Patents
Literature
1305 results about "Radioactive agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
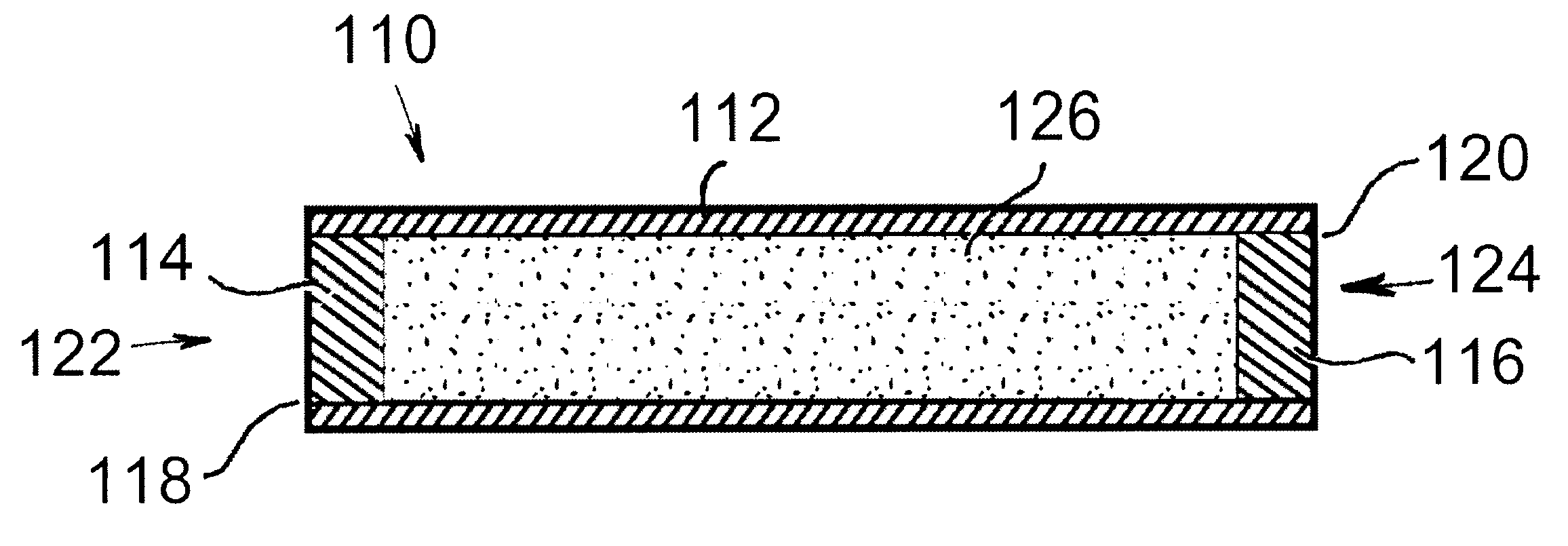
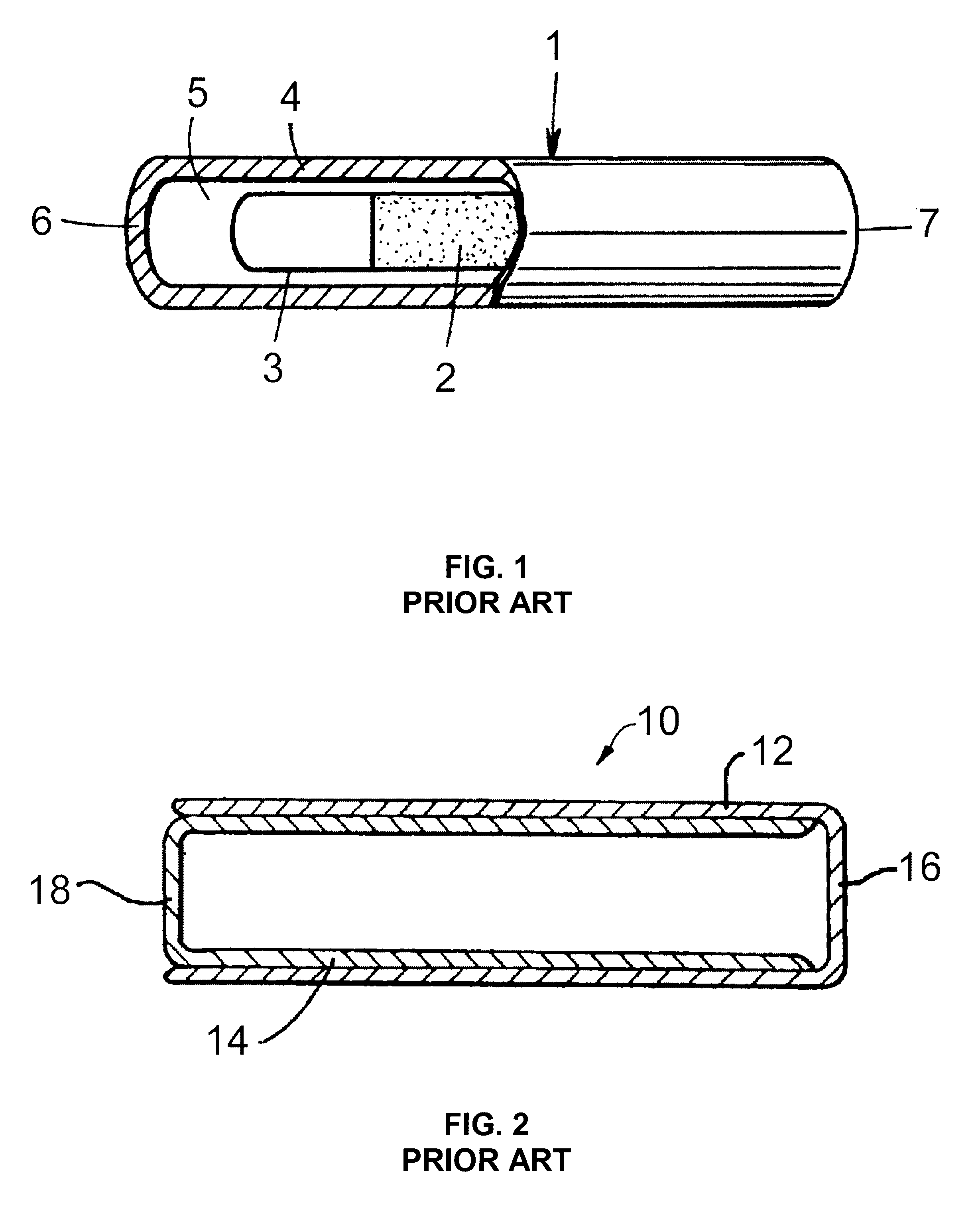
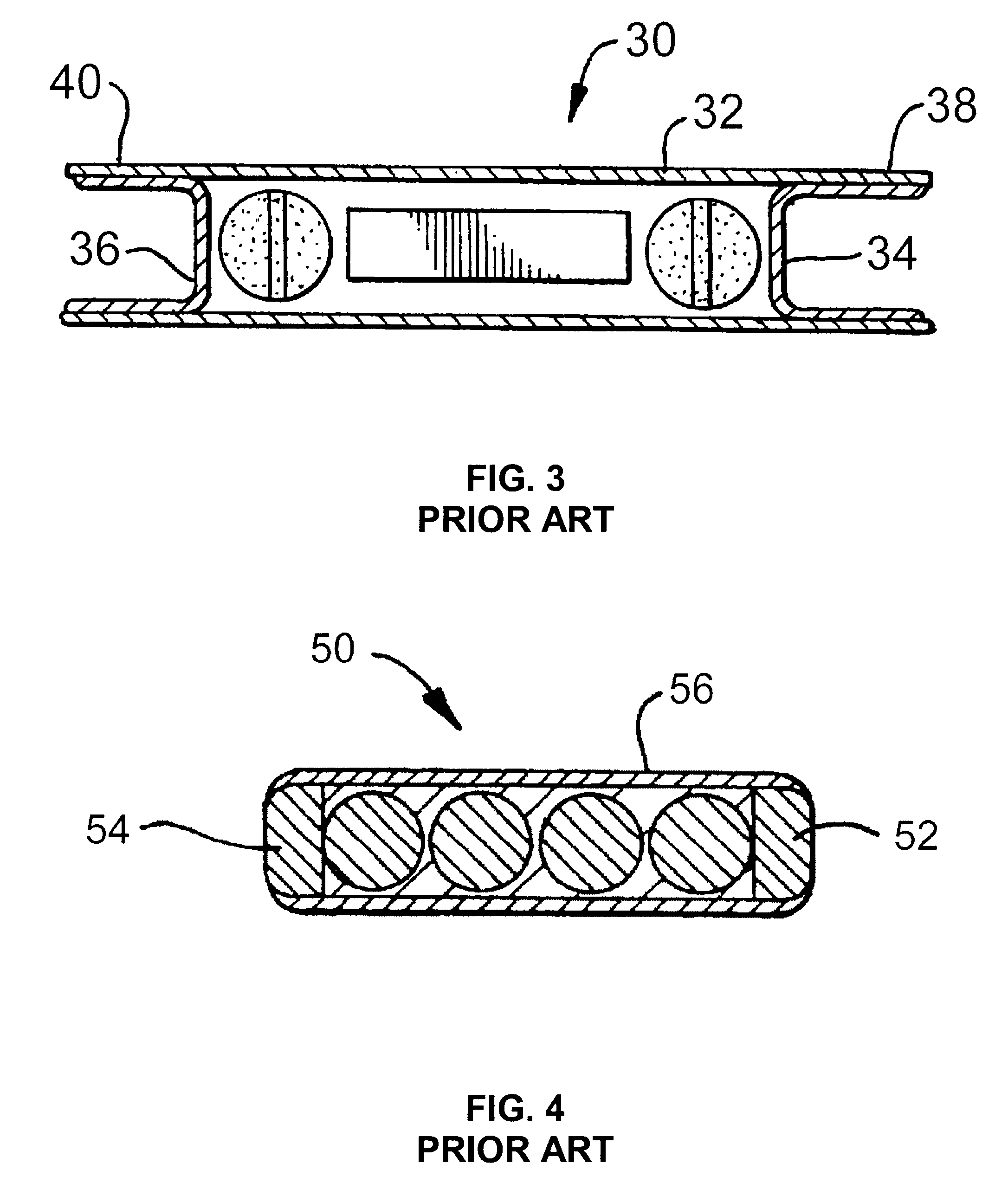
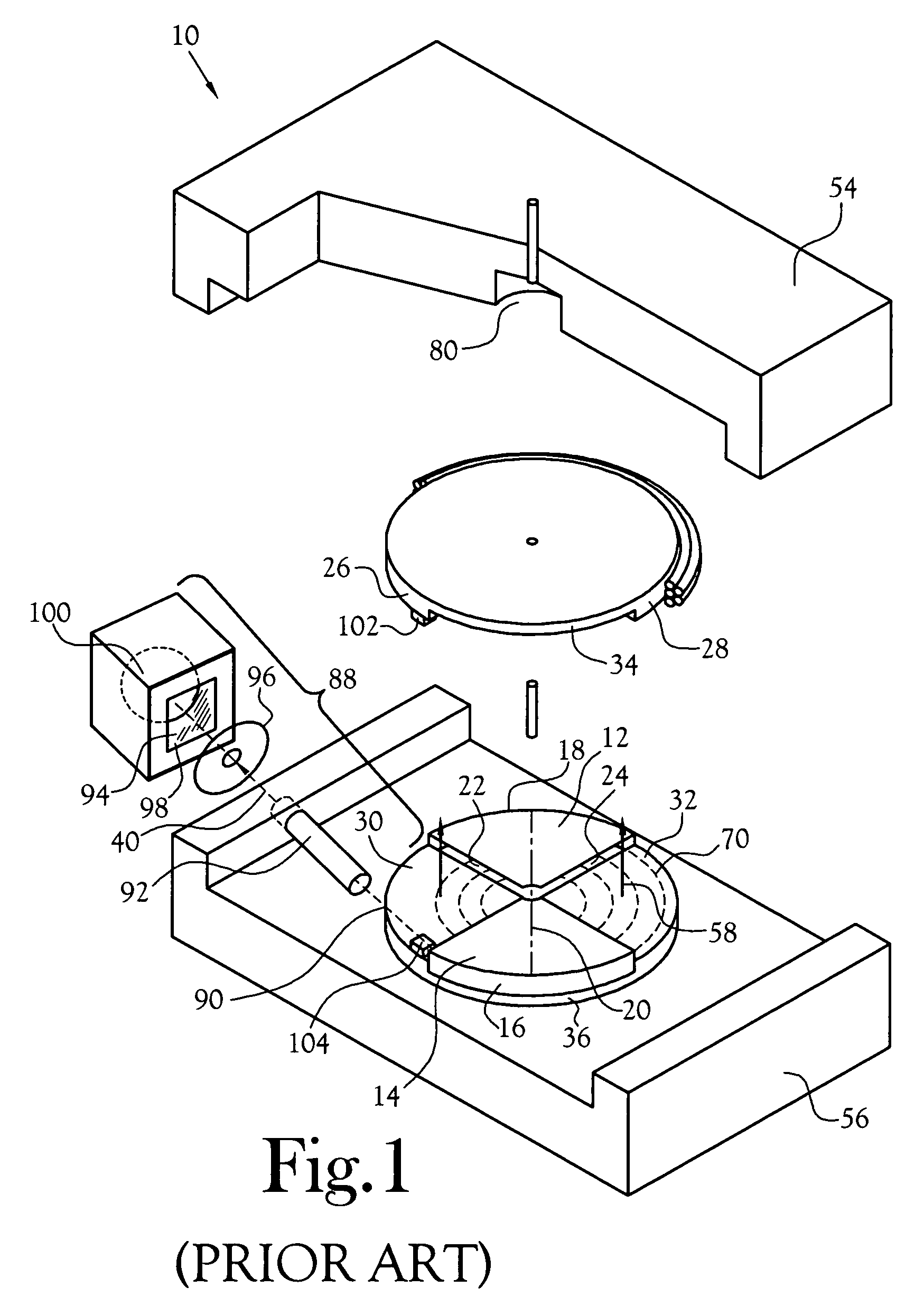
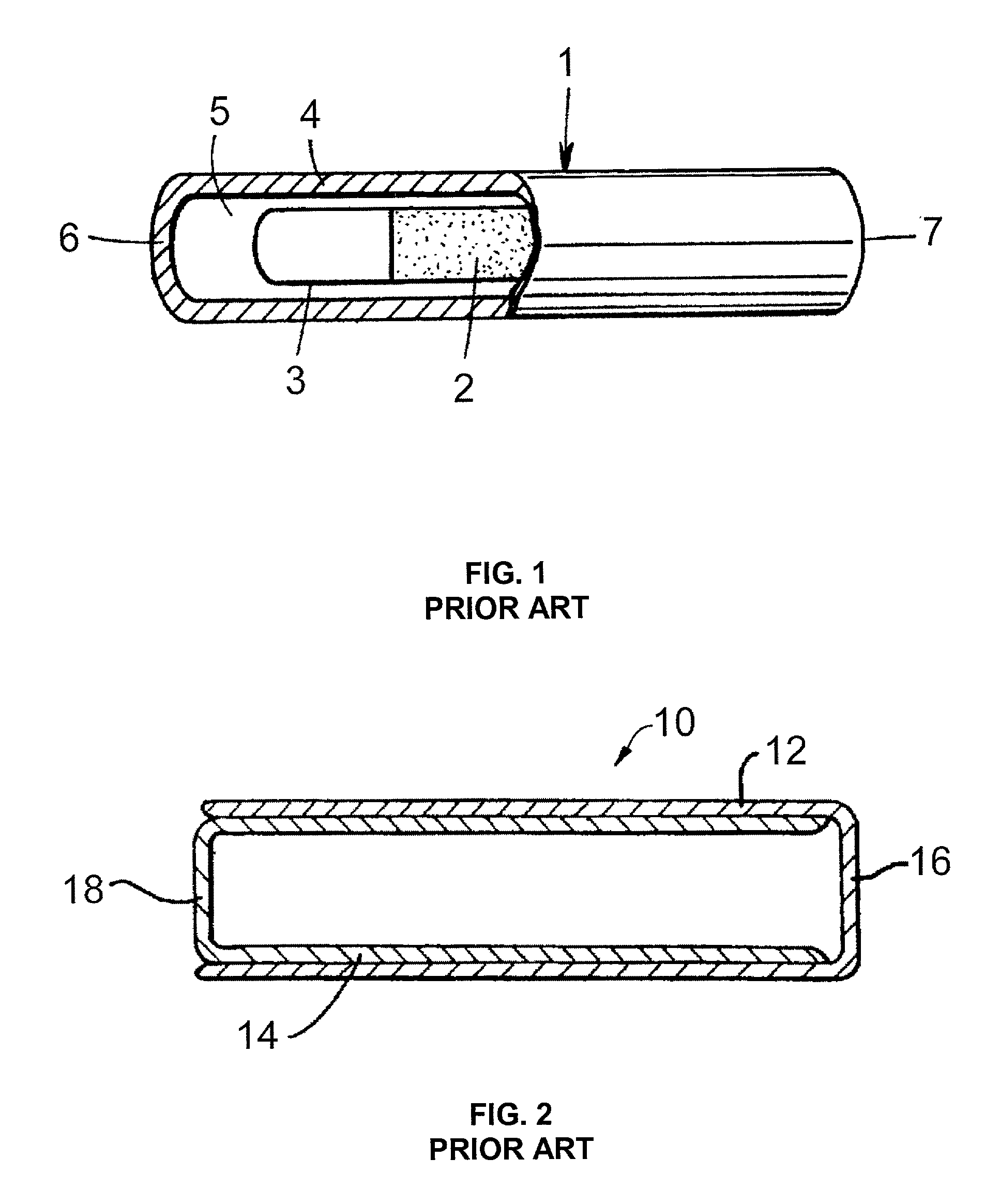
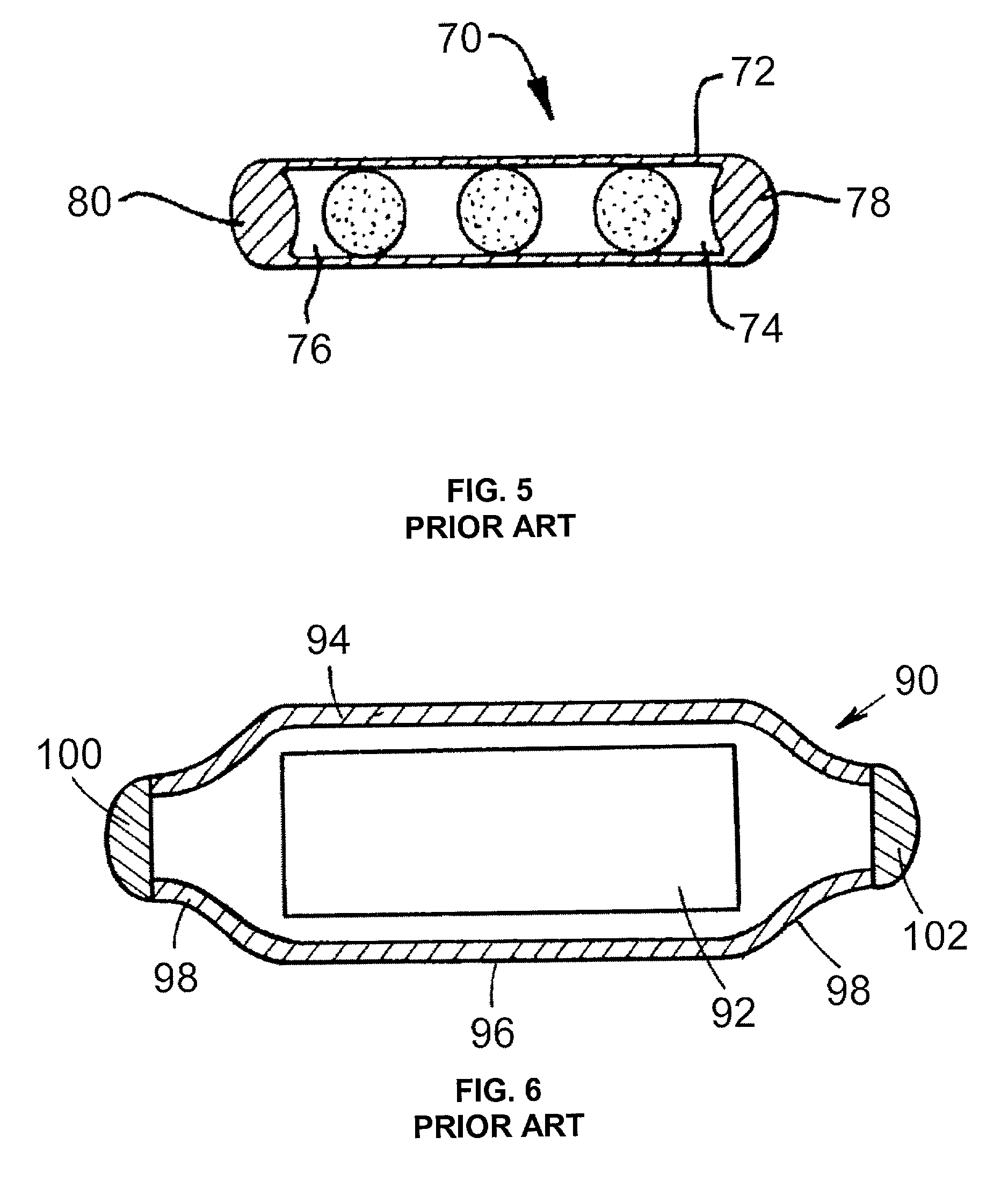
Bioabsorbable brachytherapy device
InactiveUS6575888B2Controlled release rateMinimally shieldsRadioactive preparation formsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapy deviceRadiopaque medium
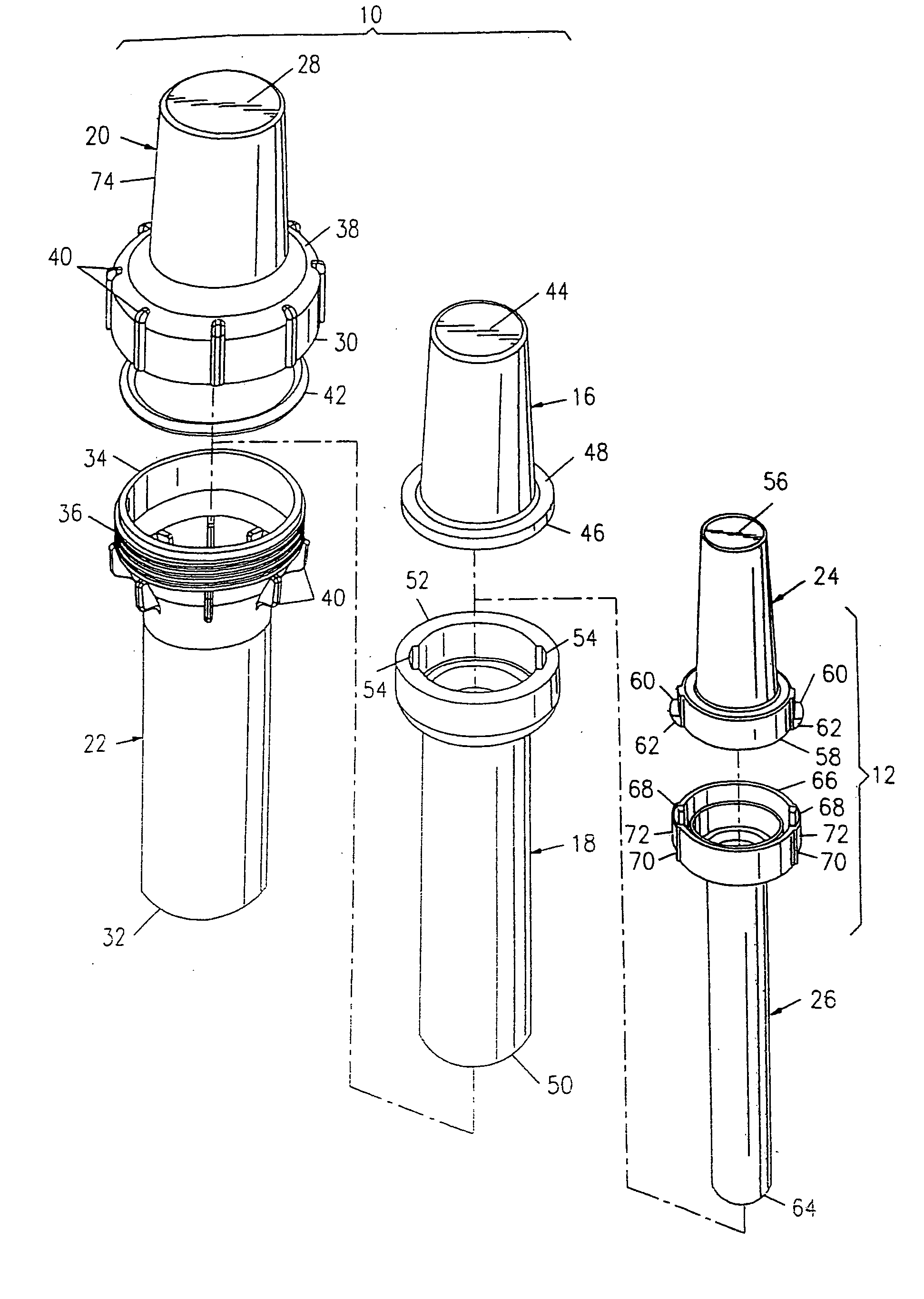
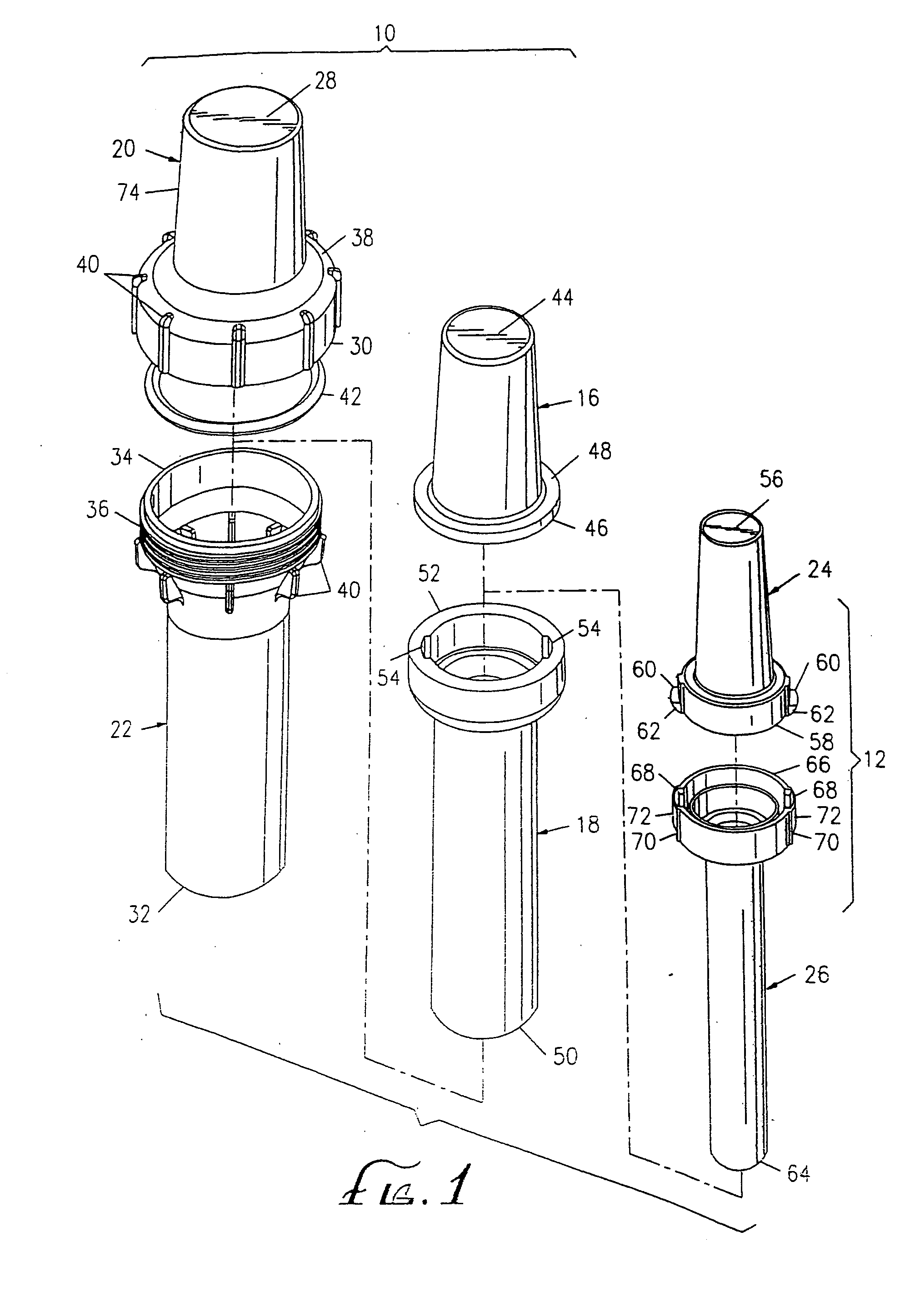
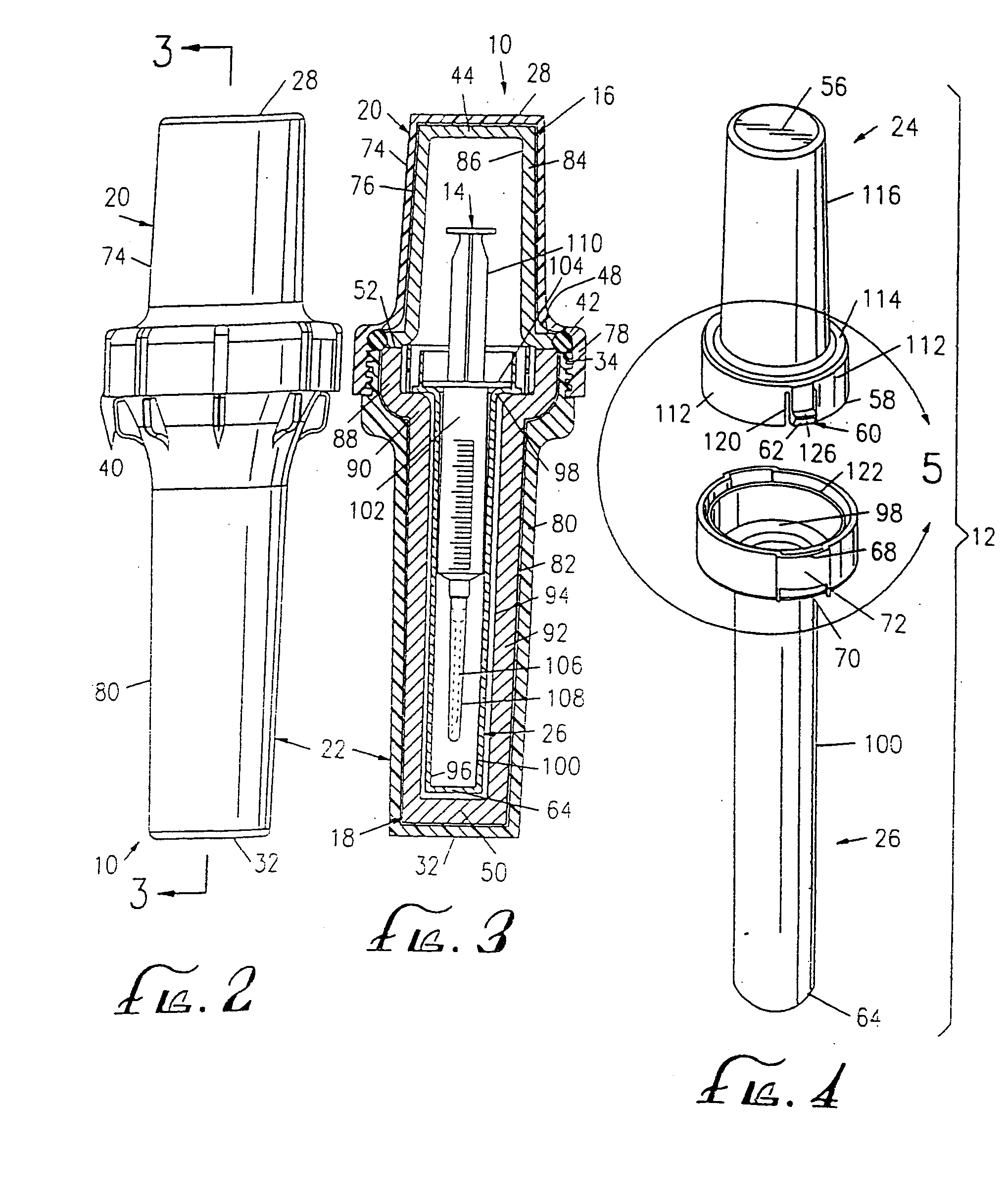
A bioabsorbable brachytherapy device includes a tubular housing with sealed ends and an enclosed radioactive material. The radioactive material includes a radioisotope, such as palladium-103 or iodine-125. The tubular housing is made from a biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymeric material, and is sealed by means such as heat welding or solvent fixing. The device may further include a radiopaque medium and one or more therapeutic drugs.
Owner:FERRING BV
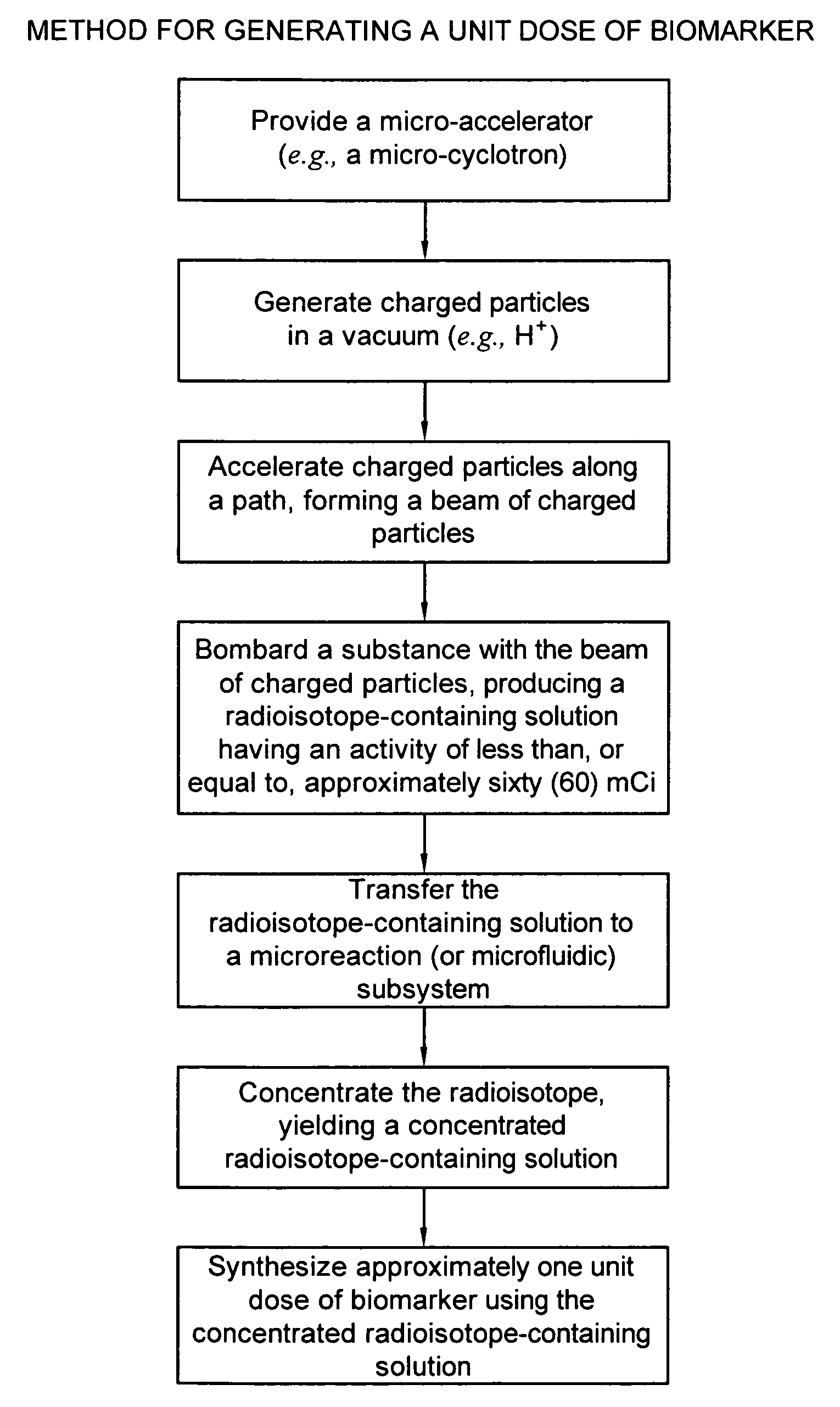
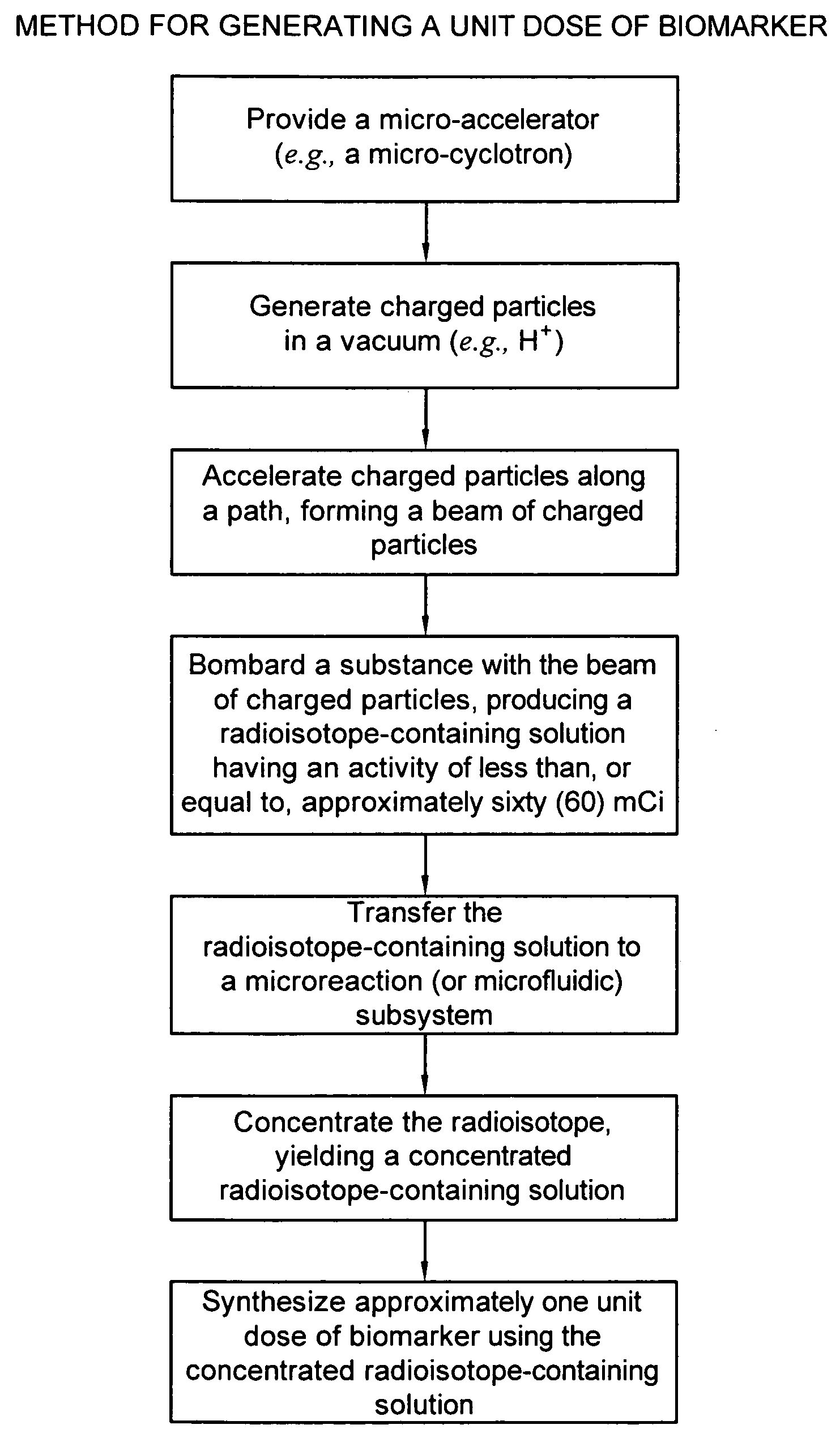
Biomarker generator system
ActiveUS7476883B2Efficient dosingEfficient productionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope delivery systemsChemical synthesisMicroreactor
A biomarker generator system for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker. The biomarker generator system includes a small, low-power particle accelerator (“micro-accelerator”) and a radiochemical synthesis subsystem having at least one microreactor and / or microfluidic chip. The micro-accelerator is provided for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a radioactive substance, such as a substance that emits positrons. The radiochemical synthesis subsystem is provided for receiving the radioactive substance, for receiving at least one reagent, and for synthesizing the approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker.
Owner:BEST ABT INC
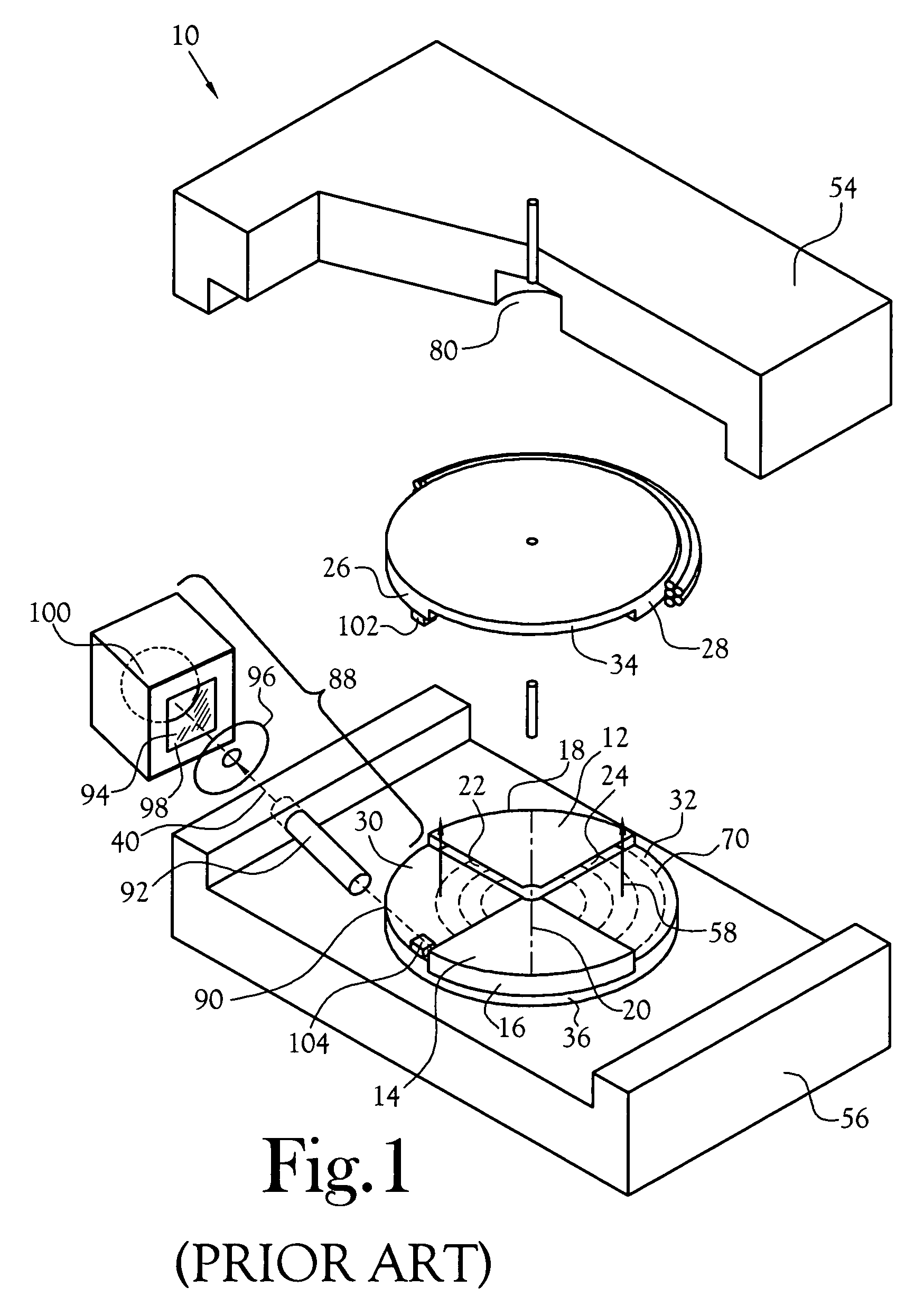
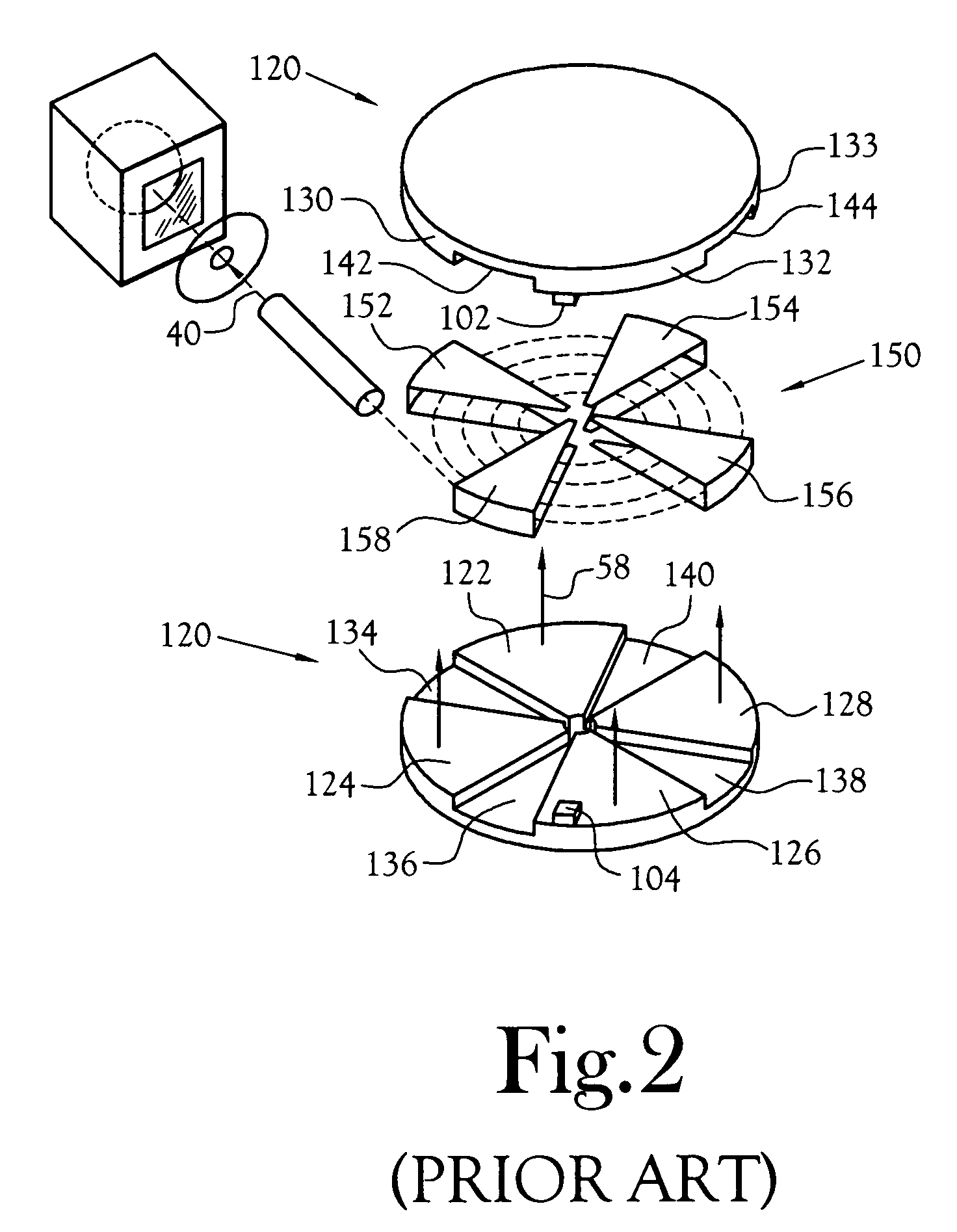
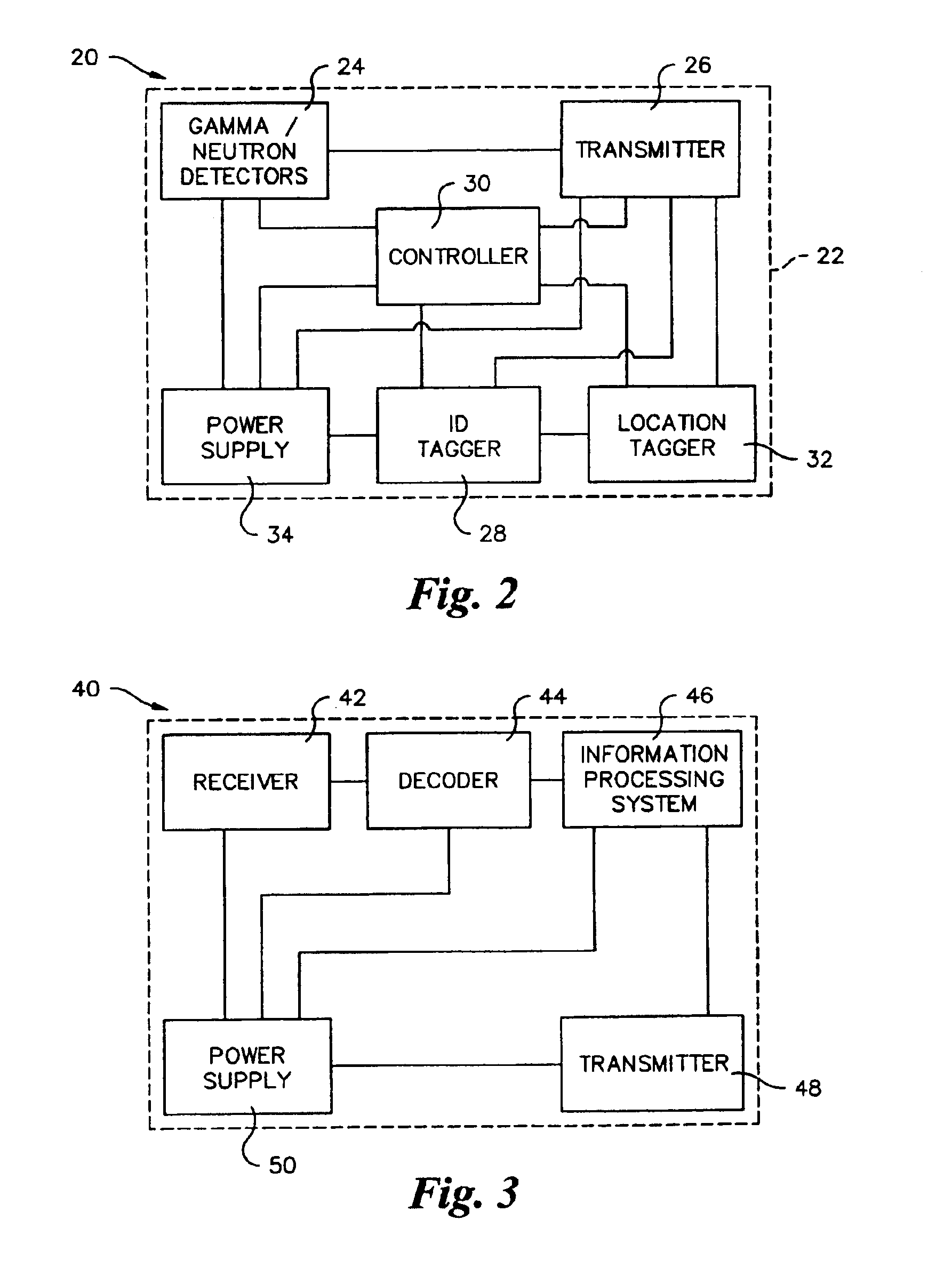
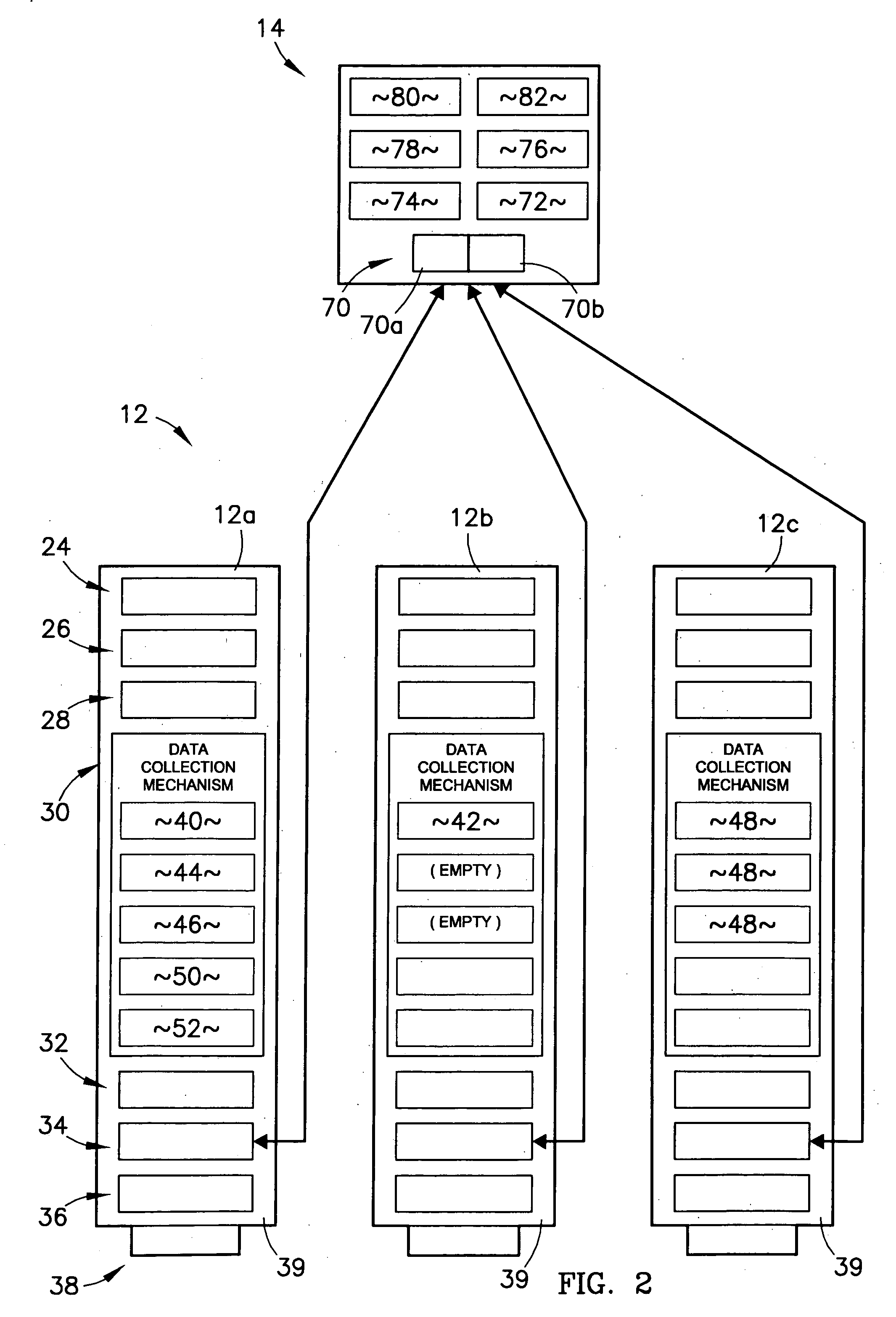
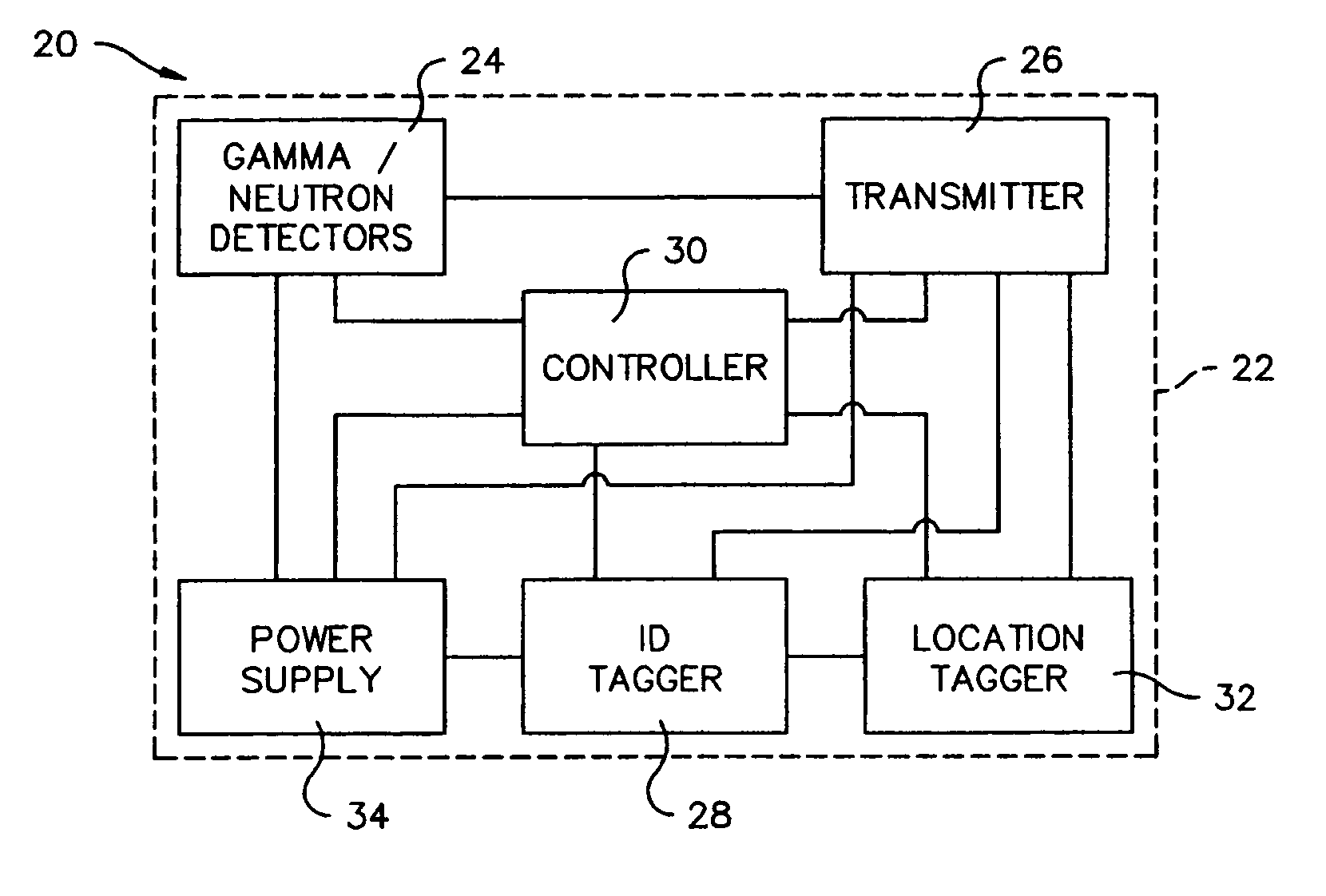
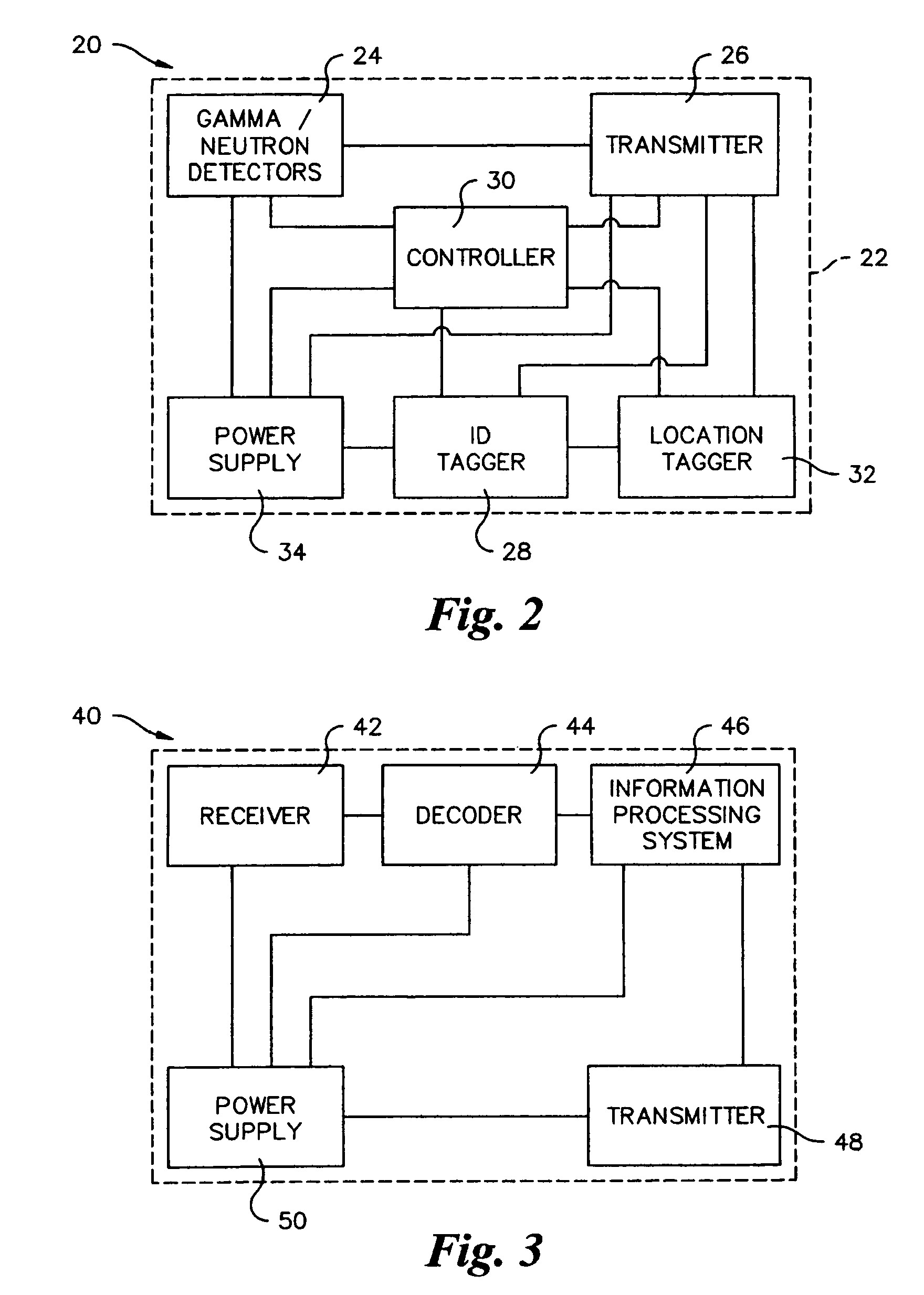
Method and apparatus for detection of radioactive material
ActiveUS6891470B2Electric testing/monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A radioactive material detection apparatus includes a transmitter, a radiation sensor and a controller. The transmitter is capable of transmitting information in correspondence with a signal. The radiation sensor has a sensor output and is configured to detect radiation over a predetermined period of time. The controller is configured to receive the sensor output from the radiation sensor and to send the signal to the transmitter for transmission.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
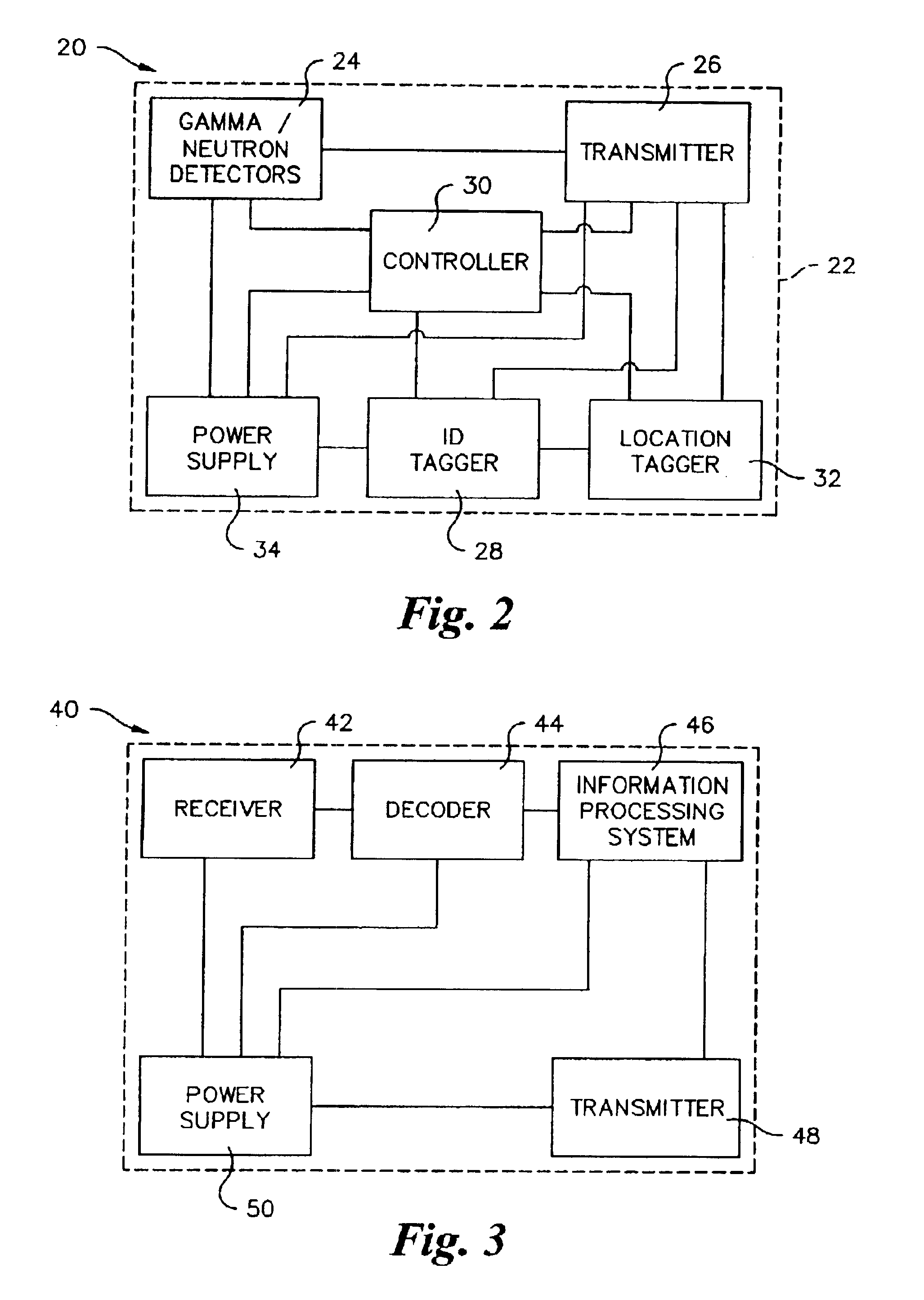
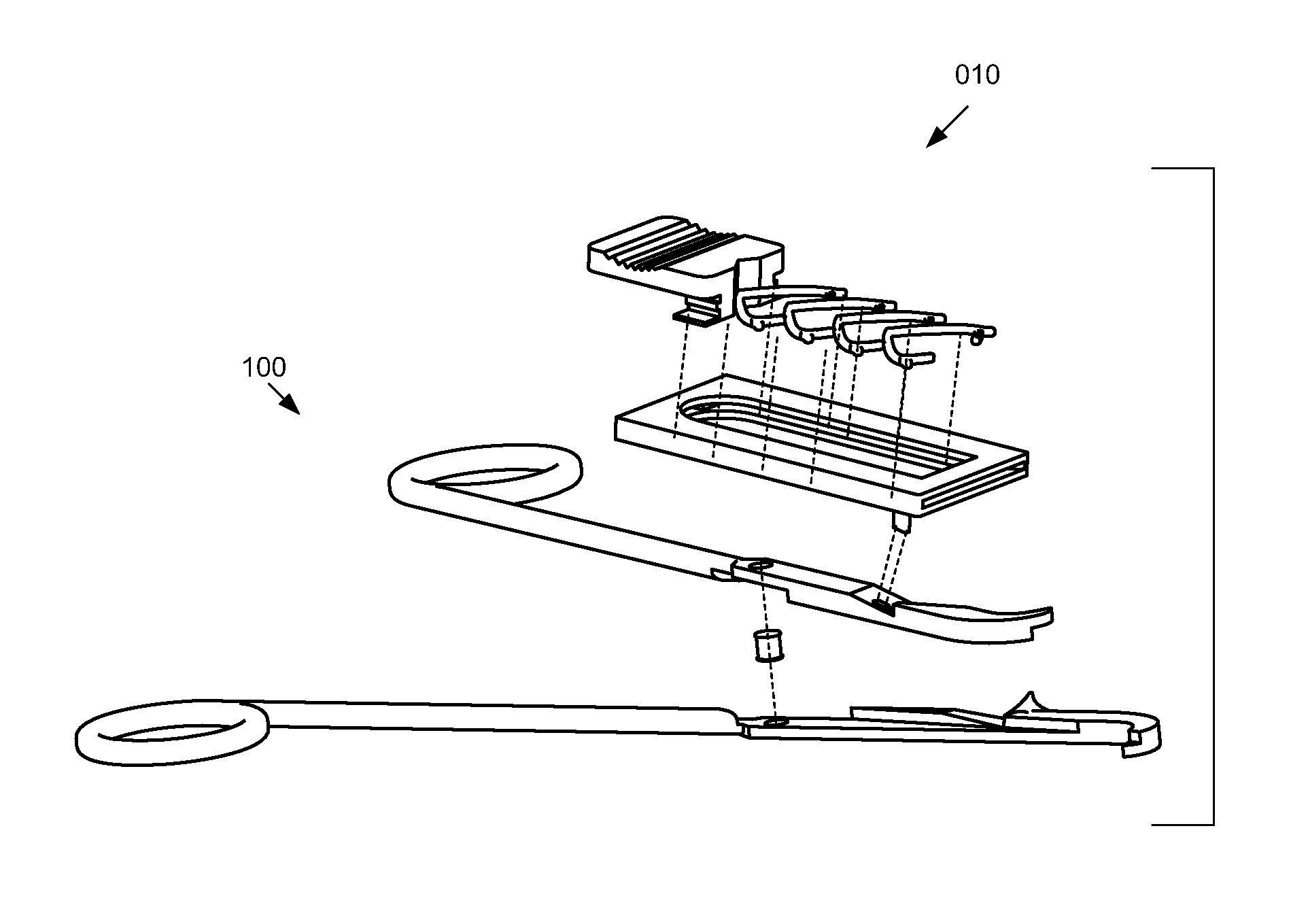
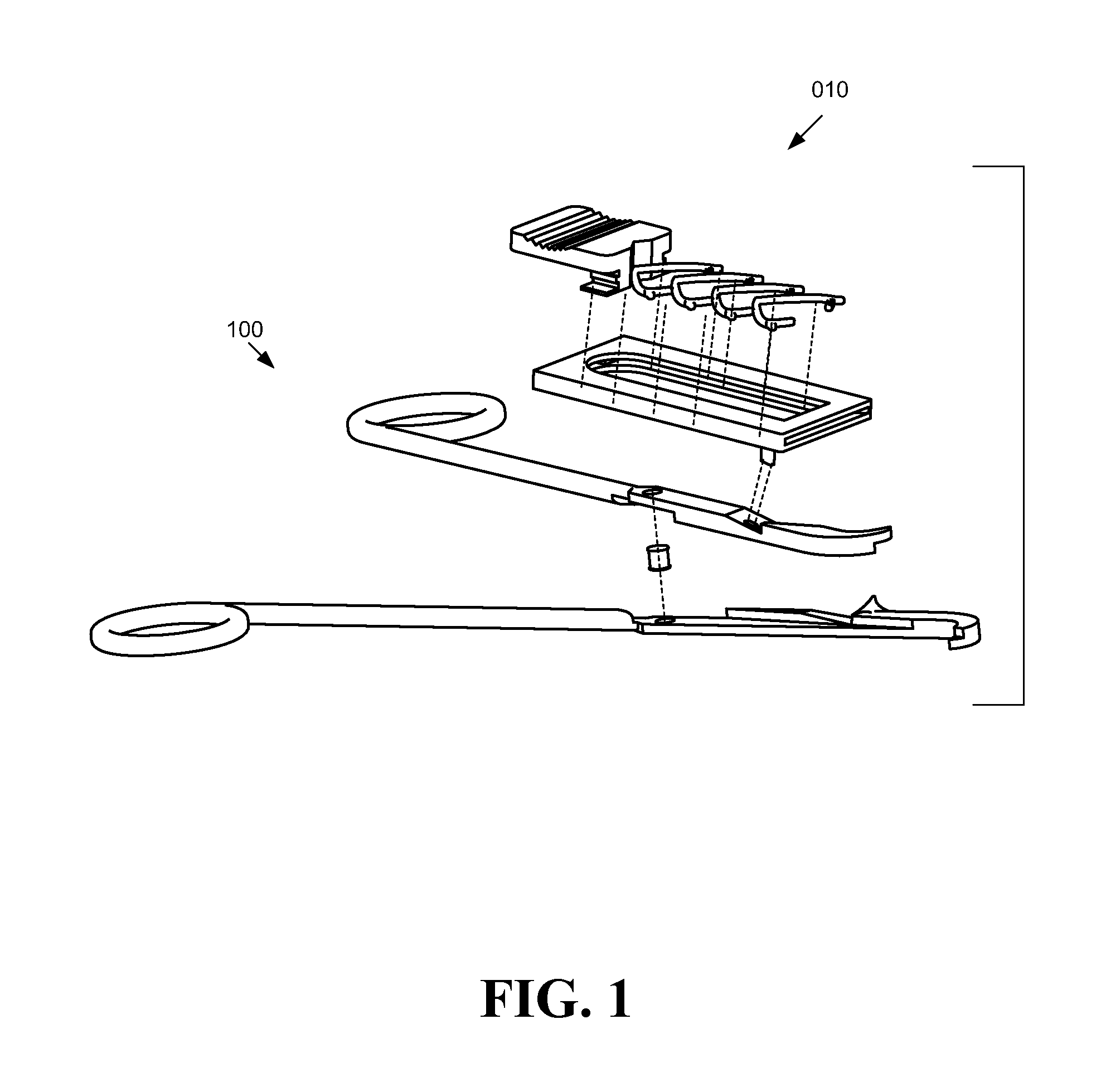
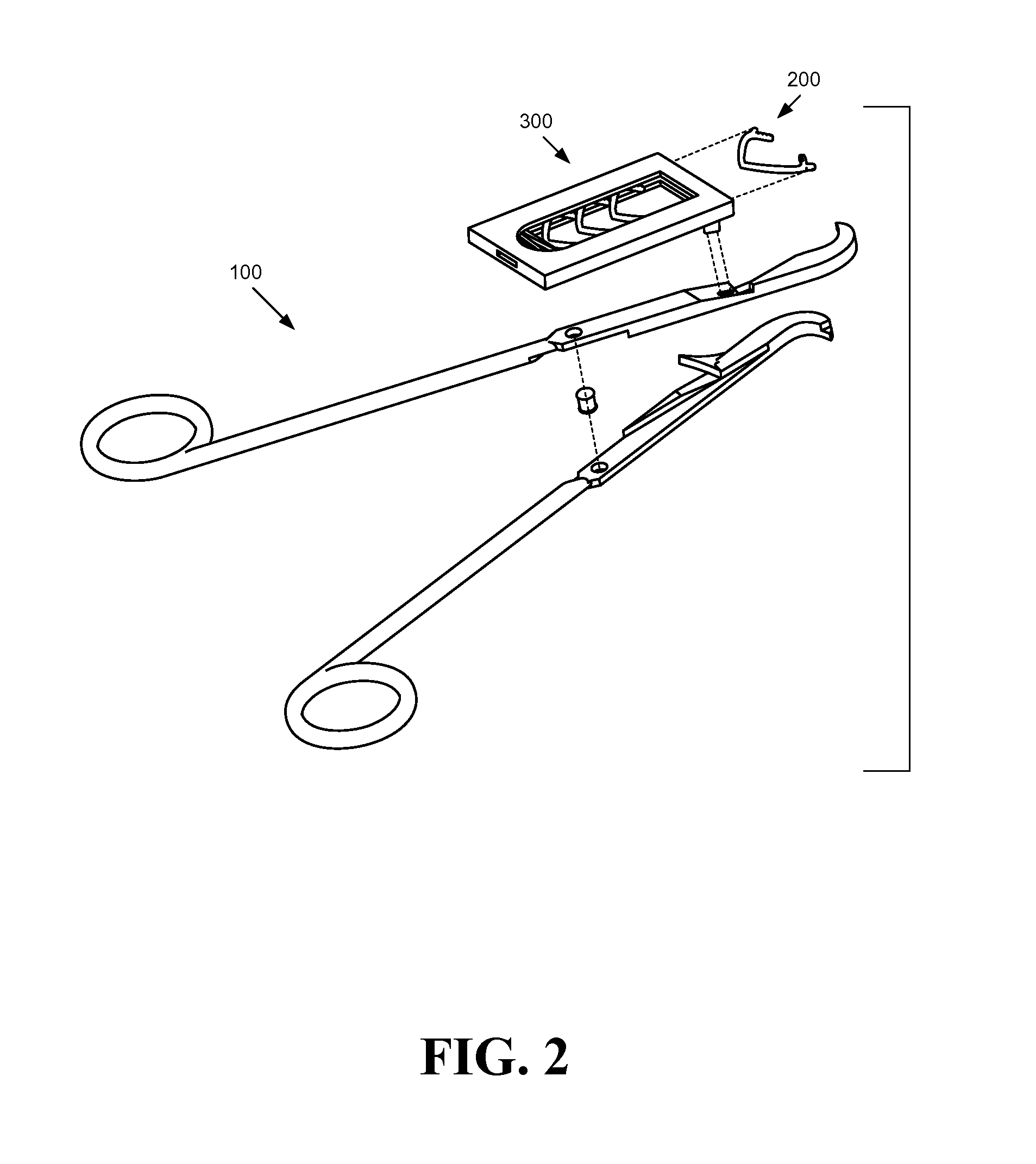
Bio-absorbable tissue closure system
InactiveUS20080103510A1Easy to closeFacilitates rapid closureStaplesNailsRadioactive agentInternal wounds
A surgical fastening system, utilizing surgical clips made from bio-absorbable materials, for use in the rapid closing of deep internal wounds in humans or animals is disclosed. Elements of the system include surgical clips, applicators of surgical clips and dispensers of surgical clips. The surgical clips may contain small amounts of prophylactic antibiotic medication, long-acting time-release pain medication, radio-opaque markers, small amounts of radioactive material, colors, and / or patterns.
Owner:APOGEE SURGICAL INSTR
Container and method for transporting a syringe containing radioactive material
InactiveUSRE36693E1Reduced Possibility of ContaminationDurable shellDispensing apparatusOther accessoriesRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A method and apparatus for transporting syringes containing radioactive material. The apparatus includes a radiopharmaceutical pig having an inner chamber in which a sharps container can be secured. The sharps container has a housing and an attachable cap. The method includes assembling the radiopharmaceutical pig so that the chamber of the radiopharmaceutical pig contains the syringe in the sharps container housing. The radiopharmaceutical pig is disassembled, where upon the syringe is removed, discharged, and then replaced in the sharps container housing. The cap of the sharps container is affixed to the housing of the sharps container, thus enclosing the contaminated syringe therein. The radiopharmaceutical pig is assembled so that its chamber contains the sharps container and the syringe. The radiopharmaceutical pig is transported to a disposal area, where it is disassembled and the sharps container containing the syringe is placed in a particular disposal container.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH INC
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
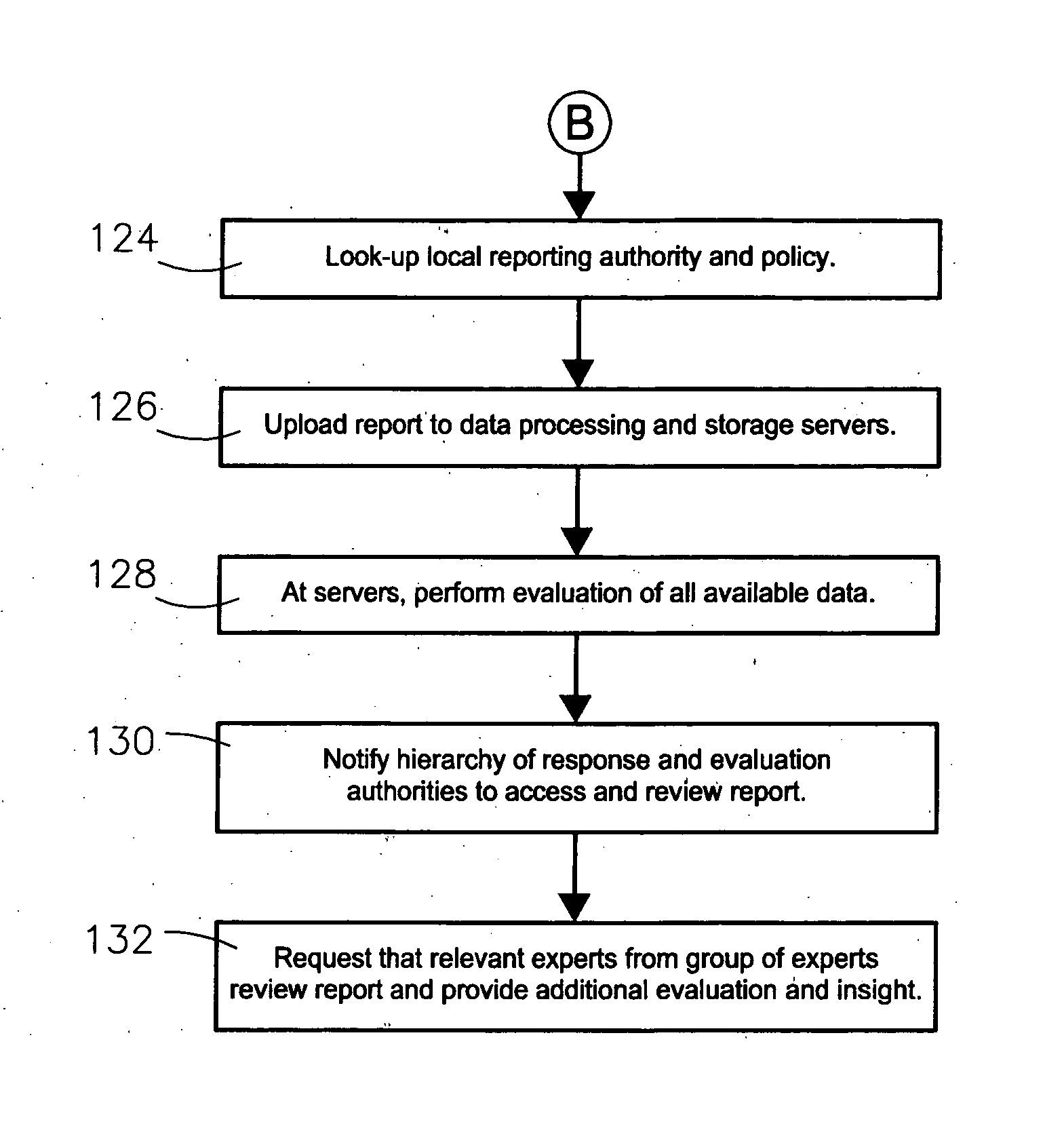
ActiveUS20120030130A1Rapid deploymentEliminates exposure riskComponent separationDigital data processing detailsRadioactive agentComputer science
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
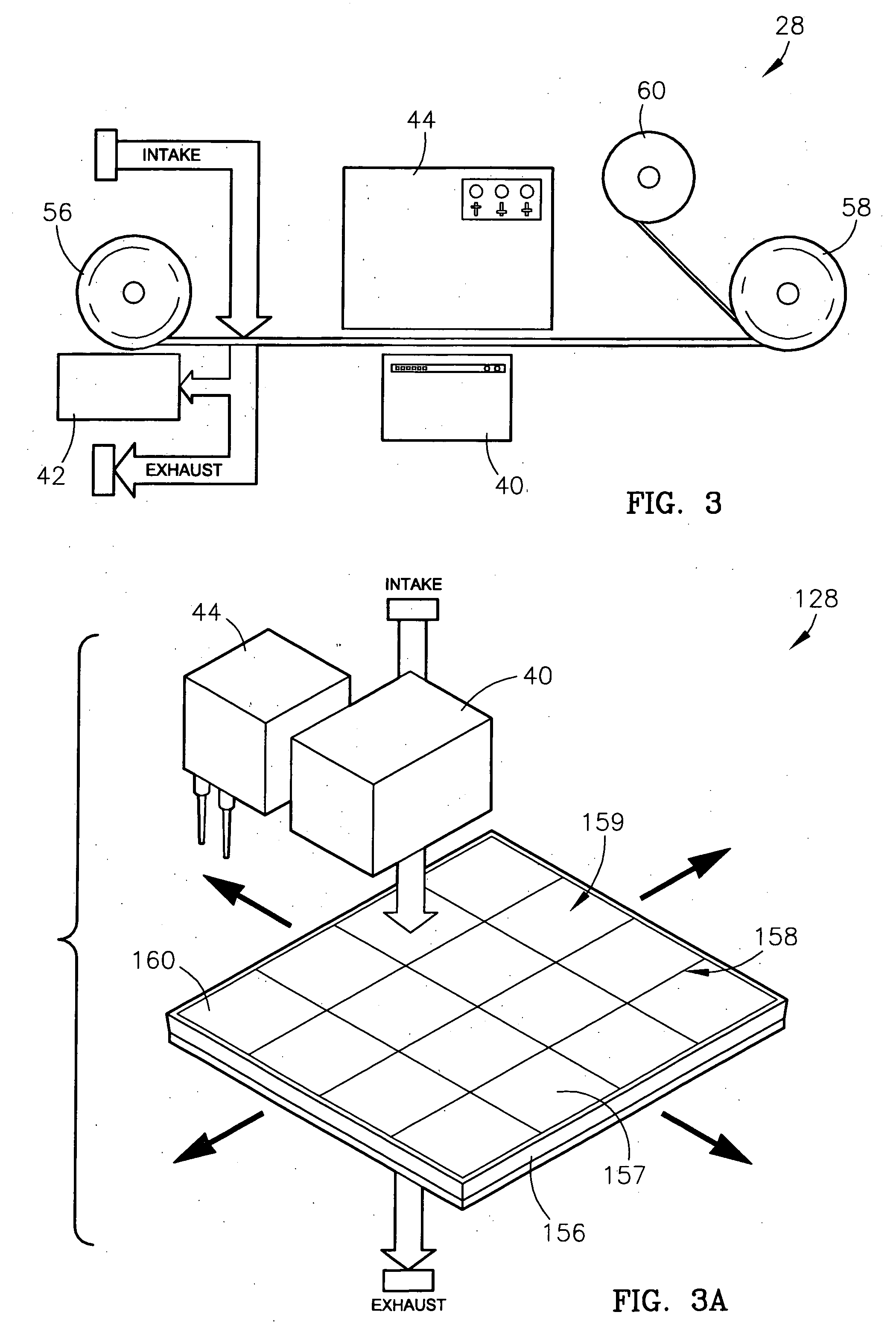
Controlled delivery of therapeutic agents from medical articles
The present invention provides novel adenosine receptor antagonists, more particularly, A1 adenosine receptor antagonists. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising an A1 adenosine receptor antagonist disclosed herein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier are further provided. Compositions also include diagnostic assay-type probes comprising a novel A1 adenosine receptor antagonist that is labeled or conjugated with radioactive or non-radioactive material. Methods for treating A1 adenosine receptor related disorders comprising administering an A1 adenosine receptor antagonist of the invention are also disclosed. The novel A1 adenosine receptor antagonist compositions find further use in diagnostic and imaging methods.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
Apparatus and method for asynchronously analyzing data to detect radioactive material
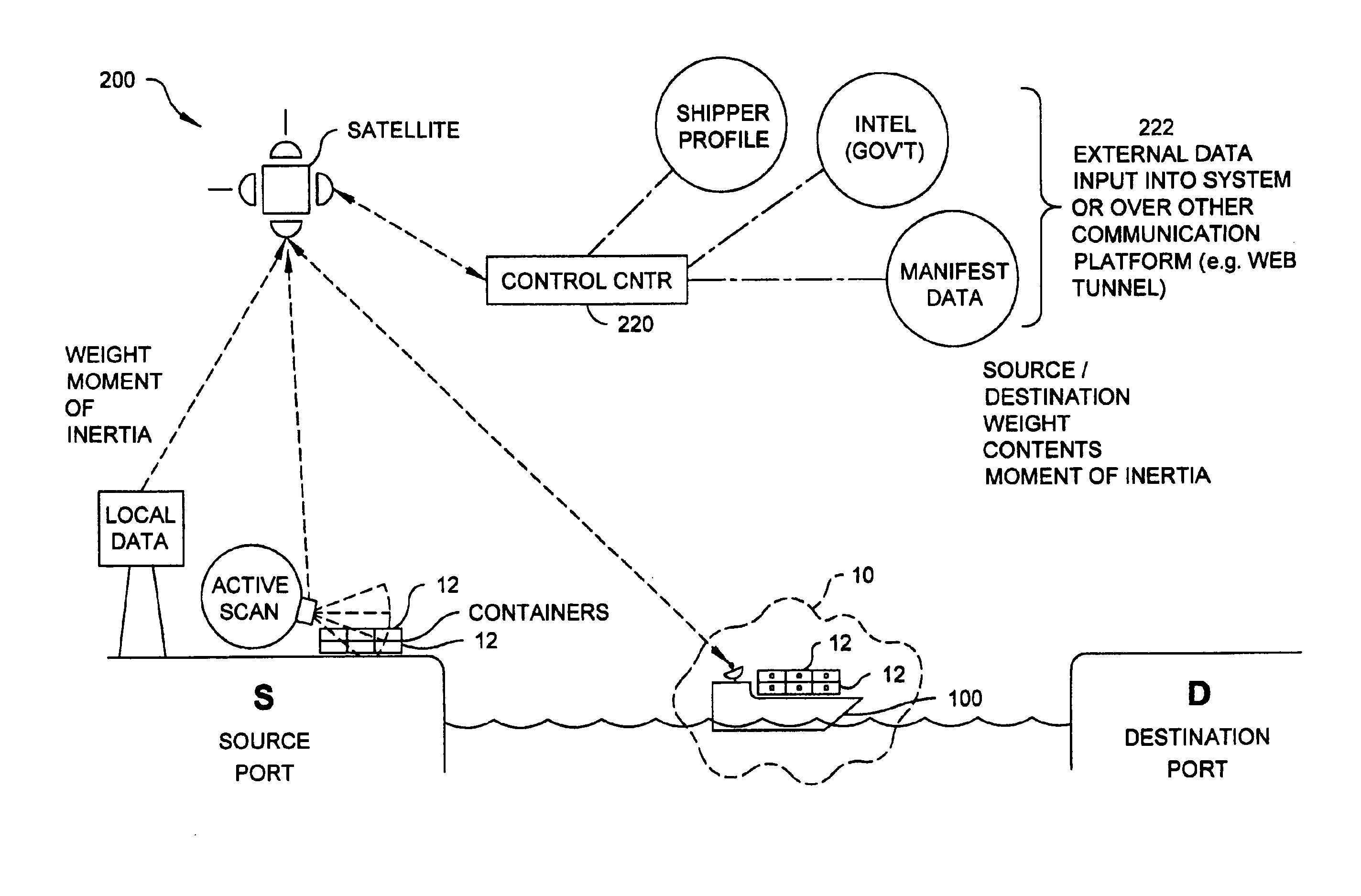
InactiveUS6965314B2High sensitivityEasy to identifyElectric testing/monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverRadioactive agent
A radioactive material detection system includes a cargo container monitoring system and a control center. The cargo container monitoring system has a radiation sensor configured to detect radiation over a predetermined or commanded period of time and a transceiver configured to send the information received from the radiation sensor. The control center is in communication with the transceiver of the cargo container monitoring system. The control center is configured to receive data from at least one additional source other than the cargo container monitoring system and to asynchronously analyze the data from the at least one additional source and the information from the radiation sensor, during transit, so as to detect radioactive material in a cargo container.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
A method and apparatus for detection of radioactive materials
InactiveUS20070001123A1Enhanced gamma ray sensitivityReducing background radiation interferenceMeasurement by spectrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh energy
In the present invention there is a provided an array of radiation detectors comprising at least one detector capable of detecting both low and high energy gamma radiation and adapted to provide spectrometric identification of the gamma source; at least one detector capable of detecting and providing spectrometric identification of fast neutrons and low resolution gamma spectra; at least one detector adapted to detect thermal neutrons; and, at least one plastic scintillator to give enhanced gamma ray sensitivity.
Owner:BUBBLE TECH INDS
Embolic compositions with non-cyanoacrylate rheology modifying agents
Compositions for embolization are disclosed herein. The compositions disclosed can have a matrix-forming component, a solid-aggregate material, and a rheology modifying agent, wherein the matrix-forming component includes at least alkyl cyanoacrylate monomers, a stabilizer, and a plasticizer, and the solid-aggregate material includes at least a radiopacifier. The composition and a method of administering the composition are useful for treating vasculature abnormalities, particularly when the composition solidifies upon contact with an ionic environment, such as blood.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Tissue interventions using nuclear-emission image guidance
InactiveUS20070167749A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadioactive agentPosition dependent
A method and apparatus for marking a lesion in a body part is provided. The method includes the steps of obtaining a first nuclear-emission image of the body part; determining a position of the lesion from the first image; percutaneously introducing a cannula to the determined position; inserting a wire into the cannula, the wire including radioactive material; retracting the cannula while holding the wire in place; and obtaining a second nuclear-emission image of the body part. The second image includes data relating to a position of the lesion and data relating to a position of the wire.
Owner:COMPANIA MEXICANA DE RADIOLOGIA CGR S A DE
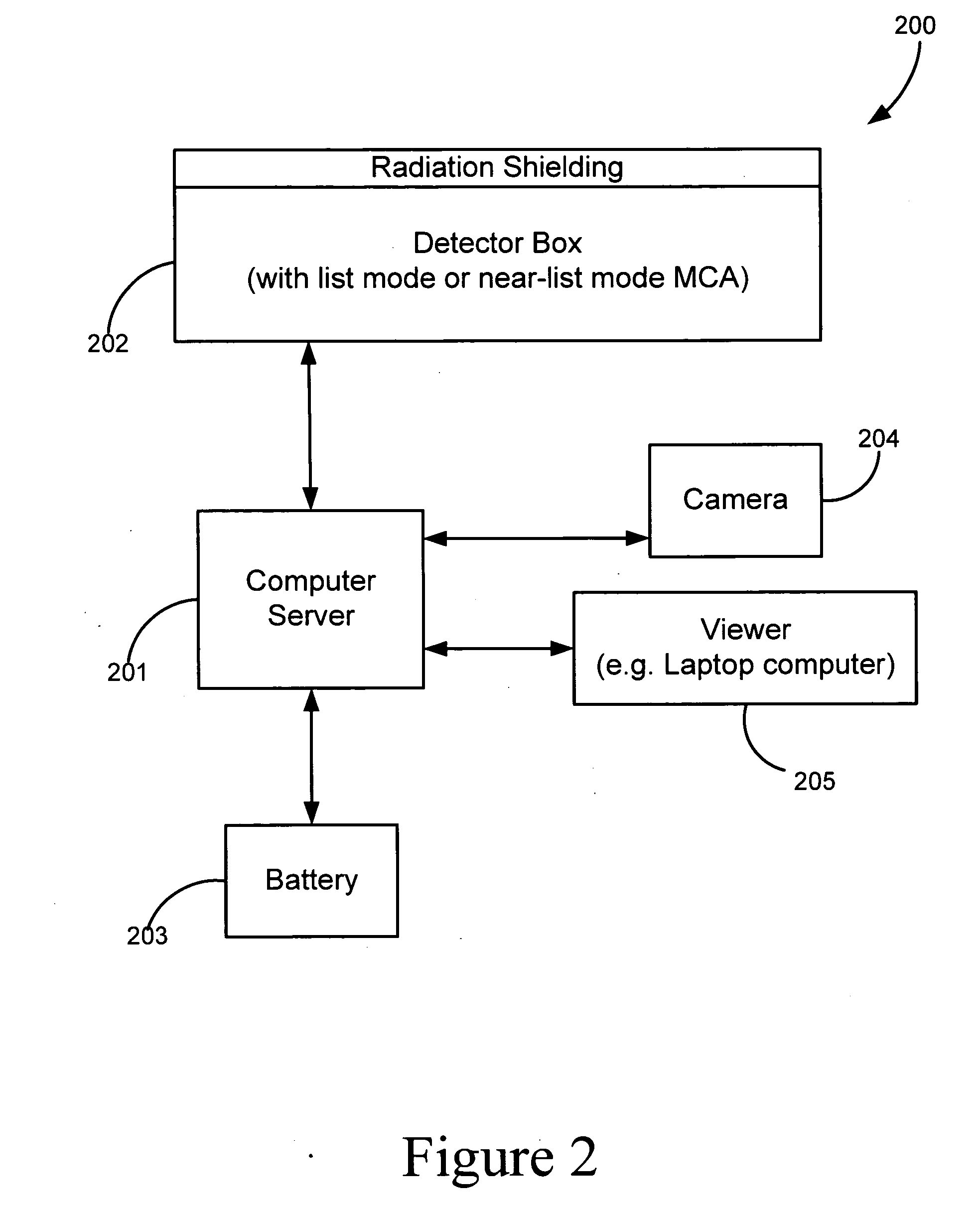
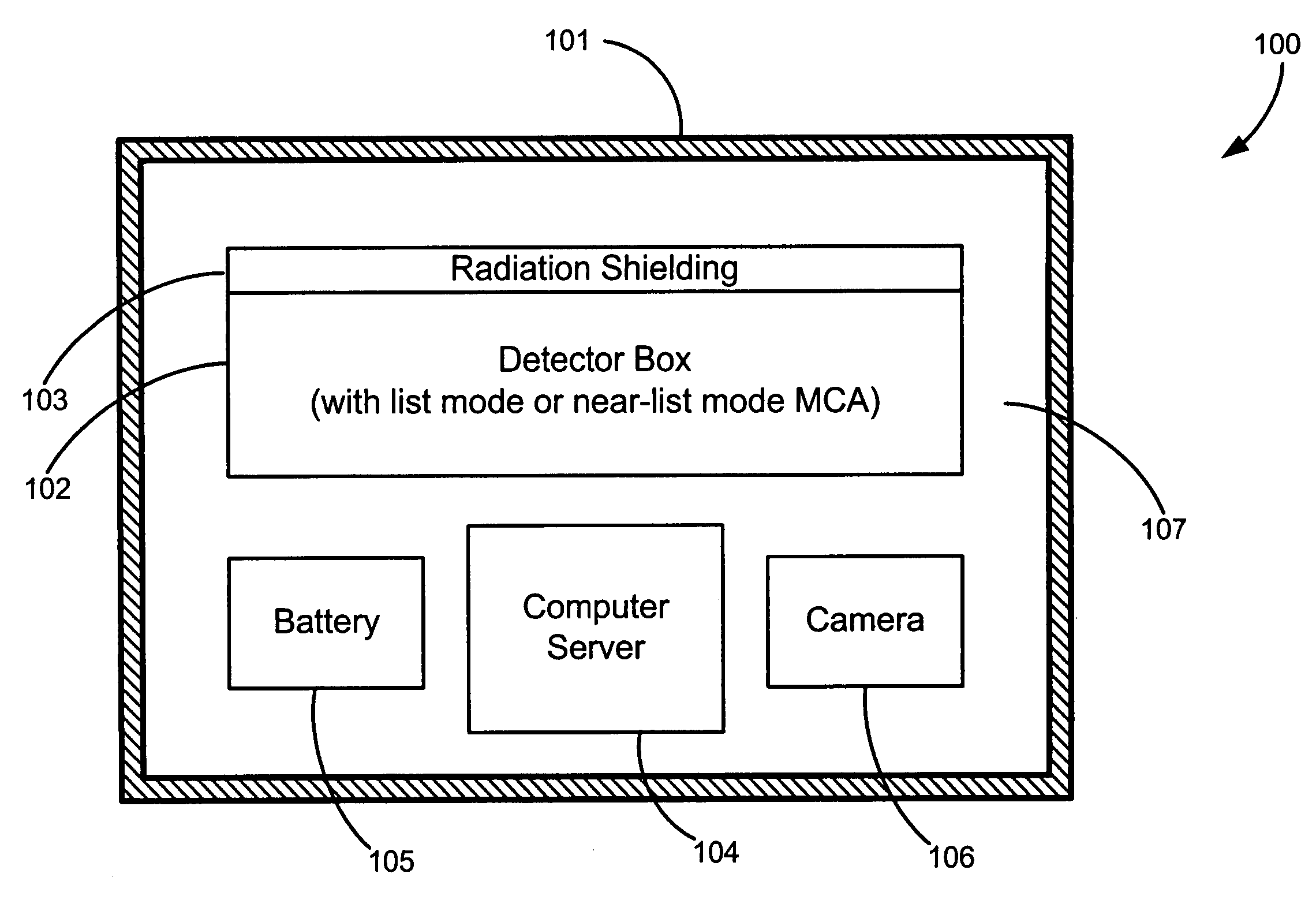
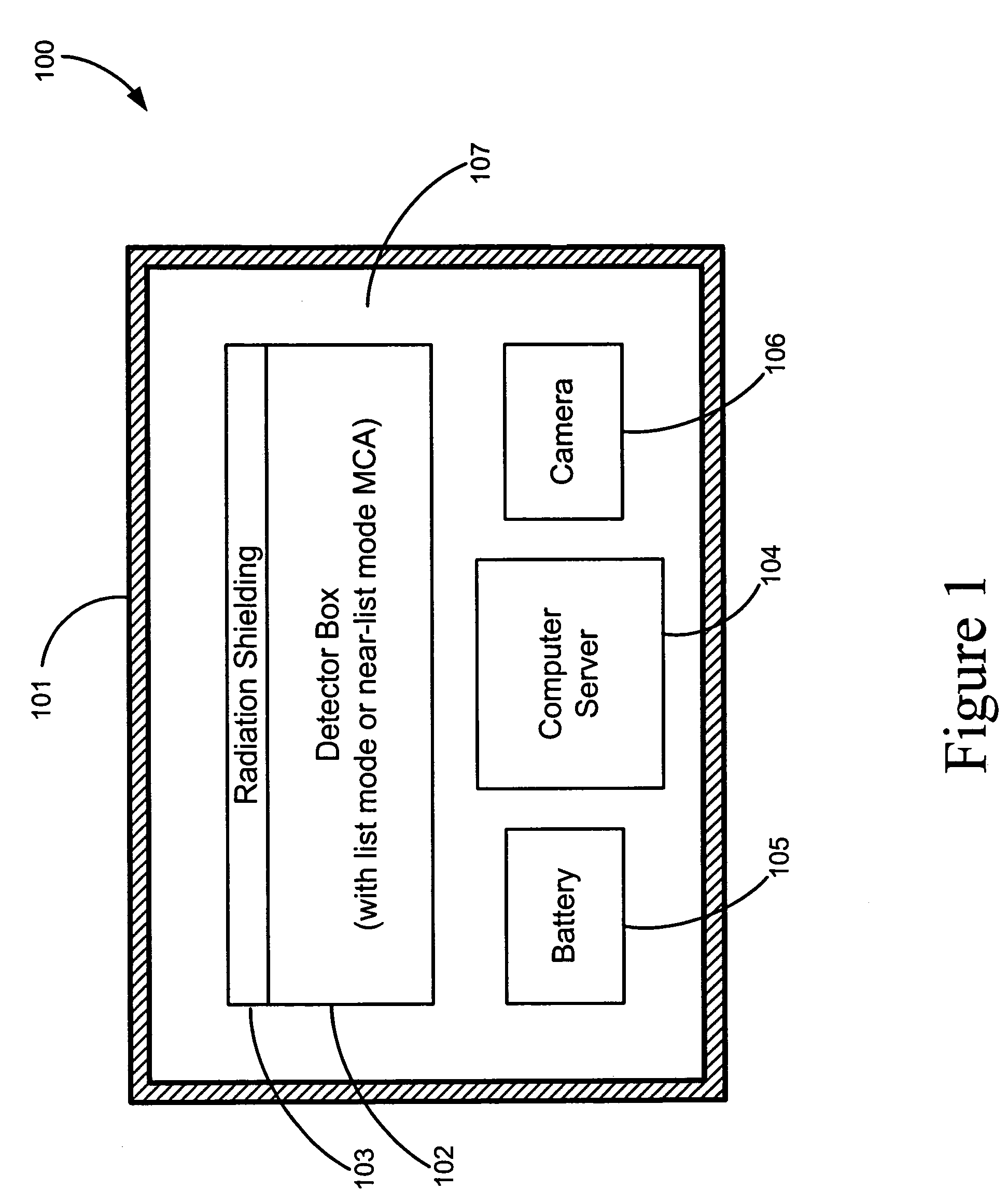
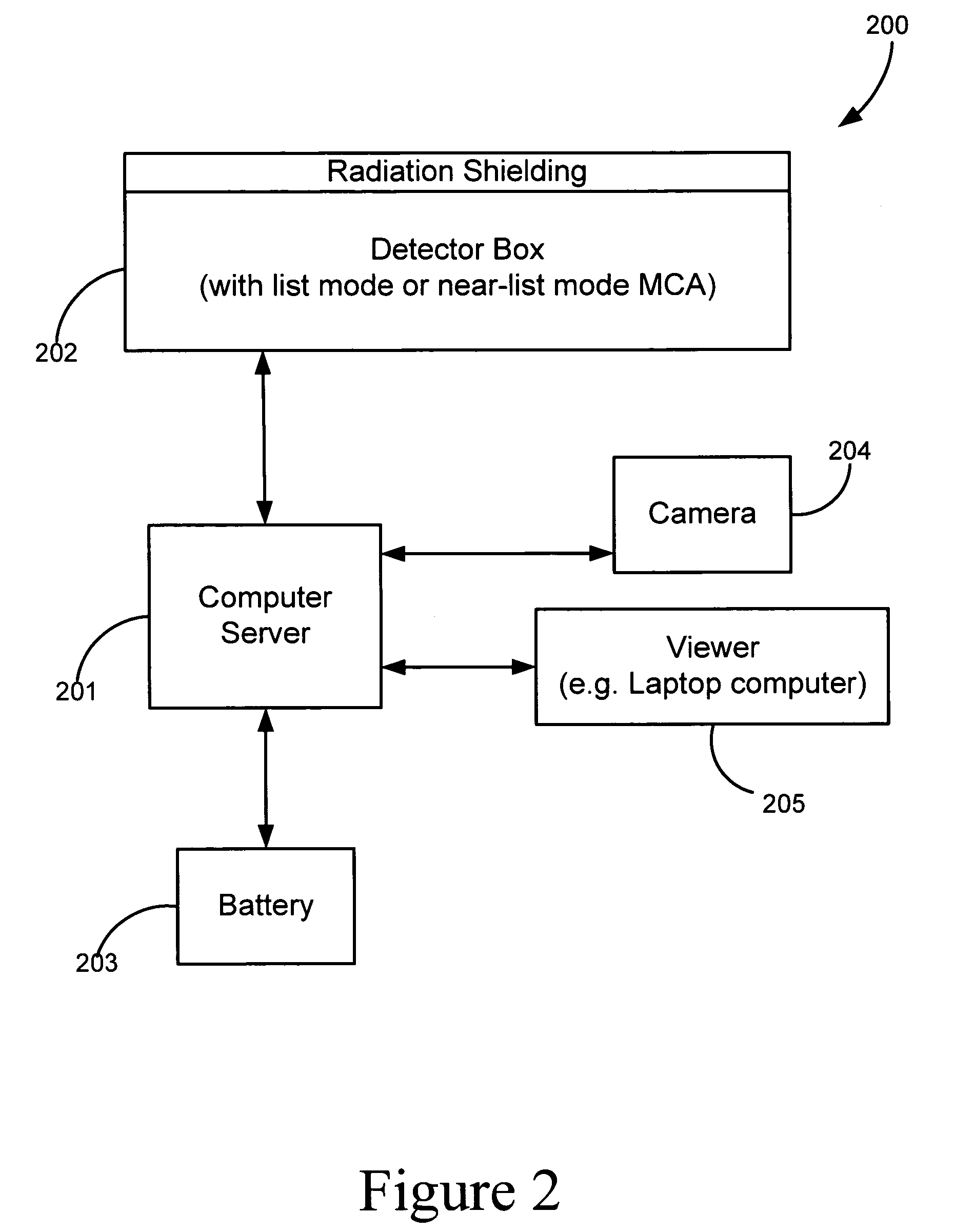
Adaptable radiation monitoring system and method
A portable radioactive-material detection system capable of detecting radioactive sources moving at high speeds. The system has at least one radiation detector capable of detecting gamma-radiation and coupled to an MCA capable of collecting spectral data in very small time bins of less than about 150 msec. A computer processor is connected to the MCA for determining from the spectral data if a triggering event has occurred. Spectral data is stored on a data storage device, and a power source supplies power to the detection system. Various configurations of the detection system may be adaptably arranged for various radiation detection scenarios. In a preferred embodiment, the computer processor operates as a server which receives spectral data from other networked detection systems, and communicates the collected data to a central data reporting system.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
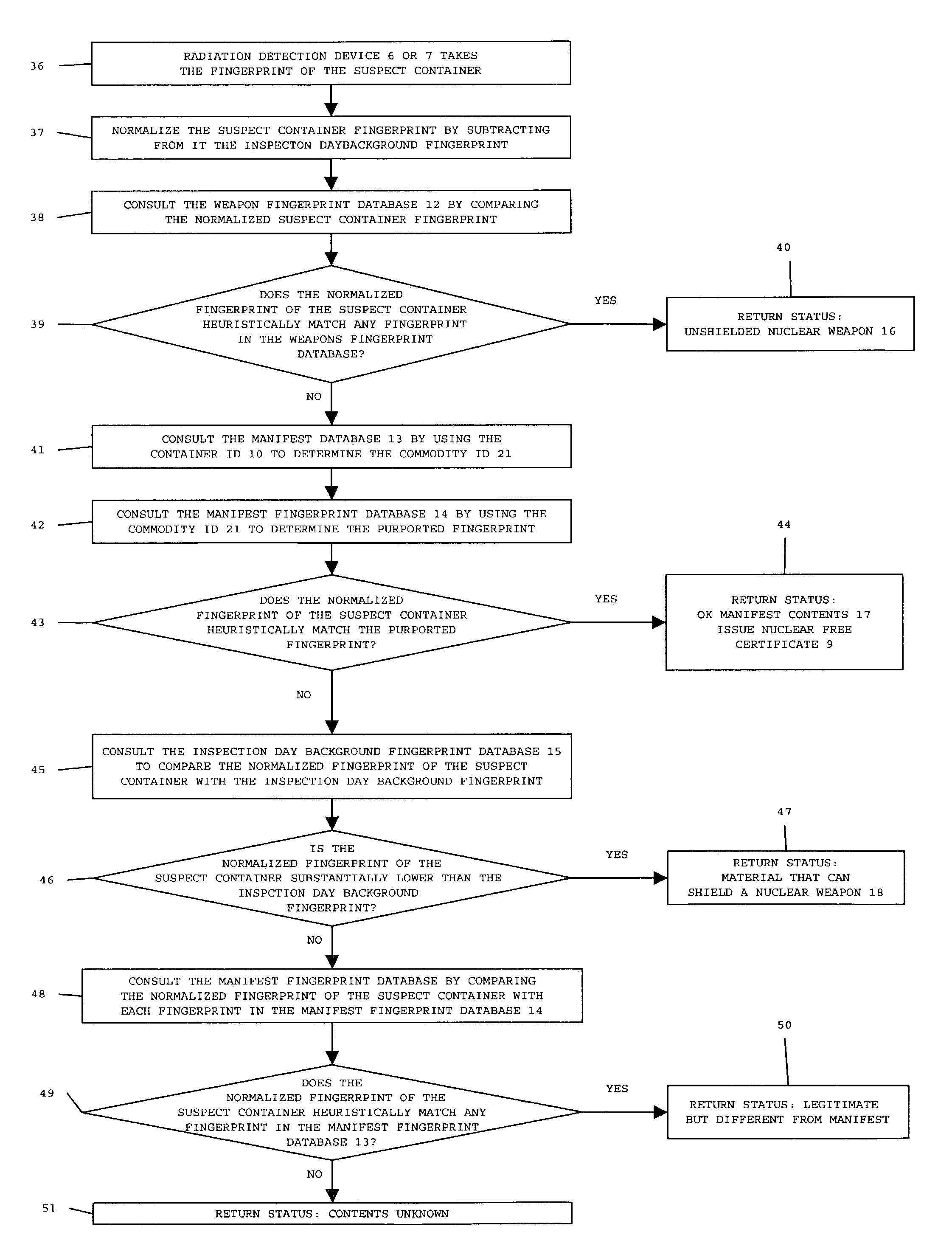
Apparatus and method for detecting radiation or radiation shielding in containers
InactiveUS7026944B2Inspection is accurateTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadioactive agentEngineering
A computer program, database and method for the detection of fissile or radioactive material or radiation shielding material in a container works with detection devices brought into proximity to containers so that the presence of fissile or radioactive material, or shielding materials to conceal the presence of such fissile or radioactive materials, may be detected. A comparison may then be made of the output of the detector to a threshold to determine subsequent action regarding the shipping container. The threshold may be based on the output of known, dangerous radioactive materials, known legitimate contents or empty containers.
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
Container and method for transporting a syringe containing radioactive material
InactiveUS20050198800A1Reduced Possibility of ContaminationDurable shellDispensing apparatusAssembly machinesRadioactive agentEngineering
A method and apparatus for transporting syringes containing radioactive material. The apparatus includes a radiopharmaceutical pig having an inner chamber in which a sharps container can be secured. The sharps container has a housing and an attachable cap. The method includes assembling the radiopharmaceutical pig so that the chamber of the radiopharmaceutical pig contains the syringe in the sharps container housing. The radiopharmaceutical pig is disassembled, where upon the syringe is removed, discharged, and then replaced in the sharps container housing. The cap of the sharps container is affixed to the housing of the sharps container, thus enclosing the contaminated syringe therein. The radiopharmaceutical pig is assembled so that its chamber contains the sharps container and the syringe. The radiopharmaceutical pig is transported to a disposal area, where it is disassembled and the sharps container containing the syringe is placed in a particular disposal container.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH INC
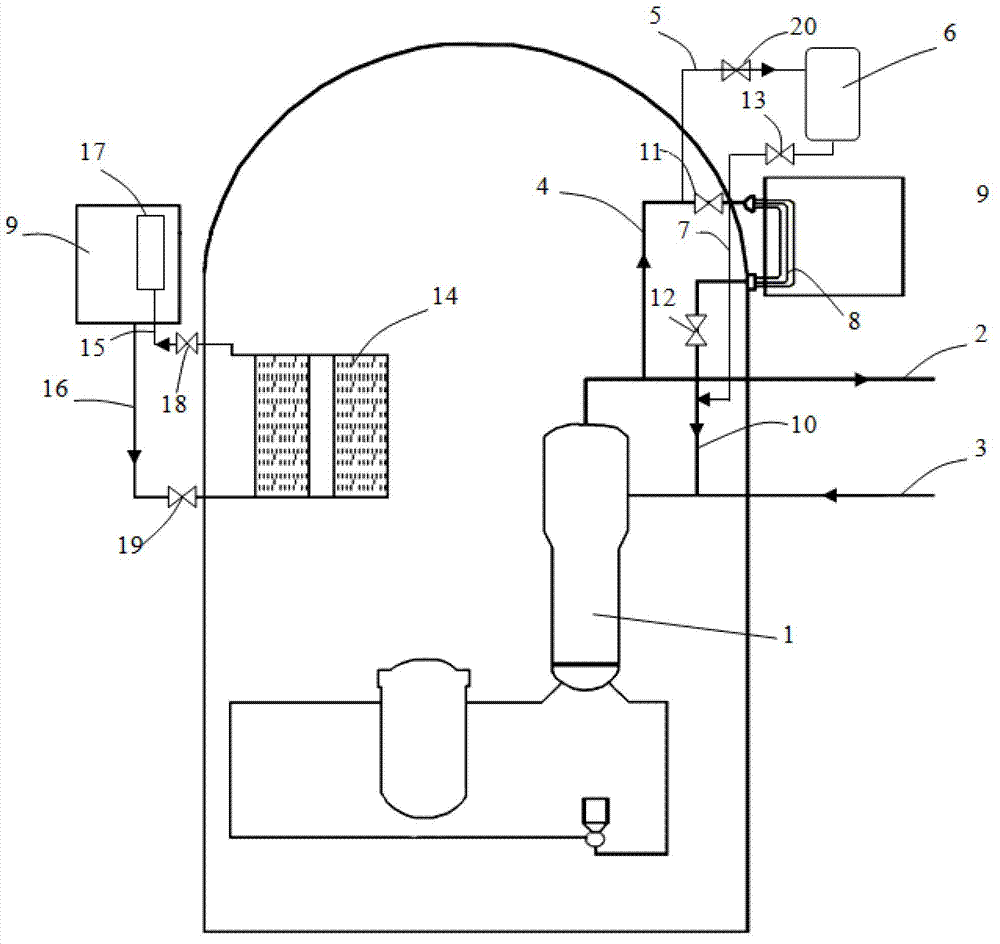
Active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system for nuclear power station
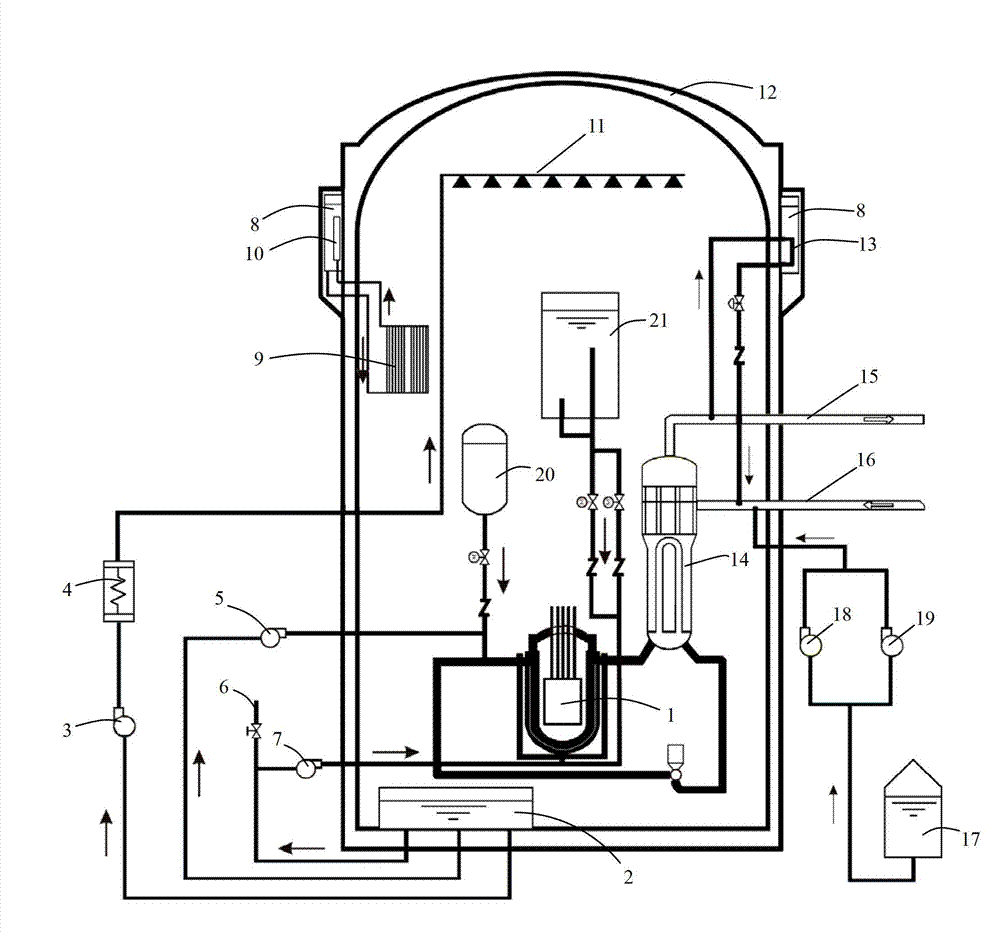
ActiveCN102903404AReduced risk of serious accidentsGuaranteed completeness of security functionsNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention relates to an active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system for a nuclear power station. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system comprises a safety injection system, a containment spraying system, an auxiliary water supply system, a reactor cavity water injection system, a secondary side passive residual heat removal system, a passive containment heat leading-out system and related valves and pipelines. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system provided by the invention realizes three safety functions of controlling reactivity, discharging reactor core heat and containing radioactive substance when an accident occurs in an active-passive combined multi-redundancy diversity manner. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system provided by the invention can completely realize the safety functions of safety injection and safety spraying under the condition that the accident occurs in a nuclear power plant, reactor cavity water injection under the serious accident working condition and the like, effectively improve reliability of a safety system, enhance coping capability of the safety system under the working condition that the accident occurs in the nuclear power station, can effectively prevent and relieve the serious accident, reduce the reactor core melting probability and risk probability of large-scale radioactivity release and greatly improve safety performance of the nuclear power station.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
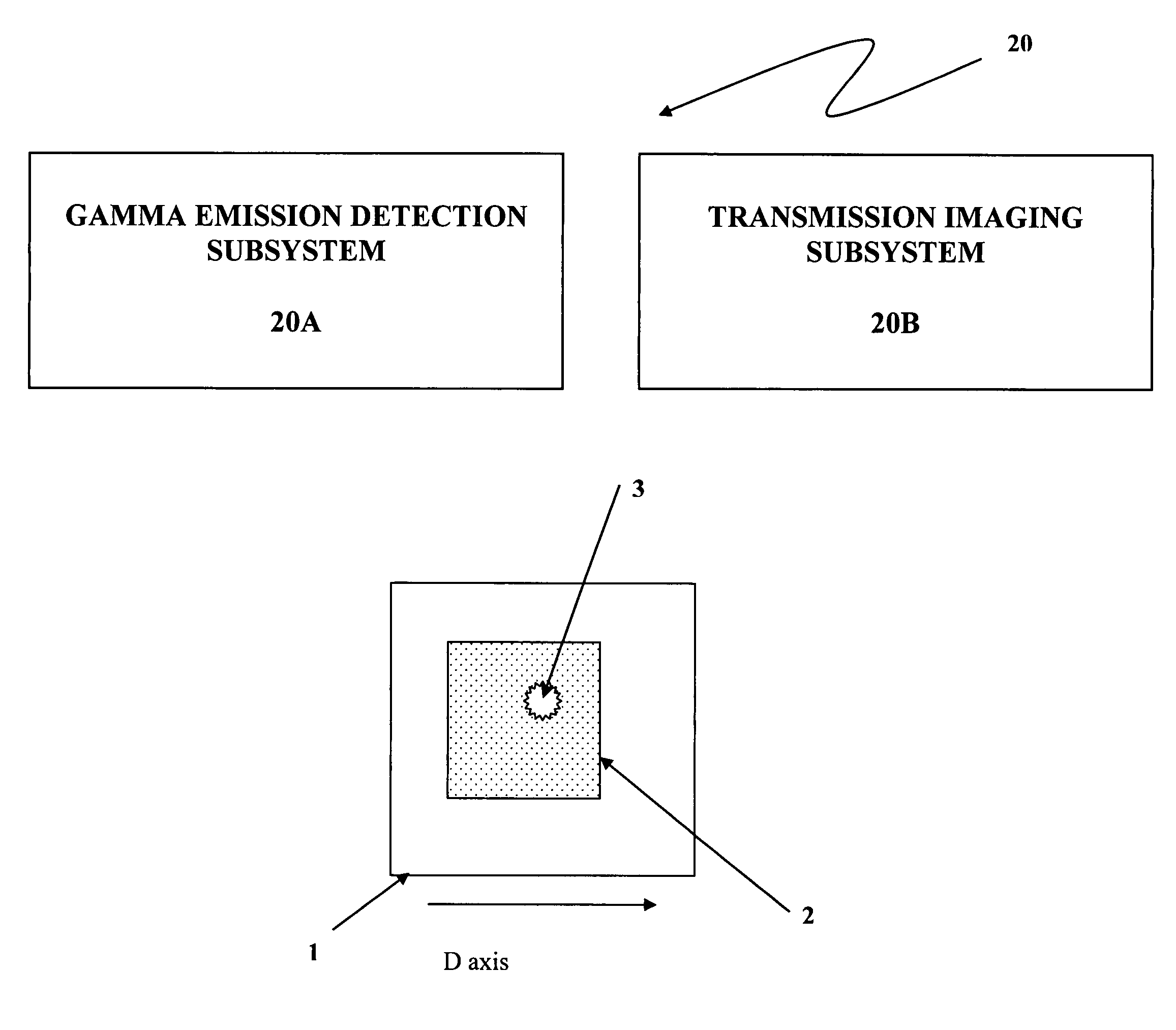
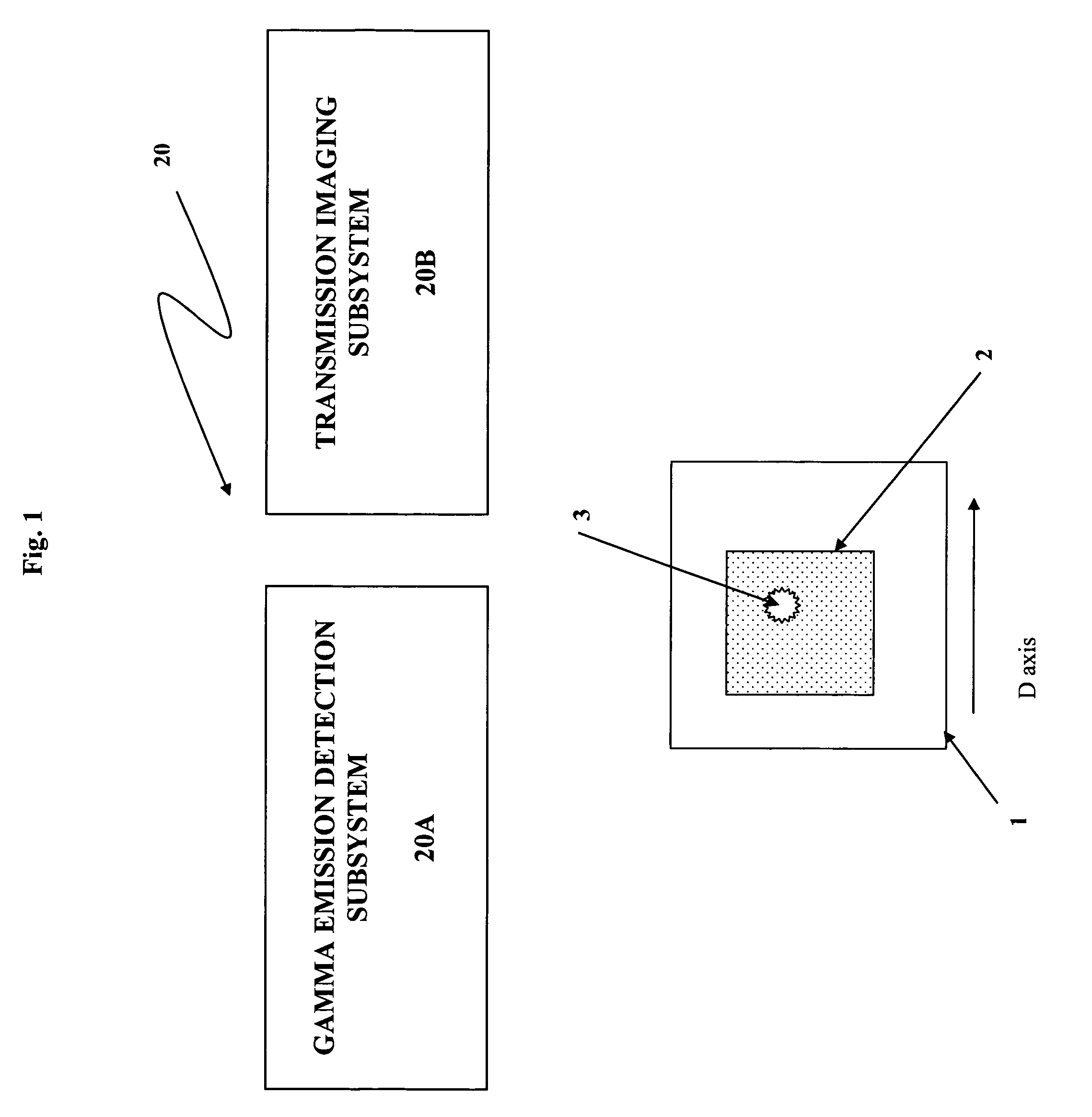
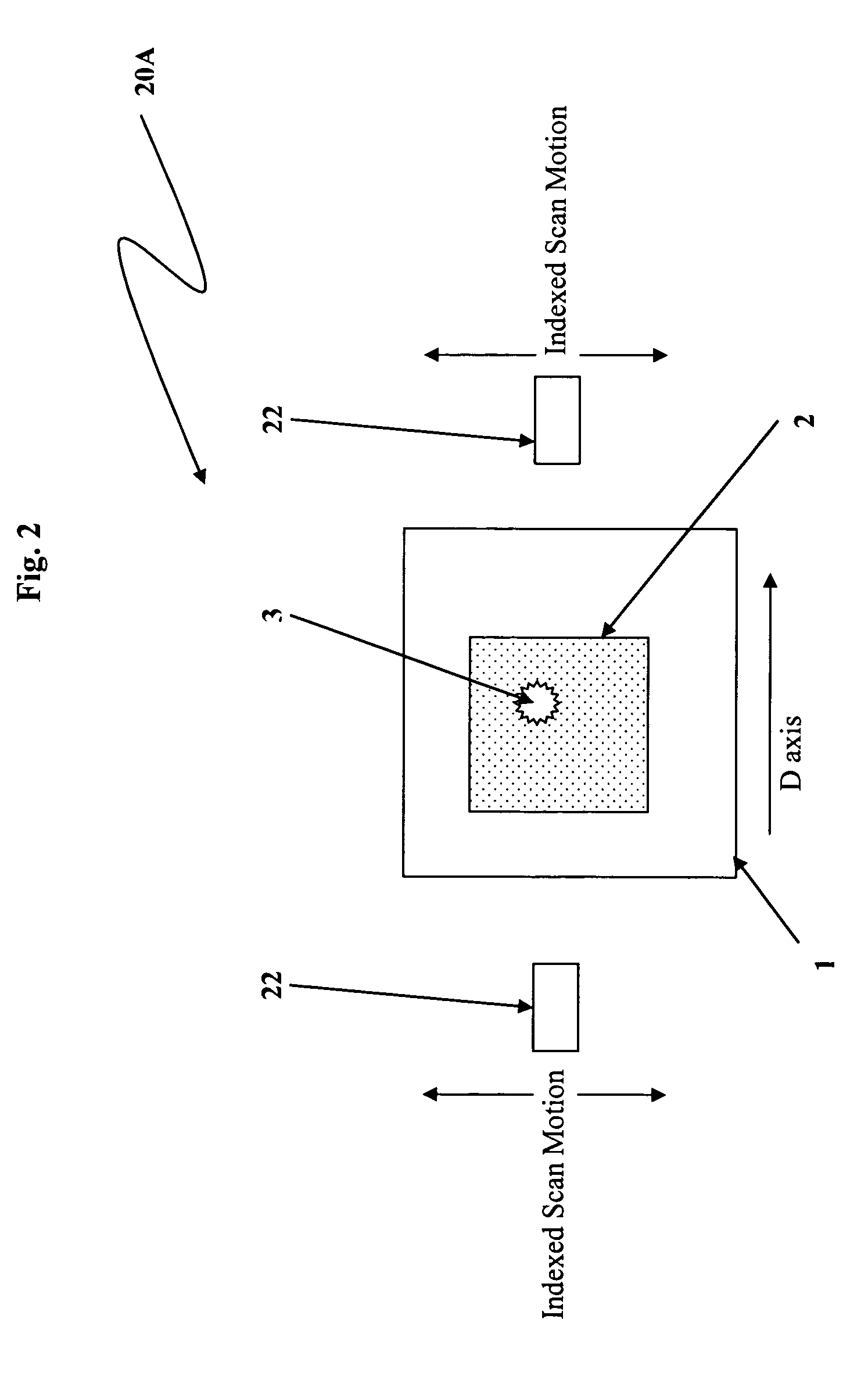
Quantitative transmission/emission detector system and methods of detecting concealed radiation sources
InactiveUS7317195B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesRadioactive agentFast scanning
Owner:EIKMAN EDWARD A
Biomarker generator system
ActiveUS20080067413A1Efficient dosingEfficient productionIsotope delivery systemsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroreactorParticle accelerator
A biomarker generator system for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker. The biomarker generator system includes a small, low-power particle accelerator (“micro-accelerator”) and a radiochemical synthesis subsystem having at least one microreactor and / or microfluidic chip. The micro-accelerator is provided for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a radioactive substance, such as a substance that emits positrons. The radiochemical synthesis subsystem is provided for receiving the radioactive substance, for receiving at least one reagent, and for synthesizing the approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker.
Owner:BEST ABT INC
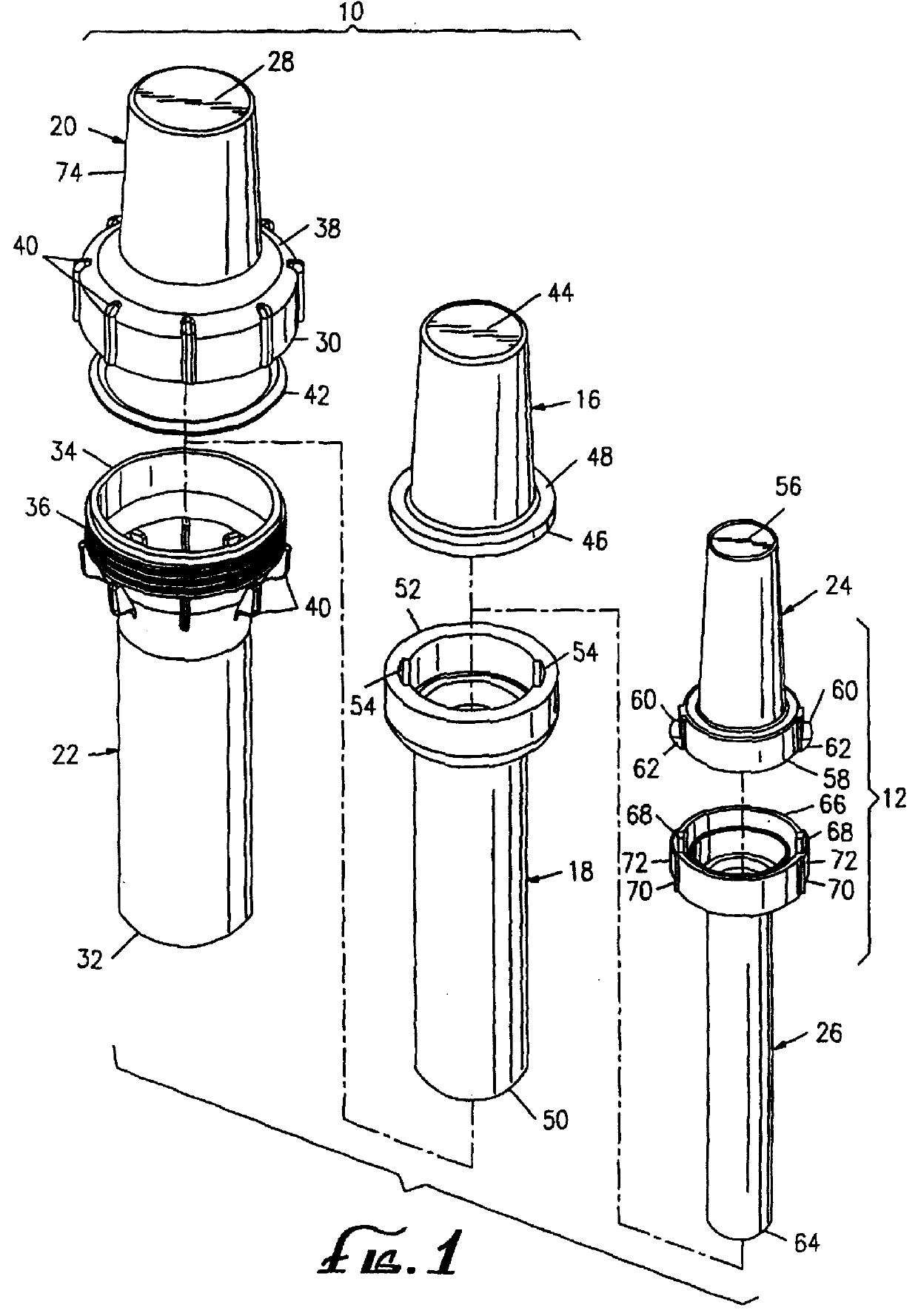
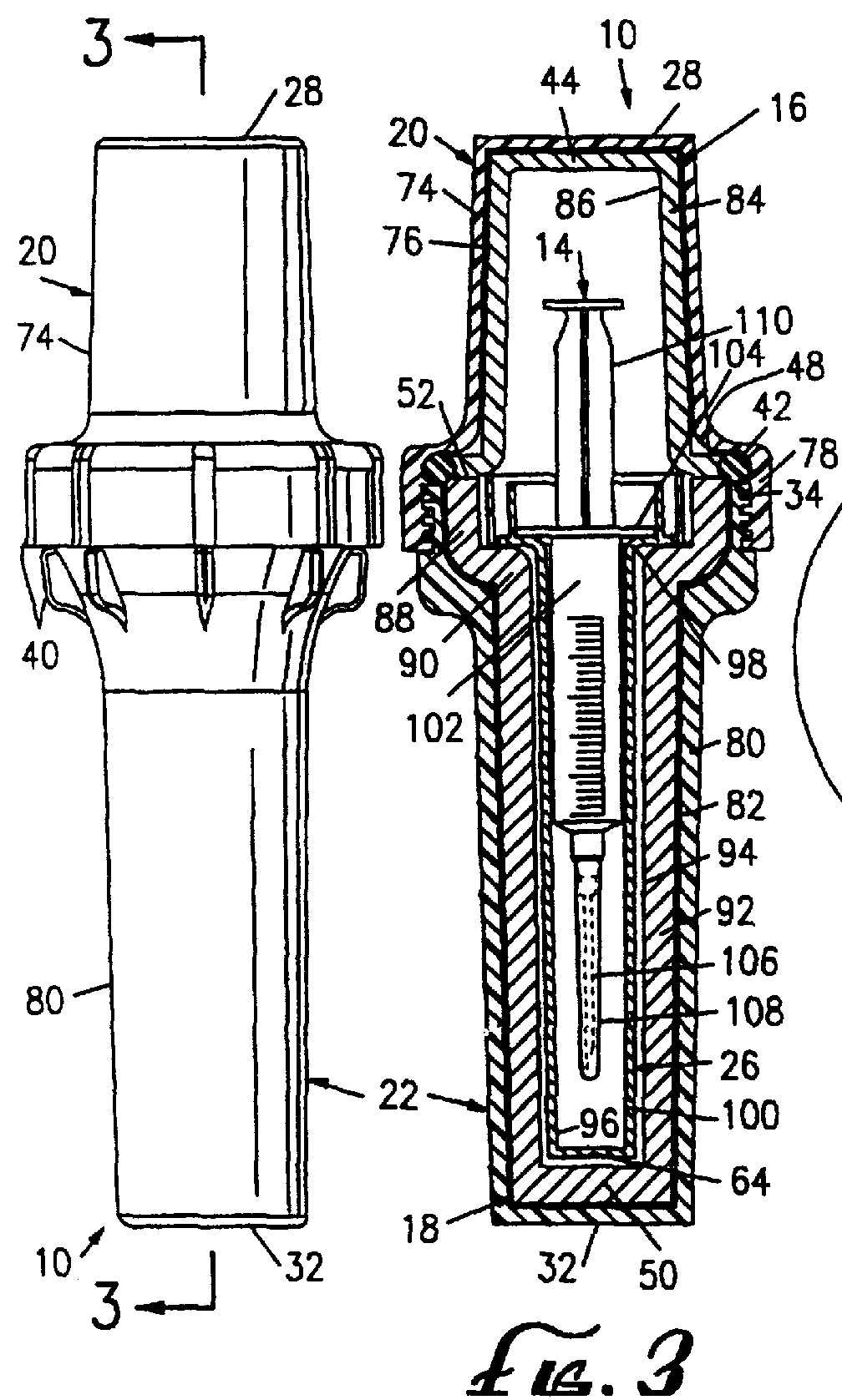
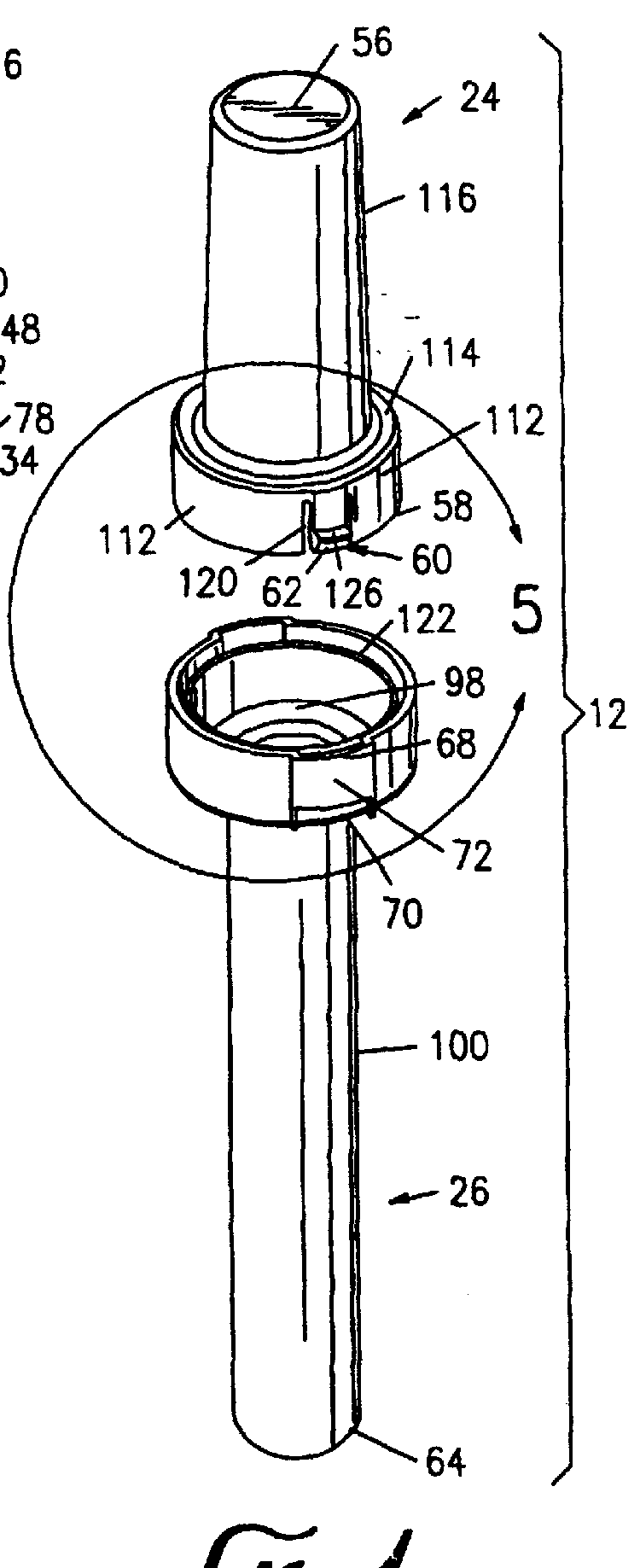
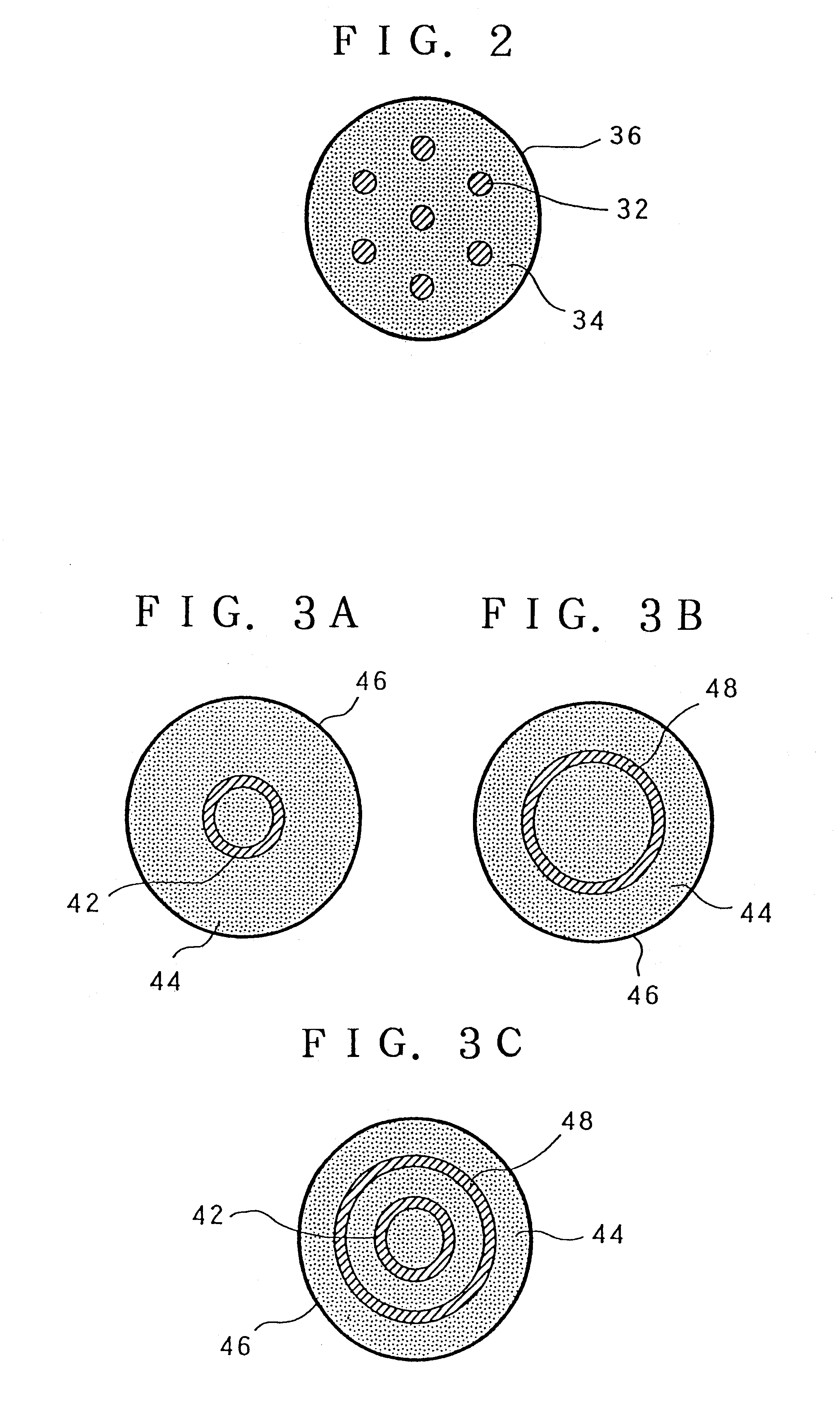
Bioabsorbable brachytherapy device
InactiveUS20010044567A1Radioactive preparation formsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapy deviceRadiopaque medium
A bioabsorbable brachytherapy device includes a tubular housing with sealed ends and an enclosed radioactive material. The radioactive material includes a radioisotope, such as palladium-103 or iodine-125. The tubular housing is made from a biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymeric material, and is sealed by means such as heat welding or solvent fixing. The device may further include a radiopaque medium and one or more therapeutic drugs.
Owner:FERRING BV
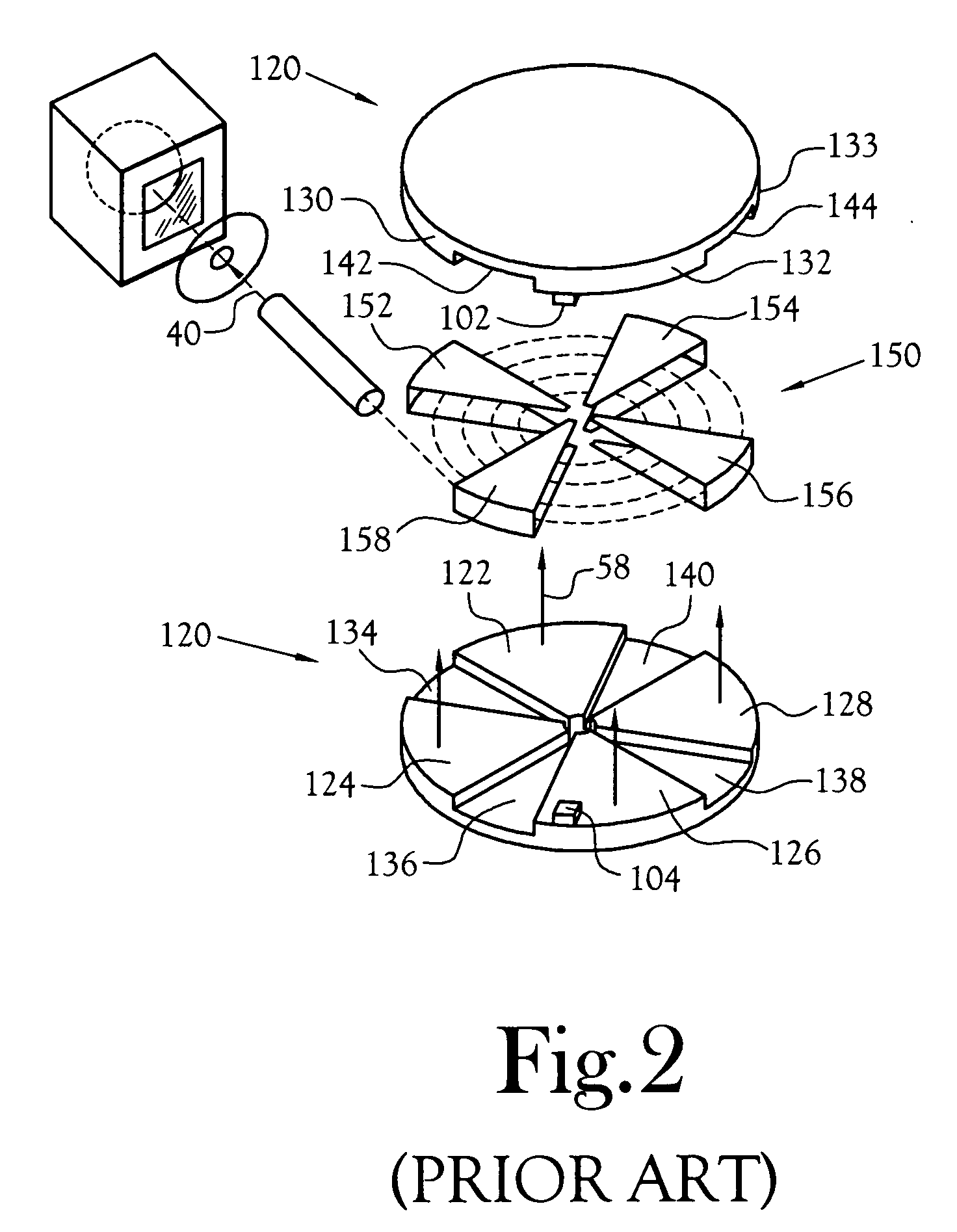
Intraocular brachytherapy device and method
ActiveUS20050027156A1Good effectMedical preparationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapy deviceRadioactive agent
An ocular brachytherapy device, generally comprising a catheter and wire, impregnated with radioactive material, are provided. The wire is formed having a desired treatment shape and size such that it can be placed near an area requiring treatment and effectuate treatment while not affecting adjacent areas. For ease in placement near such areas the wire is preferably formed using materials having properties that permit formation into a desired shape while allowing the wire to be straightened for retraction into the catheter, the shape returning upon removal from the catheter. The wire is preferably impregnated with radioactive material. When the catheter is placed near the area of treatment and the wire is pushed out of the catheter, the wire retakes the desired form and provides a therapeutic radioactive treatment to the area. Preferably, the radioactive material is placed on one edge of the wire, such that the radiation can be directed to the affected area, and non-affected areas can be shielded from radiation.
Owner:SALUTARIS MEDICAL DEVIES INC
Methods of vitrifying waste with low melting high lithia glass compositions
InactiveUS6258994B1Reduce pointsReduce the temperatureSludge treatmentSolid waste disposalAlkali metal oxideRadioactive agent
The invention relates to methods of vitrifying waste and for lowering the melting point of glass forming systems by including lithia formers in the glass forming composition in significant amounts, typically from about 0.16 wt % to about 11 wt %, based on the total glass forming oxides. The lithia is typically included as a replacement for alkali oxide glass formers that would normally be present in a particular glass forming system. Replacement can occur on a mole percent or weight percent basis, and typically results in a composition wherein lithia forms about 10 wt % to about 100 wt % of the alkali oxide glass formers present in the composition. The present invention also relates to the high lithia glass compositions formed by these methods. The invention is useful for stabilization of numerous types of waste materials, including aqueous waste streams, sludge solids, mixtures of aqueous supernate and sludge solids, combinations of spent filter aids from waste water treatment and waste sludges, supernate alone, incinerator ash, incinerator offgas blowdown, or combinations thereof, geological mine tailings and sludges, asbestos, inorganic filter media, cement waste forms in need of remediation, spent or partially spent ion exchange resins or zeolites, contaminated soils, lead paint, etc. The decrease in melting point achieved by the present invention desirably prevents volatilization of hazardous or radioactive species during vitrification.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS20040120857A1Easy to removeEasy to replaceSolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsRadioactive agentComputer science
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
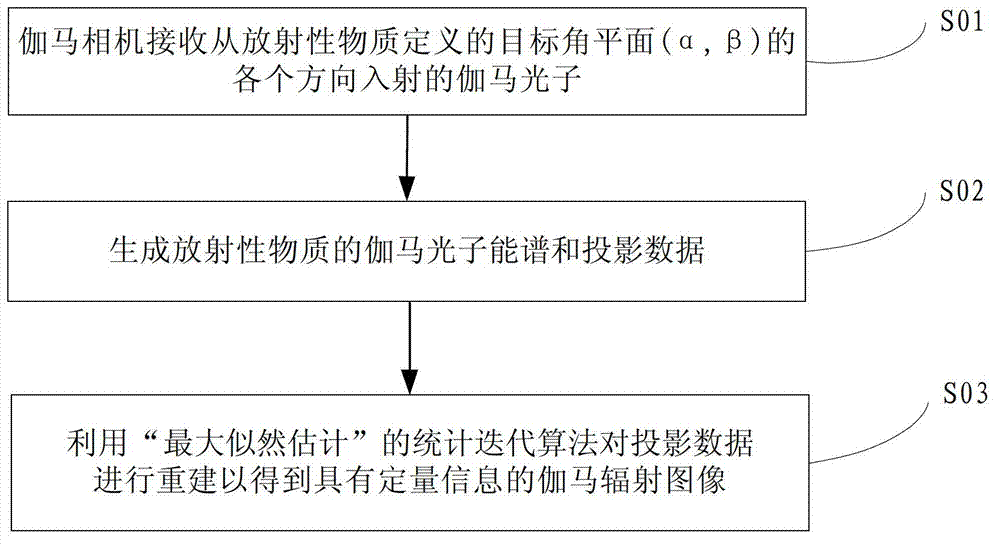
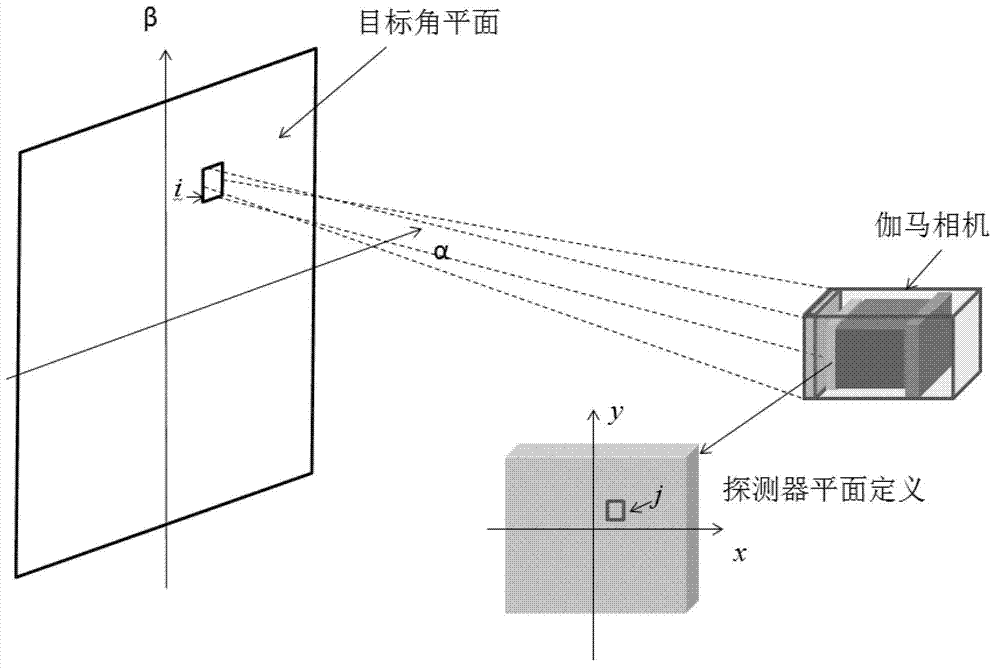
Radioactive substance detection method, device and system based on gamma camera
ActiveCN103163548AImprove spatial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhotographic dosimetersRadioactive agentNuclide
The invention provides a radioactive substance detection method, a radioactive substance detection device and a radioactive substance detection system based on a gamma camera. The detection method comprises the following steps of: receiving gamma photons incident from all directions of a target angle plane (alpha, beta) defined by radioactive substances by using the gamma camera; generating gamma photon energy spectrums and projection data of the radioactive substances; and reconstructing the projection data by using a 'maximum likelihood estimation' statistical iterative algorithm to obtain a gamma radiation image with quantitative information. By the method, the spatial resolution and the signal to noise ratio of the gamma radiation image are increased, spaces of the radioactive substances are positioned, the radiation dose is measured, nuclide types of the radioactive substances are identified, and the radioactive activity is measured.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL MEDICAL EQUIP LTD +1
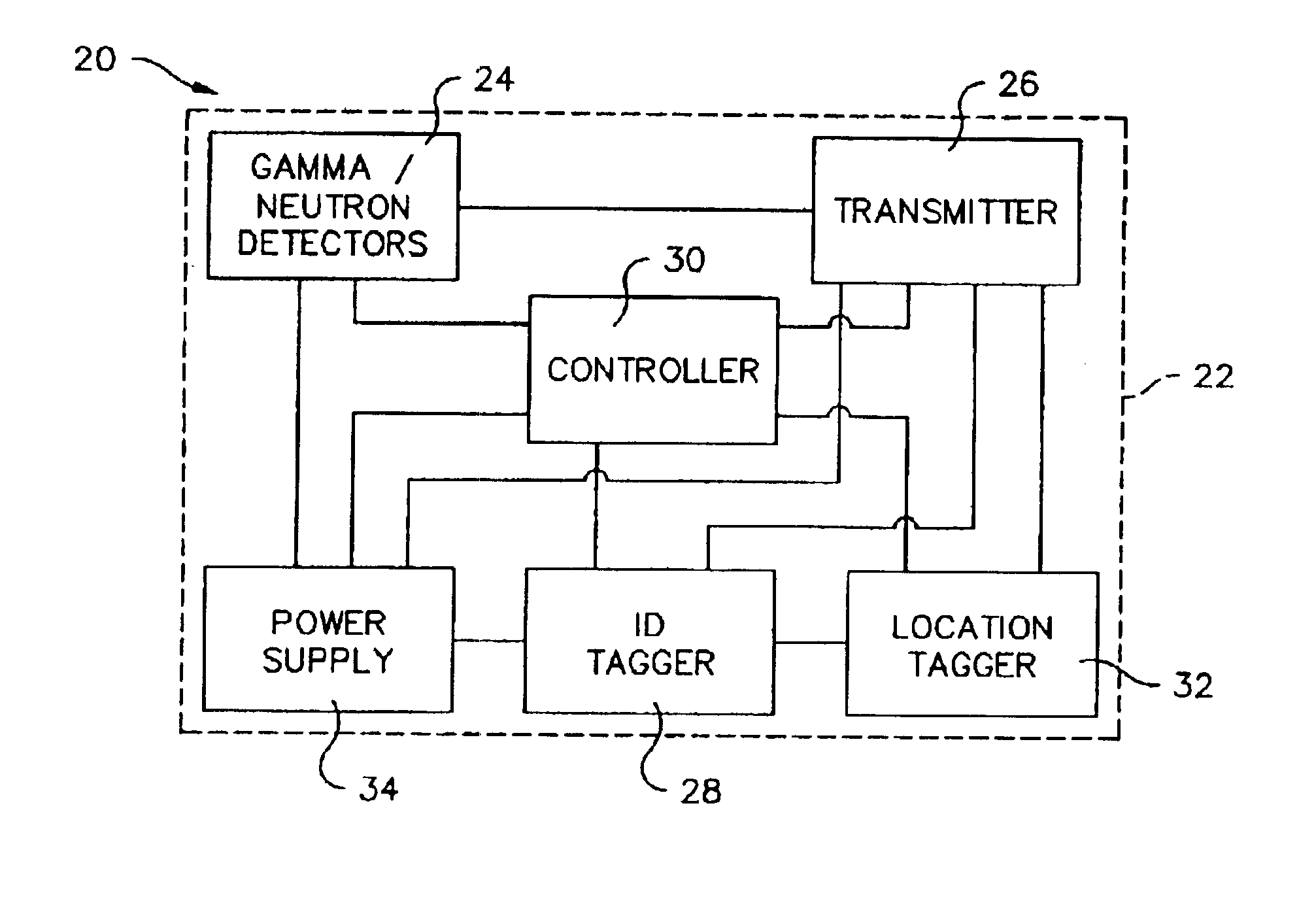
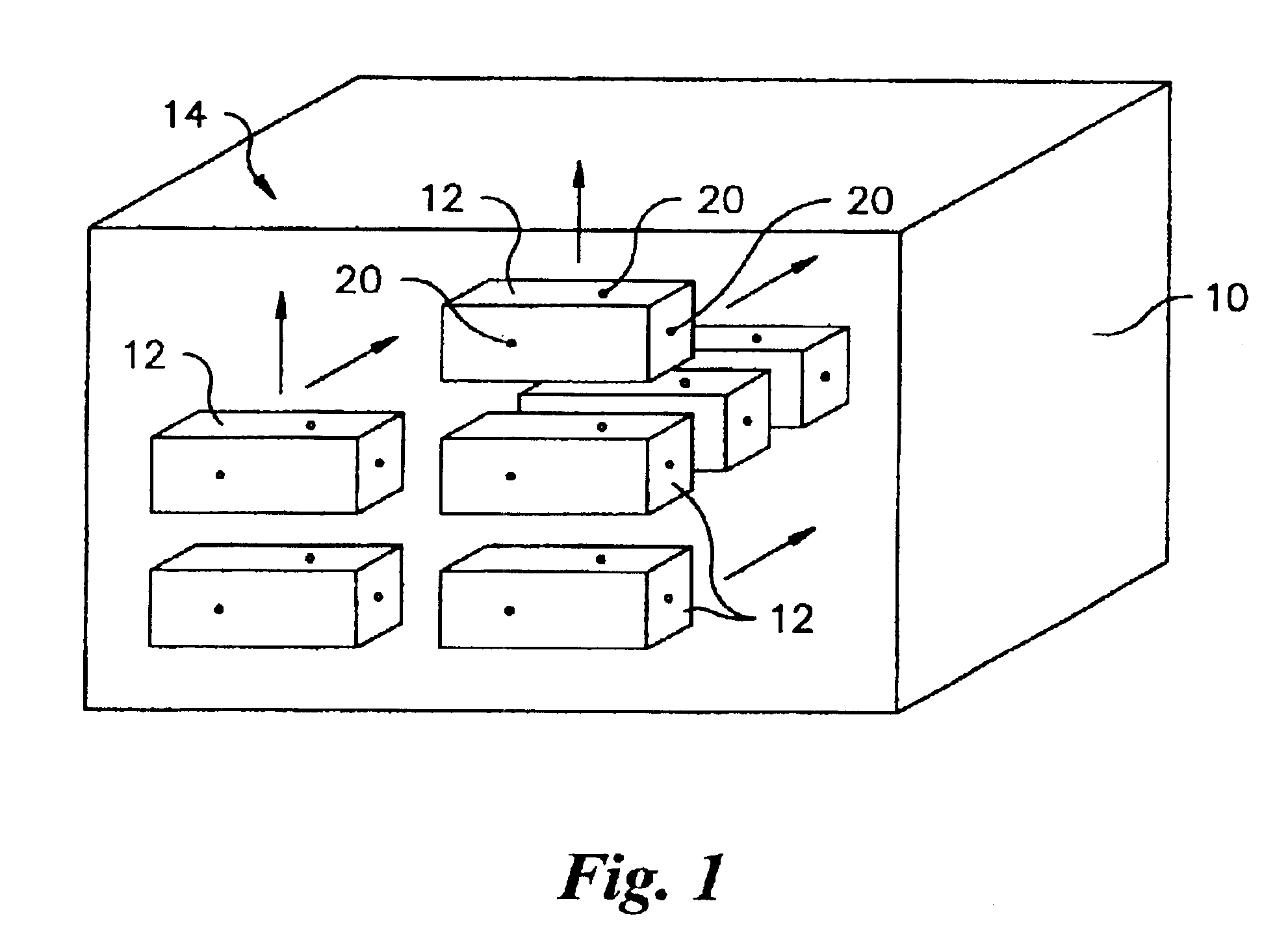
Method and apparatus for detection of radioactive material
InactiveUS20050205793A1Electric testing/monitoringMaterial analysis by optical meansNuclear engineeringRadioactive agent
A radioactive material detection system includes a plurality of radioactive material detection apparatuses and a master unit / master module. Each apparatus is disposed in or on a cargo receptacle and each apparatus has a wireless transmitter, a radiation sensor and a detection controller. The master unit / master module has a receiver configured to receive the wirelessly transmitted information from each of the wireless transmitters and a master controller. The system detects fissile or nuclear material that emits radiation by (i) calculating and storing at the master unit / master module an initial average measured radiation level at each radioactive material detection apparatus location throughout the entire array of radioactive material detection apparatuses and (ii) comparing the current measured radiation at each radioactive material detection apparatus location to the initial radiation level at each location in order to identify an anomaly amongst the plurality of cargo receptacles.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
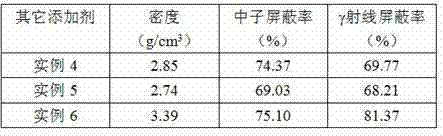
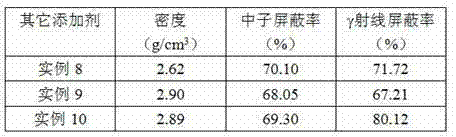
Composite shielding material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite shielding material and a preparation method thereof, in particular to the composite shielding material applied to nuclear radiation places such as nuclear reactor, spent fuel assembly storage and radioactive substance storage and transportation and the like. The composite shielding material is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 0 to 30 percent of w and compound thereof, 0 to 70 percent of B4C, 0 to 90 percent of aluminum or aluminum alloy, 0 to 8 percent of other elements and the like. The composite shielding material comprising tungsten B4C / aluminum alloy is uniform in distribution of W2B5 and B4C, high in densification degree, high in strength and toughness, and particularly applicable to the field of neutron / gamma ray shielding.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
Adaptable radiation monitoring system and method
A portable radioactive-material detection system capable of detecting radioactive sources moving at high speeds. The system has at least one radiation detector capable of detecting gamma-radiation and coupled to an MCA capable of collecting spectral data in very small time bins of less than about 150 msec. A computer processor is connected to the MCA for determining from the spectral data if a triggering event has occurred. Spectral data is stored on a data storage device, and a power source supplies power to the detection system. Various configurations of the detection system may be adaptably arranged for various radiation detection scenarios. In a preferred embodiment, the computer processor operates as a server which receives spectral data from other networked detection systems, and communicates the collected data to a central data reporting system.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method for removing metal ions from aqueous solution by use of hydrotalcite
InactiveCN102336461AImprove removal efficiencyHigh ion exchange capacityOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMetal ions in aqueous solutionRadioactive agent
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, specifically to a method for removing metal ions from an aqueous solution by the use of hydrotalcite. The method provided by the invention comprises the step of removing metal ions from an aqueous solution by the use of hydrotalcite. The metal ions, which refer to heavy metal ions or radioactive substance ions, comprise one or more selected from the group consisting of mercury, chromium, lead, arsenic, cadmium, tin, copper and zinc heavy metal ions. The radioactive substance ions comprise uranium, thorium and radium ions. According to the invention, hydrotalcite is applied in metal ions-containing sewage processing, leading to high metal ion removing efficiency and obvious effects. In the meanwhile, raw material sources for the preparation of hydrotalcite are extensive, the cost is low, the preparation method is simple, energy consumption is low and the investment is also low. Therefore, the method provided by the invention has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Passive heat removal device for dealing with station blackout accident
InactiveCN102867550AIntegrity guaranteedNo action requiredNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementRadioactive agentReactor design
The invention relates to reactor design technology, in particular to a passive heat removal device for dealing with a station blackout accident. The passive heat removal device structurally comprises a secondary side passive residual heat removal system and a passive containment heat export system, and the secondary side passive residual heat removal system is used for exporting residual heat of a reactor core and sensible heat of various devices of a reactor coolant system, so that a reactor is maintained to be in a safe shutdown state. The passive containment heat export system is used for exporting heat in a containment released by the reactor core so as to maintain integrity of the containment. The secondary side passive residual heat removal system and the passive containment heat export system share a hot water tank. The passive heat removal device for dealing with the station blackout accident is capable of exporting decay heat of the reactor core and heat in containment space released by the reactor core under the working condition of the station blackout accident, and melting probability of the reactor core and probability of radioactive substances released to the environment are evidently lowered.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Method of removing radioactive materials from a submerged state and/or preparing spent nuclear fuel for dry storage
ActiveUS20090069621A1Quantity maximizationIncreasing transfer procedure cycleNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A system, apparatus and method of processing and / or removing radioactive materials from a body of water that utilizes the buoyancy of the water itself to minimize the load experienced by a crane and / or other lifting equipment. In one aspect, the invention is a method comprising: a) submerging a container having a top, a bottom, and a cavity in a body of water having a surface level, the cavity filling with water; b) positioning radioactive material within the cavity of the submerged container; c) raising the submerged container until the top of the containment apparatus is above the surface level of the body of water while a major portion of the container remains below the surface level of the body of water; and d) removing bulk water from the cavity while the top of the container remains above the surface level of the body of water and a portion of the container remains submerged. The bulk water can be added back into the cavity to add neutron shielding after the container is placed in a staging area and prior to personnel performing the desired operations to the container. As a result, gamma radiation and neutron shielding of the container can be maximized for any crane capacity.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com