Patents
Literature
51 results about "Replacement implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
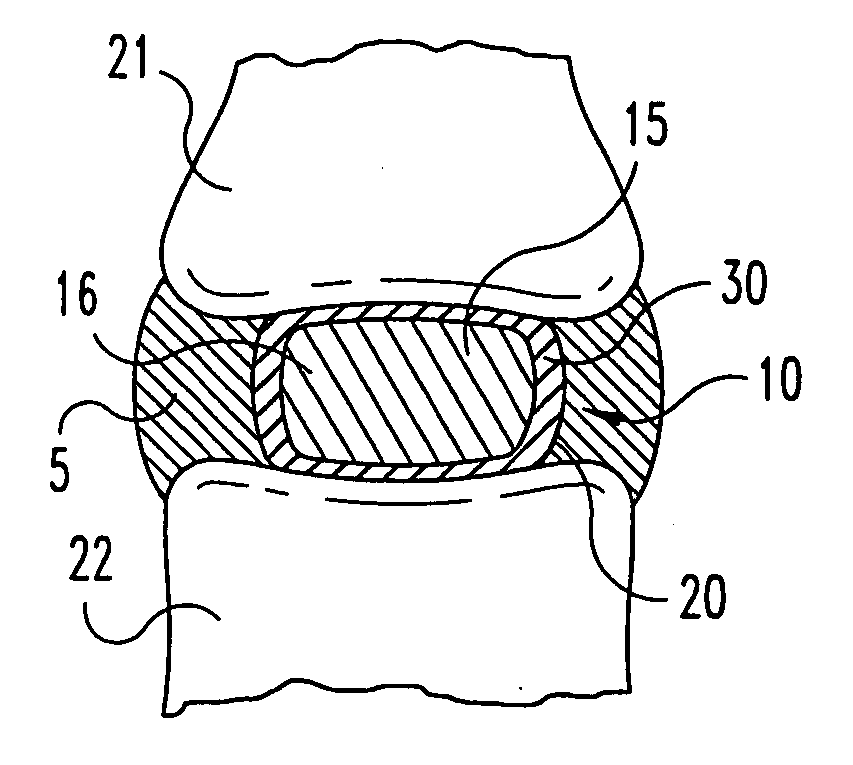
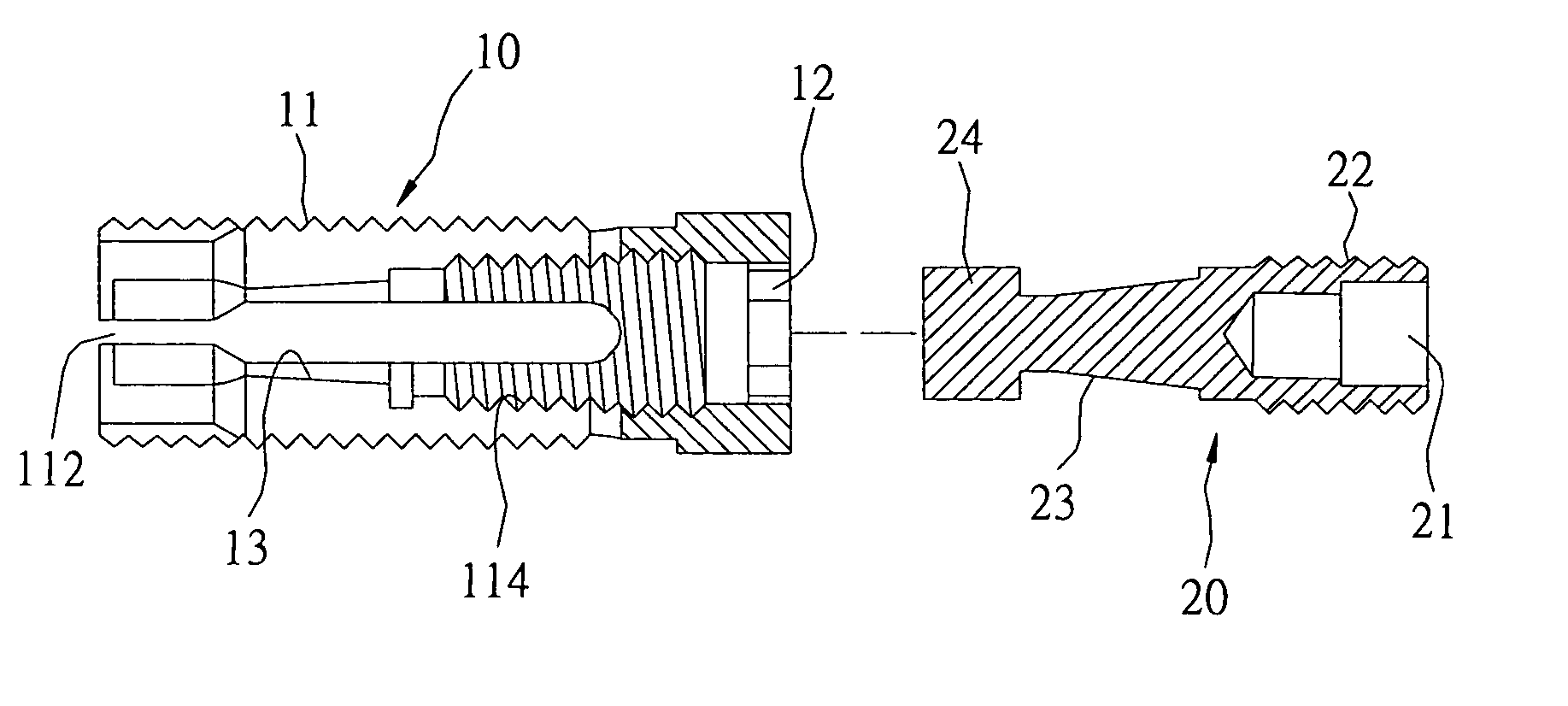
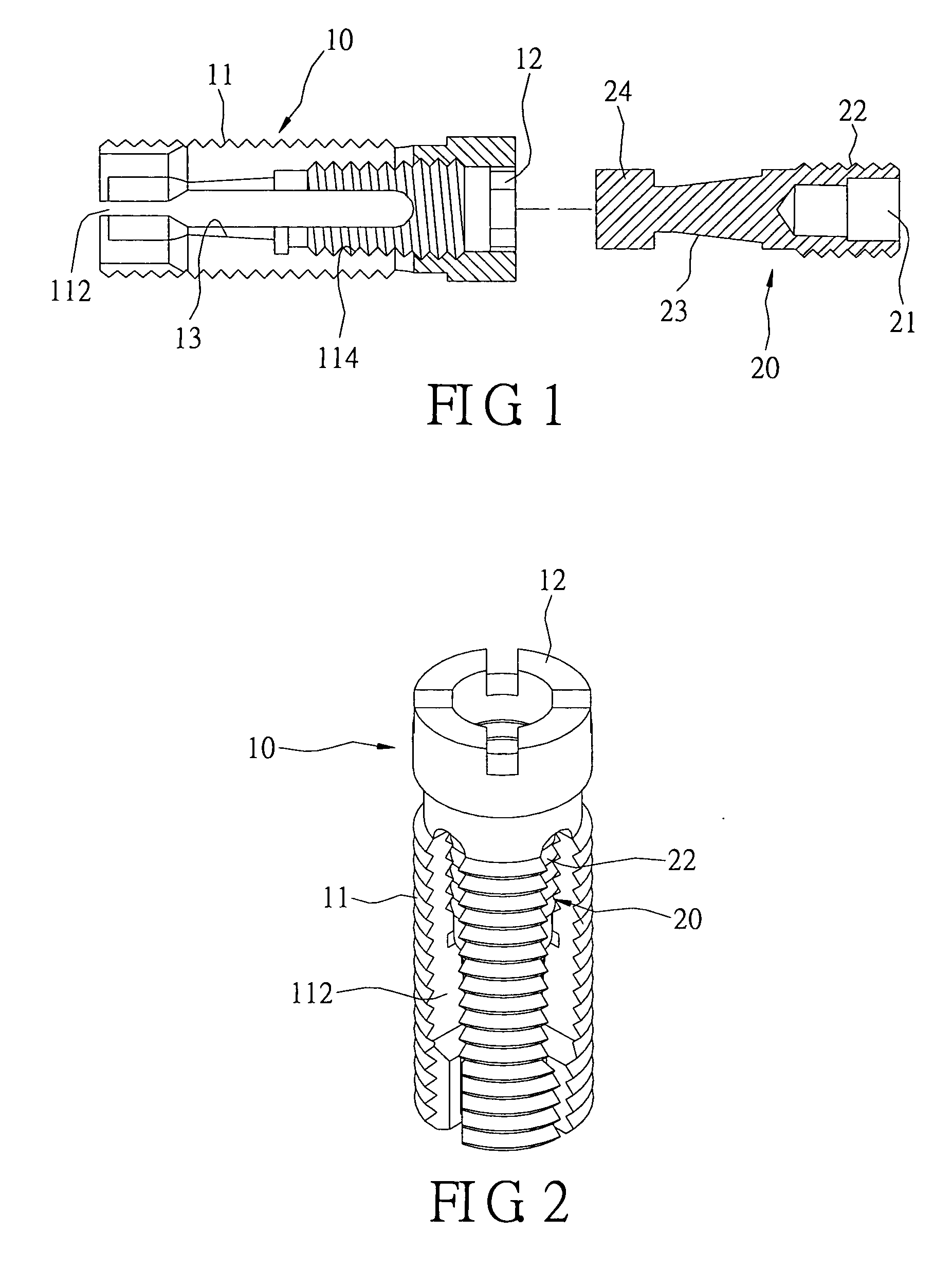
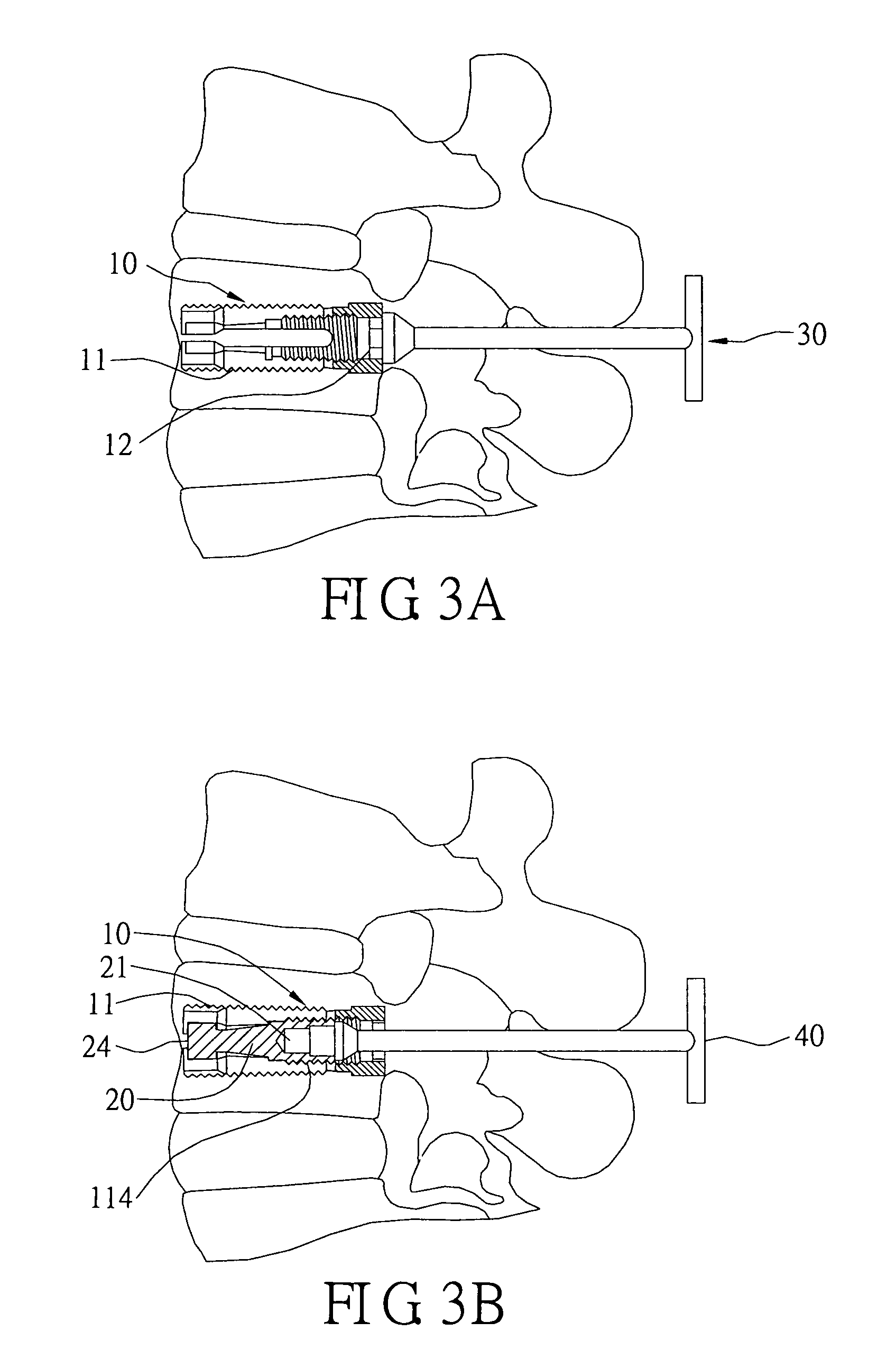
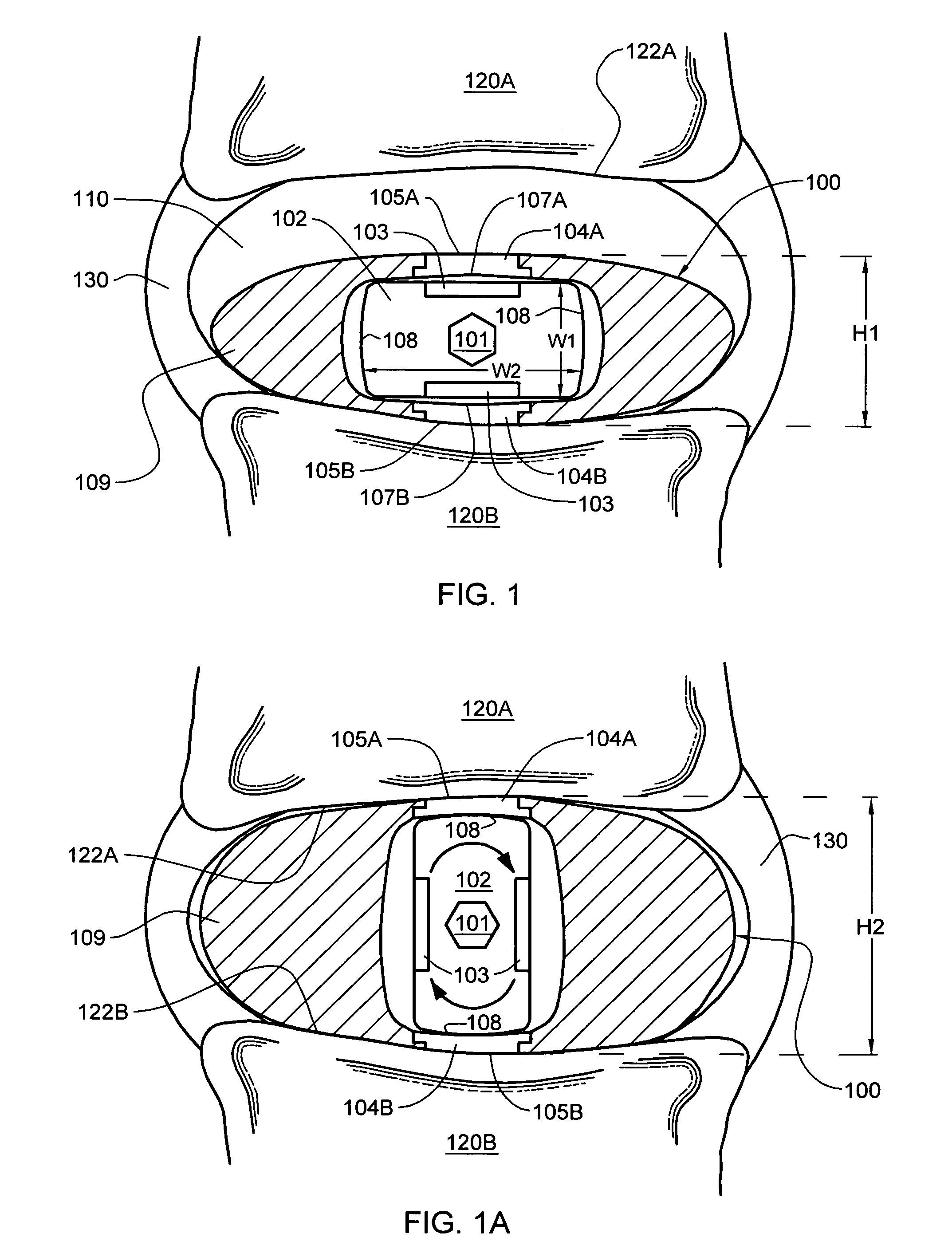
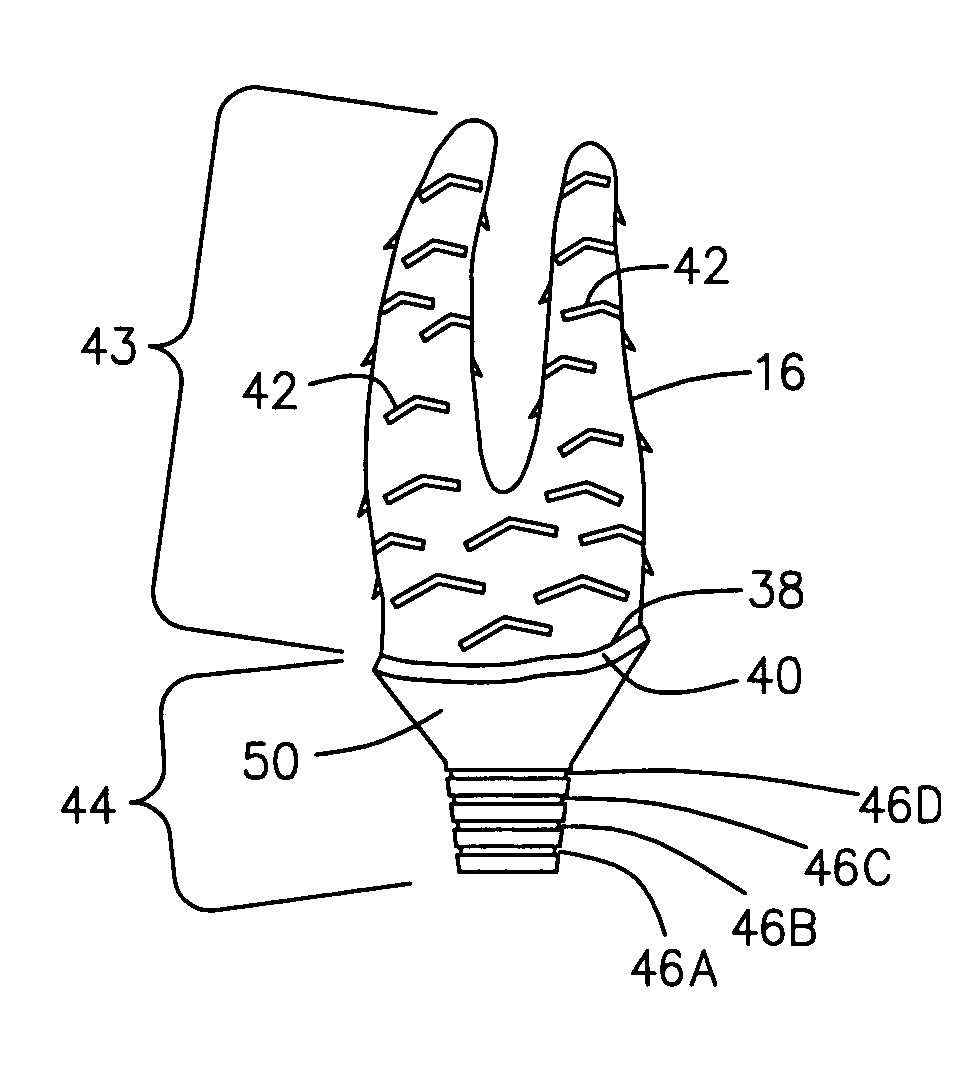
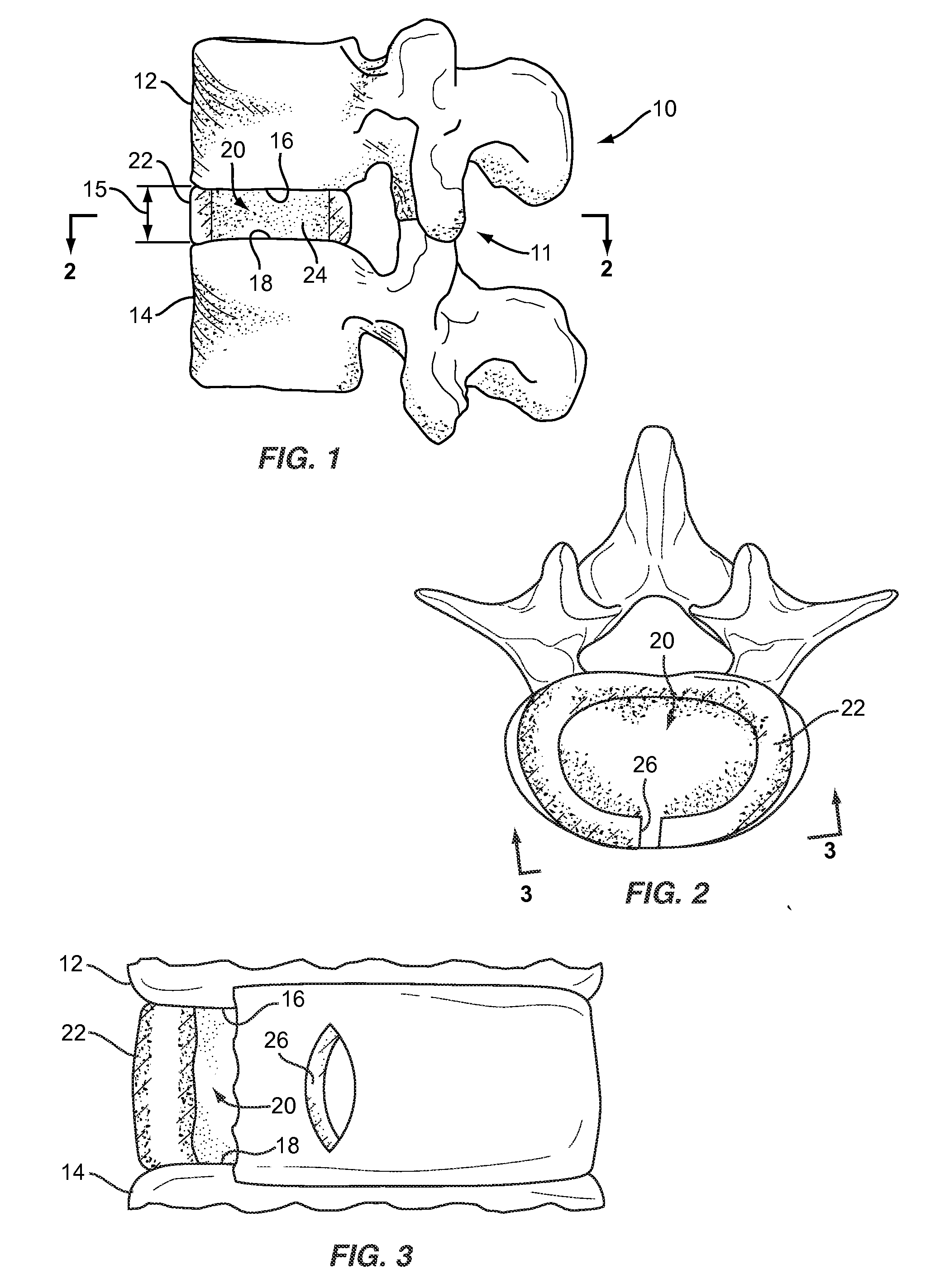
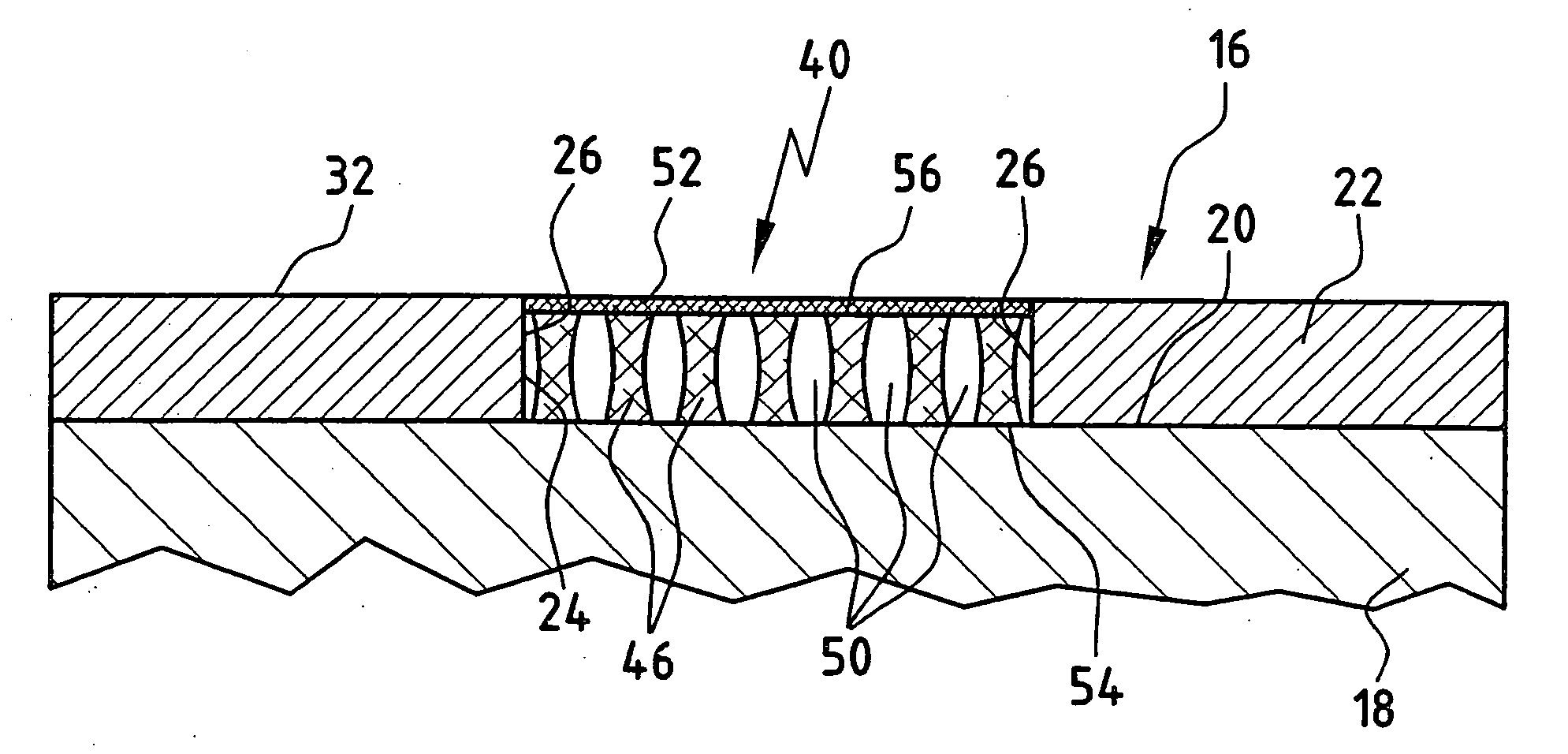
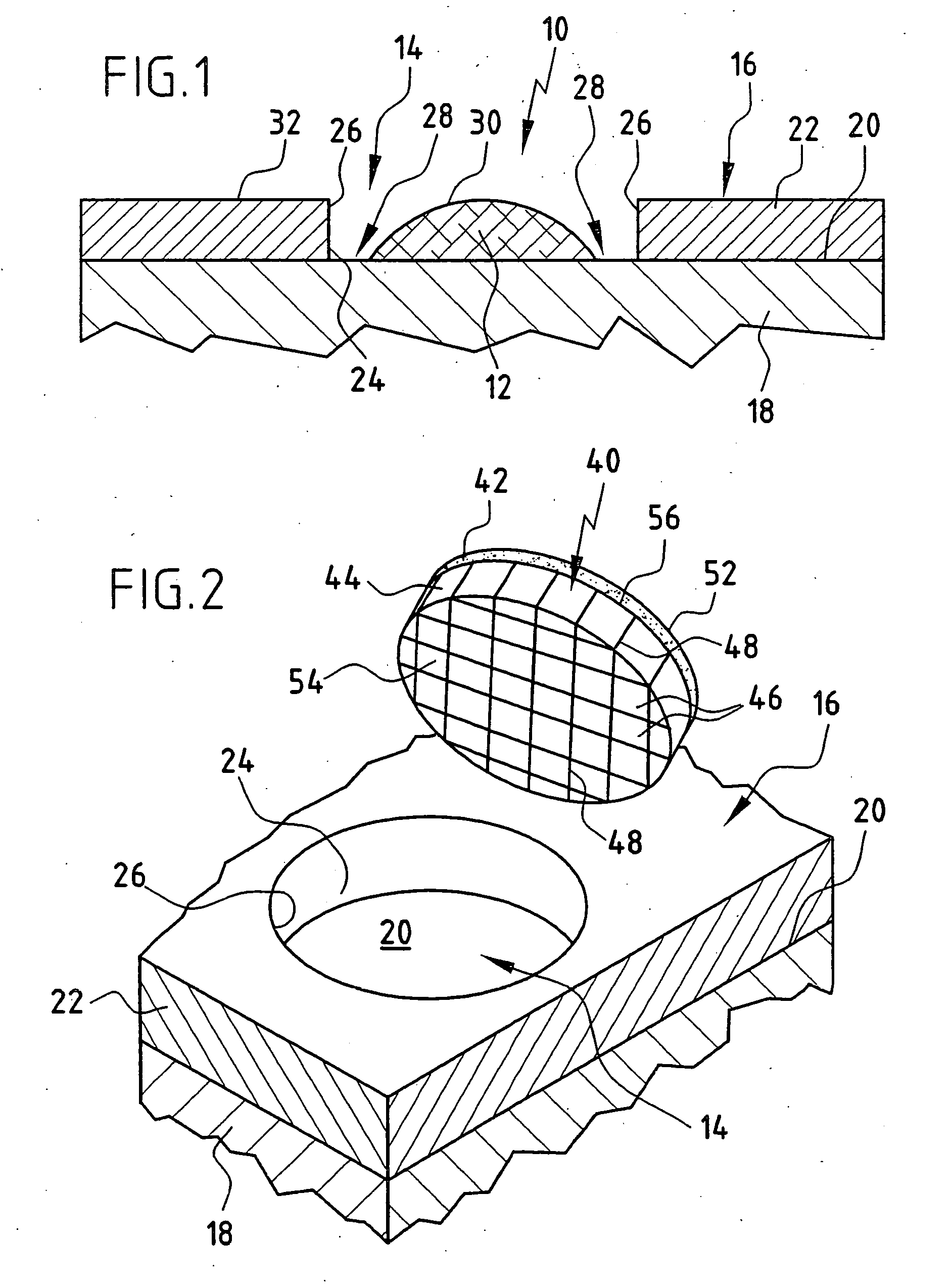
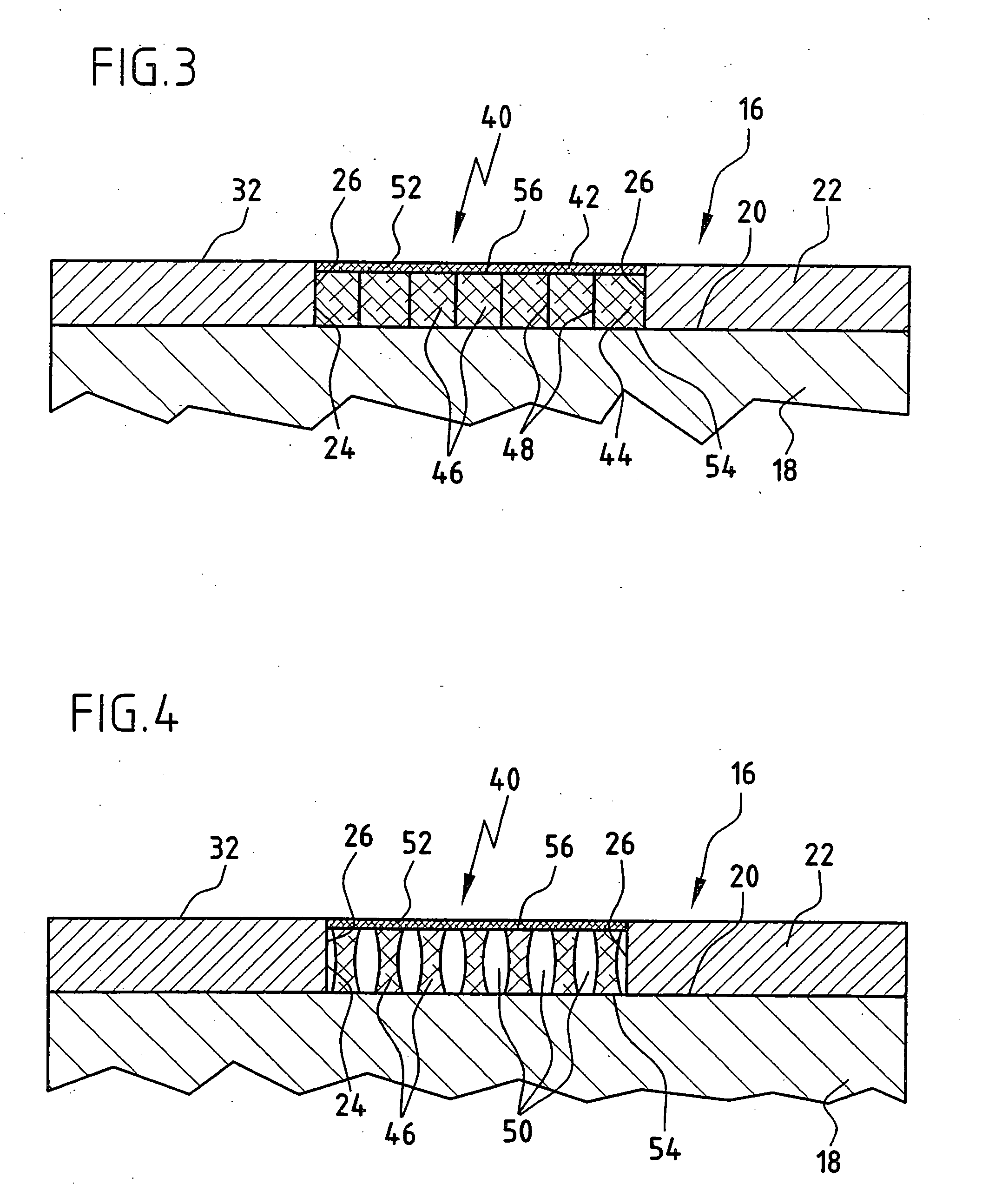
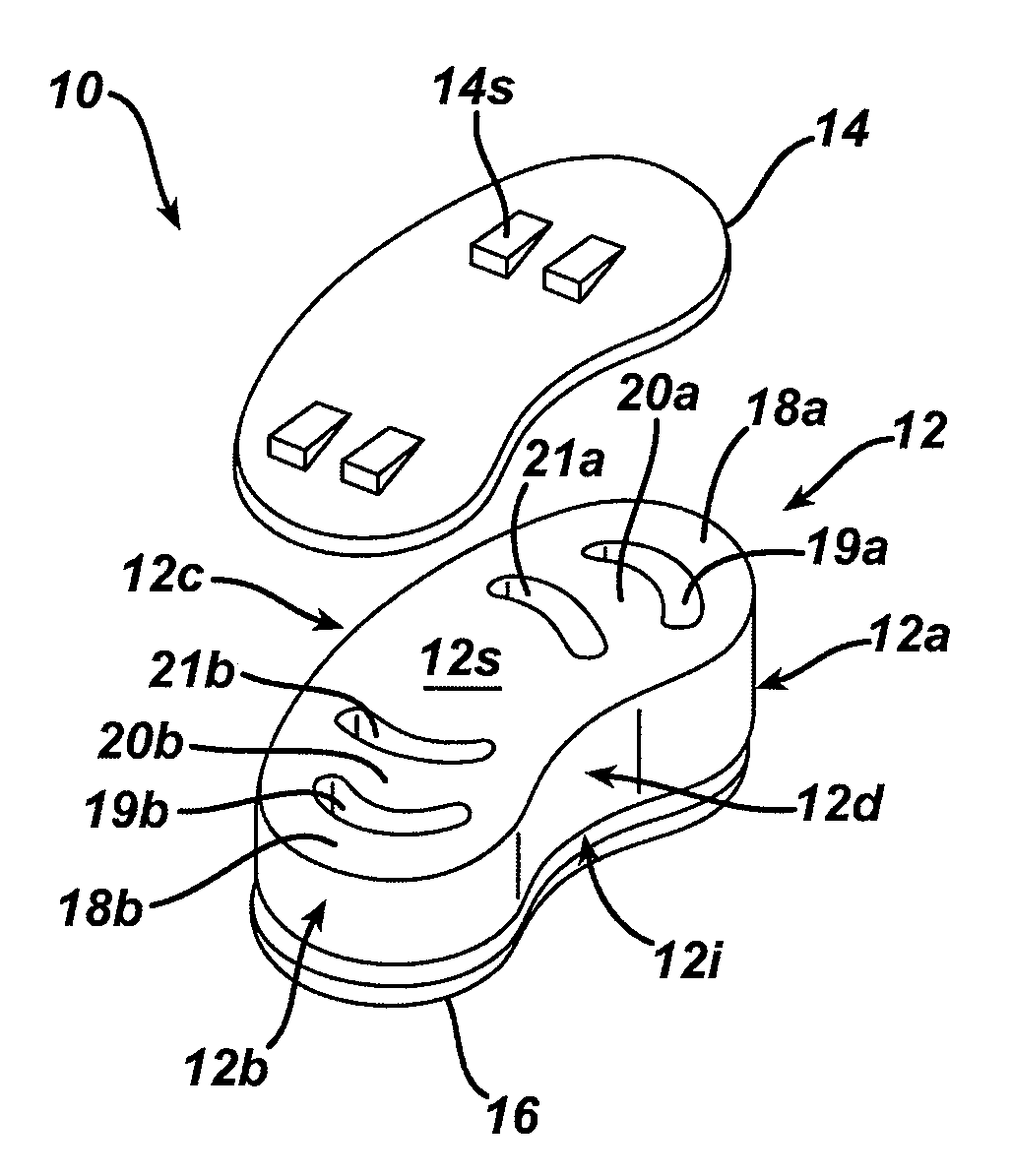
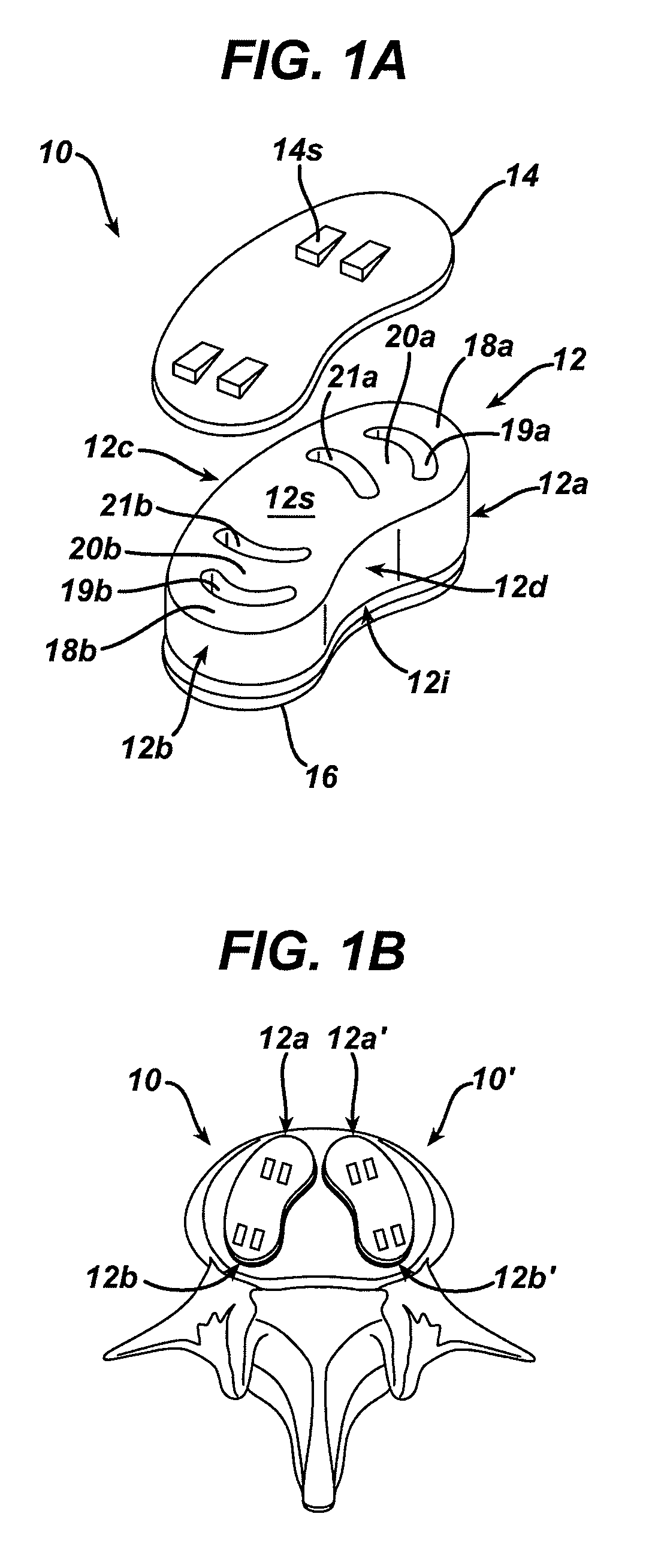
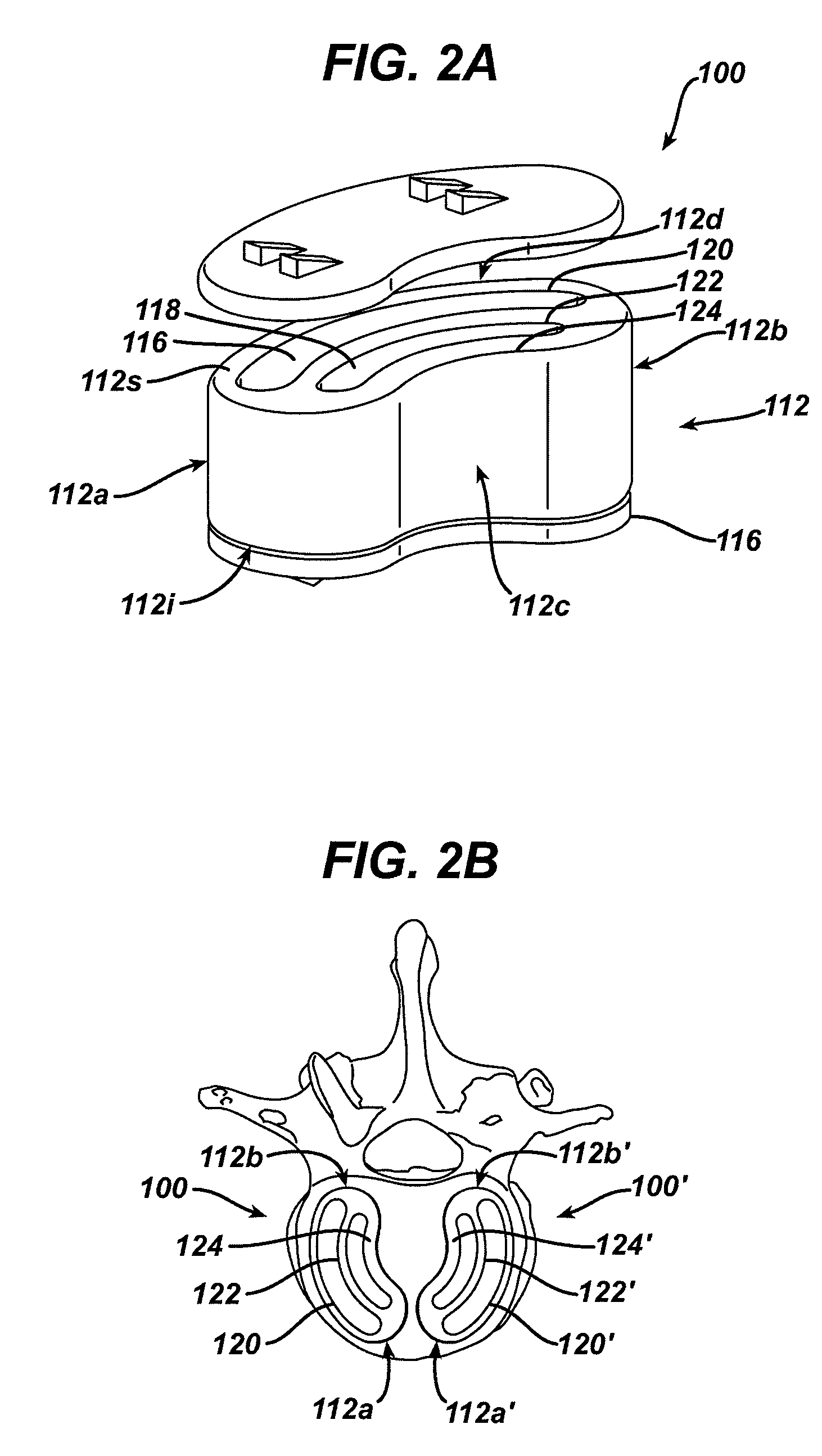
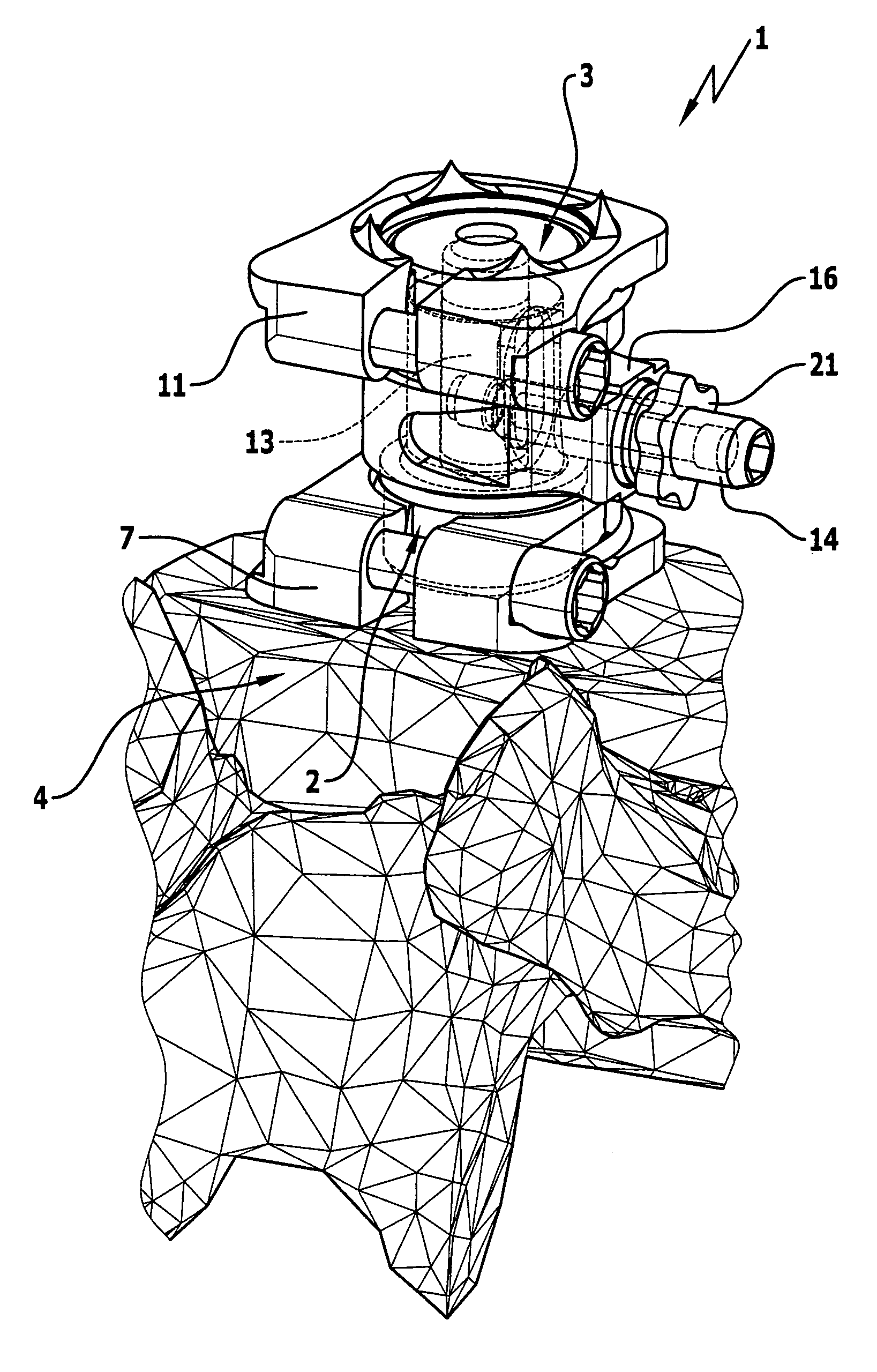
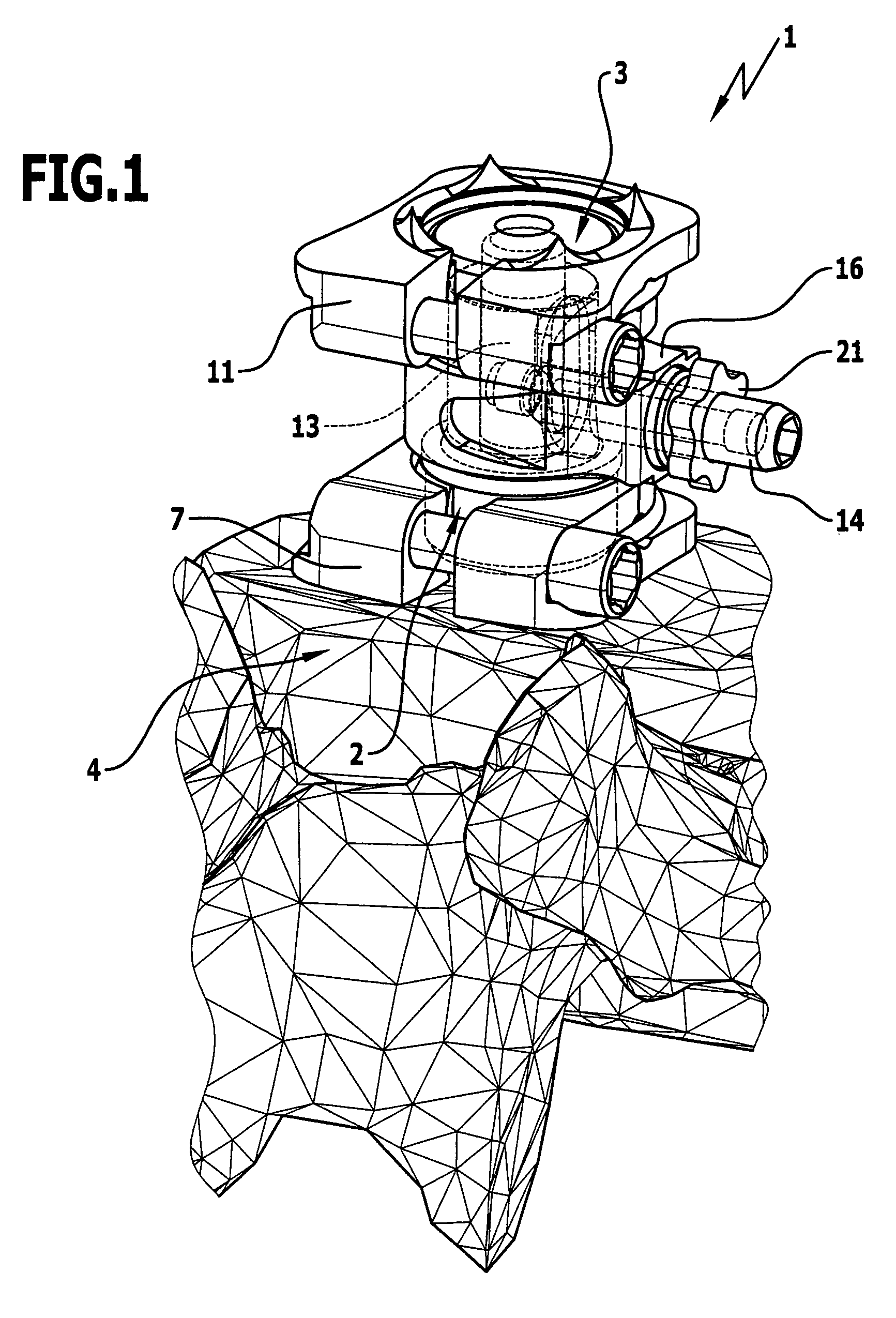
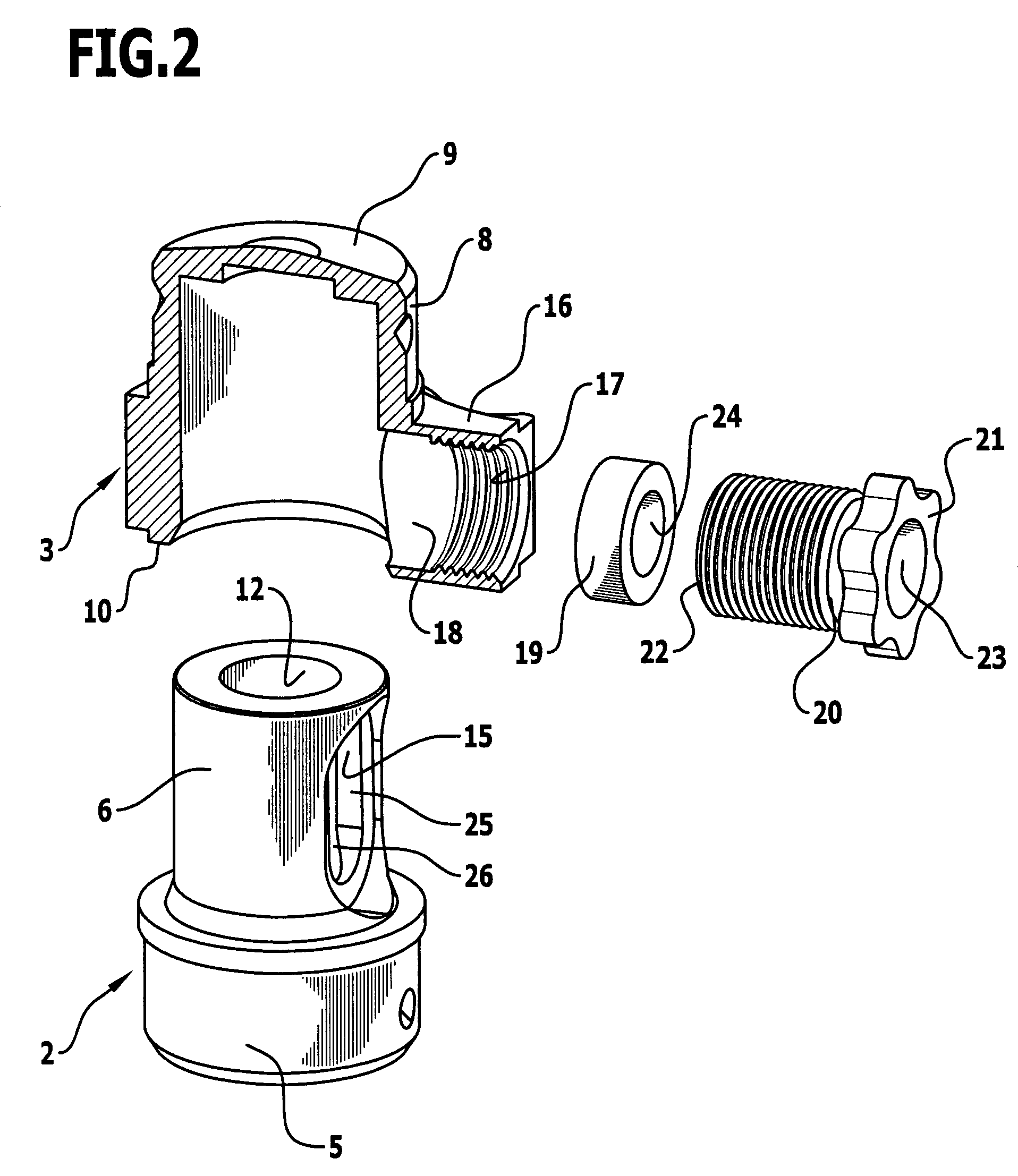
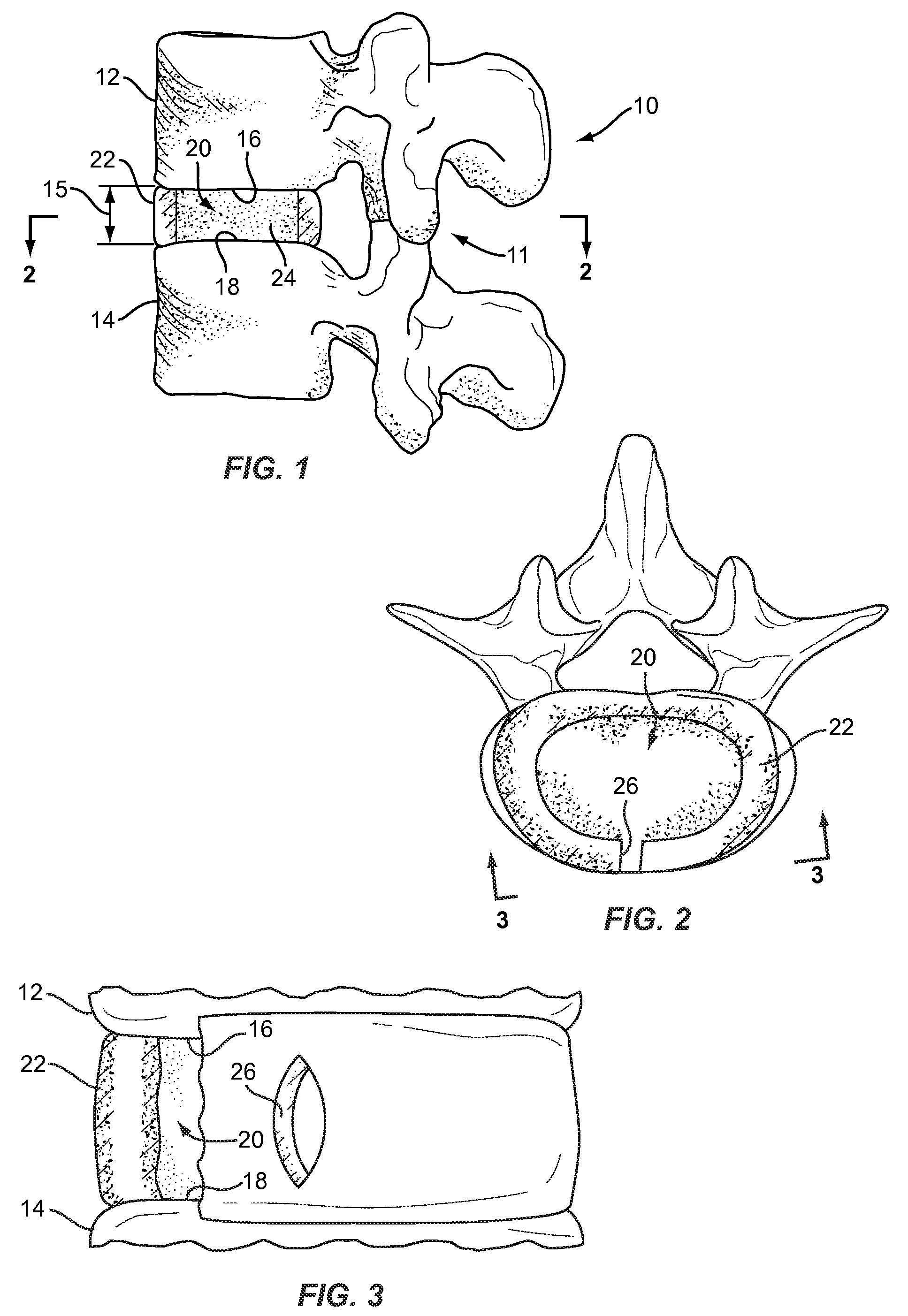
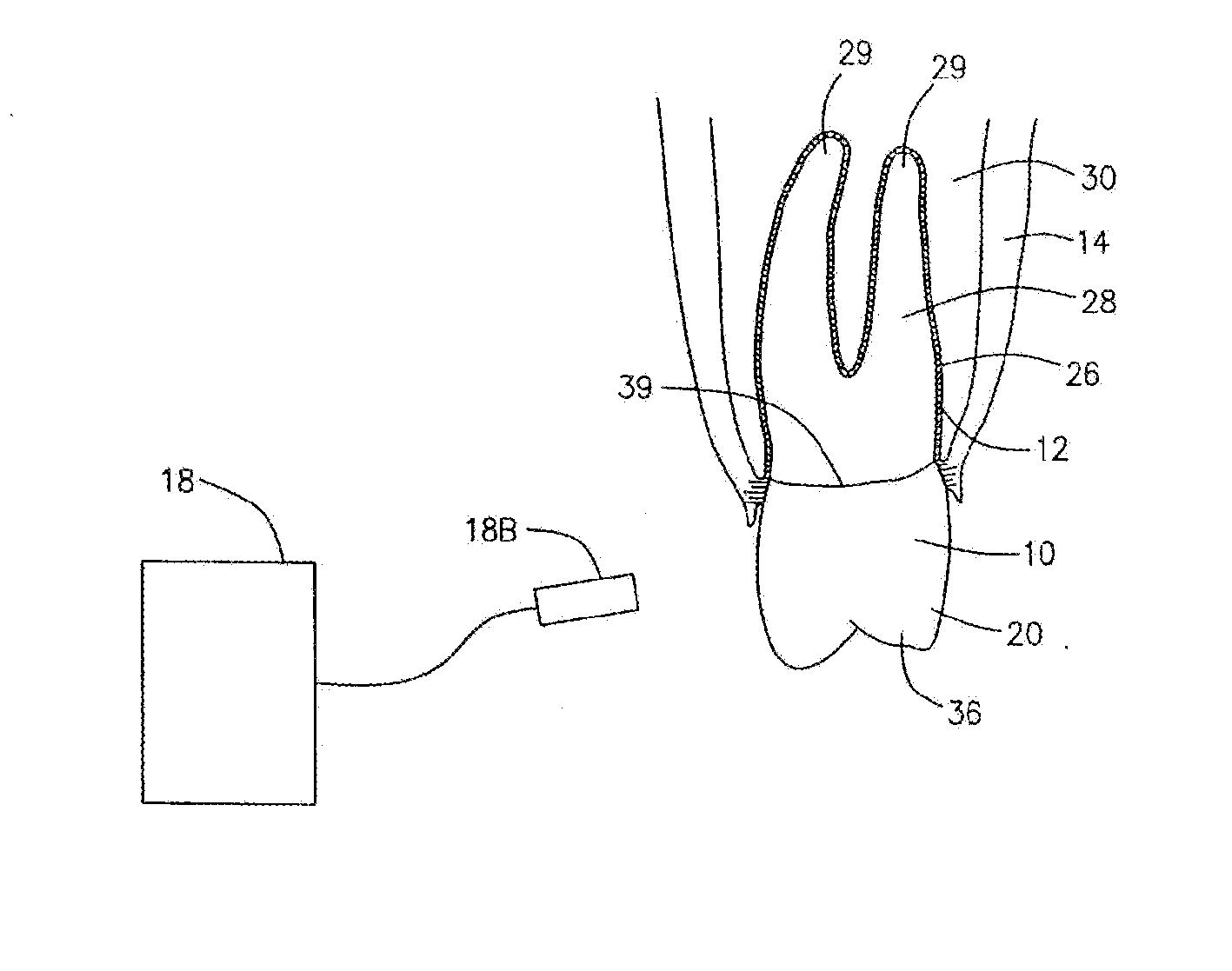
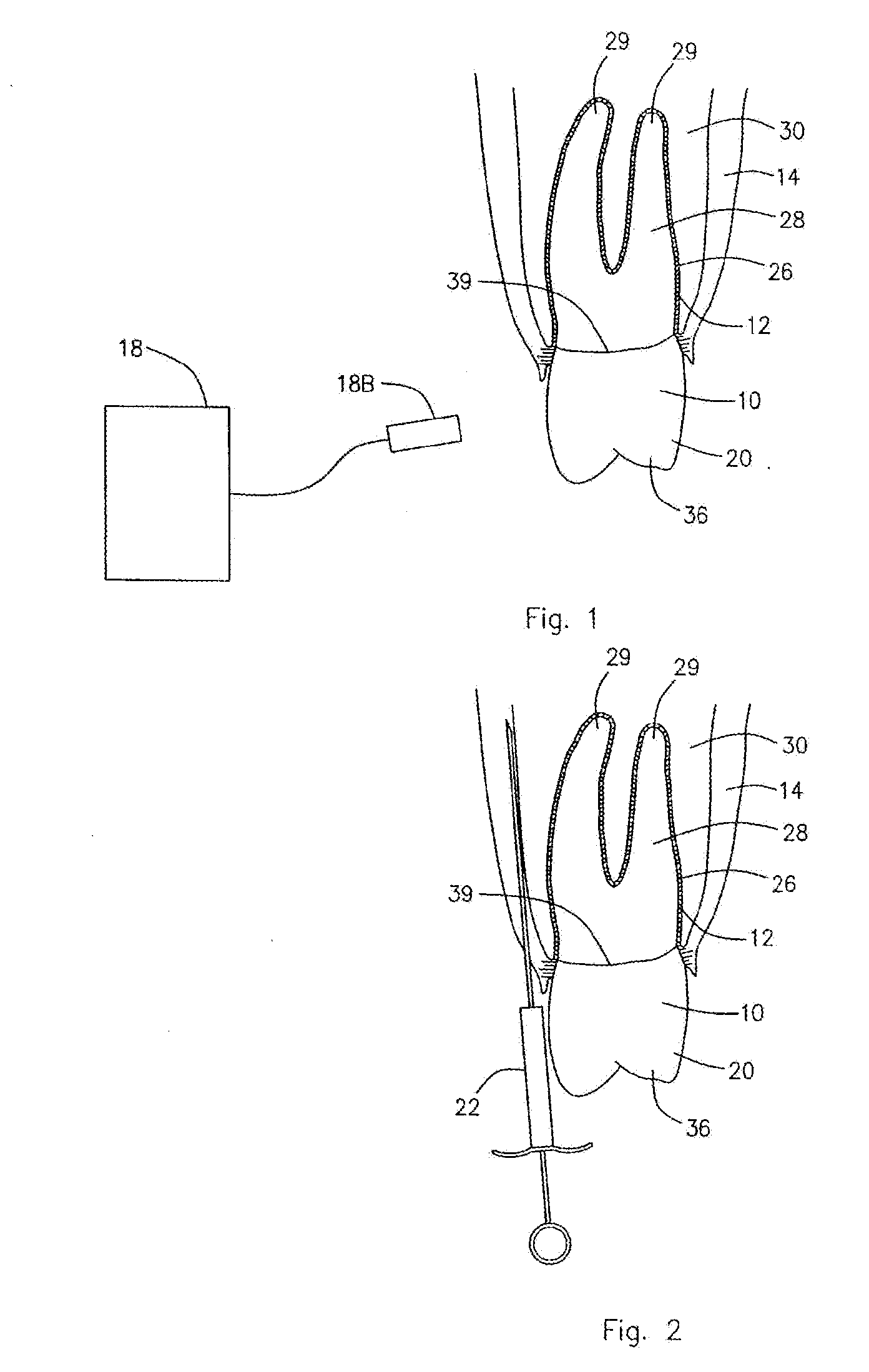
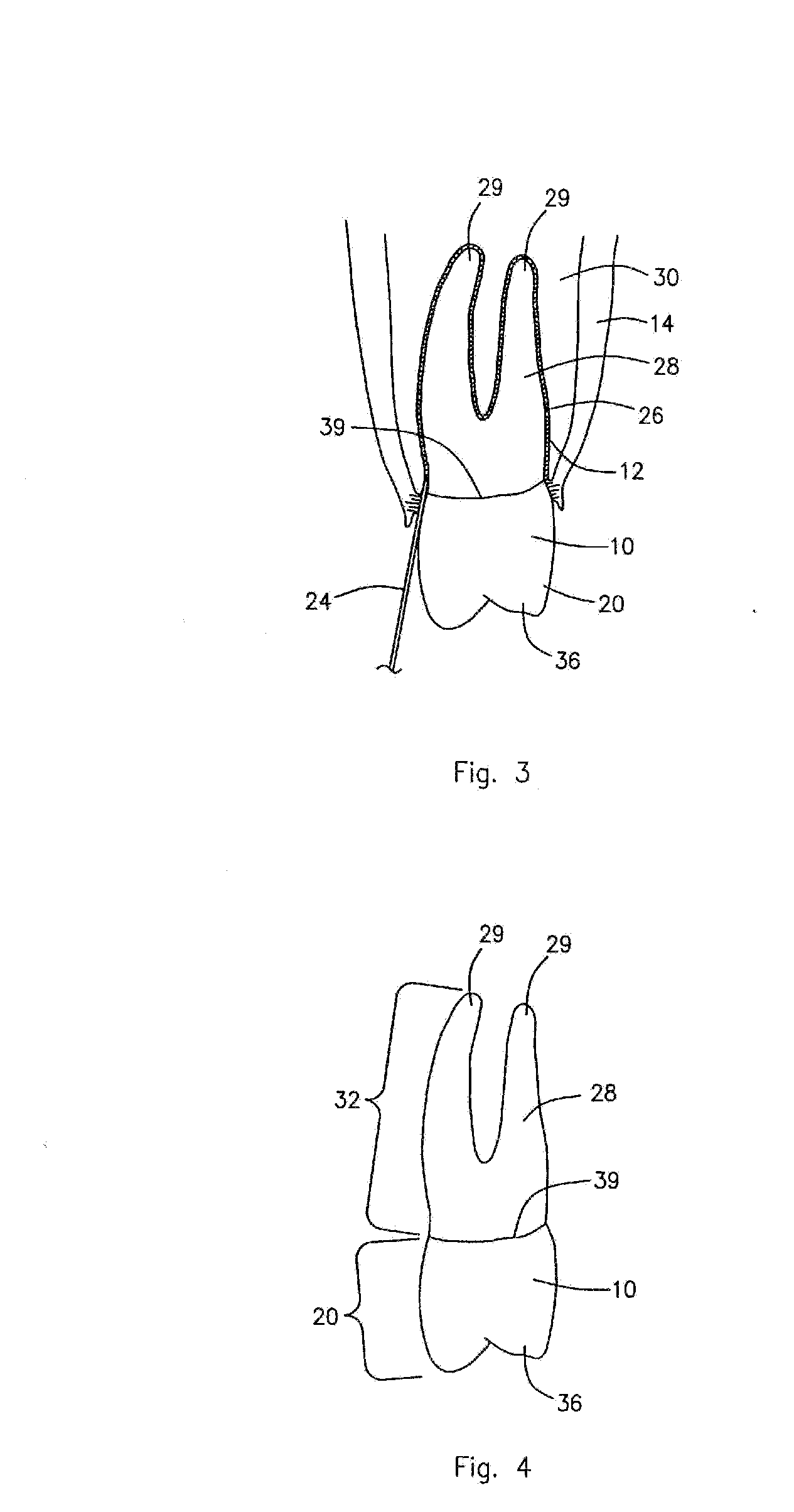
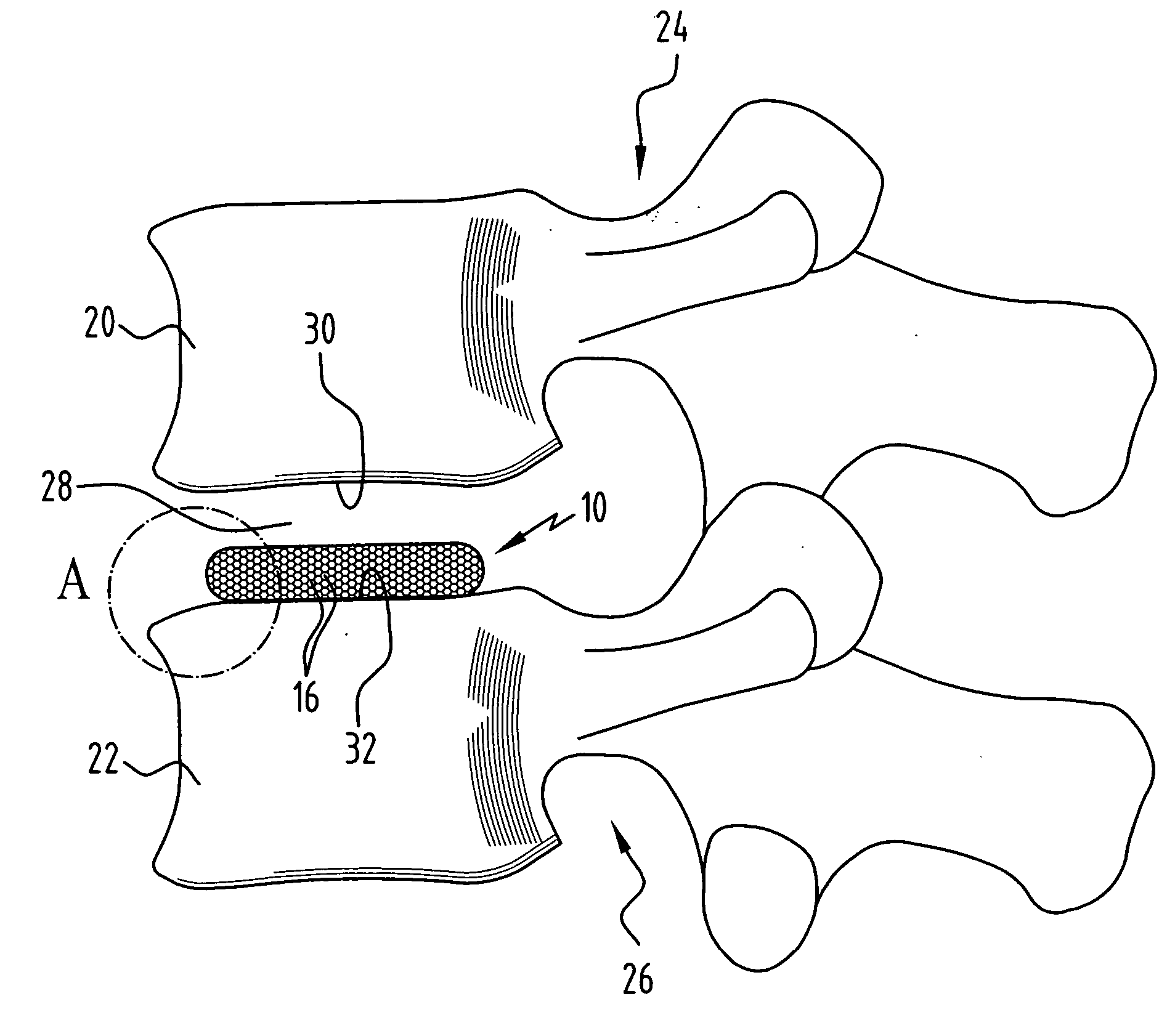
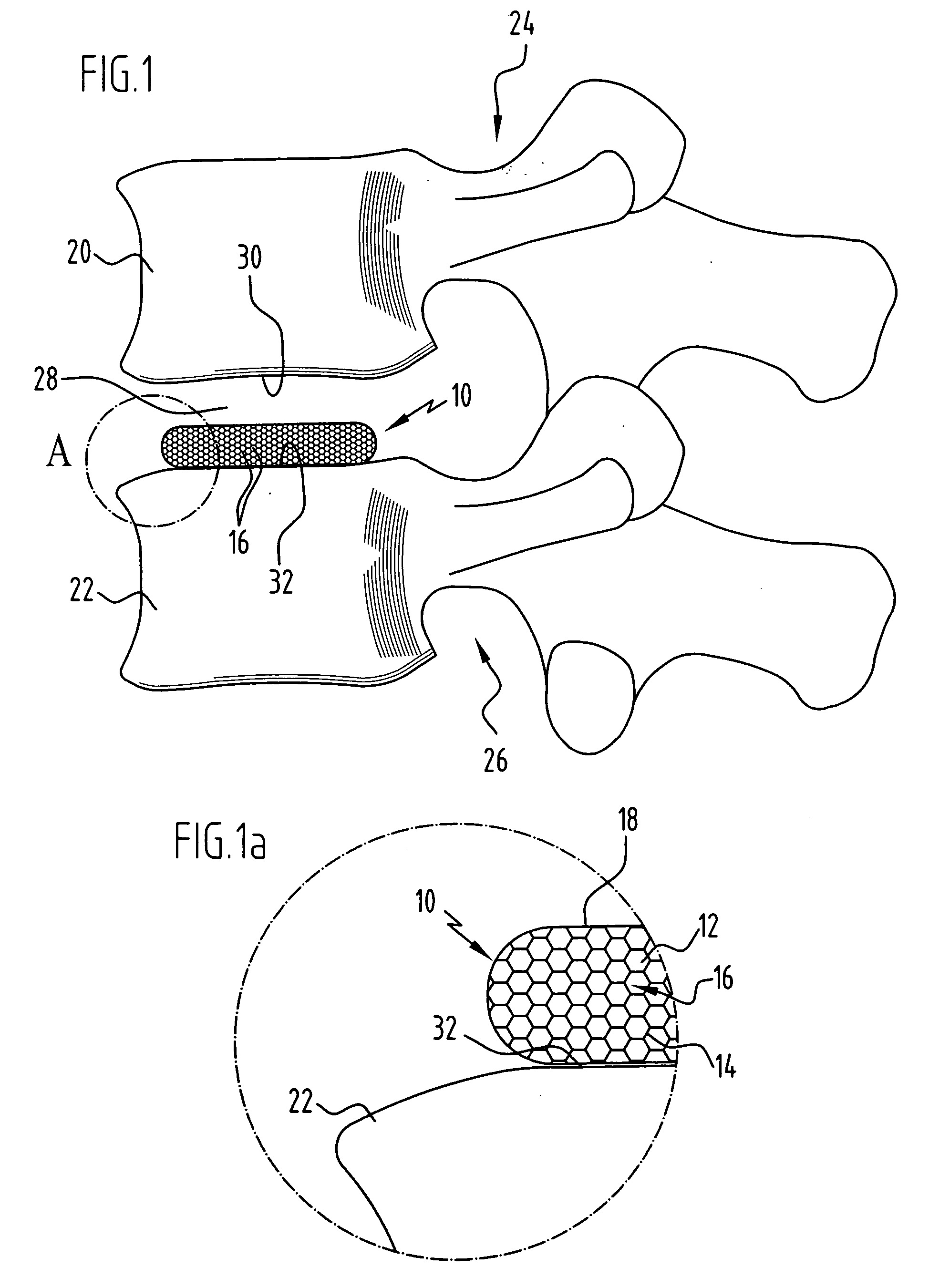
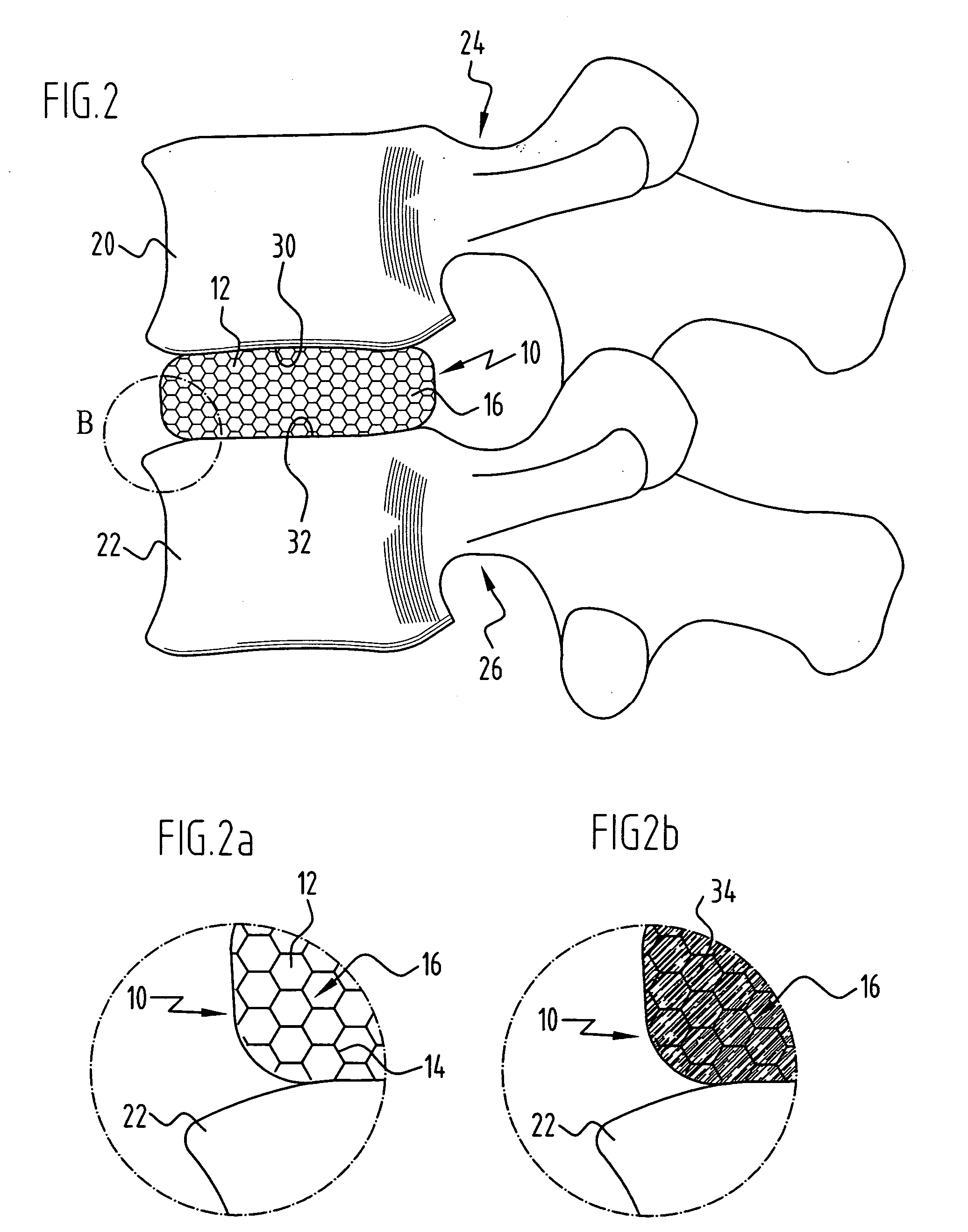
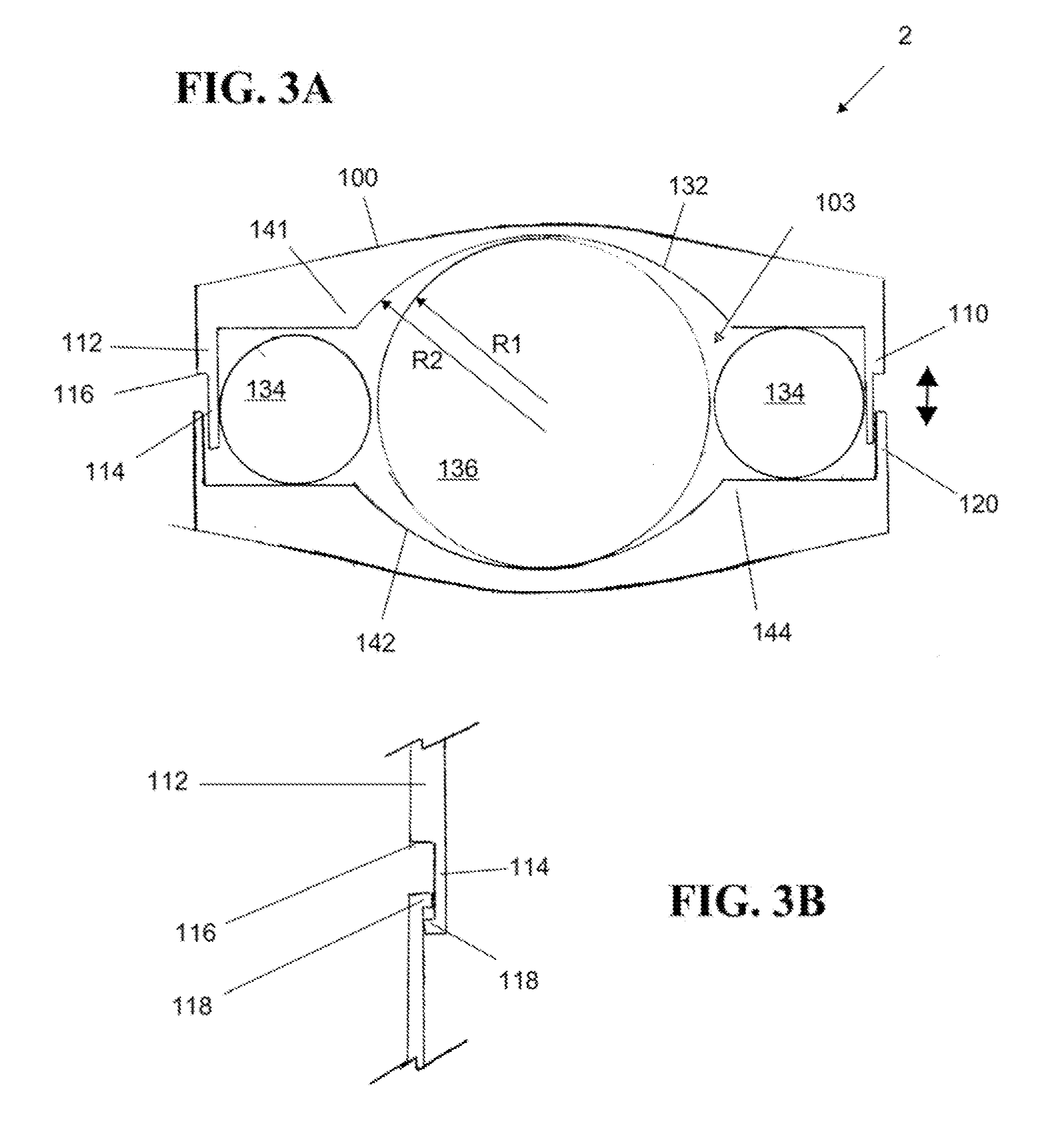
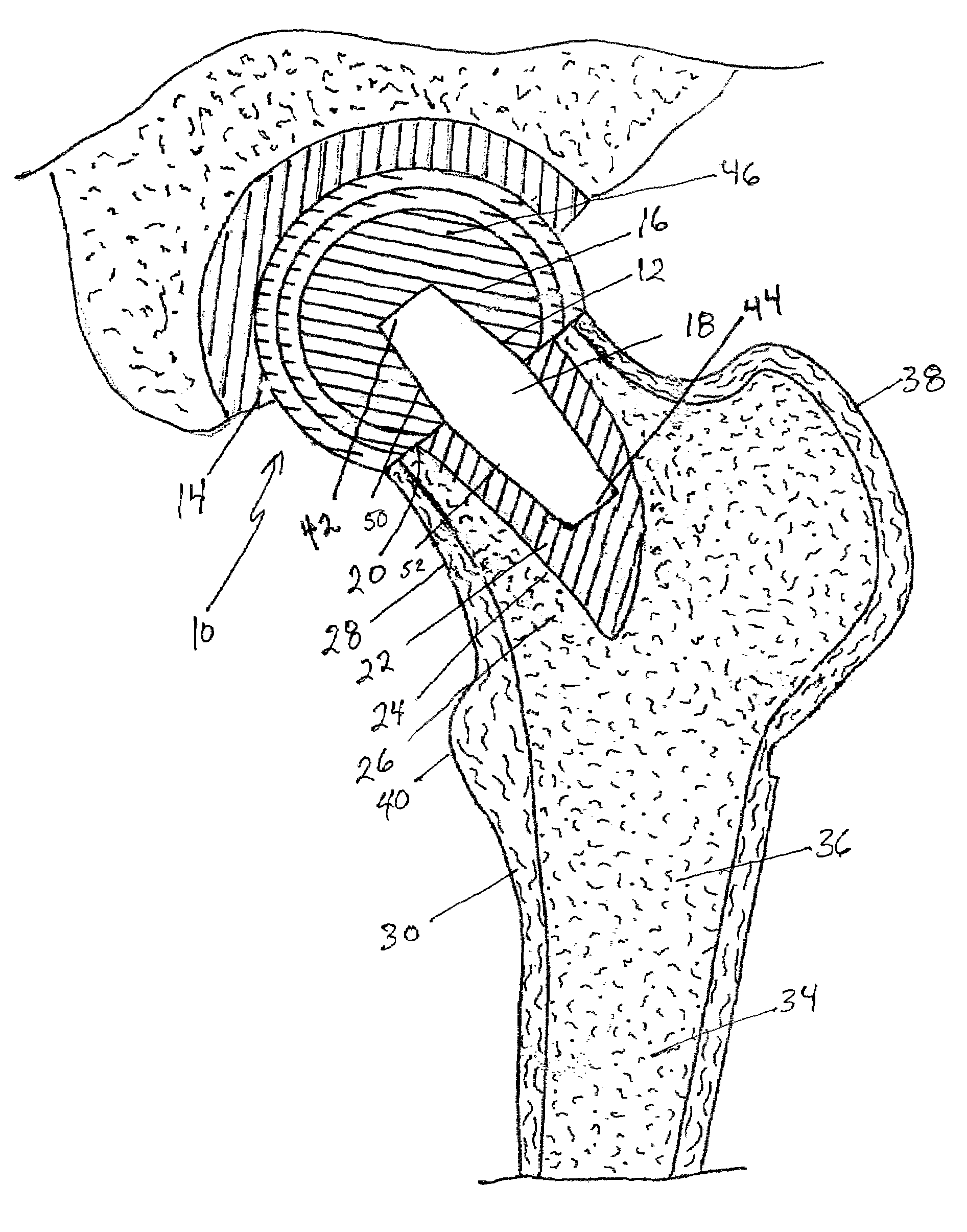
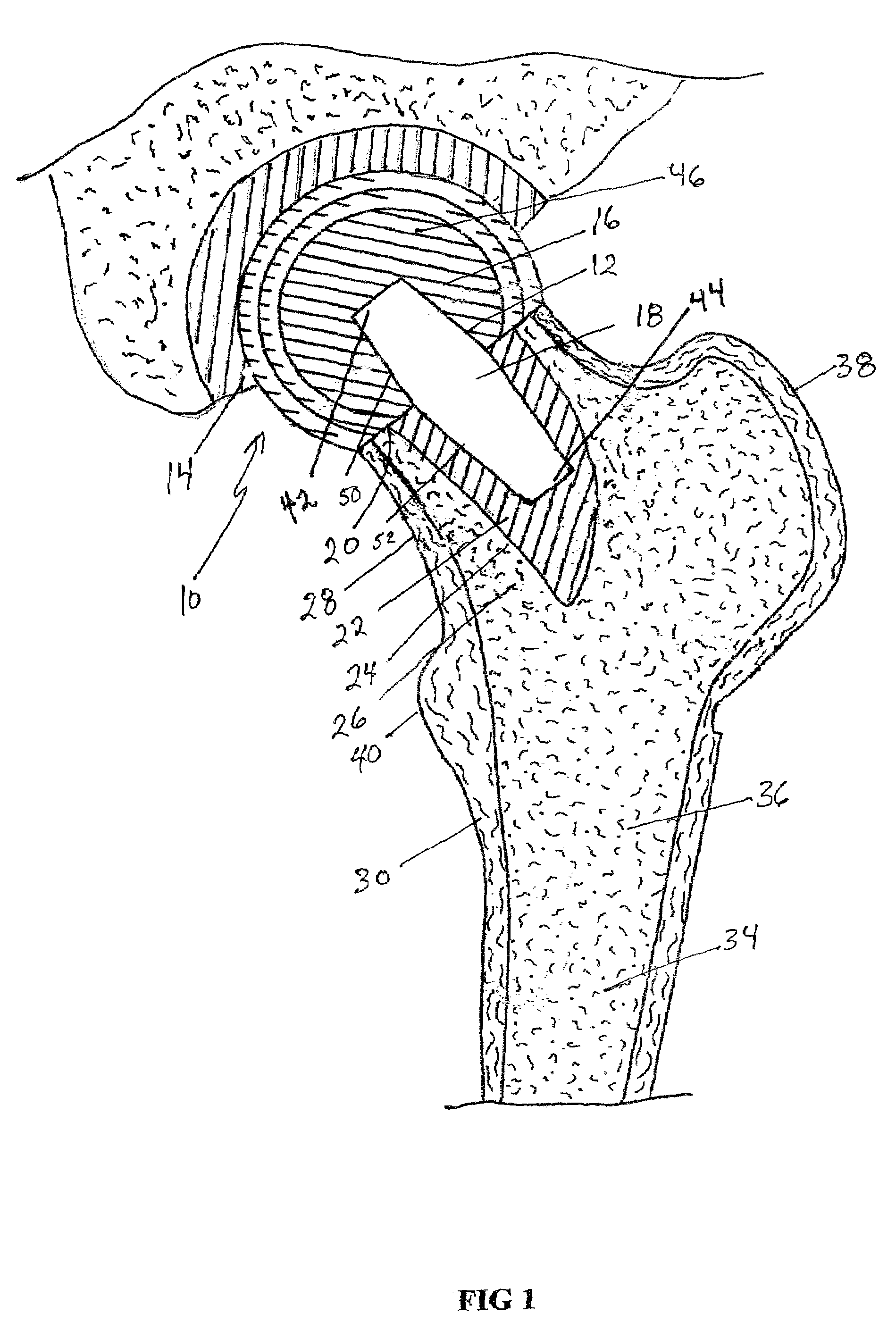
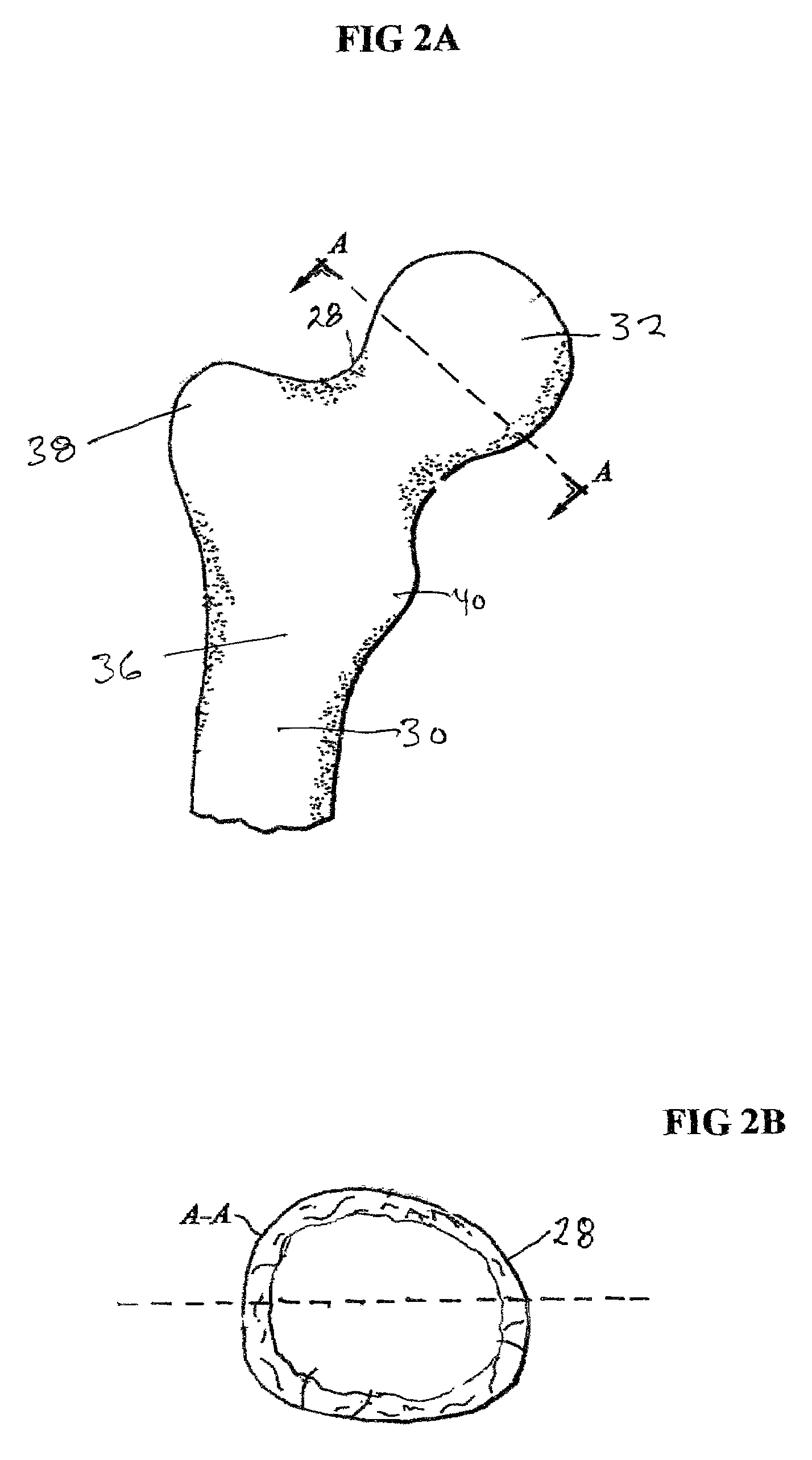
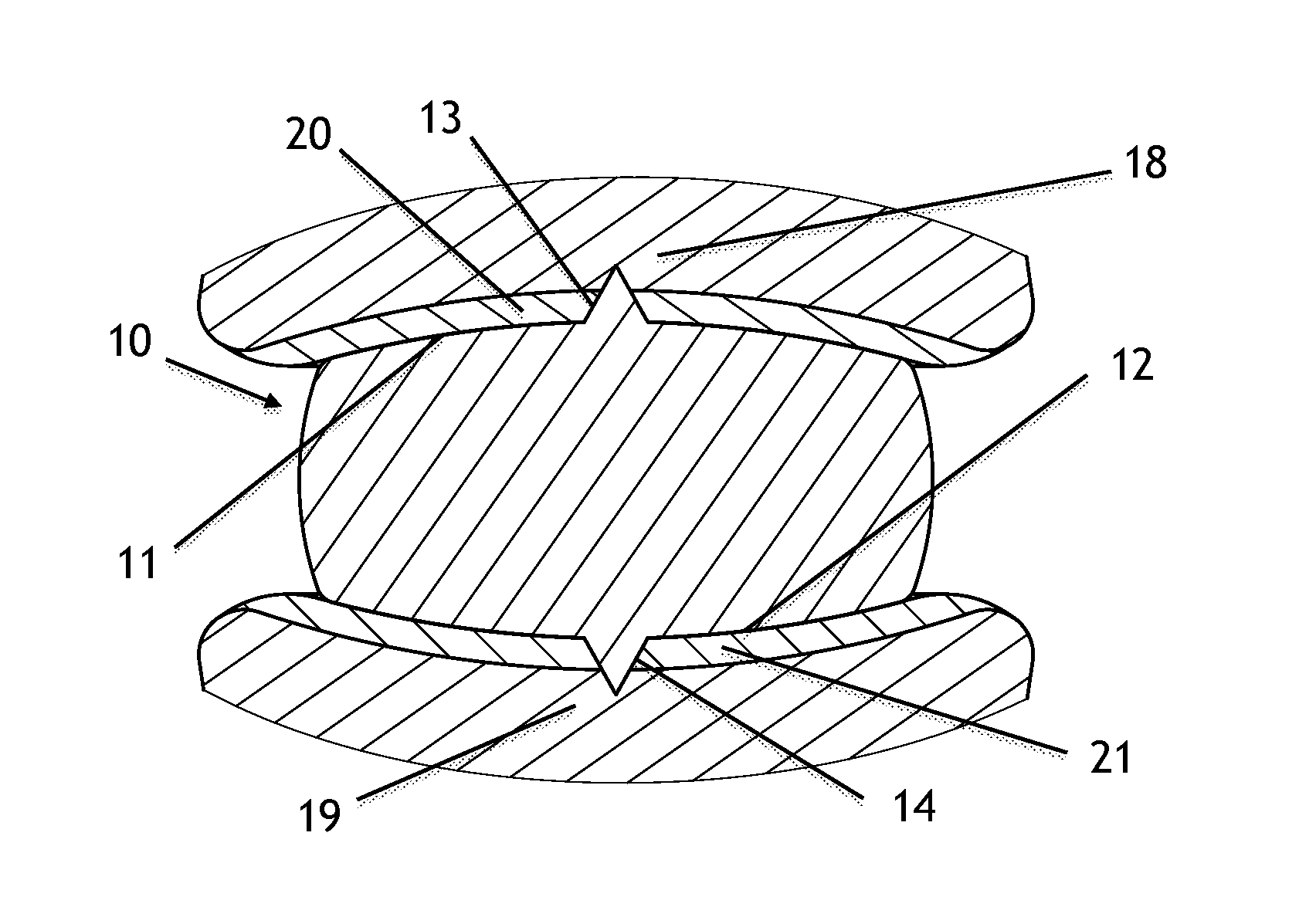
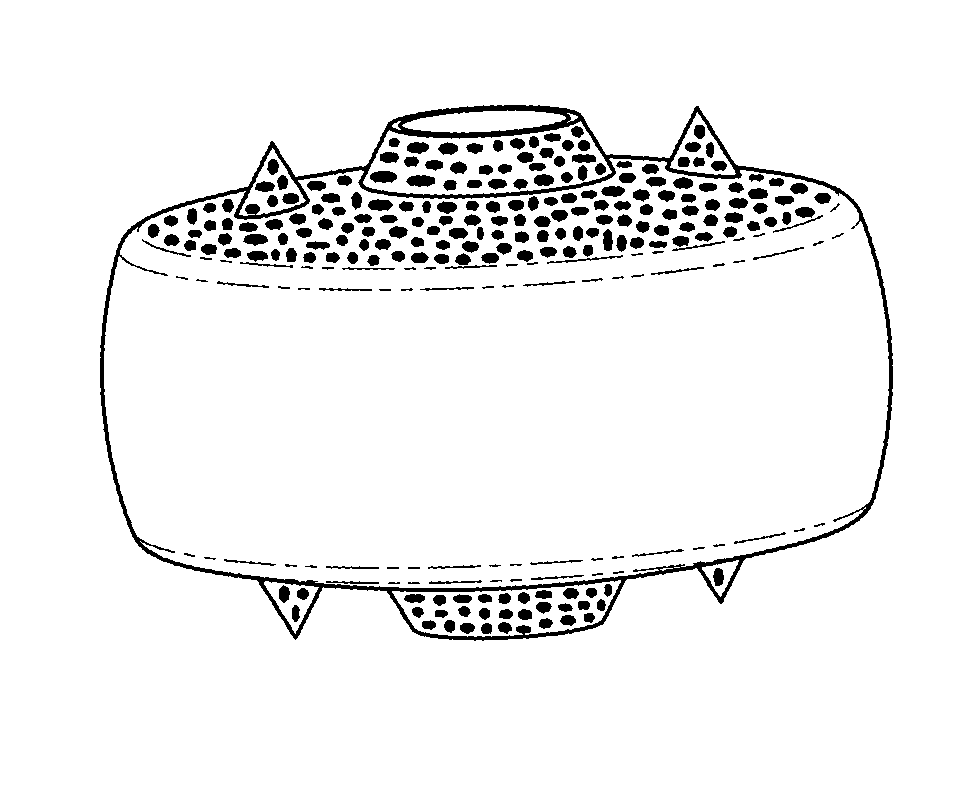
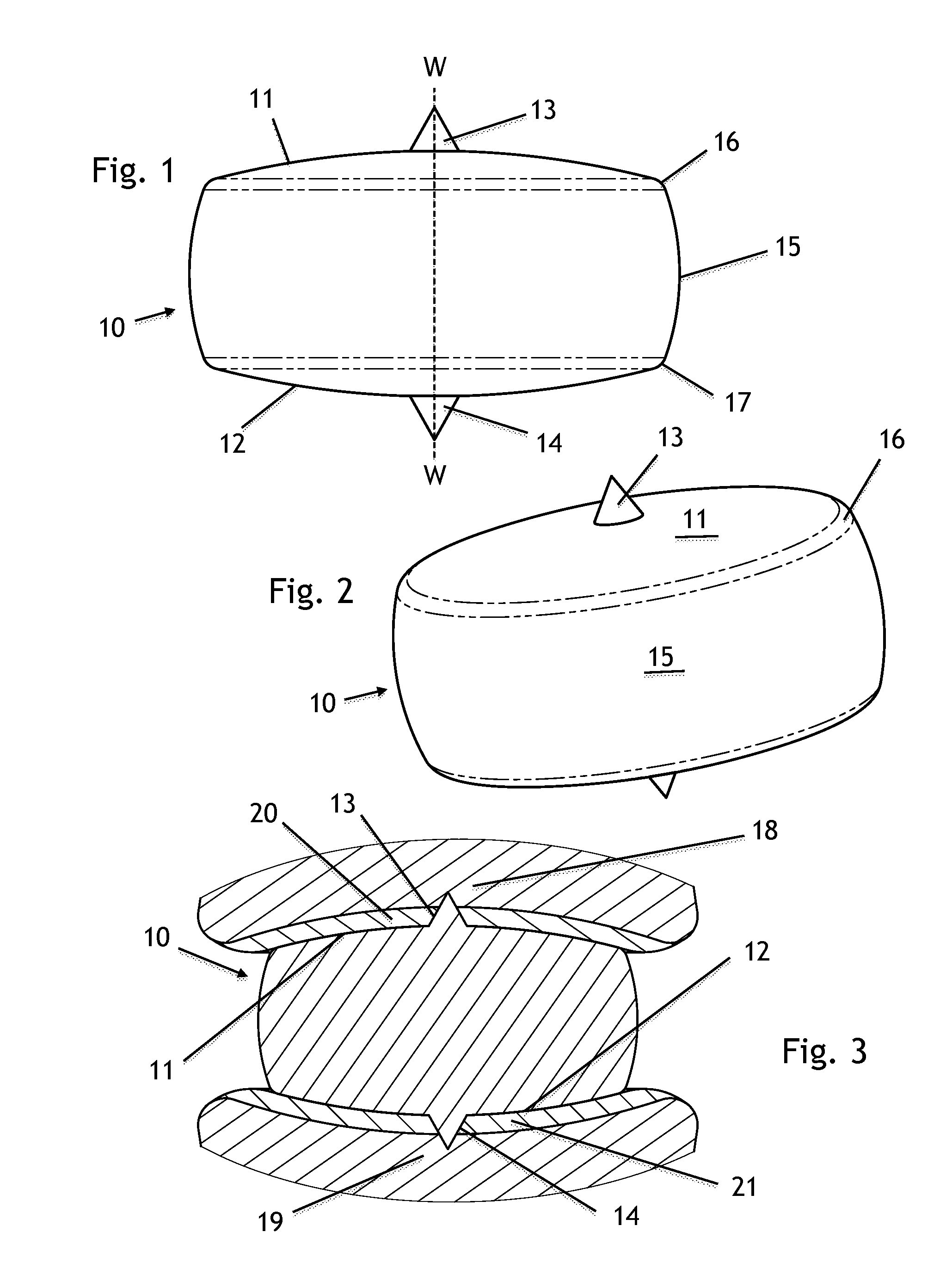
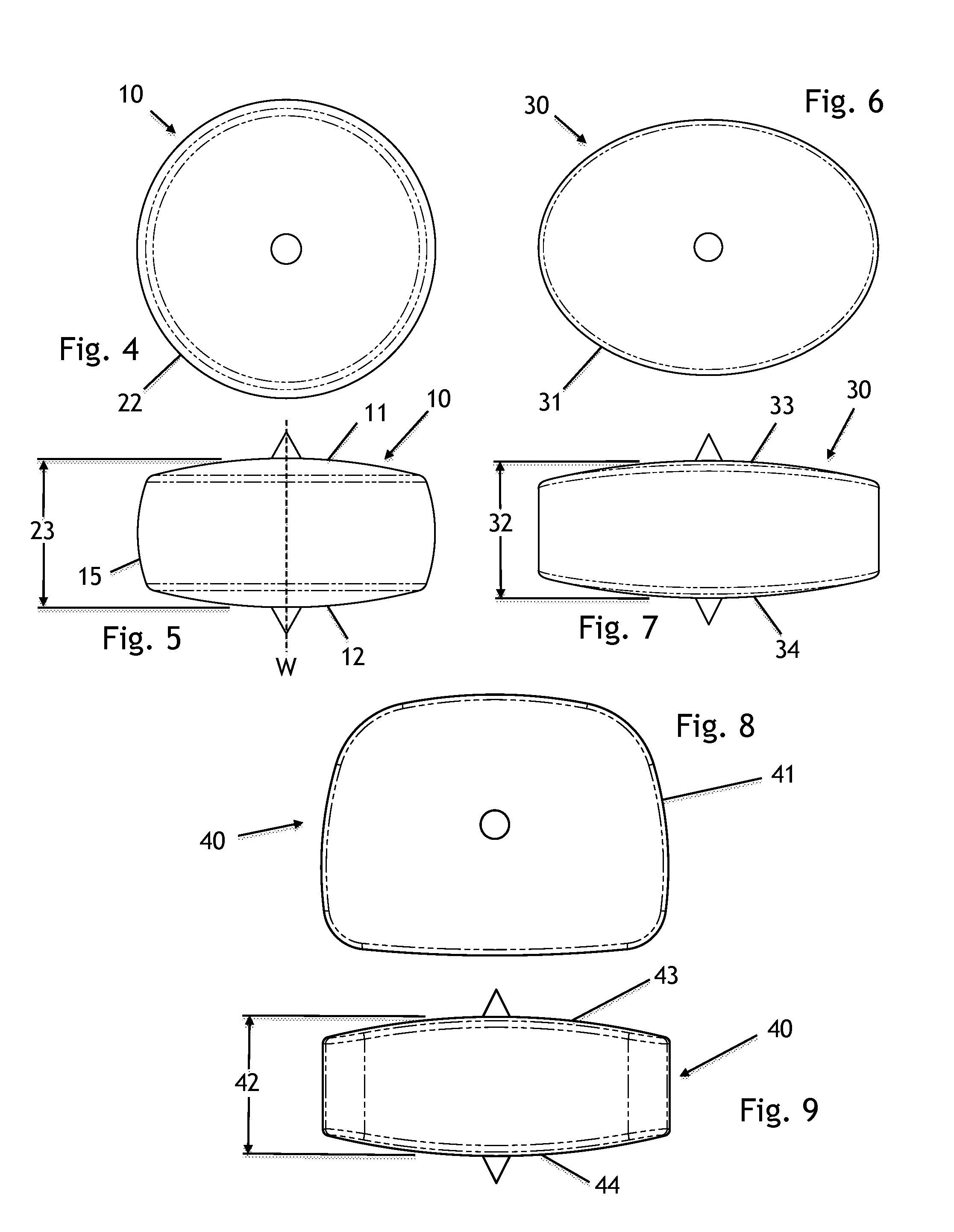
Spinal nucleus replacement implants and methods
InactiveUS20050154463A1Extended range of motionHelp positioningBone implantSurgeryReplacement implantRadiography
Improved nucleus pulposus implants are provided to better accommodate the disc nucleus space, to provide a modified compressive modulus, to facilitate positioning, to enhance fixation, and to facilitate effective implantation and use. Some implants have sloped upper and / or lower surfaces to provide a “wedge-shaped” implant, while other implants have circumferential grooves, and / or have radiographic markers, and / or are modified by including a material having a compression profile that differs from the compression profile of the predominant material of the implant. Some implants have surface features to enhance fixation to surrounding surfaces.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
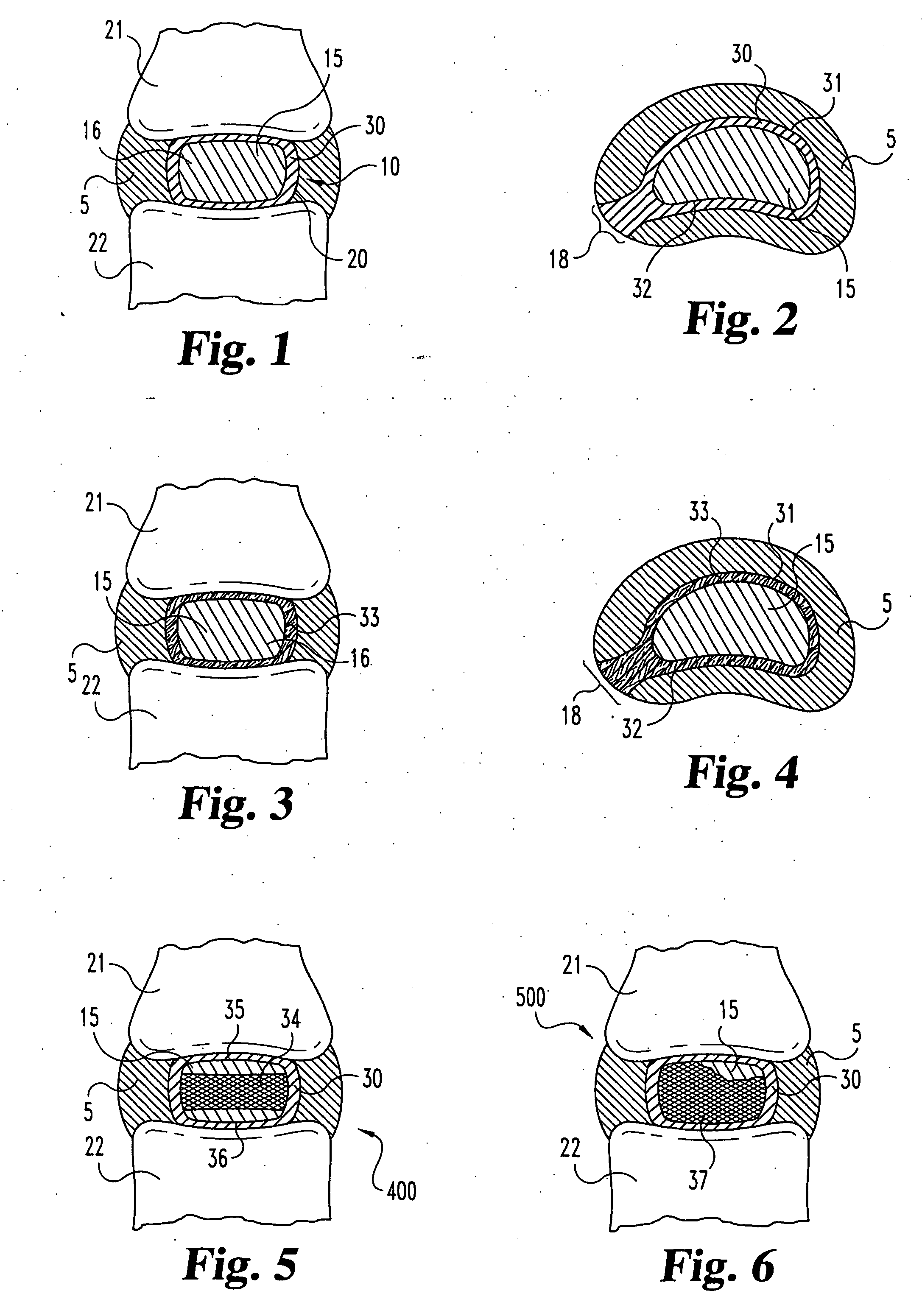
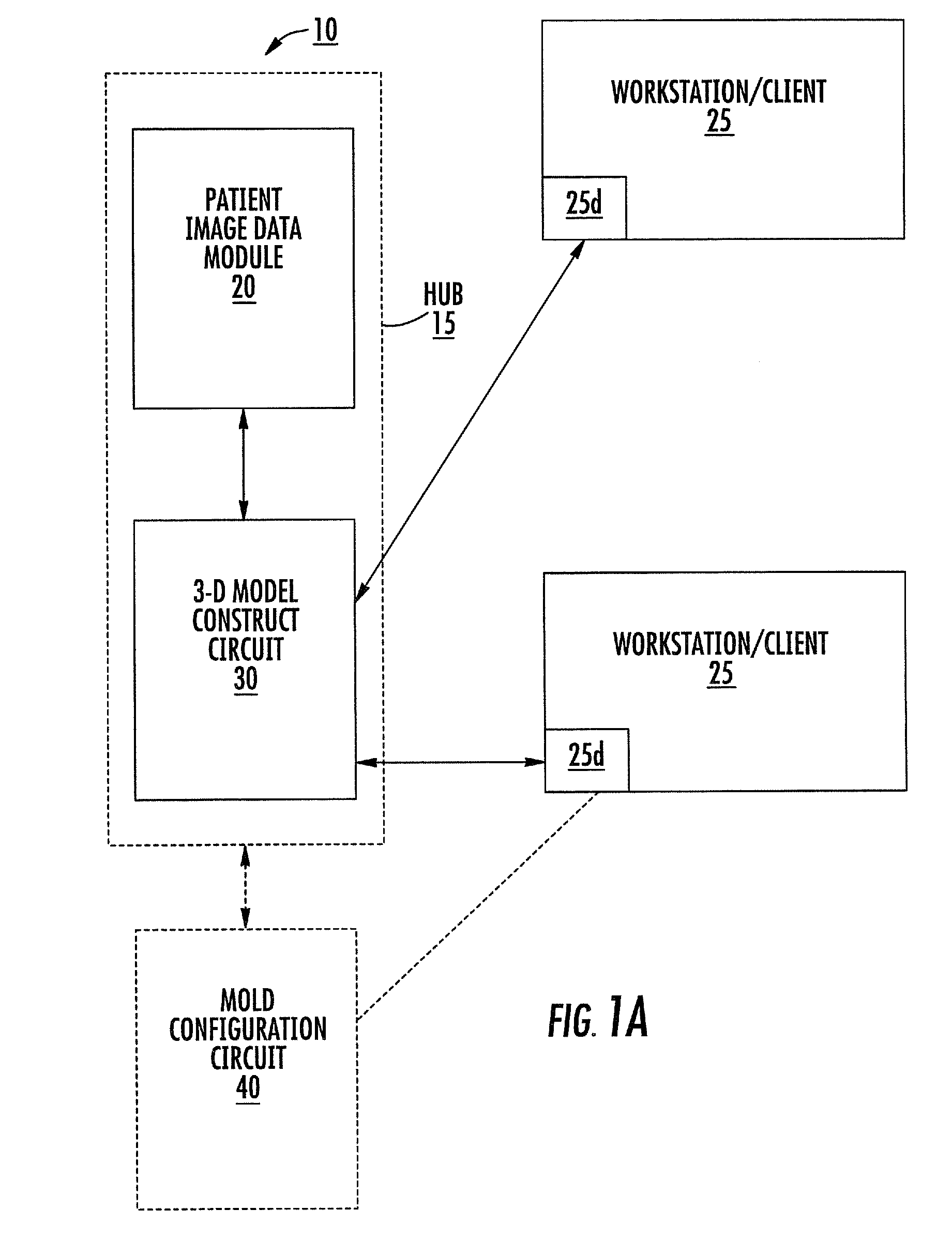
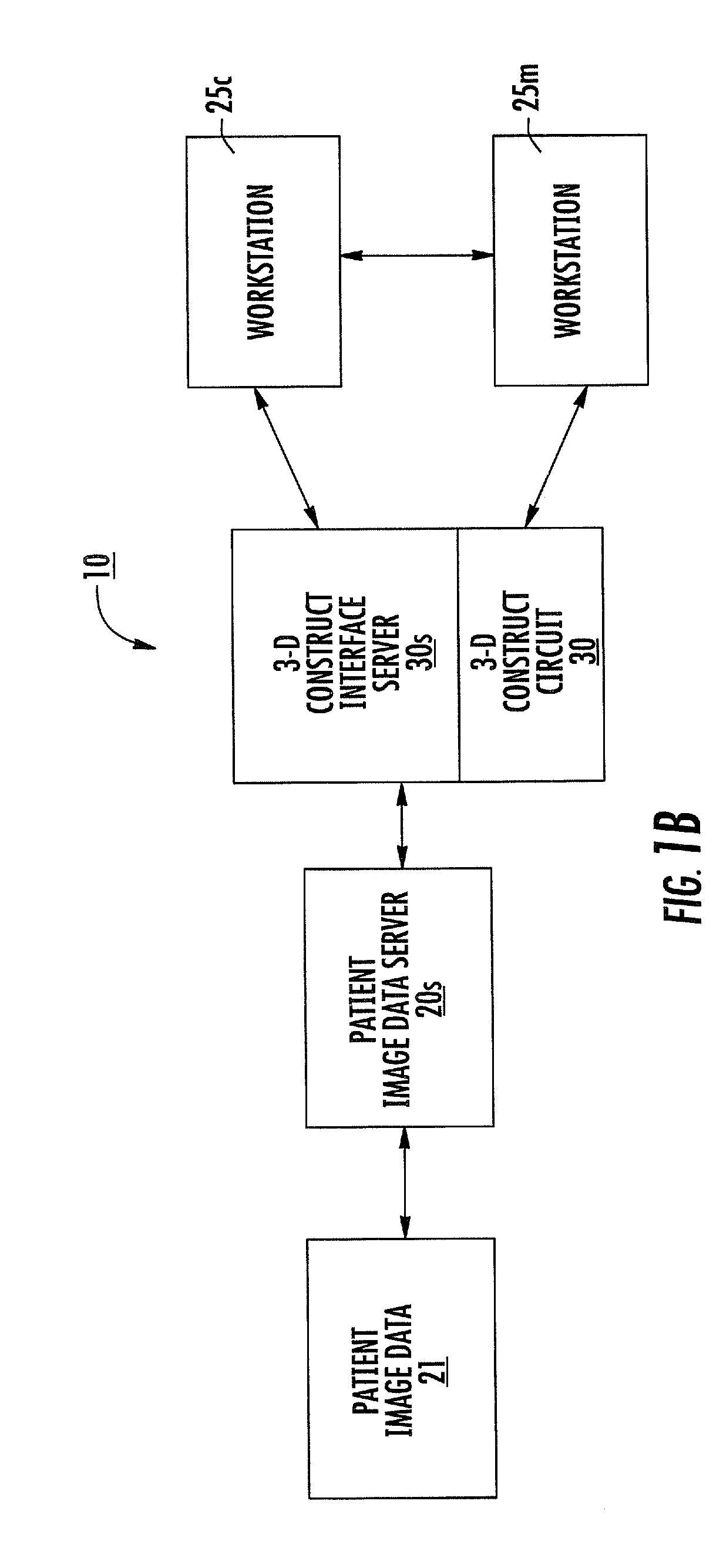
Patient-specific spinal implants and related systems and methods
InactiveUS8246680B2Easy to implantAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisCustom made implantReplacement implant
Methods and systems for generating custom implants by programmatically analyzing a patient's image data to electronically obtain shapes and dimensions of relevant anatomical features of a target region of the patient; and fabricating a patient-specific replacement implant for the patient using the analyzed patient image data. Related patient-specific spinal implants are also described.
Owner:MIMEDX PROCESSING SERVICES LLC
Lumbar disc replacement implant for posterior implantation with dynamic spinal stabilization device and method
ActiveUS20080269904A1Resist shorteningReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnReplacement implant
The invention consists of disc replacement implant for the lumbar spine designed for insertion into the disc space via a posterior approach. The implant can be stabilized in the disc space by connection to the vertebra or can be connected to dynamic spinal stabilization device consisting of interconnected bullets nested in a spring nested in a woven sleeve. By controlling the limits of elongation and compression the device prevents movement beyond normal physiological limits. In the midrange of movement flexibility is allowed. A method for using the dynamic spinal stabilization device is also provided.
Owner:VOORHIES RAND M
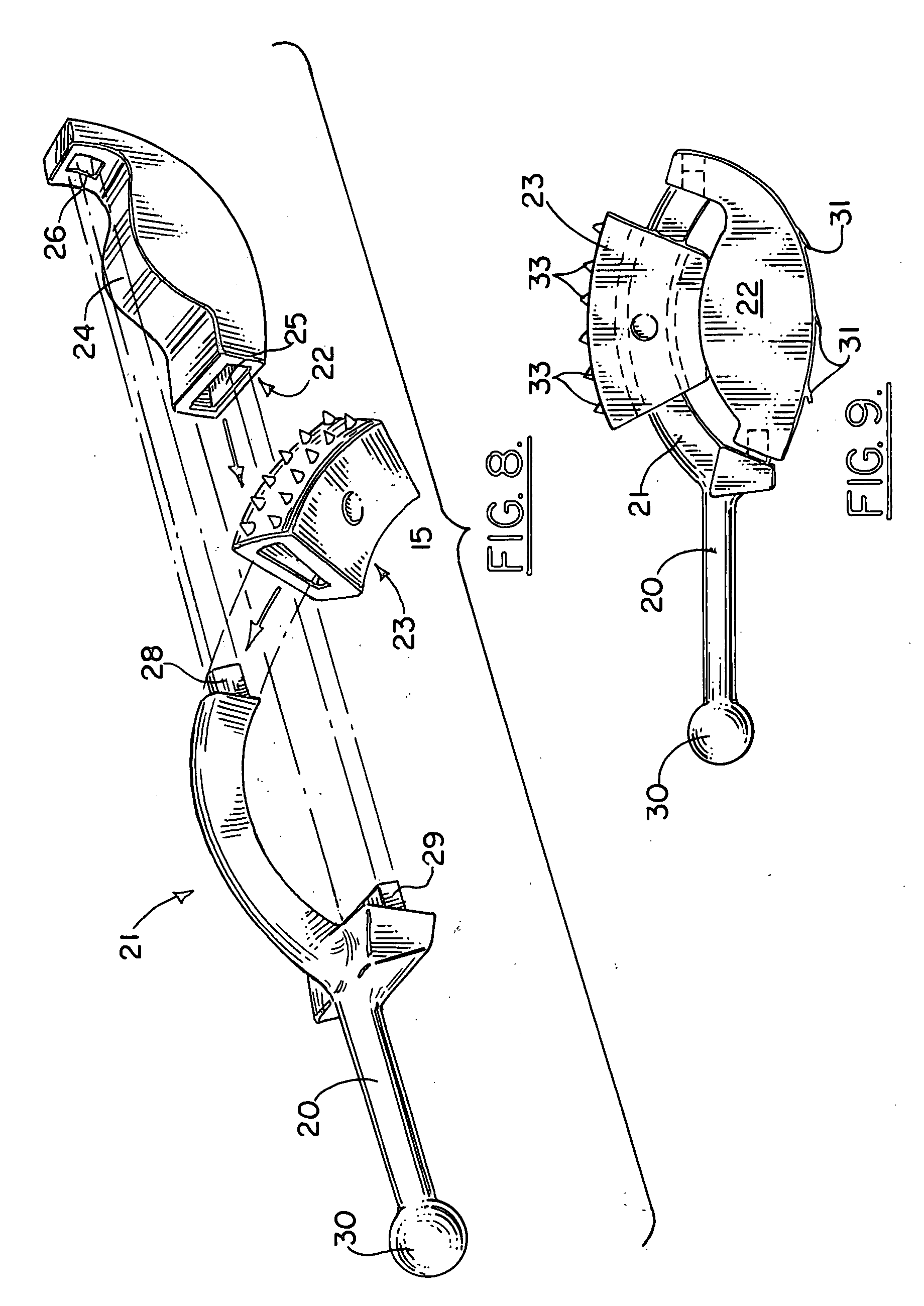
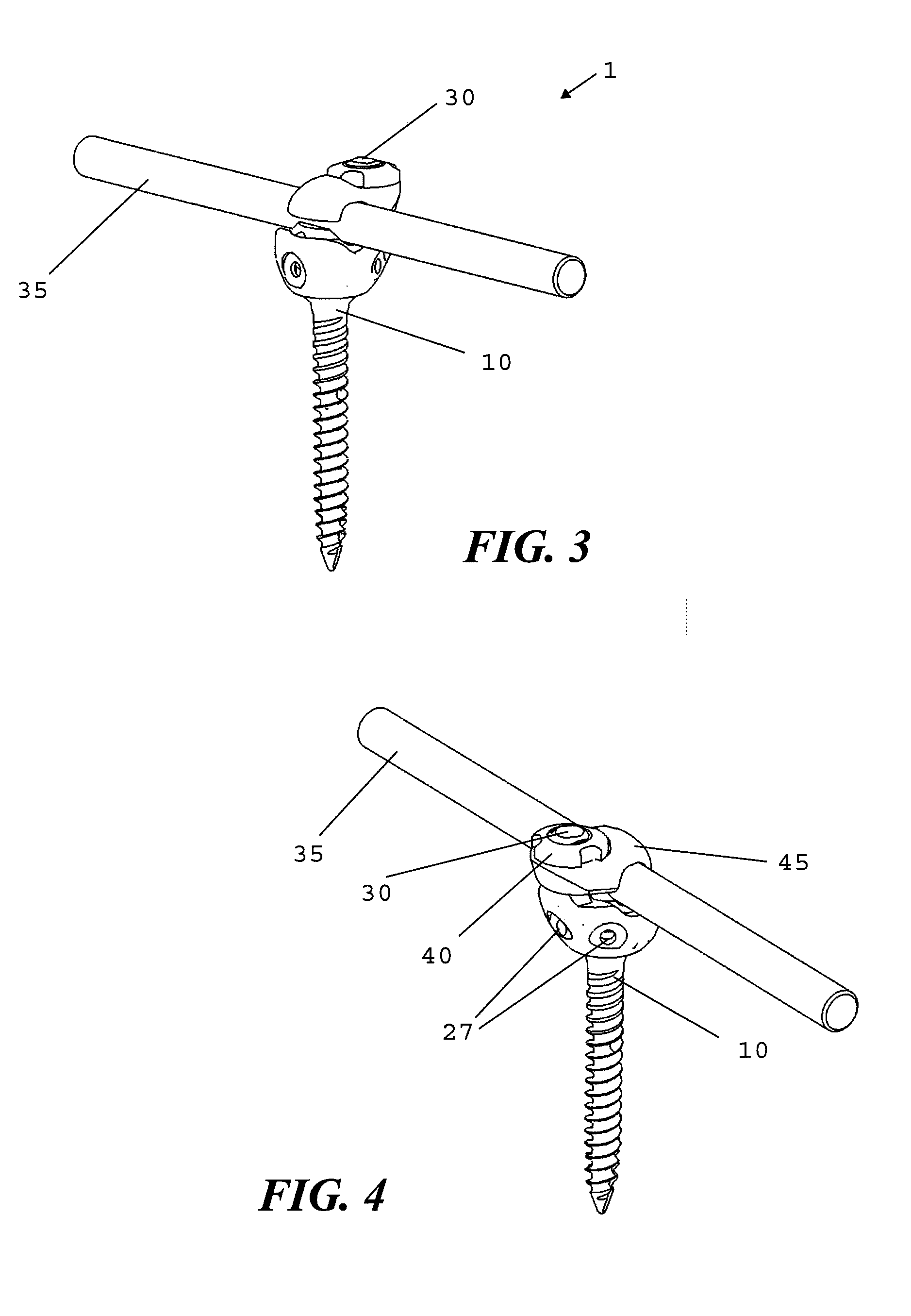
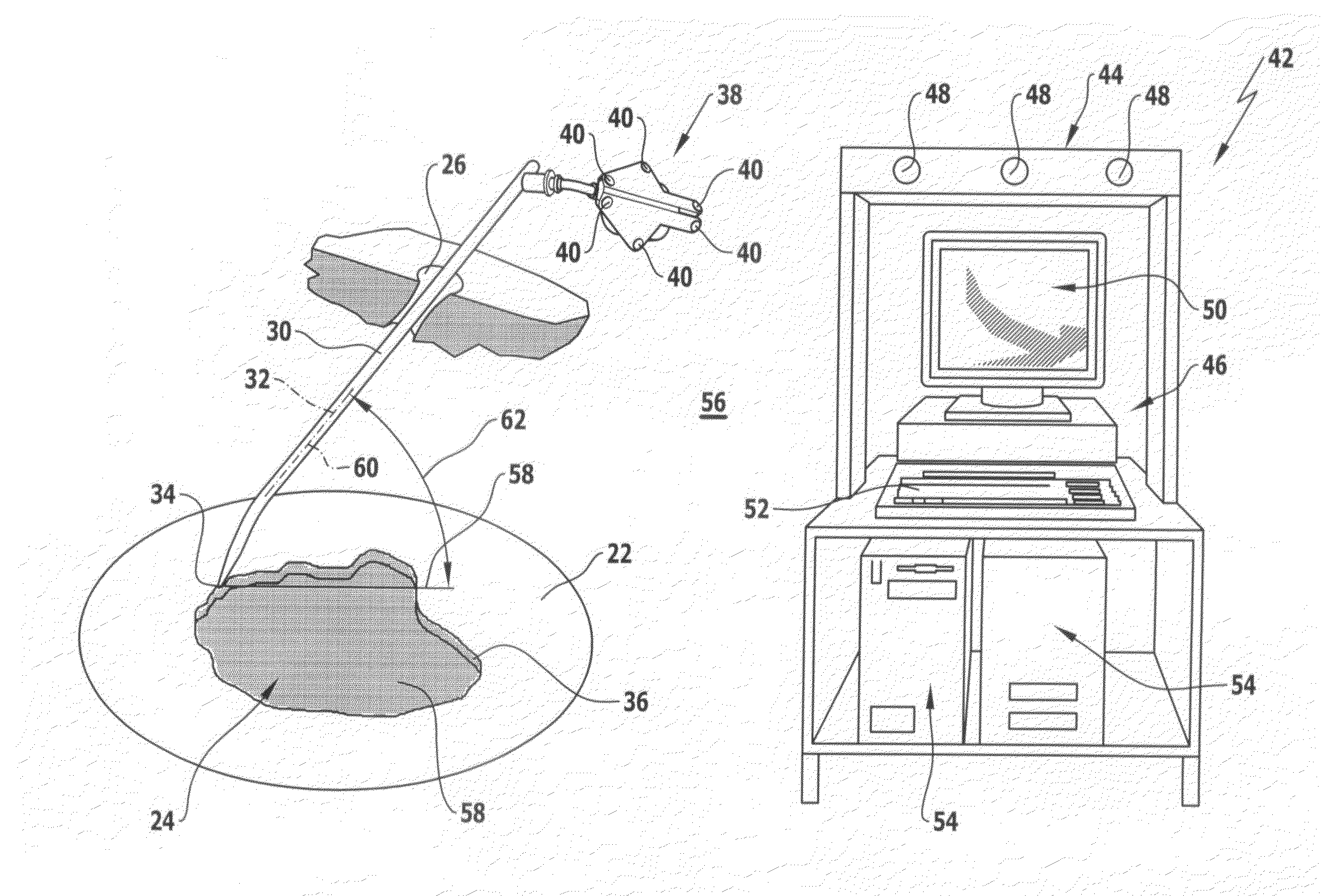
Arrangement and method for the intra-operative determination of the position of a joint replacement implant
InactiveUS20050149050A1Easy to operateLow risk of errorPerson identificationJoint implantsReference vectorMeasurement point
Arrangement for the intra-operative determination of the spatial position and angular position of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip socket or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, or a vertebral replacement implant, especially a lumbar or cervical vertebral implant, using a computer tomography method, having: a computer tomography modeling device for generating and storing a three-dimensional image of a joint region or vertebral region to be provided with the joint replacement implant, an optical coordinate-measuring arrangement for providing real position coordinates of defined real or virtual points of the joint region or vertebral region and / or position reference vectors between such points within the joint region or vertebral region or from those points to joint-function-relevant points on an extremity outside the joint region or vertebral region, the coordinate-measuring arrangement comprising a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of transducer signals, at least one multipoint transducer, which comprises a group of measurement points rigidly connected to one another, and an evaluation unit for evaluating sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducer(s) and recorded by the stereocamera, and a matching-processing unit for real position matching of the image to the actual current spatial position of the joint region or vertebral region with reference to the real position coordinates of the defined points, the matching-processing unit being configured for calculating transformation parameters with minimalization of the normal spacings.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Human bone substitutional implant
A human bone substitutional implant comprises a main body and a push body. The main body is a hollow cylinder with a thread portion or a ratchet portion disposed on its outer wall. The thread portion or the ratchet portion has at least a slit dividing it into four equal parts. An inner thread is disposed on the inner wall of the thread portion or the ratchet portion. An outer thread is disposed on the outer surface of the push body and corresponds to the inner thread. The push body and the main body are joined together via screw connection of the outer thread and the inner thread. Because the main body has a conical passage therein, the main body will be held open a certain angle to support and enhance a fractured bone of the human body when the push body is axially pushed into the main body.
Owner:WU SHING SHENG
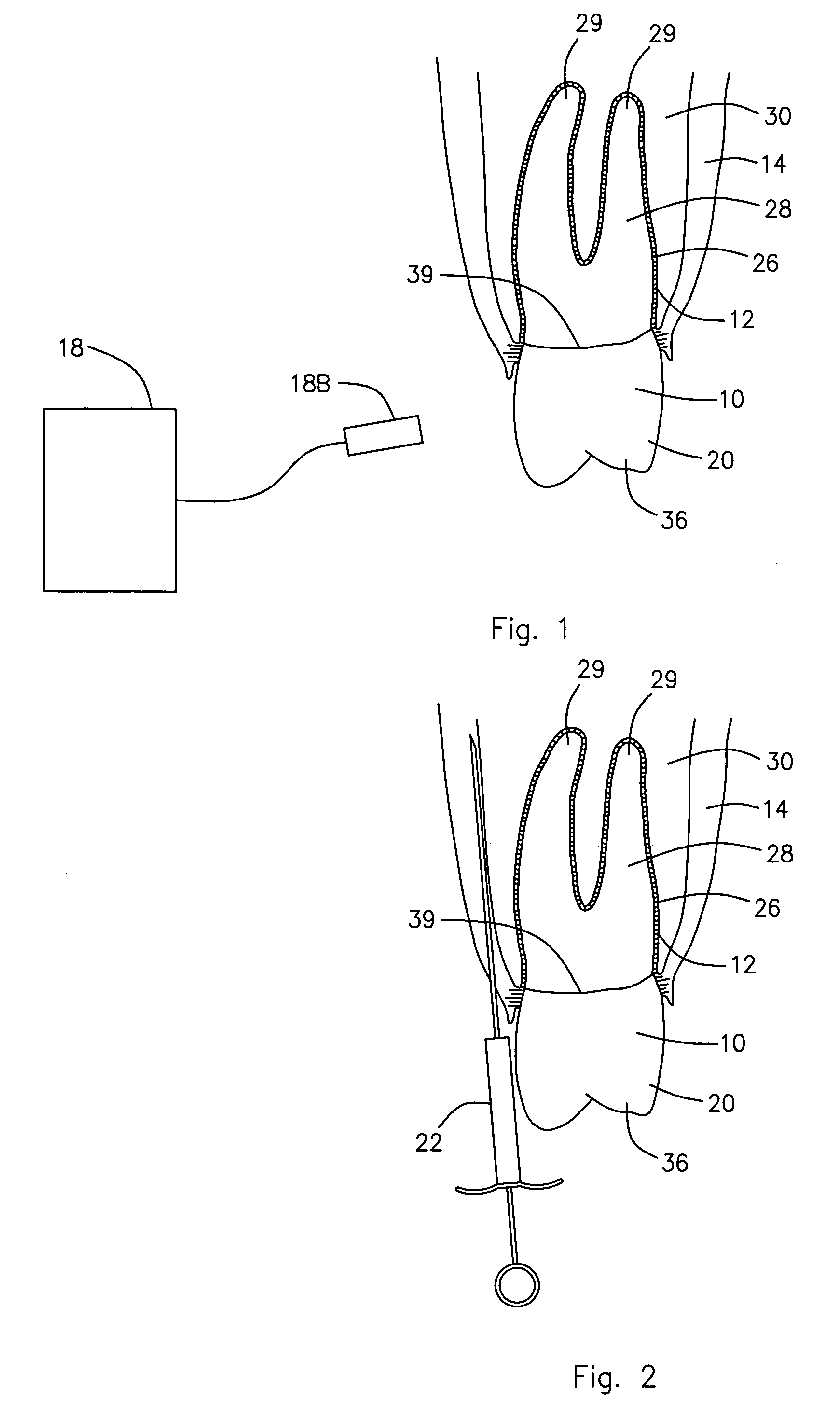
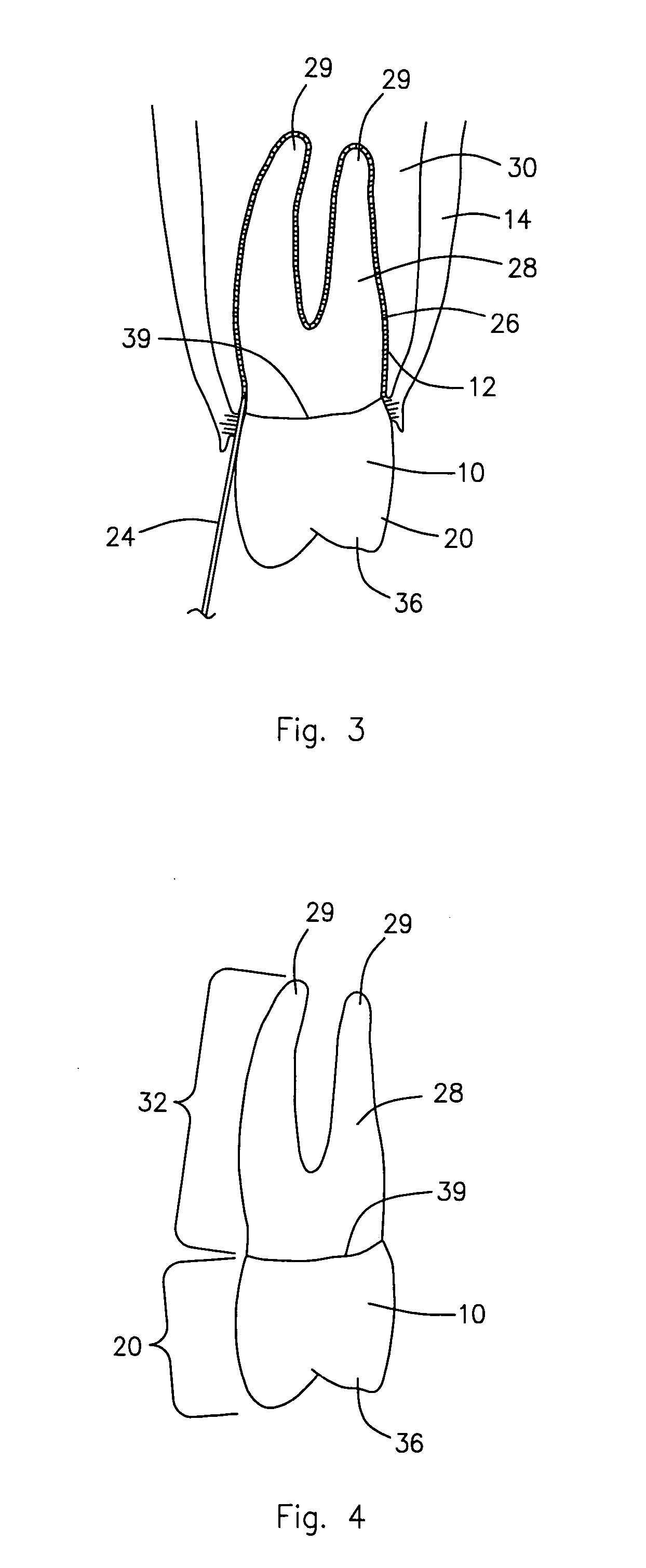
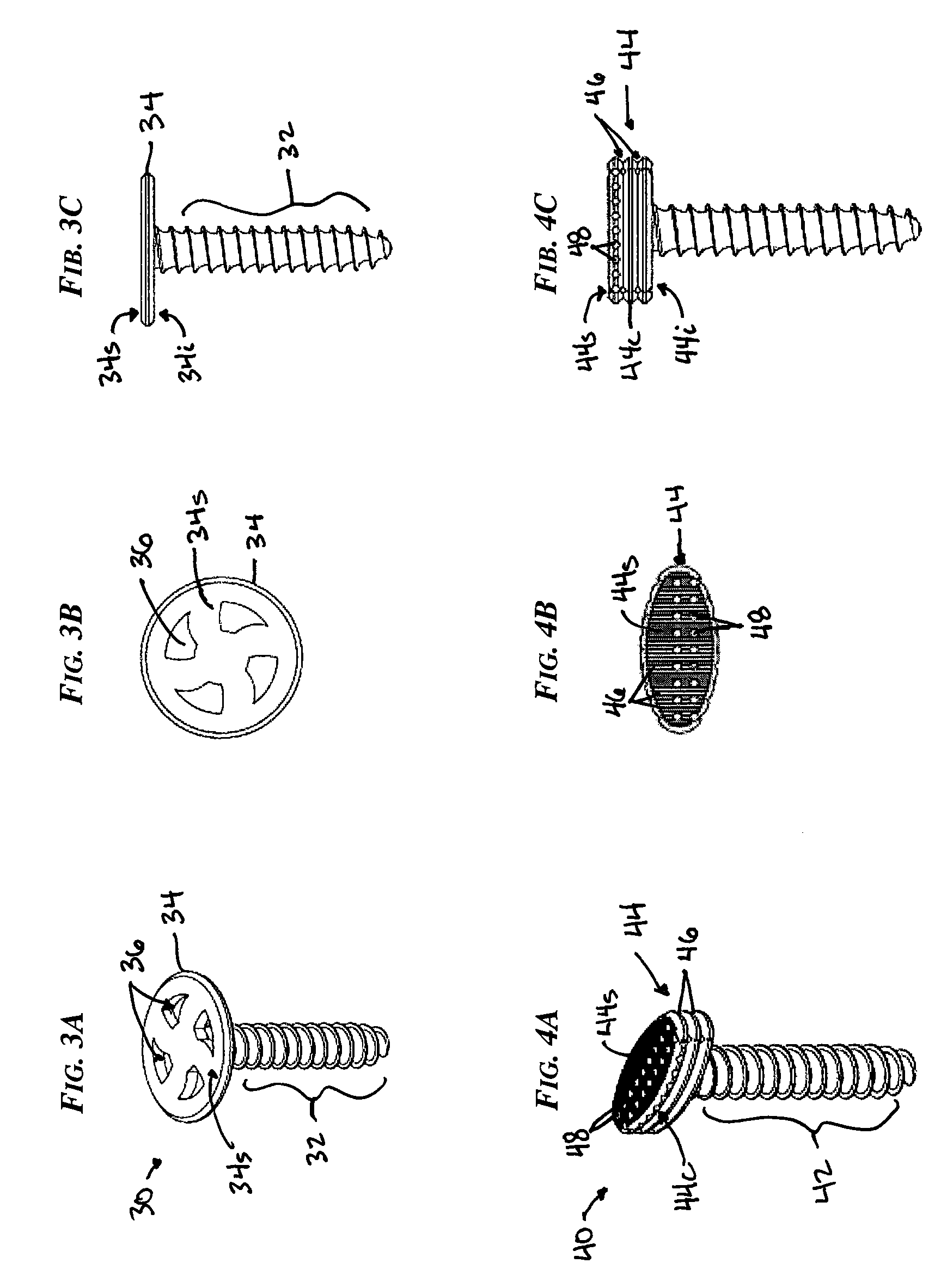
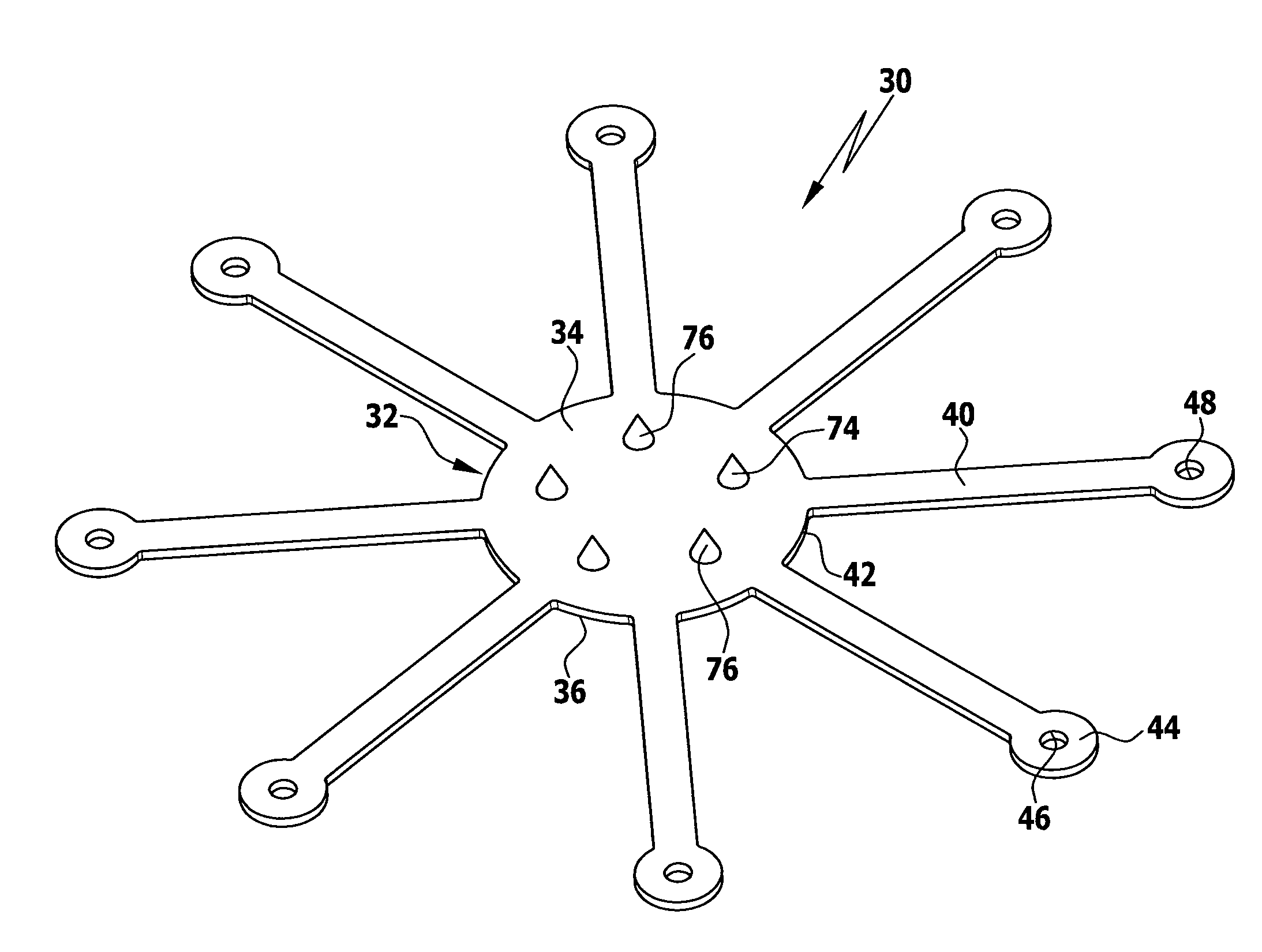
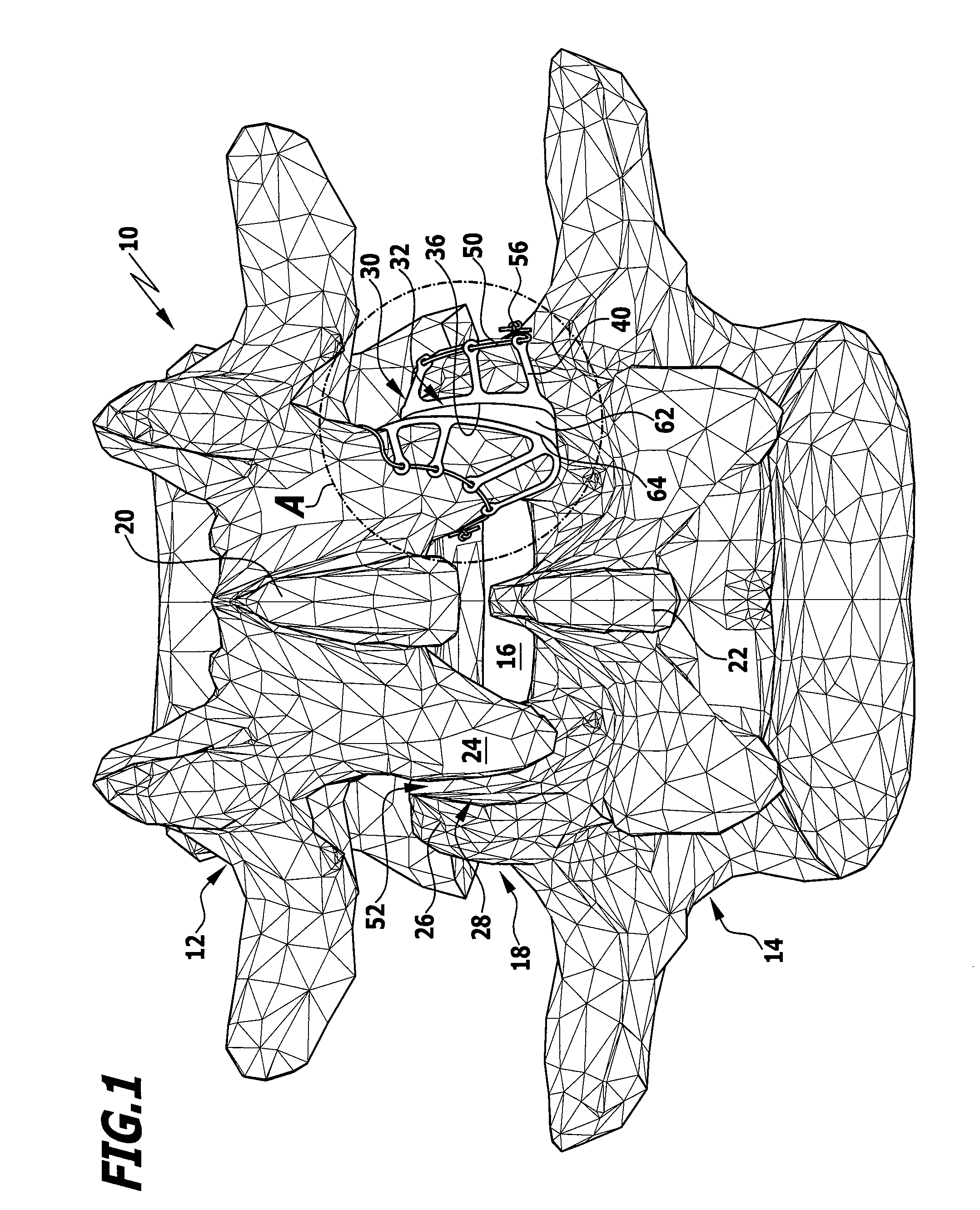
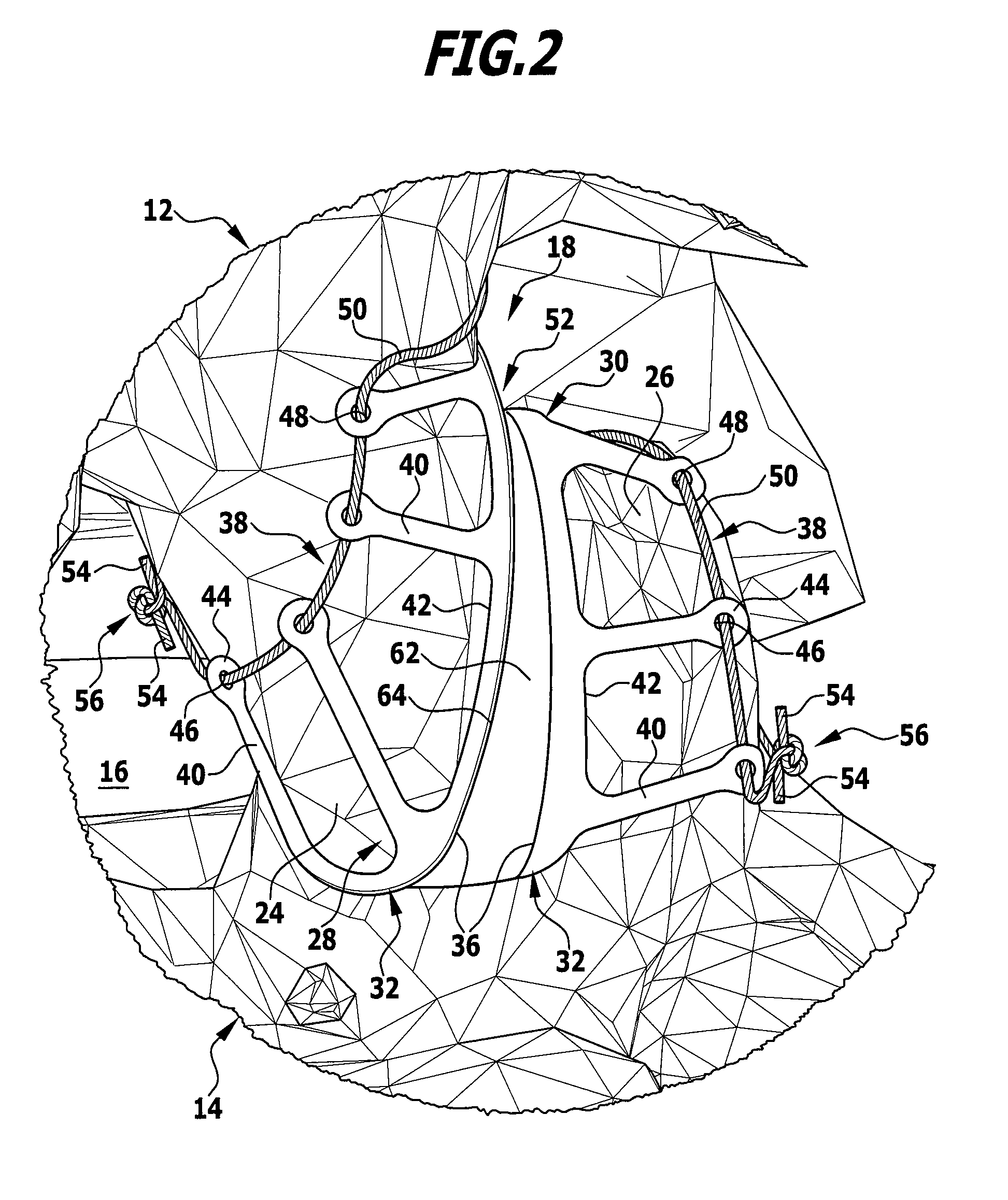
Intervertebral disc nucleus replacement implants and methods
InactiveUS7766967B2Increase stiffnessSmooth rotationSpinal implantsReplacement implantIntervertebral disc
Intervertebral disc nucleus replacement implants and methods are provided. The nucleus replacement implant, which is configured to reside within an intervertebral disc nucleus space, includes a core support structure, including a rotatable member and multiple vertebral support structures. The vertebral support structures are disposed in spaced relation with the rotatable member positioned therebetween. The implant further includes an elastic body at least partially surrounding the core support structure. When the rotatable member is in the first orientation, the implant is in a compressed height configuration to facilitate insertion of the implant into the intervertebral disc nucleus space, and when the rotatable member is in the second orientation, the implant is in an extended height configuration to facilitate use of the implant as a prosthetic intervertebral disc nucleus replacement.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
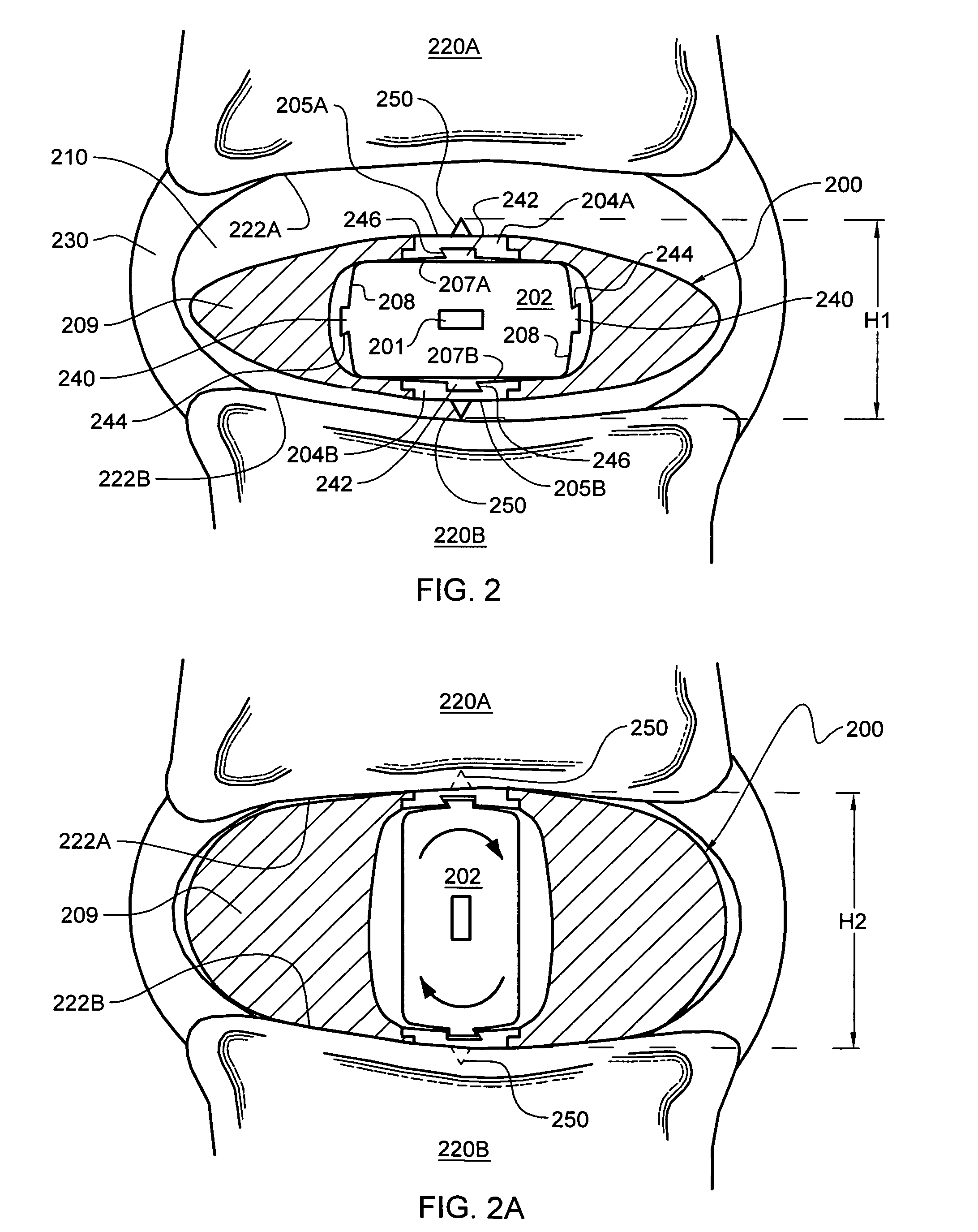
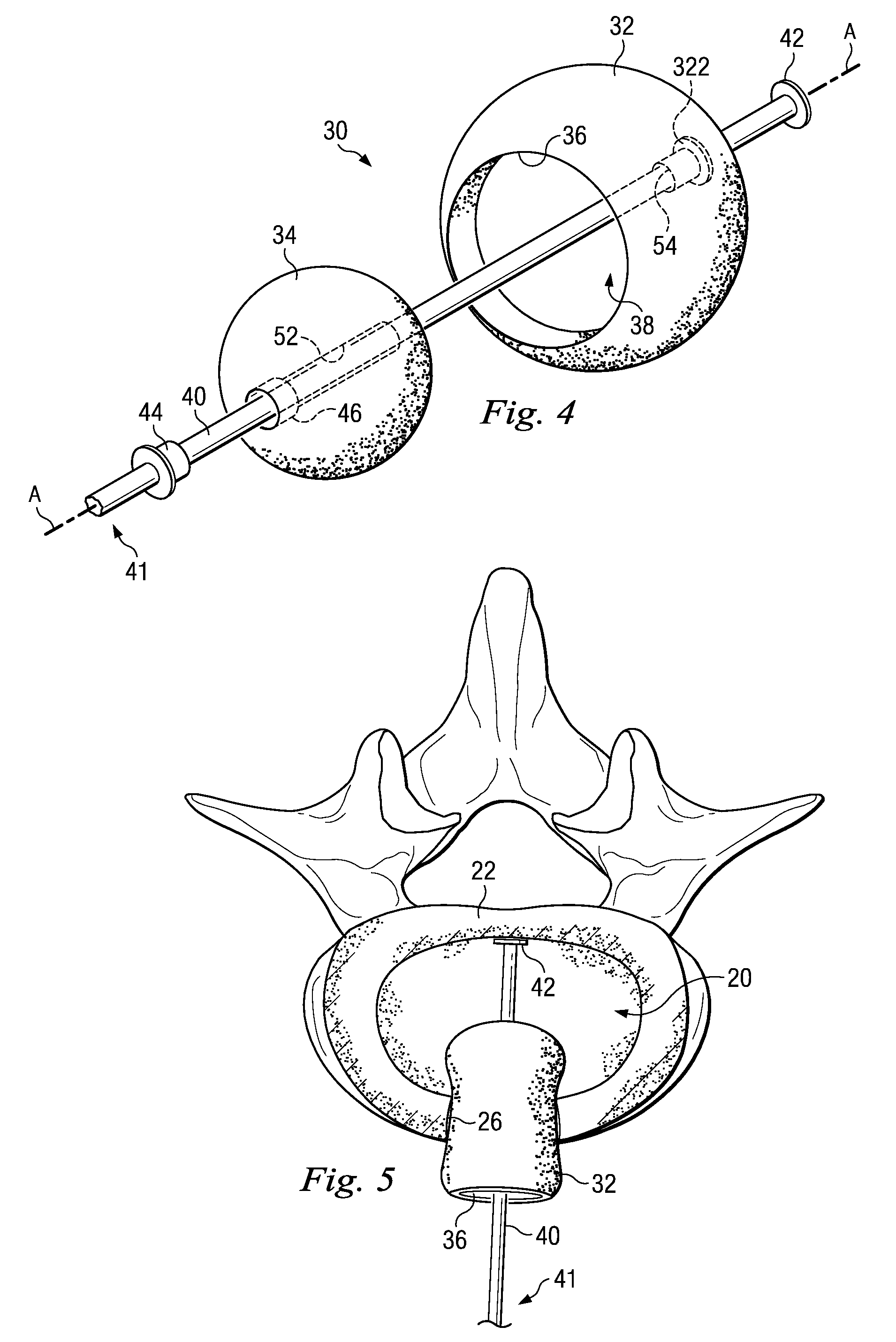
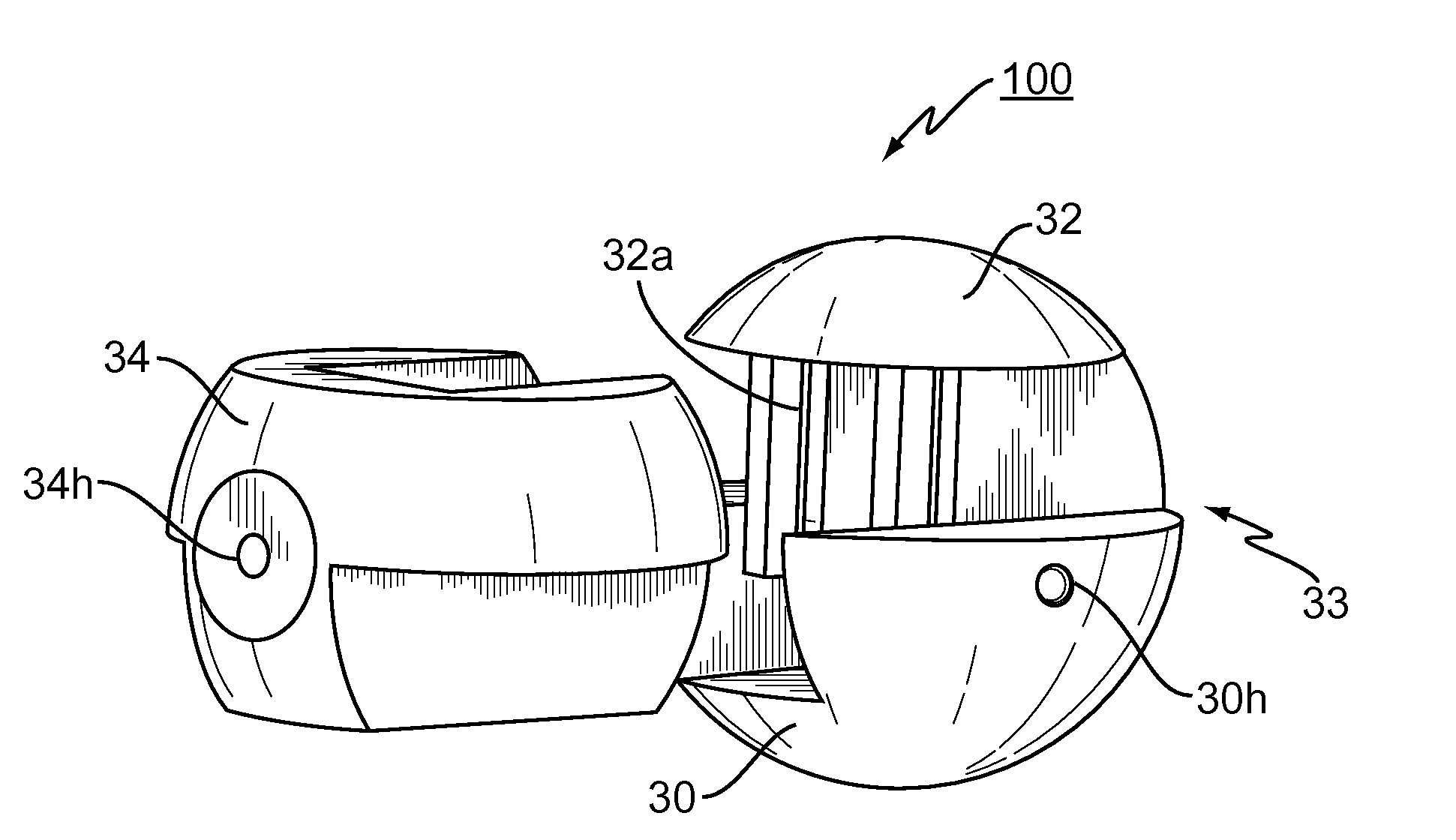
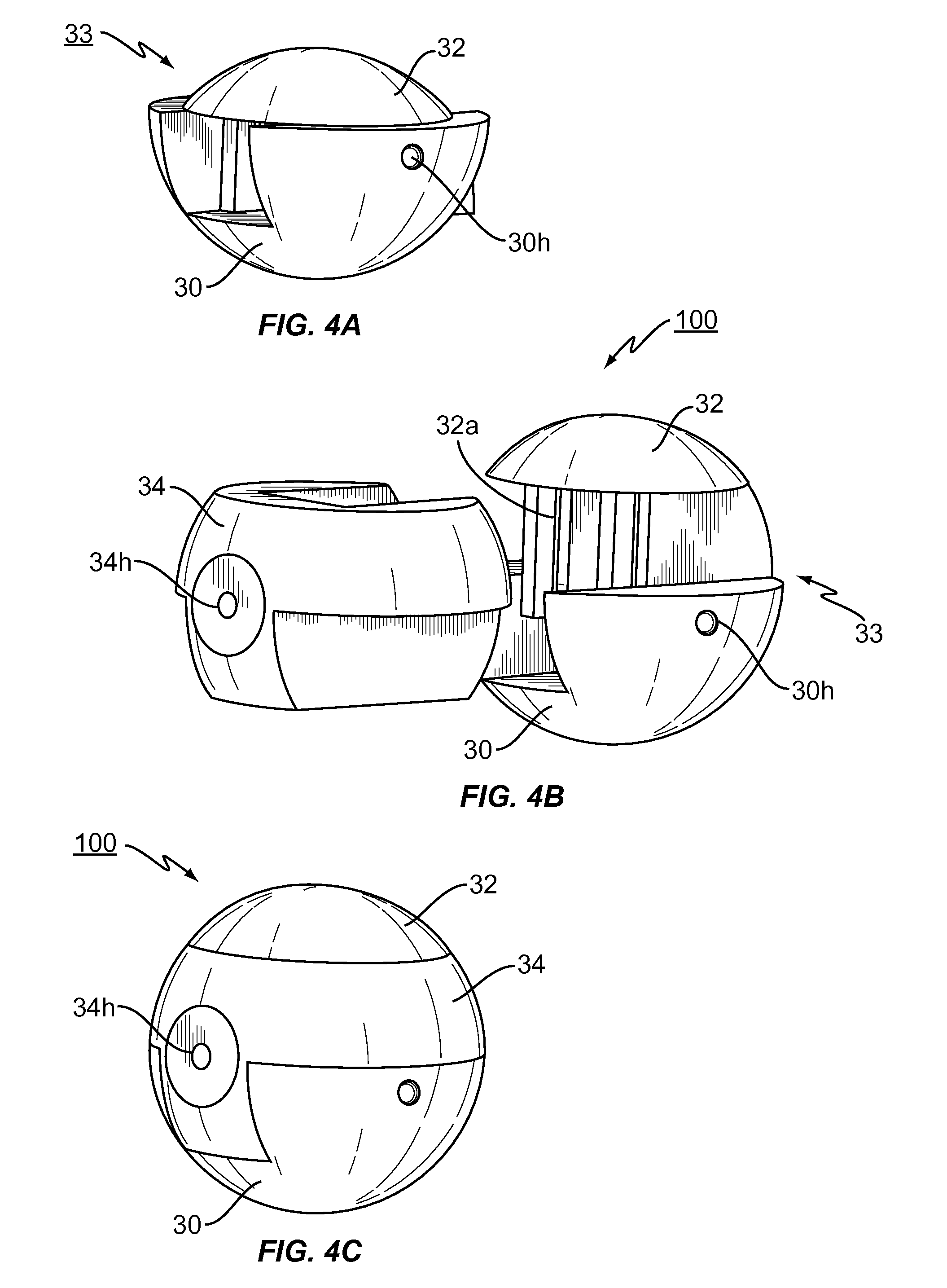
Spinal nucleus replacement implants
InactiveUS20100185287A1Spinal implantsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryReplacement implantSpinal cord
A multi-piece intervertebral disc augmentation implant that may be assembled within the annulus fibrosus is disclosed. The implant may be guided into a precise location through a relatively small opening in the annulus fibrosus with the aid of an elongated guide.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
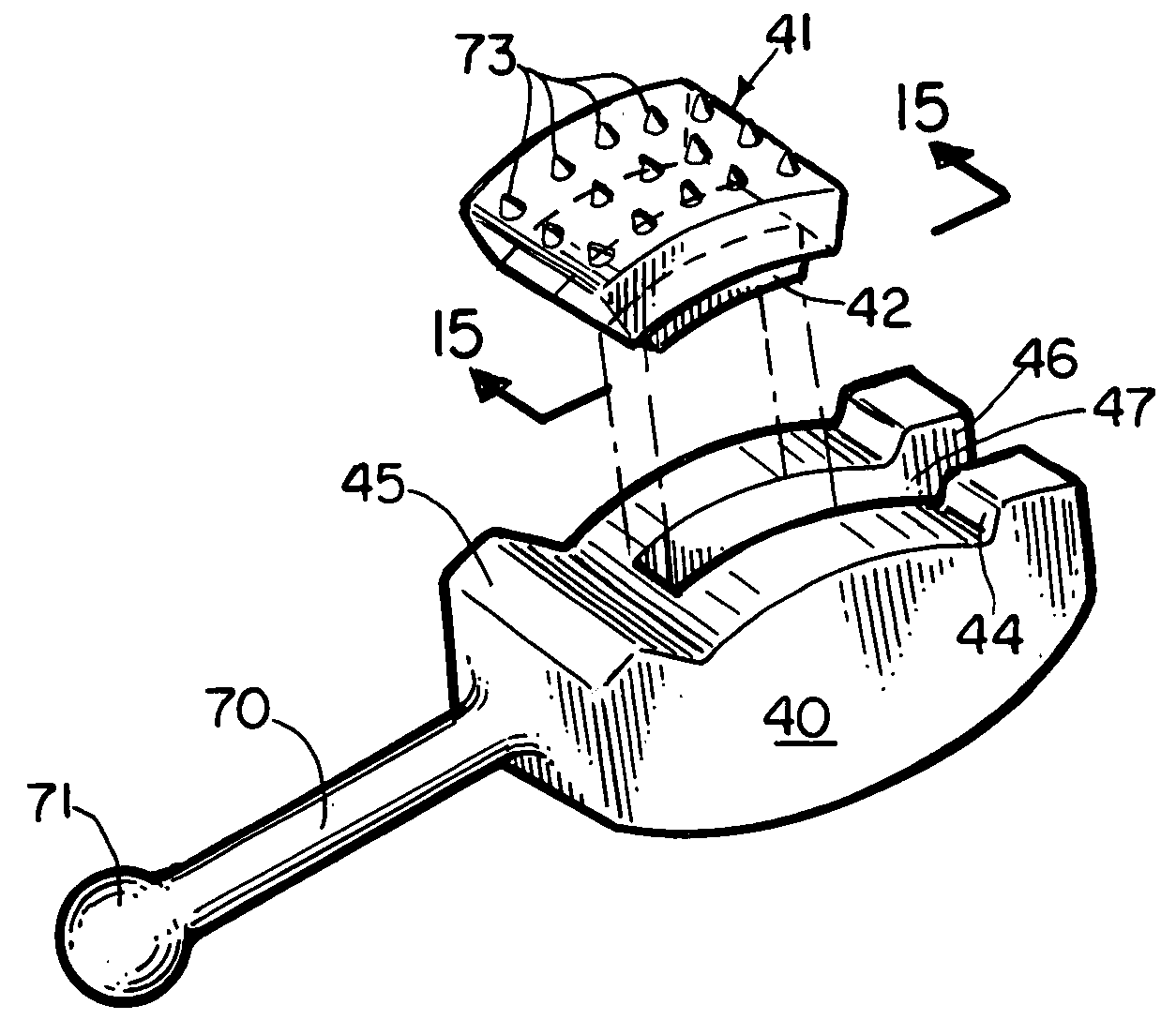
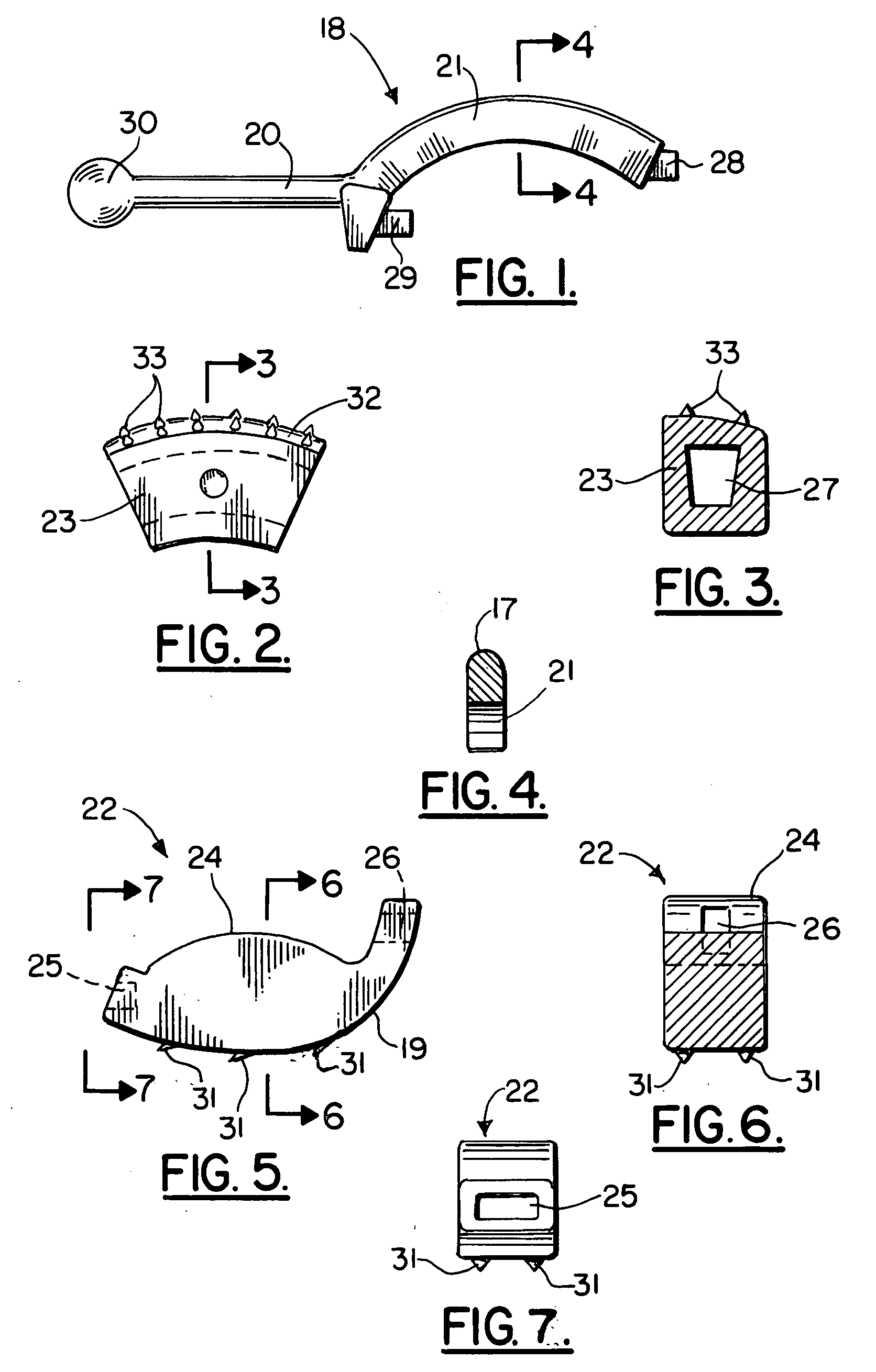
Dental implant and method for making and installing same
InactiveUS20070264612A1Promote bone growthEasy to disassembleDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCementoenamel junctionReplacement implant
A method for making a dental implant by obtaining images of the tooth pre-atraumatic tooth extraction and post extraction and using those images to computer generate and mill a titanium replacement implant employing CAD / CAM equipment. The implant includes a scalloped neck interface similar to the replaced tooth's scalloped cementoenamel junction, a polished neck area between a root portion and a crown portion, and the numeral for the tooth number imprinted on the implant's facial surface. Chevron retention fins are provided on the root portion for engaging the bone of the tooth socket or osteotomy when the implant is tapped into position. Retention grooves are provided on the crown portion to which a provisional crown is cemented slightly out of occlusion at the time the implant is placed. The provisional crown will be replaced with a permanent crown after osteointegration of the implant has occurred.
Owner:MOUNT K TIM
Spinal nucleus replacement implant
An intervertebral prosthesis implantable within a disc space and disposed between upper and lower vertebral endplates is provided. The prosthesis comprises a plurality of prosthesis modules insertable into the disc space, wherein the modules have at least one set of complementarily-shaped and sized surfaces, and wherein at least one of the modules is expandable. The modules have surfaces configured to engage within the disc space in a manner such that the modules form an assembled prosthesis of a size substantially preventing it from being outwardly expelled from the disc space, and the modules have bearing surfaces slidably engageable with the endplates to permit articulation between upper and lower vertebral endplates. In one embodiment, the at least one expandable module of the intervertebral prosthesis expands by inflation. In another embodiment, the at least one expandable module expands by unfolding into its intended form.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Cartilage replacement implant and method for producing a cartilage replacement implant
ActiveUS20060241756A1Easy to anchorEasy to sutureSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisReplacement implantSacroiliac joint
To improve a cartilage replacement implant for the biological regeneration of a damaged cartilage area of articular cartilage in the human body, comprising a cell carrier which has a defect-contacting surface for placement on the damaged cartilage area and is formed and designed for colonization with human cells, so that after implantation of the cartilage replacement implant, formation of a gap between adjacent contact surfaces of the implant and surrounding recipient tissue is minimized, it is proposed that the cell carrier rest with surface-to-surface contact on a carrier and be joined to the carrier at a cell carrier surface that faces away from the defect-contacting surface. A method for producing a cartilage replacement implant is also proposed.
Owner:TETEC TISSUE ENG TECH
Insert for nucleus implant
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Patient-specific instrumentation for implant revision surgery
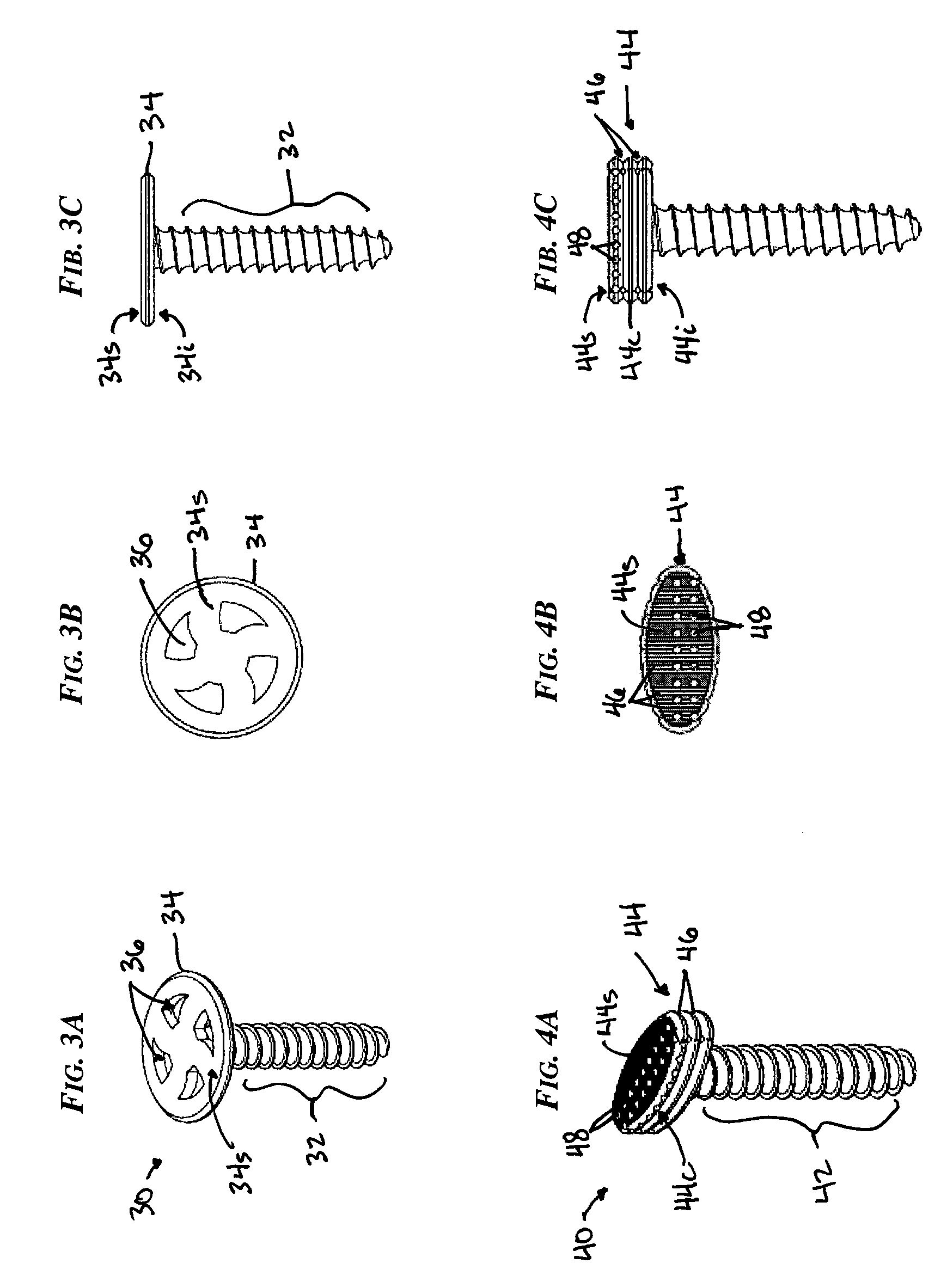
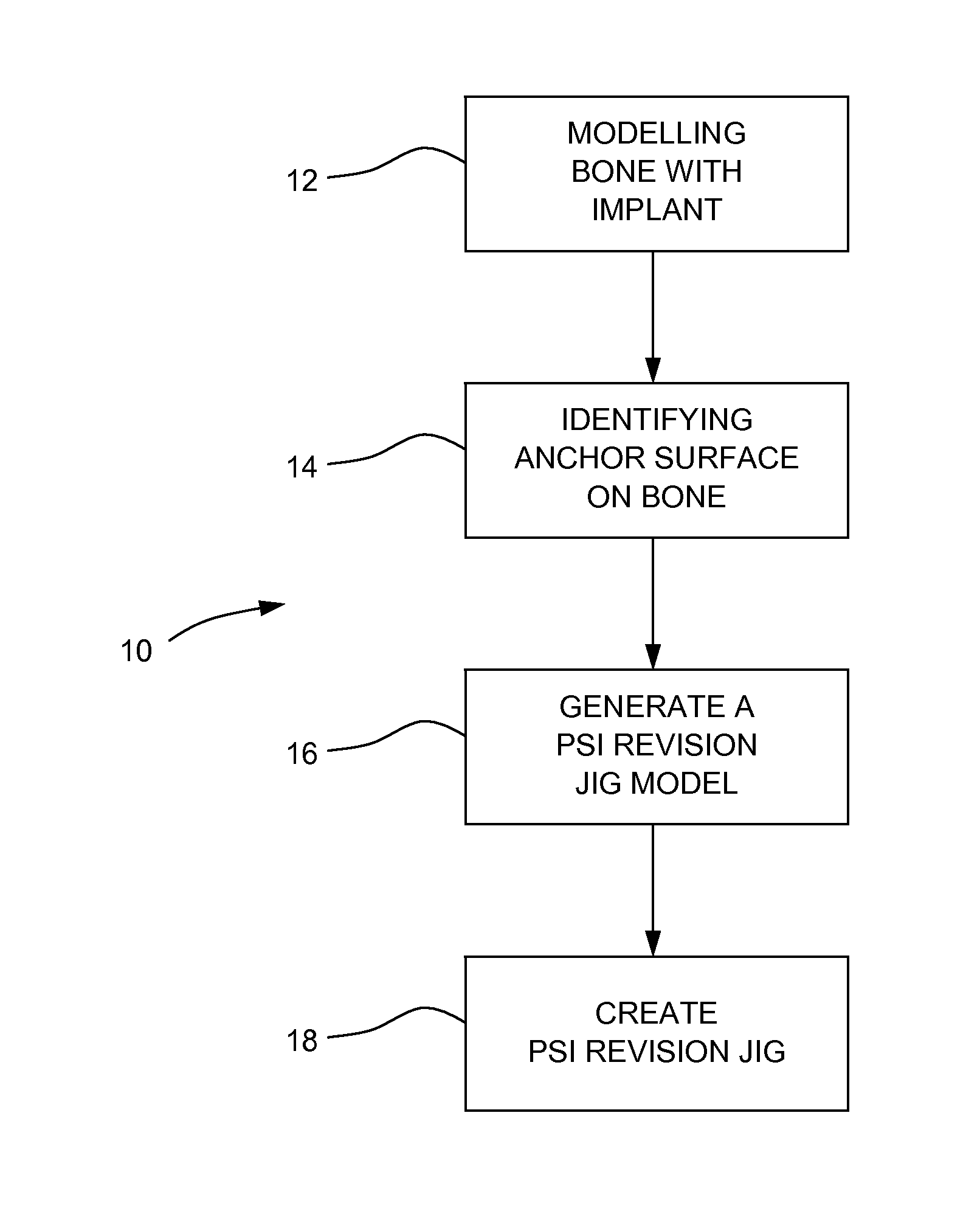
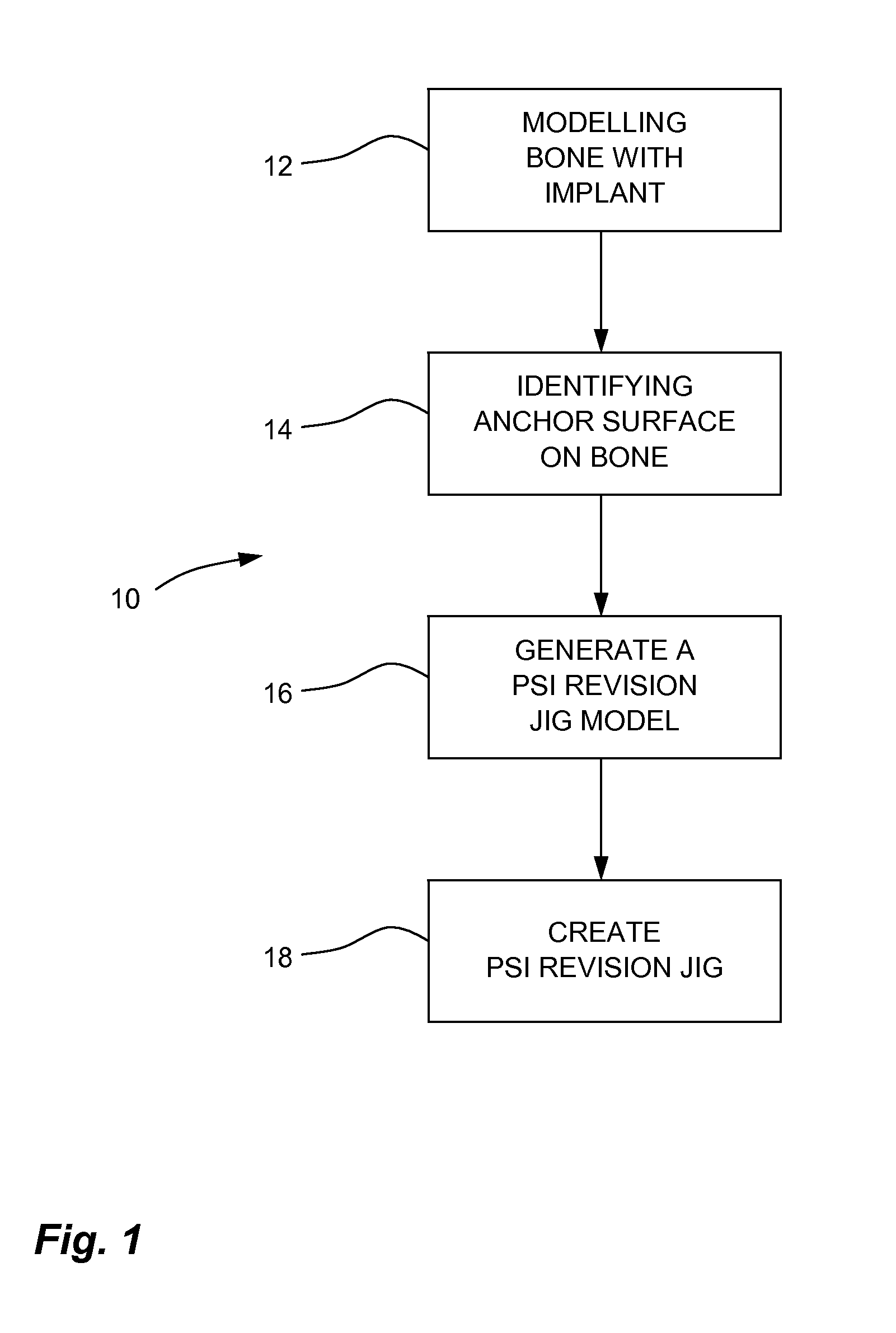
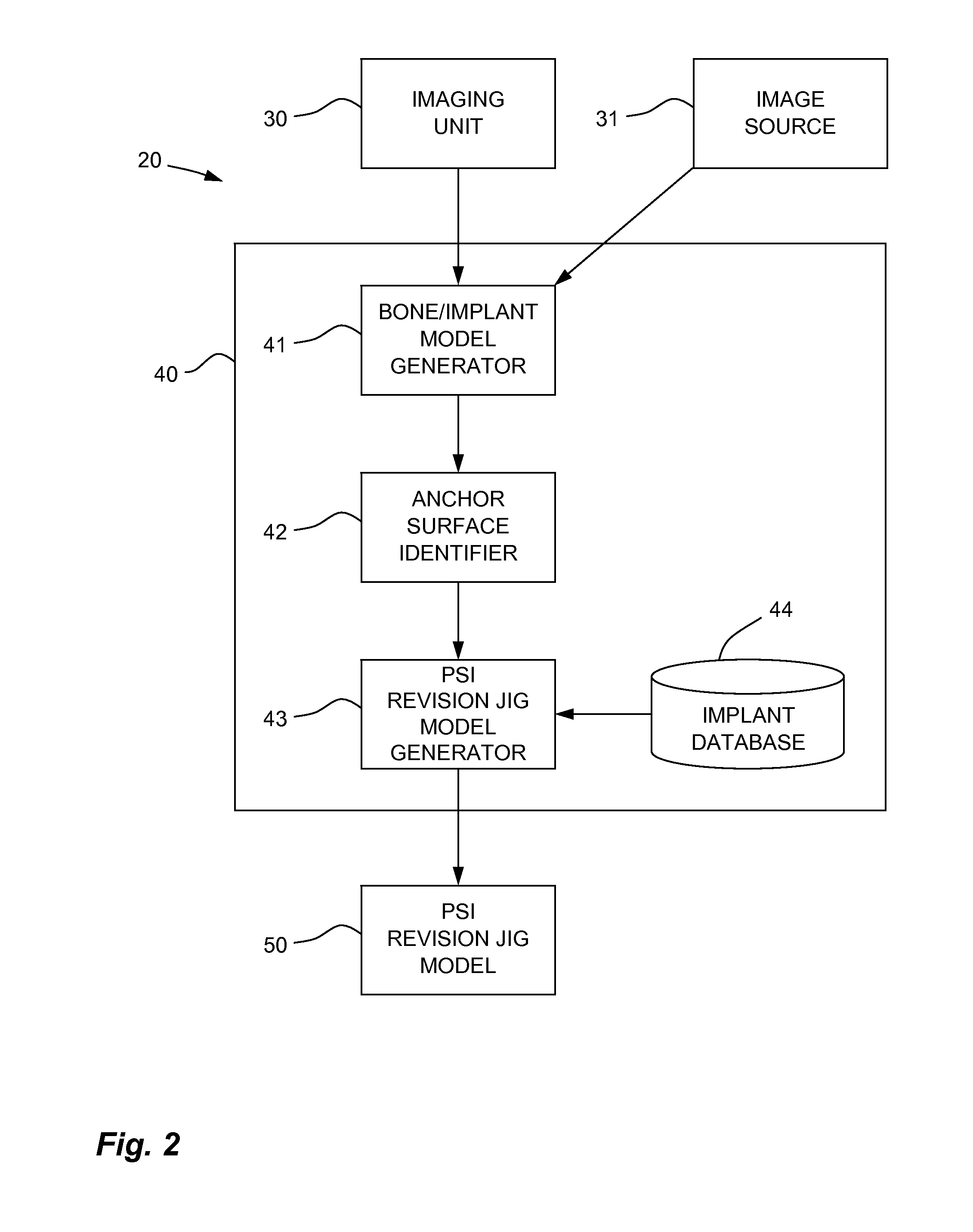
A system and method for generating a patient specific instrumentation jig model for implant revision comprises an anchor surface identifier to identify anchor surface(s) from a patient specific bone model of a bone requiring implant revision and from data related to an implanted implant on the bone. The anchor surface is in close proximity to the implanted implant. A PSI revision jig model generator generates a jig model using at least the identified anchor surface and a model of a replacement implant, the PSI revision jig model generator outputting a jig model comprising patient specific contact surface(s) corresponding to the identified anchor surface, and at least one tool interface portion positioned and / or oriented relative to the at least one contact surface, the at least one tool interface portion adapted to be interfaced to a tool altering the bone for subsequently installing an implant on the bone.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Buckling disc replacement
Devices and methods are provided for replacing a spinal disc, and in particular devices and methods are provided that rely on buckling to control movement of adjacent vertebrae. In one embodiment, an artificial disc replacement implant is provided and includes an implantable body having a superior surface adapted to be positioned adjacent to an endplate of a superior vertebra, and an opposite inferior surface adapted to be positioned adjacent to an endplate of an adjacent inferior vertebrae. The implantable body includes at least one wall formed therein and extending between the superior and inferior surfaces. The wall(s) can be adapted such that, when the implantable body is disposed between the endplates of adjacent superior and inferior vertebrae, the wall(s) will buckle by moving laterally and shorting in height under a load applied thereto by movement of the adjacent vertebrae. The implantable body can also include at least one opening formed adjacent to the wall(s) and extending between the superior and inferior surfaces of the implantable body.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Poly(ester urea) polymers and methods of use
InactiveUS20070128250A1Easy to produceImprove mechanical propertiesOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryAntibiotic YHard tissue
The invention provides high molecular weight, crystalline or semi crystalline biodegradable and biocompatible poly(ester urea) (PEU) polymers useful for making vascular stents and hard tissue replacement implants, such as bone substitutes. The PEU polymers are based on α amino acids and are made by a polycondensation reaction. PEU polymer compositions can contain a therapeutic diol incorporated into the polymer backbone that is released from such an implant in situ. Bioactive agents, such as analgesics, antibiotics, and the like, can also be covalently attached to certain PEU polymers for release into tissue surrounding an implant during biodegradation of the polymer.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
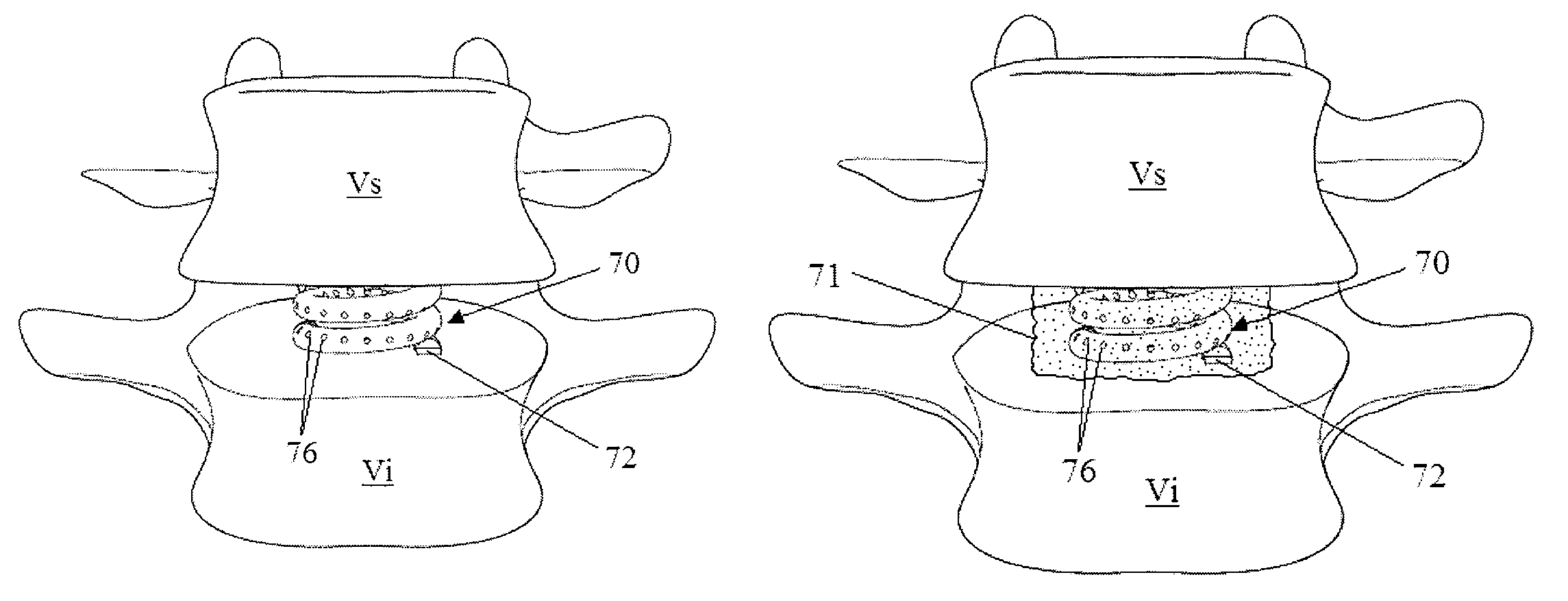
Vertebral replacement and distraction device for placing said implant
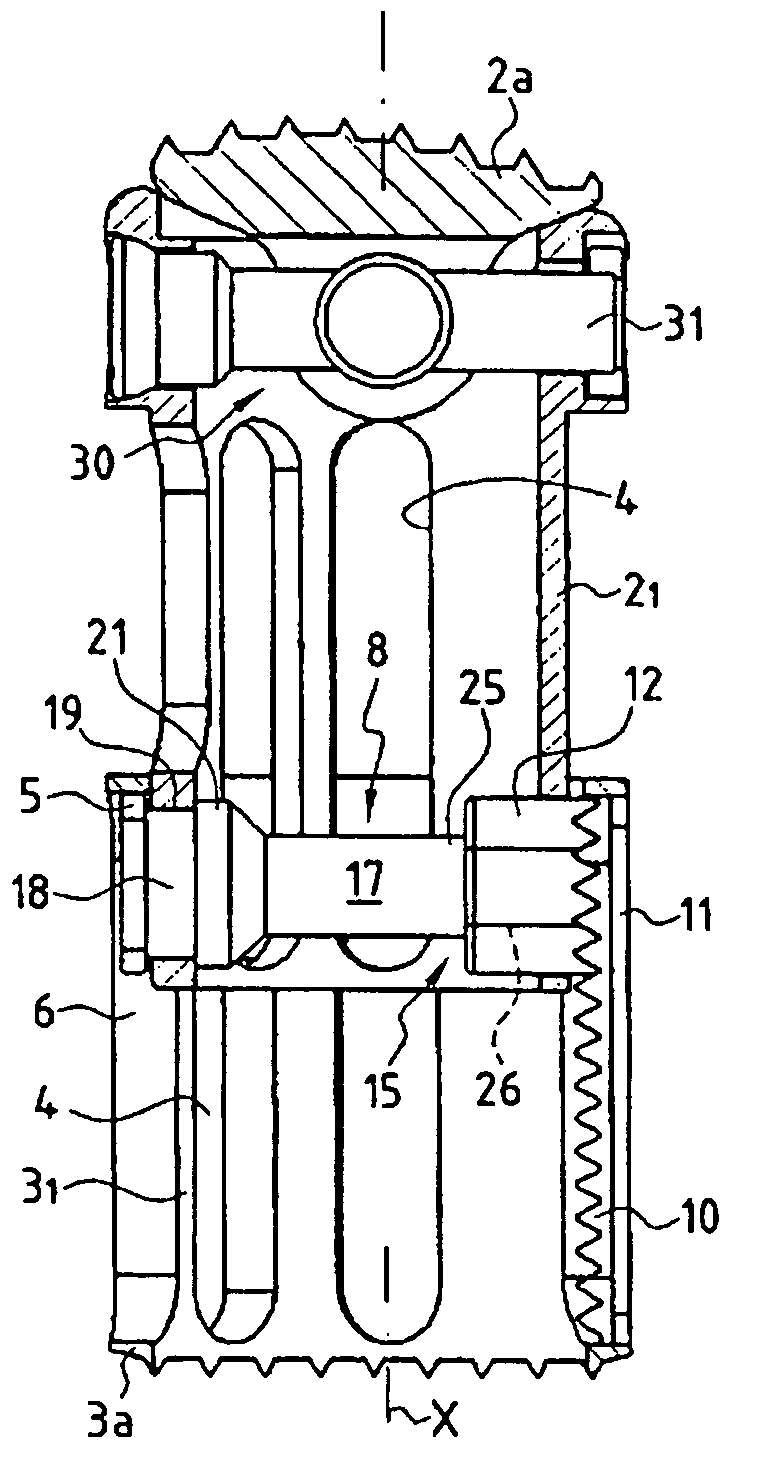
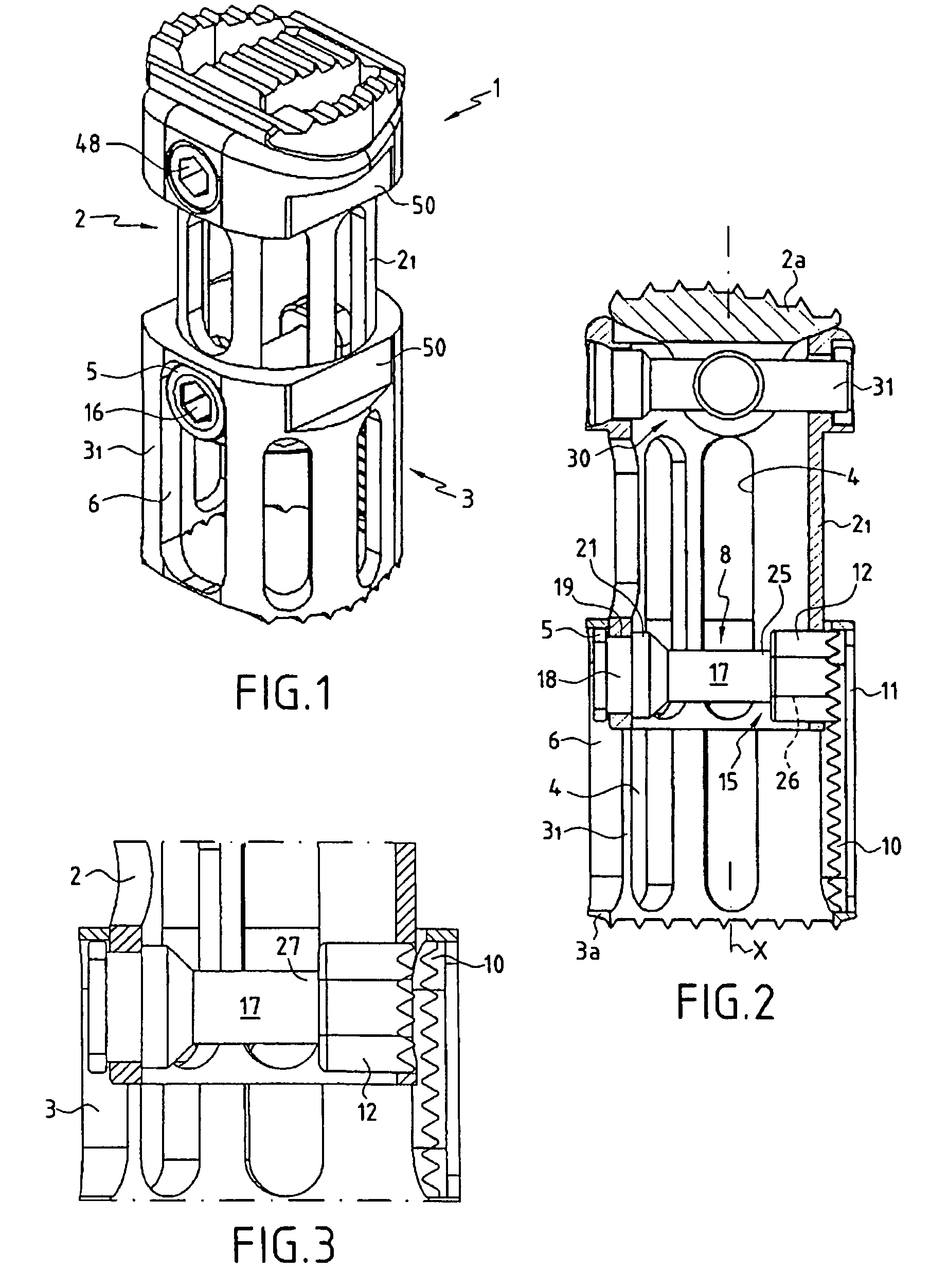
InactiveUS7819920B2Fast and easy and reversible changeoverInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionReplacement implant
A vertebral replacement implant includes two longitudinal elements slidably mounted with respect to each other, and locking elements. These locking elements include, on one of the longitudinal elements, an anchor surface, and on the other of the longitudinal elements, an anchor shoe guided in translation to take up a first position in which the elements slide freely with respect to each other, and a second position in which the anchor shoe cooperates with the anchor surface to lock the elements together, with a system converting a rotational movement into a translational movement transmitted to the anchor shoe.
Owner:SCIENTX
Cartilage replacement implant and method for producing a cartilage replacement implant
ActiveUS20110238180A1Shape longStructure longSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisHuman bodyReplacement implant
To improve a cartilage replacement implant for the biological regeneration of a damaged cartilage area of articular cartilage in the human body, comprising a cell carrier which has a defect-contacting surface for placement on the damaged cartilage area and is formed and designed for colonization with human cells, so that after implantation of the cartilage replacement implant, formation of a gap between adjacent contact surfaces of the implant and surrounding recipient tissue is minimized, it is proposed that the cell carrier rest with surface-to-surface contact on a carrier and be joined to the carrier at a cell carrier surface that faces away from the defect-contacting surface. A method for producing a cartilage replacement implant is also proposed.
Owner:TETEC TISSUE ENG TECH
Vertebral body replacement implant
ActiveUS8337558B2Strengthen the relative fixedEffectively fixedSpinal implantsReplacement implantMedicine
In a vertebral body replacement implant having a bottom locating part for positioning against a lower vertebral body and having a top locating part for positioning against an upper vertebral body, wherein both locating parts are steplessly displaceable relative to one another along a displacement path so that the height of the vertebral body replacement implant is variable, having a clamping device for fixing the two locating parts in any desired intermediate position along the displacement path, which clamping device comprises a clamping element that is mounted on one locating part so as to be variable in position and can be pressed towards a clamping face on the other locating part, in order to improve the clamping action it is proposed that the clamping face is inclined slightly relative to the displacement path, so that when the locating parts are pushed together the clamping face moves progressively closer to the clamping element.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Spinal nucleus replacement implants
An intervertebral prosthesis implantable within a disc space and disposed between upper and lower vertebral endplates is provided. The prosthesis comprises a plurality of prosthesis components insertable into the disc space, wherein the components have at least one set of complementarily-shaped and sized surfaces, and wherein the at least one set of complementarily-shaped surfaces comprises a slot, and a rod that fits in the slot. A method of implanting an intervertebral prosthesis according to the present invention also is provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Bone anchoring member with clamp mechanism
A multi-piece disc replacement implant for replacing a disc removed by a discectomy including an upper plate member, a lower plate member, and an intermediate resilient member providing movement between te two plate members replicating the natural movement of the spine. The plate members are rigid and have orthogonal sidewalls forming an enclosure. The resilient member is an elastic solid or a multi-chamber balloon structure of fluid-filled sacks that collectively define a non-uniform shape such as an oblate spheroid, or a helically coiled string of beads. Such an implant is capable of supporting the compressive and cyclic loads required of a natural disc. The upper and lower plate members are cooperatively formed to selectively limit the allowable range of motion in any given direction and a provided with protrusions to be received in one or more channels cooperatively formed in the vertebrae and secured in place by a bone screw.
Owner:ELIASEN KENNETH ARDEN +2
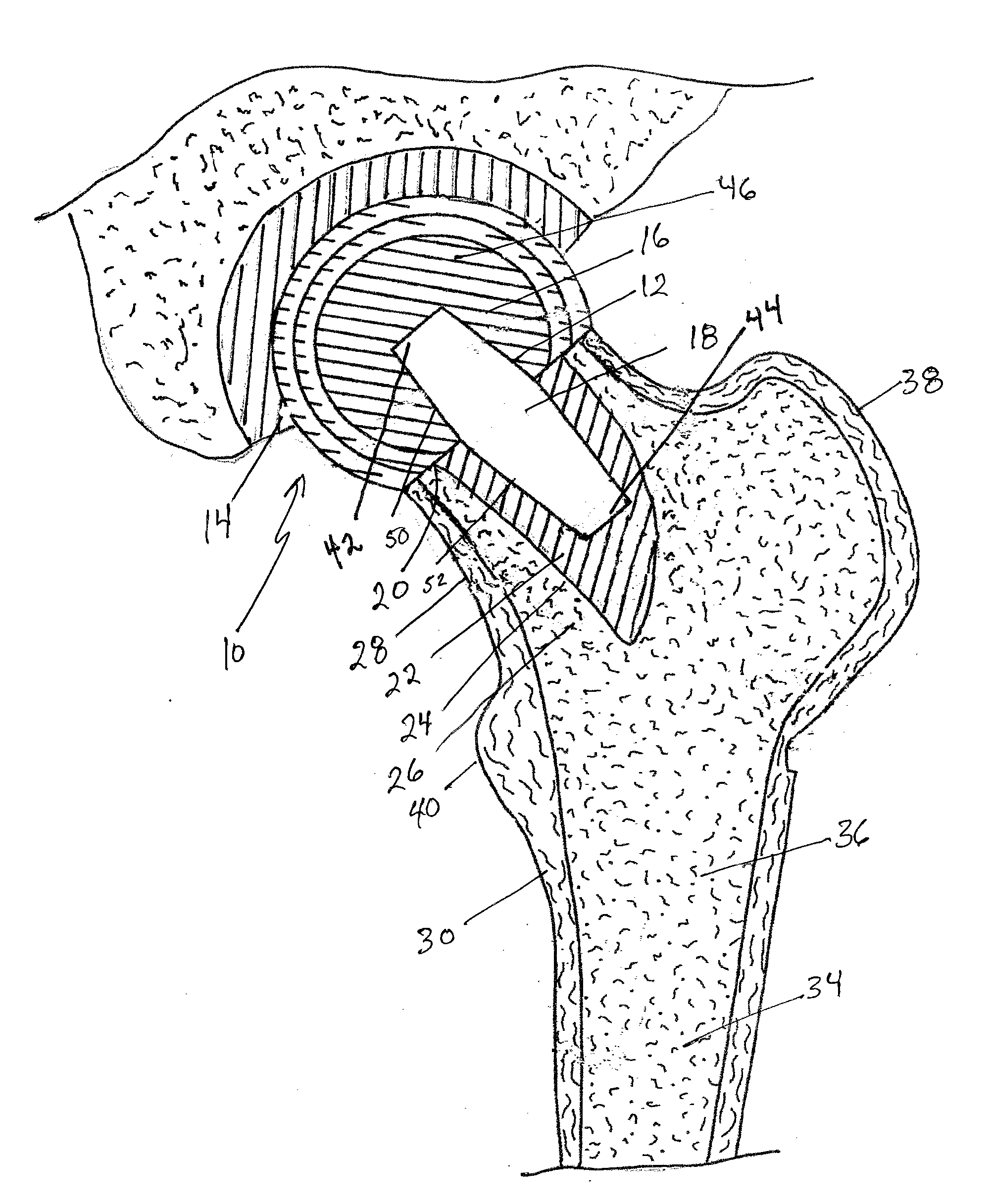
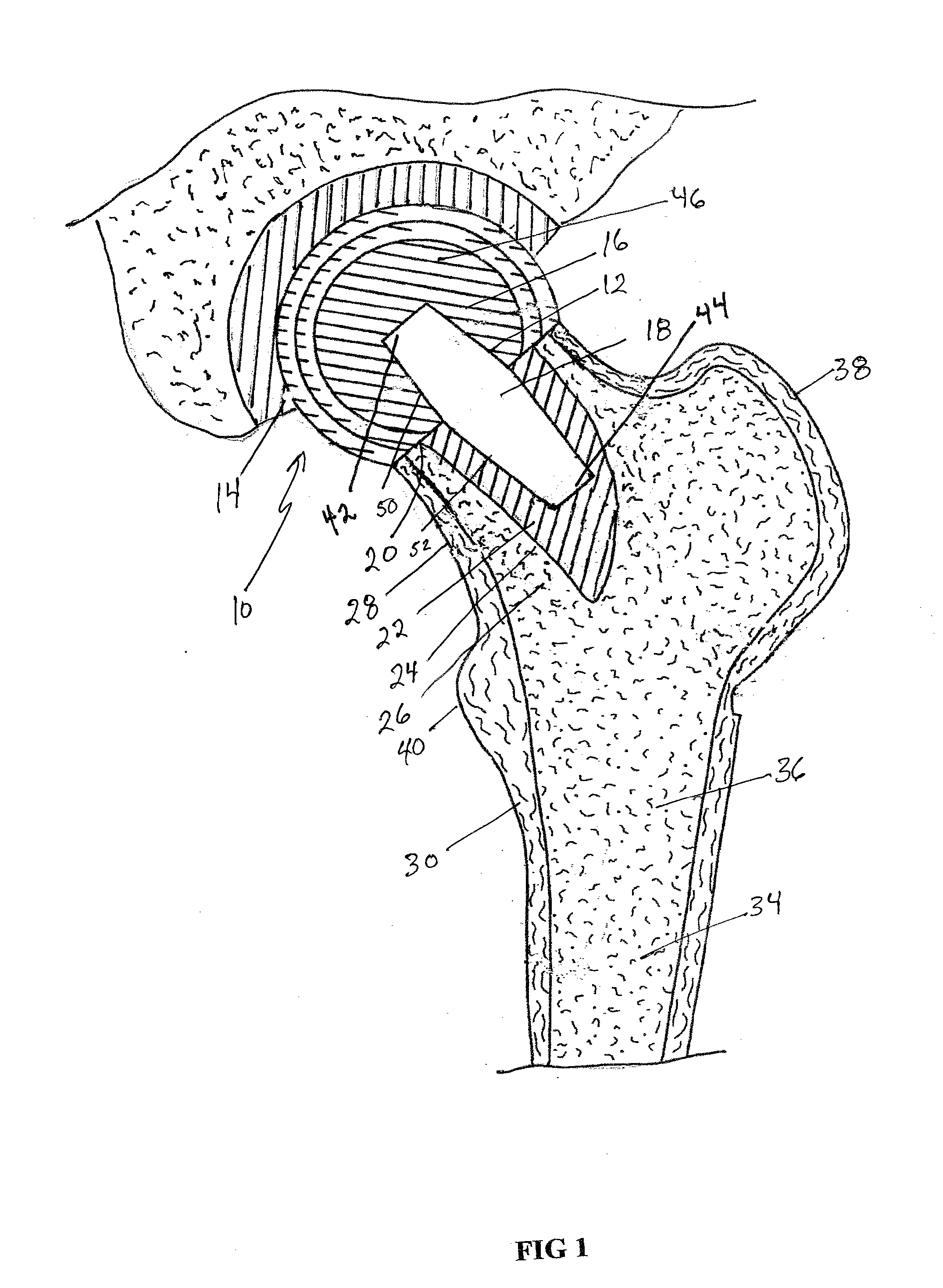
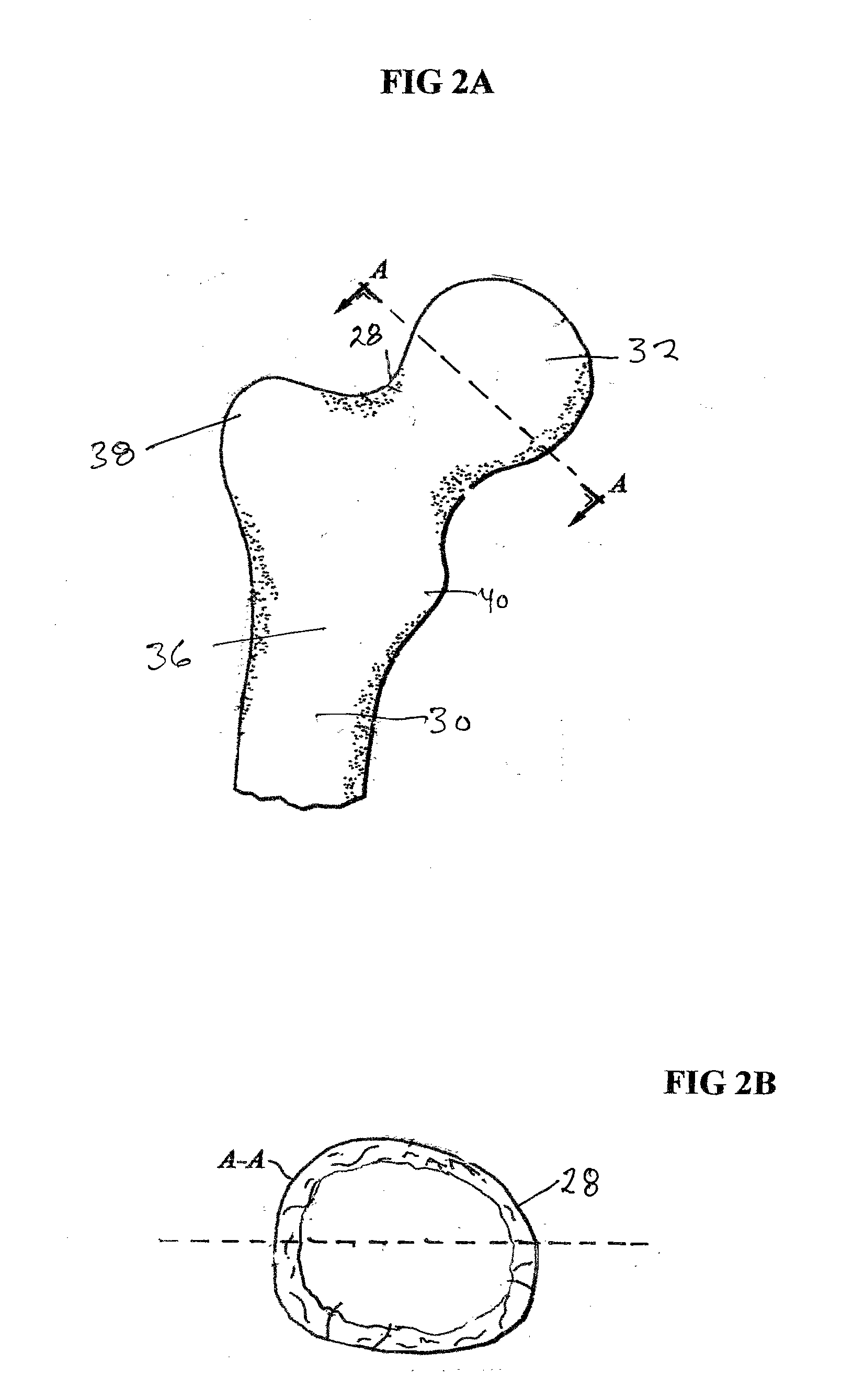
Femoral head calcar loading prosthesis
Provided is a novel hip replacement implant system that includes a ball assembly having a ball trunion, the ball assembly being configured as a replacement for the head of the femur and capable of being secured by the ball assembly trunion to a calcar implant element that can be securely seated in the calcar bone of the femoral neck, thus maintaining the load transfer function of the calcar bone of the femoral neck. A method of using the device is also provided.
Owner:CONCEPT DESIGN & DEV
Dental implant and method for making and installing same
InactiveUS20080020343A1Easy to disassemblePromote bone growthDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCementoenamel junctionReplacement implant
A method for making a dental implant by obtaining images of the tooth pre-atraumatic tooth extraction and post extraction and using those images to computer generate and mill a titanium replacement implant employing CAD / CAM equipment. The implant includes a scalloped neck interface similar to the replaced tooth's scalloped cementoenamel junction, a polished neck area between a root portion and a crown portion, and the numeral for the tooth number imprinted on the implant's facial surface. Chevron retention fins are provided on the root portion for engaging the bone of the tooth socket or osteotomy when the implant is tapped into position. Retention grooves are provided on the crown portion to which a provisional crown is cemented slightly out of occlusion at the time the implant is placed. The provisional crown will be replaced with a permanent crown after osteointegration of the implant has occurred.
Owner:MOUNT K TIM
Implant
InactiveUS20060009844A1Good dimensional stabilityReduces healing periodSpinal implantsReplacement implantBone chamber
In order to improve an implant, in particular a bone replacement implant for insertion into a bone cavity, or an intervertebral implant for insertion between two adjacent vertebral bodies of a human or animal spine, which can be brought from a normal position, in which the implant encompasses a maximum total volume, into an insertion position, in which the implant encompasses an insertion volume, which is smaller than the maximum total volume, such that the implant can be inserted through as small as possible an opening in a human or animal body and nevertheless have a high inherent stability, it is proposed that the implant has a plurality of cavities in fluidic connection with one another, and that a net volume encompassed in the normal position by the plurality of cavities in fluidic connection with one another is smaller than the maximum total volume.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Artificial disc prosthesis for replacing a damaged nucleus
ActiveUS20120116516A1Resists hyper extension of the jointLimit wearSpinal implantsOblate spheroidReplacement implant
A multi-piece disc replacement implant for replacing a disc removed by a discectomy including an upper plate member, a lower plate member, and an intermediate resilient member providing movement between the two plate members replicating the natural movement of the spine. The plate members are rigid and have orthogonal sidewalls forming an enclosure. The resilient member is an elastic solid or a multi-chamber balloon structure of fluid-filled sacks that collectively define a non-uniform shape such as an oblate spheroid, or a helically coiled string of beads. Such an implant is capable of supporting the compressive and cyclic loads required of a natural disc. The upper and lower plate members are cooperatively formed to selectively limit the allowable range of motion in any given direction and a provided with protrusions to be received in one or more channels cooperatively formed in the vertebrae and secured in place by a bone screw.
Owner:AFLATOON KAMRAN
Connective tissue substitutes, method of preparation and uses thereof
The present invention relates to connective tissue substitute implant and method of preparation thereof. The implant is essentially composed of two bone anchors joined at the proximal ends by matrix layers and / or filaments coated by supplementary biocompatible matrix coating layer which can contain living stem cells isolated from injured connective tissue.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
Femoral head calcar loading prosthesis
Provided is a novel hip replacement implant system that includes a ball assembly having a ball trunnion, the ball assembly being configured as a replacement for the head of the femur and capable of being secured by the ball assembly trunnion to a calcar implant element that can be securely seated in the calcar bone of the femoral neck, thus maintaining the load transfer function of the calcar bone of the femoral neck. A method of using the device is also provided.
Owner:CONCEPT DESIGN & DEV
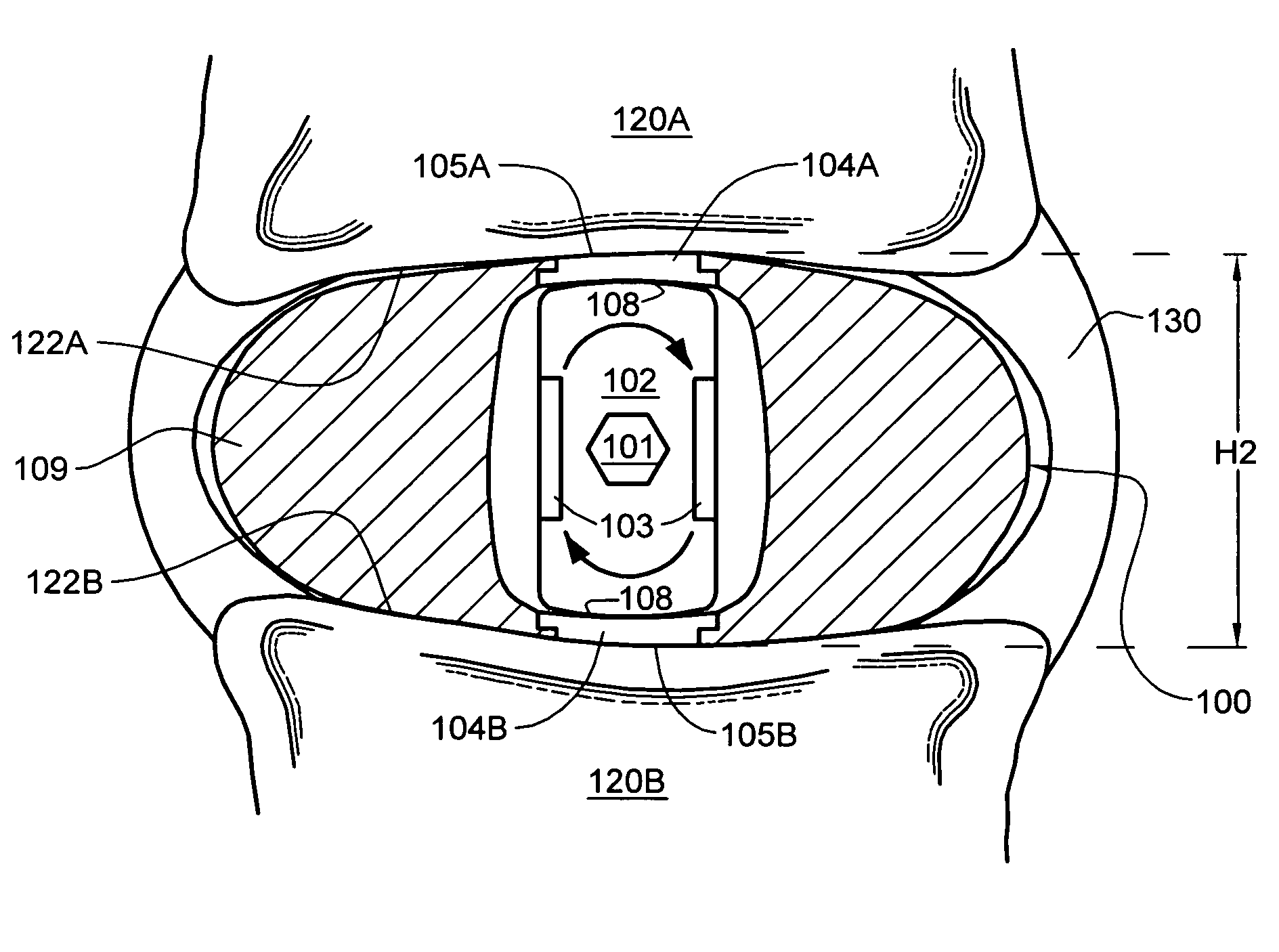
Unitary spinal disc implant
ActiveUS9408711B2Limited flexion and rotationPreserve and restore near-normal motionJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral jointNon fusion
Owner:BURKINSHAW BRIAN D +1
Insert for nucleus implant
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a nucleus of a spinal disc, and in particular for preventing nucleus disc replacement expulsion. The nucleus of a spinal disc can be removed from the annulus by forming a small opening in the annulus. Once the nucleus is removed, one or more insert devices can be implanted within the annulus of a spinal disc and they can be mated to one or both endplates of the adjacent vertebrae. The insert(s) is configured to interact with a nucleus disc replacement implant to prevent expulsion of the implant from the annulus.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Facet joint implant
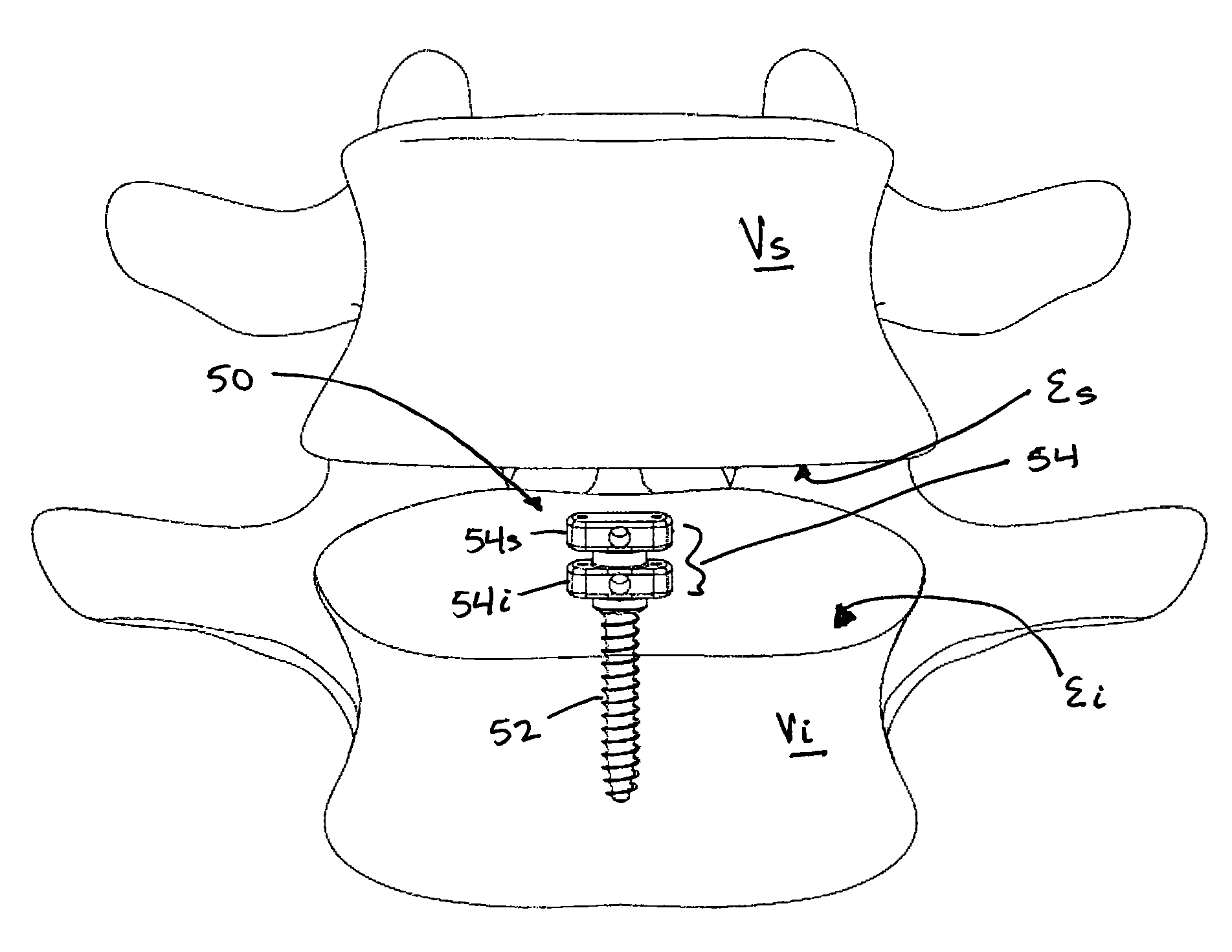
A facet joint implant includes a joint surface replacement implant and a fastening device for fixing the joint surface replacement implant in the joint gap of a facet joint of a human or animal spinal column. The fastening device includes at least two fastening elements that protrude from the joint surface replacement implant. The at least two fastening elements are each provided in the region of their free ends with at least one fixing element through hole. The facet joint implant includes a fixing element which is fed through at least two fixing element through holes of at least two fastening elements. The free ends of the fixing element are connectable to one another.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Unitary Spinal Disc Implant
ActiveUS20150245916A1Limited flexion and rotationPreserve and restore near-normal motionSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral jointNon fusion
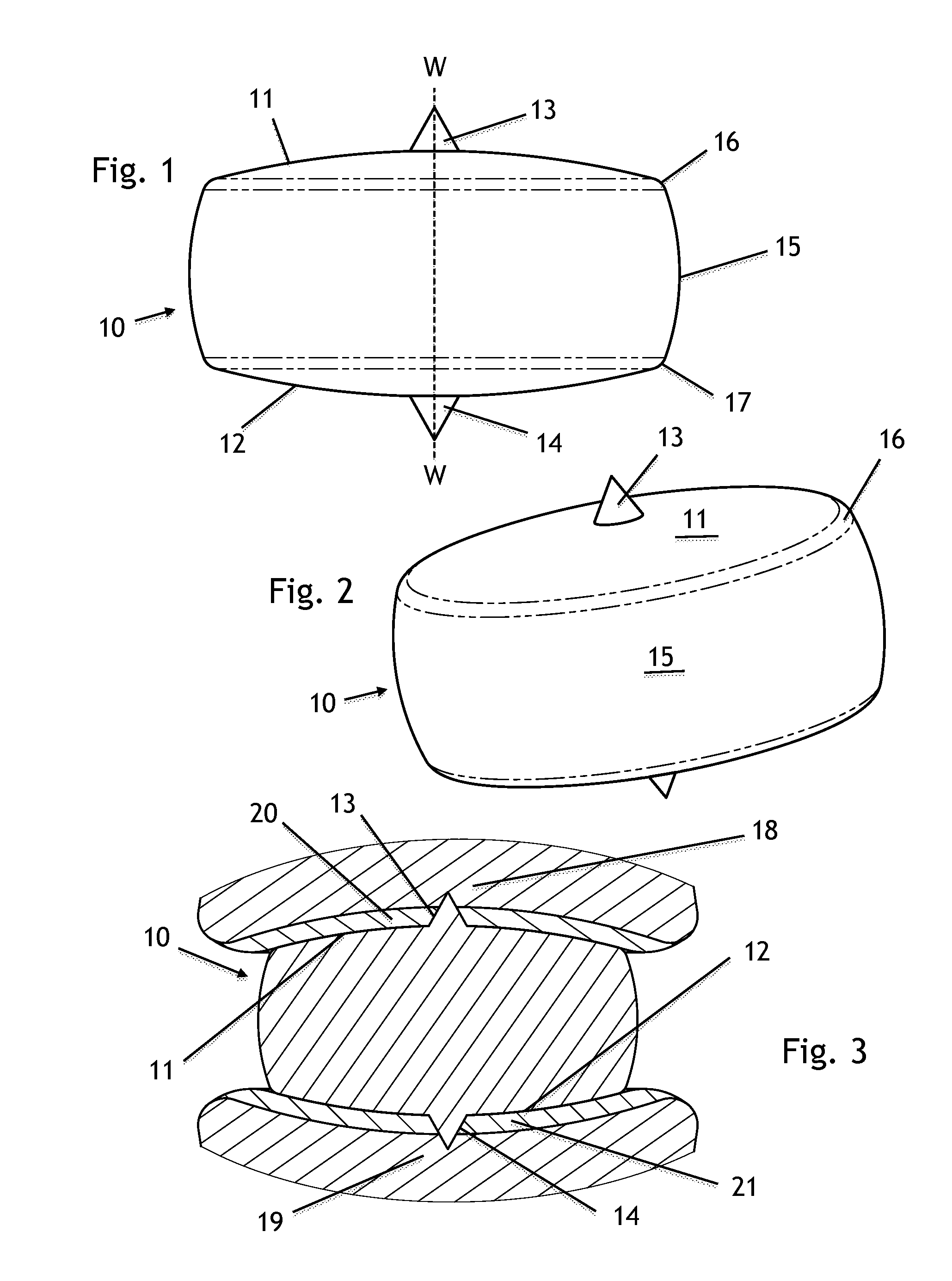
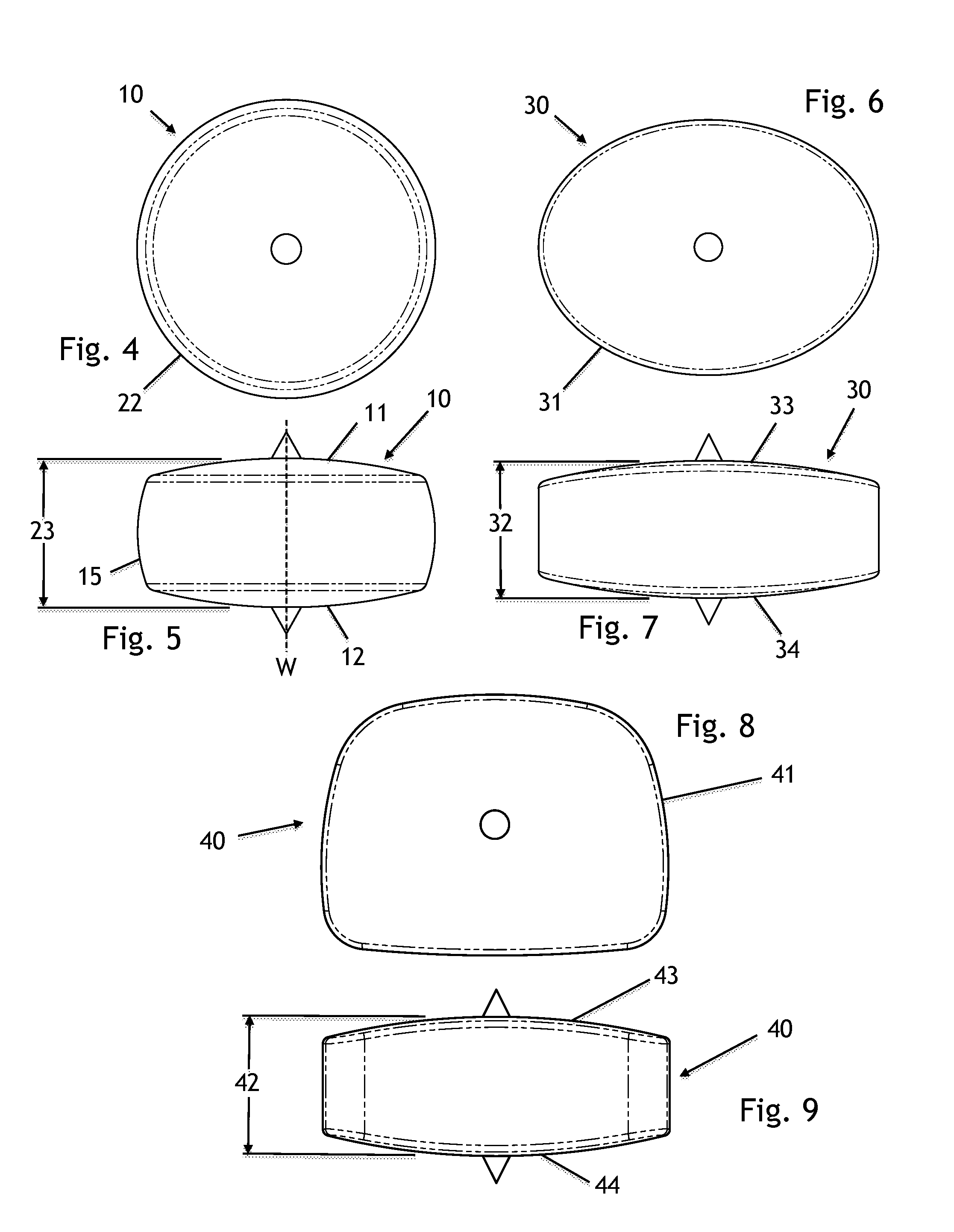
A unitary intervertebral device, having no moving components is provided for non-fusion articulation applications. The interbody articulating device allows for limited flexion and rotation between adjacent vertebrae, helping to preserve or restore near-normal motion between adjacent vertebrae. Rotational motion is achieved through one or more protrusions incorporated into the spinal interbody device. In one articulating form, a first protrusion extends perpendicularly from the superior aspect of the disc-shaped interbody device to form a spike or rotational protrusion, while a second protrusion extends axially from the inferior aspect of the interbody device to form a second spike or rotational protrusion. Protrusions preferably extend perpendicular from the apex of both the first and second arcuate articulating surfaces. In another form, a single protrusion extends axially from the superior aspect of a circular-shape of the interbody device to form a spike or anchoring protrusion, while the inferior surface may be slightly rounded and / or comprising a bone-ingrowth promoting surface. In another form, one or both of the first and / or second arcuate surfaces may be highly polished. Numerous planar geometries are described to define various profiles of the disc replacement implant which may be utilized, including irregular Reuleaux polygons. Numerous variations of the disc replacement and methods of use are described. Similarly configured fusion salvage devices are also described.
Owner:BURKINSHAW BRIAN D +1
Method for treating a cartilage defect, surgical instrumentation and surgical navigation system
The invention relates to a method for treating a cartilage defect by implanting a cartilage replacement implant through an arthroscopic access, comprising: determining at least one parameter for describing the arthroscopic access, providing a surgical instrumentation comprising at least two different applicator instruments for grasping the cartilage replacement implant, choosing one of the at least two applicator instruments of the instrumentation in dependence upon the at least one parameter determined for describing the arthroscopic access, and grasping and inserting the cartilage replacement implant into the patient's body with the chosen instrument through the arthroscopic access.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com