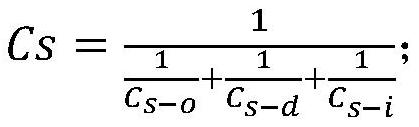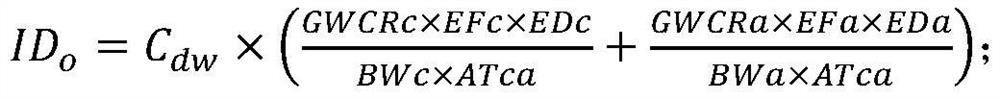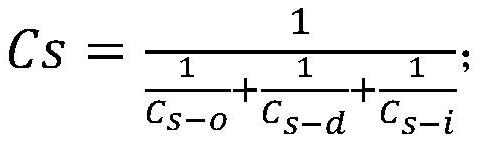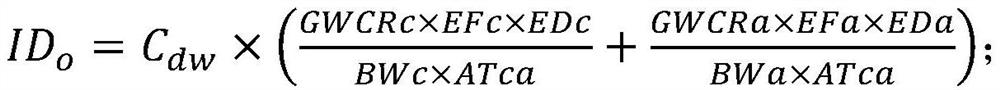Patents
Literature
33 results about "Equivalent dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Equivalent dose is a dose quantity H representing the stochastic health effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body which represents the probability of radiation-induced cancer and genetic damage. It is derived from the physical quantity absorbed dose, but also takes into account the biological effectiveness of the radiation, which is dependent on the radiation type and energy. In the SI system of units, the unit of measure is the sievert (Sv).
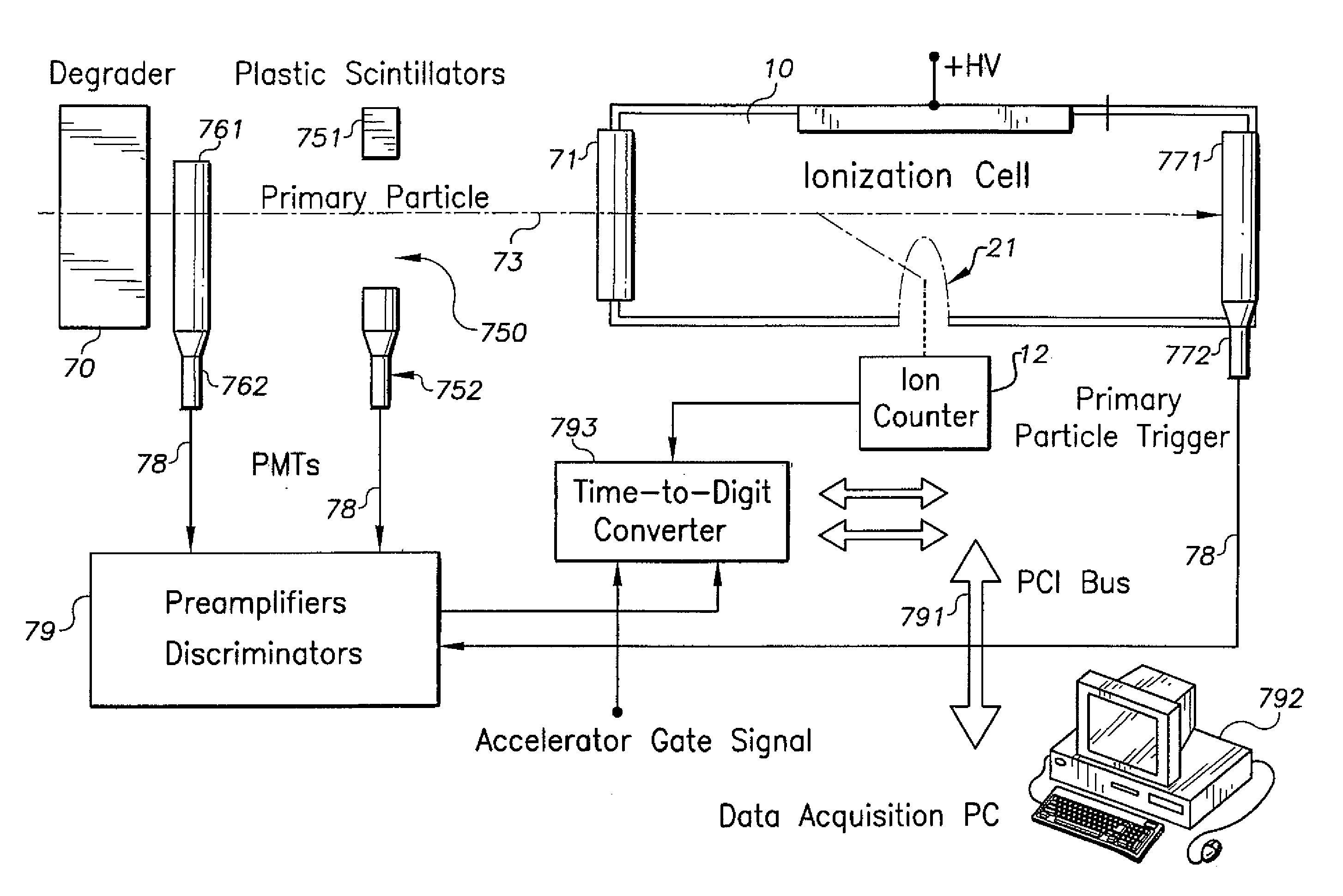
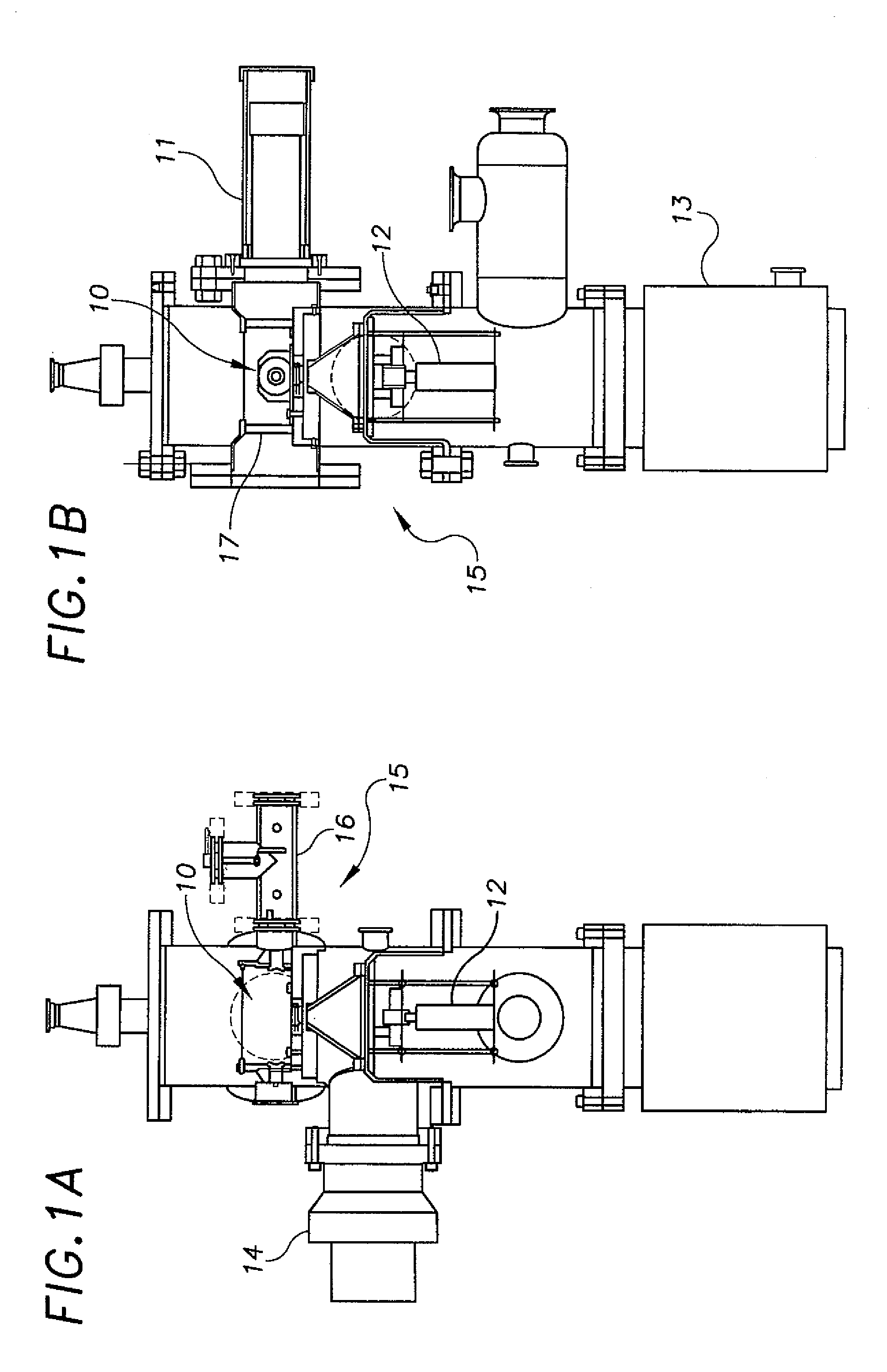
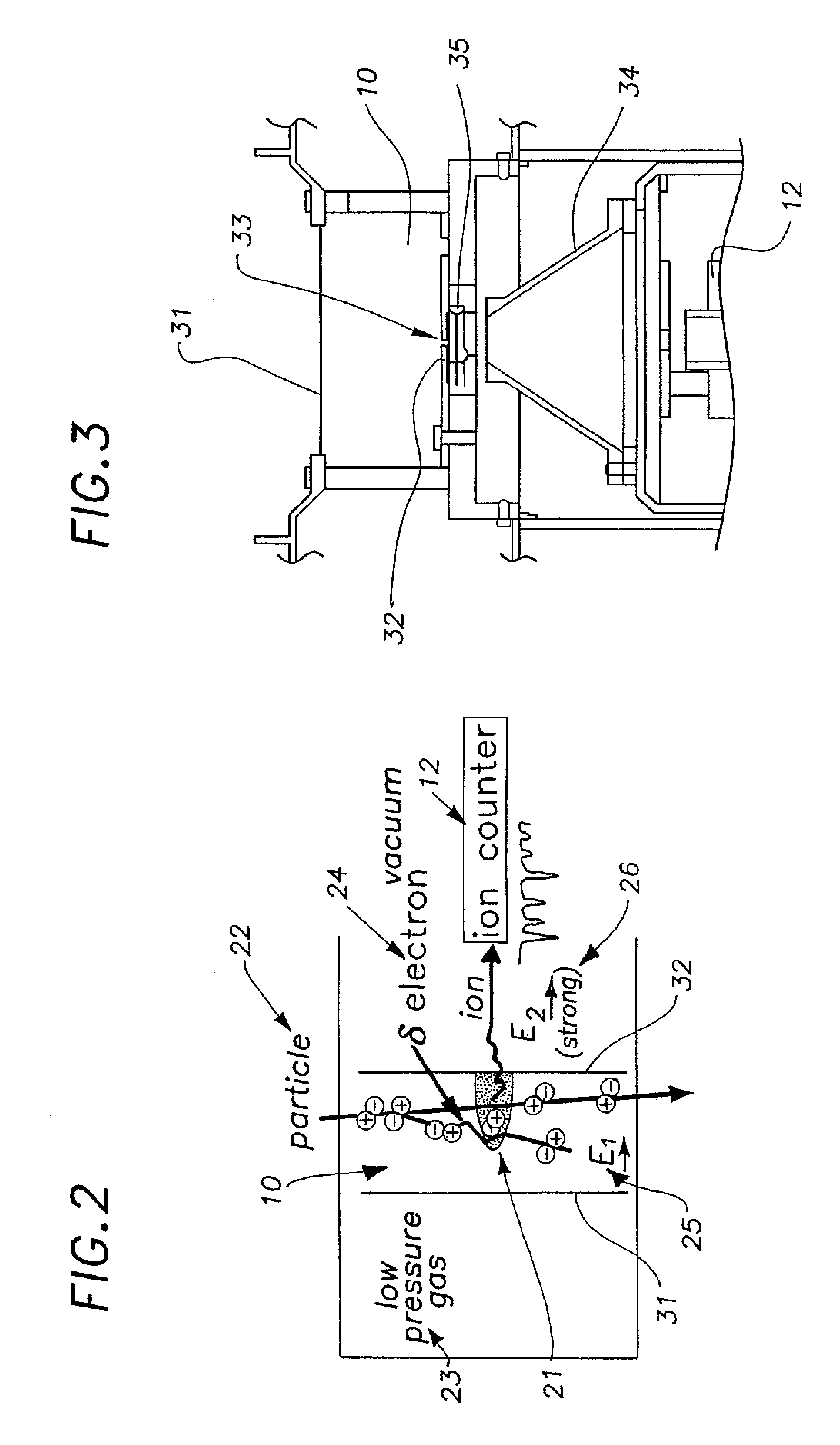
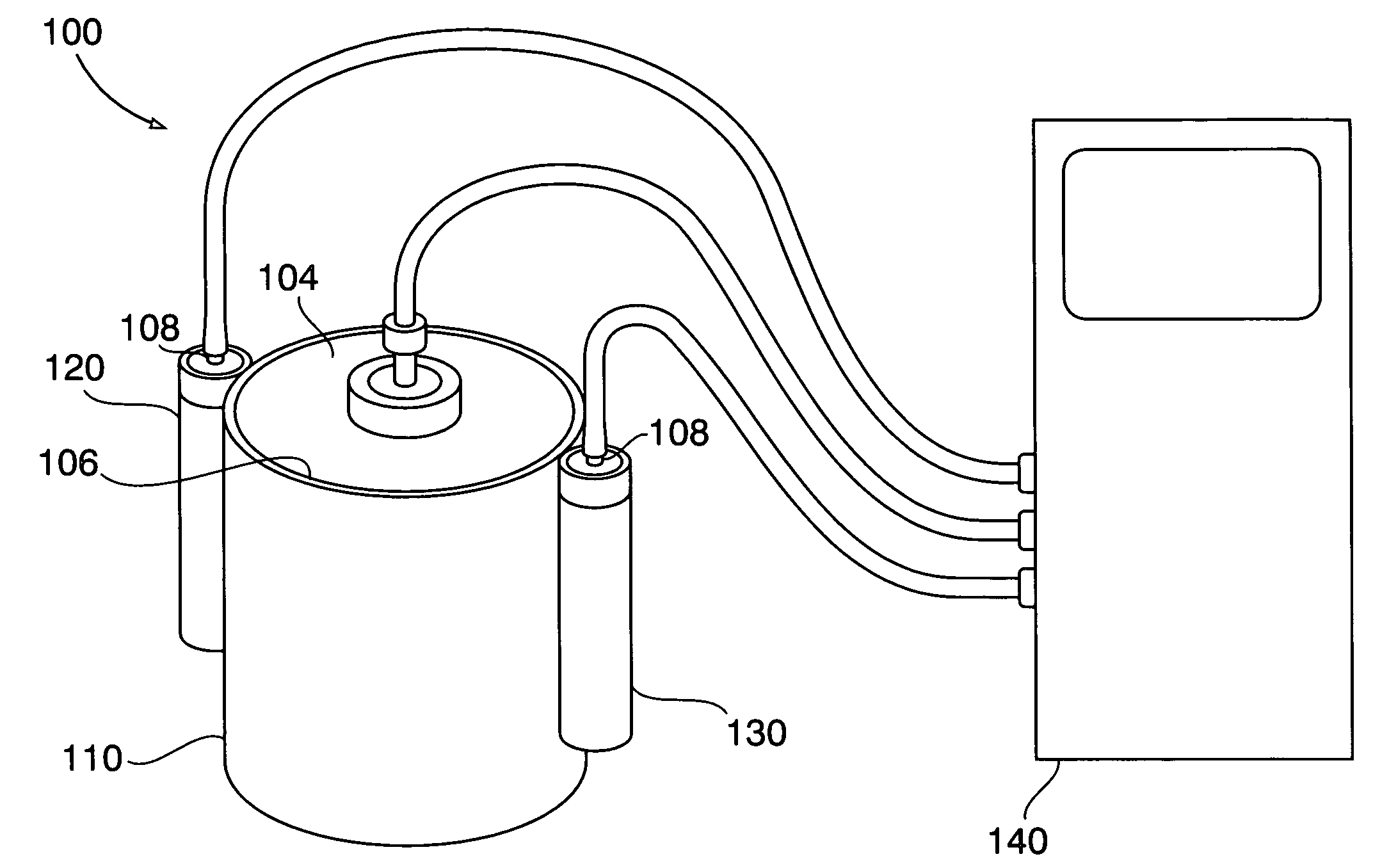
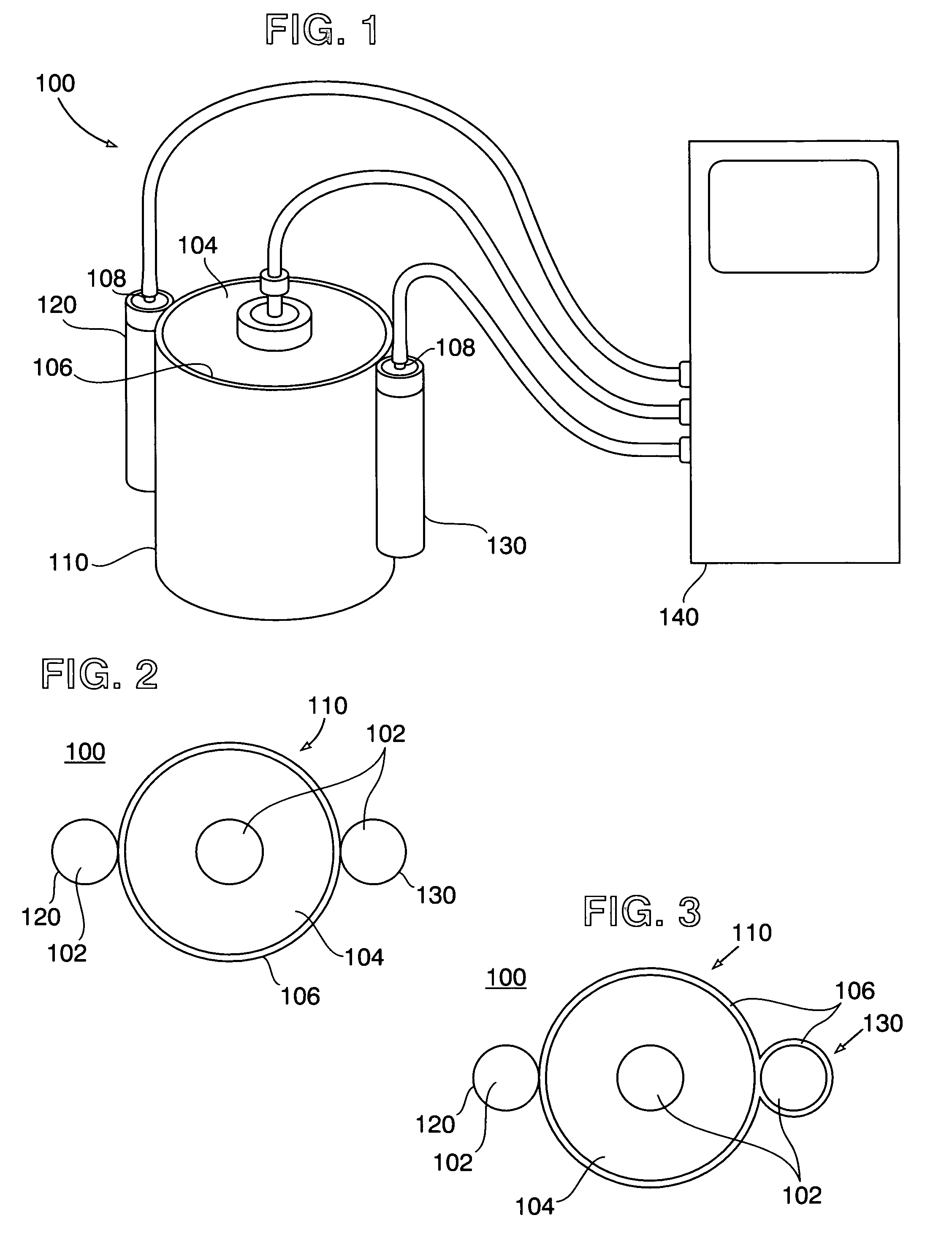
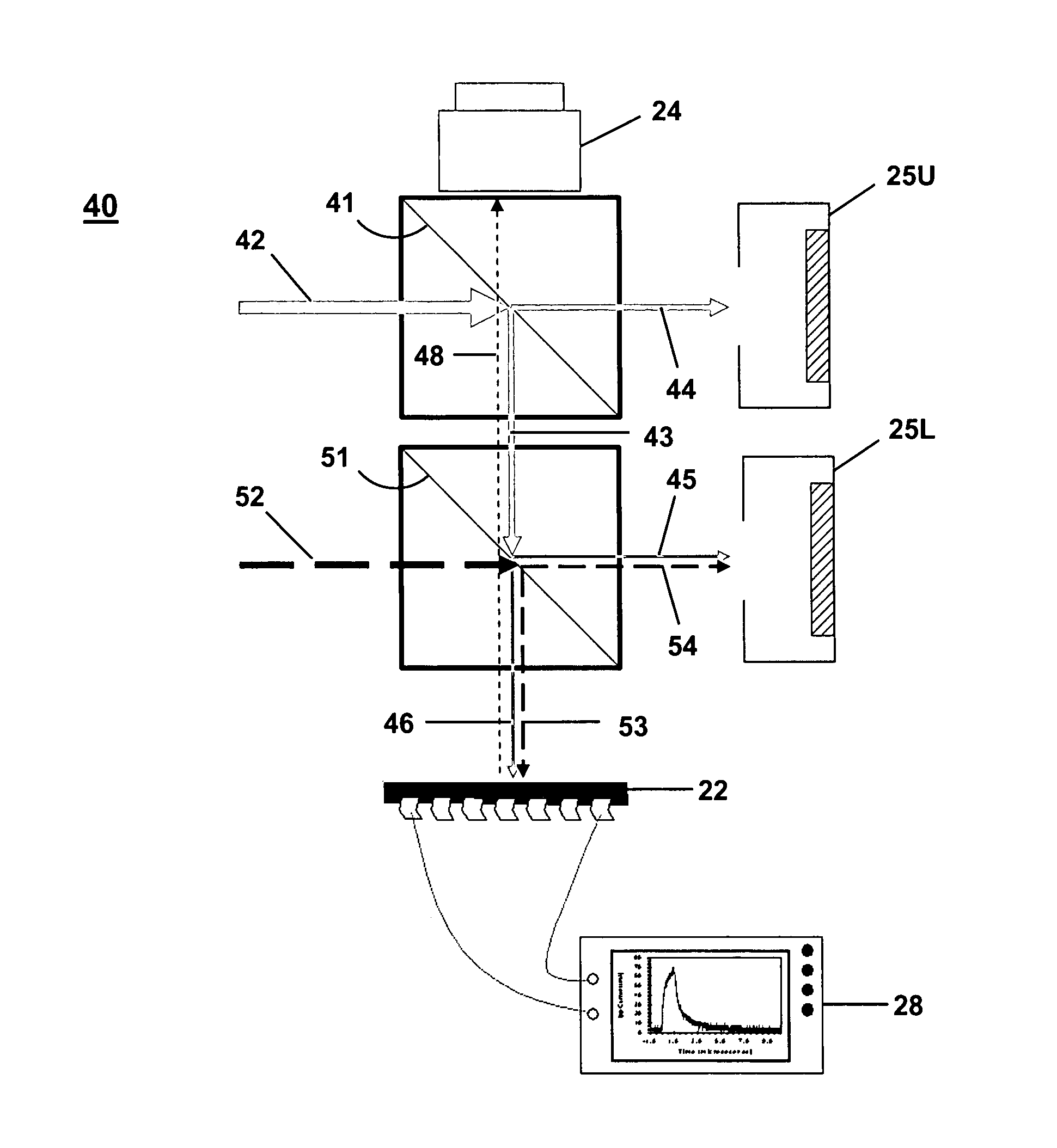
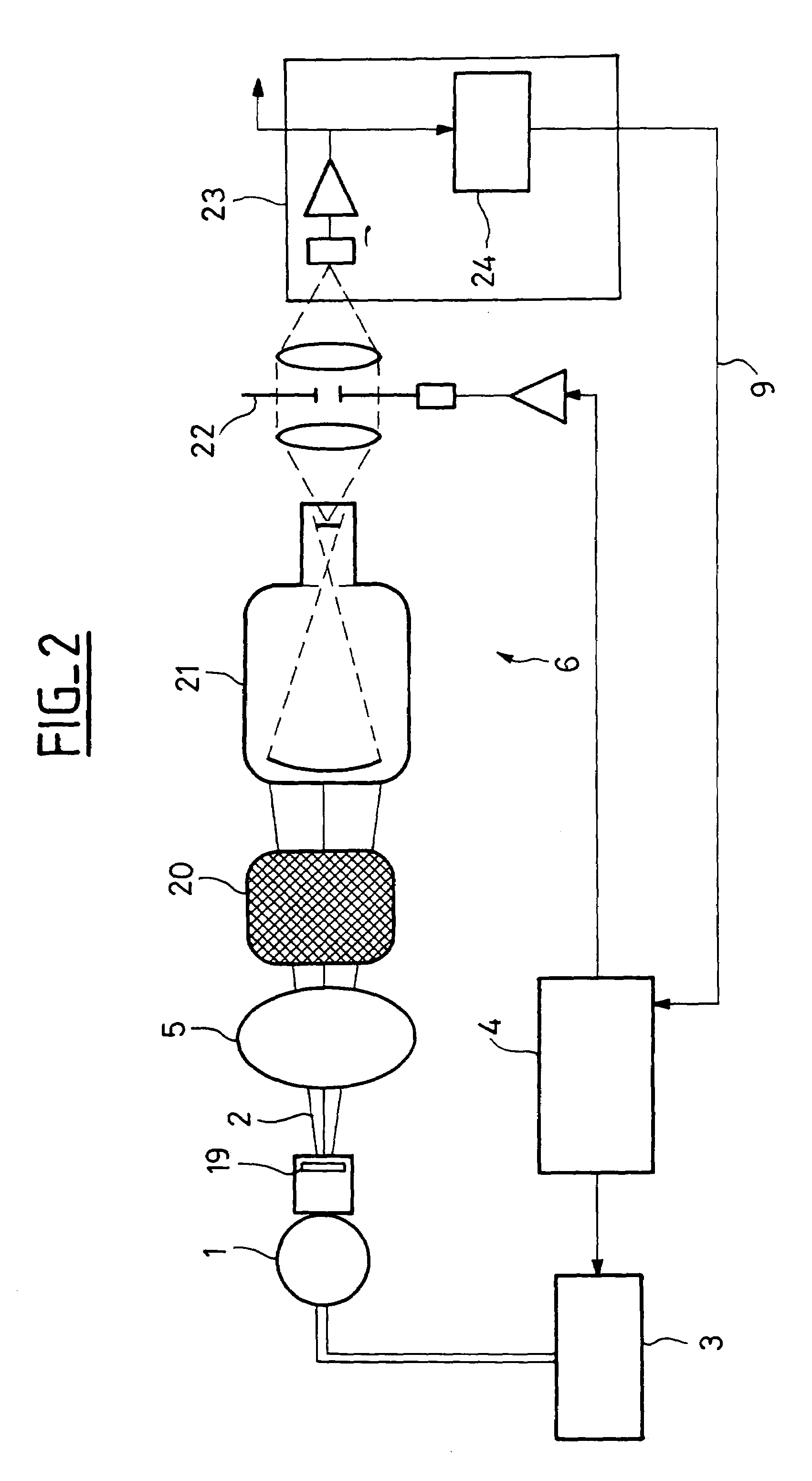
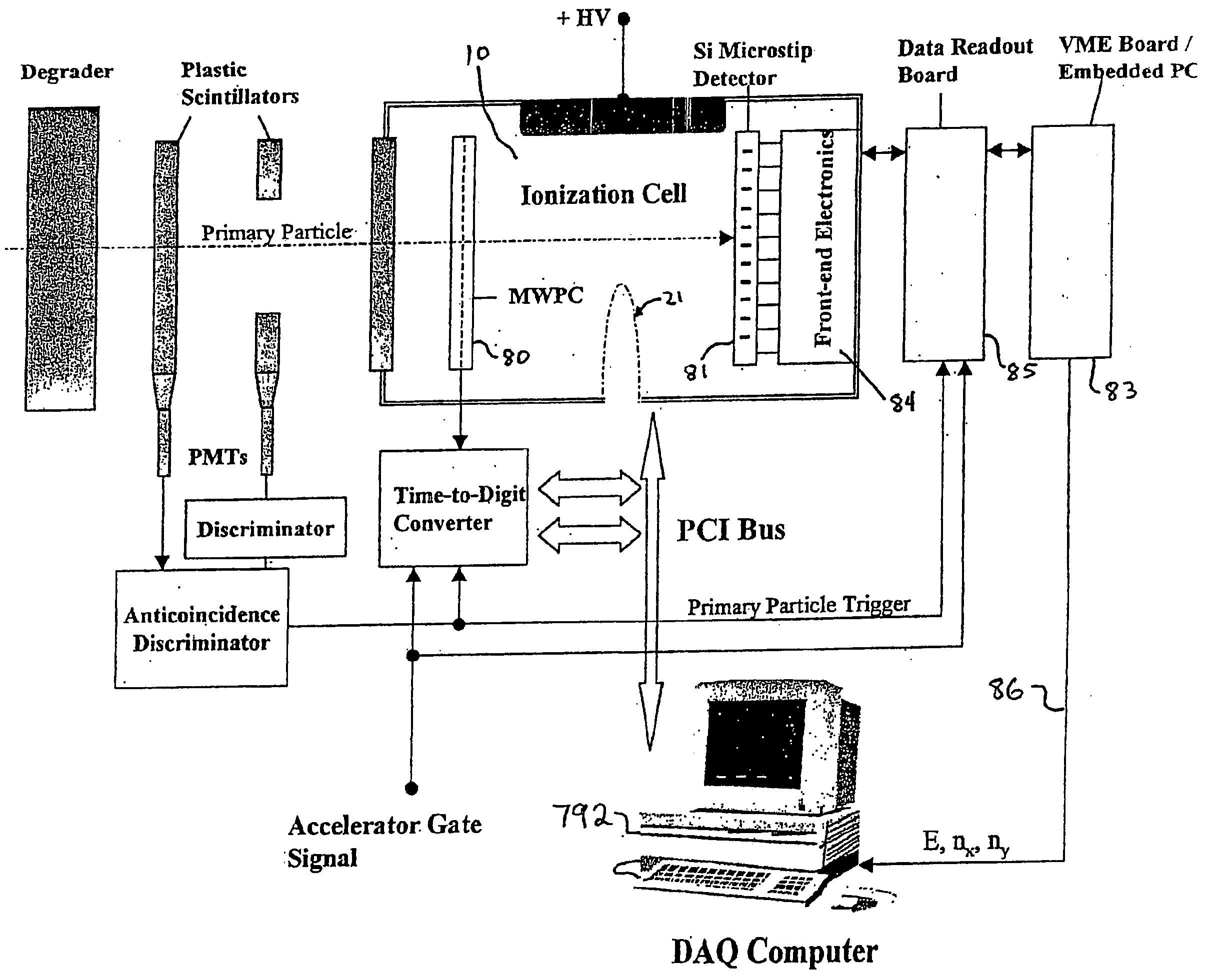
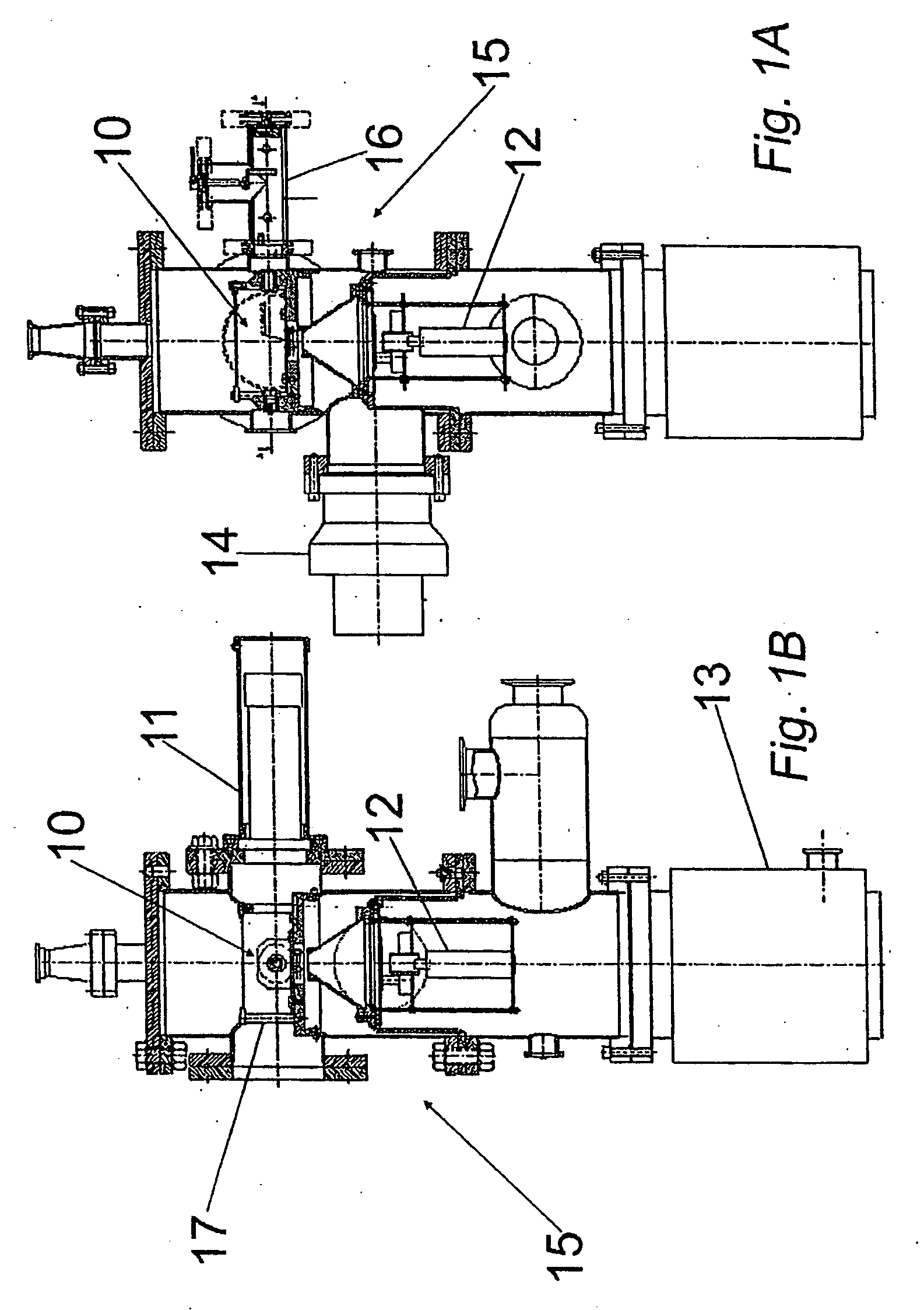
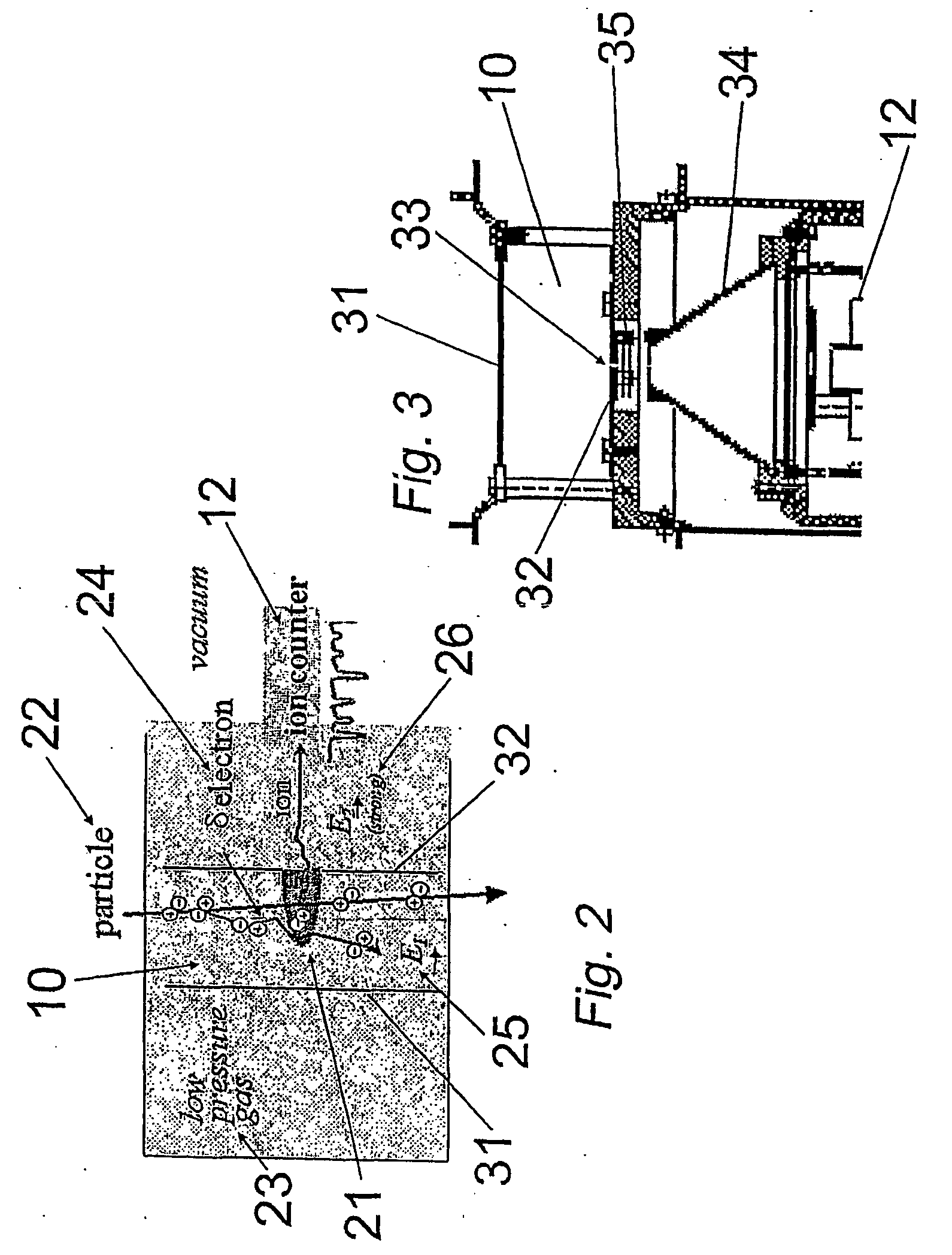
Nanodosimeter based on single ion detection
InactiveUS7081619B2Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluenceDosimeter
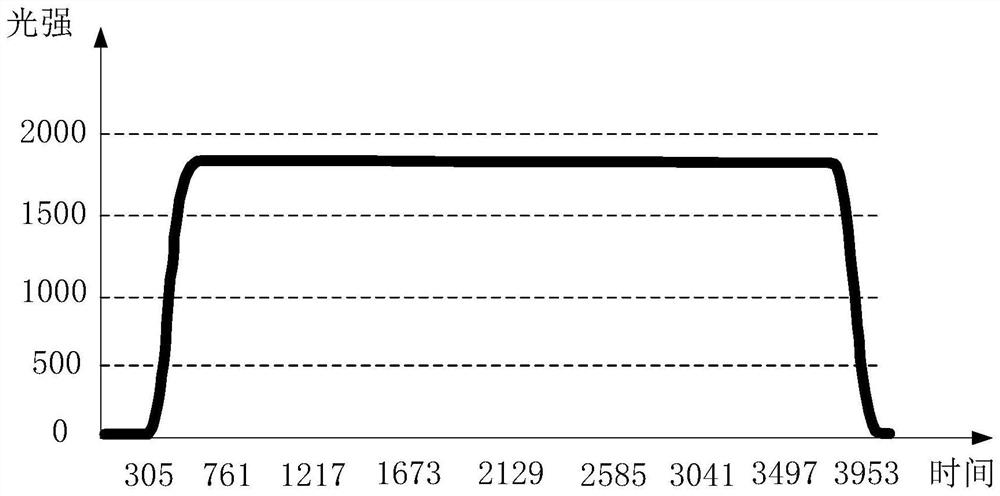
A nanodosimeter device (15) for detecting positive ions induced in a sensitive gas volume by a radiation field of primary particle, comprising an ionization chamber (10) for holding the sensitive gas volume to be irradiated by the radiation field of primary particles; an ion counter system connected to the ionization chamber (10) for detecting the positive ions which pass through the aperture opening and arrive at the ion counter (12) at an arrival time; a particle tracking system for position-sensitive detection of the primary particles passing through the sensitive gas volume; and a data acquisition system capable of coordinating the readout of all data signals and of performing data analysis correlating the arrival time of the positive ions detected by the ion counter system relative to the position sensitive data of primary particles detected by the particle tracking system. The invention further includes the use of the nanodosimeter for method of calibrating radiation exposure with damage to a nucleic acid within a sample. A volume of tissue-equivalent gas is radiated with a radiation field to induce positive ions. The resulting positive ions are measured and compared with a determination of presence or extent of damage resulting from irradiating a nucleic acid sample with an equivalent dose of radiation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +1
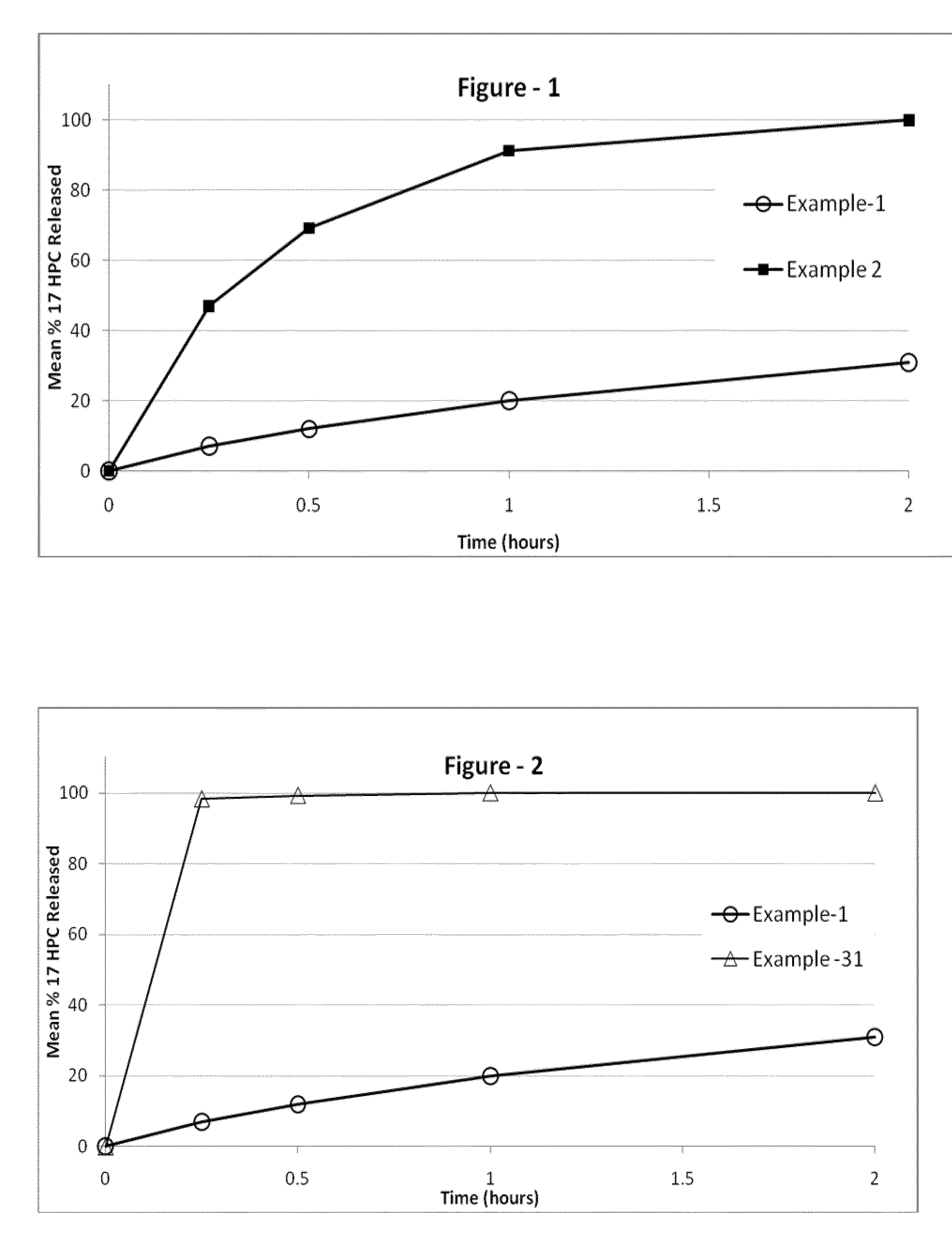
17-Hydroxyprogesterone Ester-Containing Oral Compositions and Related Methods
ActiveUS20130029957A1Effectively delivered orallyHigh percent w/w loadingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsEquivalent dose17α-Hydroxyprogesterone
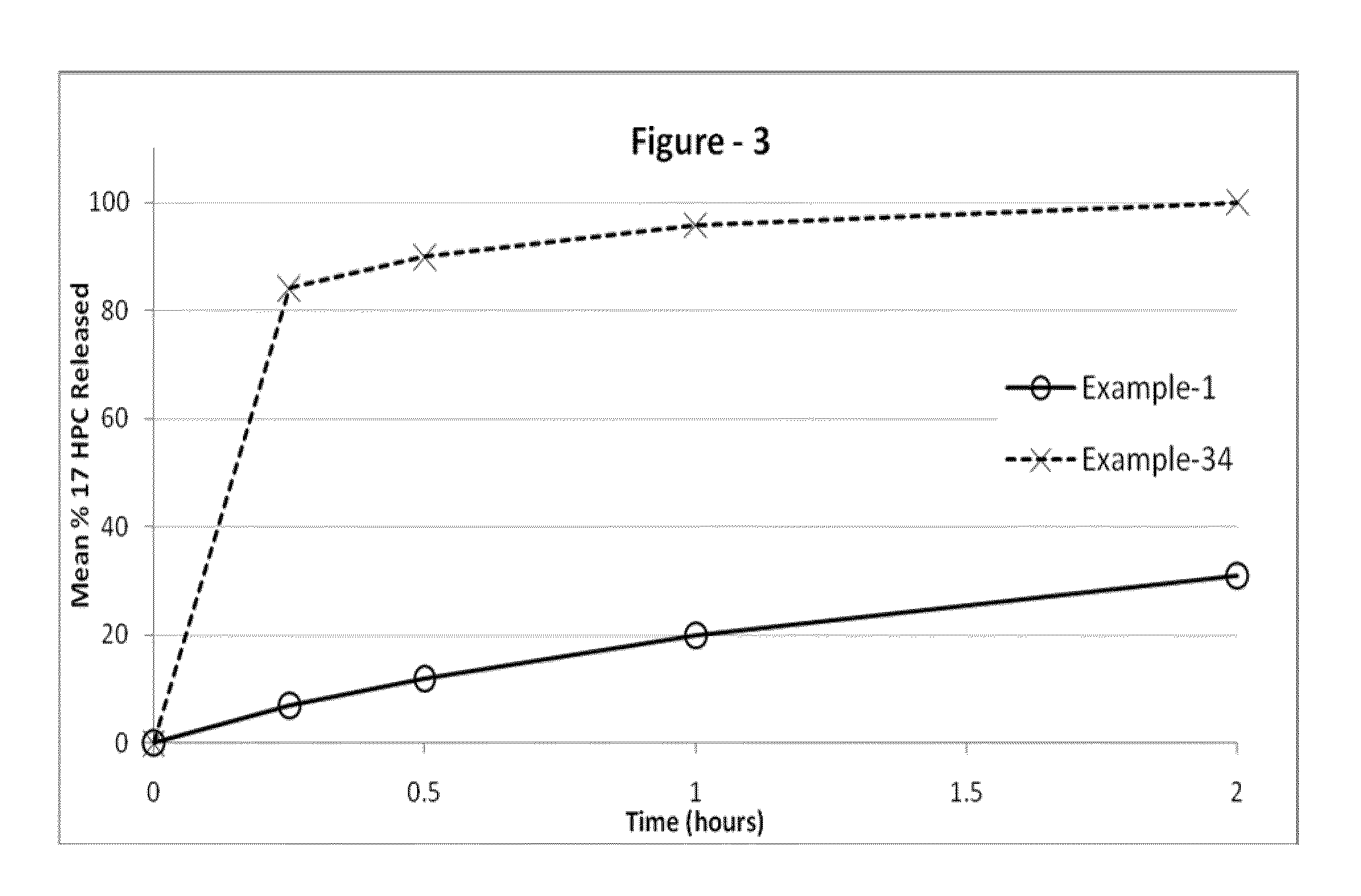
The present invention provides for bioavailable oral dosage forms containing esters of 17-hydroxyprogesterone as well as related methods. The oral dosage forms can be formulated for pregnancy support and can include a therapeutically effective amount of an ester of 17-hydroxyprogesterone and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In another embodiment, a pharmaceutically acceptable oral dosage form for pregnancy support is provided. The pharmaceutically acceptable oral dosage can include a therapeutically effective amount of an ester of 17-hydroxyprogesterone and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The oral dosage form can, when measured using a USP Type-II dissolution apparatus in 900 mL of deionized water with 0.5 (w / v) of sodium lauryl sulfate at 50 RPM at 37° C., release at least 20 wt % of the dose of the ester of 17-hydroxyprogesterone after 60 minutes, or in the alternative release at least 20 wt % more after 60 minutes than an equivalently dosed oral dosage form without the carrier.
Owner:LIPOCINE
Ship reactor shielding design optimization method based on neural network and genetic algorithm
ActiveCN104933245AReduce time consumptionReduce programming difficultySpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkComputation process
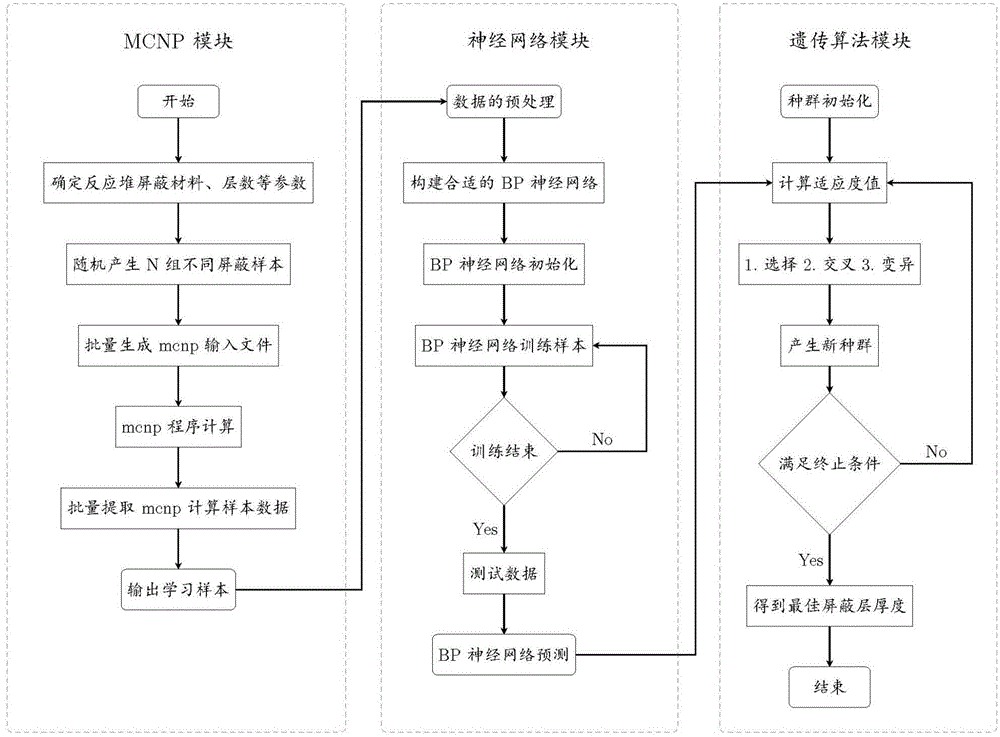
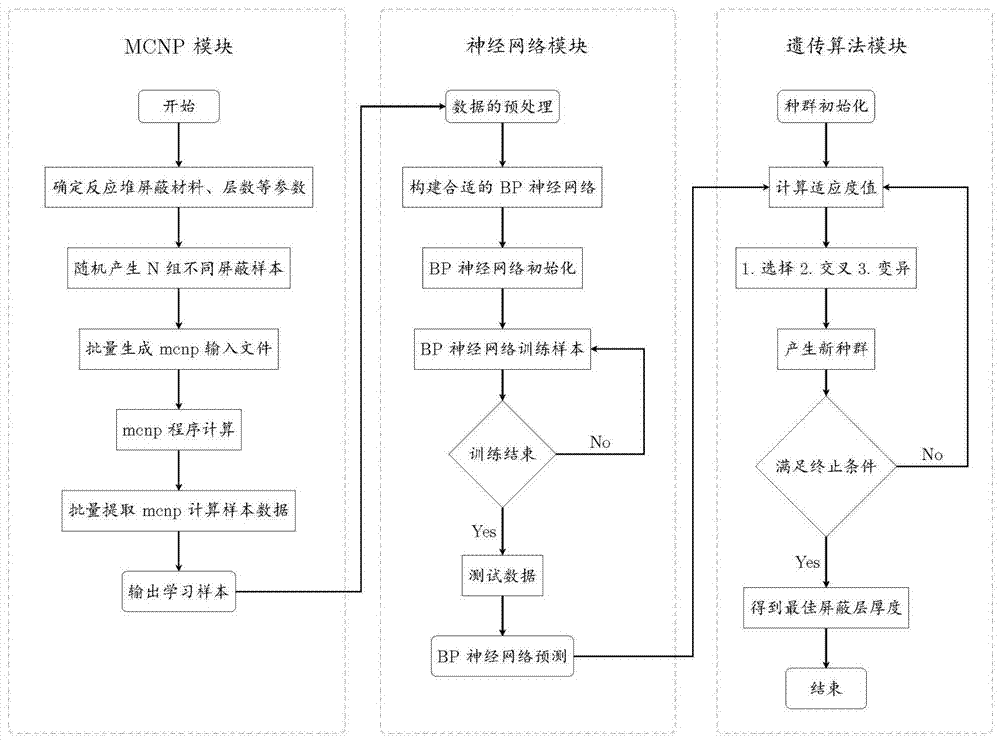
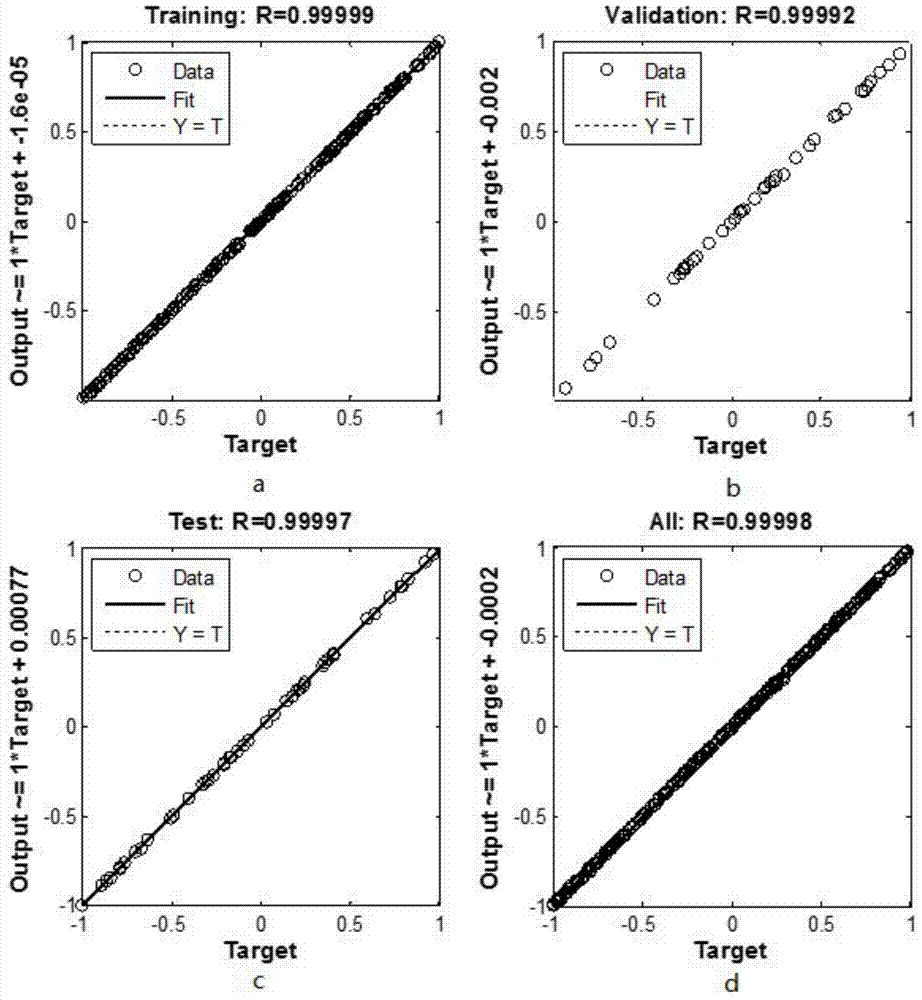
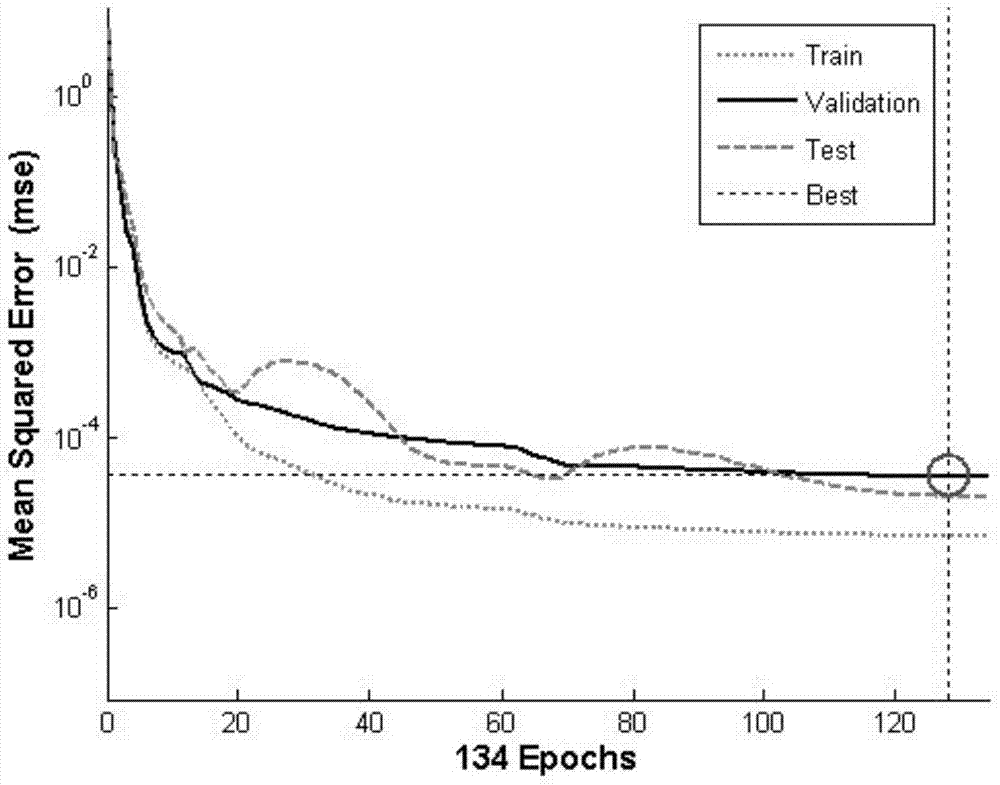
The invention discloses a ship reactor shielding design optimization method based on a neural network and a genetic algorithm. A Monte Carlo method is used for simulating and calculating the reactor neutron and photon transport process; an MCNP (Monte Carlo N Particle Transport Code) program is used for carrying out simulation and calculation on a ship reactor layered shielding model; a neutron and photon flux after the reactor shielding is obtained; the total equivalent dose is worked out; a topological structure of a BP (Back Propagation) neural network is determined according to the input parameter number n1 and the output parameter number n2 of a sample; an adaptation degree function of the genetic algorithm is determined according to a reactor shielding problem objective; the recommended adaptation degree function is selected; and the strong optimization capacity of the genetic algorithm is used and is mutually coupled with the neural network to find the optimum shielding parameter. The ship reactor shielding design optimization method has the advantages that the high fitting capability of the neural network is used; the time consumption of the MCNP program in the particle transport process is reduced; the good optimization capacity of the genetic algorithm is used; and the optimum shielding parameter can be found in few iteration steps.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Lightweight neutron remmeter
InactiveUS6930311B1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentThermal energyHydrogen
A lightweight neutron remmeter for measuring neutron equivalent dose with a response range from the thermal energy levels to around 14 MeV is achieved using a center BF3 proportional neutron detector moderated by enclosure within a cylindrical center tube and two adjacent BF3 proportional neutron detectors. A cylindrical hydrogenous material covered by a boron loaded rubber wrap moderates the center detector within the center tube. The adjacent neutron detectors are uncovered. In this manner the center detector responds to fast neutrons and the over response to thermal and intermediate energy neutrons is corrected by the adjacent neutron detectors readings and an algorithm implemented by a RADIAC.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System and method for reducing radiation dosage
ActiveCN109493951AAvoid radiationImprove image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionObject based
The invention discloses a method for reducing the radiation dosage, and the method comprises the steps: acquiring first image data related to an ROI (region of interest) of a first object, wherein thefirst image data is corresponding to a first equivalent dosage, and the first image data may be acquired by a first device; obtaining a noise reduction model associated with the first image data anddetermining second image data corresponding to the second equivalent dosage based on the first image data and the noise reduction model, wherein the second equivalent dosage is greater than the firstequivalent dosage. In some embodiments, the method may further comprise the steps: determining information related to the ROI of the first object based on the second image data, and recording information related to the ROI of the first object. The present application converts low dosage images into high dosage images through a noise reduction model, and avoids exposure of the patient to excessiveradiation while obtaining equal or higher quality images.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Laser-based irradiation apparatus and method to measure the functional dose-rate response of semiconductor devices
A broad-beam laser irradiation apparatus can measure the parametric or functional response of a semiconductor device to exposure to dose-rate equivalent infrared laser light. Comparisons of dose-rate response from before, during, and after accelerated aging of a device, or from periodic sampling of devices from fielded operational systems can determine if aging has affected the device's overall functionality. The dependence of these changes on equivalent dose-rate pulse intensity and / or duration can be measured with the apparatus. The synchronized introduction of external electrical transients into the device under test can be used to simulate the electrical effects of the surrounding circuitry's response to a radiation exposure while exposing the device to dose-rate equivalent infrared laser light.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
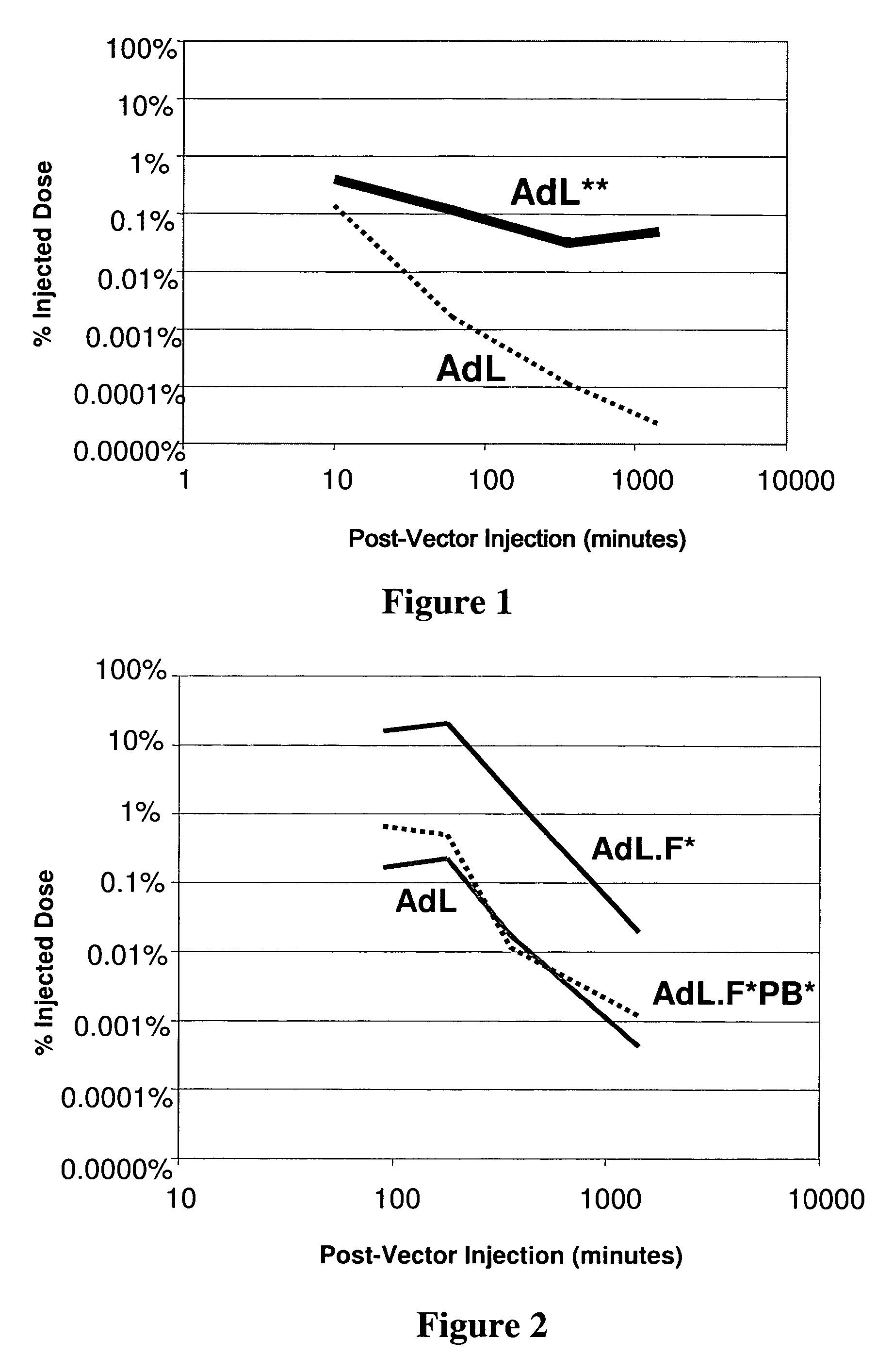
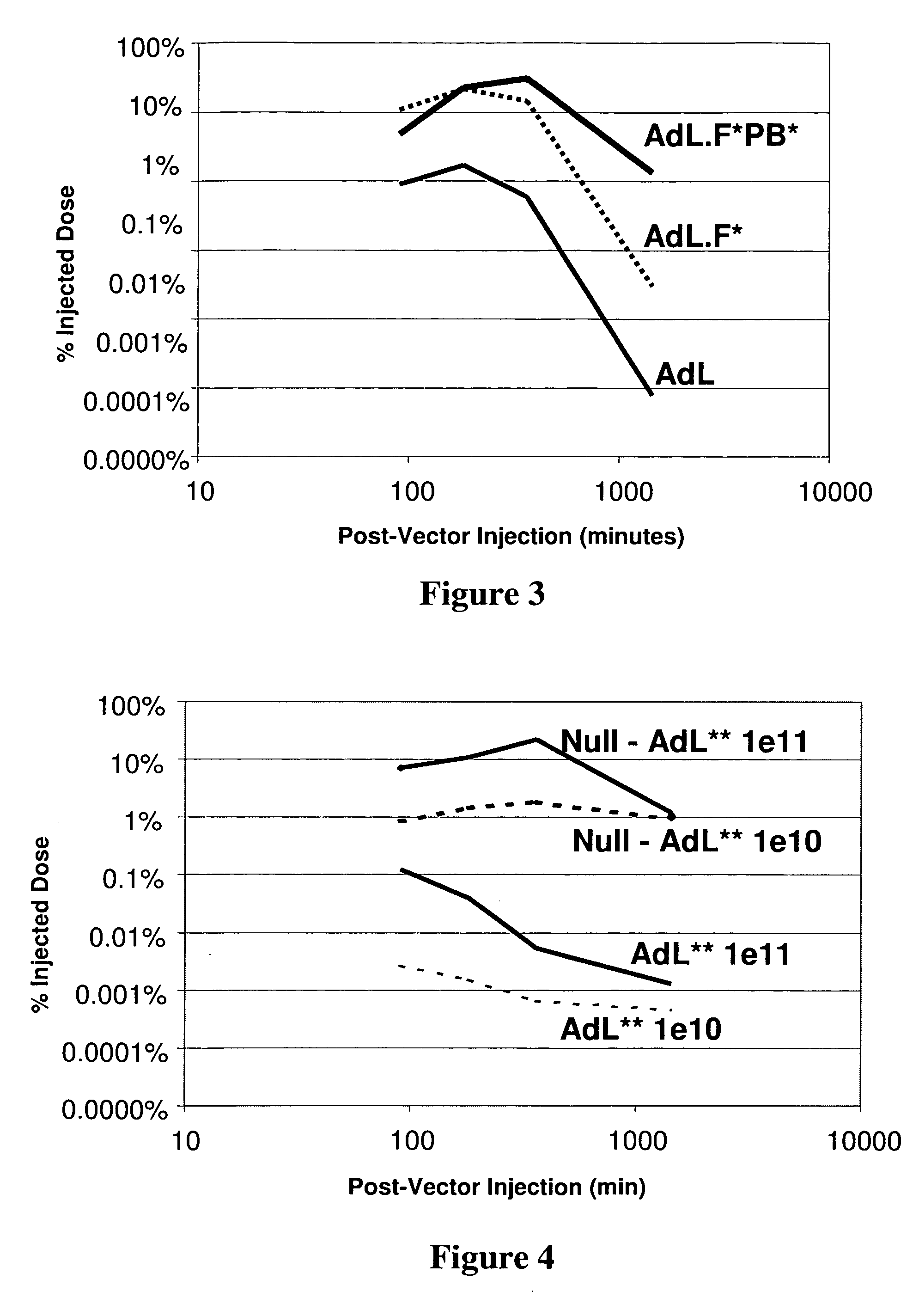
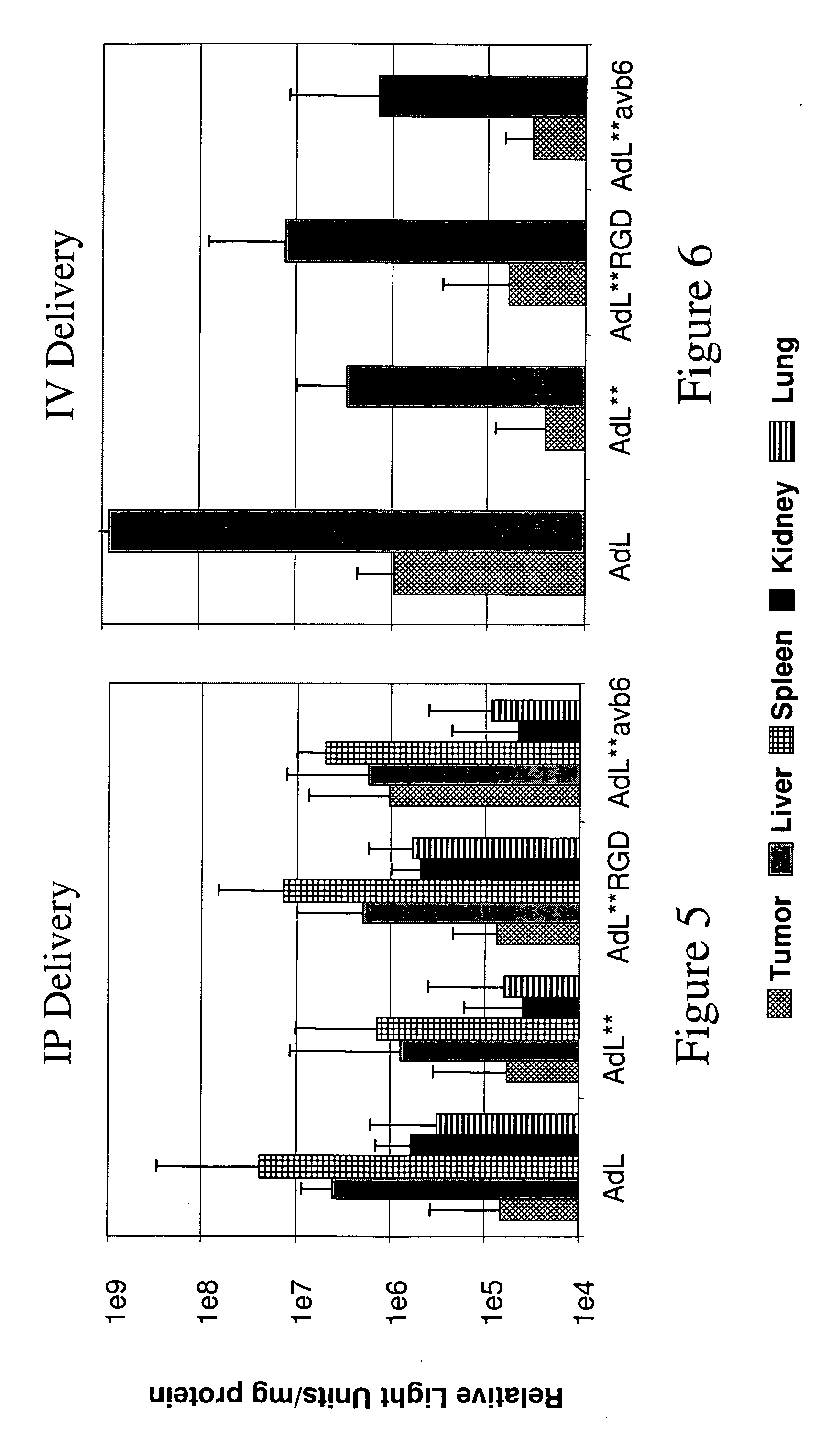
Method of using adenoviral vectors with increased persistence in vivo
The invention provides a method of expressing an exogenous nucleic acid in a mammal. The method comprises slowly releasing into the bloodstream a dose of replication-deficient or conditionally-replicating adenoviral vector having reduced ability to transduce mesothelial cells and hepatocytes. The normalized average bloodstream concentration of the adenovirus over 24 hours post-administration is at least about 1%. Alternatively, the normalized average bloodstream concentration over 24 hours post-administration is at least about 5-fold greater than the normalized average bloodstream concentration for an equivalent dose of a wild-type adenoviral vector. A method of destroying tumor cells in a mammal also is provided, as is a replication-deficient adenoviral vector comprising a serotype 5 or serotype 35 adenoviral genome with a serotype 41 fiber protein, wherein the replication-deficient adenoviral vector exhibits reduced native binding to integrins.
Owner:GEN VEC INC +1
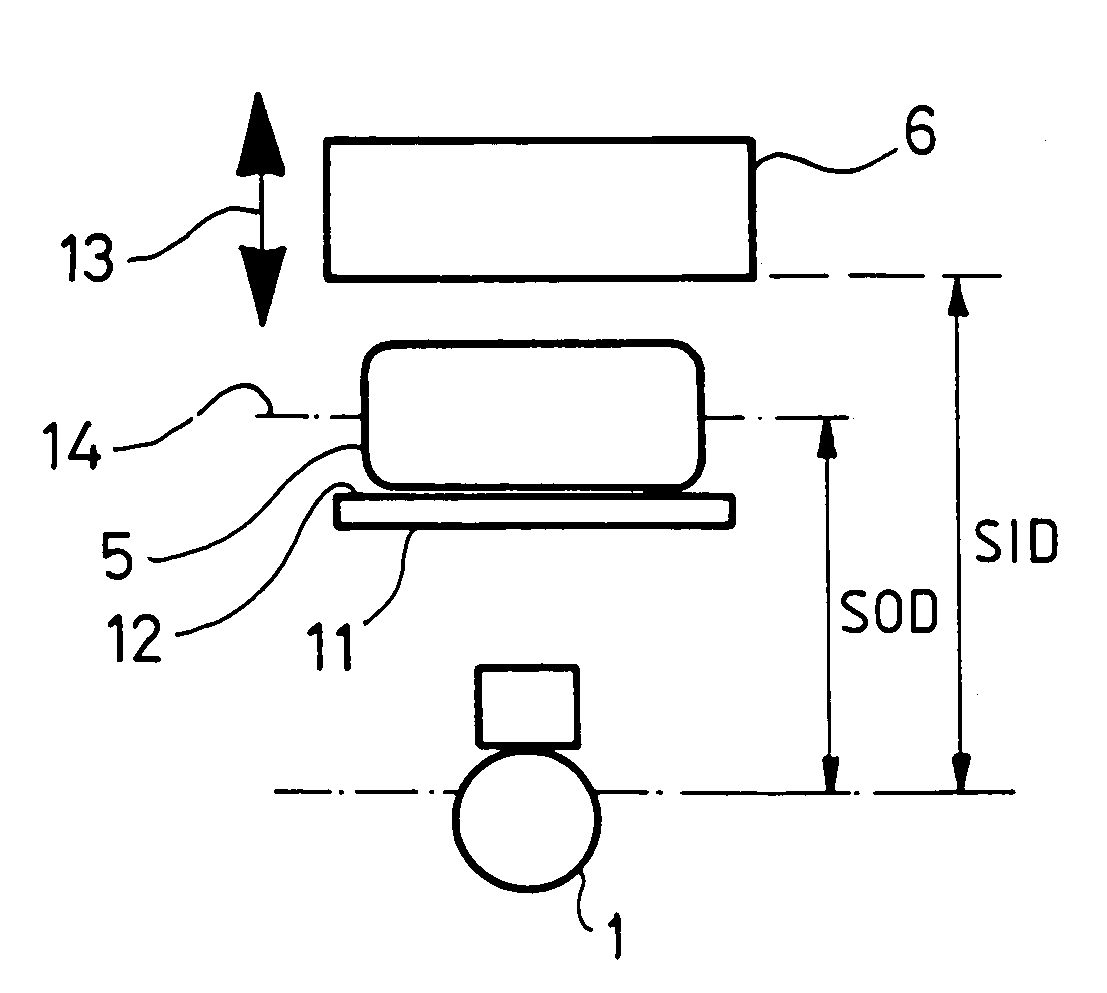
Method and apparatus for control of exposure in radiological imaging systems
InactiveUS7194065B1Without increasing X-ray dose receivedPatient positioning for diagnosticsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEquivalent doseX ray beam
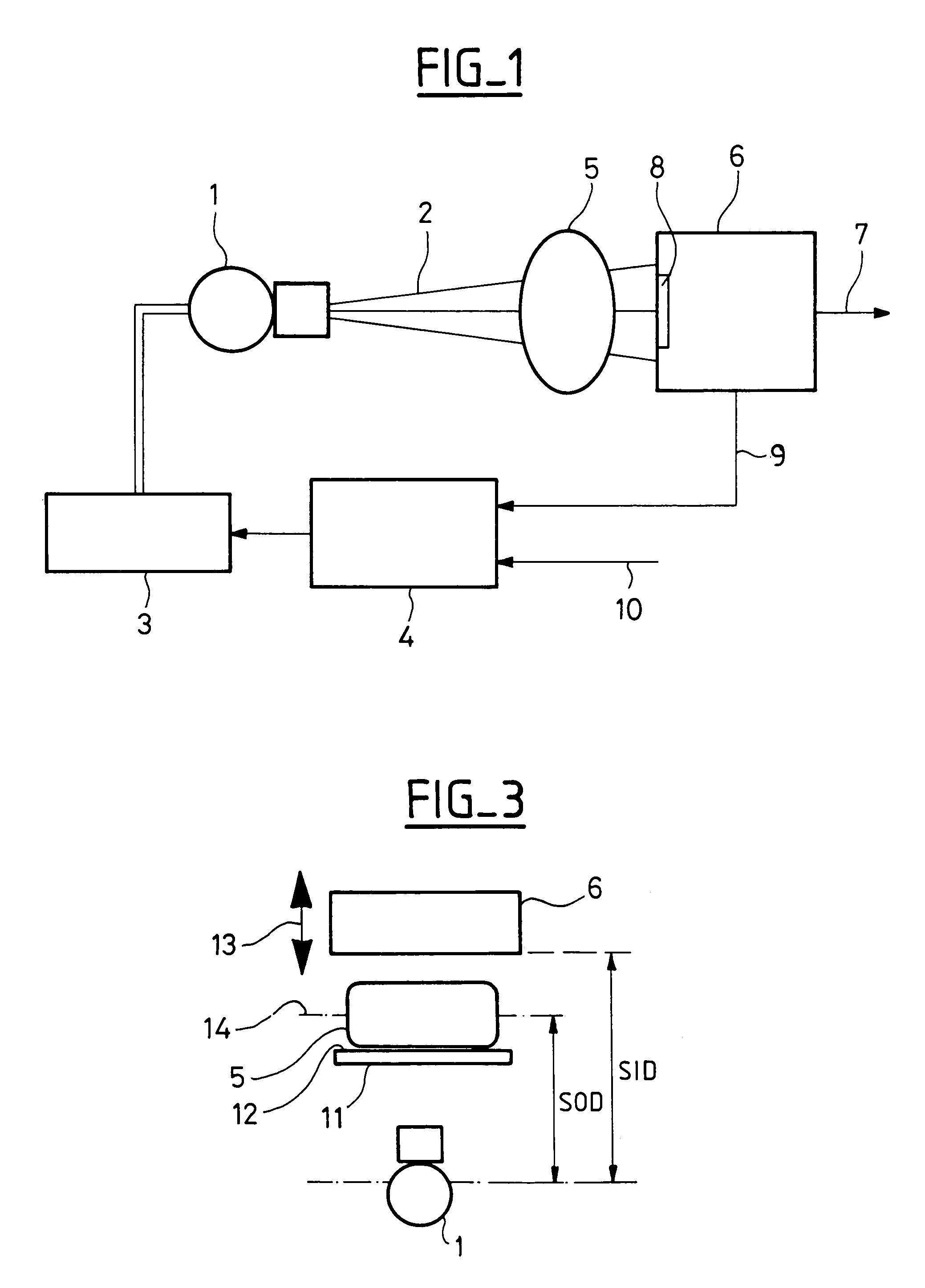
Method and apparatus for adjustment of the entrance dose of a radiology apparatus of the type containing a means of X-ray beam emission, a means of detection of the X-ray beam after it has crossed an object having to be visualized, and a means of visualization connected to the means of detection, in which the distance between the means of emission and the object is estimated and, when the distance between the means of emission and the object or the distance between the means of emission and the means of detection varies, the entrance dose is modified according to said distances in order to maintain an appreciably constant equivalent dose in the plane containing the object, the distance between the means of emission and the means of detection being known.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
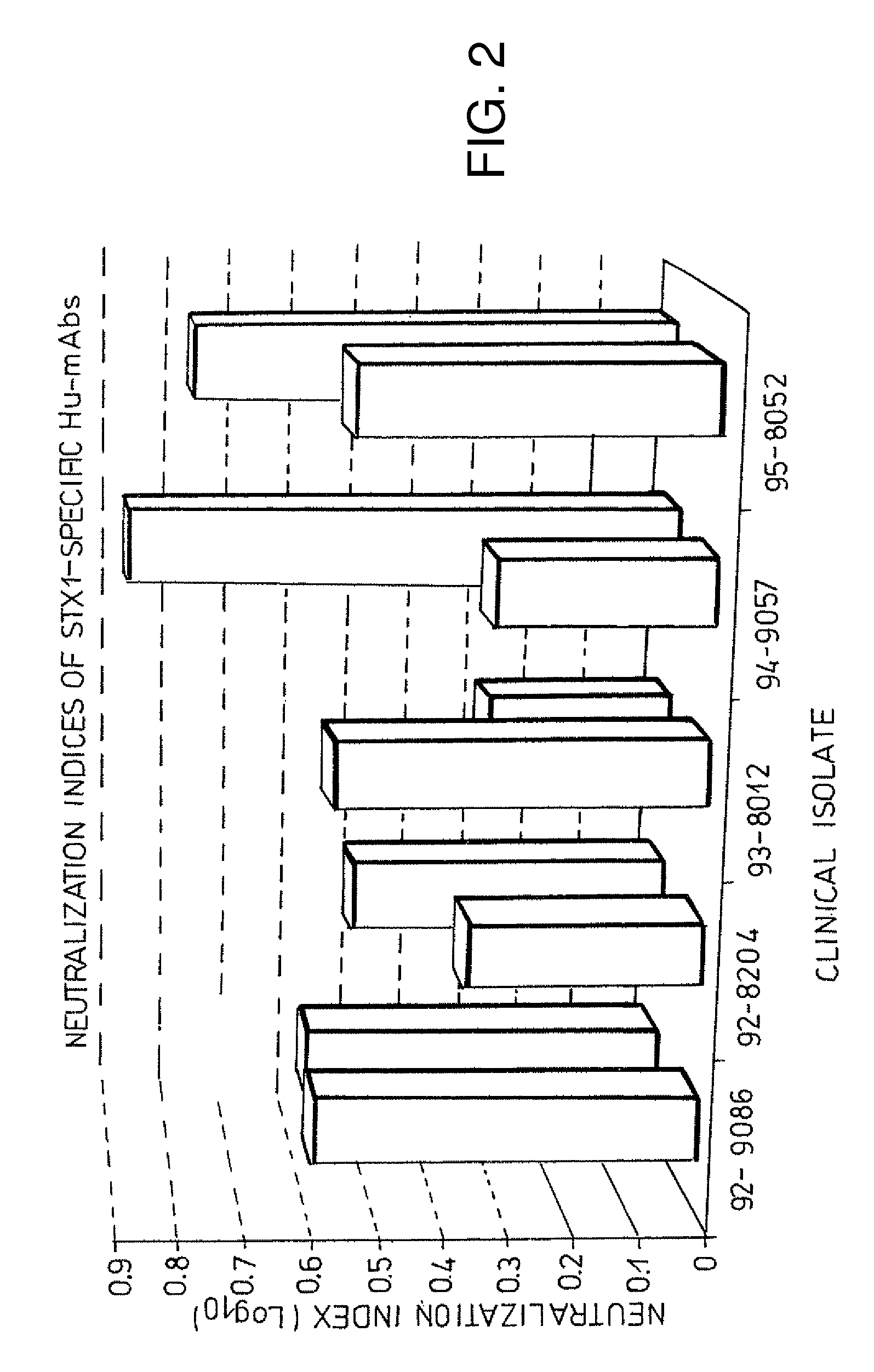
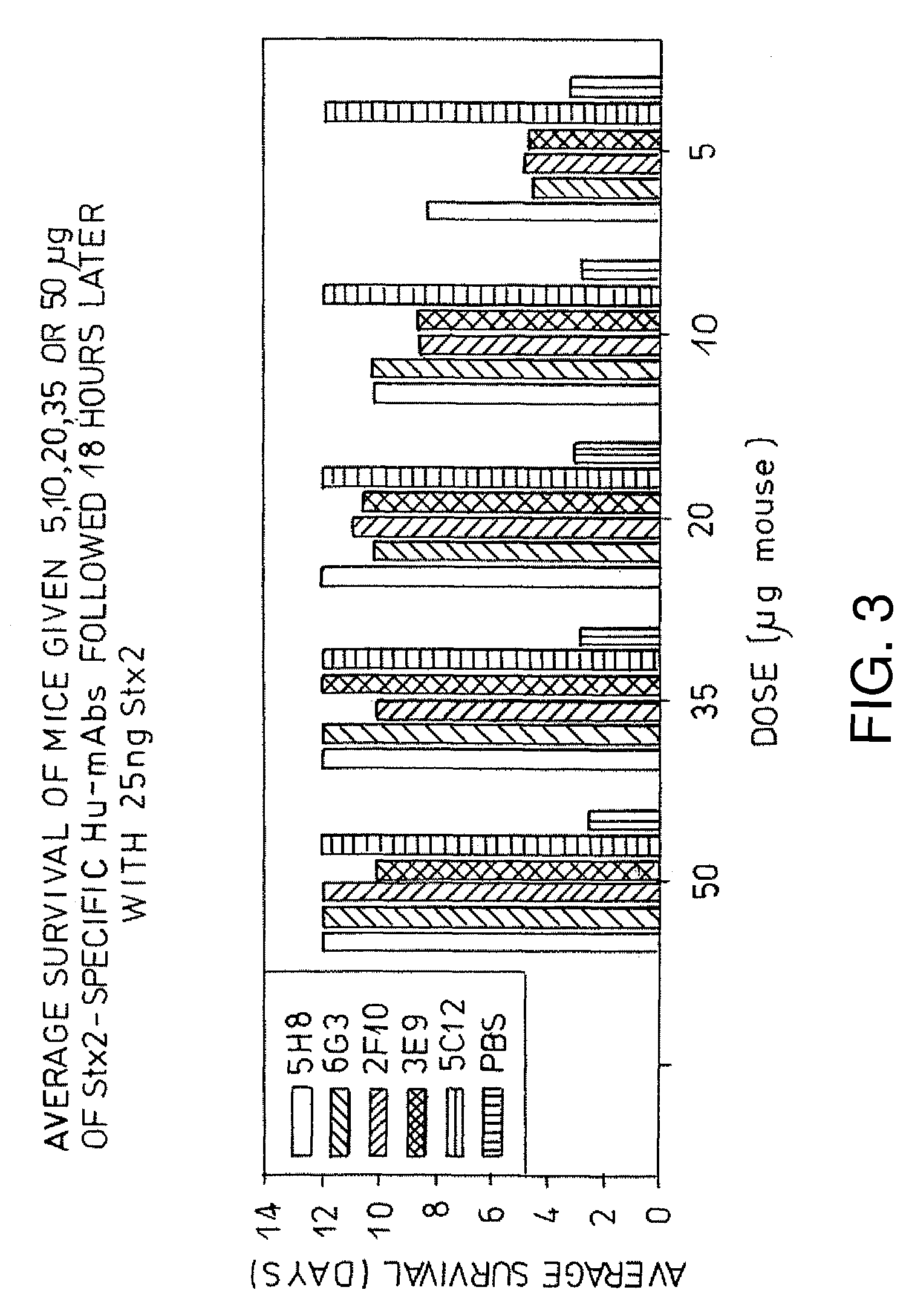
Human neutralizing antibodies against hemolytic uremic syndrome
Human and humanized monoclonal antibodies which binds specifically to subunit A of Shiga like toxin II have been developed which are effective to prevent or ameliorate one or more symptoms of HUS in a human. Effective dosages for treatment or prevention range from approximately 0.1 to 5.0 mg of antibody / kg of patient weight. The examples demonstrate the preferred dosage ranges based on the pig model, and what is being tested in phase I clinical trials. Antibodies are preferably transfused over a period of two hours, although this will depend on the patient and the disease state at the time of treatment. Preferred dosages for treatment of humans are between 0.1 mg / kg-5.0 mg / kg of 5C120, or an equivalent dosage of another antibody to subunit A of STX2. In the most preferred embodiments, dosages of 0.1 mg / kg, 0.5 mg / kg, or 5.0 mg / kg of 5C12 (low dose, anticipated therapeutic dose based on animal data and high dose) are administered.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
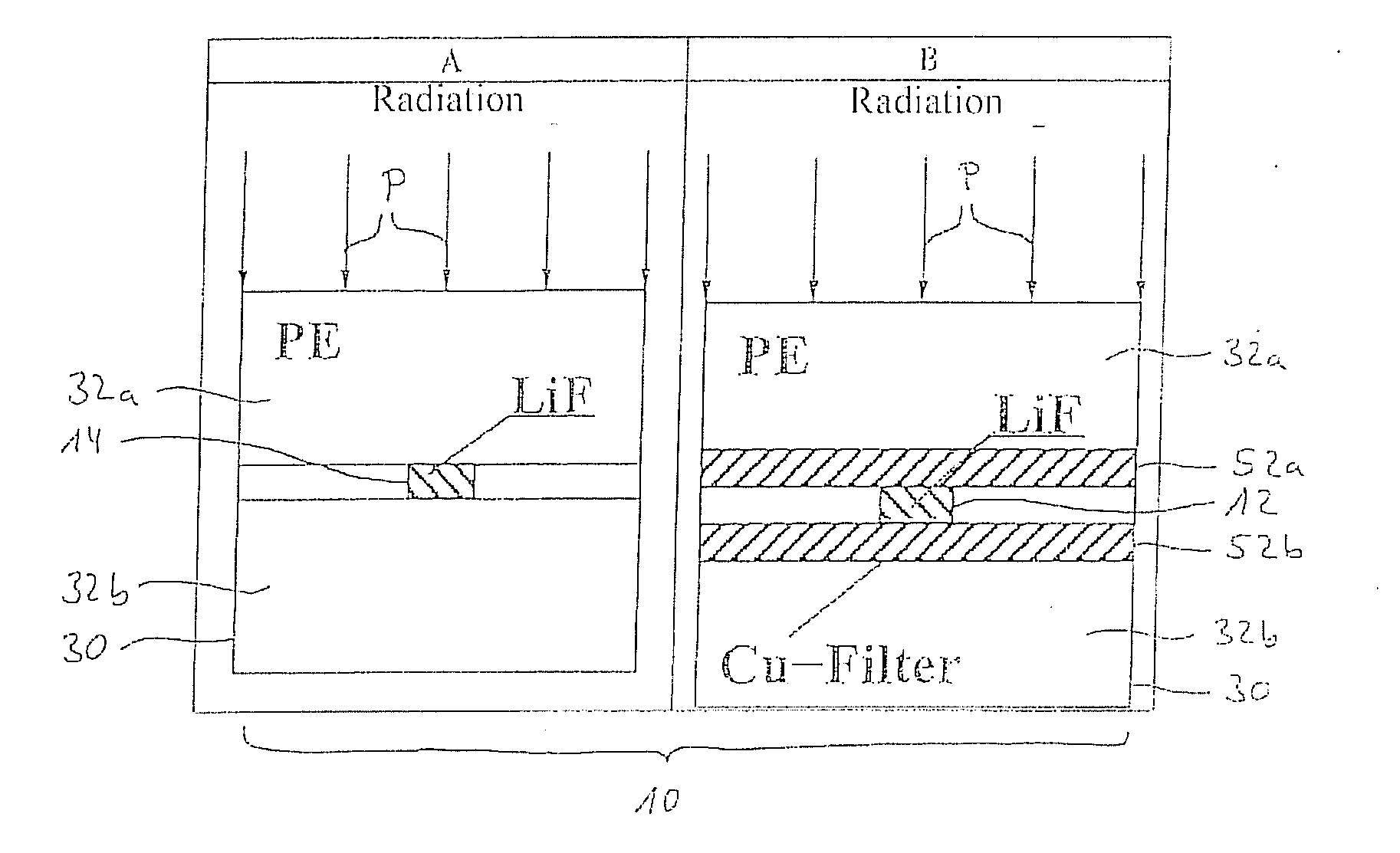
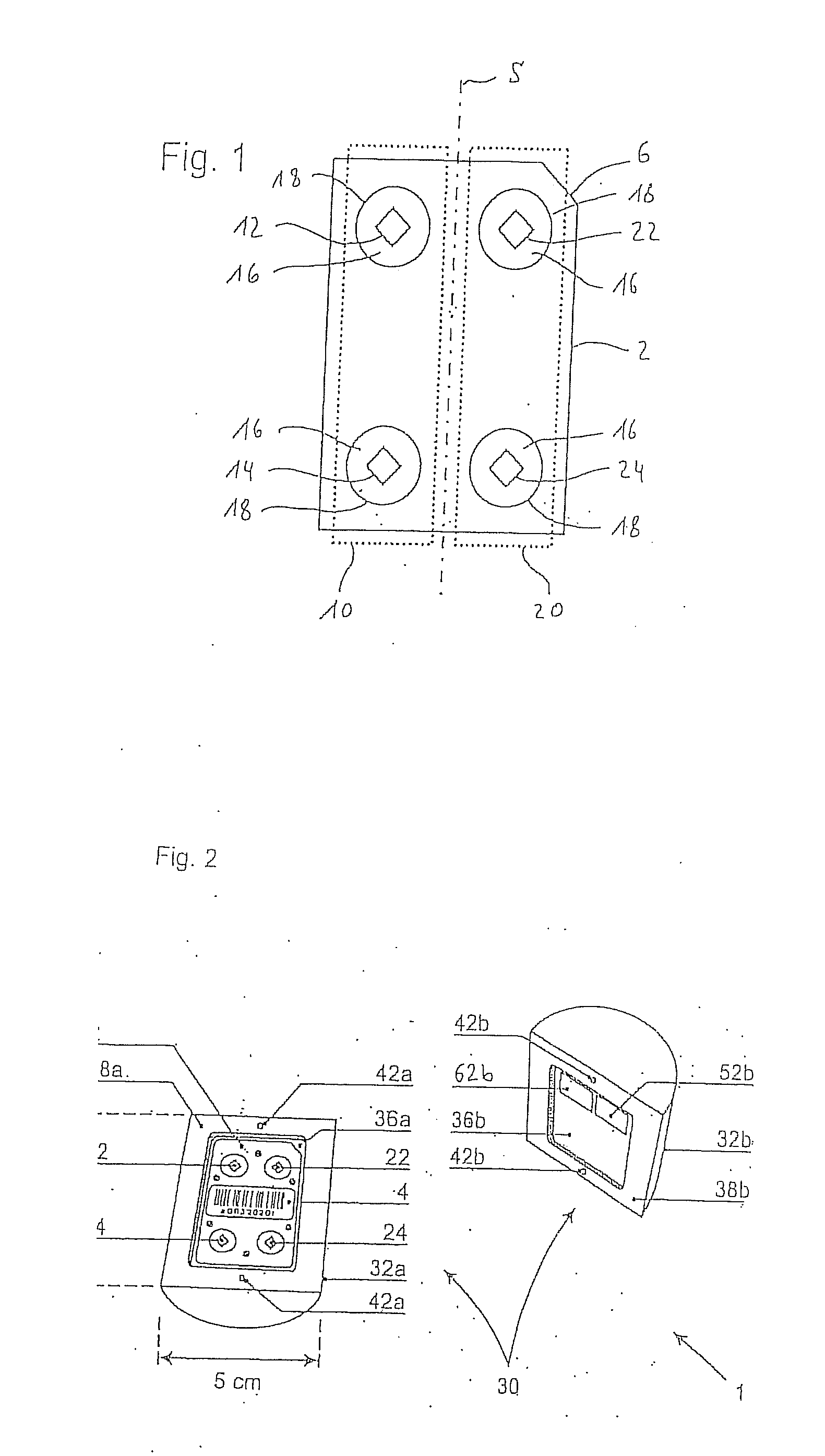
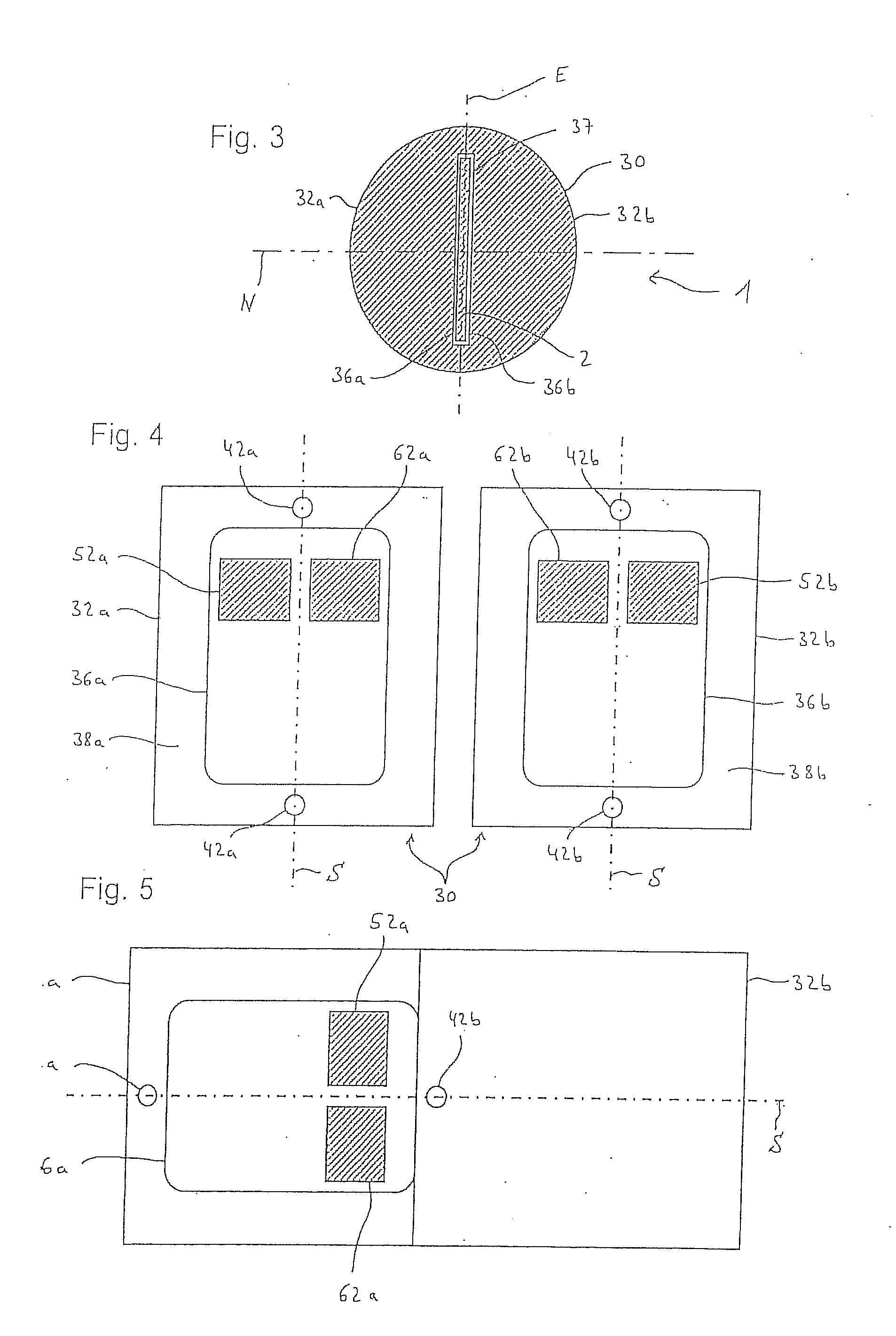
Local Dosimeter for Measuring the Ambient Equivalent Dose of Photon Radiation, and Reading Method
InactiveUS20100302533A1Luminescent dosimetersPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsDosimeterPhoton radiation
The invention consists of an area dosimeter for measuring the ambient equivalent dose (H*(10)) of photon radiation with a diffuser, a detector card with at least one pair of detection elements, preferably LiF-chips,whereby the first of the two detection elements is positioned between two filters in order to spectrally filter the photon radiation,whereby the second of the two detection elements is not positioned between such filters as those of the first detection element, in order that the photon radiation arriving at the second detection element have a different spectral distribution as the spectrally filtered photon radiation arriving at the first detection element. The two measurement values are used to obtain a weighted sum in order to achieve an optimized response characteristic, in particular in the range below 30 keV and if applicable in the range above 1.3 MeV.
Owner:GSI HELMHOLTZZENT FUR SCHWERIONENFORSCHUNG
Nanodosimeter based on single ion detection
InactiveUS20050109929A1Location can be detectedTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimeterFluence
A nanodosimeter device (15) for detecting positive ions induced in a sensitive gas volume by a radiation field of primary particle, comprising an ionization chamber (10) for holding the sensitive gas volume to be irradiated by the radiation field of primary particles; an ion counter system connected to the ionization chamber (10) for detecting the positive ions which pass through the aperture opening and arrive at the ion counter (12) at an arrival time; a particle tracking system for position-sensitive detection of the primary particles passing through the sensitive gas volume; and a data acquisition system capable of coordinating the readout of all data signals and of performing data analysis correlating the arrival time of the positive ions detected by the ion counter system relative to the position sensitive data of primary particles detected by the particle tracking system. The invention further includes the use of the nanodosimeter for method of calibrating radiation exposure with damage to a nucleic acid within a sample. A volume of tissue-equivalent gas is radiated with a radiation field to induce positive ions. The resulting positive ions are measured and compared with a determination of presence or extent of damage resulting from irradiating a nucleic acid sample with an equivalent dose of radiation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +1
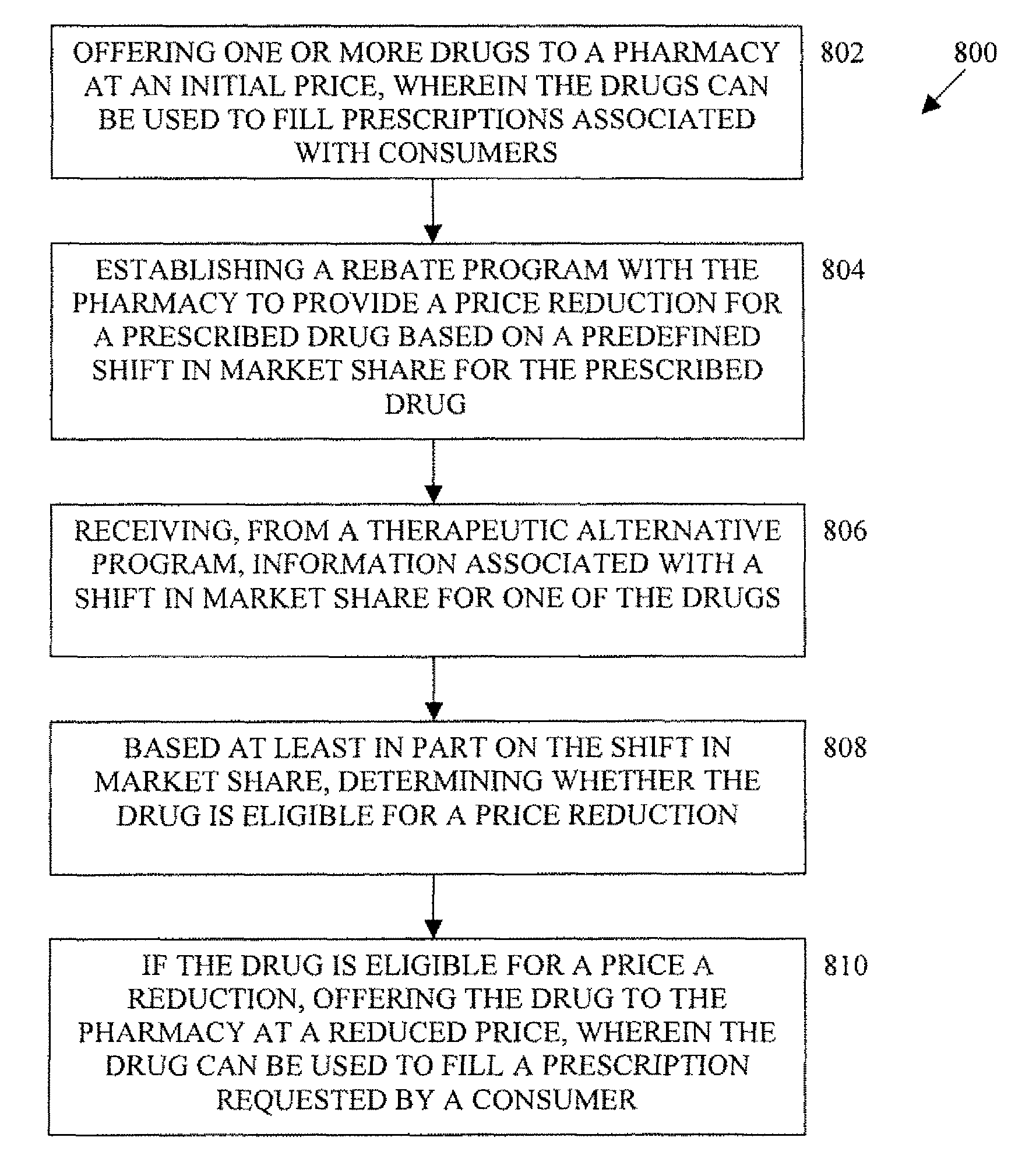
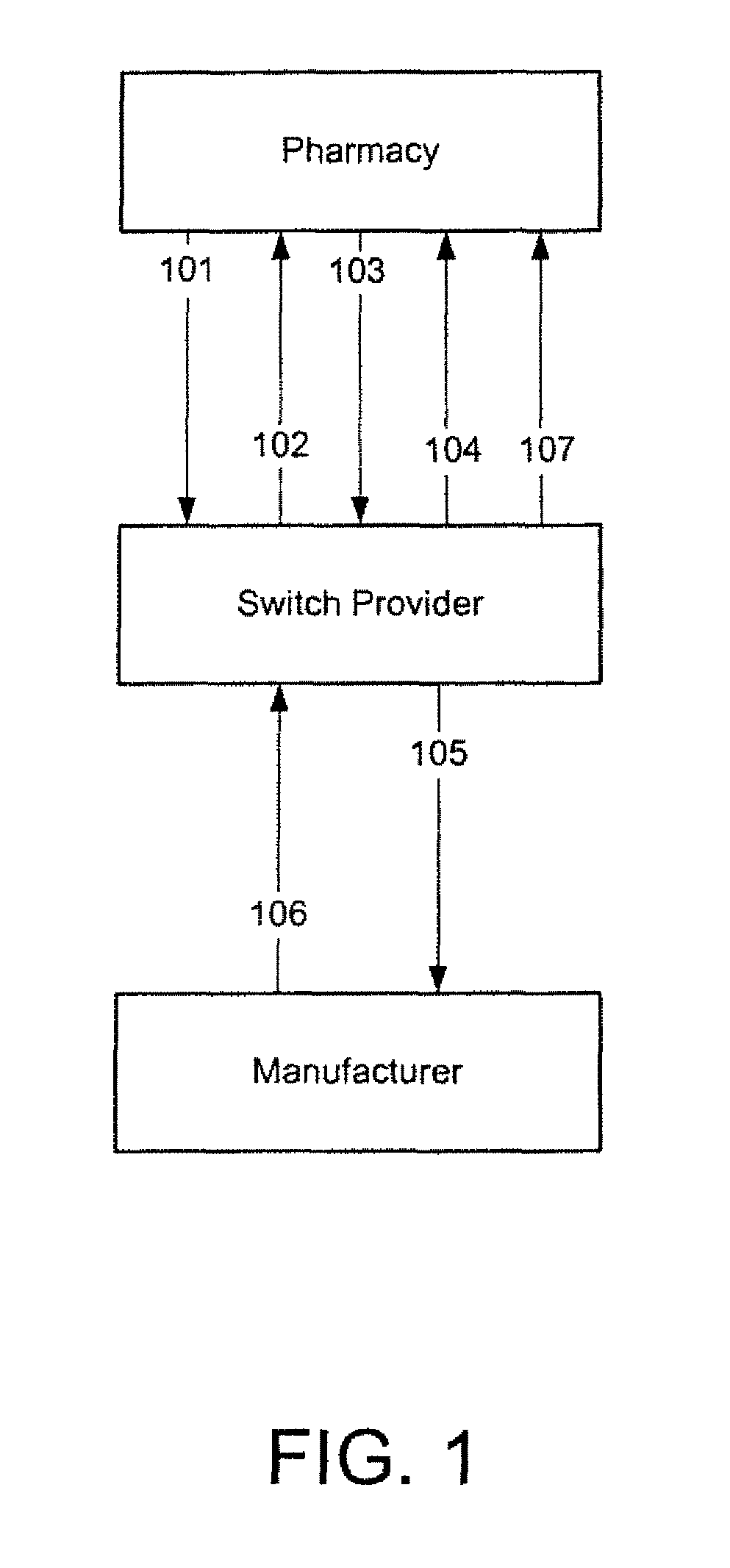
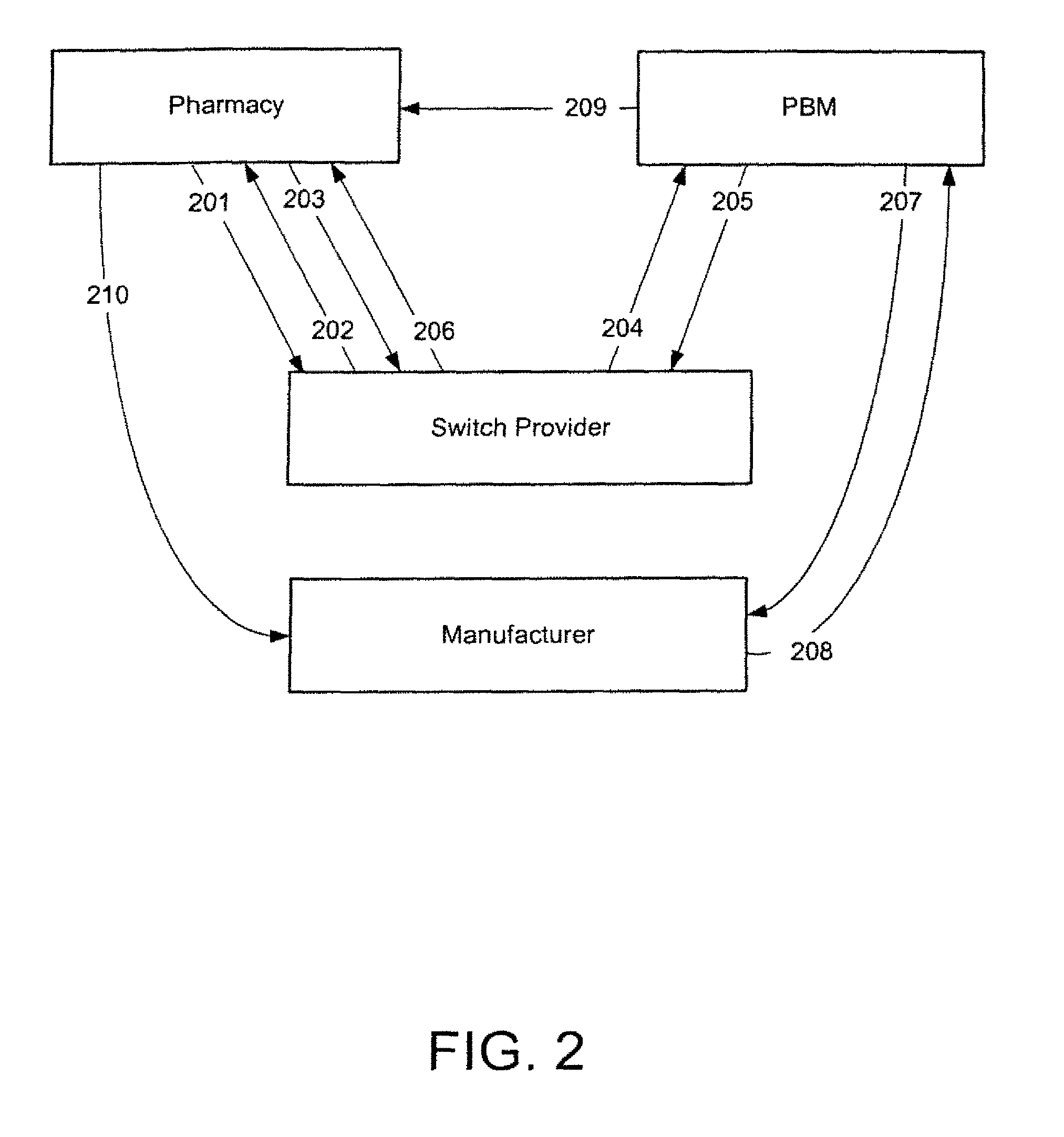
Systems and methods for shifting prescription market share by presenting pricing differentials for therapeutic alternatives
While a pharmacist may know of other medications approved by the FDA for the same medical condition, the pharmacist typically does not know what the therapeutically equivalent dose of those products is when compared to the originally prescribed item. In addition to this lack of equivalent dosage information, the pharmacist also is unable to determine if any of those other FDA approved items will save the consumer any money. Accordingly, embodiments of the invention can provide pharmacists and / or consumers with equivalent dosage information as well as pricing information for the equivalent dosage. Accordingly, based at least in part on this information, consumers may have an incentive to and may decide to purchase to another prescription drug, thereby shifting market share to a preferred prescription drug or pharmaceutical manufacturer or provider.
Owner:NDCHEALTH CORP
Portable energy adjusting device for heat energy-100 MeV neutron
ActiveCN101750623AImproved energy responseHigh sensitivityNeutron radiation measurementInelastic scatteringEnergy regulation
The invention discloses a portable energy adjusting device for equivalent dose detection of a heat energy-100 MeV neutron, which comprises an inelastic scatterer, a fast neutron moderator, an energy adjustor and a thermal neutron detector. The whole device takes the shape of a ball, the thermal neutron detector is arranged at the center of a ball body and coated with the spherical fast neutron moderator; the fast neutron moderator is coated with a spherical ultrafast neutron inelastic scatterer; and the energy reaction adjustor is positioned between the fast neutron moderator and the fast neutron inelastic scatterer. The portable energy adjusting device has the advantages of compact structure and light weight and can improve the reaction of a high-energy neutron by about 30 percent as well as the sensitivity of the neutron by about 18-40 times through experimental evidence compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR CONTROL SYST ENG
System for determining UV dose in a reactor system
InactiveUS20160130159A1Accurate RED valueReduce the amount requiredWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationReactor systemMedicine
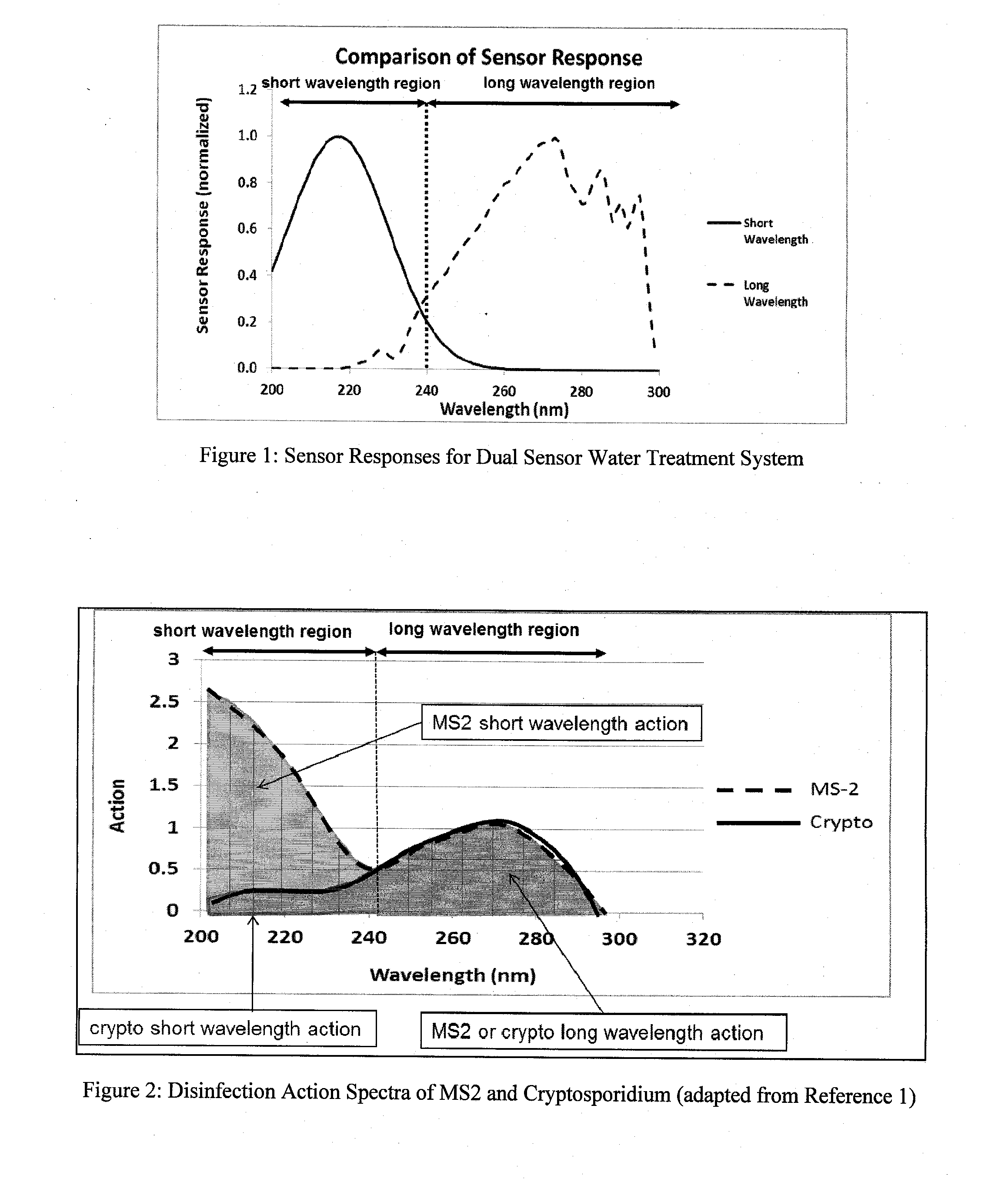
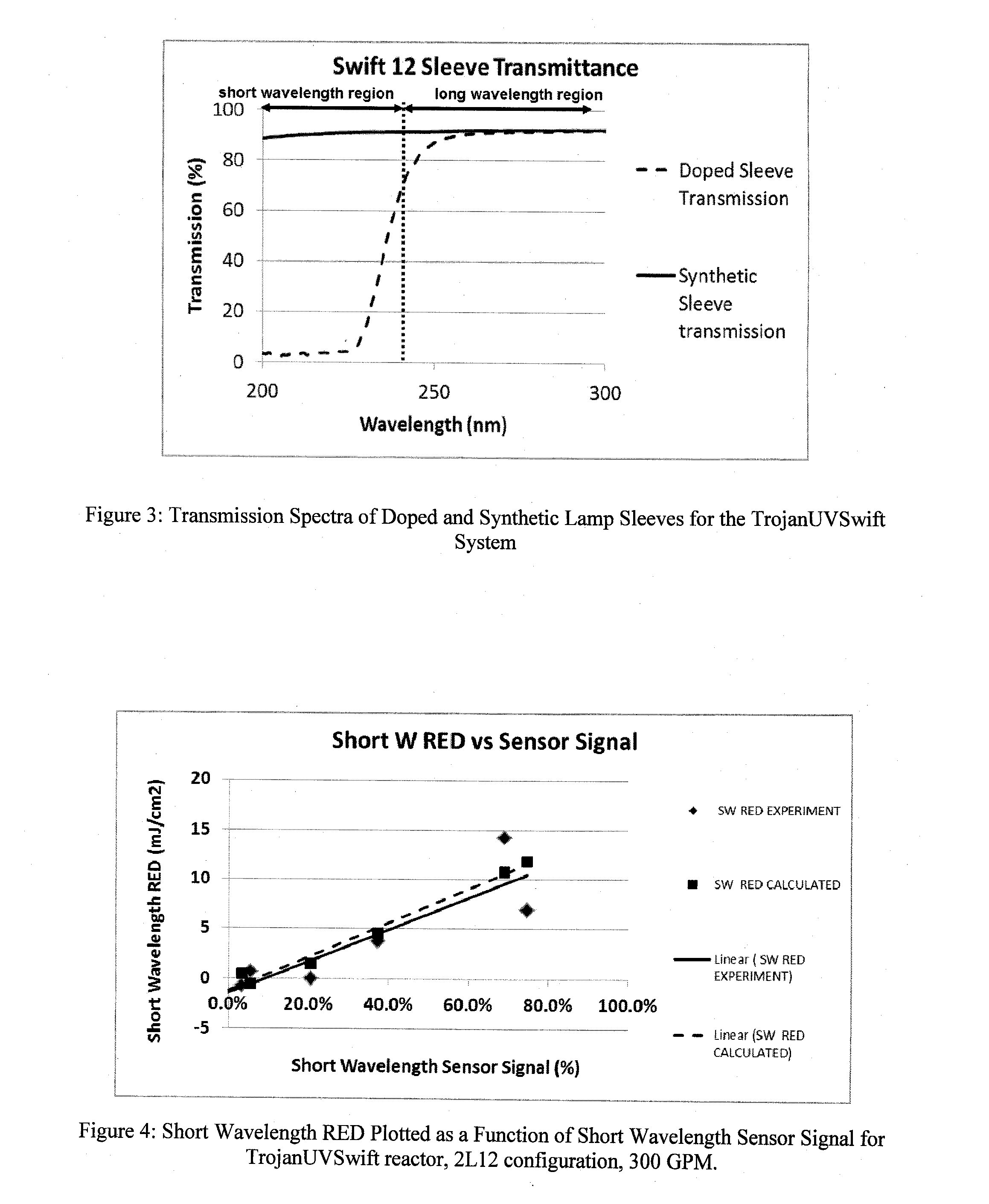
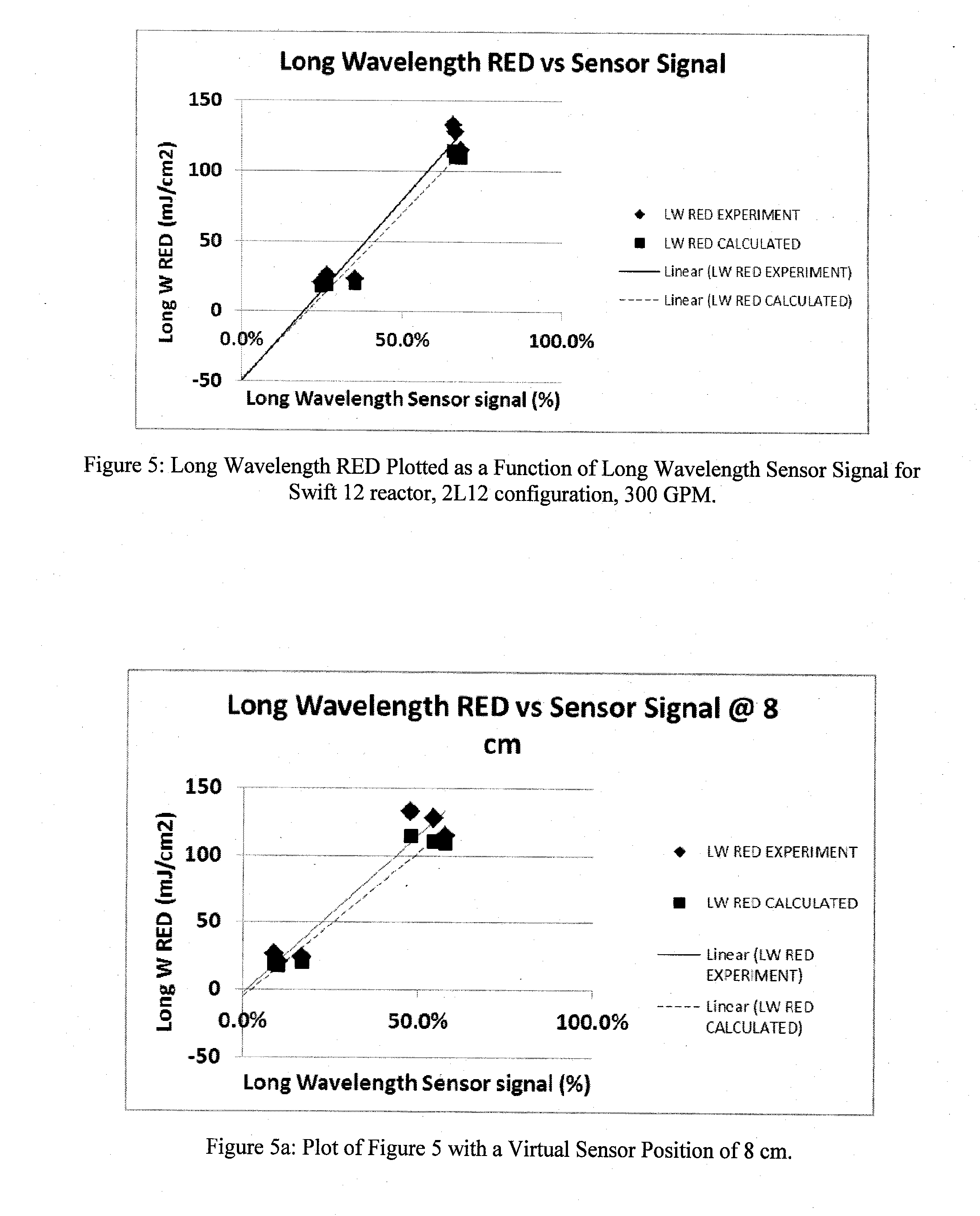
The is described a process for determining a validated Reduction Equivalent Dose for reducing the concentration of a target contaminant contained in a fluid in a radiation fluid treatment system. In one embodiment, the process comprises the steps of: (a) determining a short wavelength Reduction Equivalent Dose for the target contaminant or a challenge contaminant in a first region of the electromagnetic spectrum having a wavelength of less than or equal to about 240 nm; (b) determining a long wavelength Reduction Equivalent Dose for the target contaminant or a challenge contaminant in a second region of the electromagnetic spectrum having a wavelength of greater than about 240 nm; and (c) summing the short wavelength Reduction Equivalent Dose and the long wavelength Reduction Equivalent Dose to produce the validated Reduction Equivalent Dose for the target contaminant. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a useful approach for determining the relevant Reduction Equivalent Dose (RED) for Cryptosporidium disinfection and accomplishes this by using the discovered relation between the short wavelength sensor signal and the short wavelength RED, and subtracting the short wavelength RED from the RED determined using a challenge microbe with synthetic lamp sleeves, to obtain the long wavelength RED applicable to Cryptosporidium disinfection. In a bioassay, one would only need the short wavelength sensor reading and the challenge microbe RED using synthetic lamp sleeves to determine the applicable RED, once the relationship between the short wavelength sensor reading and the short wavelength RED was established.
Owner:TROJAN TECH
Wide-range TEPC (tissue-equivalent proportional counter) and application thereof
ActiveCN106772536AIncrease surface areaLow Flux RateRadiation intensity measurementCollection systemRadiation field
The invention relates to a radiation detection device and provides a wide-range TEPC (tissue-equivalent proportional counter) and an application thereof in order to solve the problem that an existing TEPC is hard to give consideration to radiation field measurement with larger differences of fluence rate and equivalent dose rate levels. The wide-range TEPC comprises a casing, a voltage division circuit, a multichannel signal collection system as well as a conductive tissue equivalent material negative plate, a conductive tissue equivalent material plate, a GEM membrane and a positive plate which are located in the casing and overlaid in sequence from top to bottom. The application method of the wide-range TEPC comprises steps as follows: step one, the wide-range TEPC is placed in a to-be-detected radiation field; step two, signals are collected; step three, the signals are processed. The wide-range TEPC has a quite wide measuring range, can realize measurement of the radiation fields with low fluence rate and high fluence rate conveniently, is smaller in size, relatively simple in structure, easy to manufacture and quite wide in applicable range, and can be applicable to radiation monitoring of various occasions.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
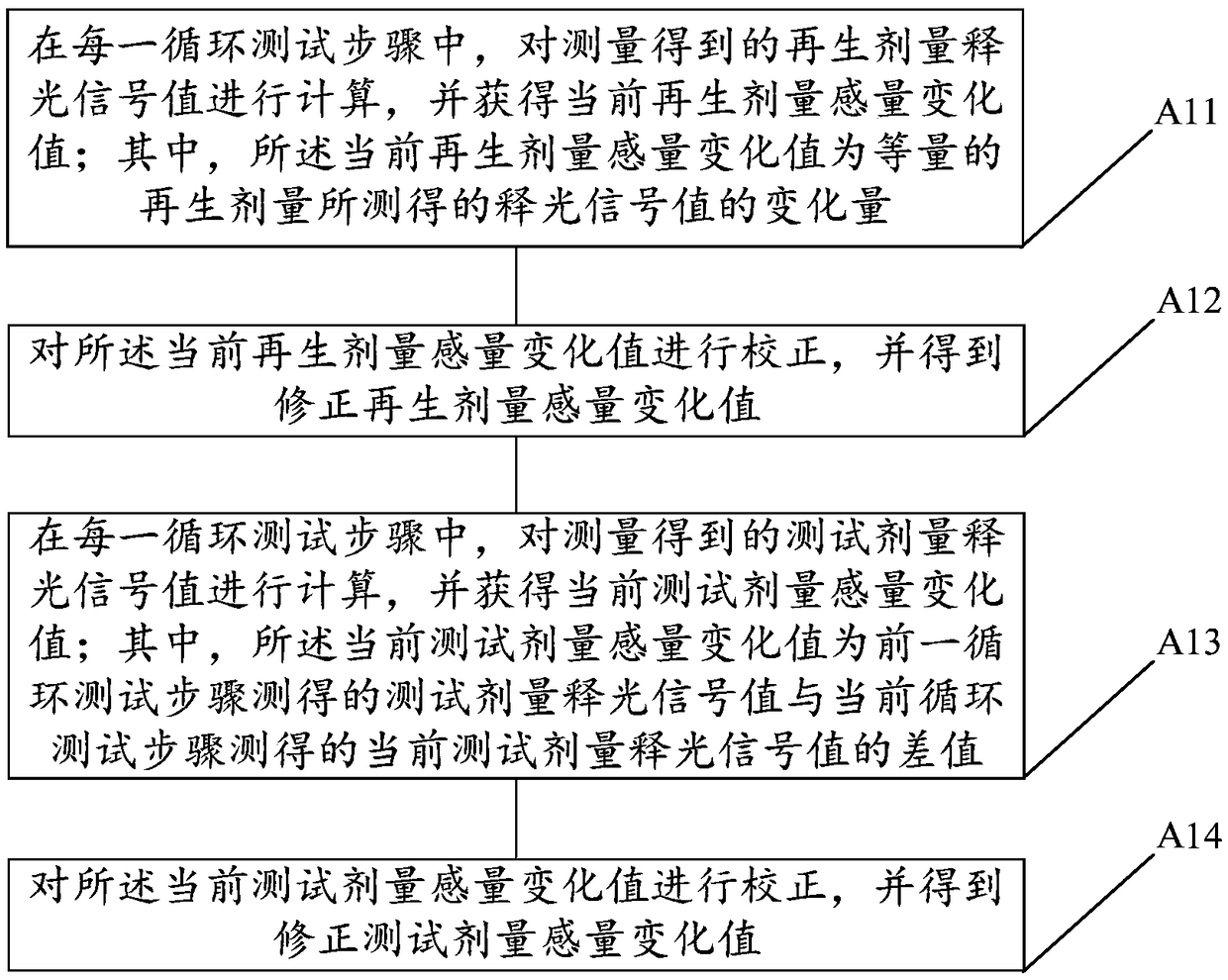
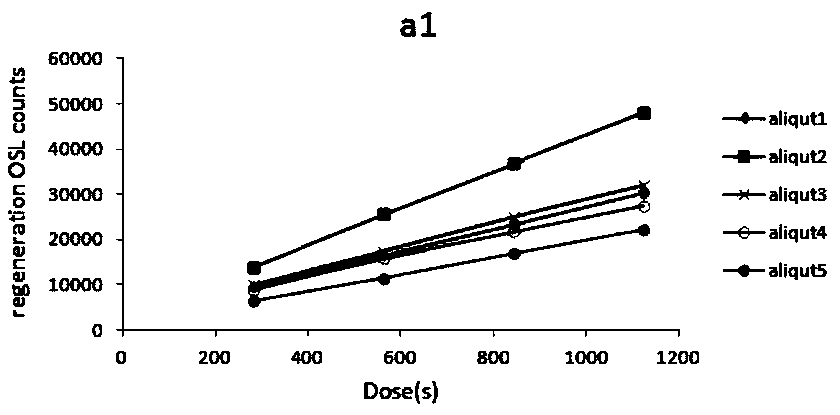
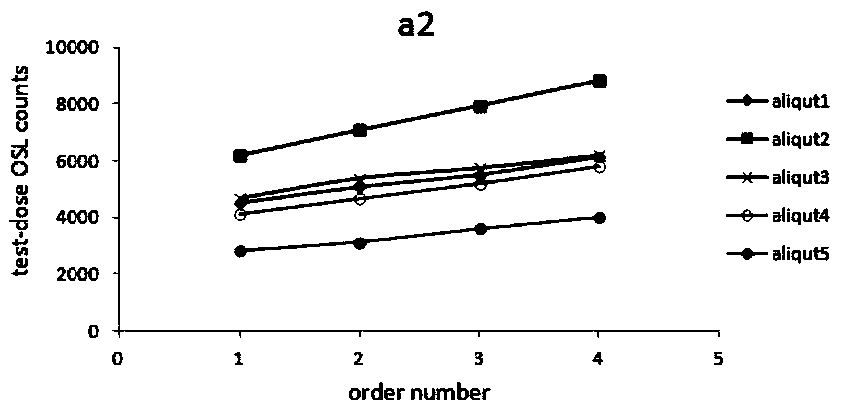
Sensitivity correction method of optically stimulated luminescence dating experiment
ActiveCN109115732AThe equivalent dose value is reasonableSensitivity Variation CorrectionAnalysis by material excitationCorrection methodEquivalent dose
The invention provides a sensitivity correction method of an optically stimulated luminescence dating experiment. The sensitivity correction method comprises the following steps of, in each loop teststep, calculating a regenerative-dose luminescence signal value and a test-dose luminescence signal value which are obtained through measurement, and acquiring a current regenerative-dose sensitivitychange value, wherein the current regenerative-dose sensitivity change value is a change quantity of the luminescence signal value measured by an equivalent regenerative dose; correcting the current regenerative-dose sensitivity change value, and obtaining a corrected regenerative-dose sensitivity change value, wherein a current test-dose sensitivity change value is a difference value between thetest-dose luminescence signal value measured in a previous loop test step and a current test-dose luminescence signal value measured in a current loop test step; and correcting the current test-dose sensitivity change value, and obtaining a corrected test-dose sensitivity change value. The sensitivity correction method can be used for effectively optimizing a correction method of a sensitivity change, so as to improve the test accuracy and reliability of an equivalent dose of a sample.
Owner:GUANGZHOU COLLEGE OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Liposomal corticosteroids for treatment of inflammatory disorders in humans
InactiveCN104144679AEfficient removalOvercome inherent problemsOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticLipid formationCorticosteroid preparation
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising liposomes composed of non-charged vesicle-forming lipids, optionally including not more than 10 mole percent of negatively charged vesicle- forming lipids and / or not more than 10 mole percent of PEGylated lipids, the liposomes having a selected mean particle diameter in the size range of 40-200 nm and comprising a first corticosteroid in water soluble form, for the site-specific treatment of inflammatory disorders in humans, providing in human patients a fast, strong, and durable anti-inflammatory effect for at least 2 weeks at a dose of at most 5 mg / kg body weight of prednisolone or an equipotent dose corticosteroid other than prednisolone at a treatment frequency of at most once per two weeks. Furthermore the present invention relates to the application of the above-mentioned pharmaceutical composition given as intervention therapy in inflammatory disorders such as rheumatic disease or a related inflammatory connective tissue disorder, inflammatory diseases of the kidney or inflammatory bowel disorders, in combination with chronic therapy with a second free corticosteroid formulation or in combination with chronic treatment with a disease- modifying agent such as methotrexate.
Owner:ENCELADUS PHARMA BV
System and method for reducing radiation dose
PendingCN113724841AAvoid radiationImprove image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionRadiation equivalent doseEquivalent dose
The invention discloses a method for reducing radiation dose. The method includes the step: acquiring first image data related to a region of interest (ROI) of a first object. The first image data corresponds to a first equivalent dose, and the first image data can be acquired by a first device. The method may further include the steps of obtaining a noise reduction model associated with the first image data and determining second image data corresponding to a second equivalent dose based on the first image data and the noise reduction model, wherein the second equivalent dose being higher than the first equivalent dose. In some embodiments, the method may further include the steps of determining information related to a region of interest (ROI) of the first object based on the second image data, and recording the information related to the region of interest (ROI) of the first object. According to the method, the low-dose image is converted into the high-dose image through the noise reduction model, and the patient can be prevented from being exposed to excessive radiation under the condition that the image with the same quality or higher quality is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Local dosimeter for measuring the ambient equivalent dose of photon radiation, and reading method
An area dosimeter for measuring the ambient equivalent dose of photon radiation with a diffuser, and a detector card with at least one pair of detection elements, preferably LiF-chips. A first of the two detection elements is positioned between two filters in order to spectrally filter the photon radiation. A second of the two detection elements is not positioned between such filters in order that the photon radiation arriving at the second detection element will have a different spectral distribution from the spectrally filtered photon radiation arriving at the first detection element. The two measurement values are used to obtain a weighted sum in order to achieve an optimized response characteristic.
Owner:GSI HELMHOLTZZENT FUR SCHWERIONENFORSCHUNG
Optimization method for shielding design of marine reactor based on neural network and genetic algorithm
ActiveCN104933245BReduce time consumptionReduce programming difficultySpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkNeural network topology
The invention discloses a method for optimizing the shielding design of a marine reactor based on a neural network and a genetic algorithm. The Monte Carlo method is used to simulate and calculate the transport process of neutrons and photons in the reactor, and the MCNP program is used to simulate and calculate the layered shielding model of the marine reactor to obtain the reactor. Neutron and photon flux after shielding, and calculate the total equivalent dose; according to the number of input parameters n of samples 1 and the number of output parameters n 2 To determine the topology of the BP neural network; determine the fitness function of the genetic algorithm according to the objective of the reactor shielding problem, select the recommended fitness function, and use the strong optimization ability of the genetic algorithm to couple with the neural network to find the best shielding parameters. The invention has the advantages of reducing the time consumption of the MCNP program in the particle transport calculation process by using the strong fitting ability of the neural network and using the good optimization ability of the genetic algorithm, and can find the optimal shielding in few iteration steps parameter.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Portable energy adjusting device for heat energy-100 MeV neutron
ActiveCN101750623BImproved energy responseHigh sensitivityNeutron radiation measurementInelastic scatteringHigh energy
The invention discloses a portable energy adjusting device for equivalent dose detection of a heat energy-100 MeV neutron, which comprises an inelastic scatterer, a fast neutron moderator, an energy adjustor and a thermal neutron detector. The whole device takes the shape of a ball, the thermal neutron detector is arranged at the center of a ball body and coated with the spherical fast neutron moderator; the fast neutron moderator is coated with a spherical ultrafast neutron inelastic scatterer; and the energy reaction adjustor is positioned between the fast neutron moderator and the fast neutron inelastic scatterer. The portable energy adjusting device has the advantages of compact structure and light weight and can improve the reaction of a high-energy neutron by about 30 percent as well as the sensitivity of the neutron by about 18-40 times through experimental evidence compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR CONTROL SYST ENG
Exposure dose control method based on exposure dose control system
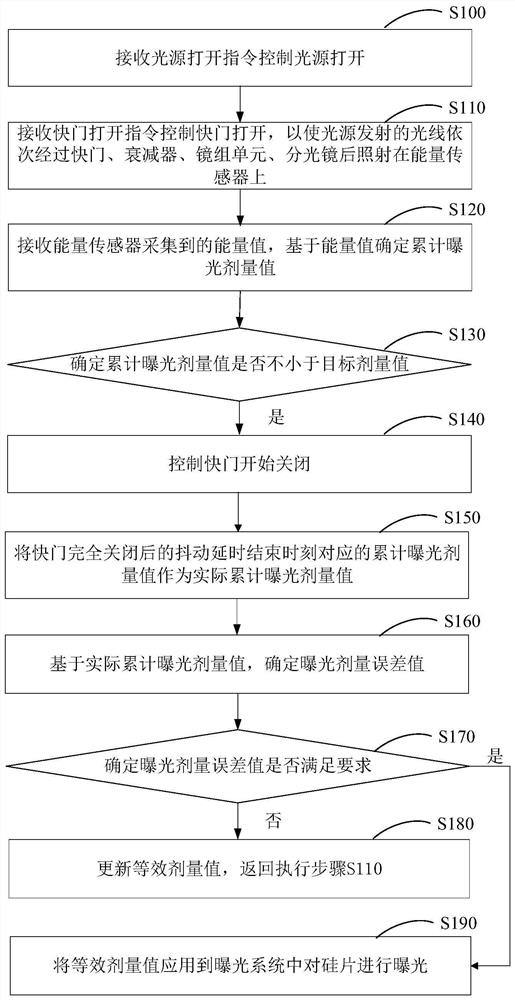
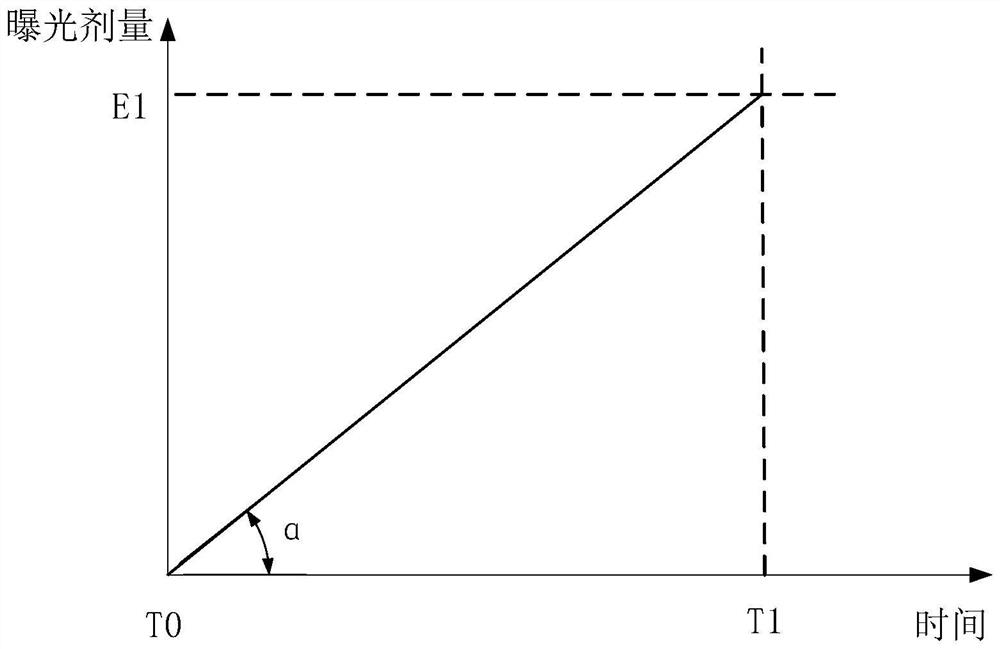
PendingCN114578658AHigh precisionSolve the problem of low control precisionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusDose errorShutter
The invention provides an exposure dose control method based on an exposure dose control system. The method comprises the following steps: controlling a shutter to open; receiving an energy value collected by an energy sensor, and determining an accumulated exposure dose value based on the energy value; determining whether the accumulated exposure dose value is not less than a target dose value; if the accumulated exposure dose value is not less than the target dose value, controlling the shutter to start to close; taking the accumulated exposure dose value corresponding to the jitter delay ending moment after the shutter is completely closed as an actual accumulated exposure dose value; determining an exposure dose error value based on the actual accumulated exposure dose value; determining whether the exposure dose error value meets requirements or not; if the exposure dose error value does not meet the requirement, updating the equivalent dose value, and returning to execute the first step; and if the exposure dose error value meets the requirement, applying the equivalent dose value to the exposure system. Through the exposure dose control method based on the exposure dose control system, the problem of low exposure dose control precision is solved.
Owner:BEIJING SEMICON EQUIP INST THE 45TH RES INST OF CETC
Special liquid soap controller used on fixed hand-washing dais
The invention relates to a special liquid soap controller used on a fixed hand-washing dais. The special liquid soap controller comprises a liquid soap container, and is characterized in that the bottom end of the liquid soap container is connected with a square liquid-outlet pipe, a gear-shaped equivalent-dose dispenser is arranged in the square liquid-outlet pipe and is installed on a horizontal shaft through key connection; and a pin shaft is horizontally arranged on the inner wall of the square liquid-outlet pipe, one end of the horizontal shaft is arranged on the pin shaft in an inserted way and is in sliding fit with the pin shaft, and the other end of the horizontal shaft extends out of the square liquid-outlet pipe and is mounted with a manual knob. Liquid soap can be output quantitatively to avoid causing waste, and the operation is very convenient.
Owner:张庆争
Novel mixing glue barrel
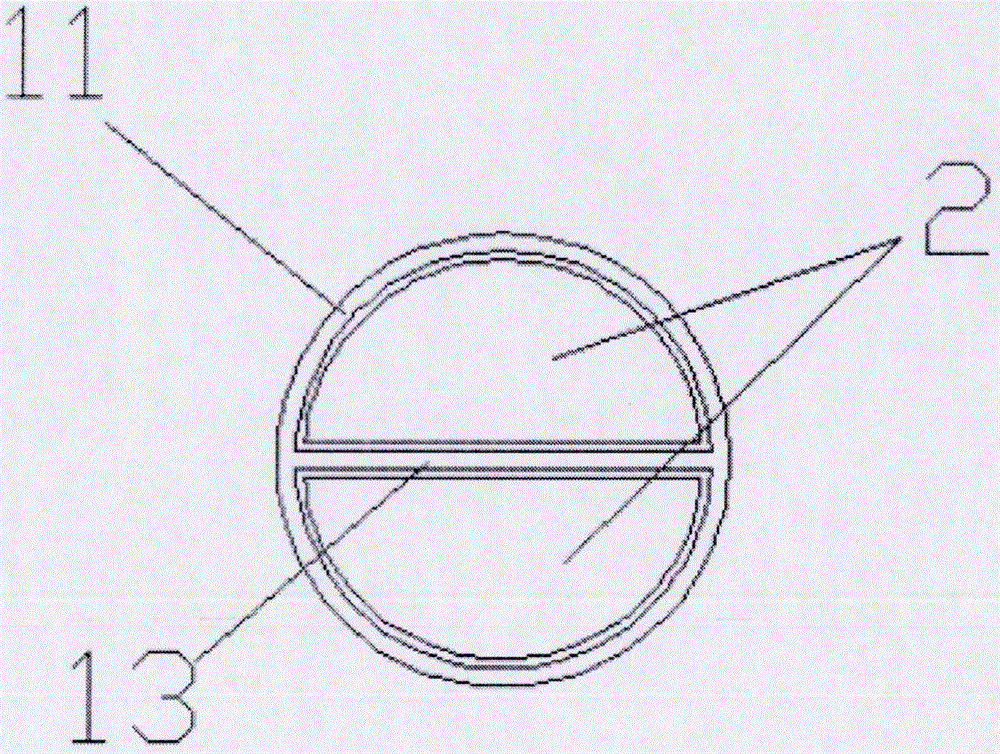
InactiveCN106516440ASimple structureDispensing apparatusContainers with multiple articlesEquivalent doseHollow cylinder
The invention discloses a novel mixing glue barrel which comprises a glue barrel main body and a barrel plug; the glue barrel main body comprises a barrel body and a glue outlet nozzle which are fixedly connected; the barrel body is in the shape of hollow cylinder with a bottom-end opening; the glue outlet nozzle is positioned on the center of the top end of the barrel body; a partition is arranged inside the glue barrel main body for dividing the barrel body and the glue outlet nozzle into two symmetrical cavities; sections of the two cavities in the barrel body are in the shape of two circles which are bilaterally symmetrical; and the barrel plug is separately arranged in the semicircular cavities of the barrel body. The novel mixing glue barrel disclosed by the invention is simple in structure; the single cylindrical barrel body is divided into two cavities through one partition, and a mixture of a component A and a component B is respectively placed in the two cavities, an opening of the glue outlet nozzle is opened through a pair of scissors first, and then the barrel plug is extruded through a glue gun, so that the mixture of the component A and the component B can be extruded with equivalent dose.
Owner:朱娉婷
A Space Telescope for Charged Particles Based on Cadmium Zinc Telluride
ActiveCN112462409BRealize the measurement functionGood energy resolutionX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementCrystal systemRadiation equivalent dose
The invention discloses a space charged particle telescope based on cadmium zinc telluride. The top of the outer cover is provided with an opening, the outer cover is provided with a mounting seat, and the mounting seat is provided with a Si semiconductor detector, a first CZT detector and a second CZT The detector, the Si semiconductor detector and the first CZT detector form a first group of ΔE‑E detector systems, the first CZT detector and the second CZT detector form a second group of ΔE‑E detector systems, and the first group ΔE The ‑E detector system and the second group of ΔE‑E detector systems work together to measure charged particles of different energies. The invention can measure components such as charged particles, thermal neutrons and gamma rays in the space environment. It can effectively measure the linear energy transfer (LET), equivalent dose, charged particle energy spectrum, total dose, dose rate and other information of charged particles in space, which is of great significance for astronaut radiation risk assessment. Compared with traditional scintillation The crystal system can improve the resolution of particle energy spectrum and enhance the ability of particle identification.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
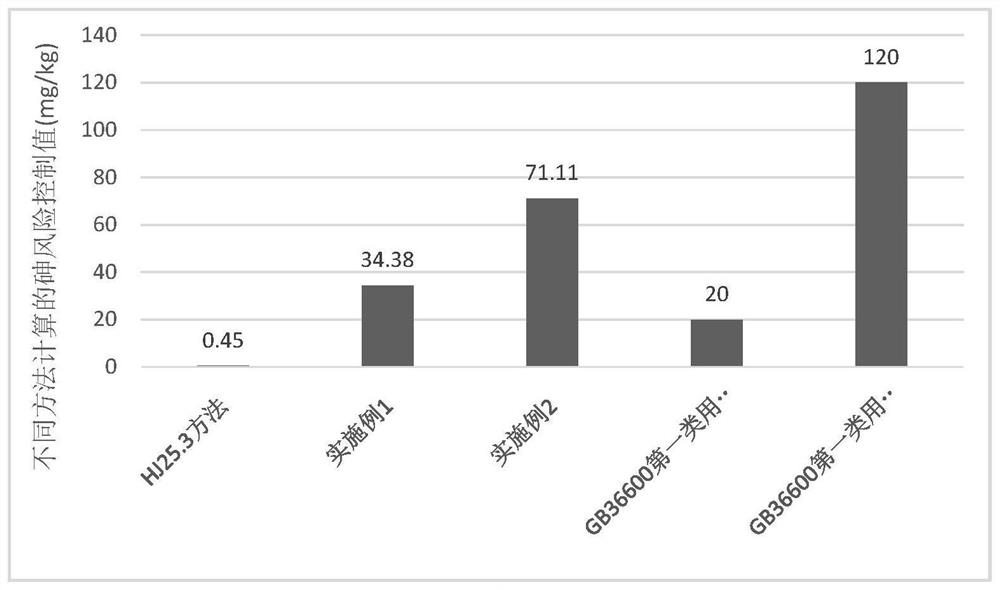
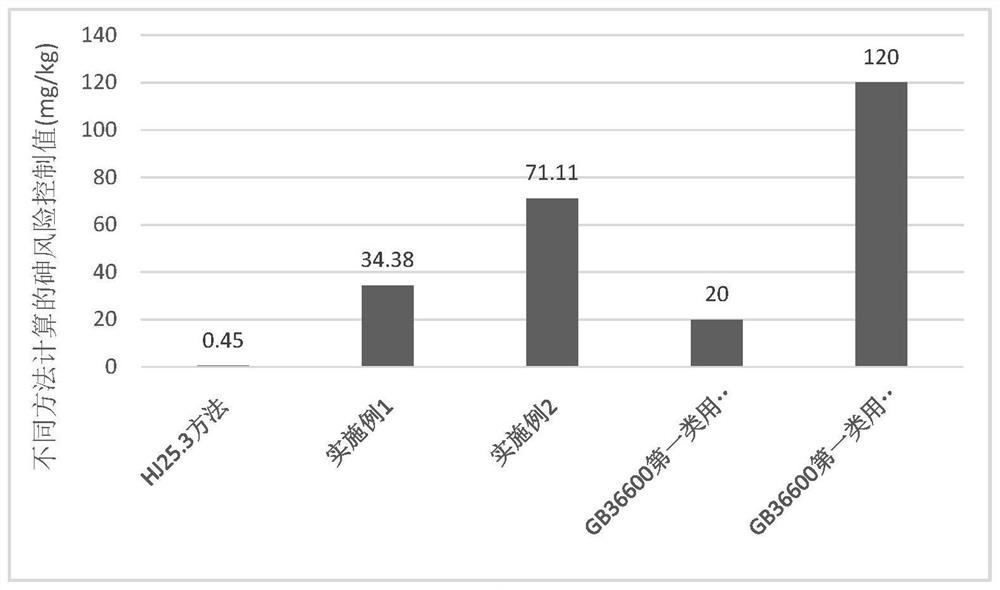
A calculation method and application of arsenic risk control value in soil
ActiveCN114141314BConvenient guidanceSolve the problem of invalid calculationHealth-index calculationComputational theoretical chemistrySoil scienceArsenic pollution
The invention discloses a method for calculating the risk control value of arsenic in soil and its application. The calculation method includes the following steps: S1, calculating the equivalent dose of each route based on different media; S2, calculating the equivalent dose of each route based on the equivalent dose Soil risk control value; S3, calculating the total soil risk control value Cs based on the equivalent dose. The calculation method of the present invention is based on the equivalent dosage of different media, and provides a basis for formulating the soil remediation target value of the arsenic-contaminated site in my country, and avoids excessive remediation of the polluted site.
Owner:北京市生态环境保护科学研究院
Systems and methods for reducing radiation dose
ActiveCN109493951BAvoid radiationImprove image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionRadiation equivalent doseHigh doses
The present application discloses a method for reducing radiation dose, the method comprising acquiring first image data related to a region of interest ROI of a first object. The first image data corresponds to a first equivalent dose, and the first image data can be acquired by a first device. The method may further include acquiring a noise reduction model associated with the first image data and determining second image data corresponding to a second equivalent dose higher than the specified dose based on the first image data and the noise reduction model. The first equivalent dose mentioned above. In some embodiments, the method may further include determining information related to the ROI of the first object based on the second image data, and recording the information related to the ROI of the first object. This application uses a noise reduction model to convert low-dose images into high-dose images, which can prevent patients from being exposed to excessive radiation while obtaining images of equal or higher quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Space charged particle telescope based on cadmium zinc telluride
ActiveCN112462409ARealize the measurement functionRealize type discriminationX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementNuclear engineeringRadiation equivalent dose
The invention discloses a space charged particle telescope based on cadmium zinc telluride. An opening is formed in the top end of an outer cover of the space charged particle telescope, a mounting base is arranged in the outer cover, a Si semiconductor detector, a first CZT detector and a second CZT detector are arranged on the mounting base, and the Si semiconductor detector and the first CZT detector form a first delta EE detector system; and the first CZT detector and the second CZT detector form a second group of delta EE detector systems, and the first delta EE detector system and the second delta EE detector system are matched to respectively measure charged particles with different energies. According to the invention, charged particles, thermal neutrons, gamma rays and other components in a space environment can be measured. The telescope can effectively measure information such as energy transfer linear density spectrum (LET), equivalent dose, charged particle energy spectrum, total dose, dose rate and the like of charged particles in space, has very important significance for astronaut radiation risk assessment, and can improve the resolution of the particle energy spectrum and enhance the particle identification capability compared with a traditional scintillation crystal system.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
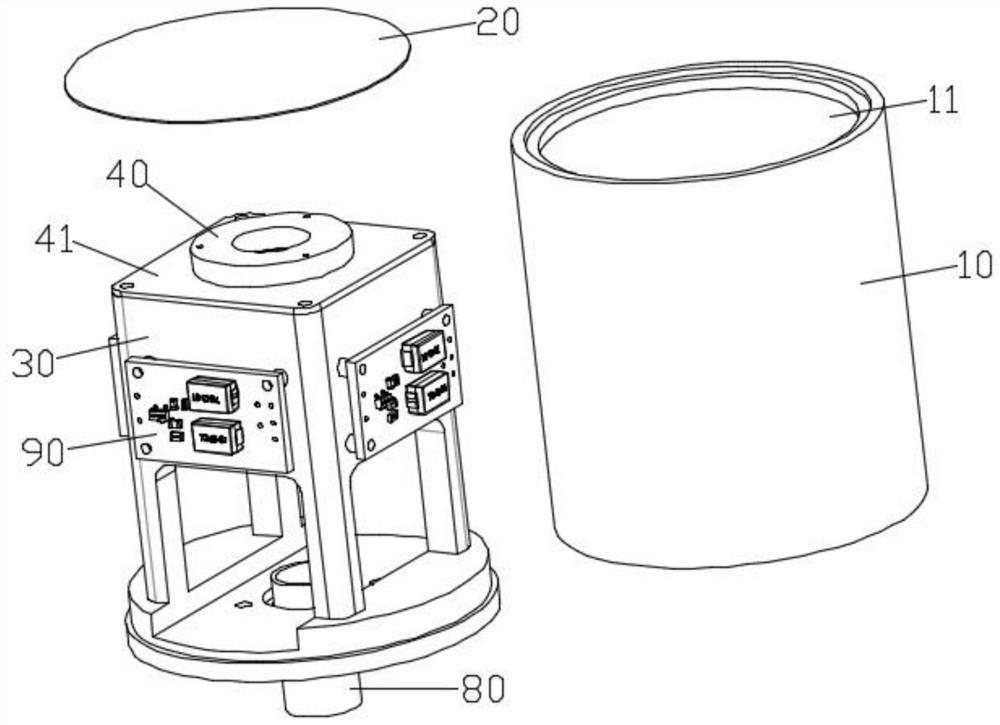
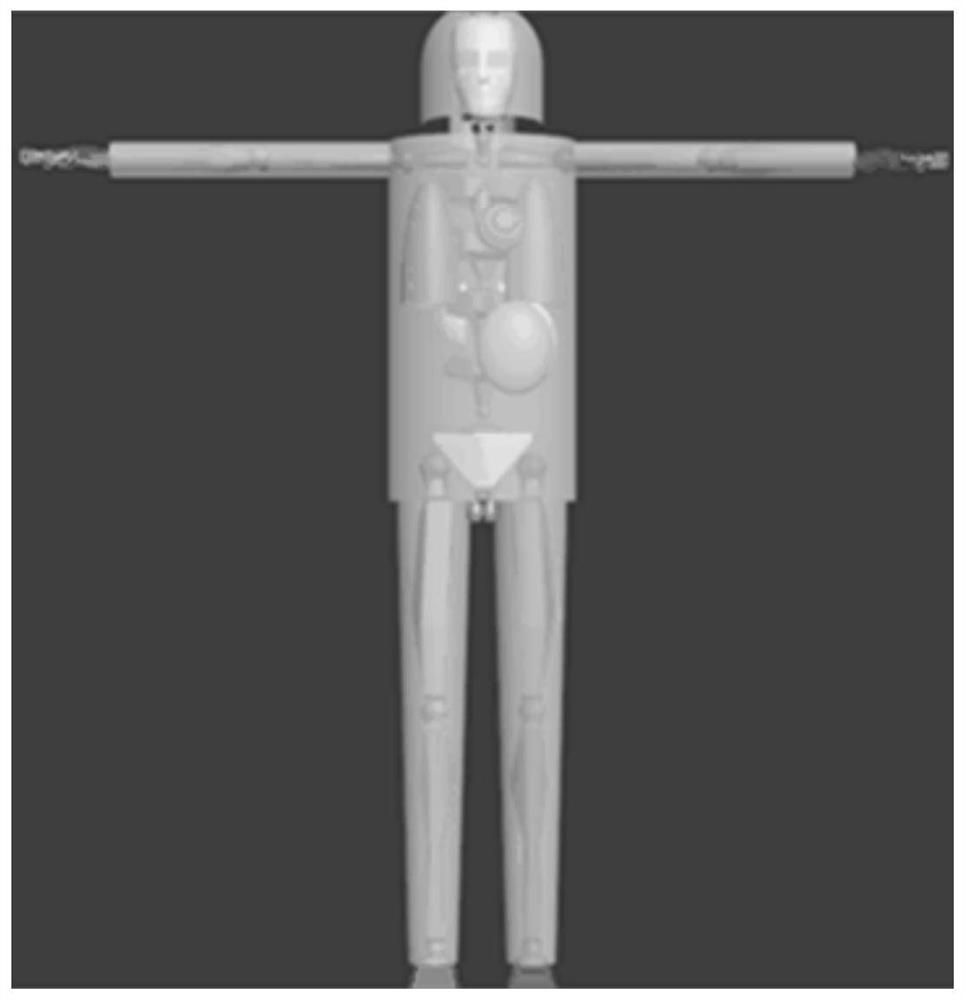
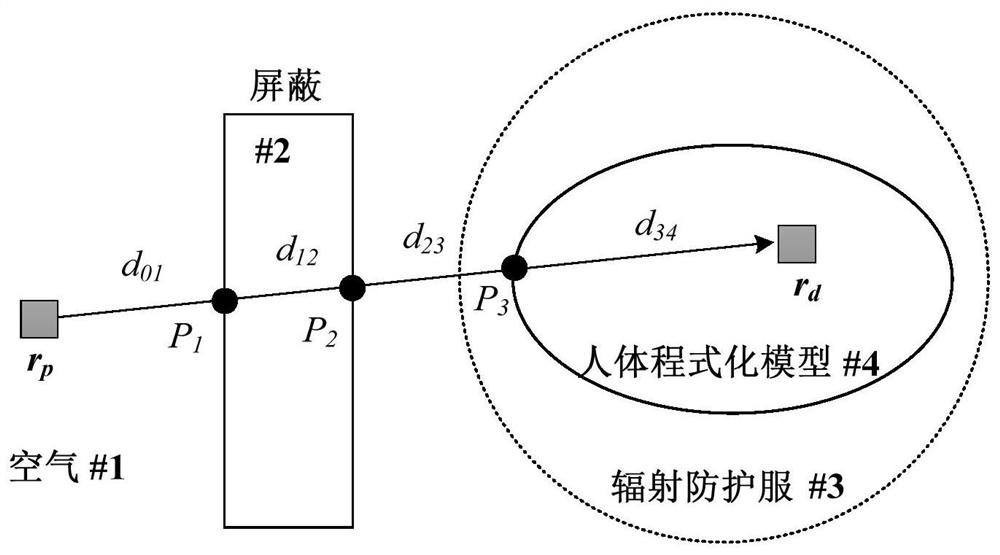
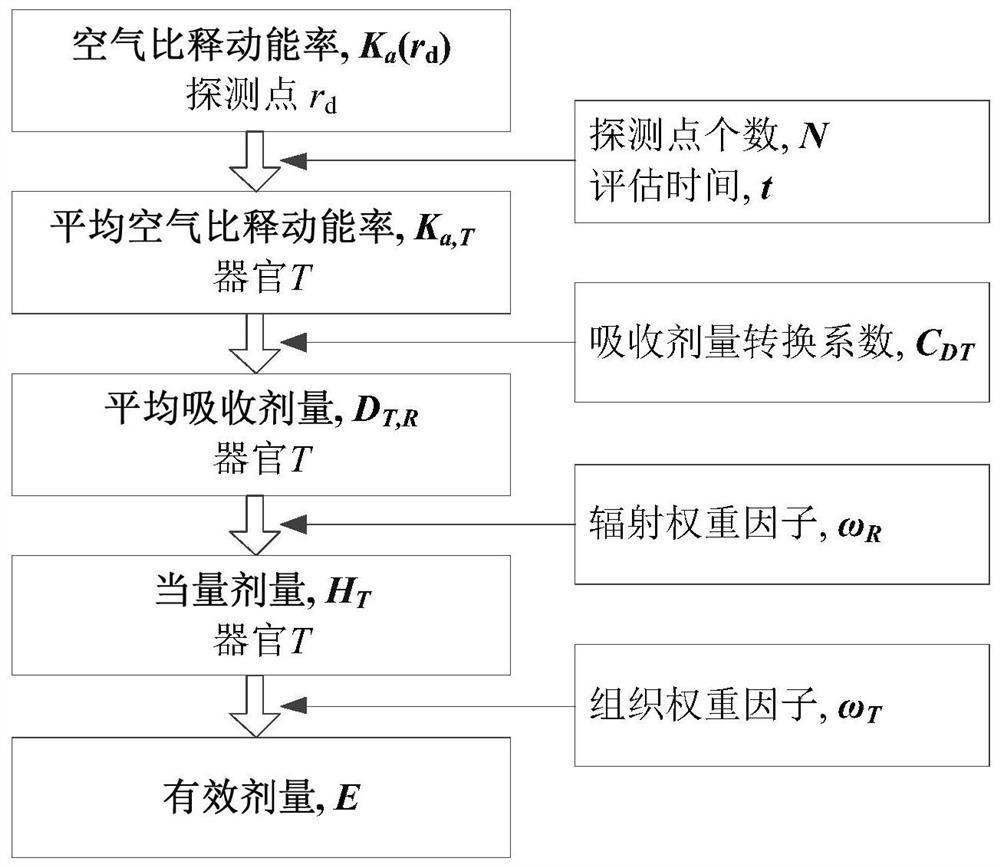
A Method for Estimating Exposure Dose of Decommissioned Humans in Nuclear Facilities
ActiveCN110110456BRealize dynamic calculationDesign optimisation/simulationResourcesHuman bodyHuman exposure
The invention discloses a method for assessing human body exposure dose for decommissioned nuclear facilities, and specifically relates to a simulation method based on a point-core integral method, which simplifies nuclear decommissioned staff into a stylized model and dynamically calculates human body exposure dose. The invention includes: adopting a stylized model to construct a virtual human model; converting the key tissues of the stylized model into a series of detection points; calculating the equivalent dose of the key tissue detection points by using a point kernel integral method; Dose, to realize the dose assessment of workers in the decommissioning process. The invention includes three modules of decommissioning environment modeling, stylized human body model modeling, and human exposure dose calculation, and realizes dynamic calculation of exposure dose of workers wearing nuclear radiation protective clothing during the decommissioning process of nuclear facilities.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Calculation method for risk control value of arsenic in soil and application thereof
ActiveCN114141314AConvenient guidanceSolve the problem of invalid calculationHealth-index calculationComputational theoretical chemistryRisk ControlArsenic pollution
The invention discloses a calculation method for a risk control value of arsenic in soil and application thereof. The calculation method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating equivalent doses of various approaches based on different media; s2, calculating a soil risk control value of each approach based on an equivalent dose; and S3, calculating a soil total risk control value Cs based on the equivalent dose. According to the calculation method, the basis is provided for formulating the soil remediation target value of the arsenic-contaminated site in China based on the equivalent doses of different media, and excessive remediation of the contaminated site is avoided.
Owner:北京市生态环境保护科学研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com