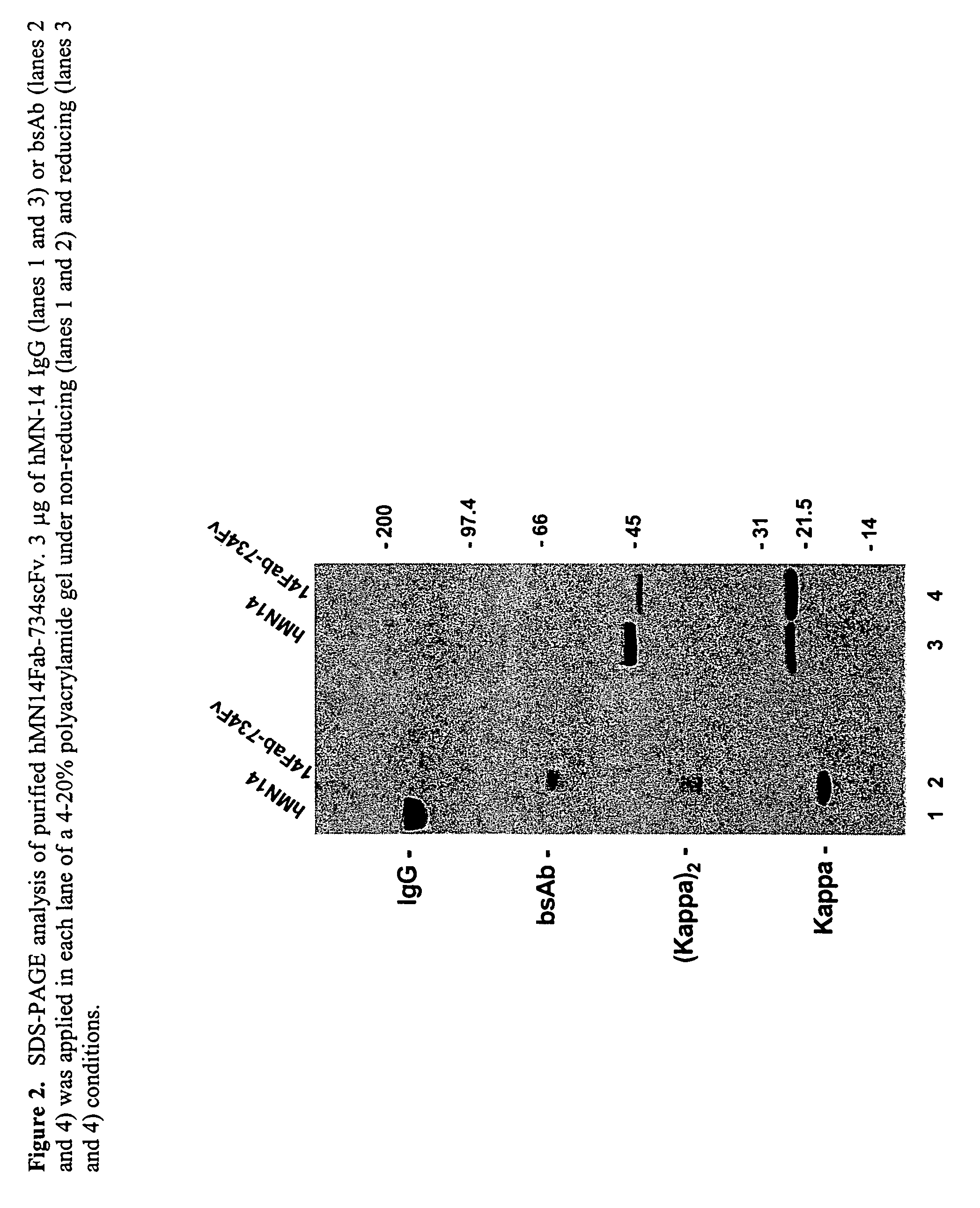
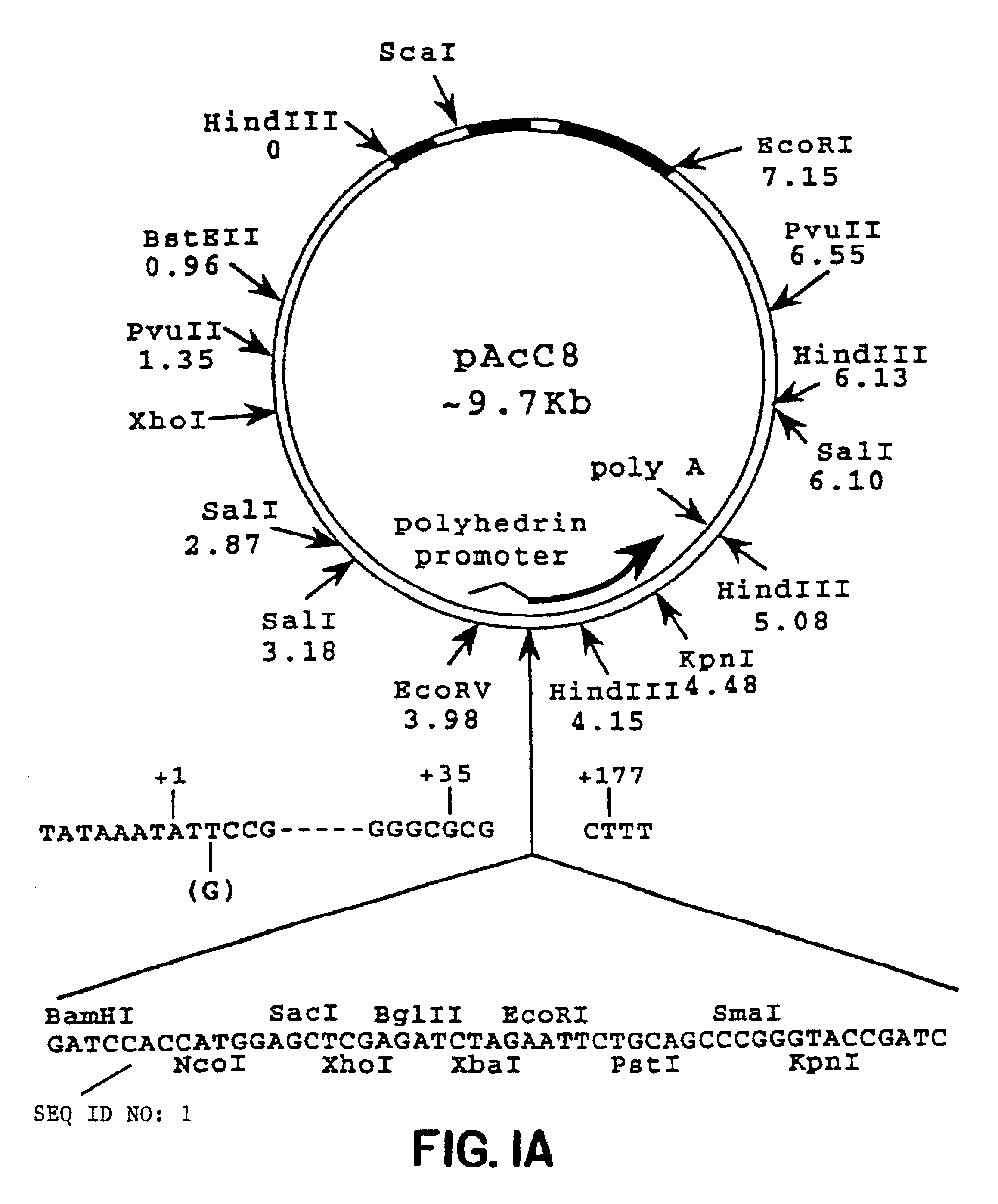
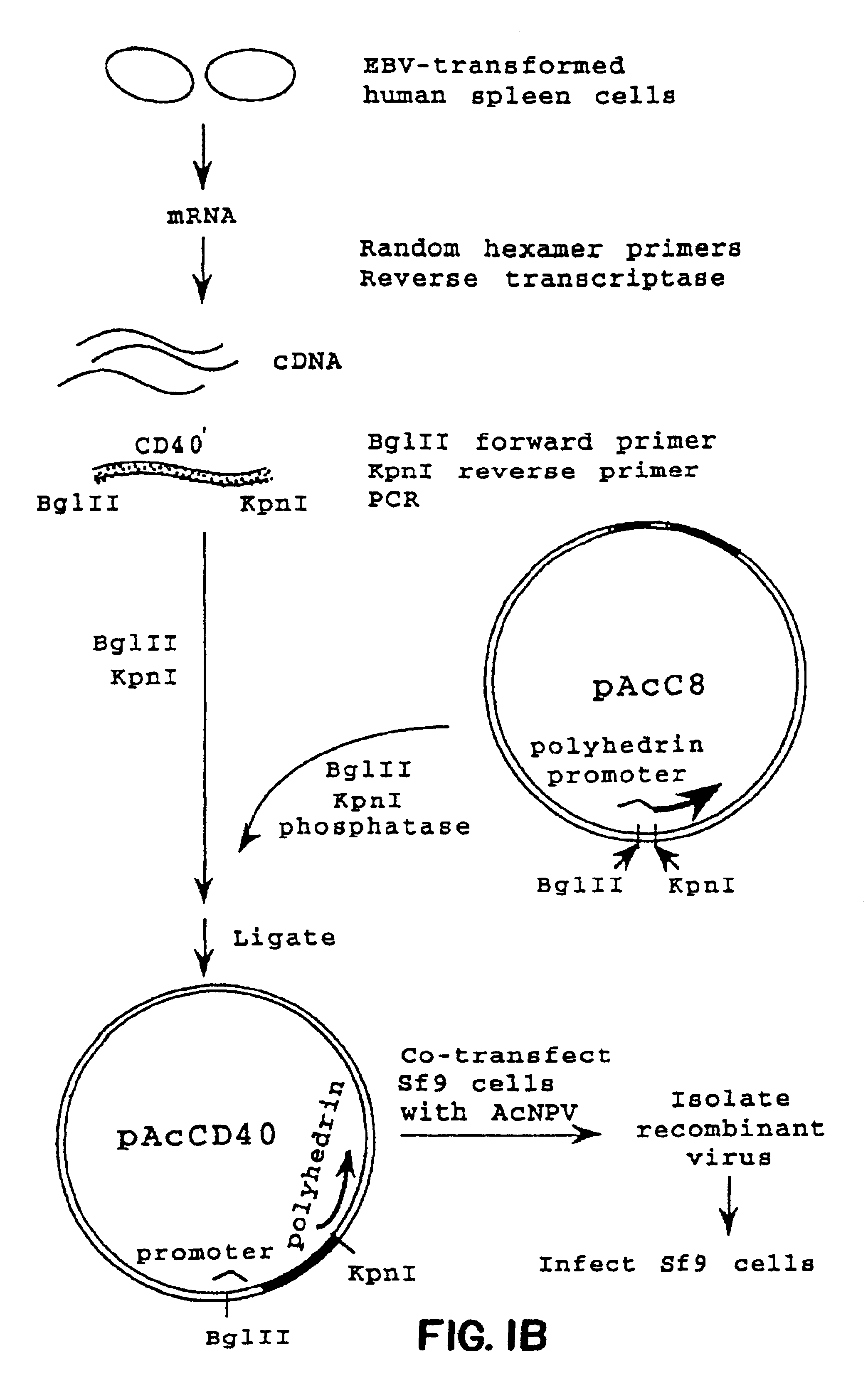
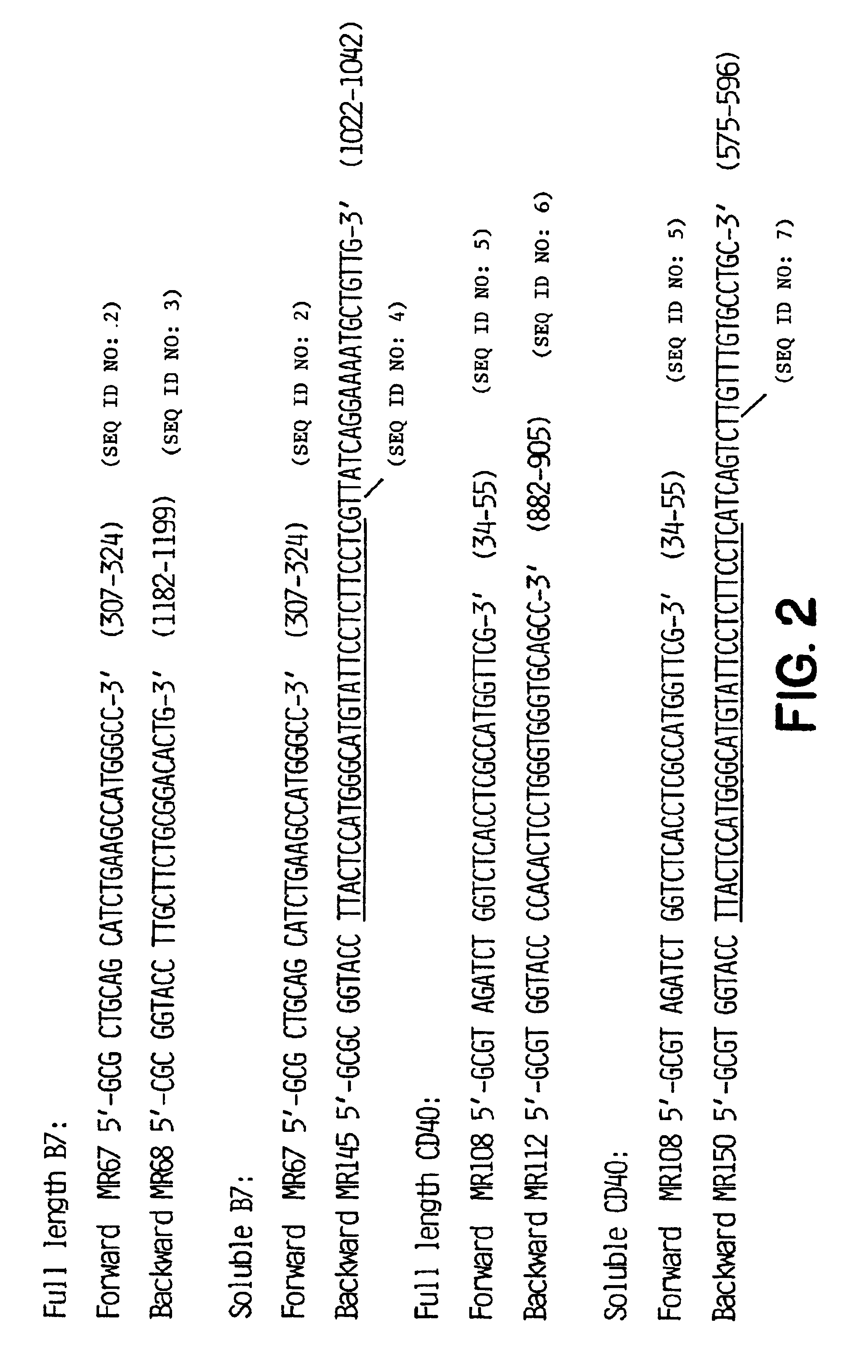
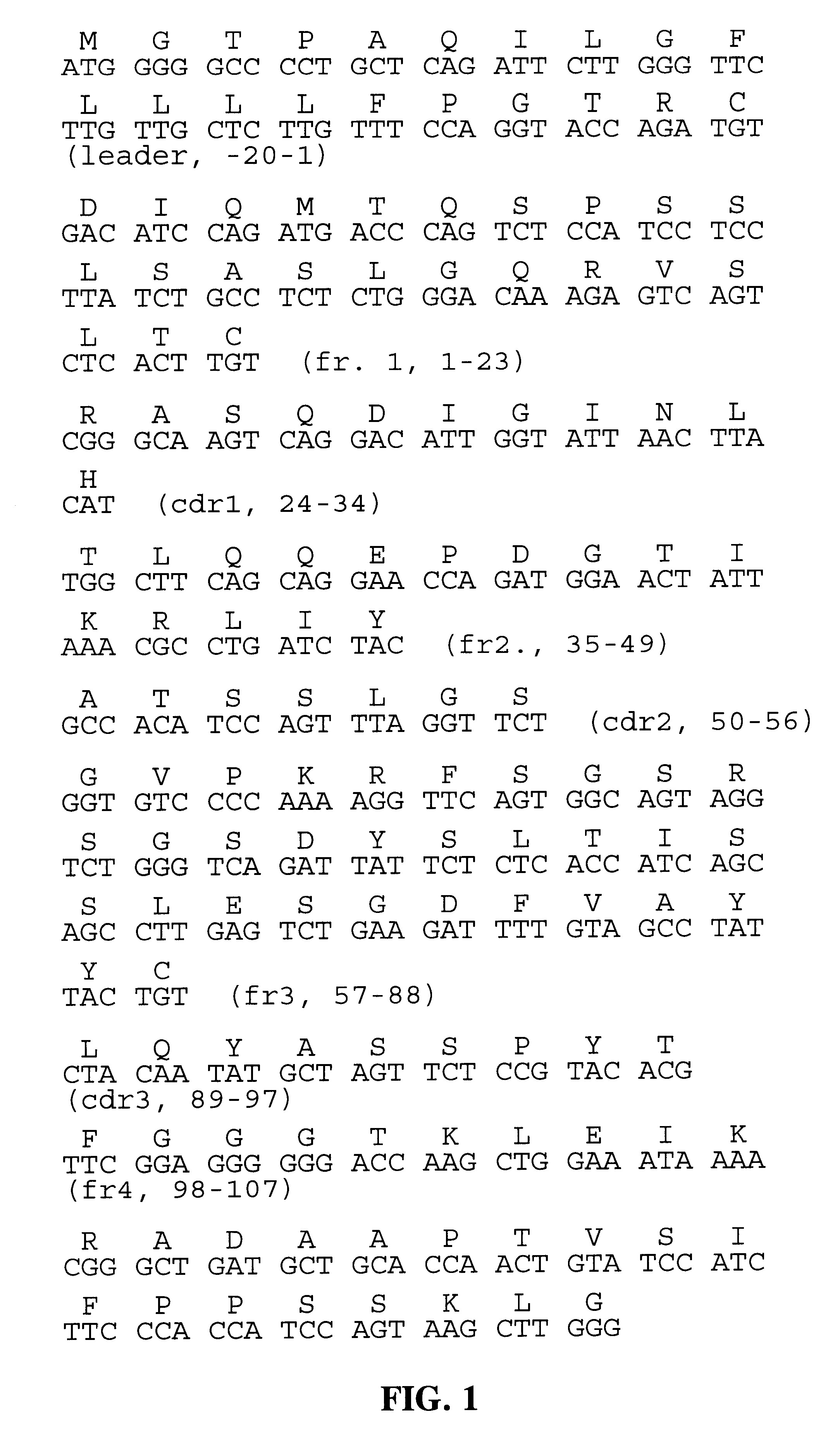Patents
Literature
4705 results about "Epitope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. For example, the epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes.
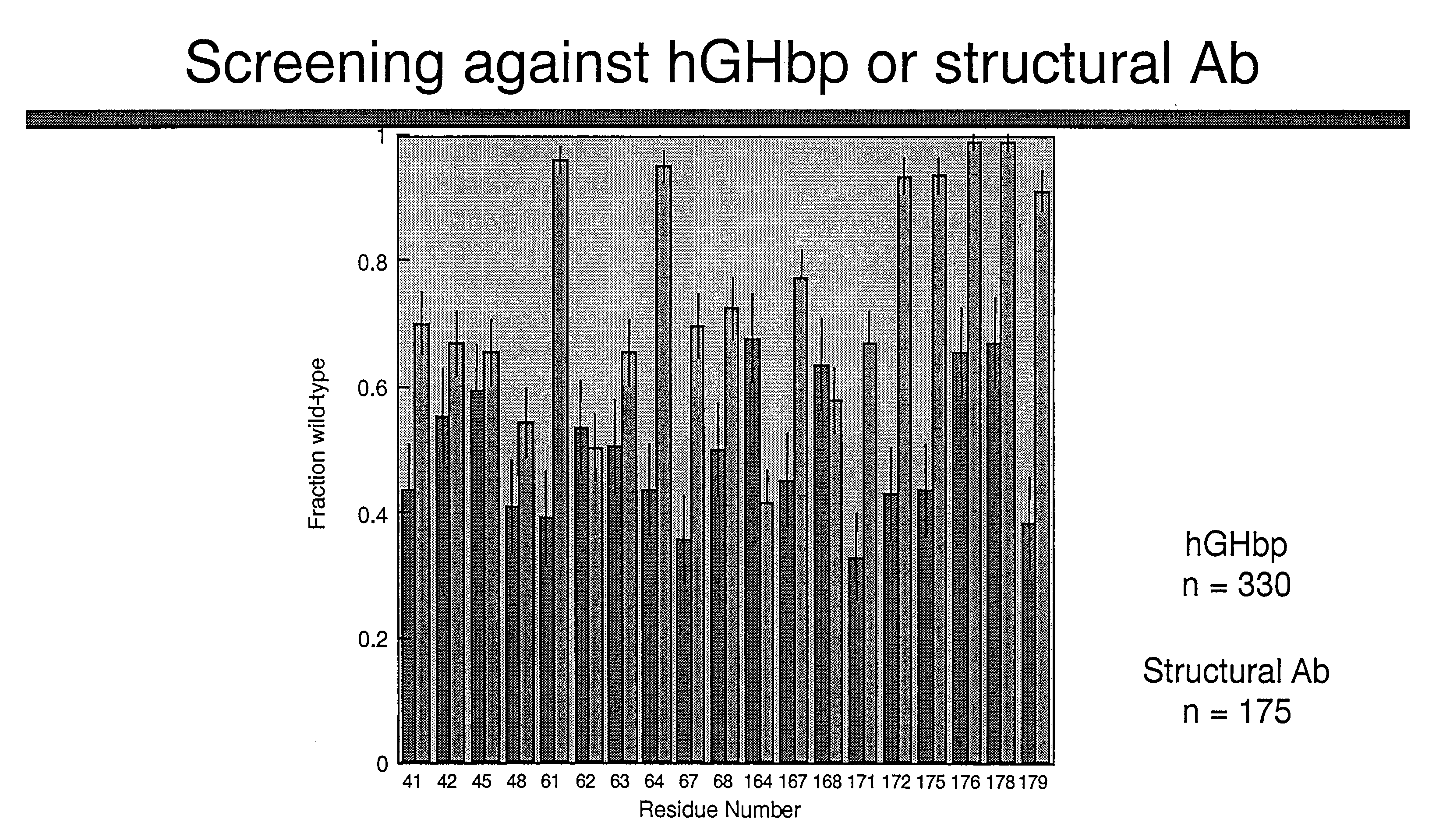
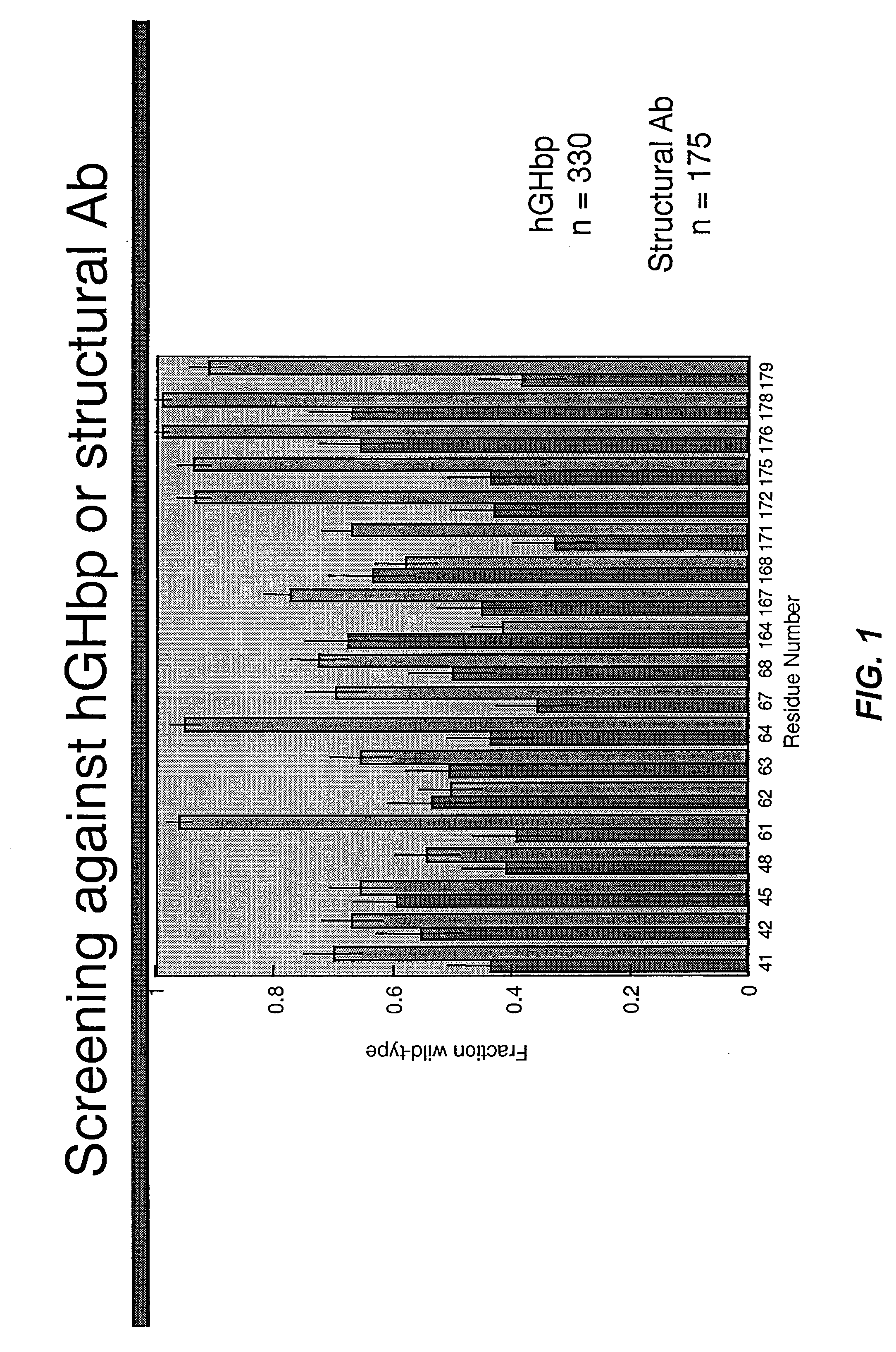
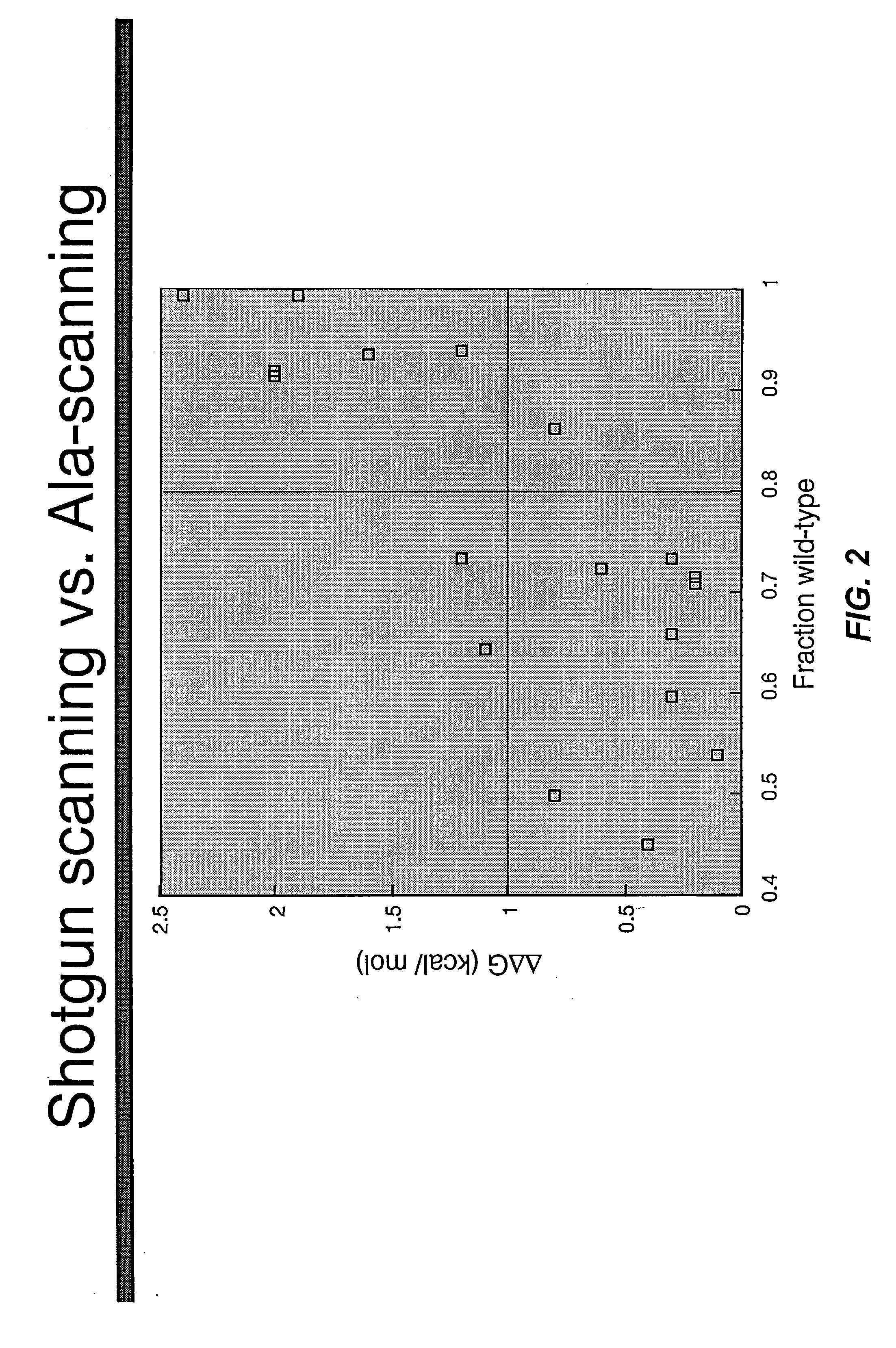
Shotgun scanning
A combinatorial method that uses statistics and DNA sequence analysis rapidly assesses the functional and structural importance of individual protein side chains to binding interactions. This general method, termed “shotgun scanning”, enables the rapid mapping of functional protein and peptide epitopes and is suitable for high throughput proteomics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
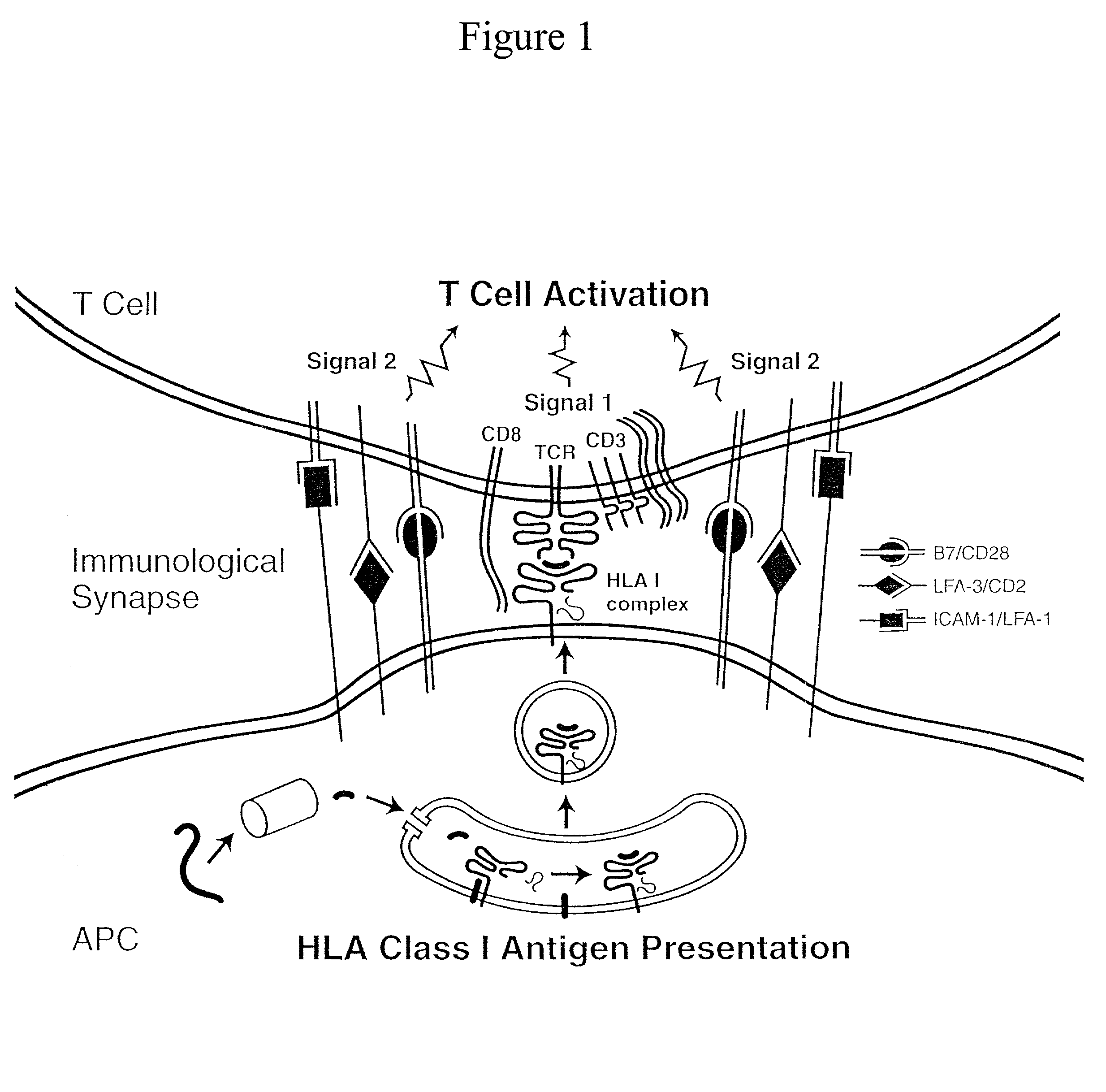
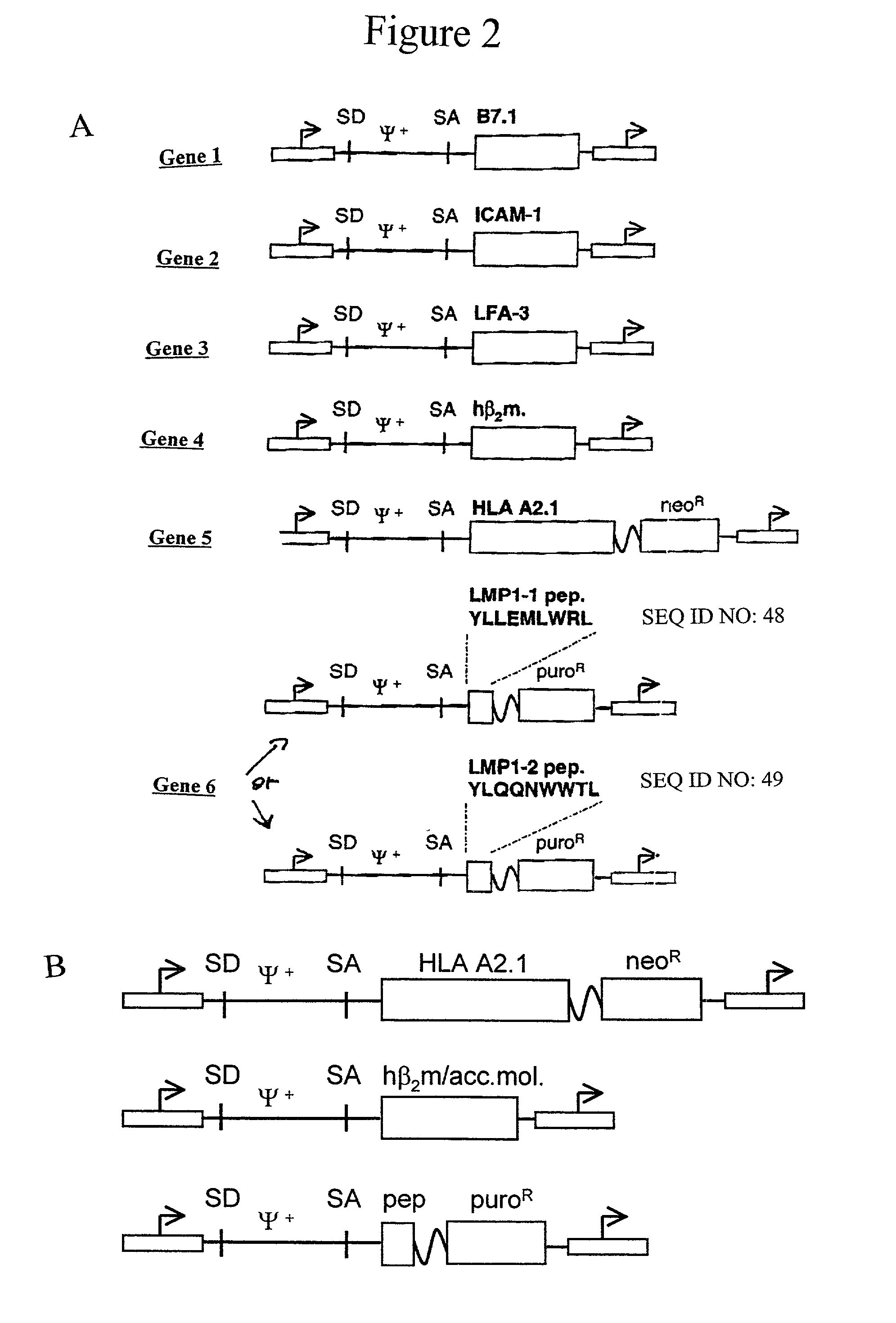
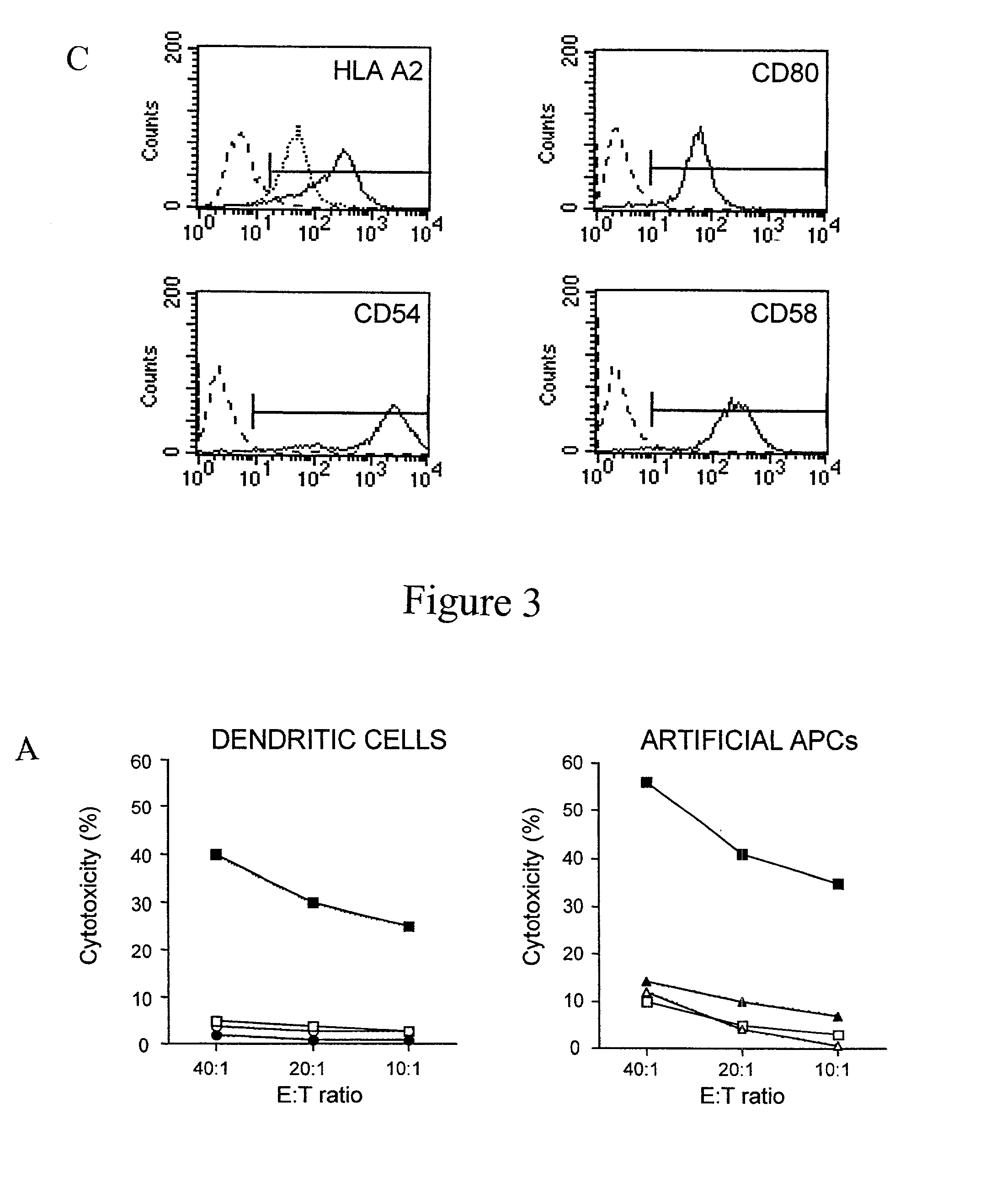
Artificial antigen presenting cells and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20020131960A1Palliating their conditionReduce riskBiocideCompound screeningEpitopeAccessory molecule
The invention provides an artificial antigen presenting cell (AAPC) comprising a eukaryotic cell expressing an antigen presenting complex comprising a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecule of a single type, at least one exogenous accessory molecule and at least one exogenous T cell-specific epitope. Methods of use for activation of T lymphocytes are also provided.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
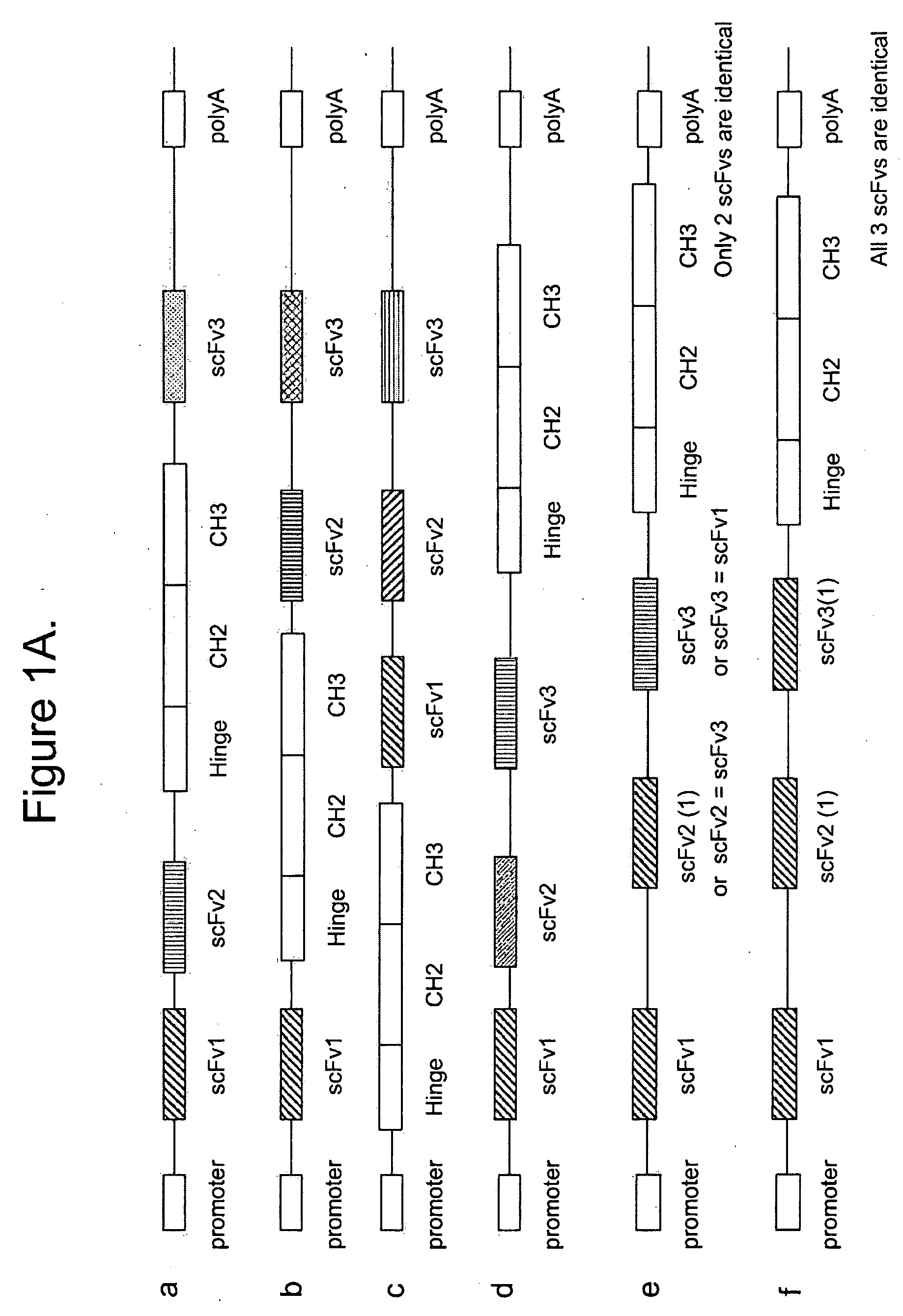
Multispecific epitope binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090155275A1Stimulate immune responseEnhanced interactionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeDisease
The present invention relates to multispecific epitope binding proteins, methods of making, and uses thereof in the prevention, management, treatment or diagnosis of acute or chronic diseases.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
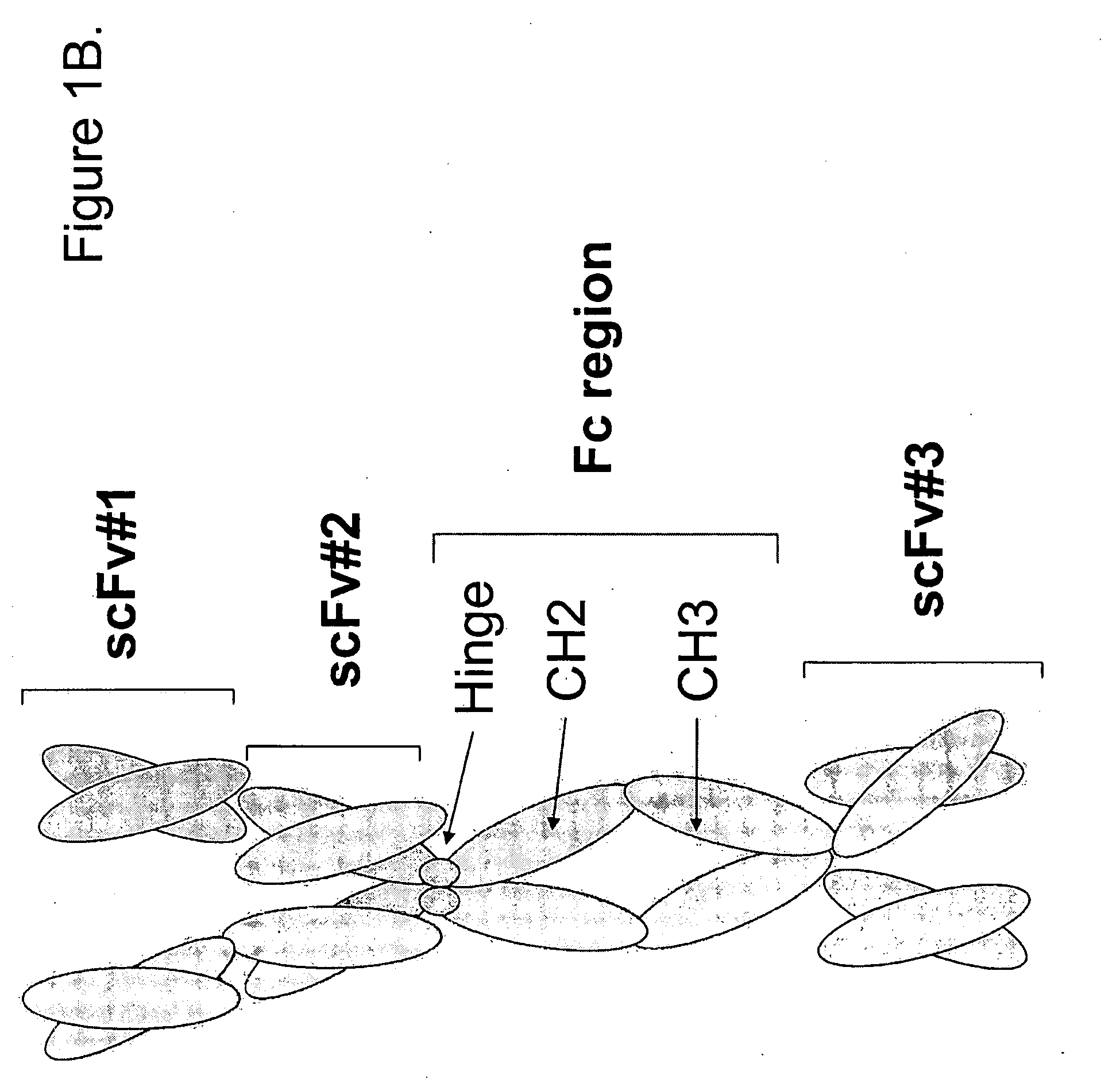
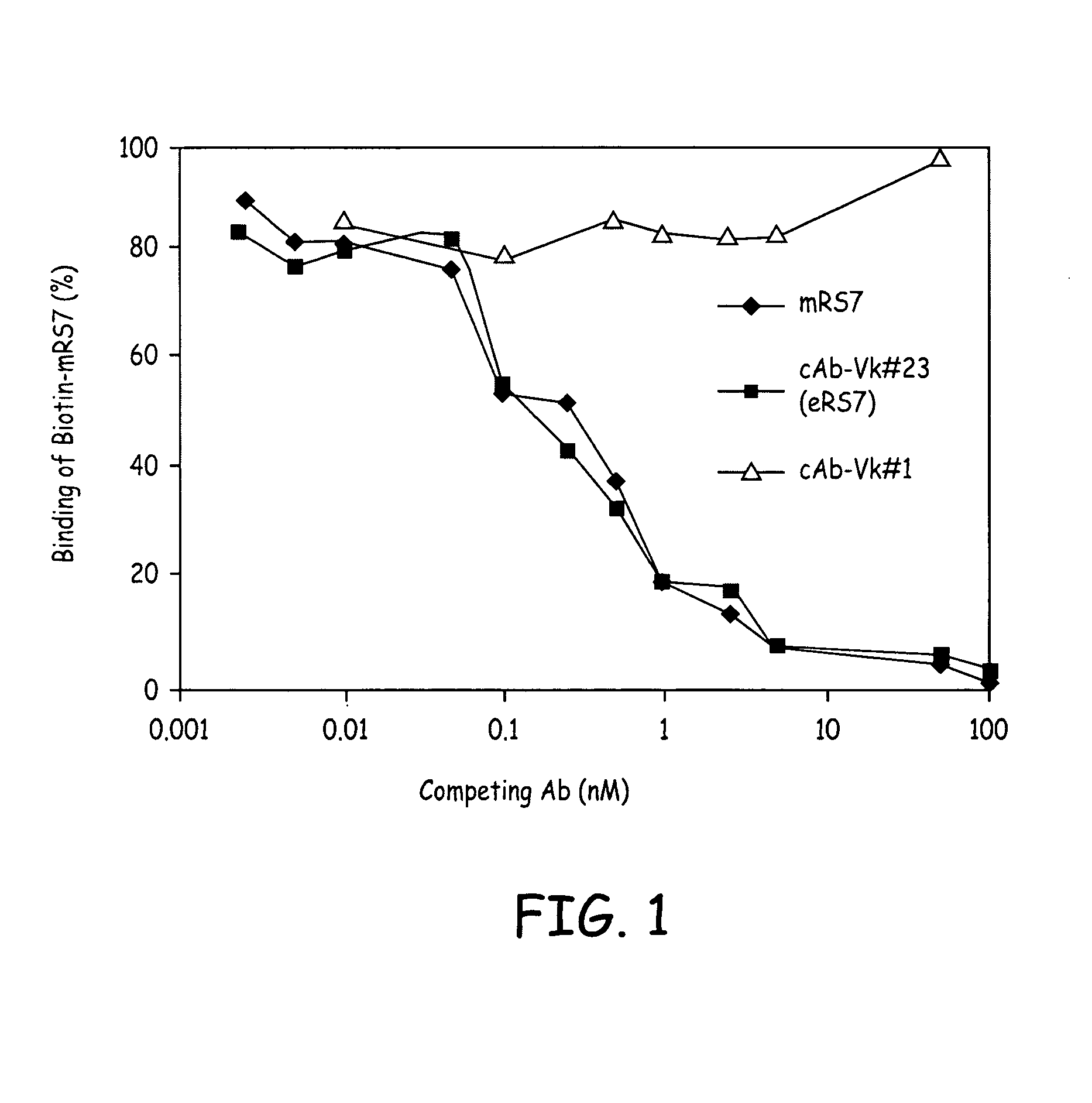
RS7 antibodies
InactiveUS7238785B2Diagnosing and treating malignancyRadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeBinding site
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
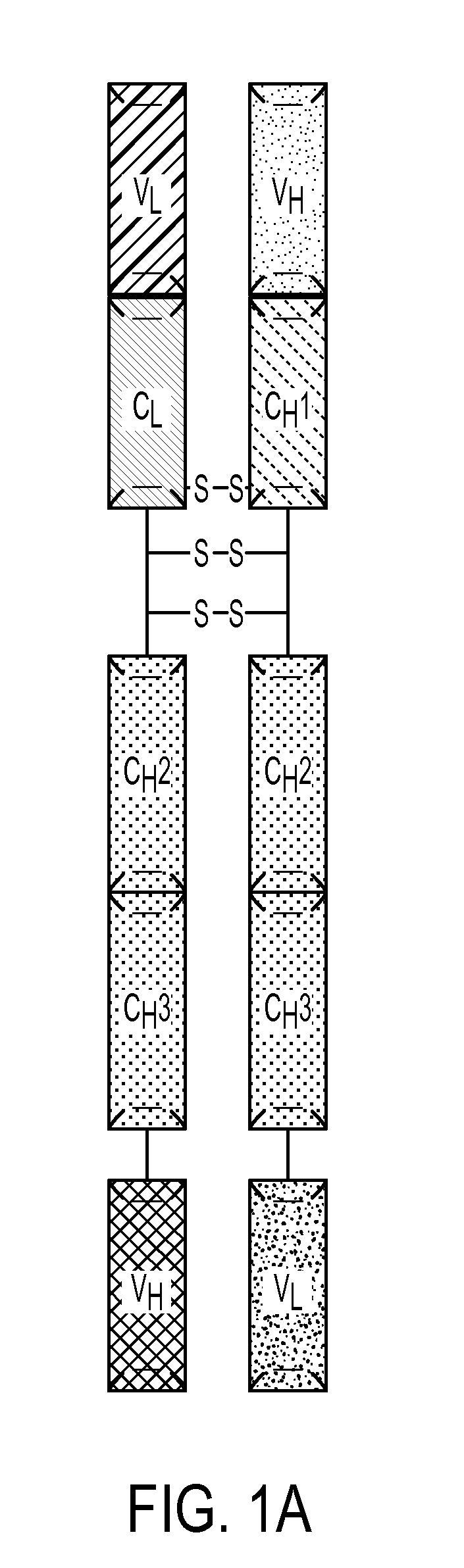
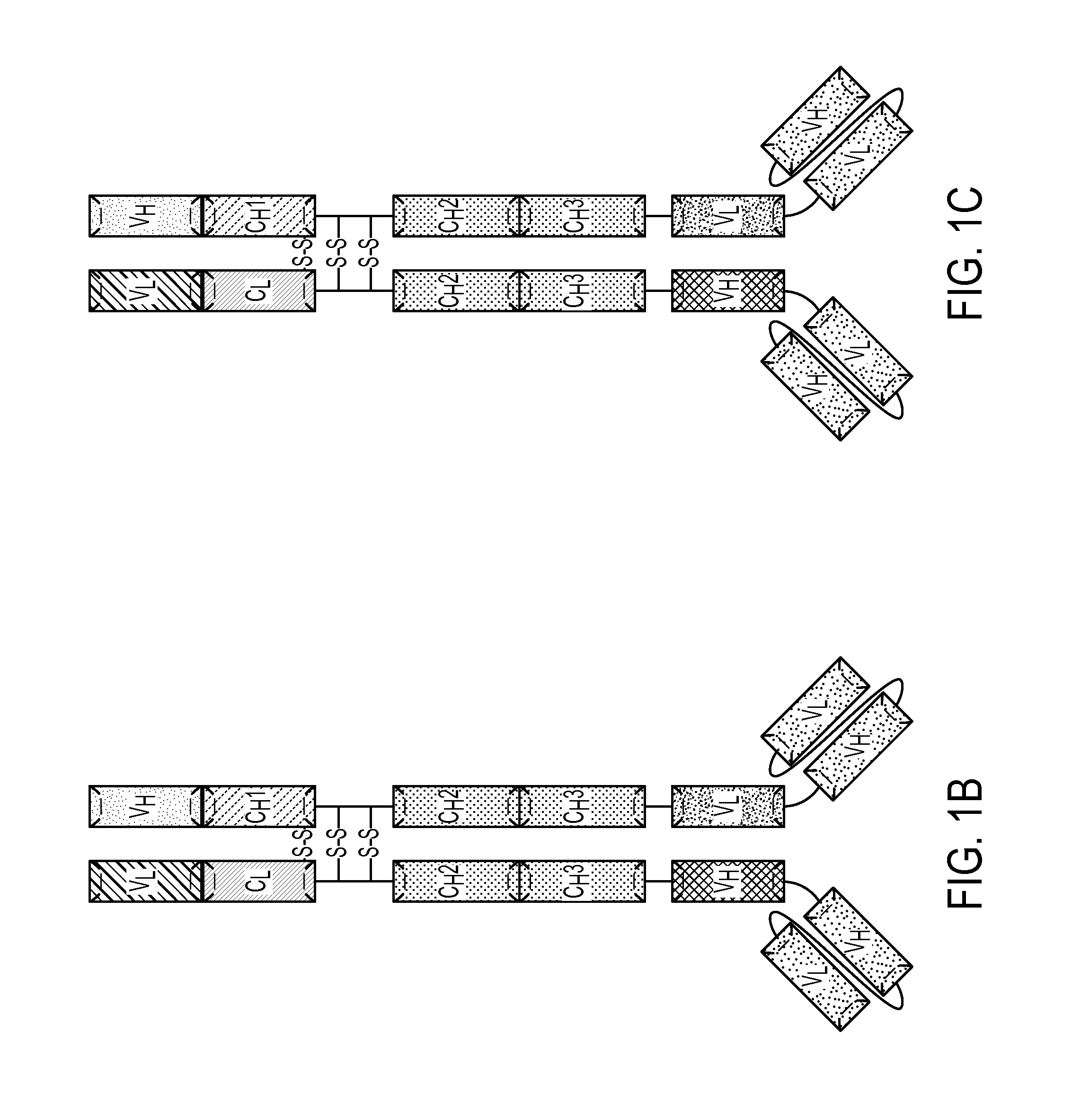
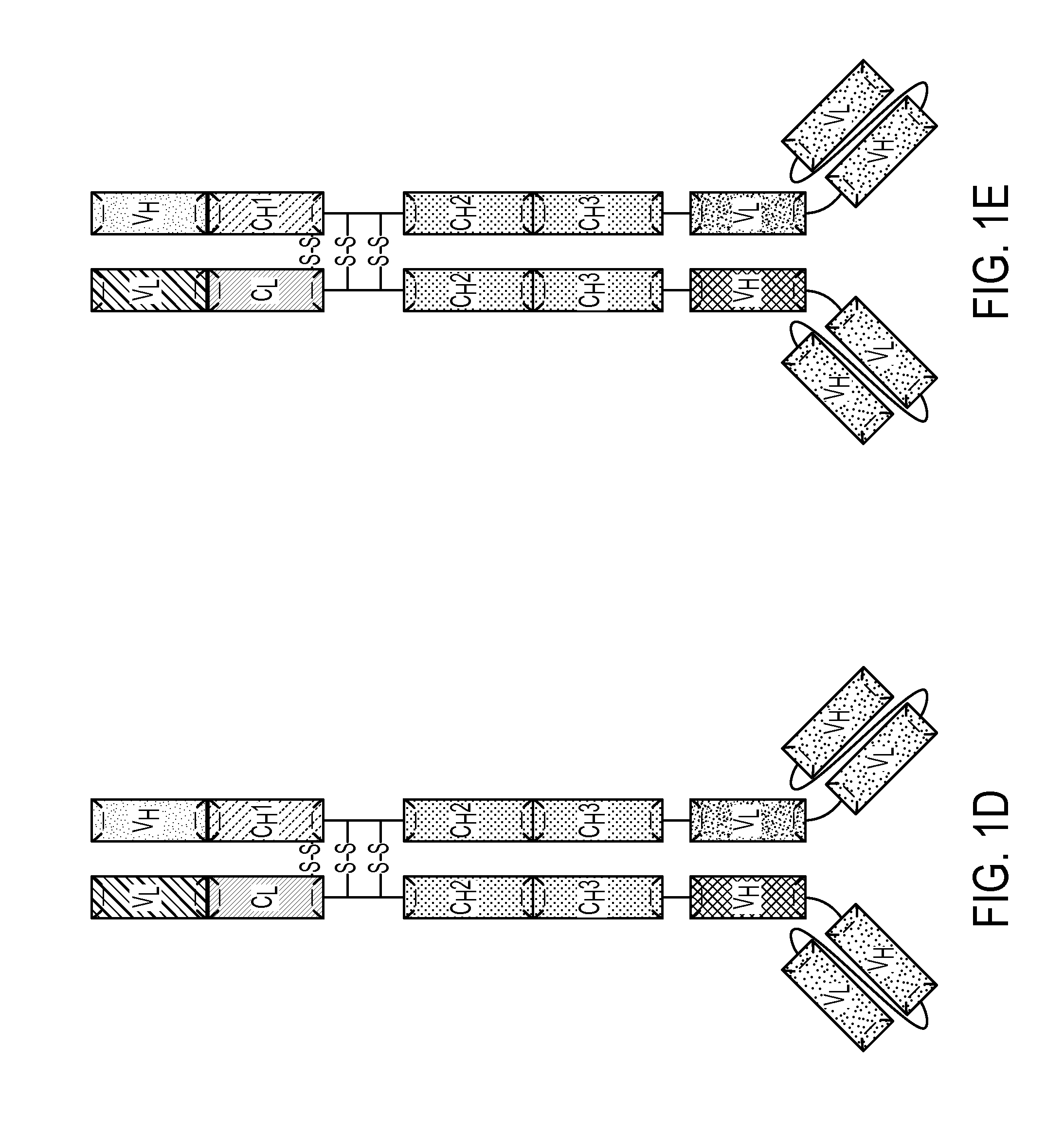
Production of Heteromultimeric Proteins
ActiveUS20110287009A1Reduction in yieldDecreased/elimination of effector functionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeBiochemistry
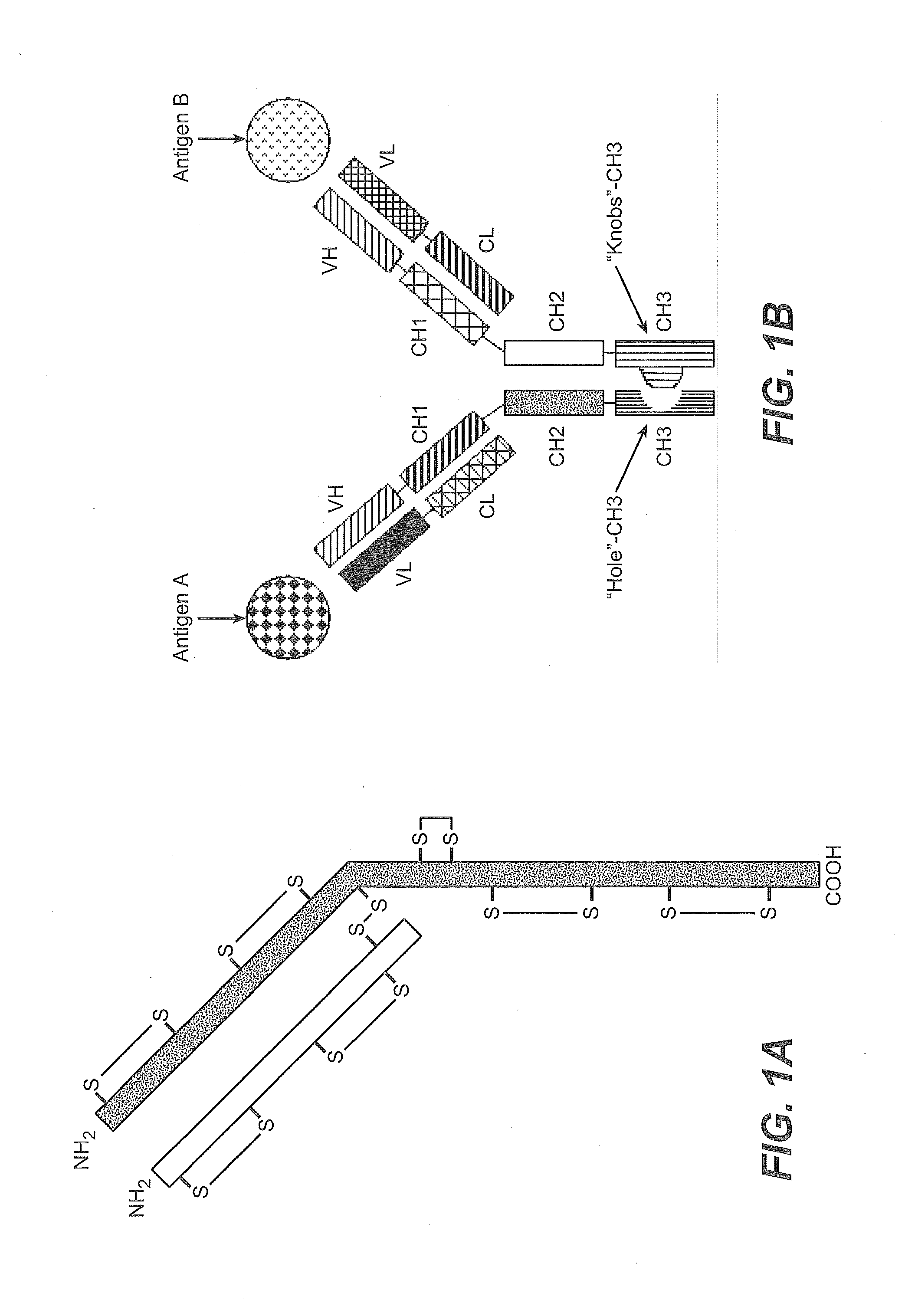
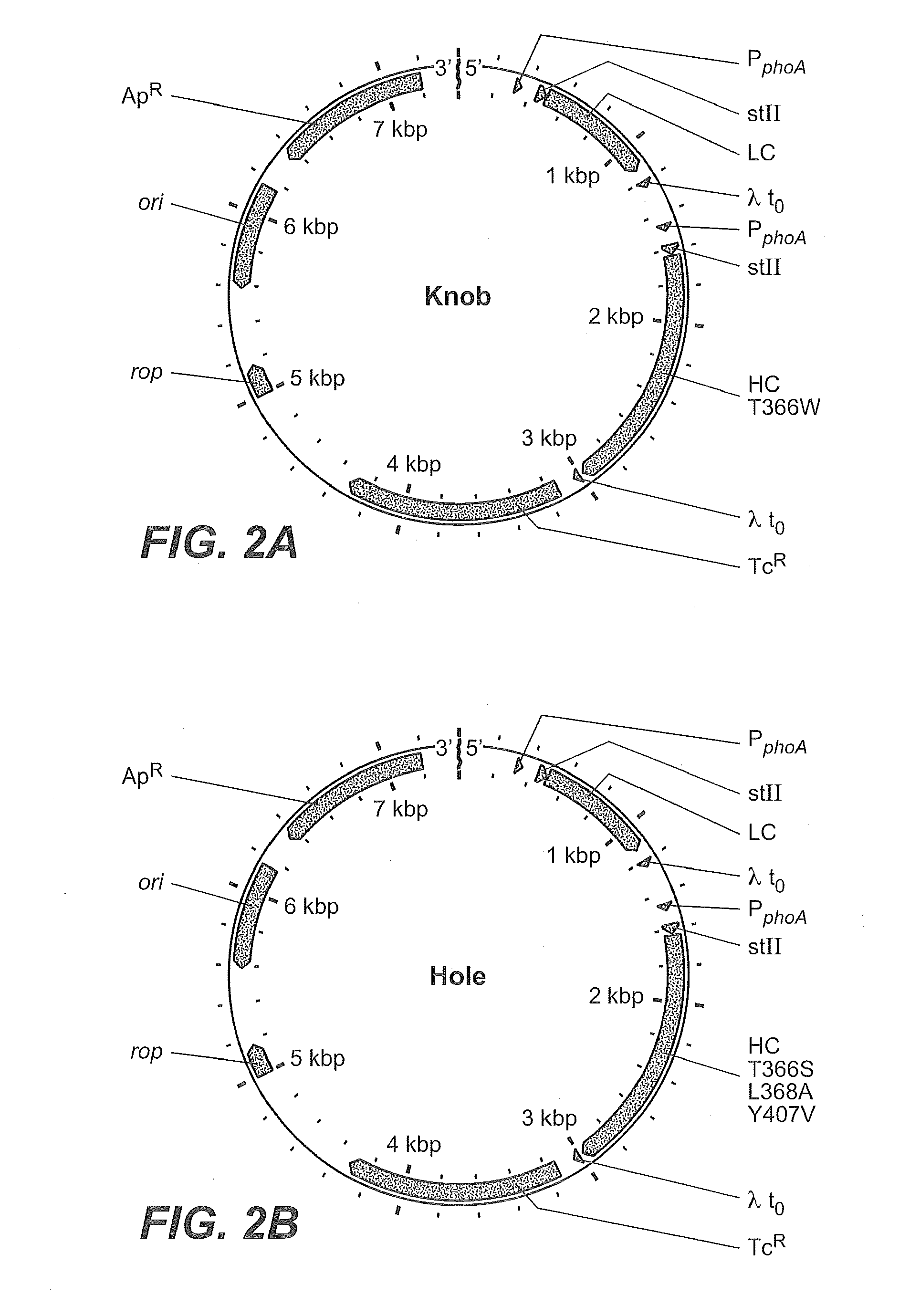
Described herein are methods for the efficient production of antibodies and other multimeric protein complexes (collectively referred to herein as heteromultimeric proteins) capable of specifically binding to more than one target. The targets may be, for example, different epitopes on a single molecule or located on different molecules. The methods combine efficient, high gene expression level, appropriate assembly, and ease of purification for the heteromultimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods of using these heteromultimeric proteins, and compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising these antibodies.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
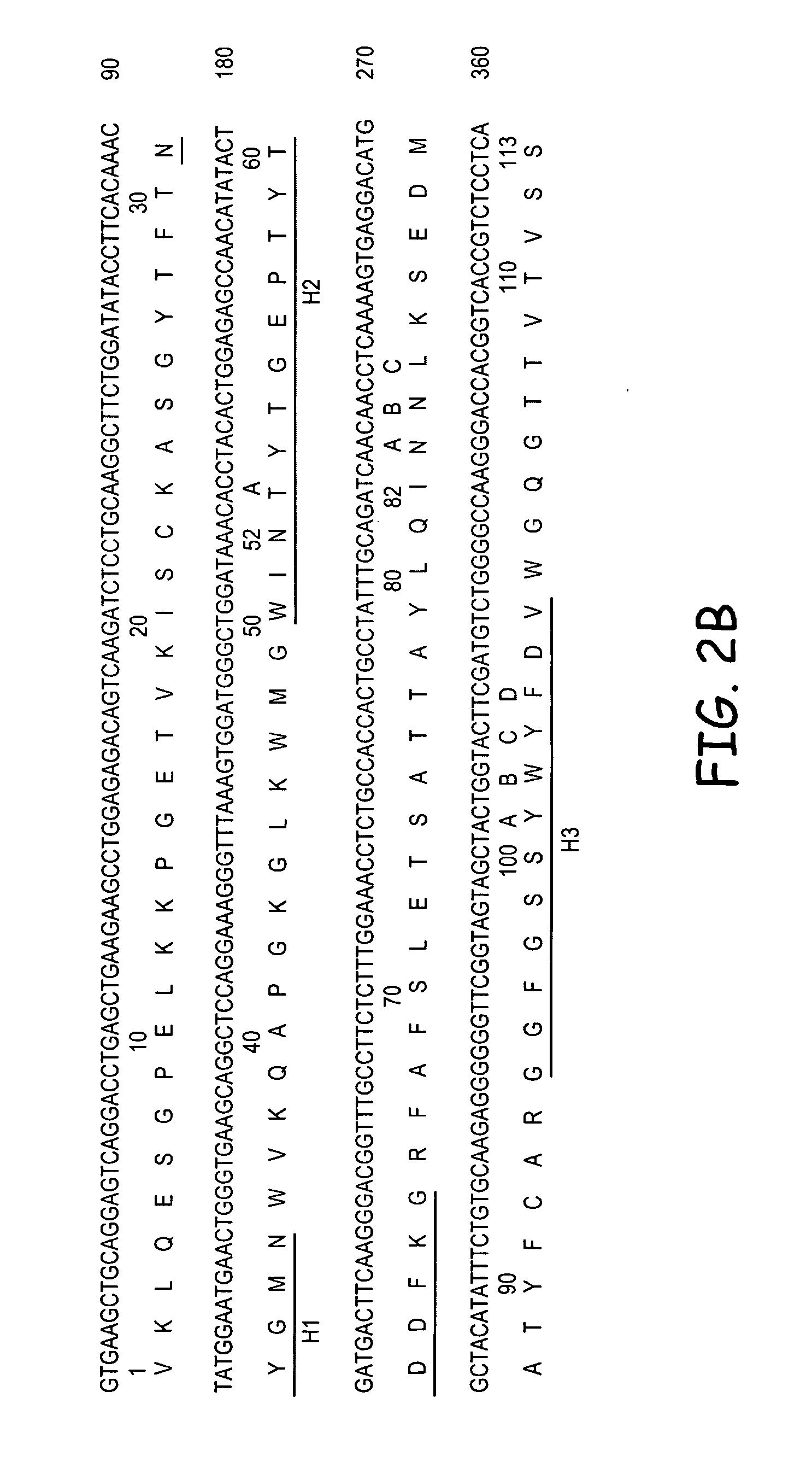
Humanized immunoglobulins
Novel methods for producing, and compositions of, humanized immunoglobulins having one or more complementarity determining regions (CDR's) and possible additional amino acids from a donor immunoglobulin and a framework region from an accepting human immunoglobulin are provided. Each humanized immunoglobulin chain will usually comprise, in addition to the CDR's, amino acids from the donor immunoglobulin framework that are, e.g., capable of interacting with the CDR's to effect binding affinity, such as one or more amino acids which are immediately adjacent to a CDR in the donor immunoglobulin or those within about about 3Å as predicted by molecular modeling. The heavy and light chains may each be designed by using any one or all of various position criteria. When combined into an intact antibody, the humanized immunoglobulins of the present invention will be substantially non-immunogenic in humans and retain substantially the same affinity as the donor immunoglobulin to the antigen, such as a protein or other compound containing an epitope.
Owner:PDL BIOPHARMA INCORPORATED
Antibody for 4-1BB
The present invention includes the receptor protein 4-1BB and the cDNA gene encoding for receptor protein 4-1BB. The nucleotide sequence of the isolated cDNA is disclosed herein along with the deduced amino acid sequence. The 4-1BB protein and fragments and derivatives can be used: 1) as a probe to isolate ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB, 2) to stimulate proliferation of B-cell's expressing 4-1BB, or 3) to block 4-1BB ligand binding. A monoclonal antibody against 4-1BB was developed which specifically recognizes an epitope on the extracellular domain of receptor protein 4-1BB. The monoclonal antibody can be used enhance T-cell proliferation and activation by treating T-cells that have expressed receptor protein 4-1BB with the monoclonal antibody. The effectiveness of the treatment was enhanced when conducted in the presence of protein tyrosinase kinase. A fusion protein for detecting cell membrane ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB was developed. It comprises the extracellular portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB and a detection protein bound to the portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
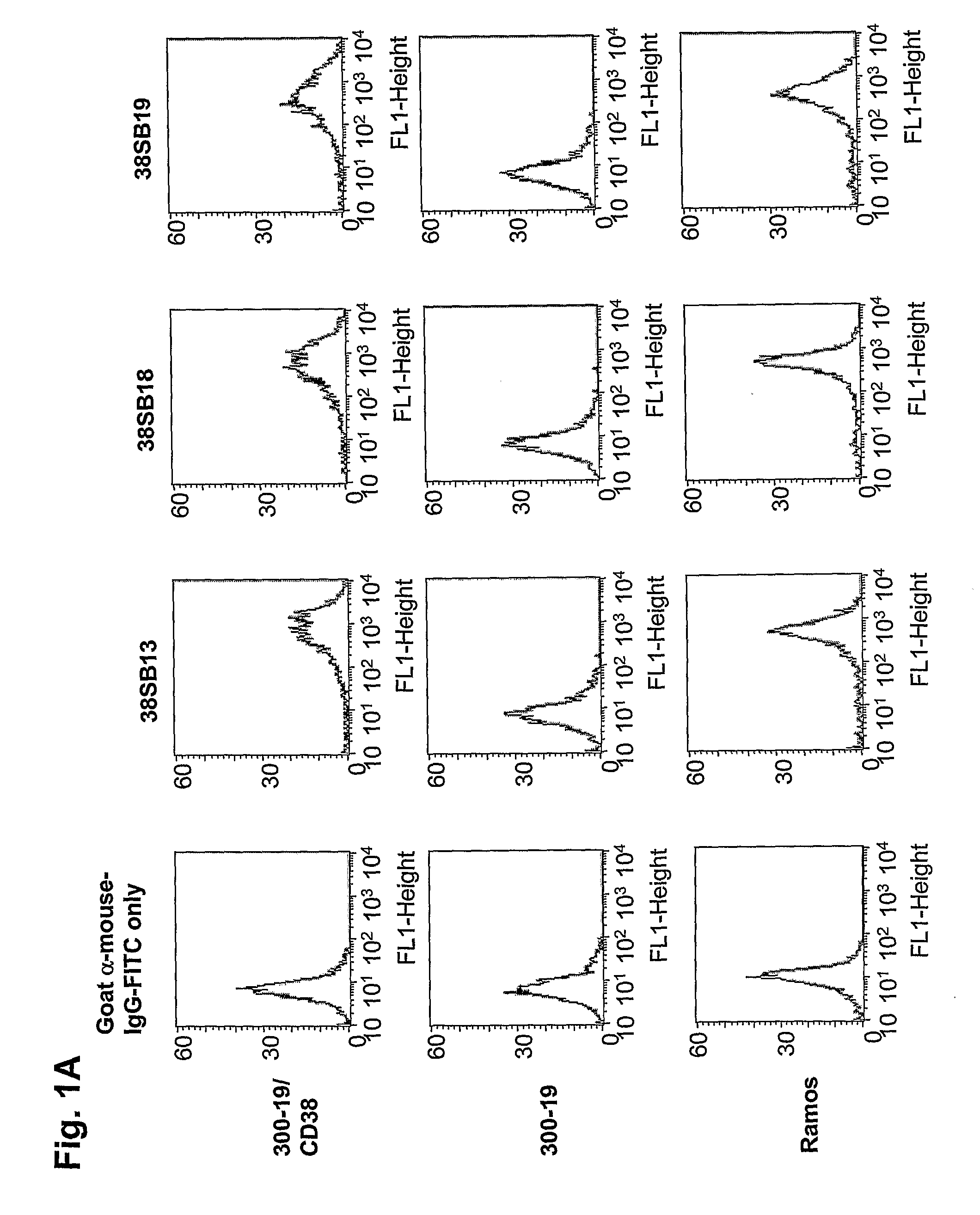
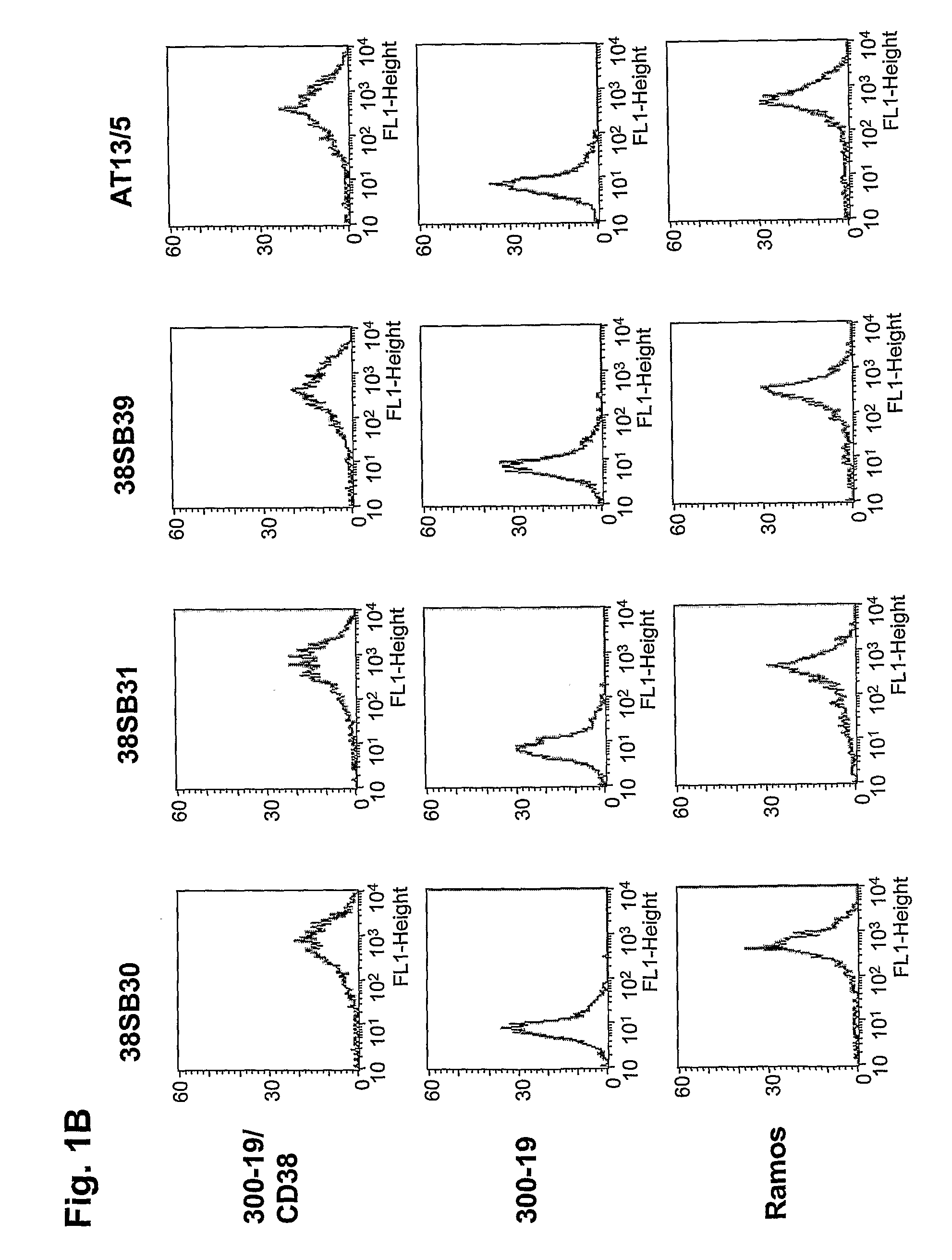
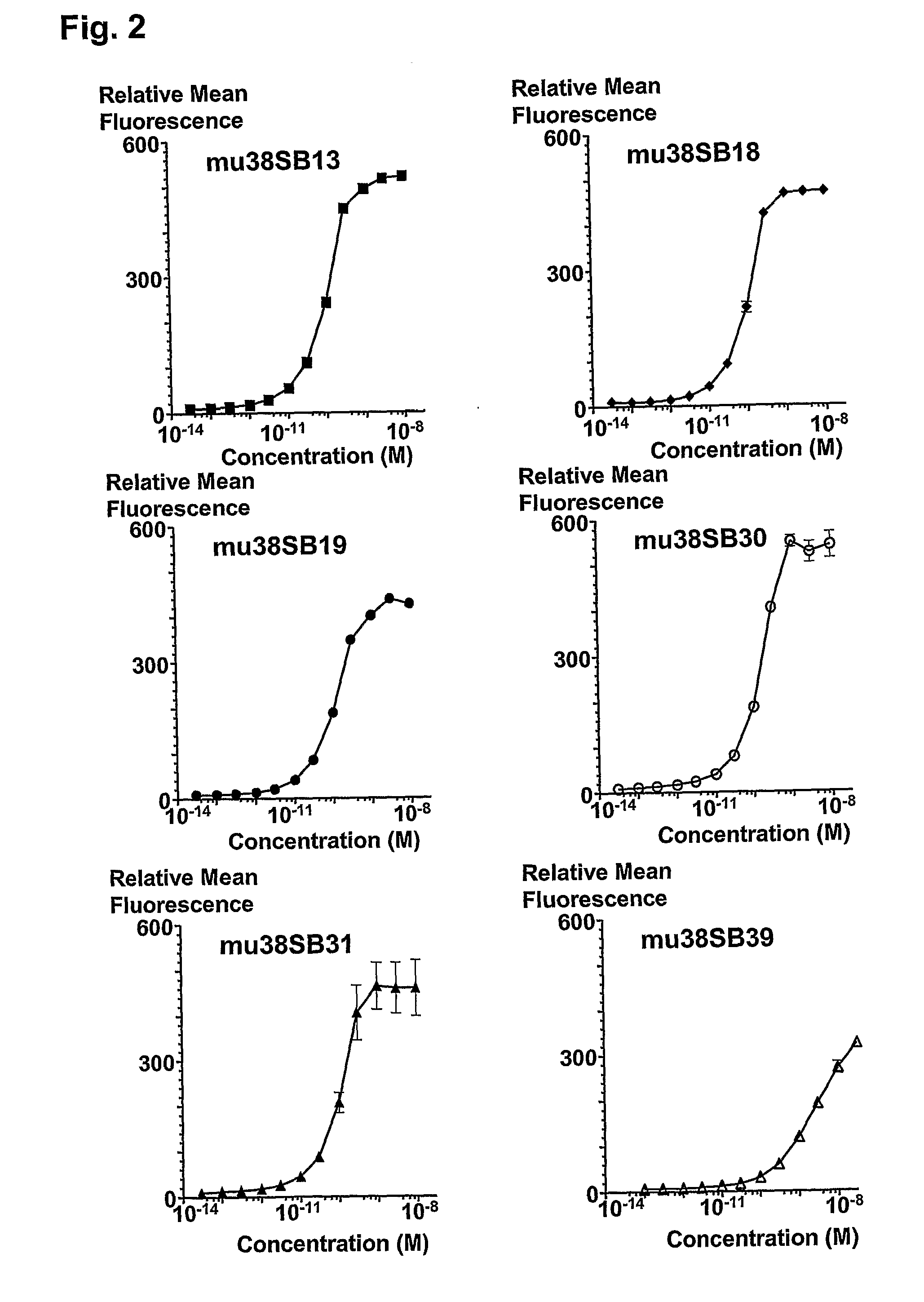
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
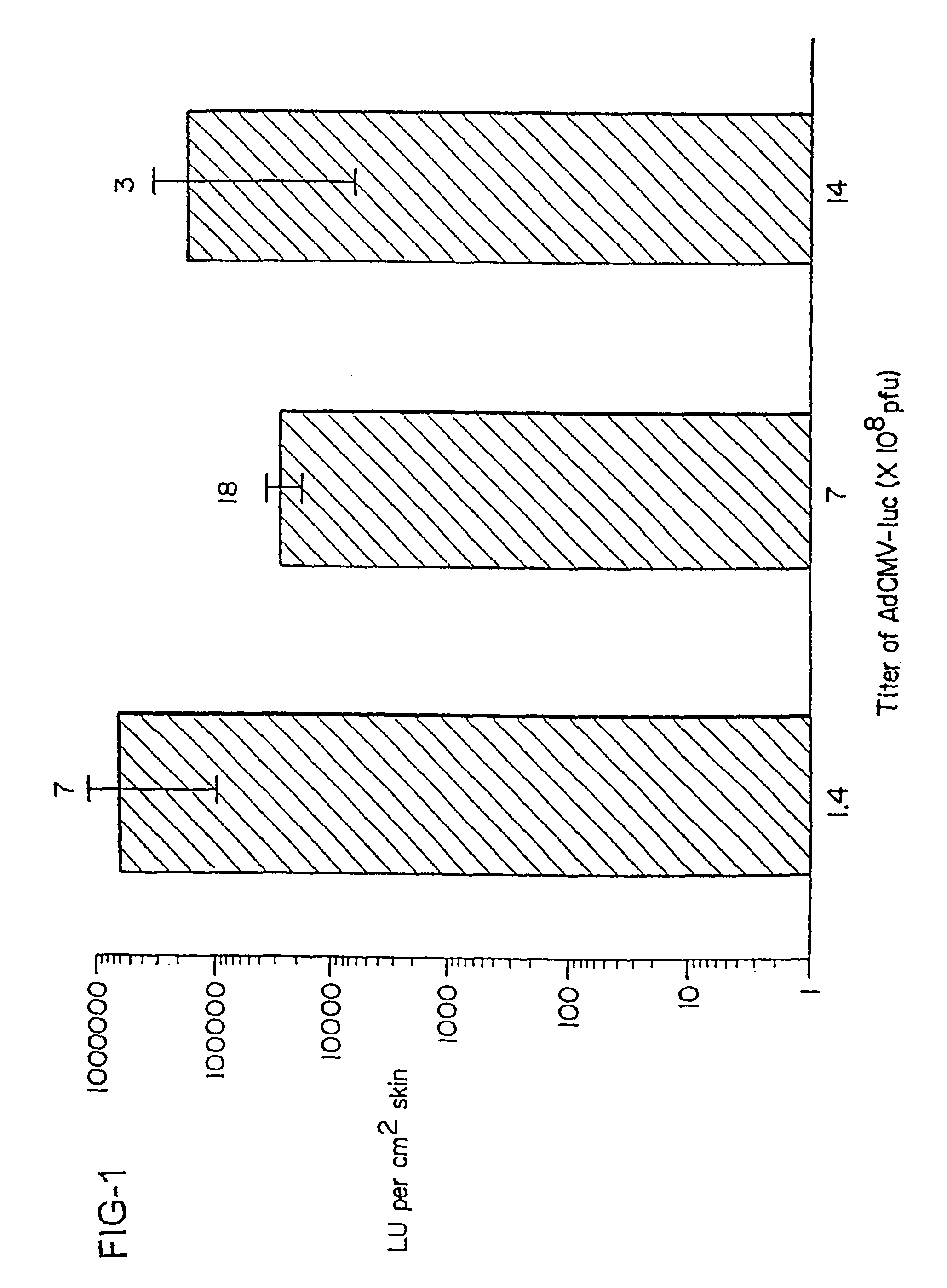
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom and uses thereof
InactiveUS6348450B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideHemagglutininWhole body
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, HIV gp 120, human carcinoembryonic antigen, and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
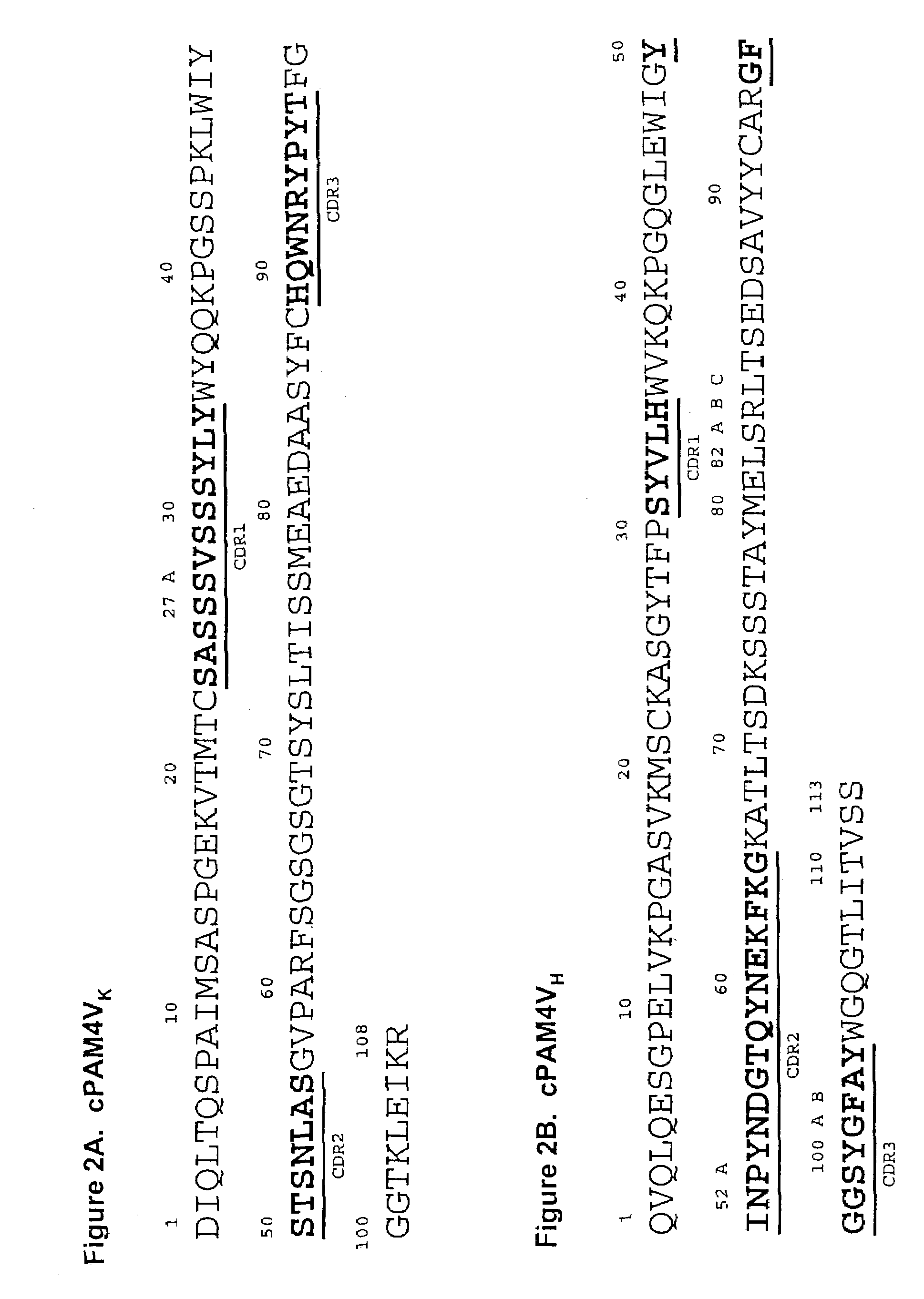
Monoclonal antibody hPAM4
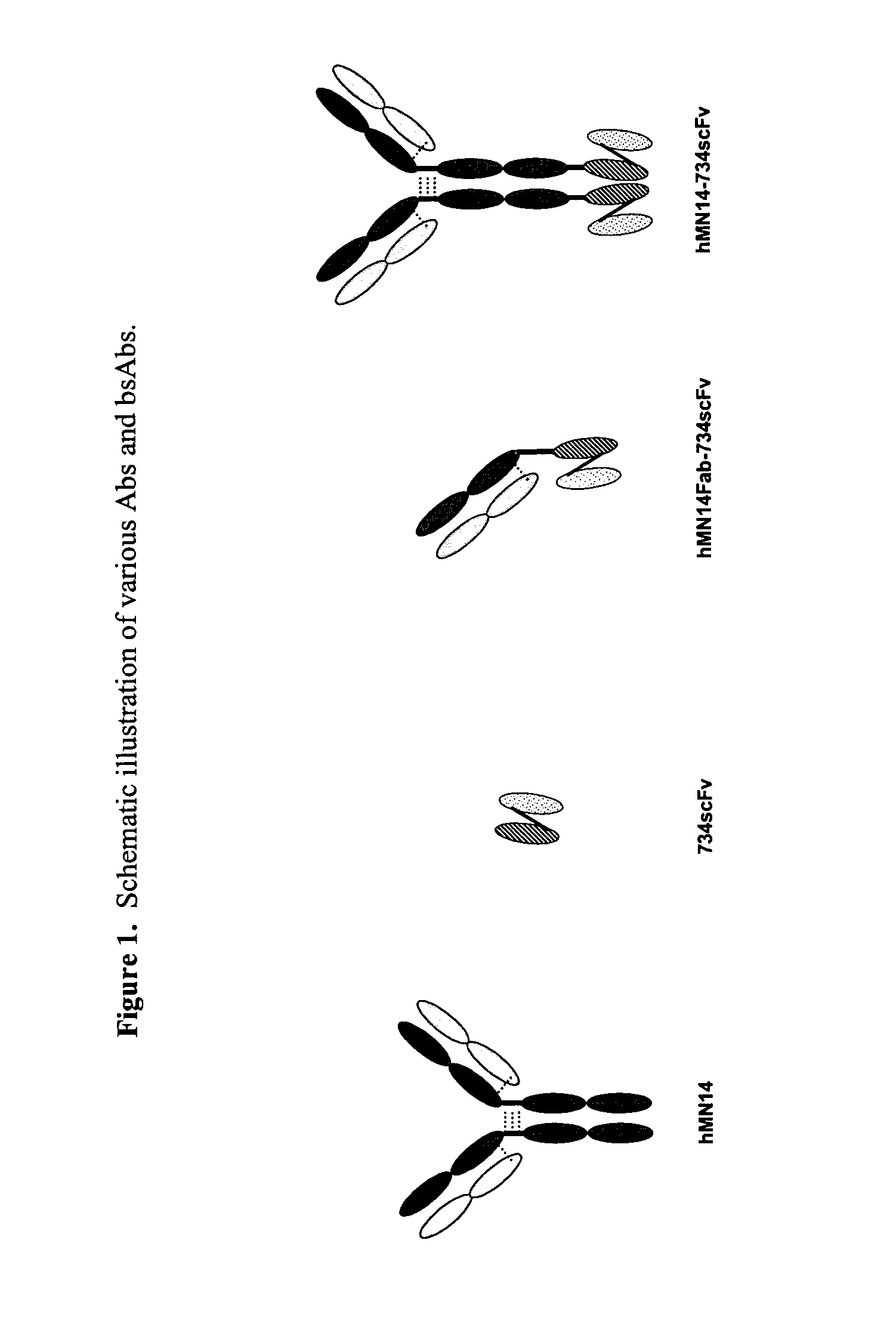
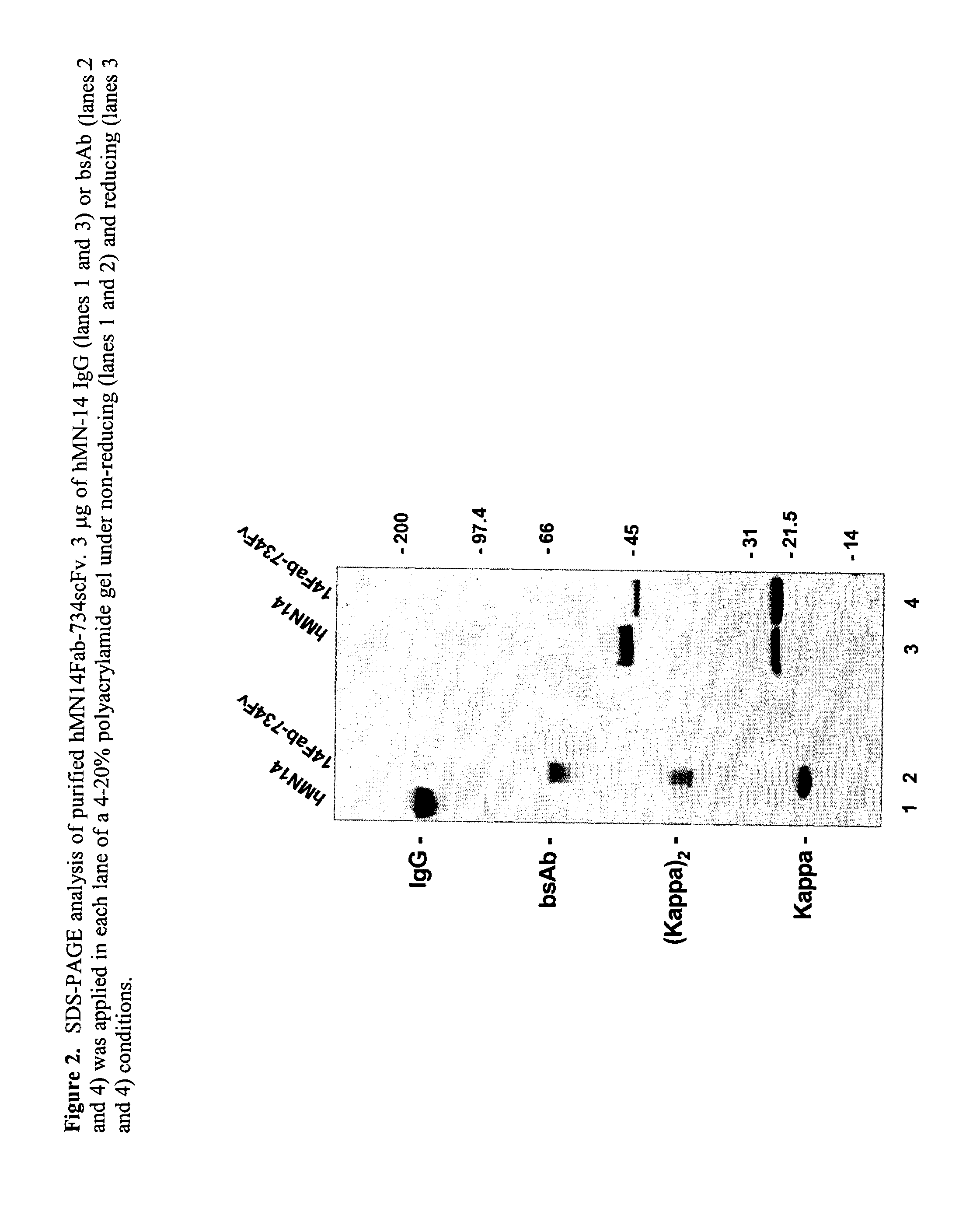
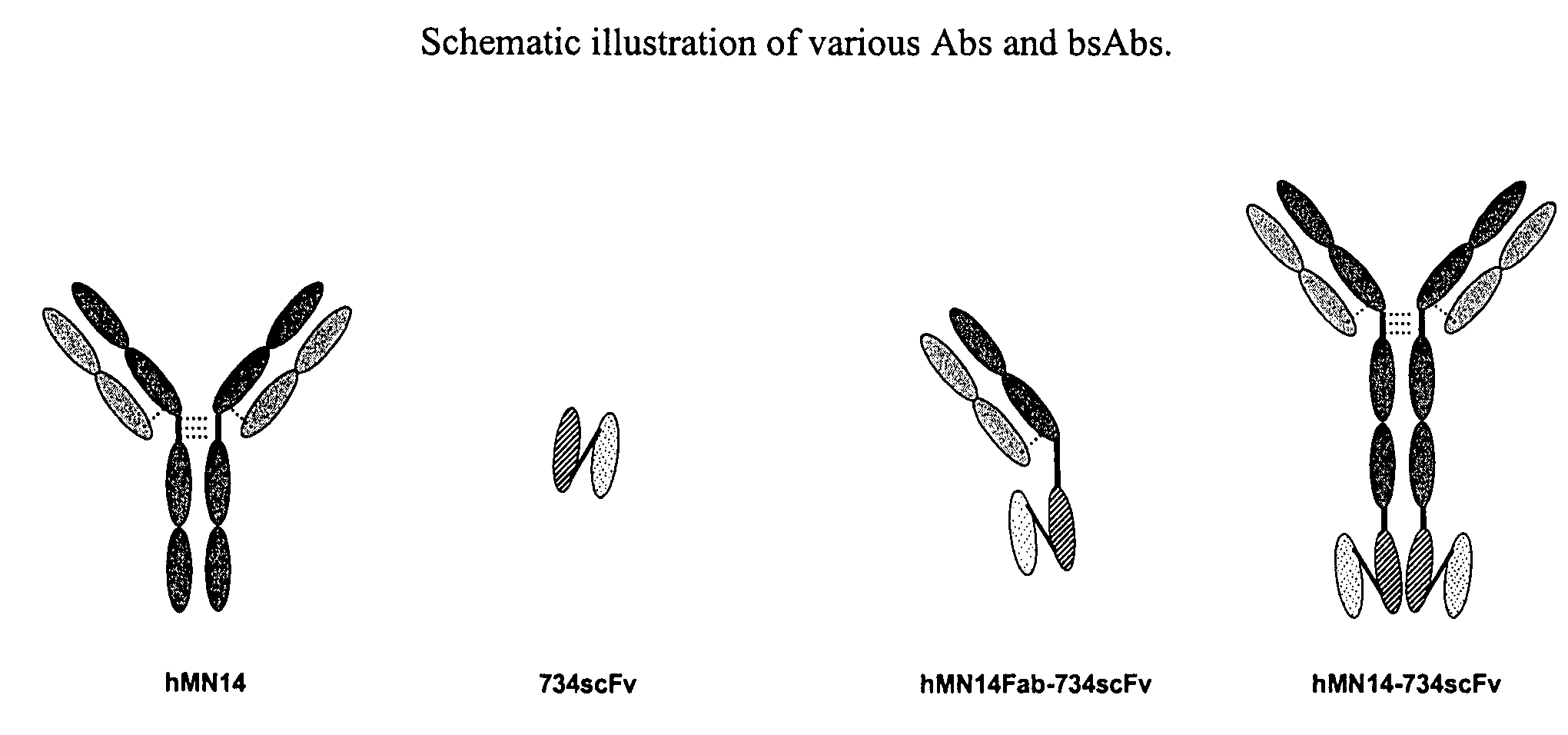
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to humanized and human PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Fc fusion
InactiveUS20060083747A1Extended half-lifeHigh affinityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderEpitopeIn vivo
The present invention relates to a simple method for generating antibody-based structures suitable for in vivo use. In particular, the invention relates to a method for the generation of antibody-based structures suitable for in vivo use comprising the steps of: (a) selecting an antibody single variable domain having an epitope binding specificity; and (b) attaching the single domain of step (a) to an effector group. Uses of molecules generated using the method of the Invention are also described.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Humanized antibodies that sequester abeta peptide
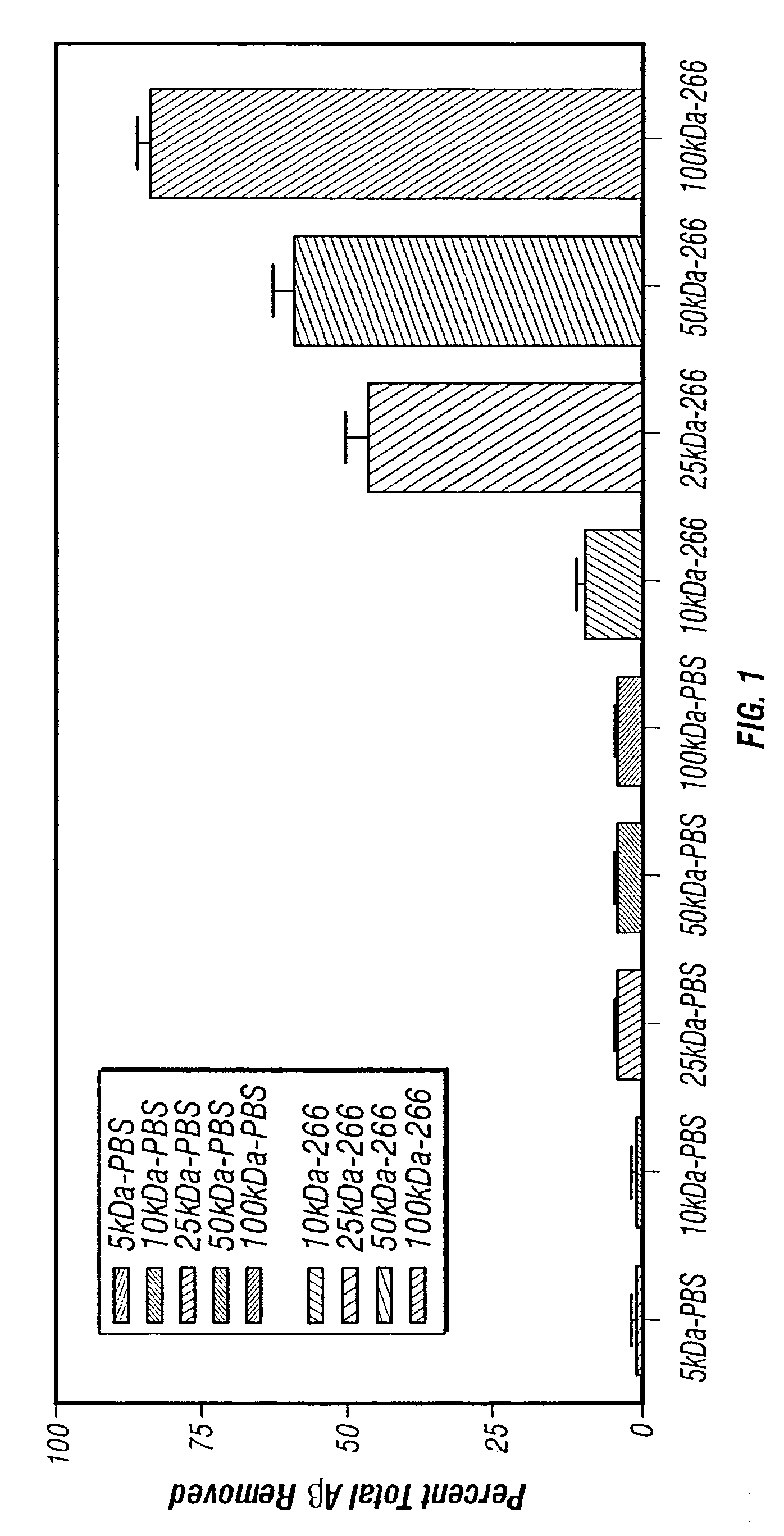
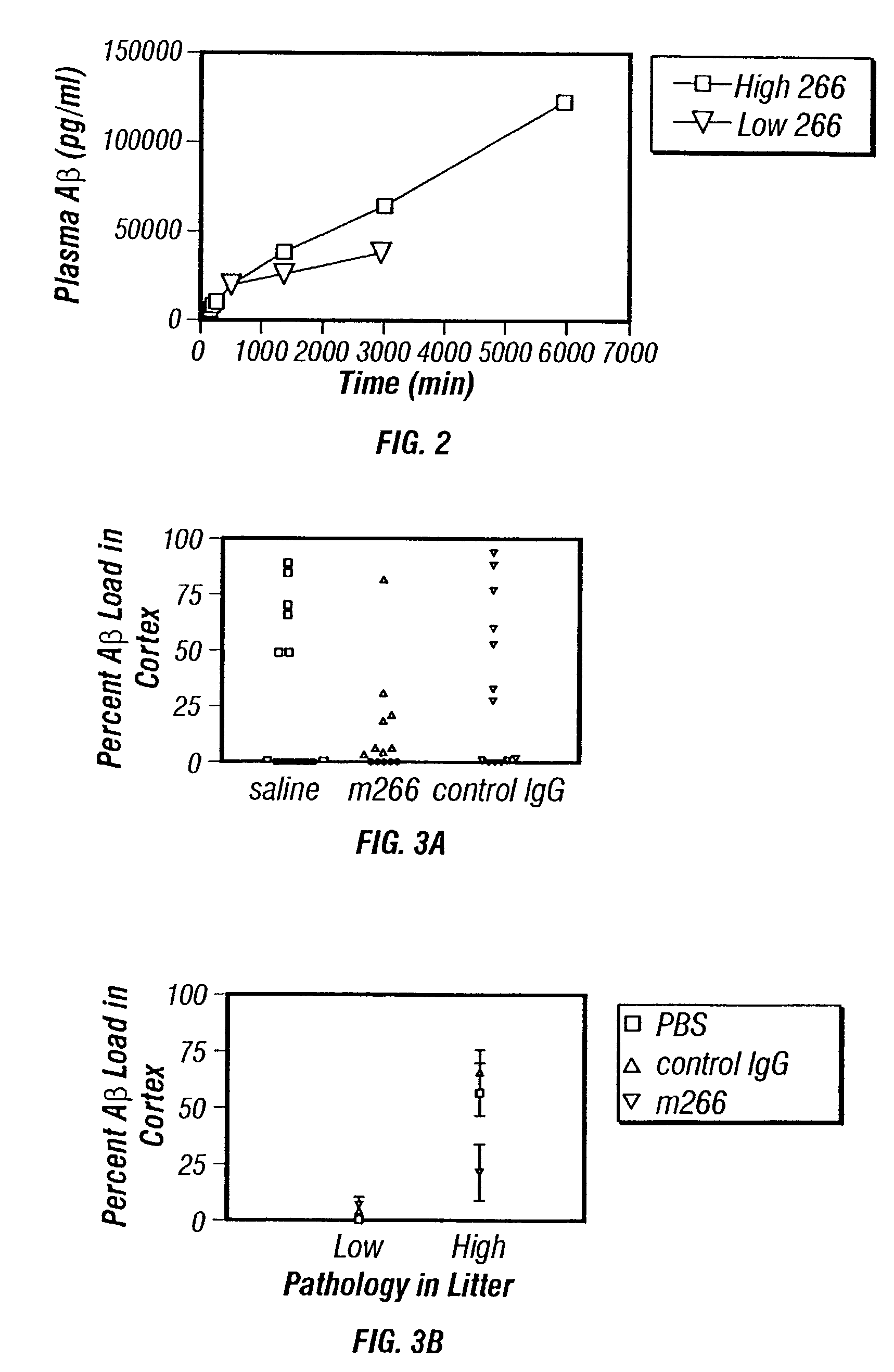
A method to treat conditions characterized by formation of amyloid plaques both prophylactically and therapeutically is described. The method employs humanized antibodies which sequester soluble Aβ peptide from human biological fluids or which preferably specifically bind an epitope contained within position 13–28 of the amyloid beta peptide Aβ.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
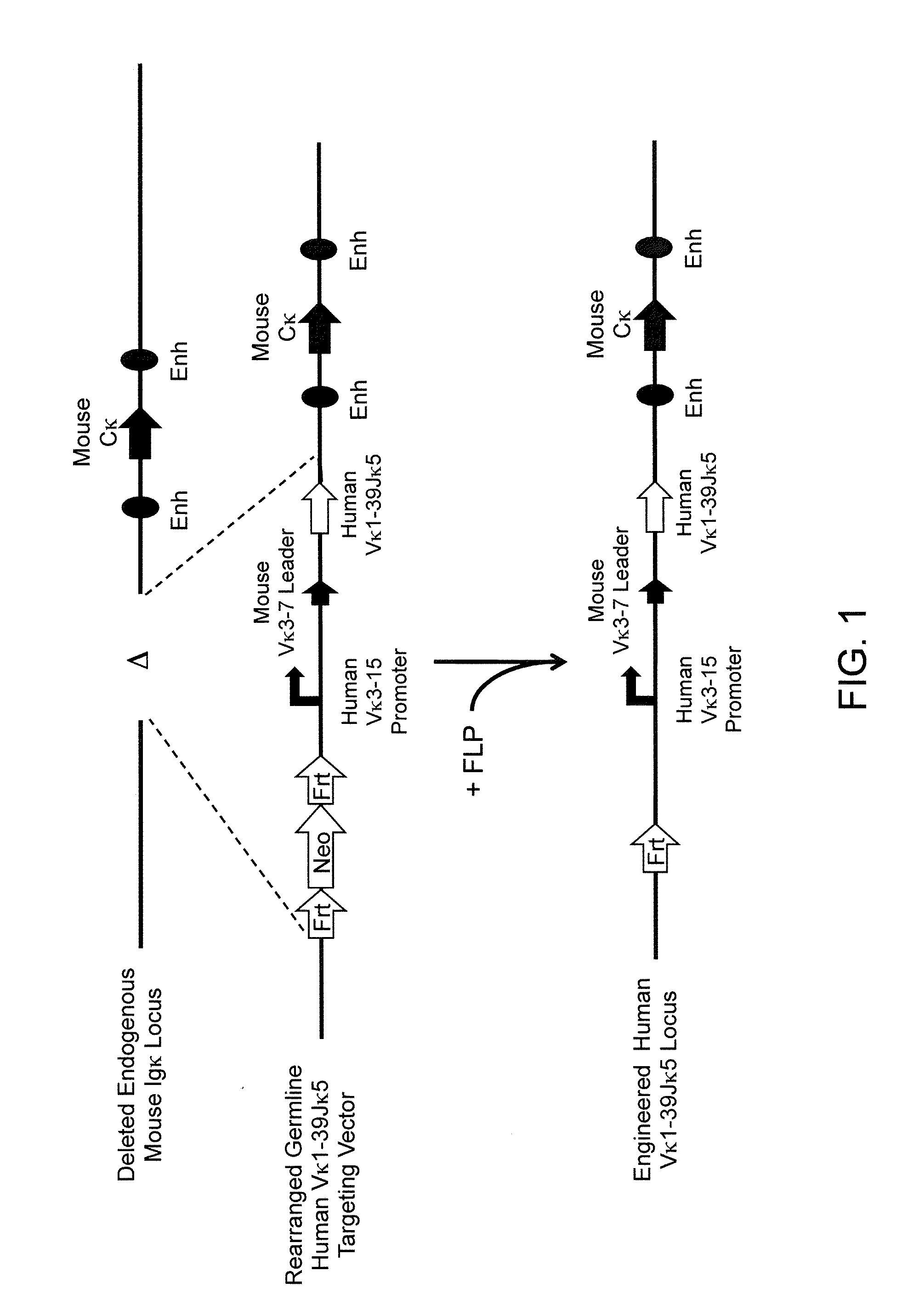
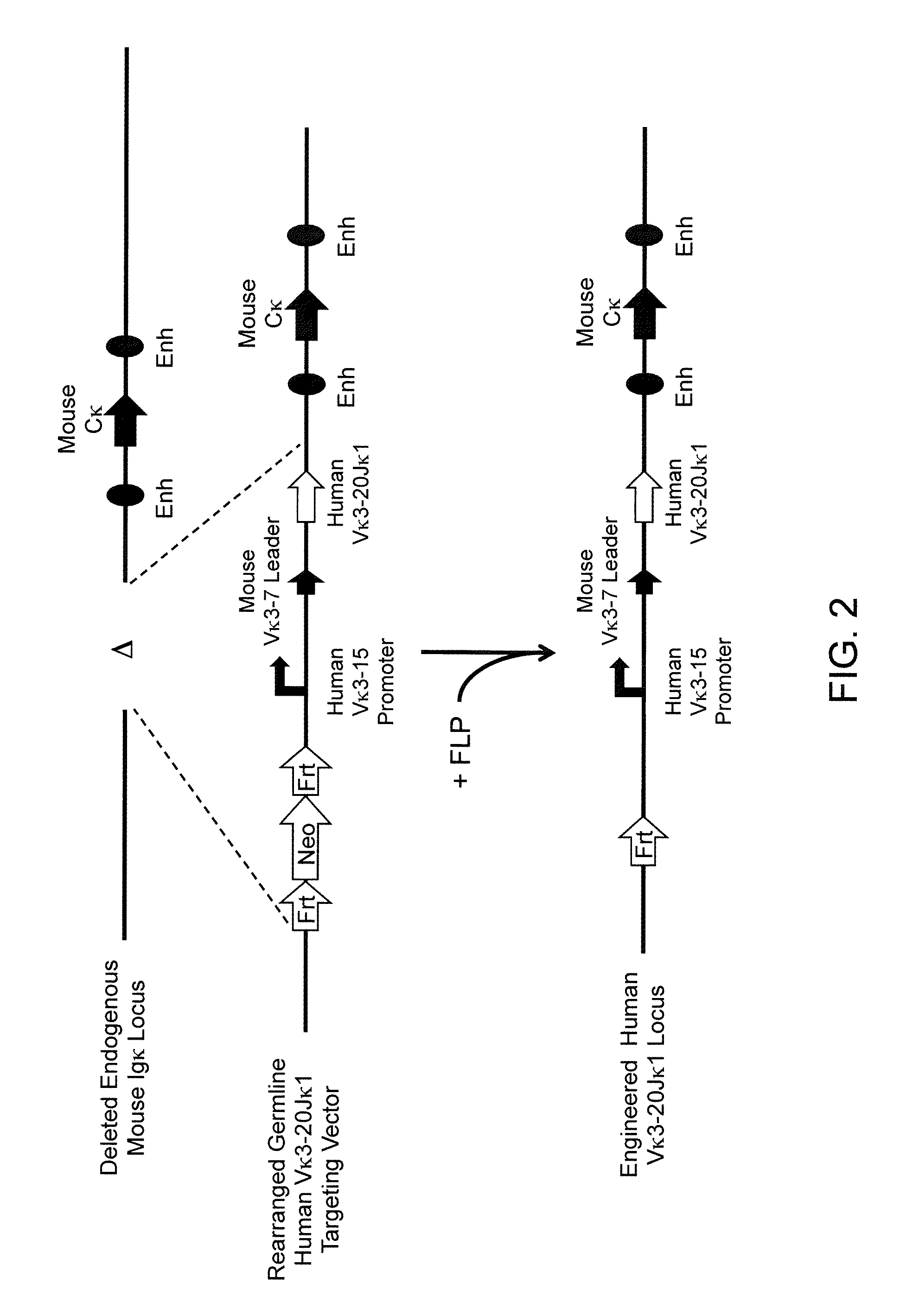
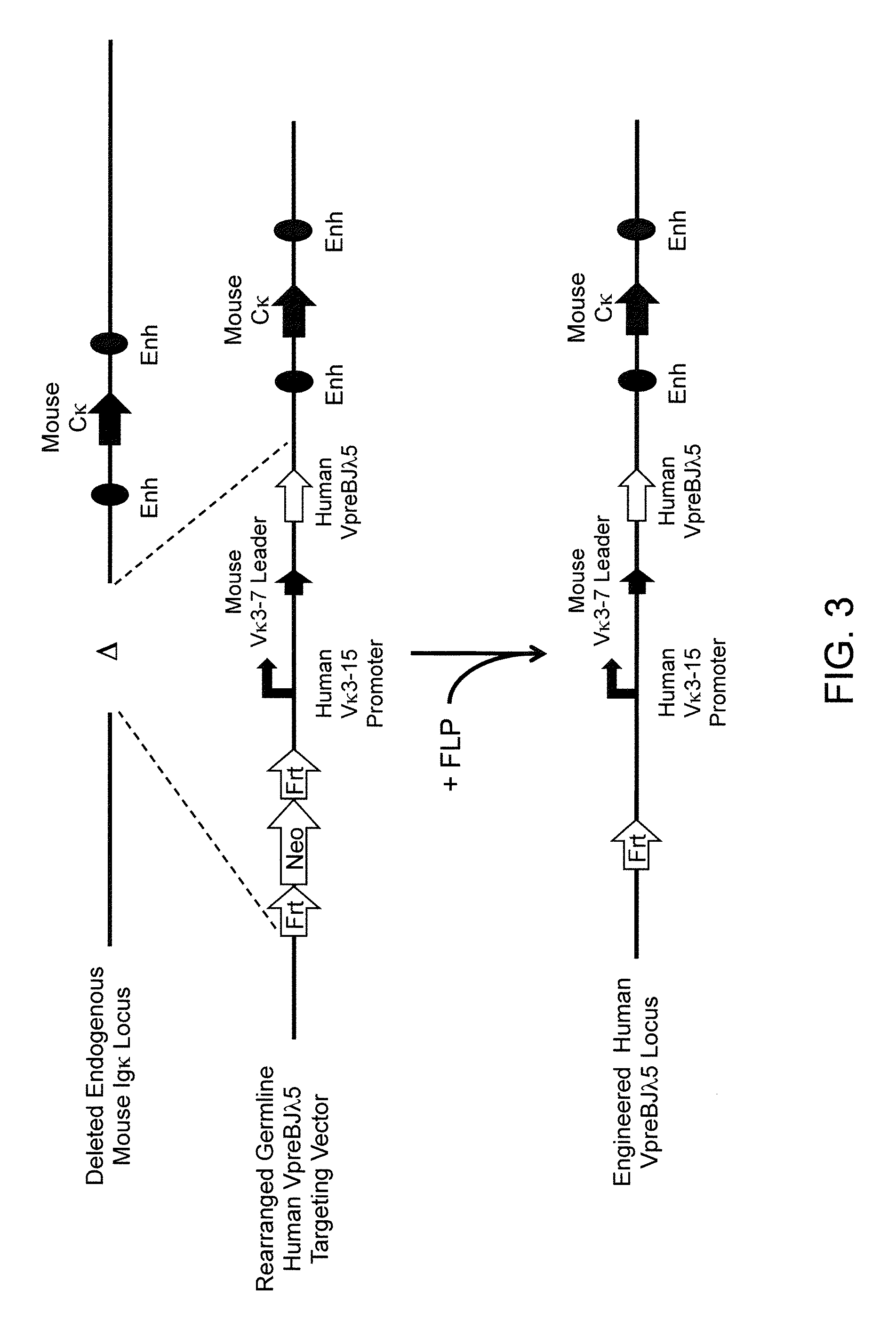
Methods For Making Fully Human Bispecific Antibodies Using A Common Light Chain
InactiveUS20130045492A1Reduce in quantitySimple methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeProtein insertion
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making bispecific antibodies having universal light chains using mice as described herein, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, and host cells are provided. Bispecific antibodies capable of binding first and second antigens are provided, wherein the first and second antigens are separate epitopes of a single protein or separate epitopes on two different proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
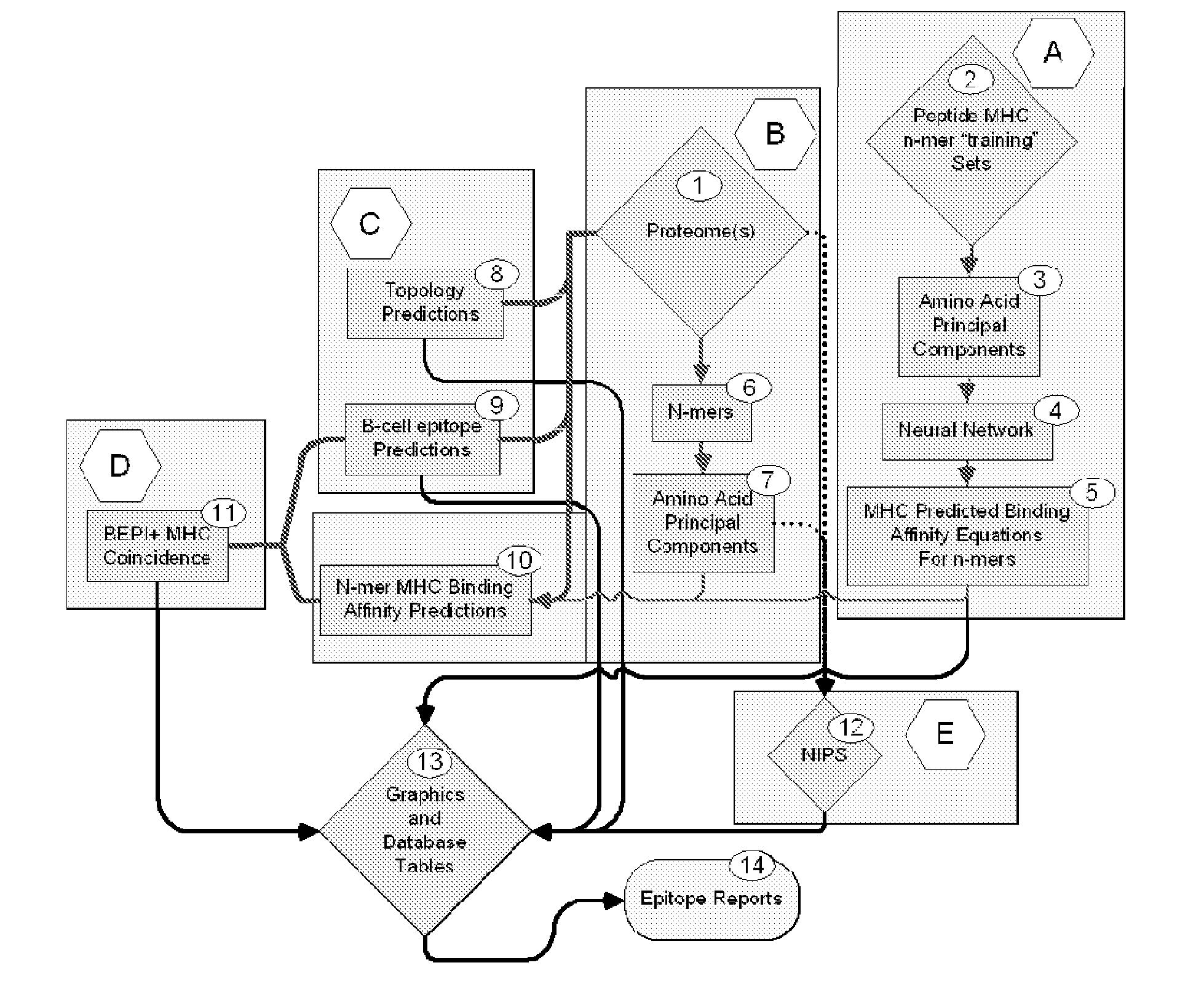
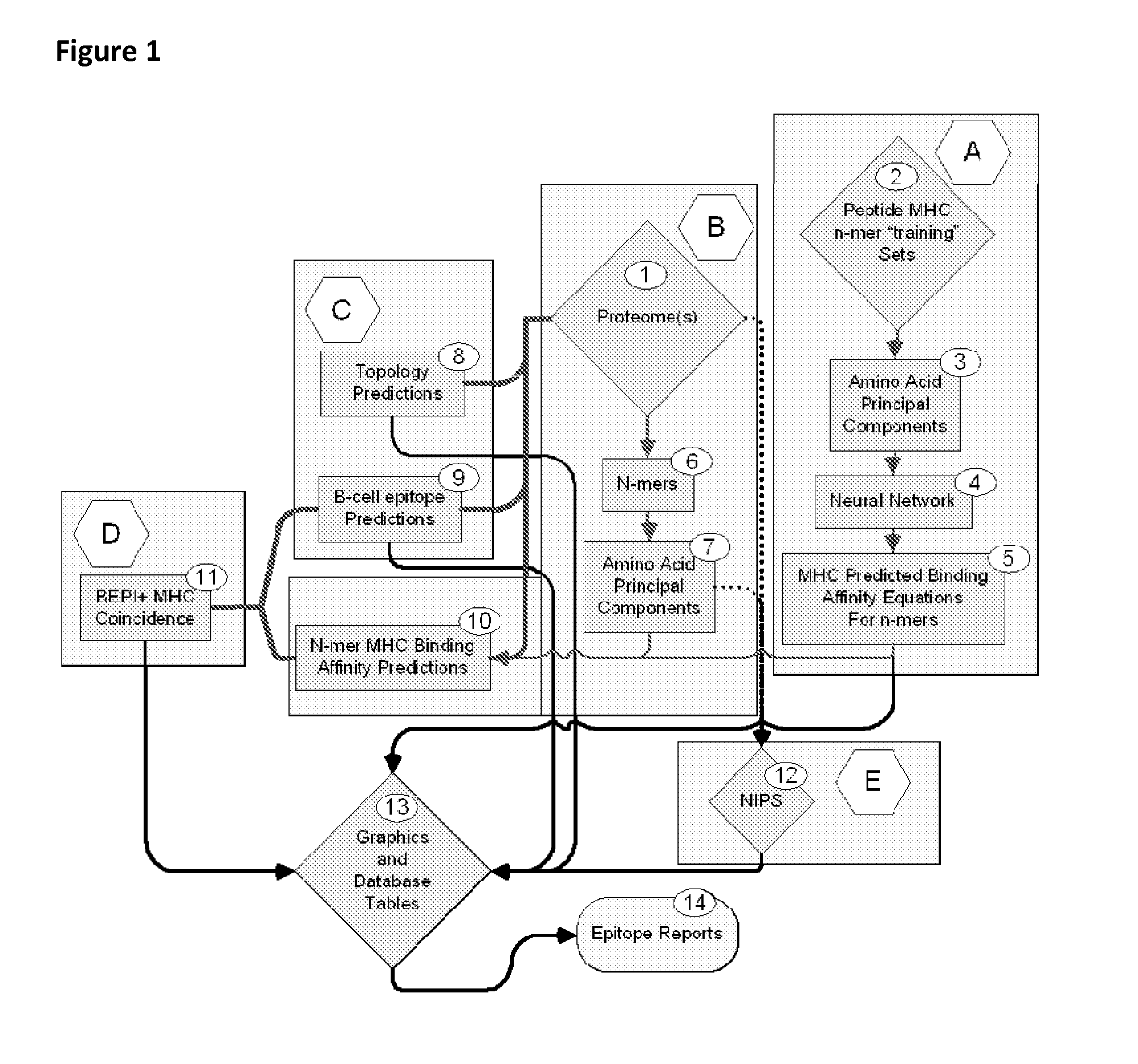
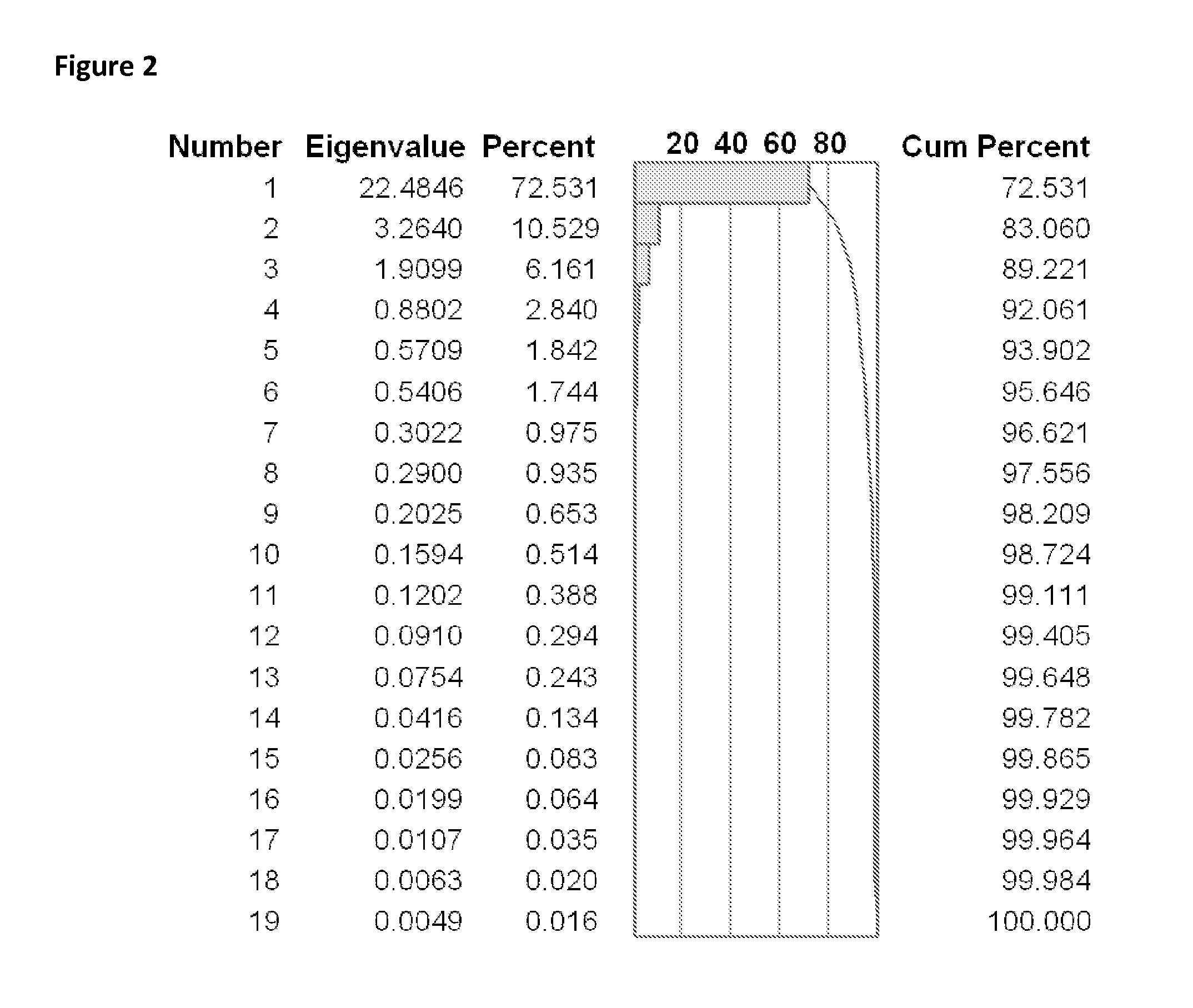
Bioinformatic processes for determination of peptide binding
ActiveUS20130330335A1Increase probabilityHigh responsePeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsEpitopeMicroorganism
This invention relates to the identification of peptide binding to ligands, and in particular to identification of epitopes expressed by microorganisms and by mammalian cells. The present invention provides polypeptides comprising the epitopes, and vaccines, antibodies and diagnostic products that utilize or are developed using the epitopes.
Owner:IOGENETICS
Sclerostin-binding antibody
Owner:UCB SA +1
Reduction of porcine circovirus-2 viral load with inactivated PCV-2
InactiveUS6517843B1Improving immunogenicityImprove performanceBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseStaining
Porcine circovirus-2 (PCV-2) is a recently identified agent wherein the potential spectrum of PCV-2-associated disease has been expanded by evidence of vertical and sexual transmission and associated reproductive failure in swine populations. PCV-2 was isolated from a litter of aborted piglets from a farm experiencing late term abortions and stillbirths. Severe, diffuse myocarditis was present in one piglet associated with extensive immunohistochemical staining for PCV-2 antigen. Variable amounts of PCV-2 antigen were also present in liver, lung and kidney of multiple fetuses. Inoculation of female pigs with a composition including an immunogen from PCV-2 or an epitope of interest from such an immunogen or with a vector expressing such an immunogen or epitope of interest prior to breeding, such as within the first five weeks of life, or prior to the perinatal period, or repeatedly over a lifetime, or during pregnancy, such as between the 6th and 8th and / or the 10th and 13th weeks of gestation, can prevent myocarditis, abortion and intrauterine infection associated with porcine circovirus-2. In addition, innoculation of male and / or female pigs with the aforementioned compositions can be carried out to prevent transmission of PCV-2 from male to female (or vice versa) during mating. Thus, the invention involves methods and compositions for preventing myocarditis, abortion and intrauterine infection associated with porcine circovirus-2.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF BELFAST +4
Epitopes
ActiveUS20070072797A1Block inhibitory effectPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderEpitopeSclerostin
Compositions and methods relating to epitopes of sclerostin protein, and sclerostin binding agents, such as antibodies capable of binding to sclerostin, are provided.
Owner:UCB SA +1
Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6288214B1Prevent and lessen adhesionReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsCarrier protein
Disclosed are the cna gene and cna-derived nucleic acid segments from Staphylococcus aureus, and DNA segments encoding cna from related bacteria. Also disclosed are Col binding protein (CBP) compositions and methods of use. The CBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to Col. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(Col binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of bacterial colonization in an animal such as a human. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of S. aureus infection.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Use of bi-specific antibodies for pre-targeting diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS7074405B1Increased toxicityLow toxicityHybrid immunoglobulinsInorganic boron active ingredientsEpitopeDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to a bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment having at least one arm that specifically binds a targeted tissue and at least one other arm that specifically binds a targetable conjugate. The targetable conjugate comprises a carrier portion which comprises or bears at least one epitope recognizable by at least one arm of said bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment. The targetable conjugate further comprises one or more therapeutic or diagnostic agents or enzymes. The invention provides constructs and methods for producing the bi-specific antibodies or antibody fragments, as well as methods for using them.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Bi-specific antibodies for pre-targeting diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS7052872B1Increased toxicityLow toxicityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesEpitopeDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to a bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment having at least one arm that specifically binds a targeted tissue and at least one other arm that specifically binds a targetable conjugate. The targetable conjugate comprises a carrier portion which comprises or bears at least one epitope recognizable by at least one arm of said bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment. The targetable conjugate further comprises one or more therapeutic or diagnostic agents or enzymes. The invention provides constructs and methods for producing the bi-specific antibodies or antibody fragments, as well as methods for using them.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Method for treating an IgE-mediated disease in a patient using anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS6899879B2Inhibition of differentiationInhibit growthOrganic active ingredientsVirusesDiseaseEpitope
Methods for preventing or treating an IgE-mediated allergic disease in a patient are presented, the methods comprising administration of a monoclonal antibody capable of binding to a human CD40 antigen located on the surface of a human B cell, wherein binding of the antibody to the CD40 antigen prevents the growth or differentiation of the B cell. Monoclonal antibodies useful in these methods, and epitopes immunoreactive with such monoclonal antibodies are also presented.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Immunobiologically-active linear peptides and method of identification
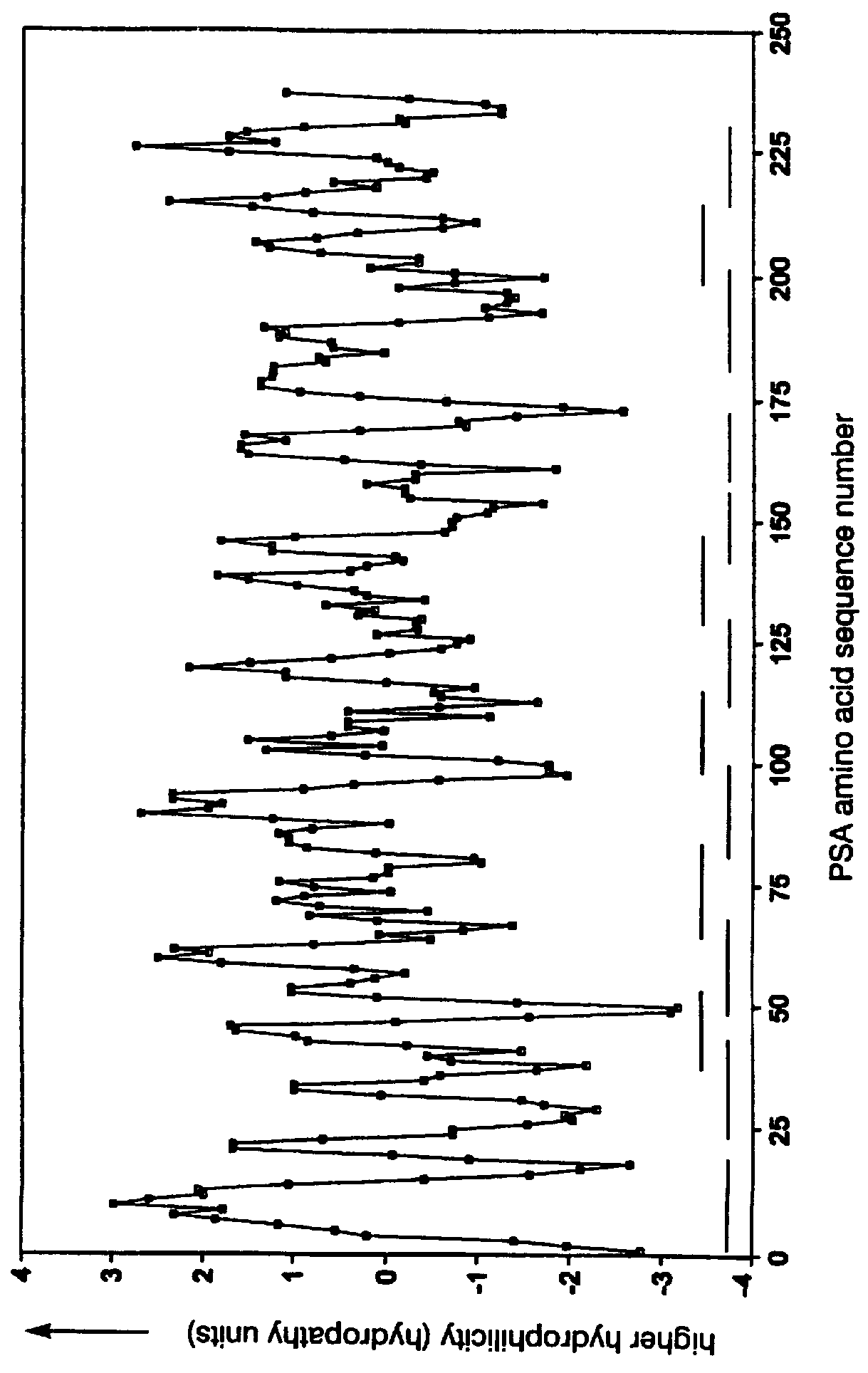
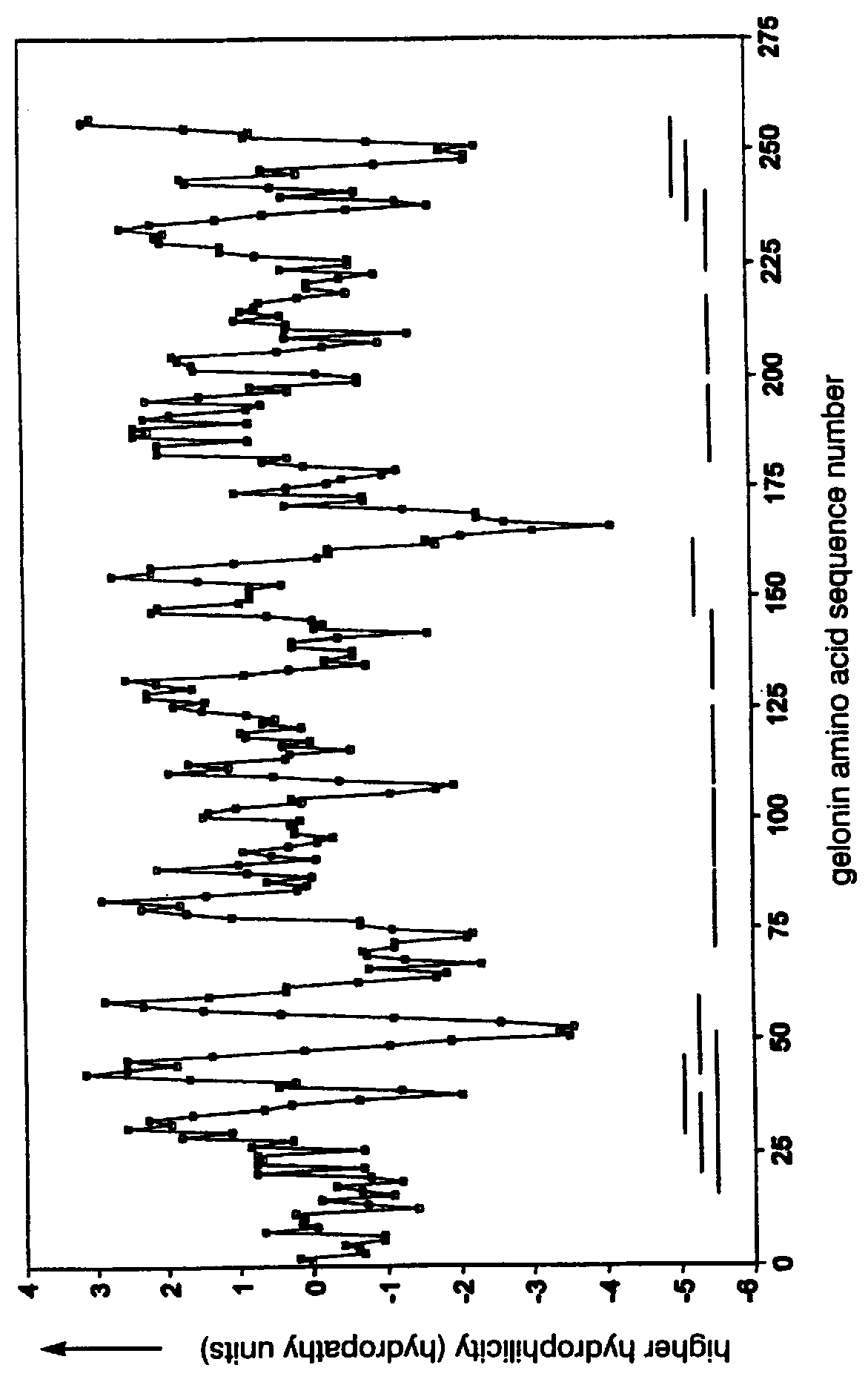
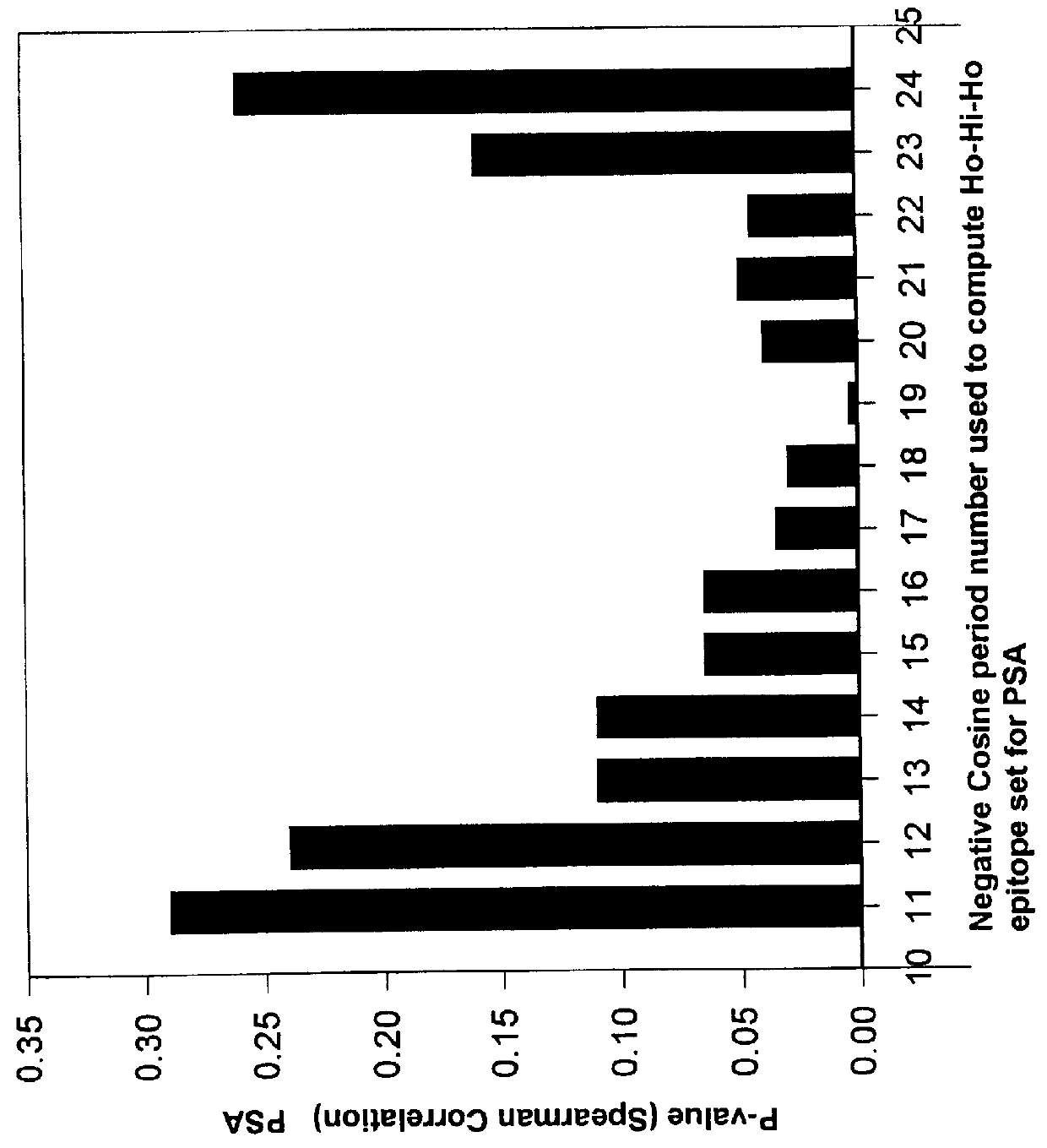
The present invention relates to identifying protein epitopes and more particularly to a novel method for identifying, determining the location, optimal length of amino acid residues and immunobiological potency of protein epitopes by applying a custom negative cosine function fit algorithm to a protein hydropathy scale. This fit analysis is supplemented with experimental immunobiological data. The amino acid sequence of the protein epitopes of the present invention exhibit a hydrophobic-hydrophilic-hydrophobic hydropathy pattern of an approximately fixed length in a given protein.
Owner:KOKOLUS WILLIAM J
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6716823B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideMalariaNon invasive
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, influenza M2, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, rabies glycoprotein, HBV surface antigen, HIV gp 120, HIV gp 160, human carcinoembryonic antigen, malaria CSP, malaria SSP, malaria MSP, malaria pfg, and mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP; and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The animal's cells can be epidermal cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector. The animal can be a vertebrate, e.g., a mammal, such as human, a cow, a horse, a dog, a cat, a goat, a sheep or a pig; or fowl such as turkey, chicken or duck. The vector can be one or more of a viral vector, including viral coat, e.g., with some or all viral genes deleted therefrom, bacterial, protozoan, transposon, retrotransposon, and DNA vector, e.g., a recombinant vector; for instance, an adenovirus, such as an adenovirus defective in its E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 region(s). The method can encompass applying a delivery device including the vector to the skin of the animal, as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can have all viral genes deleted therefrom. The vector can induce a therapeutic and / or an anti-tumor effect in the animal, e.g., by expressing an oncogene, a tumor-suppressor gene, or a tumor-associated gene. Immunological products generated by the expression, e.g., antibodies, cells from the methods, and the expression products, are likewise useful in in vitro and ex vivo applications, and such immunological and expression products and cells and applications are disclosed and claimed. Methods for expressing a gene product in vivo and products therefor and therefrom including mucosal and / or intranasal administration of an adenovirus, advantageously an E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 defective or deleted adenovirus, such as a human adenovirus or canine adenovirus, are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Methods of elicit, enhance and sustain immune responses against MHC class I-restricted epitopes, for prophylactic or therapeutic purposes
InactiveUS20050079152A1Improve responseEfficient amplificationAntibacterial agentsBiocideEpitopeMHC class I
Embodiments relate to methods and compositions for eliciting, enhancing, and sustaining immune responses, preferably against MHC class I-restricted epitopes. The methods and compositions can be used for prophylactic or therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Inducing cellular immune responses to human papillomavirus using peptide and nucleic acid compositions
InactiveUS20070014810A1Reduce the possibilityImproving immunogenicitySugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsEpitopeT cell
This invention uses our knowledge of the mechanisms by which antigen is recognized by T cells to identify and prepare human papillomavirus (HPV) epitopes, and to develop epitope-based vaccines directed towards HPV. More specifically, this application communicates our discovery of pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use in the prevention and treatment of HPV infection.
Owner:GENIMMUNE NV +1
Insect cells or fractions as adjuvant for antigens
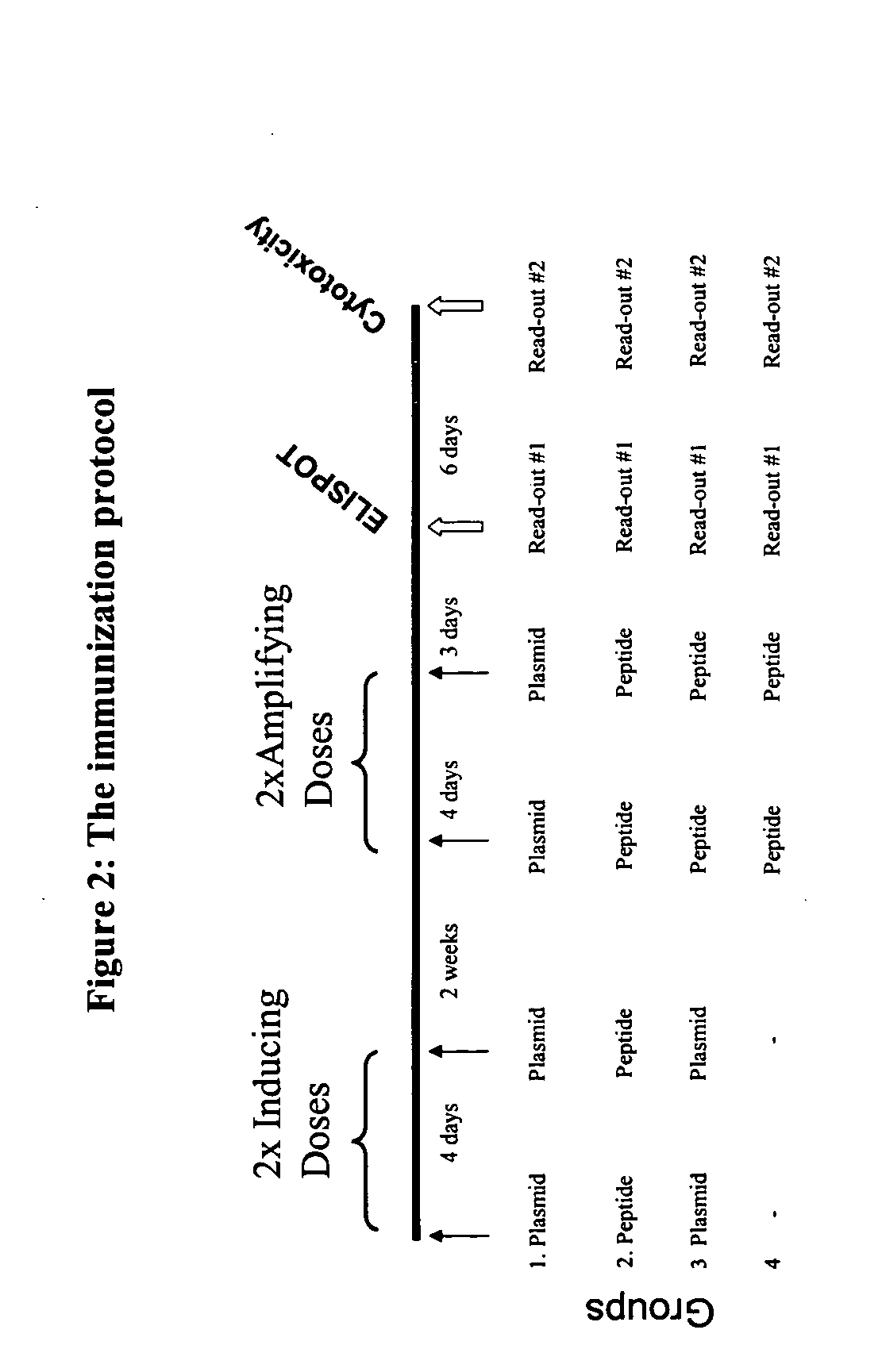
Disclosed and claimed is an adjuvant for immunogenic, immunological, antigenic or vaccine compositions. The adjuvant is composed of insect cells or fractions thereof. Disclosed and claimed are also methods for preparing and using the adjuvant and compositions containing the adjuvant. Advantageously, a recombinant baculovirus containing DNA encoding and expressing an epitope of interest or antigen can be infected into insect cells such as insect cells derived from a Lepidopteran species such as S. frugiperda for expression, and the infected insect cells or a fraction thereof can be used with the expressed epitope of interest or antigen as an inventive antigen or in an inventive immunological, antigen or vaccine composition.
Owner:MERIAL LTD
Murine monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 11D10 and methods of use thereof
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY
Multivalent antibody analogs, and methods of their preparation and use
InactiveUS20140377269A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody medical ingredientsEpitopeAntiendomysial antibodies
Multivalent antibody analogs that co-engage at least two different antigens or epitopes (also referred to “targets”, used interchangeably throughout), are provided, as well as methods for their production and use.
Owner:ADIMAB LLC
Antibodies to non-shed Muc1 and Muc16, and uses thereof
The present invention relates to antibodies, antibody fragments, conjugates of antibodies and antibody fragments with cytotoxic agents, and hybridomas producing the antibodies and antibody fragments, where the antibodies and antibody fragments recognize extracellular epitopes of plasma membrane proteins that are not released into the extracellular fluid, and to methods for the detection, monitoring and treatment of malignancies such as breast cancer and ovarian cancer using the antibodies, antibody fragments and conjugates.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Use of bi-specific antibodies for pre-targeting diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS20030198595A1Increase productionImproved chemotherapyAntibacterial agentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEpitopeDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to a bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment having at least one arm that specifically binds a targeted tissue and at least one other arm that specifically binds a targetable construct. The targetable construct comprises a carrier portion which comprises or bears at least one epitope recognizable by at least one arm of said bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment. The targetable construct further comprises one or more therapeutic or diagnostic agents or enzymes. The invention provides constructs and methods for producing the bi-specific antibodies or antibody fragments, as well as methods for using them.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com