Patents
Literature
733 results about "Wide-bandgap semiconductor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wide-bandgap semiconductors (also known as WBG semiconductors or WBGSs) are semiconductor materials which have a relatively large band gap compared to conventional semiconductors. Conventional semiconductors like silicon have a bandgap in the range of 1 - 1.5 electronvolt (eV), whereas wide-bandgap materials have bandgaps in the range of 2 - 4 eV. Generally, wide-bandgap semiconductors have electronic properties which fall in between those of conventional semiconductors and insulators.
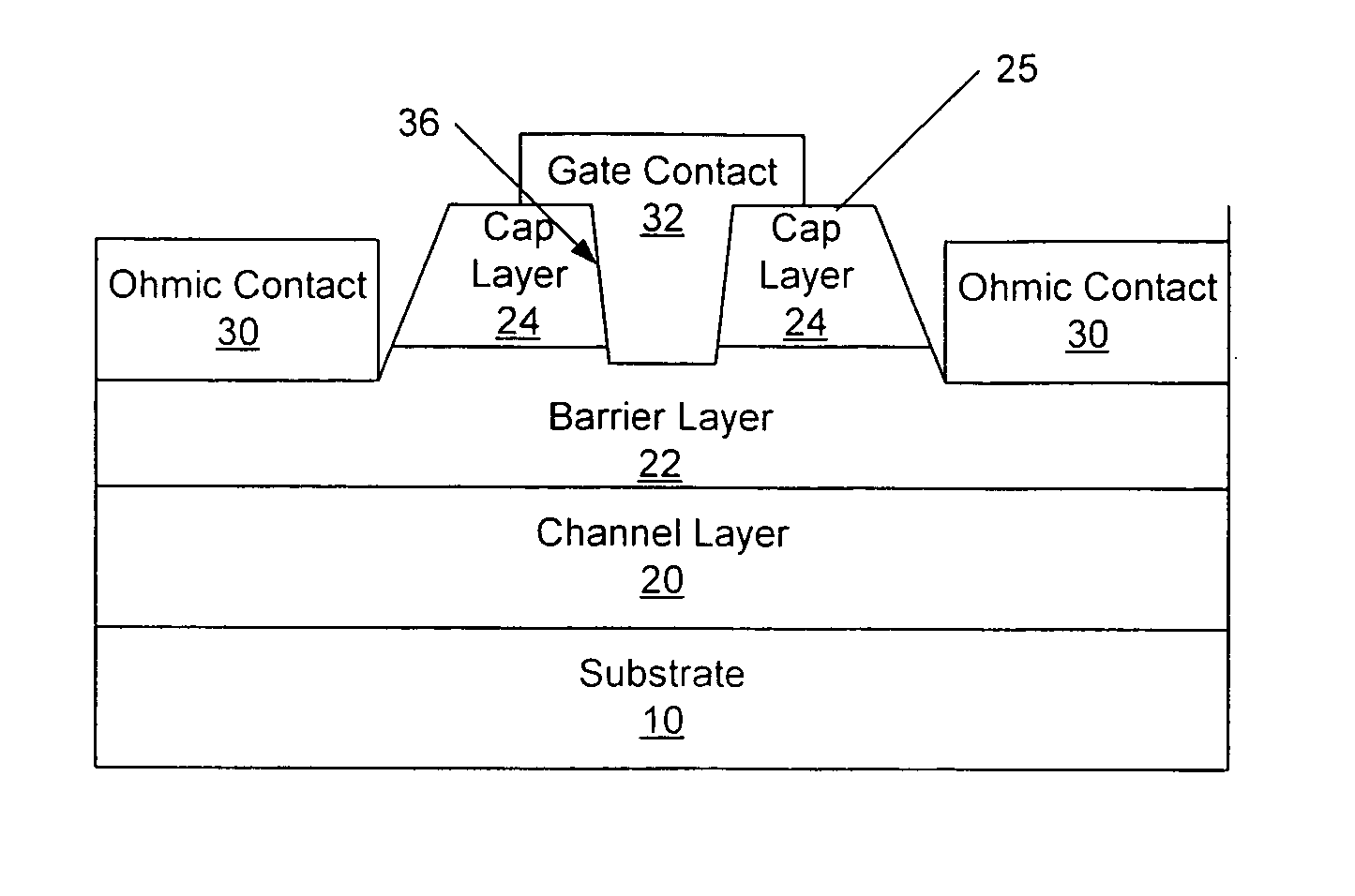
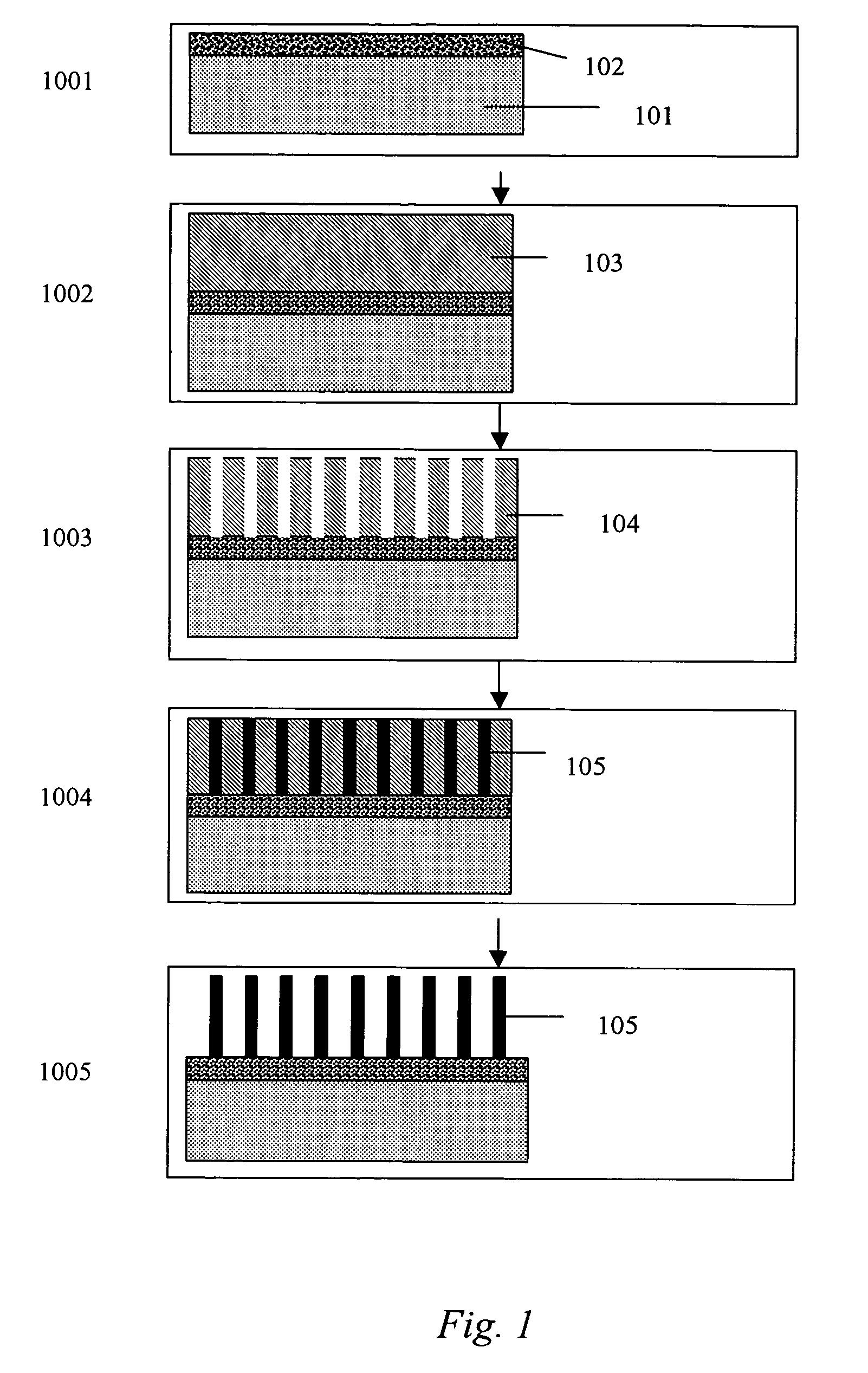
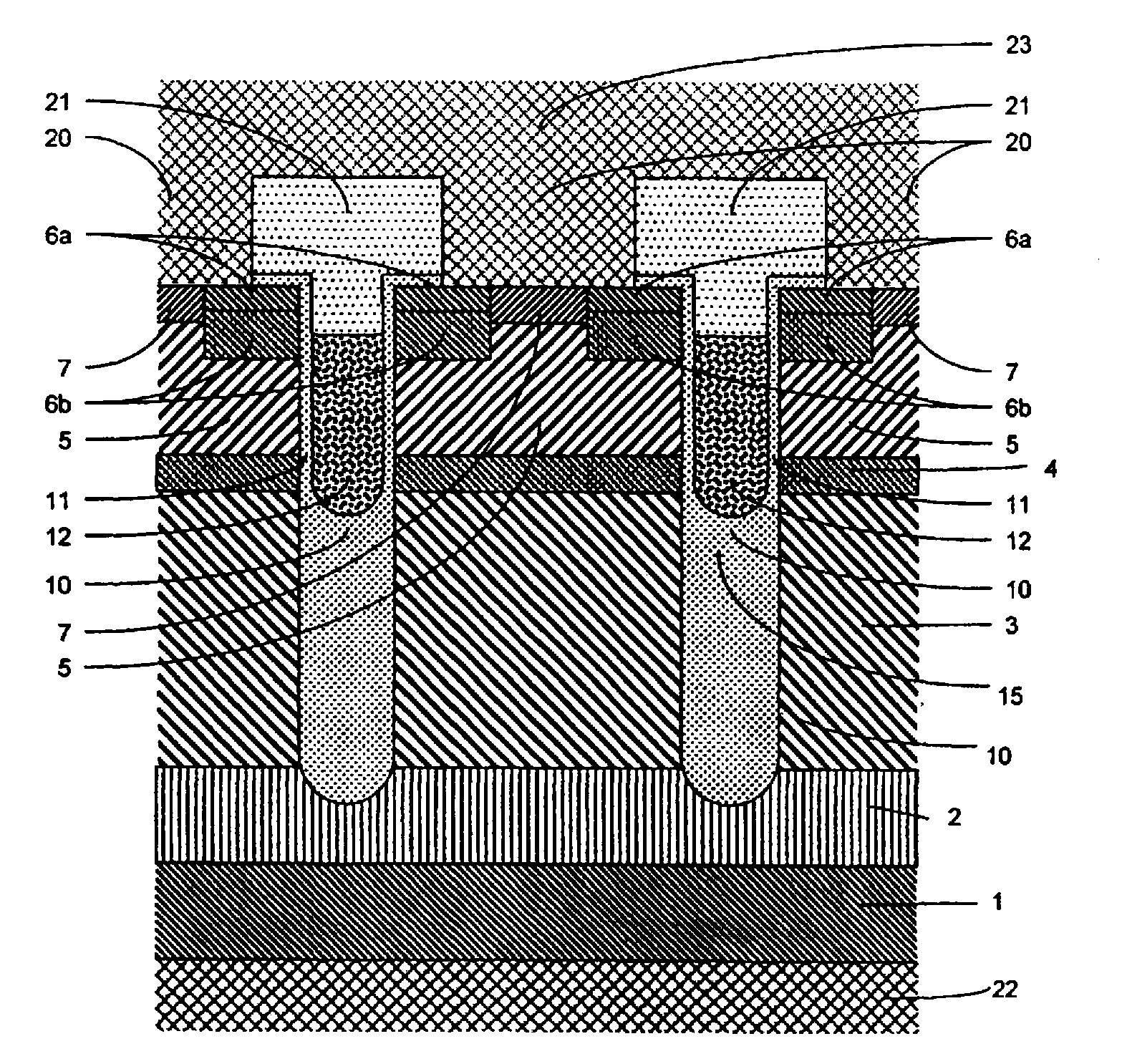
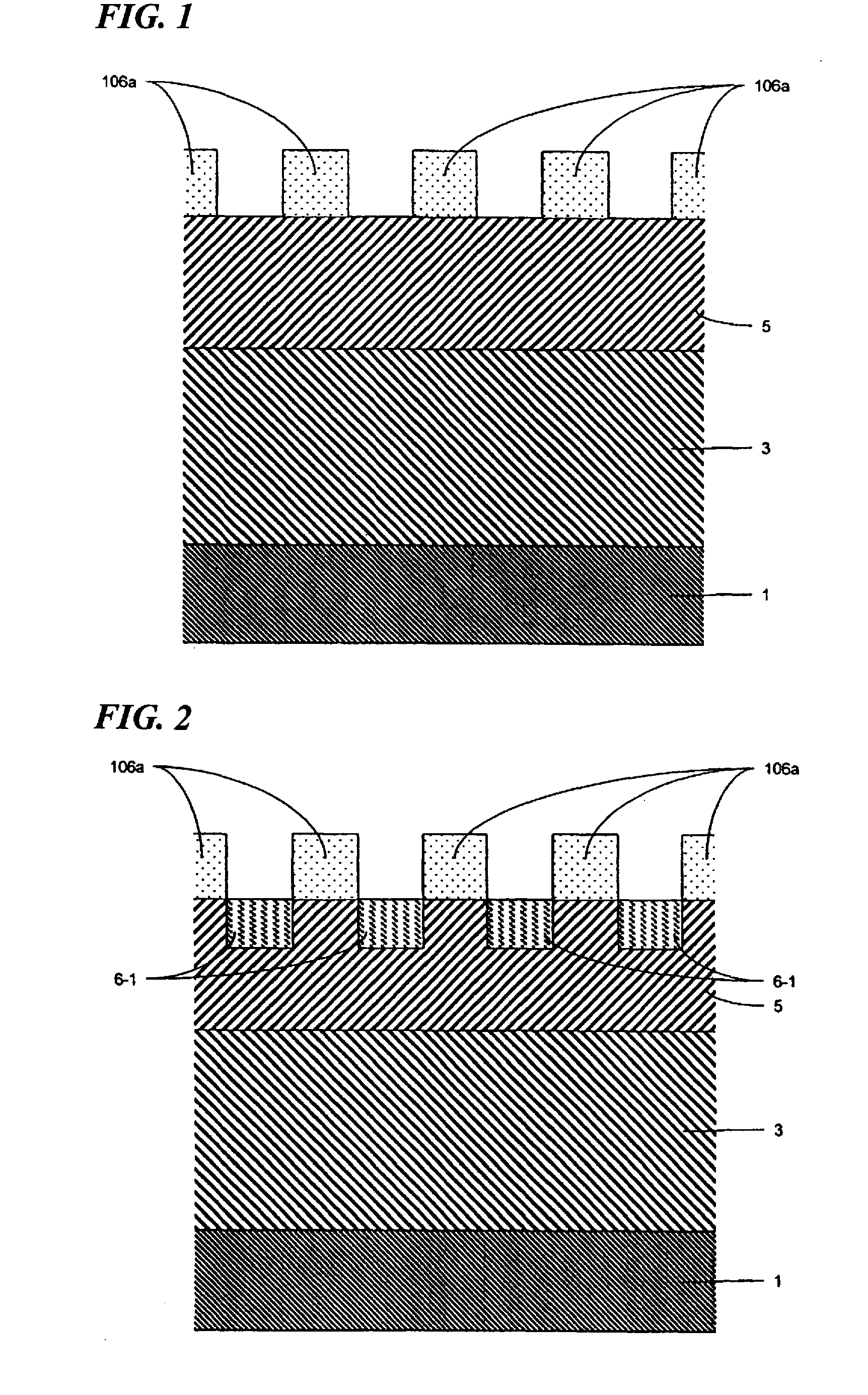
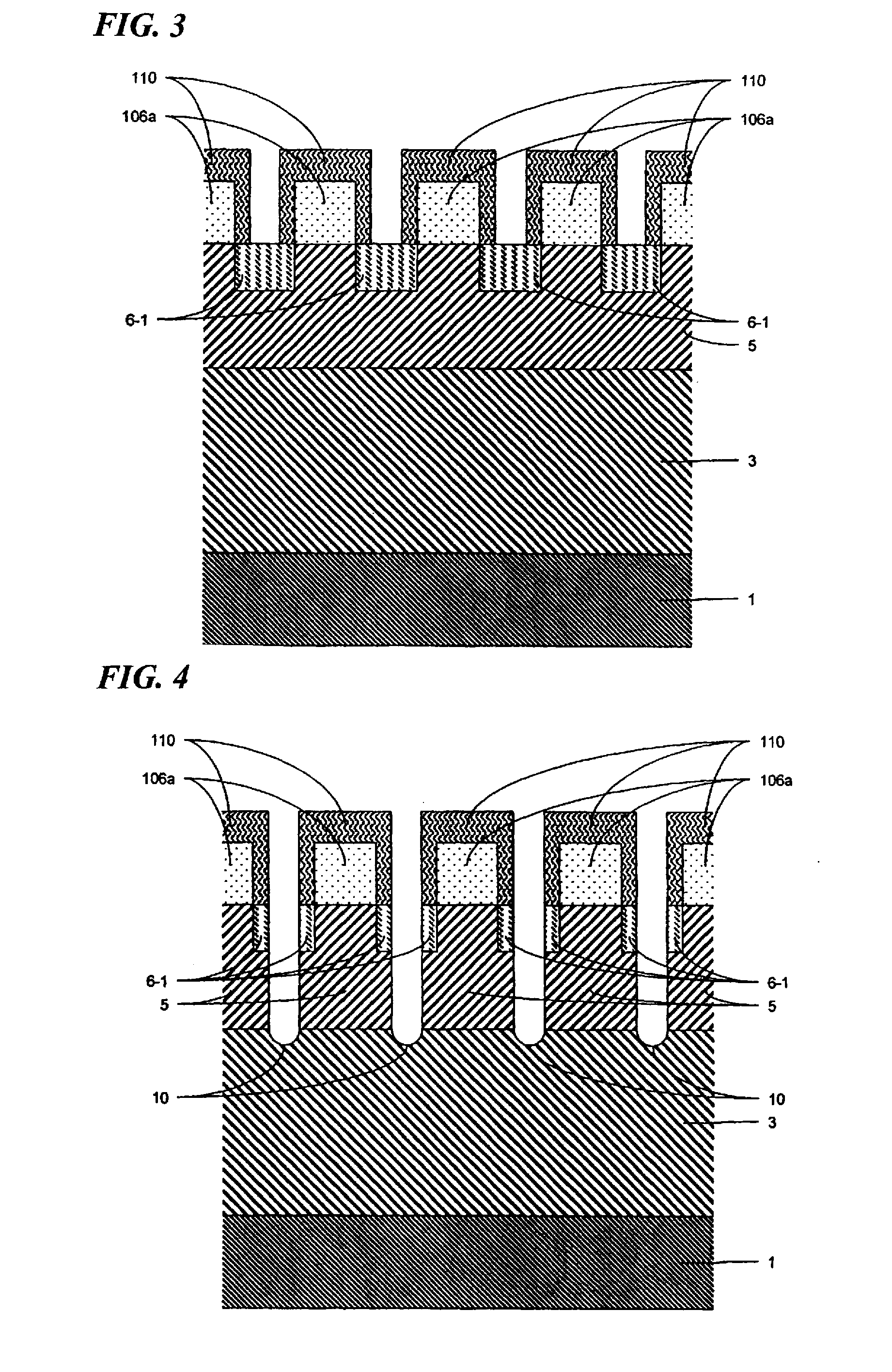
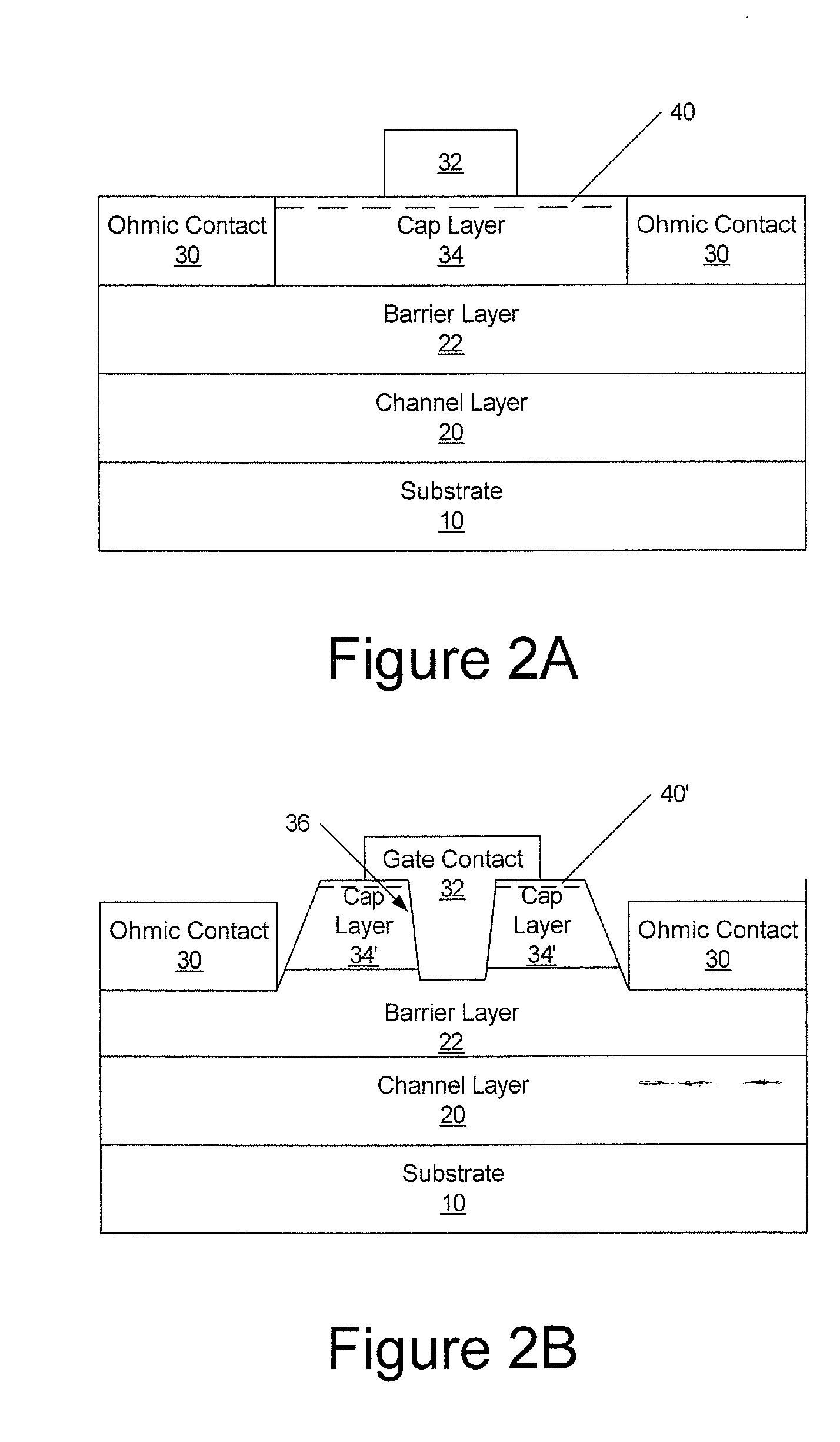
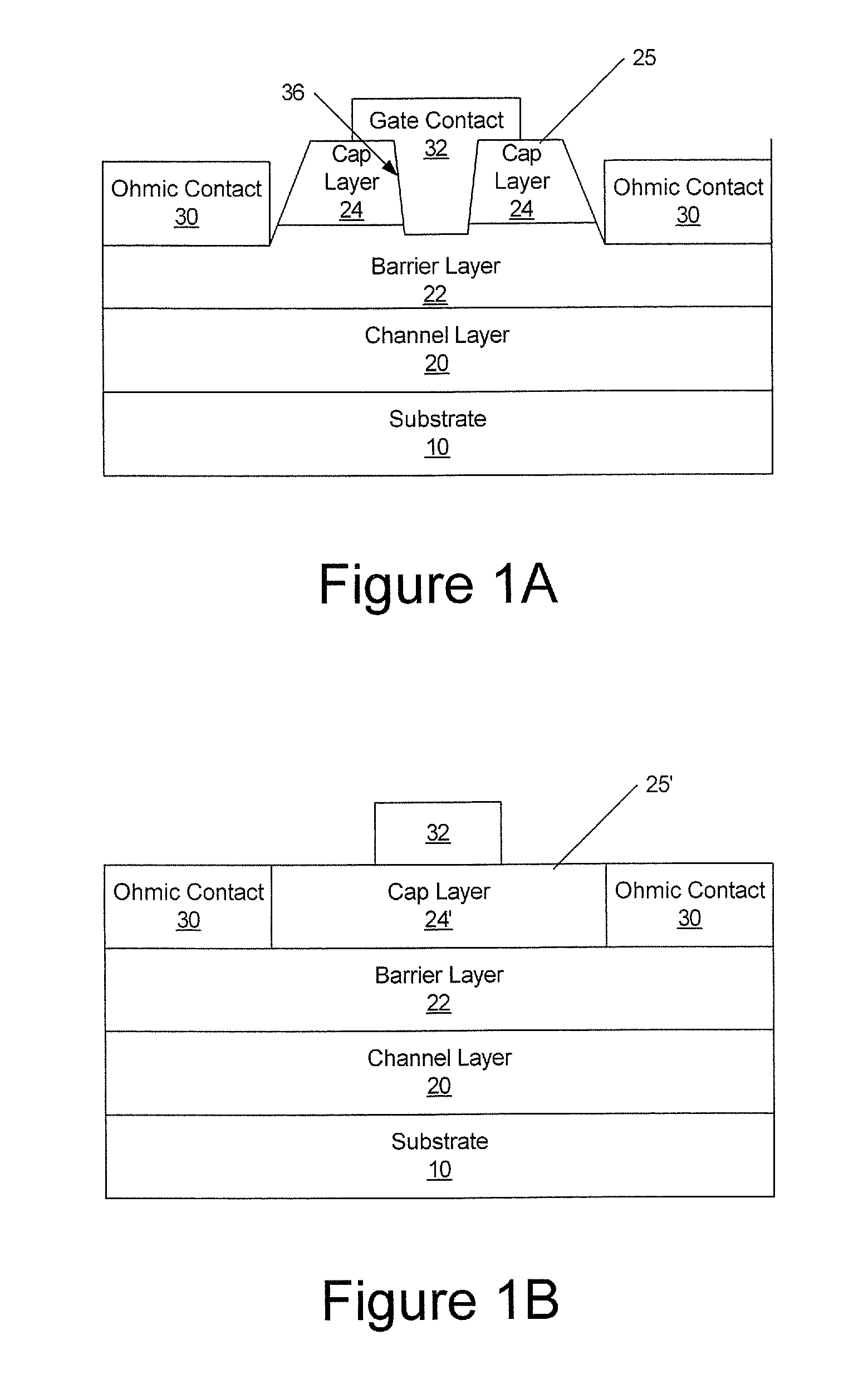
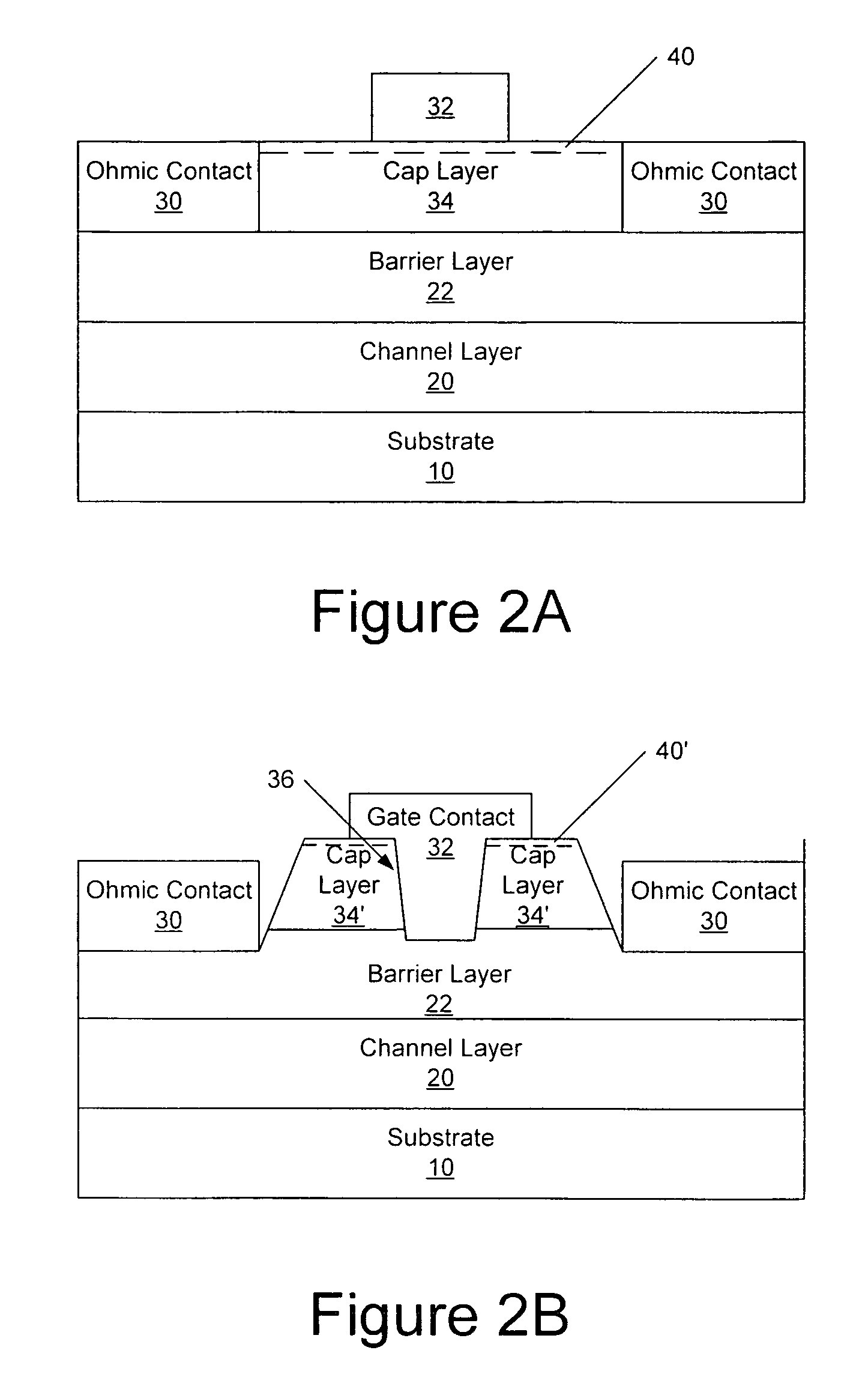
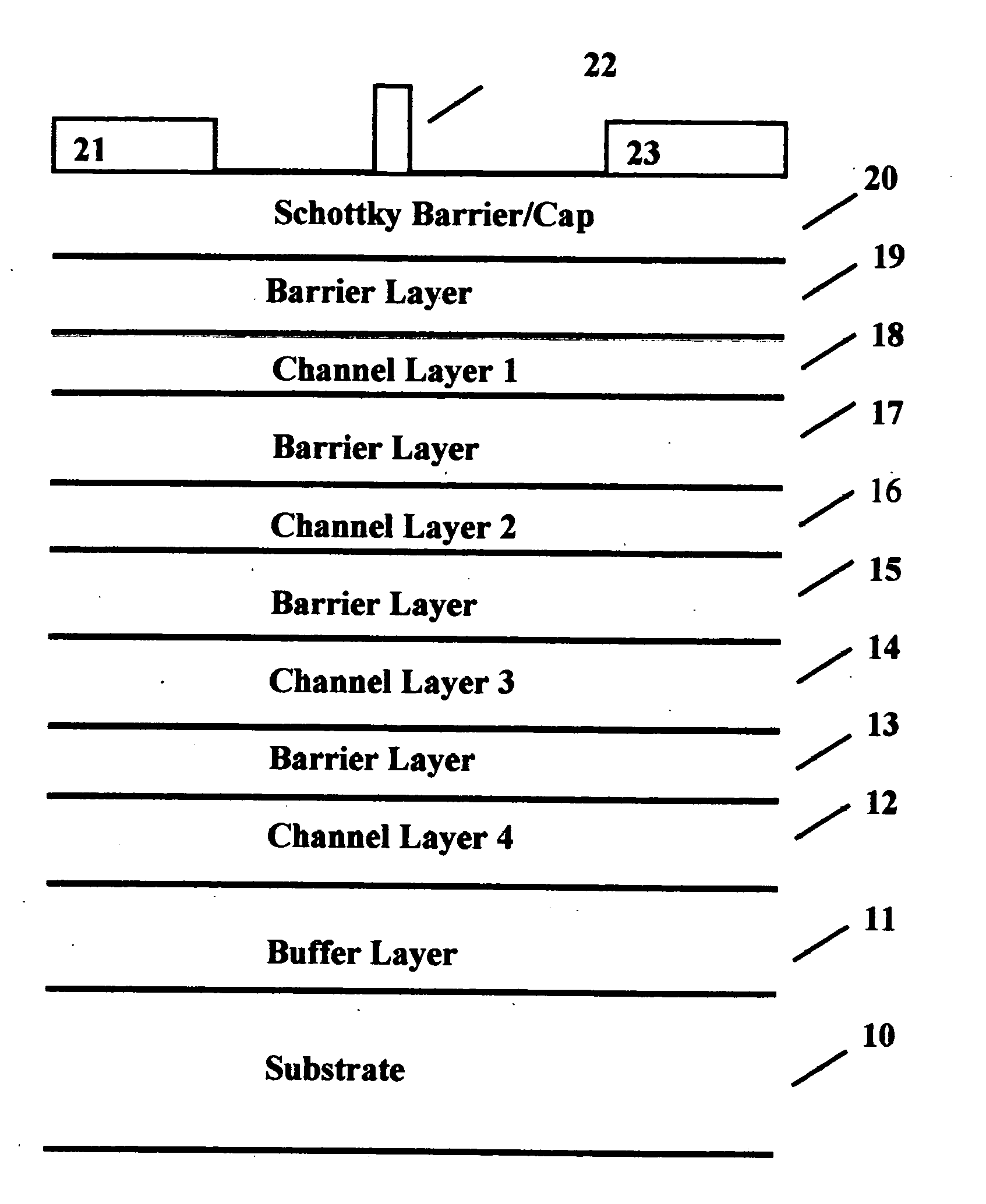
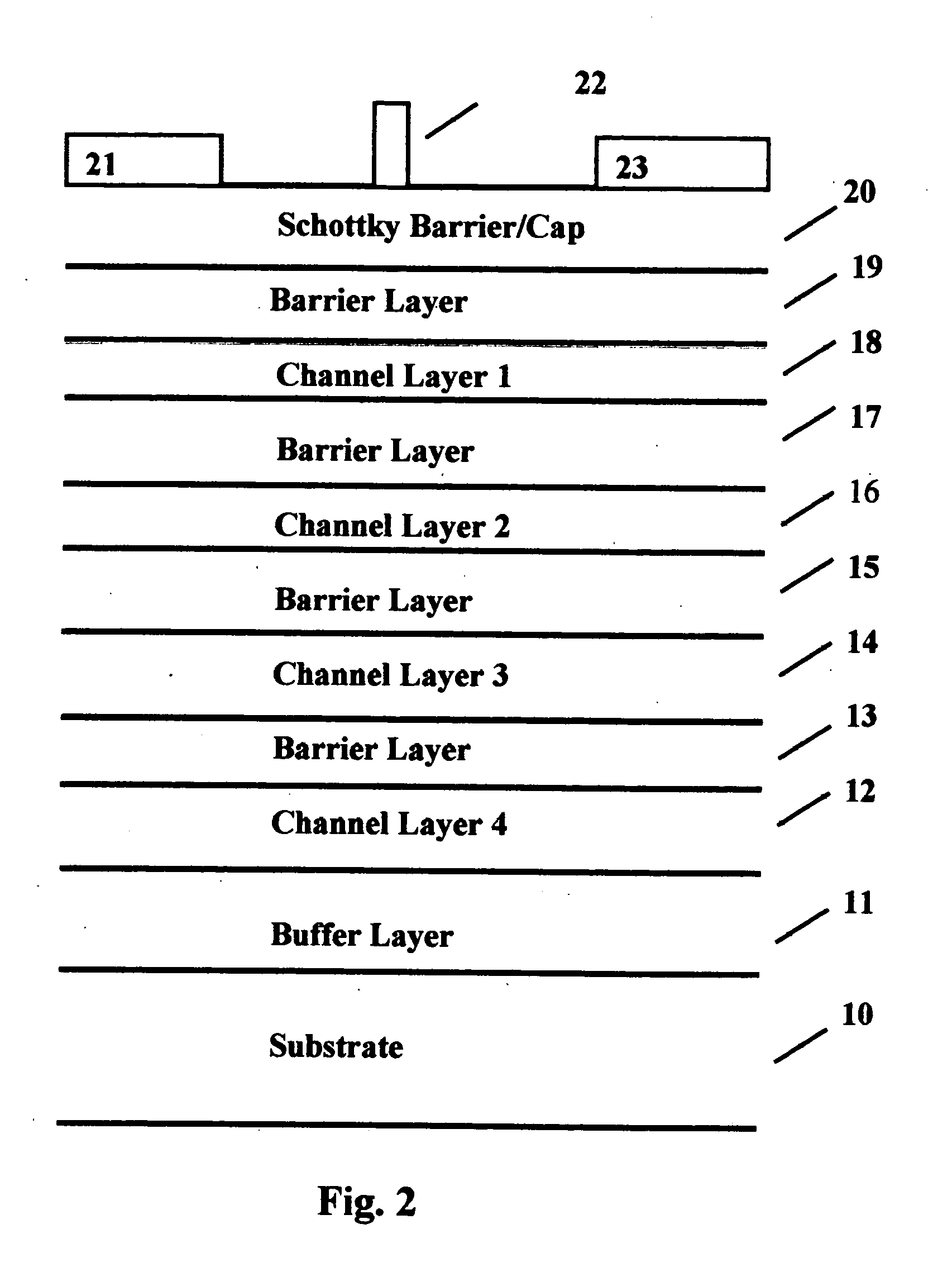
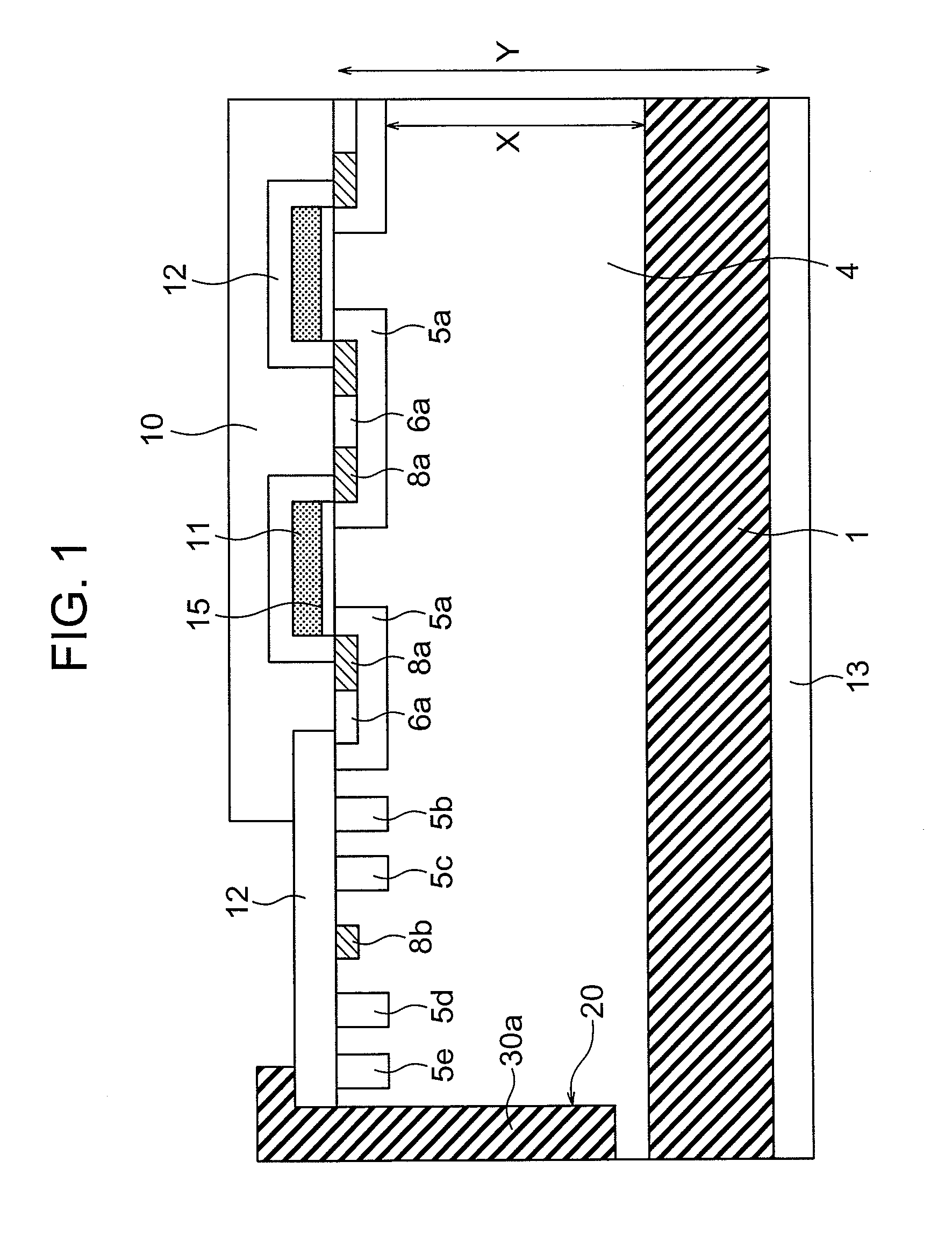
Cap layers and/or passivation layers for nitride-based transistors, transistor structures and methods of fabricating same
ActiveUS20060108606A1Increase concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactHigh electron
High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a non-uniform aluminum concentration AlGaN based cap layer having a high aluminum concentration adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a cap layer having a doped region adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. Graphitic BN passivation structures for wide bandgap semiconductor devices are provided. SiC passivation structures for Group III-nitride semiconductor devices are provided. Oxygen anneals of passivation structures are also provided. Ohmic contacts without a recess are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
Monolithic light emitting devices based on wide bandgap semiconductor nanostructures and methods for making same
InactiveUS20050082543A1Reduce defectsSmall sizeLaser detailsLaser active region structureNanolithographyPhosphor
The present invention is directed toward a method for fabricating low-defect nanostructures of wide bandgap materials and to optoelectronic devices, such as light emitting sources and lasers, based on them. The invention utilizes nanolithographically-defined templates to form nanostructures of wide bandgap materials that are energetically unfavorable for dislocation formation. In particular, this invention provides a method for the fabrication of phosphor-less monolithic white light emitting diodes and laser diodes that can be used for general illumination and other applications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
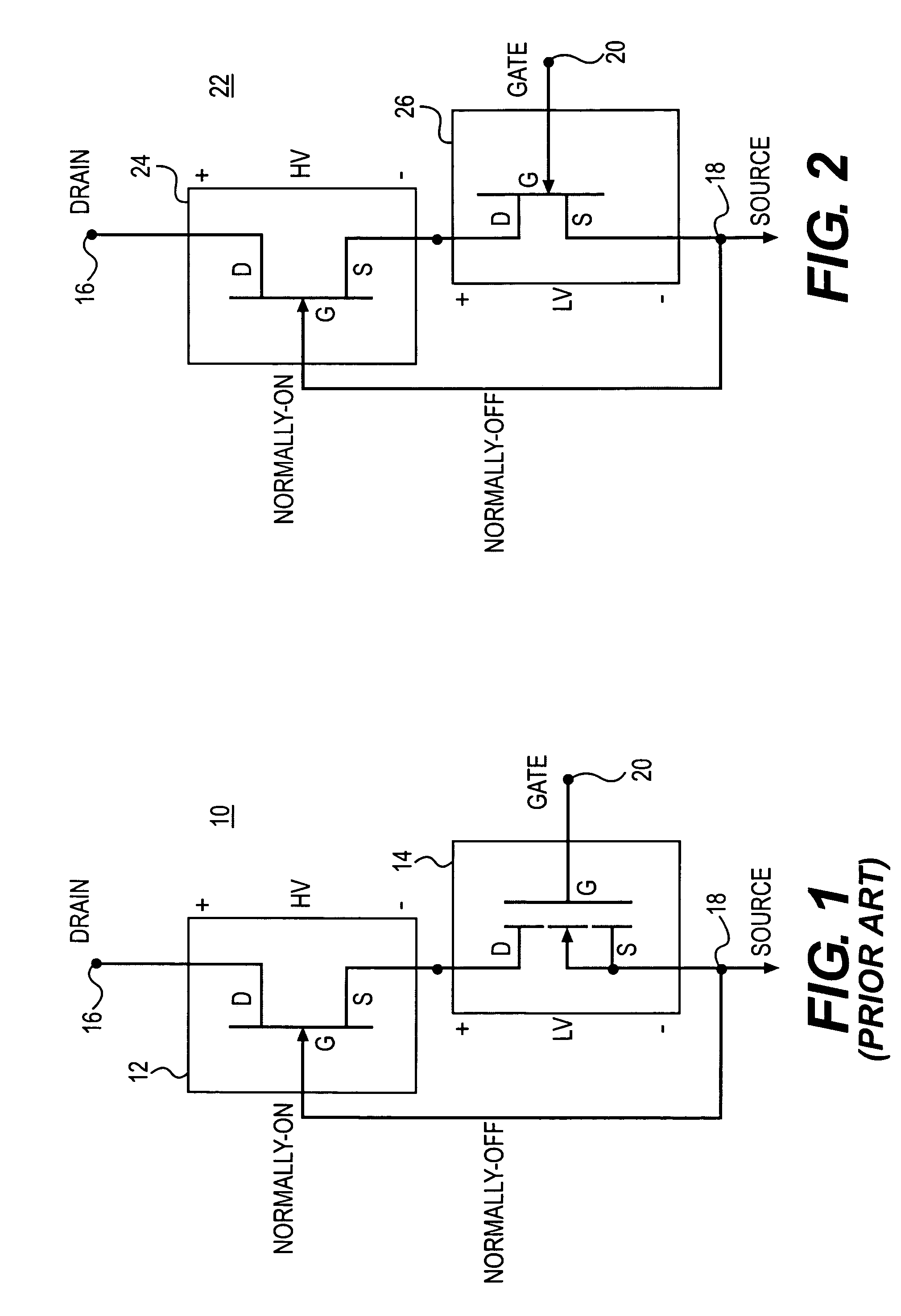
Cascode power switch topologies
ActiveUS7719055B1Increase temperatureHigh blocking voltageElectronic switchingSemiconductor devicesCascodeGallium nitride
A normally-off cascode power switch circuit is disclosed fabricated in wide bandgap semiconductor material such as silicon carbide or gallium nitride and which is capable of conducting current in the forward and reverse direction under the influence of a positive gate bias. The switch includes cascoded junction field effect transistors (JFETs) that enable increased gain, and hence blocking voltage, while minimizing specific on-resistance.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
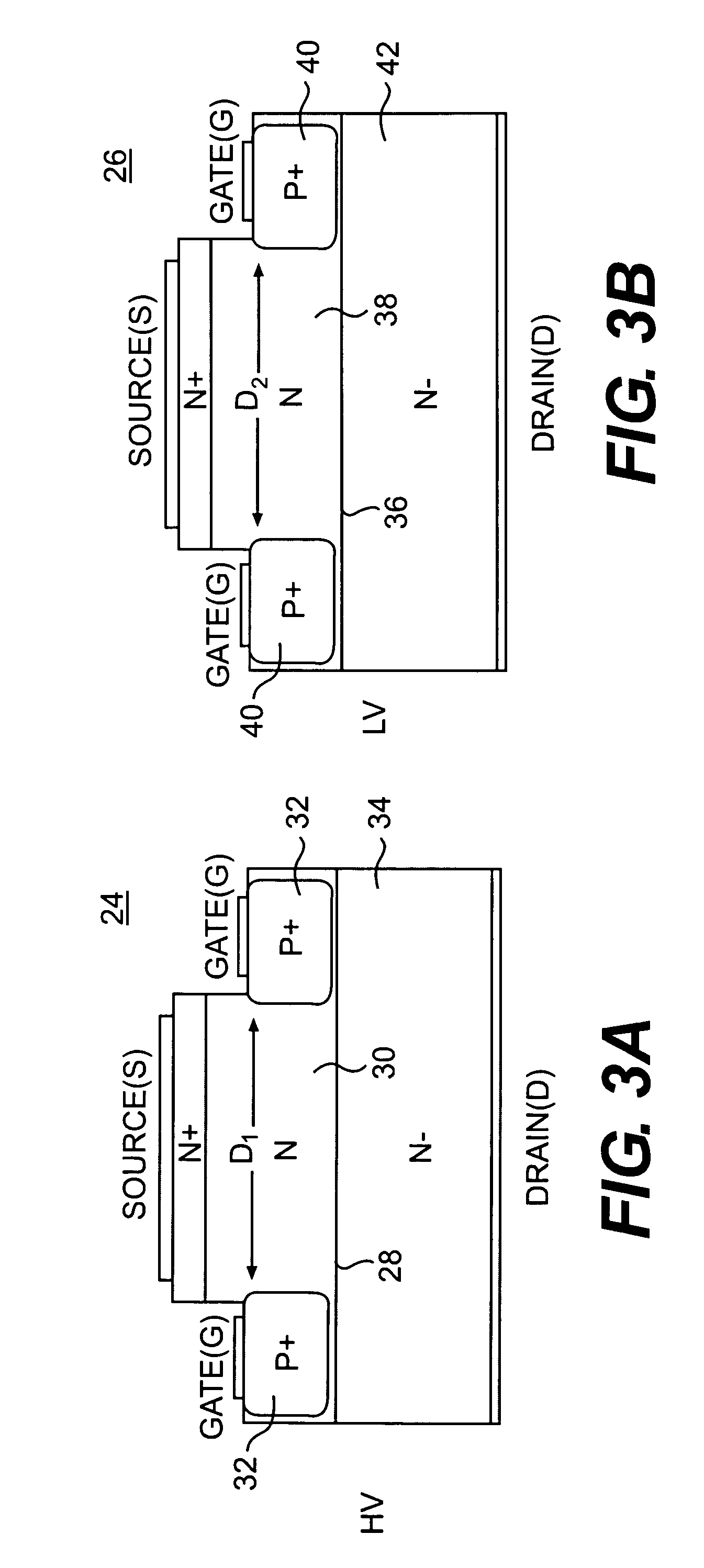
High efficiency LEDs with tunnel junctions
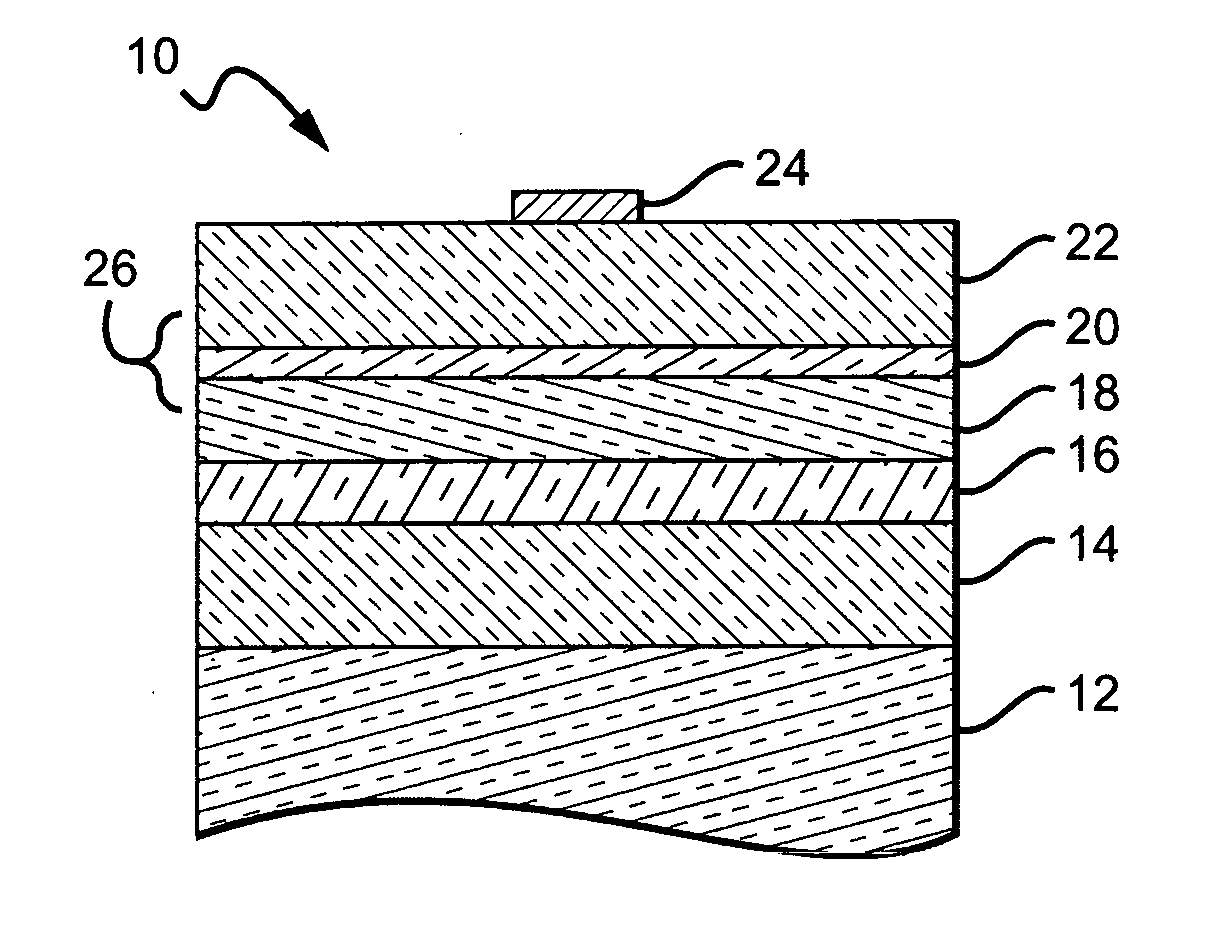
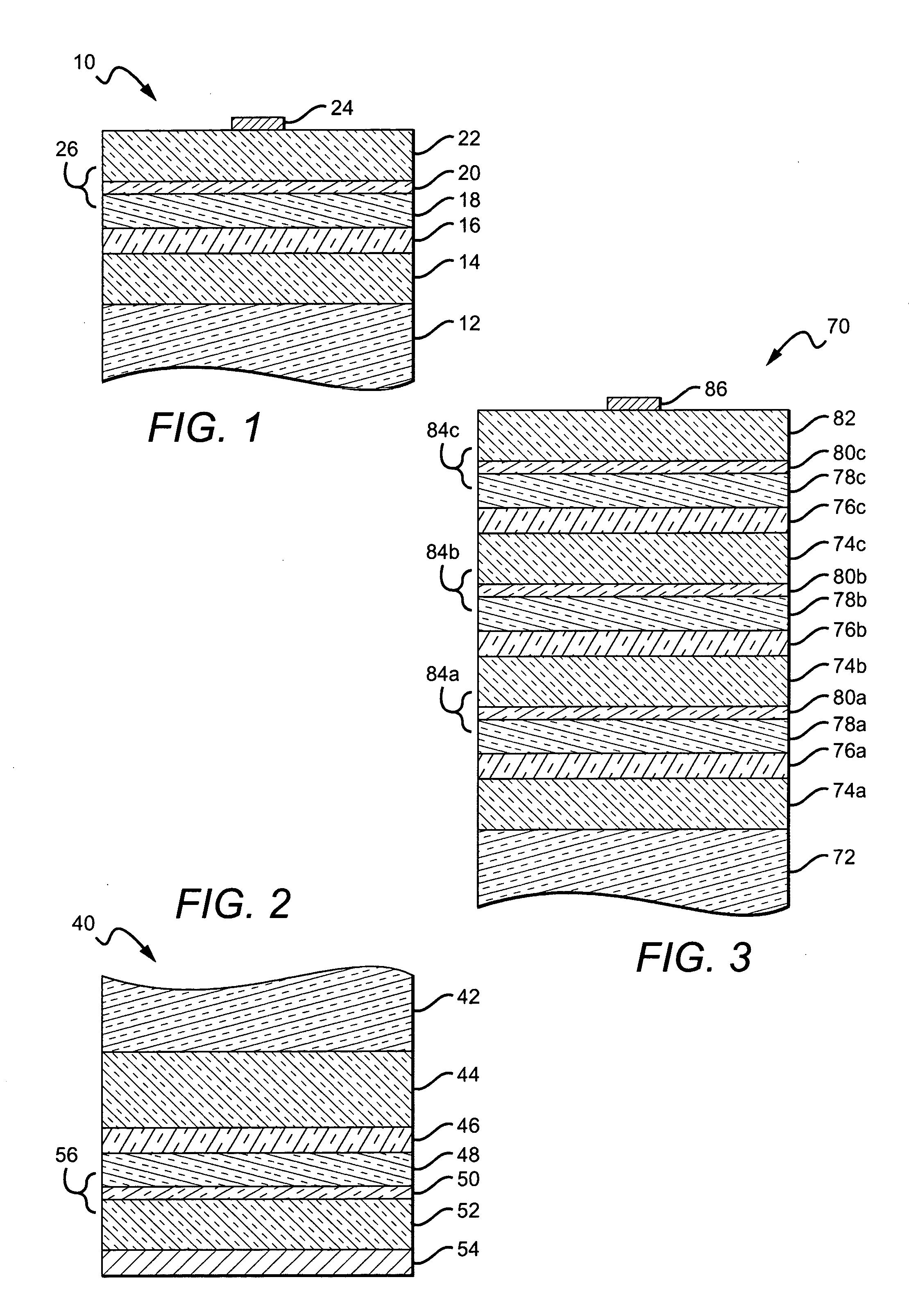
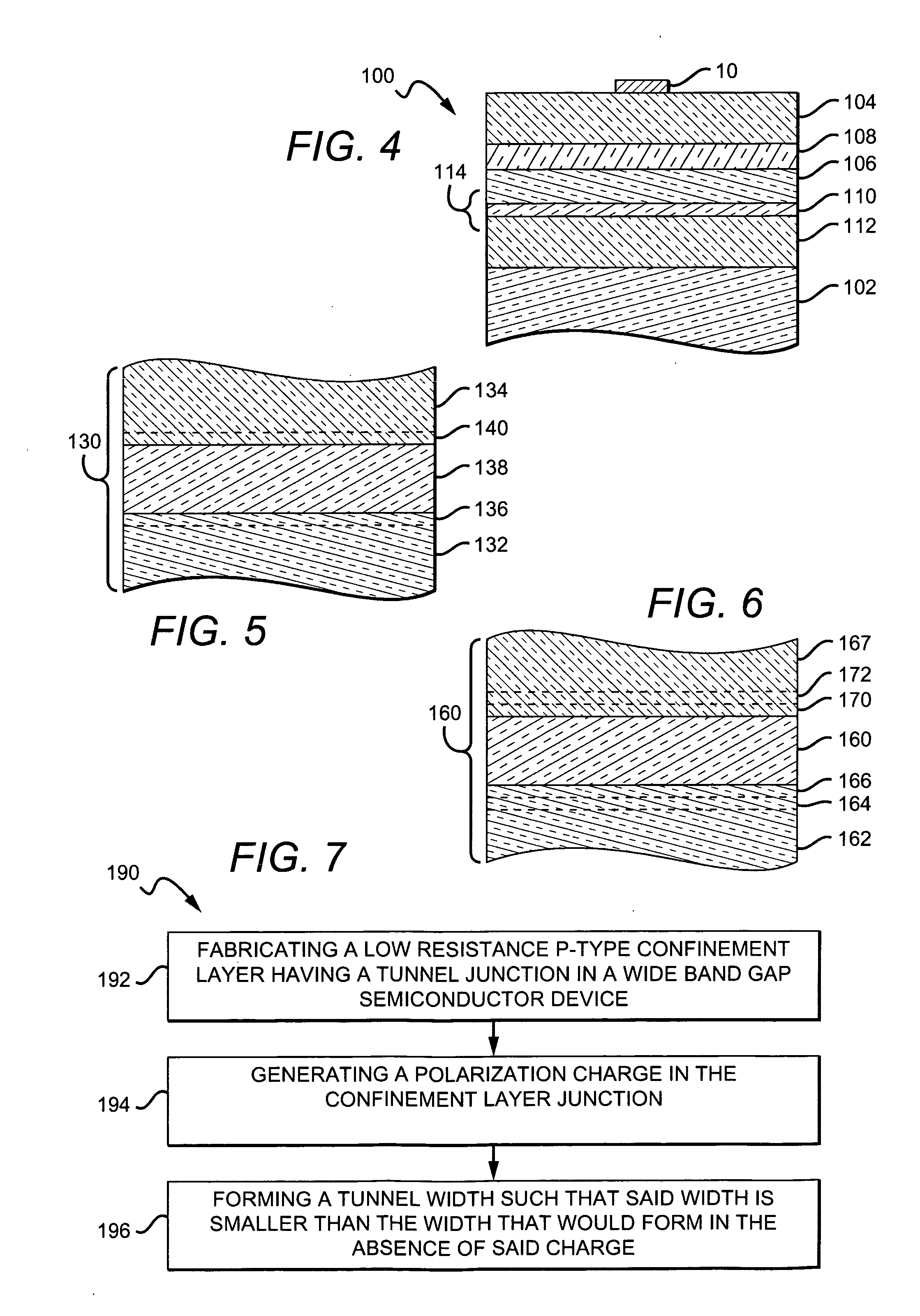
An LED made from a wide band gap semiconductor material and having a low resistance p-type confinement layer with a tunnel junction in a wide band gap semiconductor device is disclosed. A dissimilar material is placed at the tunnel junction where the material generates a natural dipole. This natural dipole is used to form a junction having a tunnel width that is smaller than such a width would be without the dissimilar material. A low resistance p-type confinement layer having a tunnel junction in a wide band gap semiconductor device may be fabricated by generating a polarization charge in the junction of the confinement layer, and forming a tunnel width in the junction that is smaller than the width would be without the polarization charge. Tunneling through the tunnel junction in the confinement layer may be enhanced by the addition of impurities within the junction. These impurities may form band gap states in the junction.
Owner:CREELED INC
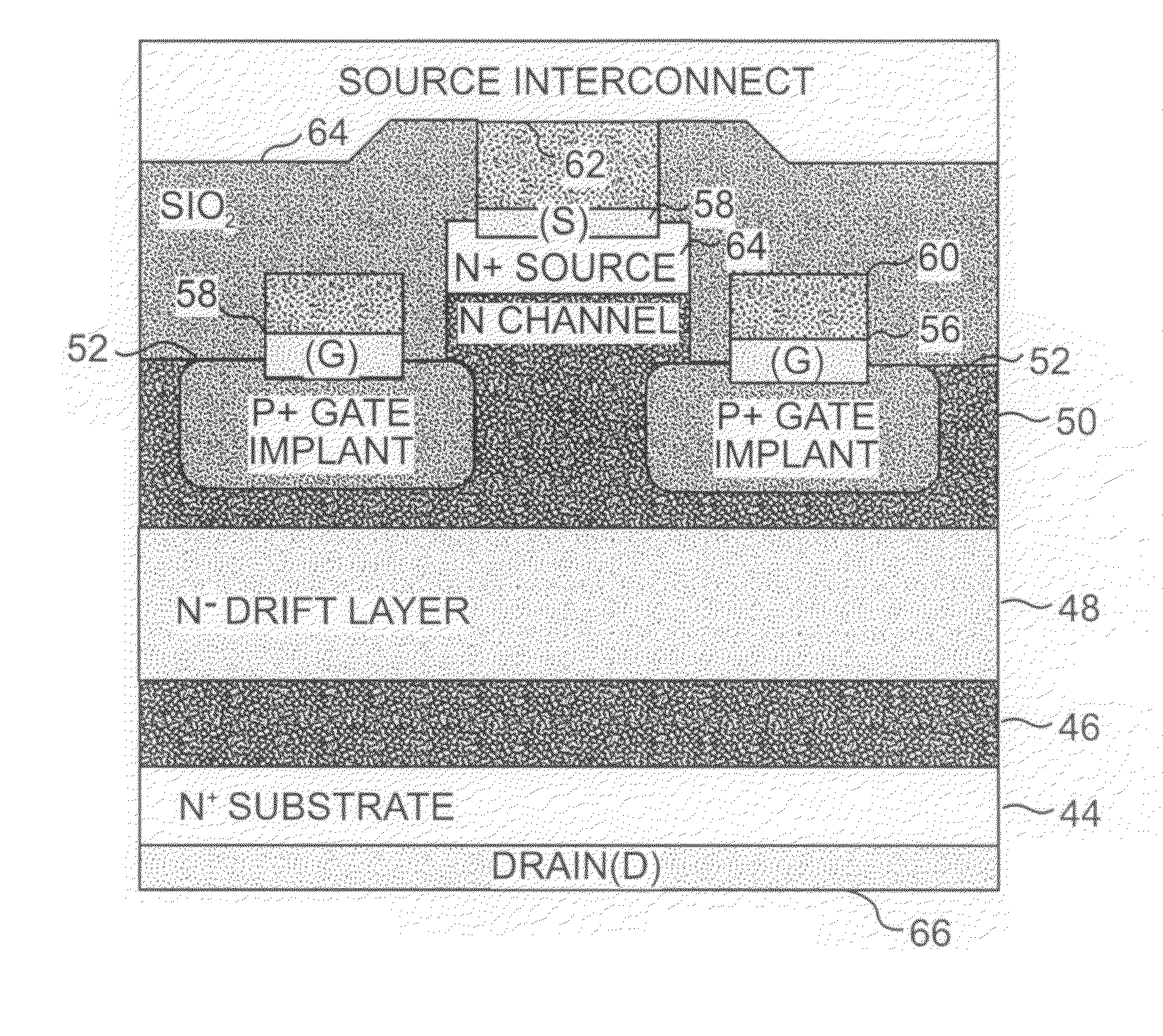
Trench gate type semiconductor device and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20090272982A1Good ohmic contactExcessive electric field is preventedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETOhmic contact
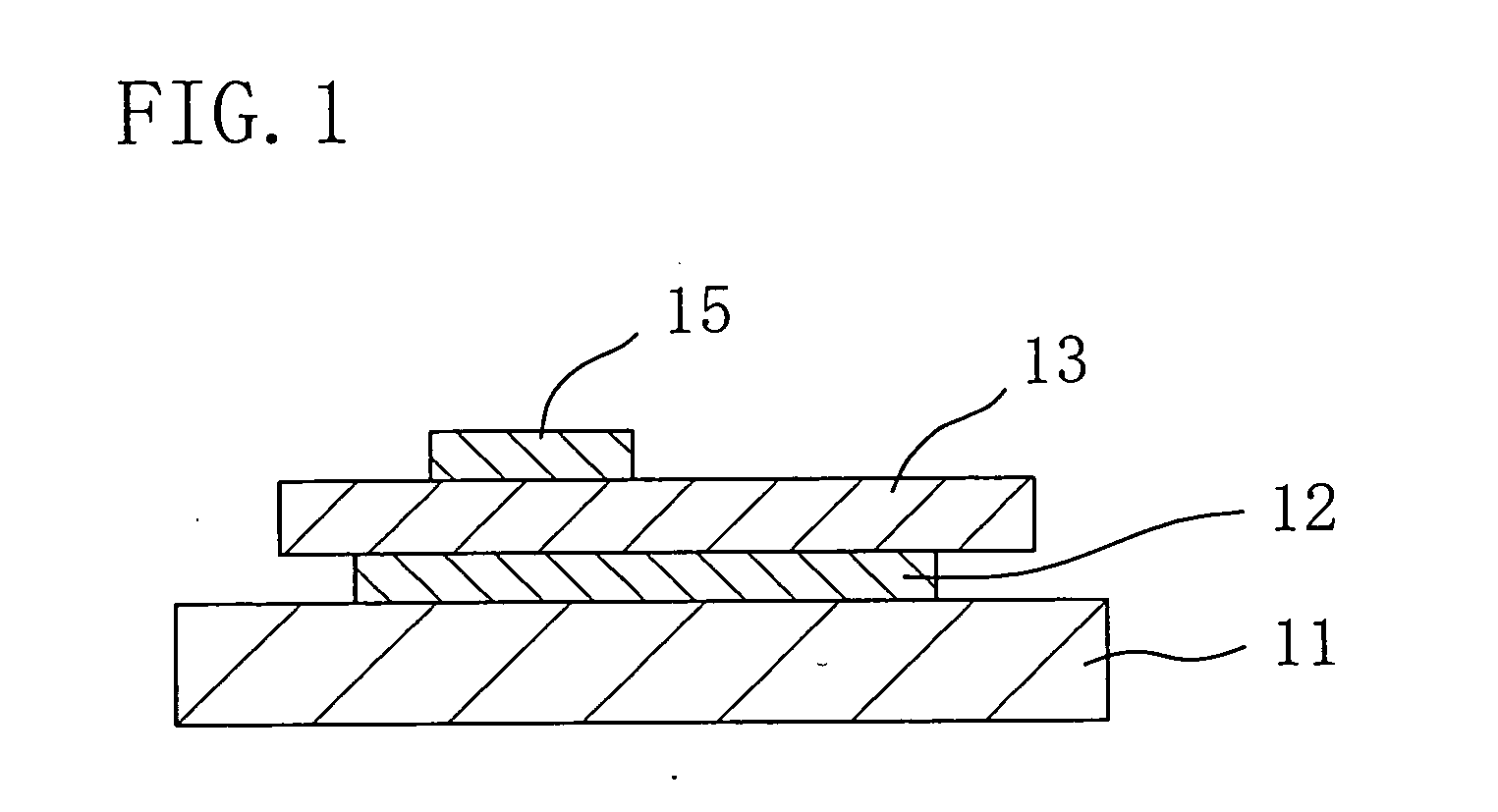
A method of producing a trench gate type MOSFET is provided in which each intersection trench is formed as a two-stage trench structure. A gate trench is backfilled with a mask material and the mask material is then patterned to form a mask used for forming each intersection trench. The intersection trench intersecting the gate trench is provided so as to be deeper than the gate trench. A Schottky electrode is provided in the bottom of each intersection trench 10p. In this manner, there is provided a trench gate type semiconductor device and a method of producing the same, in which: the cell pitch can be reduced even when a wide band gap semiconductor is used as a main semiconductor substrate; good ohmic contacts can be obtained; and an excessive electric field is prevented from being applied to an insulating film in the bottom of each trench.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
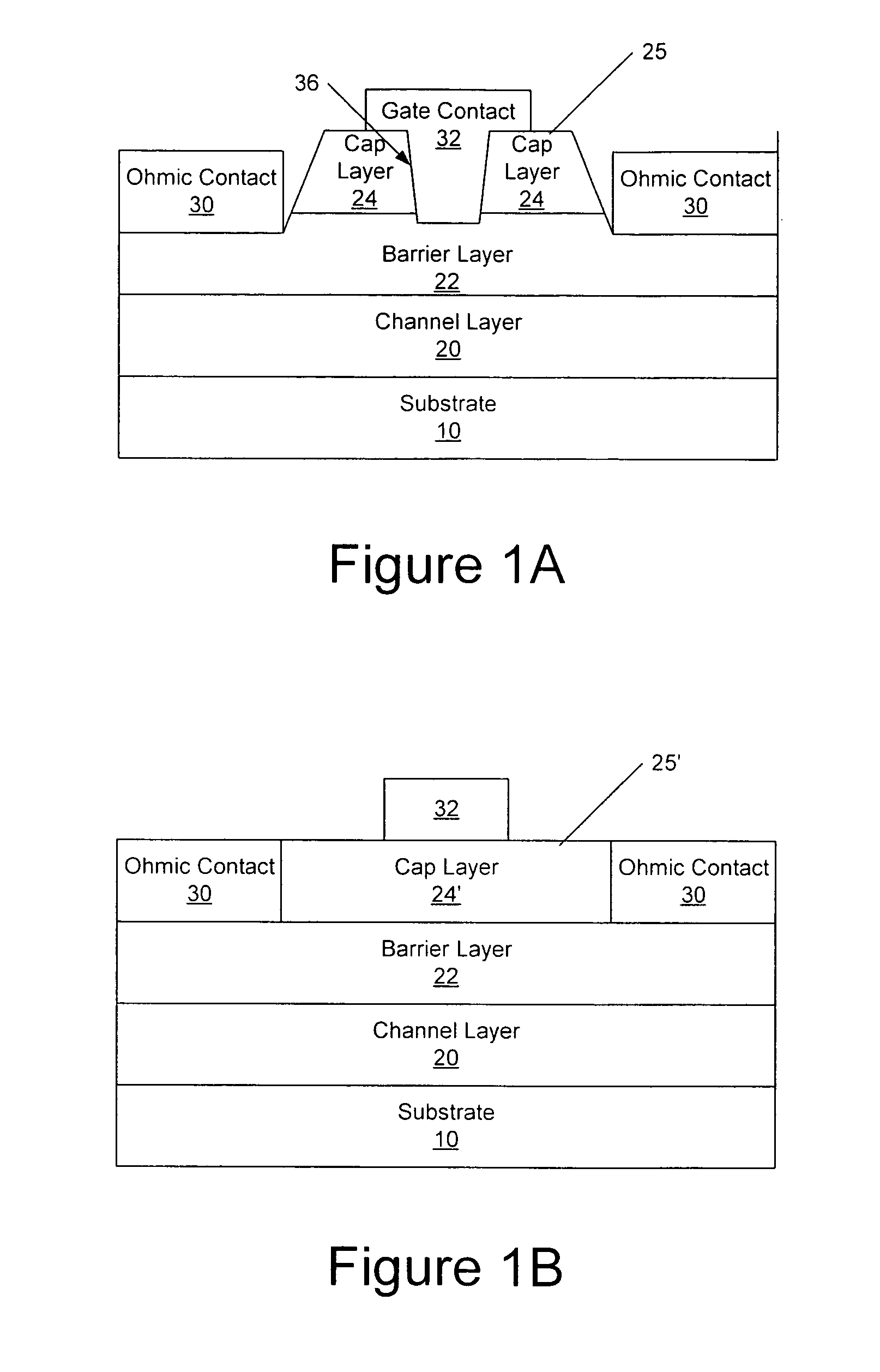
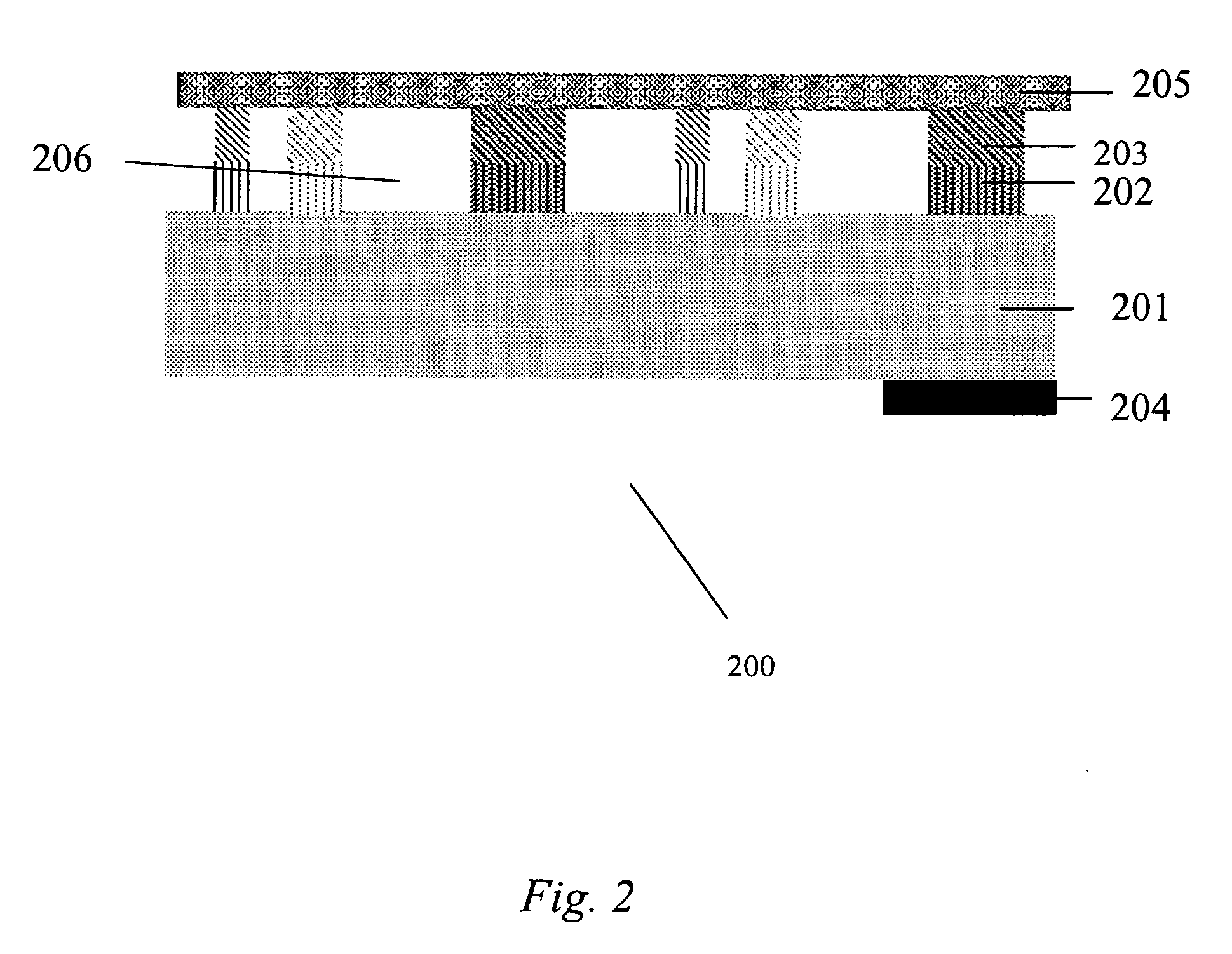
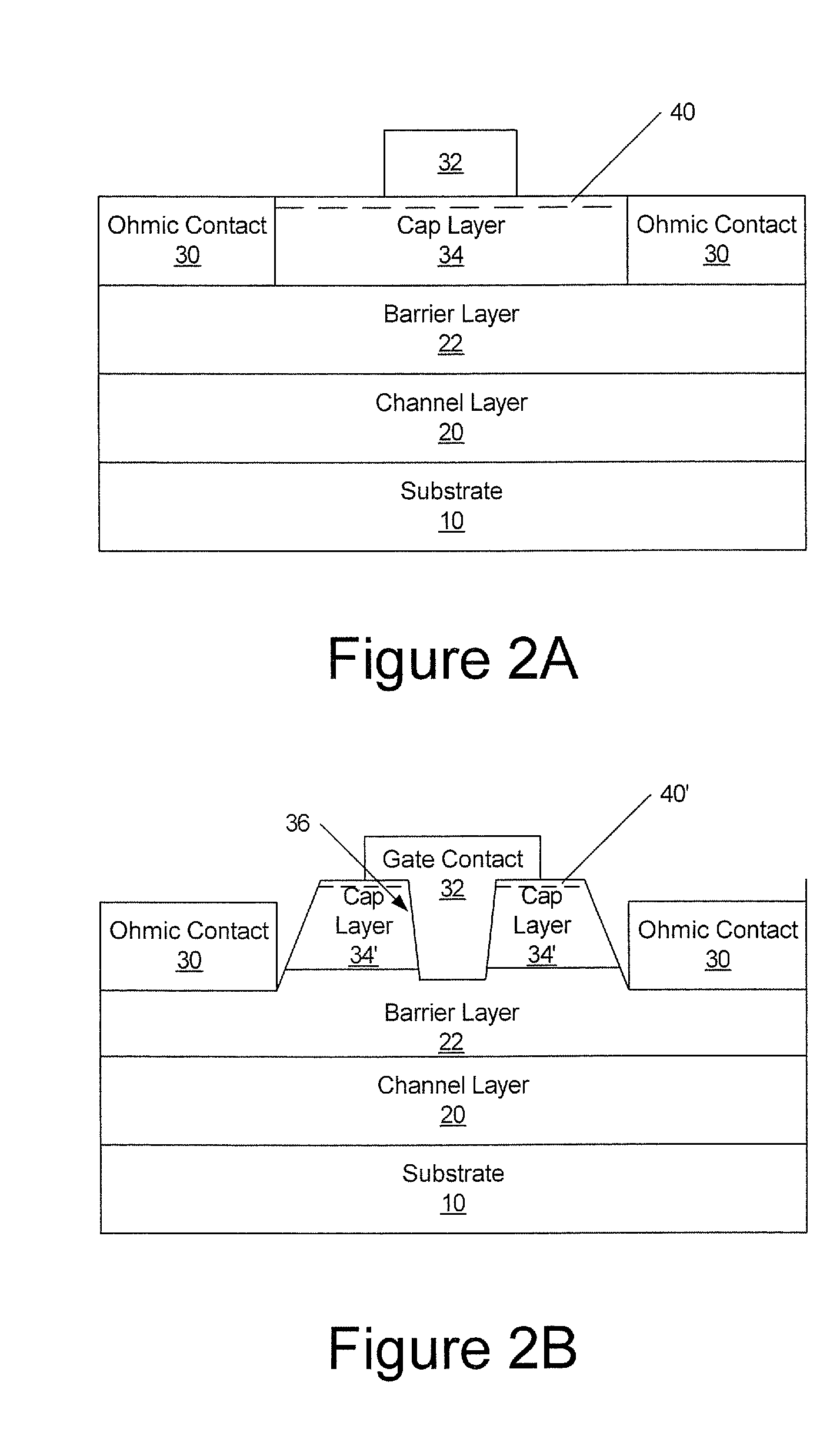
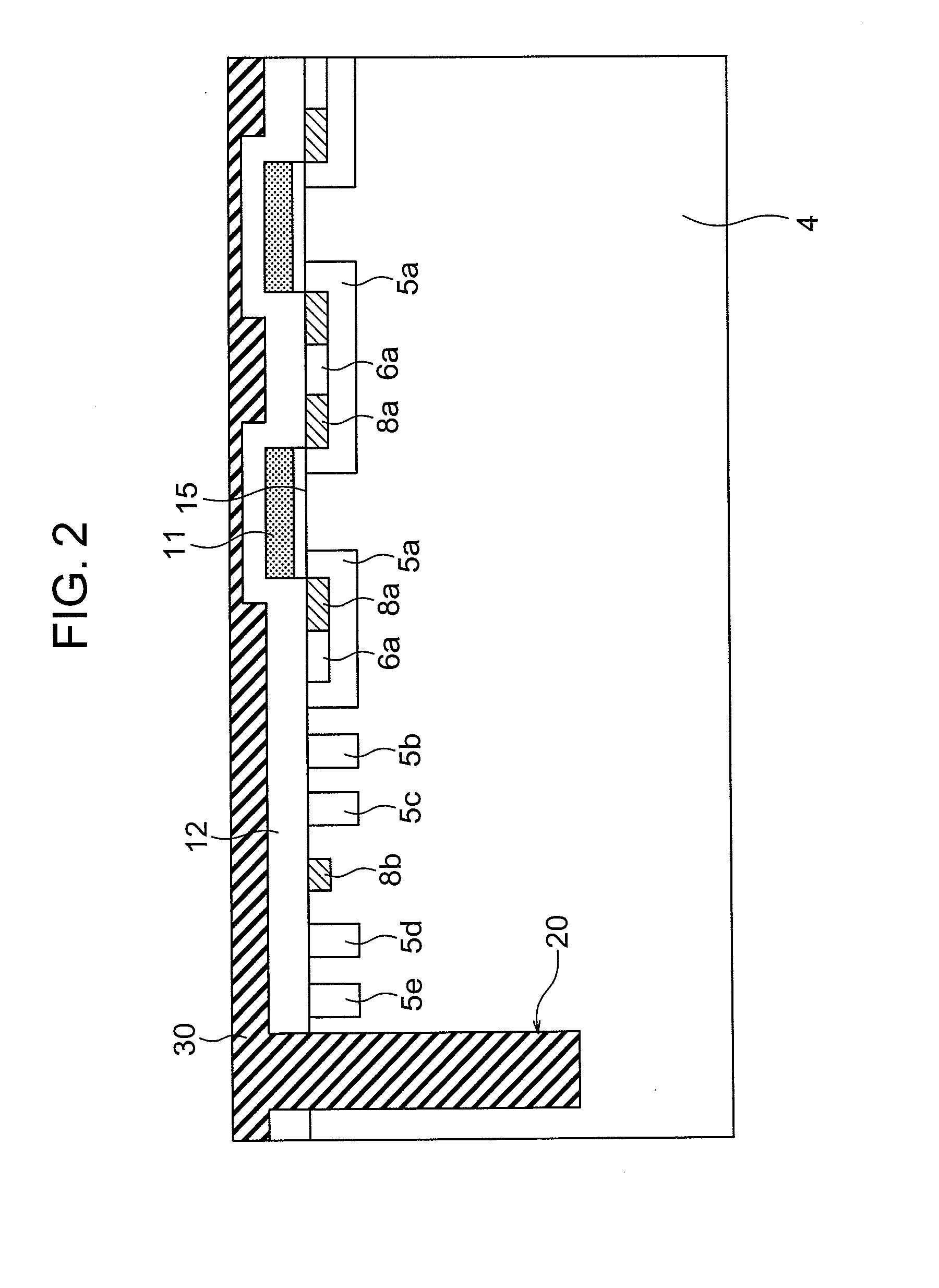
Cap Layers Including Aluminum Nitride for Nitride-Based Transistors and Methods of Fabricating Same
ActiveUS20070164315A1Increase concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactGraphite
High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a non-uniform aluminum concentration AlGaN based cap layer having a high aluminum concentration adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a cap layer having a doped region adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. Graphitic BN passivation structures for wide bandgap semiconductor devices are provided. SiC passivation structures for Group III-nitride semiconductor devices are provided. Oxygen anneals of passivation structures are also provided. Ohmic contacts without a recess are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
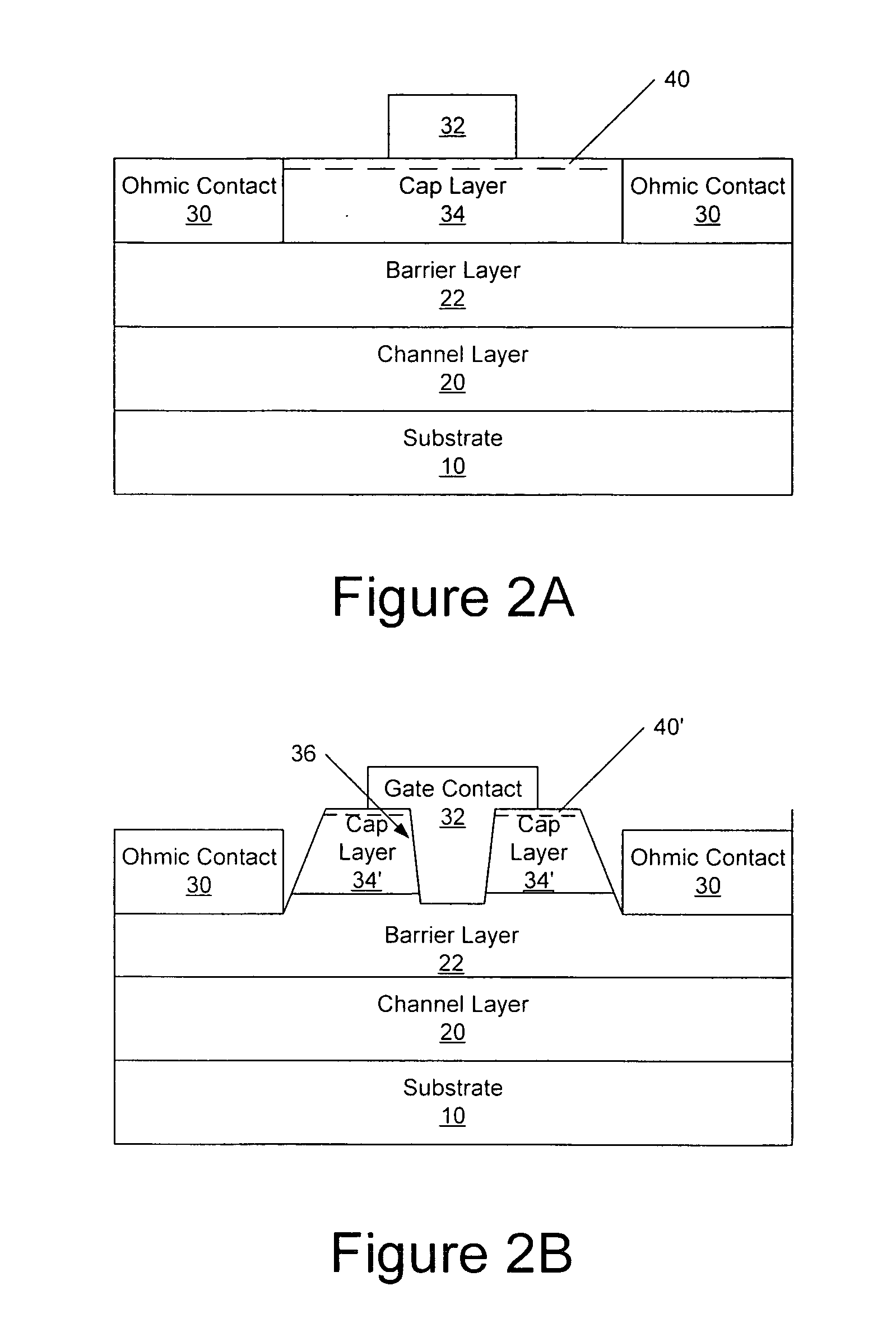
Cap layers including aluminum nitride for nitride-based transistors
ActiveUS7709859B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactHigh electron
High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a non-uniform aluminum concentration AlGaN based cap layer having a high aluminum concentration adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a cap layer having a doped region adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. Graphitic BN passivation structures for wide bandgap semiconductor devices are provided. SiC passivation structures for Group III-nitride semiconductor devices are provided. Oxygen anneals of passivation structures are also provided. Ohmic contacts without a recess are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
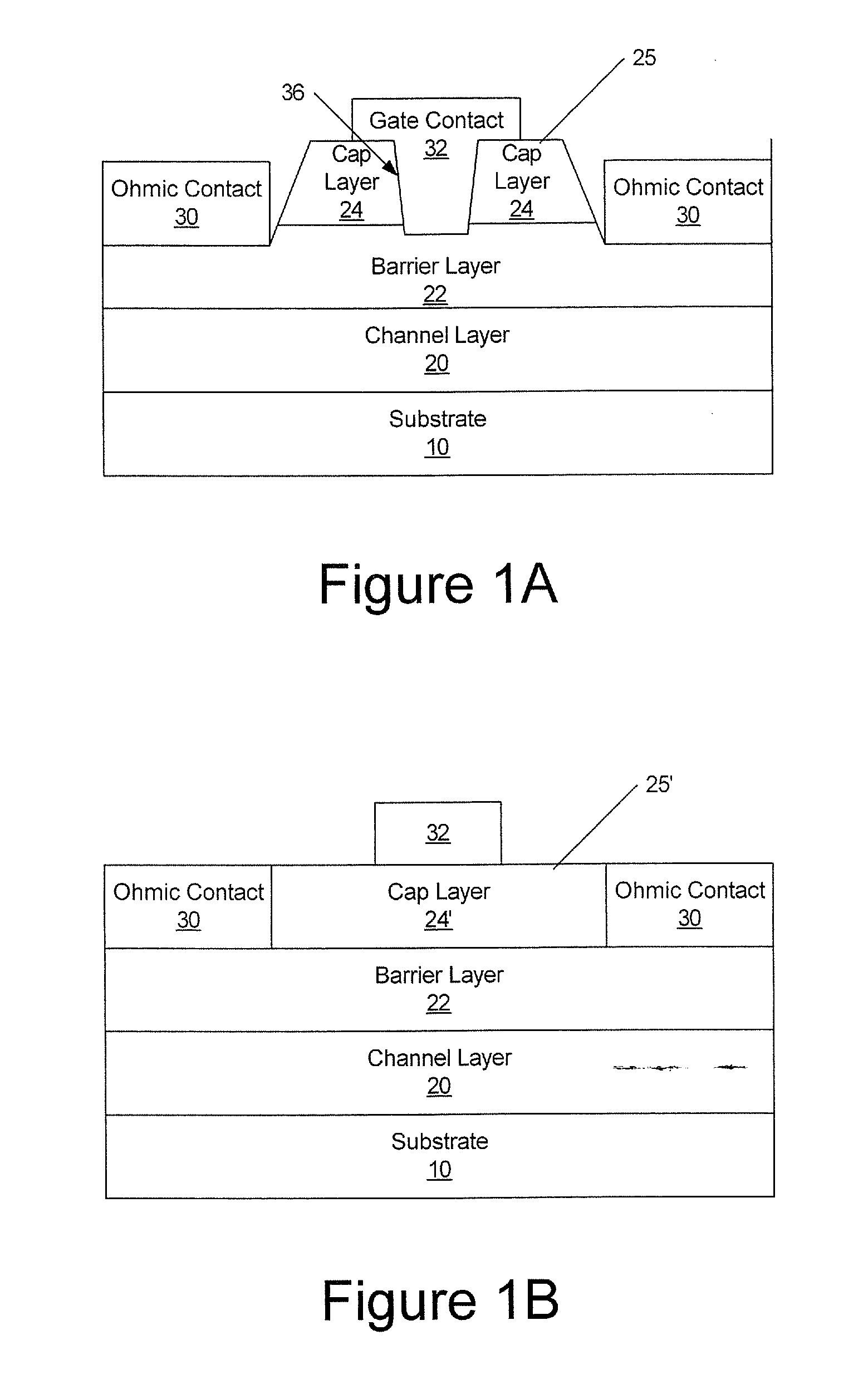
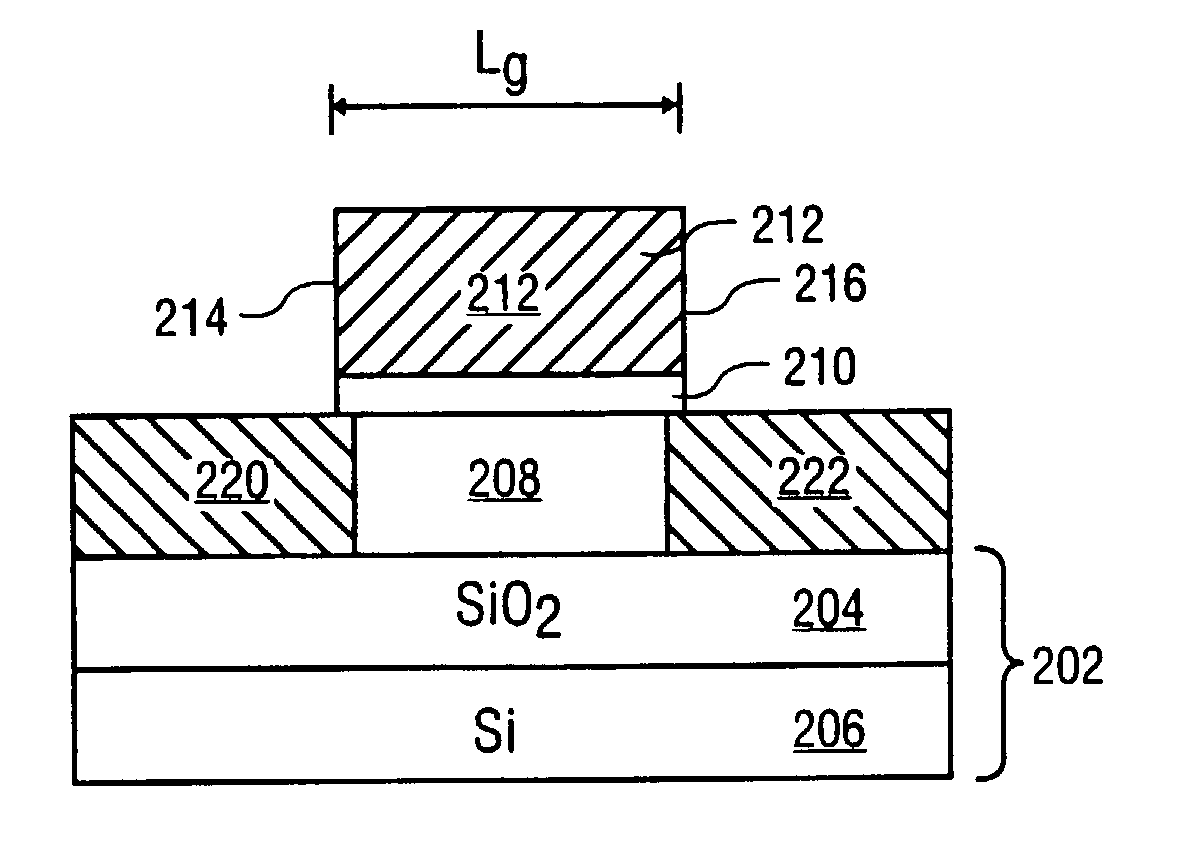
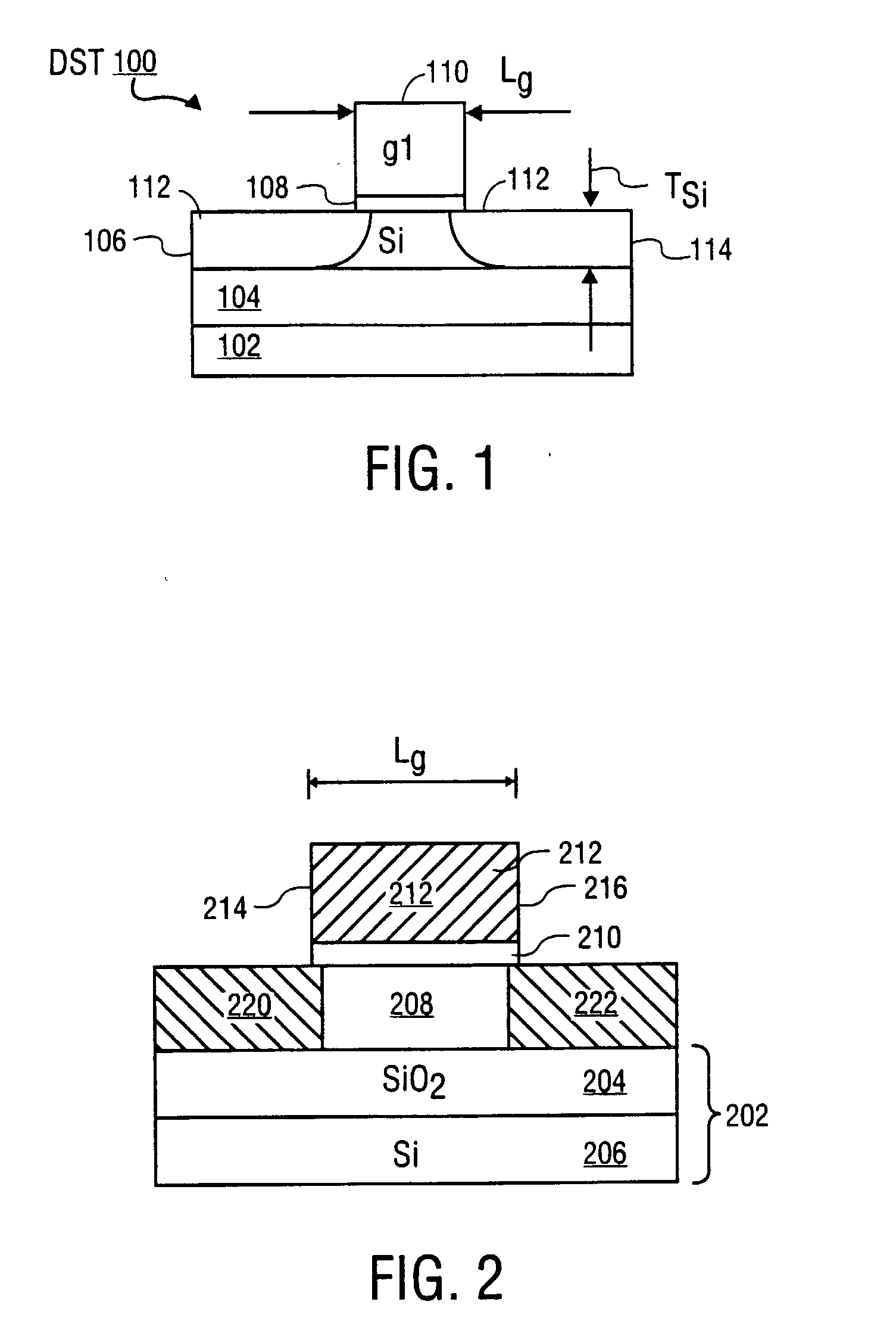
Novel field effect transistor and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20040099966A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricField-effect transistor
The present invention is a novel field effect transistor having a channel region formed from a narrow bandgap semiconductor film formed on an insulating substrate. A gate dielectric layer is formed on the narrow bandgap semiconductor film. A gate electrode is then formed on the gate dielectric. A pair of source / drain regions formed from a wide bandgap semiconductor film or a metal is formed on opposite sides of the gate electrode and adjacent to the low bandgap semiconductor film.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Wide band gap semiconductor device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090283776A1Lower on-resistanceShort reverse recovery timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeBroadbandWide band
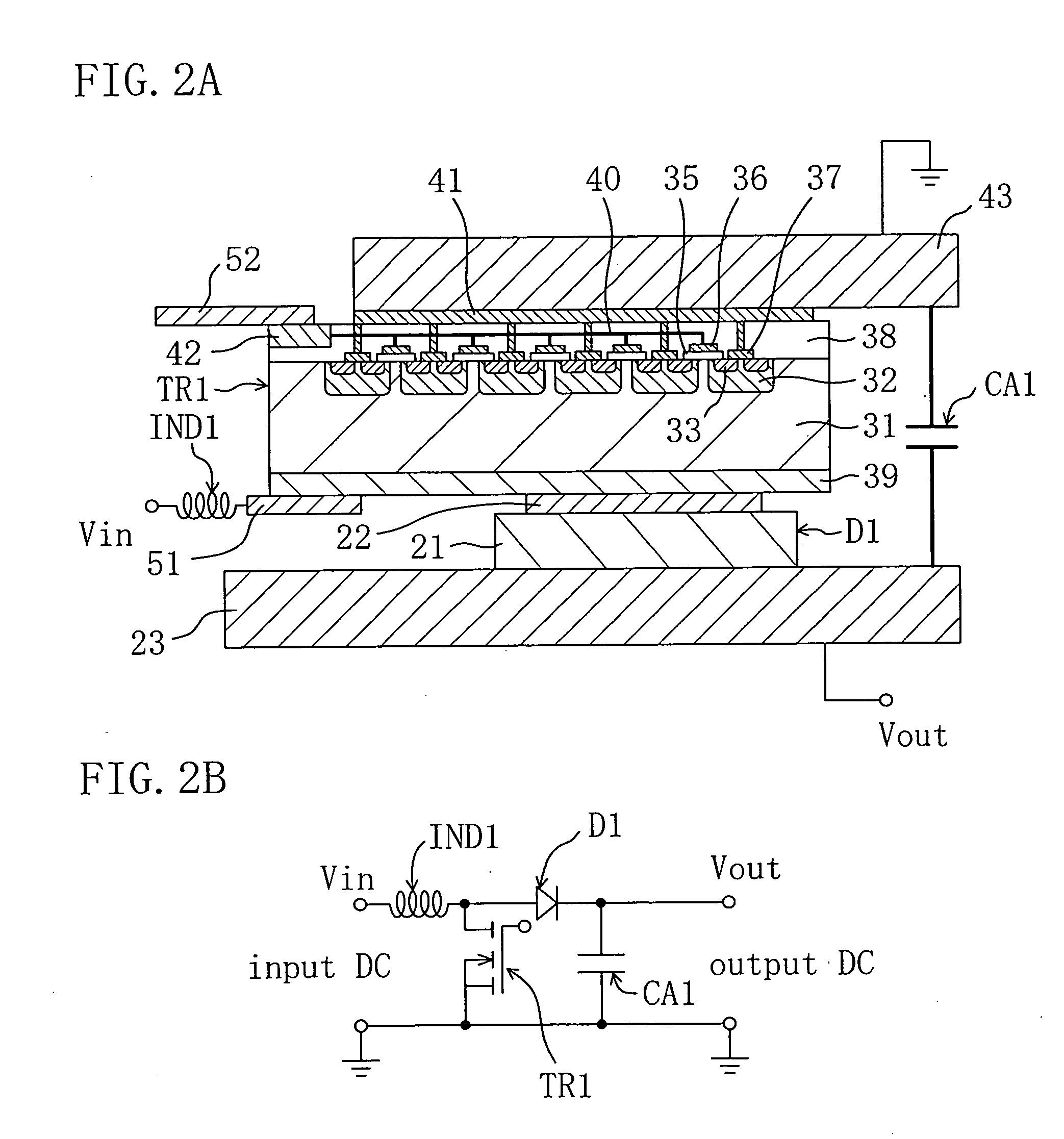
A wide band gap semiconductor device is disclosed. A first trench in a gate electrode part and a second trench in a source electrode part (Schottky diode part) are disposed so that the first and second trenches are close to each other while and the second trench is deeper than the first trench. A metal electrode is formed in the second trench to form a Schottky junction on a surface of an n-type drift layer in the bottom of the second trench. Further, a p+-type region is provided in part of the built-in Schottky diode part being in contact with the surface of the n-type drift layer, preferably in the bottom of the second trench. The result is a wide band gap semiconductor device which is small in size and low in on-resistance and loss, and in which electric field concentration applied on a gate insulating film is relaxed to suppress lowering of withstand voltage to thereby increase avalanche breakdown tolerance at turning-off time.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
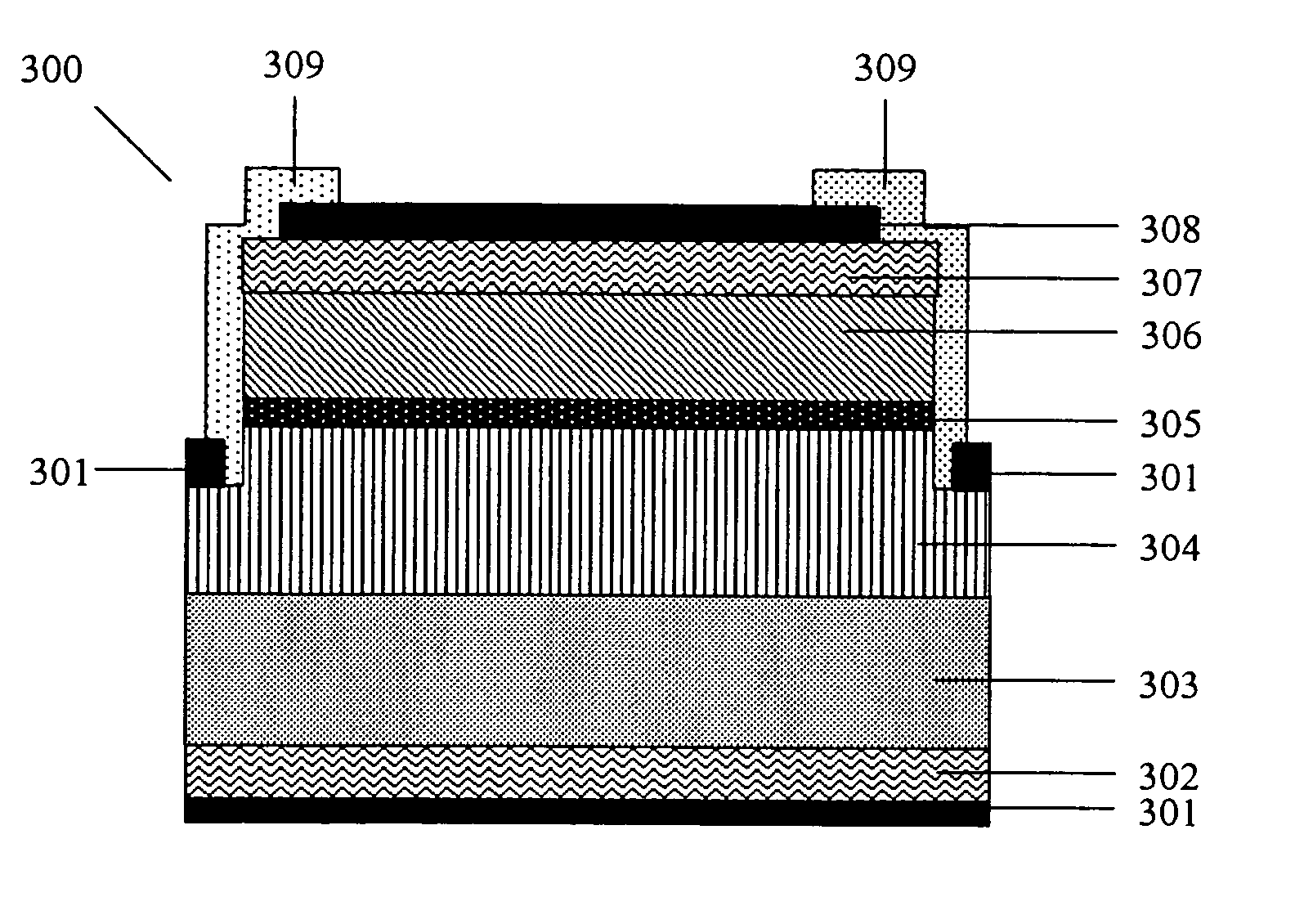
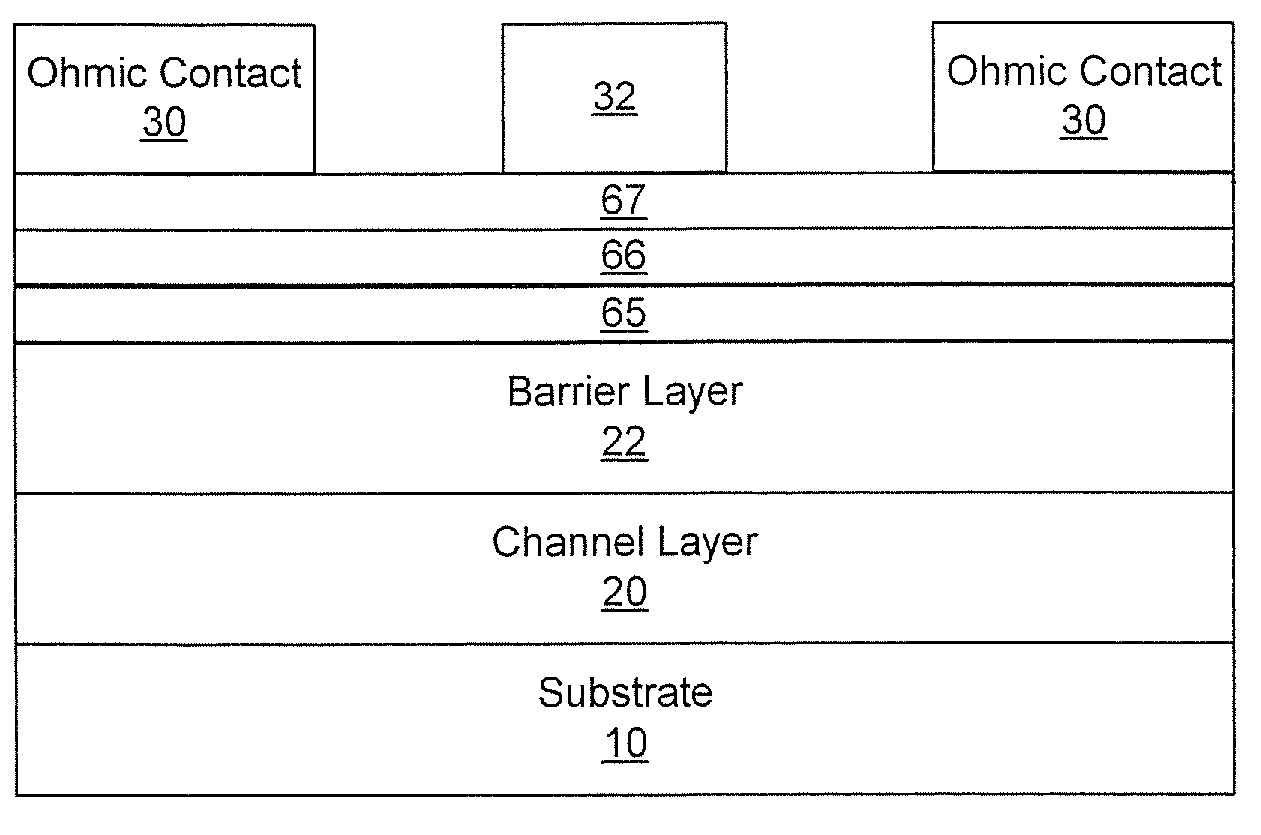
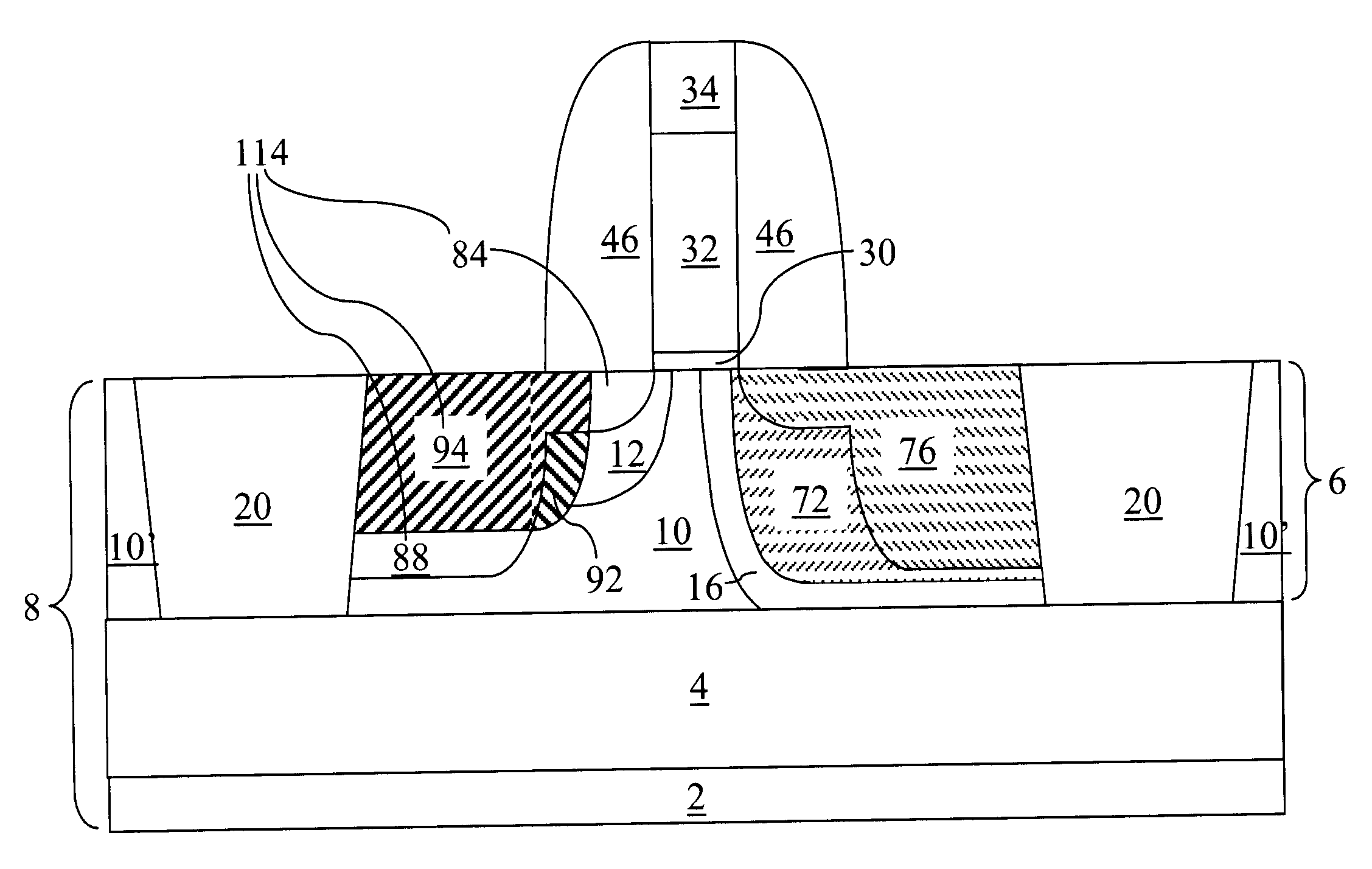
Transistors having buried n-type and p-type regions beneath the source region
High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a non-uniform aluminum concentration AlGaN based cap layer having a high aluminum concentration adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. High electron mobility transistors are provided that include a cap layer having a doped region adjacent a surface of the cap layer that is remote from the barrier layer on which the cap layer is provided. Graphitic BN passivation structures for wide bandgap semiconductor devices are provided. SiC passivation structures for Group III-nitride semiconductor devices are provided. Oxygen anneals of passivation structures are also provided. Ohmic contacts without a recess are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
Field effect transistor containing a wide band gap semiconductor material in a drain
InactiveUS20090121258A1Suppress impact ionizationLarge band gapTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsGate dielectric
A field effect transistor comprising a silicon containing body is provided. After formation of a gate dielectric, gate electrode, and a first gate spacer, a drain side trench is formed and filled with a wide band gap semiconductor material. Optionally, a source side trench may be formed and filled with a silicon germanium alloy to enhance an on-current of the field effect transistor. Halo implantation and source and drain ion implantation are performed to form various doped regions. Since the wide band gap semiconductor material as a wider band gap than that of silicon, impact ionization is reduced due to the use of the wide band gap semiconductor material in the drain, and consequently, a breakdown voltage of the field effect transistor is increased compared to transistors employing silicon in the drain region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Monolithic light emitting devices based on wide bandgap semiconductor nanostructures and methods for making same
InactiveUS7122827B2Reduce defectsSmall sizeLaser detailsLaser active region structureNanolithographyNanostructure
The present invention is directed toward a method for fabricating low-defect nanostructures of wide bandgap materials and to optoelectronic devices, such as light emitting sources and lasers, based on them. The invention utilizes nanolithographically-defined templates to form nanostructures of wide bandgap materials that are energetically unfavorable for dislocation formation. In particular, this invention provides a method for the fabrication of phosphor-less monolithic white light emitting diodes and laser diodes that can be used for general illumination and other applications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
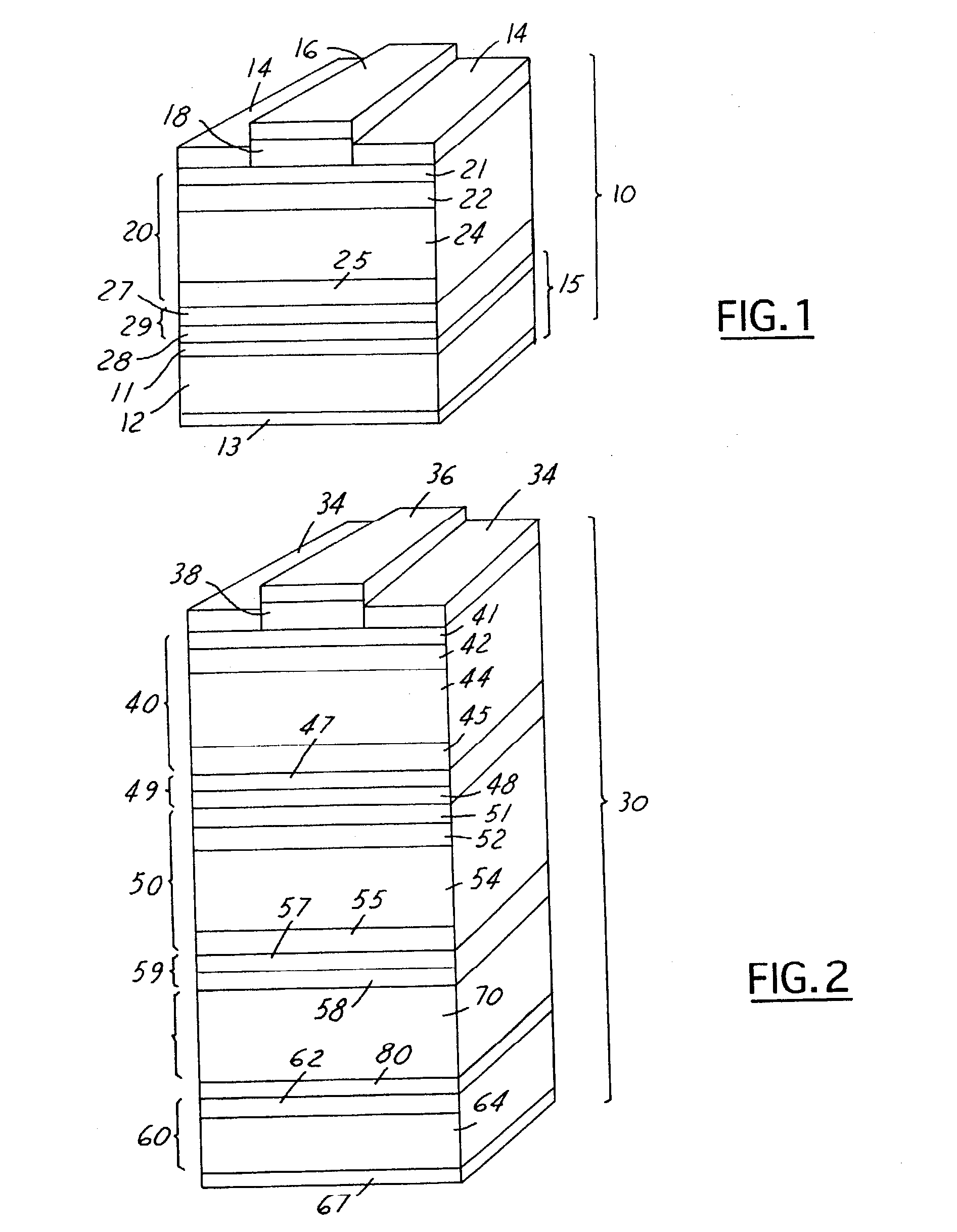
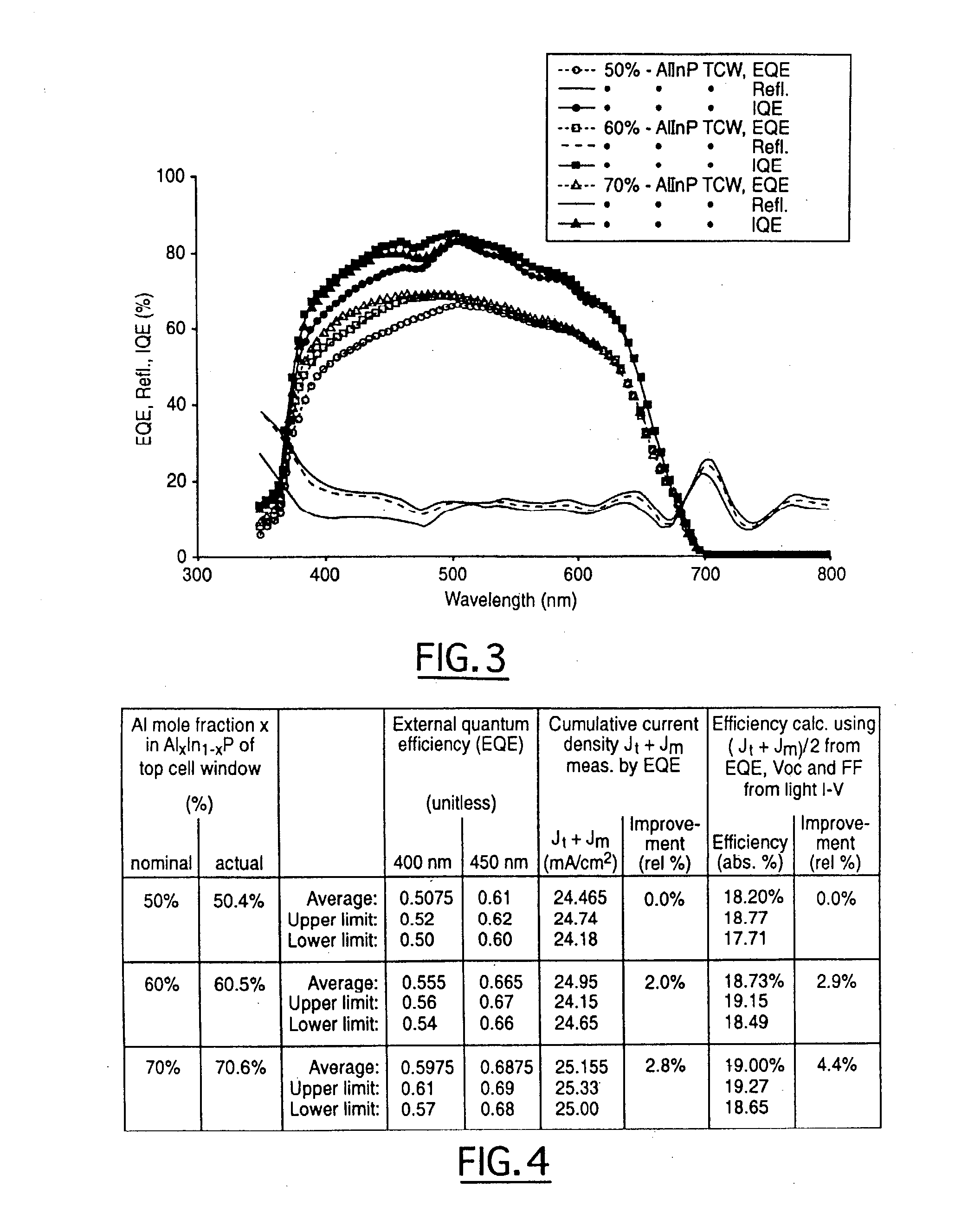
Wide-bandgap, lattice-mismatched window layer for a solar conversion device
ActiveUS7119271B2Improved surface passivationEnhanced light trapping effectPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice mismatchCell layer
A photovoltaic cell or other optoelectronic device having a wide-bandgap semiconductor used in the window layer. This wider bandgap is achieved by using a semiconductor composition that is not lattice-matched to the cell layer directly beneath it and / or to the growth substrate. The wider bandgap of the window layer increases the transmission of short wavelength light into the emitter and base layers of the photovoltaic cell. This in turn increases the current generation in the photovoltaic cell. Additionally, the wider bandgap of the lattice mismatched window layer inhibits minority carrier injection and recombination in the window layer.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Silicon Carbide on Diamond Substrates and Related Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20050164482A1Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
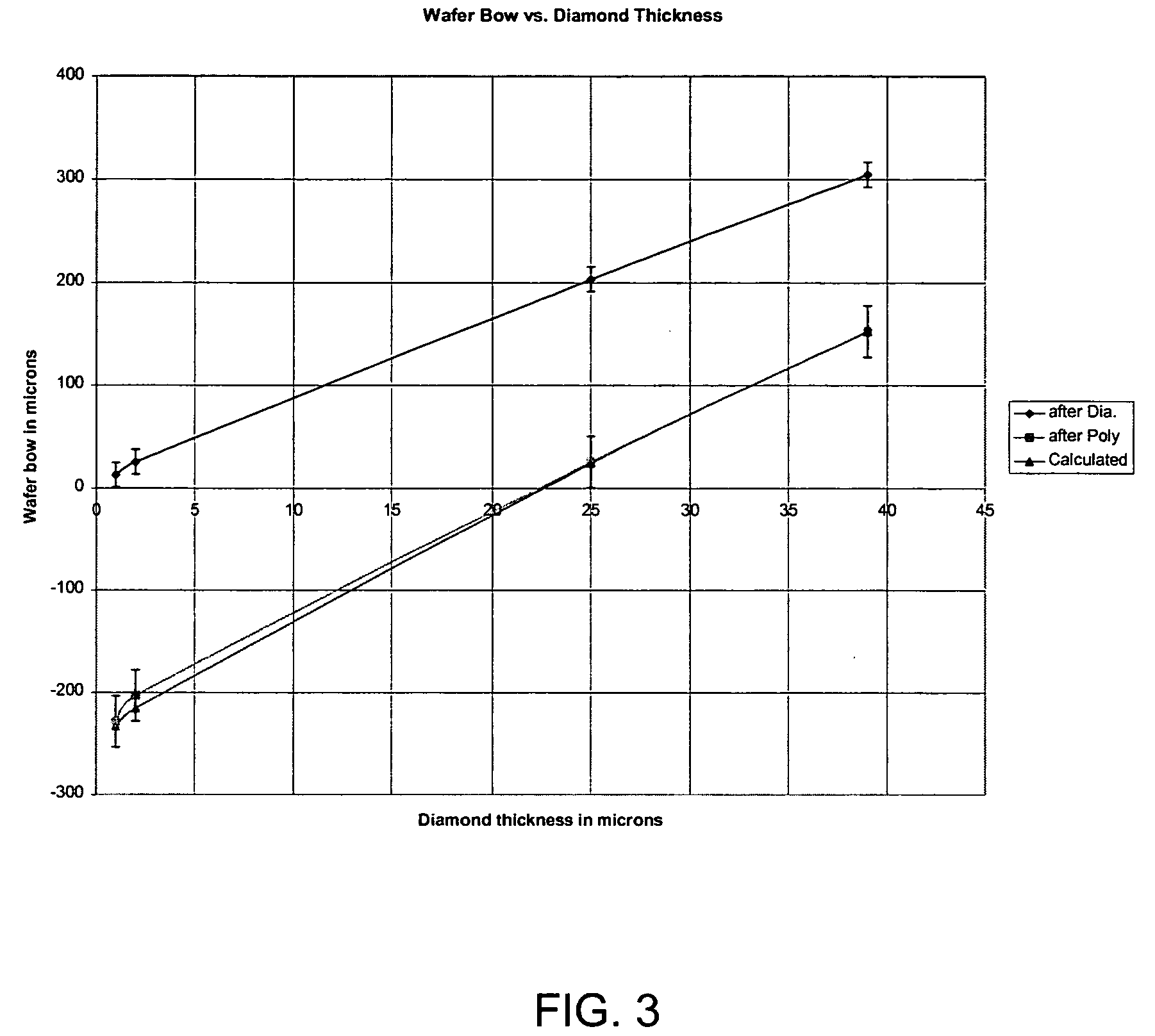
A method of forming a high-power, high-frequency device in wide bandgap semiconductor materials with reduced junction temperature, higher power density during operation and improved reliability at a rated power density is disclosed, along with resulting semiconductor structures and devices. The method includes adding a layer of diamond to a silicon carbide wafer to increase the thermal conductivity of the resulting composite wafer, thereafter reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide portion of the composite wafer while retaining sufficient thickness of silicon carbide to support epitaxial growth thereon, preparing the silicon carbide surface of the composite wafer for epitaxial growth thereon, and adding a Group III nitride heterostructure to the prepared silicon carbide face of the wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Quantum dot sensitized wide bandgap semiconductor photovoltaic devices & methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS20080216891A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
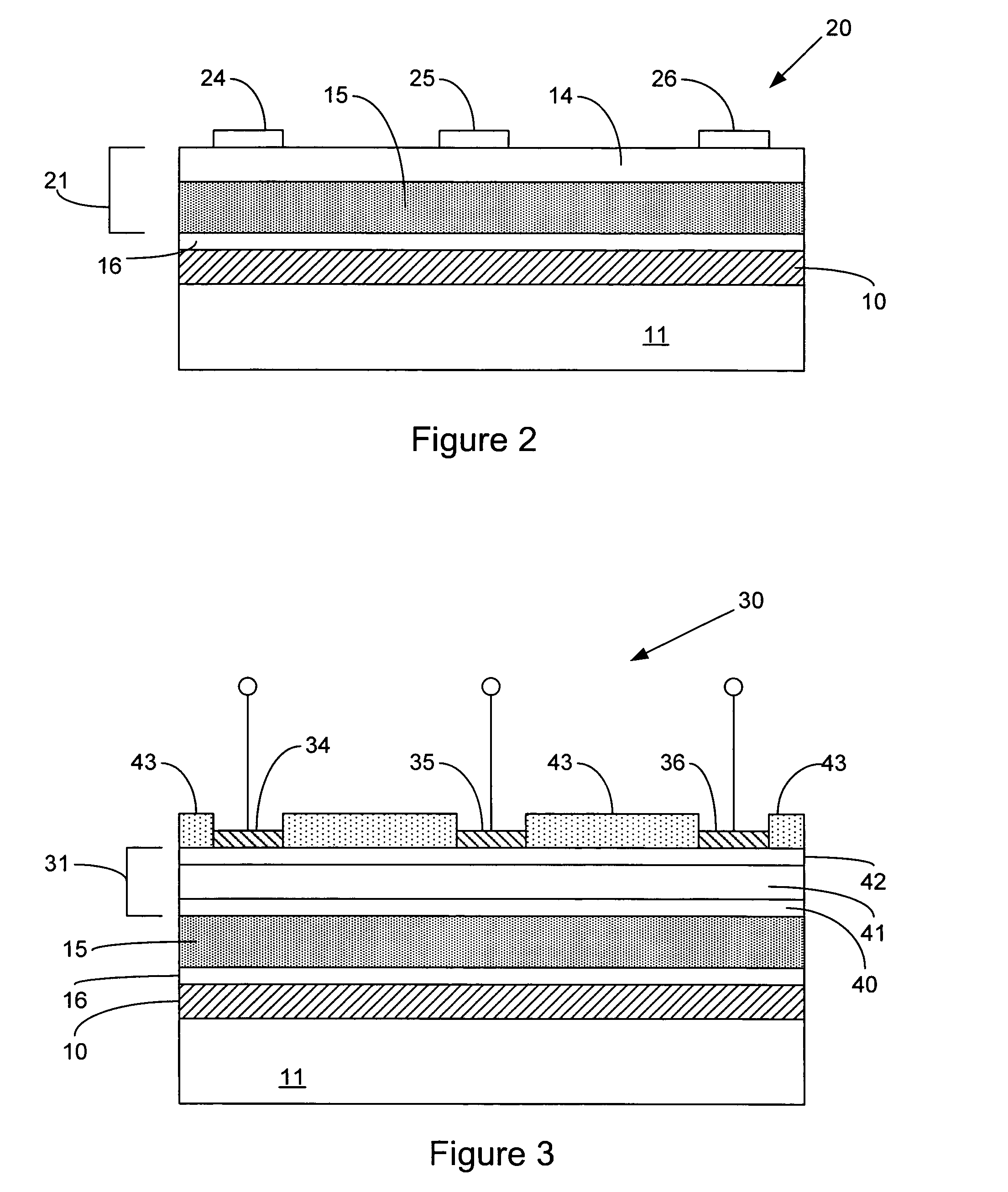
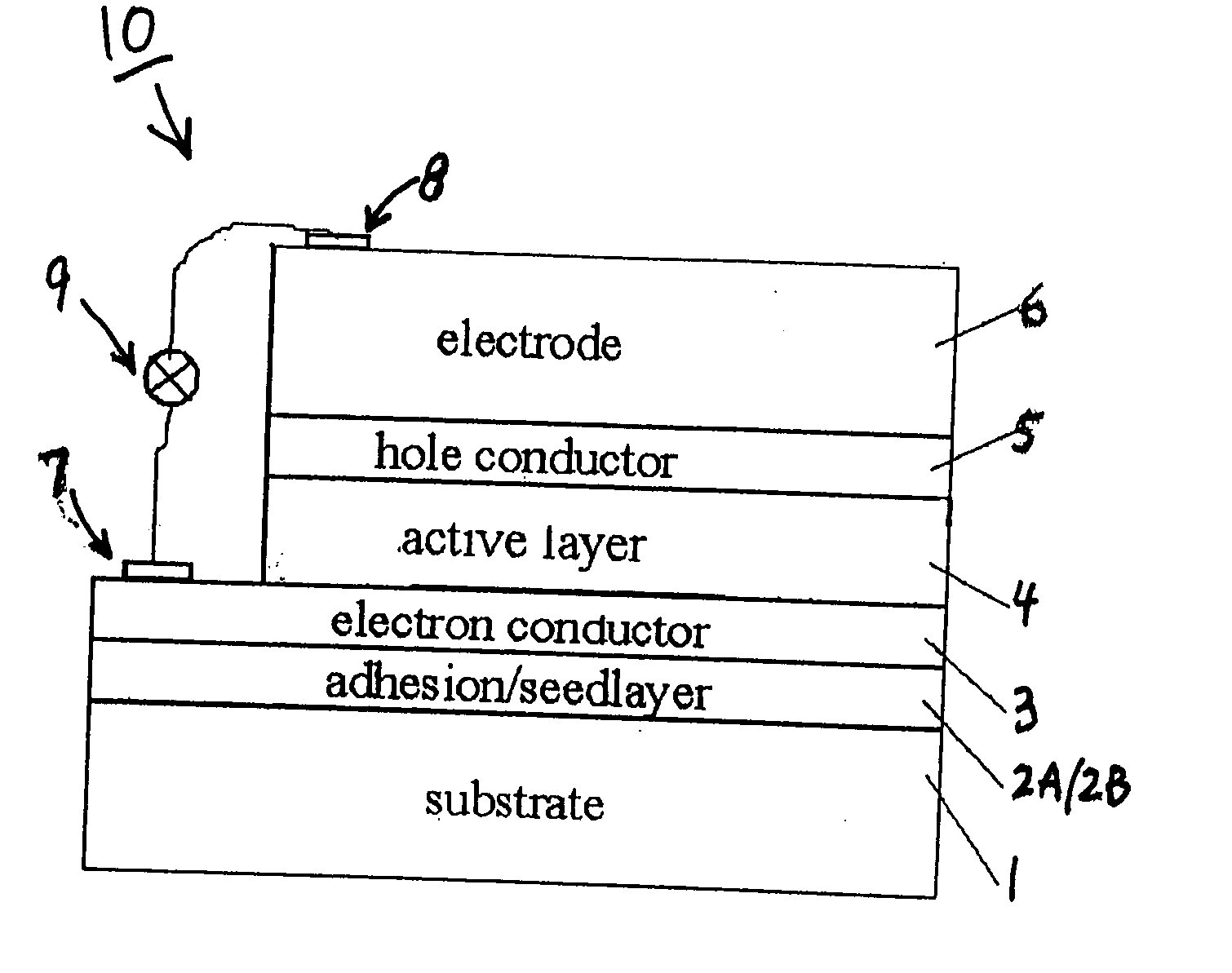
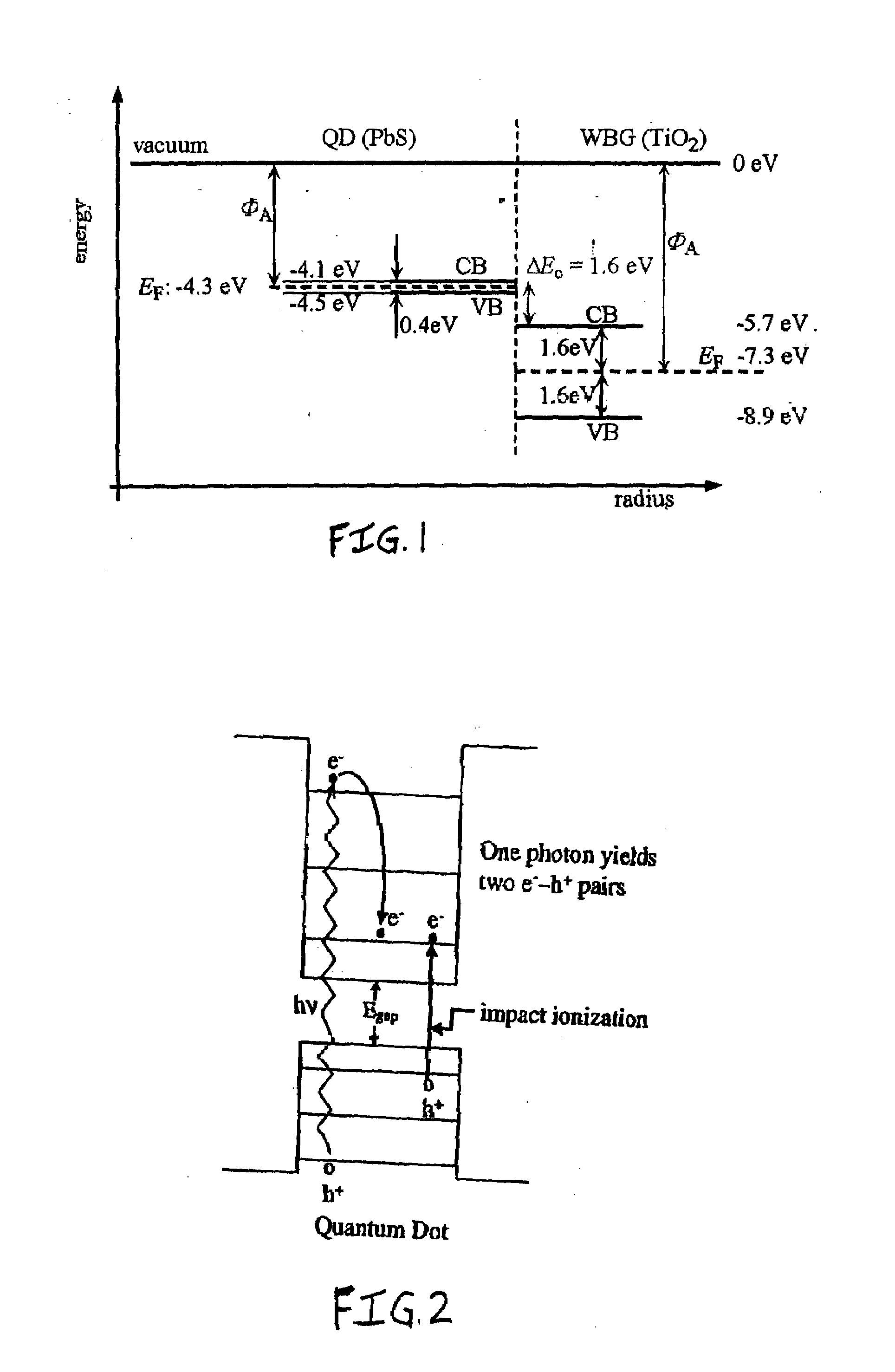
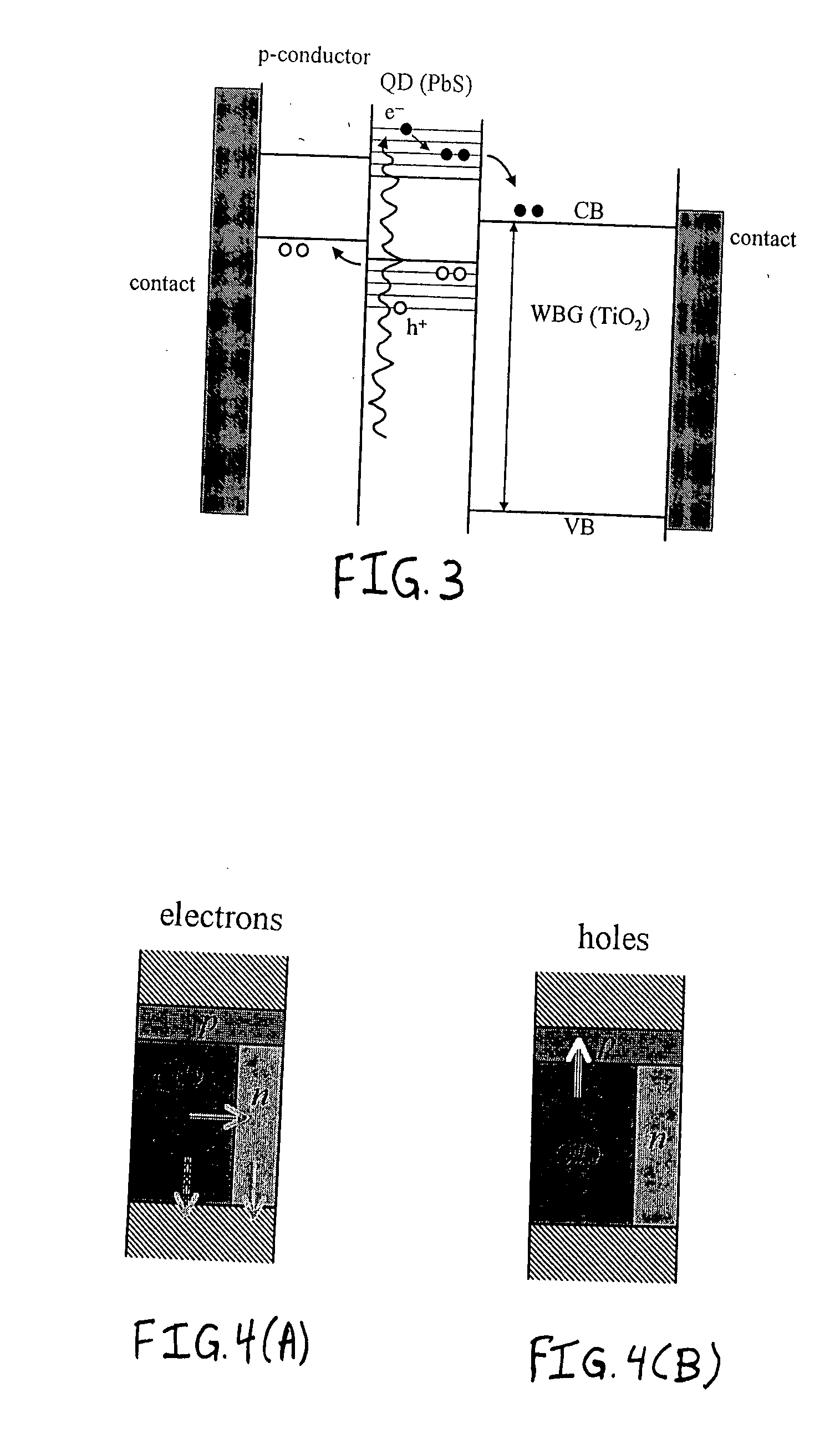
A quantum dot (QD) sensitized wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductor heterojunction photovoltaic (PV) device comprises an electron conductive layer; an active photovoltaic (PV) layer adjacent the electron conductive layer; a hole conductive layer adjacent the active PV layer; and an electrode layer adjacent the hole conductive layer. The active PV layer comprises a wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductor material with Eg≧2.0 eV, in the form of a 2-dimensional matrix defining at least two open spaces, and a narrower bandgap semiconductor material with Eg<2.0 eV, in the form of quantum dots (QD's) filling each open space defined by the matrix of WBG semiconductor material and establishing a heterojunction therewith. The active PV layer is preferably fabricated by a co-sputter deposition process, and the QD's constitute from about 40 to about 90 vol. % of the active PV layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Power converter
ActiveUS20100309700A1Low costAvoid conduction lossTransistorAc-dc conversion without reversalMOSFETEngineering
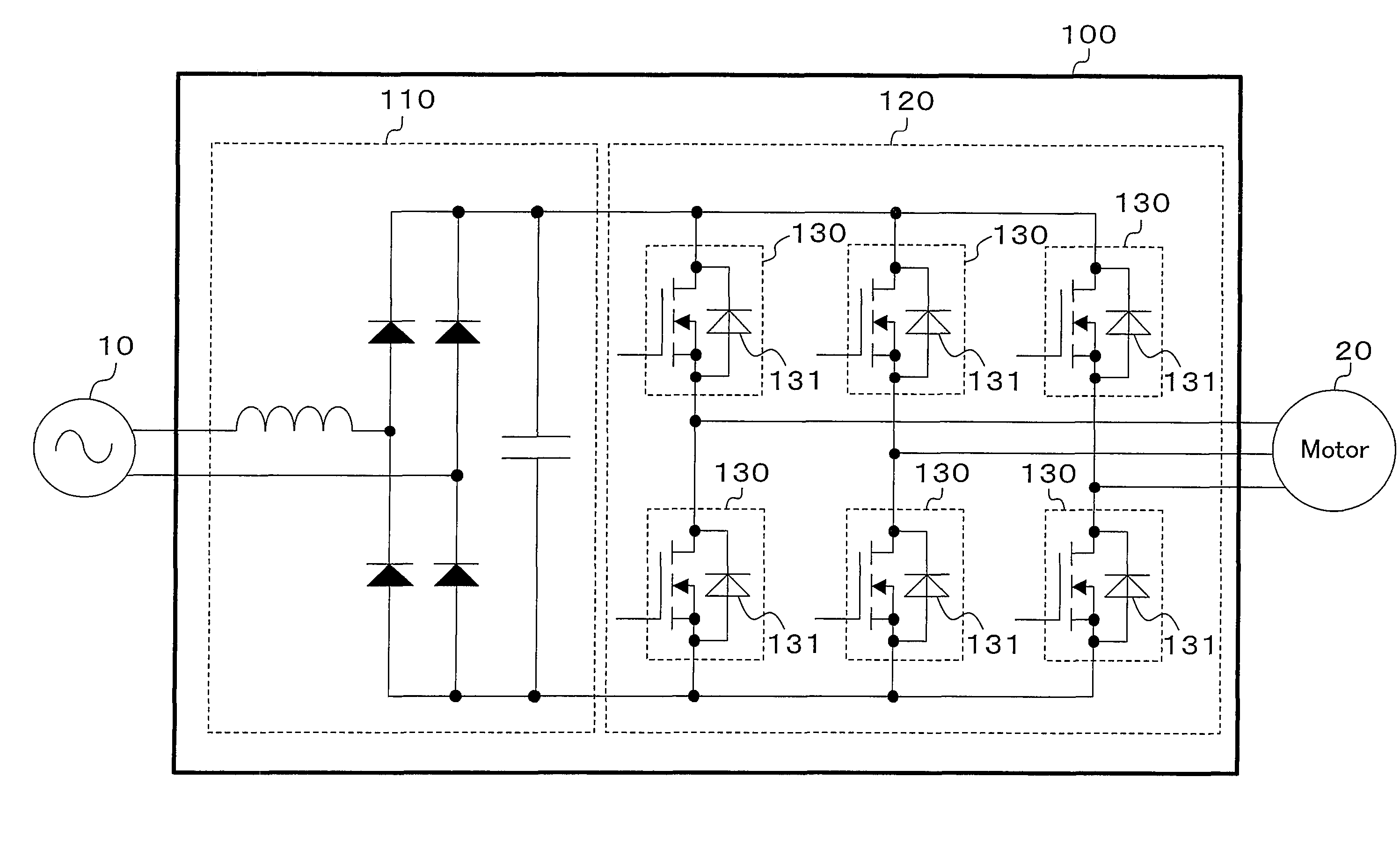
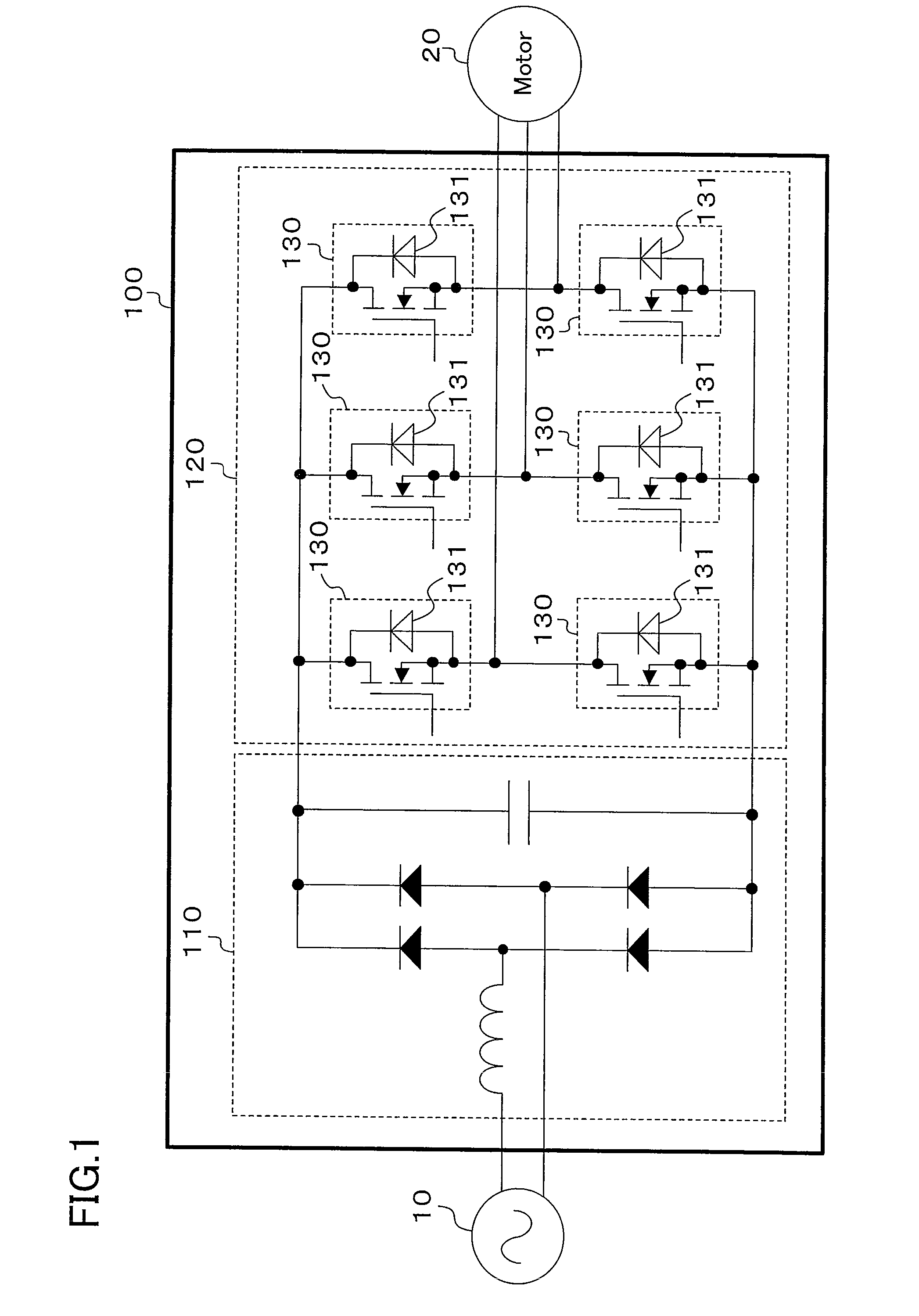
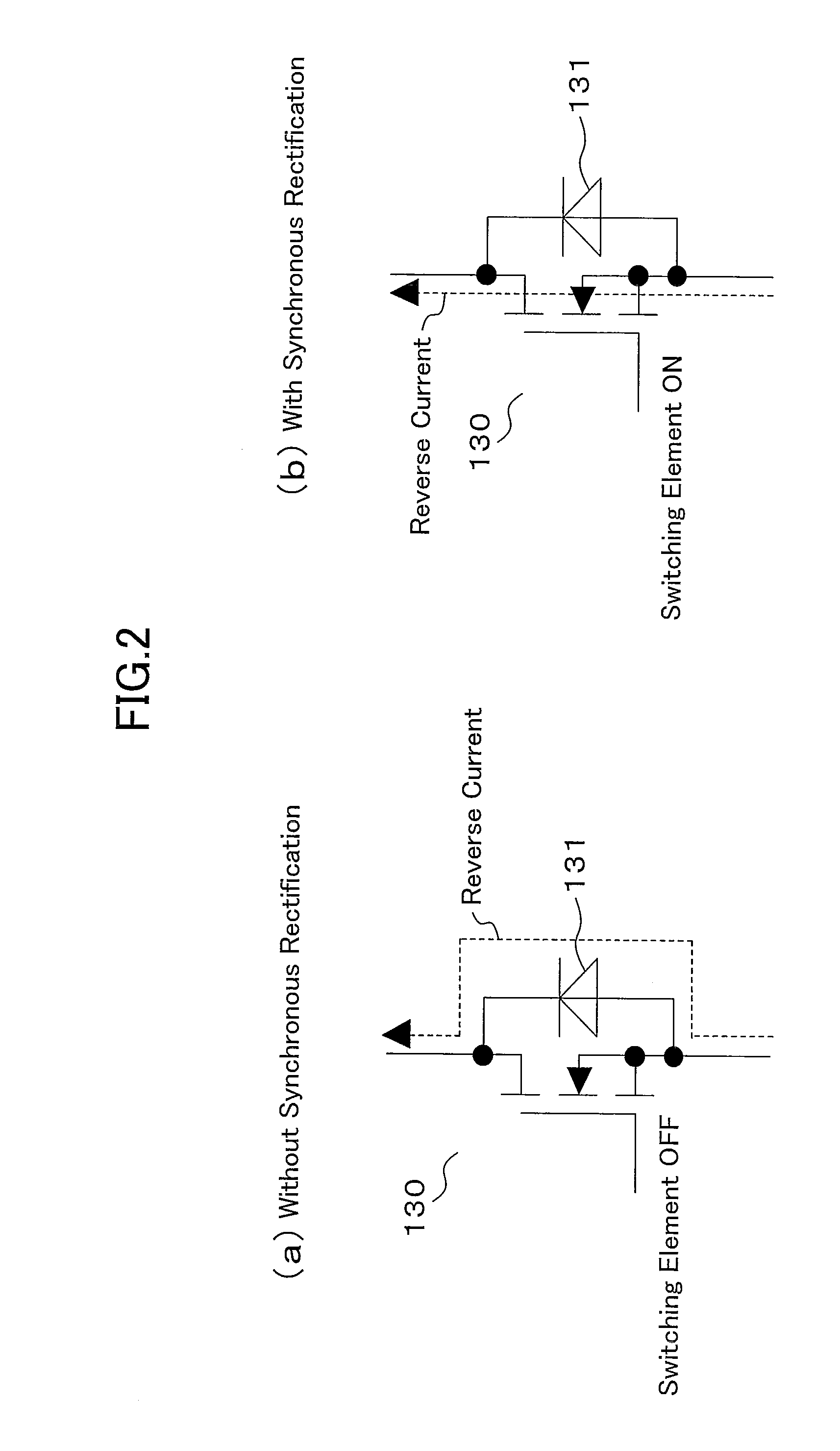
An inverter circuit (120) is configured so as to perform synchronous rectification by six switching elements (130). The switching element (130) is formed of an unipolar device (SiC MOSFET in this case) using a wideband gap semiconductor. The inverter circuit (120) uses the body diode (131) of SiC MOSFET (130) as a freewheeling diode during synchronous rectification.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
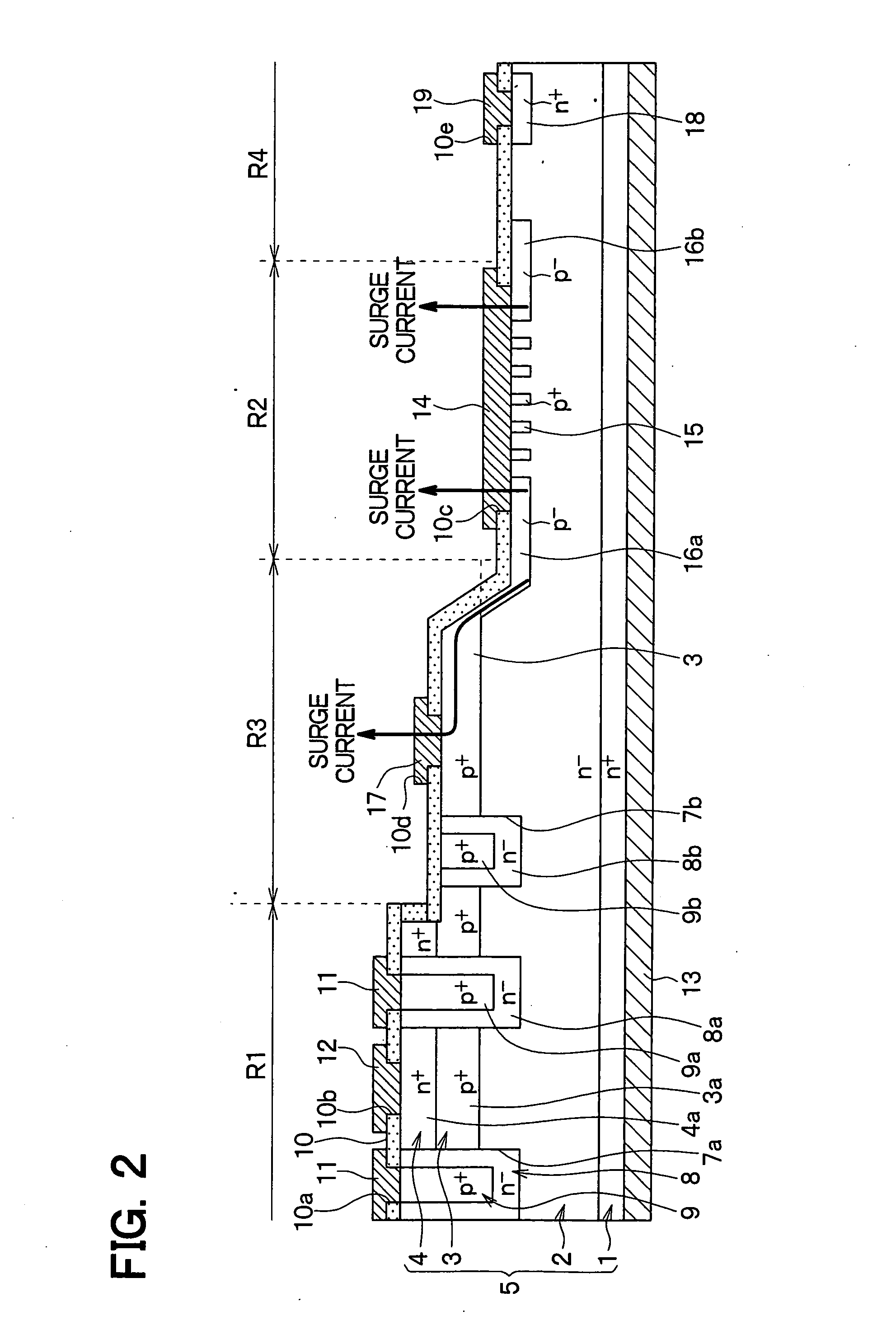
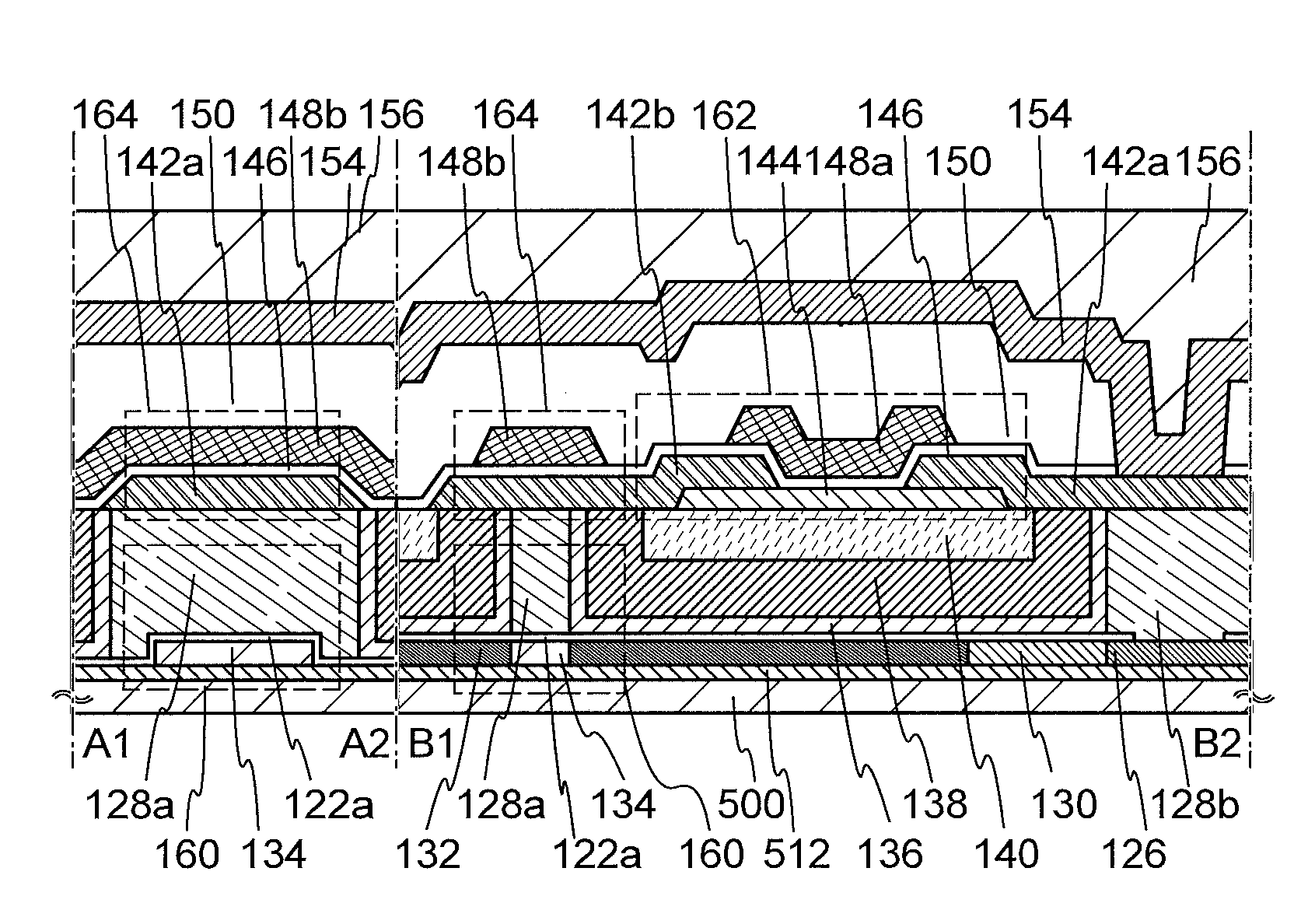
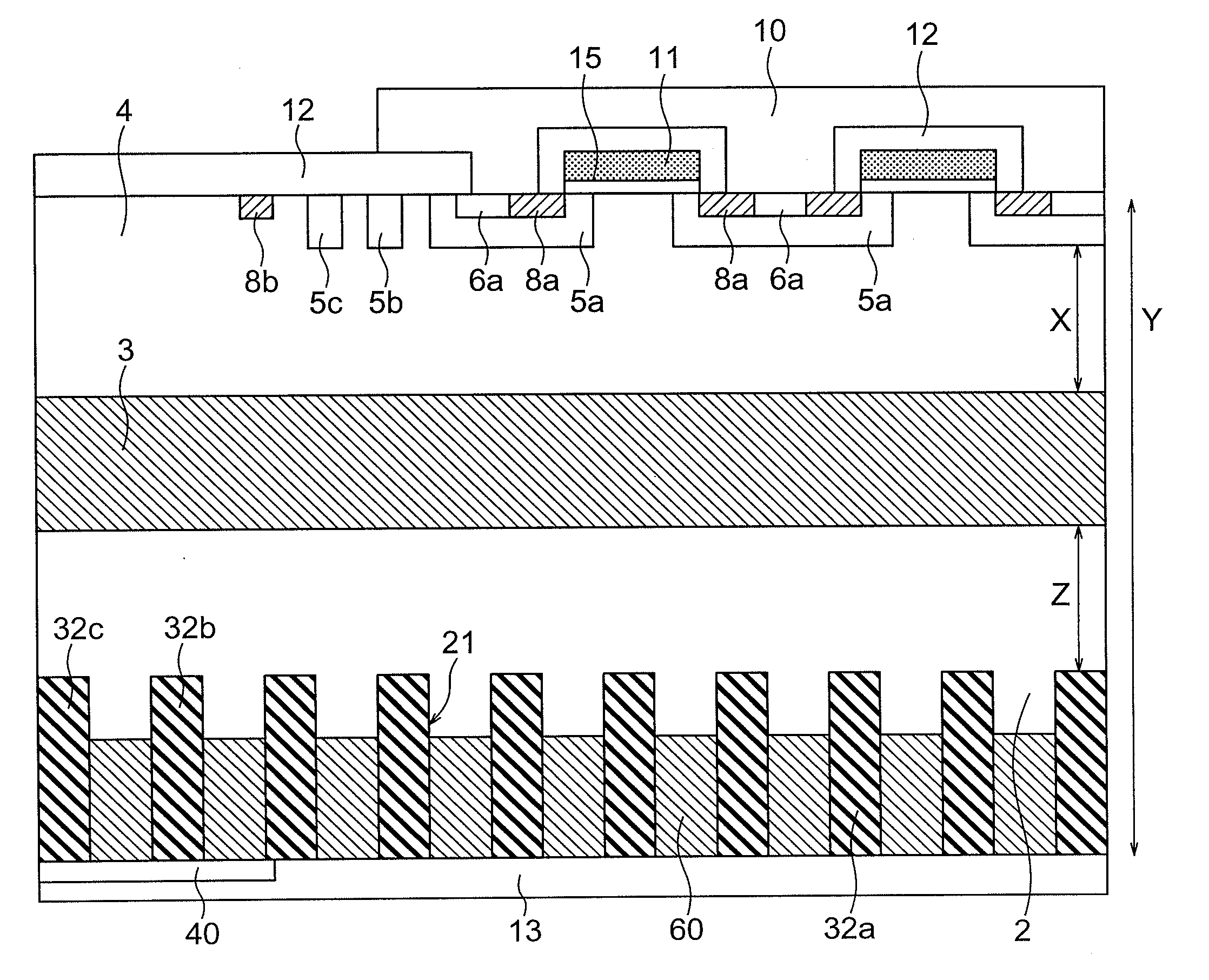
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120187475A1Occurrence can be suppressedReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTransistor
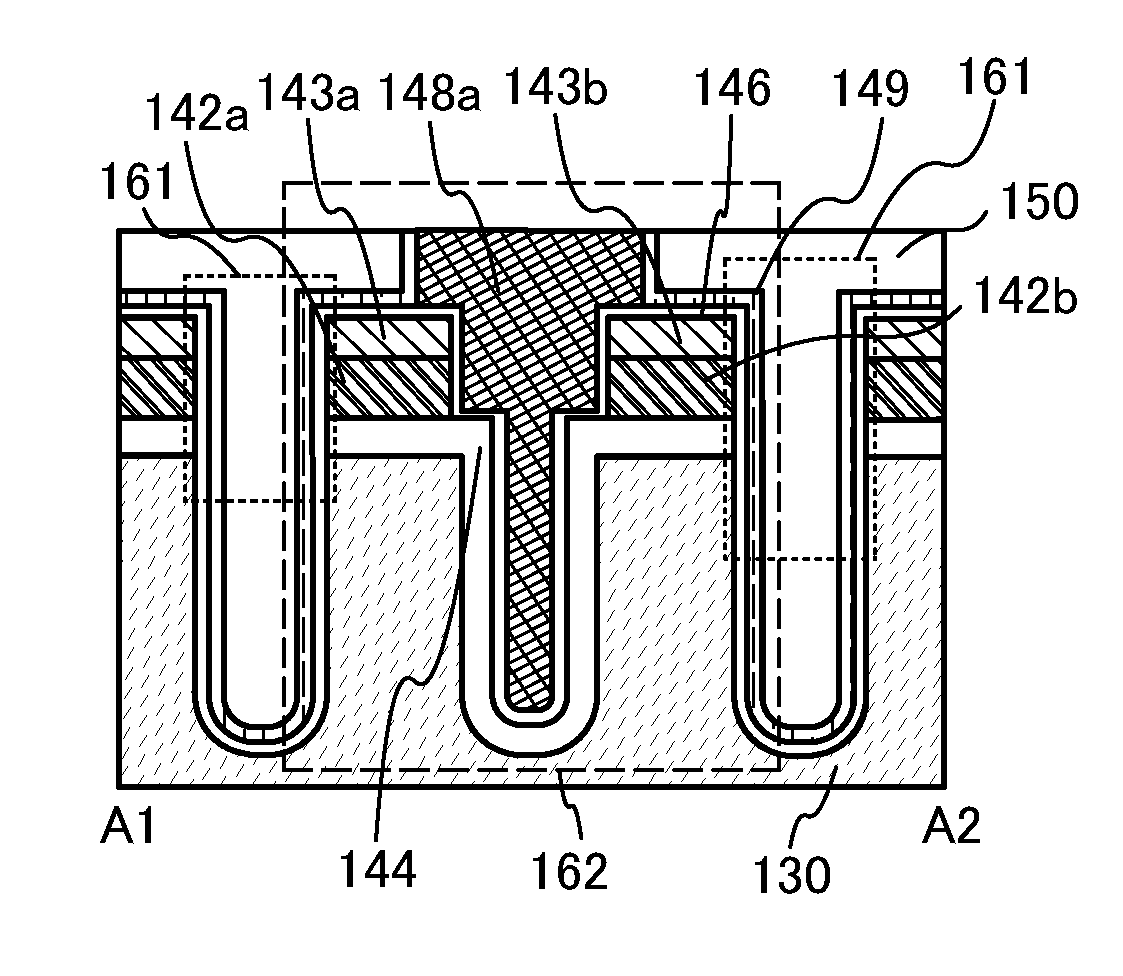
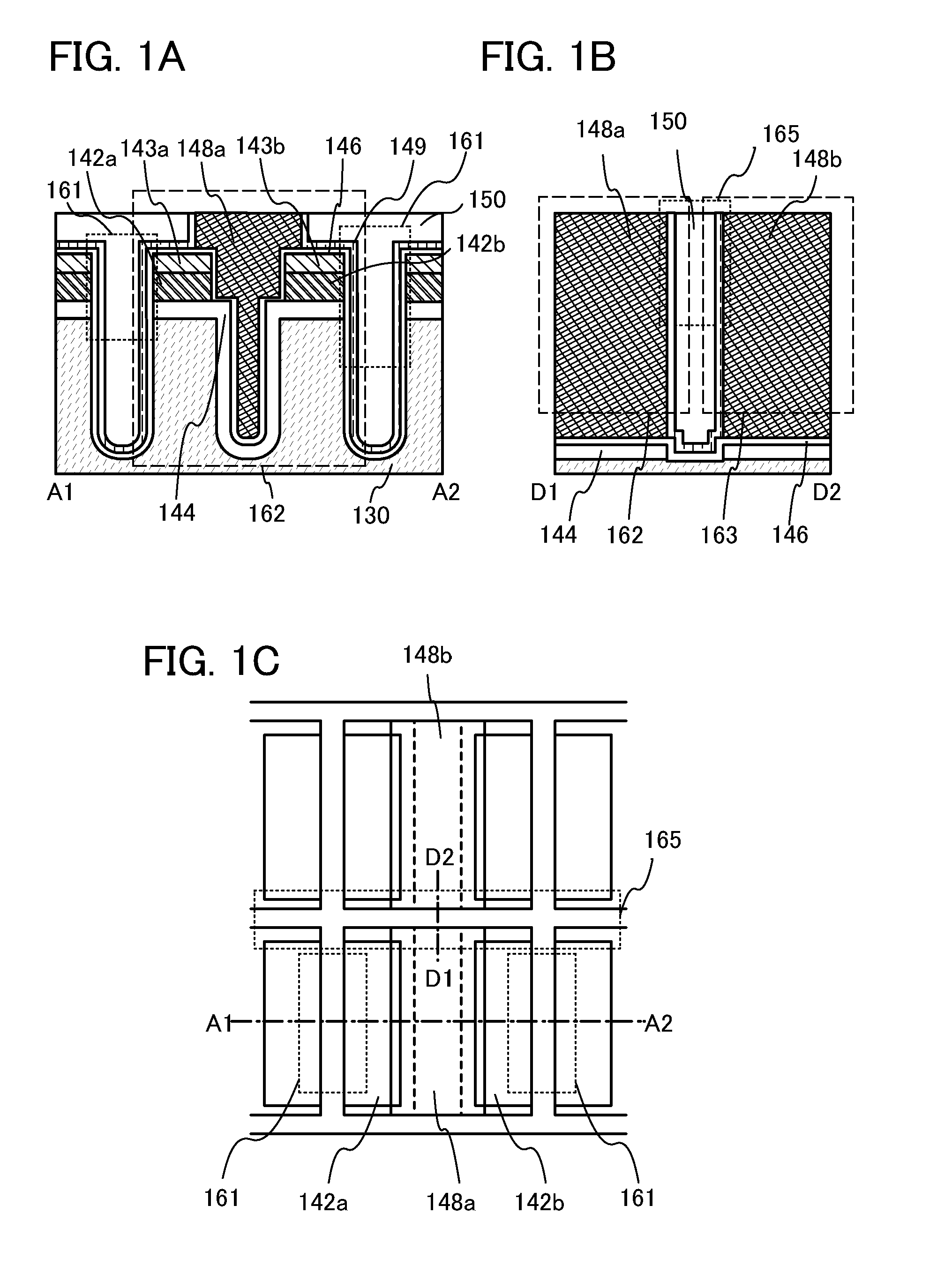
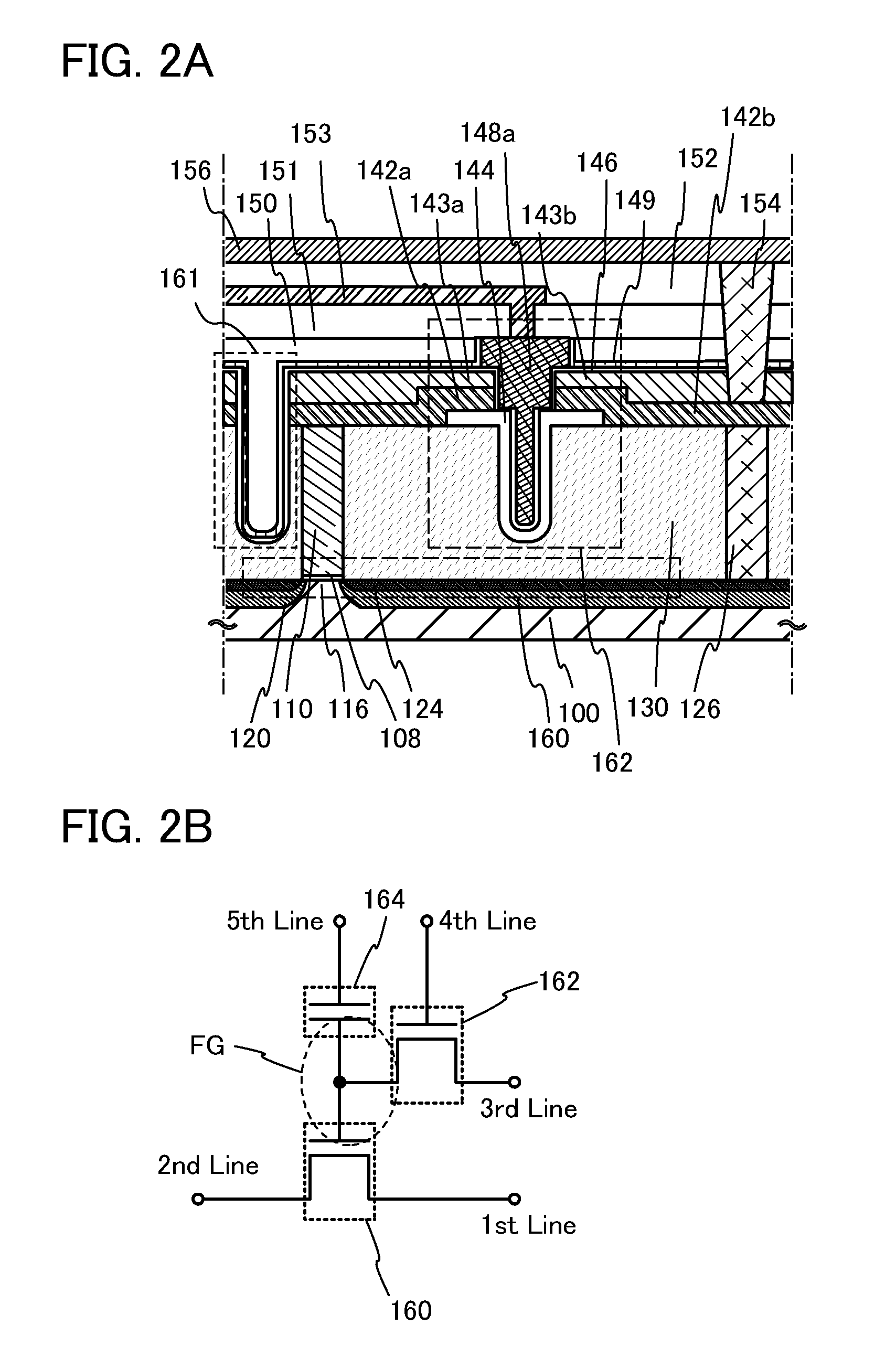
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. A transistor is provided which includes a wide-gap semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. Even when the distance between a source electrode and a drain electrode is decreased, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by setting the depth of the trench for the gate electrode as appropriate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
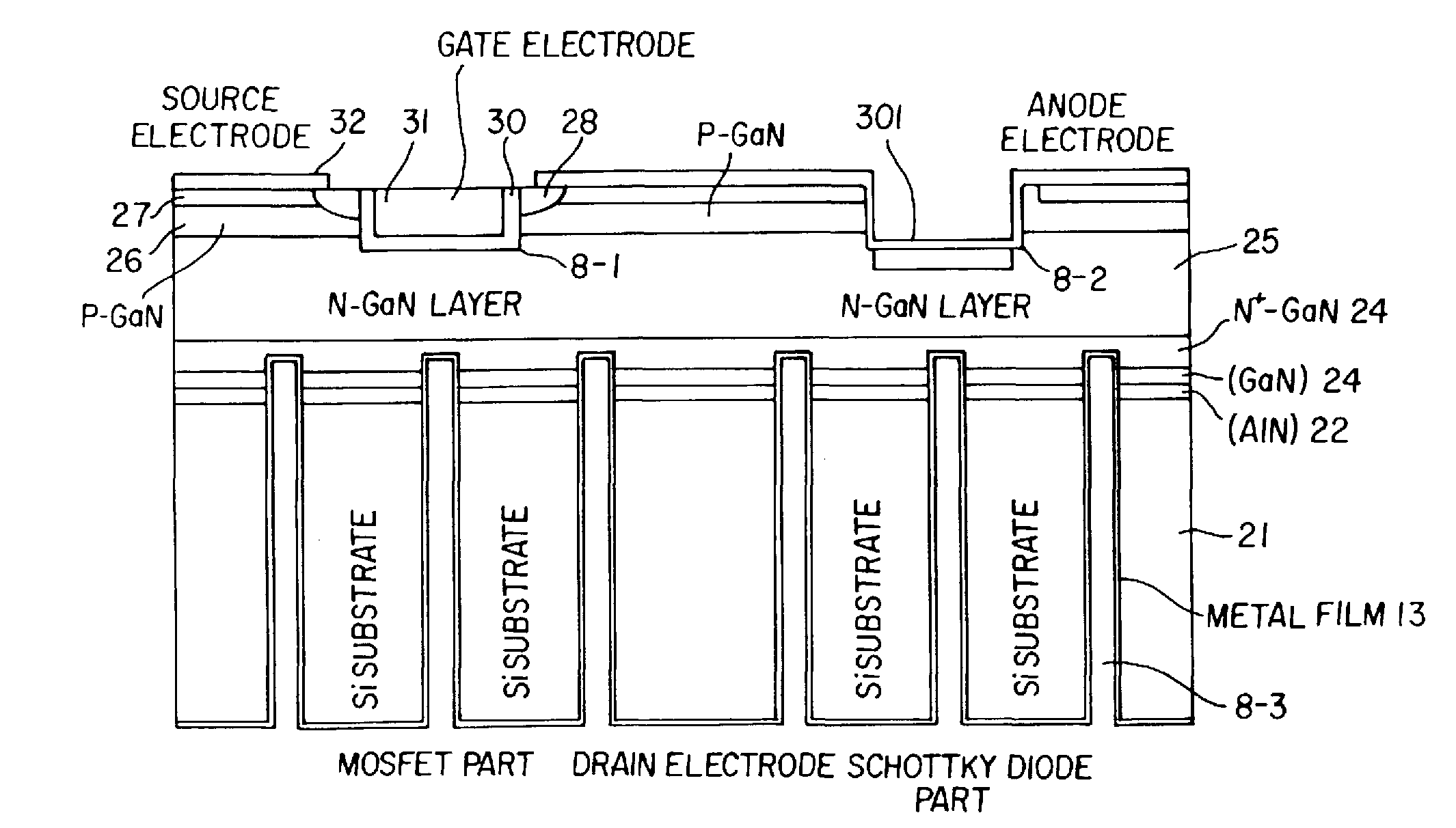
Wide band gap semiconductor device including junction field effect transistor
A wide band gap semiconductor device has a transistor cell region, a diode forming region, an electric field relaxation region located between the transistor cell region and the diode forming region, and an outer peripheral region surrounding the transistor cell region and the diode forming region. In the transistor cell region, a junction field effect transistor is disposed. In the diode forming region, a diode is disposed. In the electric field relaxation region, an isolating part is provided. The isolating part includes a trench dividing the transistor cell region and the diode forming region, a first conductivity-type layer disposed on an inner wall of the trench, and a second conductivity-type layer disposed on a surface of the first conductivity-type layer so as to fill the trench. The first conductivity-type layer and the second conductivity-type layer provide a PN junction.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
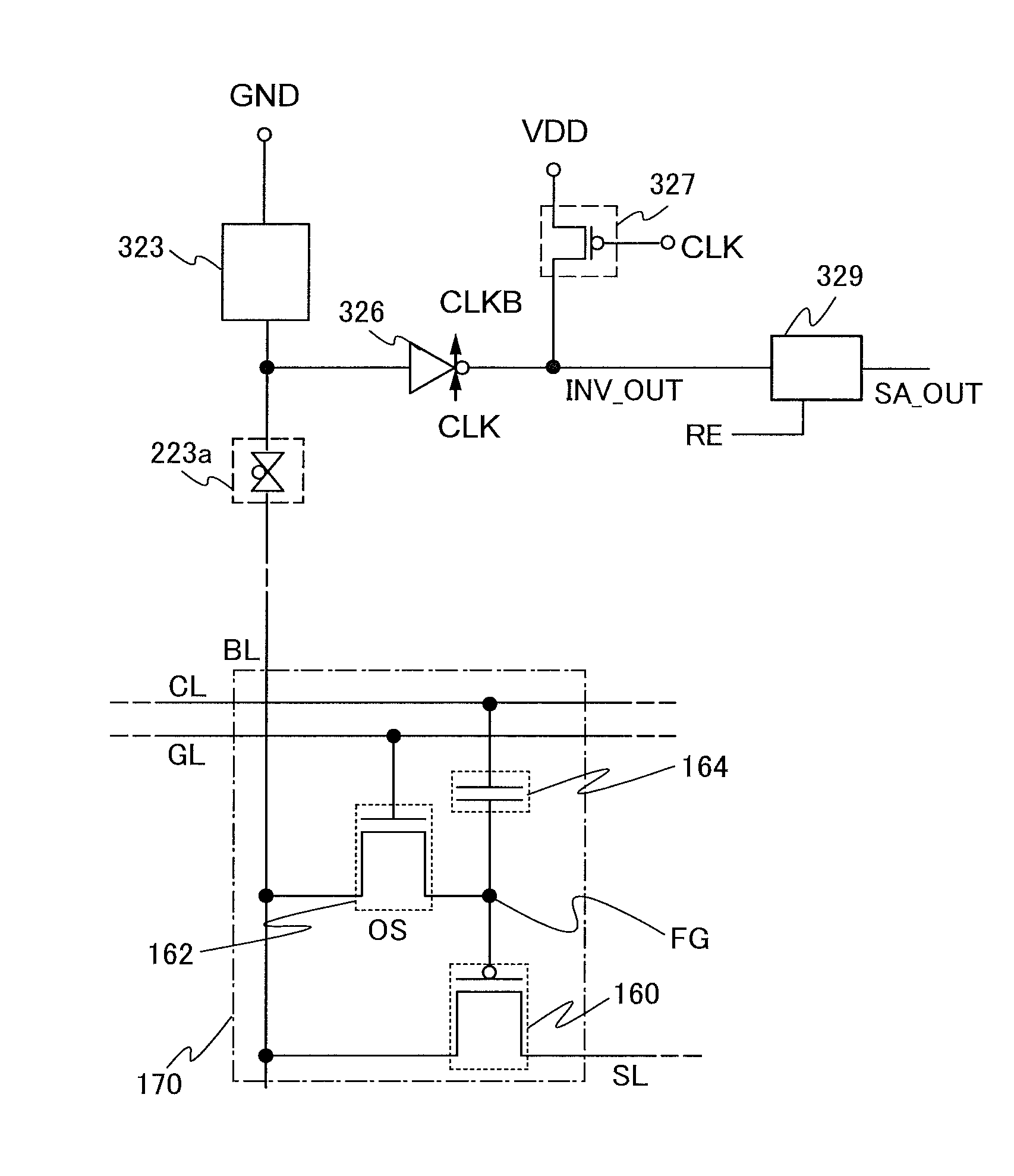
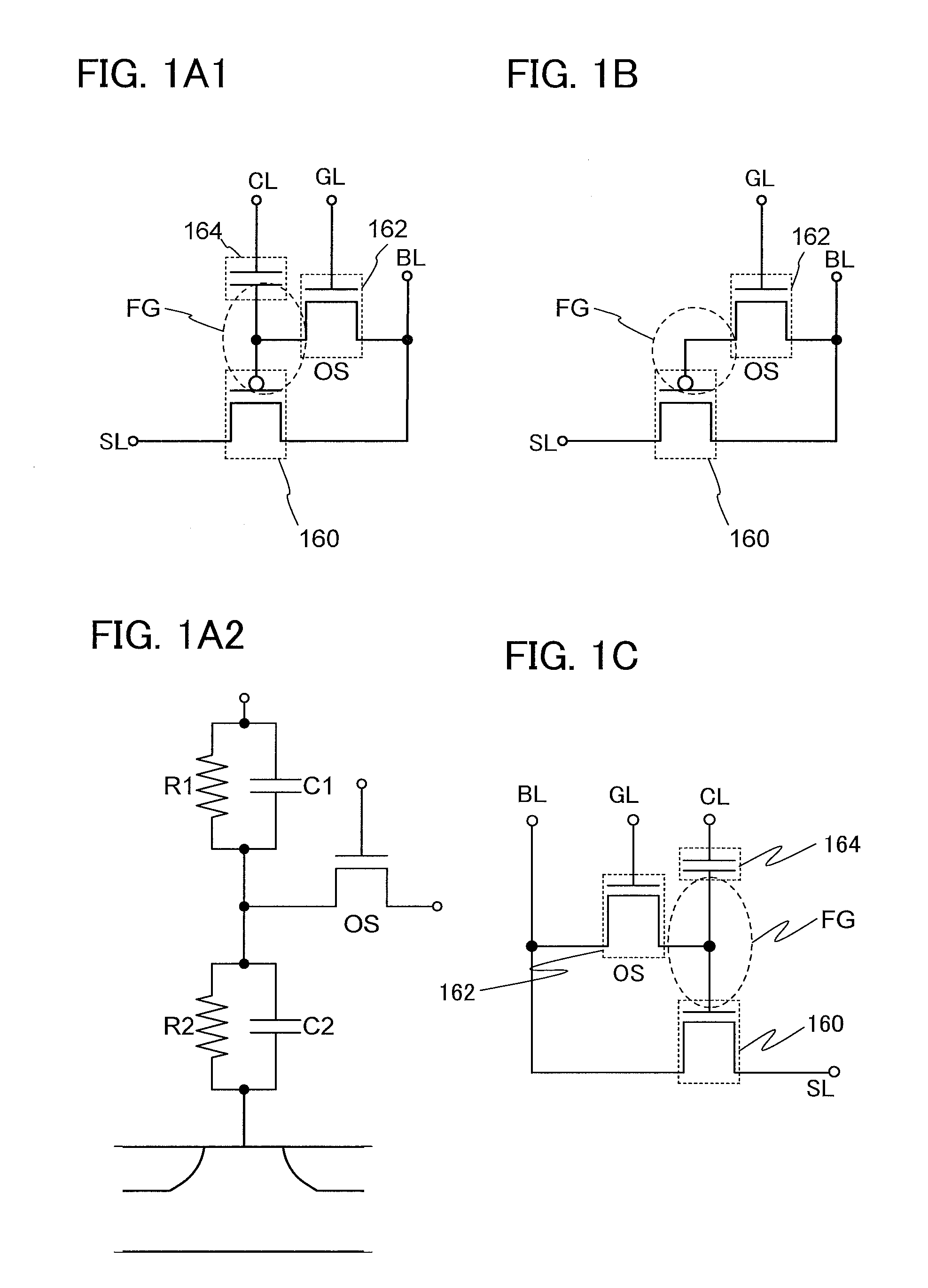
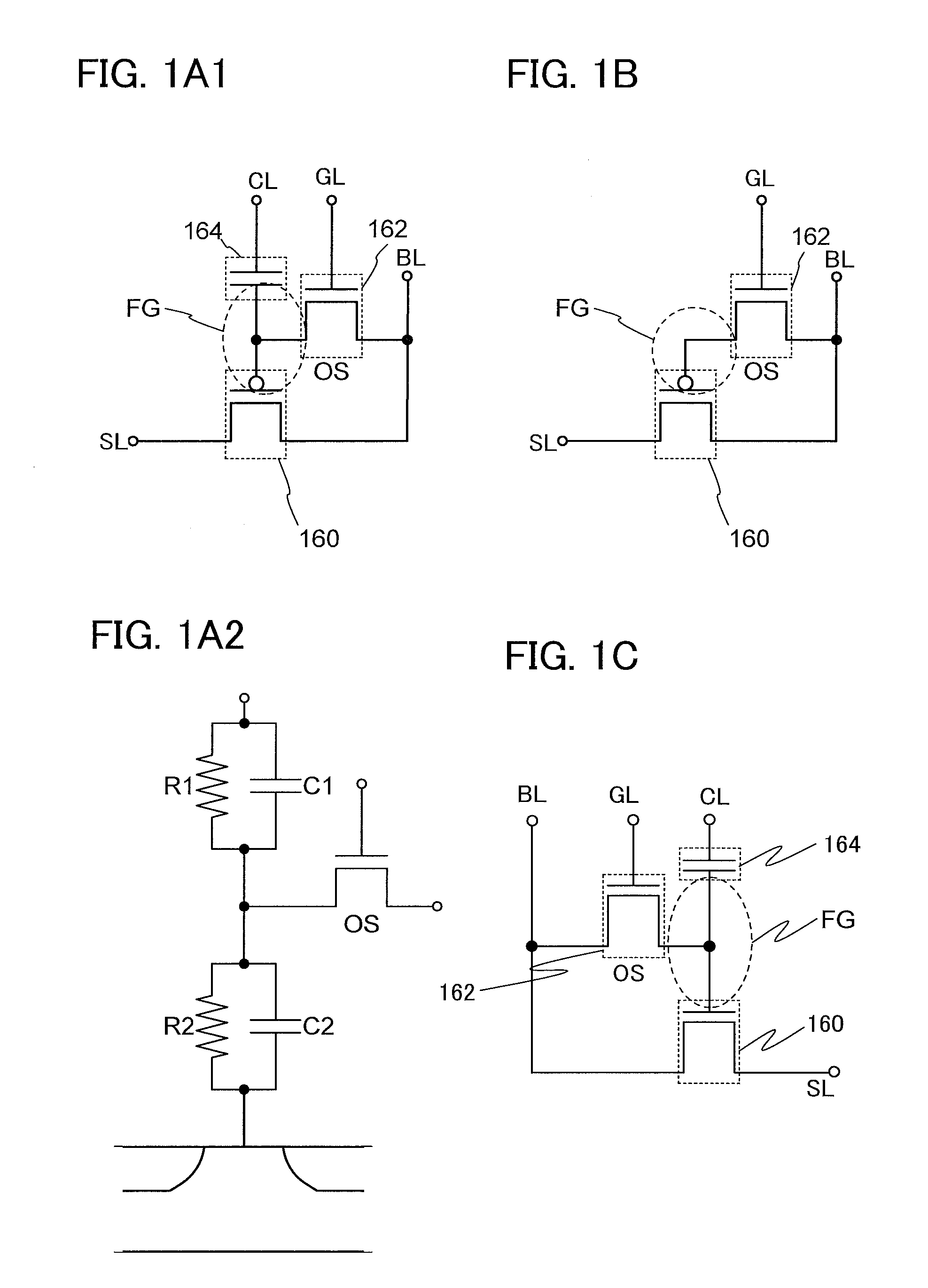
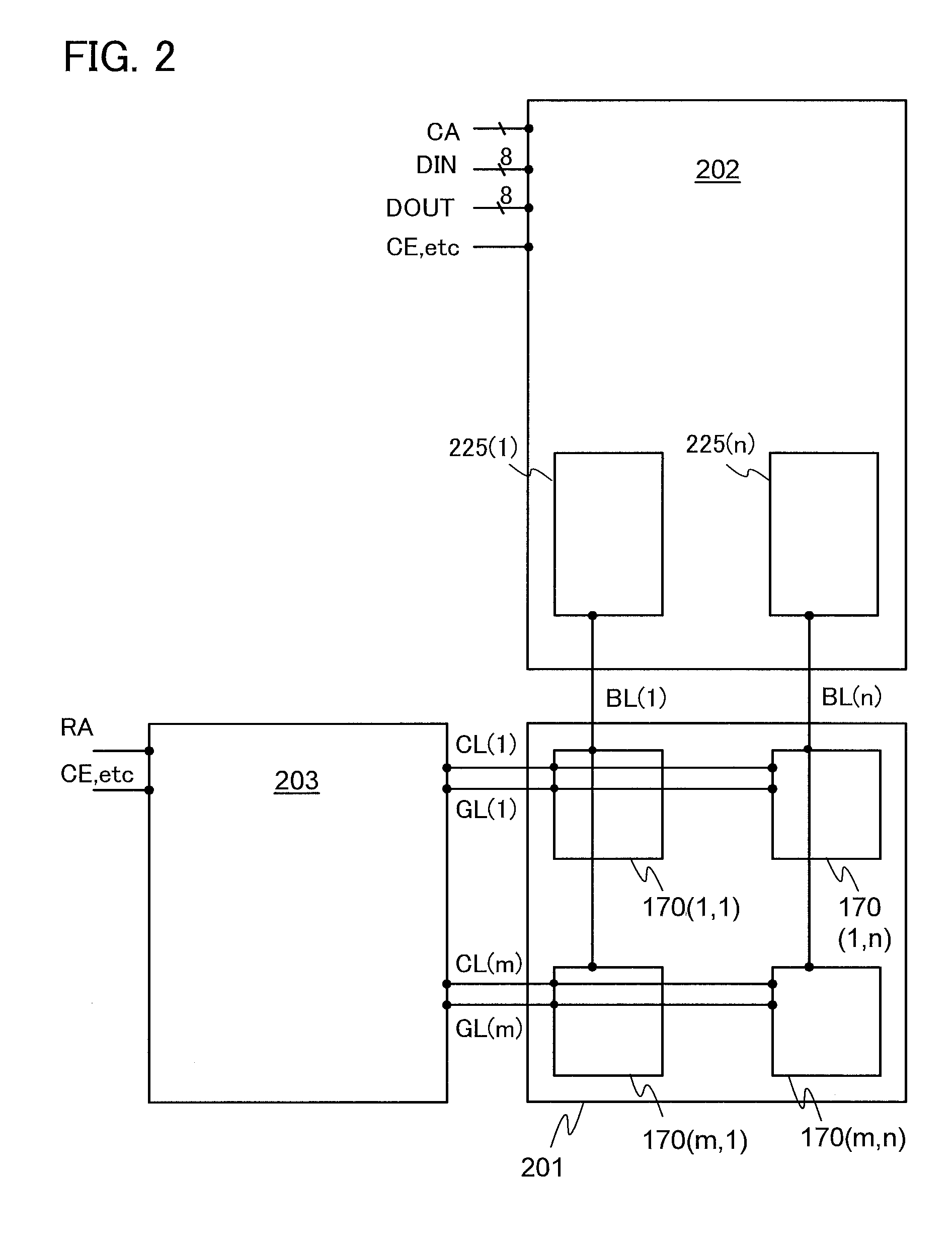
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS8614916B2Reduce off-state currentLonger heldSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPotential changeHemt circuits
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Ultra-linear multi-channel field effect transistor
InactiveUS20050285098A1Sharp impurity gradientVariation in frequencyTransistorNanoinformaticsHeterojunctionConcentration gradient
Alternate layers of wide band gap and narrow band gaps of different kinds of semiconductors are used to form multiple channels of a FET. The channels are doped or formed as 2-DEG / 2-DHG in narrow band semiconductor by charge supply layer in the wide band gap semiconductor. The different kinds of semiconductors form heterojunctions to confine the electrons / holes in separate thin spikes layers. A number of spikes (3-10 nm thick) of different doped or 2-DEG / 2-DHG concentrations in various channels can result in overall electron concentration gradient such as a 1 / x3 electron / hole concentrations profile. Such an electron / hole concentration gradient can result in a linear variation of drain current with voltage to obtain a wide dynamic range.
Owner:EPITAXIAL TECH
Low-pressure metal organic chemical vapour phase depositing apparatus for zinc oxide and process thereof
InactiveCN1644754AImprove crystal qualityImprove optical qualityFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingTransport systemGas phase
The invention was about low voltage metal organic chemistry vapour deposition equipment and the preparation. The system was made up of gas transport system, reaction chamber, sample pretreatment chamber, control system, tail gas treatment system. The sample pretreatment chamber was made up of ectotheca, sample pallet shelf, sample desk, gas bleed spore, plasma generator, flange, plate valve of switch between the sample pretreatment chamber and reaction chamber, flange of plate valve, magnetic transmit bar, magnetic cannula, flange of transmit bar. Its advantages include increased the growing of ZnO film and uniformity, benefit for the P type and intermingle of high impedance.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +2
Silicon carbide on diamond substrates and related devices and methods
ActiveUS7033912B2Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Wide bandgap semiconductor layers on SOD structures
InactiveUS20060113545A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBroadbandOpto electronic
Multi-layered structures containing GaN on SOD (silicon / diamond / silicon) substrates are described. The unique substrate / epilayer combination can provide electronic materials suitable for high-power and opto-electronic devices without commonly observed limitations due to excess heat during device operation. The resulting devices have built-in thermal heat spreading capability that result in better performance and higher reliability.
Owner:SP3 +1
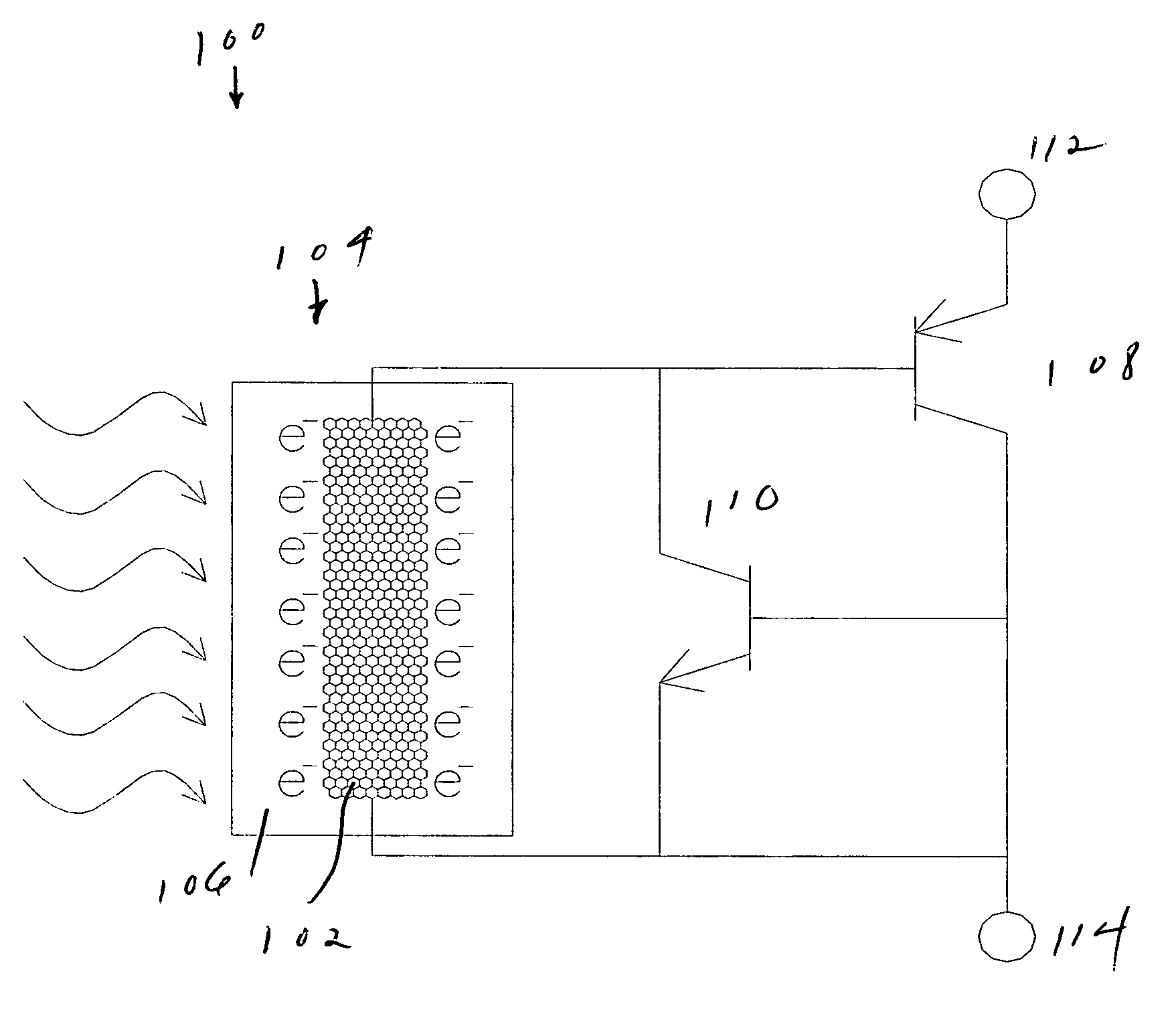
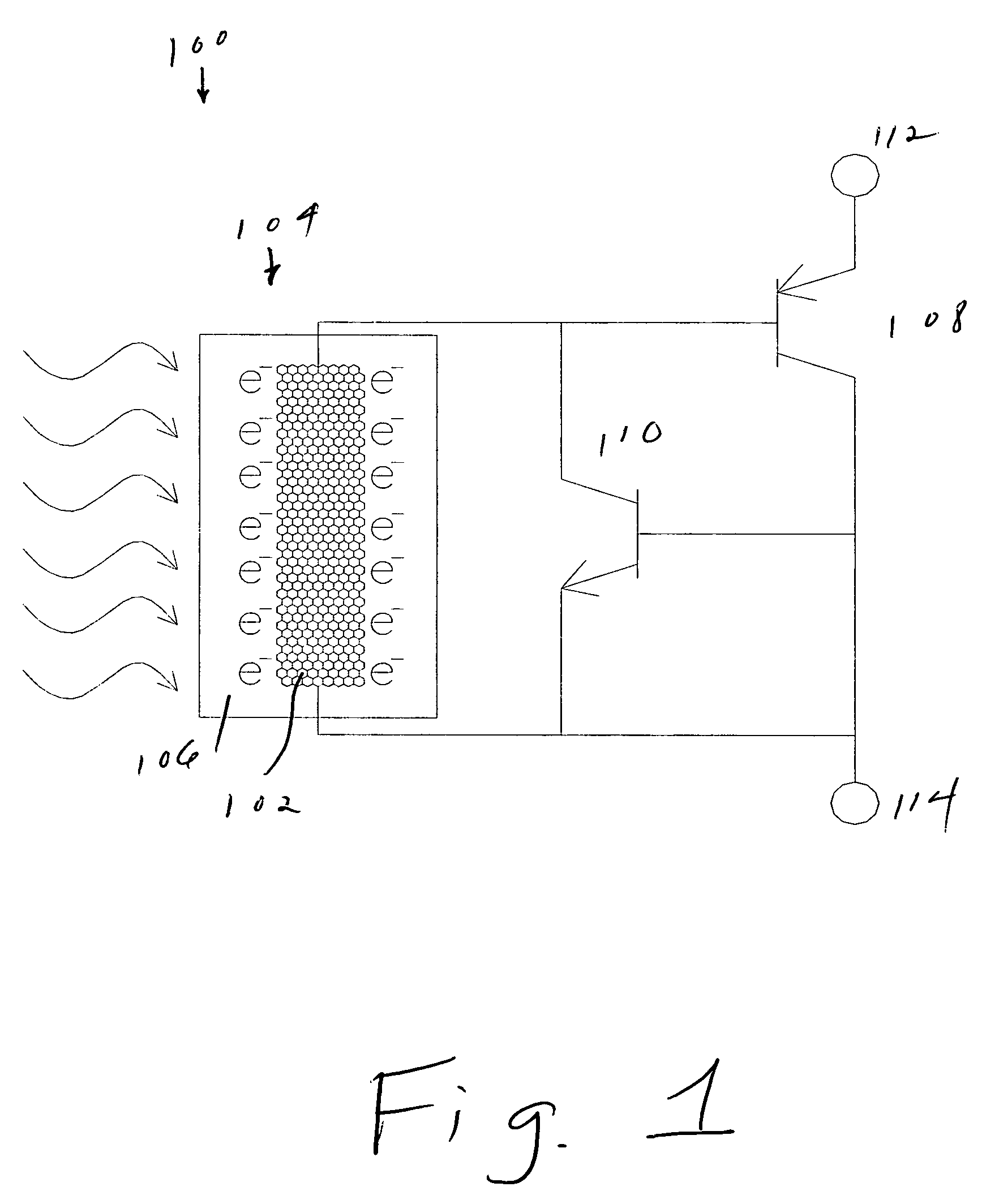
Optically controlled electrical switching device based on wide bandgap semiconductors
InactiveUS20060054922A1Improve Power Control EfficiencyHigh-temperature operationMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsPower switchingEngineering
A power switching device includes an optically controlled component using a semiconducting carbon nanotube. An optical signal transmitted over an optical fiber controls the conductivity of the nanotube. The nanotube transmits a signal controlled by the optical signal to a wide-bandgap semiconductor power switch, which switches the power.
Owner:PETTIT JOHN W
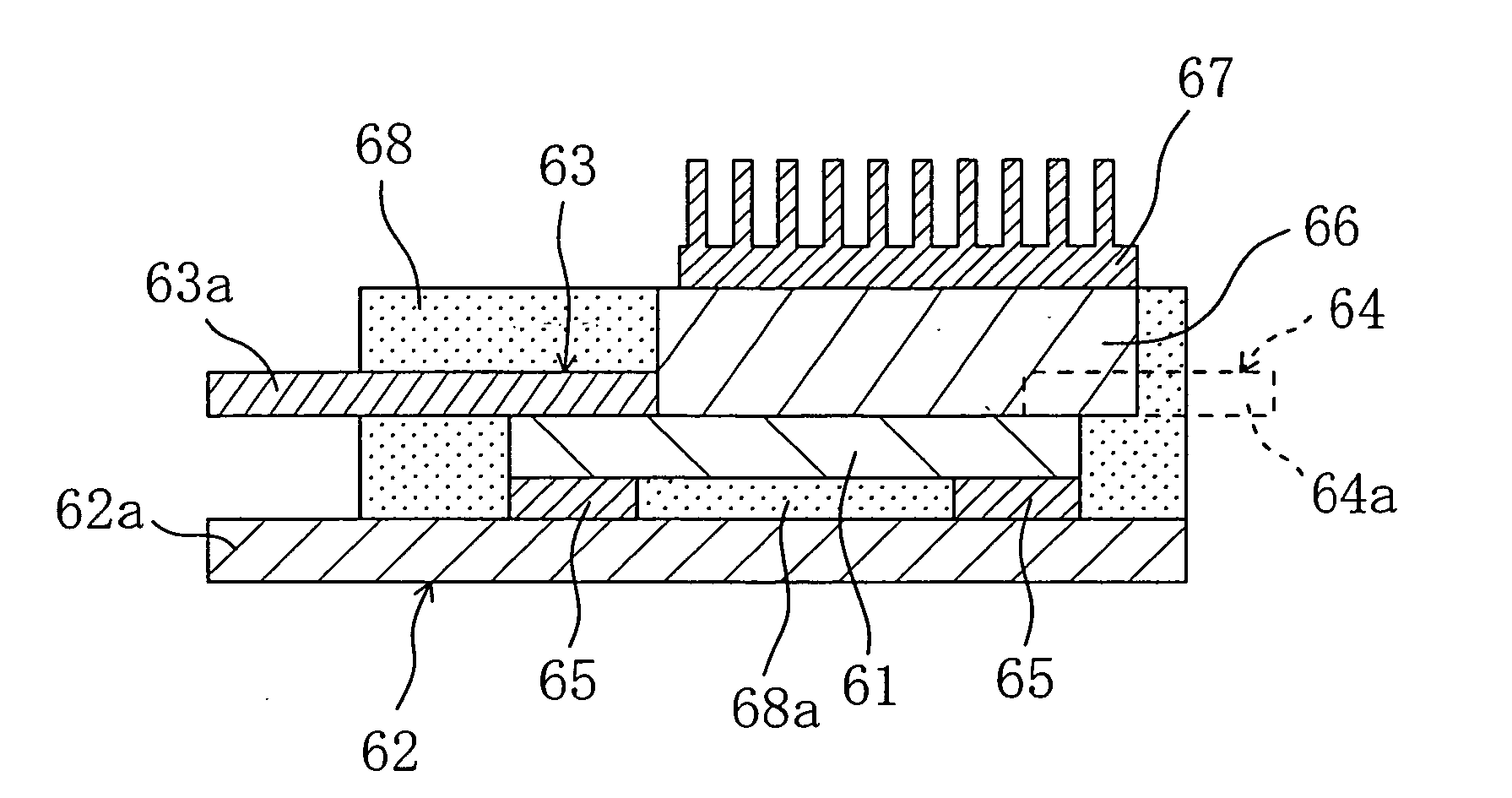
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060055027A1Efficiently flowThe connection is tight and firmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor apparatus includes a semiconductor chip 61 including a power semiconductor device using a wide band gap semiconductor, base materials 62 and 63, first and second intermediate members 65 and 68a, a heat conducting member 66, a radiation fin 67, and an encapsulating material 68 for encapsulating the semiconductor chip 61, the first and second intermediate member 65 and 68a and the heat conducting member 66. The tips of the base materials 62 and 63 work respectively as external connection terminals 62a and 63a. The second intermediate member 68a is made of a material with lower heat conductivity than the first intermediate member 65, and a contact area with the semiconductor chip 61 is larger in the second intermediate member 68a than in the first intermediate member.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Charged particle application apparatus
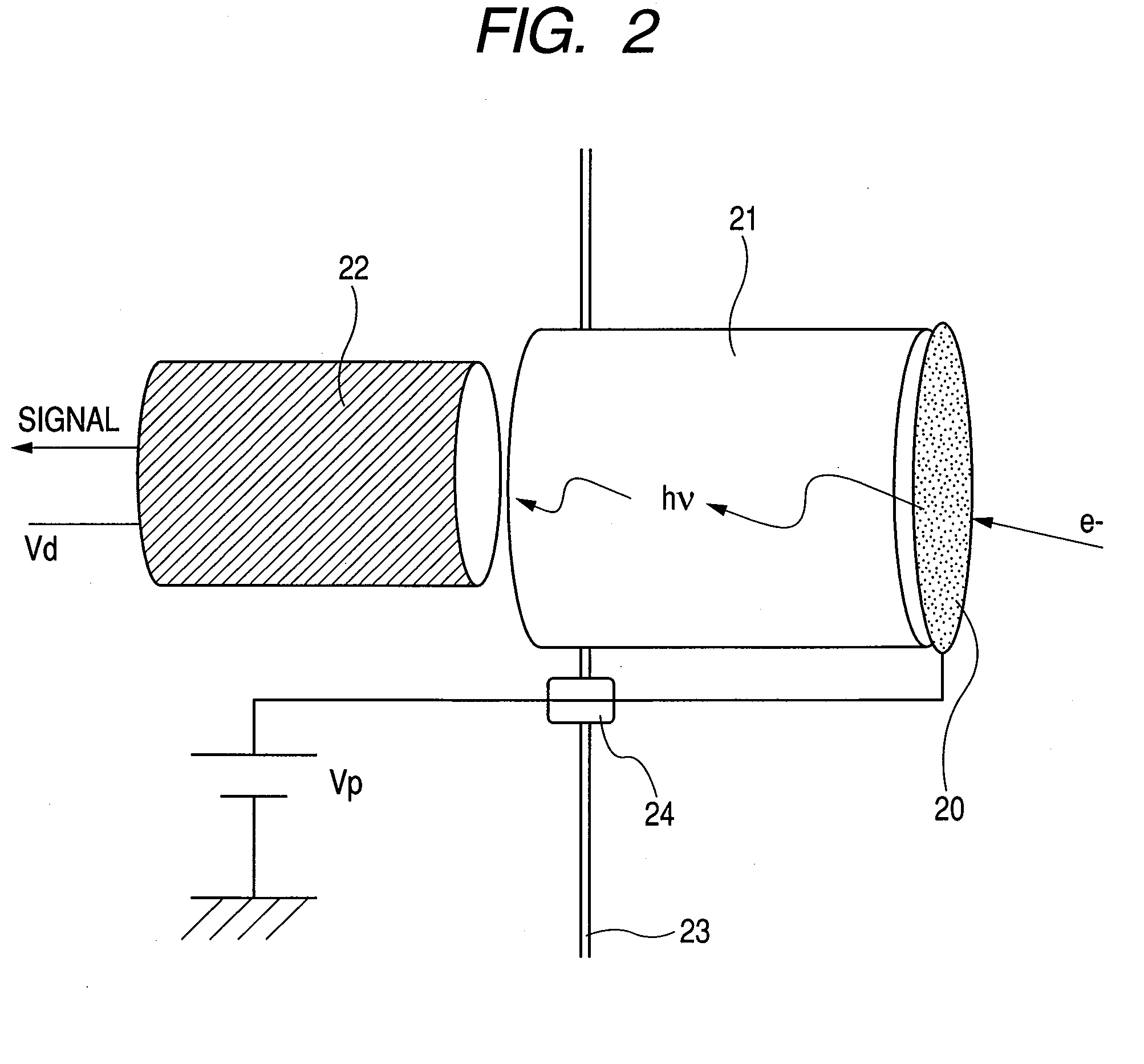
InactiveUS20090101817A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLow voltageElectron avalanche
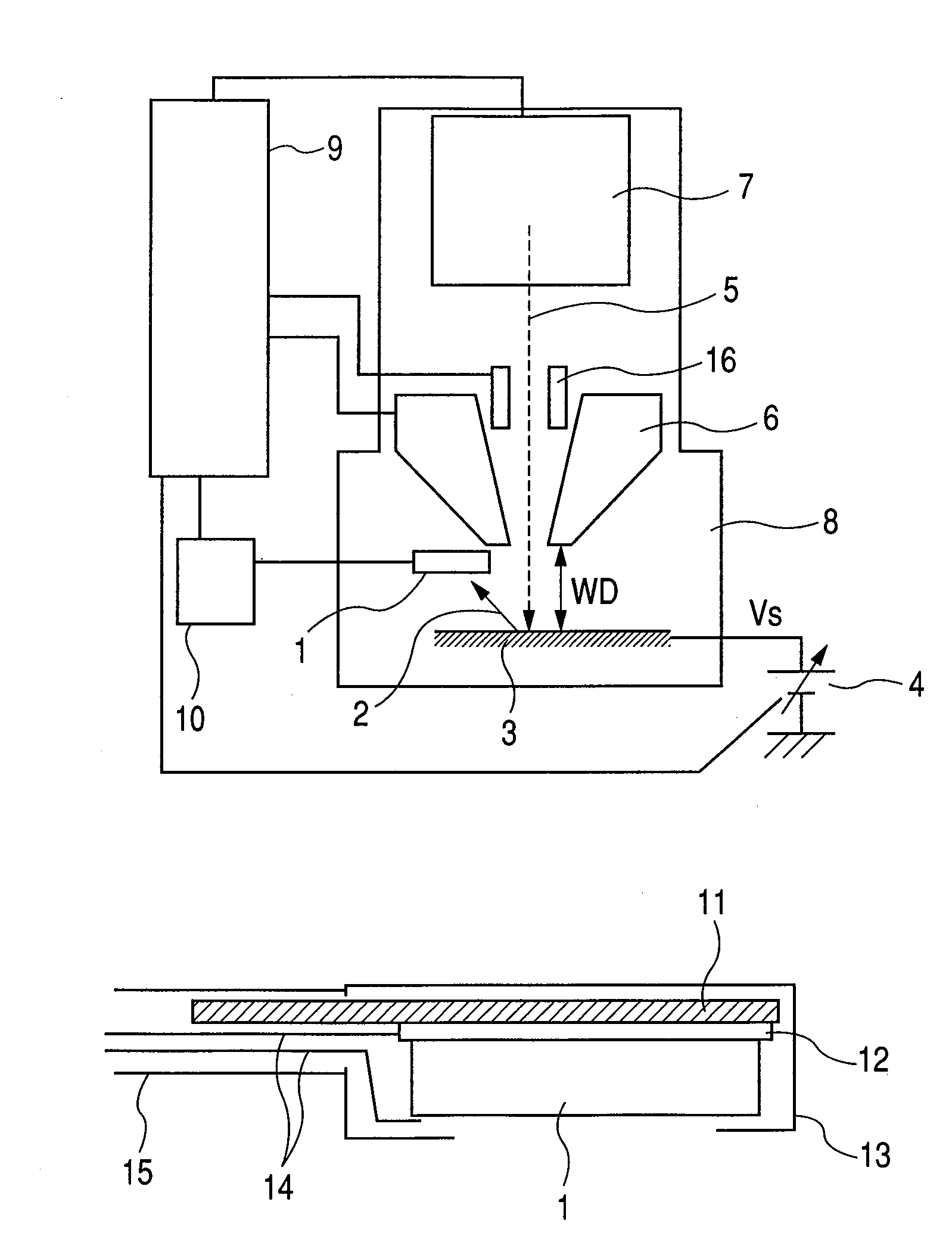
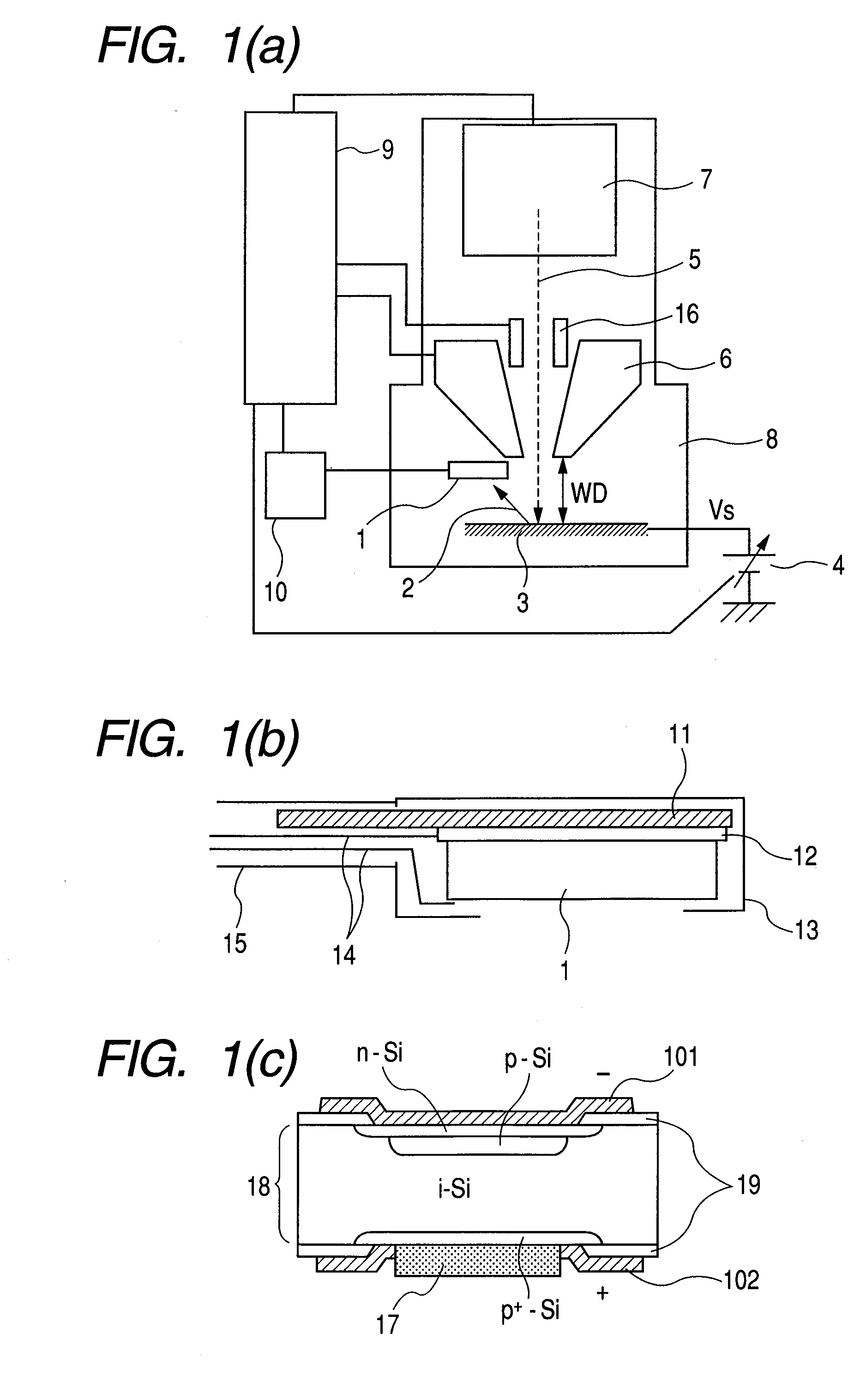
The present invention provides a highly sensitive, thin detector useful for observing low-voltage, high-resolution SEM images, and provides a charged particle beam application apparatus based on such a detector. The charged particle beam application apparatus includes a charged particle irradiation source, a charged particle optics for irradiating a sample with a charged particle beam emitted from the charged particle irradiation source, and an electron detection section for detecting electrons that are secondarily generated from the sample. The electron detection section includes a diode device that is a combination of a phosphor layer, which converts the electrons to an optical signal, and a device for converting the optical signal to electrons and subjecting the electrons to avalanche multiplication, or includes a diode device having an electron absorption region that is composed of at least a wide-gap semiconductor substrate with a bandgap greater than 2 eV.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method for the growth of large low-defect single crystals
InactiveUS7449065B1Reduce unwanted depositionImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsSingle crystalBiology
A method and the benefits resulting from the product thereof are disclosed for the growth of large, low-defect single-crystals of tetrahedrally-bonded crystal materials. The process utilizes a uniquely designed crystal shape whereby the direction of rapid growth is parallel to a preferred crystal direction. By establishing several regions of growth, a large single crystal that is largely defect-free can be grown at high growth rates. This process is particularly suitable for producing products for wide-bandgap semiconductors, such as SiC, GaN, AlN, and diamond. Large low-defect single crystals of these semiconductors enable greatly enhanced performance and reliability for applications involving high power, high voltage, and / or high temperature operating conditions.
Owner:NASA +1
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20120033488A1Reduce off-state currentLonger heldTransistorSolid-state devicesPotential changeEngineering
A semiconductor device including a memory cell formed using a wide bandgap semiconductor, for example, an oxide semiconductor is provided. The semiconductor device includes a potential change circuit having a function of outputting a potential lower than a reference potential for reading data from the memory cell. With the use of the wide bandgap semiconductor, an off-state current of a transistor included in the memory cell can be sufficiently reduced, and the semiconductor device which can hold data for a long period can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070221953A1Reduce lossImprove pressure resistanceThyristorSolid-state devicesWide bandWideband
A semiconductor device such as a reverse blocking type switching element is provided with a switching element made of a wide band gap semiconductor on the side of a first major plane where a first terminal is formed, while the wide band gap semiconductor is operable at a high voltage and in low loss. In a reverse blocking type switching element having a hetero junction diode for blocking a reverse direction current on the side of a second major plane where a second terminal is formed, a silicon semiconductor region is provided in a side surface of the semiconductor so as to prevent a deterioration of a withstanding voltage of the hetero junction diode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
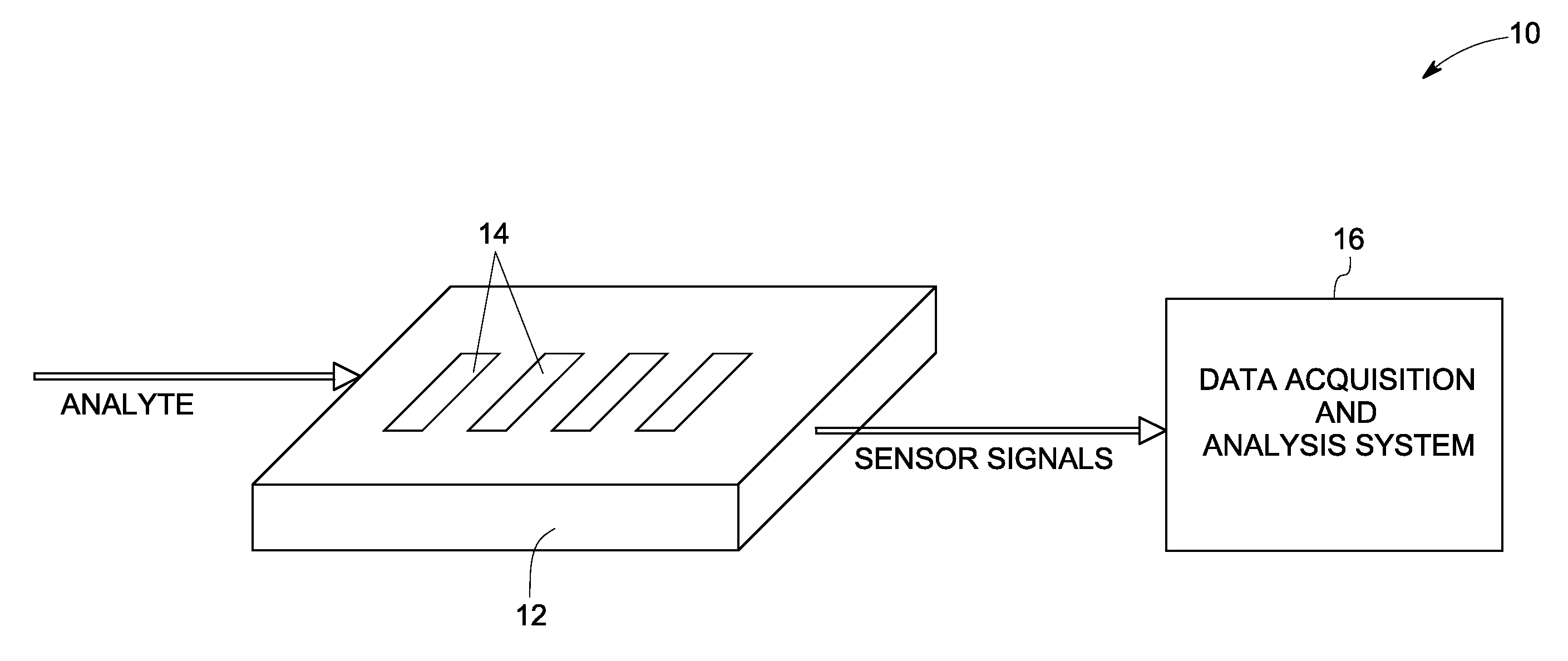
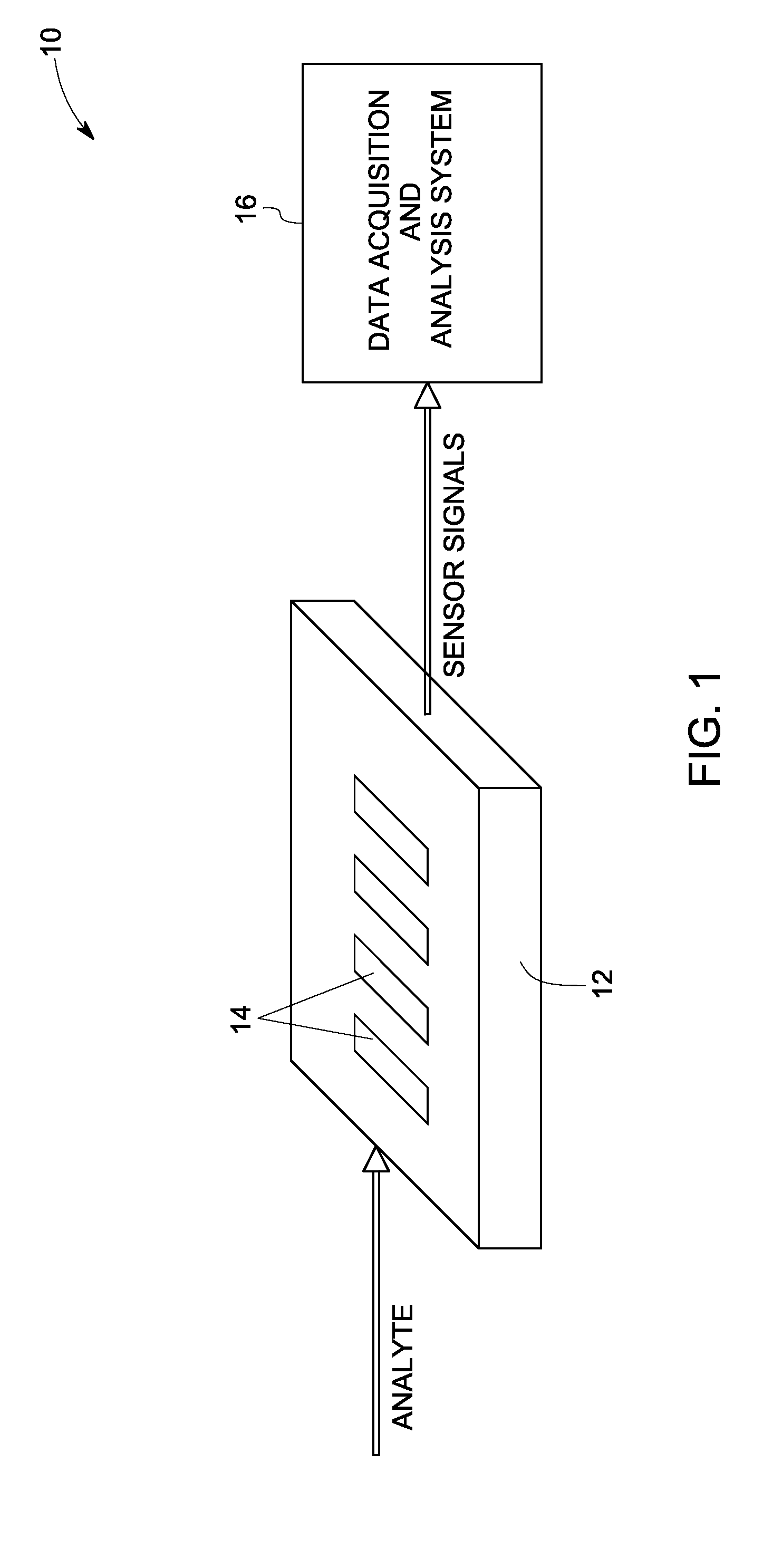
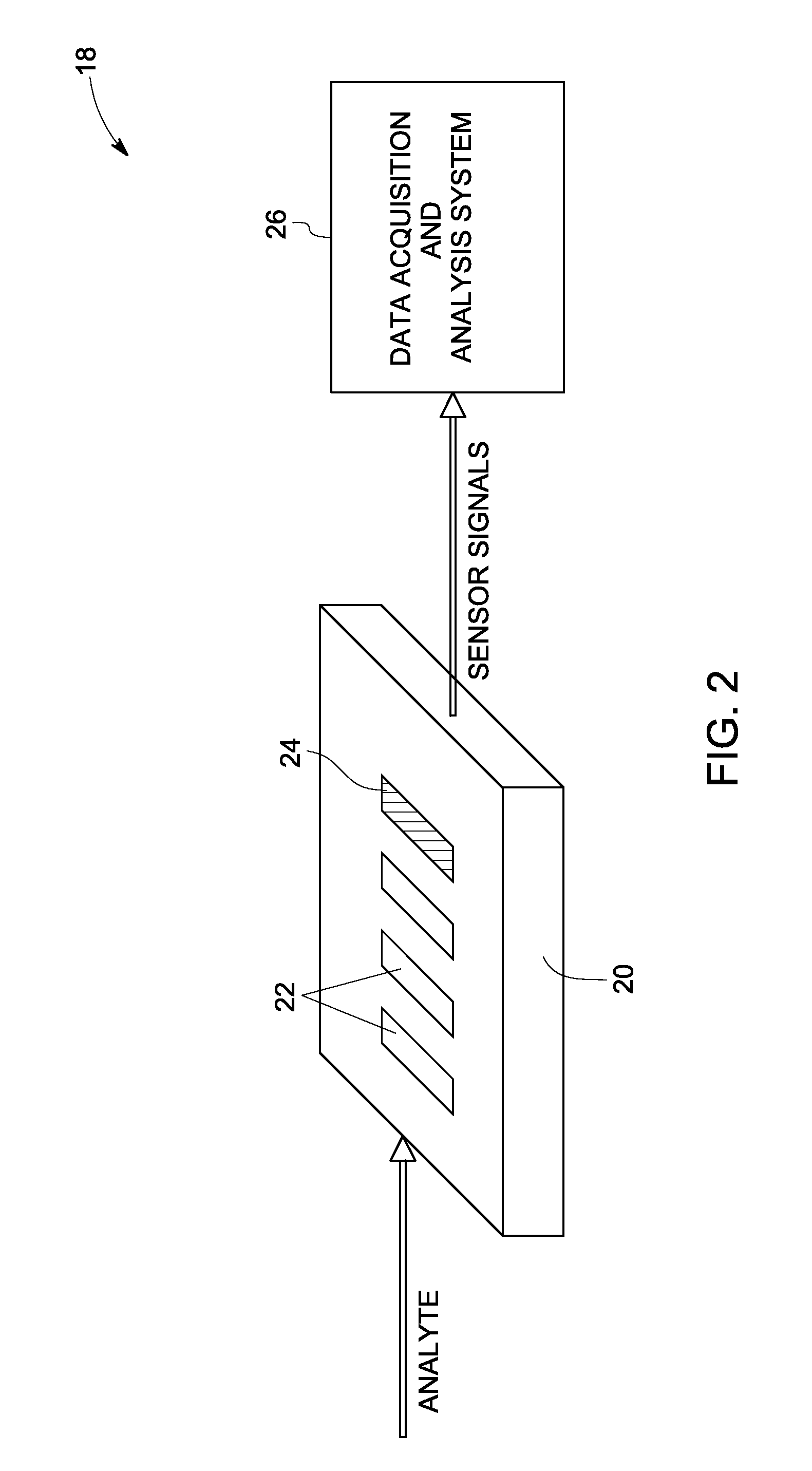
Systems and methods for sensing
InactiveUS20080302672A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteChemical species
A sensor system for measuring a plurality of chemical species is disclosed. The sensor system includes a plurality of semiconductor device sensor elements, wherein each sensor element includes at least one wide band gap semiconductor layer and at least one catalytic layer configured to have an electrical property modifiable on exposure to an analyte including one or more chemical species; and an acquisition and analysis system configured to receive sensor signals from the plurality of sensor elements and to use multivariate analysis techniques to analyze the sensor signals to provide multivariate analyte measurement data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com