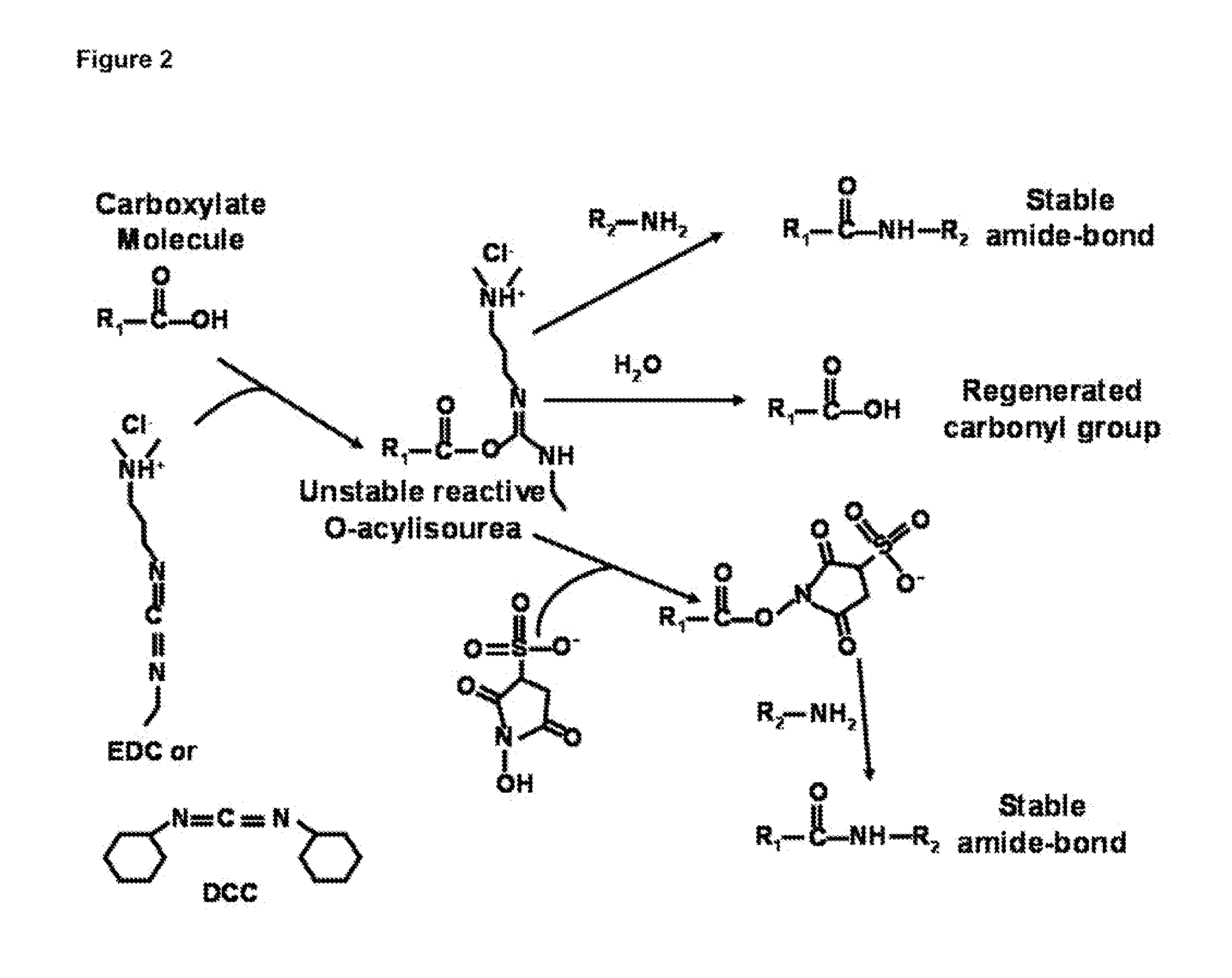
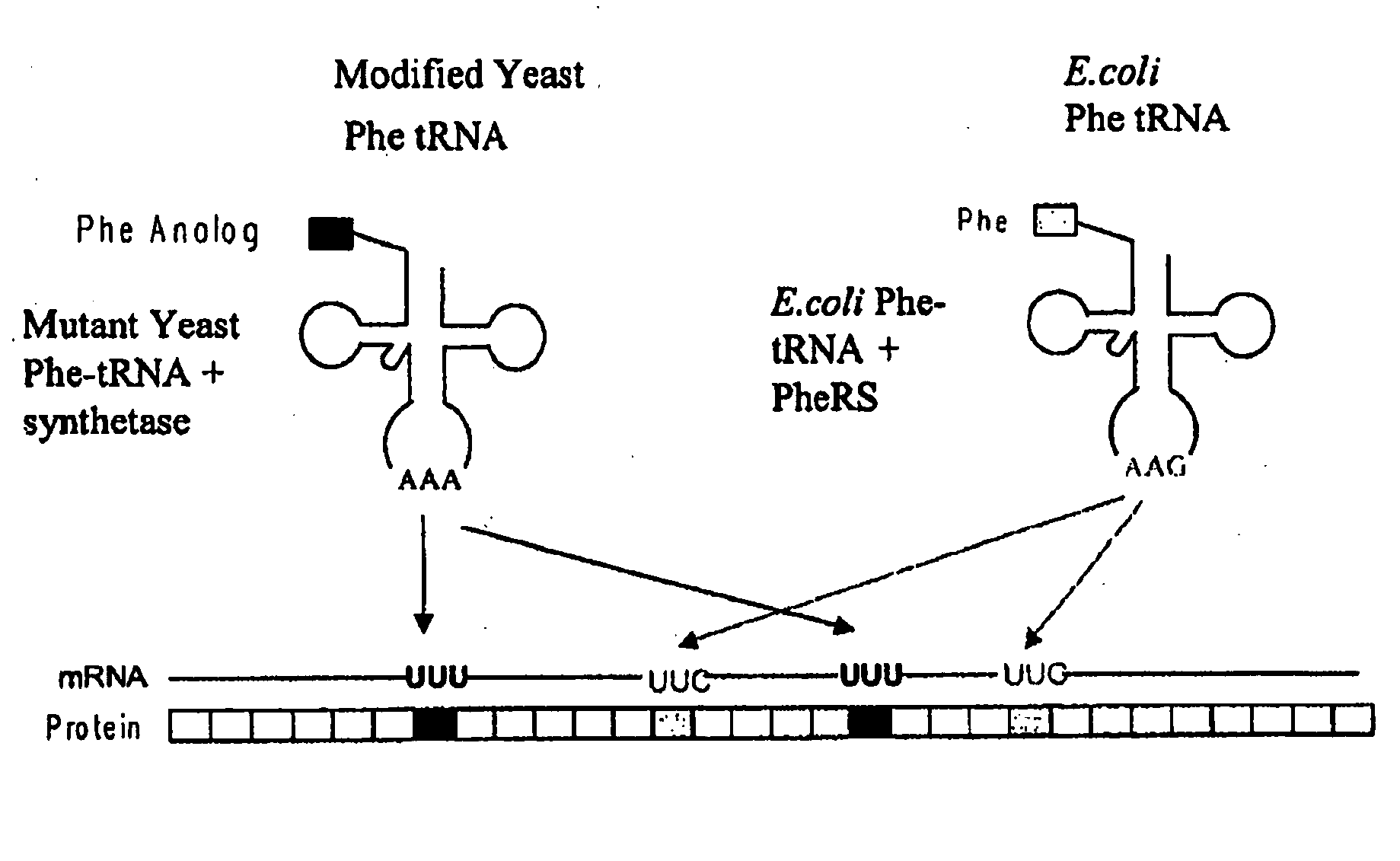
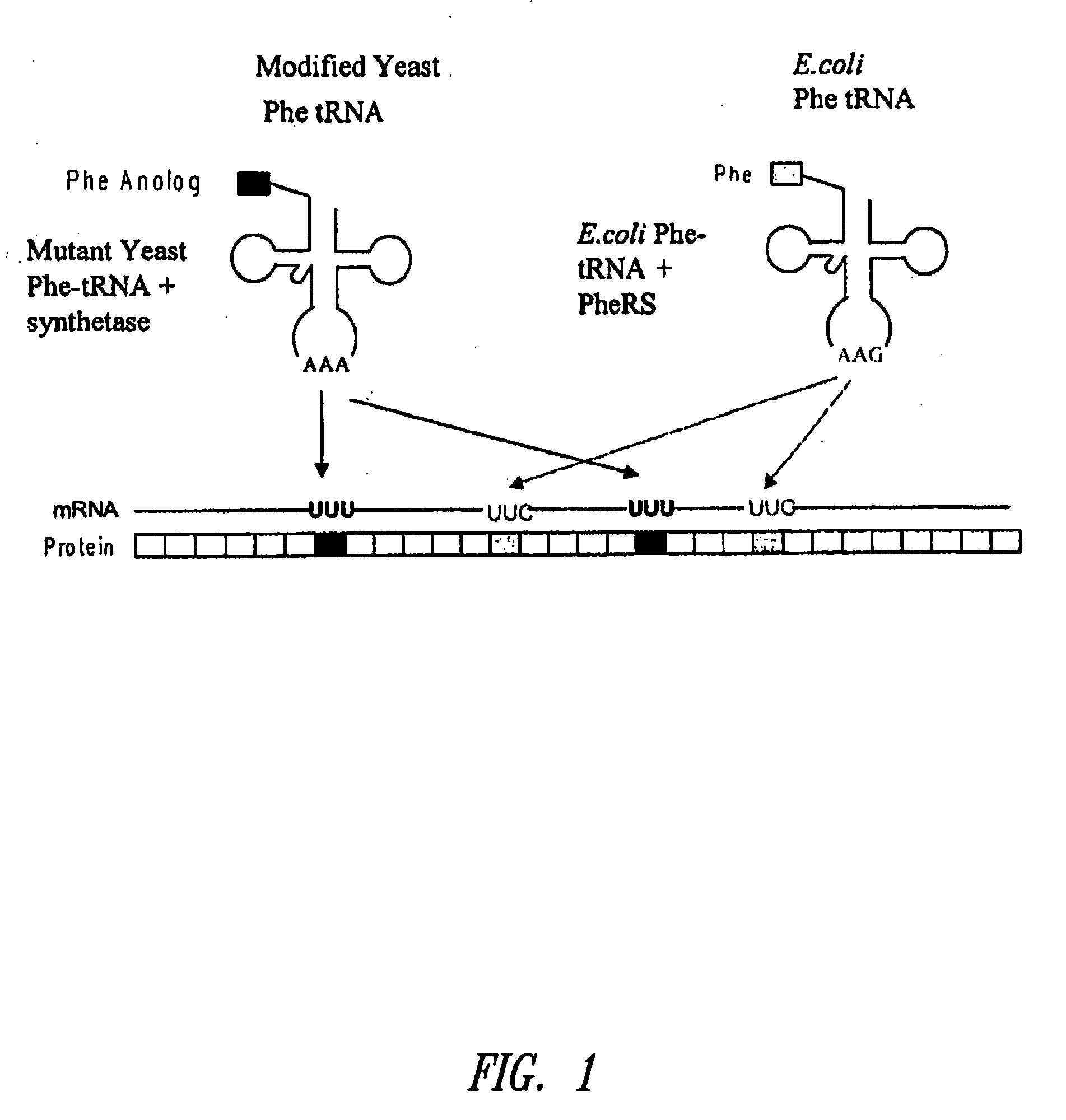
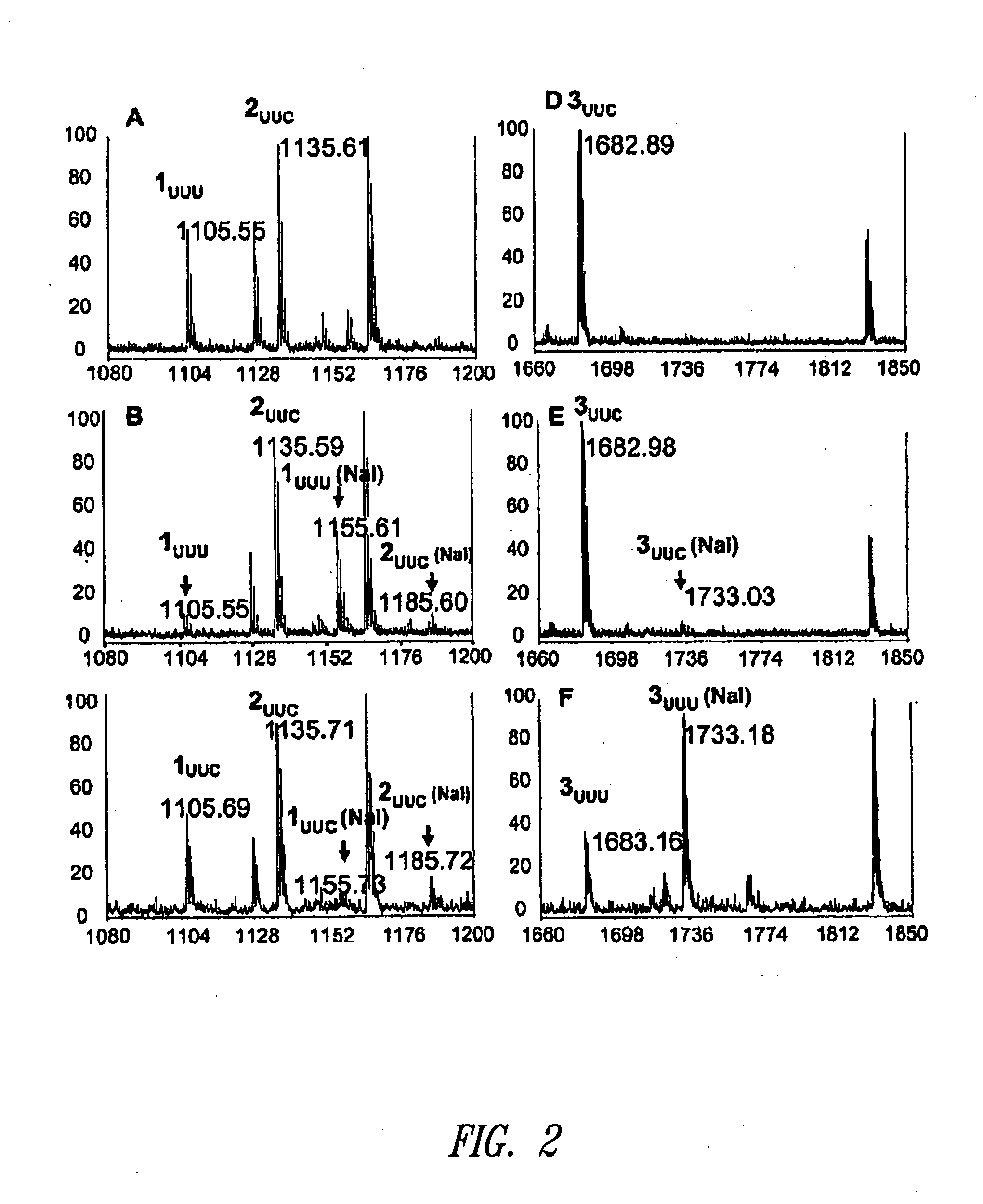
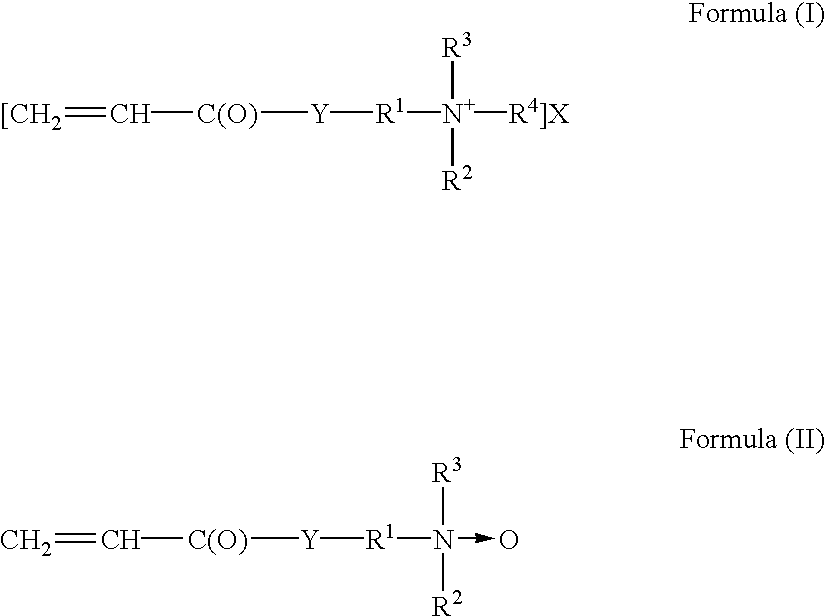
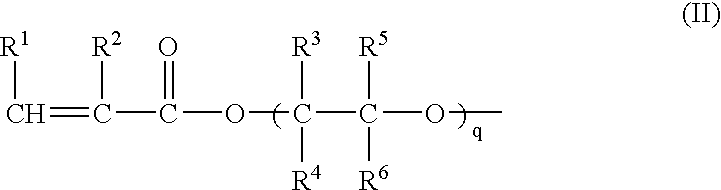
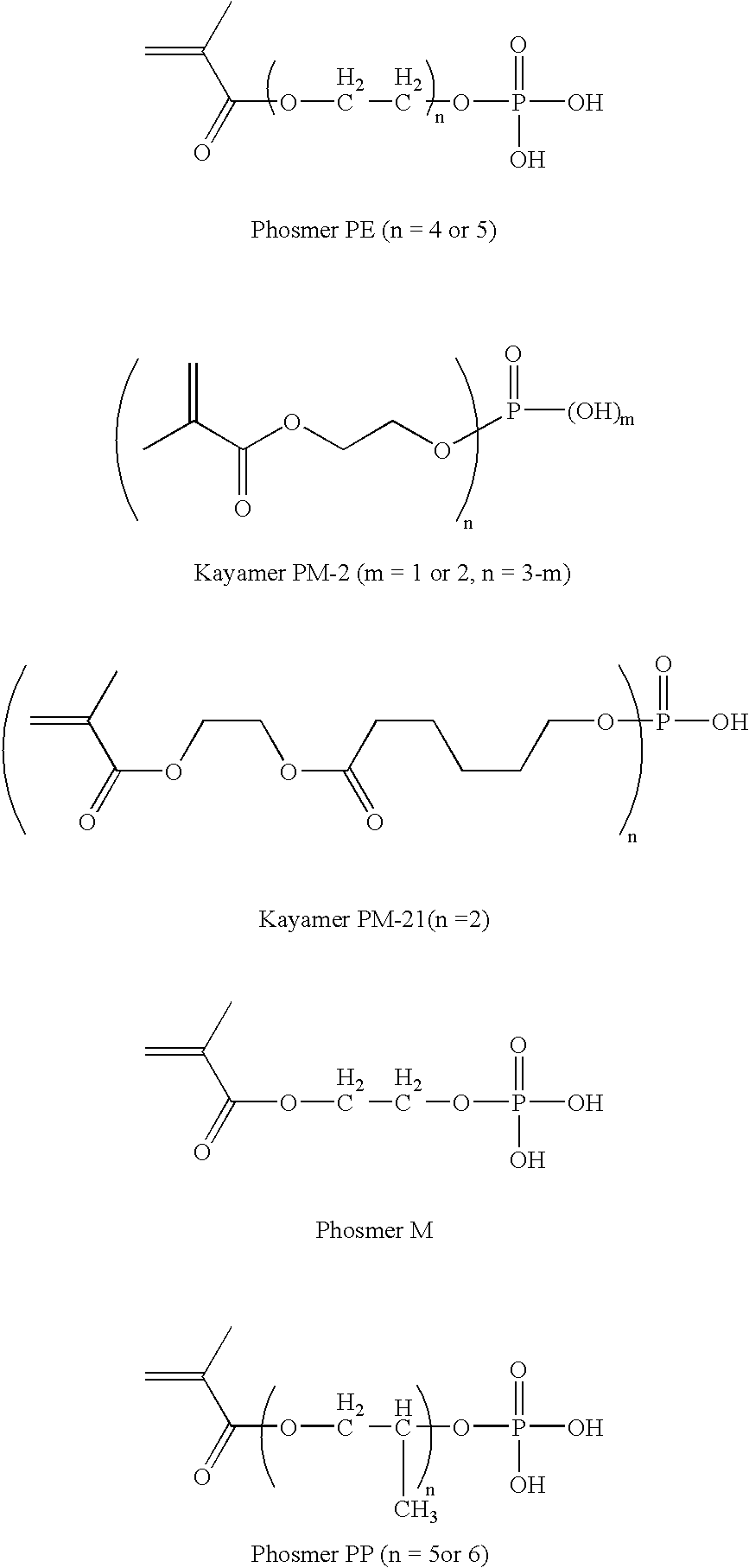
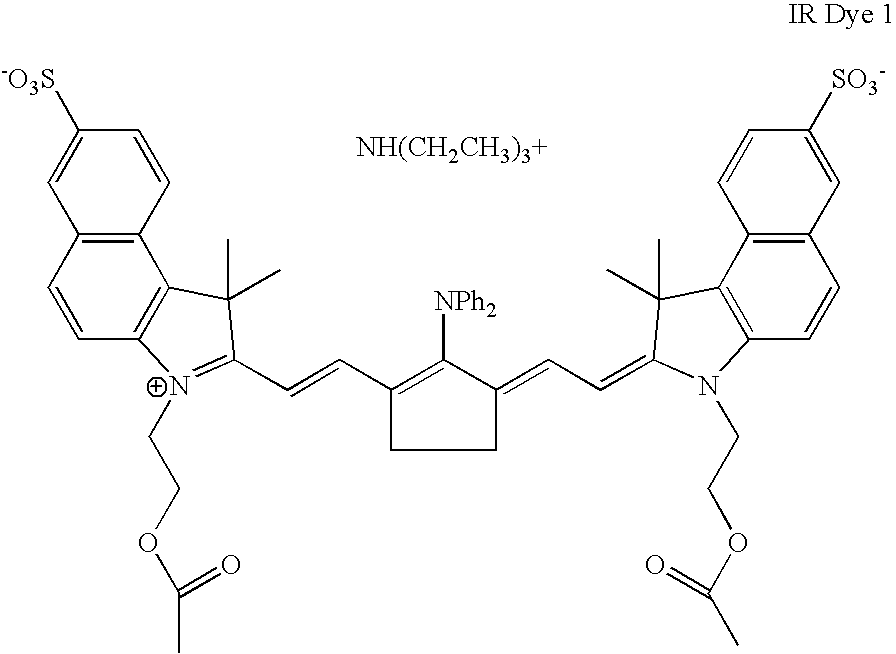
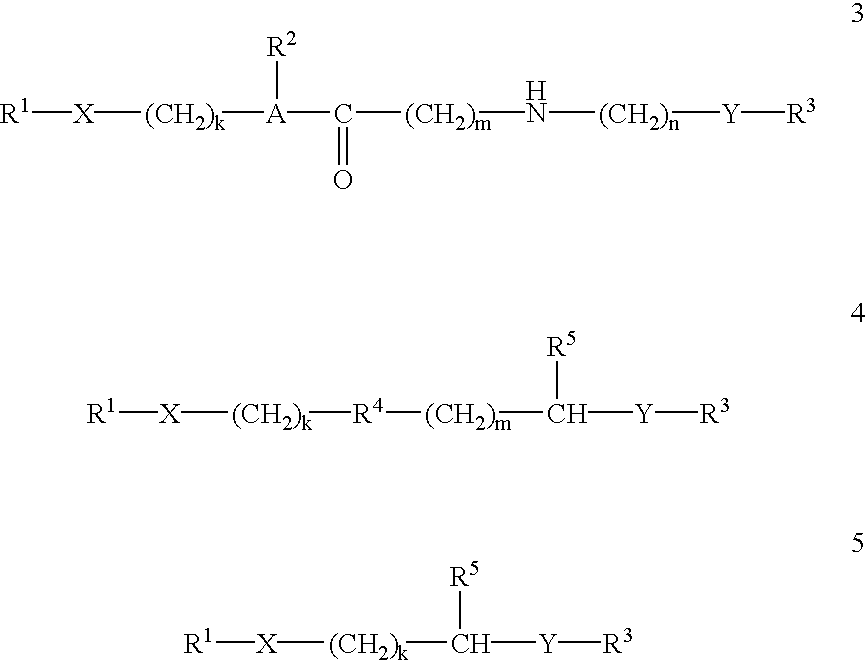Patents
Literature
10619 results about "Side chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a larger hydrocarbon backbone. It is one factor in determining a molecule's properties and reactivity. A side chain is also known as a pendant chain, but a pendant group (side group) has a different definition.
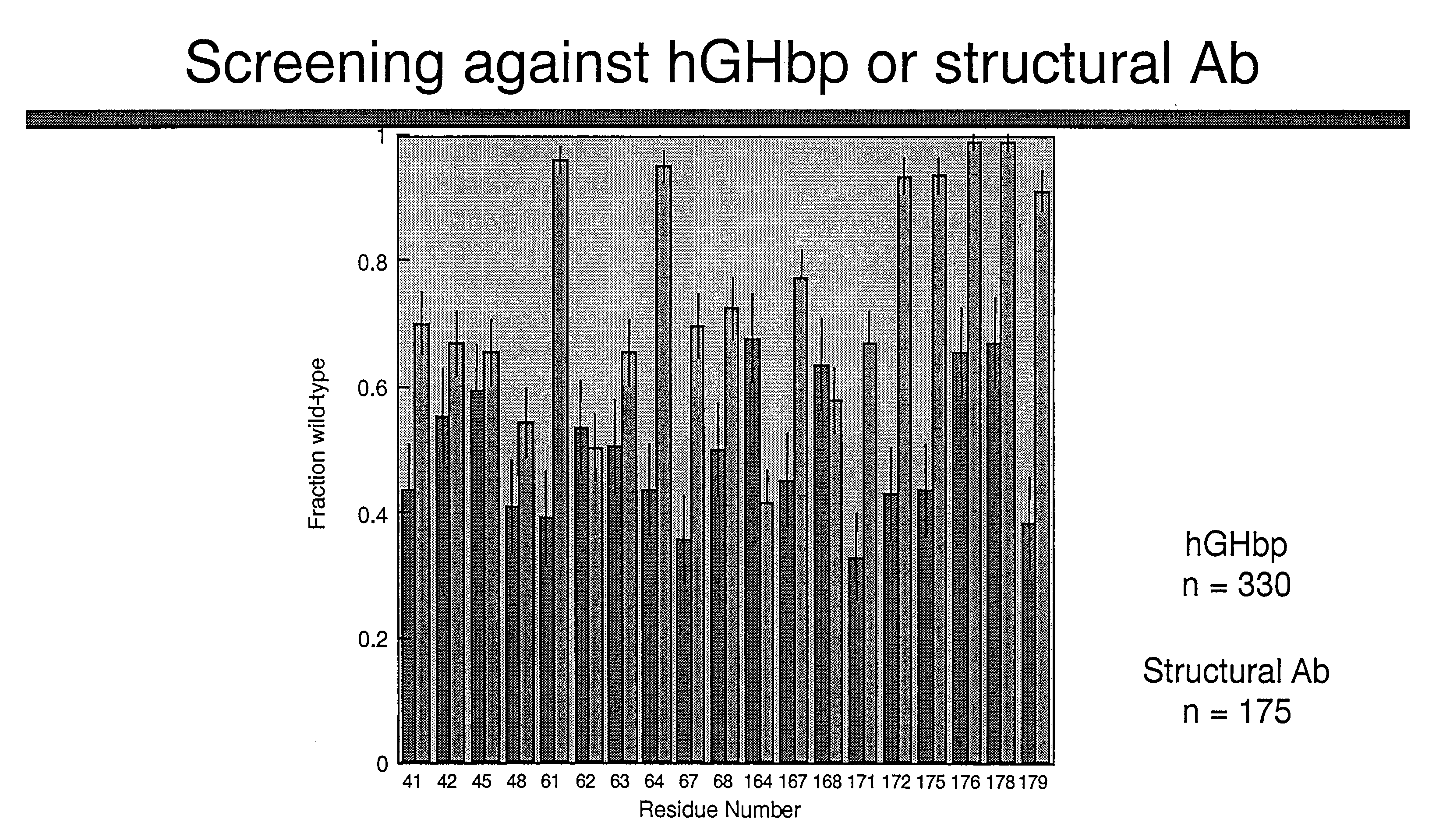
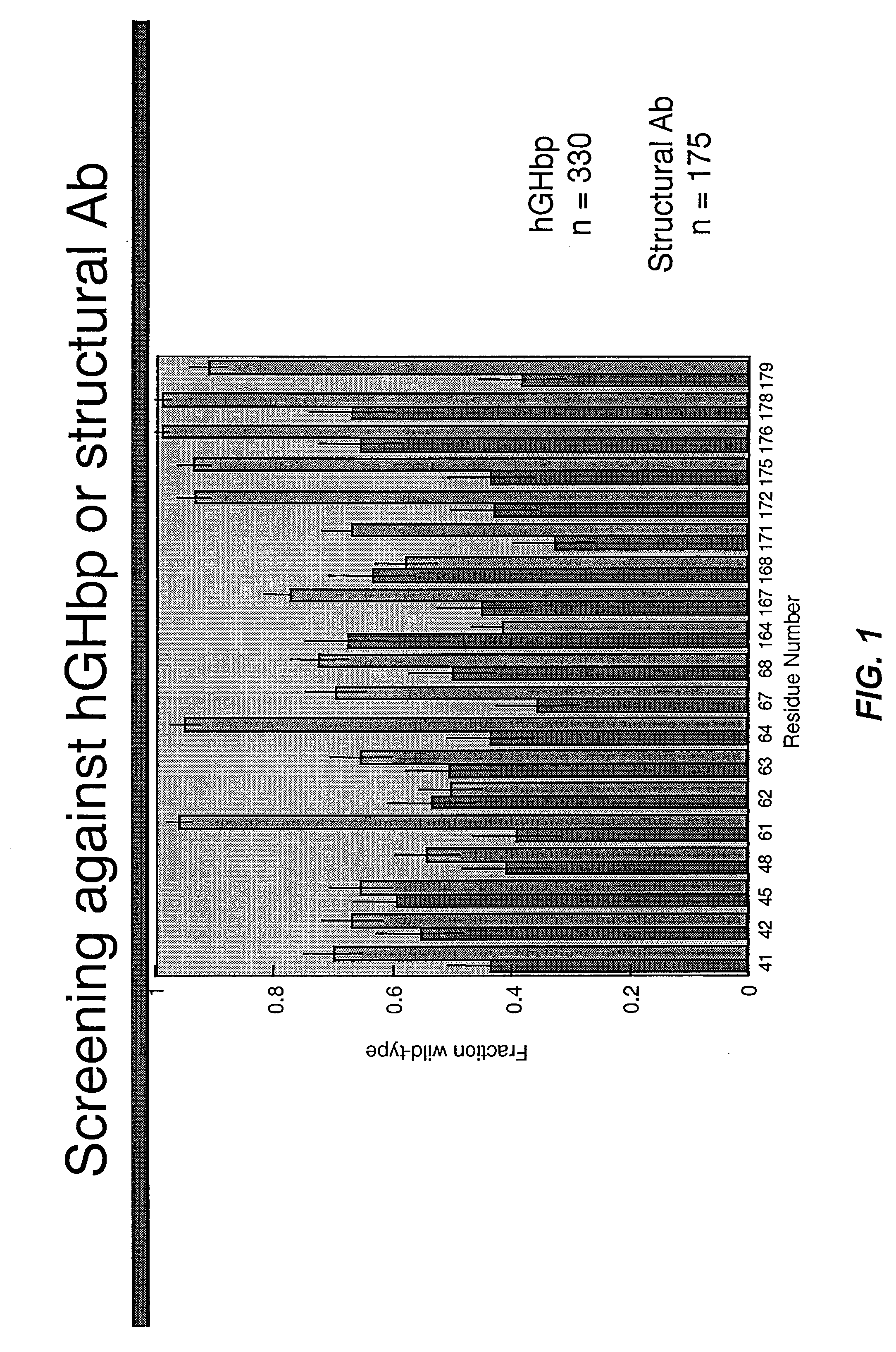
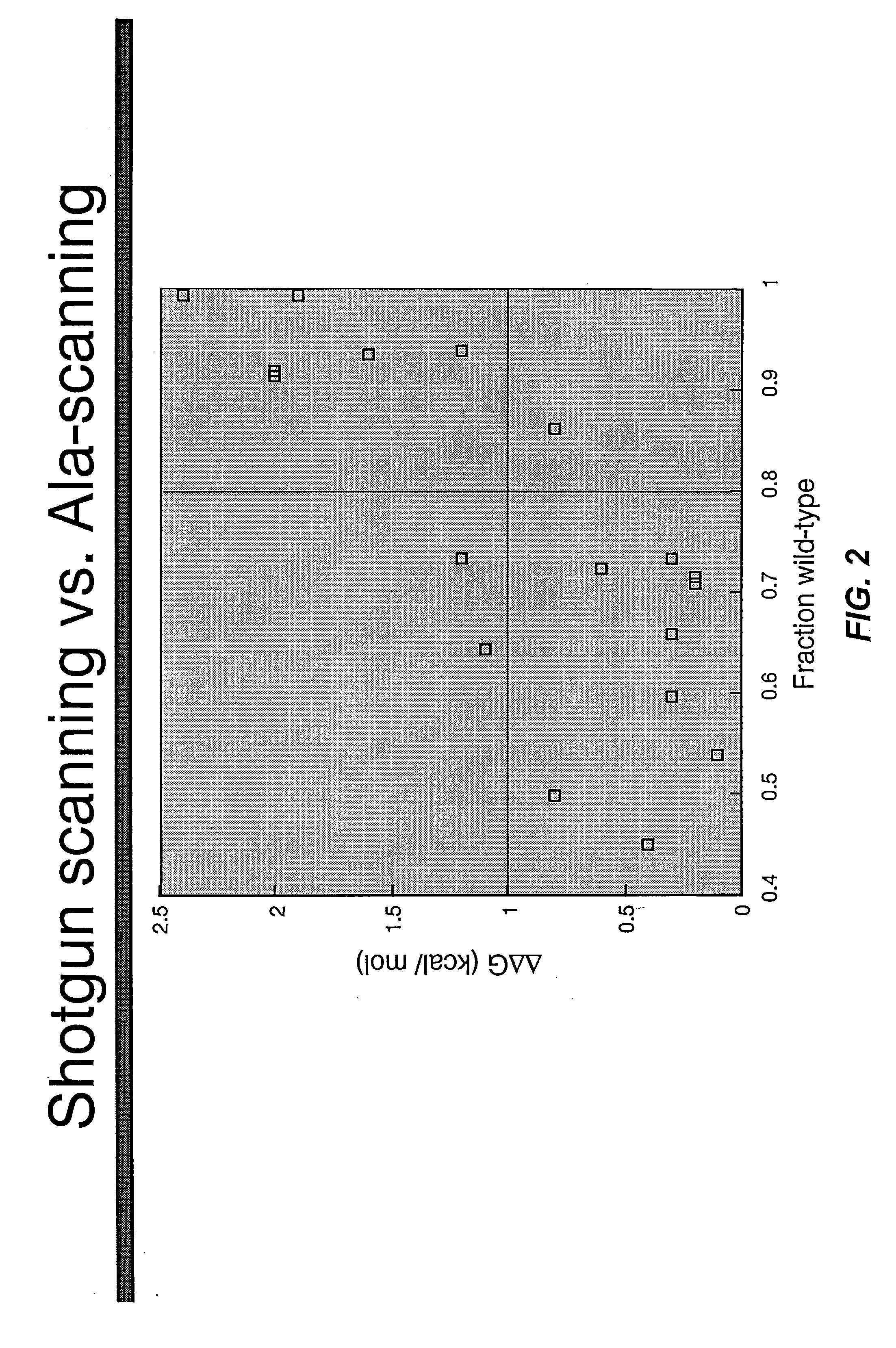
Shotgun scanning
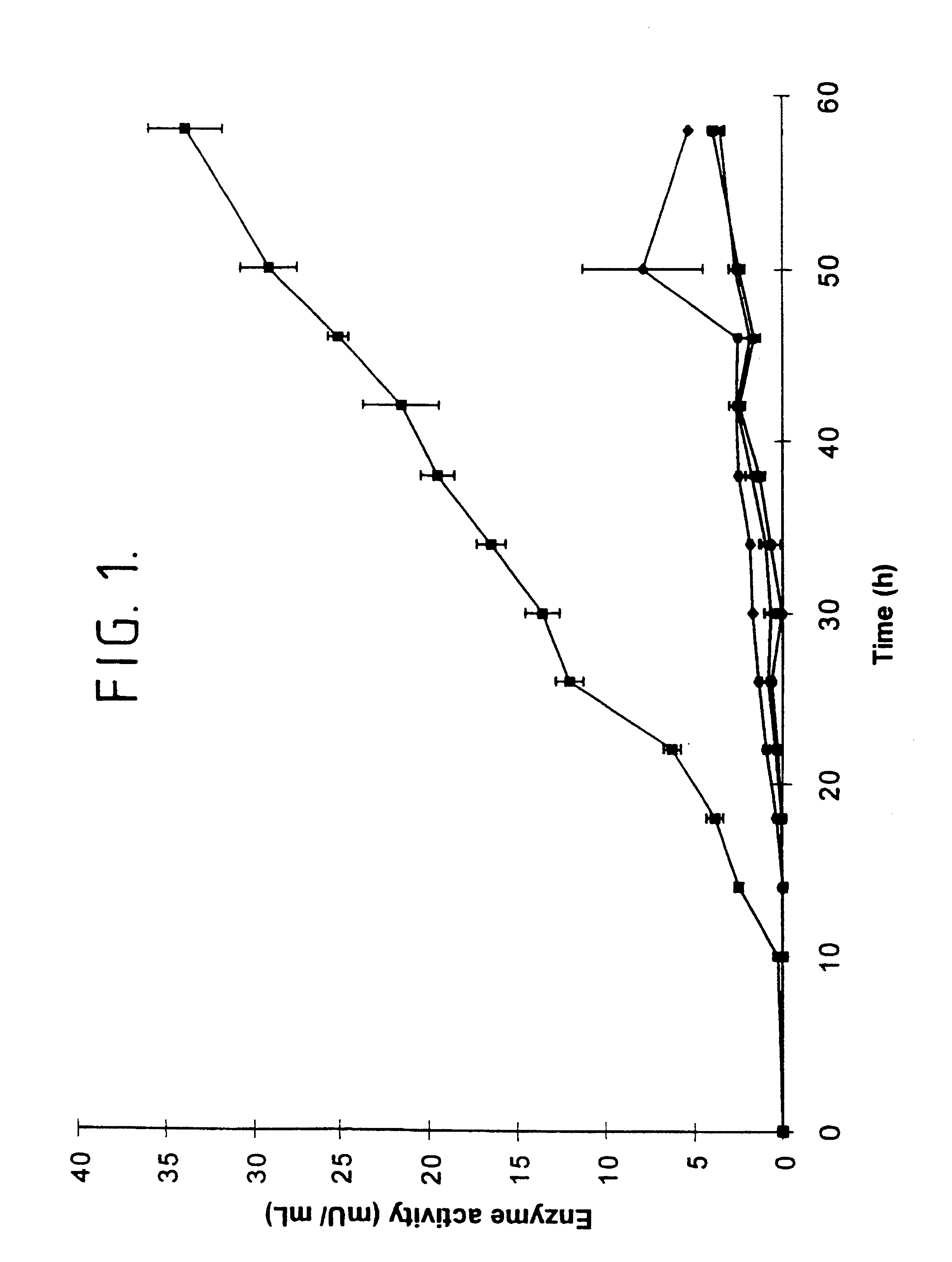
A combinatorial method that uses statistics and DNA sequence analysis rapidly assesses the functional and structural importance of individual protein side chains to binding interactions. This general method, termed “shotgun scanning”, enables the rapid mapping of functional protein and peptide epitopes and is suitable for high throughput proteomics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
On-press developable IR sensitive printing plates using binder resins having polyethylene oxide segments
InactiveUS6899994B2Prevent steppingRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePolyethylene oxide
The present invention relates to a polymerizable coating composition suitable for the manufacture of printing plates developable on-press. The coating composition comprises (i) a polymerizable compound and (ii) a polymeric binder comprising polyethylene oxide segments, wherein the polymeric binder is selected from the group consisting of at least one graft copolymer comprising a main chain polymer and polyethylene oxide side chains, a block copolymer having at least one polyethylene oxide block and at least one non-polyethylene oxide block, and a combination thereof. The invention is also directed to an imageable element comprising a substrate and the polymerizable coating composition.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
Composition for forming resist overlayer film for EUV lithography
ActiveUS20130209940A1High resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoatingsLithographic artistLithography process
There is provided a composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film that is used in an EUV lithography process, that does not intermix with the EUV resist, that blocks unfavorable exposure light for EUV exposure, for example, UV light and DUV light and selectively transmits EUV light alone, and that can be developed with a developer after exposure. A composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film used in an EUV lithography process including a resin containing a naphthalene ring in a main chain or in a side chain and a solvent, in which the resin may include a hydroxy group, a carboxy group, a sulfo group, or a monovalent organic group having at least one of these groups as a hydrophilic group.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Photoresist composition for deep UV and process thereof
InactiveUS6447980B1Radiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSide chain
The present invention relates to a chemically amplified system, which is, sensitive to wavelengths between 300 nm and 100 nm, and comprises a) a polymer that is insoluble an aqueous alkaline solution and comprises at least one acid labile group, b) a compound capable of producing an acid upon radiation. The present invention comprises a polymer that is made from a alicyclic hydrocarbon olefin, an acrylate with a pendant cyclic moeity, and a cyclic anhydride. The present invention also relates to a process for imaging such a photoresist.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
Expandable Functional TFE Copolymer Fine Powder, the Expandable Functional Products Obtained Therefrom and Reaction of the Expanded Products
A functional TFE copolymer fine powder is described, wherein the TFE copolymer is a polymer of TFE and at least one functional comonomer, and wherein the TFE copolymer has functional groups that are pendant to the polymer chain. The functional TFE copolymer fine powder resin is paste extrudable and expandable. Methods for making the functional TFE copolymer are also described. The expanded functional TFE copolymer material may be post-reacted after expansion.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Breathable polyurethanes, blends, and articles
InactiveUS6897281B2Improve breathabilityImprove moisture vapor transmission rateSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsGramSide chain
A breathable polyurethane having an upright moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) of more than about 500 gms / m2 / 24 hr comprises:(a) poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units in an amount comprising about 12 wt. % to about 80 wt. % of said polyurethane, wherein (i) alkylene oxide groups in said poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units have from 2 to 10 carbon atoms and are unsubstituted, substituted, or both unsubstituted and substituted, (ii) at least about 50 wt. % of said alkylene oxide groups are ethylene oxide, and (iii) said amount of said side-chain units is (i) at least about 30 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is less than about 600 grams / mole, (ii) at least about 15 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is from about 600 to about 1,000 grams / mole, and at least about 12 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is more than about 1,000 grams / mole, and(b) poly(ethylene oxide) main-chain units in an amount comprising less than about 25 wt. % of said polyurethane.Coatings and films for textiles and other articles and applications using such polyurethanes have excellent breathability, i.e., high moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR).
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Hydrophilic Polysiloxane Macromonomer, and Production and Use of the same
ActiveUS20090234089A1Improve compatibilityHigh oxygen permeabilitySilicon organic compoundsOptical articlesSide chainHydrophile
Problem to be Solved To provide an ophthalmic lens, which can be more safely worn, that is, to provide a material, which is transparent and has high oxygen permeability and a high hydrophilic property, and to provide a novel monomer to be a raw material thereof.Solution A hydrophilic polysiloxane macromonomer contains polyoxyethylene as a hydrophilic side chains in a polysiloxane main chain, wherein transparency, oxygen permeability, and hydrophilic properties of the material are controlled by regulating the length of the polysiloxane main chain, the length of the hydrophilic polyoxyethylene side chains, and the number of the side chains.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Electrophoretic particles and processes for the production thereof
In electrophoretic media, it is advantageous to use pigment particles having about 1 to 15 percent by weight of a polymer chemically bonded to, or cross-linked around, the pigment particles. The polymer desirably has a branched chain structure with side chains extending from a main chain. Charged or chargeable groups can be incorporated into the polymer or can be bonded to the particles separately from the polymer. The polymer-coated particles can be prepared by first attaching a polymerizable or polymerization-initiating group to the particle and then reacting the particle with one or more polymerizable monomers or oligomers.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Particles incorporating surfactants for pulmonary drug delivery
Improved aerodynamically light particles for drug delivery to the pulmonary system, and methods for their synthesis and administration are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the aerodynamically light particles are made of a biodegradable material and have a tap density less than 0.4 g / cm3 and a mass mean diameter between 5 mum and 30 mum. The particles may be formed of biodegradable materials such as biodegradable polymers. For example, the particles may be formed of a functionalized polyester graft copolymer consisting of a linear alpha-hydroxy-acid polyester backbone having at least one amino acid group incorporated therein and at least one poly(amino acid) side chain extending from an amino acid group in the polyester backbone. In one embodiment, aerodynamically light particles having a large mean diameter, for example greater than 5 mum, can be used for enhanced delivery of a therapeutic agent to the alveolar region of the lung. The aerodynamically light particles incorporating a therapeutic agent may be effectively aerosolized for administration to the respiratory tract to permit systemic or local delivery of wide variety of therapeutic agents.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
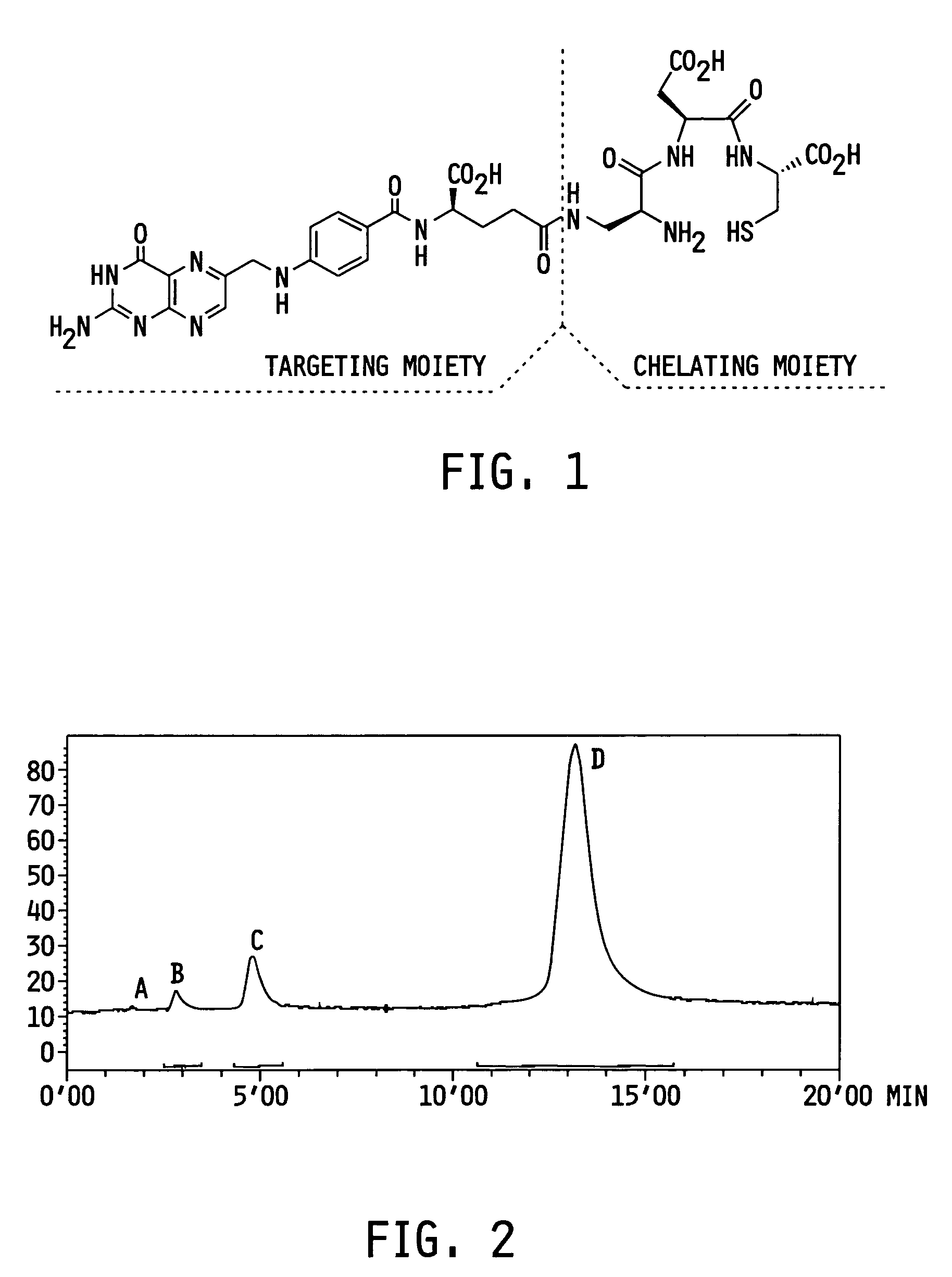
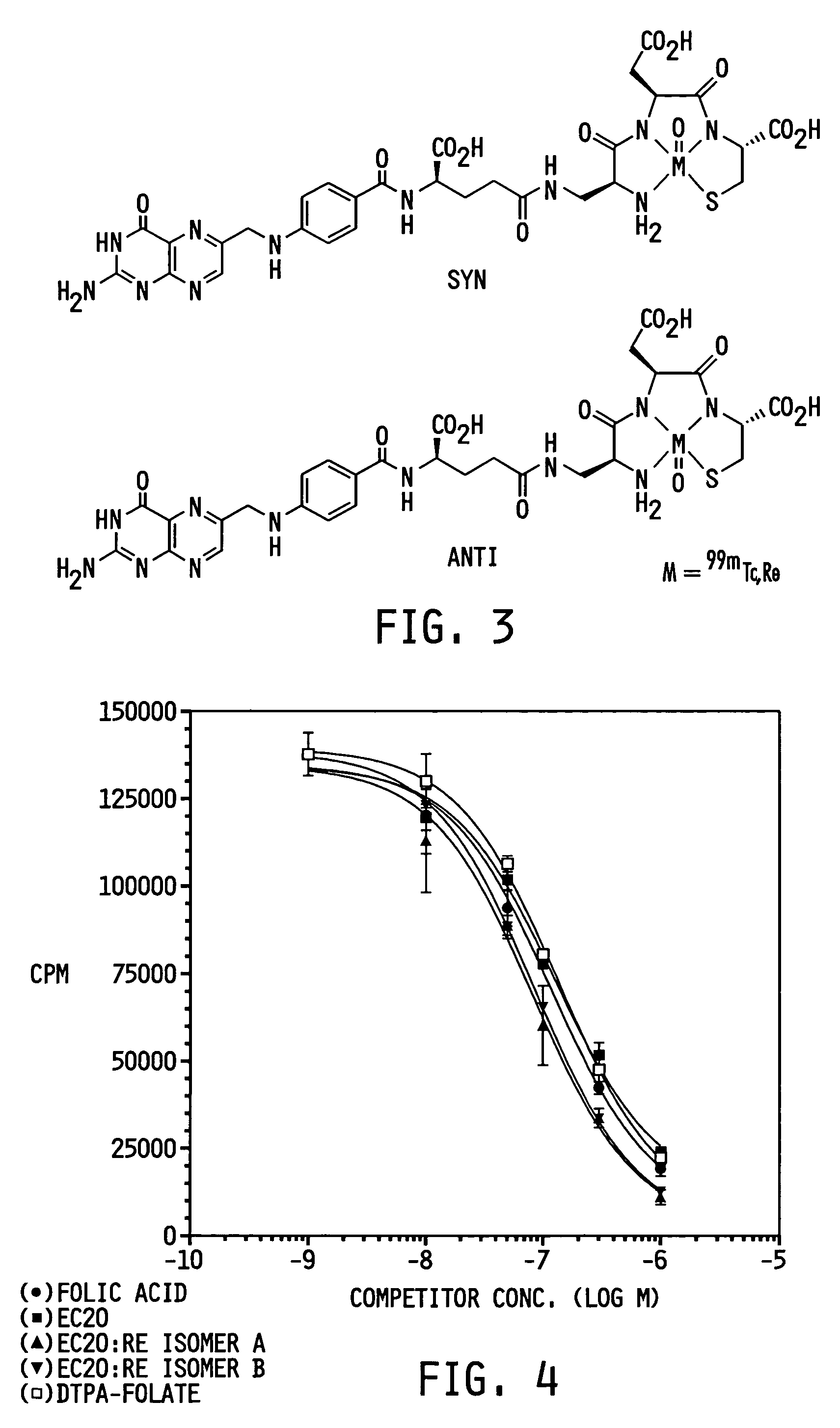
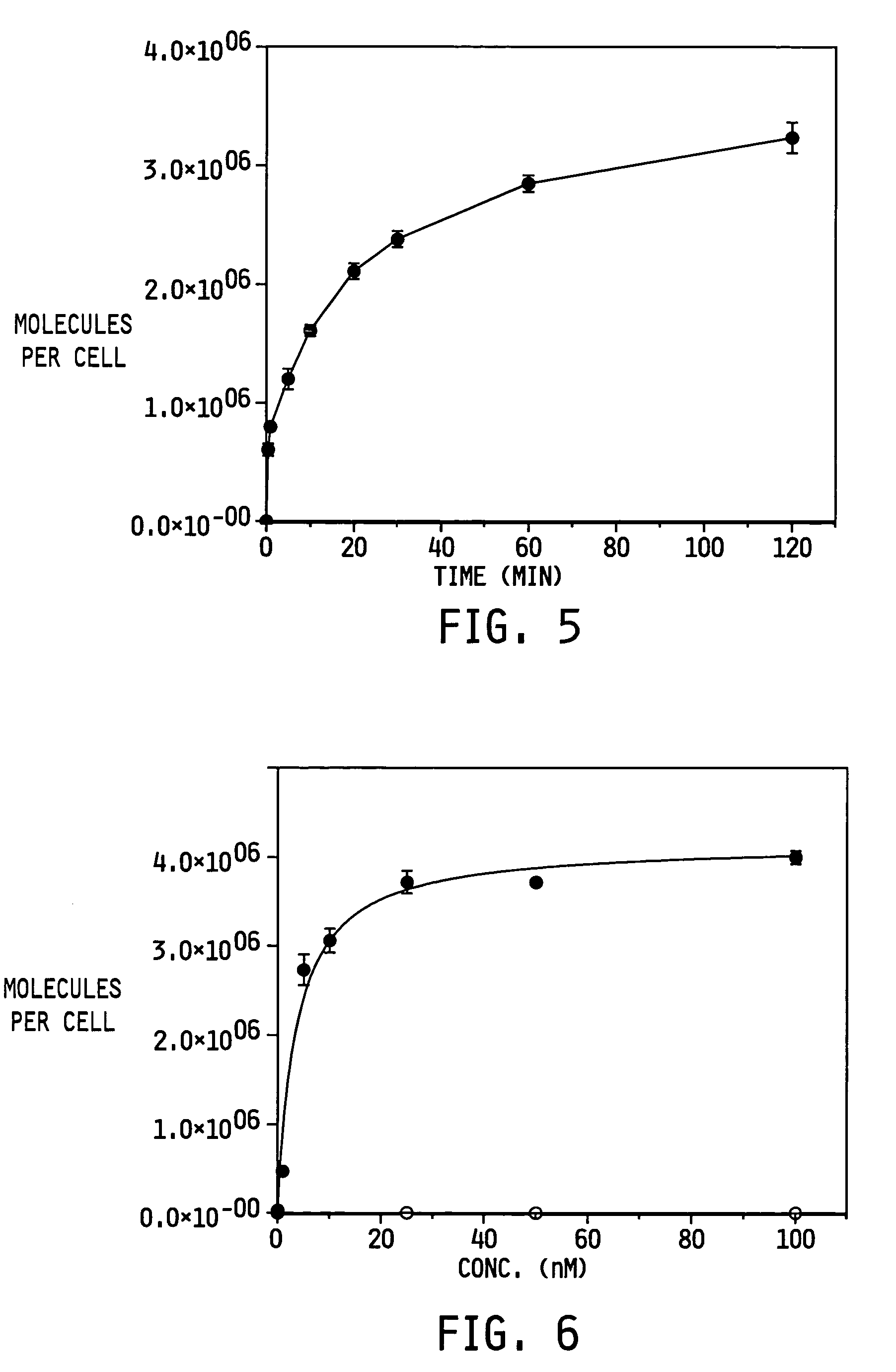
Vitamin-targeted imaging agents
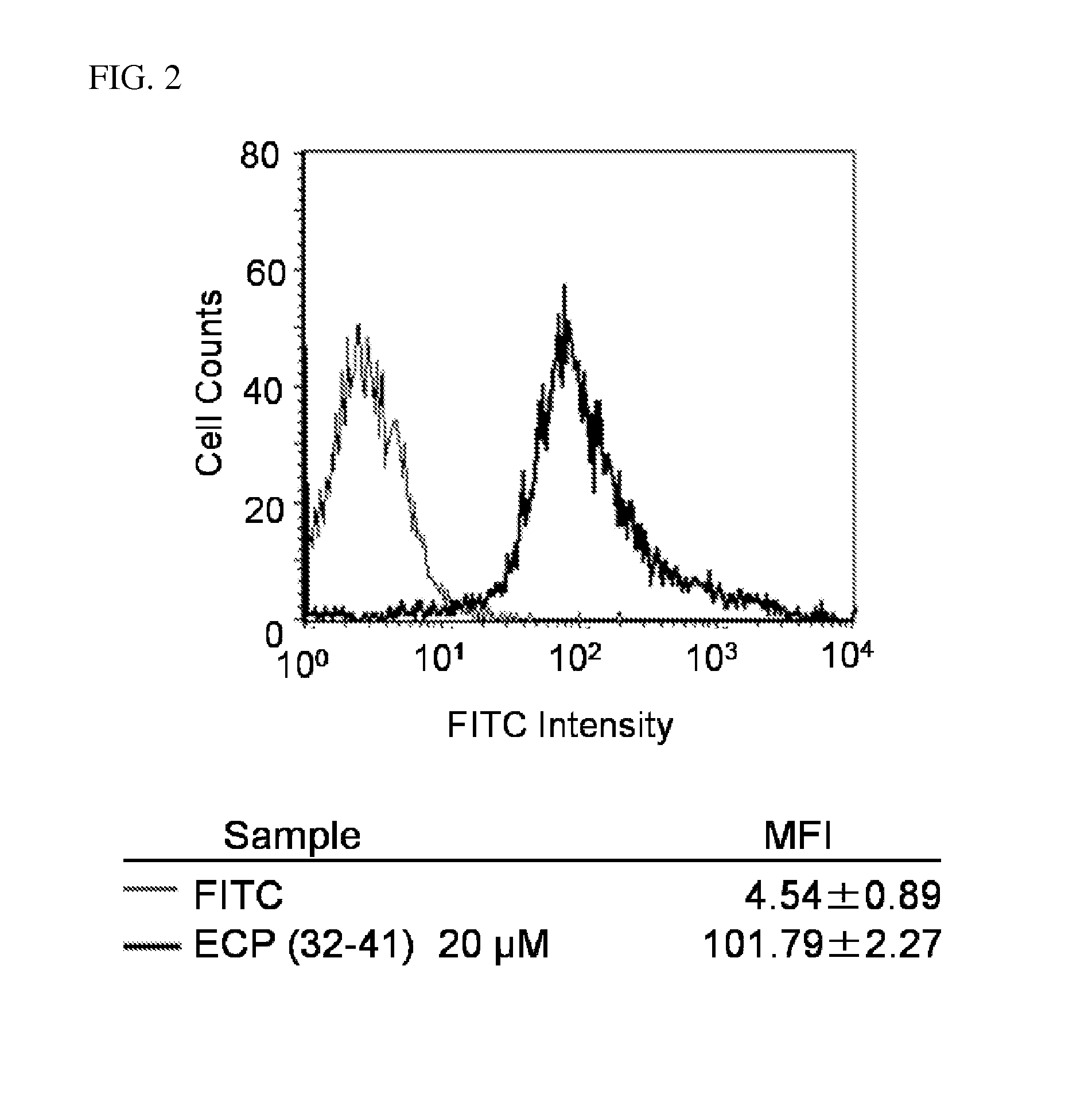
ActiveUS7128893B2Easy to getProducing cost is highPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersVitamin receptorSide chain
The invention relates to compounds and methods for targeting radionuclide-based imaging agents to cells having receptors for a vitamin, or vitamin receptor binding derivative or analog thereof, by using such a vitamin as the targeting ligand for the imaging agent. The invention provides a compound of the formulafor use in such methods. In the compound, V is a vitamin that is a substrate for receptor-mediated transmembrane transport in vivo, or a vitamin receptor binding derivative or analog thereof, L is a divalent linker, R is a side chain of an amino acid, M is a cation of a radionuclide, n is 1 or 0, K is 1 or 0, and the compound can be in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier therefor. The vitamin-based compounds can be used to target radionuclides to cells, such as a variety of tumor cell types, for use in diagnostic imaging of the targeted cells.
Owner:ENDOCTYE INC
PNA monomer and precursor
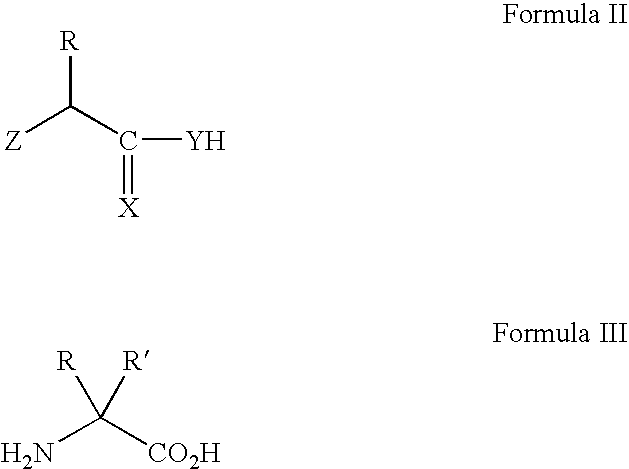
InactiveUS7022851B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBase JOligomer
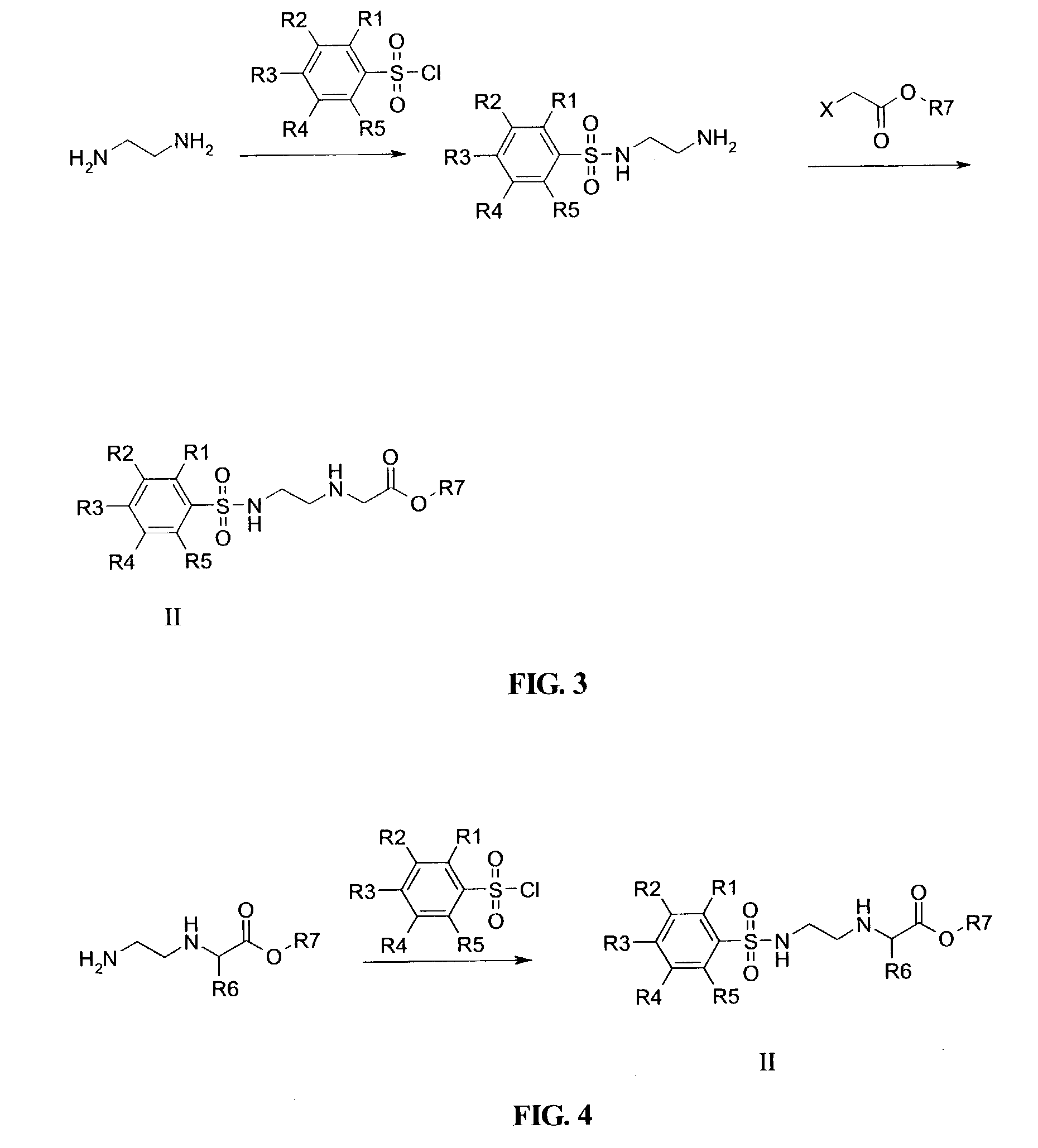
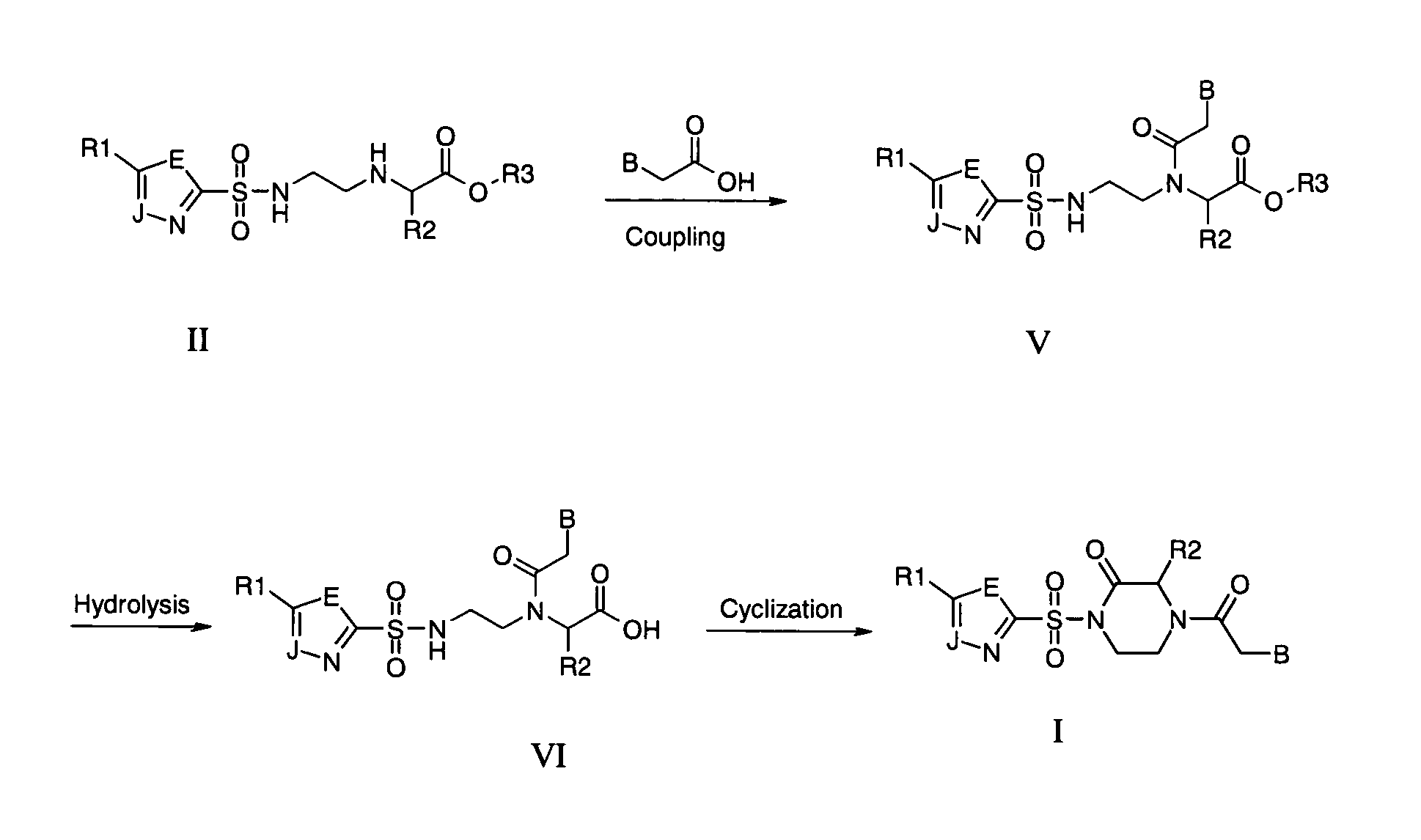
This application relates to monomers of the general formula (I) for the preparation of PNA (peptide nucleic acid) oligomers and provides method for the synthesis of both predefined sequence PNA oligomers and random sequence PNA oligomers: whereinR1, R2, R3, R4, R5 is independently H, halogen, C1–C4 alkyl, nitro, nitrile, C1–C4 alkoxy, halogenated C1–C4 alkyl, or halogenated C1–C4 alkoxy, wherein at least one of R1, R3, and R5 is nitro;R6 is H or protected or unprotected side chain of natural or unnatural α-amino acid; andB is a natural or unnatural nucleobase, wherein when said nucleobase has an exocyclic amino function, said function is protected by protecting group which is labile to acids but stable to weak to medium bases.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
PNA monomer and precursor
ActiveUS7211668B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSide chainNucleobase
Owner:PANAGENE INC
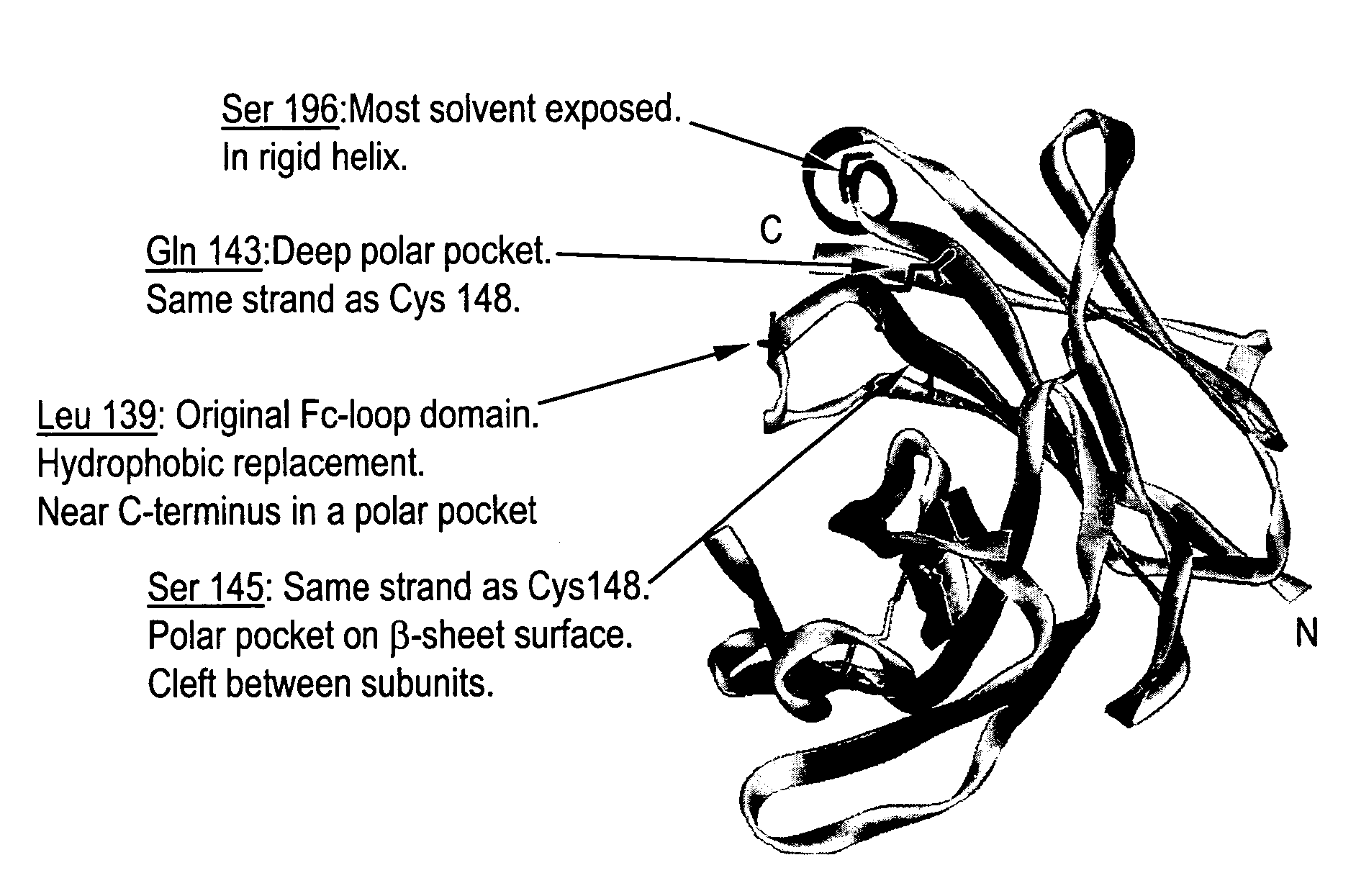
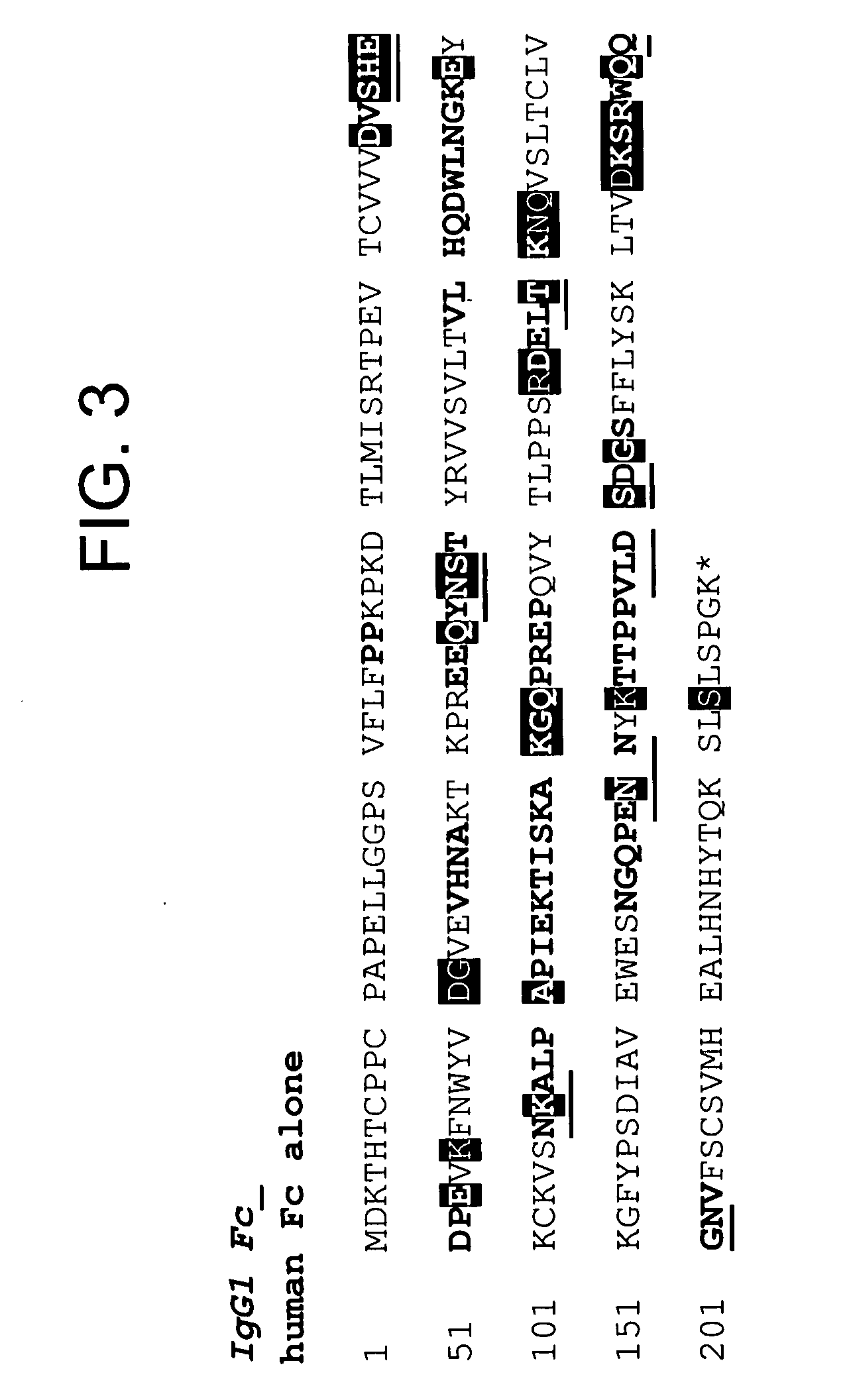
Modified Fc molecules
Disclosed is a process for preparing a pharmacologically active compound, in which at least one internal conjugation site of an Fc domain sequence is selected that is amenable to conjugation of an additional functional moiety by a defined conjugation chemistry through the side chain of an amino acid residue at the conjugation site. An appropriate amino acid residue for conjugation may be present in a native Fc domain at the conjugation site or may be added by insertion (i.e., between amino acids in the native Fc domain) or by replacement (i.e., removing amino acids and substituting different amino acids). In the latter case, the number of amino acids added need not correspond to the number of amino acids removed from the previously existing Fc domain. This technology may be used to produce useful compositions of matter and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. A DNA encoding the inventive composition of matter, an expression vector containing the DNA, and a host cell containing the expression vector are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Printing plates using binder resins having polyethylene oxide segments
InactiveUS20050170286A1Prevent steppingRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePolyethylene oxide
The present invention relates to a polymerizable coating composition suitable for the manufacture of printing plates, which may be developable on-press. The coating composition comprises (i) a polymerizable compound and (ii) a polymeric binder comprising polyethylene oxide segments, wherein the polymeric binder is selected from the group consisting of at least one graft copolymer comprising a main chain polymer and polyethylene oxide side chains, a block copolymer having at least one polyethylene oxide block and at least one non-polyethylene oxide block, and a combination thereof. The invention is also directed to an imageable element comprising a substrate and the polymerizable coating composition.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Compositions and methods for enhancing drug delivery across and into epithelial tissues
This invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing delivery of drugs and other agents across epithelial tissues, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary epithelium, and the like. The compositions and methods are also useful for delivery across endothelial tissues, including the blood brain barrier. The compositions and methods employ a delivery enhancing transporter that has sufficient guanidino or amidino sidechain moieties to enhance delivery of a compound conjugated to the reagent across one or more layers of the tissue, compared to the non-conjugated compound. The delivery-enhancing polymers include, for example, poly-arginine molecules that are preferably between about 6 and 25 residues in length.
Owner:KAI PHARMA
Oligonucleotide Core Carrier Compositions for Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Containing Therapeutic Agents, Methods of Making and Using the Same
ActiveUS20090053169A1Easy to adjustSafe and effective and readily adjustedAntibacterial agentsBiocideSide chainOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates, in part, to an oligonucleotide-core carrier comprising a carrier, and oligonucleotide groups covalently linked to the carrier. The oligonucleotide groups are capable of dissociably linking load molecules such as therapeutic agents. The oligonucleotide-core carrier may also comprise protective side chains, and targeting molecules.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
Modulating ph-sensitive binding using non-natural amino acids
InactiveUS20090035836A1High affinitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSide chain
The invention provides methods, systems and reagents for regulating pH-sensitive protein interaction by incorporating non-natural amino acids into the protein (e.g. an antibody, or its functional fragment, derivative, etc.). The invention also relates to specific uses in regulating pH-sensitive binding of antibodies to tumor site, by conferring enhanced tumor-specificity / selectivity. In that embodiment, the non-natural amino acids preferably have desirable side-chain pKa's, such that at below physiological pH (e.g. about pH 6.3-6.5) the non-natural amino acid confer enhanced binding to tumor antigens in acidic environments. Such non-natural amino acids can be incorporated by any suitable means, such as by utilizing a modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to charge the nonstandard amino acid to a modified tRNA, which forms strict Watson-Crick base-pairing with a codon that normally forms wobble base-pairing with natural tRNAs (e.g. the degenerate codon orthogonal system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Thiol-modified hyaluronan
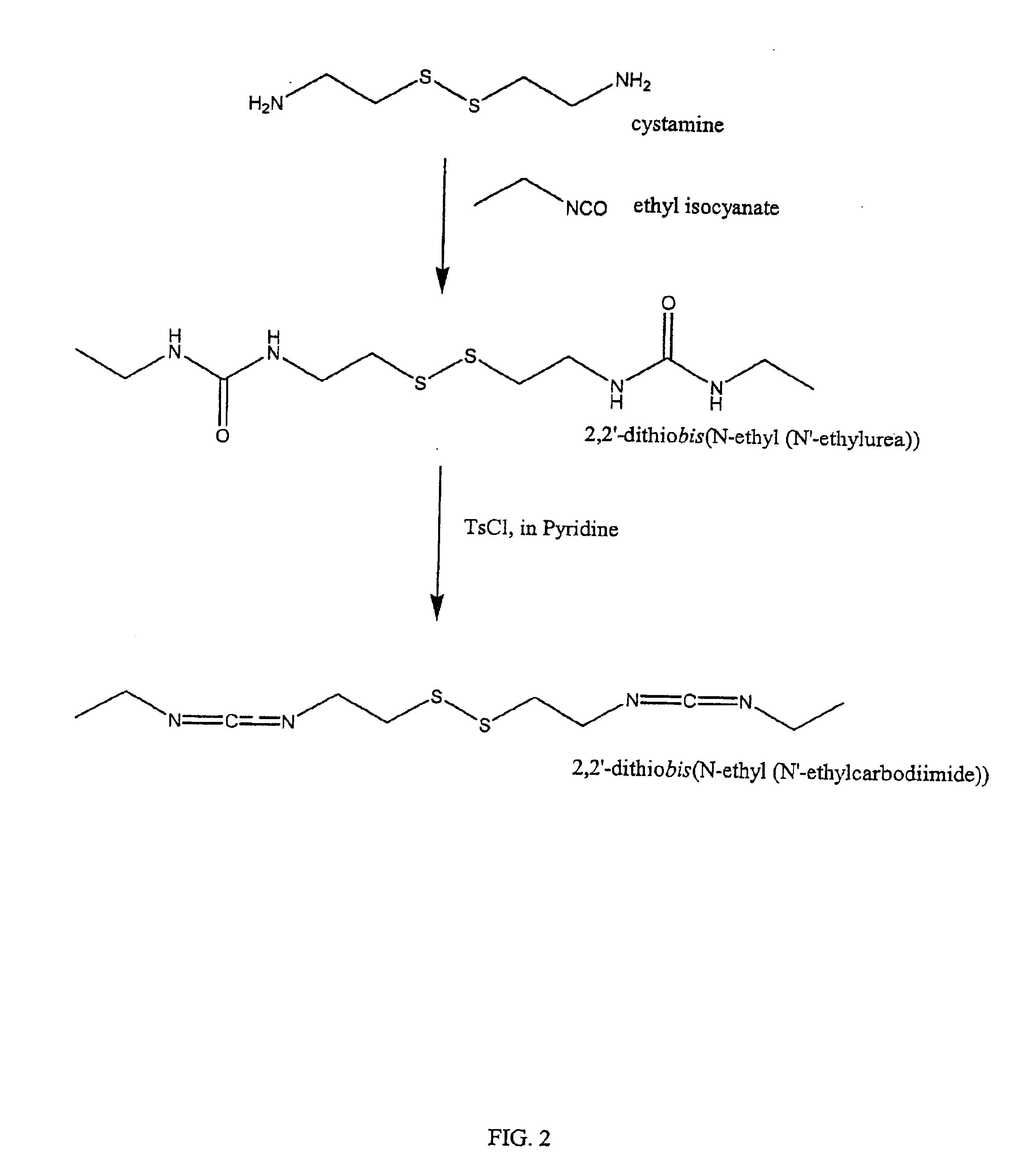
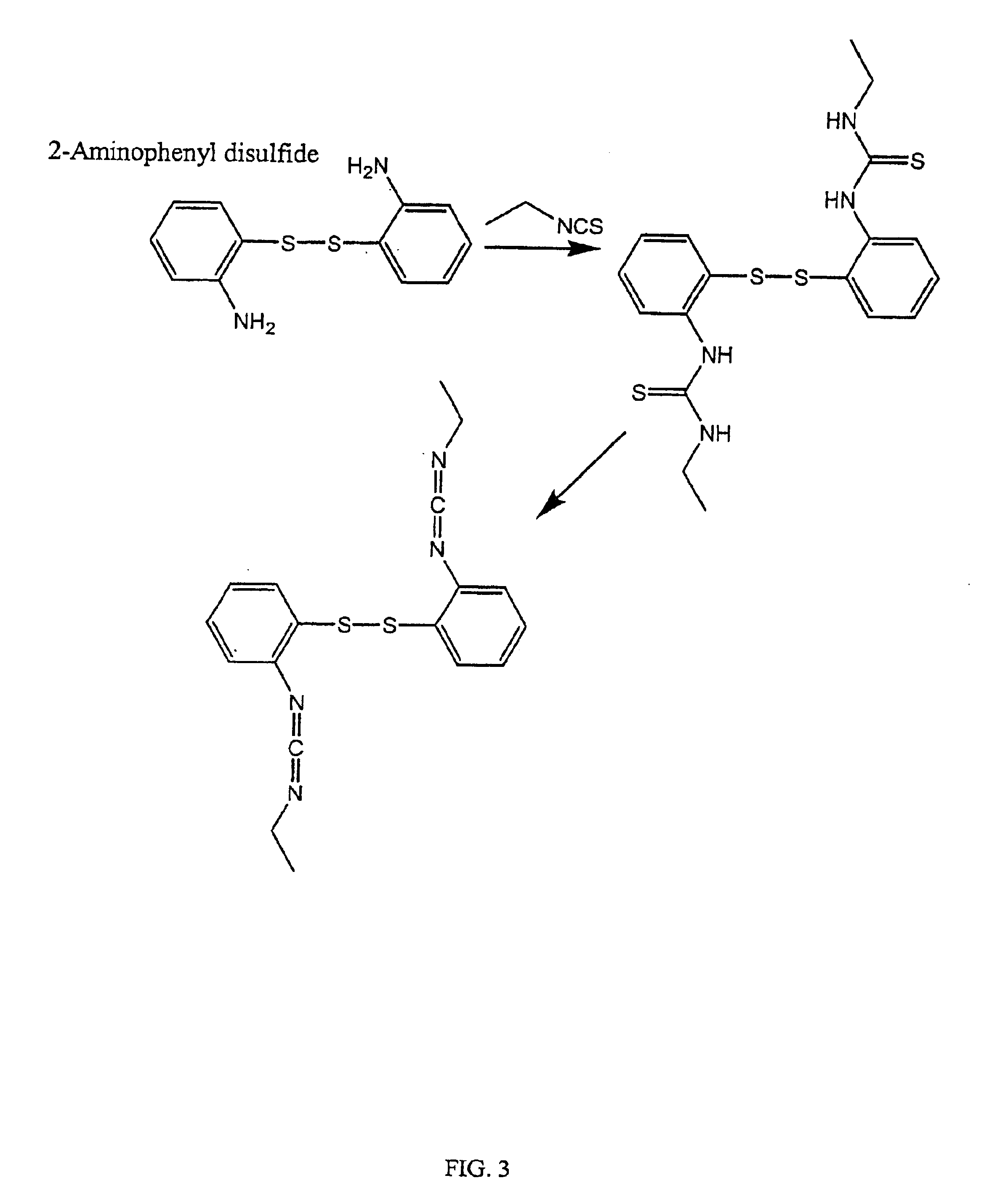
InactiveUS6884788B2High activityControl moreBiocideOrganic active ingredientsUrea derivativesCross-link
The present invention relates to biscarbodiimides, thiourea derivatives, urea derivatives, and cross-linked hyaluronan derivatives having at least one intramolecular disulfide bond, and methods of preparation thereof. The invention also includes thiolated hyaluronan derivatives and salts thereof having at least one pendant thiol group or a modified pendant thiol group, and methods of preparation thereof. An example of a modified pendant thiol group is a sulfhydryl group linked to a small molecule such as a bioactive agent, for example a drug or pharmaceutically active moiety. A hyaluronan derivative having a sulfhydryl group linked to a pharmaceutically active moiety is useful as a sustained or controlled release drug delivery vehicle. Compositions containing the hyaluronan derivatives of the invention can reversibly viscosify in vivo or in vitro, in response to mild changes in condition, and are thus useful in ophthalmic surgery and in tissue engineering.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS INC
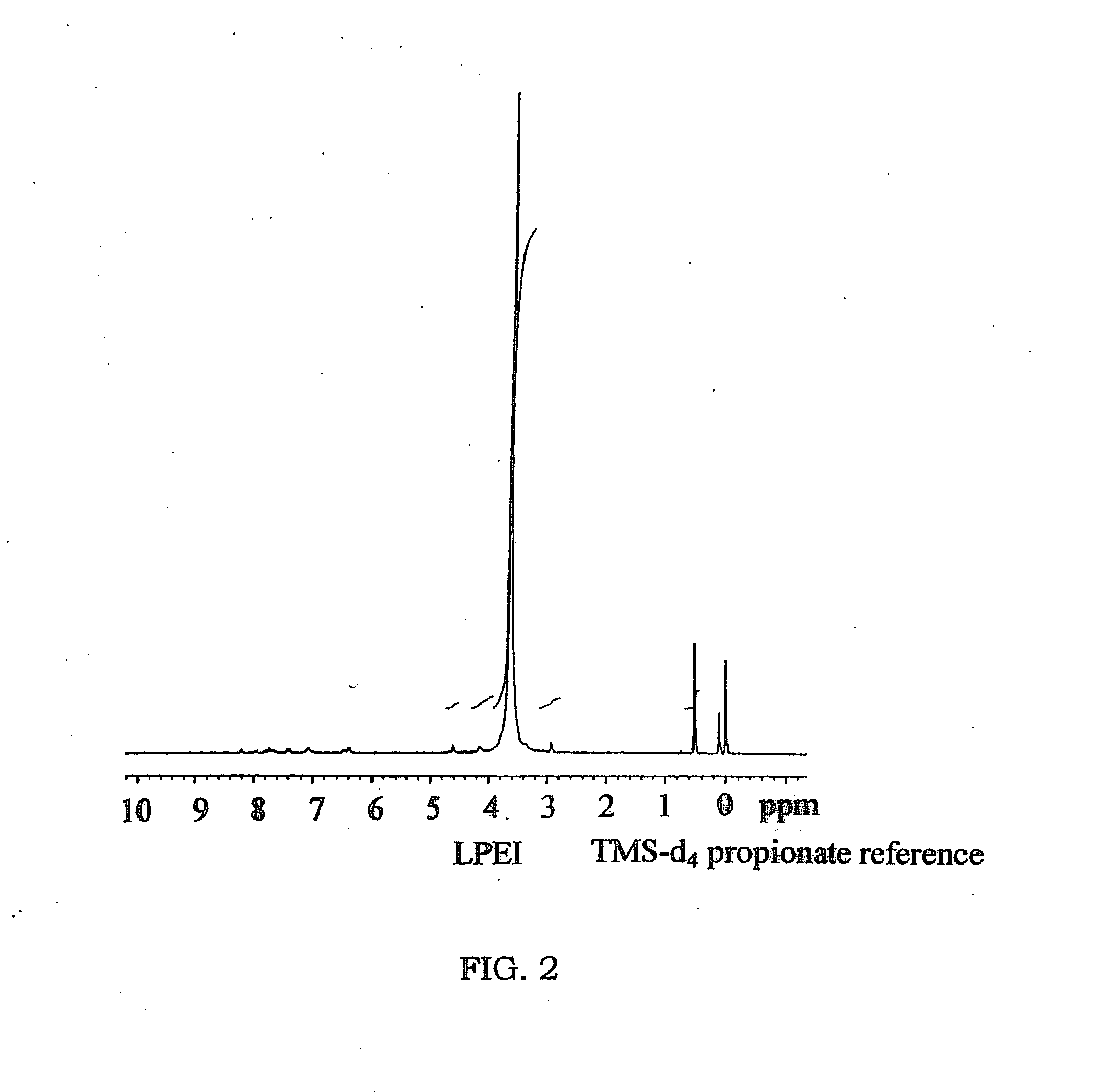
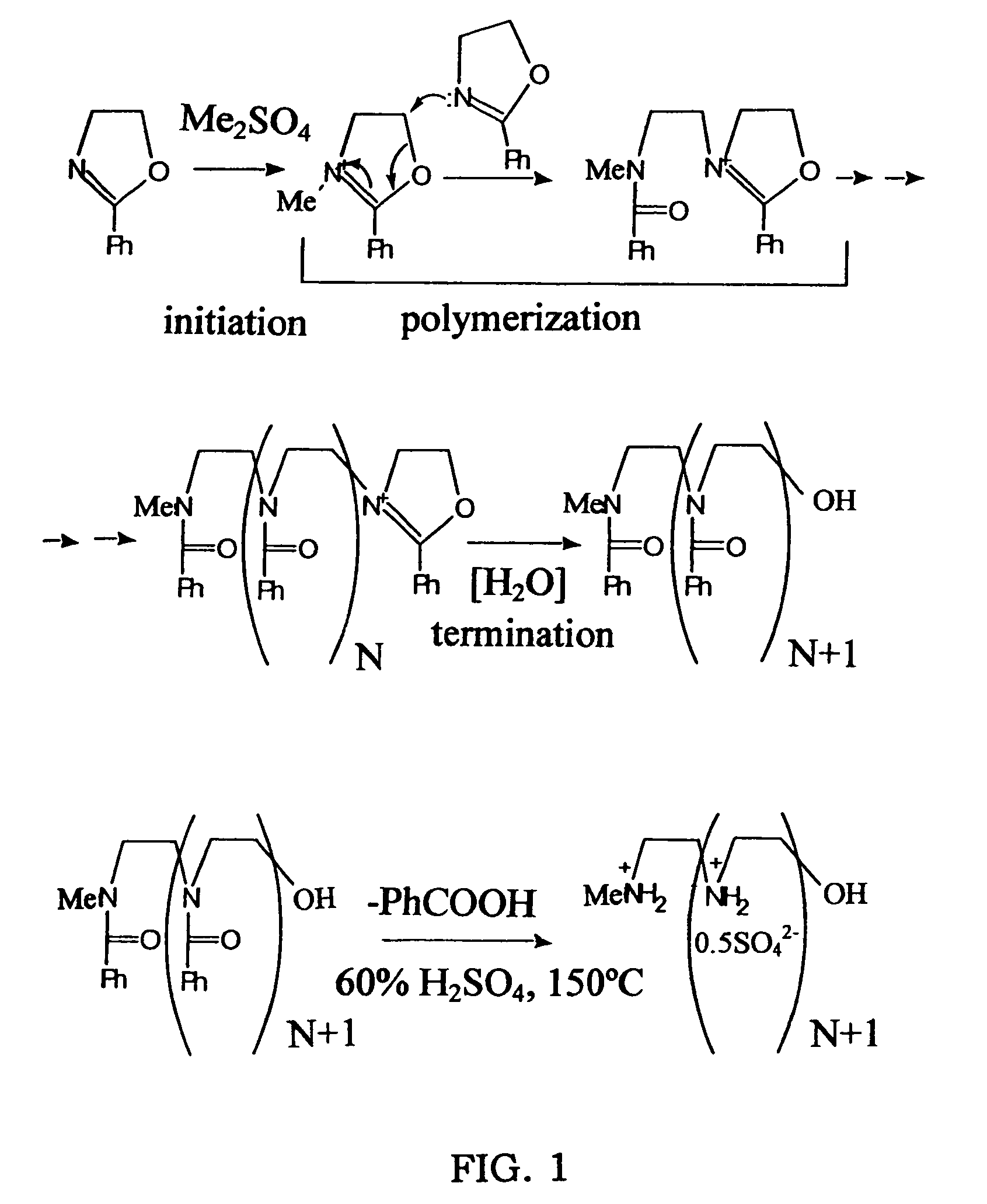
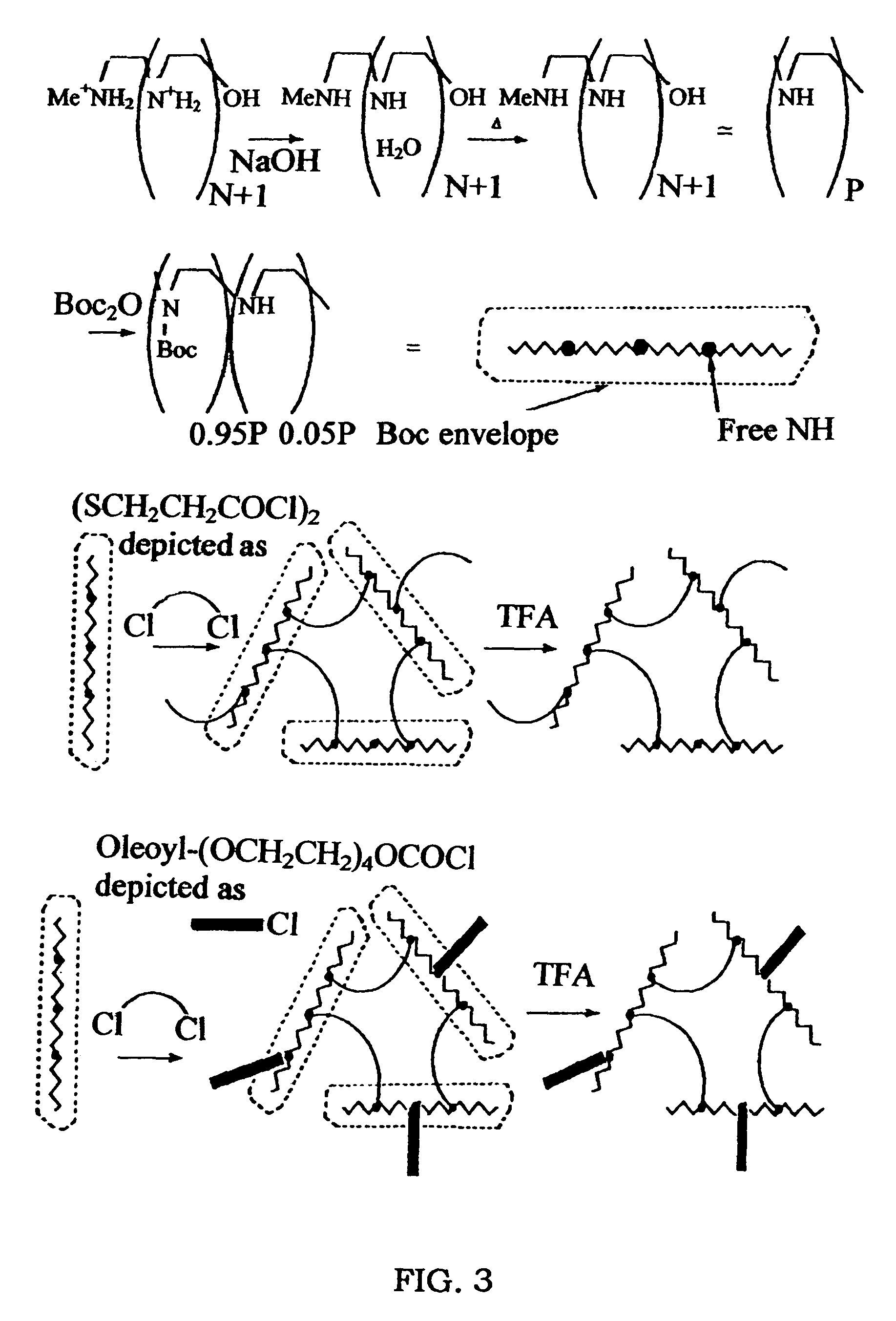
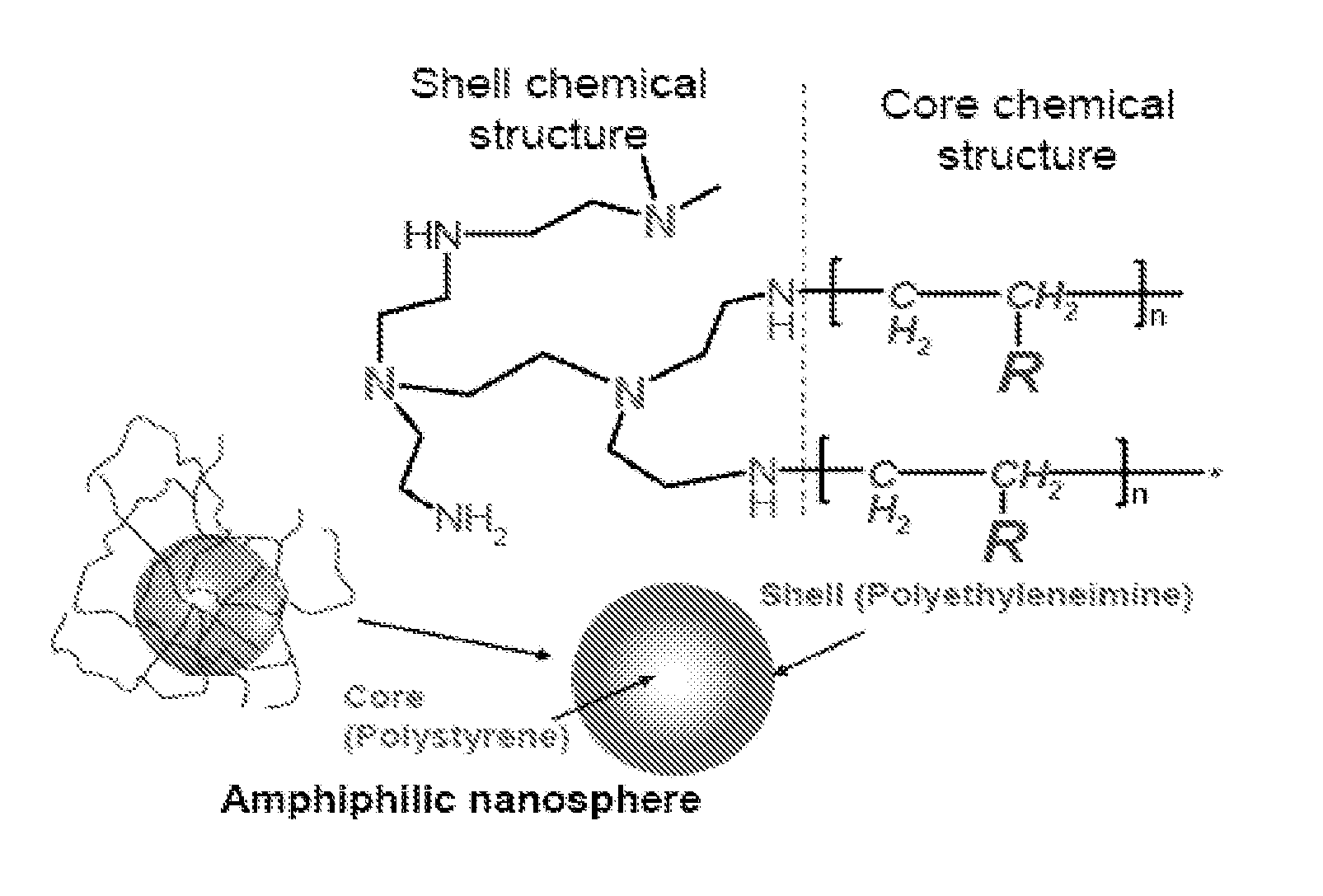
Biodegradable Cross-Linked Cationic Multi-block Copolymers for Gene Delivery and Methods of Making Thereof
ActiveUS20120009145A1Easy to controlGuaranteed effective sizeCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkGene delivery
A biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer of linear polyethylenimine (LPEI) wherein the LPEI blocks are linked together by hydrophilic linkers with a biodegradable disulfide bond and methods of making thereof. The biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer may also contain pendant functional moieties which are preferably receptor ligands, membrane permeating agents, endosomolytic agents, nuclear localization sequences, pH sensitive endosomolytic peptides, chromogenic or fluorescent dyes.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Positively charged membrane
InactiveUS6780327B1High rateHigh charge densityCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPorous substrateFiltration
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
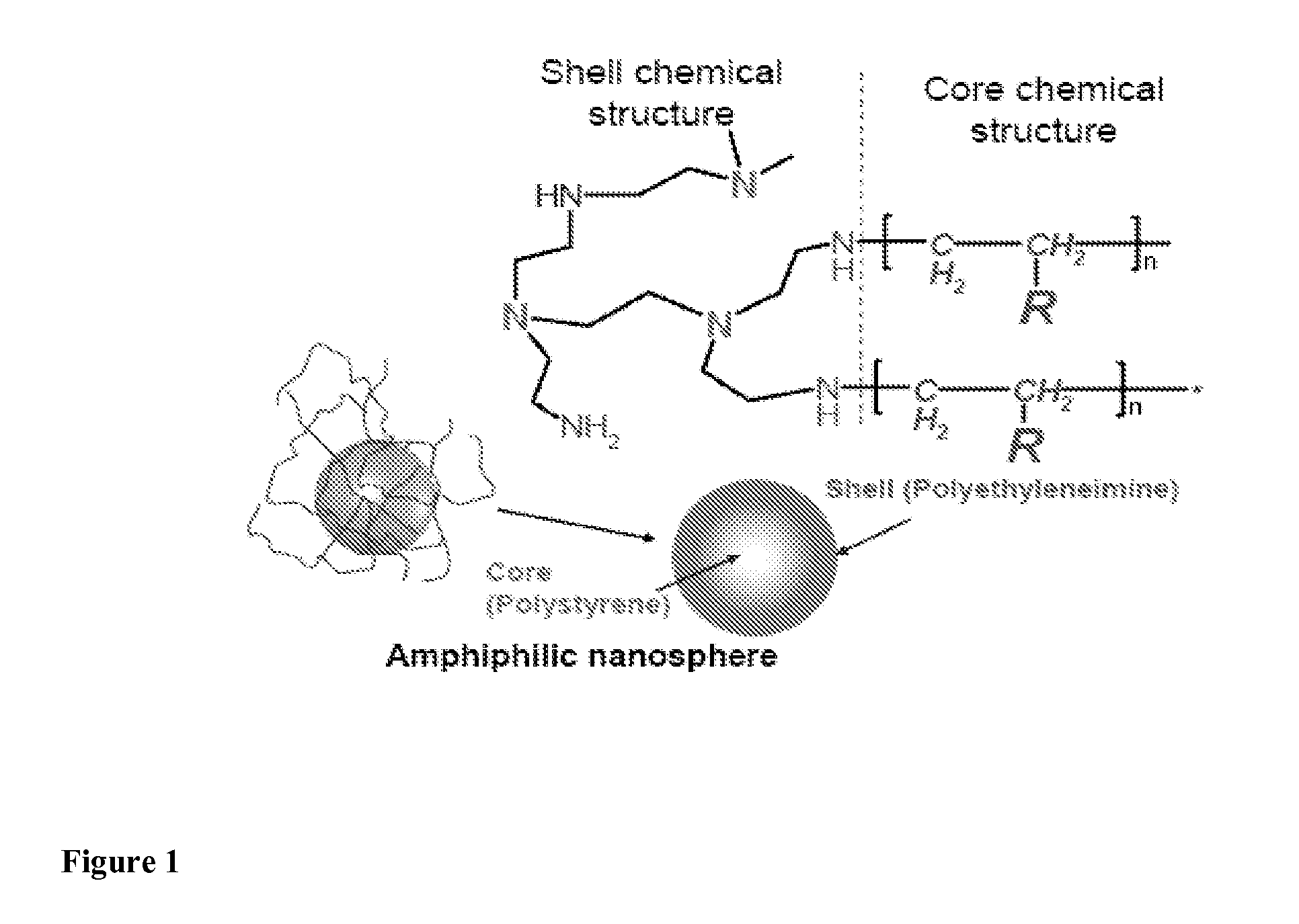
Biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymers for gene delivery and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS8057821B2Easy to controlGuaranteed effective sizePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCross-linkGene delivery
A biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer of linear polyethylenimine (LPEI) wherein the LPEI blocks are linked together by hydrophilic linkers with a biodegradable disulfide bond and methods of making thereof. The biodegradable cross-linked cationic multi-block copolymer may also contain pendant functional moieties which are preferably receptor ligands, membrane permeating agents, endosomolytic agents, nuclear localization sequences, pH sensitive endosomolytic peptides, chromogenic or fluorescent dyes.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Cell penetrating peptides for intracellular delivery
ActiveUS8372951B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographySide chain
A cell penetrating peptide which has following sequence: NYBX1BX2BNQX3, wherein B represents a basic amino acid, X1 represents an amino acid with an aromatic, a hydrophobic or an uncharged side chain, X2 represents any amino acid, and X3 represents N or none is described. A method for delivering a cargo into a subject by administrating a complex comprising the cell penetrating peptide and the desired cargo to the subject is also described.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Toughened fiber reinforced polymer composite with core-shell particles
Embodiments disclosed herein include a resin composition comprising two or more different kinds of thermosetting resins, wherein at least one of the two or more different kinds of the thermosetting resins is a multifunctional resin, and a core-shell particle having a core and a shell, wherein a composition of the core is different from a composition of the shell and the composition of the shell has a branched polymer structure comprising at least one main chain and at least one side chain, the main chain or the side chain containing at least one functional group that reacts with the thermosetting resin, a method of manufacturing the resin composition, and a composite comprising a reinforcing fiber and the resin composition.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Modulating pH-sensitive binding using non-natural amino acids
InactiveUS20050260711A1Prolong half-life in vivoSame effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSide chainTumor antigen
The invention provides methods, systems and reagents for regulating pH-sensitive protein interaction by incorporating non-natural amino acids into the protein (e.g. an antibody, or its functional fragment, derivative, etc.). The invention also relates to specific uses in regulating pH-sensitive binding of antibodies to tumor site, by conferring enhanced tumor-specificity / selectivity. In that embodiment, the non-natural amino acids preferably have desirable side-chain pKa's, such that at below physiological pH (e.g. about pH 6.3-6.5) the non-natural amino acid confer enhanced binding to tumor antigens in acidic environments. Such non-natural amino acids can be incorporated by any suitable means, such as by utilizing a modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to charge the nonstandard amino acid to a modified tRNA, which forms strict Watson-Crick base-pairing with a codon that normally forms wobble base-pairing with natural tRNAs (e.g. the degenerate codon orthogonal system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern from the same
InactiveUS20040110085A1Small line edge roughnessHigh resolutionRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityMethacrylate
There is provided a positive type resin composition comprising (A) a resin component comprising within the principal chain a structural unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester and incorporating an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group on an ester side chain section, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, and (C) an organic solvent, wherein the component (A) comprises both a structural unit derived from a methacrylate ester and a structural unit derived from an acrylate ester. According to such a resist composition, a resist pattern can be formed which displays little surface roughness and line edge roughness on etching, and also offers excellent resolution and a wide depth of focus range.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Film-forming compositions and methods
InactiveUS6838078B2Reduce bacterial loadLess irritatingCosmetic preparationsBiocideWater dispersibleActive agent
Film-forming compositions, as well as methods of making and using, wherein the compositions include an optional active agent, water, a surfactant, and a water-soluble or water-dispersible vinyl polymer comprising amine group-containing side-chains and a copolymerized hydrophobic monomer; wherein the amine equivalent weight of the polymer is at least about 300 grams polymer per equivalent of amine group.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Cure on demand adhesives and window module with cure on demand adhesive thereon
InactiveUS6355127B1Improve stabilityHigh green strengthManual label dispensersGlass/slag layered productsActive agentSide chain
In one embodiment the invention is An adhesive composition comprisinga) a polymer having a flexible backbone and a reactive moiety capable of cross-linking,b) a particle comprising an active agent encapsulated in an encapsulating agent wherein the active agent comprises a catalyst for cross-linking of the reactive moiety, a curing agent for the reactive moiety, an accelerator for the curing reaction or a mixture thereof; and the encapsulating agent comprises a side chain crystallizable polymer wherein the active agent is not substantially extractable from the particle at ambient conditions in a first extraction after particle formation.This composition is used in binding two subtracters together.
Owner:ESSEX SPECIALITY PROD INC +1
Method of preparing negative-working radiation-sensitive elements
ActiveUS7175969B1Excellent developabilityReduced background stainingPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsSide chainMoisture
A method of preparing negative-working, single-layer imageable elements improves their storage stability in a humid environment. The method includes enclosing the coated imageable elements in a water-impermeable sheet material that substantially inhibits the transfer of moisture to and from the imageable element. Such imageable elements include a radiation-sensitive composition that includes a radically polymerizable component, an initiator composition to provide radicals upon exposure to imaging radiation, a radiation absorbing compound, and a polymeric binder having poly(alkylene glycol) side chains.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Compositions and methods for enhancing drug delivery across and into epithelial tissues
InactiveUS20020127198A1Reduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainGastrointestinal tract
This invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing delivery of drugs and other agents across epithelial tissues, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary epithelium, ocular tissues and the like. The compositions and methods are also useful for delivery across endothelial tissues, including the blood brain barrier. The compositions and methods employ a delivery enhancing transporter that has sufficient guanidino or amidino sidechain moieties to enhance delivery of a compound conjugated to the reagent across one or more layers of the tissue, compared to the non-conjugated compound. The delivery-enhancing polymers include, for example, poly-arginine molecules that are preferably between about 6 and 25 residues in length.
Owner:KAI PHARMA
Non-maltogenic exoamylases and their use in retarding retrogradation of starch
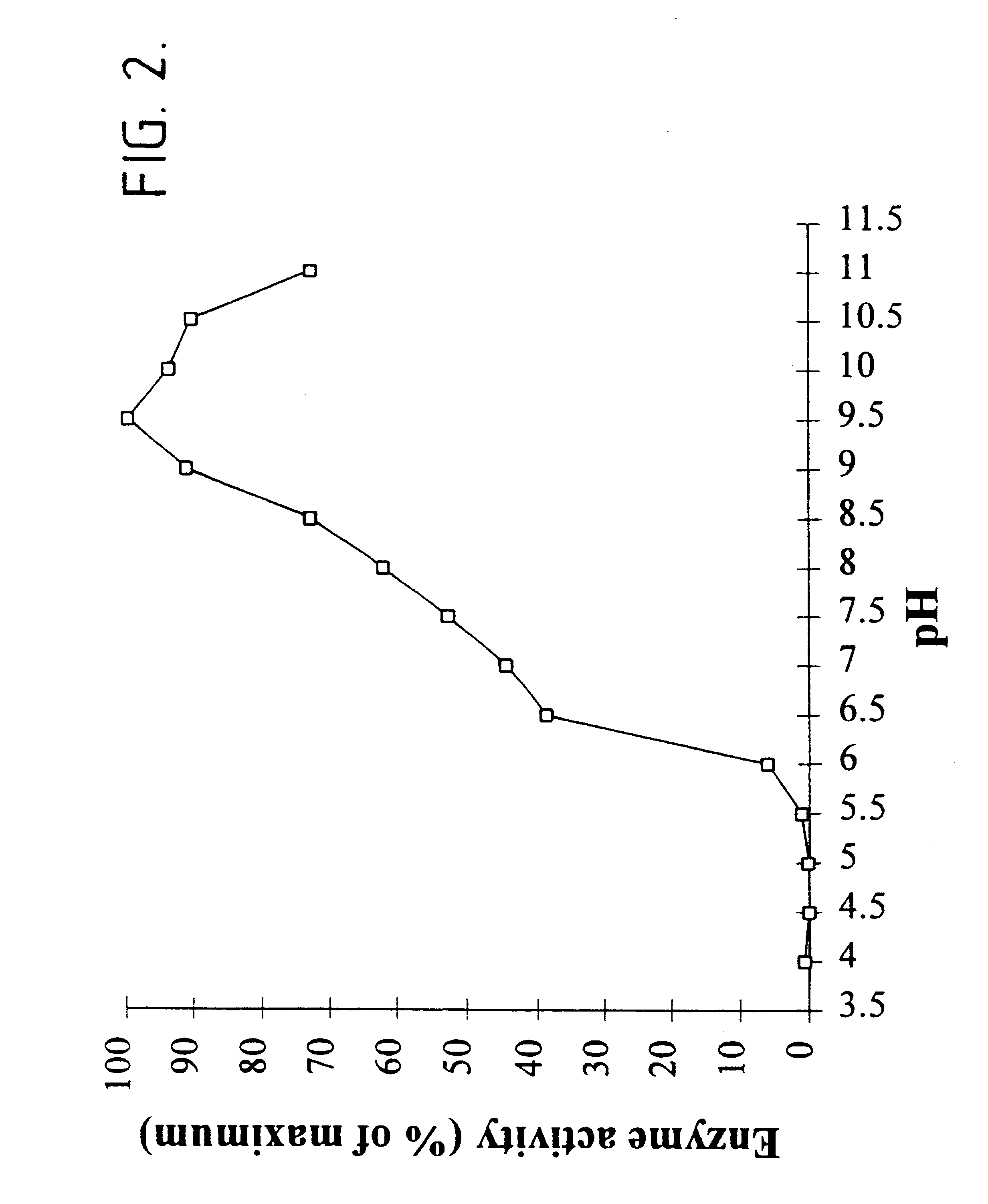
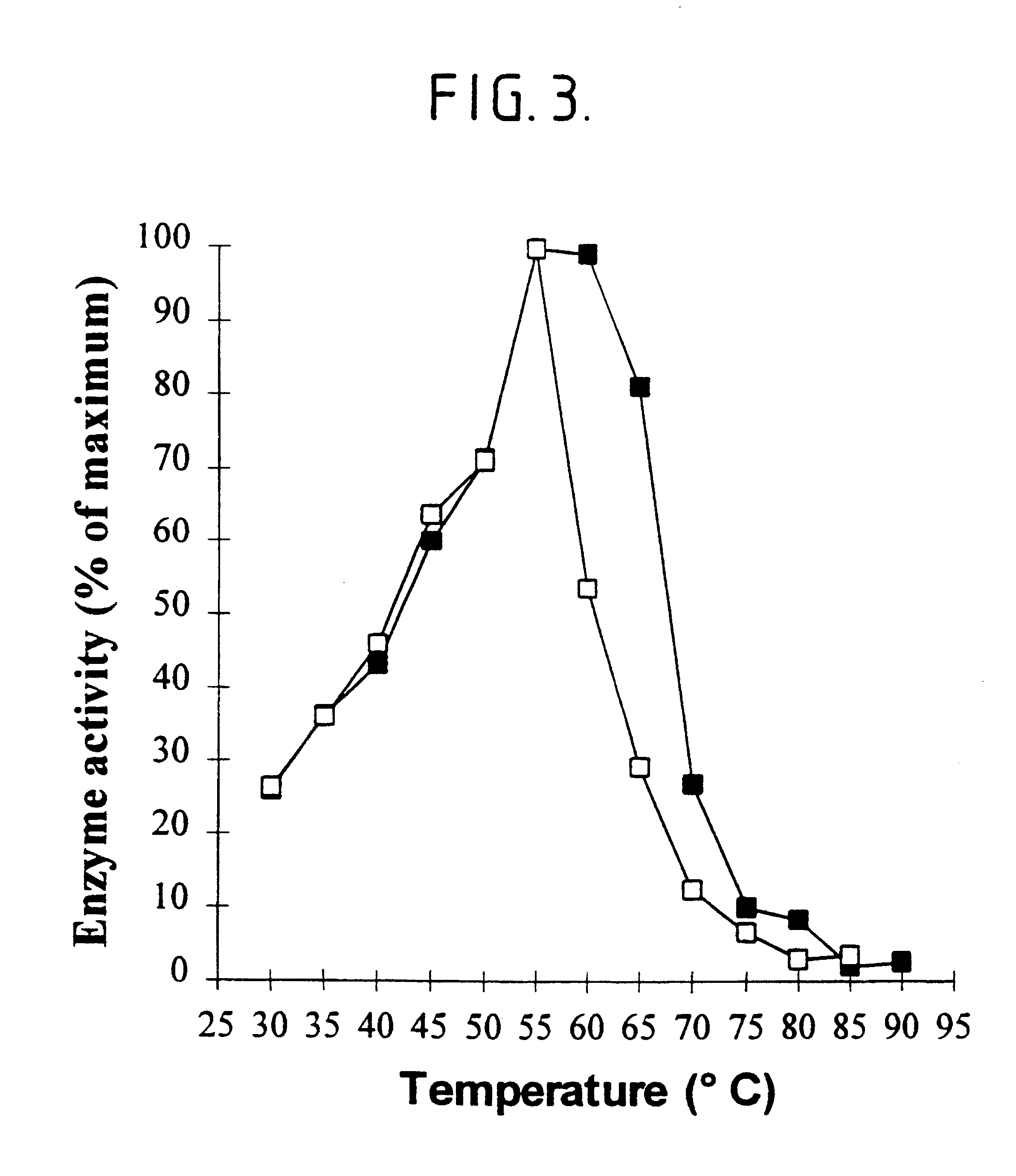
InactiveUS6667065B1Highly effective in retarding or reducing detrimental retrogradationImprove propertiesDough treatmentHydrolasesAmylosucrase activitySide chain
The present invention relates to a process for making a bread product. The process includes the addition of a non-maltogenic exoamylase that hydrolyses starch to a starch medium, and the application of heat to the starch medium. The non-maltogenic exomylase cleaves one or more linear malto-oligosaccharides, predominantly consisting of from four to eight D-glucopyranosyl units, from non-reducing ends of amylopectin side chains. The non-maltogenic exoamylase has an endoamylase activity of less than 0.5 endoamylase units (EAU) per unit of exoamylase activity.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com