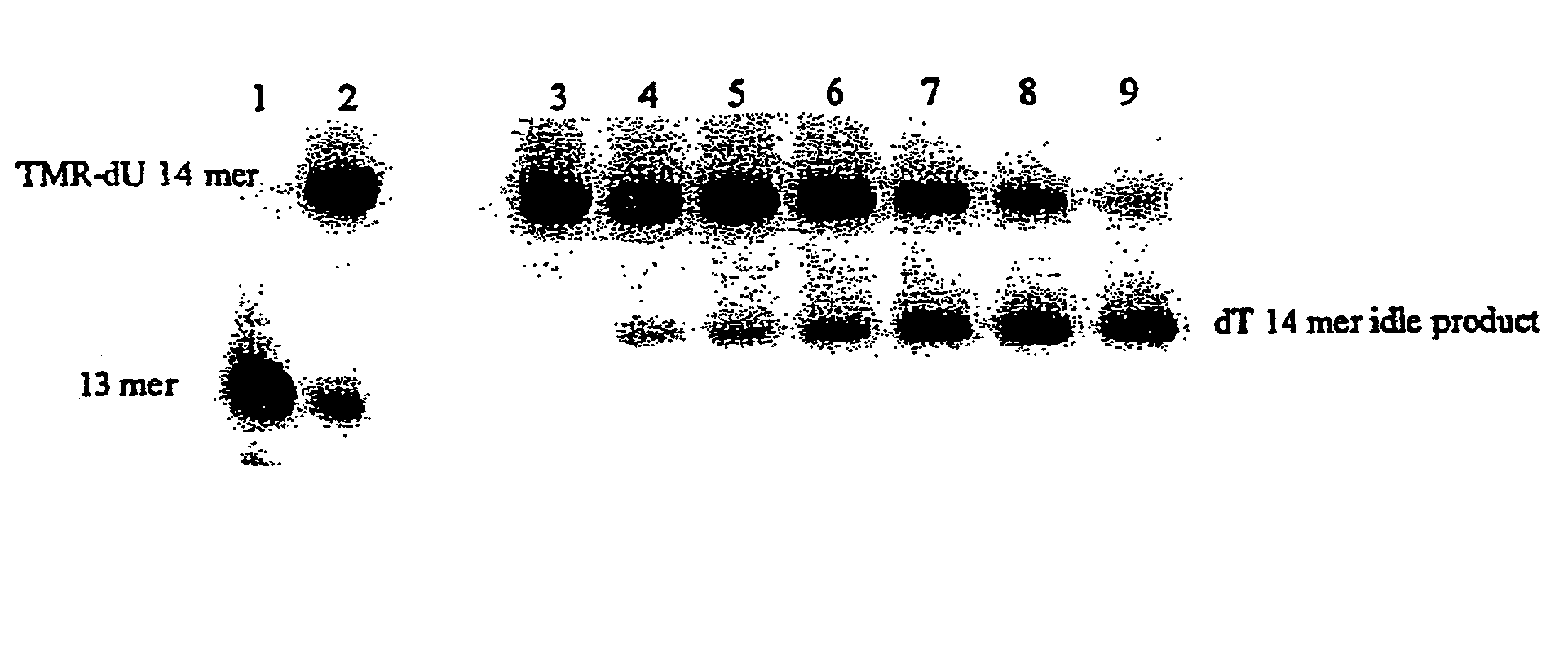Patents
Literature
248 results about "Sequence determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sequence determination is a type of examination conducted by a forensic document examiner. This type of forensic examination is done in an attempt to determine which of two events occurred first in the preparation of a document. Another term used for this type of examination is "sequence of intersections" since the evaluation requires intersection of physical materials on the document.
Polynucleotide sequencing
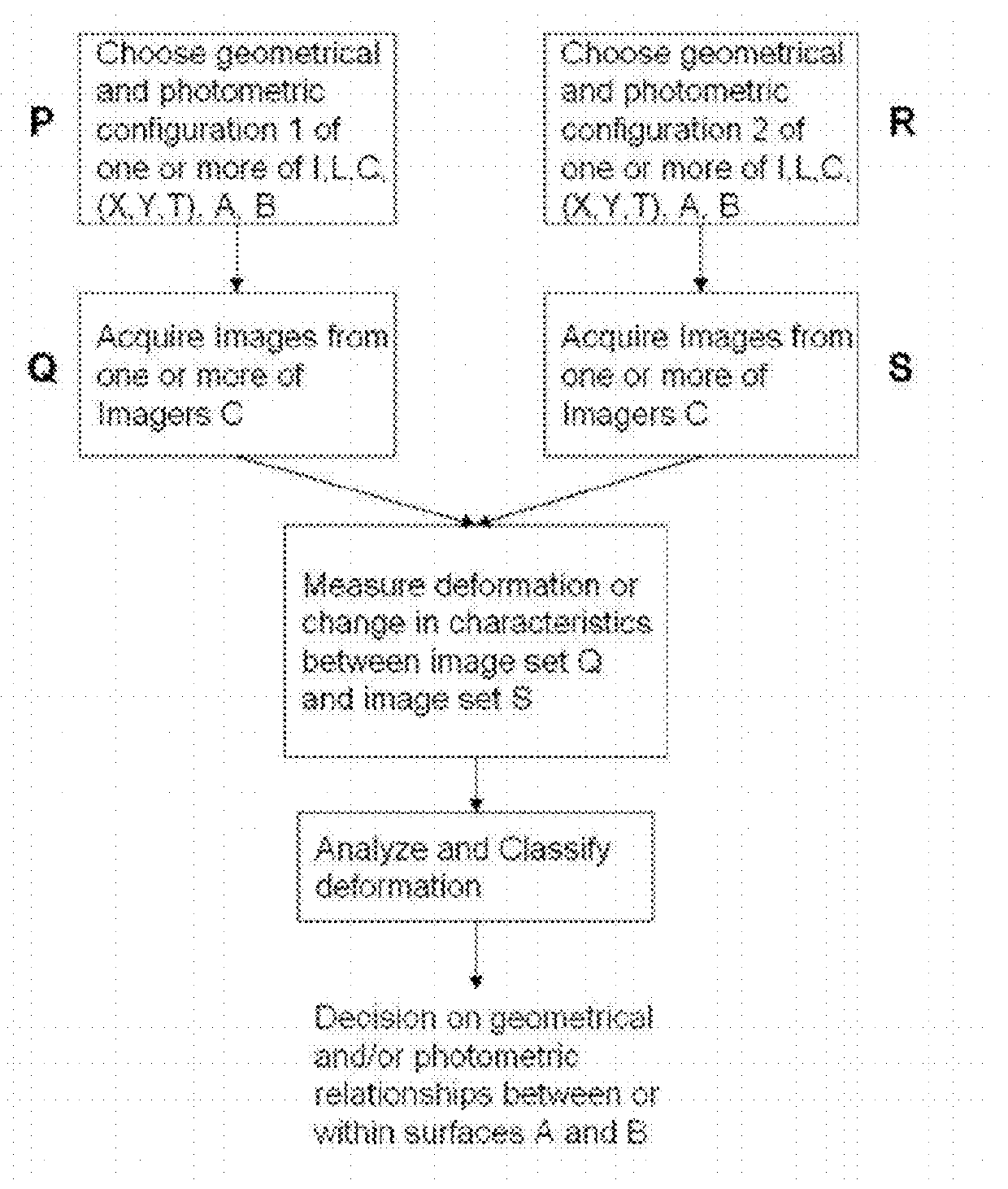
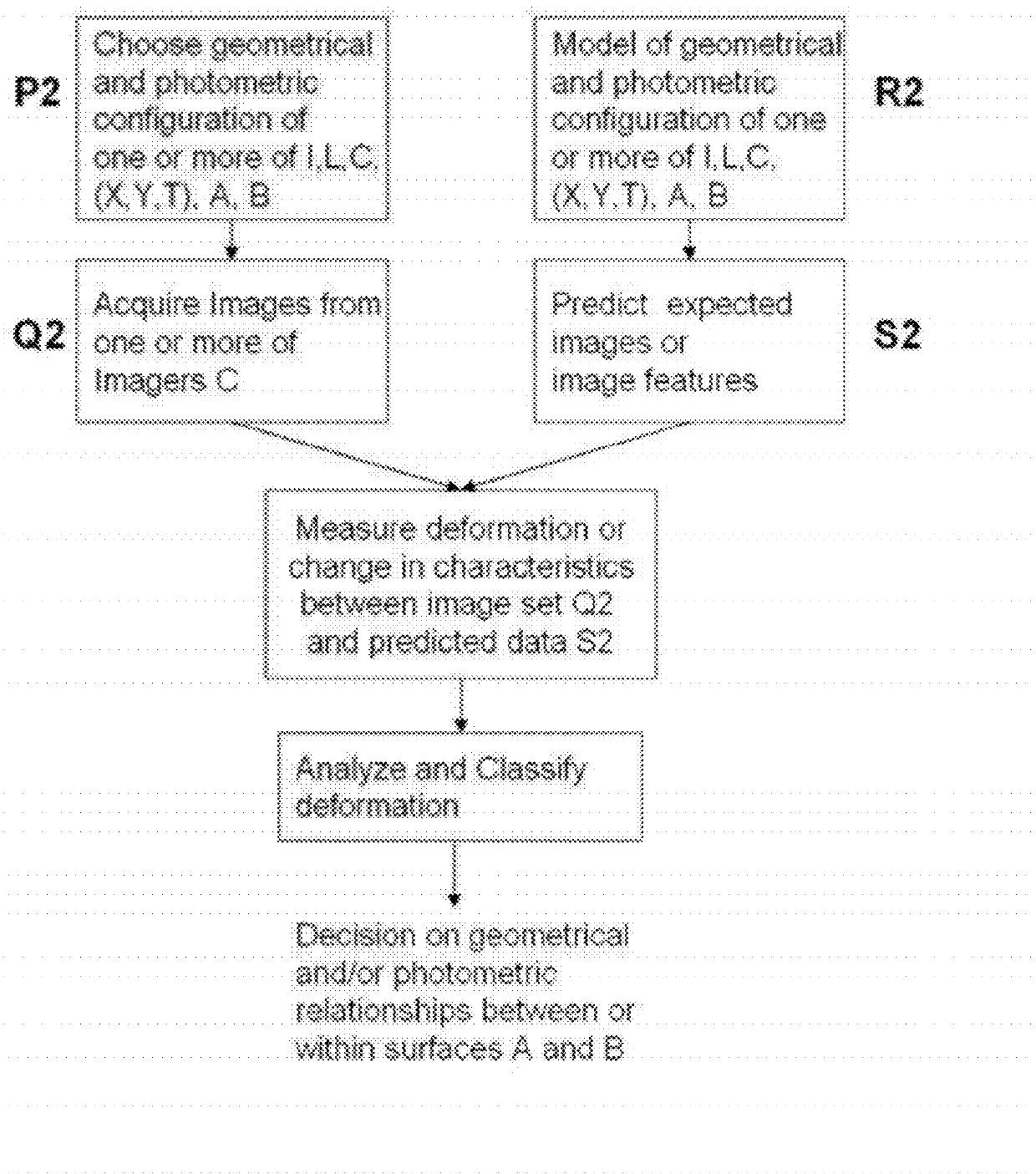
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
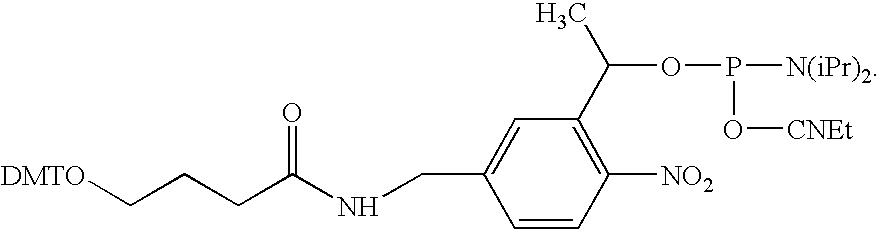
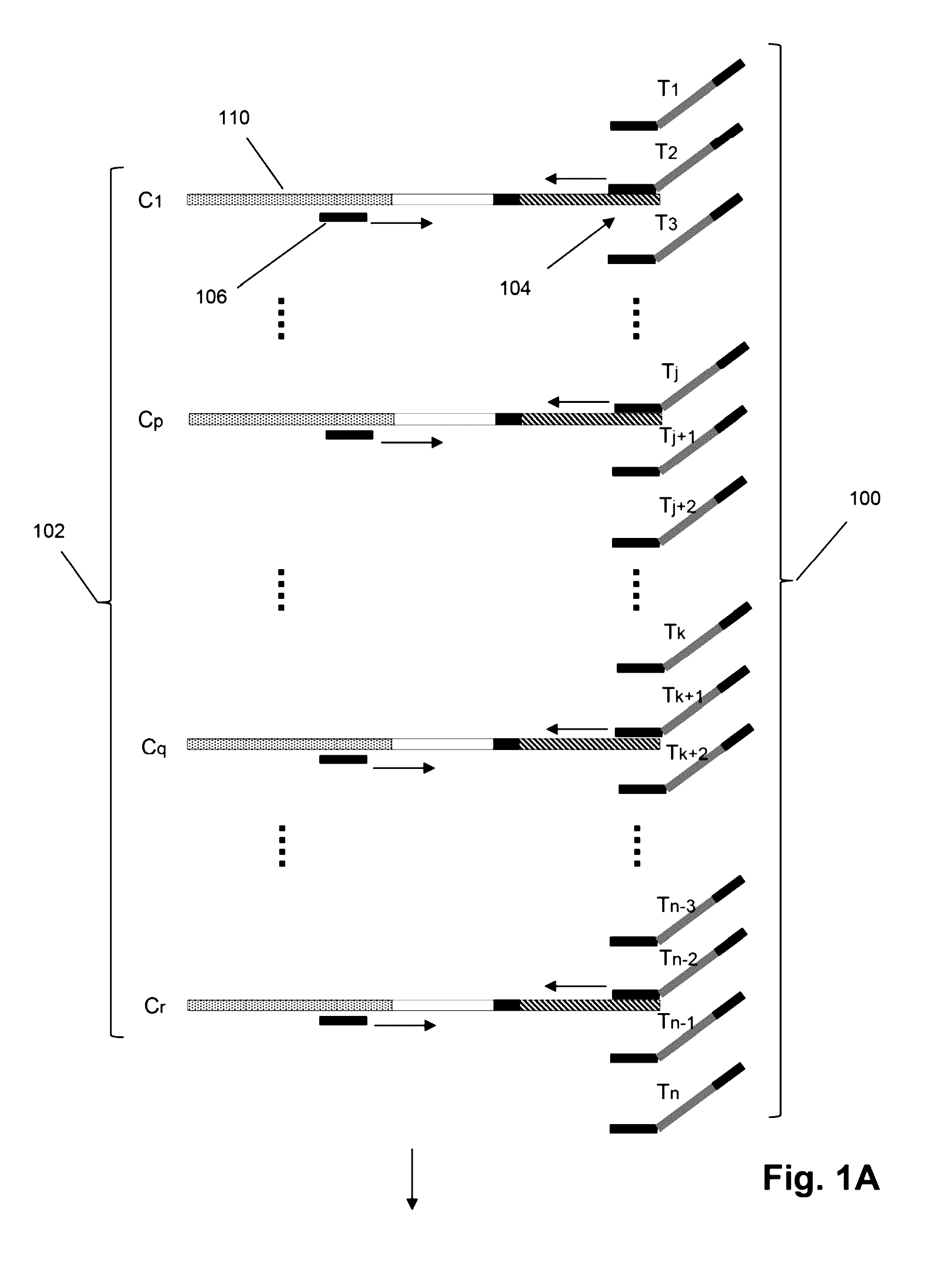
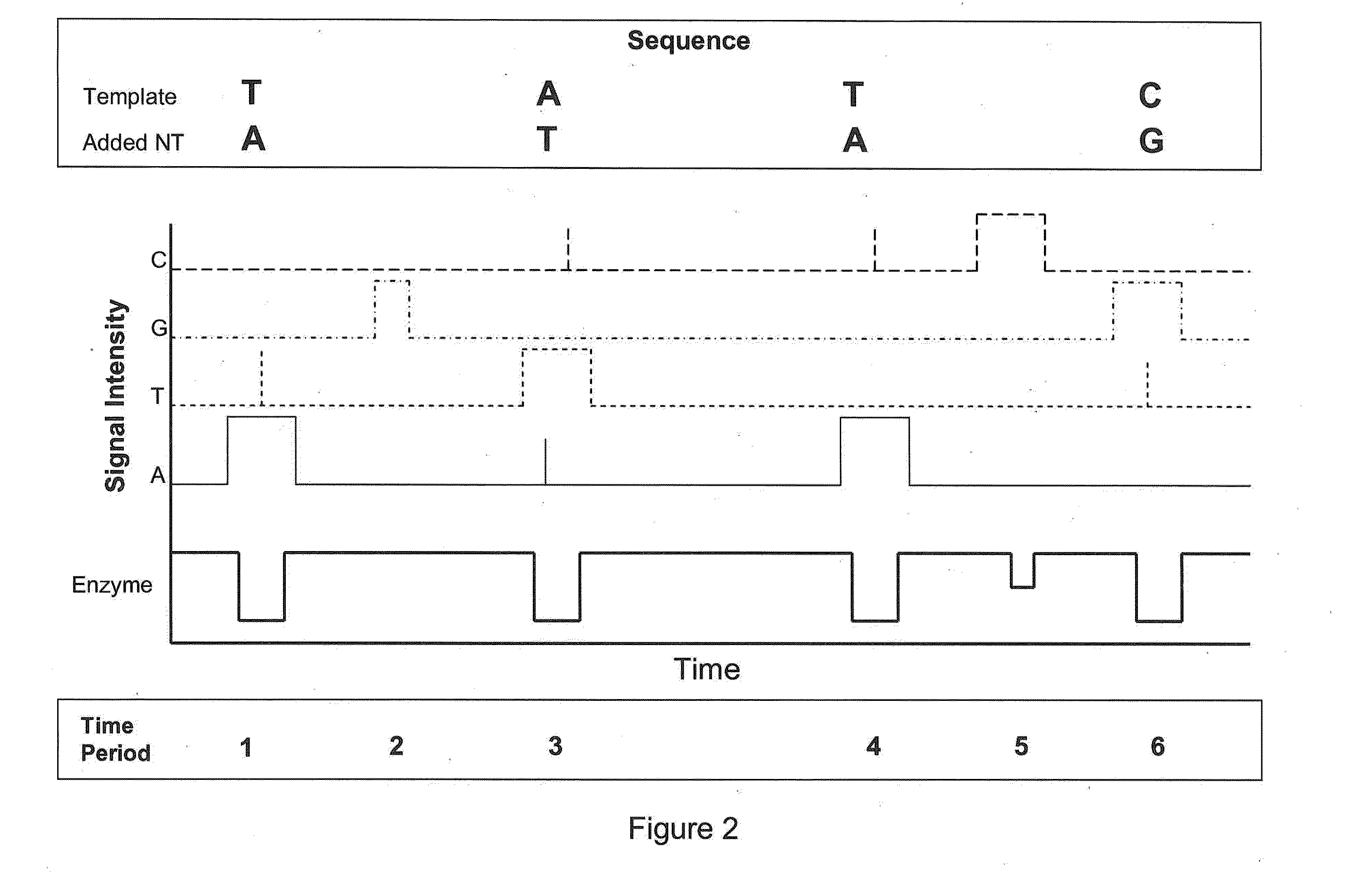
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Analying polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6054270AStable duplexReduce impactSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesHybridization reactionSequence determination
This invention provides an apparatus and method for analyzing a polynucleotide sequence; either an unknown sequence or a known sequence. A support, e.g. a glass plate, carries an array of the whole or a chosen part of a complete set of oligonucleotides which are capable of taking part in hybridization reactions. The array may comprise one or more pair of oligonucleotides of chosen lengths. The polynucleotide sequence, or fragments thereof, are labelled and applied to the array under hybridizing conditions. Applications include analyses of known point mutations, genomic fingerprinting, linkage analysis, characterization of mRNAs, mRNA populations, and sequence determination.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH
Algorithms for sequence determination
ActiveUS8370079B2Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
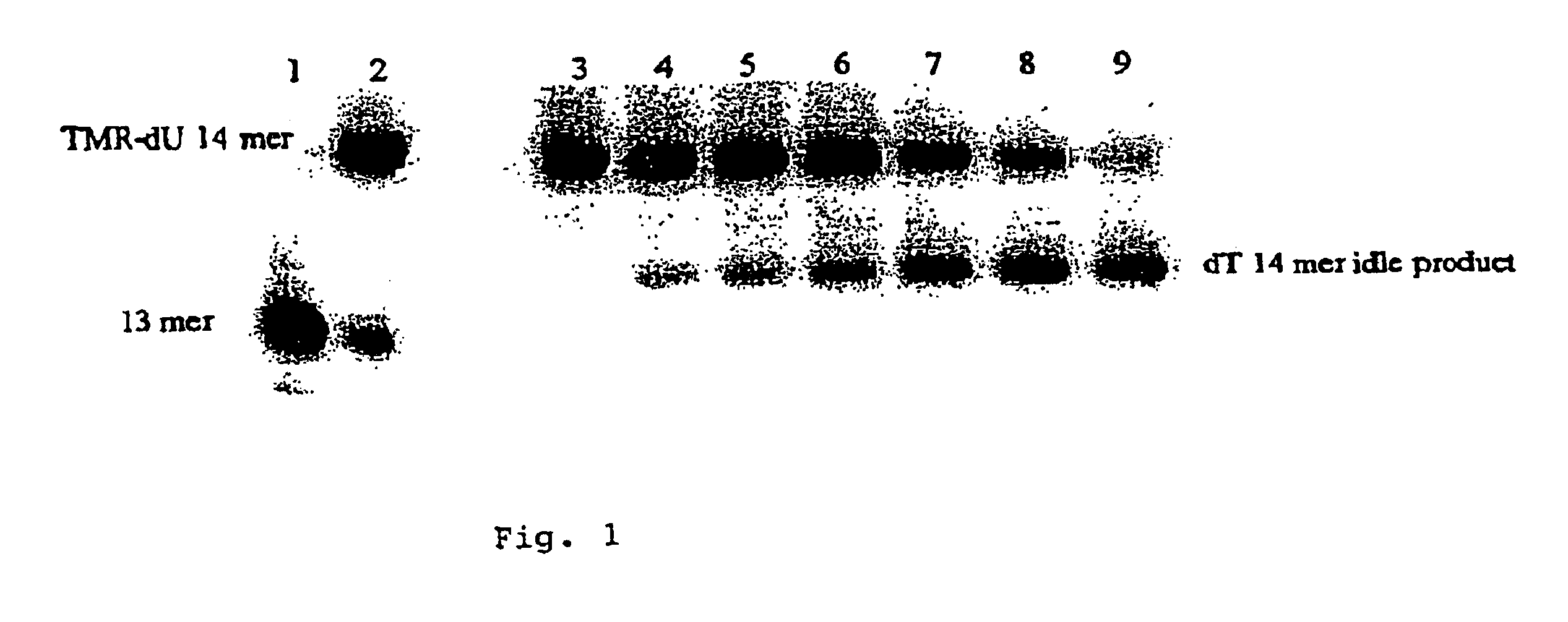
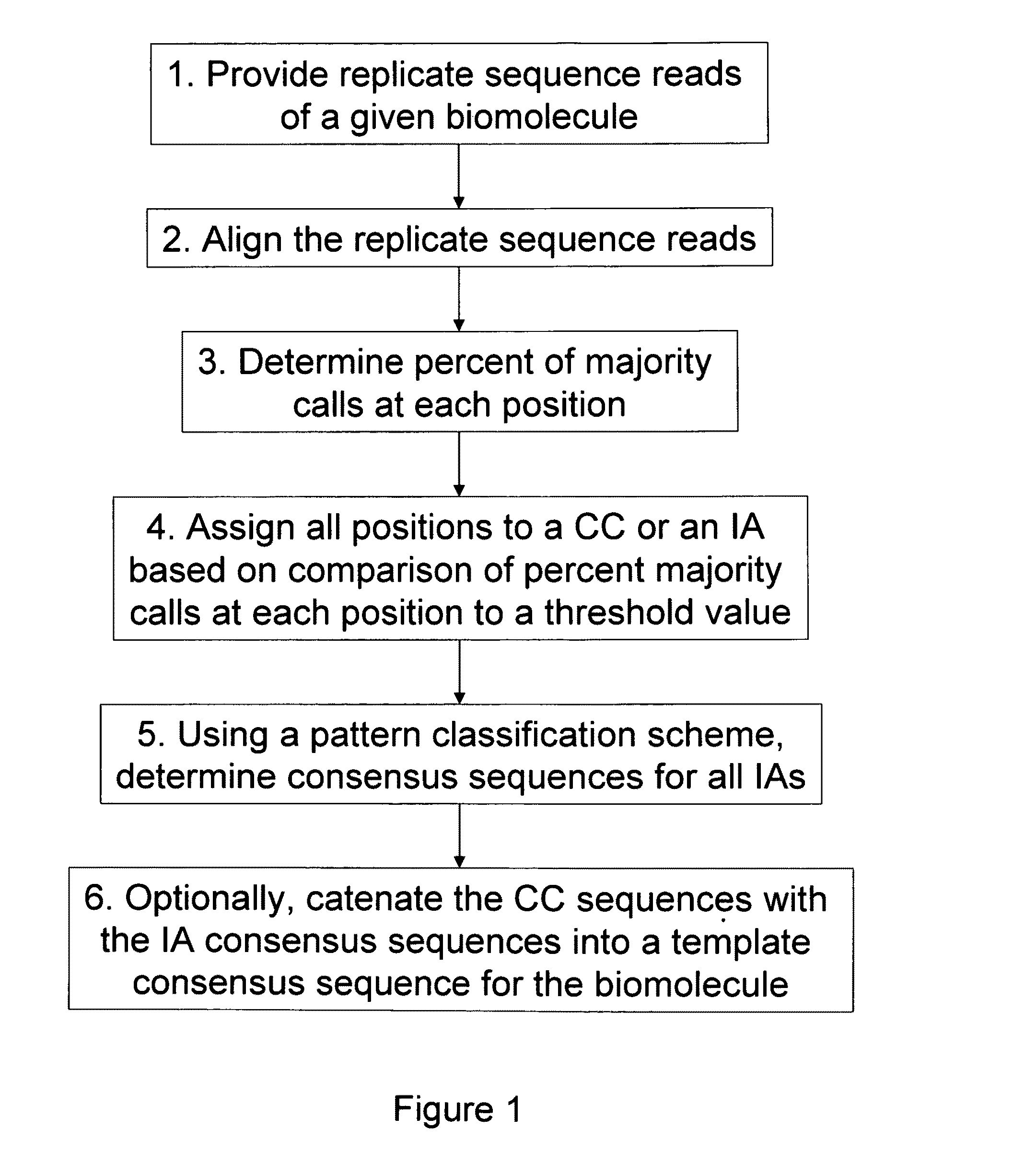
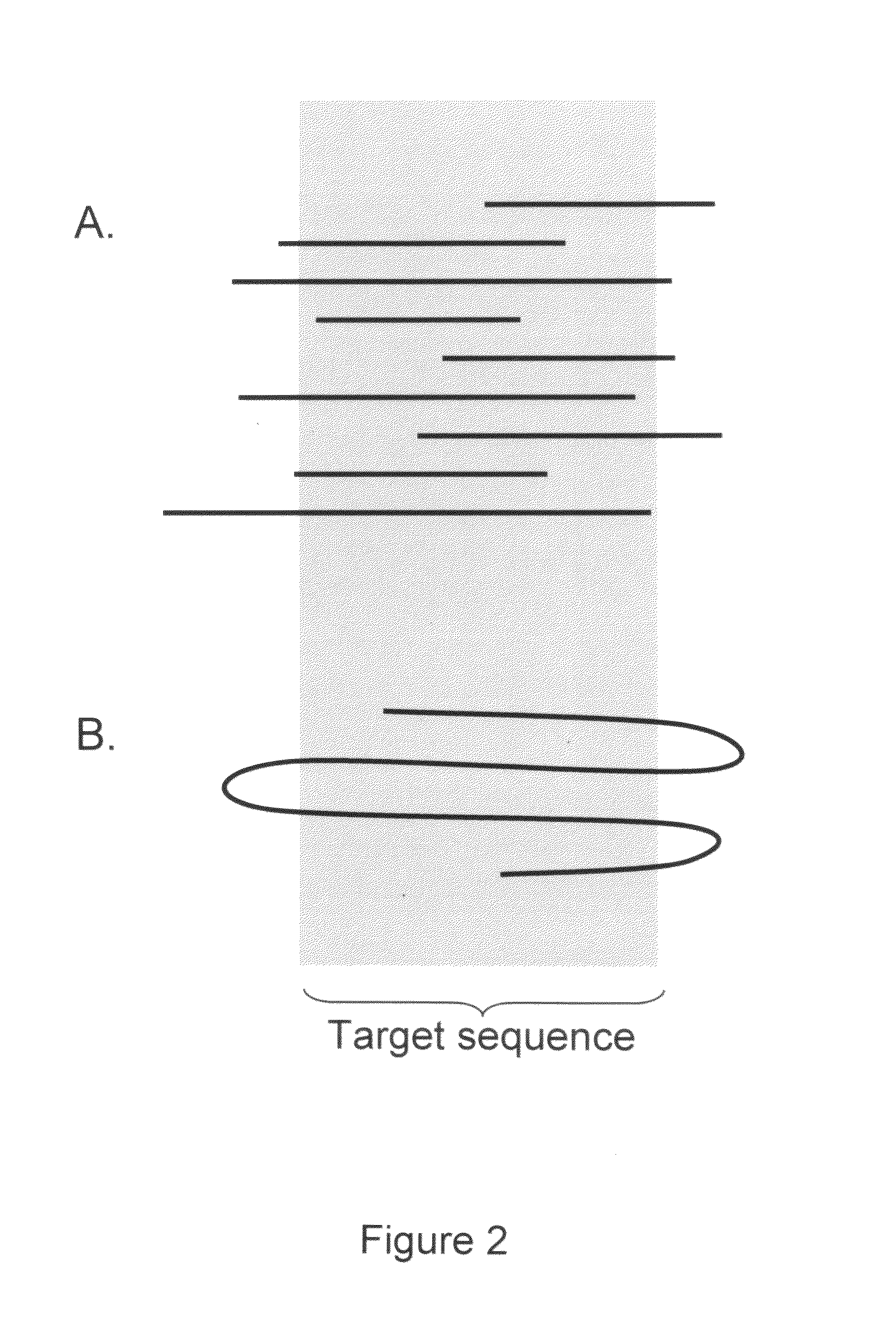
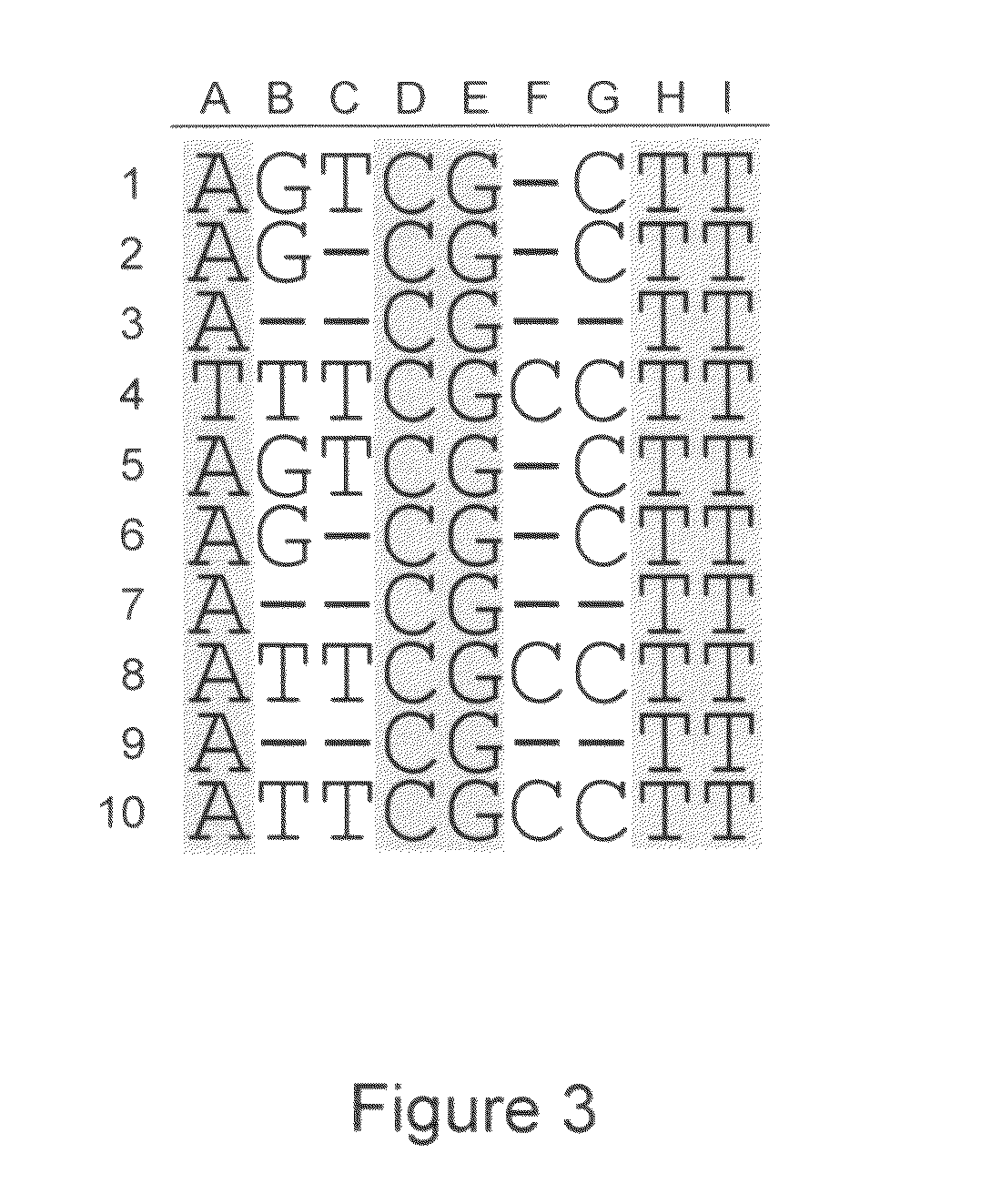
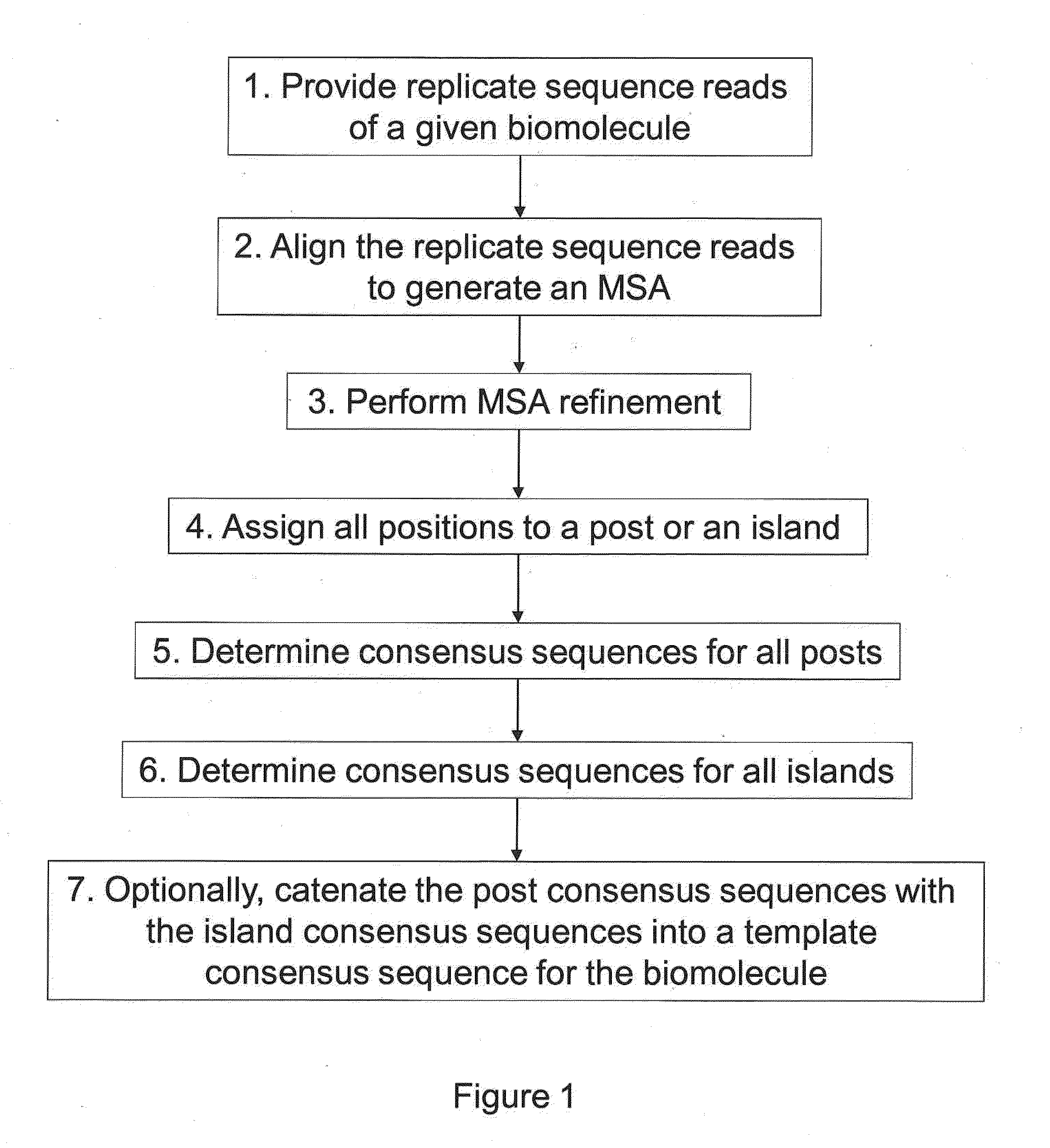
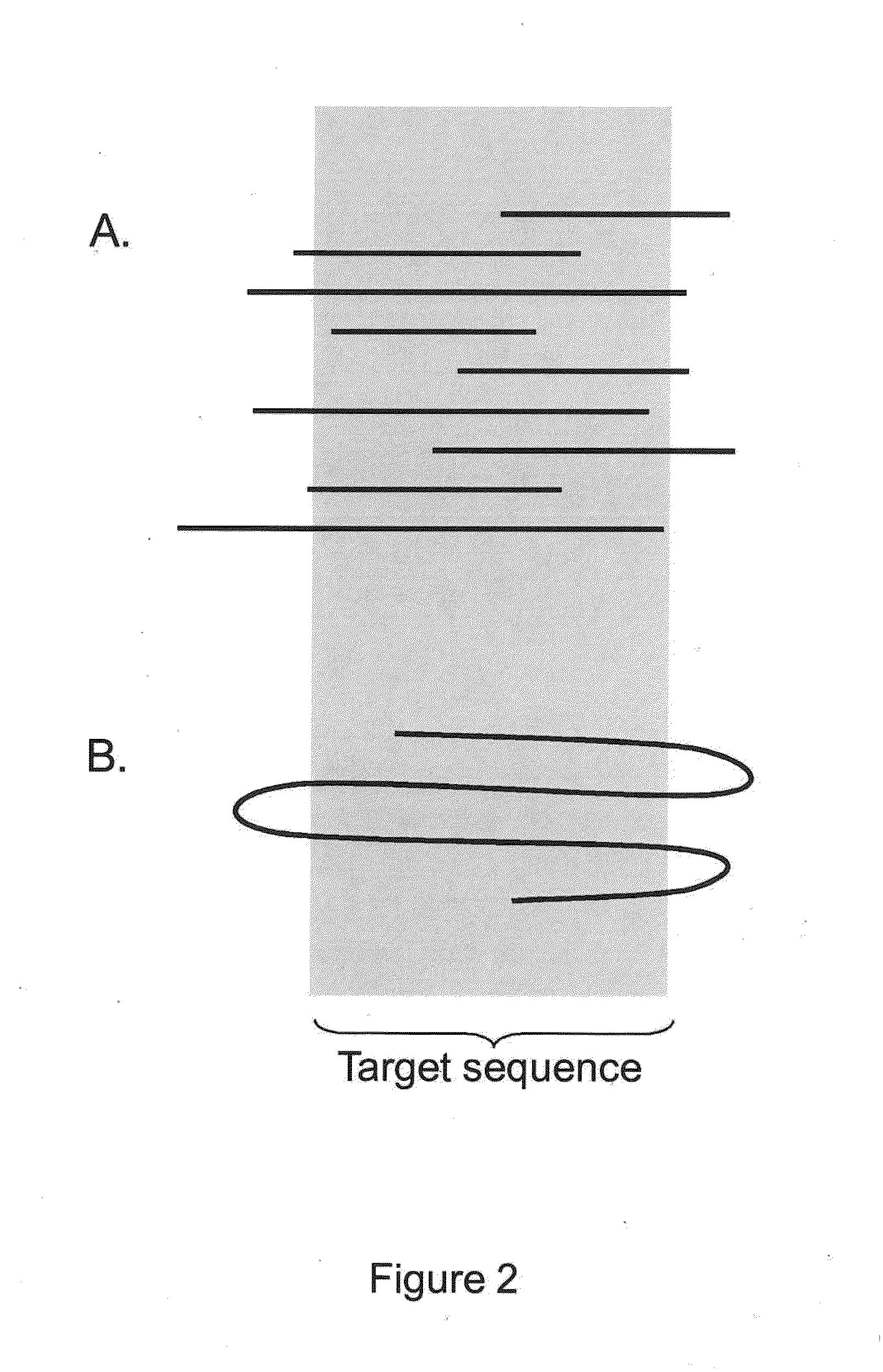
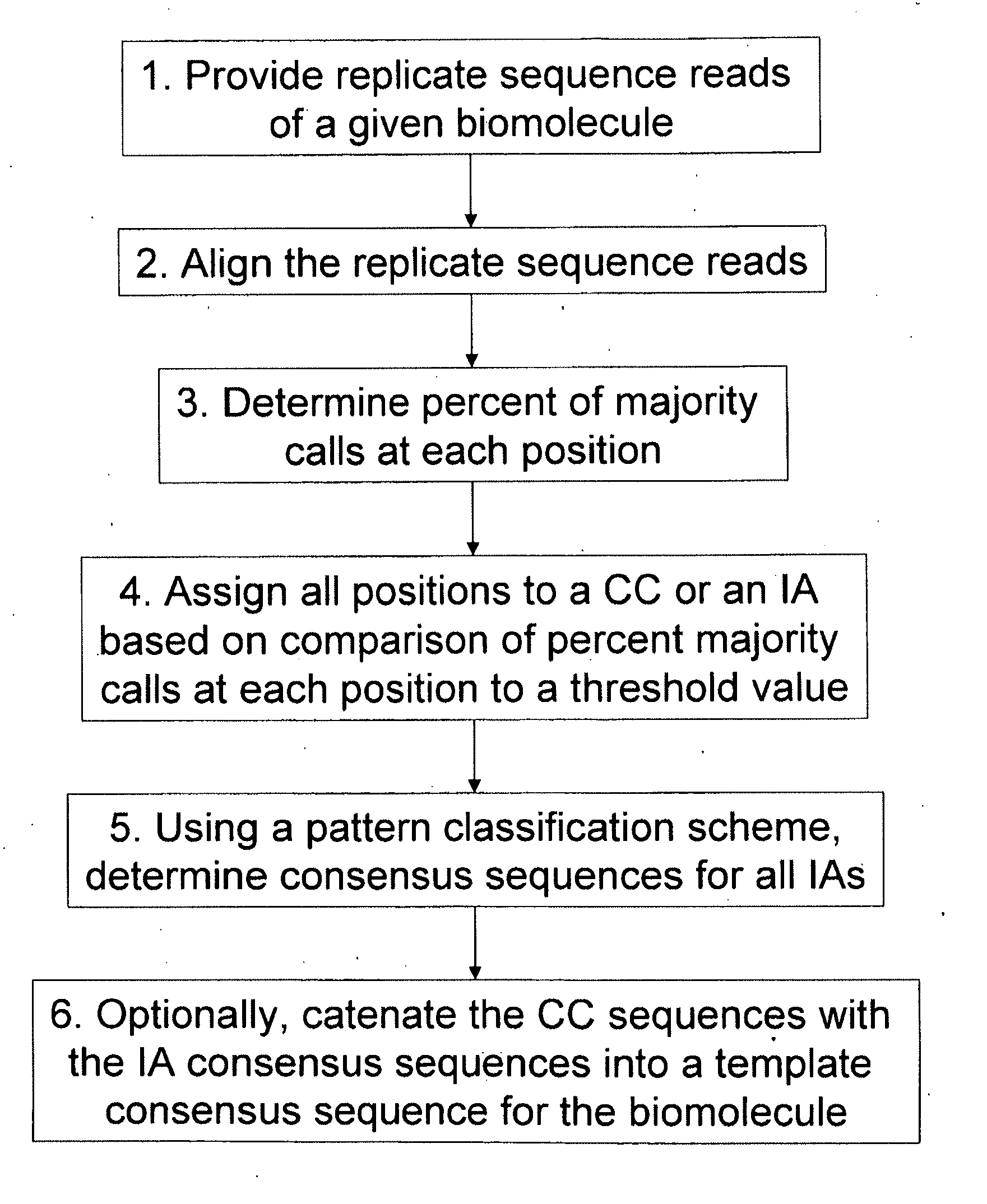
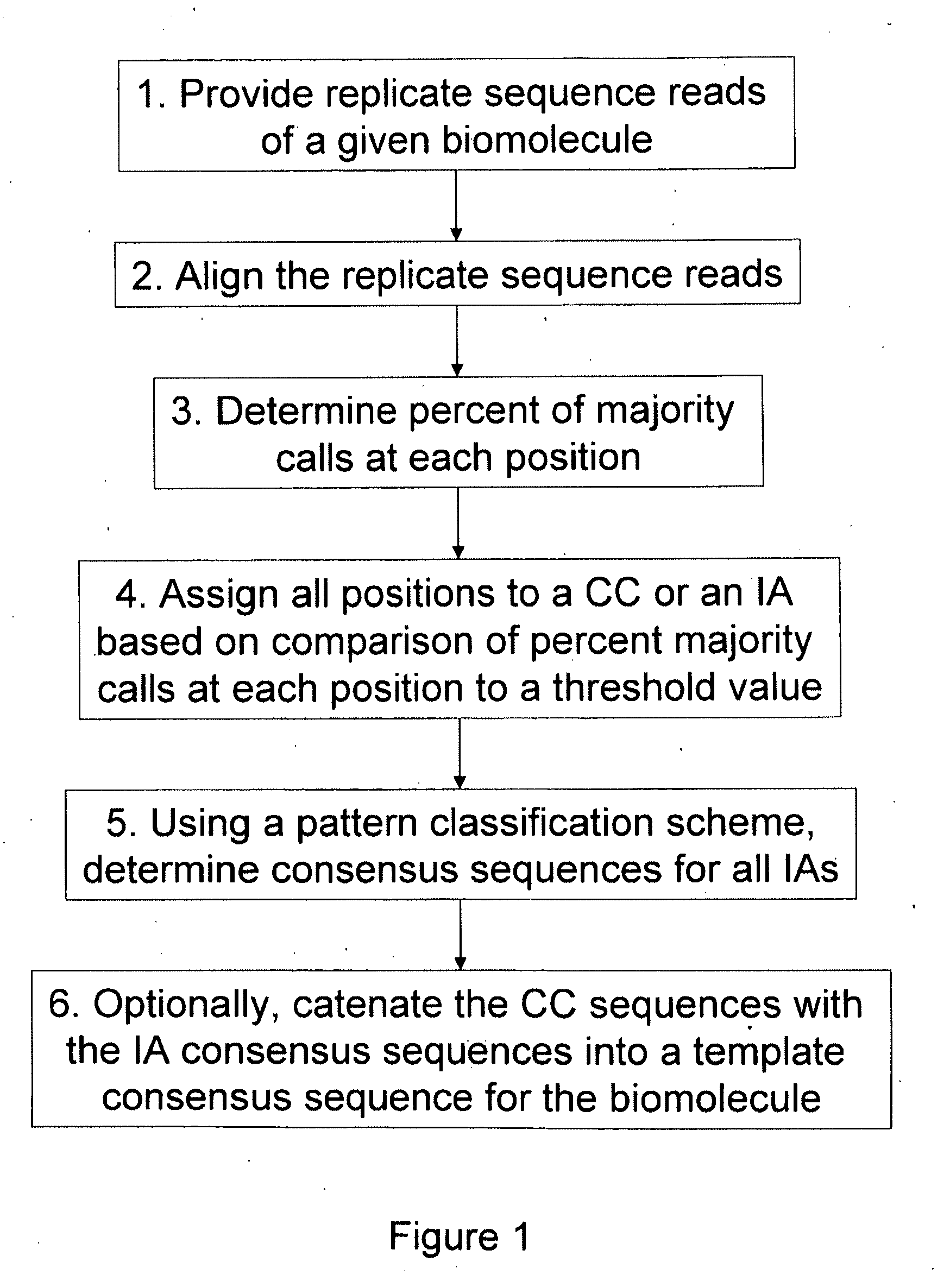
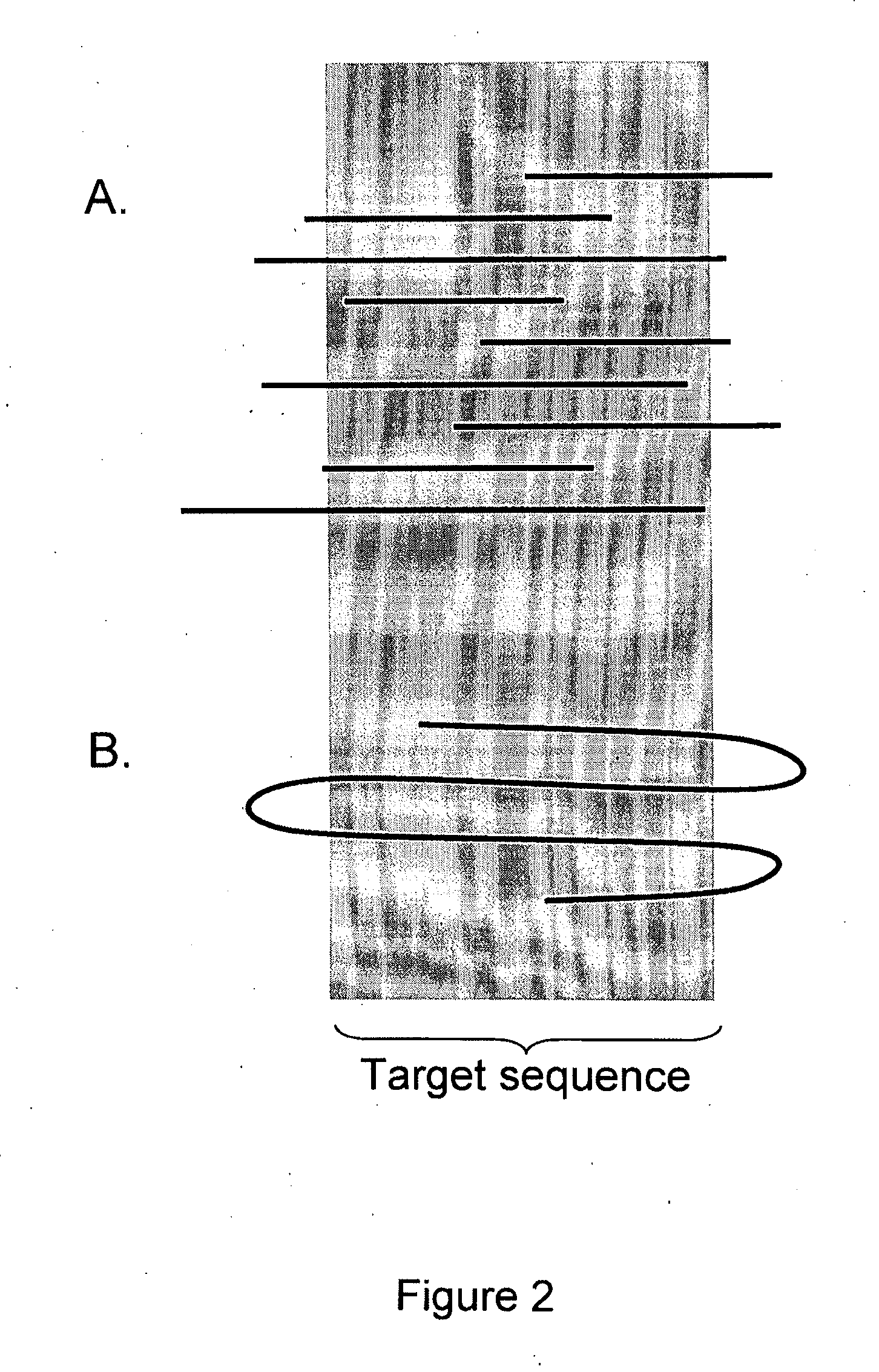
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Ultra-high multiplex analytical systems and methods
ActiveUS8247216B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsLiquid surface applicatorsDirect illuminationSequence determination
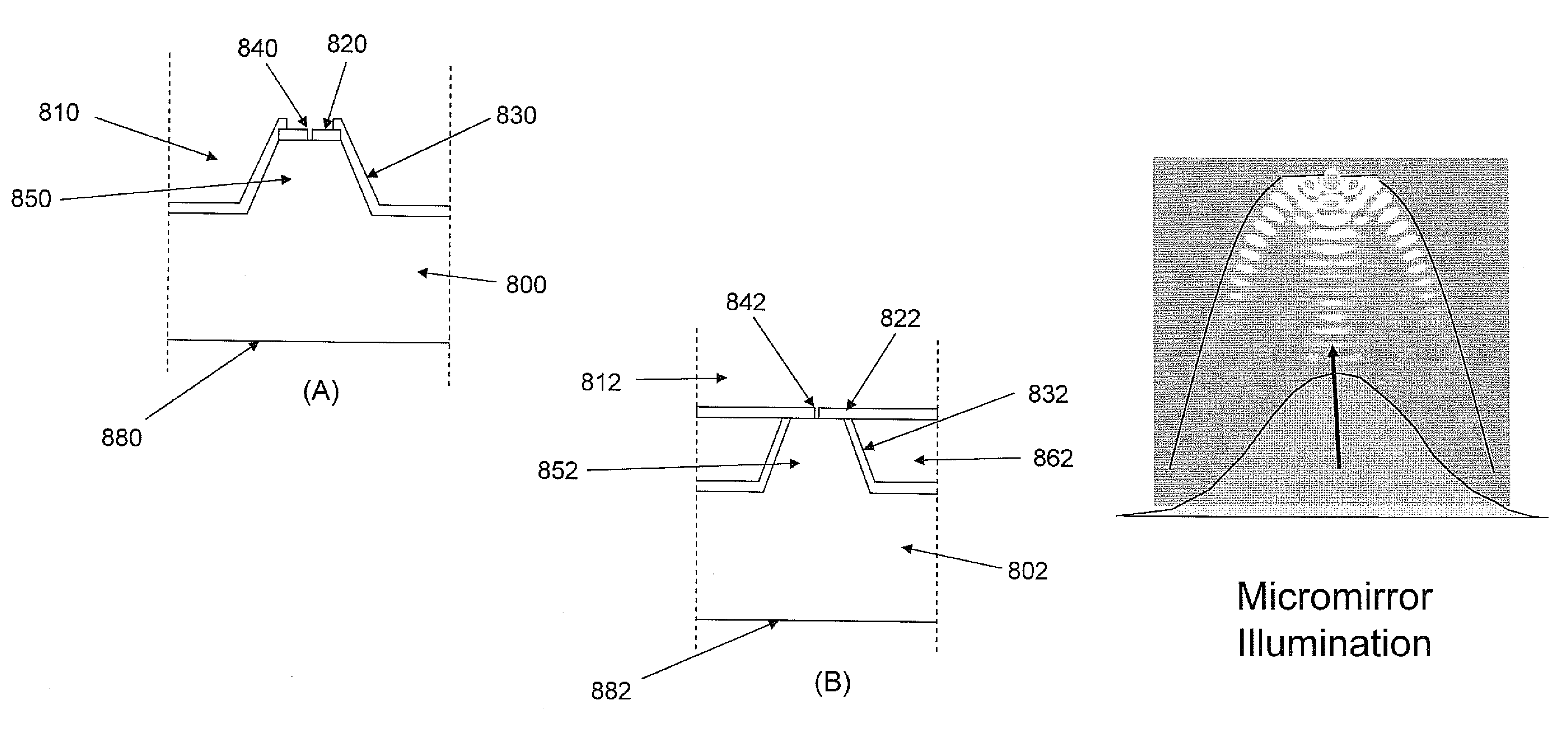
Apparatus, systems and methods for use in analyzing discrete reactions at ultra high multiplex with reduced optical noise, and increased system flexibility. Apparatus include substrates having integrated optical components that increase multiplex capability by one or more of increasing density of reaction regions, improving transmission of light to or collection of light from discrete reactions regions. Integrated optical components include reflective optical elements which re-direct illumination light and light emitted from the discrete regions to more efficiently collect emitted light. Particularly preferred applications include single molecule reaction analysis, such as polymerase mediated template dependent nucleic acid synthesis and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods for performing biometric recognition of a human eye and corroboration of same
A method of biometric recognition is provided. Multiple images of the face or other non-iris image and iris of an individual are acquired. If the multiple images are determined to form an expected sequence of images, the face and iris images are associated together. A single camera preferably acquires both the iris and face images by changing at least one of the zoom, position, or dynamic range of the camera. The dynamic range can be adjusted by at least one of adjusting the gain settings of the camera, adjusting the exposure time, and / or adjusting the illuminator brightness. The expected sequence determination can be made by determining if the accumulated motion vectors of the multiple images is consistent with an expected set of motion vectors and / or ensuring that the iris remains in the field of view of all of the multiple images.
Owner:EYELOCK
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS20030013101A1Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
Owner:SOLEXA
Method for sequencing a polynucleotide template
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method of sequence determination using sequence tags
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
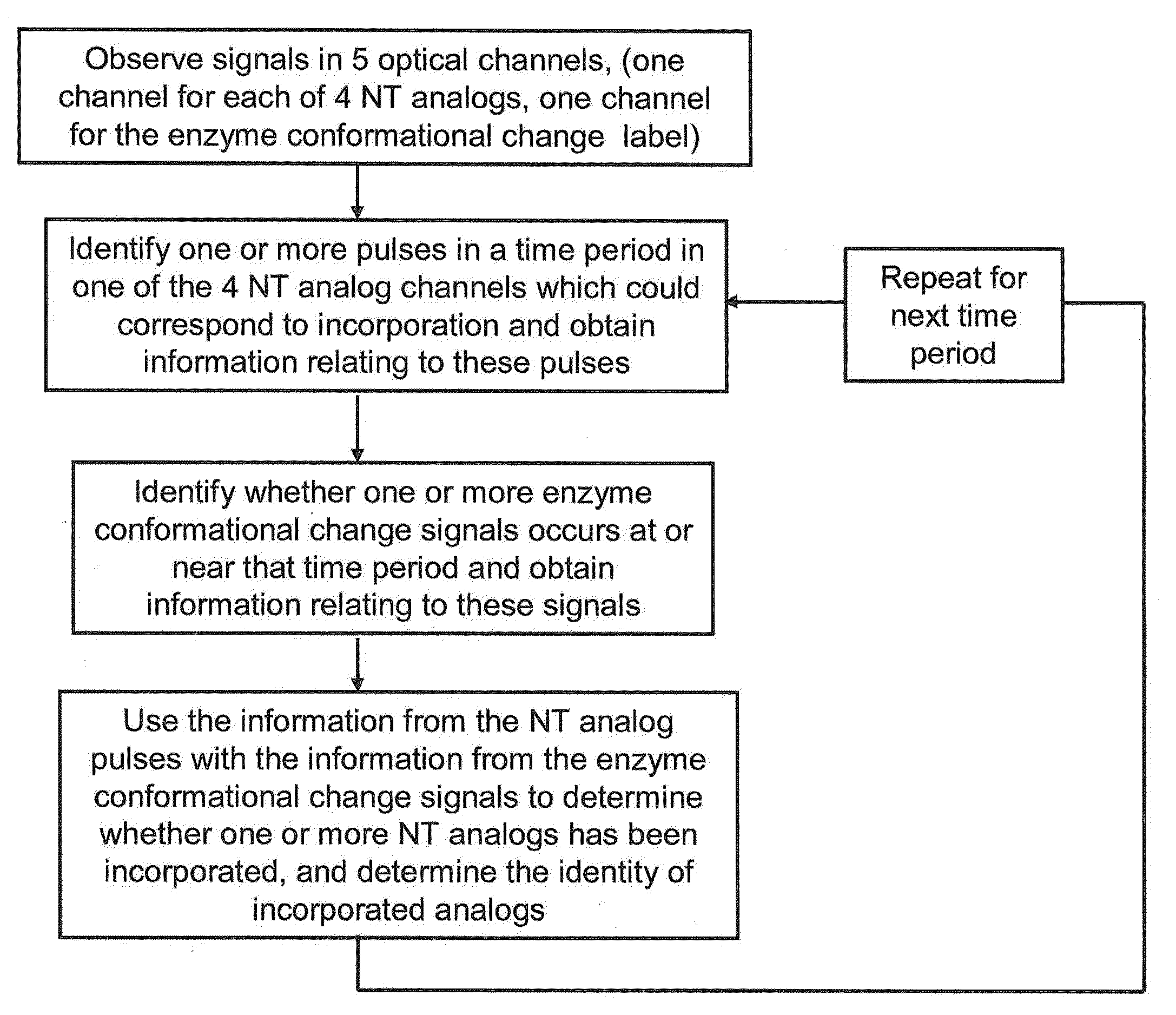
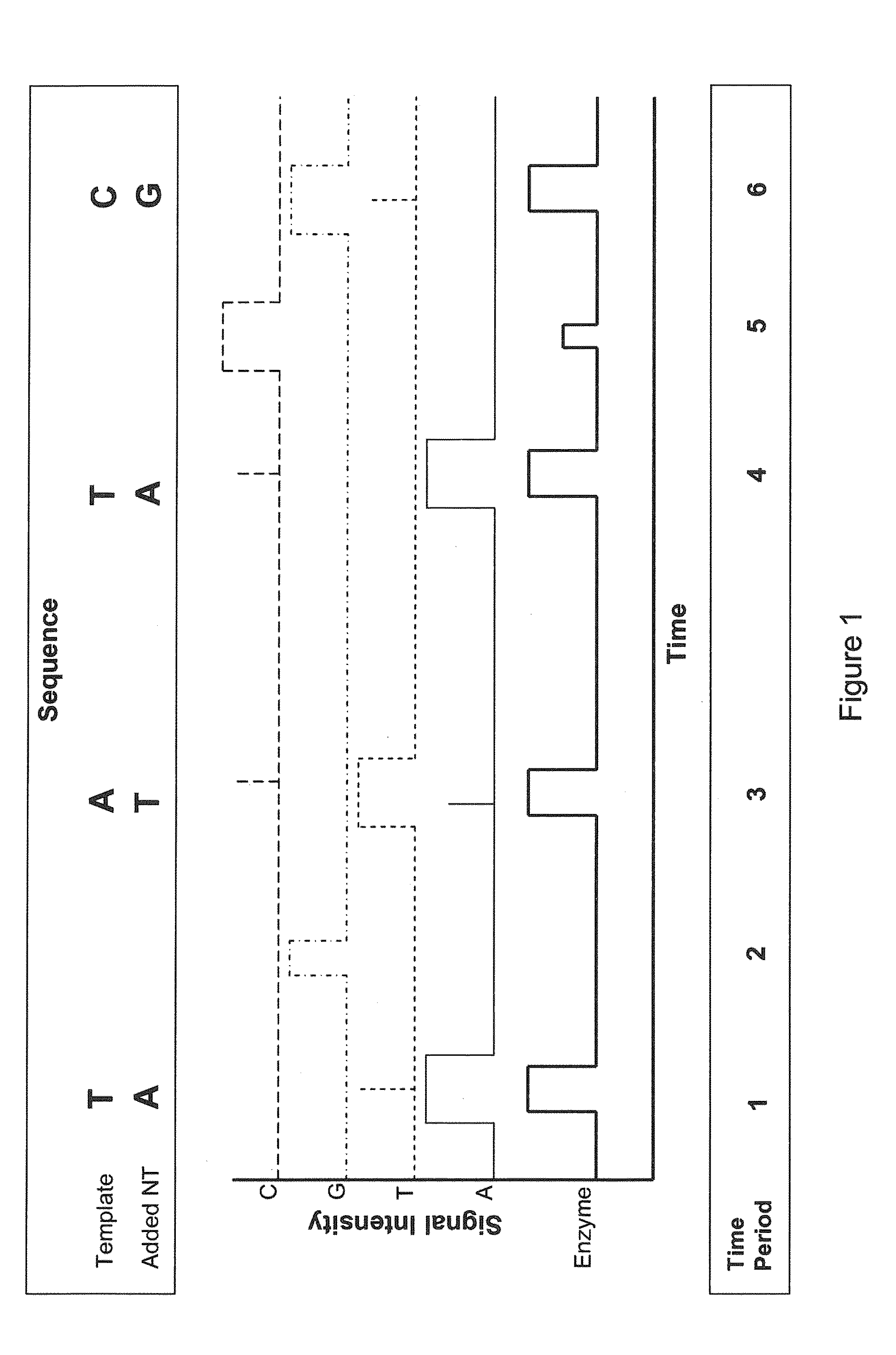
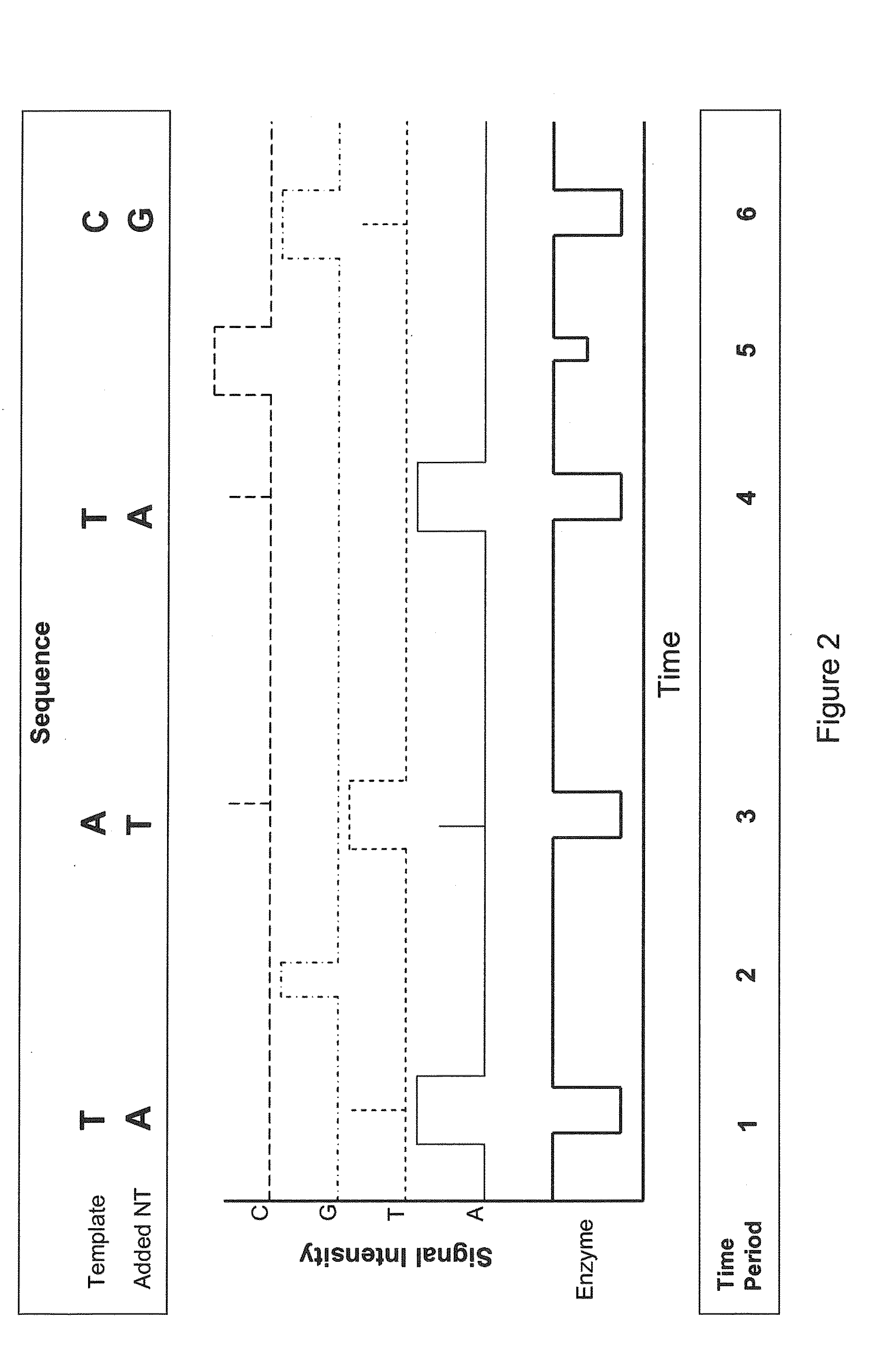
Sequencing methods using enzyme conformation
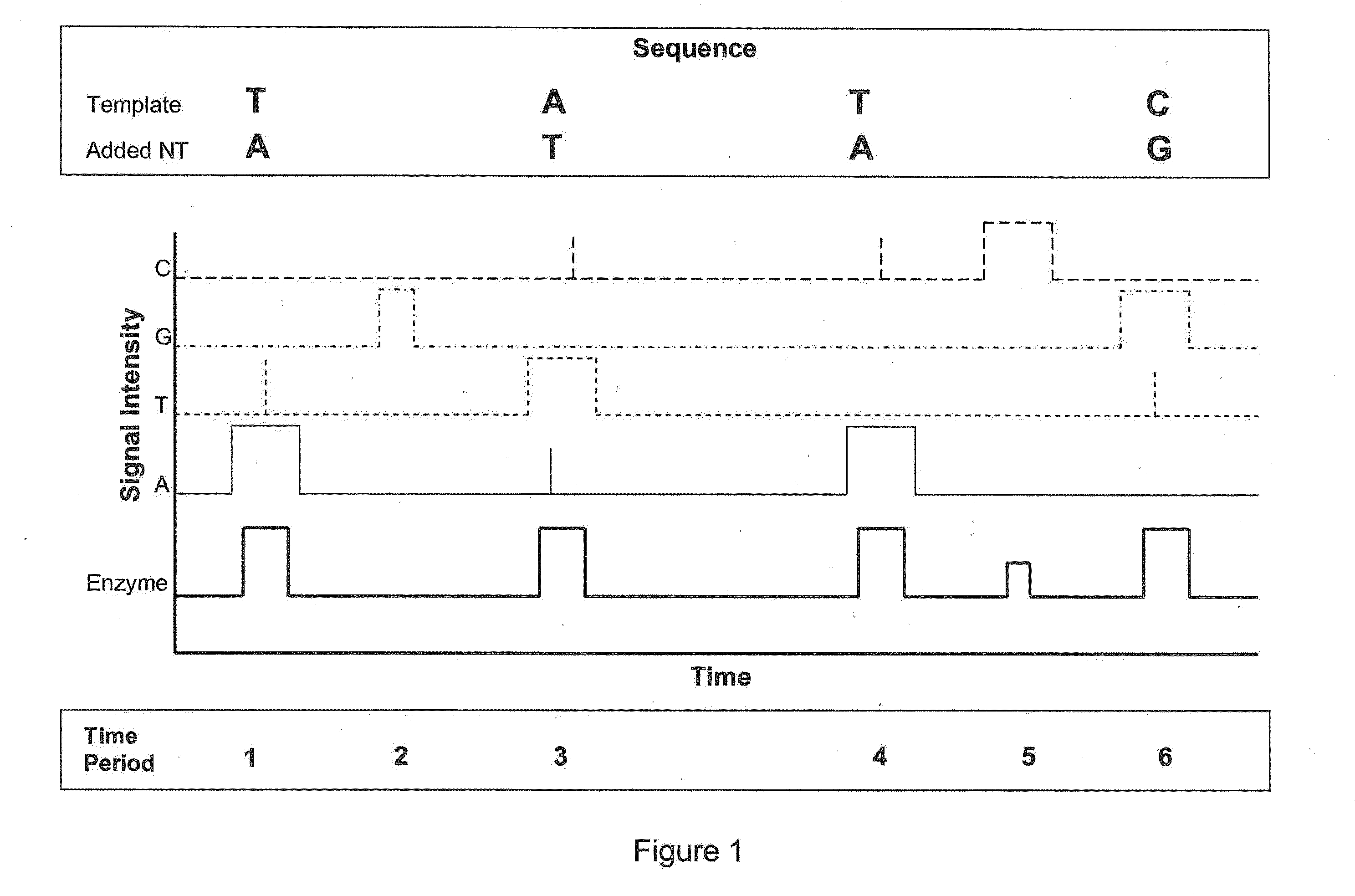
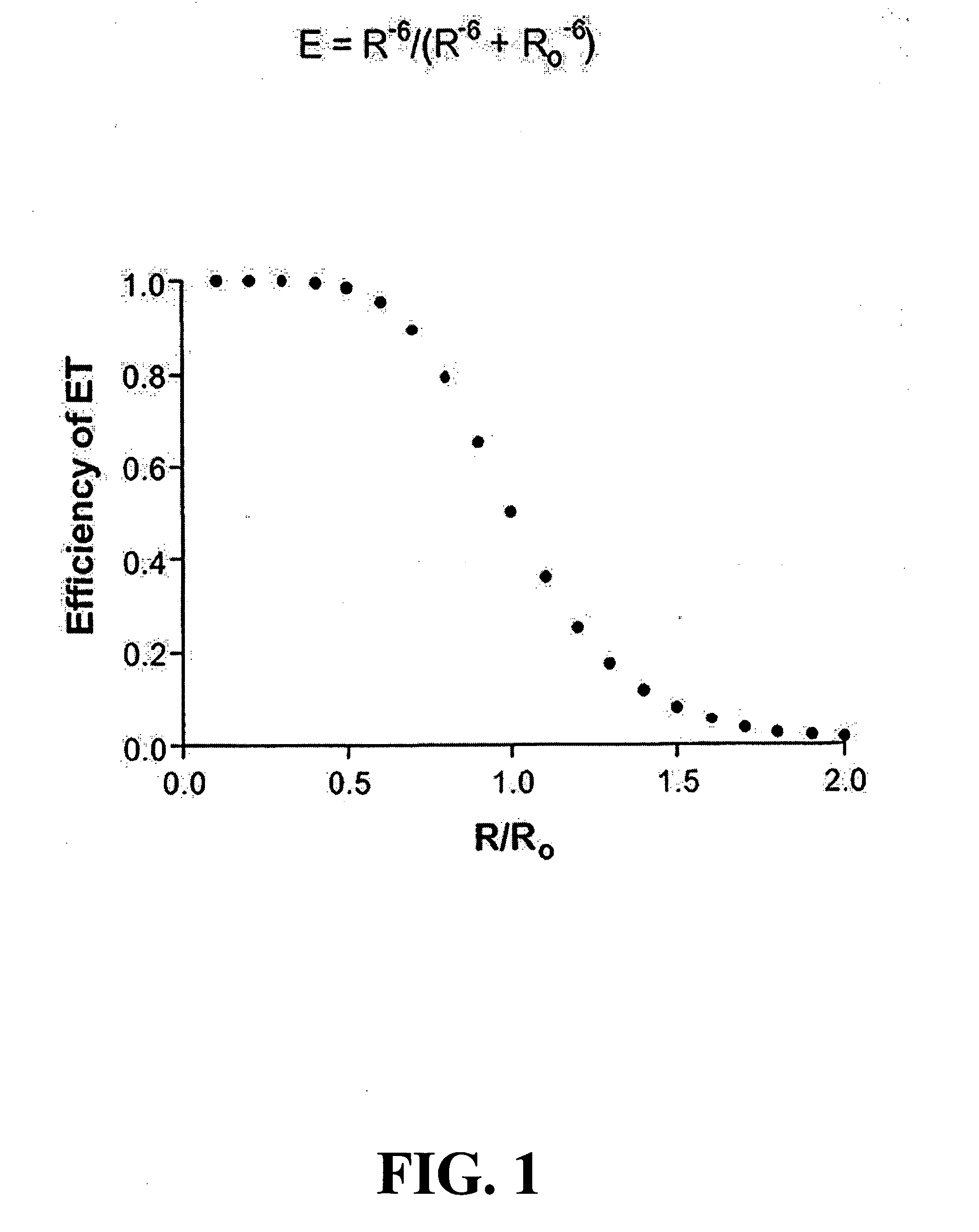
Systems and methods are provided for single-molecule sequencing of template nucleic acids in which the signal from a label attached to a polymerase enzyme is used to monitor conformational changes in the polymerase which occur while labeled nucleotides or nucleotide analogs are added to a growing nucleic acid chain which is complementary to the template nucleic acid. The signal indicative of the conformational state of the enzyme is used to determine with higher confidence when true nucleotide or nucleotide analog incorporation events occur, allowing for the improved quality of base calls and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
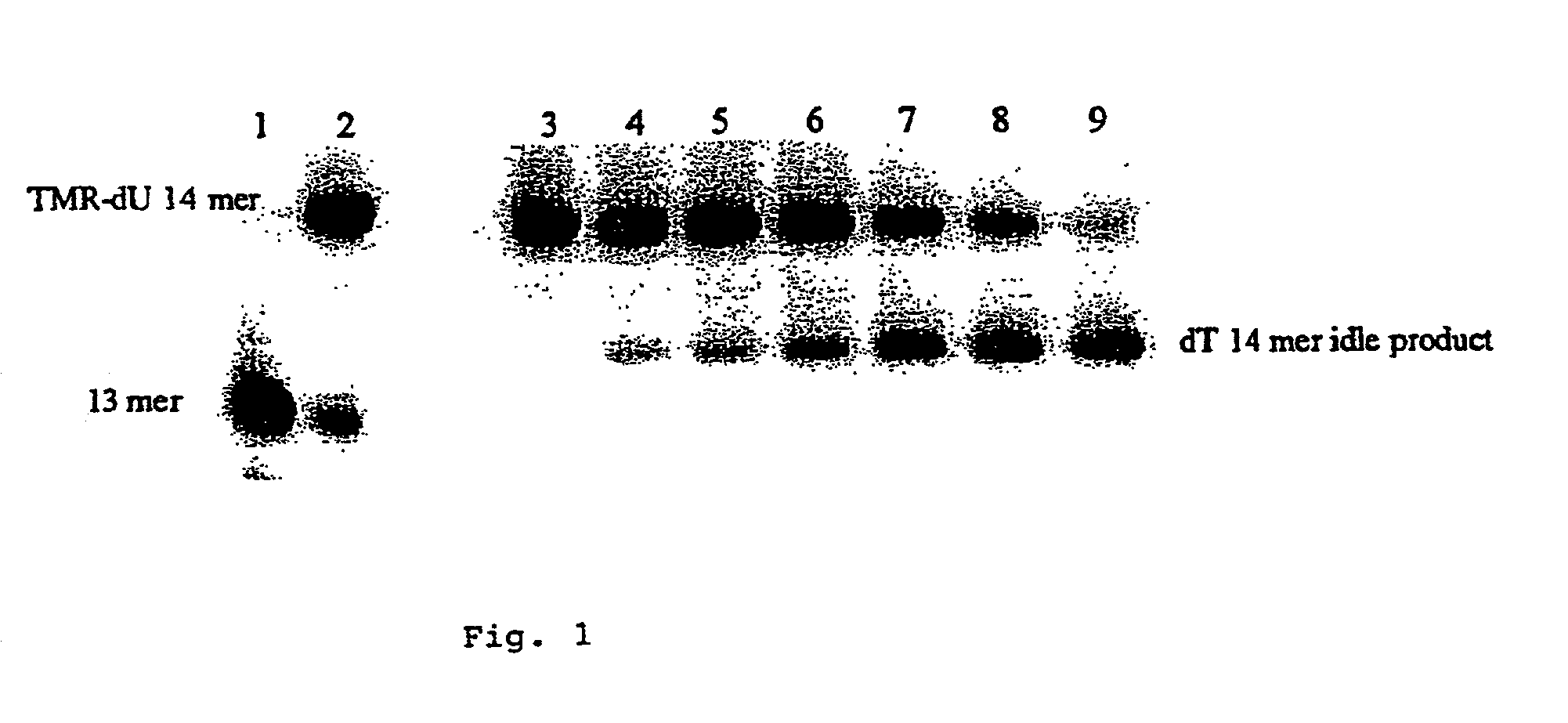
Methods for sequence determination using depolymerizing agent
InactiveUS20070172866A1Enhanced interactionQuick checkSugar derivativesHydrolasesPolymerase LSequence determination
A sequencing methodology is disclosed that allows a single DNA or RNA molecule or portion thereof to be sequenced directly and in substantially real time. The methodology involves engineering a polymerase and / or dNTPs with atomic and / or molecular tags that have a detectable property that is monitored by a detection system.
Owner:HARDIN SUSAN +4
Communications device
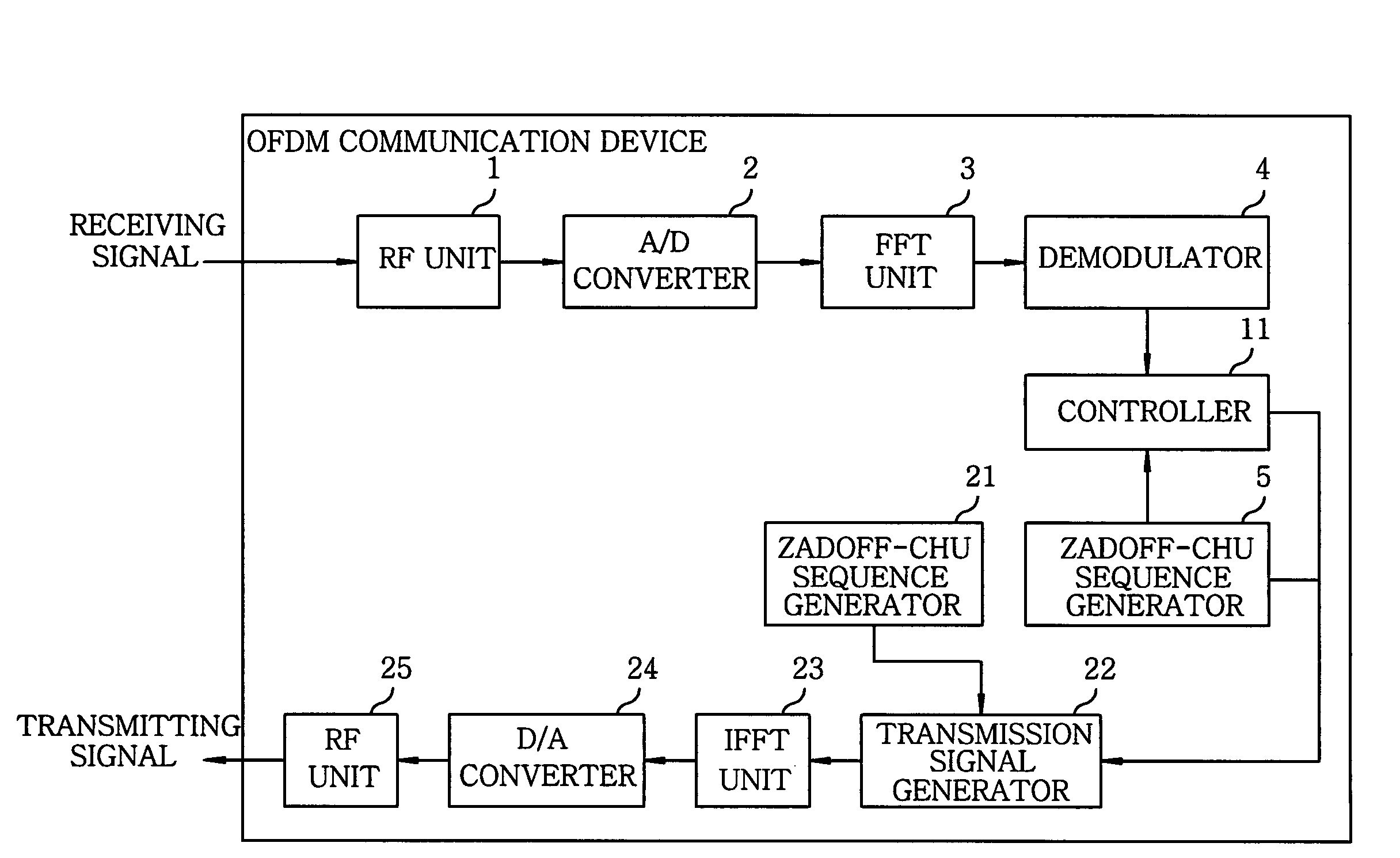
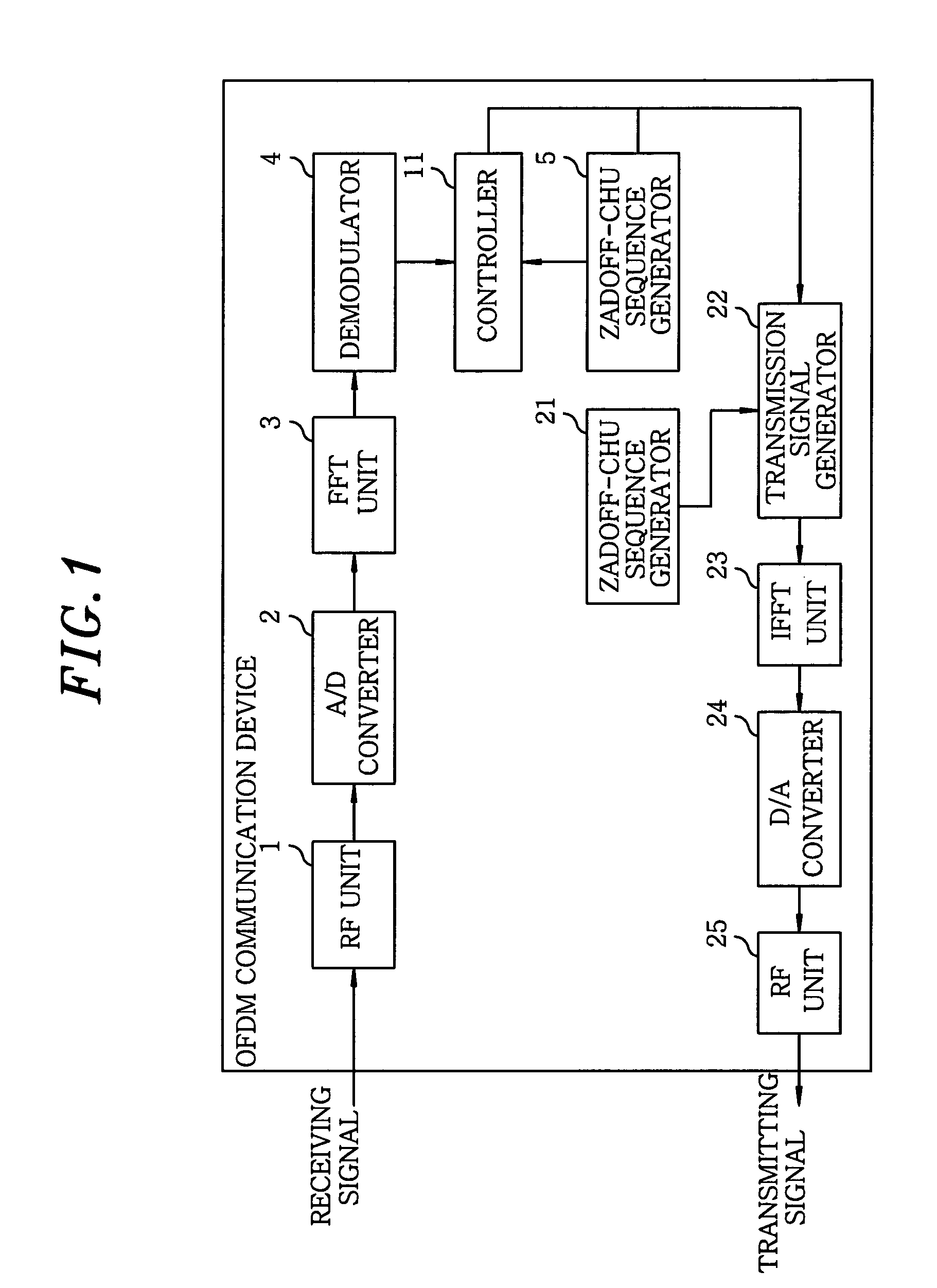
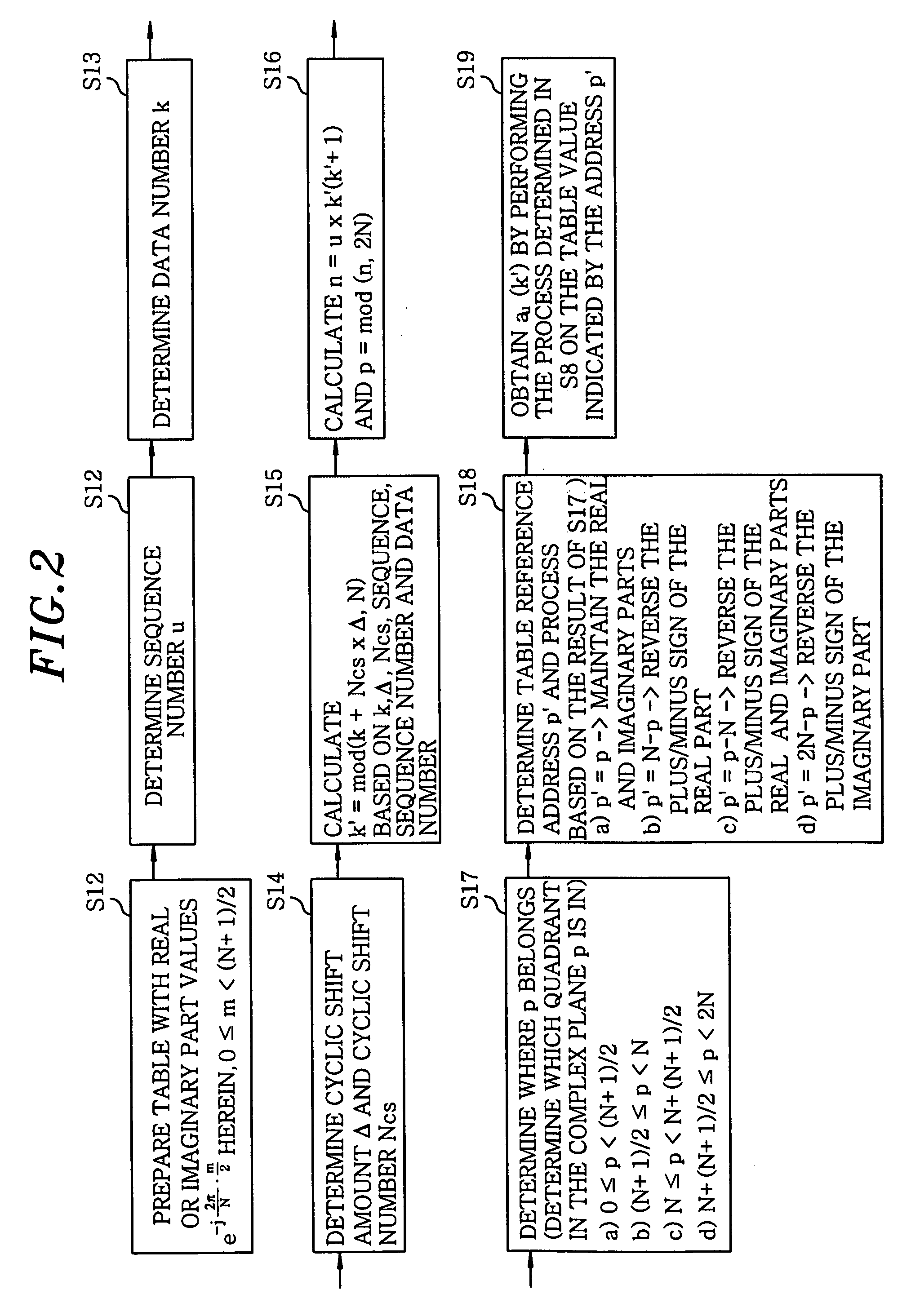
ActiveUS20090080550A1Generate efficientlyImprove accuracyCode division multiplexDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSequence determinationComputer science
A communications device for generating a Zadoff-Chu sequence includes a storage unit storing real and imaginary part values of exp{−j·(2π / N)·(m / 2)} for the Zadoff-Chu sequence of the sequence length N, wherein m is an integer (0≦m<(N+1) / 2); a parameter acquisition unit acquiring a sequence number u, data number k, cyclic shift amount Δ and cyclic shift number Ncs; a phase position detecting unit detecting a phase position of the Zadoff-Chu sequence with acquired parameters; and a sequence determination unit determining m to read a real and an imaginary part value in the storage unit based on the phase position and determining a plus / minus sign of each of the real and the imaginary part value. The device further includes a sequence acquisition unit acquiring the Zadoff-Chu sequence by using the real and the imaginary part values according to m determined by the sequence determination unit and the signs thereof determined.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Algorithms for sequence determination
InactiveUS20130138358A1Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Adaptive brain-computer interface device
InactiveUS20110152710A1Accurately determineIncrease the number ofElectroencephalographySensorsBrain computer interfacingSequence determination
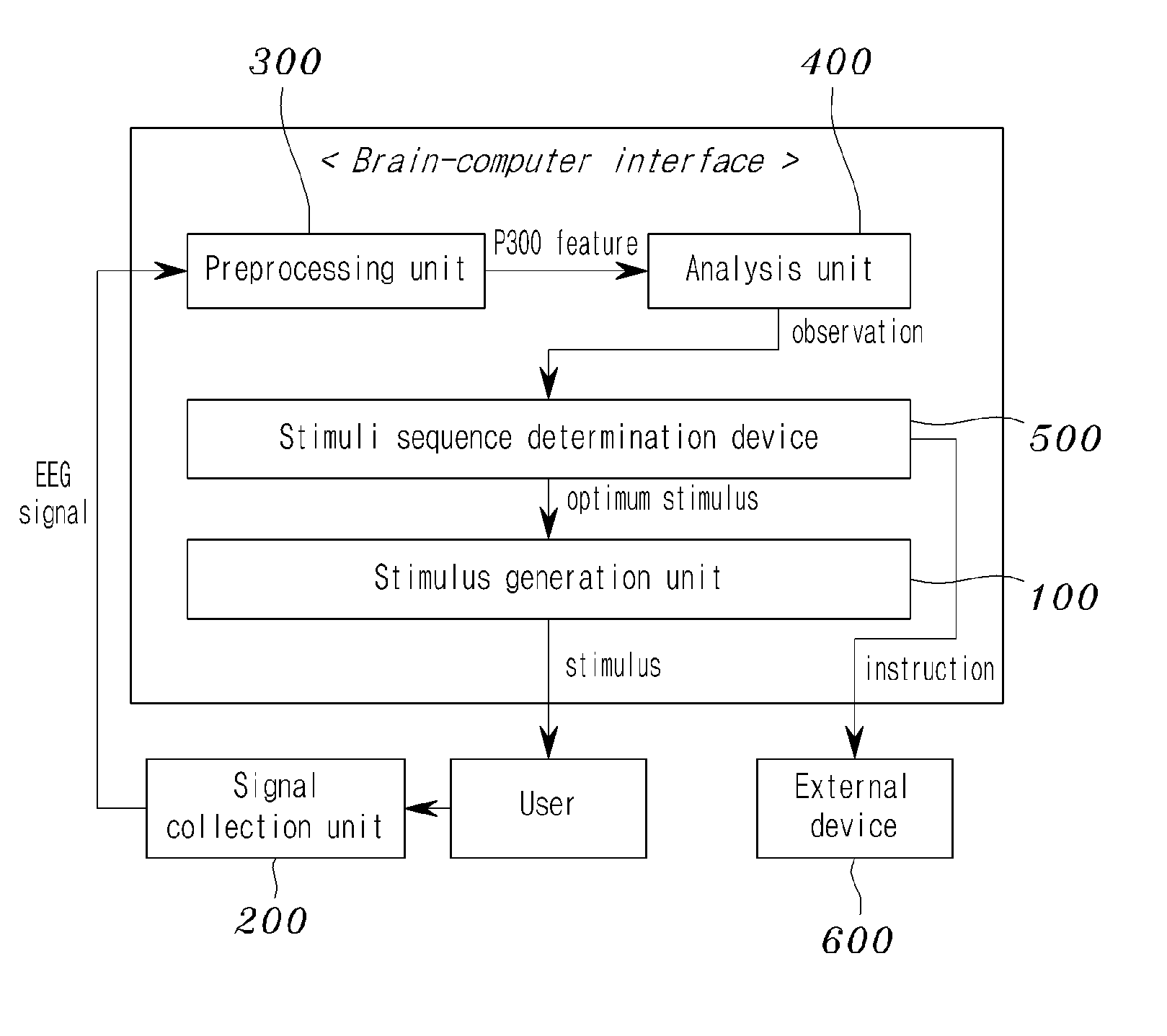
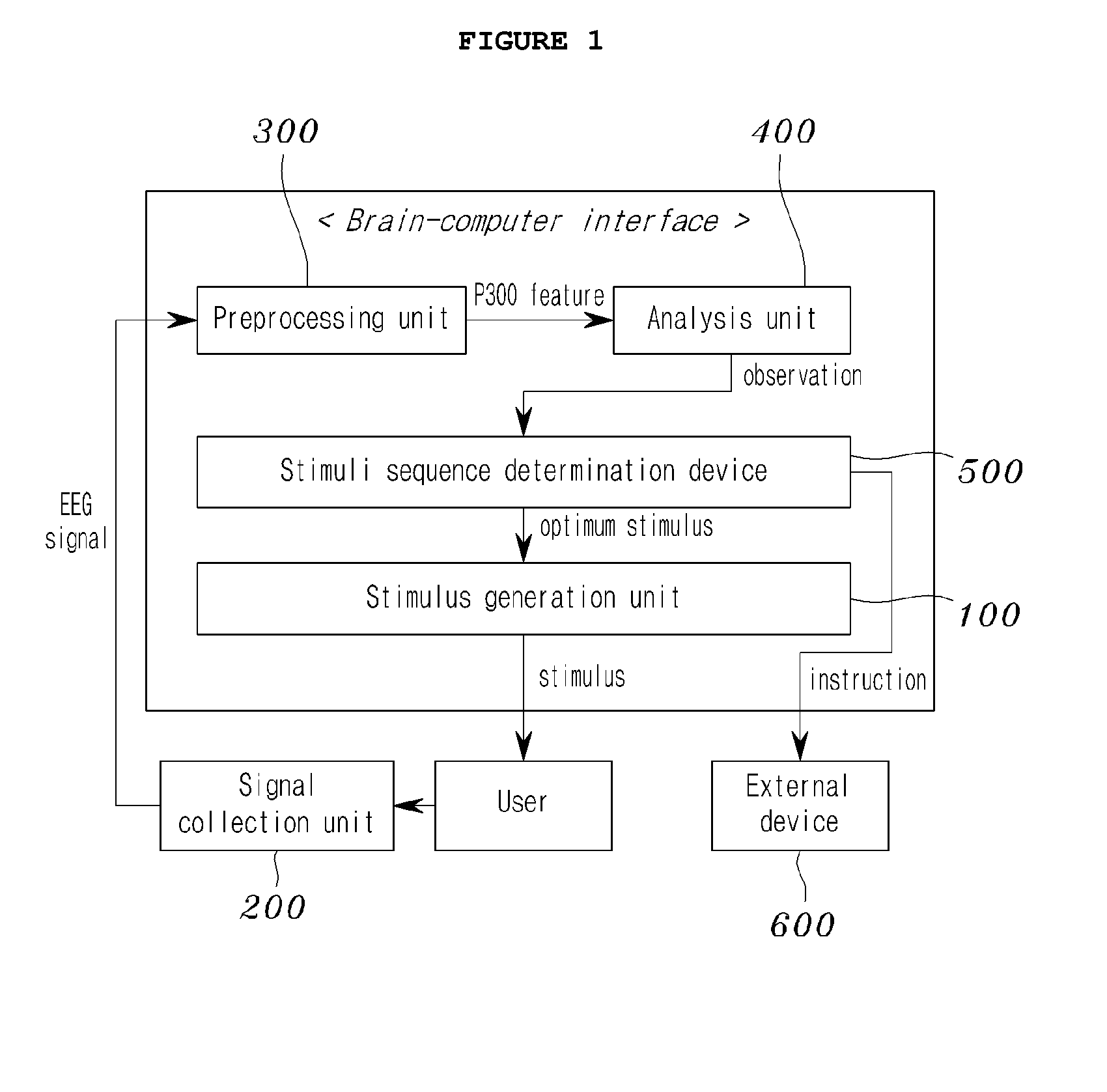
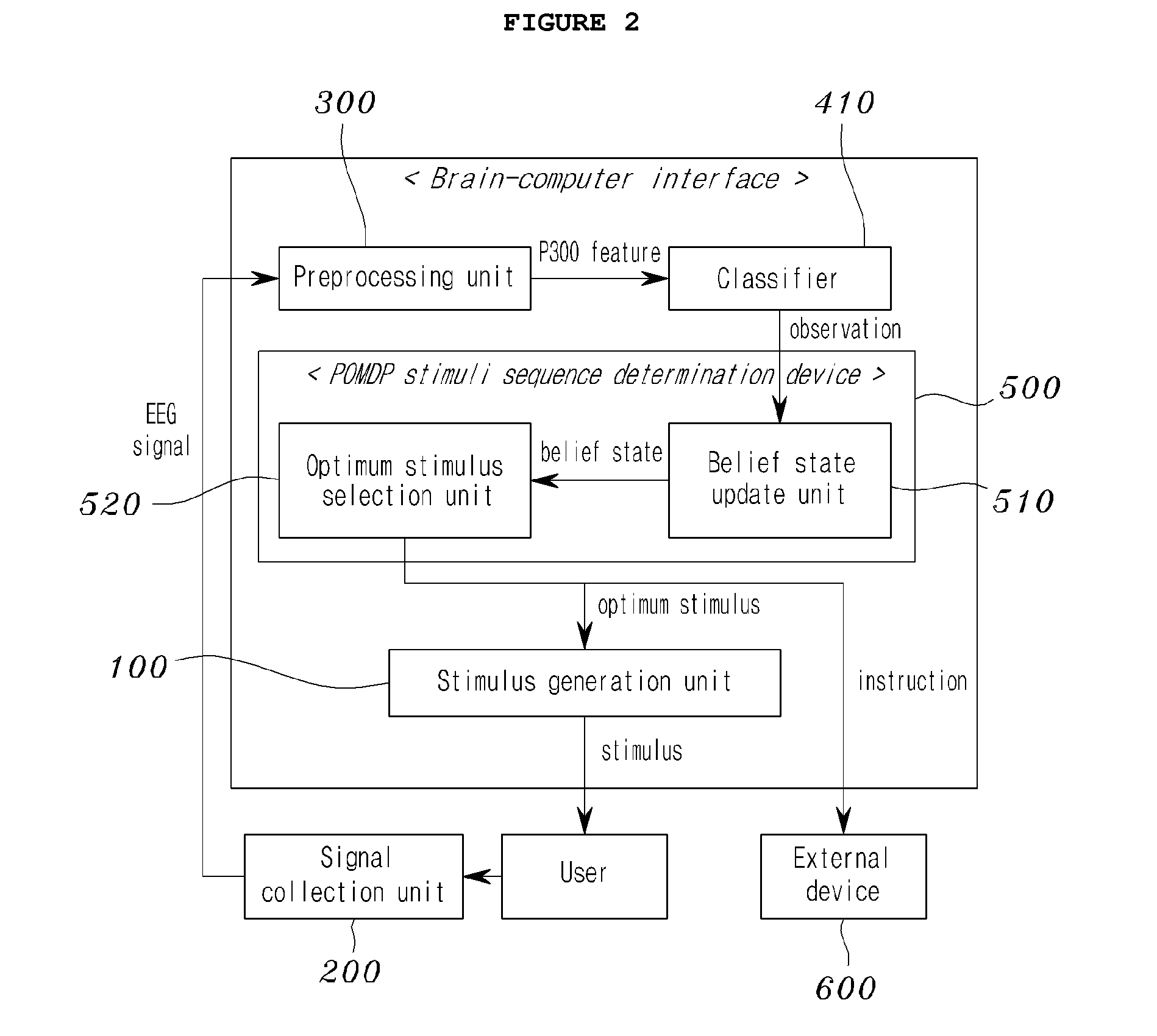
Disclosed herein is an adaptive brain-computer interface device. The brain-computer interface device includes a stimulus generation unit, a signal collection unit, a preprocessing unit, an analysis unit, and a stimuli sequence determination unit. The stimulus generation unit generates stimuli and applies the stimuli to a user. The signal collection unit records the user's Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals generated by the stimuli. The preprocessing unit extracts the feature of P300 on the basis of one of the stimulus from the EEG signals. The analysis unit determines whether P300 is present in the signal extracted by the preprocessing unit. The stimuli sequence determination unit determines the sequence of the stimuli of the stimulus generation unit by inferring a current state from the observations of the analysis unit and selecting an optimum stimulus for the current state.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Sequence determination of nucleic acids using electronic detection
ActiveUS7935481B1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementSelf-assembled monolayerNucleophilic substitution
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of self-assembled monolayers to electronically detect nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC +1
Sequencing methods using enzyme conformation
Systems and methods are provided for single-molecule sequencing of template nucleic acids in which the signal from a label attached to a polymerase enzyme is used to monitor conformational changes in the polymerase which occur while labeled nucleotides or nucleotide analogs are added to a growing nucleic acid chain which is complementary to the template nucleic acid. The signal indicative of the conformational state of the enzyme is used to determine with higher confidence when true nucleotide or nucleotide analog incorporation events occur, allowing for the improved quality of base calls and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
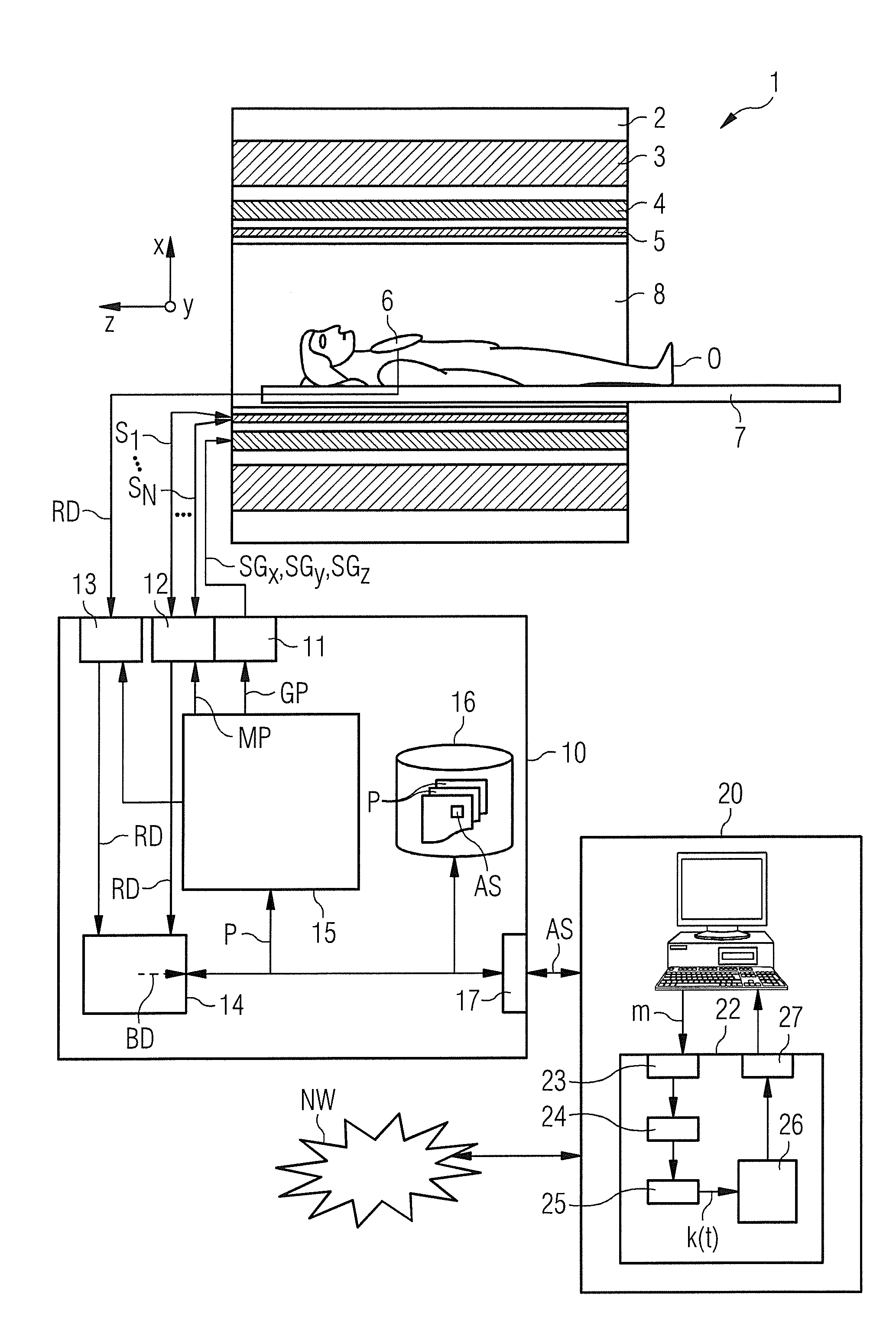
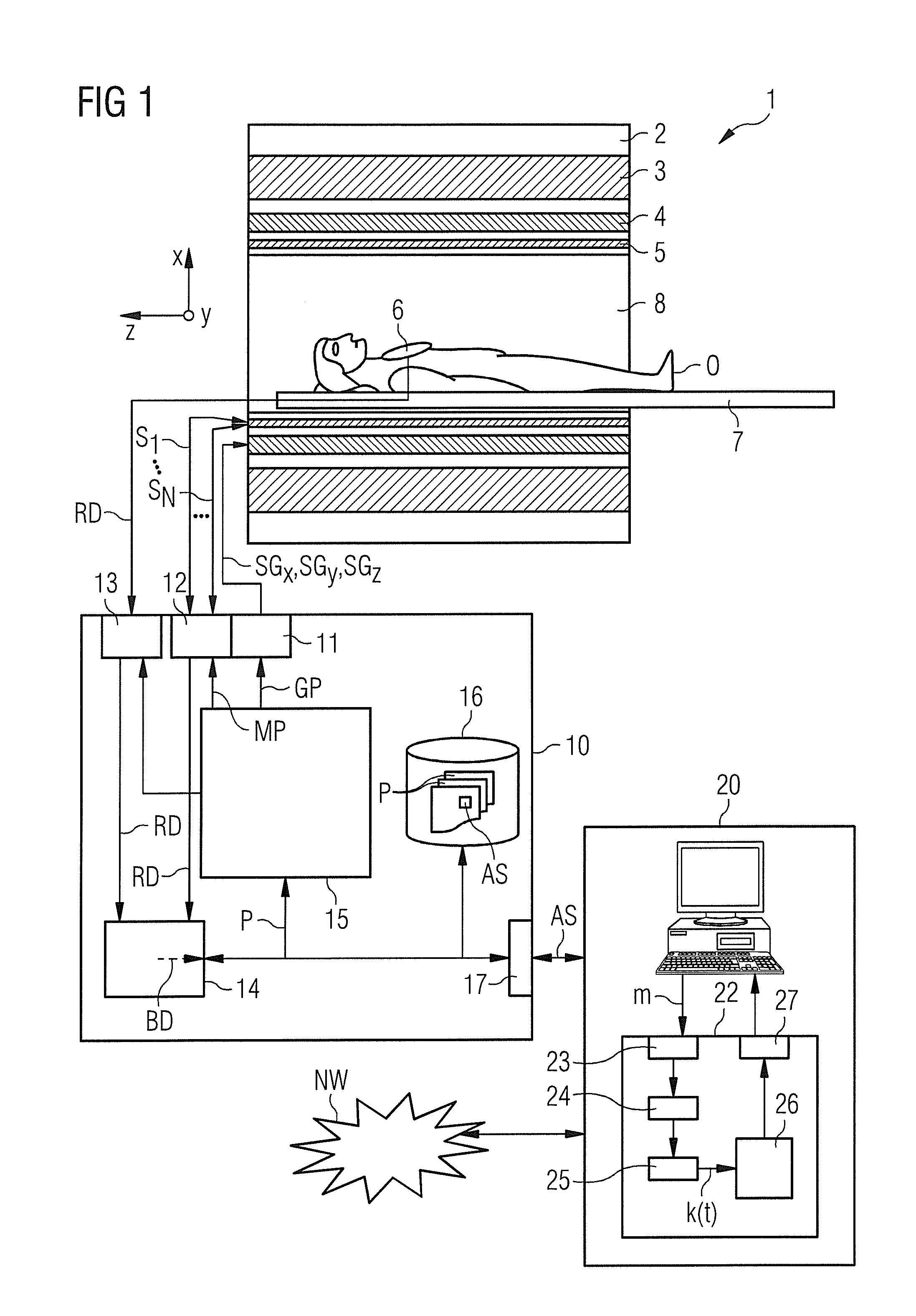
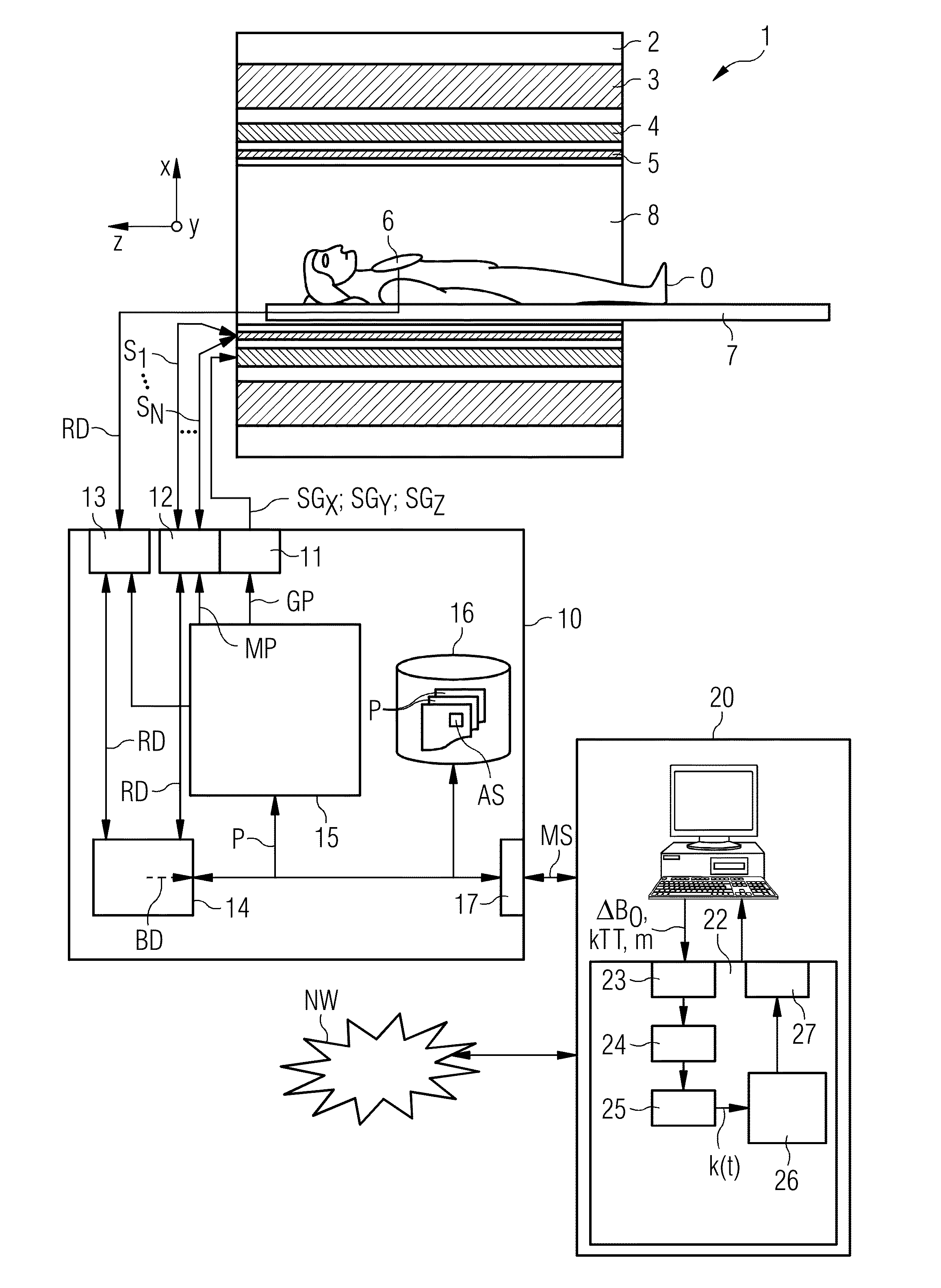
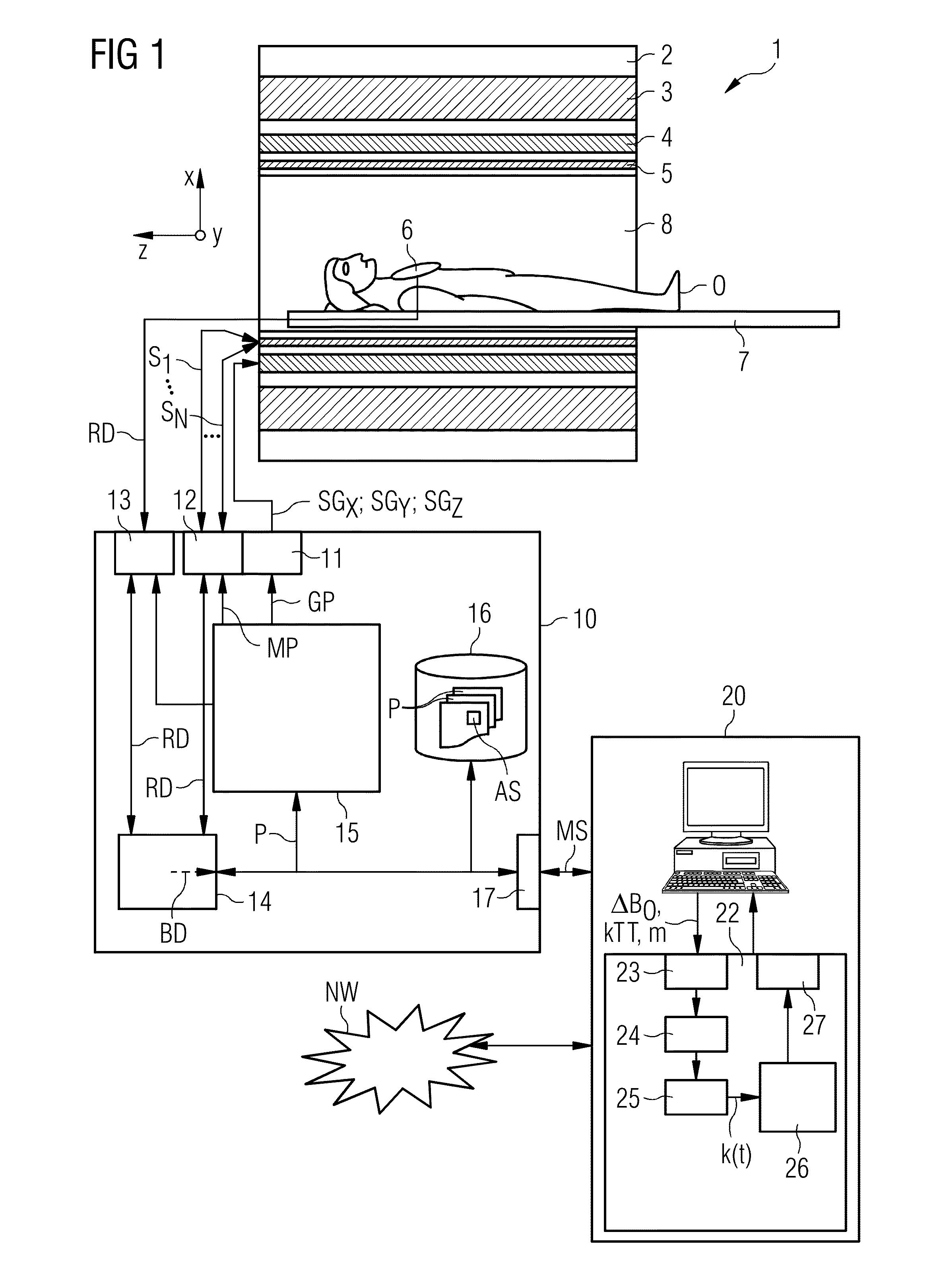
Method and device for a magnetic resonance system control sequence
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
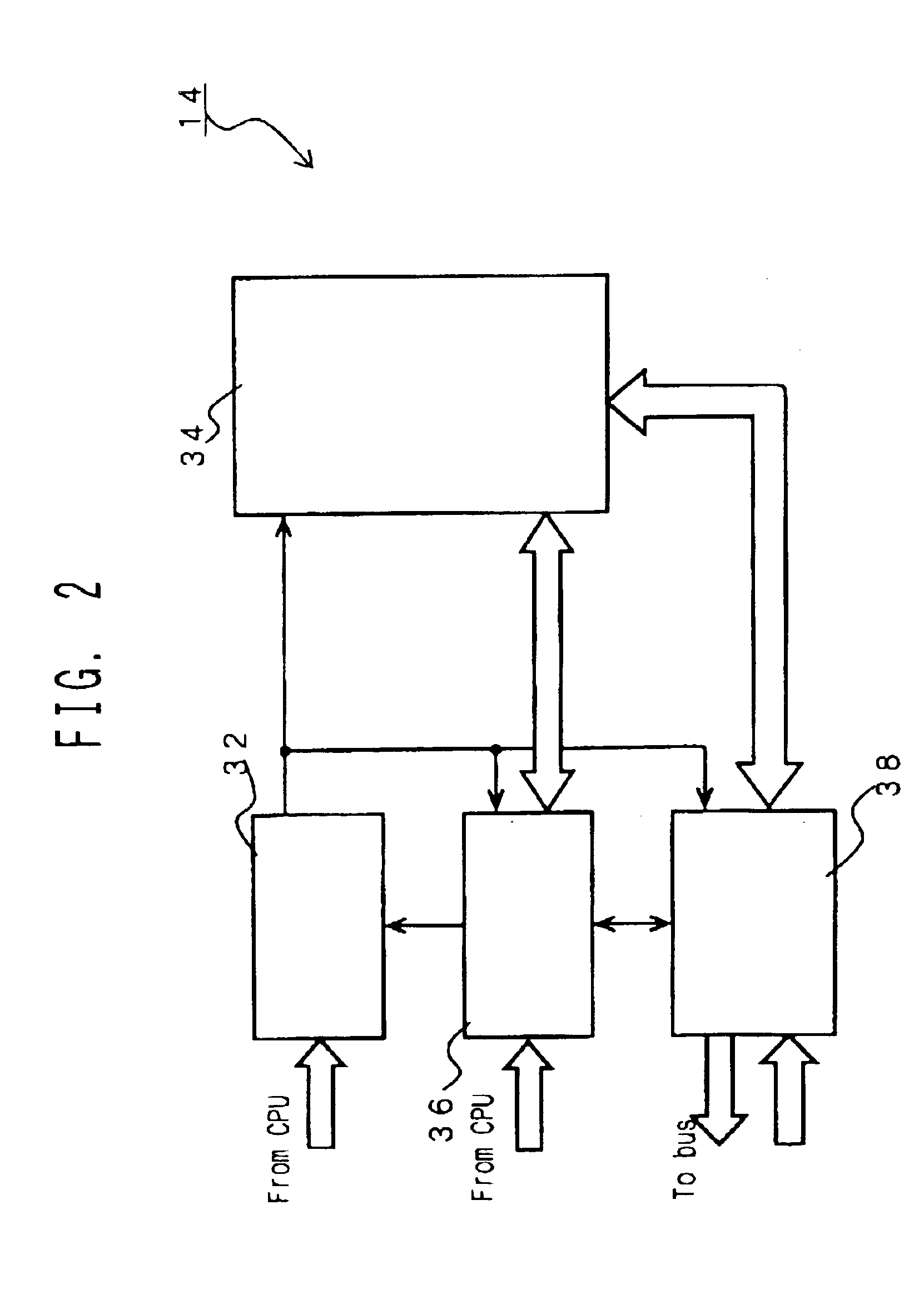
Information processing system
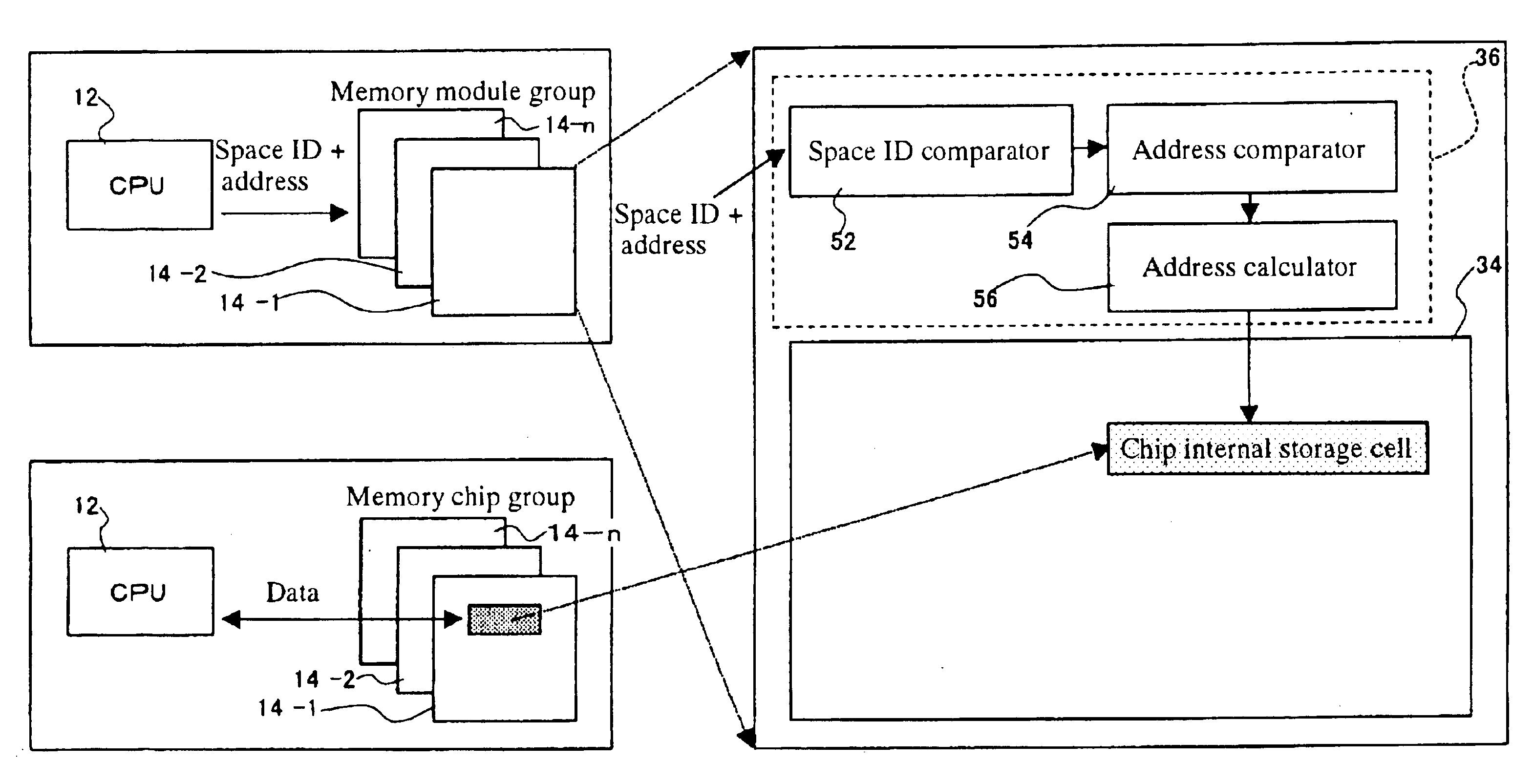
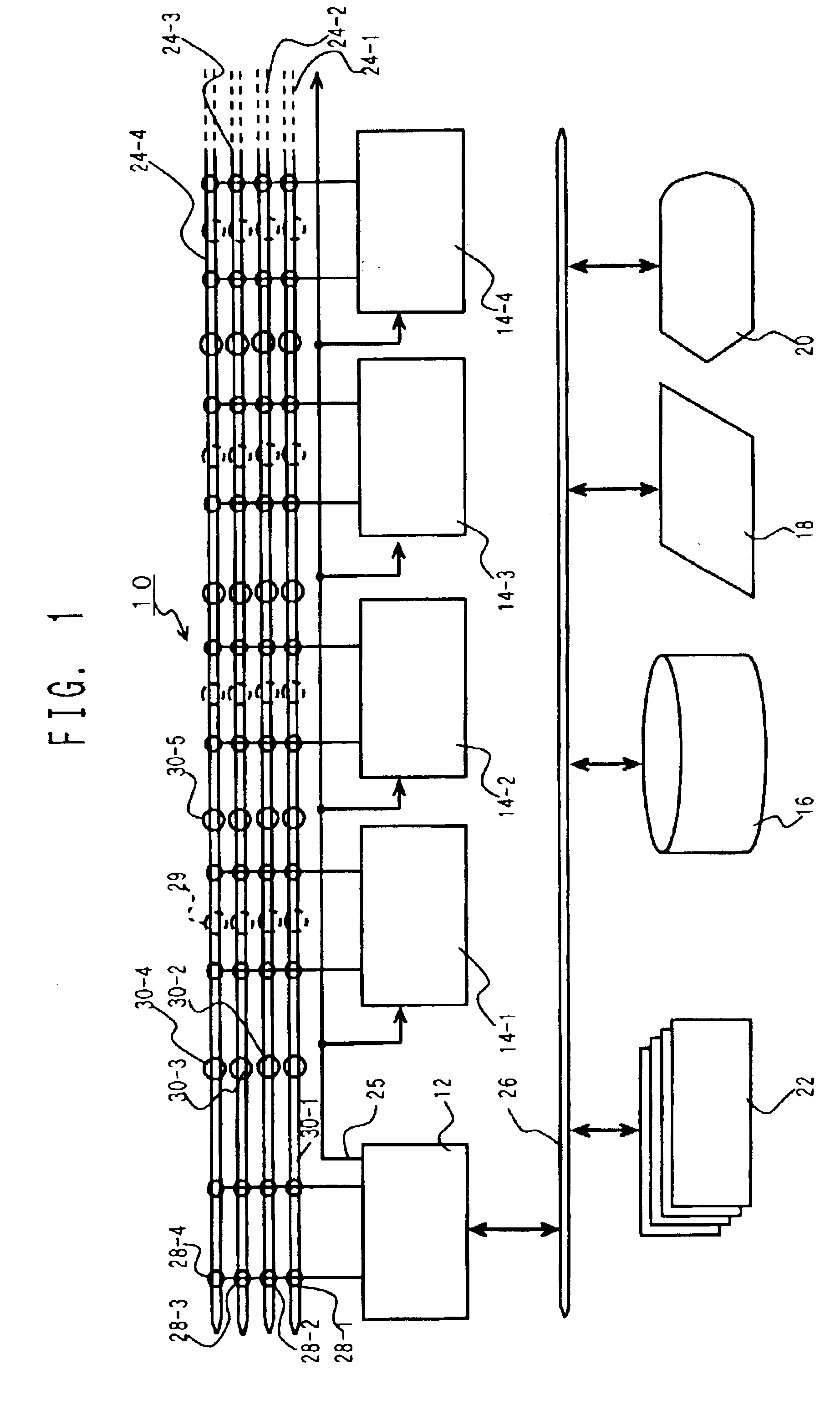
InactiveUS6886082B1Bus collisions can be avertedEliminate redundancyDatabase updatingData processing applicationsInformation processingDistributed memory
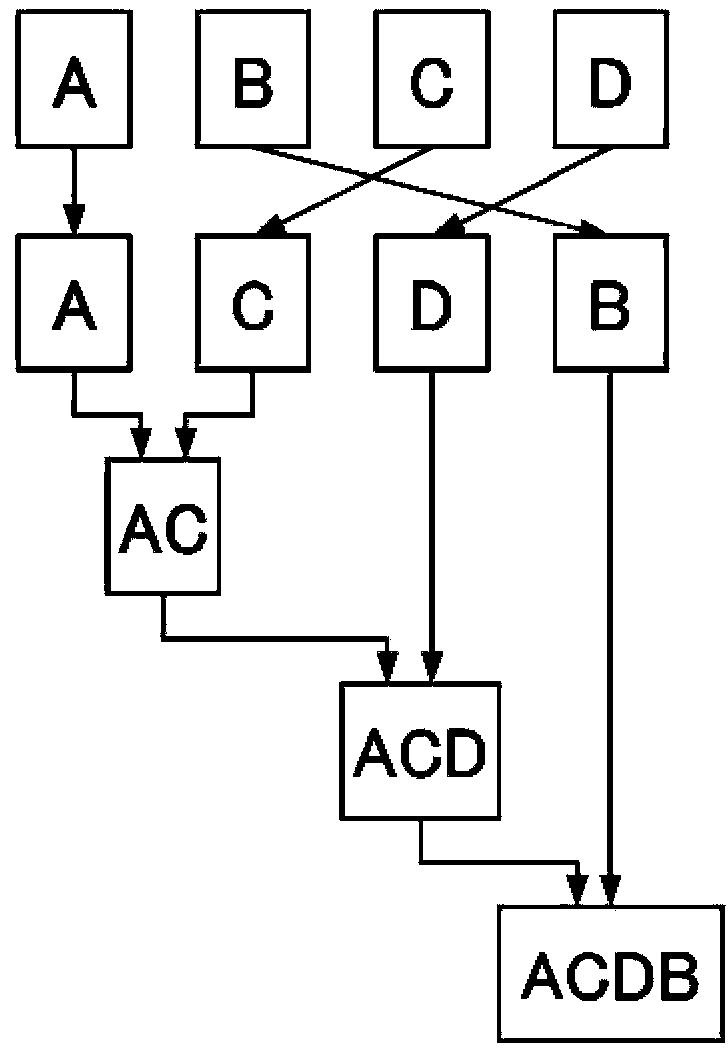
The object of this invention is to perform the sorting, compiling and joining of data at extremely high speeds. This is achieved by a distributed memory type information processing system comprising: a CPU module, a plurality of memory modules, each of which having a processor and RAM core, and a plurality of sets of buses that make connections between the CPU and memory modules and / or connections among memory modules, where the processors of the various memory modules execute the processing of arrays managed by the one or more memory modules based on instructions given by the CPU to the processors of the various memory modules. In this system, the processor of the memory module comprises: sorting means that executes a sort on the elements that make up those portions of the array that it itself manages, and reorders the elements according to a specific order, I / O that, depending on the positions that the portions managed by itself occupy within the array, sends the sorted elements together with their sequence numbers to another memory module via a stipulated bus, or receives the elements and sequence numbers from another memory module via a stipulated bus, sequence number calculation means that, upon receipt of the element and sequence number, compares it with the elements that it manages itself and calculates a virtual sequence number which is a candidate for the sequence number of the received element, and returns it to the other memory module, and sequence determination means that, upon receipt of the virtual sequence number, determines the sequence of elements according to the virtual sequence numbers. Thus, the sequence numbers of elements of the array are determined by means of communication between a presentation memory module on the side that sends the element and sequence number and a determination memory module on the side that receives the element and sequence number and calculates the virtual sequence number.
Owner:TURBO DATA LAB INC
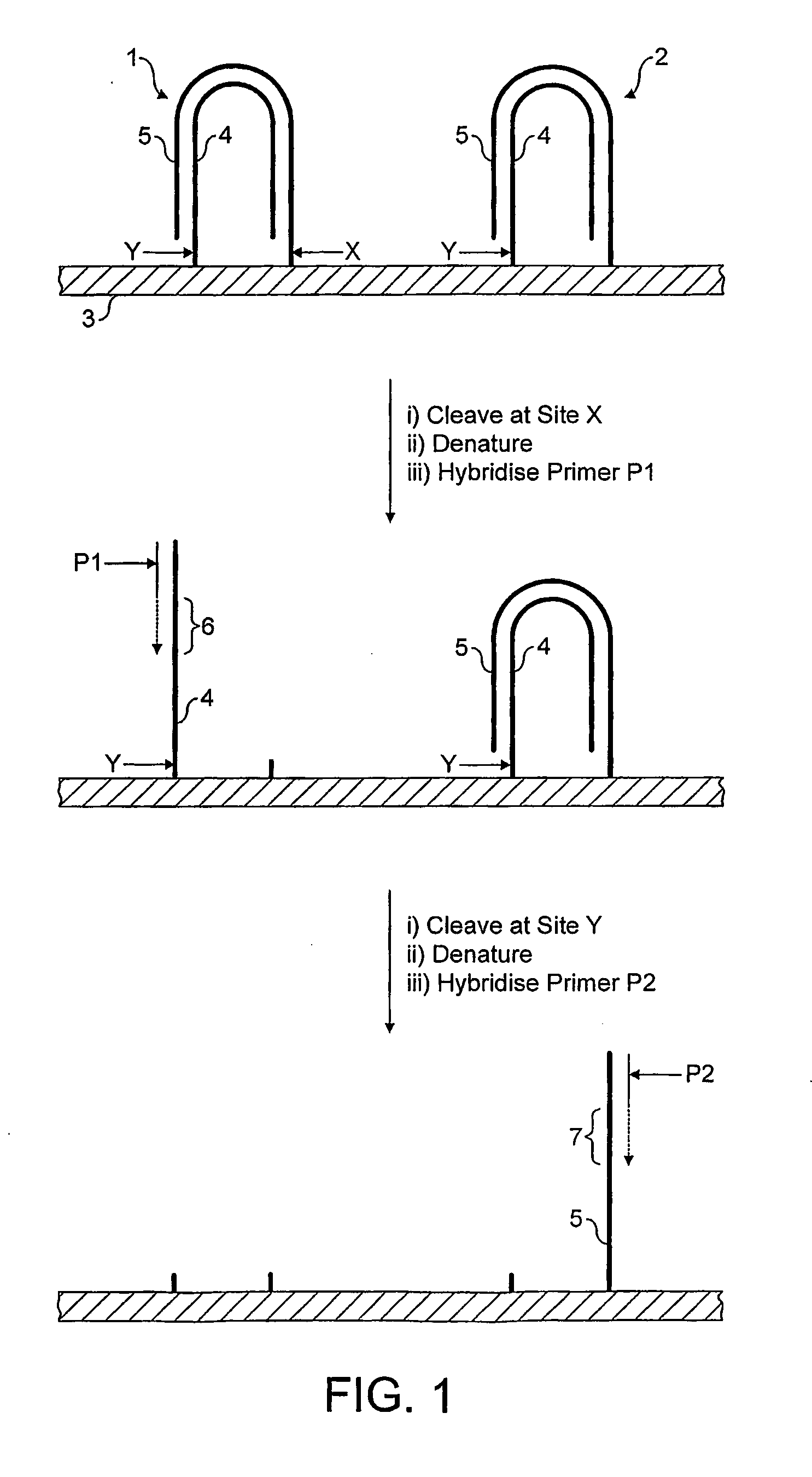
Method for Sequencing a Polynucleotide Template
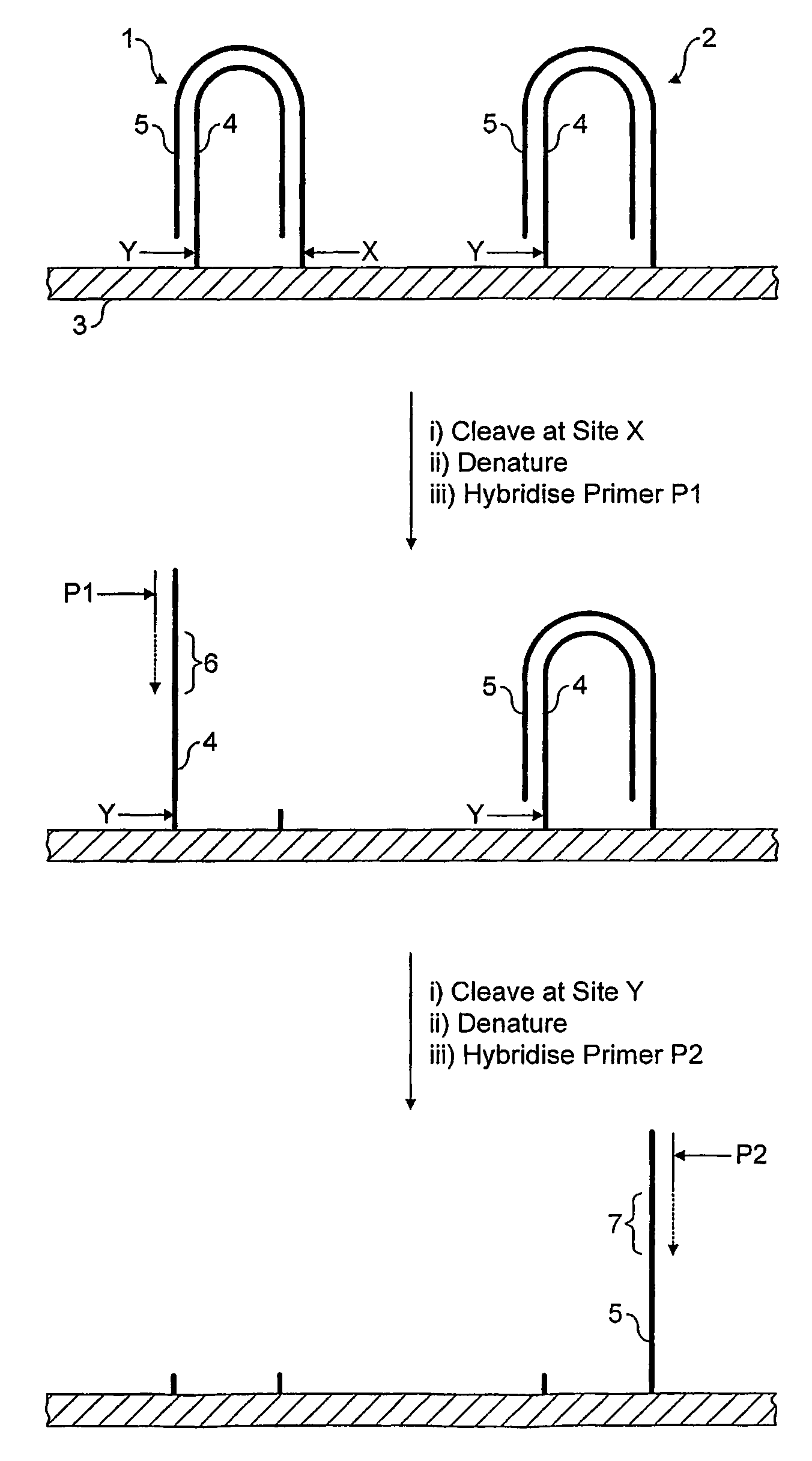
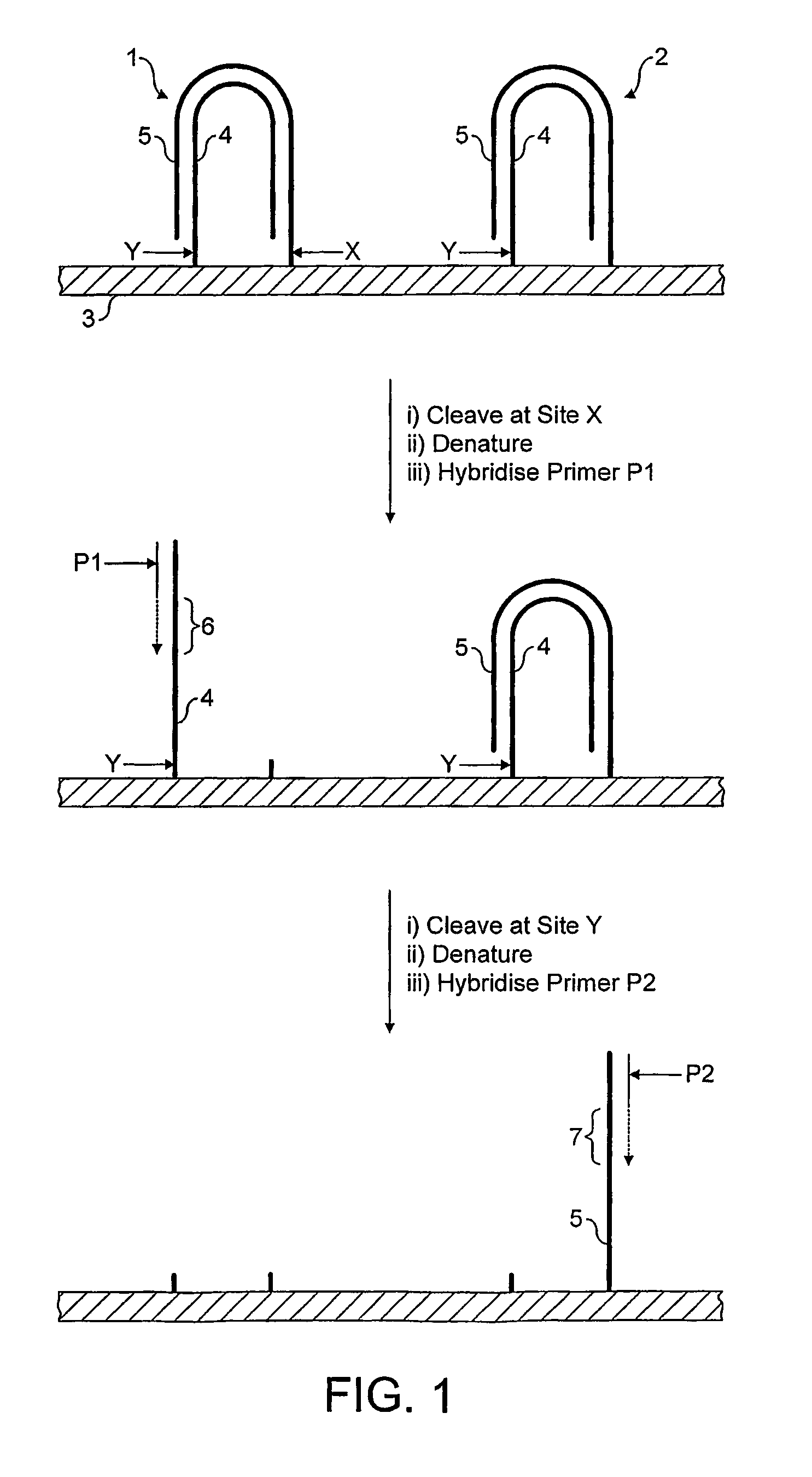
The invention relates to methods for pairwise sequencing of a double-stranded polynucleotide template, which permit the sequential determination of nucleotide sequences in two distinct and separate regions on complementary strands of the double-stranded polynucleotide template. The two regions for sequence determination may or may not be complementary to each other.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
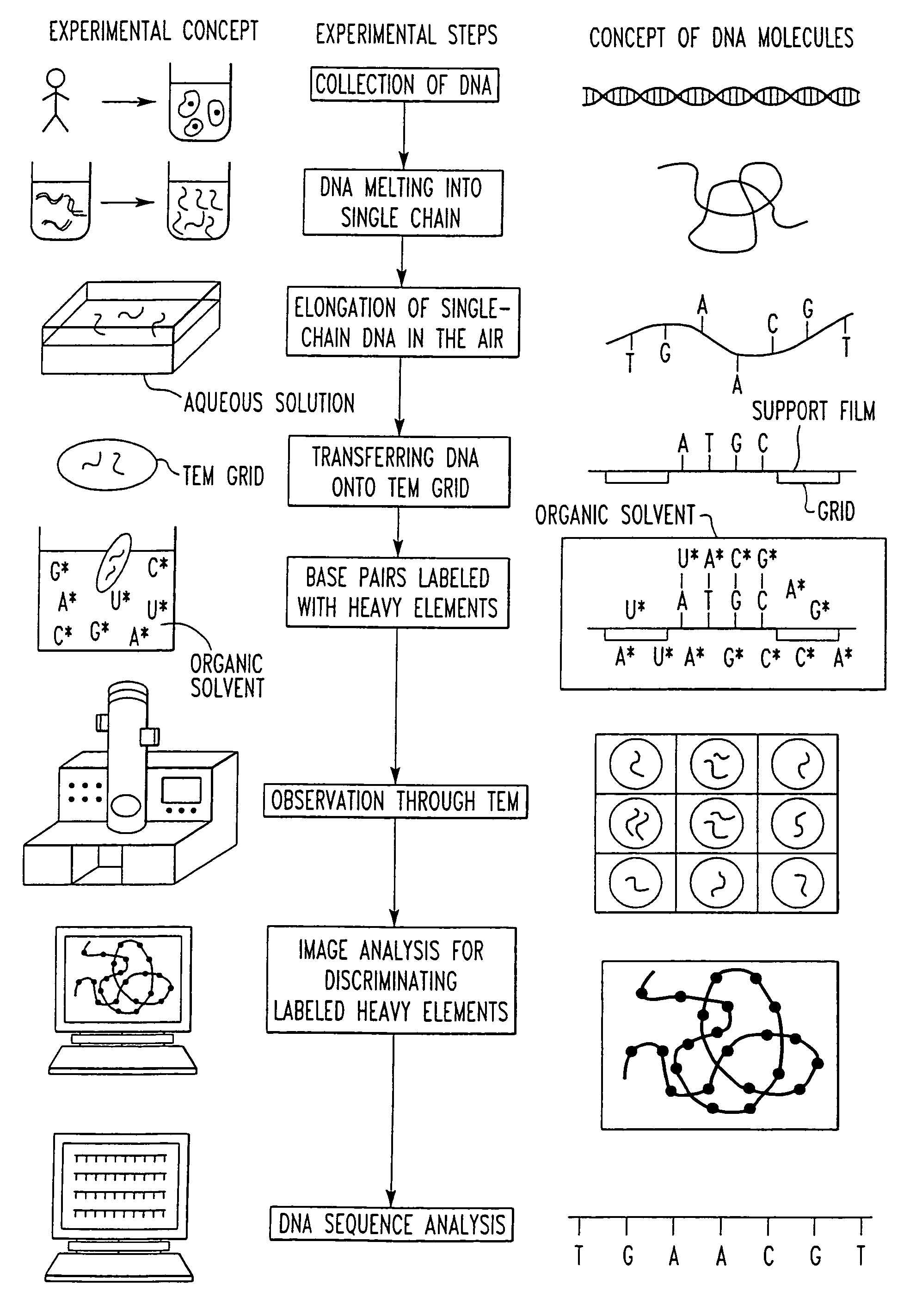
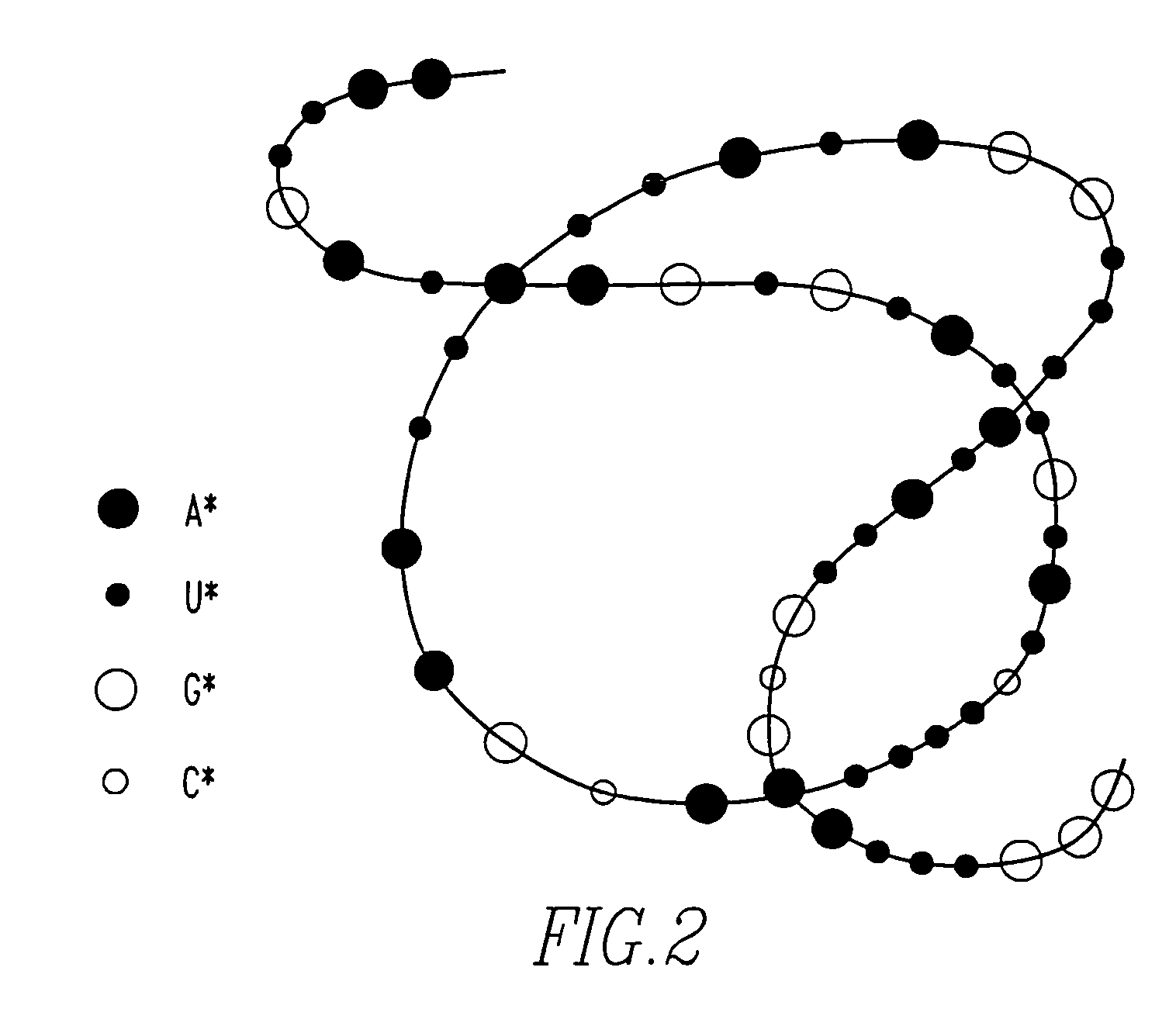
Method of determining base sequence of DNA or RNA using heavy element labeling and imaging by transmission electron microscopy
InactiveUS7332284B2Accurate analysisRemove overlapBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophoresisDNA sequencer
Novel DNA sequence determination method and DNA sequencer system providing a sequencing speed 103 to 104 times faster than the current DNA sequencing speed (105 bases per day with a lane at maximum) of the existing DNA sequencer based on electrophoresis. The method includes the step of discriminating base-specific labels of heavy elements using a magnified image of elongated single-chain DNA or RNA produced by a transmission electron microscope (TEM). The DNA sequencer system uses this method. The invention provides a DNA sequencing speed that is higher than the existing speed by 3 or 4 orders of magnitude.
Owner:NAGAYAMA IP HLDG
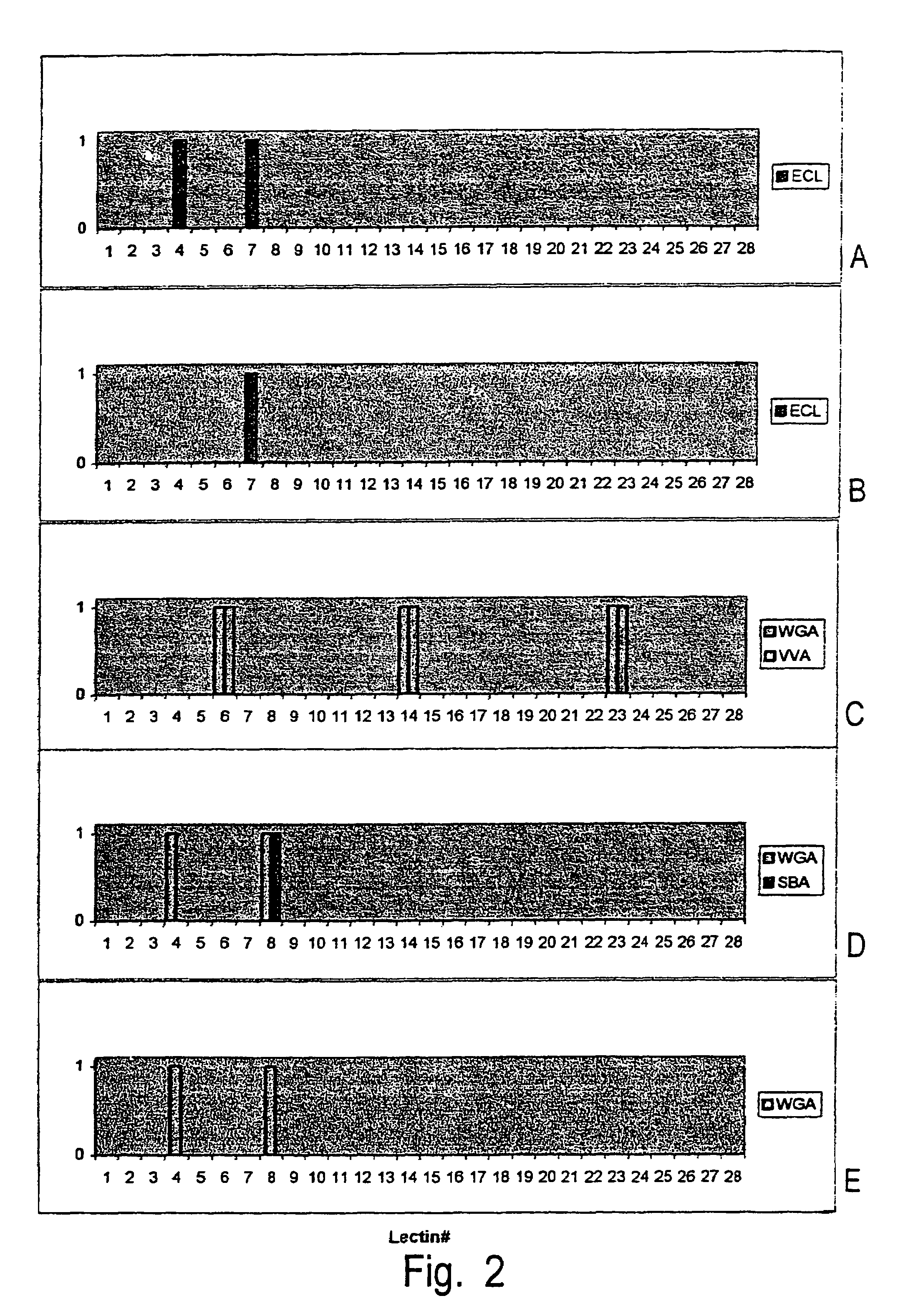
Polysaccharide structure and sequence determination
The invention provides a method for the structural analysis of a saccharide, comprising: a) providing on a surface a plurality of essentially sequence- and / or site-specific binding agents; b) contacting said surface with a saccharide to be analyzed, or with a mixture comprising a plurality of fragments of said saccharide; c) washing or otherwise removing unbound saccharide or saccharide fragments; d) adding to the surface obtained in step c) an essentially sequence- and / or site-specific marker, or a mixture of essentially sequence- and / or site-specific markers; e) acquiring one or more images of the markers that are bound to said surface; and f) deriving information related to the identity of the saccharide being analyzed from said image.
Owner:PROCOGNIA ISRAEL
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
InactiveCN103533232ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingSequence determination
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
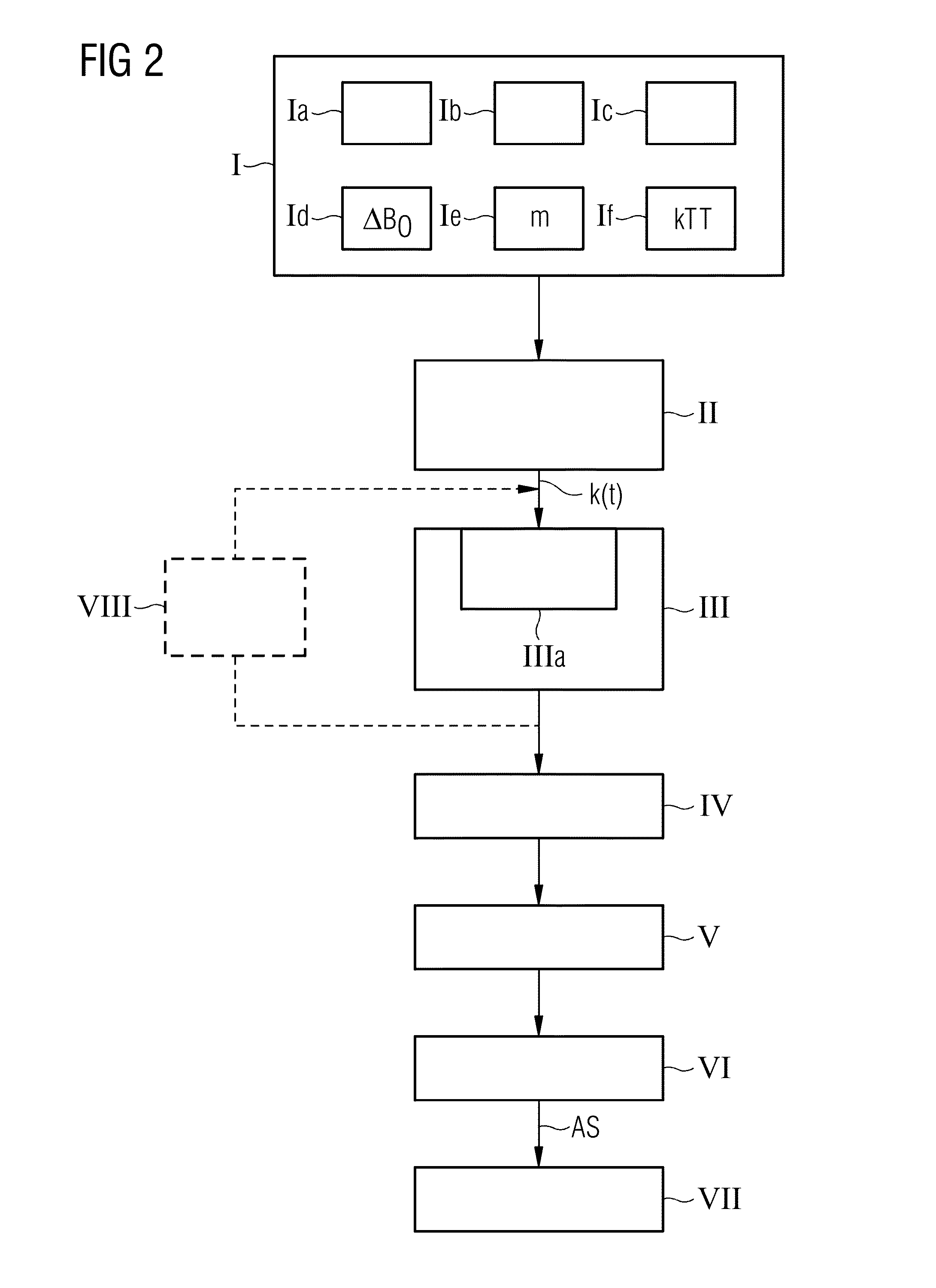
Determination of a magnetic resonance system control sequence
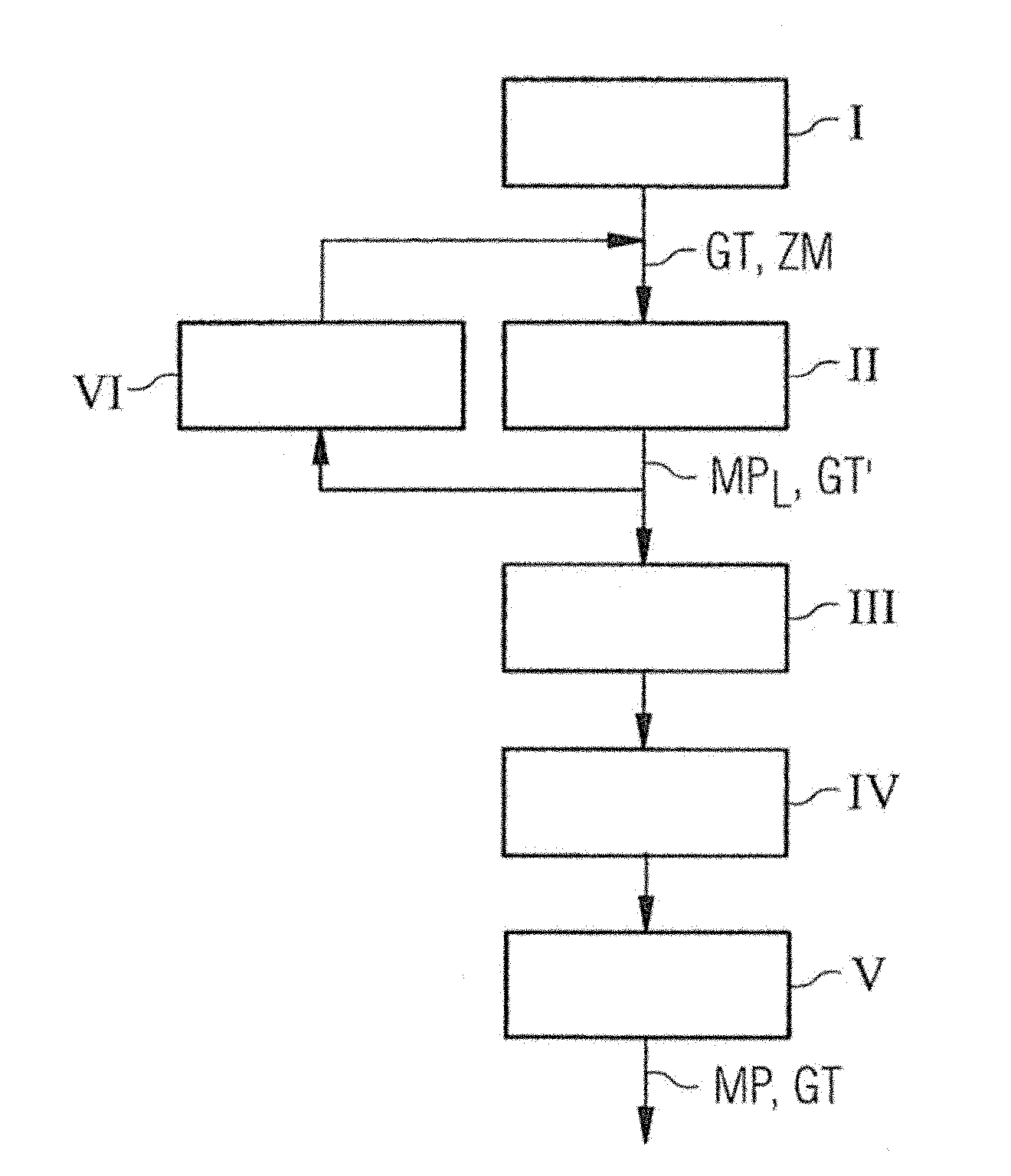
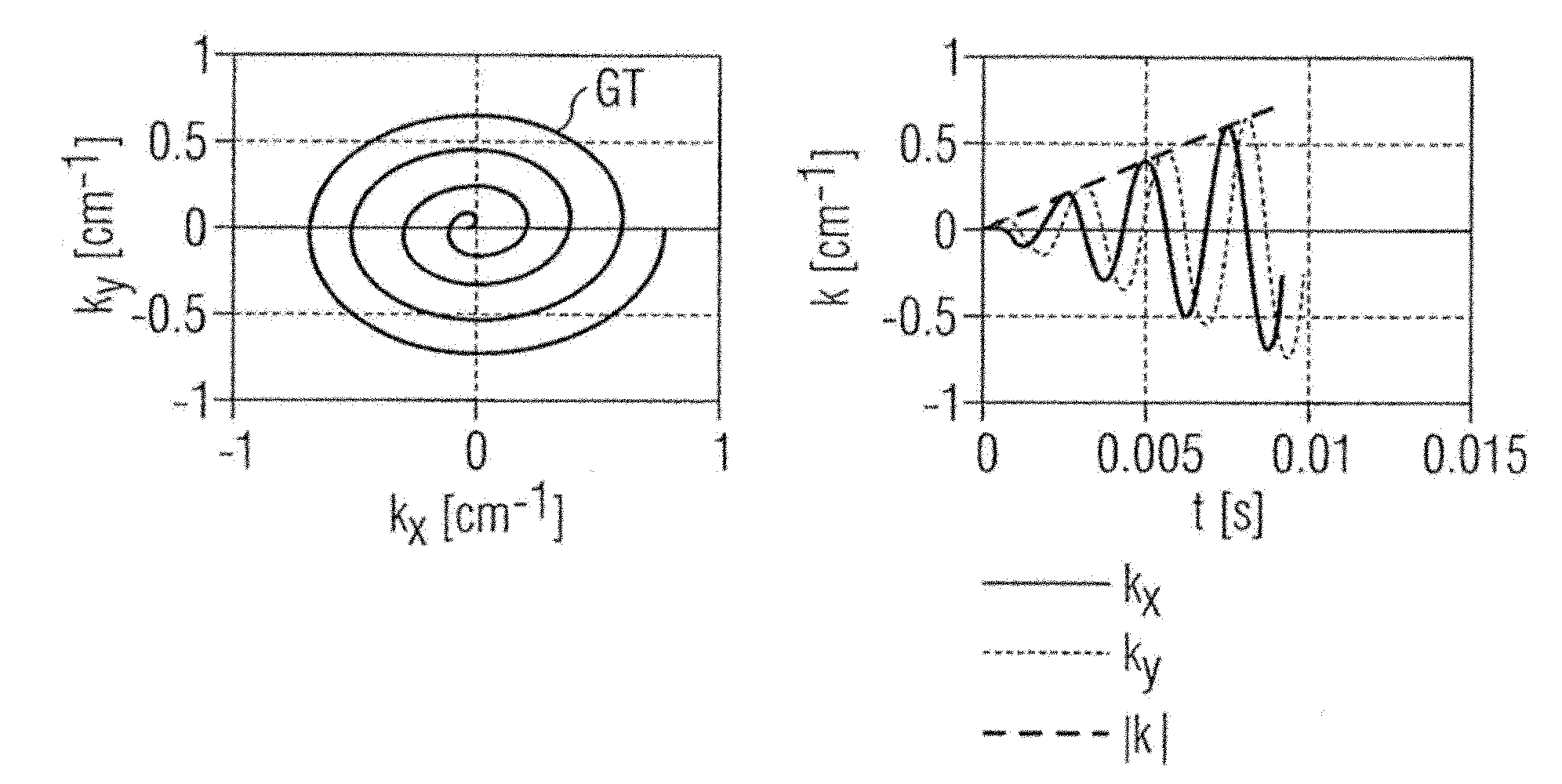
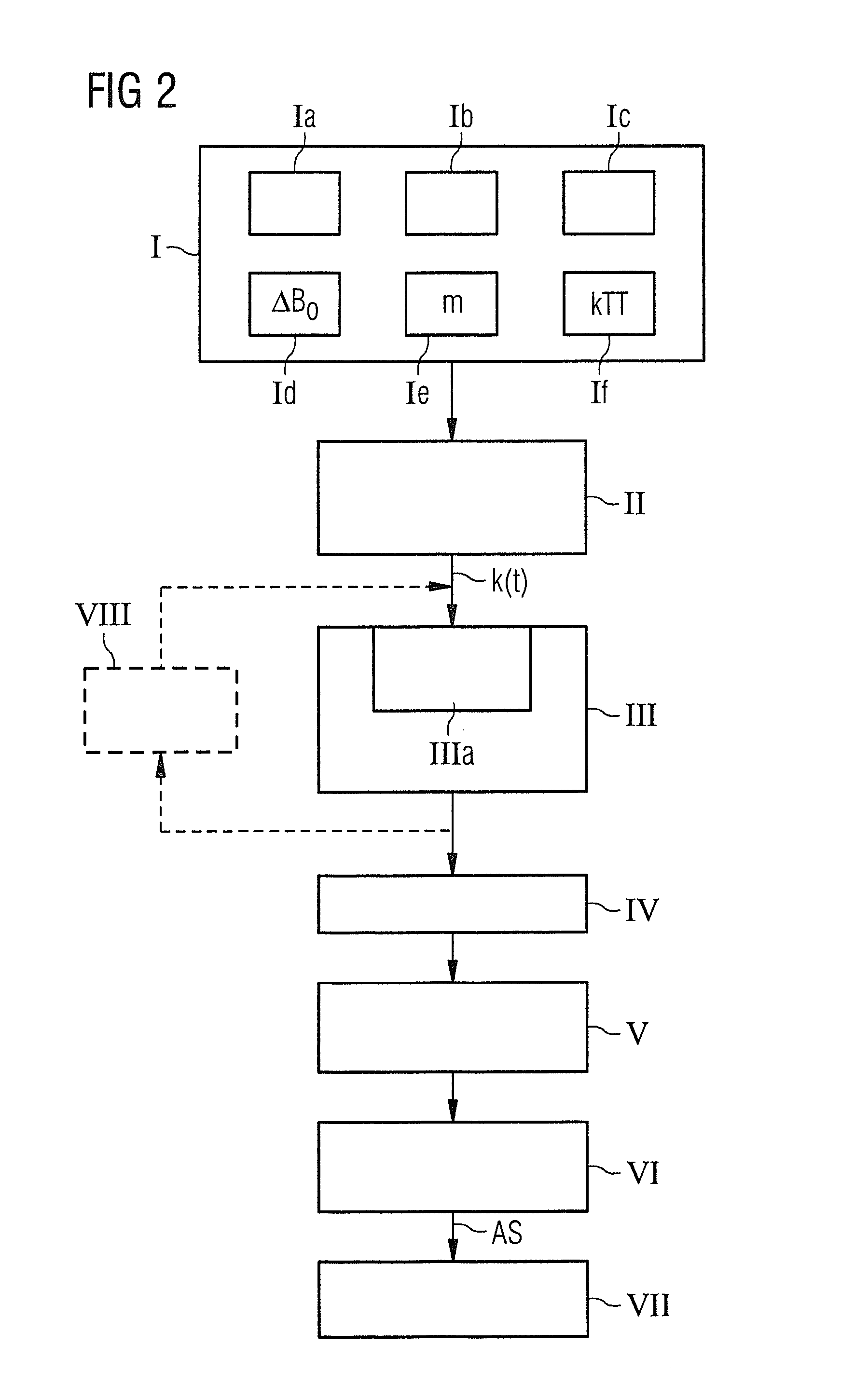
ActiveUS20130249549A1Fast and optimally robust calculationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingResonanceMagnetization
In method and a control sequence determination device to determine a magnetic resonance system control sequence that includes at least one radio-frequency pulse train to be emitted by a magnetic resonance system, a target magnetization (m) is initially detected, and an energy distribution function in k-space is determined on the basis of the target magnetization. A k-space trajectory is then determined under consideration of the energy distribution function in k-space, for which the radio-frequency pulse train is then determined in an RF pulse optimization method. The method is suitable for operation of a magnetic resonance system, and a magnetic resonance system includes such a control sequence determination device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Methods for real-time single molecule sequence determination
InactiveUS20050260614A1Enhanced interactionQuick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LSequence determination
A sequencing methodology is disclosed that allows a single DNA or RNA molecule or portion thereof to be sequenced directly and in substantially real time. The methodology involves engineering a polymerase and / or dNTPs with atomic and / or molecular tags that have a detectable property that is monitored by a detection system.
Owner:VISIGEN BIOTECH
Layout analyzing method and system
ActiveCN104516891AAccurate Layout Analysis ResultsImproved layout analysis resultsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData informationTheoretical computer science
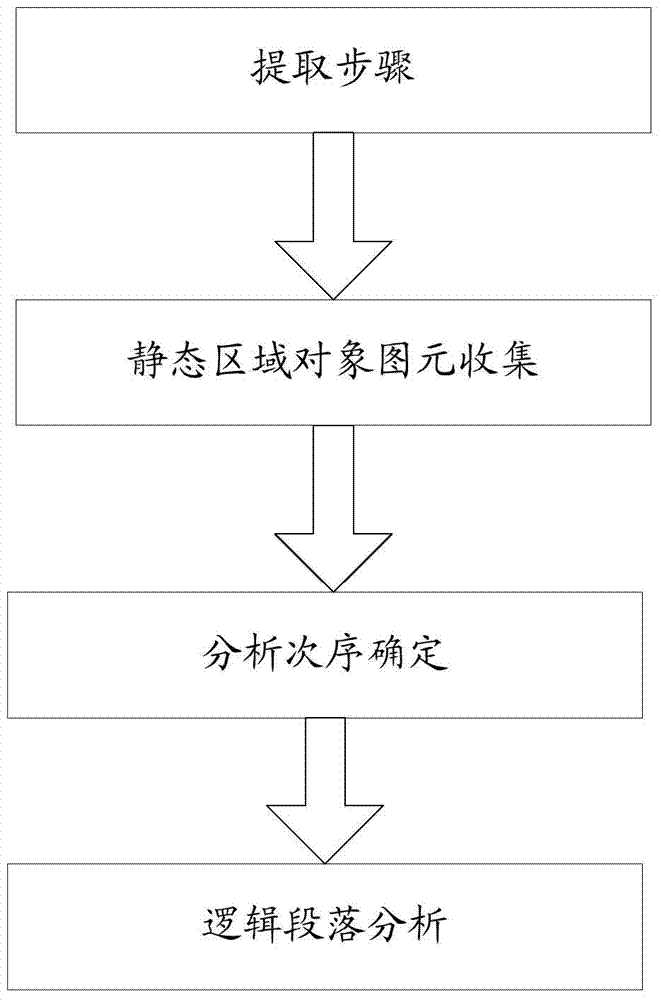
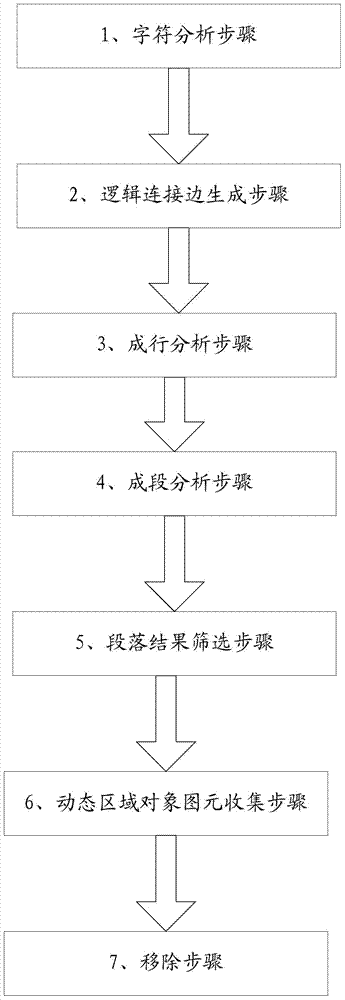
Embodiments of the present invention provide a layout analysis method, comprising: extraction, collection of basic elements with respect to static area objects, analysis sequence determination and logical paragraph analysis, wherein the logical paragraph analysis comprises character analyzing, logical connection edge generating, line forming analyzing, paragraph forming analyzing, paragraph result filtering, basic elements collecting with respect to the dynamic area objects and basic element removing. According to the embodiments of the present invention, logical reference information and basic element data information are combined, and the logical reference information is fully used during layout analysis, such that a more accurate layout analysis result with respect to a fixed-layout document is acquired, and the layout analysis result is effectively improved.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +1
Rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi
The invention relates to a rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi, which specially comprises the following steps: (1) culturing fungi on a solid culture medium; (2) taking fresh fungi, and extracting the DNA of the fungi by using a microwave method; (3) amplifying DNA fragments between ribosomal spacers of the fungi by using ITS1 and ITS4 primers through PCR (polymerase chain reaction); (4) after recovering the PCR fragments, carrying out sequence determination on the fragments; and (5) carrying out comparison on the obtained sequences by using the Blast of NCBI. According to the invention, the identification of unknown pathogenic fungi can be performed within a shorter time and under relatively simple experimental conditions, thereby facilitating the rapid diagnosis for diseases occurring in fields so as to guide the prevention and control of diseases. According to the method, through the identification on 21 kinds of pathogenic fungi on different crops, and the coincidence rate is 100% through sequence comparison. The method is not only applicable to the identification on fresh mycelia, but also is applicable to the identification on conidium and sclerotium of pathogenic fungi, and has the characteristics of rapidness and high efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Determination of a Magnetic Resonance System Activation Sequence
InactiveUS20130253876A1Rapid and robust calculationQuick calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMagnetization
A method and a control sequence determination device for the determination of a magnetic resonance system activation sequence including at least one high-frequency pulse sequence to be transmitted by a magnetic resonance system are provided. A current B0 map and optionally a target magnetization are acquired. In addition, a k-space trajectory type is determined. An error density is calculated in a k-space based on the current B0 map and optionally based on the target magnetization using an analytic function. This analytic function defines an error density in the k-space as a function of the current B0 map and optionally the target magnetization. Taking account of the error density in the k-space, a k-space trajectory of the specified k-space trajectory type is determined. The high-frequency pulse sequence is determined for the k-space trajectory in an HF pulse optimization process.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
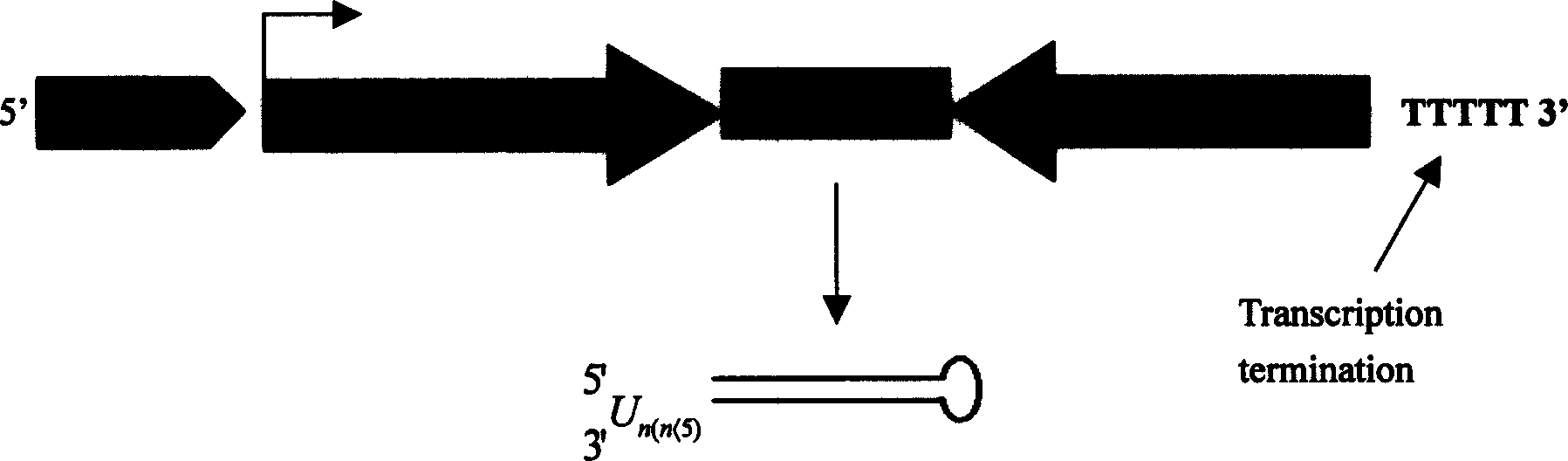
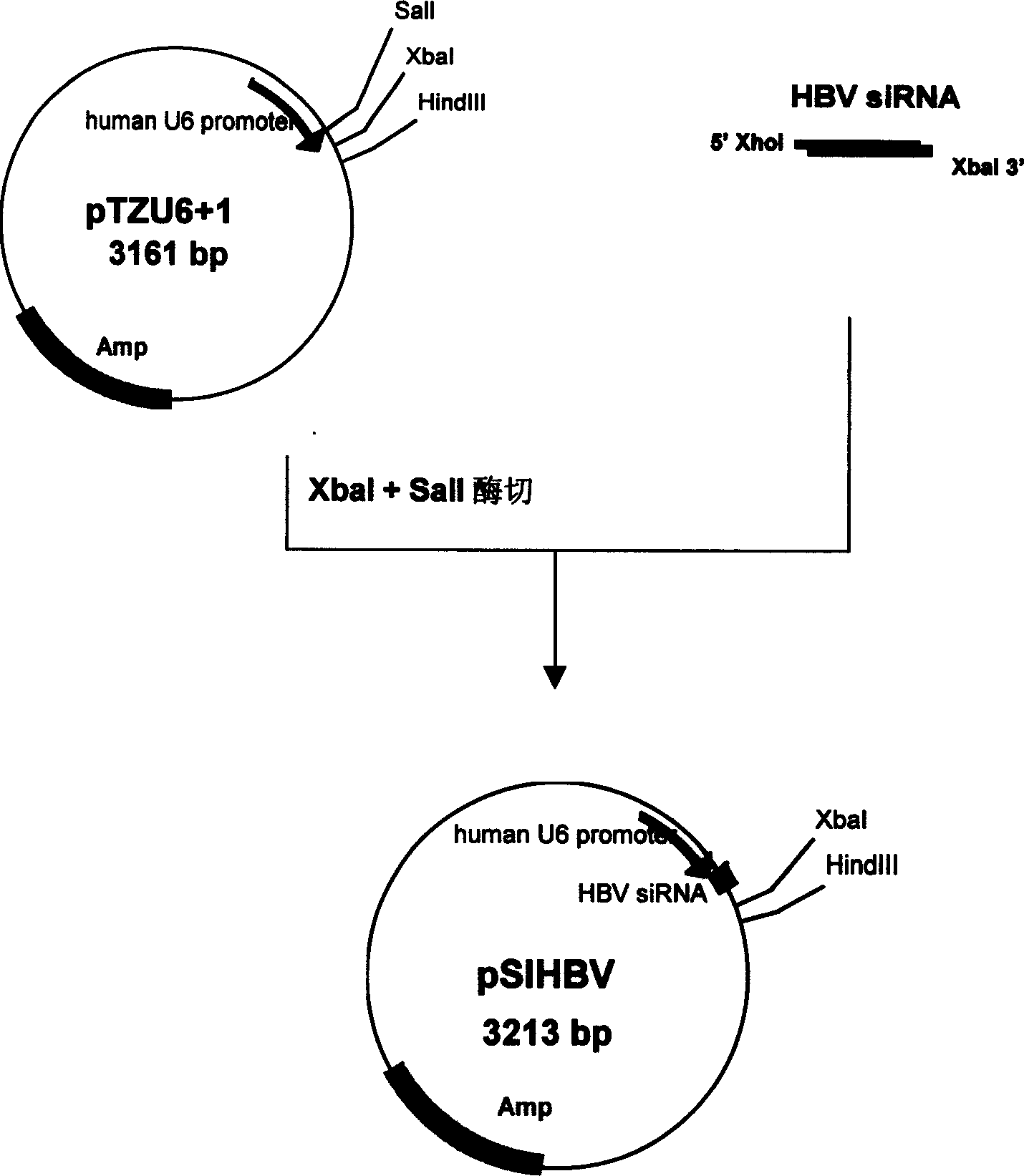
Construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its application in antivirus treatment
InactiveCN1523113AInhibit expressionInhibition of replicationGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyChemical synthesisConserved sequence
The present invention relates to construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its antiviral therapeutic application. According to the design principle said construction includes the following steps: respectively selecting nucleotide sequence of HBV envelope protein (MS) coding region 69nt-87nt, polymerase(p) coding region 708nt-726nt and core protein (c) coding region 2052 nt-2070nt, designing correspondent siRNA sequence, using BLAST software to analyze homogenously to confirm that it is HBV highly conservative sequence, then chemically synthesizing single-stranded oligonucleotide, external annearing to form double-stranded DNA, connecting it with eukaryotic expression vector pTZU6+1, enzyme excision identification and sequence determination and analysis show that siRNA extression vectors of three target hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene sequences are constructed. The tests show that HBV siRNA has the strong action of inhibiting virus replication and expression.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Algorithms for sequence determination
InactiveUS20130217006A1Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisRepetitive Sequences
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Contaminated soil phenanthrene and application thereof in contaminated soil restoration
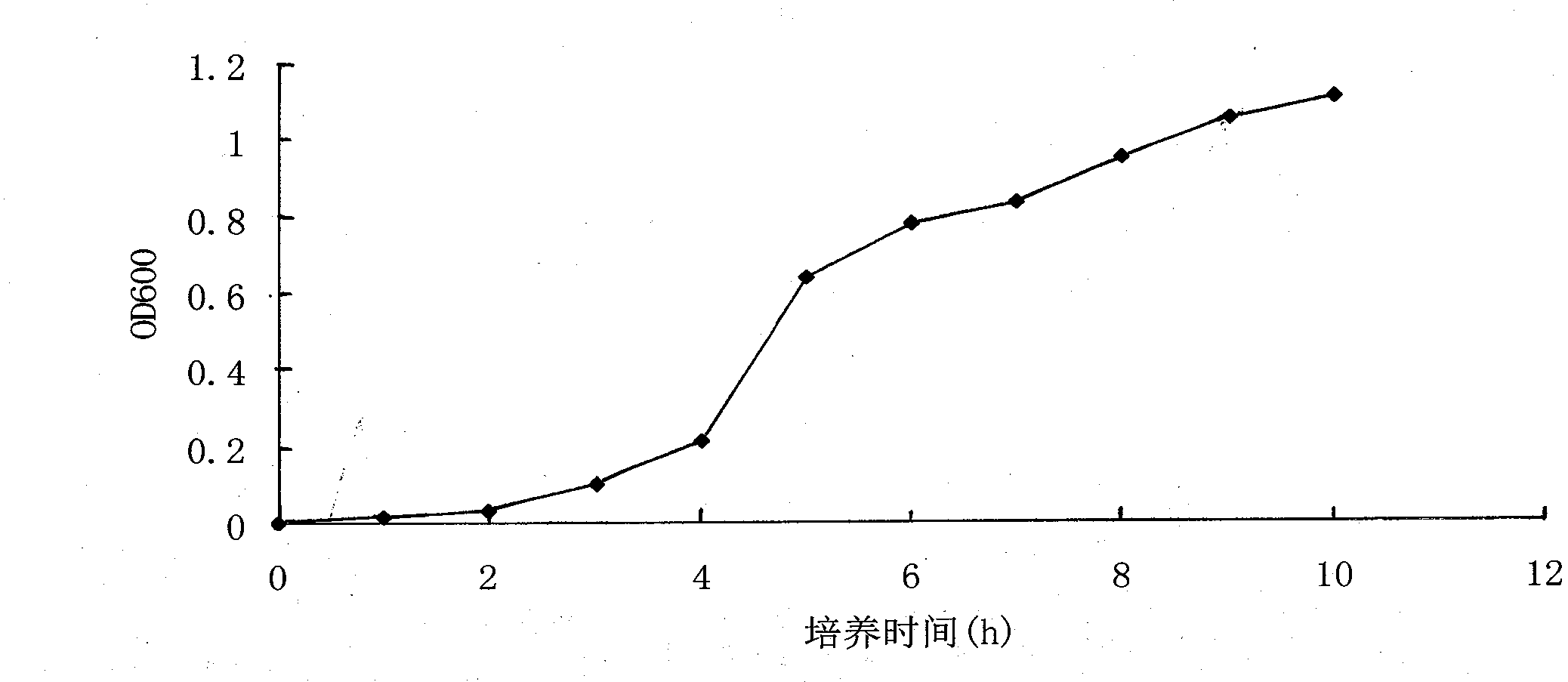
The invention discloses a contaminated soil phenanthrene and an application thereof in contained soil restoration. A bacterial strain with a contaminated soil restoration function is obtained by screening the strain in kelamayi oilfield oil-contaminated soil sample; the bacteria y-8 is determined as pseudomonasgeniculata CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6763 by further screening, domesticating and breeding, and carrying out morphological characteristic, 16SrRNA sequence determination and phylogenetic analysis to the obtained bacterial strain; according to the measured degradation property of the phenanthrene and the intensive study of the action of the phenanthrene in contaminated soil restoration, the contaminated soil phenanthrene has an outstanding technical effect in the contaminated soil restoration.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus, system, and method for automated conversion of content having multiple representation versions
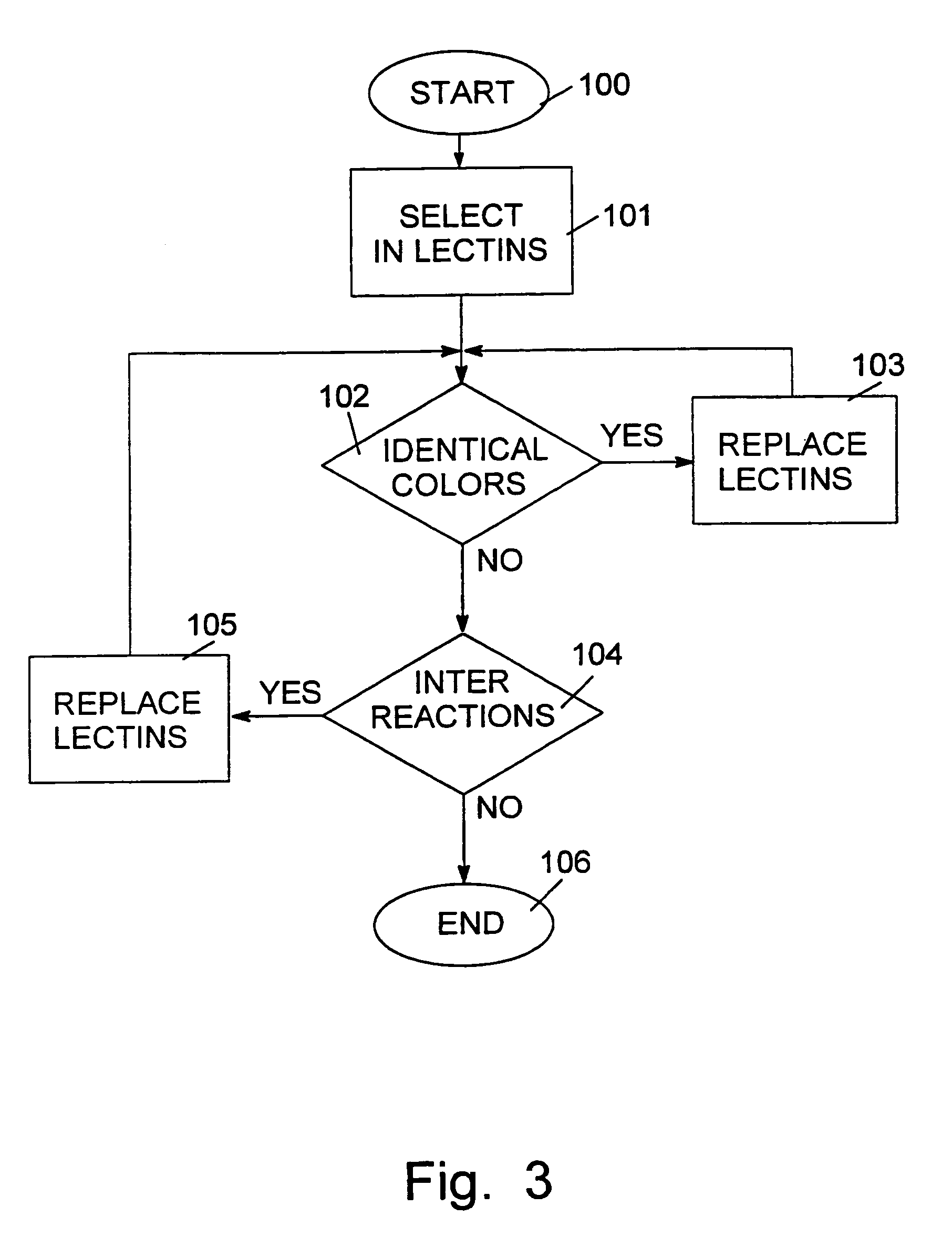
InactiveUS20060010175A1Low costReduce complexityVersion controlSpecific program execution arrangementsSequence determinationDatabase
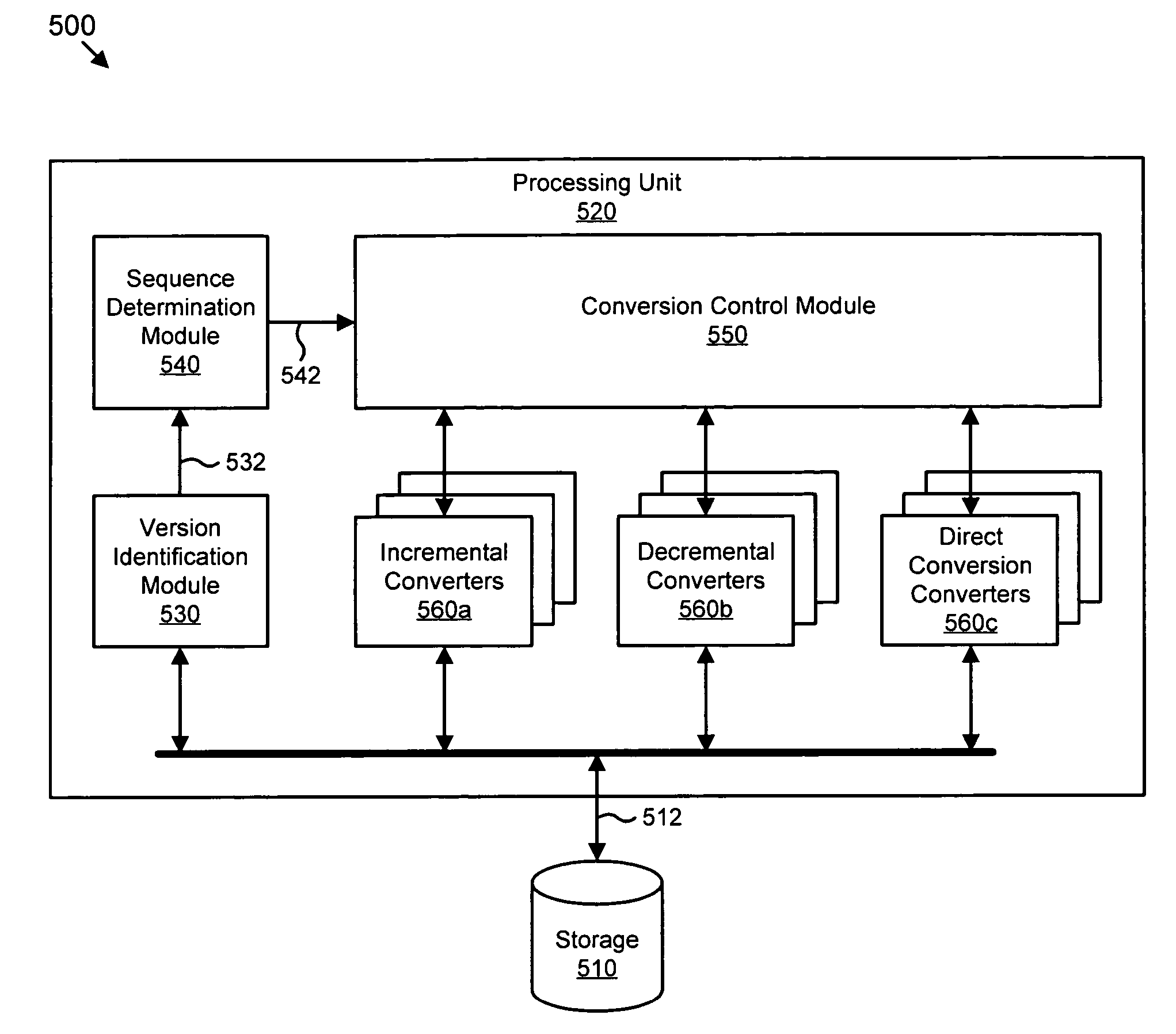
An apparatus, system, and method for automated conversion of content reduces the development and support burden associated with multiple content representation versions such as those associated with various releases of a software program. In one embodiment, a version identification module determines a source version identifier for specified content, a sequence determination module receives the source version identifier along with a target version identifier and determines a minimum length conversion sequence. Furthermore, a conversion control module invokes one or more content converters corresponding to the conversion sequence and provides the specified content in the target representation. The ability to cascade multiple content converters into a composite converter increases the permutation of content representations that may be supported with a small number of converters.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com