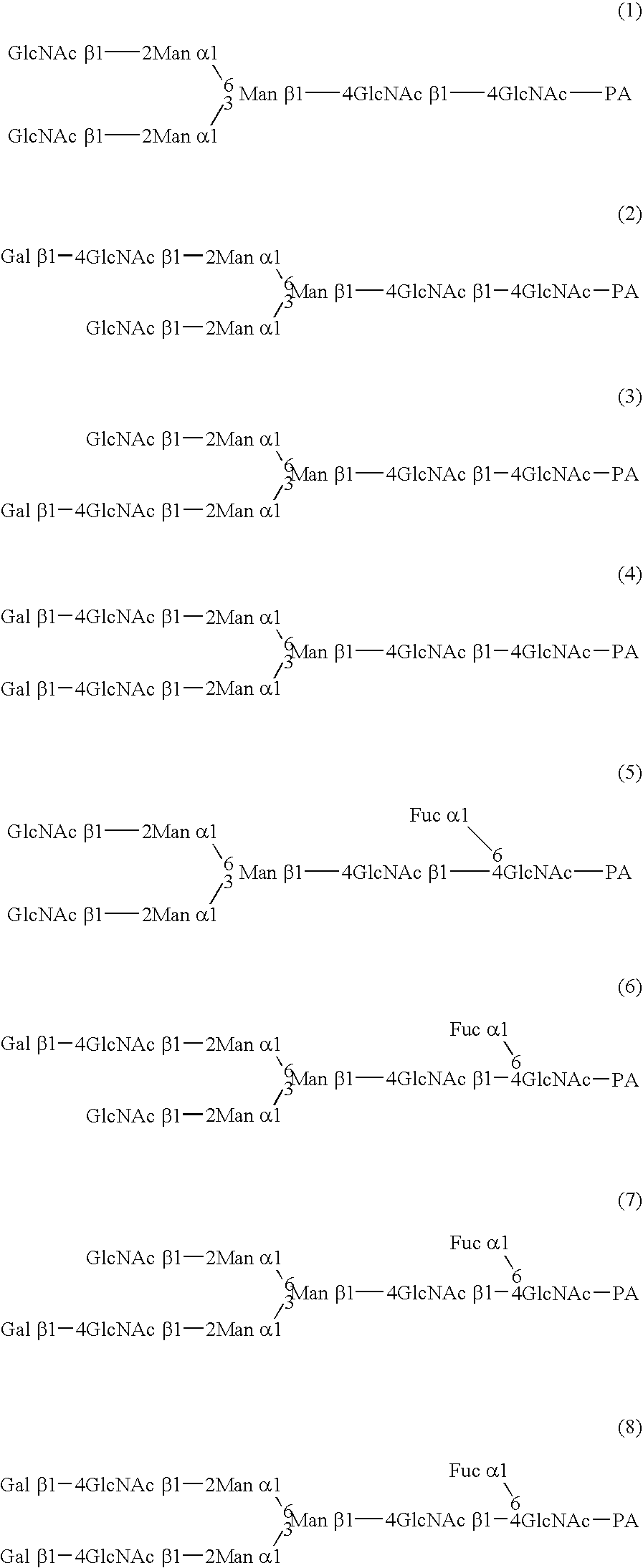Patents
Literature
15756 results about "Genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is the genetic material of an organism. It consists of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The genome includes both the genes (the coding regions) and the noncoding DNA, as well as mitochondrial DNA and chloroplast DNA. The study of the genome is called genomics.
Cells of which genome is modified
InactiveUS20040110704A1Raise the ratioDecreased and deleted activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticGlycosideN-Acetylglucosamine
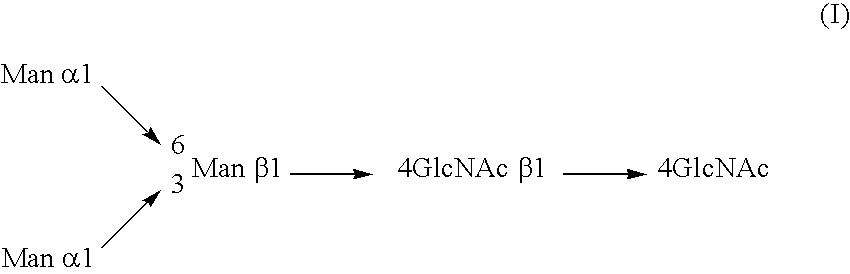
A cell in which genome is modified so as to have a more decreased or deleted activity of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain than its parent cell, and a process for producing an antibody composition using the cell.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
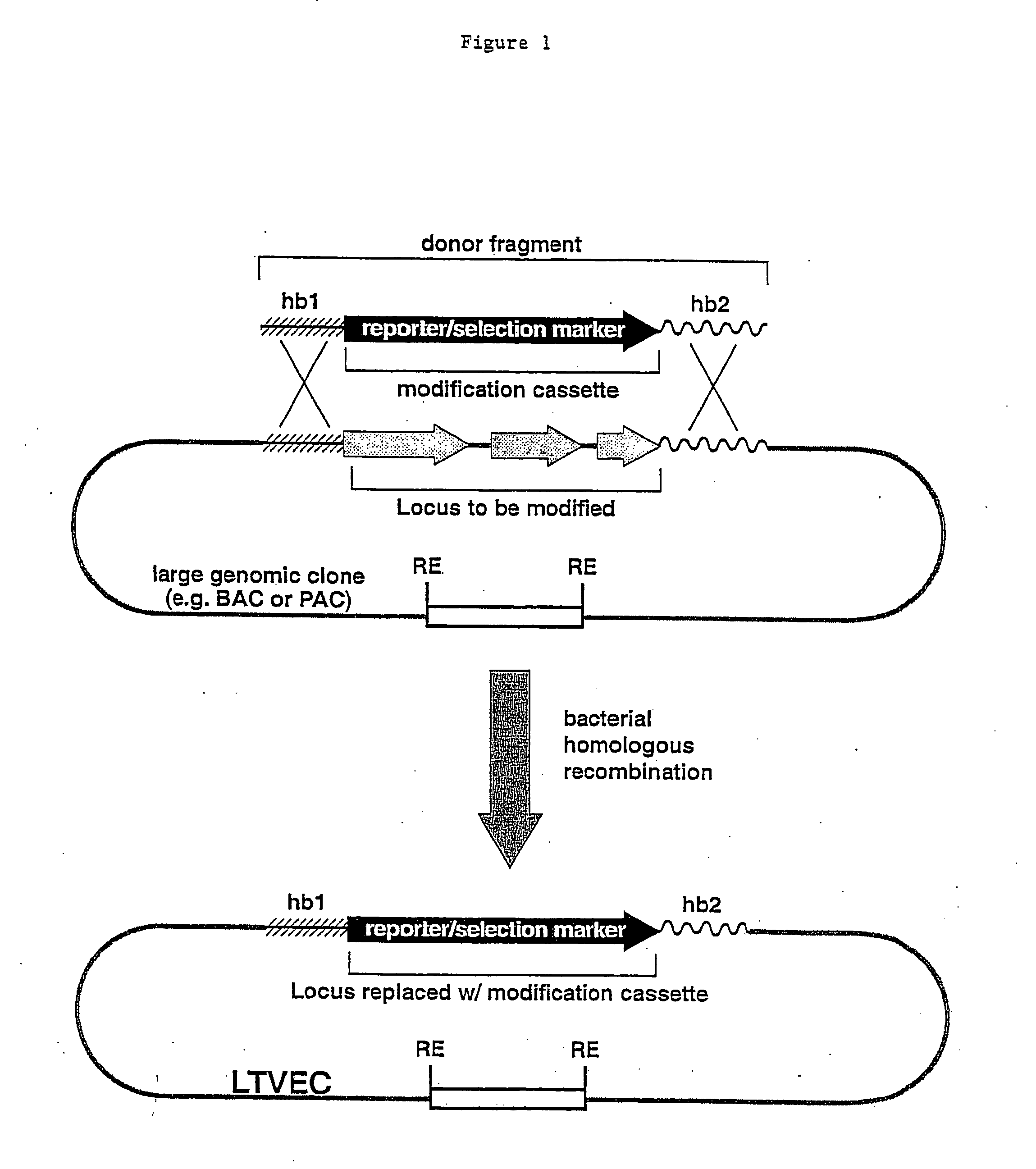
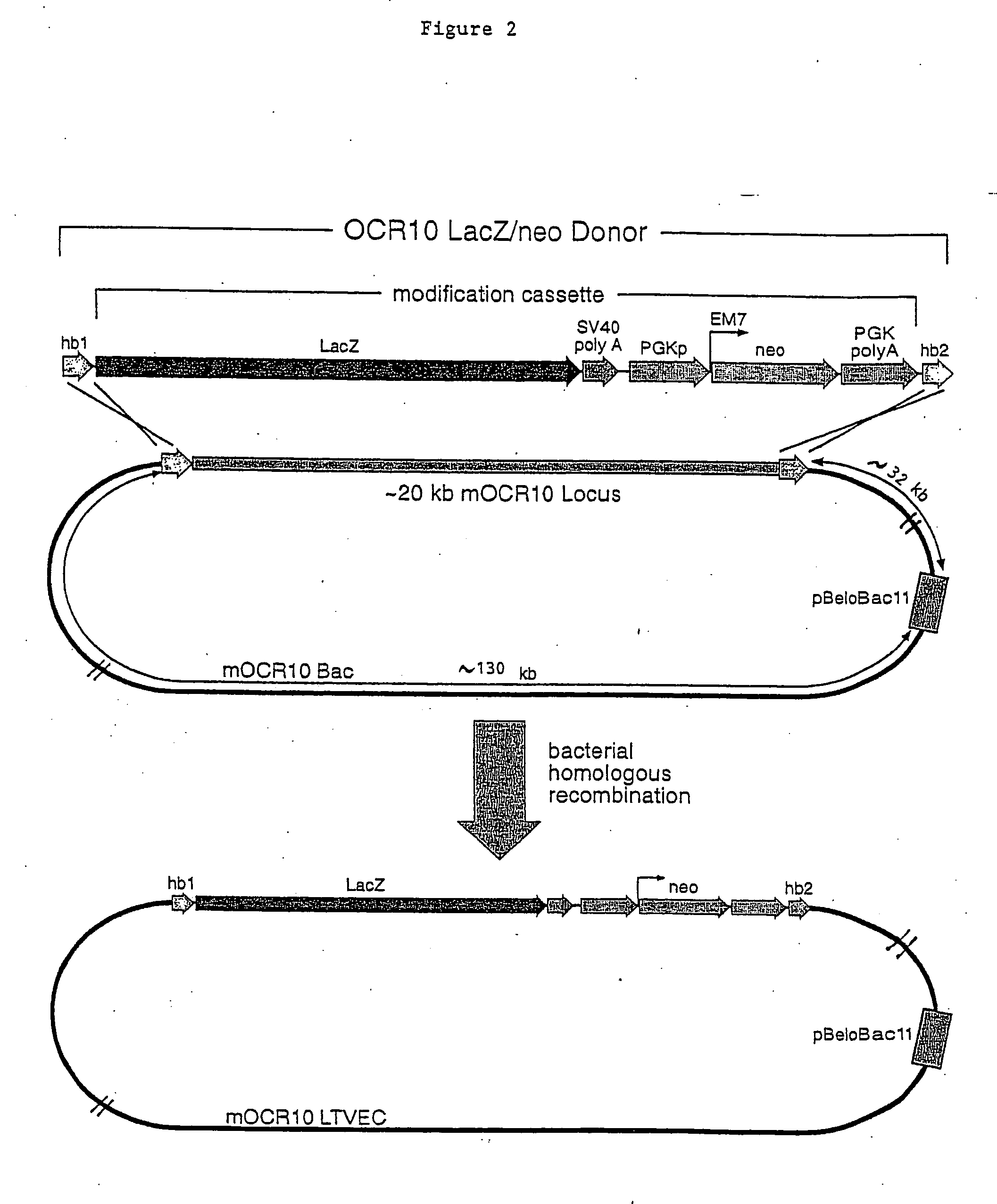
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
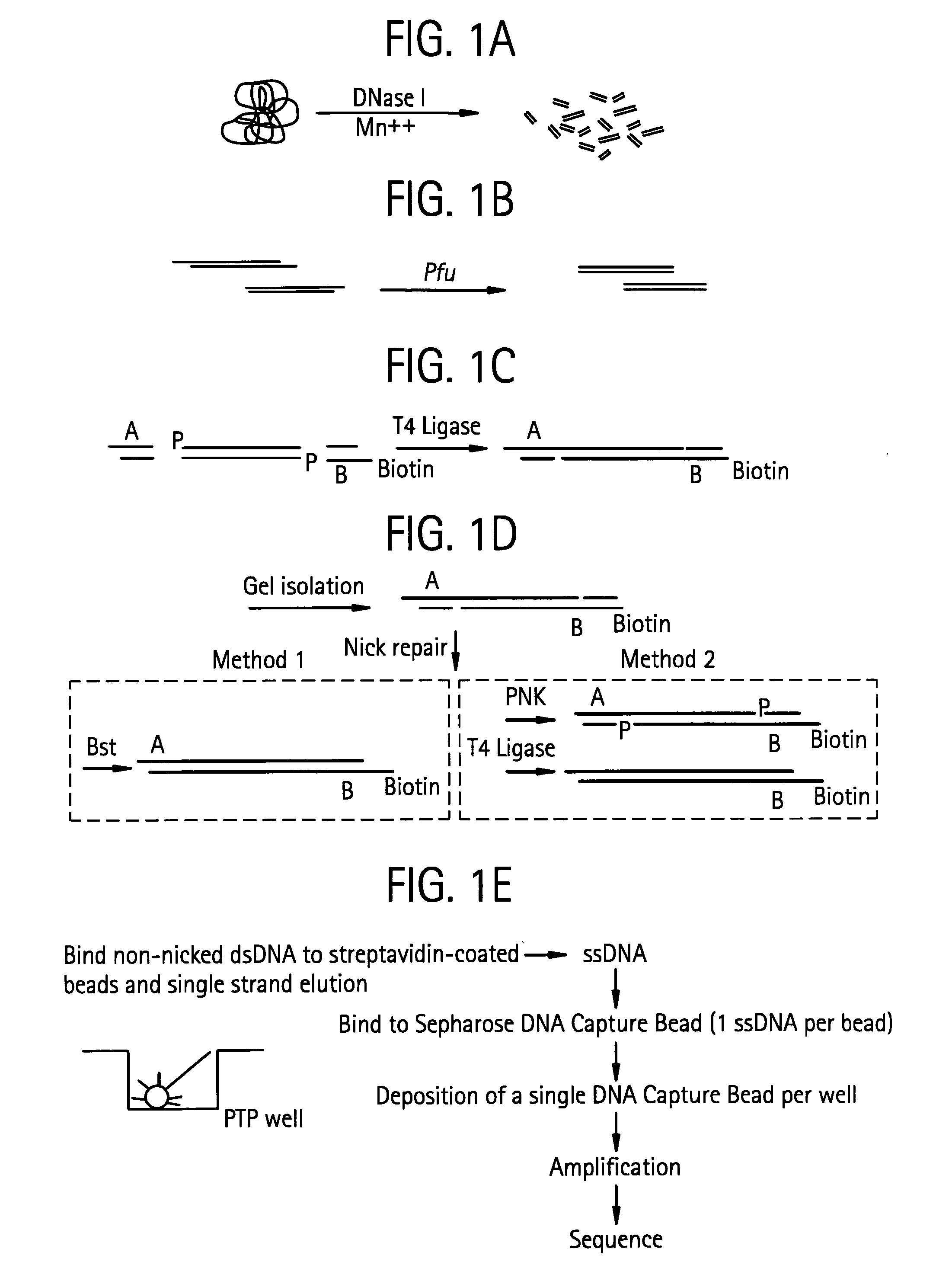
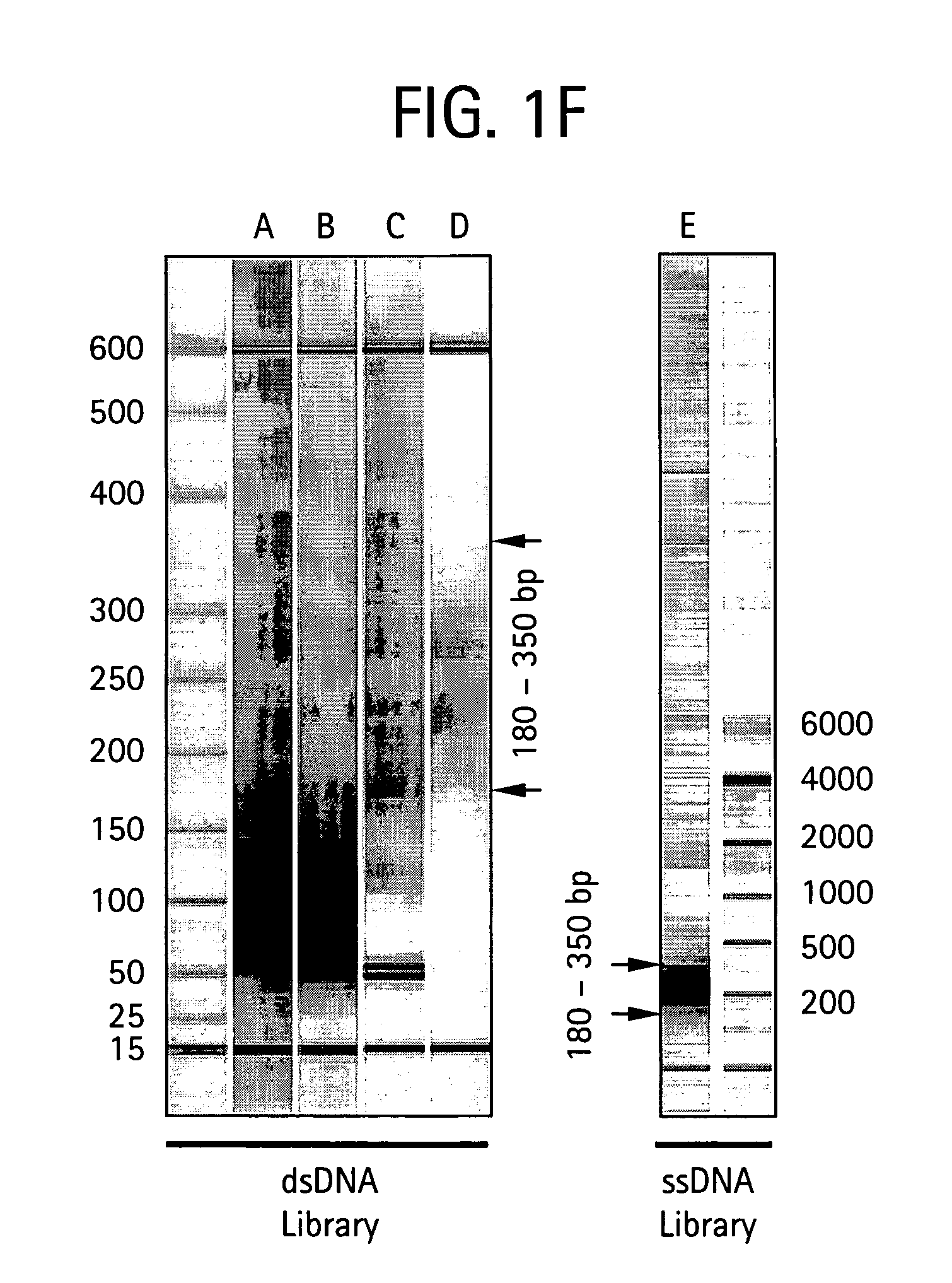
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
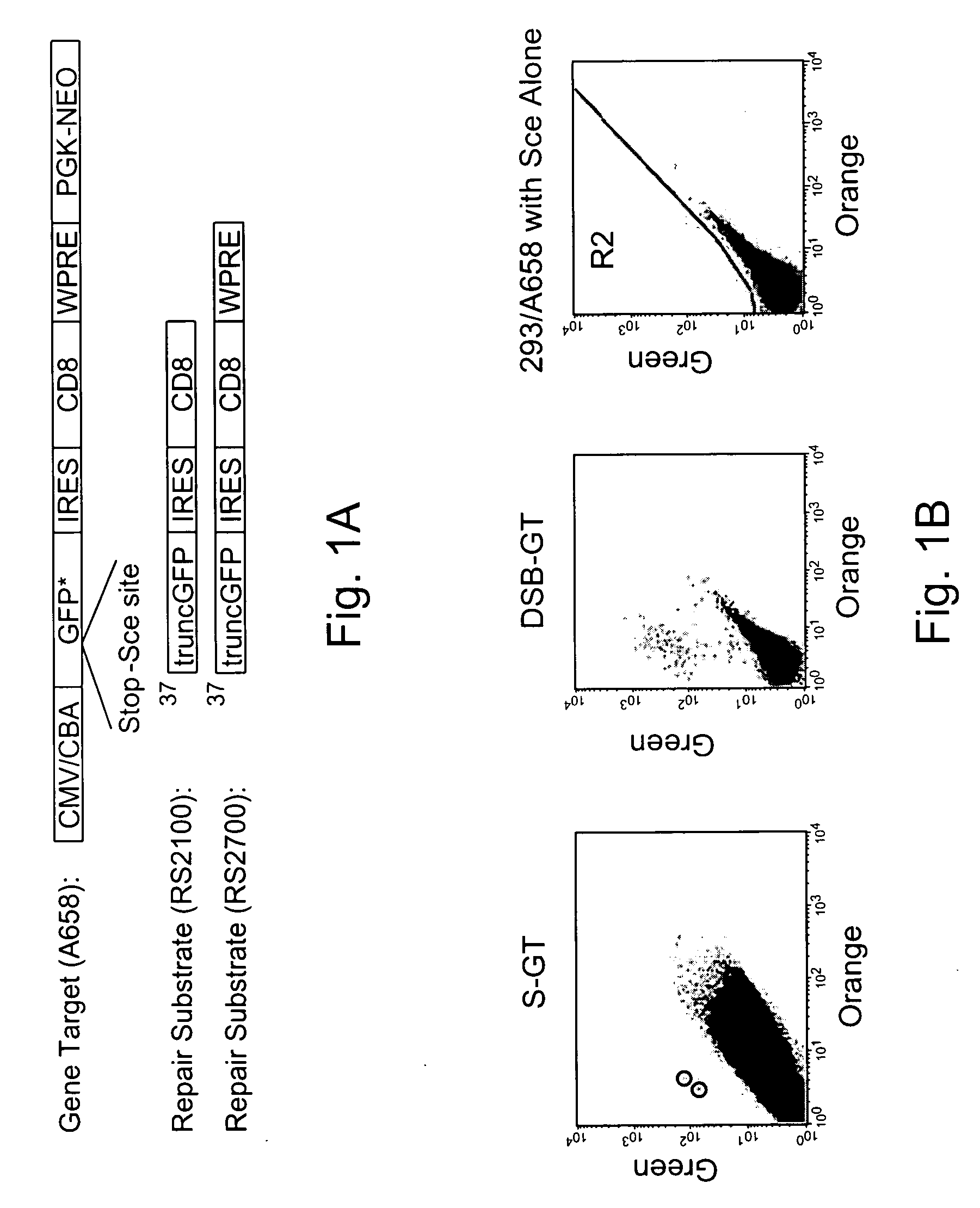
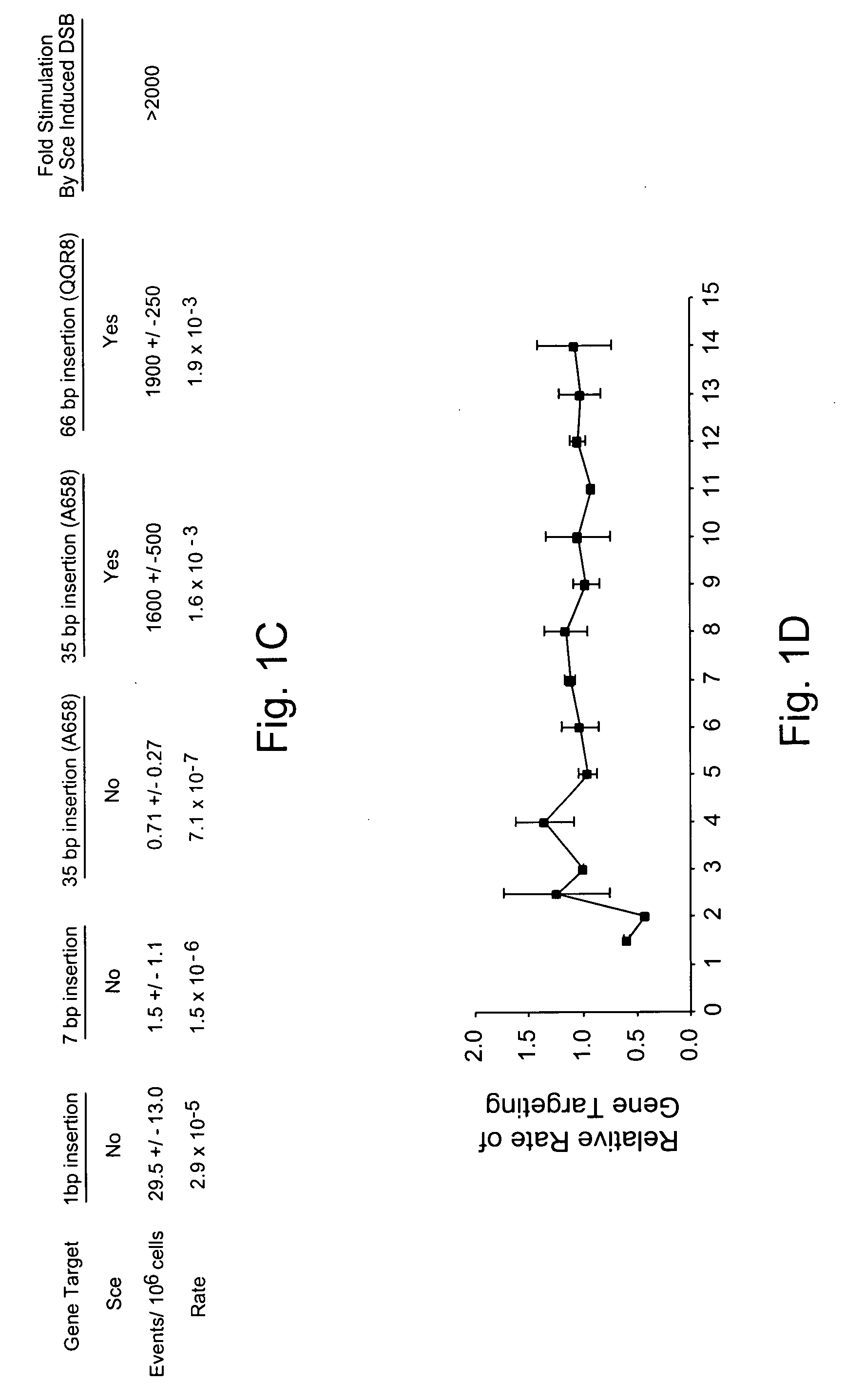
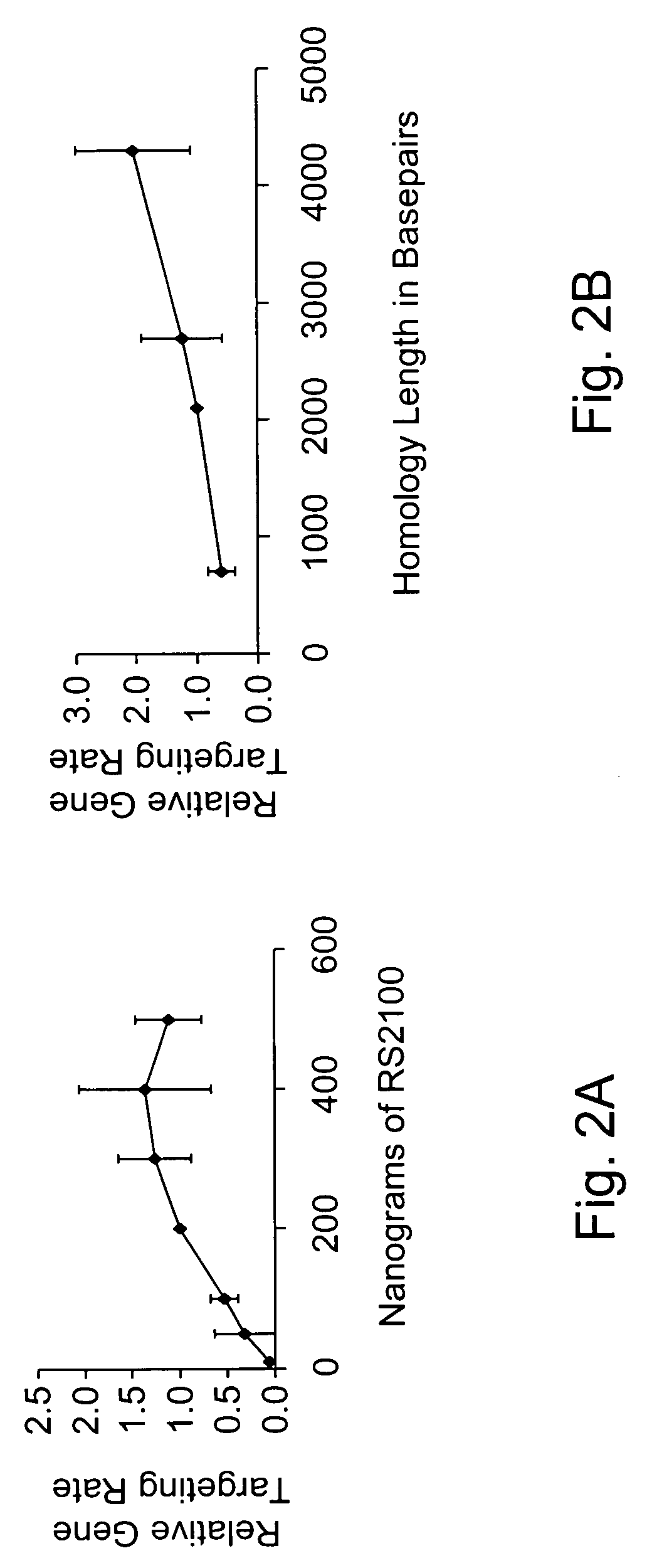
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Analying polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6054270AStable duplexReduce impactSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesHybridization reactionSequence determination
This invention provides an apparatus and method for analyzing a polynucleotide sequence; either an unknown sequence or a known sequence. A support, e.g. a glass plate, carries an array of the whole or a chosen part of a complete set of oligonucleotides which are capable of taking part in hybridization reactions. The array may comprise one or more pair of oligonucleotides of chosen lengths. The polynucleotide sequence, or fragments thereof, are labelled and applied to the array under hybridizing conditions. Applications include analyses of known point mutations, genomic fingerprinting, linkage analysis, characterization of mRNAs, mRNA populations, and sequence determination.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH
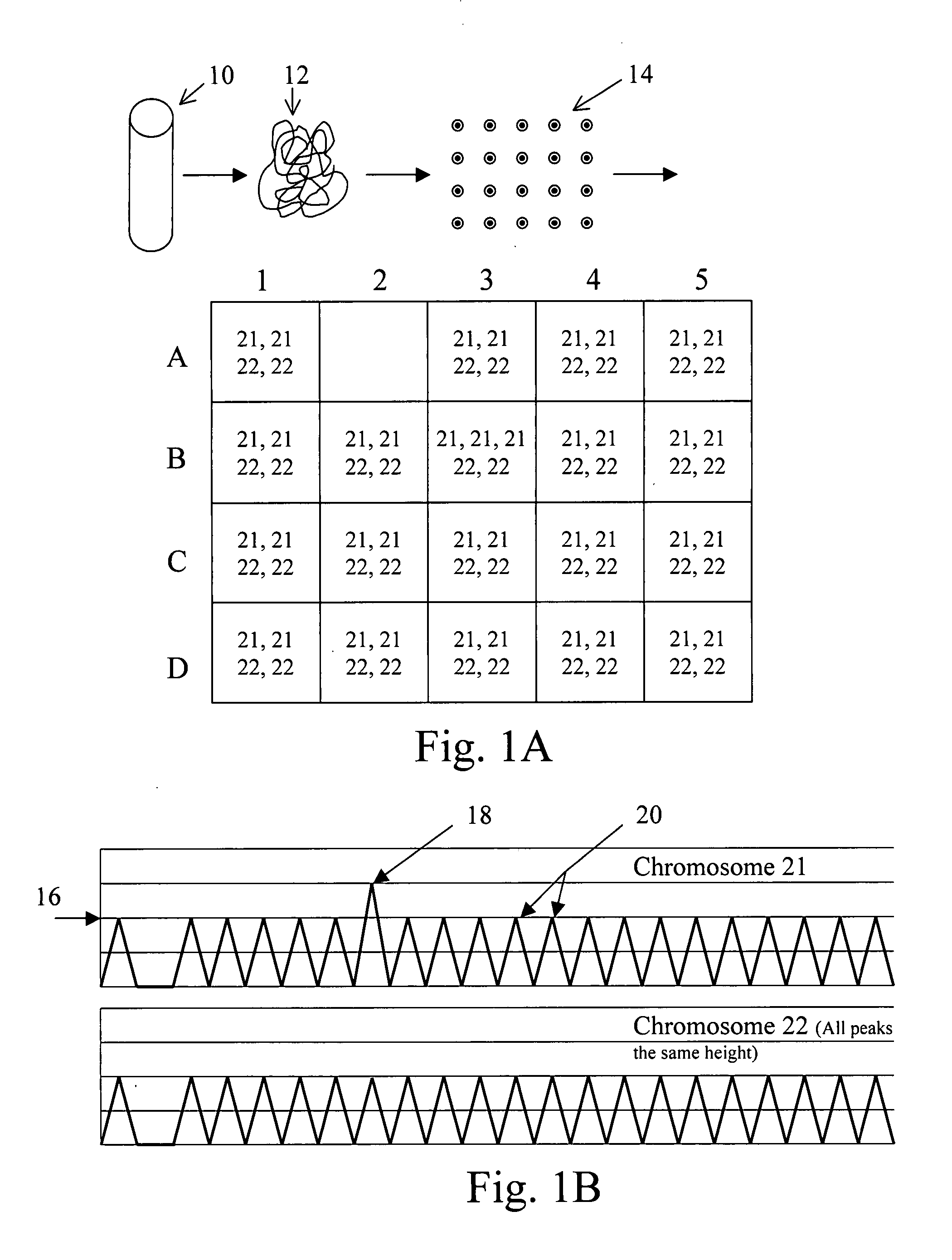
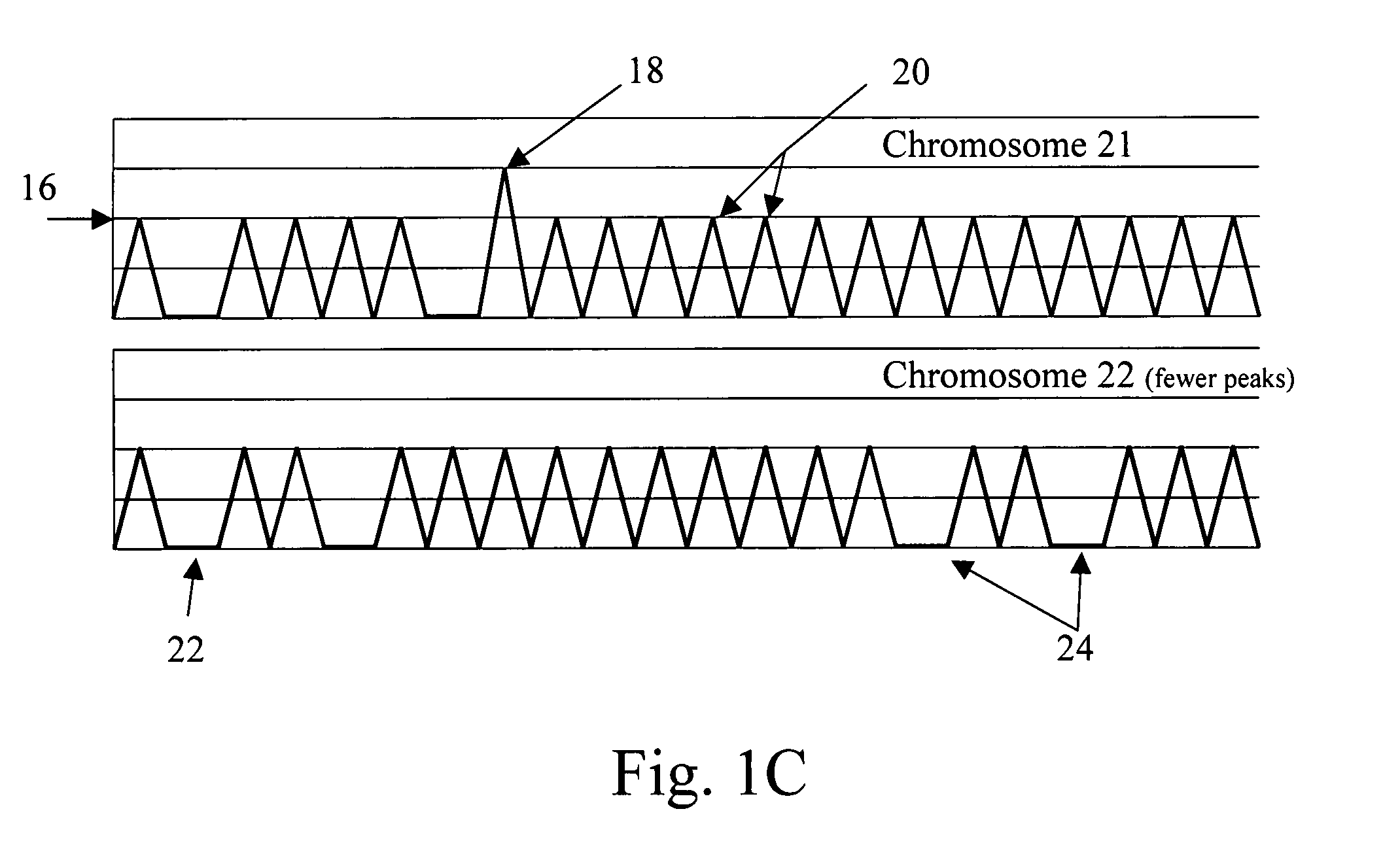
Non-invasive fetal genetic screening by digital analysis
ActiveUS20070202525A1Enriching fetal DNAMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationChorionic villiMassively parallel
The present methods are exemplified by a process in which maternal blood containing fetal DNA is diluted to a nominal value of approximately 0.5 genome equivalent of DNA per reaction sample. Digital PCR is then be used to detect aneuploidy, such as the trisomy that causes Down Syndrome. Since aneuploidies do not present a mutational change in sequence, and are merely a change in the number of chromosomes, it has not been possible to detect them in a fetus without resorting to invasive techniques such as amniocentesis or chorionic villi sampling. Digital amplification allows the detection of aneuploidy using massively parallel amplification and detection methods, examining, e.g., 10,000 genome equivalents.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Plants and processes for obtaining them
InactiveUS6013861AIncrease depositionAlteration of fine structureOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch synthaseStarch synthesis
Plants, particularly cereal plants, which have improved ability to synthesise starch at elevated or lowered temperatures and / or to synthesise starch with an altered fine structure are produced by inserting into the genome of the plant (i) a gene(s) encoding a form of an enzyme of the starch or glycogen biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which display an activity which continues to increase over a temperature range over which the activity would normally be expected to decrease, and / or (ii) a gene(s) encoding sense and anti-sense constructs of enzymes of the starch biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which alters the natural ratios of expression of the said enzymes or inserts enzymes with special structural characteristics which alter the natural branching pattern in starch.
Owner:ZENECA LTD
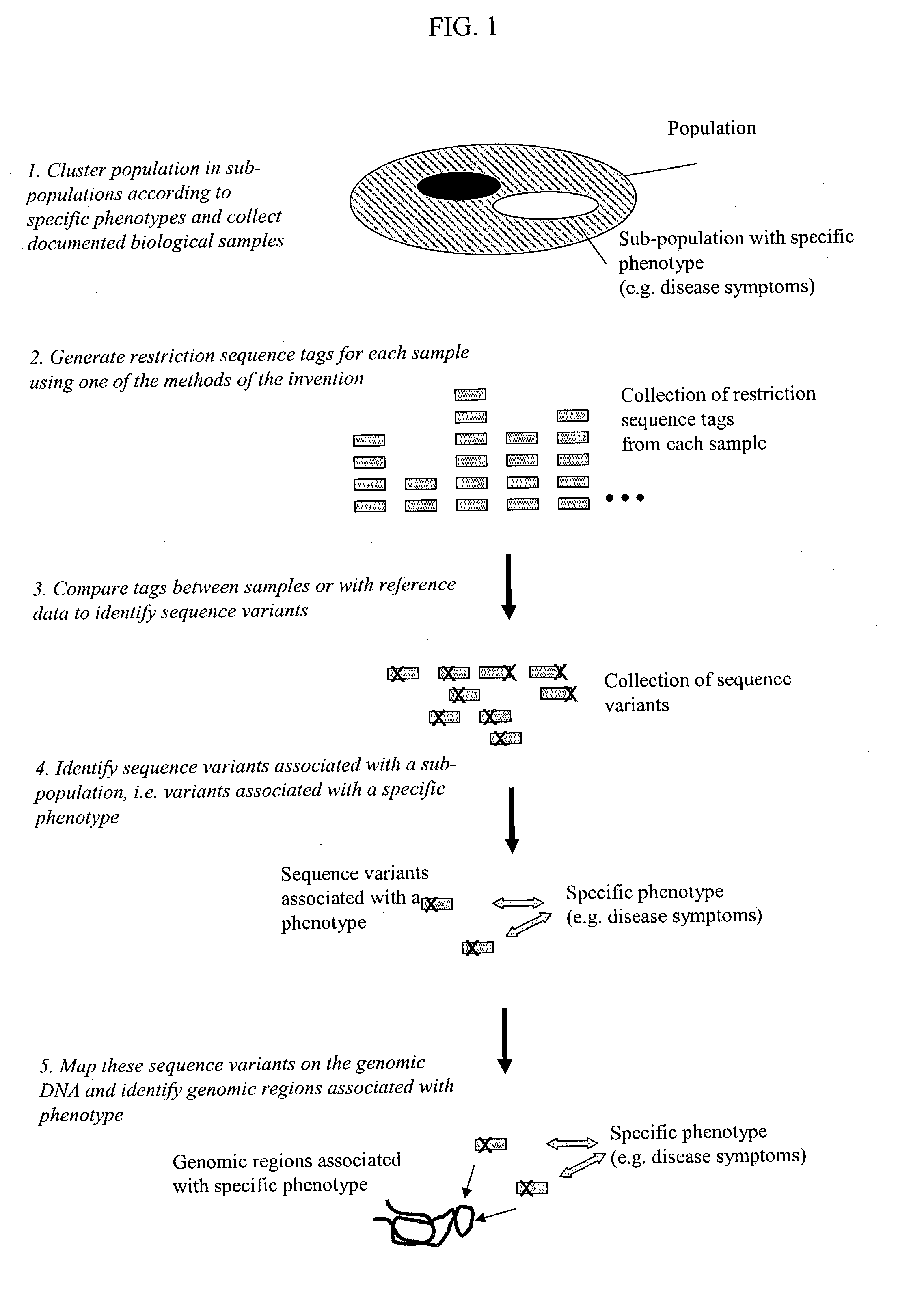
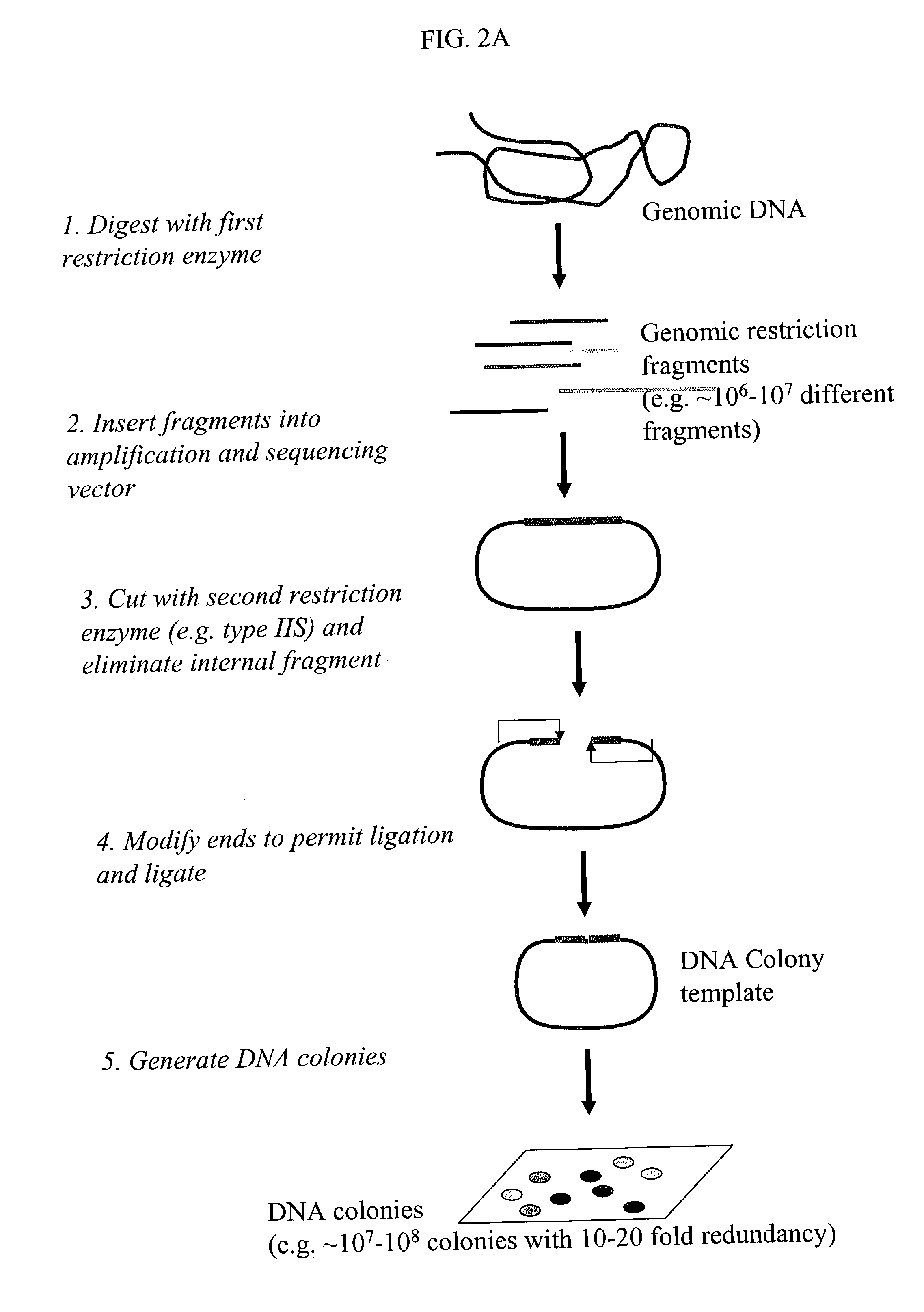
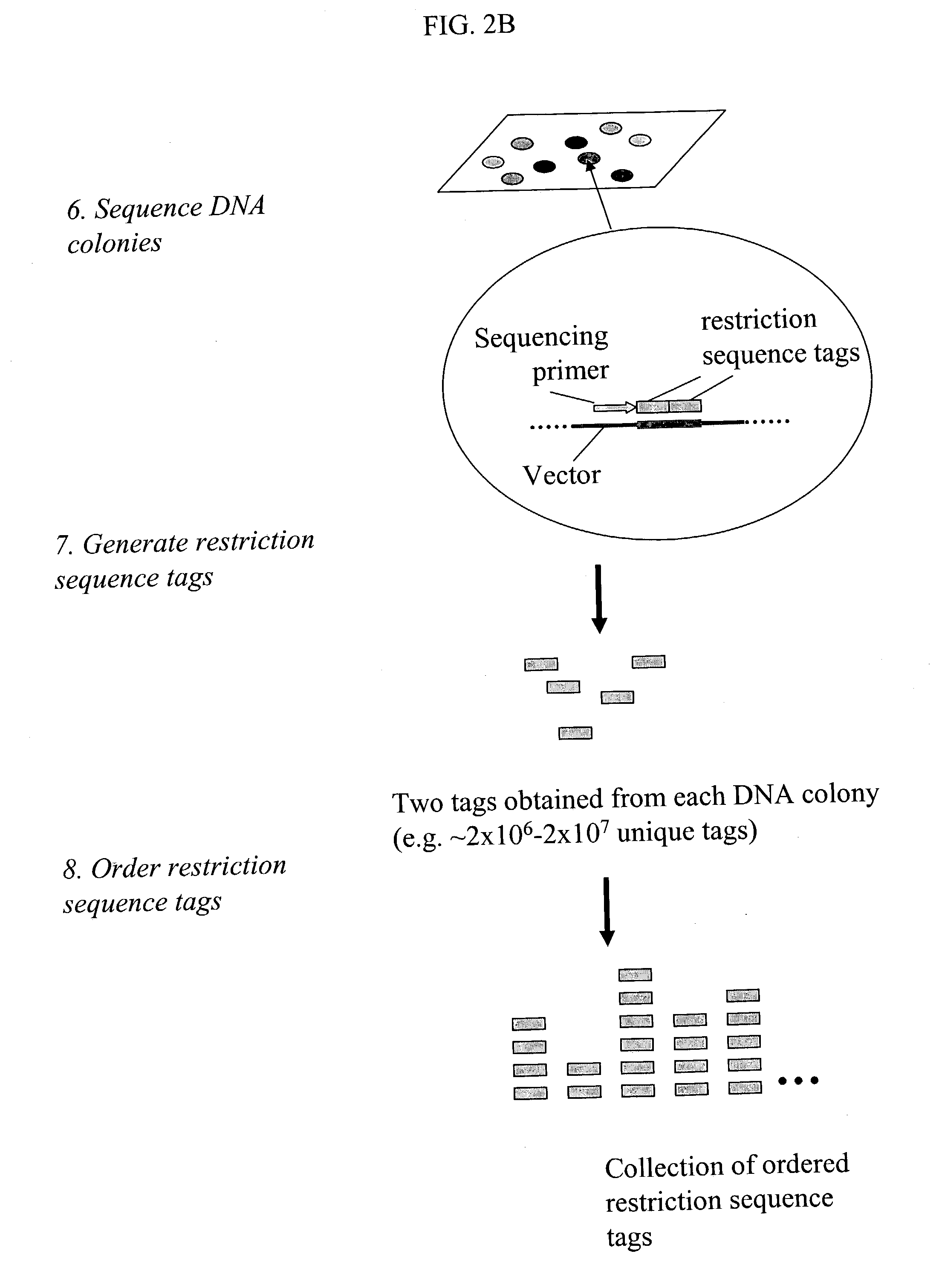
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
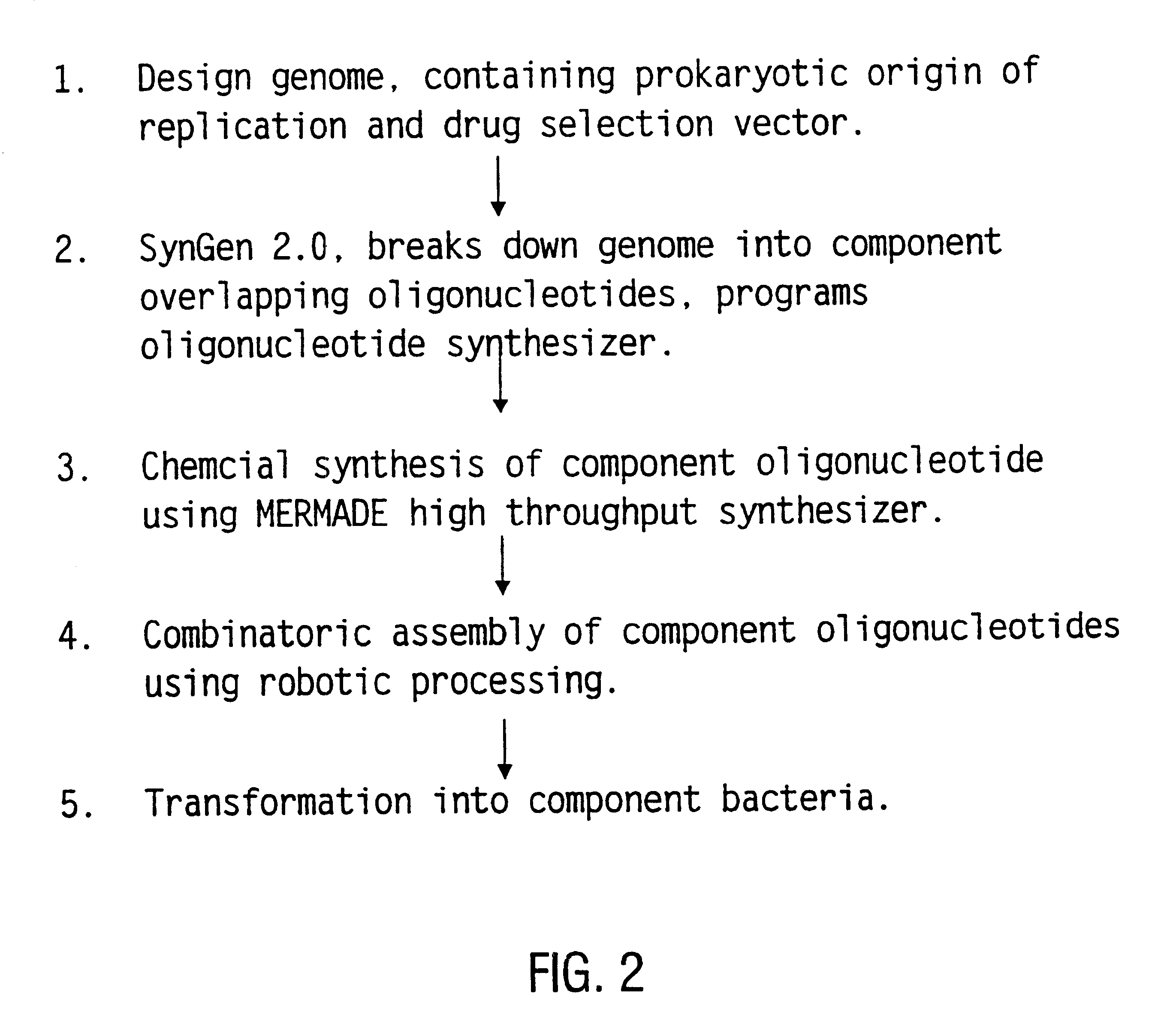
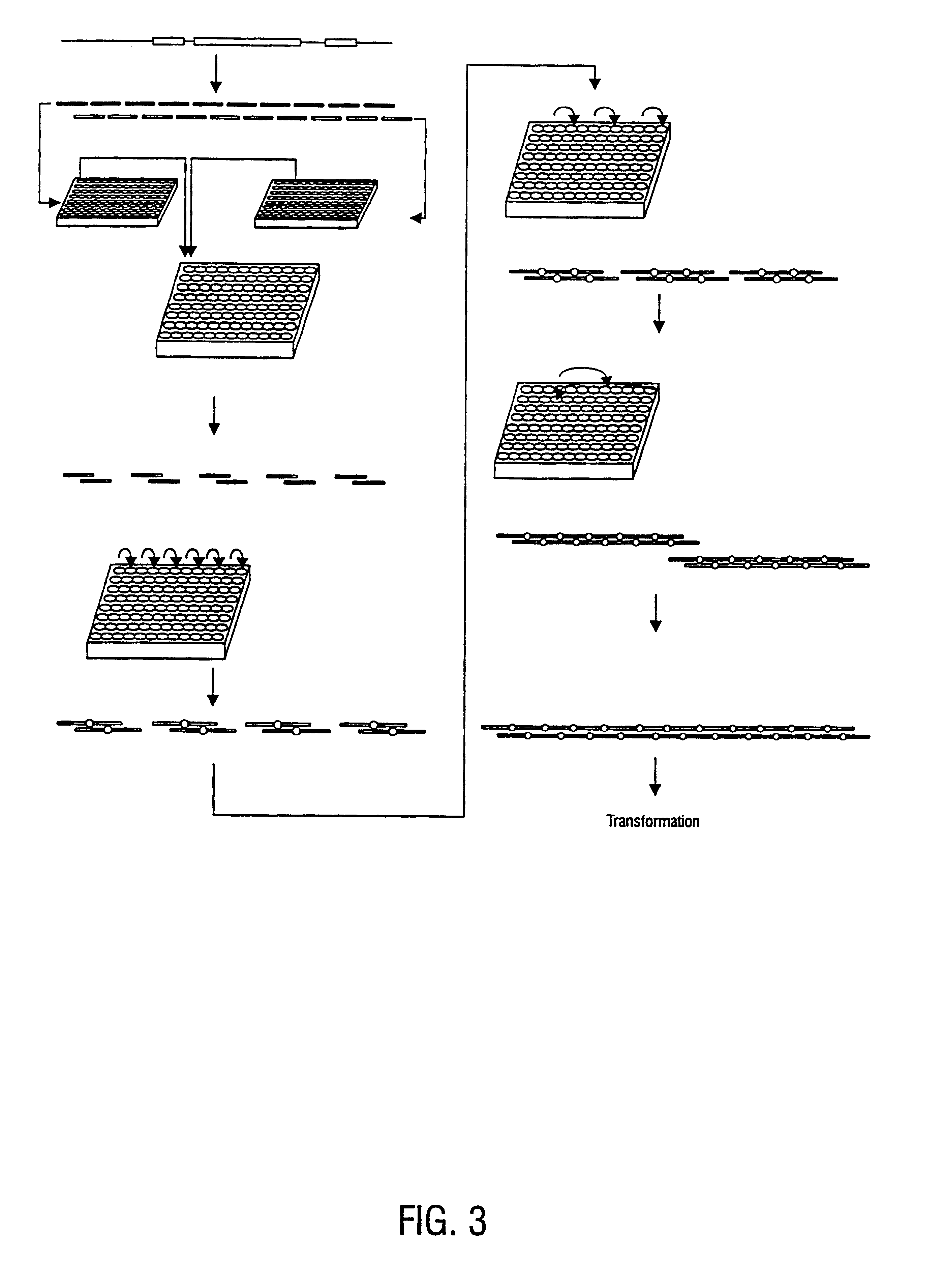
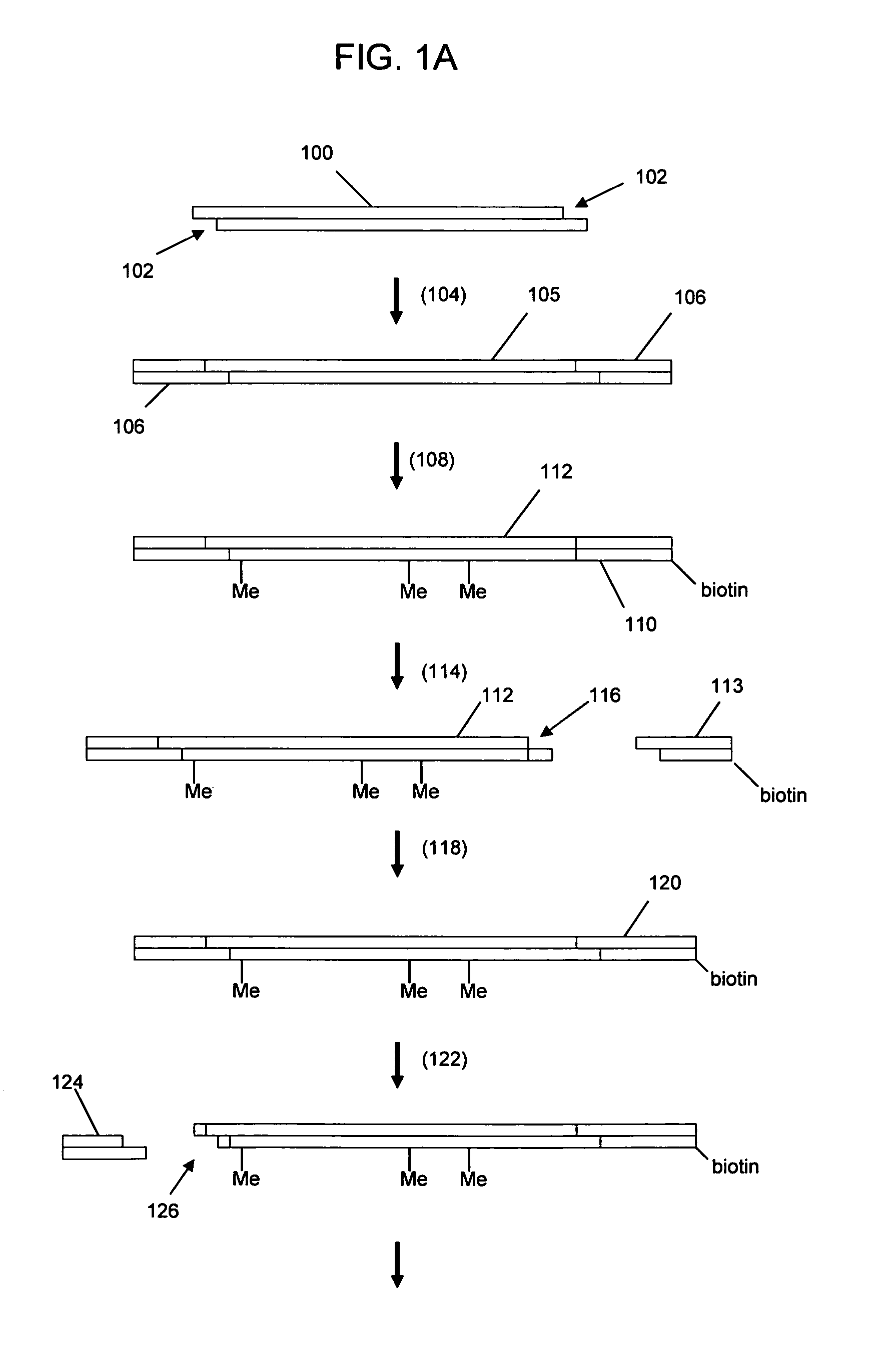
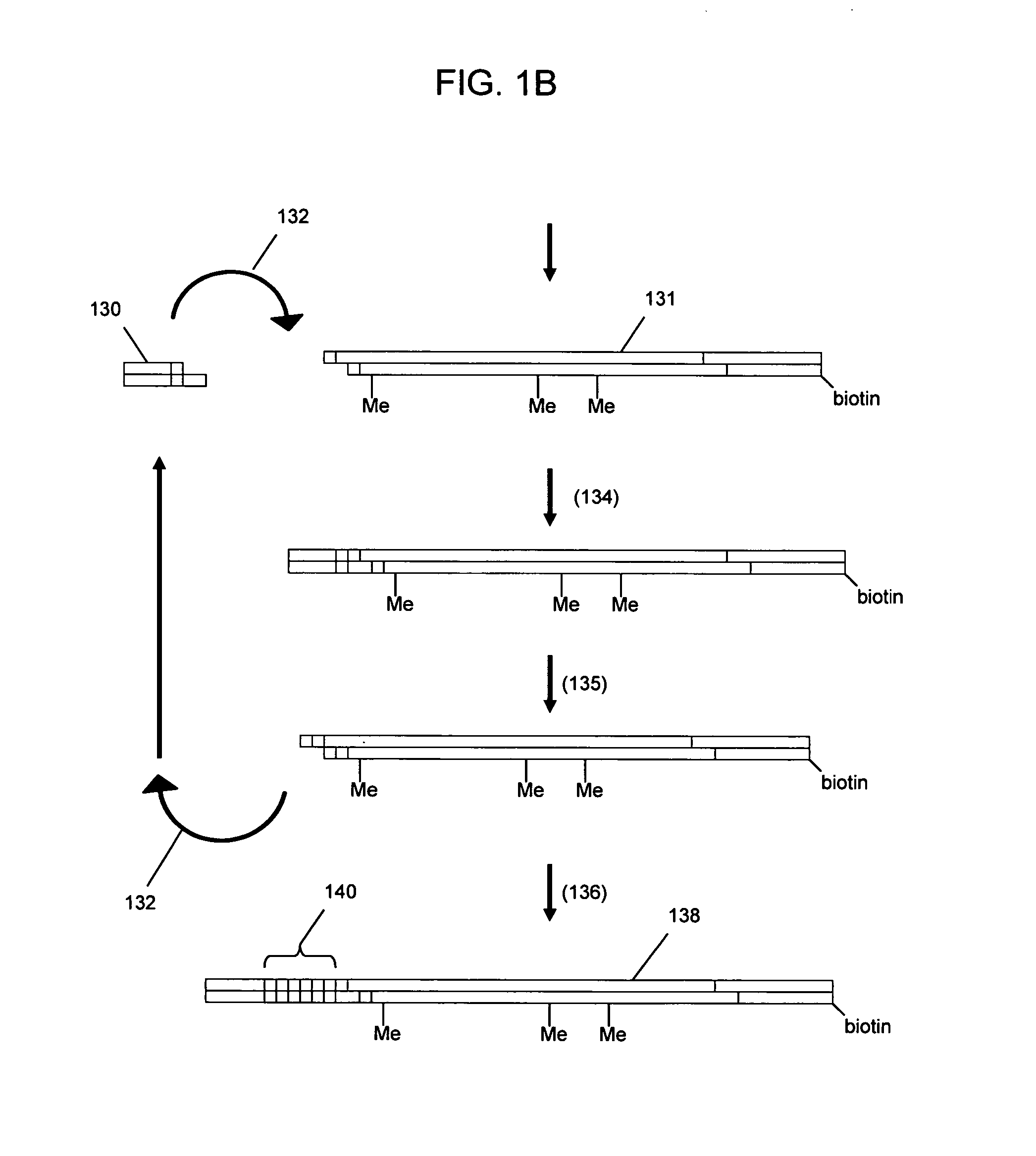
Method for the complete chemical synthesis and assembly of genes and genomes
InactiveUS6521427B1BiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisHuman genome database
The present invention relates generally to the fields of oligonucleotide synthesis. More particularly, it concerns the assembly of genes and genomes of completely synthetic artificial organisms. Thus, the present invention outlines a novel approach to utilizing the results of genomic sequence information by computer directed gene synthesis based on computing on the human genome database. Specifically, the present invention contemplates and describes the chemical synthesis and resynthesis of genes defined by the genome sequence in a host vector and transfer and expression of these sequences into suitable hosts.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US) +3
Nucleic acid analysis using sequence tokens
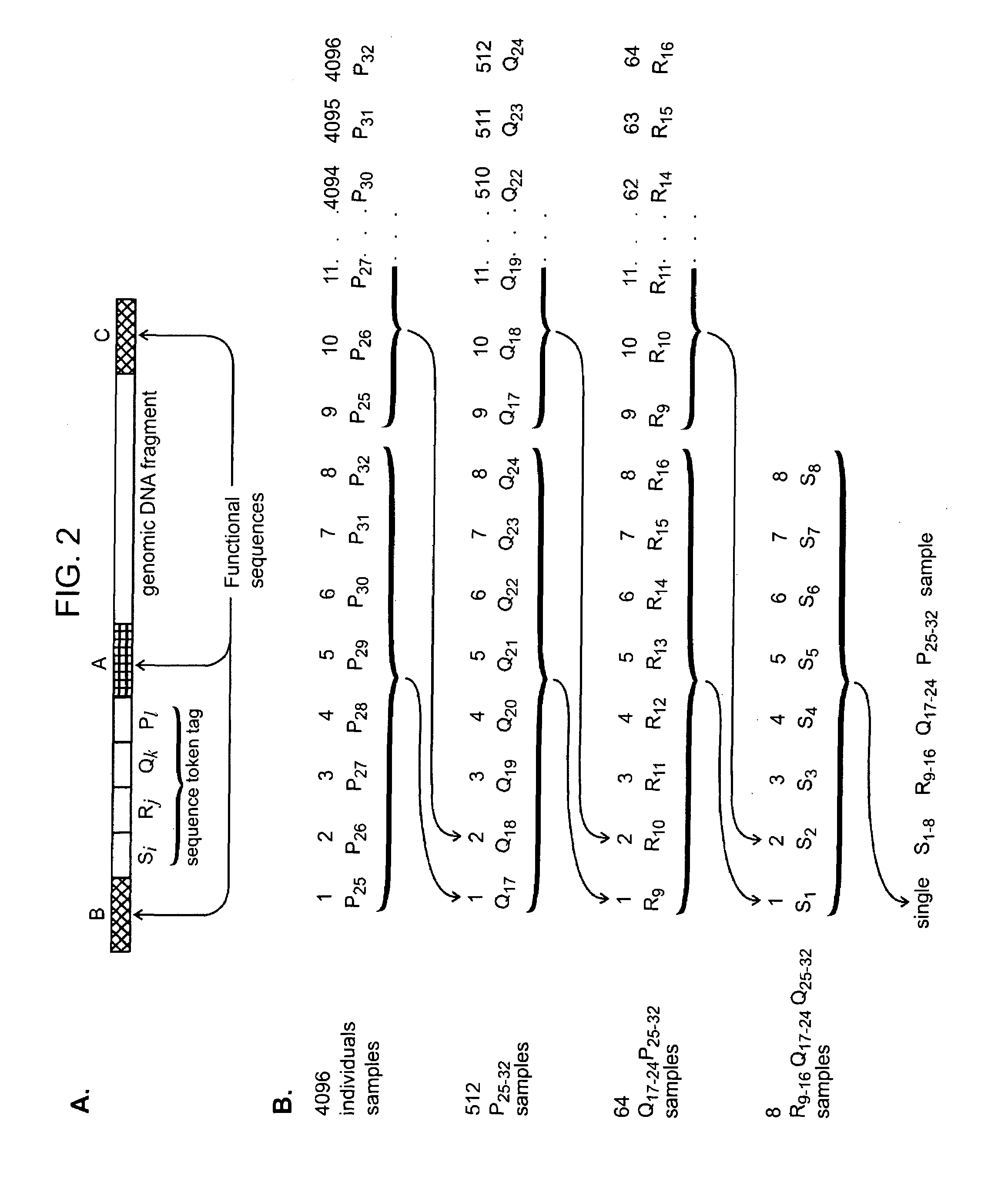
ActiveUS7544473B2Efficiently determine variations in nucleotide sequences in the associated nucleic acid sequence fragmentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDon't repeat yourselfNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods and compositions for tagging nucleic acid sequence fragments, e.g., a set of nucleic acid sequence fragments from a single genome, with one or more unique members of a collection of oligonucleotide tags, or sequence tokens, which, in turn, can be identified using a variety of readout platforms. As a general rule, a given sequence token is used once and only once in any tag sequence. In addition, the present invention also provides methods for using the sequence tokens to efficiently determine variations in nucleotide sequences in the associated nucleic acid sequence fragments.
Owner:PERSONAL GENOME DIAGNOSTICS INC
Soybean event dp-305423-1 and compositions and methods for the identification and/or detection thereof
ActiveUS20080312082A1Improve farming efficiencyImprove toleranceBiocideSugar derivativesHigh oleic acidInsertion site
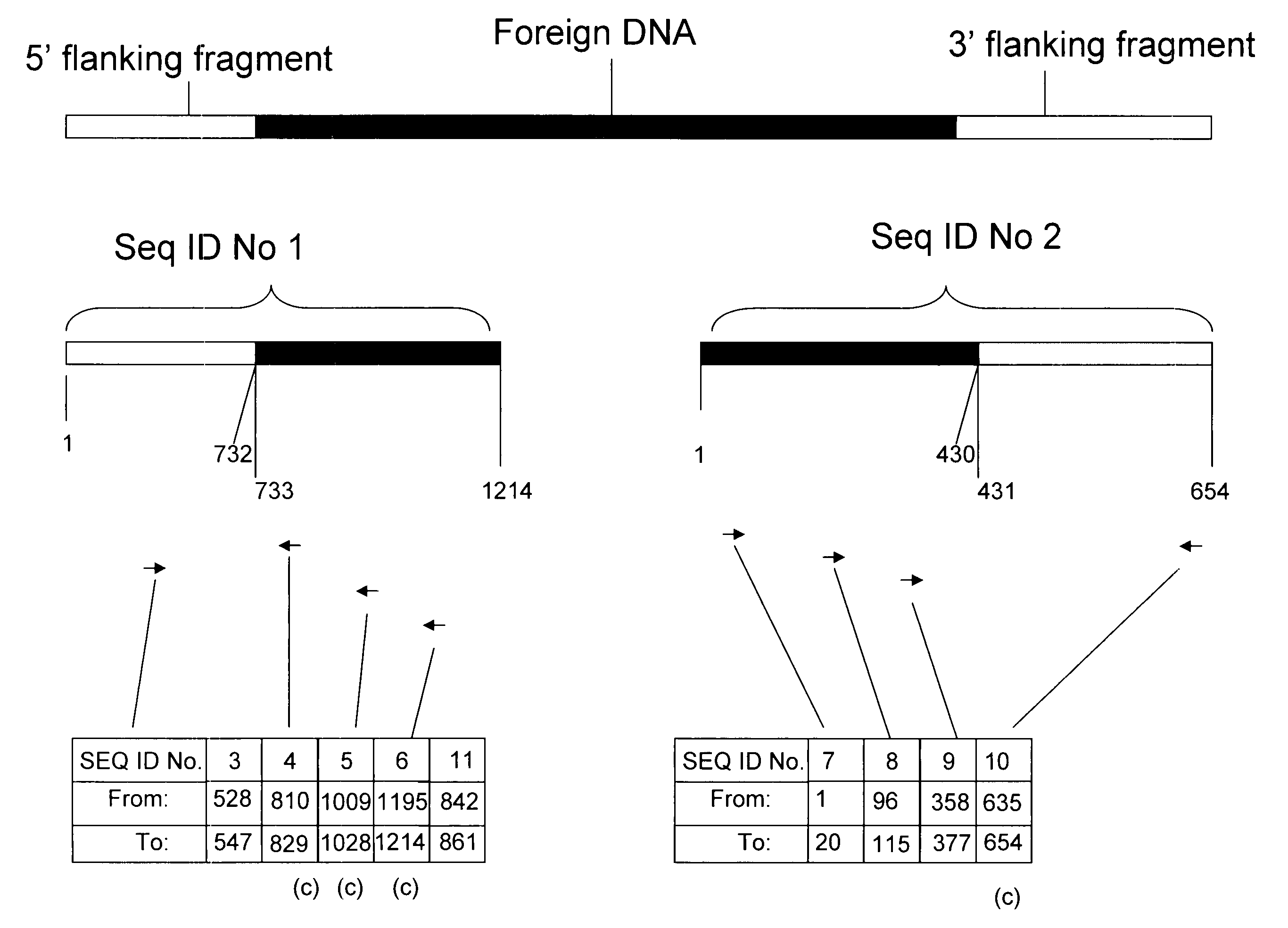
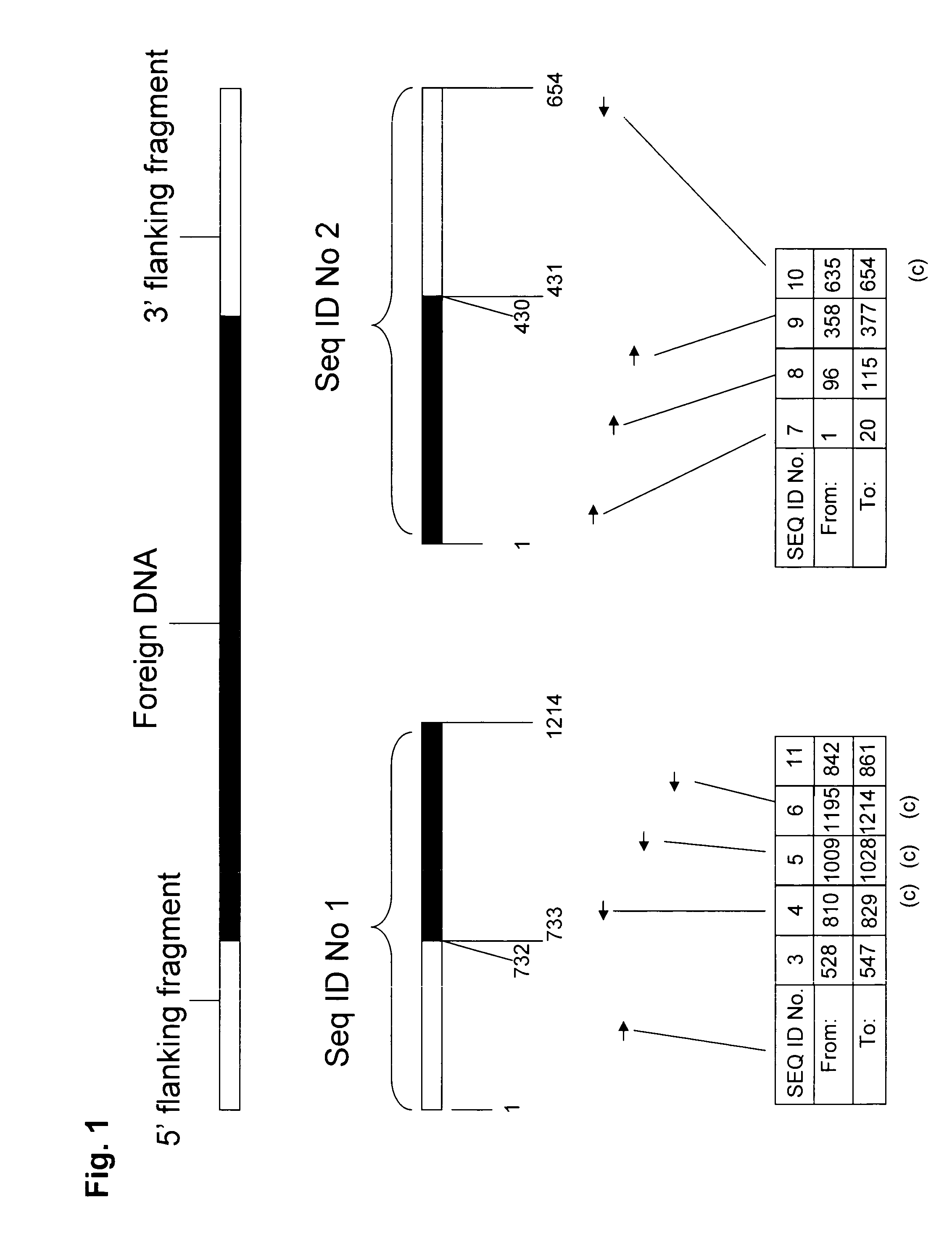
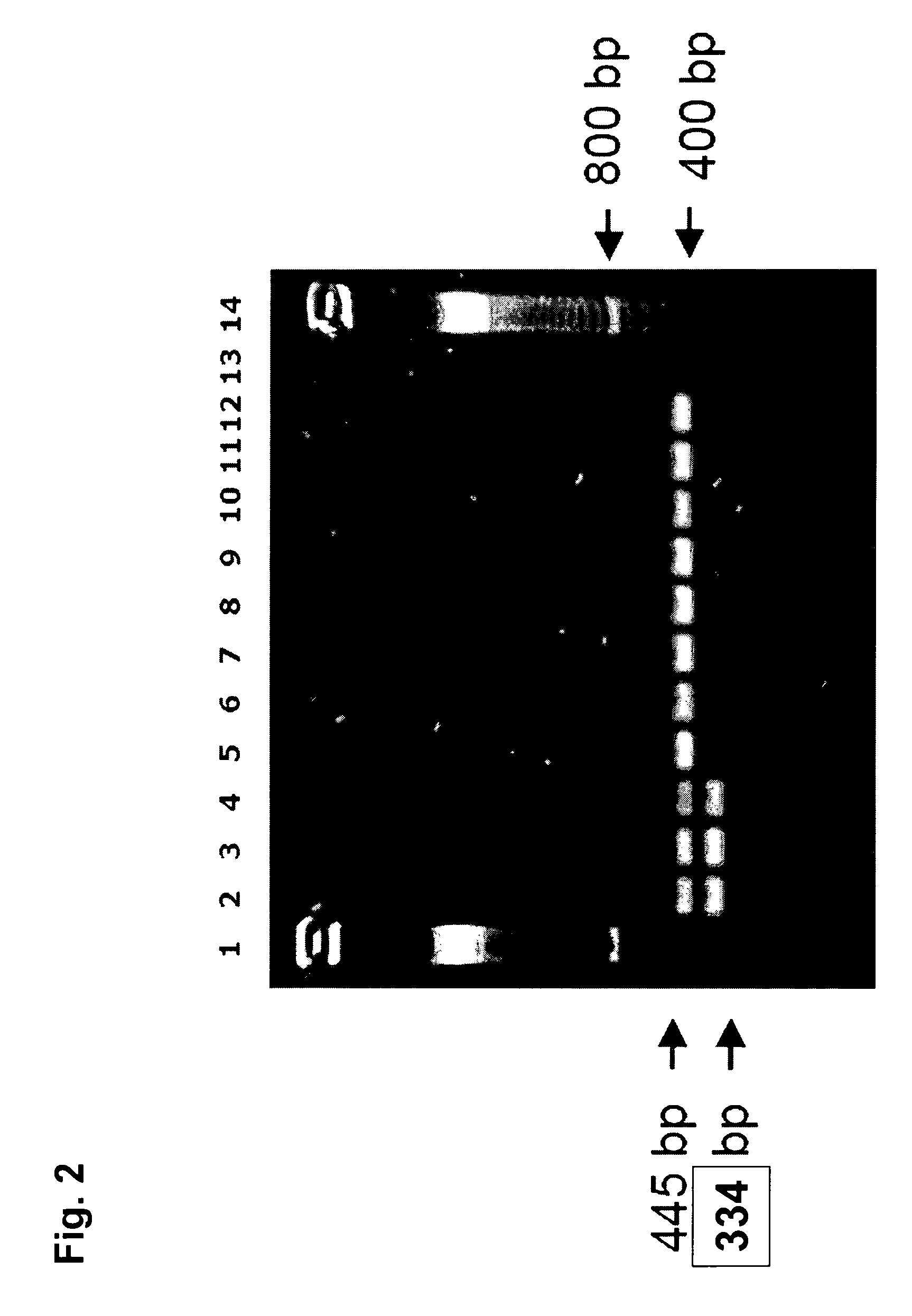
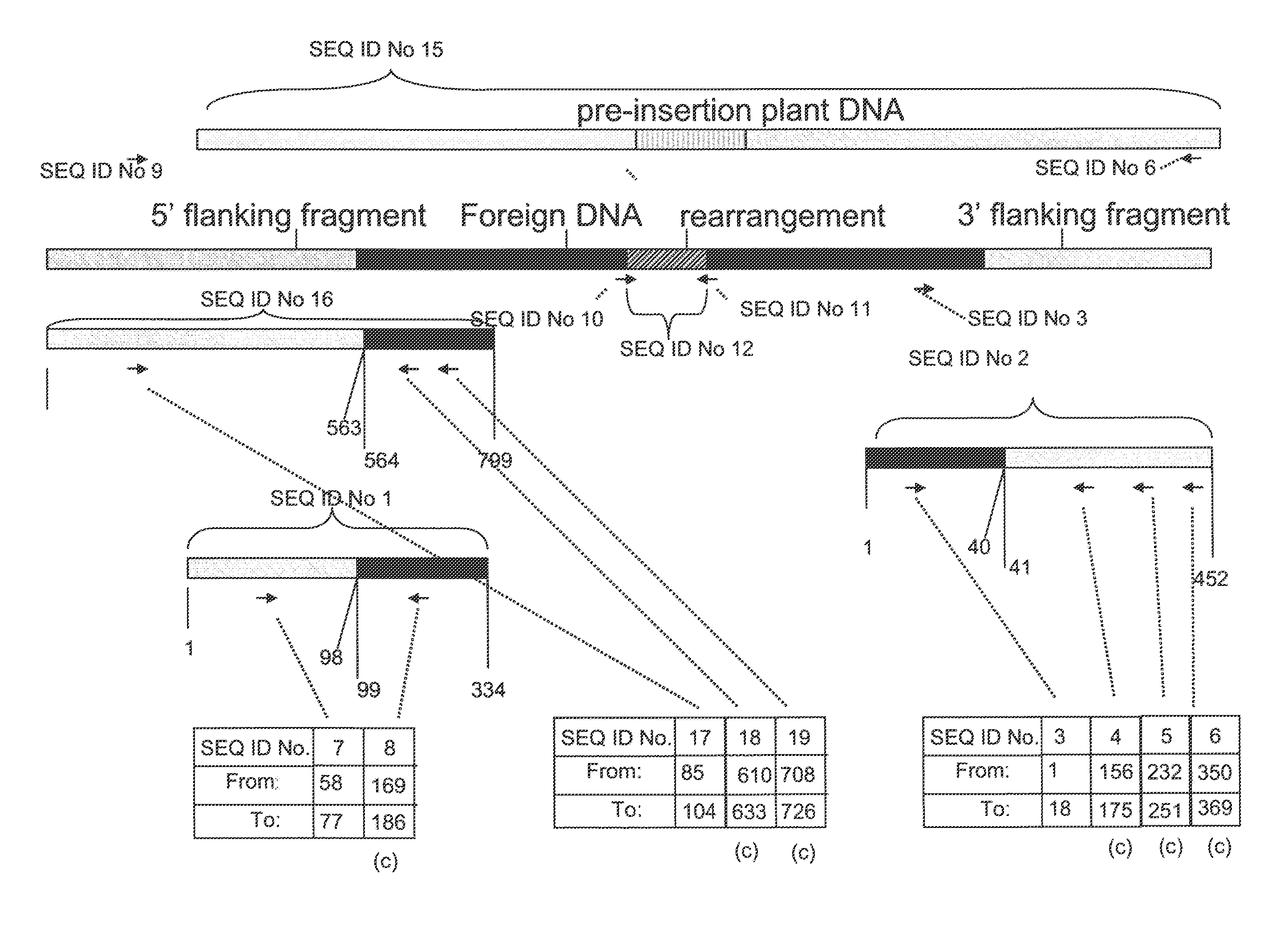
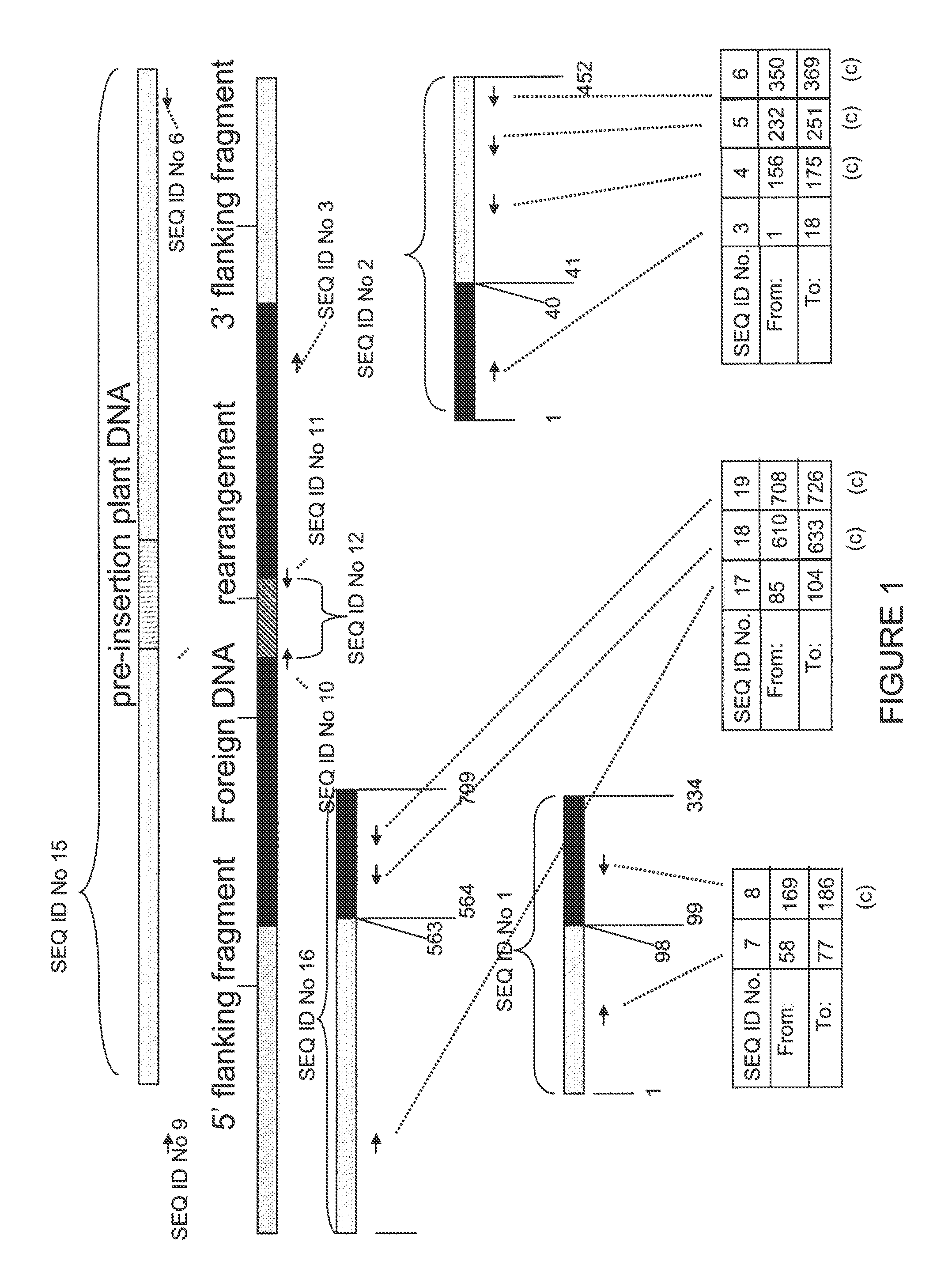
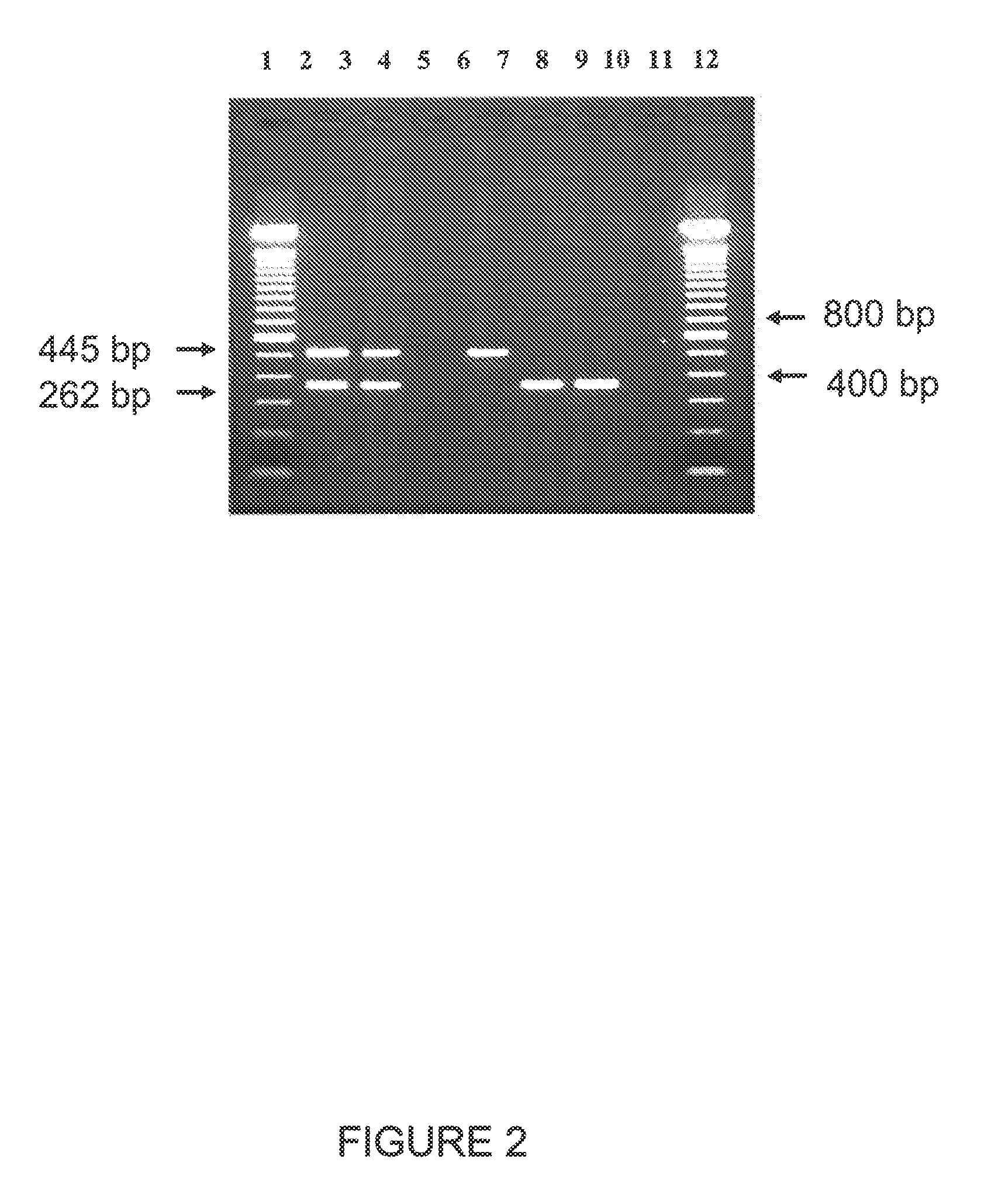
Compositions and methods related to transgenic high oleic acid / ALS inhibitor-tolerant soybean plants are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides soybean plants having a DP-305423-1 event which imparts a high oleic acid phenotype and tolerance to at least one ALS-inhibiting herbicide. The soybean plant harboring the DP-305423-1 event comprises genomic / transgene junctions having at least the polynucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:8, 9, 14, 15, 20, 21, 83 or 84. The characterization of the genomic insertion site of the DP-305423-1 event provides for an enhanced breeding efficiency and enables the use of molecular markers to track the transgene insert in the breeding populations and progeny thereof. Various methods and compositions for the identification, detection, and use of the soybean DP-305423-1 events are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
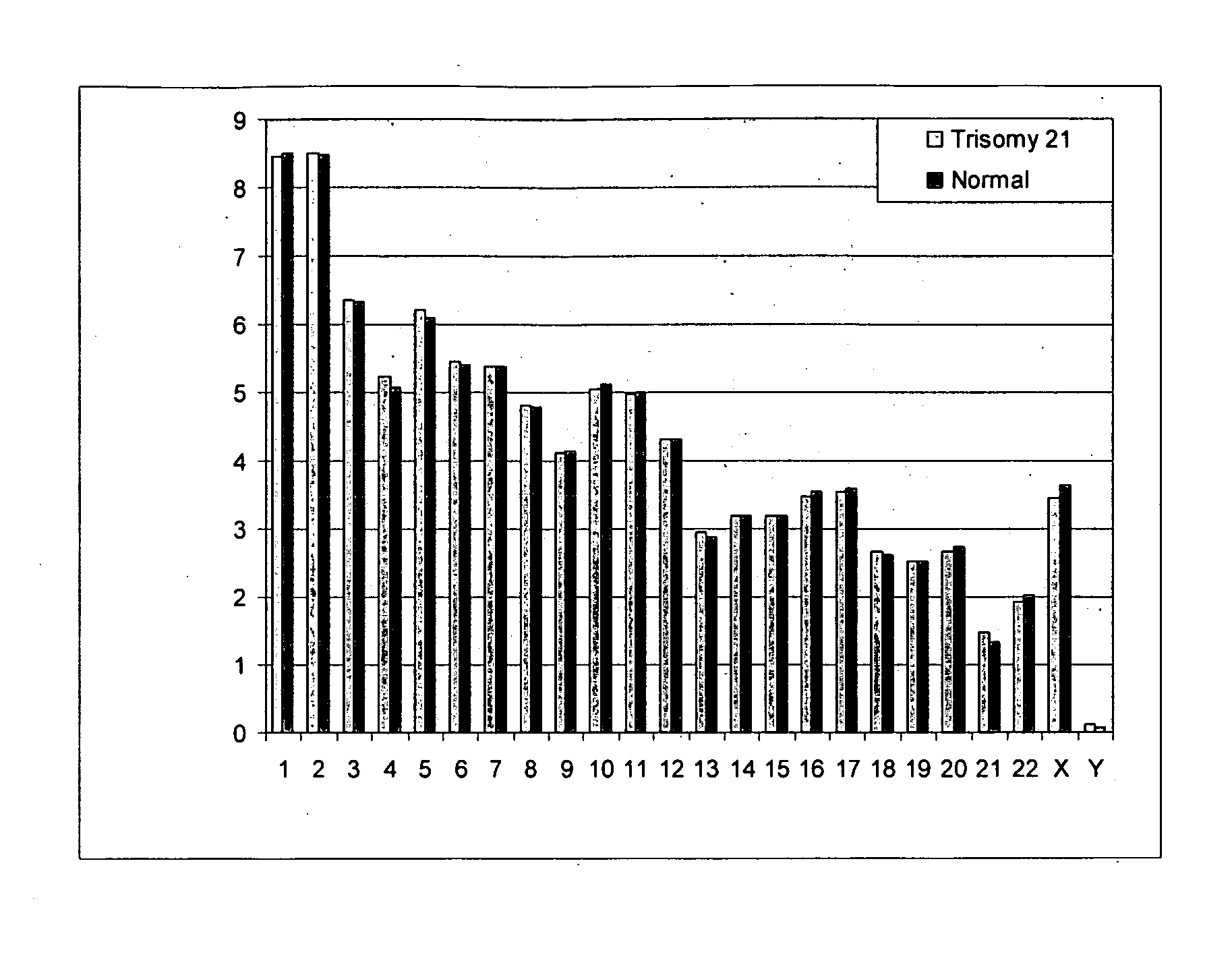
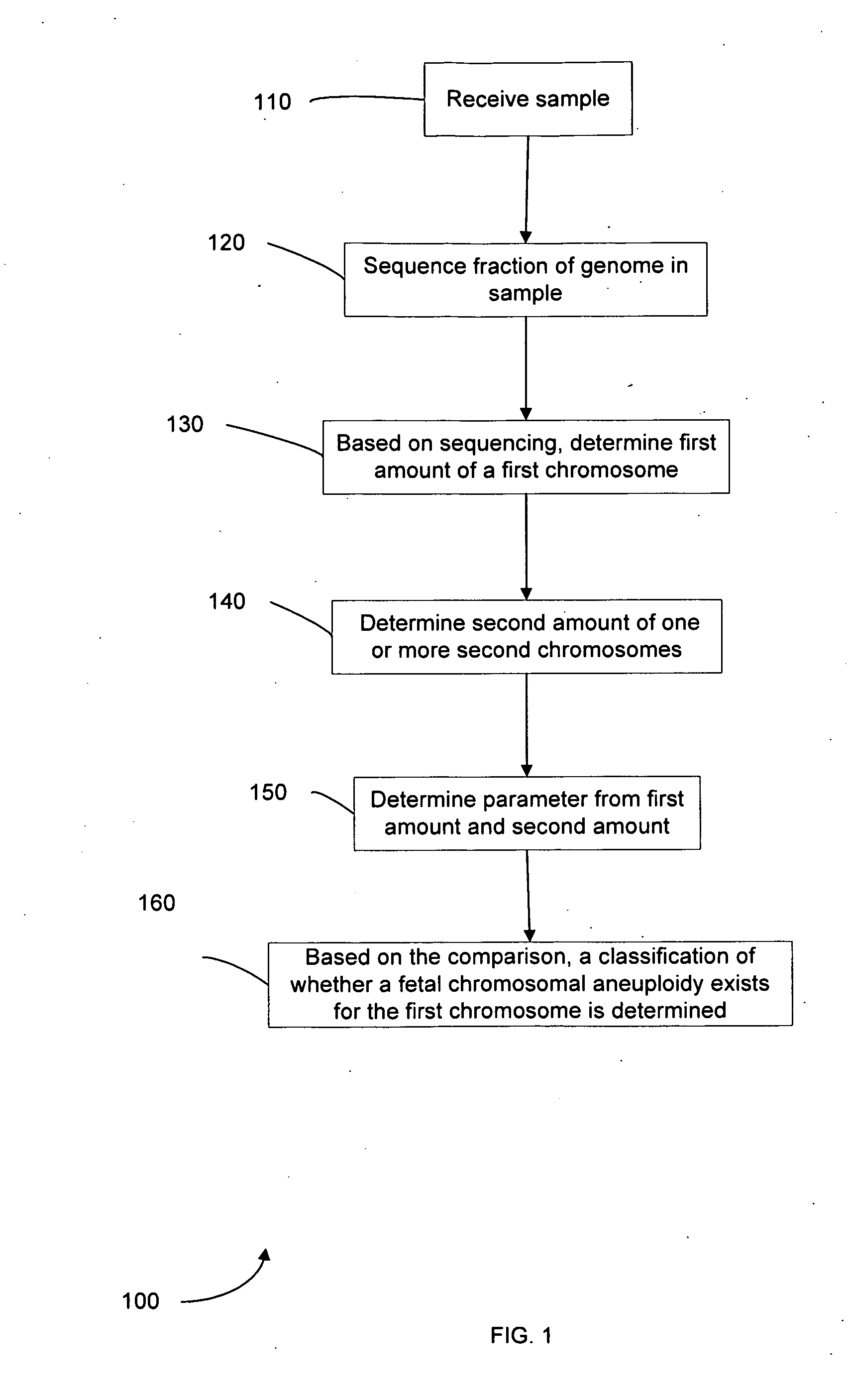
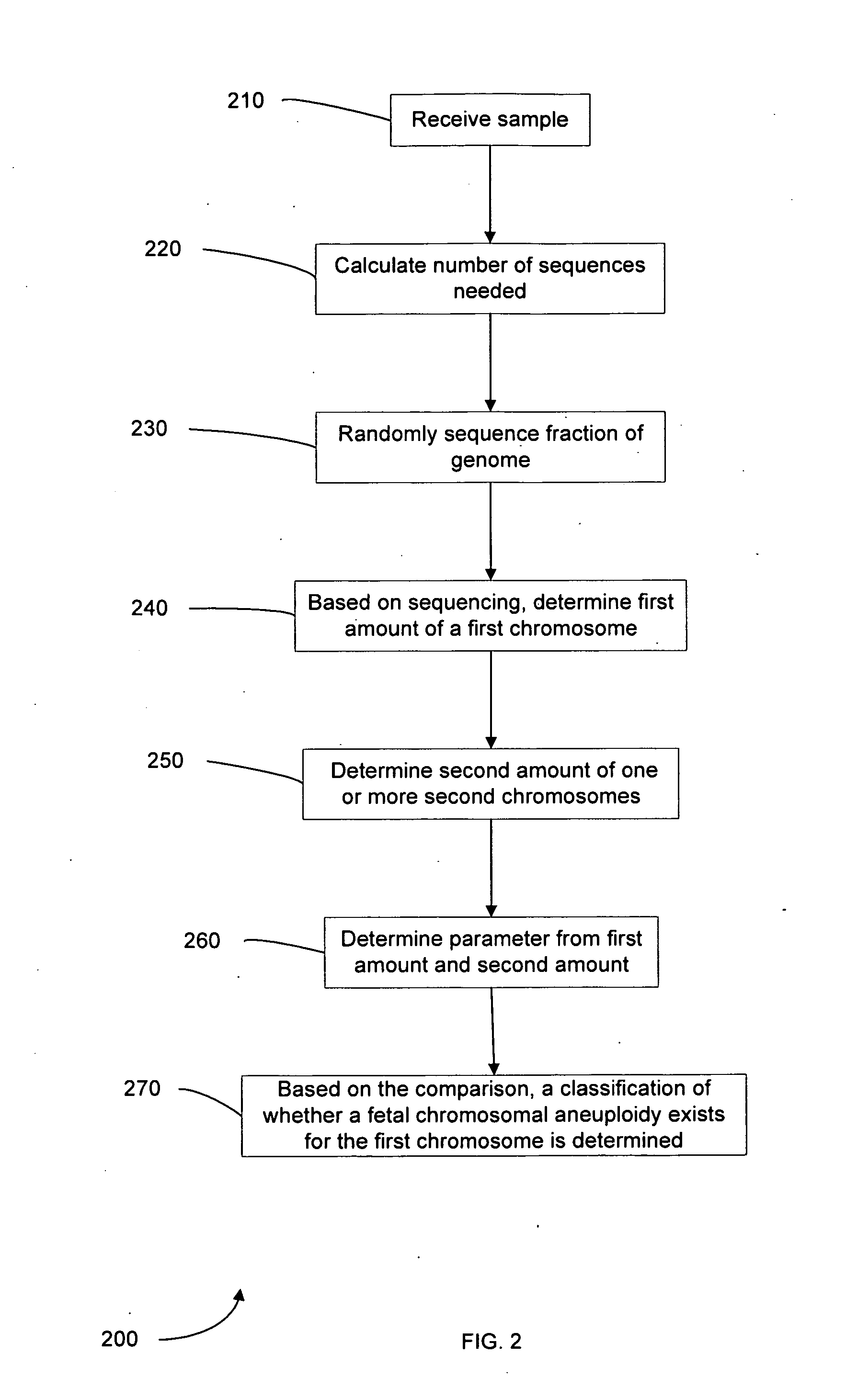
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20090029377A1Quantity maximizationSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenomic sequencingGenome
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
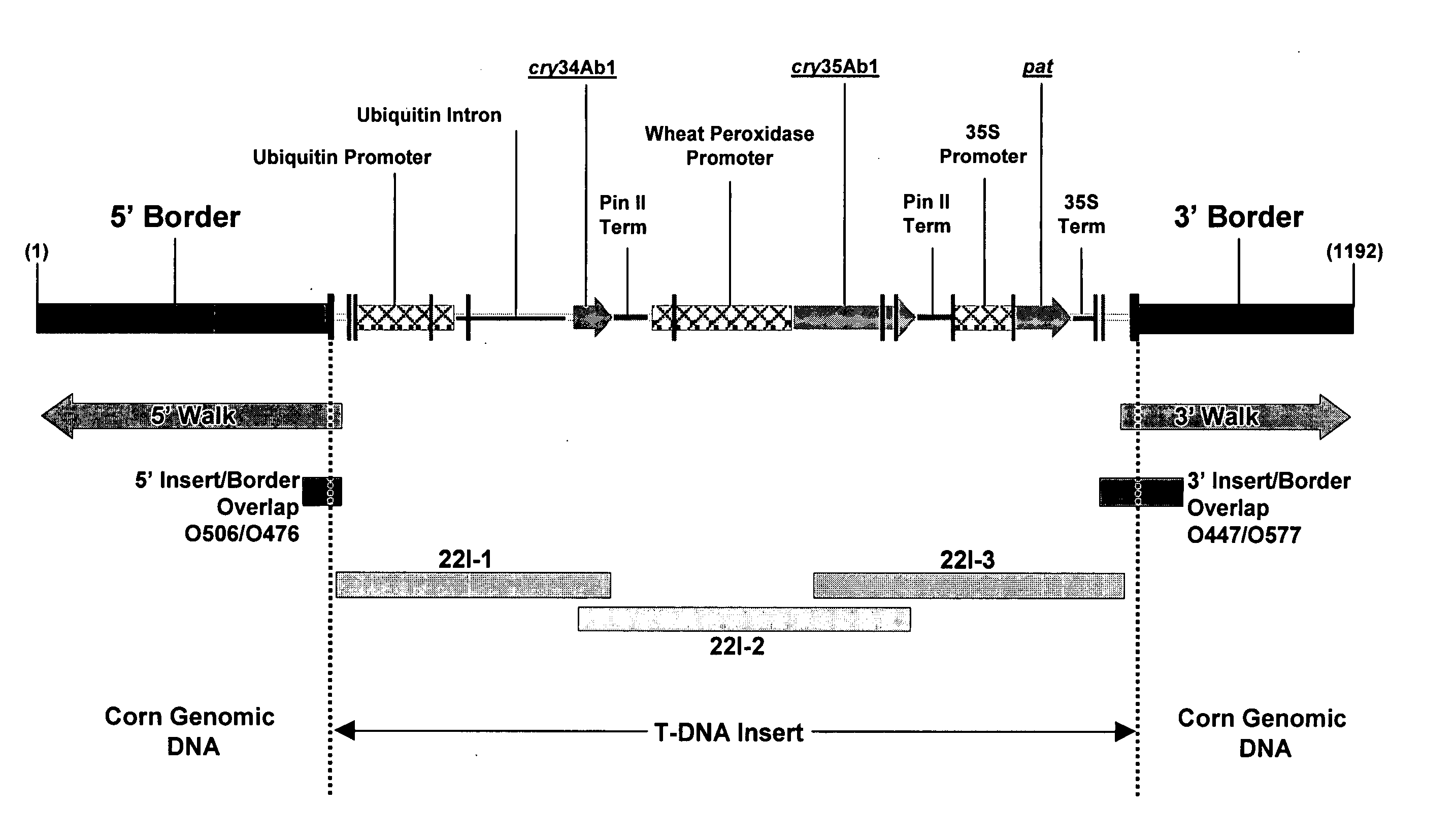
Corn event DAS-59122-7 and methods for detection thereof
The invention provides DNA compositions that relate to transgenic insect resistant maize plants. Also provided are assays for detecting the presence of the maize DAS-59122-7 event based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the maize genome and the DNA sequences flanking the insertion site. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
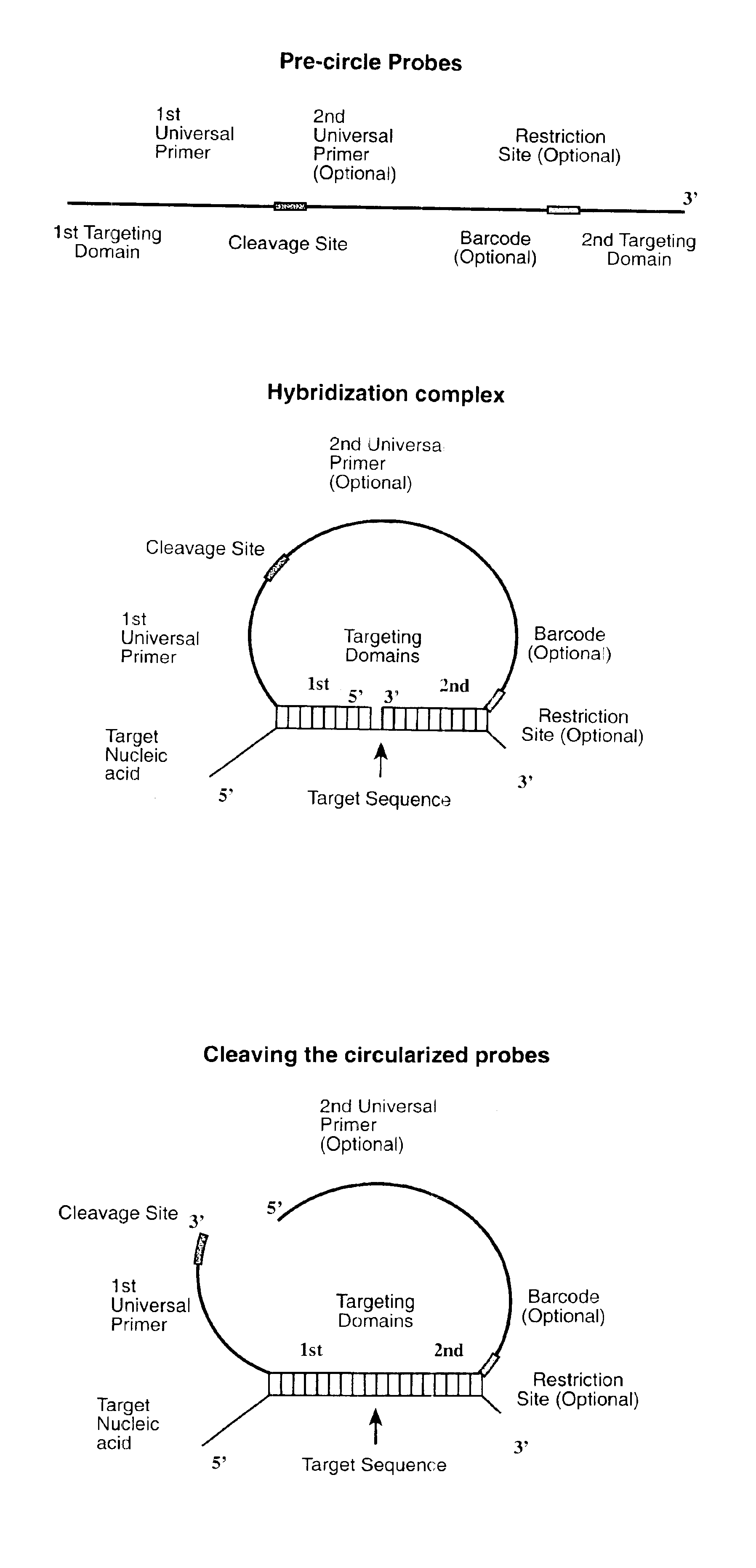
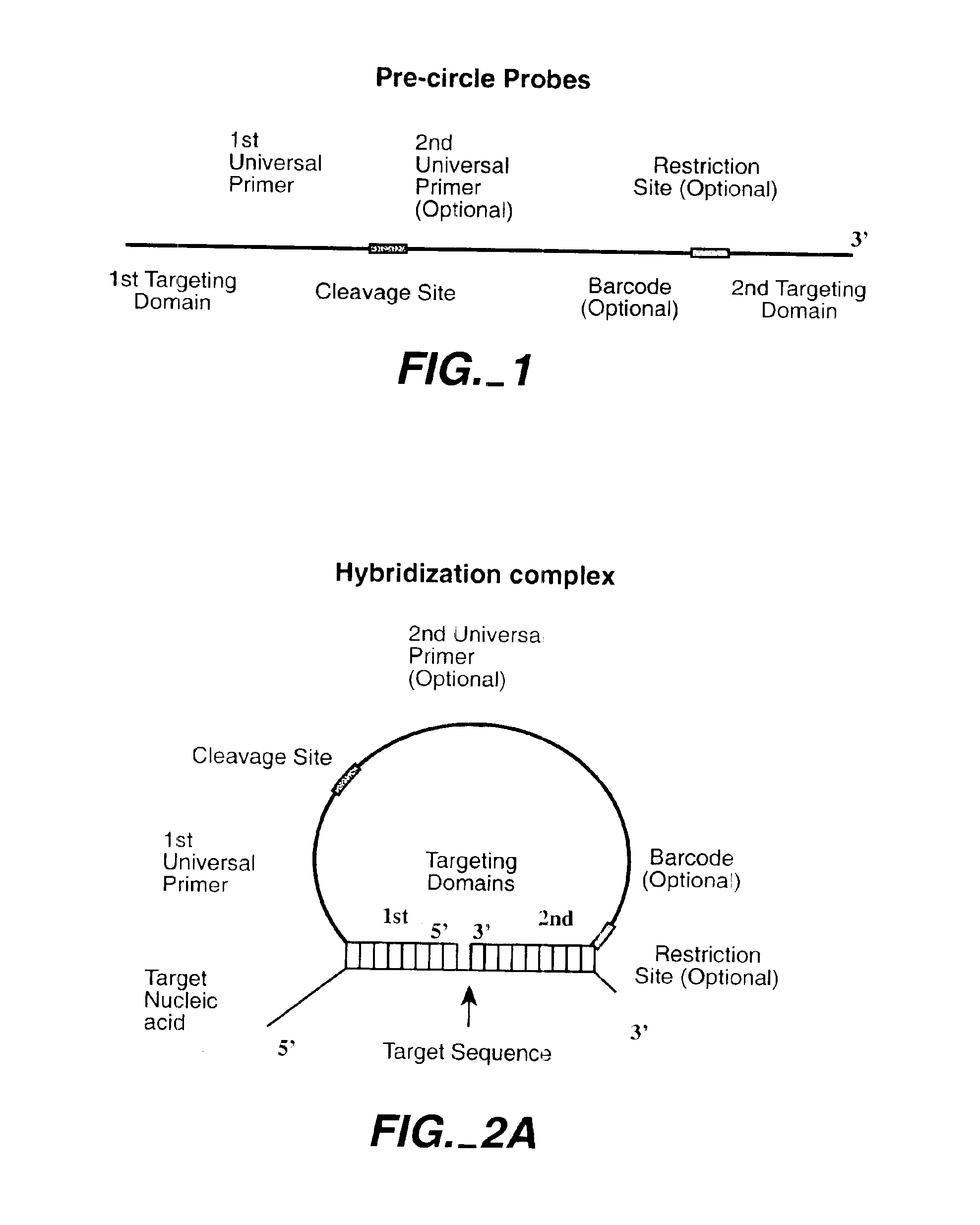
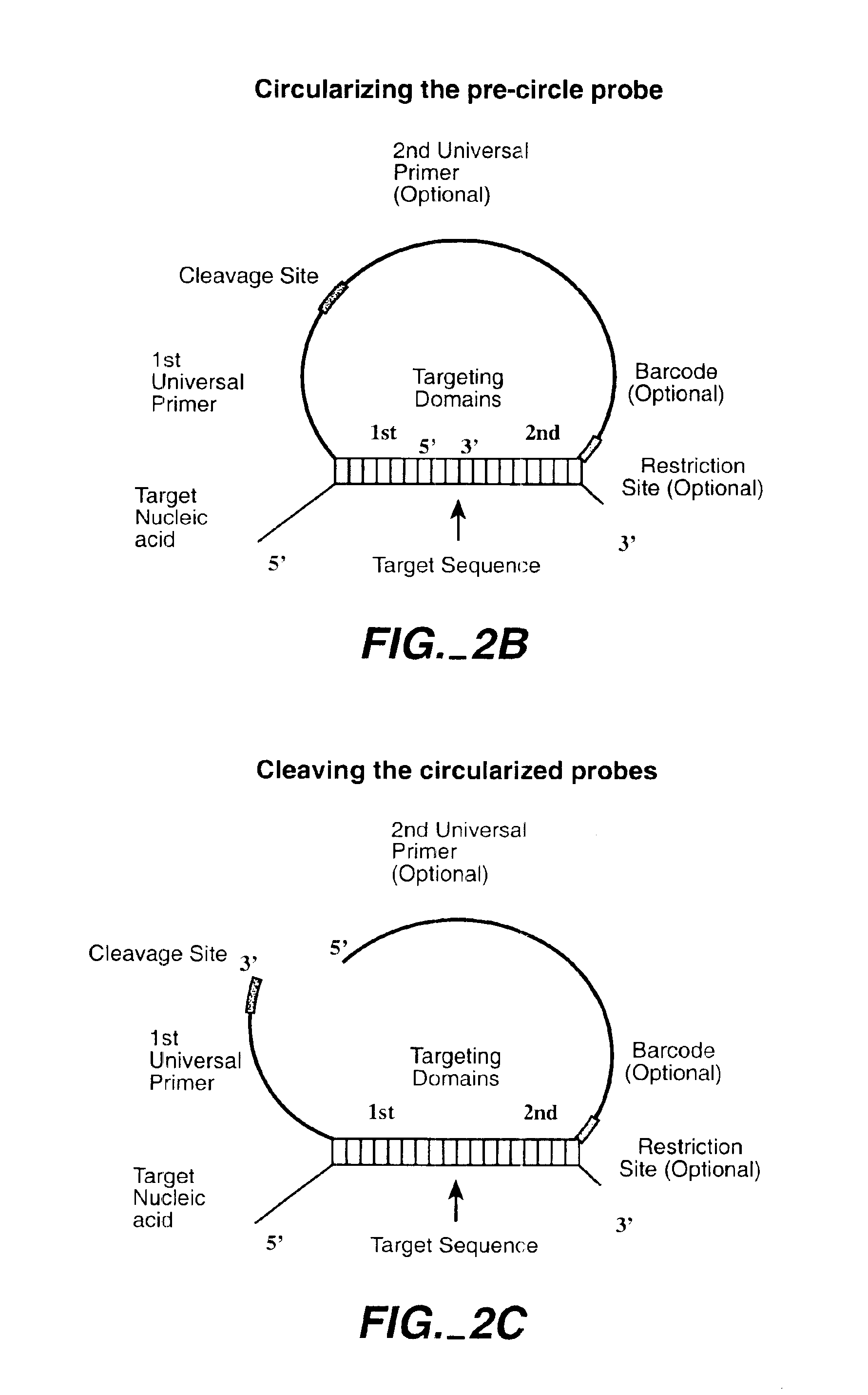
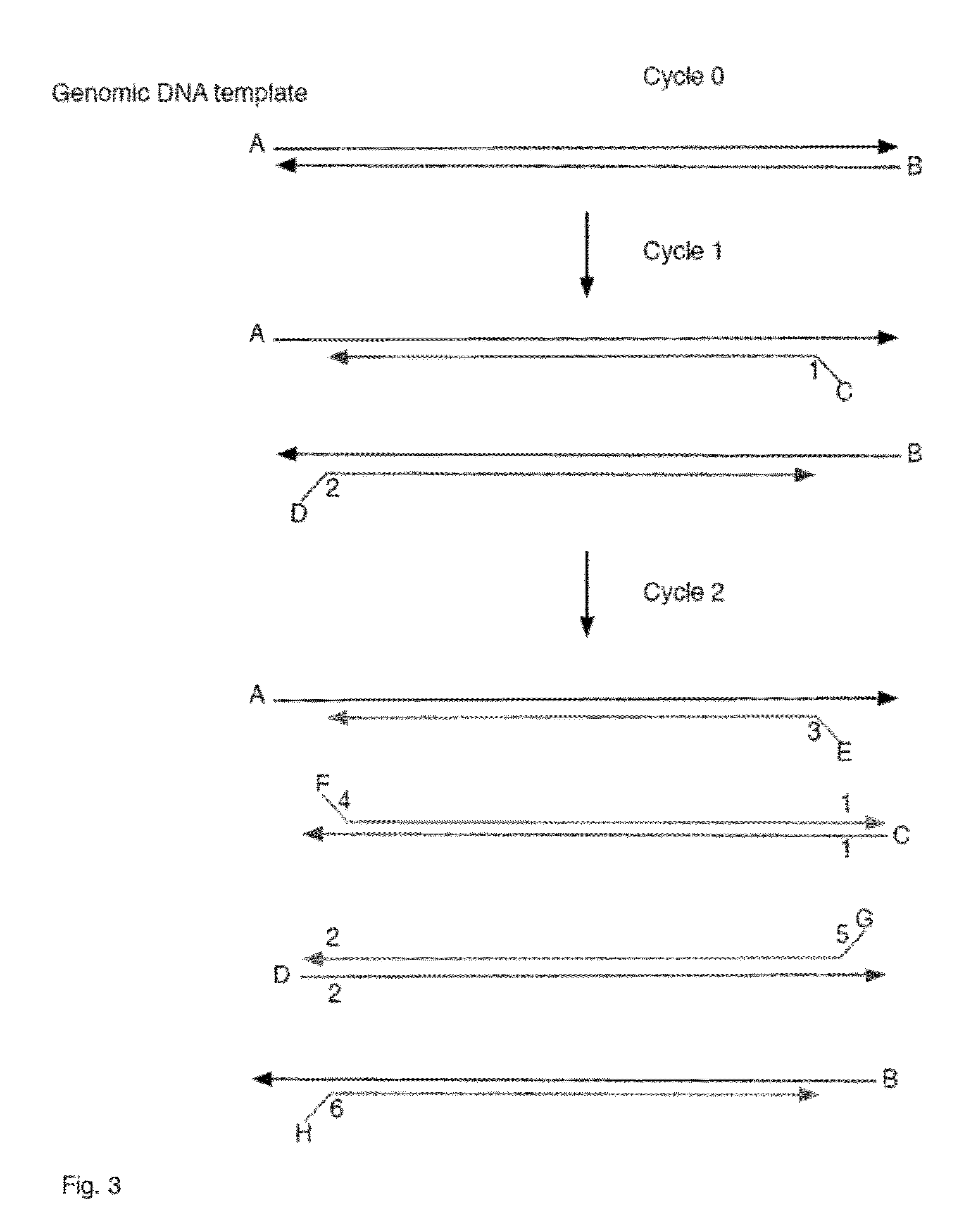
Direct multiplex characterization of genomic DNA
The invention is directed to novel methods of multiplexing nucleic acid reactions, including amplification, detection and genotyping. The invention relies on the use of precircle probes that are circularized in the presence of the corresponding target nucleic acids, cleaved, and then amplified.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
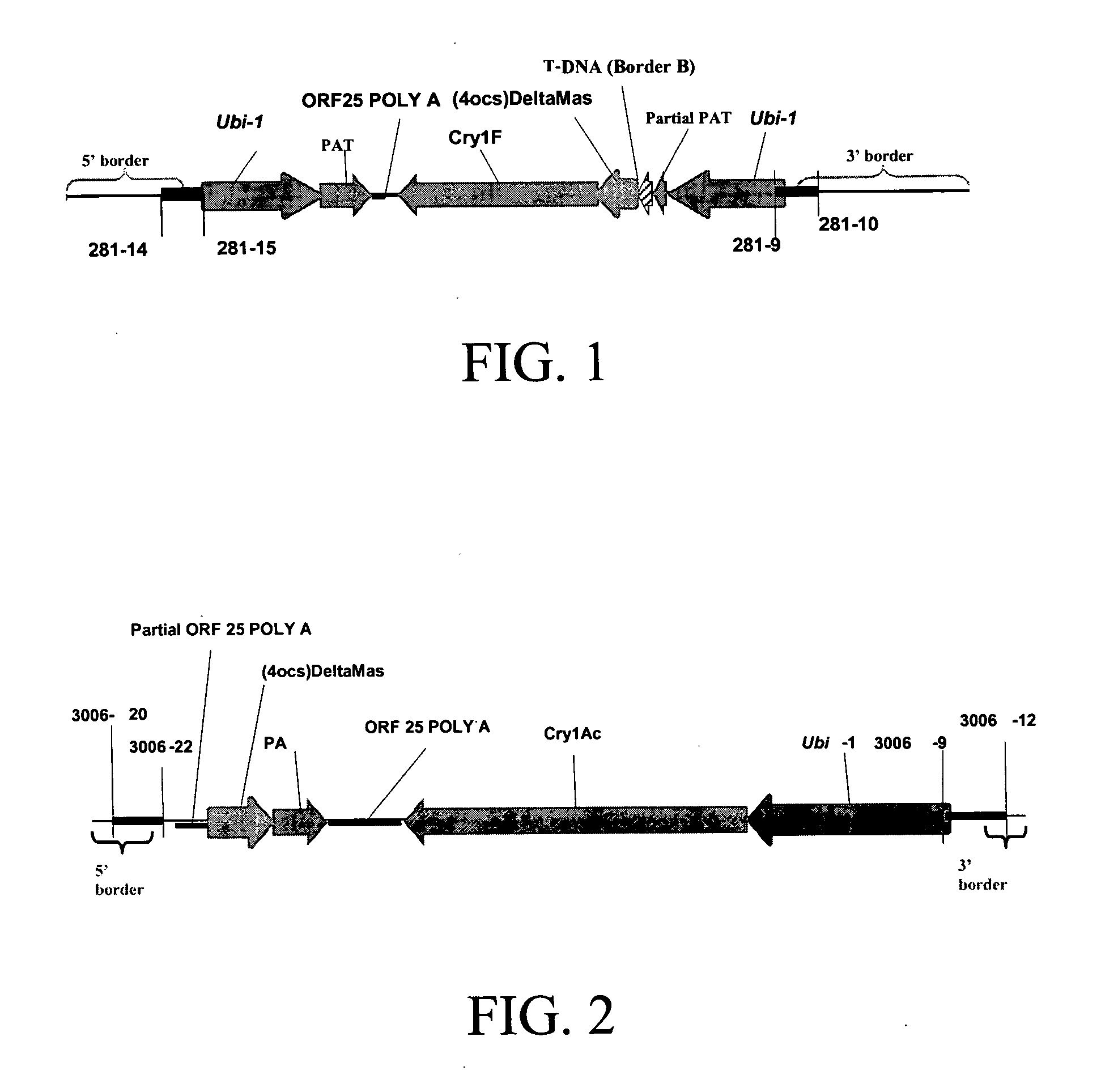
Cry1F and Cry1AC transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
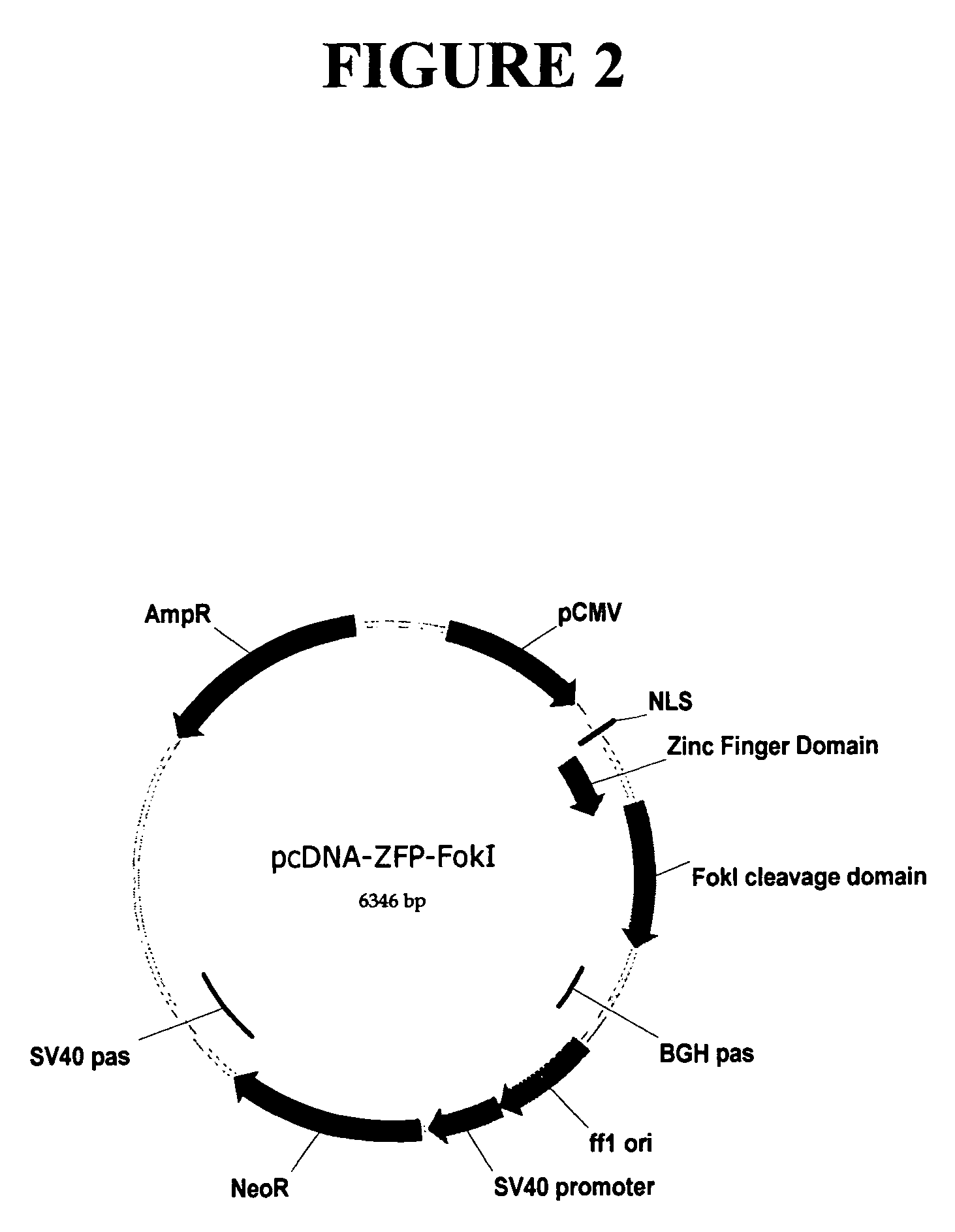
Methods and compositions for targeted cleavage and recombination
ActiveUS7888121B2High frequencyInhibitory activityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesPolynucleotideGenome
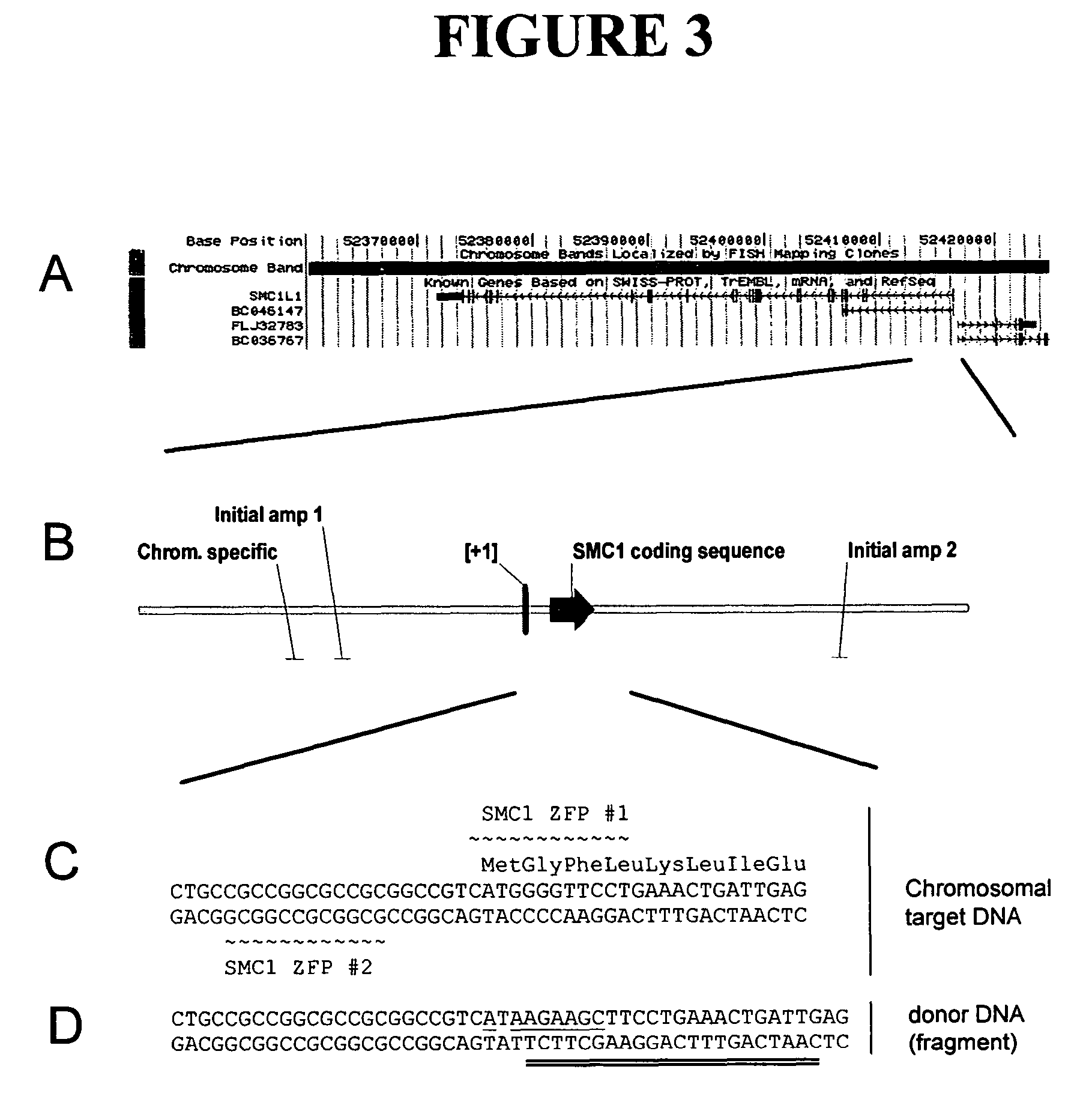
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for targeted cleavage of a genomic sequence, targeted alteration of a genomic sequence, and targeted recombination between a genomic region and an exogenous polynucleotide homologous to the genomic region. The compositions include fusion proteins comprising a cleavage domain (or cleavage half-domain) and an engineered zinc finger domain and polynucleotides encoding same. Methods for targeted cleavage include introduction of such fusion proteins, or polynucleotides encoding same, into a cell. Methods for targeted recombination additionally include introduction of an exogenous polynucleotide homologous to a genomic region into cells comprising the disclosed fusion proteins.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Corn event pv-zmir13 (mon863) plants and compositions and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides compositions and methods for detecting the presence of the corn event MON863 DNA inserted into the corn genome from the transformation of the recombinant construct containing a Cry3Bb gene and of genomic sequences flanking the insertion site. The present invention also provides the corn event MON863 plants, progeny and seeds thereof that contain the corn event MON863 DNA.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Seed specific highly effective promoter and its application
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Cotton event PV-GHGT07(1445) and compositions and methods for detection thereof
InactiveUS20020120964A1Improve stabilityHigh selectivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyInsertion site
The present invention provides DNA compositions and assays for detecting the presence of the DNA compositions in PV-GHGT07(1445) cotton event based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion site. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Canola event PV-BNGT04(RT73) and compositions and methods for detection thereof
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Herbicide Tolerant Cotton Plants and Methods for Identifying the Same
ActiveUS20100050282A1Superior agronomic phenotypeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHerbicide resistanceGenome
The invention provides specific transgenic cotton plants, plant material and seeds, characterized in that these products harbor a specific transformation event at a specific location in the cotton genome. Tools are also provided which allow rapid and unequivocal identification of the event in biological samples.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Insect resistant cotton plants and methods for identifying same
ActiveUS20100077501A1Superior agronomic phenotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGenomeAgronomy
The invention provides specific transgenic cotton plants, plant material and seeds, characterized in that these products harbor a specific transformation event at a specific location in the cotton genome. Tools are also provided which allow rapid and unequivocal identification of the event in biological samples.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
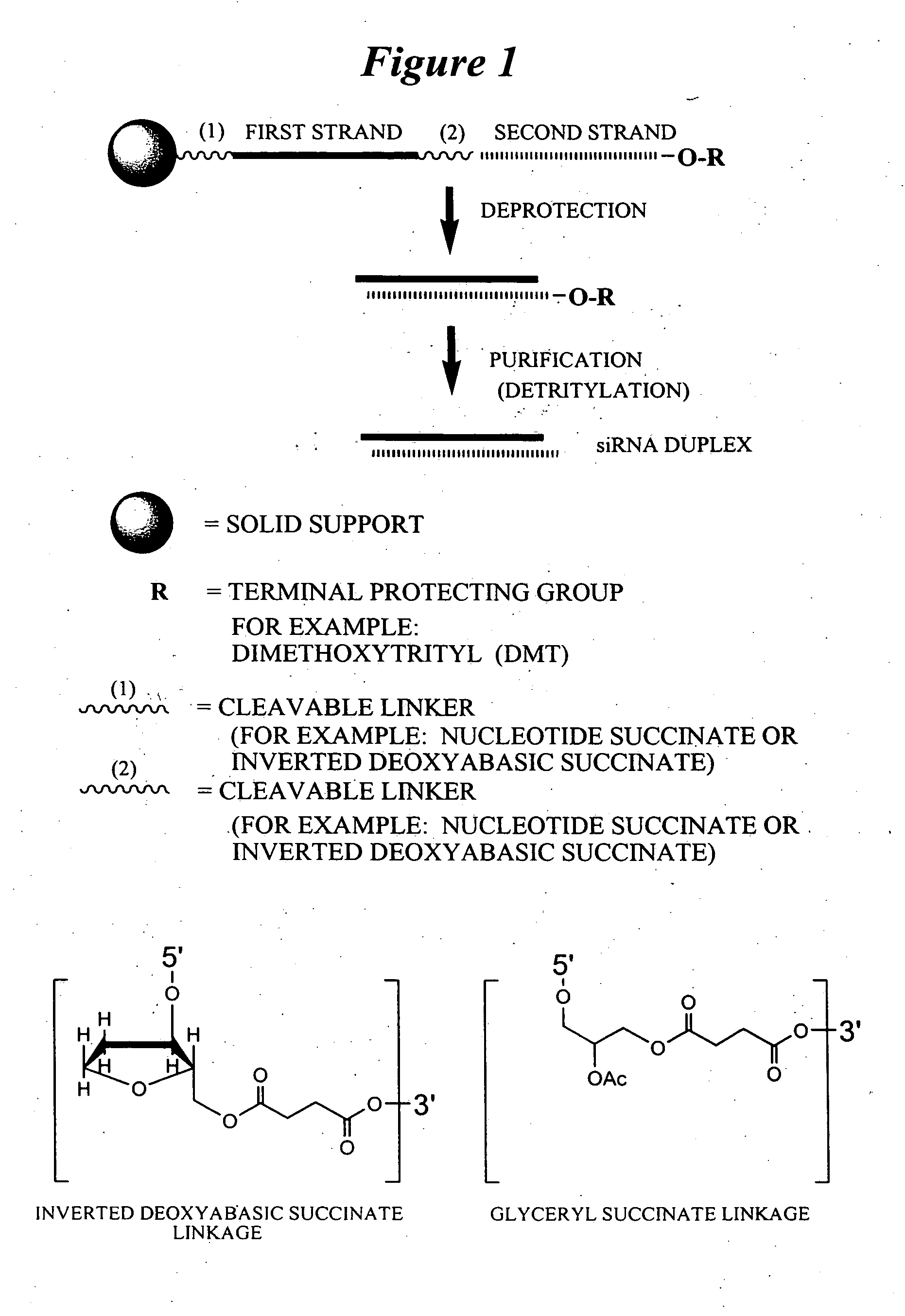
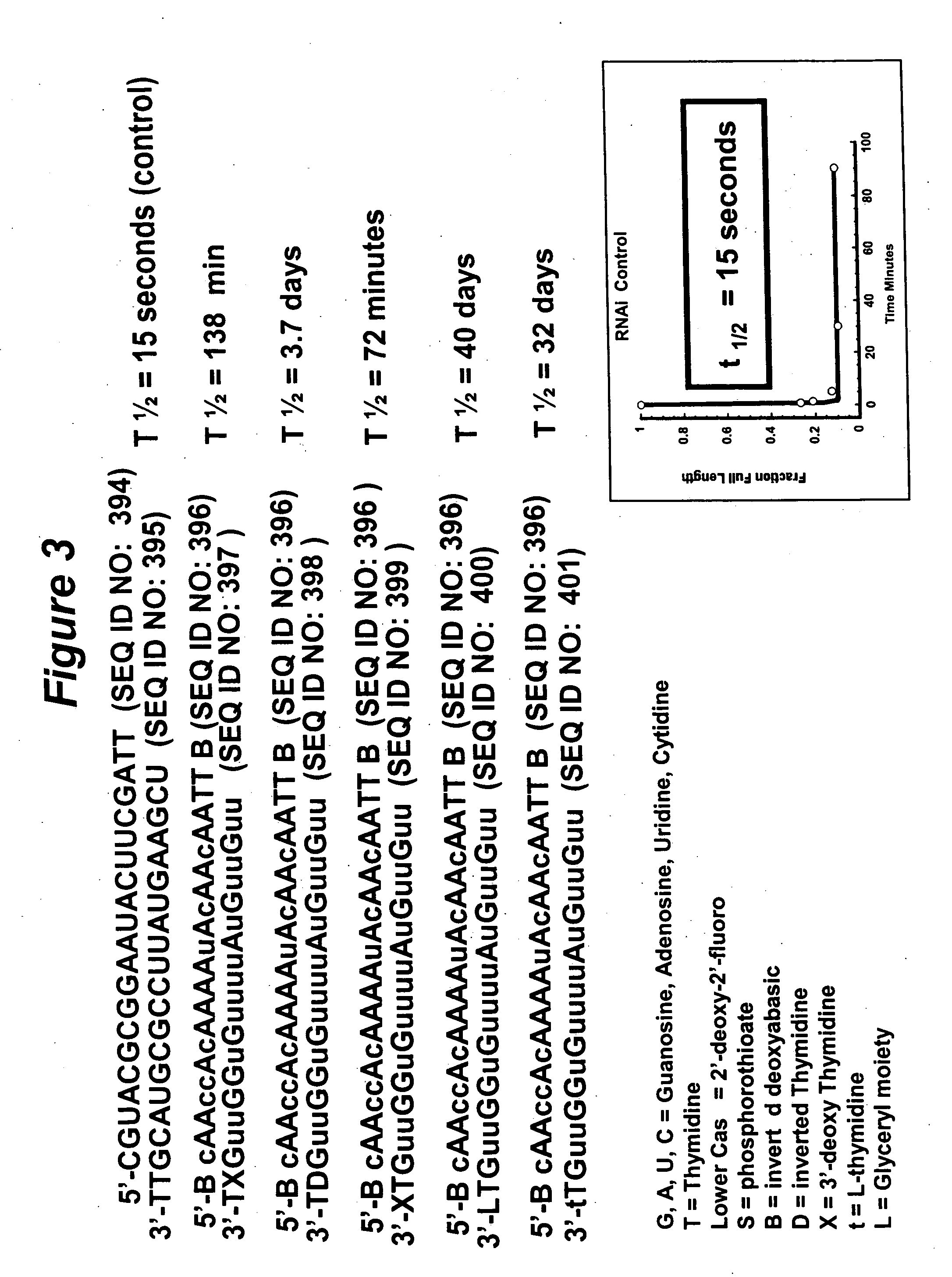
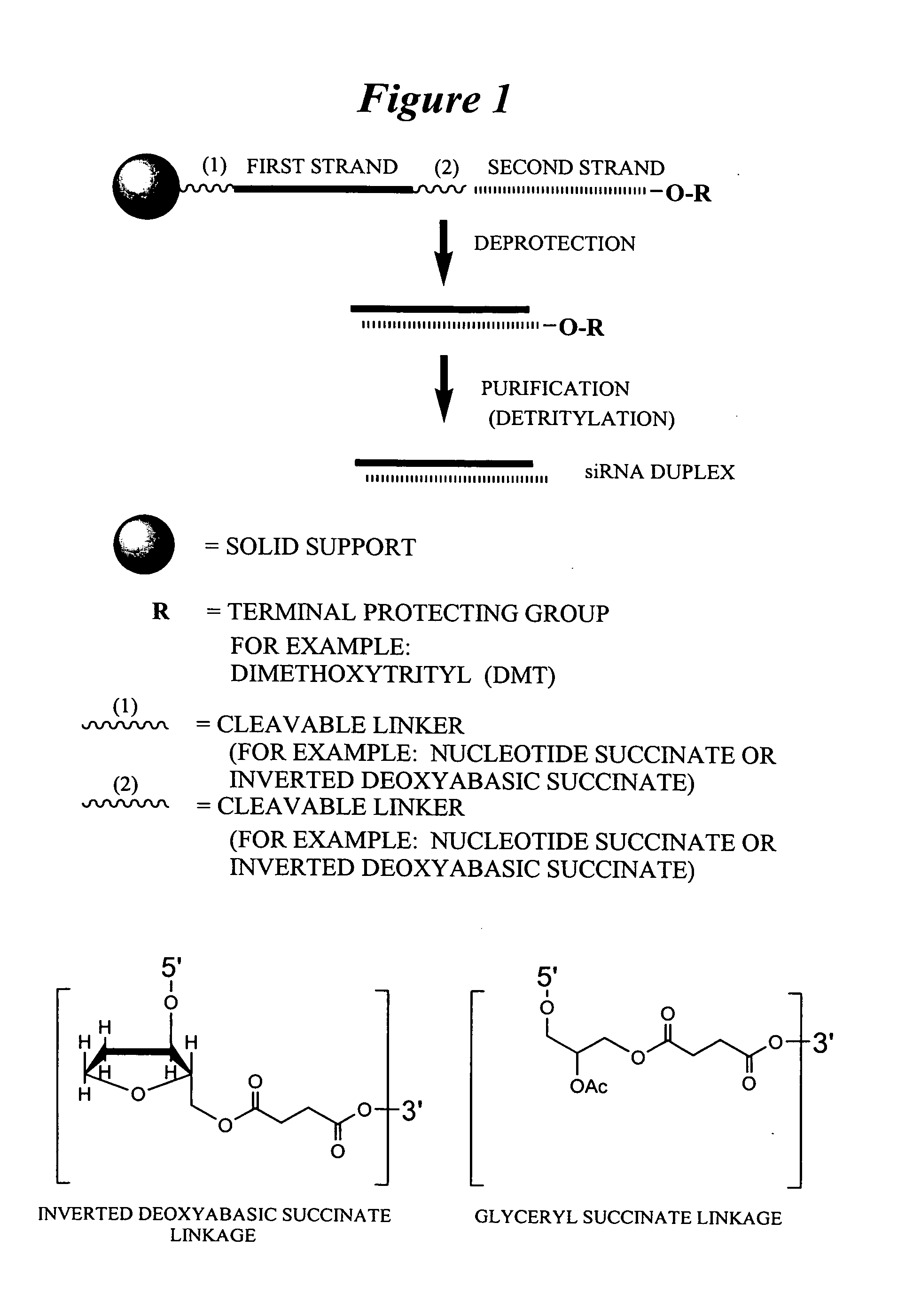
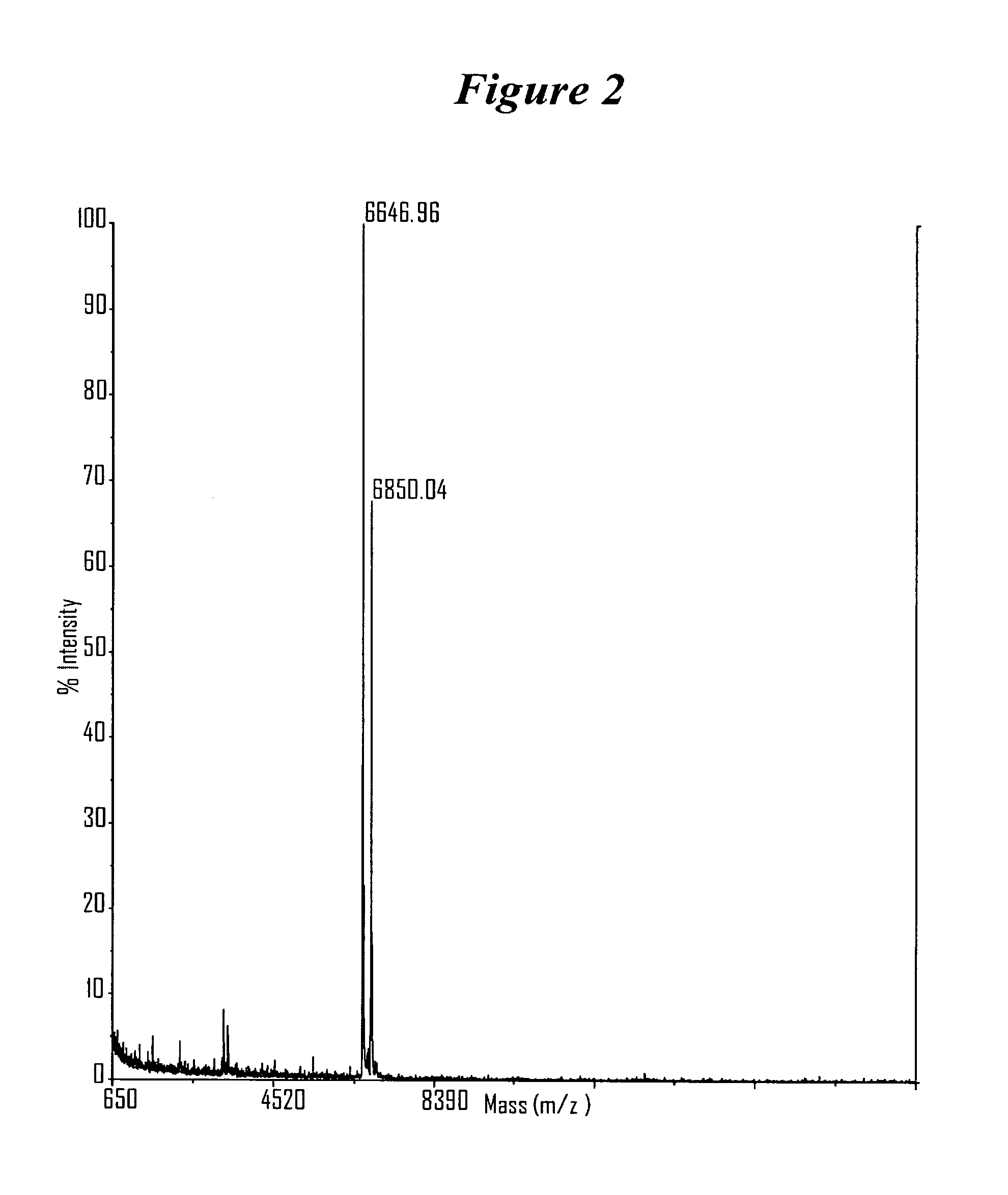
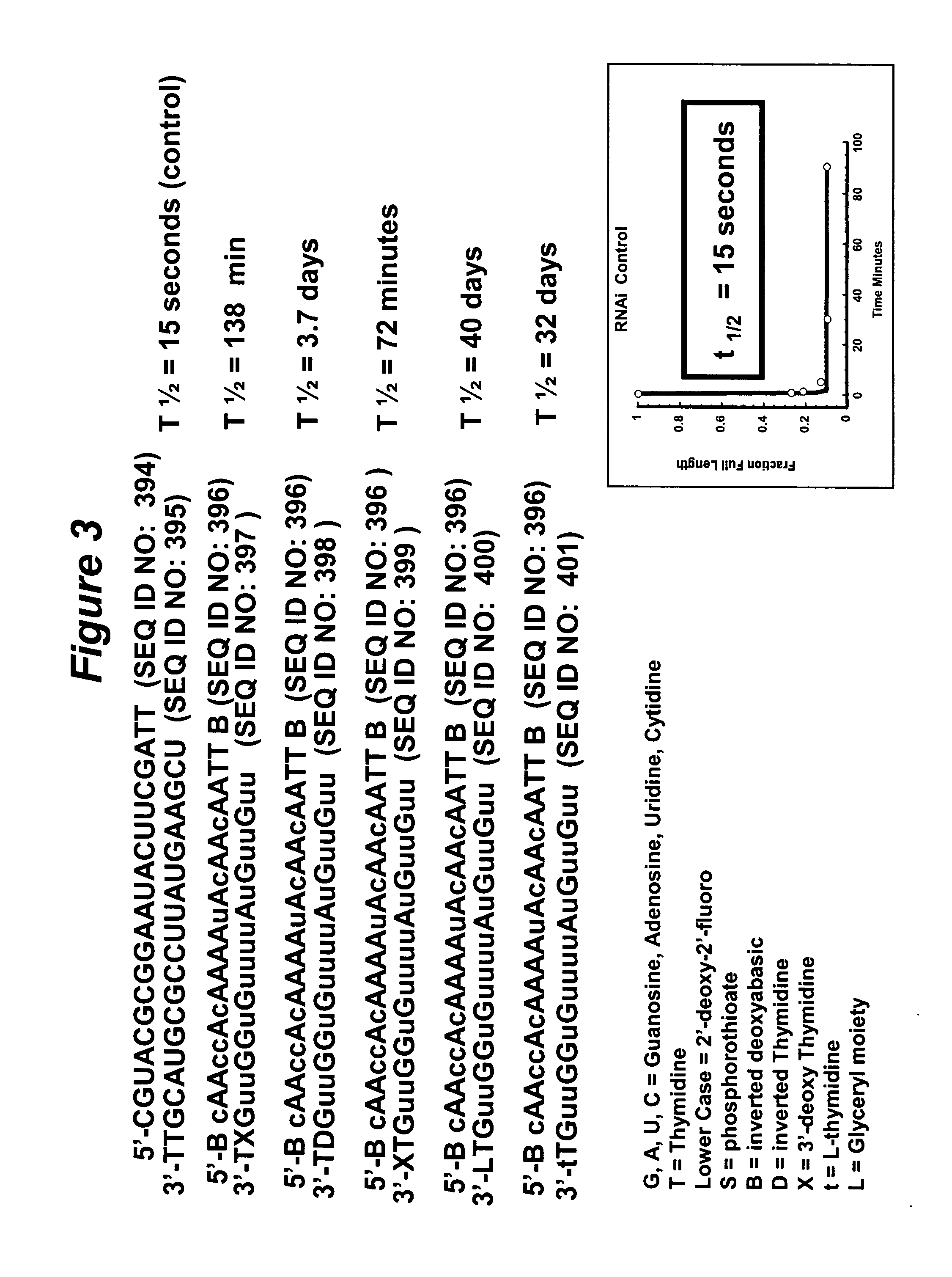
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050020525A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesDouble strandOrganism
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIMA THERAPEUTICS ICN
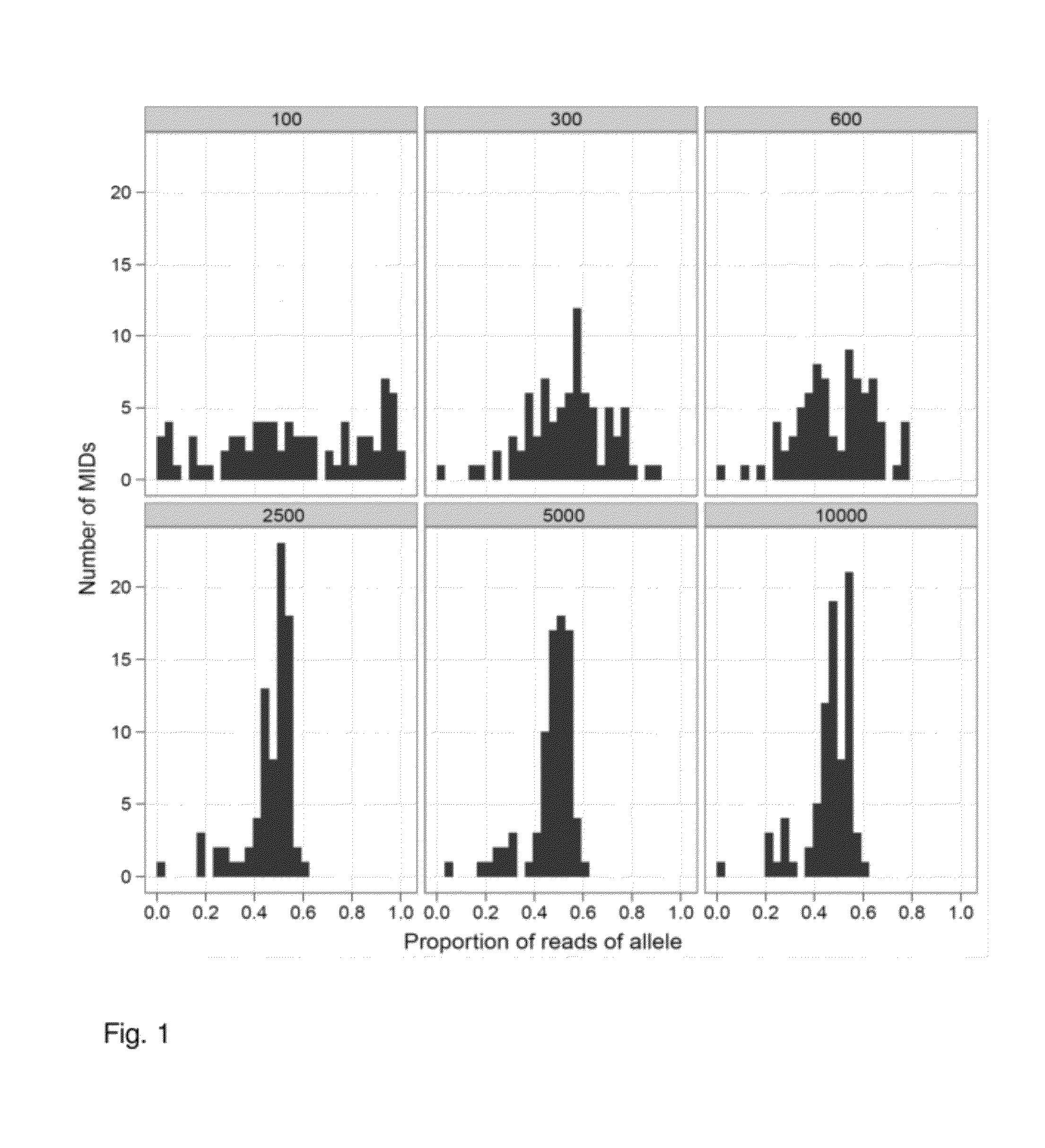
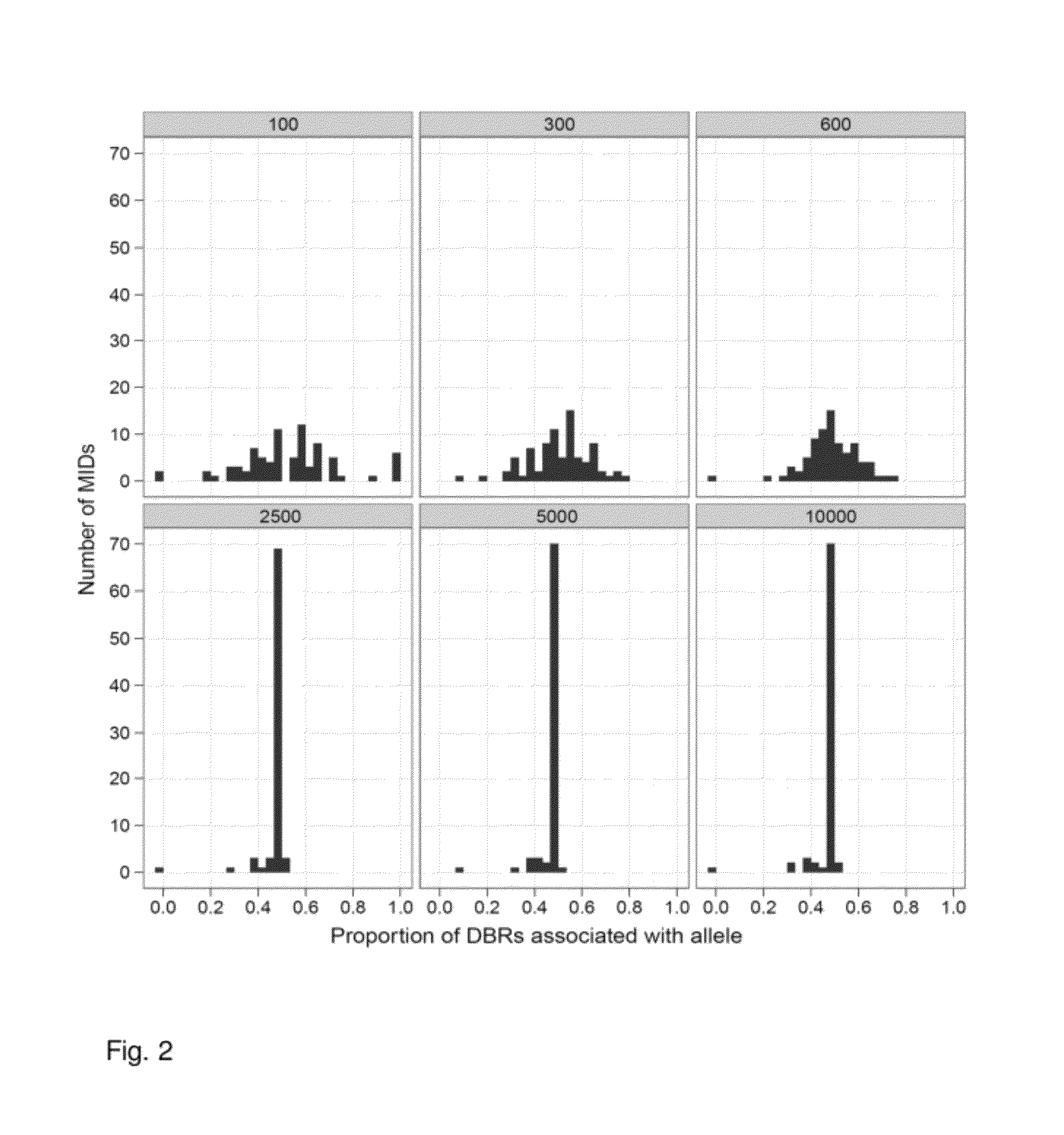
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS8481292B2Easy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotide
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (SiNA)
InactiveUS20050032733A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryBiological bodyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
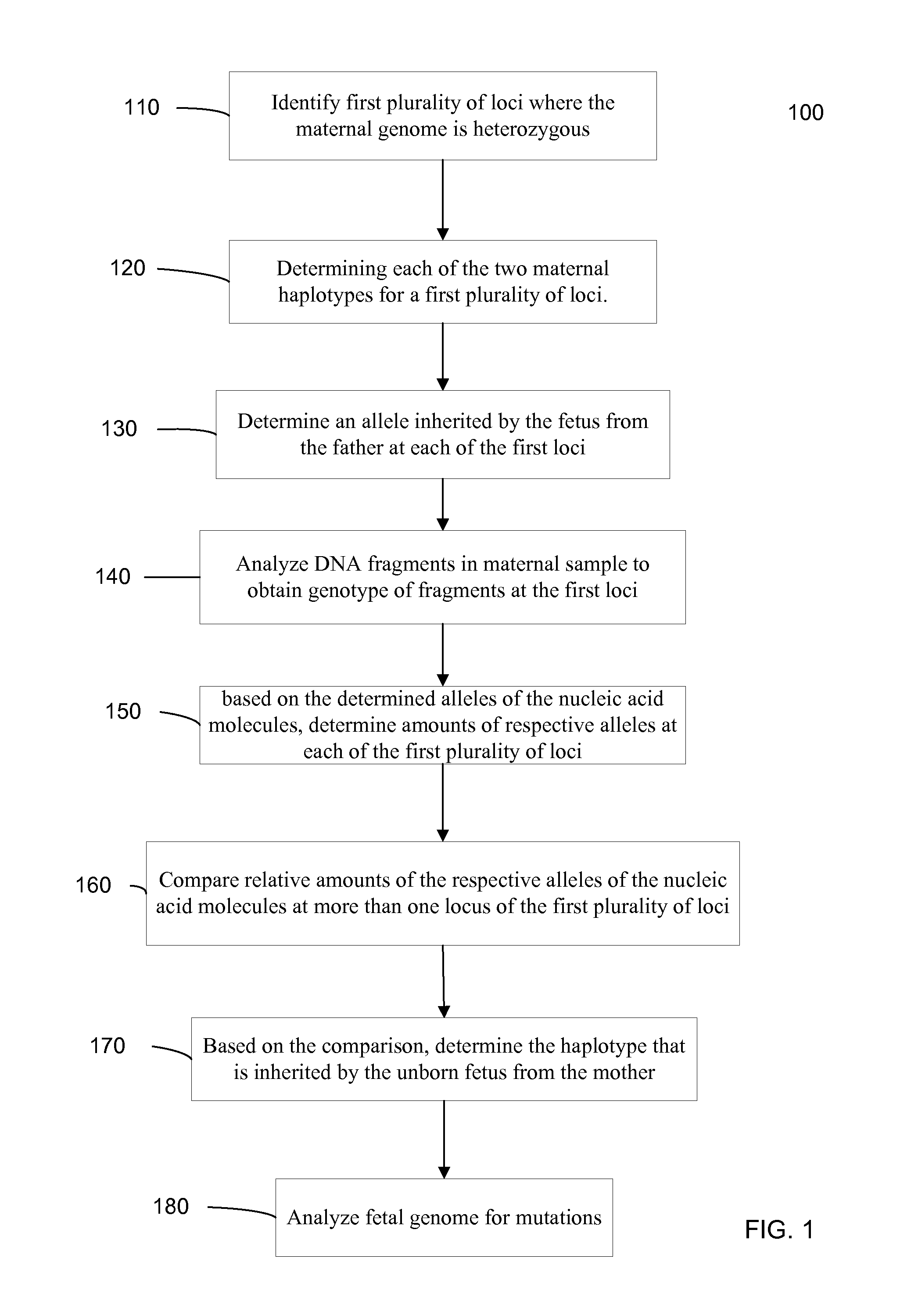
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
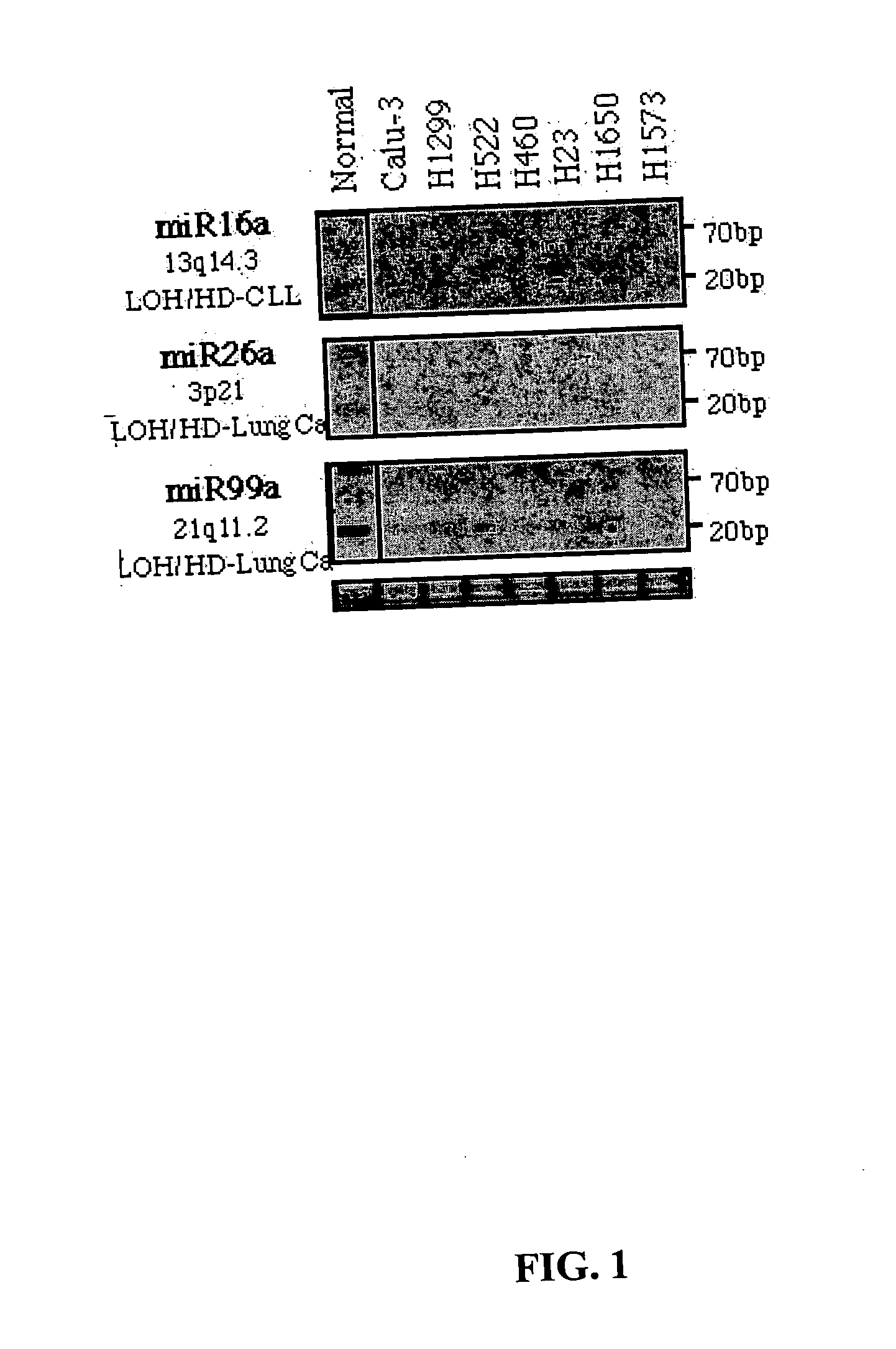
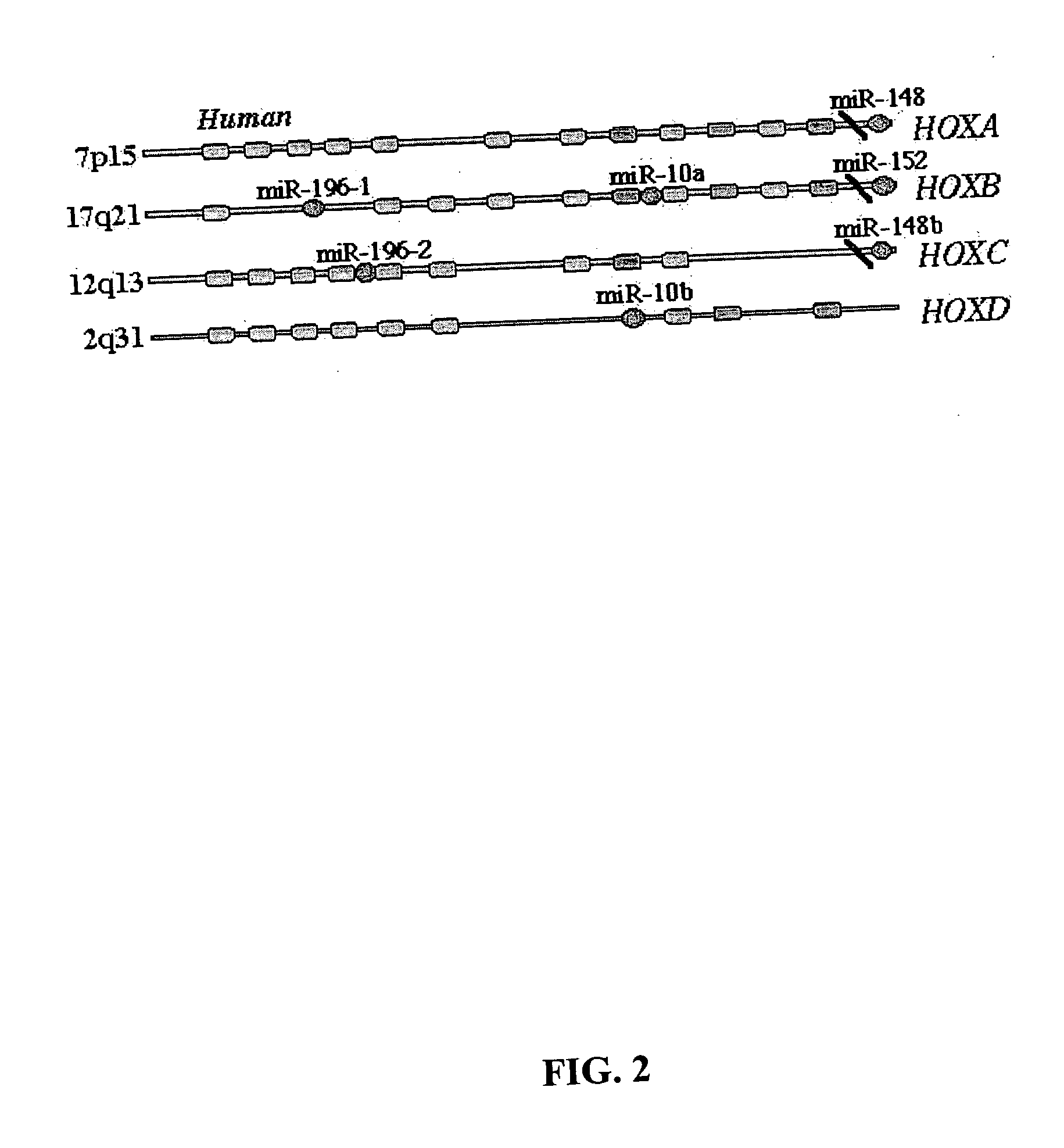
Diagnosis and treatment of cancers with microRNA located in or near cancer associated chromosomal features
InactiveUS20060105360A1Restore levelOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyMicroRNA Gene
MicroRNA genes are highly associated with chromosomal features involved in the etiology of different cancers. The perturbations in the genomic structure or chromosomal architecture of a cell caused by these cancer-associated chromosomal features can affect the expression of the miR gene(s) located in close proximity to that chromosomal feature. Evaluation of miR gene expression can therefore be used to indicate the presence of a cancer-causing chromosomal lesion in a subject. As the change in miR gene expression level caused by a cancer-associated chromosomal feature may also contribute to cancerigenesis, a given cancer can be treated by restoring the level of miR gene expression to normal. microRNA expression profiling can be used to diagnose cancer and predict whether a particular cancer is associated with an adverse prognosis. The identification of specific mutations associated with genomic regions that harbor miR genes in CLL patients provides a means for diagnosing CLL and possibly other cancers.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
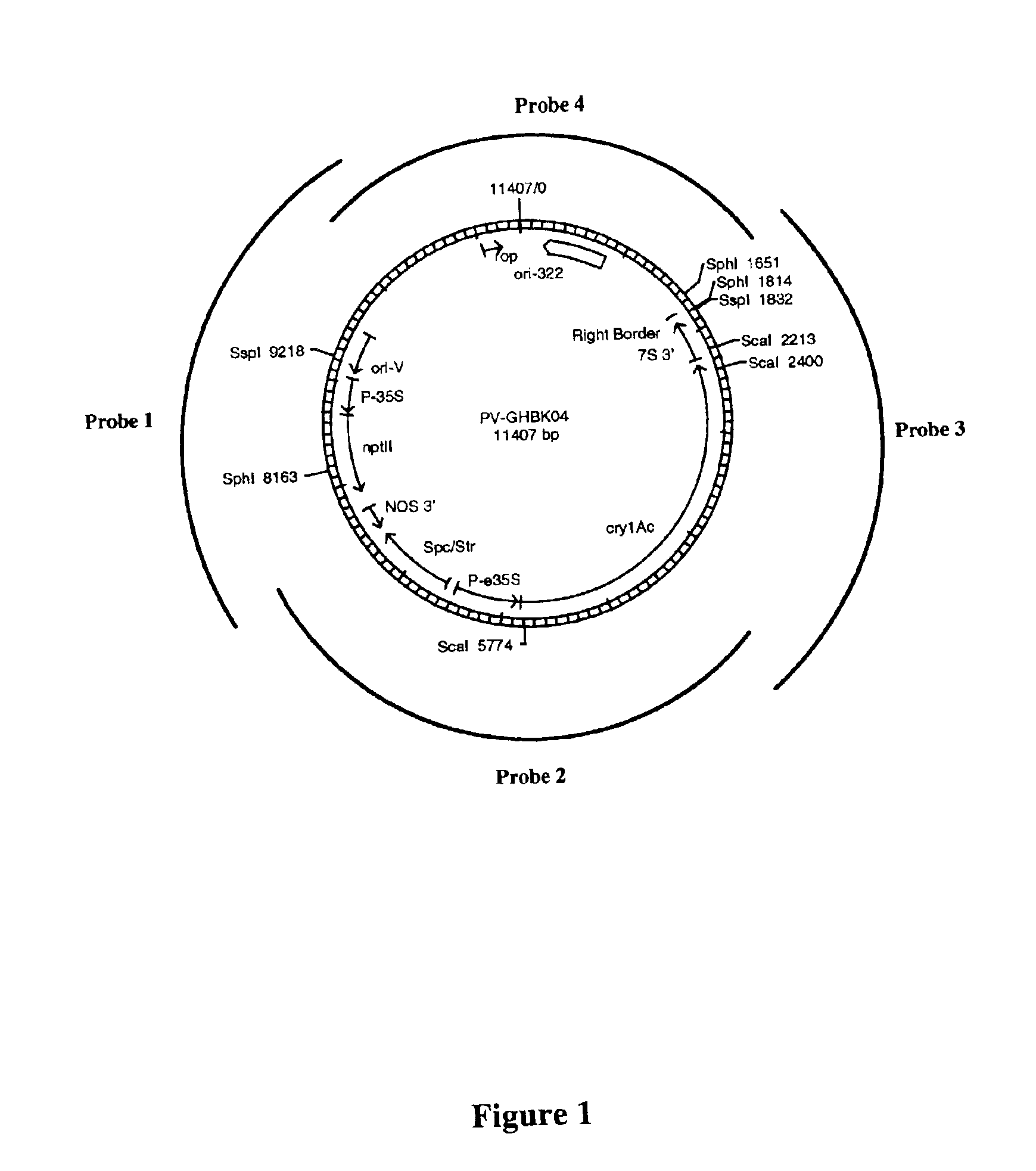
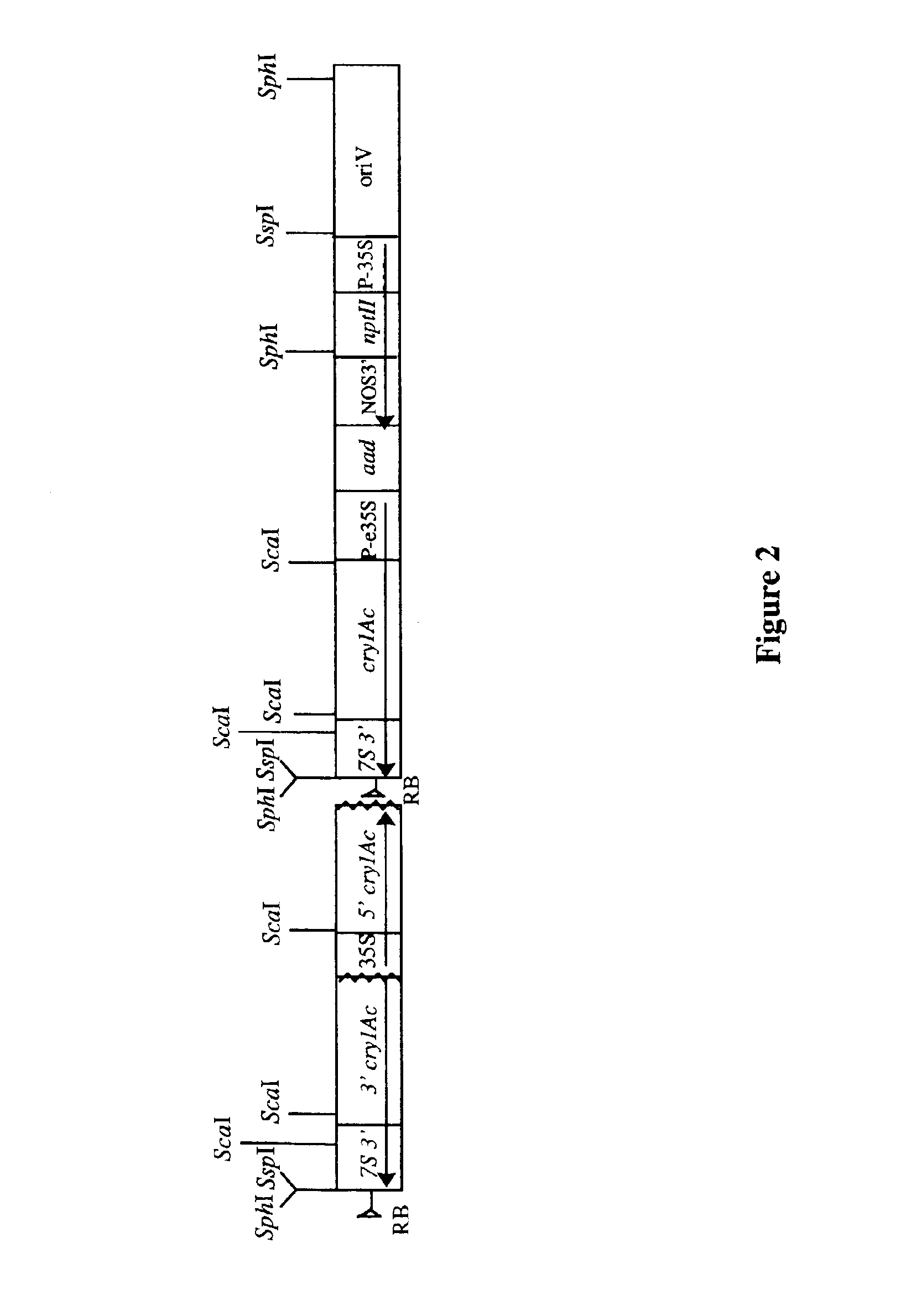
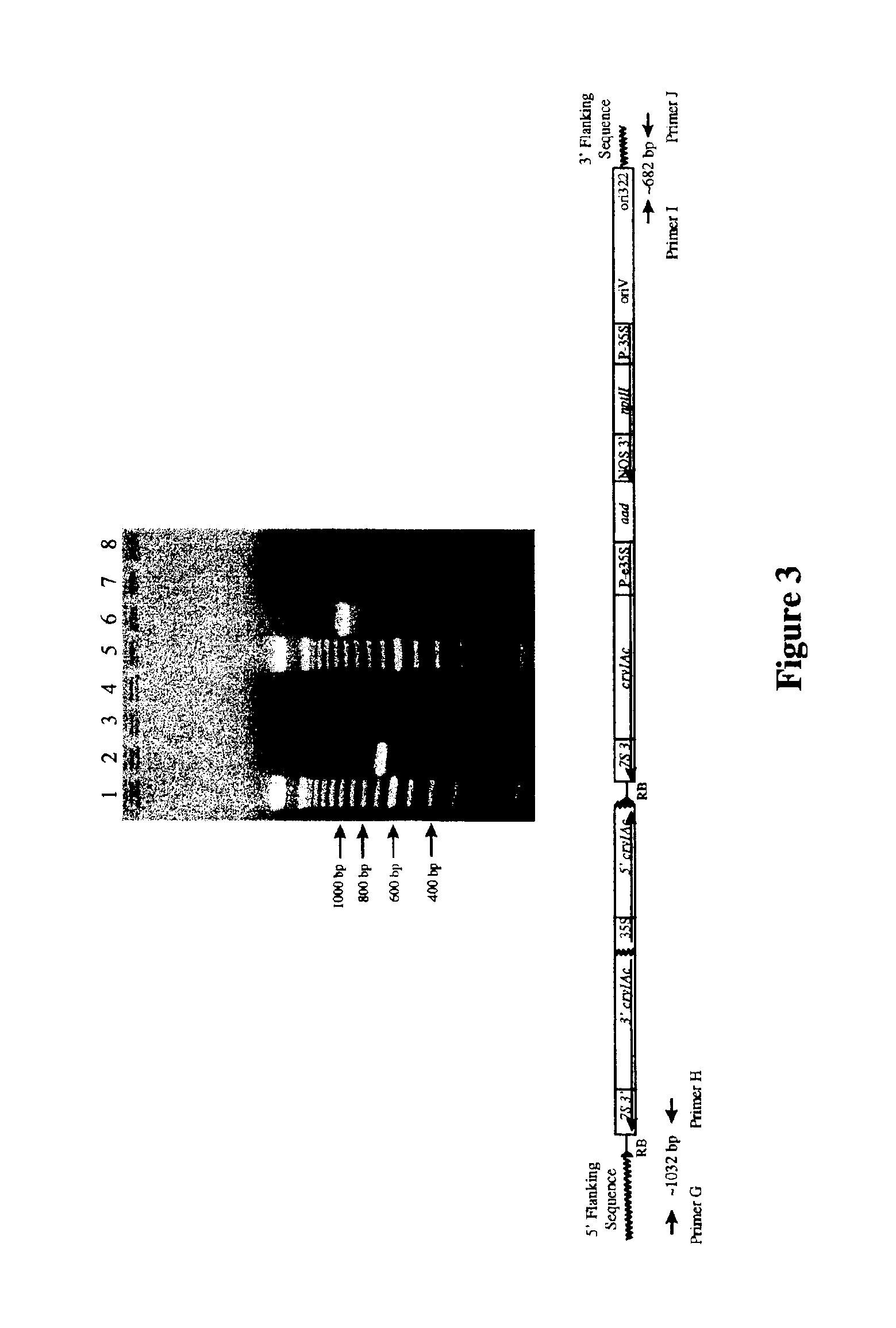
Cotton event PV-GHBK04 (757) and compositions and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides a cotton event PV-GHBK04 (757), a cotton plant that contains PV-GHBK04 (757) DNA molecules and its progeny thereof, and methods for producing cotton event PV-GHBK04 (757). The present invention also provides assays for detecting the presence of the 757 cotton event DNA sequences in a sample based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the cotton genome and of genomic sequences flanking the insertion site, and provides amplicons and sequences which are diagnostic for the presence of event 757 nucleic acids in a sample.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
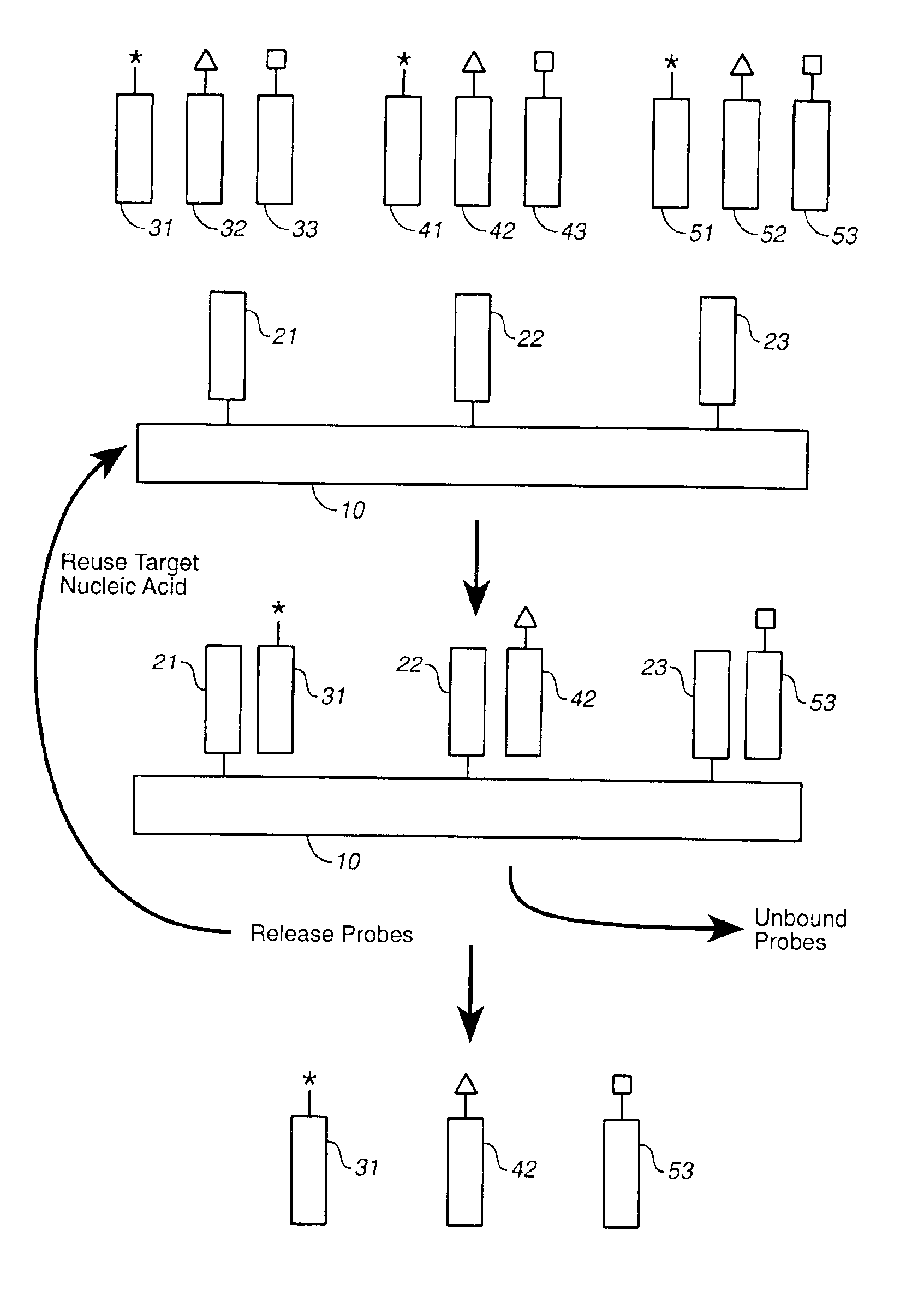
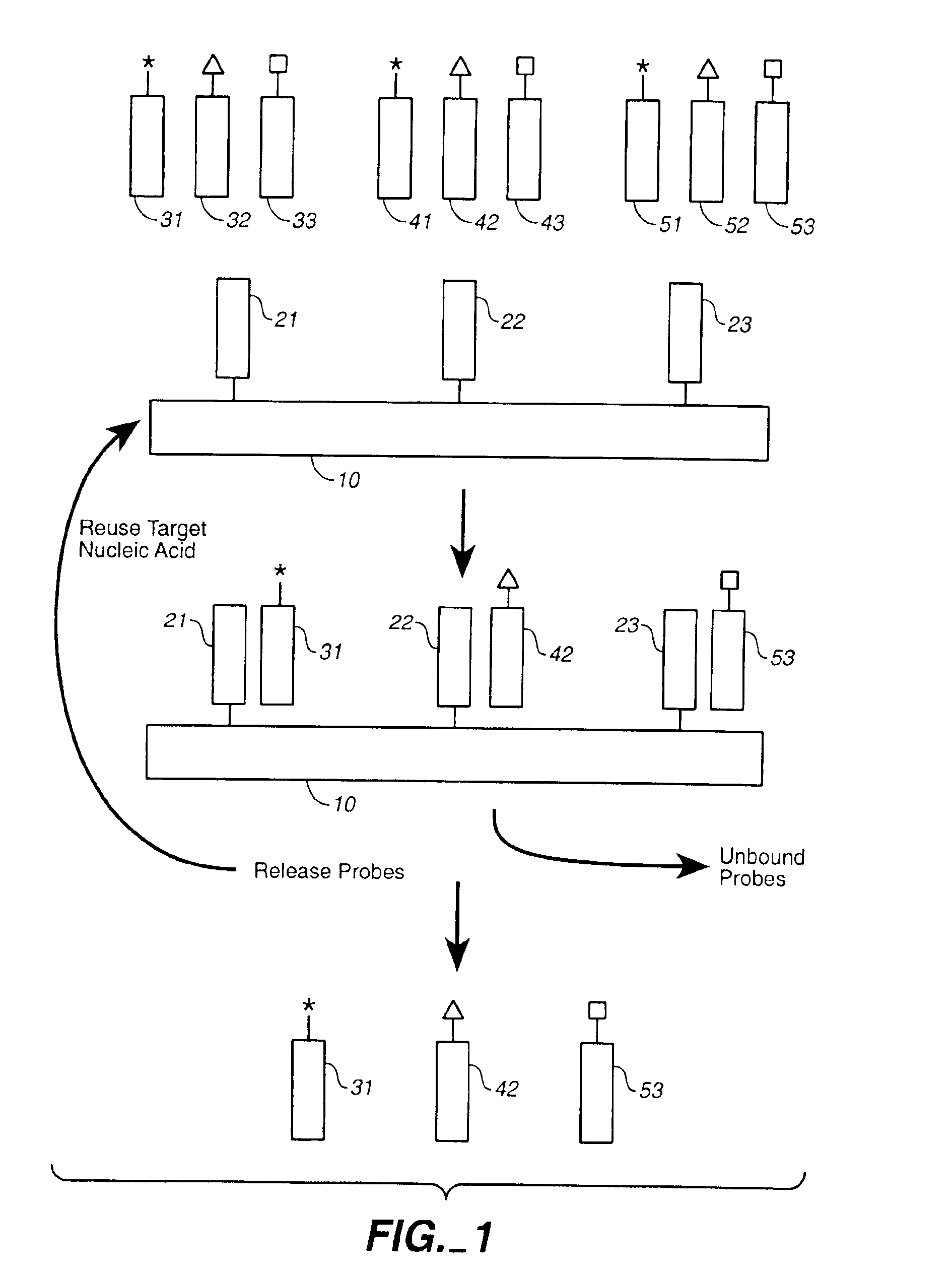
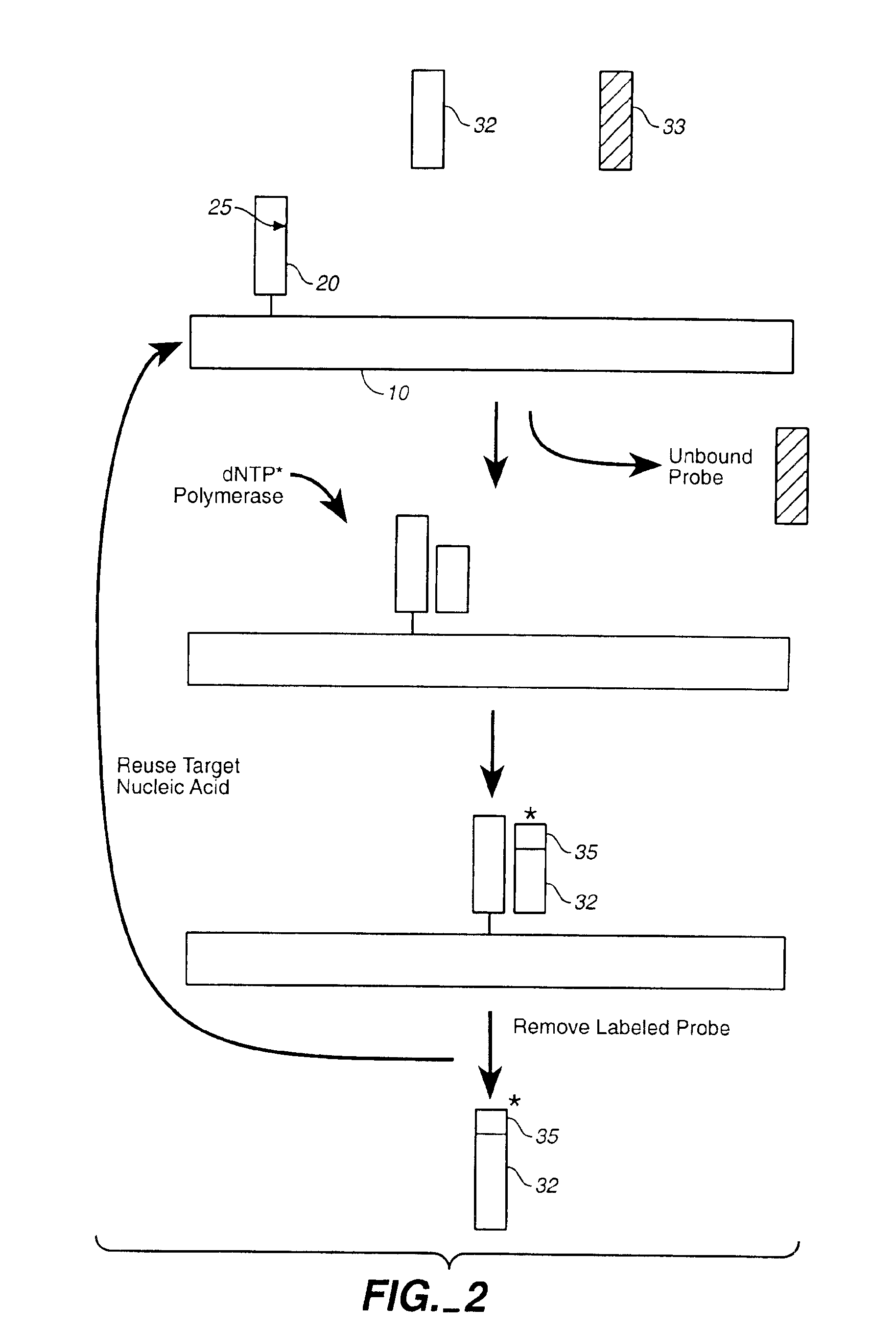
Compositions and methods for repetitive use of genomic DNA
The present invention relates to detection or genotyping (or other sample analysis) of target nucleic acids following immobilization of the target nucleic acids onto a surface. The target nucleic acids can be re-used multiple times, thus conserving sample materials and simplifying sample preparation.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
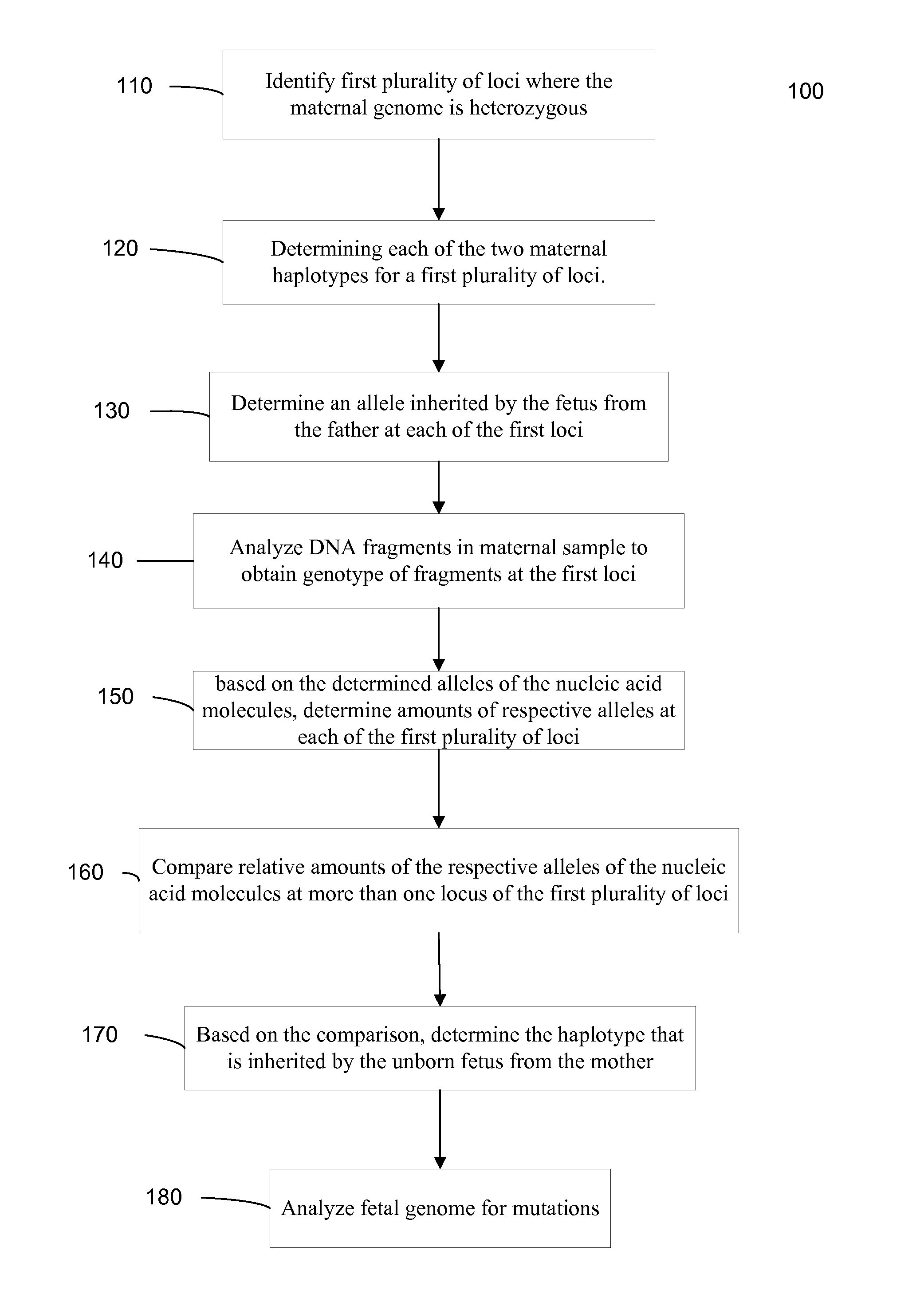
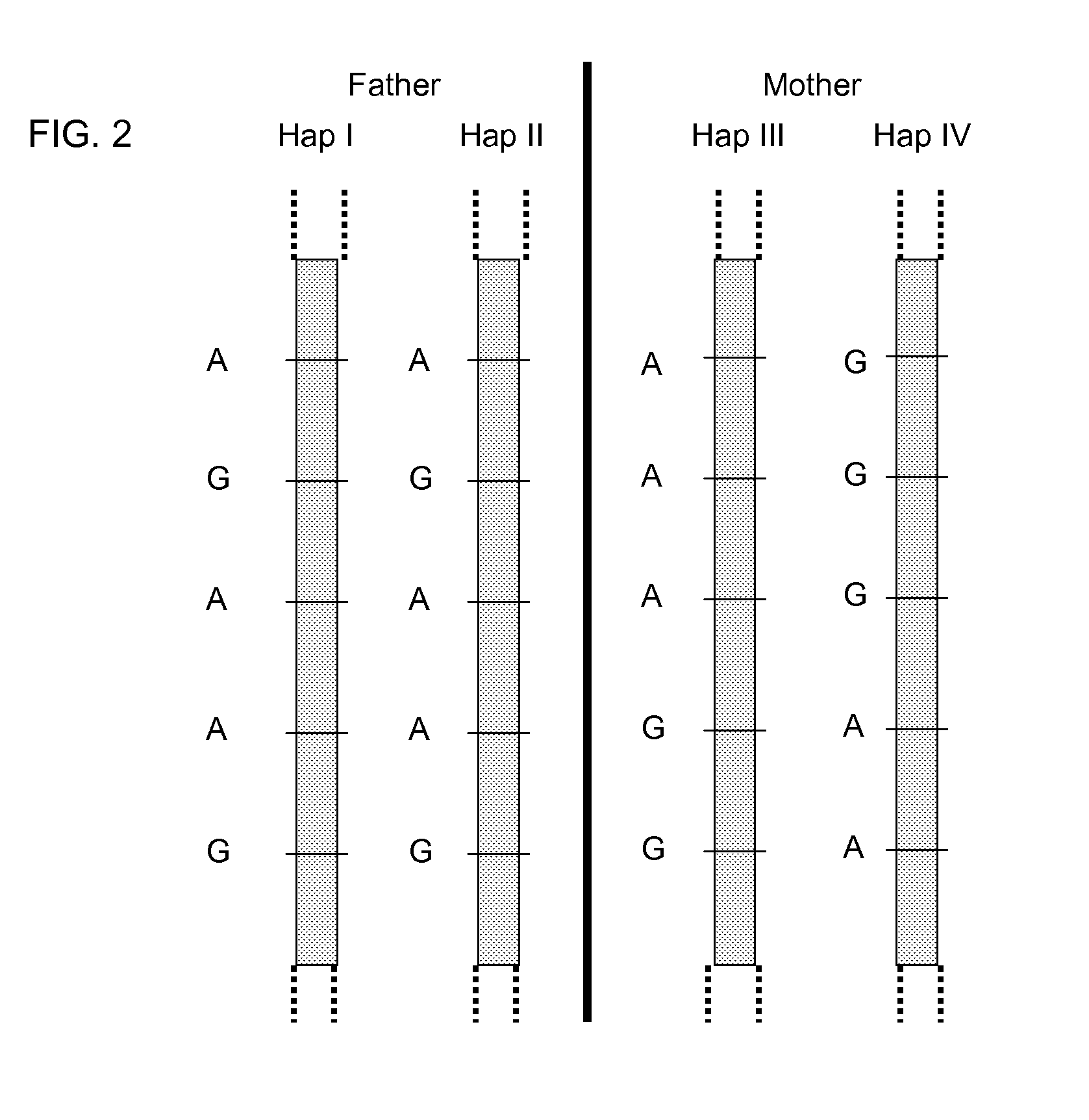
Fetal Genomic Analysis From A Maternal Biological Sample
ActiveUS20110105353A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDna concentrationPopulation
Systems, methods, and apparatus for determining at least a portion of fetal genome are provided. DNA fragments from a maternal sample (maternal and fetal DNA) can be analyzed to identify alleles at certain loci. The amounts of DNA fragments of the respective alleles at these loci can be analyzed together to determine relative amounts of the haplotypes for these loci and determine which haplotypes have been inherited from the parental genomes. Loci where the parents are a specific combination of homozygous and heterozygous can be analyzed to determine regions of the fetal genome. Reference haplotypes common in the population can be used along with the analysis of the DNA fragments of the maternal sample to determine the maternal and paternal genomes. Determination of mutations, a fractional fetal DNA concentration in a maternal sample, and a proportion of coverage of a sequencing of the maternal sample can also be provided.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com