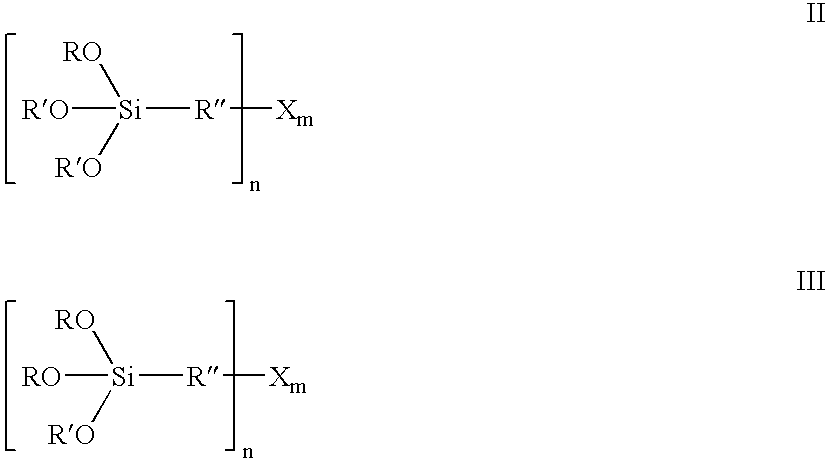Patents
Literature
4276 results about "Iodine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a lustrous, purple-black non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at 114 degrees Celsius, and boils to a violet gas at 184 degrees Celsius. The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811. It was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac from this property, after the Greek ἰώδης "violet-coloured".
Nmos metal gate materials, manufacturing methods, and equipment using CVD and ald processes with metal based precursors
ActiveUS20110263115A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseMetallic materials
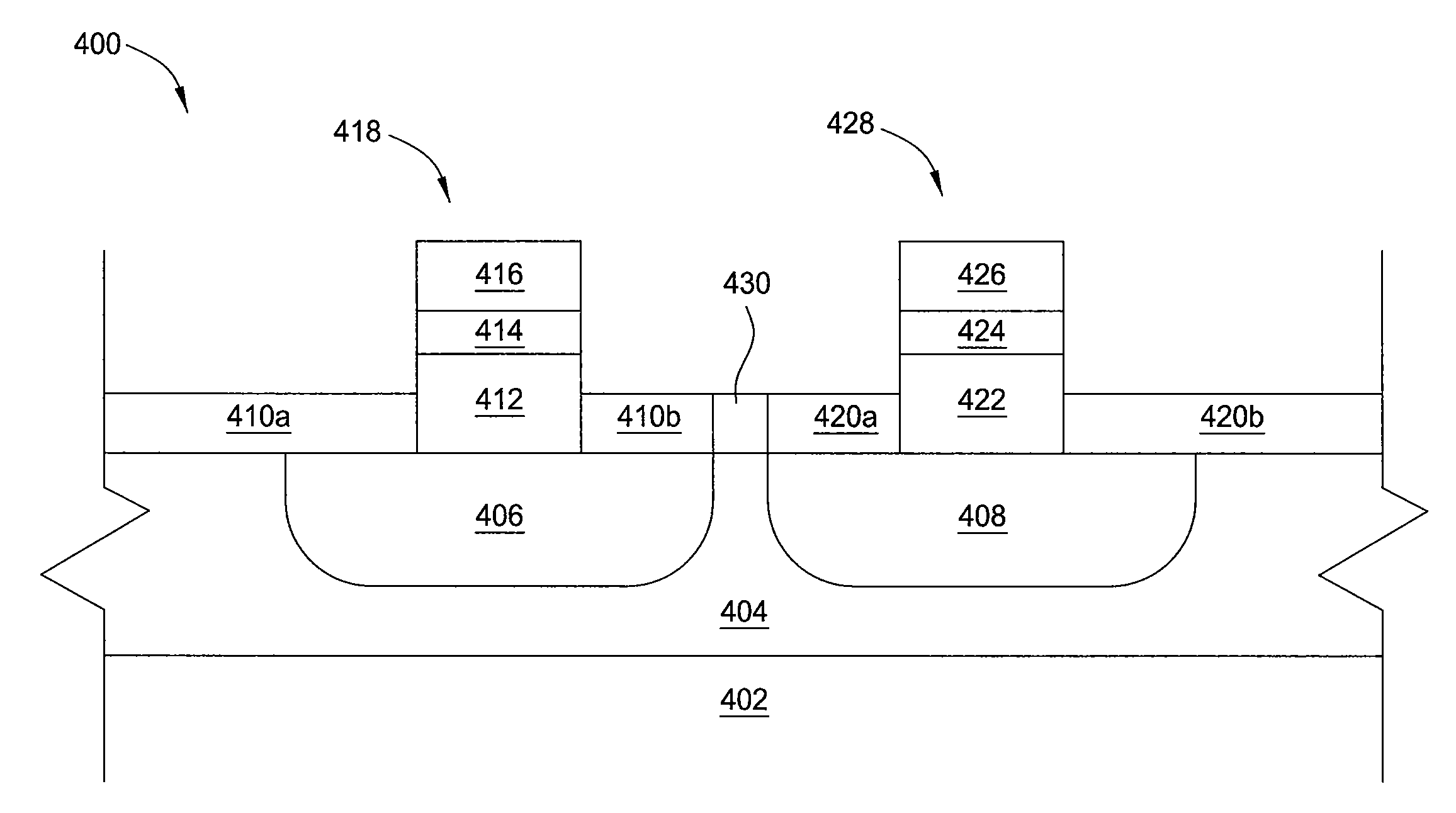
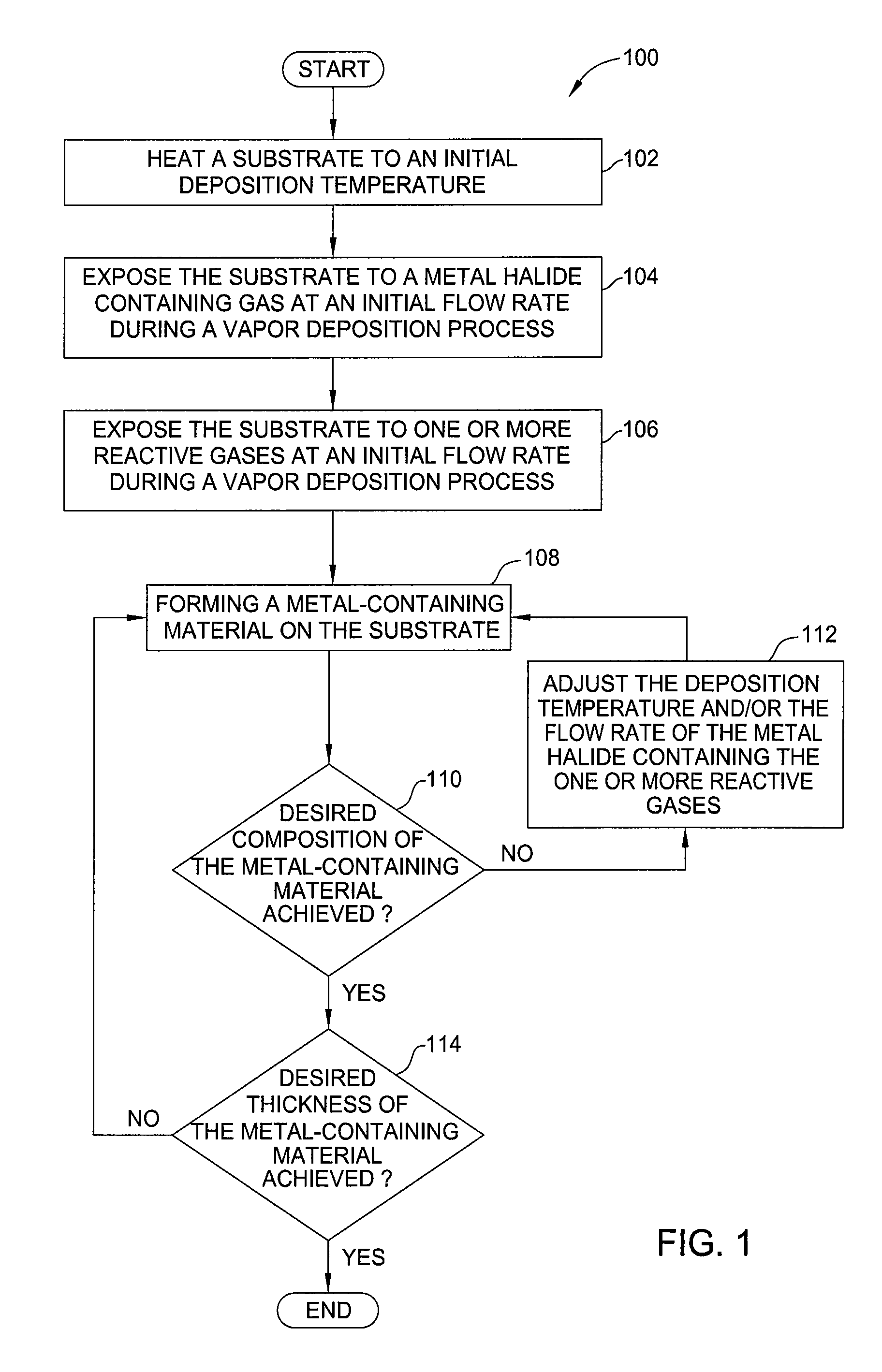
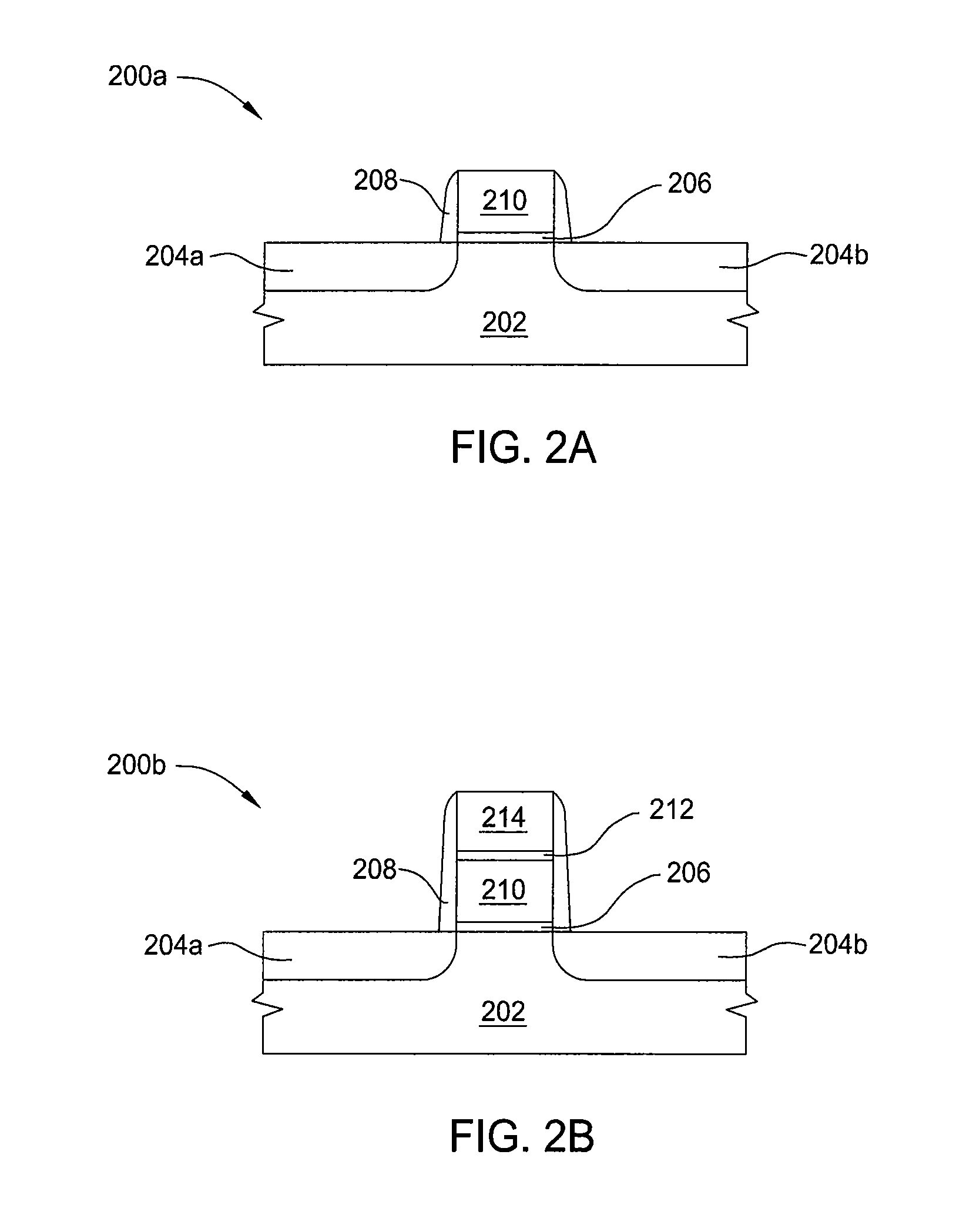
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for depositing metal-containing materials and compositions thereof. The methods include deposition processes that form metal, metal carbide, metal silicide, metal nitride, and metal carbide derivatives by a vapor deposition process, including thermal decomposition, CVD, pulsed-CVD, or ALD. In one embodiment, a method for processing a substrate is provided which includes depositing a dielectric material having a dielectric constant greater than 10, forming a feature definition in the dielectric material, depositing a work function material conformally on the sidewalls and bottom of the feature definition, and depositing a metal gate fill material on the work function material to fill the feature definition, wherein the work function material is deposited by reacting at least one metal-halide precursor having the formula MXY, wherein M is tantalum, hafnium, titanium, and lanthanum, X is a halide selected from the group of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine, and y is from 3 to 5.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Precursors and processes for low temperature selective epitaxial growth
InactiveUS20090087967A1Practical and cost-effective SEGReduce processingDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBromineGas phase
This invention generally relates to low temperature epitaxy. More specifically, this invention relates to processes for achieving low temperature selective epitaxial growth by chemical vapor deposition of source precursors containing Si or Ge in the presence of bromine or iodine, compositions containing precursors and brominated or iodinated compounds suitable for achieving selective epitaxial growth using the processes, epitaxial layers made using the processes, devices and other types of structures made using the processes, and processes for cleaning epitaxy reactor chambers using a bromine etchant source.
Owner:TODD MICHAEL A
Process for control of the shape of the etch front in the etching of polysilicon
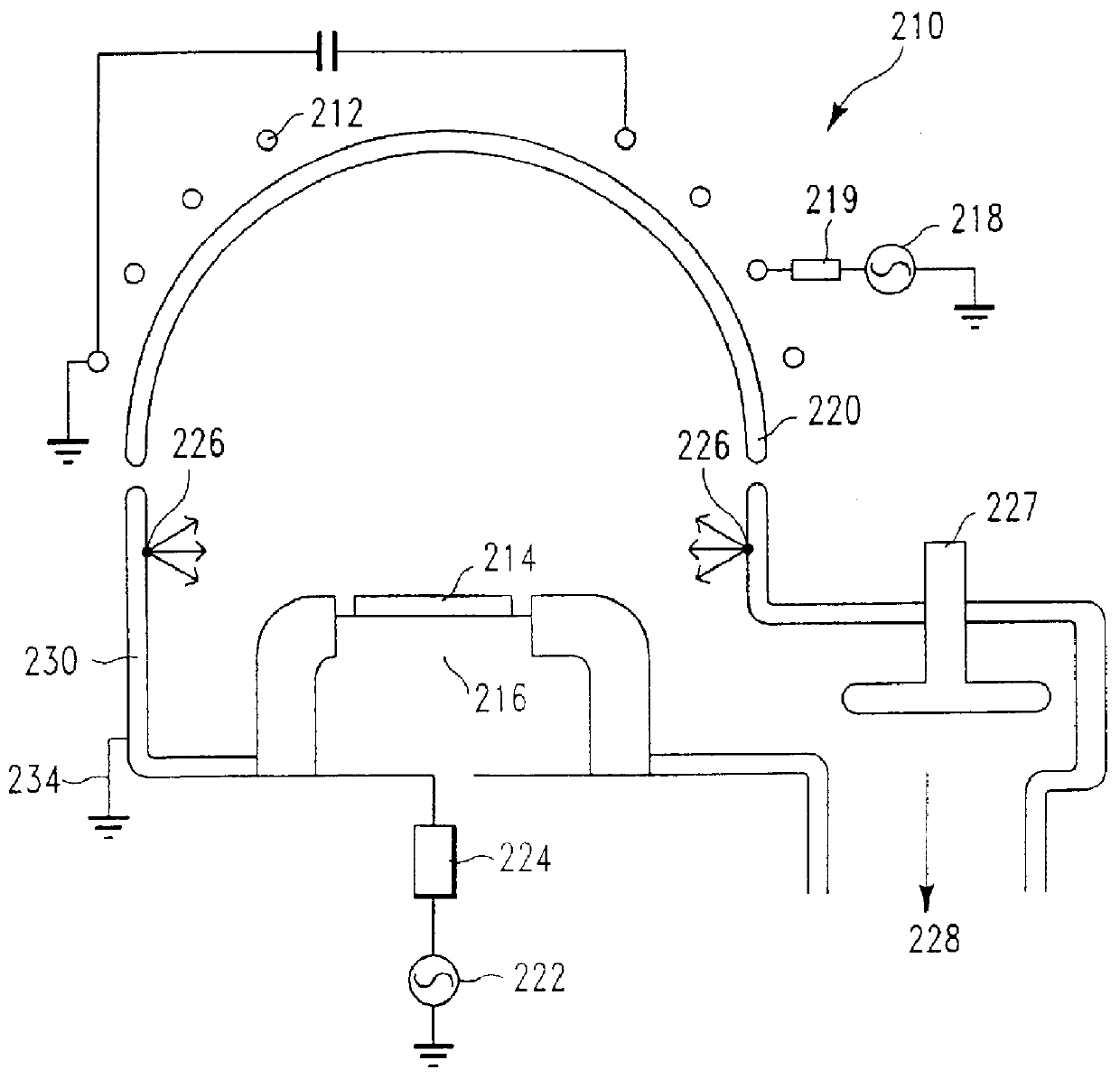
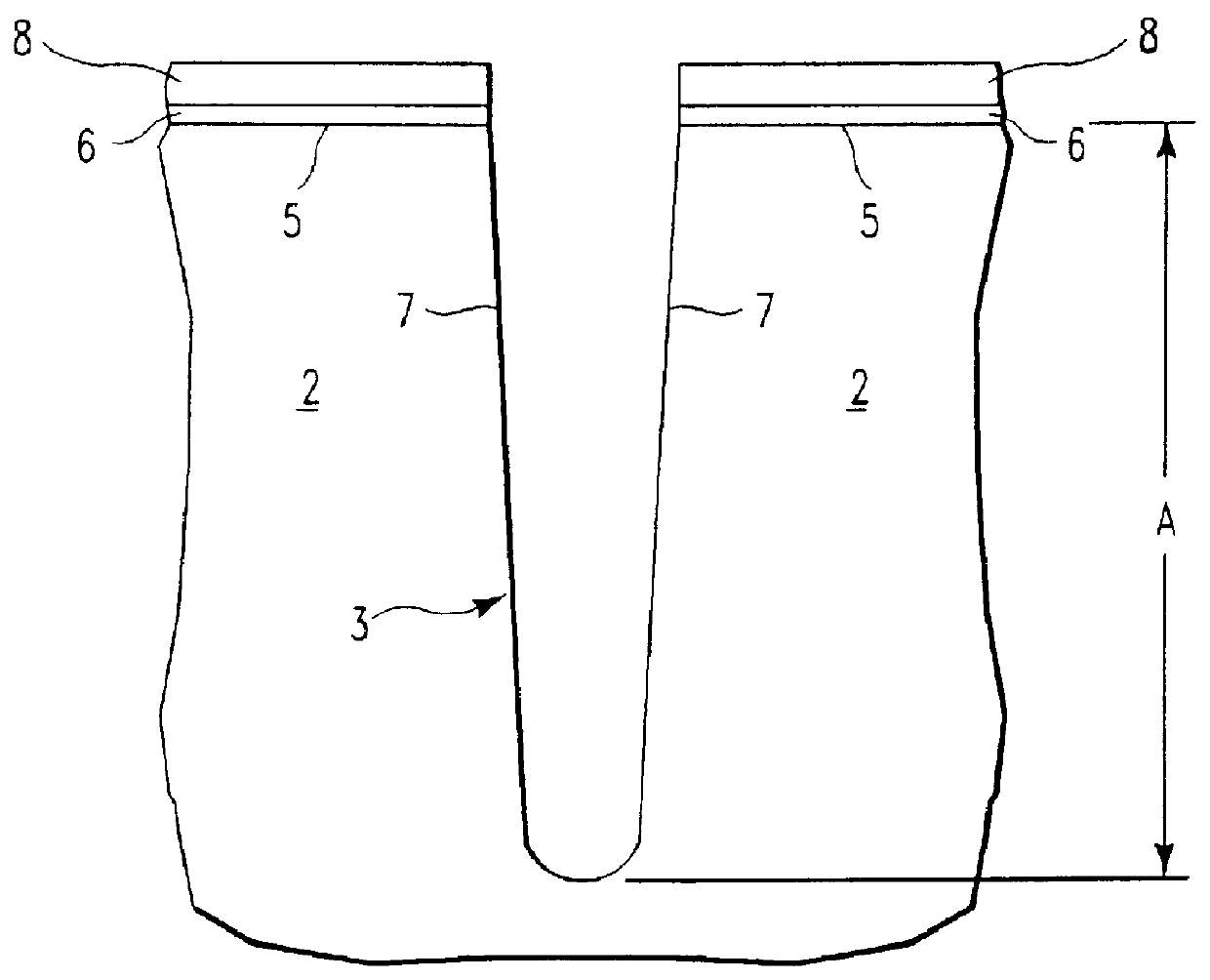
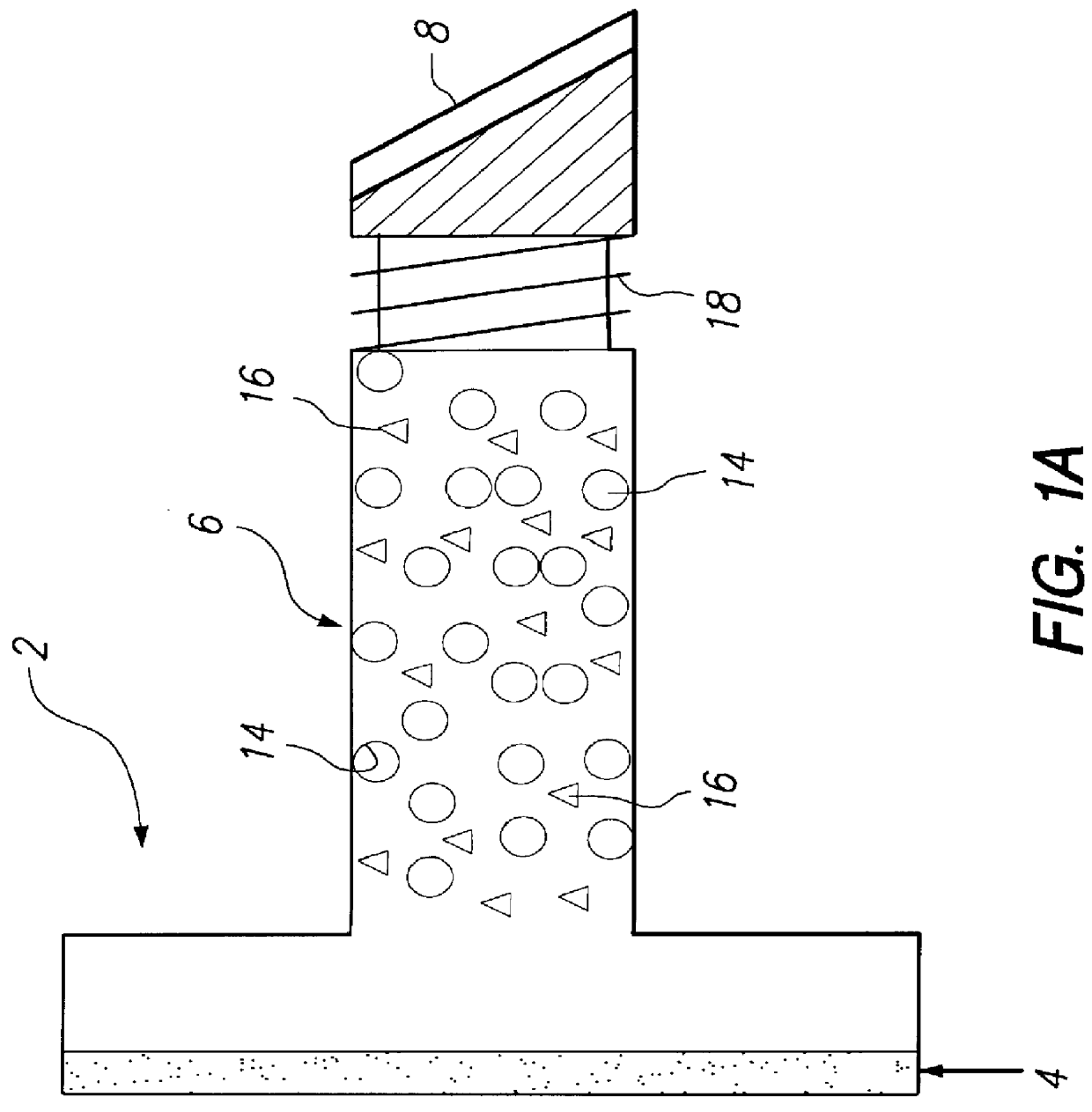
The present disclosure pertains to our discovery that the use of a particular combination of etchant gases results in the formation of a substantially flat etch front for polysilicon etching applications. In general, the process of the invention is useful for controlling the shape of the etch front during the etchback of polysilicon. Typically, the process comprises isotropically etching the polysilicon using a plasma produced from a plasma source gas comprising a particular combination of reactive species which selectively etch polysilicon. The plasma source gas comprises from about 80% to about 95% by volume of a fluorine-comprising gas, and from about 5% to about 20% by volume of an additive gas selected from a group consisting of a bromine-comprising gas, a chlorine-comprising gas, an iodine-comprising gas, or a combination thereof. One preferred mixture is SF6, Cl2 and HBr. A preferred method of the invention, used to perform recess etchback of a polysilicon-filled trench in a substrate, comprises the following steps: a) providing a trench 3 formed in a semiconductor structure, wherein the structure includes a substrate 2, at least one gate dielectric layer 6 overlying a surface of the substrate, and at least one etch barrier layer 8 overlying the gate dielectric layer; b) forming a conformal dielectric film 10 overlying the etch barrier layer and the sidewall and bottom of the trench; c) filling the trench with a layer of polysilicon 12 which overlies the conformal dielectric film; and d) isotropically etching the polysilicon back to a predetermined depth within the trench using a plasma produced from the invention plasma source gas. Also disclosed herein is a method of forming a trench capacitor in a single-crystal silicon substrate, the trench capacitor including a dielectric collar and a buried strap.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Chemical treatment to retard diffusion in a semiconductor overlayer
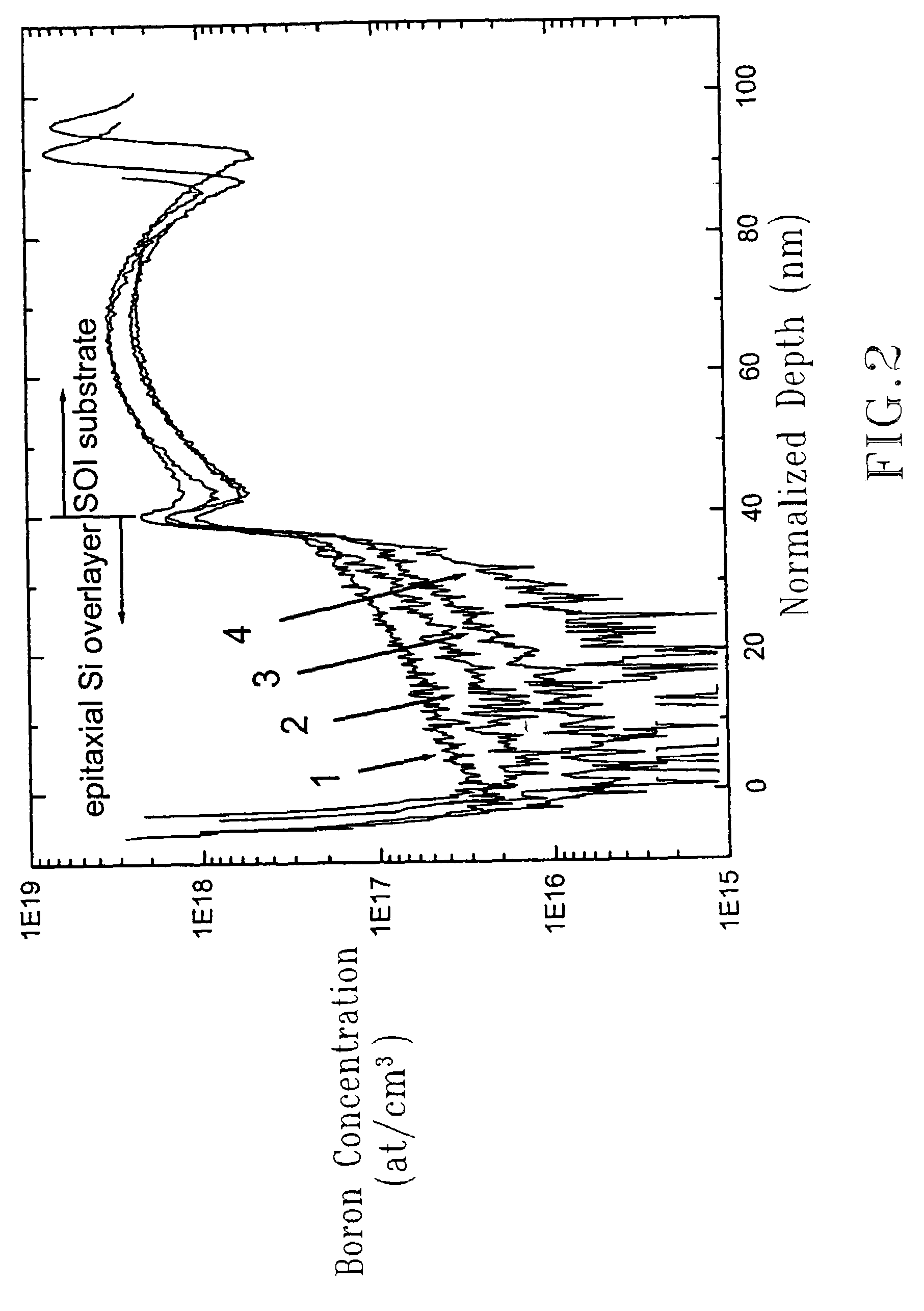
InactiveUS7071103B2Diffusion slowSimple technologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantChemical treatment
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Reducing mercury emissions from the burning of coal
Processes and compositions are provided for decreasing emissions of mercury upon combustion of fuels such as coal. Various sorbent compositions are provided that contain components that reduce the level of mercury and / or sulfur emitted into the atmosphere upon burning of coal. In various embodiments, the sorbent compositions are added directly to the fuel before combustion; are added partially to the fuel before combustion and partially into the flue gas post combustion zone; or are added completely into the flue gas post combustion zone. In preferred embodiments, the sorbent compositions comprise a source of halogen and preferably a source of calcium. Among the halogens, iodine and bromine are preferred. In various embodiments, inorganic bromides make up a part of the sorbent compositions.
Owner:NOX II LTD
Reducing mercury emissions from the burning of coal
Processes and compositions are provided for decreasing emissions of mercury upon combustion of fuels such as coal. Various sorbent compositions are provided that contain components that reduce the level of mercury and / or sulfur emitted into the atmosphere upon burning of coal. In various embodiments, the sorbent compositions are added directly to the fuel before combustion; are added partially to the fuel before combustion and partially into the flue gas post combustion zone; or are added completely into the flue gas post combustion zone. In preferred embodiments, the sorbent compositions comprise a source of halogen and preferably a source of calcium. Among the halogens, iodine and bromine are preferred. In various embodiments, inorganic bromides make up a part of the sorbent compositions.
Owner:NOX II LTD
Metabolic capacity enhancing compositions and methods for use in a mammal
InactiveUS20060024385A1Increase vitalityImproved and increased energy processing of given caloric foods)BiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationMammal
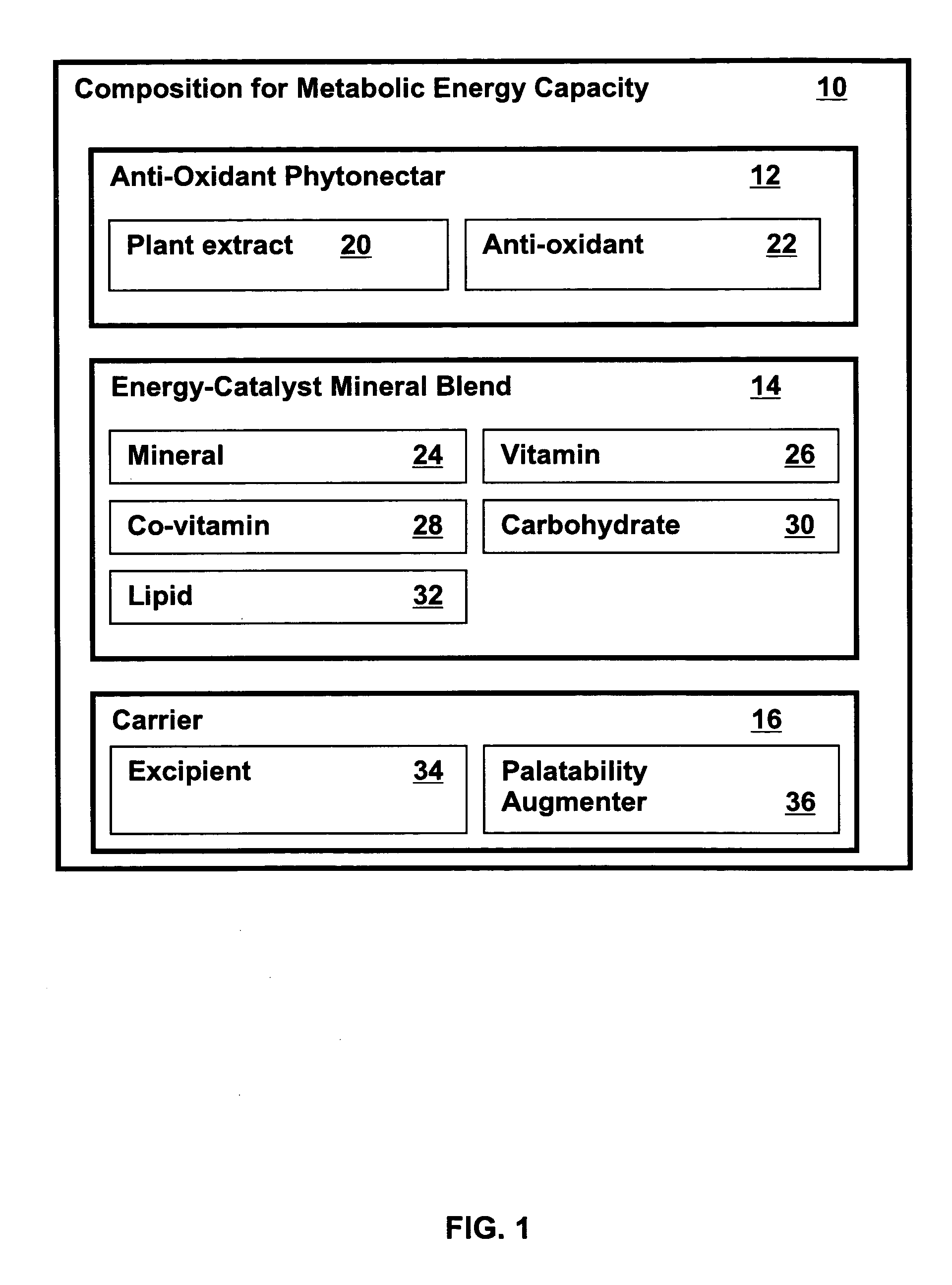
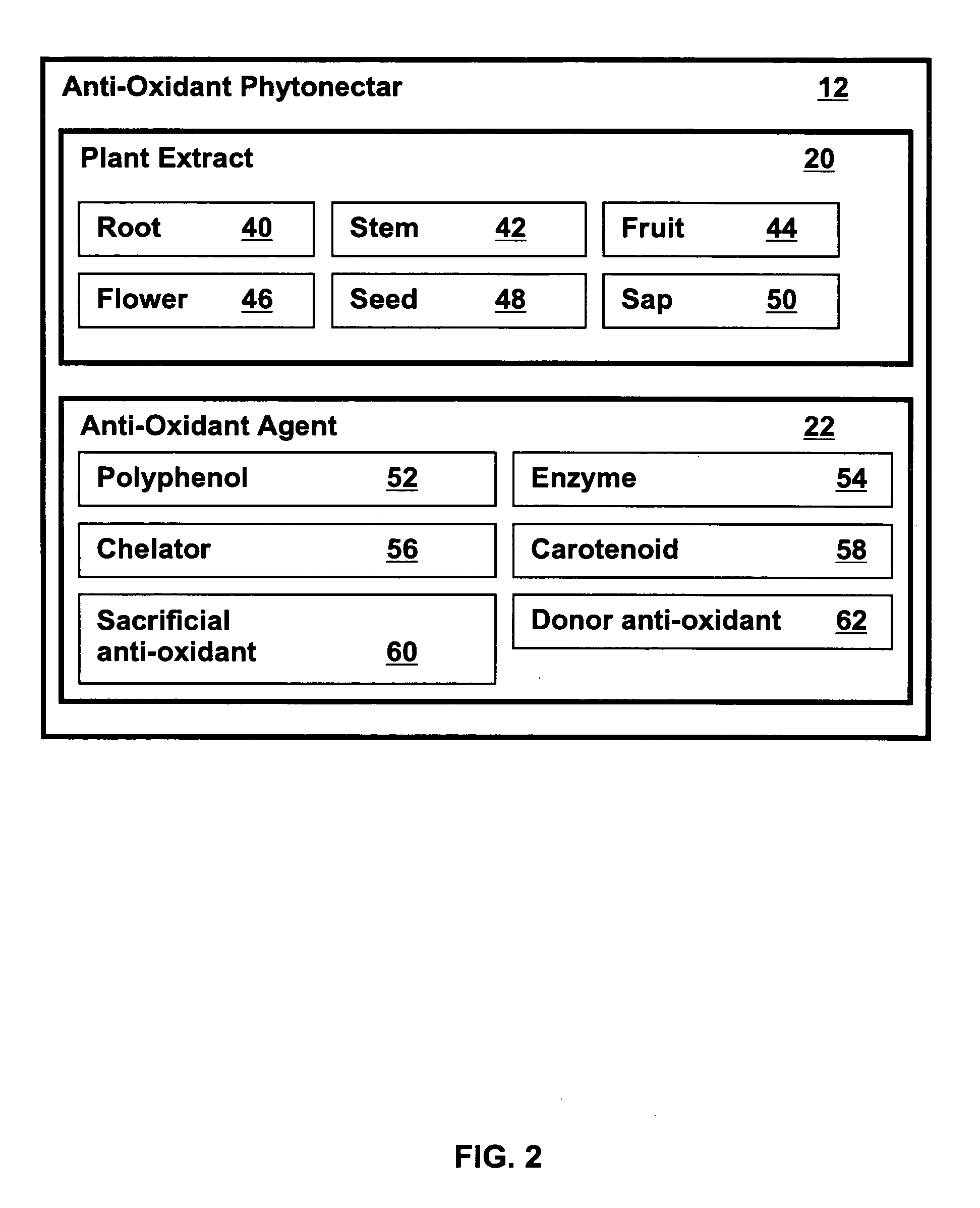
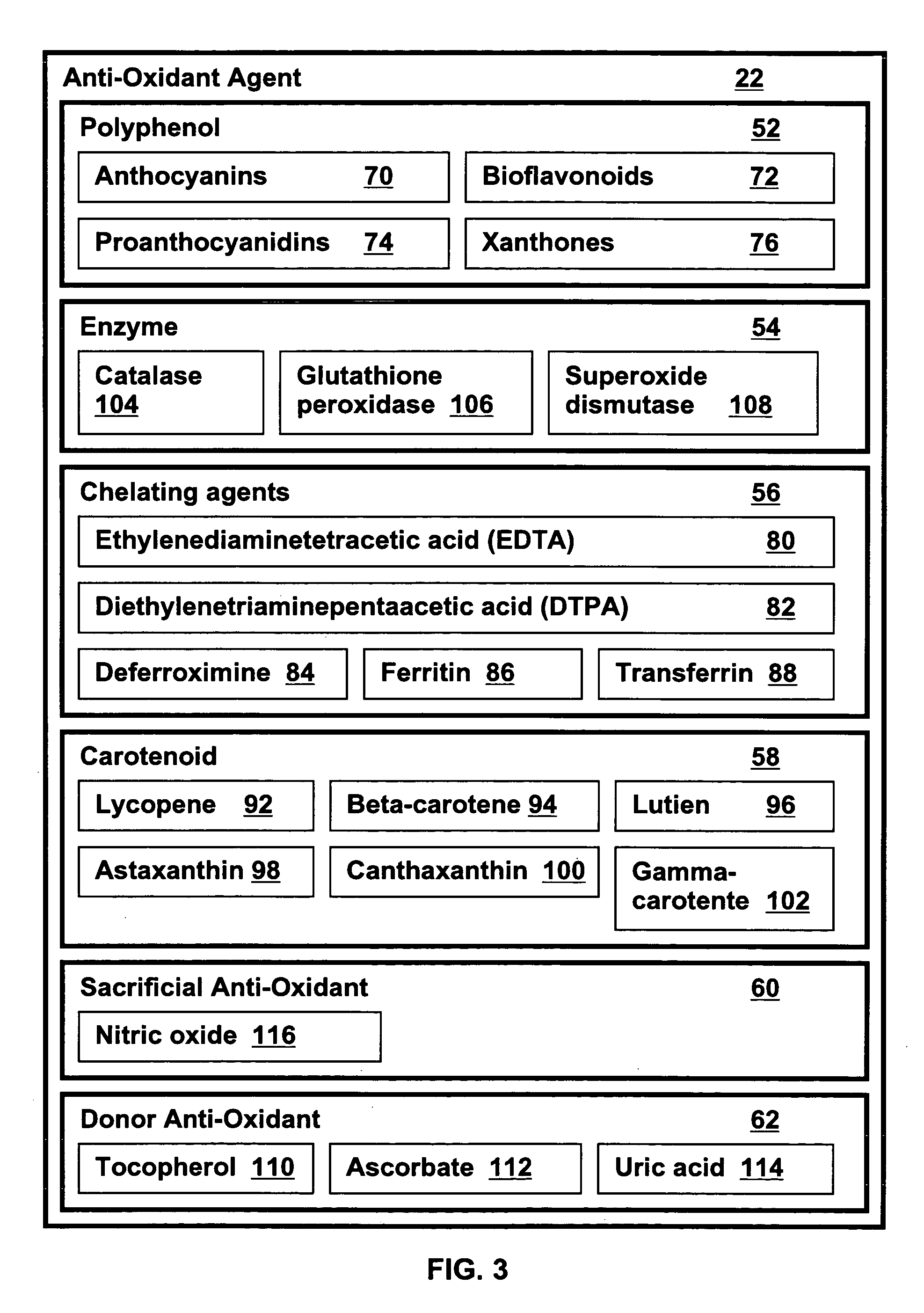
Metabolic energy capacity enhancing compositions and methods for reducing oxidative stress and improving vitality in a mammal are disclosed. A composition for increasing metabolic energy capacity may be in a palatable liquid formulation or a solid dosage form and typically includes an anti-oxidant containing phytonectar and an energy catalyst. An anti-oxidant may include a polyphenol, anthrocyanin, bioflavonoid, proanthocyanidin, and a xanthone. An energy catalyst may include a mineral, vitamin, co-vitamin, carbohydrate and a lipid. In a presently preferred embodiment a composition includes phytonectar extracts from grape, aloe vera, apple, morinda citrifolia, scullcap, blueberry, prune, cranberry, elderberry, bilberry, and gentain and a mineral blend containing calcium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, chromium, selenium, iron, copper, molybdenum, vanadium, potassium, iodine, and cobalt. A method for increasing metabolic energy capacity in a mammal may include consuming a chemical component having the ability to undergo oxidation, producing free radicals and administering a composition having an anti-oxidant containing phytonectar and an energy catalyst.
Owner:PEDERSEN MARK A
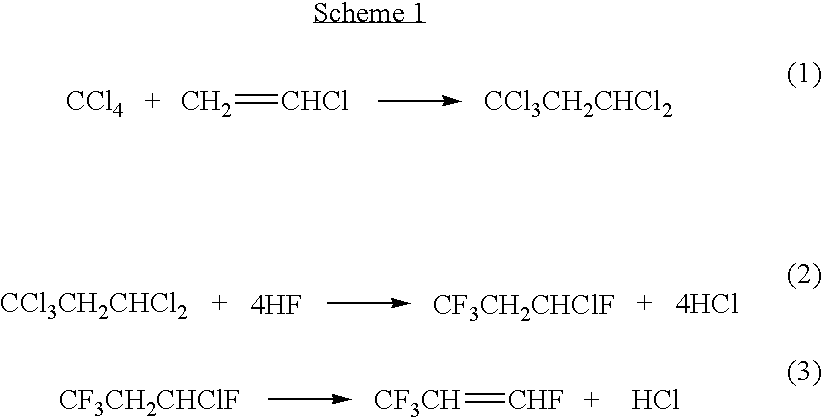
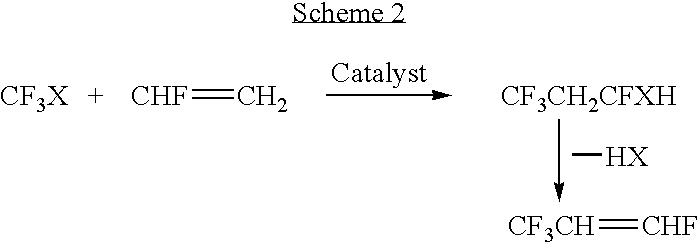
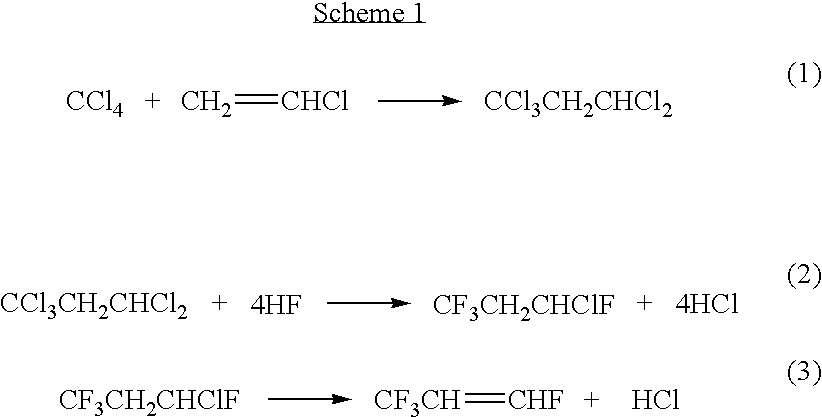
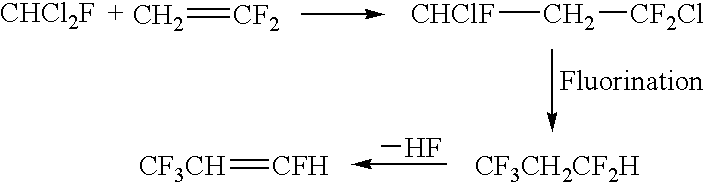
Process for synthesis of fluorinated olefins
ActiveUS20090099396A1Preparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogenBromine
Disclosed is a process for the synthesis of fluorinated olefins, and in particularly preferred embodiments tetrafluorinated olefins having F on an unsaturated, non-terminal carbon, such as 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene. The preferred processes of the present invention in accordance with one embodiment generally comprise:(a) reacting a compound of formula (I)X1X2 (I)with a compound of formula (II)CX1X2X3CX1═CX1X2 (II)to produce a reaction product comprising a compound of formula (III)CF3CHX1CH2X2 (III), and(b) exposing said compound of formula (III) to reaction conditions effective to convert said compound of formula (III) to a compound of formula (IV)CF3CZ=CH2 (IV)wherein X1, X2, and X3 are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, chlorine, bromine, fluorine and iodine, provided that X1 and X2 in formula (I) are not both hydrogen and Z is Cl, I, Br, or F.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
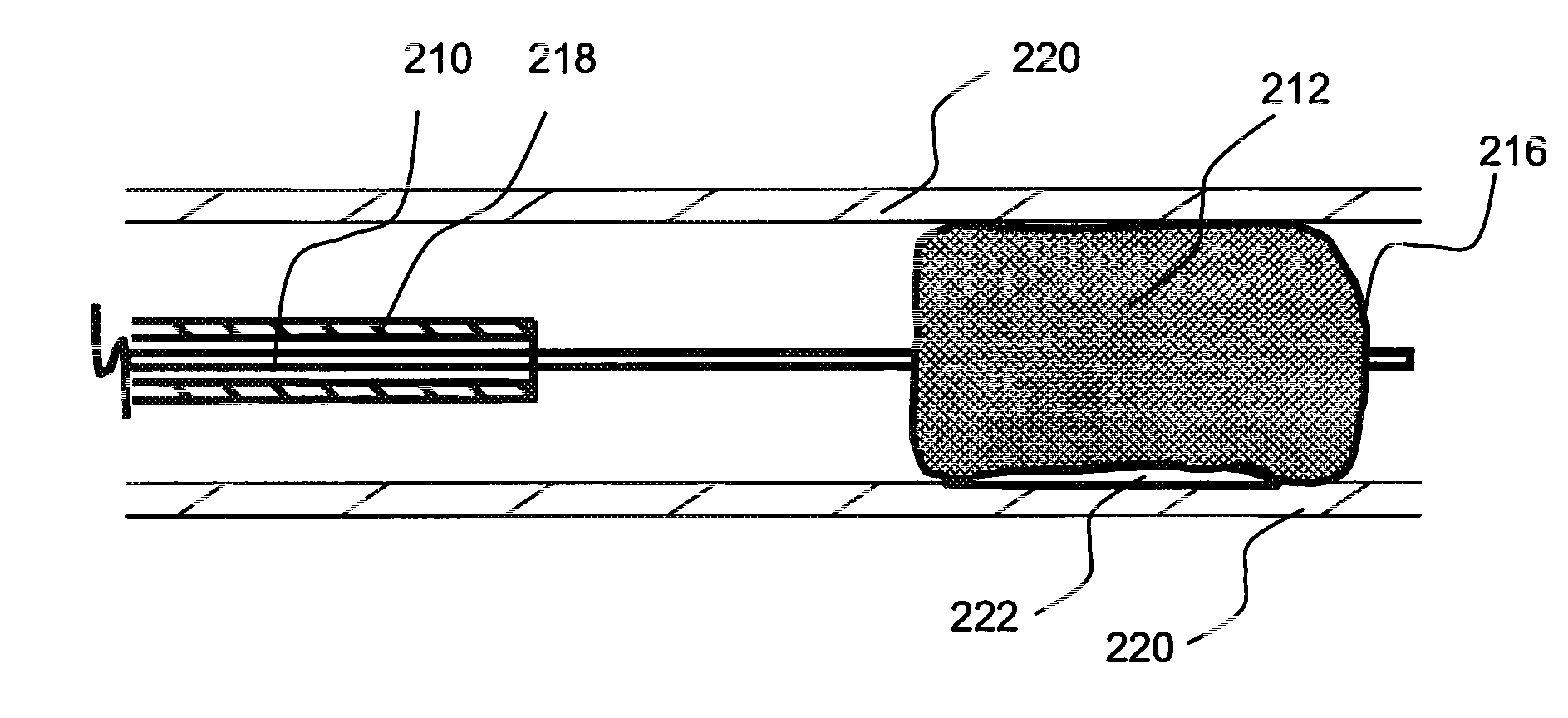
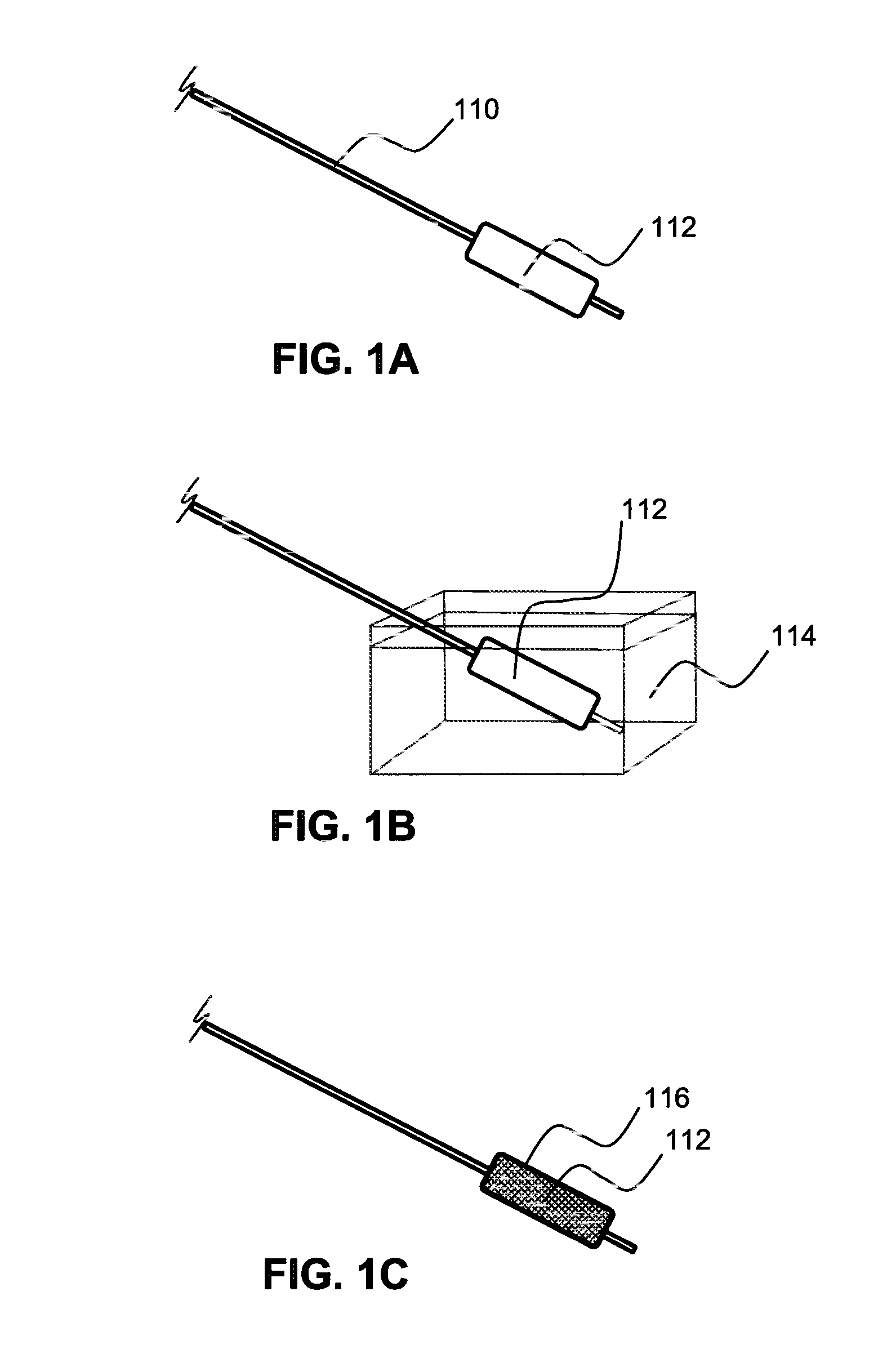
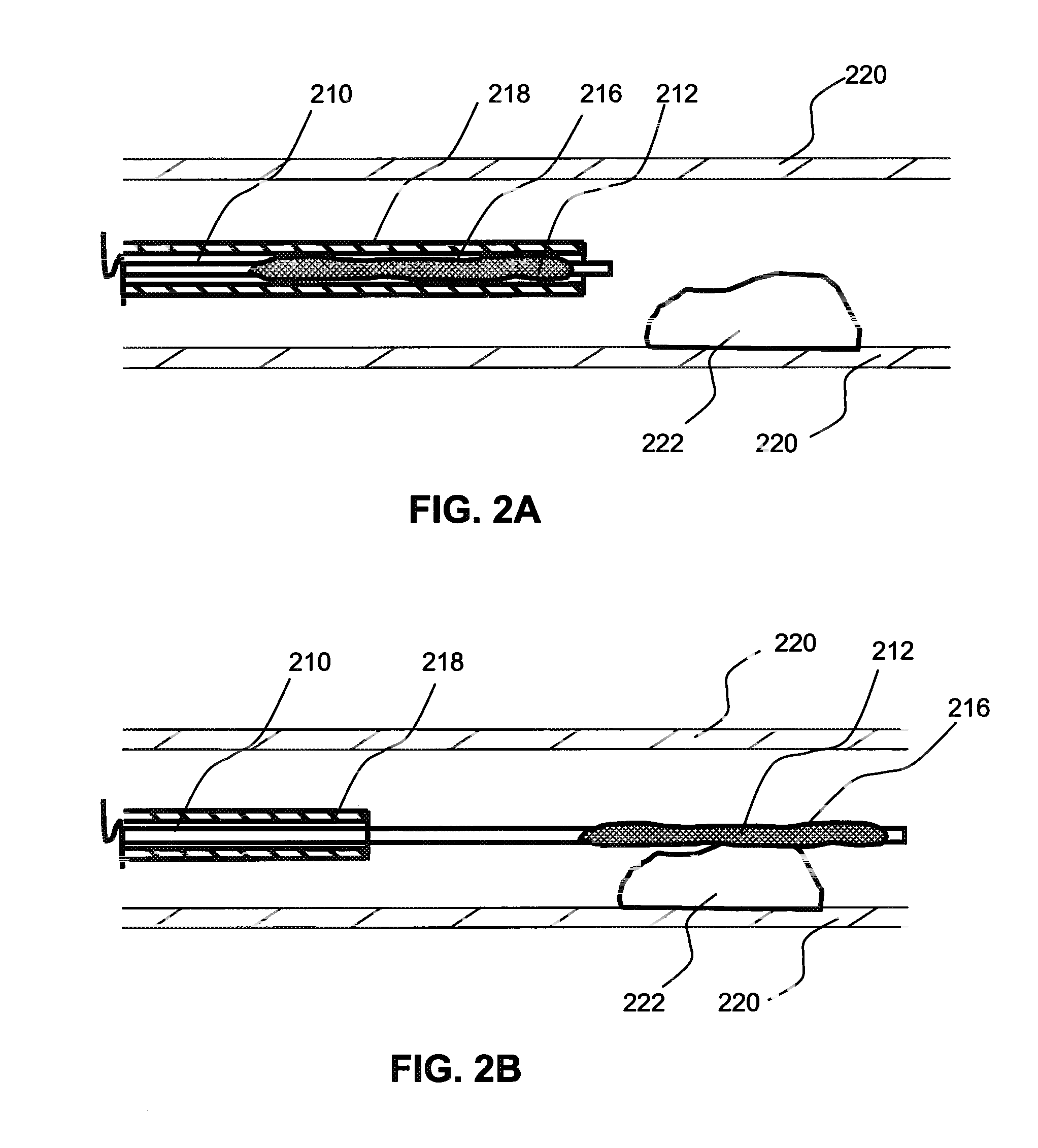
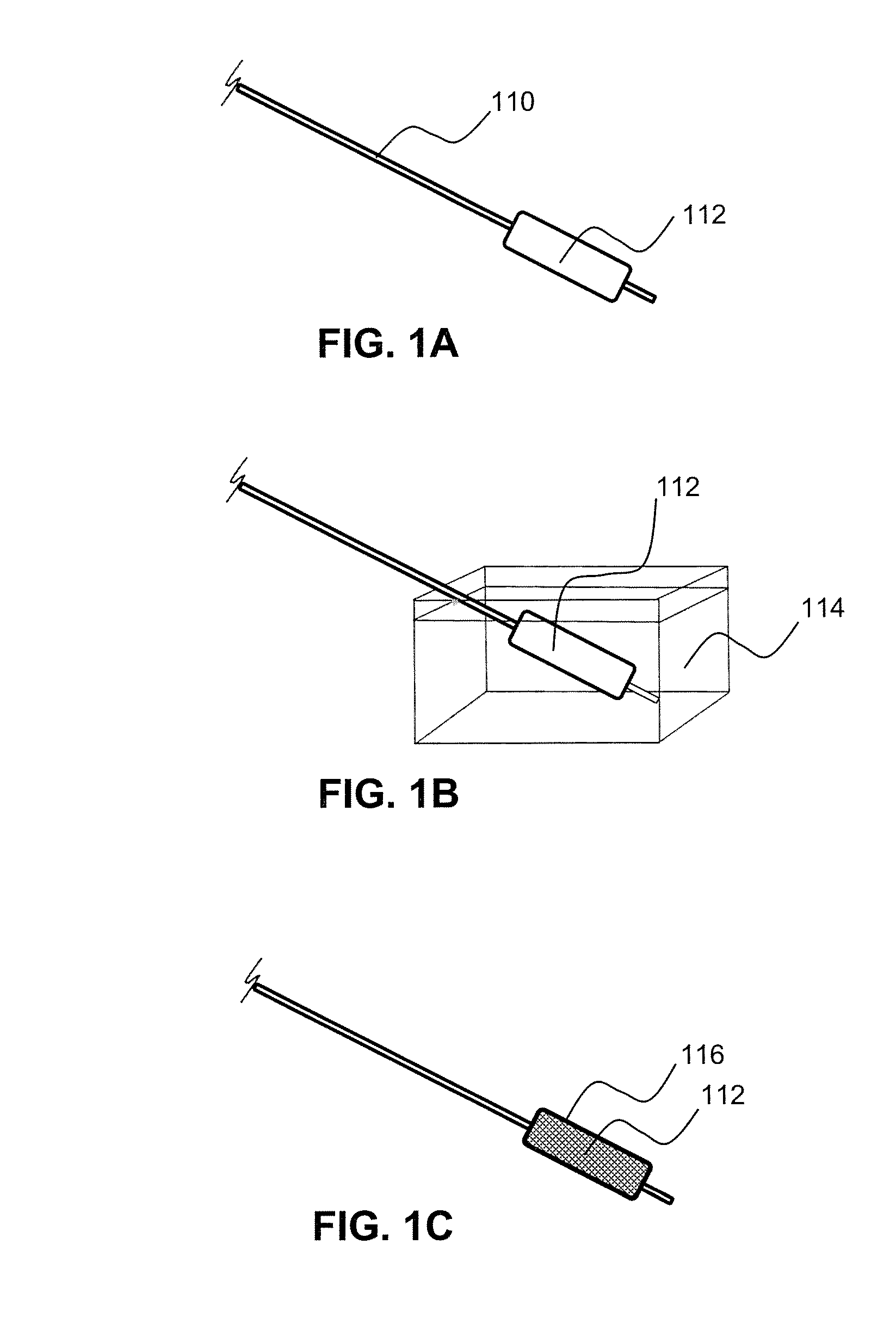
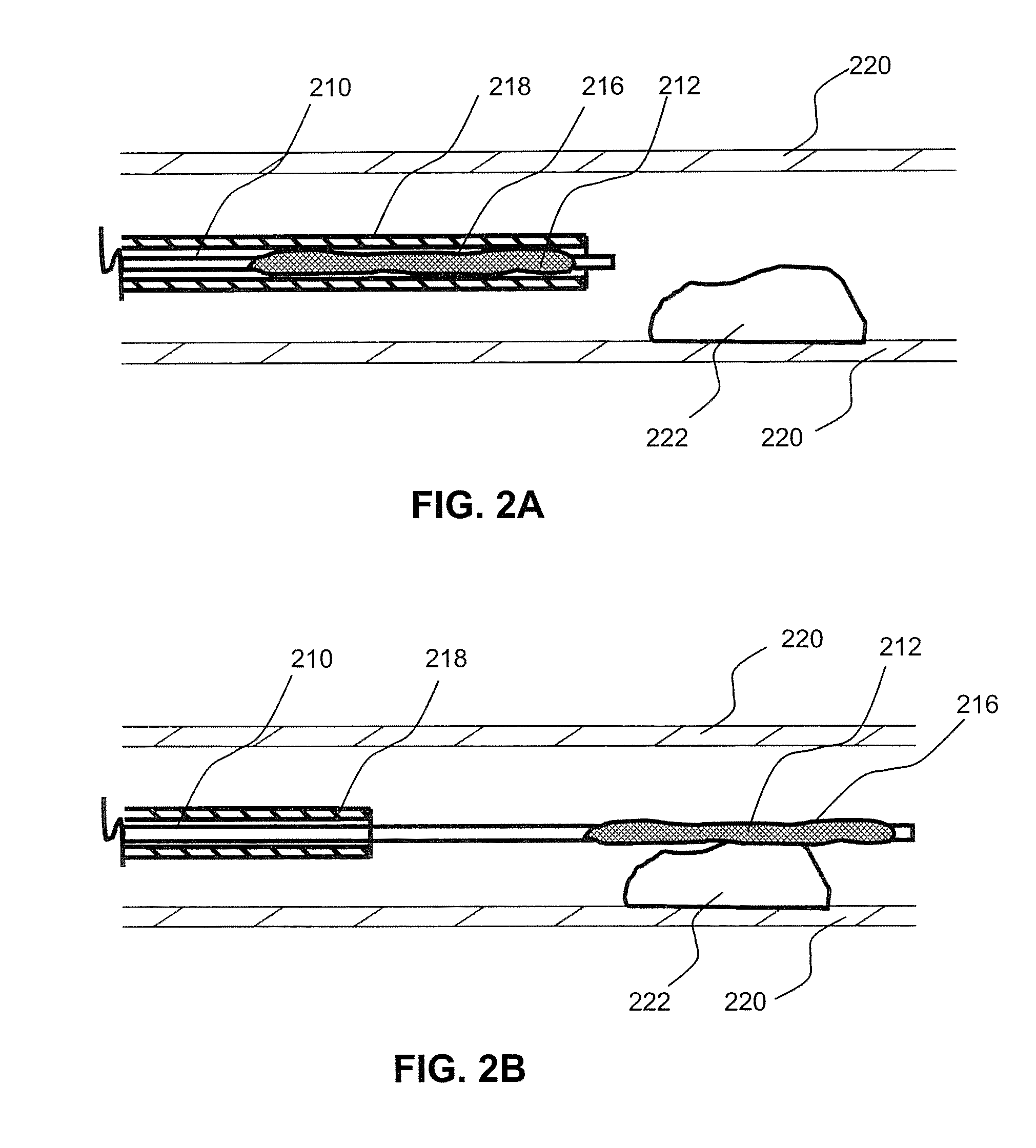
Local delivery of water-soluble or water-insoluble therapeutic agents to the surface of body lumens
ActiveUS20100198190A1Improve treatment efficiencyEasy to processStentsOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleIodine
A method and device for local delivery of water-soluble or water-insoluble therapeutic agents to the tissue of a normal or diseased body lumen is disclosed. An expandable structure of a medical disposable device, such as a balloon of a balloon catheter, is coated with a non-durable coating which is complexed with iodine and has a substantially water-insoluble therapeutic agent dispersed therein. The medical disposable device is inserted into a body lumen, and expanded to contact the non-durable coating against the body lumen and deliver the substantially water-insoluble therapeutic agent to the body lumen tissue.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
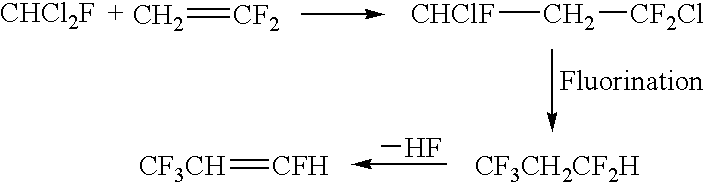
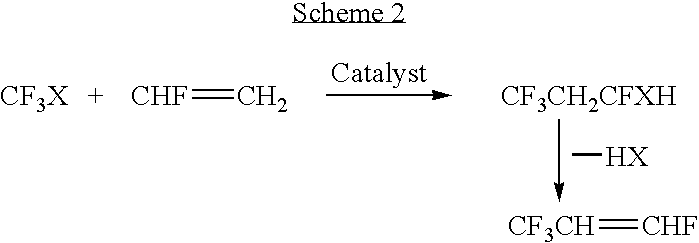
Processes for synthesis of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
InactiveUS7345209B2Preparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-off1,3,3,3-TetrafluoropropeneBromine
Disclosed is a process for the synthesis of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene that comprises, in one preferred embodiment, providing a compound of the formula CF3CH2CHFX, wherein X is a selected from the group consisting of chlorine, bromine and iodine, and exposing said compound to reaction conditions effective to convert said compound to 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene. Other processes for forming 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Foamable iodine composition
The present invention is related to a foamable composition of matter comprising iodine, water, a foam adjuvant, a surface-active agent and a gelling agent. This foamable composition, which may be provided in a propellant free foaming device, or alternatively may further comprise a propellant, evolves into foam, which is effective in the topical treatment and prevention of various skin disorders.
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Stabilized thyroxine medications
InactiveUS6190696B1High strengthWider marginHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsIodised saltThyroxine measurement
Thyroxine medications which include combinations of levothyroxine, and / or liothronine, or dextrothyroxine, or thyroid, and one or more iodine salts, or iodine donor compounds are described, which produce a stable thyroxine medication, with a long shelf life. A method for manufacturing the medications is also described.
Owner:GROENEWOUD PIETER J
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
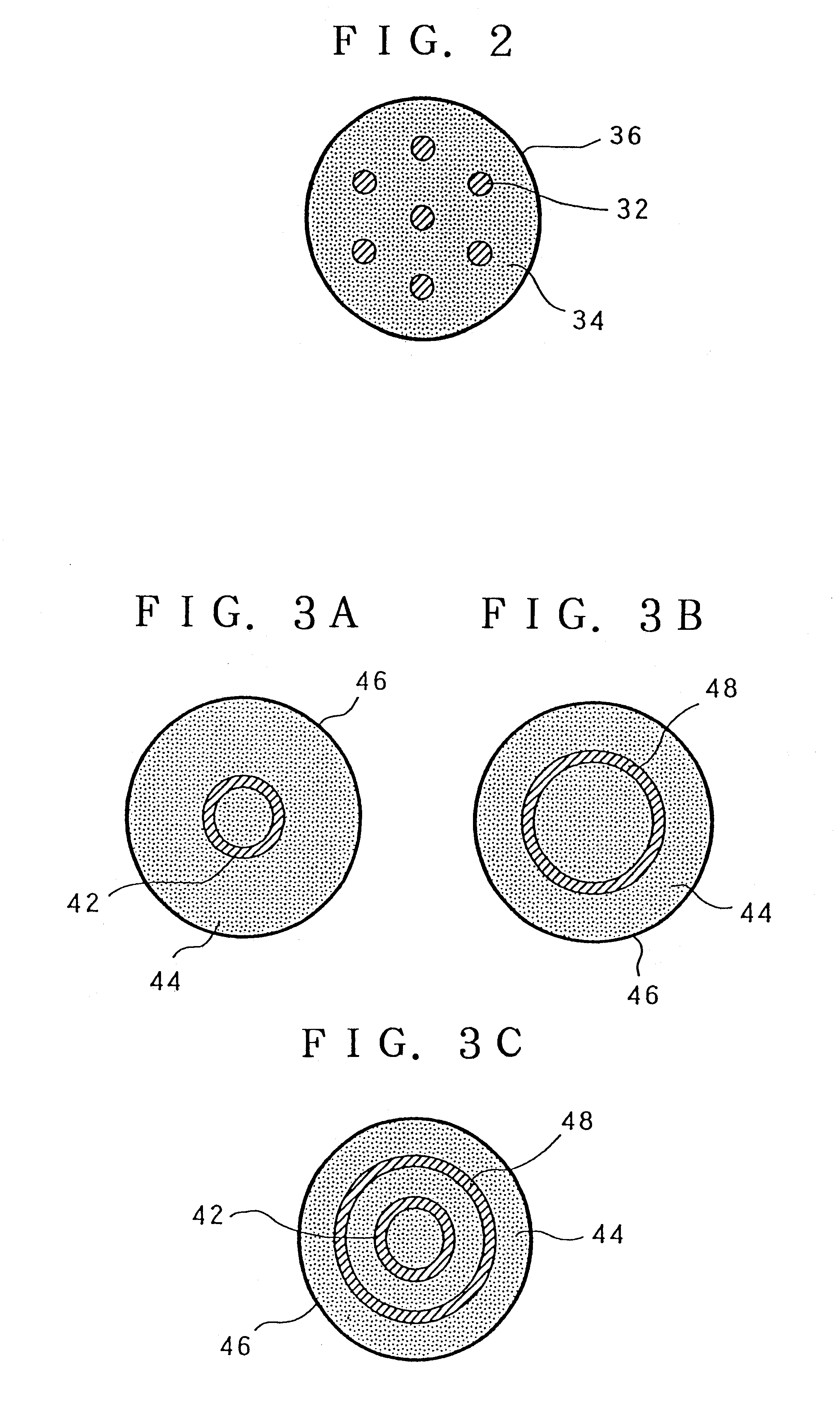
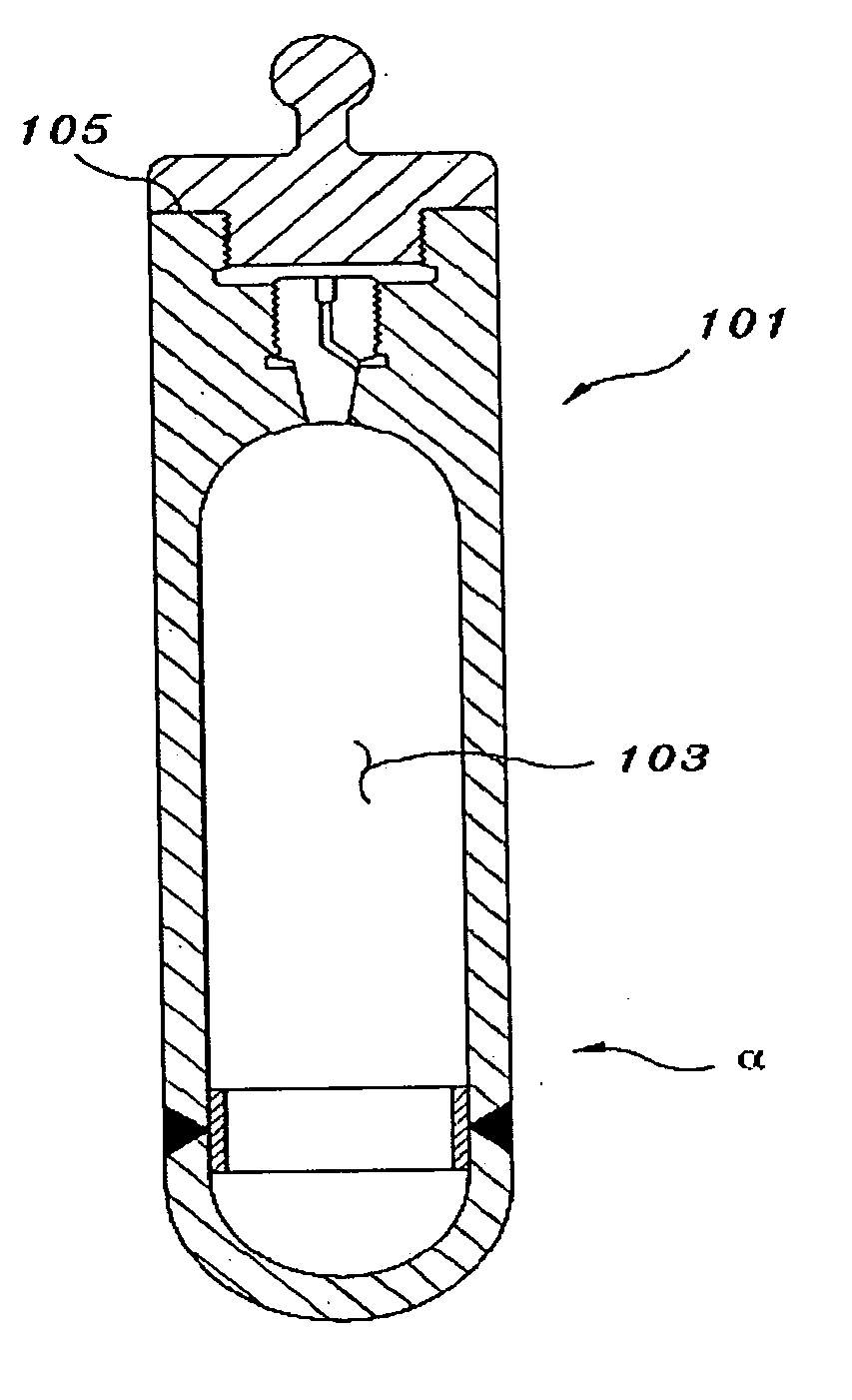
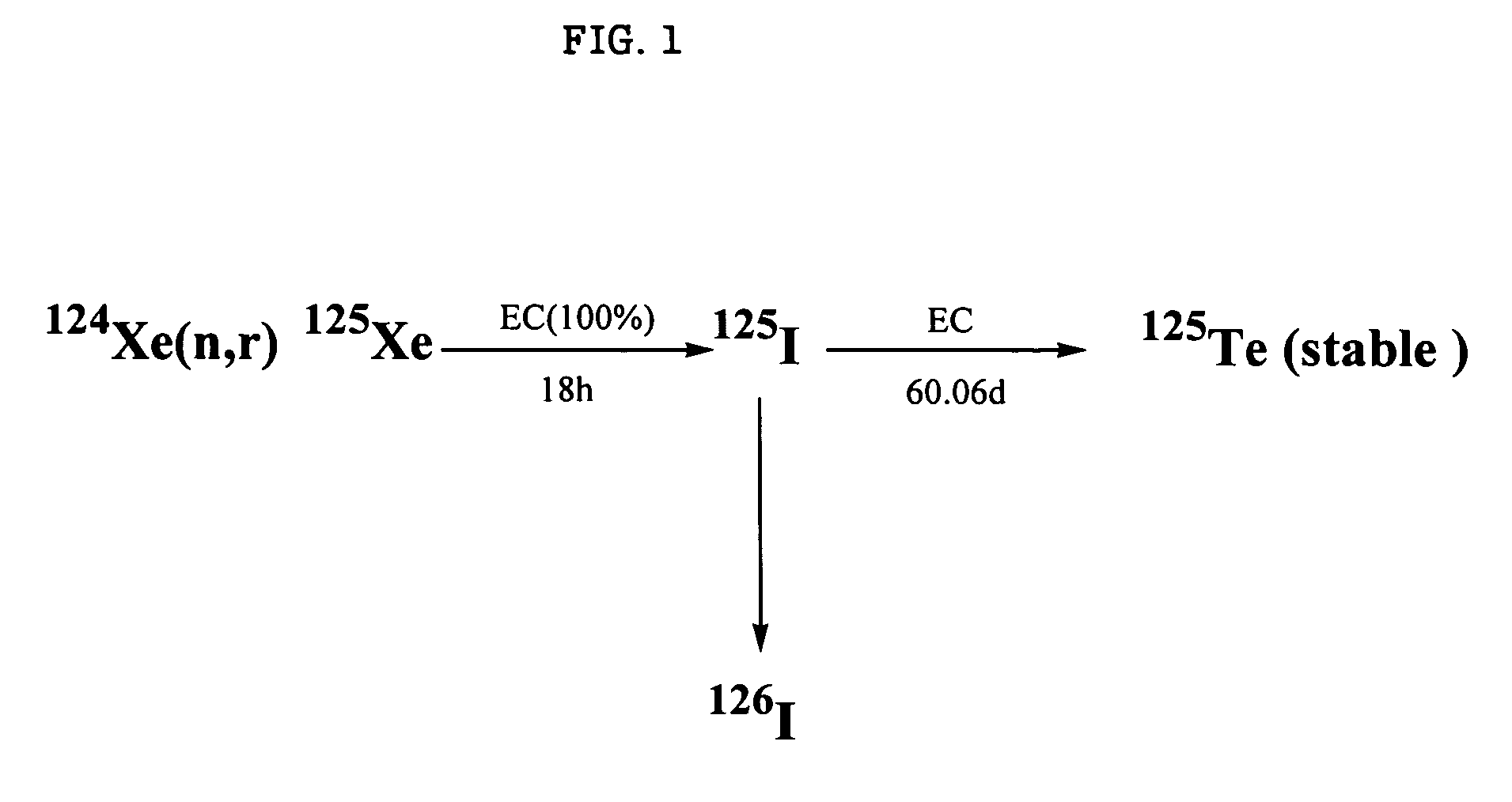
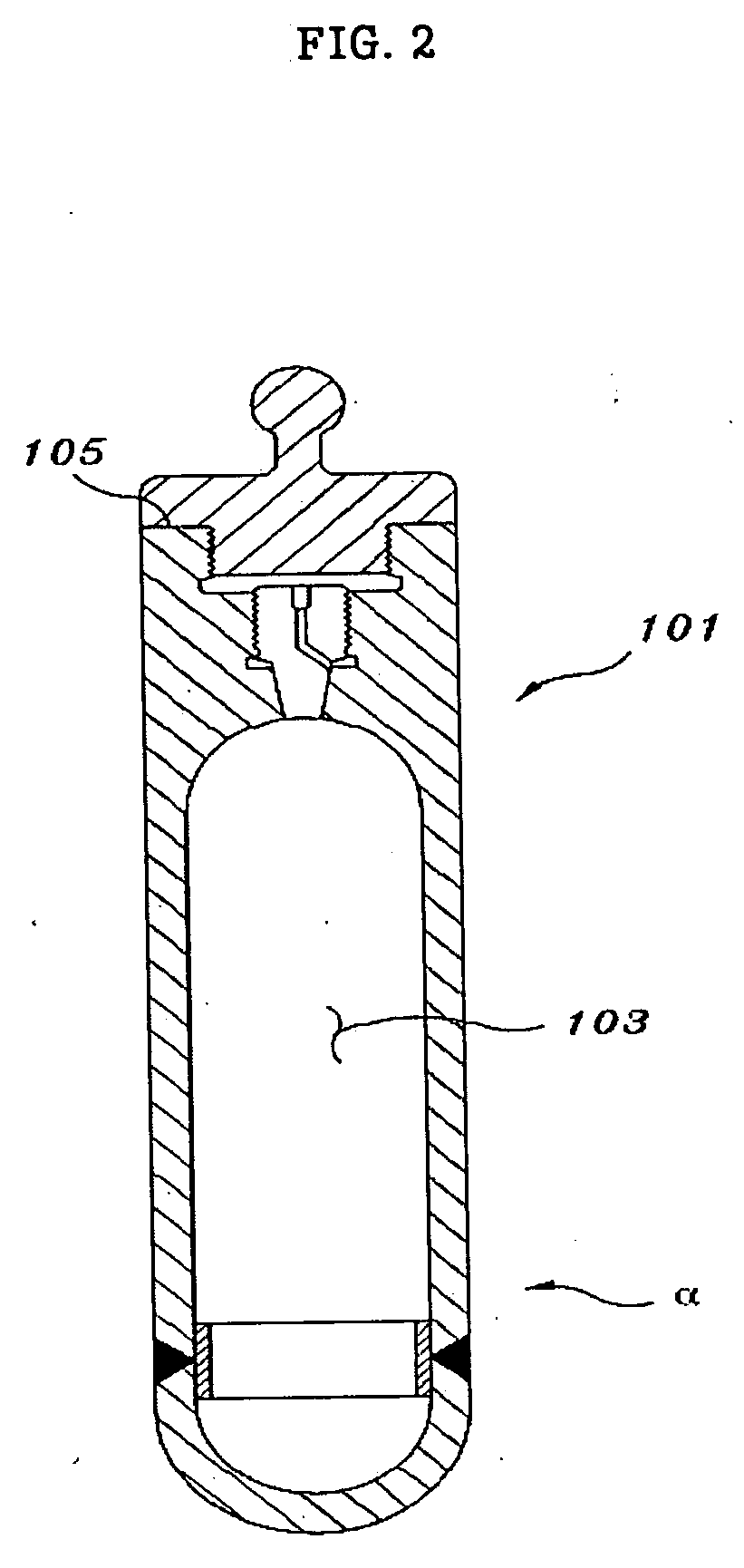
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveUS20060126774A1Reduce neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationIodine
A present invention provides an internal circulating irradiation capsule available for the production of iodine-125 and a related production method. The irradiation capsule filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation part, an upper irradiation part, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into an irradiation hole of a reactor core and irradiated with a large quantity of neutron directly. When neutron is radiated to the xenon gas, iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas. The upper irradiation part protrudes from the irradiation hole, and iodine-125 is transferred to the upper irradiation part by convection and solidified in the upper part. The neutron control member reduces neutron in the upper part to produce iodine-125 of high purity and radioactivity in a large quantity.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Processes for synthesis of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
InactiveUS20050245773A1Overcome deficienciesPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide addition1,3,3,3-TetrafluoropropeneBromine
Disclosed is a process for the synthesis of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene that comprises, in one preferred embodiment, providing a compound of the formula CF3CH2CHFX, wherein X is a selected from the group consisting of chlorine, bromine and iodine, and exposing said compound to reaction conditions effective to convert said compound to 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene. Other processes for forming 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Local delivery of water-soluble or water-insoluble therapeutic agents to the surface of body lumens
ActiveUS20100198150A1Improve treatment efficiencyEasily manufacturable application processOrganic active ingredientsStentsWater insolubleIodine
A method and device for local delivery of a water-insoluble therapeutic agent to the tissue of a normal or diseased body lumen is disclosed. An expandable structure of a medical disposable device, such as a balloon of a balloon catheter, is coated with a non-durable coating which comprises poly(HEMA) complexed with iodine and has a substantially water-insoluble therapeutic agent dispersed therein. The medical disposable device is inserted into a body lumen, and expanded to contact the non-durable coating against the body lumen and deliver the substantially water-insoluble therapeutic agent to the body lumen tissue.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Pneumatic tire
The invention is directed to a pneumatic tire having a tread including a vulcanizable rubber composition including, expressed as parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of elastomer (phr),(A) 60 to 95 phr of solution-polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber with a bound styrene content of from 20 to 30 percent by weight, a vinyl 1,2 content of from 50 to 70 percent by weight based on the butadiene content, and a Tg of from about −40° C. to about −20° C.;(B) 5 to 15 phr of cis-1,4 polybutadiene having a Tg of from −95° C. to −105° C.;(C) 10 to 20 phr of 3,4-polyisoprene;(D) 30 to 70 phr of processing oil;(E) 10 to 30 phr of carbon black having an Iodine absorption ranging from 192 to 212 g / kg according to ASTM D-1510 and an oil absorption ranging from 126 to 142 cc / 100 g according to ASTM D-2414;(F) 90 to 110 phr of silica;(G) 0.5 to 20 phr of a sulfur containing organosilicon compound; and(H) 10 to 20 phr of resin.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
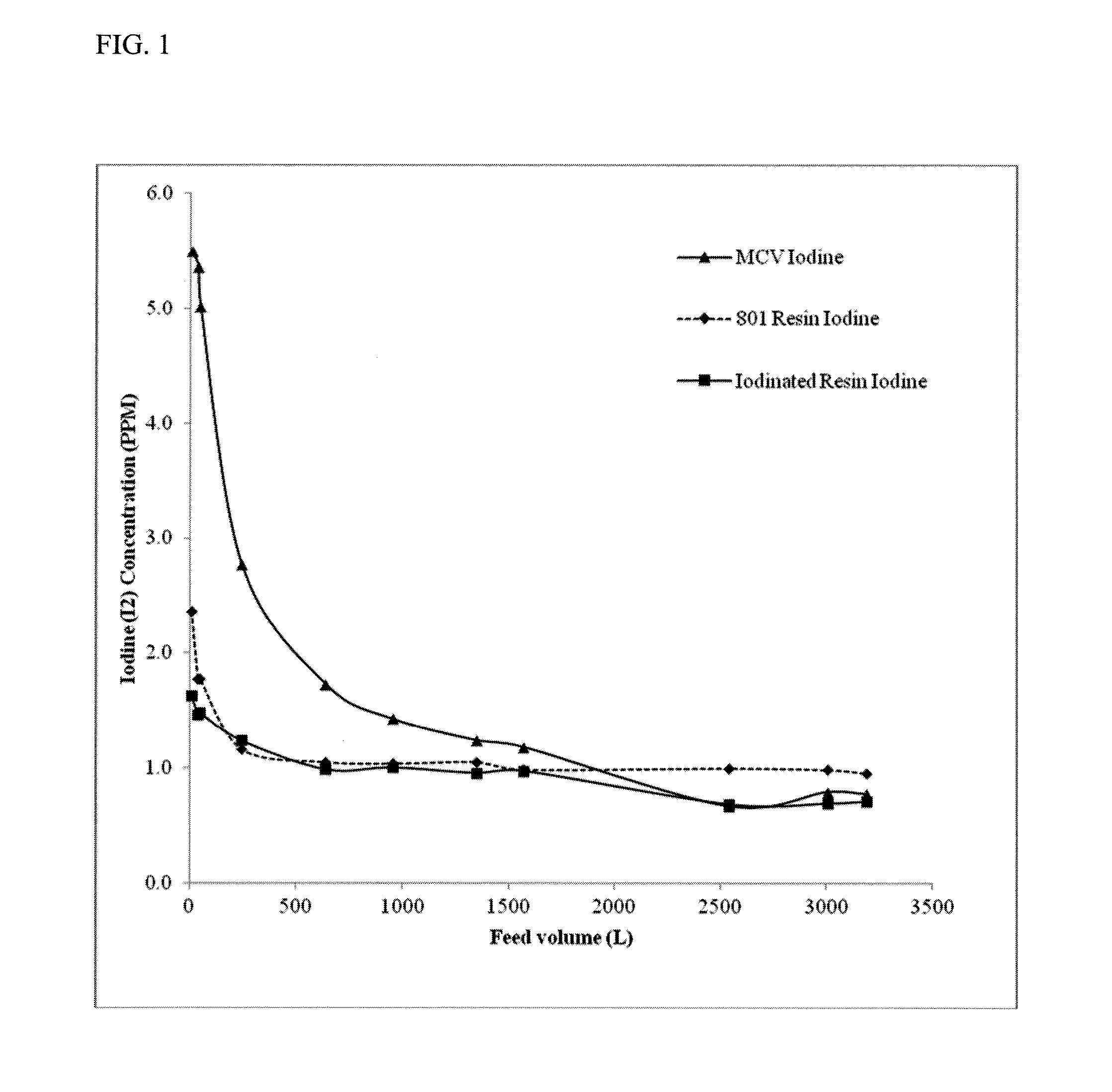
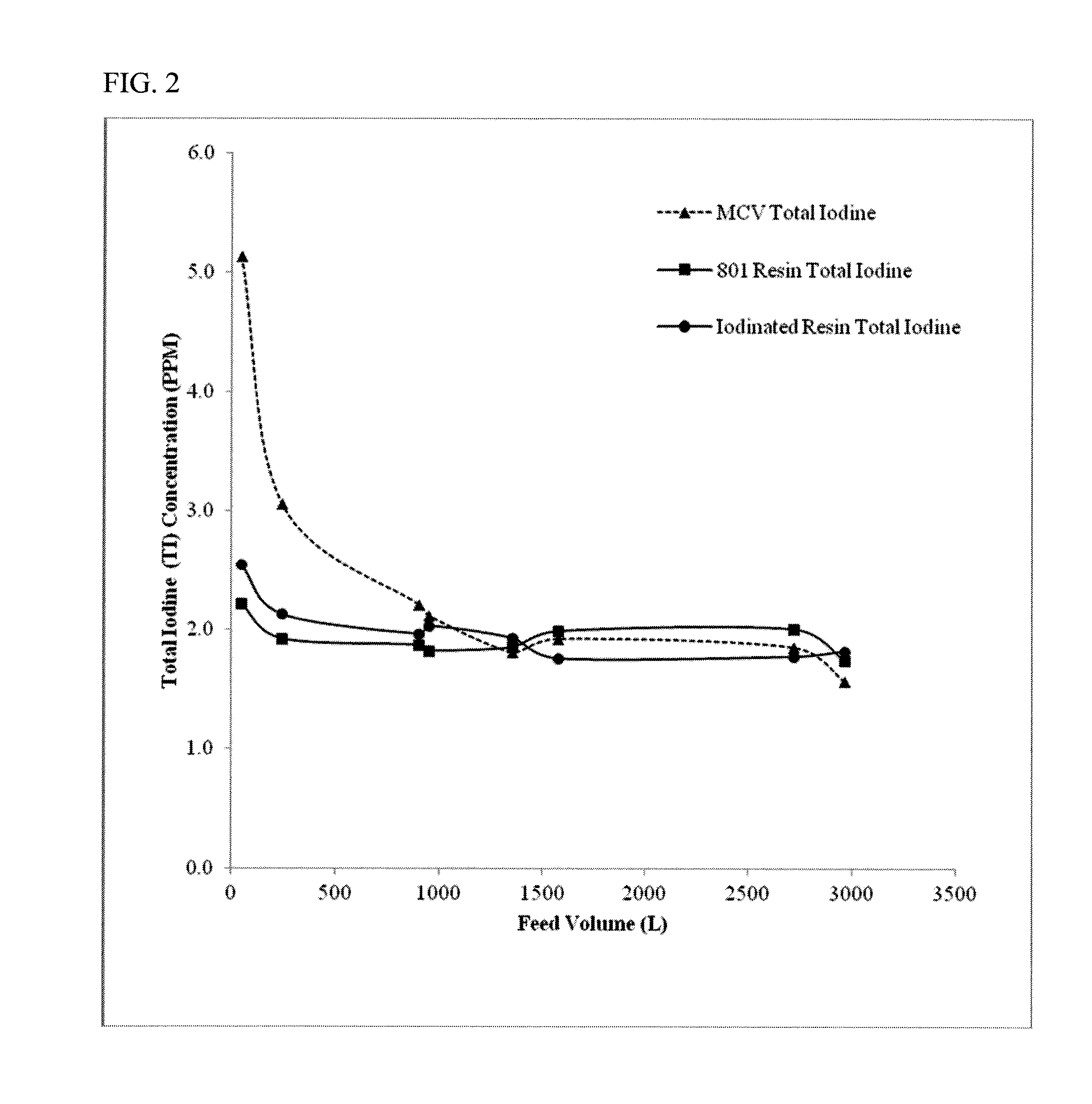
Methods of producing iodinated resins
Methods for producing or regenerating an iodinated resin are presented. The methods include converting iodide residues on a surface of and in pores of an iodide loaded anion exchange resin to iodine and iodine intermediates using a source of active halogen to form an iodinated resin having iodine and iodine intermediate residues on the surface of and in the pores of the iodinated resin. The iodinated resins show reduced and stable levels of iodine elution compared to conventional iodinated anion exchange resins and may utilizes less iodine raw materials during the manufacturing process. The iodinated resin can also act as an end-of life indicator in a water purification system that incorporates the iodinated resin to reduce microbial, including bacterial and viral, contamination in drinking water sources. Methods and systems for purifying water are also presented.
Owner:WATER SECURITY CORP
Prepolymer compositions comprising an antimicrobial agent
Disclosed are biocompatible prepolymer compositions comprising a compatible antimicrobial agent and, in particular, a compatible iodine containing antimicrobial agent. These compositions provide for in situ formation of an antimicrobial polymeric film on mammalian skin.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
Organic electroluminescent device
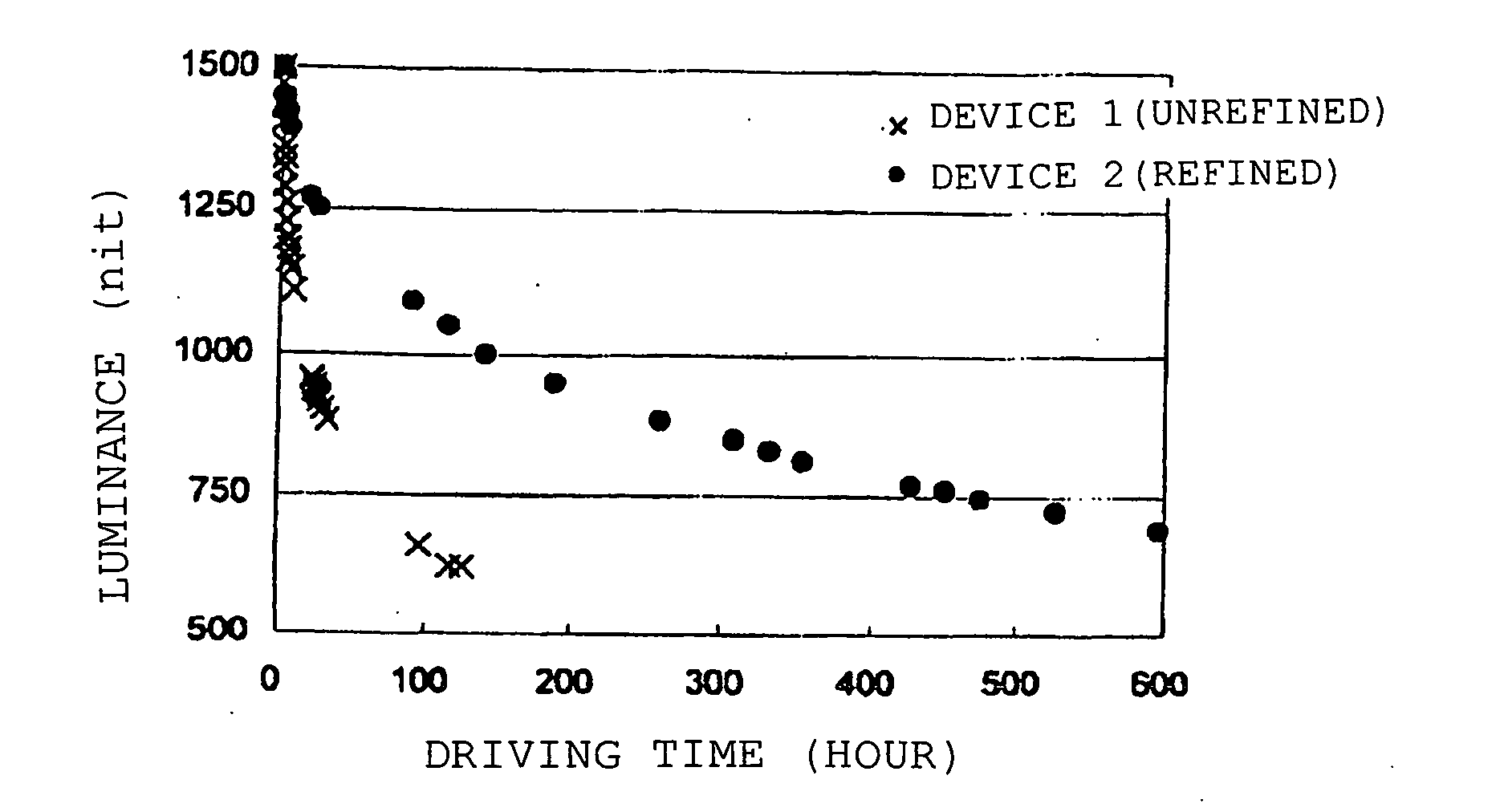
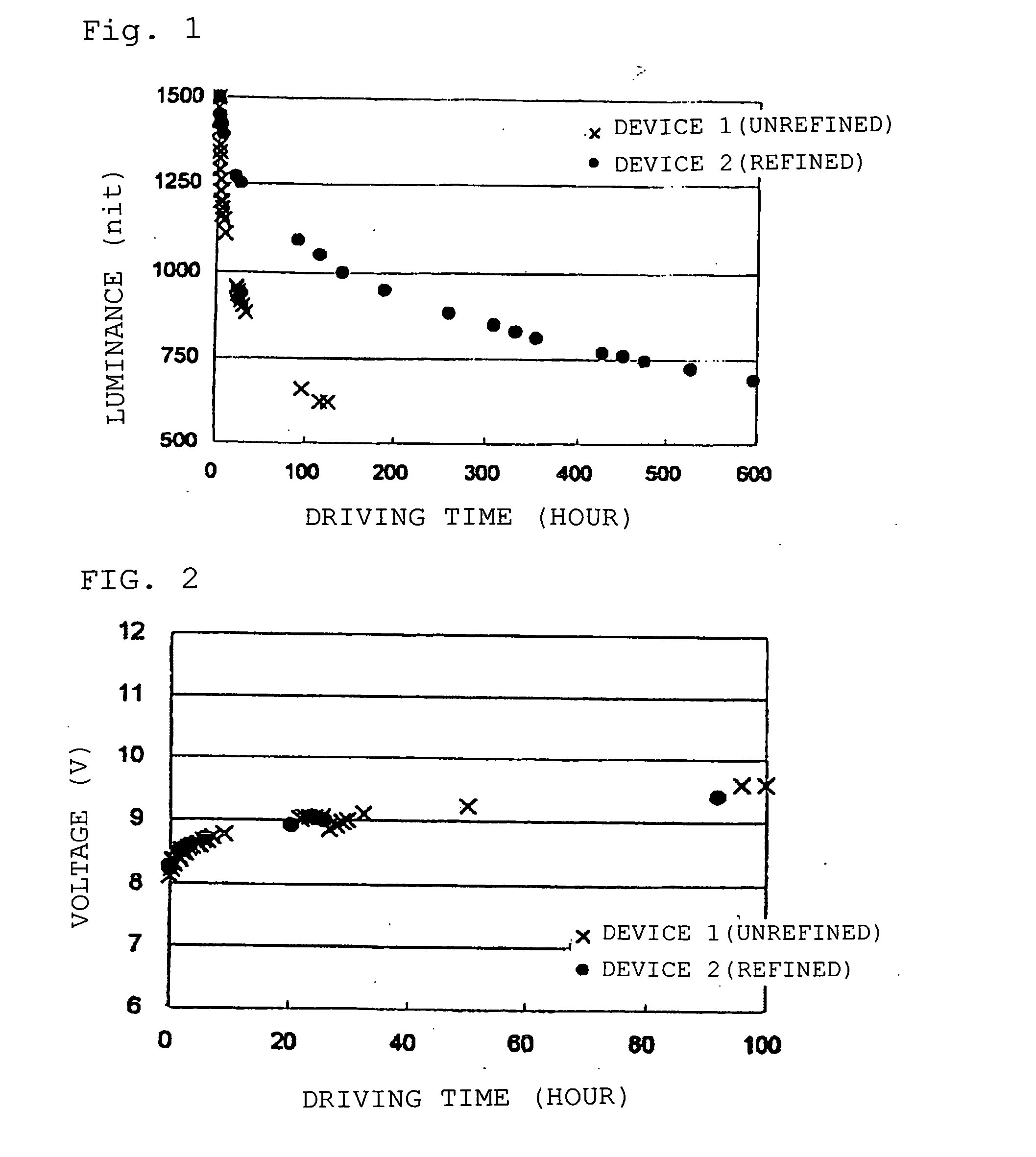
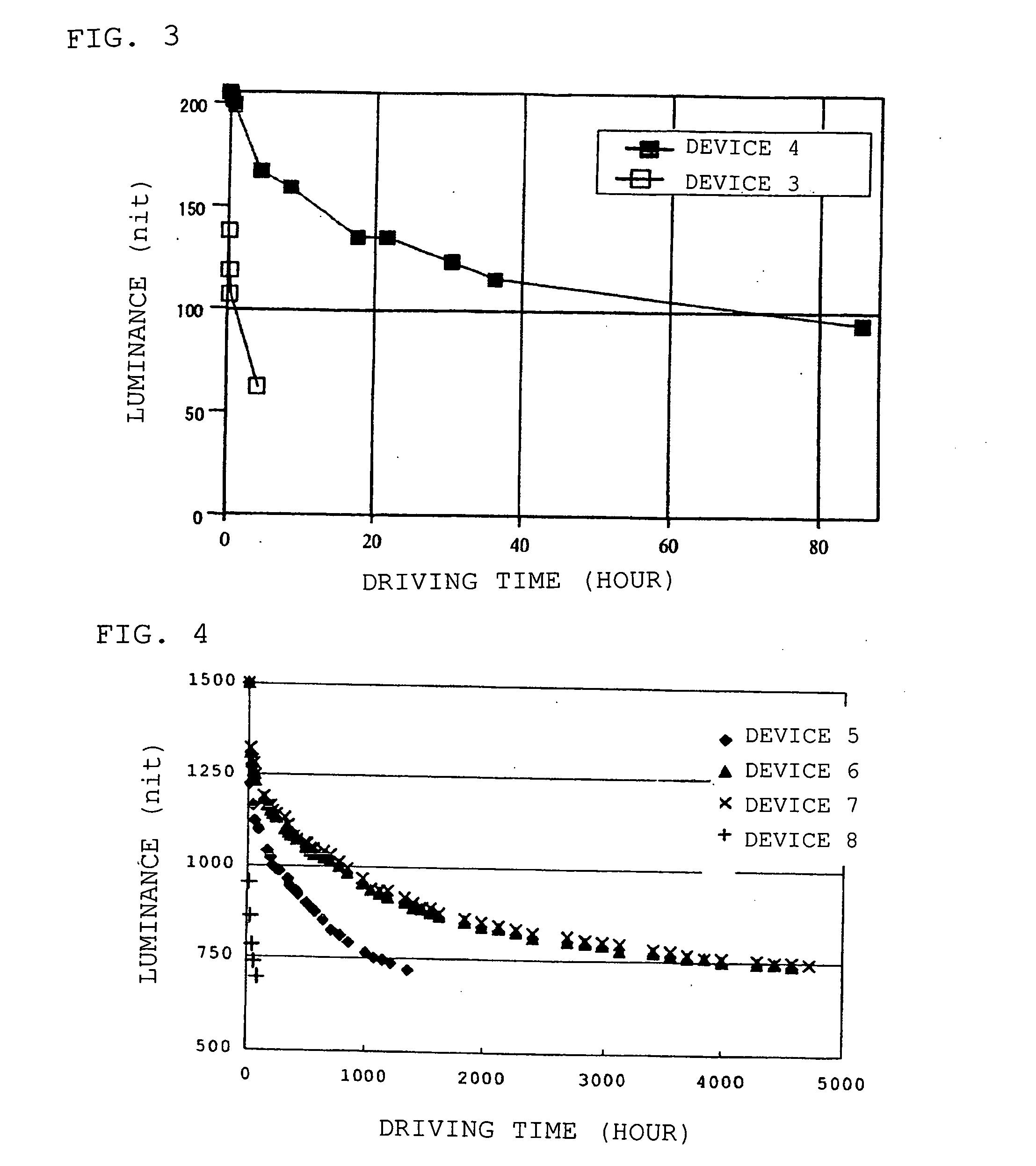
ActiveUS20070172698A1High luminous efficiencySolution to short lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesImpurityMultiple layer
Provided is an organic electroluminescent device in which an organic thin film layer comprising a single layer or plural layers comprising a phosphorescence light-emitting layer containing at least a host material and a phosphorescent organic metal complex is interposed between a cathode and an anode, wherein the total of the halogen element mass concentrations of bromine, iodine and chlorine which are contained as impurities in the host material constituting the light-emitting layer described above is 50 ppm or less. It has a high emission luminance, a high luminous efficiency and a long life.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Color changing skin sealant
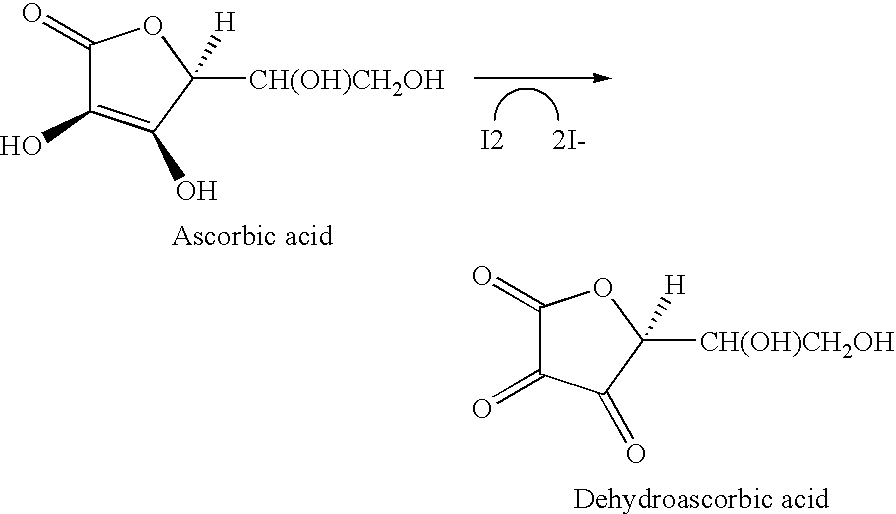
Iodine is used in about 80 percent of surgeries in the US to remove some level of microbial load on the skin prior to making an incision. Skin sealants are applied over skin preps to seal the skin and hold any remaining bacteria in place. Iodine produces a characteristic orange-brown color on skin. A skin sealant is provided that has a decolorant that reacts with the iodine found in most skin preps, rendering the skin prep colorless. A skin sealant containing ascorbic acid (vitamin C), Indigo Carmine or Indigo will react with the iodine, thus visually indicating where the skin prep and sealant have been applied and allowing an unobstructed view of the incision.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
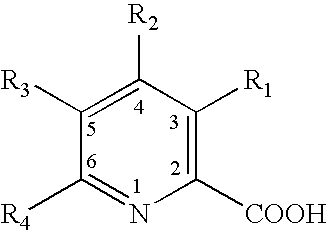
Compositions and methods useful for treatment of acne
Methods and compositions related to treating, controlling or inhibiting acne vulgaris by reducing or inhibiting growth of Proprionibacterium acnes employing a compound having the following structure: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are selected from a group consisting of a carboxyl group, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, isobutyl group, secondary butyl group, tertiary butyl group, pentyl group, isopentyl group, neopentyl group, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and hydrogen.
Owner:NOVACTYL
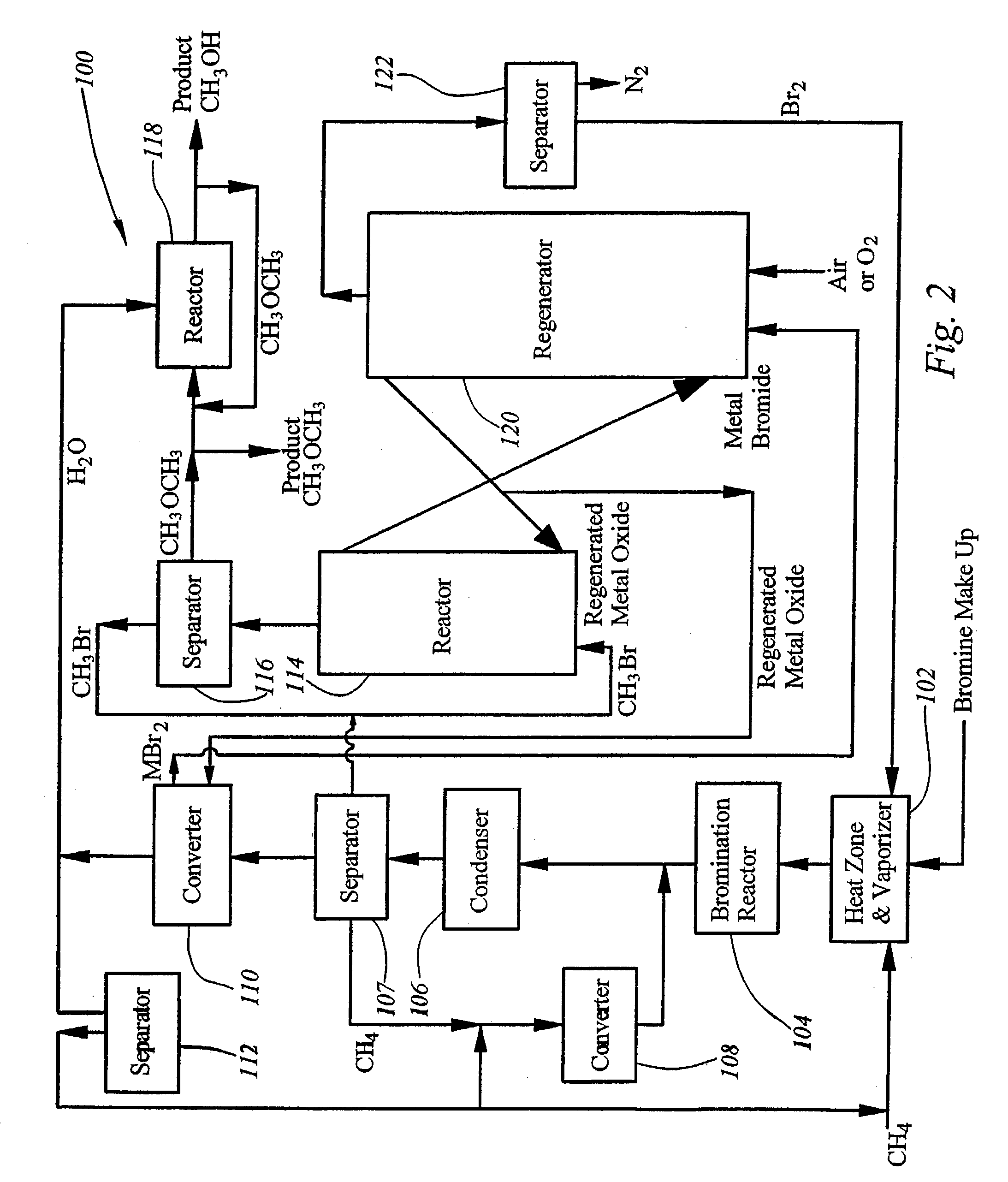
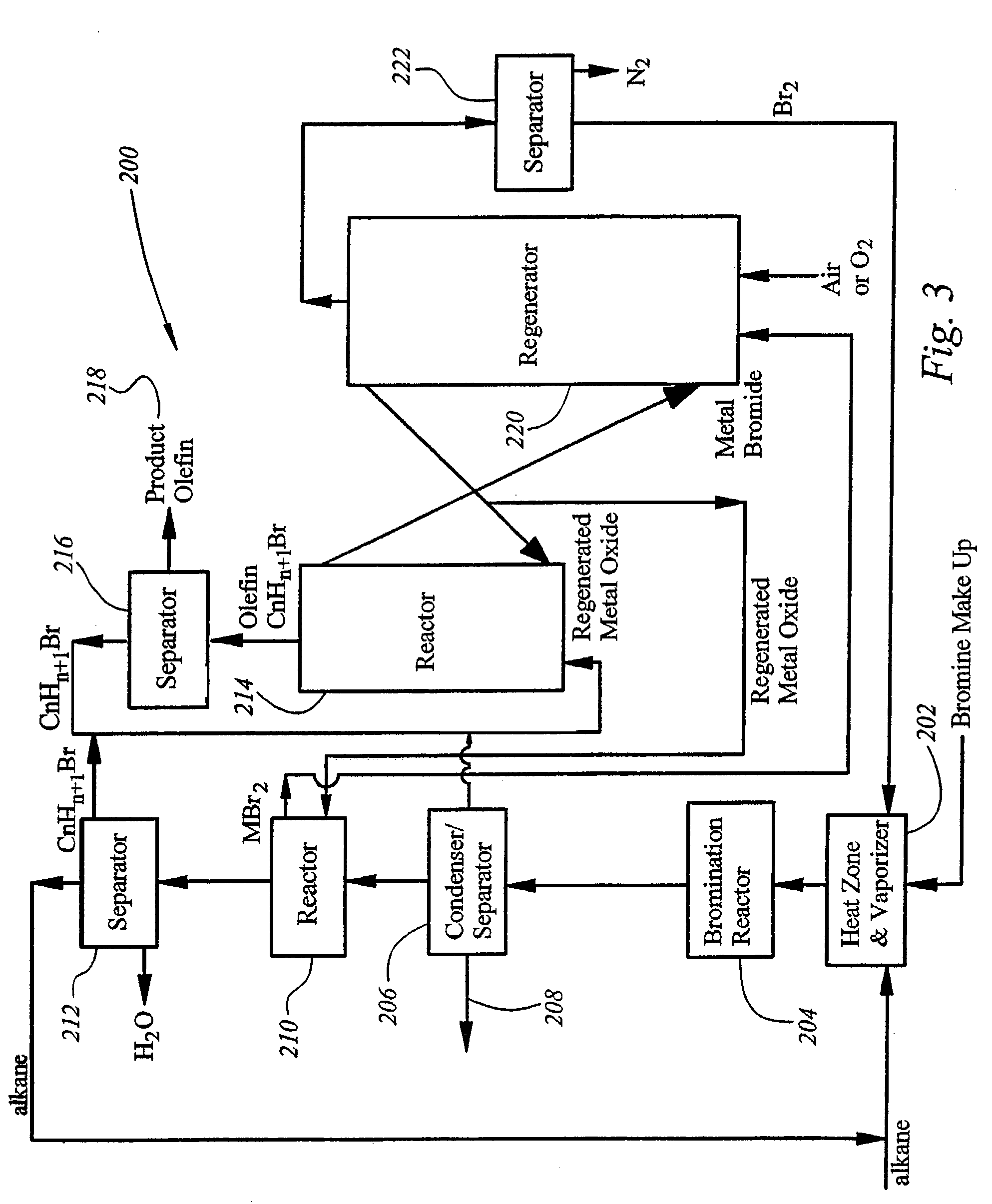
Integrated process for synthesizing alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and olefins from alkanes
InactiveUS7148390B2Less corrosiveImprove securityOrganic compound preparationChemical industryHydrogen halideAlkane
Alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and olefins are manufactured from alkanes by mixing an alkane and a halogen selected from the group including chlorine, bromine, and iodine in a reactor to form alkyl halide and hydrogen halide. The alkyl halide only or the alkyl halide and the hydrogen halide are directed into contact with metal oxide to form an alcohol and / or an ether, or an olefin and metal halide. The metal halide is oxidized to form original metal oxide and halogen, both of which are recycled.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Thermoelectric material, thermoelectric element, thermoelectric module and methods for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20070095383A1Reduce in quantityAvoid decompositionThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermoelectric materialsBromine
T provide an N type thermoelectric material having figure of the merit improved to be comparable to or higher than that of P type thermoelectric material, the N type thermoelectric material of the present invention contains at least one kind of Bi and Sb and at least one kind of Te and Se as main components, and contains bromine (Br) and iodine (I) to have carrier in such a concentration that corresponds to the contents of bromine (Br) and iodine (I).
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Kits containing cyanoacrylate compositions comprising an antimicrobial agent
Disclosed are kits of parts comprising a first container comprising a cyanoacrylate composition and a second container comprising a compatible antimicrobial agent and, in particular, a compatible iodine containing antimicrobial agent. Mixture of these compositions provide for in situ formation of an antimicrobial polymeric cyanoacrylate film on mammalian skin.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
Systems and methods for the cyclotron production of iodine-124
ActiveUS20070064858A1Good physical propertiesSimple processConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDistillationIodine
The present invention relates to targets, systems and methods for the cyclotron production of 124I from aluminum telluride (Al2Te3) targets. The systems and methods utilize low energy proton cyclotrons to produce 124I by the 124Te(p,n) reaction from enriched Al2Te3 glassy melts. The 124I is recovered in high yield from the glassy melt by adapted methods of common thermal distillation techniques.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
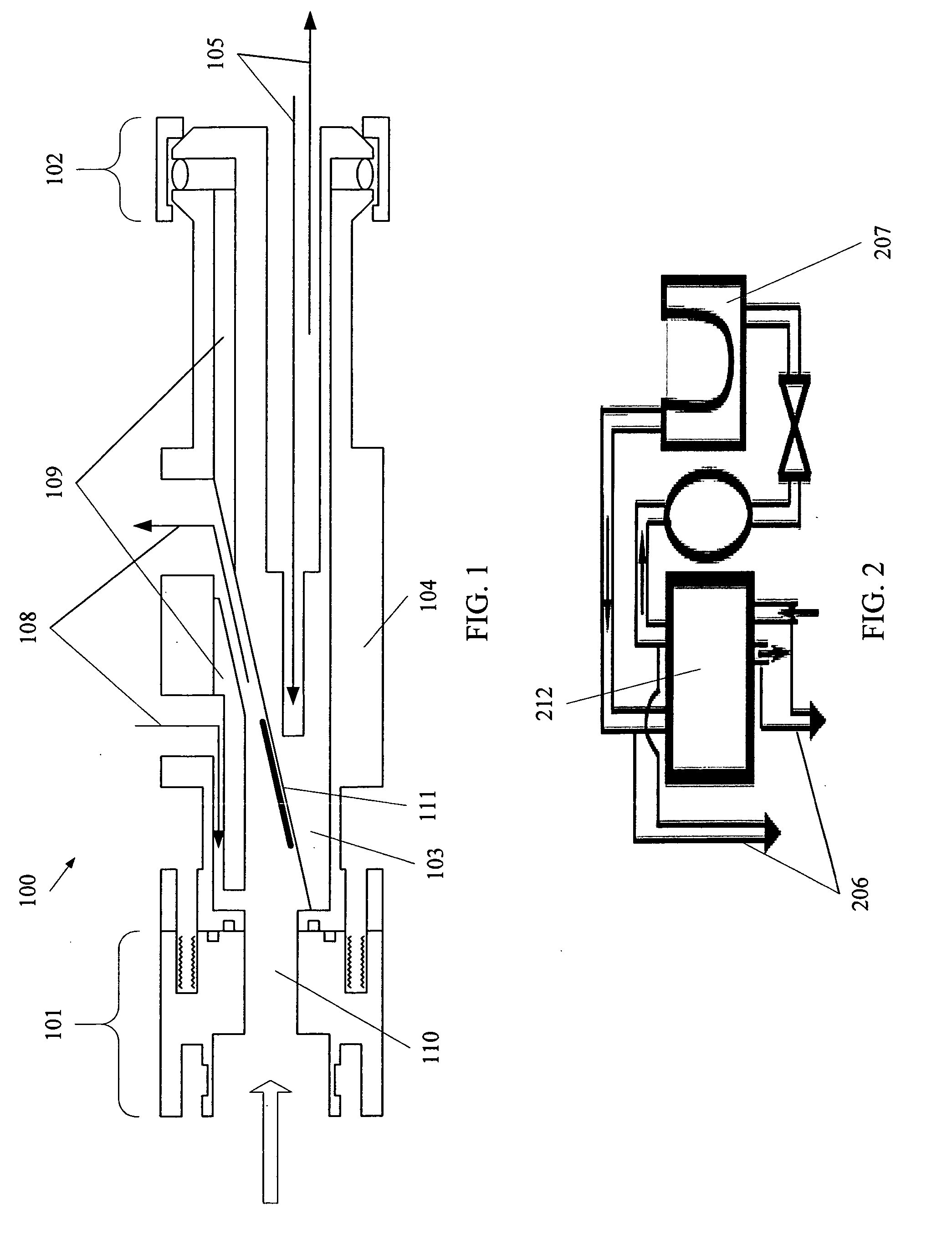
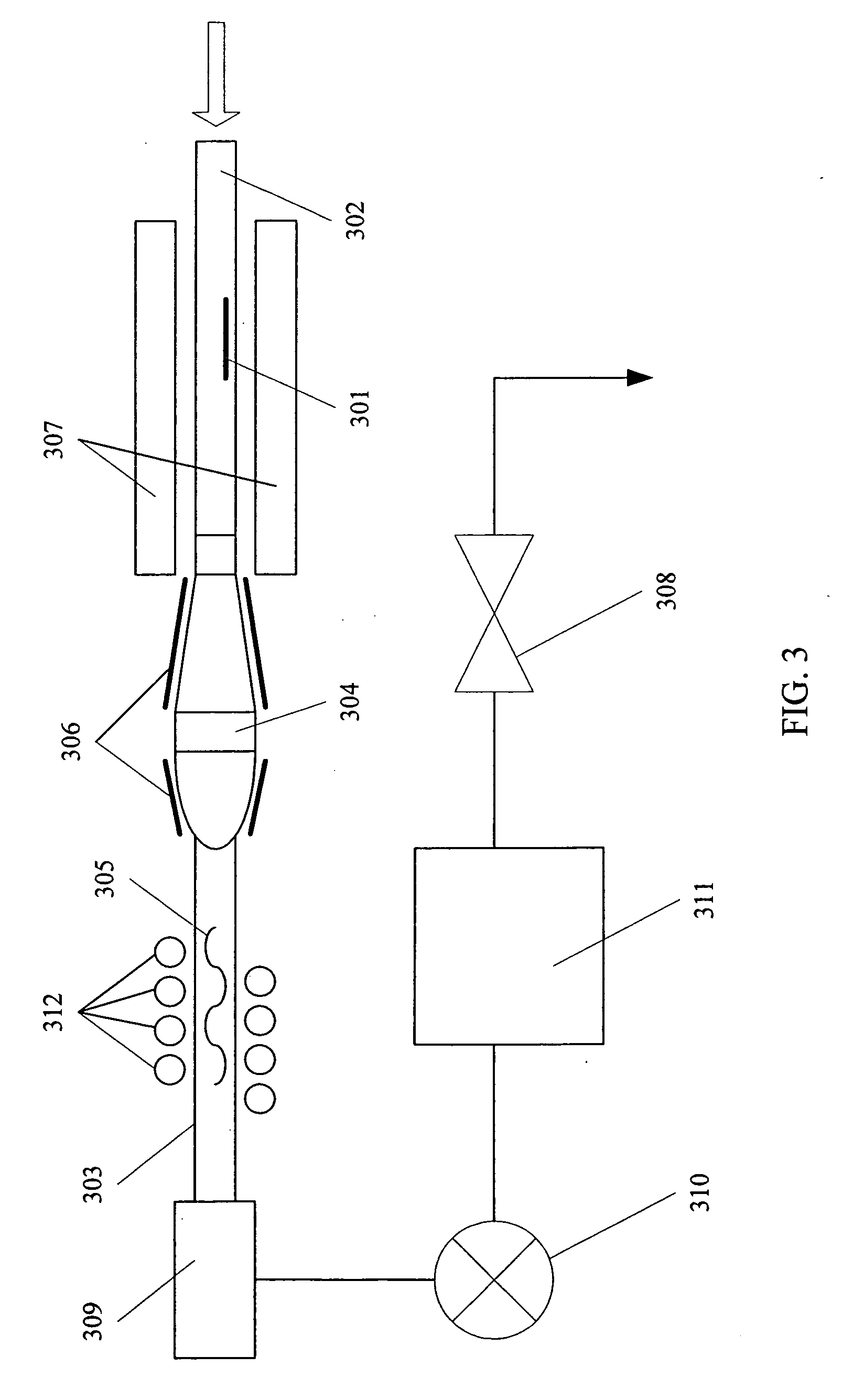
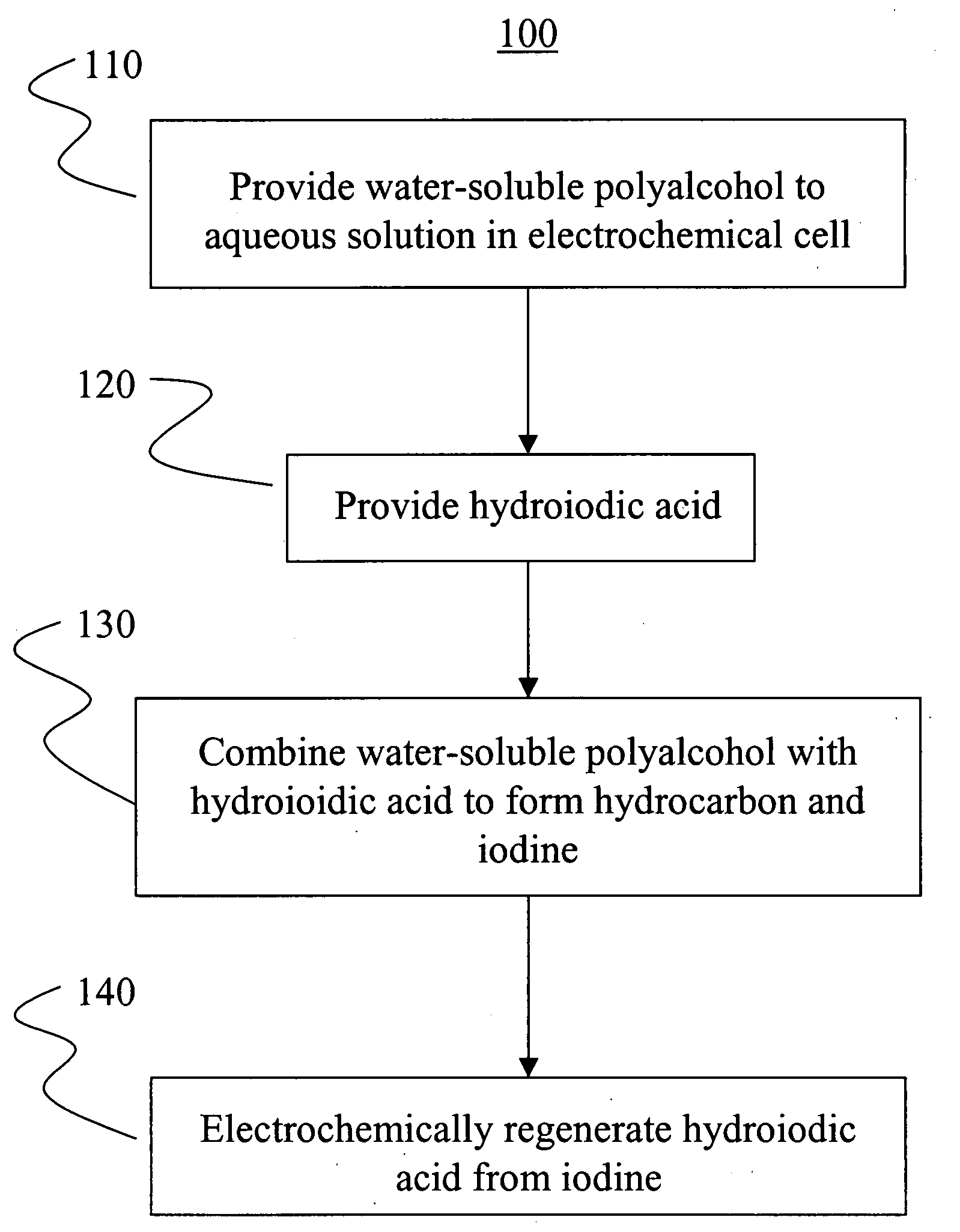
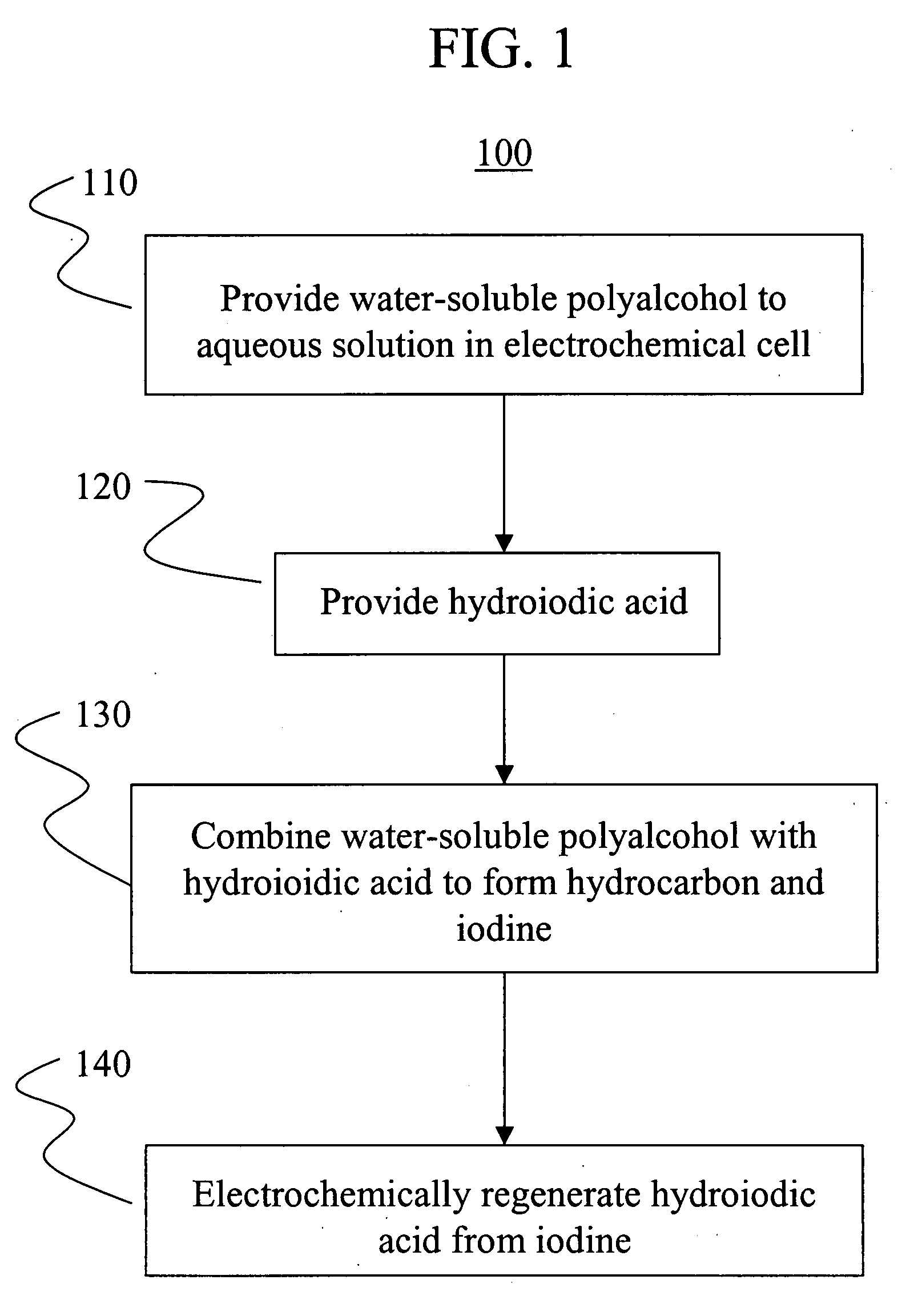
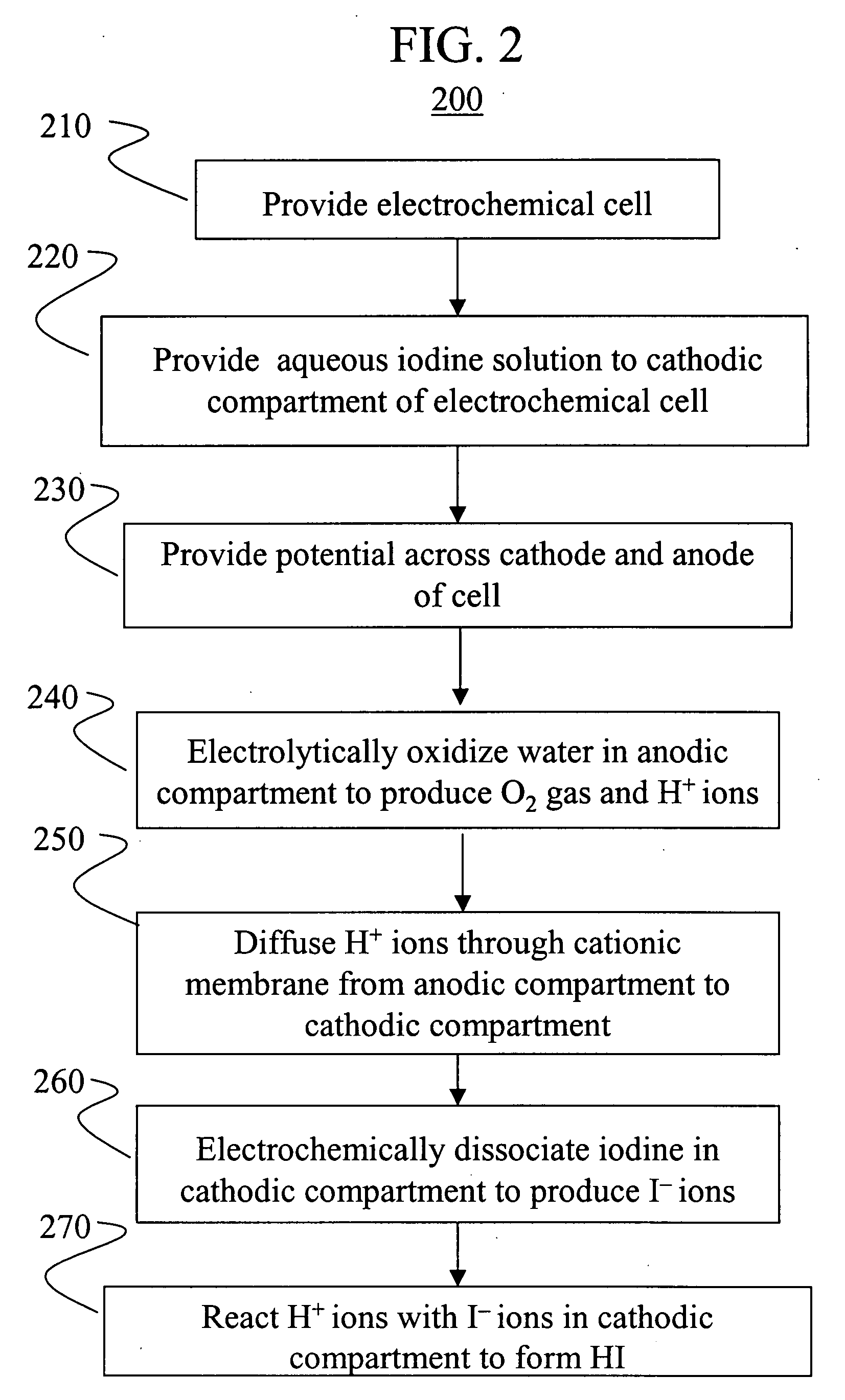
Electrochemical conversion of polyalcohols to hydrocarbons
A method of making hydrocarbons from polyalcohols, such as carbohydrates. The polyalcohols and carbohydrates may be provided from biomass, including paper, cardboard or urban generated paper product waste; wood and wood products, including forest slash and deadfall; agricultural waste; and the like. The polyalcohols and carbohydrates are combined with hydroiodic acid in aqueous solution to form the hydrocarbon and elemental iodine. Hydroiodic acid is then electrochemically regenerated by reducing the elemental iodine in a parallel reaction. A method of electrochemically generating hydroiodic acid from elemental iodine in aqueous solution is also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hoof bath system
InactiveUS20070074672A1Enhanced inhibitory effectStrong killing abilityVeterinary washing devicesAnimal shoeingInorganic saltsMicroorganism
The present invention is directed to methods for applying bovine foot and hoof treatment compositions having two or more specific and complimentary antimicrobial components in a hoof bath just prior to use to work more effectively. These antimicrobial components may include antimicrobial inorganic salts of certain heavy metals, cationic agents, peroxides, aldehydes, fatty acids, iodines or other suitable compounds effective in the killing of microorganisms.
Owner:GEA FARM TECH
Sanitizing device and method for sanitizing articles
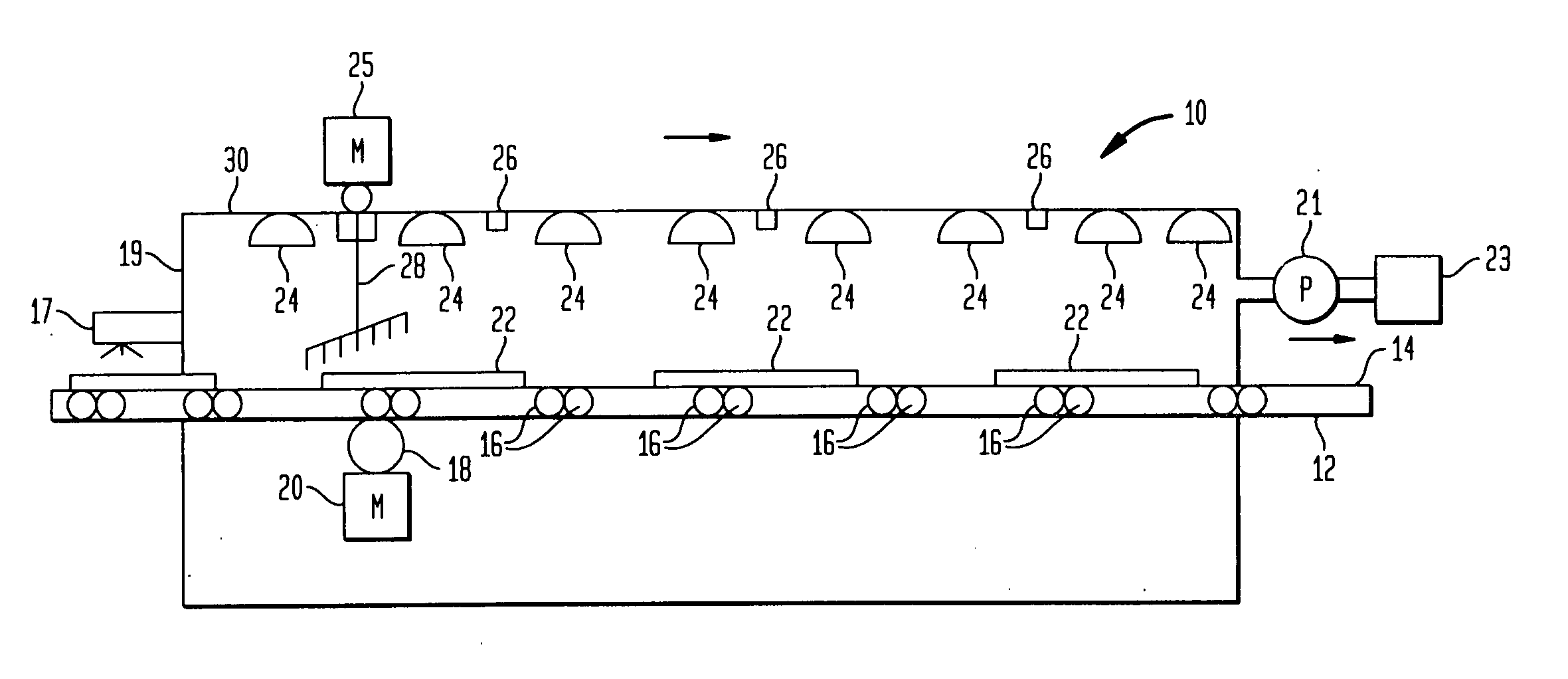
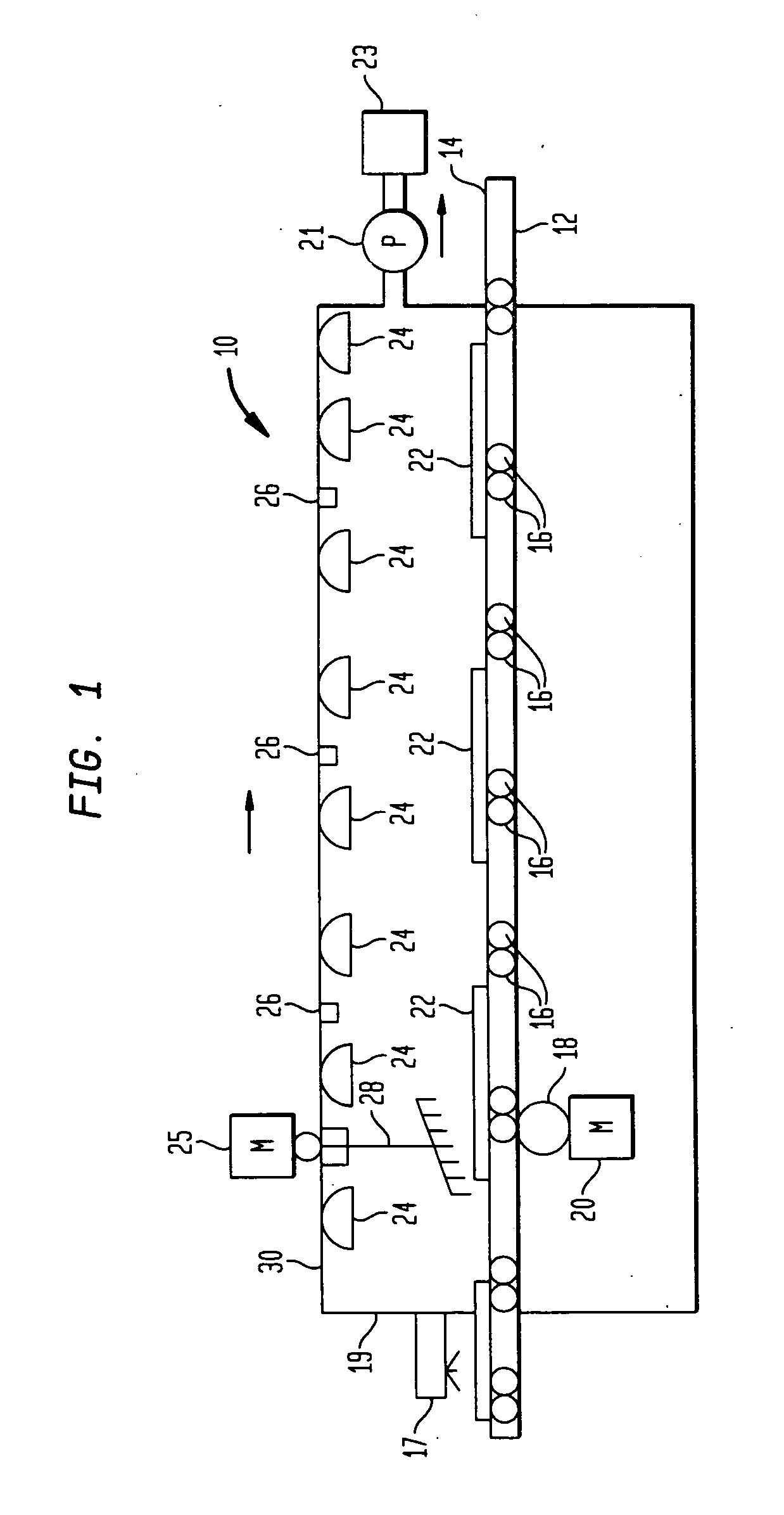
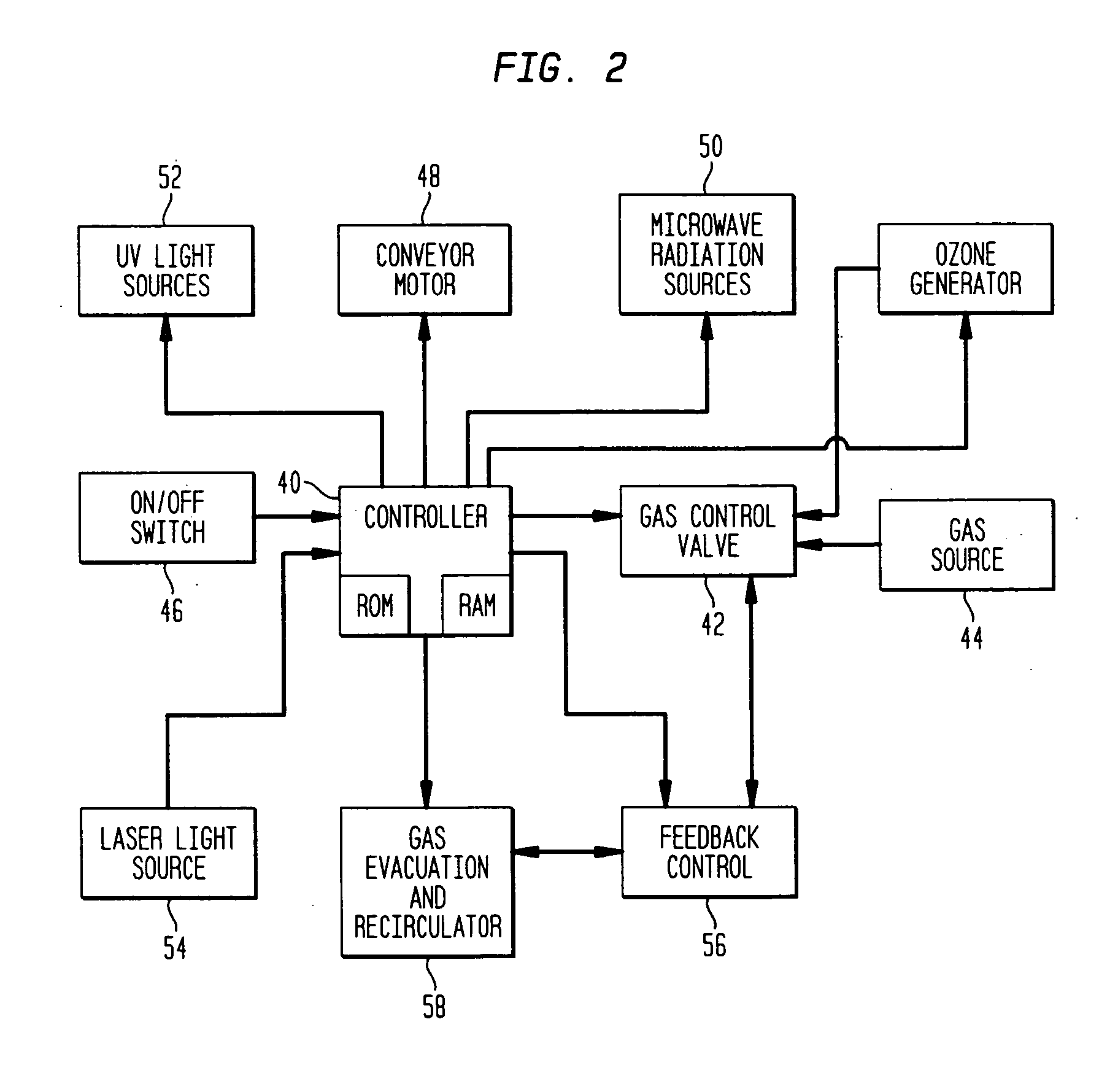
The invention provides an apparatus for sanitizing a plurality of articles, which comprises a housing enclosing a sanitizing zone, the housing having a seal for preventing leakage of gas or fluid from the sanitizing zone; a pump for introducing an antimicrobial fluid into the sanitizing zone; and a pump for withdrawing the fluid from the sanitizing zone. The device also includes at least one high power microwave source and at least one ultraviolet irradiating source, or a microwave source that also generates ultraviolet radiation. Preferably, the gas is a halogen, such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine, or a gas or fluid containing chlorine or bromine ions, but it can be ozone or another gas which kills bacteria, microbes, viruses, and other pathogens. The fluid can also be sprayed droplets or vaporized sodium hypochlorite, or similar antiseptic agent.
Owner:WEN SHEREE H
Foamable iodine compositions
ActiveUS20090317338A1Efficient use ofImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAdjuvantActive agent
The present invention is related to a foamable composition of matter comprising iodine, water, a foam adjuvant, a surface-active agent and a gelling agent. This foamable composition, which may be provided in a propellant free foaming device, or alternatively may further comprise a propellant, evolves into foam, which is effective in the topical treatment and prevention of various skin disorders.
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com