Patents
Literature
5458 results about "Tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning, through the use of any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word tomography is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος tomos, "slice, section" and γράφω graphō, "to write" (see also Etymology). A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram.
Imaging and eccentric atherosclerotic material laser remodeling and/or ablation catheter
Devices, systems, and methods for treating atherosclerotic lesions and other disease states, particularly for treatment of vulnerable plaques, can incorporate optical coherence tomography or other imaging techniques which allow a structure and location of an eccentric plaque to be characterized. Remodeling and / or ablative laser energy can then be selectively and automatically directed to the appropriate plaque structures, often without imposing mechanical trauma to the entire circumference of the lumen wall.
Owner:VESSIX VASCULAR
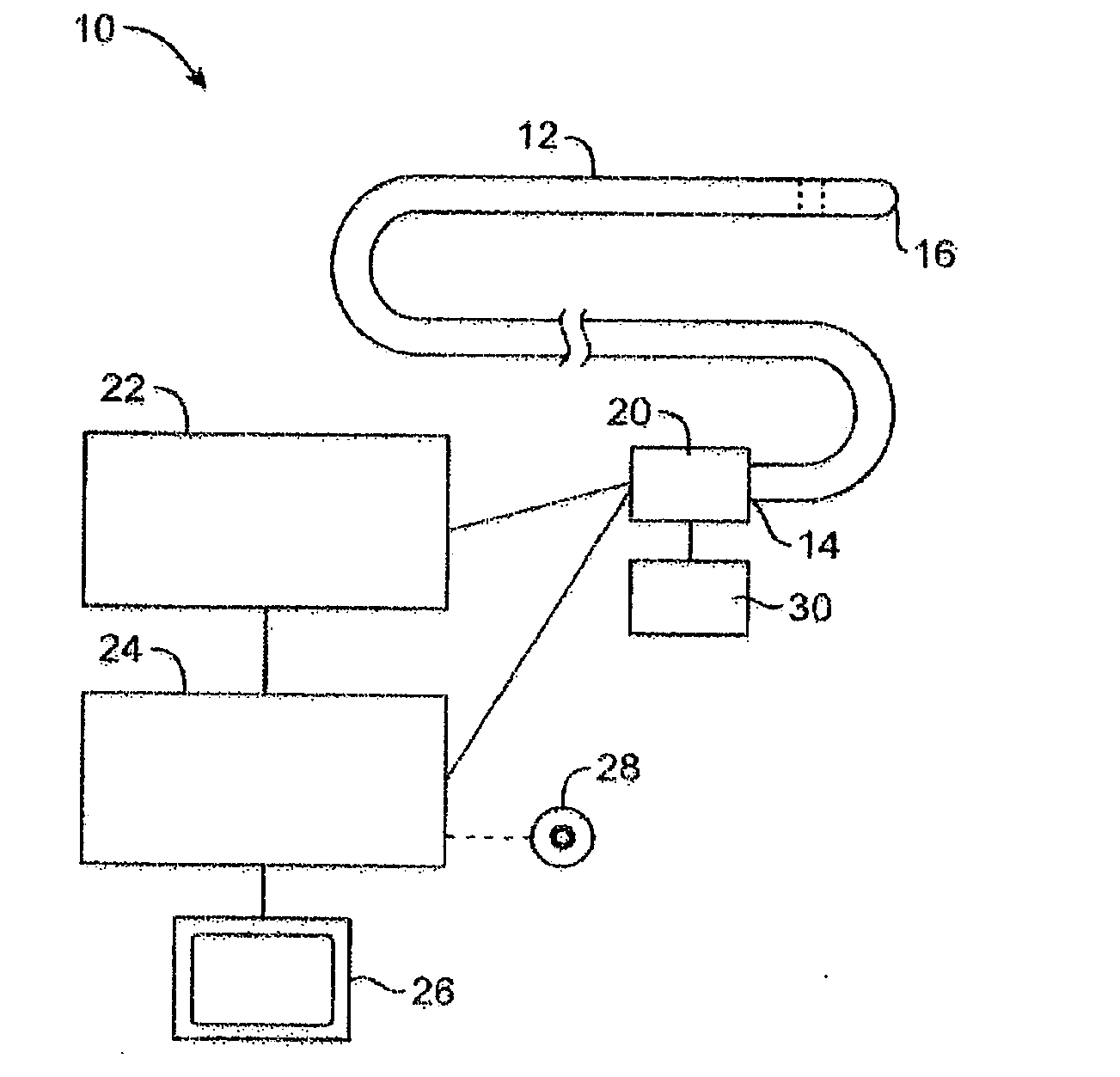
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
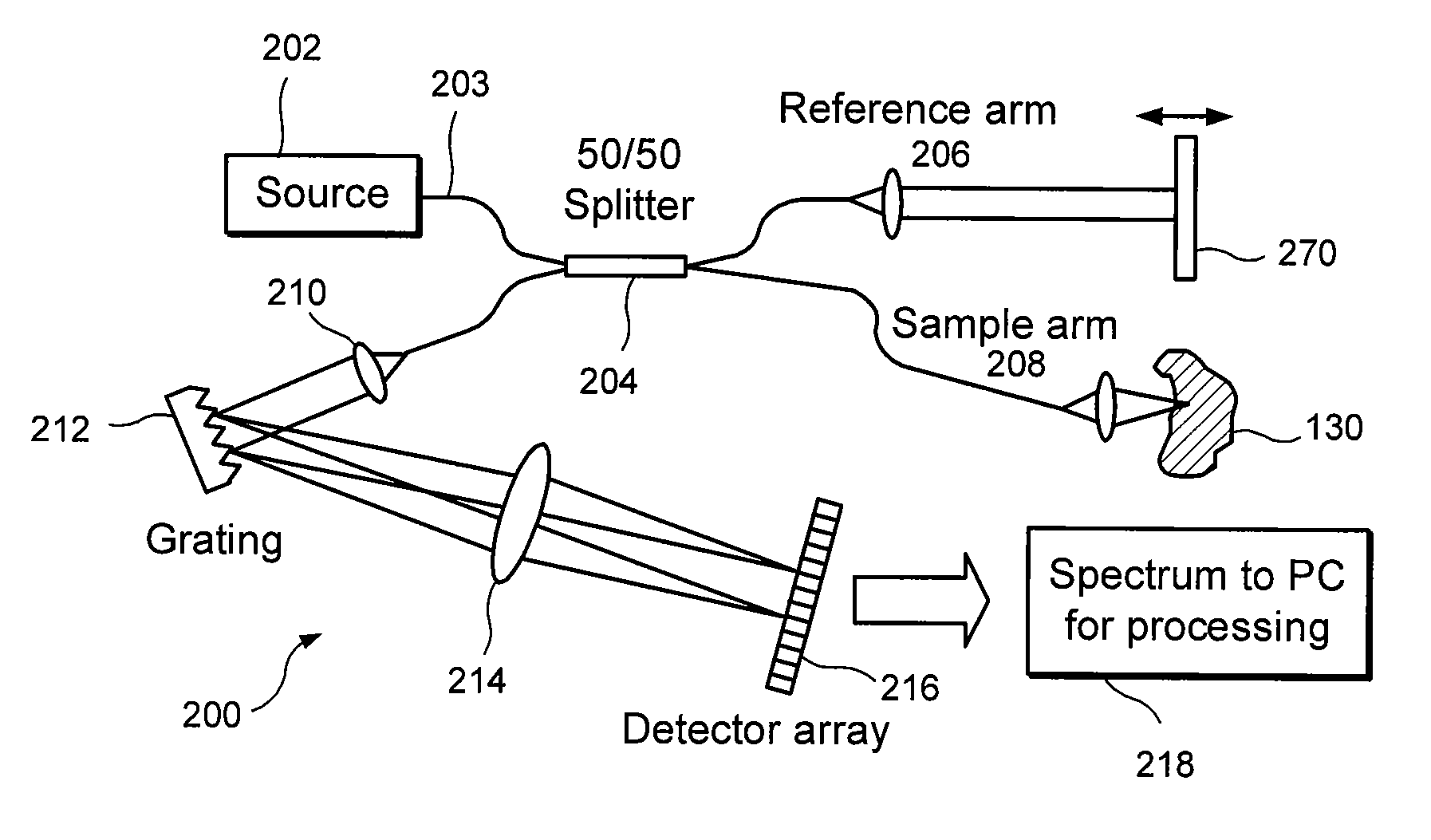
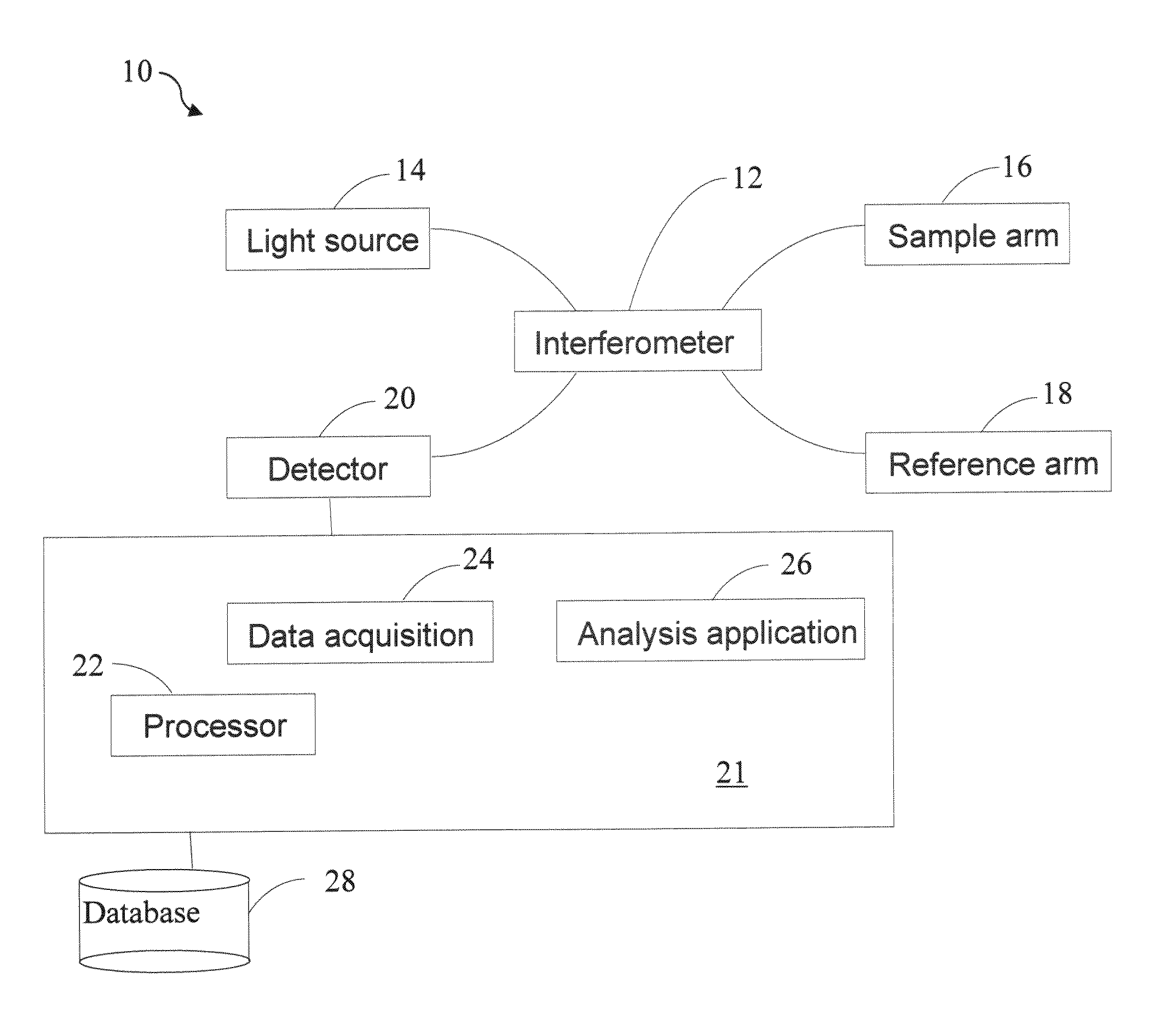
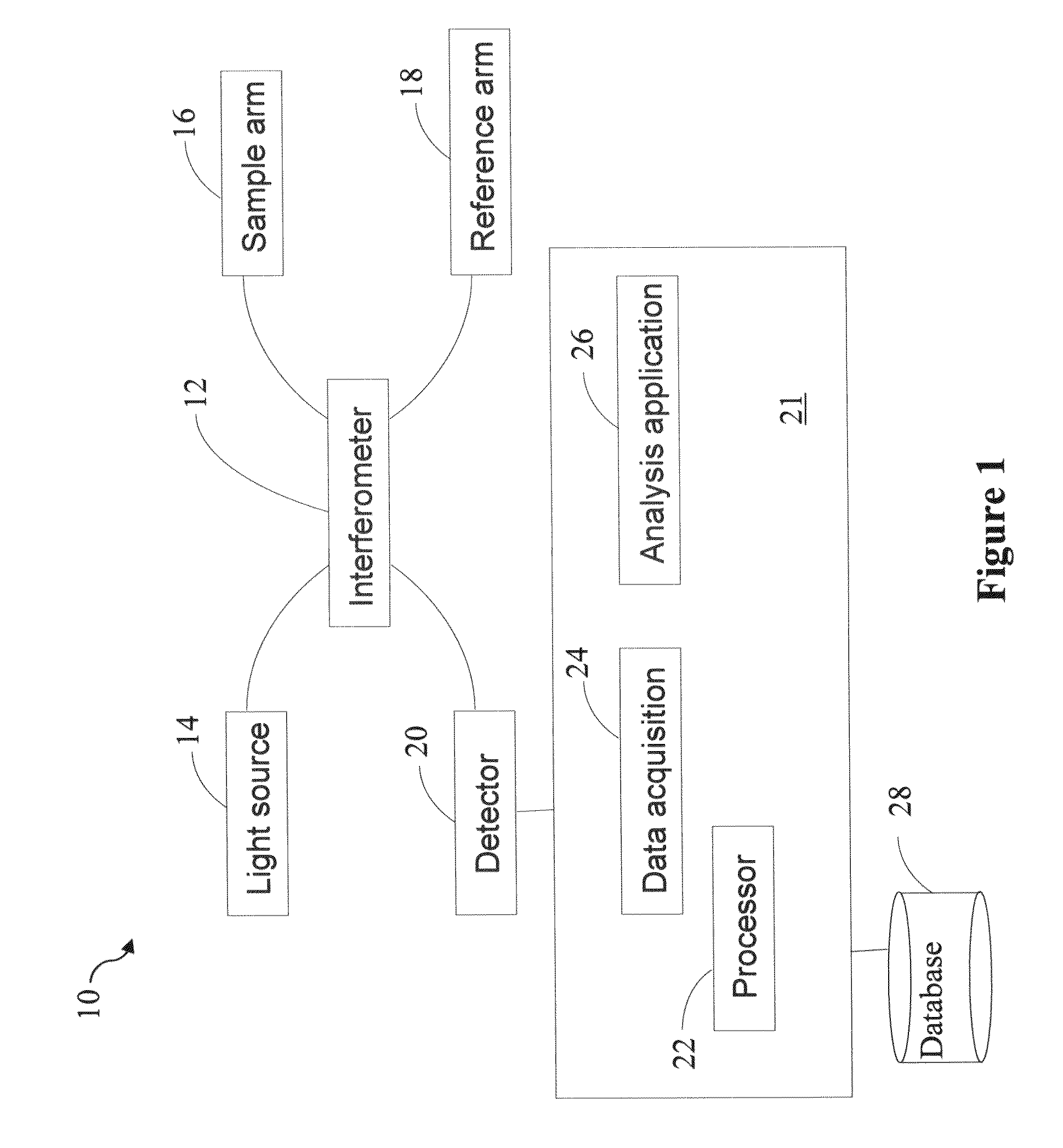
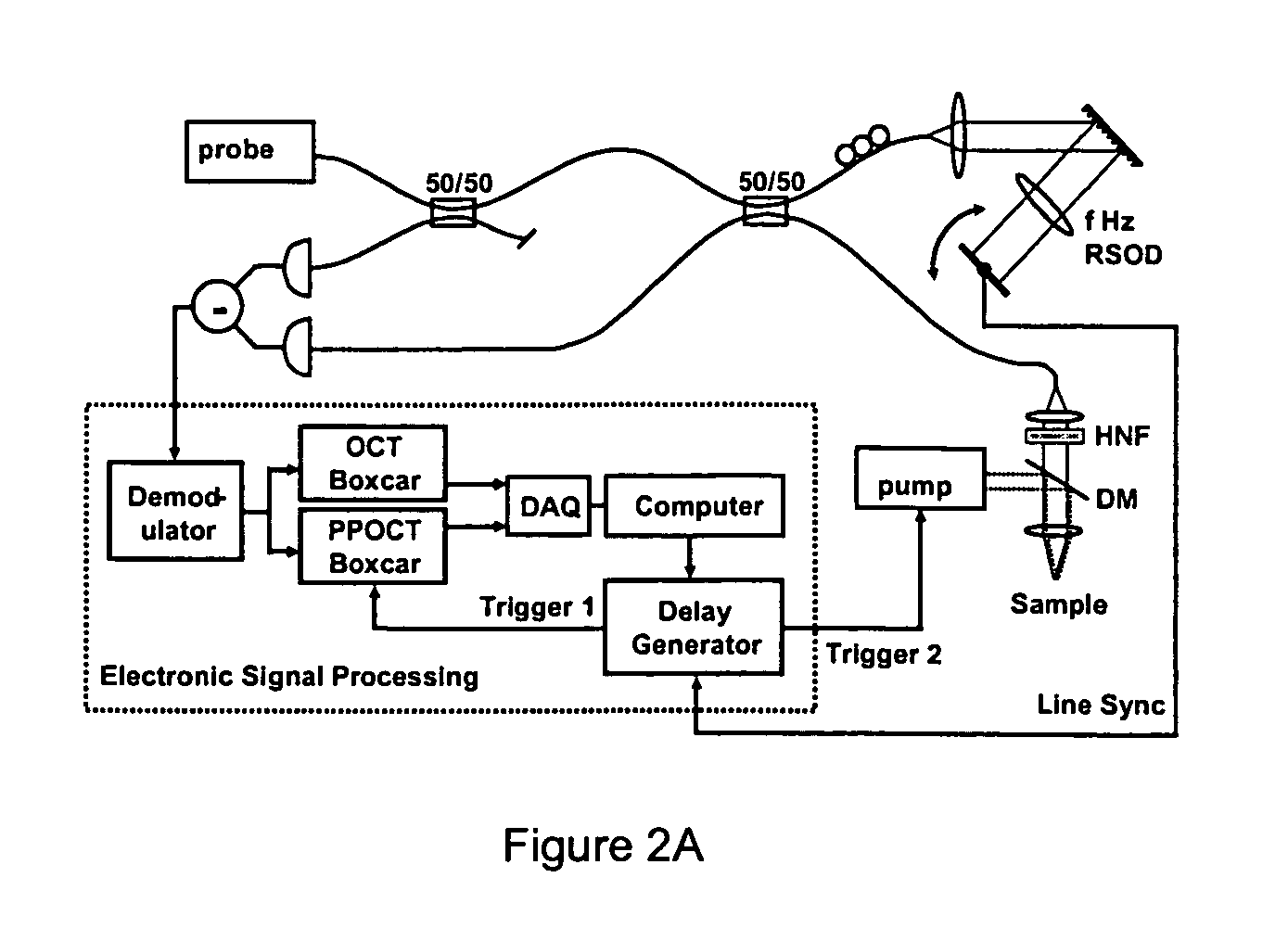
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
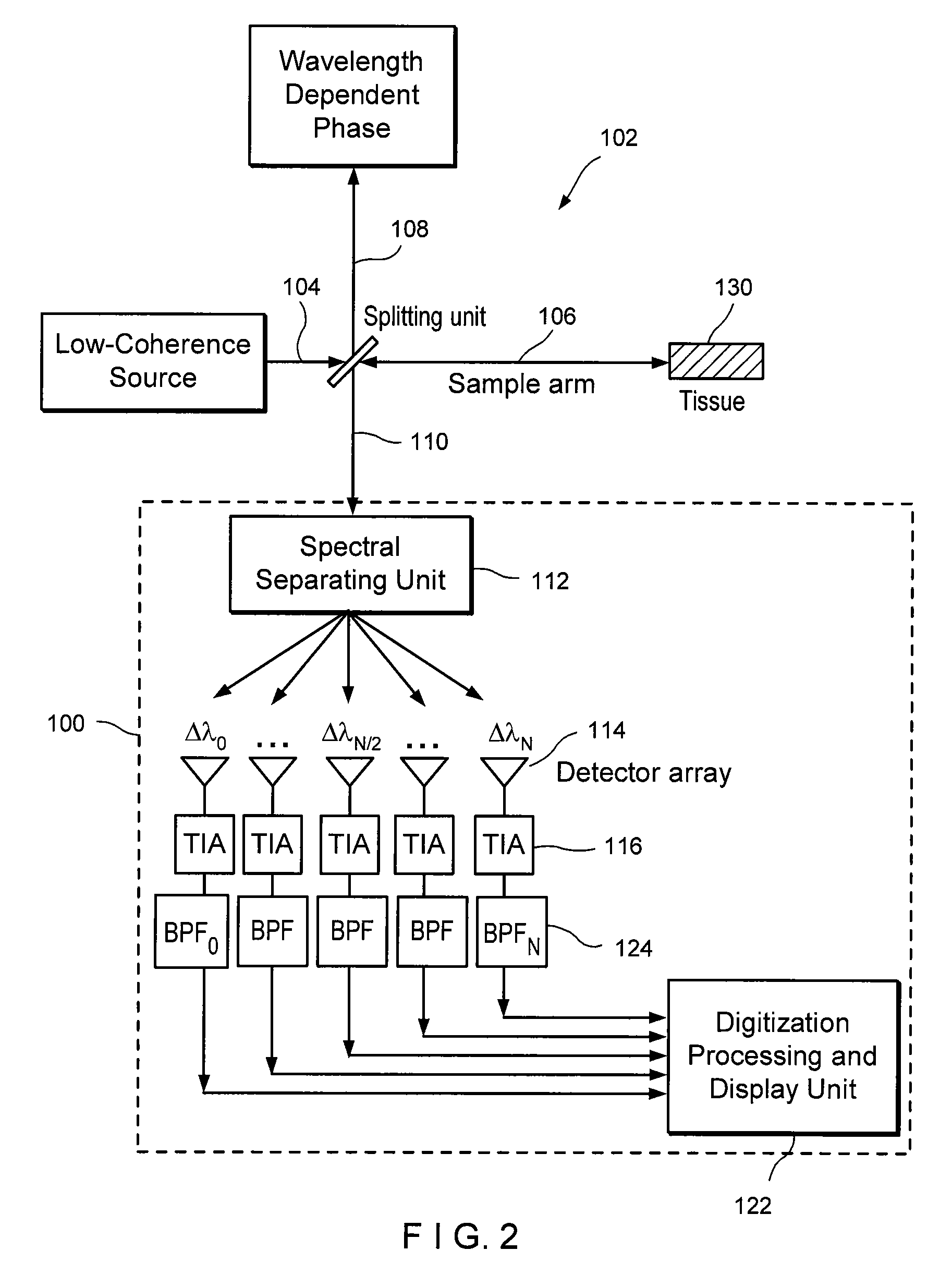
InactiveUS7355716B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
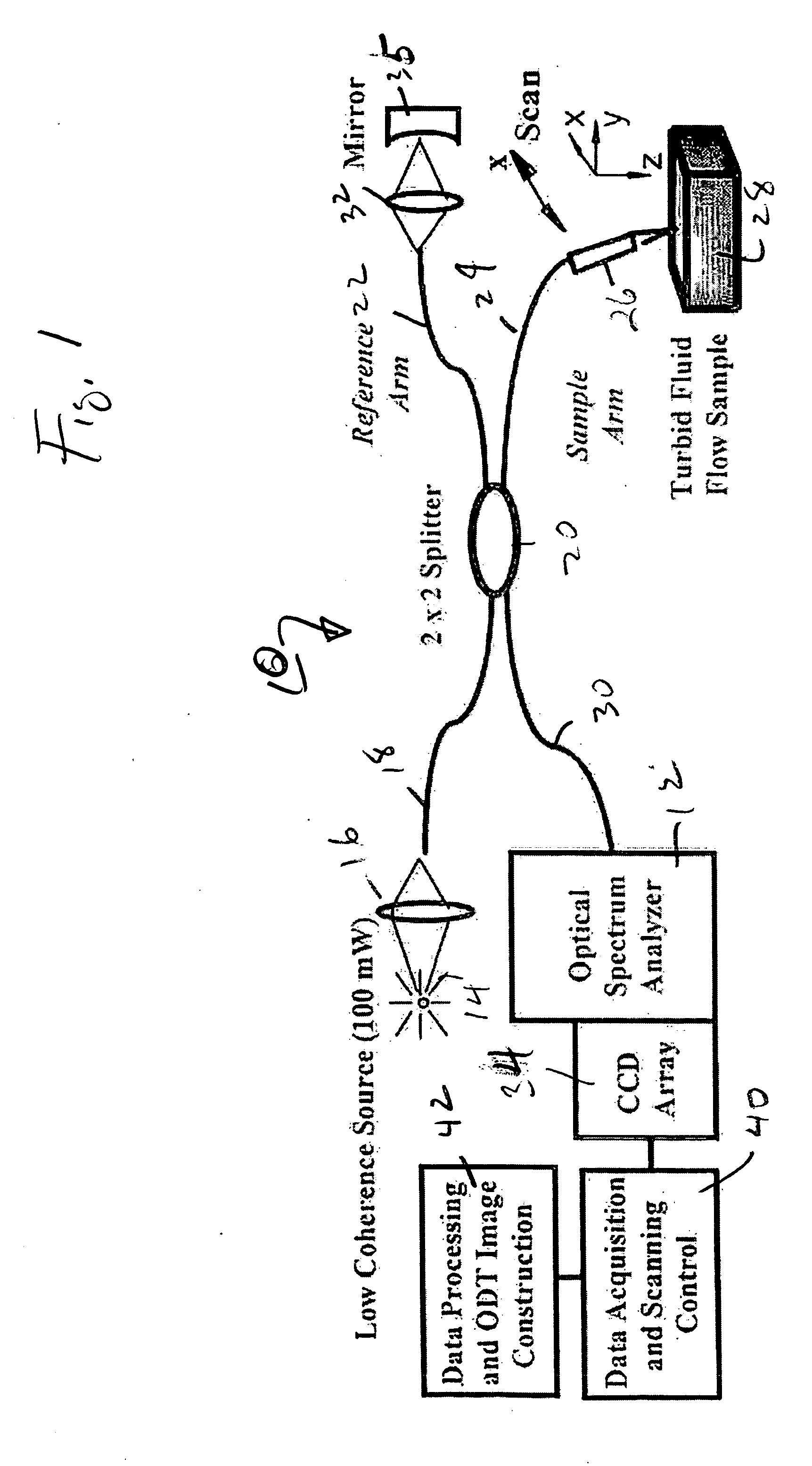
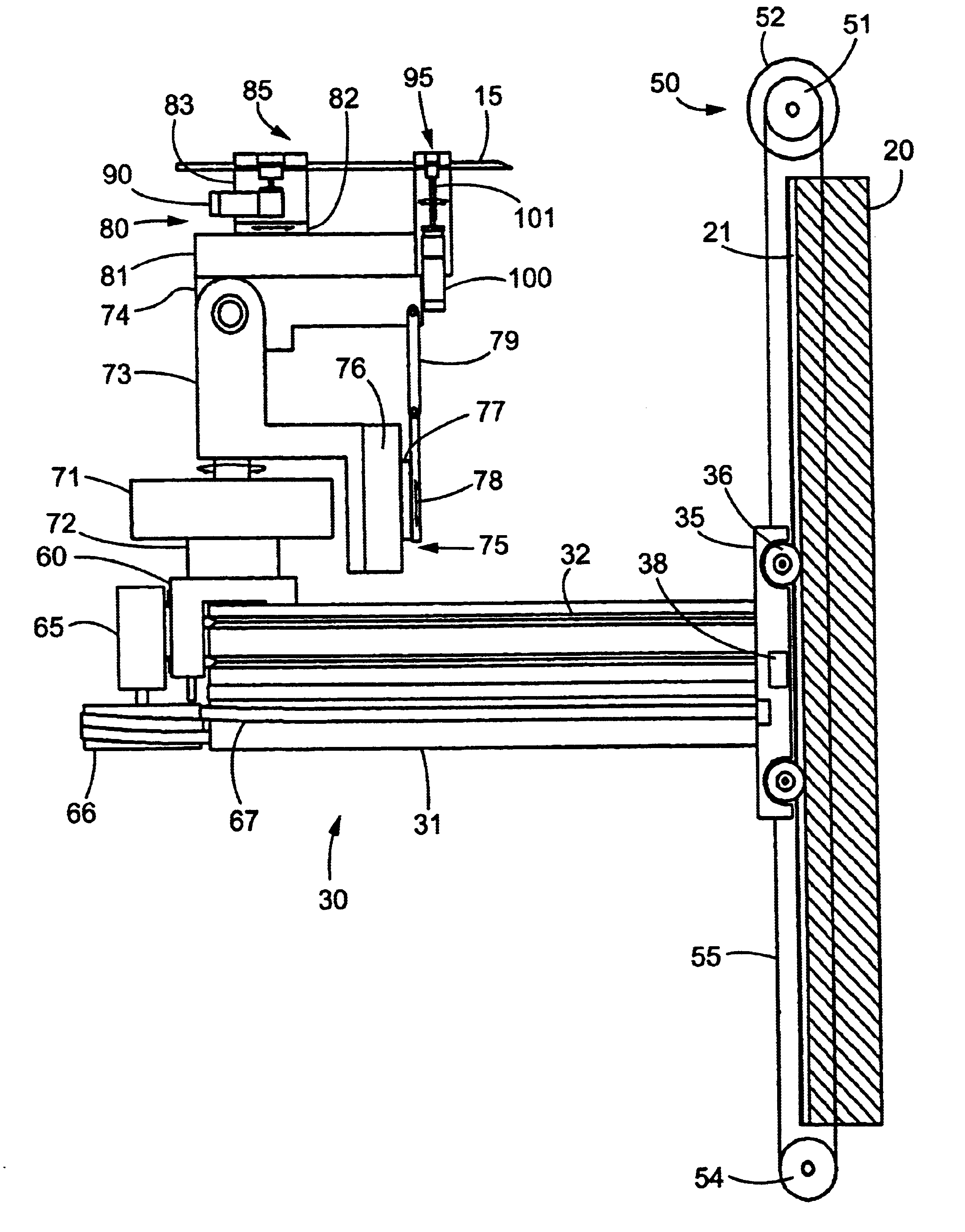
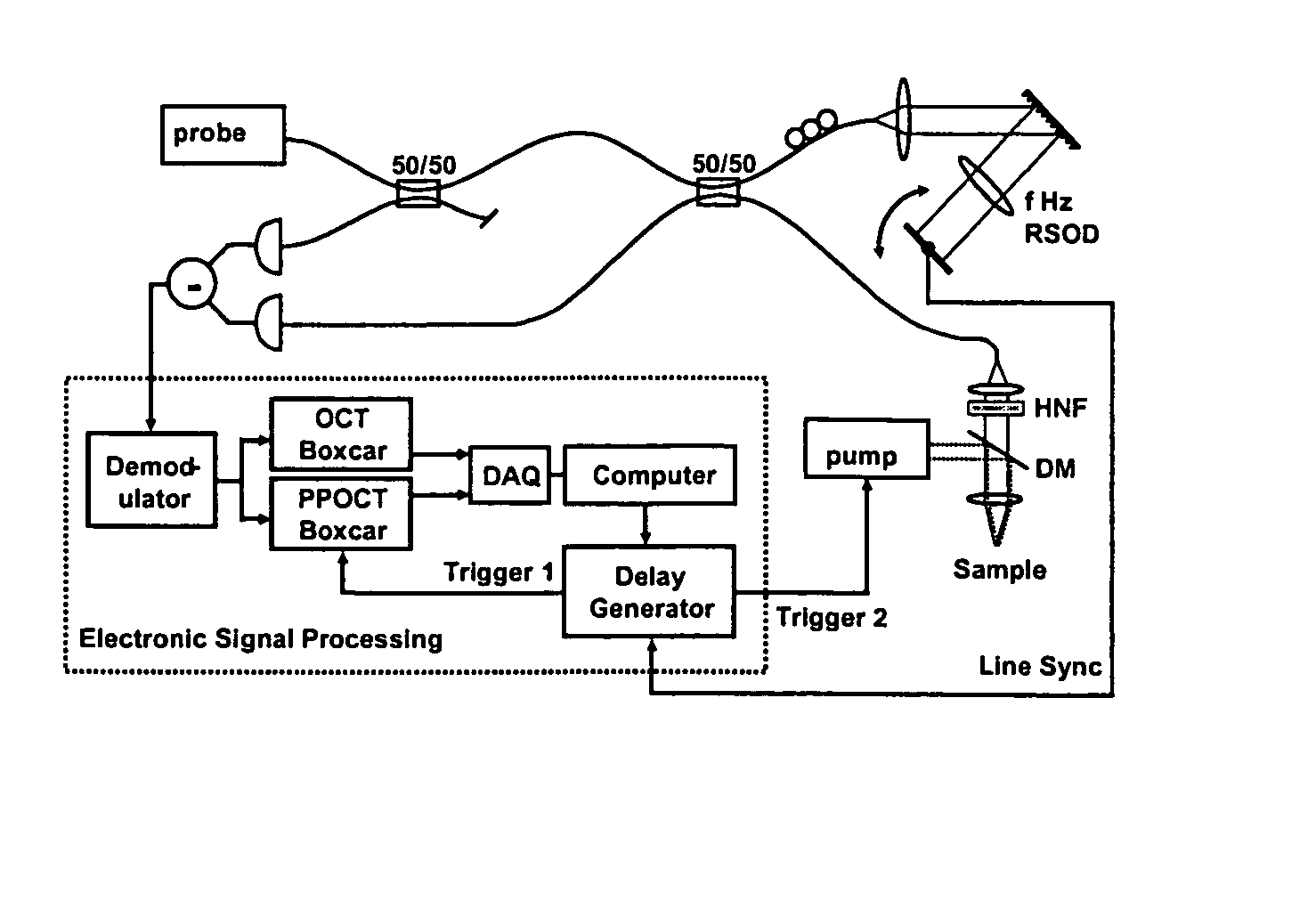
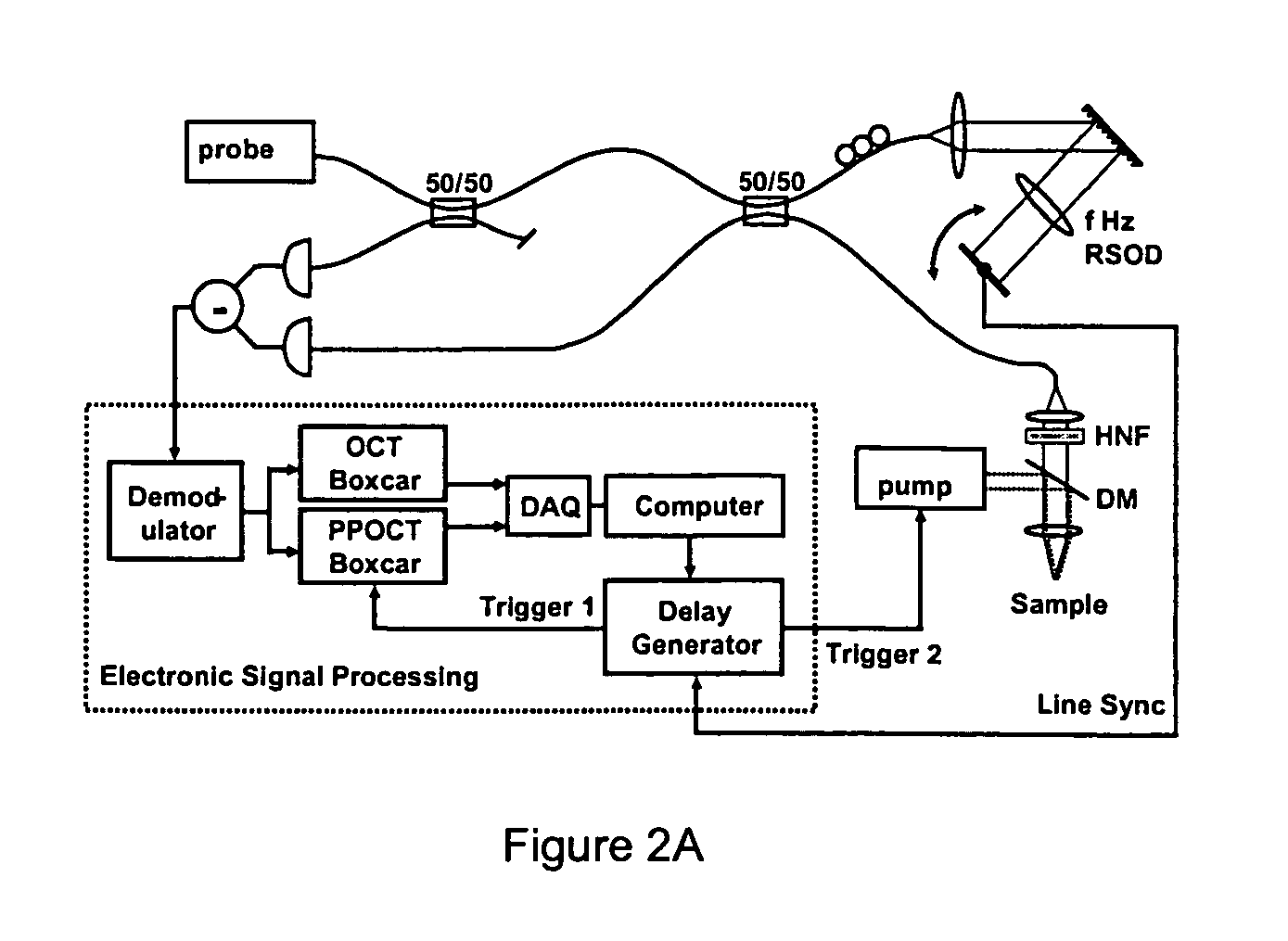
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
ActiveUS20050171438A1Accurate settingImprove system sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood flowIn vivo
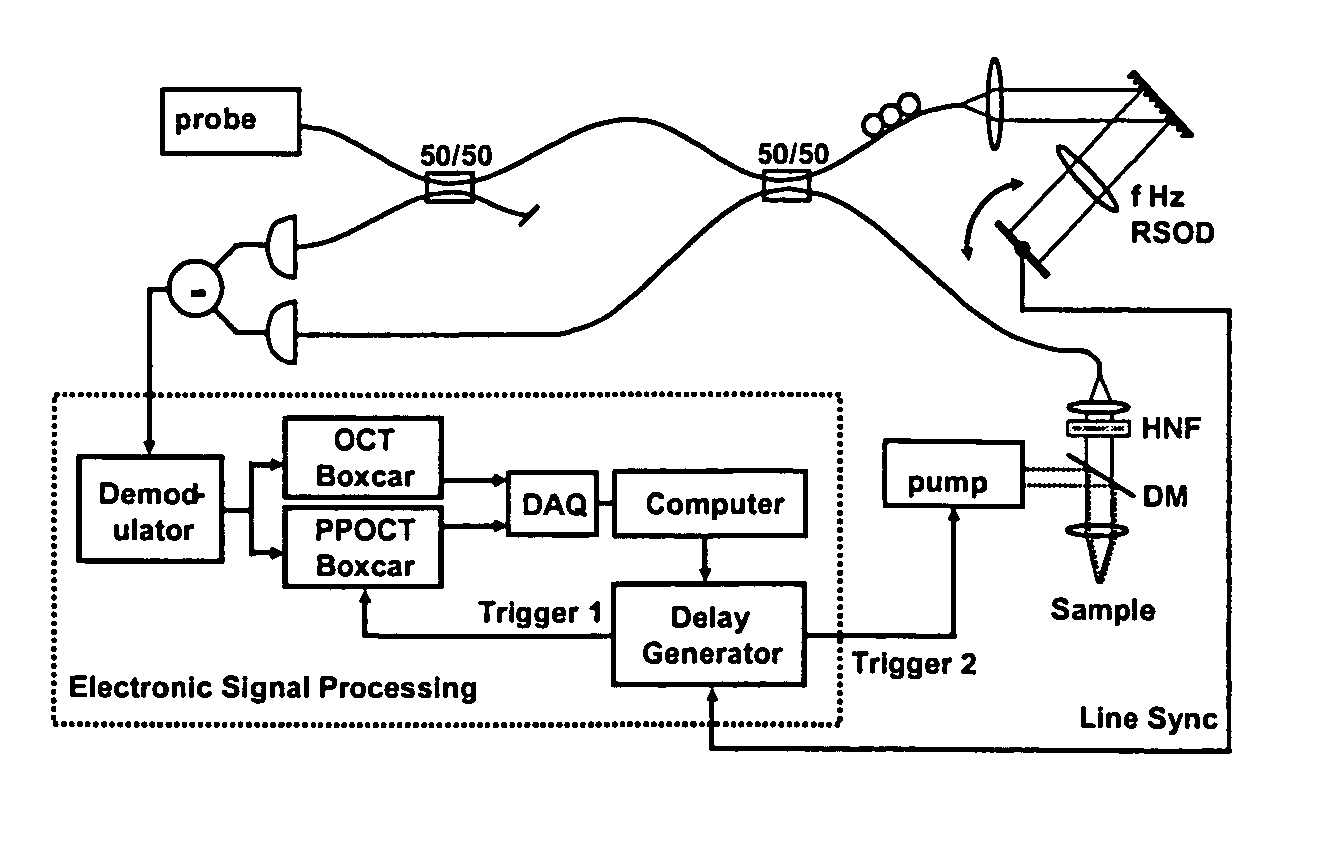
A method for tomographic imaging comprises the steps of providing a source of at least partially coherent radiation and a frequency-swept laser source through an interferometer; phase modulating the radiation in the interferometer at a modulation frequency for elimination of DC and autocorrelation noises as well as the mirror image; detecting interference fringes of the radiation backscattered from the sample into the interferometer to obtain a spectral signal; transforming the spectral signal of the detected backscattered interference fringes to obtain a time and location dependent signal, including the Doppler shift and variance, at each pixel location in a data window; and generating a tomographic image of the fluid flow in the data window and of the structure of the scanned fluid flow sample in the data window from the time and location dependent signal. The apparatus comprises a system for tomographic imaging operating according to the above method.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Medical manipulator for use with an imaging device
InactiveUS6665554B1Easy to insertLess stressSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDegrees of freedomEngineering
A manipulator for use in medical procedures can manipulate a medical tool with one or more degrees of freedom with respect to a patient. The manipulator is particularly useful for positioning a medical tool with respect to a patient disposed inside an imaging device such as a computer tomography machine.
Owner:MICRODEXTERITY SYST
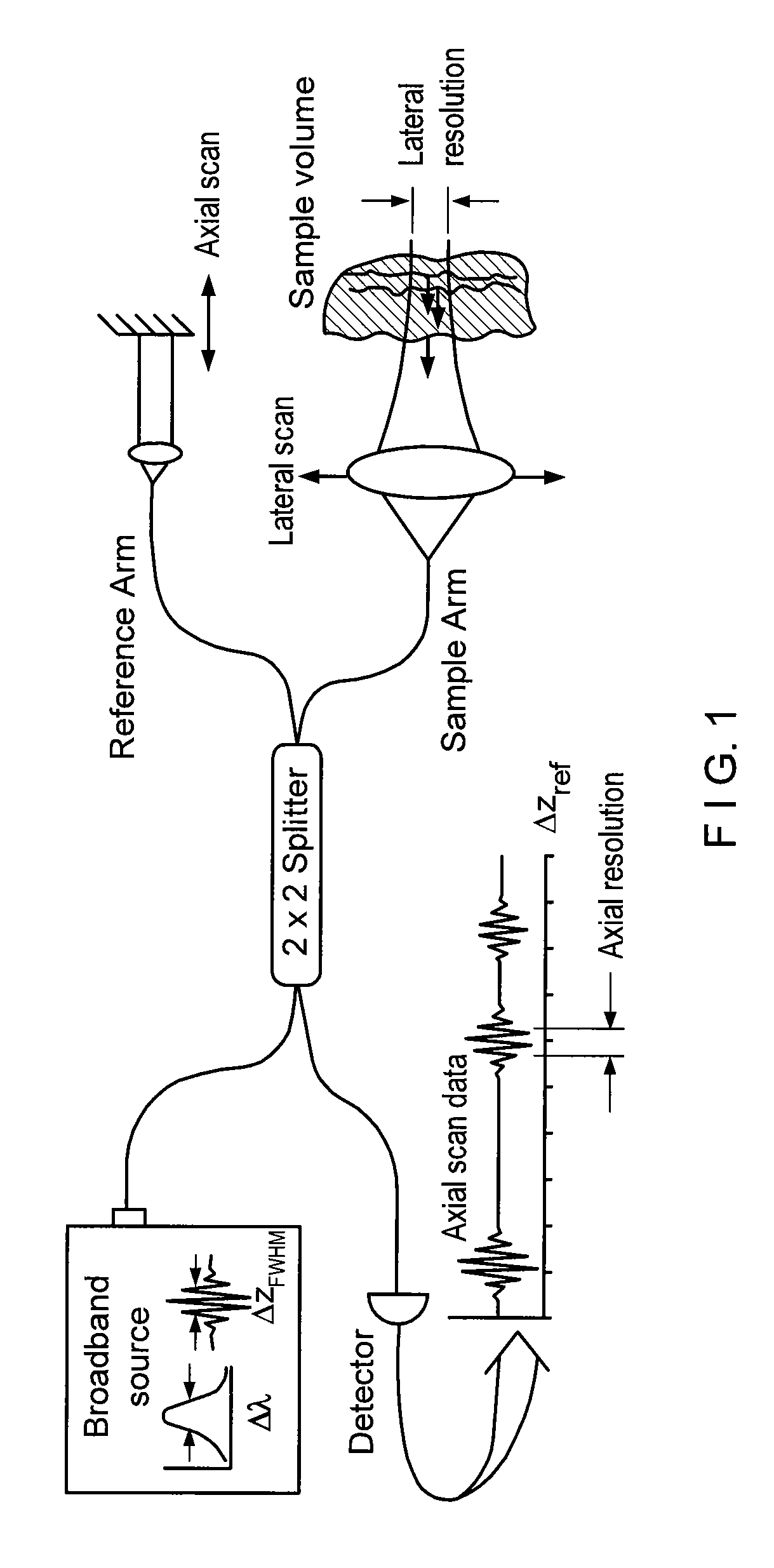
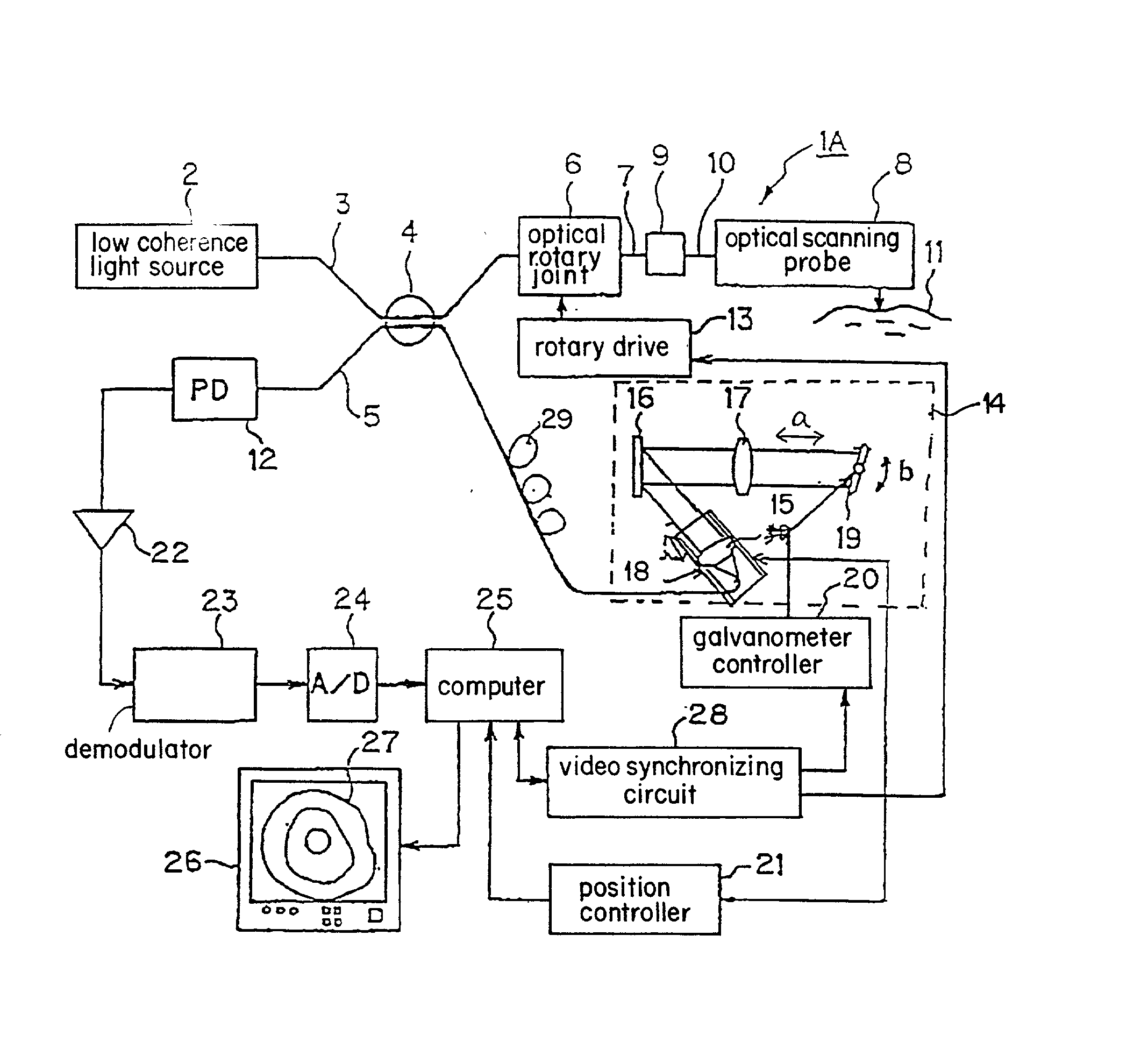
Methods and apparatus for optical coherence tomography scanning
ActiveUS20060187462A1Large and substantially motion error freePrecise positioningEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyComputer science
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
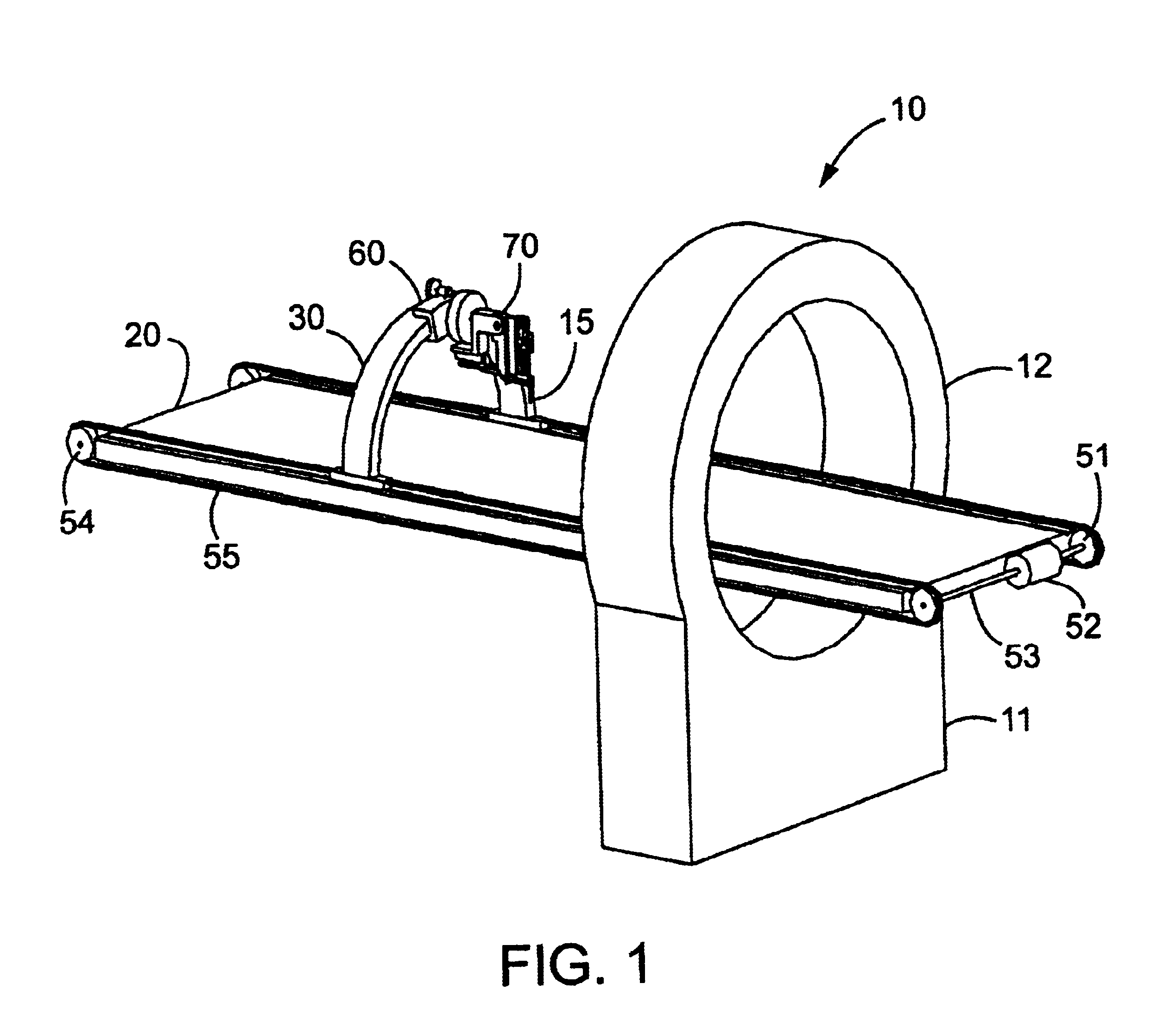
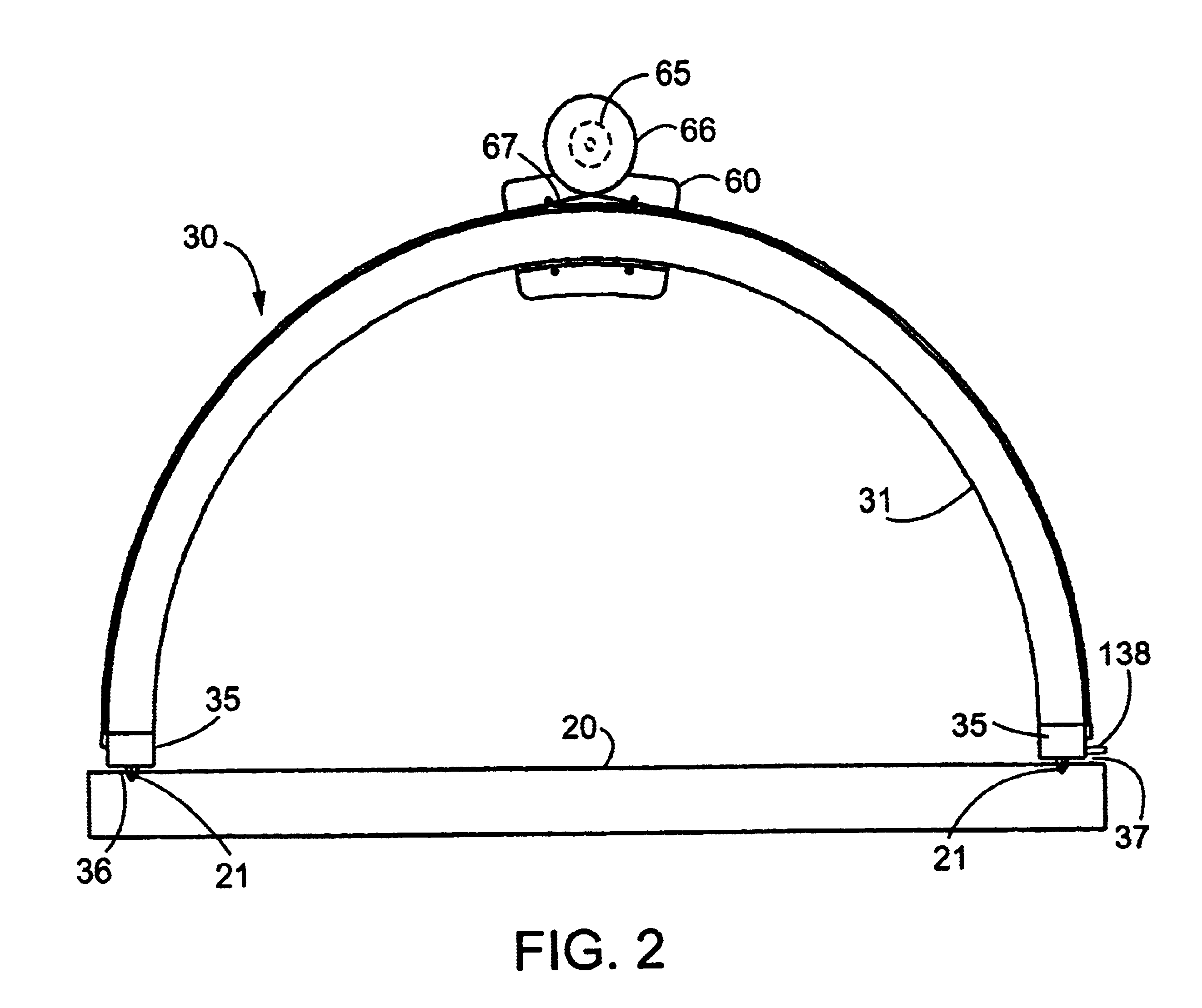
Cantilevered gantry apparatus for x-ray imaging
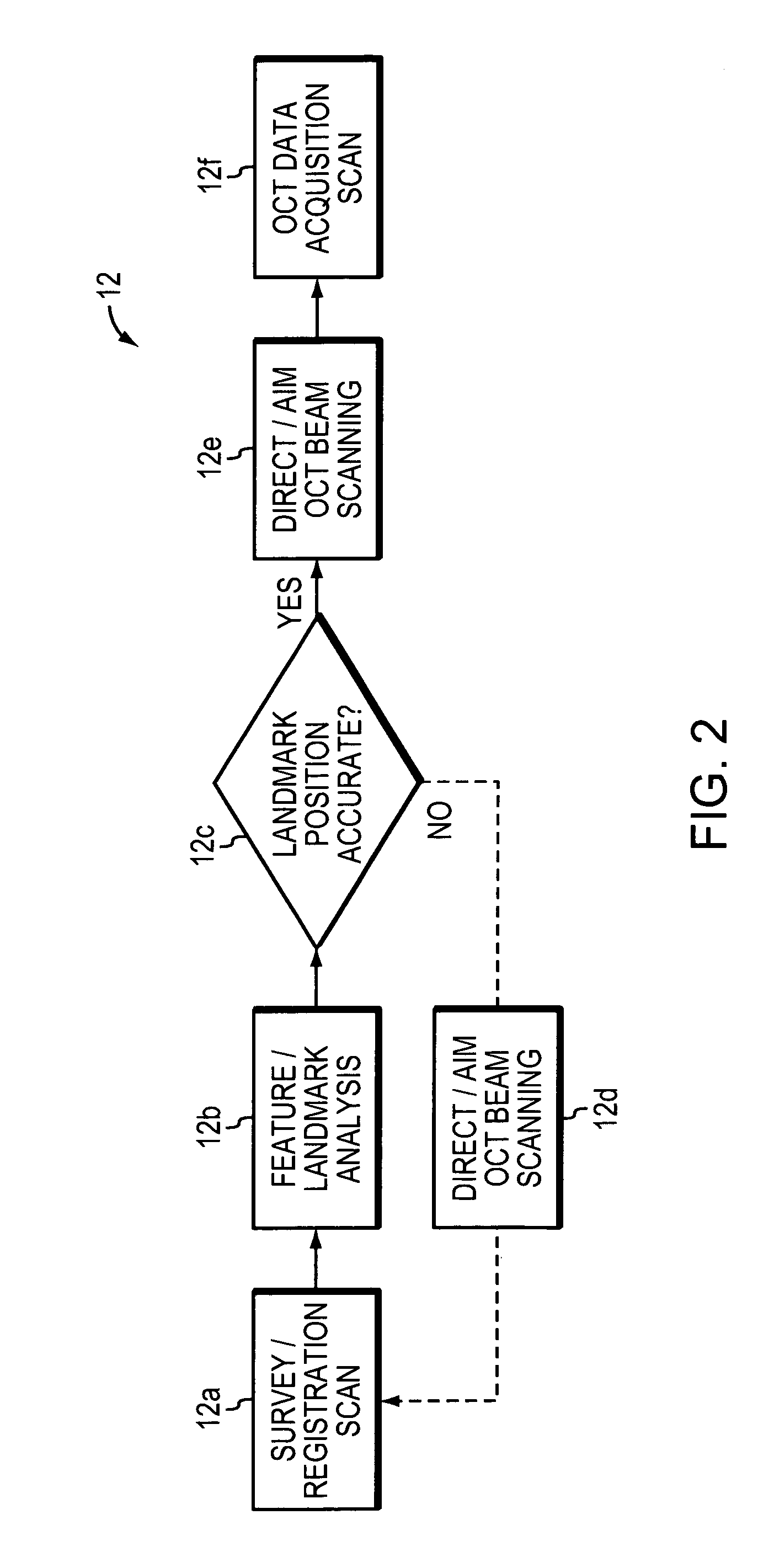
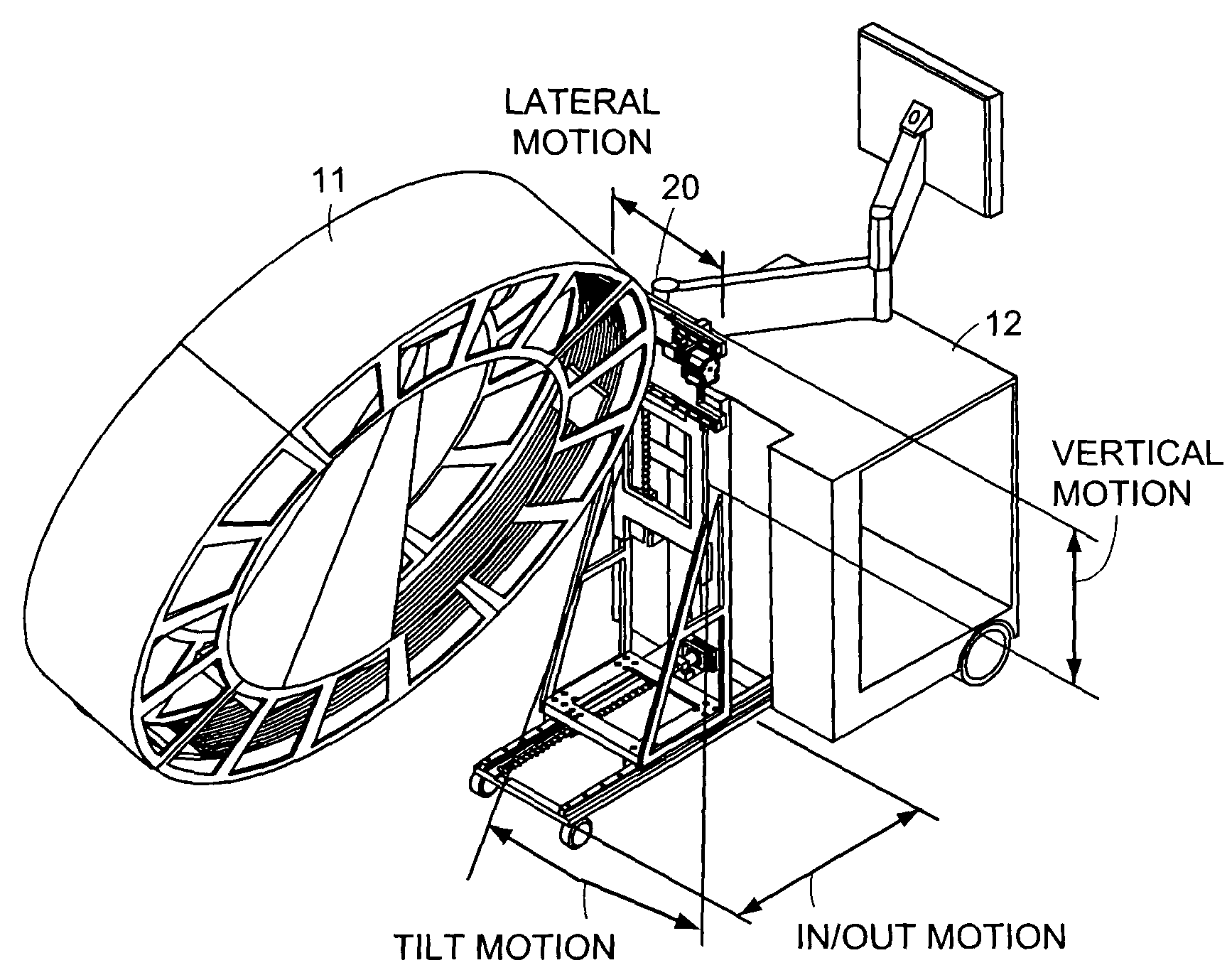
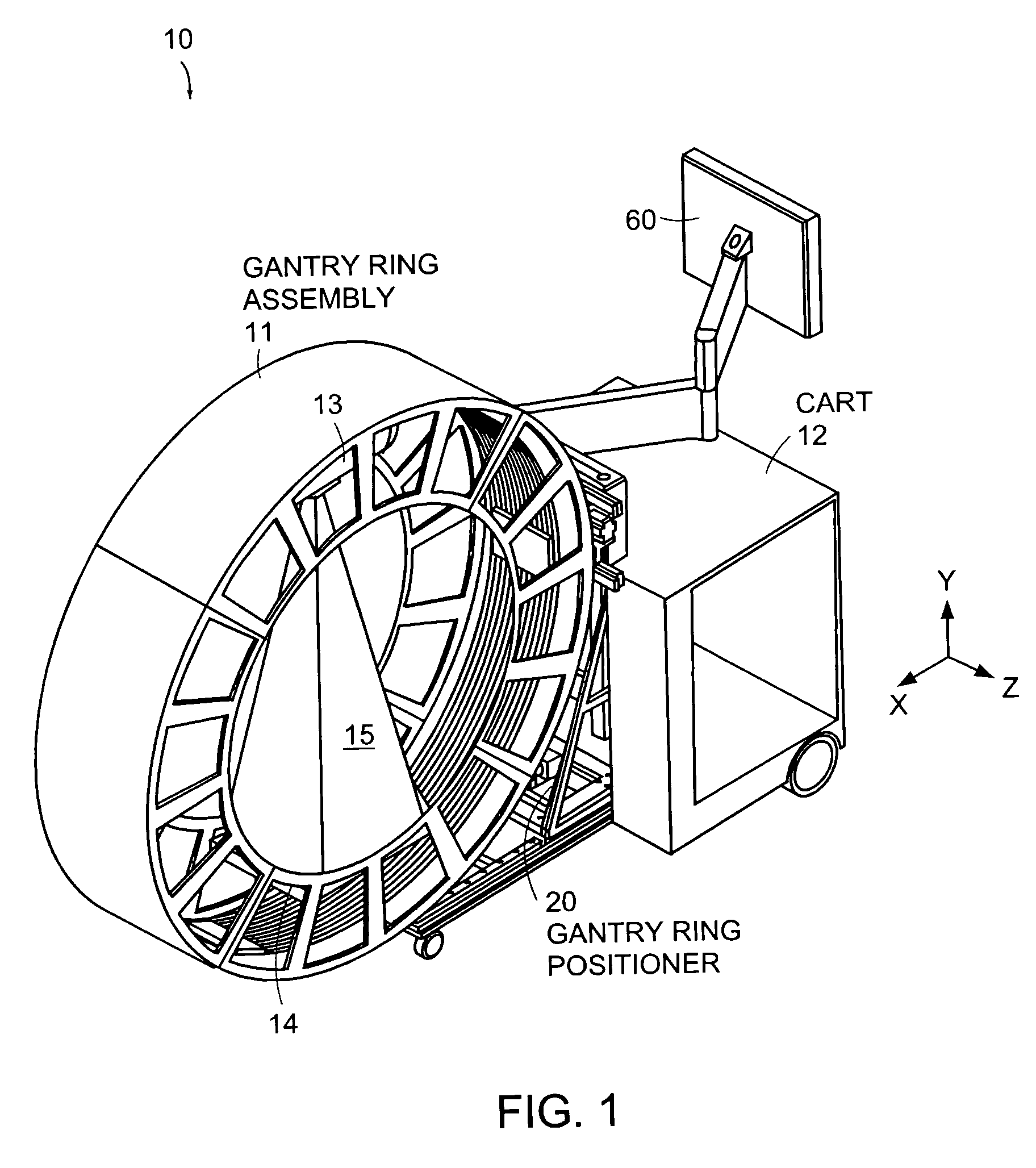
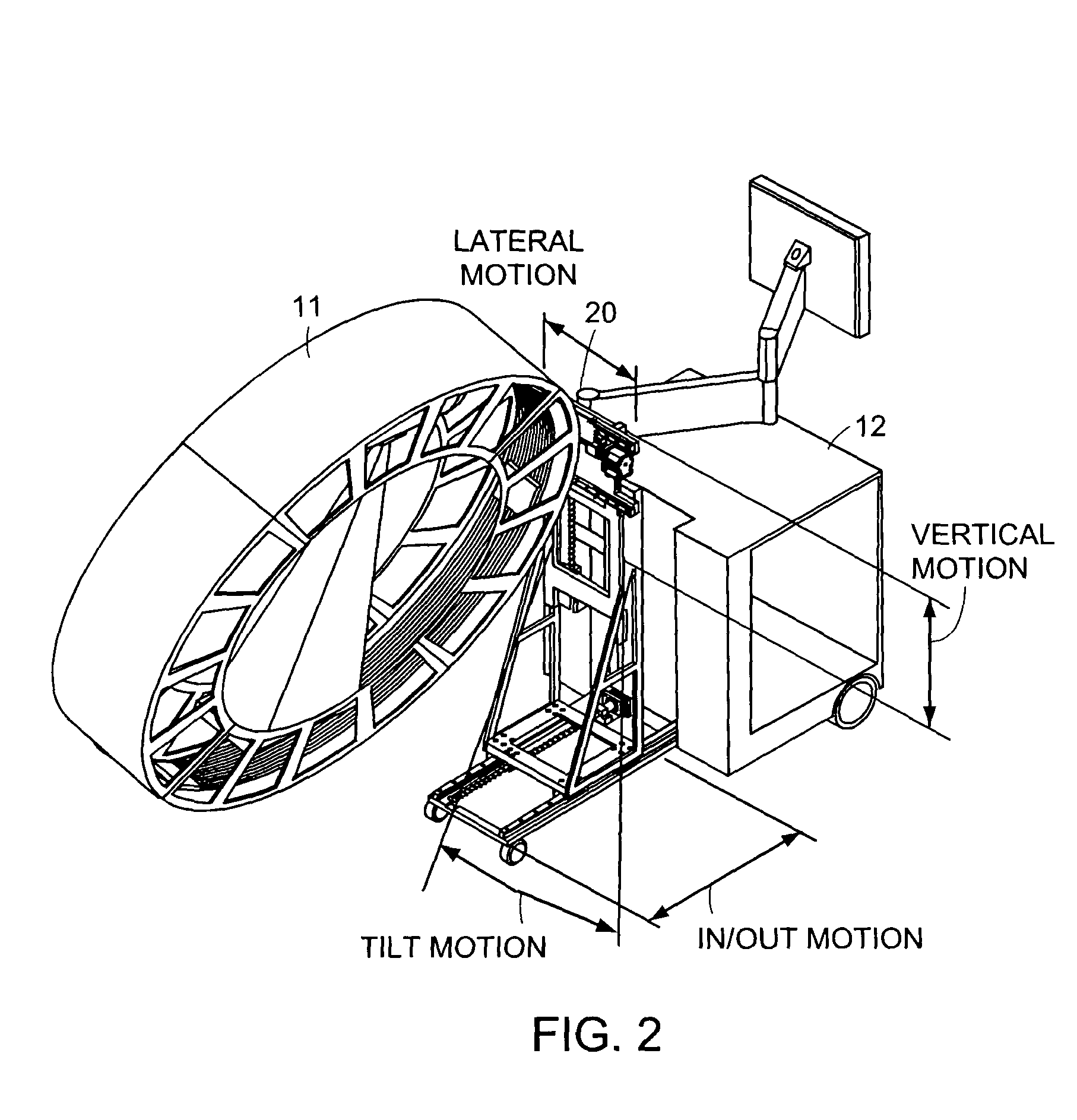
An x-ray scanning imaging apparatus with a rotatably fixed generally O-shaped gantry ring, which is connected on one end of the ring to support structure, such as a mobile cart, ceiling, floor, wall, or patient table, in a cantilevered fashion. The circular gantry housing remains rotatably fixed and carries an x-ray image-scanning device that can be rotated inside the gantry around the object being imaged either continuously or in a step-wise fashion. The ring can be connected rigidly to the support, or can be connected to the support via a ring positioning unit that is able to translate or tilt the gantry relative to the support on one or more axes. Multiple other embodiments exist in which the gantry housing is connected on one end only to the floor, wall, or ceiling. The x-ray device is particularly useful for two-dimensional multi-planar x-ray imaging and / or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) imaging applications
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
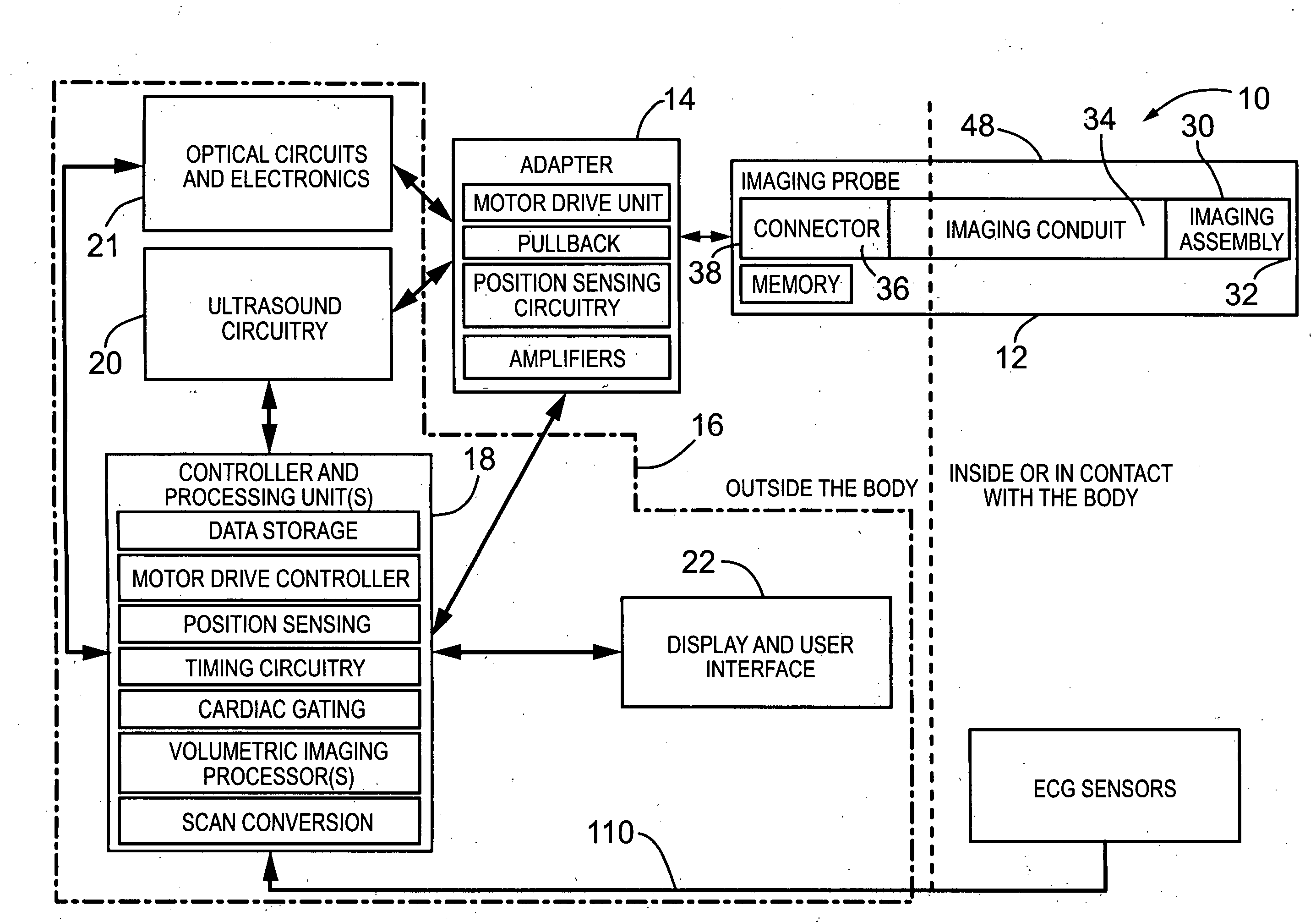
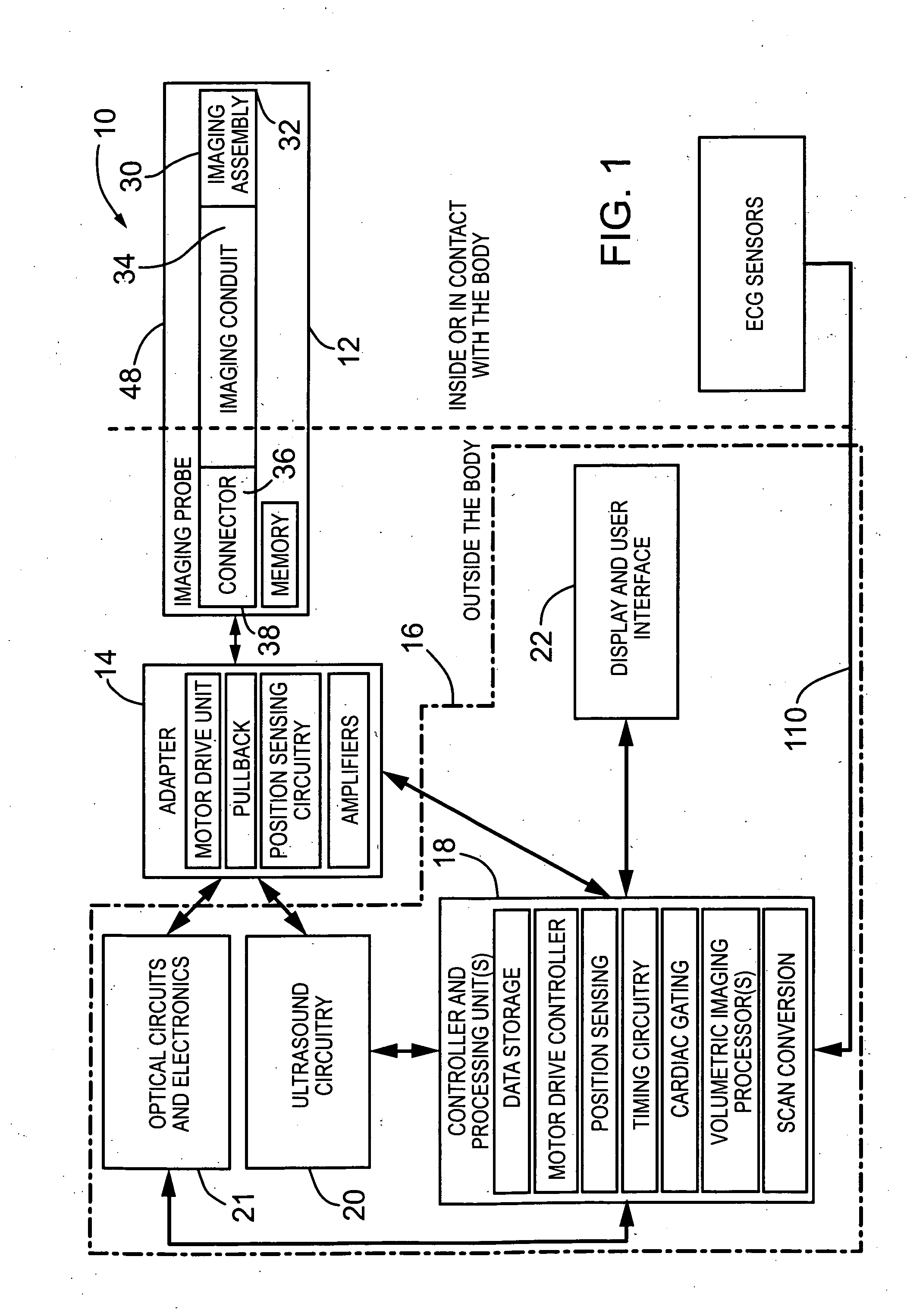
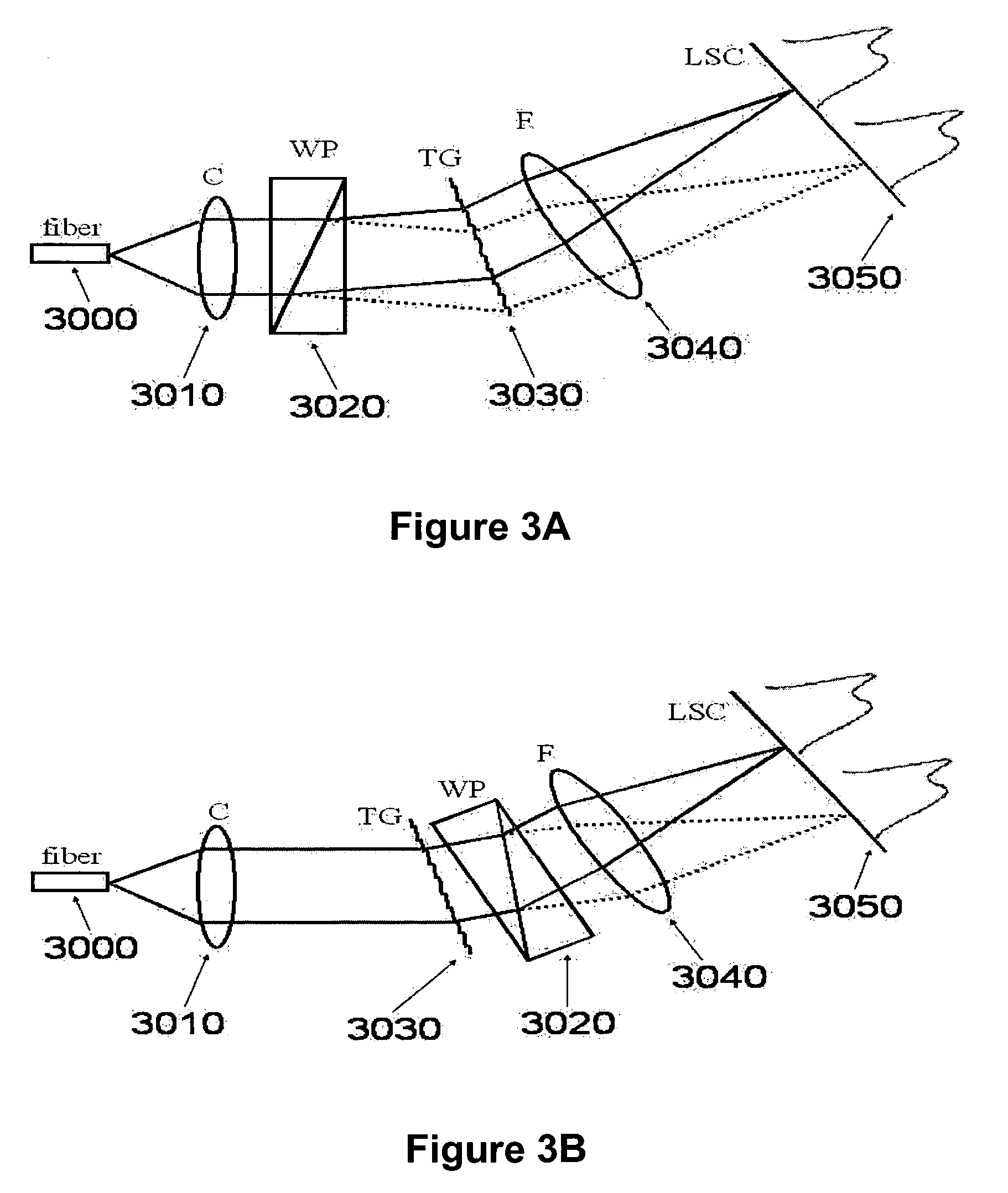
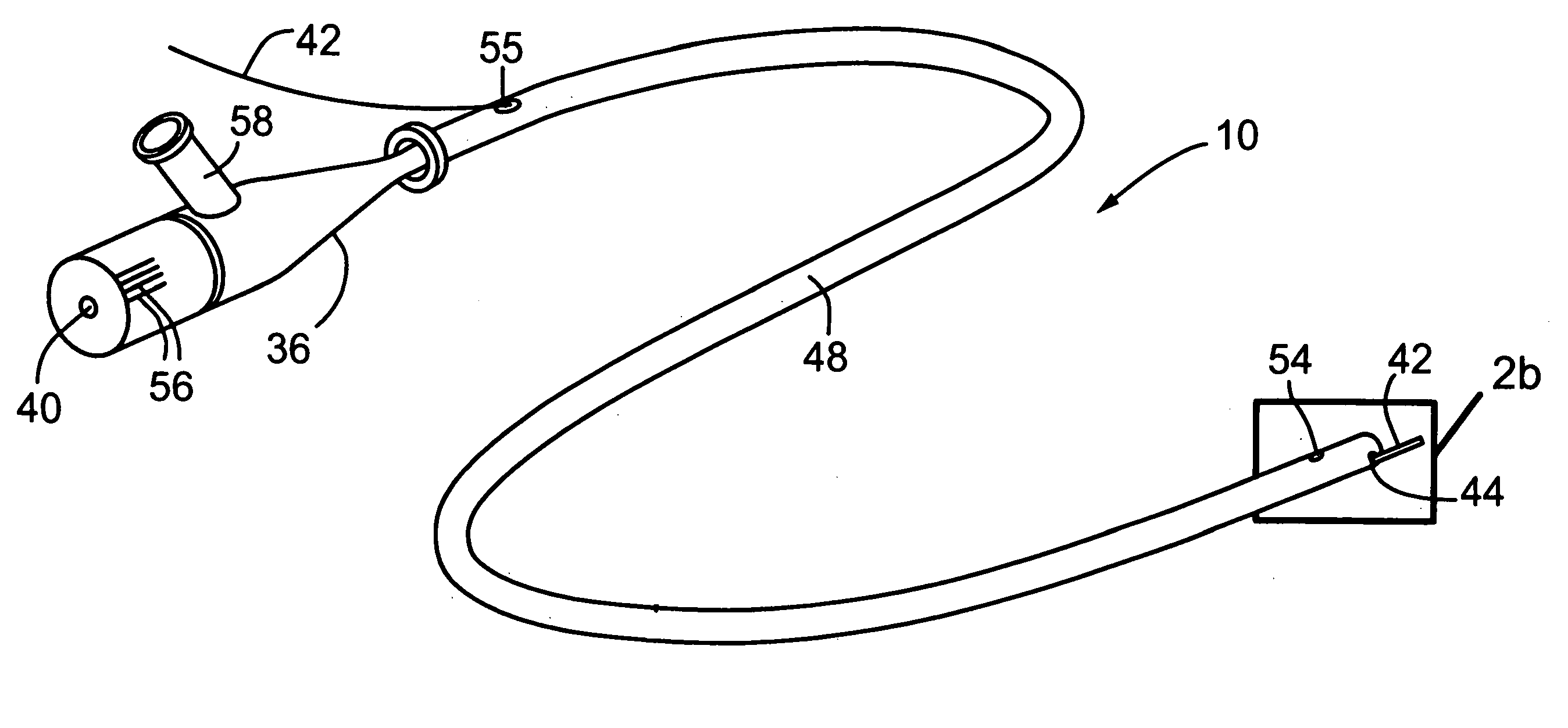
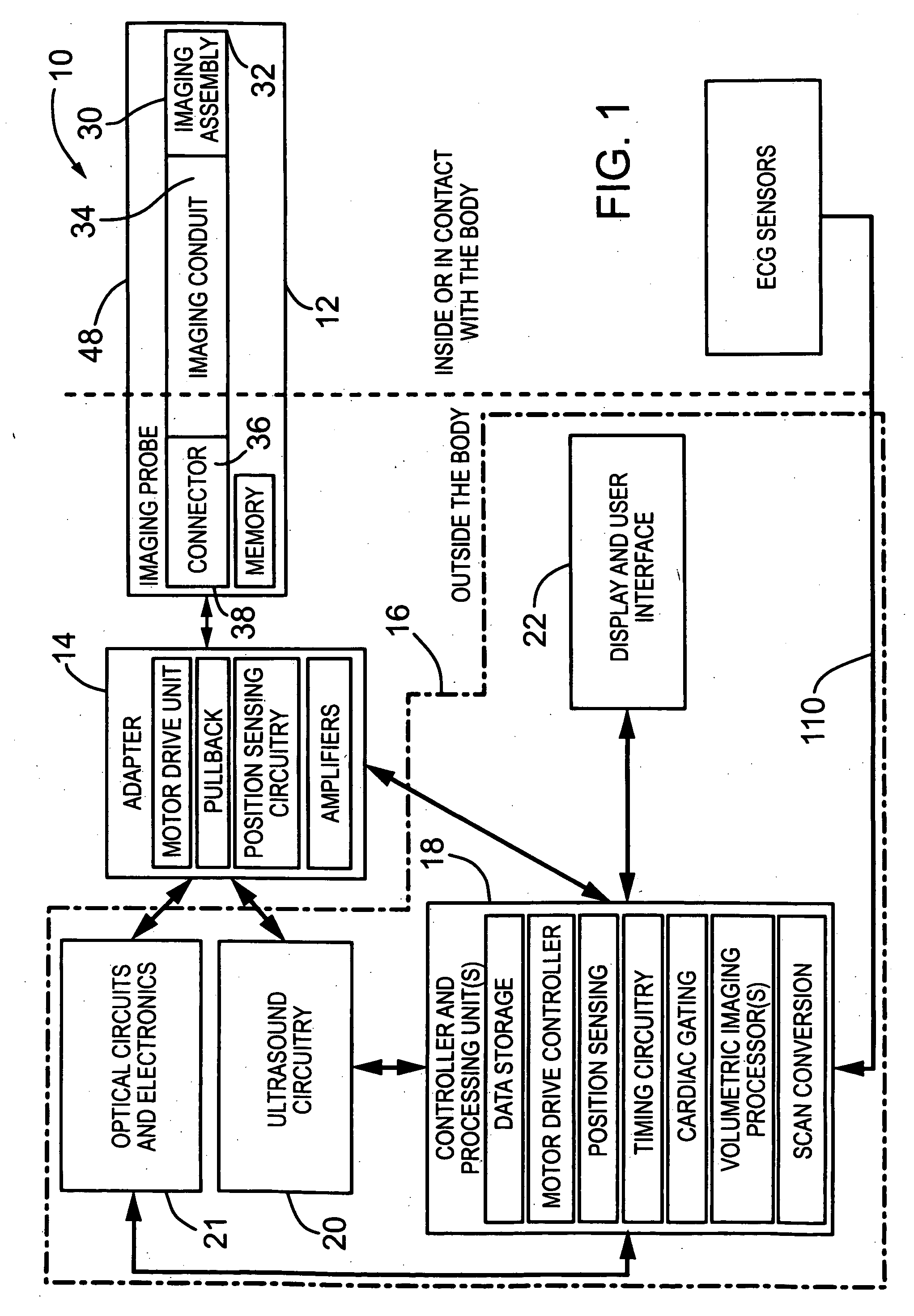
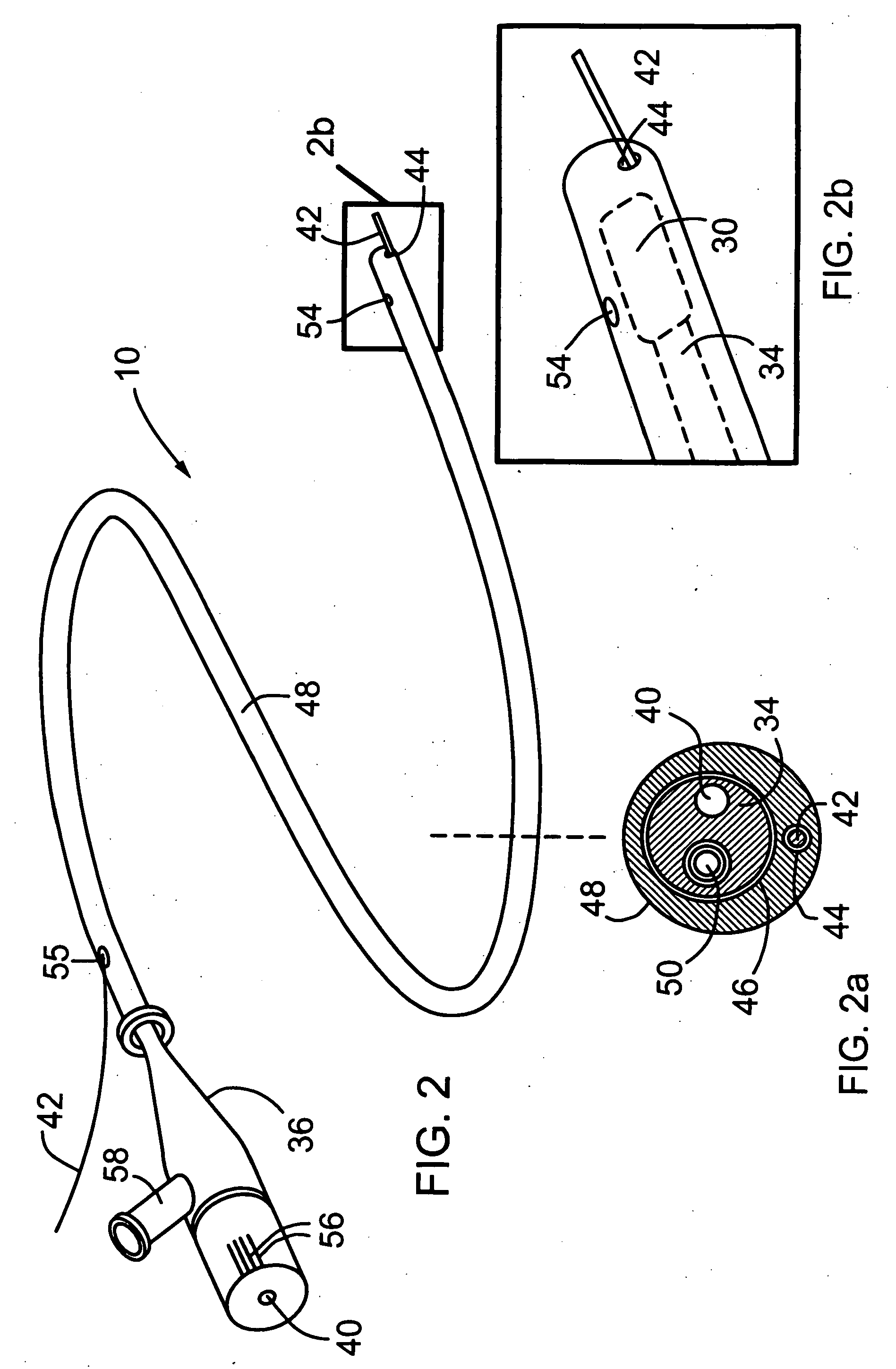
Imaging probe with combined ultrasounds and optical means of imaging
ActiveUS20080177183A1Provide goodFacilitates simultaneous imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryHigh resolution imagingMammalian tissue
The present invention provides an imaging probe for imaging mammalian tissues and structures using high resolution imaging, including high frequency ultrasound and optical coherence tomography. The imaging probes structures using high resolution imaging use combined high frequency ultrasound (IVUS) and optical imaging methods such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and to accurate co-registering of images obtained from ultrasound image signals and optical image, signals during scanning a region of interest.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
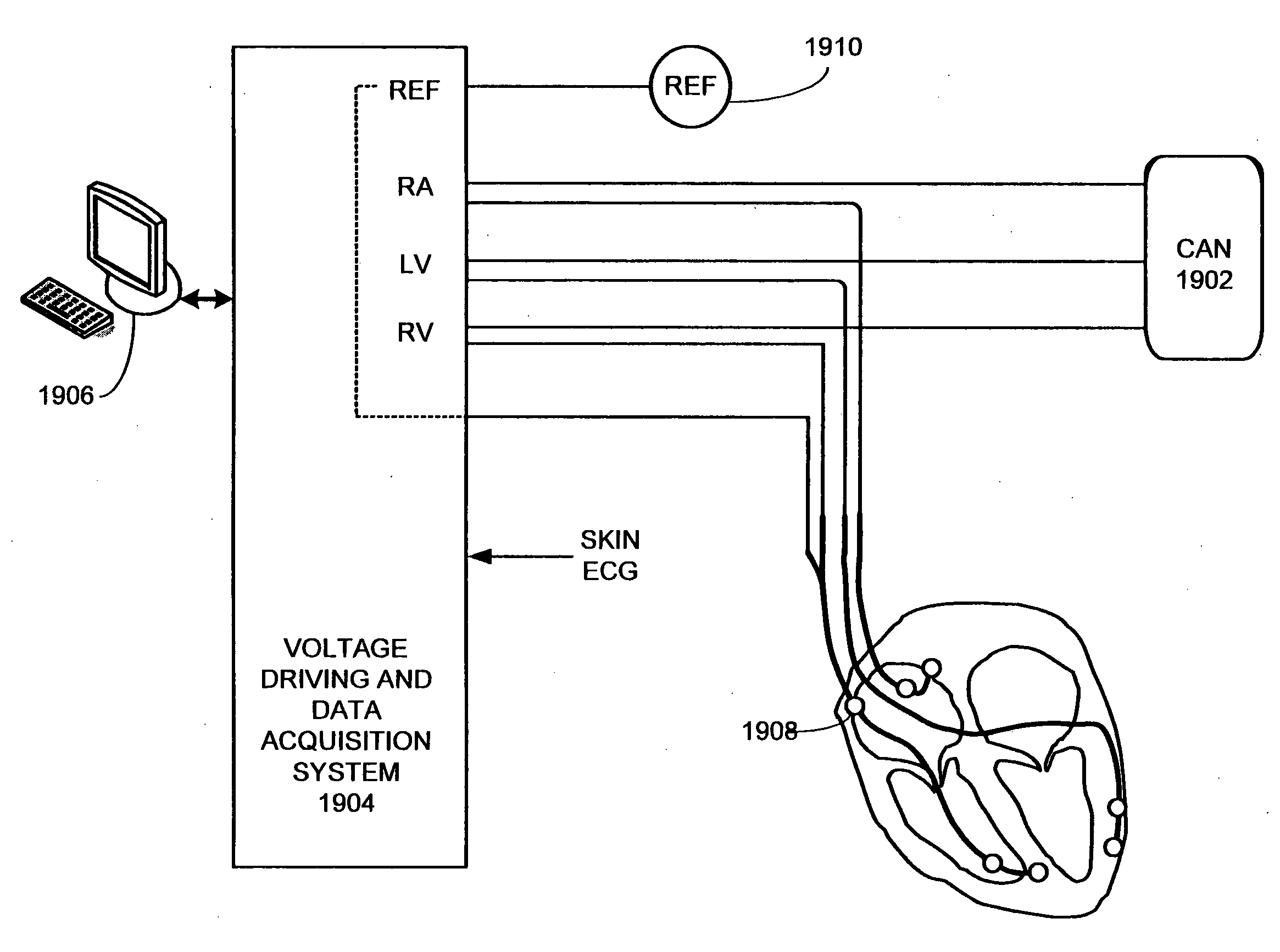
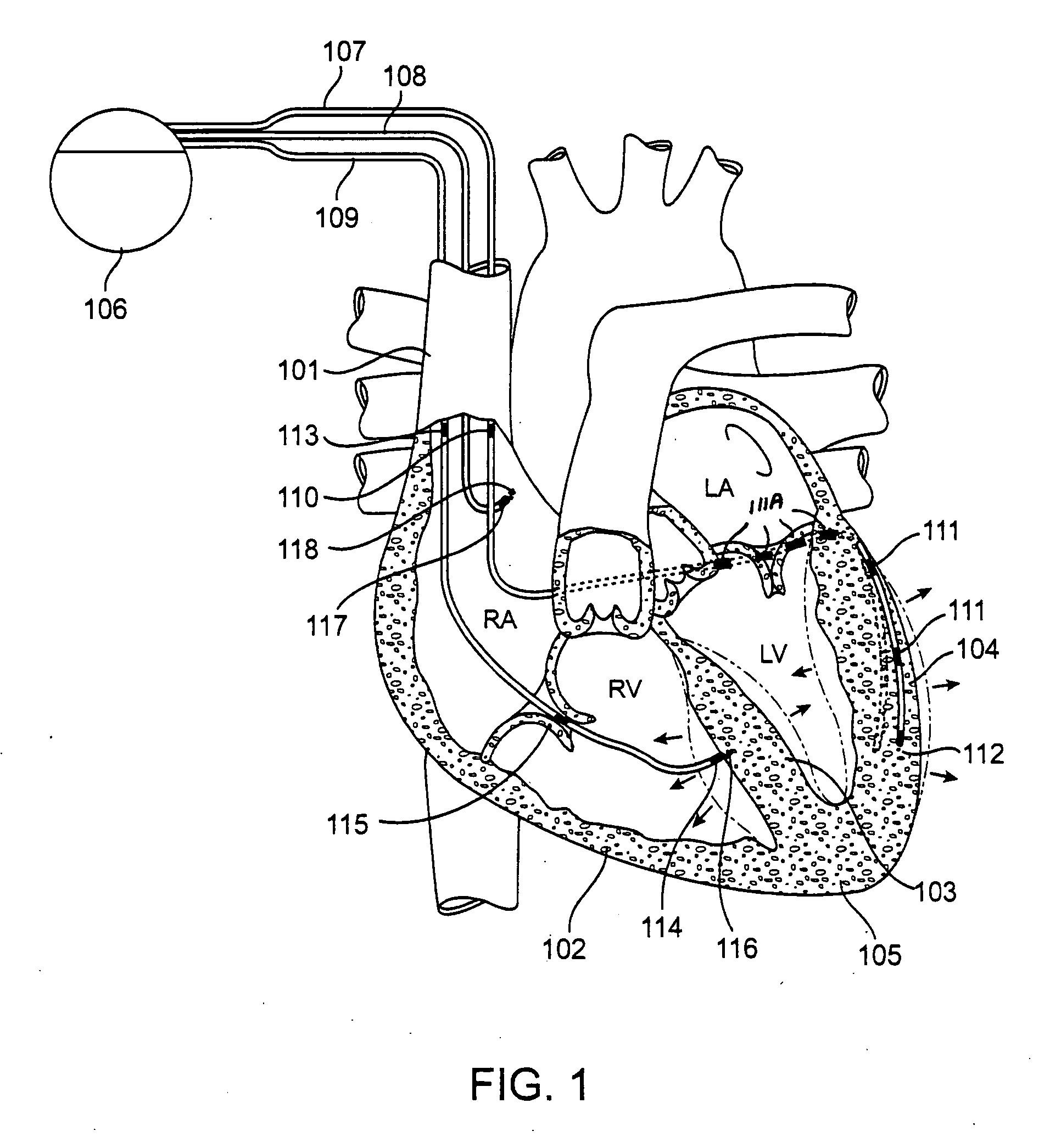
Electric tomography
Methods for evaluating motion of a tissue, such as of a cardiac location, e.g., heart wall, via electrical field tomography are provided. In the subject methods, an sensing element is stably associated with a tissue location of interest. Signals obtained from the sensing element are obtained to evaluate movement of the tissue location. Also provided are systems and devices for practicing the subject methods. In addition, innovative data displays and systems for producing the same are provided. The subject methods and devices find use in a variety of different applications, including cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Optical imaging device
An Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) device irradiates a biological tissue with low coherence light, obtains a high resolution tomogram of the inside of the tissue by low-coherent interference with scattered light from the tissue, and is provided with an optical probe which includes an optical fiber having a flexible and thin insertion part for introducing the low coherent light. When the optical probe is inserted into a blood vessel or a patient's body cavity, the OCT enables the doctor to observe a high resolution tomogram. In a optical probe, generally, a fluctuation of a birefringence occurs depending on a bend of the optical fiber, and this an interference contrast varies depending on the condition of the insertion. The OCT of the present invention is provided with polarization compensation means such as a Faraday rotator on the side of the light emission of the optical probe, so that the OCT can obtain the stabilized interference output regardless of the state of the bend.
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND +1
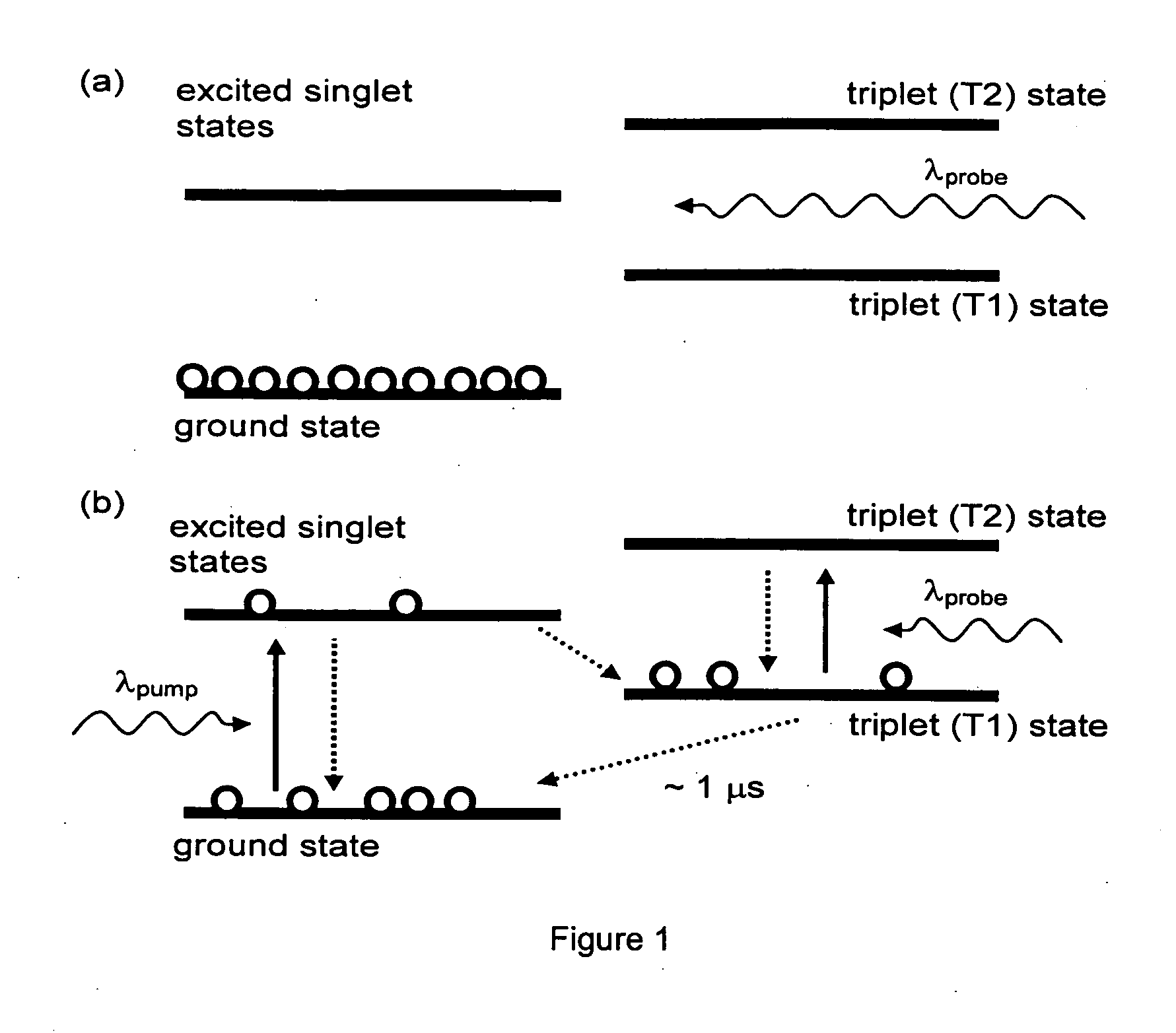
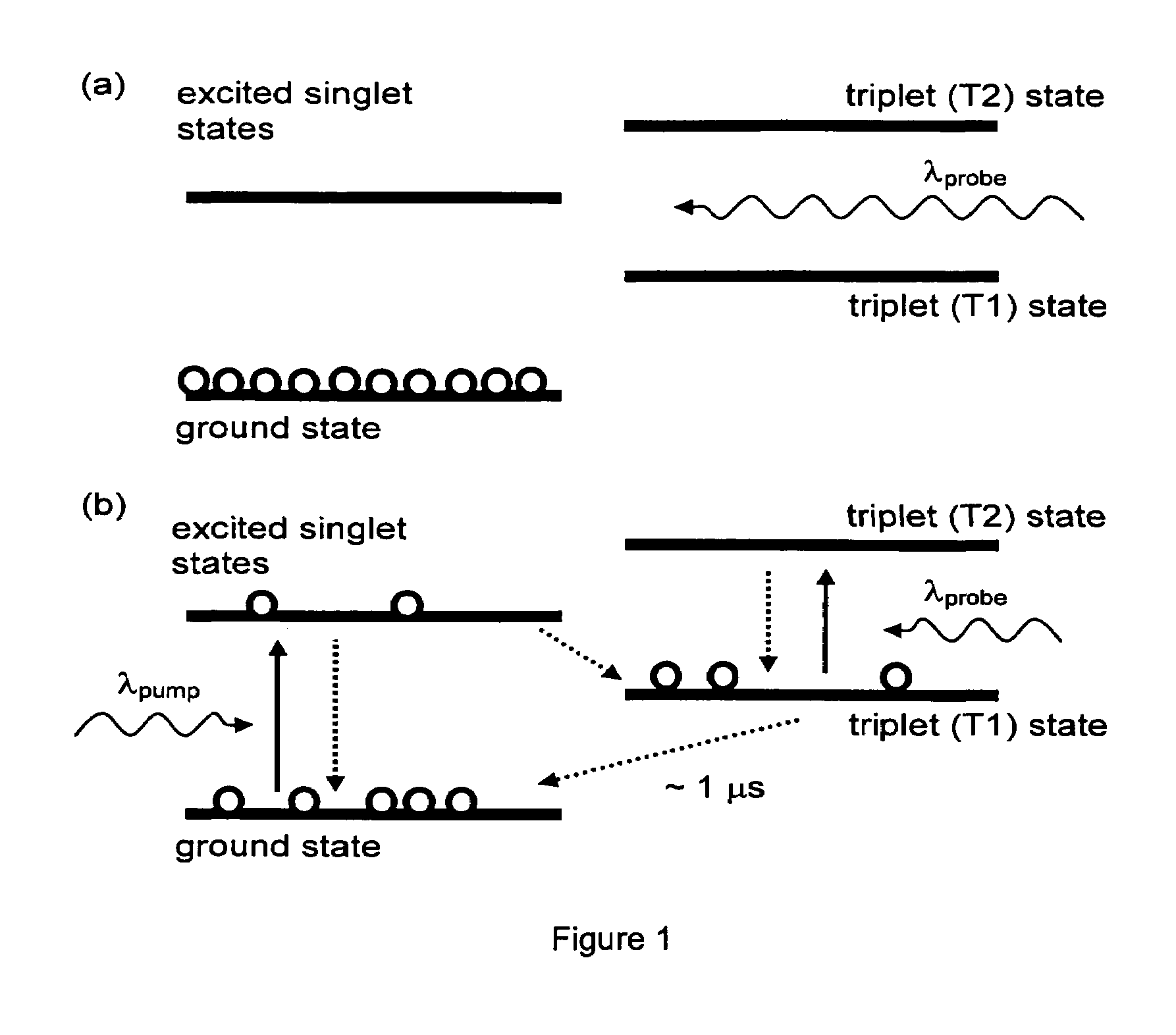
Method for optical coherence tomography imaging with molecular contrast
Spatial information, such as concentration and displacement, about a specific molecular contrast agent, may be determined by stimulating a sample containing the agent, thereby altering an optical property of the agent. A plurality of optical coherence tomography (OCT) images may be acquired, at least some of which are acquired at different stimulus intensities. The acquired images are used to profile the molecular contrast agent concentration distribution of the sample.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
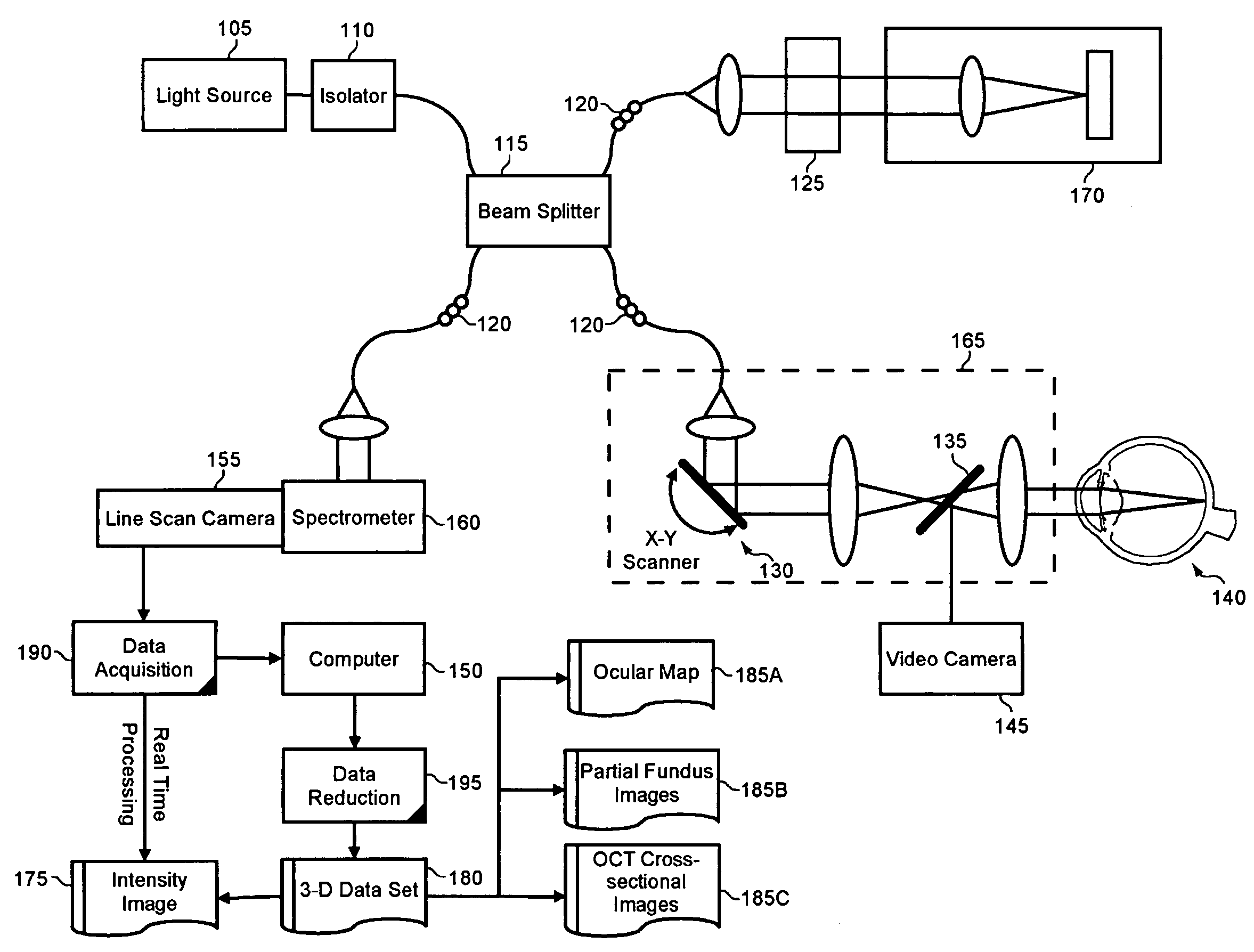
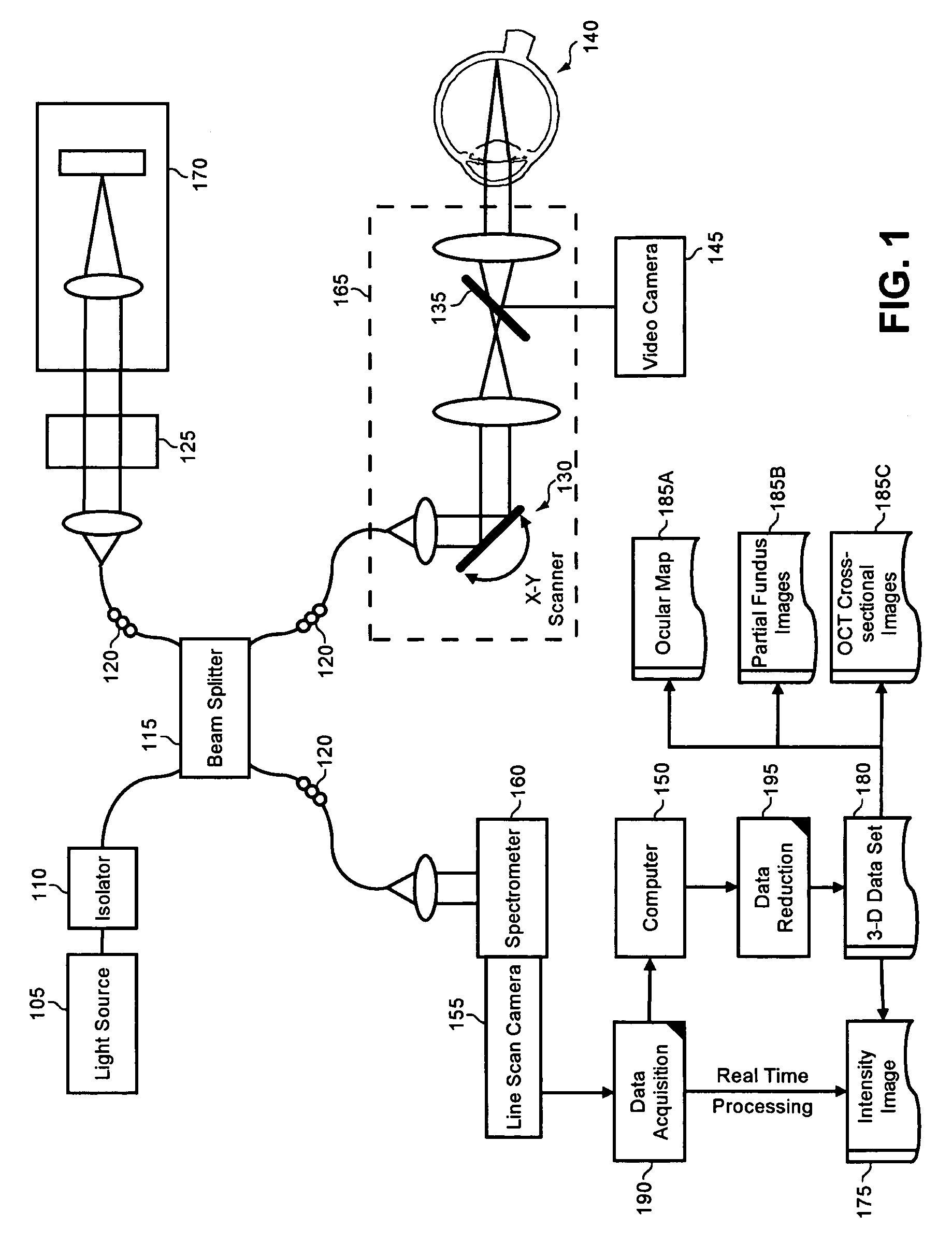
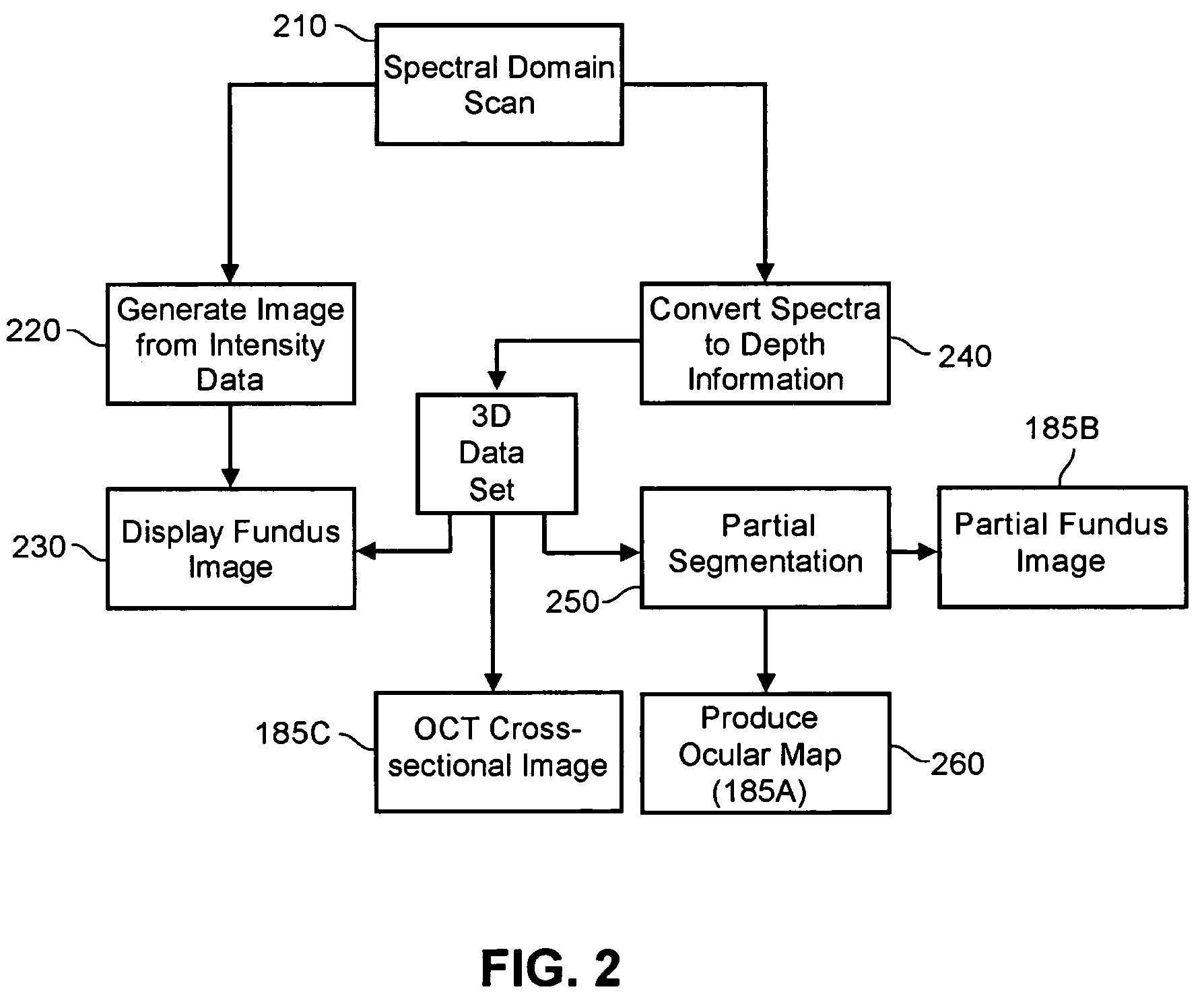
Enhanced optical coherence tomography for anatomical mapping
A system, method and apparatus for anatomical mapping utilizing optical coherence tomography. In the present invention, 3-dimensional fundus intensity imagery can be acquired from a scanning of light back-reflected from an eye. The scanning can include spectral domain scanning, as an example. A fundus intensity image can be acquired in real-time. The 3-dimensional data set can be reduced to generate an anatomical mapping, such as an edema mapping and a thickness mapping. Optionally, a partial fundus intensity image can be produced from the scanning of the eye to generate an en face view of the retinal structure of the eye without first requiring a full segmentation of the 3-D data set. Advantageously, the system, method and apparatus of the present invention can provide quantitative three-dimensional information about the spatial location and extent of macular edema and other pathologies. This three-dimensional information can be used to determine the need for treatment, monitor the effectiveness of treatment and identify the return of fluid that may signal the need for re-treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
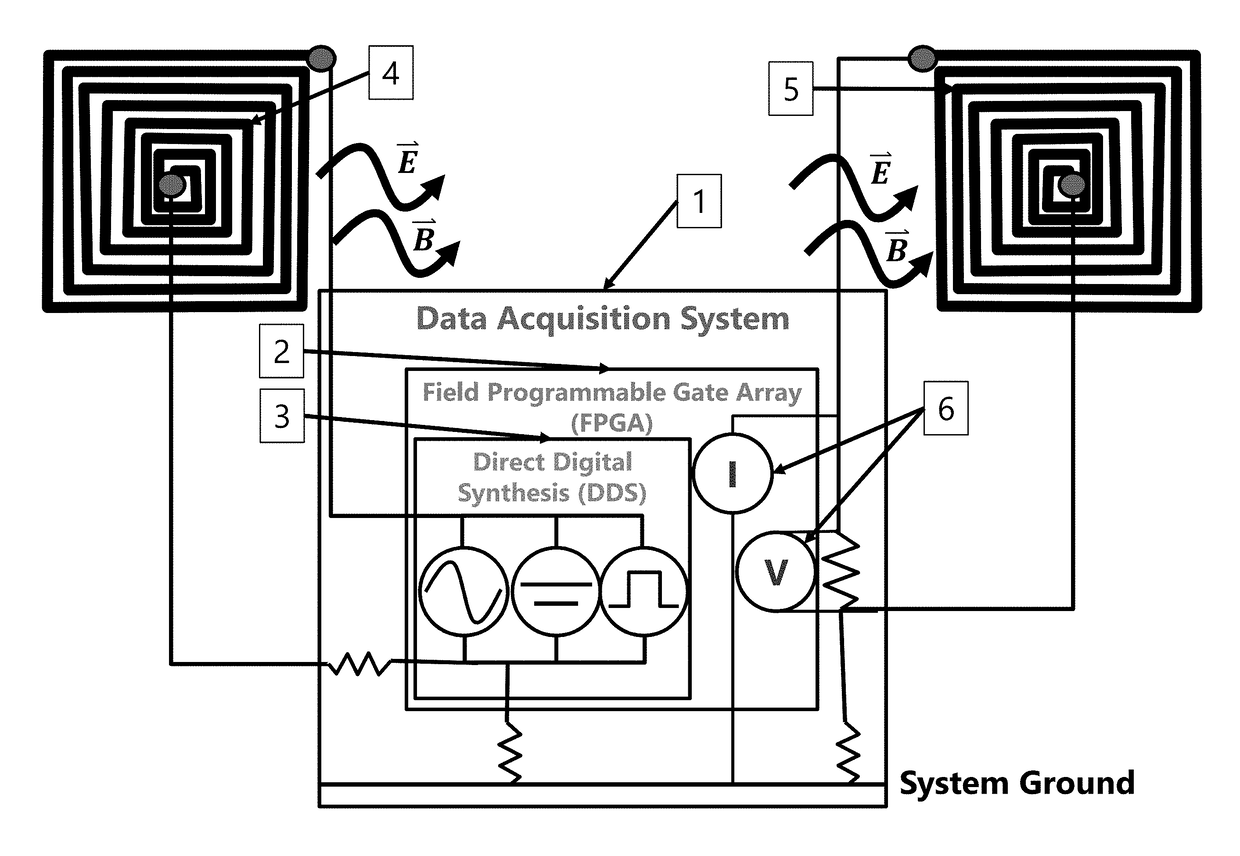
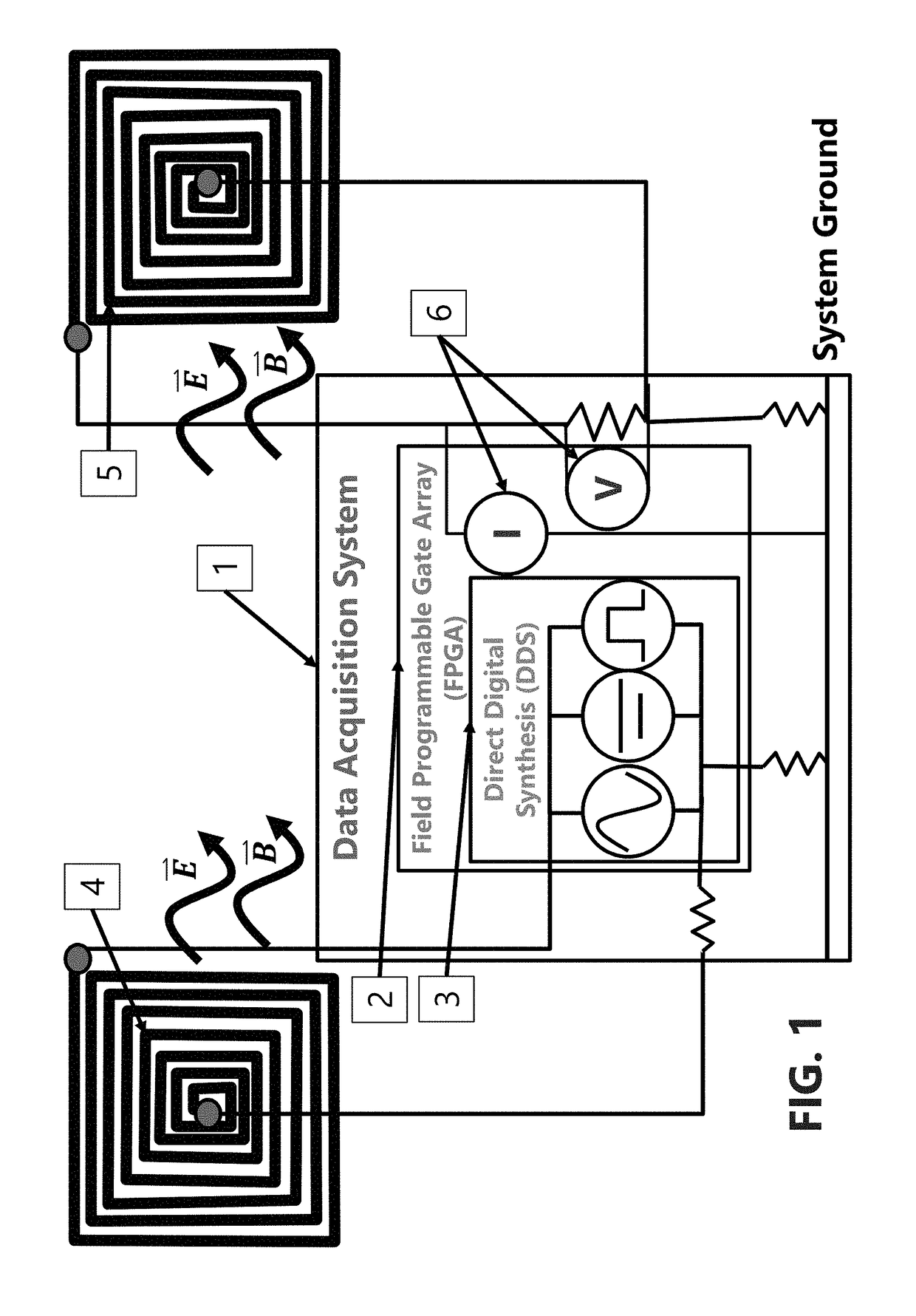
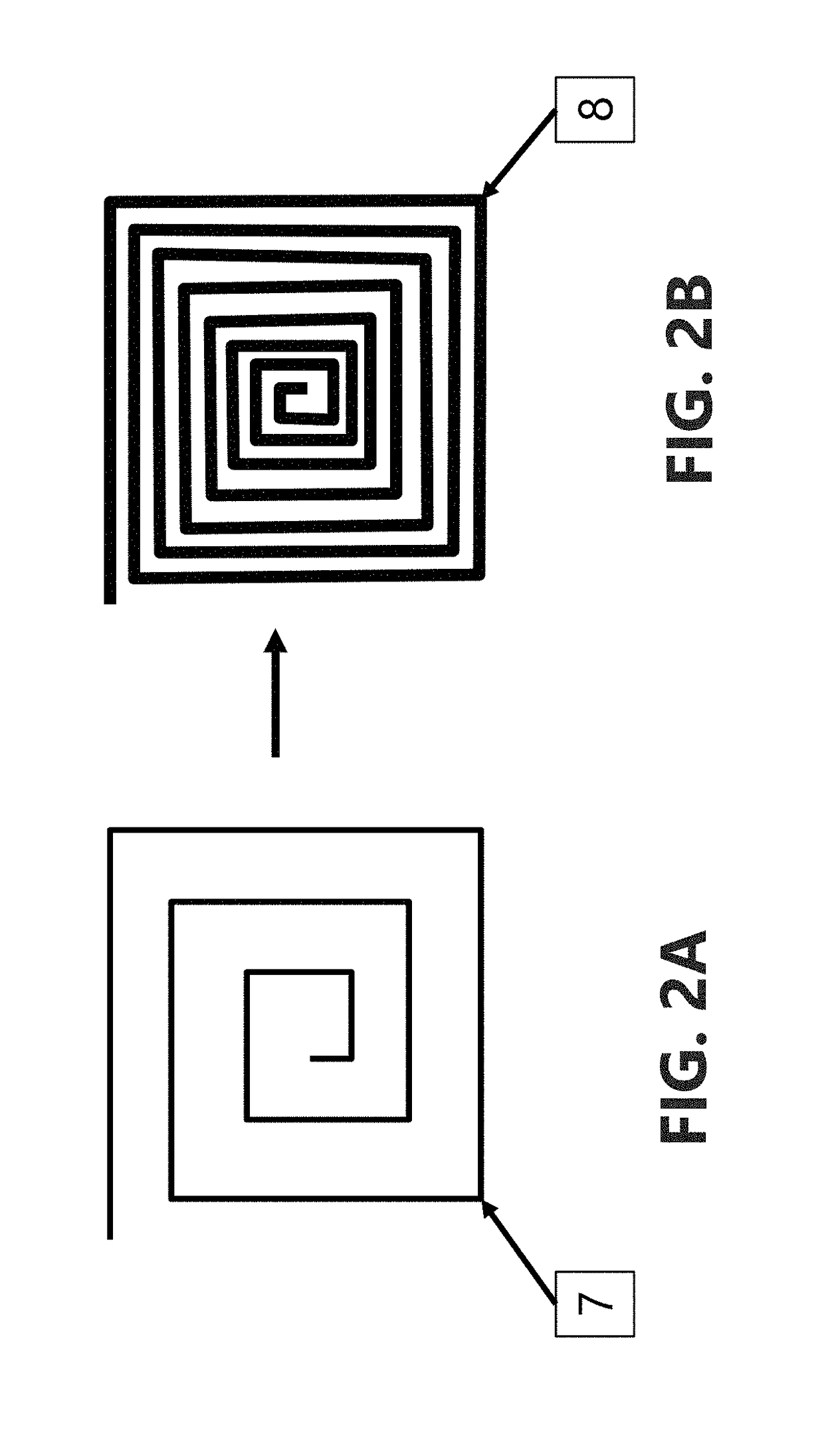
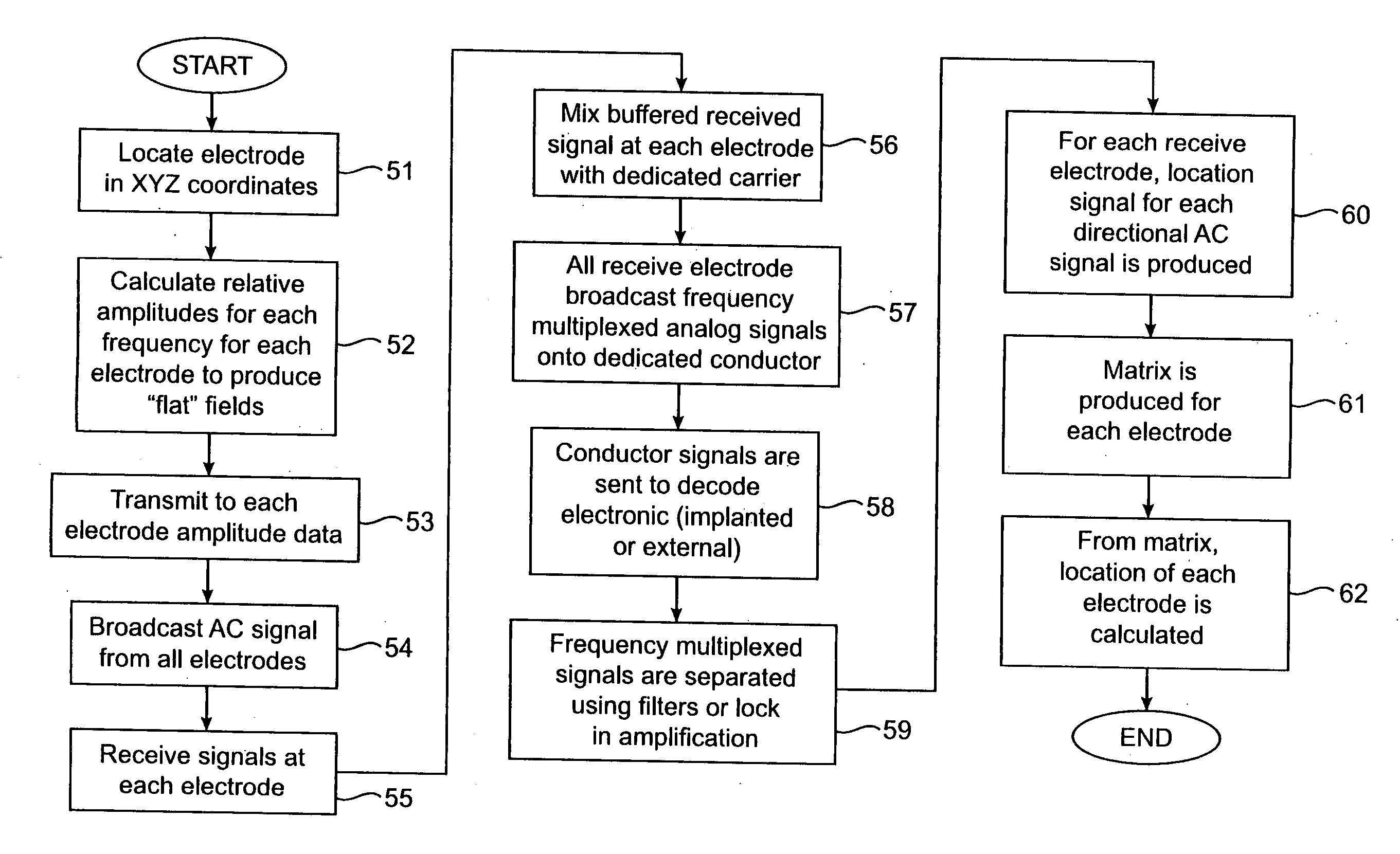
Electro-magneto volume tomography system and methodology for non-invasive volume tomography
InactiveUS20180325414A1Maximize surface areaMaximize number of turnReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapacitanceImage resolution
A system and method capable of performing multiple types of non-invasive tomographic techniques. The system is capable, via electronic control, of detecting and imaging materials within a volume using electrical capacitance, displacement phase current, magnetic inductance, and magnetic pressure sensing. The system is also able to control the amplitude, phase, and frequency of individual electrode excitation to increase imaging resolution and phase detection. This allows many dimensions of non-invasive data to be captured without the need for multiple instruments or moving parts, at a high data capture rate.
Owner:TECH4IMAGING
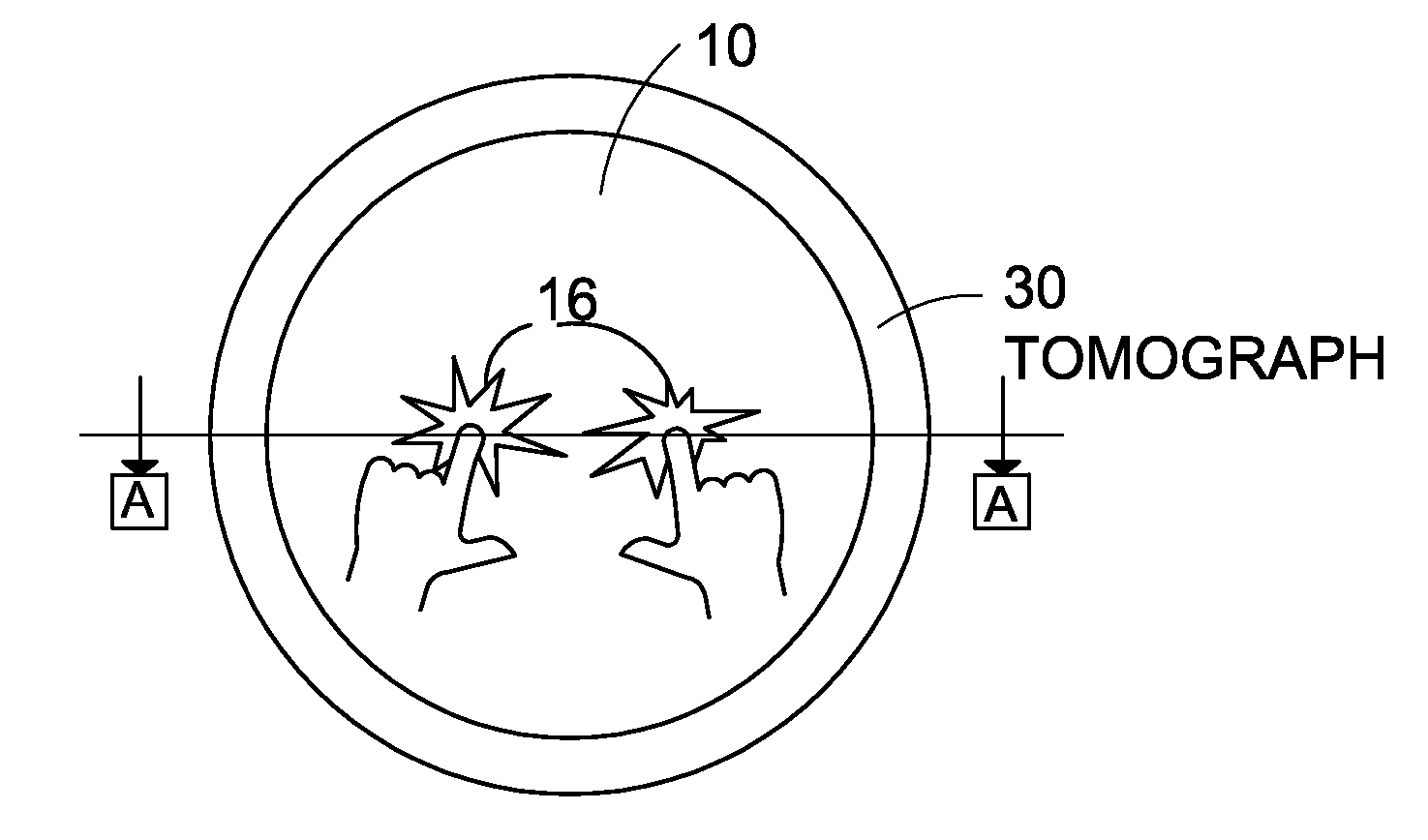
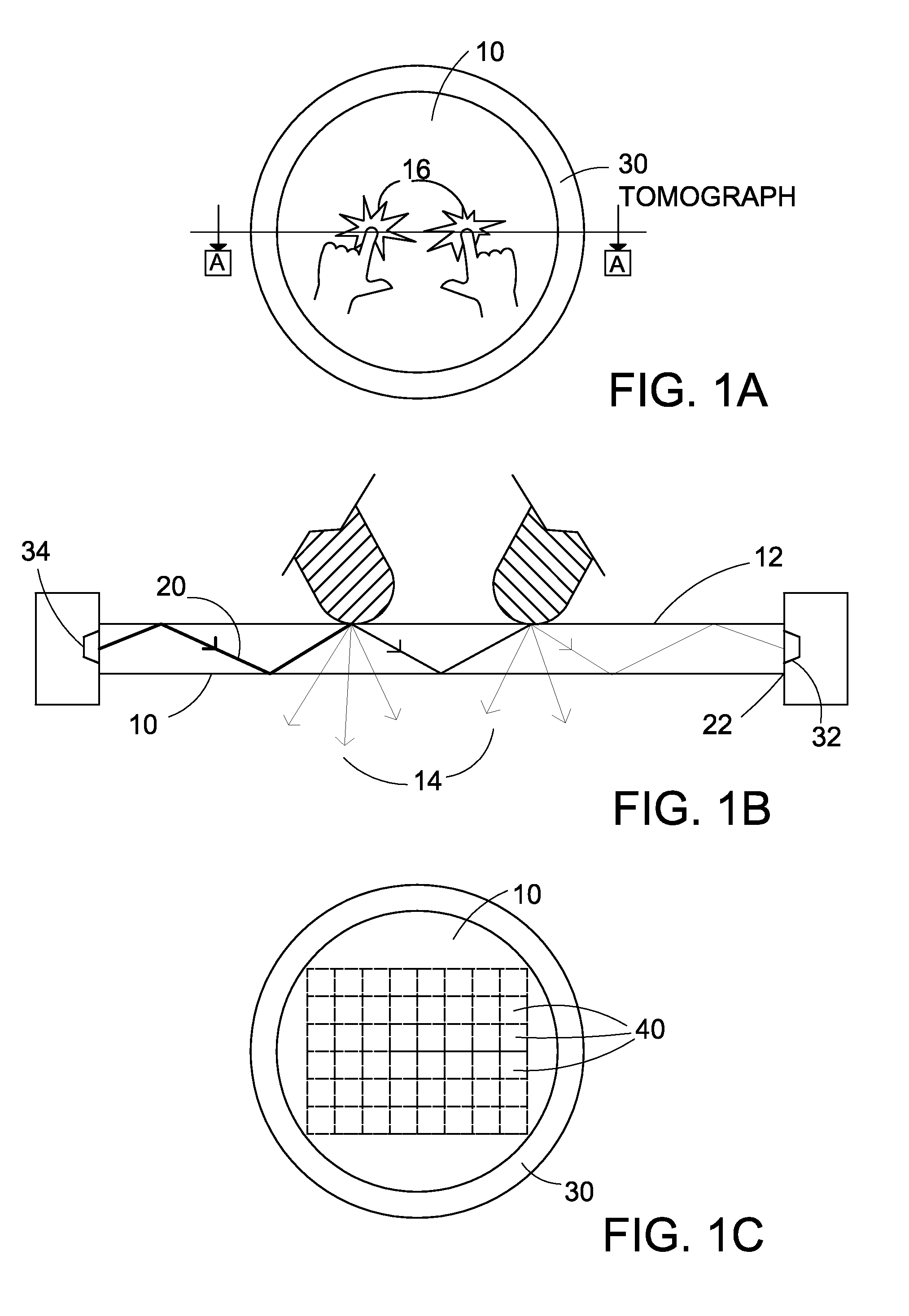
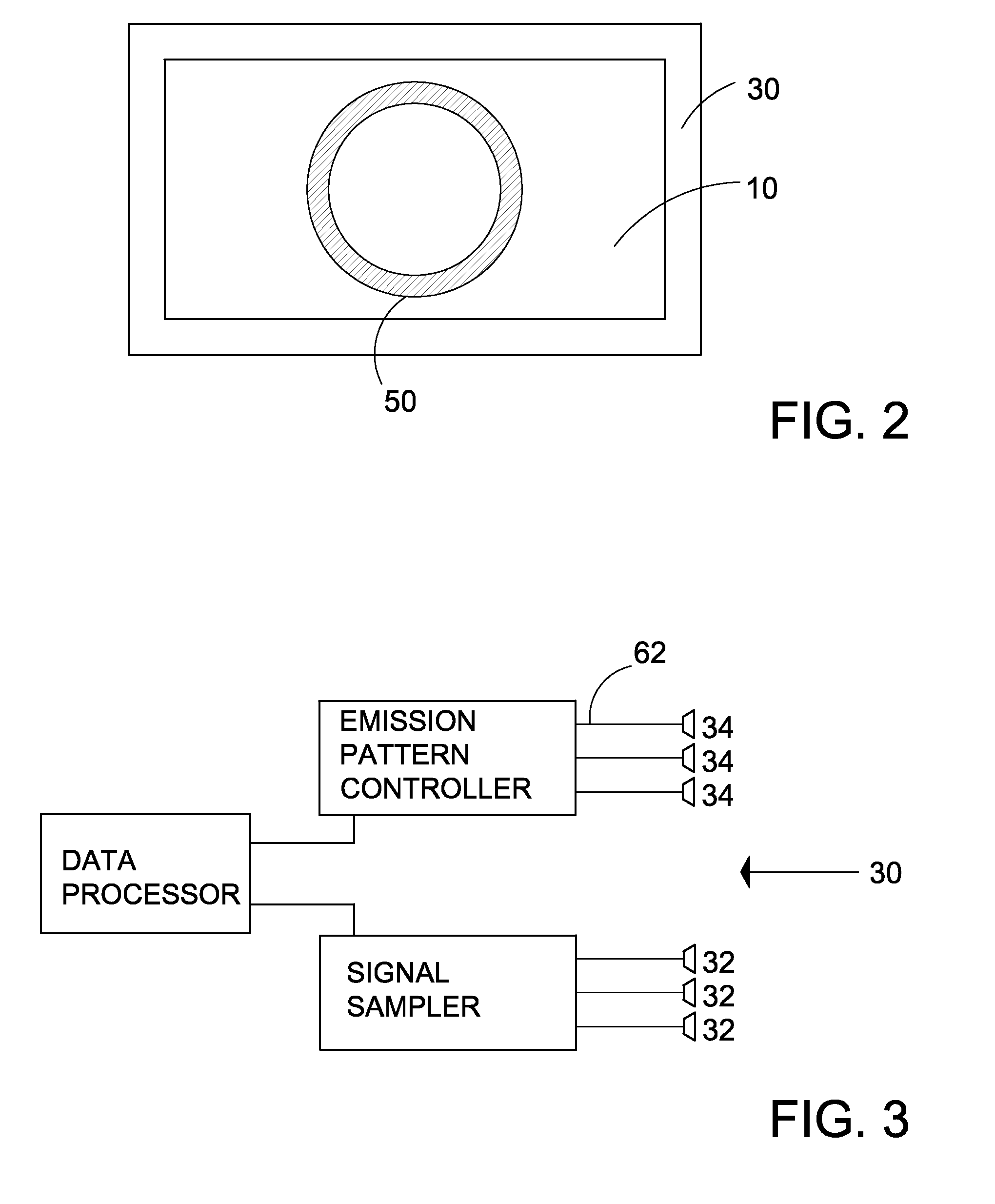
Method and apparatus for tomographic touch imaging and interactive system using same
ActiveUS20090153519A1System to be portableIncrease surface areaInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTomography
A touch screen in the form of a panel is capable of conducting signals and a tomograph including signal flow ports is positioned adjacent the panel with the signal flow ports arrayed around the border of the panel at discrete locations. Signals are introduced into the panel to pass from each discrete border location to a plurality of other discrete border locations for being detected and tomographically processed to determine if any change occurred to signals due to the panel being touched during signal passage through the panel, and therefrom determine any local area on the panel where a change occurred. The tomograph computes and outputs a signal indicative of a panel touch and location, which can be shown on a display.
Owner:SUAREZ ROVERE VICTOR MANUEL
Cone-beam computerized tomography with a flat-panel imager
InactiveUS20030007601A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAmorphous siliconX-ray
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Quantitative methods for obtaining tissue characteristics from optical coherence tomography images
InactiveUS20090306520A1Improve tissue type classificationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight beam
A method and apparatus for determining properties of a tissue or tissues imaged by optical coherence tomography (OCT). In one embodiment the backscatter and attenuation of the OCT optical beam is measured and based on these measurements and indicium such as color is assigned for each portion of the image corresponding to the specific value of the backscatter and attenuation for that portion. The image is then displayed with the indicia and a user can then determine the tissue characteristics. In an alternative embodiment the tissue characteristics is classified automatically by a program given the combination of backscatter and attenuation values.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
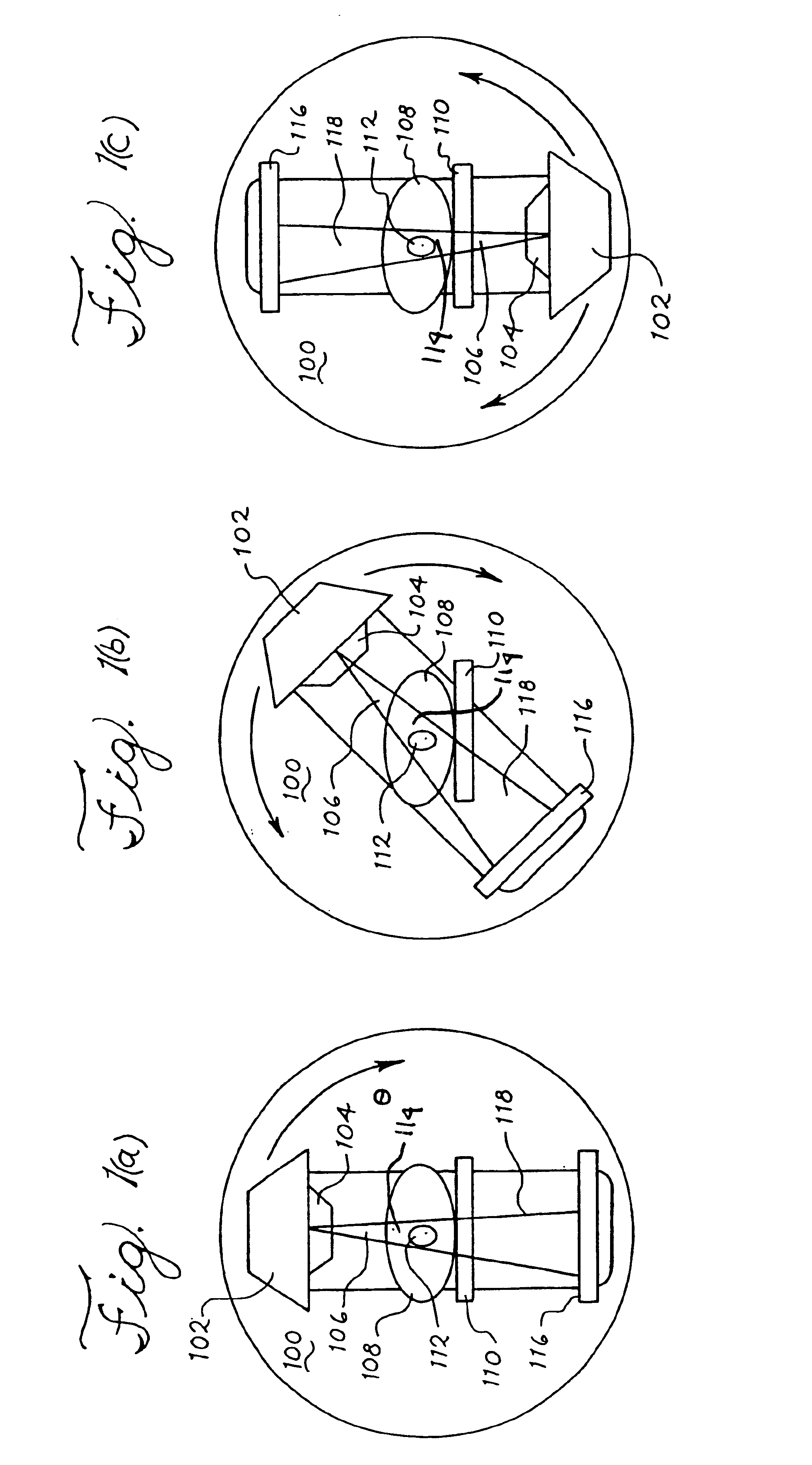
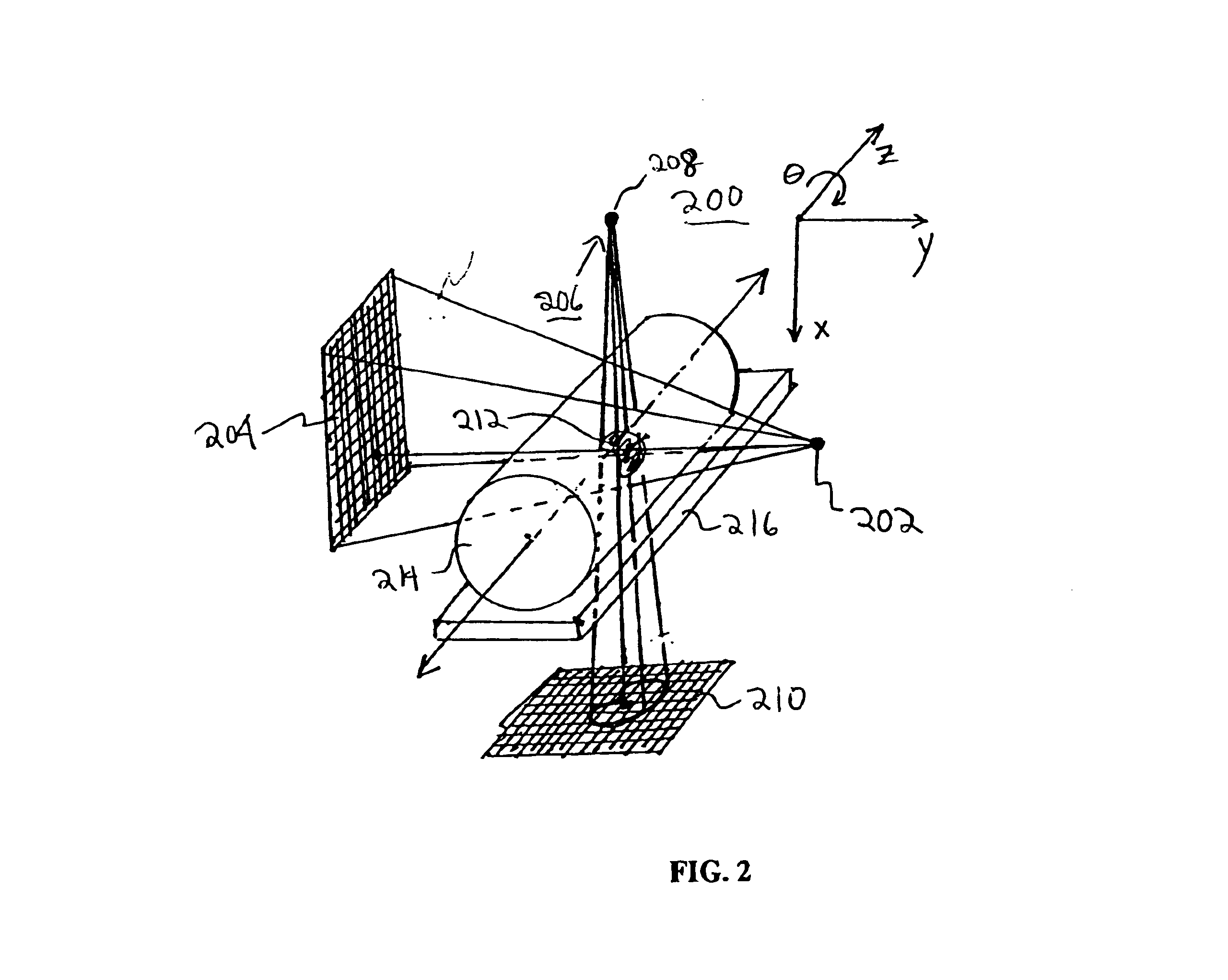
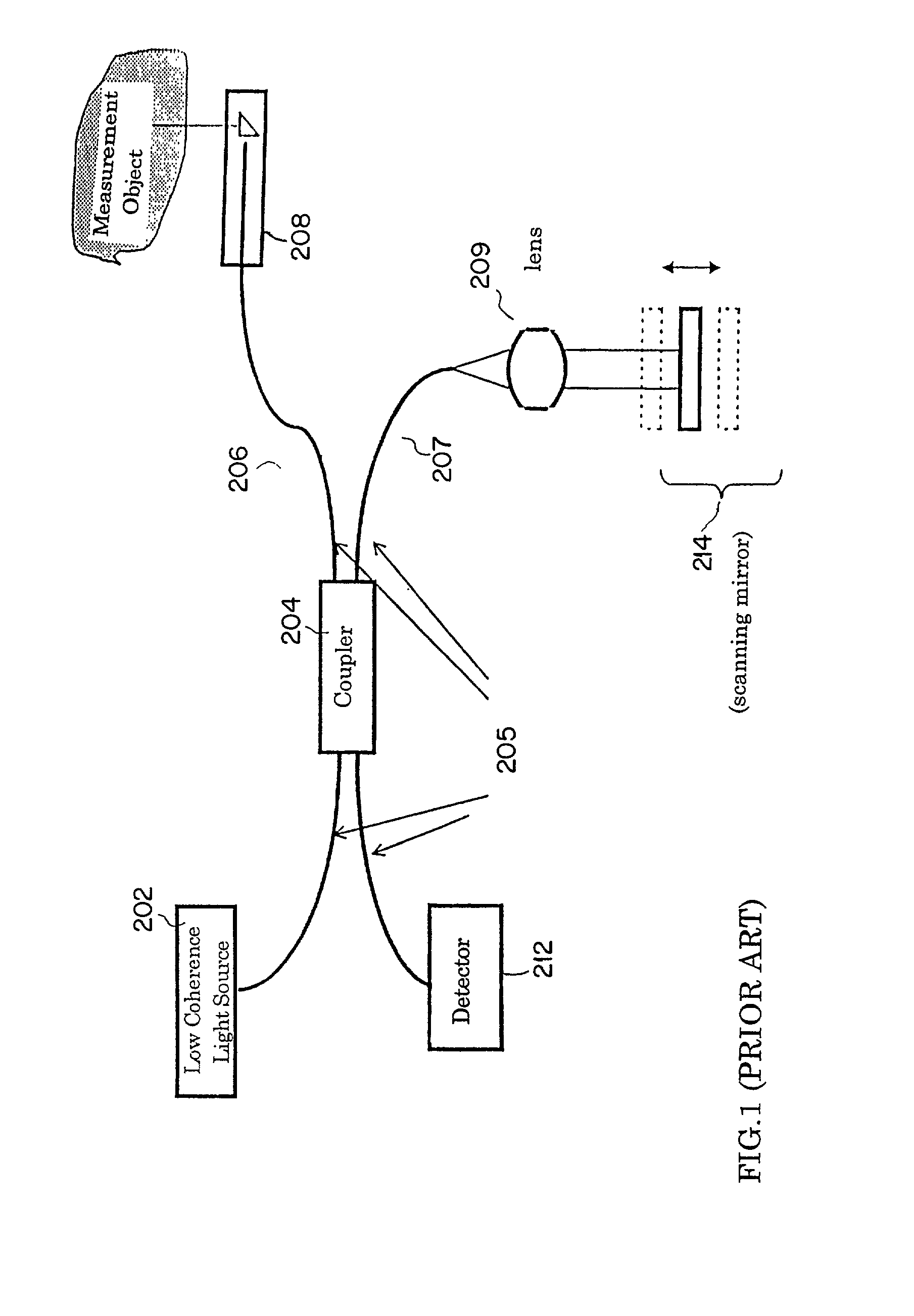
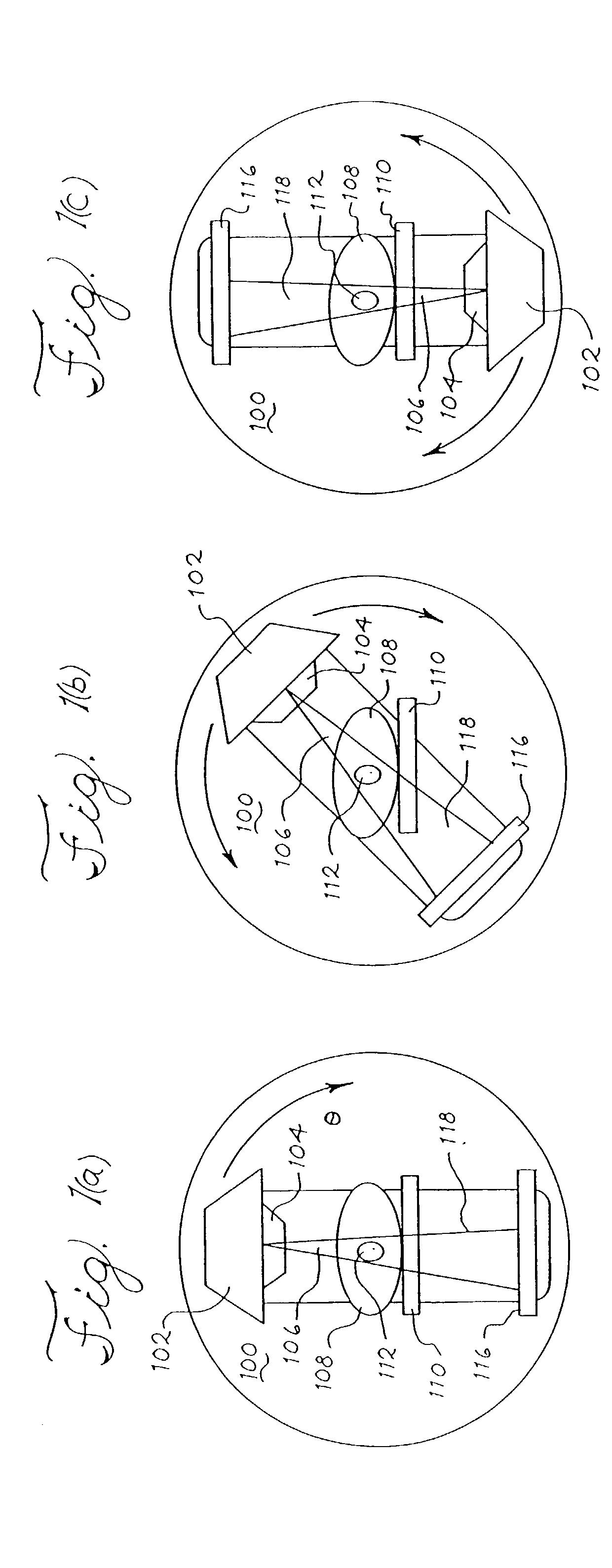
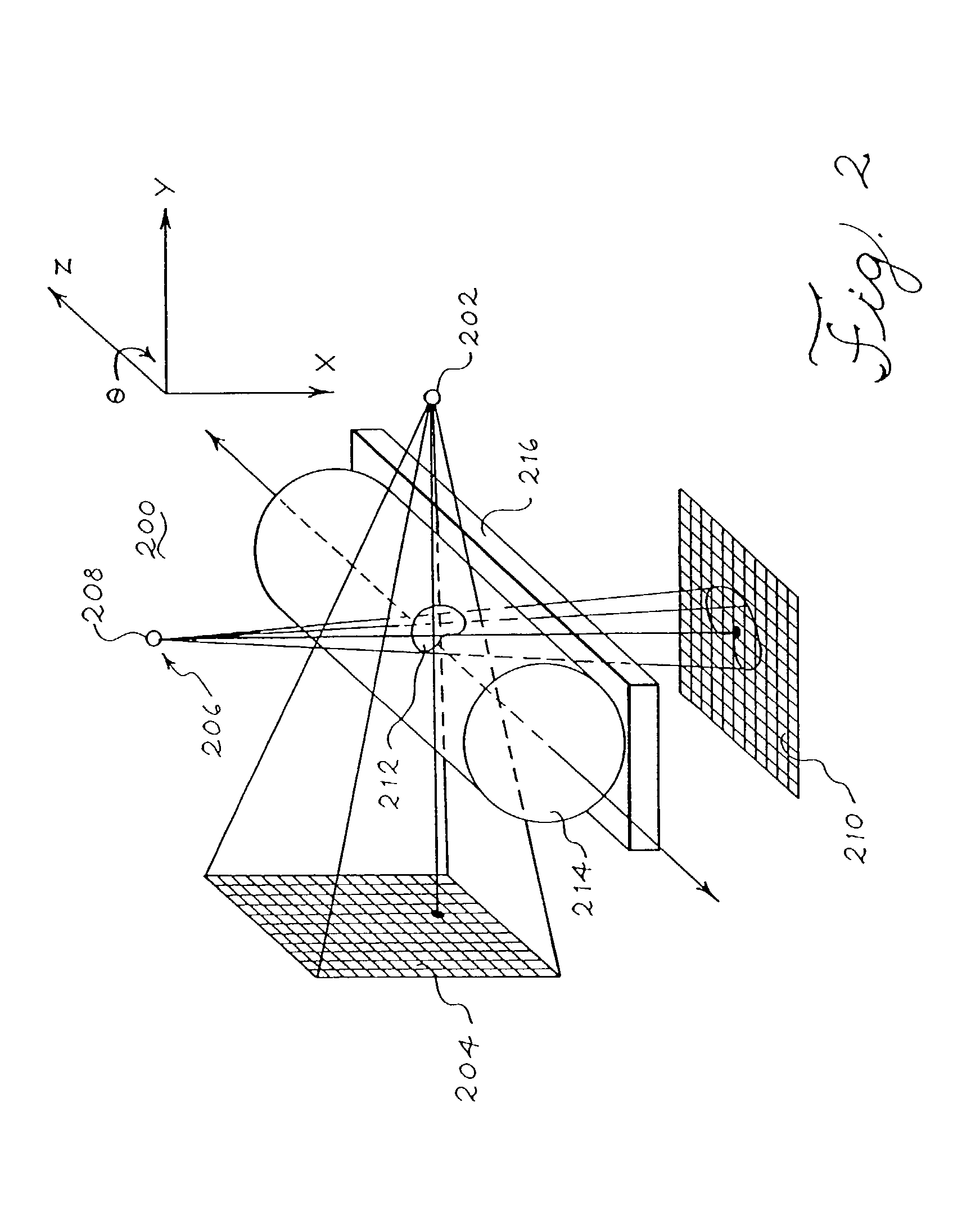
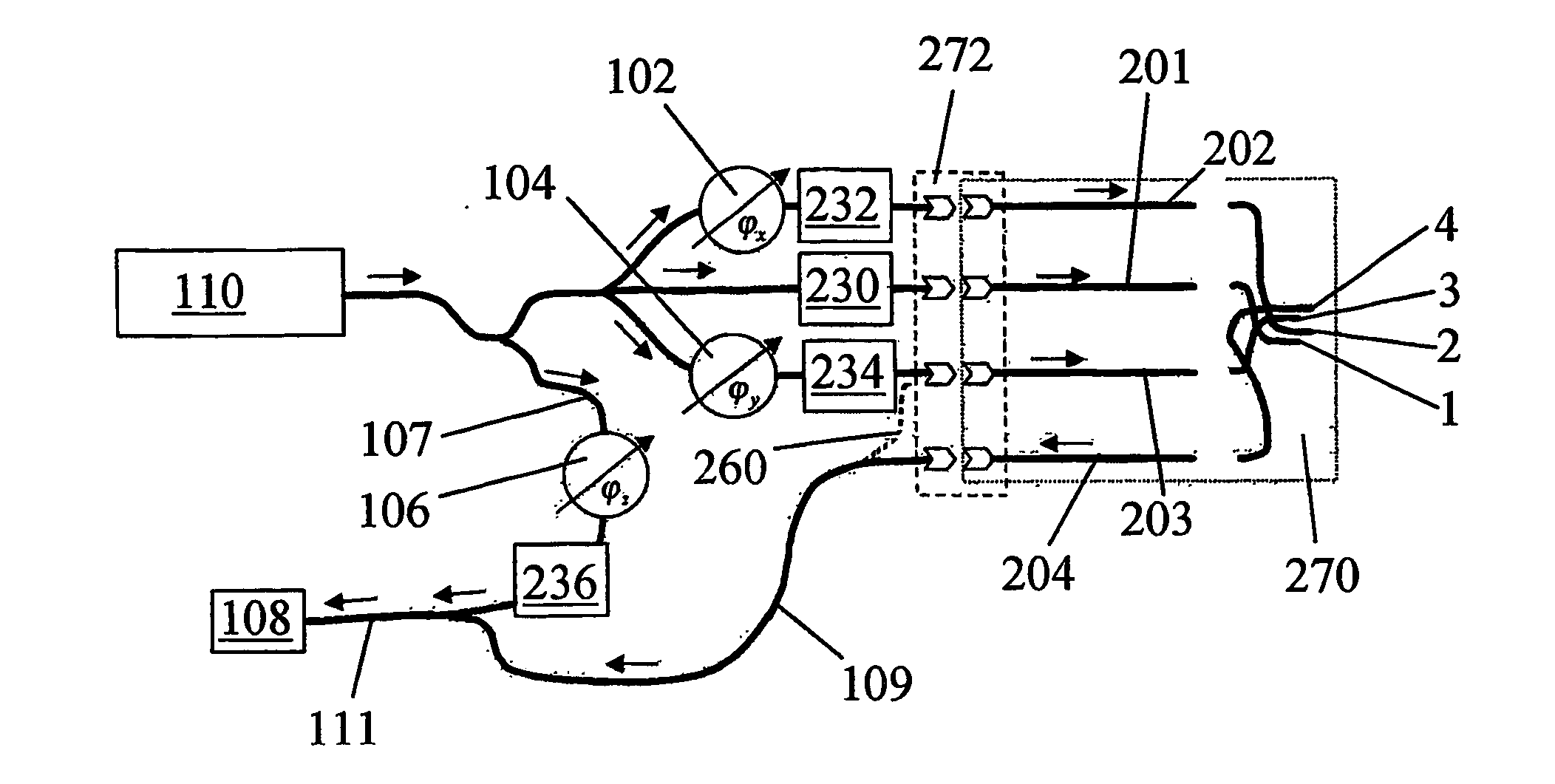
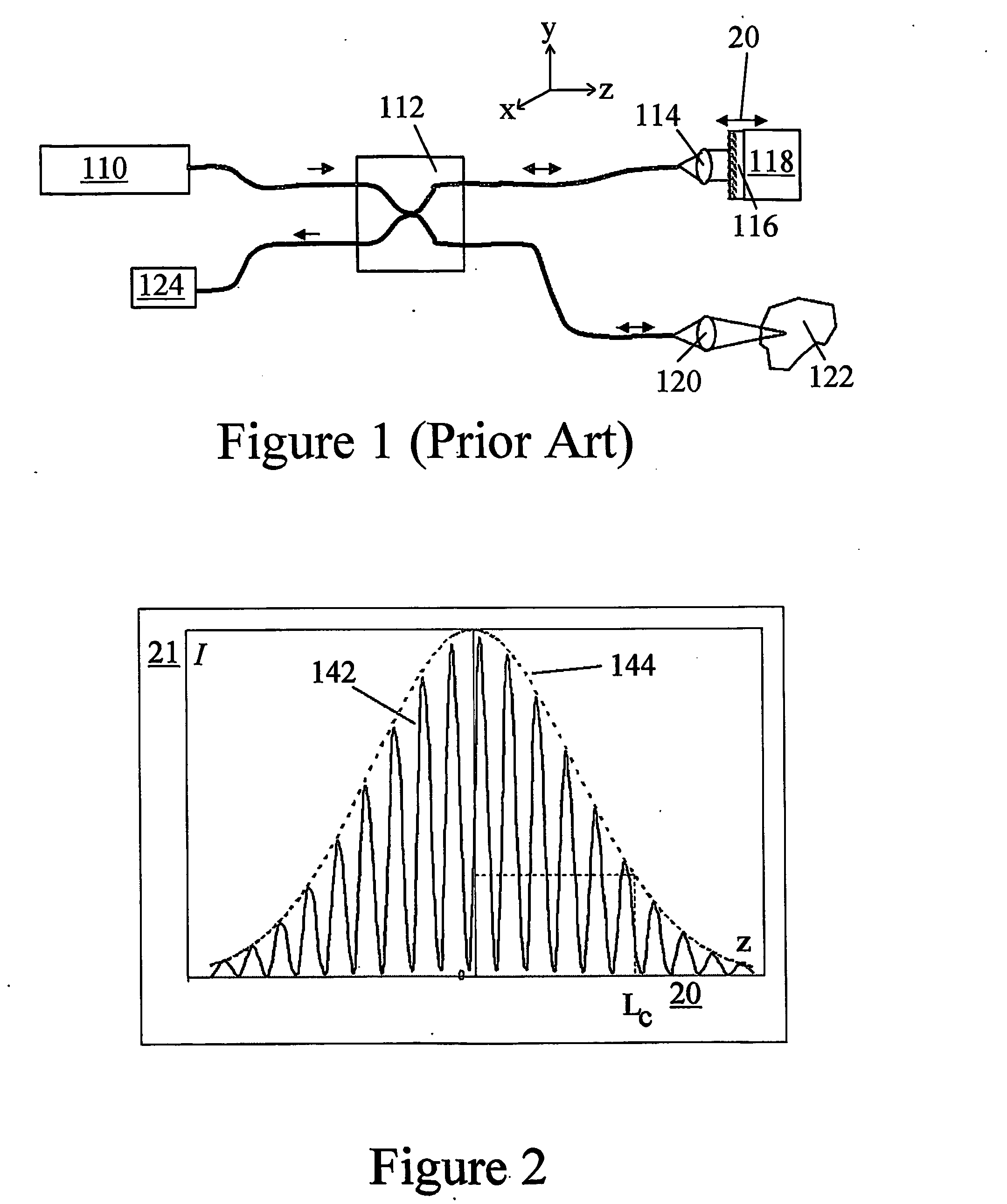
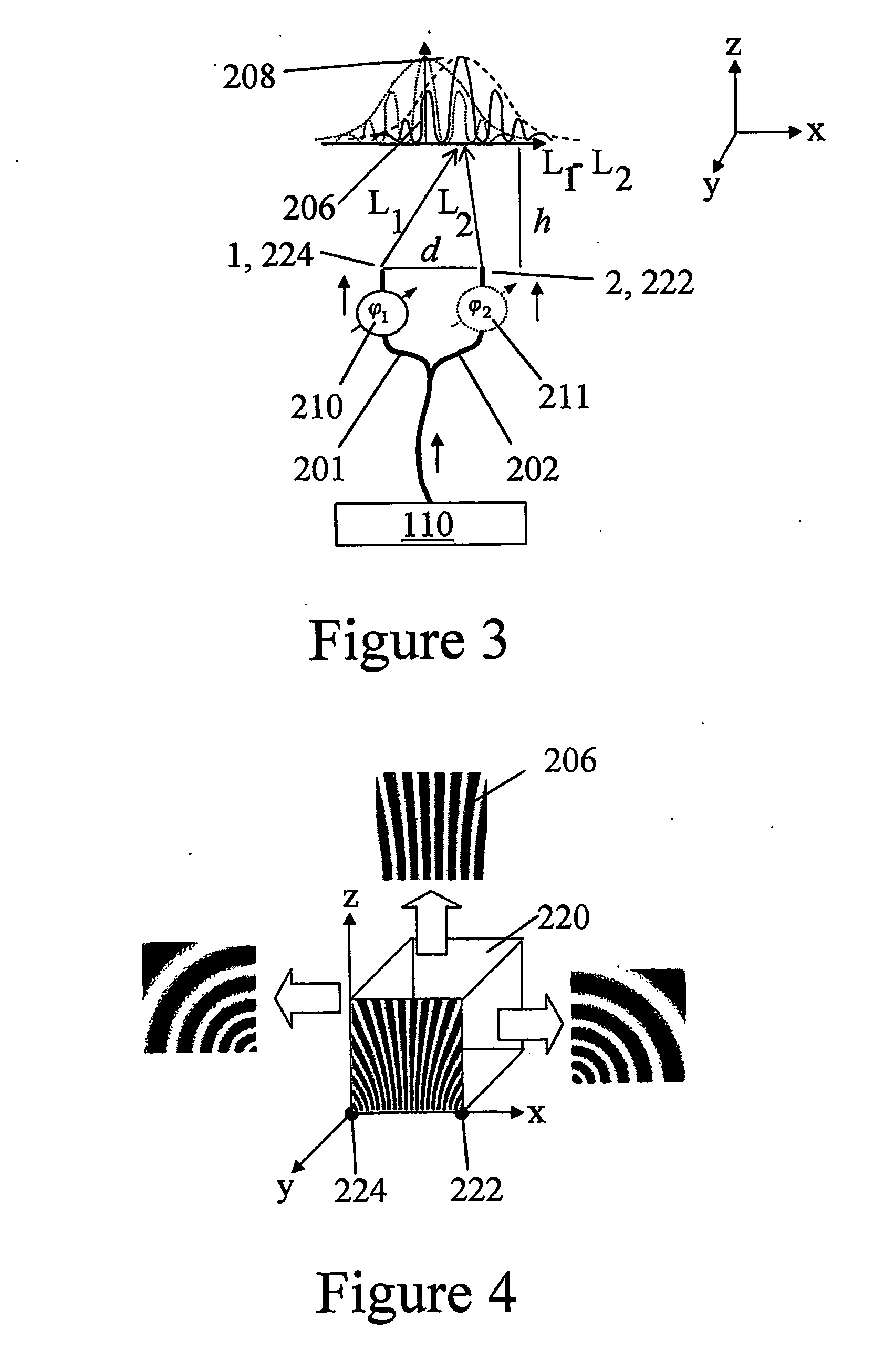
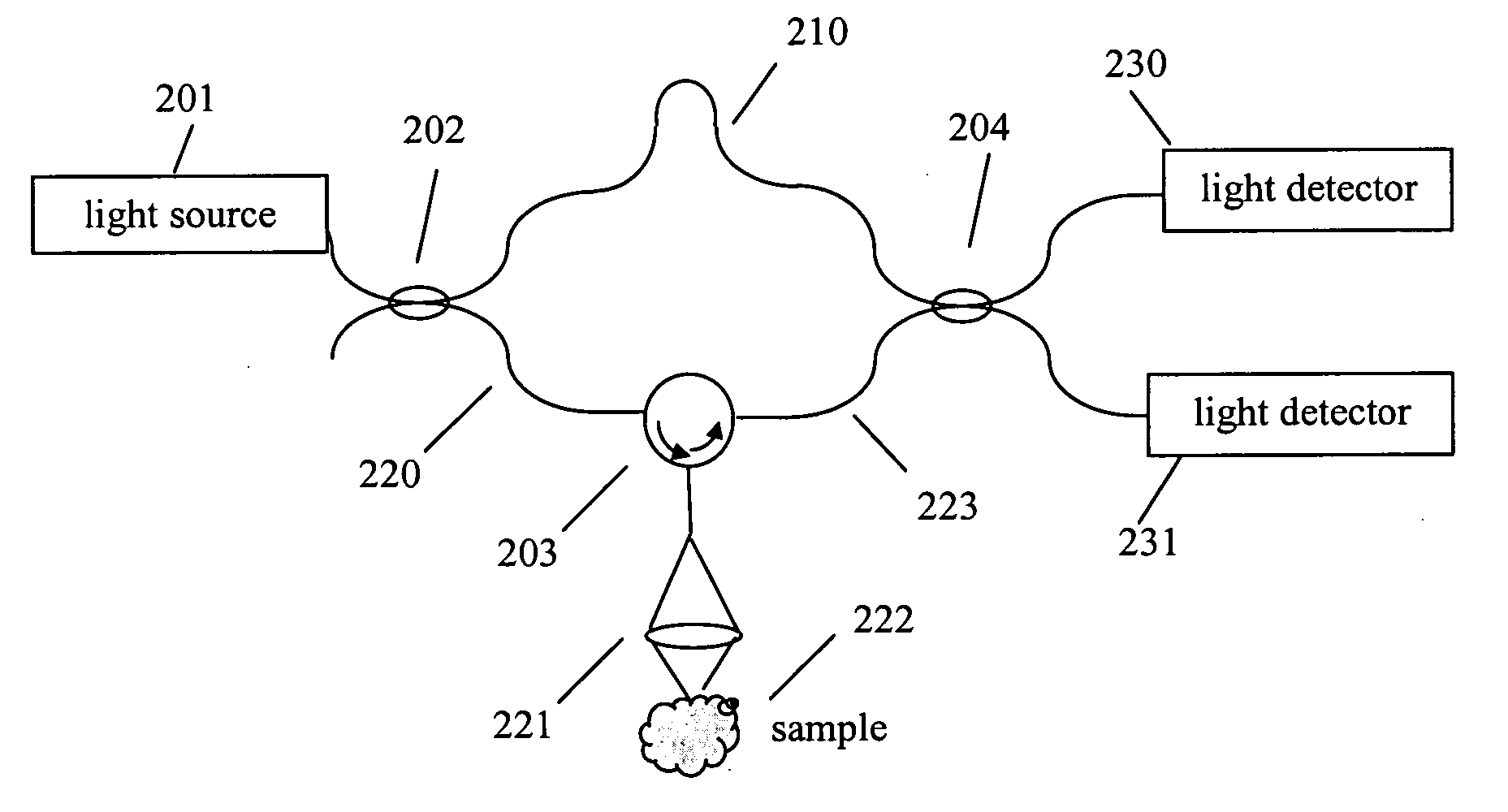
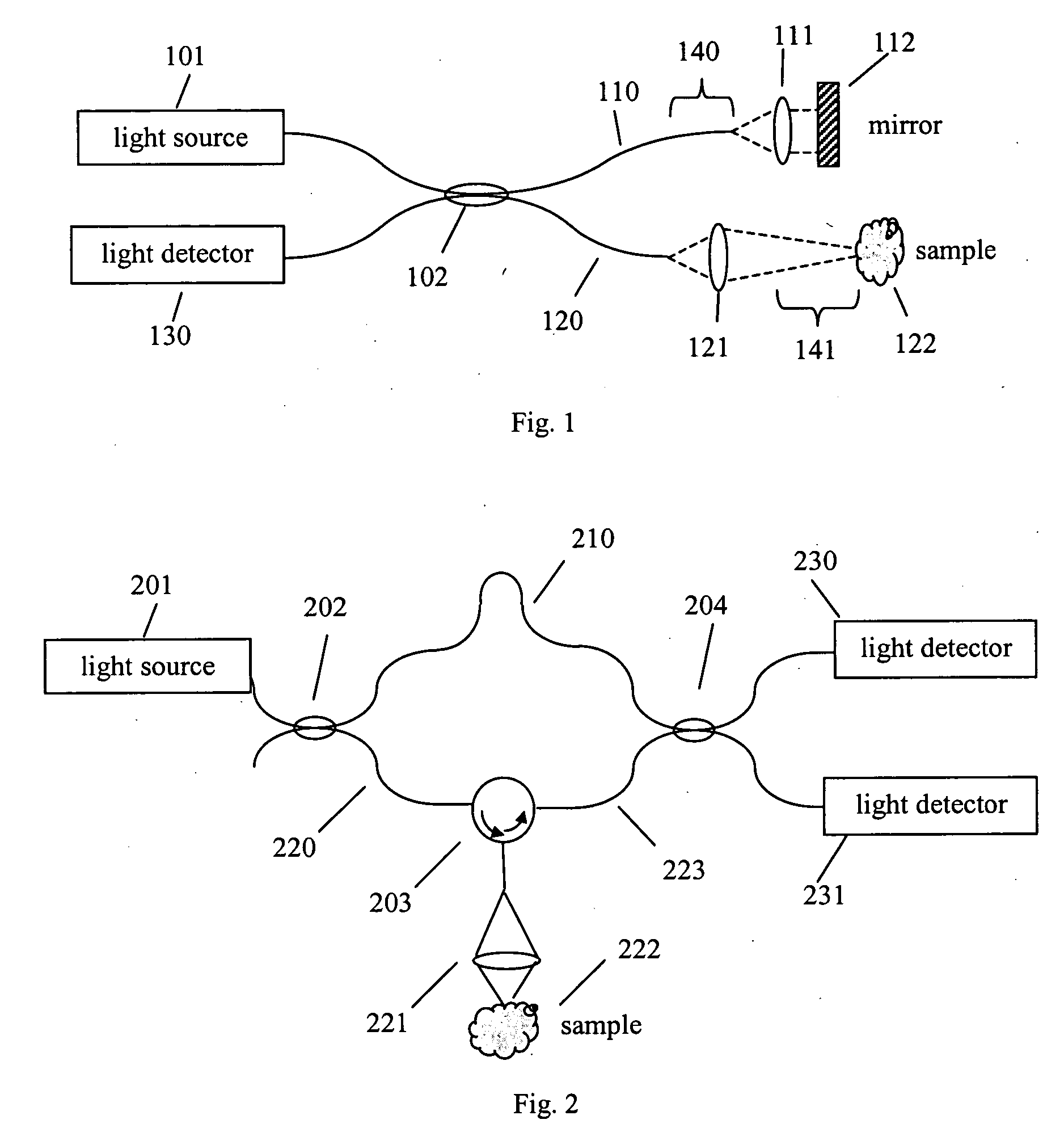
Optical coherence tomography with 3d coherence scanning
Optical coherence tomography with 3D coherence scanning is disclosed, using at least three fibers (201, 202, 203) for object illumination and collection of backscattered light. Fiber tips (1, 2, 3) are located in a fiber tip plane (71) normal to the optical axis (72). Light beams emerging from the fibers overlap at an object (122) plane, a subset of intersections of the beams with the plane defining field of view (266) of the optical coherence tomography apparatus. Interference of light emitted and collected by the fibers creates a 3D fringe pattern. The 3D fringe pattern is scanned dynamically over the object by phase shift delays (102, 104) controlled remotely, near ends of the fibers opposite the tips of the fibers, and combined with light modulation. The dynamic fringe pattern is backscattered by the object, transmitted to a light processing system (108) such as a photo detector, and produces an AC signal on the output of the light processing system (108). Phase demodulation of the AC signal at selected frequencies and signal processing produce a measurement of a 3D profile of the object.
Owner:APPLIED SCI INNOVATIONS +1
Arrangements, systems and methods capable of providing spectral-domain polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20070038040A1Improve measurement reliabilityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsSpectral domainTomography
Systems, arrangements and methods for separating an electromagnetic radiation and obtaining information for a sample using an electromagnetic radiation are provided. In particular, the electromagnetic radiation can be separated into at least one first portion and at least one second portion according to at least one polarization and at least one wave-length of the electromagnetic radiation. The first and second separated portions may be simultaneously detected. Further, a first radiation can be obtained from the sample and a second radiation may be obtained from a reference, and the first and second radiations may be combined to form a further radiation, with the first and second radiations being associated with the electro-magnetic radiation. The information is provided as a function of first and second portions of the further radiations that have been previously separated and can be analyzed to extract birefringent information characterizing the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
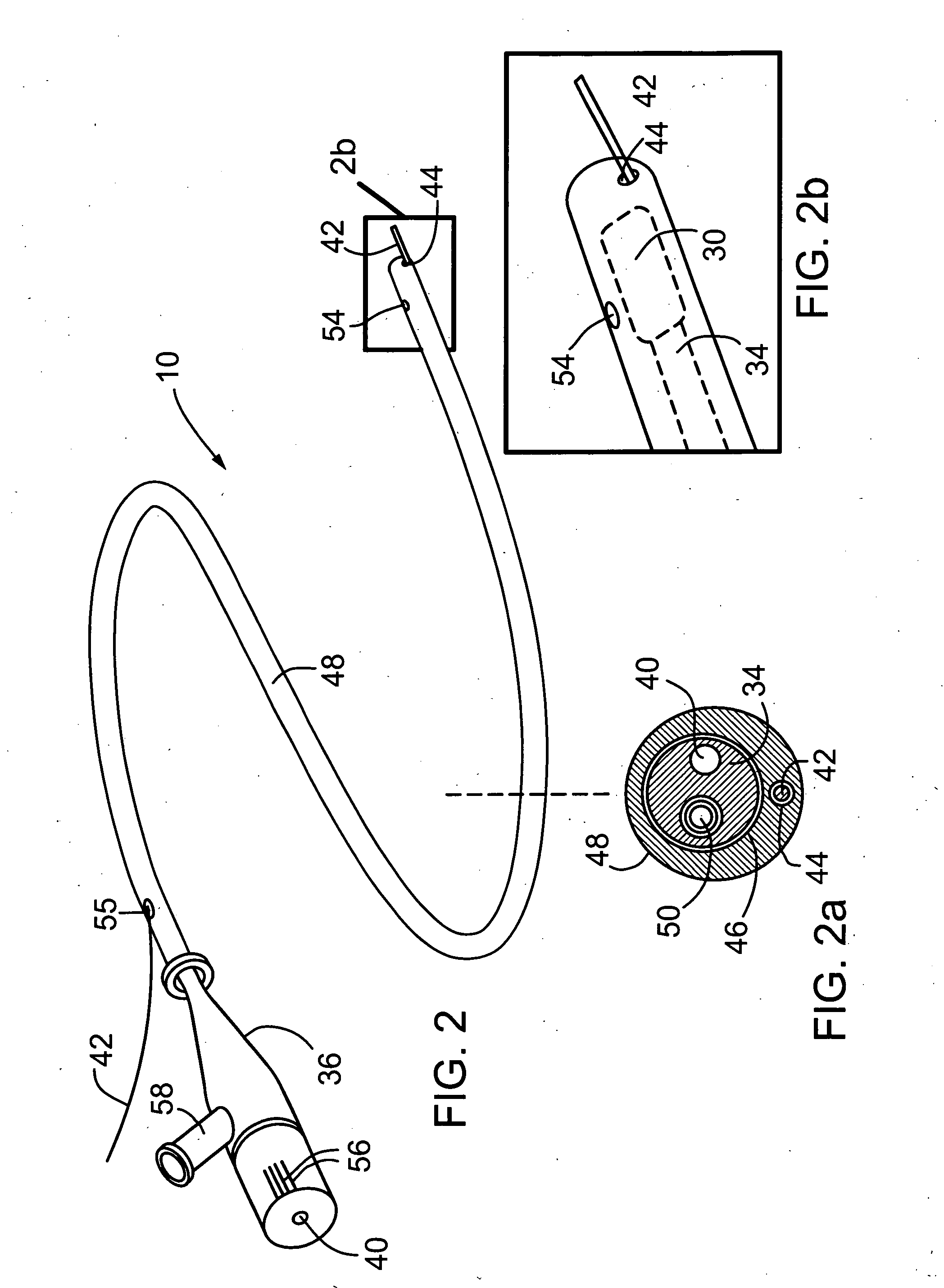
Scanning mechanisms for imaging probe
ActiveUS20080177138A1High resolutionQuantity minimizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPhysicsMammalian tissue
The present invention provides scanning mechanisms for imaging probes using for imaging mammalian tissues and structures using high resolution imaging, including high frequency ultrasound and / or optical coherence tomography. The imaging probes include adjustable rotational drive mechanism for imparting rotational motion to an imaging assembly containing either optical or ultrasound transducers which emit energy into the surrounding area. The imaging assembly includes a scanning mechanism having including a movable member configured to deliver the energy beam along a path out of said elongate hollow shaft at a variable angle with respect to said longitudinal axis to give forward and side viewing capability of the imaging assembly. The movable member is mounted in such a way that the variable angle is a function of the angular velocity of the imaging assembly.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Methods and apparatuses for positioning within an internal channel
InactiveUS20060135870A1Reduce congestionEliminate and reduce blockage effect of bloodStentsSurgeryPhotodynamic therapyDistal portion
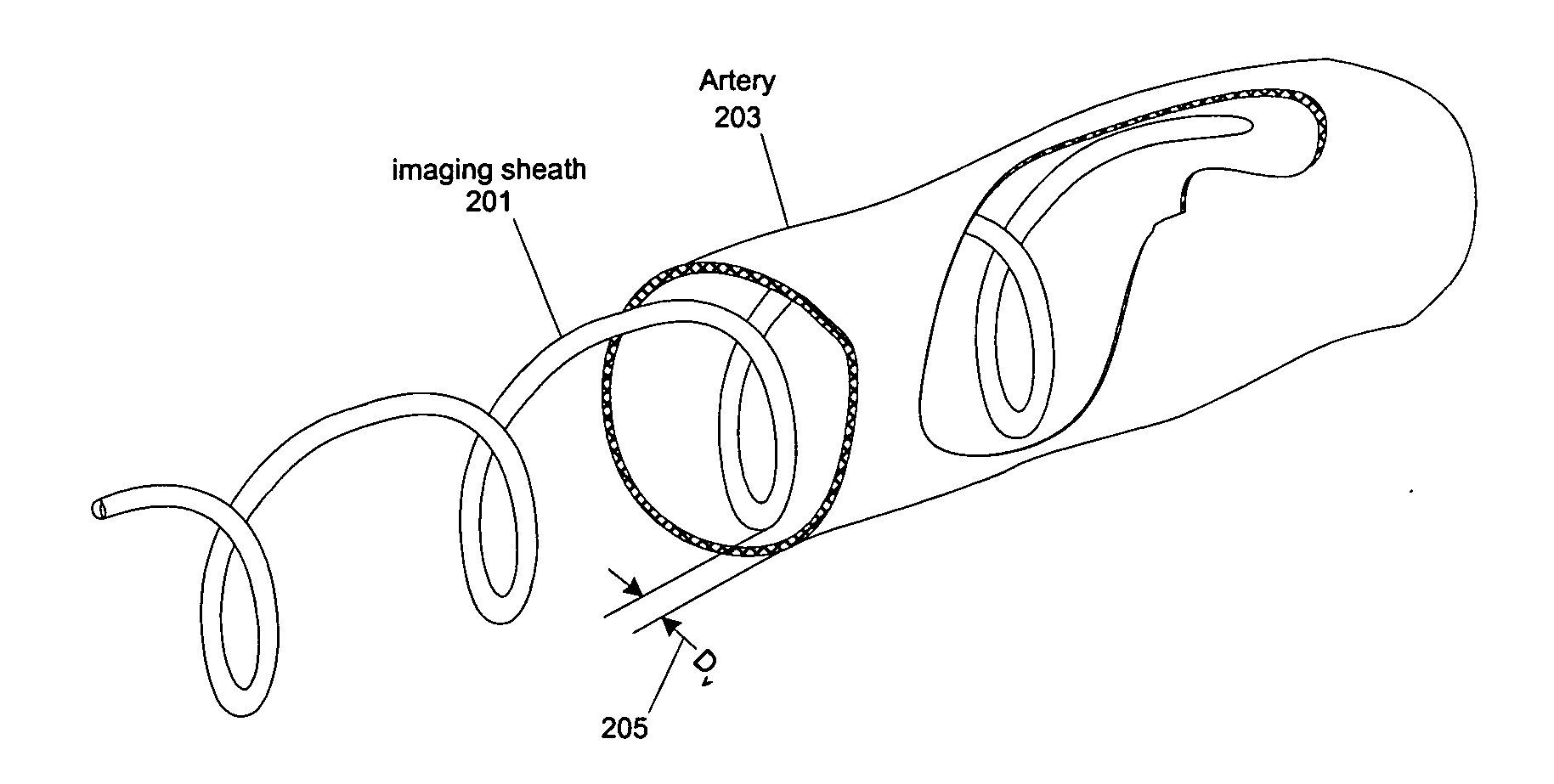
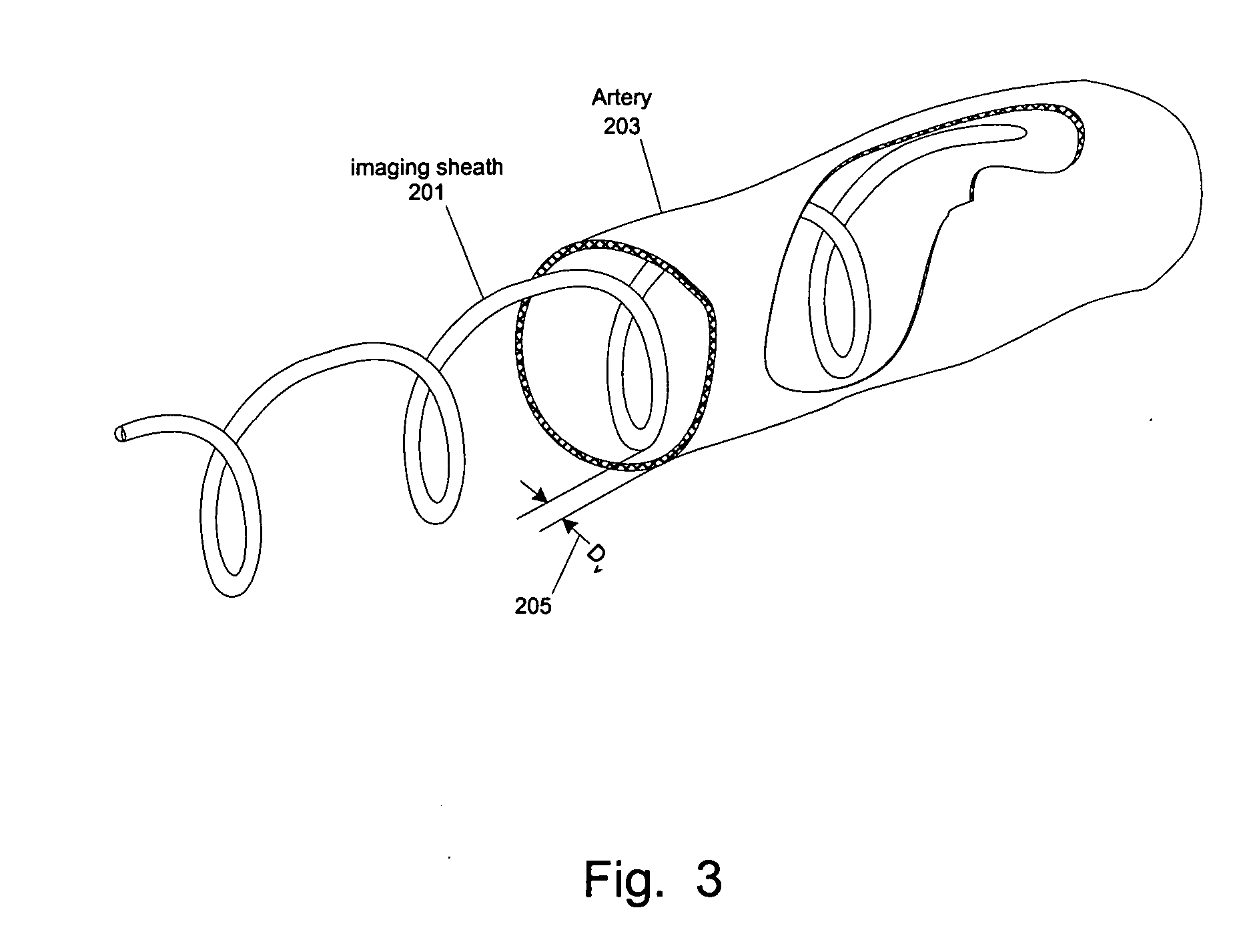
Methods and apparatuses for positioning medical devices onto (or close to) a desired portion of the interior wall of an internal channel, such as for scan imaging, for photodynamic therapy and / or for optical temperature measurement. In one embodiment, a catheter assembly has a distal portion that can be changed from a configuration suitable for traversing the internal channel to another configuration suitable for scan at least a spiral section of the interior wall of an internal channel, such as an artery. In one example, the distal portion spirals into gentle contact with (or close to) a spiral section of the artery wall for Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scanning. The spiral radius may be changed through the use of a guidewire, a tendon, a spiral balloon, a tube, or other ways.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Optical coherence tomography apparatus and methods
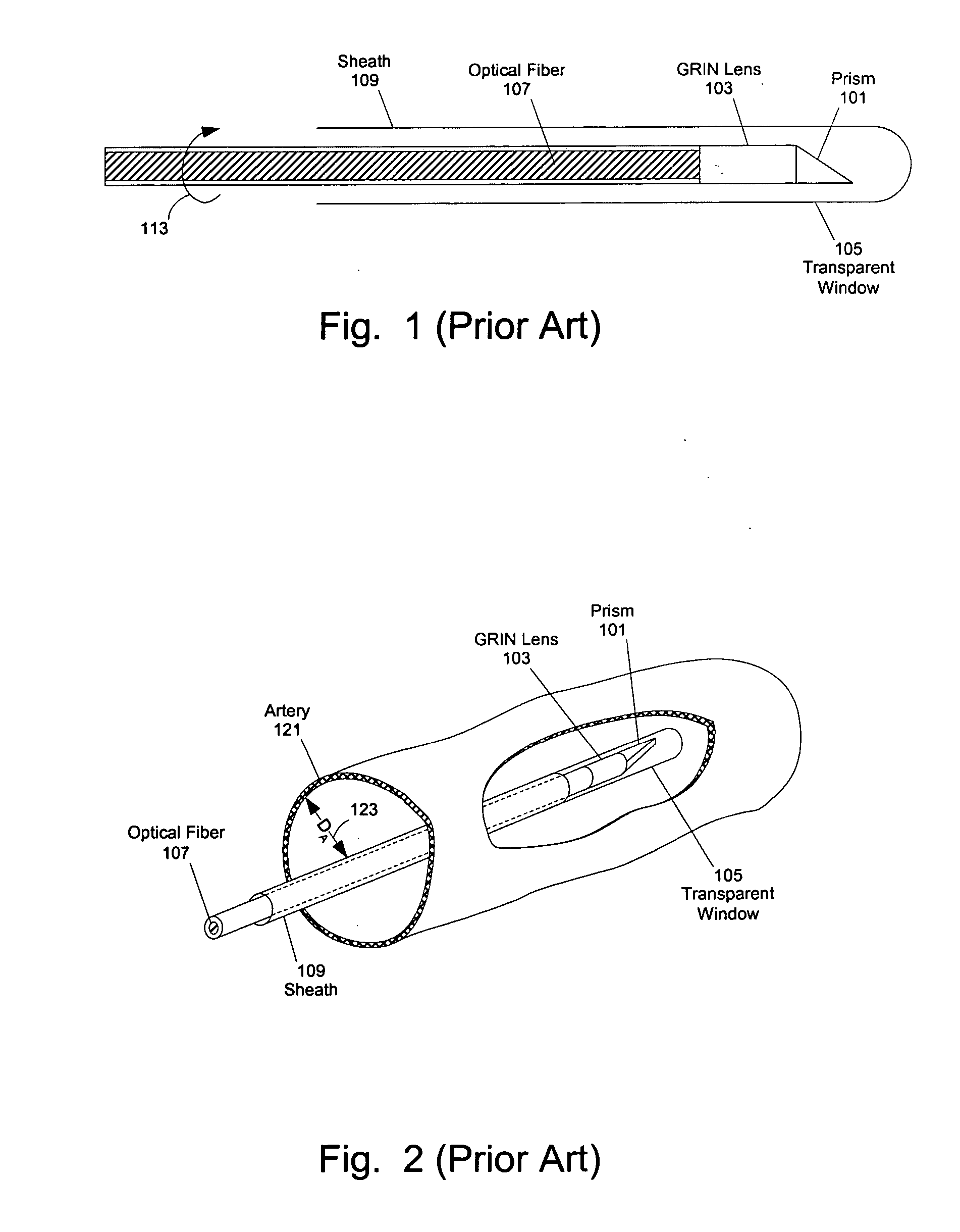
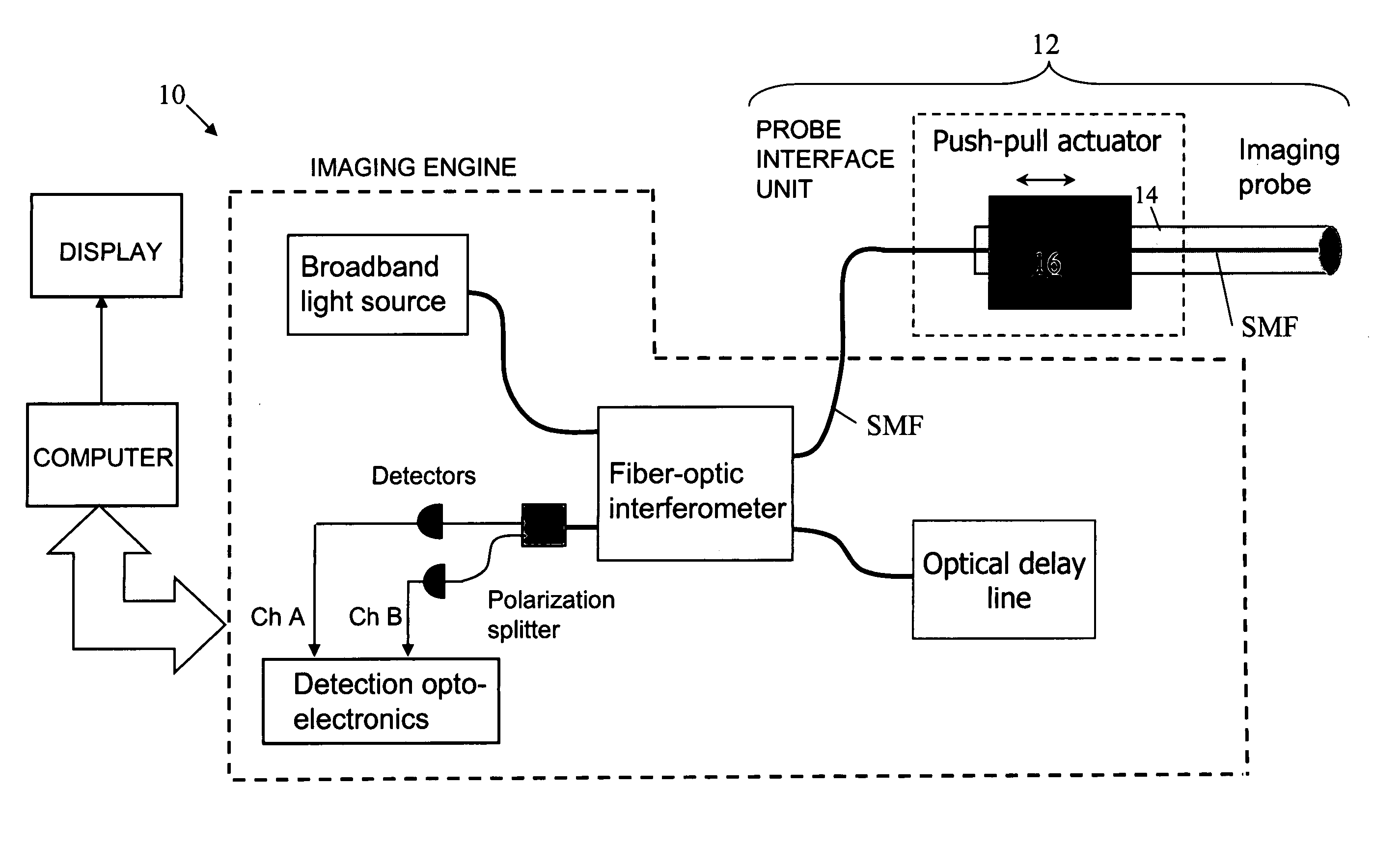
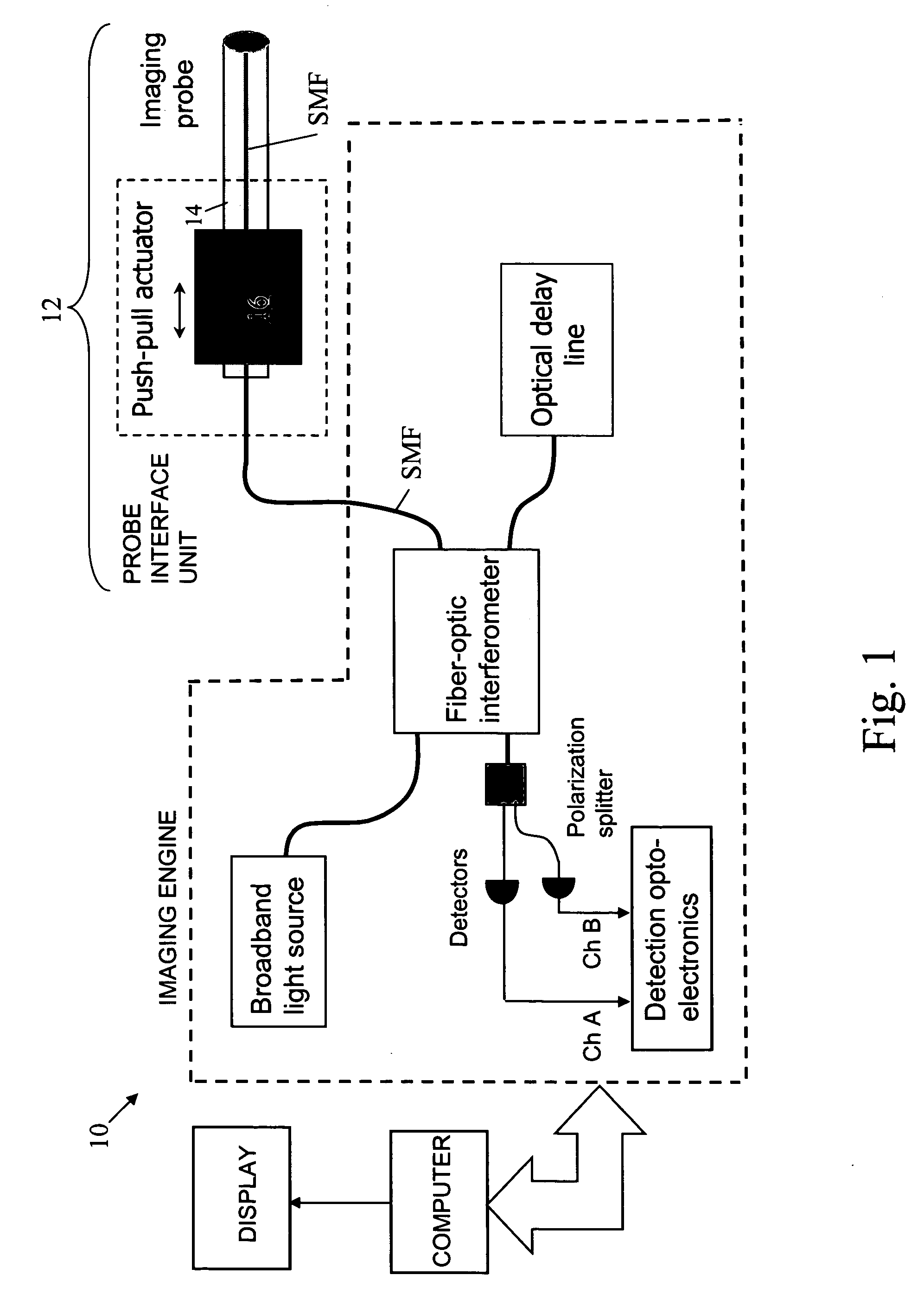
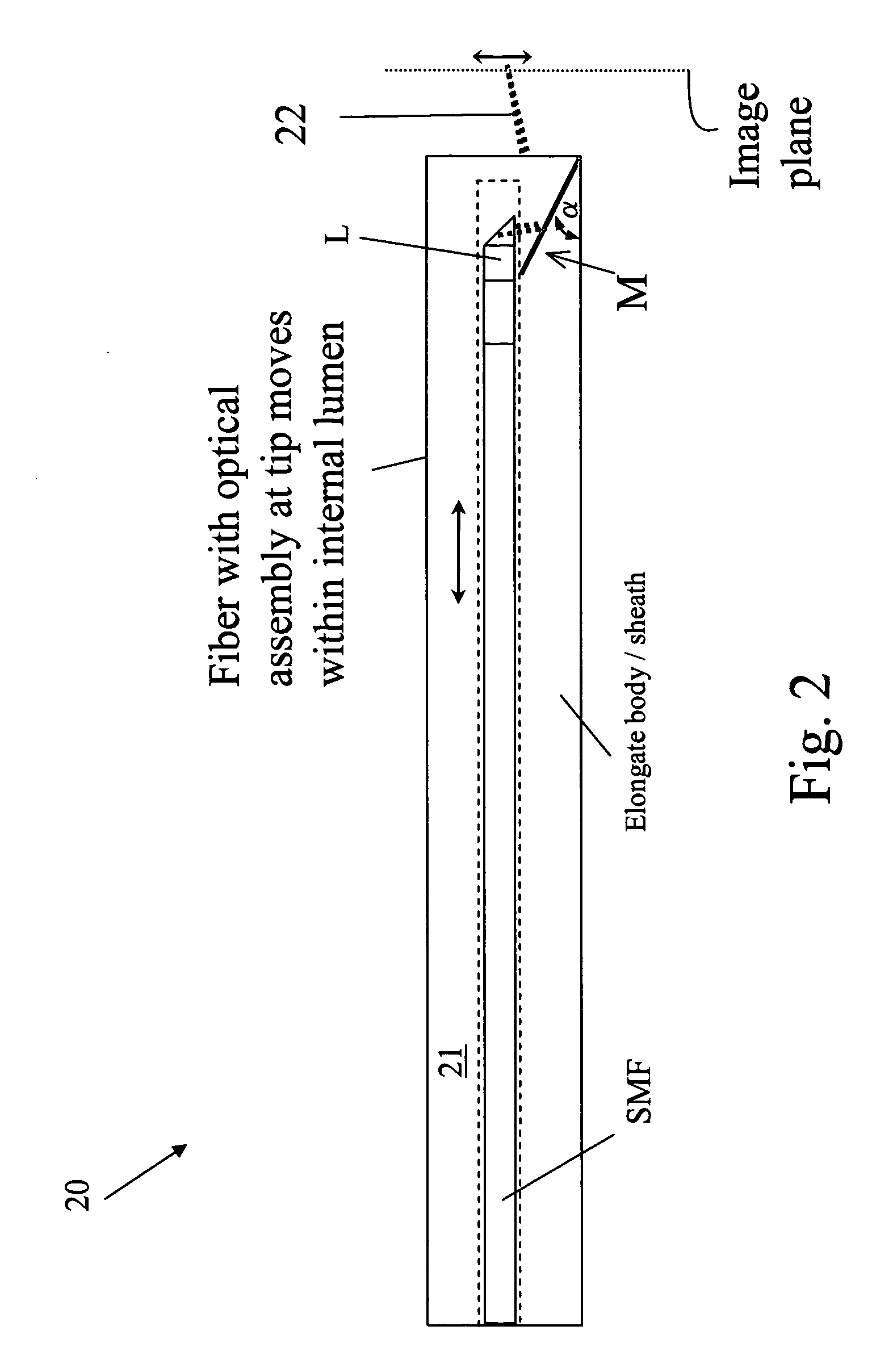
In one aspect, the invention relates to an imaging probe. The imaging probe includes an elongate body having a proximal end and distal end, the elongate body adapted to enclose a portion of a slidable optical fiber, the optical fiber having a longitudinal axis; and a first optical assembly attached to a distal end of the fiber. The first optical assembly includes a beam director adapted to direct light emitted from the fiber to a plane at a predetermined angle to the longitudinal axis, a linear actuator disposed at the proximal portion of the elongated body, the actuator adapted to affect relative linear motion between the elongate body and the optical fiber; and a second optical assembly located at the distal portion of the elongate body and attached thereto, the second optical assembly comprising a reflector in optical communication with the first optical assembly, the reflector adapted to direct the light to a position distal to the elongate body.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Method for optical coherence tomography imaging with molecular contrast
Spatial information, such as concentration and displacement, about a specific molecular contrast agent, may be determined by stimulating a sample containing the agent, thereby altering an optical property of the agent. A plurality of optical coherence tomography (OCT) images may be acquired, at least some of which are acquired at different stimulus intensities. The acquired images are used to profile the molecular contrast agent concentration distribution of the sample.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
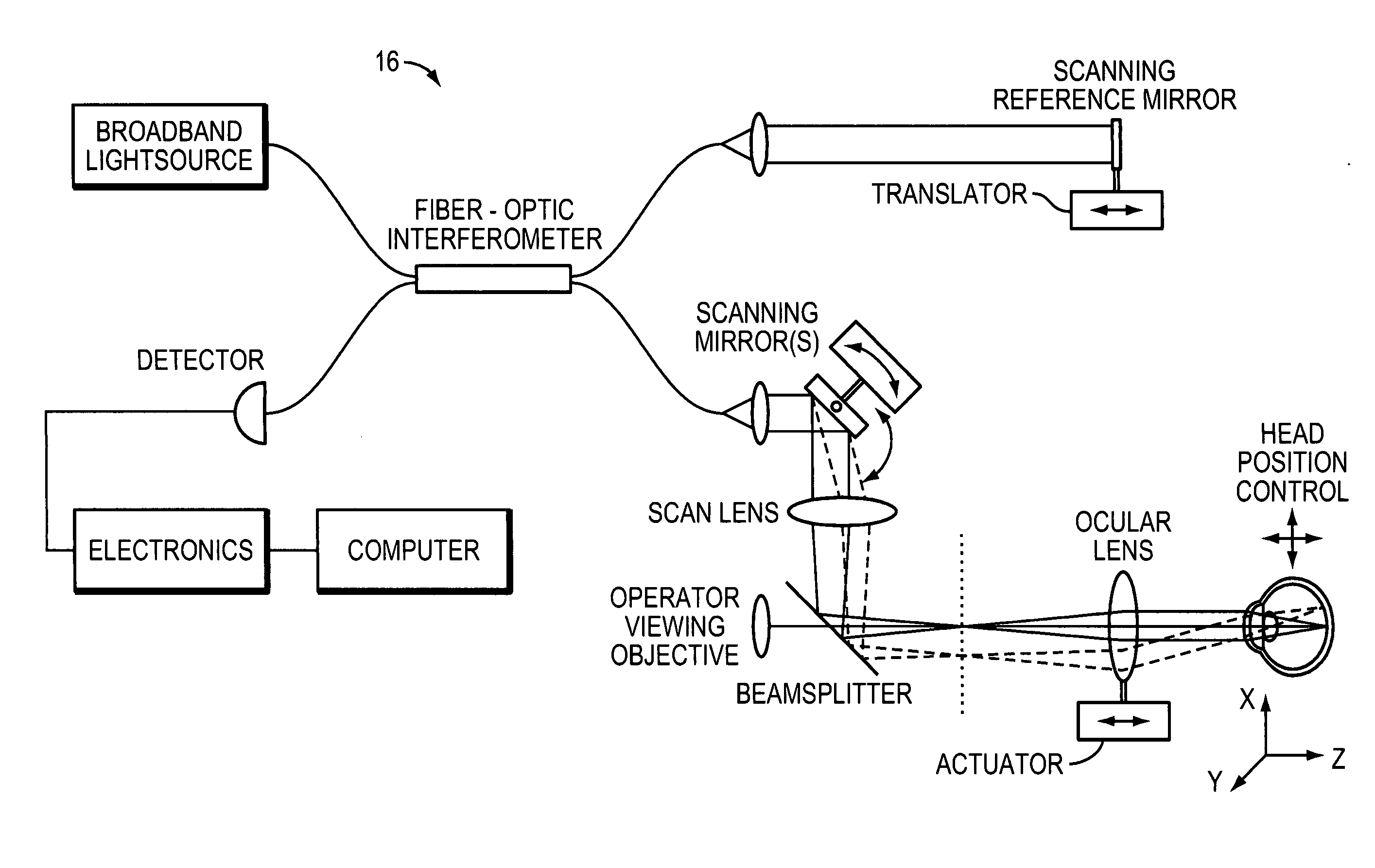
Optical apparatus and method of use for non-invasive tomographic scan of biological tissues
The present invention relates to a non-invasive optical system equipped with optical tomographic scanning method and algorithm for quantifying scattering and absorption properties and chromophore concentrations of highly scattering medium such as biological tissues, for 3D mapping and imaging reconstruction of the spatial and temporal variations in such properties. The invention further relates to a method and an apparatus for simultaneous measurement of concentrations of biochemical substances and blood oxygen saturation inside a biological tissue and arterial blood.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH +1
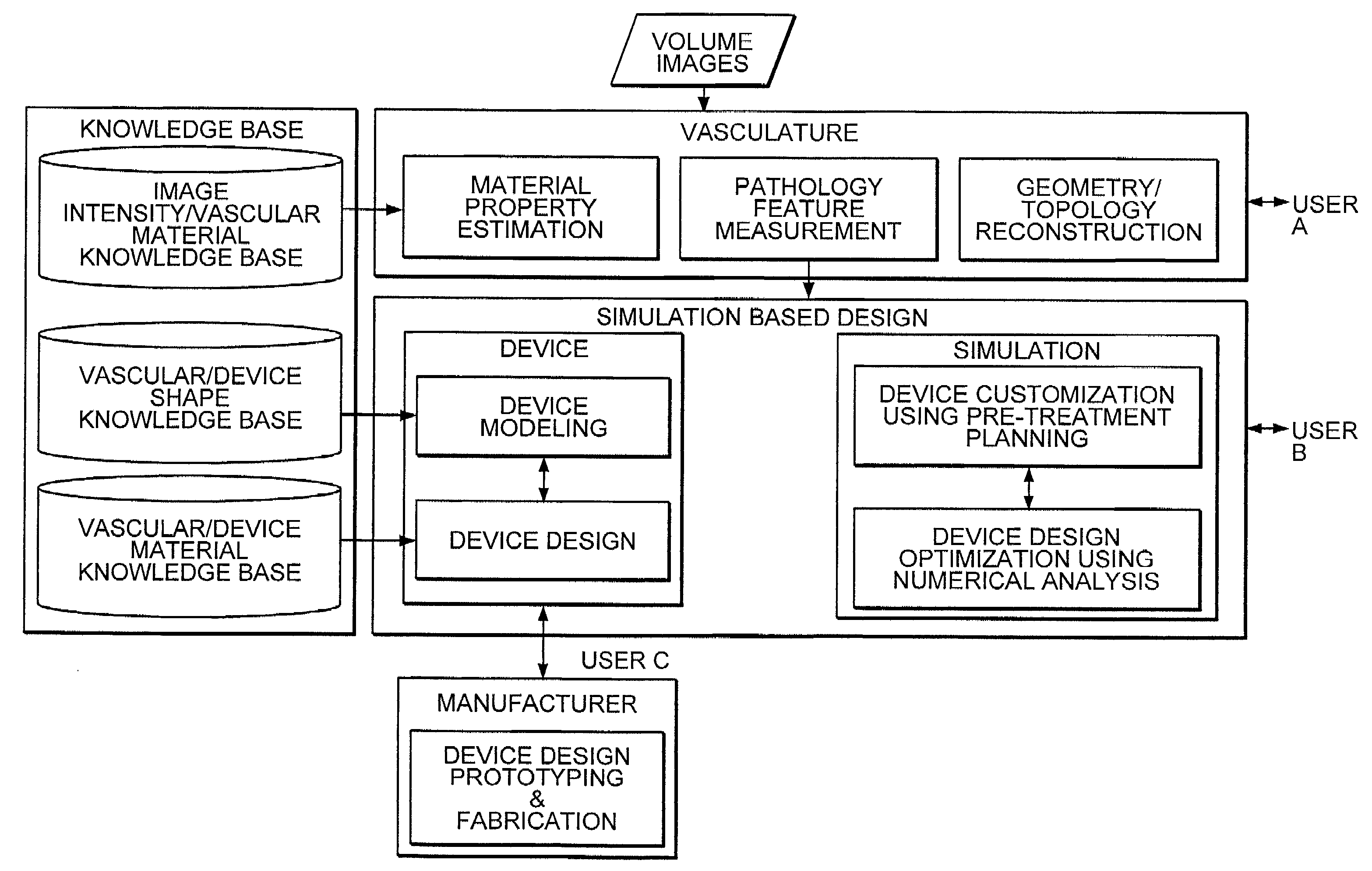
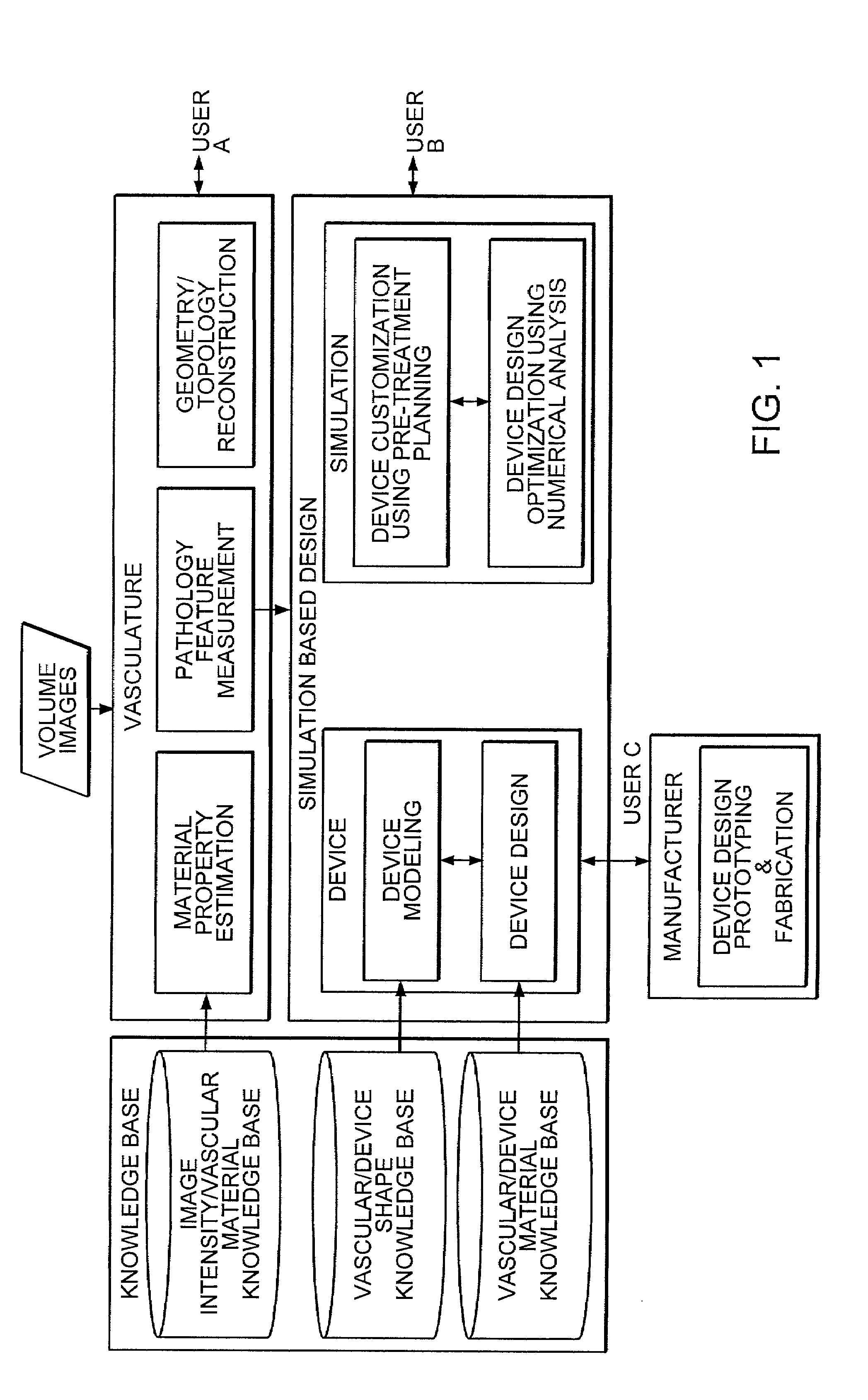
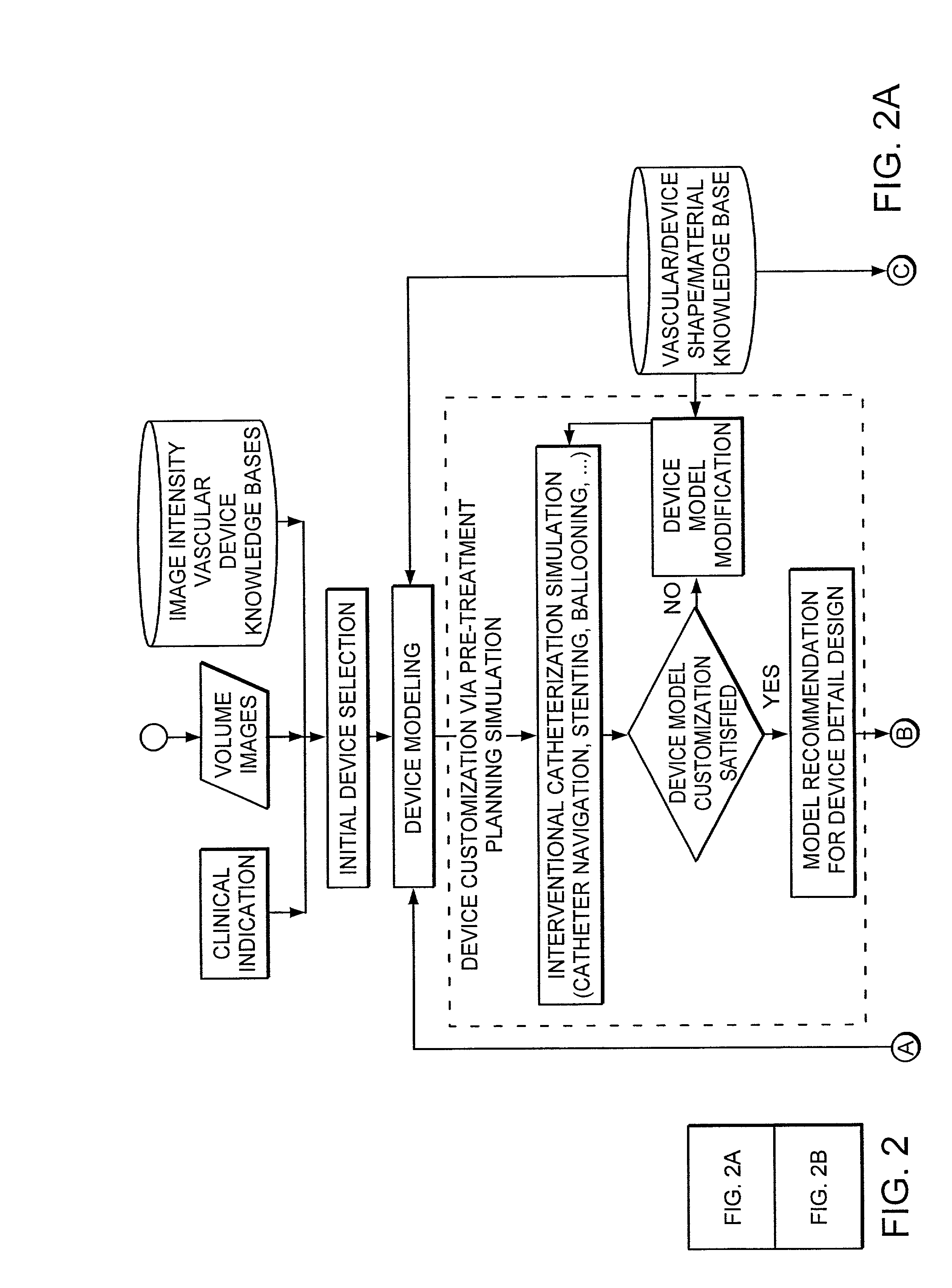
Simulation method for designing customized medical devices
The invention provides a system for virtually designing a medical device conformed for use with a specific patient. Using the system, a three-dimensional geometric model of a patient-specific body cavity or lumen is reconstructed from scanned volume images such as obtained x-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computer tomography (CT), ultrasound (US), angiography or other imaging modalities. Knowledge of the physical properties of the cavity / lumen is obtained by determining the relationship between image density and the stiffness or elasticity of tissues in the body cavity or lumen and is used to model interactions between a simulated device and a simulated body cavity or lumen.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
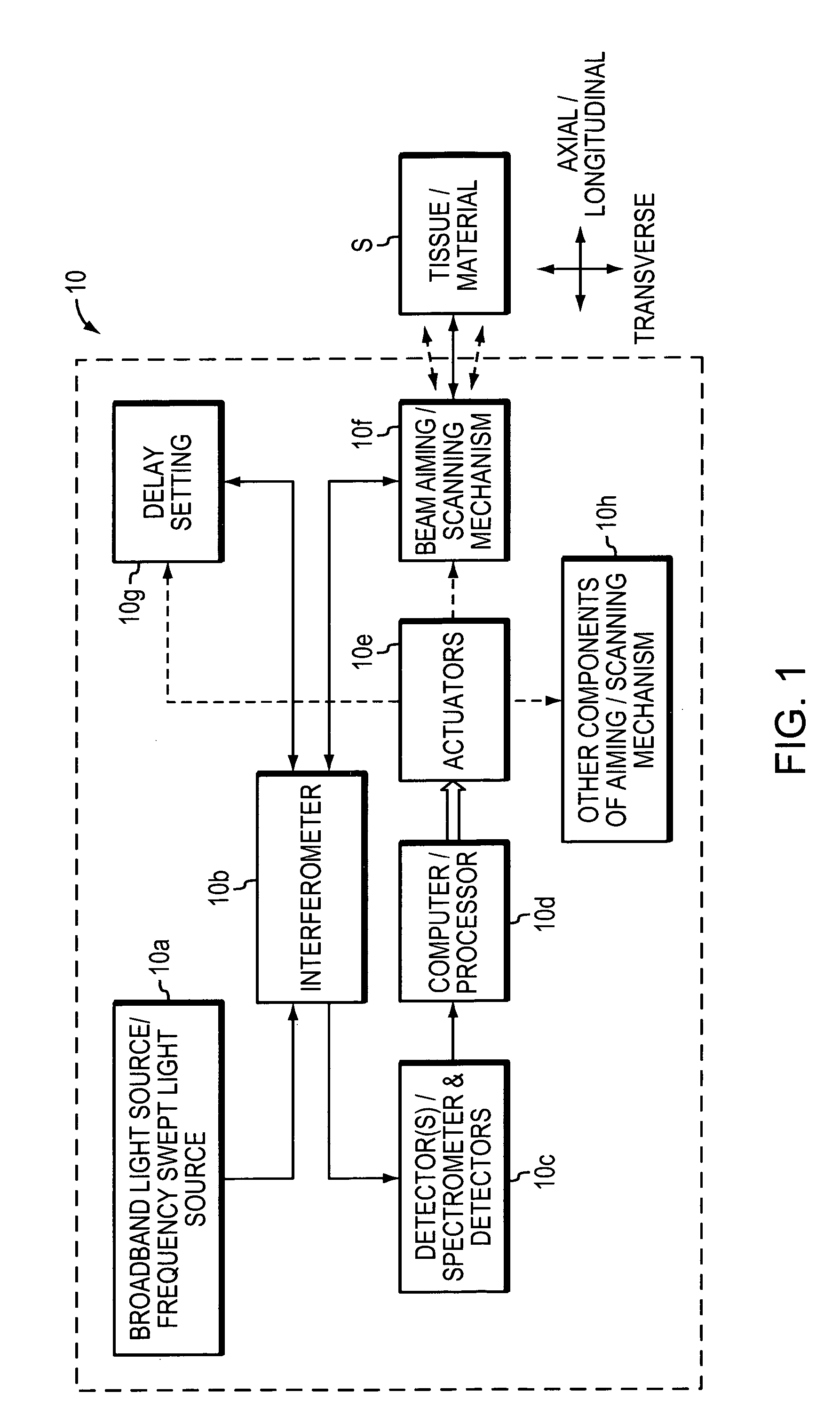
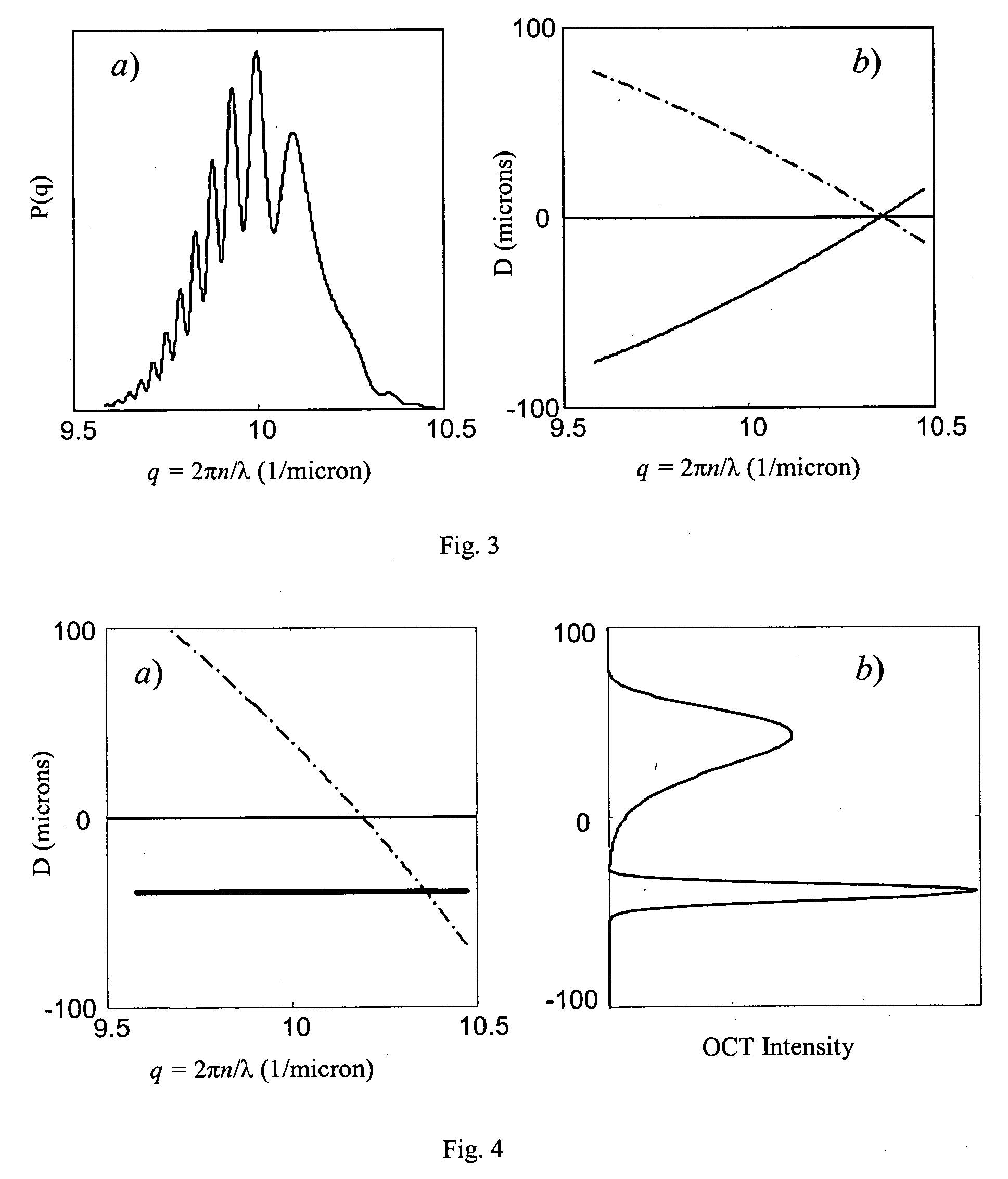
Method to suppress artifacts in frequency-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20060171503A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomographyFrequency domain optical coherence tomography
One embodiment of the present invention is a method for suppressing artifacts in frequency-domain OCT images, which method includes (a) providing sample and reference paths with a significant difference in their chromatic dispersion (b) correcting for the effects of the mismatch in chromatic dispersion, for the purpose of making artifacts in the OCT image readily distinguishable from the desired image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
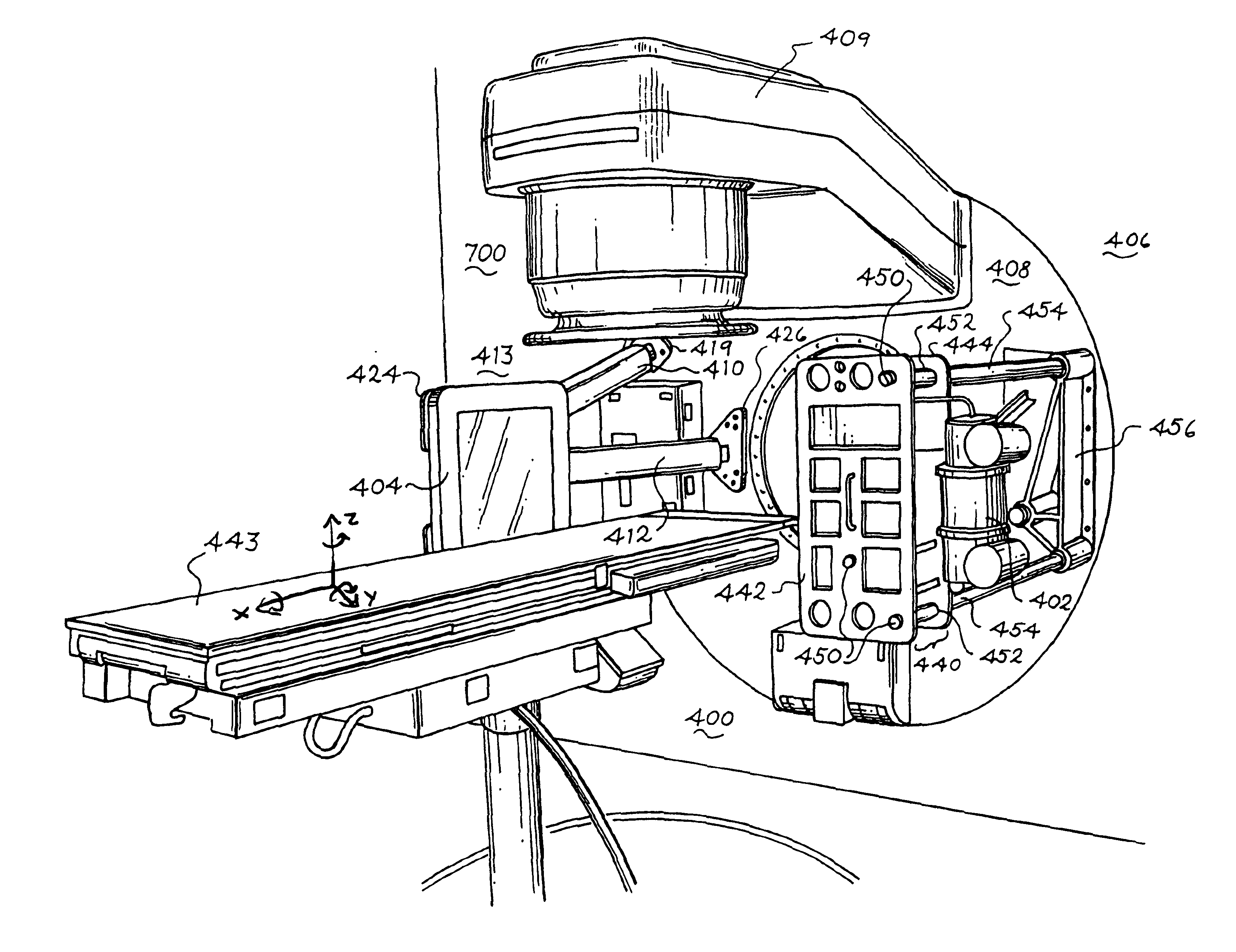
C-arm computerized tomography system
ActiveUS9044190B2Reducing effect of motion of C-armCharacter and pattern recognitionX-ray apparatusData setVideo sequence
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
External continuous field tomography
Methods for evaluating tissue motion of a tissue location, e.g., a cardiac location, via external continuous field tomography are provided. Aspects of the methods include generating at least one substantially linear continuous field gradient across the tissue location of interest, and using a resultant signal from a sensing element stably associated with the tissue location to evaluate motion of the tissue location. Also provided are systems, devices and related compositions for practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and devices find use in a variety of different applications, including cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
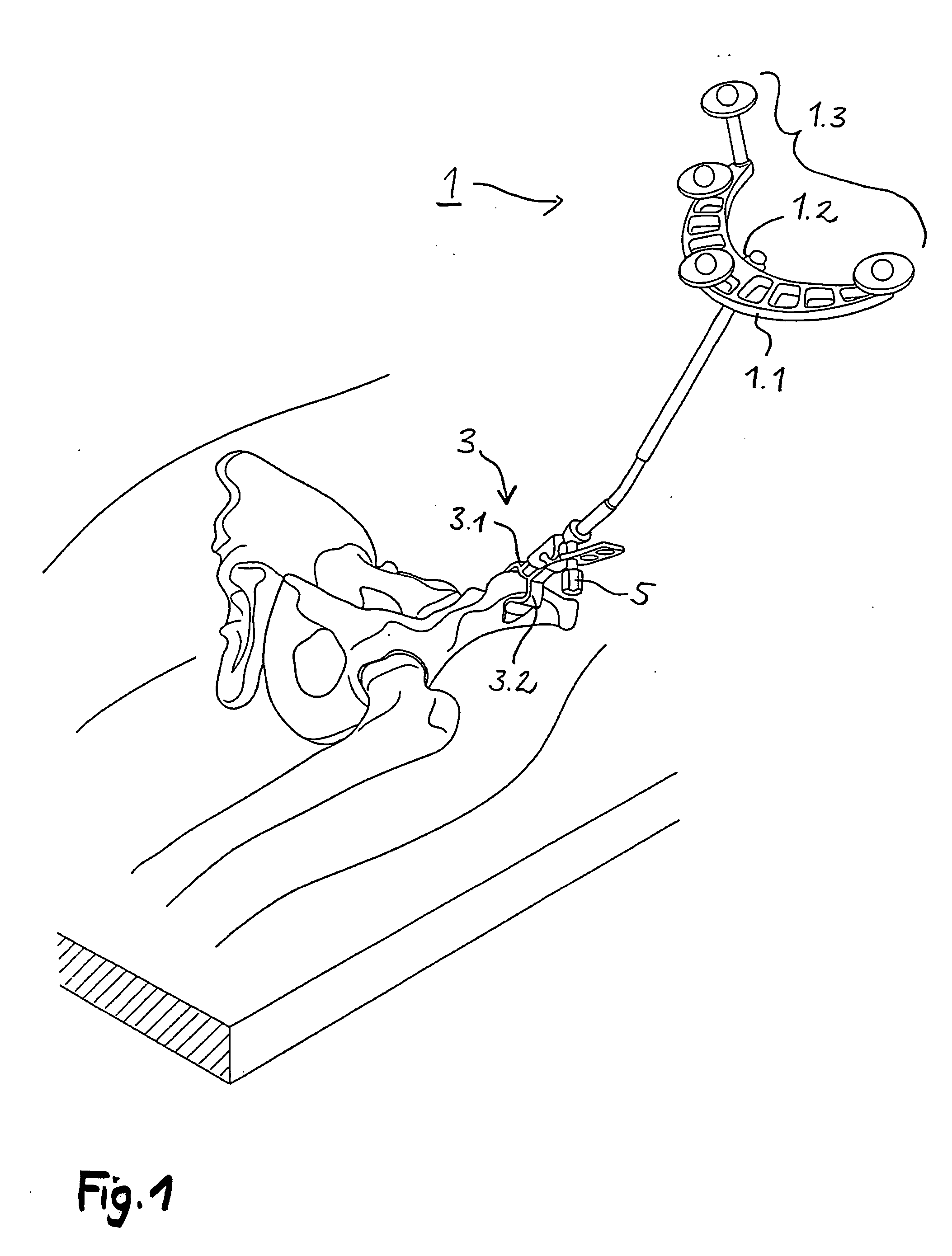
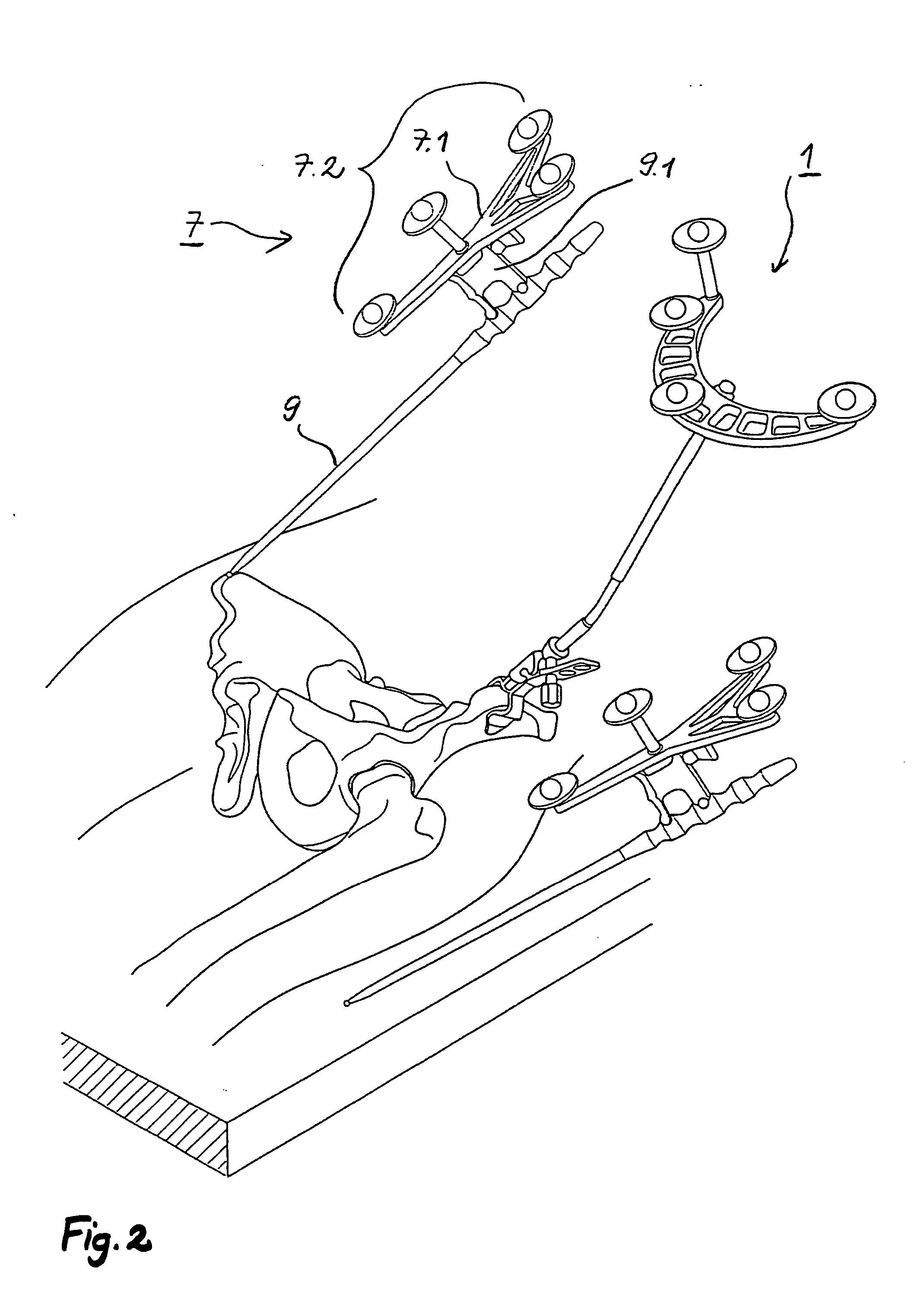
Arrangement and method for the intra-operative determination of the position of a joint replacement implant
InactiveUS20050149050A1Easy to operateLow risk of errorPerson identificationJoint implantsReference vectorMeasurement point
Arrangement for the intra-operative determination of the spatial position and angular position of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip socket or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, or a vertebral replacement implant, especially a lumbar or cervical vertebral implant, using a computer tomography method, having: a computer tomography modeling device for generating and storing a three-dimensional image of a joint region or vertebral region to be provided with the joint replacement implant, an optical coordinate-measuring arrangement for providing real position coordinates of defined real or virtual points of the joint region or vertebral region and / or position reference vectors between such points within the joint region or vertebral region or from those points to joint-function-relevant points on an extremity outside the joint region or vertebral region, the coordinate-measuring arrangement comprising a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of transducer signals, at least one multipoint transducer, which comprises a group of measurement points rigidly connected to one another, and an evaluation unit for evaluating sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducer(s) and recorded by the stereocamera, and a matching-processing unit for real position matching of the image to the actual current spatial position of the joint region or vertebral region with reference to the real position coordinates of the defined points, the matching-processing unit being configured for calculating transformation parameters with minimalization of the normal spacings.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Assisted Guidance and Navigation Method in Intraoral Surgery
InactiveUS20140234804A1Shorten the construction periodGood curative effectRadiation diagnostic image/data processingTeeth fillingVisual positioningSurgical department
An assisted guidance and navigation method in intraoral surgeries is a method using computerized tomography (CT) photography and an optical positioning system to track medical appliances, the method including: first providing an optical positioning treatment instrument and an optical positioning device; then obtaining image data of the intraoral tissue receiving treatment through CT photography, precisely displaying actions of the treatment instrument in the image data, and real-time checking an image and guidance and navigation. Therefore, during the surgery, the existing use habits of the physicians are not affected and accurate and convenient auxiliary information is provided, and attention is paid to using the treatment instrument in physical environments such as a patient's tooth or dental model.
Owner:HUANG JERRY T +1
Endoscopy device with removable tip
The present invention provides an endoscope for in vivo imaging the cells, tissue, organs or body cavities of humans or other animals to observe and locate, diagnosis and / or treat disease. Illumination sources, image detectors, sensors may be provided alone or in combination on the removable tip allowing functional alterations or optimization for a particular procedure. Endoscope features such as an instrument channel supporting tissue sampling, suction, treatment, micro-surgery, optical computed tomography, confocal microscopy, laser or drug treatments, injections, gene-therapy, marking, implanting or other medical techniques are maintained.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com