Patents
Literature
6606 results about "Ohmic contact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
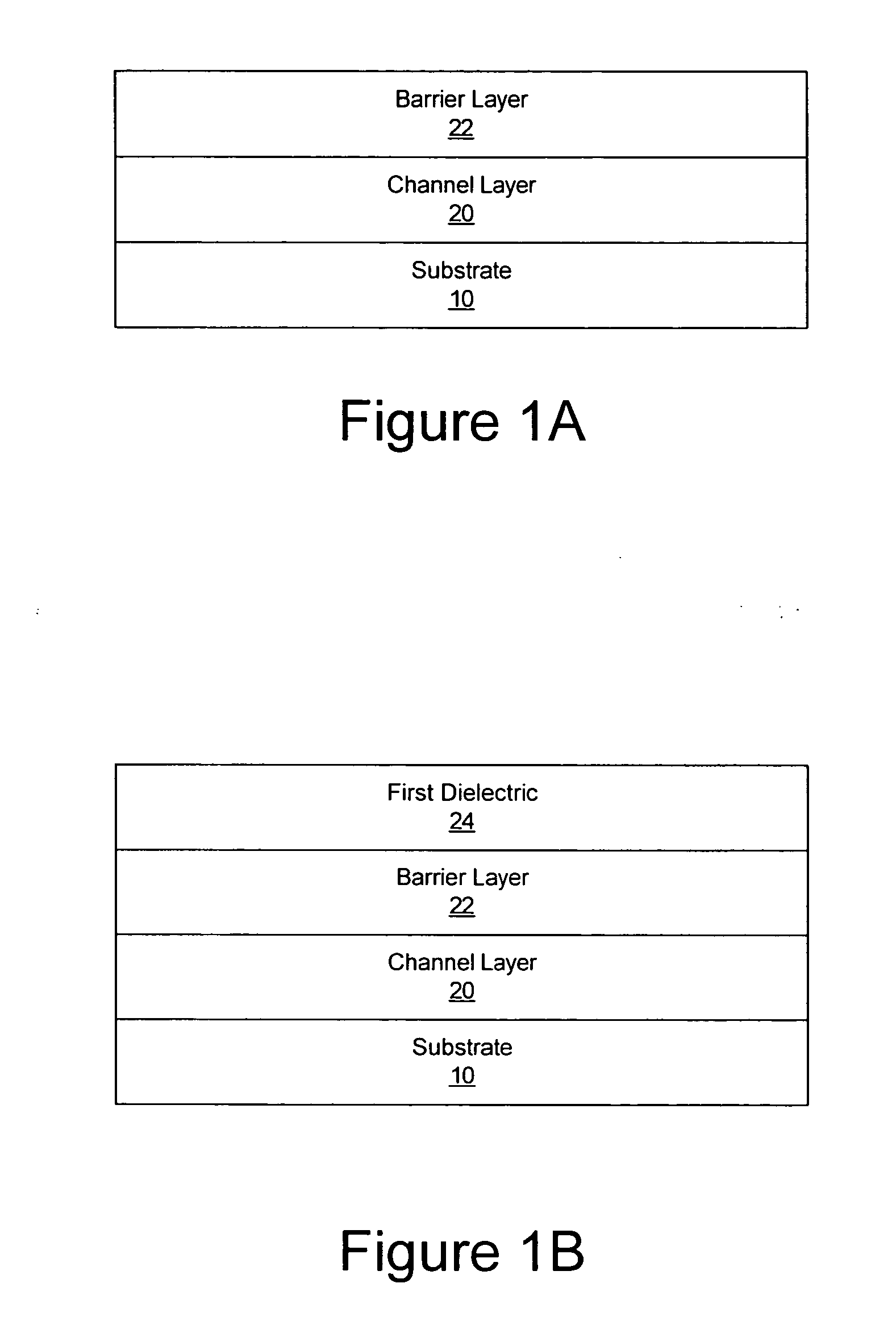
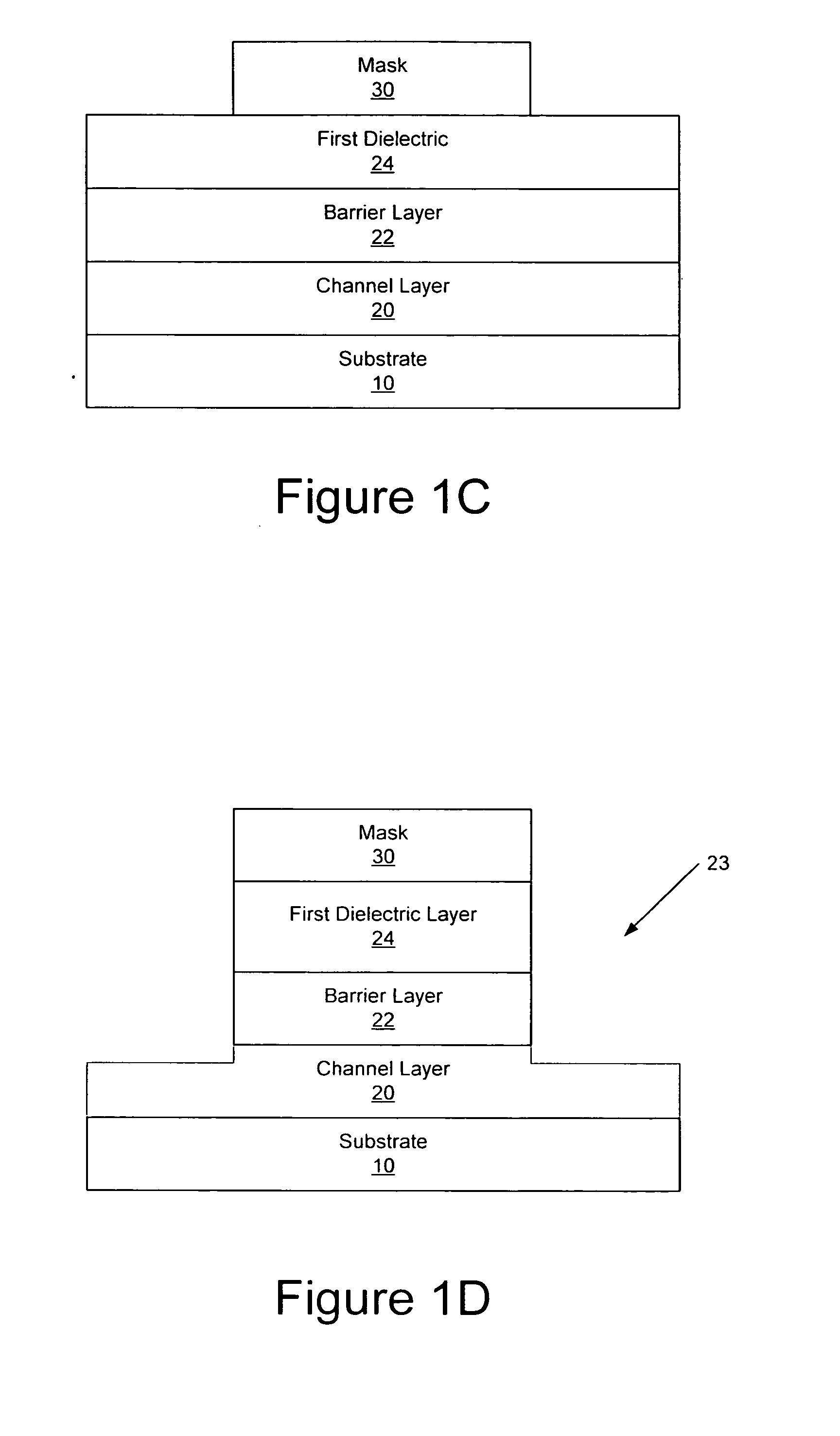
An ohmic contact is a non-rectifying electrical junction: a junction between two conductors that has a linear current–voltage (I-V) curve as with Ohm's law. Low resistance ohmic contacts are used to allow charge to flow easily in both directions between the two conductors, without blocking due to rectification or excess power dissipation due to voltage thresholds.
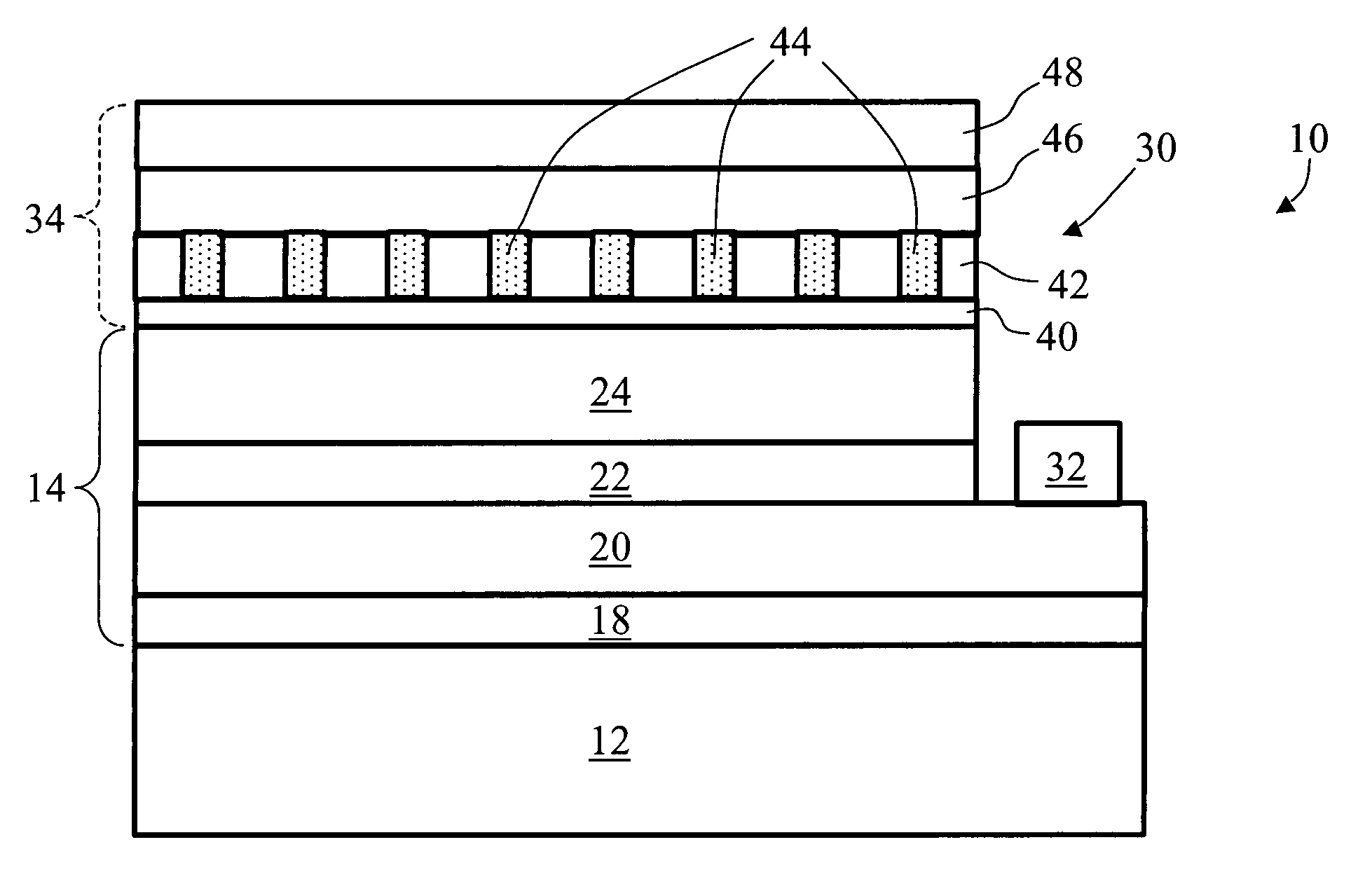
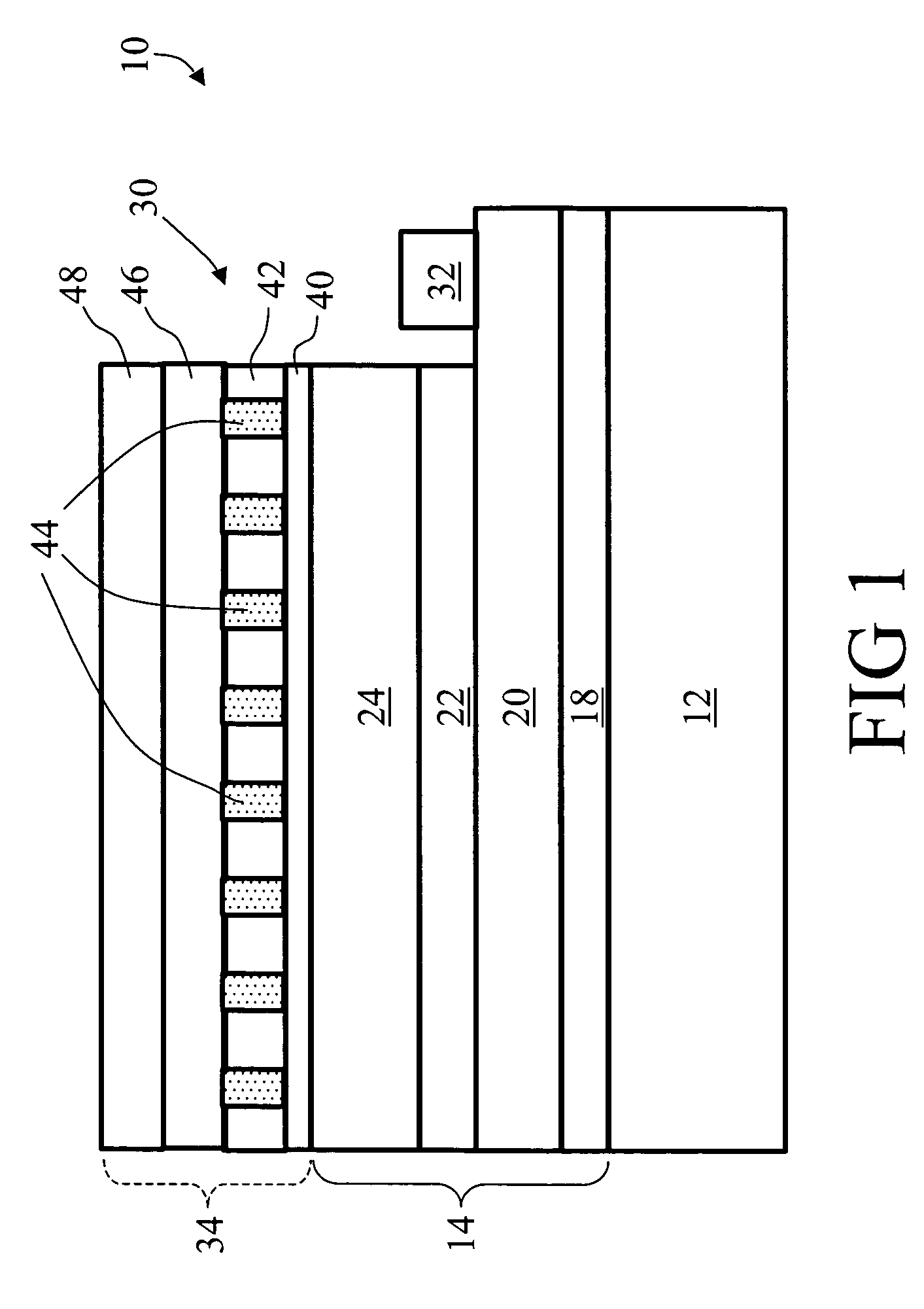
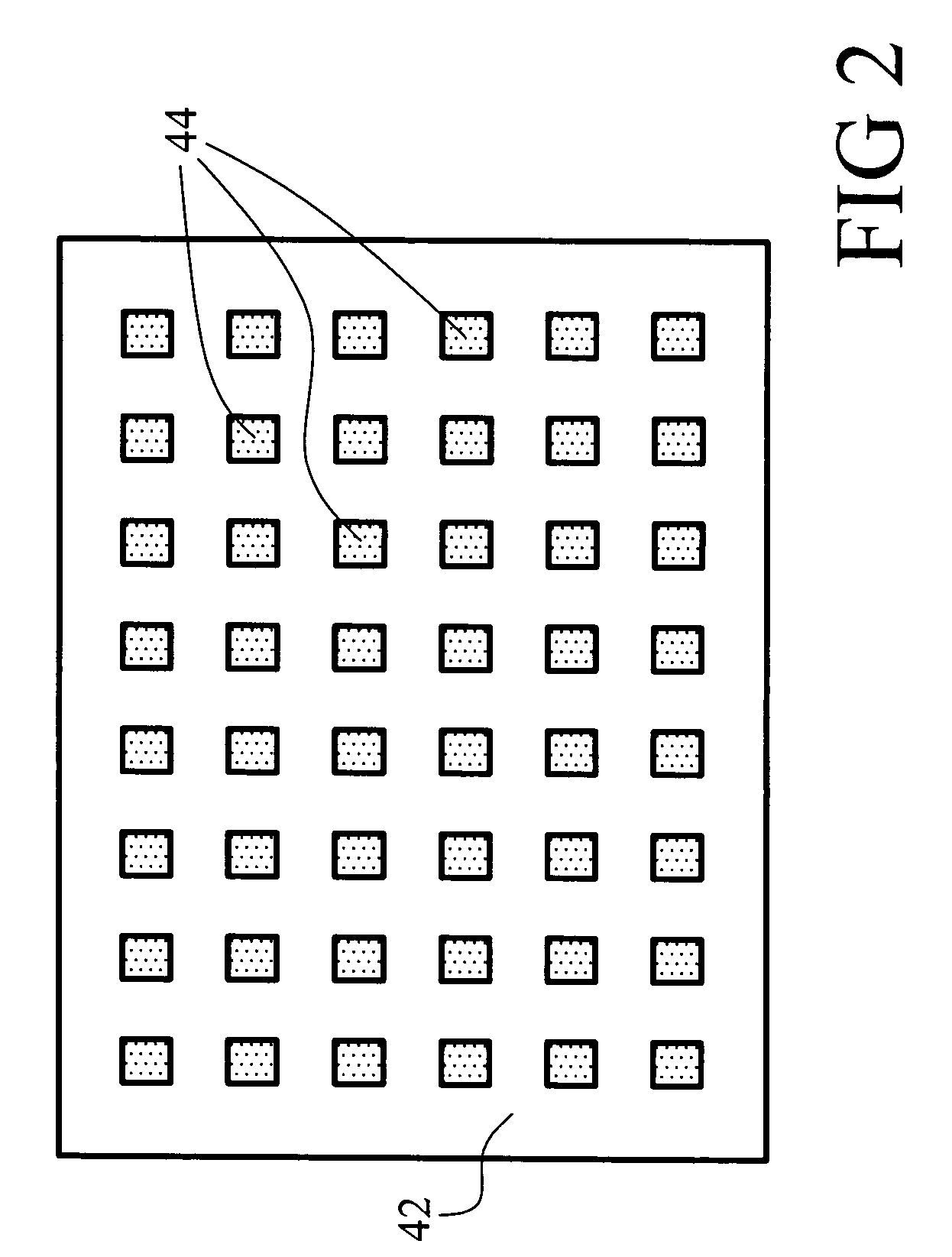
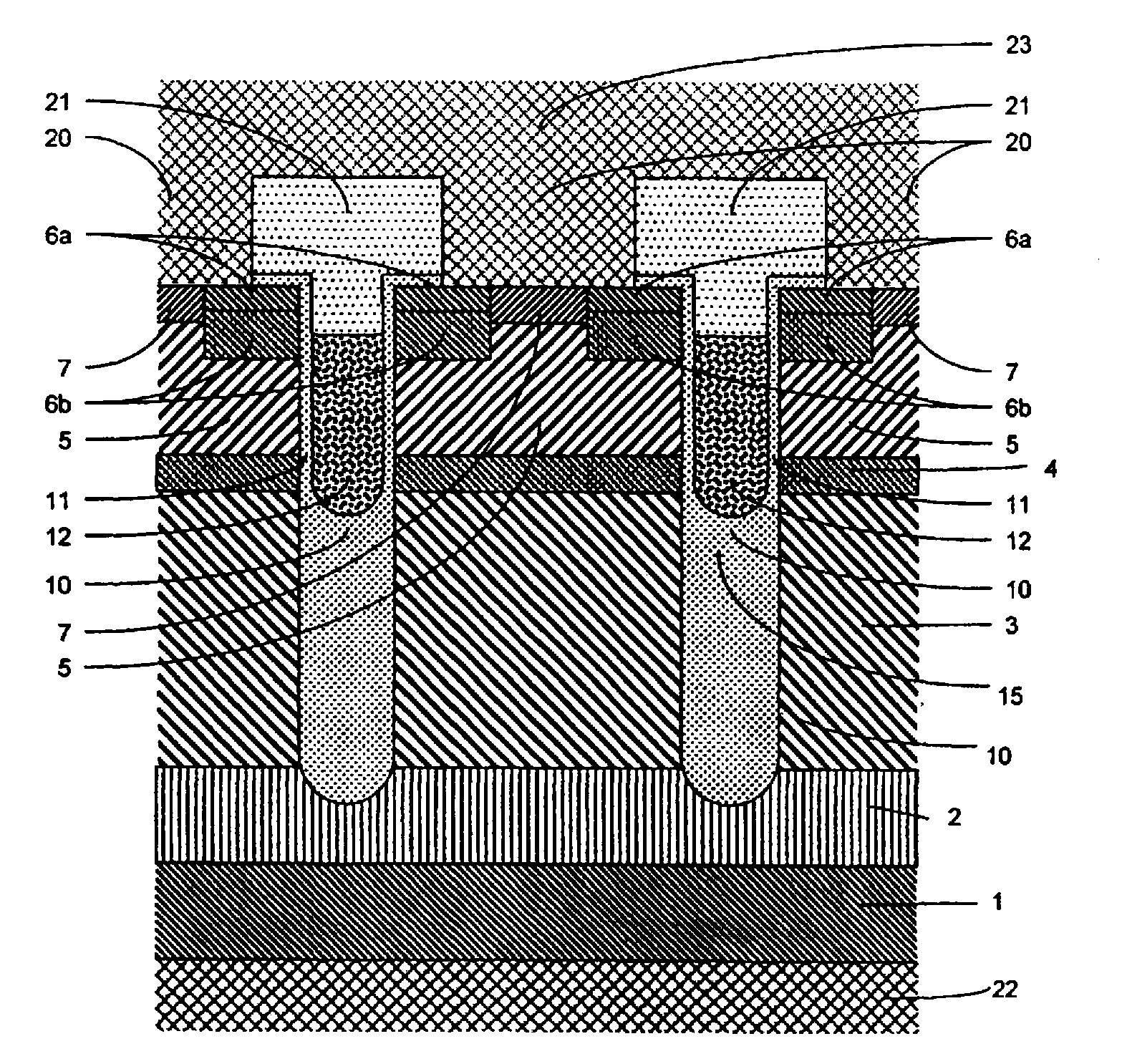
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100025678A1Comparatively-easy manufacturing processRun at high speedTransistorSolid-state devicesProduction rateOhmic contact
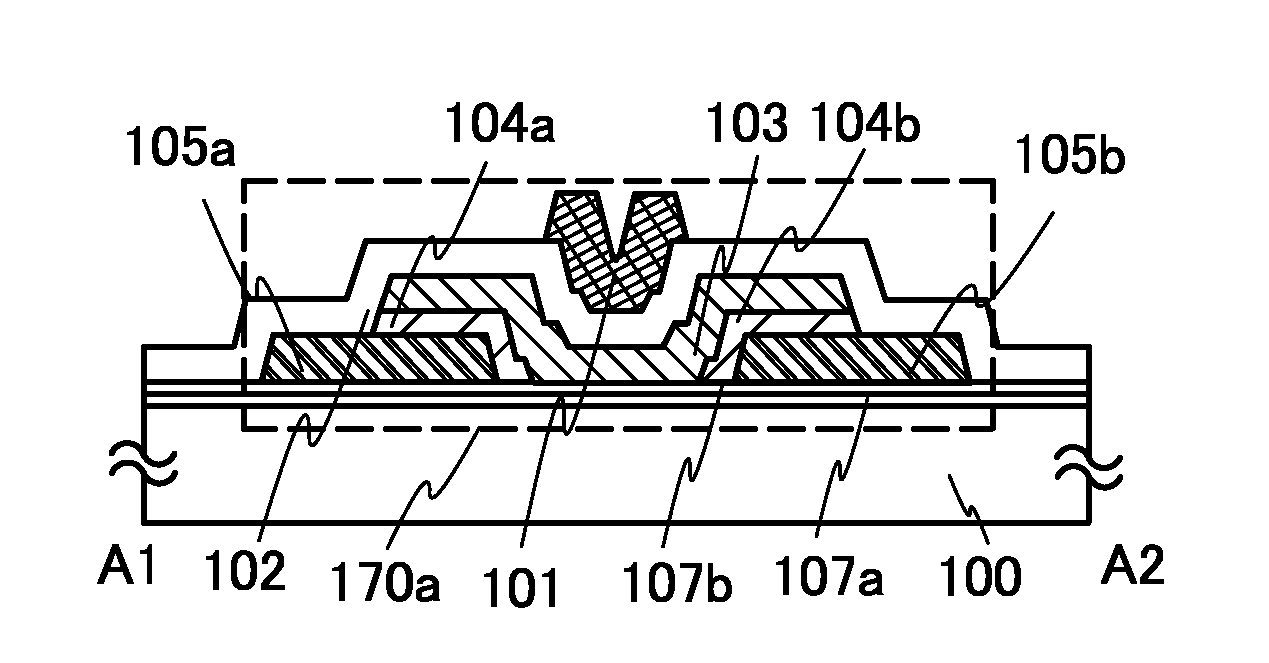
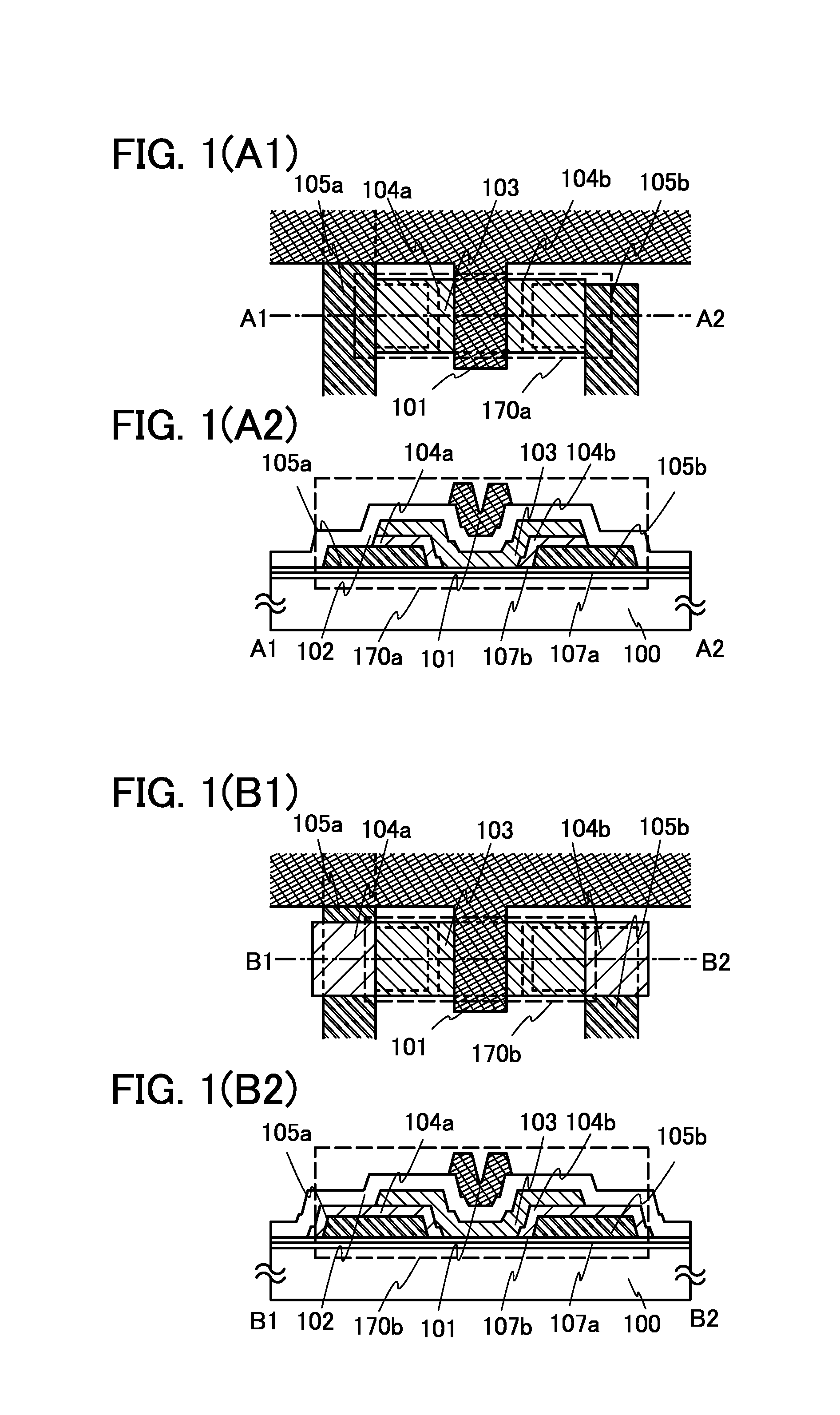
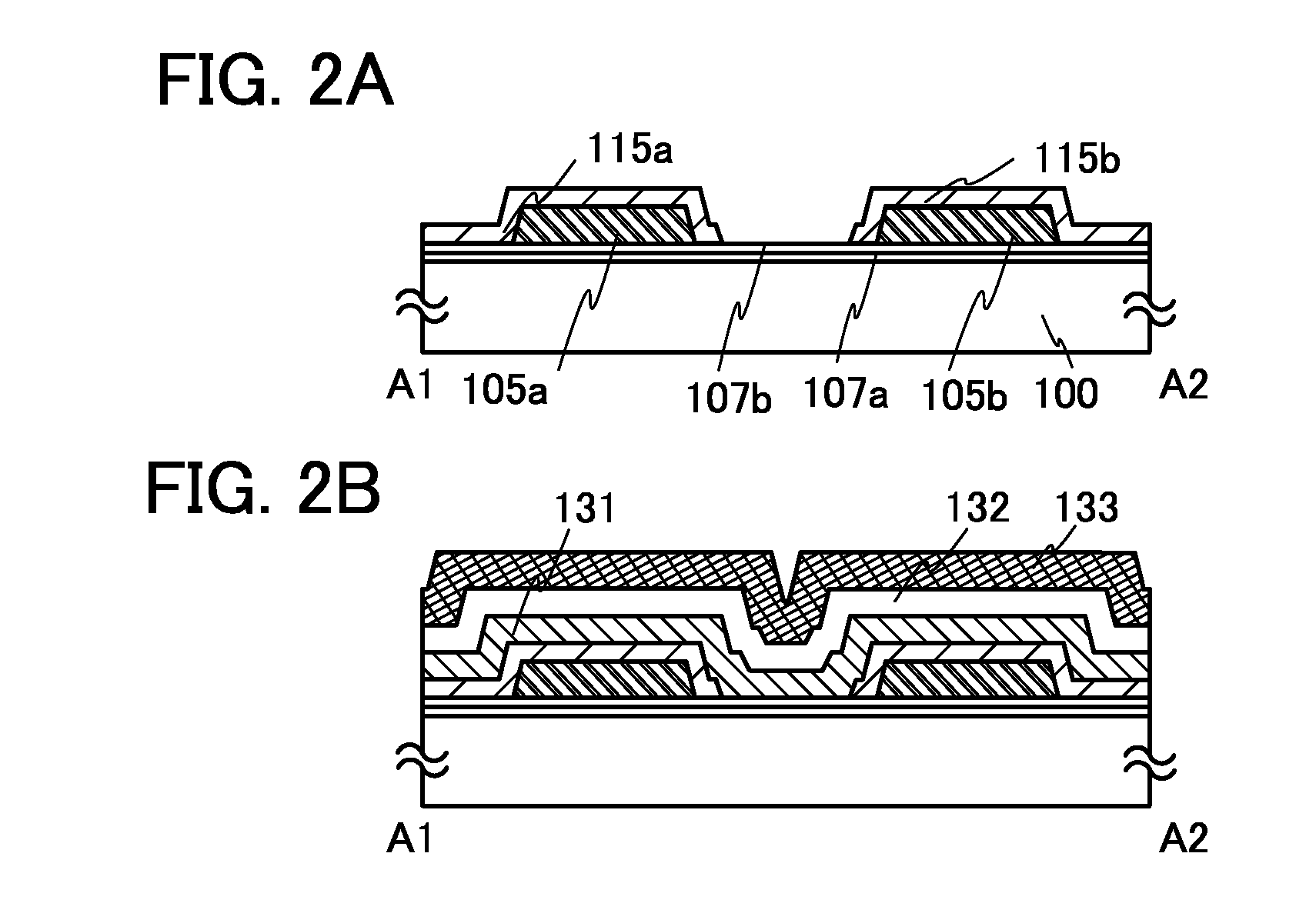
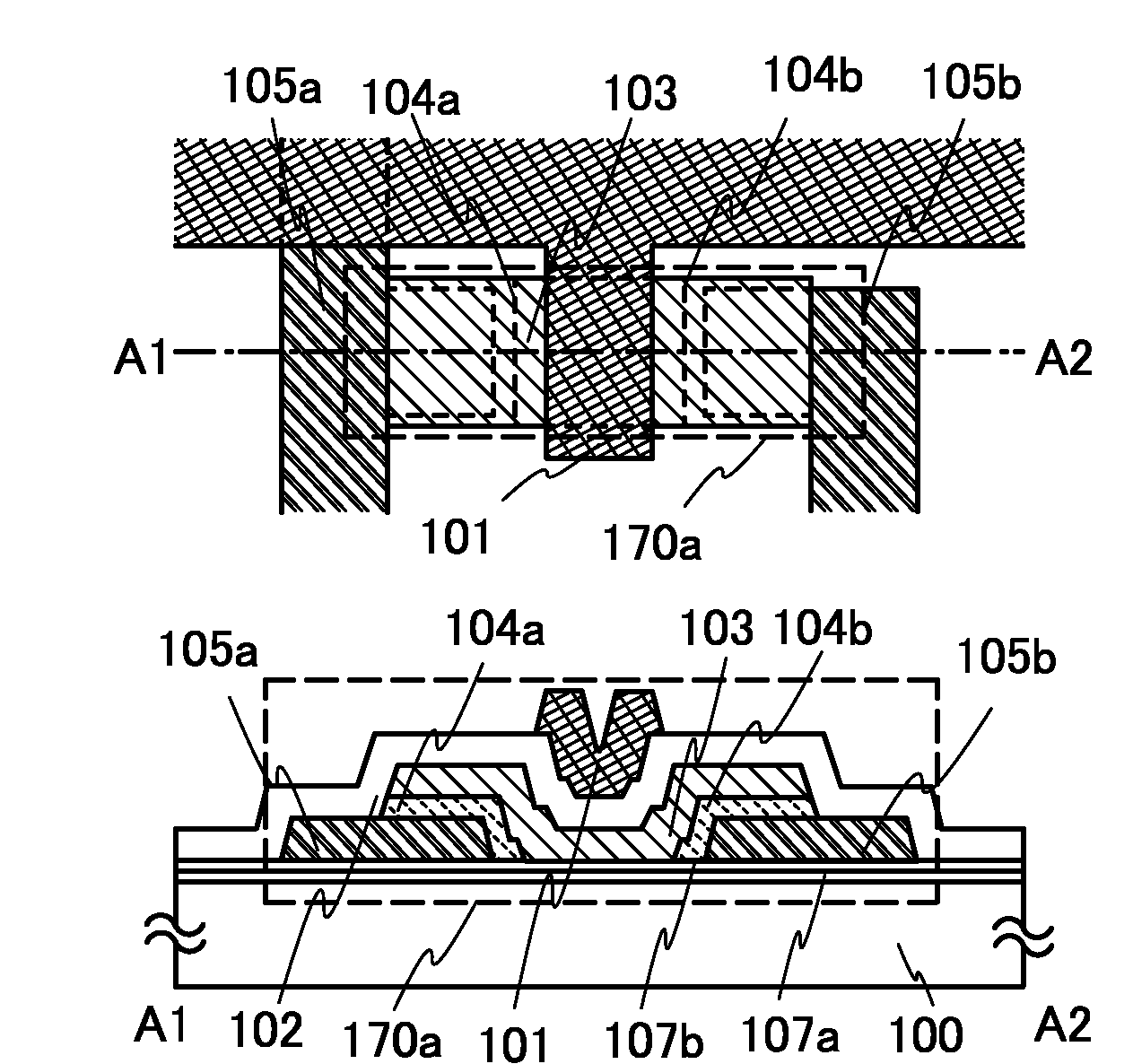
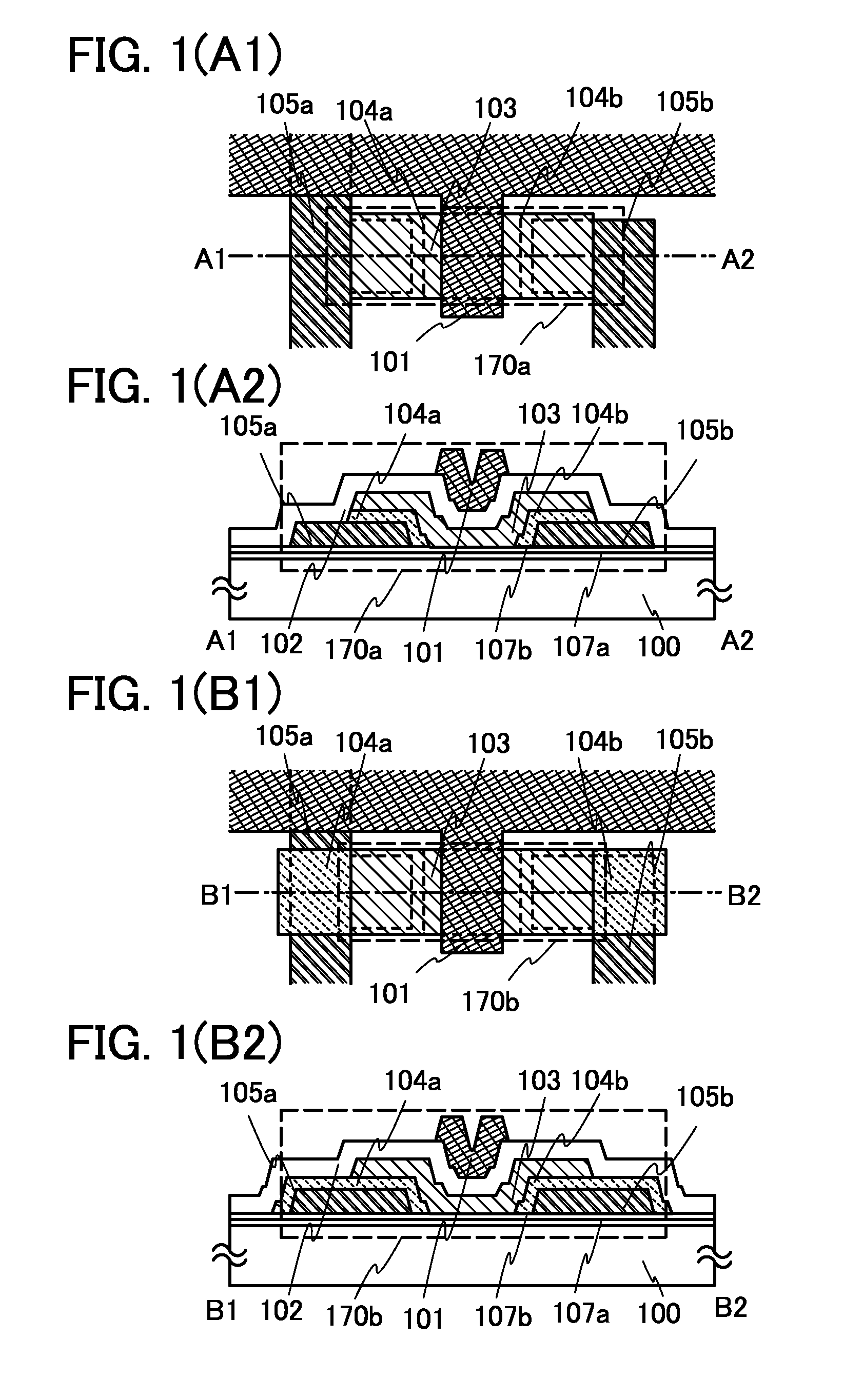
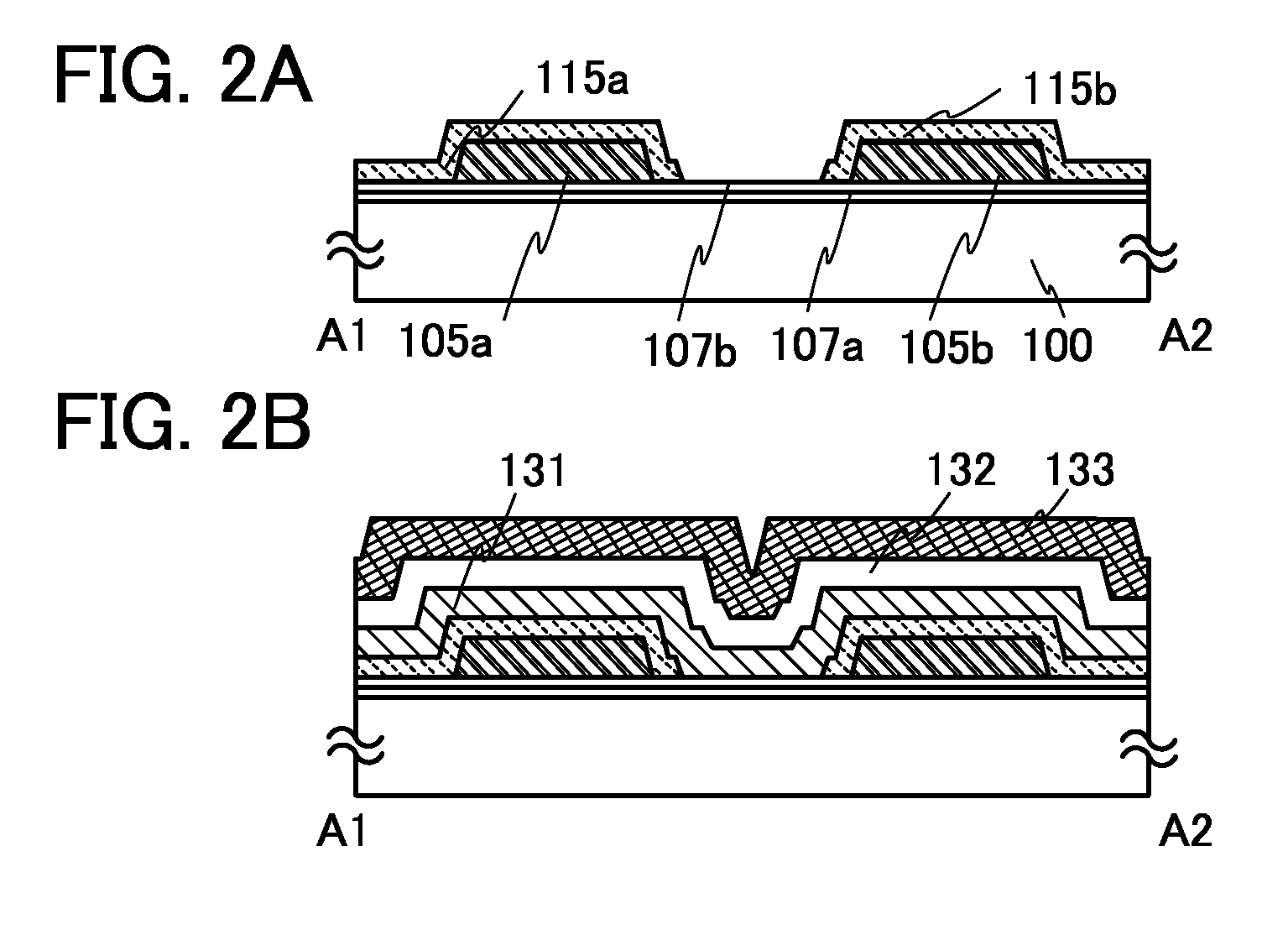
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor with favorable electric properties and high reliability, and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device with high productivity. In an inverted staggered (bottom gate) thin film transistor, an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used as a semiconductor layer, and a buffer layer formed using a metal oxide layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and a source and drain electrode layers. The metal oxide layer is intentionally provided as the buffer layer between the semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrode layers, whereby ohmic contact is obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
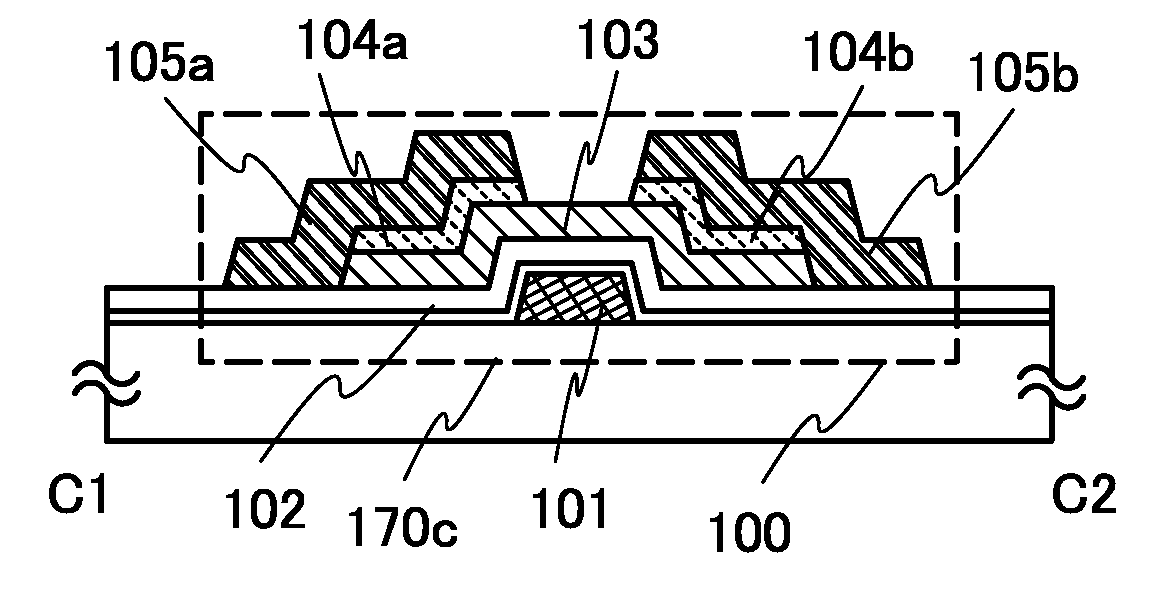
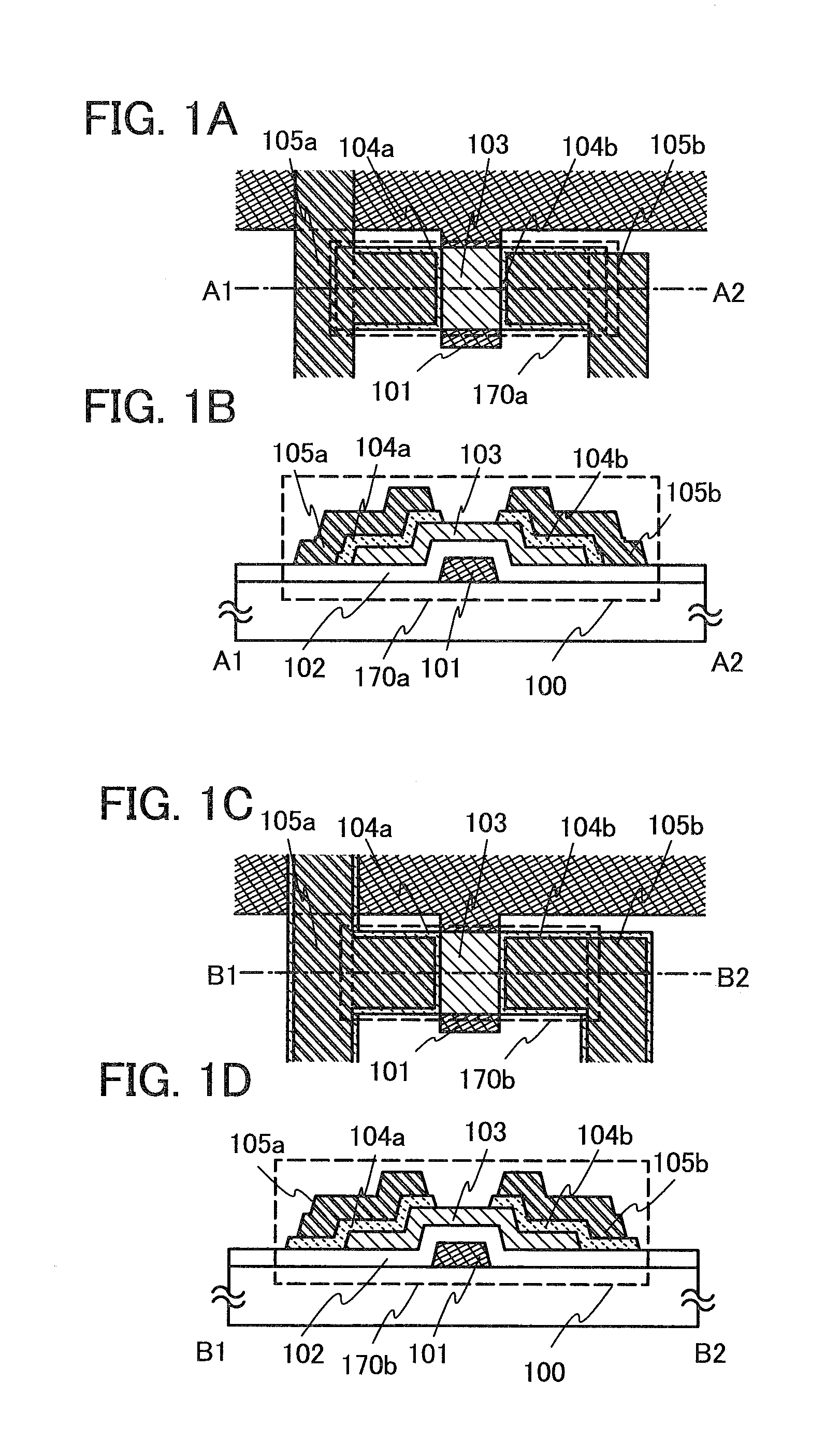
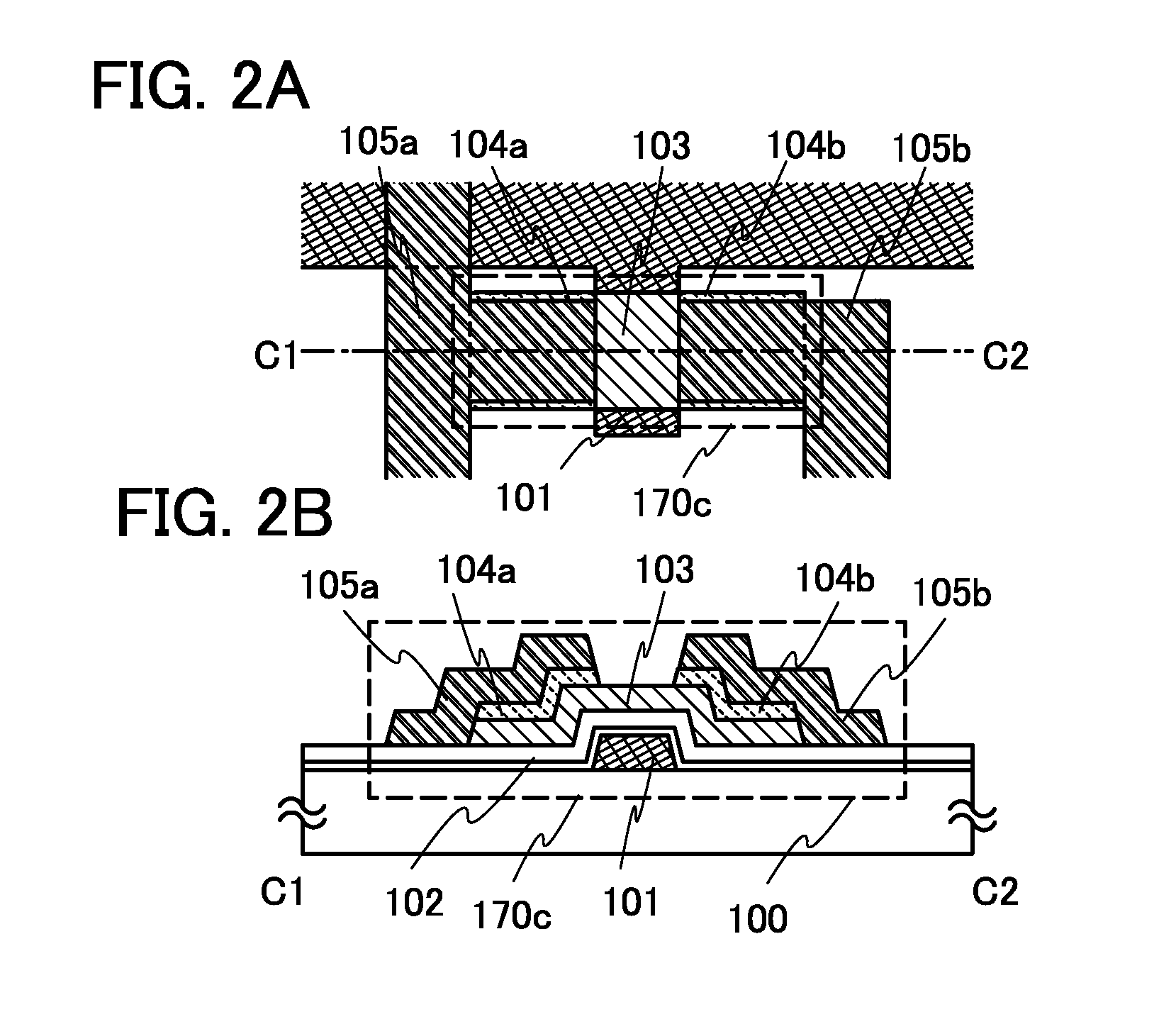
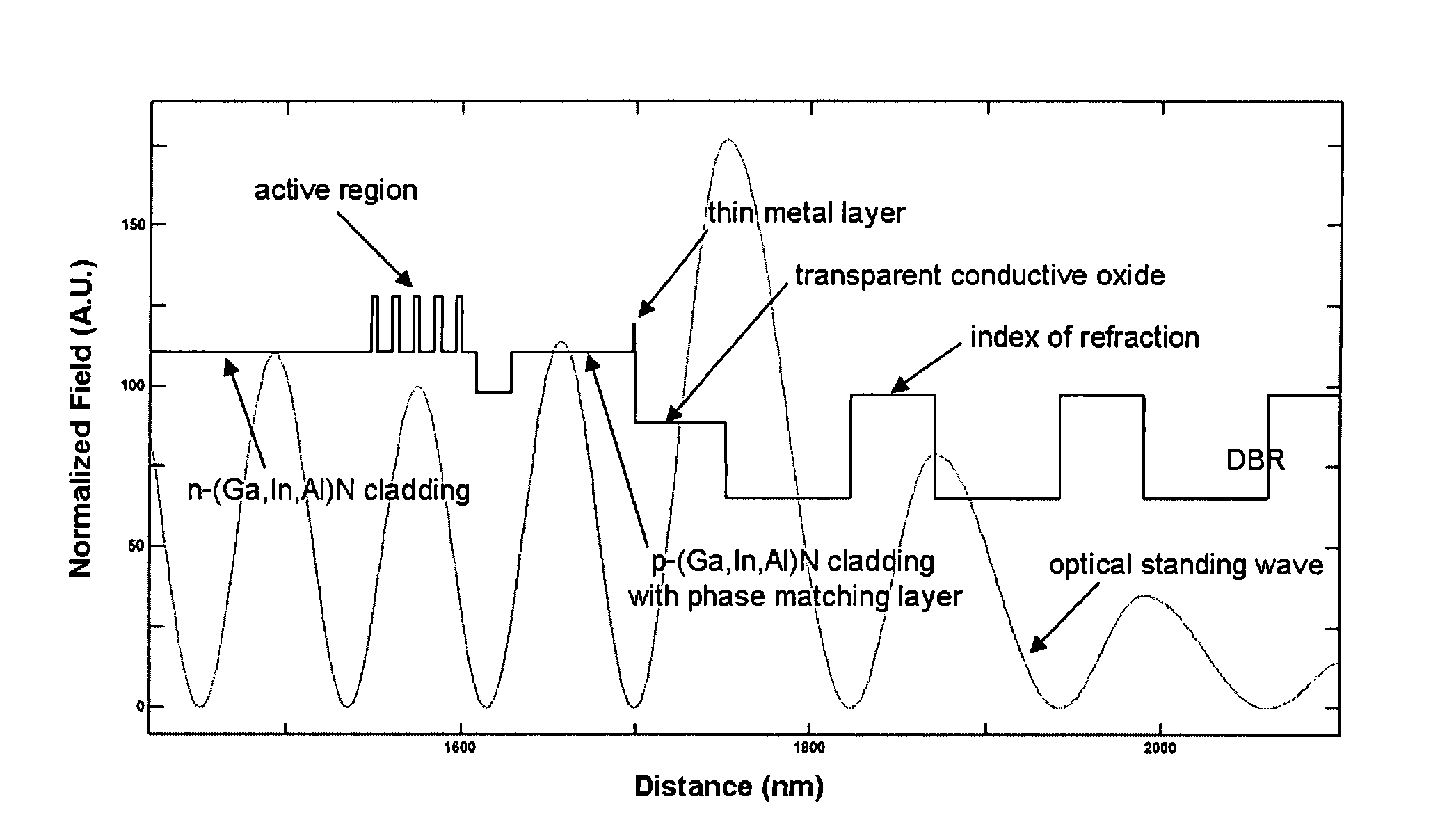
Electrically-pumped (Ga,In,Al)N vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
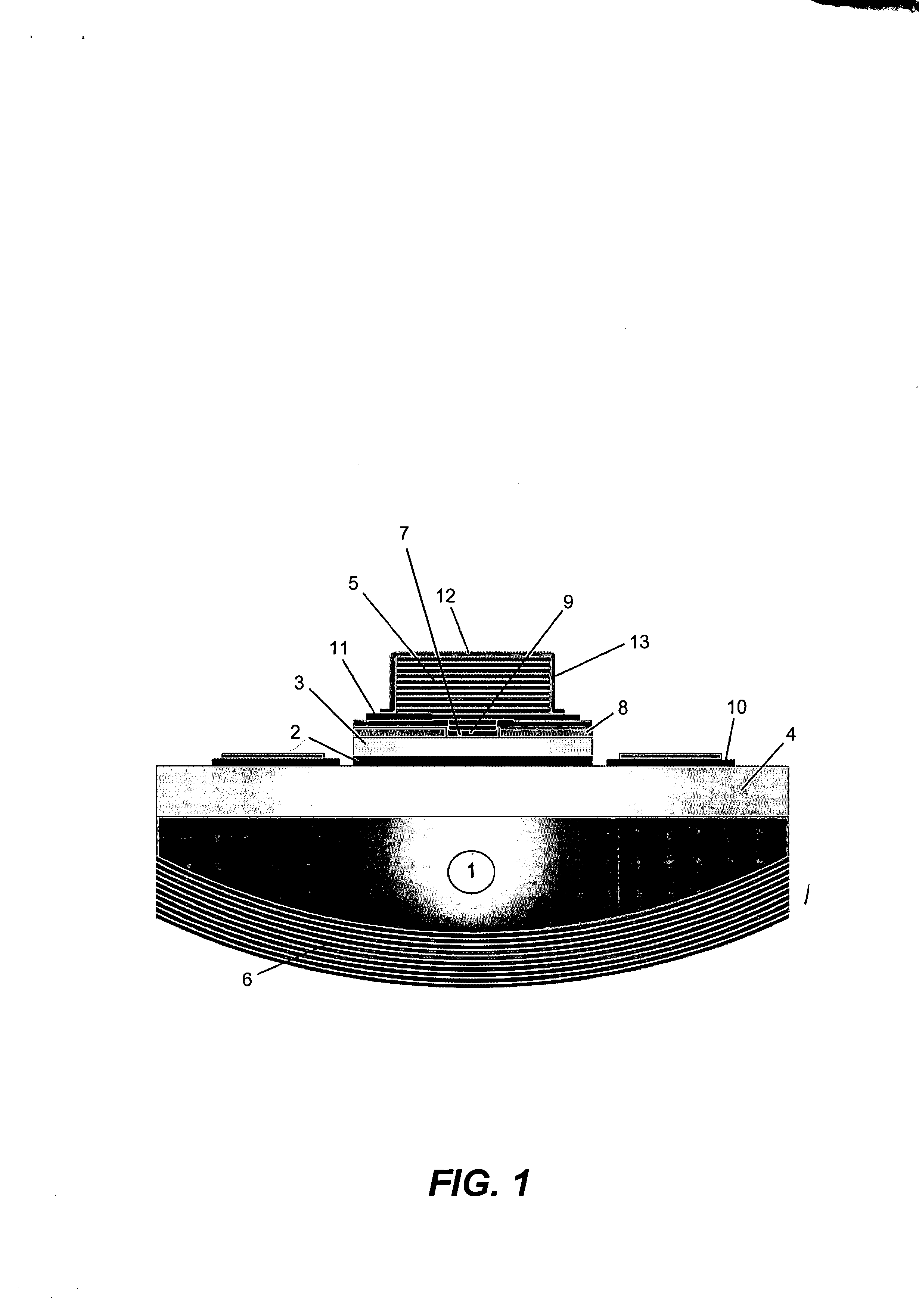
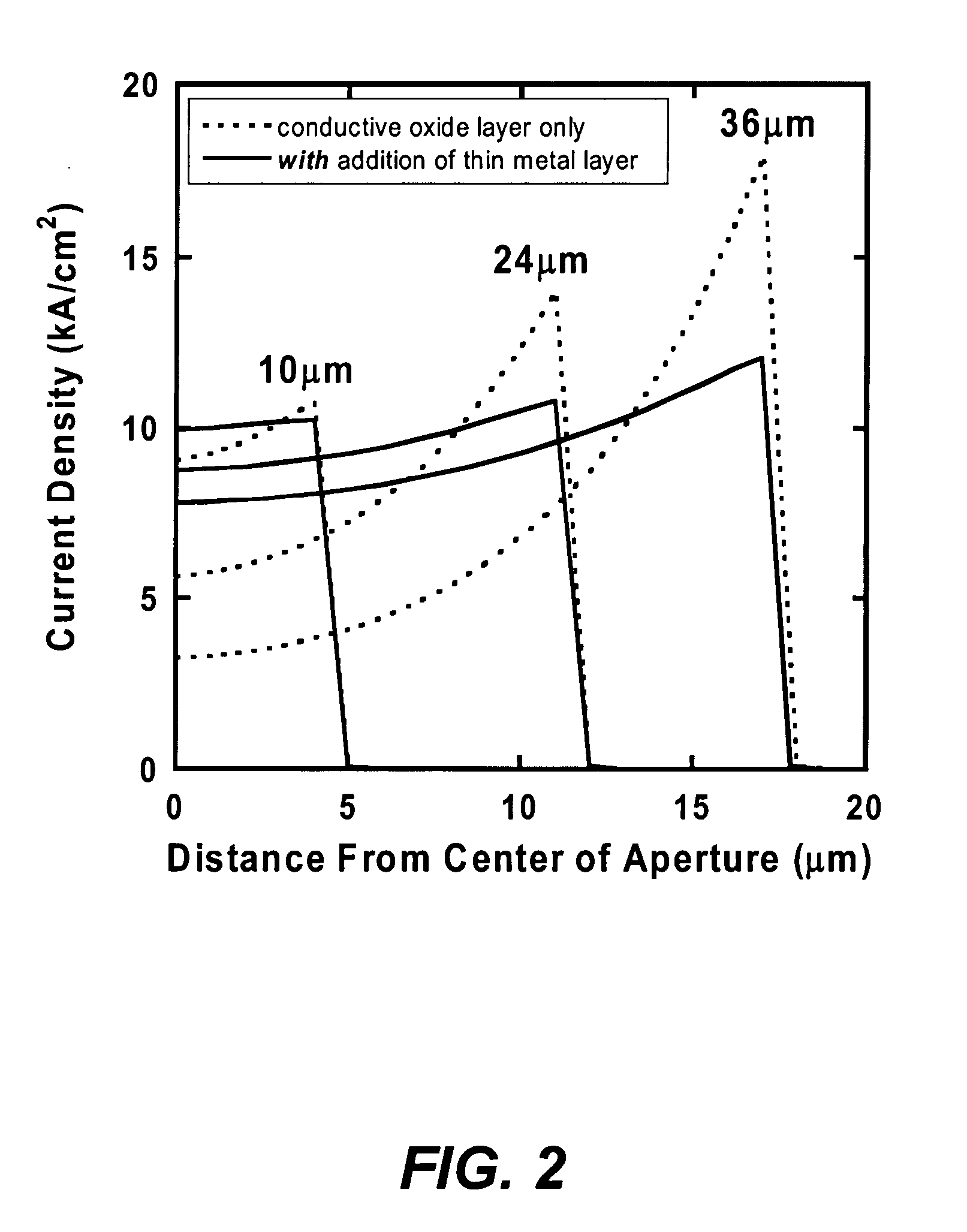
InactiveUS20070280320A1Good ohmic contactOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersThin metalVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
A vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) comprising a low-loss thin metal contact and current spreading layer within the optical cavity that provides for improved ohmic contact and lateral current distribution, a substrate including a plano-concave optical cavity, a (Ga,In,Al)N multiple quantum well (MQW) active region contained within the optical cavity that generates light when injected by an electrical current, and an integrated micromirror fabricated onto the substrate that provides for optical mode control of the light generated by the active region. A relatively simple process is used to fabricate the VCSEL.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor light-emitting device
A semiconductor light-emitting device capable of attaining a surface plasmon effect while attaining excellent ohmic contact is provided. This semiconductor light-emitting device comprises a semiconductor layer formed on an emission layer, a first electrode layer formed on the semiconductor layer and a second electrode layer, formed on the first electrode layer, having a periodic structure. The first electrode layer is superior to the second electrode layer in ohmic contact with respect to the semiconductor layer, and the second electrode layer contains a metal exhibiting a higher plasma frequency than the first electrode layer.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100025677A1Small amount of photocurrentReduce parasitic capacitanceTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesProduction rateCharge carrier
To provide a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor having excellent electric characteristics and high reliability and a manufacturing method of the semiconductor device with high mass productivity. The summary is that an inverted-staggered (bottom-gate) thin film transistor is included in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used as a semiconductor layer, a channel protective layer is provided in a region that overlaps a channel formation region of the semiconductor layer, and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and source and drain electrodes. An ohmic contact is formed by intentionally providing the buffer layer having a higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer between the semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
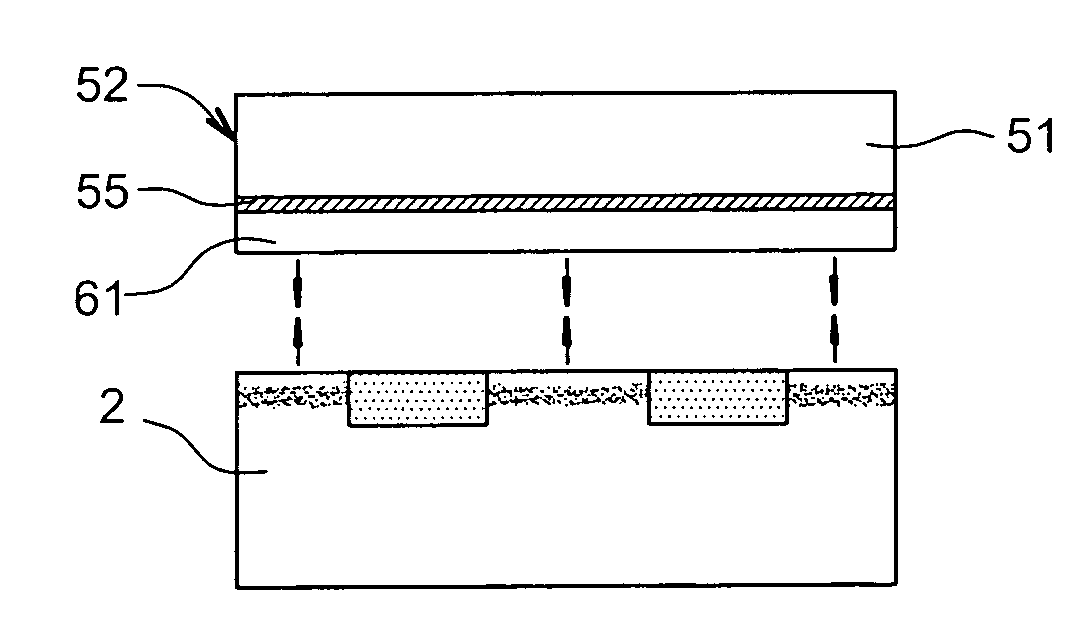
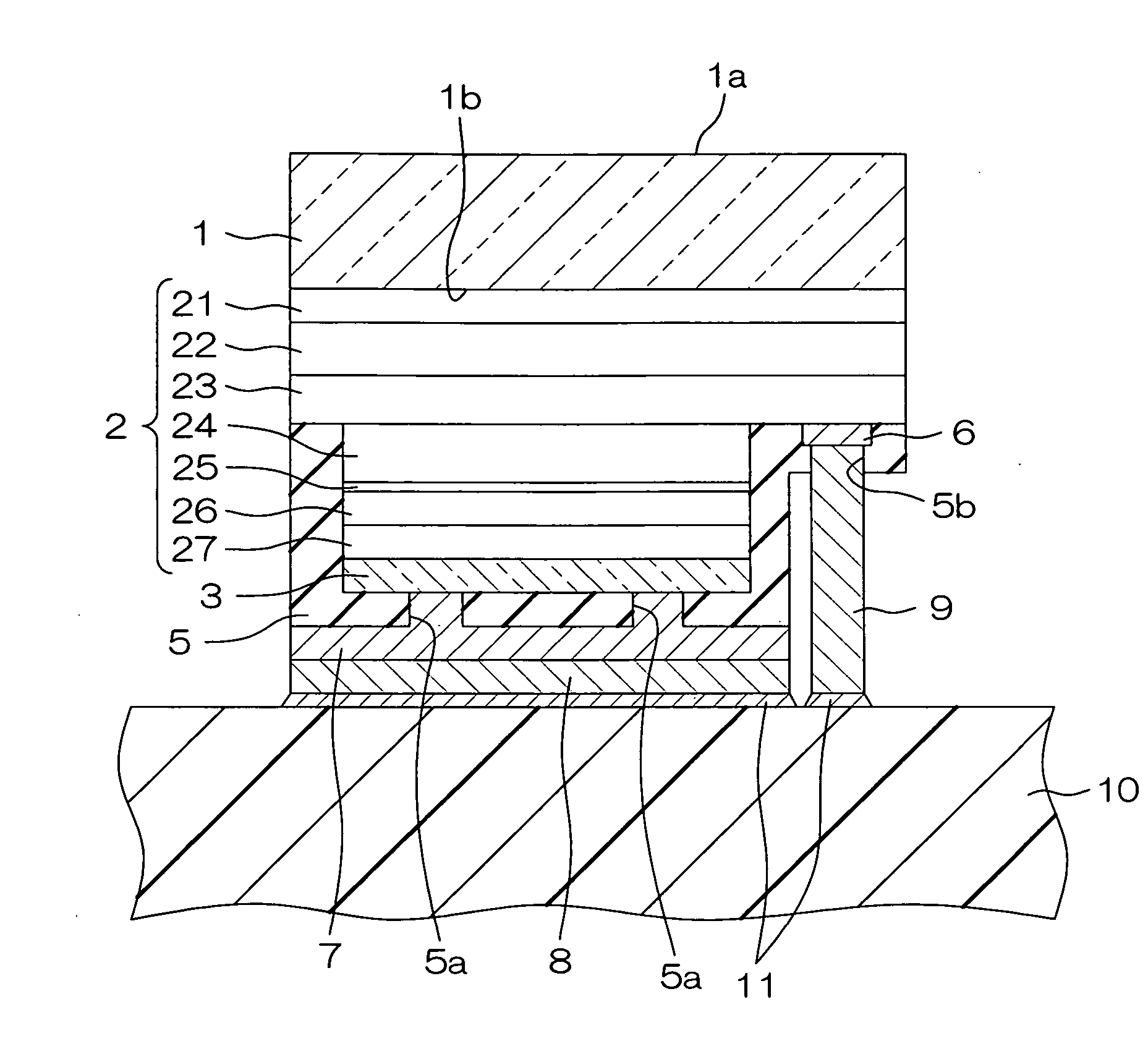
Method of sealing two plates with the formation of an ohmic contact therebetween
InactiveUS20070072391A1Reduce depthBudget is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
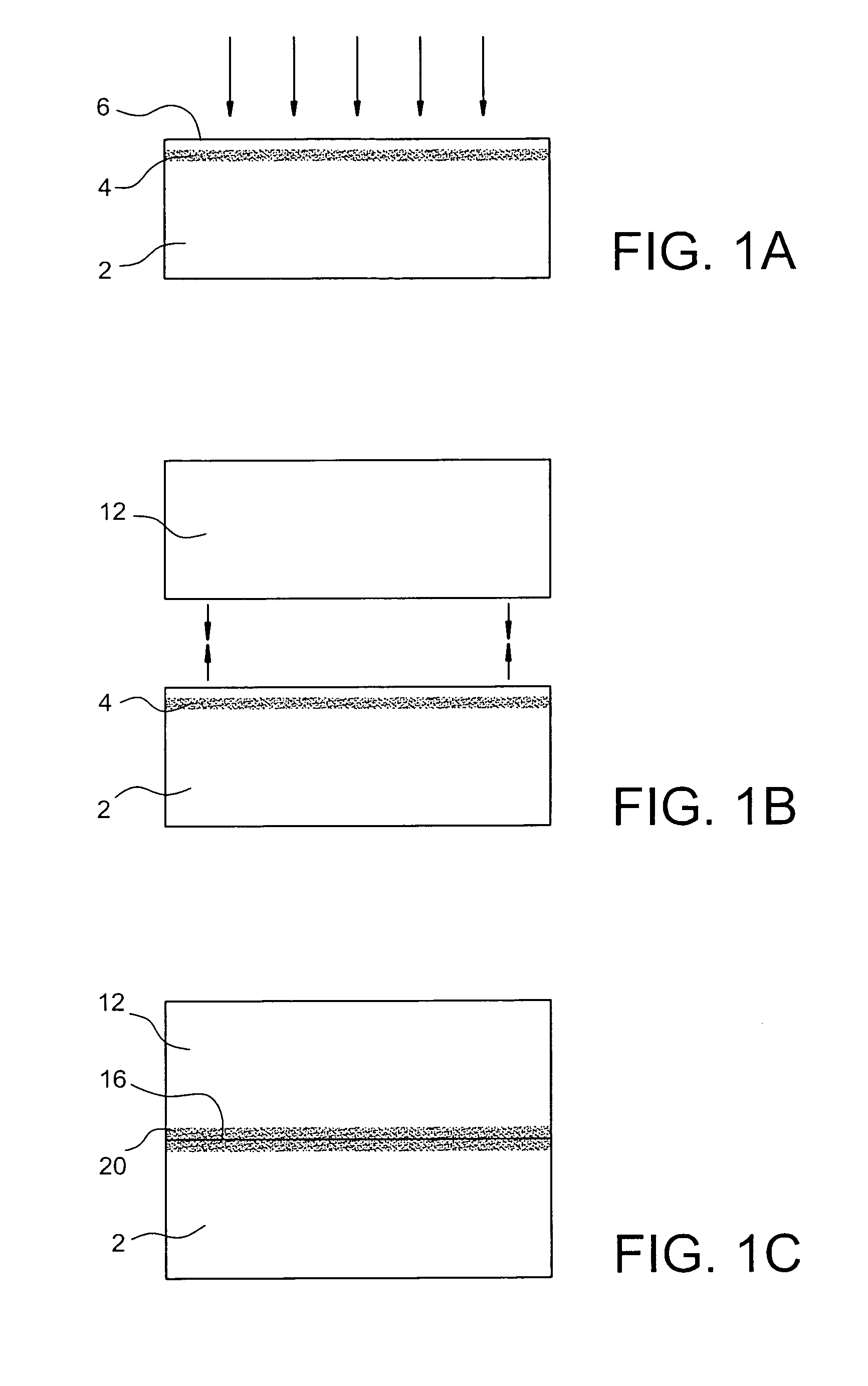
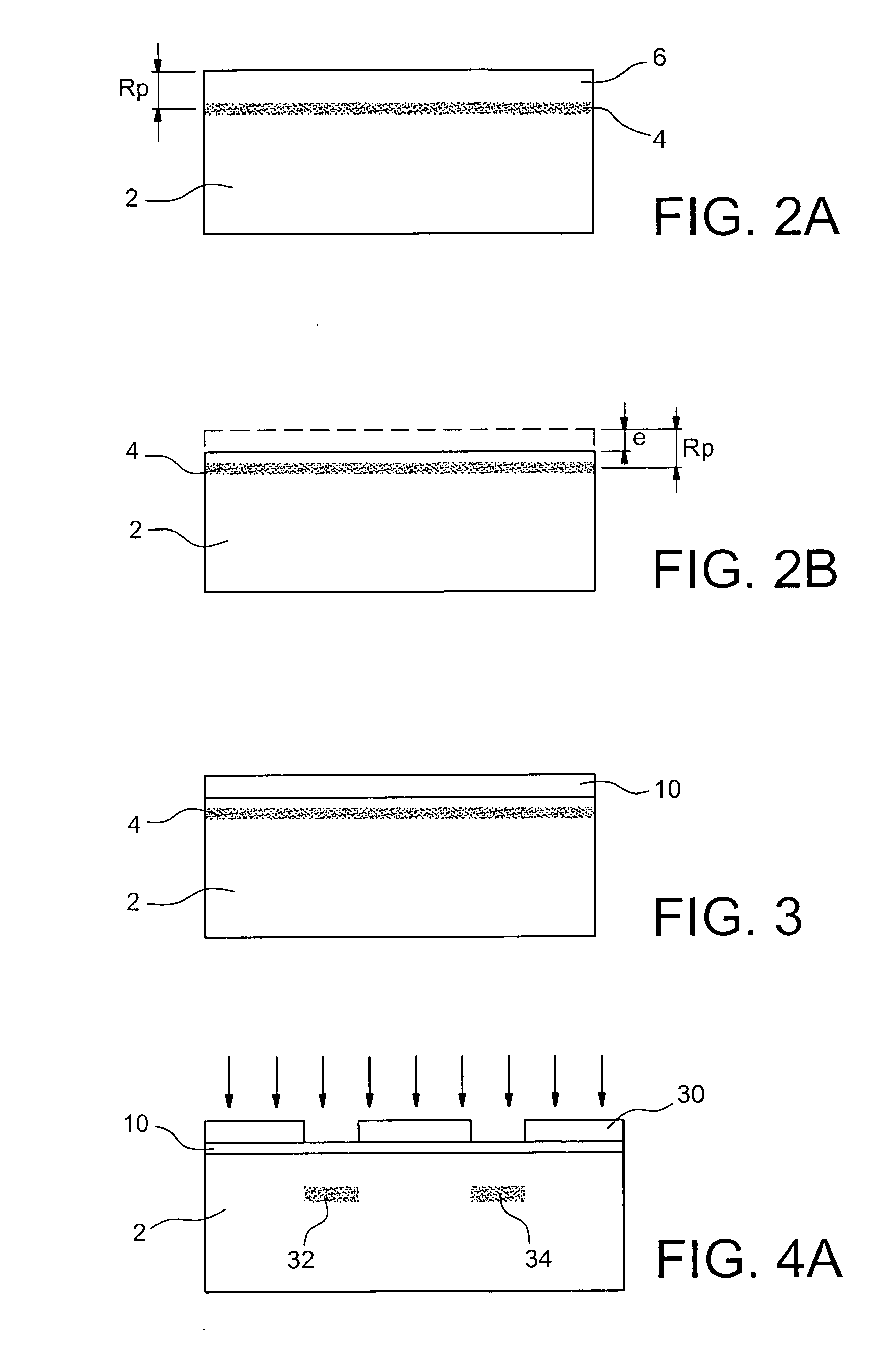
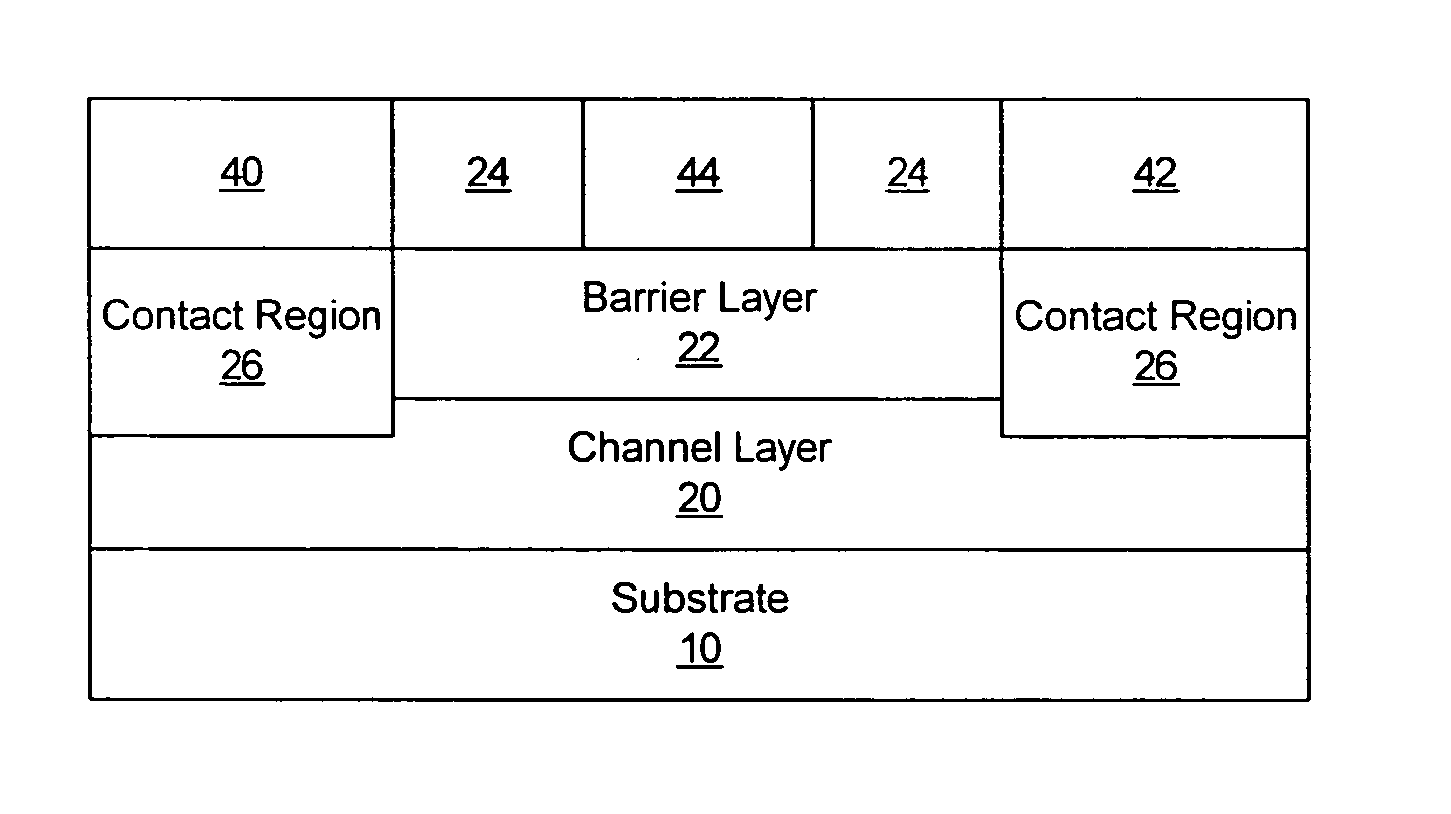
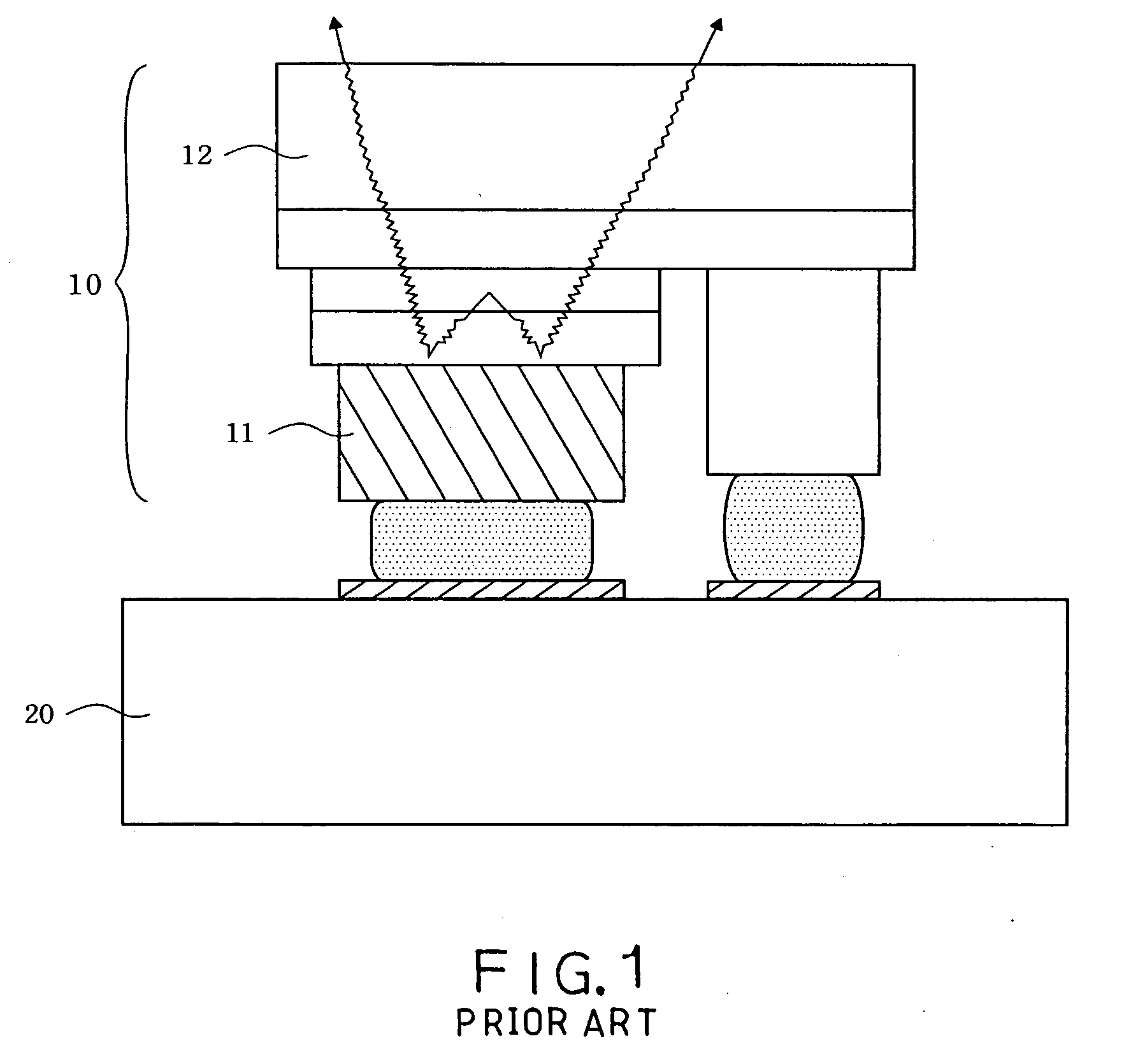
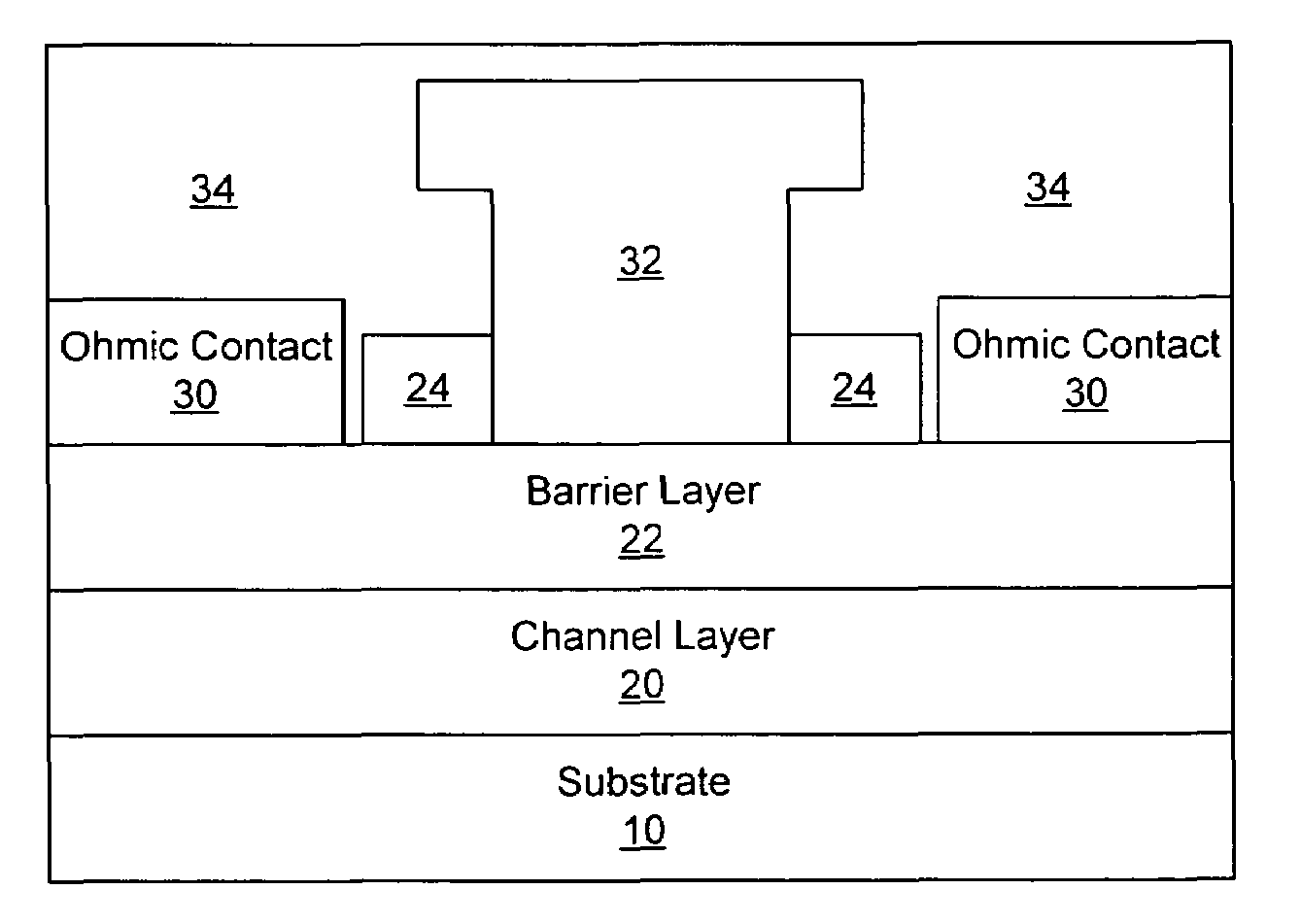
Methods of fabricating nitride-based transistors having regrown ohmic contact regions and nitride-based transistors having regrown ohmic contact regions
ActiveUS20050258451A1High electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow temperature depositionSemiconductor materials
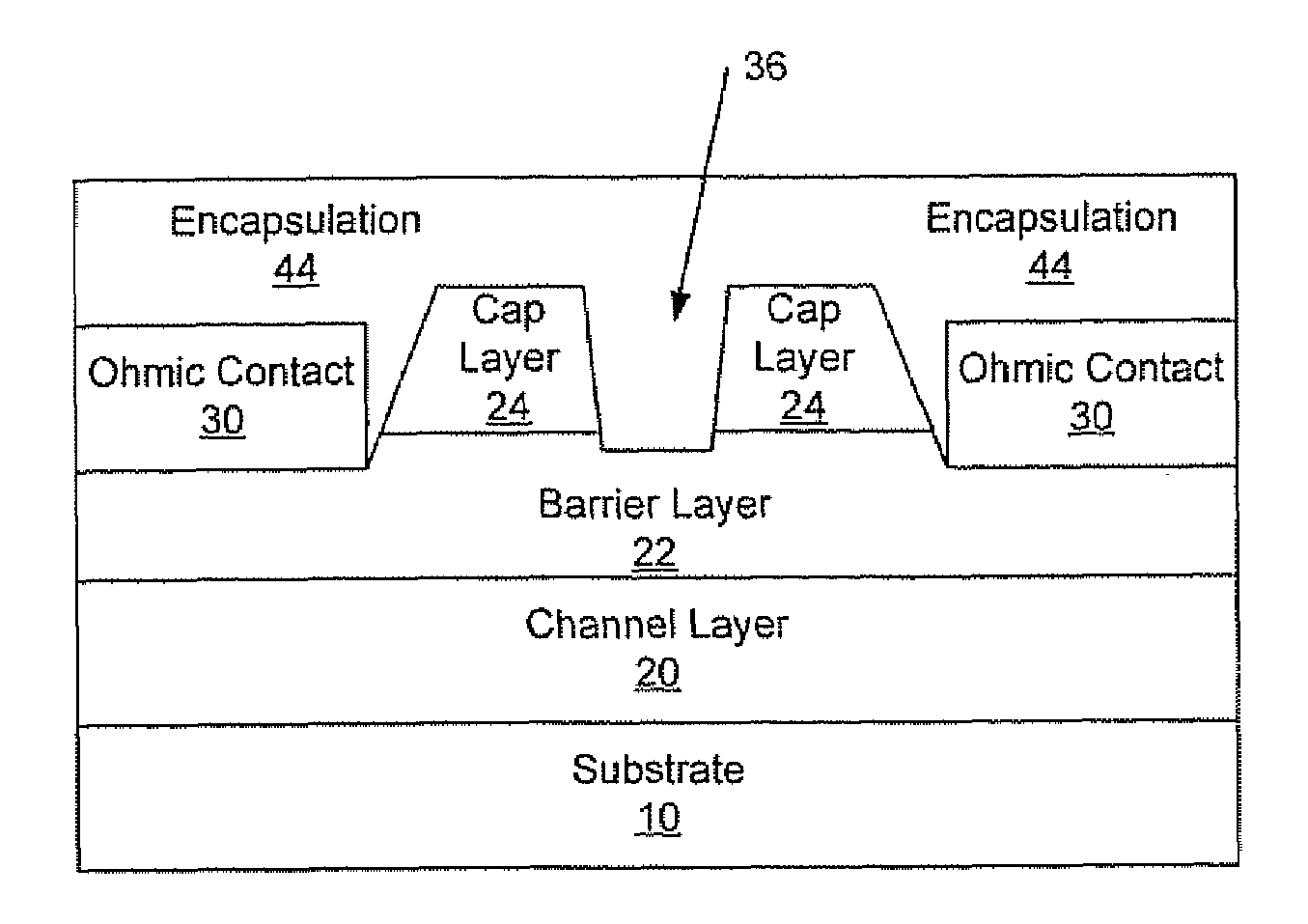
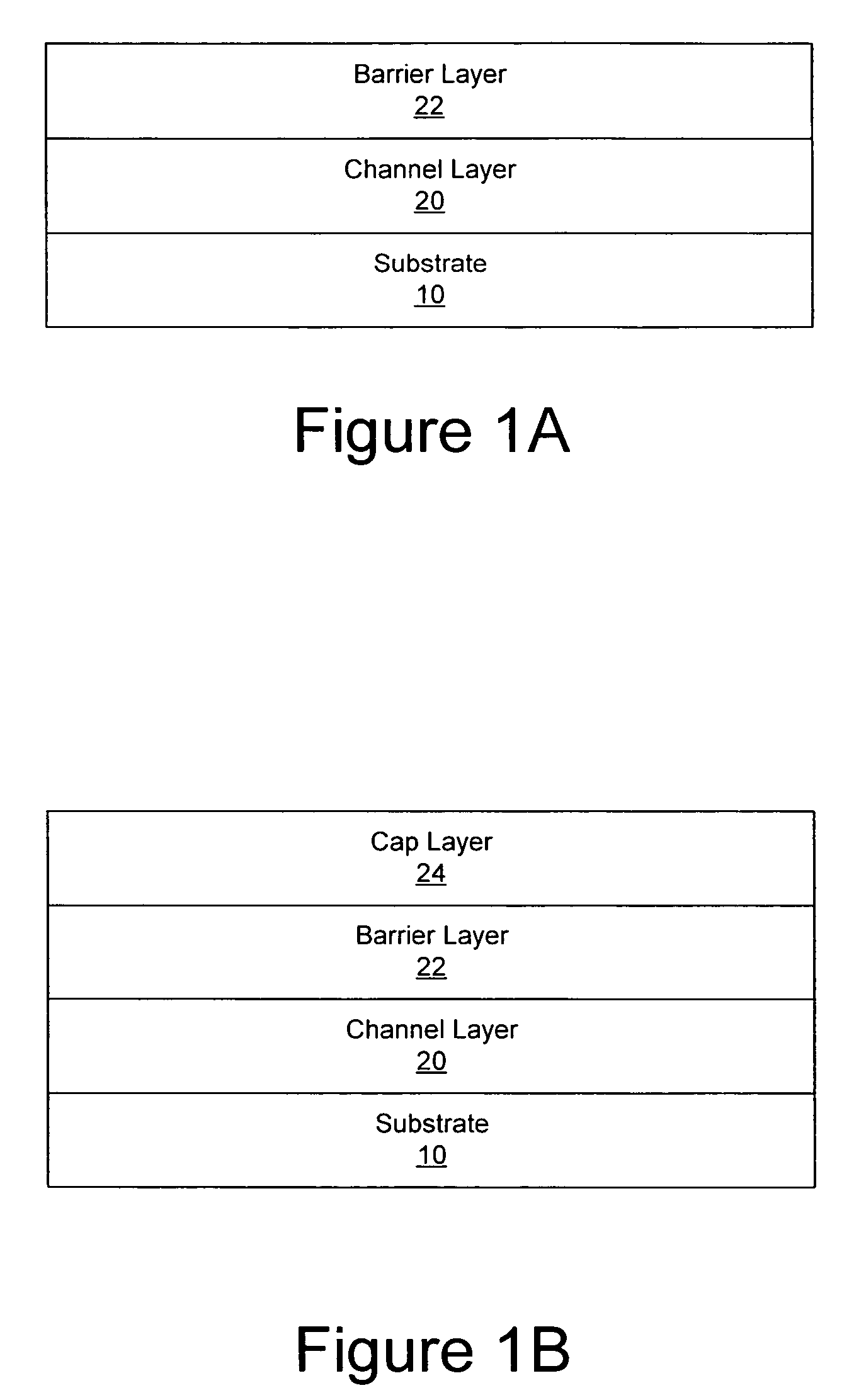
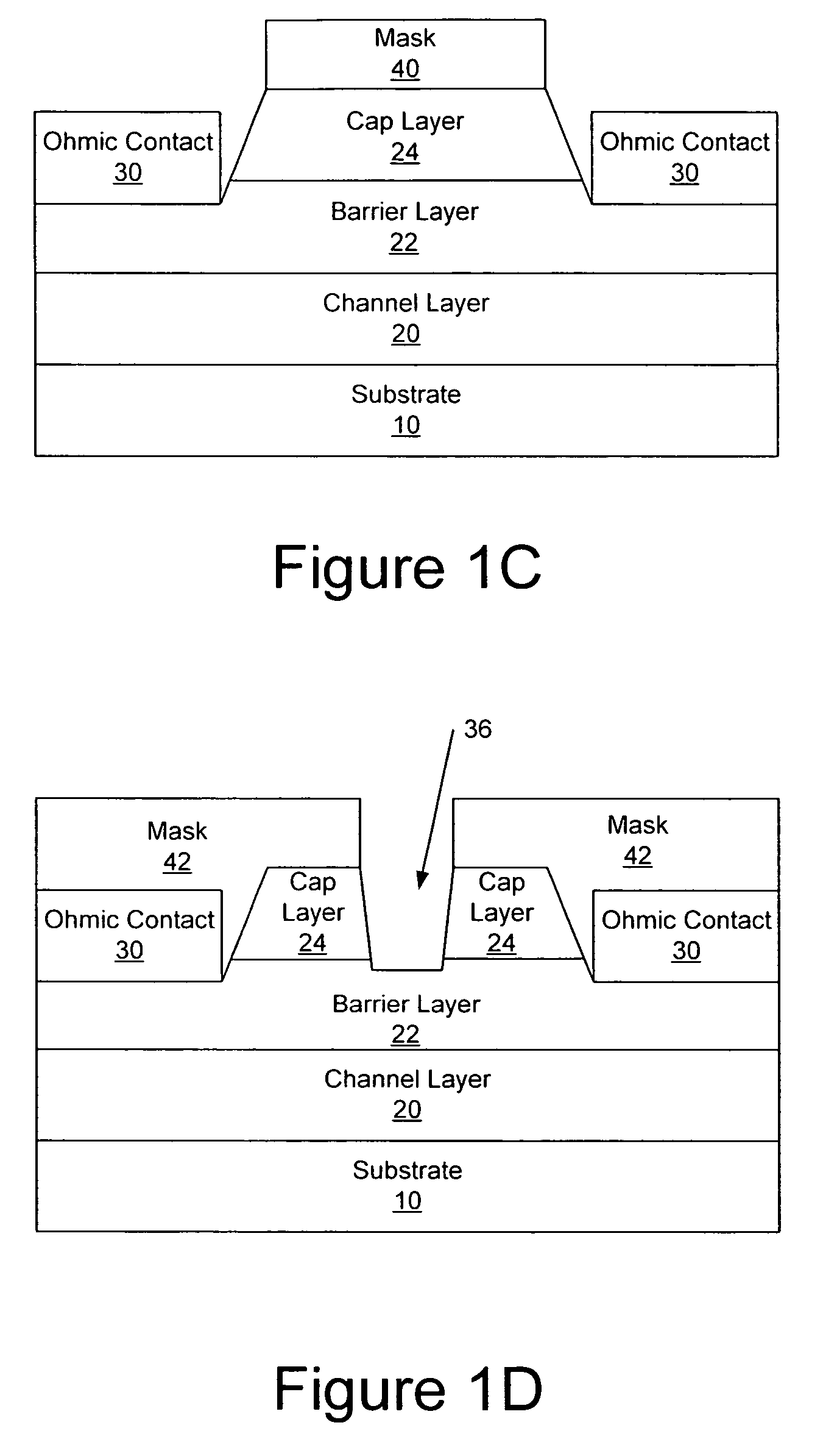
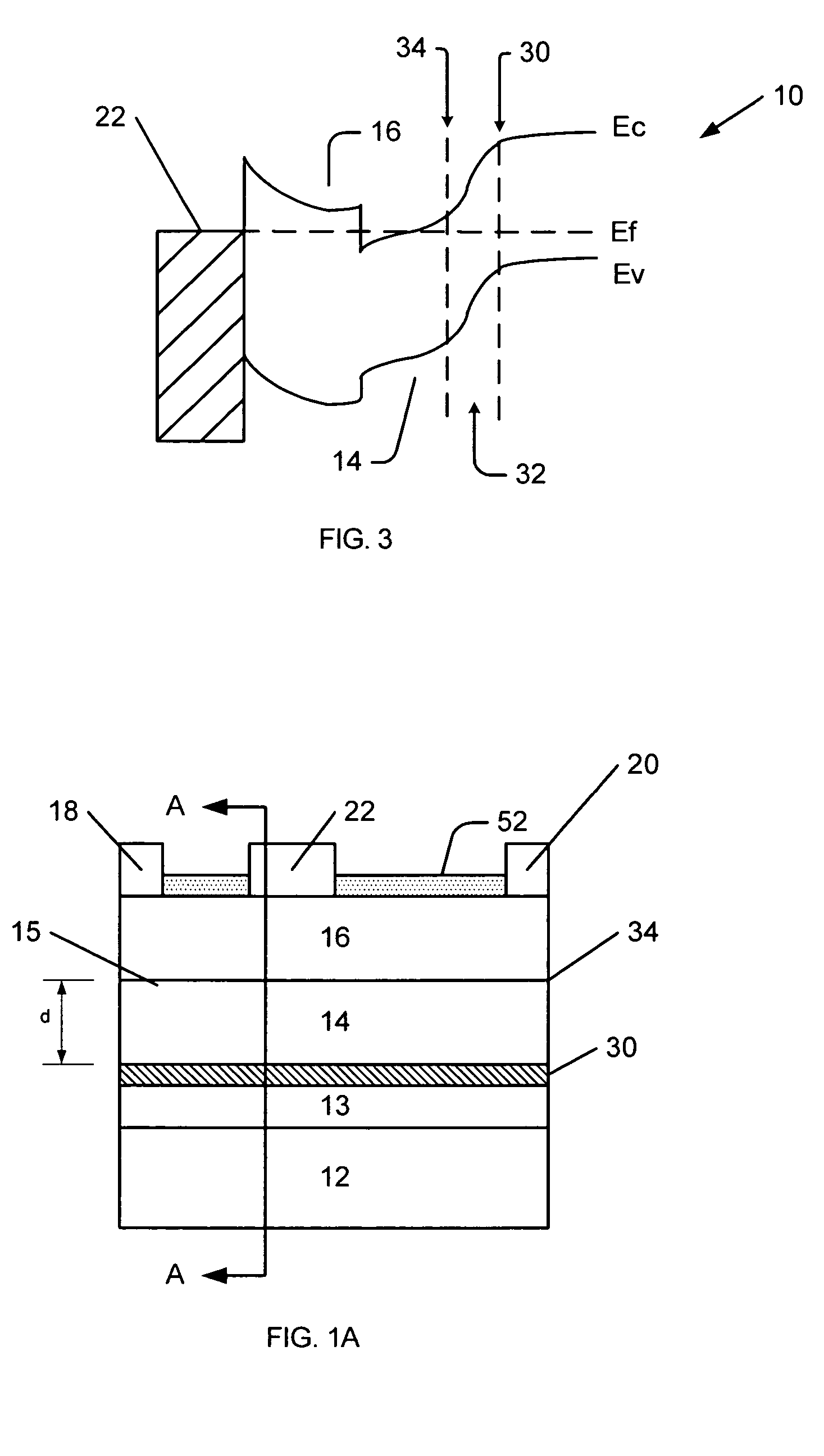
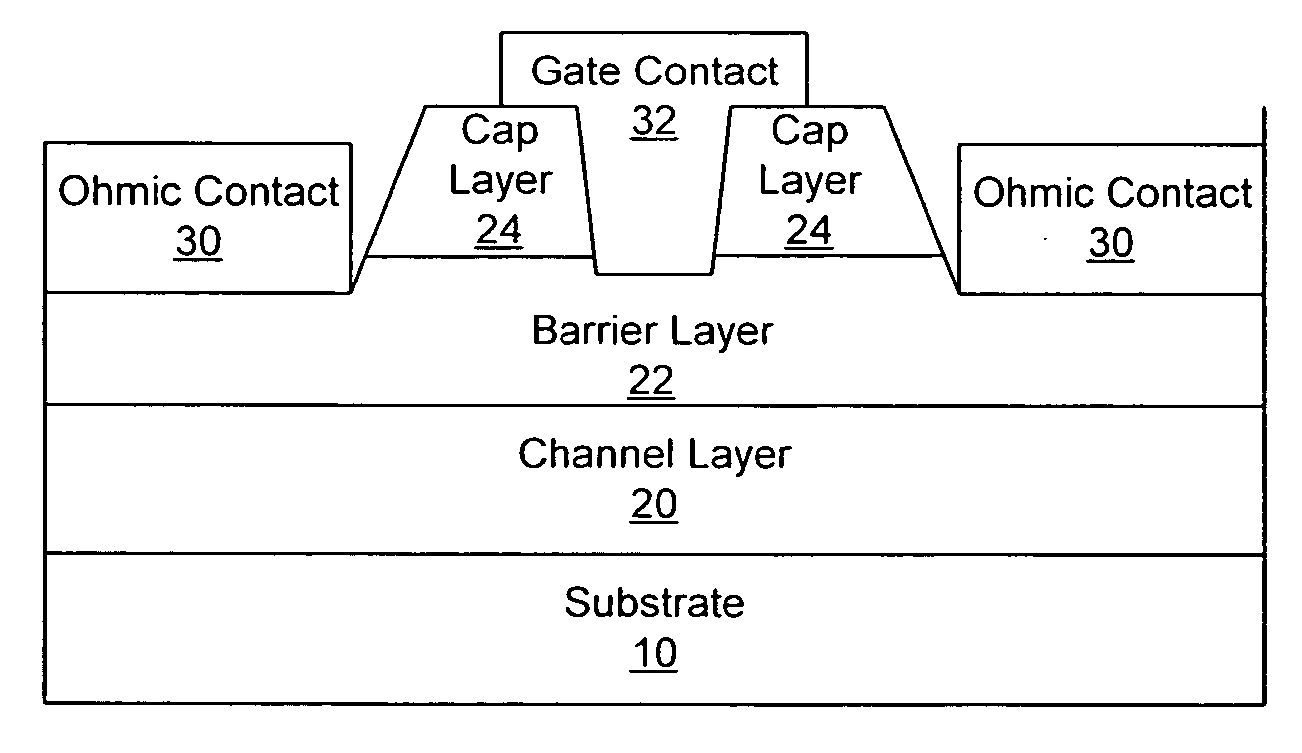
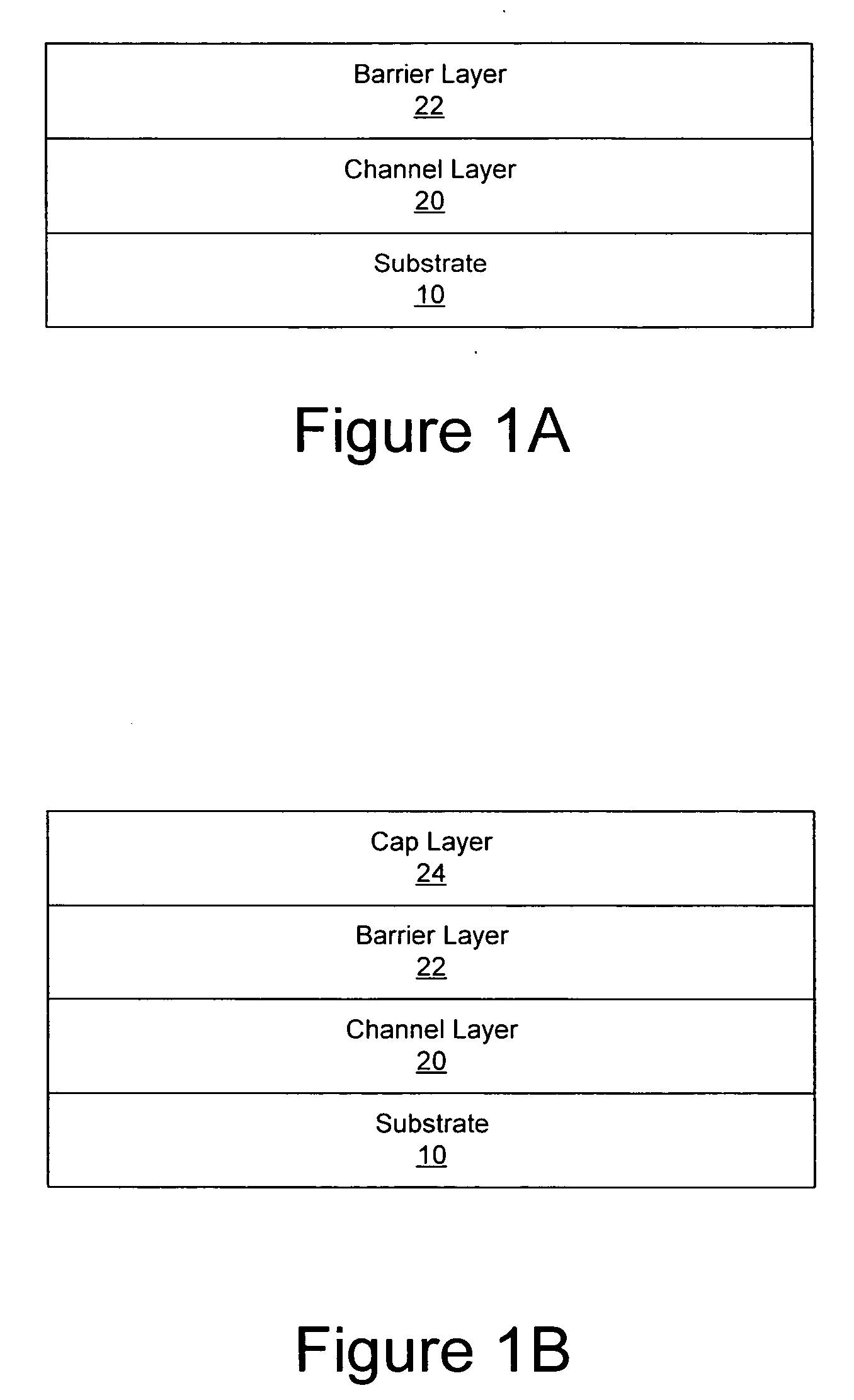
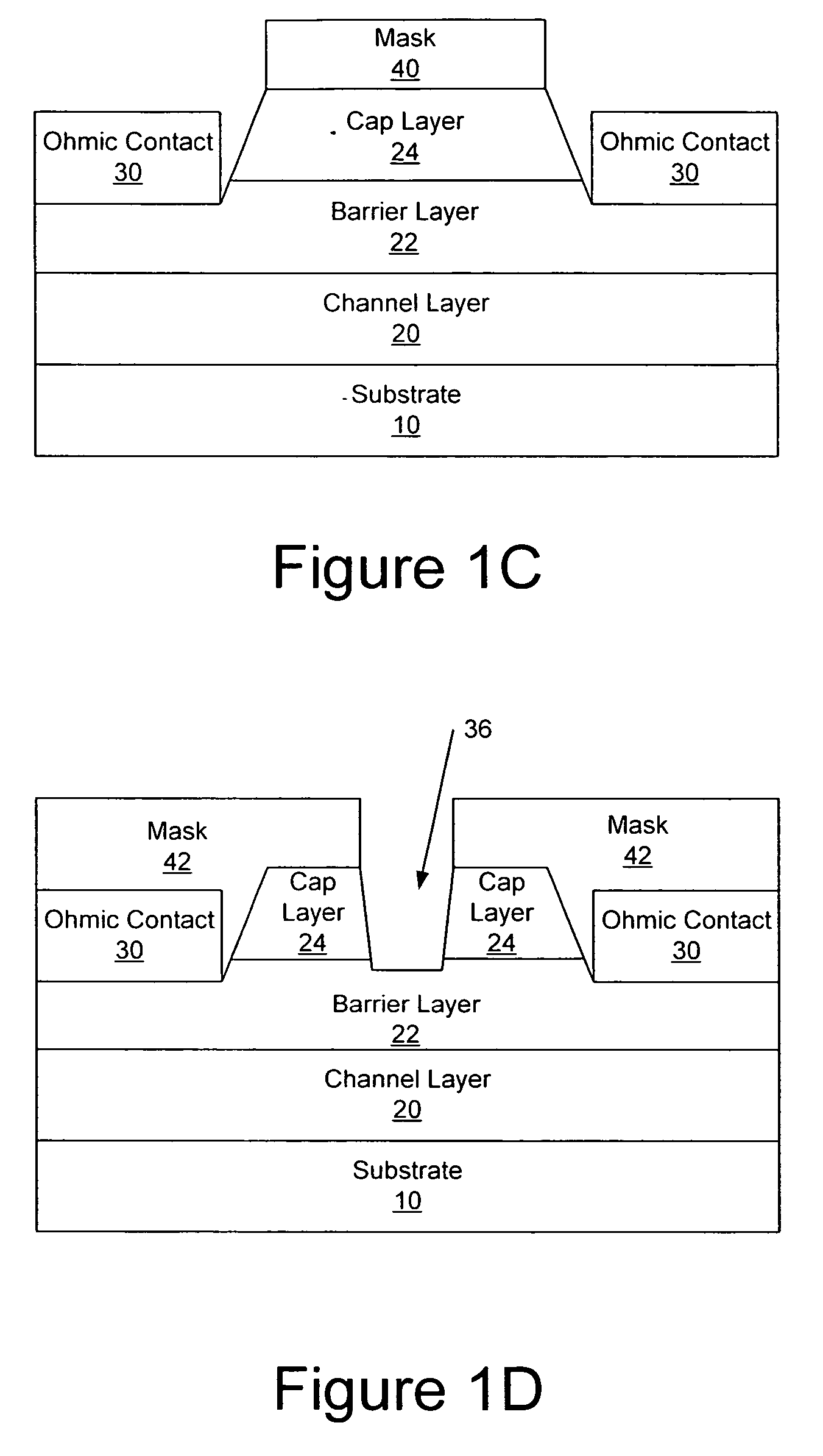
Transistor fabrication includes forming a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, forming a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact recess in the barrier layer to expose a contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact layer on the exposed contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, for example, using a low temperature deposition process, forming an ohmic contact on the contact layer and forming a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) and methods of fabricating a HEMT are also provided. The HEMT includes a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, a contact recess in the barrier layer that extends into the channel layer, an n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region on the nitride-based channel layer in the contact recess, an ohmic contact on the nitride-based contact region and a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. The n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region and the nitride-based channel layer include a surface area enlargement structure.
Owner:CREE INC
Silicon carbide based field effect gas sensor for high temperature applications
InactiveUS20180011052A1Change electrical propertiesLong-term reliable operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactSemiconductor structure
A field effect gas sensor, for detecting a presence of a gaseous substance in a gas mixture, the field effect gas sensor comprising: a SiC semiconductor structure; an electron insulating layer covering a first portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; a first contact structure at least partly separated from the SiC semiconductor structure by the electron insulating layer; and a second contact structure conductively connected to a second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure, wherein at least one of the electron insulating layer and the first contact structure is configured to interact with the gaseous substance to change an electrical property of the SiC semiconductor structure; and wherein the second contact structure comprises: an ohmic contact layer in direct contact with the second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; and a barrier layer formed by an electrically conducting mid-transition-metal oxide covering the ohmic contact layer.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100032665A1Easy to makeGuaranteed high speed operationTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesOhmic contactCharge carrier
An embodiment is to include a staggered (top gate structure) thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used as a semiconductor layer and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and a source and drain electrode layers. The buffer layer having higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer is provided intentionally between the source and drain electrode layers and the semiconductor layer, whereby an ohmic contact is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods of fabricating nitride-based transistors with a cap layer and a recessed gate
ActiveUS7238560B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactNitride
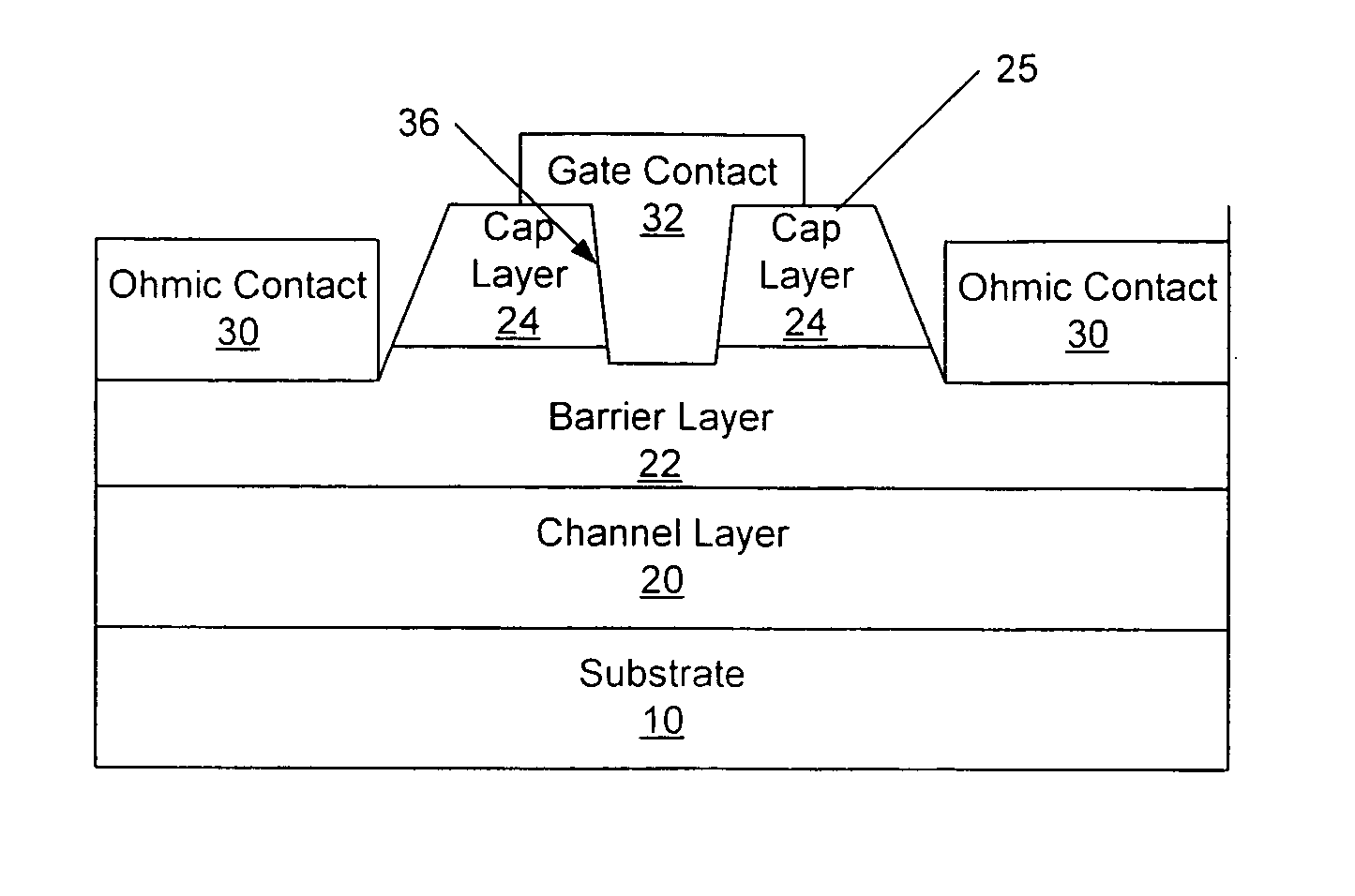
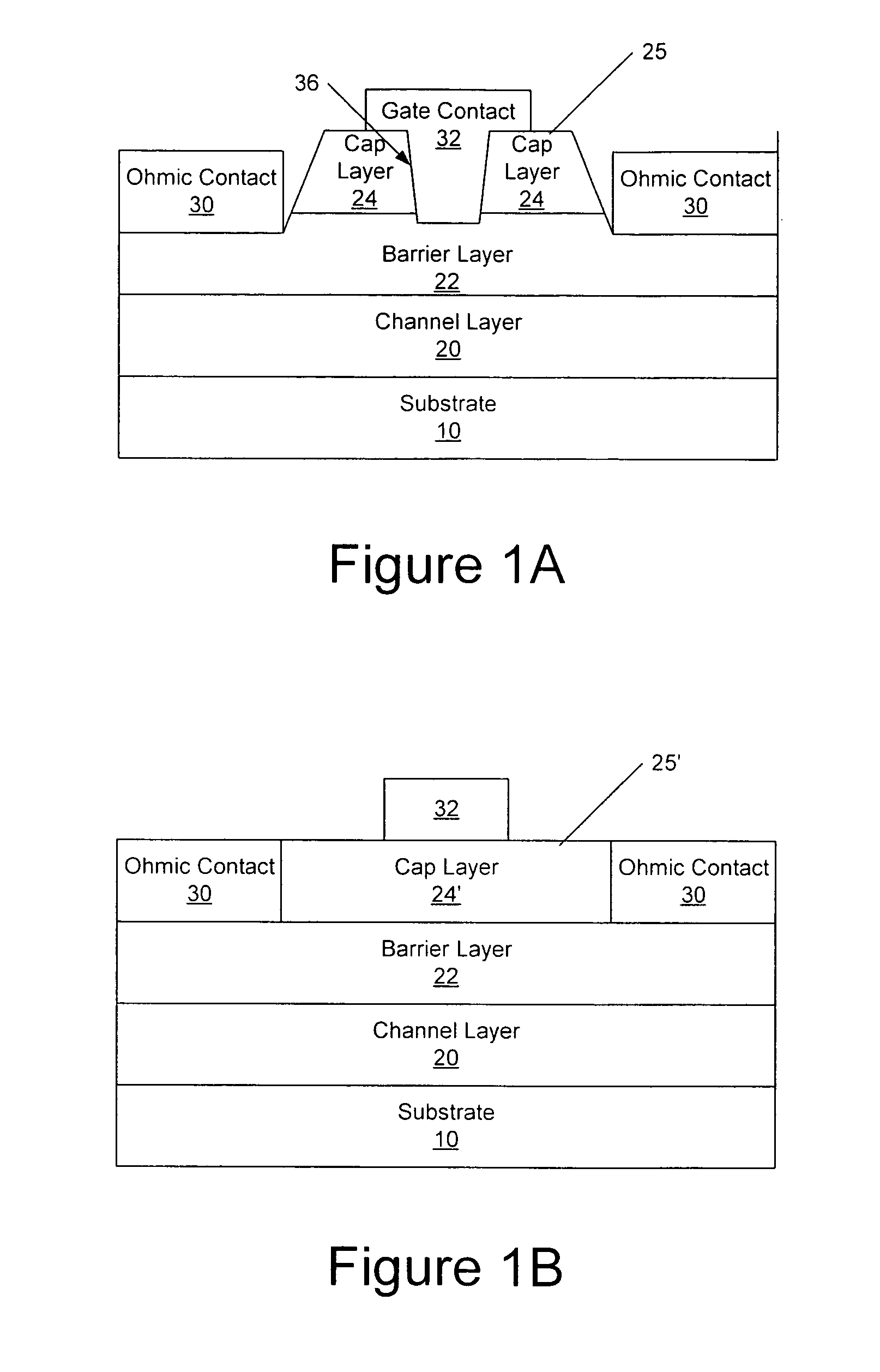
An anneal of a gate recess prior to formation of a gate contact, such as a Schottky contact, may reduce gate leakage and / or provide a high quality gate contact in a semiconductor device, such as a transistor. The use of an encapsulation layer during the anneal may further reduce damage to the semiconductor in the gate recess of the transistor. The anneal may be provided, for example, by an anneal of ohmic contacts of the device. Thus, high quality gate and ohmic contacts may be provided with reduced degradation of the gate region that may result from providing a recessed gate structure as a result of etch damage in forming the recess.
Owner:CREE INC
Flip-chip electrode light-emitting element formed by multilayer coatings
InactiveUS20060081869A1High reflective functionLuminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesInter layerOhmic contact
A flip-chip electrode light-emitting element formed by multilayer coatings where a translucent conducting layer and a highly reflective metal layer acts as flip-chip electrode for enhancing the LED luminous efficiency. The flip-chip electrode light-emitting element includes a translucent substrate, a semiconductor die structure attached on the translucent substrate and made of group III nitride compounds, and an intermediate layer adapted to support the inverted semiconductor die structure on a submount. The flip-chip electrode formed by multiplayer coatings includes a current-spreading transparent conducting layer formed on a top side of the second type semiconductor layer, a highly reflective metal layer formed on a top side of the transparent conducting layer, a metallic diffusion barrier layer formed on a top side of the highly reflective metal layer, and a bonding layer electrically coupled to the intermediate layer and formed on a top side of the barrier layer. Moreover, an ohmic contact layer is formed on the transparent conducting layer. And a passivation layer encloses the die structure for insulating p / n interface and for avoiding the creation of the leakage current.
Owner:ARIMA OPTOELECTRONICS
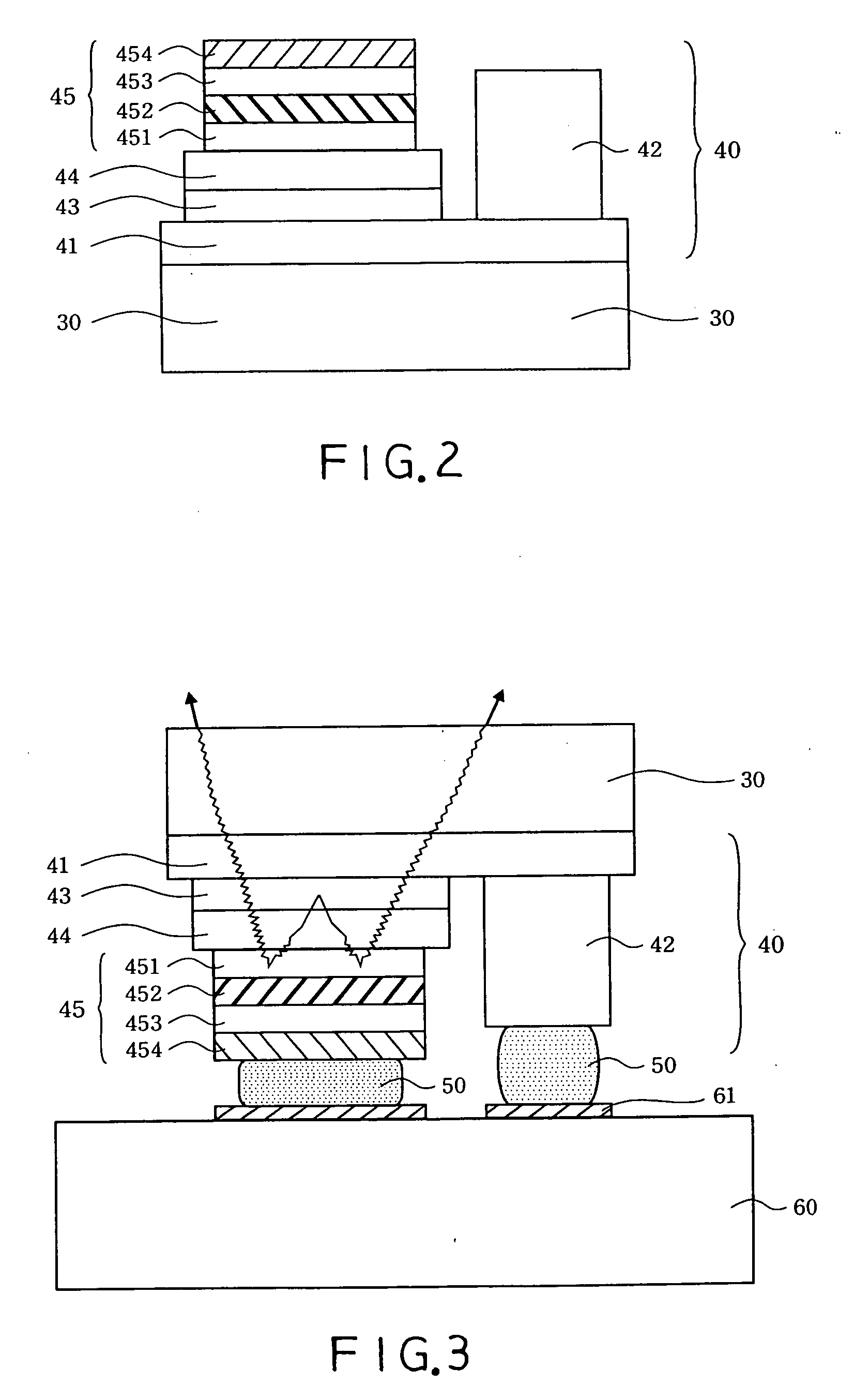
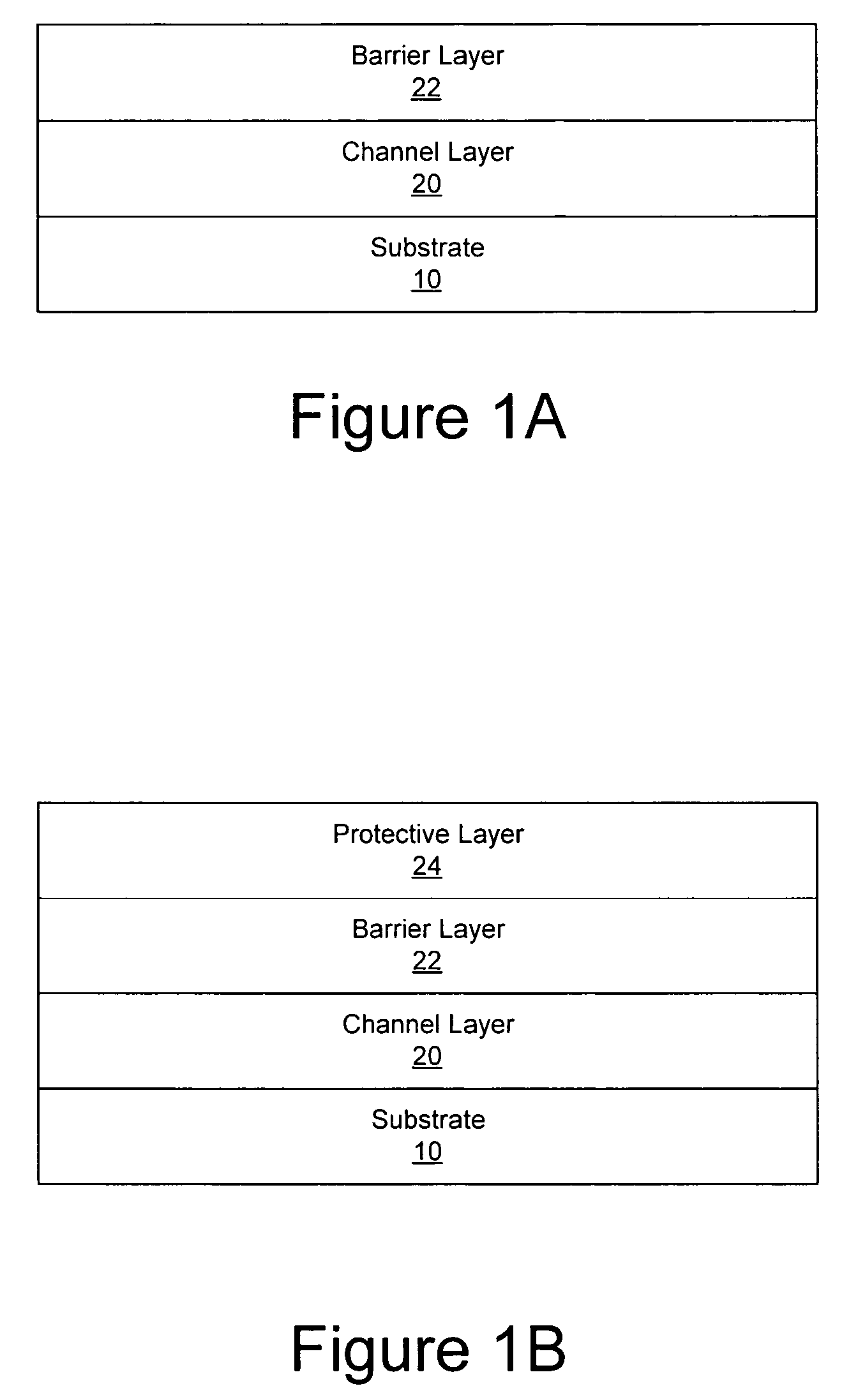
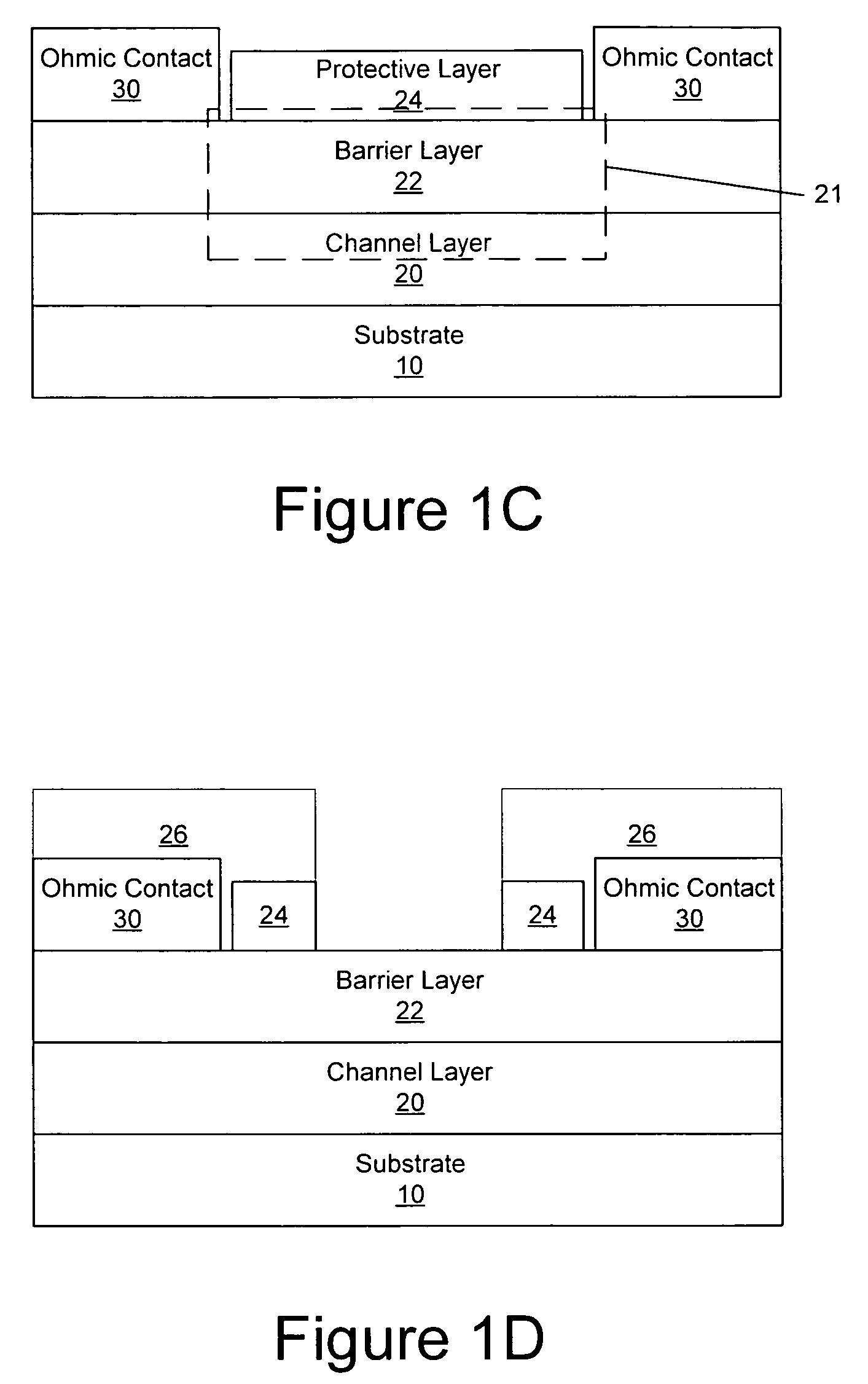
Nitride-based transistors with a protective layer and a low-damage recess and methods of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7045404B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactNitride
Transistors are fabricated by forming a nitride-based semiconductor barrier layer on a nitride-based semiconductor channel layer and forming a protective layer on a gate region of the nitride-based semiconductor barrier layer. Patterned ohmic contact metal regions are formed on the barrier layer and annealed to provide first and second ohmic contacts. The annealing is carried out with the protective layer on the gate region. A gate contact is also formed on the gate region of the barrier layer. Transistors having protective layer in the gate region are also provided as are transistors having a barrier layer with a sheet resistance substantially the same as an as-grown sheet resistance of the barrier layer.
Owner:CREE INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100025679A1Small currentHigh on-off ratioStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesOhmic contactCharge carrier
An embodiment is to include an inverted staggered (bottom gate structure) thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used as a semiconductor layer and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and a source and drain electrode layers. The buffer layer having higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer is provided intentionally between the source and drain electrode layers and the semiconductor layer, whereby an ohmic contact is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100032668A1Easy to makeGuaranteed high speed operationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierOhmic contact
An embodiment is to include a staggered (top gate structure) thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used as a semiconductor layer and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and a source and drain electrode layers. A metal oxide layer having higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer is provided intentionally as the buffer layer between the source and drain electrode layers and the semiconductor layer, whereby an ohmic contact is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Field-effect transistor and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060273347A1Small gateHigh currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactOptoelectronics
An AlN buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer, an undoped AlGaN layer, a p-type GaN layer and a heavily doped p-type GaN layer are formed in this order. A gate electrode forms an Ohmic contact with the heavily doped p-type GaN layer. A source electrode and a drain electrode are provided on the undoped AlGaN layer. A pn junction is formed in a gate region by a two dimensional electron gas generated at an interface between the undoped AlGaN layer and the undoped GaN layer and the p-type GaN layer, so that a gate voltage can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Nitride heterojunction transistors having charge-transfer induced energy barriers and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050173728A1Affect performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionElectron source
A nitride-based field effect transistor includes a substrate, a channel layer comprising InAlGaN formed on the substrate, source and drain ohmic contacts in electrical communication with the channel layer, and a gate contact formed on the channel layer. At least one energy barrier opposes movement of carriers away from the channel layer. The energy barrier may comprise an electron source layer in proximity with a hole source layer which generate an associated electric field directed away from the channel. An energy barrier according to some embodiments may provide a built-in potential barrier in excess of about 0.5 eV. Method embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CREE INC
Cap layers and/or passivation layers for nitride-based transistors, transistor structures and methods of fabricating same
ActiveUS20060108606A1Increase concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactHigh electron
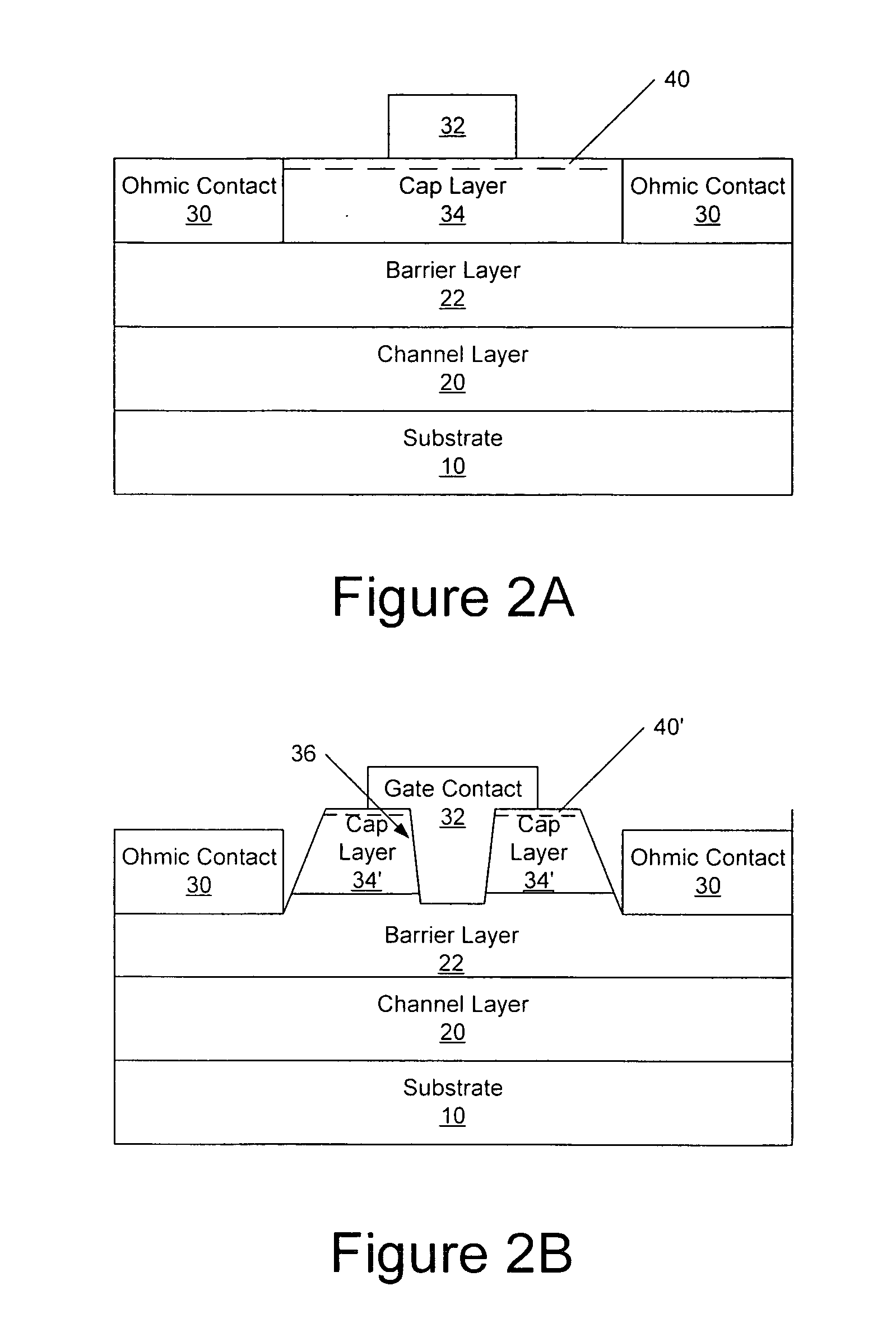
High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a non-uniform aluminum concentration AlGaN based cap layer having a high aluminum concentration adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a cap layer having a doped region adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. Graphitic BN passivation structures for wide bandgap semiconductor devices are provided. SiC passivation structures for Group III-nitride semiconductor devices are provided. Oxygen anneals of passivation structures are also provided. Ohmic contacts without a recess are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100025676A1Small amount of photocurrentReduce parasitic capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge carrierOhmic contact
To offer a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor having excellent characteristics and high reliability and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device without variation. The summary is to include an inverted-staggered (bottom-gate structure) thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used for a semiconductor layer and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and source and drain electrode layers. An ohmic contact is formed by intentionally providing a buffer layer containing In, Ga, and Zn and having a higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer between the semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrode layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods of fabricating nitride-based transistors with a cap layer and a recessed gate
ActiveUS20060019435A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactDevice material
An anneal of a gate recess prior to formation of a gate contact, such as a Schottky contact, may reduce gate leakage and / or provide a high quality gate contact in a semiconductor device, such as a transistor. The use of an encapsulation layer during the anneal may further reduce damage to the semiconductor in the gate recess of the transistor. The anneal may be provided, for example, by an anneal of ohmic contacts of the device. Thus, high quality gate and ohmic contacts may be provided with reduced degradation of the gate region that may result from providing a recessed gate structure as a result of etch damage in forming the recess.
Owner:CREE INC
Method of preparing solar cell front contacts
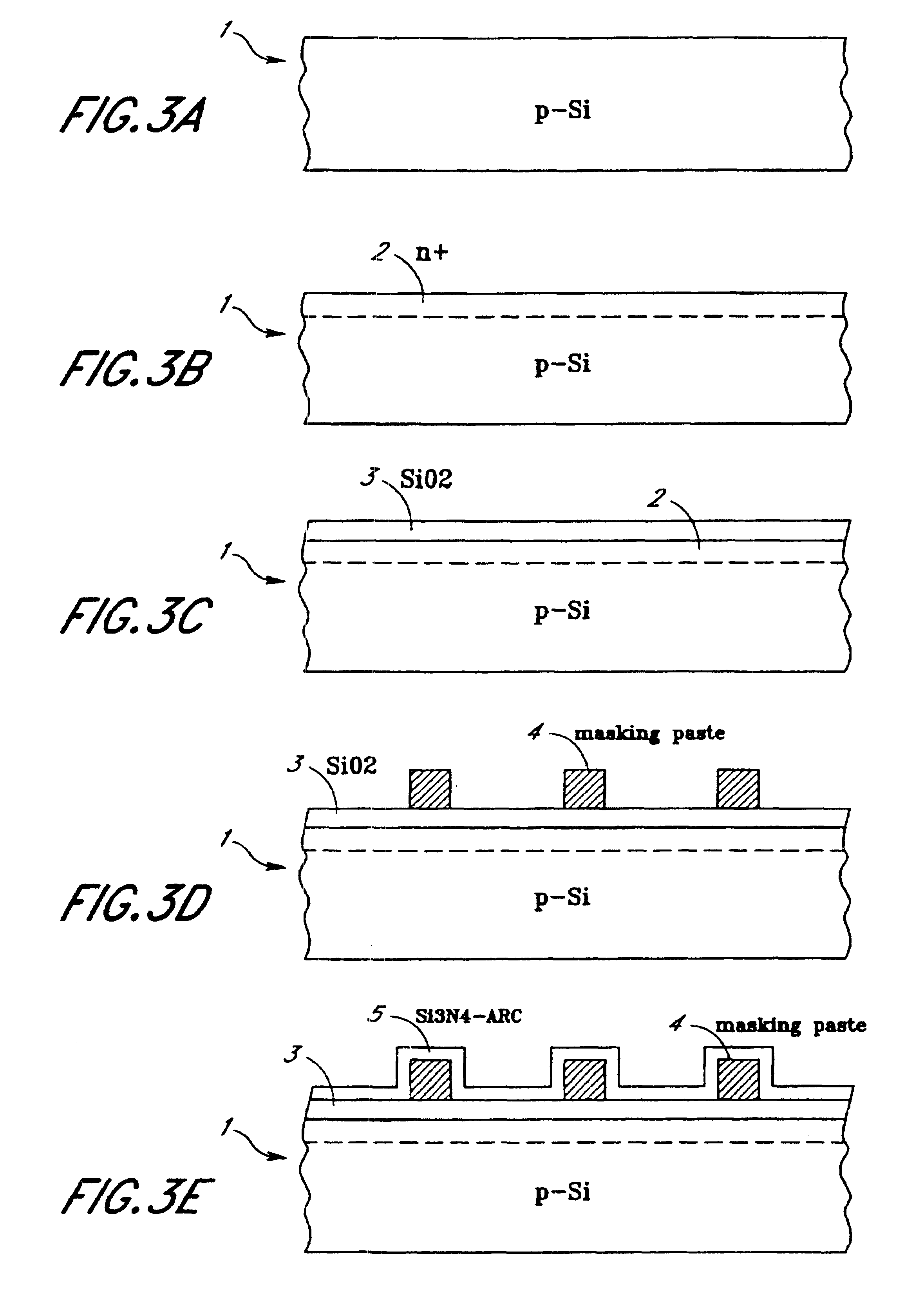
InactiveUSRE37512E1Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove barrier propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationScreen printingOhmic contact
Method of preparing on a solar cell the top contact pattern which consists of a set of parallel narrow finger lines and wide collector lines deposited essentially at right angles to the finger lines on the semiconductor substrate, characterized in that it comprises at least the following steps:(a) screen printing and drying the set of contact finger lines;(b) printing and drying the wide collector lines on the top of the set of finger lines in a subsequent step;(c) firing both finger lines and collector lines in a single final step in order to form an ohmic contact between the finger lines and the semiconductor substrate and between the finger lines and the wide collector lines.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Flip-chip light emitting diode
InactiveUS20050087884A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactLight-emitting diode
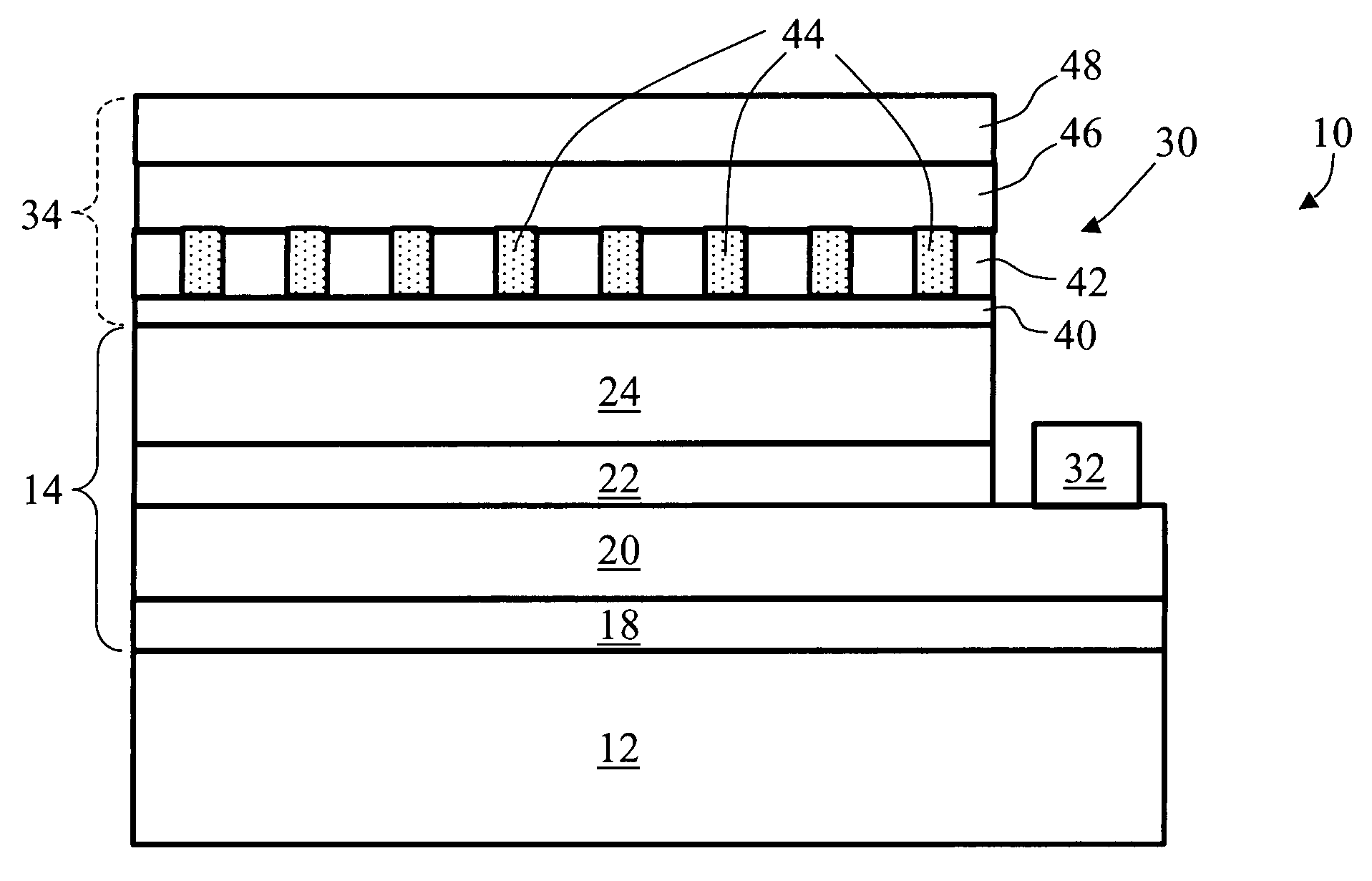
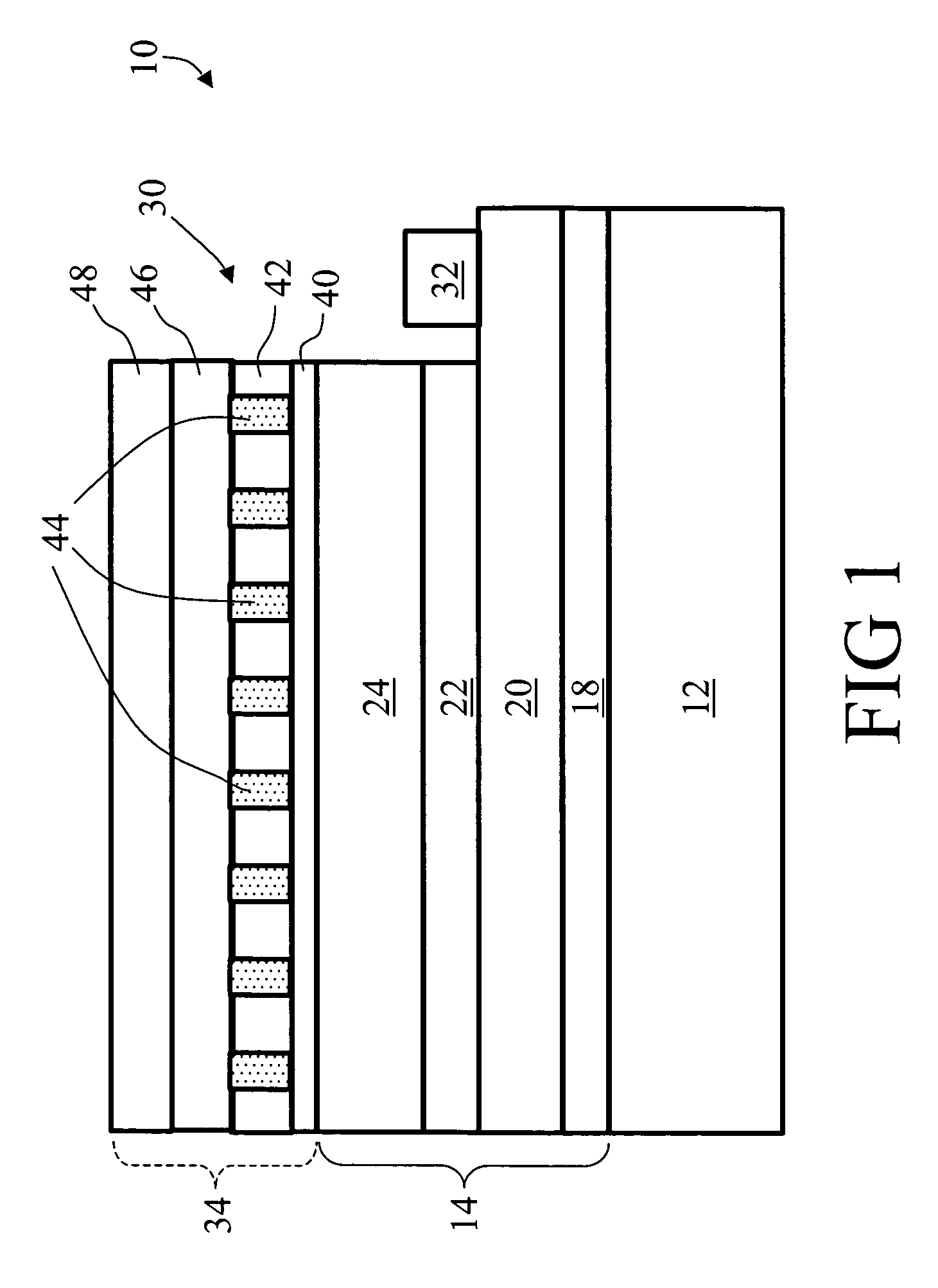
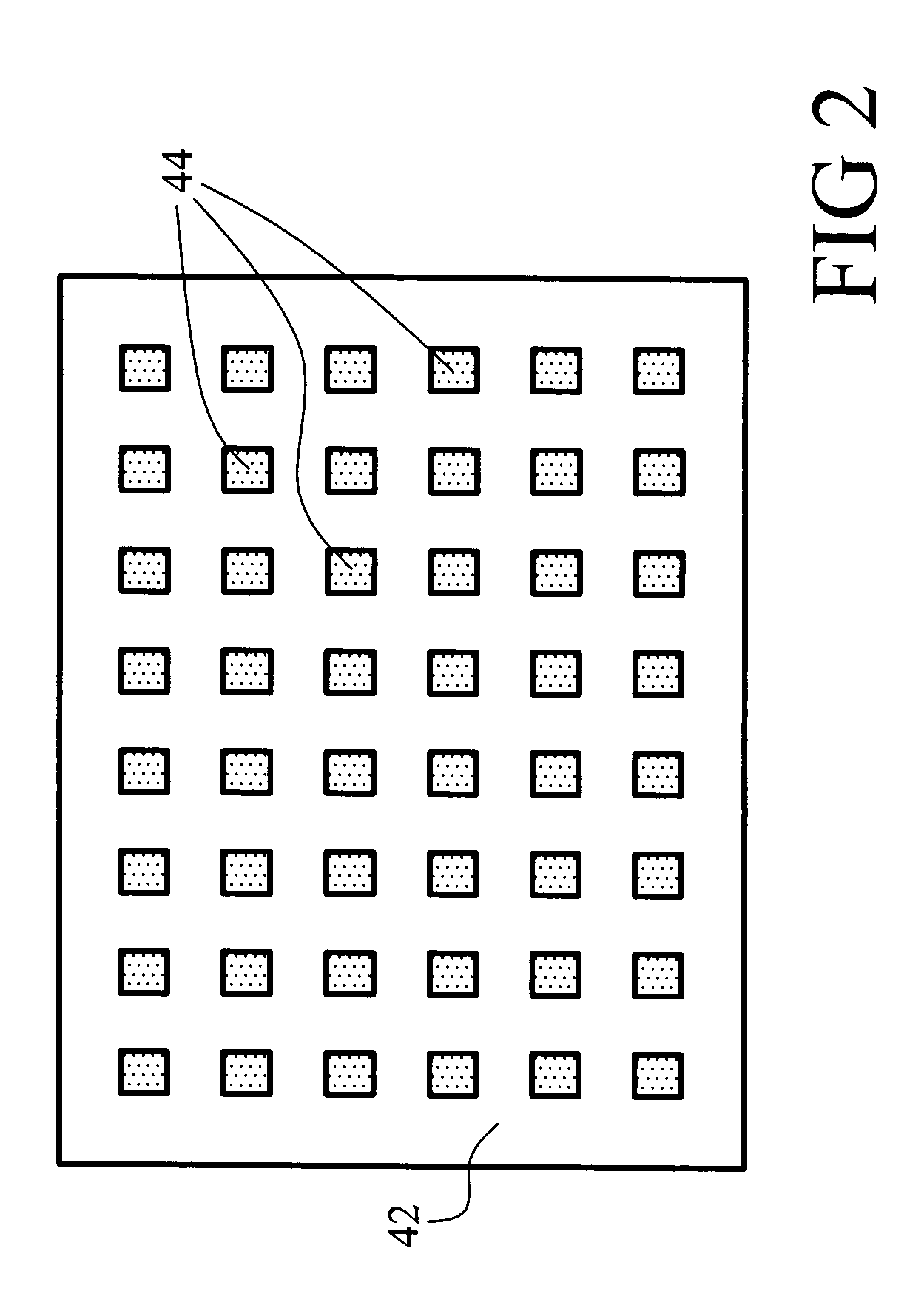
A flip chip light emitting diode die (10, 10′, 10″) includes a light-transmissive substrate (12, 12′, 12″) and semiconductor layers (14, 14′, 14″) that are selectively patterned to define a device mesa (30, 30′, 30″). A reflective electrode (34, 34′, 34″) is disposed on the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″). The reflective electrode (34, 34′, 34″) includes a light-transmissive insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) disposed over the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″), an ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62) disposed at openings of the insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) and making ohmic contact with the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″), and an electrically conductive reflective film (46, 46′, 46″) disposed over the insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) and the ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62). The electrically conductive reflective film (46, 46′, 46″) electrically communicates with the ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62).
Owner:GELCORE LLC (US)
Flip-chip light emitting diode
InactiveUS7119372B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactLight-emitting diode
A flip chip light emitting diode die (10, 10′, 10″) includes a light-transmissive substrate (12, 12′, 12″) and semiconductor layers (14, 14′, 14″) that are selectively patterned to define a device mesa (30, 30′, 30″). A reflective electrode (34, 34′, 34″) is disposed on the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″). The reflective electrode (34, 34′, 34″) includes a light-transmissive insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) disposed over the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″), an ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62) disposed at openings of the insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) and making ohmic contact with the device mesa (30, 30′, 30″), and an electrically conductive reflective film (46, 46′, 46″) disposed over the insulating grid (42, 42′, 60, 80) and the ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62). The electrically conductive reflective film (46, 46′, 46″) electrically communicates with the ohmic material (44, 44′, 44″, 62).
Owner:GELCORE LLC (US)
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20060273335A1Good ohmic contactReduce contact resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactLength wave
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a semiconductor light emitting portion having a first contact layer of a first conductivity, a second contact layer of a second conductivity and an active layer sandwiched between the first and second contact layers. The device further includes a transparent electrode which substantially entirely covers a surface of the second contact layer in ohmic contact with the surface of the second contact layer and is transparent to a wavelength of light emitted from the semiconductor light emitting portion, and a metal reflection film which is opposed to substantially the entire surface of the transparent electrode and electrically connected to the transparent electrode, and reflects the light emitted from the semiconductor light emitting portion and passing through the transparent electrode toward the semiconductor light emitting portion.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method for manufacturing thin film transistor array panel for liquid crystal display
Simplified method of manufacturing liquid crystal displays. A gate wire including a gate line, a gate pad and a gate electrode is formed on the substrate by using the first mask. A gate insulating layer, a semiconductor layer, a ohmic contact layer and a metal layer are sequentially deposited to make a quadruple layers, and patterned by a dry etch of using the second mask. At this time, the quadruple layers is patterned to have a matrix of net shape layout and covering the gate wire. An opening exposing the substrate is formed in the display area and a contact hole exposing the gate pad is formed in the peripheral area. Next, ITO is deposited and a photoresist layer coated on the ITO. Then, the ITO layer is patterned by using the third mask and a dry etch, and the data conductor layer and the ohmic contact layer not covered by the ITO layer is dry etched. After depositing a passivation layer, a opening is formed by using the fourth mask and the exposed semiconductor layer through the opening is etched to separate the semiconductor layer under the adjacent data line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
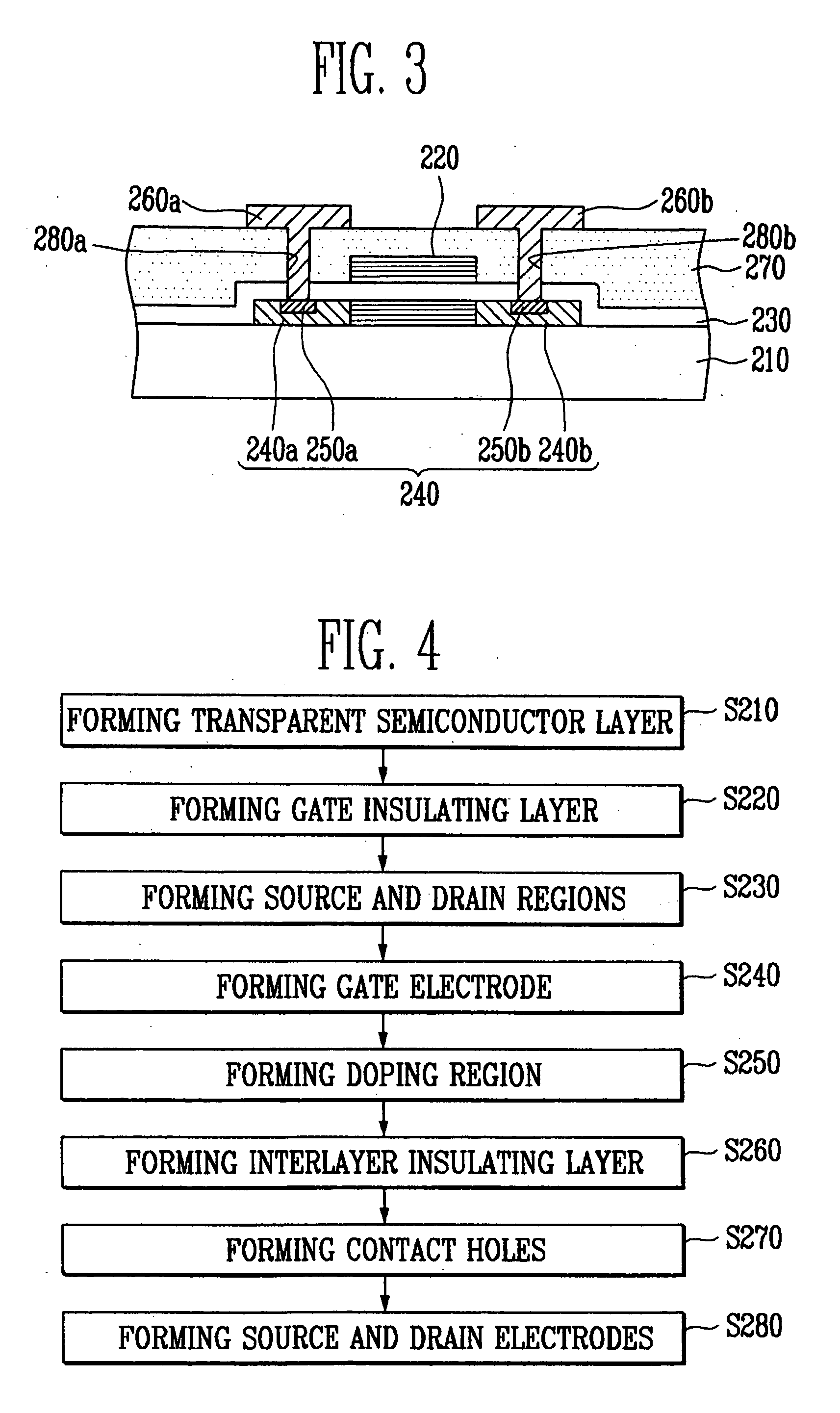
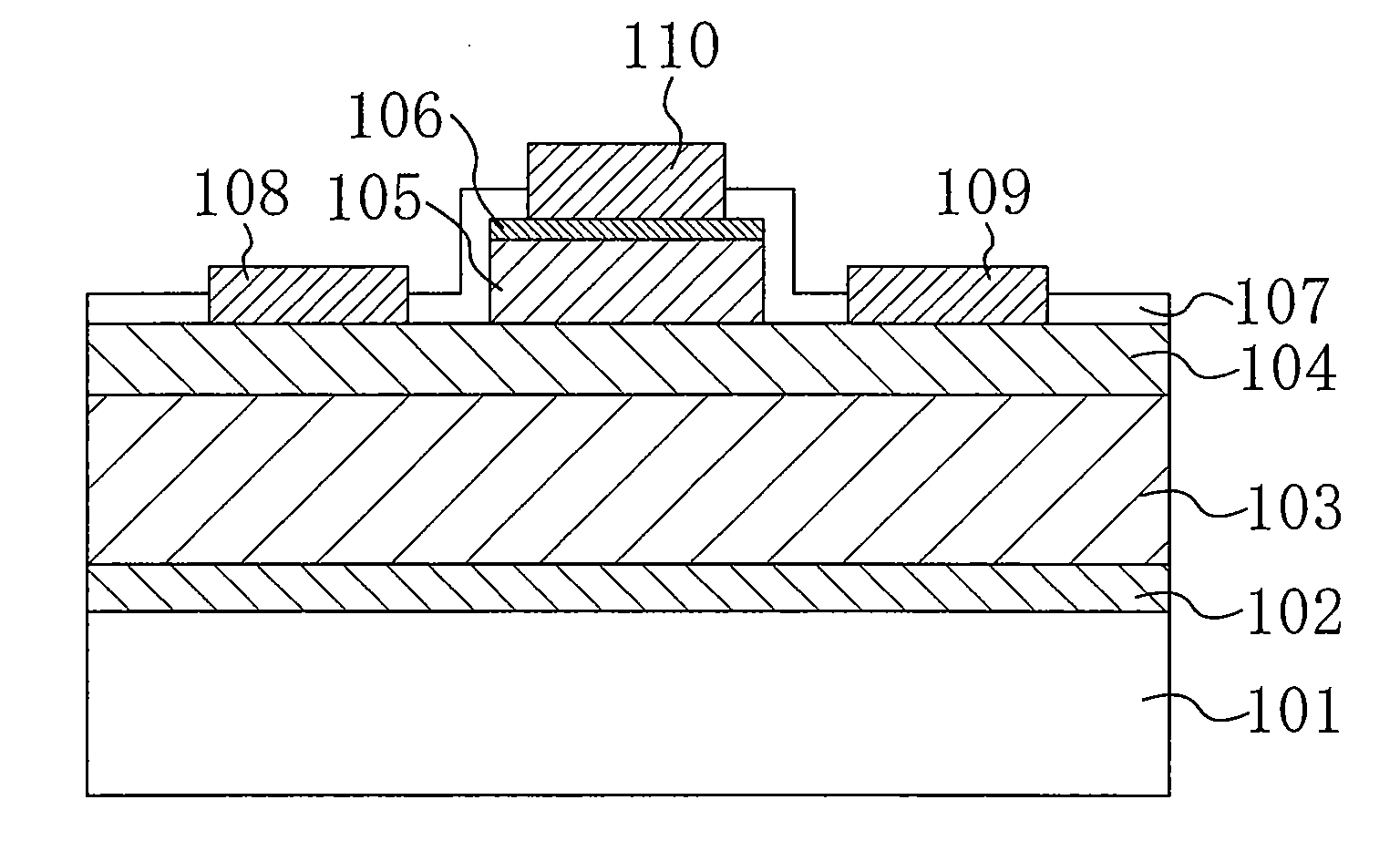
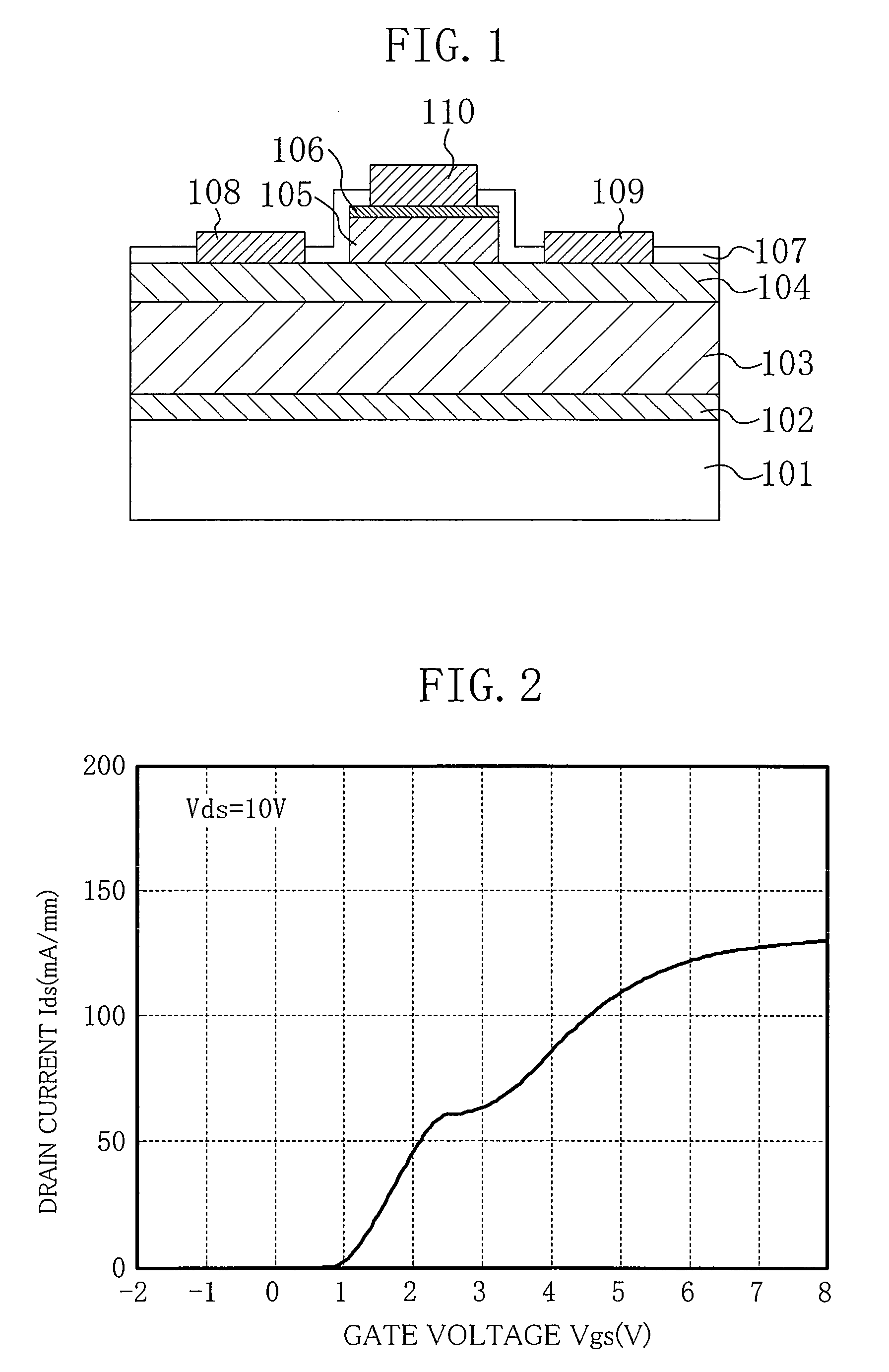
Transparent thin film transistor (TFT) and its method of manufacture
InactiveUS20070069209A1Eliminate the problemGood ohmic contactSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactBiological activation
A transparent thin film transistor (TFT) and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The transparent TFT includes transparent source and drain electrodes formed of transparent material, a transparent semiconductor activation layer that contacts the source and drain electrodes, that is formed of transparent semiconductor, and in which source and drain regions are formed, and a doping section provided between the transparent source and drain electrodes and the transparent activation layer to have the same doping type as that of the source and drain regions and to have doping concentration different from that of the source and drain regions. At this time, doping during the formation of the doping section is performed by an in-situ method in which a gas containing impurities is sprayed in the same apparatus as the apparatus used for the previous step. Therefore, it is possible to reduce high contact resistance generated when the transparent semiconductor activation layer contacts the transparent electrodes and to thus form ohmic contact.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
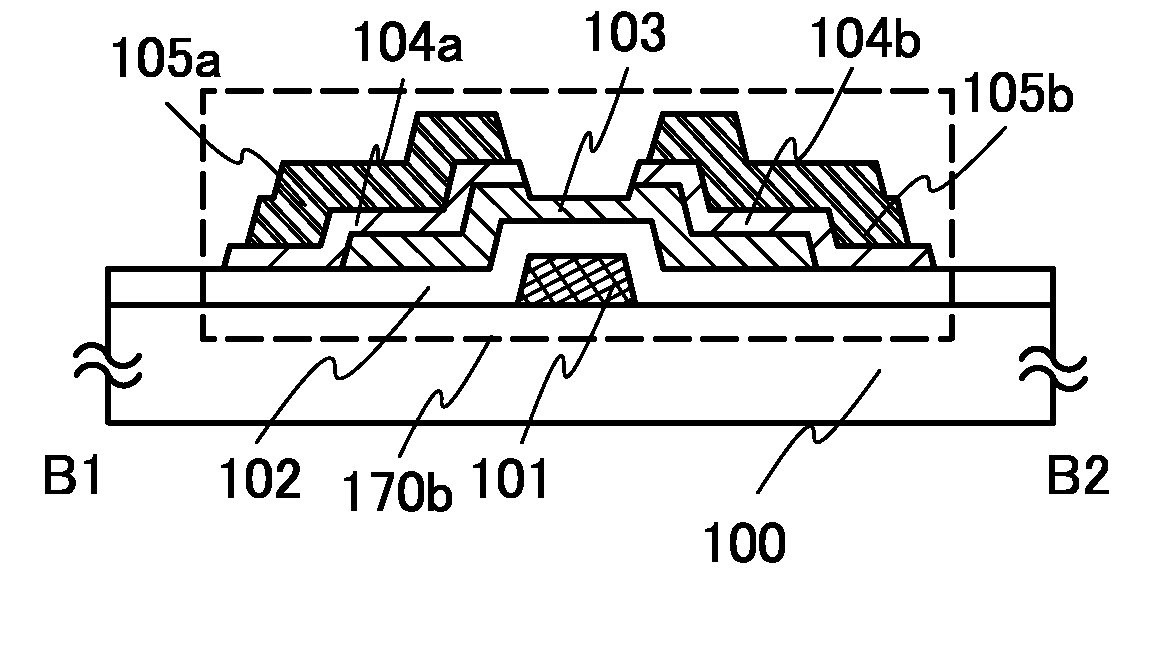
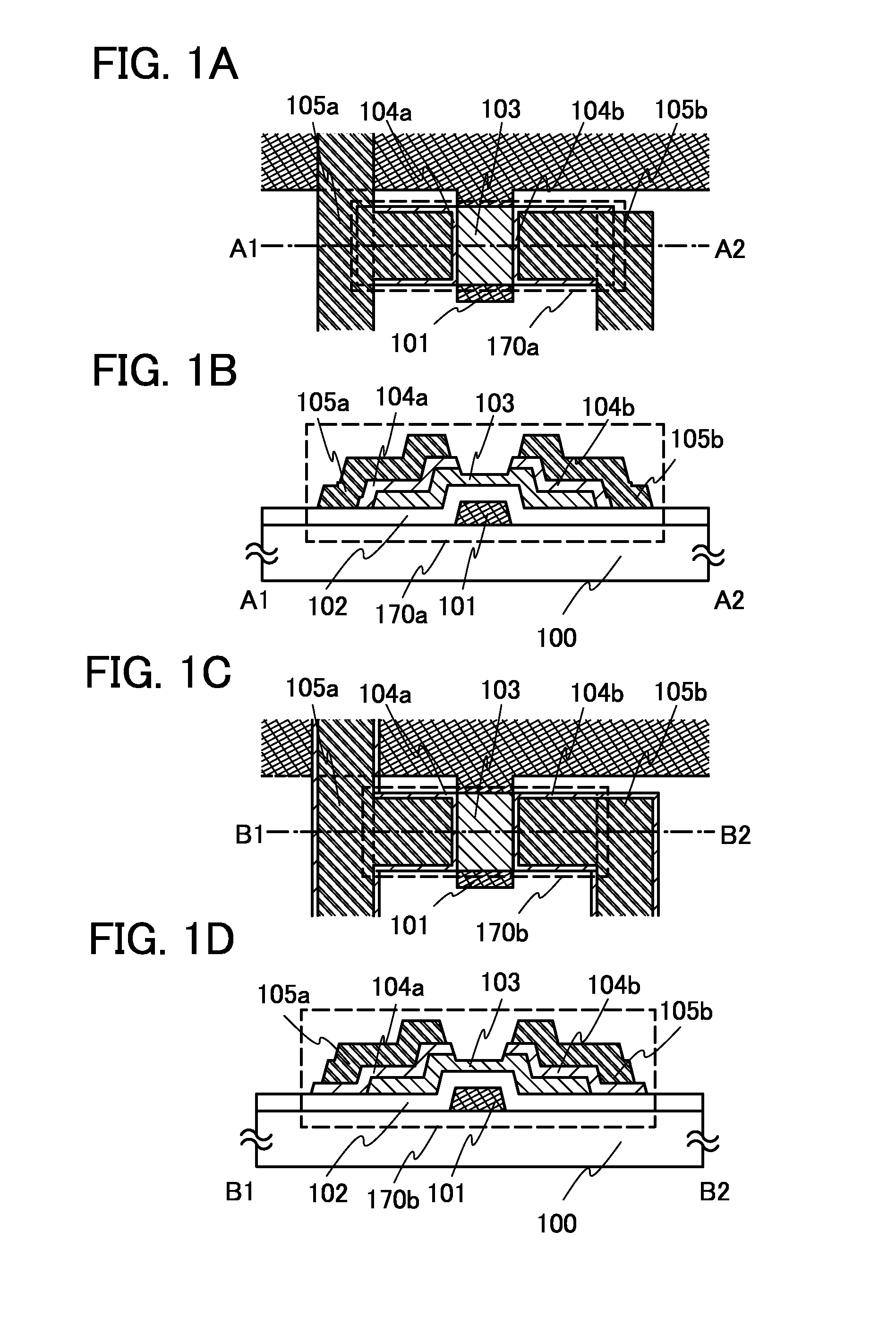
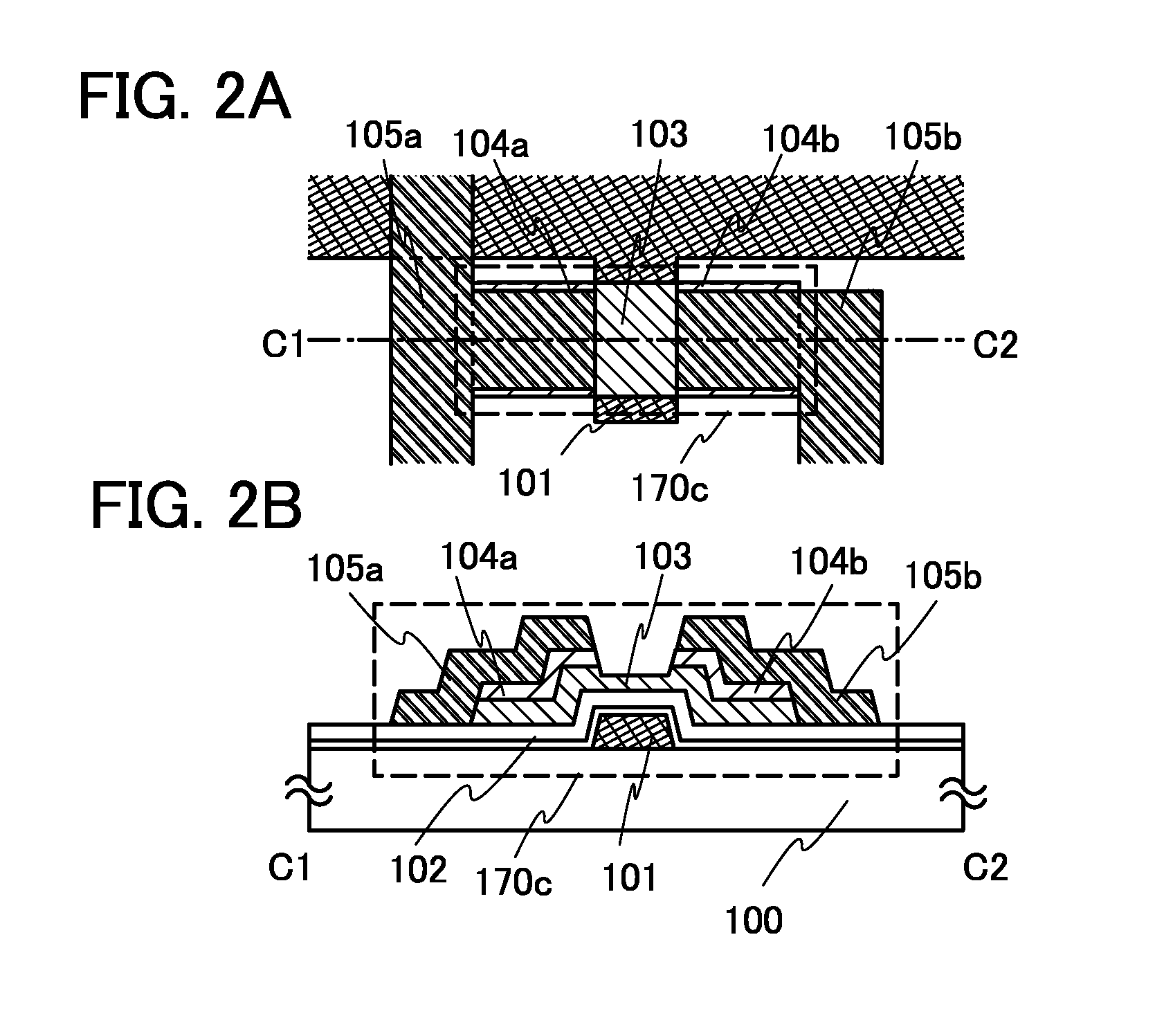
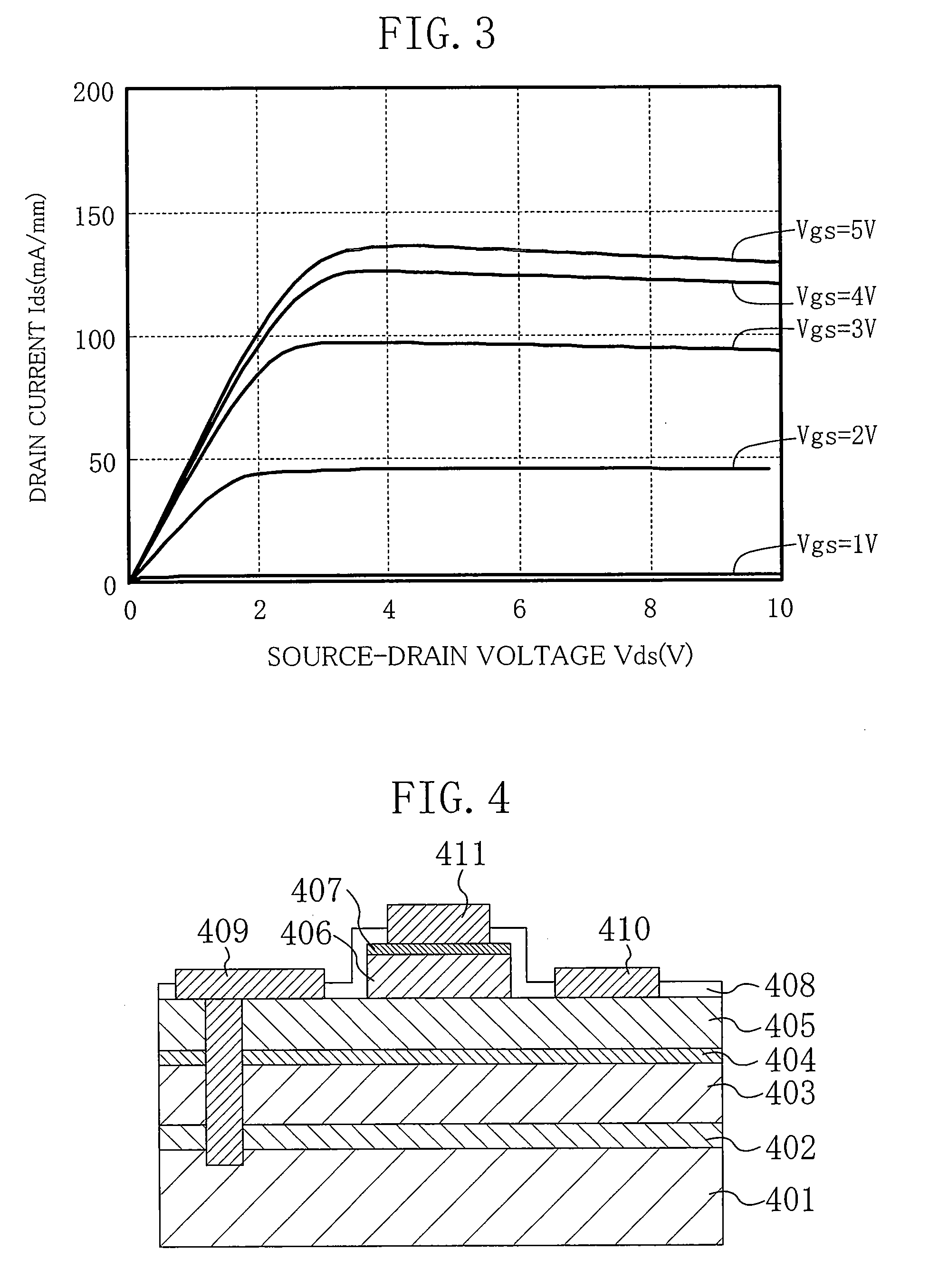
Transistor and method for operating the same
ActiveUS20090121775A1Promote generationIncrease current channelElectronic switchingSemiconductor devicesControl layerOhmic contact
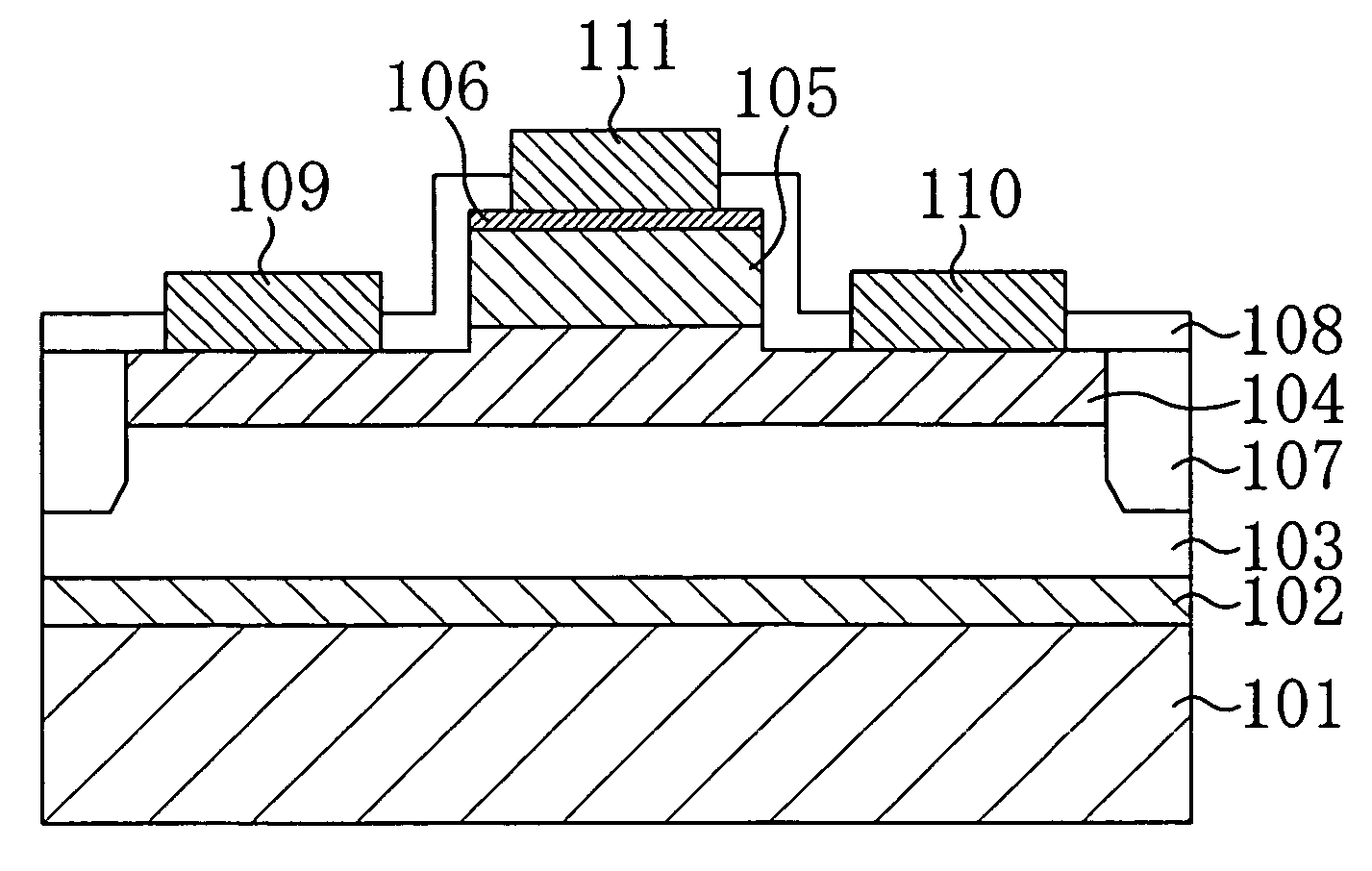
In a transistor, an AlN buffer layer 102, an undoped GaN layer 103, an undoped AlGaN layer 104, a p-type control layer 105, and a p-type contact layer 106 are formed in this order on a sapphire substrate 101. The transistor further includes a gate electrode 110 in ohmic contact with the p-type contact layer 106, and a source electrode 108 and a drain electrode 109 provided on the undoped AlGaN layer 104. By applying a positive voltage to the p-type control layer 105, holes are injected into a channel to increase a current flowing in the channel.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light emiting diodes with current spreading layer
A light-emitting diode (LED) for both AlGaInP- and GaN-based materials needs a good transparent current spreading layer to disseminate electrons or holes from the electrode to the active layer. The present invention utilizes a conductive and transparent ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) thin film with an ultra-thin (to minimize the absorption) composite metallic layer to serve as a good ohmic contact and current spreading layer. The present invention avoids the Schottky contact due to direct deposition of ITO on the semiconductor. For AlGaInP materials, a thick GaP current spreading layer is omitted by the present invention. For GaN-based LEDs with the present invention, semi-transparent Ni / Au contact layer is avoided. Therefore, the light extraction of LED can be dramatically improved by the present invention. Holes may be etched into the semiconductor cladding layer forming a Photonic Band Gap structure to improve LED light extraction.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Nitride semiconductor light emitting diode and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080064133A1Simple electrode structureGood effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactTransmittance
A flip chip-type nitride semiconductor light emitting diode includes a light transmittance substrate, an n-type nitride semiconductor layer, an active layer, a p-type nitride semiconductor layer and a mesh-type DBR reflecting layer. The mesh-type DBR reflecting layer has a plurality of open regions. The mesh-type DBR reflecting layer is composed of first and second nitride layers having different Al content. The first and second nitride layers are alternately stacked several times to form the mesh-type DBR reflecting layer. An ohmic contact layer is formed on the mesh-type DBR reflecting layer and on the p-type nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting diodes with current spreading layer
A light-emitting diode (LED) for both AlGaInP- and GaN-based materials needs a good transparent current spreading layer to disseminate electrons or holes from the electrode to the active layer. The present invention utilizes a conductive and transparent ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) thin film with an ultra-thin (to minimize the absorption) composite metallic layer to serve as a good ohmic contact and current spreading layer. The present invention avoids the Schottky contact due to direct deposition of ITO on the semiconductor. For AlGaInP materials, a thick GaP current spreading layer is omitted by the present invention. For GaN-based LEDs with the present invention, semi-transparent Ni / Au contact layer is avoided. Therefore, the light extraction of LED can be dramatically improved by the present invention. Holes may be etched into the semiconductor cladding layer forming a Photonic Band Gap structure to improve LED light extraction.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Nitride heterojunction transistors having charge-transfer induced energy barriers and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7170111B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionElectron source
A nitride-based field effect transistor includes a substrate, a channel layer comprising InAlGaN formed on the substrate, source and drain ohmic contacts in electrical communication with the channel layer, and a gate contact formed on the channel layer. At least one energy barrier opposes movement of carriers away from the channel layer. The energy barrier may comprise an electron source layer in proximity with a hole source layer which generate an associated electric field directed away from the channel. An energy barrier according to some embodiments may provide a built-in potential barrier in excess of about 0.5 eV. Method embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Trench gate type semiconductor device and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20090272982A1Good ohmic contactExcessive electric field is preventedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETOhmic contact
A method of producing a trench gate type MOSFET is provided in which each intersection trench is formed as a two-stage trench structure. A gate trench is backfilled with a mask material and the mask material is then patterned to form a mask used for forming each intersection trench. The intersection trench intersecting the gate trench is provided so as to be deeper than the gate trench. A Schottky electrode is provided in the bottom of each intersection trench 10p. In this manner, there is provided a trench gate type semiconductor device and a method of producing the same, in which: the cell pitch can be reduced even when a wide band gap semiconductor is used as a main semiconductor substrate; good ohmic contacts can be obtained; and an excessive electric field is prevented from being applied to an insulating film in the bottom of each trench.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com