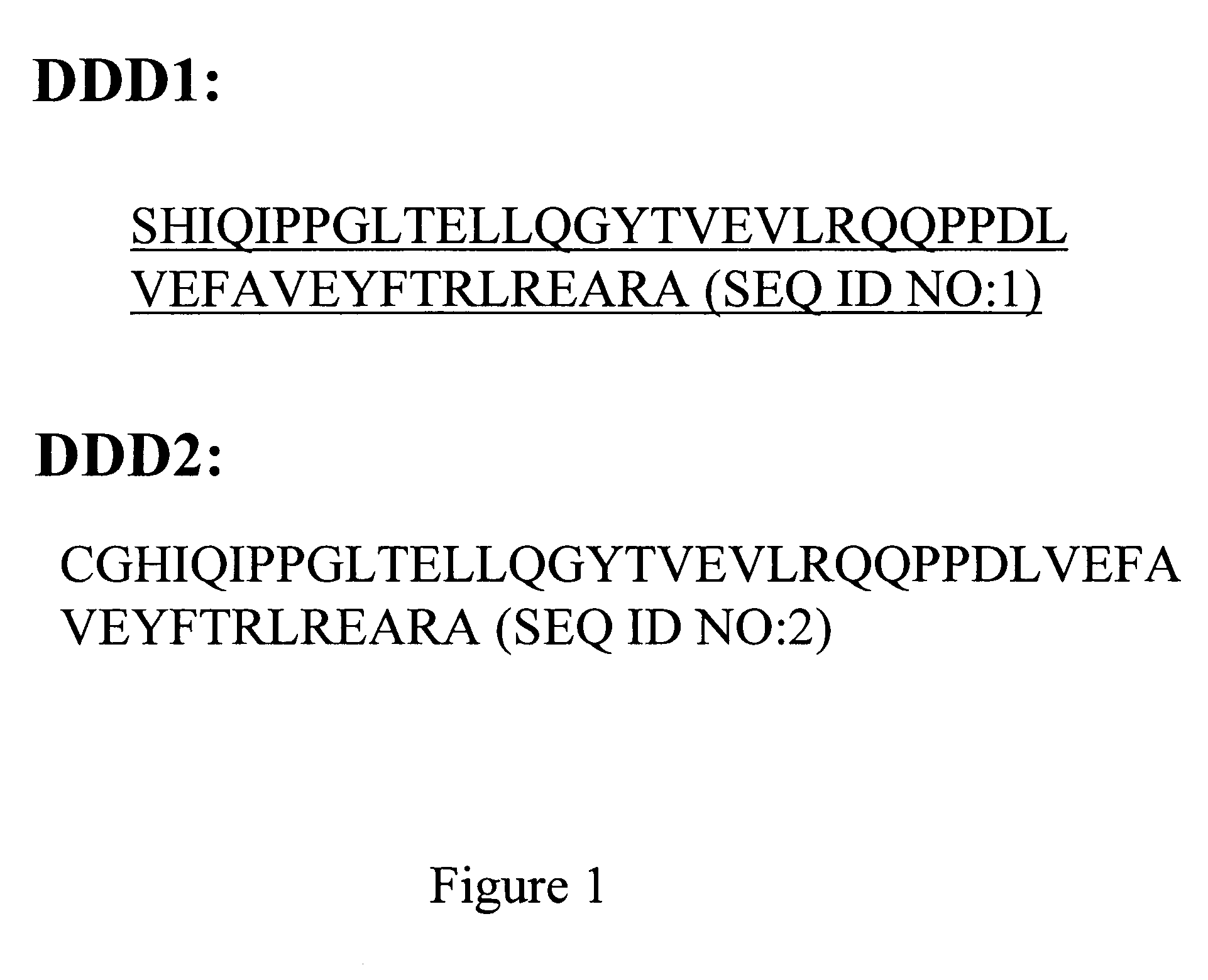
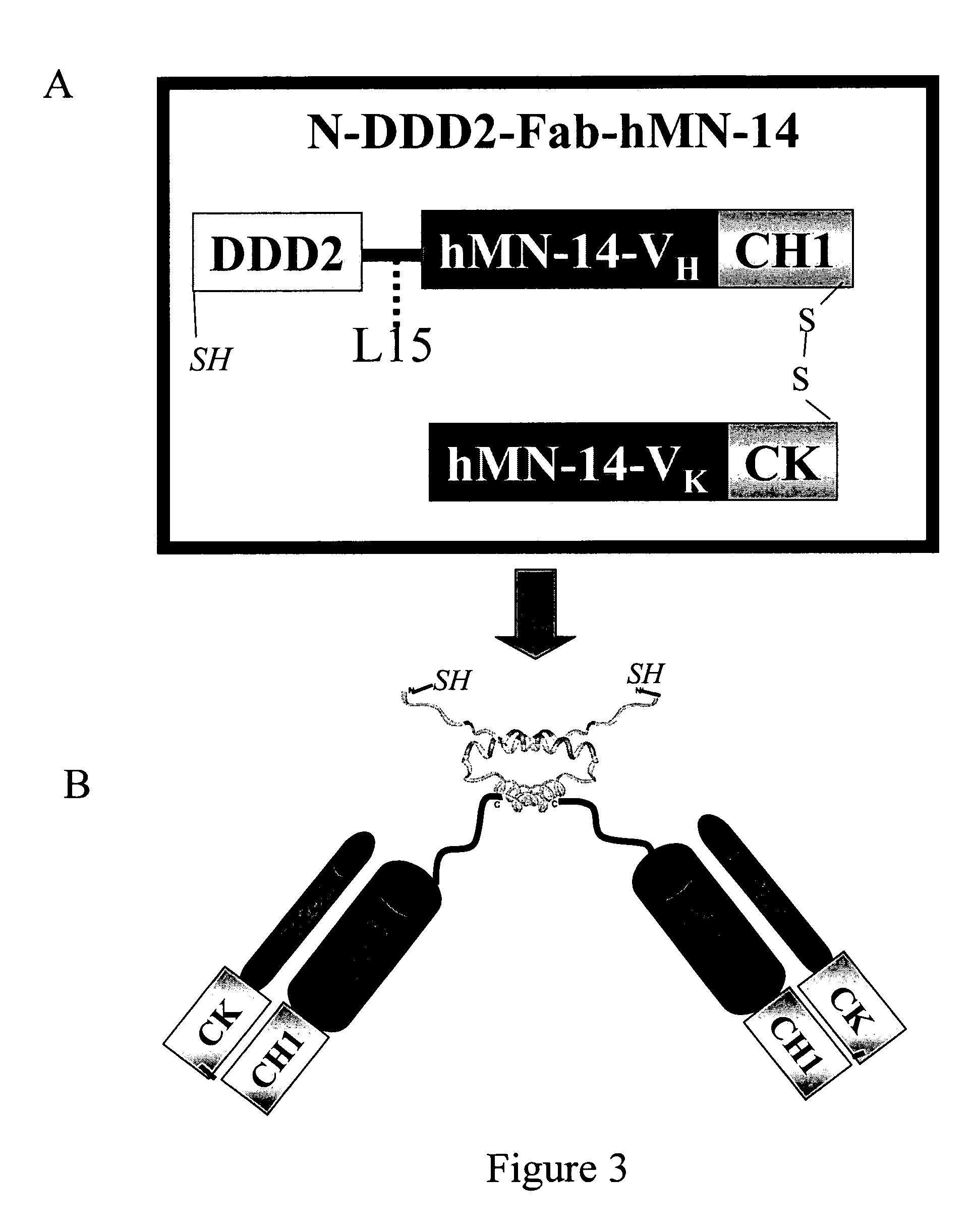
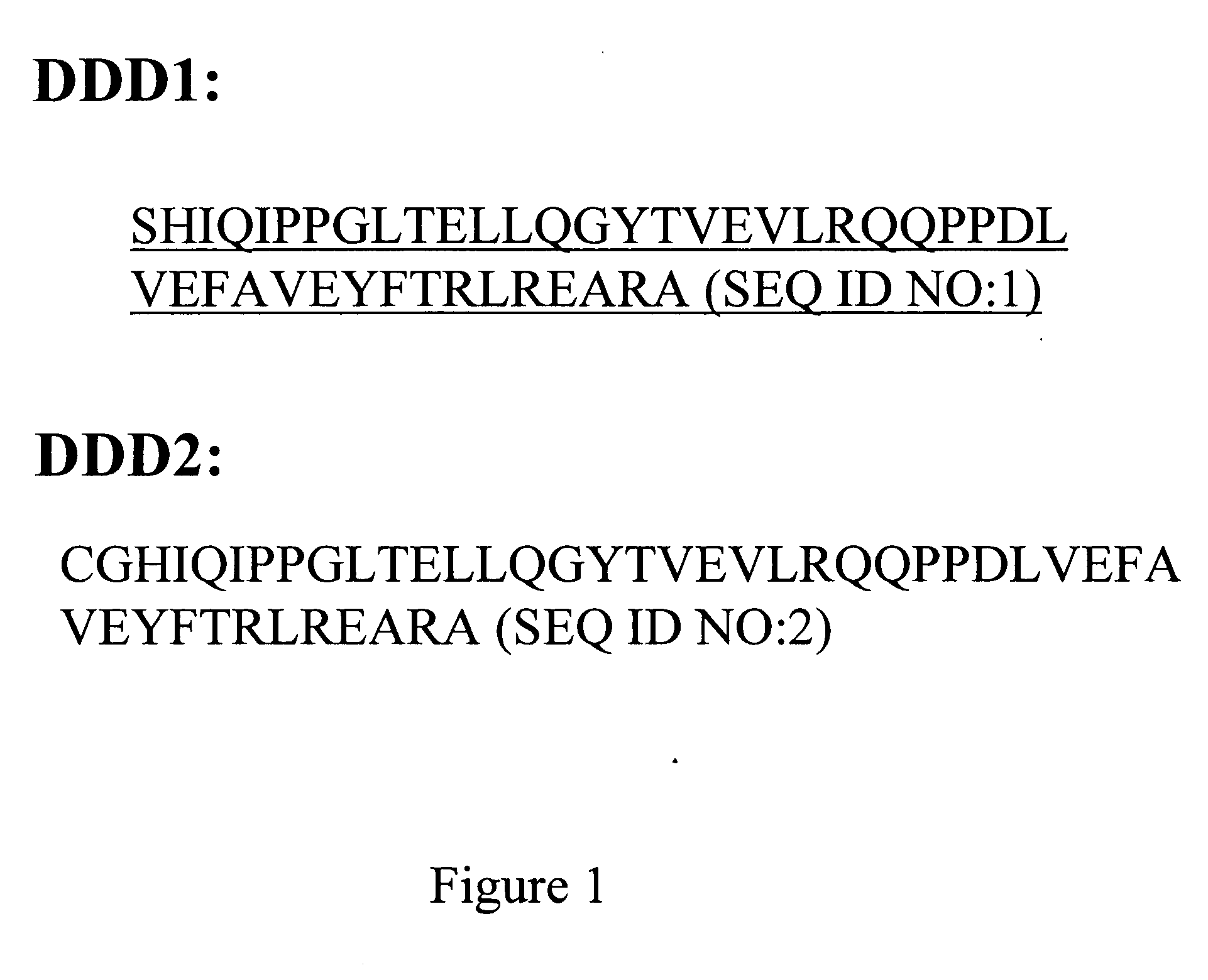
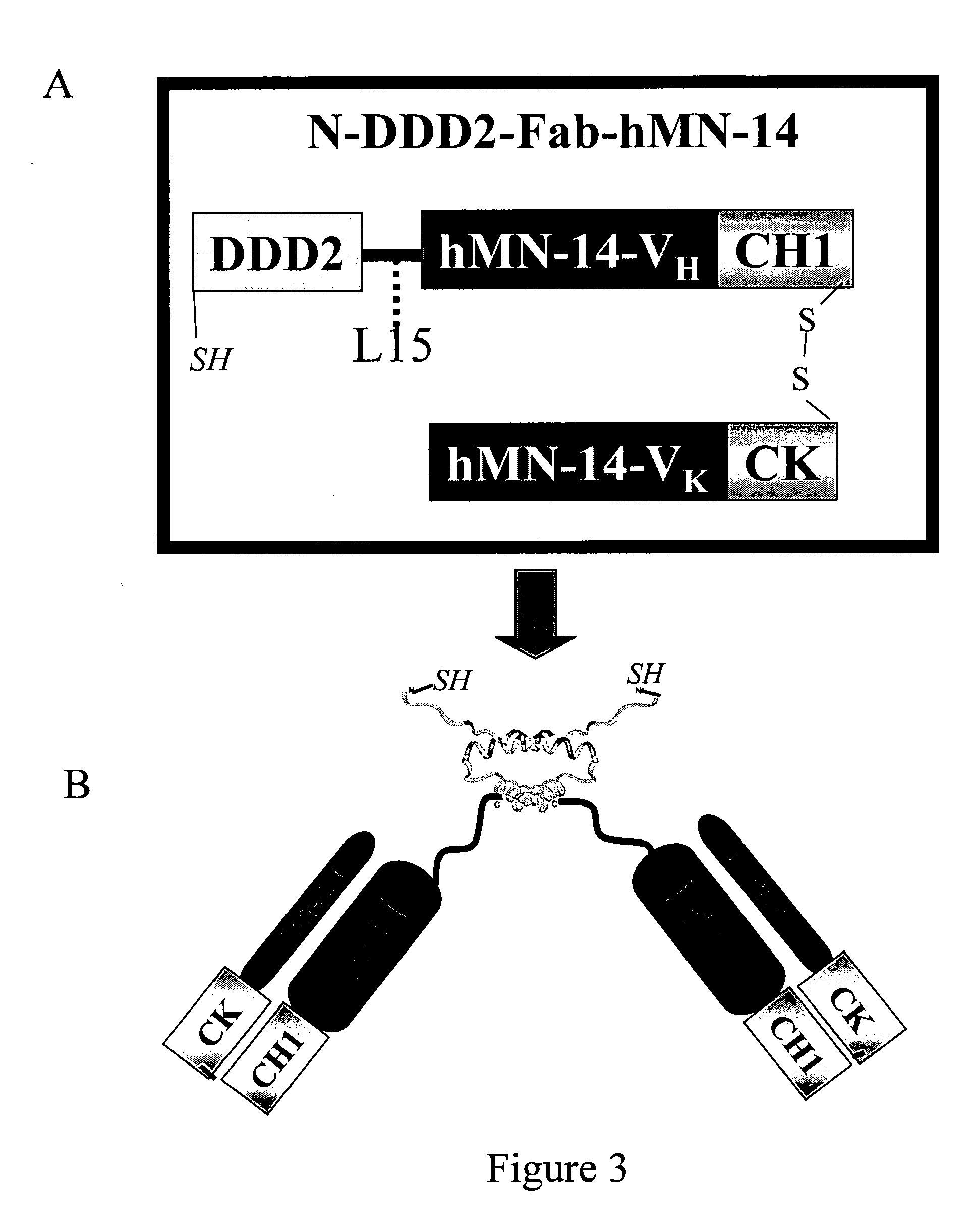
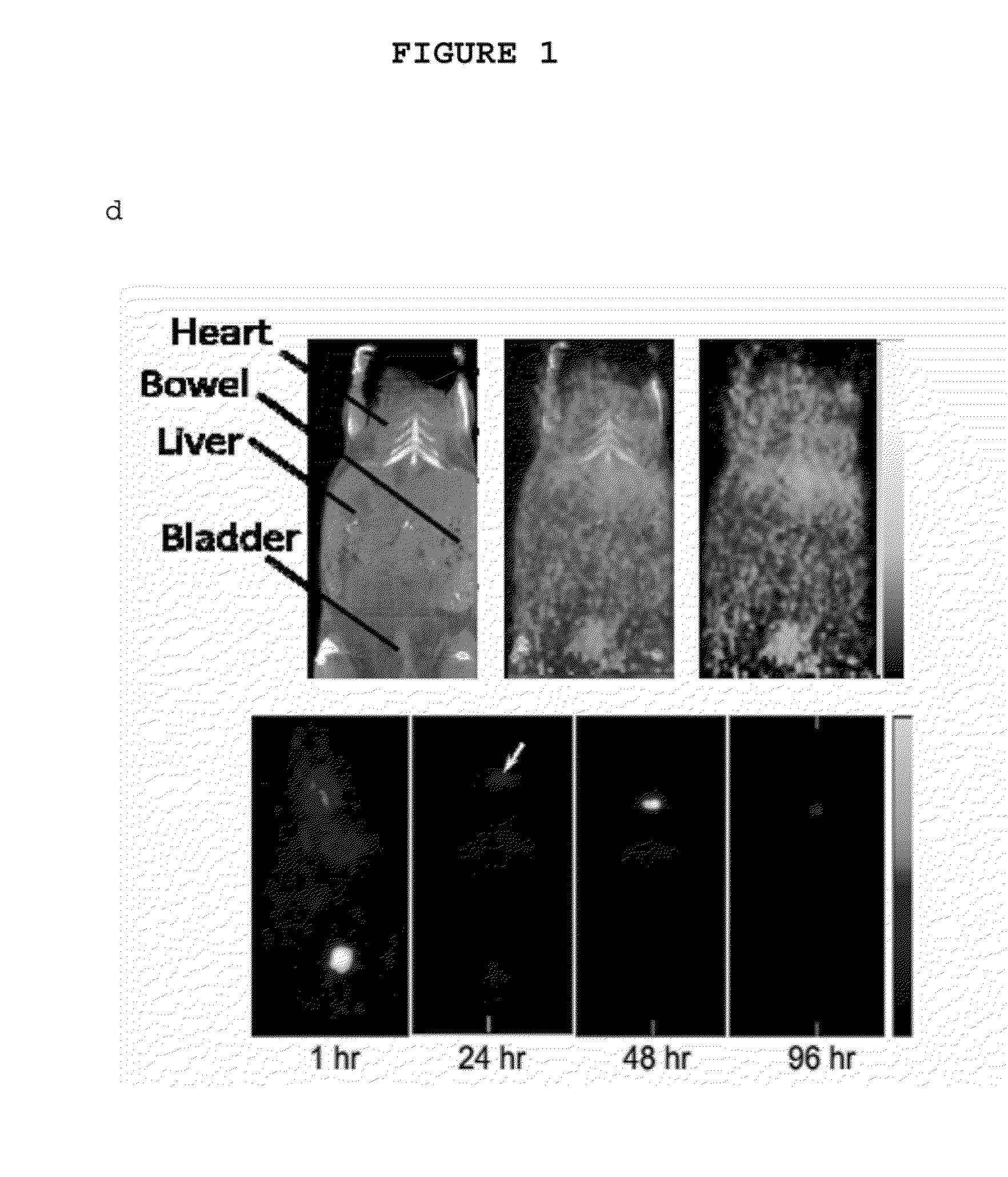
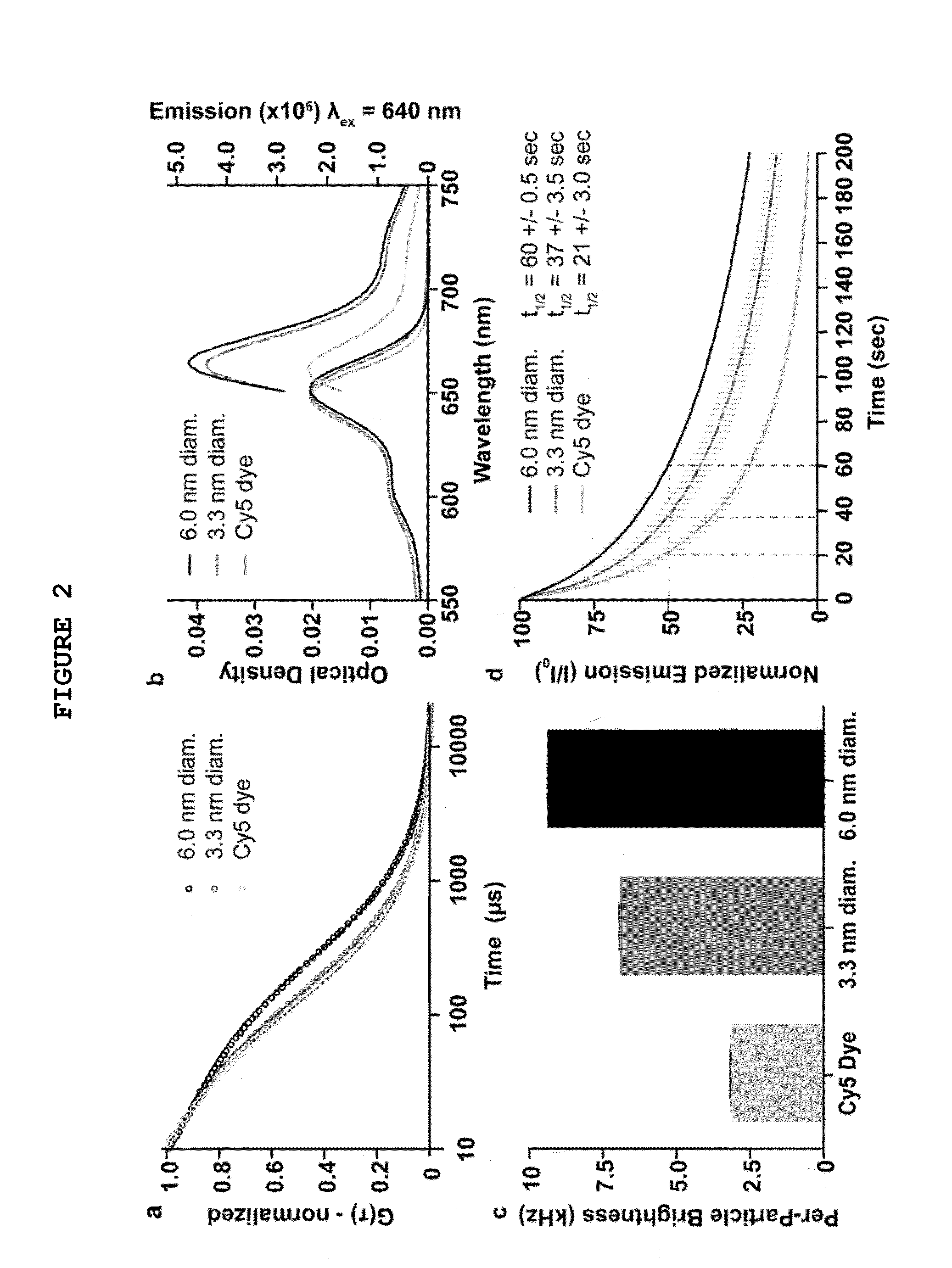
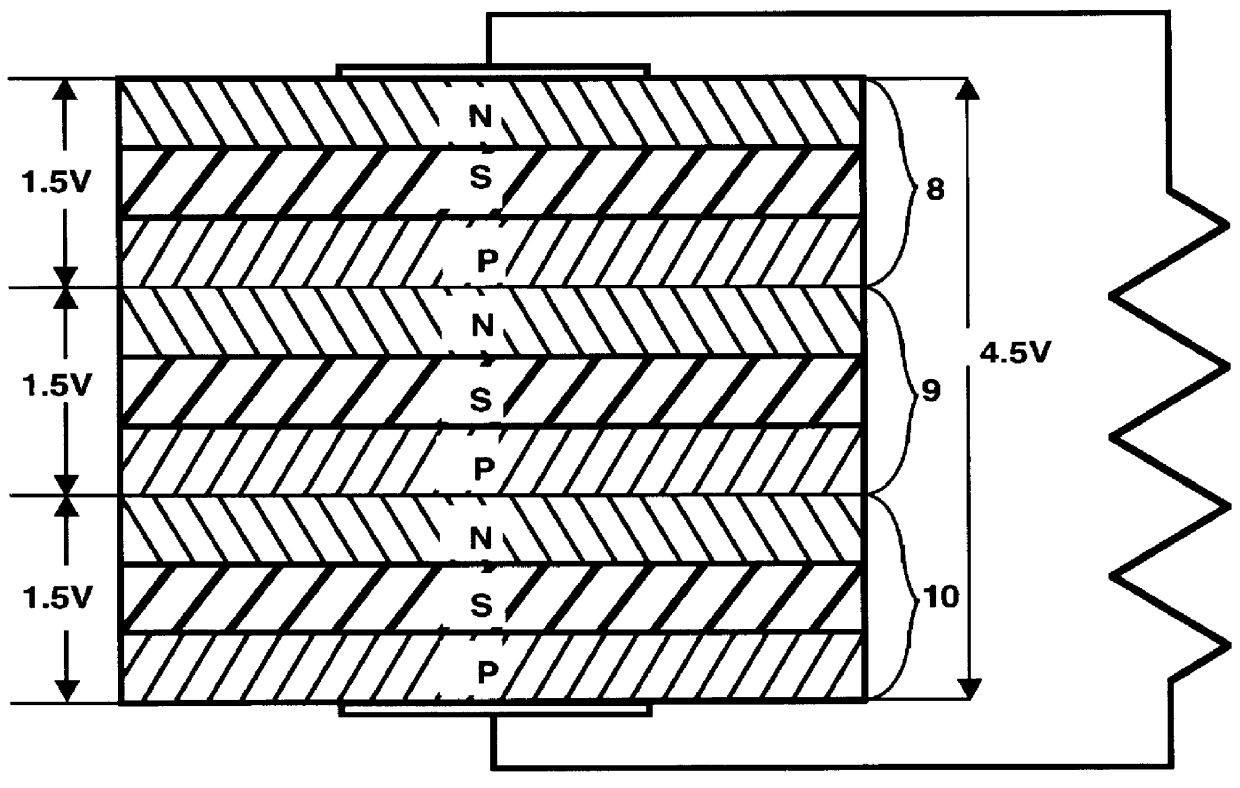
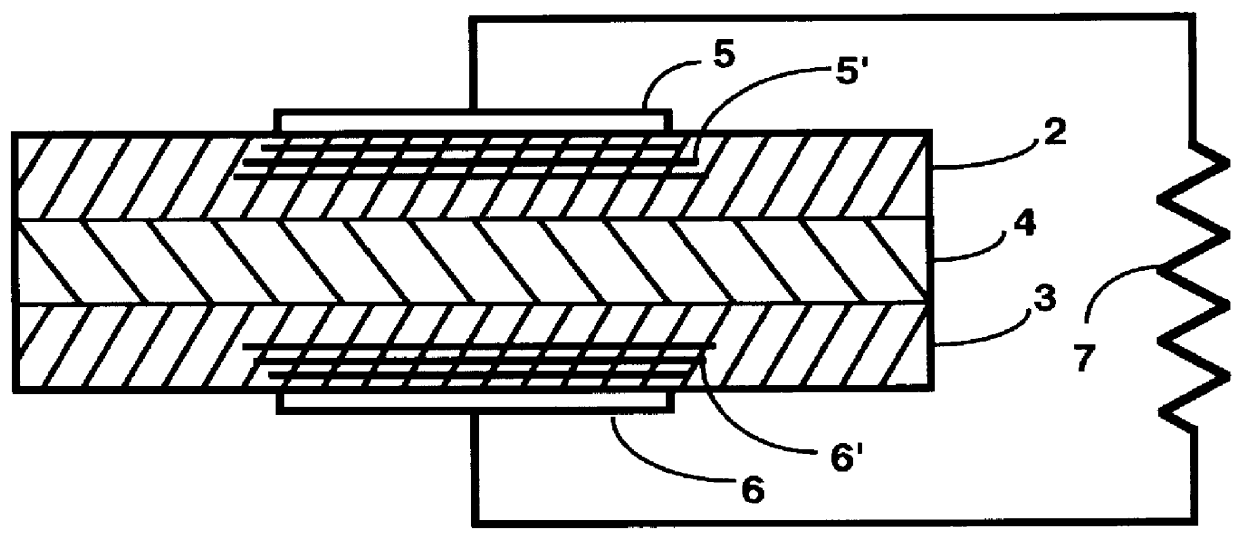
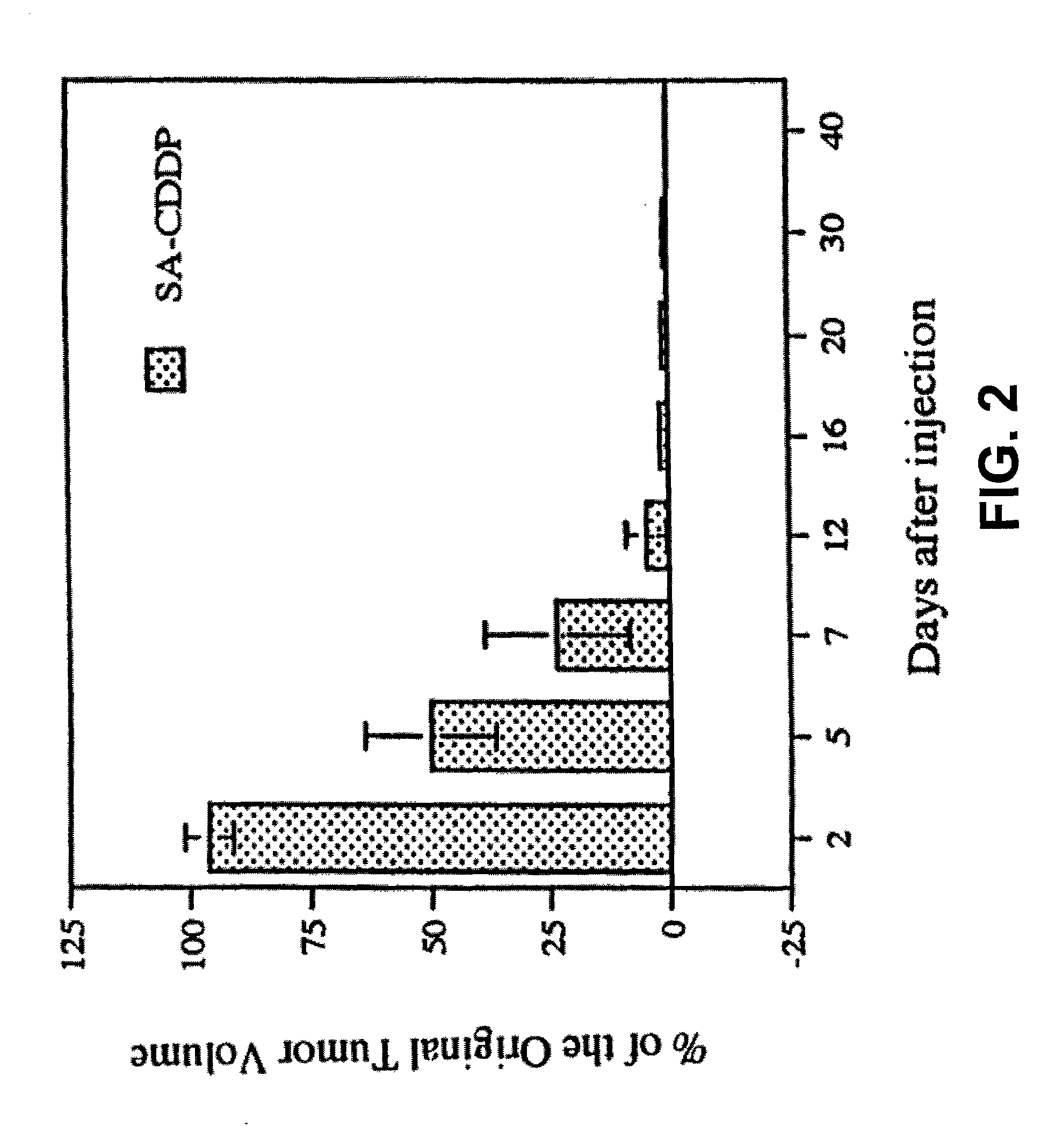
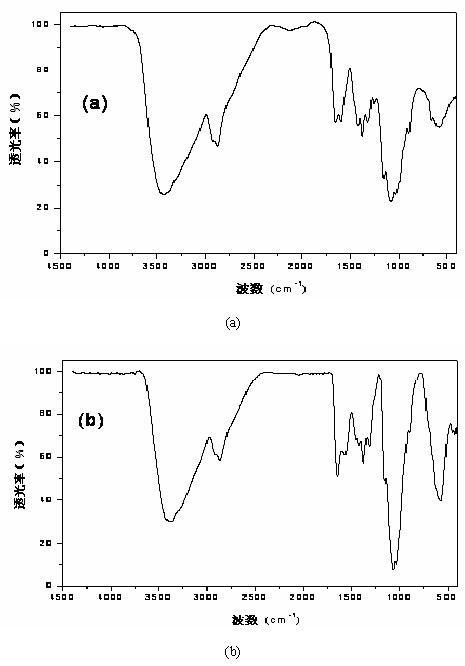
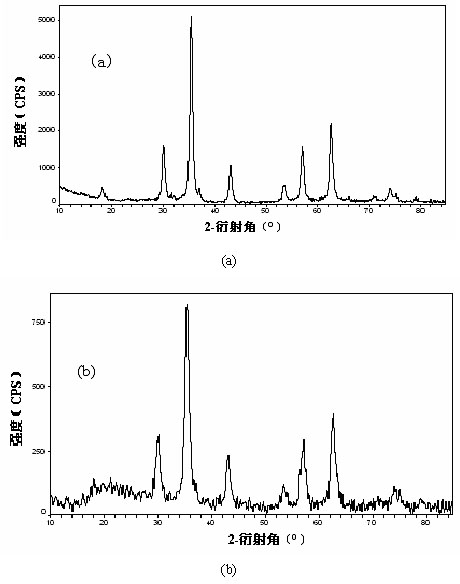
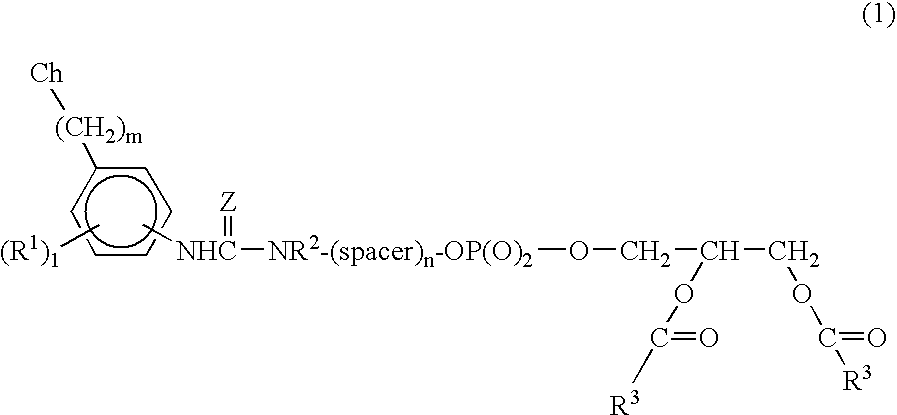Patents
Literature
793 results about "Radionuclide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is an atom that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are powerful enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single element the decay rate, and thus the half-life (t₁⸝₂) for that collection can be calculated from their measured decay constants. The range of the half-lives of radioactive atoms have no known limits and span a time range of over 55 orders of magnitude.
Multivalent immunoglobulin-based bioactive assemblies
ActiveUS7527787B2Efficacious for arrestingInhibition formationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseDiagnostic agent
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Multivalent immunoglobulin-based bioactive assemblies
ActiveUS20070140966A1Prevent further clot formationHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiagnostic agentAutoimmune condition
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions, which may have multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Preferred embodiments concern hexameric stably tethered structures comprising one or more IgG antibody fragments and which may be monospecific or bispecific. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a facile and general way to obtain stably tethered structures of virtually any functionality and / or binding specificity. The stably tethered structures may be administered to subjects for diagnostic and / or therapeutic use, for example for treatment of cancer or autoimmune disease. The stably tethered structures may bind to and / or be conjugated to a variety of known effectors, such as drugs, enzymes, radionuclides, therapeutic agents and / or diagnostic agents.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Vitamin-targeted imaging agents
ActiveUS7128893B2Easy to getProducing cost is highPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersVitamin receptorSide chain
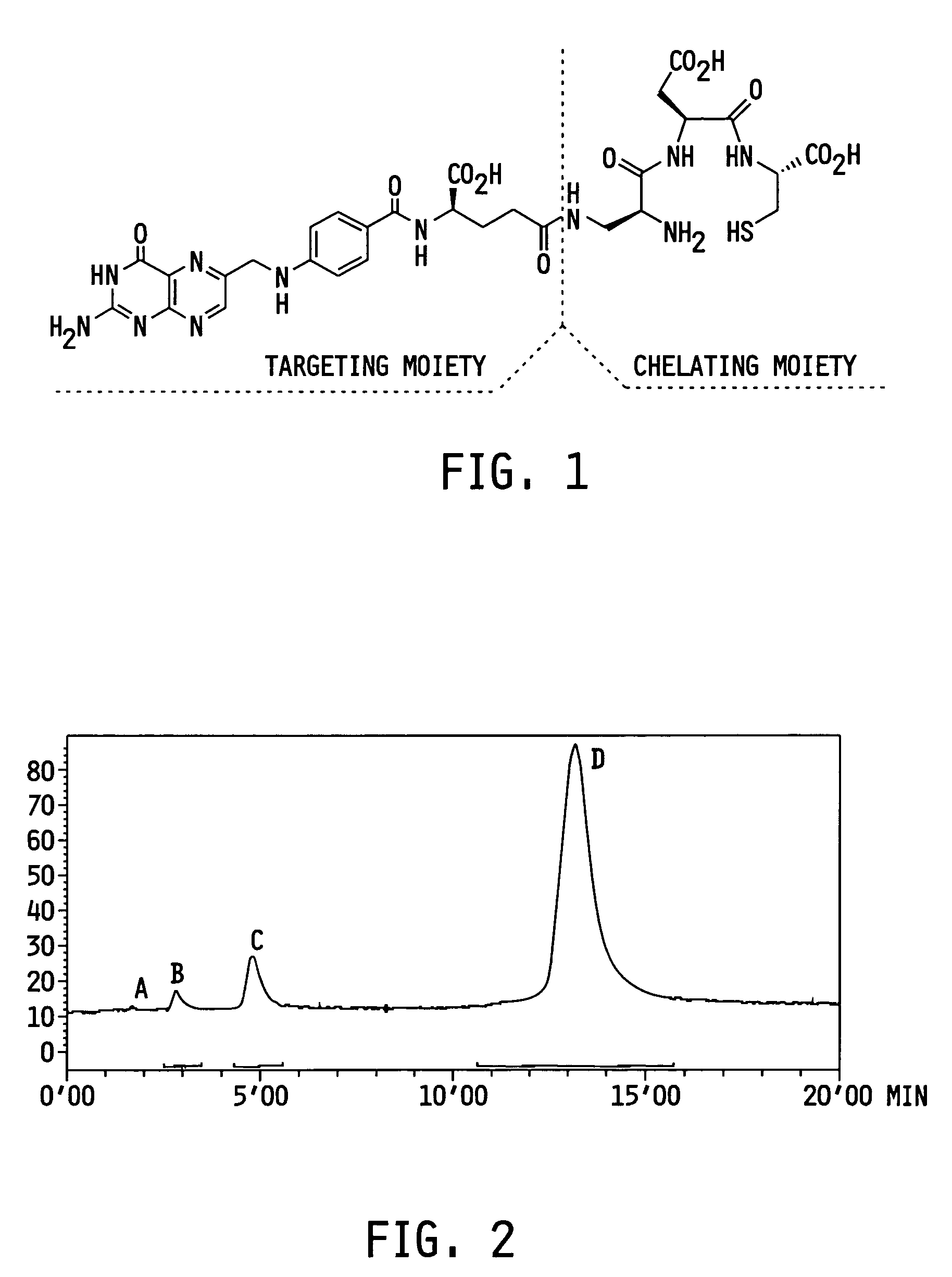
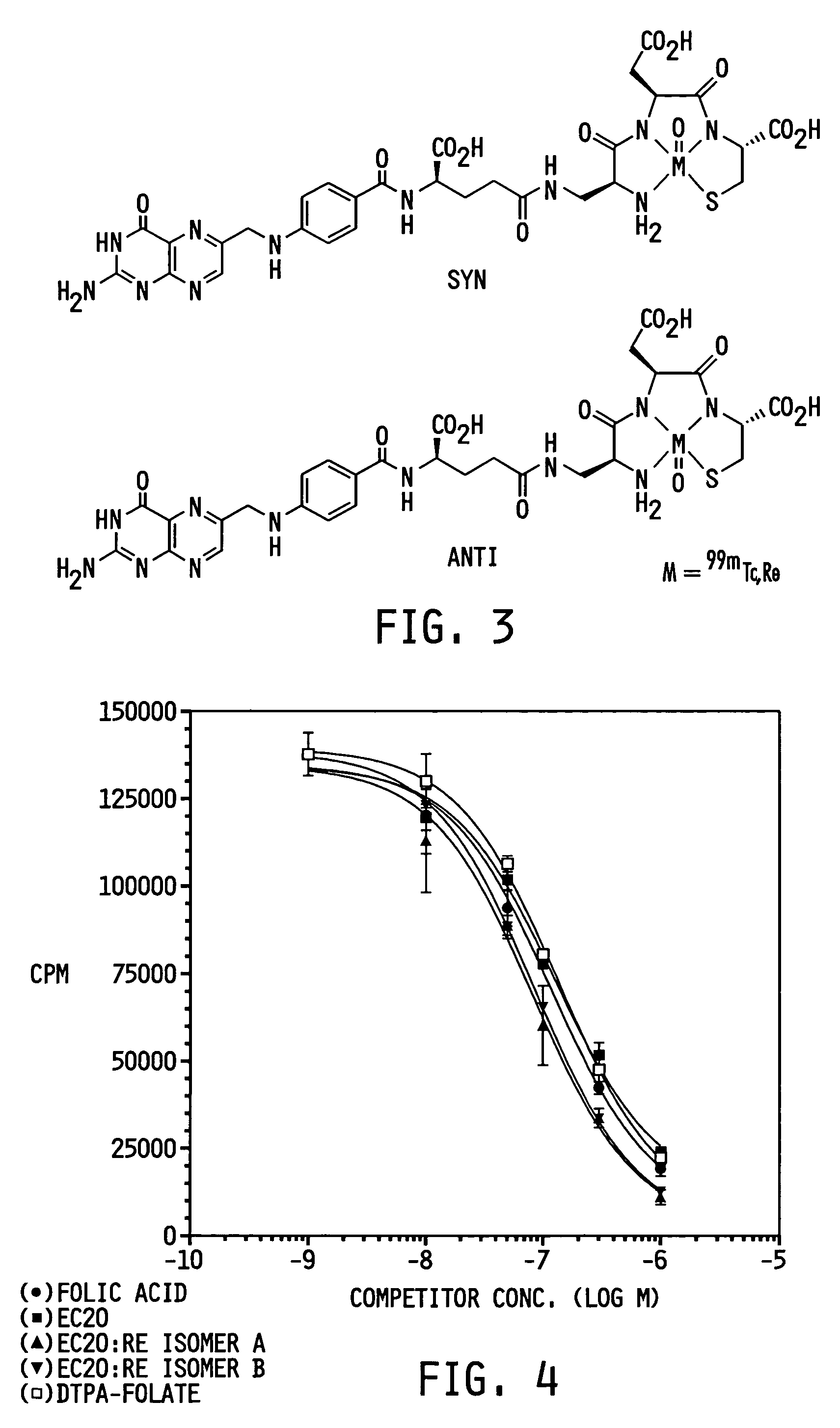
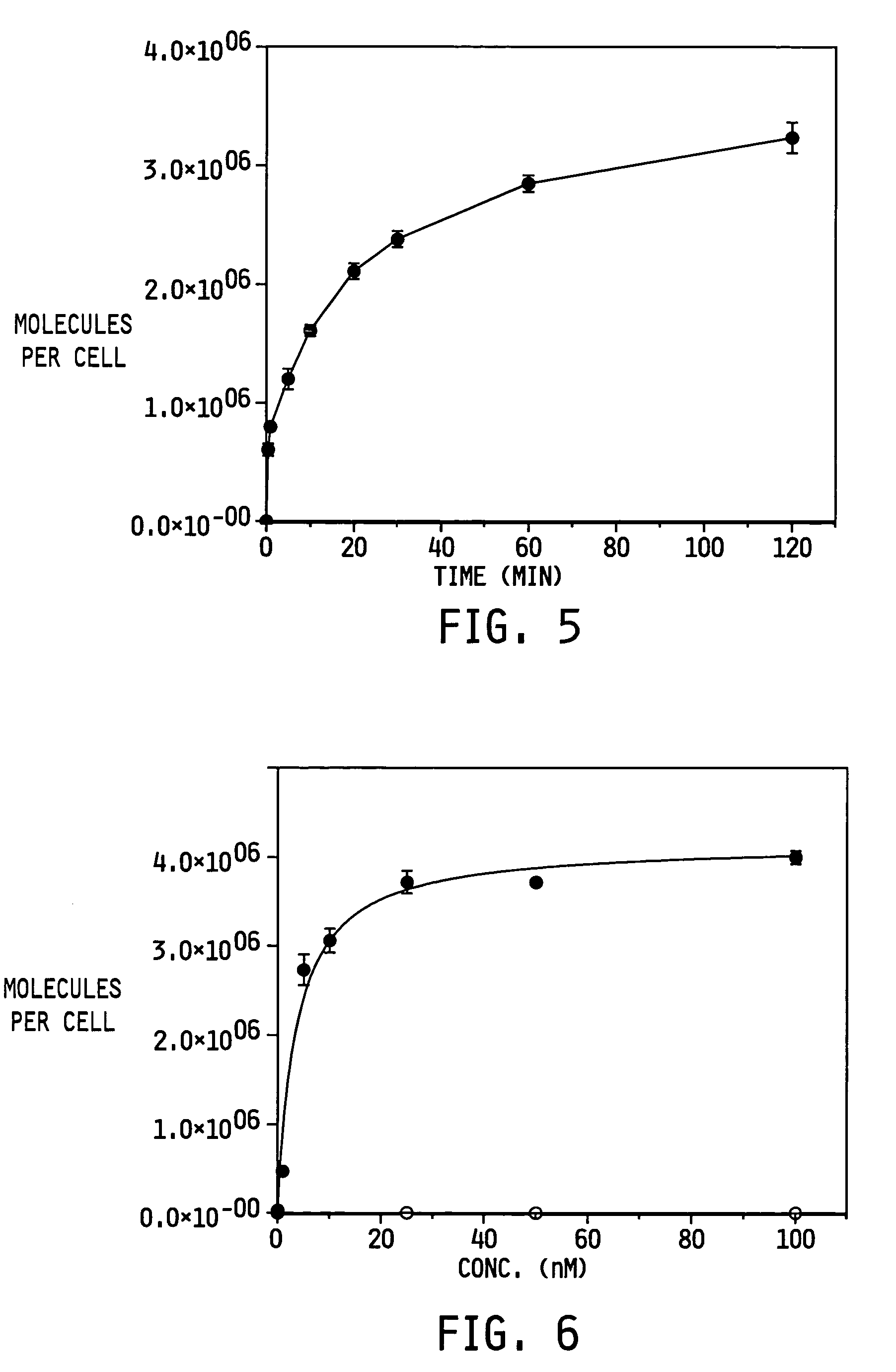
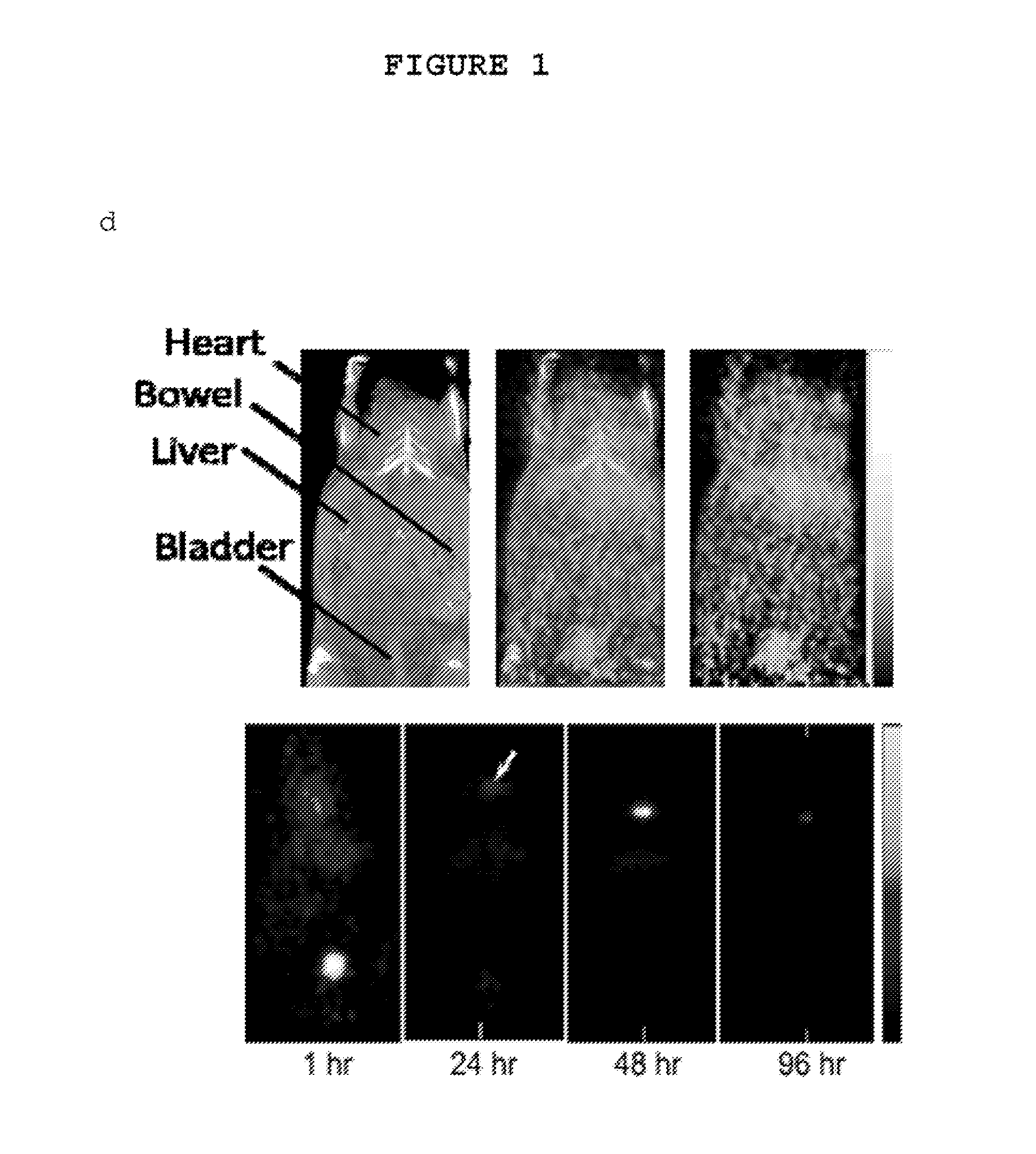
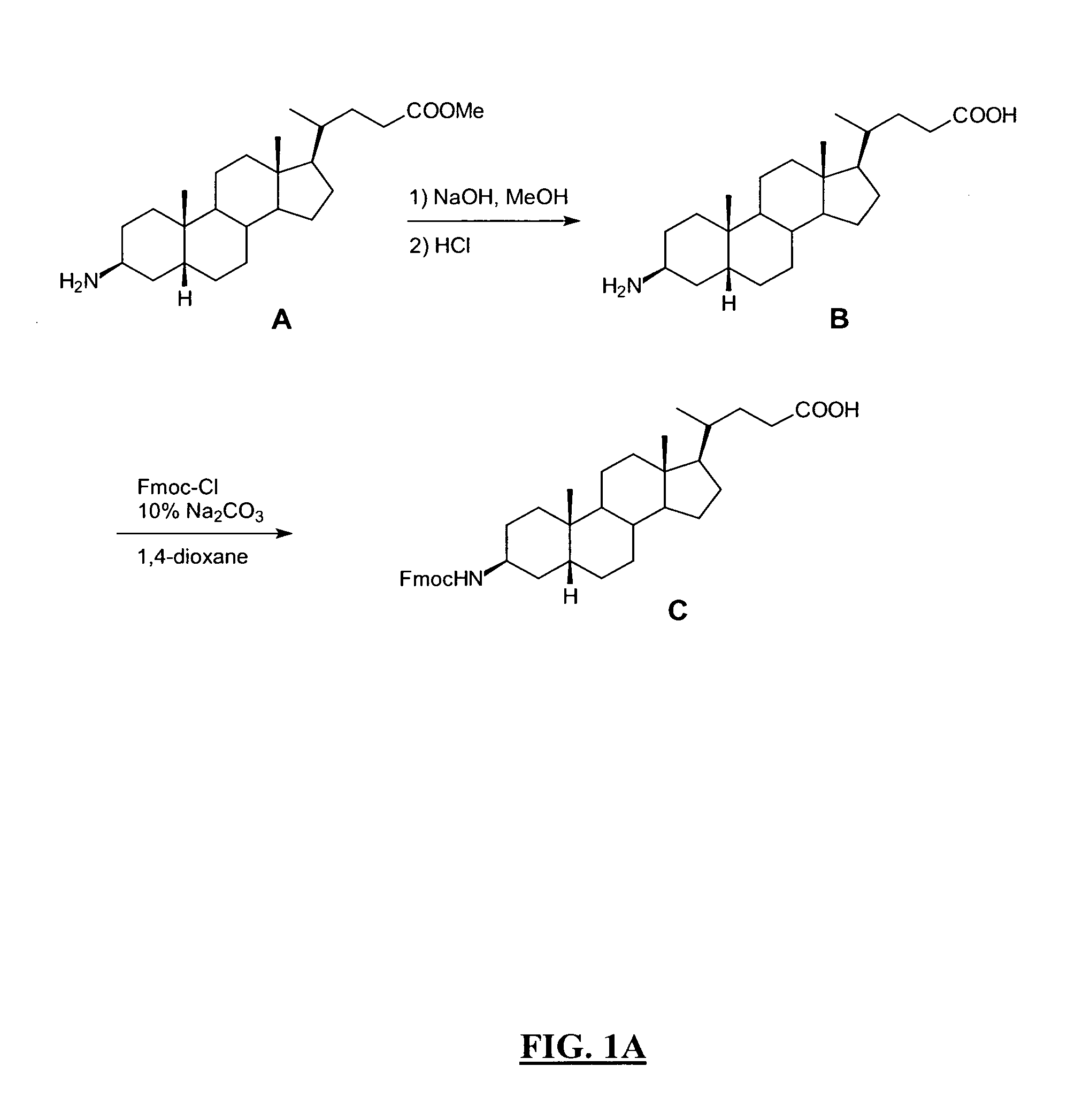
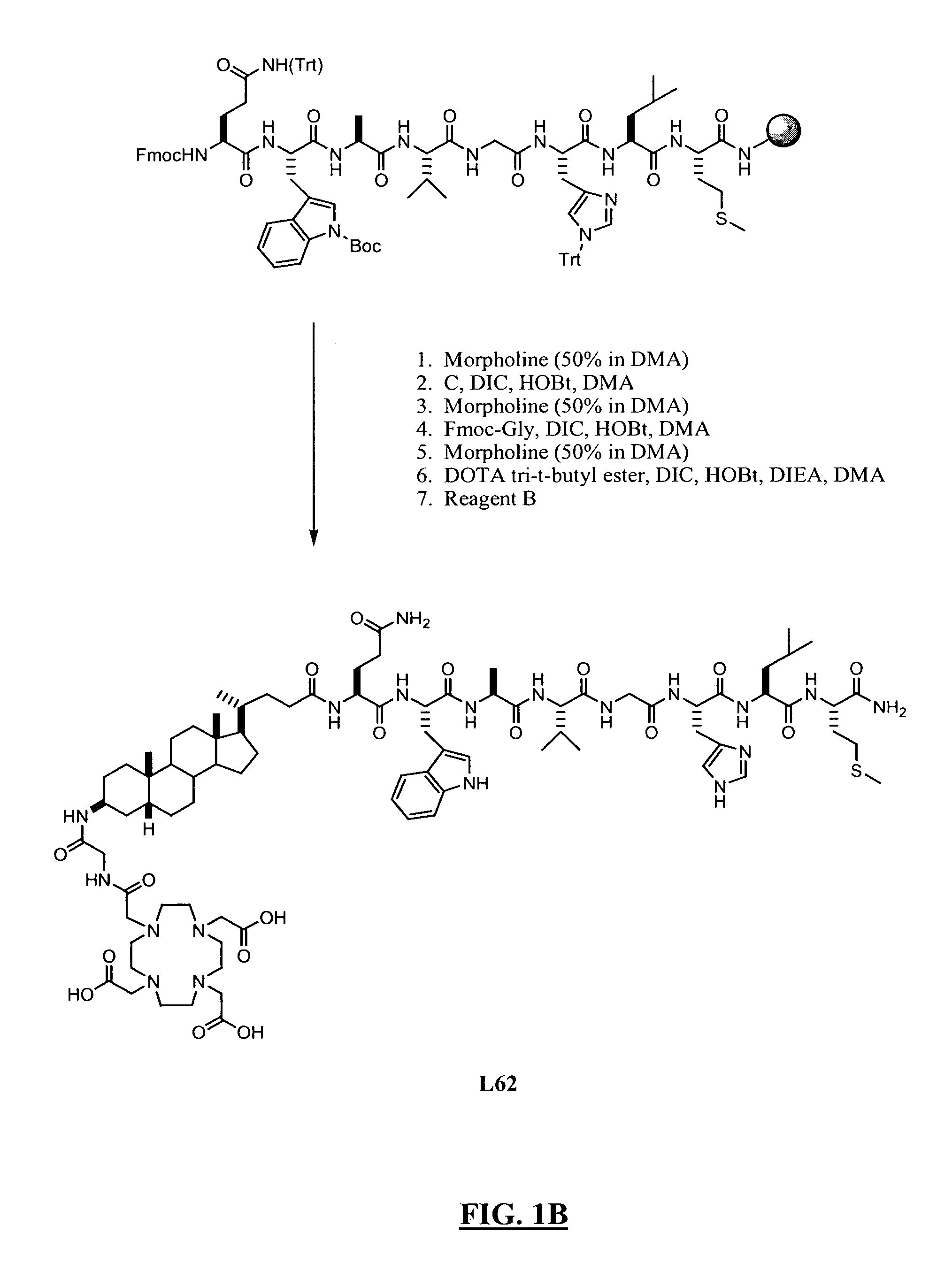
The invention relates to compounds and methods for targeting radionuclide-based imaging agents to cells having receptors for a vitamin, or vitamin receptor binding derivative or analog thereof, by using such a vitamin as the targeting ligand for the imaging agent. The invention provides a compound of the formulafor use in such methods. In the compound, V is a vitamin that is a substrate for receptor-mediated transmembrane transport in vivo, or a vitamin receptor binding derivative or analog thereof, L is a divalent linker, R is a side chain of an amino acid, M is a cation of a radionuclide, n is 1 or 0, K is 1 or 0, and the compound can be in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier therefor. The vitamin-based compounds can be used to target radionuclides to cells, such as a variety of tumor cell types, for use in diagnostic imaging of the targeted cells.
Owner:ENDOCTYE INC
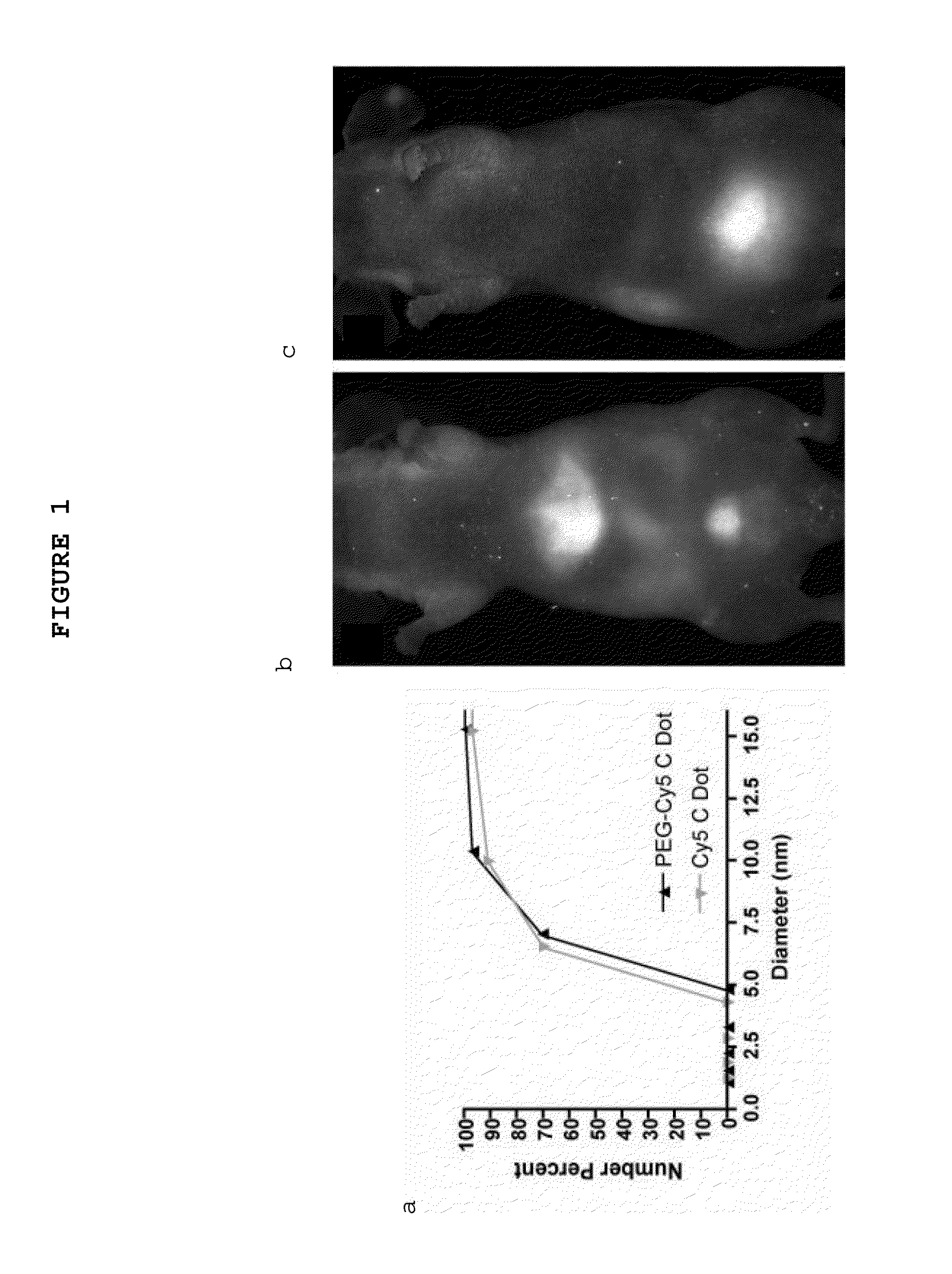
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20130039848A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseCellular component
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as polyethylene glycol) (PEG) The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo The nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker A therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle Radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle to permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by various imaging techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
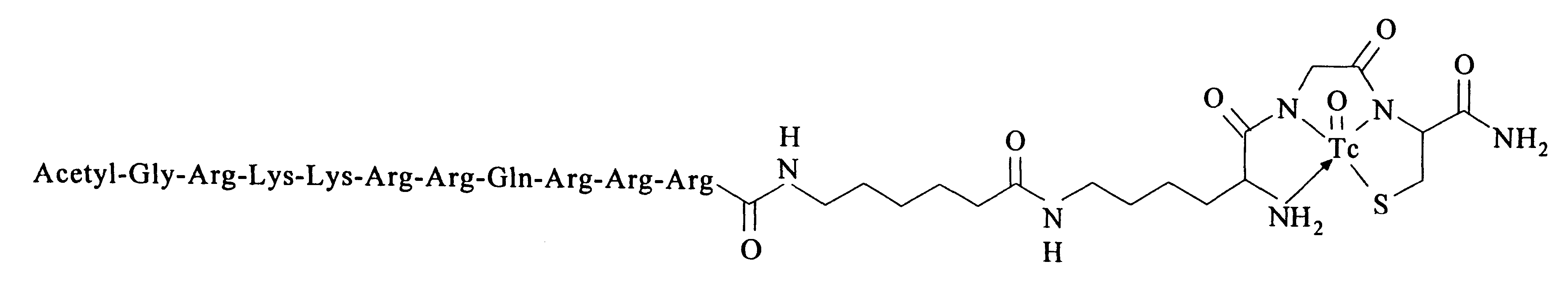
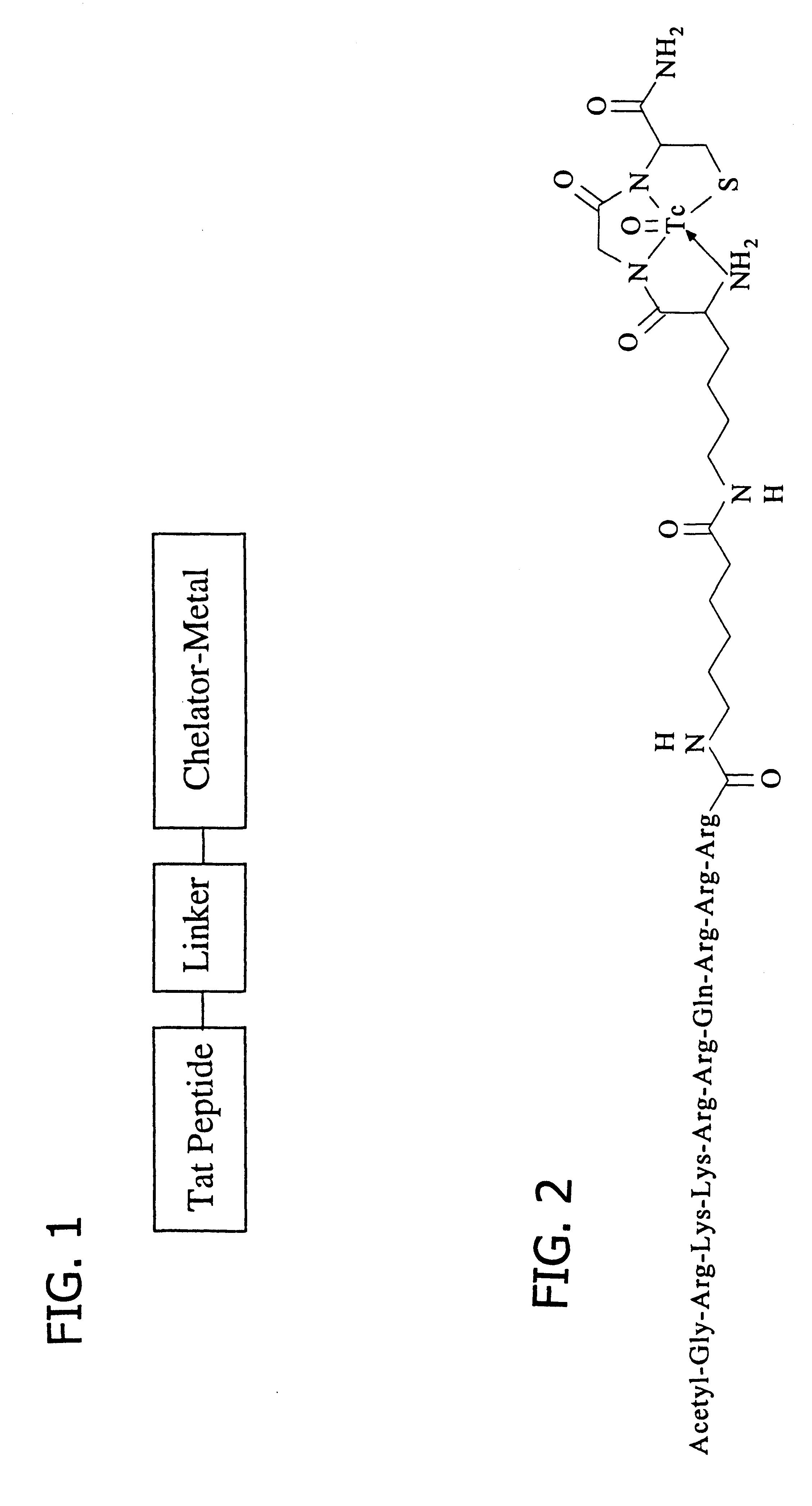
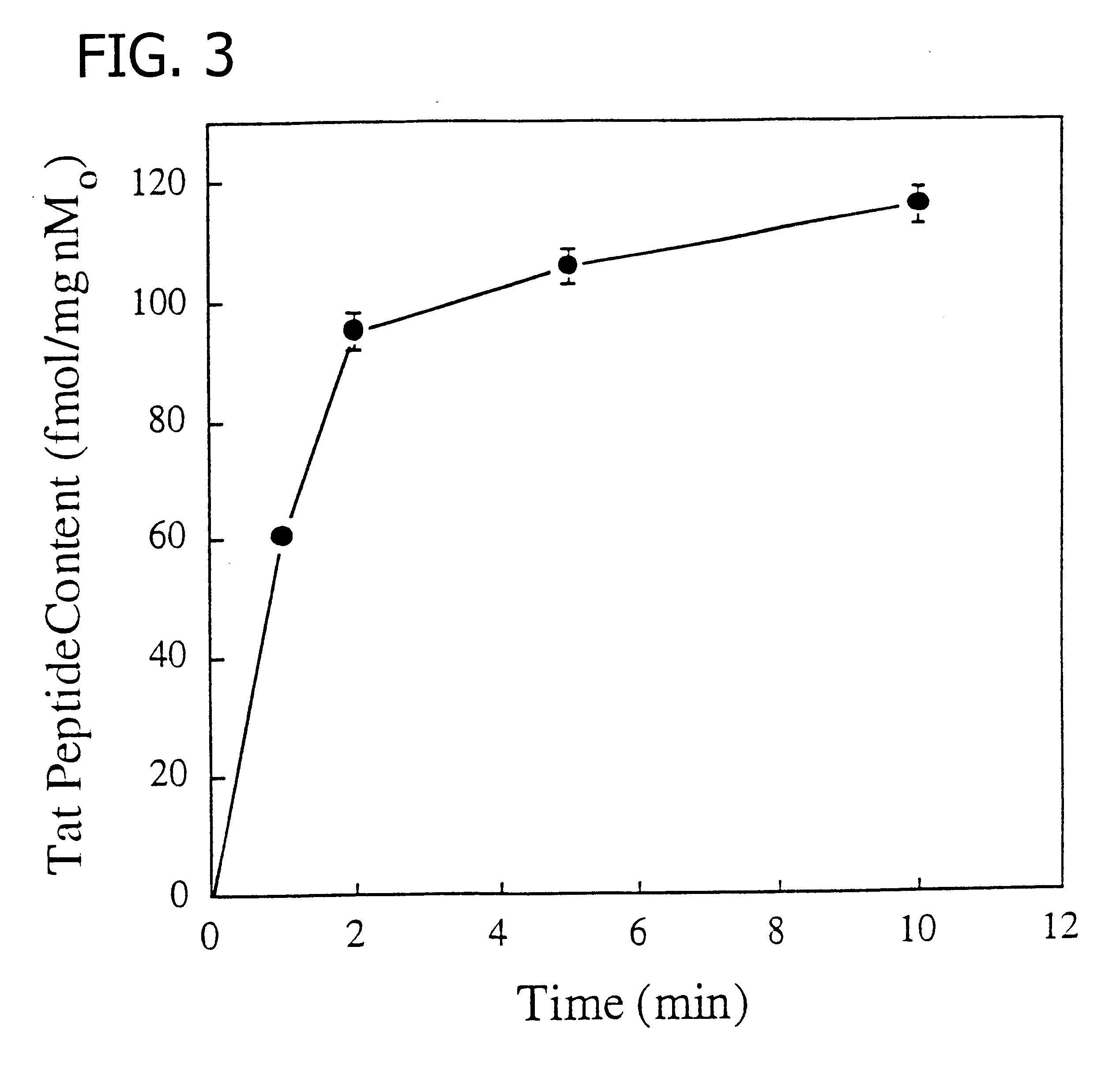
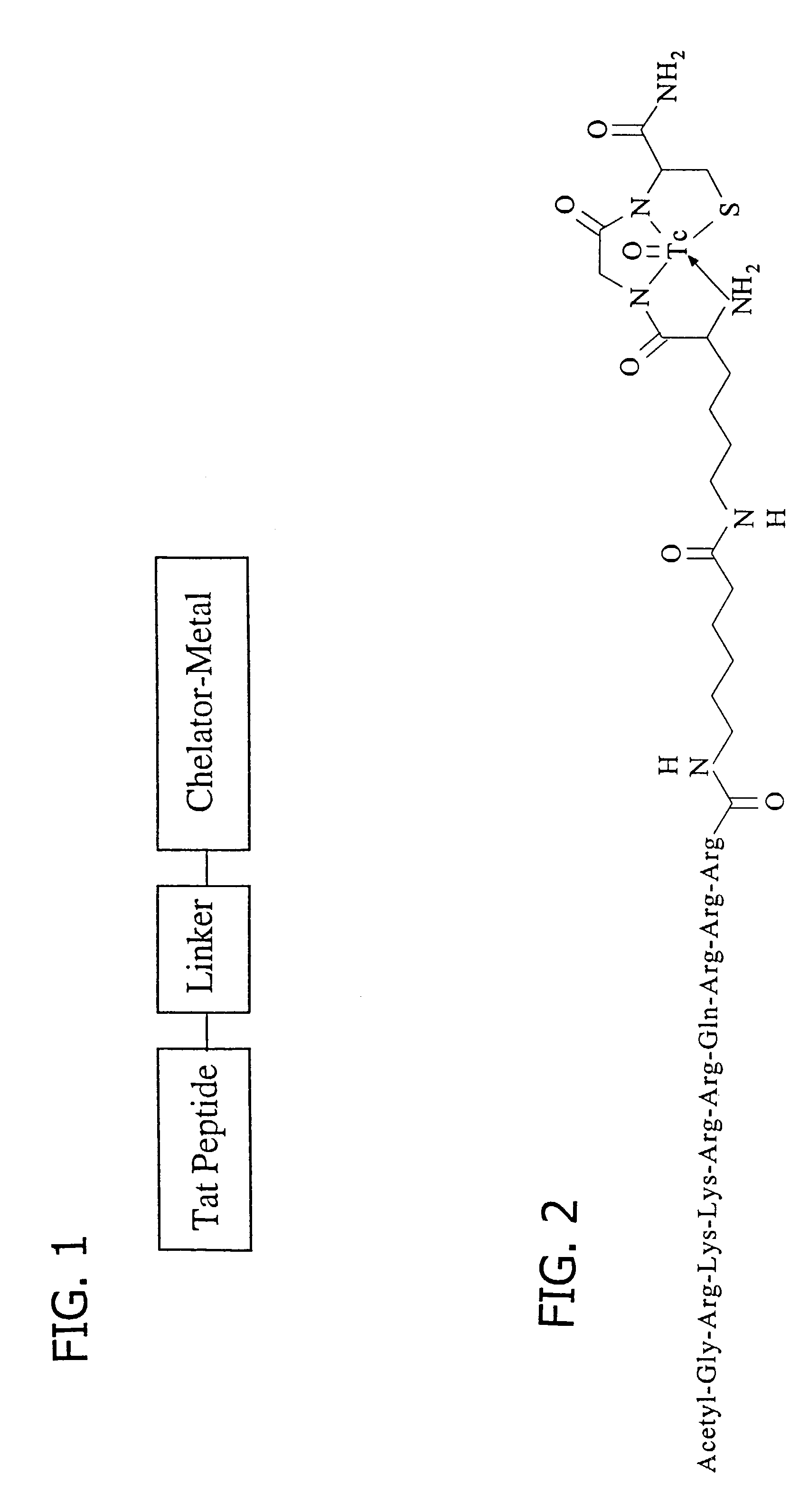
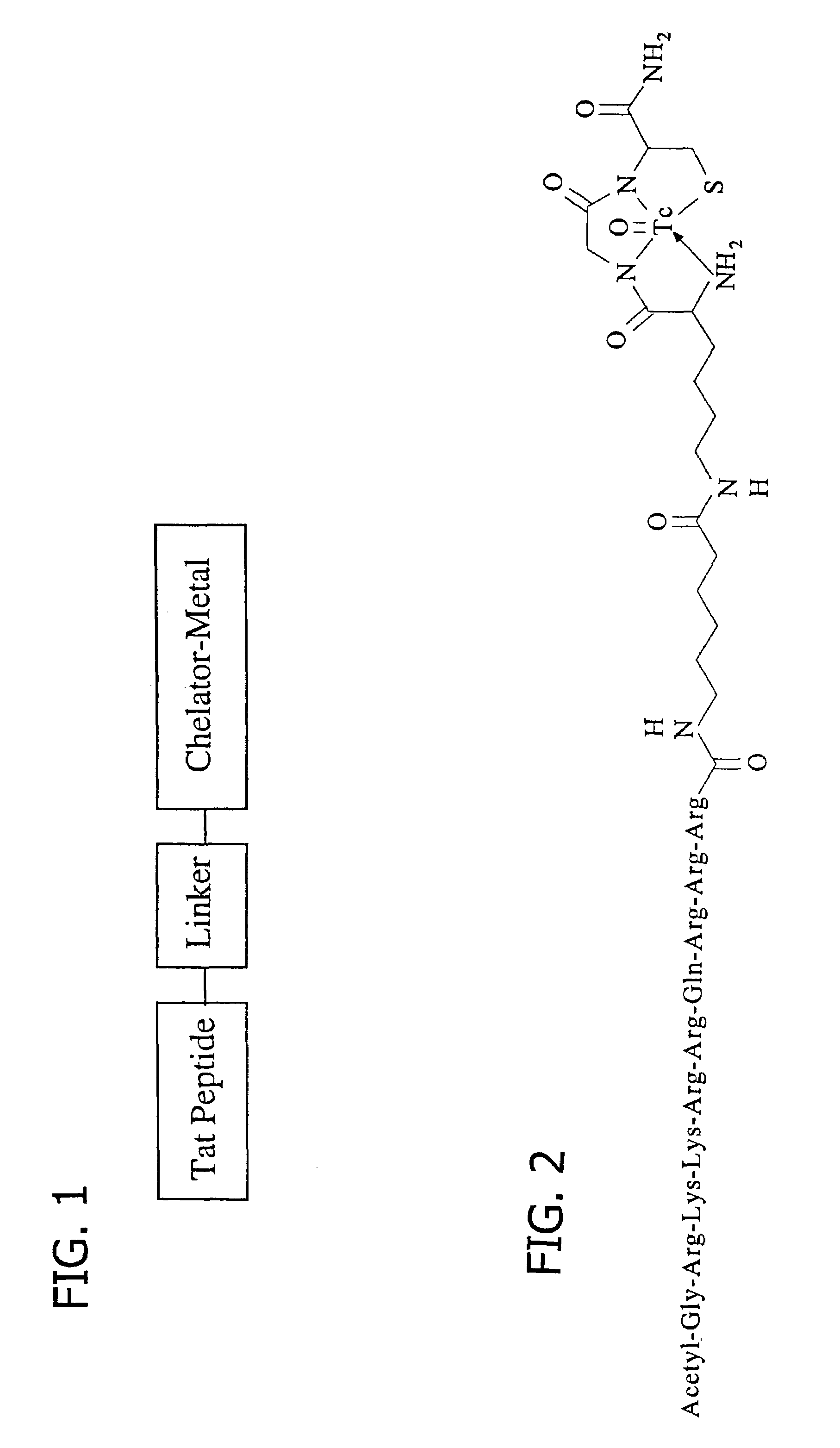
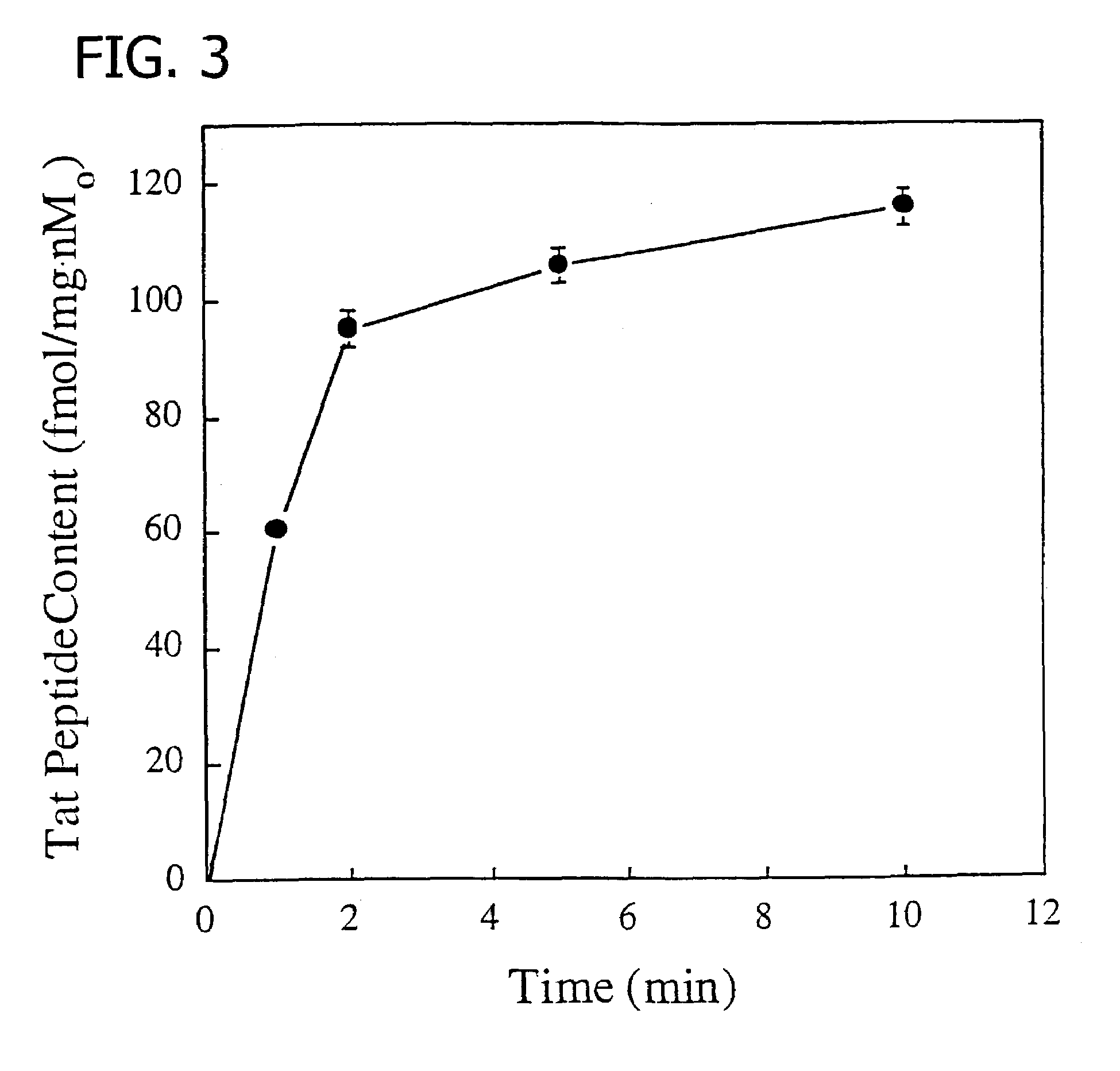
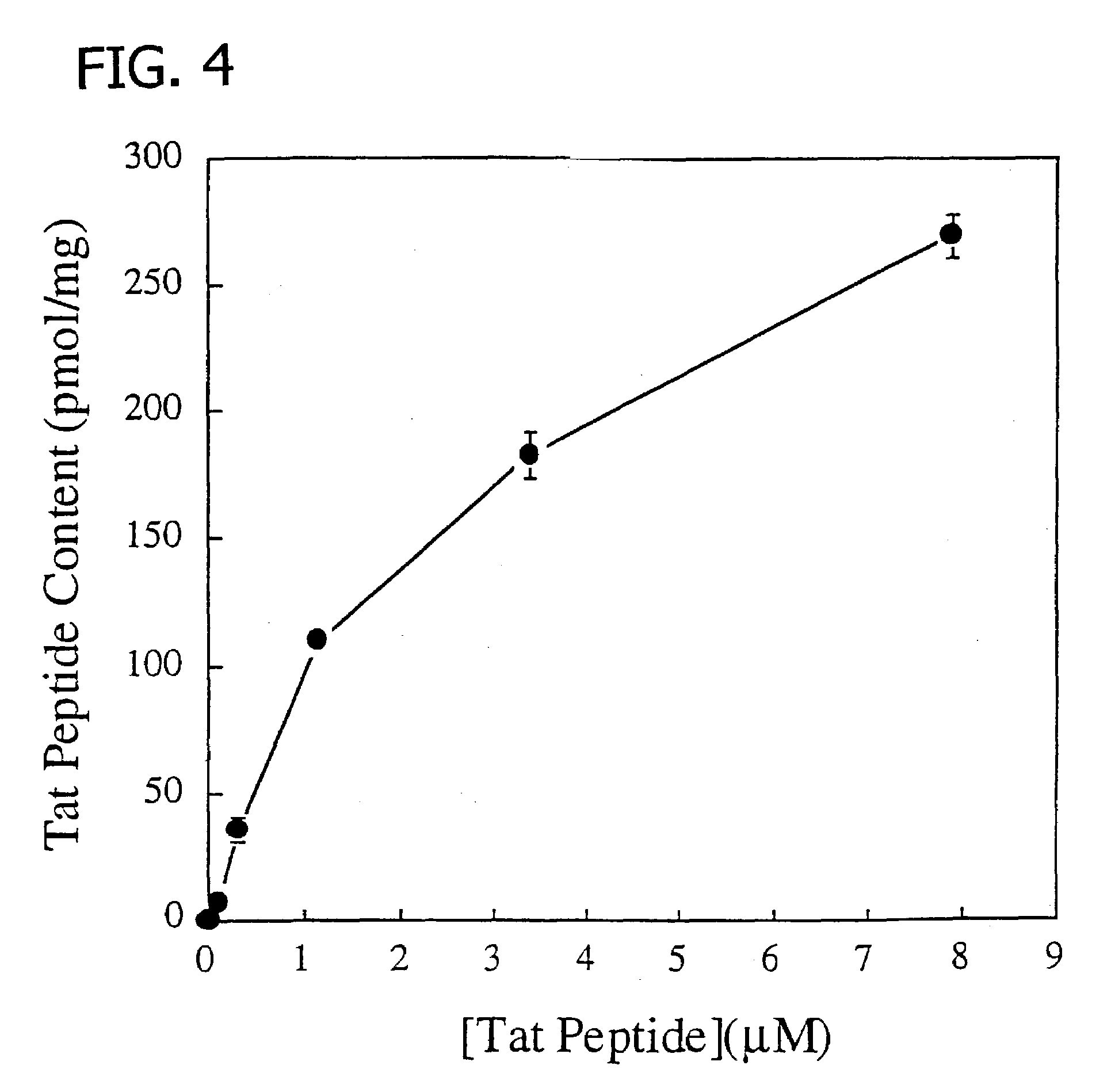
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
InactiveUS7306783B2Accelerate the accumulation processImprove clearance rateVirusesHydrolasesCell membraneMedical imaging
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Detection of necrotic malignant tissue and associated therapy
InactiveUS6017514AGuaranteed monitoring effectShrink tumorPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
Disclosed is a method for measuring the effectiveness of therapy intended to kill malignant cells in vivo in a mammal, comprising the steps of obtaining monoclonal antibody that is specific to an internal cellular component of the mammal but not to external cellular components, wherein the monoclonal antibody is labeled; contacting the labeled antibody with tissue of a mammal that has received therapy to kill malignant cells in vivo, and determining the effectiveness of the therapy by measuring the binding of the labeled antibody to the internal cellular component. The internal cellular component is preferably insoluble intracellular antigen, and the label is preferably a radionuclide, a radiopaque material, or a magnetic resonance-enhancing material. Also disclosed is a method whereby the antibody to insoluble intracellular antigen is conjugated to an antineoplastic agent, so that upon administration of the antibody-antineoplastic agent conjugate, antineoplastic agent may be delivered to the tumor. Also disclosed are antibodies for use with the foregoing methods.
Owner:PEREGRINE PHARMA INC +1
Conjugation methods
ActiveUS20110003969A1Reduce potential steric hindrancePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsBiochemistryAntibody
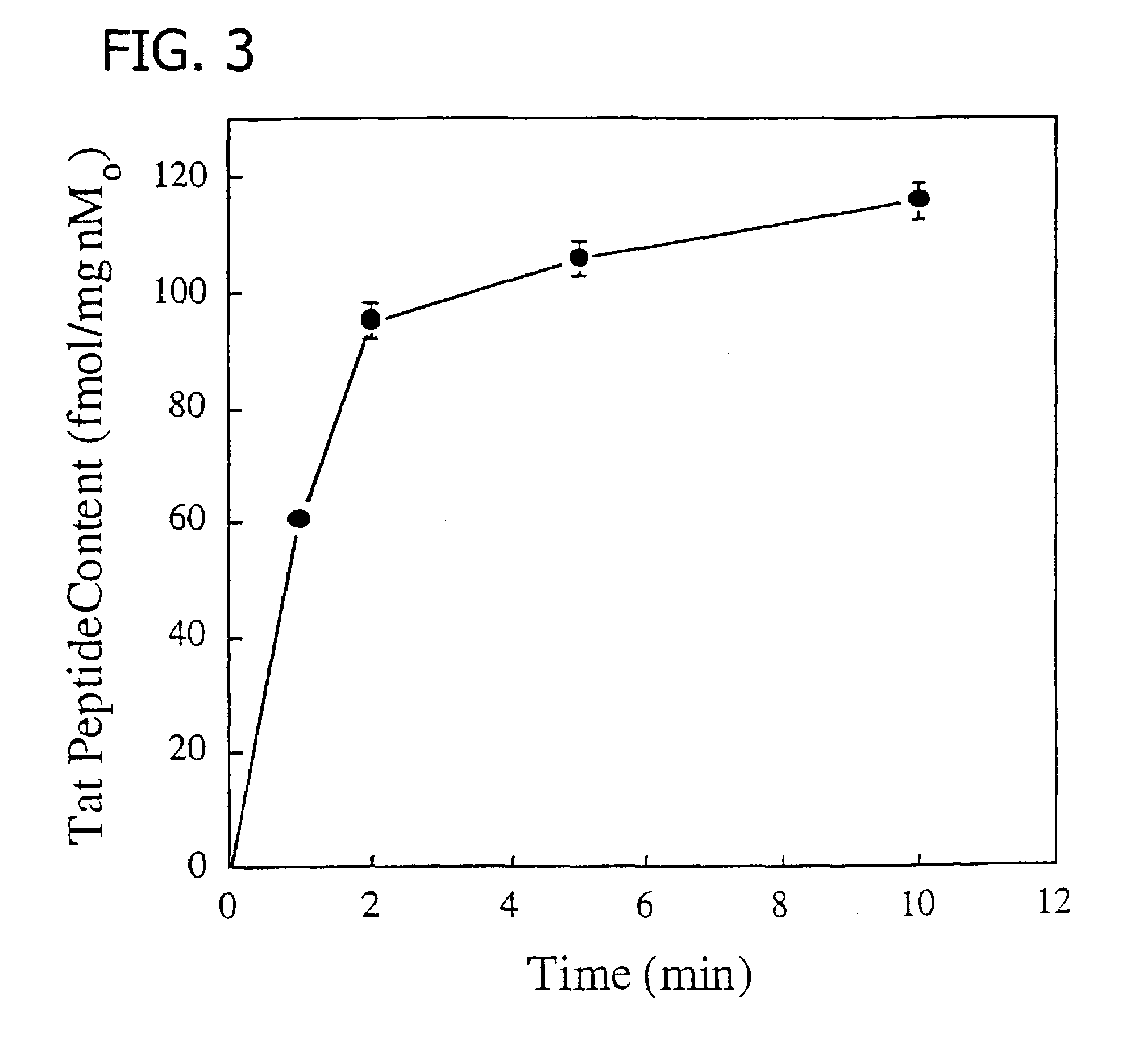
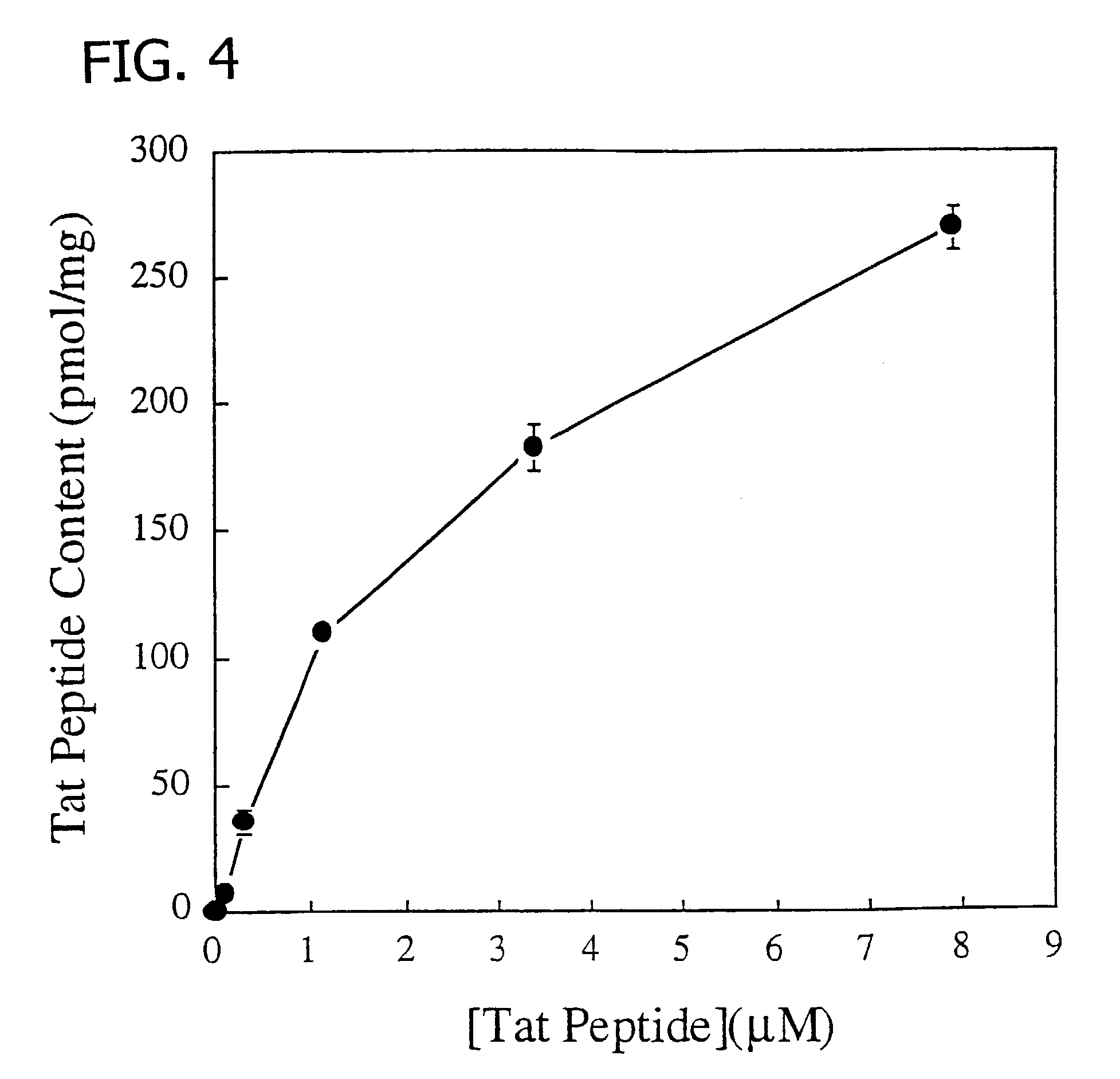
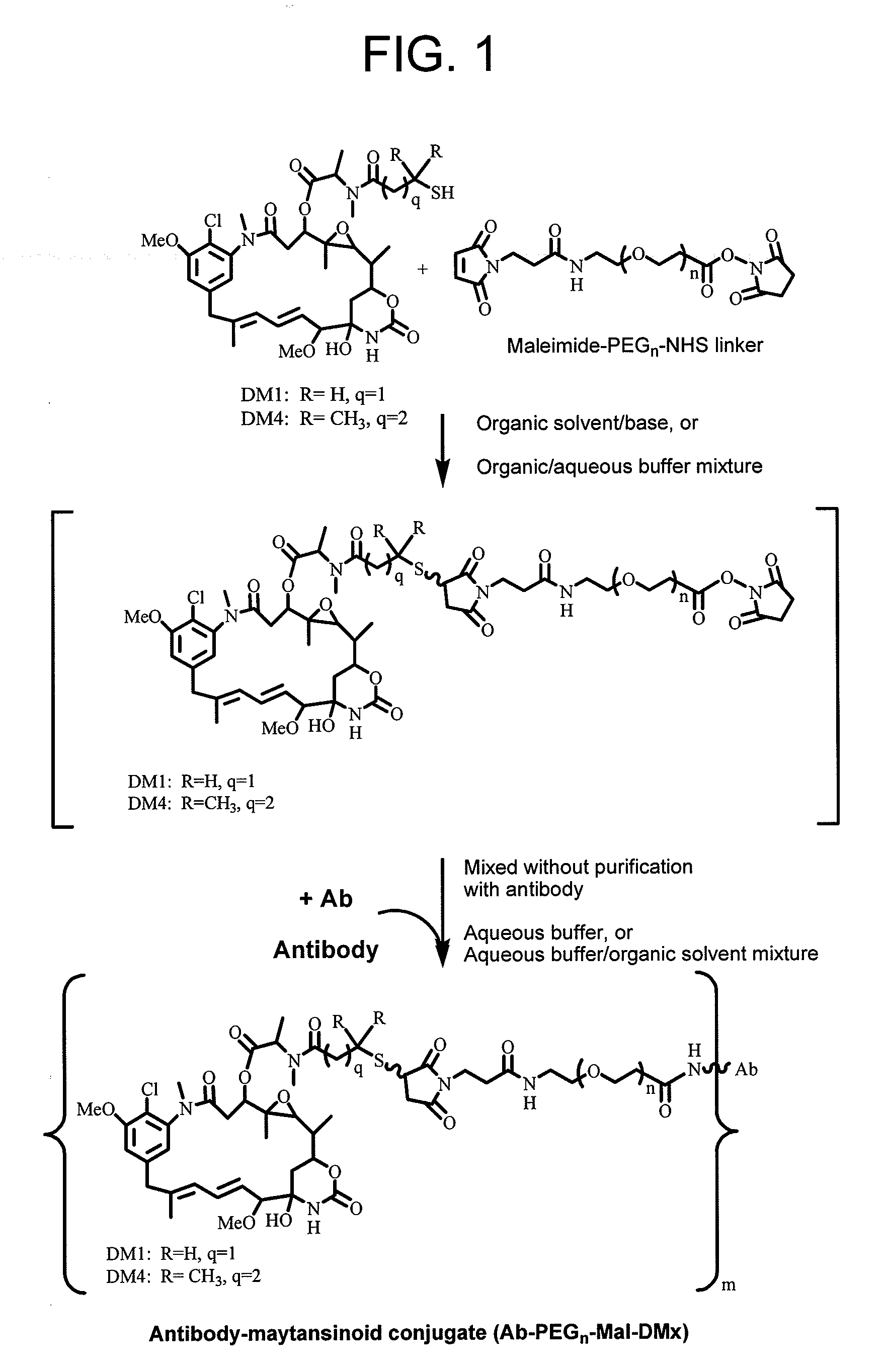
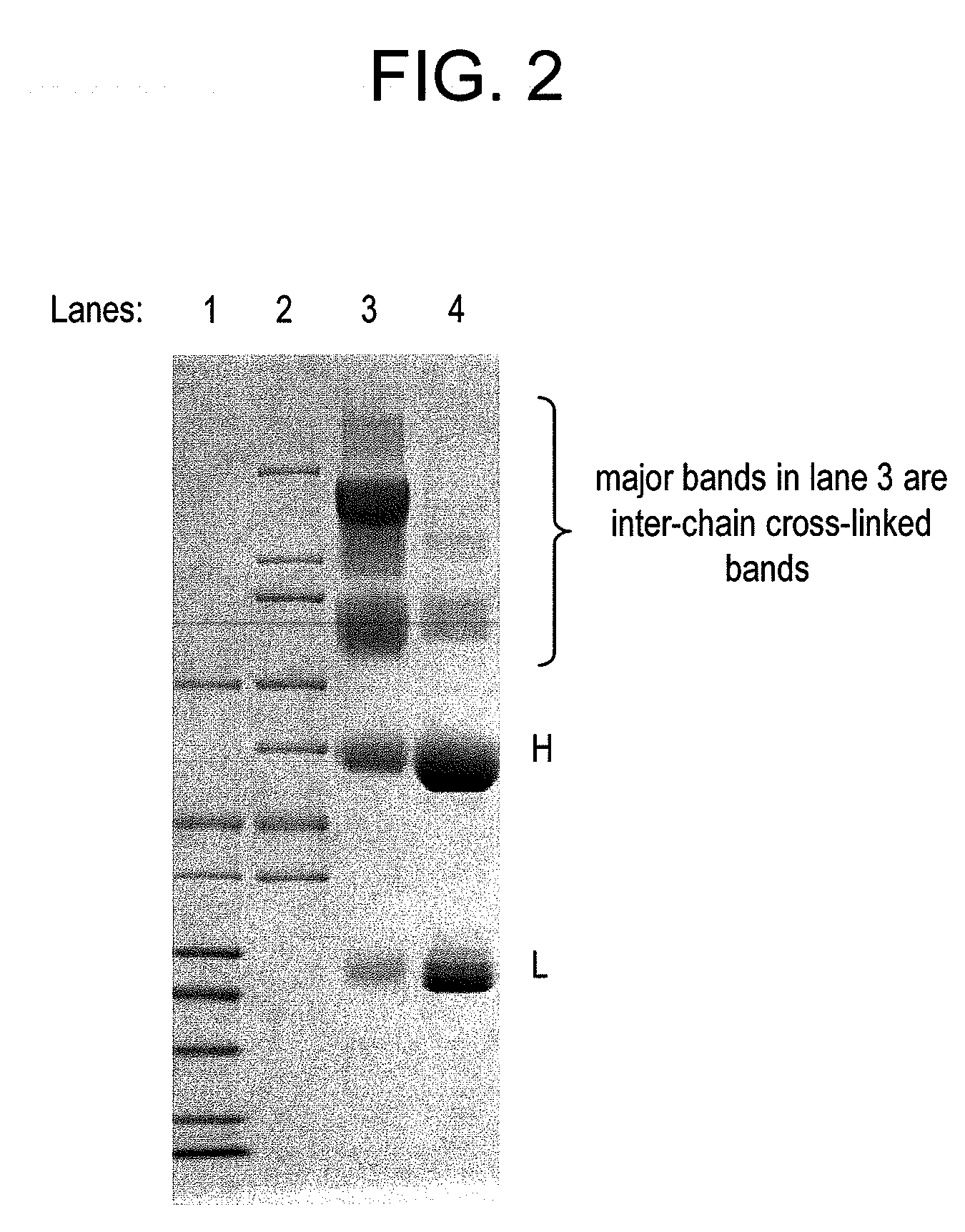
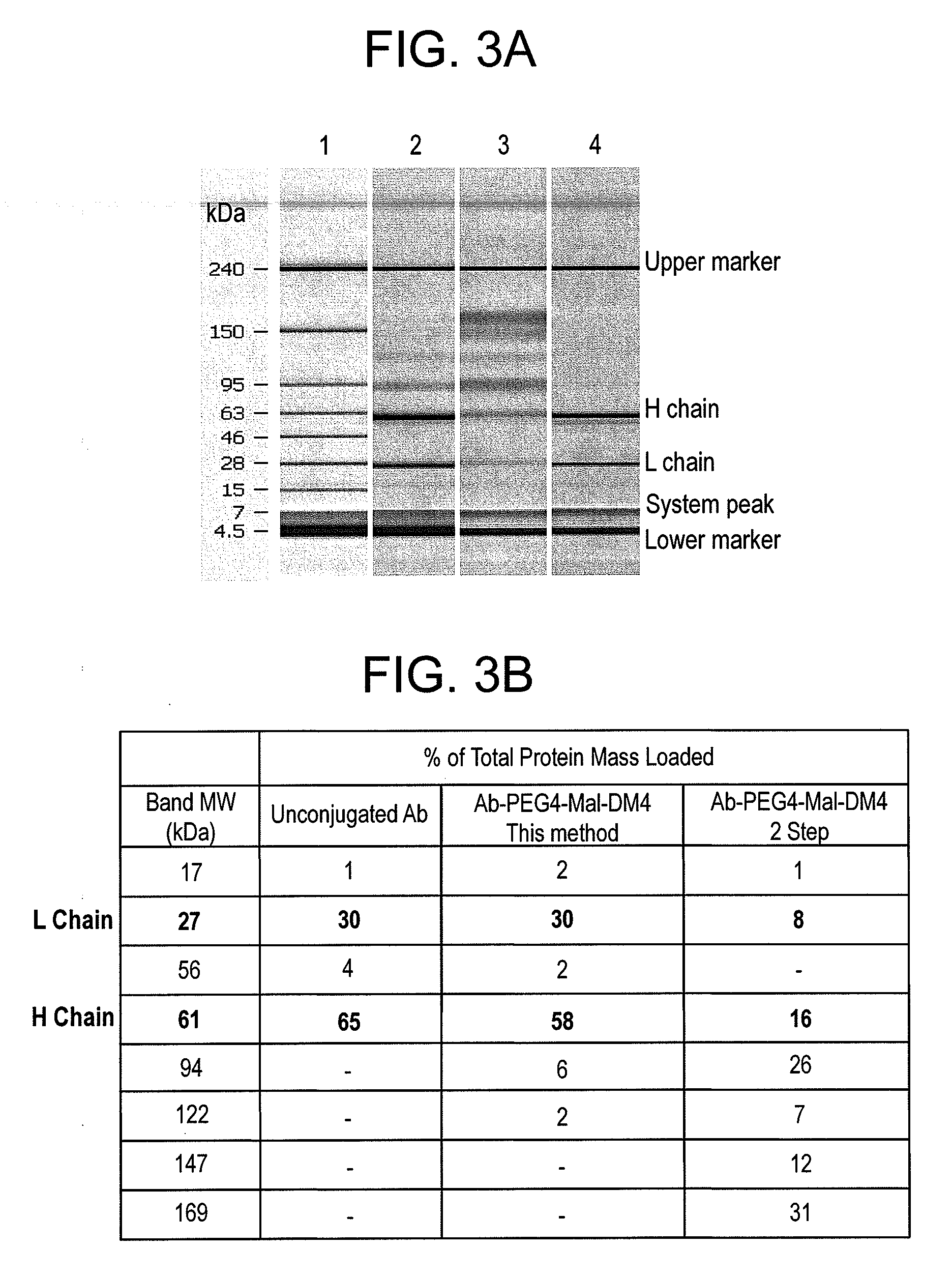
This invention describes a method of conjugating a cell binding agent such as an antibody with an effector group (e.g., a cytotoxic agent) or a reporter group (e.g., a radionuclide), whereby the reporter or effector group is first reacted with a bifunctional linker and the mixture is then used without purification for the conjugation reaction with the cell binding agent. The method described in this invention is advantageous for preparation of stably-linked conjugates of cell binding agents, such as antibodies with effector or reporter groups. This conjugation method provides in high yields conjugates of high purity and homogeneity that are without inter-chain cross-linking and inactivated linker residues
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
InactiveUS7306784B2Accelerate the accumulation processImprove clearance rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHydrolasesCell membranePharmacologic therapy
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
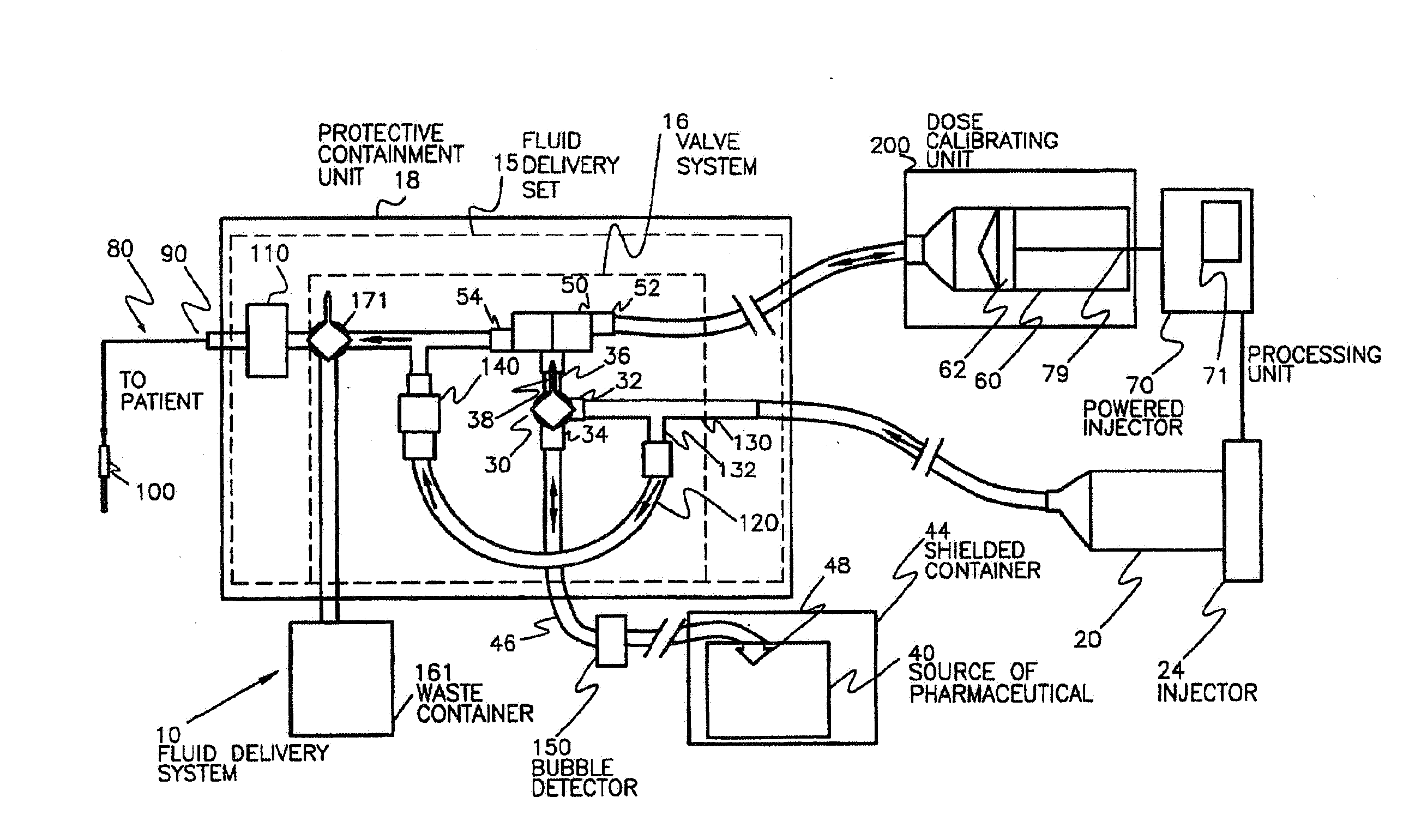
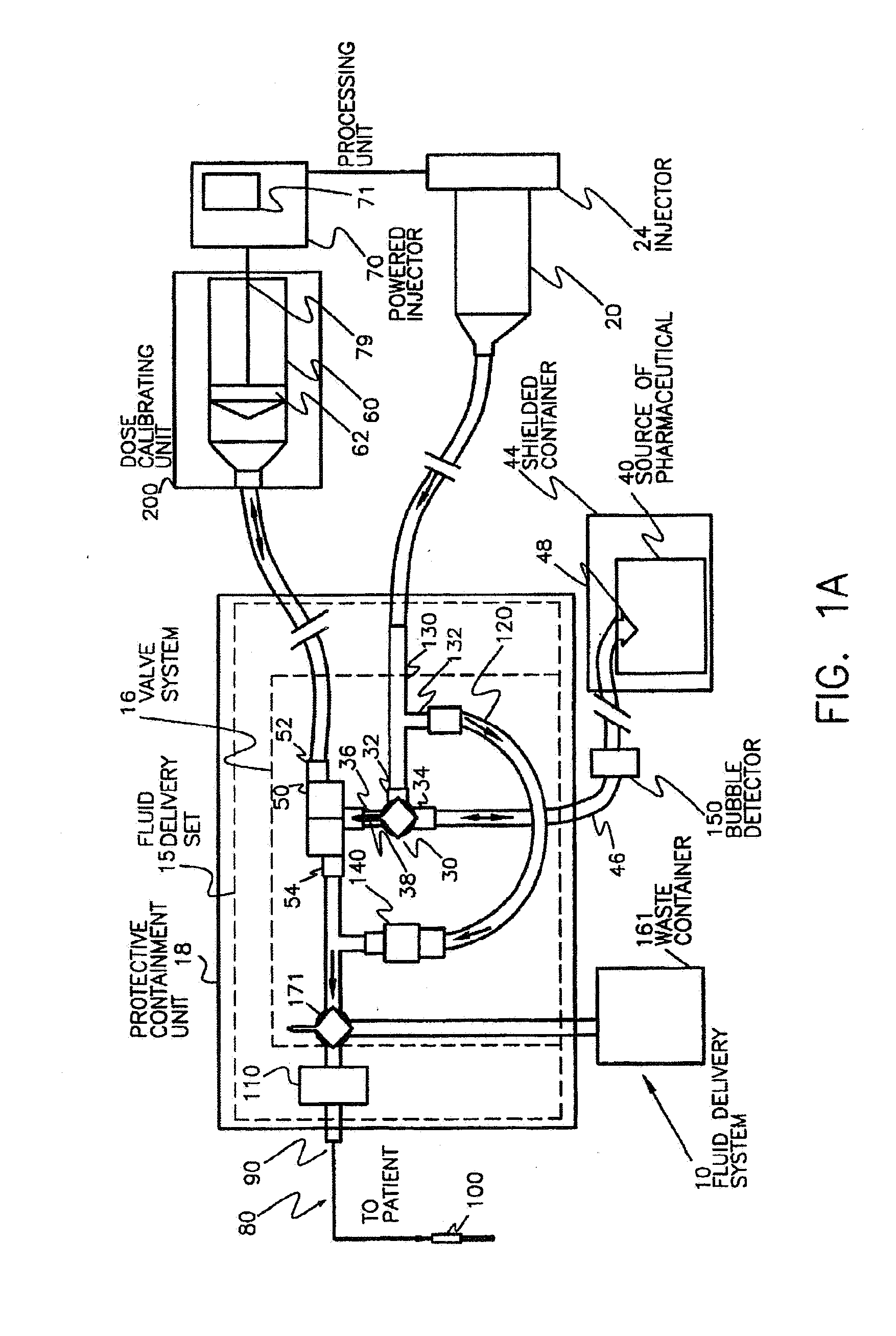
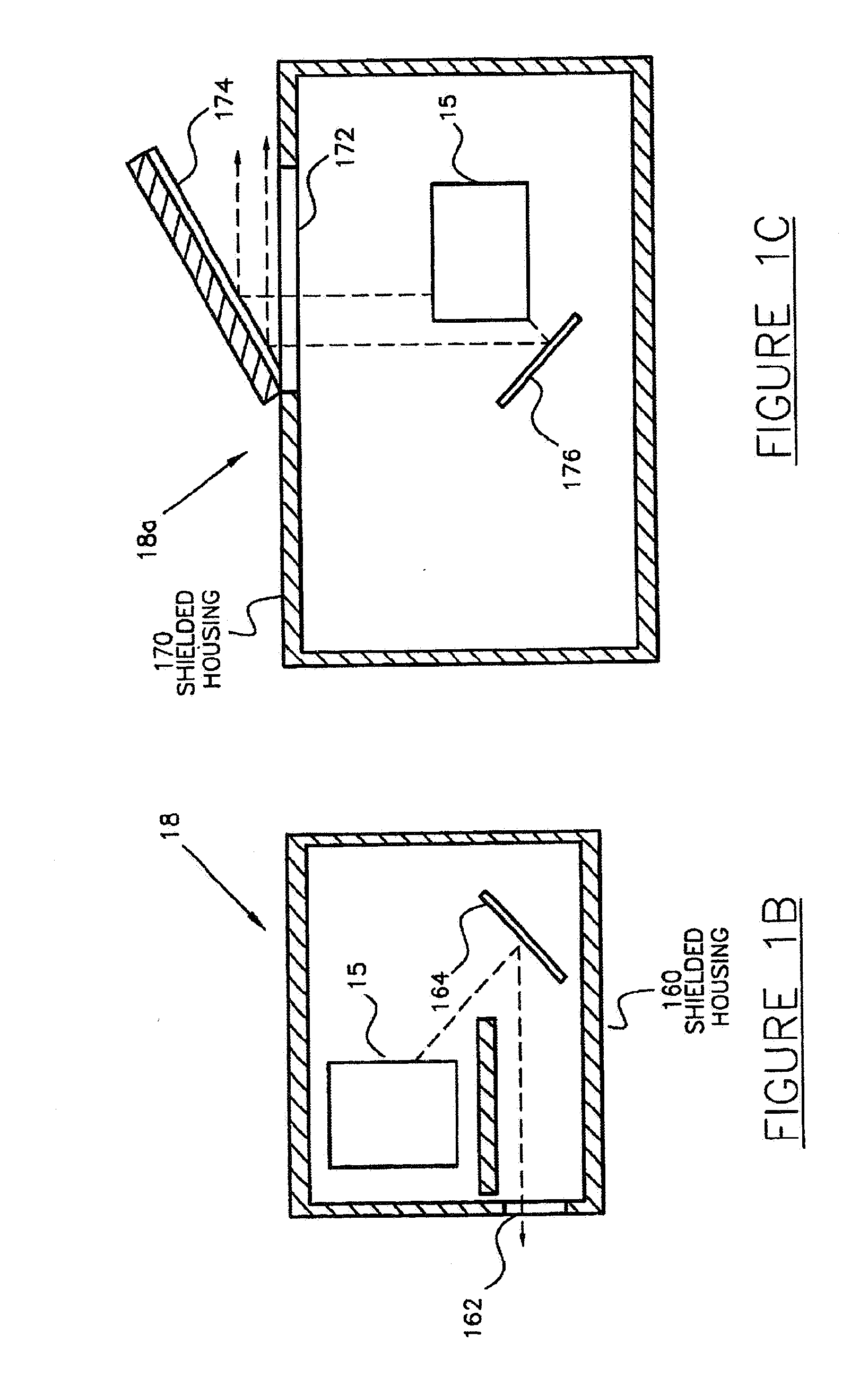
Pharmaceutical Dosing Method
InactiveUS20080166292A1Accurately determineMedical simulationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsTime factorTime standard
Systems, devices, and methods for more accurately determining a radiopharmaceutical dose administered to a patient by relying on a time factor. Particularly, broadly contemplated herein is the administration of a dose on the basis of an elapsed time from when a dose was last accurately measured in the past to when it is injected into the patient. As such, when a dose is first measured, that timepoint is preferably recorded whereupon the time of injection or administration into a patient is also recorded. Based on the original measured dose, the radionuclide (and thus its known decay rate) and the time elapsed, the dose is calculated and not directly measured on injection. The clocks on the filling station and the transport cart are synchronized to each other or to a known and accepted time standard. In this manner, there is temporal continuity and no inaccuracies of time or loss of time occurs between measurement and injection.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
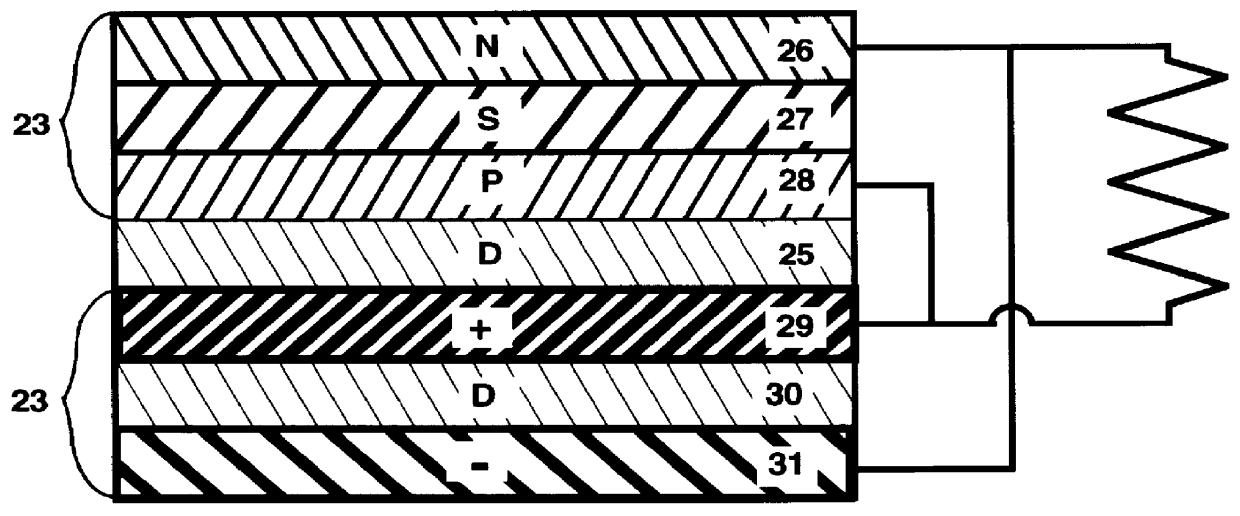
Layered metal foil semiconductor power device
InactiveUS6118204AIncrease motivationGood energyRadiation electrical energyThermoelectric devicesSemiconductor materialsMetal foil
The present invention is a power cell for directly converting ionizing radiation into electrical energy. The invented isotopic electric converter provides an electrical power source that includes an electronegative material layered in a semiconductor, to form a first region that has a high density of conduction electrons, and an electropositive material also layered in the semiconductor material to form a second region with a high density of holes. Said N-layers region and P-layers region are separated by a neutral zone of semiconductor material doped with a radioactive isotope, such as, but not limited to, tritium. No junction is formed between the N and P layers regions. Rather, the potential gradient across the neutral zone is provided by the difference between the work functions of the electronegative and electropositive electrodes. Electrical contacts are affixed to the respective regions of the first and second type conductivity which become the anode and cathode of the cell, respectively. Beta particles emitted by the tritium generate electron-hole pairs within the neutral zone, which are swept away by the potential gradient between the first and second regions, thereby producing an electric current.
Owner:BROWN PAUL M
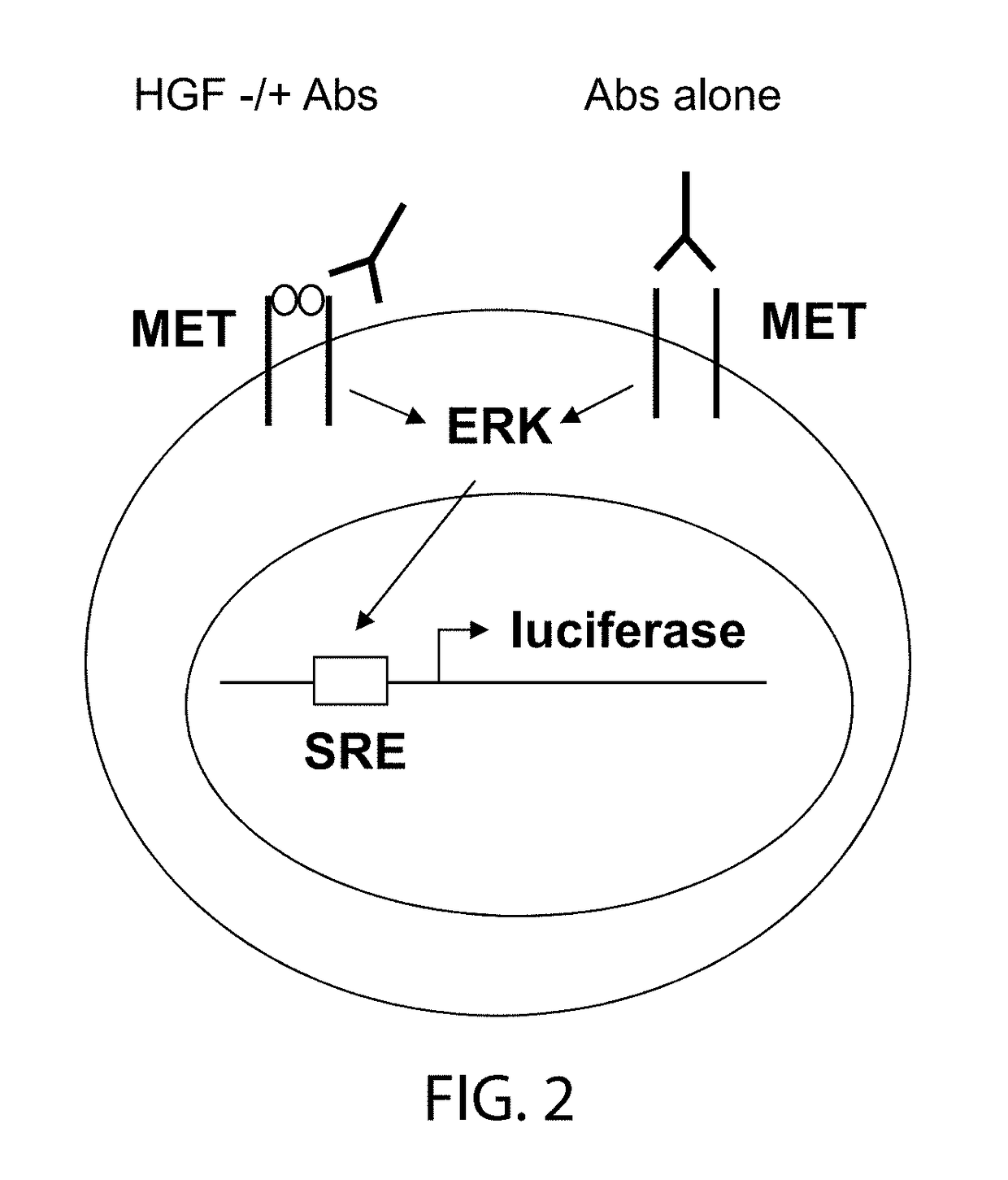
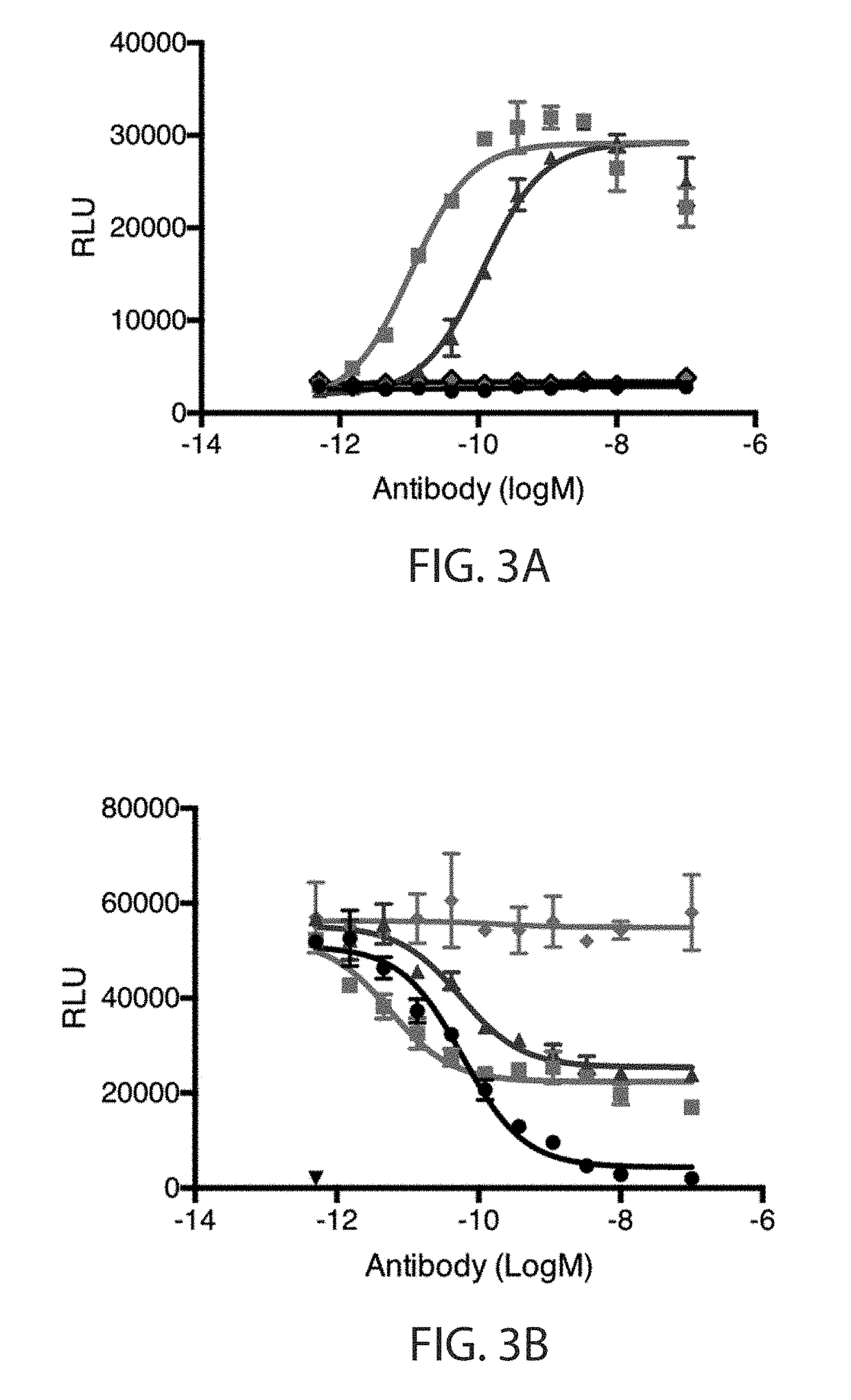
Anti-met antibodies, bispecific antigen binding molecules that bind met, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180134794A1Organic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeExtracellular Structure
Provided herein are antibodies and bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind MET and methods of use thereof. The bispecific antigen-binding molecules comprise a first and a second antigen-binding domain, wherein the first and second antigen-binding domains bind to two different (preferably non-overlapping) epitopes of the extracellular domain of human MET. The bispecific antigen-binding molecules are capable of blocking the interaction between human MET and its ligand HGF. The bispecific antigen-binding molecules can exhibit minimal or no MET agonist activity, e.g., as compared to monovalent antigen-binding molecules that comprise only one of the antigen-binding domains of the bispecific molecule, which tend to exert unwanted MET agonist activity. Also included are antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) comprising the antibodies or bispecific antigen-binding molecules provided herein linked to a cytotoxic agent, radionuclide, or other moiety, as well as methods of treating cancer in a subject by administering to the subject a bispecific antigen-binding molecule or an ADC thereof.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Gastrin Releasing Peptide Compounds
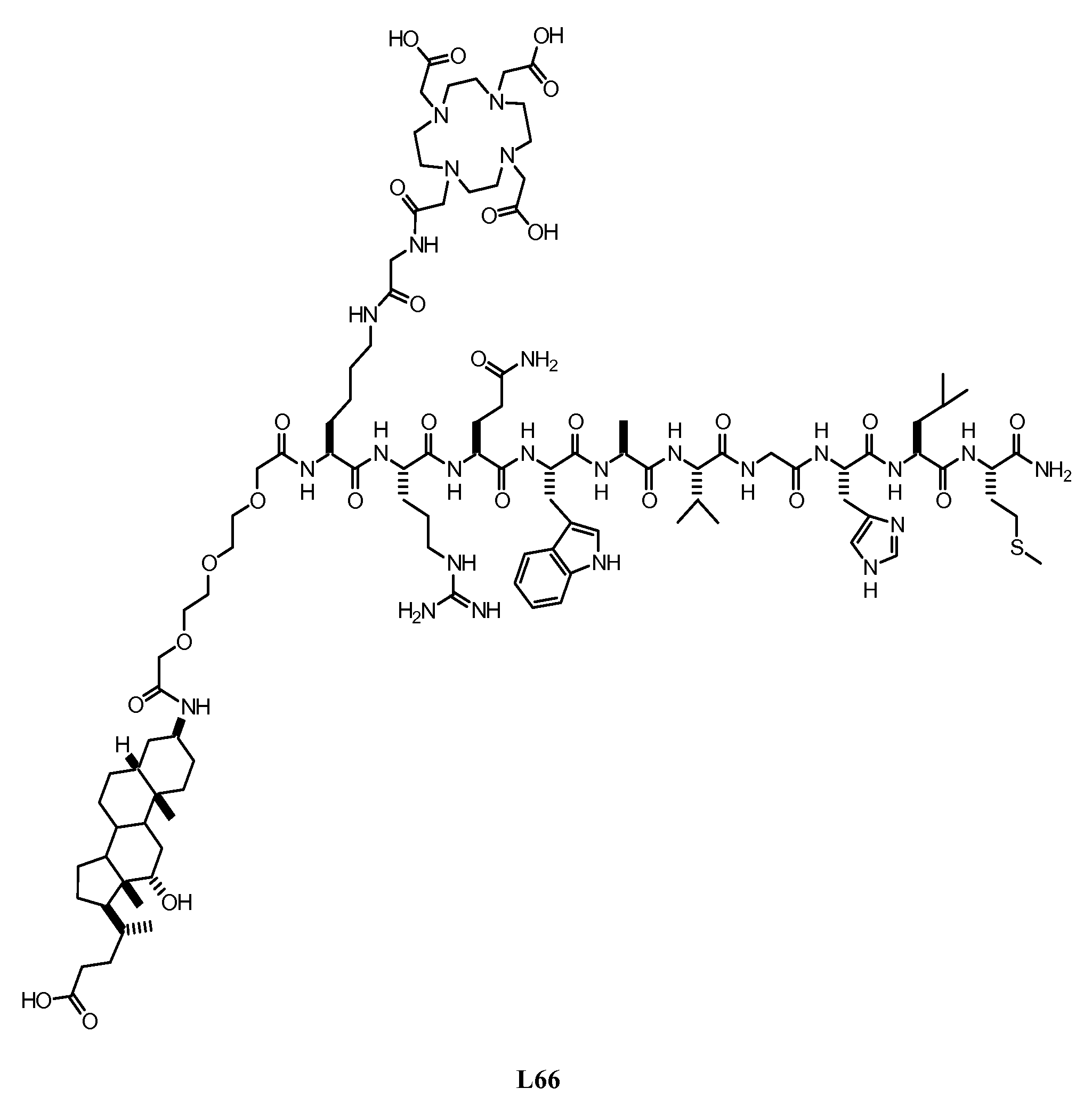
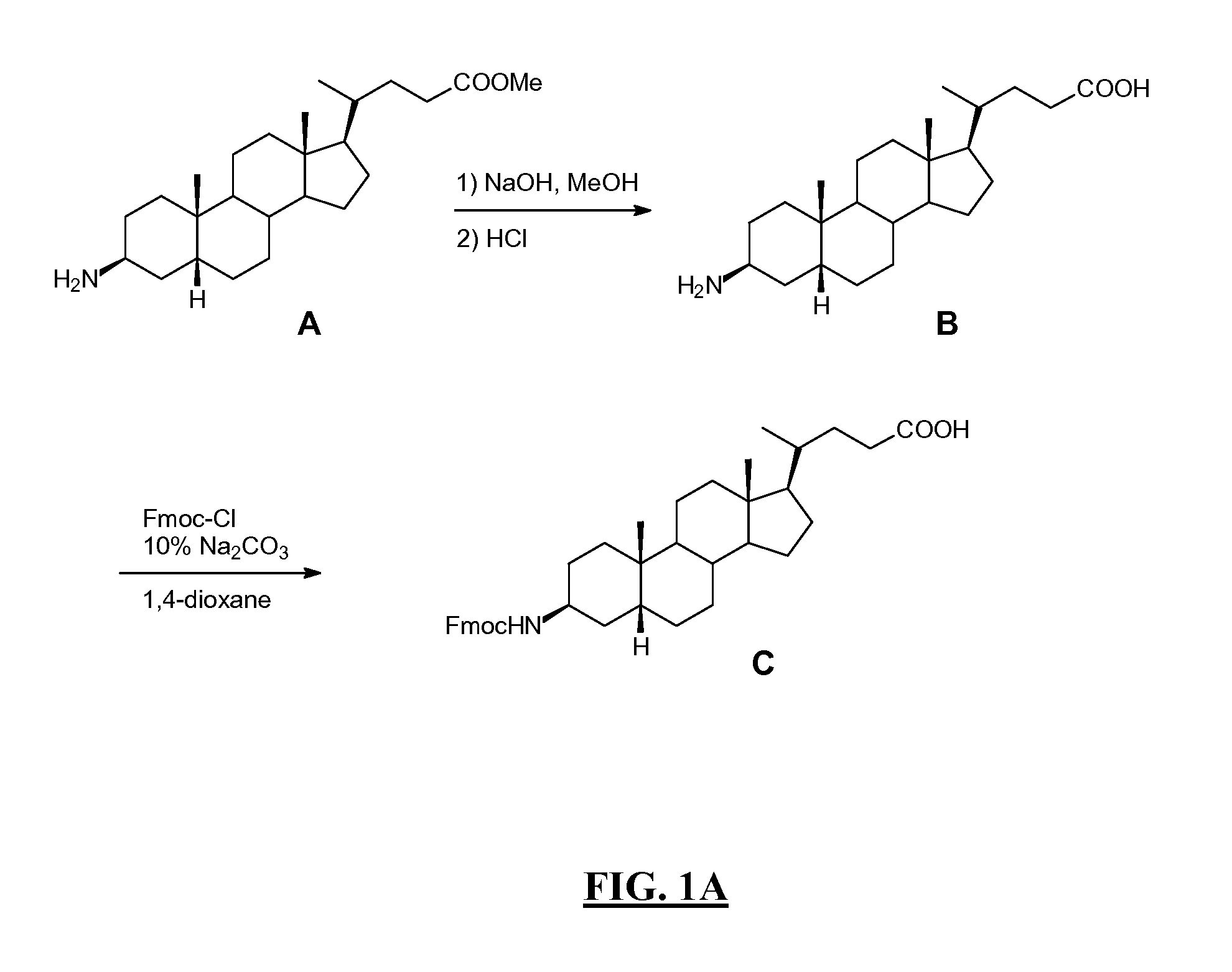
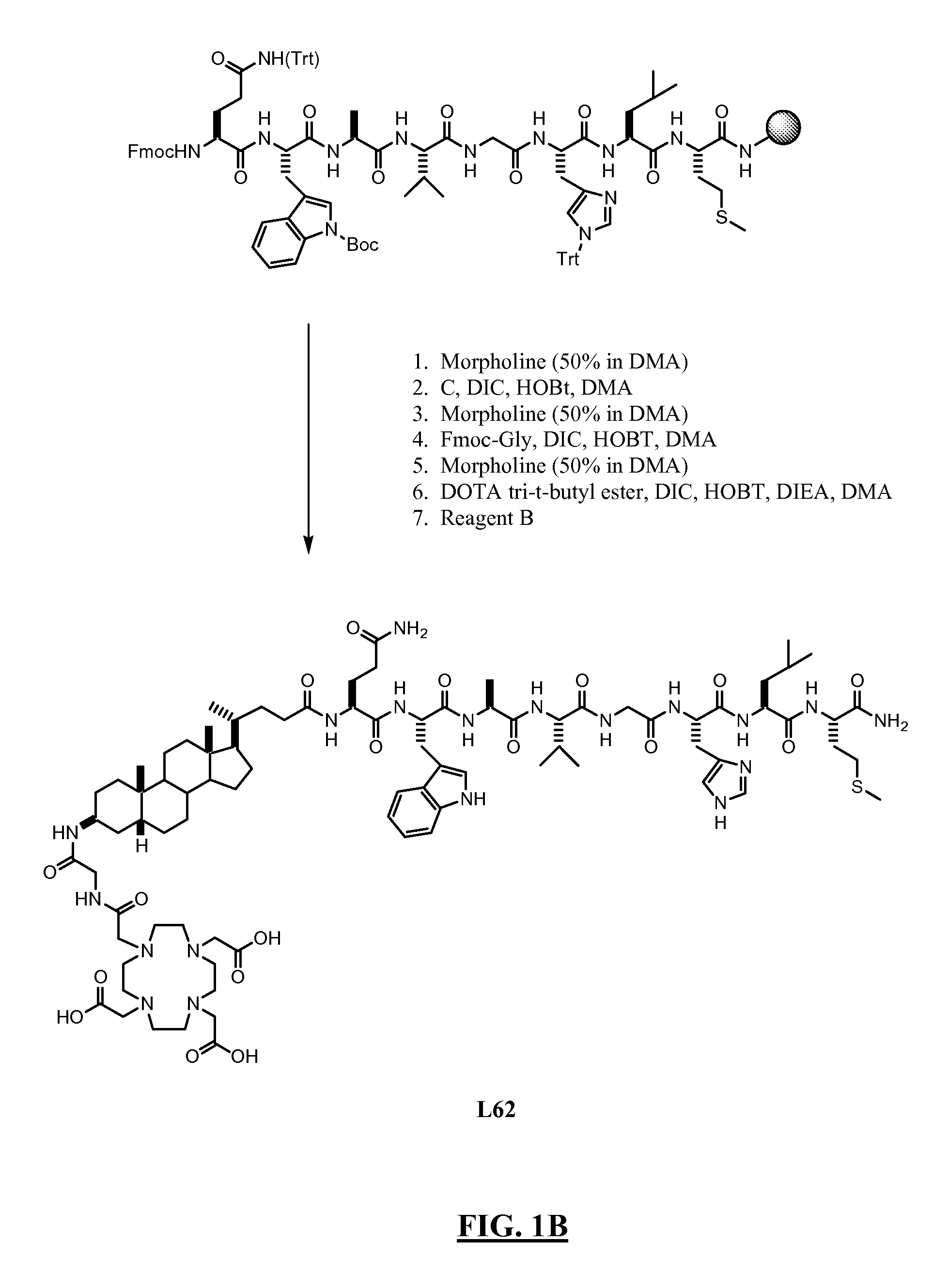
InactiveUS20080008649A1Improve targetingDecreasing aberrant vascular permeabilityRadioactive preparation carriersGastrin releasing peptideCholic acidTherapeutic Hormone
New and improved compounds for use in diagnostic imaging or therapy having the formula M-N—O—P-G, wherein M is a metal chelator having the structure: wherein R1-R5 and FG are as defined herein (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N—O—P is the linker containing at least one non-alpha amino acid with a cyclic group, at least one substituted bile acid or at least one non-alpha amino acid, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. In the preferred embodiment, M is an Aazta metal chelator or a derivative thereof. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy or phototherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. Methods and kits for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. Methods and kits for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent are further provided. Novel methods of treating prostate tumors or of delaying the progression of prostate tumors are also provided, including, methods of treating bone or soft tissue metastases of prostate cancer, methods for treating hormone sensitive and hormone refractory prostate cancer, methods for delaying the progression of hormone sensitive prostate cancer, for facilitating combination therapy in patients with hormone sensitive prostate cancer and for decreasing aberrant vascular permeability in patients with hormone sensitive prostate cancer.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Method and apparatus for noise tomography
The subject invention pertains to an imaging technique and apparatus which can utilize an array of RF probes to measure the non-resonant thermal noise which is produced within a sample, such as a body, and produce a non-resonant thermal noise correlation. The detected noise correlation is a function of the spatial overlap of the electromagnetic fields of the probes and the spatial distribution of the conductivity of the sample. The subject technique, which can be referred to as Noise Tomography (NT), can generate a three-dimensional map of the conductivity of the sample. Since the subject invention utilizes detection of the thermal noise generated within the body, the subject method can be non-invasive and can be implemented without requiring external power, chemicals, or radionuclides to be introduced into the body. The subject imaging method can be used as a stand along technique or can be used in conjunction with other imaging techniques.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Non-antigenic toxin-conjugate and fusion protein of internalizing receptor system
InactiveUS7033572B2Effective and less toxicIncrease valuePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEphA ReceptorsCytokine
A conjugate of a toxin and a cytokine, and a fusion protein comprising a bispecific antibody that has a first specificity for a cell marker specific to a malignant cell and a second specificity for a region of IL-15α, each optionally further comprising a radionuclide, are useful therapeutic reagents for treating leukemias and lymphomas.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Local regional chemotherapy and radiotherapy using in situ hydrogel
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for treating radioactive wastewater
ActiveCN103177784AImprove processing precisionReduce competitionGeneral water supply conservationRadioactive contaminantsStrong acidsIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for treating radioactive wastewater. The method for treating the radioactive wastewater comprises the steps of firstly carrying out reverse osmosis treatment on the radioactive wastewater, then enabling the radioactive wastewater to enter a continuous electrodeionization unit to be treated, and further removing radionuclide so as to enable treated wastewater to reach discharge requirements; and respectively filling different mixed ion exchange resin in a plain water chamber and a thick water chamber in a continuous electrodeionization membrane stack of the continuous electrodeionization unit, wherein mixed ion exchange resin filled in the plain water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 30%-60% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, 40%-60% of strong-base anion exchange resin, and 0%-30% of weak-base anion exchange resin, mixed ion exchange resin filled in the thick water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 20%-50% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, and the balance strong-base anion exchange resin. A weak dissociation polymer portion is used for improving selectivity of continuous electrodeionization membrane stack to trace amount radionuclide, radionuclide with extremely concentration can be effectively removed, and the method for treating the radioactive wastewater ensures that the final discharged water satisfies the discharge requirements.
Owner:BEIJING QINGHE CHAOHUA TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof
InactiveCN102079823AWide variety of sourcesEasy to makeOther chemical processesMagnetic liquidsMicrosphereWastewater
The invention relates to a method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing acidic aqueous solution of chitosan and a water-based magnetofluid first, then crosslinking by using glutaraldehyde, then adjusting the pH value to form a gelatinous precipitate, then modifying by using ethylenediamine and epichlorohydrin, and washing and drying to obtain a final product. The product has good absorption effect on radionuclide aranium and metal ions such as heavy metal Pb, Cr and the like; the removal rate reaches over 95 percent when the initial concentration of various ions is within the range of 200mg / L; and the product has quick absorption rate and good regeneration performance. The ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres can be used for metal recovery and pollution remediation in mines, radioactive waste water, smelteries, electronics factories and waste water of electroplating factories.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Methods and computer readable medium for improved radiotherapy dosimetry planning
InactiveUS20020046010A1Simple methodImprove calculation accuracyMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDosimetry radiationHigh energy
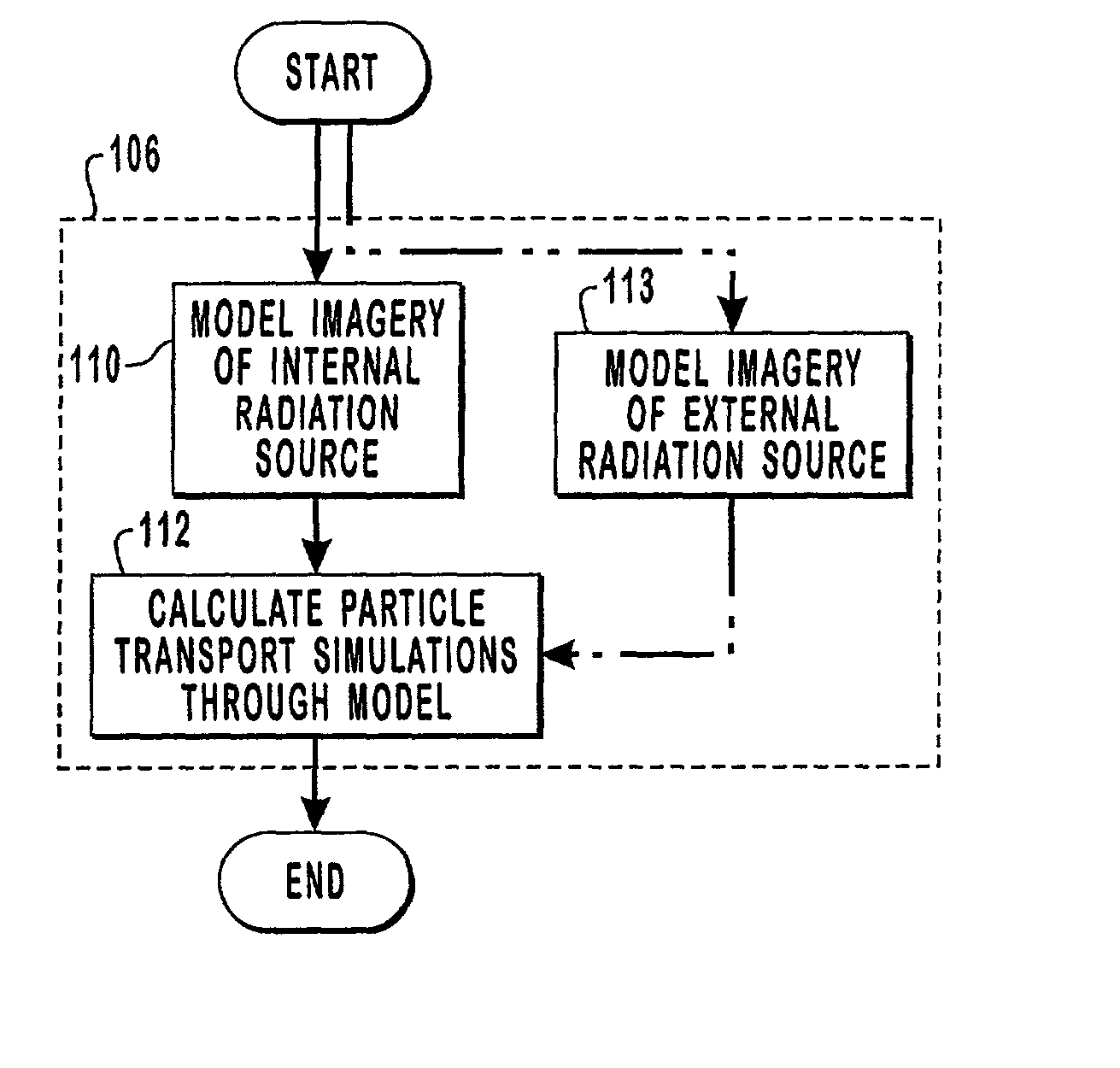
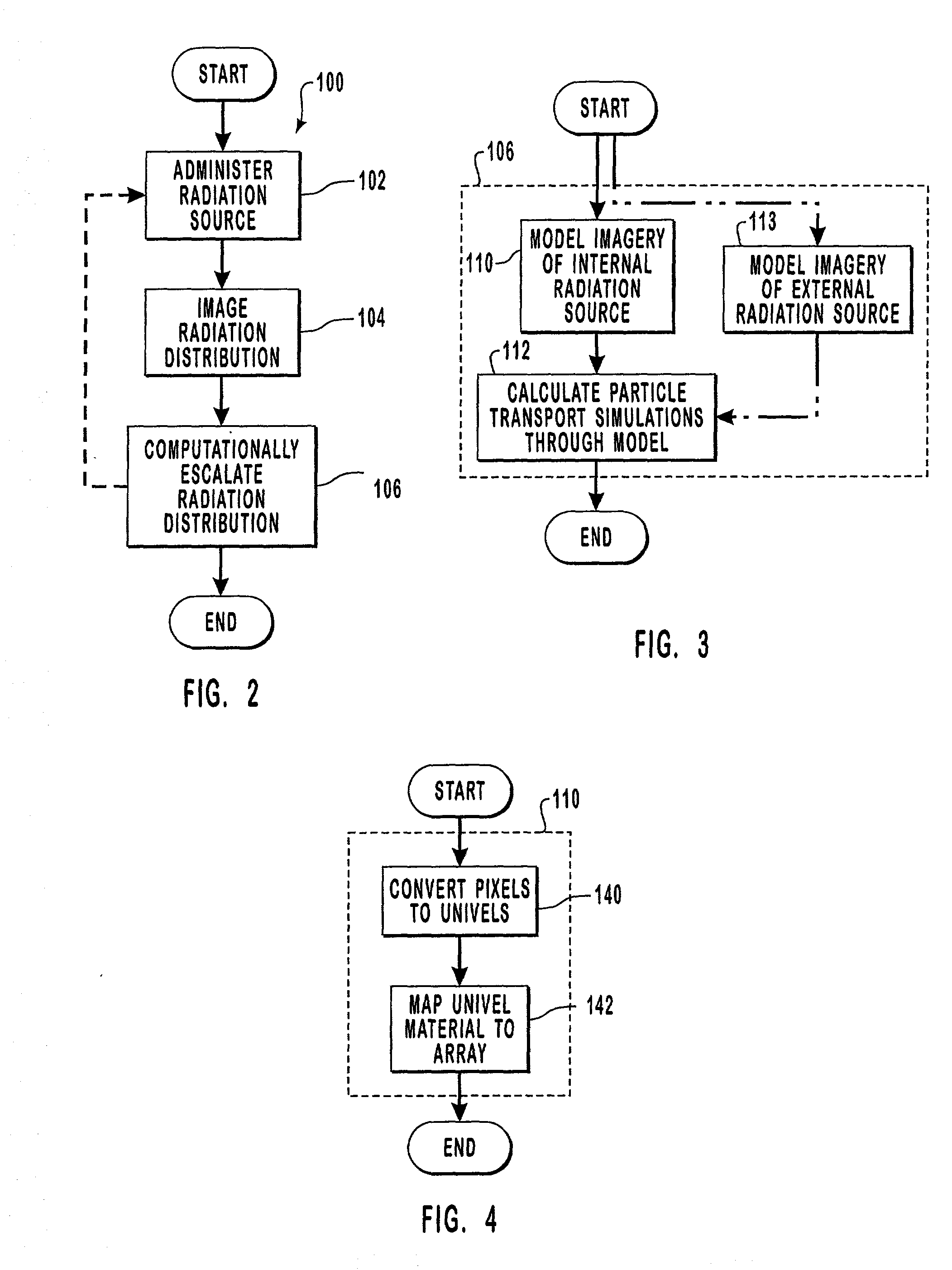
Methods and computer readable media are disclosed for ultimately developing a dosimetry plan for a treatment volume irradiated during radiation therapy with a radiation source concentrated internally within a patient or incident from an external beam. The dosimetry plan is available in near"real-time" because of the novel geometric model construction of the treatment volume which in turn allows for rapid calculations to be performed for simulated movements of particles along particle tracks therethrough. The particles are exemplary representations of alpha, beta or gamma emissions emanating from an internal radiation source during various radiotherapies, such as brachytherapy or targeted radionuclide therapy, or they are exemplary representations of high-energy photons, electrons, protons or other ionizing particles incident on the treatment volume from an external source. In a preferred embodiment, a medical image of a treatment volume irradiated during radiotherapy having a plurality of pixels of information is obtained.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Core-Excited Nanoparticles and Methods of Their Use in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20130195979A1Cost-effectiveEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseExternal energy
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
Psma-binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110142760A1Satisfies long standingSharp contrastUrea derivatives preparationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAntigenProstate cancer cell
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Low density radionuclide-containing particulate material
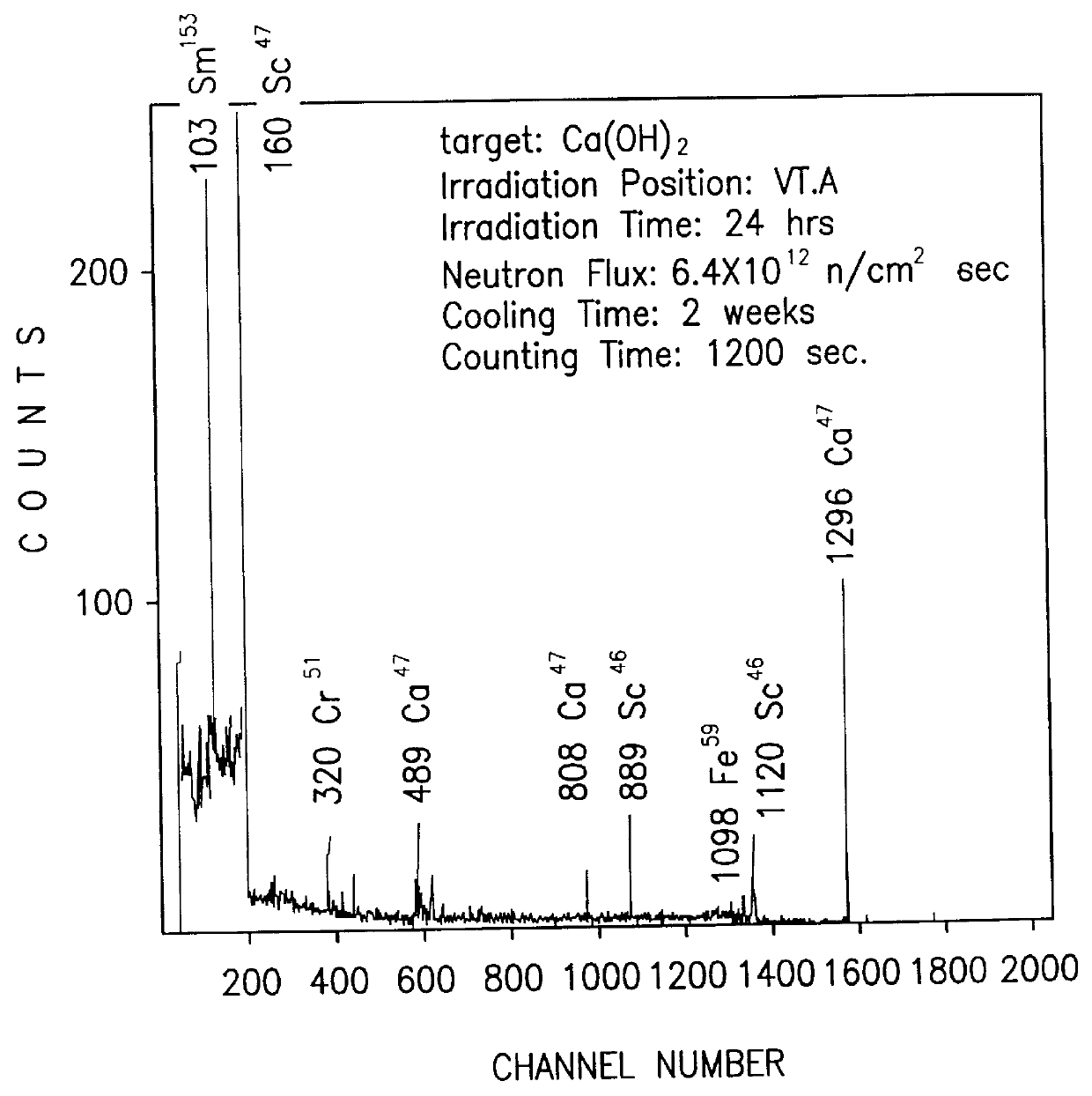
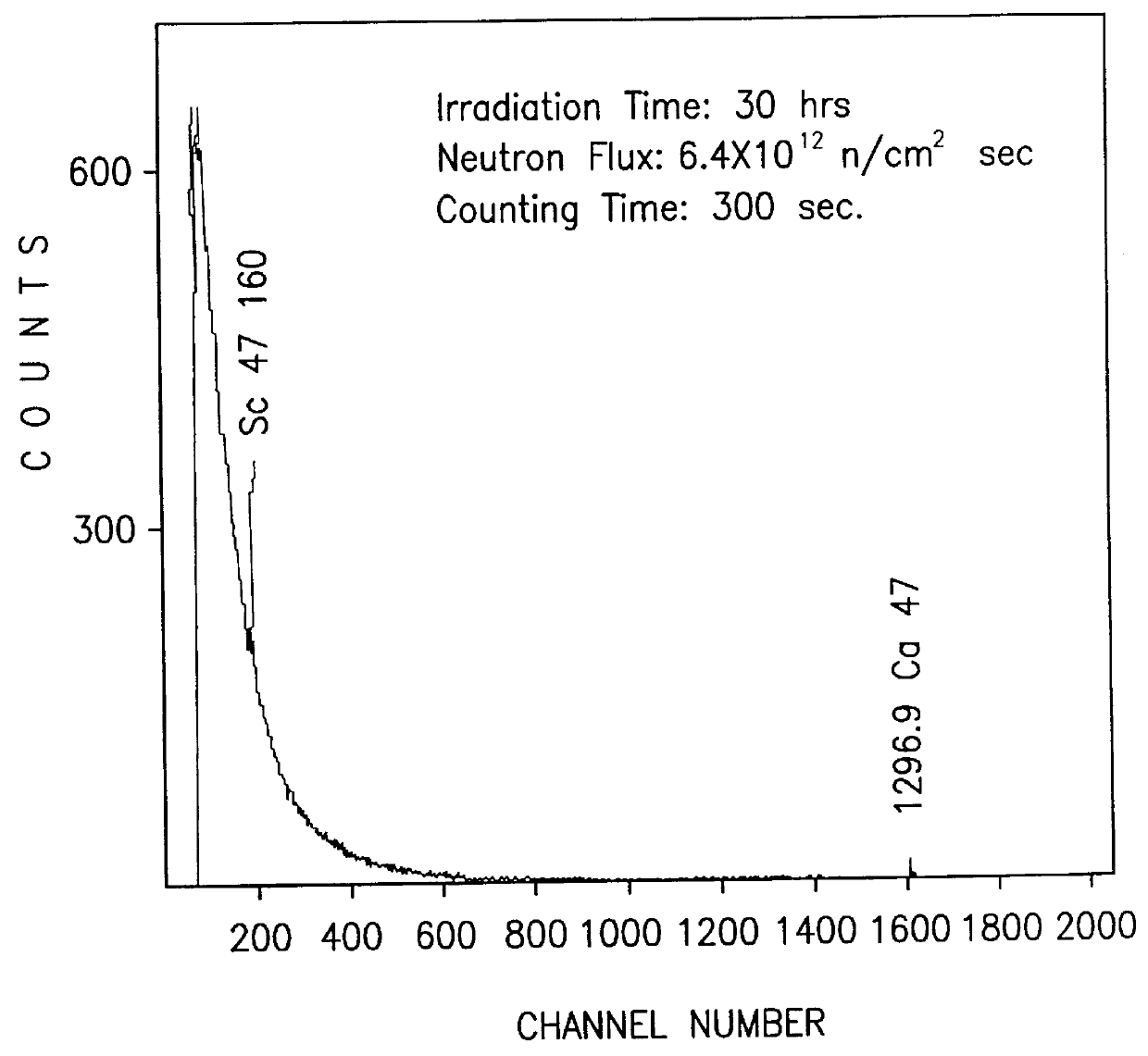
The invention relates to a particulate material consisting of a low density radiation-tolerant glass and a radionuclide incorporated into the low density glass or coated on the low density glass, the glass having a density of less than 2.5 g / cm3, processes for its production and a method of radiation therapy utilising the patentable material.
Owner:SIRTEX MEDICAL LTD
Biocompatible Microbubbles to Deliver Radioactive Compounds to Tumors, Atherosclerotic Plaques, Joints and Other Targeted Sites
A composition and method for targeted use of radionuclide therapy for the treatment of cancer and cancerous tumors, atherosclerotic plaques, joints and other targeted sites. Microparticles, microbubbles, or nanoparticles deliver therapeutic doses of radiation, included radiation from alpha emitting radionuclides, to sites in a patient. The delivery may be targeted by targeting agents linked to the microparticles, microbubbles, or nanoparticles or by the external application of energy, or both.
Owner:CROWLEY ROSEMARY C
Graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating radioactive wastewater
InactiveCN105664738AHigh retention rateAchieve enrichmentSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiltrationIon
The invention relates to a graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating radioactive wastewater and a preparation method thereof.According to the membrane, a porous carrier is pre-modified through a silane coupling agent, and the graphene oxide-based composite membrane is prepared from a polydopamine and graphene oxide compound by adopting a vacuum filtration method.The method is characterized in that a polydopamine bionic self-assembly technology and a graphene oxide sheet are compounded, the size dimension of a membrane nanochannel is accurately adjusted, the selectivity or the rejection rate of the membrane on radionuclide ions is increased, and concentration and removal of radionuclide are achieved.According to the graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating the radioactive wastewater and the preparation method thereof, the preparation process is simple and easy to operate, good repeatability is achieved, the water flux and ion rejection rate of the composite membrane are significantly increased, the separating property of a long-time operating membrane is stable, and a wide application prospect in the fields such as membrane-method radioactive wastewater treatment and heavy metal wastewater treatment is achieved.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Radioactive particles and methods for preparing same
InactiveUS6149889AMinimizing damageLong lastingPowder deliveryRadioactive preparation carriersGlass particleRadioactive decay
A nuclear medical drug for localize radiotheraphy of a tumor and methods for its preparation. The drug includes a radioactive ceramic or glass particle having biocompatiblity. Ceramic or glass particles prepared by traditional processes become radioactive particles with pure beta -particle-emitting radionuclides after being irradiated with an appropriate flux of neutrons. The radioactive particle with suitable particle size can then be dispersed into a contrast medium for injection or can be implanted by operation.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH THE EXECUTIVE YUAN REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS7226577B2Peptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemGastrin-releasing peptideImaging agent
New and improved compounds for use in radiodiagnostic imaging or radiotherapy having the formula M-N-O-P-G, wherein M is the metal chelator (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N-O-P is the linker, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. A method for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. A method for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent is further provided.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Method and apparatus for noise tomography
The subject invention pertains to an imaging technique and apparatus which can utilize an array of RF probes to measure the non-resonant thermal noise which is produced within a sample, such as a body, and produce a non-resonant thermal noise correlation. The detected noise correlation is a function of the spatial overlap of the electromagnetic fields of the probes and the spatial distribution of the conductivity of the sample. The subject technique, which can be referred to as Noise Tomography (NT), can generate a three-dimensional map of the conductivity of the sample. Since the subject invention utilizes detection of the thermal noise generated within the body, the subject method can be non-invasive and can be implemented without requiring external power, chemicals, or radionuclides to be introduced into the body. The subject imaging method can be used as a stand along technique or can be used in conjunction with other imaging techniques.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Tetrazine-trans-cyclooctene Ligation for the Rapid Construction of Radionuclide Labeled Probes
A Diels-Alder adduct of a trans-cyclooctene with a tetrazine is provided, wherein the adduct bears a substituent labeled with a radionuclide. A method of producing a PET or other image of an organ in an animal or human includes forming the Diels-Alder adduct in the animal or human. Trans-cyclooctenes and tetrazines suitable for preparing the adducts are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
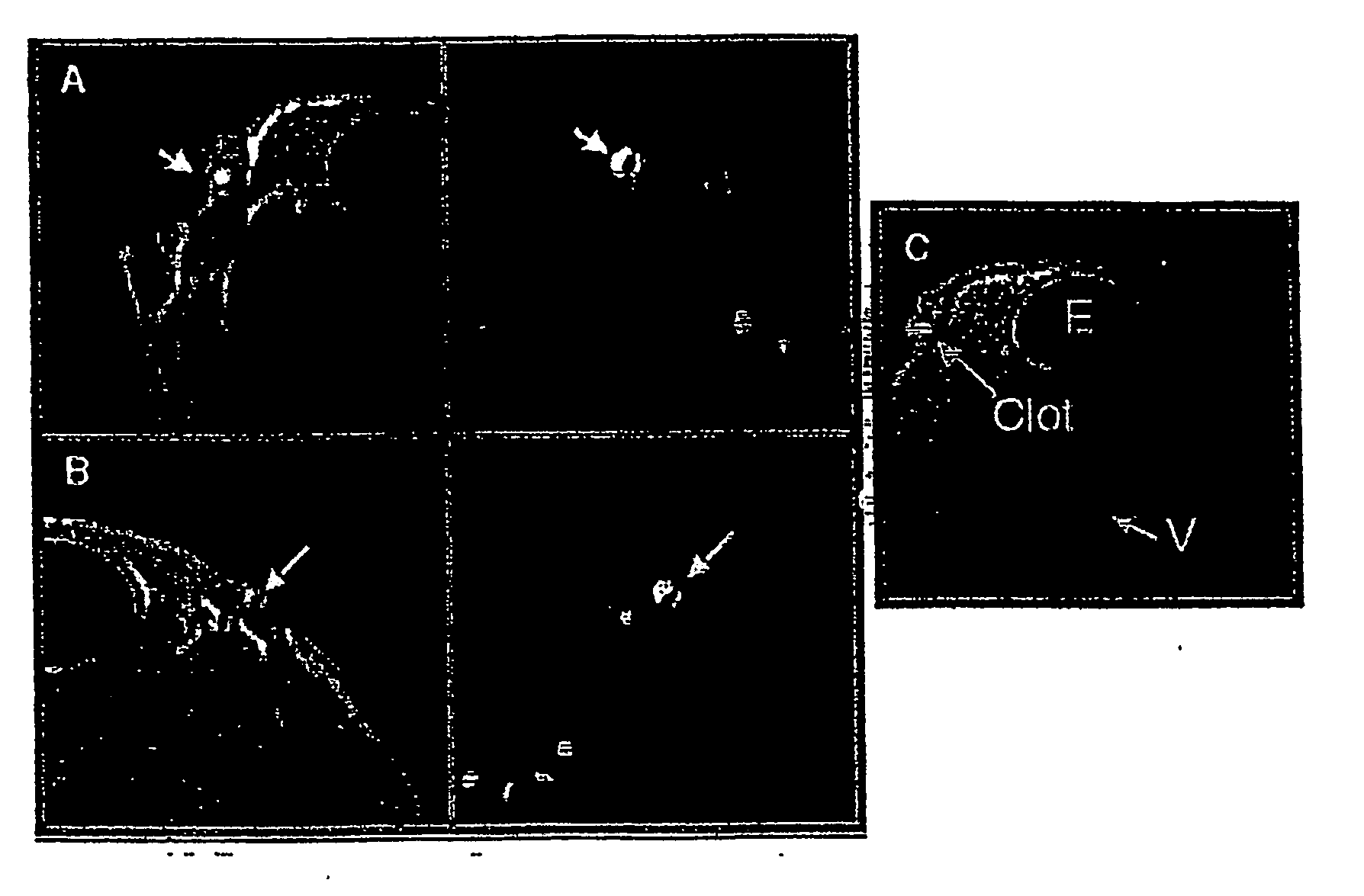
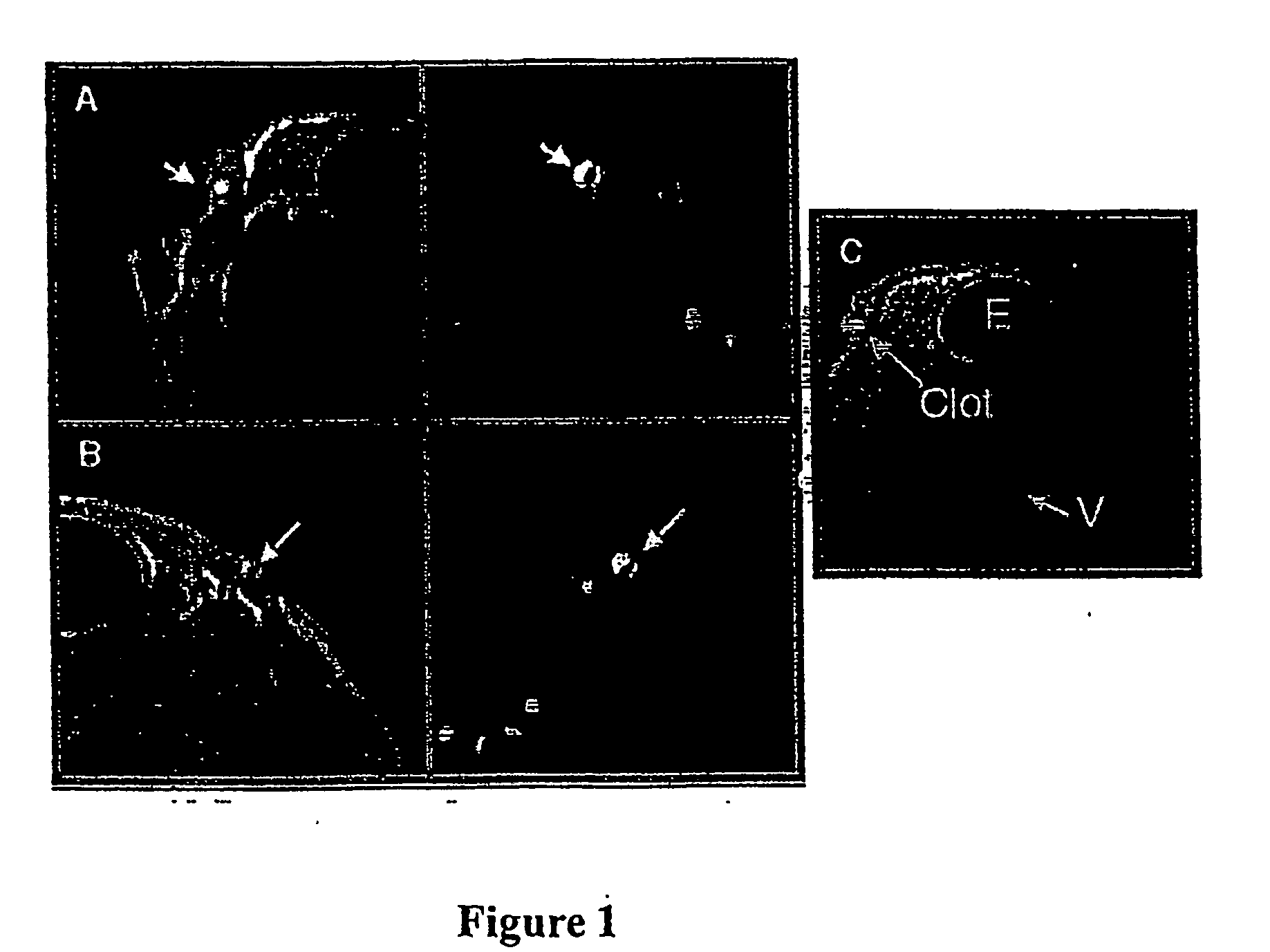
Blood Clot-Targeted Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080247943A1Stroke preventionUseful in detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideLipid formationEmulsion
Emulsions comprising nanoparticles formed from high boiling perfluorochemical substances, said particles coated with a lipid / surfactant coating are made target-specific by directly coupling said nanoparticles to a targeting ligand. The nanoparticle may further include biologically active agents, radionuclides, and / or other imaging agents, and are used to image and / or lyse blood clots in human subjects.
Owner:BARNES JEWISH HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com