Patents
Literature
305 results about "Multivariate analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multivariate analysis (MVA) is based on the statistical principle of multivariate statistics, which involves observation and analysis of more than one statistical outcome variable at a time. Typically, MVA is used to address the situations where multiple measurements are made on each experimental unit and the relations among these measurements and their structures are important. A modern, overlapping categorization of MVA includes...
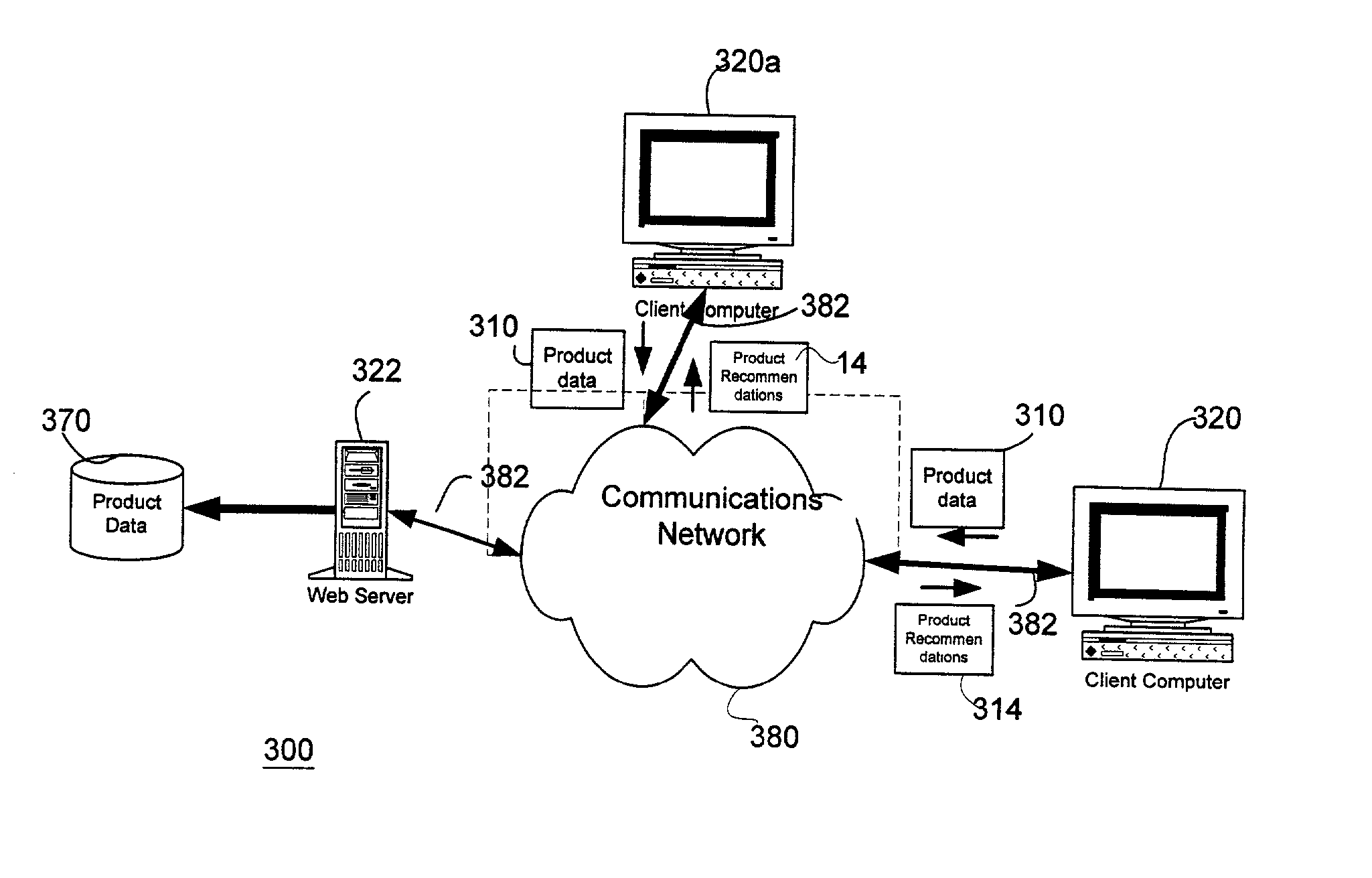
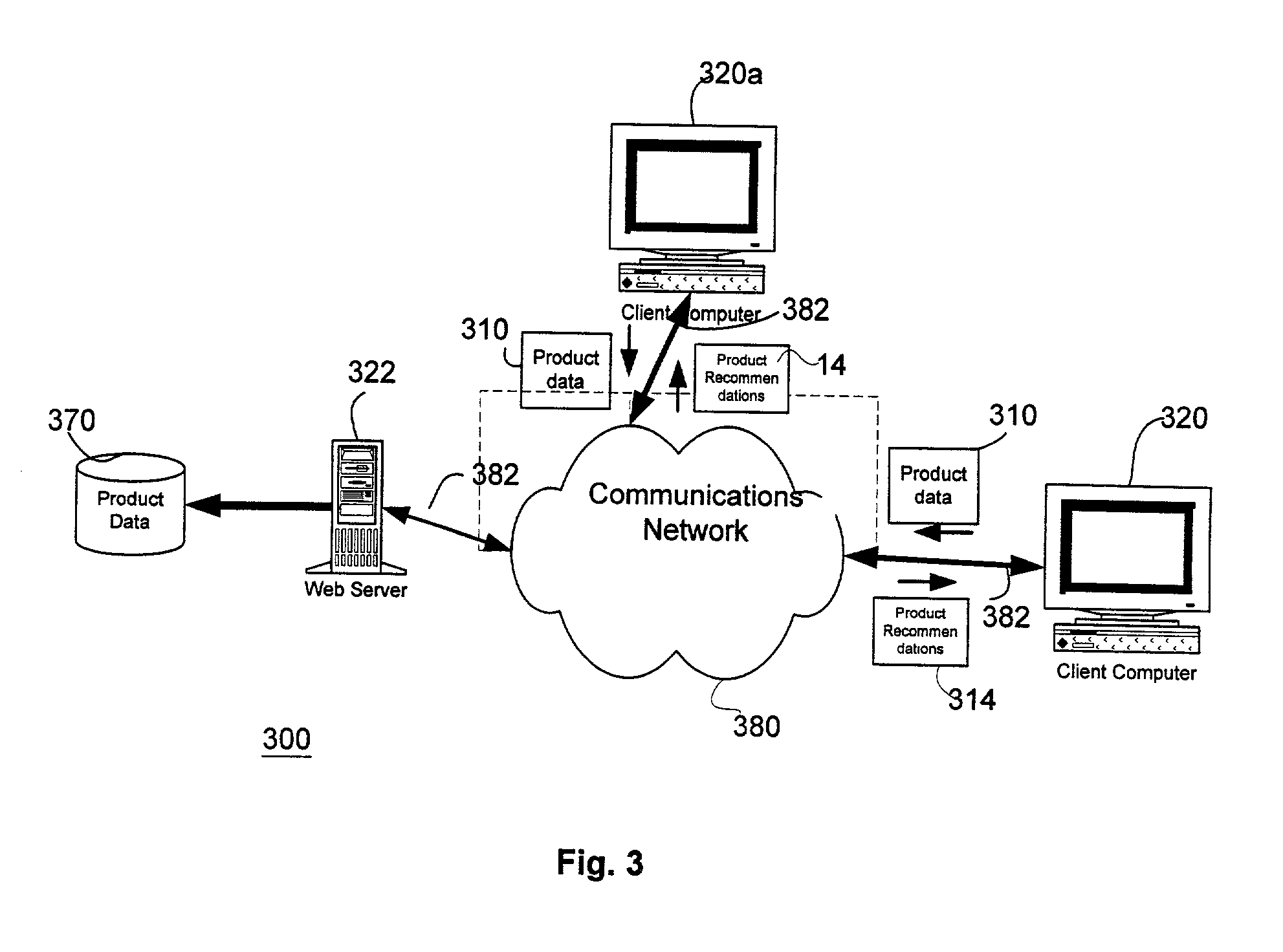
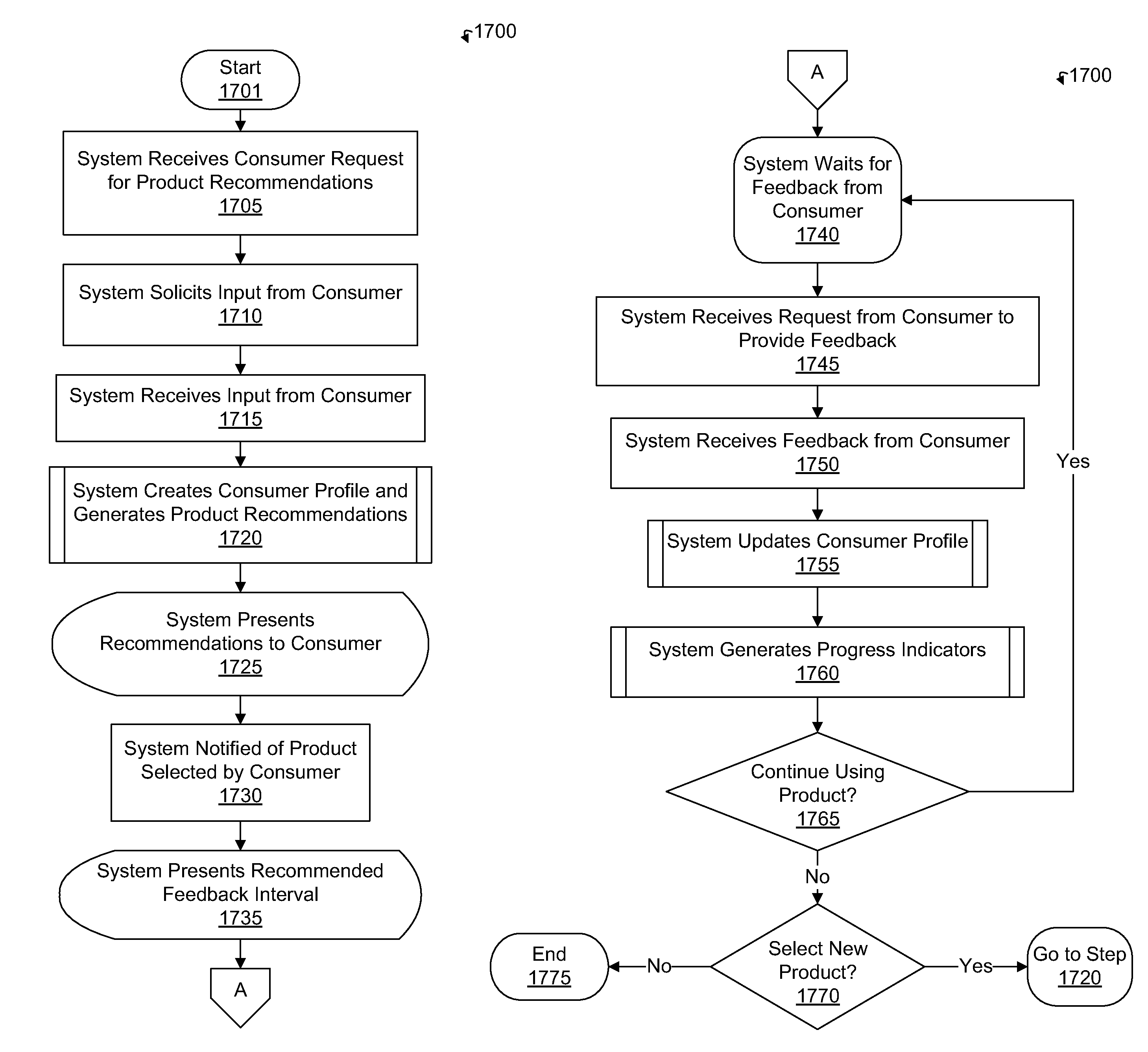
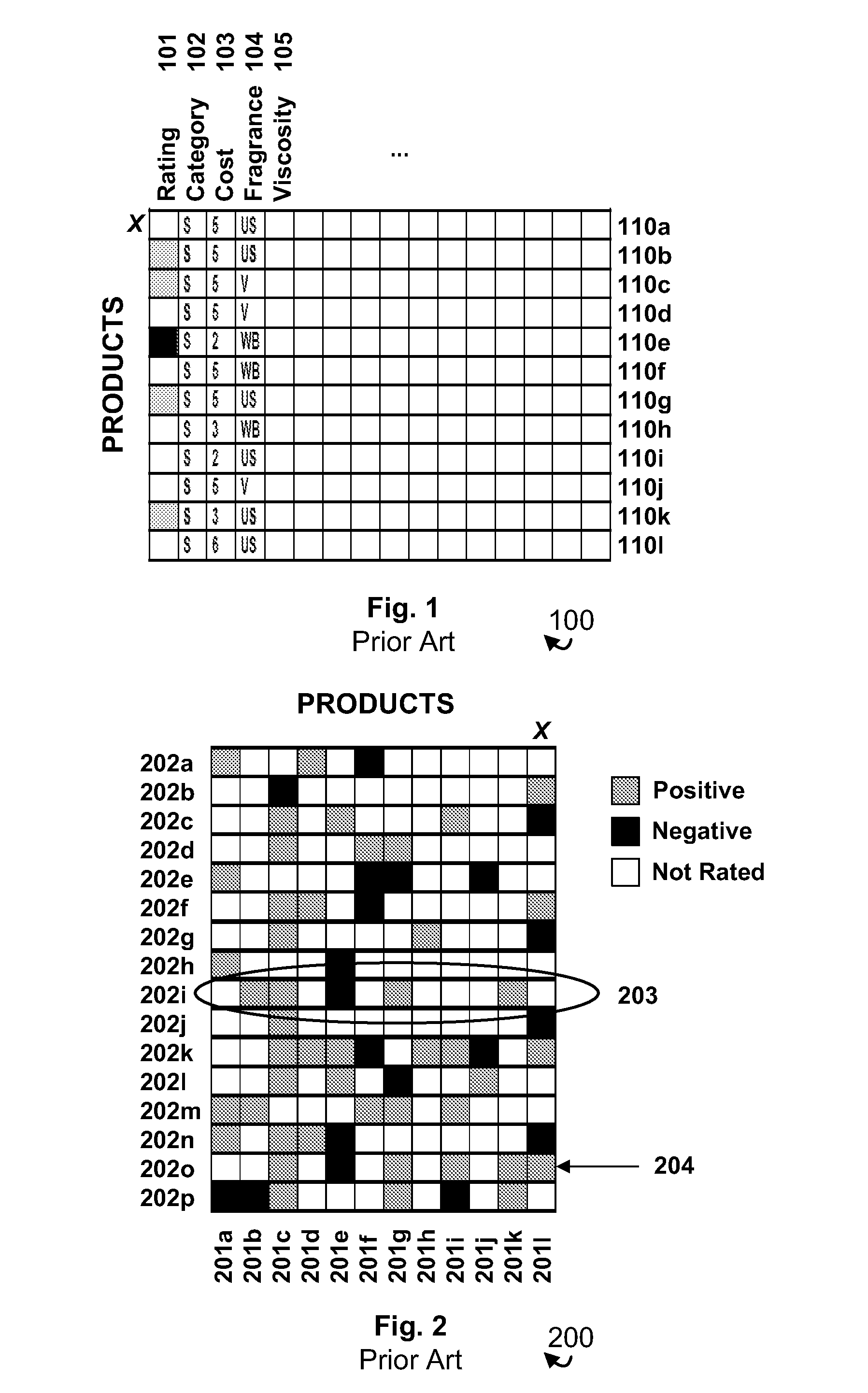
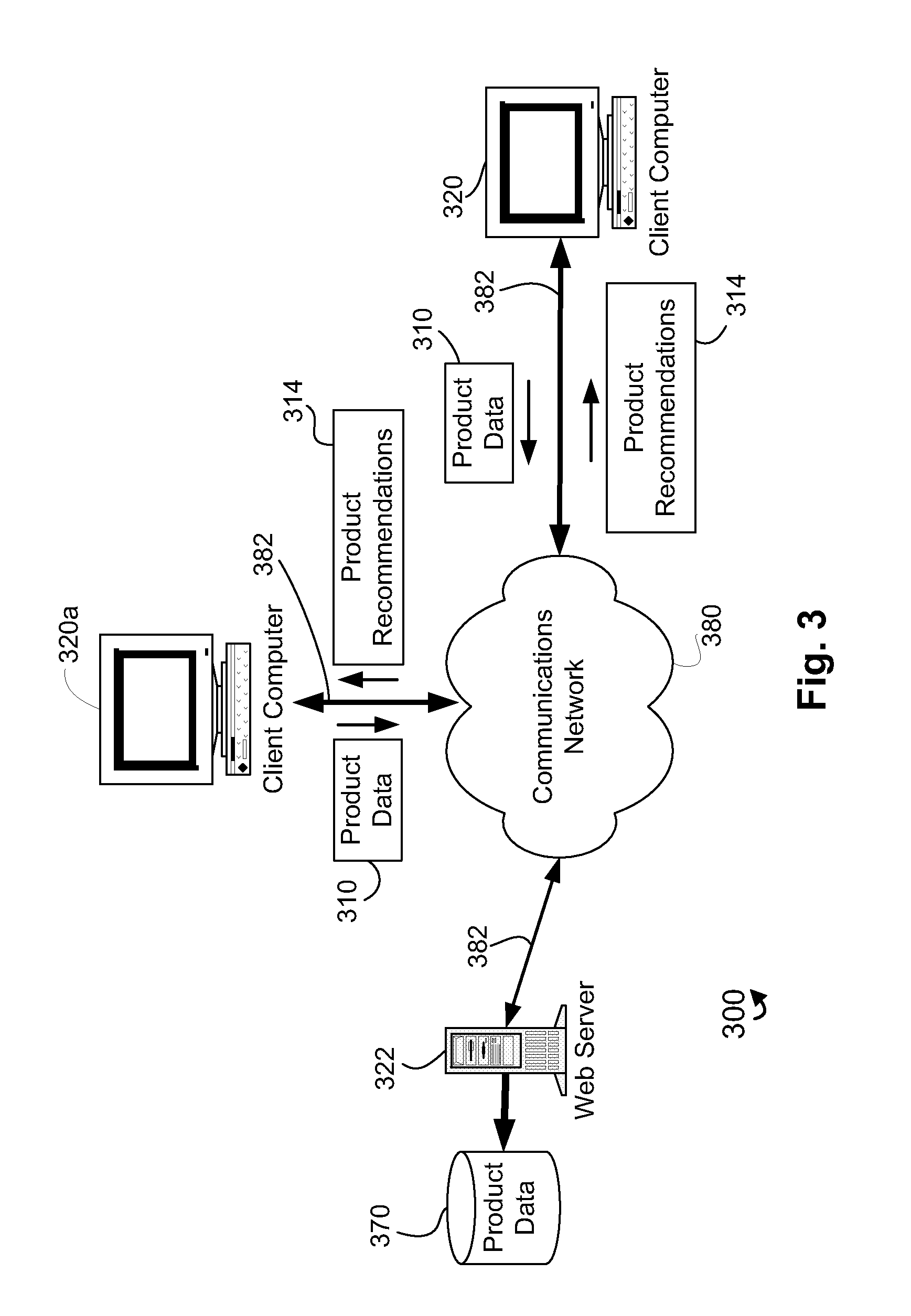
Intelligent performance-based product recommendation system
ActiveUS20020161664A1Accurately predict product performanceAccurately consumer preferenceSpecial data processing applicationsMarketingThe InternetProcessing element
Systems and methods of utilizing communications networks and multivariate analysis to predict or recommend optimal products from a predefined population of commercially available products are disclosed. The recommendations are based on intelligence contained in processing elements and subjective and / or objective product information received from consumers or input to the systems as part of their initial setup. The output of the systems comprise sets of products that they predict the consumer will prefer and / or perform well for the problem or concern identified by the consumer. The performance and preference predictions are a function of consumer problems and product responsiveness patterns. Objective product information is generally obtained with diagnostic instruments. Data measured with the diagnostic instruments may be communicated to the data processing portions of the invention via the Internet. The outputs of the data processing portion of the system may be presented to consumers via the Internet as well.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
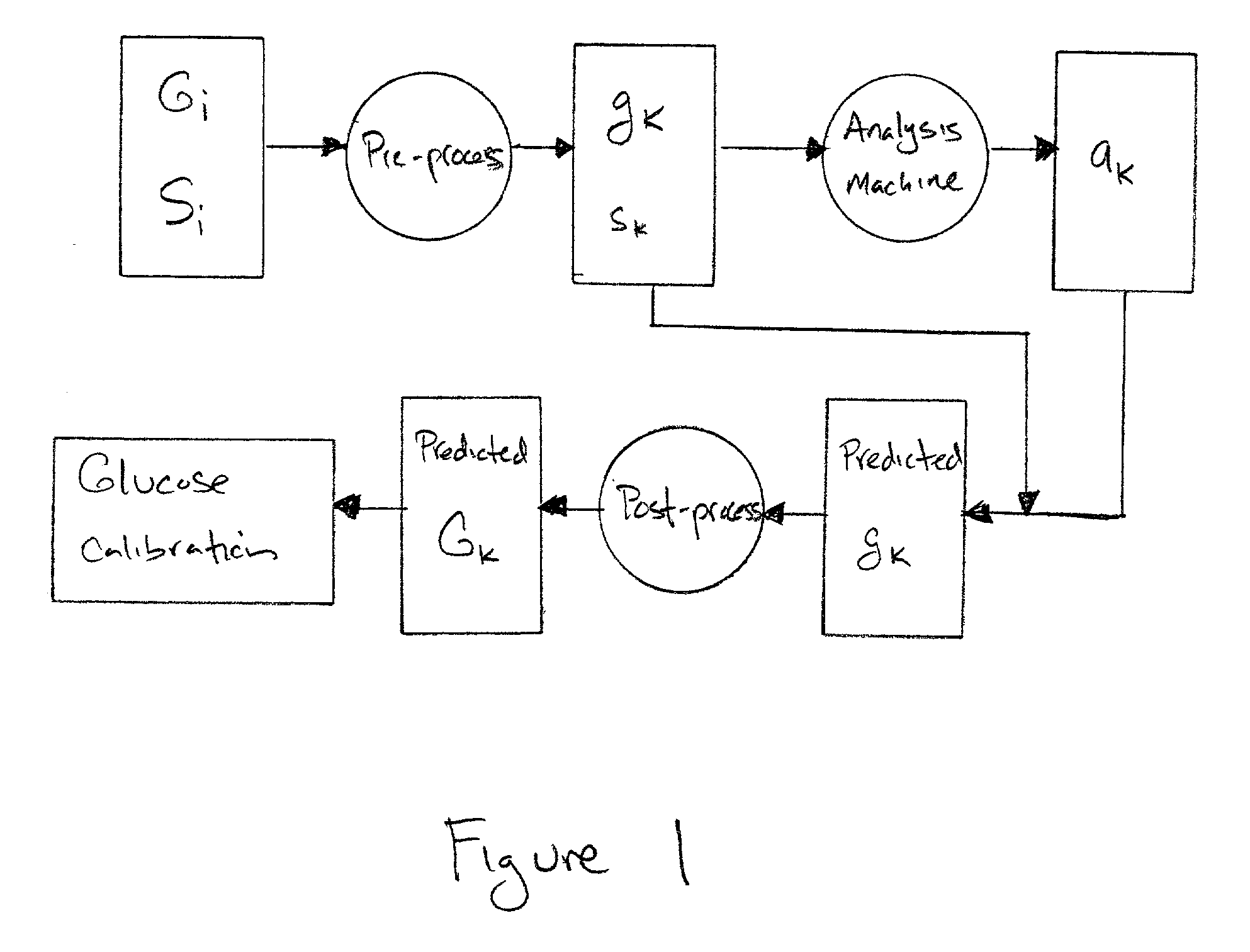
Pre- and post-processing of spectral data for calibration using mutivariate analysis techniques
Owner:ARGOSE
Multivariate analysis of green to ultraviolet spectra of cell and tissue samples
InactiveUS20010034477A1Diagnostics using lightSpectrum investigationMultivariate classificationTissue sample
This invention relates to methods for processing in vivo skin auto-fluorescence spectra for determining blood glucose levels. The invention also relates to methods of classifying cells or tissue samples or quantifying a component of a cell or tissue using a multivariate classification or quantification model.
Owner:ARGOSE
Intelligent performance-based product recommendation system
ActiveUS7809601B2Accurate performanceGood precisionSpecial data processing applicationsMarketingThe InternetProcessing element
Systems and methods of utilizing communications networks and multivariate analysis to predict or recommend optimal products from a predefined population of commercially available products are disclosed. The recommendations are based on intelligence contained in processing elements and subjective and / or objective product information received from consumers or input to the systems as part of their initial setup. The output of the systems comprise sets of products that they predict the consumer will prefer and / or perform well for the problem or concern identified by the consumer. The performance and preference predictions are a function of consumer problems and product responsiveness patterns. Objective product information is generally obtained with diagnostic instruments. Data measured with the diagnostic instruments may be communicated to the data processing portions of the invention via the Internet. The outputs of the data processing portion of the system may be presented to consumers via the Internet as well.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
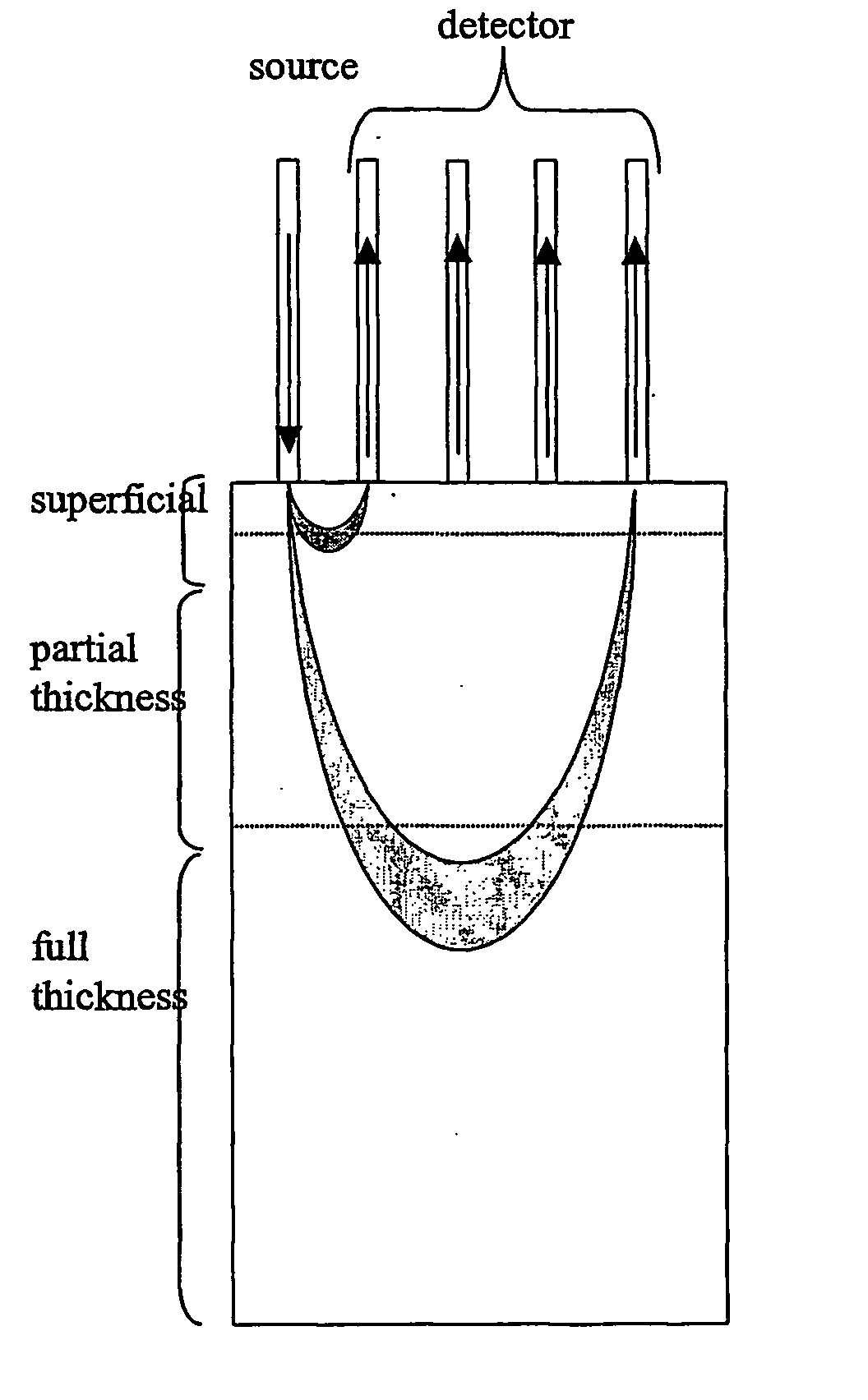
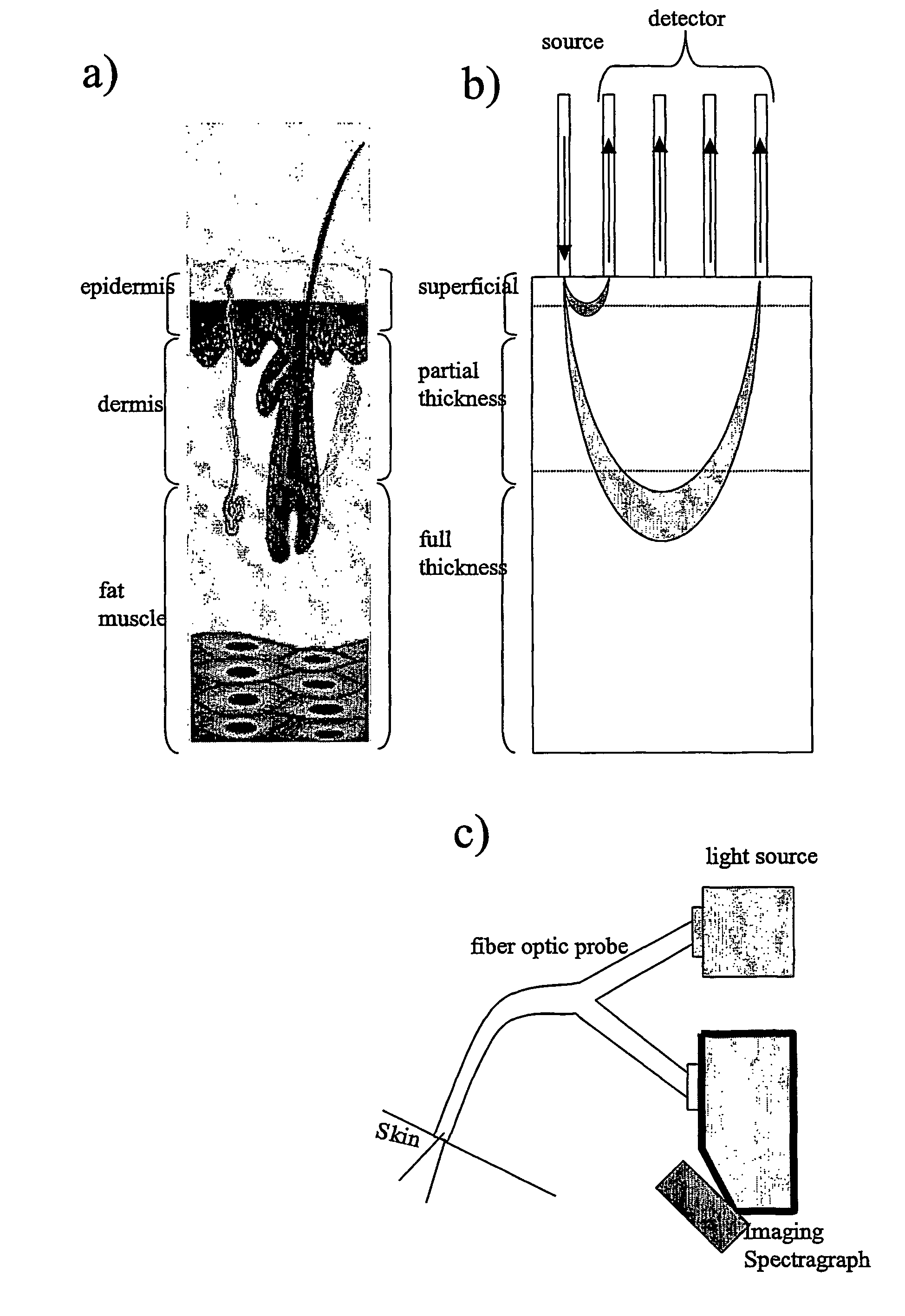
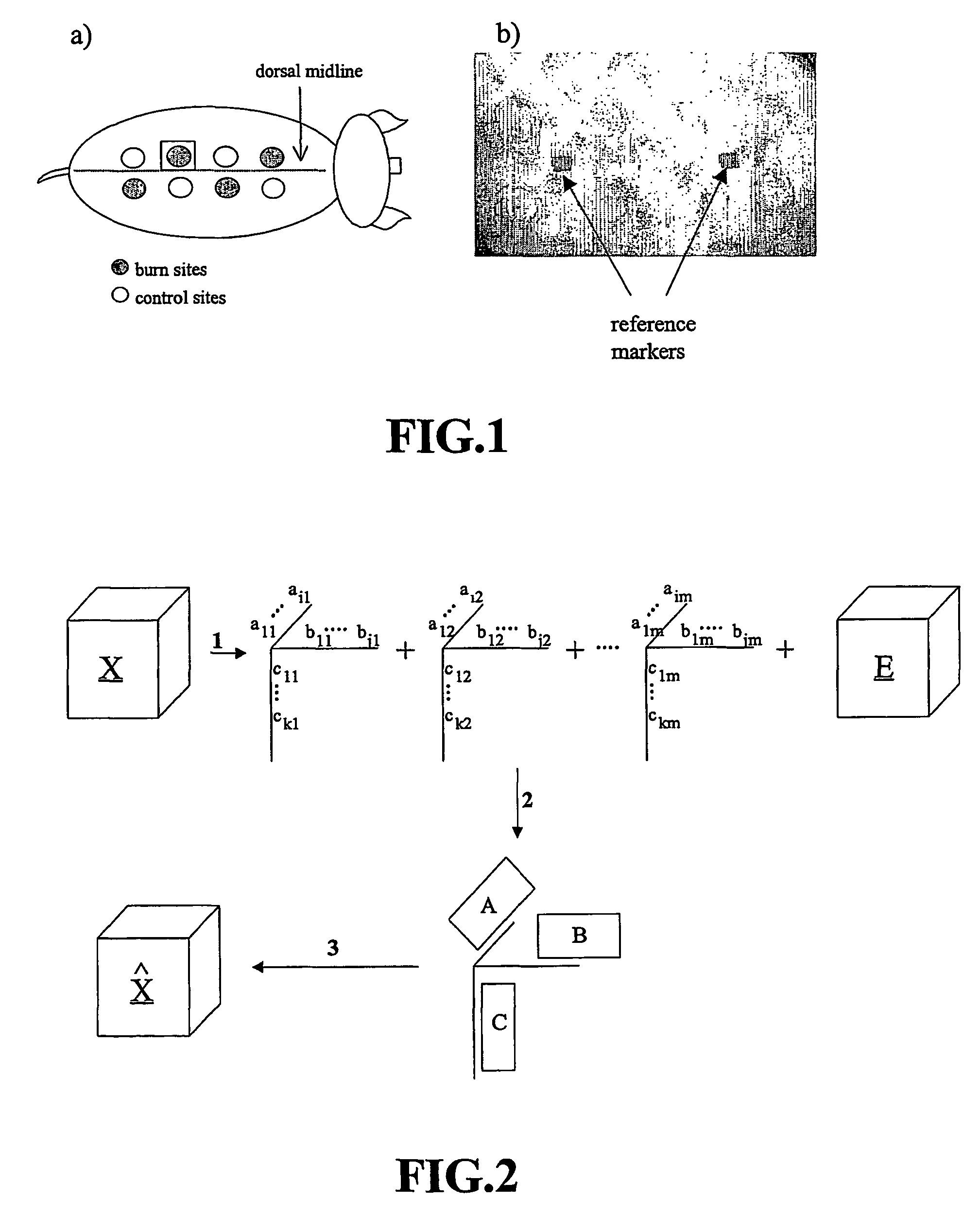
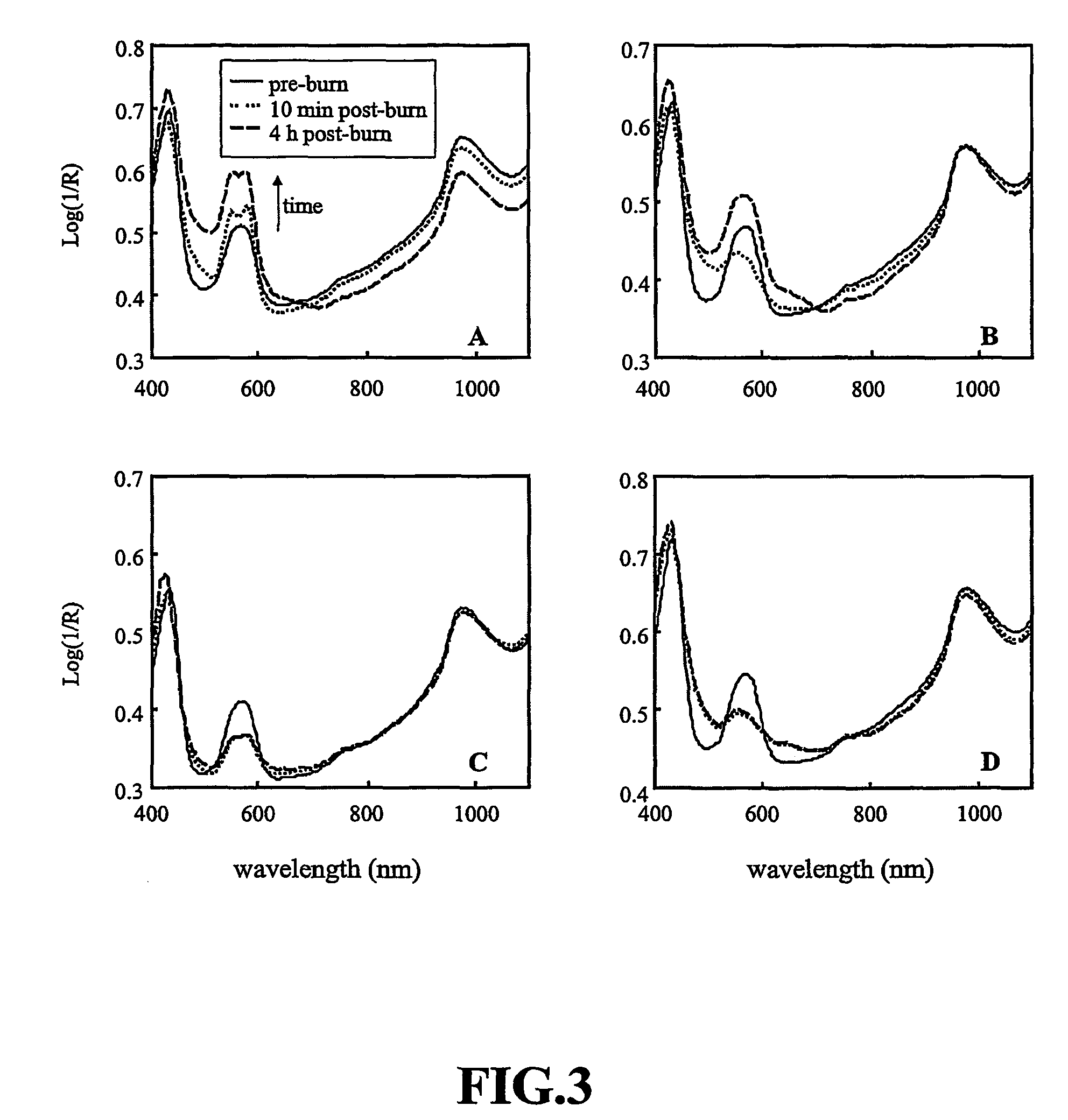
Visible-near infrared spectroscopy in burn injury assessment
ActiveUS20060155193A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyBurning tissueFull thickness burn
A non-invasive method of characterizing burn injuries using near infrared spectroscopy is described. In the method, a beam of light is emitted into the burnt tissue portion at two or more different tissue depths. The spectra are then compared using multivariate analysis to determine diagnostic regions of the spectra. This information is used to categorize the burn. In some cases, the diagnostic regions correspond to wavelengths related to the hemodynamics of the tissue portion. The spectra can also be repeated over time, thereby allowing trends and changes in the spectra to be measured. This data is in turn used to categorize the burn as either a superficial burn, partial thickness burn, deep partial burn or a full thickness burn. Once the burn has been categorized, the clinician can intervene as needed to treat the burn.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
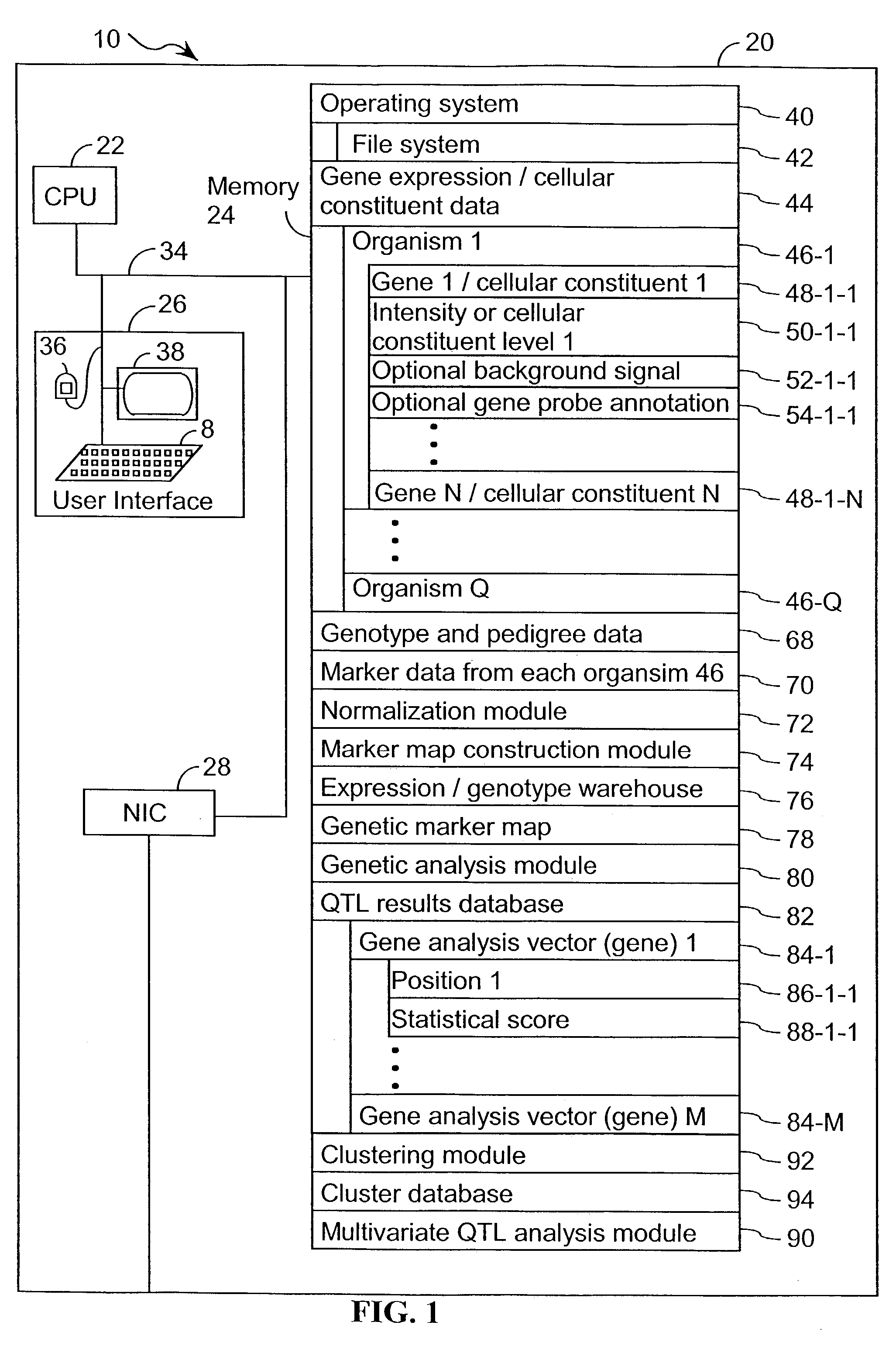
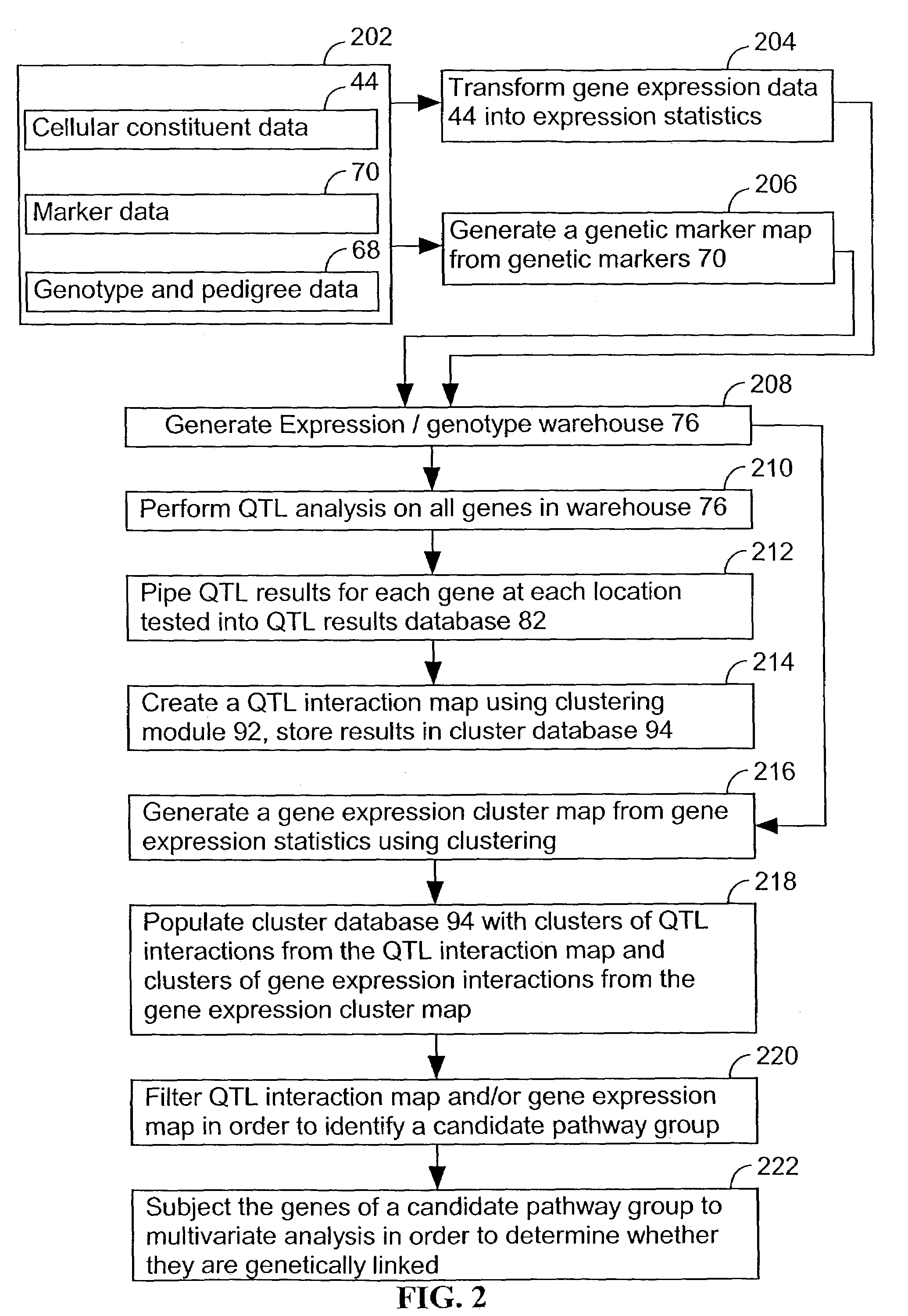
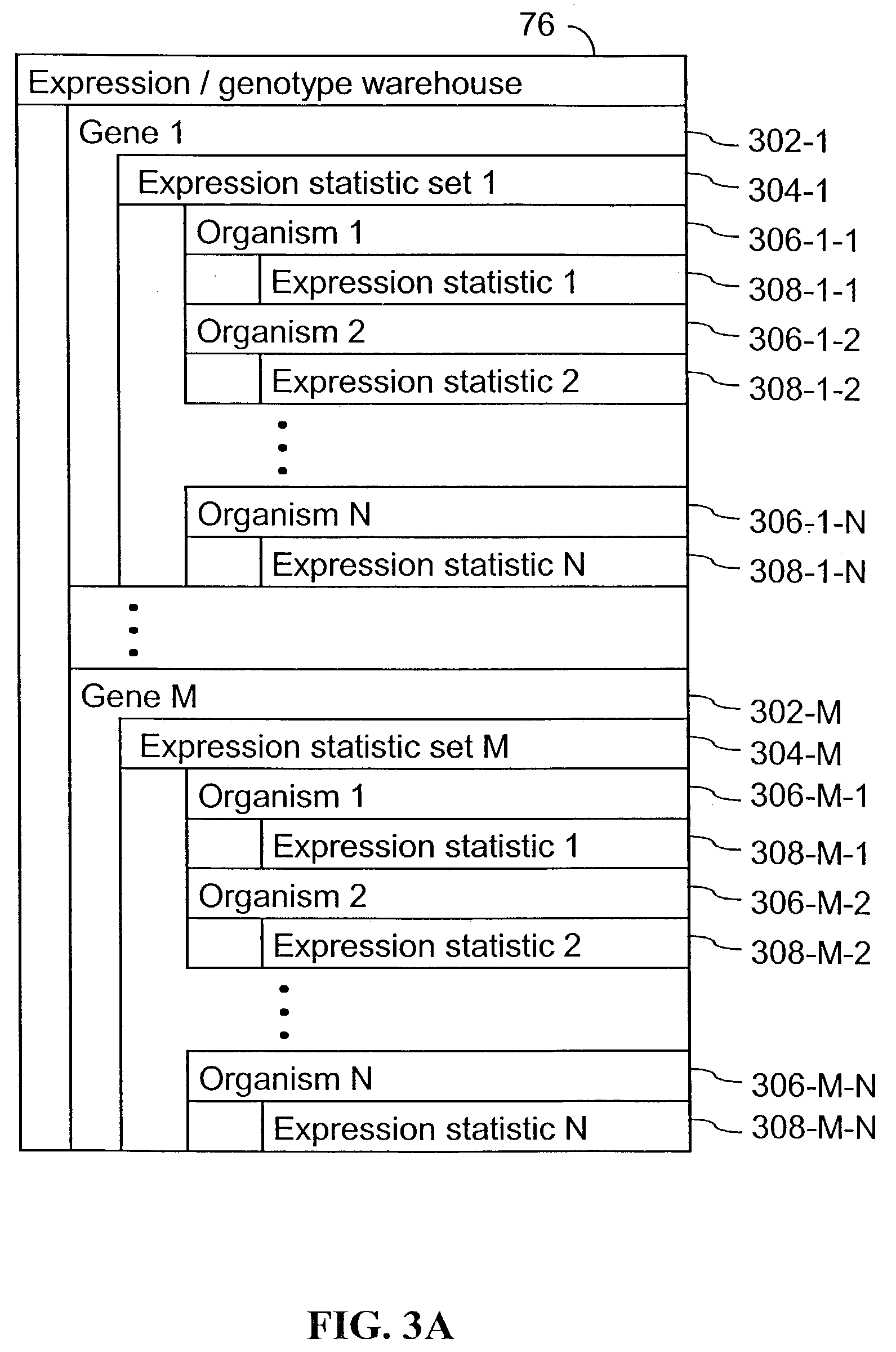
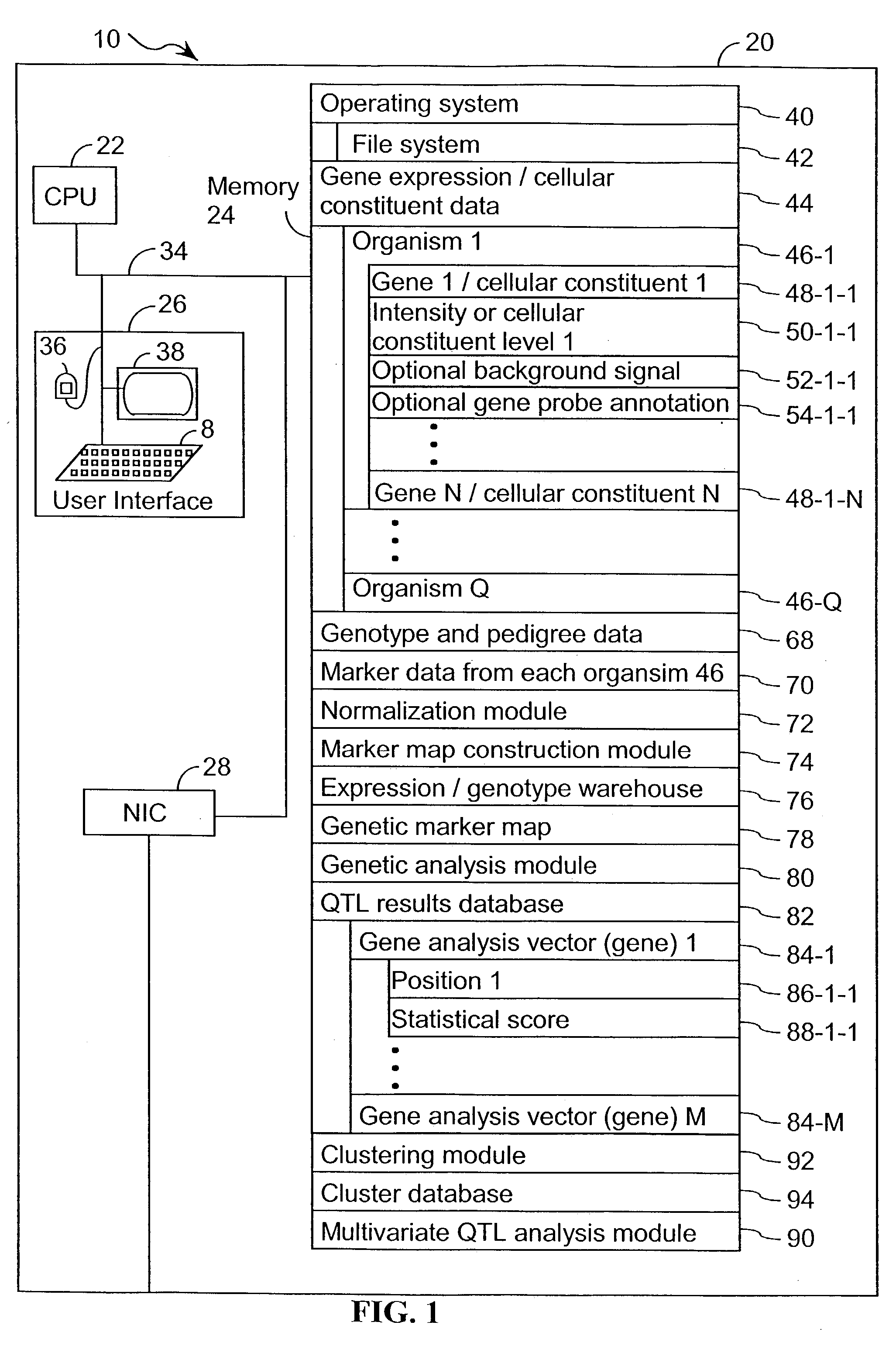
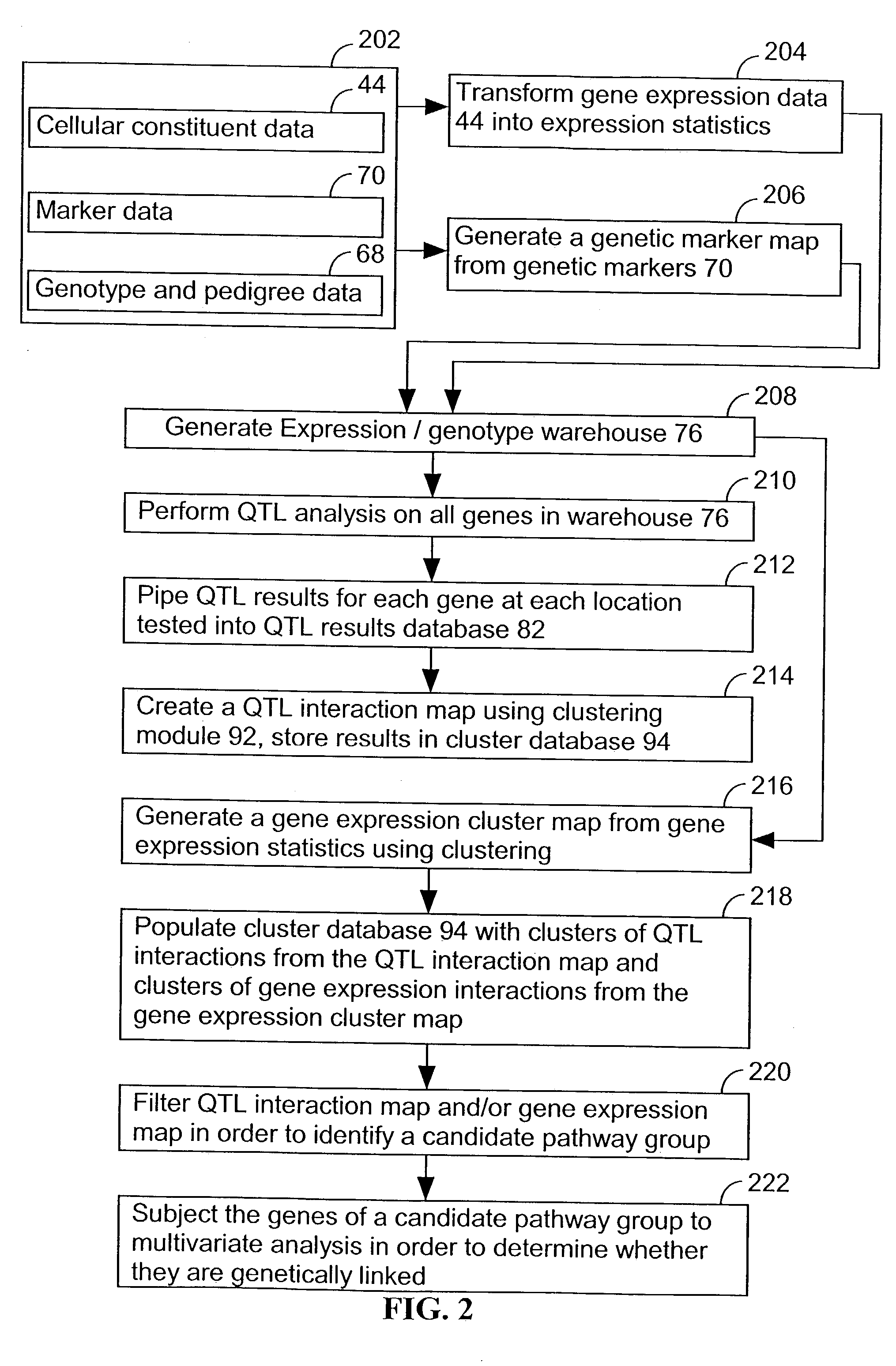
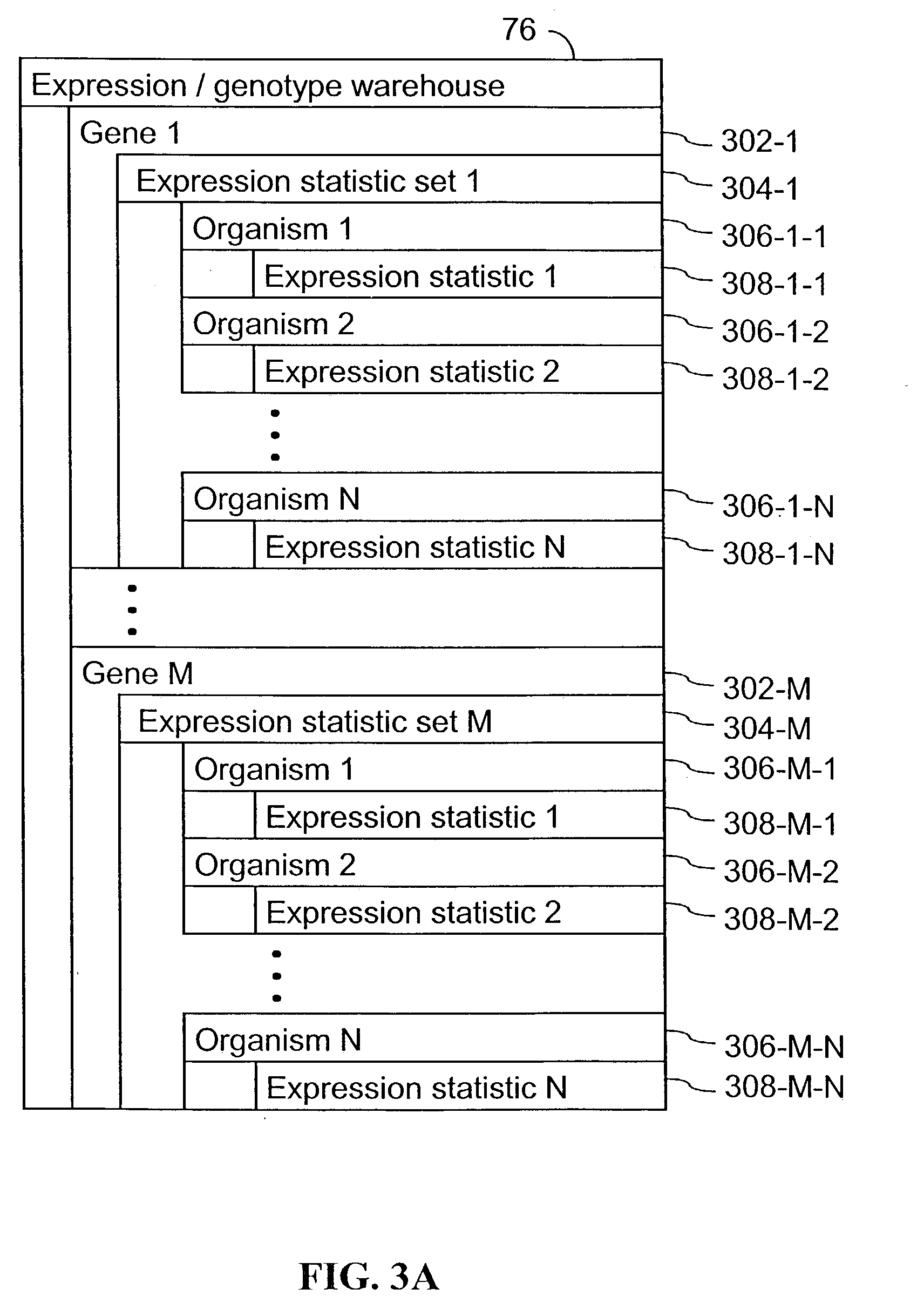
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS7035739B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
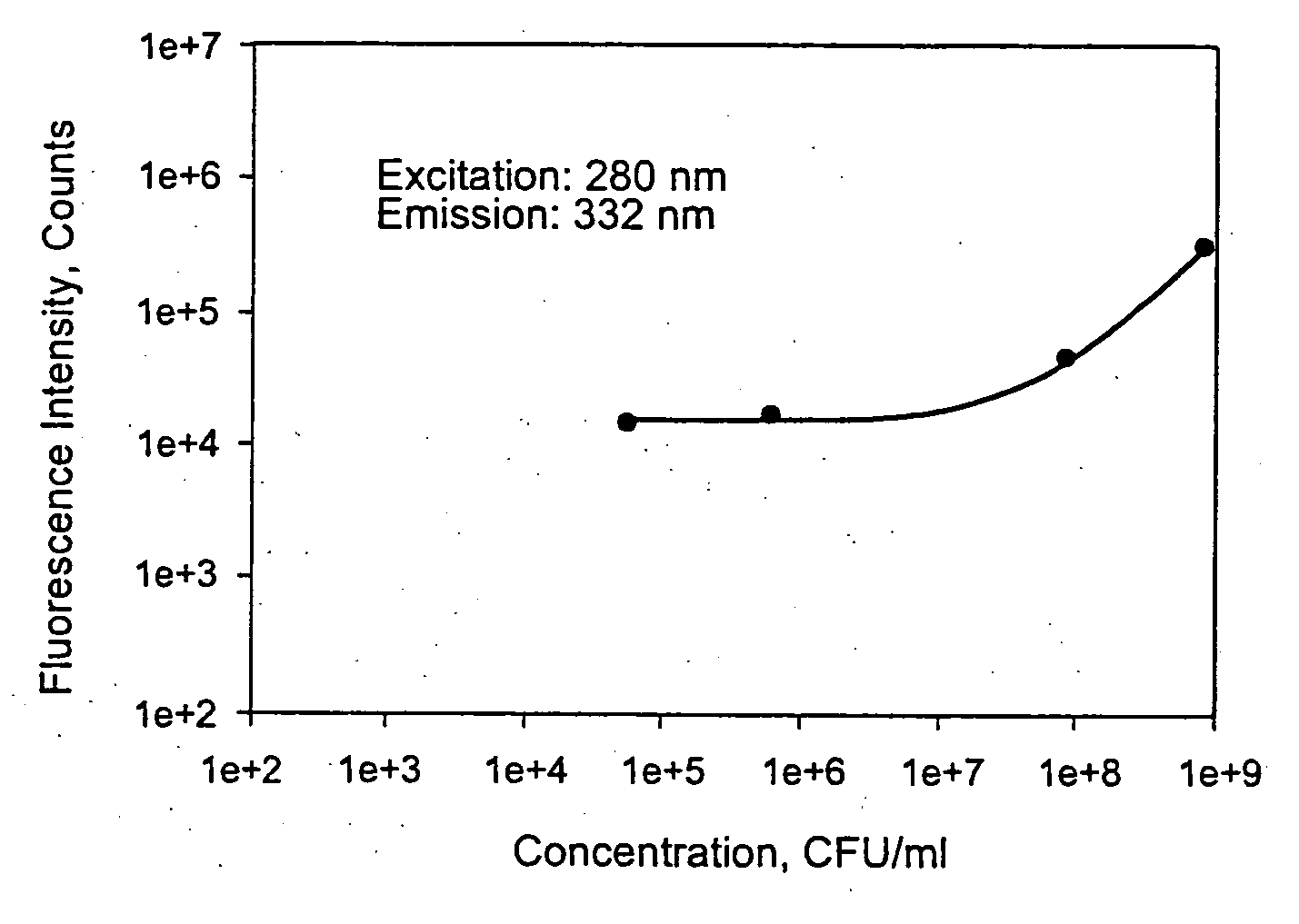
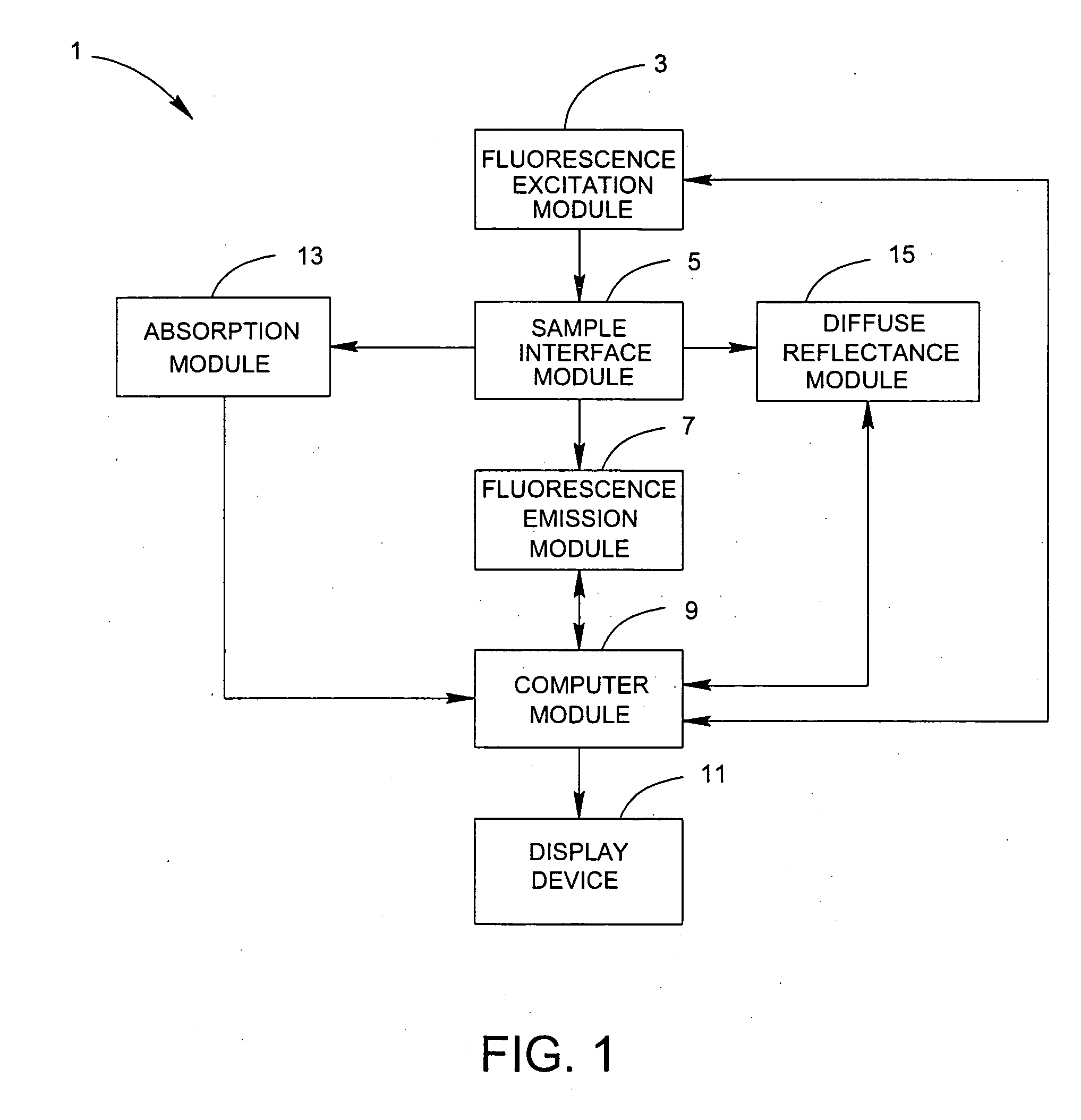
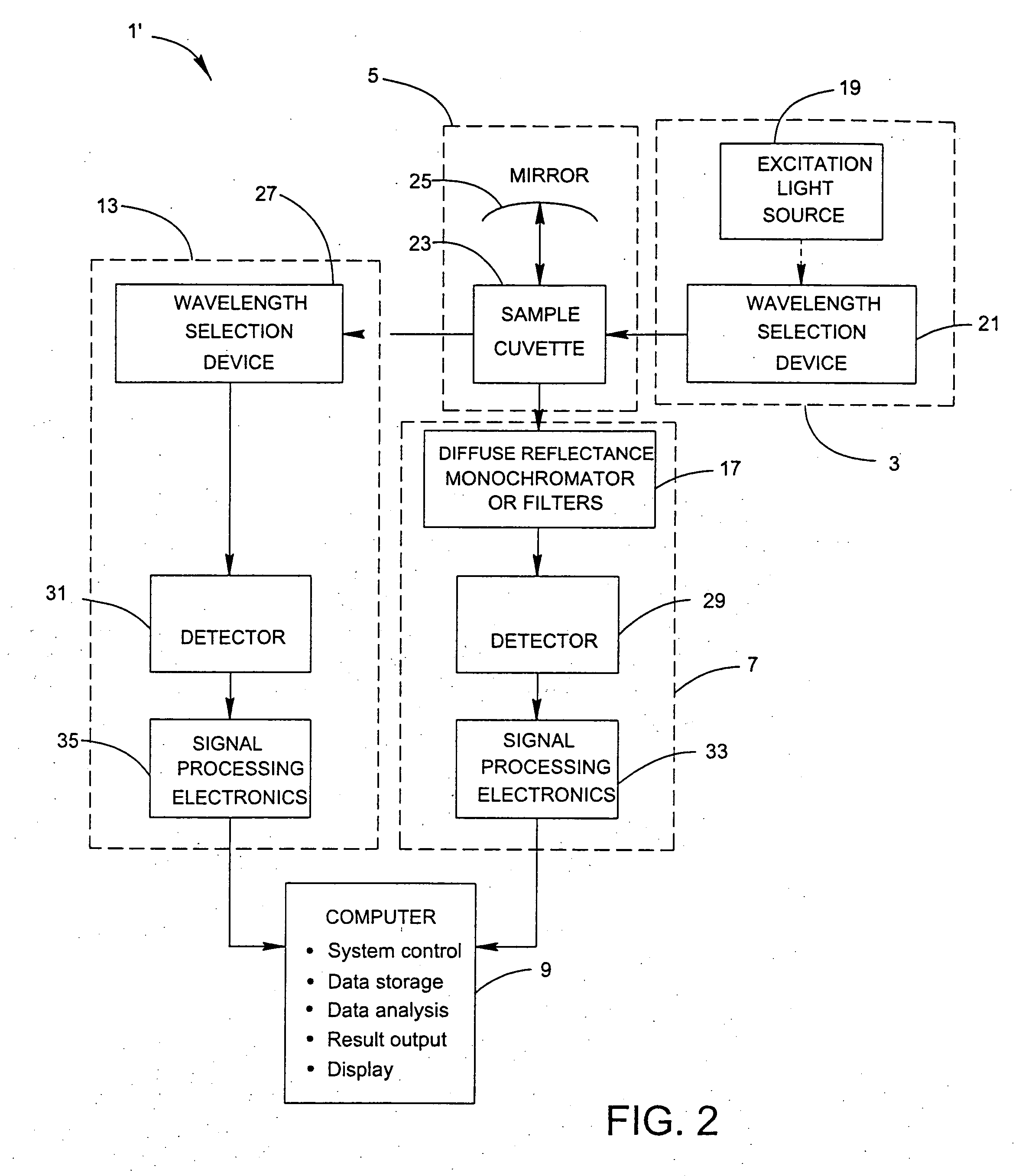
System and method for the identification and quantification of a biological sample suspended in a liquid
InactiveUS20070037135A1Low costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceComputer module
A system for the identification and quantification of a biological sample suspended in a liquid includes a fluorescence excitation module with at least one excitation light source; a sample interface module optically coupled to the fluorescence excitation module for positioning a biological sample to receive excitation light from the at least one excitation light source; a fluorescence emission module optically coupled to the sample interface module and comprising at least one detection device for detecting fluorescence excitation-emission matrices of the biological sample; and a computer module operatively coupled to the fluorescence emission module. The computer module performs multivariate analysis on the fluorescence excitation-emission matrices of the biological sample to identify and quantify the biological sample. The multivariate analysis may comprise extended partial least squared analysis for identification and quantification of the biological sample. A method for the identification and quantification of a biological sample suspended in a liquid is also provided.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
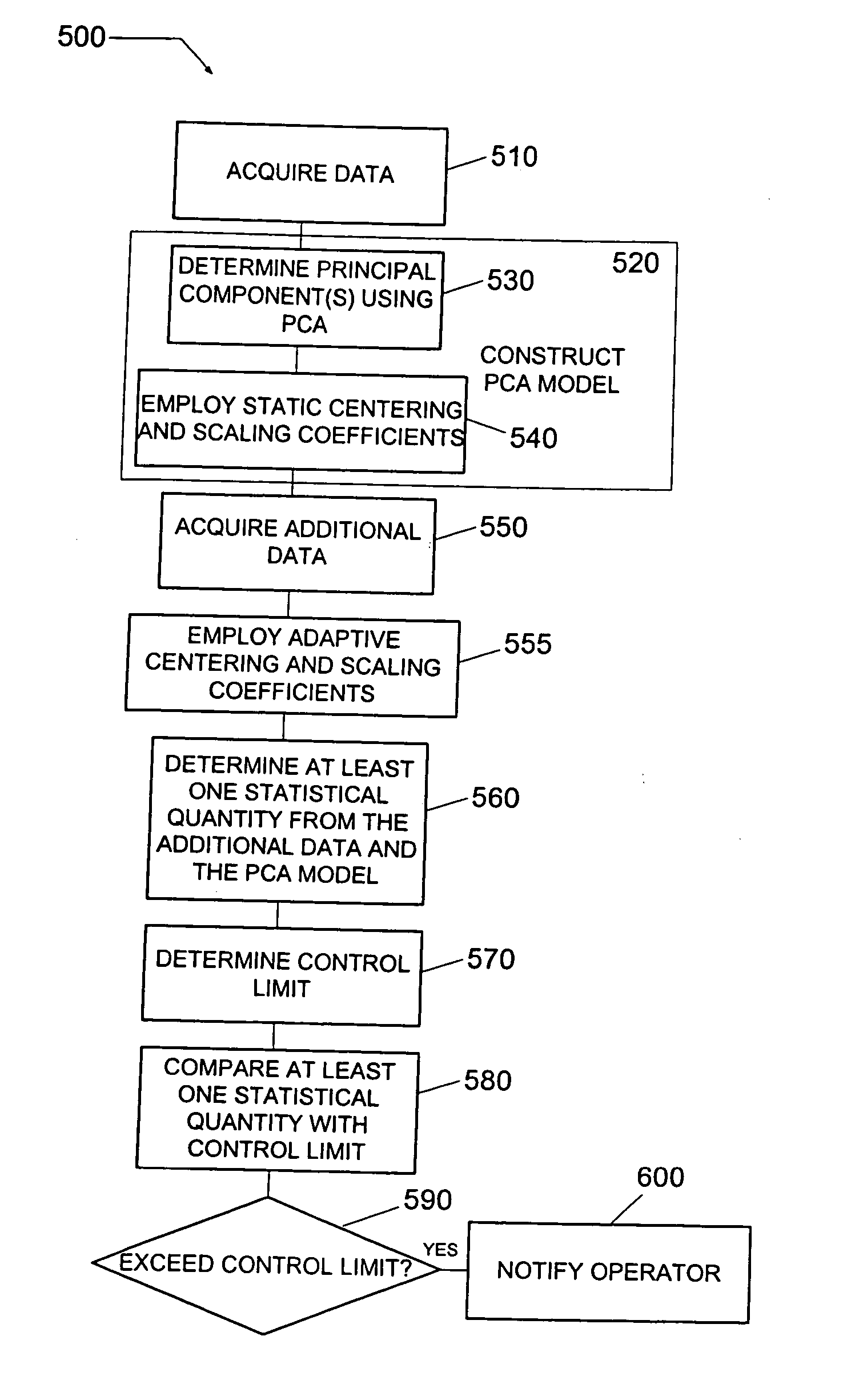
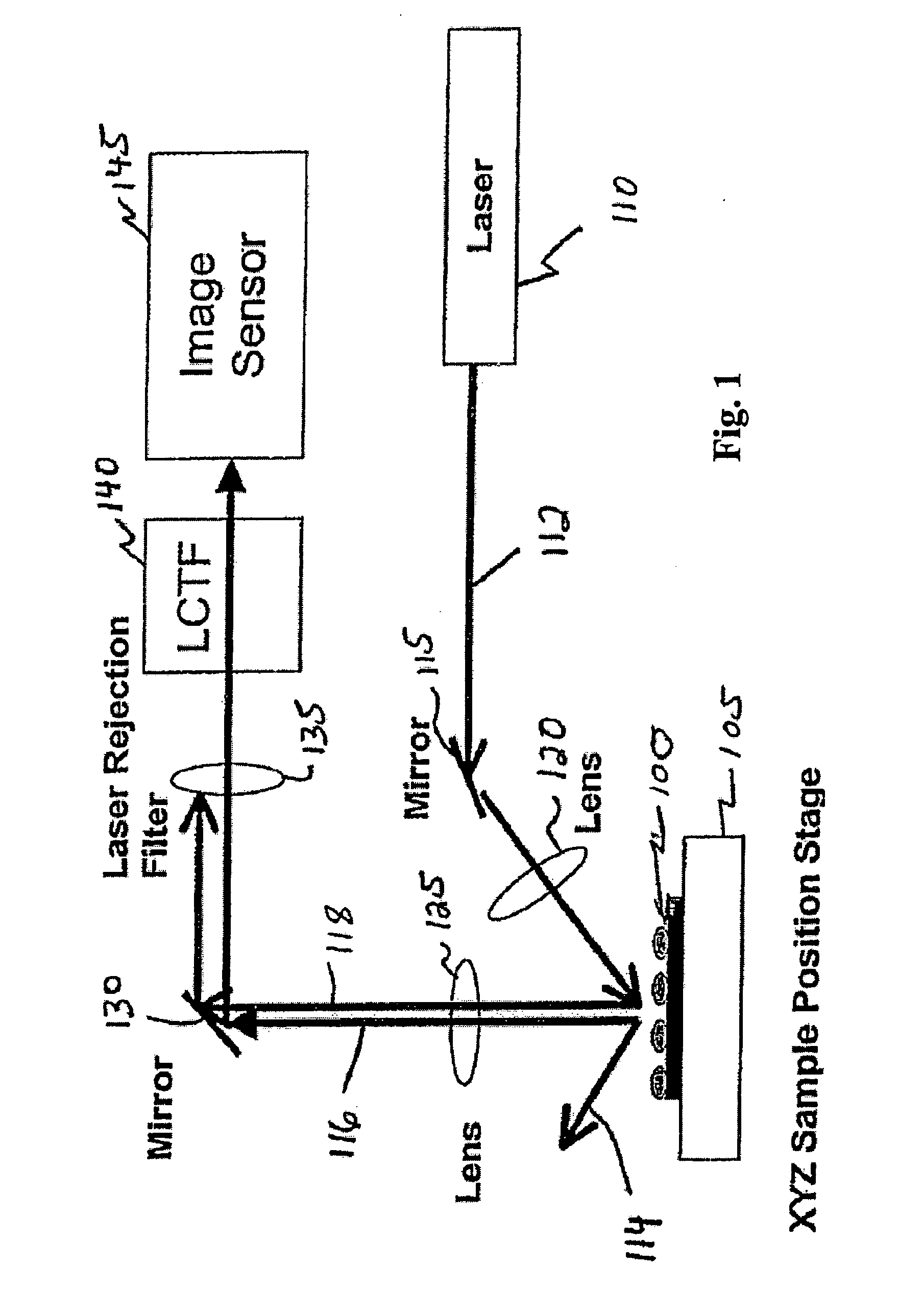
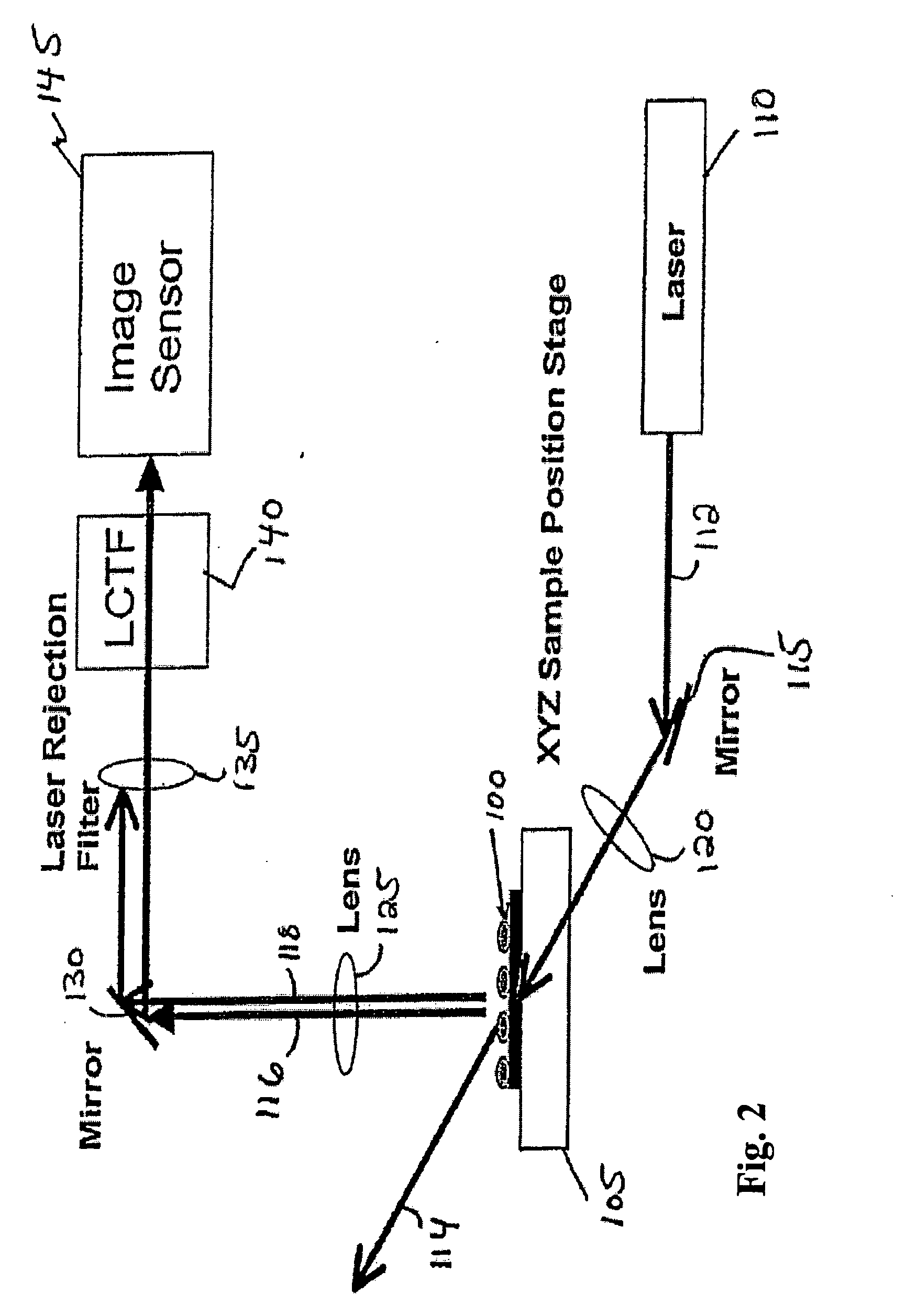
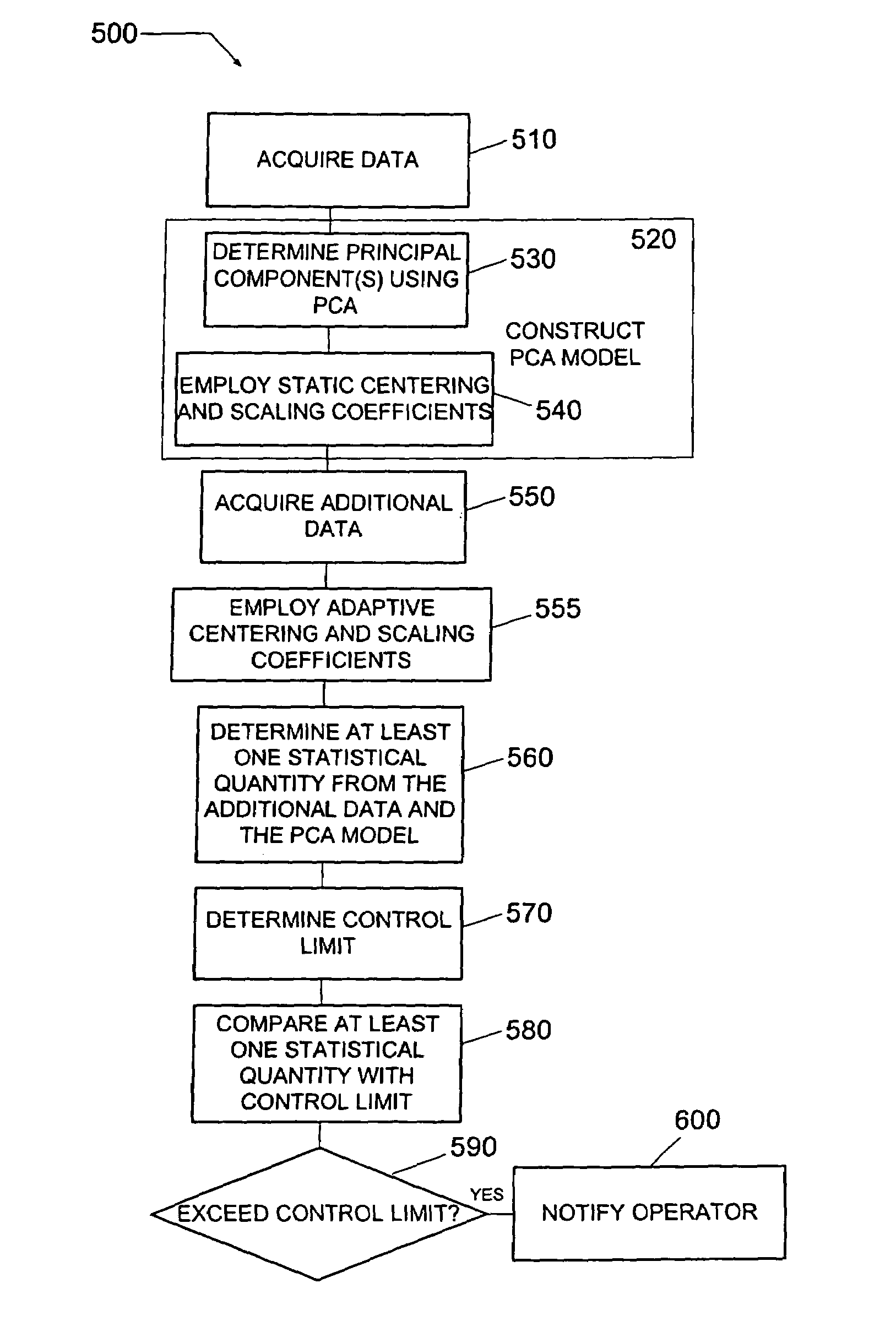
Method and system of diagnosing a processing system using adaptive multivariate analysis
ActiveUS20050060103A1Useful applicationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPrincipal component analysisControl limits
A method and system of monitoring a processing system and for processing a substrate during the course of semiconductor manufacturing. As such, data is acquired from the processing system for a plurality of observations, the data including a plurality of data parameters. A principal components analysis (PCA) model is constructed from the data and includes centering coefficients. Additional data is acquired from the processing system, the additional data including an additional observation of the plurality of data parameters. The centering coefficients are adjusted to produce updated adaptive centering coefficients for each of the data parameters in the PCA model. The updated adaptive centering coefficients are applied to each of the data parameters in the PCA model. At least one statistical quantity is determined from the additional data using the PCA model. A control limit is set for the statistical quantity and compared to the statistical quantity.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS20030224394A1Improve artBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
A method for associating a gene with a trait exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms from a species. A genetic marker map is constructed from a set of genetic markers associated with the plurality of organisms. For each gene in a plurality of genes, a quantitative trait locus analysis is performed using the genetic marker map and a quantitative trait. The quantitative trait locus analysis produces quantitative trait locus data. A quantitative trait comprises an expression statistic for a gene. The expression statistic for a gene is derived from a cellular constituent level that corresponds to the gene in each organism in the plurality of organisms. The quantitative trait locus data are clustered from each quantitative trait locus analysis to form a quantitative trait locus interaction map. Clusters of genes in the map are identified as a candidate pathway group. An expression cluster map is used to refine the candidate pathway group. Multivariate analysis is used to validate the candidate pathway group as a set of genes that are genetically interacting.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
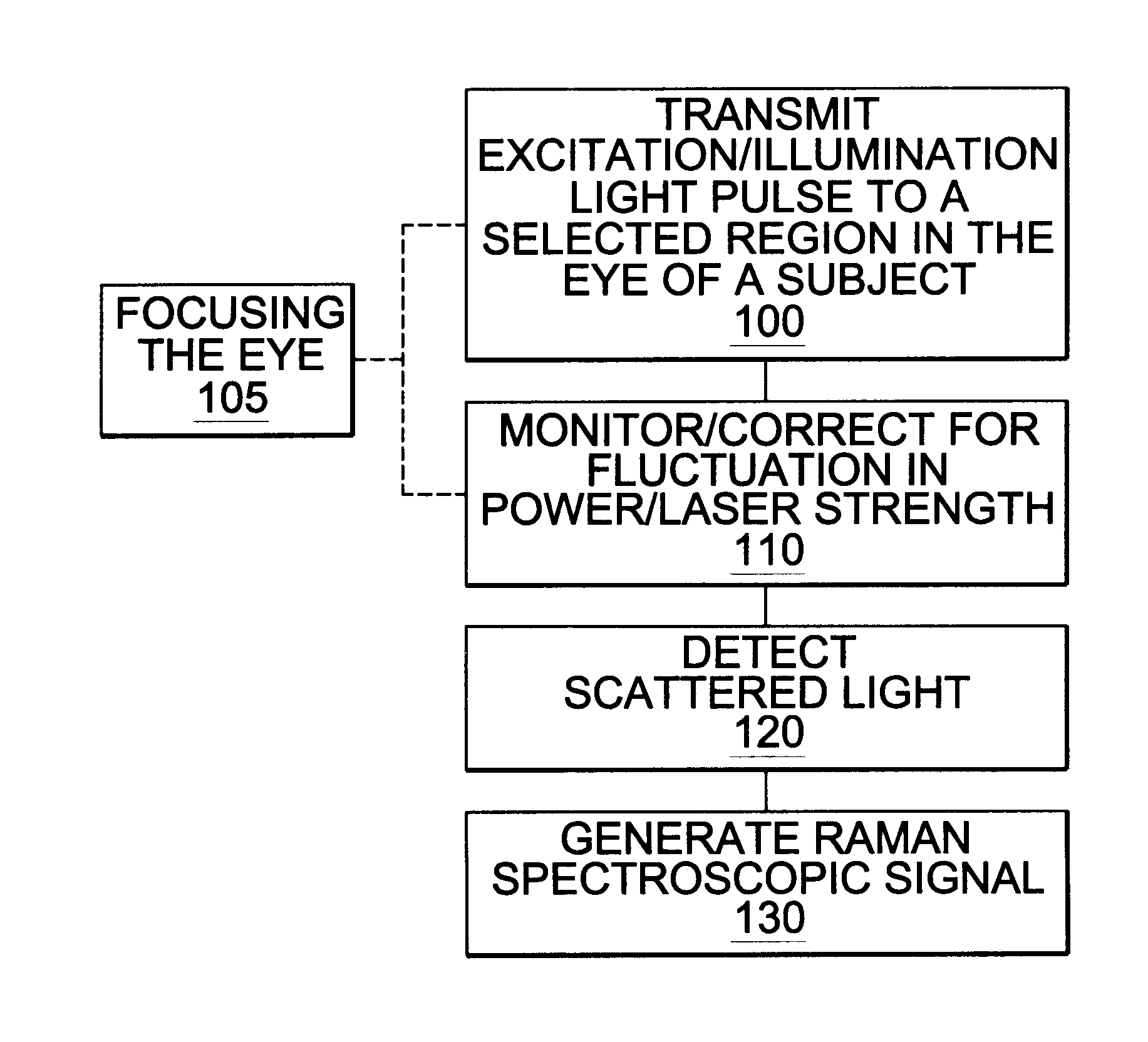
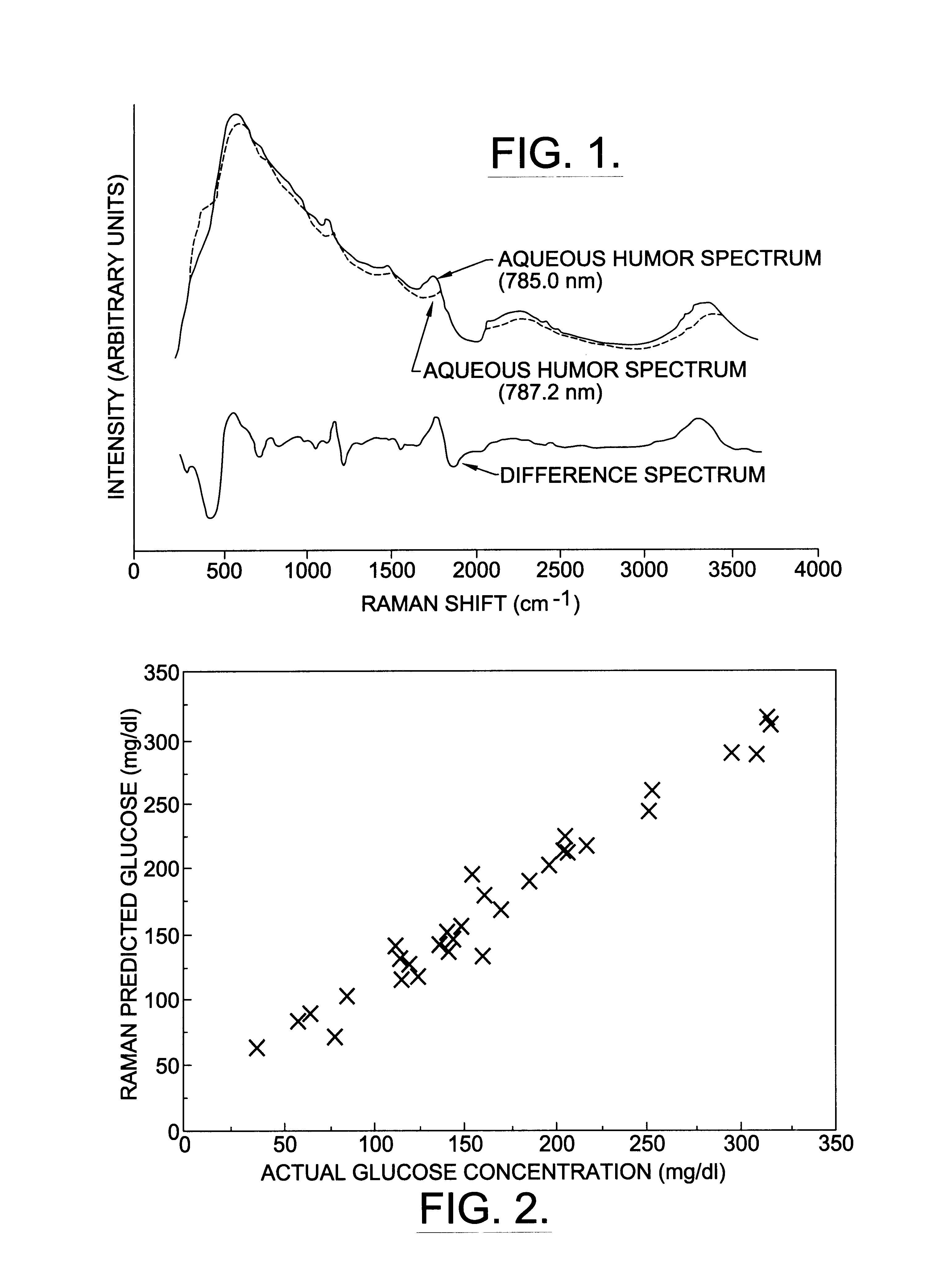
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances or toxins in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals of selected regions in the eye
InactiveUS6574501B2Reduced energy/density exposure ratingImproved margin of safetyRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringConjunctivaNon invasive
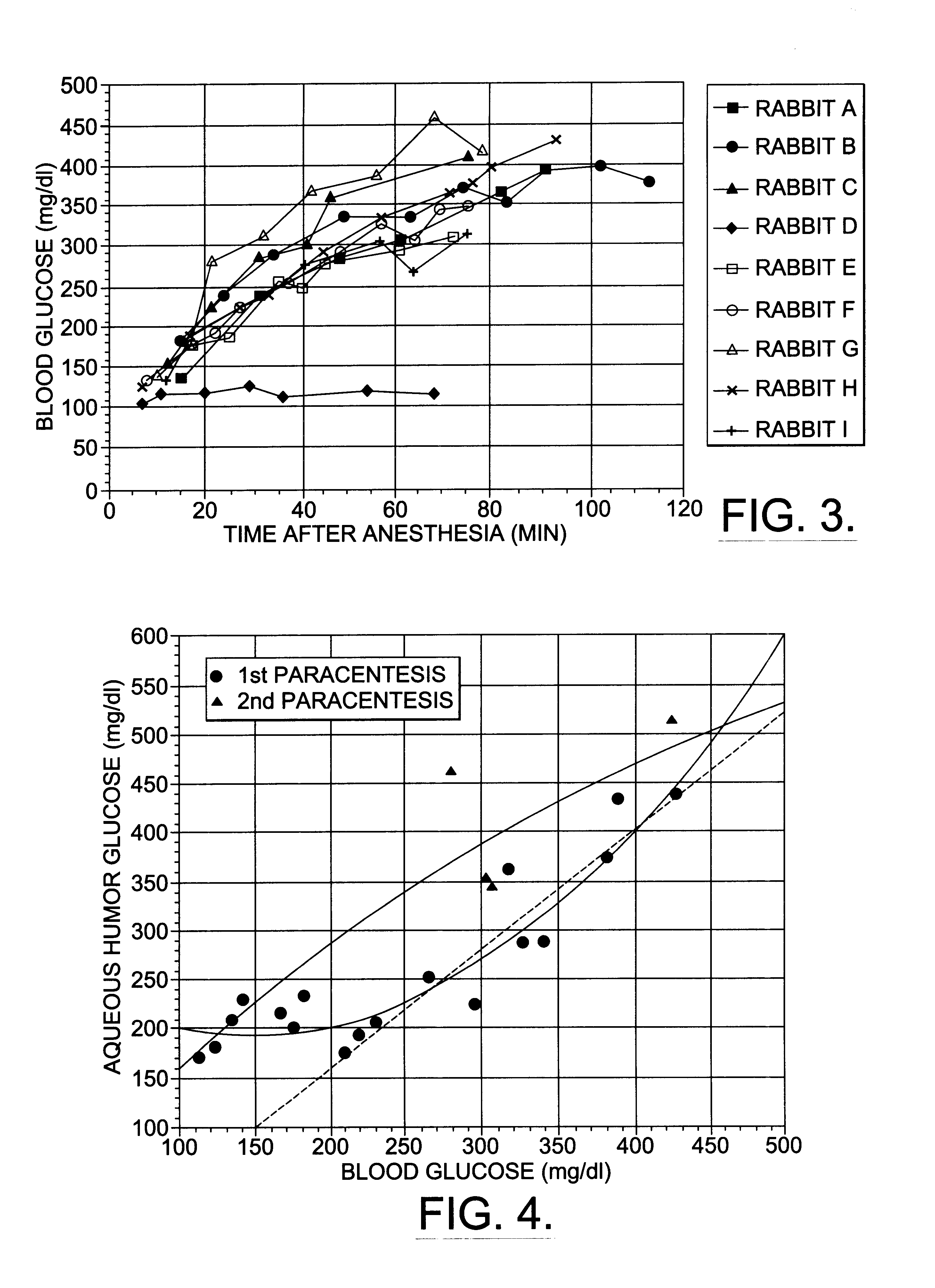
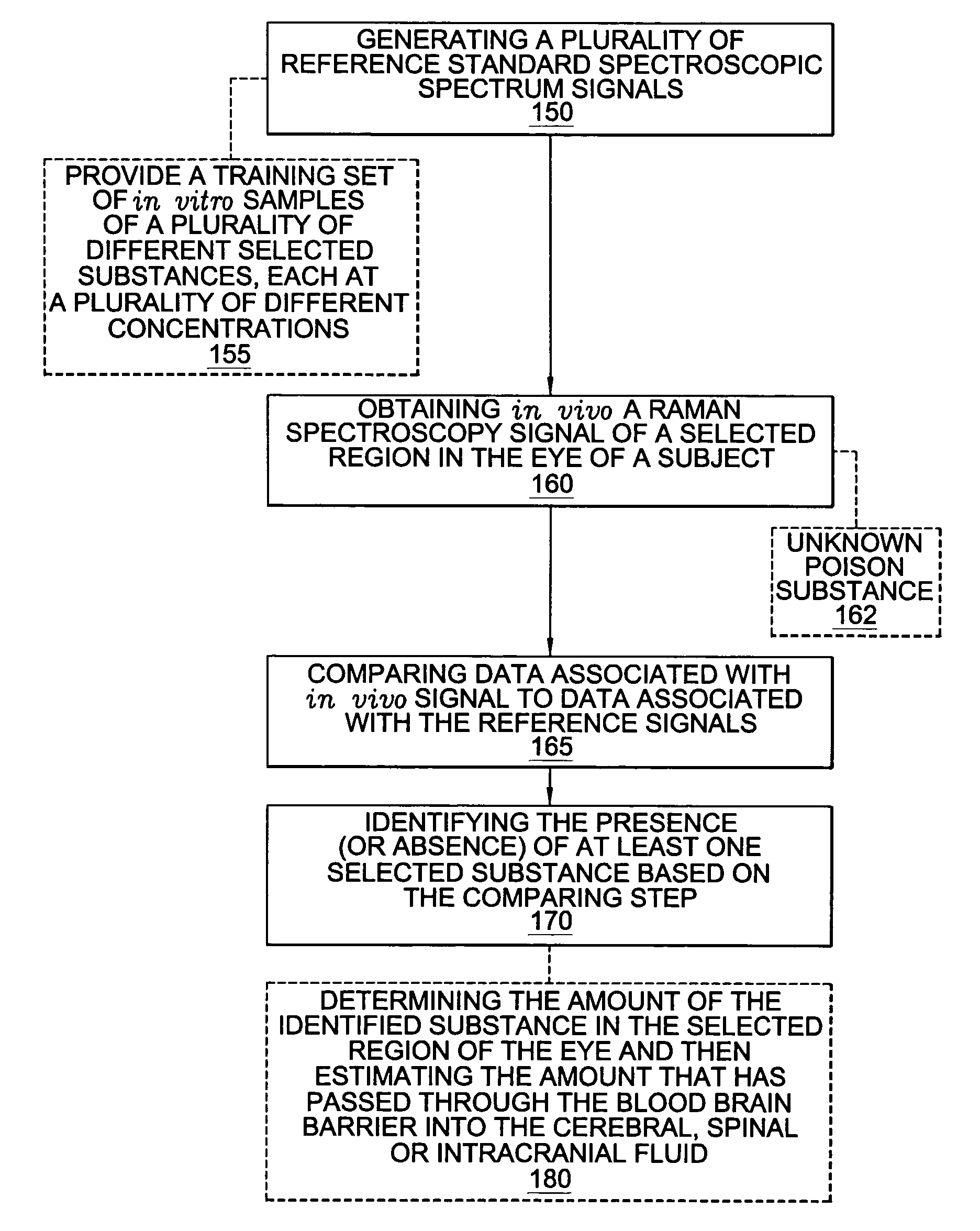
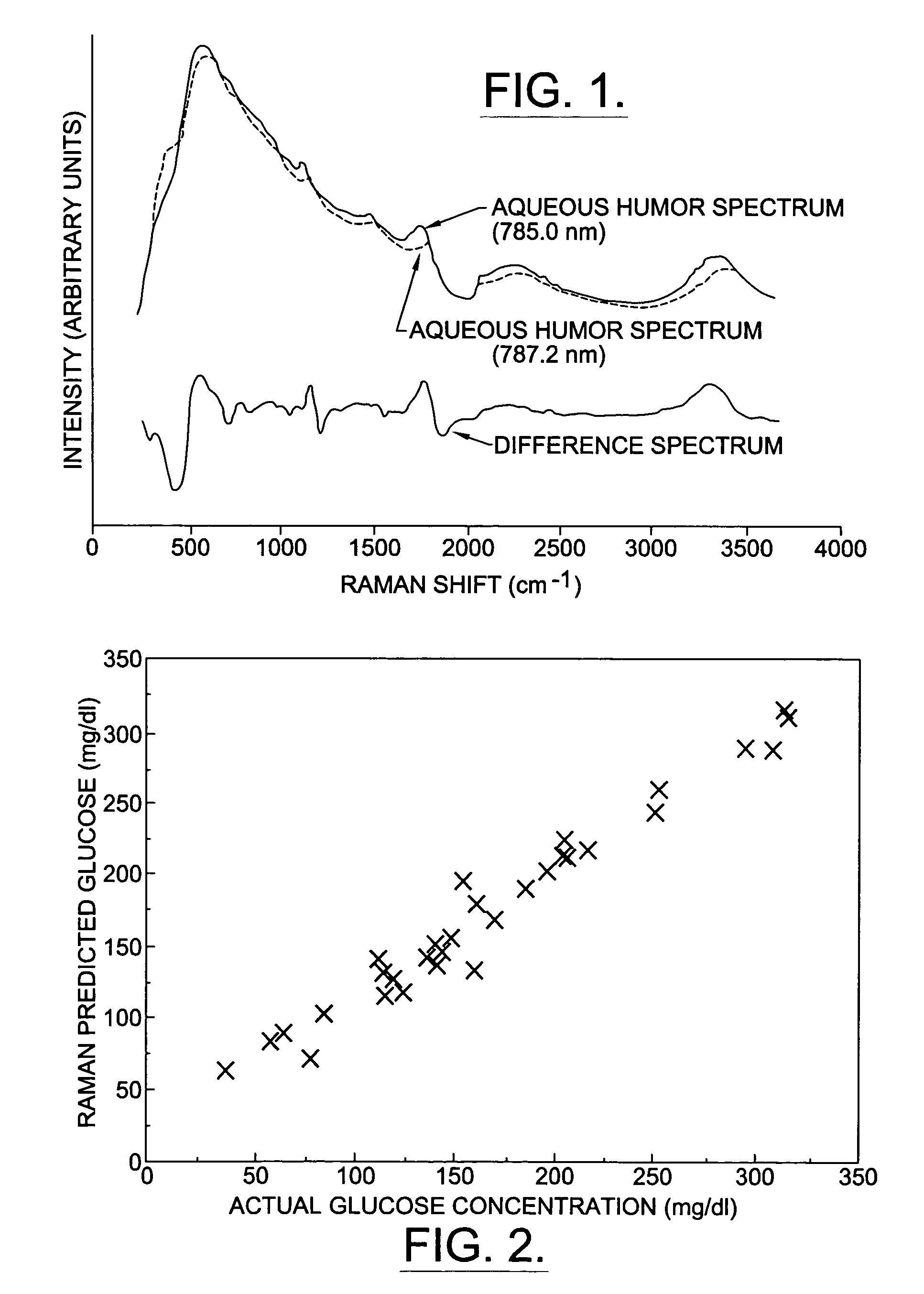
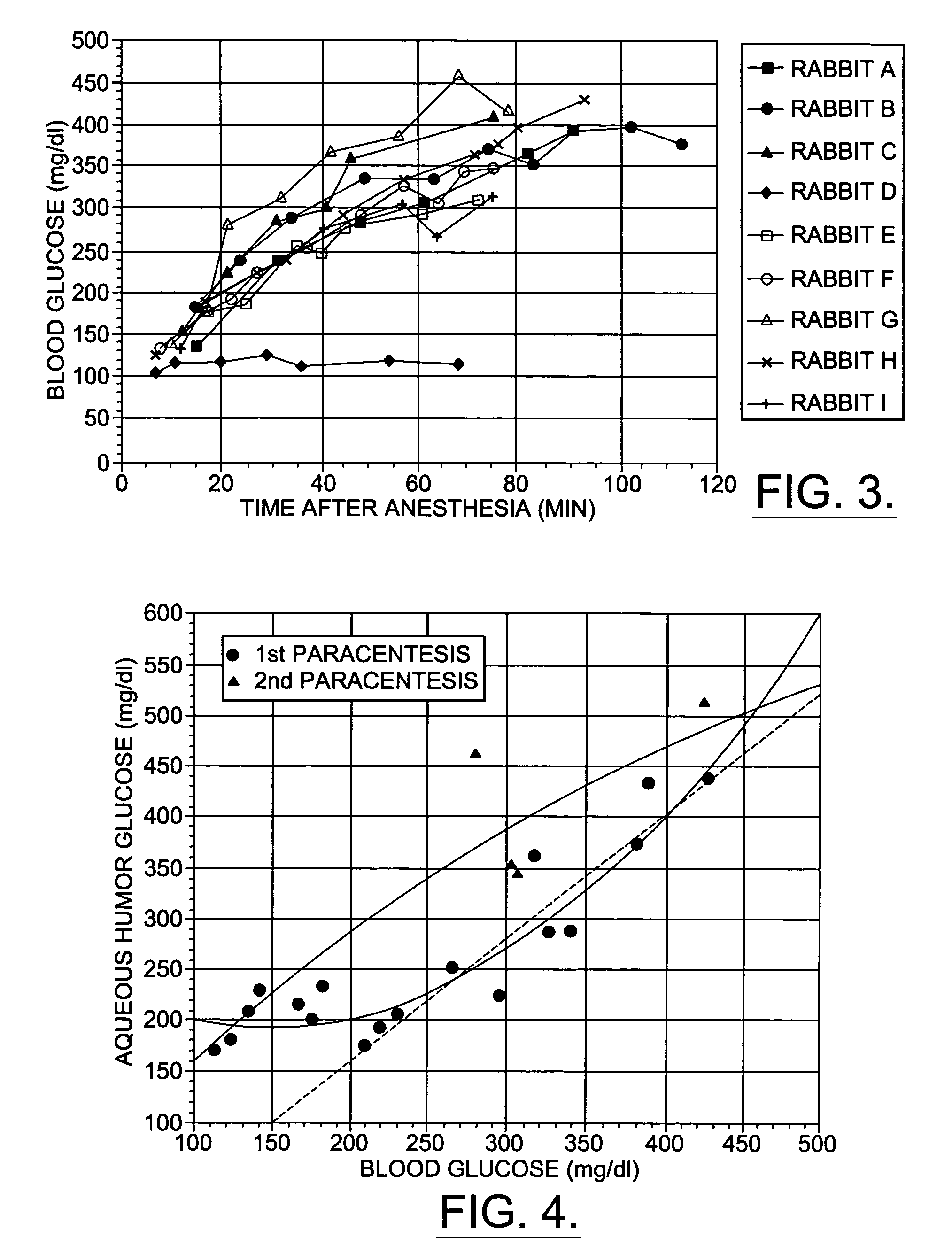
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier. Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam (e.g., at a wavelength of 600 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES +1
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances, including ethanol or toxins, in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals
InactiveUS7398119B2Fast “ triage ” assessmentReliable and faster treatment decisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon invasivePhysics
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier.Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam at a selected wavelength (e.g., at a wavelength of about 400 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Wearable Wireless Multisensor Health Monitor with Head Photoplethysmograph
InactiveUS20140275888A1Accurate measurementFacilitate early detectionMachine supportsEvaluation of blood vesselsRemote computerWearable eeg
Ambulatory monitoring of human health is provided by a multi-component multi-sensor wireless wearable biosignal acquisition system comprising a torso device and a peripheral device communicating wirelessly, and a mobile phone for receiving collected data and uploading it over cellular network or WiFi to a remote computer for multivariate analysis. Biosignals include EKG and PPG, from which a determination of pulse transit time can be made.
Owner:VENTURE GAIN L L C
Statistical signatures used with multivariate analysis for steady-state detection in a process
ActiveUS20080082181A1Easy to detectReduce dimensionalityData processing applicationsTesting/monitoring control systemsSteady state detectionPrincipal component analysis
Methods and systems to detect steady-state operations in a process of a process plant include collecting process data. The collected process data is generated from a plurality of process variables of the process. A multivariate statistical model of the operation of the process is generated using the process data. The multivariate statistical model may be generated from a principal component analysis. The model is executed to generate outputs corresponding to the most significant variations in the process. Statistical measures of the outputs are generated and used to determine whether a steady-state or unsteady-state is related to the process.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
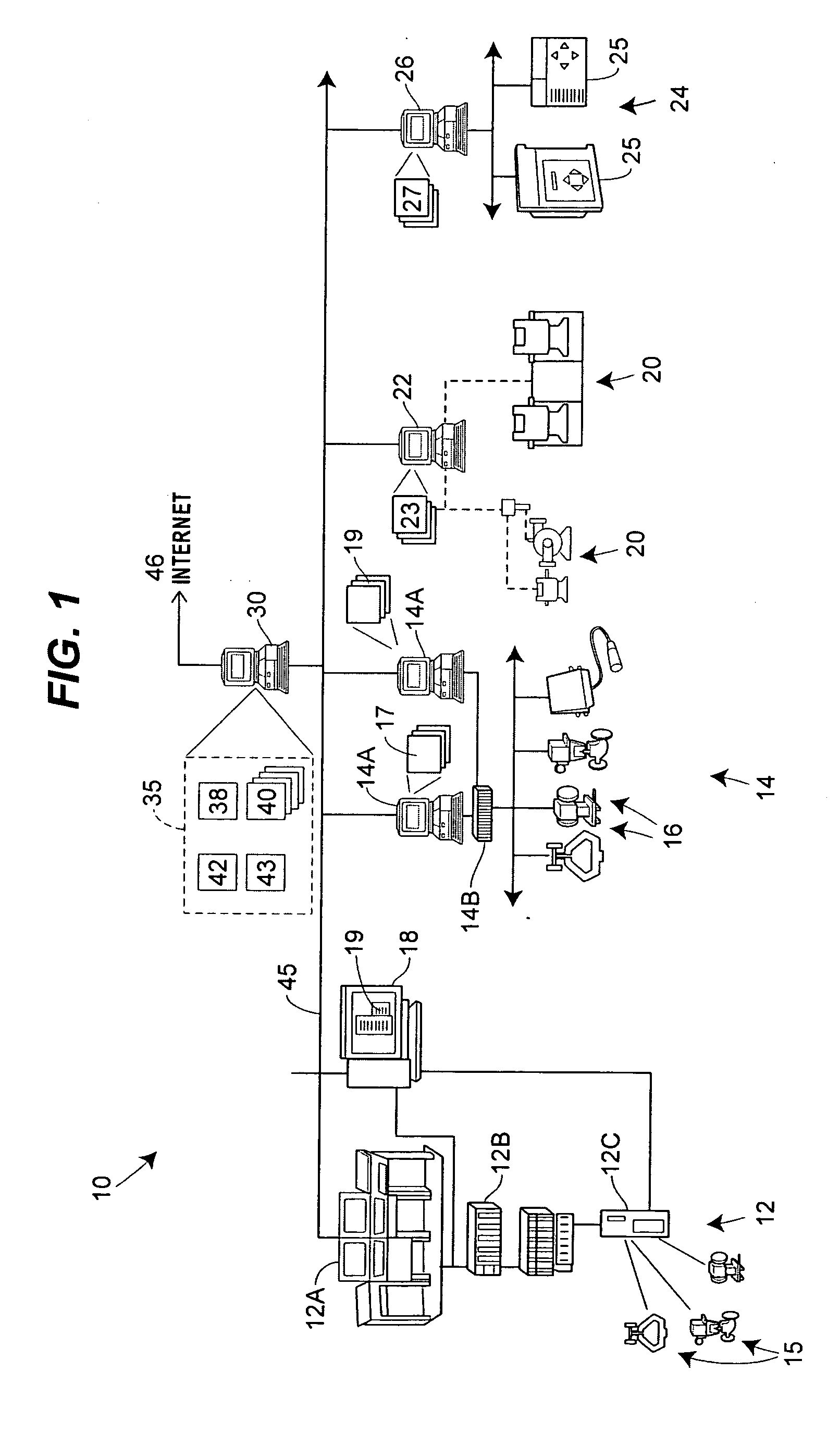
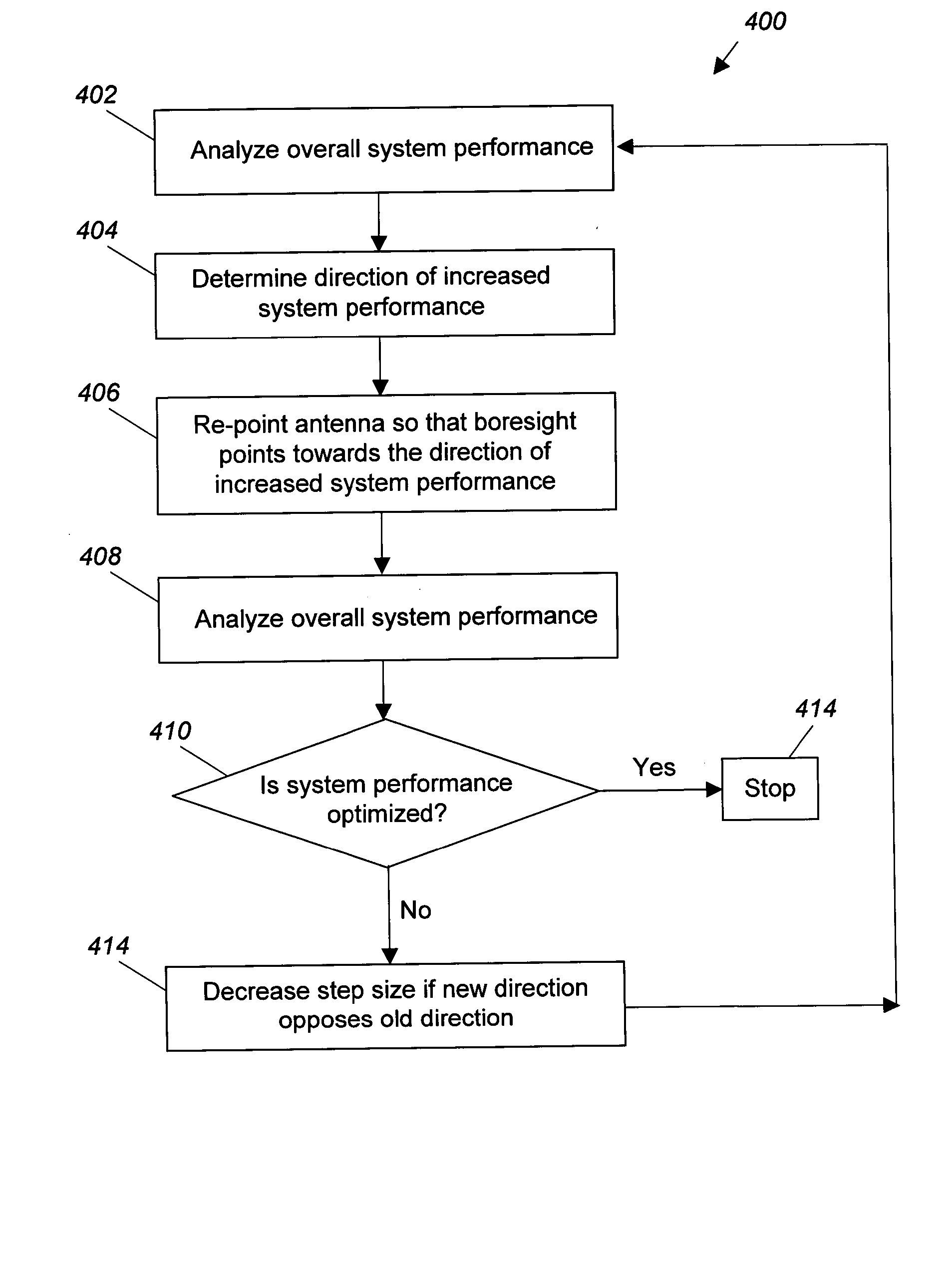
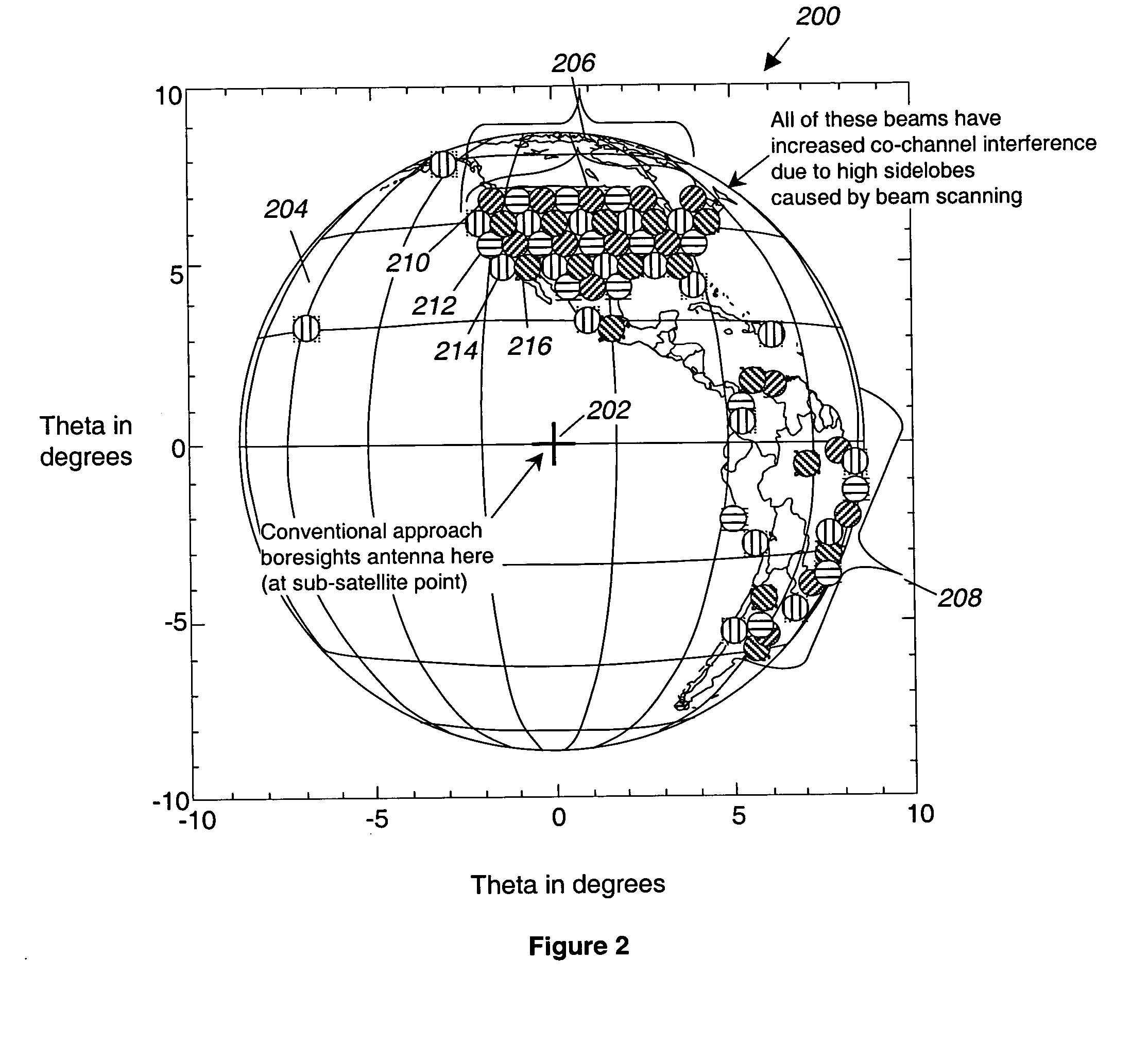
Reducing co-channel interference in satellite communications systems by antenna re-pointing
ActiveUS20050068230A1Improve performanceMinimizes CCIAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionCommunications systemHigh density
A system and method for increasing the performance of a satellite communication system by using a multivariate analysis approach to optimize the pointing of the boresight of a satellite-mounted antenna. Optimizing the pointing of the boresight of the antenna minimizes sidelobe generation, and thus Co-Channel Interference (CCI) in geographic areas served by the system. By minimizing CCI, the overall system performance of the communication system is optimized. To optimize the pointing of the boresight of the antenna, the overall performance of the satellite communication system is determined, and the boresight of the antenna is iteratively repointed in the direction of increasing system performance until the optimized boresight pointing is determined. Alternatively, the frequency re-use plan of the satellite communication system may be analyzed to determine a high density cell region and the boresight may be pointed to the high density cell region.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
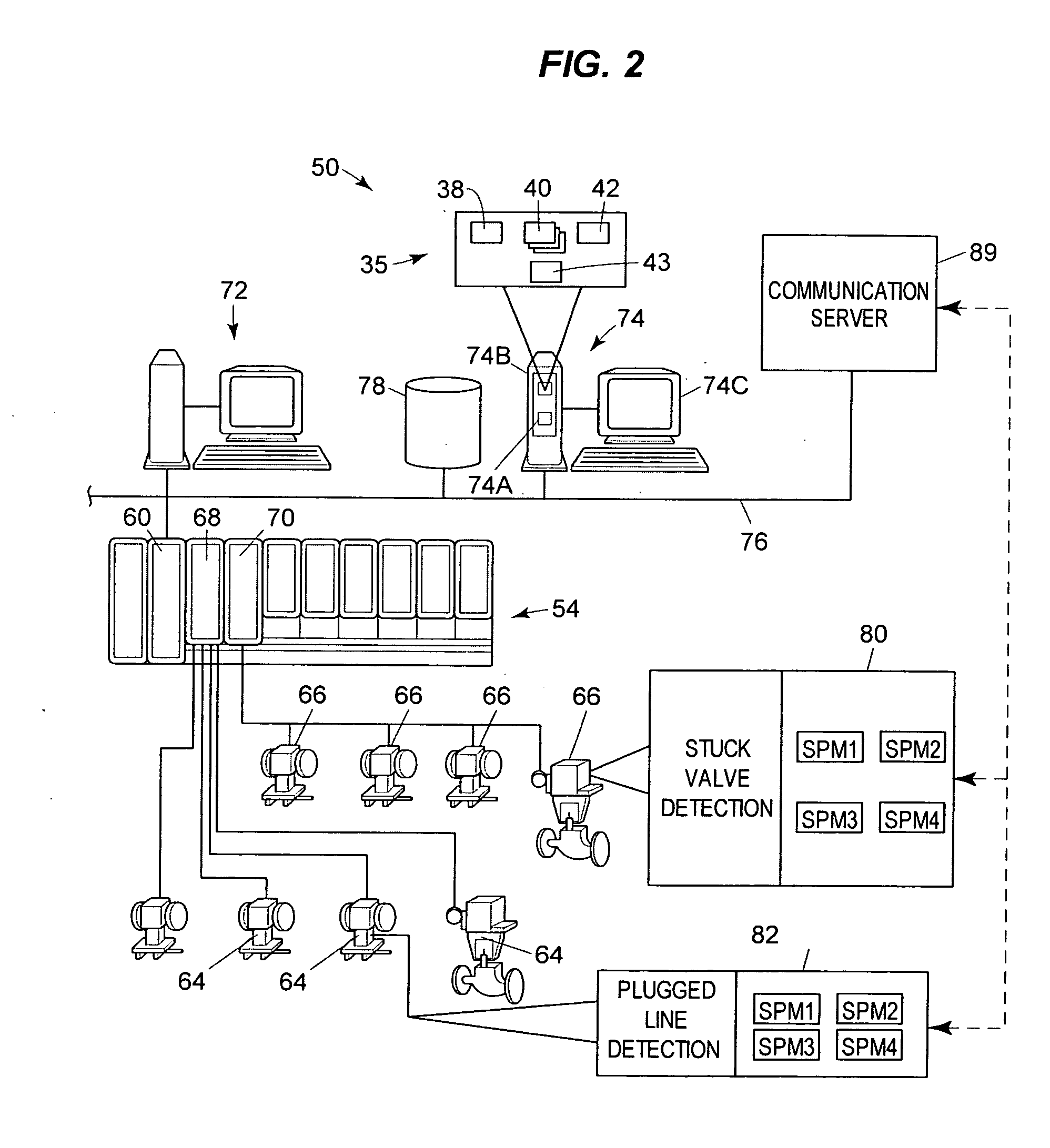
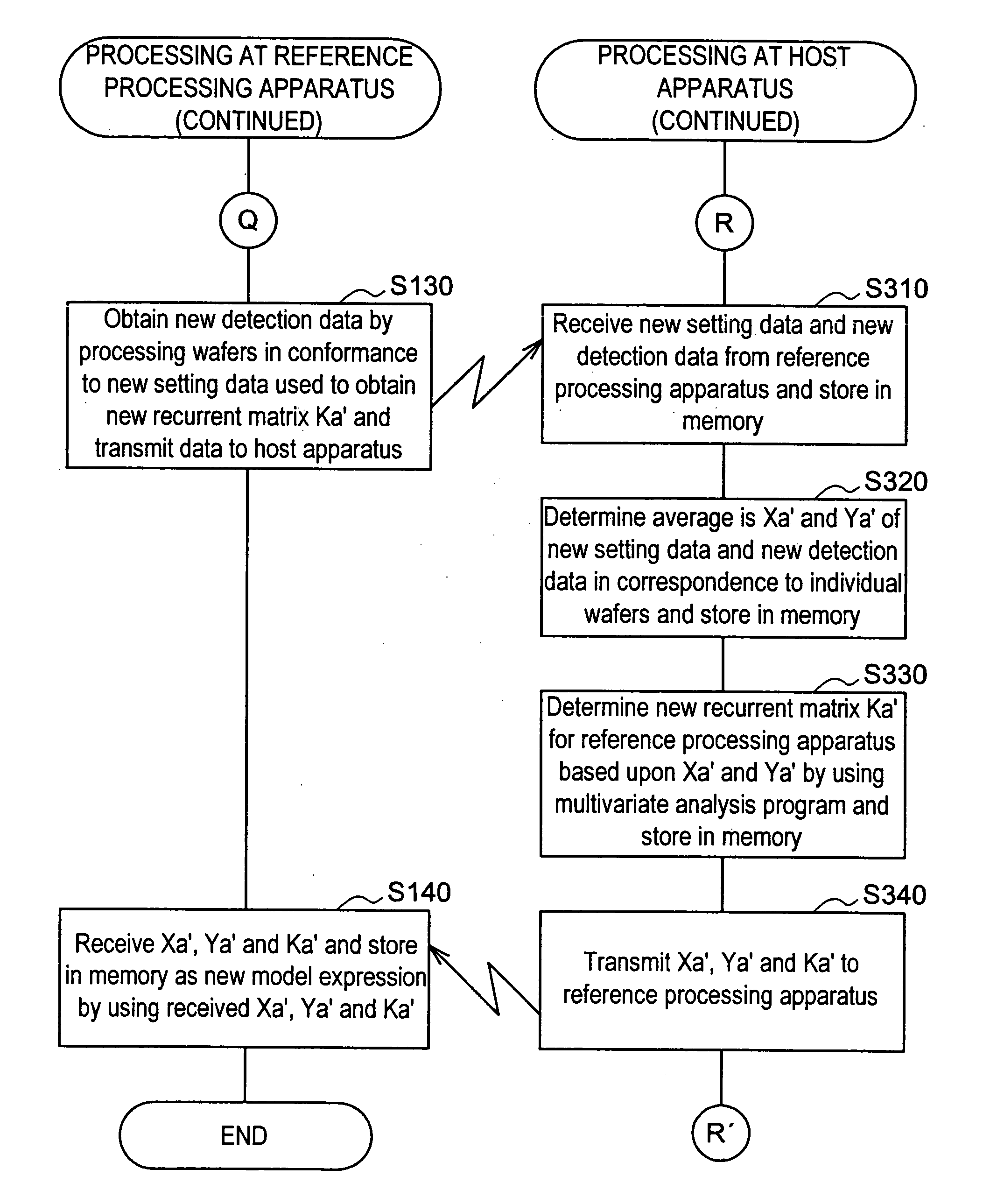
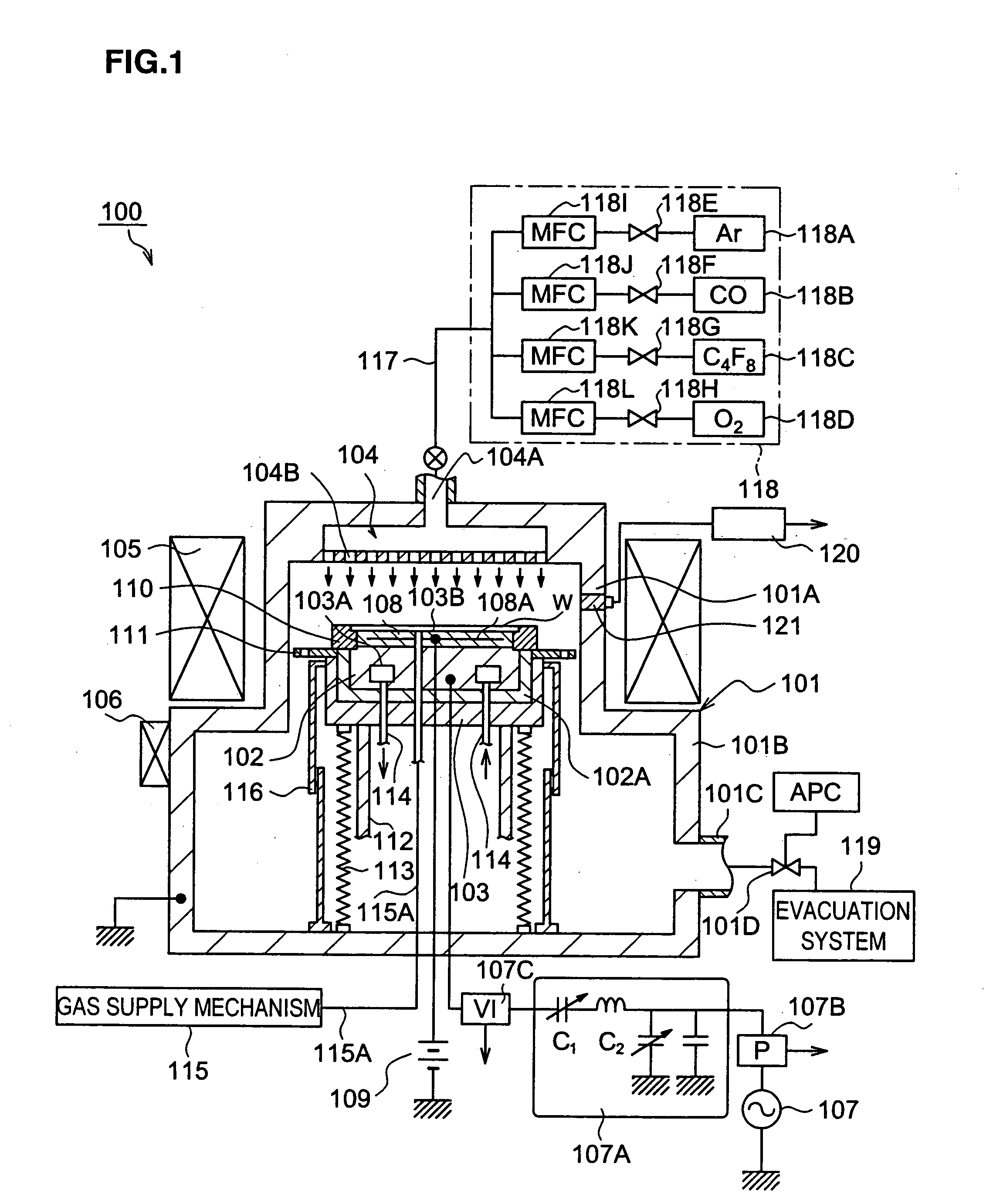
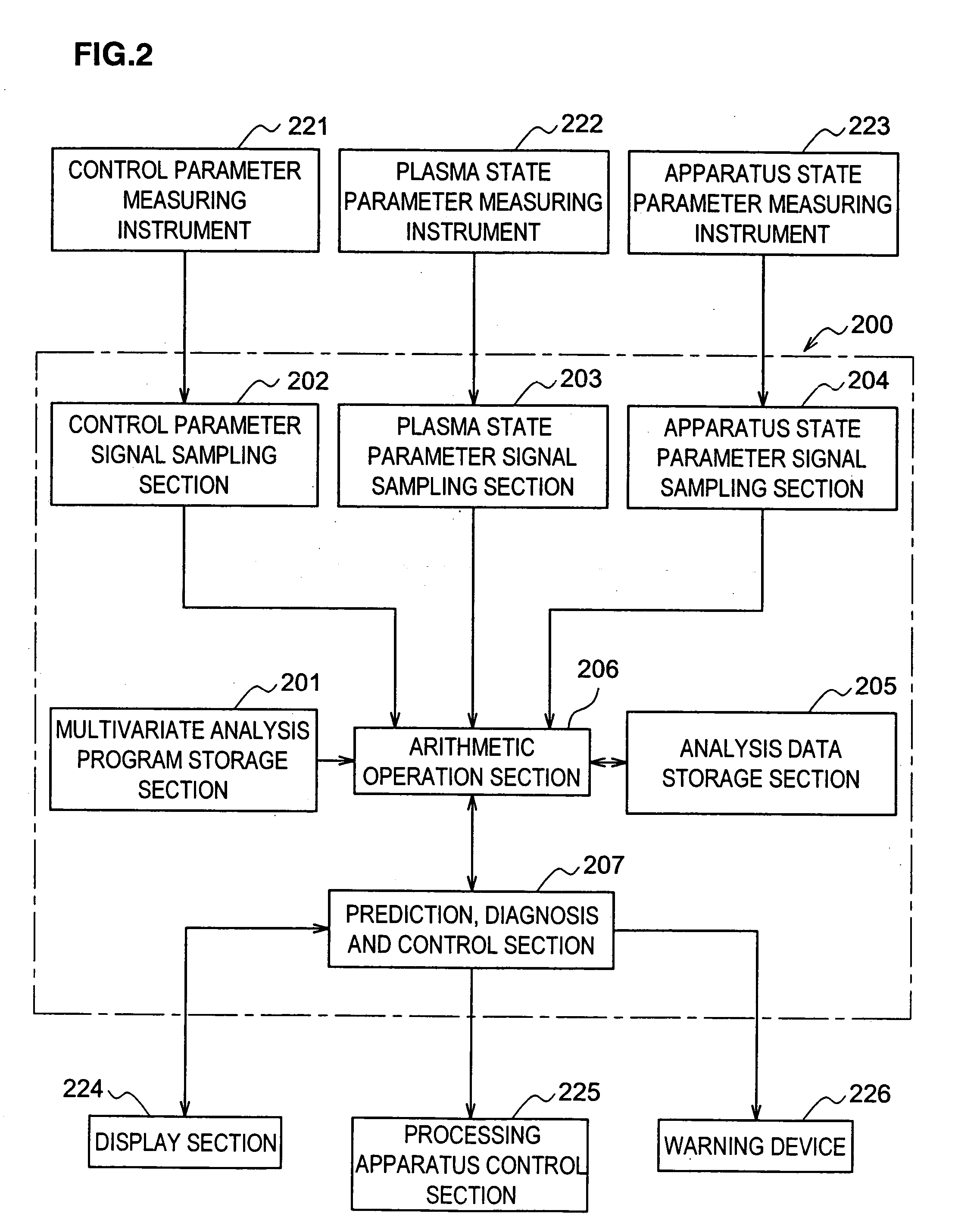
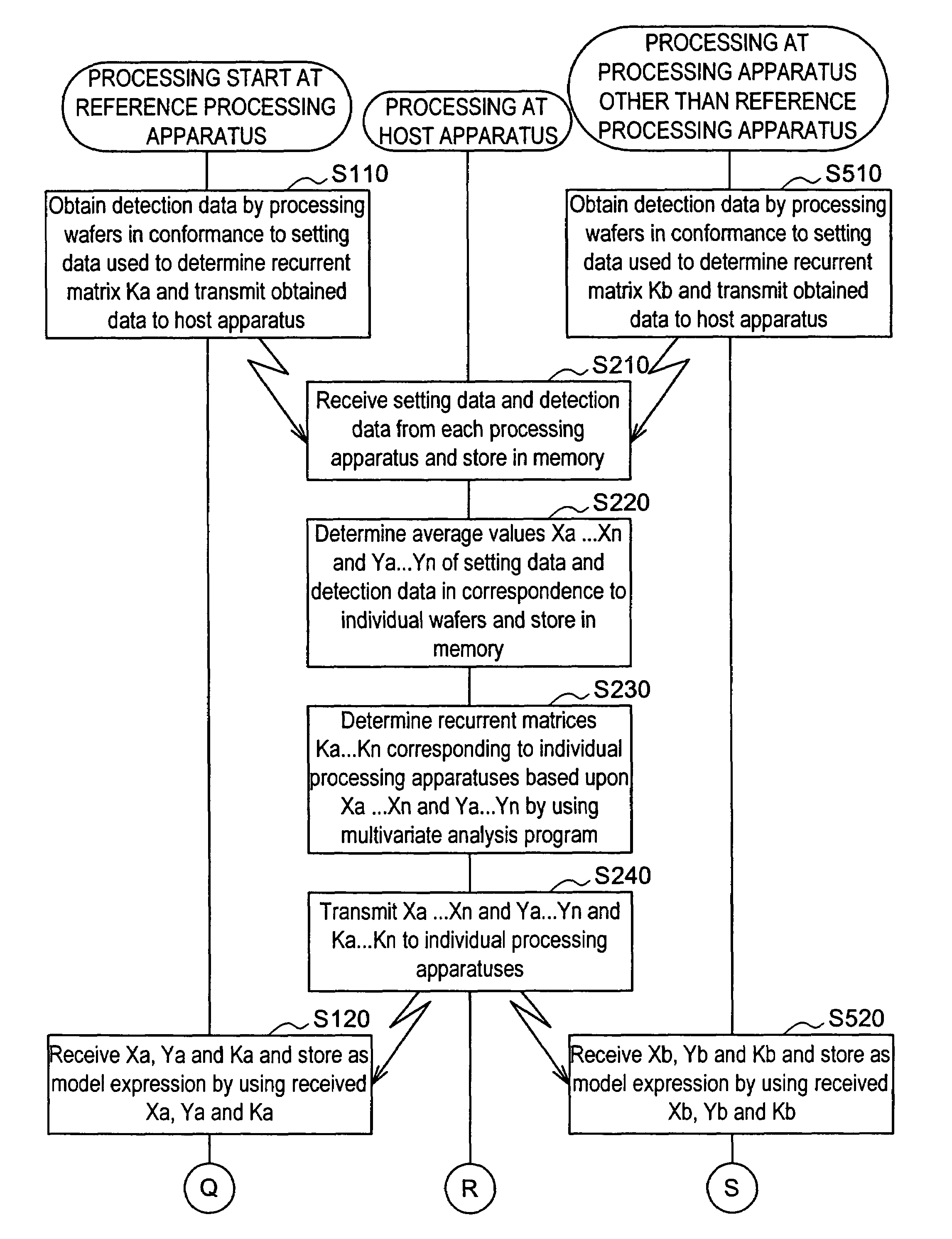
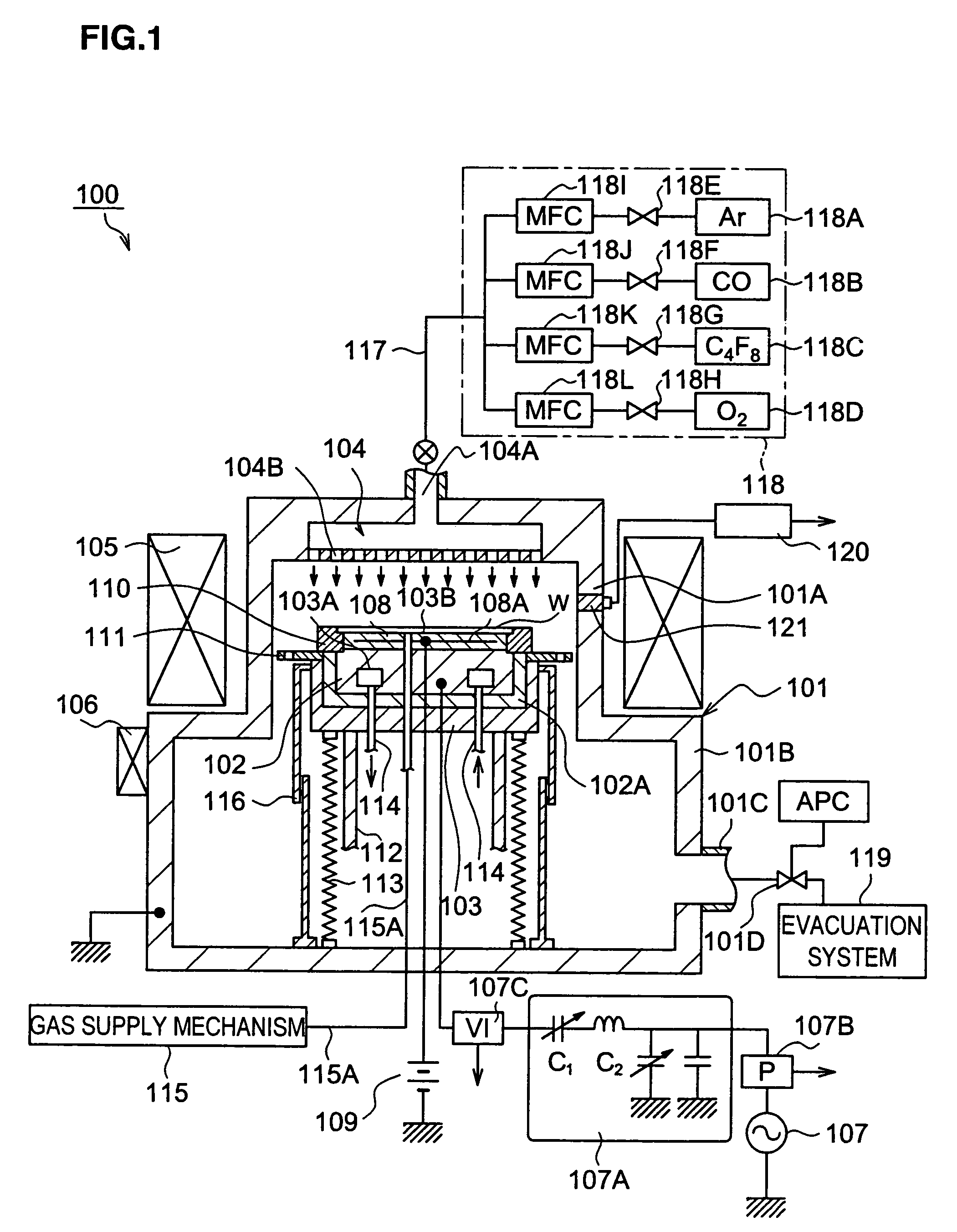
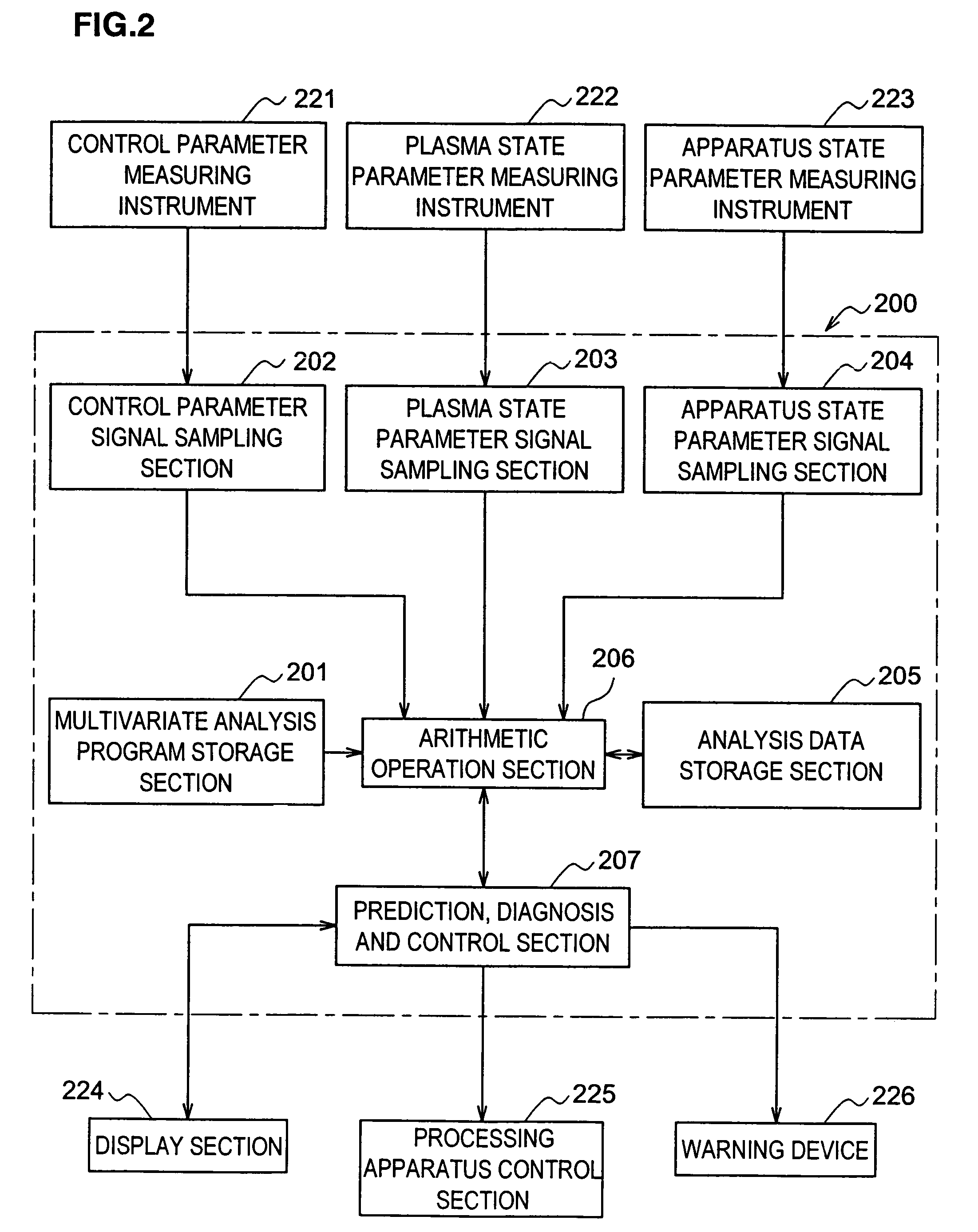
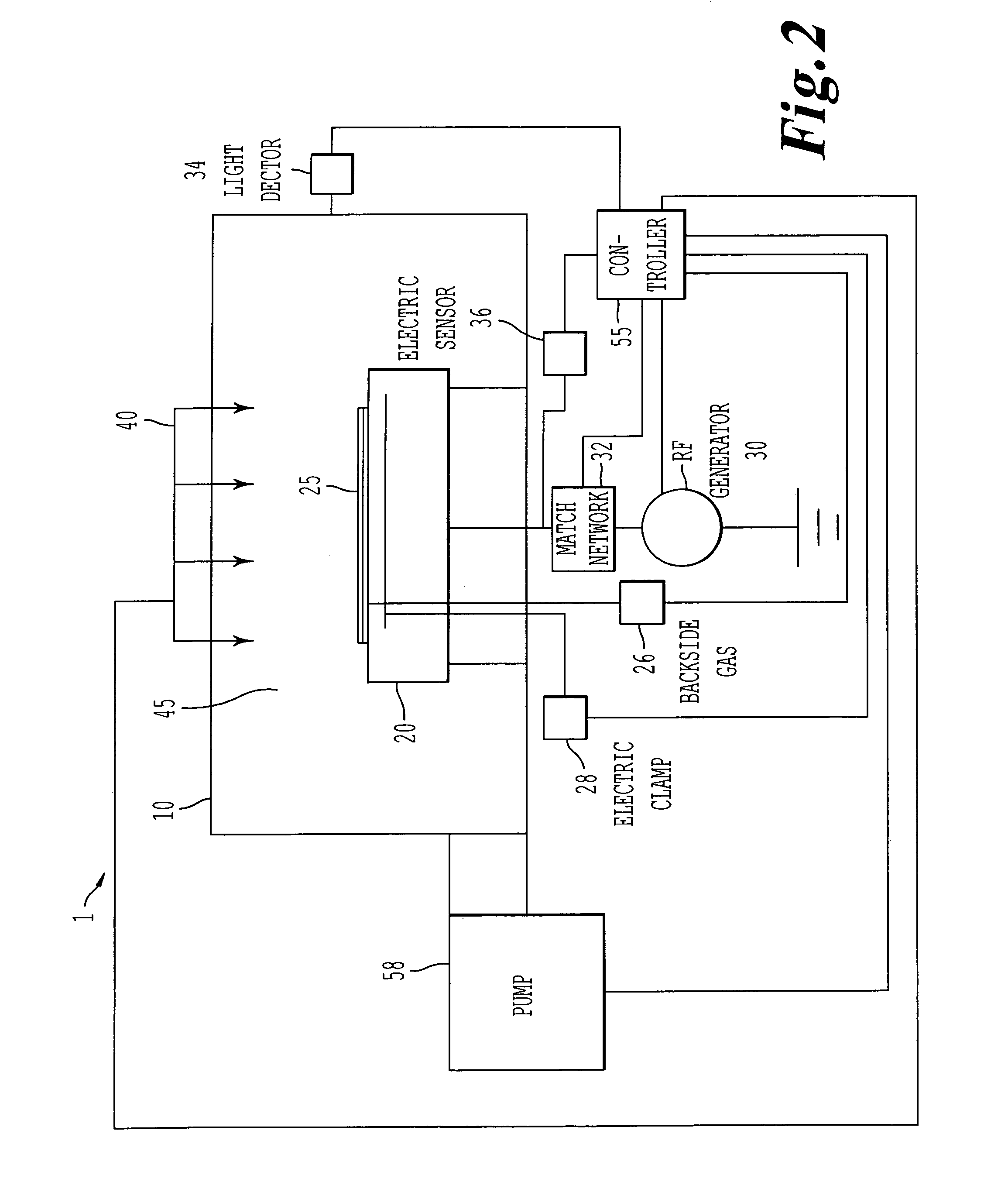
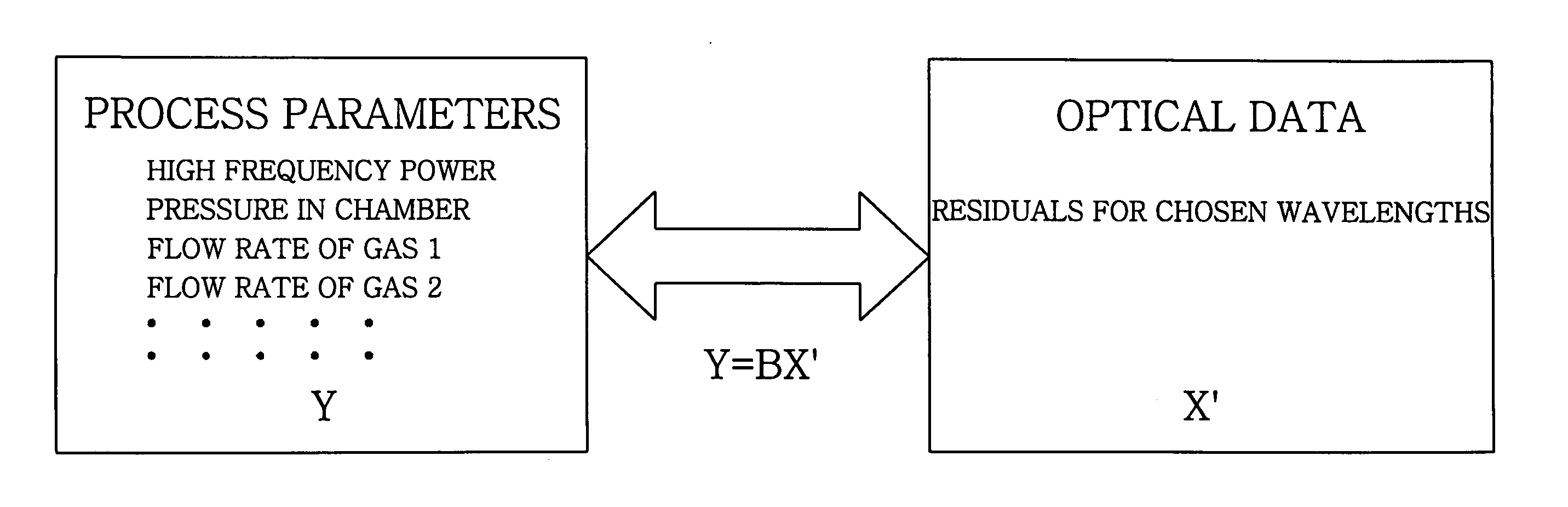
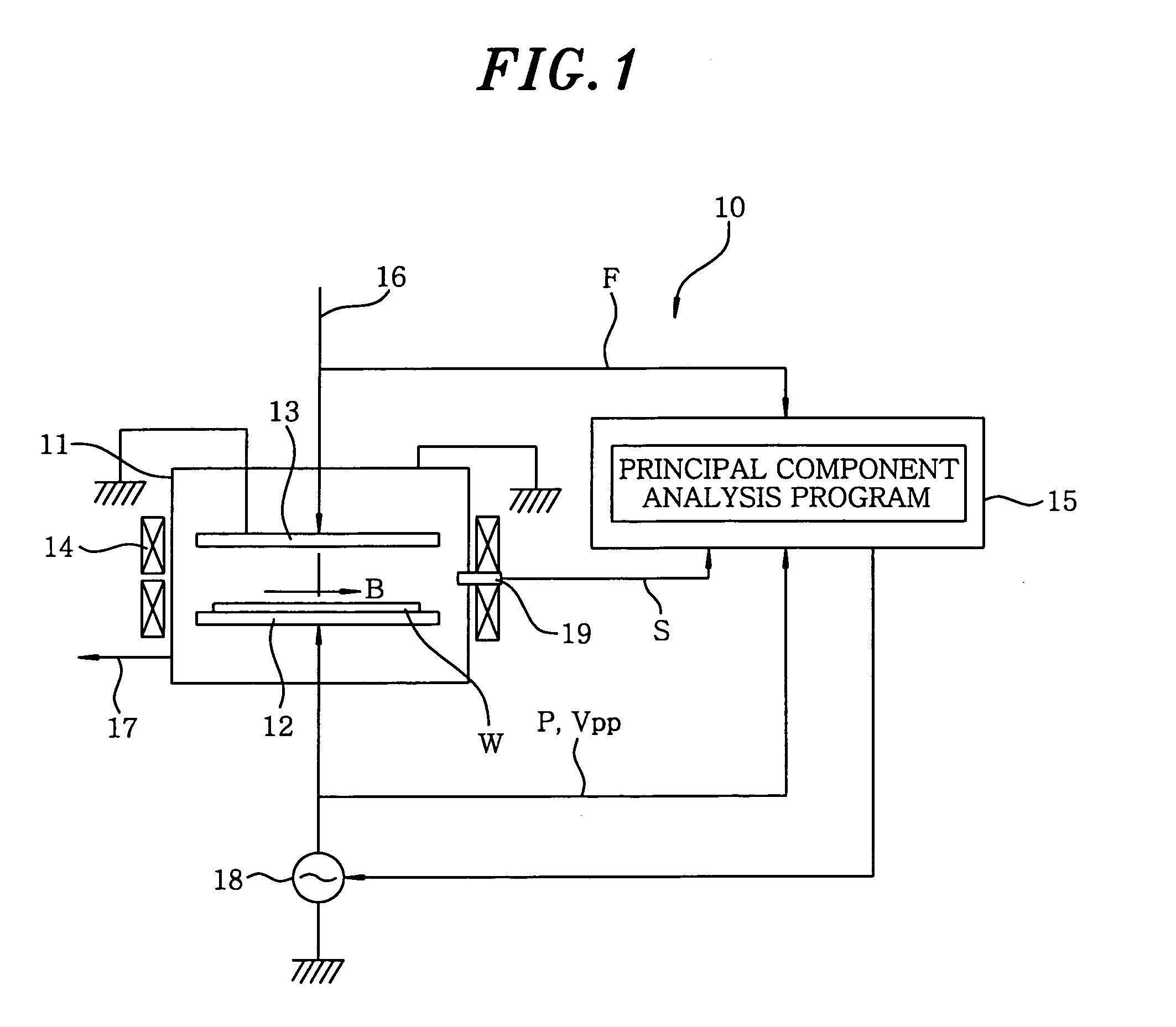
Method for generating multivariate analysis model expression for processing apparatus, method for executing multivariate analysis of processing apparatus, control device of processing apparatus and control system for processing apparatus
ActiveUS20050143952A1Electric discharge tubesDigital computer detailsControl systemParallel computing
According to the present invention, multivariate analysis model expressions are generated for a plasma processing apparatus 100A and a plasma processing apparatus 100B by executing a multivariate analysis of detection data provided by a plurality of sensors included in each plasma processing apparatus when the plasma processing apparatuses 100A and 100B operate based upon first setting data. Then, when the plasma processing apparatus 100A operates based upon new second setting data, detection data provided by the plurality of sensors in the plasma processing apparatus 100A are used to generate a corresponding multivariate analysis model expression, and by using the new multivariate analysis model expression corresponding to the plasma processing apparatus 100A generated based upon the second setting data and to the plasma processing apparatus 100B, a multivariate analysis model expression corresponding to the new second setting data is generated four the plasma processing apparatus 100B.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
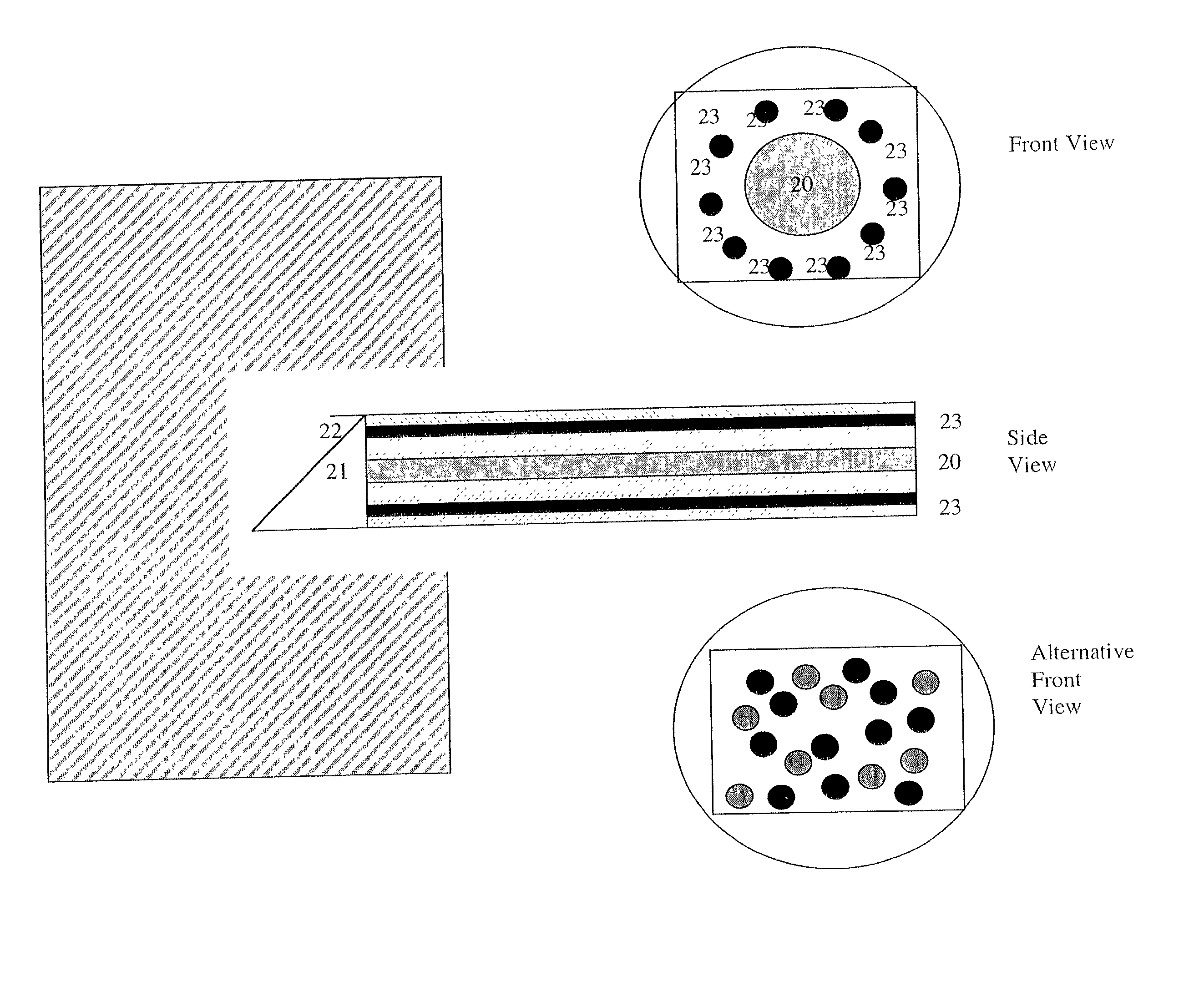
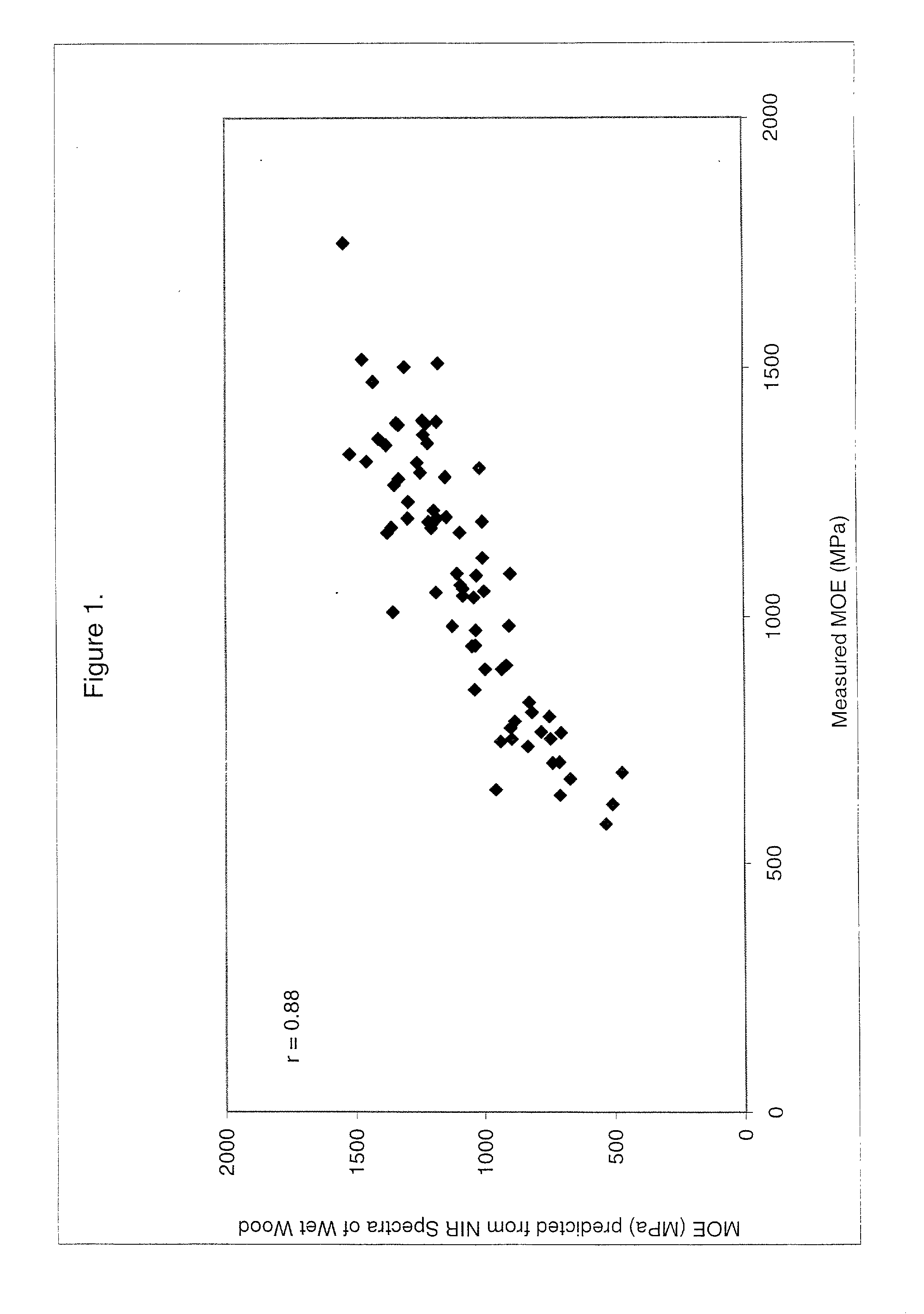
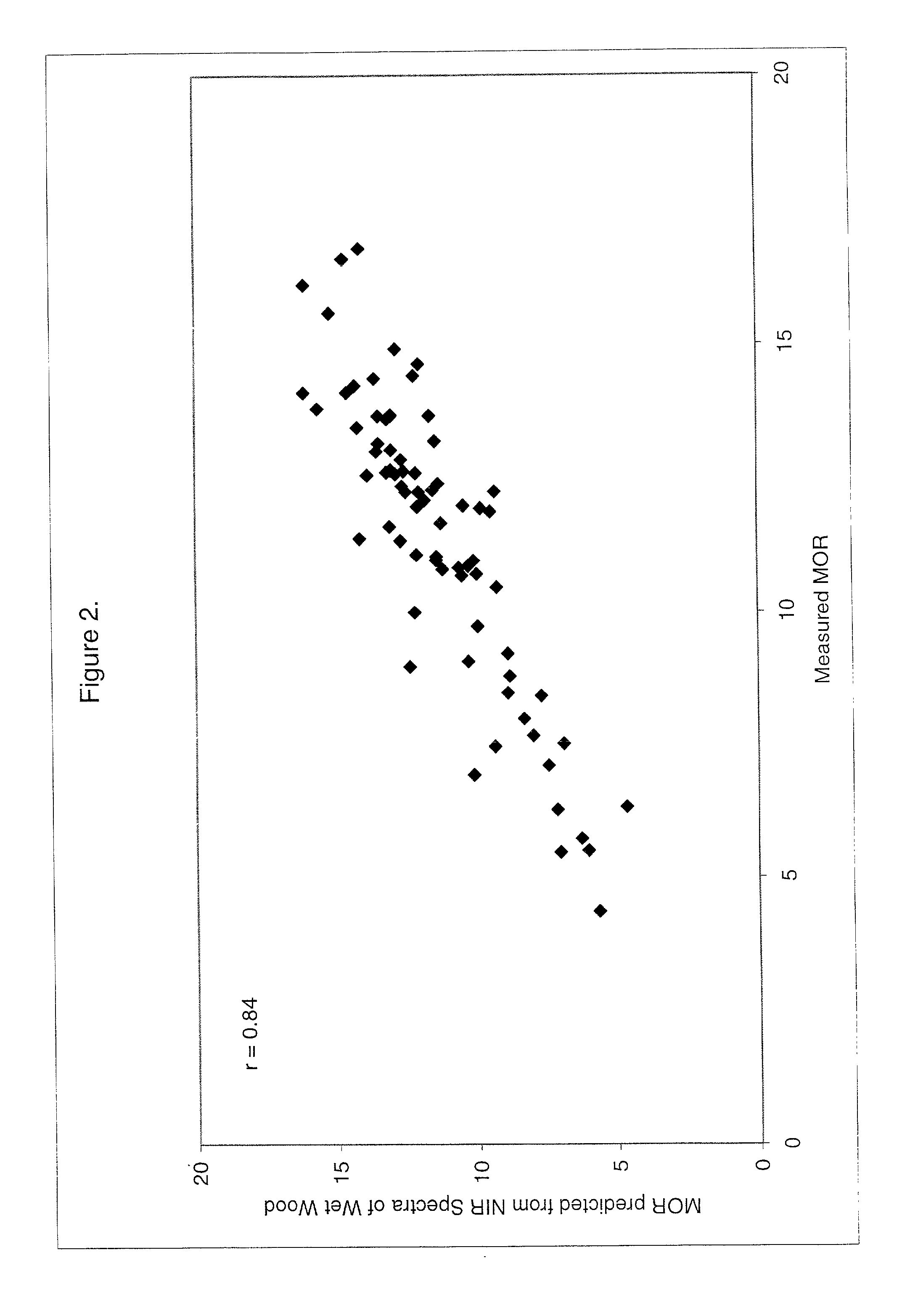
Use of a region of the visible and near infrared spectrum to predict mechanical properties of wet wood and standing trees
InactiveUS20020113212A1The process is fast and accurateEasy accessRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsGreen woodNir spectra
In a method for determining the dry mechanical strength for a green wood, the improvement comprising: (a) illuminating a surface of the wood to be determined with a reduced range of wavelengths in the VIS-NIR spectra 400 to 1150 nm, said wood having a green moisture content; (b) analyzing the surface of the wood using a spectrometric method, the method generating a first spectral data of a reduced range of wavelengths in VIS-NIR spectra; and (c) using a multivariate analysis technique to predict the mechanical strength of green wood when dry by comparing the first spectral data with a calibration model, the calibration model comprising a second spectrometric method of spectral data of a reduced range of wavelengths in VIS-NIR spectra obtained from a reference wood having a green moisture content, the second spectral being correlated with a known mechanical strength analytical result obtained from the reference wood when dried and a having a dry moisture content.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Method for generating multivariate analysis model expression for processing apparatus, method for executing multivariate analysis of processing apparatus, control device of processing apparatus and control system for processing apparatus
According to the present invention, multivariate analysis model expressions are generated for a plasma processing apparatus 100A and a plasma processing apparatus 100B by executing a multivariate analysis of detection data provided by a plurality of sensors included in each plasma processing apparatus when the plasma processing apparatuses 100A and 100B operate based upon first setting data. Then, when the plasma processing apparatus 100A operates based upon new second setting data, detection data provided by the plurality of sensors in the plasma processing apparatus 100A are used to generate a corresponding multivariate analysis model expression, and by using the new multivariate analysis model expression corresponding to the plasma processing apparatus 100A generated based upon the second setting data and to the plasma processing apparatus 100B, a multivariate analysis model expression corresponding to the new second setting data is generated four the plasma processing apparatus 100B.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
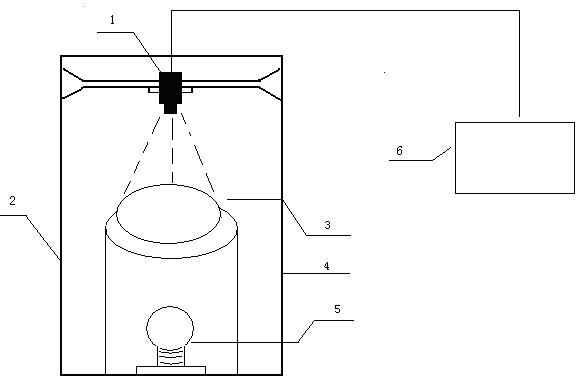
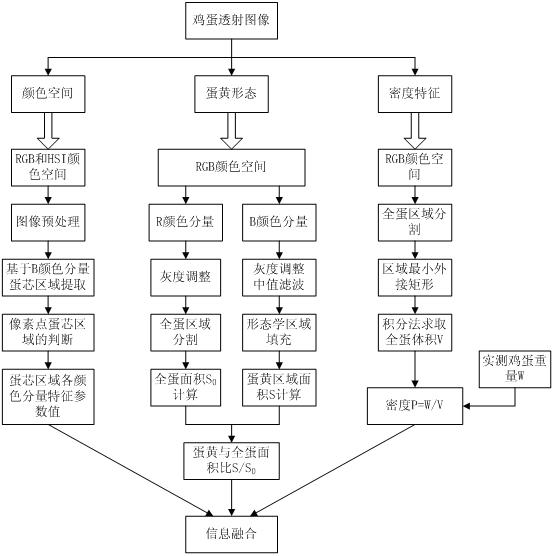
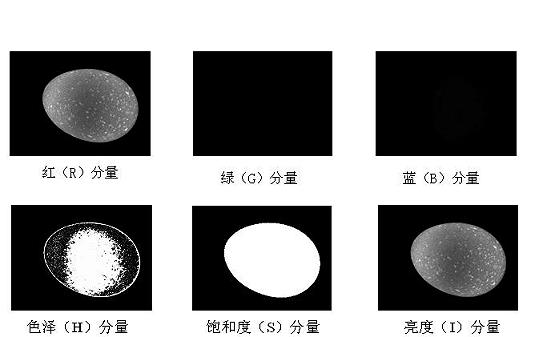
Machine vision technology based method for rapidly detecting egg freshness
InactiveCN102147402AImprove robustnessReduce complexityTesting eggsCharacter and pattern recognitionYolkEggshell
The invention relates to a machine vision technology based method for rapidly detecting egg internal quality, belonging to non-destructive testing technologies for agricultural and animal products. According to the method, a machine vision technology is used for acquiring characteristics on three aspects including a color space, an eggshell shape and an egg density from an egg transmission image so as to comprehensively judge the freshness characteristic of the egg. The machine vision technology based method specifically comprises the steps: acquiring the transmission image of an egg under a certain illumination condition, transmitting the transmission image to a computer through image acquisition equipment, acquiring the information on the three aspects including the color space, an egg yolk area and the egg density from the acquired egg image, fusing and screening the information on the three aspects, and finally obtaining a detection result of the egg freshness by means of a multi-variable analysis model in a standard library, wherein the information on the three aspects including the color space, the egg yolk area and the egg density is in one-to-one correspondence to three phenomena of diluted concentrated egg white, enlarged egg yolk area and raised gas cell height which are expressed under an egg freshness drop condition. In addition, grading can be carried out according to standards so that the egg freshness can be detected more objectively and accurately.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
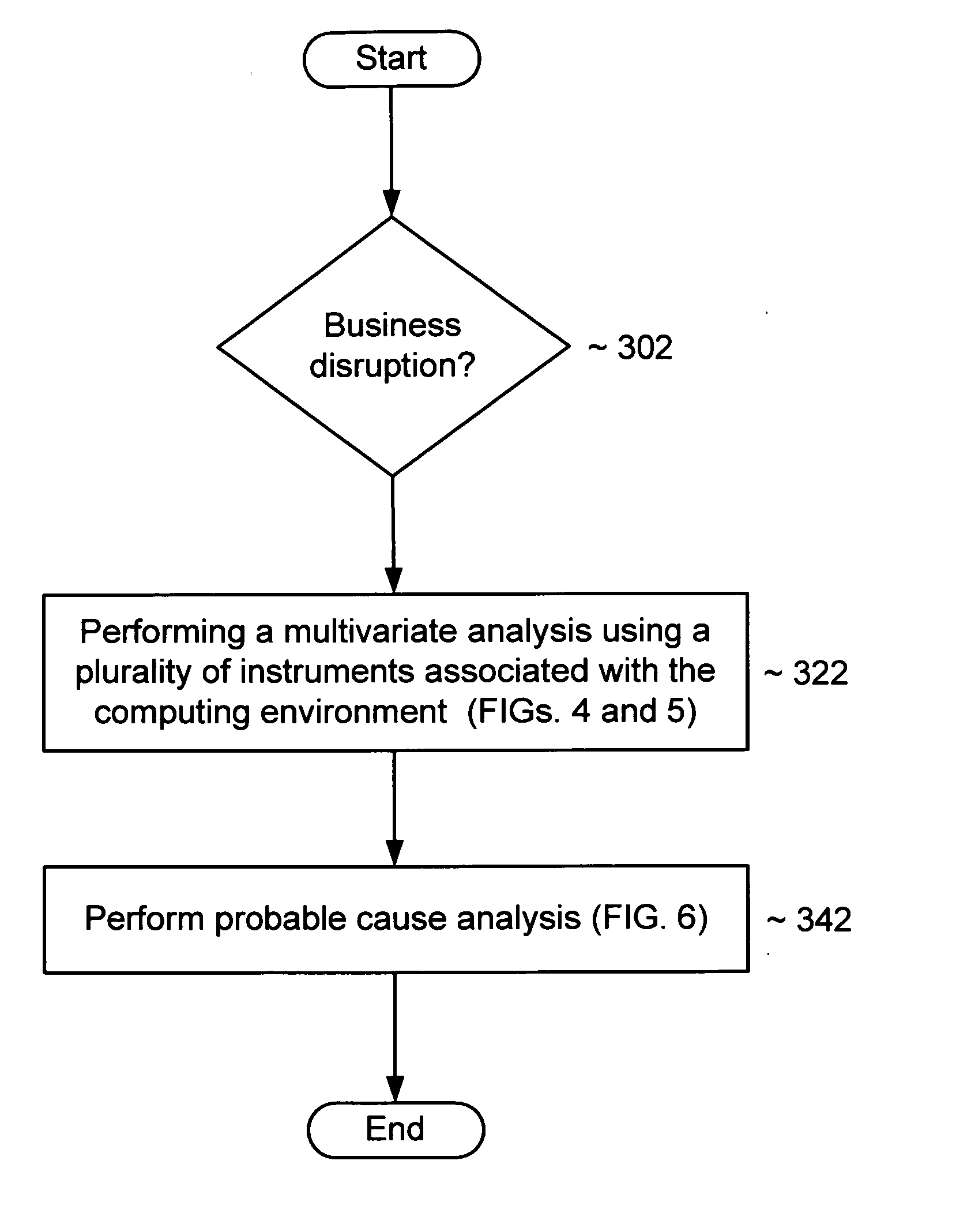
Methods and systems to detect business disruptions, determine potential causes of those business disruptions, or both
InactiveUS20070168915A1Non-redundant fault processingSpecific program execution arrangementsPredictive modellingStatistical analysis
Multivariate analysis can be performed to determine whether a computing environment is encountering a business disruption (e.g., relatively long end-user response times) or other problem. Cluster analysis (comparing more recent data with a particular cluster of good operating data), predictive modeling, or other suitable multivariate analysis can be used. A probable cause analysis may be performed in conjunction with the multivariate analysis. A probable cause analysis may be used when one or more abnormal instruments, abnormal components, abnormal load patterns, suspicious actions (such as resource provisioning or deprovisioning activities), software or hardware updates or failures, recent changes to the computing environment (component provisioning, change of a control, etc.), or any combination thereof. The probable cause analysis can include ranking potential causes based on likelihood, and such ranking can include statistical analysis, policy violations, recent changes to the computing environment, or any combination thereof.
Owner:CESURA
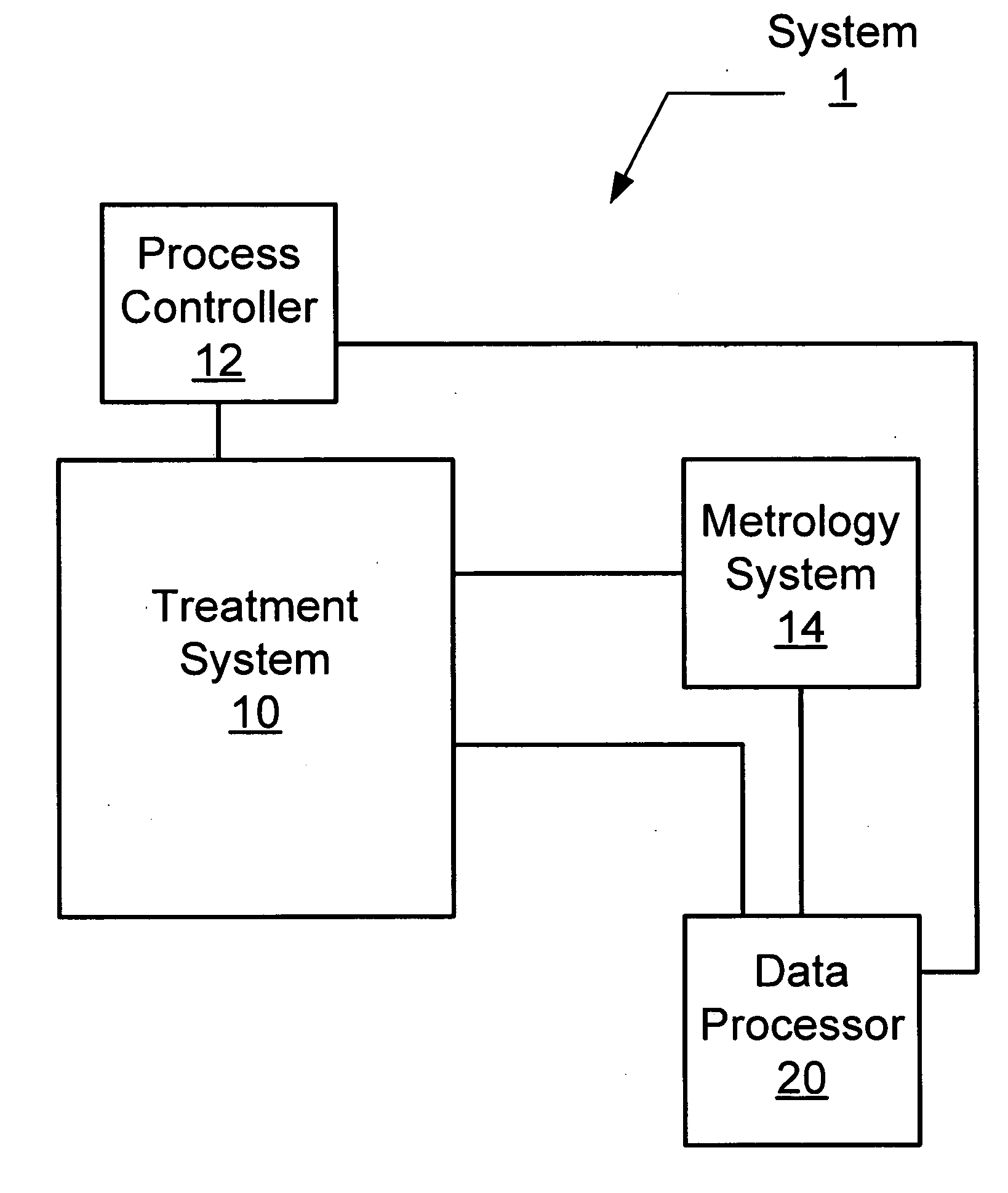
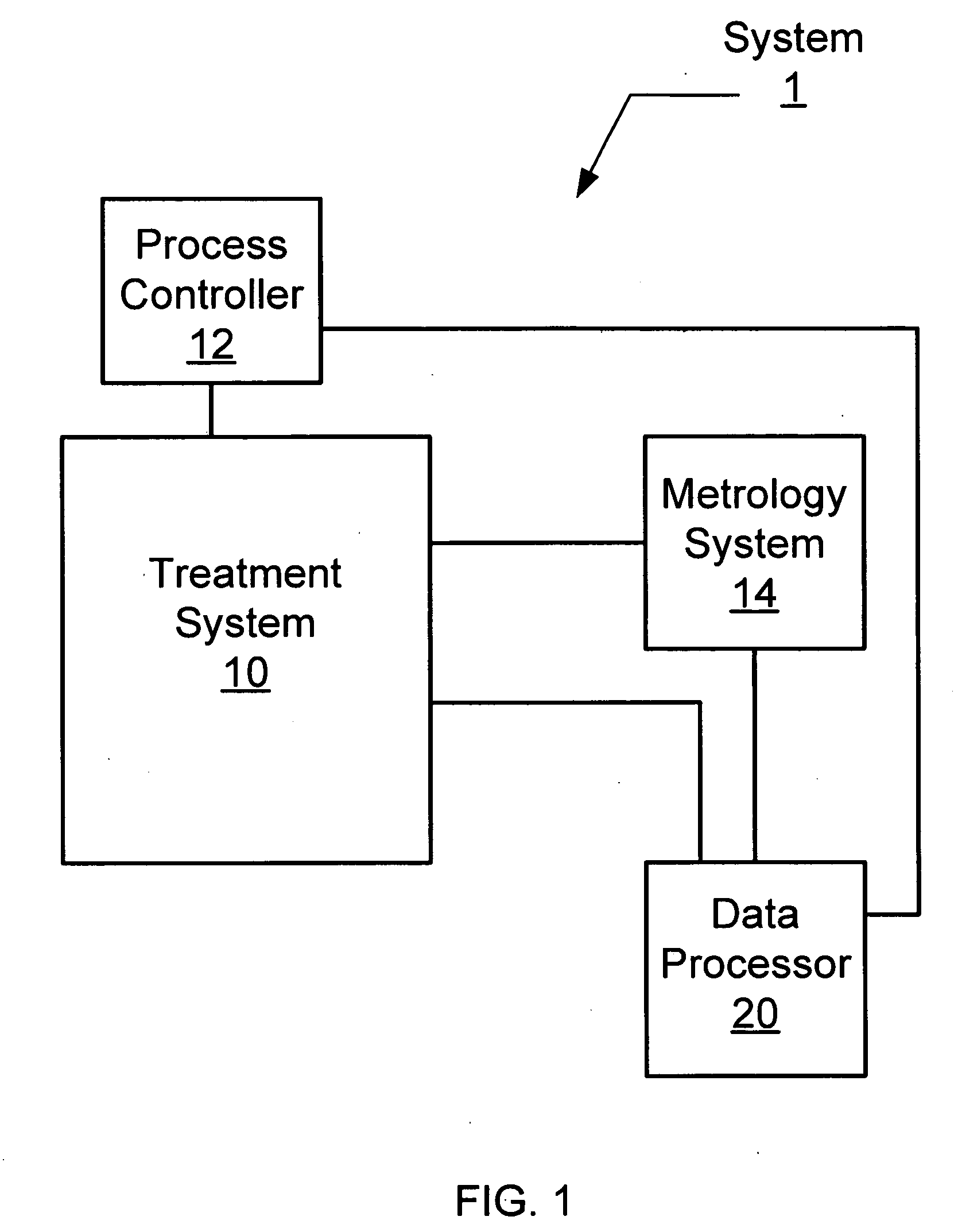
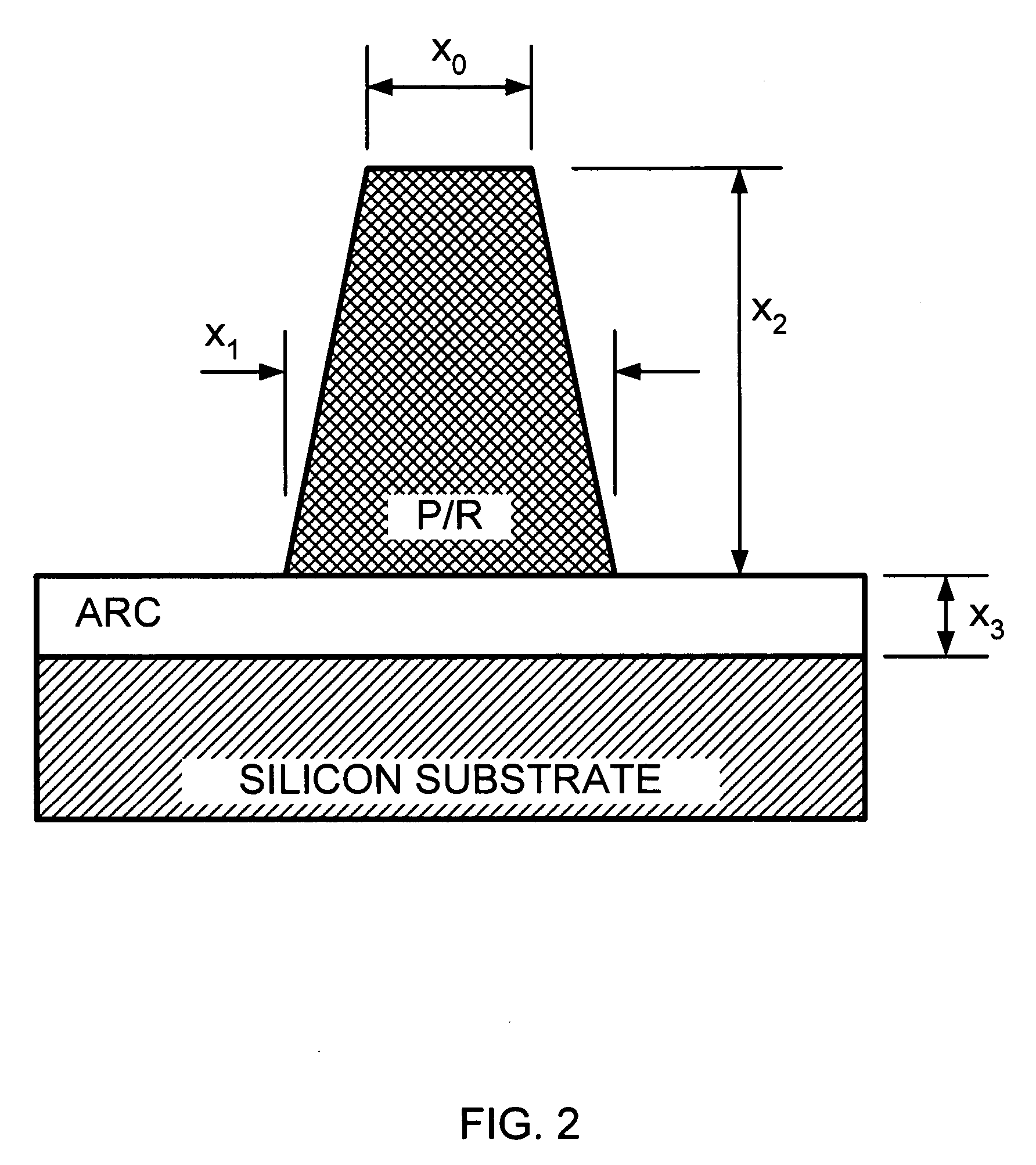
Transforming metrology data from a semiconductor treatment system using multivariate analysis
Metrology data from a semiconductor treatment system is transformed using multivariate analysis. In particular, a set of metrology data measured or simulated for one or more substrates treated using the treatment system is obtained. One or more essential variables for the obtained set of metrology data is determined using multivariate analysis. A first metrology data measured or simulated for one or more substrates treated using the treatment system is obtained. The first obtained metrology data is not one of the metrology data in the set of metrology data earlier obtained. The first metrology data is transformed into a second metrology data using the one or more of the determined essential variables.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
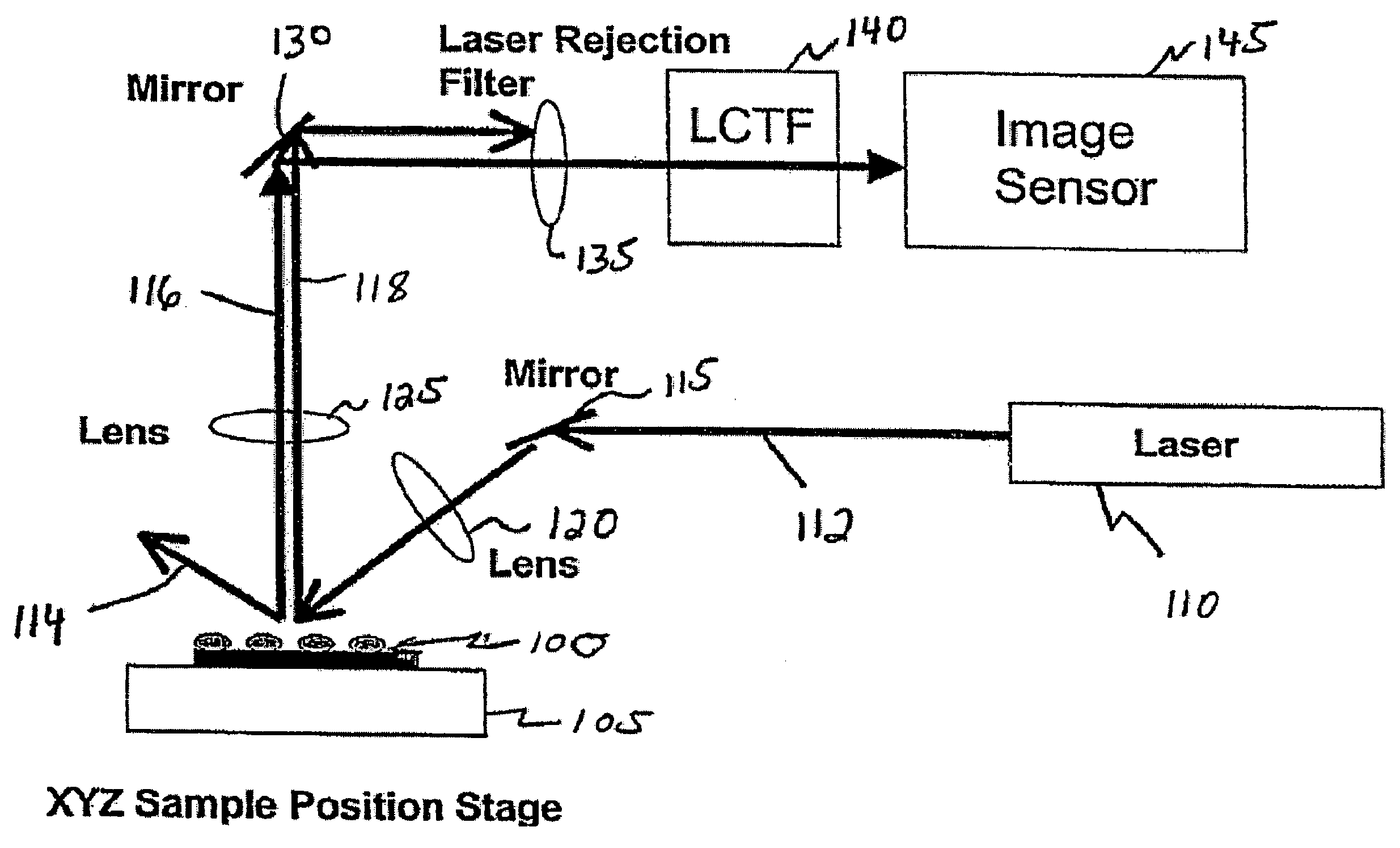
Dynamic imaging of biological cells and other subjects
ActiveUS20070182959A1Quick observationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscopic imageMultivariate analysis
The invention relates to methods of dynamic chemical imaging, including methods of cellular imaging. The method comprises illuminating at least a portion of a cell with substantially monochromatic light and assessing Raman-shifted light scattered from the illuminated portion at a plurality of discrete times. The Raman-shifted light can be assessed at a plurality of Raman shift (RS) values at each of the discrete times, and the RS values can be selected to be characteristic of a pre-selected component at each of the discrete times. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectral features of the images thus obtained can yield the location and chemical identity of components in the field of view. This information can be combined or overlaid with other spectral data (e.g., a visible microscopic image) obtained from the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Method and system of diagnosing a processing system using adaptive multivariate analysis
InactiveUS7328126B2Useful applicationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPrincipal component analysisHandling system
A method and system of monitoring a processing system and for processing a substrate during the course of semiconductor manufacturing. As such, data is acquired from the processing system for a plurality of observations, the data including a plurality of data parameters. A principal components analysis (PCA) model is constructed from the data and includes centering coefficients. Additional data is acquired from the processing system, the additional data including an additional observation of the plurality of data parameters. The centering coefficients are adjusted to produce updated adaptive centering coefficients for each of the data parameters in the PCA model. The updated adaptive centering coefficients are applied to each of the data parameters in the PCA model. At least one statistical quantity is determined from the additional data using the PCA model. A control limit is set for the statistical quantity and compared to the statistical quantity.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
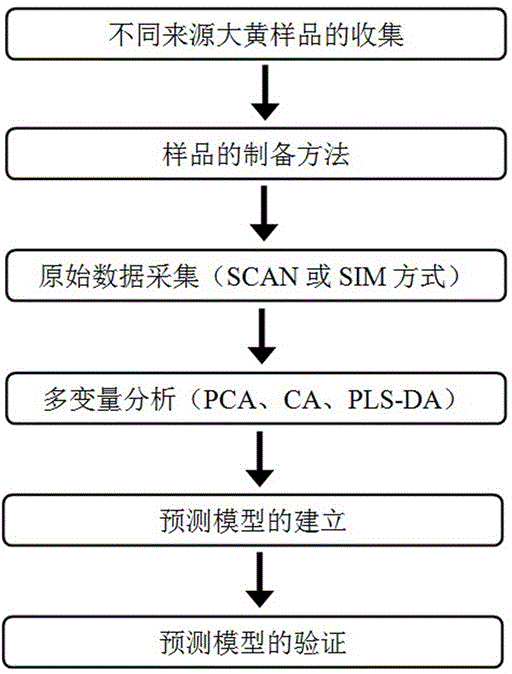
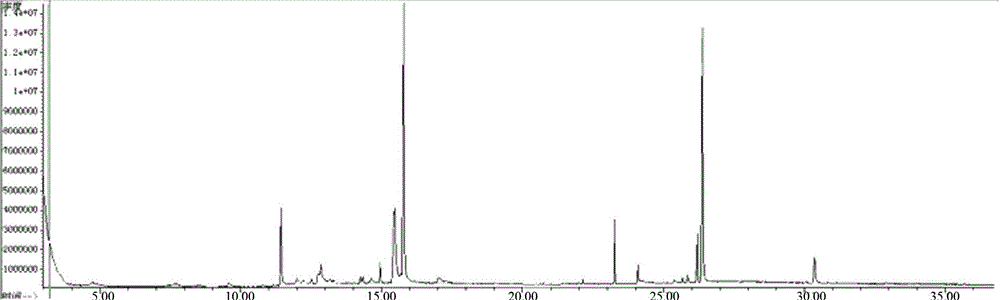
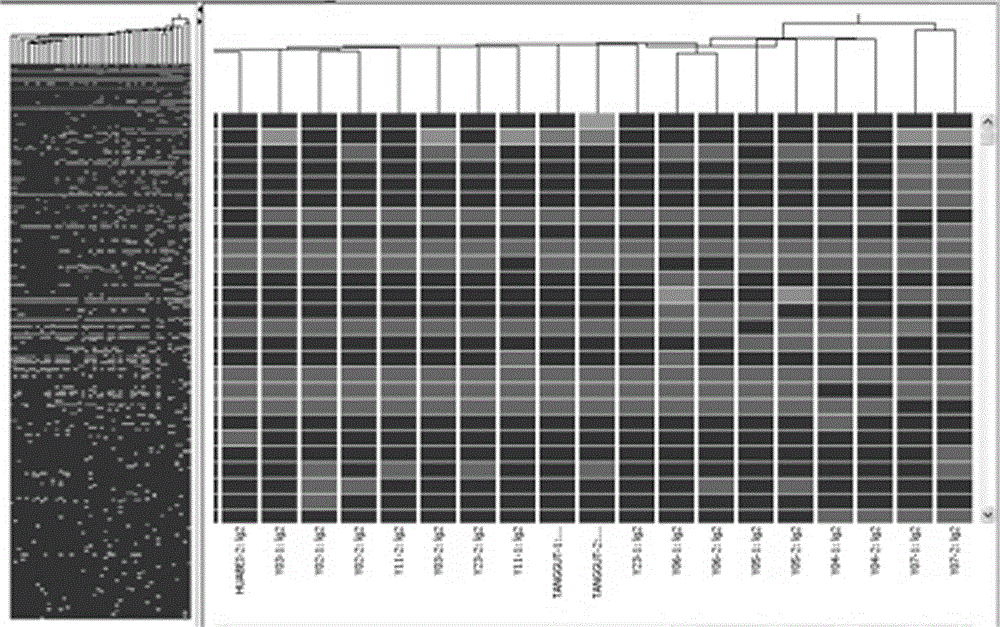
Building method for rhubarb medicinal material trueness/falseness and species prediction model
The invention provides a building method for a rhubarb medicinal material trueness / falseness and species prediction model. According to the model, category identification of quality rhubarb, fake rhubarb and three rhubarb species is realized on the basis of a gas chromatography-mass spectrum technology in combination with partial least square discriminant analysis. The building method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting samples; (2) preparing the samples; (3) acquiring GC-MS data; (4) performing data processing and multivariate analysis, wherein cluster analysis and principal component analysis are performed by comparing the differences of chromatographic behaviors of rhubarb of different sources; (5) building the prediction model; and (6) verifying the model. Two built category prediction models are proved to have 100 percent identification accuracy and prediction accuracy. Through adoption of the method, trueness / falseness and species identification of rhubarb are realized by modeling, so that a reliable conclusion and high integrity are achieved; the defects of an existing method are overcome; and a more feasible and reliable new thought is provided for the trueness / falseness and species identification of rhubarb medicinal materials and decoction pieces.
Owner:青岛市食品药品检验研究院
Method and apparatus for evaluating processing apparatus status and predicting processing result
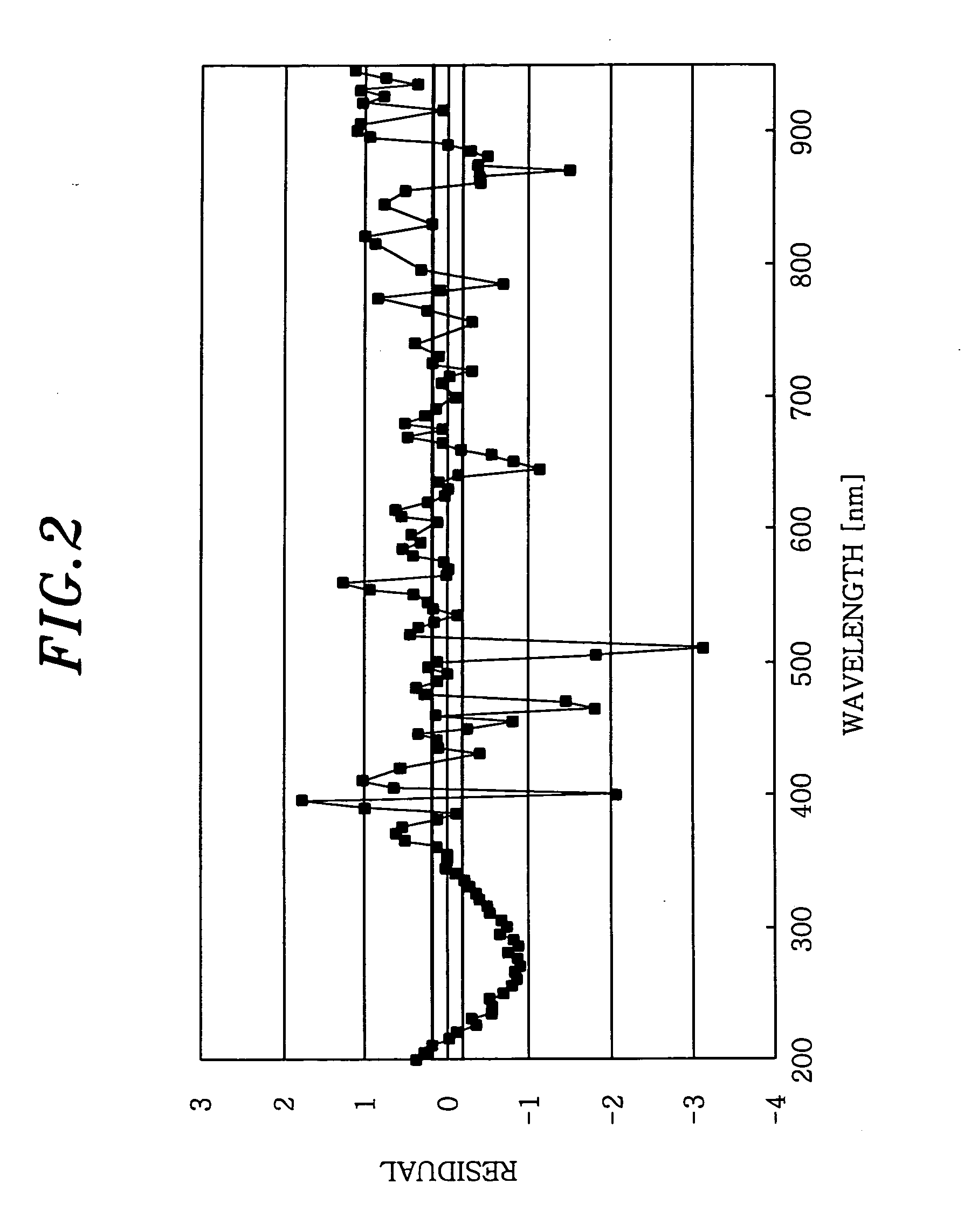
InactiveUS20050125090A1Reliable inspectionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesPrincipal component analysisMultivariate analysis
A method for predicting a processing result includes a process of performing a principal component analysis on a plurality of detected data obtained during a first standard processing, to construct a principal component analysis model; a process of obtaining residuals of the principal component analysis model as first residuals; a process of performing a second standard processing; and a process of obtaining a plurality of detected data from a plurality of detectors during the second standard processing. And, the detected data obtained during the second standard processing are applied to the principal component analysis model, to obtain second residuals. The method further includes a process of weighting the second residuals based on weighting references, and constructing a new multivariate analysis model with use of the weighted second residuals; and a process of predicting a processing result of the second standard processing with use of the multivariate analysis model.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Visible-near infrared spectroscopy in burn injury assessment
A non-invasive method of characterizing burn injuries using near infrared spectroscopy is described. In the method, a beam of light is emitted into the burnt tissue portion at two or more different tissue depths. The spectra are then compared using multivariate analysis to determine diagnostic regions of the spectra. This information is used to categorize the burn. In some cases, the diagnostic regions correspond to wavelengths related to the hemodynamics of the tissue portion. The spectra can also be repeated over time, thereby allowing trends and changes in the spectra to be measured. This data is in turn used to categorize the burn as either a superficial burn, partial thickness burn, deep partial burn or a full thickness burn. Once the burn has been categorized, the clinician can intervene as needed to treat the burn.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Temperature independent pressure sensor and associated methods thereof
InactiveUS20110320142A1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFlow propertiesEngineeringElectromagnetic field
A temperature independent pressure sensor for selectively determining pressure is provided. The sensor comprises a resonance sensor circuit, a pressure sensitive component disposed on the sensor circuit, and an electromagnetic field modulator. A temperature independent pressure sensor system comprises a resonance sensor circuit, a pressure sensitive component disposed on the sensor circuit, an electromagnetic field modulator, and a processor that generates a multivariate analysis of sensor response pattern that is based on a change in an environmental pressure of the sensor system. A method of detecting a pressure response pattern in a temperature independent manner is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
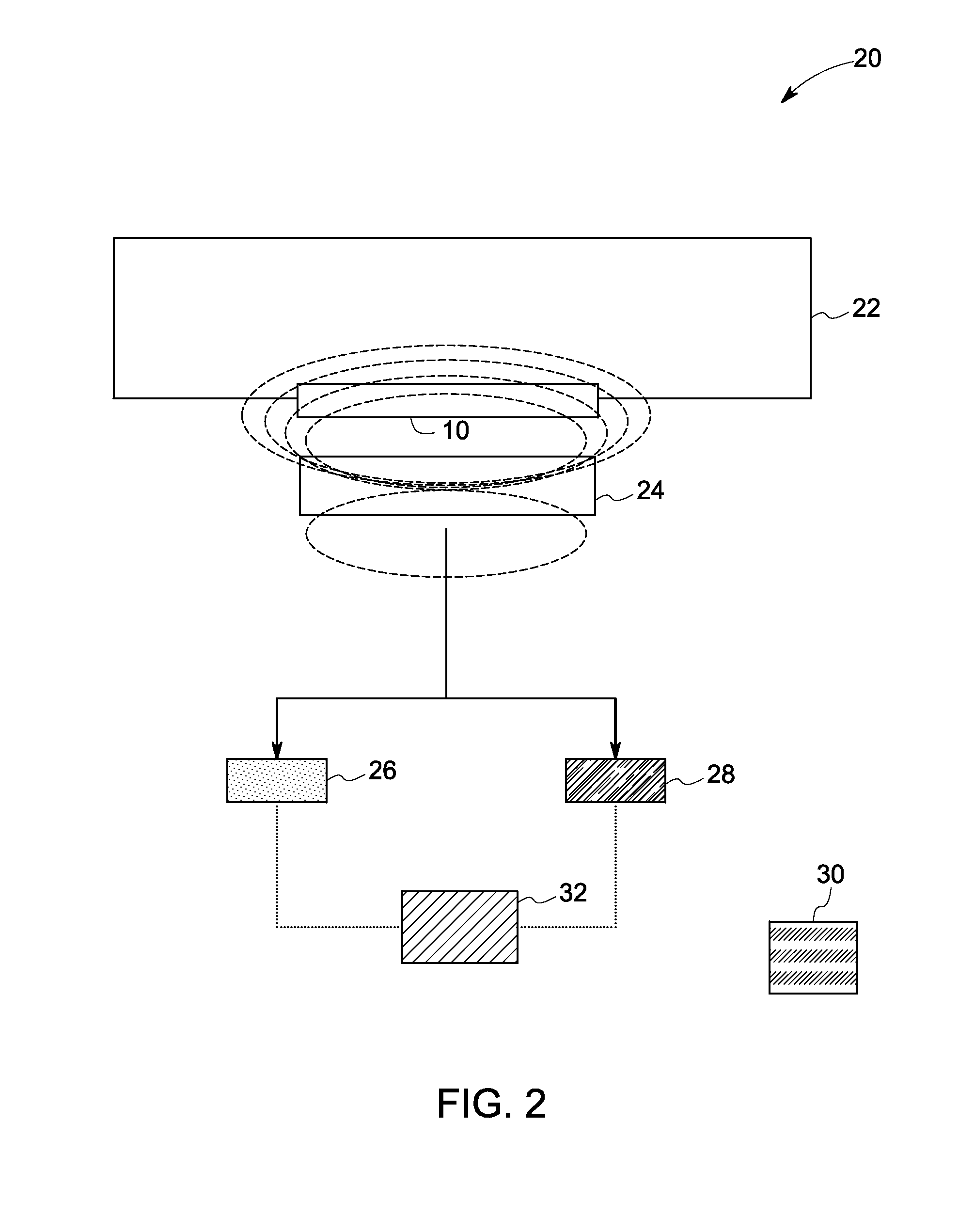
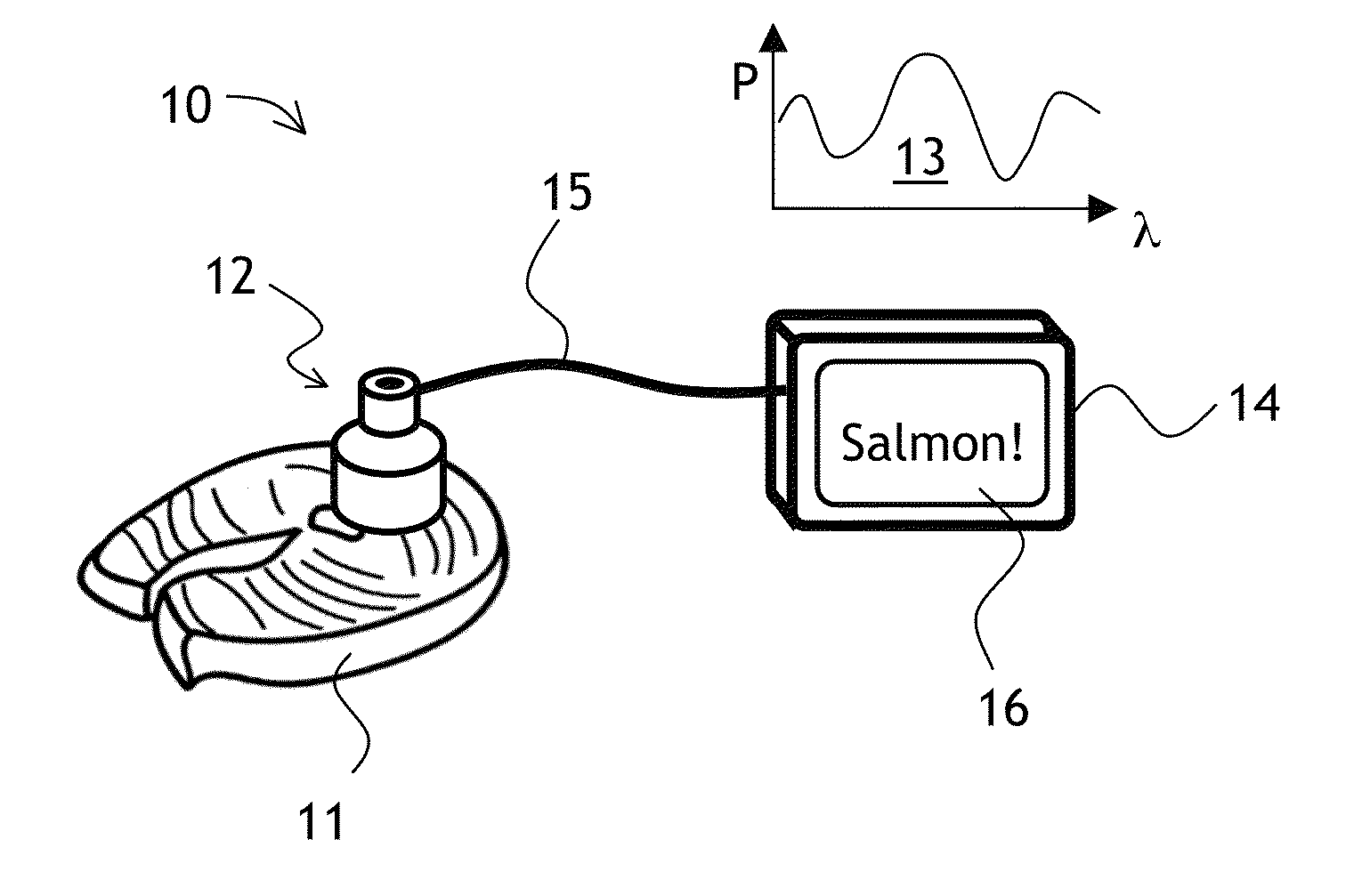
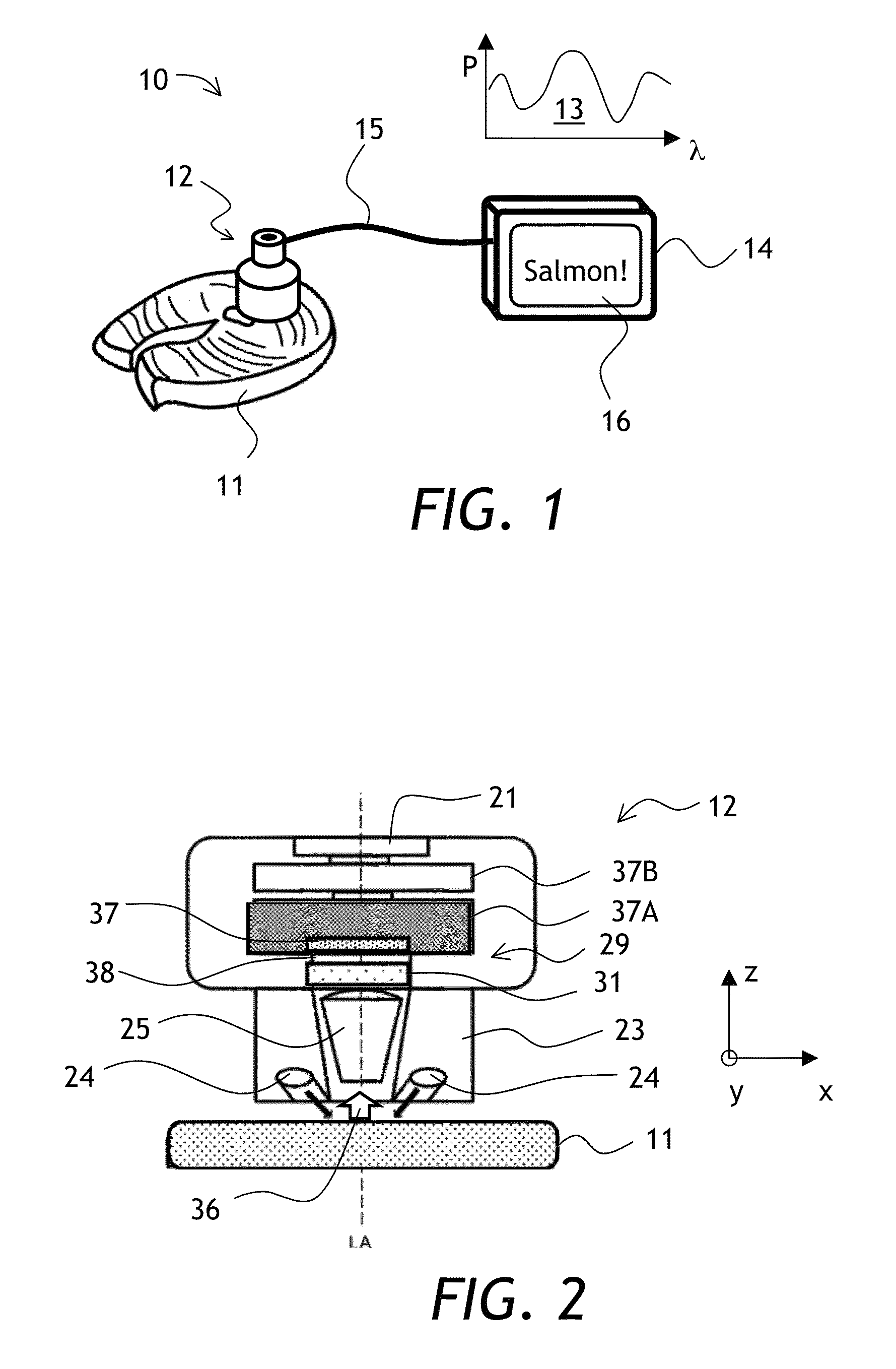
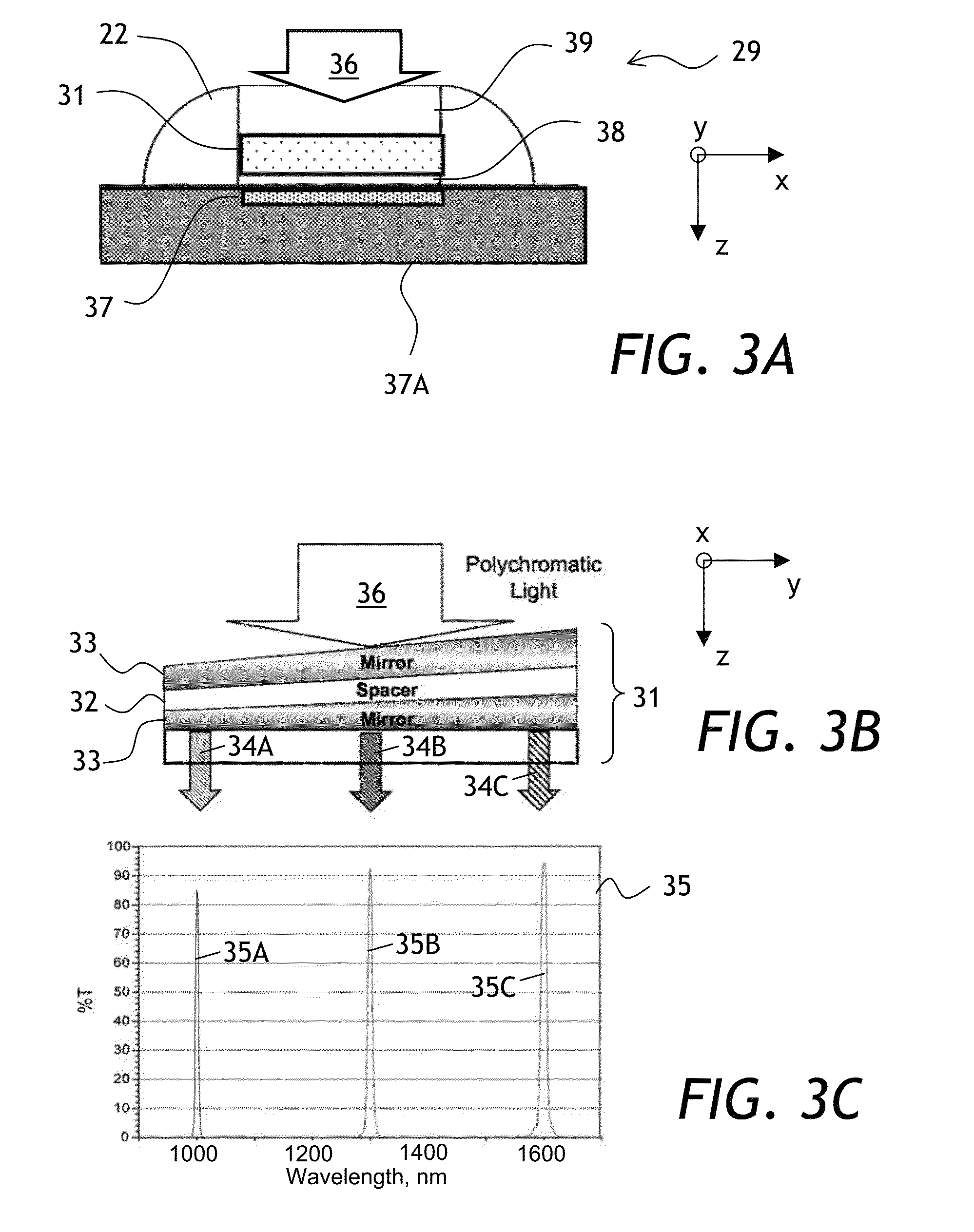
Spectroscopic characterization of seafood
ActiveUS20150204833A1Reduce the impactReduce impactRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsMultivariate analysisSeafood sample
A method and apparatus for field spectroscopic characterization of seafood is disclosed. A portable NIR spectrometer is connected to an analyzer configured for performing a multivariate analysis of reflection spectra to determine qualitatively the true identities or quantitatively the freshness of seafood samples.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
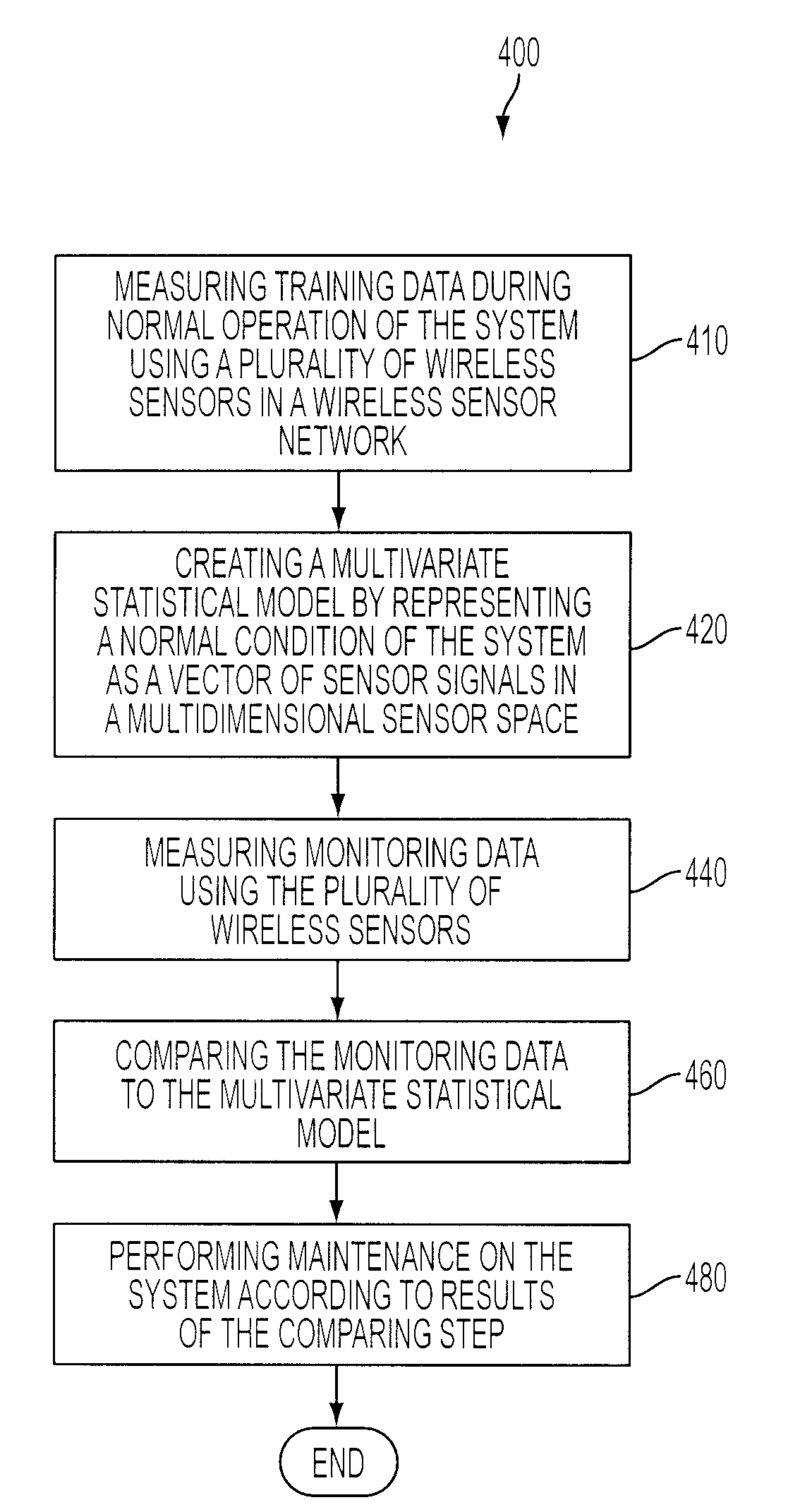
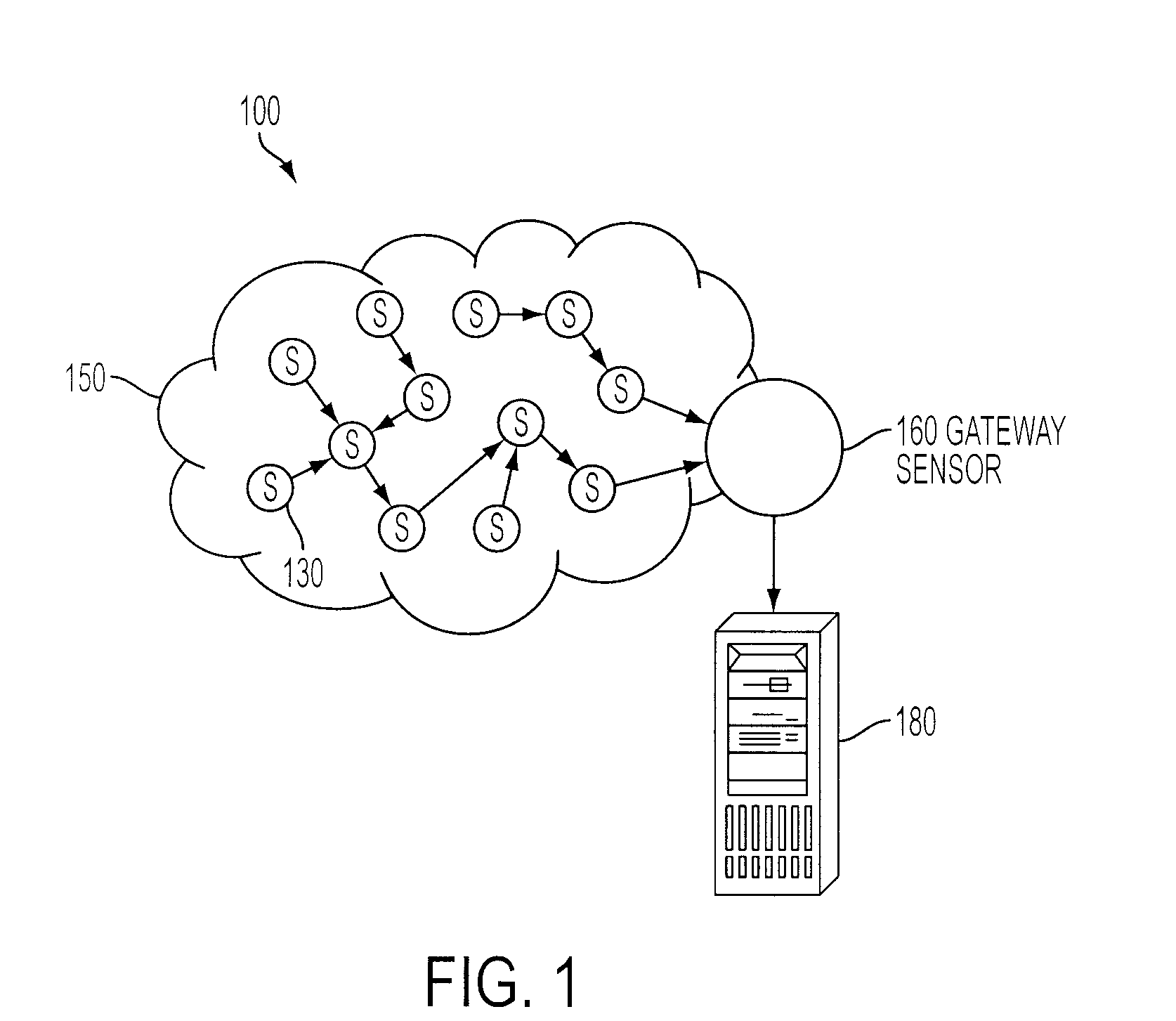
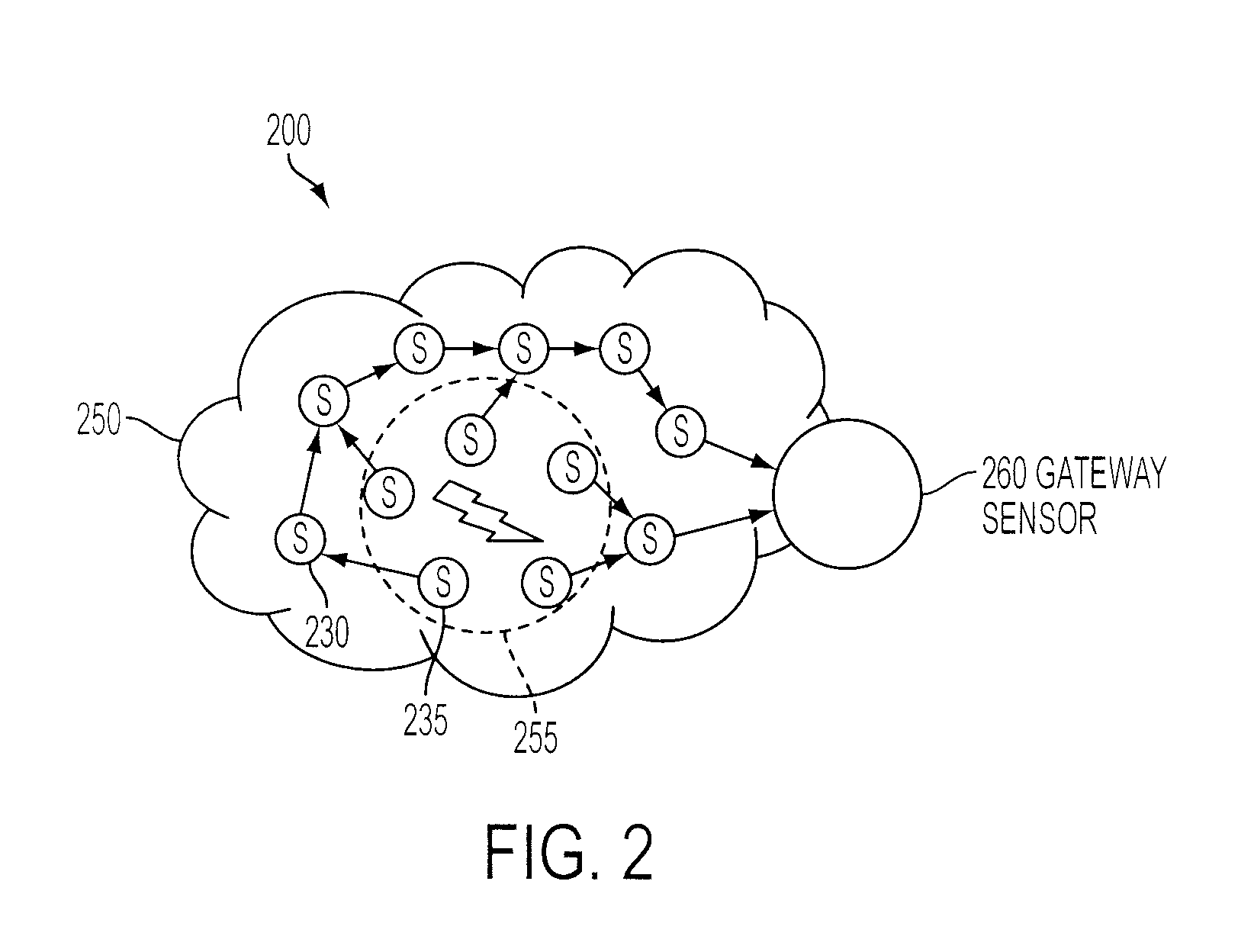
Multivariate Analysis of Wireless Sensor Network Data for Machine Condition Monitoring
ActiveUS20090119243A1Probabilistic networksFuzzy logic based systemsLine sensorDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Machine condition monitoring on a system utilizes a wireless sensor network to gather data from a large number of sensors. The data is processed using a multivariate statistical model to determine whether the system has deviated from a normal condition. The wireless sensor network permits the acquisition of a large number of distributed data points from plural system modalities, which, in turn, yields enhanced prediction accuracy and a reduction in false alarms.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
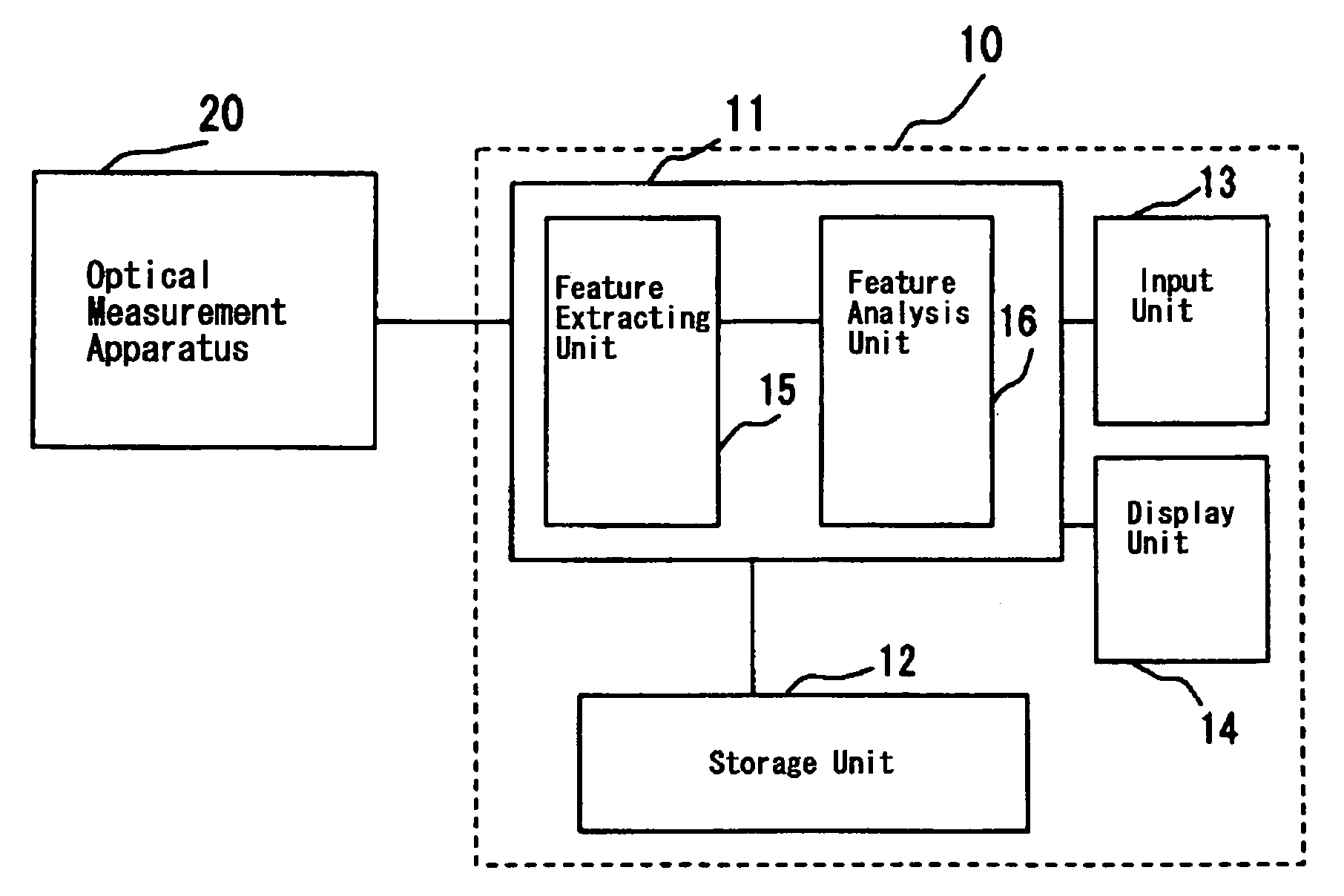
Optical measurement apparatus for living body
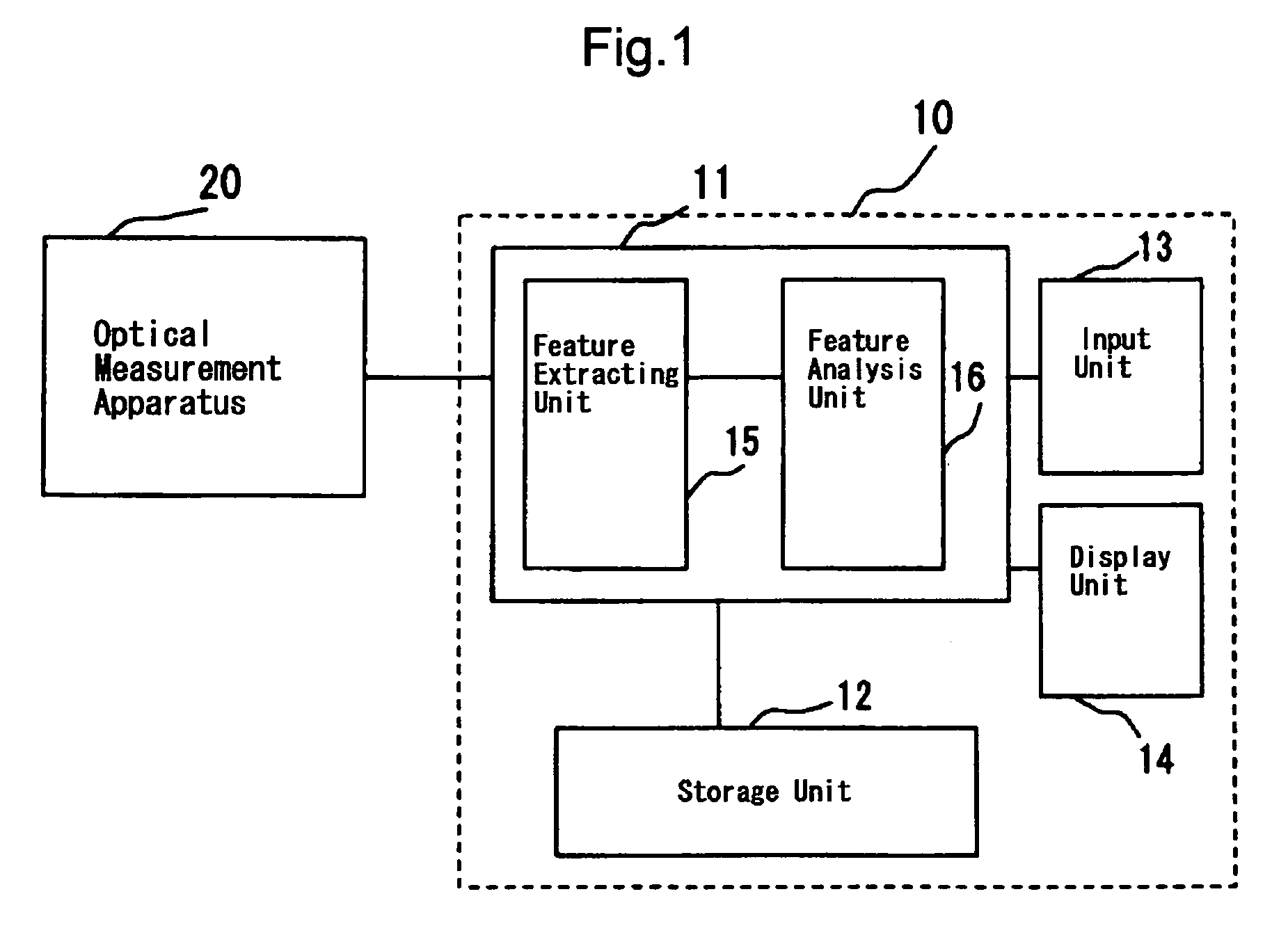
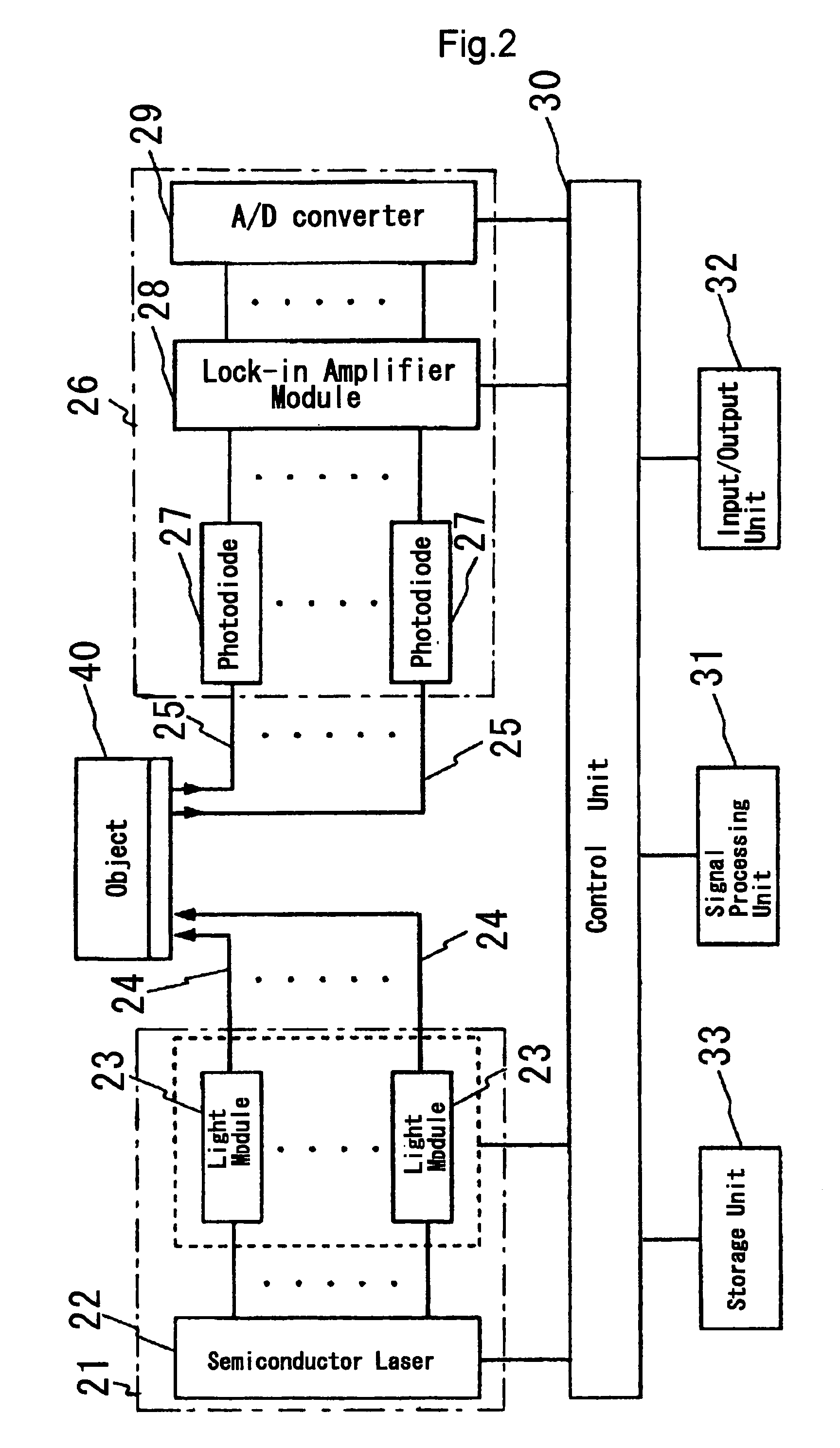
InactiveUS7353054B2Accurate assessmentAssess disease easily and objectivelySensorsBlood characterising devicesBiological bodyFeature extraction
An apparatus which can objectively assess and display to what extent and to which disease the subject belongs based on the signals of changes in hemoglobin amount measured by the optical measurement apparatus is provided. The disease assessment apparatus comprises the feature extraction unit 15 for extracting features of the hemoglobin waveform, the feature analysis unit 16 and the storage unit 12 for storing features by each disease as database. The disease is assessed by extracting various kinds of feature amounts from the hemoglobin signals of the subject measured by the optical measurement apparatus in the feature extraction unit 15 and by applying multivariate analysis of similarities between feature amounts extracted and feature amounts stored by disease in the storage unit 12. Results of assessment are shown as scores expressing similarity with each disease group in a bar graph.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
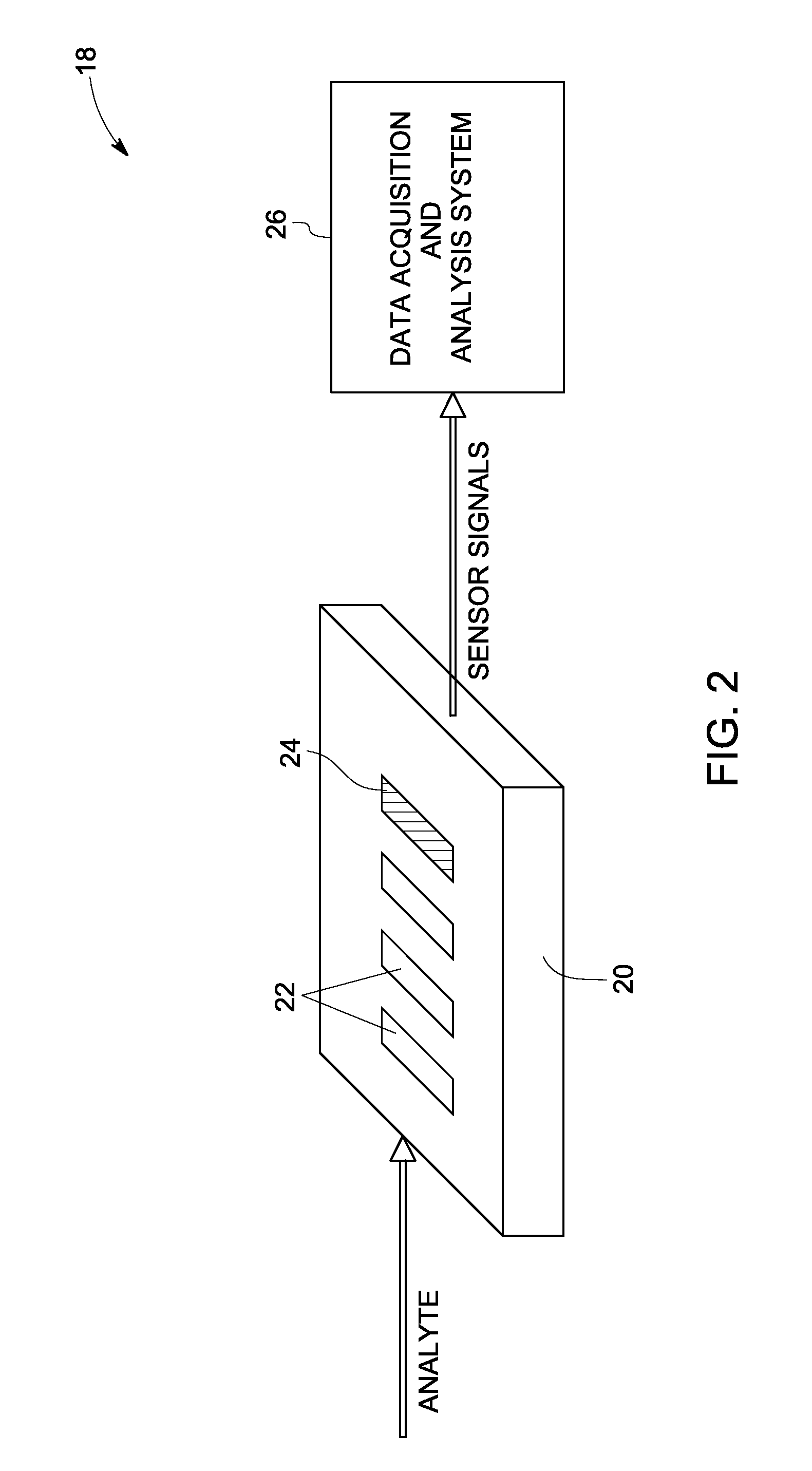
Systems and methods for sensing
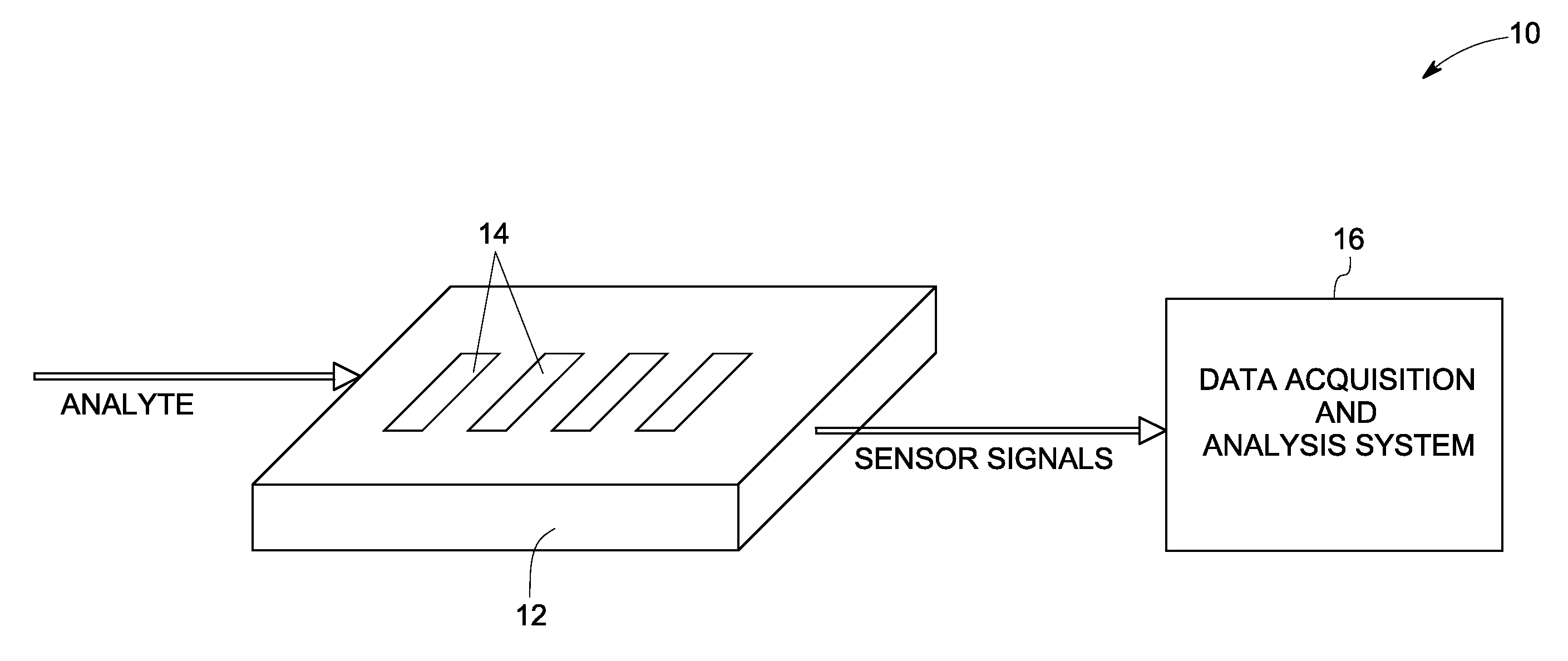
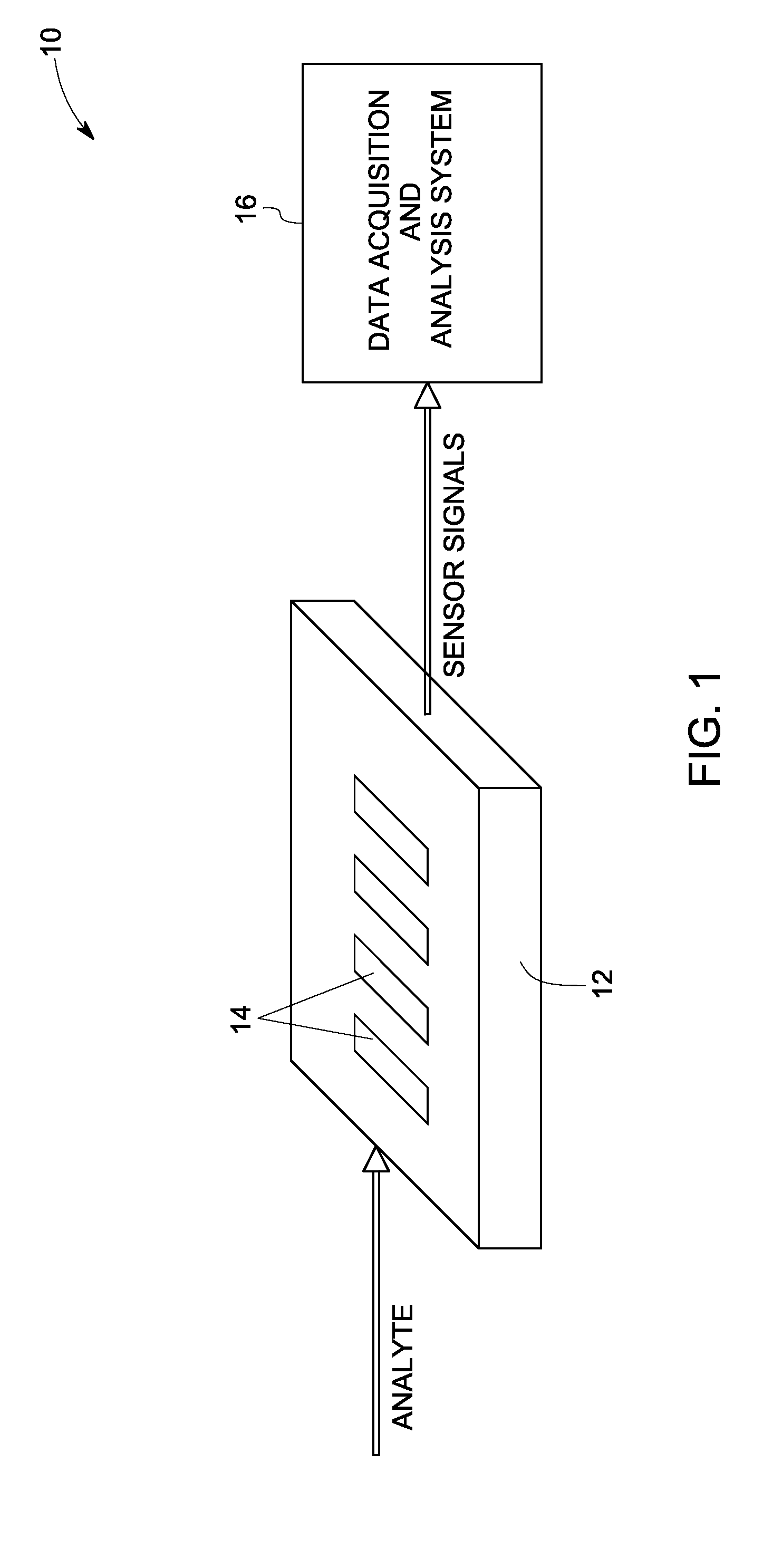
InactiveUS20080302672A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteChemical species
A sensor system for measuring a plurality of chemical species is disclosed. The sensor system includes a plurality of semiconductor device sensor elements, wherein each sensor element includes at least one wide band gap semiconductor layer and at least one catalytic layer configured to have an electrical property modifiable on exposure to an analyte including one or more chemical species; and an acquisition and analysis system configured to receive sensor signals from the plurality of sensor elements and to use multivariate analysis techniques to analyze the sensor signals to provide multivariate analyte measurement data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com