Patents
Literature
71 results about "Chemical imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
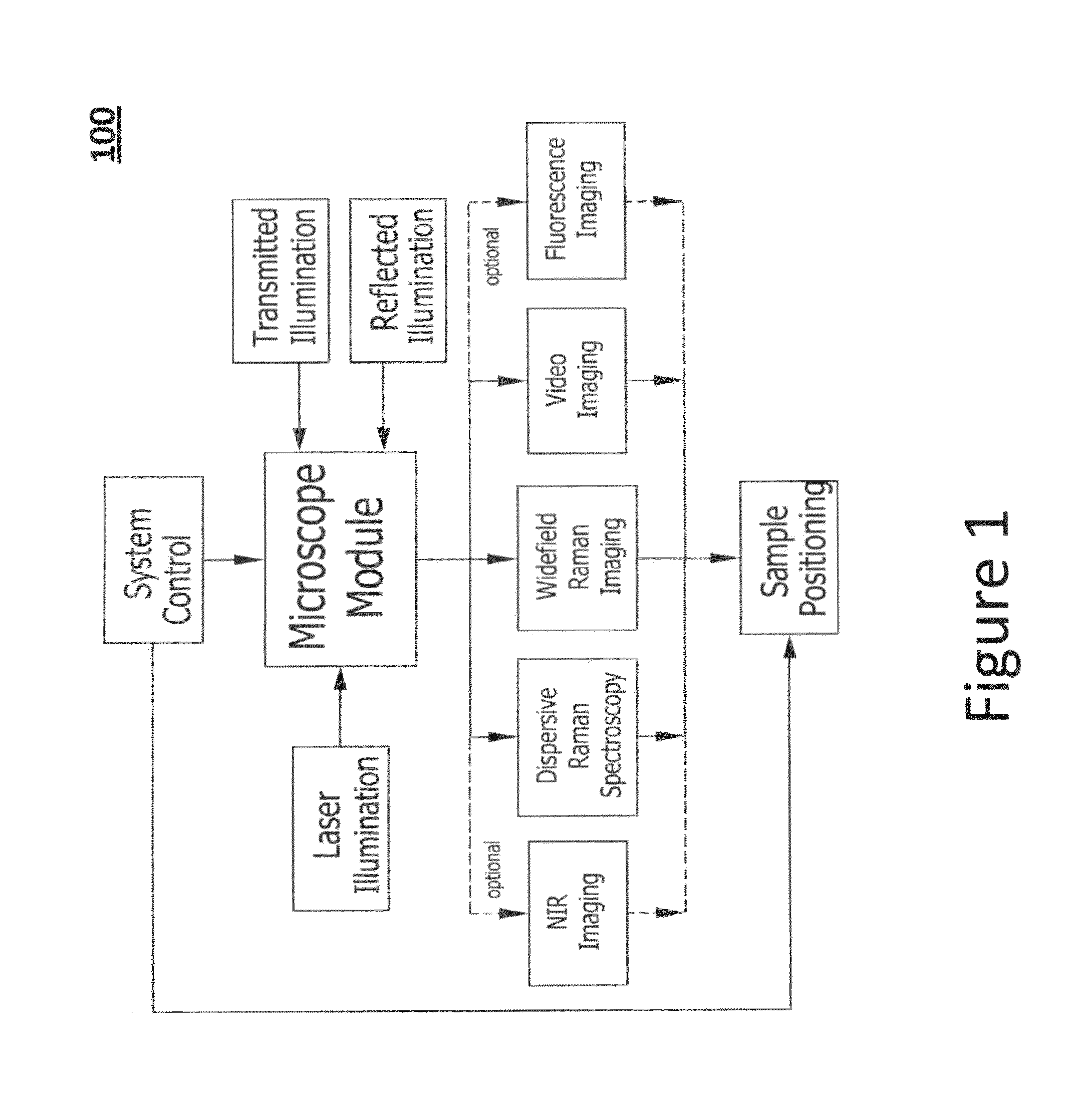
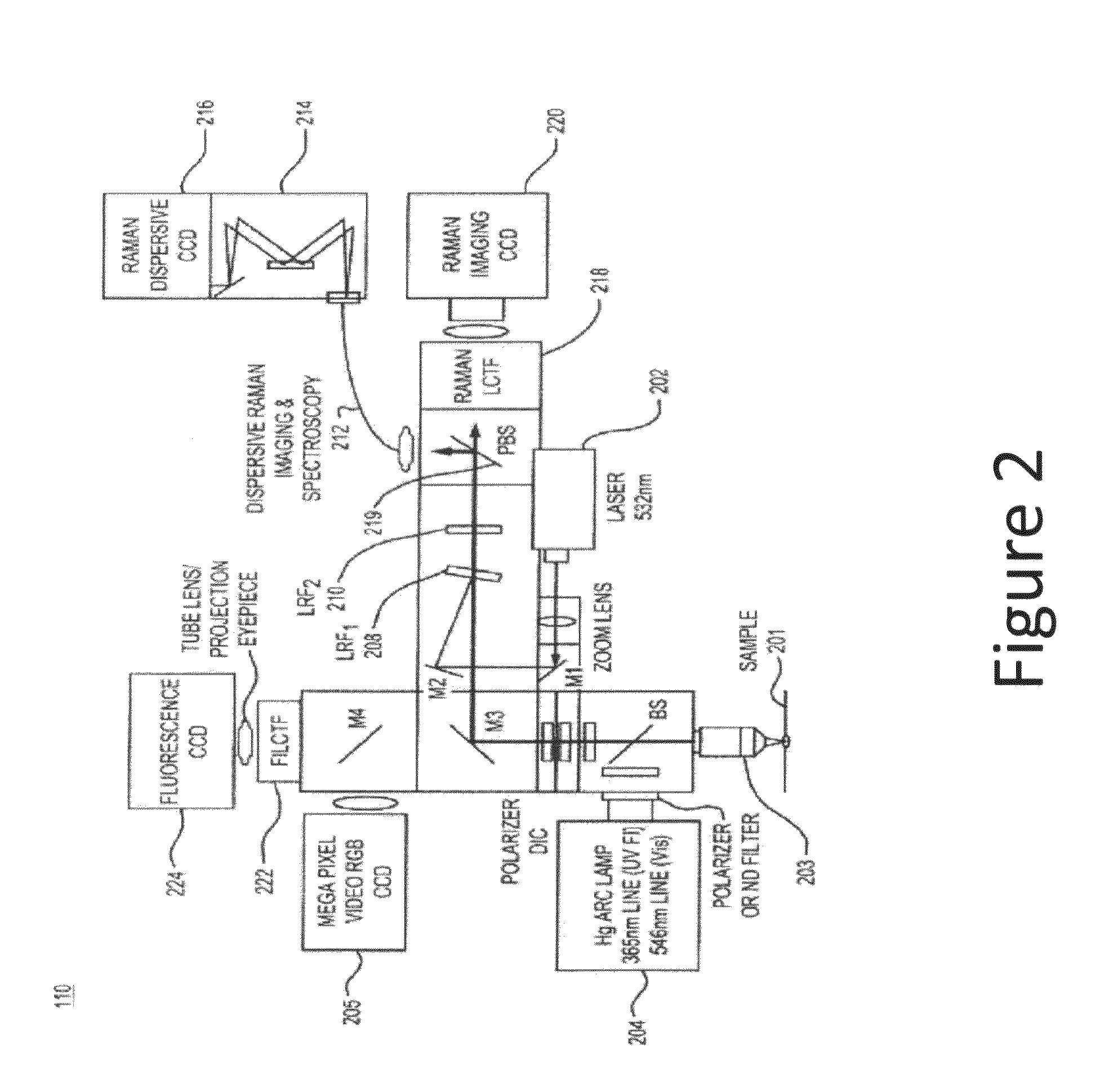
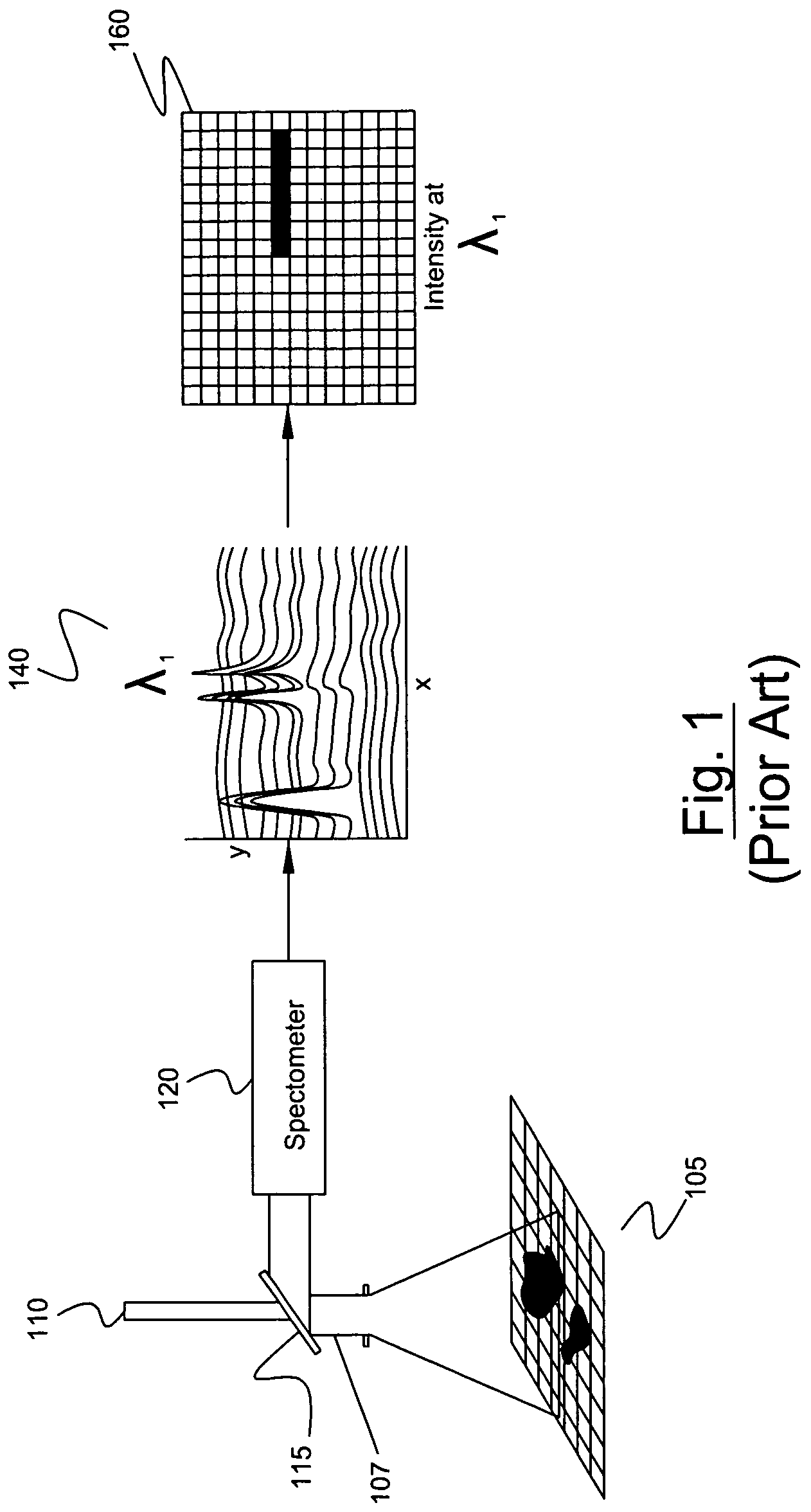
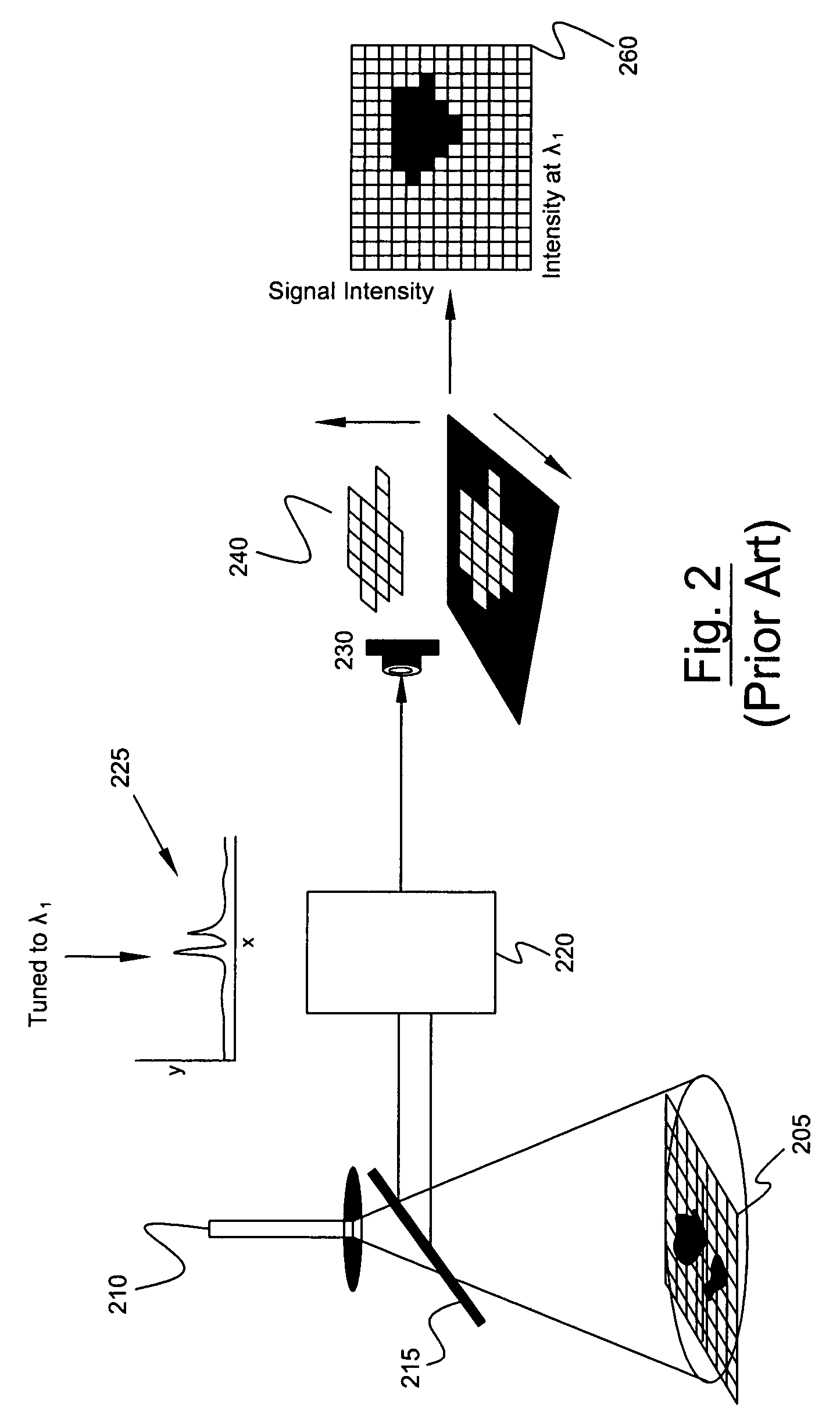
Chemical imaging (as quantitative – chemical mapping) is the analytical capability to create a visual image of components distribution from simultaneous measurement of spectra and spatial, time information. Hyperspectral imaging measures contiguous spectral bands, as opposed to multispectral imaging which measures spaced spectral bands.
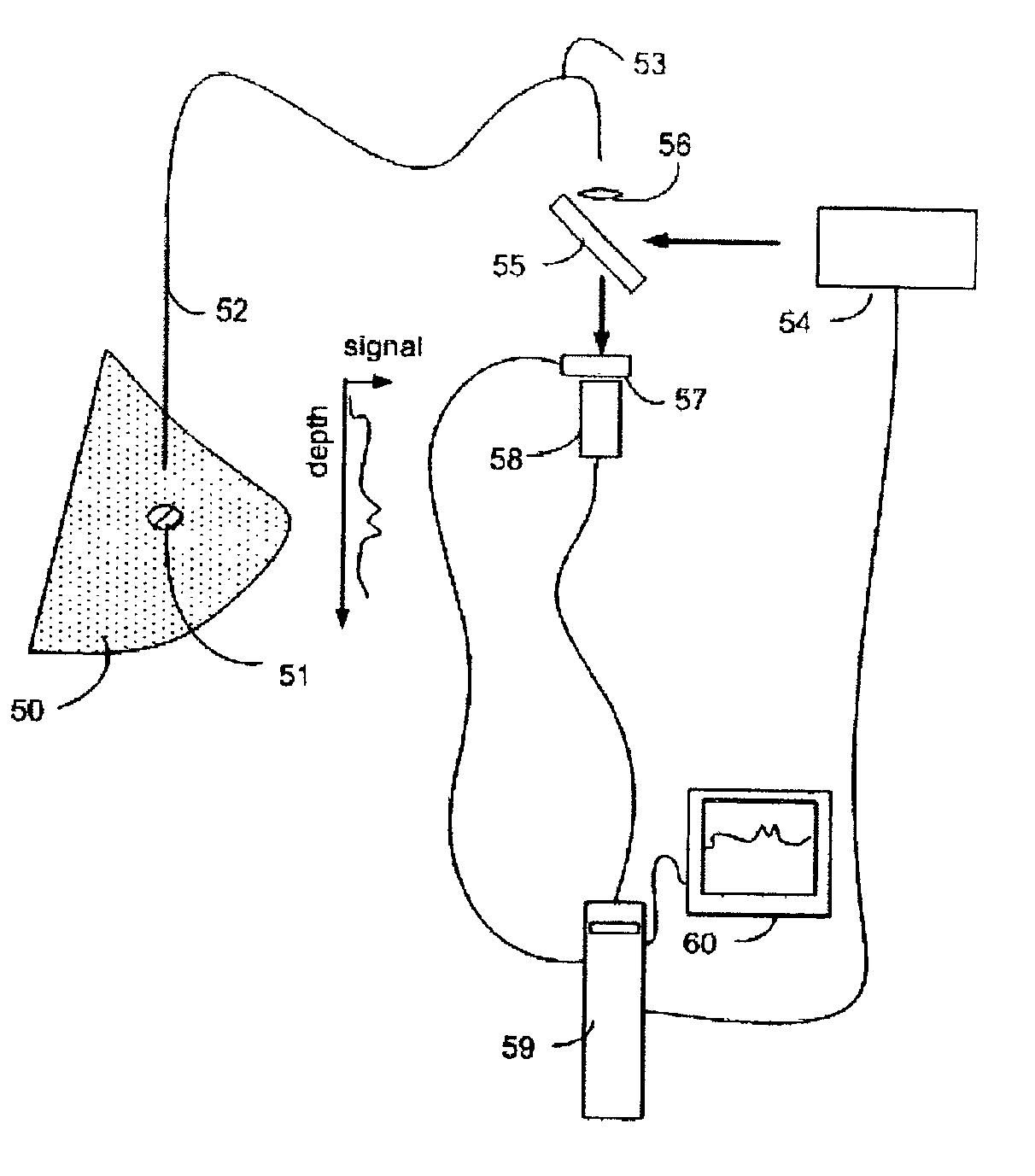
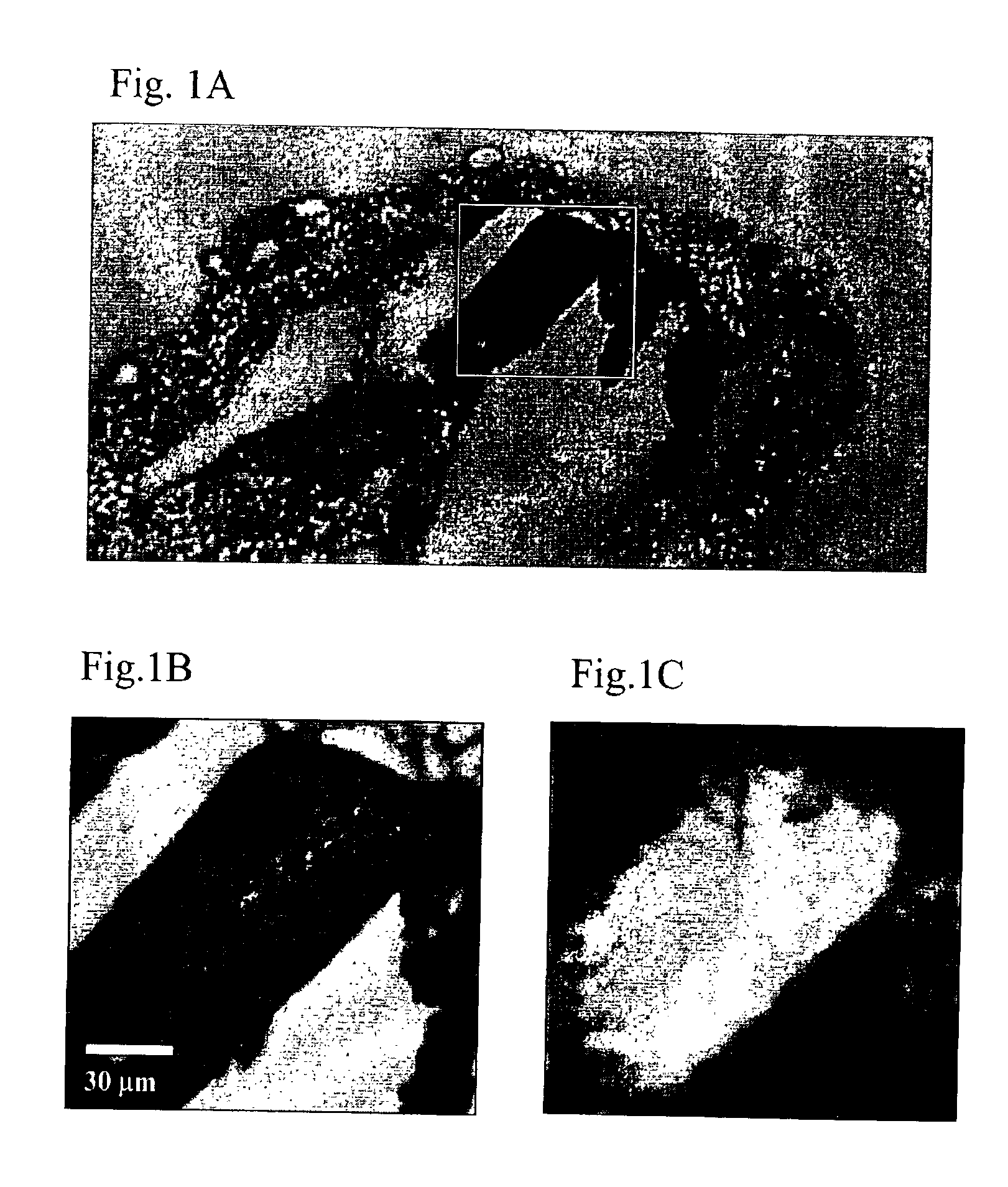
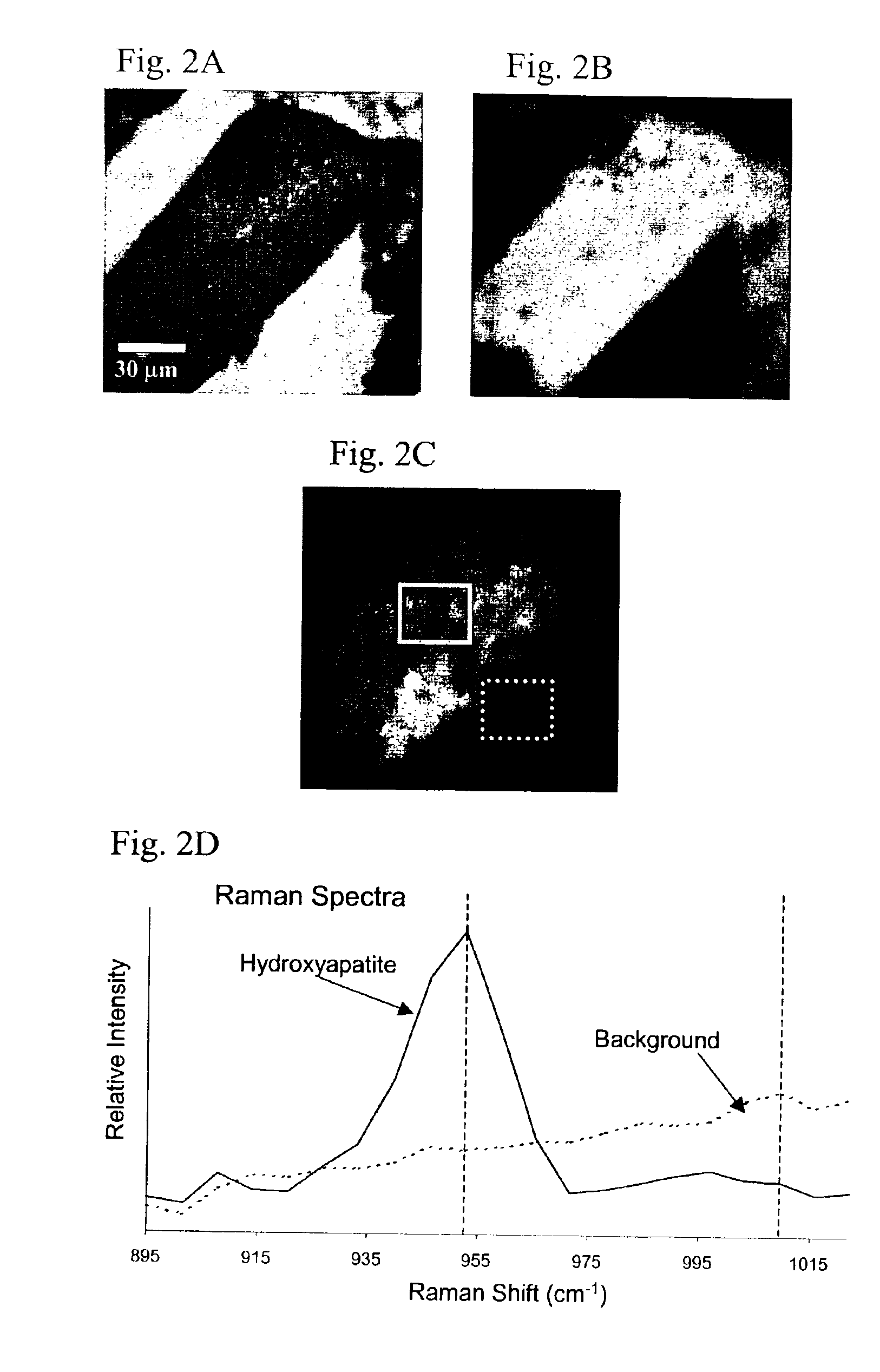
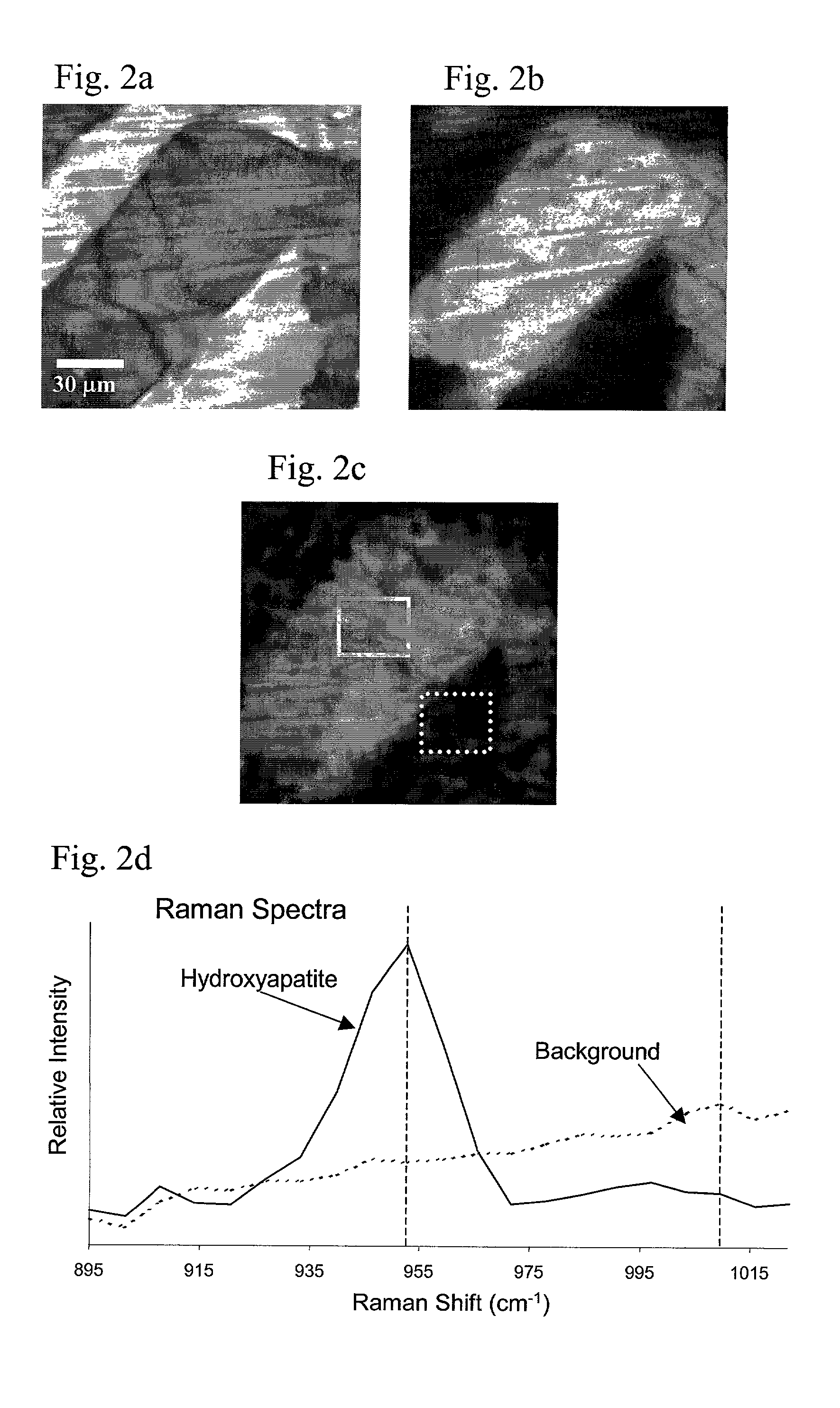
Method for Raman chemical imaging and characterization of calcification in tissue
Apparatus and methods for spatially resolved Raman detection of calcification in tissues are disclosed. A region of soft non-arterial biological tissue is illuminated with monochromatic light. A spatially organized first area of calcified tissue is then detected in the region by detecting a Raman shifted light signal. The Raman shifted light signal is spatially resolved in at least one direction.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
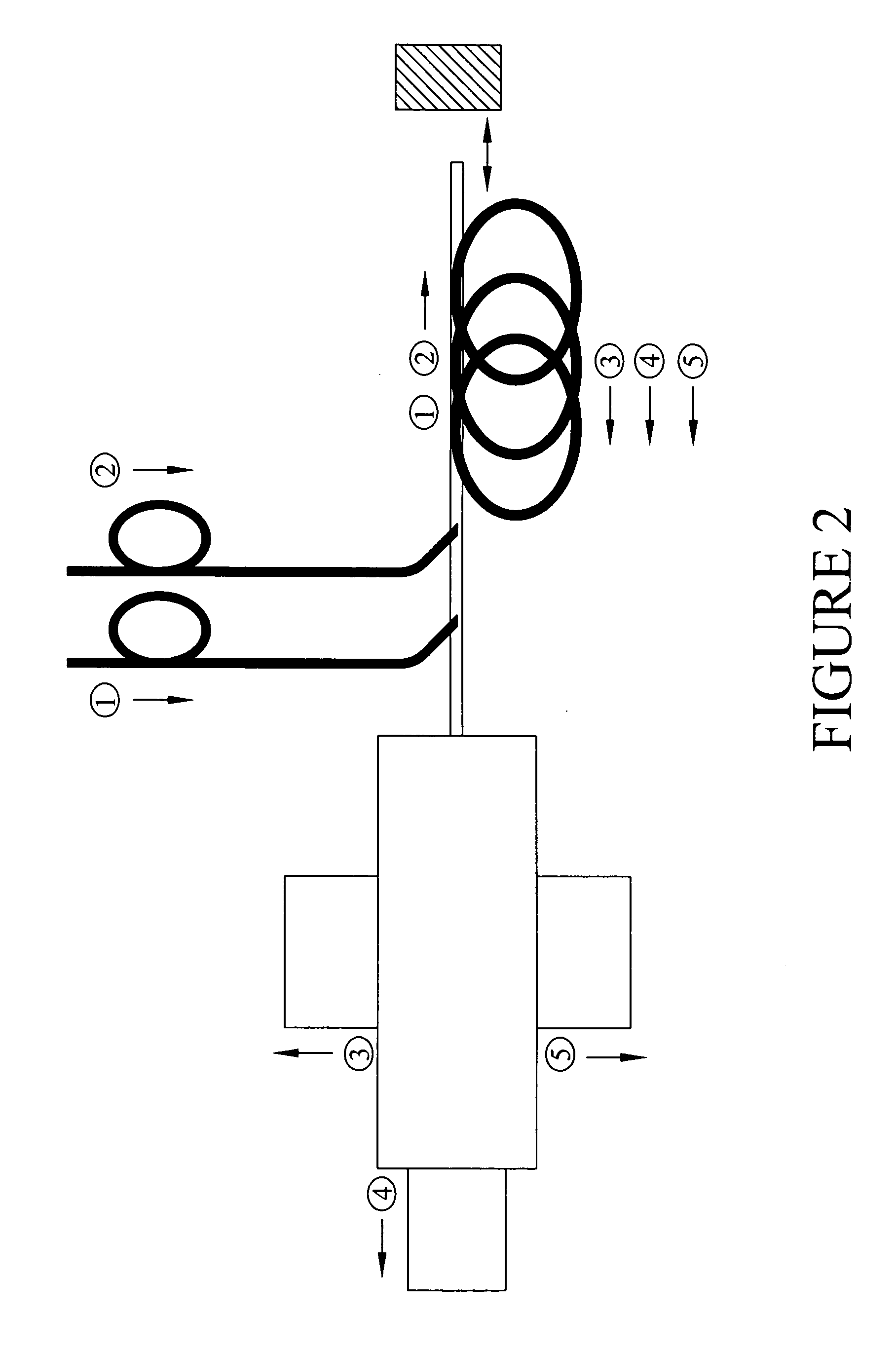
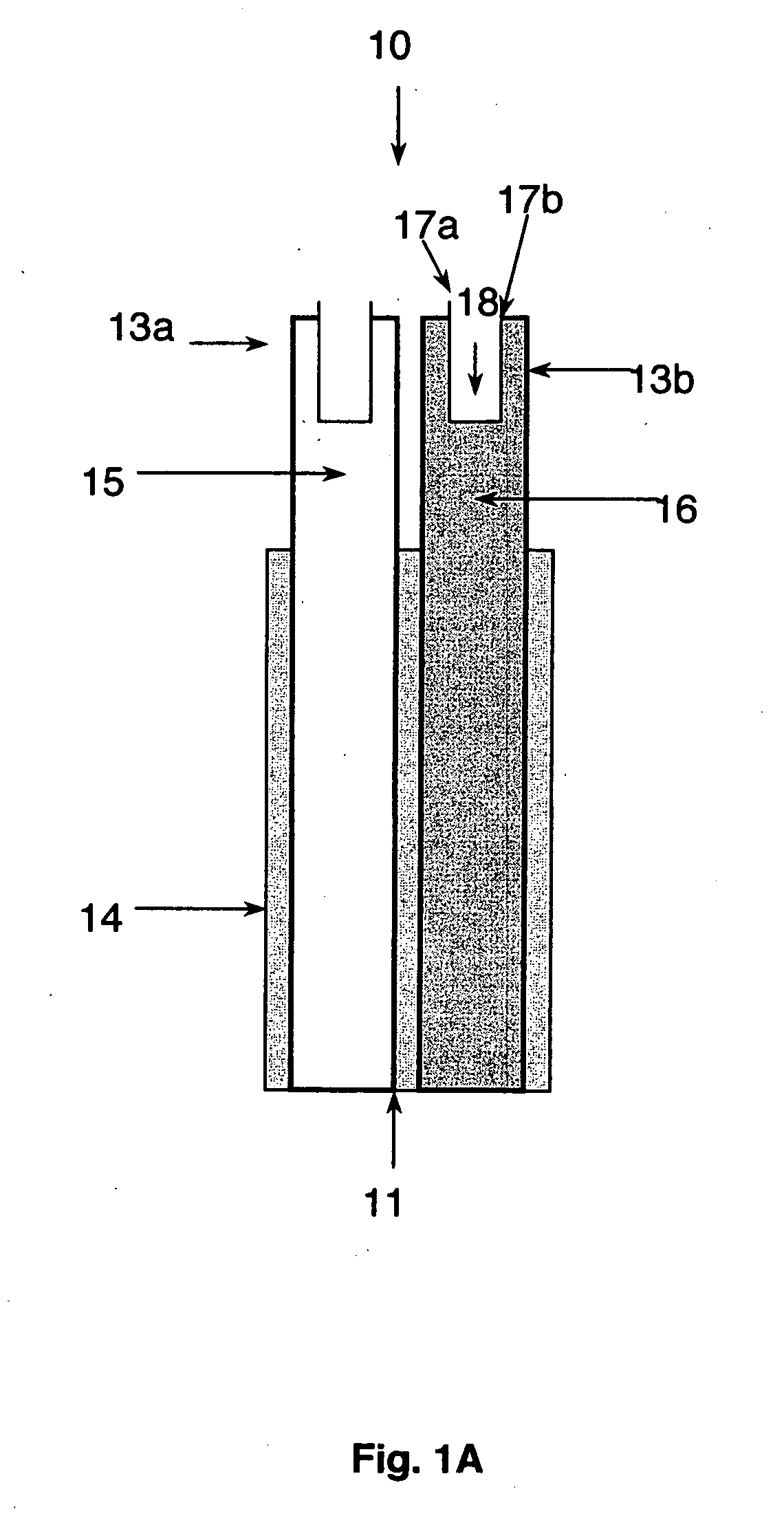
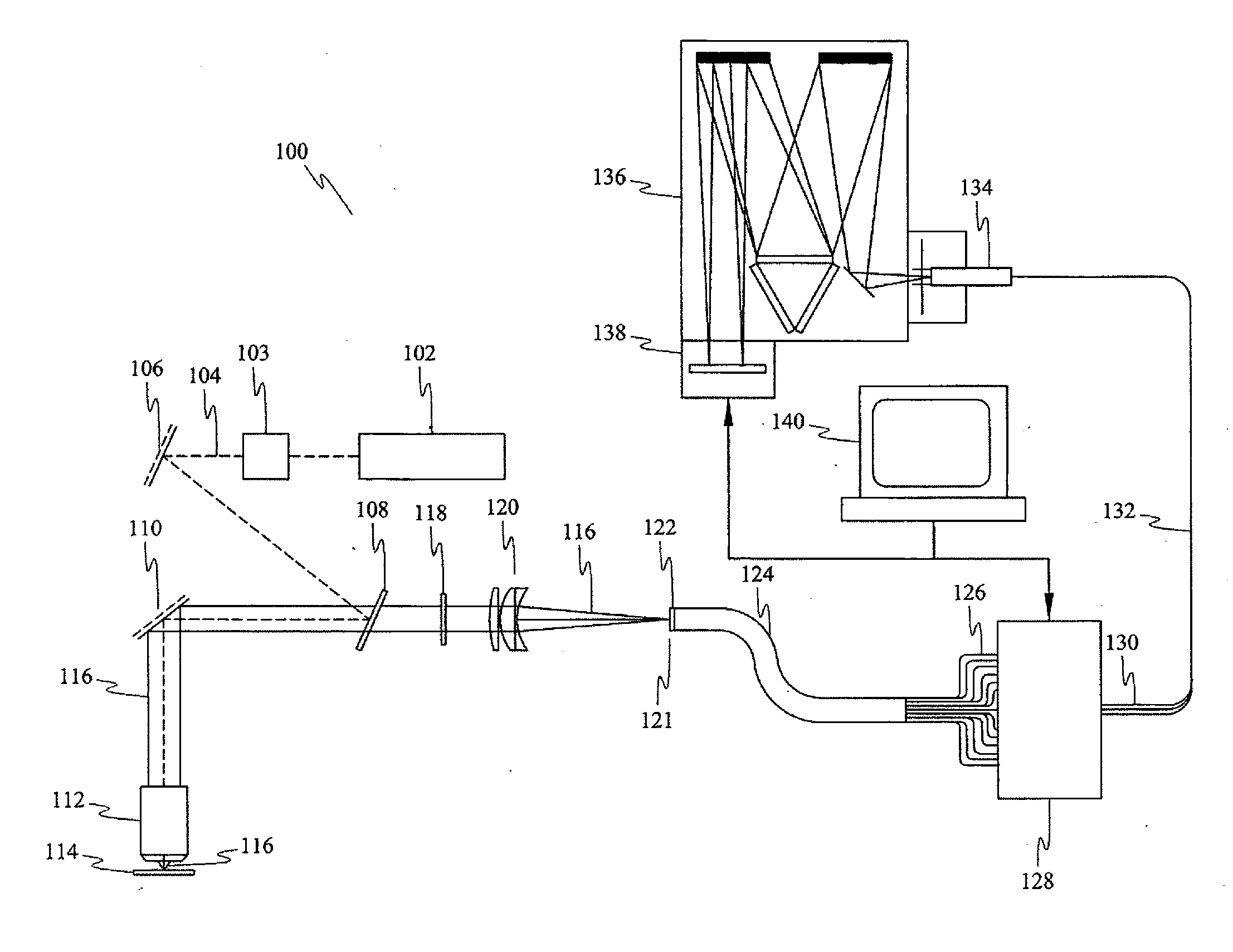
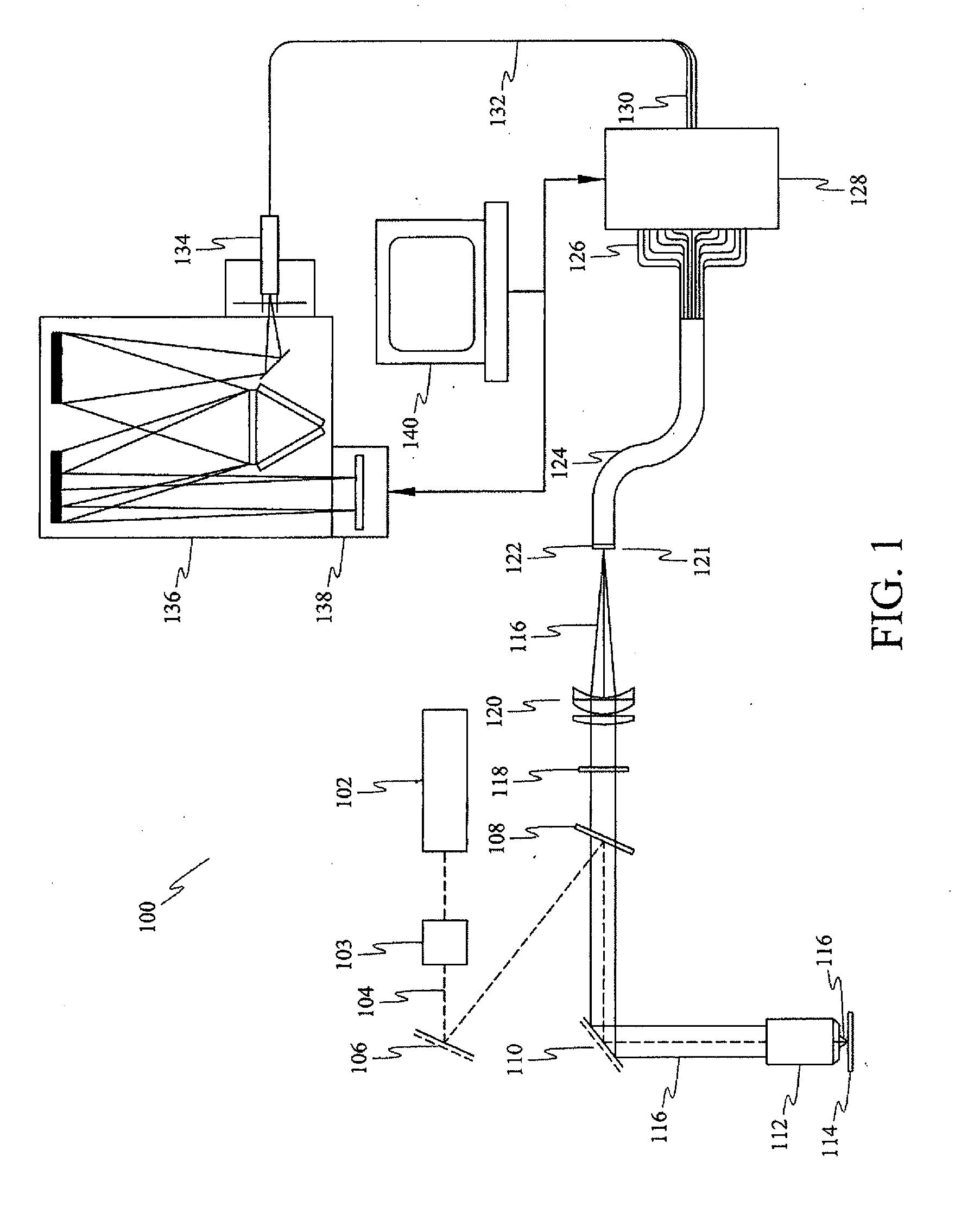
Method and apparatus for fiberscope
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for a fiberscope. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a chemical imaging fiberscope for imaging and collecting optical spectra from a sample having at least one illumination fiber for transmitting light from a first an a second light source to a distal end of a fiberscope; a dichroic mirror disposed at said distal end of the fiberscope such that light from said first light source passes substantially straight through said mirror and light of a predetermined wavelength from said second light source is substantially reflected by said mirror toward said sample to thereby illuminate said sample; and at least one collection fiber for receiving light from said illuminated sample and transmitting the received light to an optical device.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Method for Raman chemical imaging of endogenous chemicals to reveal tissue lesion boundaries in tissue
Apparatus and methods for spatially resolved Raman detection of molecules indicative of the borders of lesions with normal tissue are disclosed. A region of biological tissue was illuminated with monochromatic light. A Raman shifted light signal is detected from endogenous molecules in the region, the molecules being spatially organized in a localized first area of the region. These molecules are indicative of a border between normal tissue and a lesion. The Raman shifted light signal is then spatially resolved in at least one direction.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
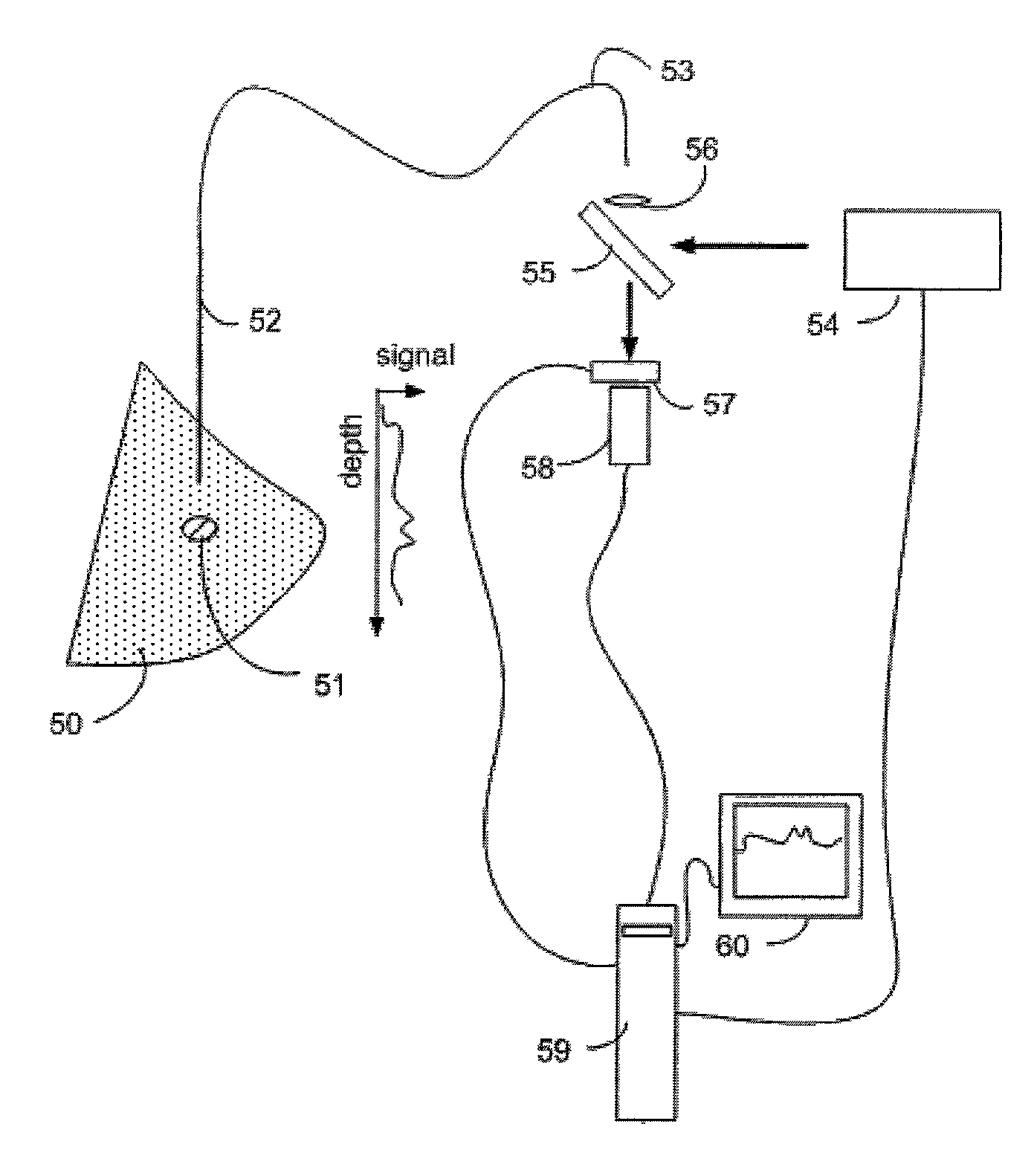
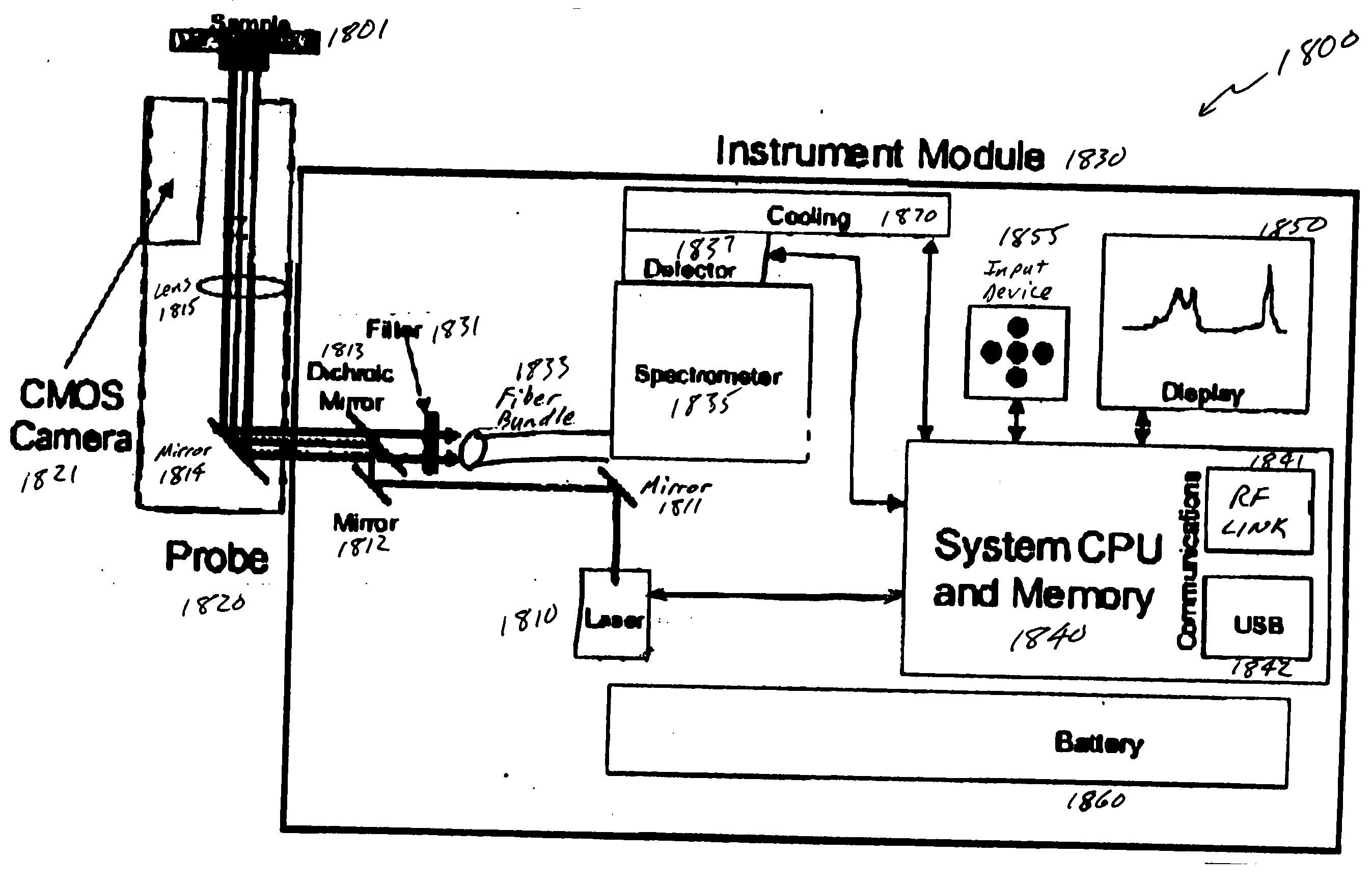
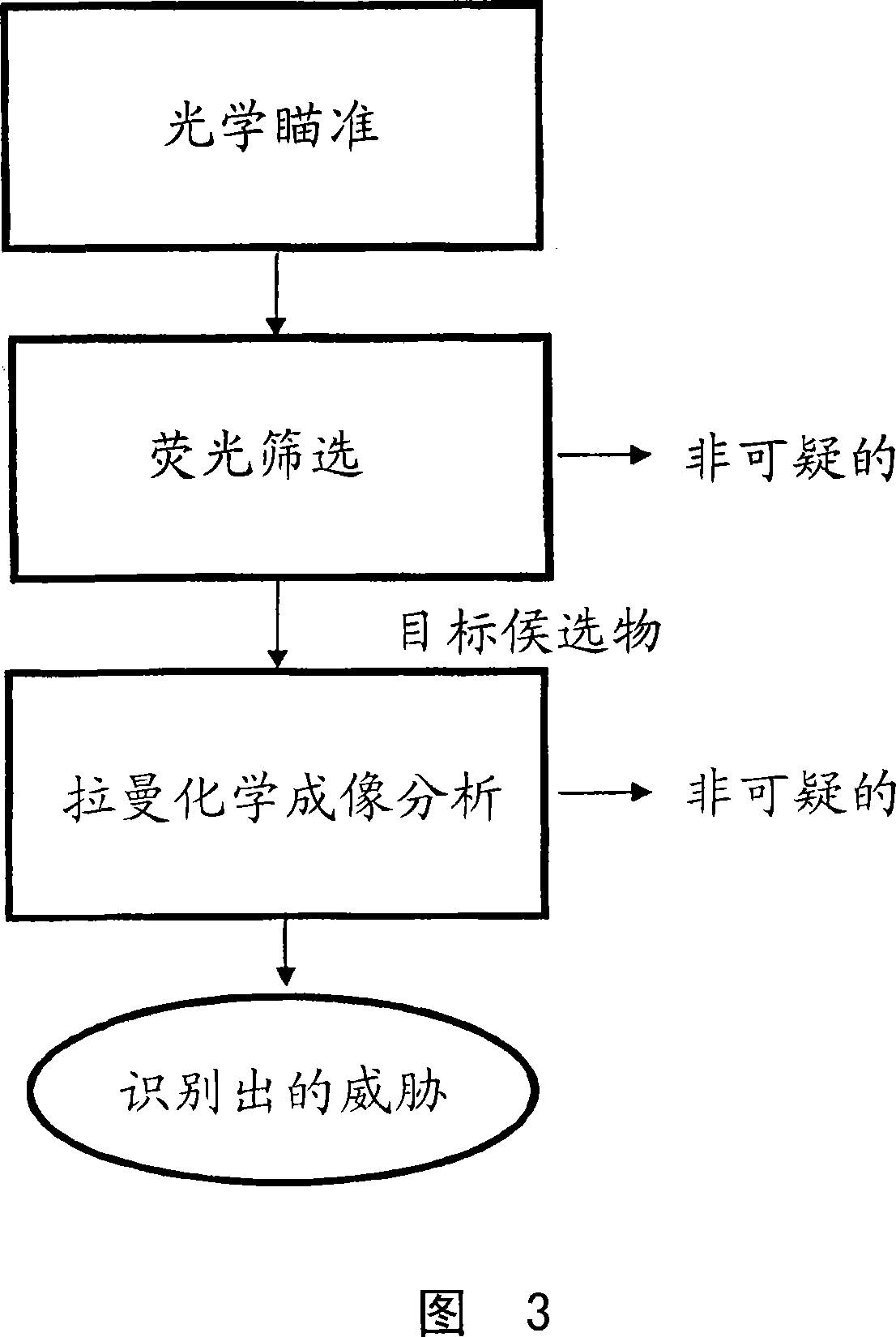
System and method for a chemical imaging threat assessor with a probe
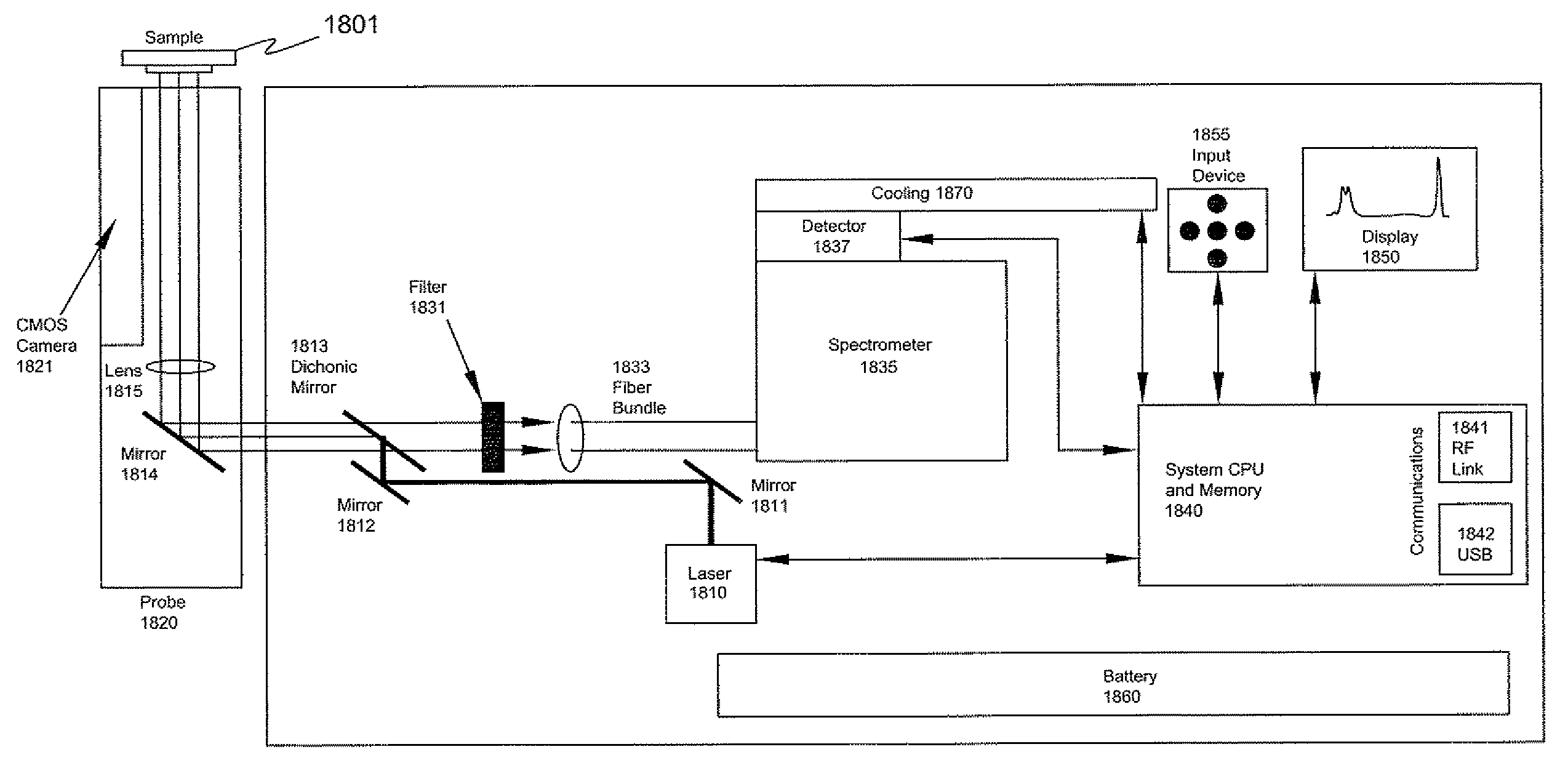
The disclosure relates to a portable and / or handheld bioagent detector and methodology described herein that is based in part on advanced Raman Chemical Imaging (“RCI”) technology. According to one embodiment of the present disclosure, the detection system may include a fiber array spectral translator (“FAST”) and may also include a probe which may include a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) camera. The probe alleviates the need to place the main instrument close to an unconfined release of a potentially hazardous material and facilitates analysis of a sample that is situated in a hard-to-reach location while minimizing contamination of the detector and operator.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
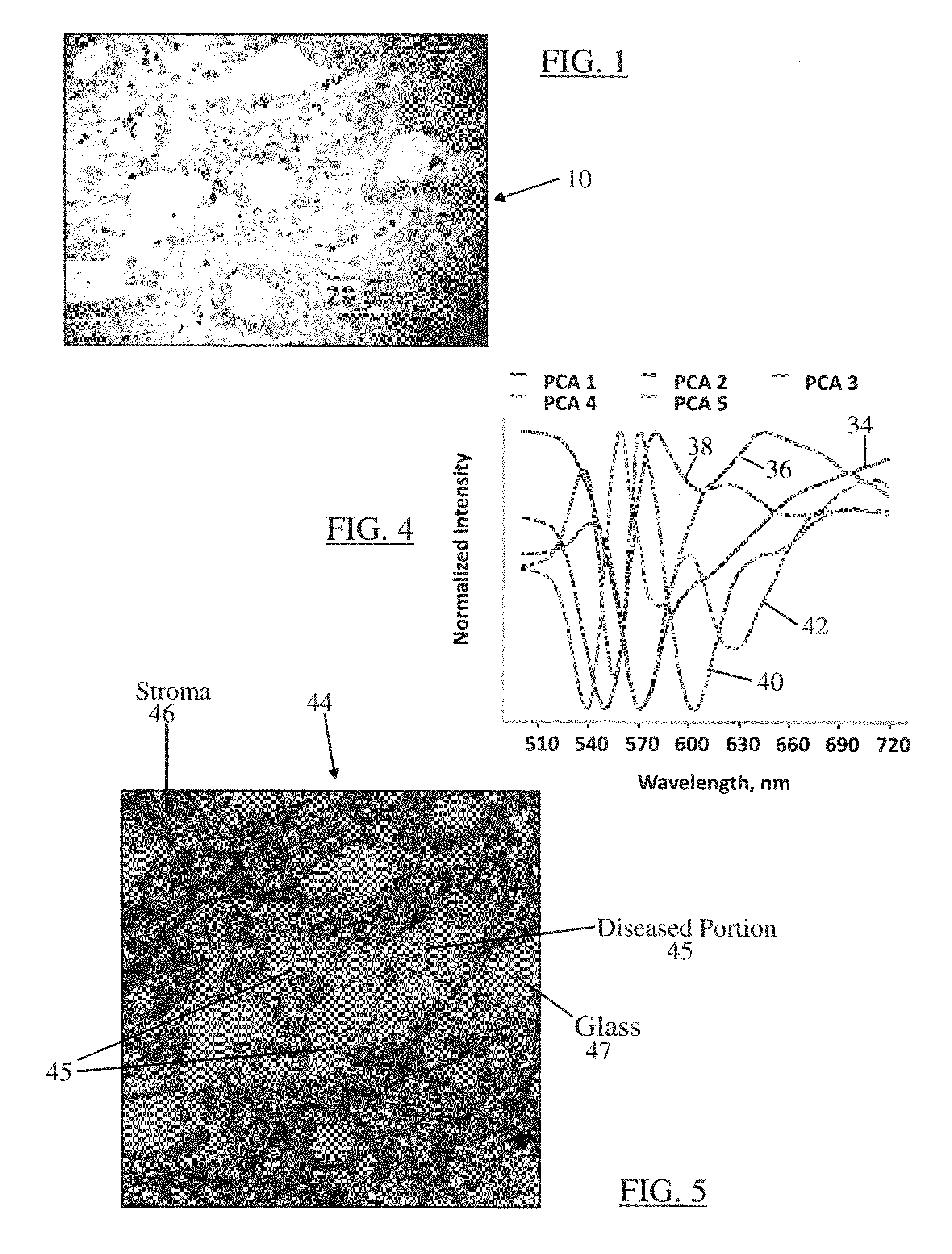
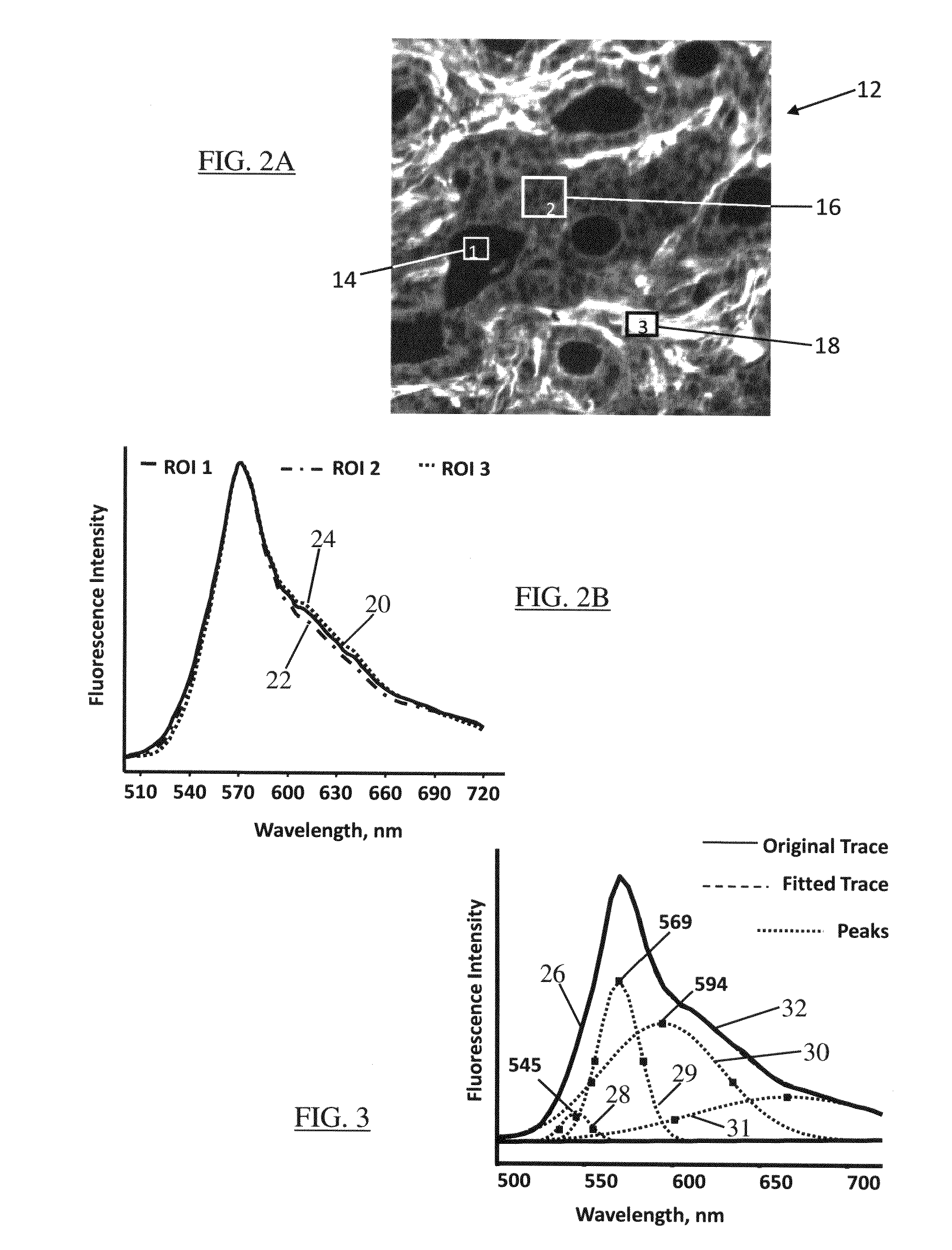
Hyperspectral fluorescence and absorption bioimaging
InactiveUS20080272312A1Strong specificityDetailed analysisPhotometrySolid-state devicesABSORPTION BASECellular component
A system and method of hyperspectral chemical imaging (fluorescence or absorption based) to provide an automated approach for a more detailed analysis of disease status of a biological sample. When a biological sample is labeled with a fluorescent or light-absorbing contrast-enhancing agent, interactions between the contrast-enhancing agent and one or more constituents (or cellular components) of the biological sample may be manifested through spectral contents of a plurality of regions in a hyperspectral chemical image of the sample. Observations of such manifestations through analysis of corresponding spectral contents may greatly assist a user (e.g., a pathologist) in detecting and differentiating diseased portions of the stained sample. Hyperspectral chemical imaging may allow to identify multiple cellular components within a biological sample and to image their distribution within the sample, thereby assisting a pathologist to successfully and more accurately identify diseased portion(s) of the sample for further diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Dynamic imaging of biological cells and other subjects
ActiveUS20070182959A1Quick observationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscopic imageMultivariate analysis
The invention relates to methods of dynamic chemical imaging, including methods of cellular imaging. The method comprises illuminating at least a portion of a cell with substantially monochromatic light and assessing Raman-shifted light scattered from the illuminated portion at a plurality of discrete times. The Raman-shifted light can be assessed at a plurality of Raman shift (RS) values at each of the discrete times, and the RS values can be selected to be characteristic of a pre-selected component at each of the discrete times. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectral features of the images thus obtained can yield the location and chemical identity of components in the field of view. This information can be combined or overlaid with other spectral data (e.g., a visible microscopic image) obtained from the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
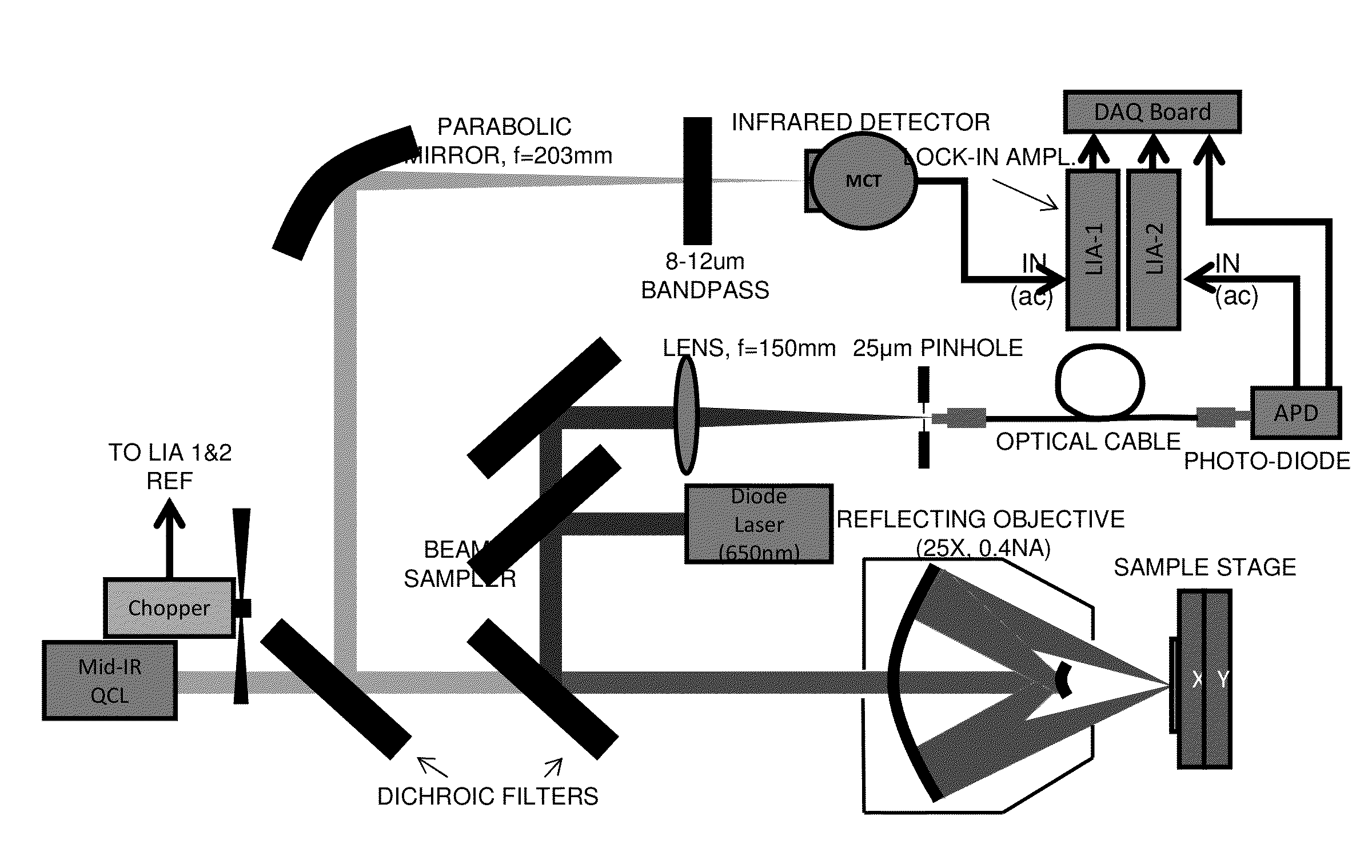
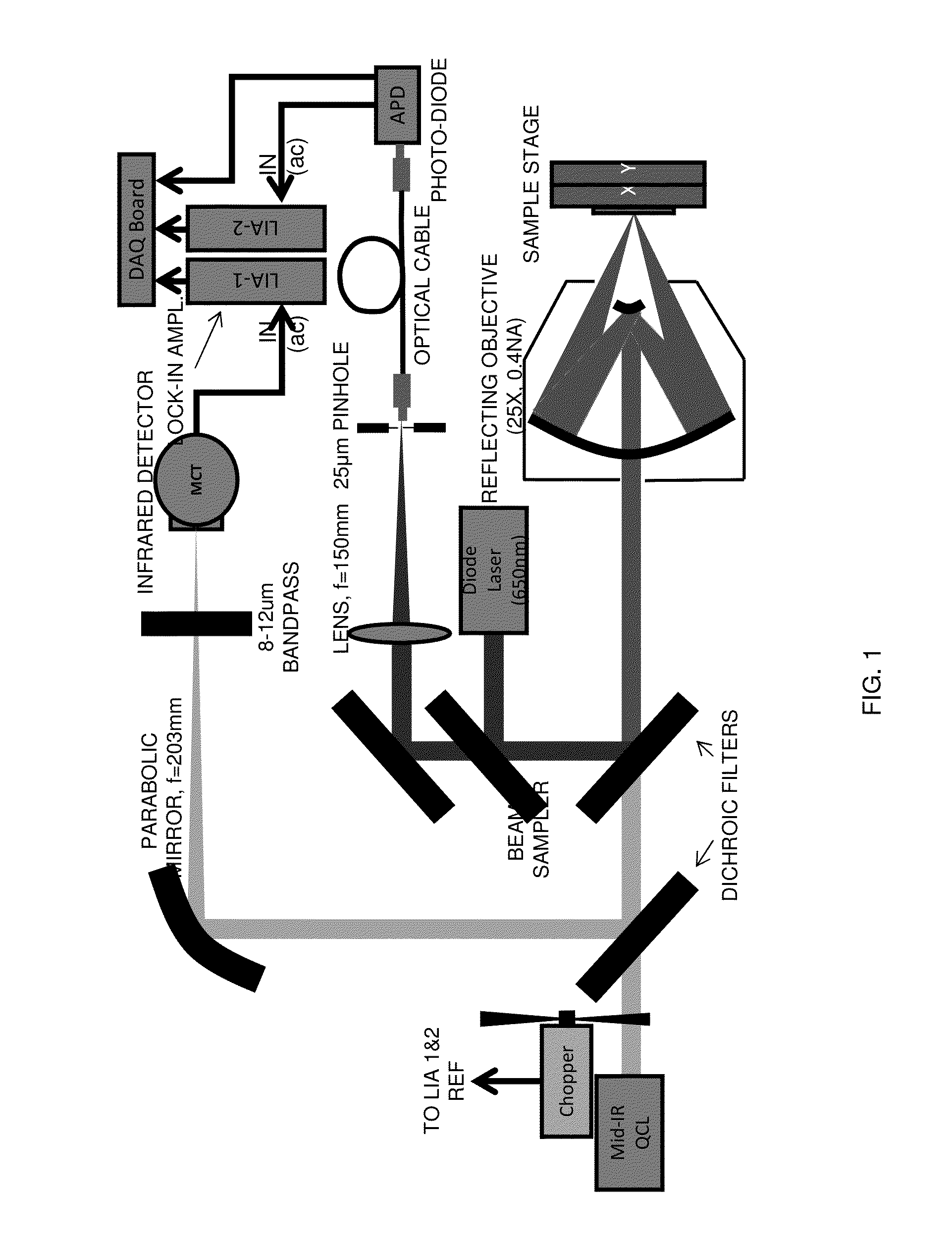
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and NANO scales
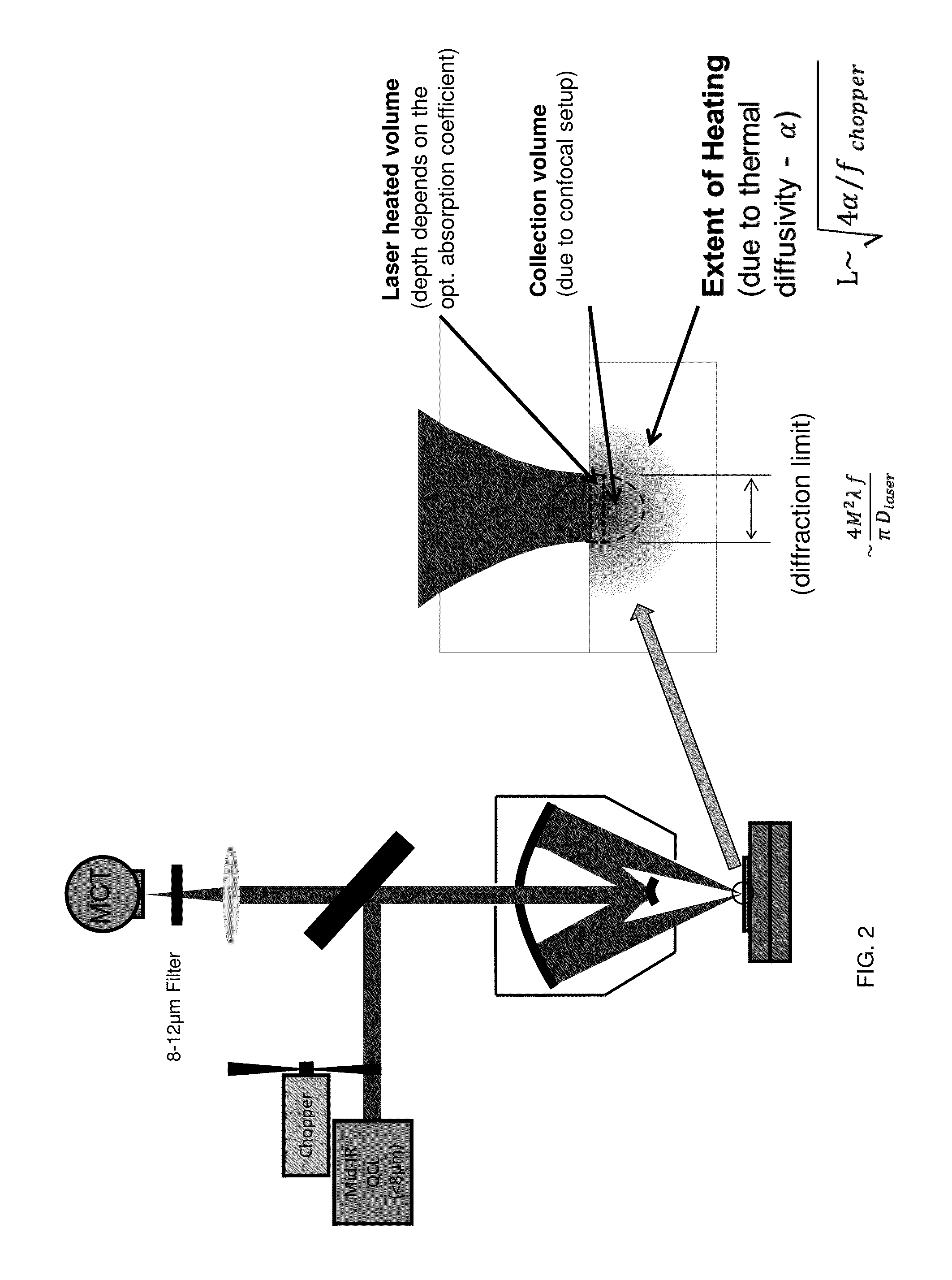
ActiveUS20130134310A1Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
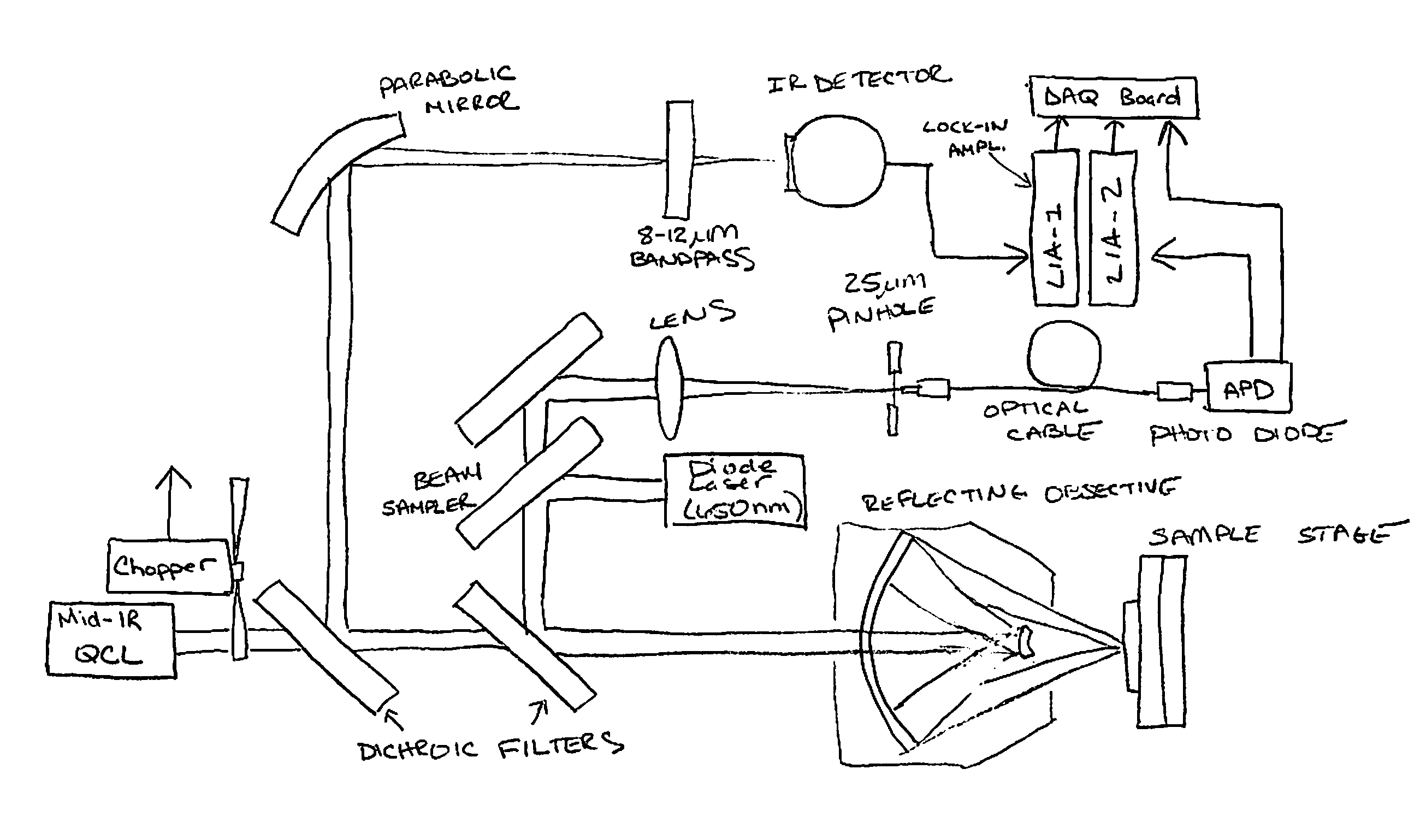
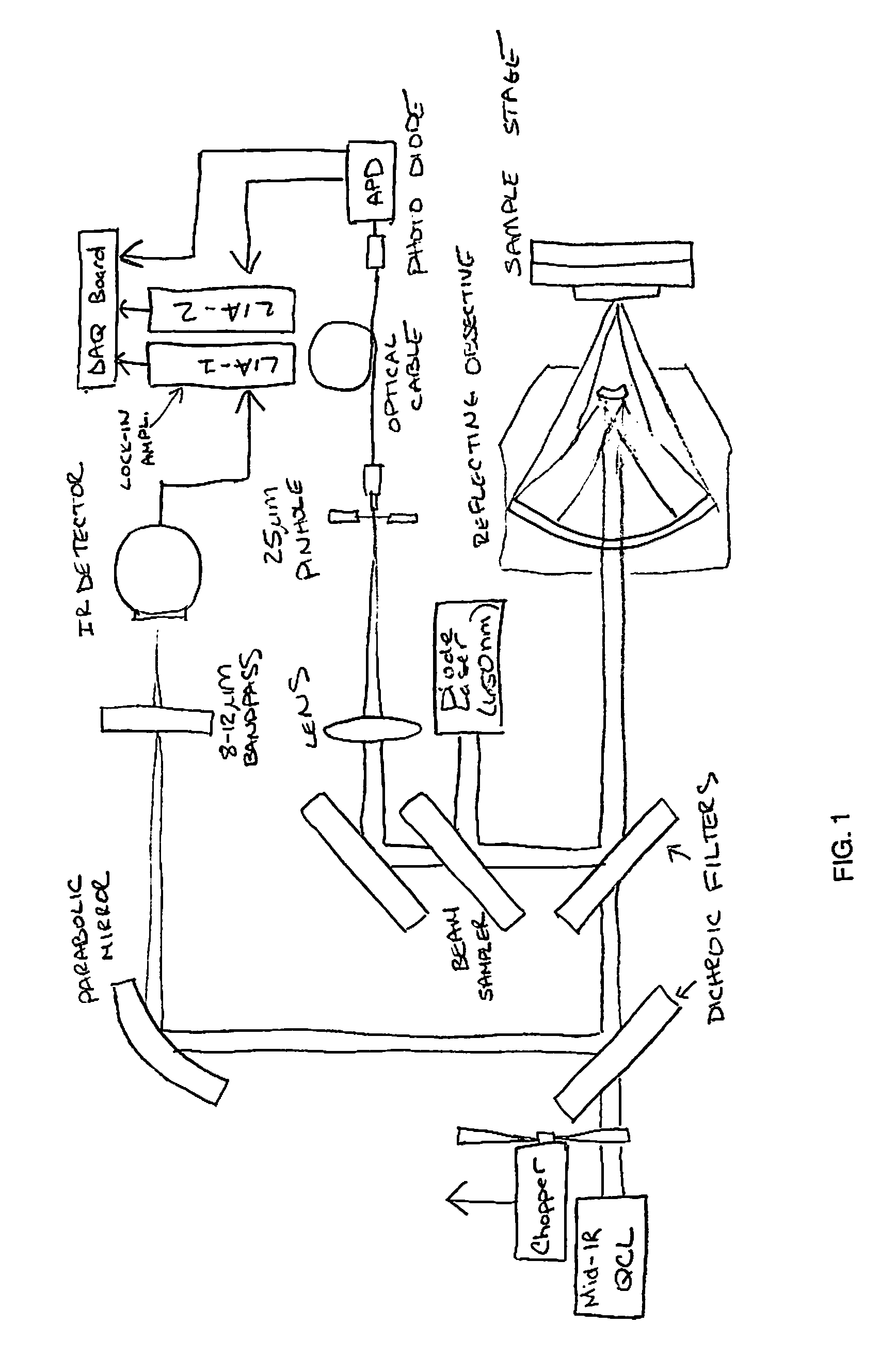
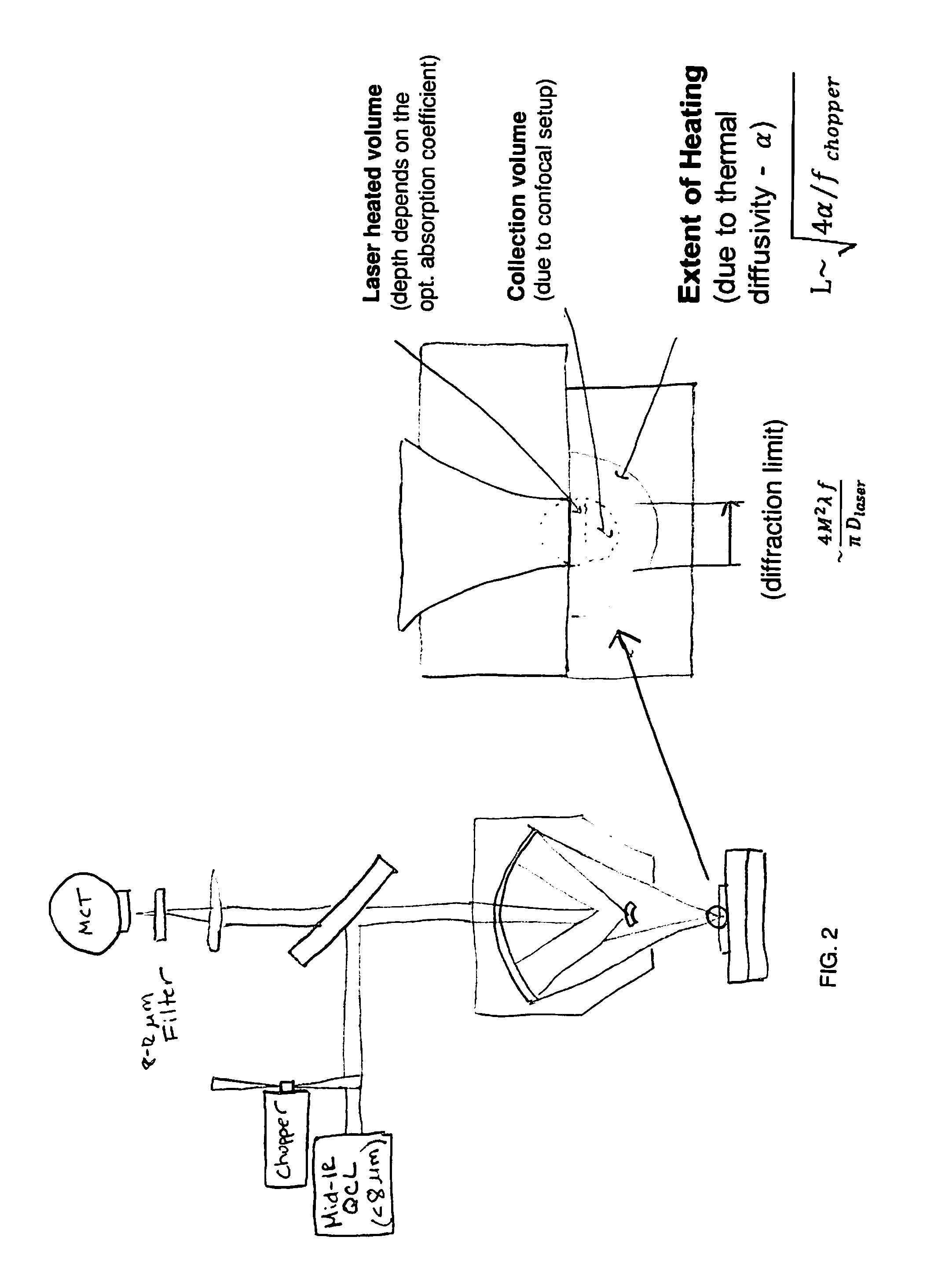
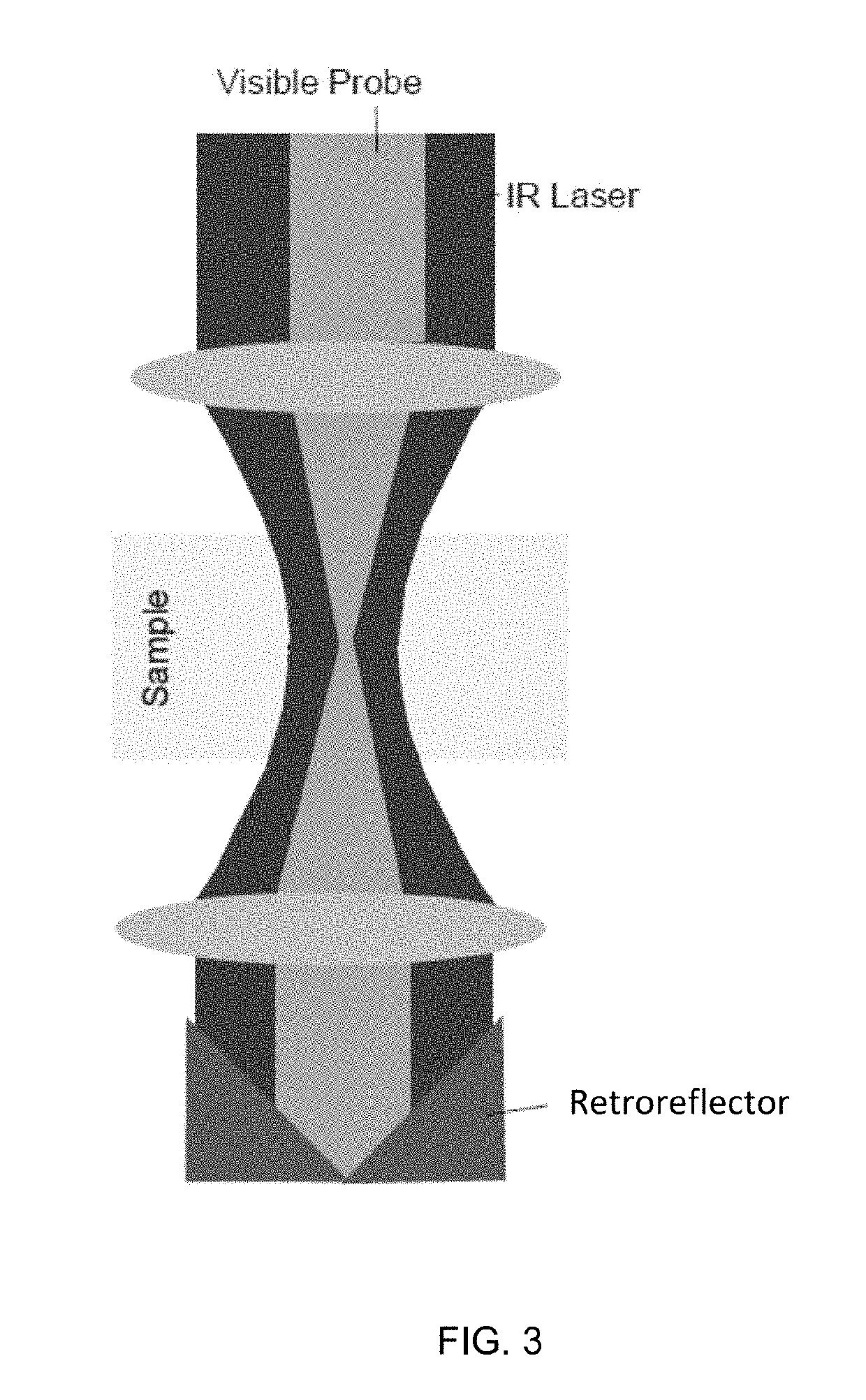
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic nano-imaging probe and uses therefor
Provided herein is a reusable nano-imaging probe useful in surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) applications demonstrating nanometer scale resolution. The nano-imaging probe generally comprises a fiber optic imaging bundle of fiber optic elements each having a tapered etched end and a non-tapered non-etched end. The tapered etched ends further comprise a SERS-active metal substrate deposited thereon effective to create a uniform SERS enhancement for an analyte or other substance of interest. Also provided is a SERS nanoimager for dynamic chemical imaging using the nano-imaging probe and methods of imaging and Raman spectral analysis and identification using the nano-imaging probe.
Owner:UNIV OF MARLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY THE
Method and apparatus for fiberscope
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for a fiberscope. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a chemical imaging fiberscope for imaging and collecting optical spectra from a sample having at least one illumination fiber for transmitting light from a first an a second light source to a distal end of a fiberscope; a dichroic mirror disposed at said distal end of the fiberscope such that light from said first light source passes substantially straight through said mirror and light of a predetermined wavelength from said second light source is substantially reflected by said mirror toward said sample to thereby illuminate said sample; and at least one collection fiber for receiving light from said illuminated sample and transmitting the received light to an optical device.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Method and apparatus for microlens array/fiber optics imaging
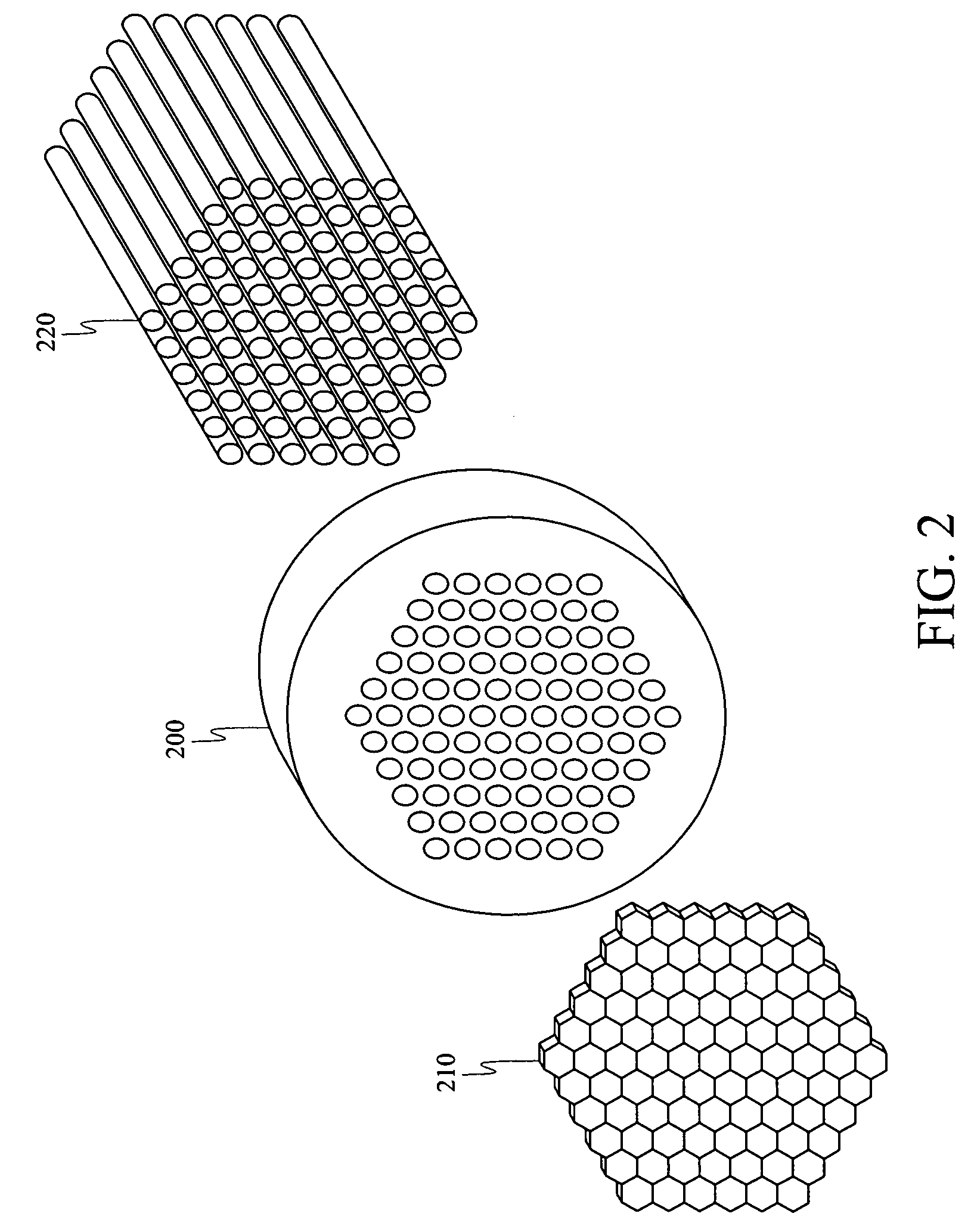
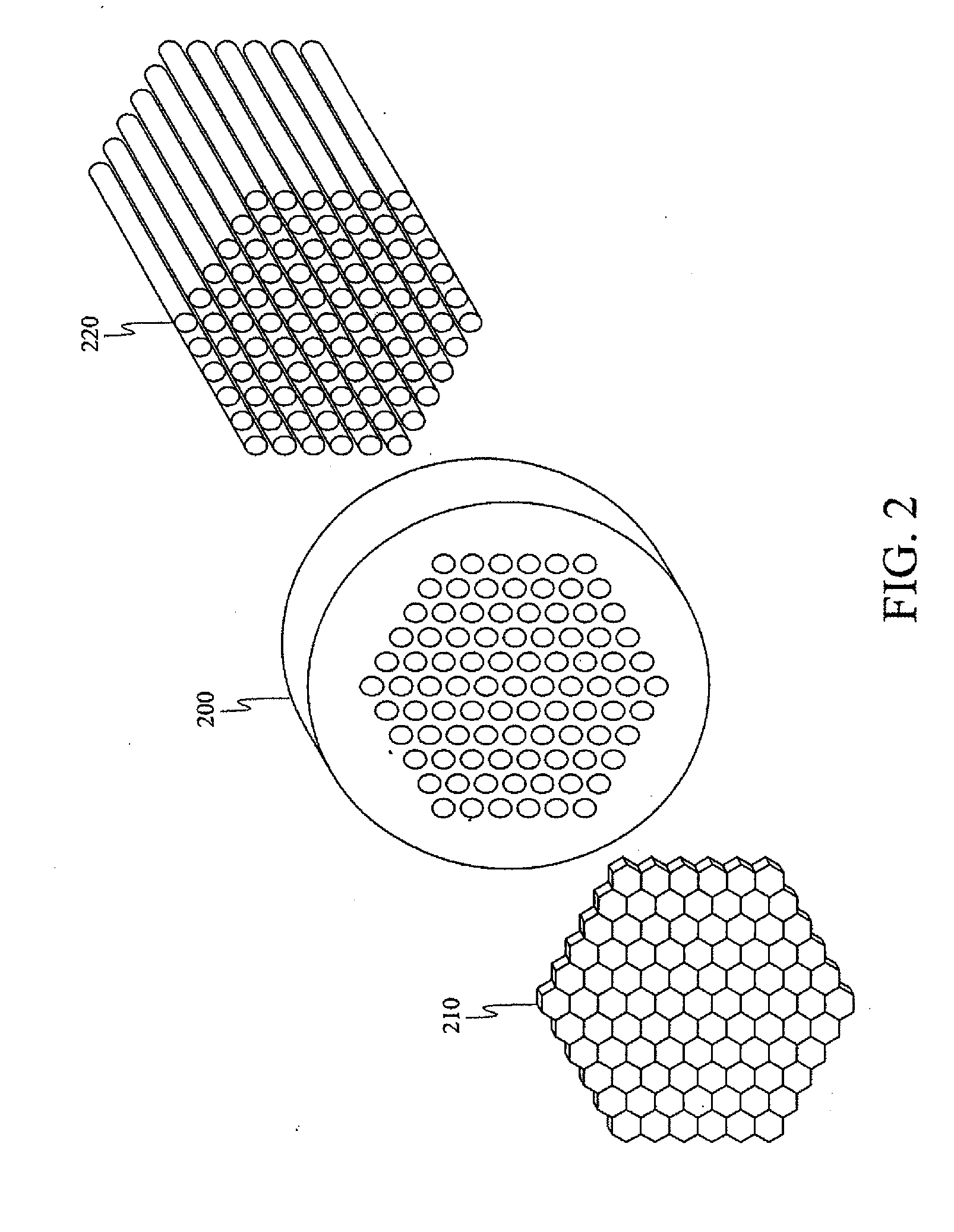
A novel approach for chemical imaging is disclosed. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a system for producing a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample from photons scattered from the sample, comprising an optical lens; a first optical fiber bundle of M fibers; a second optical fiber bundle of N fibers; an optical fiber switch; and a charge coupled device, wherein the image comprises plural sub-images, and wherein each sub-image is formed from photons scattered from a predetermined two spatial dimension portion of the sample, and wherein the scattered photons forming each sub-image have a predetermined wavelength different from a predetermined wavelength of scattered photons forming the other sub-images, and wherein the scattered photons for each sub-image are collected substantially simultaneously.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
System and method for raman chemical analysis of lung cancer with digital staining
InactiveUS20120083678A1Accurate and reliable diagnostic informationOvercome limitationsRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using spectroscopyData setMesothelioma
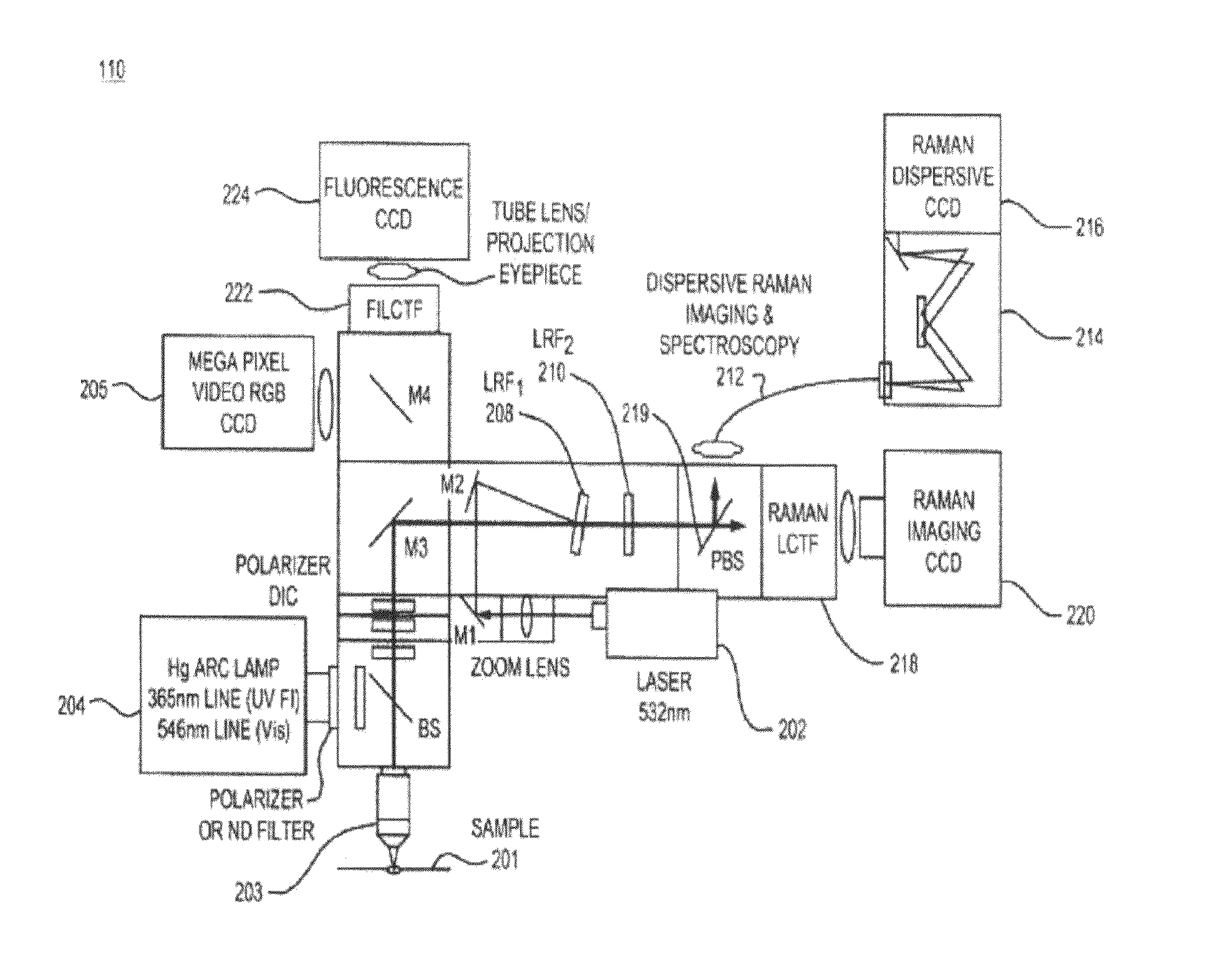
The present disclosure provides for a system and method for diagnosing biological samples that combines the visual staining features familiar to pathologists with the accurate, reliable, and nondestructive capabilities of Raman chemical imaging. The invention disclosed herein may be applied to diagnose lung cancer samples. A method may comprise illuminating a biological sample to generate interacted photons, filtering said interacted photons using a tunable filter, and detecting interacted photons to generate a test Raman data set representative of said sample. The method may further comprise applying at least one chemometric technique and / or a digital stain to said test Raman data set. This test Raman data set may be analyzed to diagnose said sample as comprising at least one of: adenocarcinoma, mesothelioma, and combinations thereof. A system may comprise an illumination source, a tunable filter, and a detector configured to generate a test Raman data set representative of a biological sample.
Owner:CLEMLMAGE
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and nano scales
ActiveUS9091594B2Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
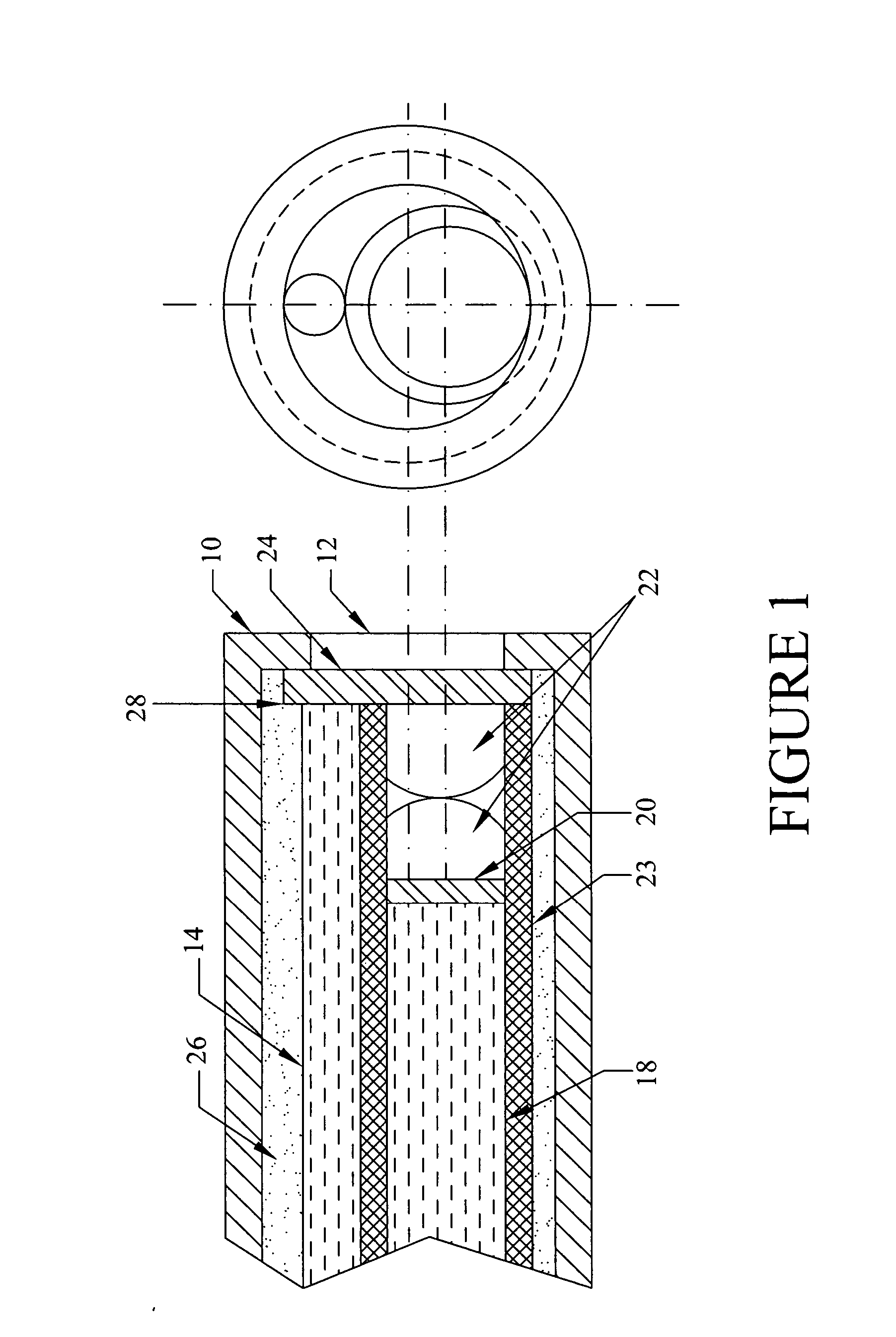
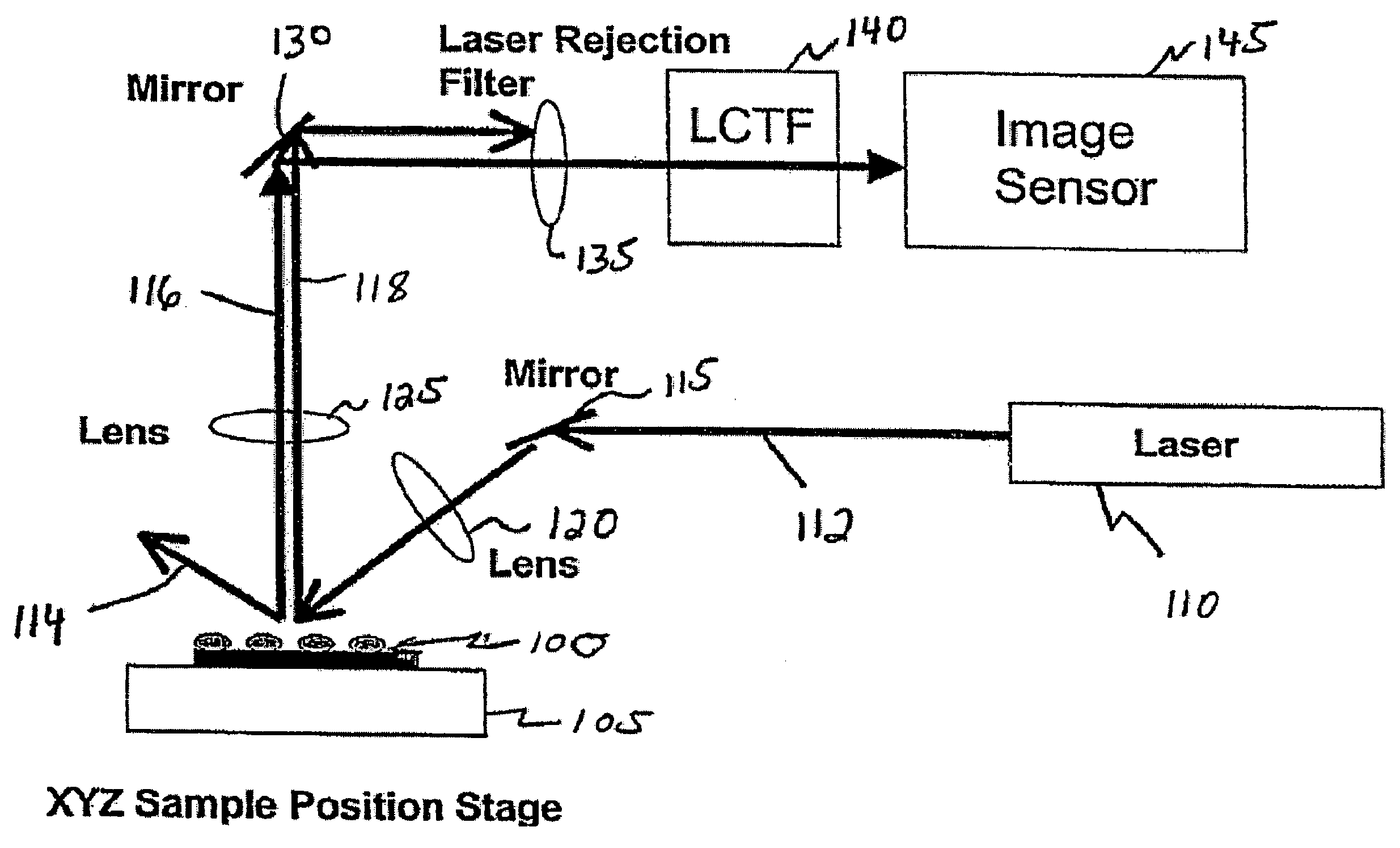
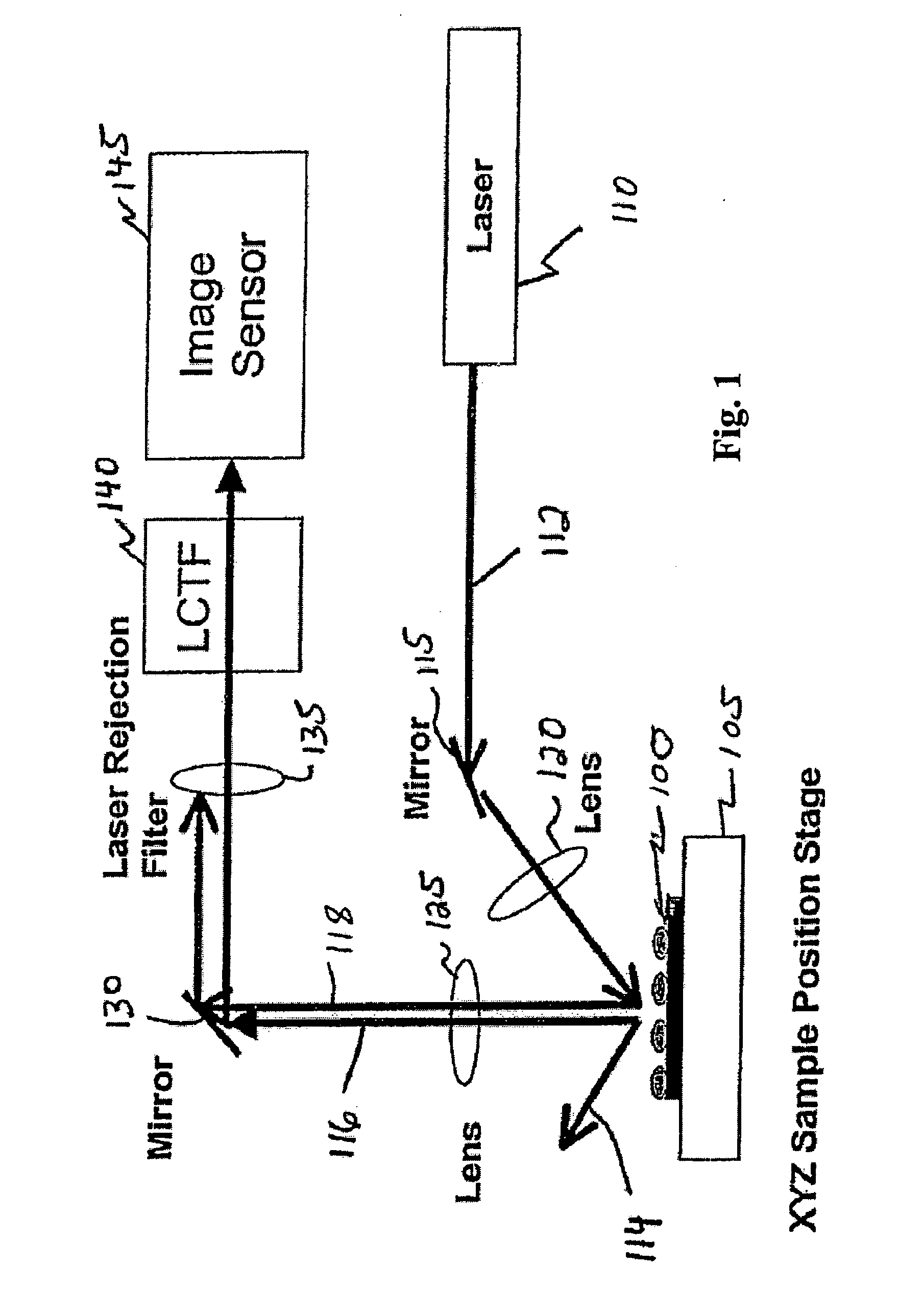
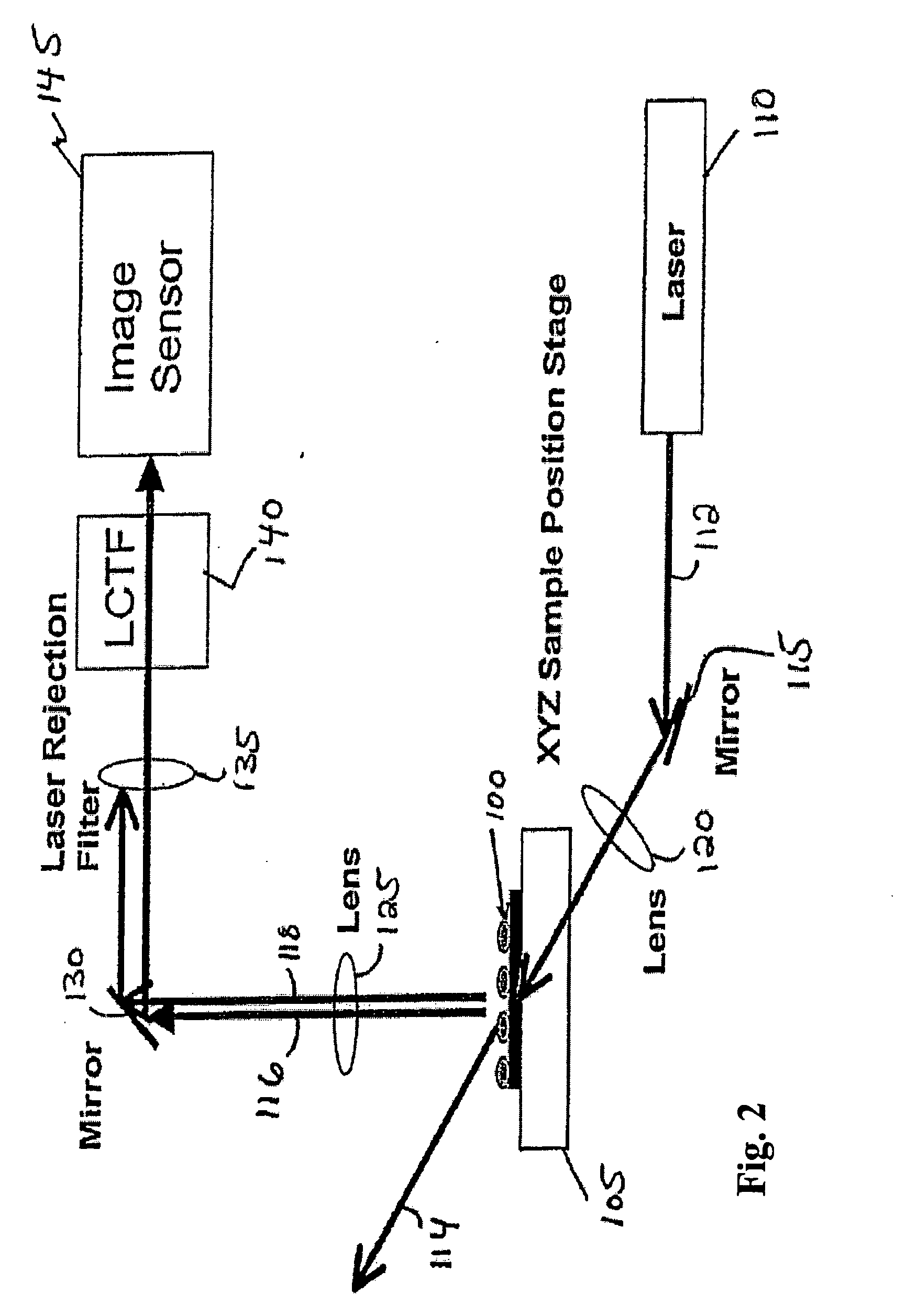
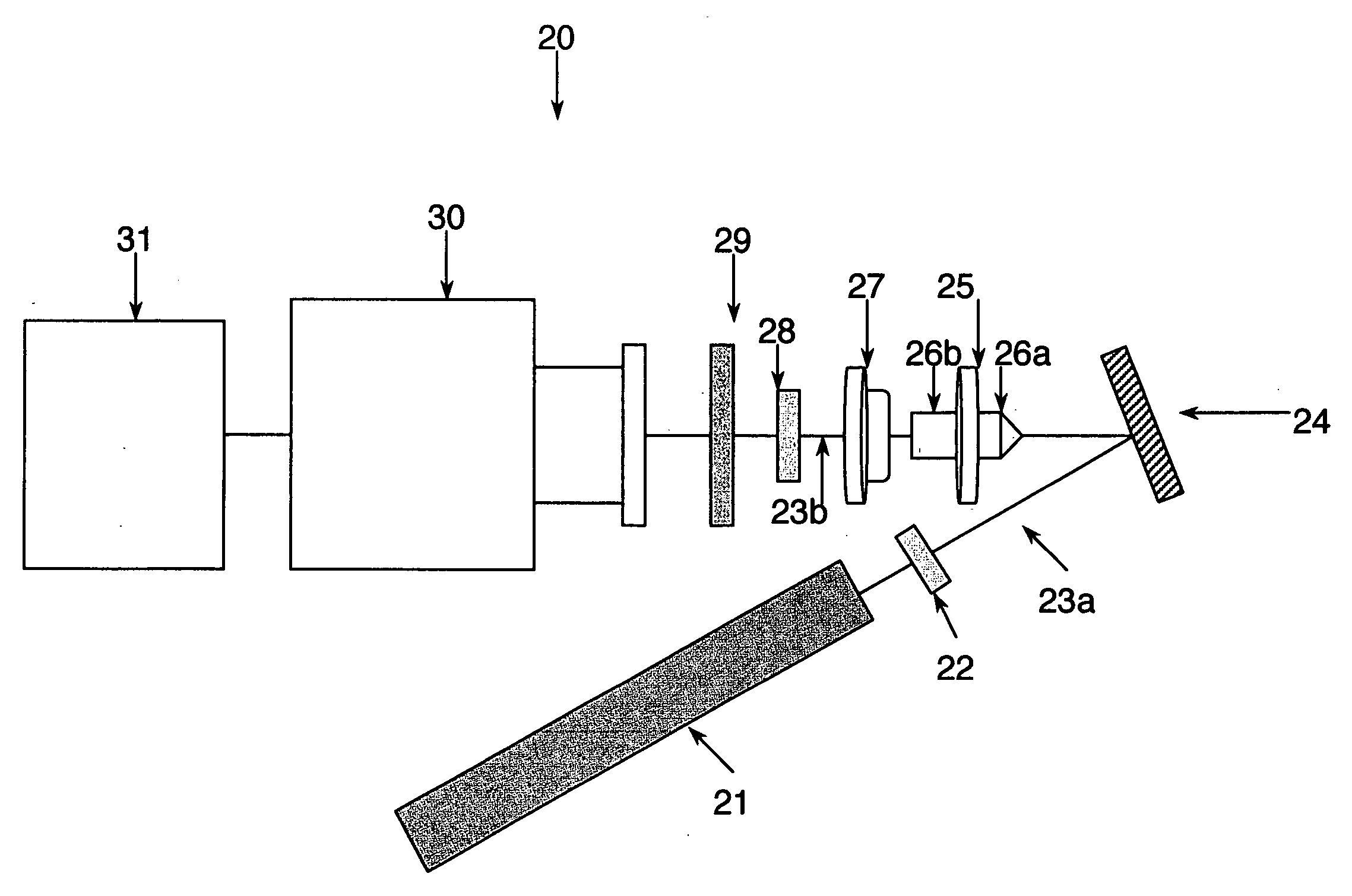
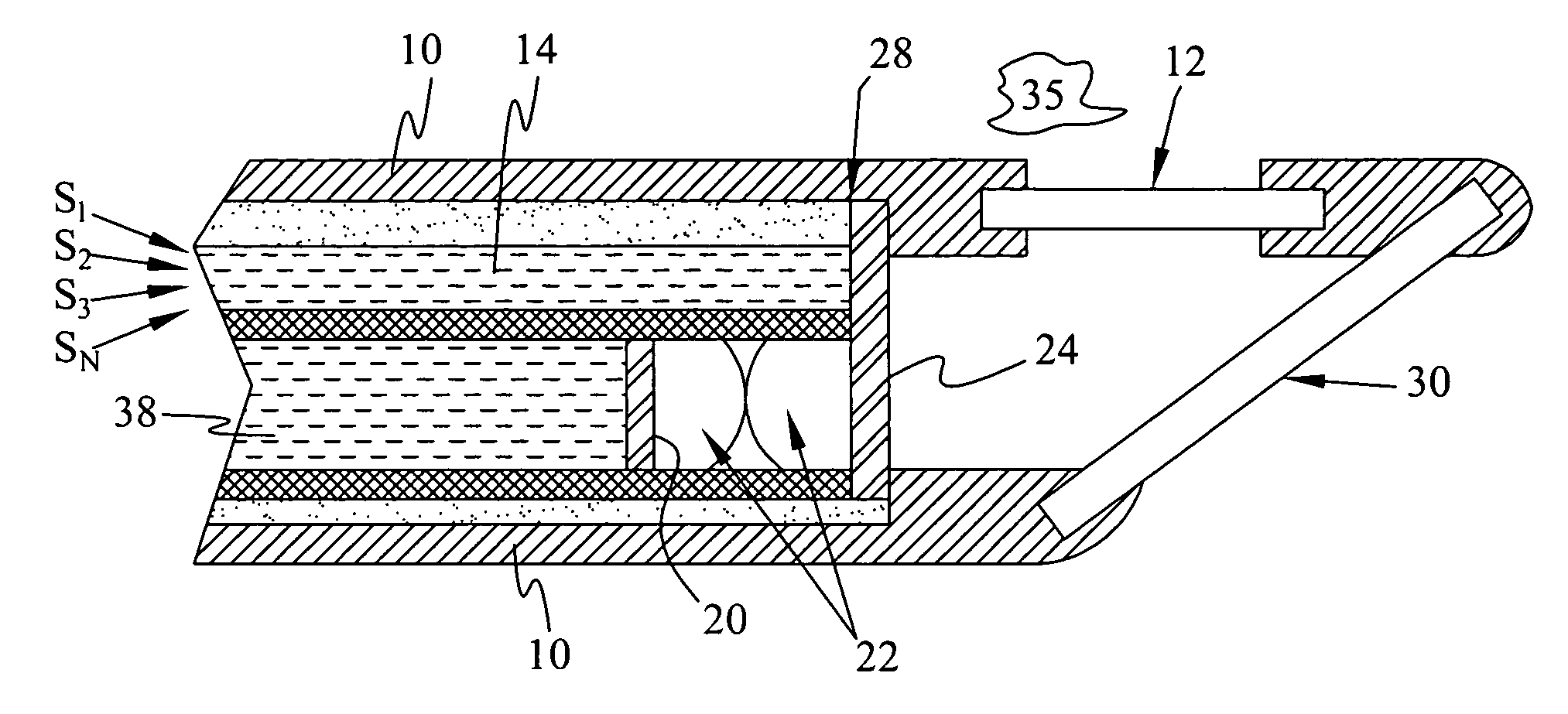
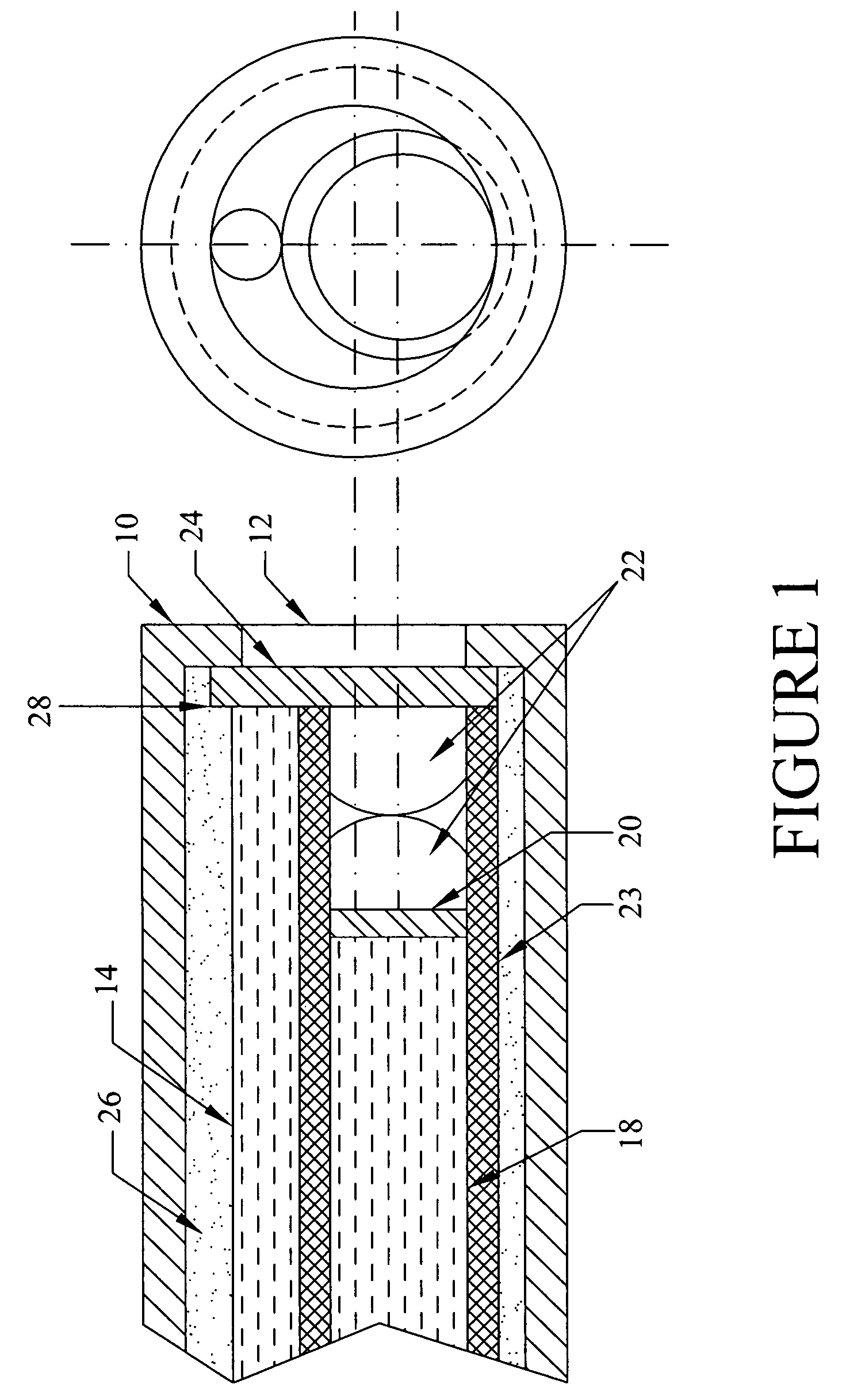
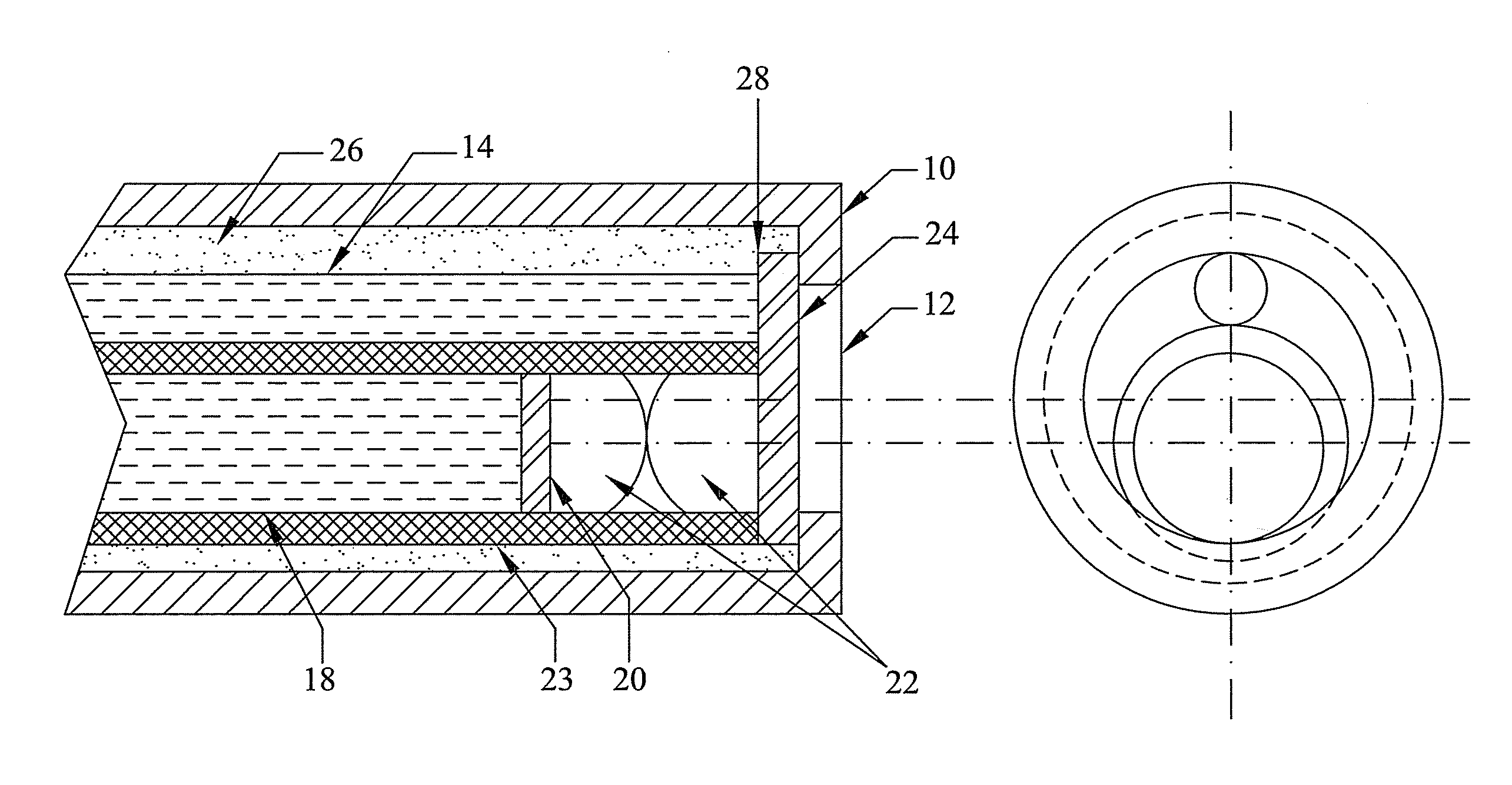
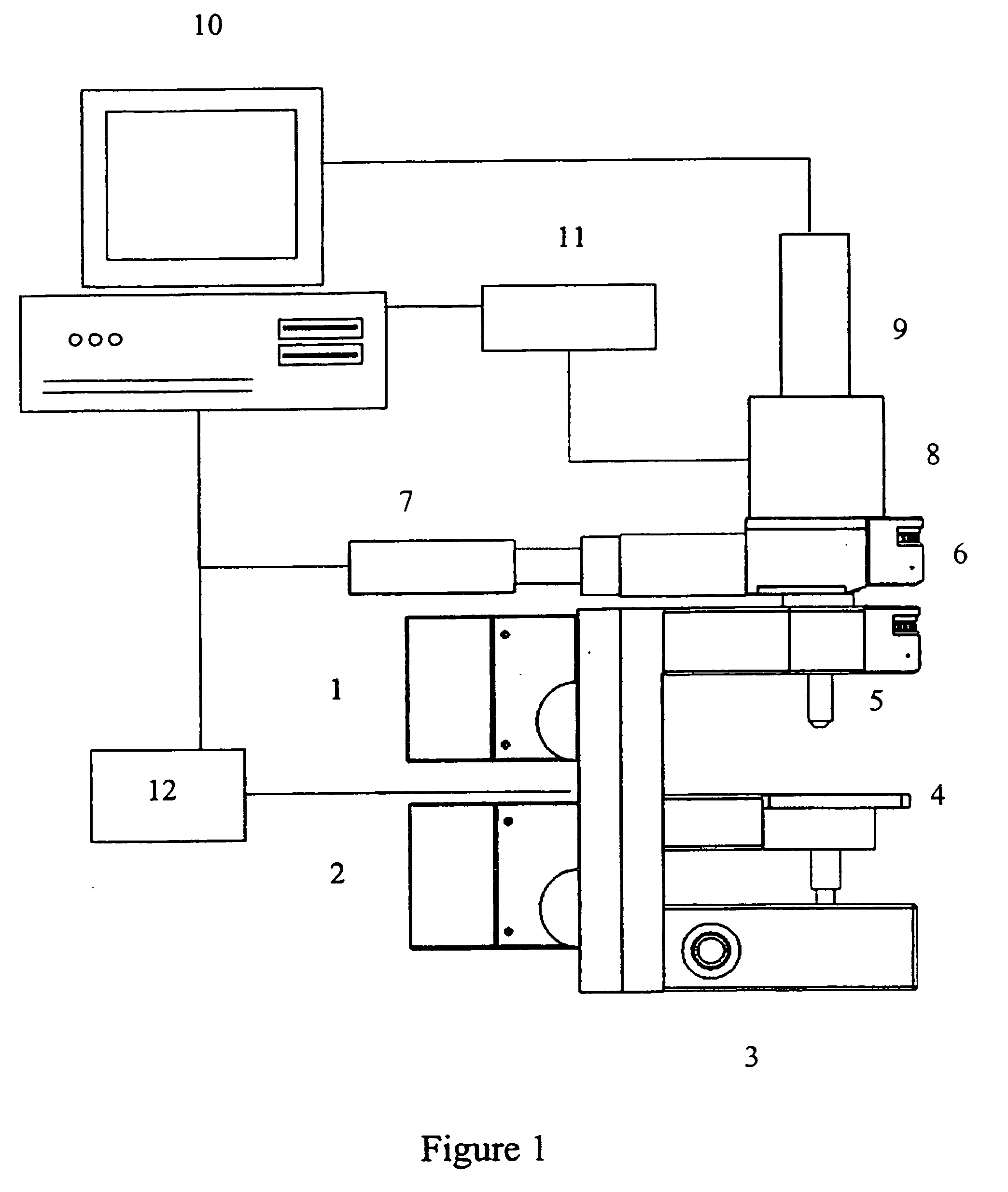
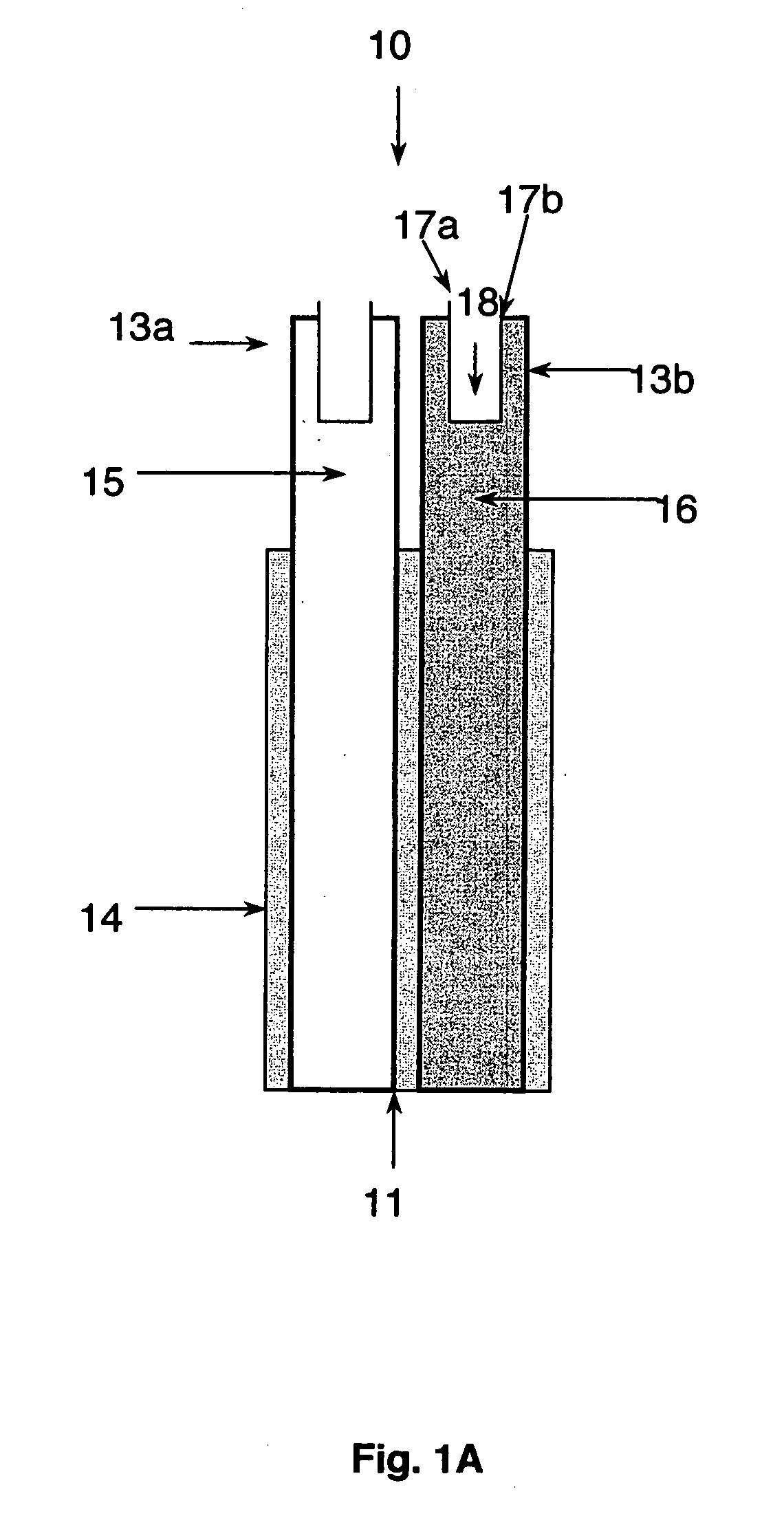
Chemical imaging fiberscope
ActiveUS7239782B1Effectively to humidityEffectively to temperature changeRadiation pyrometrySurgeryBiological materialsMoisture
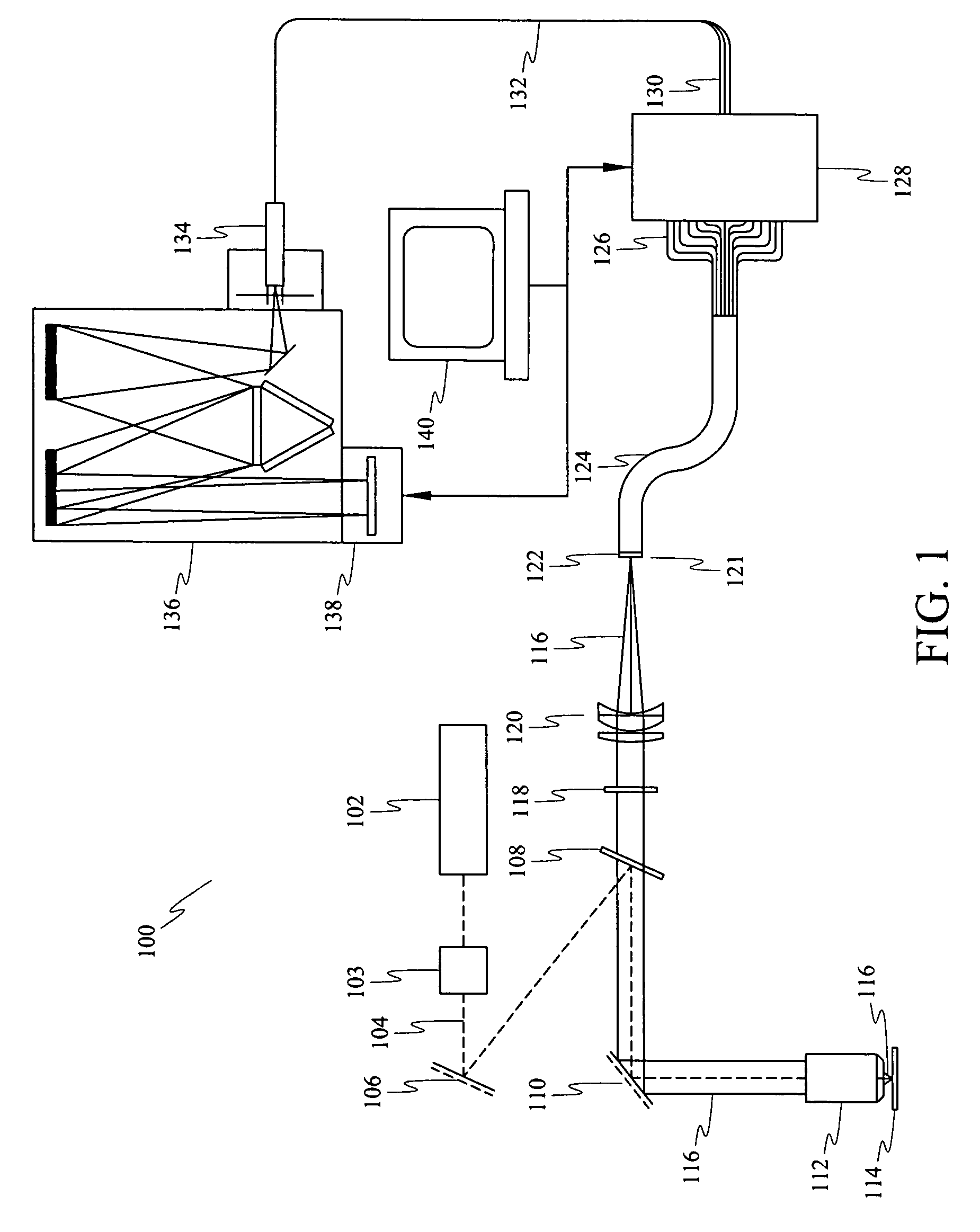
A fiberscope device is disclosed which is suitable for video imaging, laser Raman spectroscopy and laser Raman spectroscopic (i.e. chemical) imaging. The fiberscope design minimizes fiber background interference arising from the laser delivery fiber optic and the coherent fiber optic light gathering bundle while maintaining high light throughput efficiency through the use of integrated spectral filters. In the fiberscope design, the laser delivery fiber optic is offset from the coherent fiber optic light gathering bundle. The laser delivery field is captured entirely by the light gathering field of view of the coherent fiber bundle. The fiberscope incorporates spectral filter optical elements that provide environmental insensitivity, particularly to temperature and moisture. The fiberscope is suited to the analysis of a wide range of condensed phase materials (solids and liquids), including the analysis of biological materials such as breast tissue lesions and arterial plaques, in such a manner to delineate abnormal from normal tissues.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
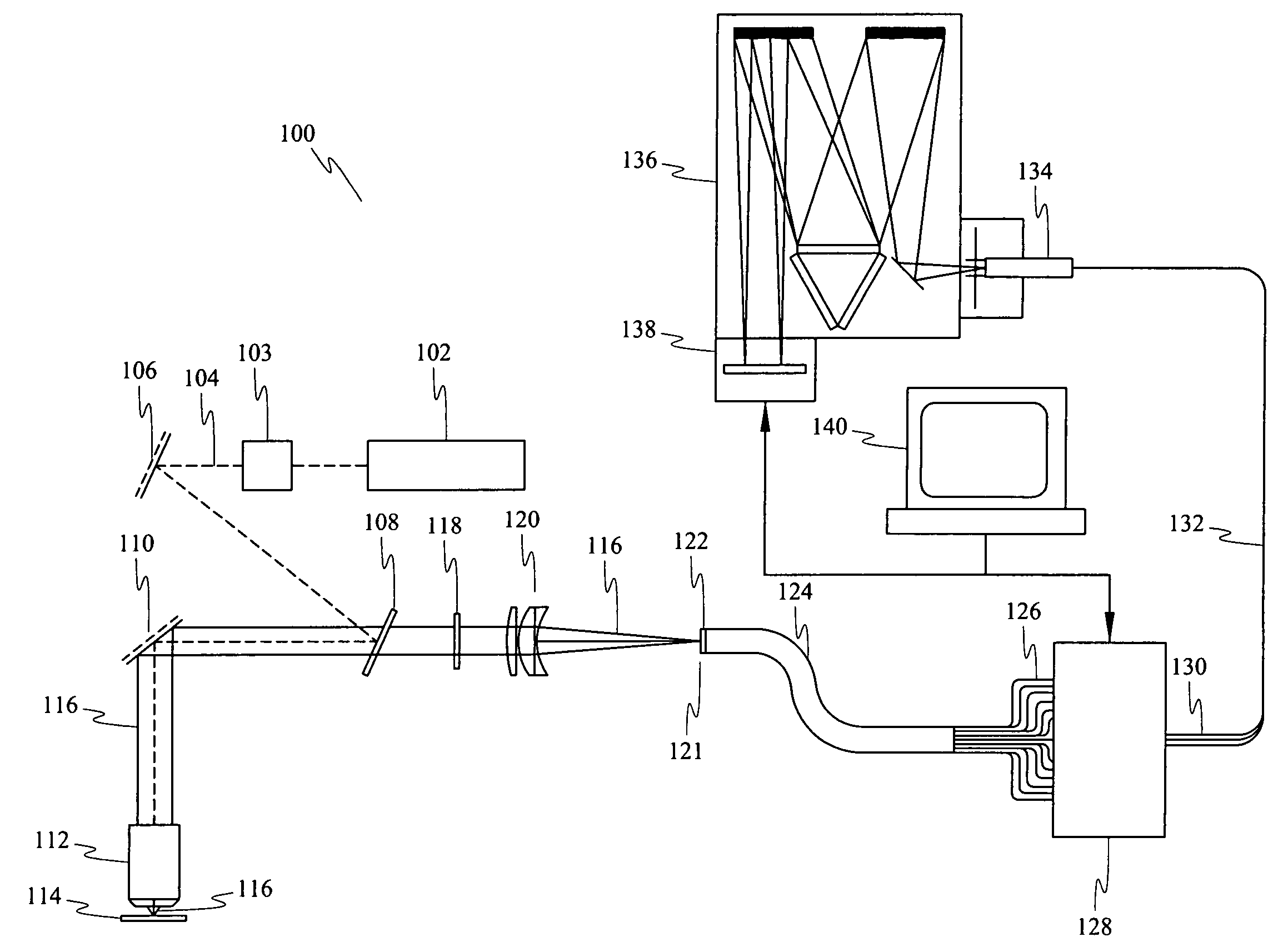
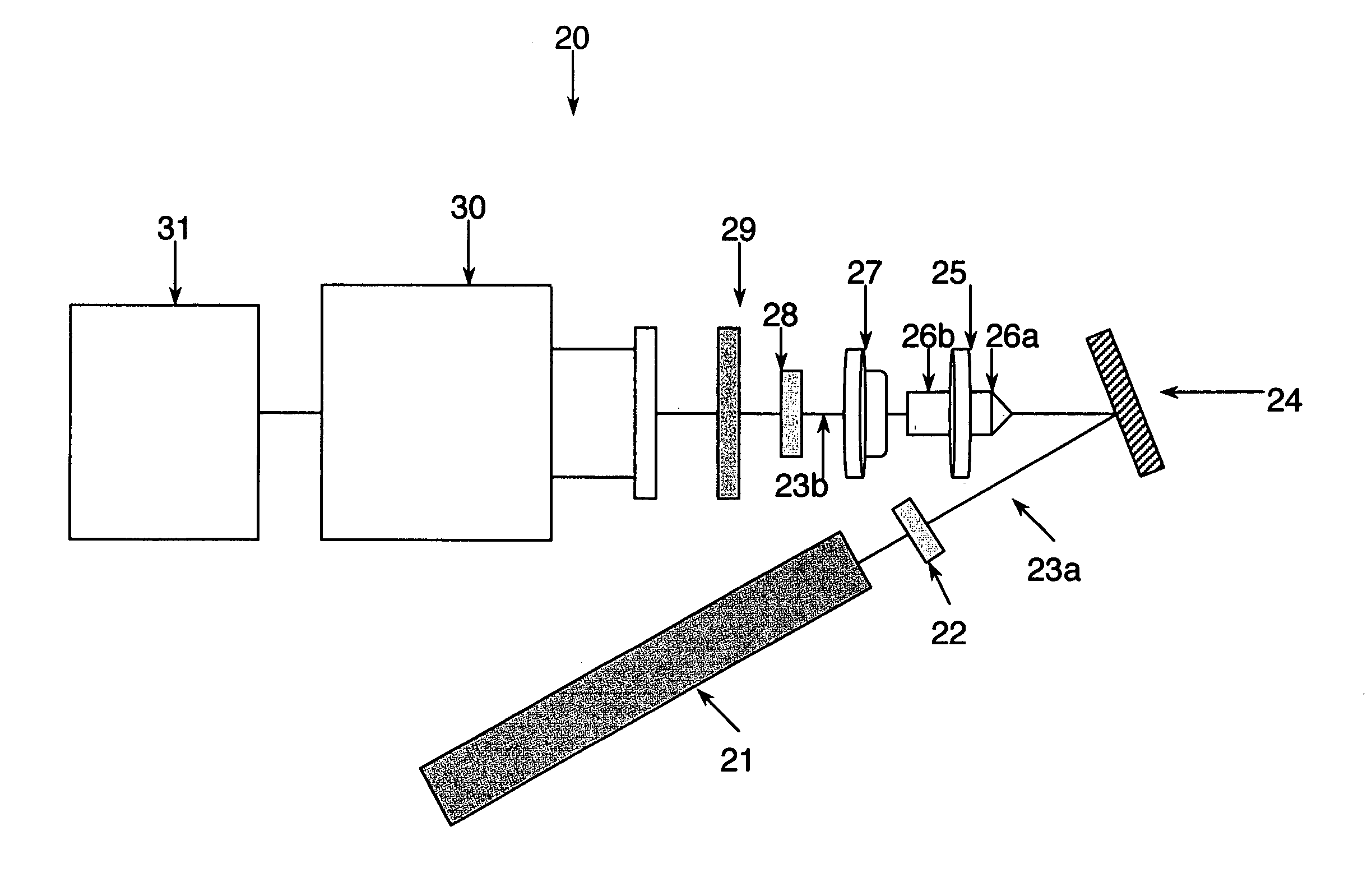
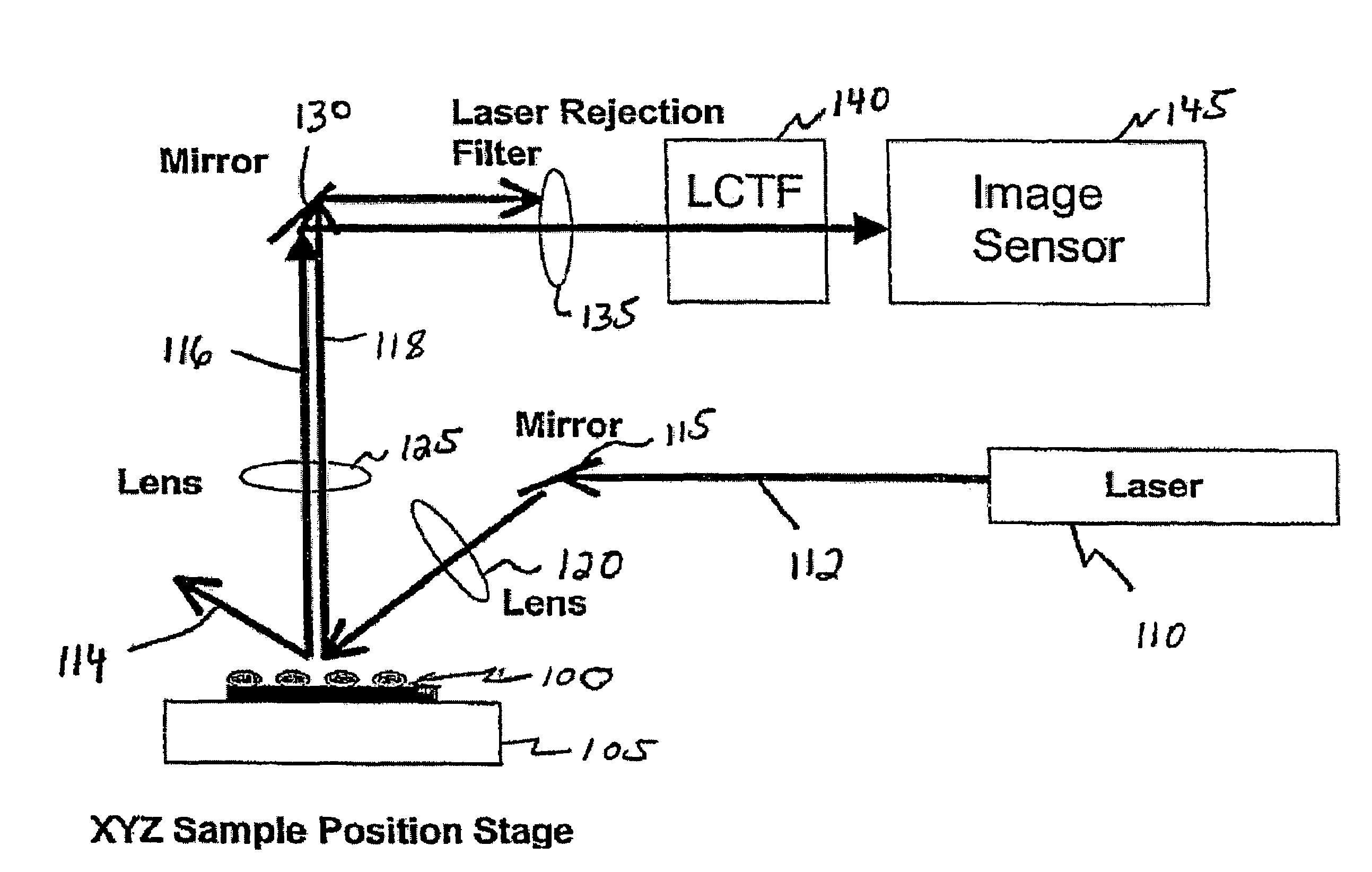
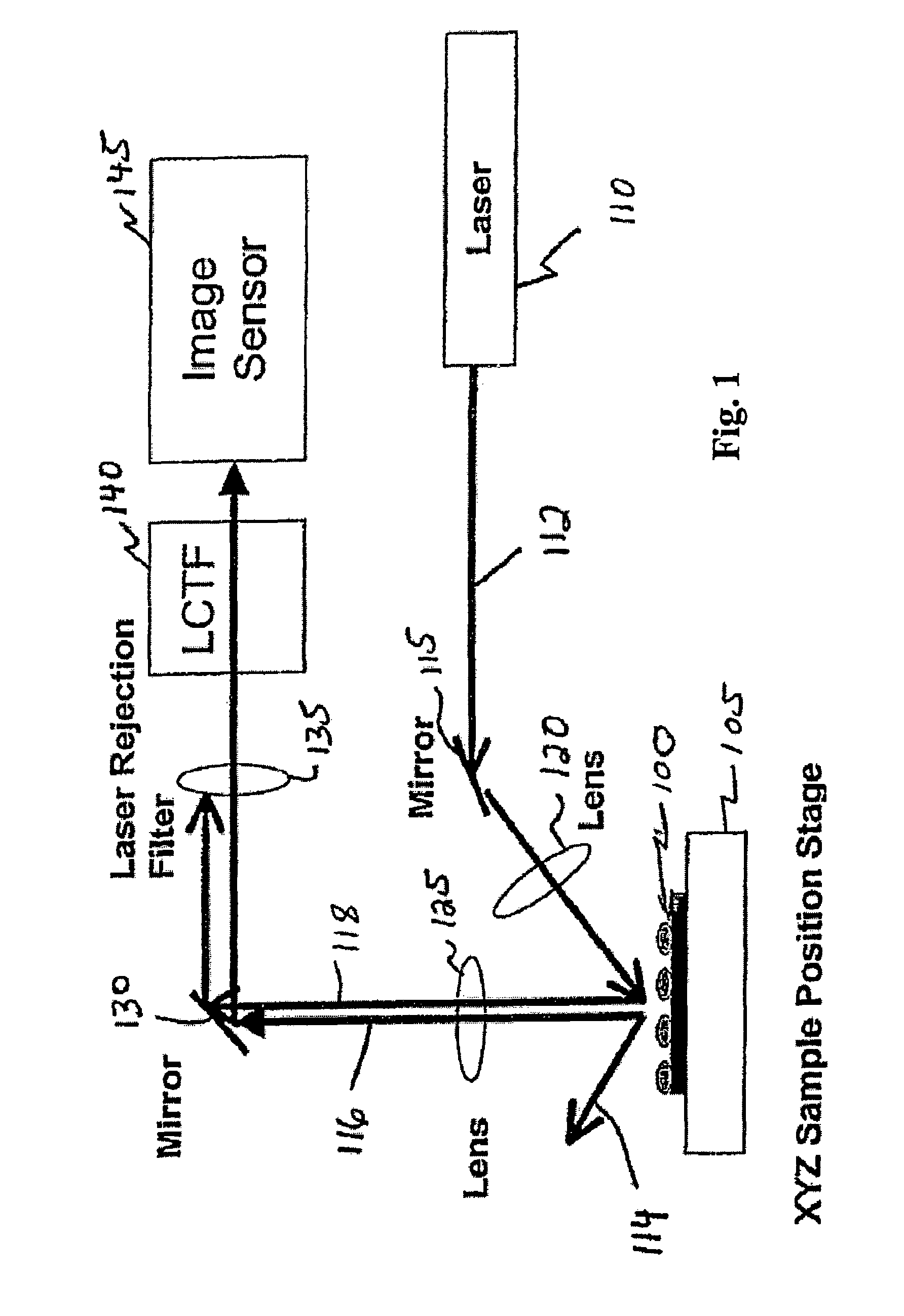
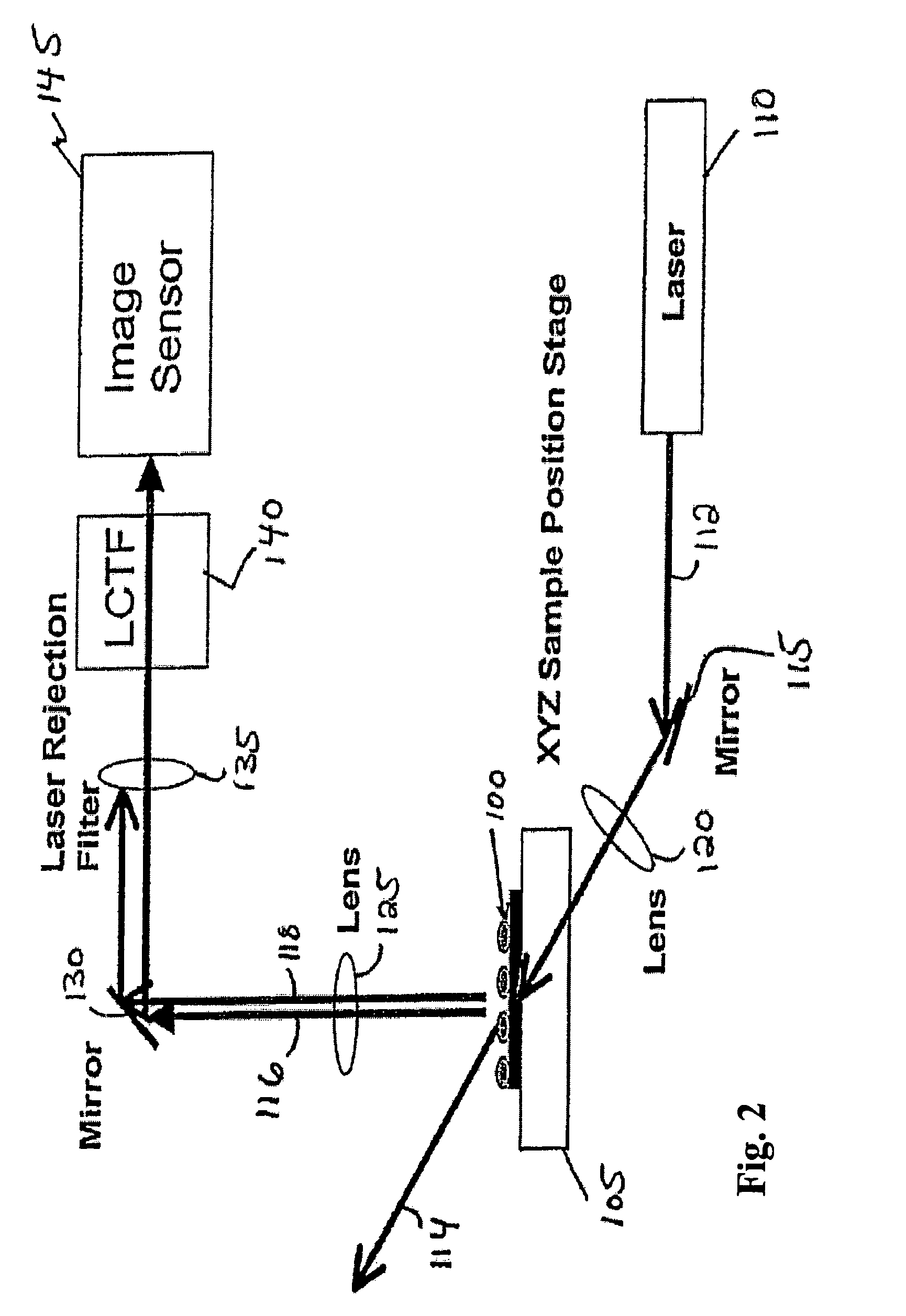
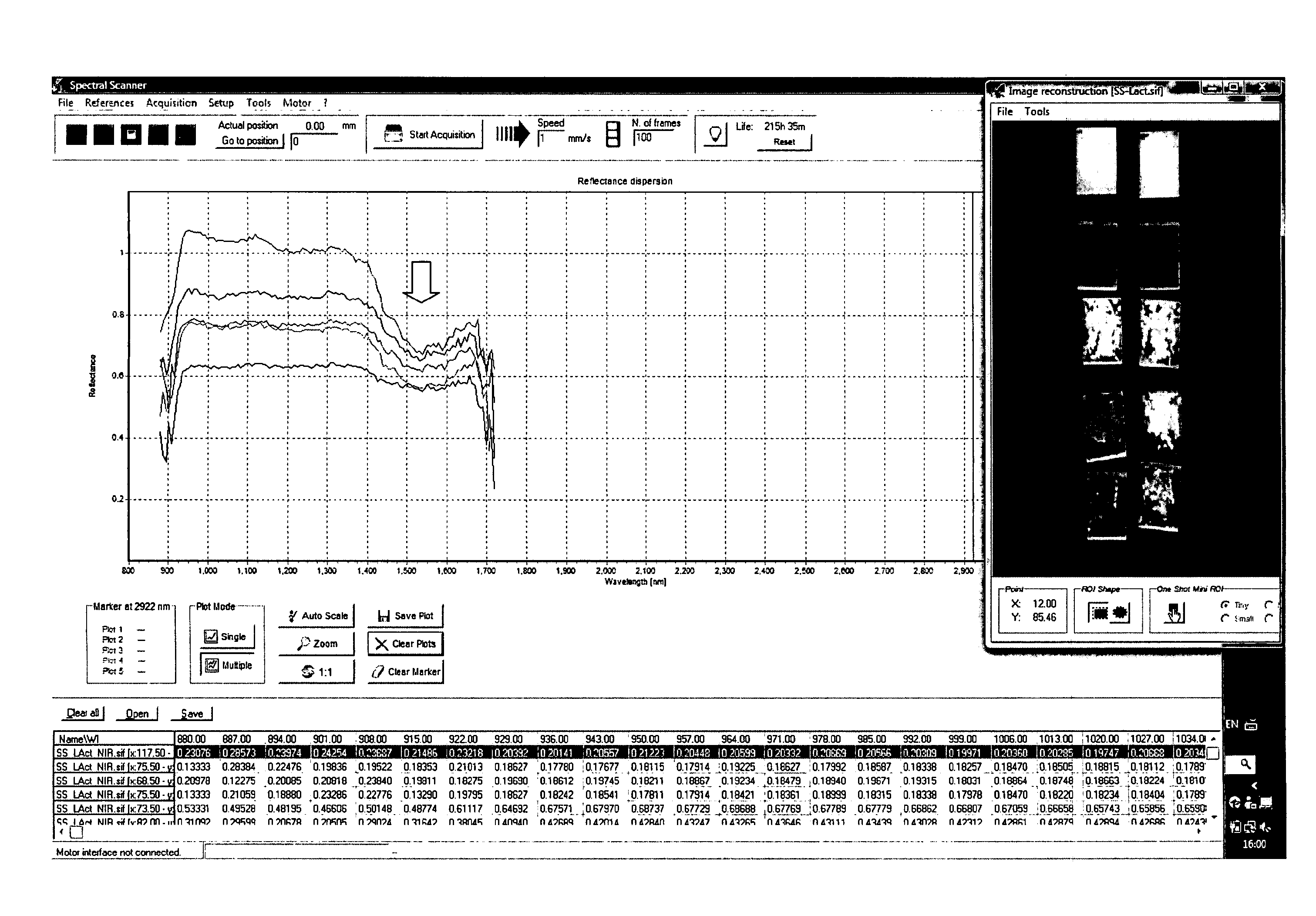
Near infrared chemical imaging microscope
A chemical imaging system is provided which uses a near infrared radiation microscope. The system includes an illumination source which illuminates an area of a sample using light in the near infrared radiation wavelength and light in the visible wavelength. A multitude of spatially resolved spectra of transmitted, reflected, emitted or scattered near infrared wavelength radiation light from the illuminated area of the sample is collected and a collimated beam is produced therefrom. A near infrared imaging spectrometer is provided for selecting a near infrared radiation image of the collimated beam. The filtered images are collected by a detector for further processing. The visible wavelength light from the illuminated area of the sample is simultaneously detected providing for the simultaneous visible and near infrared chemical imaging analysis of the sample. Two efficient means for performing three dimensional near infrared chemical imaging microscopy are provided.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic nano-imaging probe and uses therefor
Provided herein is a reusable nano-imaging probe useful in surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) applications demonstrating nanometer scale resolution. The nano-imaging probe generally comprises a fiber optic imaging bundle of fiber optic elements each having a tapered etched end and a non-tapered non-etched end. The tapered etched ends further comprise a SERS-active metal substrate deposited thereon effective to create a uniform SERS enhancement for an analyte or other substance of interest. Also provided is a SERS nanoimager for dynamic chemical imaging using the nano-imaging probe and methods of imaging and Raman spectral analysis and identification using the nano-imaging probe.
Owner:UNIV OF MARLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY THE
Method and apparatus for microlens array/fiber optic imaging
A novel approach for chemical imaging is disclosed. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a system for producing a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample from photons scattered from the sample, comprising an optical lens; a first optical fiber bundle of M fibers; a second optical fiber bundle of N fibers; an optical fiber switch; and a charge coupled device, wherein the image comprises plural sub-images, and wherein each sub-image is formed from photons scattered from a predetermined two spatial dimension portion of the sample, and wherein the scattered photons forming each sub-image have a predetermined wavelength different from a predetermined wavelength of scattered photons forming the other sub-images, and wherein the scattered photons for each sub-image are collected substantially simultaneously.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
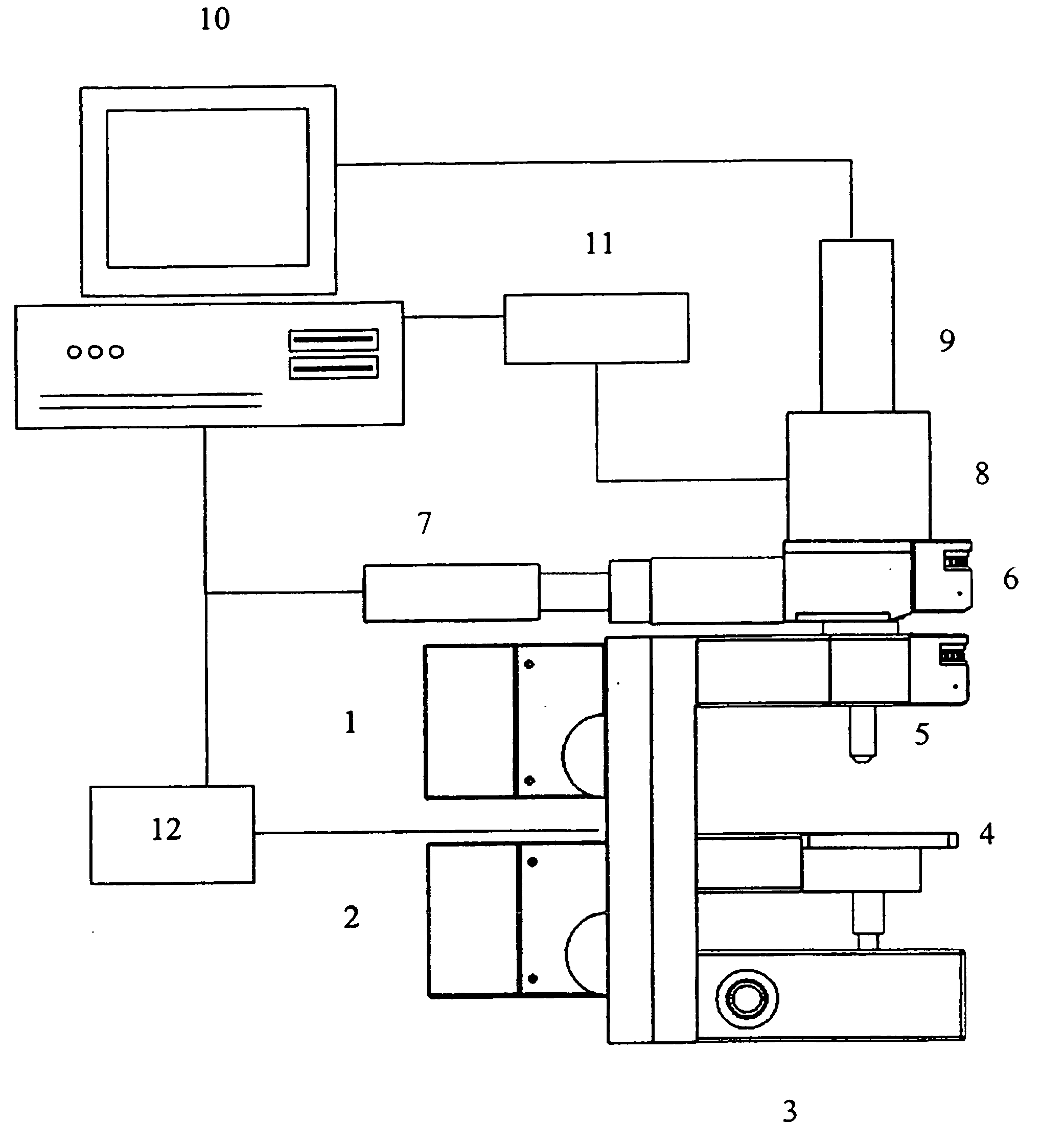
Local electrochemical imaging test system based on surface plasma resonance
ActiveCN103675053AReal-time dynamic detectionLarge dynamic detection rangeScattering properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseData acquisition
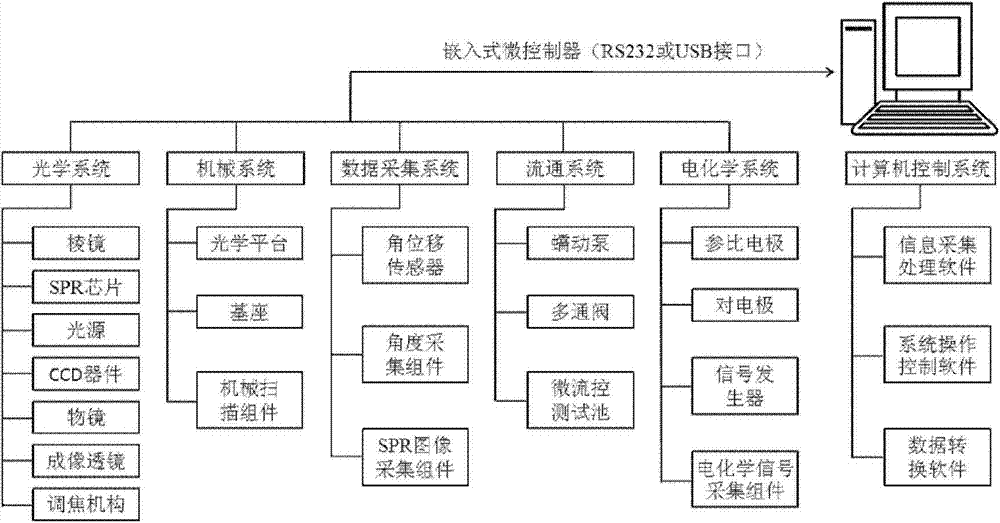
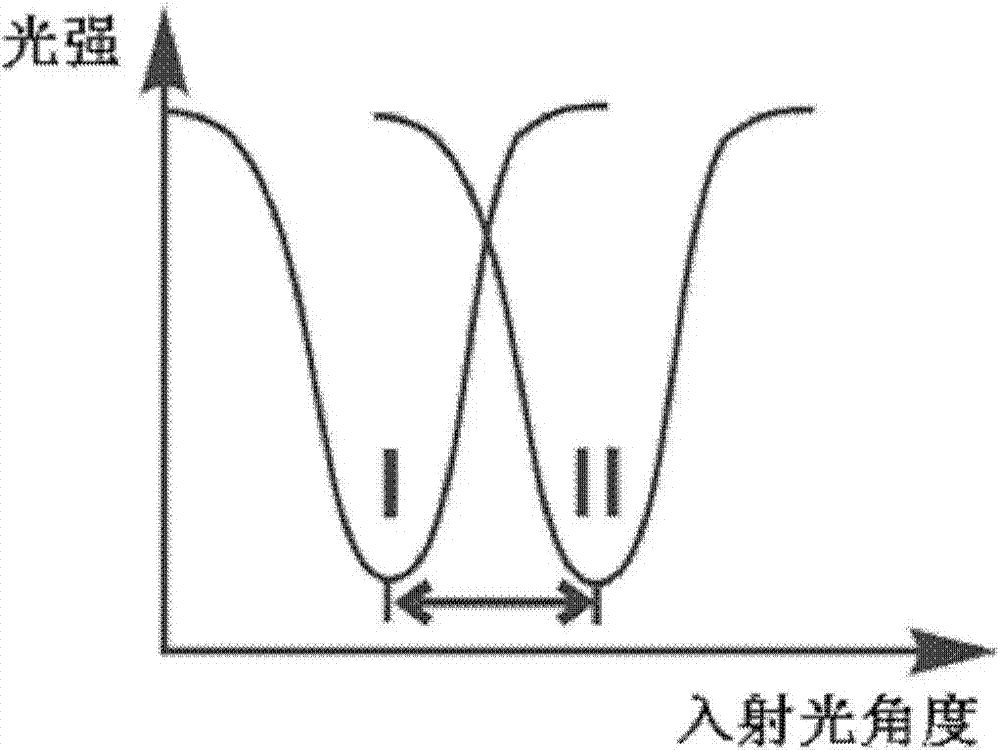
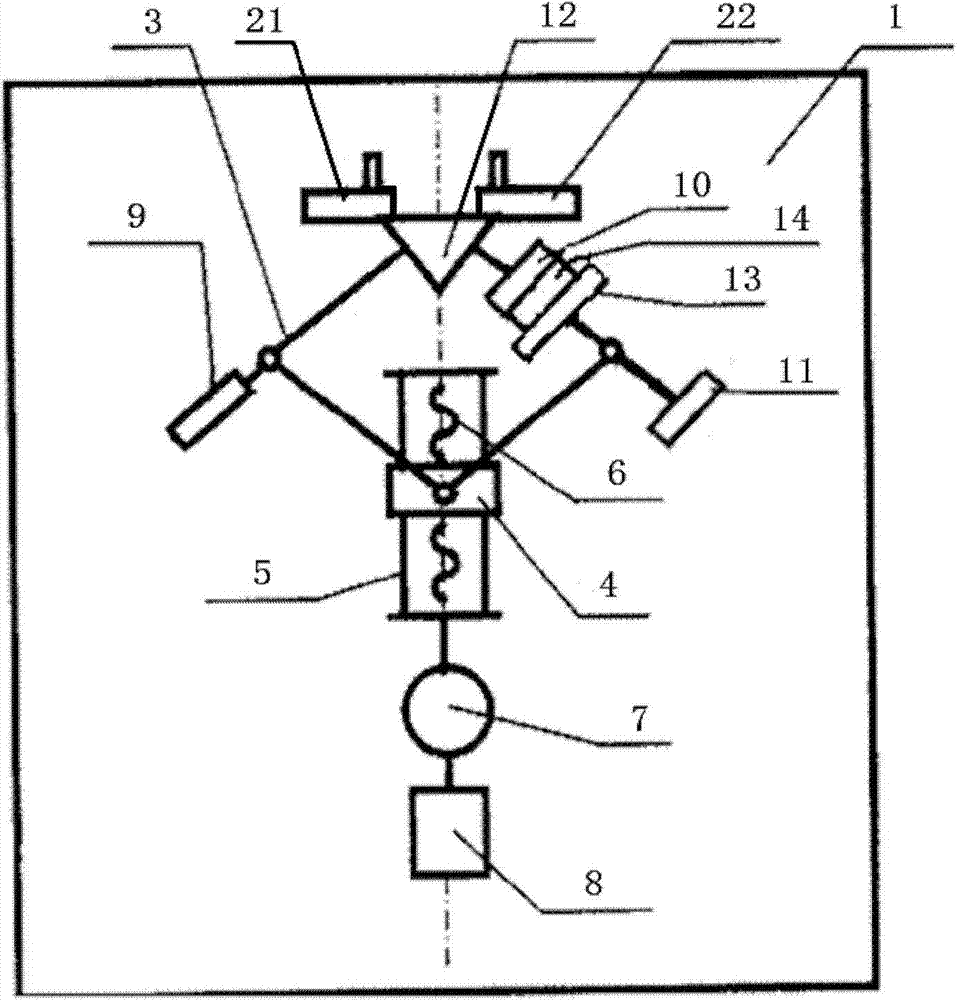
The invention discloses a local electrochemical imaging test system based on surface plasma resonance. The local electrochemical imaging test system comprises an optical system, a mechanical system, a data acquiring system, a circulation system, an electrochemical system and a computer control system, wherein the optical system comprises an SPR (surface plasma resonance) chip, an optical prism and a light source; the light source emits an incident laser and irradiates to the optical prism; the circulation system comprises a micro-fluidic test tank, wherein a to-be-tested article flows through the upper surface of the SPR chip via the micro-fluidic test tank to cause the change of a surface plasma resonance absorption peak; the electrochemical system provides electrical stimulation to the to-be-tested article to carry out the electrochemical reaction on the to-be-tested article and acquires corresponding electrochemical signals; the data acquiring system acquires the change of the surface plasma resonance absorption peak; the mechanical system is used for adjusting the angle of the incident laser emitted from the light source; and the computer system obtains corresponding information of the to-be-tested article according to the electrochemical signal and the change of the surface plasma resonance absorption peak.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system and method based on high spectrum
ActiveCN103398994AResolve resolutionSolve efficiency problemsRaman scatteringColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological cellFood borne
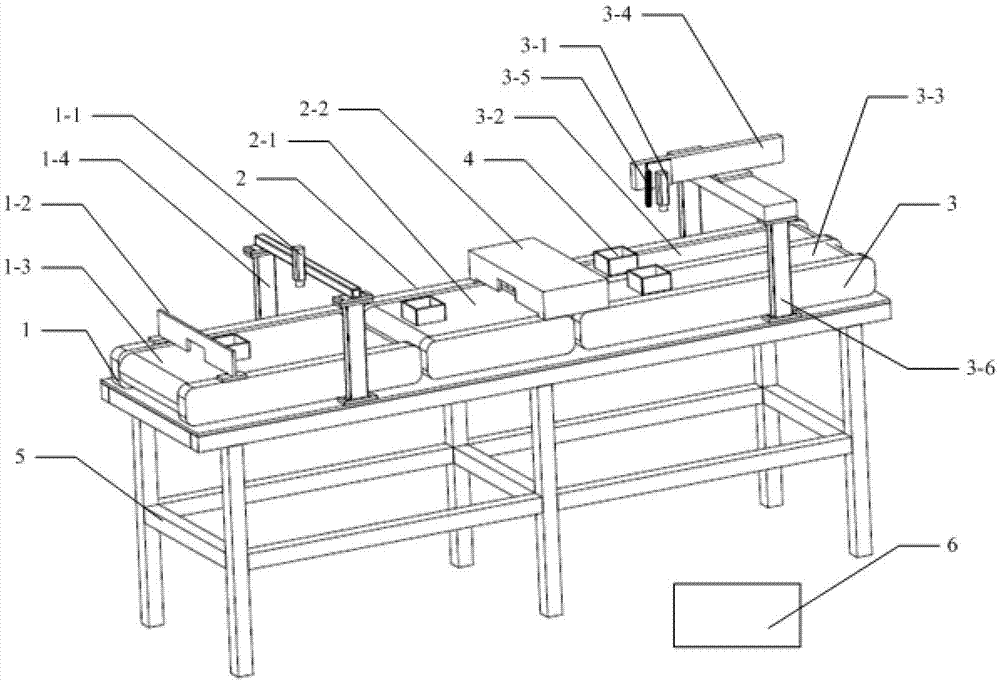
The invention discloses a food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system based on a high spectrum. The food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system comprises a surface detection line, a sorting line, a qualified product conveying belt and a point detection line, which are connected with a control system respectively. The invention further discloses a detection method of the food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system based on the high spectrum. The surface detection line based on a near-infrared high-spectrum system is used for rapidly positioning food-borne pathogenic bacteria; the sorting line is used for conveying pork polluted by the food-borne pathogenic bacteria to the point detection line; Raman chemical imaging is used for realizing species identification of the food-borne pathogenic bacteria. According to the food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system disclosed by the invention, the problems that the resolution ratio of detecting a microorganism cell structure by the near-infrared high-spectrum system is limited and the large-area scanning and imaging efficiency of the Raman chemical imaging is low are solved; the food-borne pathogenic bacterium detection system based on the high spectrum has the advantages of convenience for utilization and obvious detection efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
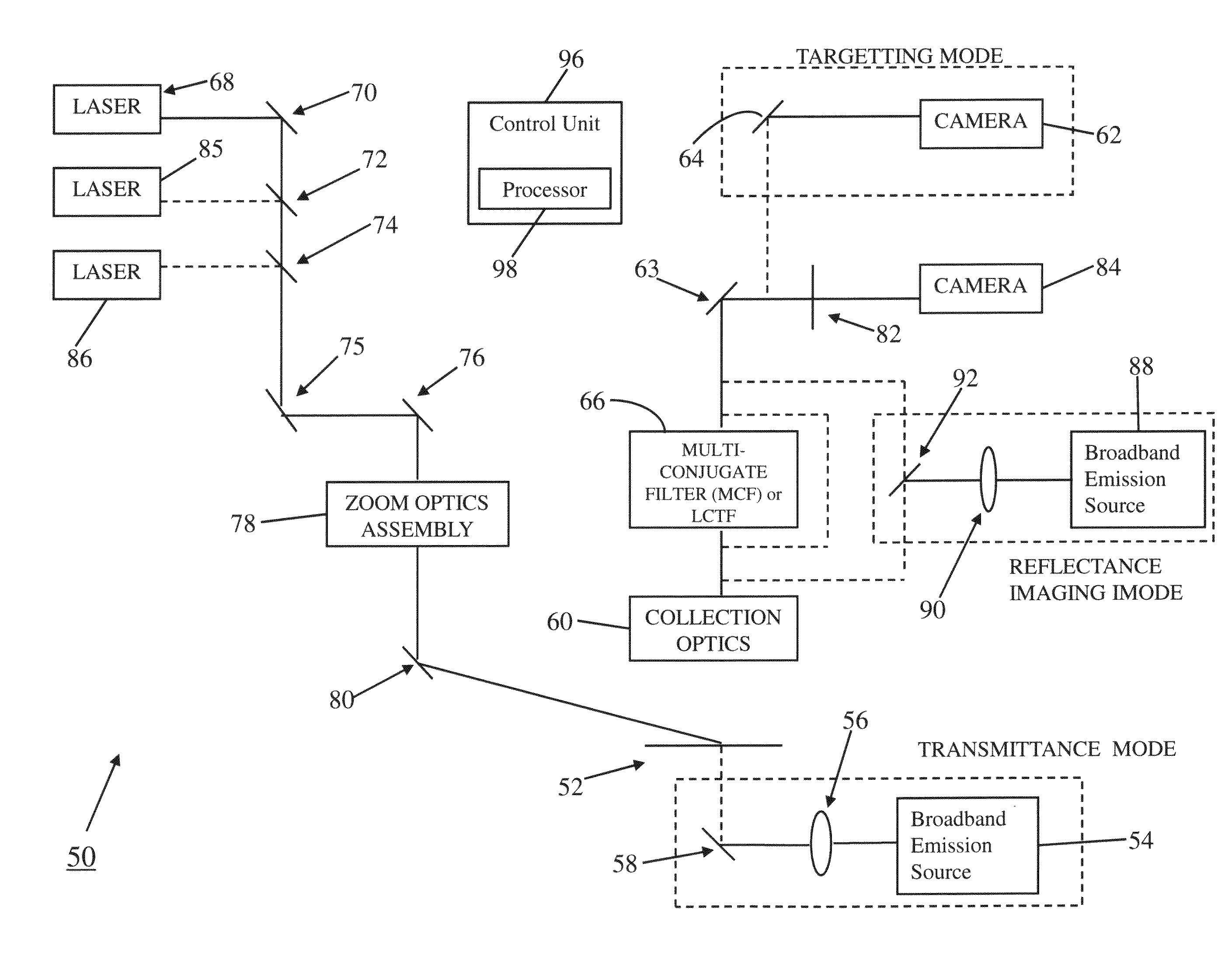
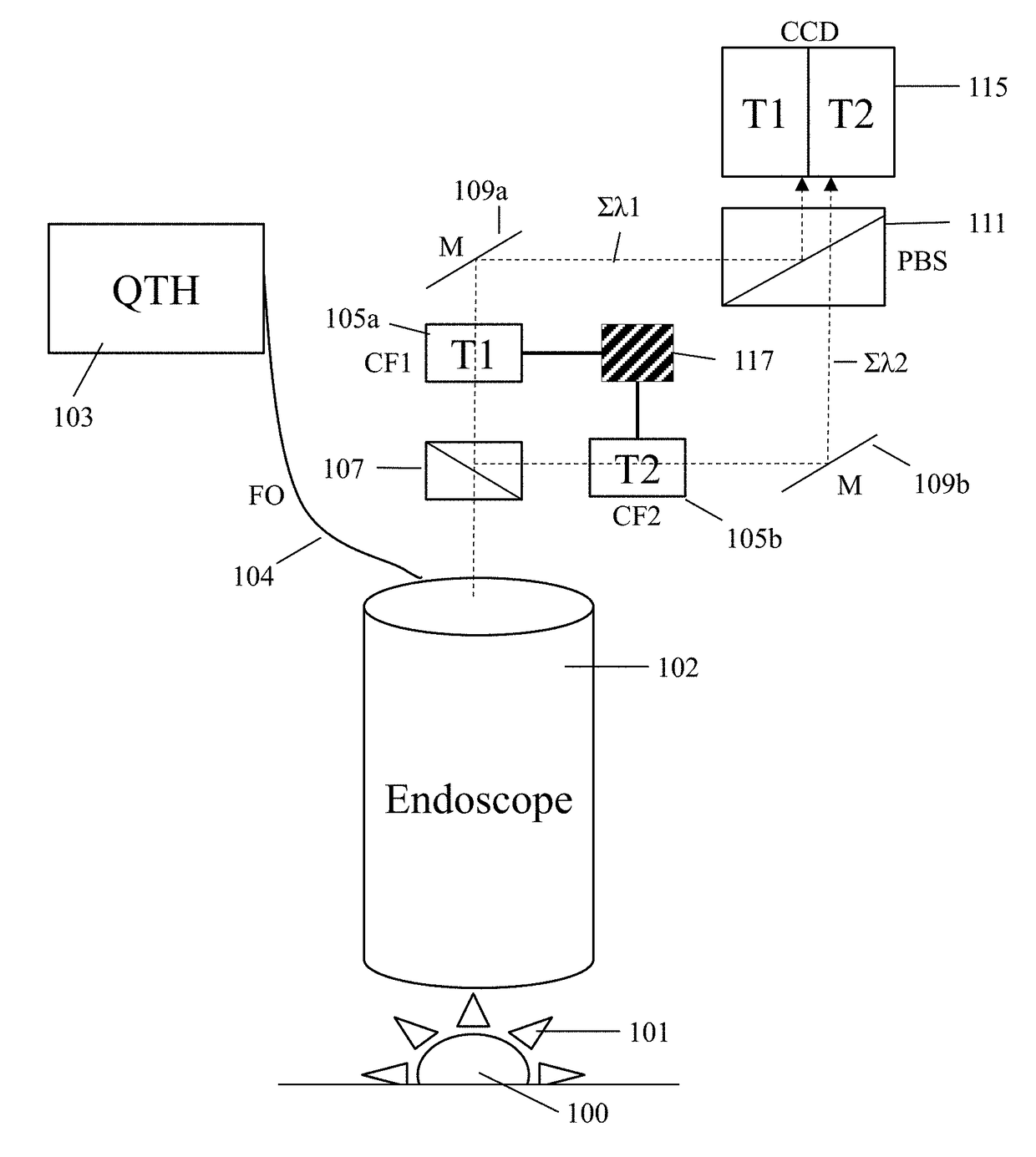
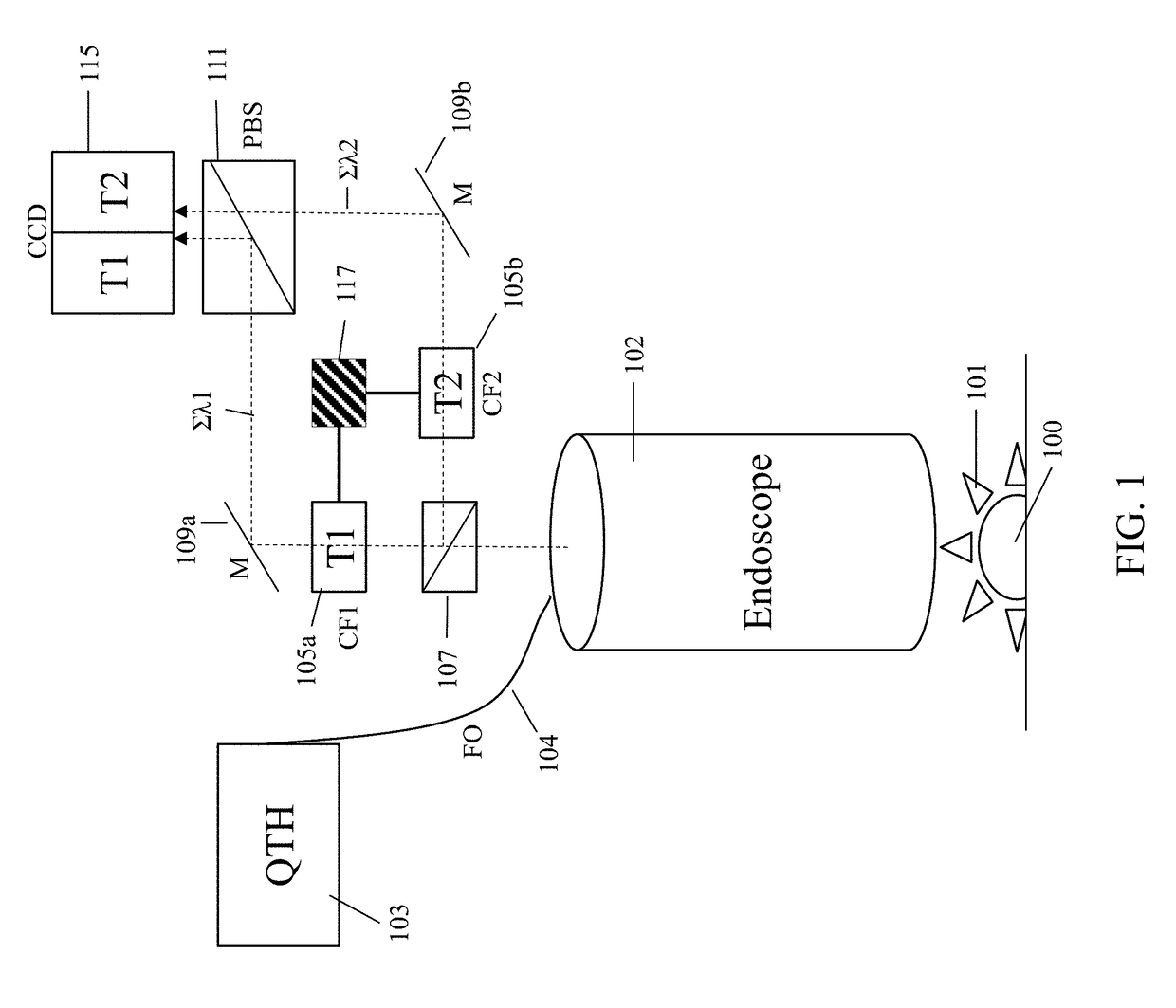
Molecular chemical imaging endoscopic imaging systems
Medical imaging systems for use in conjunction with an endoscope are described. Generally, the medical imaging system includes an illumination source configured to generate illuminating photons. The illuminating photons are transmitted to one or more filters configured to filter a first plurality of illuminating photons and generate a first plurality of filtered photons comprising a first passband wavelength and a second plurality of filtered photons comprising a second passband wavelength. A sample is then illuminated with the first plurality of filtered photons and the second plurality of filtered photons to generate a first plurality of interacted photons and a second plurality of interacted photons. One or more detectors are configured to detect the first plurality of interacted photons and the second plurality of interacted photons and generate one or more image data sets.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
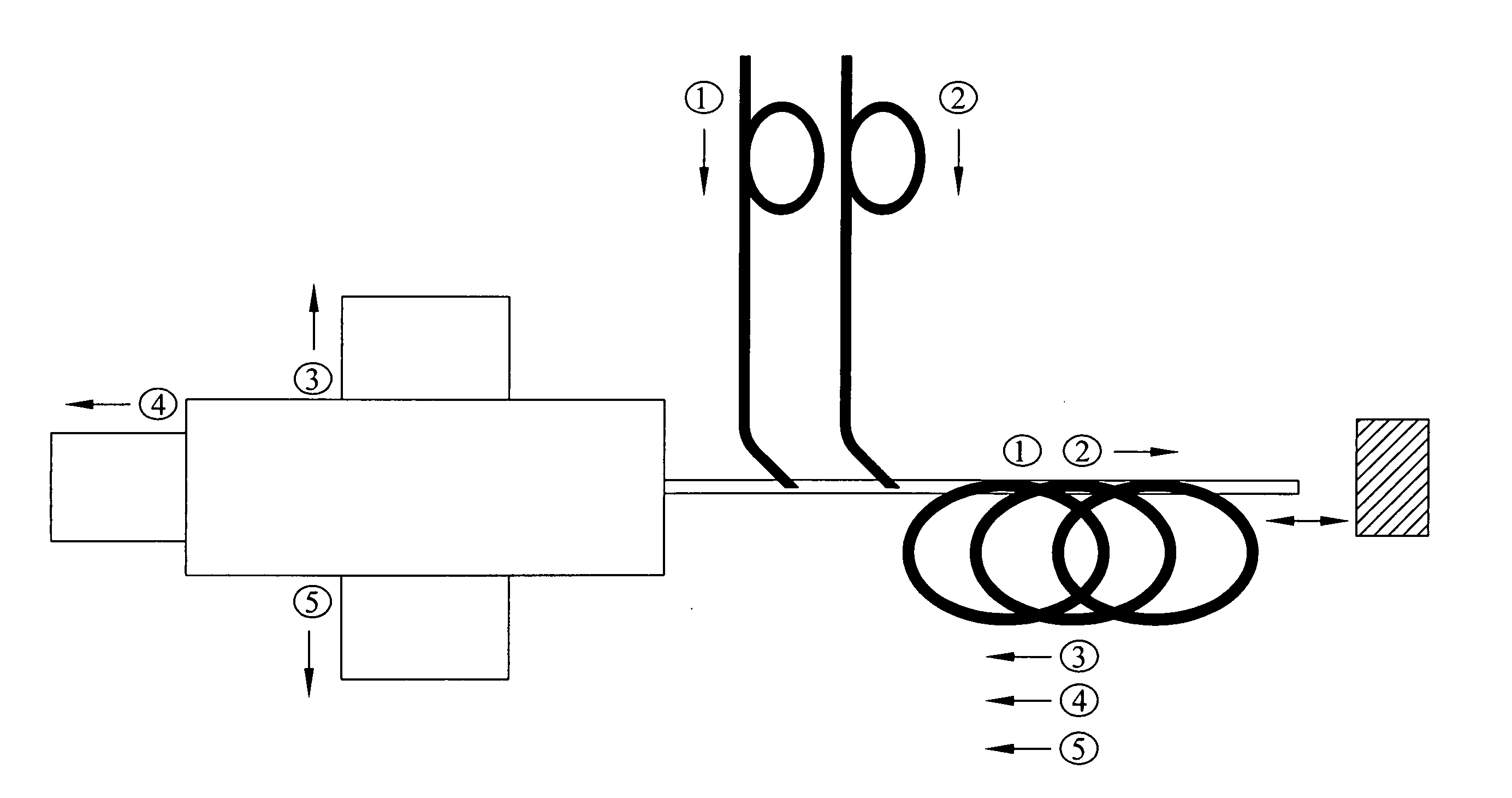
Microfluidic electrochemical device and process for chemical imaging and electrochemical analysis at the electrode-liquid interface in-situ
ActiveUS20140038224A1Quick fixEasy to appreciateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricitySurface layer
A microfluidic electrochemical device and process are detailed that provide chemical imaging and electrochemical analysis under vacuum at the surface of the electrode-sample or electrode-liquid interface in-situ. The electrochemical device allows investigation of various surface layers including diffuse layers at selected depths populated with, e.g., adsorbed molecules in which chemical transformation in electrolyte solutions occurs.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Multimodal method for identifying hazardous agents
The invention relates to methods of dynamic chemical imaging, including methods of cellular imaging. The method comprises illuminating at least a portion of a cell with substantially monochromatic light and assessing Raman-shifted light scattered from the illuminated portion at a plurality of discrete times. The Raman-shifted light can be assessed at a plurality of Raman shift (RS) values at each of the discrete times, and the RS values can be selected to be characteristic of a pre-selected component at each of the discrete times. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectral features of the images thus obtained can yield the location and chemical identity of components in the field of view. This information can be combined or overlaid with other spectral data (e.g., a visible microscopic image) obtained from the field of view.The invention relates to apparatus and methods for assessing occurrence of a hazardous agent in a sample by performing multimodal spectral analysis of the sample. Methods of employing Raman spectroscopy for entities in a sample which exhibit one or more optical properties characteristic of a hazardous agent are disclosed. Devices and systems suitable for performing such methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Dynamic imaging of biological cells and other subjects
ActiveUS7564546B2Quick observationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscopic imageOrganism
The invention relates to methods of dynamic chemical imaging, including methods of cellular imaging. The method comprises illuminating at least a portion of a cell with substantially monochromatic light and assessing Raman-shifted light scattered from the illuminated portion at a plurality of discrete times. The Raman-shifted light can be assessed at a plurality of Raman shift (RS) values at each of the discrete times, and the RS values can be selected to be characteristic of a pre-selected component at each of the discrete times. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectral features of the images thus obtained can yield the location and chemical identity of components in the field of view. This information can be combined or overlaid with other spectral data (e.g., a visible microscopic image) obtained from the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
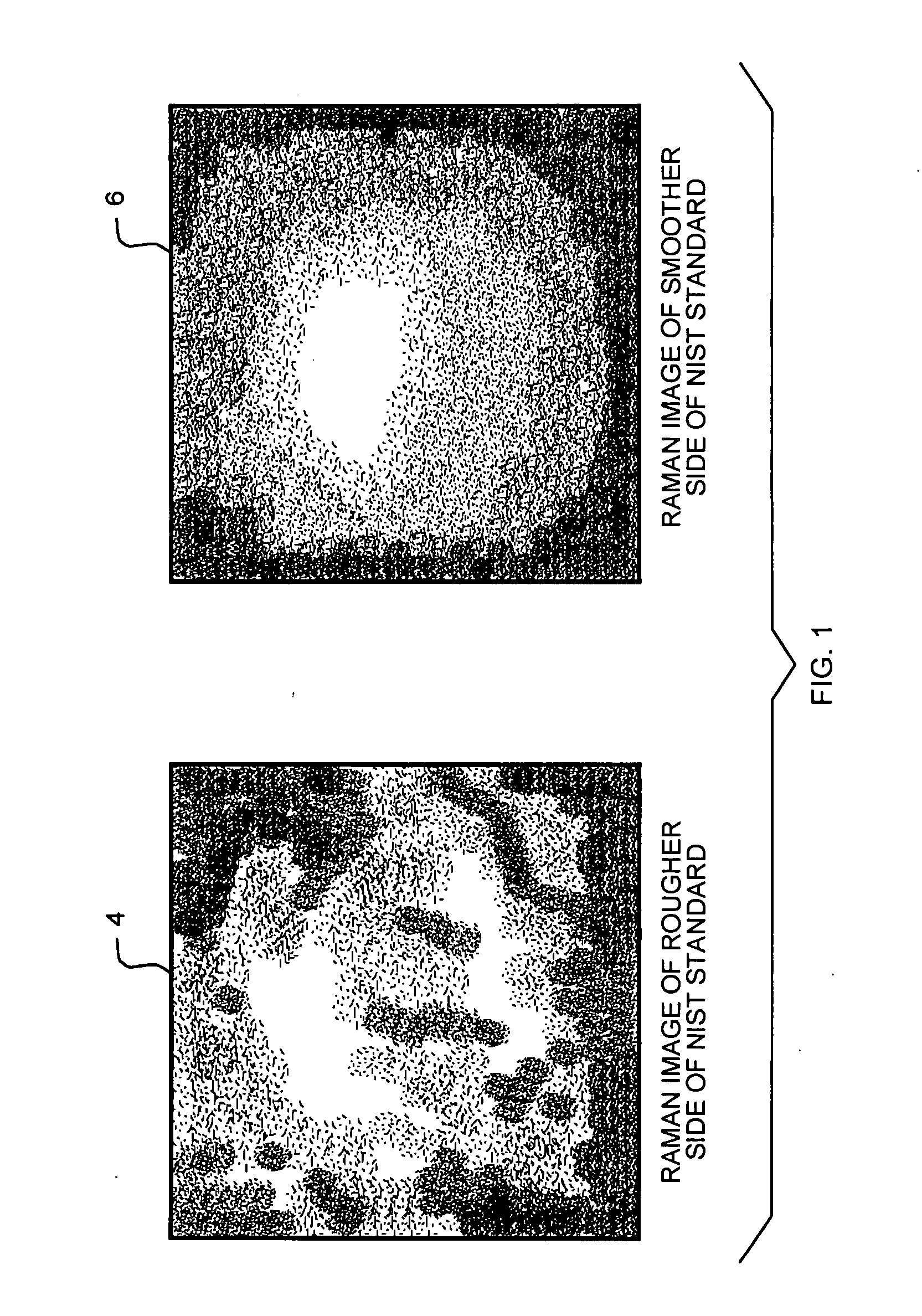
Optical Spectroscopy Instrument Response Correction
A system and method for correction of instrument response of an optical spectroscopy instrument using a Raman standard sample supplied by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). The smoother side of the NIST sample is placed facing a light collection optics in the spectroscopy instrument, whereas the non-smooth or rough side remains away from the light collection optics, but in contact with a platform or sample placement surface in the spectroscopy instrument. An instrument response function is determined with the NIST sample so placed. Thereafter, spectra or spectral images of target samples obtained using the spectroscopy instrument are divided by the instrument response function to correct for imperfections in the response of the optical spectroscopy instrument. The target sample spectra may be non-Raman spectra. The optical spectroscopy instrument may be a gratings-based or a tunable filter based chemical imaging system.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
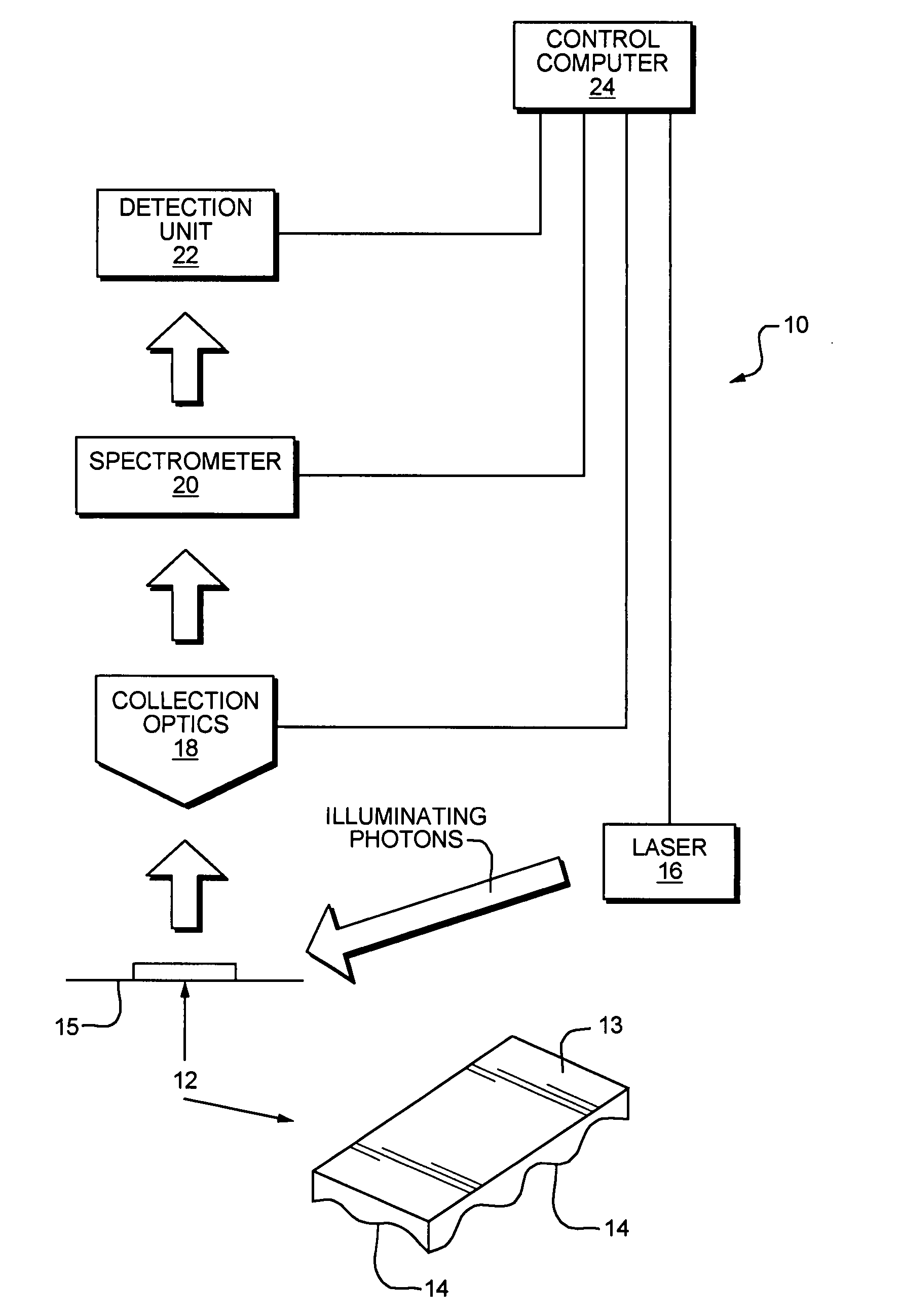
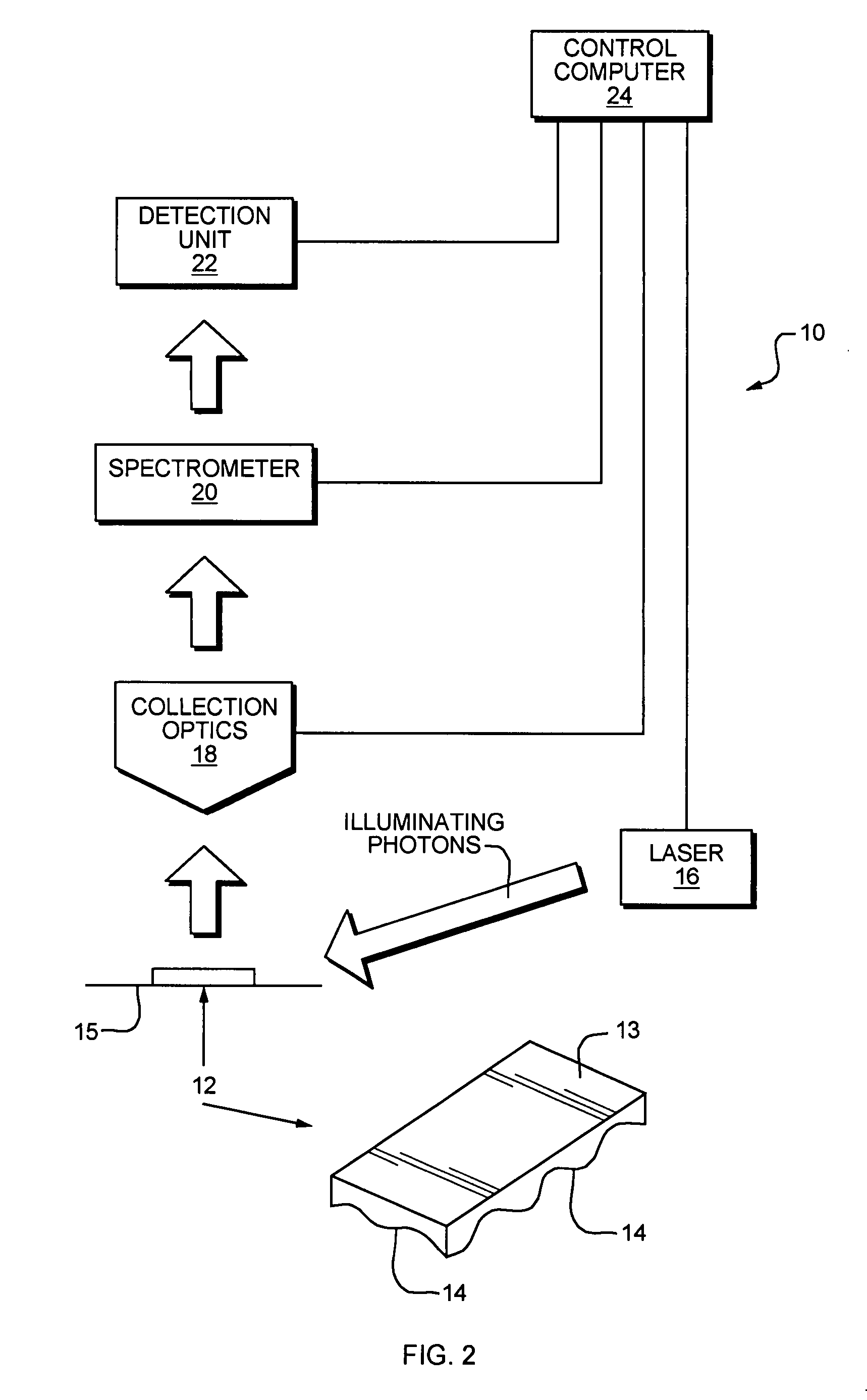
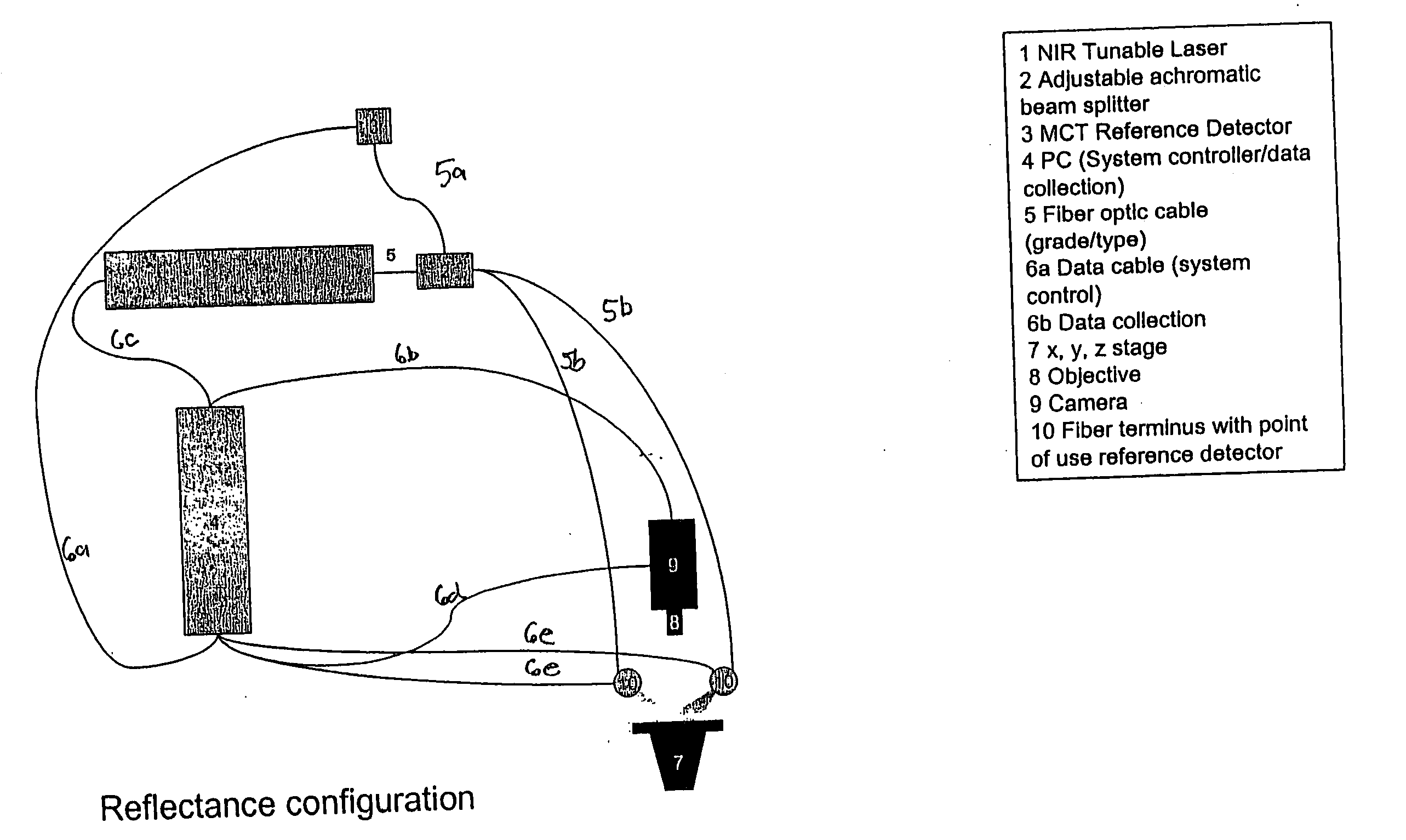
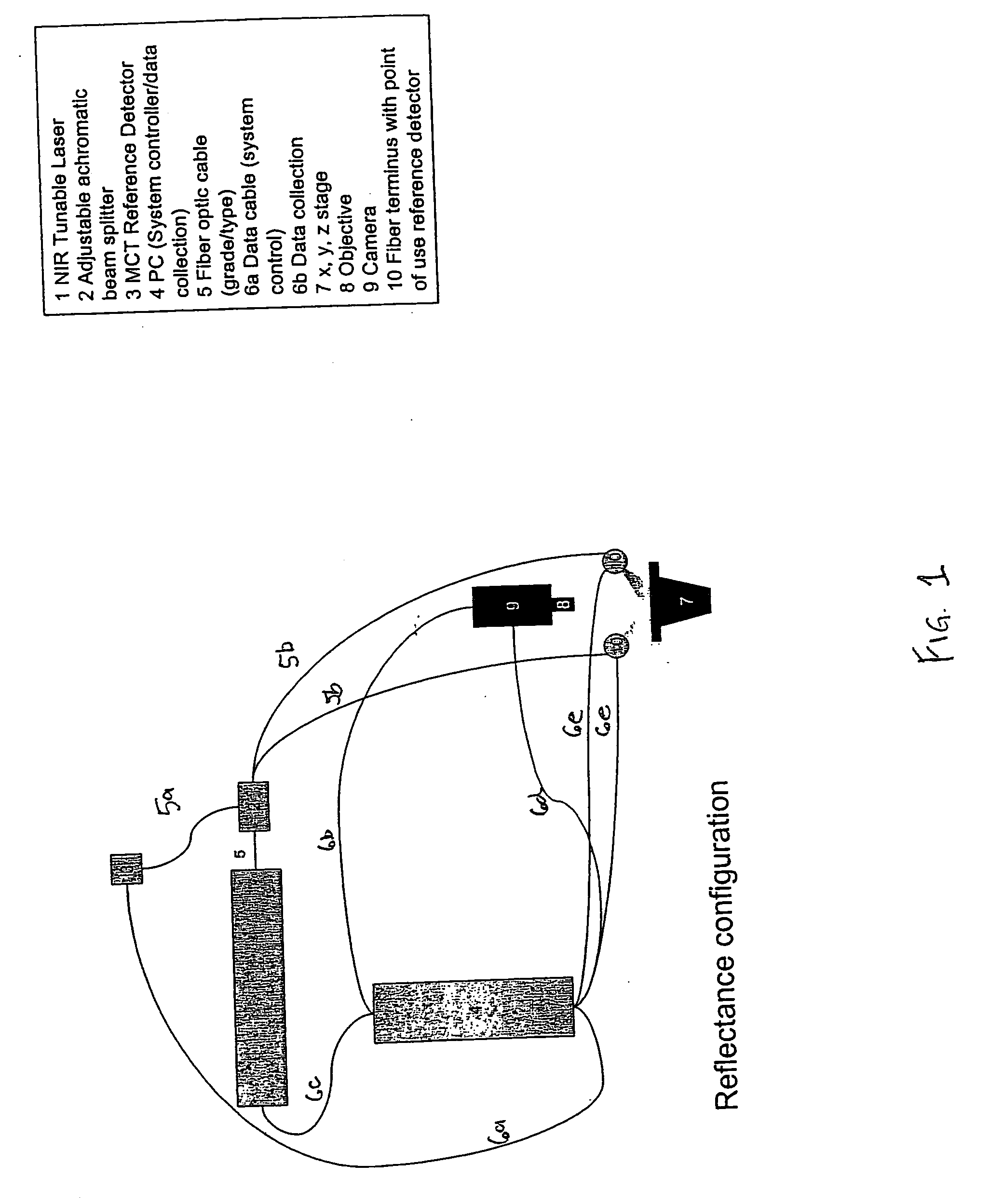
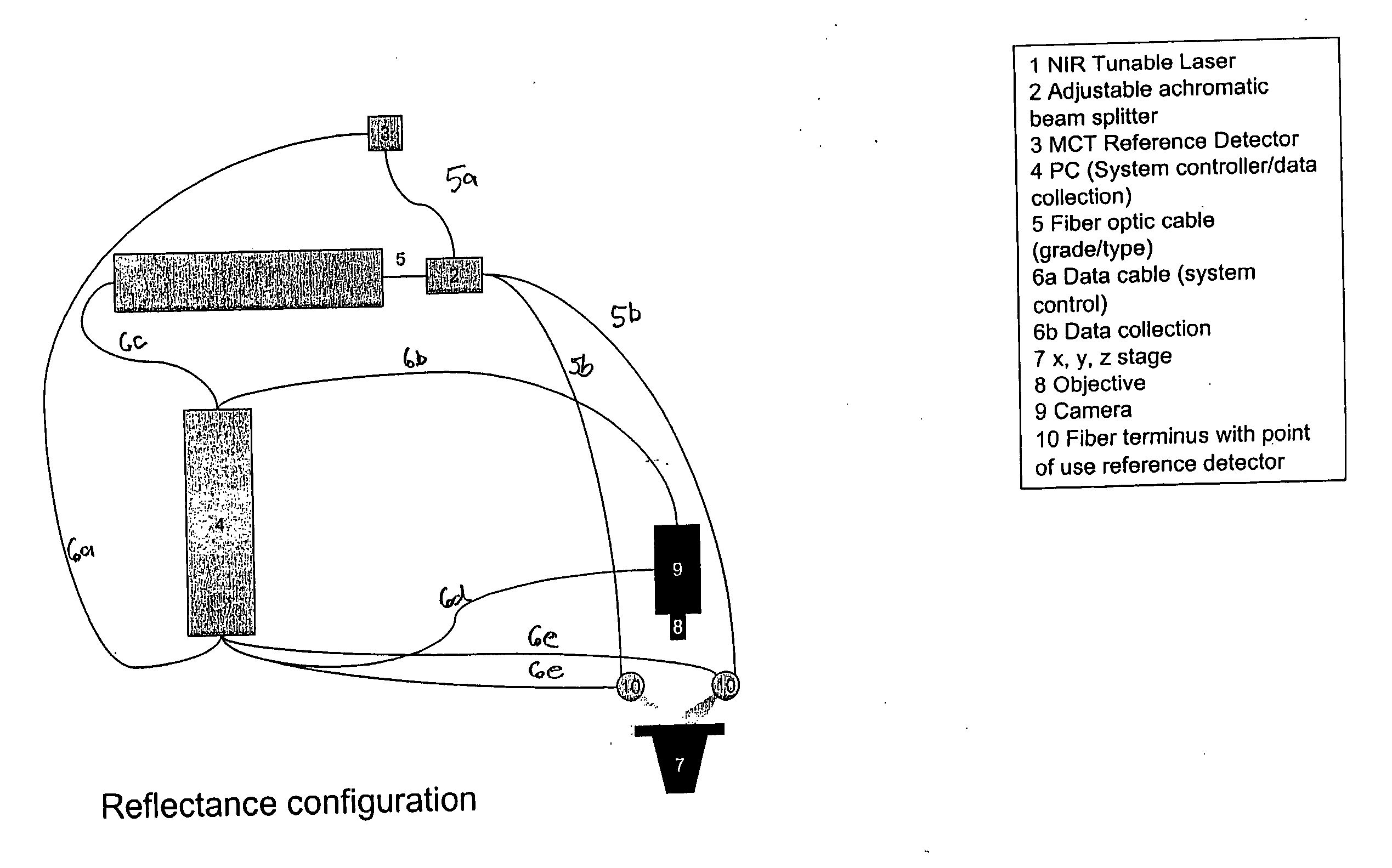
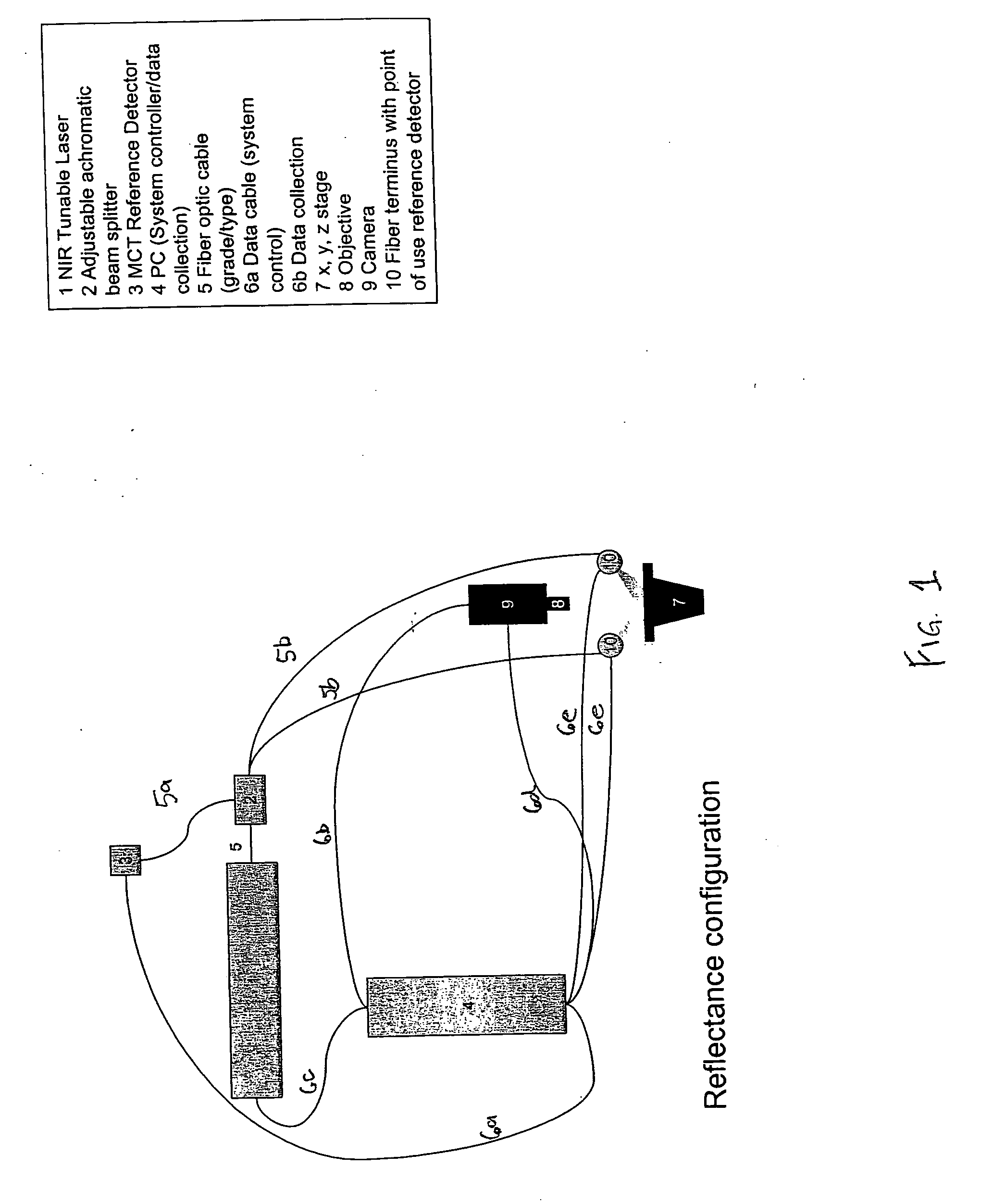
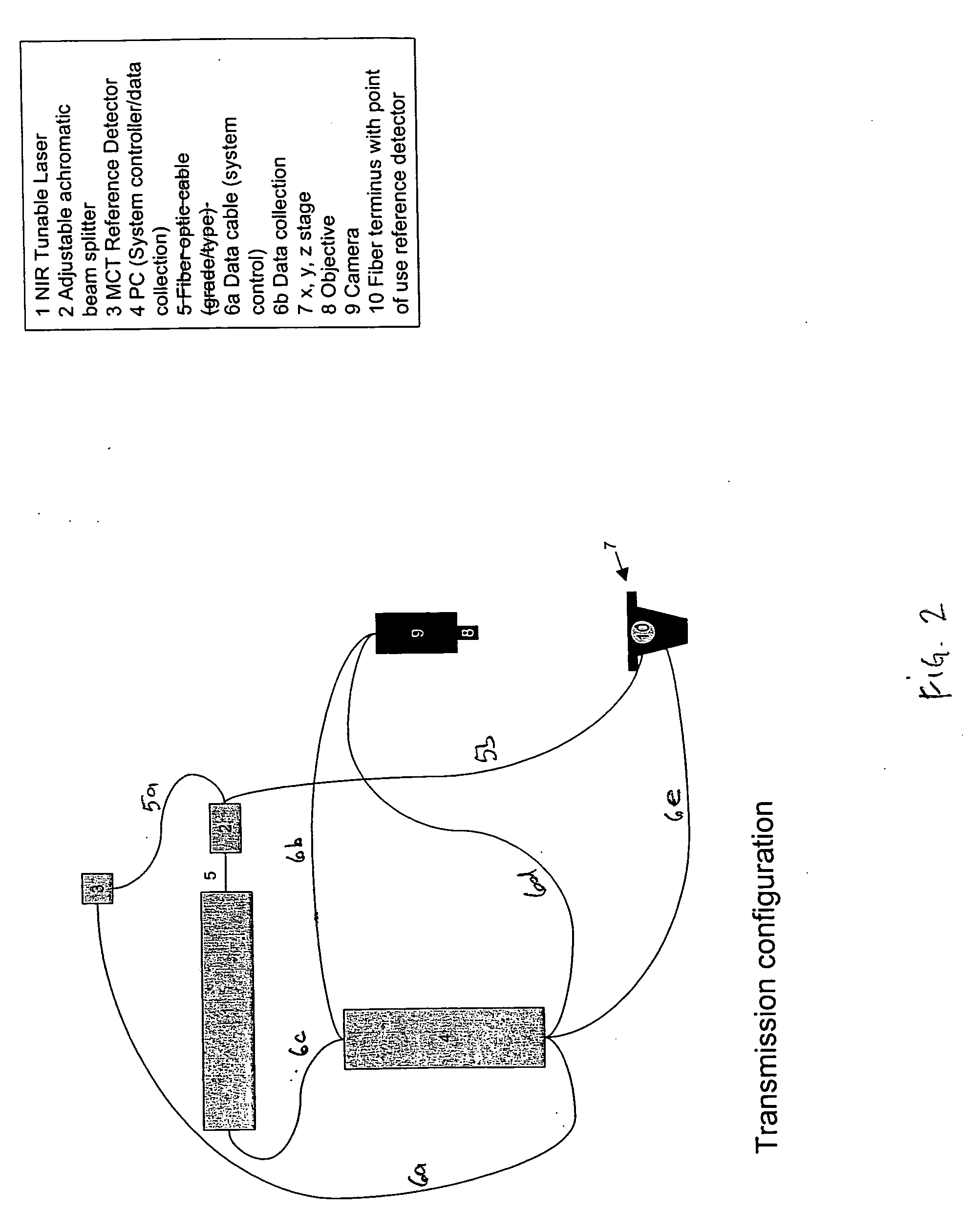
Tunable laser-based process monitoring apparatus
InactiveUS20060152729A1Easy to operateEasy to modifyPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryLight deliveryMonitor equipment
A chemical imaging and process monitoring device which utilizes a computer controlled tunable laser to provide light at discrete wavelengths in the near infrared band and a focal plane array to image or a single-point photo detector to detect the intensity of light reflected from a sample illuminated at various wavelengths of light. The device also provides light intensity reference detectors at the source and terminus of the light delivery pathway for normalizing the collected data and for detecting defects in the light delivery pathway.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
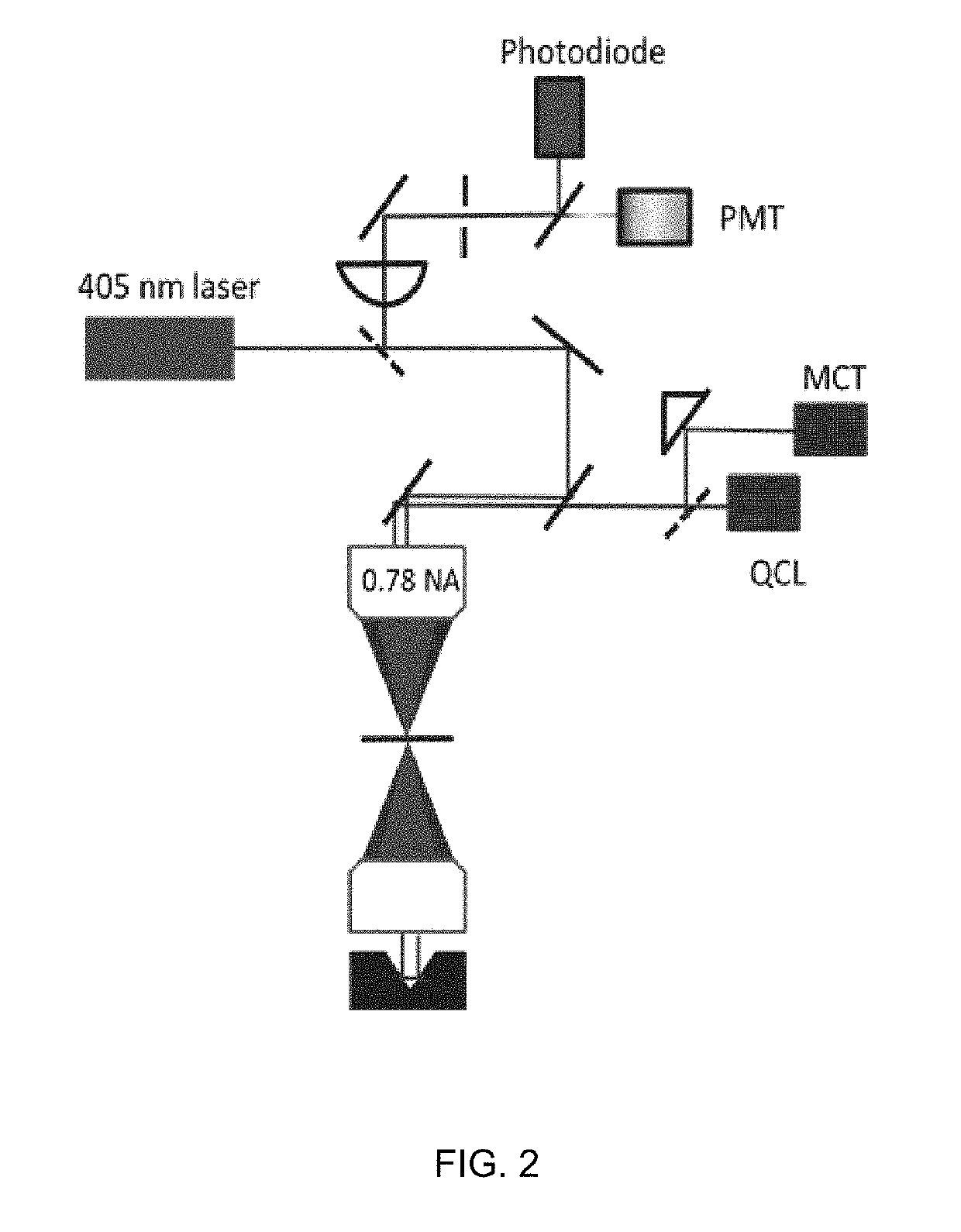
Rapid multiplexed infrared 3D nano-tomography
ActiveUS20190317012A1Sufficient speedIncrease ratingsColor/spectral properties measurementsInelastic scatteringFractography
A method and system for rapid, label free nanoscale chemical imaging and tomography (3D) with multiplexing for speed, and engineered coherent illumination and detection to achieve 3-D resolution at twice the Abbe limit. A sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using a modulated infrared light source and the resulting probe beam modulation is measured with one or more visible laser probes. Varying the infrared wavelength results in a spectrum which characterizes the chemical composition of the sample. Optionally, inelastically scattered light generated as a result of the probe beam interacting with the sample is collected simultaneously to yield additional chemical information.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System and method for a chemical imaging threat assessor with a probe
The disclosure relates to a portable and / or handheld bioagent detector and methodology described herein that is based in part on advanced Raman Chemical Imaging (“RCI”) technology. According to one embodiment of the present disclosure, the detection system may include a fiber array spectral translator (“FAST”) and may also include a probe which may include a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) camera. The probe alleviates the need to place the main instrument close to an unconfined release of a potentially hazardous material and facilitates analysis of a sample that is situated in a hard-to-reach location while minimizing contamination of the detector and operator.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
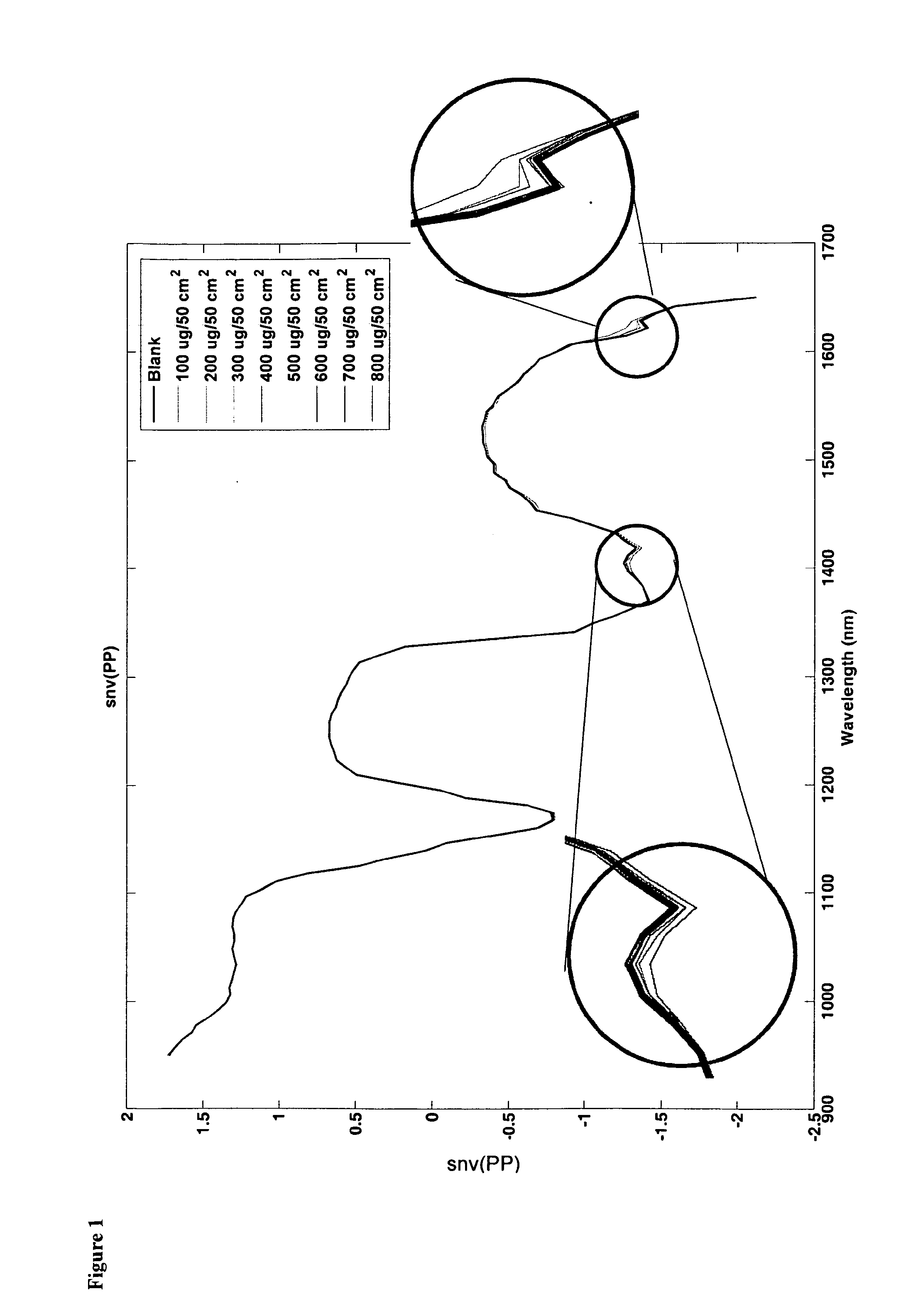
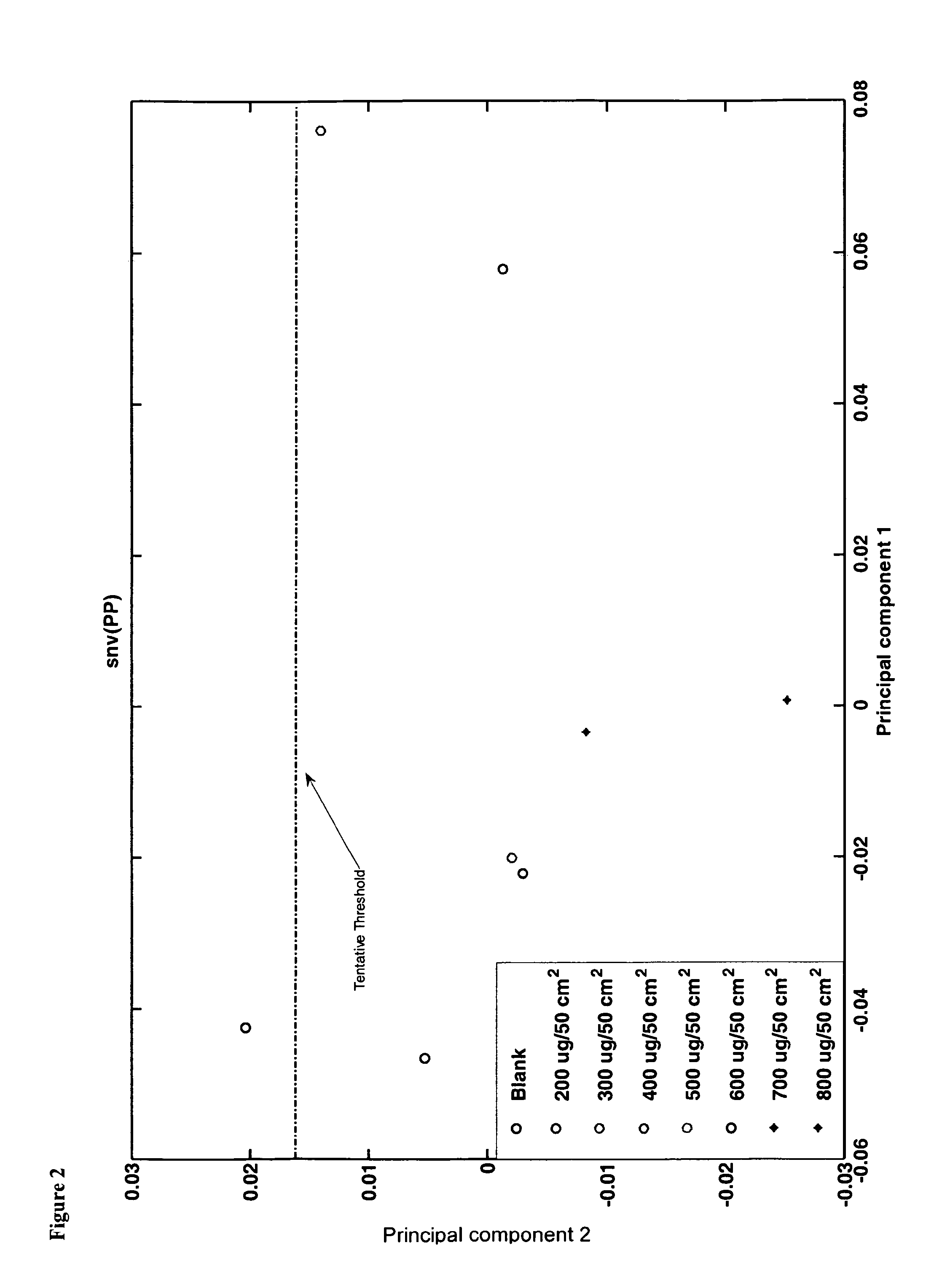
Method of validating a cleaning process
ActiveUS20130229516A1Use cleanRapid methodTelevision system detailsColor television detailsProcess engineeringEnvironmental engineering
A method of validating or verifying a process for cleaning a surface contaminated with at least one chemical substrate, comprising the steps of: capturing an infrared image of the surface using infrared chemical imaging; utilising at least one algorithm to interpret the captured image to extract an infra-red signal from the at least one chemical substrate to determine the amount of the at least one chemical substrate present on the surface; and determining if the amount of the at least one detected chemical substrate exceeds a threshold value, thereby indicating that a repeat cleaning process is required or thereby indicating that no further cleaning is required.
Owner:JONES IAN
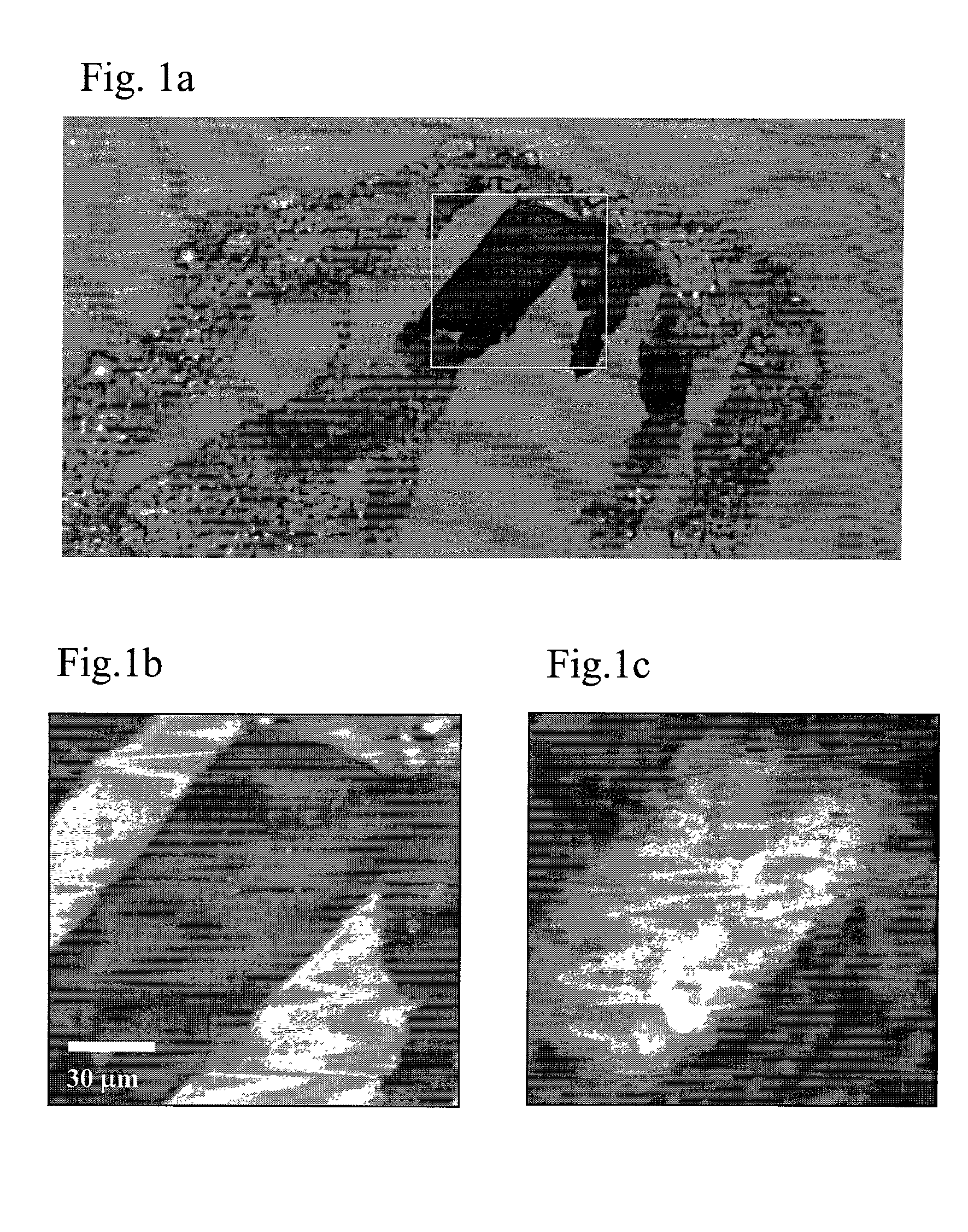
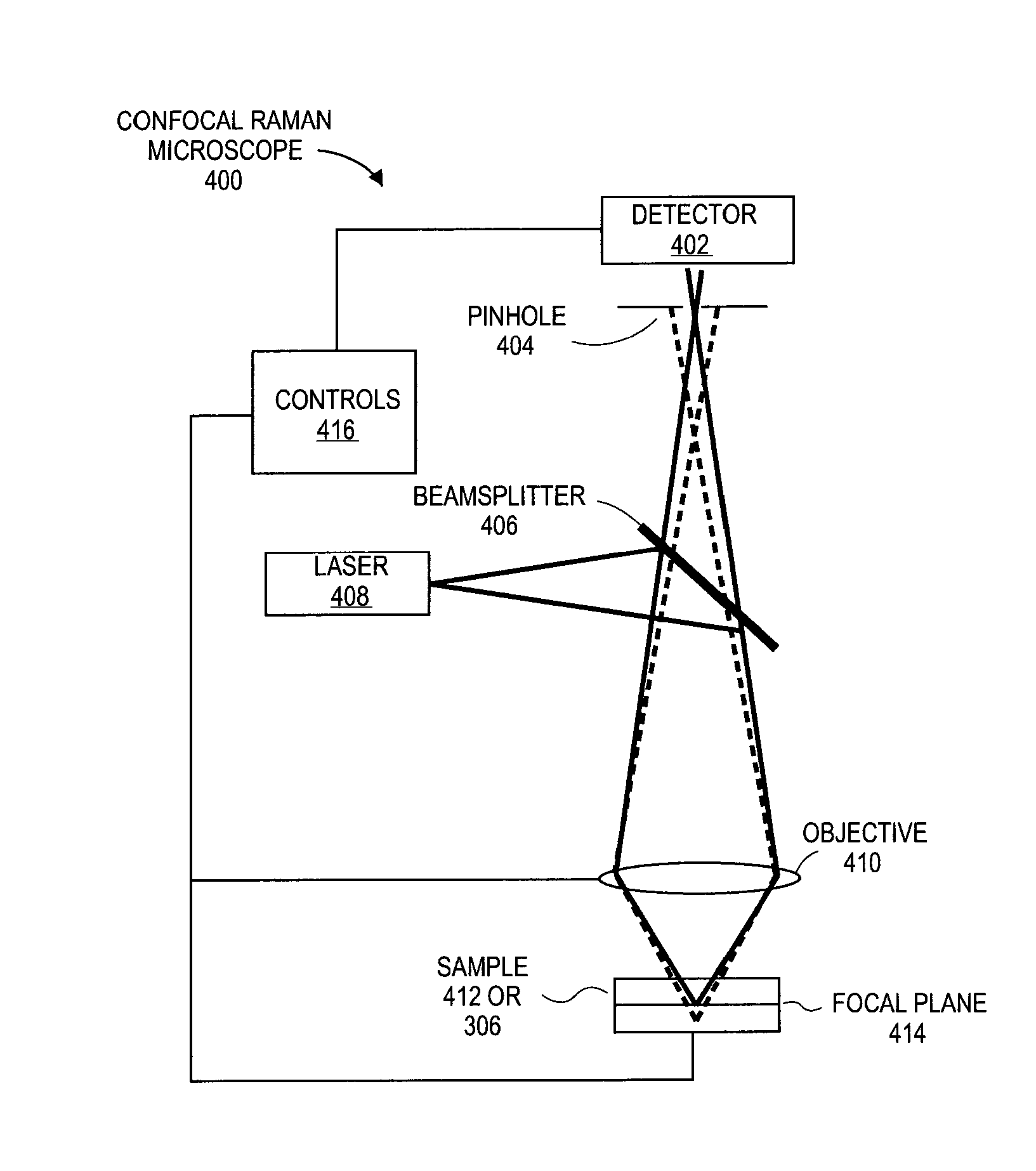
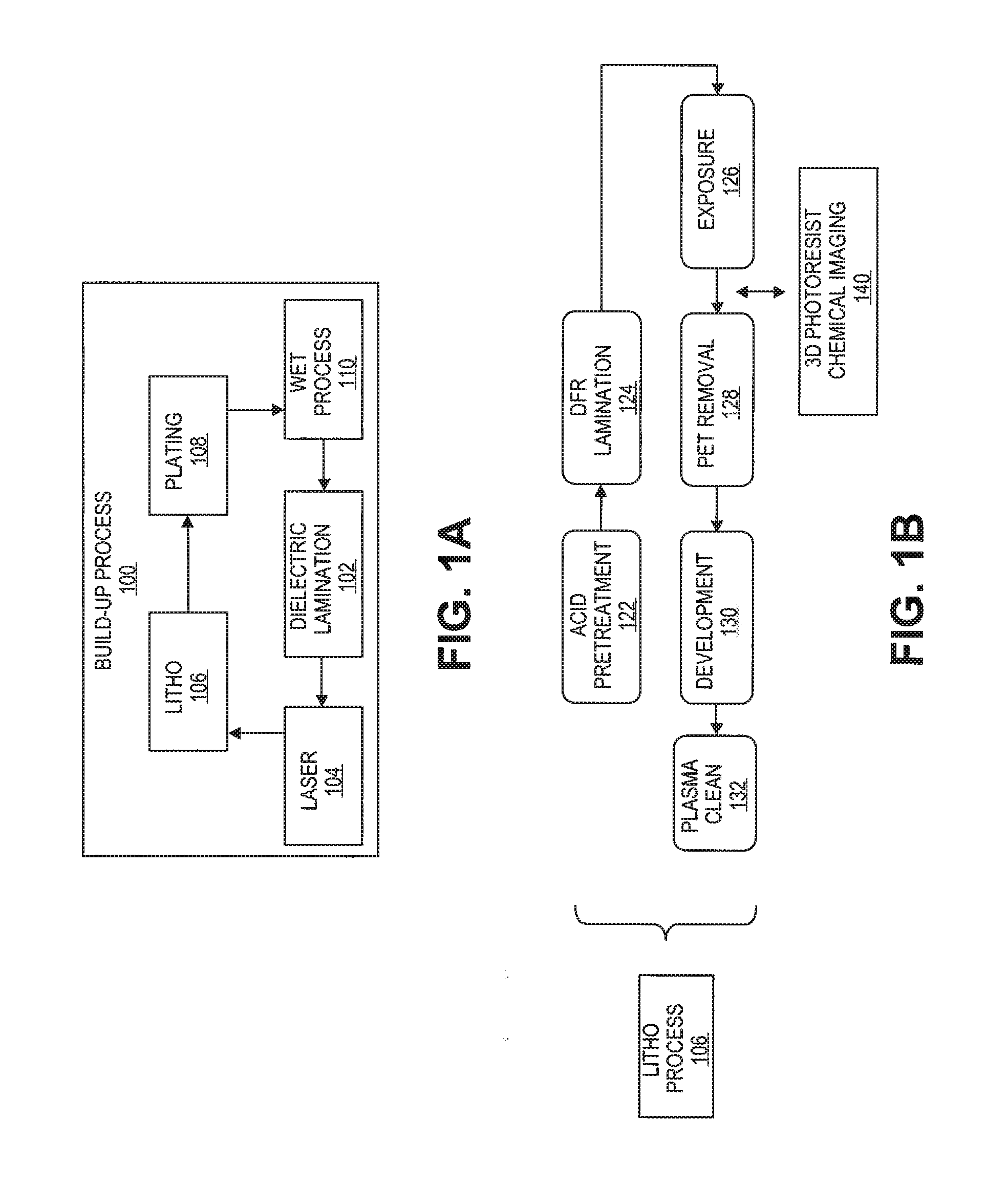
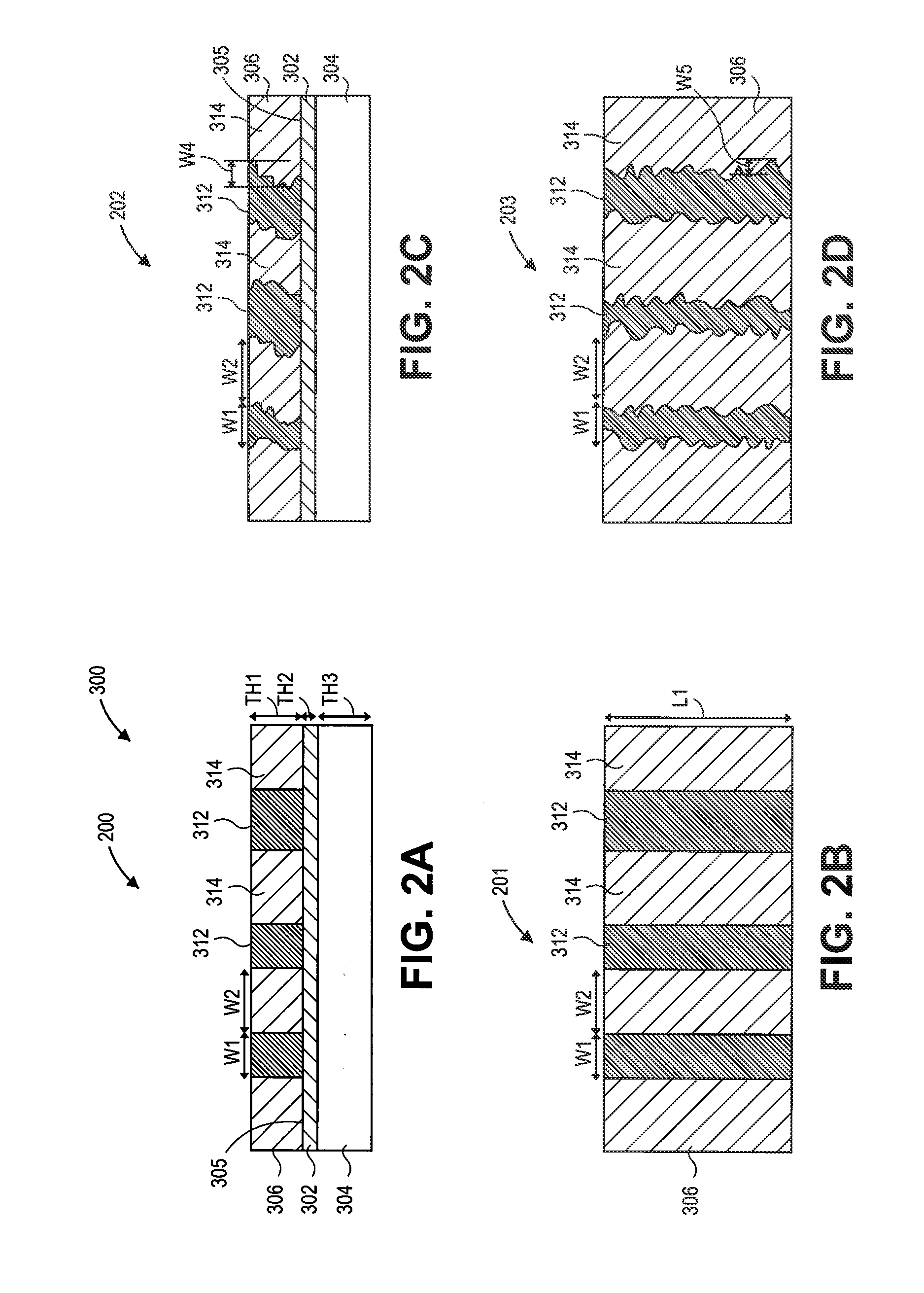
Non-Destructive 3-Dimensional Chemical Imaging Of Photo-Resist Material
Embodiments include devices, systems and processes for using a combined confocal Raman microscope for inspecting a photo resist film material layer formed on the top surface of a layer of a substrate package, to detect border defects between regions of light exposed (e.g., cured) and unexposed (e.g., uncured) resist film material. Use of the confocal Raman microscope may provide a 3D photo-resist chemical imaging and characterization technique based on combining (1) Raman spectroscopy to identify the borders between regions of light exposed and unexposed resist along XY planes, with (2) Confocal imaging to select a Z-height of the XY planes scanned. Such detection provides fast, high resolution, non-destructive in-line inspection, and improves technical development of polymerization profiles of the resist film material.
Owner:INTEL CORP
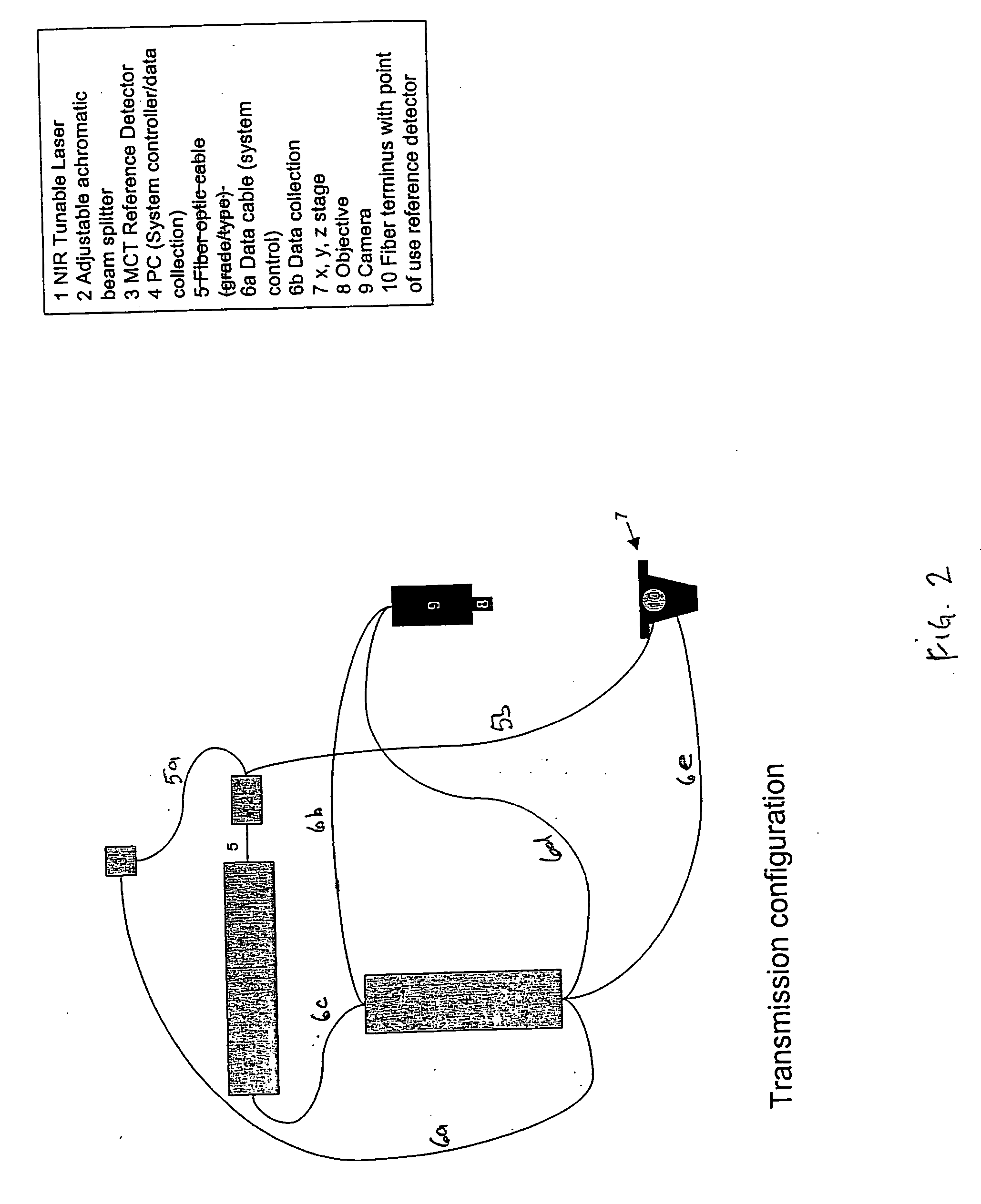
Tunable laser-based chemical imaging system
InactiveUS20060082777A1Easy to operateEasy to modifyPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryLight deliveryLength wave
A chemical imaging device which utilizes a computer controlled tunable laser to provide light of wavelengths in the near infrared band and a focal plane array to image a sample illuminated at various wavelengths of light. The device also provides light intensity reference detectors at the source and terminus of the light delivery pathway for normalizing the collected images and for detecting defects in the light delivery pathway.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
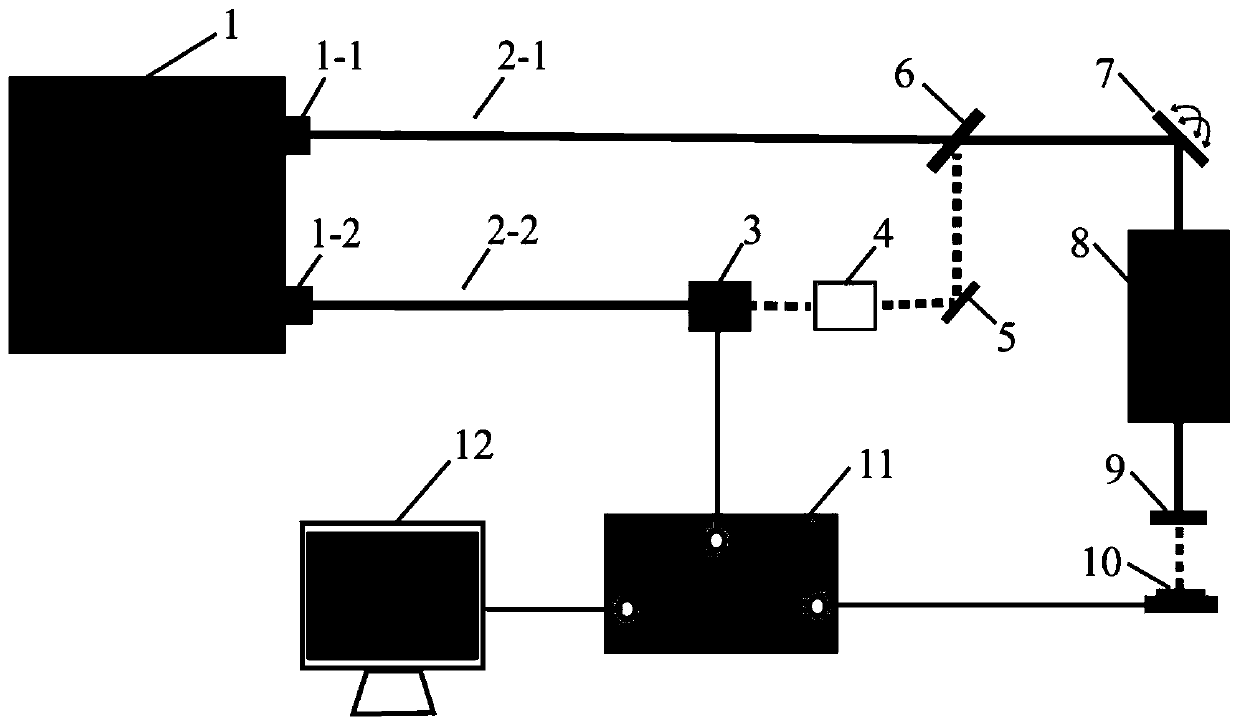
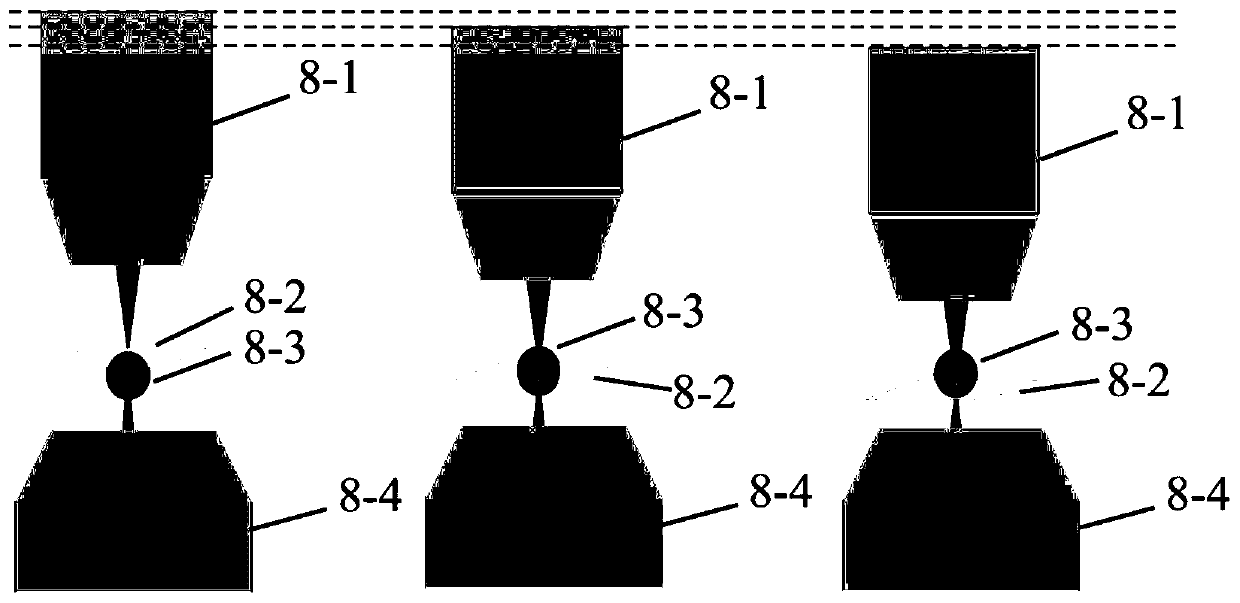
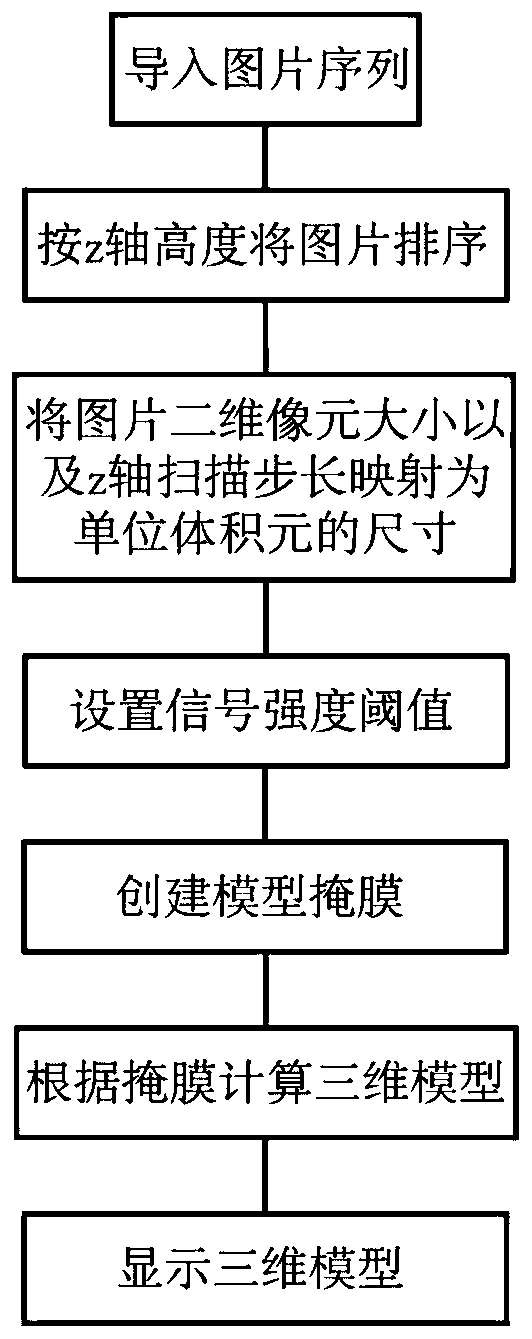
Atmospheric single particle quick three-dimensional chemical imaging method based on stimulated Raman scattering
ActiveCN110208241ADemonstrating the ability to image non-destructively and quicklyRigorous experimental verificationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationParticulatesStimulate raman scattering
The invention belongs to the technical field of nonlinear optical imaging and in particular relates to an atmospheric single particle quick three-dimensional chemical imaging method based on stimulated Raman scattering. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: detecting a standard substance of a to-be-detected substance by utilizing a stimulated Raman scattering microscope system, and obtaining specific parameters of a Raman peak in a stimulated Raman system; setting experiment parameters, performing quick x and y axis two-dimensional imaging on the to-be-detected substance, and repeating the process, thus obtaining an image sequence along a z axis; importing the image sequence into three-dimensional reconstruction software, so as to scan the size of a view fieldand number of pixel points, calculating the actual size of each pixel, combining a z axis scanning step size, and mapping the z axis scanning step size into initialization parameter setting during three-dimensional reconstruction, thus obtaining real stereoscopic structure information of a particle. The method provided by the invention can acquire a three-dimensional structure of an atmospheric single particle as well as specific component distribution information in short time; and the method dose not need to perform sample pretreatment, the most original state of the particle is reserved, and experimental procedures are simple.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com