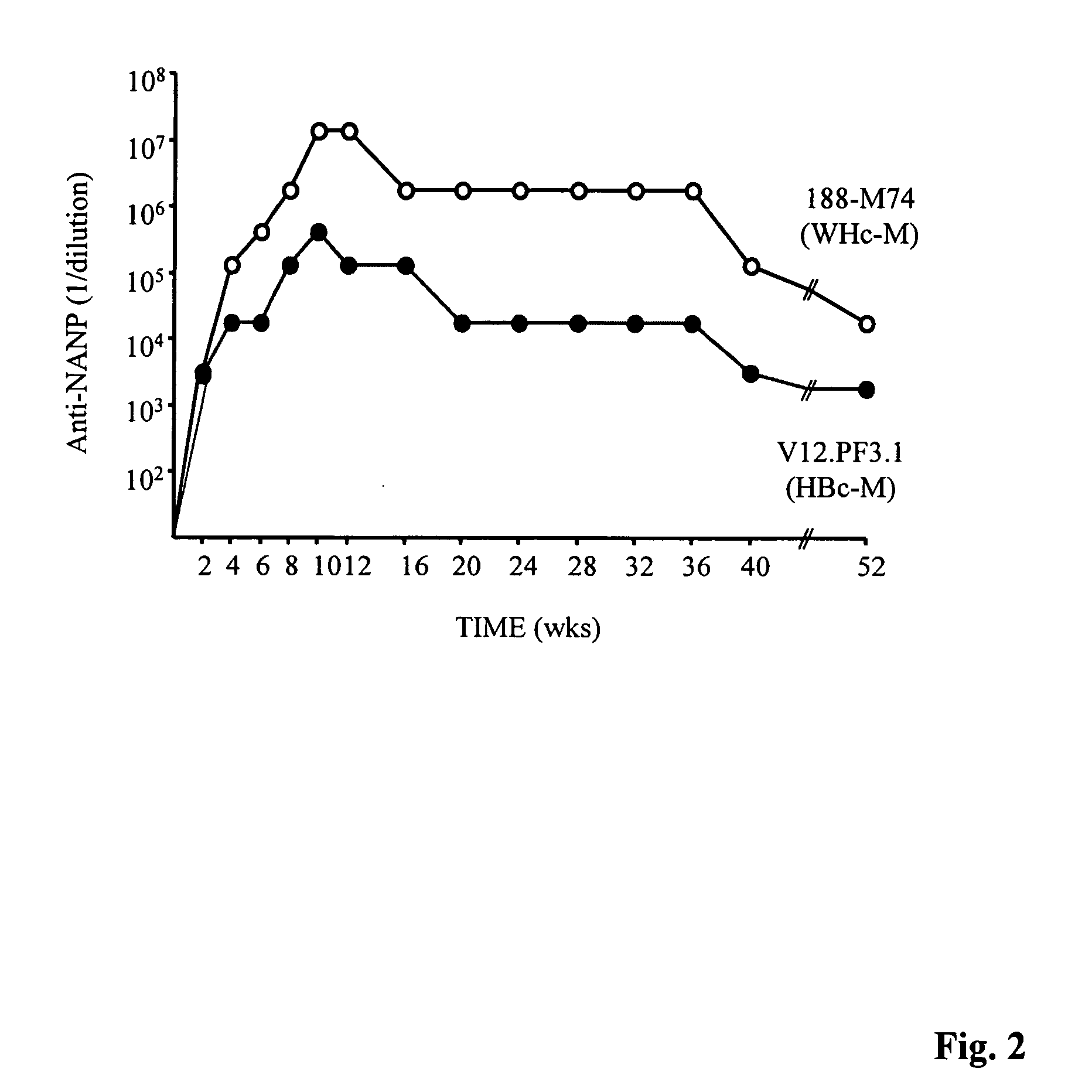
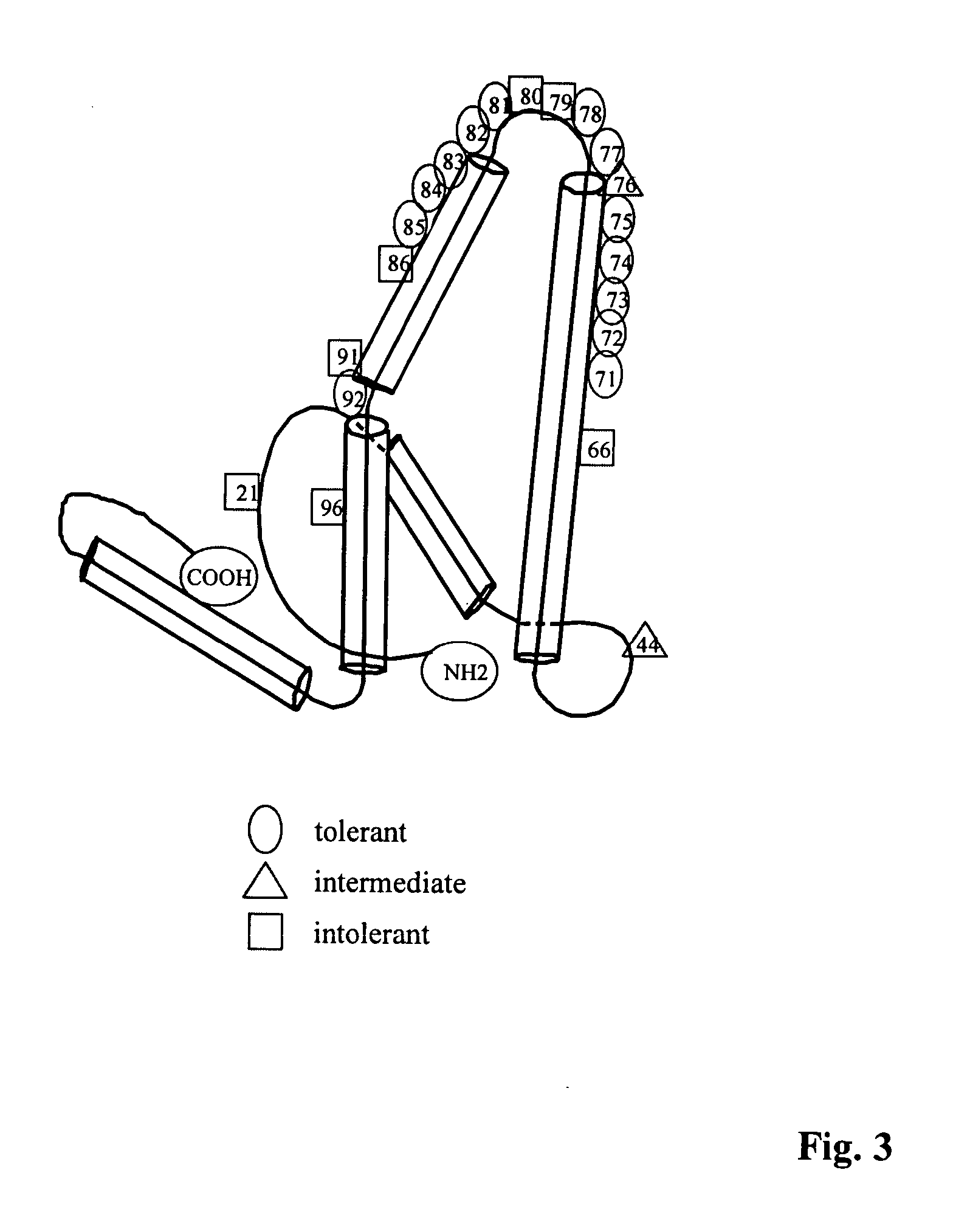
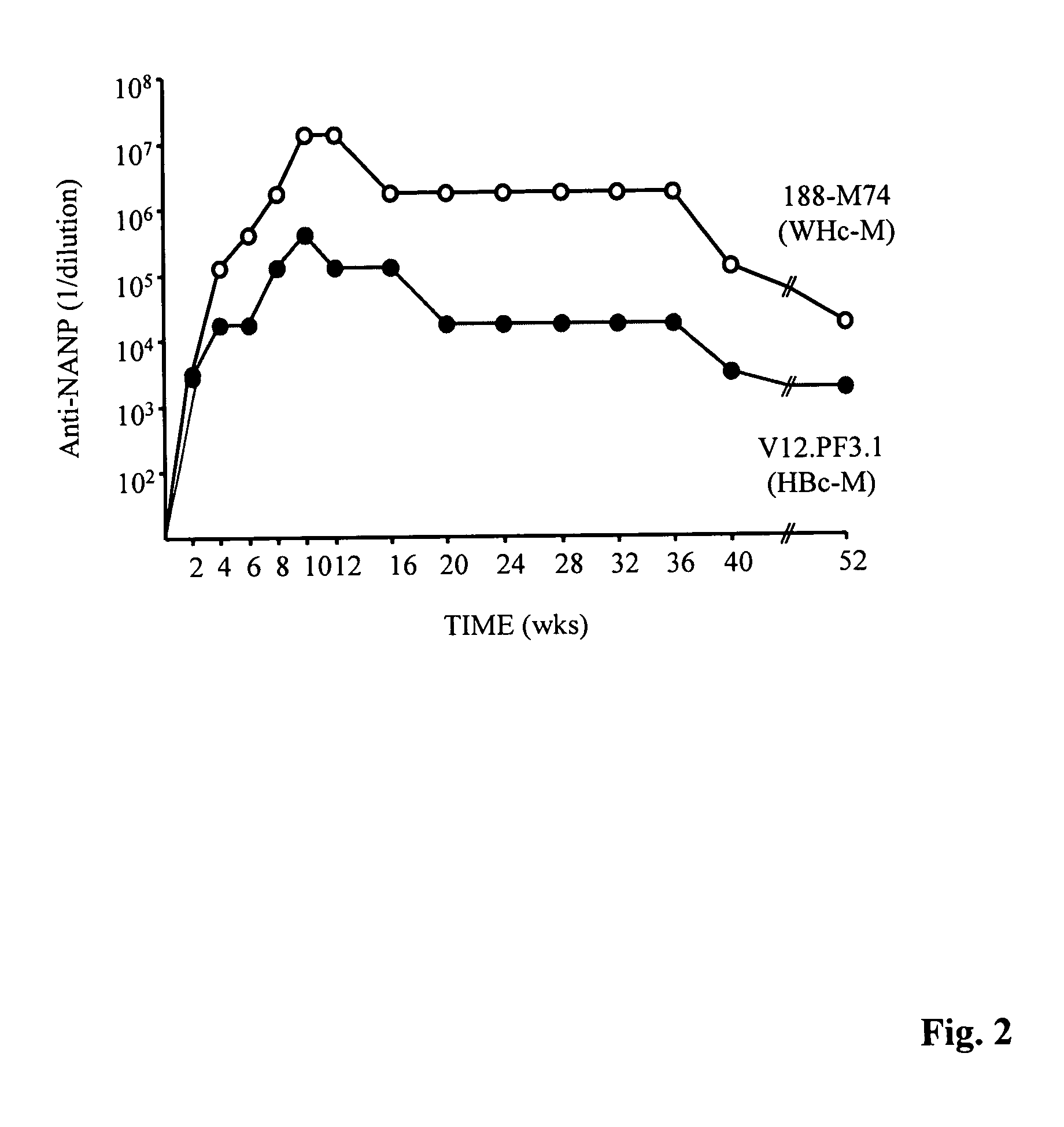
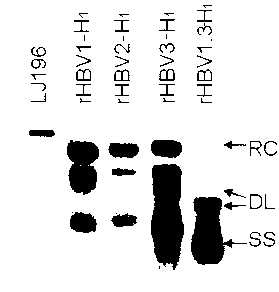Patents
Literature
178 results about "Core protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Capsid-modified recombinant adenovirus and methods of use
InactiveUS6955808B2Low yieldEfficiencyBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSingle-Chain AntibodiesNoninvasive imaging
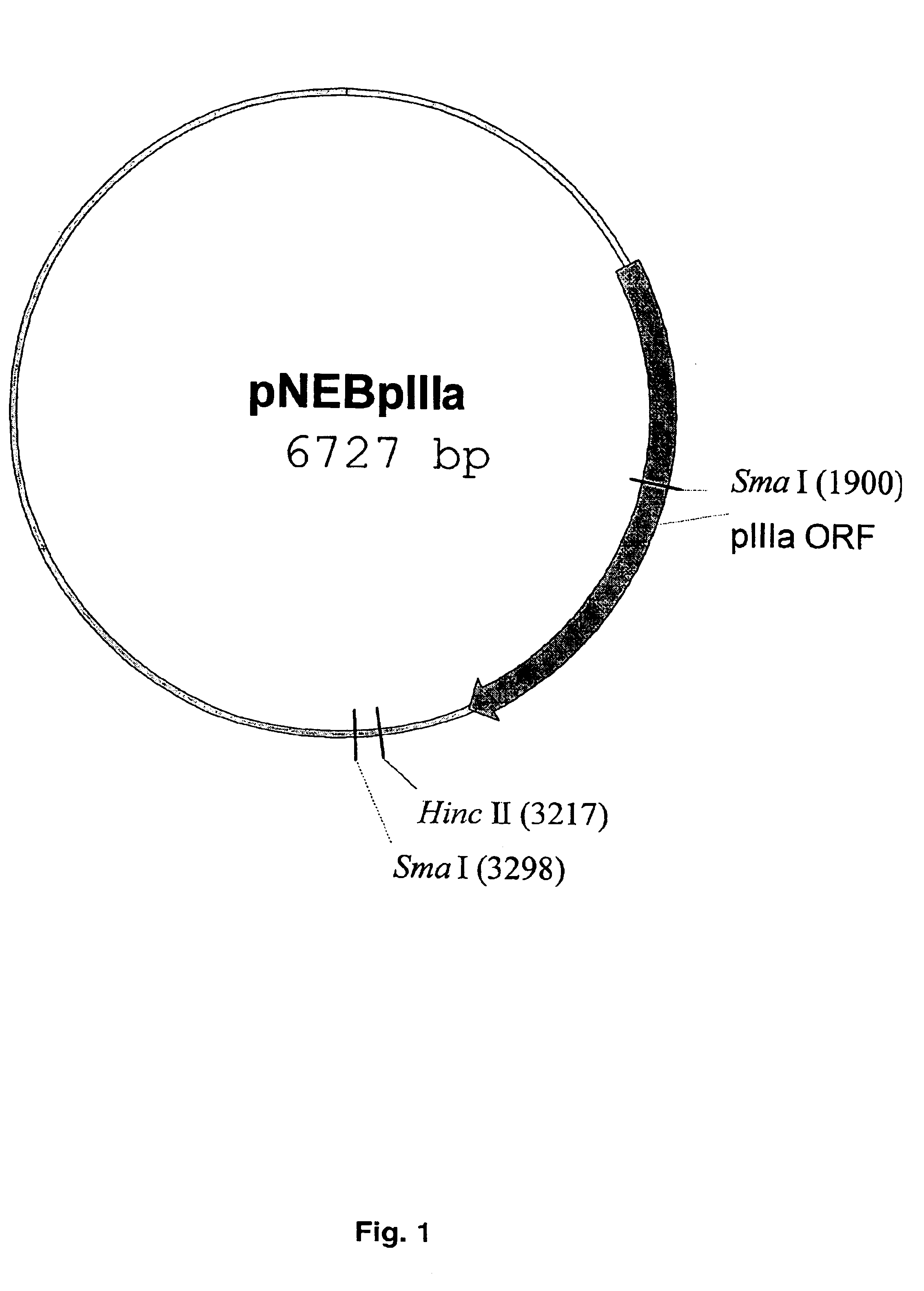
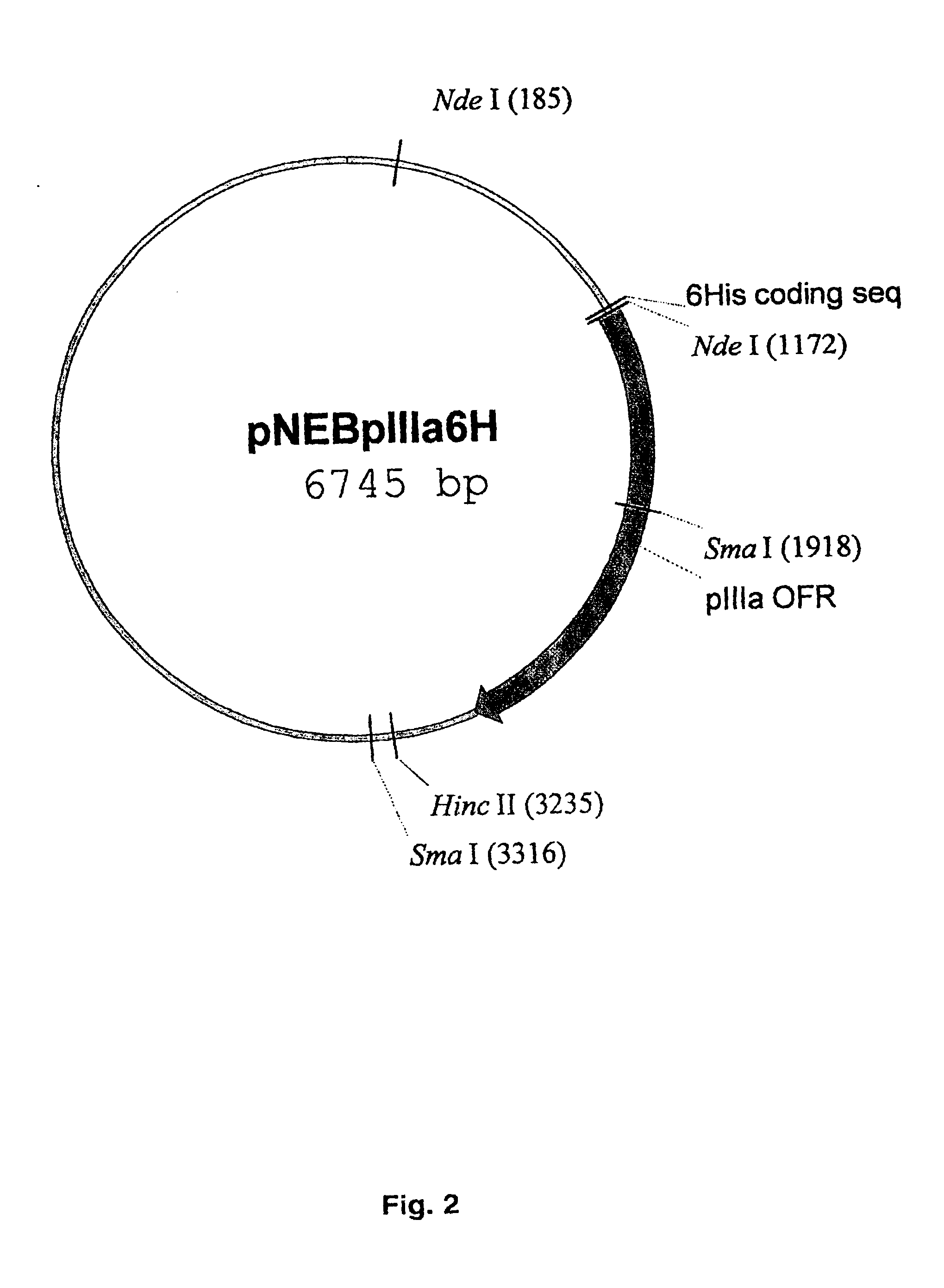
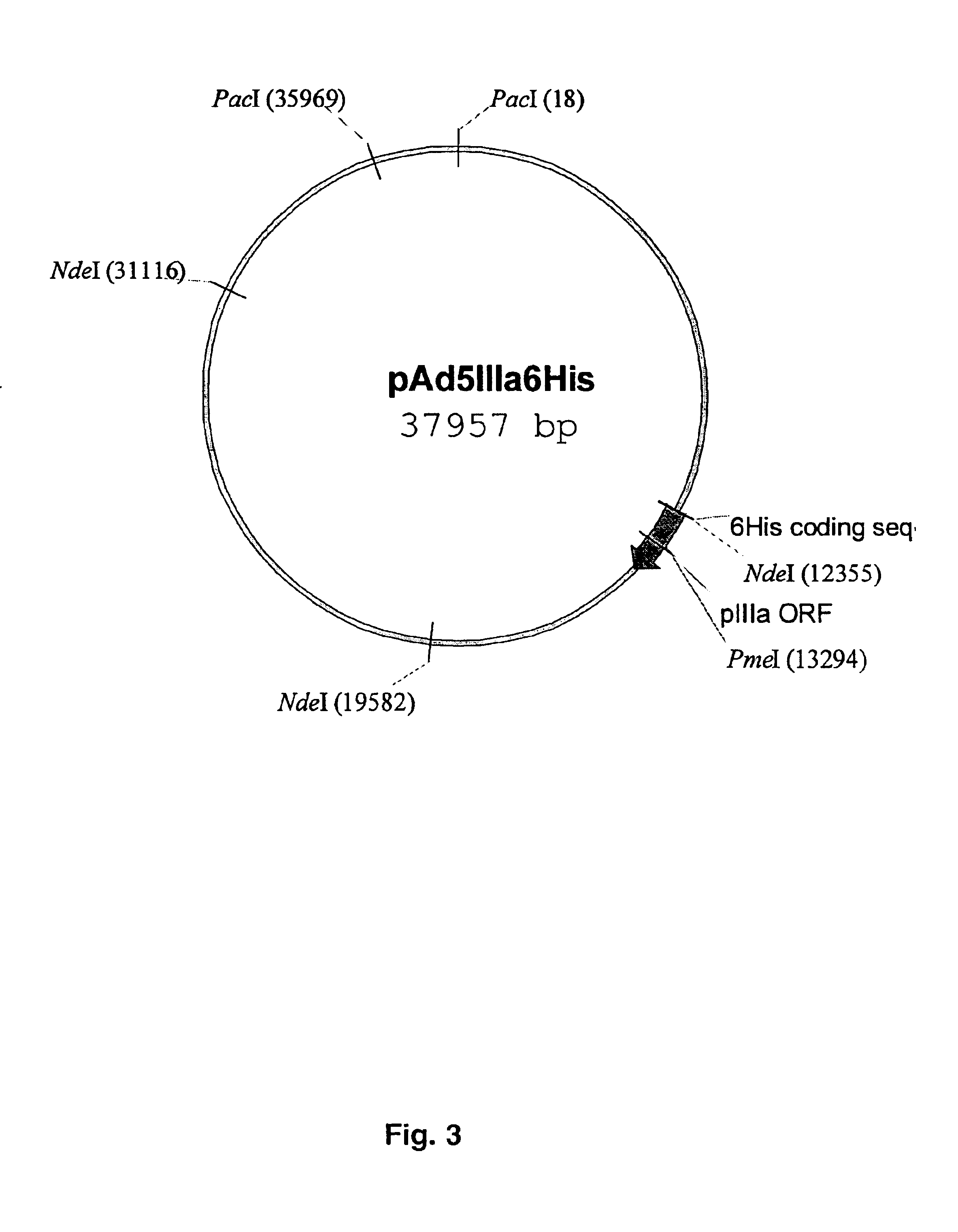
The present invention describes recombinant adenoviral vectors modified by incorporating targeting ligands or label into viral capsid or structural proteins. In one embodiment, single-chain antibody was introduced into the minor capsid proteins pIIIa or pIX so that the adenoviral vector can be targeted to a particular cell type. In another embodiment, there is provided a noninvasive imaging strategy useful for monitoring the replication and spread of conditionally replicative adenoviral vectors. Viral structural proteins such as pIX capsid protein, core proteins mu, V and VII were expressed as fusion protein with a fluorescent label. Once incorporated into the virions, detection of the structural fusion protein label would indicate the localization of the disseminated viral progeny. The detected fluorescent signals also closely correlate with the level of viral replication and progeny production.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Modified Human Hepatitis C Virus Genomic RNA That can be Autonomously Replicated
ActiveUS20090176200A1Easy to useSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
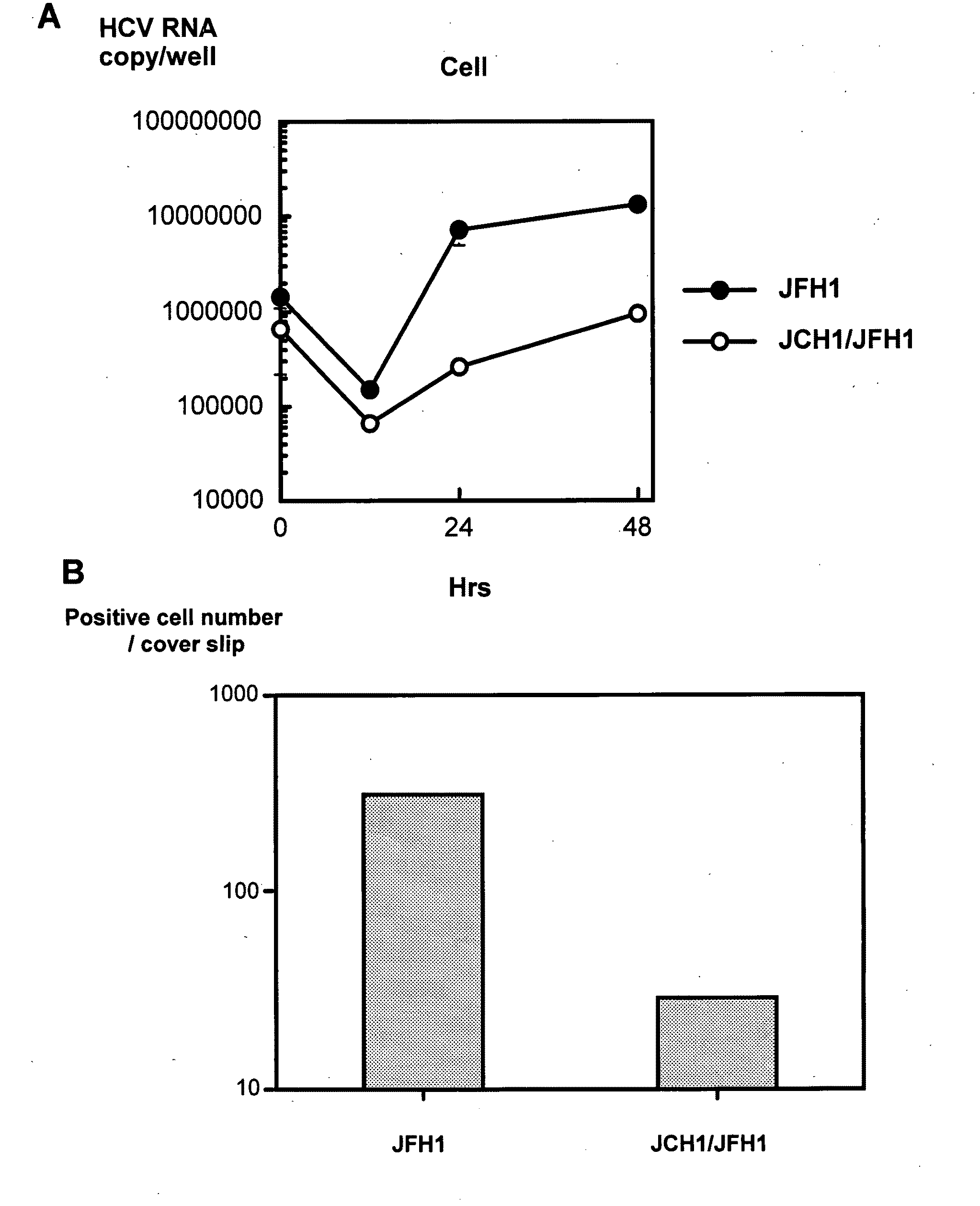
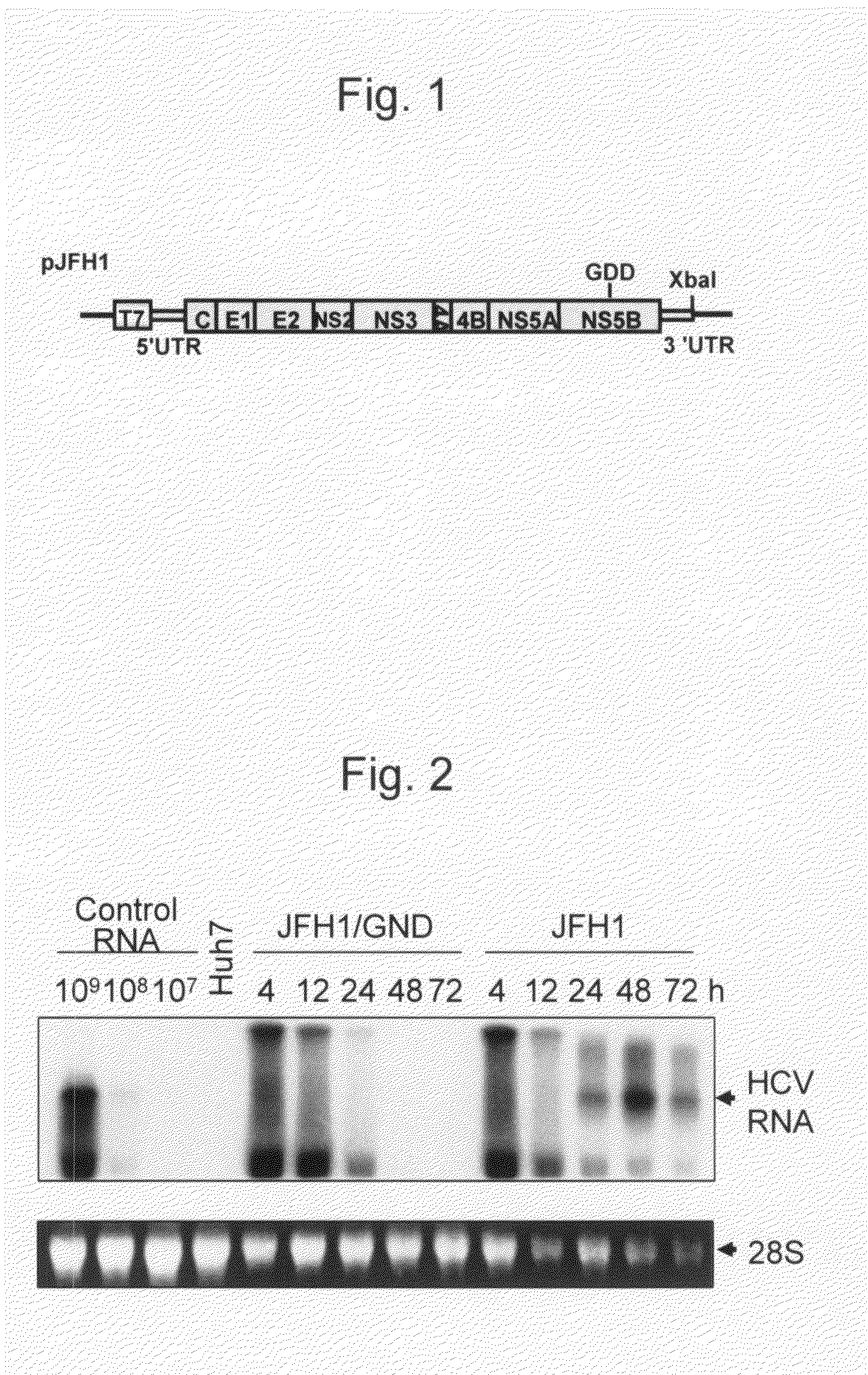
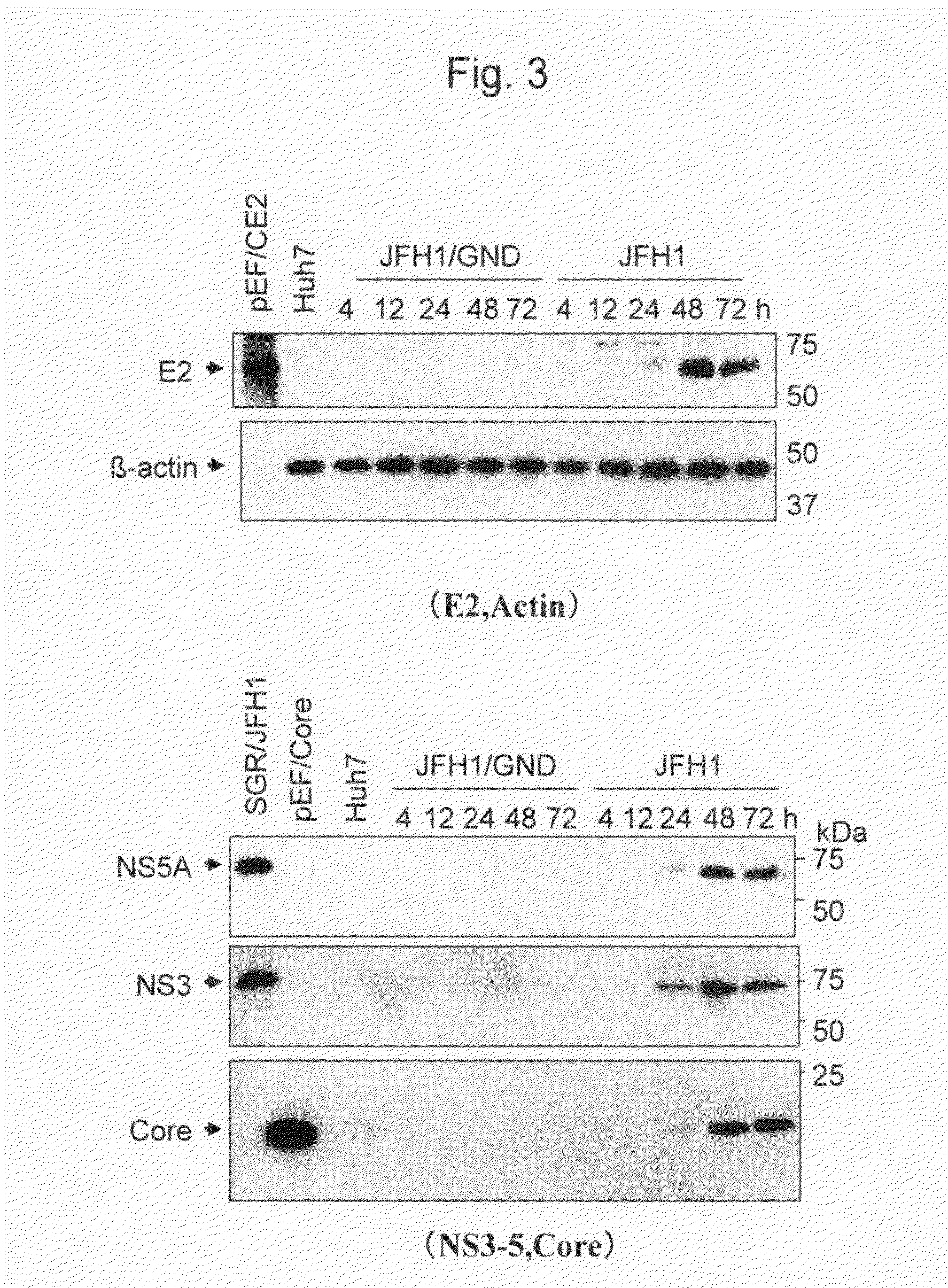
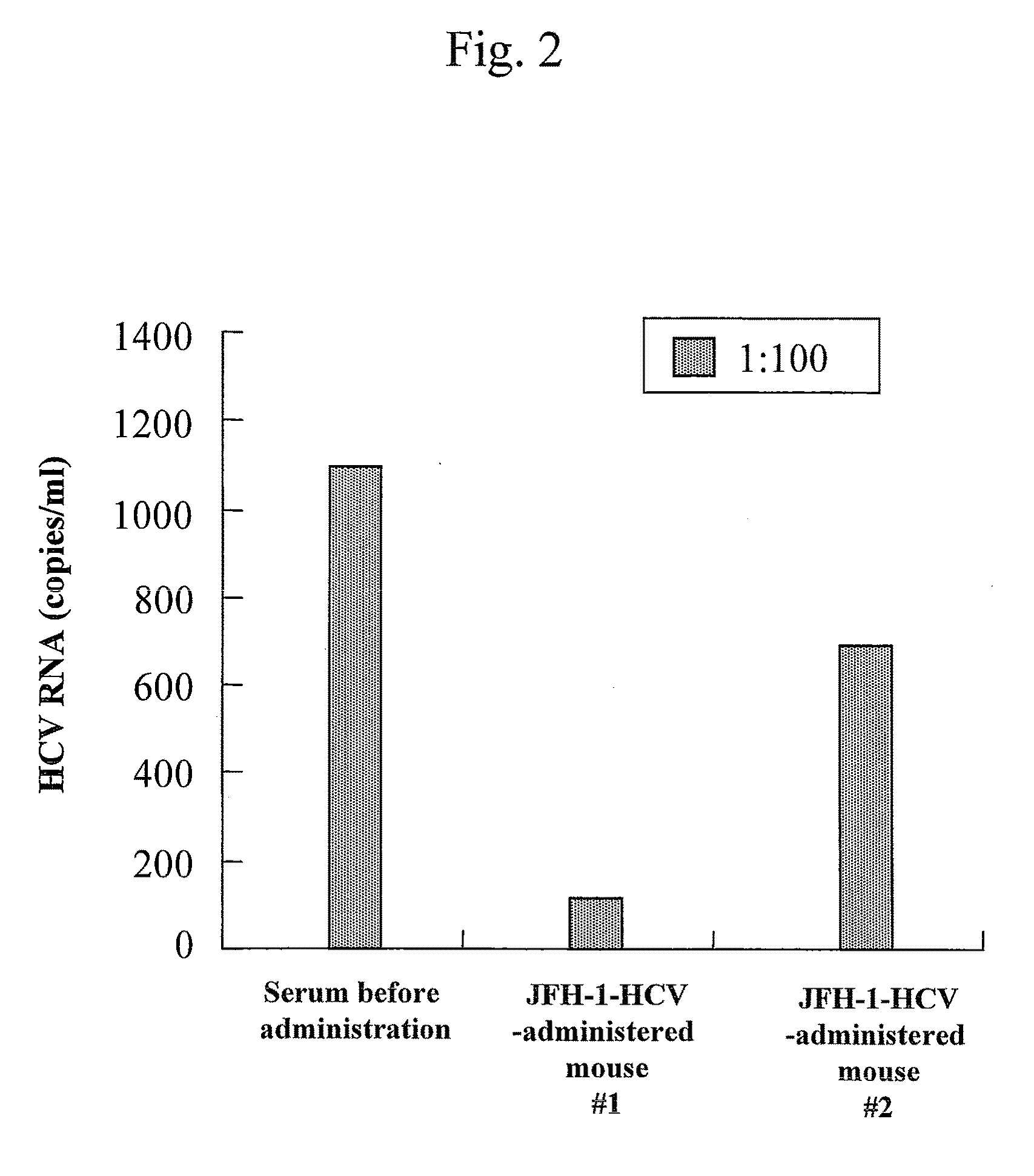
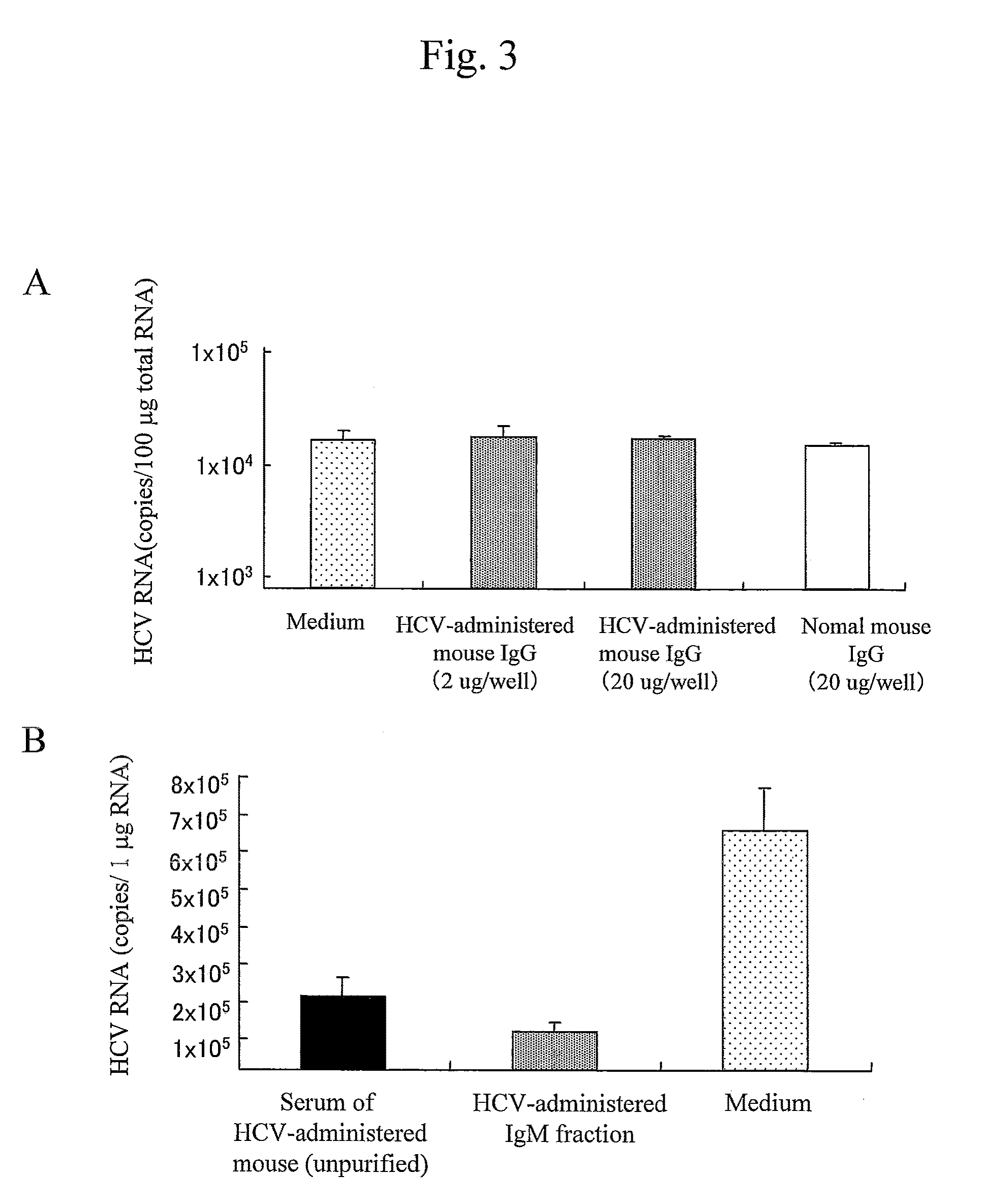
The present invention provides modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, comprising nucleotide sequences of genomic RNA portions of two or more types of hepatitis C viruses, which comprises a 5′ untranslated region, a core protein coding sequence, an E1 protein coding sequence, a p7 protein coding sequence, an E2 protein coding sequence, an NS2 protein coding sequence, an NS3 protein coding sequence, an NS4A protein coding sequence, an NS4B protein coding sequence, an NS5A protein coding sequence, an NS5B protein coding sequence, and a 3′ untranslated region, and which can be autonomously replicated. In particular, the present invention relates to modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, which can be autonomously replicated by substitution of the RNA sequence portion encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of hepatitis C virus genomic RNA with a partial RNA sequence encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of a JFH1 strain shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Cropping GST protein thermal induction fusion expression plasmid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101215573ASuitable for western blot experimentsWill not affect judgmentVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliProtein target
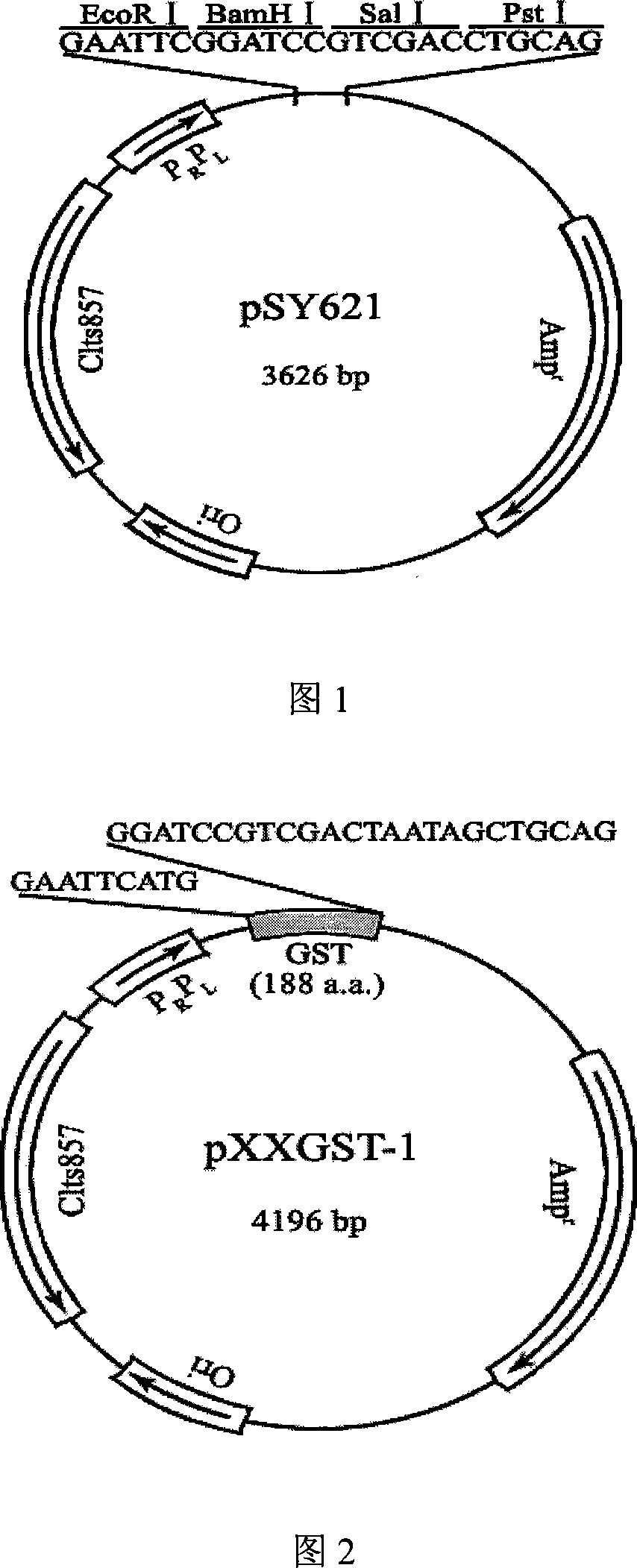
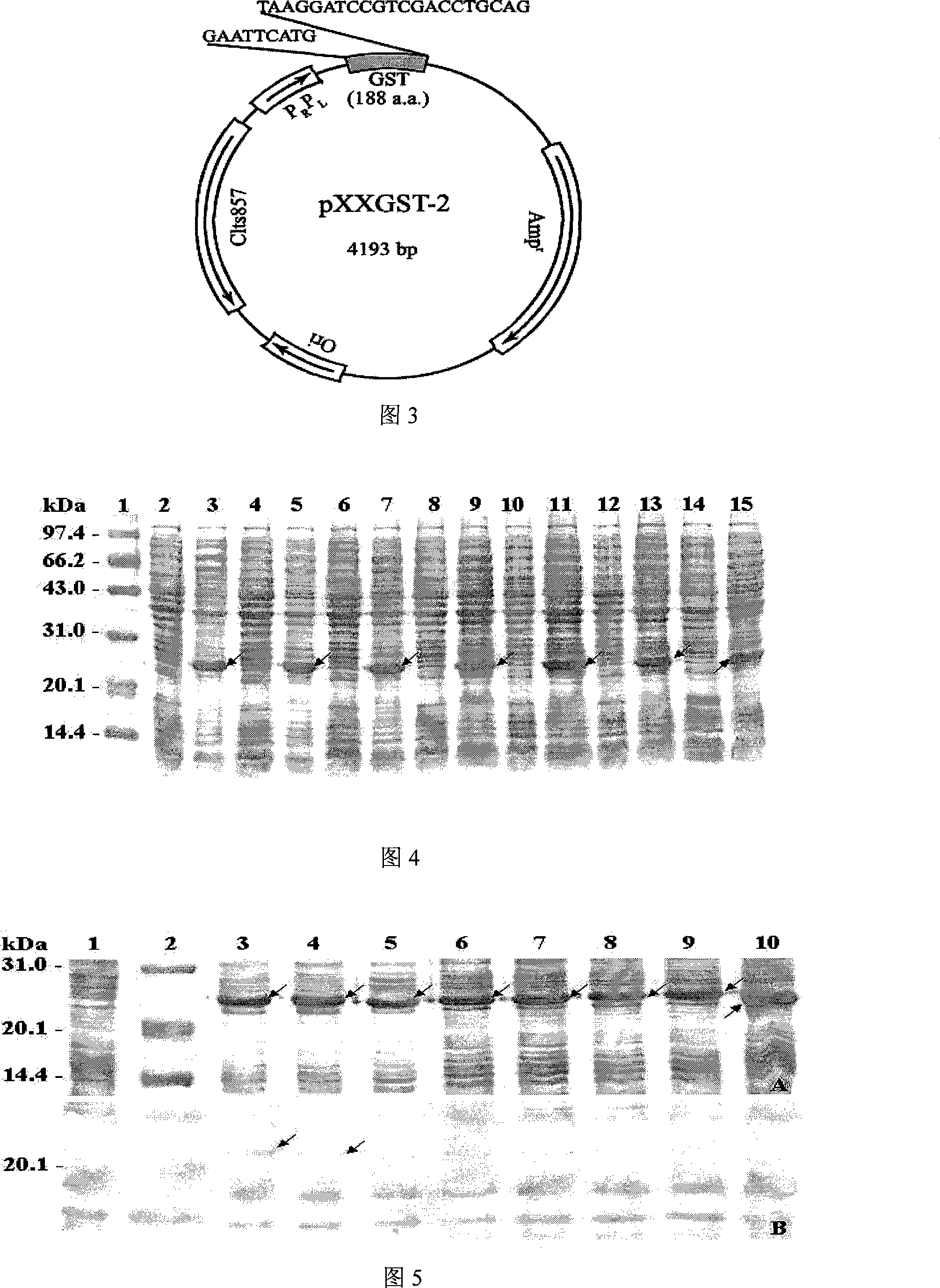
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering and in particular is a heat-induced fusion expression recombinant plasmid of truncated GST protein and a process for preparation. The invention selects utility truncated GST188 protein which is composed of 188aa as a carrier, a pXXGST-1 recombinant plasmid which expresses short peptide fusion protein in an escherichia coli heat-induced expression system and a heat-induced type pXXGST-2 recombinant plasmid which is used to express comparison to realize the aim of synthesizing short peptide creatures, which is especially provided for scanning, drawing, positioning antigen linear epitopes and identifying epitope motif. Experiments of the invention prove the adaptability and the applicability of the GST188 core protein which is used as the short peptide creatures expression vector, in antigen epitope scanning identification, and in particular when anti- recombinant target protein antiserum is used to indentify the epitope motif.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PLANNED PARENTHOOD RES +2
Cancer-associated antigen analogue peptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110229481A1Improve long-term prognosisPrevent recurrenceFungiBacteriaEpitopeActivation cells
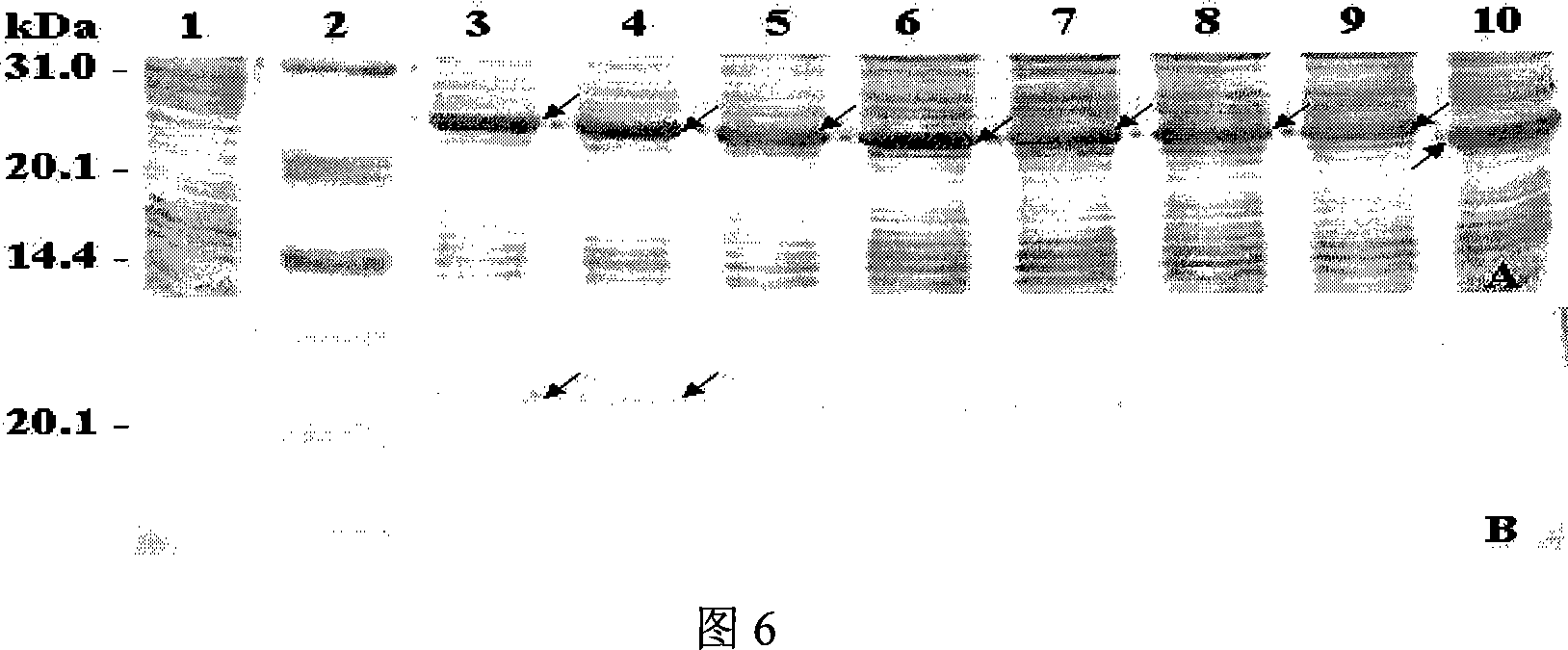
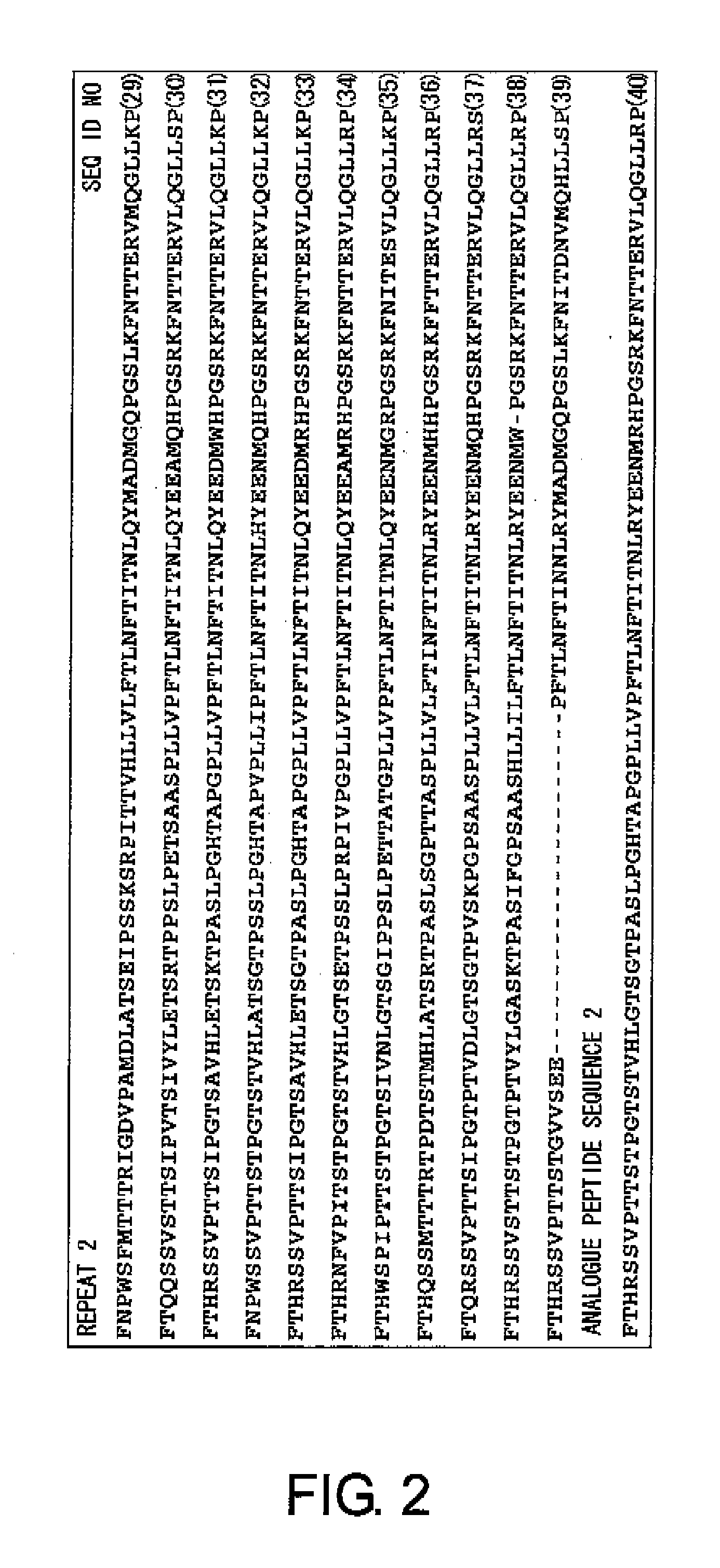
First, to solve the problems of the present invention, the present inventors confirmed the presence of ovarian cancer antigen-specific T cells in the peripheral blood of ovarian cancer patients by using an experimental system that detects combinations of CD4 and IL-4 or IFNγ. Next, using analogue peptides of the core protein MUC16 of the ovarian cancer-associated antibody C125, the present inventors revealed that antigen-specific CD4-positive T cells are present at an average frequency of about 4% in the peripheral mononuclear cells of patients and healthy subjects. Then, the present inventors analyzed the epitope for T cells in the core protein MUC16 of the ovarian cancer-associated antigen CA125, and determined the amino acid sequence FTLNFTITN (SEQ ID NO: 1) to be a shorter epitope. The present inventors further discovered that the analogue peptide OVCA11: GHTAPOPLLVPFTLNFTITN (SEQ ID NO: 11) is suitable for T cell activation.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Flavivirus expression and delivery system
InactiveUS6893866B1High expressionImprove translation efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsNucleotideStructural protein
The present invention provides a gene expression system comprising: a) a self-replicating expression vector of flavivirus origin which includes the flavivirus 5′ untranslated region (UTR), at least a portion of the 5′ coding region for flavivirus core protein, the nucleotide sequence coding for the flavivirus non-structural proteins, and the complete or most of the 3′-terminal sequence of the flavivrus 3′UTR, required for self-replication of flavivirus genomic material, which vector is adapted to receive at least a nucleotide sequence without disrupting its replication capabilities; and b) at least a second vector that is capable of expressing flavivirus structural protein(s) and any other proteins required for packaging of the self-replicating expression vector into flavivirus viral particles which vector is engineered to prevent recombination with the self-replicating vector when in its presence.
Owner:REPLIKUN BIOTECH
Advanced antigen presentation platform
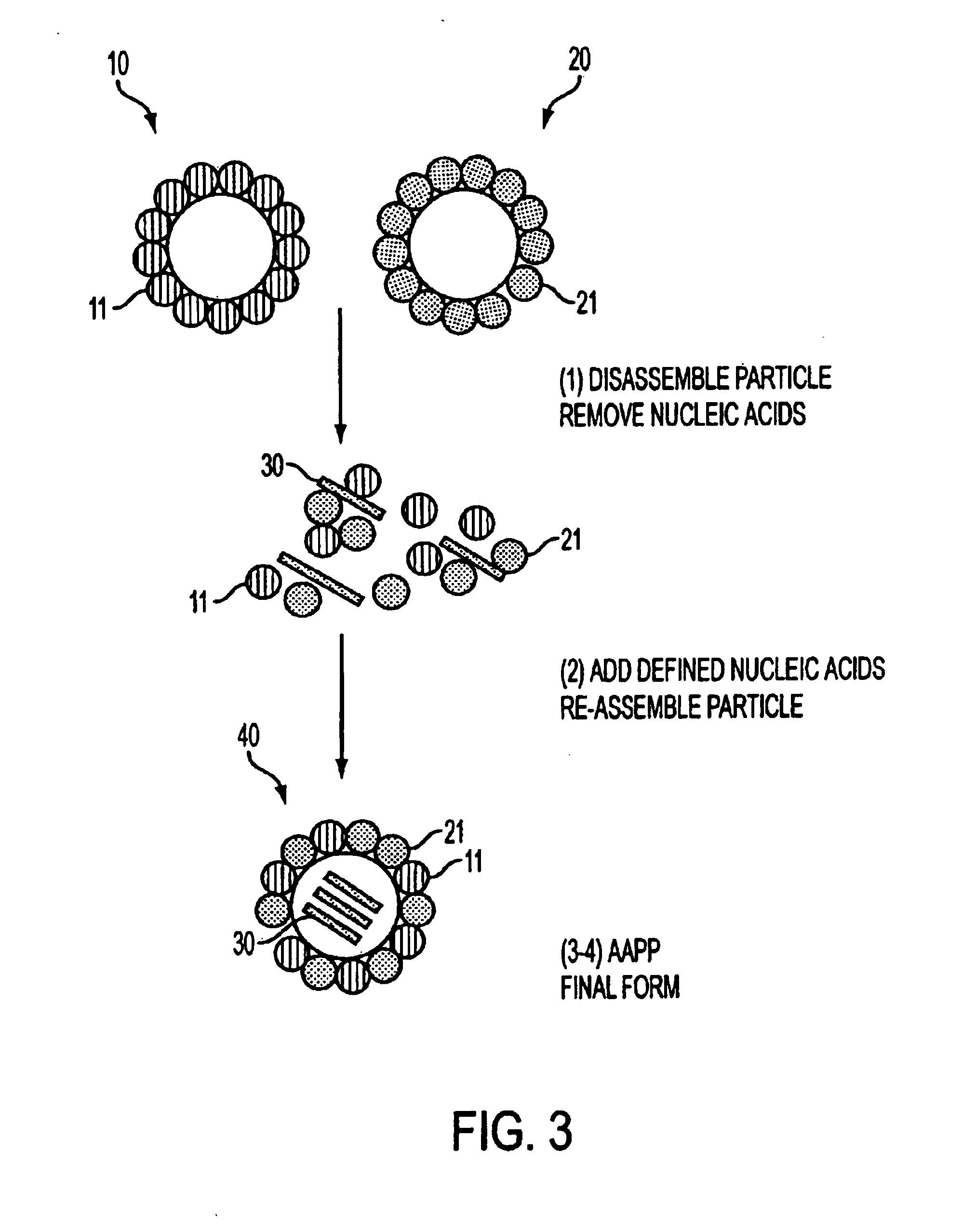
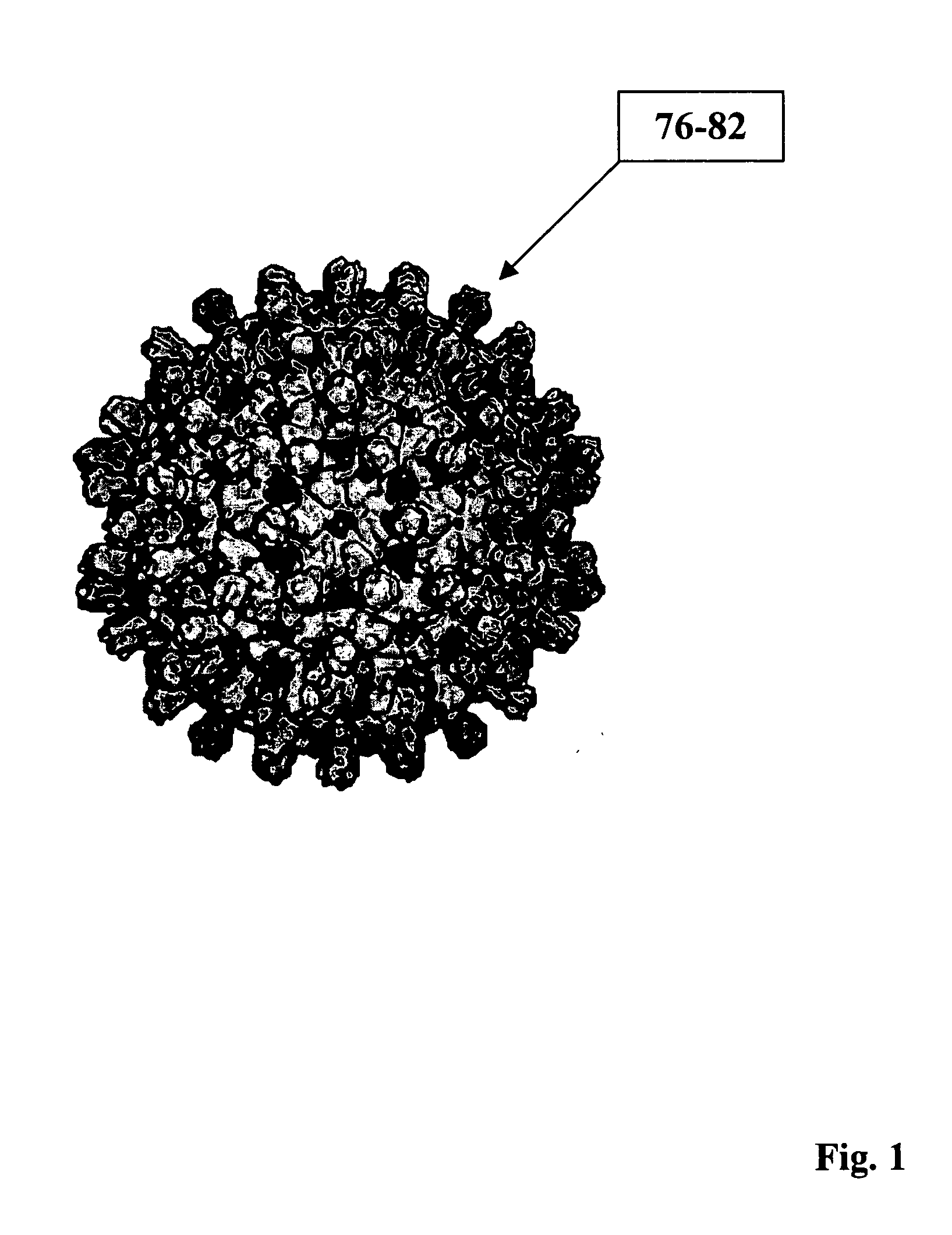
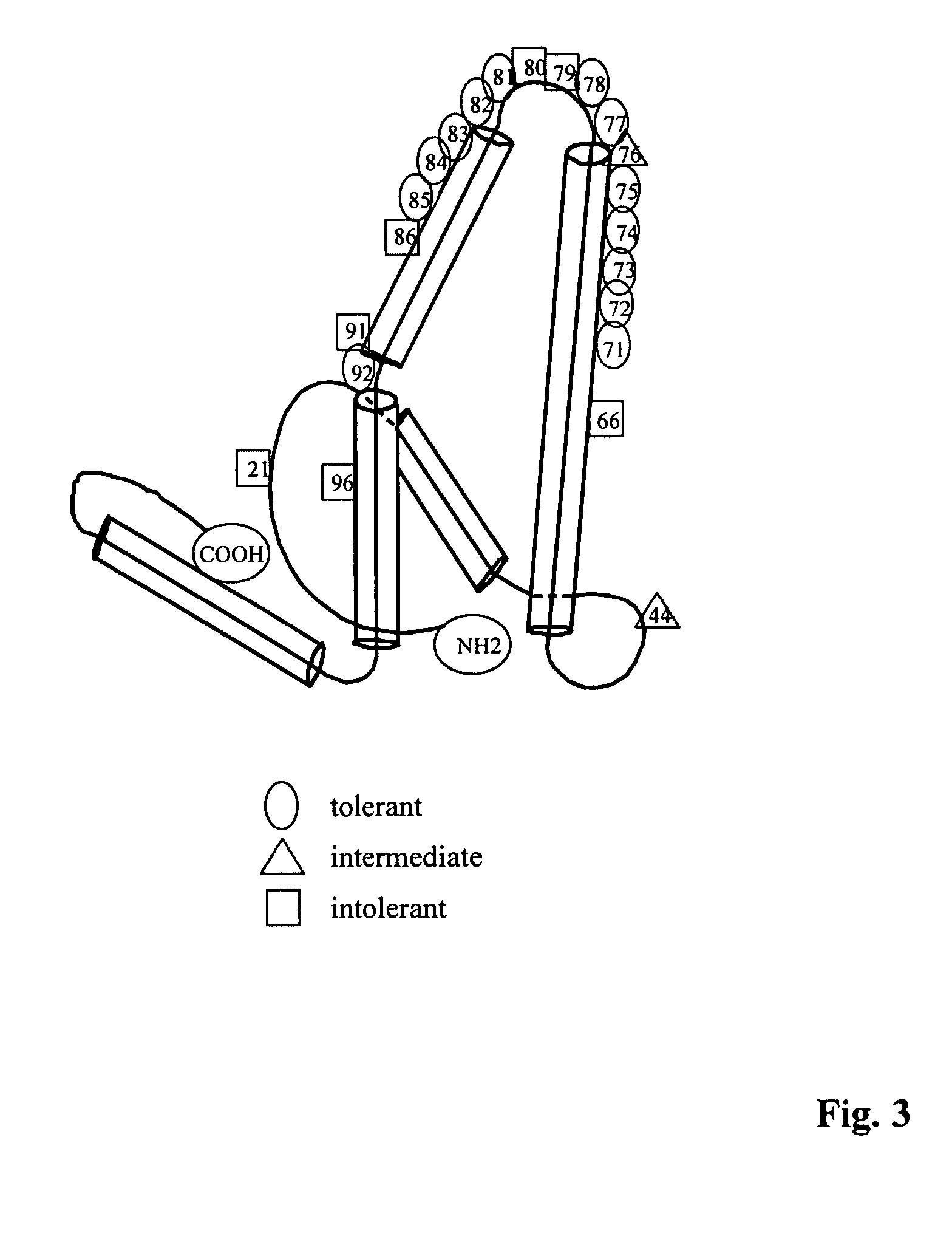
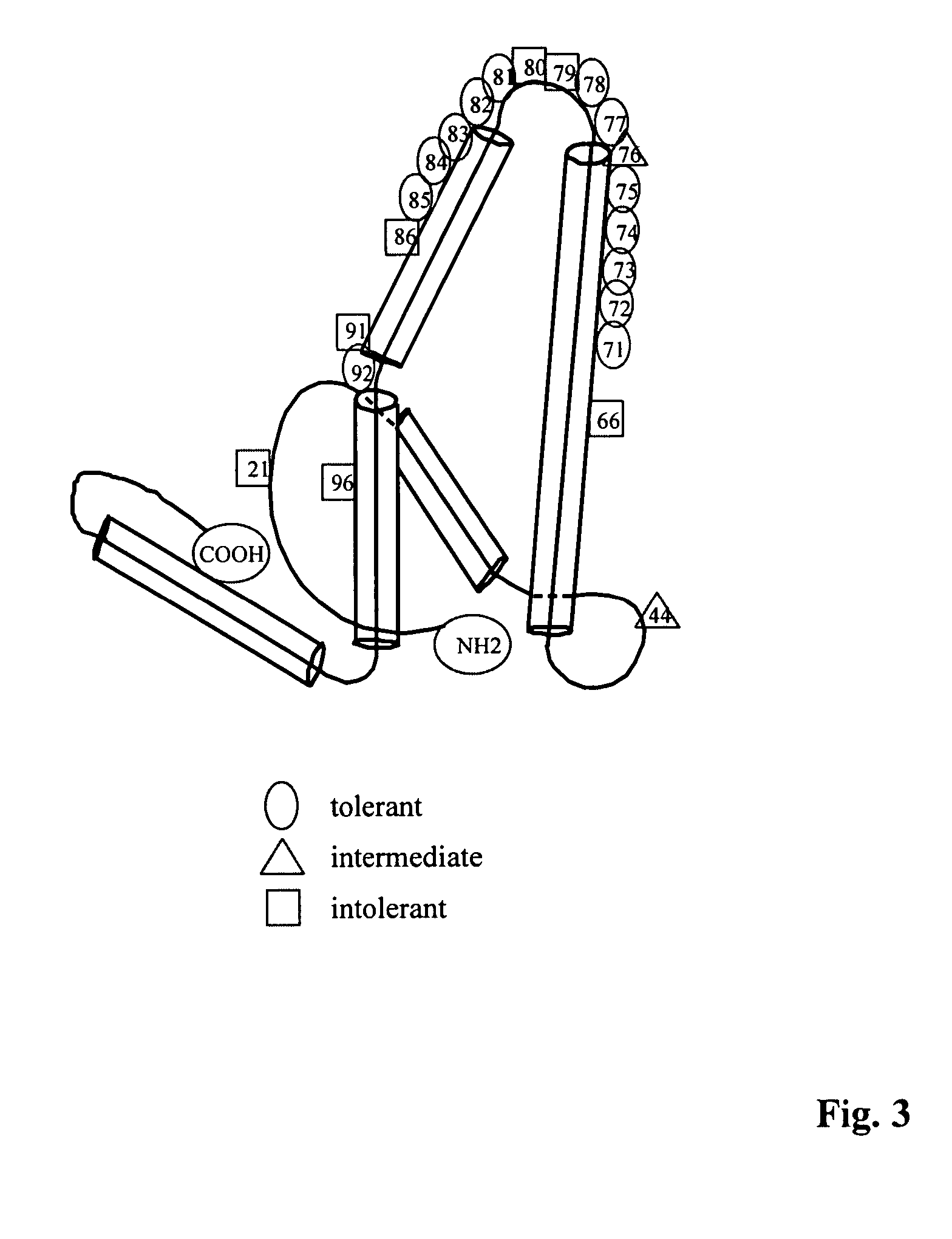
The present invention provides particles for the presentation of haptens for the purpose of eliciting an immune response. The amino acid sequences of the monomers which make up the particles are derived from duck hepatitis B virus core protein. The particles may also deliver nucleic acids. The nucleic acids may be delivered for the purpose of enhancing an immune response, or for other purposes such as gene therapy.
Owner:BIOCACHE PHARMA +1
Method for mass expressing external protein using domestic silk core protein heavy chain promoter
InactiveCN1912116AEnsure sustainable developmentConducive to long-term developmentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceHeavy chain
The invention relates to a method useing cultivated silkworm fibroin heavy chain promoter to express extraneous sources protein. It can increase extraneous sources protein content to 16% which is greatly higher by using light chain protein and fhx promoter. This can broaden cultivated silkworm application field. And it can be used to easily gain transgene silkworm concoon to get purpose extraneous sources protein by feeding purpose transgene silkworm largely.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method for pretreating sample and method for immunoassay of hcv
InactiveCN102081018APrevent agglutinationAgglutination does not occurPreparing sample for investigationTissue cultureProtein detectionVirus
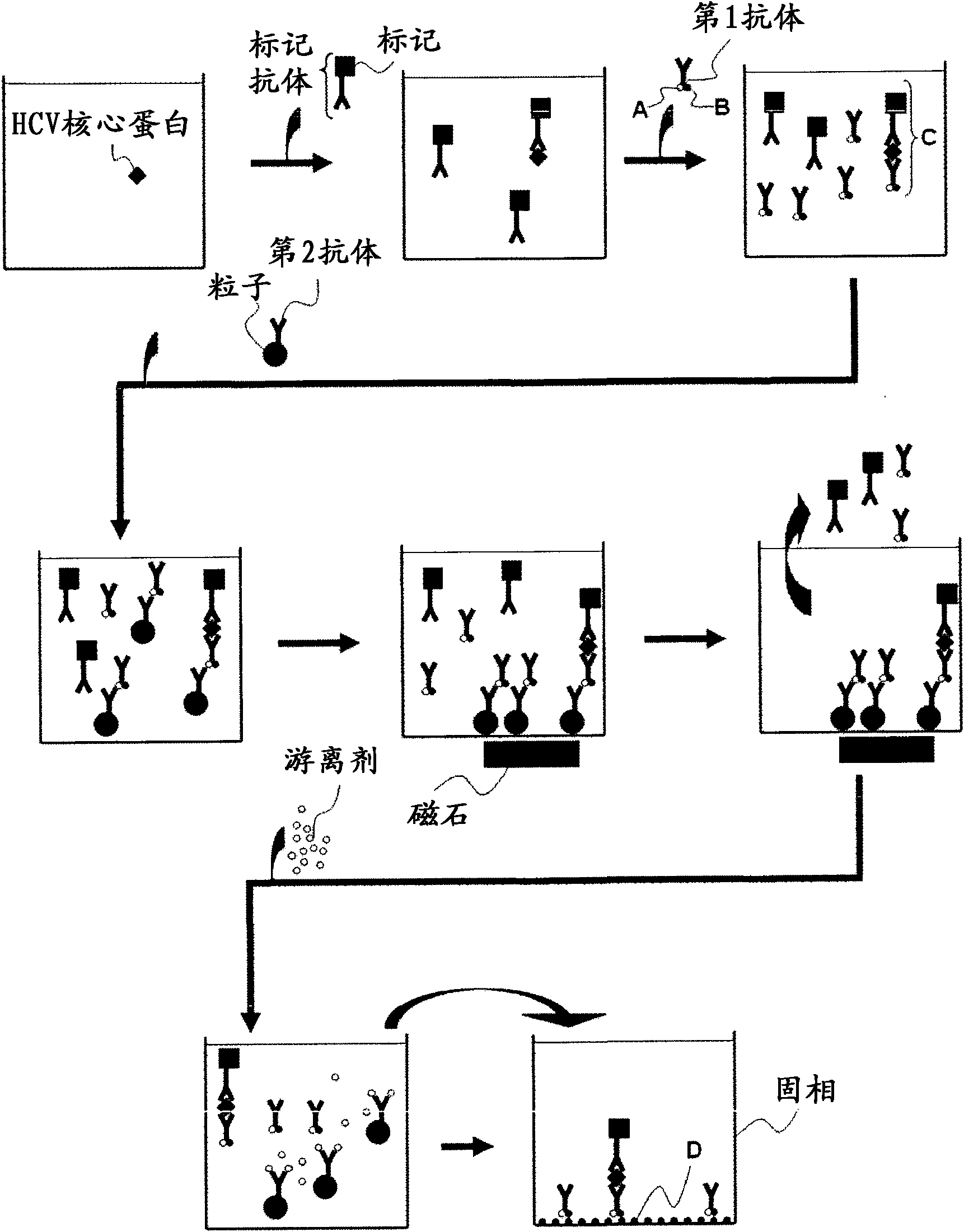
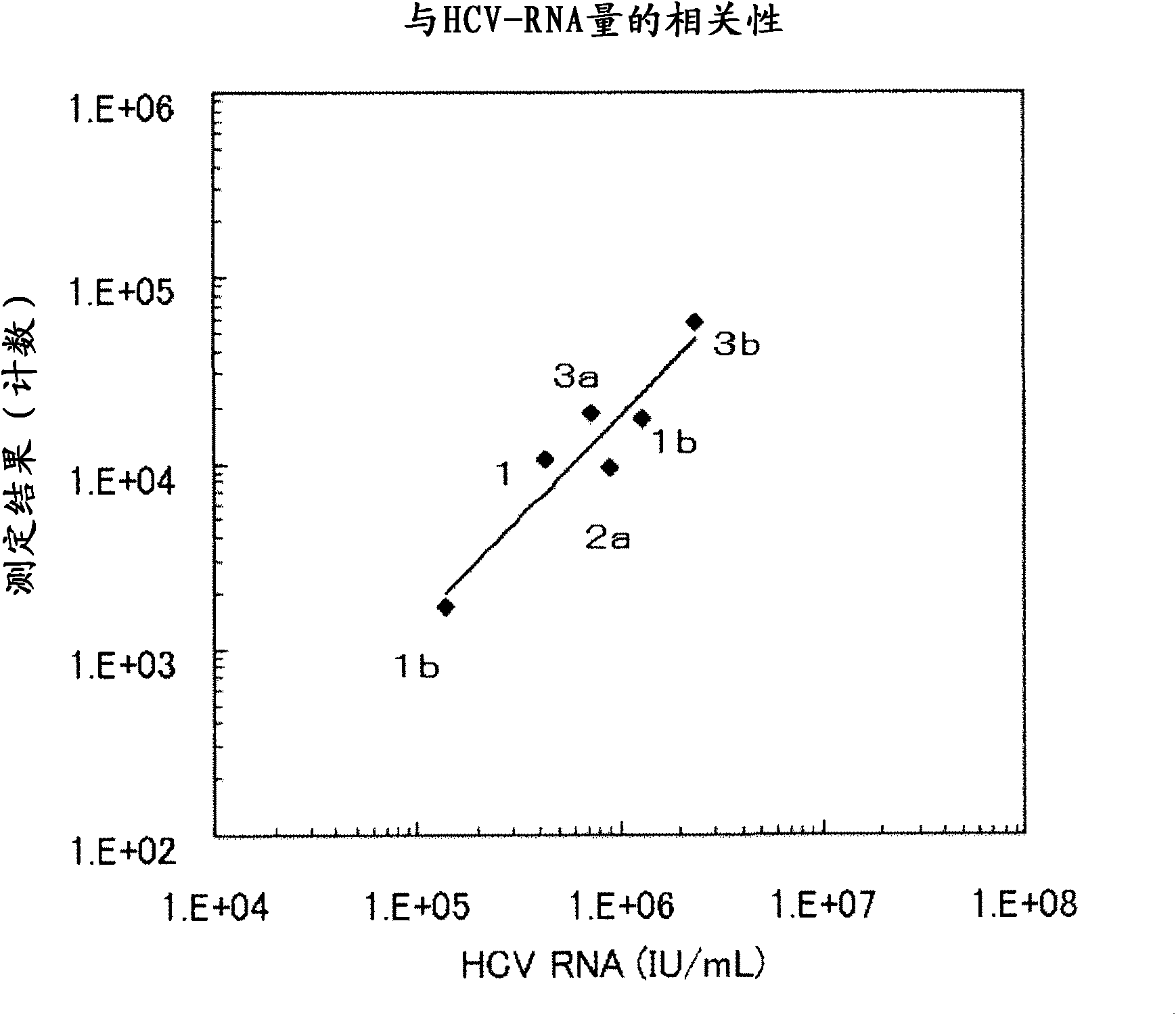
There are provided: a method for pretreating a sample for HCV core protein detection by an immunoassay using particles, which includes treating a sample suspected of containing hepatitis C virus (HCV) with an alkaline material-containing reagent and neutralizing the sample with an acid material-containing reagent, wherein at least one of the reagents contains a reducing agent; a reagent kit for HCV core protein detection; a method for determining the presence or absence of hepatitis C virus in a sample; and a method for immunoassay of HCV.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method for glucose production using endoglucanase core protein for improved recovery and reuse of enzyme
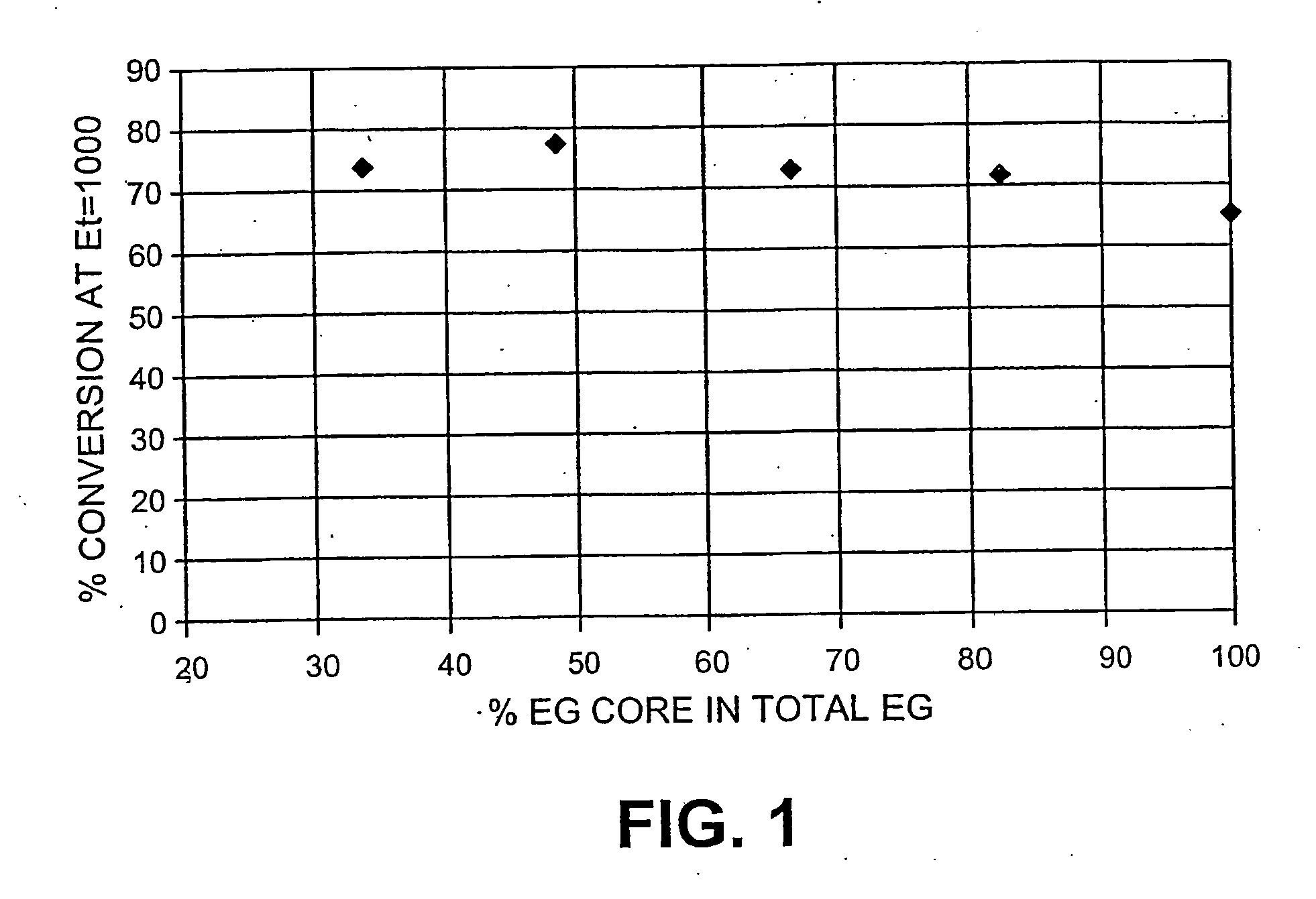
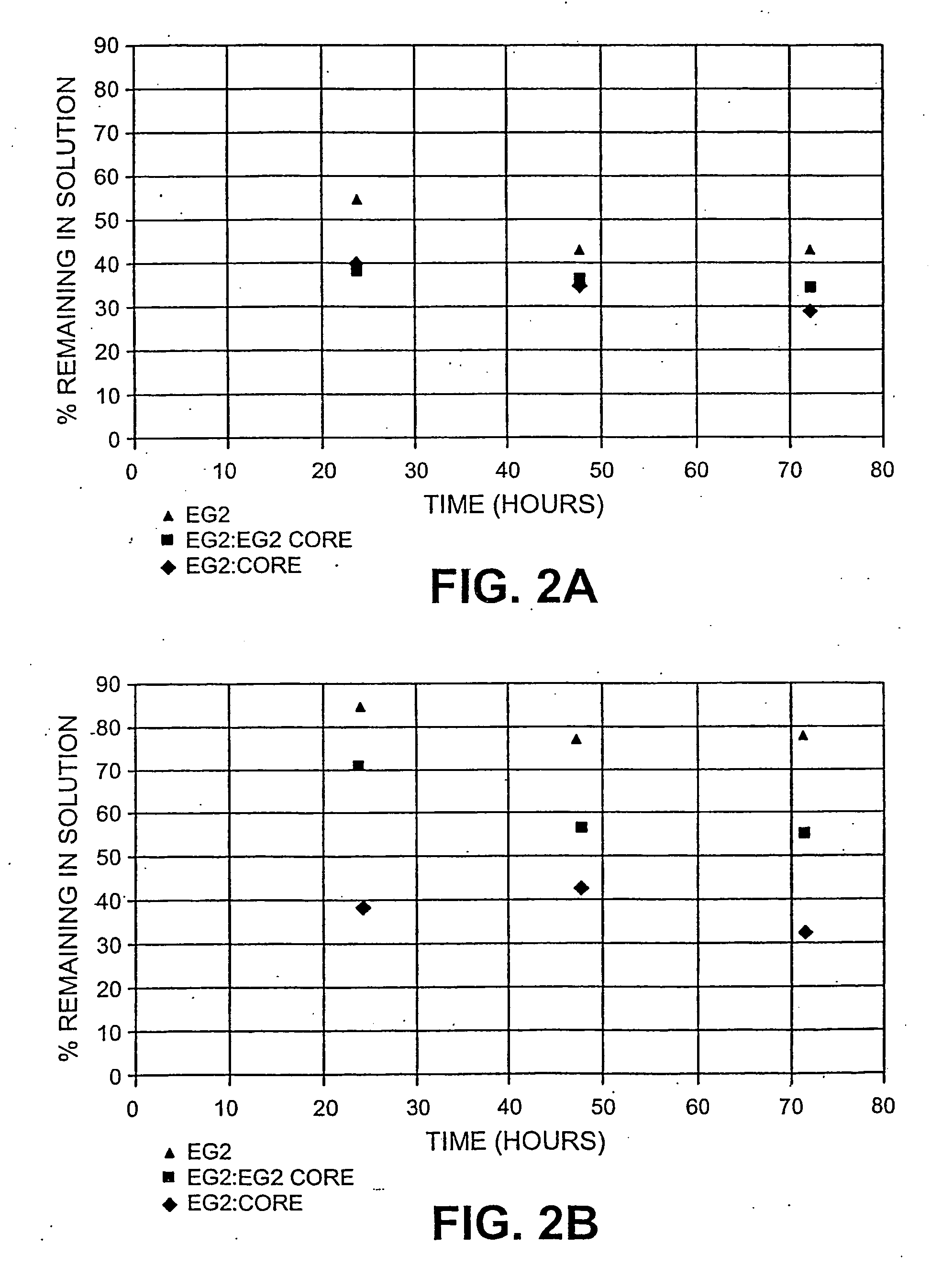
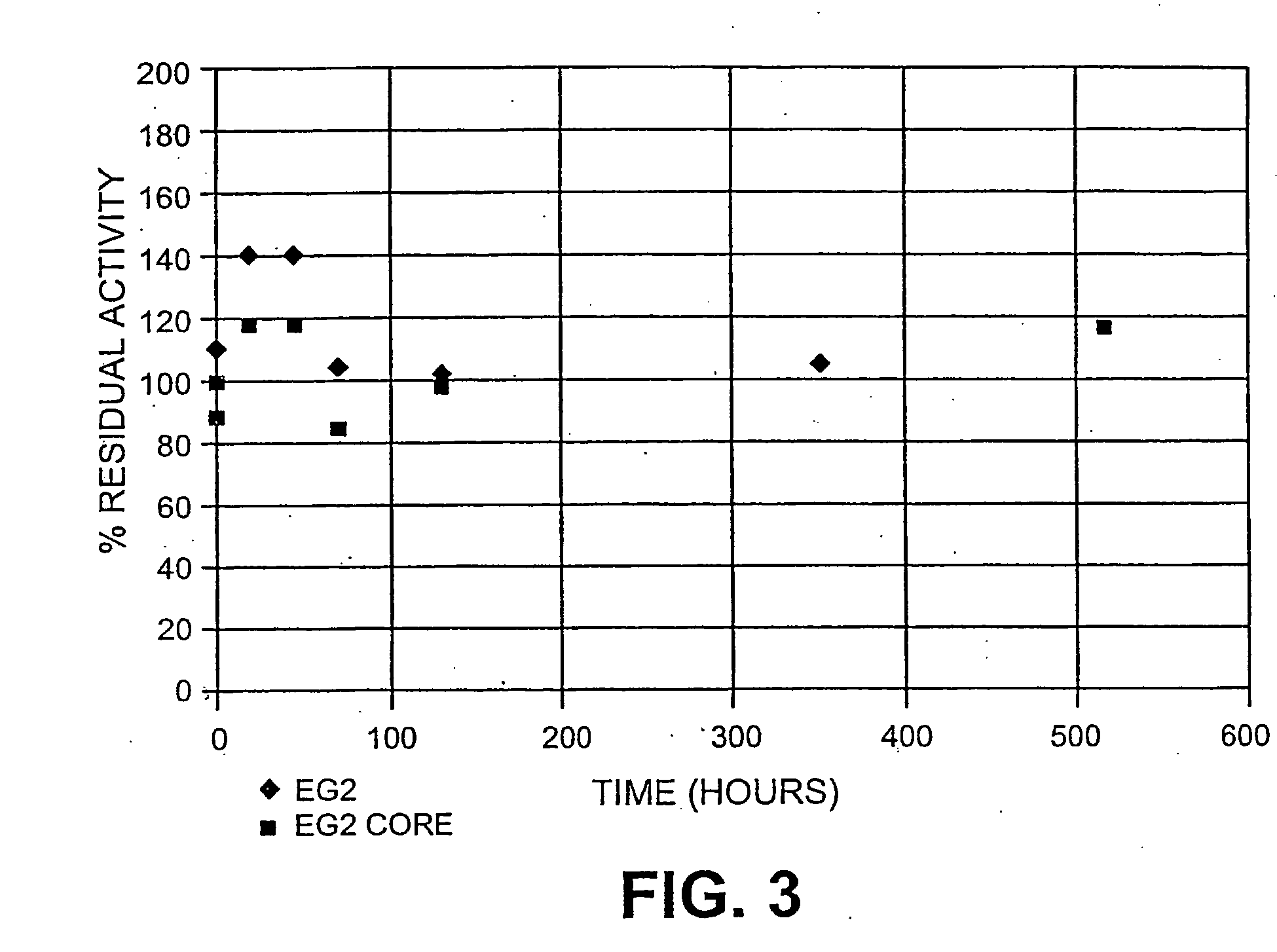
The present invention pertains to a method of converting cellulose to glucose by treating a pretreated lignocellulosic substrate with an enzyme mixture comprising cellulase enzyme and endoglucanase core proteins, wherein the endoglucanase core proteins are present in the enzyme mixture at an amount relative to all endoglucanases from about 35 wt. % to about 100 wt. % and wherein the endoglucanase cellulase enzymes are present in the enzyme mixture at an amount relative to the amount of CBH and EG enzymes from about 2 wt. % to about 50 wt. %. The pretreated lignocellulosic substrate is selected from the group consisting of agricultural residues, residues after starch or sugar removal, dedicated ethanol crops, forestry products, and pulp and paper products, or combinations thereof.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Human hepatitis B virus core proteins as vaccine platforms and methods of use thereof
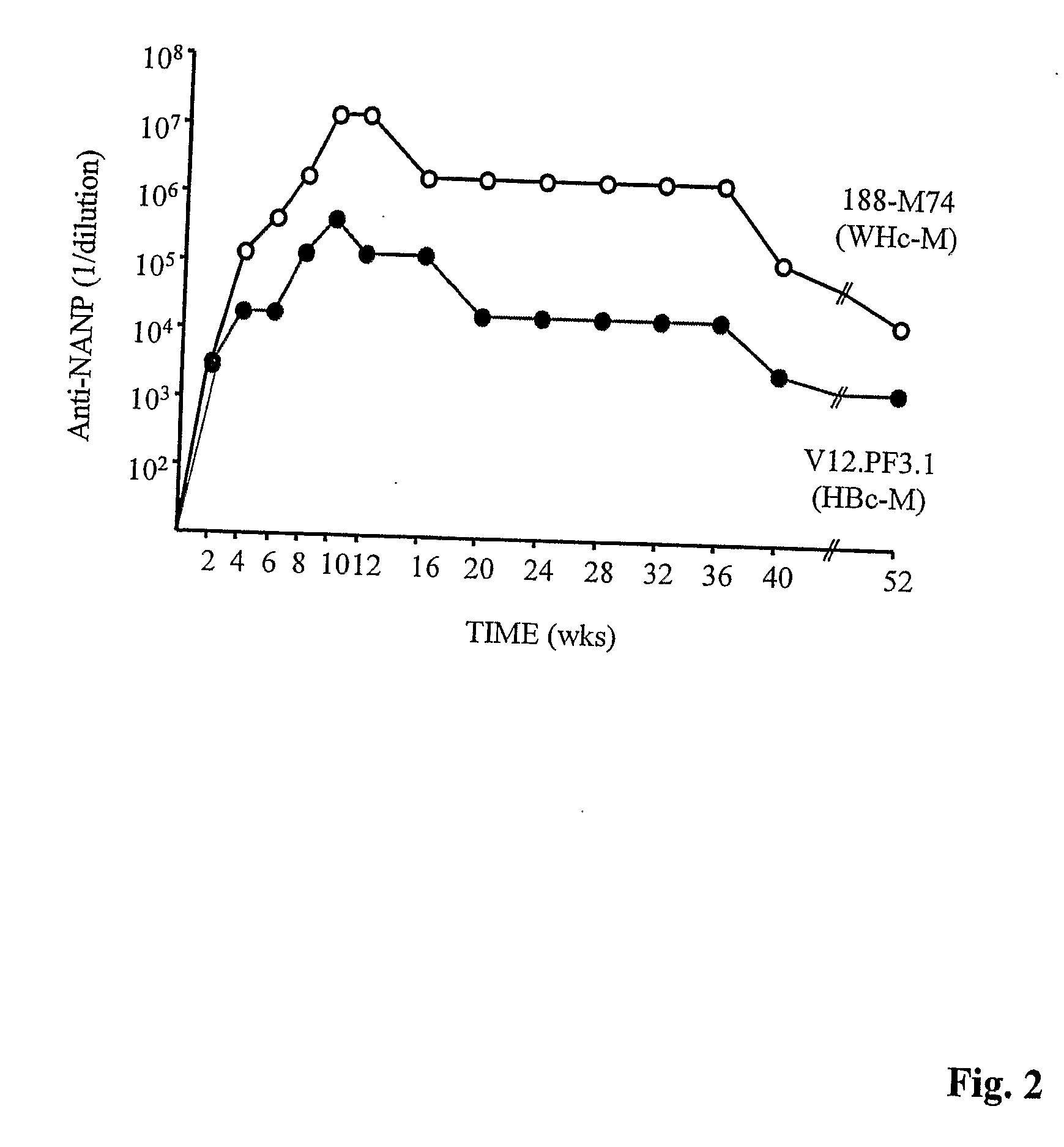
ActiveUS20050025782A1Uptake of nucleic acids by cells is enhancedPromote absorptionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsNucleic acidHepatitis virus
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Rodent hepatitis B virus core proteins as vaccine platforms and methods of use thereof
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Rodent hepatitis B virus core proteins as vaccine platforms and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050025781A1Promote absorptionOptimizationSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsHepacivirusHepatitis B virus core
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Combination hepatitis c virus antigen and antibody detection method
InactiveUS20080113339A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsWhole blood productHepatitis C virus core
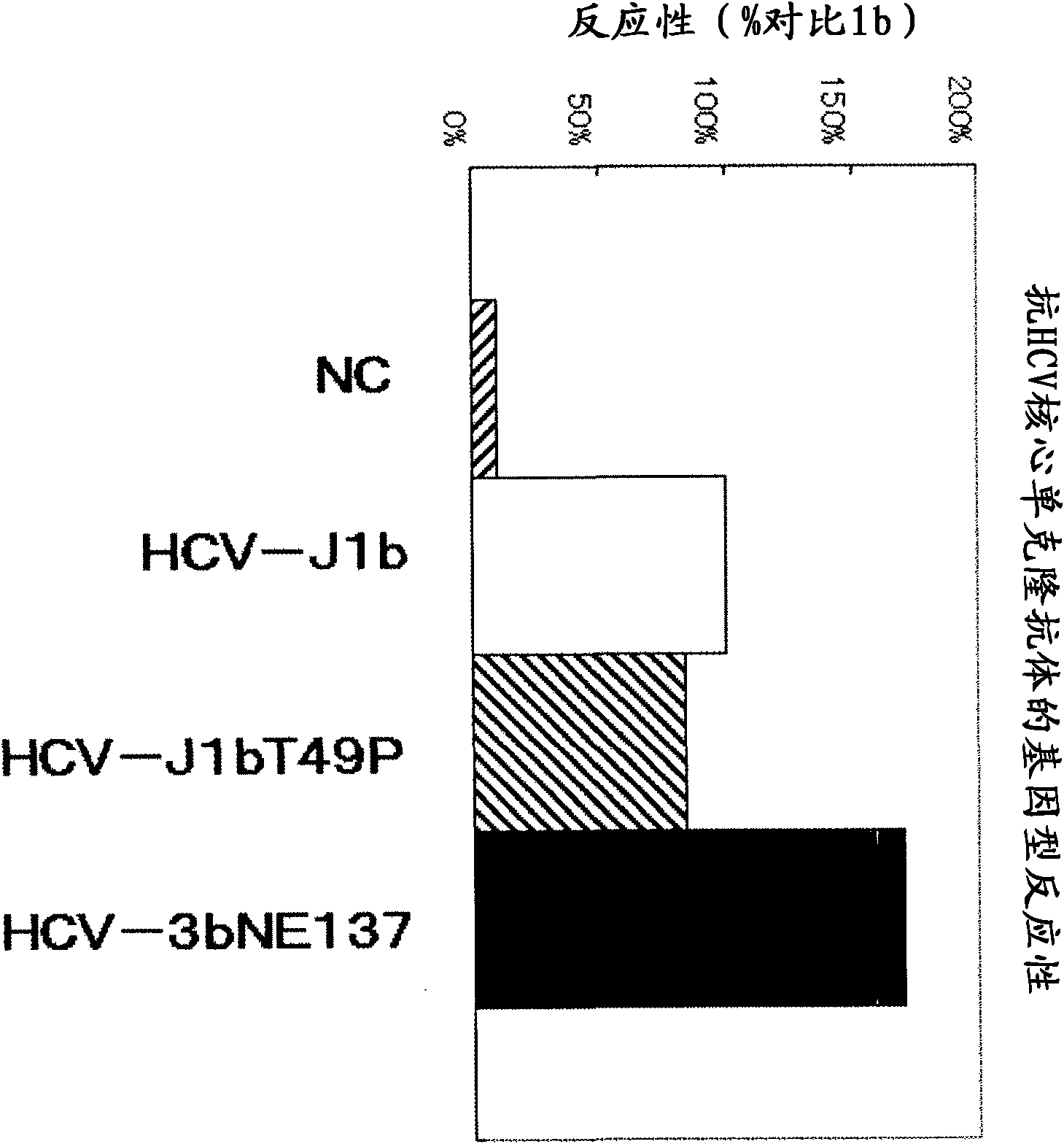
An in vitro method that allows detection of hepatitis C by detecting hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein and antibodies to HCV core protein (anti-core antibodies) in a single assay is provided. Cross-reactivity is eliminated in the method preferably by utilizing short peptides, each of which has an amino acid sequence that corresponds to an immunodominant region of the native core protein but which does not wholly encompass the epitope bound by the antibodies utilized in the method. The method can be used to detect the presence of HCV in a subject, and / or to determine the suitability of donor blood or blood products for transfusion purposes. Also provided are diagnostic kits for carrying out the method and a process for selecting suitable capture peptides and monoclonal antibodies for use in the combination method.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its application in antivirus treatment
InactiveCN1523113AInhibit expressionInhibition of replicationGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyChemical synthesisConserved sequence
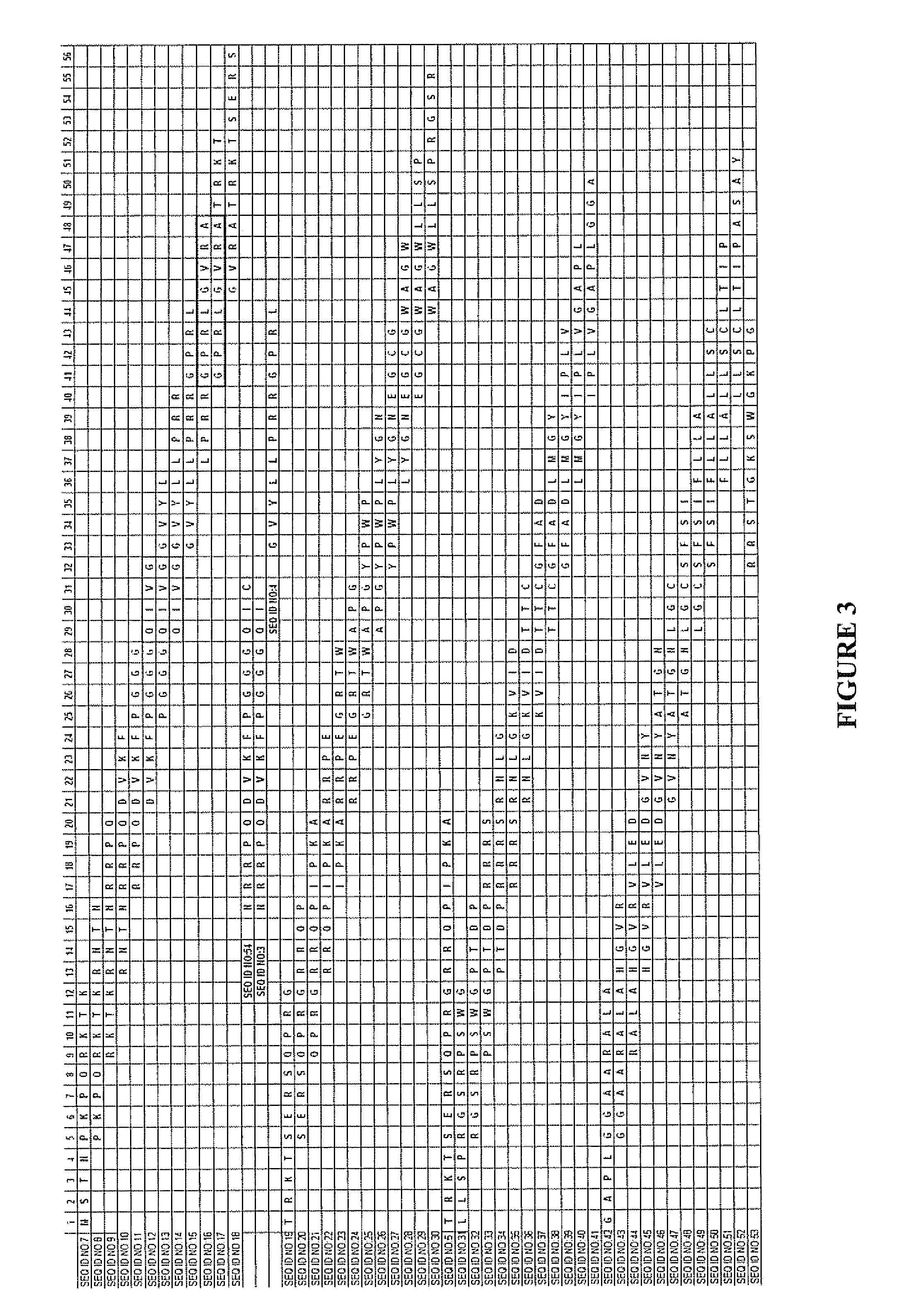
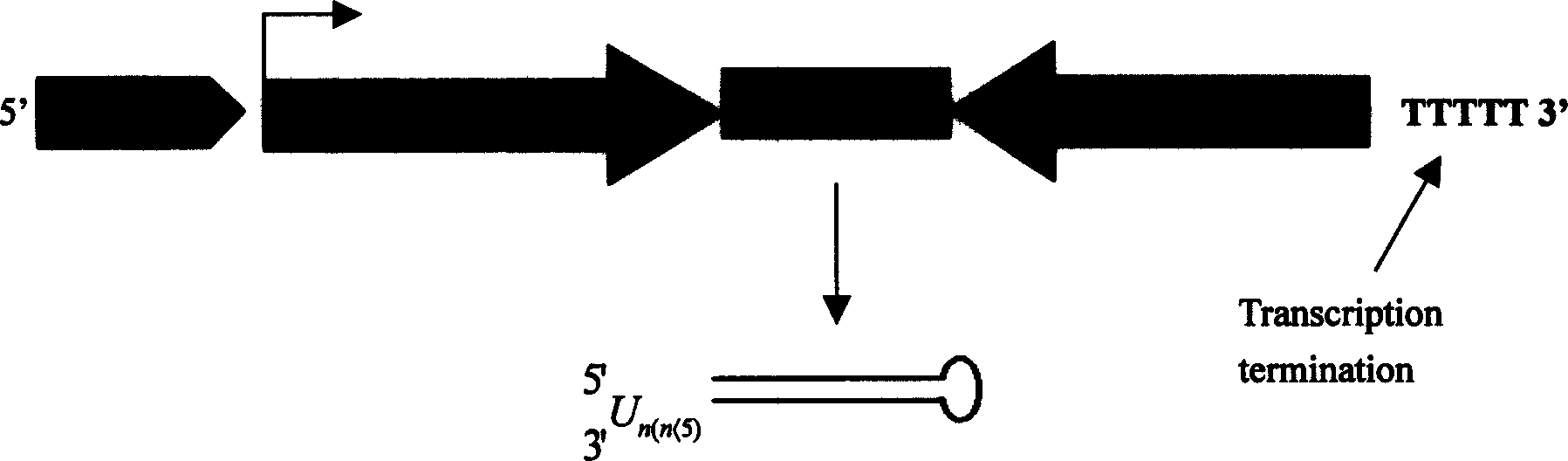
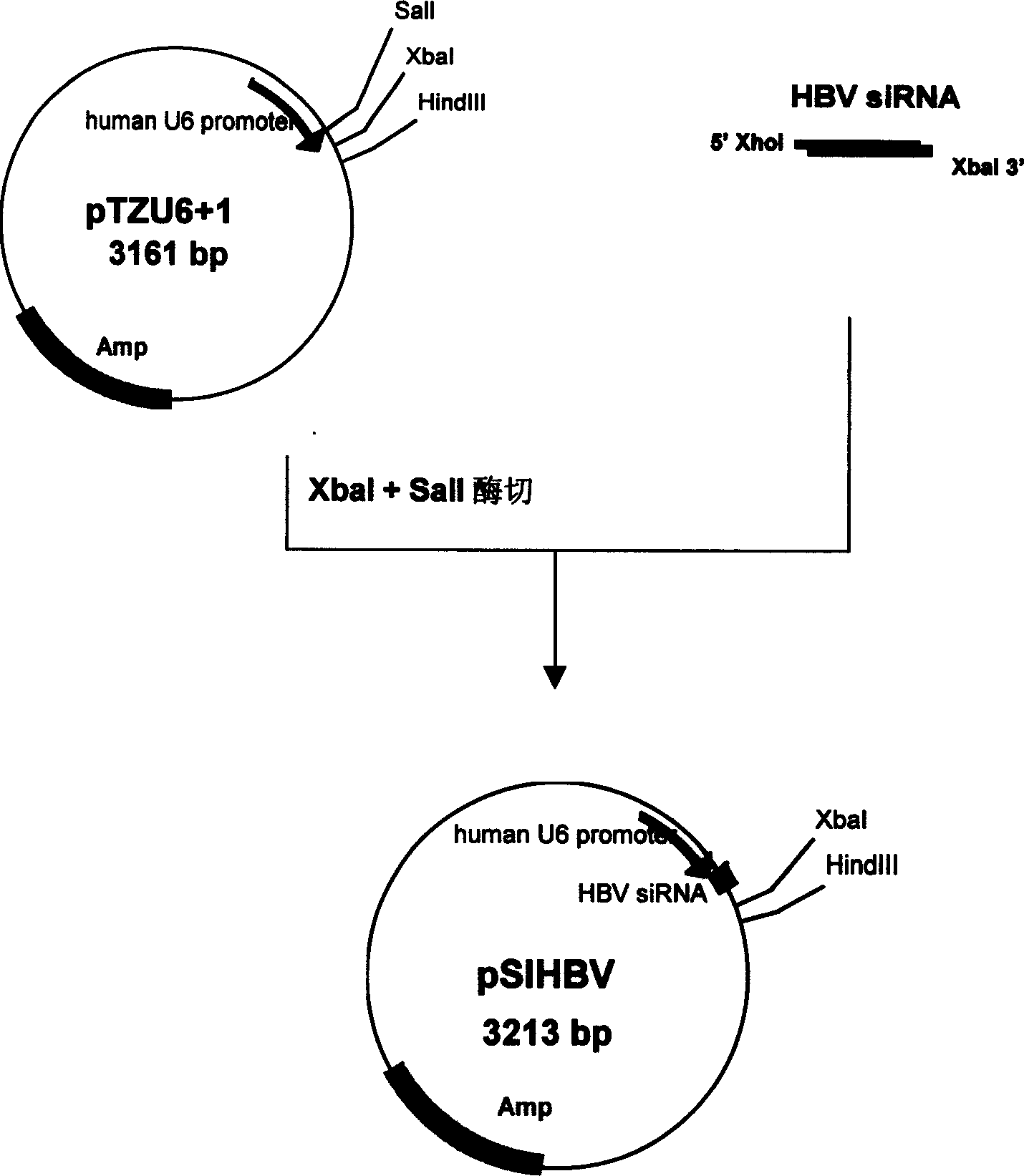
The present invention relates to construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its antiviral therapeutic application. According to the design principle said construction includes the following steps: respectively selecting nucleotide sequence of HBV envelope protein (MS) coding region 69nt-87nt, polymerase(p) coding region 708nt-726nt and core protein (c) coding region 2052 nt-2070nt, designing correspondent siRNA sequence, using BLAST software to analyze homogenously to confirm that it is HBV highly conservative sequence, then chemically synthesizing single-stranded oligonucleotide, external annearing to form double-stranded DNA, connecting it with eukaryotic expression vector pTZU6+1, enzyme excision identification and sequence determination and analysis show that siRNA extression vectors of three target hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene sequences are constructed. The tests show that HBV siRNA has the strong action of inhibiting virus replication and expression.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Antigenic epitopes and mosaic polypeptides of hepatitis C virus proteins
InactiveUS7052696B2Rapid and simple and reliable and sensitiveNot labor intensiveSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeImmunogenicity
Antigenic epitopes of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and mosaic HCV polypeptides useful as reagents in assays for the diagnosis or monitoring of HCV in a biological sample. The antigenic epitopes and mosaic polypeptides are also useful for the construction of immunogenic pharmaceutical compositions, such as vaccines. The mosaic polypeptides are artificial composite proteins constructed from diagnostically relevant antigenic regions derived from different HCV proteins. Preferably, the mosaic polypeptides contain antigenic epitopes from the core protein, NS3 protein, and NS4 protein. The preferred mosaic polypeptides optionally contain an additional antigenic epitope from either the NS4 protein or the NS5a protein or both.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
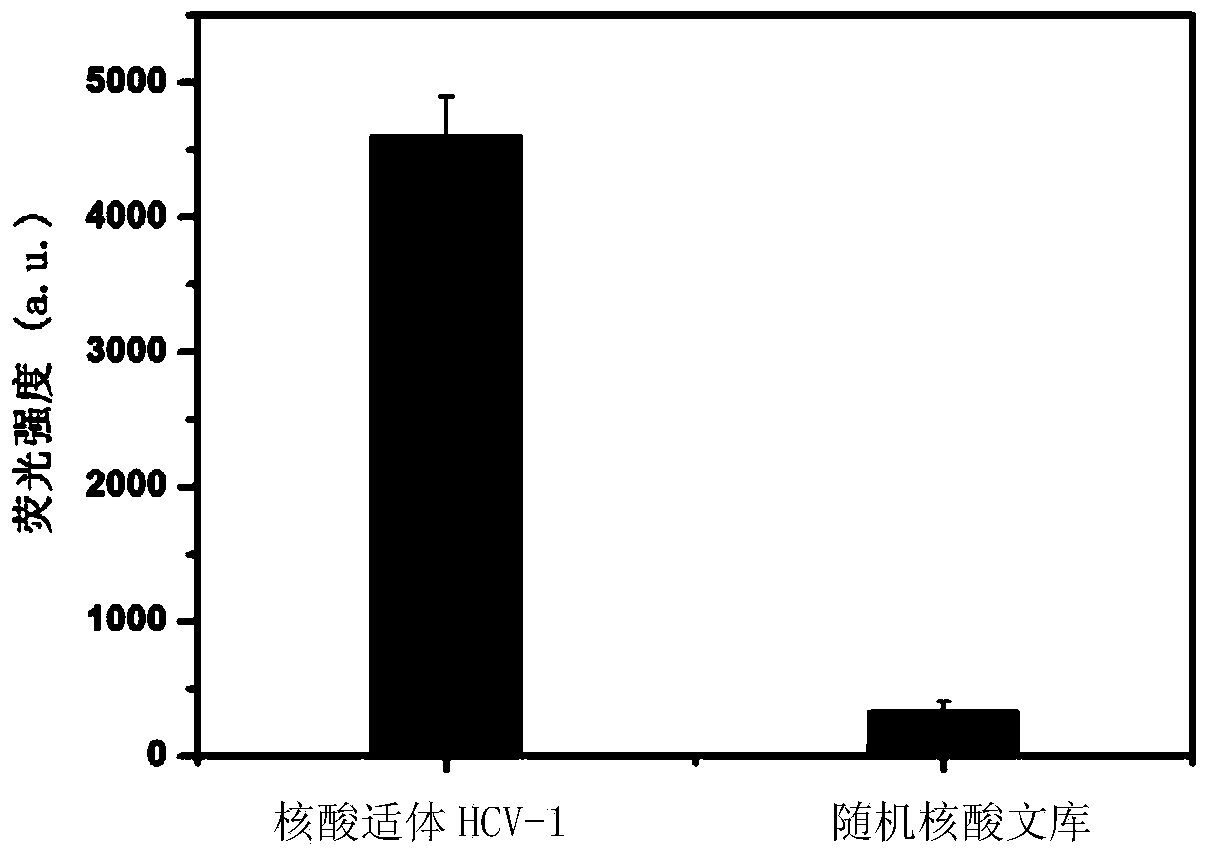
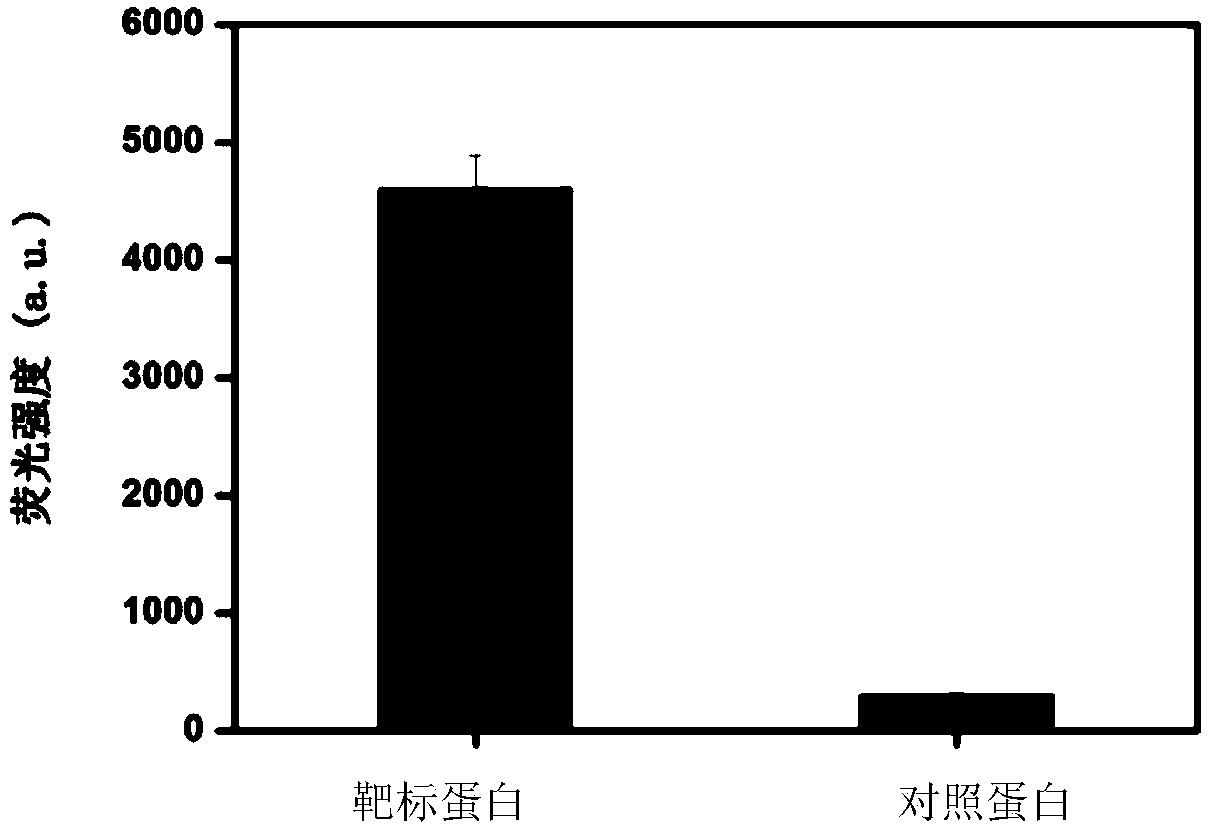
Nucleic acid aptamer specifically combined with hepatitis C virus core protein and application thereof
ActiveCN102121009ASensitive highLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer specifically combined with a hepatitis C virus core protein and application thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer is a single stranded DNA shown in a sequence 2 of a sequence table or single stranded DNA containing the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer has better affinity with a hepatitis C virus core protein. By using the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention, the hepatitis C virus core protein in a solution can be captured and can be also detected, and hepatitis C serodiagnosis and blood screening can be realized. Part of thenucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention can be used to replace a monoclonal antibody to capture the core protein for hepatitis C detection. The invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, low cost, easiness of preparation and storage, and high application value.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)-PKcs in preparation of medicine for changing drug resistance of tumor cells on MTX (Methotrexate)
ActiveCN103301447AReduce the degree of amplificationDouble minute reductionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh concentrationResearch Object
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Human hepatitis B virus core proteins as vaccine platforms and methods of use thereof
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Antibody having inhibitory activity on infection with hepatitis c virus (HCV) and use thereof
The objection of the invention is to provide an antibody that inhibits infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV). To this end, this invention provides an antibody that recognizes the hepatitis C virus (HCV) particle obtained from the hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome comprising the following (i) and (ii) ligated to each other as an antigen and has an inhibitory activity on infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV): (i) (a) the 5′-untranslated region, the core protein-encoding sequence, the E1 protein-encoding sequence, the E2 protein-encoding sequence, and the p7 protein-encoding sequence of the JFH-1 strain of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) or (b) the 5′-untranslated region, the core protein-encoding sequence, the E1 protein-encoding sequence, the E2 protein-encoding sequence, and the p7 protein-encoding sequence of the J6CF strain the hepatitis C virus (HCV); and (ii) the NS2 protein-encoding sequence, the NS3 protein-encoding sequence, the NS4A protein-encoding sequence, the NS4B protein-encoding sequence, the NS5A protein-encoding sequence, the NS5B protein-encoding sequence, and the 3′-untranslated region of the JFH-1 strain.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Protein fragments for use in protein targeting
InactiveUS6340577B1Improve efficiencyReduce compositional complexityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationADAMTS Proteins
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Recombinant HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) vector for expressing specific HBVshRNA (Hepatitis B Virus Short Hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) as well as construction method and application of vector
InactiveCN103014045AWill not mutateDoes not affect growthGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsChronic hepatitisHepatitis B virus
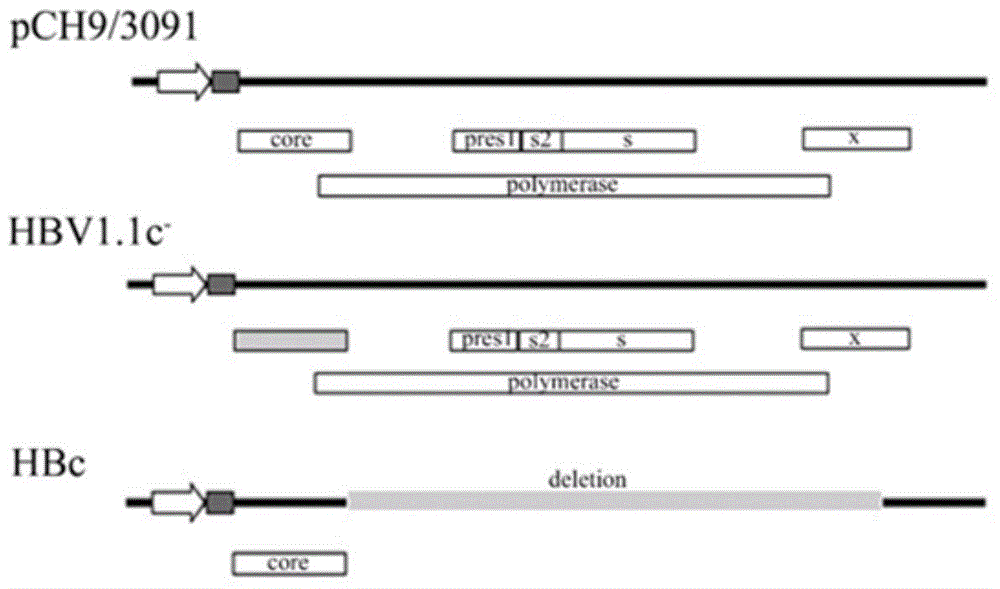
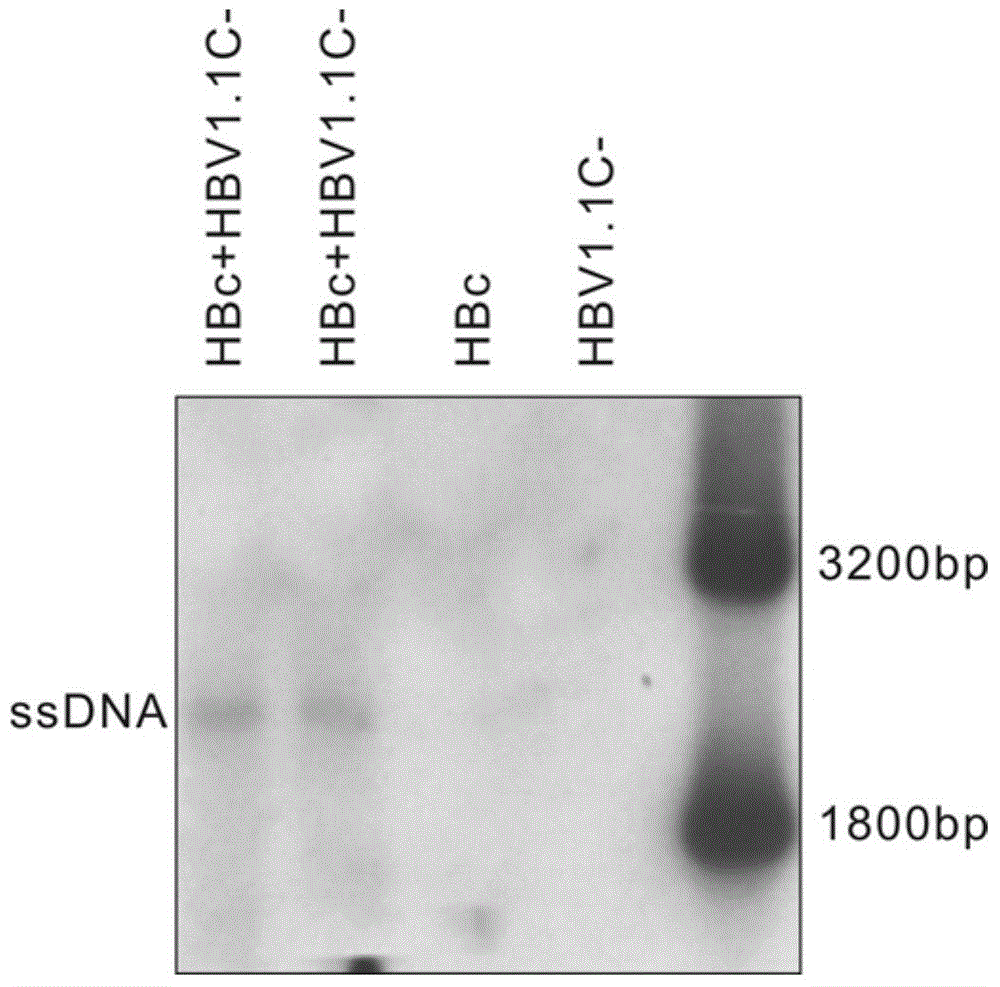
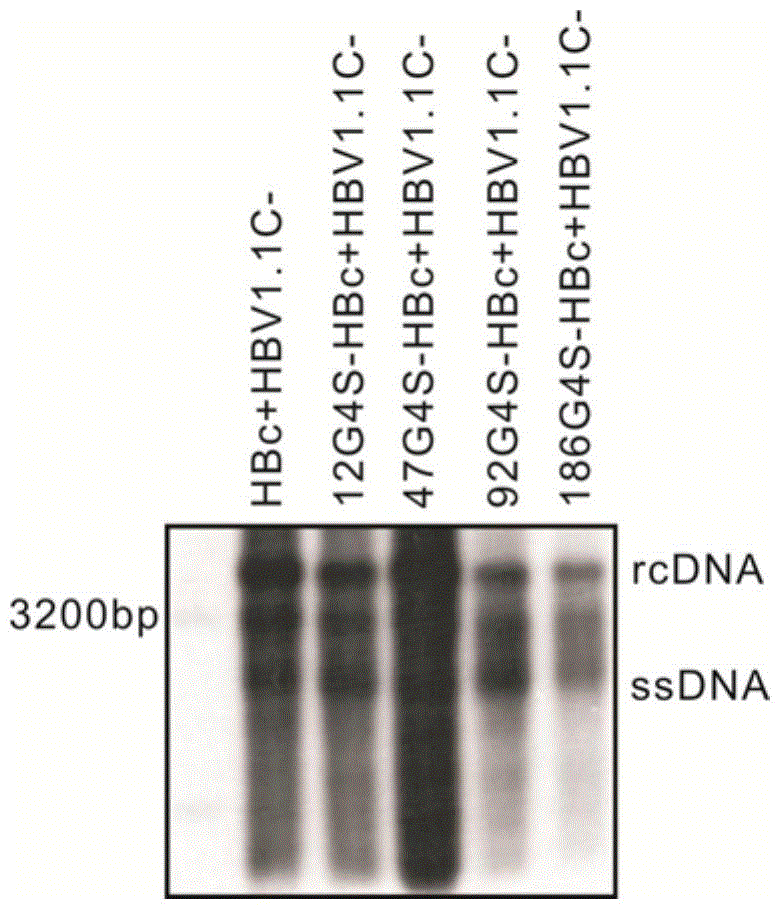
The invention relates to a recombinant HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) vector for expressing specific HBVshRNA (Hepatitis B Virus Short Hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) as well as a construction method and application of the vector. The recombinant HBV vector is formed by deleting 2111st-2643rd bases, 187th-680th bases or 1060th-1500th bases from an LJ196 vector, and replacing shRNA transcription structure units of the deleted sequences at the deleted sequence deleting positions. The preparation method is simple; RCDNA (Relaxed Circular Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be efficiently synthesized using Core protein and Pol protein of wild-type hepatitis B virus genome by adopting the recombinant HBV vector, and the synthesis efficiency is higher than that of the wild-type hepatitis B virus genome DNA, the RCDNA synthesis can compete with the duplication of the wild-type hepatitis B virus, simultaneously, the shRNA can be efficiently expressed by utilizing the characteristics of high synthesis efficiency of the recombinant HBV vector, and then the DNA duplication and HBsAg synthesis of the hepatitis B virus can be disturbed. The vector can be applied to preparation a medicine for disturbing the DNA duplication of the hepatitis B virus genome, and a new idea for treating the chronic hepatitis B virus infection is provided.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Hepatitis Virus Core Proteins as Vaccine Platforms and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080131452A1Improve the level ofViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acidCore protein
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Fusion protein of divisive ranilla luciferase and HBC (hepatitis B core) and application of fusion protein
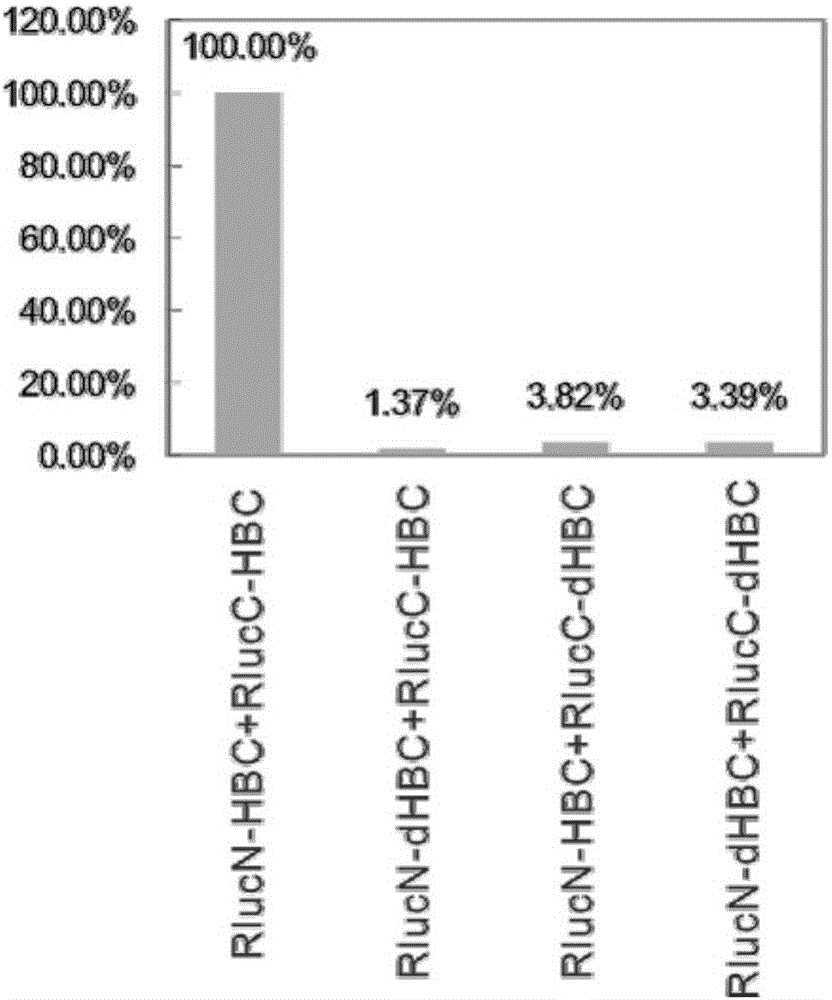
InactiveCN106188310AInhibition of replicationVirus peptidesBiological testingBiologyHepatitis b core
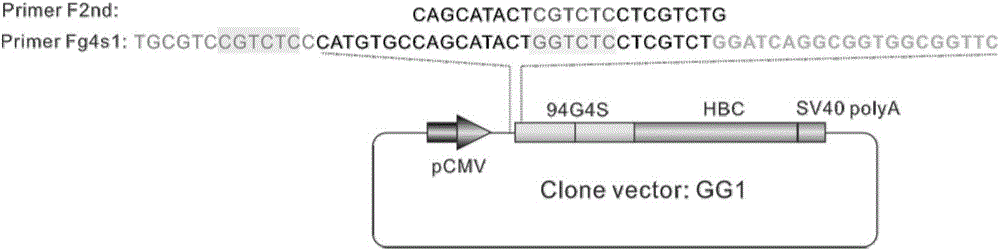
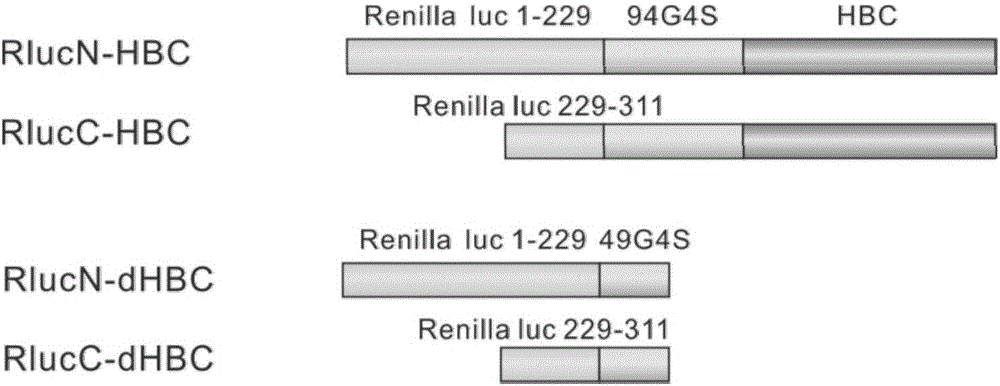
The invention discloses fusion protein of divisive ranilla luciferase and HBC (hepatitis B core). The fusion protein is obtained by joint connection of 1 to 229 amino acids of the N-terminal of the ranilla luciferase and core protein of hepatitis B virus (HBV), or obtained by joint connection of 229 to 311 amino acids of the N-terminal of the ranilla luciferase and the core protein of the HBV, the sequence of the amino acids is as shown in SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) No: 1 and No: 3 respectively, and nucleotide sequence encoding the two fusion protein is as shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and No: 4 respectively. The invention further discloses a carrier containing the nucleotide sequence as is shown in the SEQ ID No: 2 and No: 4. and discloses an application about whether the fusion protein as is shown in the SEQ ID No: 1 or the No: 3 is formed or not in indication of core protein dimers of the HBV. An importation foundation is laid for establishing cell models for drug screening in formation of the anti-HBC dimers.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
HBV core antigen particles with multiple immunogenic components attached via peptid ligands
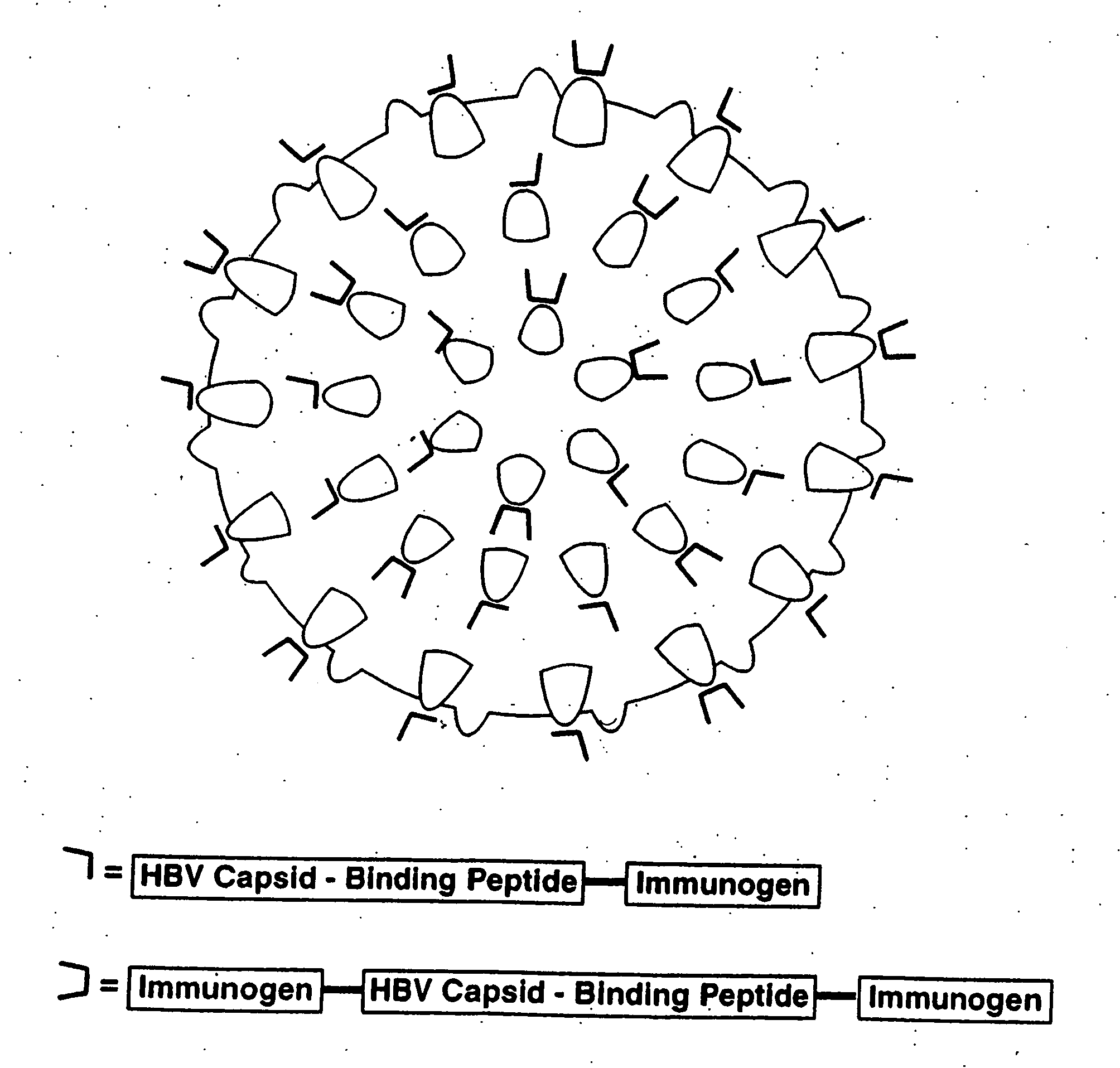
InactiveUS20070280962A1Facilitated DiffusionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHepatitis B immunizationPeptide ligand
This invention relates to hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) core antigen particles that are characterized by multiple immunogen specificities. More particularly, the invention relates to HBV core antigen particles comprising immunogens, epitopes, or other related structures, crosslinked thereto by ligands which are HBV capsid-binding peptides that selectively bind to HBV core protein. Such particles may be used as delivery systems for a diverse range of immunogenic epitopes, including the HBV capsid-binding peptides, which advantageously also inhibit and interfere with HBV viral assembly by blocking the interaction between HBV core protein and HBV surface proteins. Mixtures of different immunogens and / or capsid-binding peptide ligands may be crosslinked to the same HBV core particle. Such resulting multicomponent or multivalent HBV core particles may be advantageously used in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and compositions, as well as in diagnostic compositions and methods using them.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
HBV core antigen particles with multiple immunogenic components attached via peptide ligands
InactiveUS8168190B2Facilitated DiffusionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHepatitis B immunizationPeptide ligand
This invention relates to hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) core antigen particles that are characterized by multiple immunogen specificities. More particularly, the invention relates to HBV core antigen particles comprising immunogens, epitopes, or other related structures, crosslinked thereto by ligands which are HBV capsid-binding peptides that selectively bind to HBV core protein. Such particles may be used as delivery systems for a diverse range of immunogenic epitopes, including the HBV capsid-binding peptides, which advantageously also inhibit and interfere with HBV viral assembly by blocking the interaction between HBV core protein and HBV surface proteins. Mixtures of different immunogens and / or capsid-binding peptide ligands may be crosslinked to the same HBV core particle. Such resulting multicomponent or multivalent HBV core particles may be advantageously used in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and compositions, as well as in diagnostic compositions and methods using them.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Detection methods employing hcv core lipid and DNA binding domain monoclonal antibodies
ActiveUS20170052184A1Easy to adaptImmunoglobulins against virusesDisease diagnosisEpitopeDNA-binding domain
The present disclosure provides detection methods employing HCV core lipid binding domain and DNA binding domain monoclonal antibodies or antibody fragments. In certain embodiments, the lipid binding domain monoclonal antibody or antibody fragment recognizes an epitope in amino acids 141 to 161 of HCV core protein and the DNA binding domain antibody or antibody fragment recognizes an epitope in amino acids 95-123 (e.g., in amino acids 99-117) of HCV core protein.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +1
Nucleic acid aptamer of affinity viral hepatitis C core protein and application of nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN104004763ASensitive highLow costMaterial analysisDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer of an affinity viral hepatitis C core protein and an application of the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer is the following (a) or (b): (a) single-stranded DNA represented by sequence 2 in a sequence table; (b) single-stranded DNA containing the nucleic acid aptamer described in (a). Due to the adoption of the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention, the viral hepatitis C core protein in a solution can be captured and the viral hepatitis C core protein in a solution can also be detected, which are conductive to hepatitis C serology diagnosis and blood screening. By virtue of the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention, the monoclonal antibody can be partially replaced to capture core protein for detecting hepatitis C and the nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages of high sensitivity, low cost, and convenience in production and preservation. The nucleic acid aptamer has a relatively high application value.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hepatitis virus core proteins as vaccine platforms and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7883843B2Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHepacivirusNucleic acid
Owner:VLP BIOTECH
Combination hepatitis C virus antigen and antibody detection method
InactiveUS8865398B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesWhole blood productHepacivirus
An in vitro method that allows detection of hepatitis C by detecting hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein and antibodies to HCV core protein (anti-core antibodies) in a single assay is provided. Cross-reactivity is eliminated in the method preferably by utilizing short peptides, each of which has an amino acid sequence that corresponds to an immunodominant region of the native core protein but which does not wholly encompass the epitope bound by the antibodies utilized in the method. The method can be used to detect the presence of HCV in a subject, and / or to determine the suitability of donor blood or blood products for transfusion purposes. Also provided are diagnostic kits for carrying out the method and a process for selecting suitable capture peptides and monoclonal antibodies for use in the combination method.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Recombinant human hepatitis B virus core protein fused protein
The invention discloses a recombinant human hepatitis B virus core protein fused protein. The fused protein comprises a protein (X), a linker peptide (L) and a hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) from the end N to the end C in sequence; the linker peptide (L) has the amino acid sequence of Gly-Ser-(Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser)n, and n is an integer between 2 and 20 and is 9 or 18, particularly; the end C of the linker peptide (L) is connected with the end N of the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc); the end C of the protein (X) is connected with the end N of the linker peptide (L); and the protein (X) is a red fluorescent protein or vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein. The hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) is connected with the functional protein, and the functions of the proteins on two ends of the linker peptide (L) can be both guranteed. The problem in the prior art that the functions of the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) and the functions of the functional protein can not be both guaranteed after the hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) is fused with the functional protein is solved. The fused protein is of great importance to the research on the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com