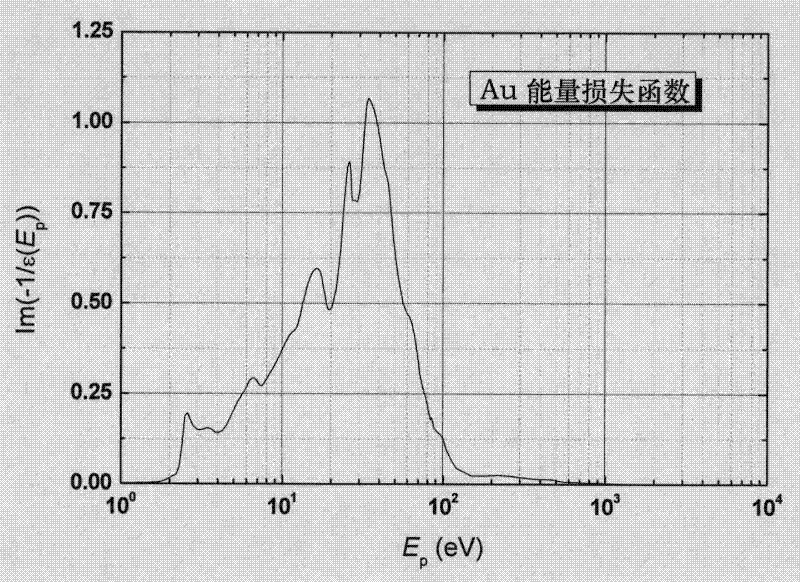
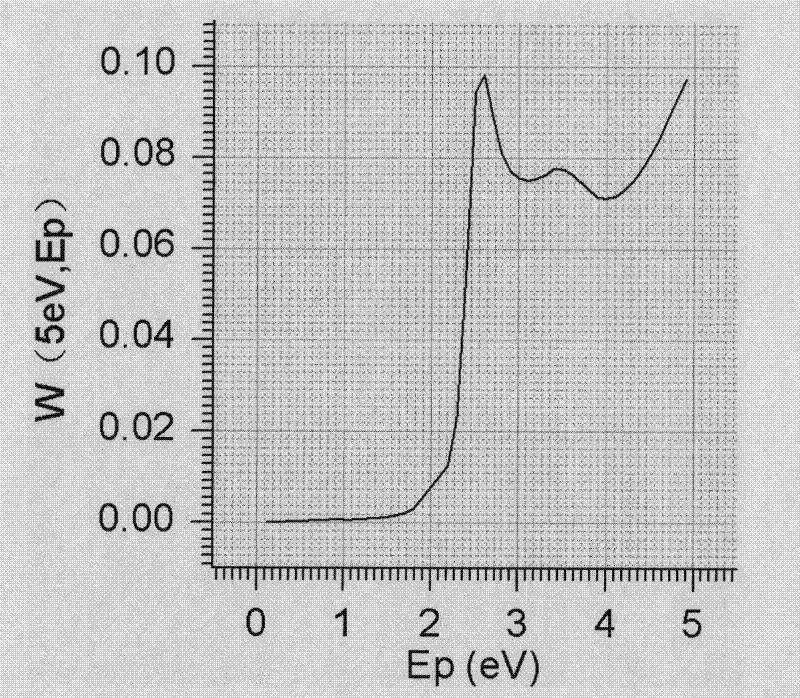
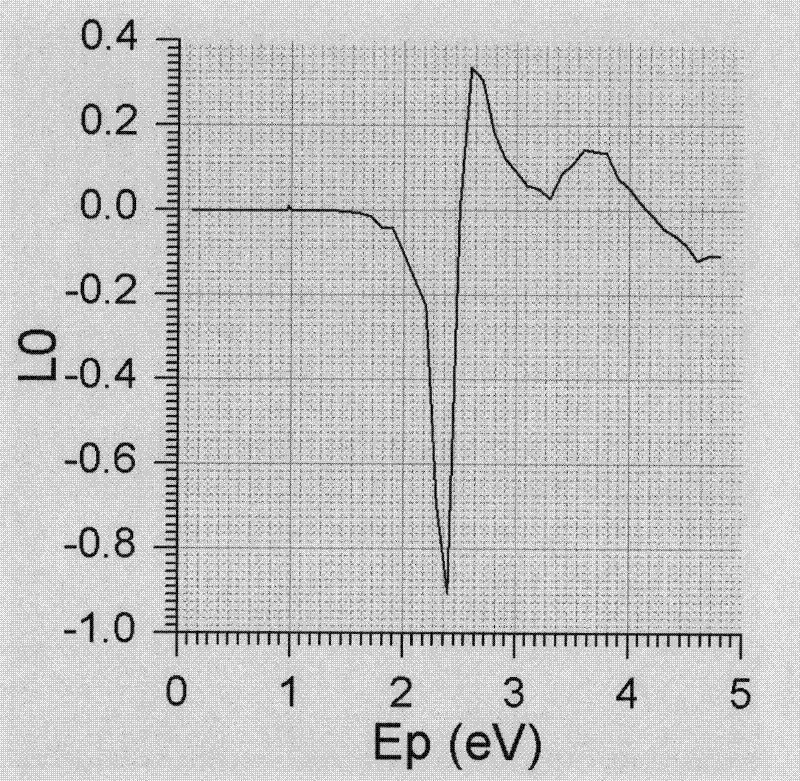
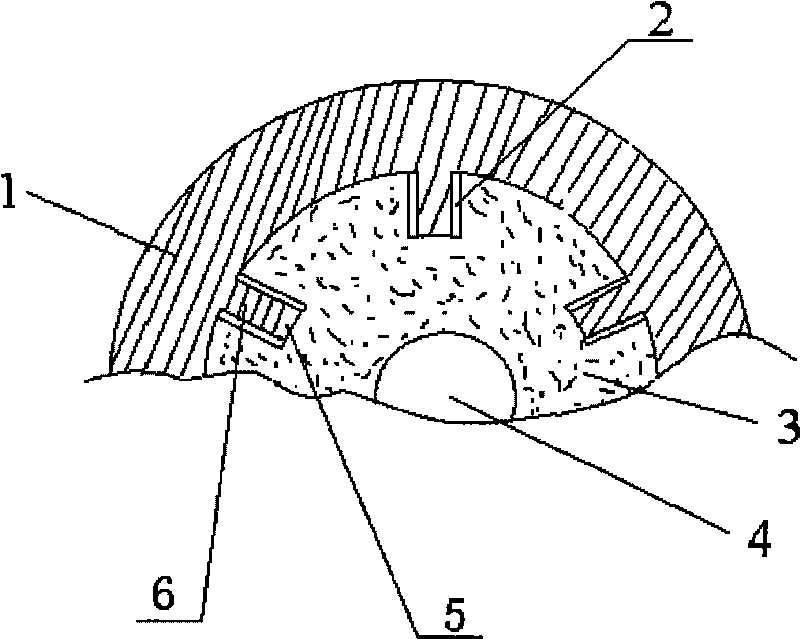
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Inelastic scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
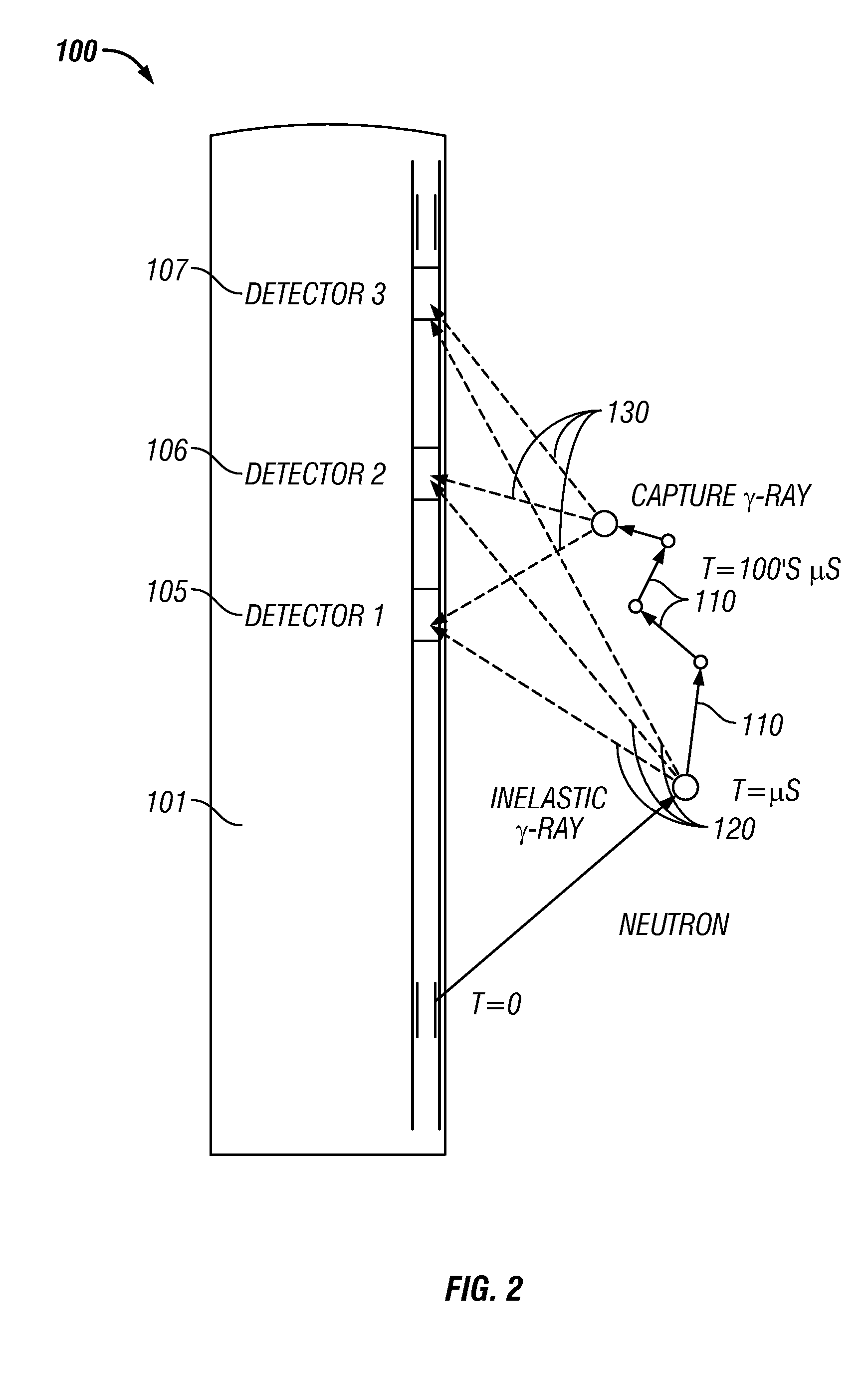
In chemistry, nuclear physics, and particle physics, inelastic scattering is a fundamental scattering process in which the kinetic energy of an incident particle is not conserved (in contrast to elastic scattering). In an inelastic scattering process, some of the energy of the incident particle is lost or increased. Although the term is historically related to the concept of inelastic collision in dynamics, the two concepts are quite distinct; inelastic collision in dynamics refers to processes in which the total macroscopic kinetic energy is not conserved. In general, scattering due to inelastic collisions will be inelastic, but, since elastic collisions often transfer kinetic energy between particles, scattering due to elastic collisions can also be inelastic, as in Compton scattering.
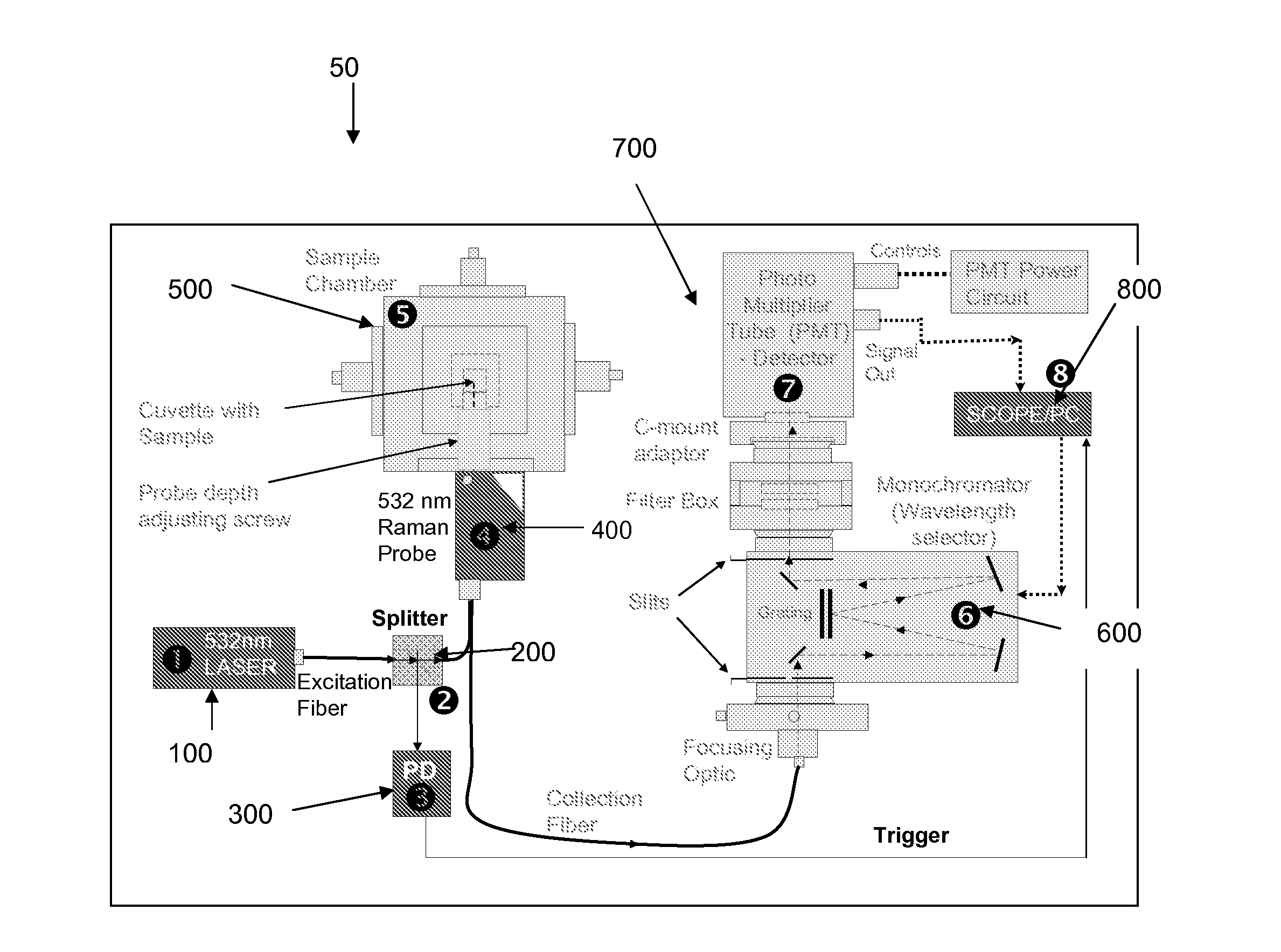
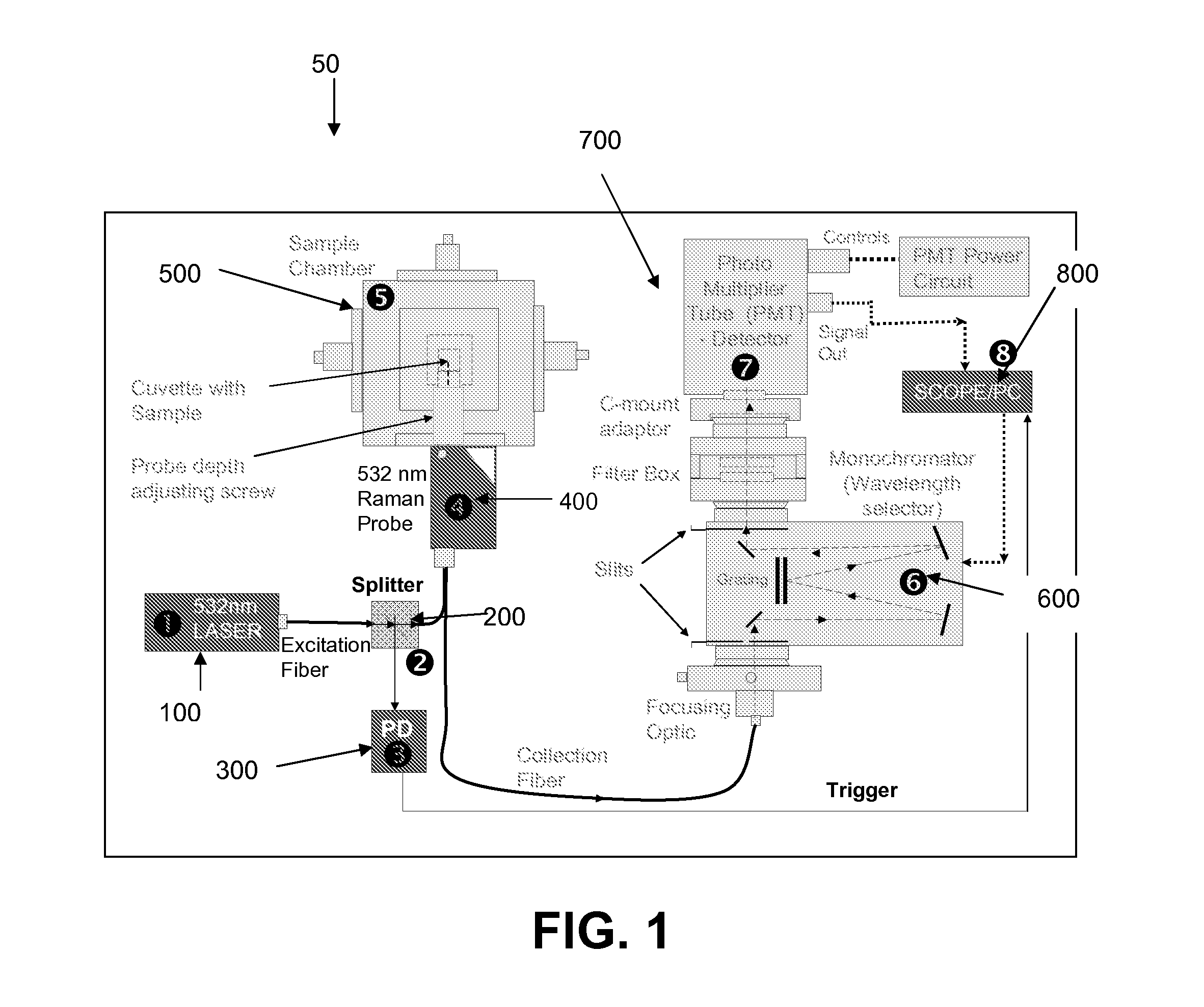
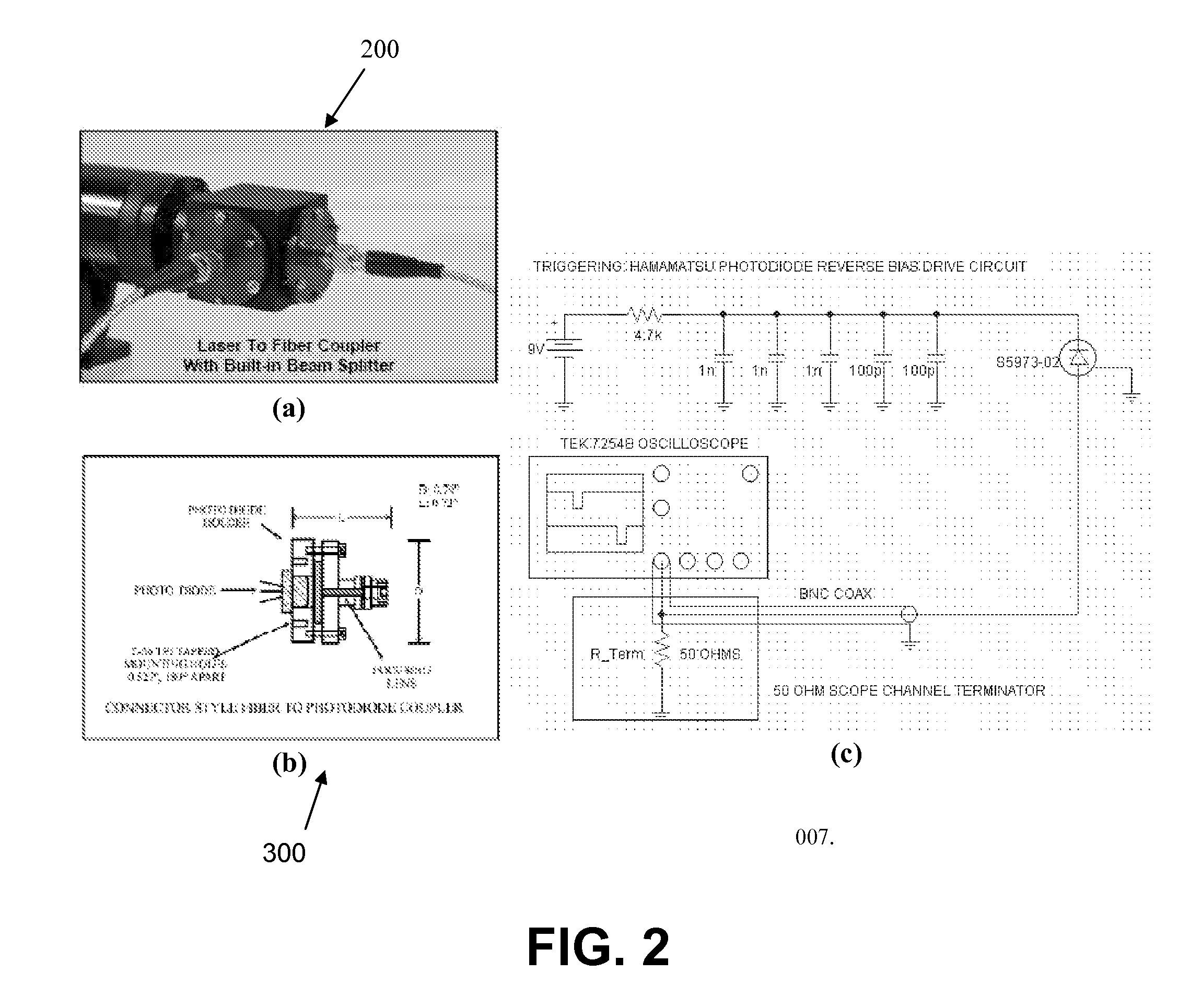
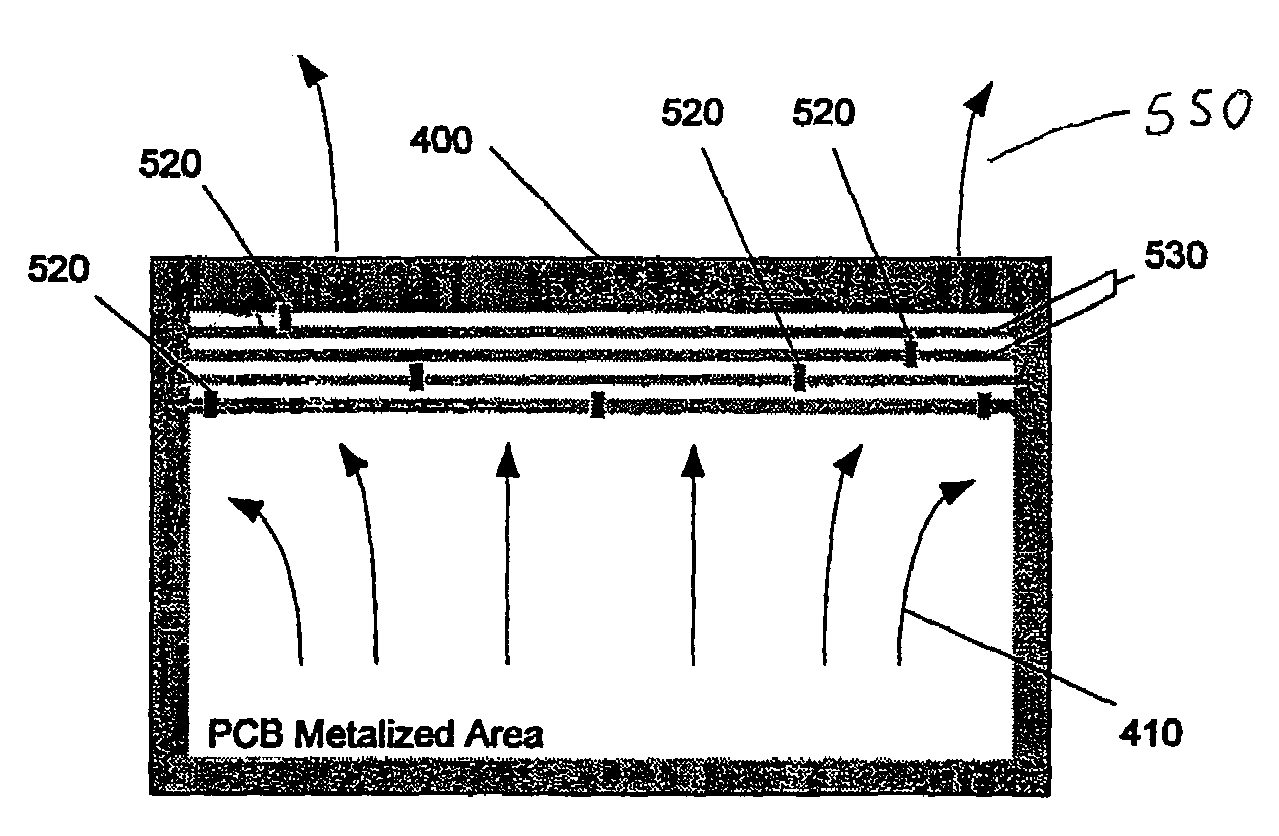
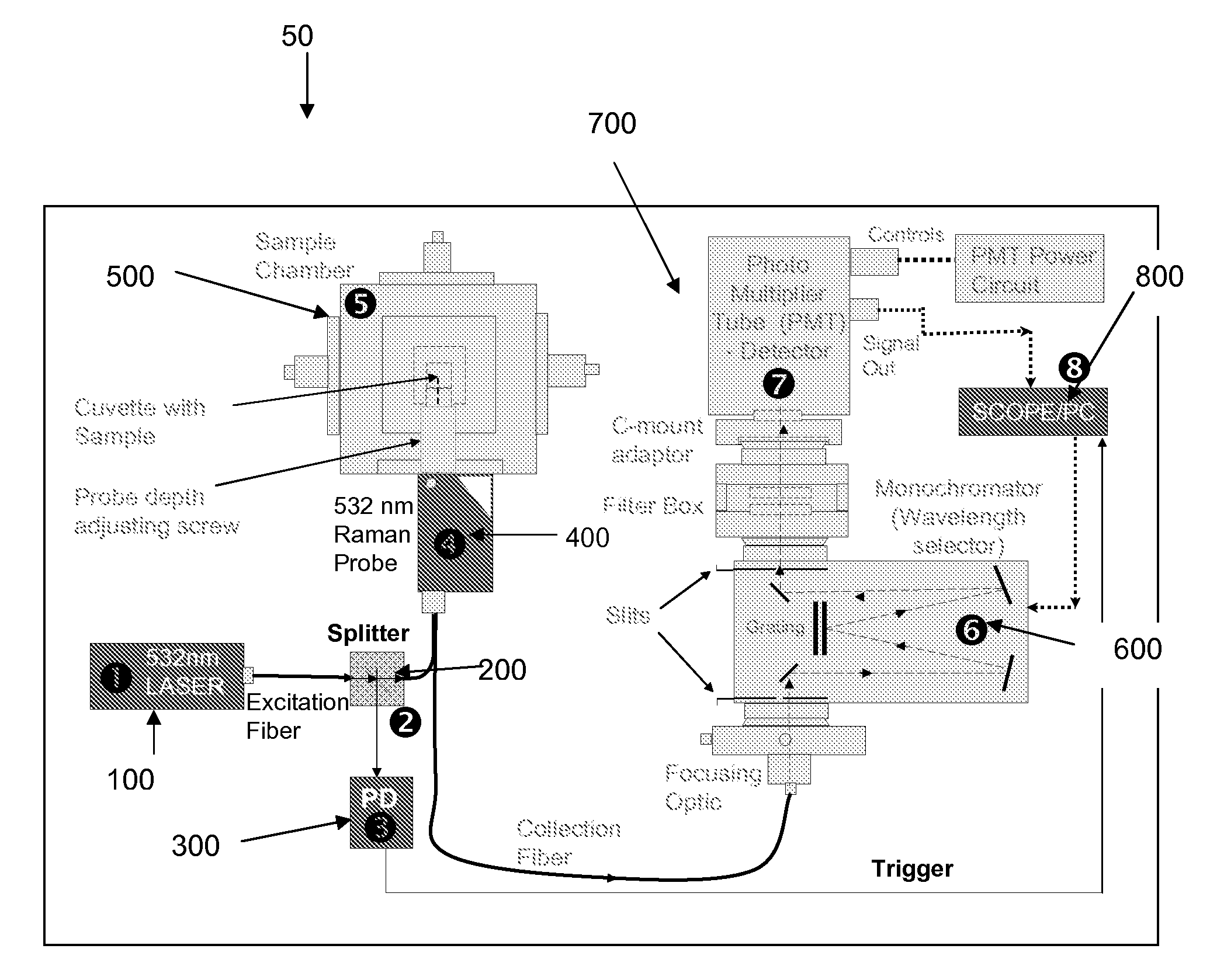
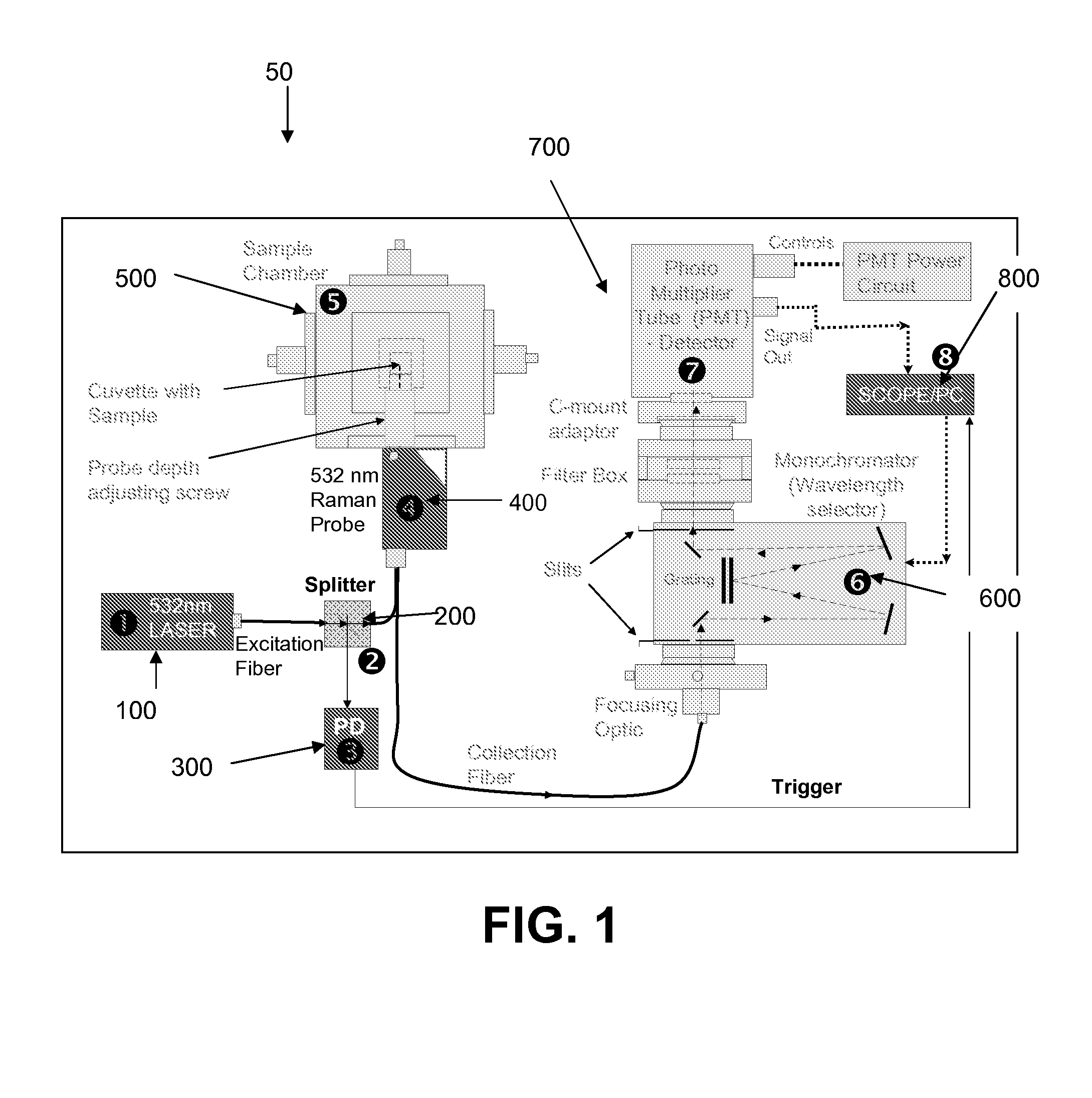
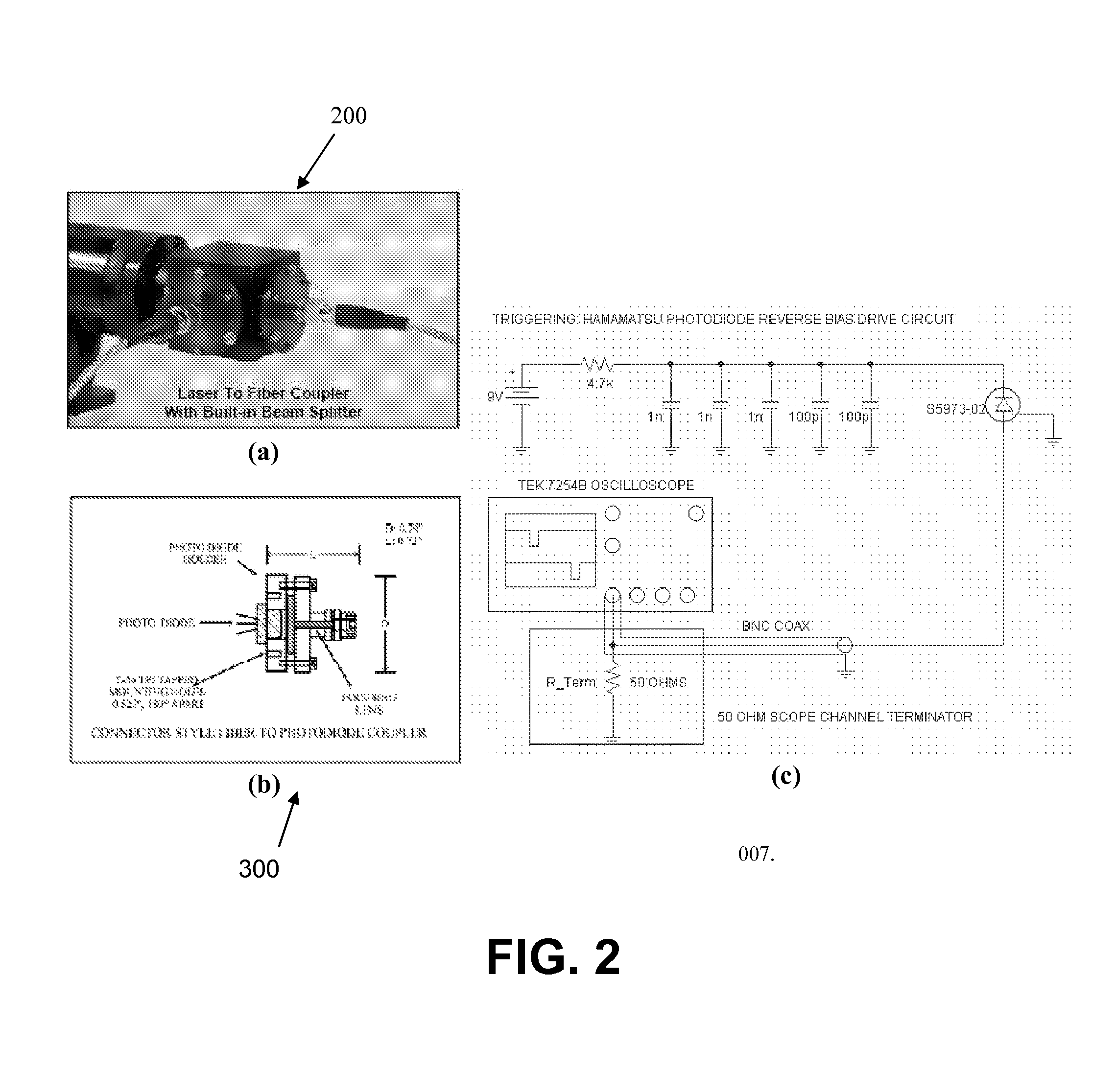
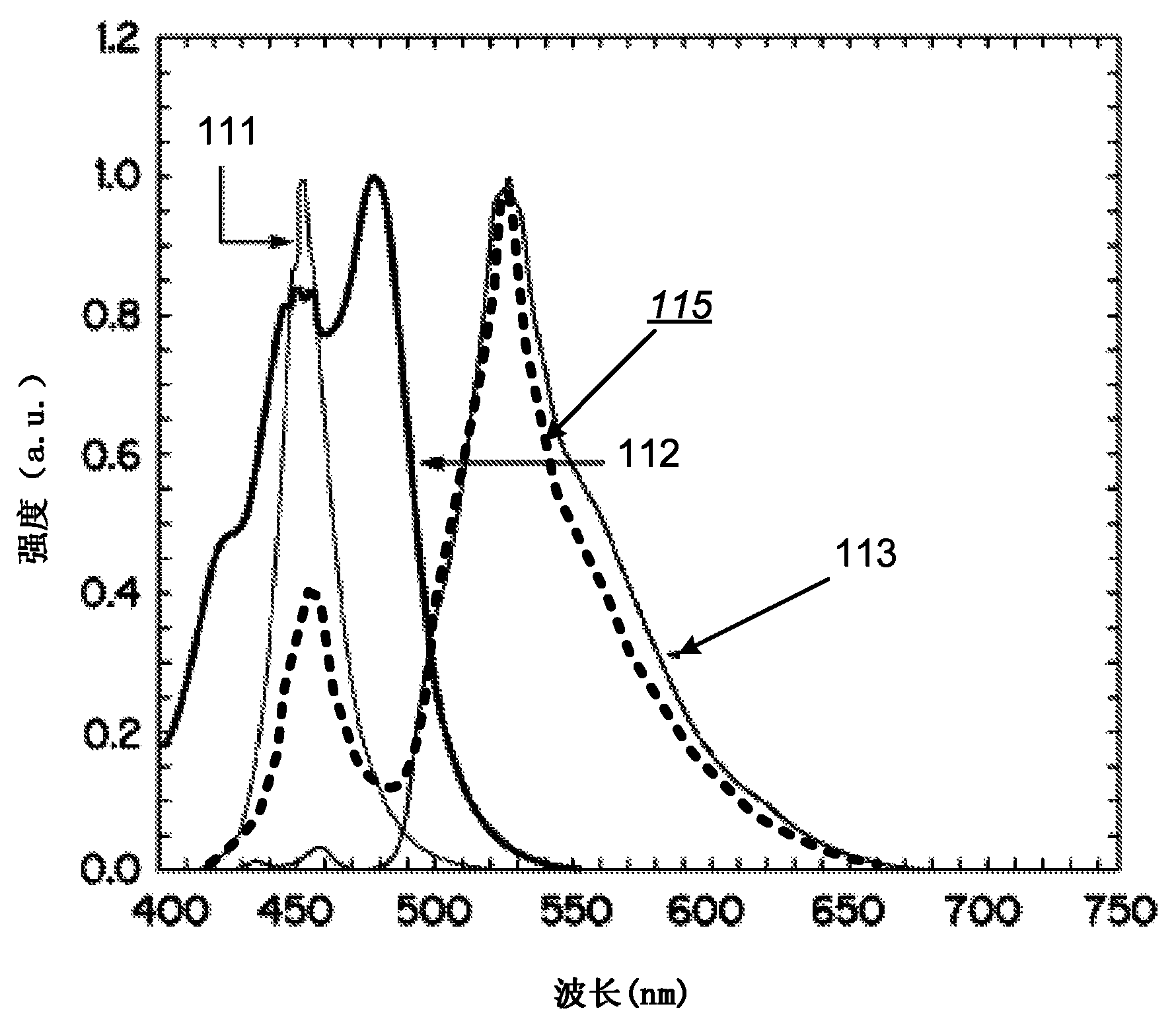
Time resolved raman spectroscopy
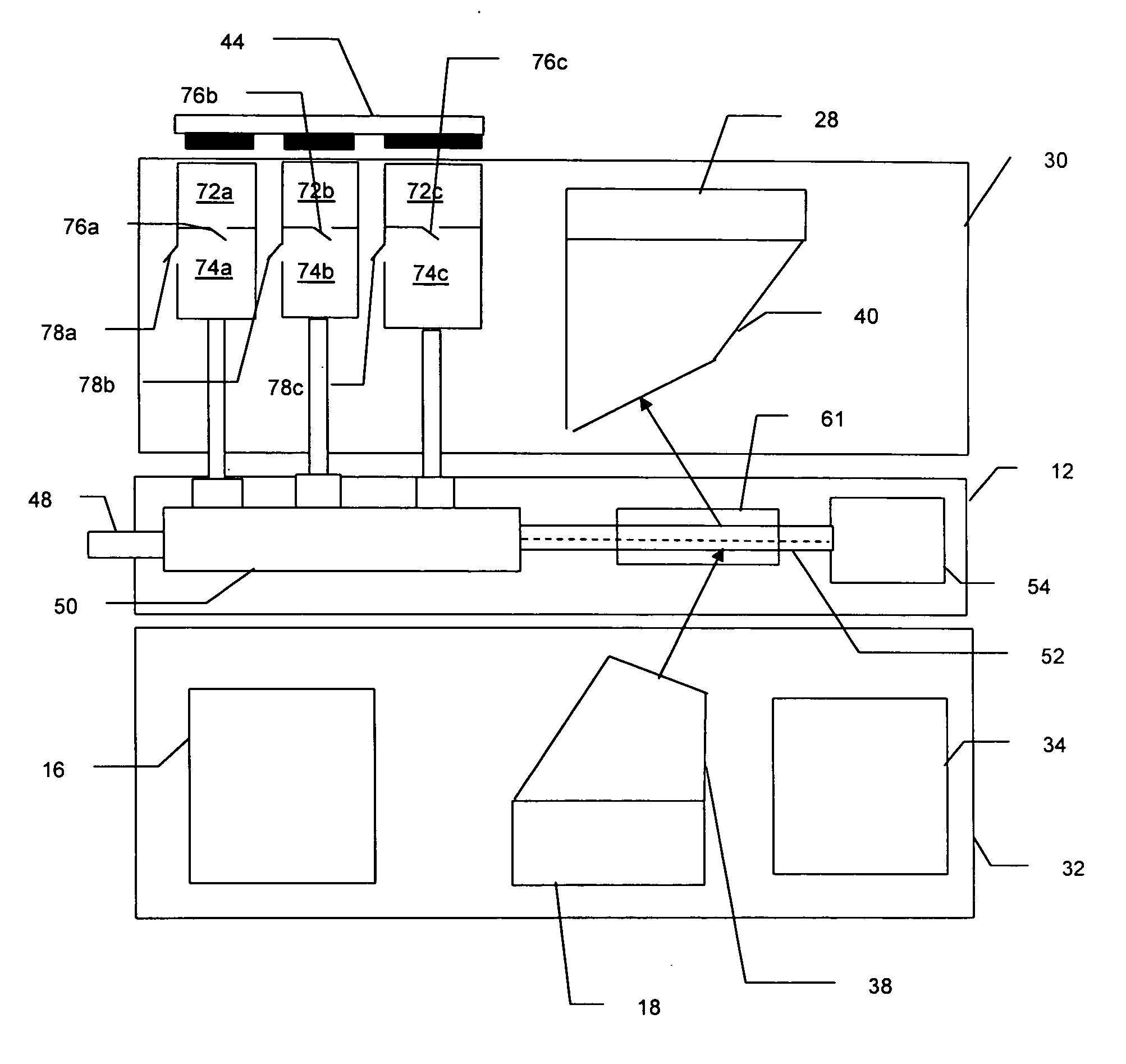
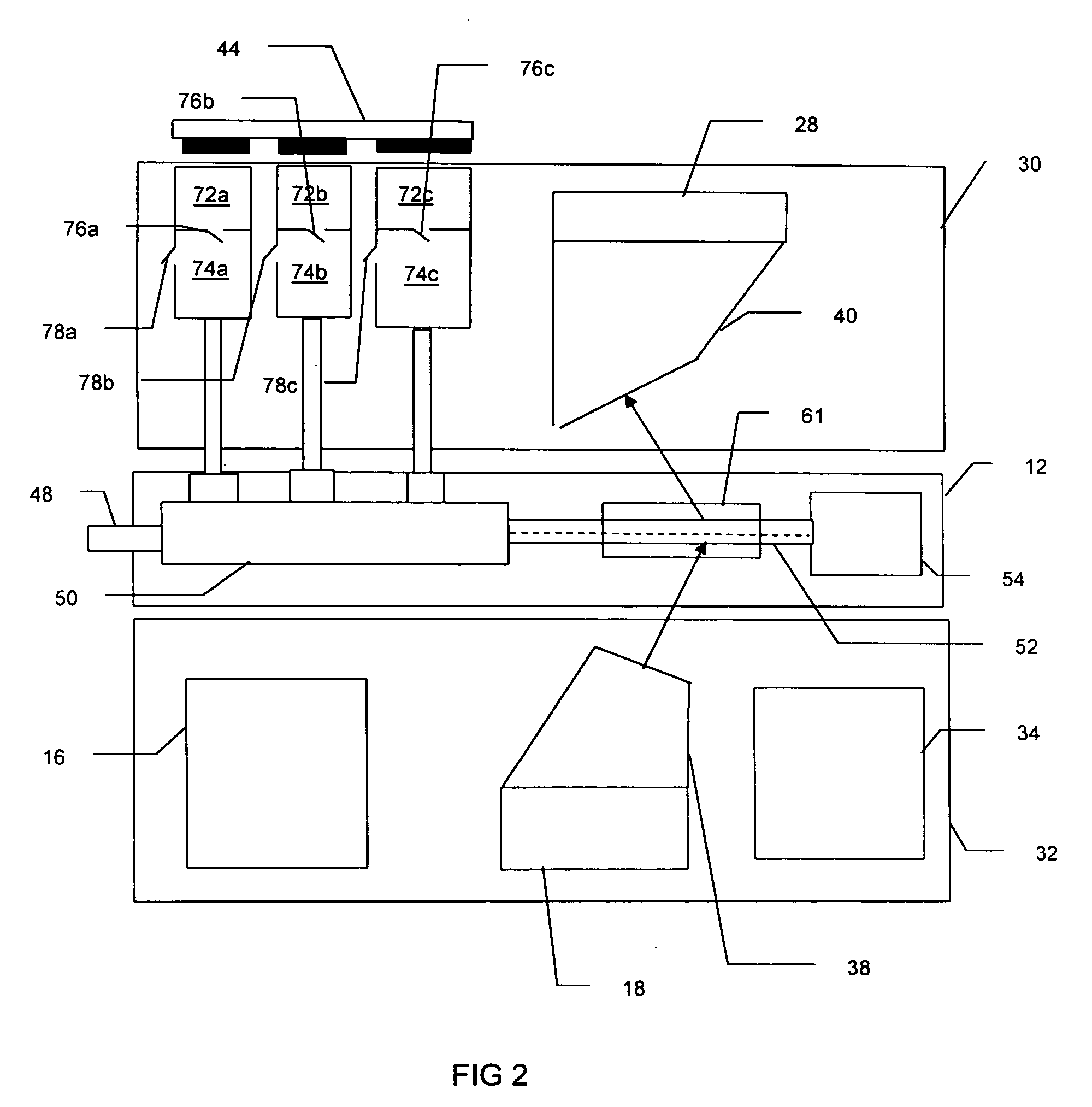
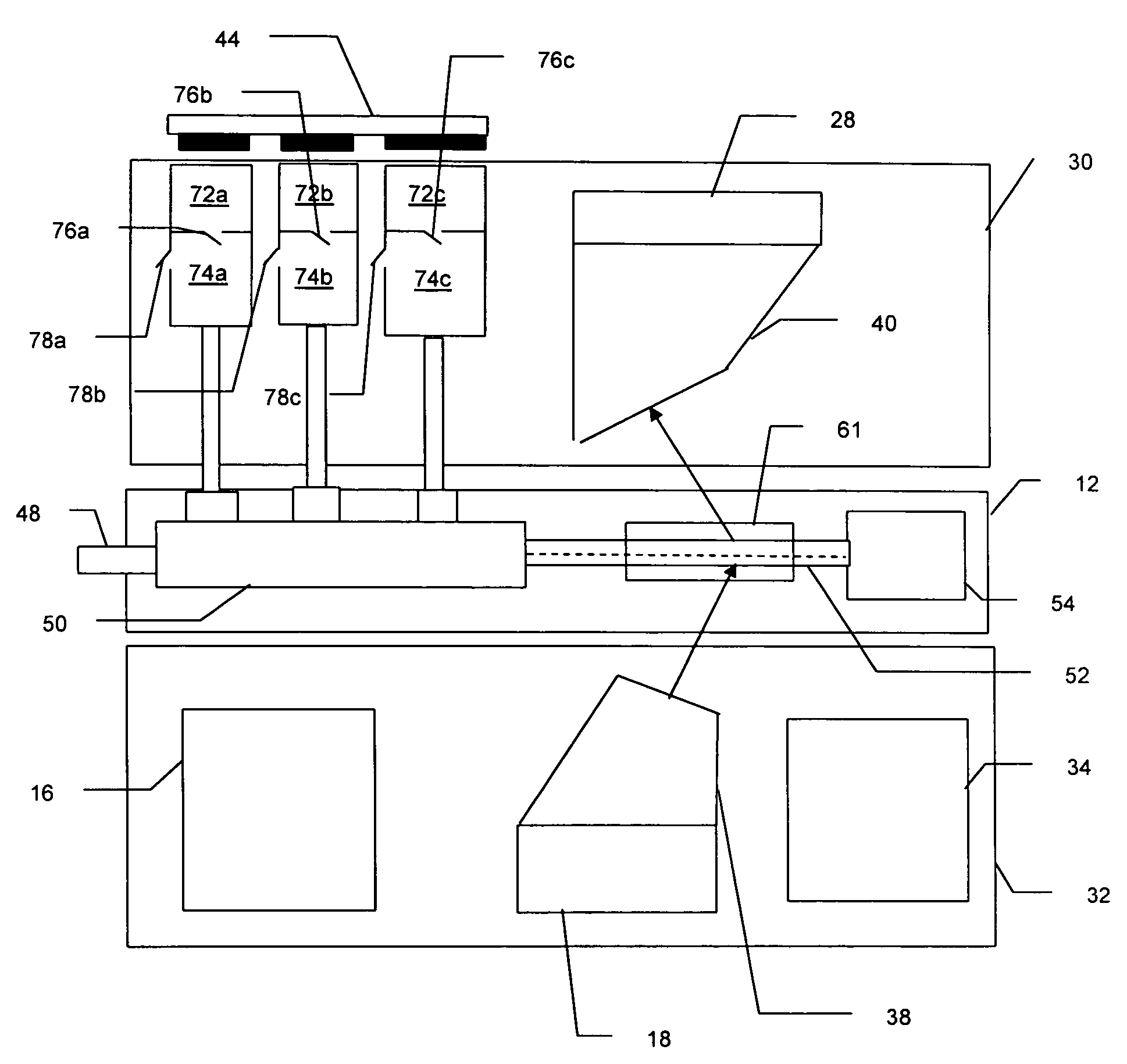
ActiveUS20110261354A1Low costHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhotometry using reference valueComputer control systemInelastic scattering
System, method, and apparatus for determining the composition of a sample of material. In one embodiment, the method pertains to the counting of photons that were inelastically scattered by the sample, and for minimizing the effects of fluorescent or phosphorescent photons. In yet another embodiment of the invention, a sample is illuminated by a repetitive pulse of monochromatic light, and the resultant scattered photons from the samples are collected and counted during a predetermined integration period. Yet other embodiments pertain to a low-cost, computer-controlled system for repetitively counting inelastically scattered photons so as to create a Raman histogram and a Raman spectrogram of the photons.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Reduction of near field electro-magnetic scattering using high impedance metallization terminations
ActiveUS7376408B2Reduce the electro-magnetic field scatteringHigh areaMagnetic/electric field screeningCurrent interference reductionInelastic scatteringGradual transition
The present invention uses metallization termination techniques to reduce the electro-magnetic field scattering at the edges of metallized areas. The metallization termination techniques provide a gradual transition from high conductivity areas to high impedance areas. The mobile phone antenna illuminates the PCB allowing currents to flow on the PCB. When the currents reach edges of the PCB they flow through a region of increasingly high impedance without reflecting back or scattering.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
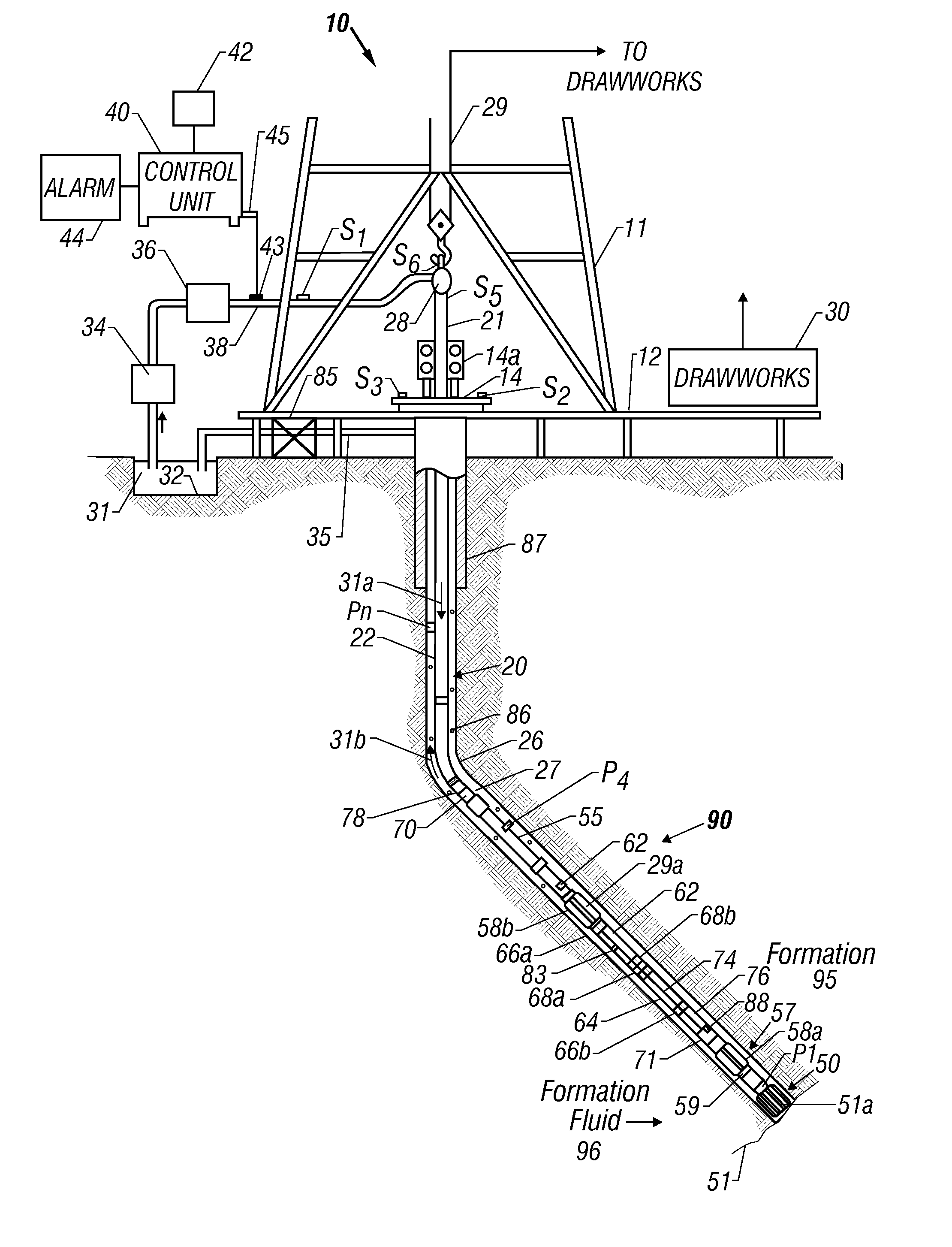
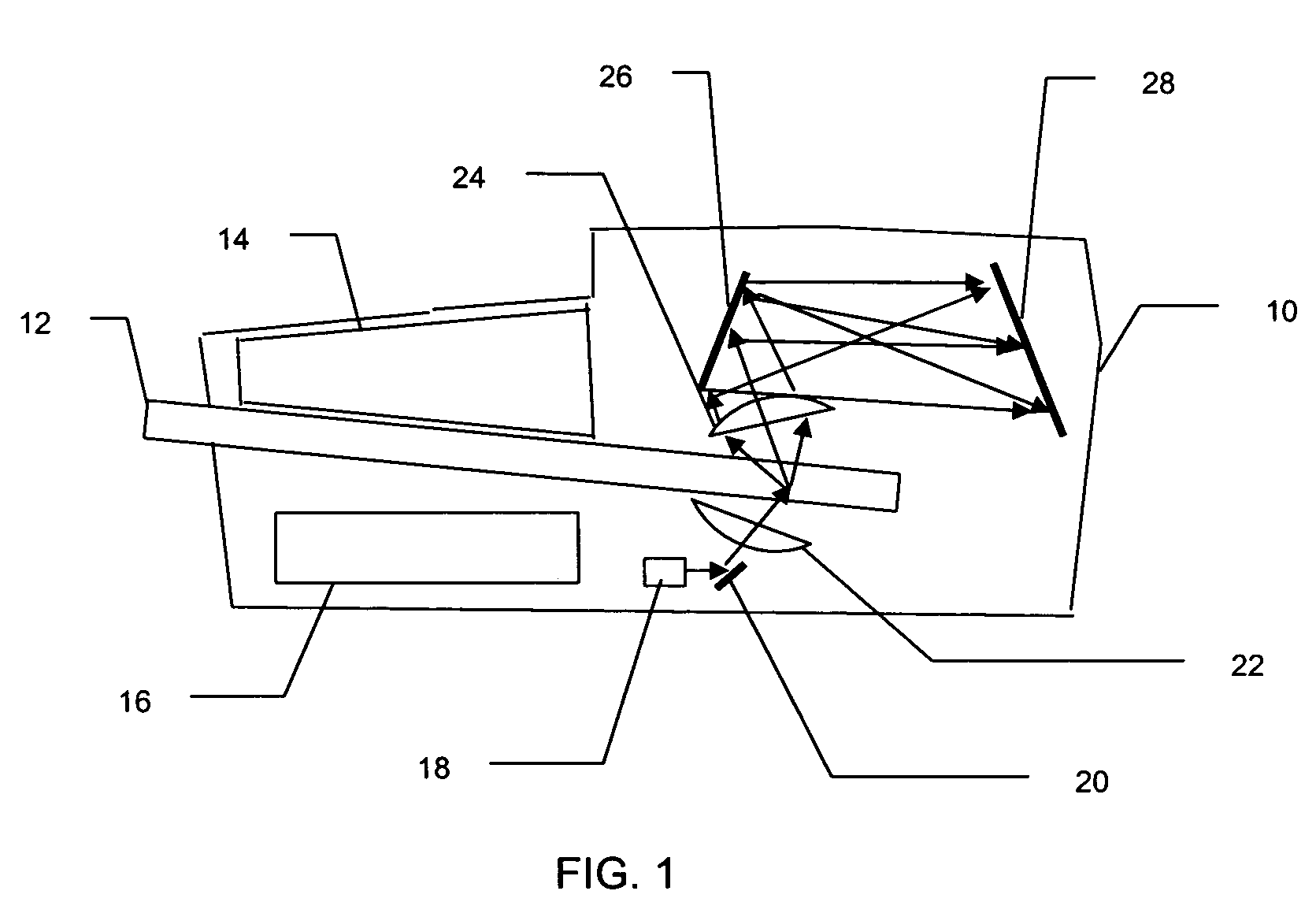
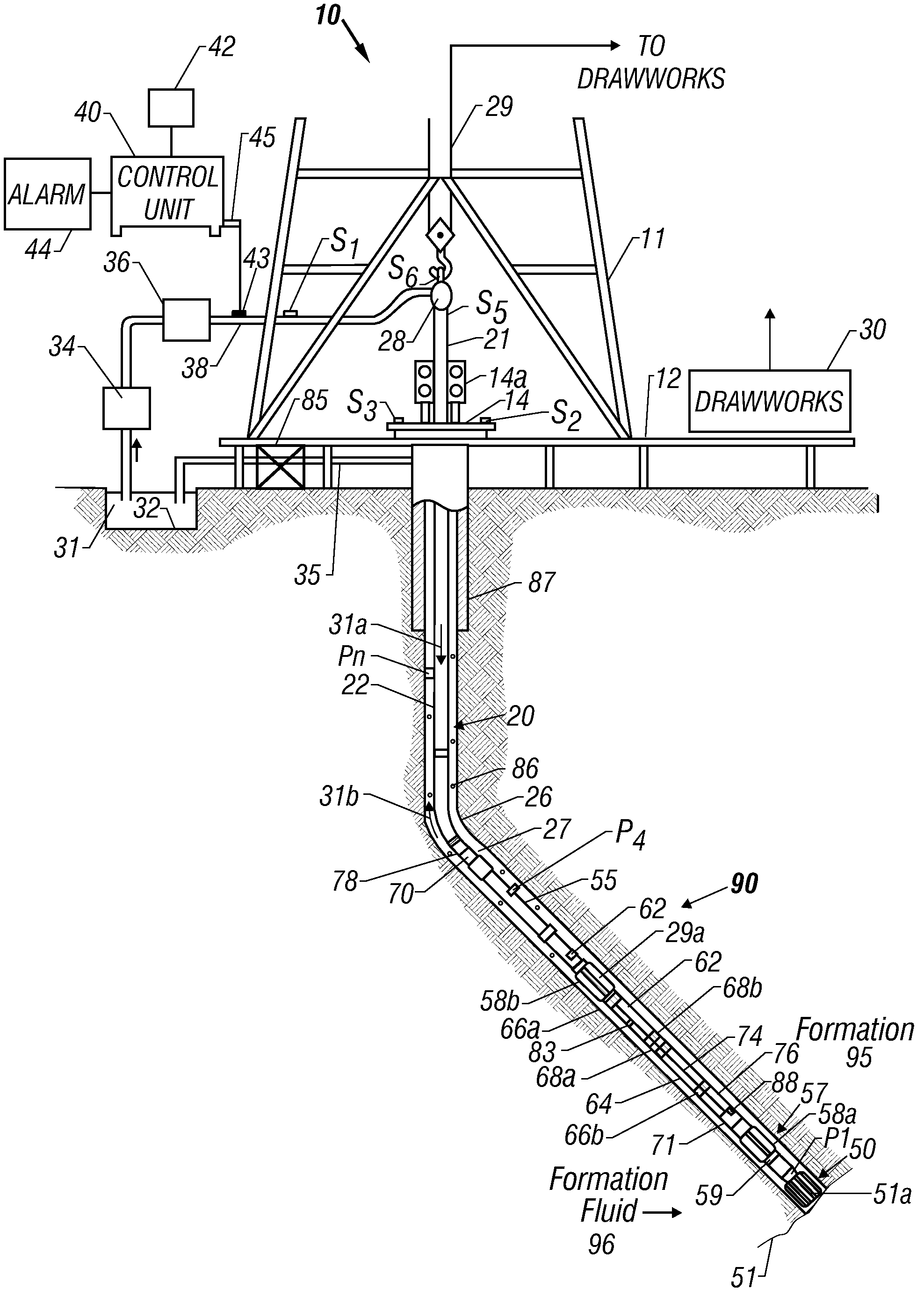
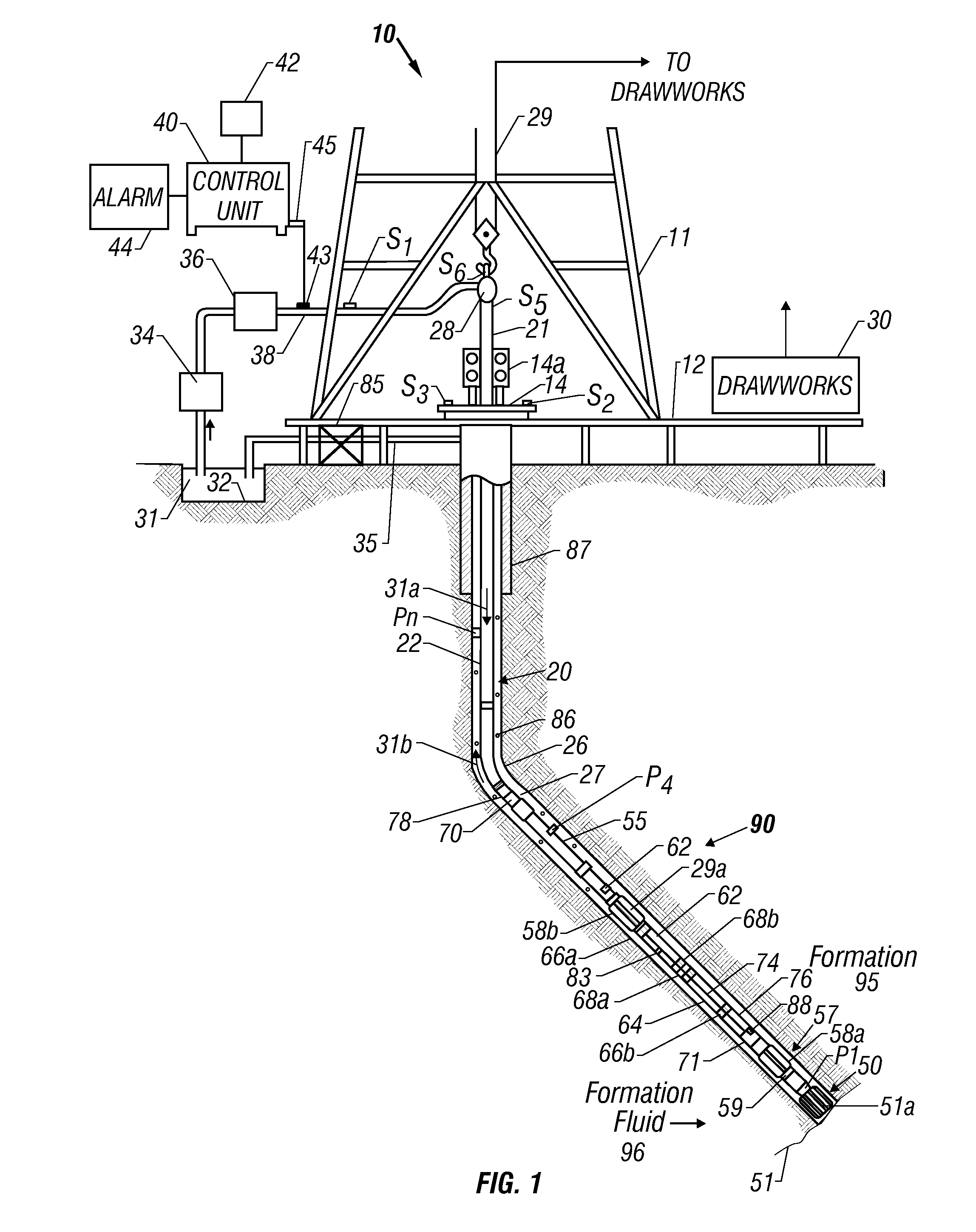
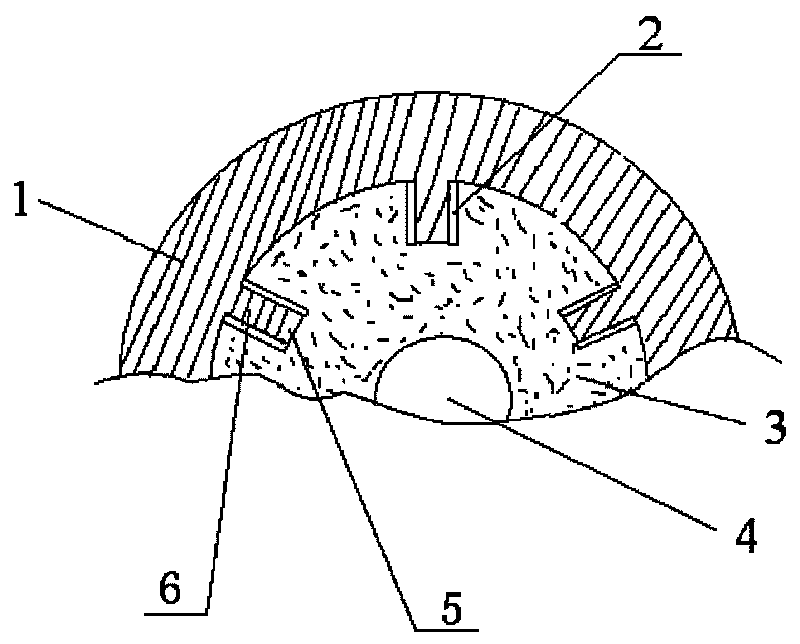
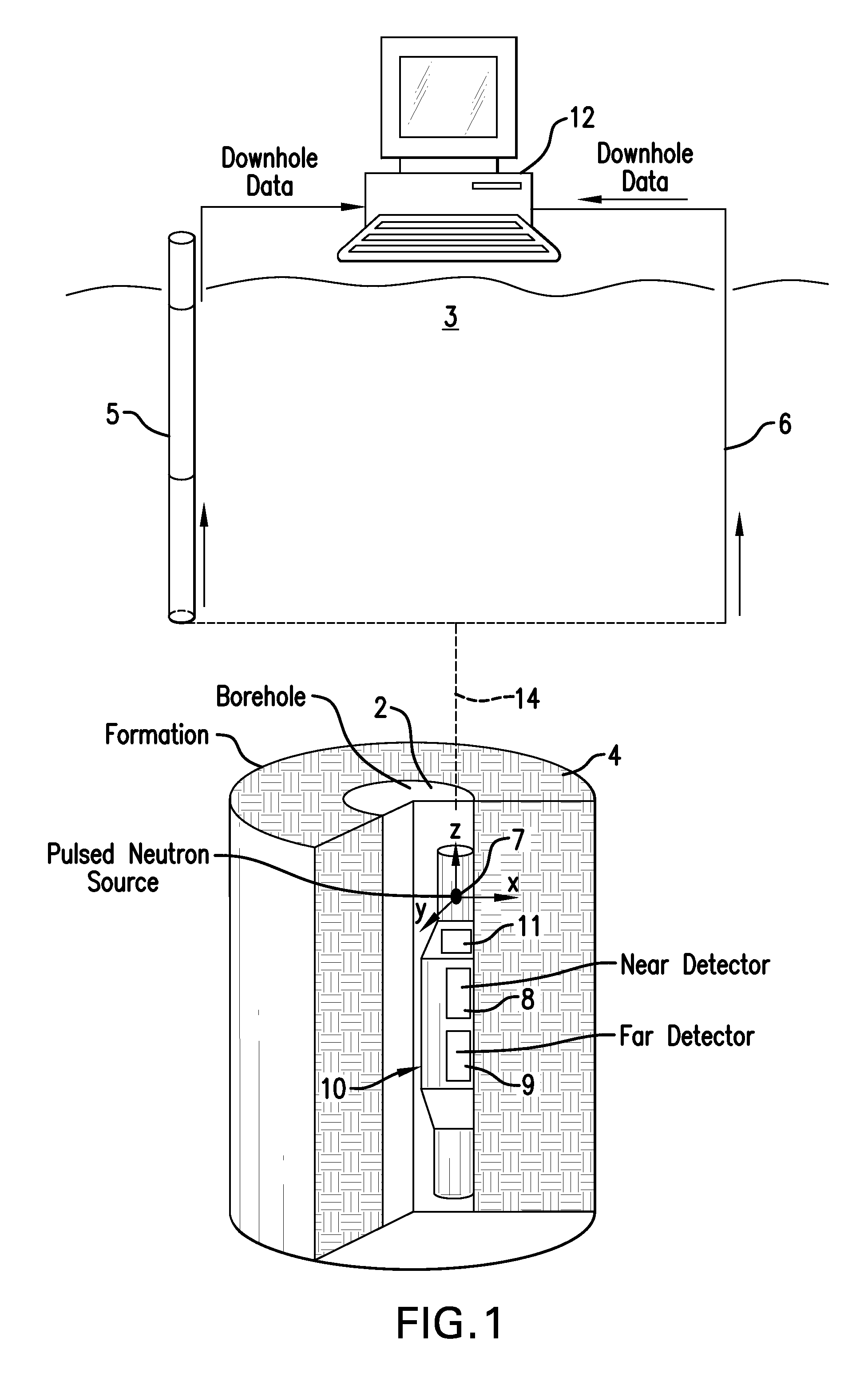
Apparatus and method for determining density, porosity and fluid saturation of formations penetrated by a borehole
InactiveUS6936812B2Reduce ambiguityMinimize adverse effectsNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringFluid saturation
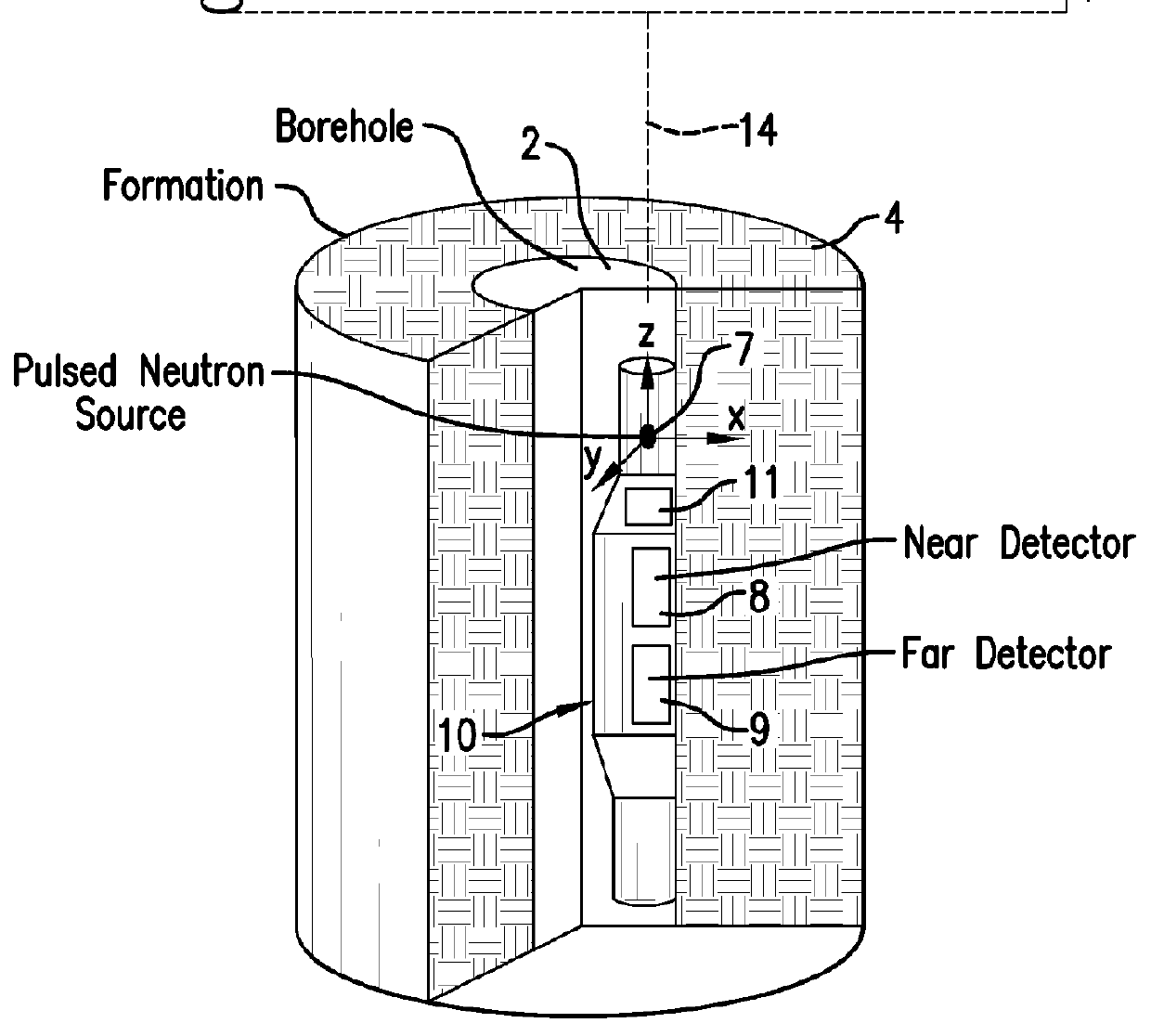
A borehole logging system for determining bulk density, porosity and formation gas / liquid fluid saturation of formation penetrated by a borehole. Measures of fast neutron radiation and inelastic scatter gamma radiation, induced by a pulsed neutron source, are combined with an iterative numerical solution of a two-group diffusion model to obtain the formation parameters of interest. Double-valued ambiguities in prior art measurements are removed by using the iterative solution of the inverted two-group diffusion model. The system requires two gamma ray detectors at different axial spacings from the source, and a single neutron detector axially spaced between the two gamma ray detectors. The system can be embodied as a wireline system or as a logging-while-drilling system.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
3-D imaging system
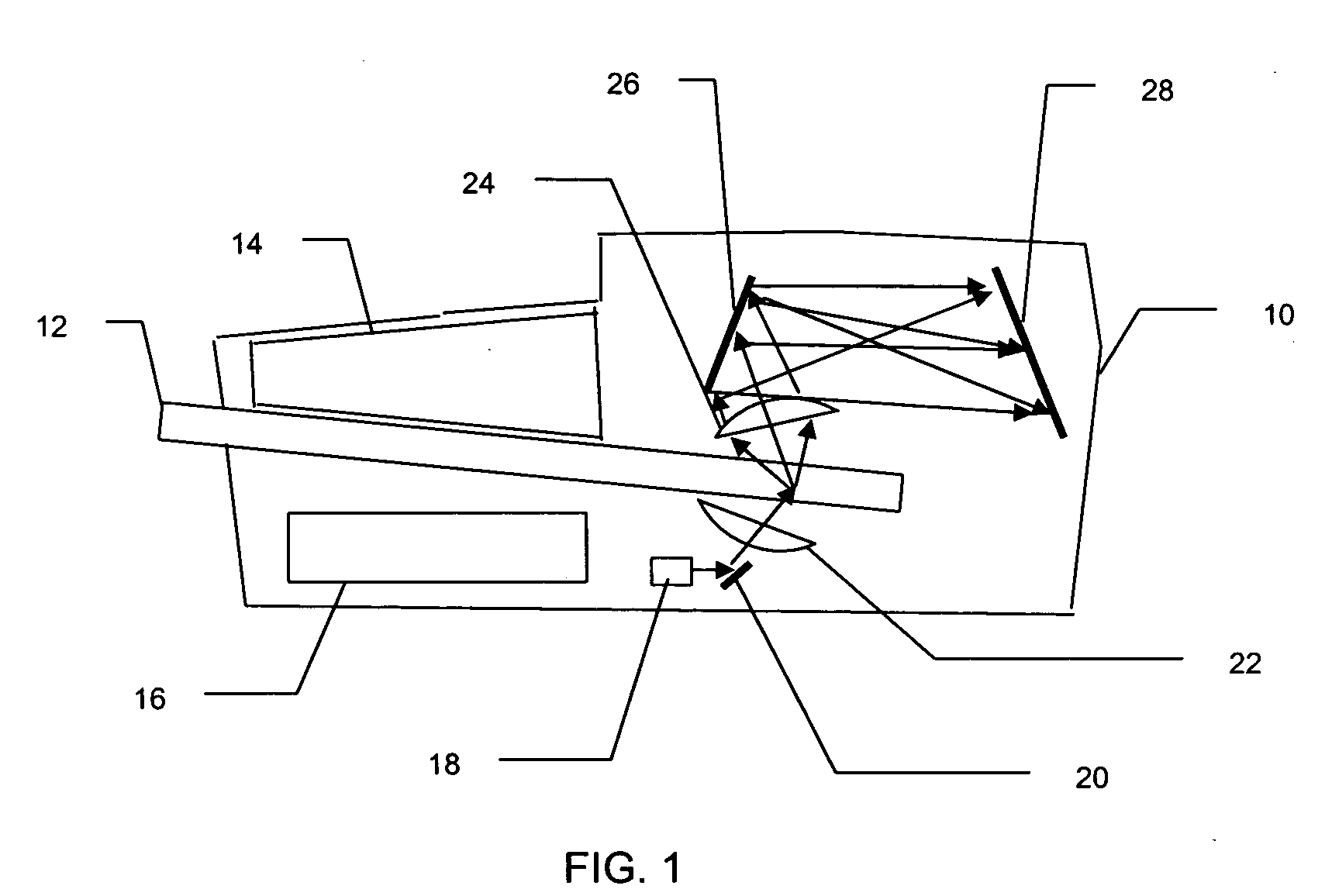
InactiveUS20050007448A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsTime gatingInelastic scattering
The invention is directed to a remote 3-D imaging system which uses a novel illumination source to establish the relationship of the image features to the system, which is displayed by virtue of calculations. In addition to static surfaces, moving surfaces may be studied and corrections due to turbidity and platform position are also easily compensated for. The instant system may also contain a plurality of sensing systems based on light, including traditional reflective or elastic scattering and novel fluorescent or non-elastic scattering still and video imaging systems, including time-gated systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
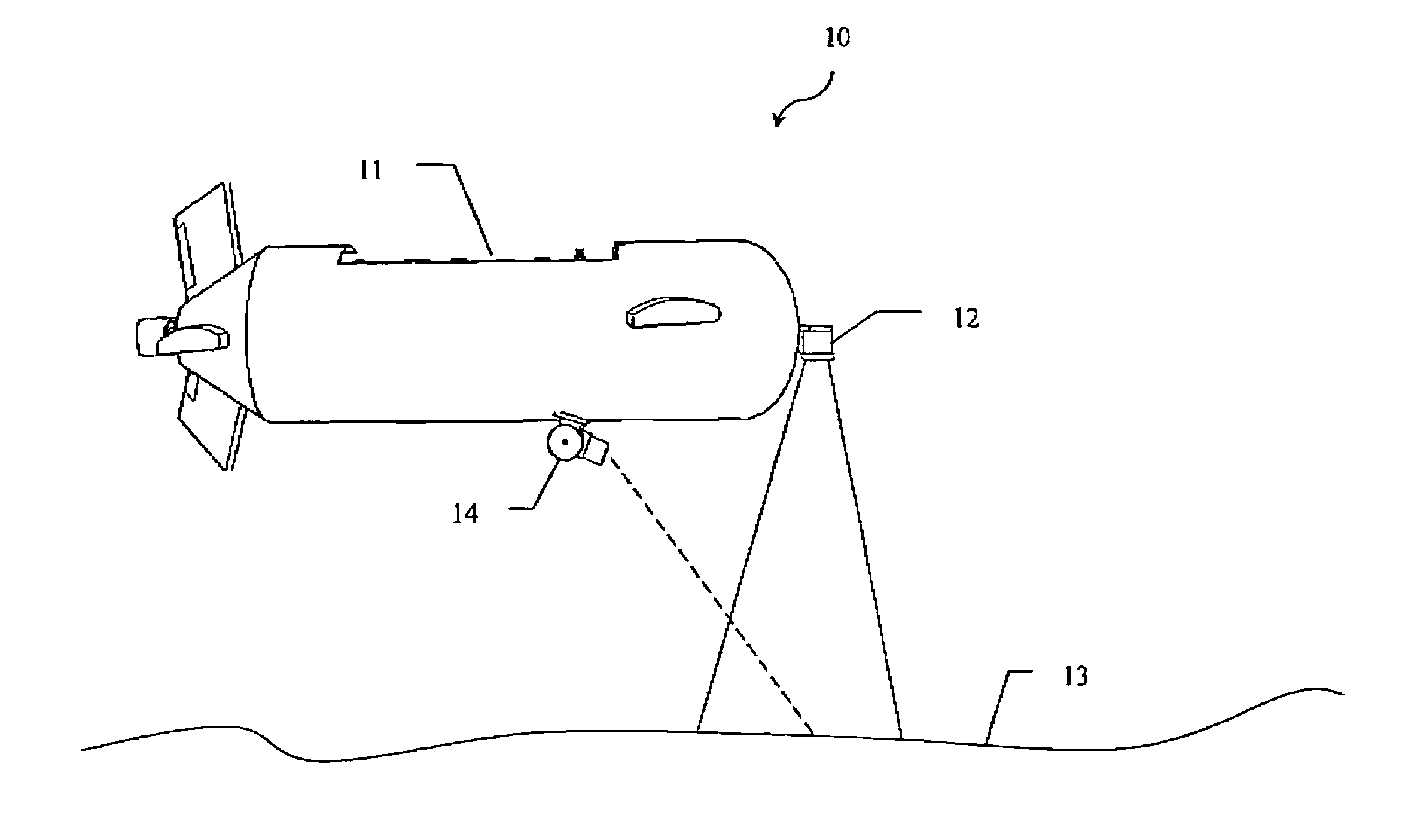
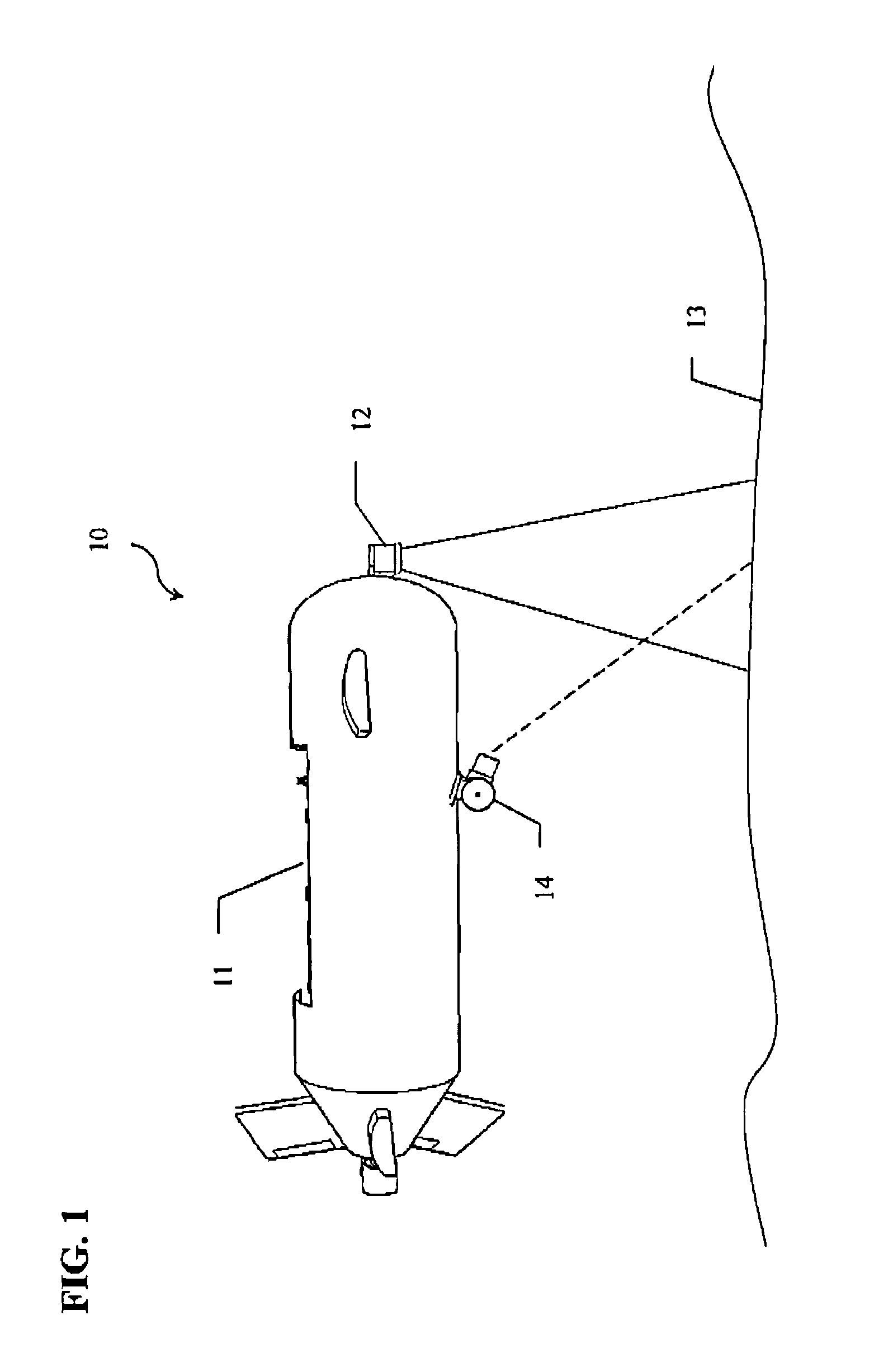
Method and Apparatus for Fluid Influx Detection While Drilling
A C / O ratio is determined using measurements of inelastically scattered gamma rays with a pulsed neutron source. Combined with look-up tables, the C / O measurement is used as an indicator of formation fluid influx into wellbore such as gas kick.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Optoelectronic device employing a microcavity including a two-dimensional carbon lattice structure
A microcavity-controlled two-dimensional carbon lattice structure device selectively modifies to reflect or to transmit, or emits, or absorbs, electromagnetic radiation depending on the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation. The microcavity-controlled two-dimensional carbon lattice structure device employs a graphene layer or at least one carbon nanotube located within an optical center of a microcavity defined by a pair of partial mirrors that partially reflect electromagnetic radiation. The spacing between the mirror determines the efficiency of elastic and inelastic scattering of electromagnetic radiation inside the microcavity, and hence, determines a resonance wavelength of electronic radiation that is coupled to the microcavity. The resonance wavelength is tunable by selecting the dimensional and material parameters of the microcavity. The process for manufacturing this device is compatible with standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) manufacturing processes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +2
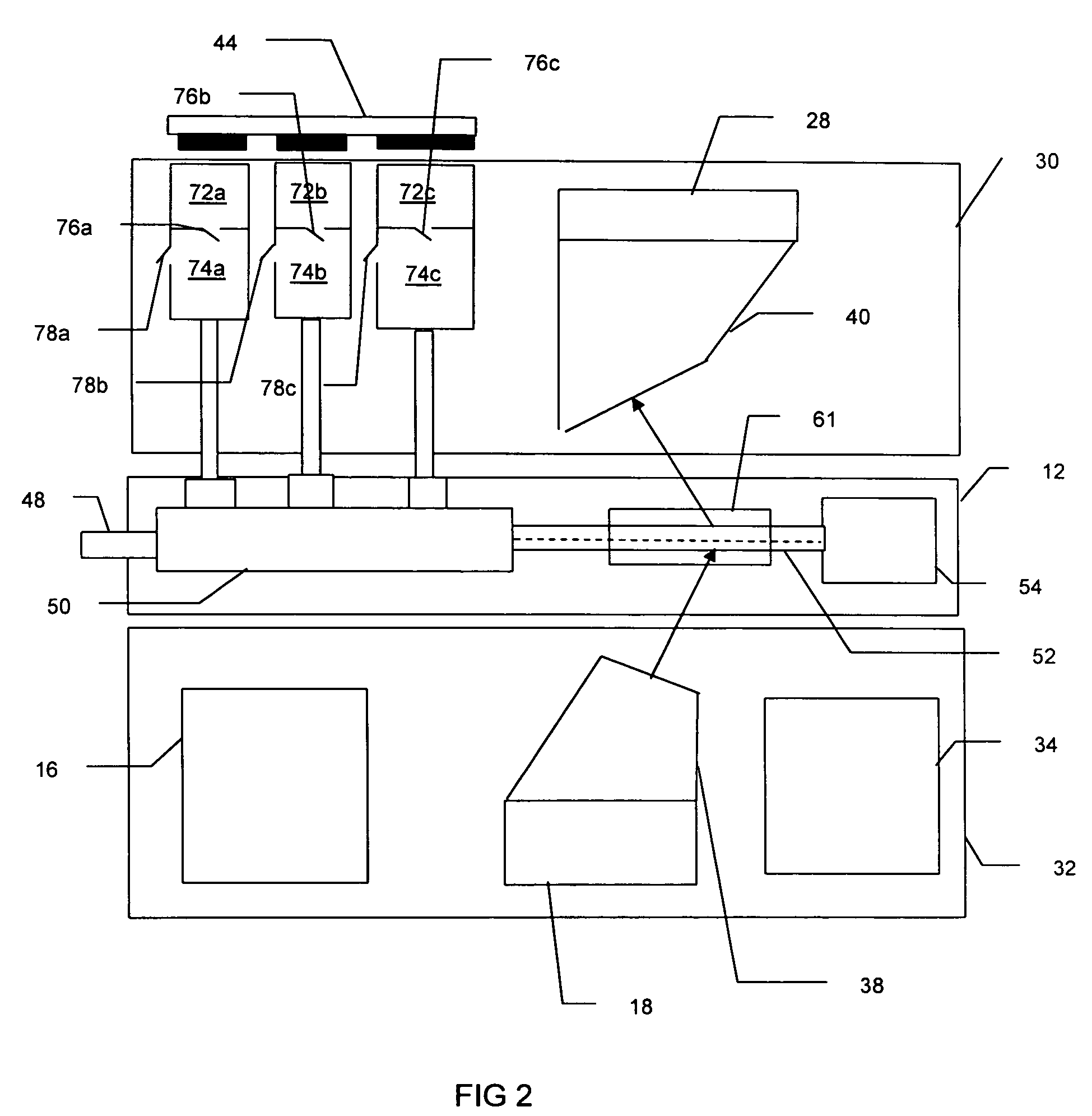
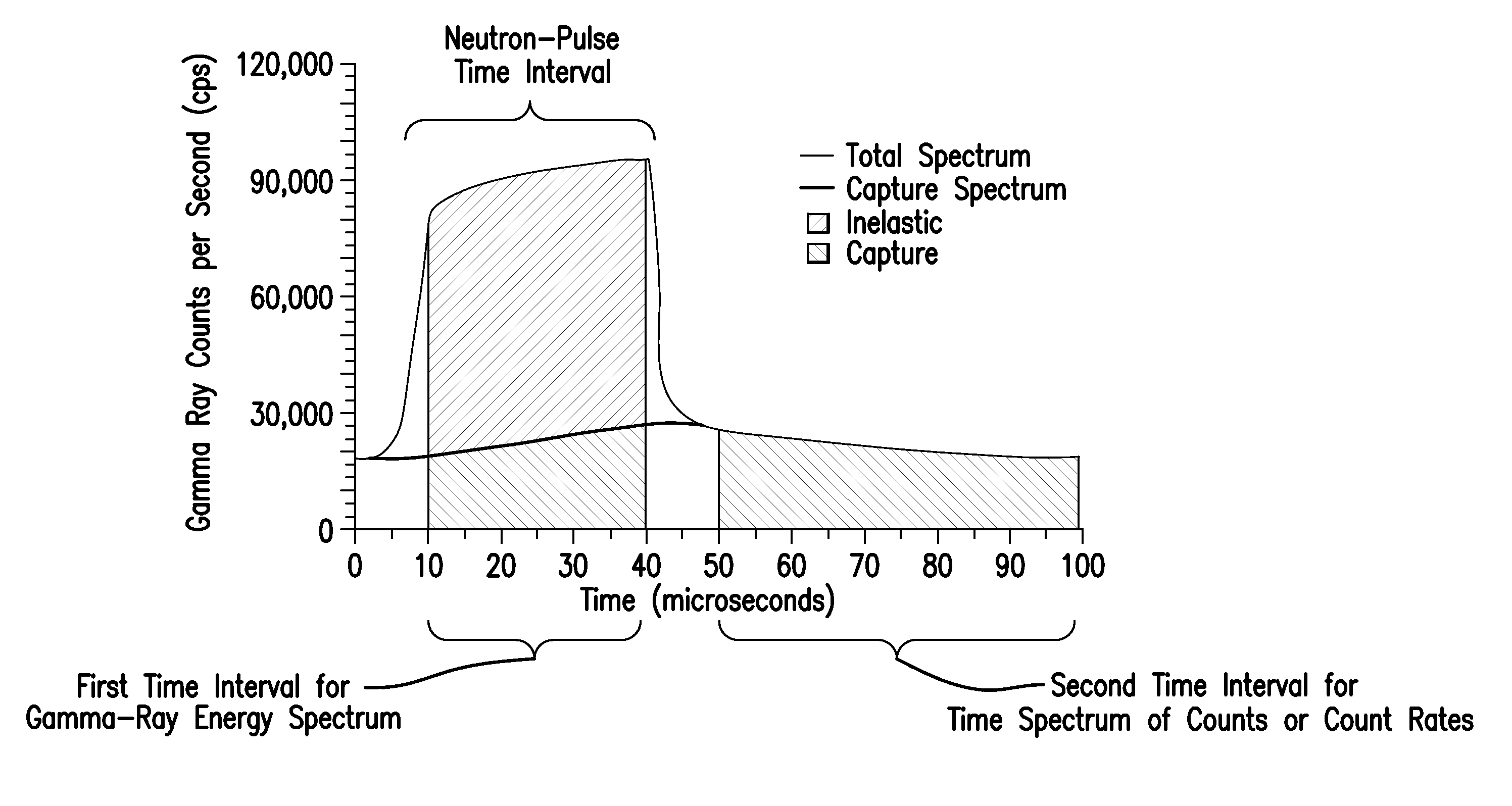
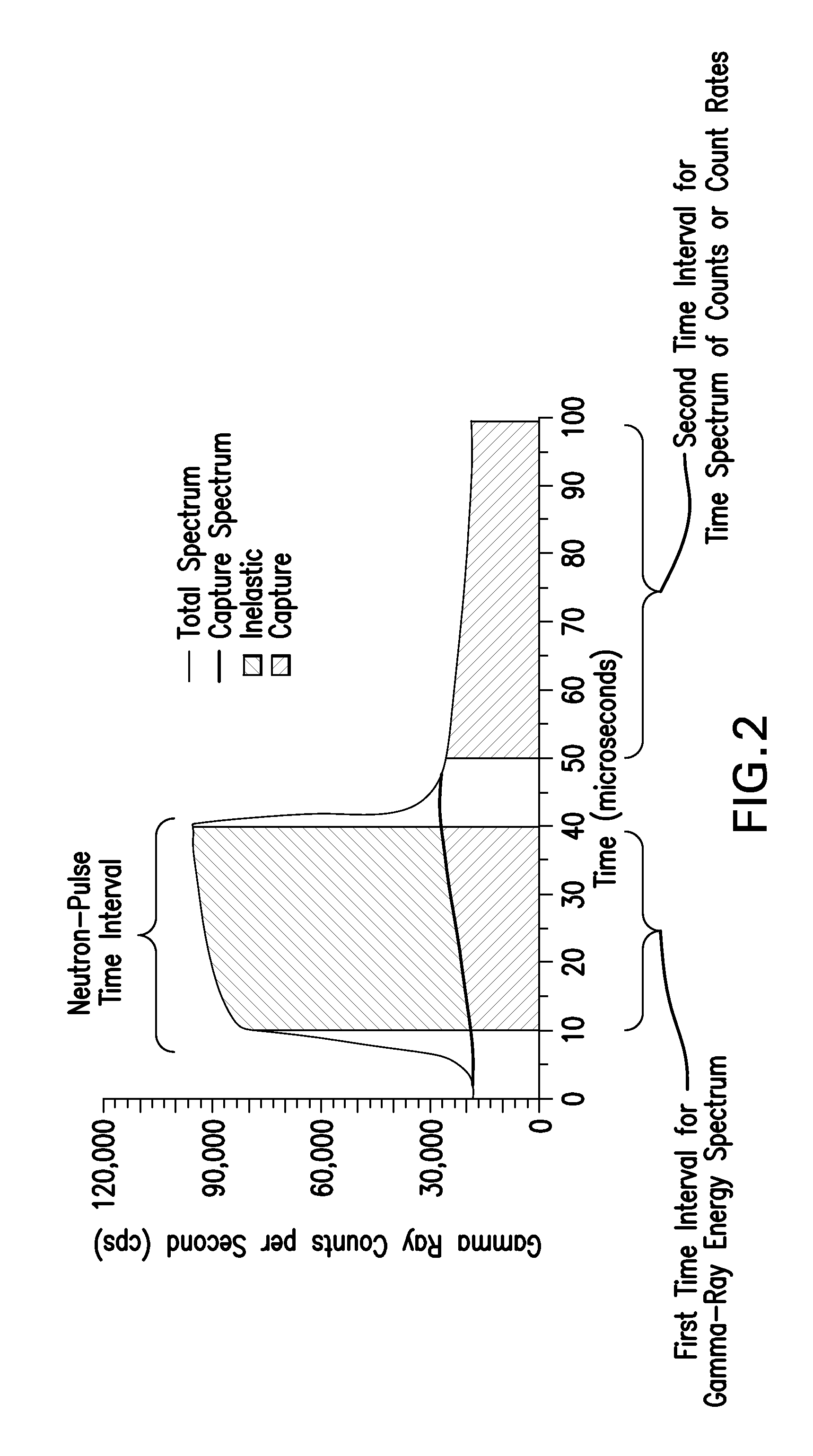
Methods for sourceless density downhole measurement using pulsed neutron generator
InactiveUS20130048849A1Radiation intensity measurementNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
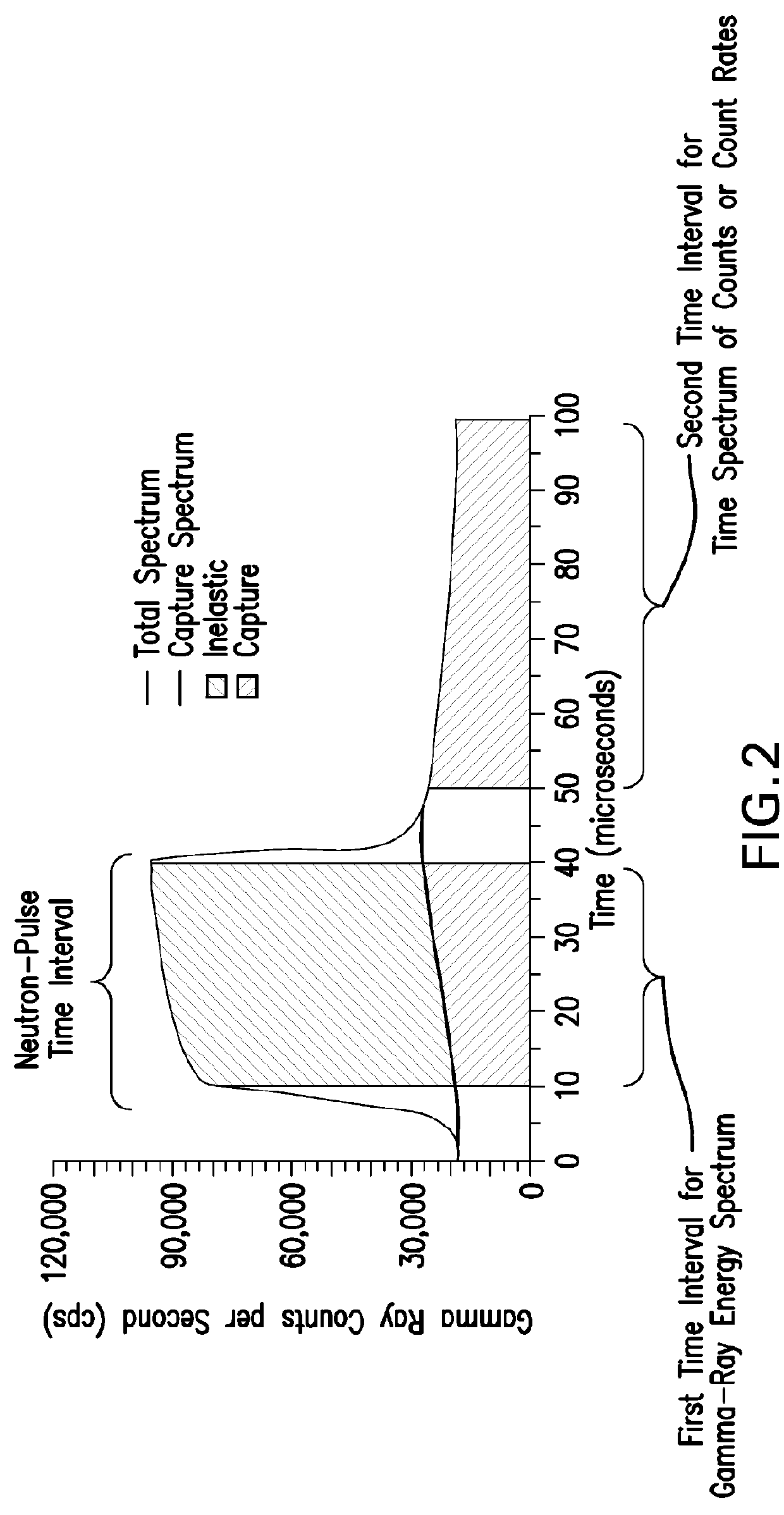
Disclosed is a method for estimating a density of an earth formation penetrated by a borehole. The method includes: emitting a pulse of fast neutrons into the formation during a neutron-pulse time interval; detecting gamma-rays due to inelastic scattering and thermal capture of the emitted neutrons in the formation to provide a gamma-ray energy spectrum due to the inelastic scattering and the thermal capture during a first time interval within the neutron-pulse time interval and to provide a time spectrum of counts or count rates due to thermal capture during a second time interval occurring after the neutron-pulse time interval; determining a macroscopic capture cross section of the formation from a decay in the time spectrum of counts or count rates; determining an elemental weight fraction from the gamma-ray energy spectrum; and estimating the density of the formation using the macroscopic capture cross section and the elemental weight fraction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
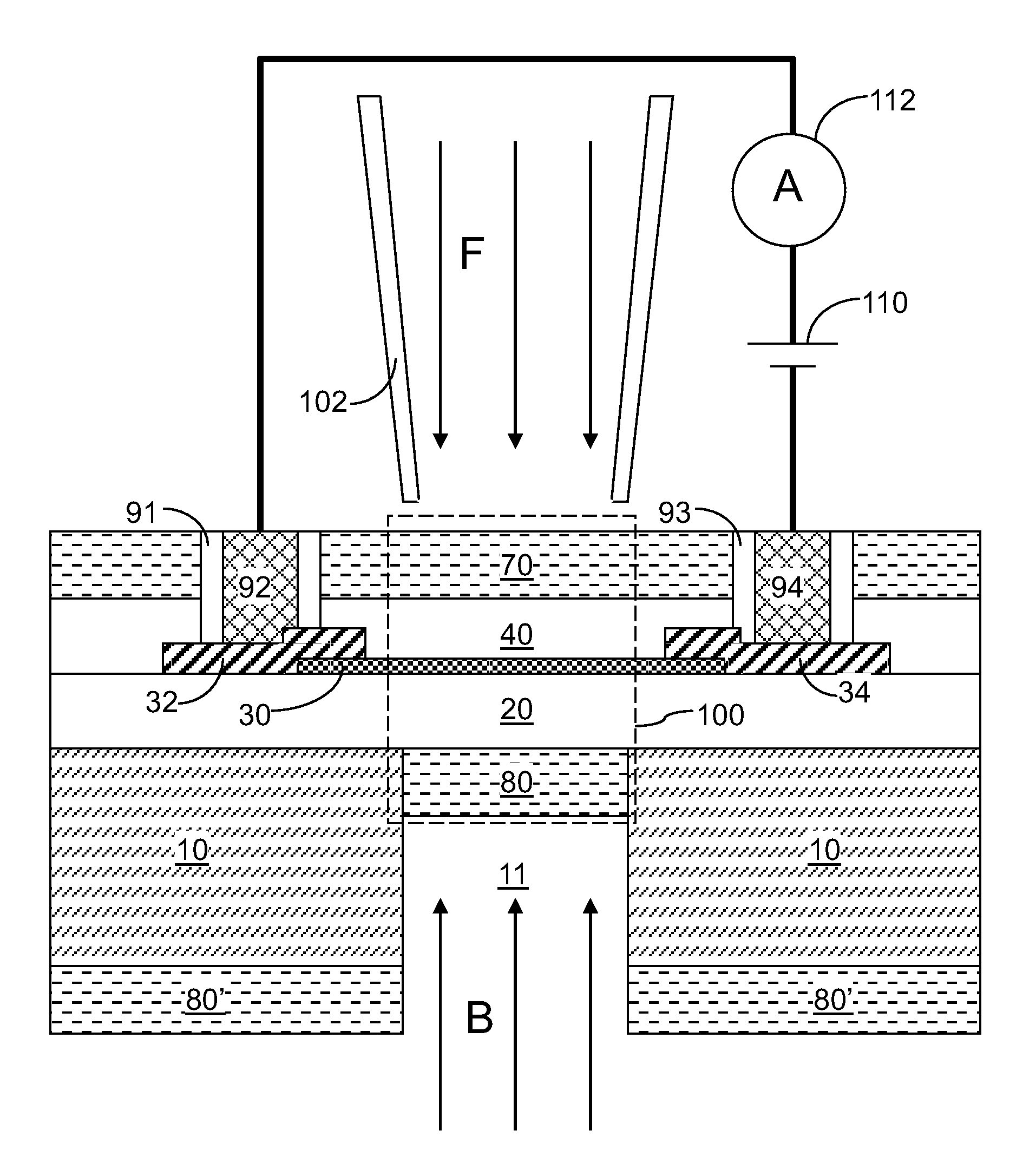
Surface contamination analyzer for semiconductor wafers, method used therein and process for fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020123161A1Improve reliabilityHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesElectricityInelastic scattering
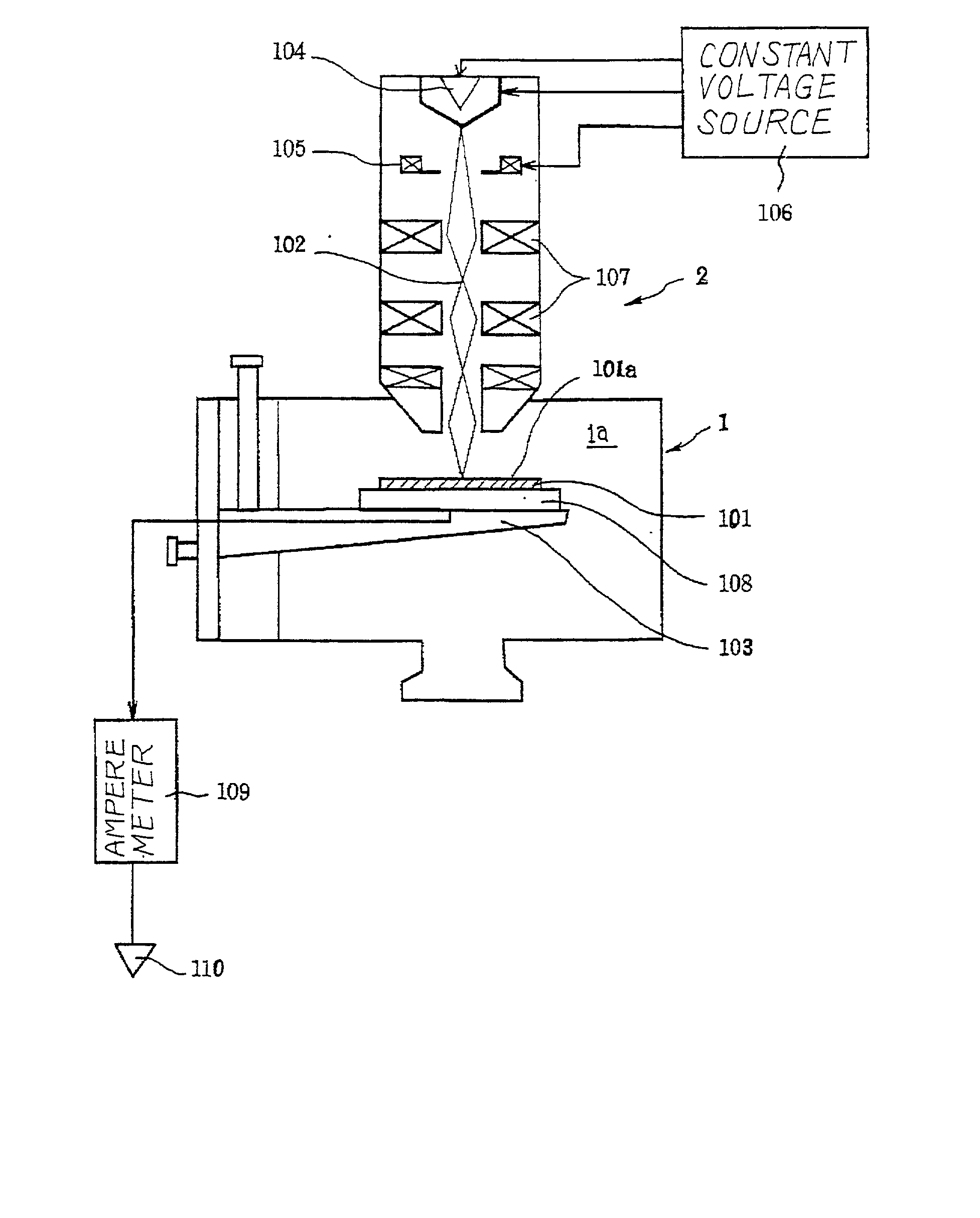
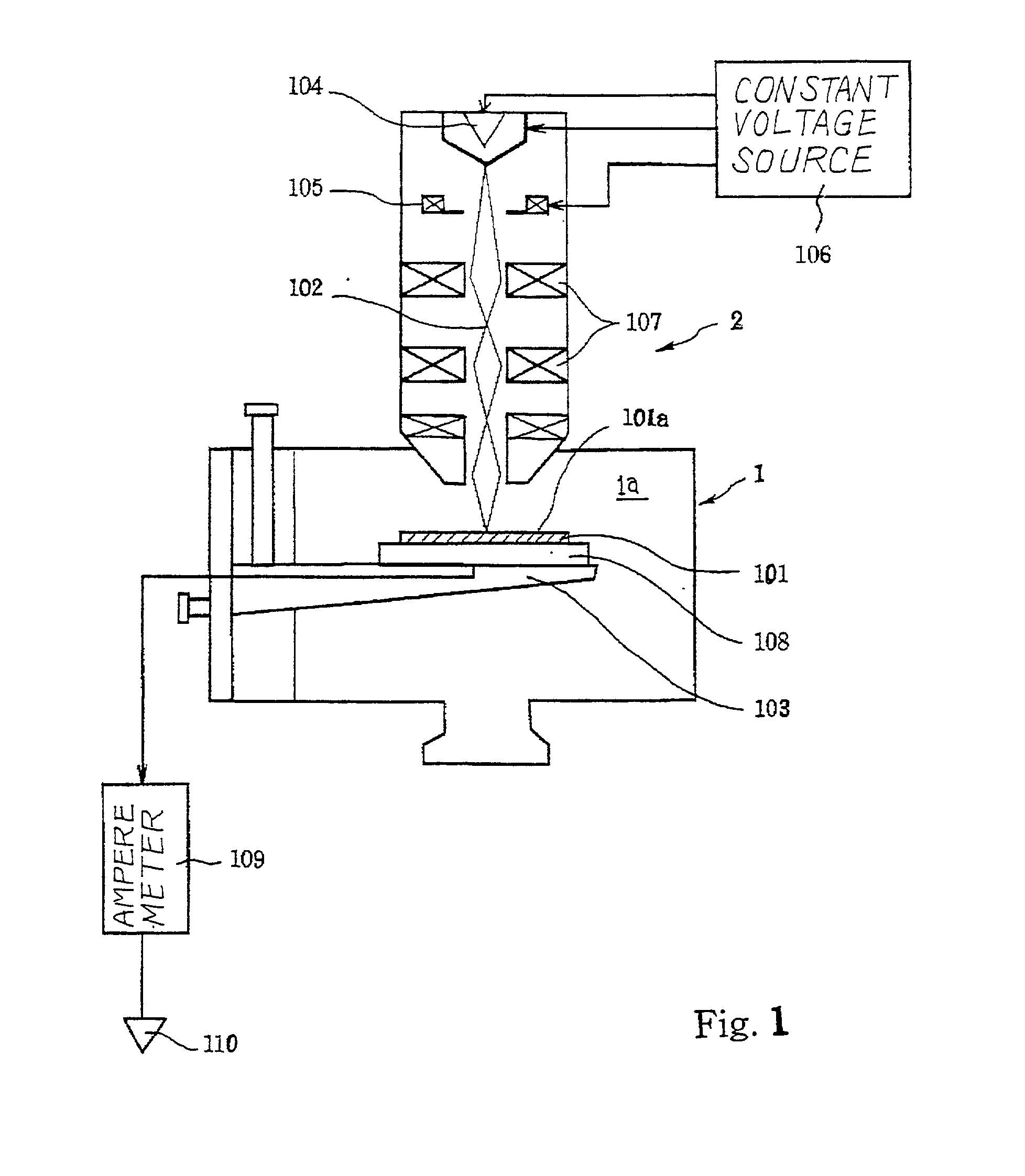
A semiconductor wafer is radiated with an electron beam so that the inelastic scattering takes place in the narrow region, and current flows out from the narrow region; the amount of current is dependent on the substance or substances in the narrow region so that the analyst evaluates the degree of contamination on the basis of the substance or substances specified in the narrow region.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Absolute elemental concentrations from nuclear spectroscopy
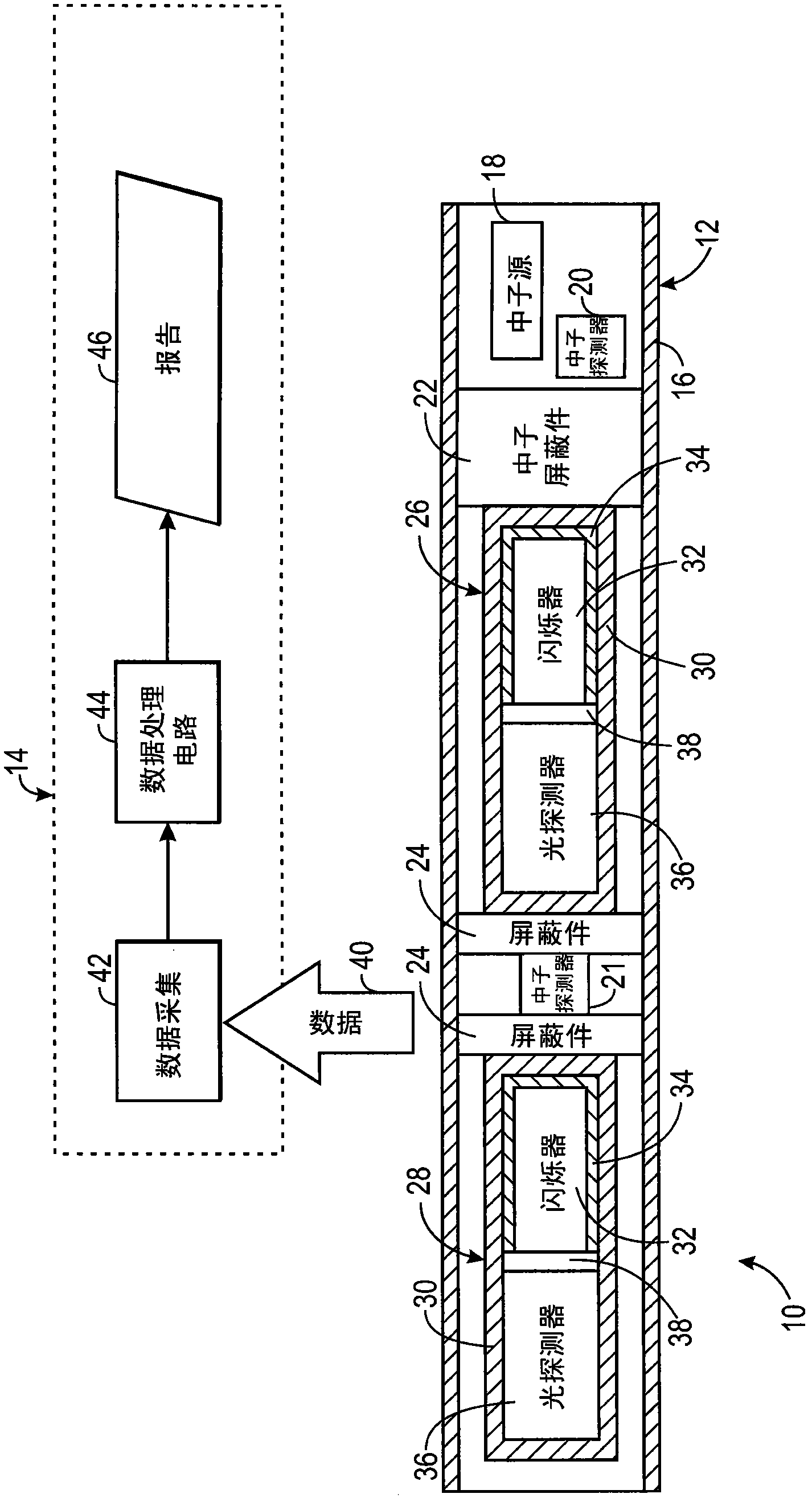
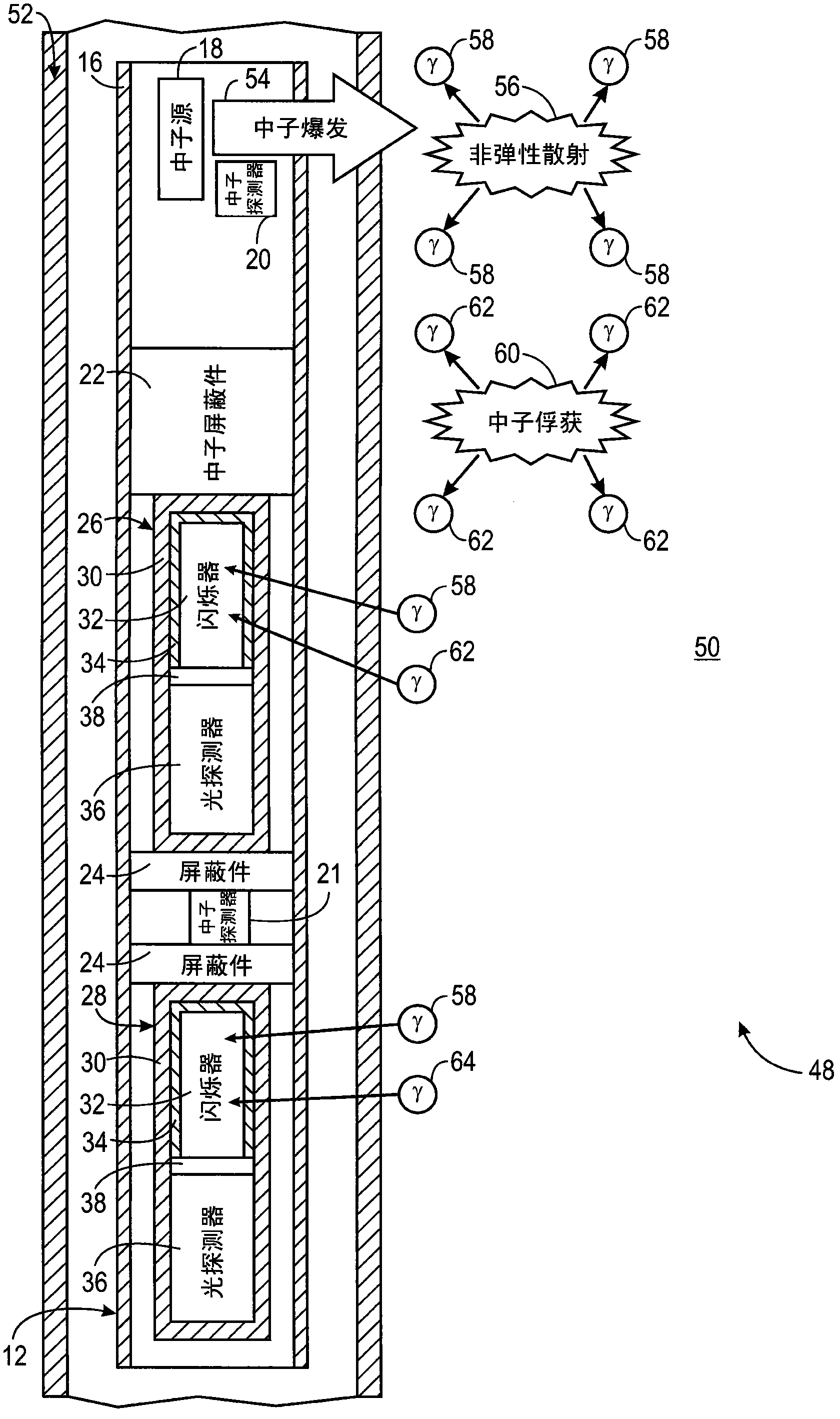
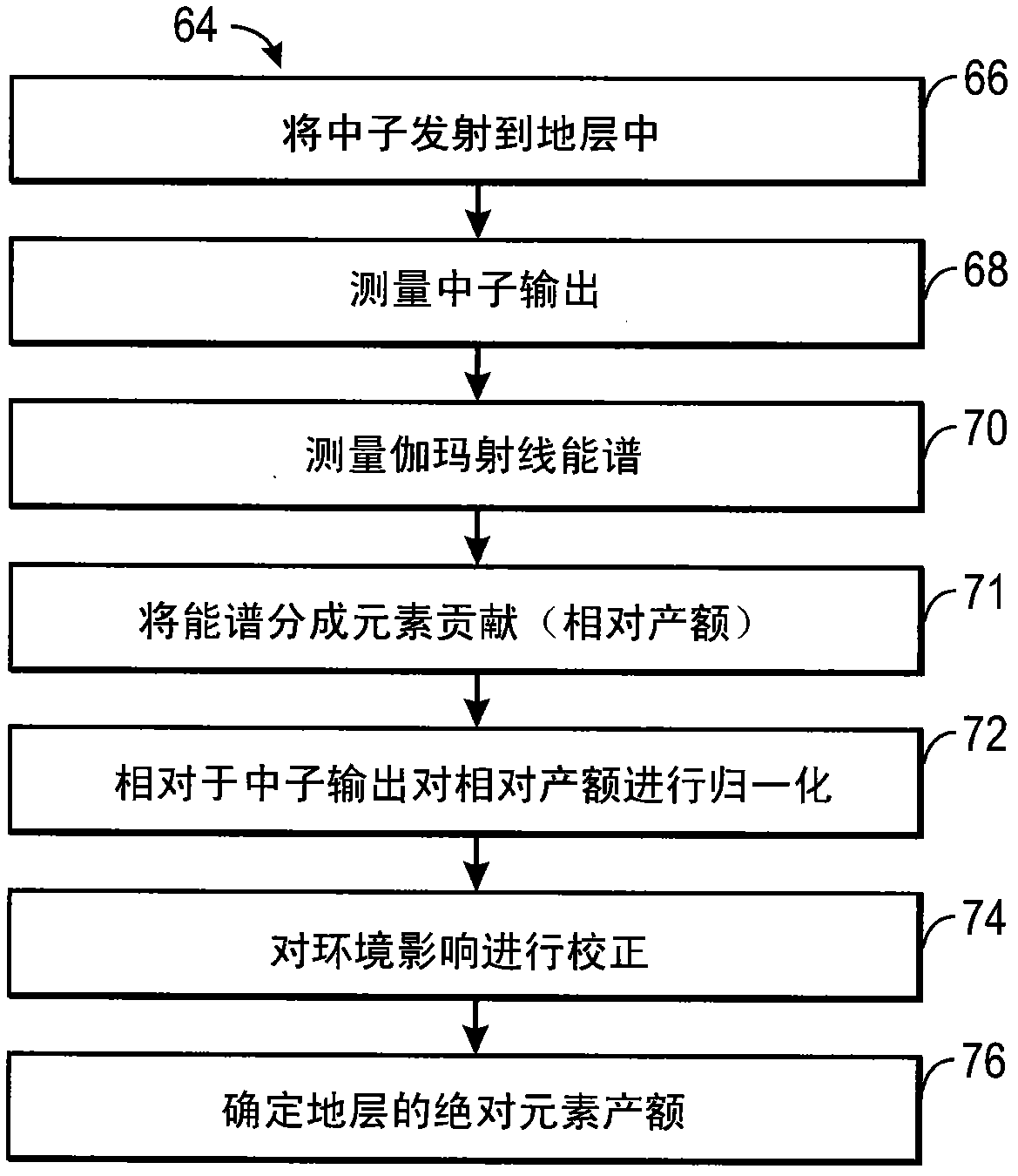
ActiveCN102084271AX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
The present invention discloses a system and method for estimating absolute elemental concentrations of a subterranean formation from neutron-induced gamma-ray spectroscopy. In one example, a system (10) for estimating an absolute yield of an element in a subterranean formation may include a downhole tool (12) and data processing circuitry (14). The downhole tool may include a neutron source (18) to emit neutrons into the formation, a neutron monitor (20) to detect a count rate of the emitted neutrons, and a gamma-ray detector (26,28) to obtain gamma-ray spectra deriving at least in part from inelastic gamma- rays produced by inelastic scattering events and neutron capture gamma-rays produced by neutron capture events. The data processing circuitry may be configured to determine a relative elemental yield from the gamma-ray spectra and to determine an absolute elemental yield based at least in part on a normalization of the relative elemental yield to the count rate of the emitted neutrons.
Owner:PRAD RES & DEV LTD
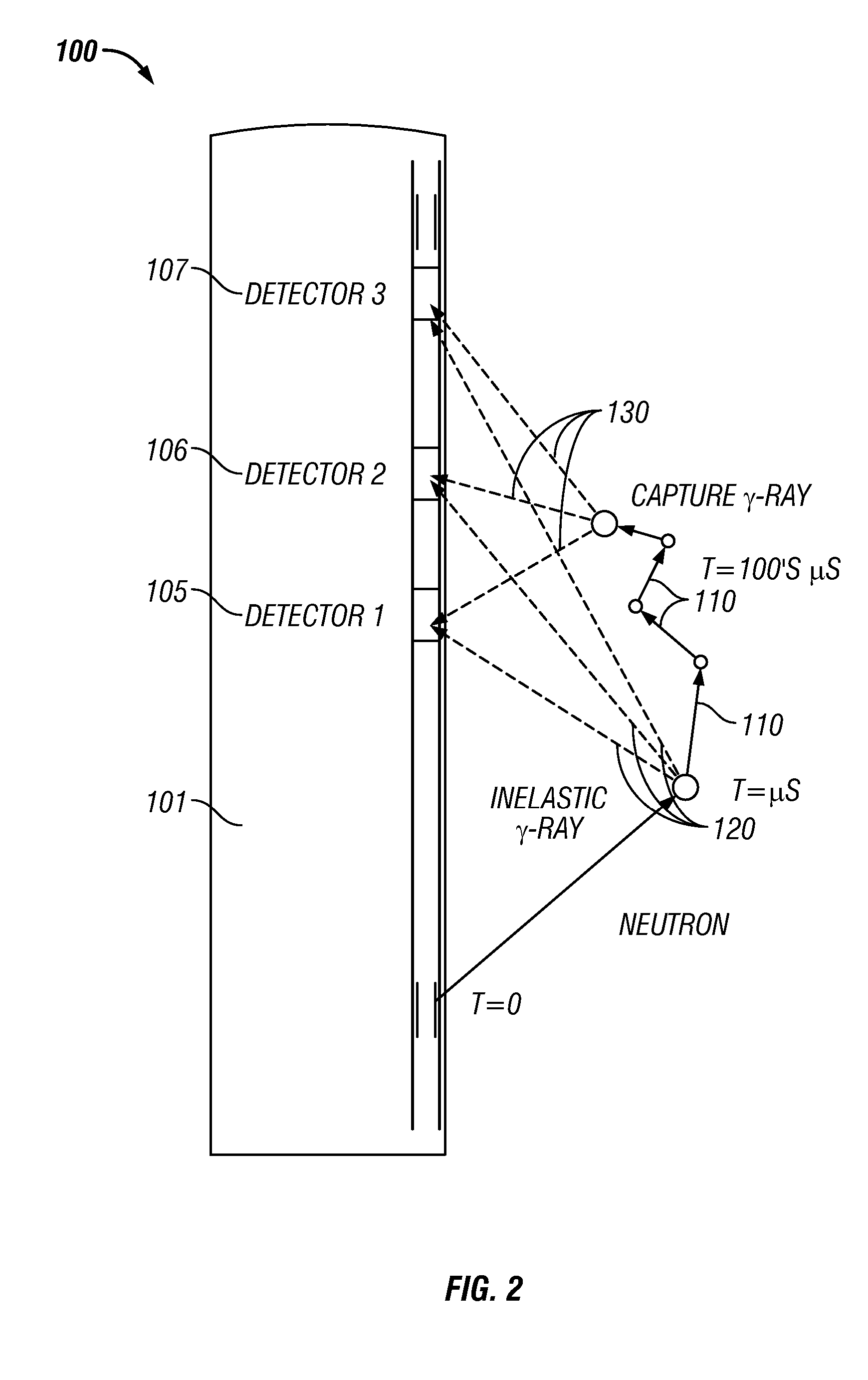
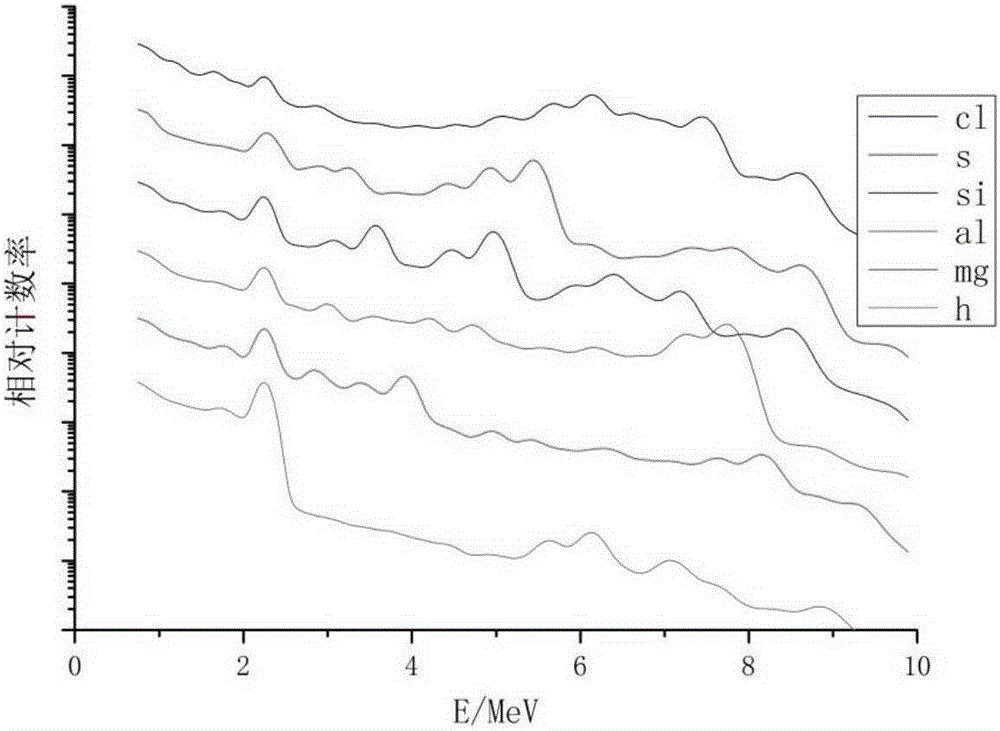
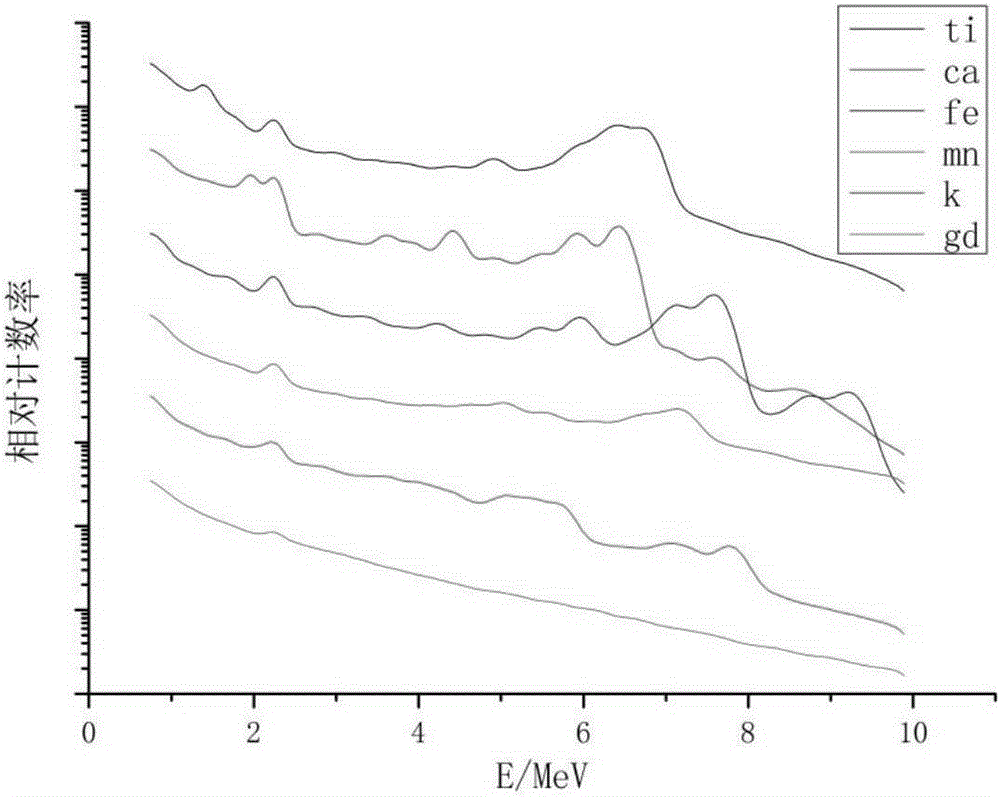
Method for obtaining pure inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra in stratum element well logging
ActiveCN104297810AAvoid double deductionAvoid the situationNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringWell logging
The invention provides a method for obtaining pure inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra in stratum element well logging. The method includes the following steps that the inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra and capture gamma-ray energy spectra of a target stratum are obtained according to well logging materials, wherein the inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra include the capture radiation reaction influence; the inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra including the capture radiation reaction influence are segmented by the adoption of the feature of the elements in the known stratum and the feature of the capture gamma rays, and corresponding deduction coefficients are arranged for all the energy spectrum segments; according to the deduction coefficients of all the energy spectrum segments and the deduction amount determined by the product of the capture gamma-ray energy spectra of the corresponding energy spectrum segments, the influence of the capture radiation reaction is deducted from the inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra of the corresponding energy spectrum segments so as to obtain the pure inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra of the target stratum. By means of the method, the more pure inelastic scattering gamma-ray energy spectra can be obtained.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Apparatus, computer-accessible medium and method for measuring chemical and/or molecular compositions of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in anatomical structures
InactiveUS20090073439A1Reduce absorptionReduce scatterDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnalogue computers for chemical processesInelastic scatteringAnatomical structures
Exemplary apparatus and method can be provided for controlling at least one electro-magnetic radiation. For example, it is possible to rotate and / or translate at least one optical waveguide. At least one of the optical waveguide(s) can receive a first radiation at a first wavelength and transmit the first radiation to at least one sample. Such optical waveguide and / or another optical waveguide may receive a second radiation at a second wavelength that is different from the first wavelength. For example, the second radiation may be produced based on an inelastic scattering of the first radiation. In addition, exemplary apparatus and method can be provided which can also be used to receive data associated with the second radiation, determine at least one characteristic of the at least one sample based on the data, and generate the image and / or the map of a portion of the arterial sample based on the at least one characteristic. Further, exemplary computer-accessible medium can be provided which includes a software arrangement thereon. When a processing arrangement executes the software arrangement, the processing arrangement is configured to modify at least one characteristic of an arrangement using certain procedures. These exemplary procedures include simulating at least one electro-magnetic radiation provided into and out of the arrangement, simulating an inelastic scattering radiation from at least one simulated sample, receiving the simulated inelastic scattering radiation into and out of the simulated arrangement, and determining a simulated characteristic of the simulated arrangement as a function of the simulated inelastic scattering radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Raman detection based flow cytometer
InactiveUS20060103840A1Radiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesInelastic scatteringParticle flow
A method and apparatus for enabling chemical identification of individual particles, cells of molecules by obtaining a Raman spectrum of a particle, cell or molecule as it flows past a sensing point in a flow cytometer. The particles, which may be cells or molecules, are associated with a suitable noble metal colloid or colloidal aggregate. Cellular particles may be associated with gold or silver colloidal particles by ultra-sonic sonification while in a sample preparation reservoir containing the gold or silver colloidal suspension. The colloid associated particles are then hydrodynamically focused into a single file by a fluid control module. The surface-enhance Raman Spectrum of individual particles are obtained by illuminating the particle with a laser as the particle flows past a sensing point and gathering the light that is non-elastically scattered (Raman scattered) by the particle. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum is then analyzed to identify the particle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Raman detection based flow cytometer
A method and apparatus for enabling chemical identification of individual particles, cells of molecules by obtaining a Raman spectrum of a particle, cell or molecule as it flows past a sensing point in a flow cytometer. The particles, which may be cells or molecules, are associated with a suitable noble metal colloid or colloidal aggregate. Cellular particles may be associated with gold or silver colloidal particles by ultra-sonic sonification while in a sample preparation reservoir containing the gold or silver colloidal suspension. The colloid associated particles are then hydrodynamically focused into a single file by a fluid control module. The surface-enhance Raman Spectrum of individual particles are obtained by illuminating the particle with a laser as the particle flows past a sensing point and gathering the light that is non-elastically scattered (Raman scattered) by the particle. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum is then analyzed to identify the particle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
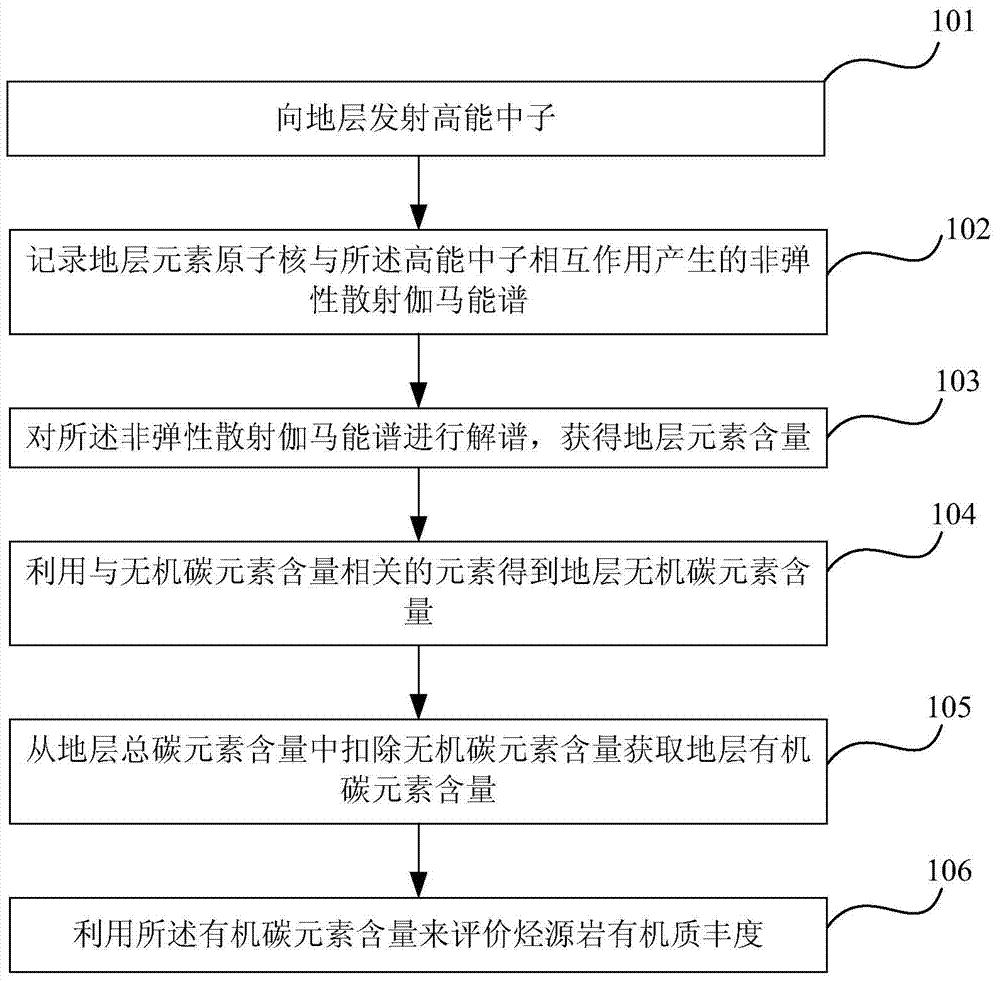
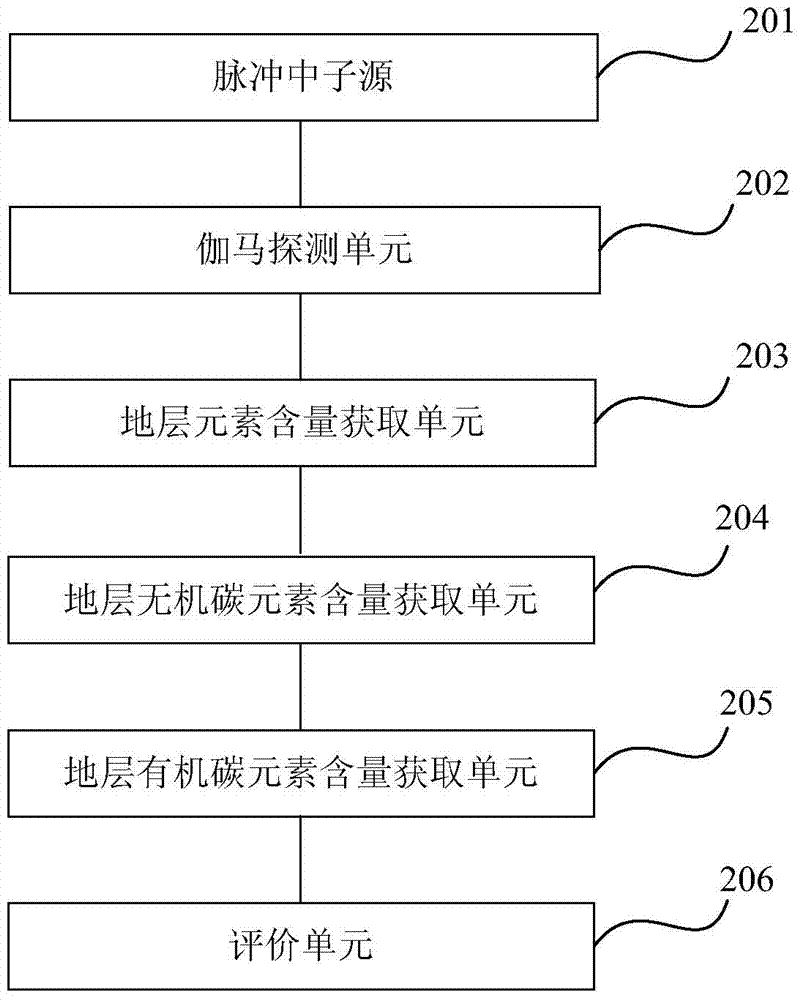
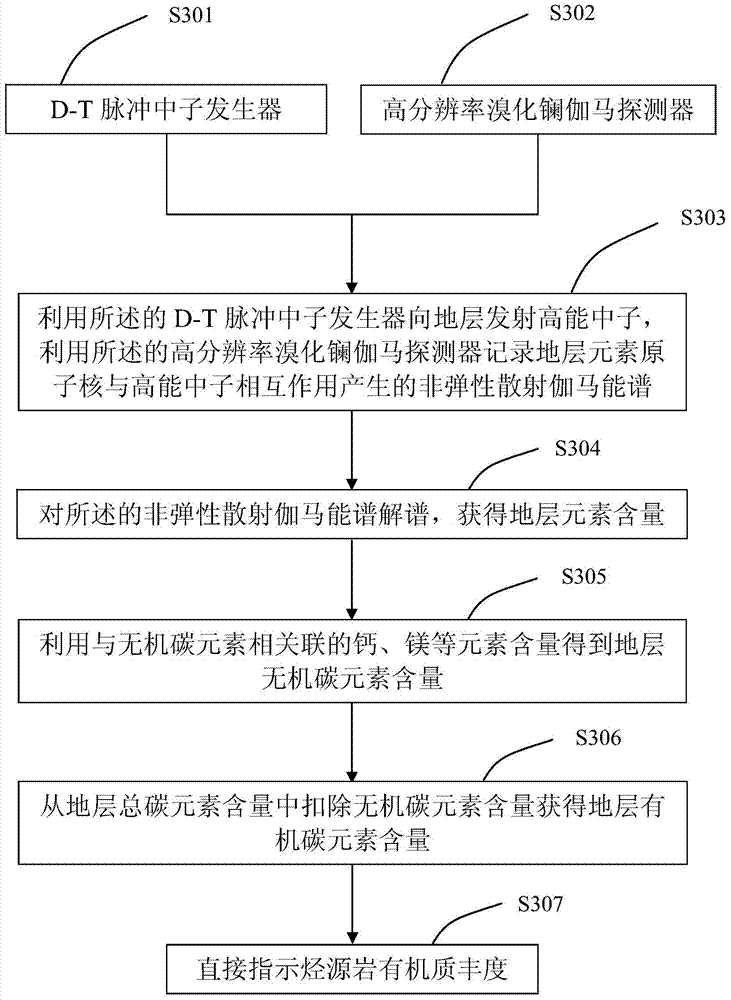
Method and device for evaluating abundance of organic matter of hydrocarbon source rock
InactiveCN103760182ASolve the technical status of evaluating organic carbon elementsMeet the needs of direct evaluation of organic matter abundance in source rocksMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationInelastic scatteringSoil organic matter
The invention provides a method and a device for evaluating abundance of organic matter of a hydrocarbon source rock, wherein the method comprises the following steps: emitting high-energy neutron to a stratum; recording an inelastic scattering gamma-ray spectra generated by the interaction of nucleus of elements in the stratum and the high-energy neutron; analyzing the inelastic scattering gamma-ray spectra, to obtain the content of elements in the stratum; obtaining the content of inorganic carbon in the stratum by using the elements associated with the content of the inorganic carbon; deducting the content of the inorganic carbon from the total carbon content of the stratum, so as to obtain the content of the organic carbon in the stratum; evaluating the abundance of organic matter of the hydrocarbon source rock by using the content of the organic carbon element.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
3-D imaging system with pre-test module
InactiveUS7796809B1Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionColor television detailsInelastic scatteringFluorescence
A remote 3-D imaging system which uses a novel angular relationship to establish the relationship of the image features to the system, which is displayed by virtue of calculations. In addition to static surfaces, moving surfaces may be studied and corrections due to turbidity and platform position are also easily compensated for. A pre-test module is also included which predicts and has the ability to re-adjust the instrumentation to the test conditions as predicted by a hybrid Monte Carlo model. The instant system may also contain a plurality of sensing systems based on light, including traditional reflective or elastic scattering and novel fluorescent or non elastic scattering still and video imaging systems, including time-gated systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Rapid multiplexed infrared 3D nano-tomography
ActiveUS20190317012A1Sufficient speedIncrease ratingsColor/spectral properties measurementsInelastic scatteringFractography
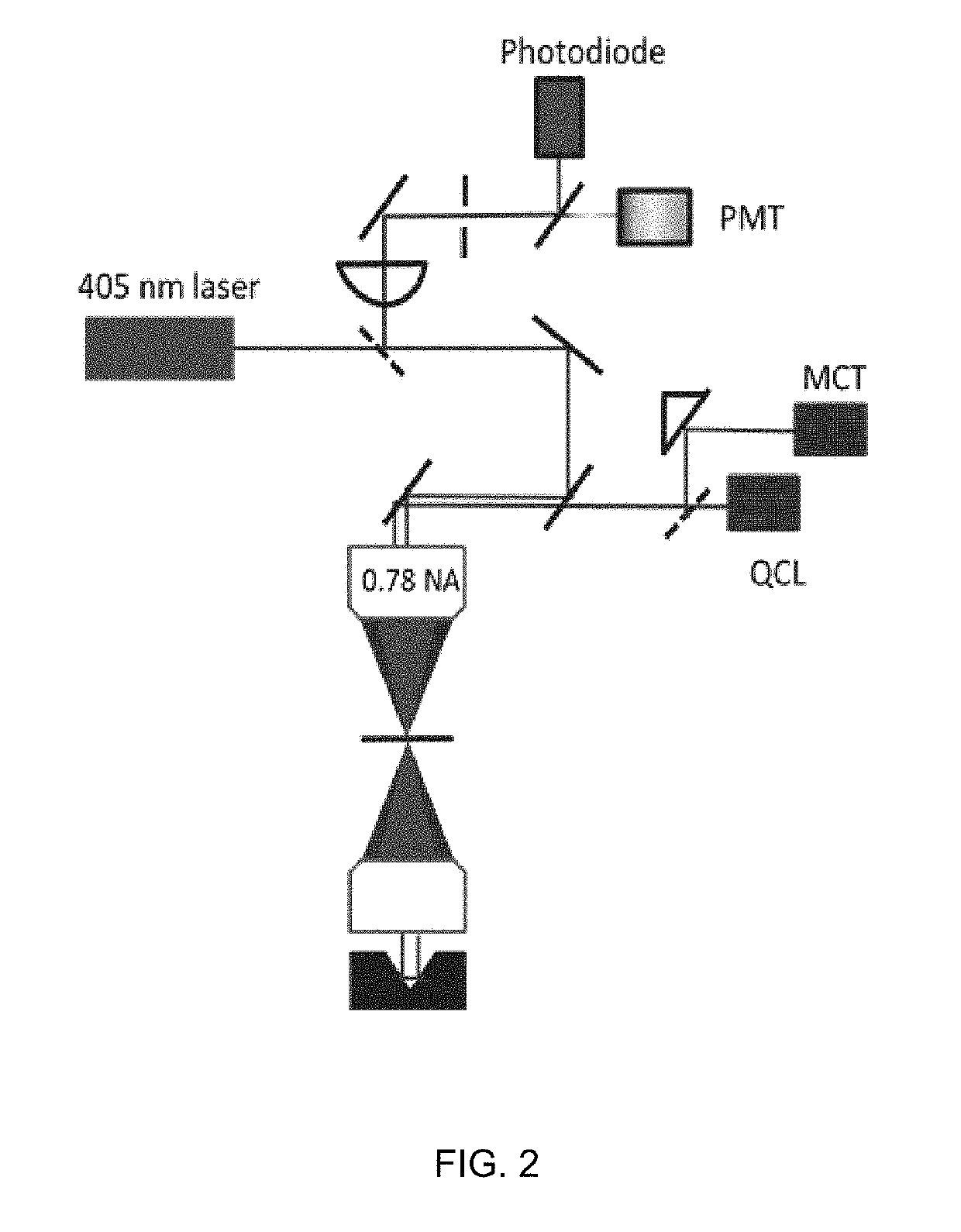
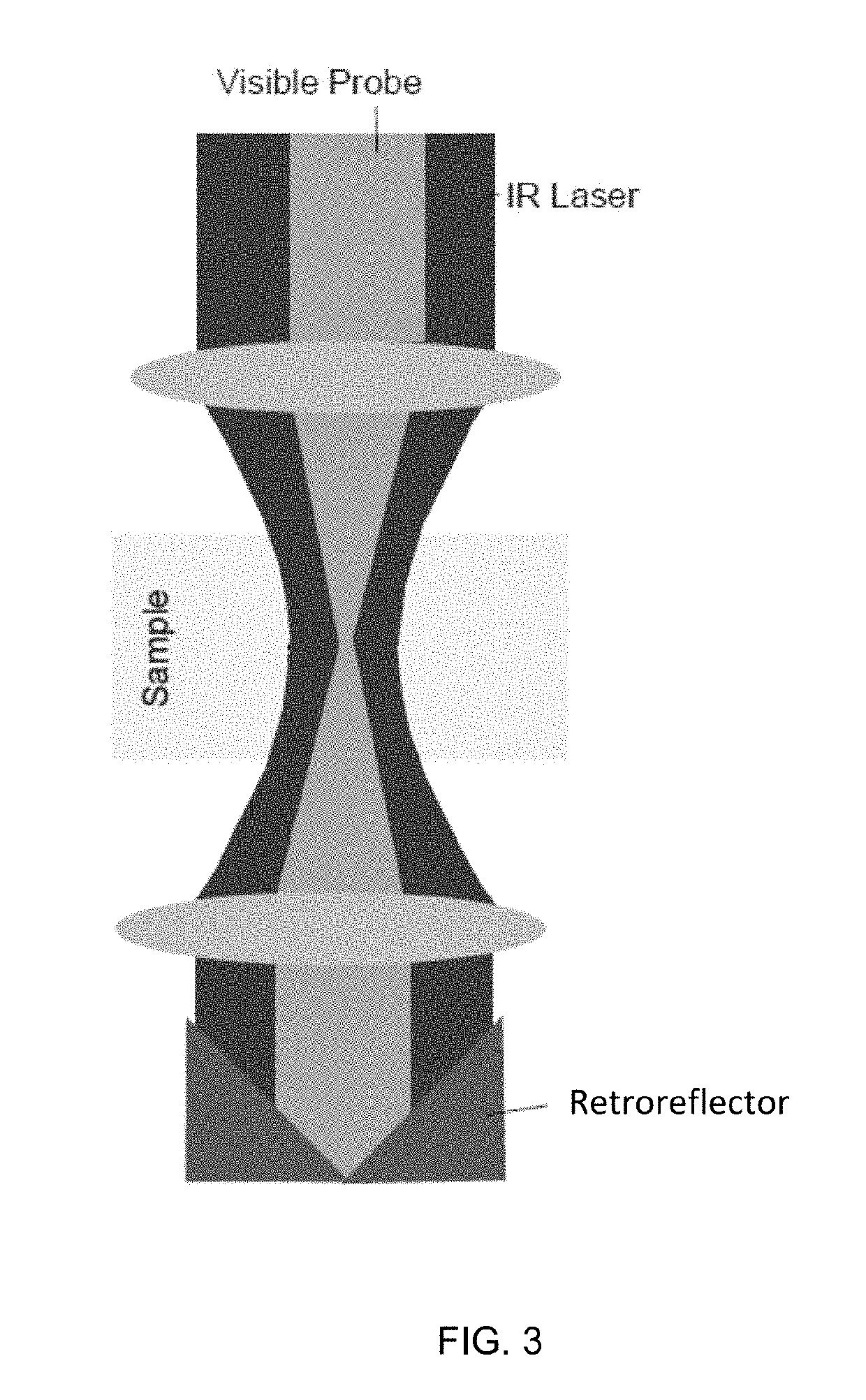
A method and system for rapid, label free nanoscale chemical imaging and tomography (3D) with multiplexing for speed, and engineered coherent illumination and detection to achieve 3-D resolution at twice the Abbe limit. A sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using a modulated infrared light source and the resulting probe beam modulation is measured with one or more visible laser probes. Varying the infrared wavelength results in a spectrum which characterizes the chemical composition of the sample. Optionally, inelastically scattered light generated as a result of the probe beam interacting with the sample is collected simultaneously to yield additional chemical information.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Stratum element logging element standard spectrum making and application method
InactiveCN105182422AShort cycleSave moneyX-ray spectral distribution measurementSeismology for water-loggingInelastic scatteringEngineering
The invention discloses a stratum element logging element standard spectrum making and application method. First of all, an element standard spectrum is made by use of a Monte Carlo value simulation method, and then, experiment verification is carried out on the element standard spectrum by use of an instrument actual measurement power spectrum so that correctness and availability of the element standard spectrum are guaranteed. After a captured gamma power spectrum and / or an inelastic scattering gamma power spectrum of stratum elements are obtained, based on the element standard spectrum, spectrum unfolding is carried out on the captured gamma power spectrum and / or the inelastic scattering gamma power spectrum through a least square method, and the contents of the stratum elements are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention, the element yield can be rapidly and accurately obtained, and the calculation accuracy and the calculation efficiency of the element contents are guaranteed.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
3-D imaging system
InactiveUS7417666B2Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsTime gatingInelastic scattering
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Time resolved raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS8325337B2Low costHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhotometry using reference valueComputer control systemInelastic scattering
System, method, and apparatus for determining the composition of a sample of material. In one embodiment, the method pertains to the counting of photons that were inelastically scattered by the sample, and for minimizing the effects of fluorescent or phosphorescent photons. In yet another embodiment of the invention, a sample is illuminated by a repetitive pulse of monochromatic light, and the resultant scattered photons from the samples are collected and counted during a predetermined integration period. Yet other embodiments pertain to a low-cost, computer-controlled system for repetitively counting inelastically scattered photons so as to create a Raman histogram and a Raman spectrogram of the photons.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for fluid influx detection while drilling
A C / O ratio is determined using measurements of inelastically scattered gamma rays with a pulsed neutron source. Combined with look-up tables, the C / O measurement is used as an indicator of formation fluid influx into wellbore such as gas kick.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
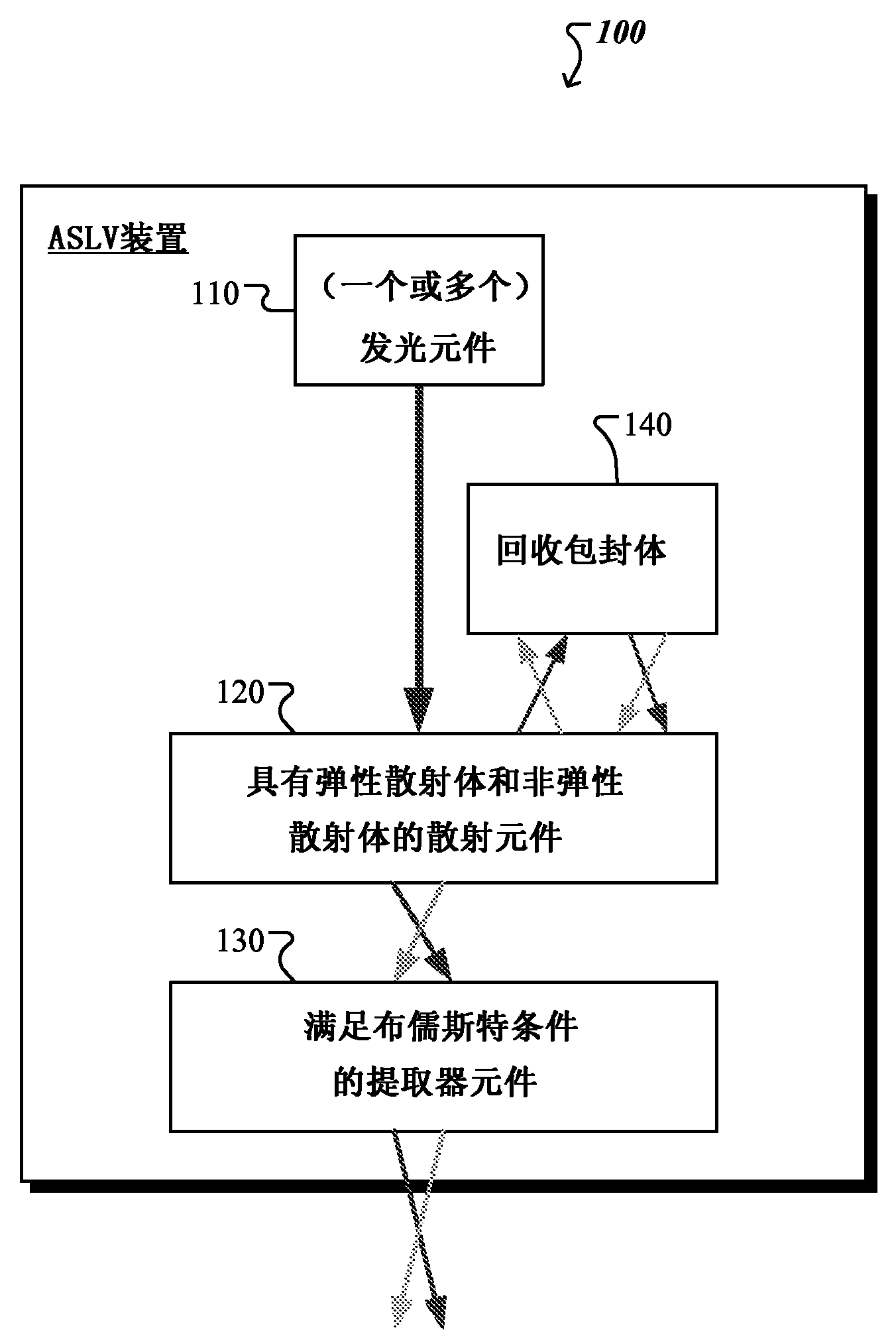
Light-emitting devices providing asymmetrical propagation of light
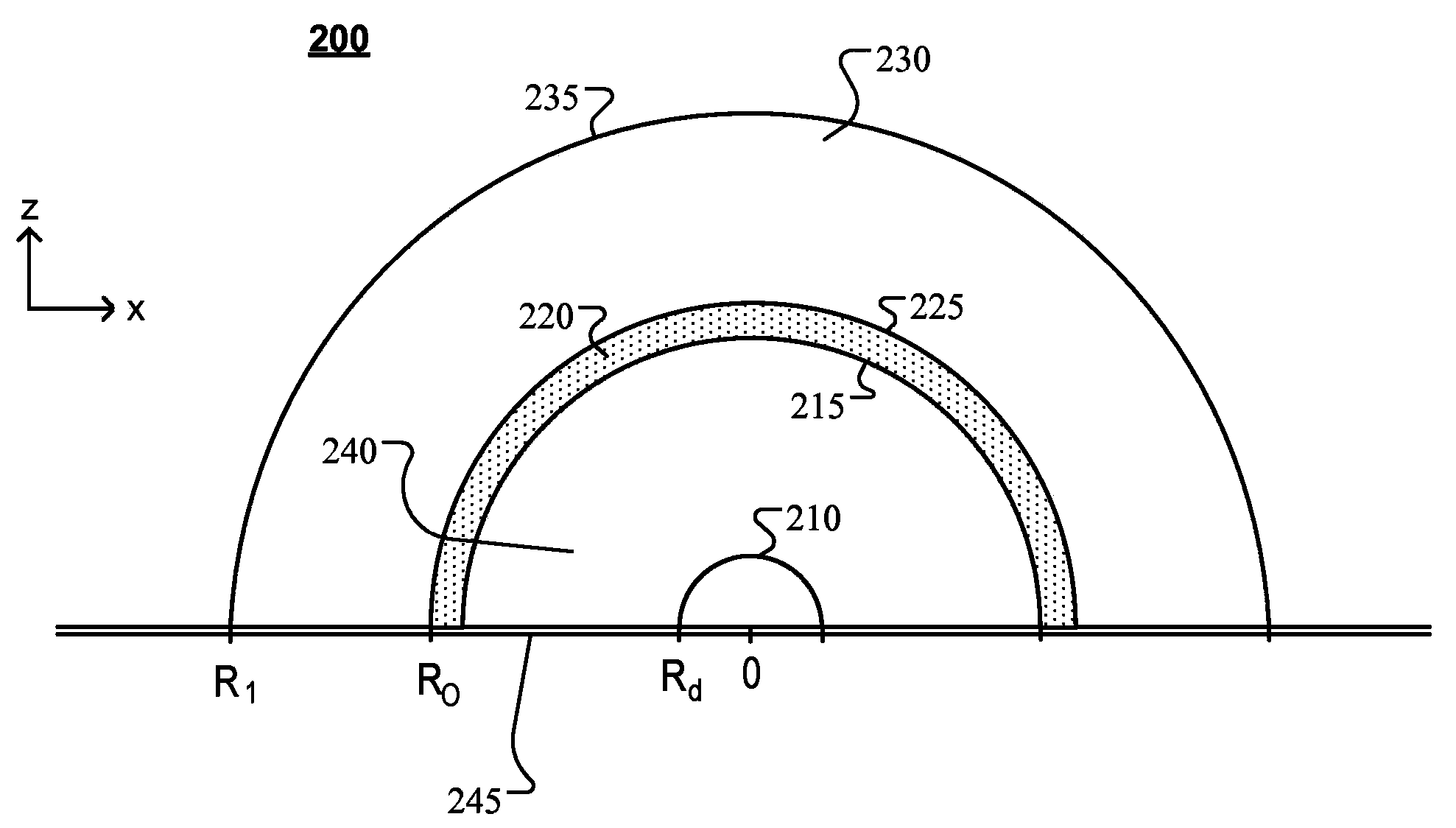
ActiveCN104115290ACondensersSemiconductor devices for light sourcesForward scatterInelastic scattering
A variety of light-emitting devices for general illumination utilizing solid state light sources (e.g., light emitting diodes) are disclosed. In general, the devices include a scattering element in combination with an extractor element. The scattering element, which may include elastic and / or inelastic scattering centers, is spaced apart from the light source element. Opposite sides of the scattering element have asymmetric optical interfaces, there being a larger refractive index mismatch at the interface facing the light emitting element than the interface between the scattering element and the extractor element. Such a structure favors forward scattering of light from the scattering element. In other words, the system favors scattering out of the scattering element into the extractor element over backscattering light towards the light source element. The extractor element, in turn, is sized and shaped to reduce reflection of light exiting the light-emitting device at the devices interface with the ambient environment.
Owner:QUARKSTAR
Thermal imaging sensor pixel unit and thermal imaging sensor pixel array
InactiveCN106949978ARaise the ratioImprove accuracyPyrometry using electric radation detectorsInelastic scatteringEngineering
The invention relates to a thermal imaging sensor pixel unit and a thermal imaging sensor pixel array. The pixel unit comprises a substrate, a heat gathering component, and a heat absorbing component. The heat absorbing component is disposed between the substrate and the heat gathering component. The heat gathering component includes a focusing lens which is embedded into a hollow frame and erected above the heat absorbing component in a suspended manner. The heat absorbing component includes a heat absorbing plate and a temperature sensor on the surface of the heat absorbing plate. The heat absorbing plate is erected above the substrate in a suspended manner through a first support rack. The focusing lens is used for gathering heat radiation to the surface of the heat absorbing plate. According to the technical scheme provided by an embodiment of the invention, as the suspended focusing lens is arranged to gather heat radiation of objects, heat scattering is reduced, the proportion of heat absorption is increased, and the accuracy of detection is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High-resolution electron energy loss spectrometer for energy and momentum two-dimensional analyses
ActiveCN103123325AIncrease sampling densityImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationInelastic scatteringHigh signal intensity
The invention provides an electron energy loss spectrometer for energy and momentum two-dimensional analyses and solves problems of high resolution and high signal intensity matching between an electron-beam source and an angle-resolution electron energy analyzer. The electron energy loss spectrometer comprises a flexible electron-beam source, an angle-resolution mode lens, an angle-resolution electron energy analyzer and the like. The angle-resolution electron energy analyzer can be used for analyzing a low-energy inelastic scattering electron beam of EELS (electron energy loss spectroscopy), flexibility and good monochromatization capability of the electron source, good parallel convergence capability to the electron beam of an angle-resolution mode lens system and the energy and momentum dual analytic capability of the angle-resolution electron energy analyzer are combined together, the momentum and the energy two-dimensional analyses of inelastic scattering electrons can be performed synchronously, and the electron energy loss spectrometer can be acquired, so that a measurement method is provided for accurately measuring complete information excited by surface elements.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining intermediate-low energy electronic inelastic scattering
ActiveCN102507608AQuick fixAccurately determineMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionInelastic scatteringScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a method for determining intermediate-low energy electronic inelastic scattering, which comprises the following steps of: a step of determining the upper limit of a center frequency of plasmons which are interacted with electrons; a step of determining a weighting function of interaction between the plasmons and the electrons on scattering energy points; a step of determining 0-order contribution and 1-order contribution of the interaction between the plasmons and the electrons; and a step of determining a scattering cross section and a scattering angle of the inelastic scattering. Due to the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the scattering cross section and the scattering angle of the inelastic scattering generated in the interacting process of the electrons and a solid can be rapidly and accurately acquired.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Portable energy adjusting device for heat energy-100 MeV neutron
ActiveCN101750623AImproved energy responseHigh sensitivityNeutron radiation measurementInelastic scatteringEnergy regulation
The invention discloses a portable energy adjusting device for equivalent dose detection of a heat energy-100 MeV neutron, which comprises an inelastic scatterer, a fast neutron moderator, an energy adjustor and a thermal neutron detector. The whole device takes the shape of a ball, the thermal neutron detector is arranged at the center of a ball body and coated with the spherical fast neutron moderator; the fast neutron moderator is coated with a spherical ultrafast neutron inelastic scatterer; and the energy reaction adjustor is positioned between the fast neutron moderator and the fast neutron inelastic scatterer. The portable energy adjusting device has the advantages of compact structure and light weight and can improve the reaction of a high-energy neutron by about 30 percent as well as the sensitivity of the neutron by about 18-40 times through experimental evidence compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR CONTROL SYST ENG
Methods for sourceless density downhole measurement using pulsed neutron generator
InactiveUS8476584B2Radiation intensity measurementNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
Disclosed is a method for estimating a density of an earth formation penetrated by a borehole. The method includes: emitting a pulse of fast neutrons into the formation during a neutron-pulse time interval; detecting gamma-rays due to inelastic scattering and thermal capture of the emitted neutrons in the formation to provide a gamma-ray energy spectrum due to the inelastic scattering and the thermal capture during a first time interval within the neutron-pulse time interval and to provide a time spectrum of counts or count rates due to thermal capture during a second time interval occurring after the neutron-pulse time interval; determining a macroscopic capture cross section of the formation from a decay in the time spectrum of counts or count rates; determining an elemental weight fraction from the gamma-ray energy spectrum; and estimating the density of the formation using the macroscopic capture cross section and the elemental weight fraction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
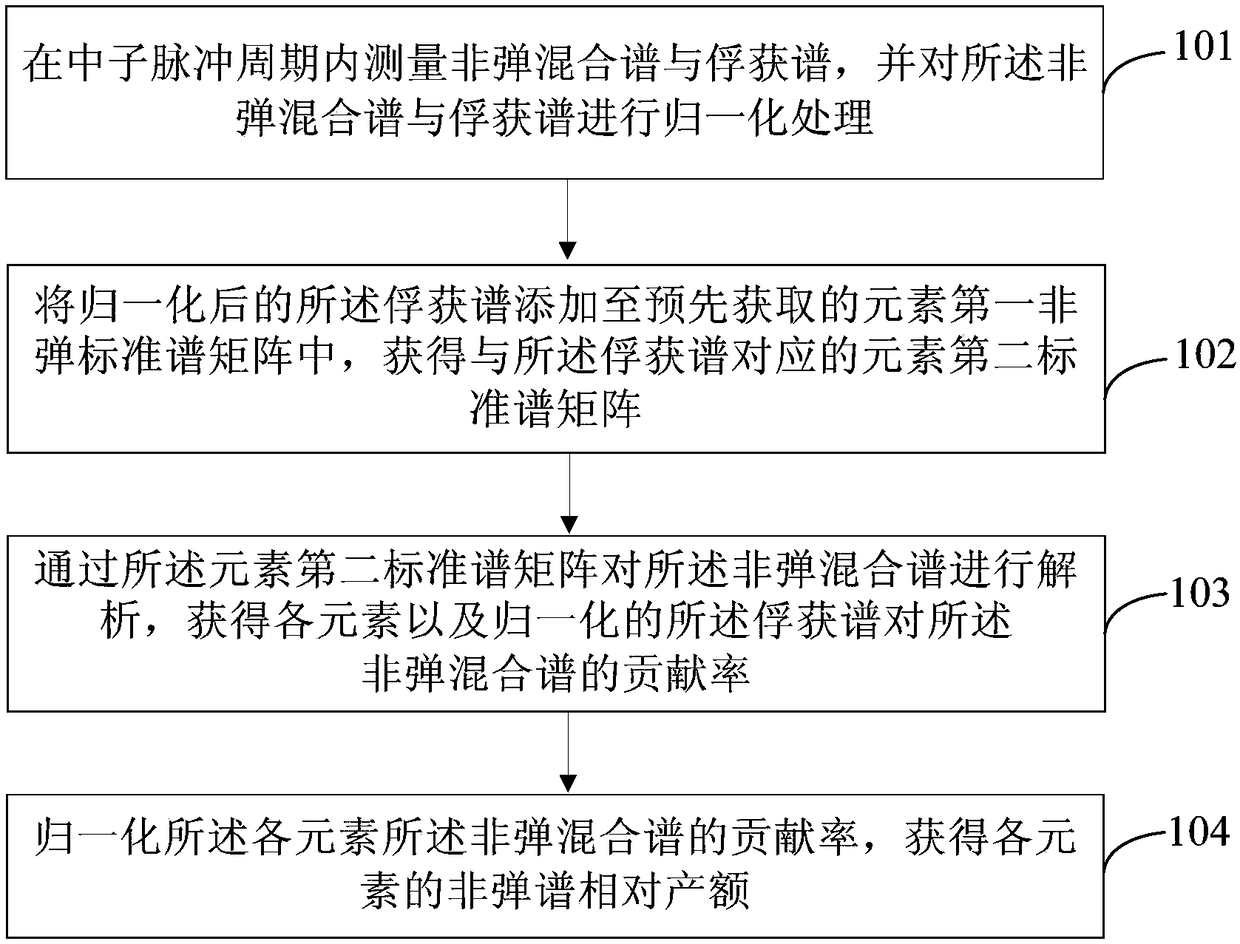
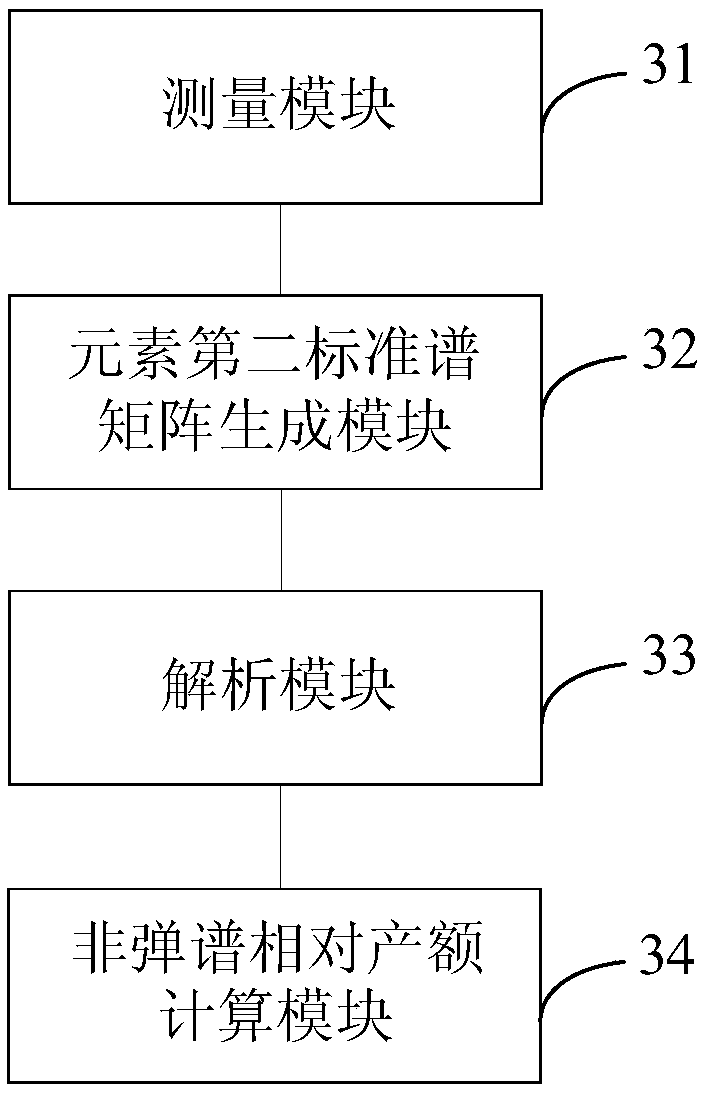
Inelastic scattering gamma-ray spectrometry analysis method and device
ActiveCN108535786AAvoid oilyAvoid accuracyNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringMixed spectrum
The invention provides an inelastic scattering gamma-ray spectrometry analysis method and device. The method comprises the steps as follows: inelastic mixed spectrum and capture spectrum are measuredin a neutron pulse cycle and subjected to normalization processing; the normalized capture spectrum is added to an element first inelastic standard spectrum matrix obtained in advance, and an elementsecond standard spectrum matrix corresponding to the capture spectrum is obtained; the inelastic mixed spectrum is analyzed through the element second standard spectrum matrix, and contribution ratesof elements and the normalized capture spectrum for the inelastic mixed spectrum are obtained; the contribution rates of all the elements for the inelastic mixed spectrum are normalized, and inelasticspectrum relative yields of all the elements are obtained. Pure inelastic spectrum is not required to be obtained firstly during measurement of inelastic spectrum relative yields of all the elements,so that the defect of inaccurate underground stratum oil saturation due to defects of a fixed pure spectrum coefficient method which is mainly adopted at present can be overcome.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
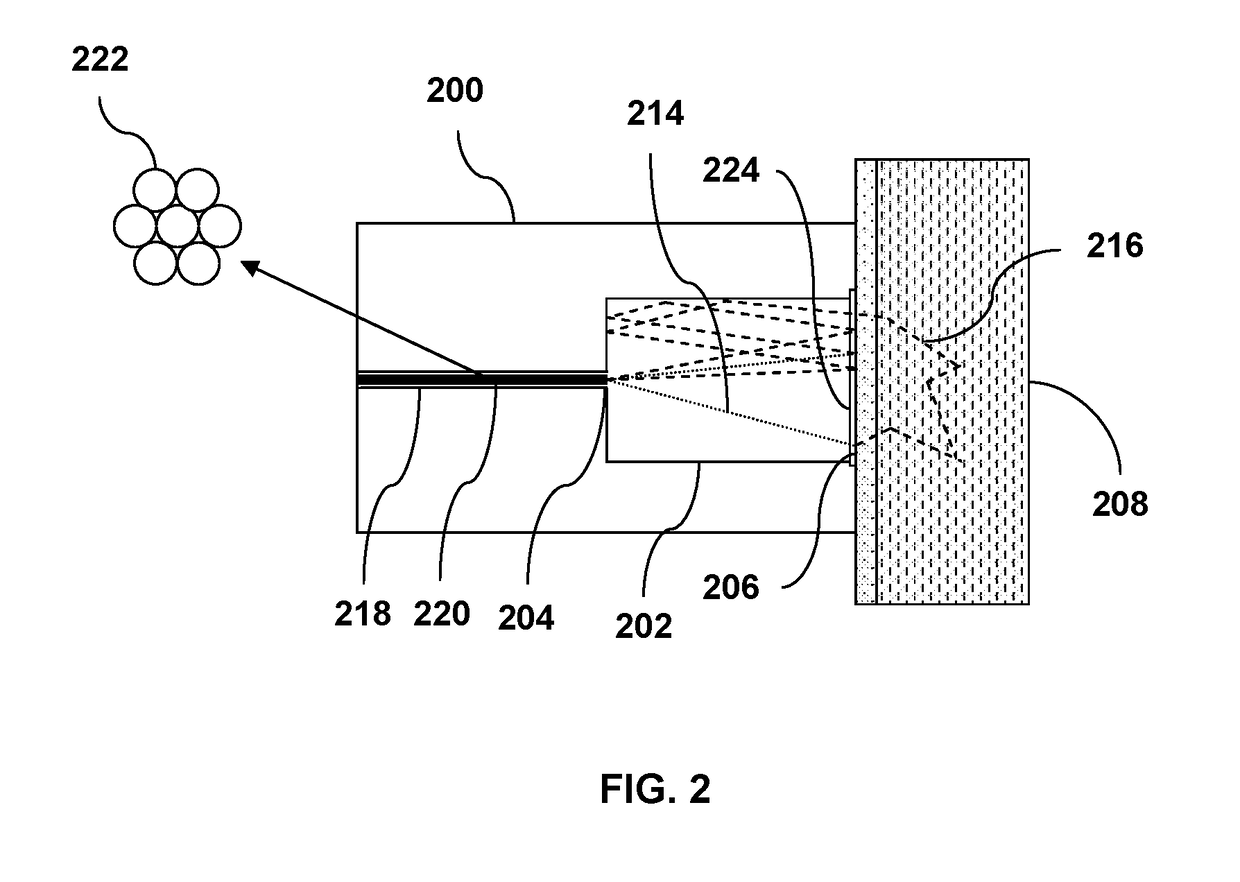
Apparatus and Method for Performing Spectroscopic Analysis of a Subject
ActiveUS20180372540A1Improve reflectivityEasy to collectRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryInelastic scatteringFluorescence
This invention relates to a light delivery and collection device for performing spectroscopic analysis of a subject. The light delivery and collection device comprises a reflective cavity with two apertures. The first aperture receives excitation light which then diverges and projects onto the second aperture. The second aperture is applied to the subject such that the reflective cavity substantially forms an enclosure covering an area of the subject. The excitation light interacts with the covered area of the subject to produce inelastic scattering and / or fluorescence emission from the subject. The reflective cavity reflects the excitation light as well as the inelastic scattering and / or fluorescence emission that is reflected and / or back-scattered from the subject and redirects it towards the subject. This causes more excitation light to penetrate into the subject hence enabling sub-surface measurement and also improves the collection efficiency of the inelastic scattering or fluorescence emission. The shape of the reflective cavity is optimized to further improve the collection efficiency.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
All reflective apparatus for injecting excitation light and collecting in-elastically scattered light from a sample
InactiveCN102449451ARaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryInelastic scatteringHigh numerical aperture
An apparatus is disclosed wherein laser radiation illuminates a sample using all reflective optics and wherein in-elastically scattered light from the sample is collected using the identical elements. The apparatus obviates the problem of contaminating the laser radiation with unwanted spectra from transmissive optics while providing very high rejection of the laser radiation with respect to the in-elastically scattered light. In addition, the apparatus can collect and launch light with high numerical aperture and large field of view.
Owner:C8 MEDISENSORS
Method for optimizing detection of inelastically scattered light from a distant target by measuring the target distance using inelastically scattered light
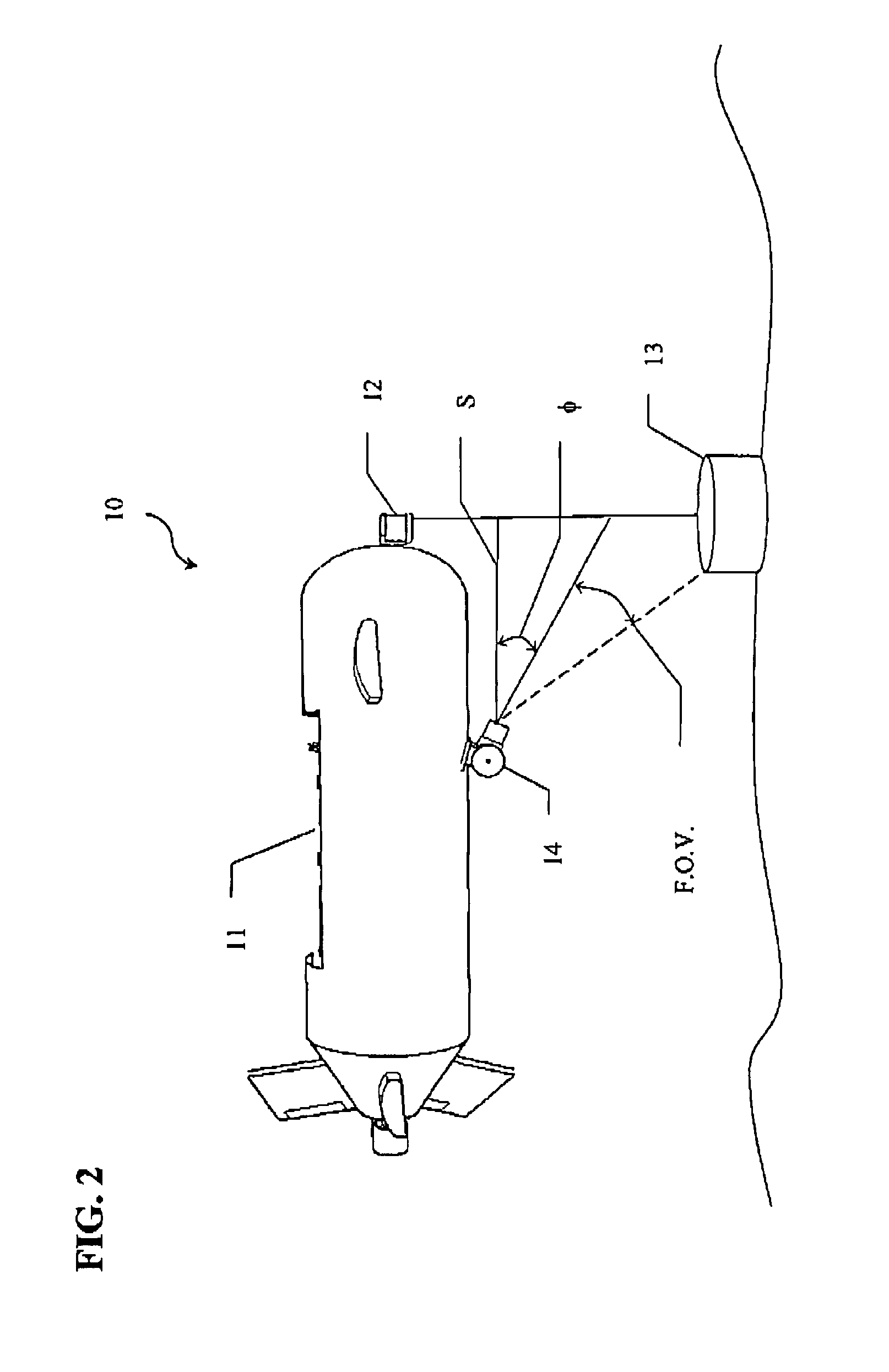
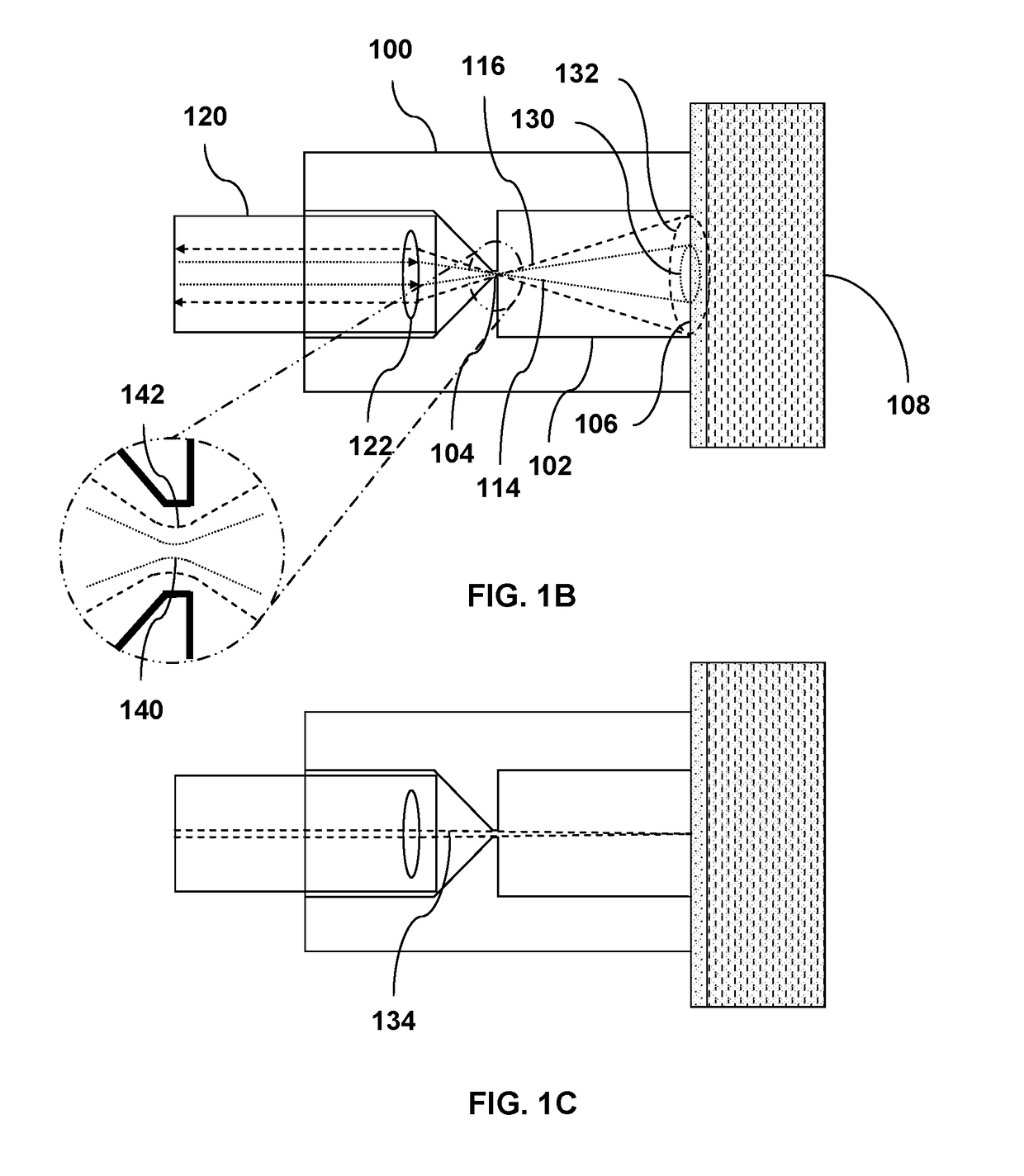
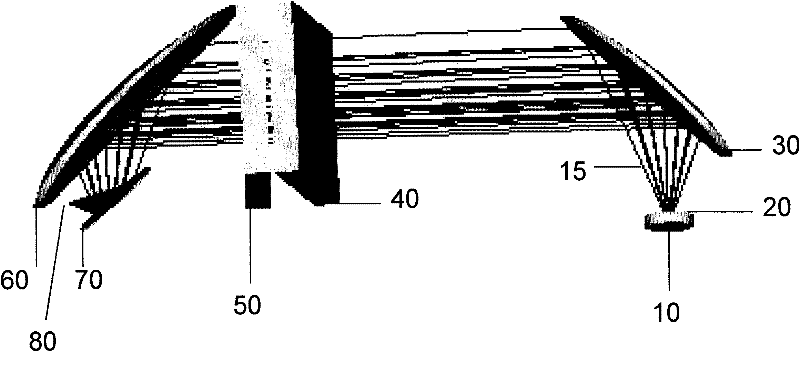
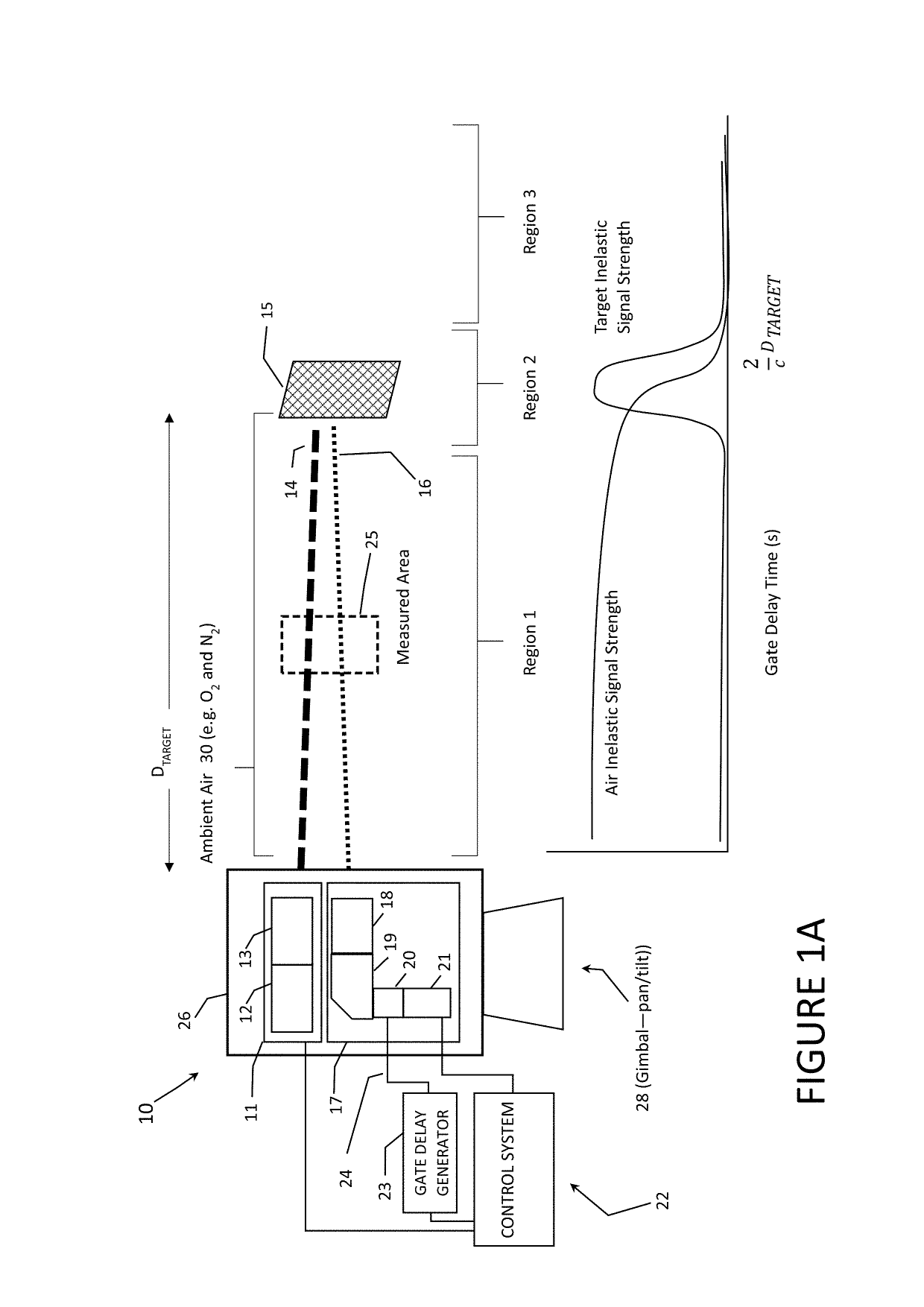
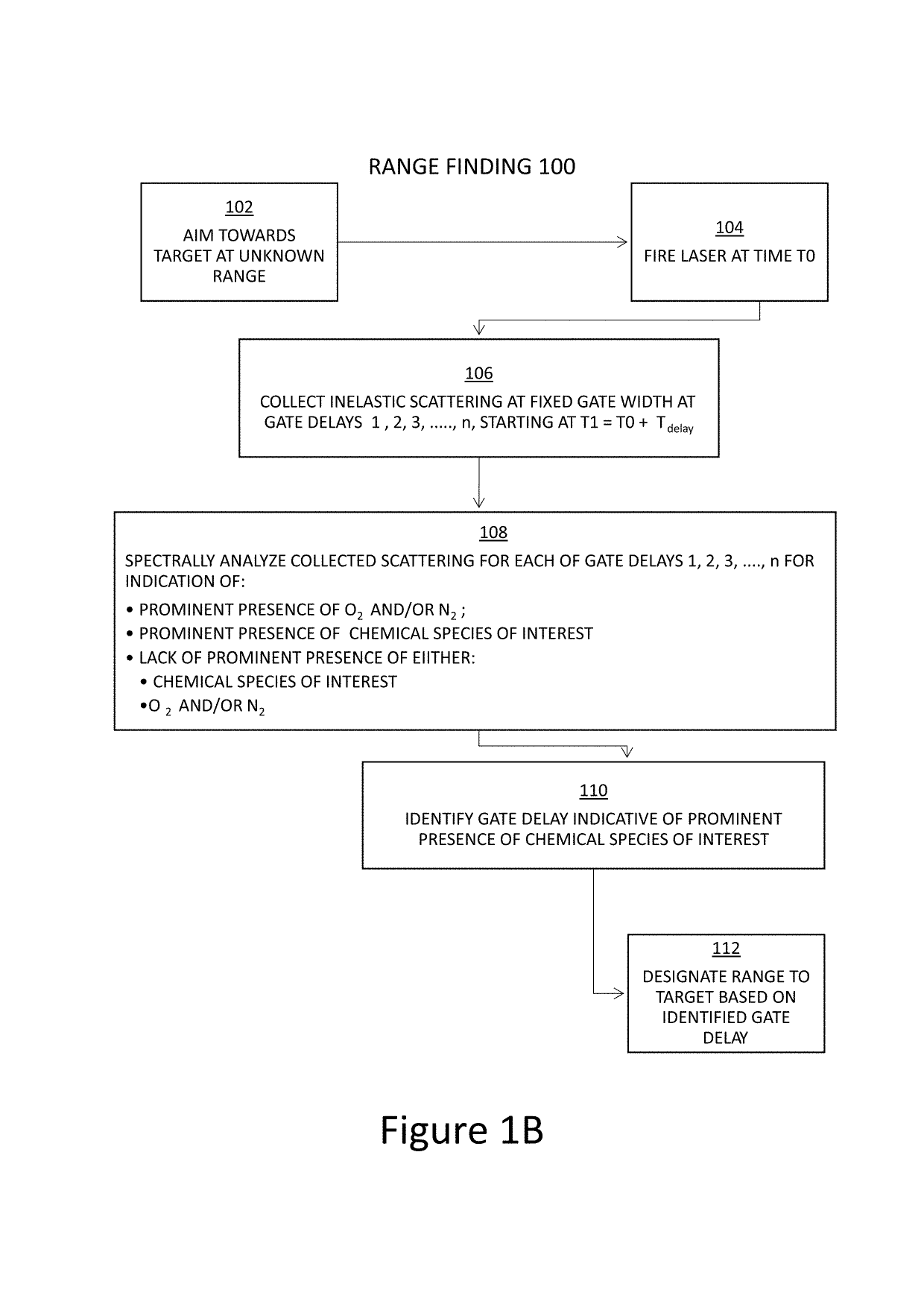
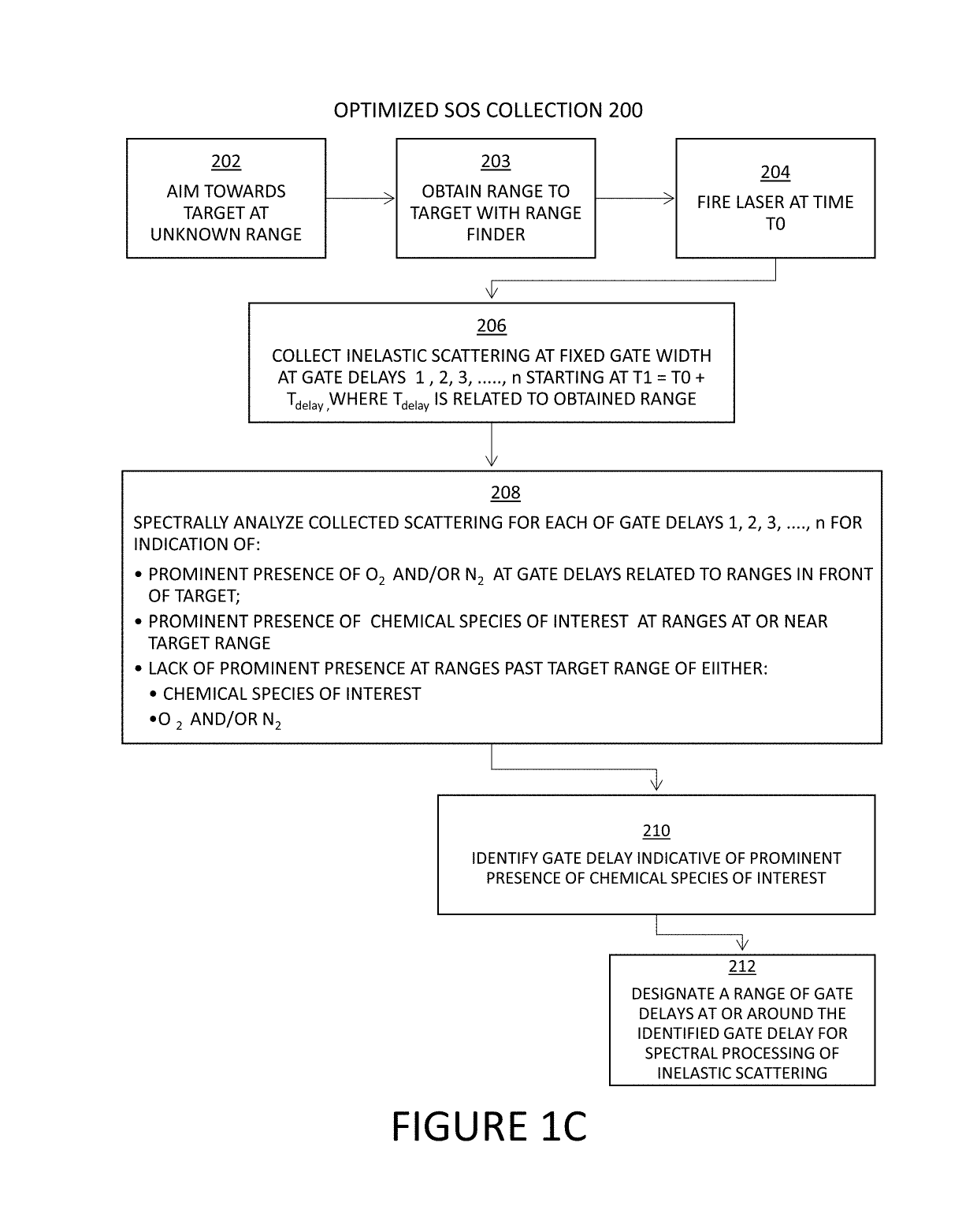
ActiveUS10352863B1Simple designEasy to operateScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringInelastic scatteringDistance measuring equipment
The present invention comprises a novel approach for optimizing detection performance of a standoff optical detection system using the inelastic scattering of light from the target and / or inelastic scattering of light from molecules between the light emitting source and the target. This is a useful approach primarily for systems which already employ a pulsed light source, a detector, and a timing mechanism but whose primary function is not the detection of range. Using this methodology removes the need to deploy a secondary device to find range or augments the ability of any included range finder to widen the overall system operating envelope, reliability, and performance.
Owner:ALAKAI DEFENSE SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com