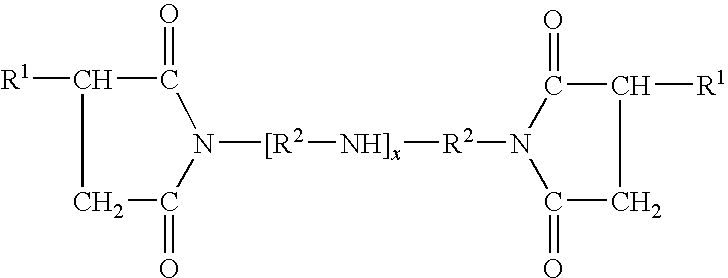Patents
Literature
44899 results about "Titanium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It is a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength. Titanium is resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine.
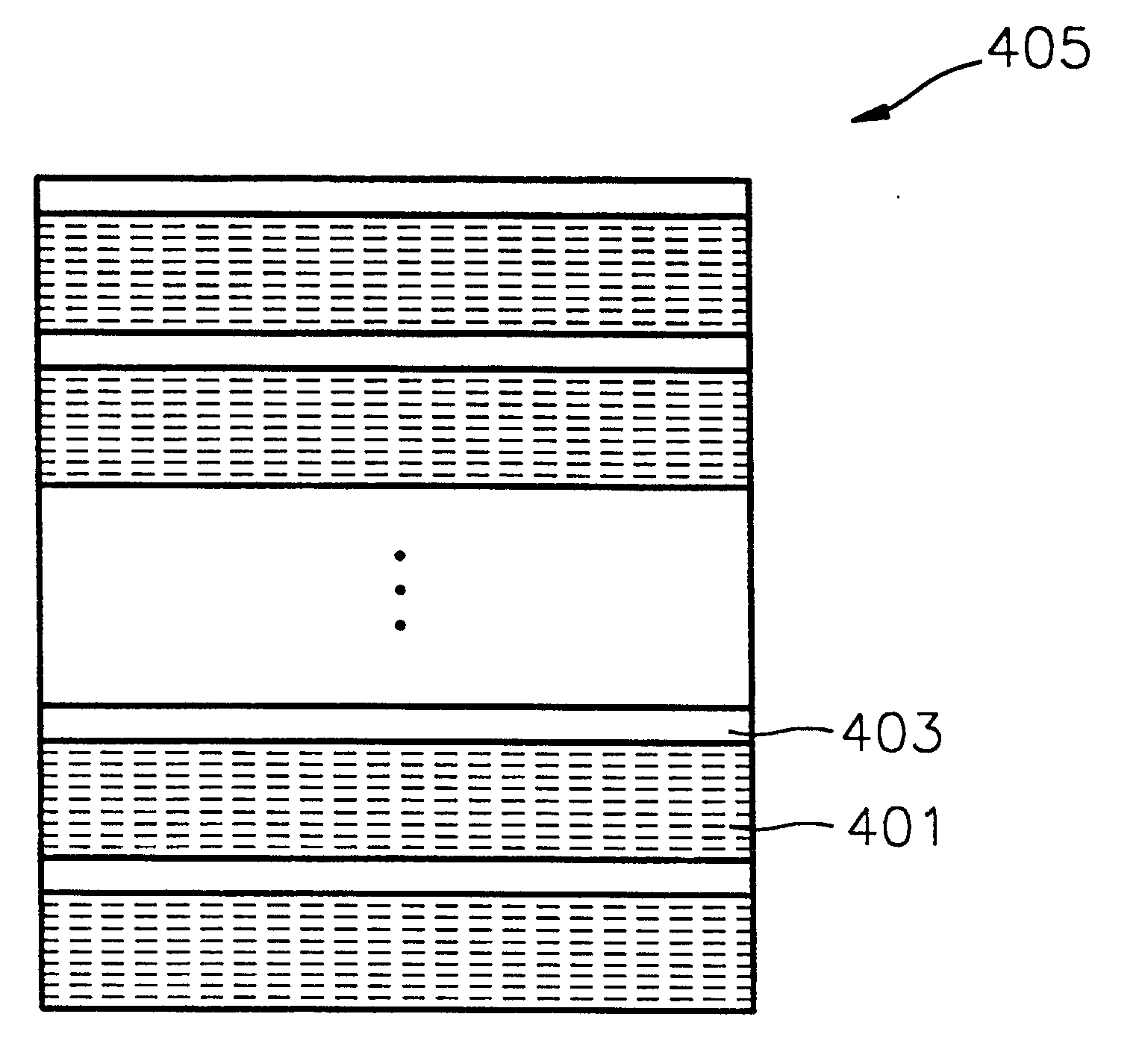
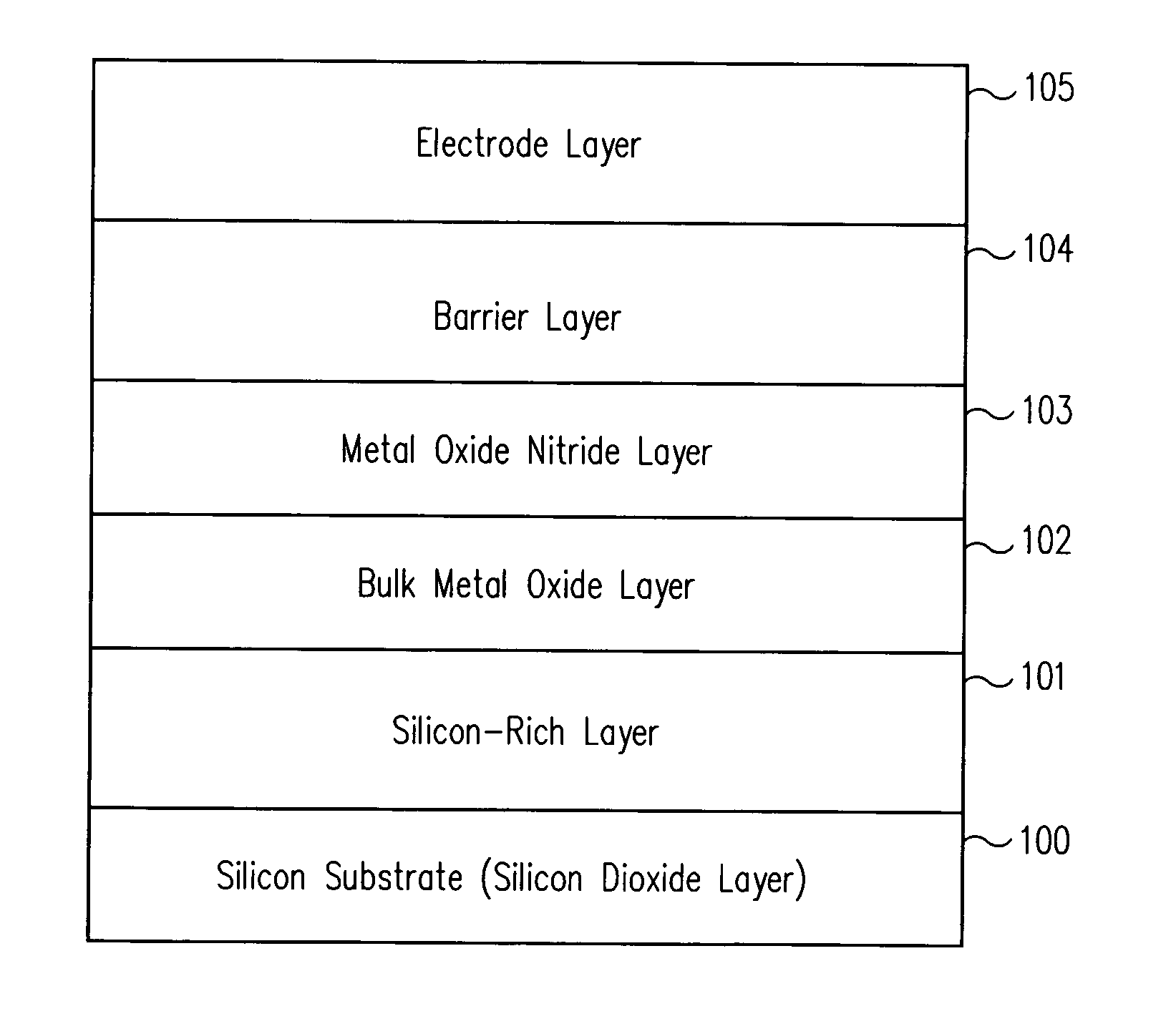
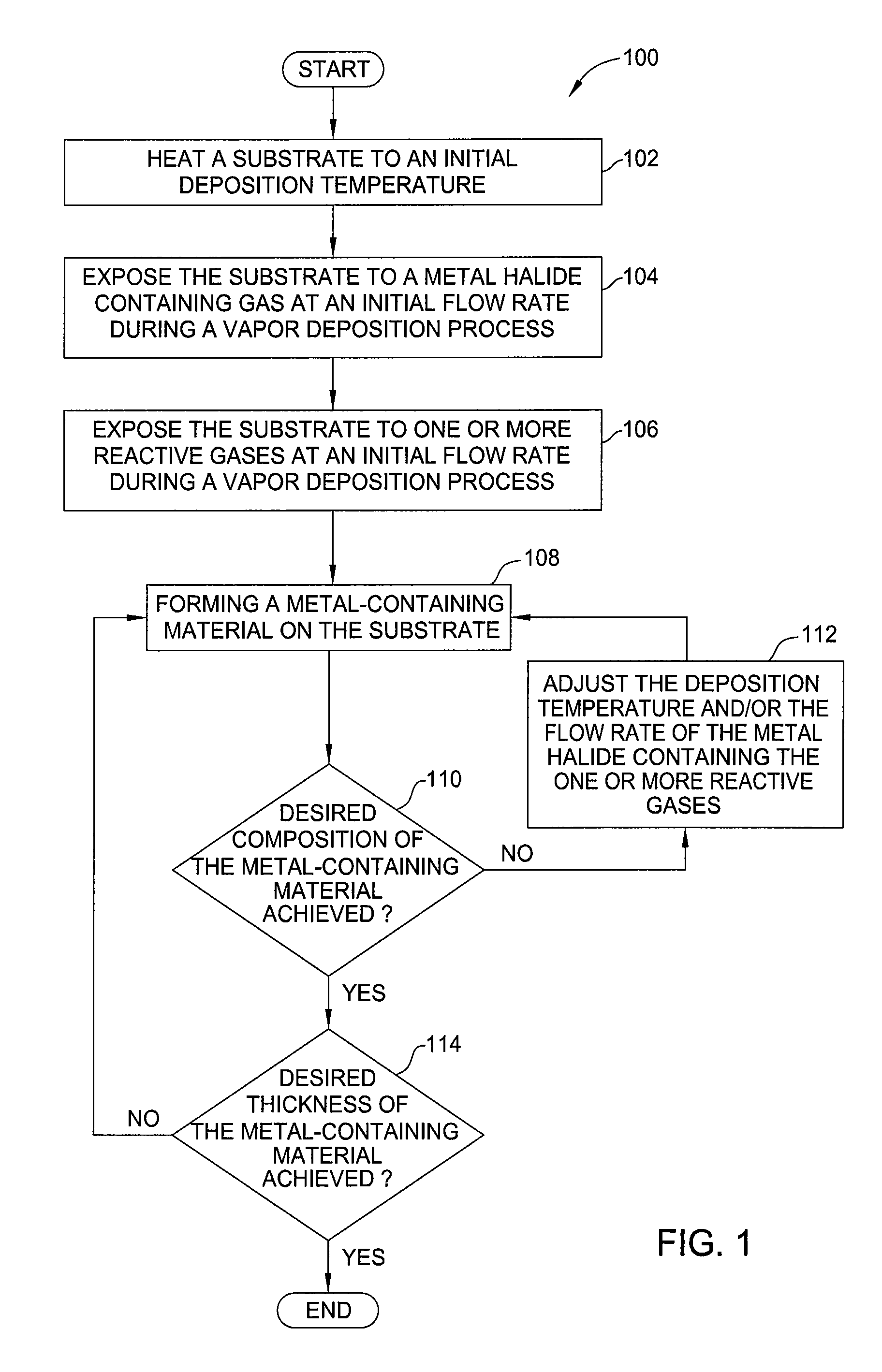
Method of forming metal layer using atomic layer deposition and semiconductor device having the metal layer as barrier metal layer or upper or lower electrode of capacitor
InactiveUS6287965B1High thermal resistantEasy to adjustSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsNiobiumDevice material
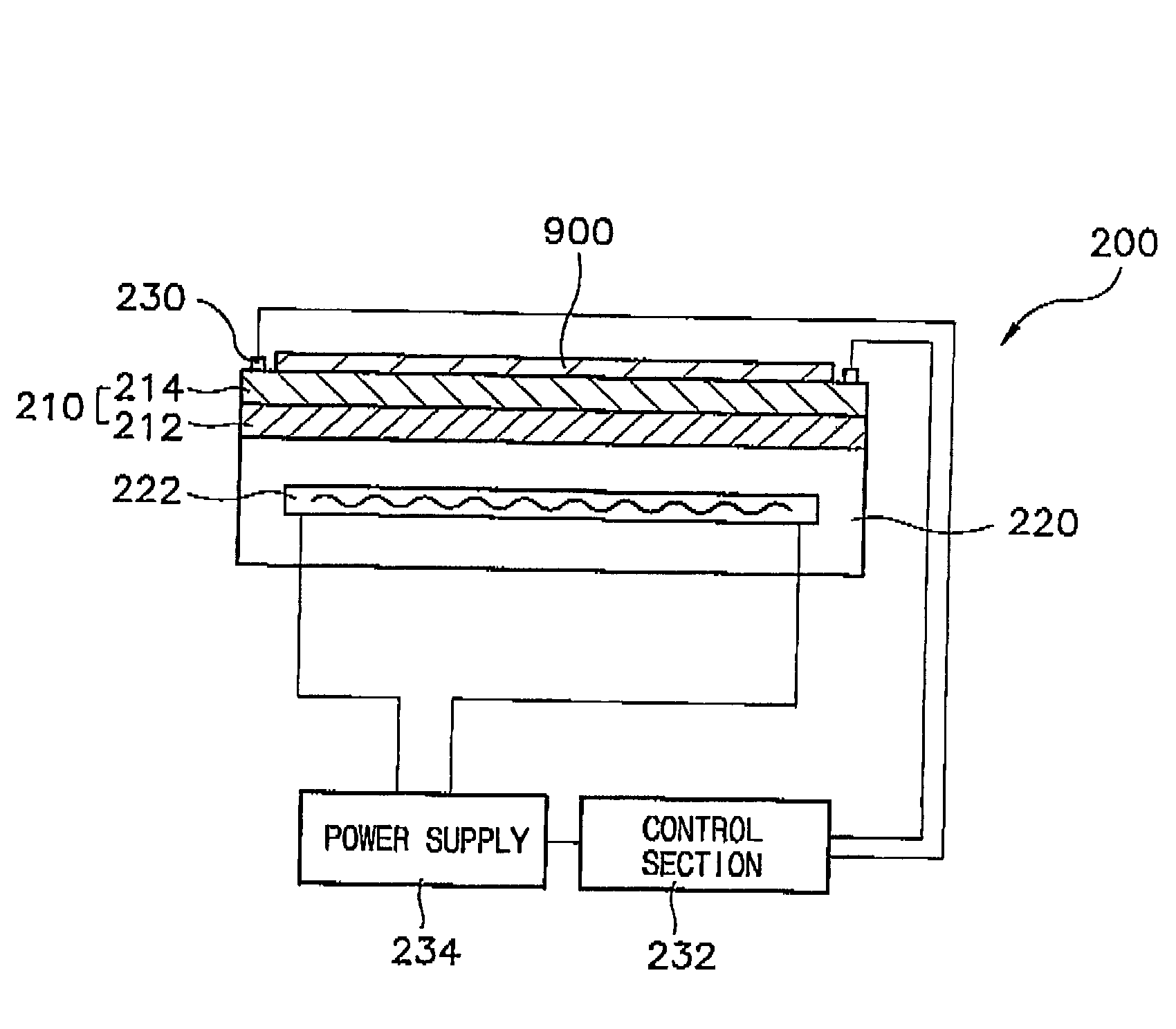
A method of forming a metal layer having excellent thermal and oxidation resistant characteristics using atomic layer deposition is provided. The metal layer includes a reactive metal (A), an element (B) for the amorphous combination between the reactive metal (A) and nitrogen (N), and nitrogen (N). The reactive metal (A) may be titanium (Ti), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), zirconium (Zr), hafnium (Hf), molybdenum (Mo) or niobium (Nb). The amorphous combination element (B) may be aluminum (Al), silicon (Si) or boron (B). The metal layer is formed by alternately injecting pulsed source gases for the elements (A, B and N) into a chamber according to atomic layer deposition to thereby alternately stack atomic layers. Accordingly, the composition ratio of a nitrogen compound (A-B-N) of the metal layer can be desirably adjusted just by appropriately determining the number of injection pulses of each source gas. According to the composition ratio, a desirable electrical conductivity and resistance of the metal layer can be accurately obtained. The atomic layers are individually deposited, thereby realizing excellent step coverage even in a complex and compact region. A metal layer formed by atomic layer deposition can be employed as a barrier metal layer, a lower electrode or an upper electrode in a semiconductor device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
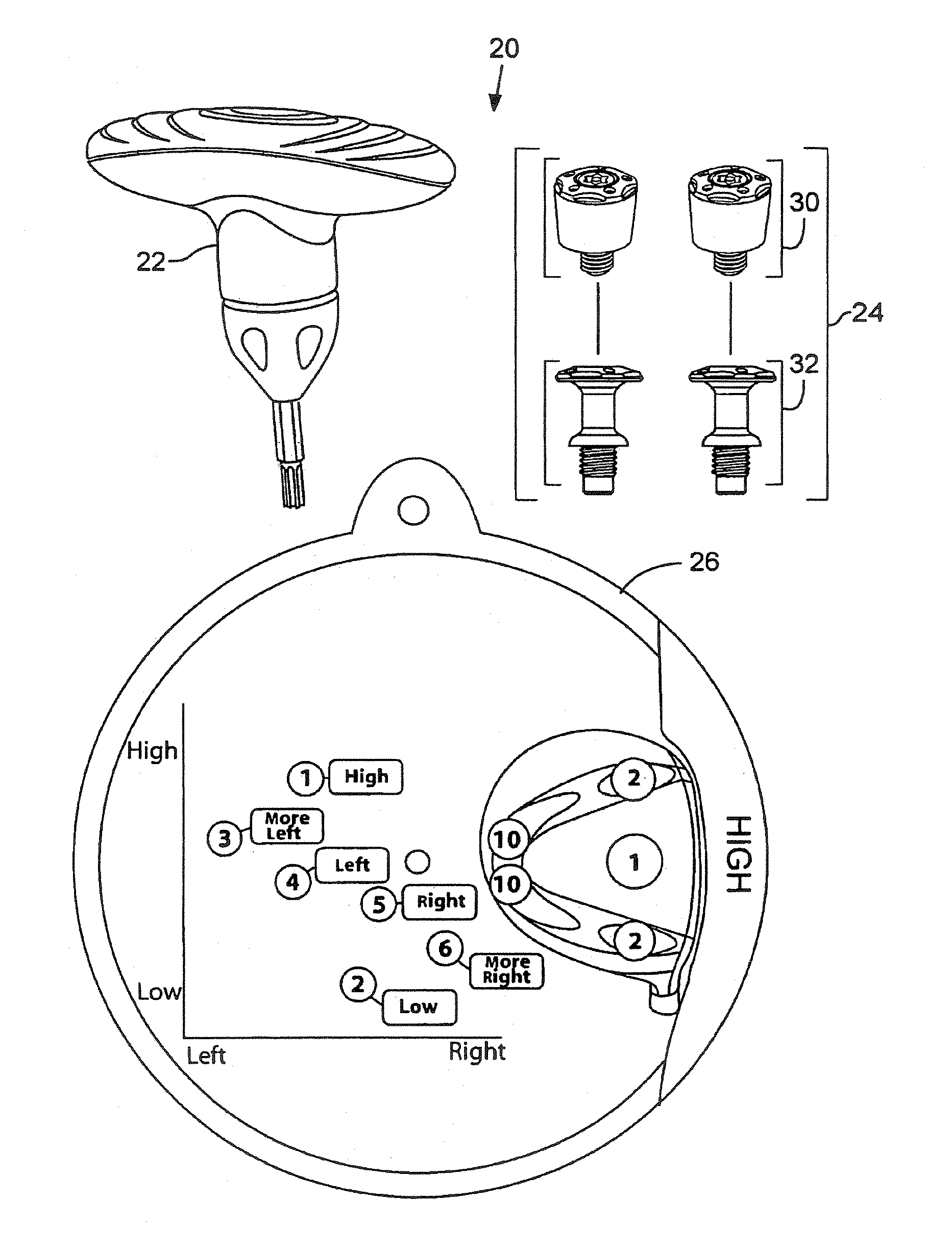
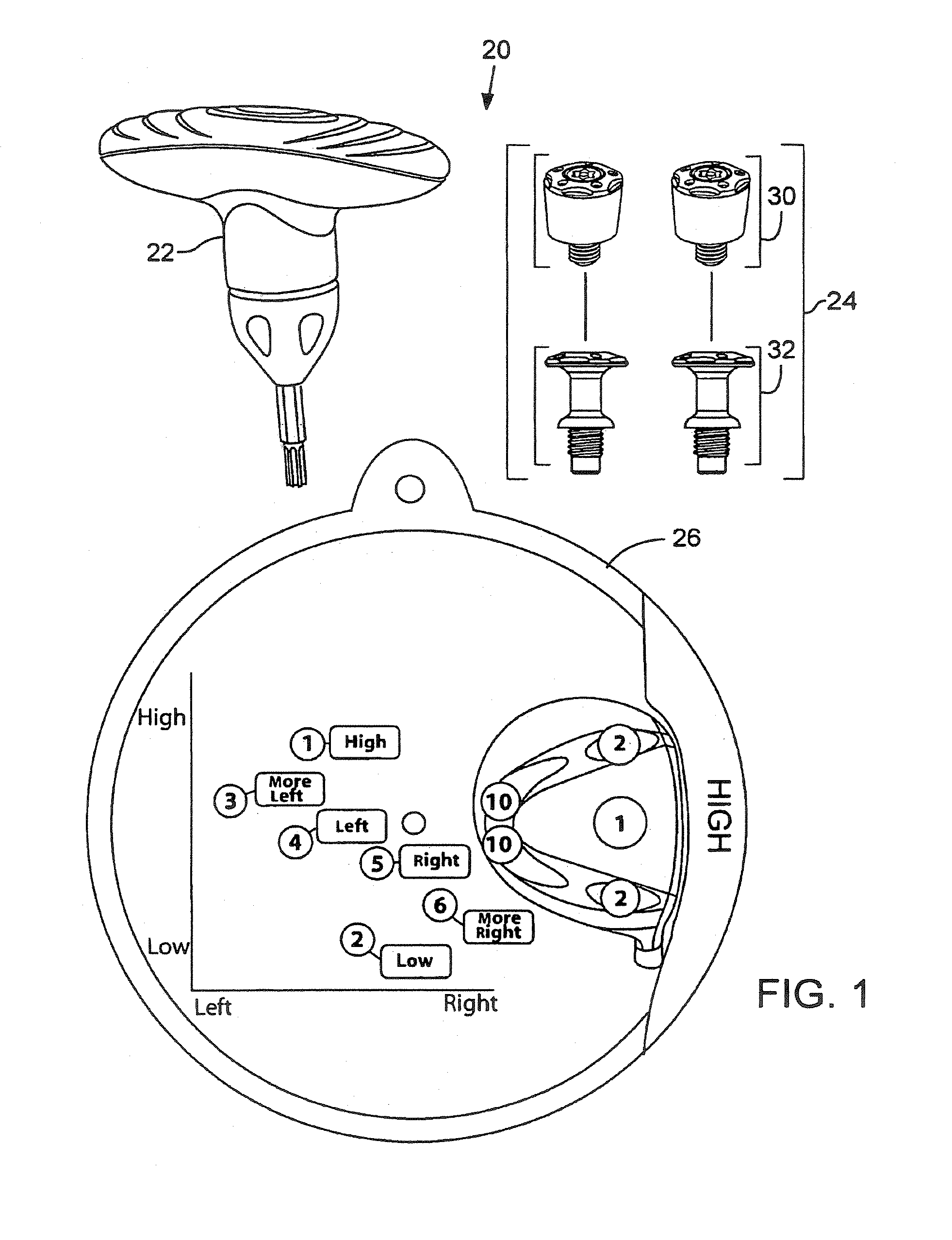
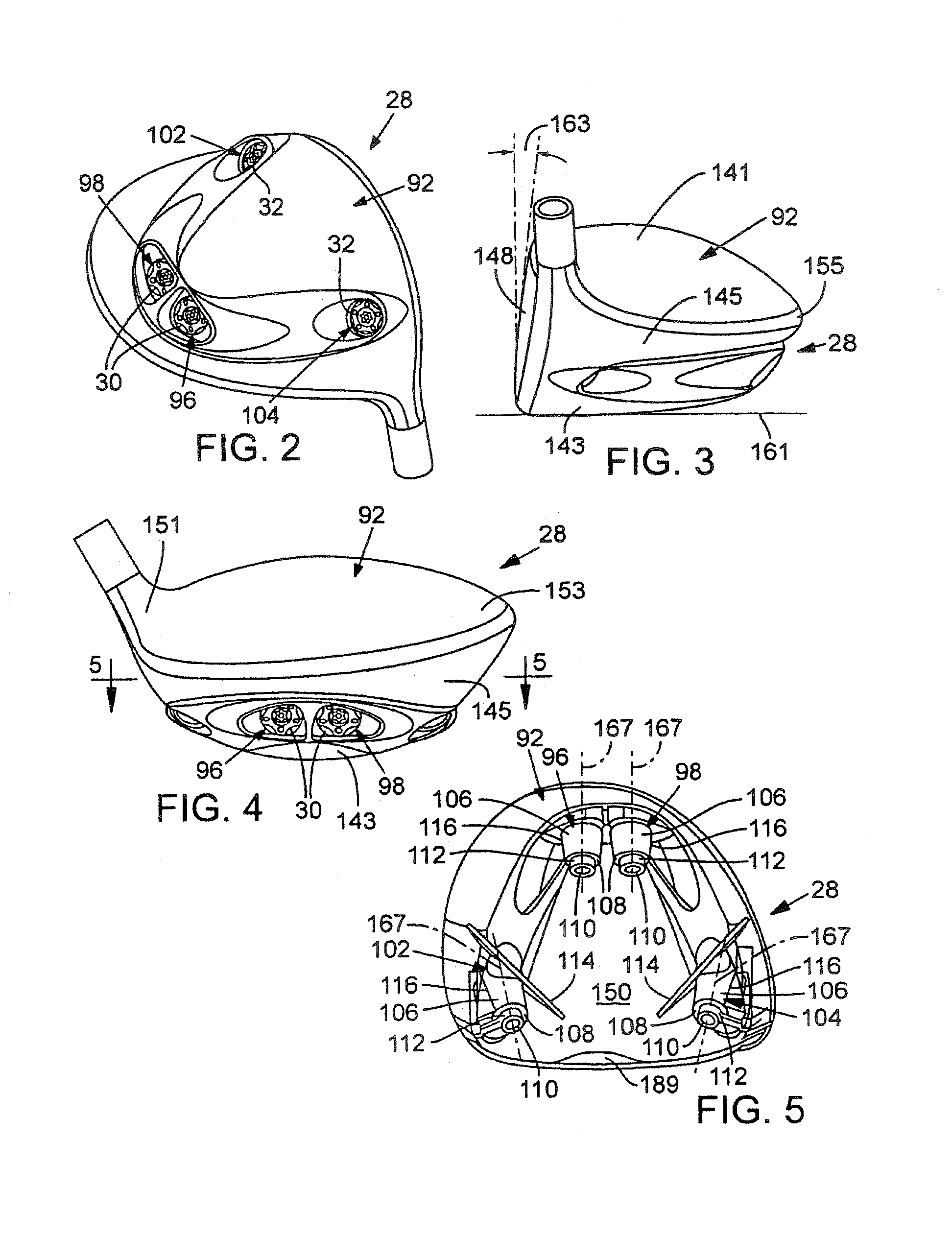
Removable weight and kit for golf club head
A weight for use with a golf club head is provided. The golf club head defines a recess for receiving removable weights, and a threaded opening in a wall of each recess. The weight comprises titanium and has a total mass between about 1 gram and about 2 grams. In addition, the weight comprises a head and a threaded body. The head defines a socket for receiving an engagement end of a tool, and is configured to substantially conform to a recess of the club head. The threaded body, extends from the head and is configured to cooperatively engage the threaded opening of the club head. The threaded body also has an annular ledge, located in an intermediate region of the threaded body, which has a diameter greater than that of a threaded portion of the body.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
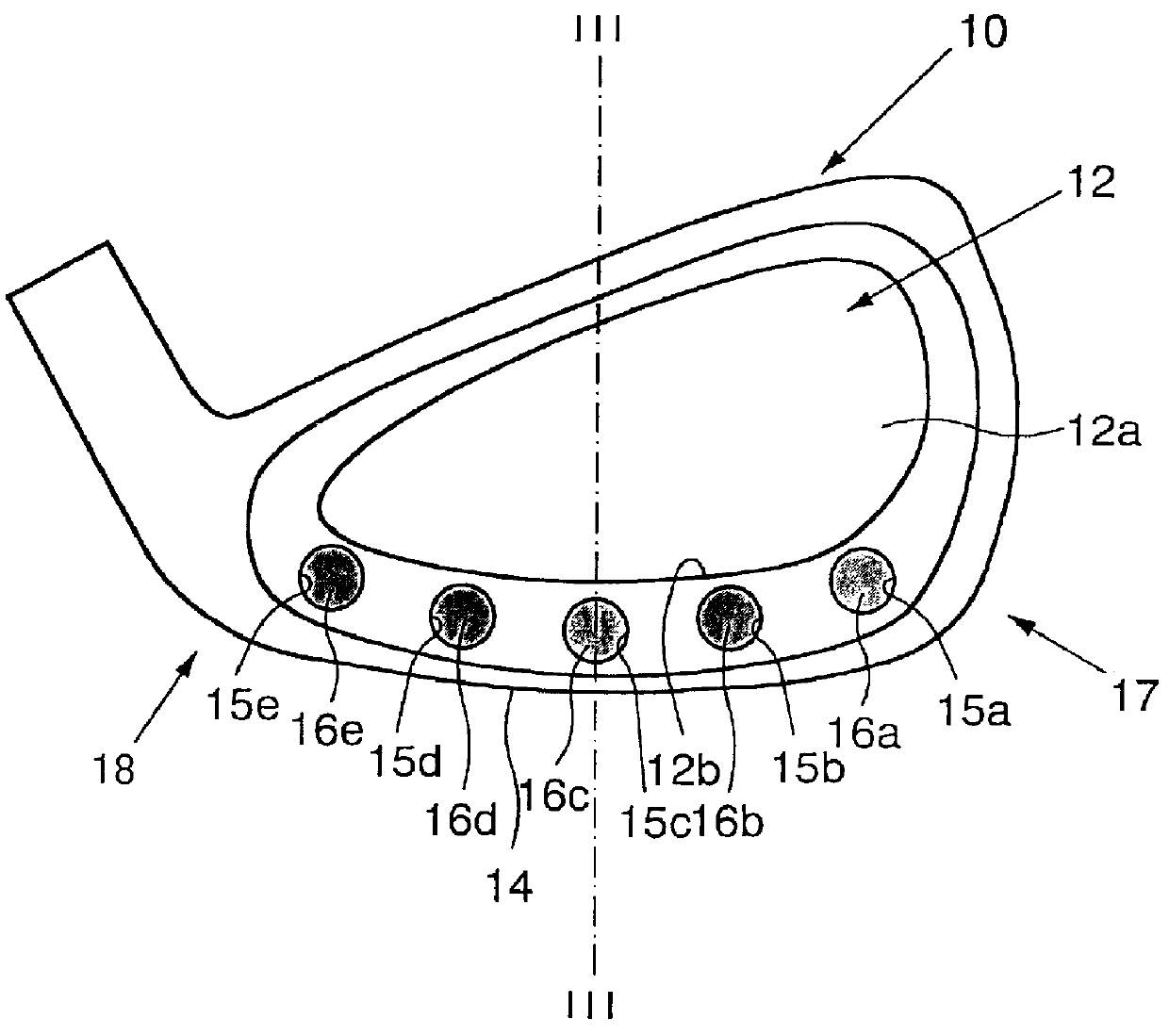
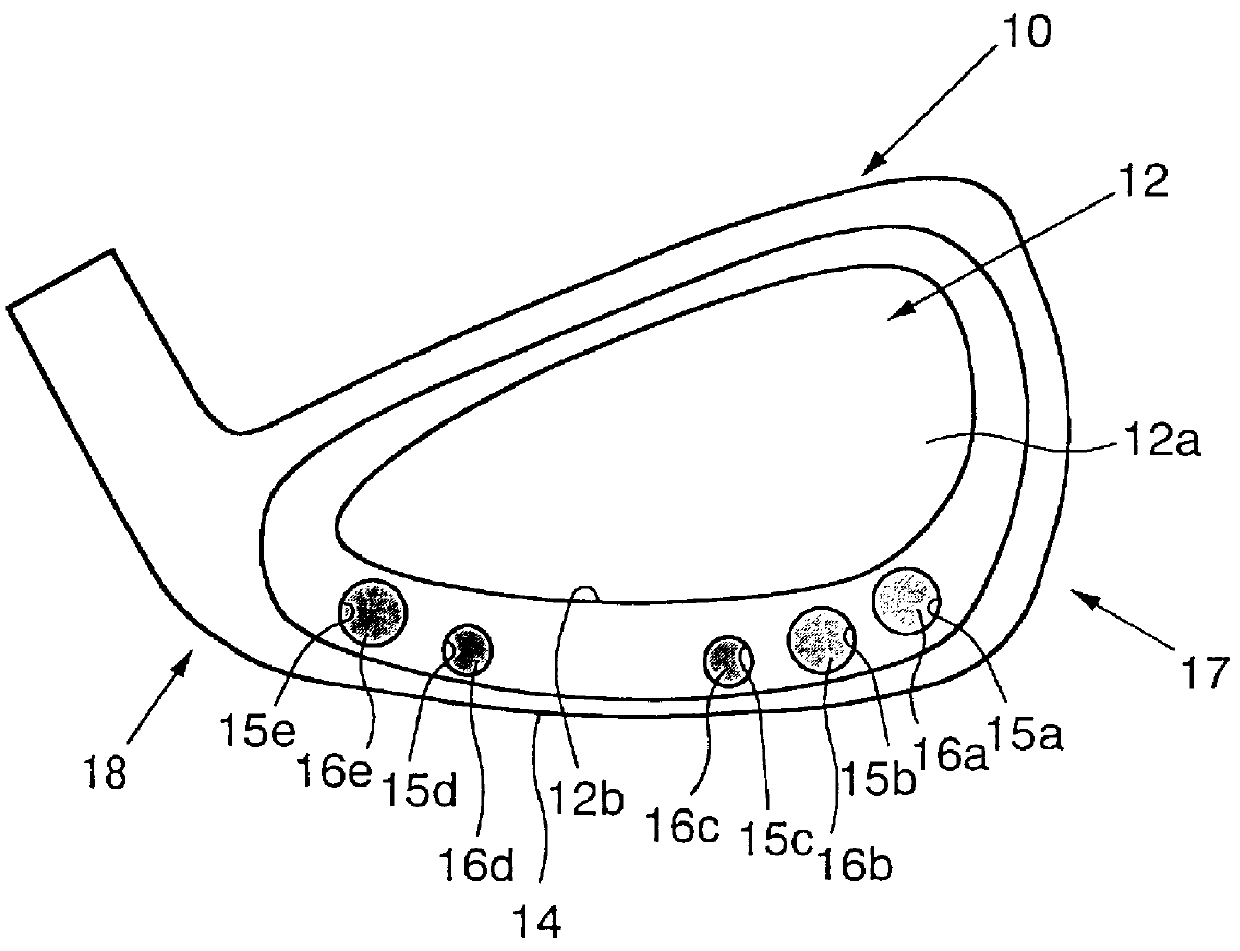
Iron golf club head including weight members for adjusting center of gravity thereof
An iron golf club head comprised of a head body 10 made of light metal such as titanium and containing a plurality of weight members 16. The head body 10 includes a front surface 13, a rear surface 13a, a cavity 12 disposed at the rear surface 13a, and a plurality of holes 15 disposed in the head body 10 at the rear surface 13a between a lower side wall 12b of the cavity 12 and a sole 14 of the head body 10 at predetermined intervals between a toe part 17 and a heel part 18. The center axis of each hole 15 is oriented substantially parallel to the sole 14 of the head body 10. The weight members 16 are press-inserted into the holes 15 in a direction going toward the front surface 13 of the head body 10 to a predetermined depth. Each weight member 16 is made of a material having a heavier specific weight than the light metal used for the aforesaid head body 10. Tungsten or tungsten alloy can be used as the material for the weight members 16. The combined weight of the weight members 16 does not exceed forty percent of the weight of the entire head.
Owner:YONEX CO LTD
Multilayer multicomponent high-k films and methods for depositing the same
InactiveUS20060264066A1Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricNitrogen
The present invention provides systems and methods for forming a multi-layer, multi-component high-k dielectric film. In some embodiments, the present invention provides systems and methods for forming high-k dielectric films that comprise hafnium, titanium, oxygen, nitrogen, and other components. In a further aspect of the present invention, the dielectric films are formed having composition gradients.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
Ampoule with a thermally conductive coating
ActiveUS20080149031A1Improve temperature uniformityChemical vapor deposition coatingConductive coatingCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention provide an apparatus and a process for generating a chemical precursor used in a vapor deposition processing system. The apparatus includes a canister (e.g., ampoule) having a sidewall, a top, and a bottom encompassing an interior volume therein, inlet and outlet ports in fluid communication with the interior volume, and a thermally conductive coating disposed on or over the outside surface of the canister. The thermally conductive coating is more thermally conductive than the outside surface of the canister. The thermally conductive coating may contain aluminum, aluminum nitride, copper, brass, silver, titanium, silicon nitride, or alloys thereof. In some embodiments, an adhesion layer (e.g., titanium or tantalum) may be disposed between the outside surface of the canister and the thermally conductive coating. In other embodiments, the canister may contain a plurality of baffles or solid heat-transfer particles to help evenly heat a solid precursor therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Solar cell and method of manufacture
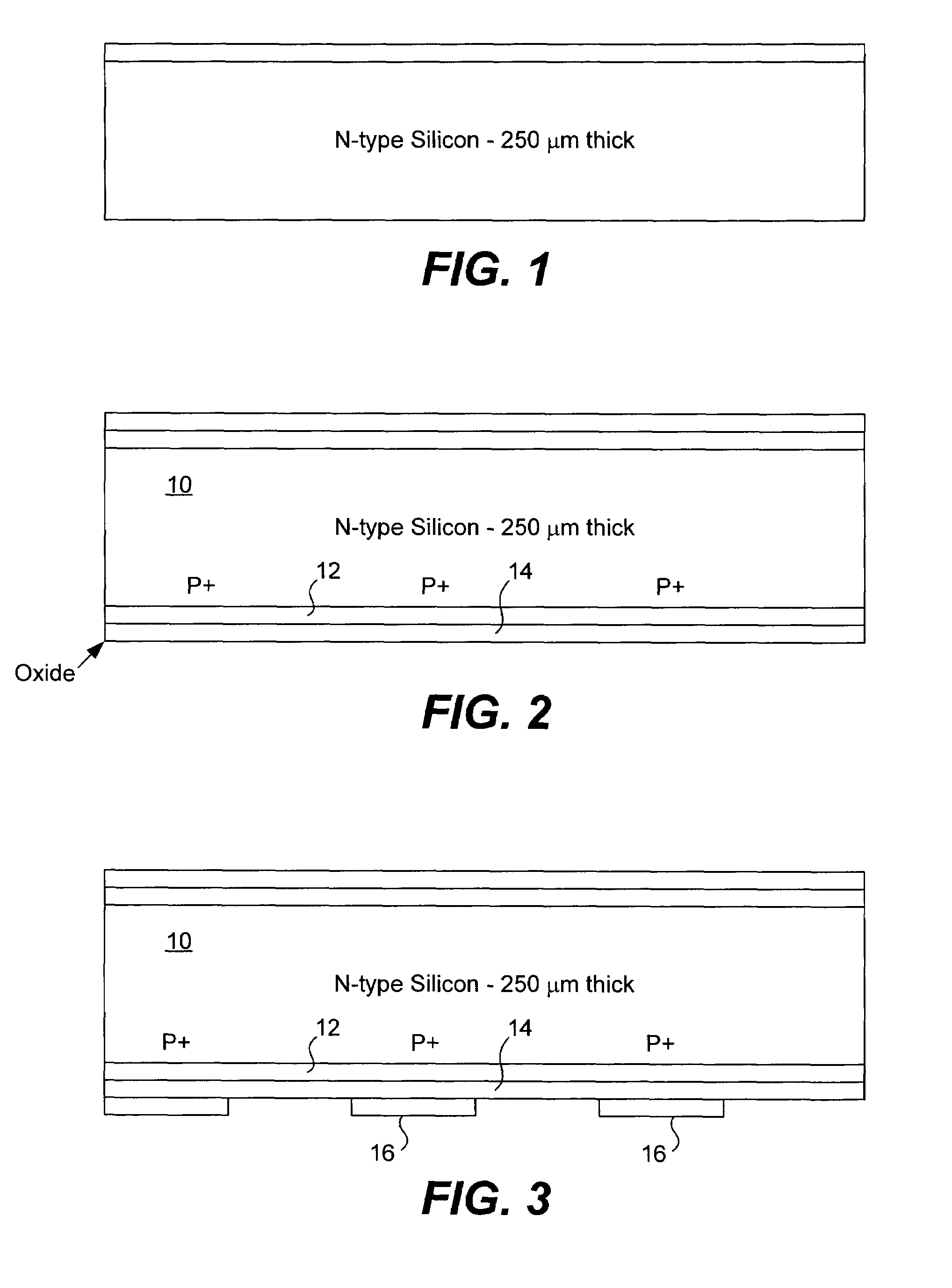
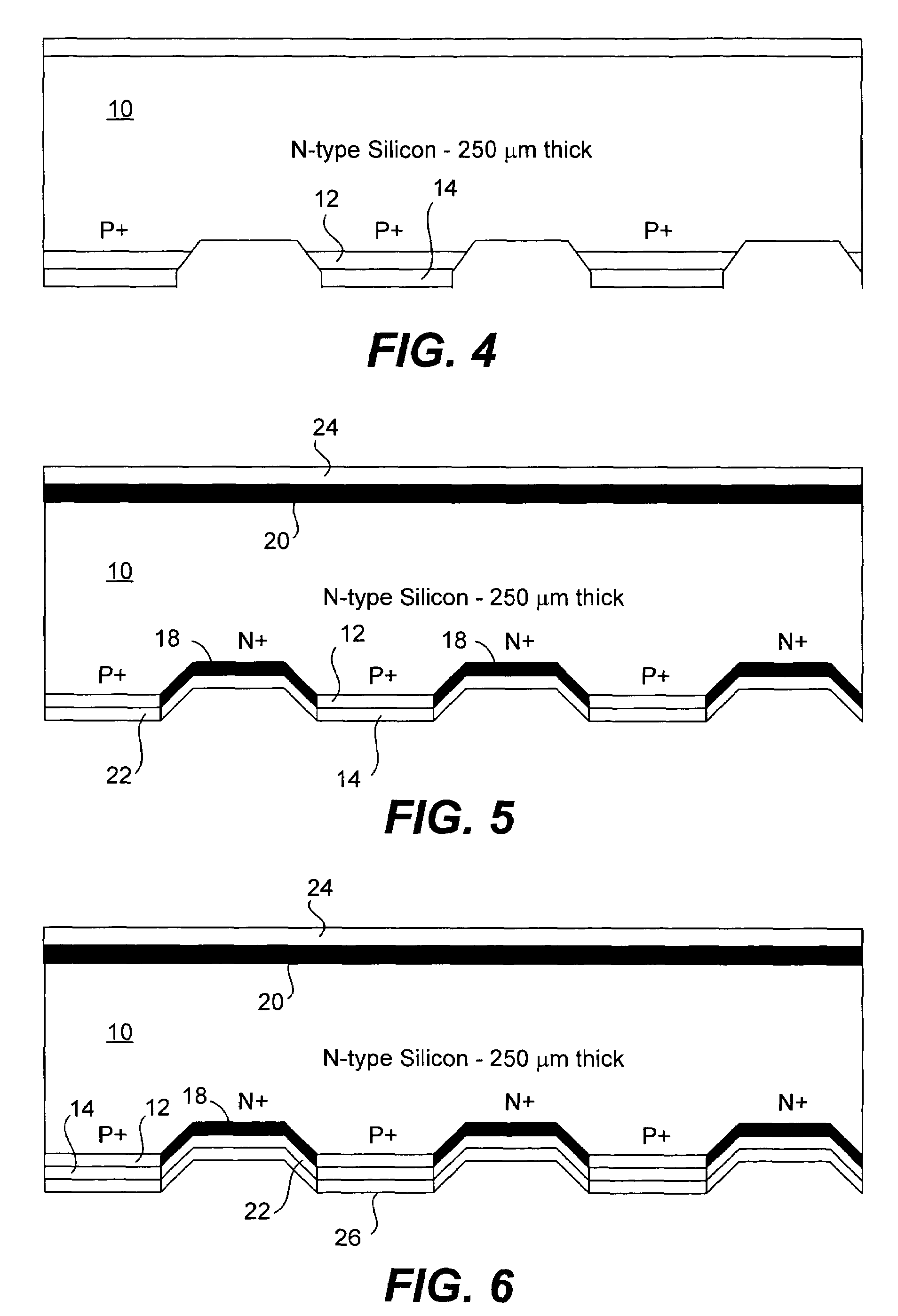
ActiveUS7339110B1Easy to manufactureLess expensiveFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSilicon oxide
A solar cell that is readily manufactured using processing techniques which are less expensive than microelectronic circuit processing. In preferred embodiments, printing techniques are utilized in selectively forming masks for use in etching of silicon oxide and diffusing dopants and in forming metal contacts to diffused regions. In a preferred embodiment, p-doped regions and n-doped regions are alternately formed in a surface of the wafer in offset levels through use of masking and etching techniques. Metal contacts are made to the p-regions and n-regions by first forming a seed layer stack that comprises a first layer such as aluminum that contacts silicon and functions as an infrared reflector, second layer such titanium tungsten that acts as diffusion barrier, and a third layer functions as a plating base. A thick conductive layer such as copper is then plated over the seed layer, and the seed layer between plated lines is removed. A front surface of the wafer is preferably textured by etching or mechanical abrasion with an antireflection layer provided over the textured surface. A field layer can be provided in the textured surface with the combined effect being a very low surface recombination velocity.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD +1
Apparatus for processing a substrate including a heating apparatus
InactiveUS20030066826A1Drying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesProduction rateDevice material
An apparatus for heating a substrate of a semiconductor device includes a hot plate, on which a semiconductor substrate is placed, and a heater for heating the hot plate. The hot plate is preferably a composite plate including a plurality of plates having different thermal conductivities from each other. For example, a first plate adjacent to the heater can be made of aluminum, which has a relatively high thermal conductivity. A second plate, laminated on top of the first plate, can be made of titanium or stainless steel, which both have a thermal conductivity lower than aluminum. A composite hot plate as disclosed herein is better able to maintain a constant temperature and a uniform temperature distribution in order to more uniformly heat a substrate and to reduce an amount of energy required for the heating process. In addition, the reliability and productivity of the semiconductor device manufactured by the apparatus can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for preparing olefin polymerization ball type catalytic component and carrier
The spherical catalyst carrier is prepared with alcoholated magnesium chloride containing double-ether compound in emulsifying pelletizer. Liquid titanium halide compound is carried onto the spherical catalyst carrier to form spherical solid catalyst component in the presence of electron donor. In the X-ray diffraction spectrogram, the spherical solid catalyst component has diffraction peak in 13.3 deg of 2theta angle, strongest diffraction peak in 26.5 deg of 2theta angle and no characteristic diffraction peak of alpha-anhydrous MgCl2 in 15 deg of 2theta angle. The catalyst of the presentinvention has very high activity and may be used to produce polymer with good form, high apparent density and less fine powder. The catalyst is used in homopolymerization and copolymerization of olefin and suitable for various polymerization process.
Owner:YINGKOU XIANGYANG CATALYST
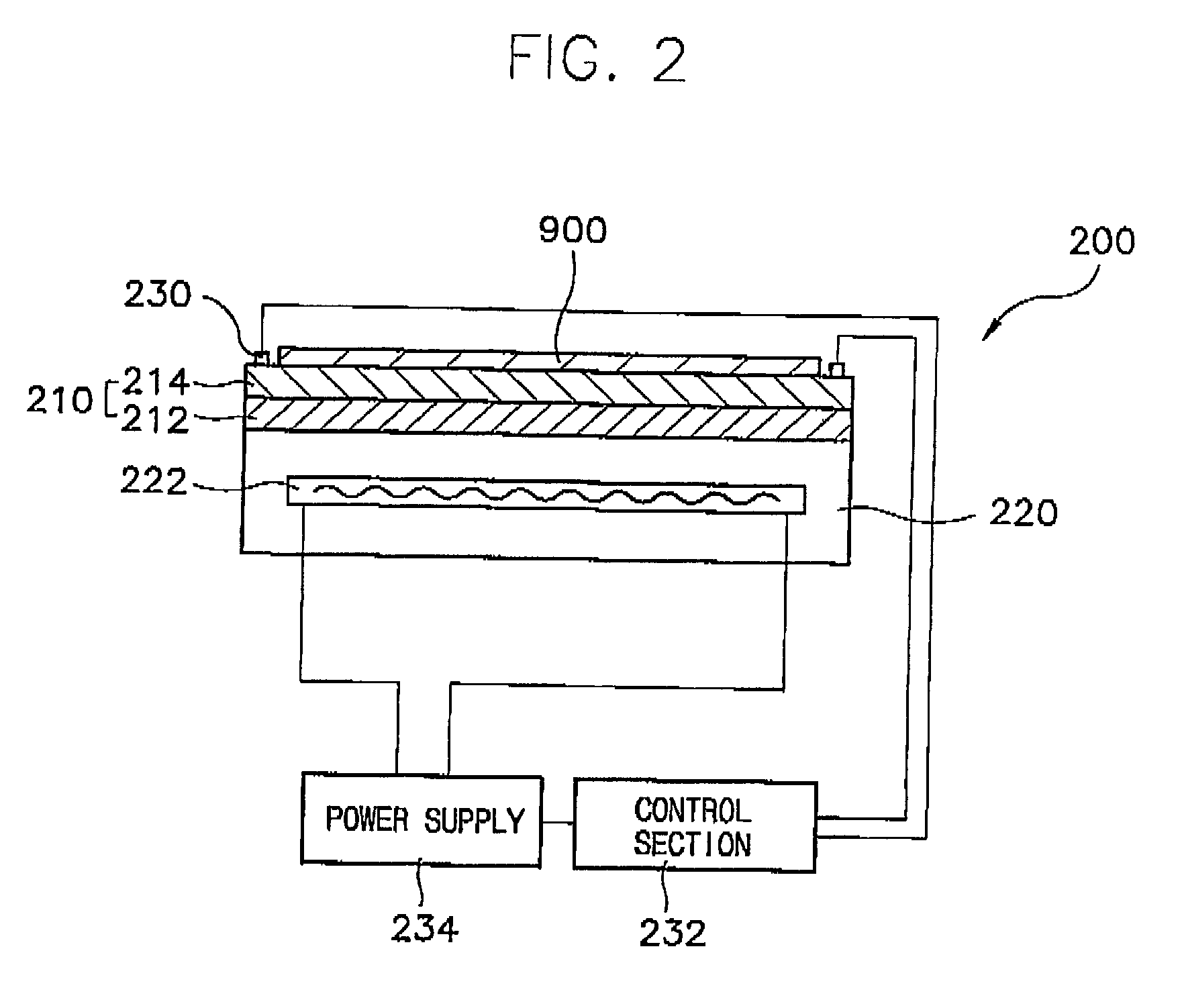
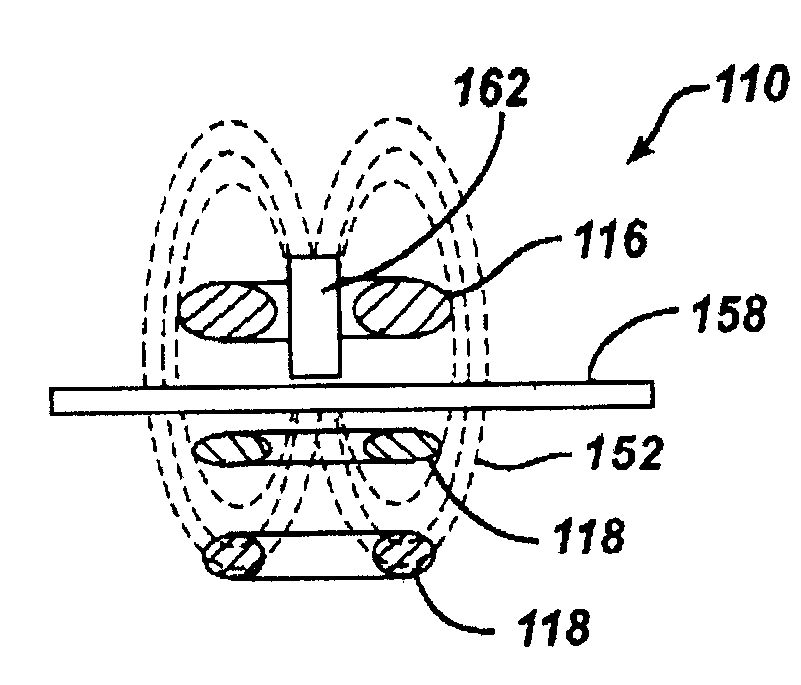
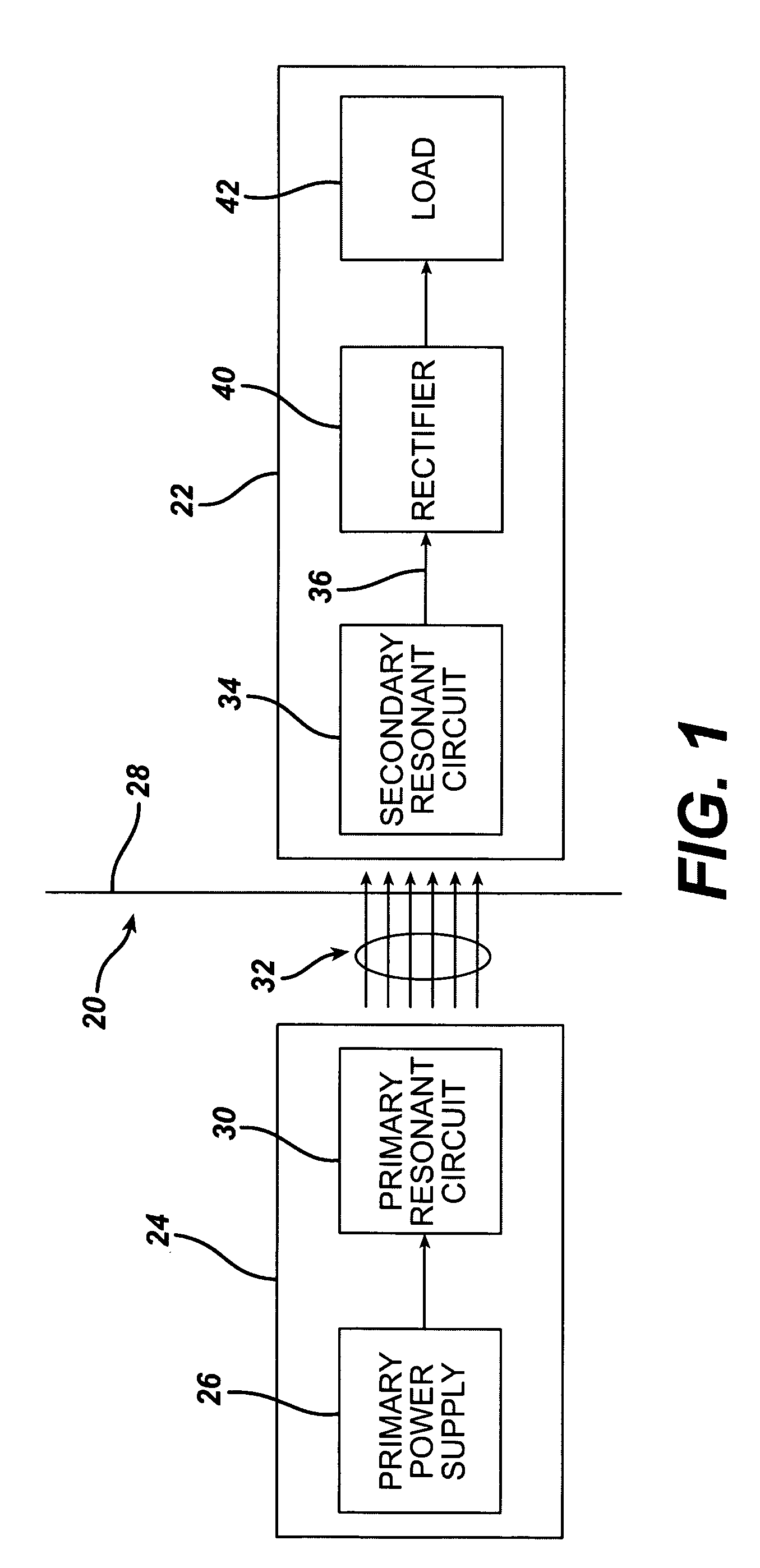
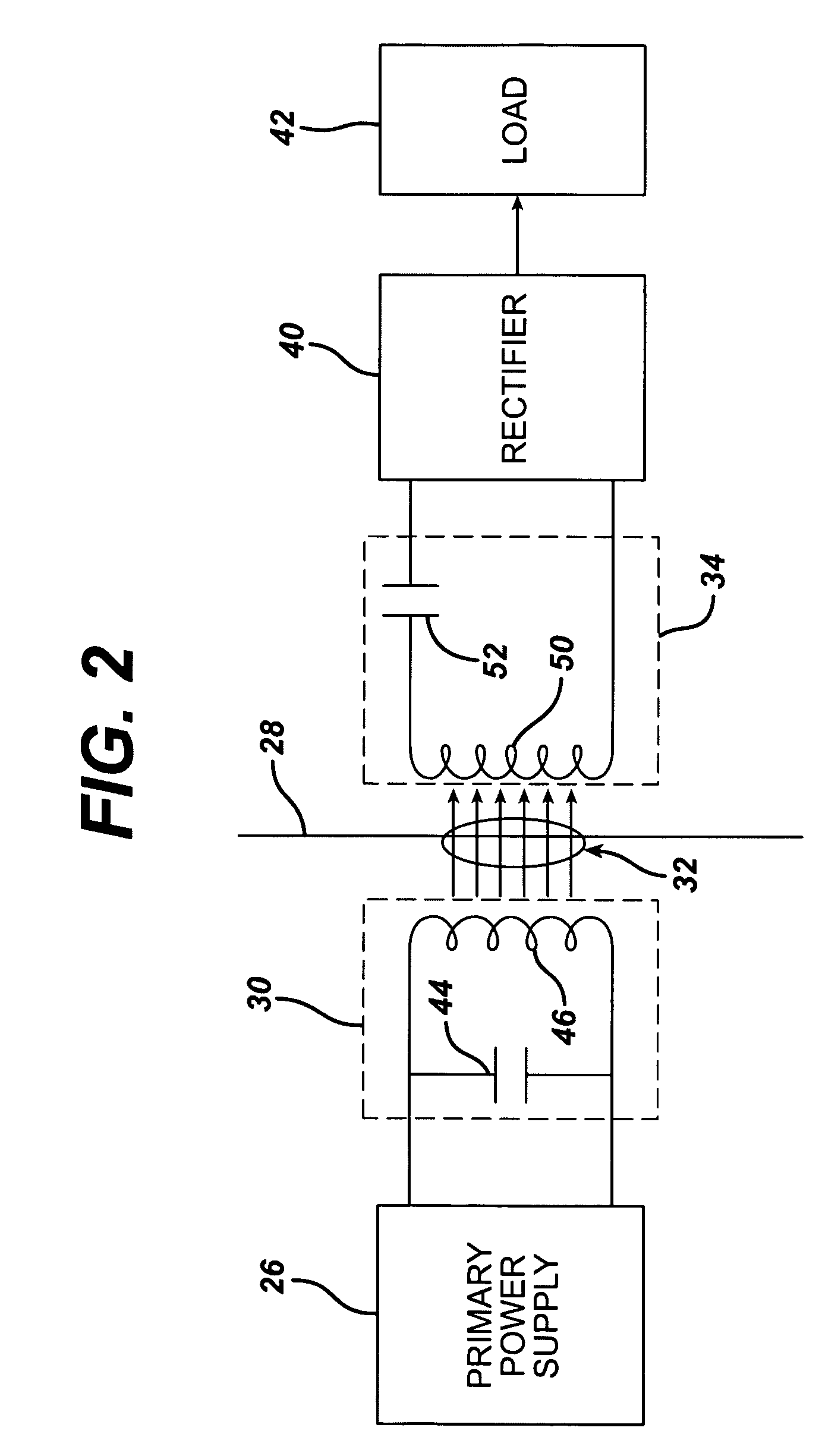
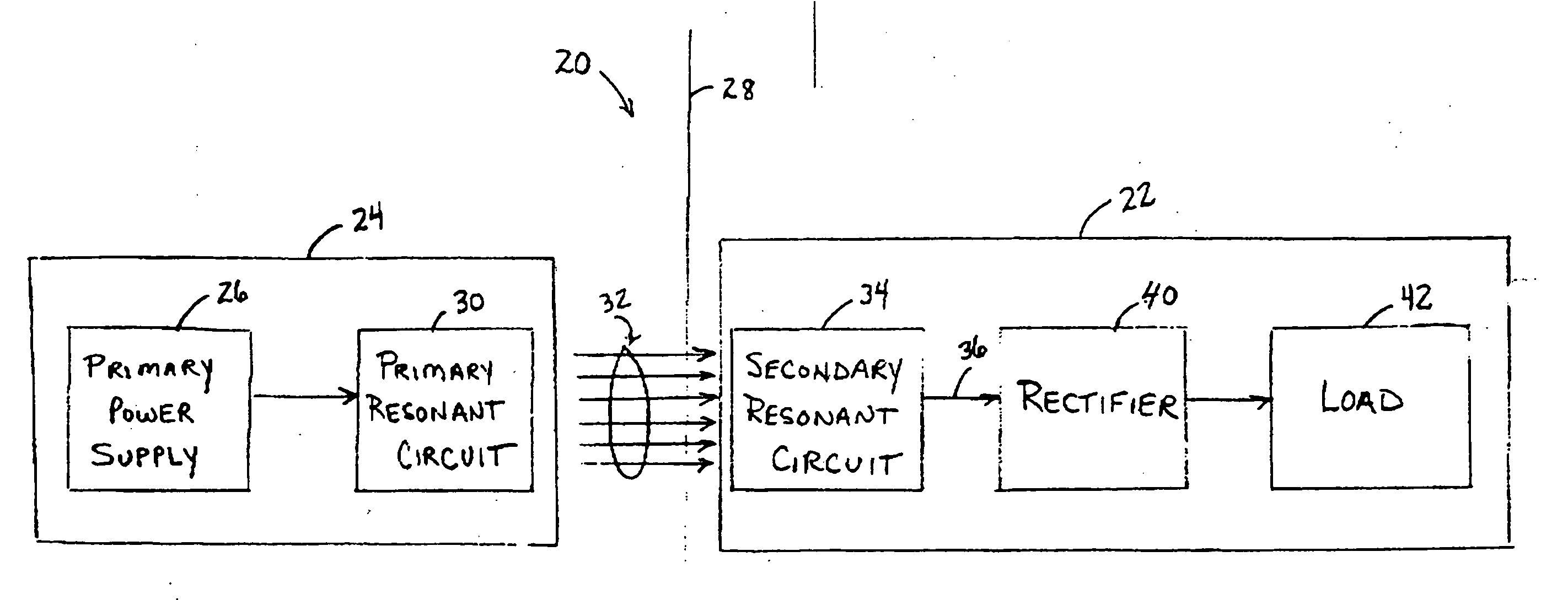
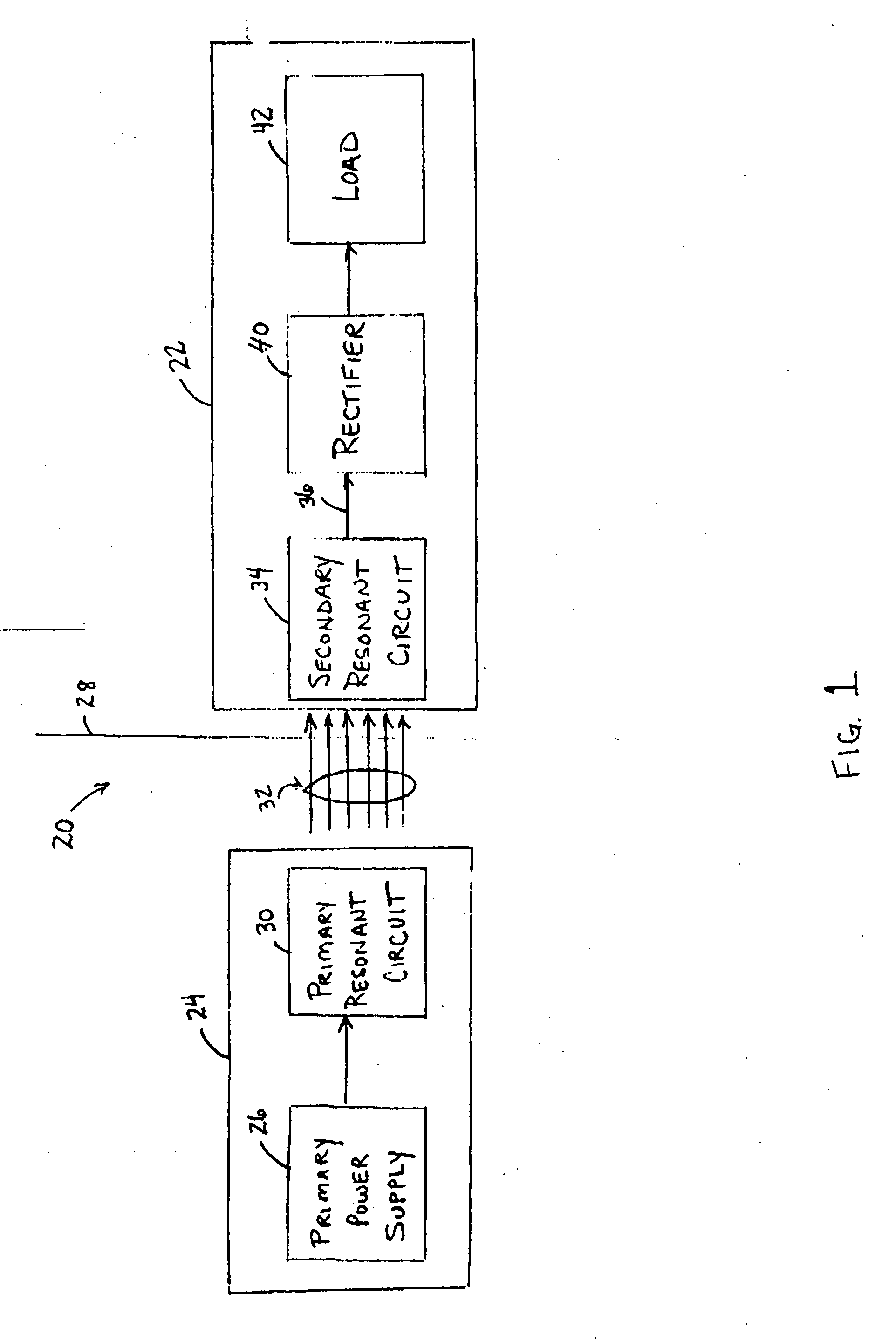
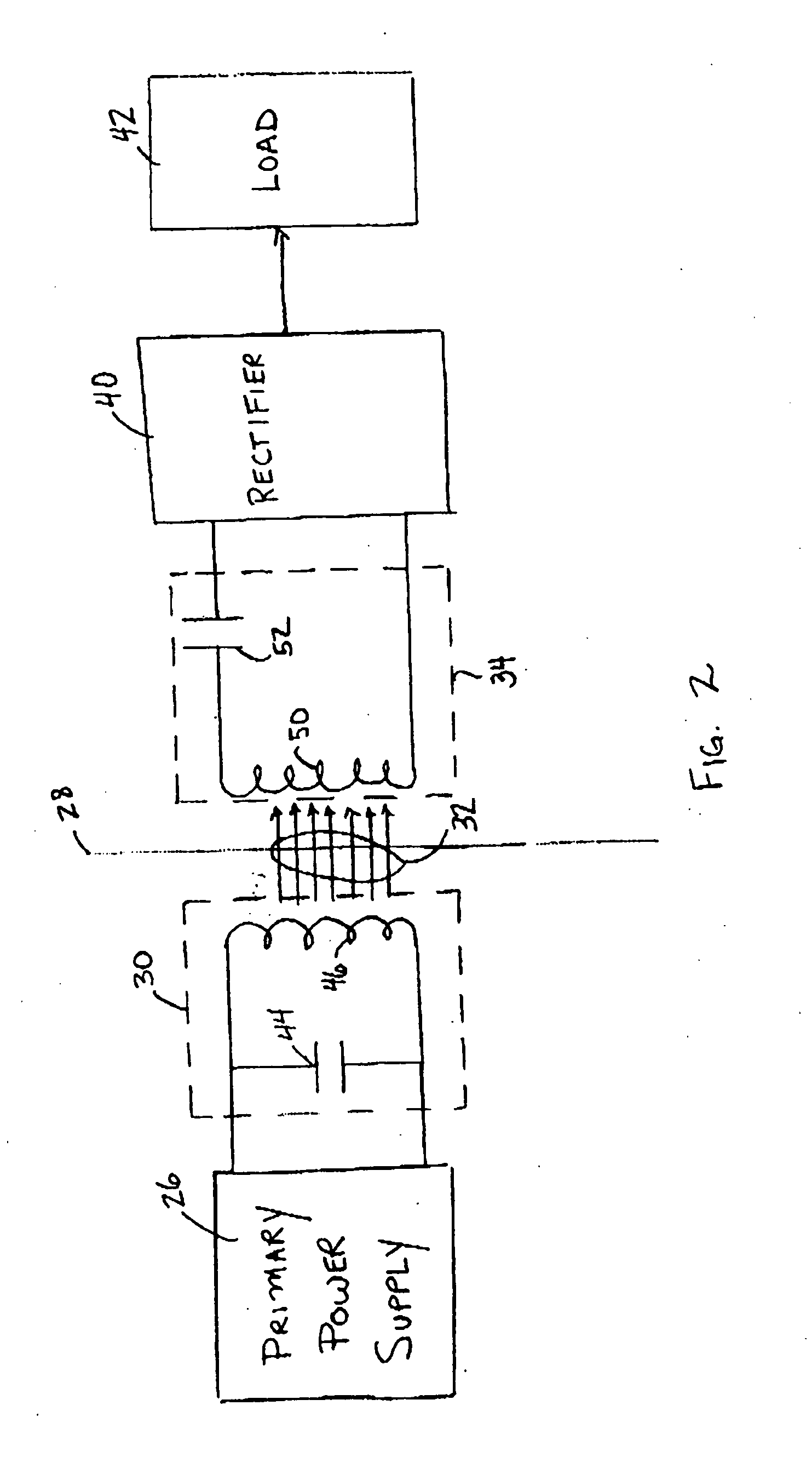
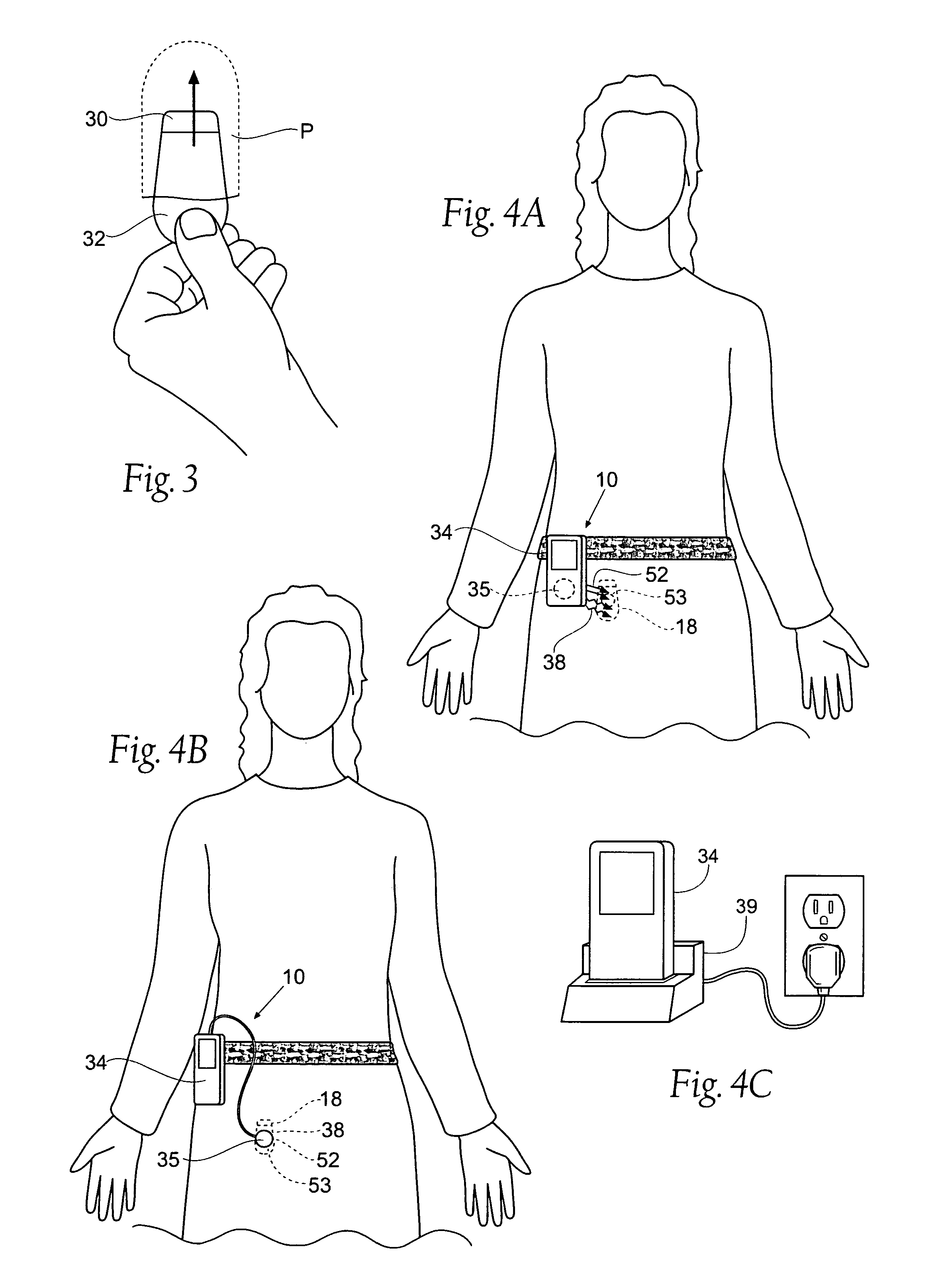
Low frequency transcutaneous energy transfer to implanted medical device
InactiveUS7599743B2Efficiently penetrate physical boundaryMore powerElectrotherapyAnti-incontinence devicesEnergy transferComputer module
An implantable medical device system advantageously utilizes low frequency (e.g., about 1-100 kHz) transcutaneous energy transfer (TET) for supplying power from an external control module to an implantable medical device, avoiding power dissipation through eddy currents in a metallic case of an implant and / or in human tissue, thereby enabling smaller implants using a metallic case such as titanium and / or allowing TET signals of greater strength thereby allowing placement more deeply within a patient without excessive power transfer inefficiencies.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
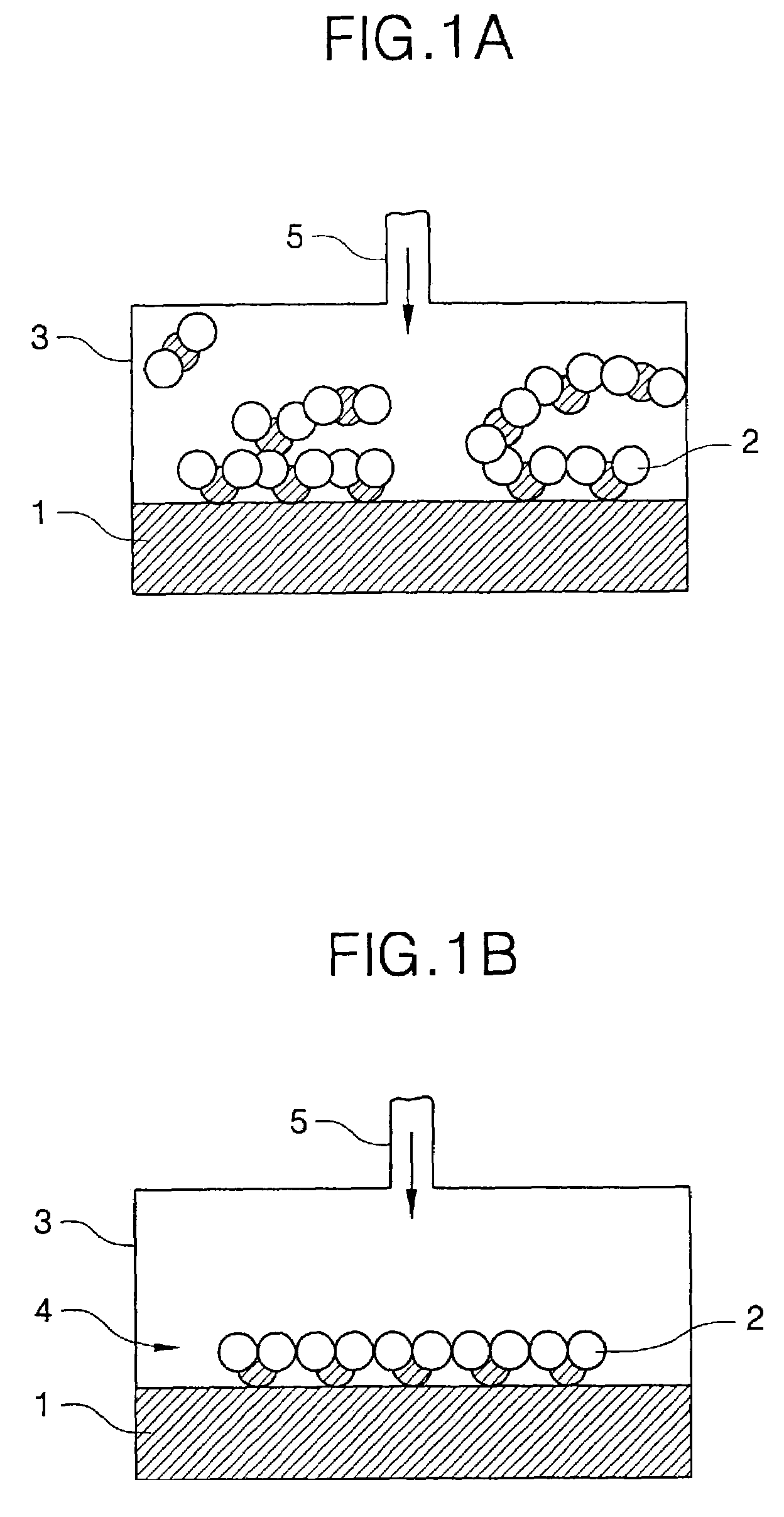
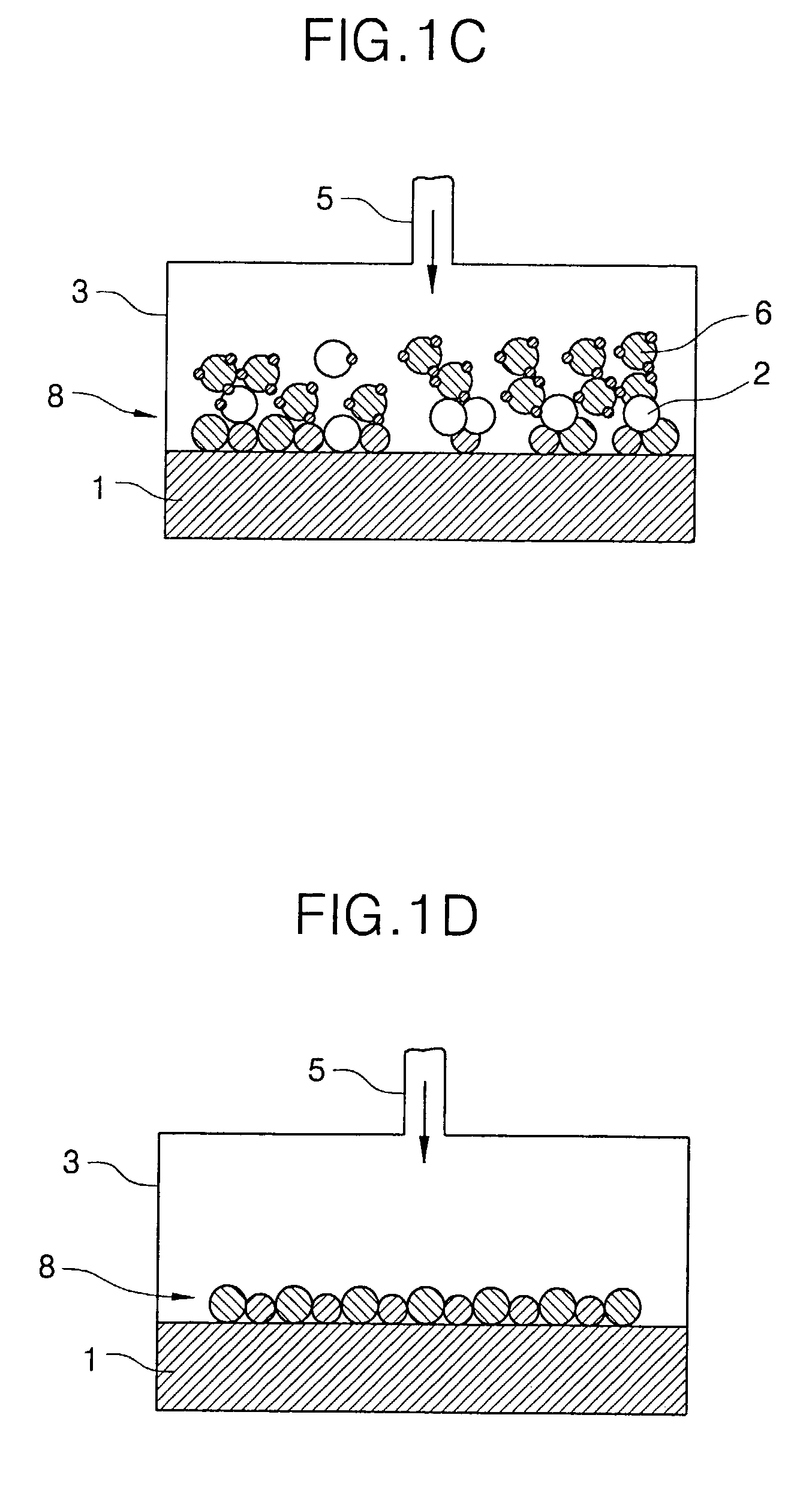
Method for Forming Ti-Containing Film by PEALD using TDMAT or TDEAT
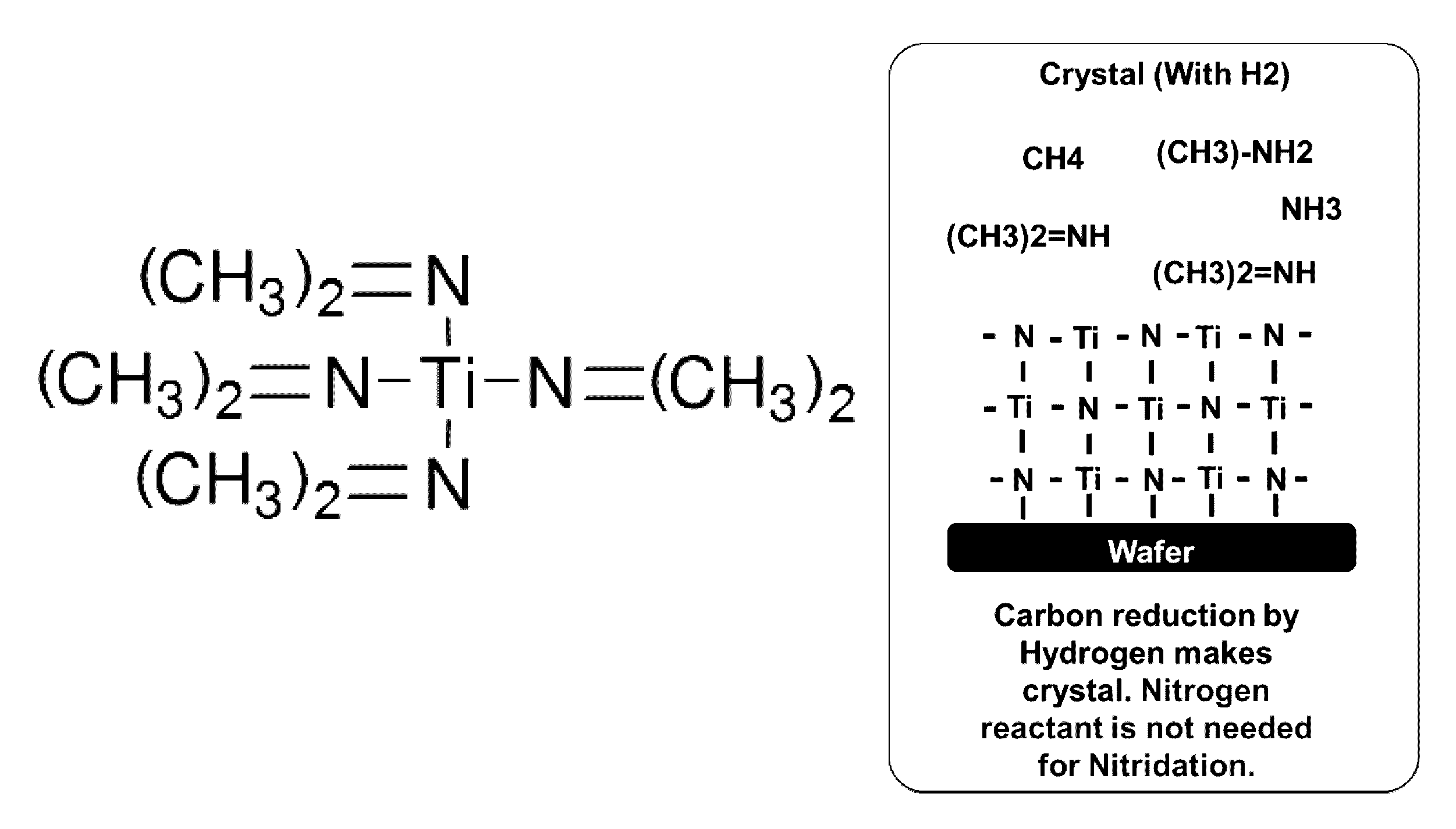
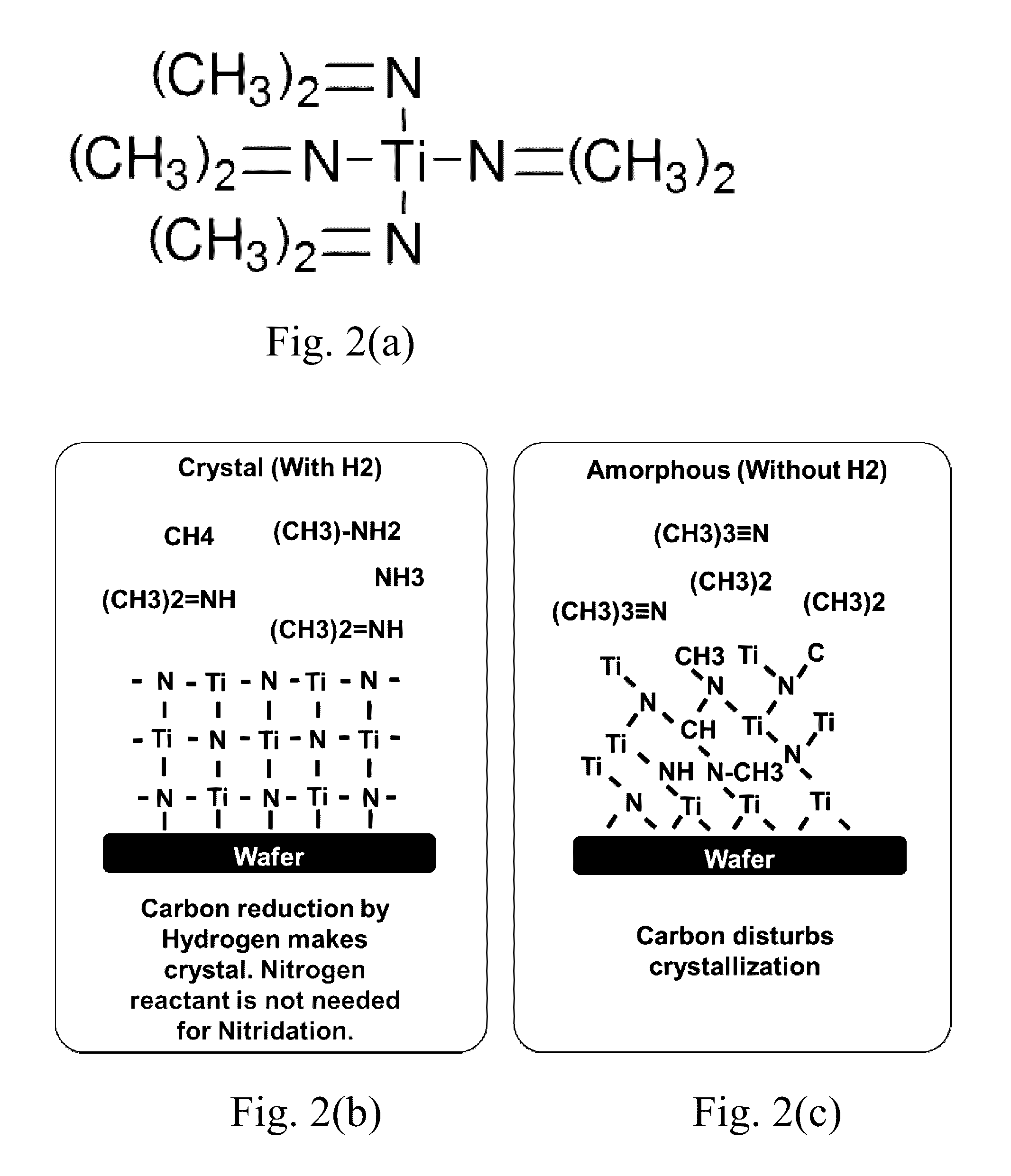
ActiveUS20150099072A1Enhance layeringQuality of filmChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueTitaniumAtomic layer deposition
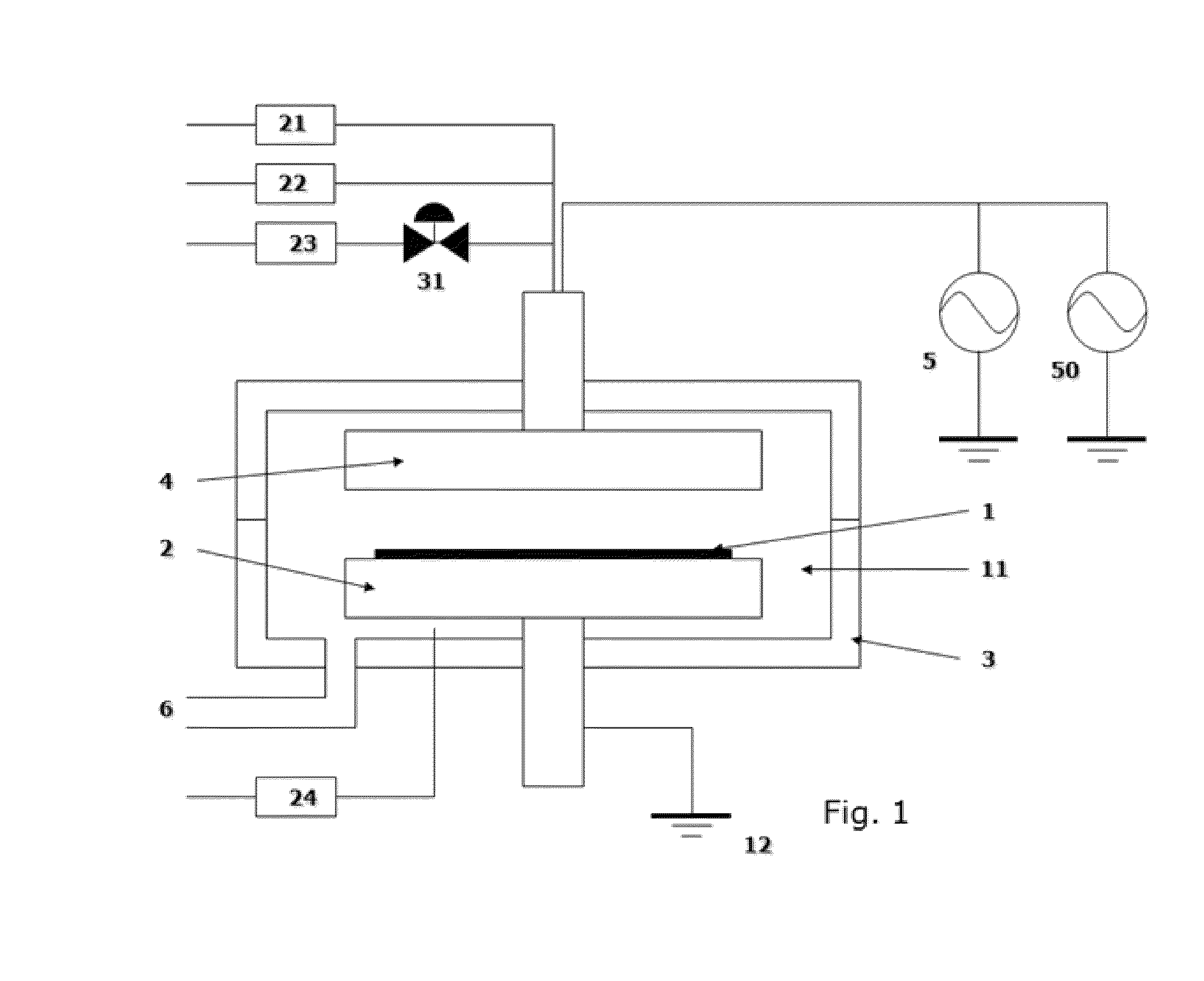
A method for forming a Ti-containing film on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium (TDMAT) or tetrakis(diethylamino)titanium (TDEAT), includes: introducing TDMAT and / or TDEAT in a pulse to a reaction space where a substrate is placed; continuously introducing a NH3-free reactant gas to the reaction space; applying RF power in a pulse to the reaction space wherein the pulse of TDMAT and / or TDEAT and the pulse of RF power do not overlap; and repeating the above steps to deposit a Ti-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
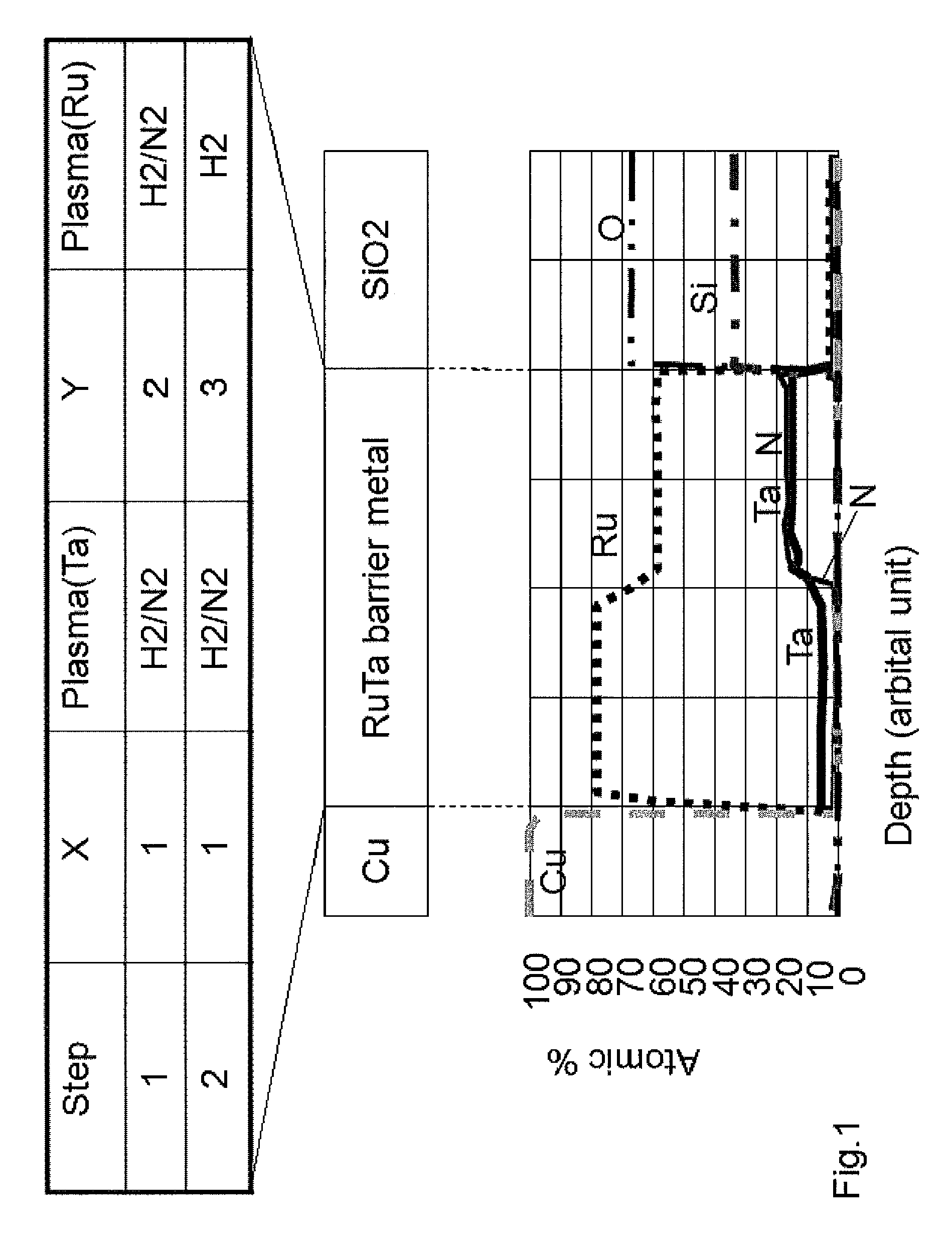
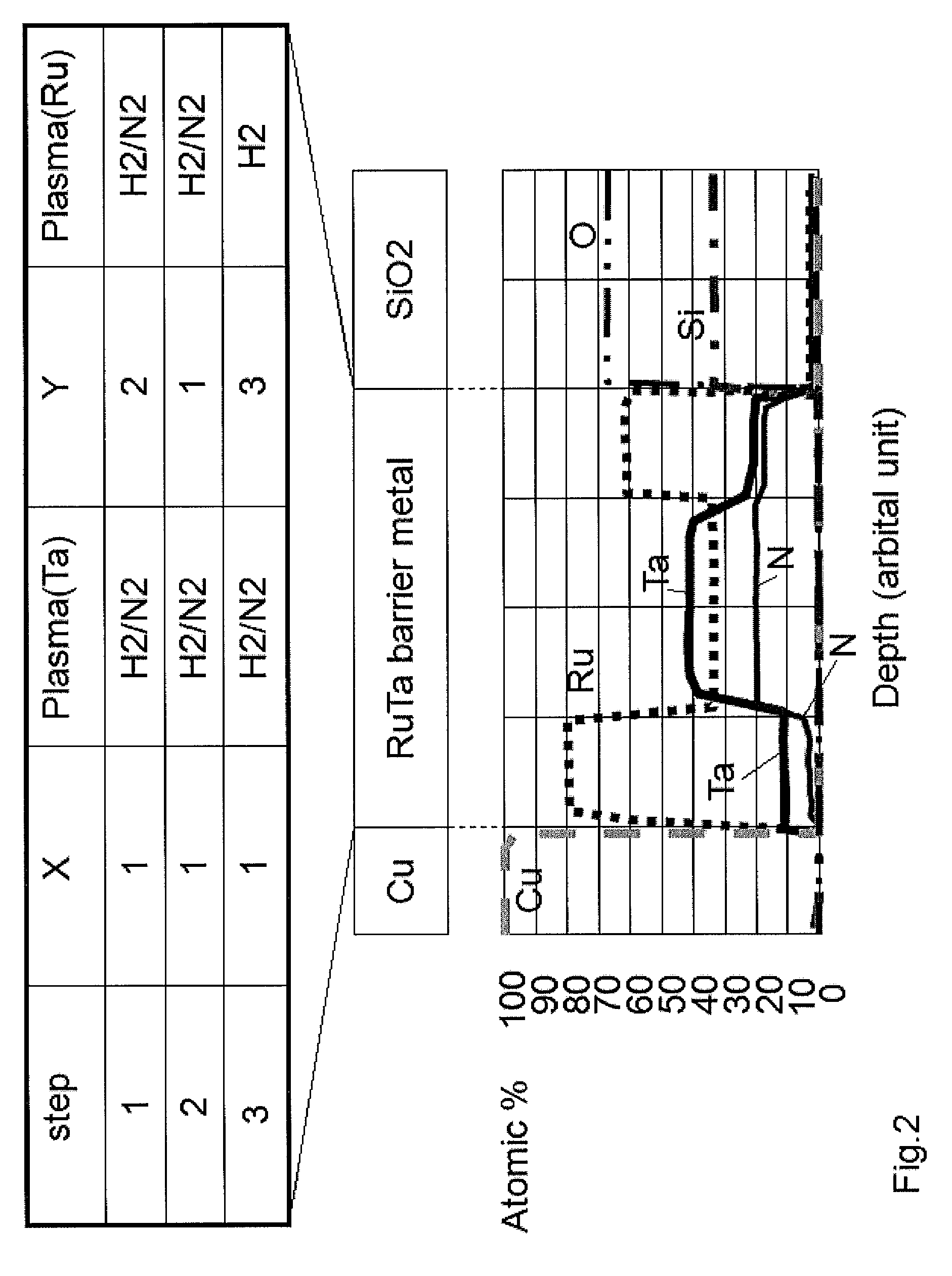
Atomic composition controlled ruthenium alloy film formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS8084104B2Reduce resistanceLow densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsRutheniumAlloy
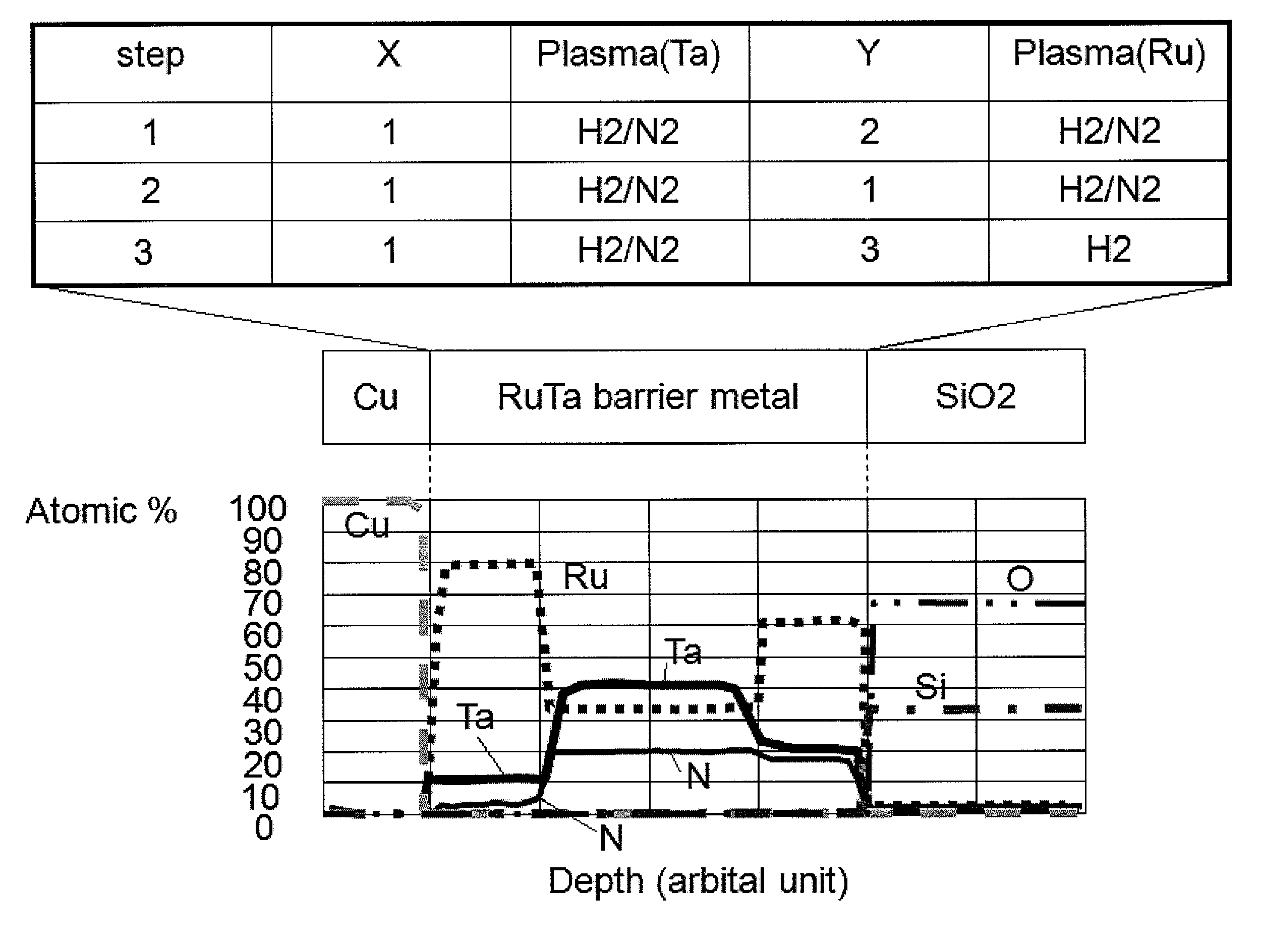
A metal film composed of multiple atomic layers continuously formed by atomic layer deposition of Ru and Ta or Ti includes at least a top section and a bottom section, wherein an atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N varies in a thickness direction of the metal film. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the top section is represented as Ru(x1)Ta / Ti(y1)N(z1) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x1) / (Ta / Ti(y1)) is no less than 15, and z1 is 0.05 or less. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the bottom section is represented as Ru(x2)Ta / Ti(y2)N(z2) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x2) / (Ta / Ti(y2)) is more than zero but less than 15, and z2 is 0.10 or greater.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
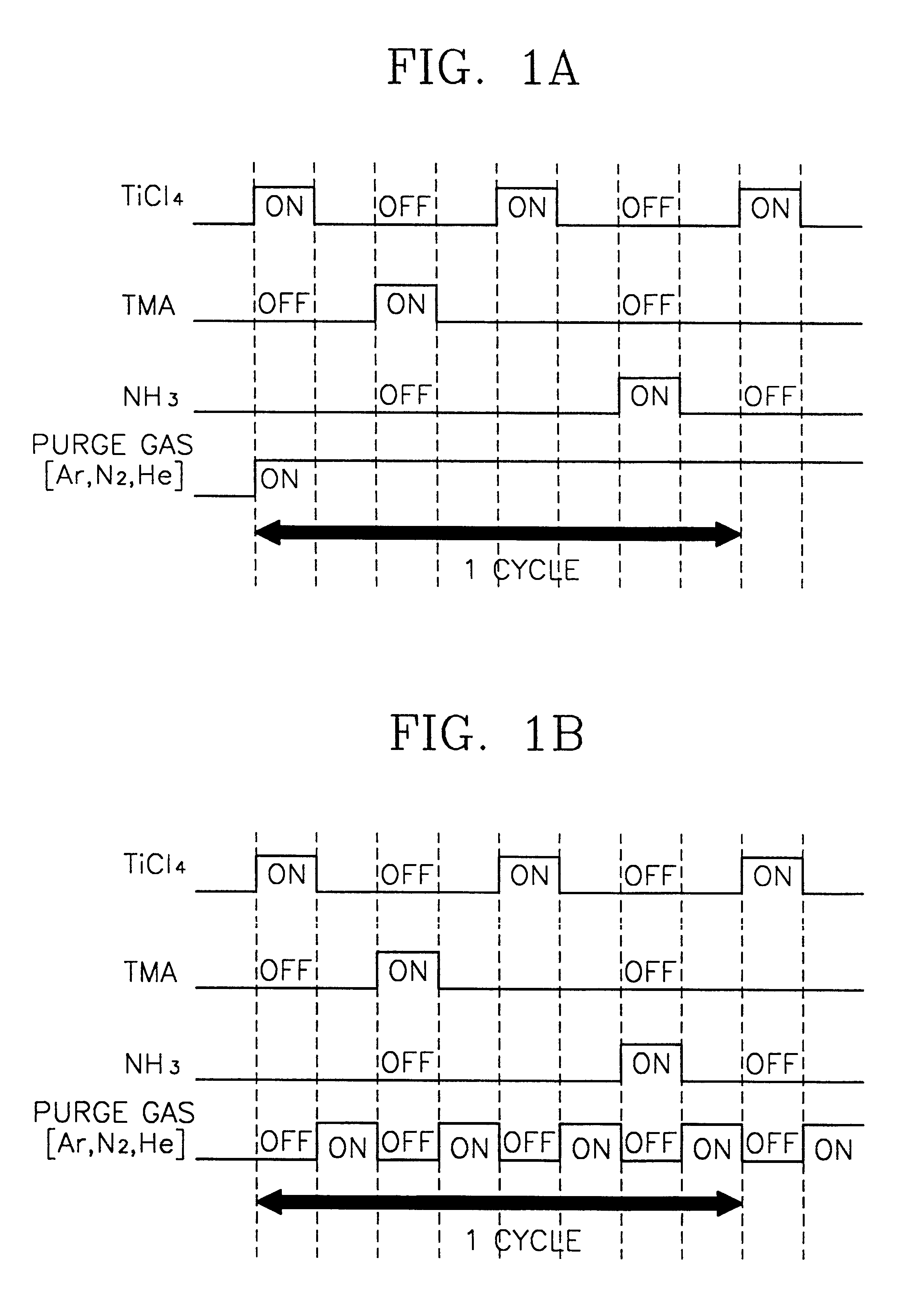
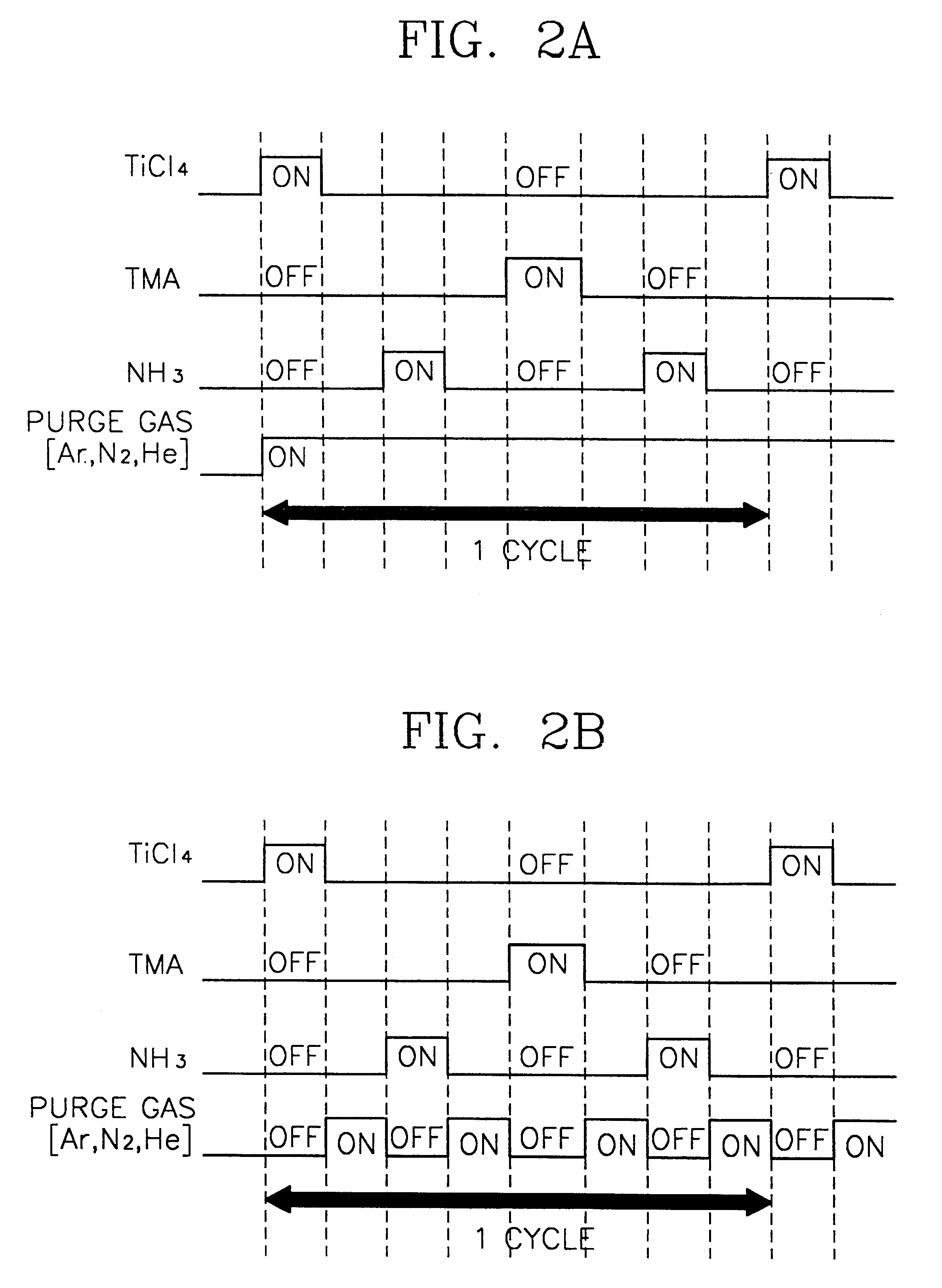
Methods of forming atomic layers of a material on a substrate by sequentially introducing precursors of the material
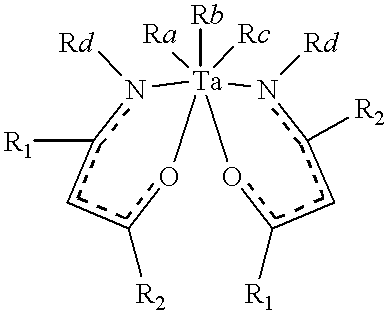
InactiveUS7201943B2Easy to integrateHigh dielectric constantVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricTitanium
A thin film is formed using an atomic layer deposition process, by introducing a first reacting material including tantalum precursors and titanium precursors onto a substrate. A portion of the first reacting material is chemisorbed onto the substrate. Then, a second reacting material including oxygen is introduced onto the substrate. A portion of the second reacting material is also chemisorbed onto the substrate, to form an atomic layer of a solid material on the substrate. The solid material may be used as a dielectric layer of the capacitor and / or a gate dielectric layer of the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of electroless plating copper on nitride barrier
InactiveUS6436816B1Insulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSolid-state devicesCopper platingElectroless deposition
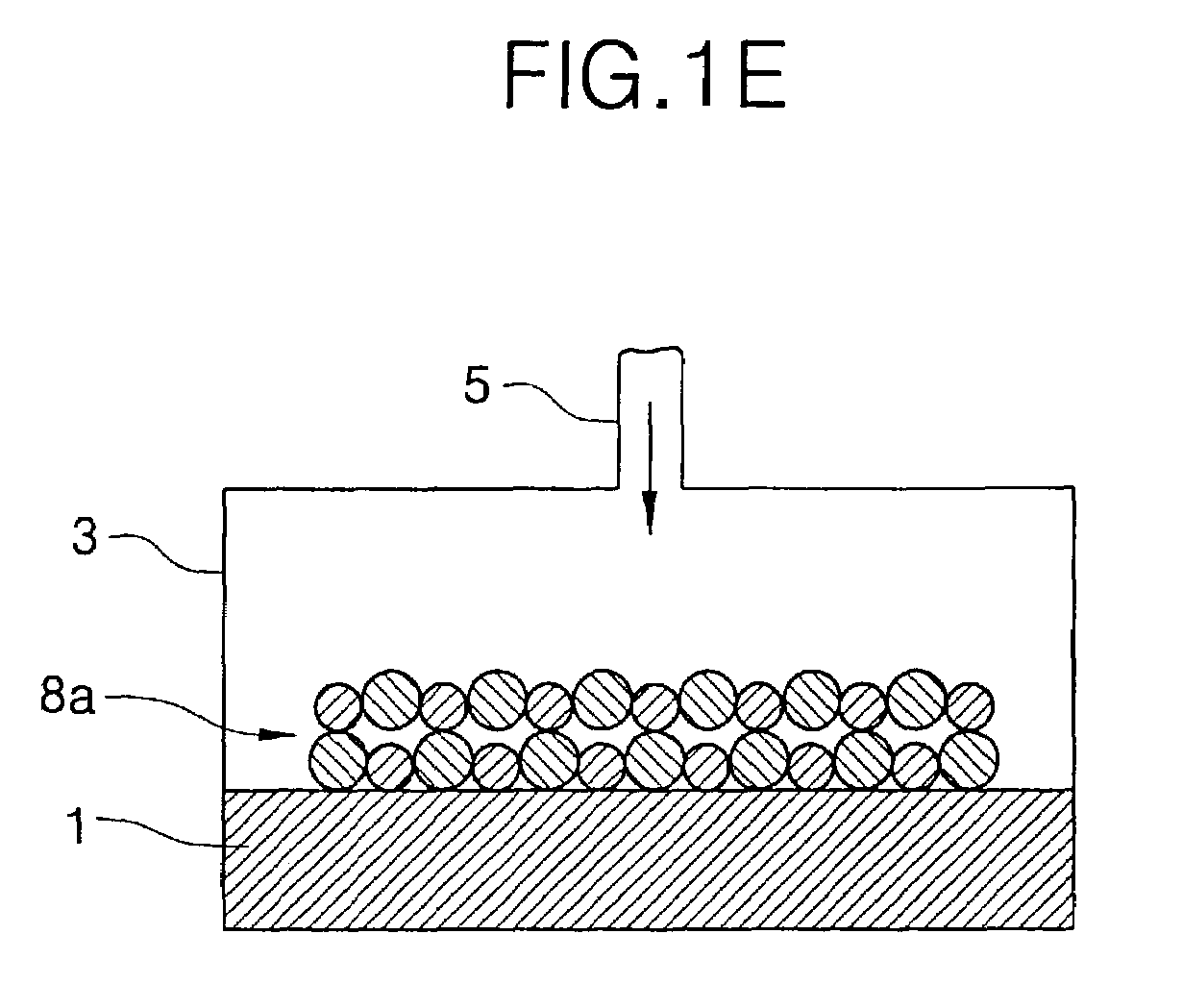
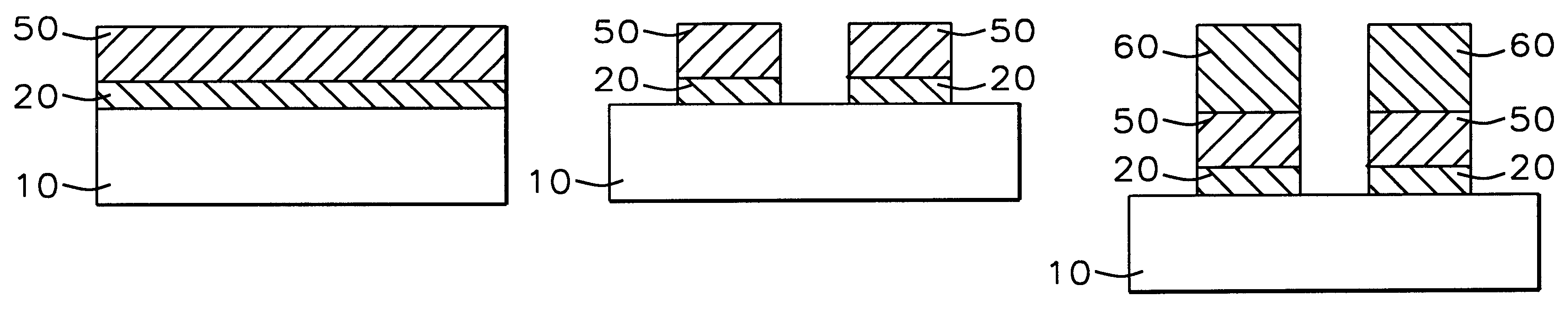
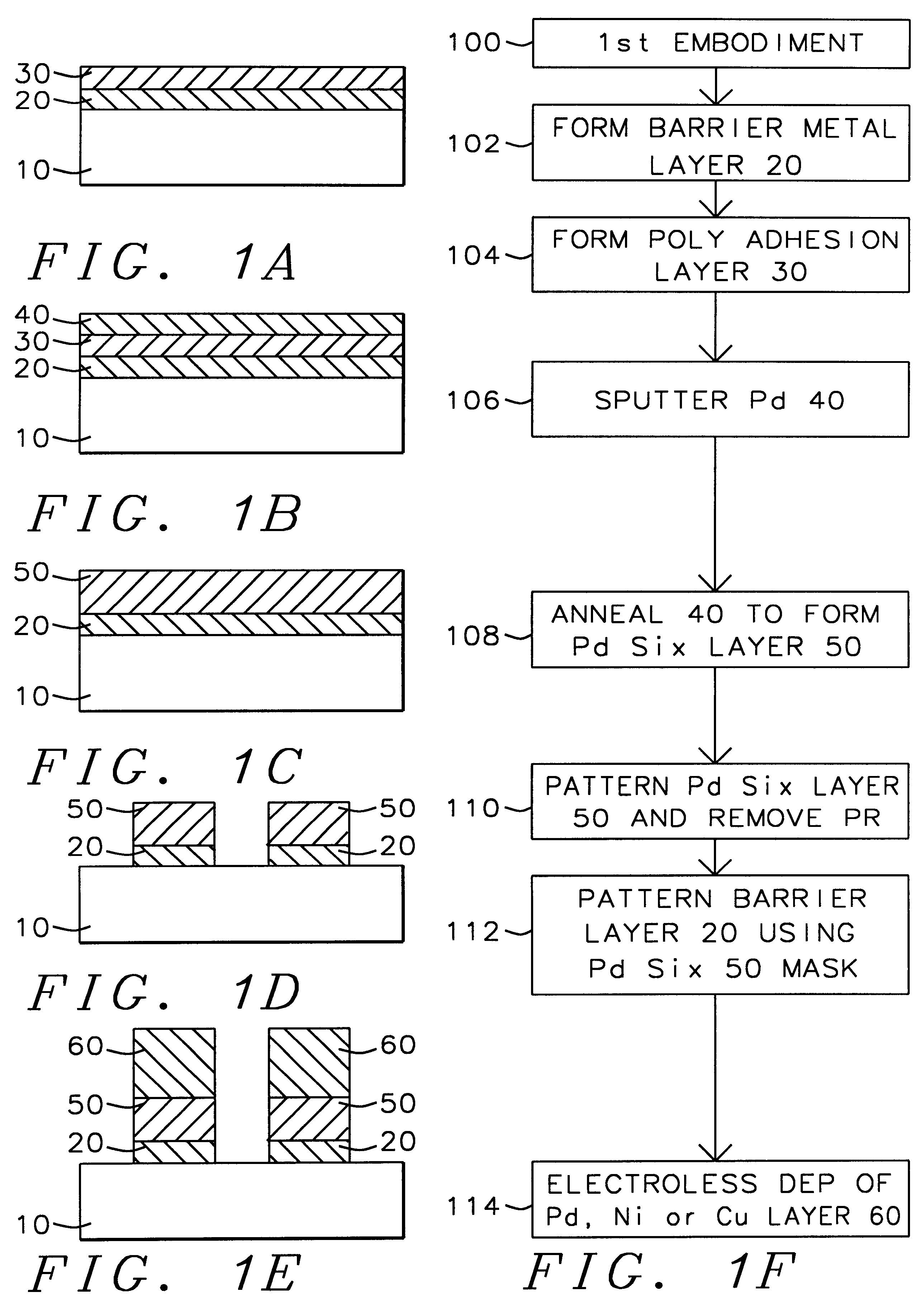
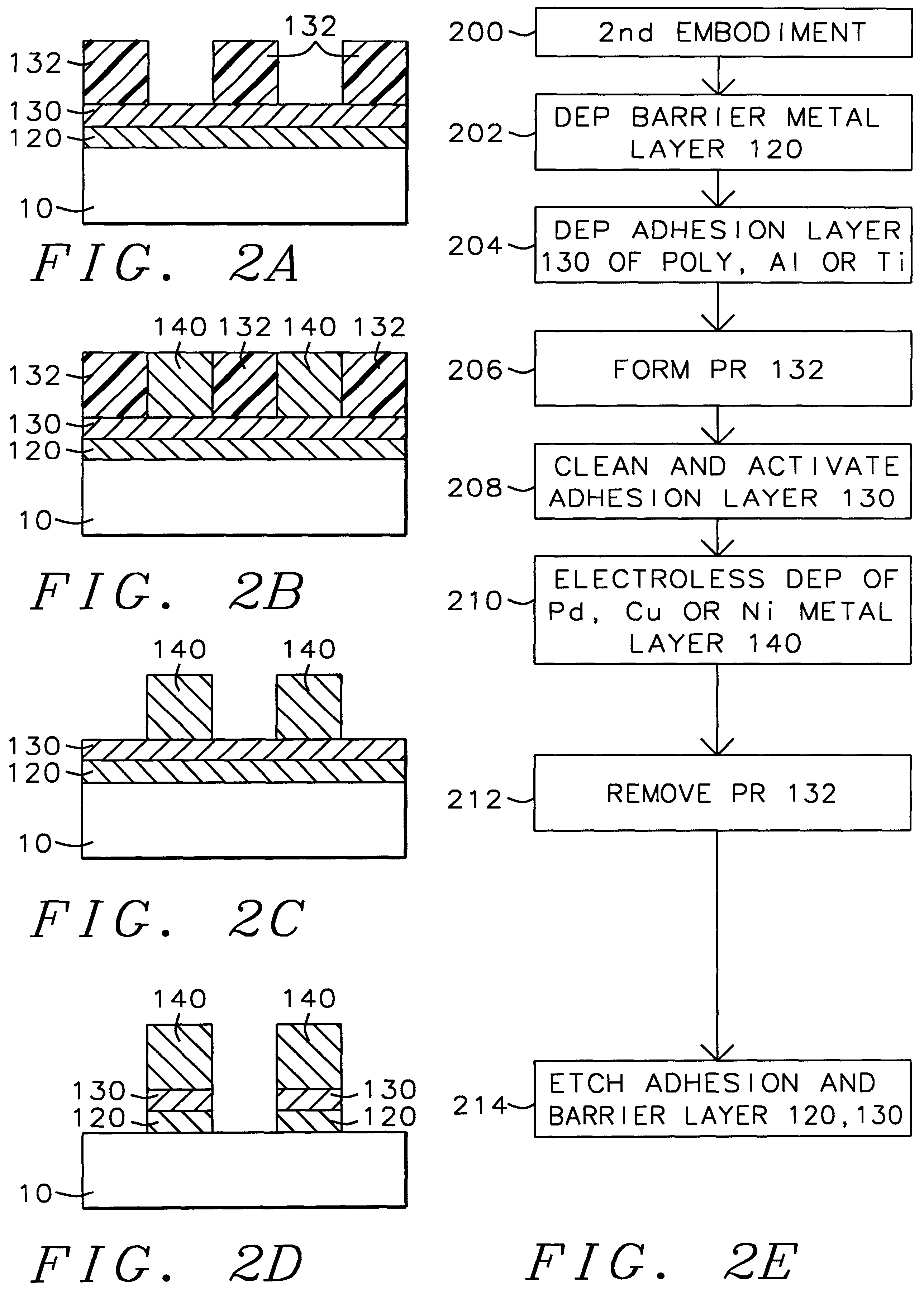
A method with three embodiments of manufacturing metal lines and solder bumps using electroless deposition techniques. The first embodiment uses a PdSix seed layer 50 for electroless deposition. The PdSix layer 50 does not require activation. A metal line is formed on a barrier layer 20 and an adhesion layer 30. A Palladium silicide seed layer 50 is then formed and patterned. Ni, Pd or Cu is electroless deposited over the Palladium silicide layer 50 to form a metal line. The second embodiment selectively electrolessly deposits metal 140 over an Adhesion layer 130 composed of Poly Si, Al, or Ti. A photoresist pattern 132 is formed over the adhesion layer. A metal layer 140 of Cu or Ni is electrolessly deposited over the adhesion layer. The photoresist layer 132 is removed and the exposed portion of the adhesion layer 130 and the underlying barrier metal layer 120 are etched thereby forming a metal line. The third embodiment electroless deposits metal over a metal barrier layer that is roughen by chemical mechanical polishing. A solder bump is formed using an electroless deposition of Cu or Ni by: depositing an Al layer 220 and a barrier metal layer 230 over a substrate 10. The barrier layer 230 is polished and activated. Next, the aluminum layer 220 and the barrier metal layer 230 are patterned. A metal layer 240 is electroless deposited. Next a solder bump 250 is formed over the electroless metal layer 240.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for forming Ti-containing film by PEALD using TDMAT or TDEAT
ActiveUS9556516B2Enhance layeringAvoid reactionChemical vapor deposition coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitaniumAtomic layer deposition
A method for forming a Ti-containing film on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium (TDMAT) or tetrakis(diethylamino)titanium (TDEAT), includes: introducing TDMAT and / or TDEAT in a pulse to a reaction space where a substrate is placed; continuously introducing a NH3-free reactant gas to the reaction space; applying RF power in a pulse to the reaction space wherein the pulse of TDMAT and / or TDEAT and the pulse of RF power do not overlap; and repeating the above steps to deposit a Ti-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Detergents having acceptable color
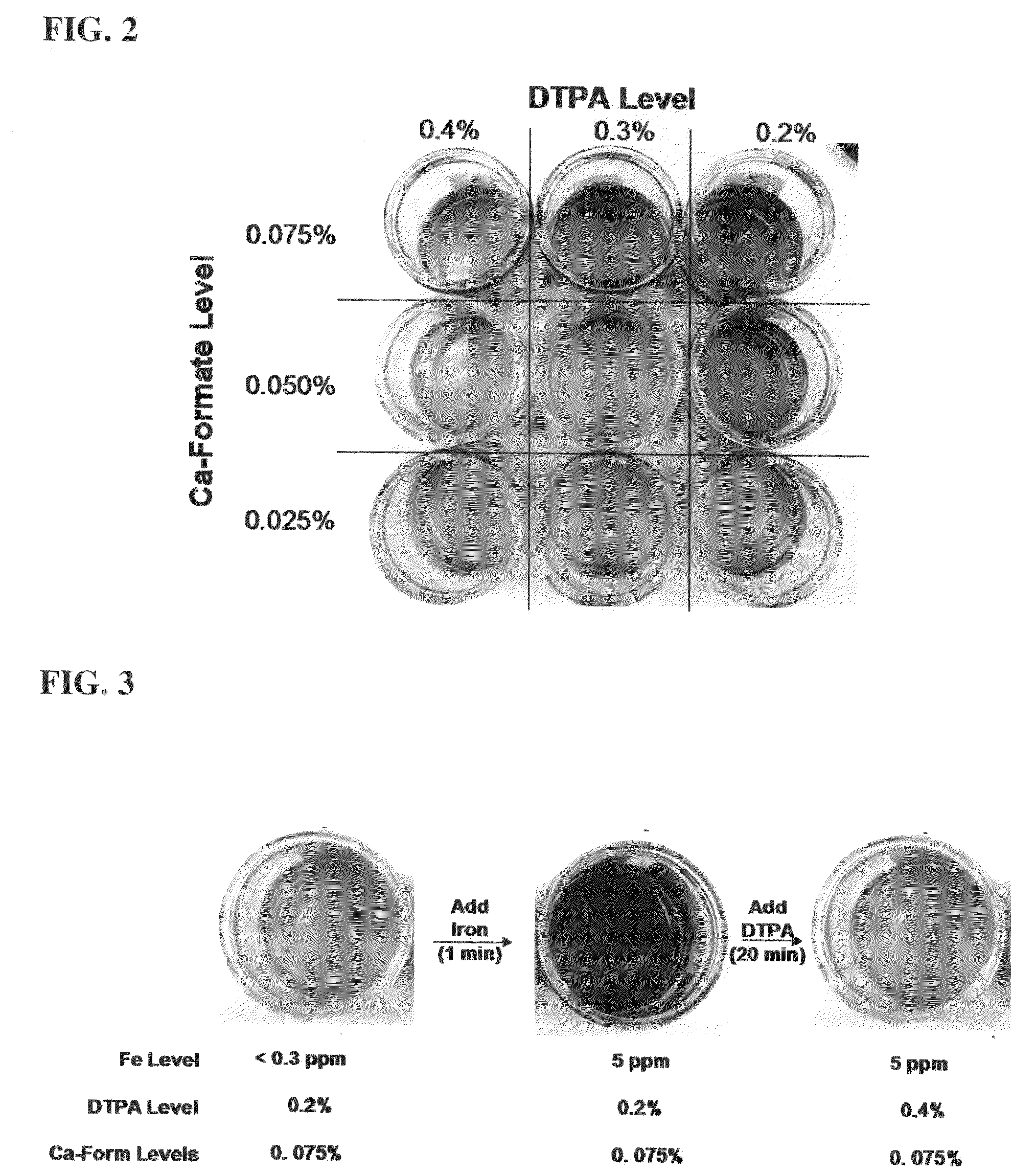
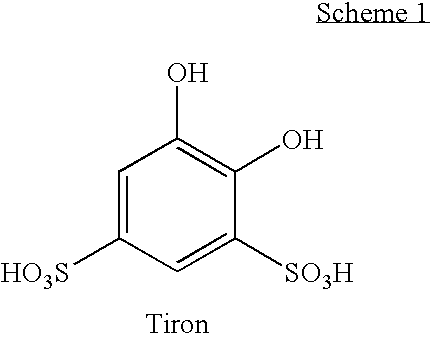
InactiveUS20090176684A1Reduce intensityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsBenzeneTitanium
Detergent compositions containing catechols, such as tiron (1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonic acid), which do not have or do not develop the reddish color associated with the catechol / ferric iron chelate are disclosed. Methods for reducing the intensity of red color in a tiron containing detergent composition are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Minimally-Invasive Approach to Bone-Obstructed Soft Tissue
InactiveUS20080177268A1Improve shielding effectLow magnetic susceptibilitySurgeryMagnetic susceptibilityImaging quality
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for placing a minimally-invasive access with respect to a patient's bone or other non-soft tissue. The subject invention can use a drilling machine incorporating an ultrasound motor. The subject drilling machine can be applied to sample, for example, bone biopsies under MRI control. In a specific embodiment, the subject ultrasound motor can be completely manufactured of non-magnetic materials, such as plastics, titanium, and titanium alloy, or ceramics and piezoceramics. The subject drilling apparatus can be placed into an MRI near field without influencing the image quality, and without the drilling apparatus itself being disturbed by the MRI magnet, gradient, or high-frequency field. The subject invention can incorporate good shielding with the subject drilling apparatus use of these materials, and can achieve minimal, if any, image distortions or so-called artifacts. Thus, the subject invention can involve the problem by use of non-magnetic materials of low magnetic susceptibility for the design of an actuation unit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
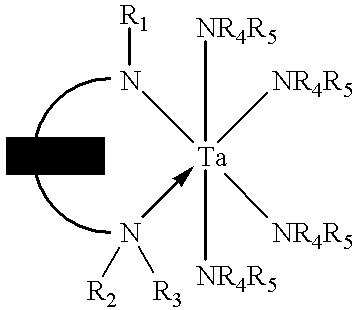
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6015917ARapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microlectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Formation of boron-doped titanium metal films with high work function
ActiveUS20170025280A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium metalWork function
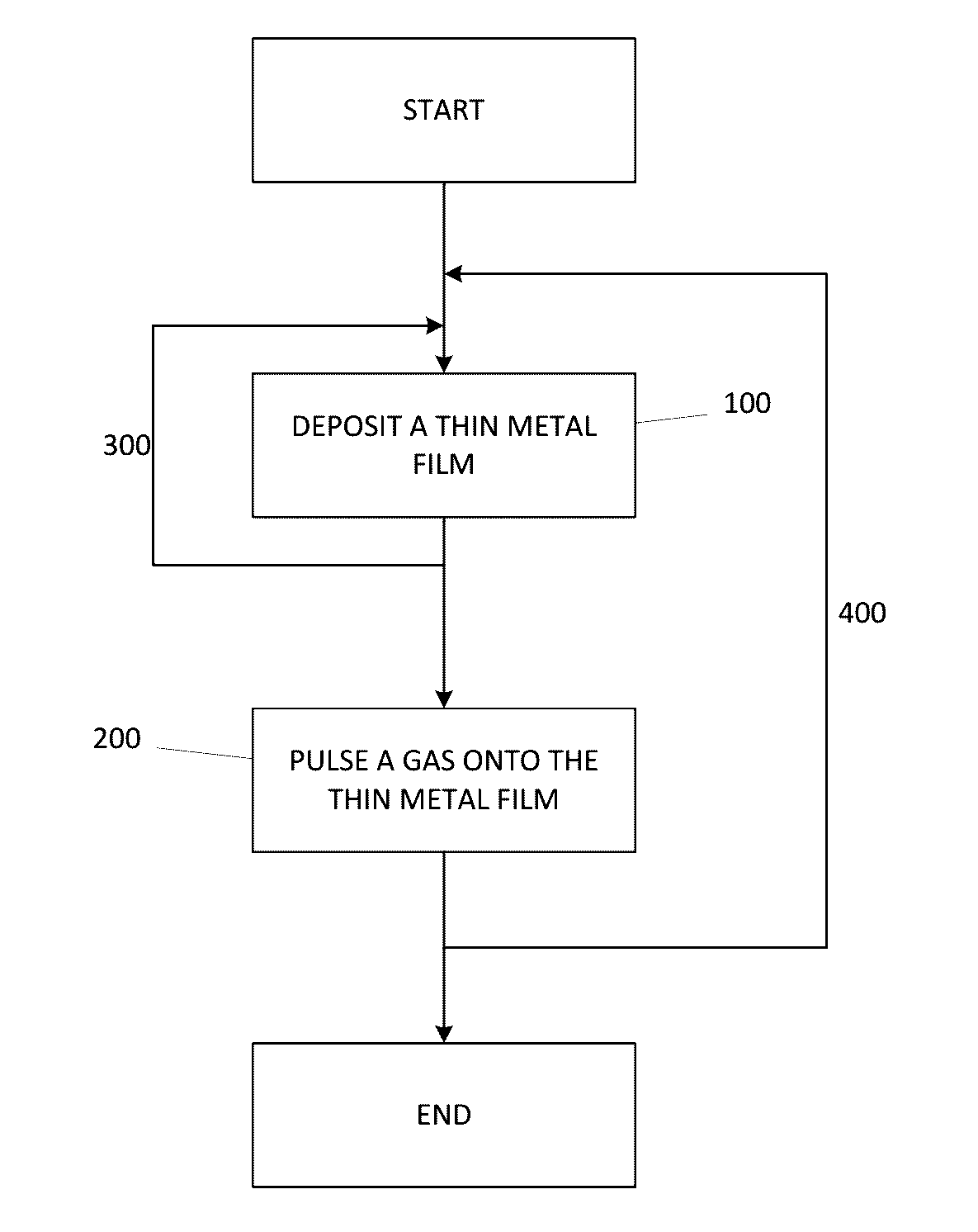
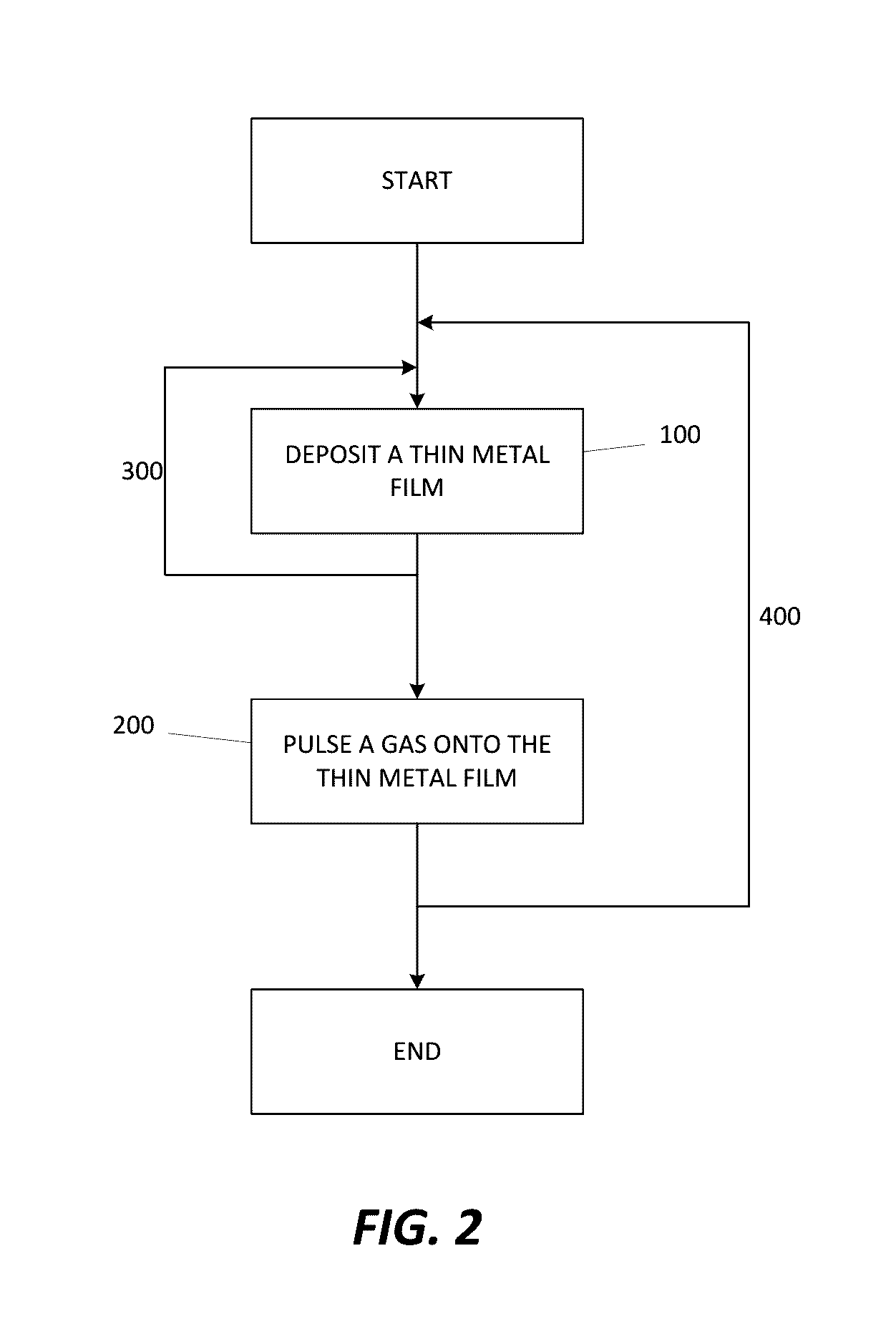
A method for forming a Boron doped metallic film, such as Titanium Boron Nitride, is disclosed. The method allows for creation of the metallic film with a high work function and low resistivity, while limiting the increase in effective oxide thickness. The method comprises a thin metallic layer deposition step as well as a Boron-based gas pulse step. The Boron-based gas pulse deposits Boron and allows for the removal of excess halogens within the metallic film. The steps may be repeated in order to achieve a desired thickness of the metallic film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Nmos metal gate materials, manufacturing methods, and equipment using CVD and ald processes with metal based precursors
ActiveUS20110263115A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseMetallic materials
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for depositing metal-containing materials and compositions thereof. The methods include deposition processes that form metal, metal carbide, metal silicide, metal nitride, and metal carbide derivatives by a vapor deposition process, including thermal decomposition, CVD, pulsed-CVD, or ALD. In one embodiment, a method for processing a substrate is provided which includes depositing a dielectric material having a dielectric constant greater than 10, forming a feature definition in the dielectric material, depositing a work function material conformally on the sidewalls and bottom of the feature definition, and depositing a metal gate fill material on the work function material to fill the feature definition, wherein the work function material is deposited by reacting at least one metal-halide precursor having the formula MXY, wherein M is tantalum, hafnium, titanium, and lanthanum, X is a halide selected from the group of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine, and y is from 3 to 5.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Chemical vapor deposition methods of forming barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layers, including such layers having a varied concentration of barium and strontium within the layer
The invention includes a chemical vapor deposition method of forming a barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layer having a varied concentration of barium and strontium, and / or titanium, within the layer. A substrate is positioned within a chemical vapor deposition reactor. Barium and strontium are provided within the reactor by flowing at least one metal organic precursor to the reactor. Titanium is provided within the reactor. One or more oxidizers are flowed to the reactor. In one aspect, conditions are provided within the reactor to be effective to deposit a barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layer on the substrate from the reactants.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Process for deposition of titanium oxynitride for use in integrated circuit fabrication
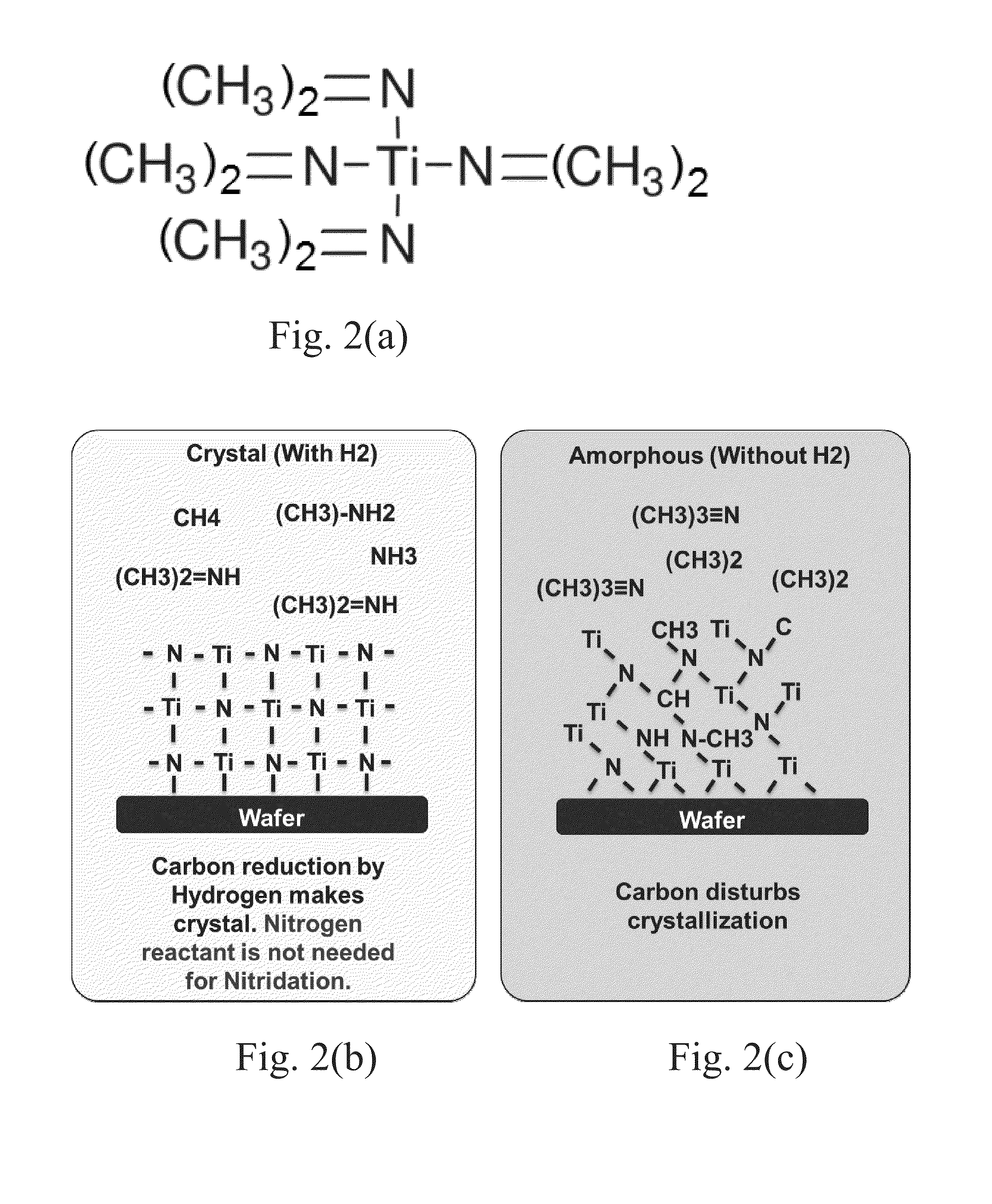
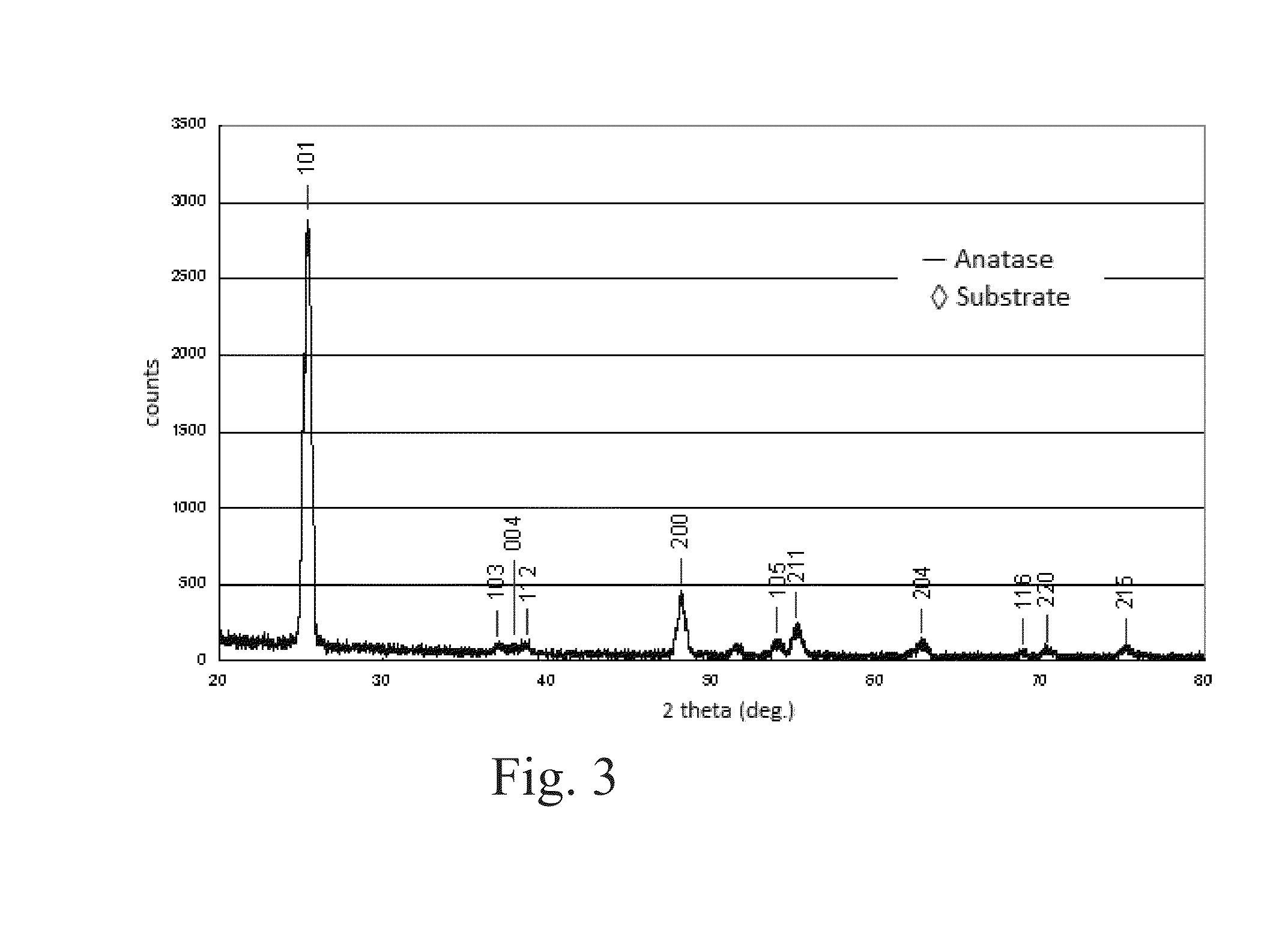
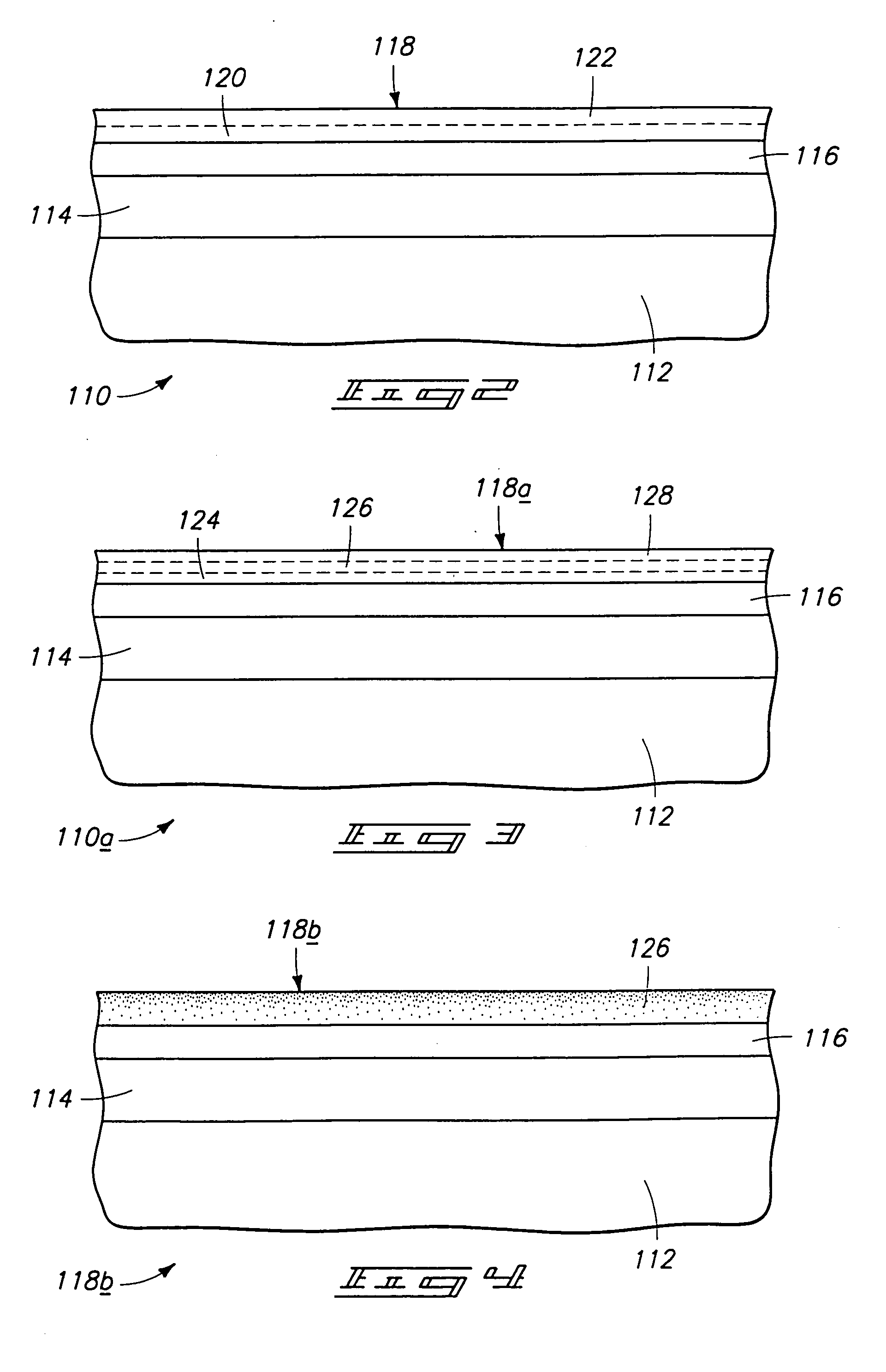
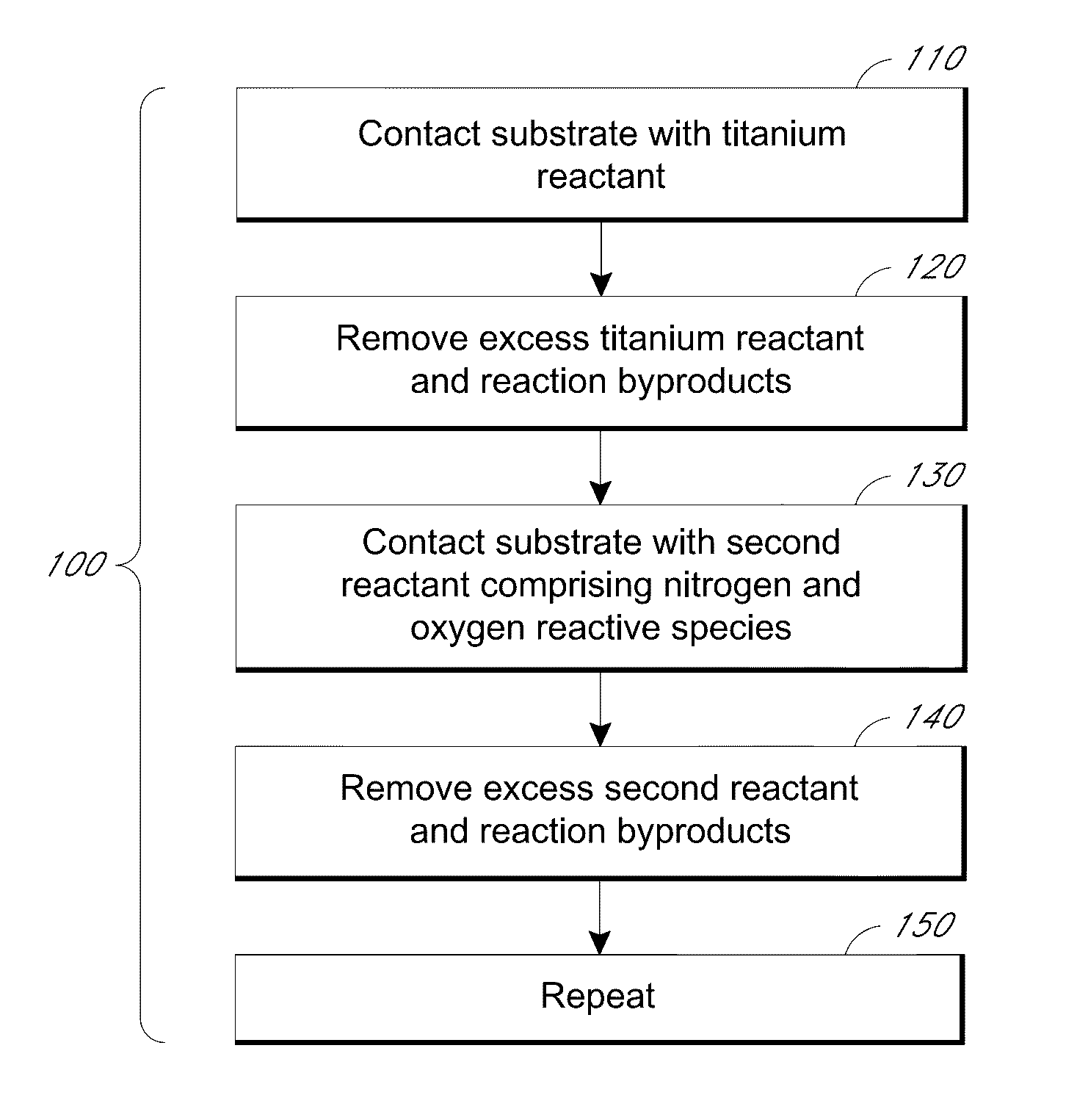
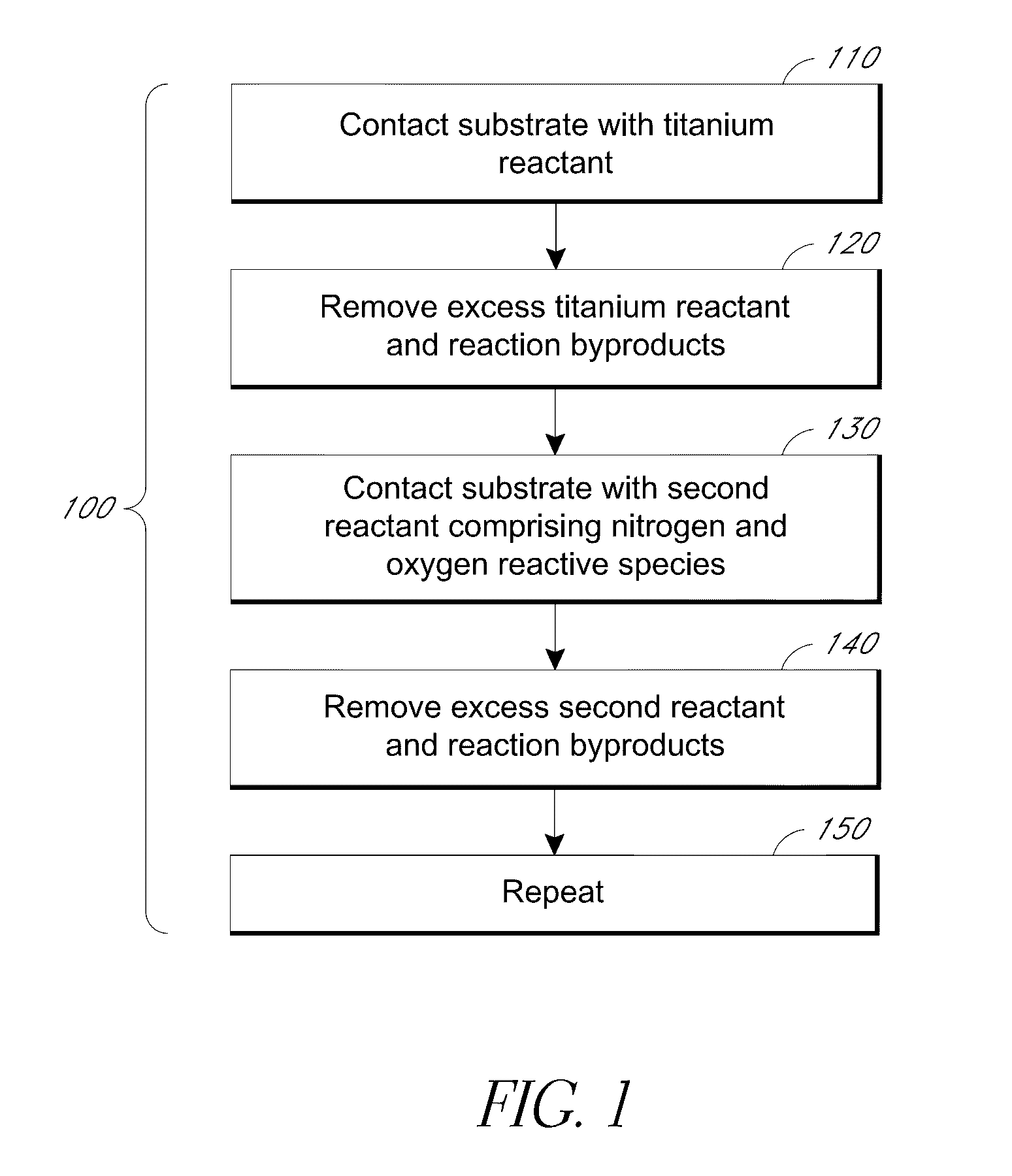
A process is provided for depositing a substantially amorphous titanium oxynitride thin film that can be used, for example, in integrated circuit fabrication, such as in forming spacers in a pitch multiplication process. The process comprises contacting the substrate with a titanium reactant and removing excess titanium reactant and reaction byproducts, if any. The substrate is then contacted with a second reactant which comprises reactive species generated by plasma, wherein one of the reactive species comprises nitrogen. The second reactant and reaction byproducts, if any, are removed. The contacting and removing steps are repeated until a titanium oxynitride thin film of desired thickness has been formed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Low frequency transcutaneous energy transfer to implanted medical device
InactiveUS20050288741A1Efficiently penetrate physical boundaryWithout excessive power lossElectrotherapyAnti-incontinence devicesEnergy transferComputer module
An implantable medical device system advantageously utilizes low frequency (e.g., about 1-100 kHz) transcutaneous energy transfer (TET) for supplying power from an external control module to an implantable medical device, avoiding power dissipation through eddy currents in a metallic case of an implant and / or in human tissue, thereby enabling smaller implants using a metallic case such as titanium and / or allowing TET signals of greater strength thereby allowing placement more deeply within a patient without excessive power transfer inefficiencies.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Titanium compounds and complexes as additives in lubricants
A lubricating composition comprising an oil of lubricating viscosity, 1 to 1000 parts per million by weight of titanium in the form of an oil-soluble titanium-containing material, and at least one additional lubricant additive provides beneficial effects on properties such as deposit control, oxidation, and filterability in engine oils.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Low resistance contacts including intermetallic alloy of nickel, platinum, titanium, aluminum and type iv semiconductor elements
ActiveUS20180068950A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPlatinumSemiconductor materials
A method of forming a contact to a semiconductor device is provided that forms an alloy composed of nickel (Ni), platinum (Pt), aluminum (Al), titanium (Ti) and a semiconductor material. The methods may include forming a nickel and platinum semiconductor alloy at a base of a via. A titanium layer having an angstrom scale thickness is deposited in the via in contact with the nickel platinum semiconductor alloy. An aluminum containing fill is deposited atop the titanium layer. A forming gas anneal including an oxygen containing atmosphere is applied to the structure to provide a contact alloy comprising nickel, platinum, aluminum, titanium and a semiconductor element from the contact surface of the semiconductor device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Implantable pulse generator for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and /or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
ActiveUS20050277999A1Efficient chargingImprove the quality of lifeElectrotherapyElectromyographyElectricityMicrocontroller
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide an implantable pulse generator for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The implantable pulse generator is sized and configured to be implanted subcutaneous a tissue region. The implantable pulse generator includes an electrically conductive case of a laser welded titanium material. Control circuitry is located within the case, the control circuitry including a rechargeable power source, a receive coil for receiving an RF magnetic field to recharge the power source, and a microcontroller for control of the implantable pulse generator. Improved assemblies, systems, and methods also provide a stimulation system for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The stimulation system provides at least one electrically conductive surface, a lead connected to the electrically conductive surface, and an implantable pulse generator electrically connected to the lead.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
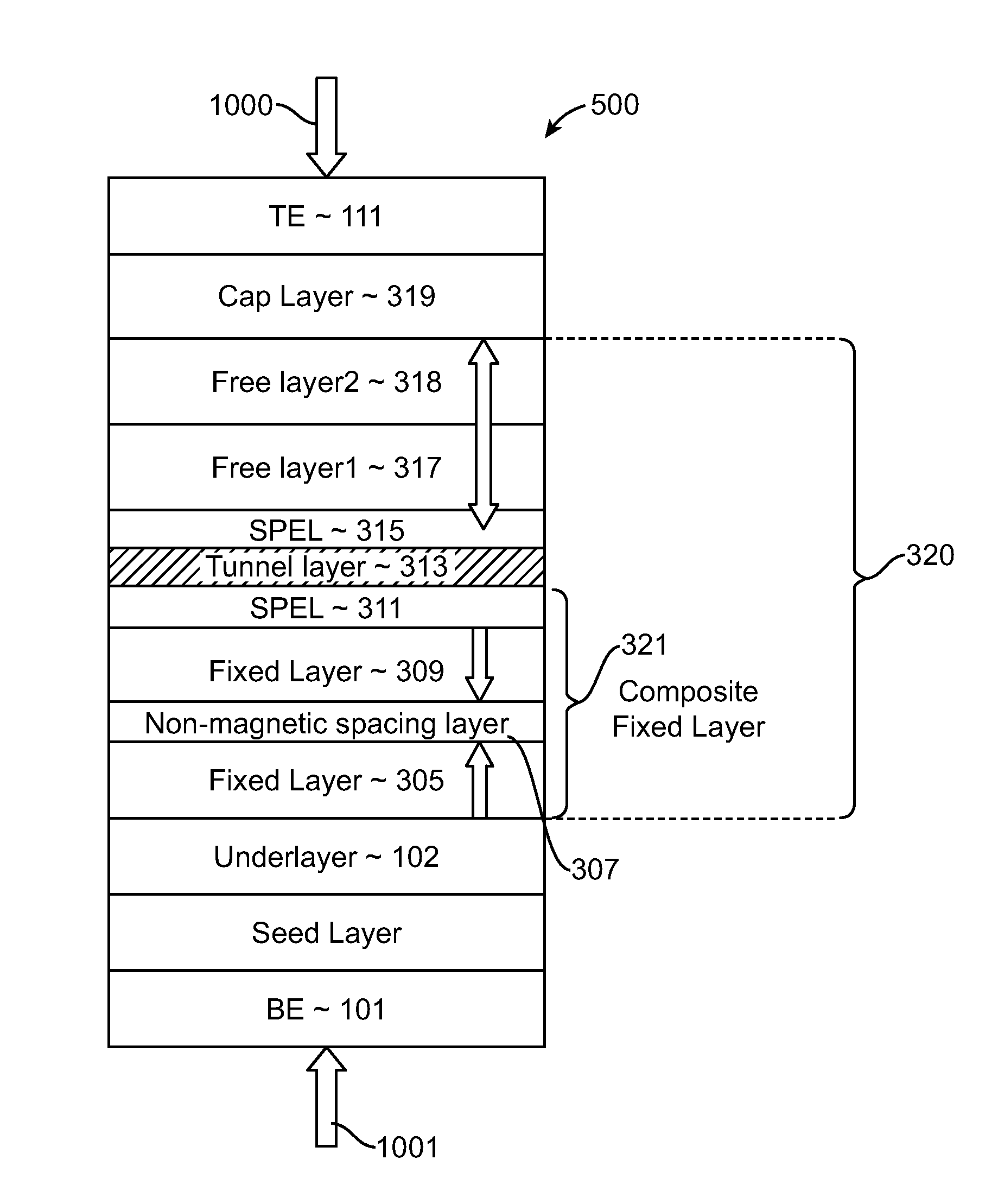
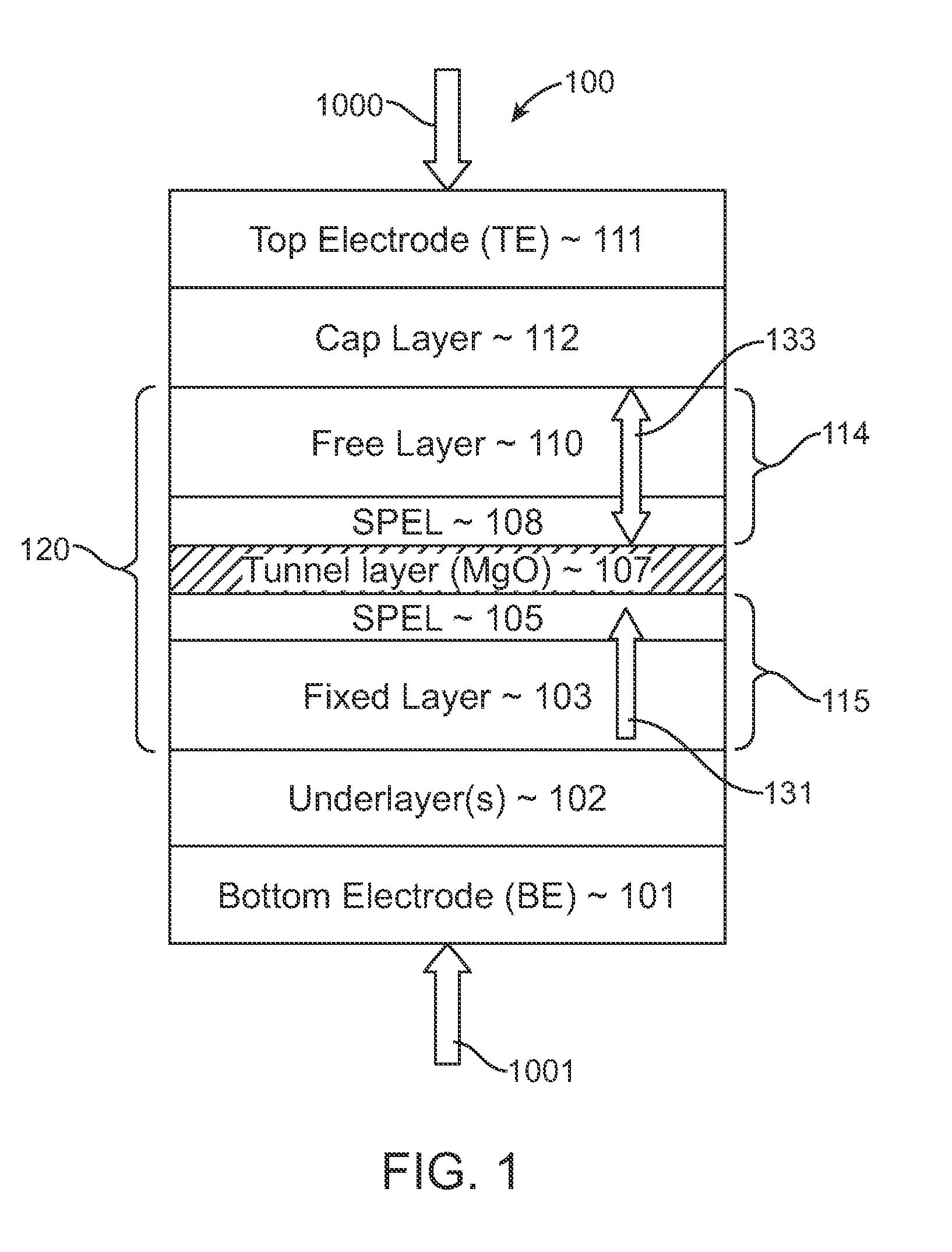
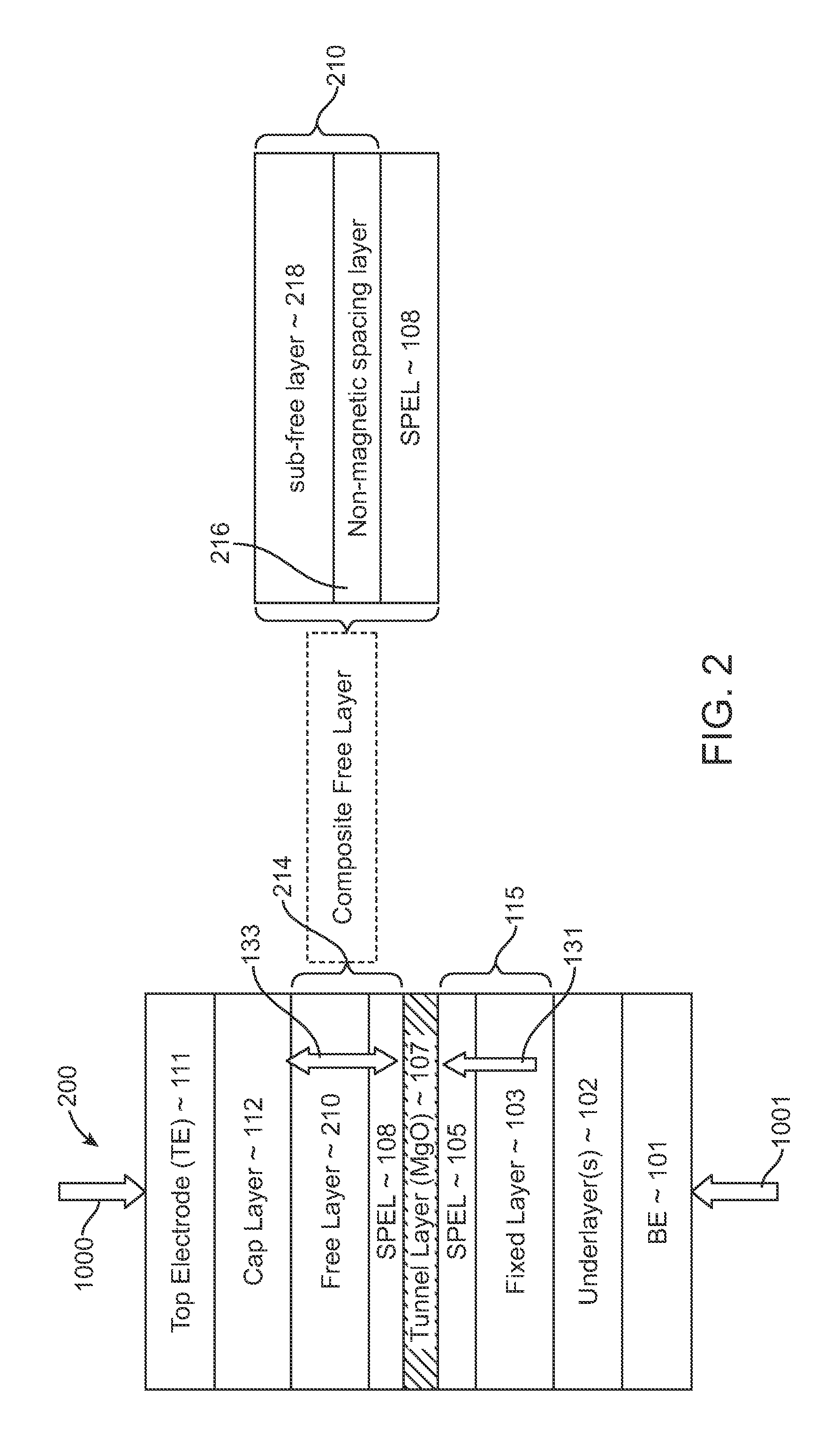
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6379748B1Rapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microelectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Implantable pulse generator for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and/or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
ActiveUS7239918B2Reliable and easy connectionEfficient chargingElectrotherapySurgeryElectricityMicrocontroller
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
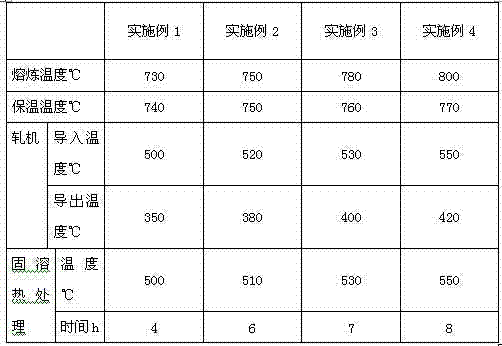
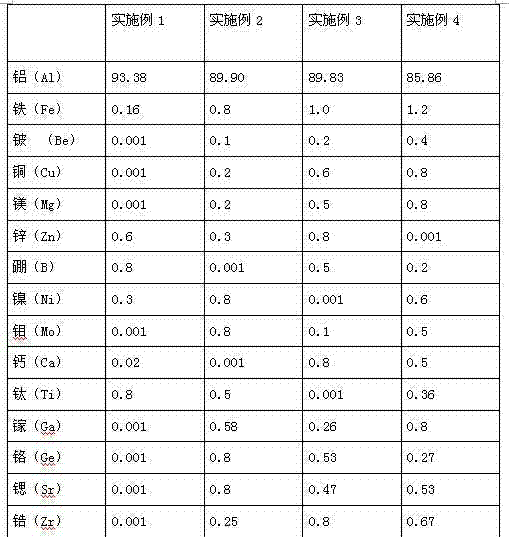
A kind of aluminum alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an aluminum alloy material which is characterized in that the aluminum alloy material comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.16-1.2% of Fe, 0.001-0.8% of Cu, 0.001-0.8% of Mg, 0.001-0.8% of Zn, 0.001-0.8% of Ca, 0.001-1.0% of rare-earth elements, a trace amount of strontium, titanium, boron, nickel, chromium, zirconium, vanadium, beryllium, cobalt, lead, tin, bismuth, molybdenum, silver, indium, niobium and barium and the balance of aluminum. The alloy has excellent mechanical strength, processing performance and corrosion resistance and is suitable for the cable armored sheath.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINYI ALUMINUM ALLOY CABLE
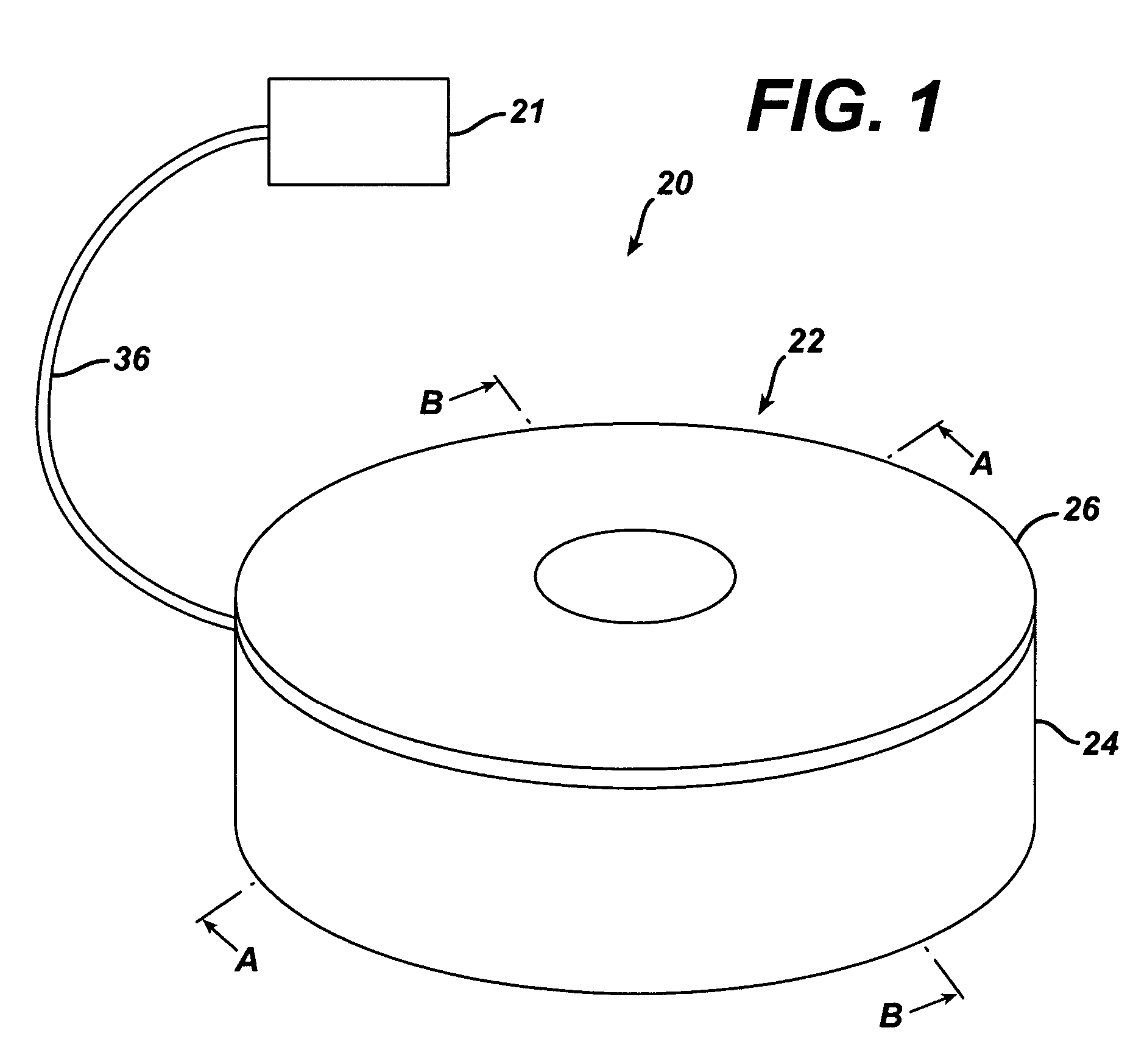
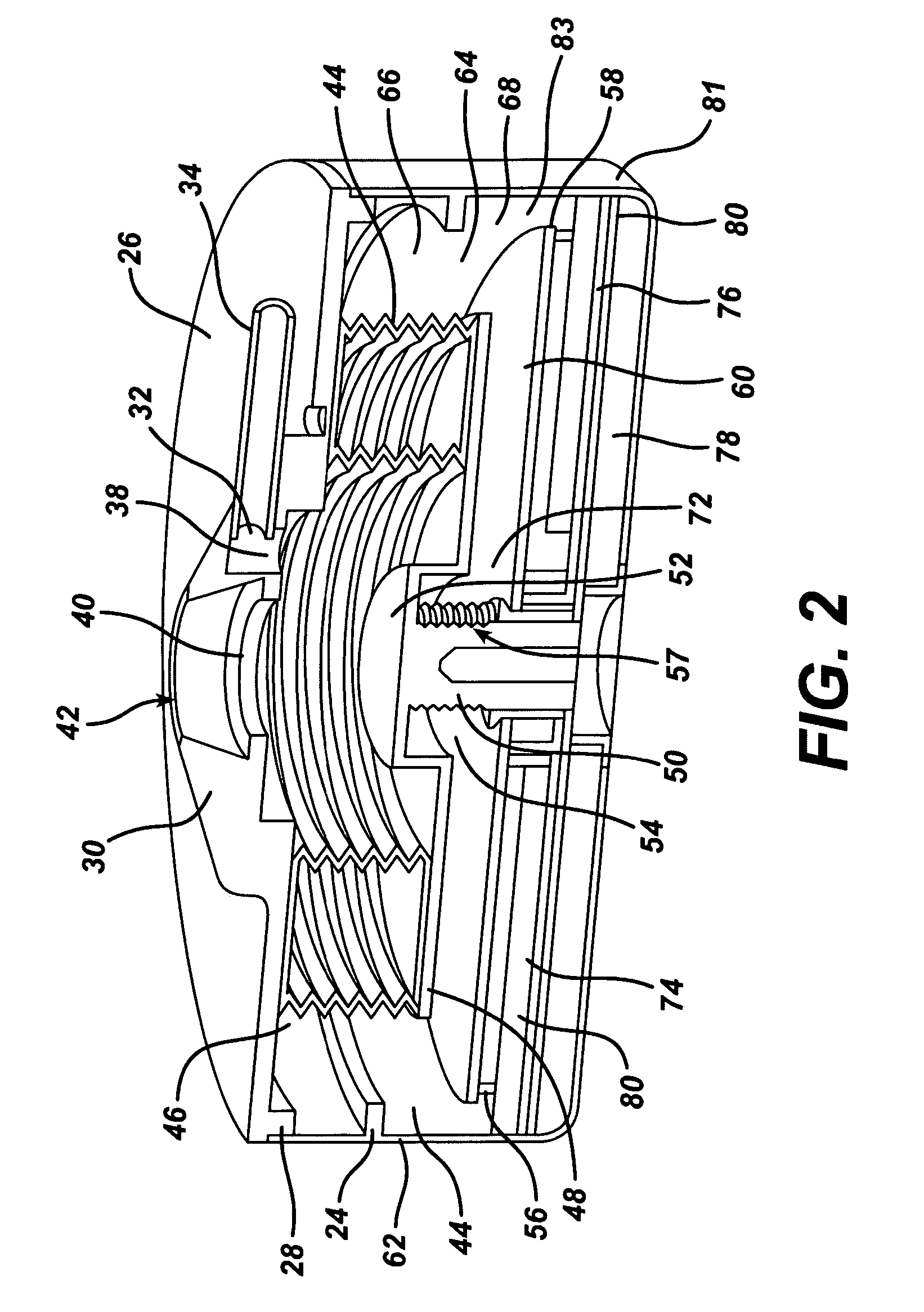
Piezo electrically driven bellows infuser for hydraulically controlling an adjustable gastric band
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume in a gastric band. A piezoelectrically driven (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic case such as titanium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com