Patents
Literature
15223results about How to "Prevent oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
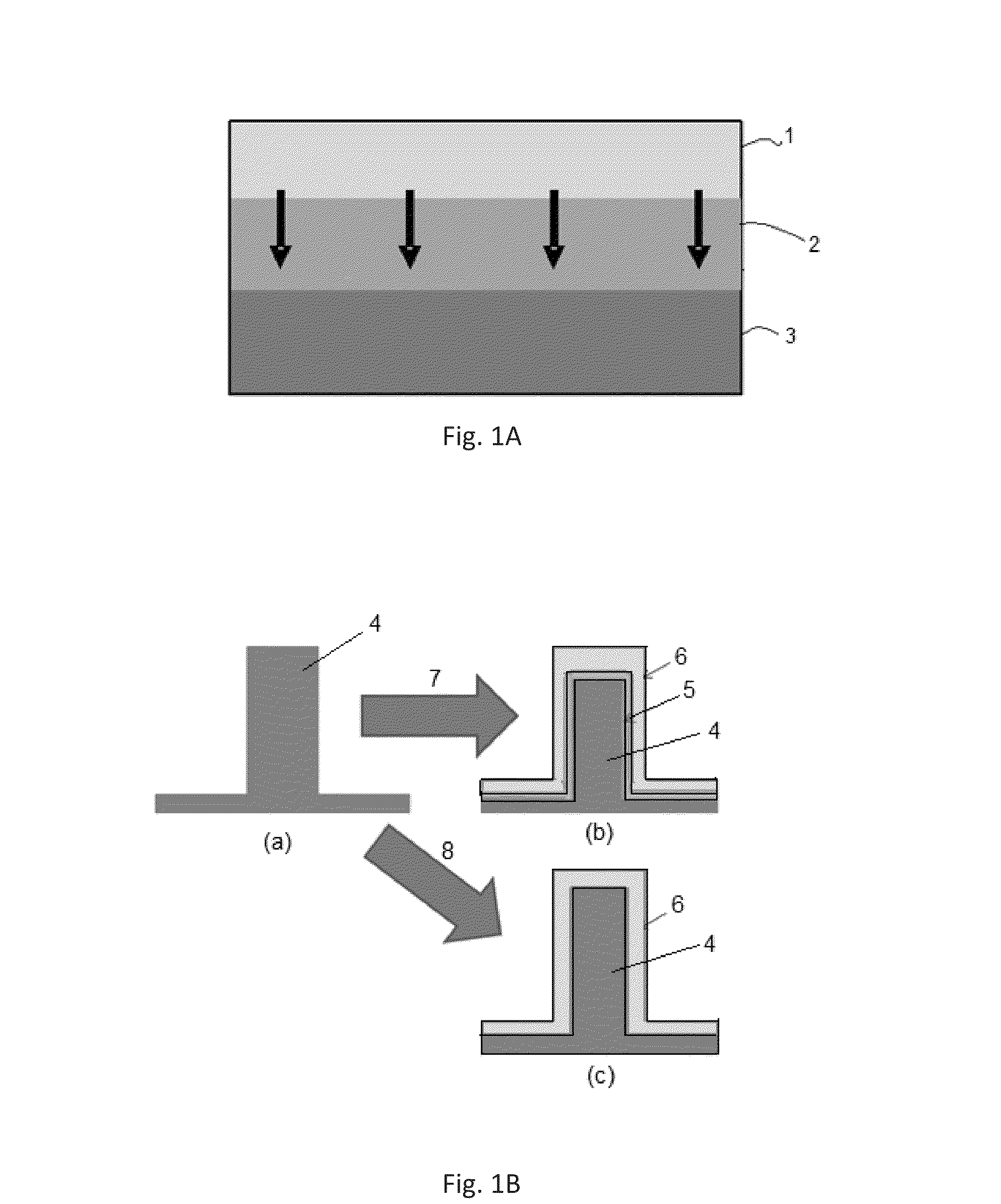
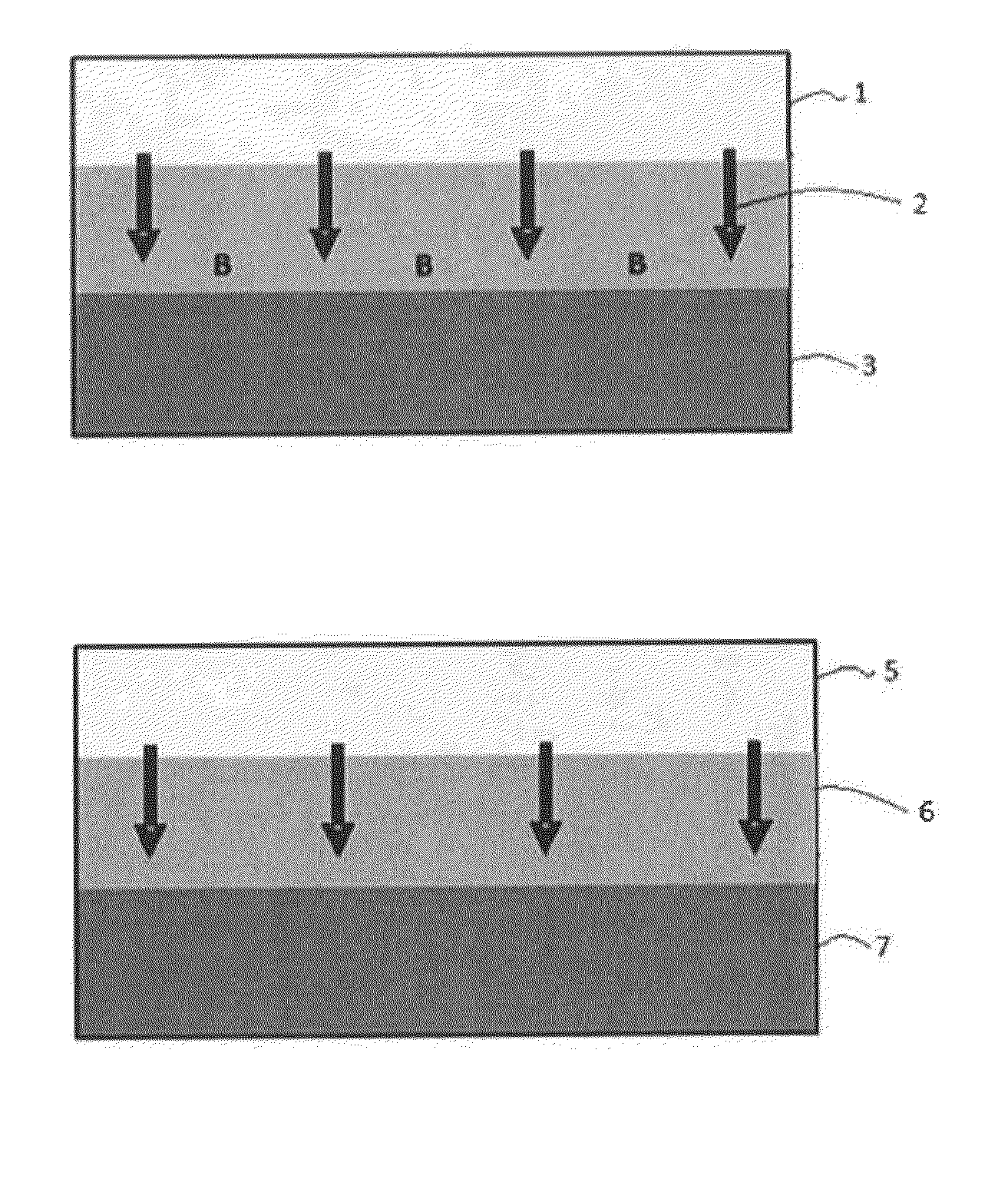
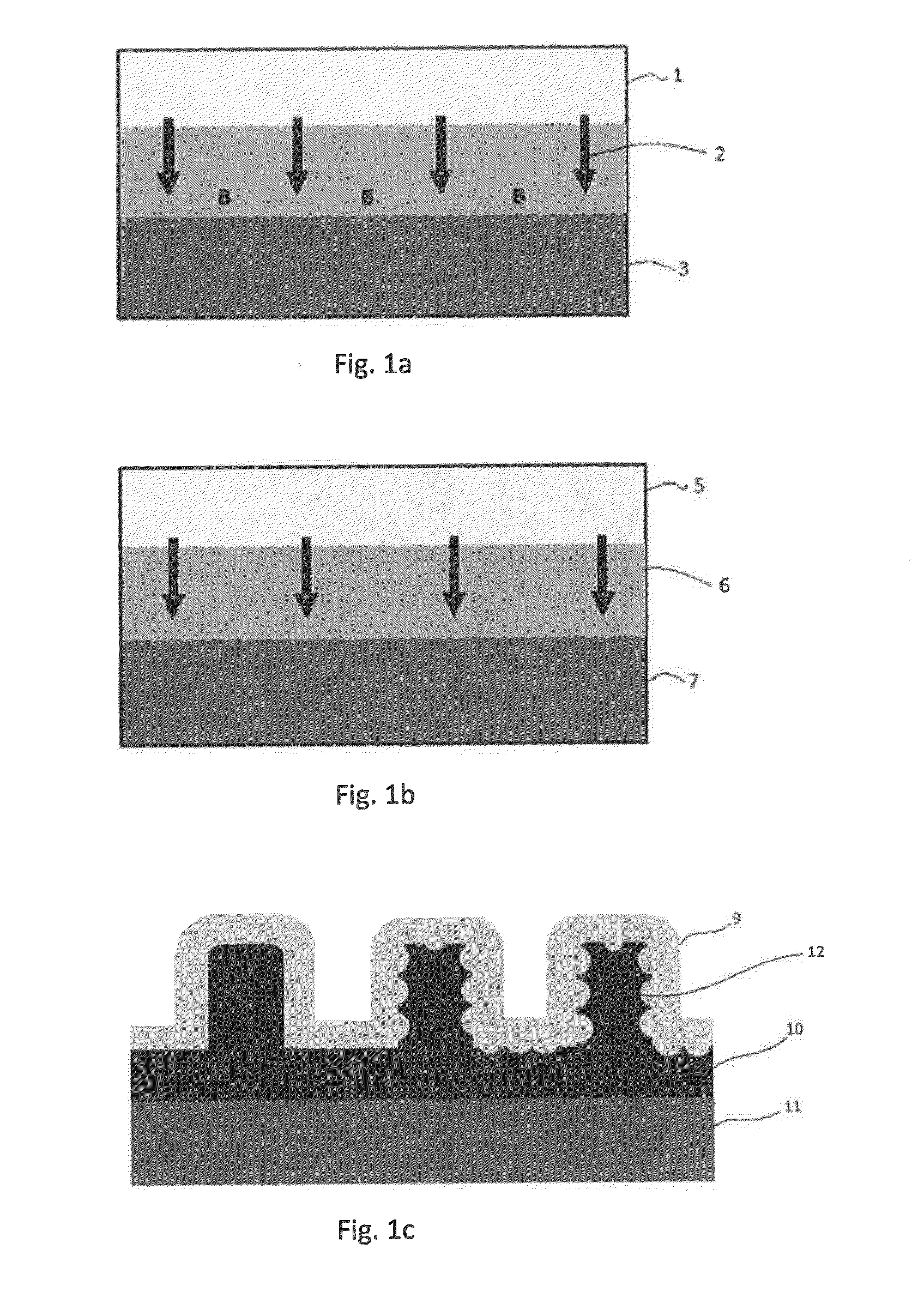
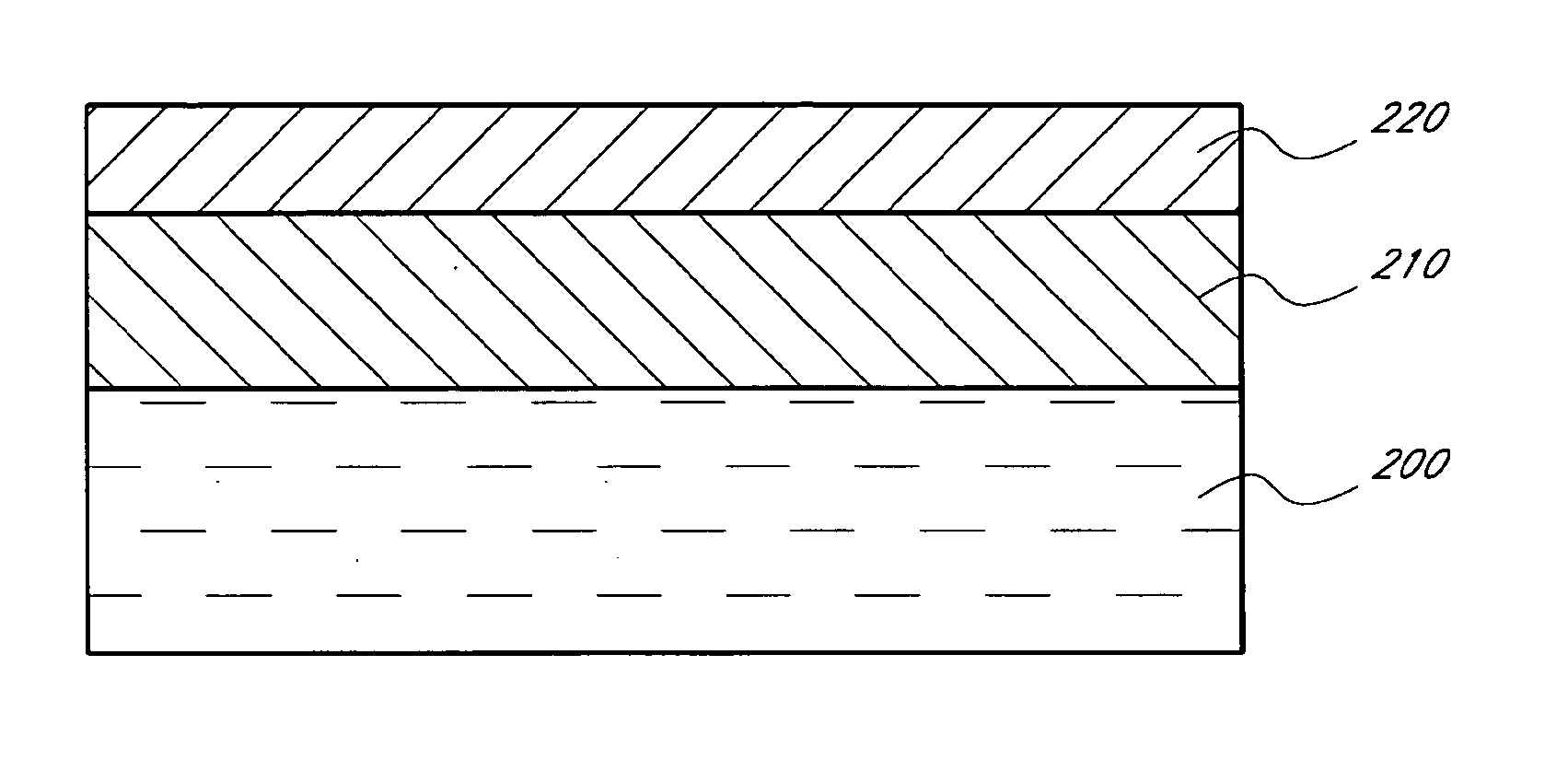
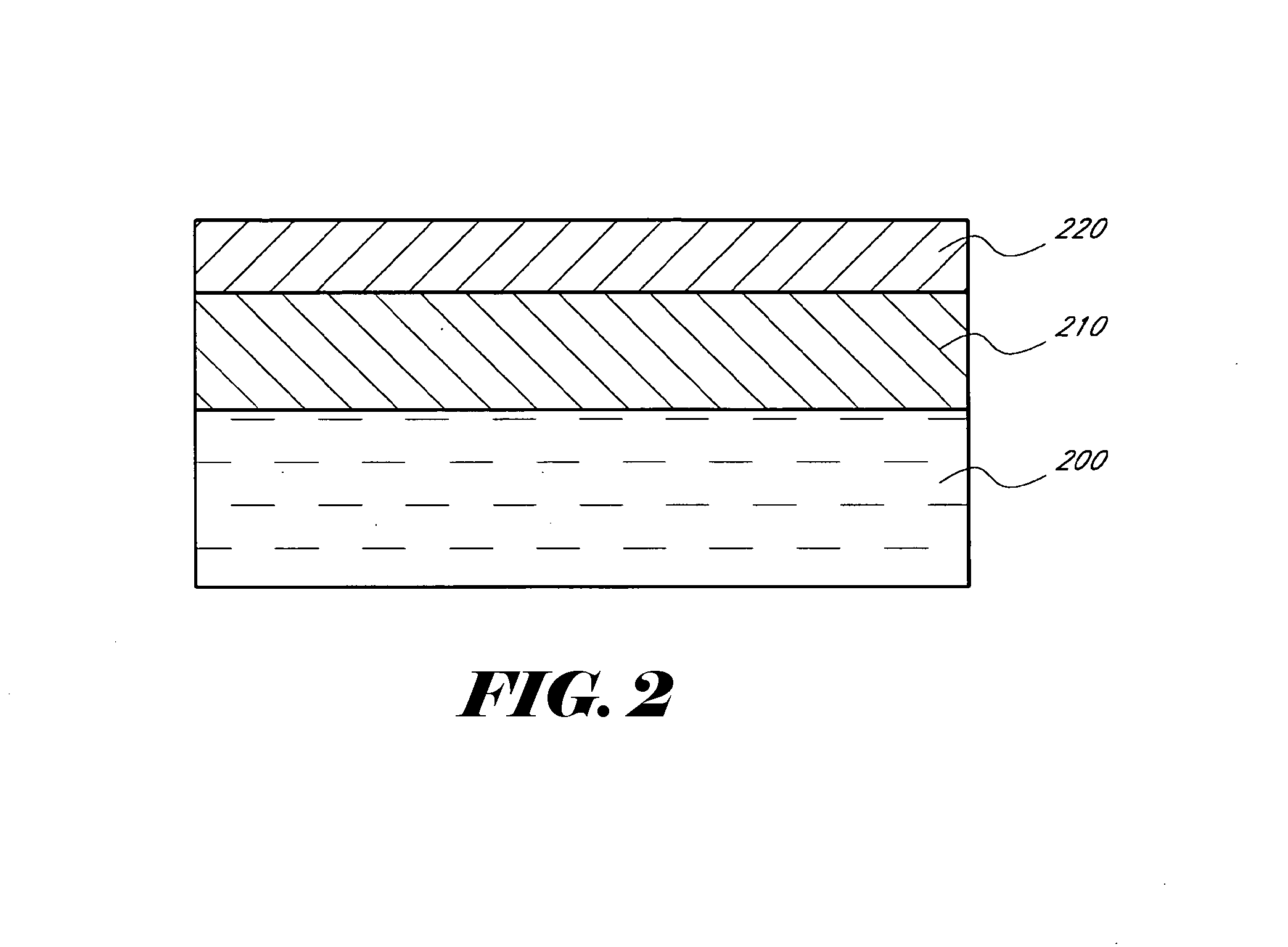
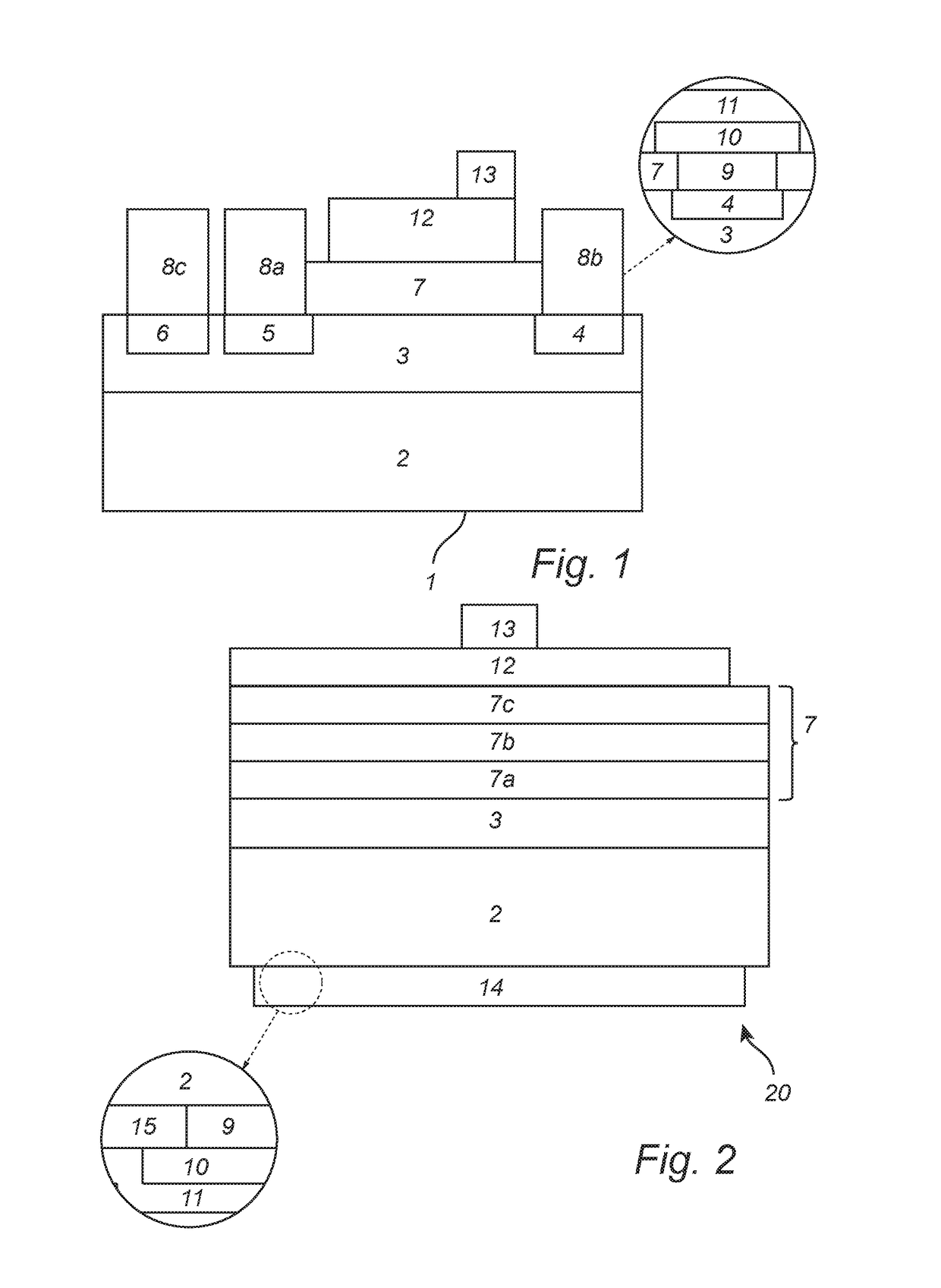
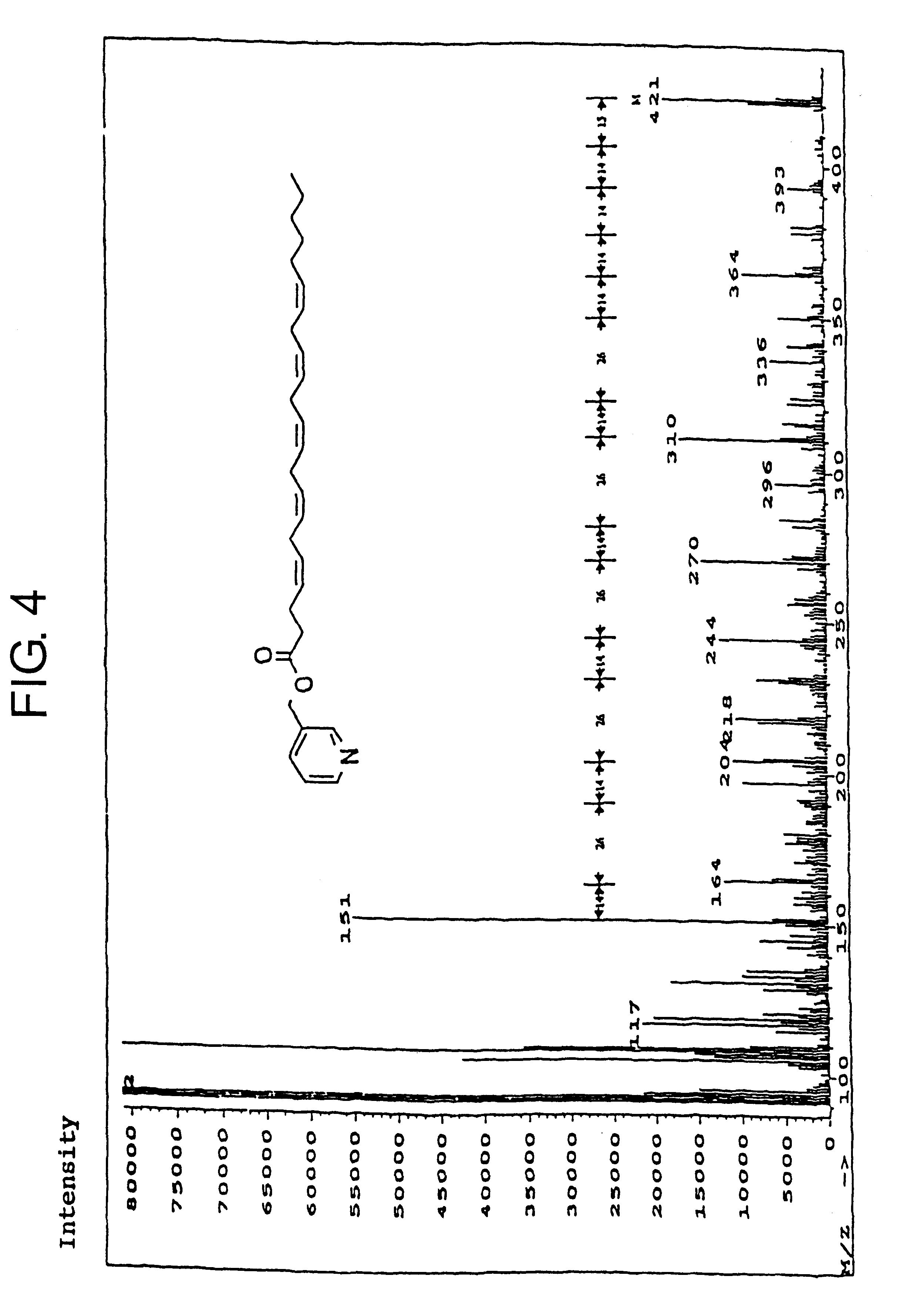
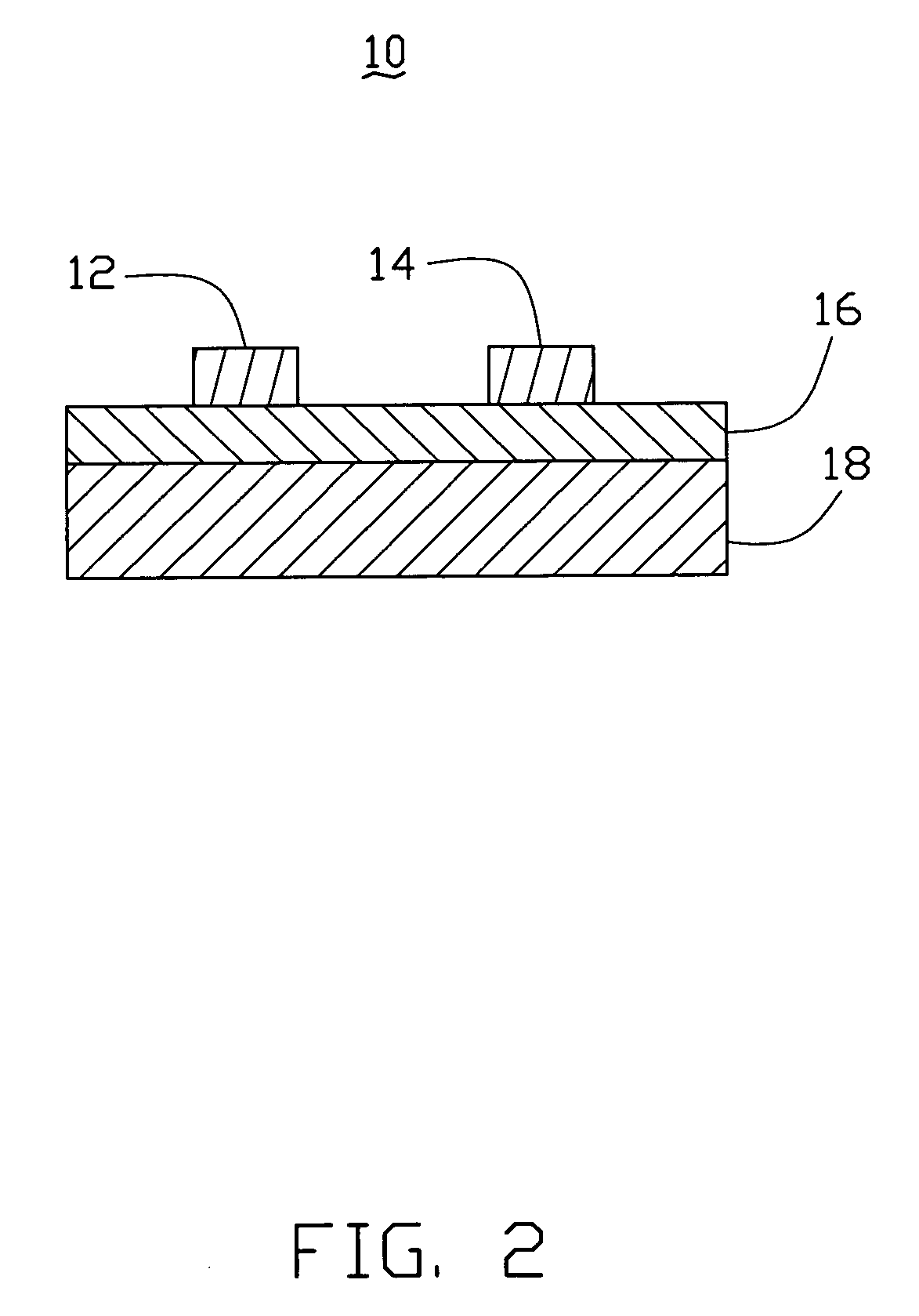
Silane and borane treatments for titanium carbide films
ActiveUS8841182B1Reduce oxidized portionPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesCompound (substance)
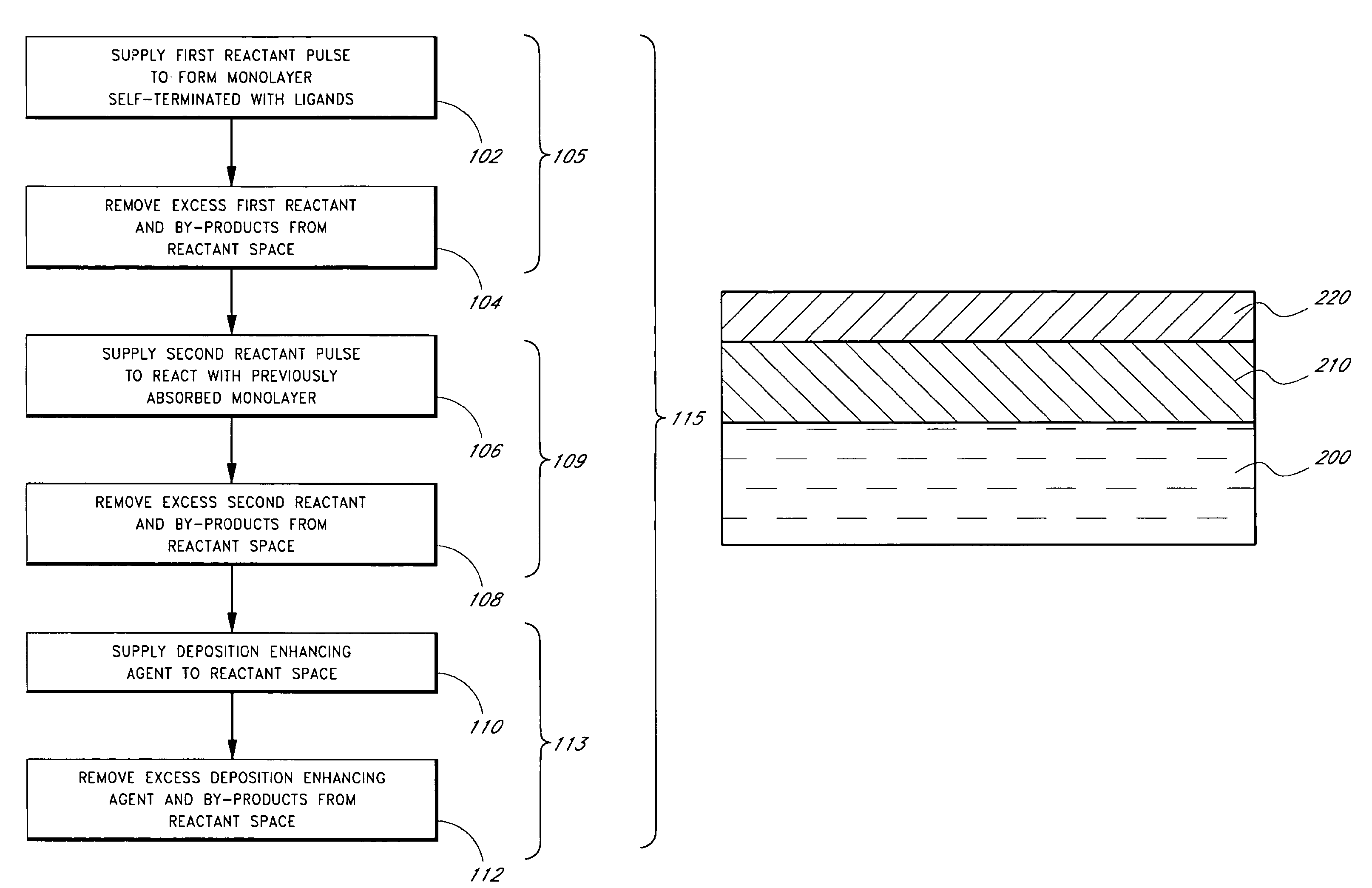
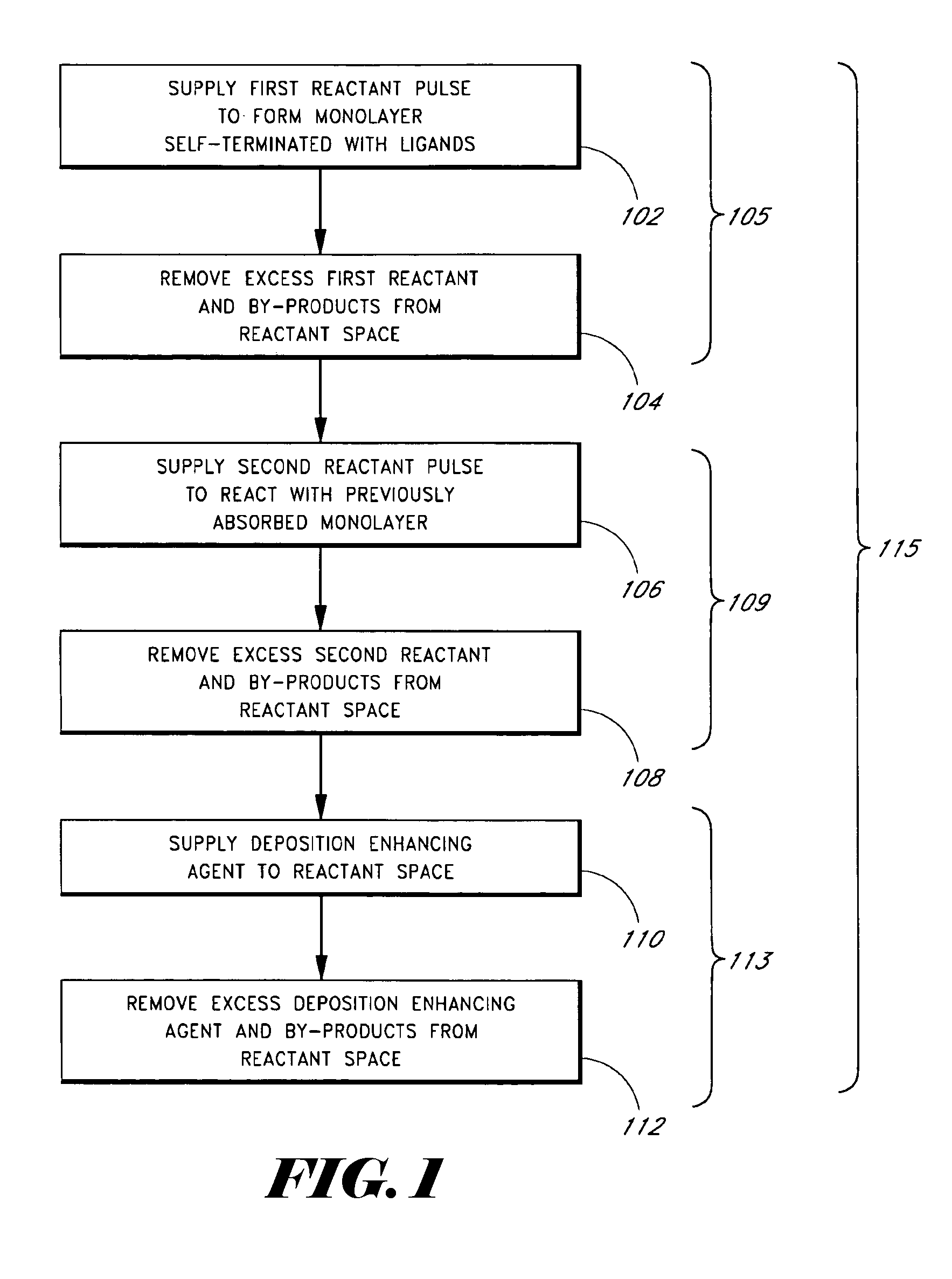
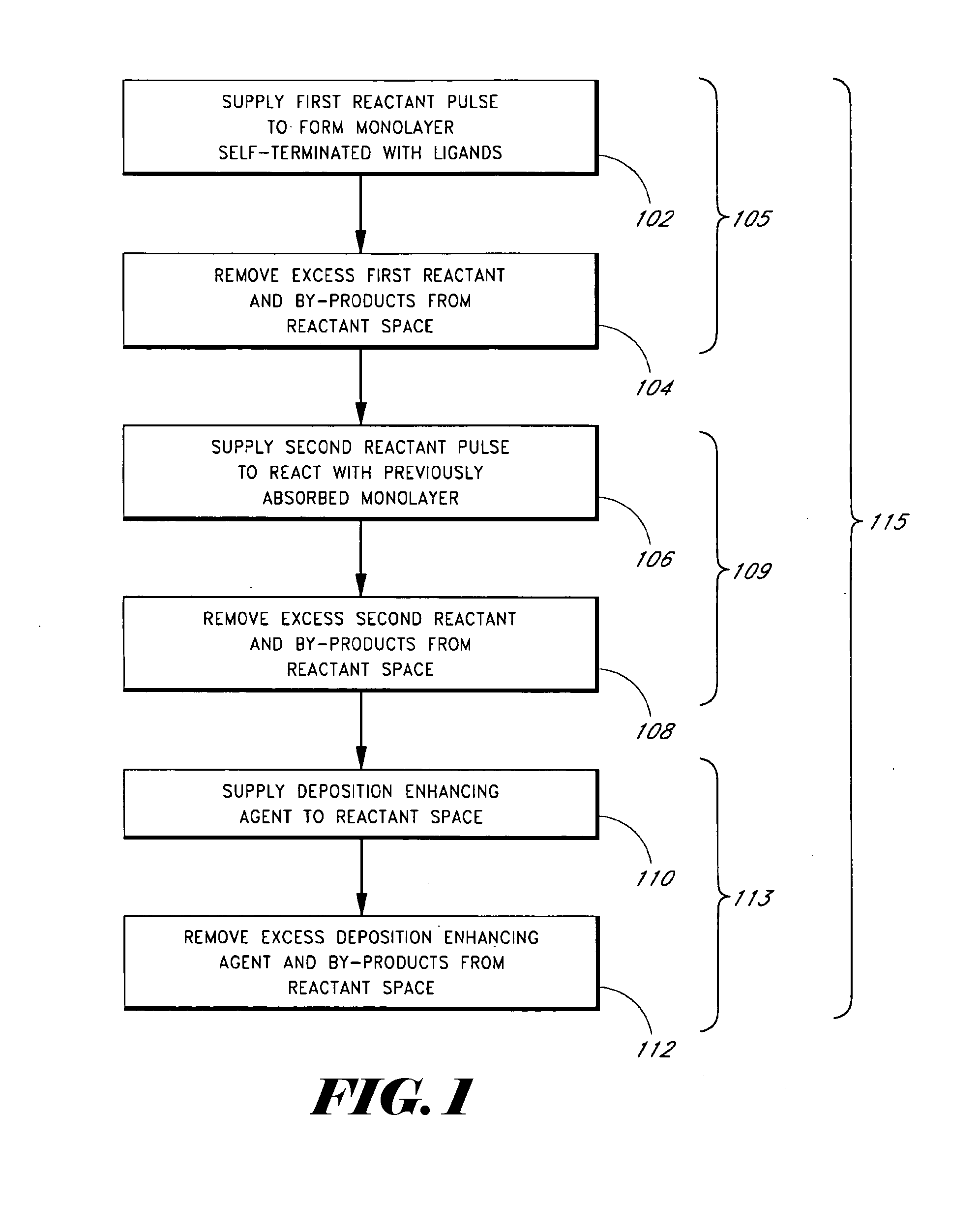
Methods of treating metal-containing thin films, such as films comprising titanium carbide, with a silane / borane agent are provided. In some embodiments a film including titanium carbide is deposited on a substrate by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The process may include a plurality of deposition cycles involving alternating and sequential pulses of a first source chemical that includes titanium and at least one halide ligand, a second source chemical that includes metal and carbon, where the metal and the carbon from the second source chemical are incorporated into the thin film, and a third source chemical, where the third source chemical is a silane or borane that at least partially reduces oxidized portions of the titanium carbide layer formed by the first and second source chemicals. The treatment can form a capping layer on the metal carbide film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
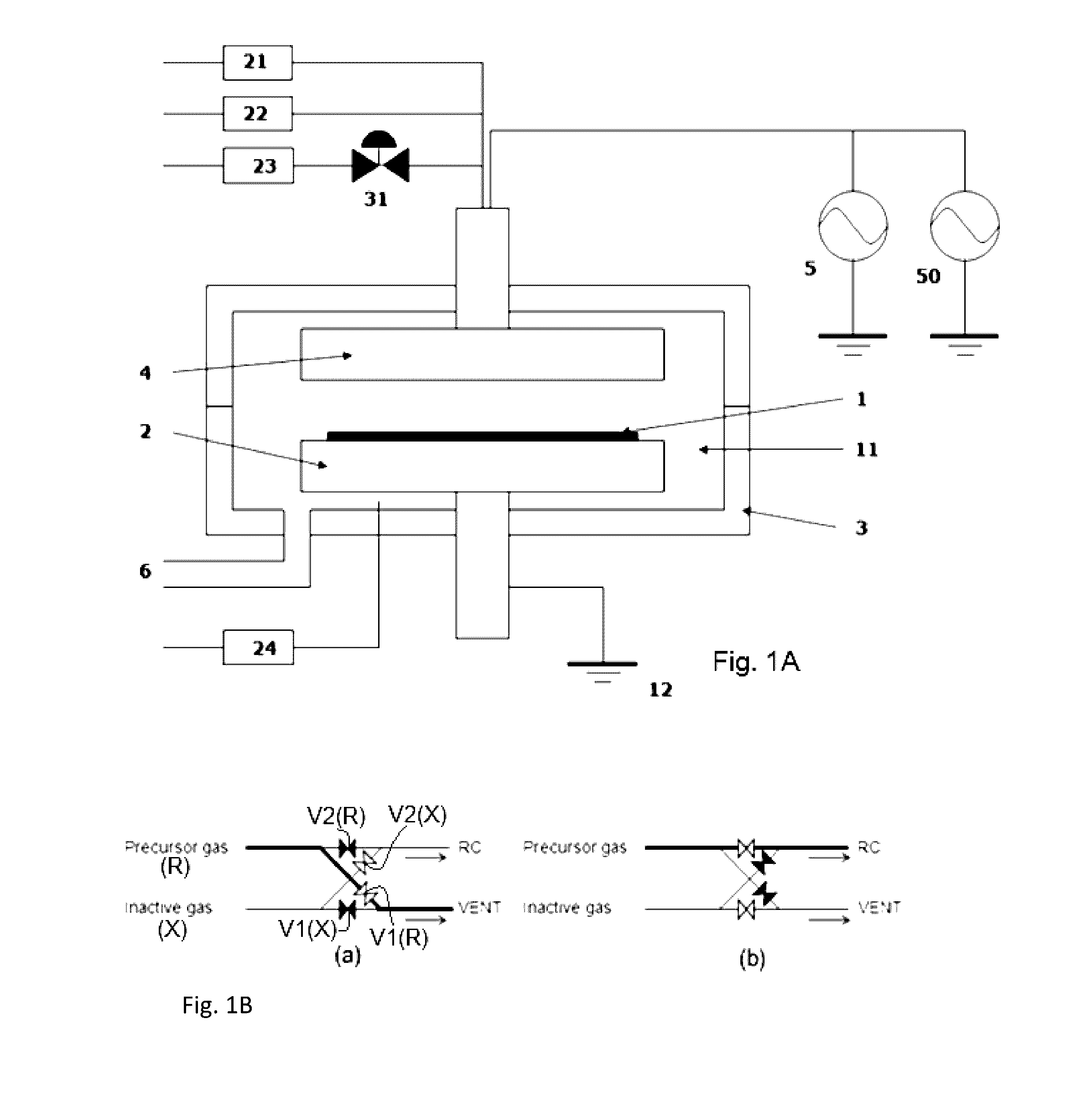
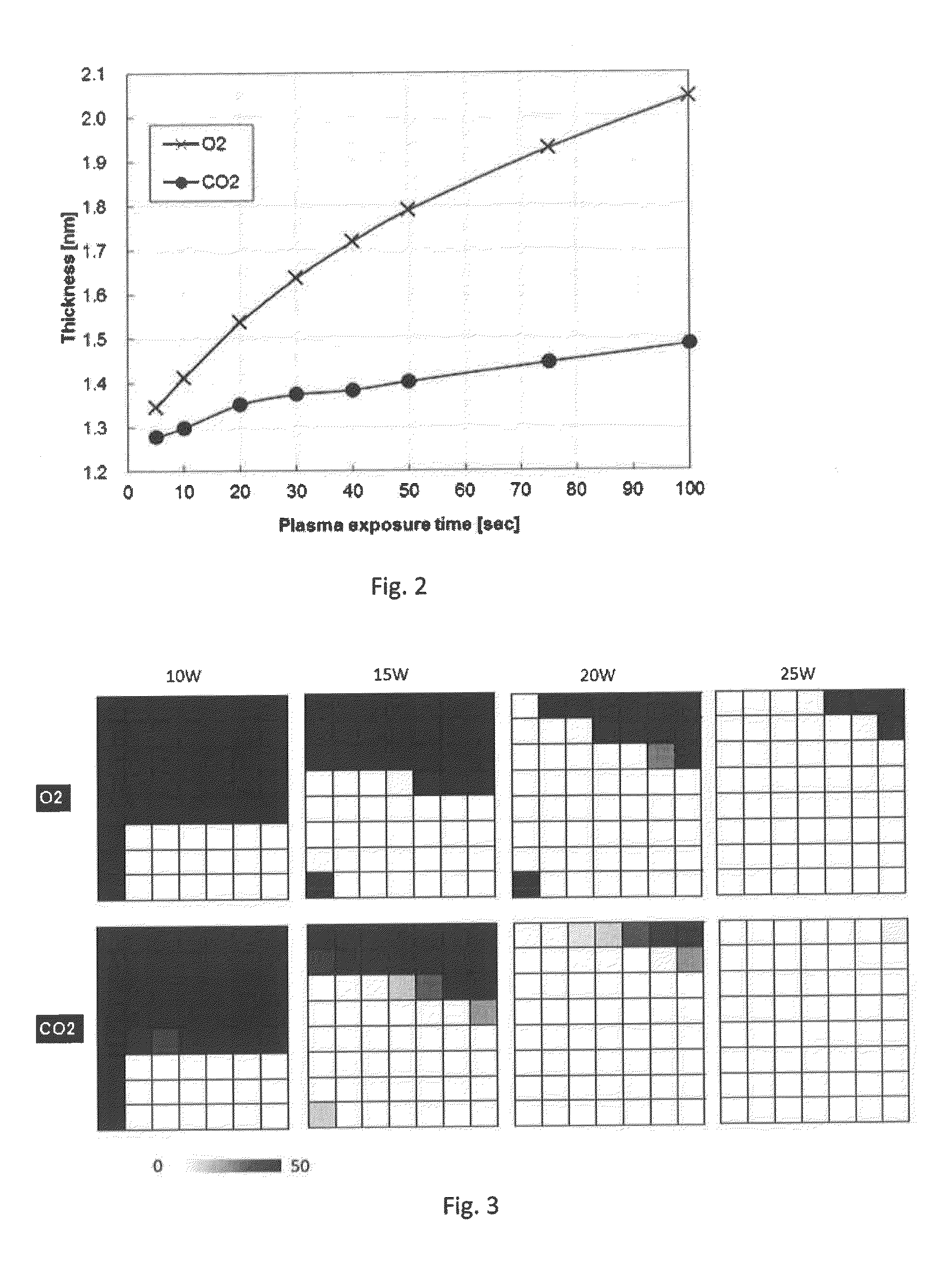
Low-Oxidation Plasma-Assisted Process
ActiveUS20150315704A1Improve film qualitySuppressing of layerElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringOxide
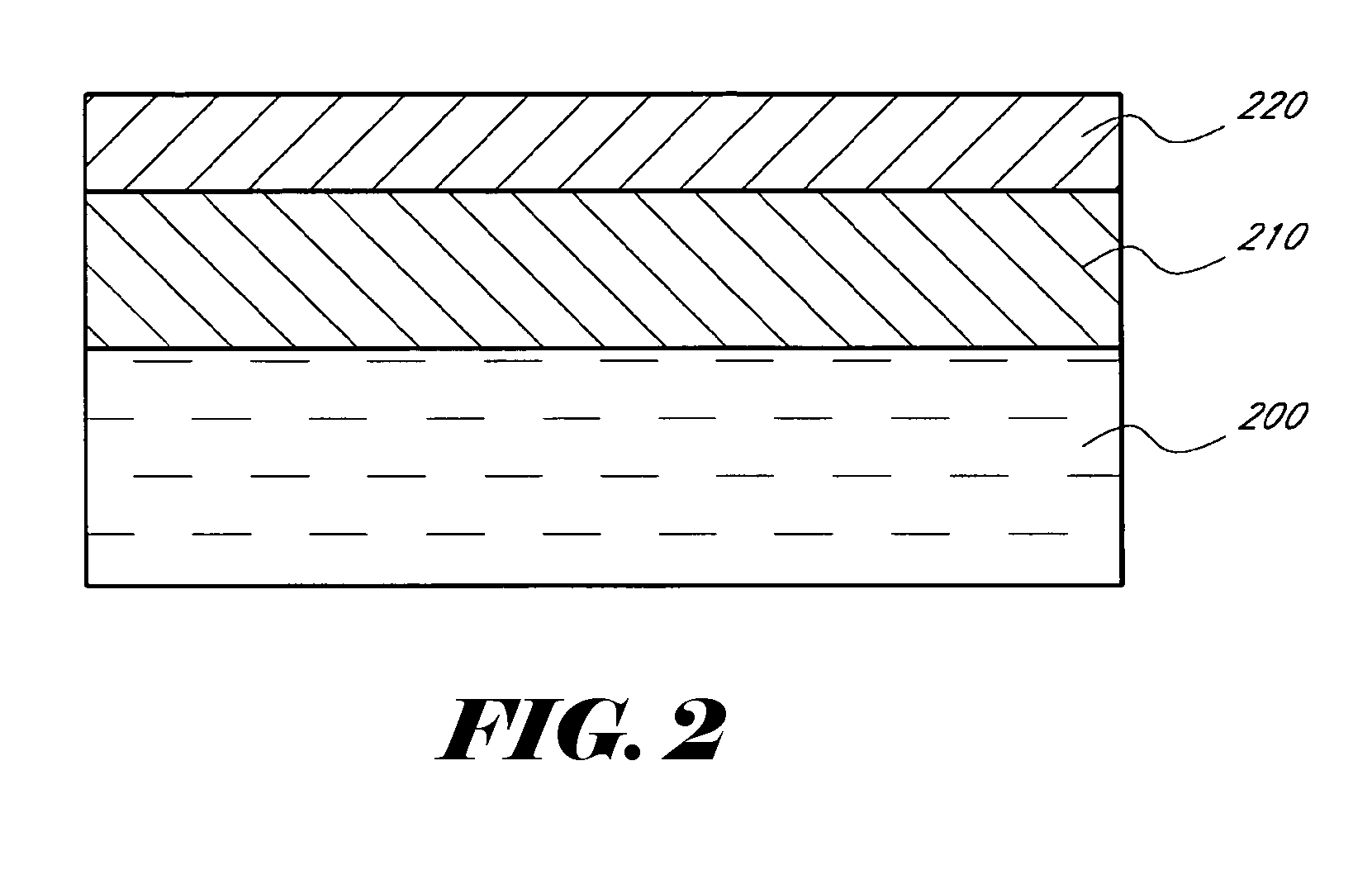
A method for forming an oxide film by plasma-assisted cyclic processing, includes: (i) supplying a precursor to a reaction space wherein a substrate is placed; (ii) applying a first RF power to the reaction space for a first period of time without supplying a precursor; and (iii) applying a second RF power to the reaction space for a second period of time without supplying the precursor, wherein the first RF power is lower than the second RF power, and / or the first period of time is shorter than the second period of time.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
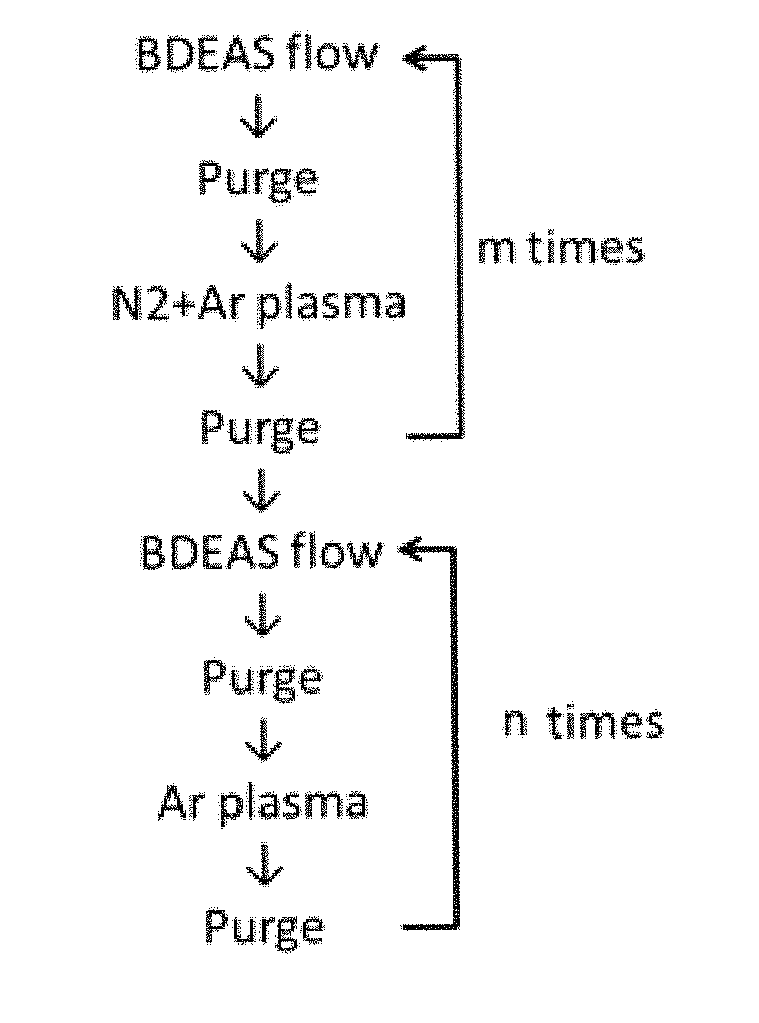
Method for protecting layer by forming hydrocarbon-based extremely thin film
ActiveUS20170018477A1Improve concentrationGood chemical resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNoble gasProtection layer
A method for protecting a layer includes: providing a substrate having a target layer and forming a protective layer on the target layer, said protective layer contacting and covering the target layer and containing a hydrocarbon-based layer constituting at least an upper part of the protective layer, which hydrocarbon-based layer is formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using an alkylaminosilane precursor and a noble gas without a reactant.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming oxide film by plasma-assisted processing
ActiveUS9284642B2Inhibition is effectiveHigh affinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygenAnalytical chemistry
A method for forming an oxide film by plasma-assisted processing includes: (i) supplying a precursor reactive to none of oxygen, CxOy, and NxOy (x and y are integers) without a plasma to a reaction space wherein a substrate is placed; (ii) exposing the precursor to a plasma of CxOy and / or NxOy in the reaction space; and (iii) forming an oxide film on the substrate using the precursor and the plasma.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for Forming Oxide Film by Plasma-Assisted Processing
ActiveUS20150079311A1Effectively inhibitIncrease in RF powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOxideAnalytical chemistry
A method for forming an oxide film by plasma-assisted processing includes: (i) supplying a precursor reactive to none of oxygen, CxOy, and NxOy (x and y are integers) without a plasma to a reaction space wherein a substrate is placed; (ii) exposing the precursor to a plasma of CxOy and / or NxOy in the reaction space; and (iii) forming an oxide film on the substrate using the precursor and the plasma.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for protecting layer by forming hydrocarbon-based extremely thin film
ActiveUS9899291B2Improve concentrationGood chemical resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNoble gasOptoelectronics
A method for protecting a layer includes: providing a substrate having a target layer and forming a protective layer on the target layer, said protective layer contacting and covering the target layer and containing a hydrocarbon-based layer constituting at least an upper part of the protective layer, which hydrocarbon-based layer is formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using an alkylaminosilane precursor and a noble gas without a reactant.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Low-oxidation plasma-assisted process
ActiveUS9464352B2Suppressing of layerImprove film qualityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryRadio frequency
A method for forming an oxide film by plasma-assisted cyclic processing, includes: (i) supplying a precursor to a reaction space wherein a substrate is placed; (ii) applying a first RF power to the reaction space for a first period of time without supplying a precursor; and (iii) applying a second RF power to the reaction space for a second period of time without supplying the precursor, wherein the first RF power is lower than the second RF power, and / or the first period of time is shorter than the second period of time.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for protecting layer by forming hydrocarbon-based extremely thin film
ActiveUS10043661B2Improve concentrationGood chemical resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNoble gasProtection layer
A method for protecting a layer includes: providing a substrate having a target layer; depositing a protective layer on the target layer, which protective layer contacts and covers the target layer and is constituted by a hydrocarbon-based layer; and depositing an oxide layer on the protective layer so that the protective layer in contact with the oxide layer is oxidized. The hydrocarbon-based layer is formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using an alkylaminosilane precursor and a noble gas without a reactant.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Silane and borane treatments for titanium carbide films
ActiveUS20140273510A1Reduce oxidized portionPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium carbideSilanes
Methods of treating metal-containing thin films, such as films comprising titanium carbide, with a silane / borane agent are provided. In some embodiments a film comprising titanium carbide is deposited on a substrate by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The process may include a plurality of deposition cycles involving alternating and sequential pulses of a first source chemical that comprises titanium and at least one halide ligand, a second source chemical comprising metal and carbon, wherein the metal and the carbon from the second source chemical are incorporated into the thin film, and a third source chemical, wherein the third source chemical is a silane or borane that at least partially reduces oxidized portions of the titanium carbide layer formed by the first and second source chemicals. In some embodiments treatment forms a capping layer on the metal carbide film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
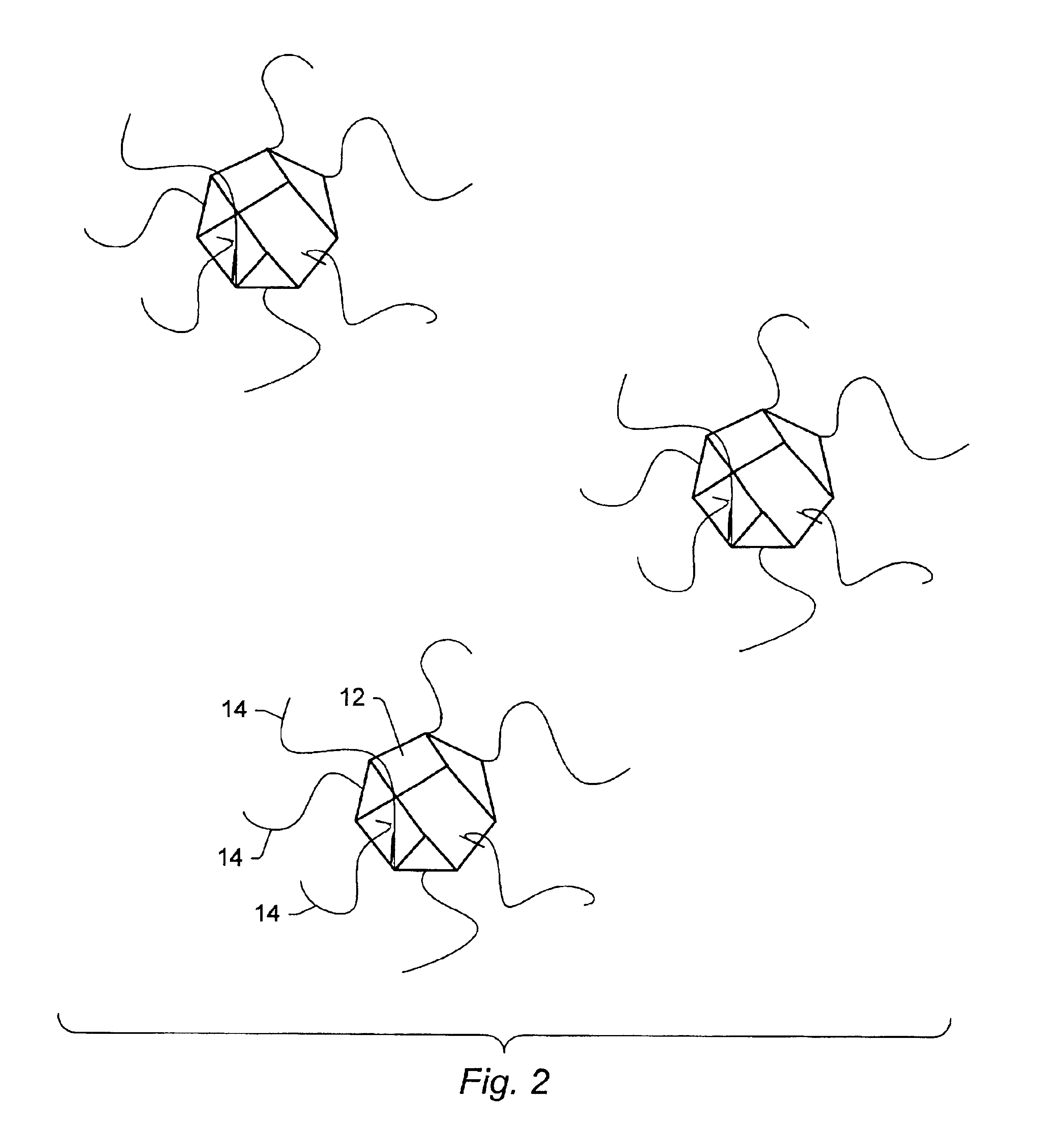
Light-emitting nanoparticles and method of making same
InactiveUS6846565B2Reduce aggregationResist formationMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH +1
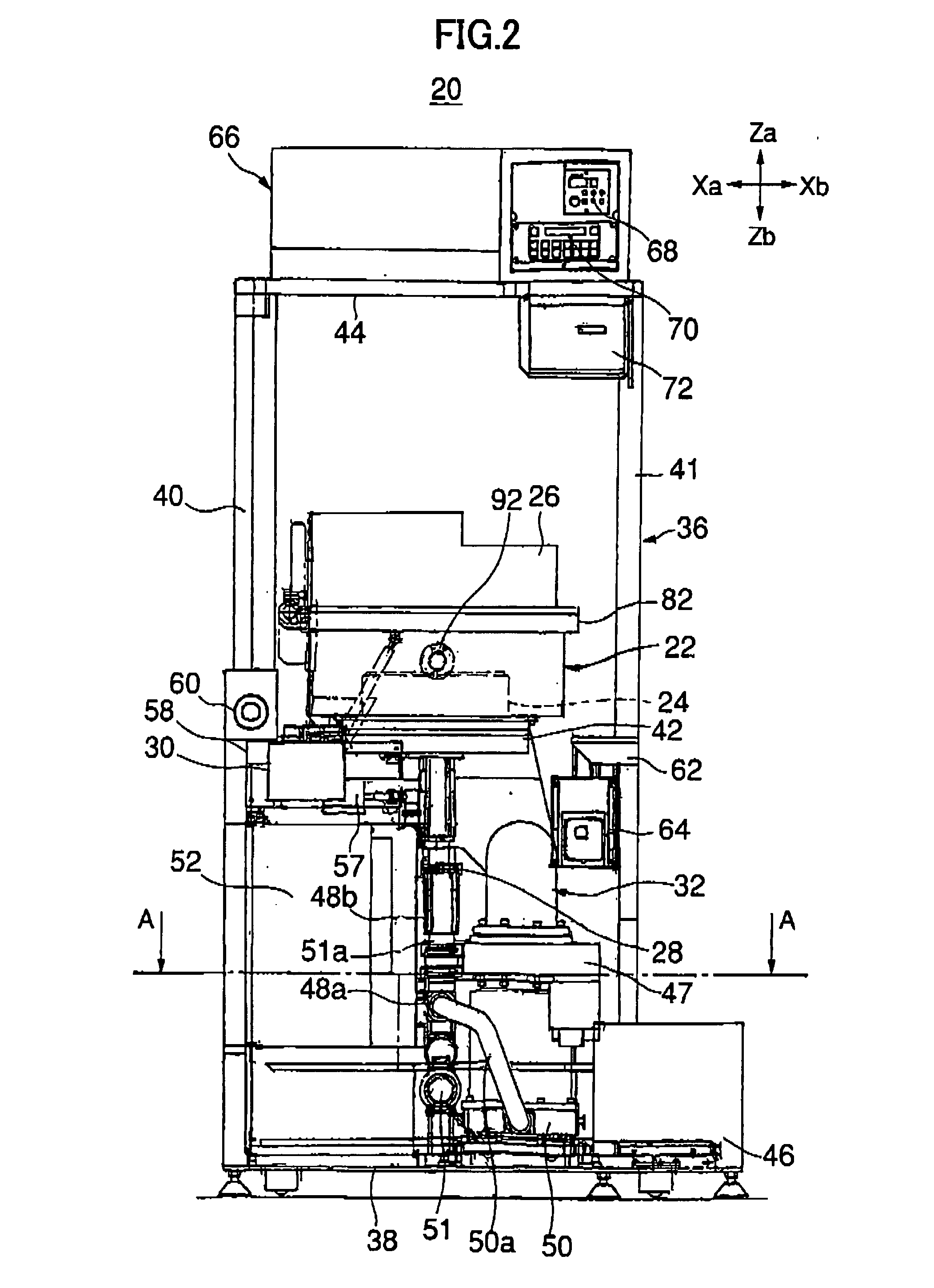
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060057799A1Reliable formingAvoid pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingUltraviolet lightsEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus stably and efficiently conducts a film forming process on a substrate to be processed. In the substrate processing apparatus, the substrate to be processed is supported at a position facing a heater portion, and a holding member for holding the substrate is rotated, whereby the temperature distribution of the substrate is kept uniform and a warp of the substrate is suppressed. The inner wall of the processing vessel is covered with a quartz liner which is made of opaque quartz, and thus protected from ultraviolet rays emitted from an ultraviolet light source. The temperature rise of the inner wall caused by heat from the heater portion is suppressed due to the heat insulating effect of the quartz liner. Consequently, the life cycle of the processing vessel can be prolonged.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
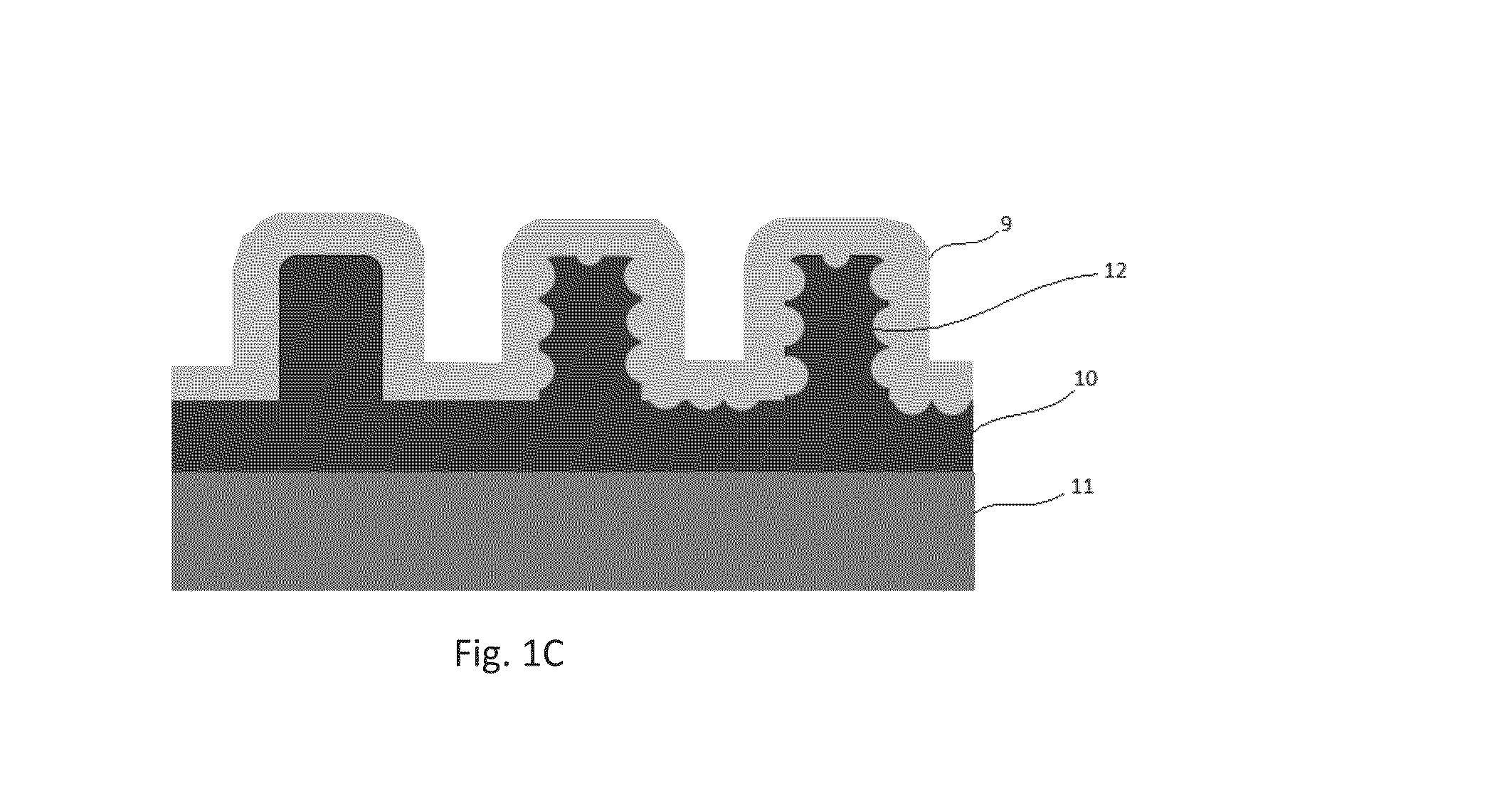
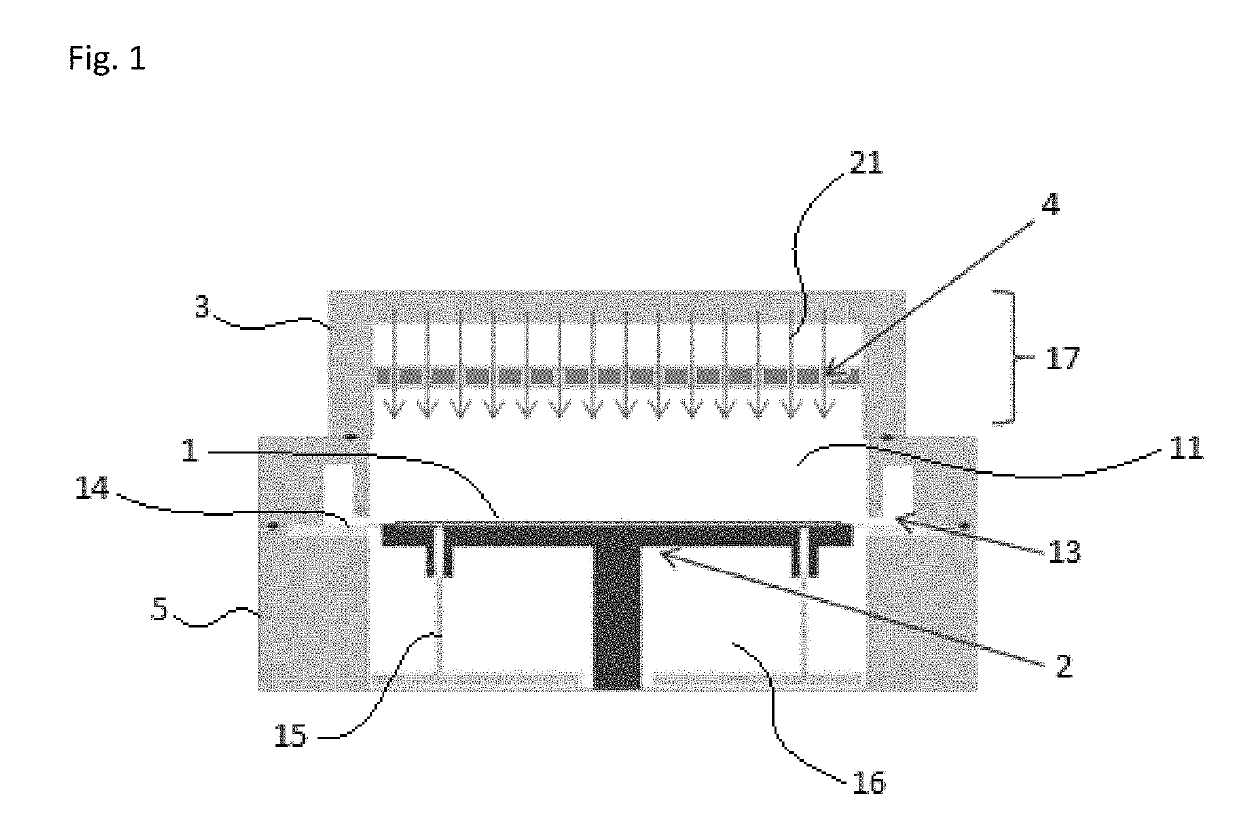
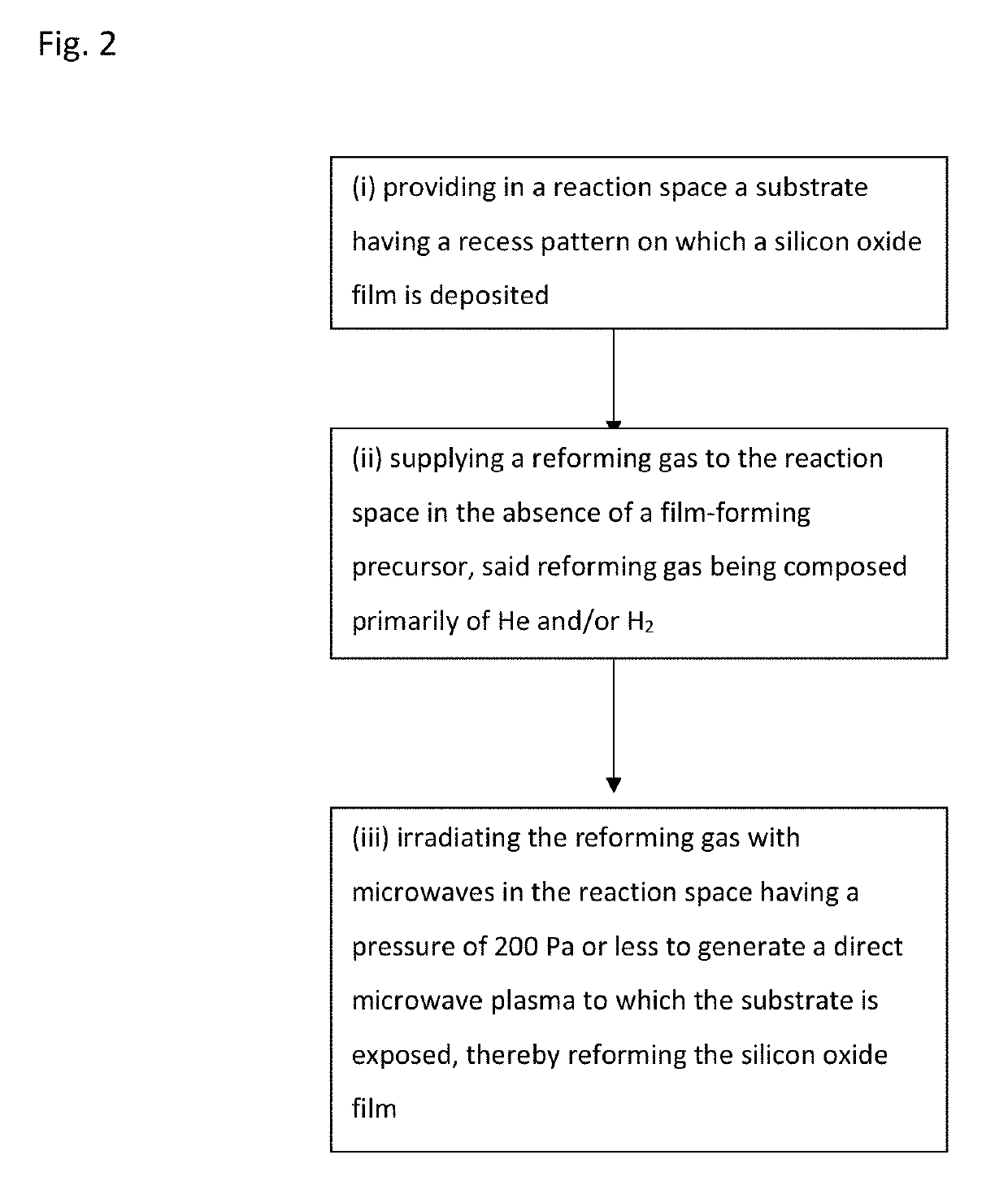
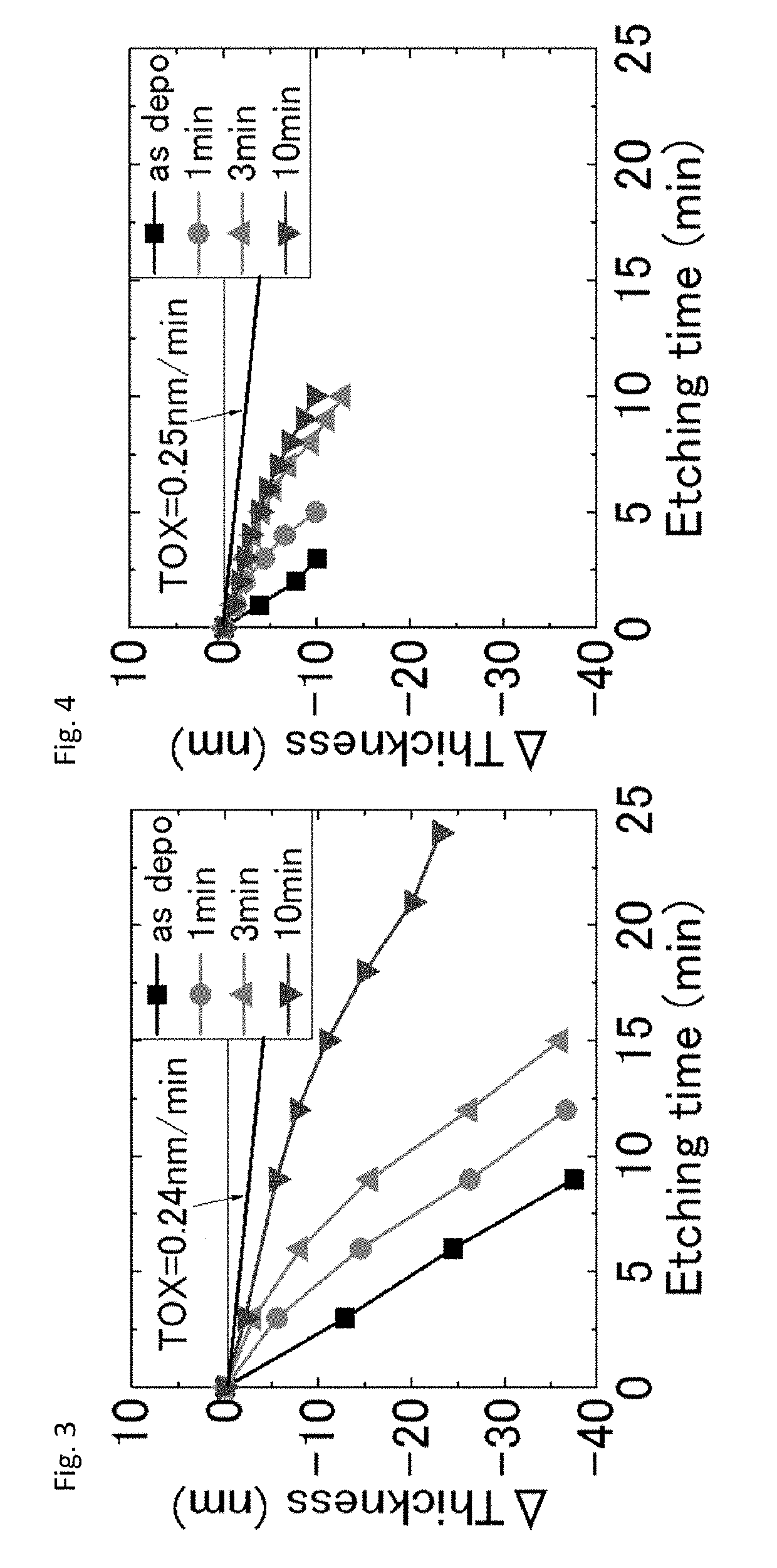
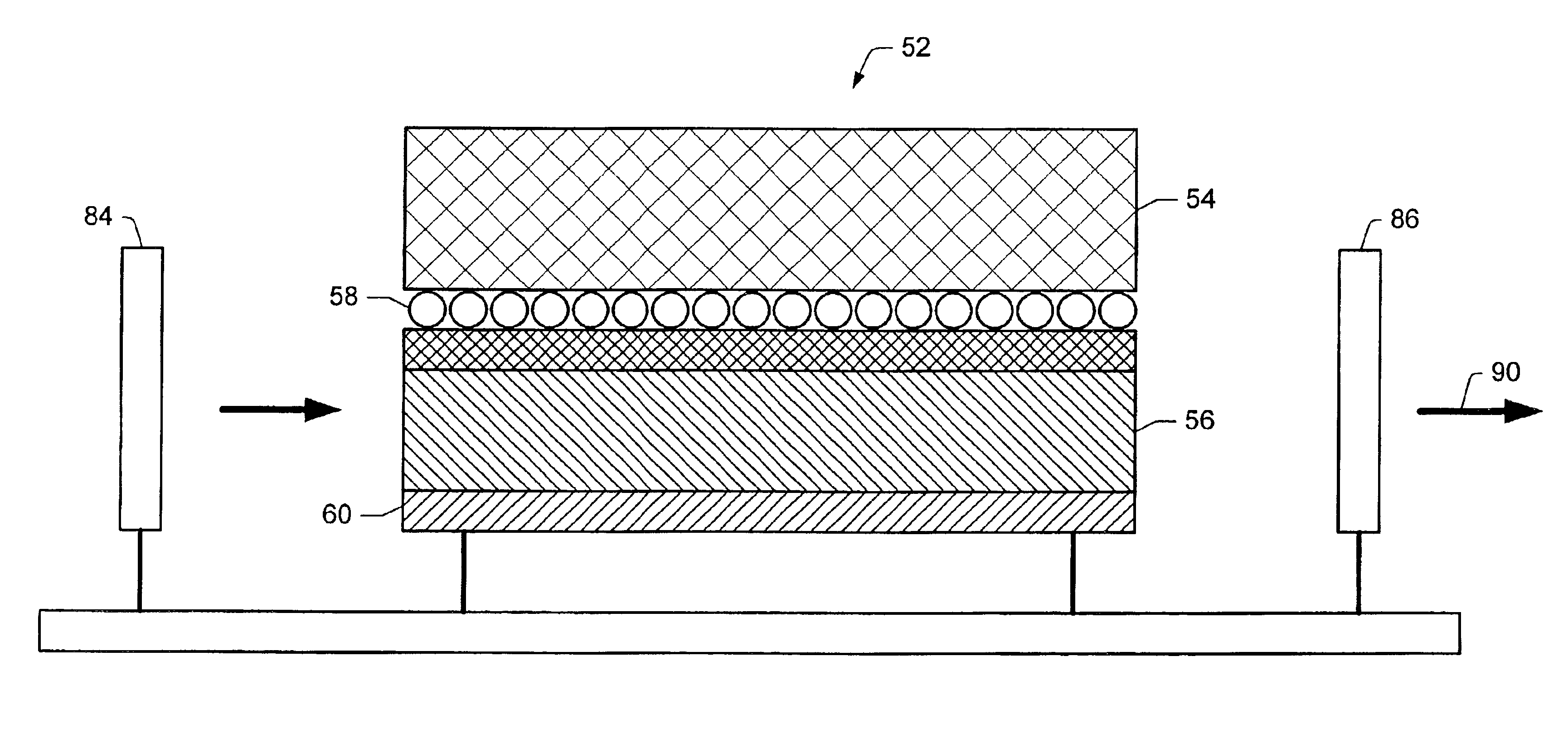
Method of post-deposition treatment for silicon oxide film
ActiveUS20190244803A1High degreeIncrease plasma densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowaveSilicon oxide
A method of post-deposition treatment for silicon oxide film includes: providing in a reaction space a substrate having a recess pattern on which a silicon oxide film is deposited; supplying a reforming gas for reforming the silicon oxide film to the reaction space in the absence of a film-forming precursor, said reforming gas being composed primarily of He and / or H2; and irradiating the reforming gas with microwaves in the reaction space having a pressure of 200 Pa or less to generate a direct microwave plasma to which the substrate is exposed, thereby reforming the silicon oxide film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Heparin barrier coating for controlled drug release
ActiveUS20050004663A1Reduce frictional forceReduce forceSuture equipmentsStentsCompound (substance)Antioxidant
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. The drugs, agents, and / or compounds may also be utilized to treat specific diseases, including vulnerable plaque. Therapeutic agents may also be delivered to the region of a disease site. In regional delivery, liquid formulations may be desirable to increase the efficacy and deliverability of the particular drug. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations as well as other therapeutic agents may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices. In each of these instances, antioxidants are utilized to prolong product integrity.
Owner:WYETH
Silicon carbide based field effect gas sensor for high temperature applications
InactiveUS20180011052A1Change electrical propertiesLong-term reliable operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactSemiconductor structure
A field effect gas sensor, for detecting a presence of a gaseous substance in a gas mixture, the field effect gas sensor comprising: a SiC semiconductor structure; an electron insulating layer covering a first portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; a first contact structure at least partly separated from the SiC semiconductor structure by the electron insulating layer; and a second contact structure conductively connected to a second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure, wherein at least one of the electron insulating layer and the first contact structure is configured to interact with the gaseous substance to change an electrical property of the SiC semiconductor structure; and wherein the second contact structure comprises: an ohmic contact layer in direct contact with the second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; and a barrier layer formed by an electrically conducting mid-transition-metal oxide covering the ohmic contact layer.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Internally-arranged sun-shading hollow shutter
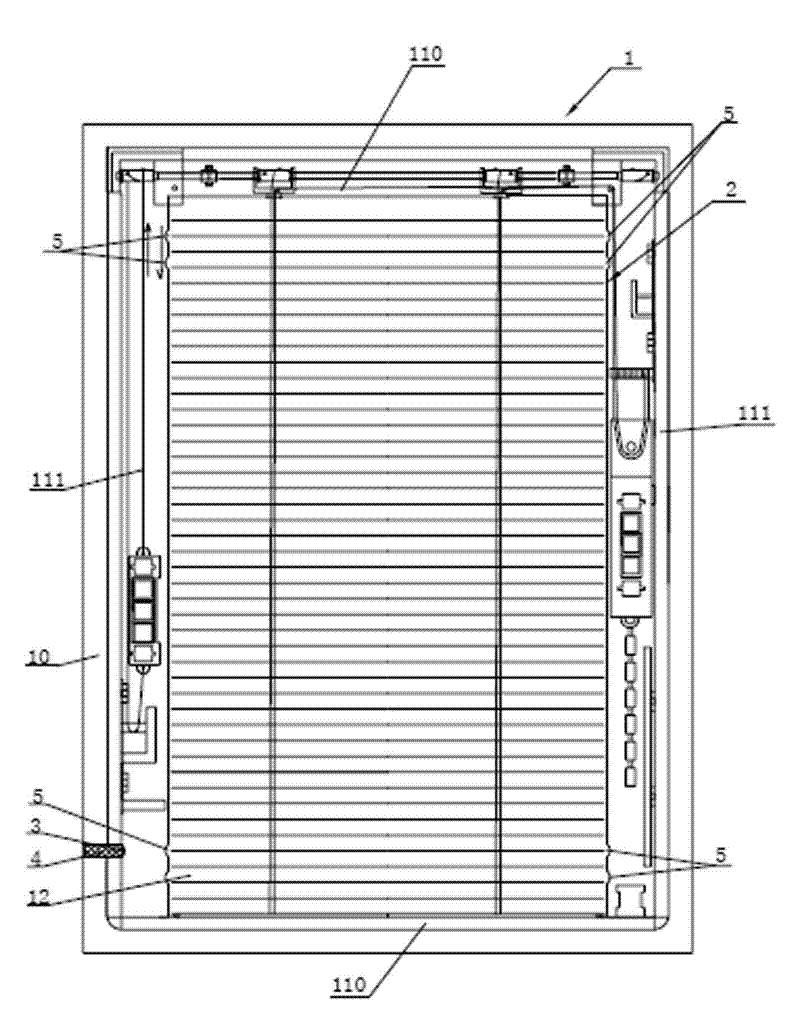
InactiveCN102444372AExtended service lifePrevent oxidationDoor/window protective devicesClimate change adaptationWindow shutterEngineering
The invention relates to an internally-arranged sun-shading hollow shutter, which comprises hollow glass, a shutter curtain and a control mechanism. The hollow glass comprises a two glass original sheets which are parallel to each other, a metal hollow frame clamped between the two glass original sheets, a hollow portion enclosed by the two glass original sheets and the metal hollow frame, and sealing glue. The shutter curtain is arranged in the hollow portion. The internally-arranged sun-shading hollow shutter further comprises a port arranged on the outer lateral side of the metal hollow frame and a sealing plug for sealing the port. The inner lateral side of the metal hollow frame is provided with an air vent hole for communicating the metal hollow frame and the hollow portion, wherein the hollow portion is filled with inertia gas. The port can be connected with a vacuumizing device to vacuumize the inside of the hollow portion, the inertia gas is delivered into the hollow portion through the port, and inertia gas environment can prevent parts such as a pull rope and a ladder rope in the hollow glass from being oxidized so as to prolong service life of the internally-arranged sun-shading hollow shutter.
Owner:张家港市虹壹玻璃制品有限公司
Applications of light-emitting nanoparticles
InactiveUS6918946B2Reduce aggregationResist formationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:KORGEL BRIAN A +1
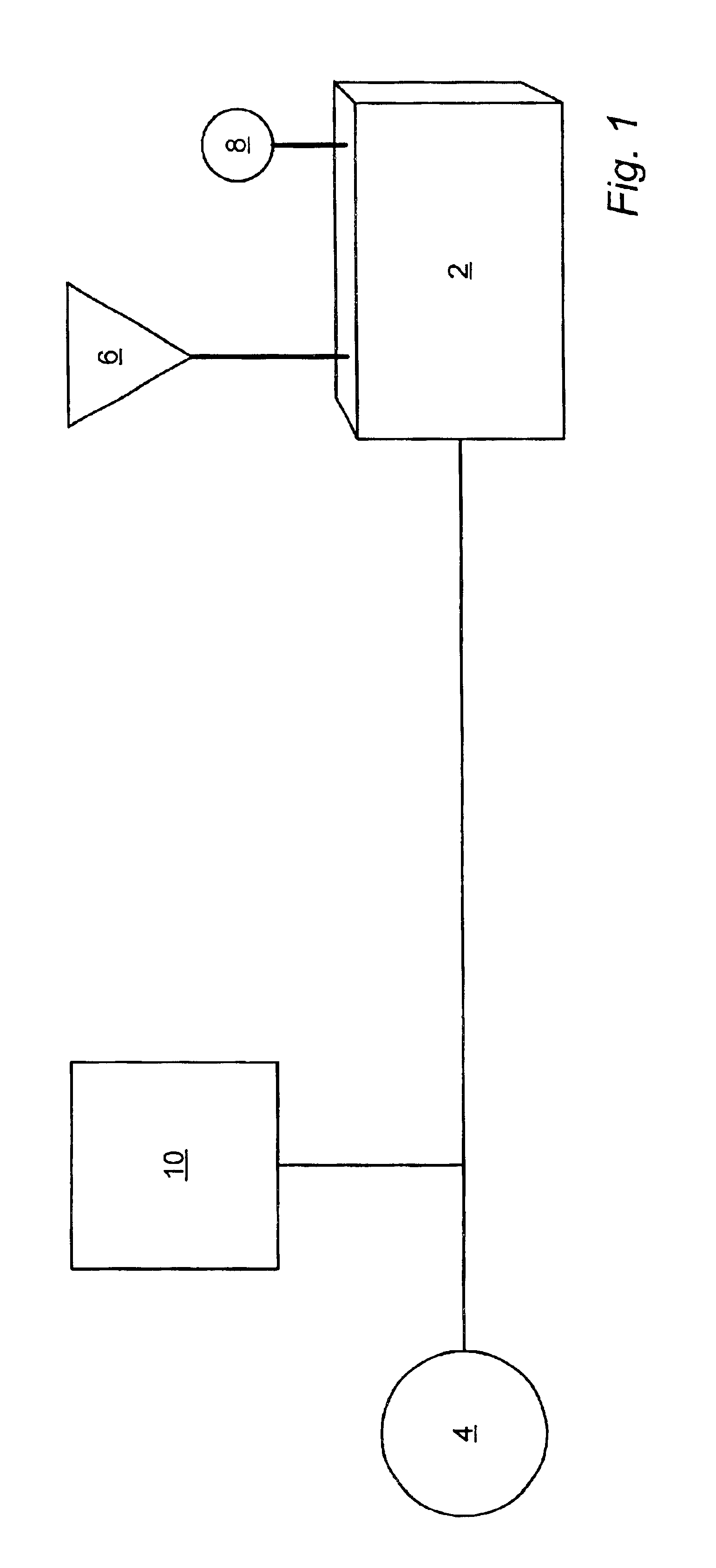
Microorganisms capable of producing highly unsaturated fatty acids and process for producing highly unsaturated fatty acids by using the microorganisms
InactiveUS6582941B1High speedIncrease productionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismSchizochytrium
The present invention relates to the Schizochytrium genus SR21 strain and a microorganism belonging to the same species as does said SR21 strain or having substantially the same fungological properties as does said SR21 strain, the said SR21 strain and microorganism having the ability to produce the (n-3) series of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the (n-6) series of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and the invention also relates to a process for preparing the (n-3) series of DHA and the (n-6) series of DPA utilizing said microorganisms. The microorganisms according to the present invention are superior in their proliferation character and their propensity to produce fat, and have the ability to produce the (n-3) series of DHA and the (n-6) series of DPA very well. Accordingly, it is possible to effectively produce the (n-3) series of DHA and / or the (n-6) series of DPA, which are useful in the fields of foods and pharmaceuticals, using the microorganisms according to the present invention. In addition, the present invention provides a fat obtained by culturing the present microorganisms. Since the fat composition contains the (n-6) series of DPA in addition to the (n-3) series of DHA having various physiological activities, it is possible to stably and effectively supply the (n-6) series of DPA and / or the (n-3) series of DHA to subjects in need of these highly unsaturated fatty acids by adding the fat composition to various feedstuffs or foods.
Owner:DIRECTOR GENERAL OF THE AGENCY OF IND SCI & TECH +1
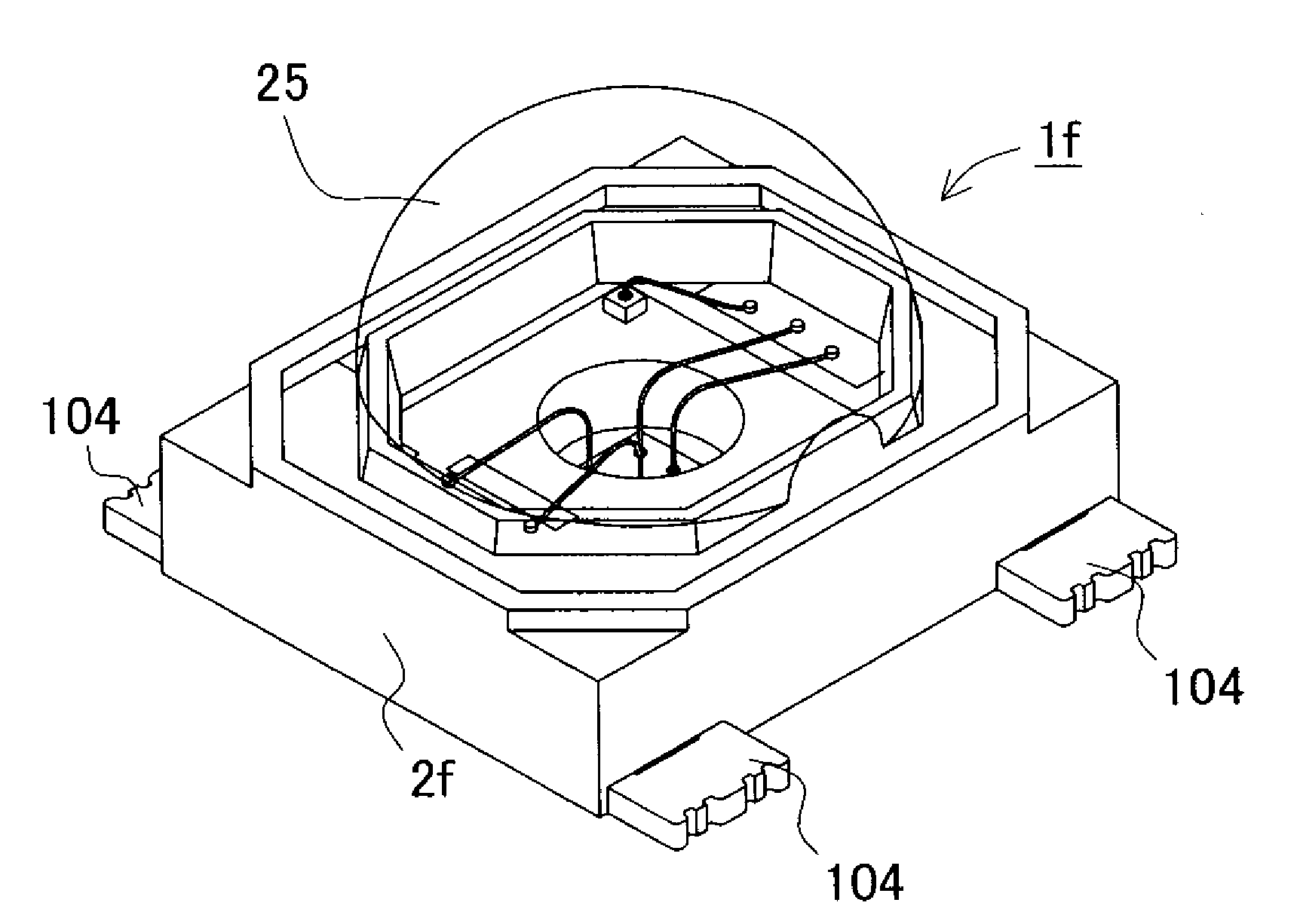
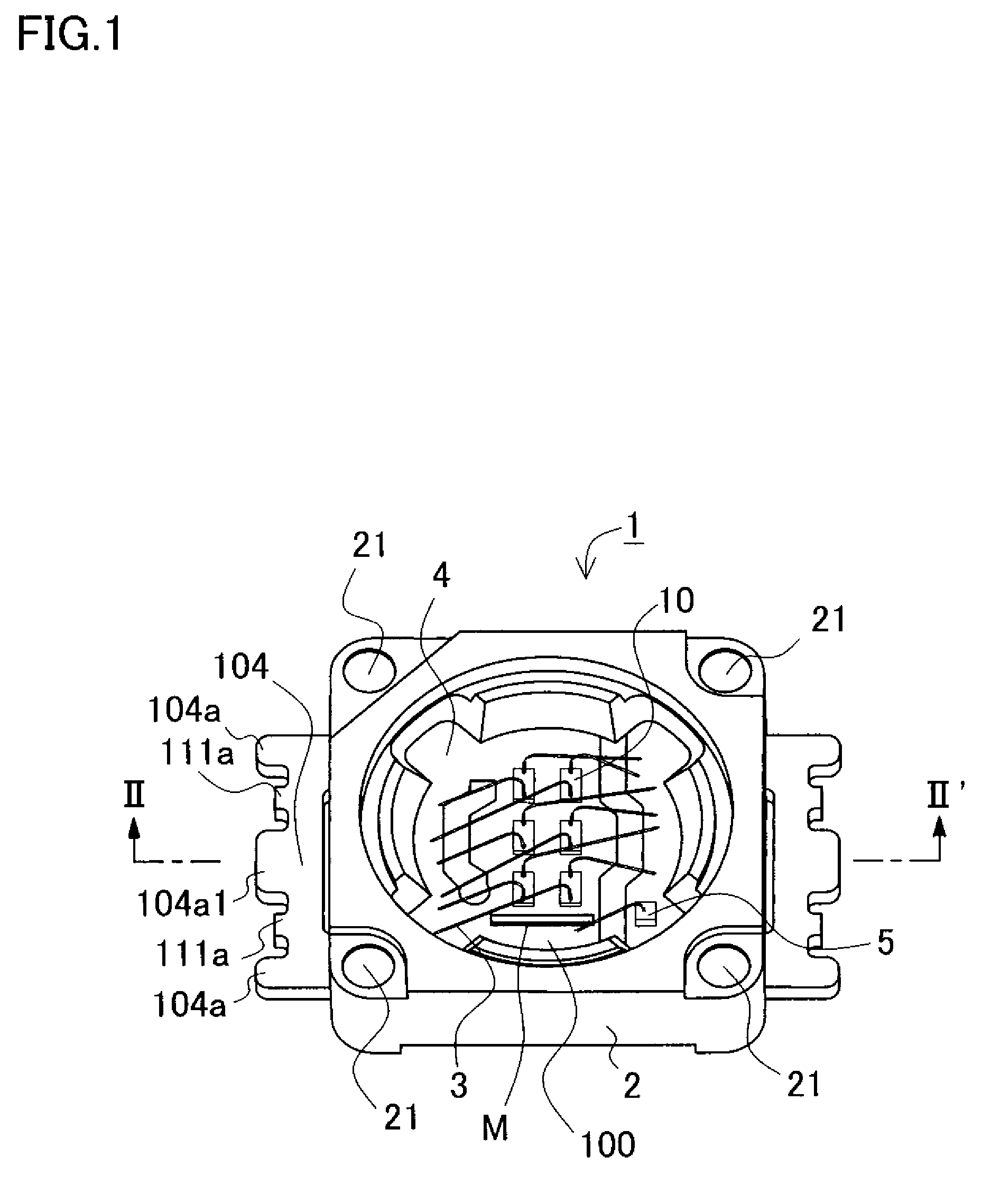
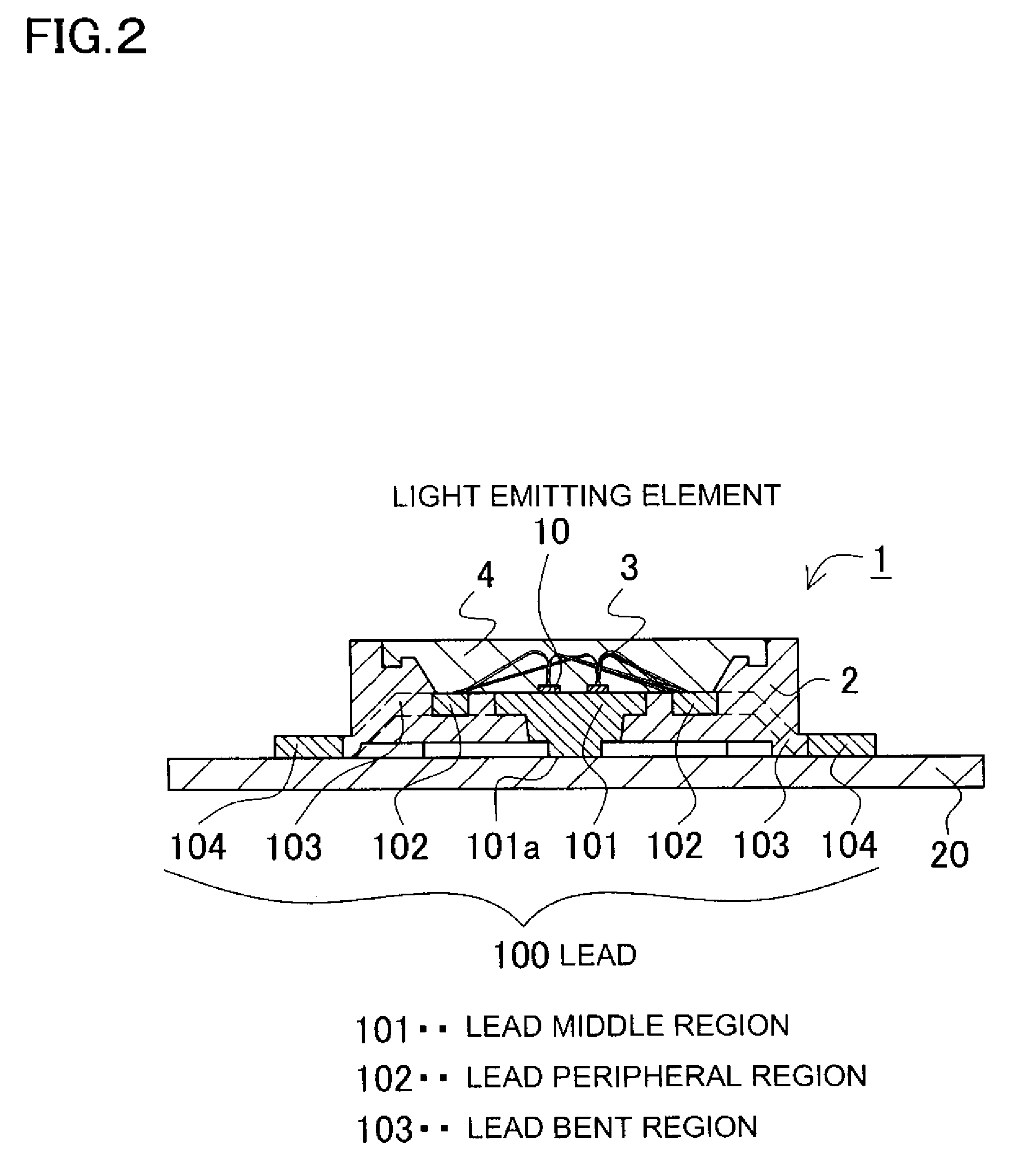
Semiconductor light emitting device and a method for producing the same
ActiveUS20070262328A1Avoid damageReduce the possibility of damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLight emitting device
Both ends of the lead arrangement project outward from side surfaces of a package to form outer lead regions. Each of the outer lead regions includes a pair of outer lead projections and lead terminal smaller projections that are located between the outer lead projections. The outer lead projections and lead terminal smaller projections project outward. Adjustment is made to the projection amount of end surfaces of the lead smaller projections lying in a plane perpendicular to a longitudinal direction of the lead arrangement, whereby the end surfaces projecting less than end surfaces of the outer lead projections. Thus, cut surfaces of lead connection portions with edged corners are not exposed. This arrangement prevents that the cut surfaces damage other devices.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
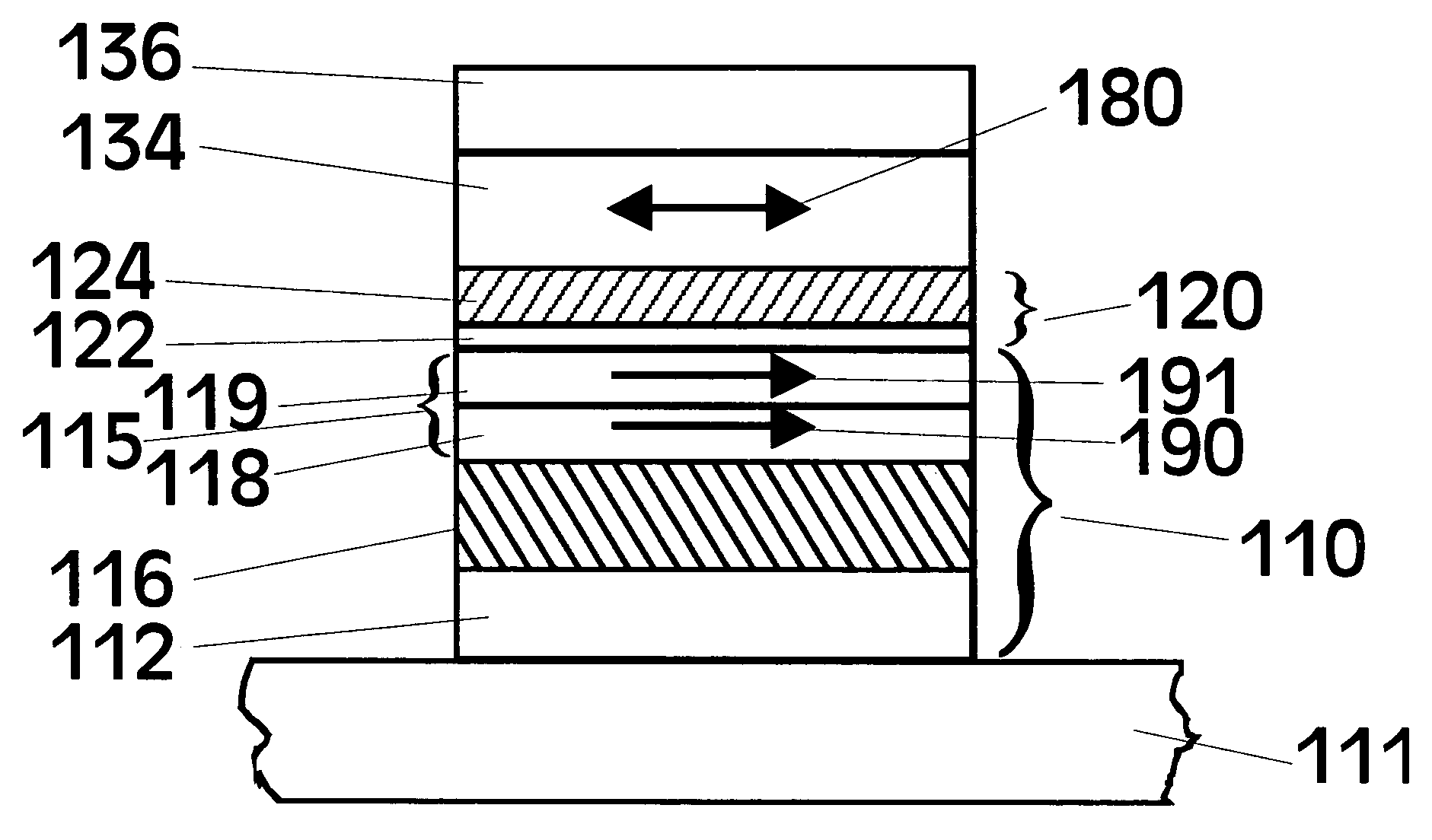
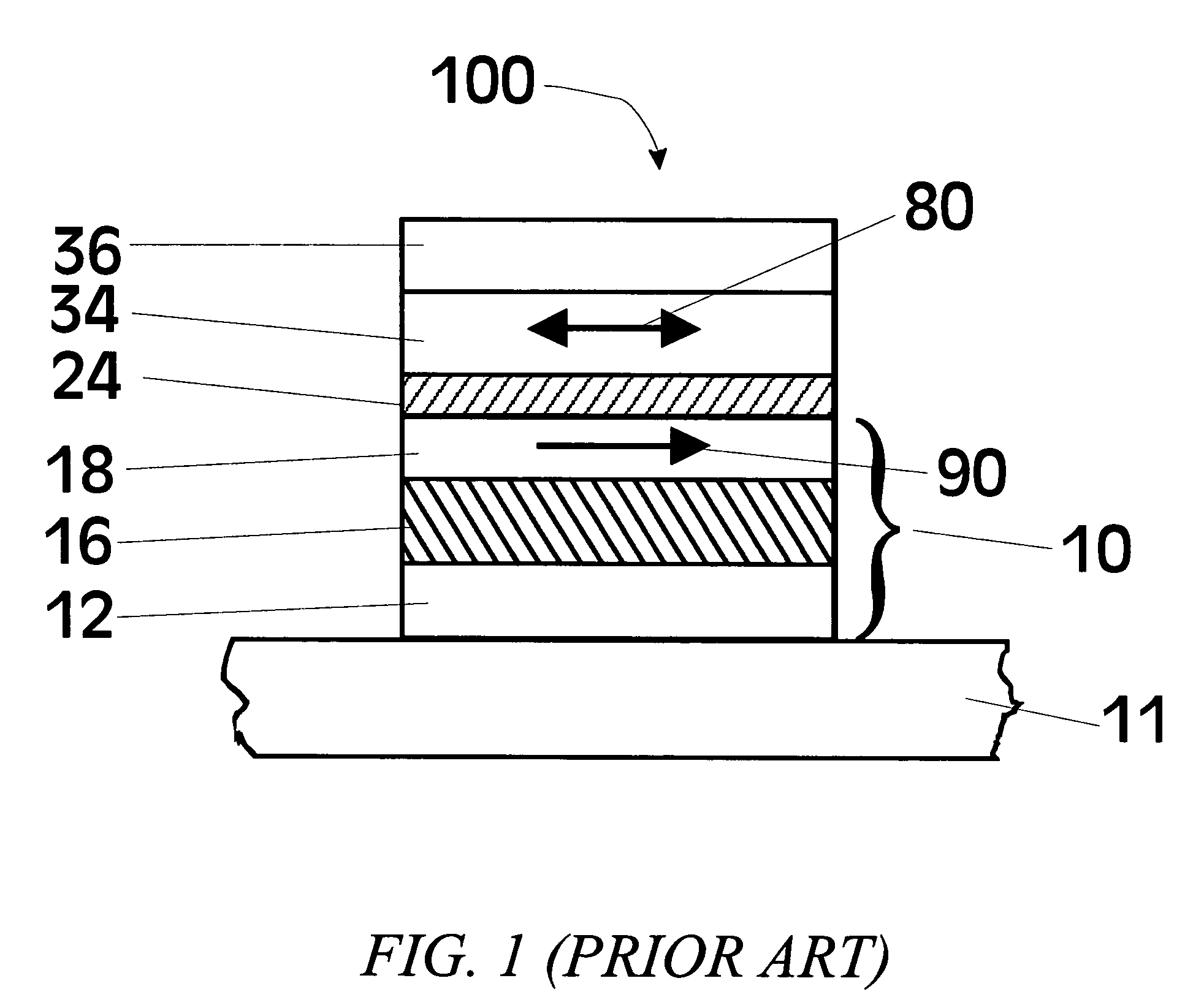
MgO tunnel barriers and method of formation
ActiveUS7598555B1Facilitate manufacturingImprove performanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetoresistanceThin layer
MgO tunnel barriers are formed by depositing a thin layer of Mg on a suitable underlayer, and then directing oxygen and additional Mg towards the Mg layer. The oxygen reacts with the additional Mg and the Mg in the Mg layer to form a MgO tunnel barrier that enjoys excellent tunneling characteristics. The MgO tunnel barriers so formed may be used in magnetic tunnel junctions having tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) values of greater than 100%. The highest TMR values are observed for junctions that have been annealed and that have a (100) crystallographic orientation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method And Apparatus for Load-Locked Printing
ActiveUS20100201749A1Prevent oxidationAvoid contaminationInking apparatusMolten spray coatingElectrical and Electronics engineering3D printing
The disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for preventing oxidation or contamination during a circuit printing operation. The circuit printing operation can be directed to OLED-type printing. In an exemplary embodiment, the printing process is conducted at a load-locked printer housing having one or more of chambers. Each chamber is partitioned from the other chambers by physical gates or fluidic curtains. A controller coordinates transportation of a substrate through the system and purges the system by timely opening appropriate gates. The controller may also control the printing operation by energizing the print-head at a time when the substrate is positioned substantially thereunder.
Owner:KATEEVA
Method of Forming a Polymer Component
ActiveUS20110153025A1Reduce oxidationPrevent oxidationMedical devicesPretreated surfacesCross-linkArticular surfaces
This invention relates to a method of forming a polymer component and comprises blending polymer particles with antioxidant to form a mixture in which the antioxidant coats the polymer particles, irradiating the mixture to cross-link the polymer particles therein and forming the irradiated mixture into a consolidated component. The invention also relates to a method of forming an articular surface for a prosthesis and a prosthesis having a polymer articular bearing surface wherein at least one pre-determined portion of the bearing surface is provided with cross-linked polymer bonds.
Owner:JOINTMEDICA LTD
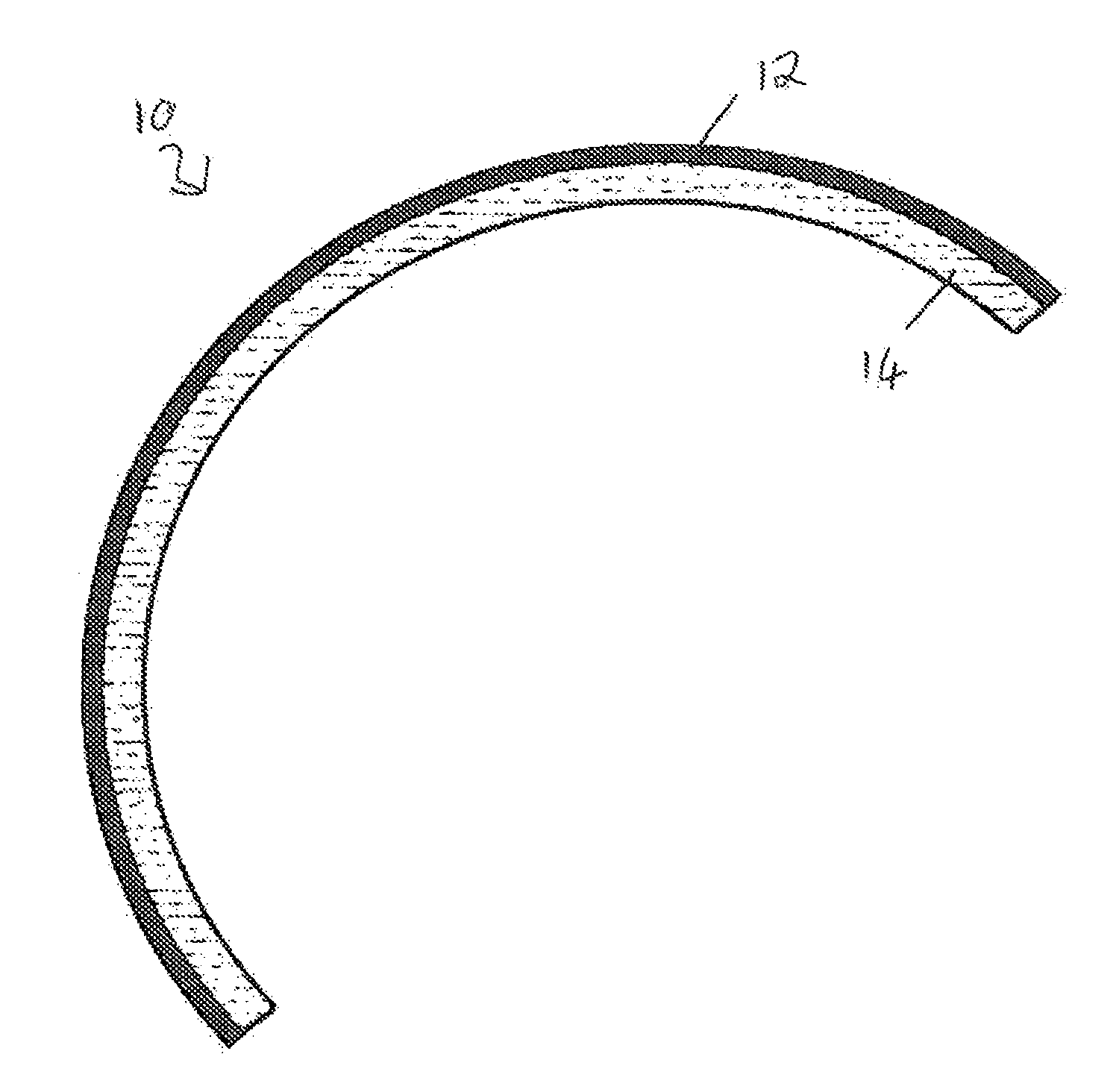
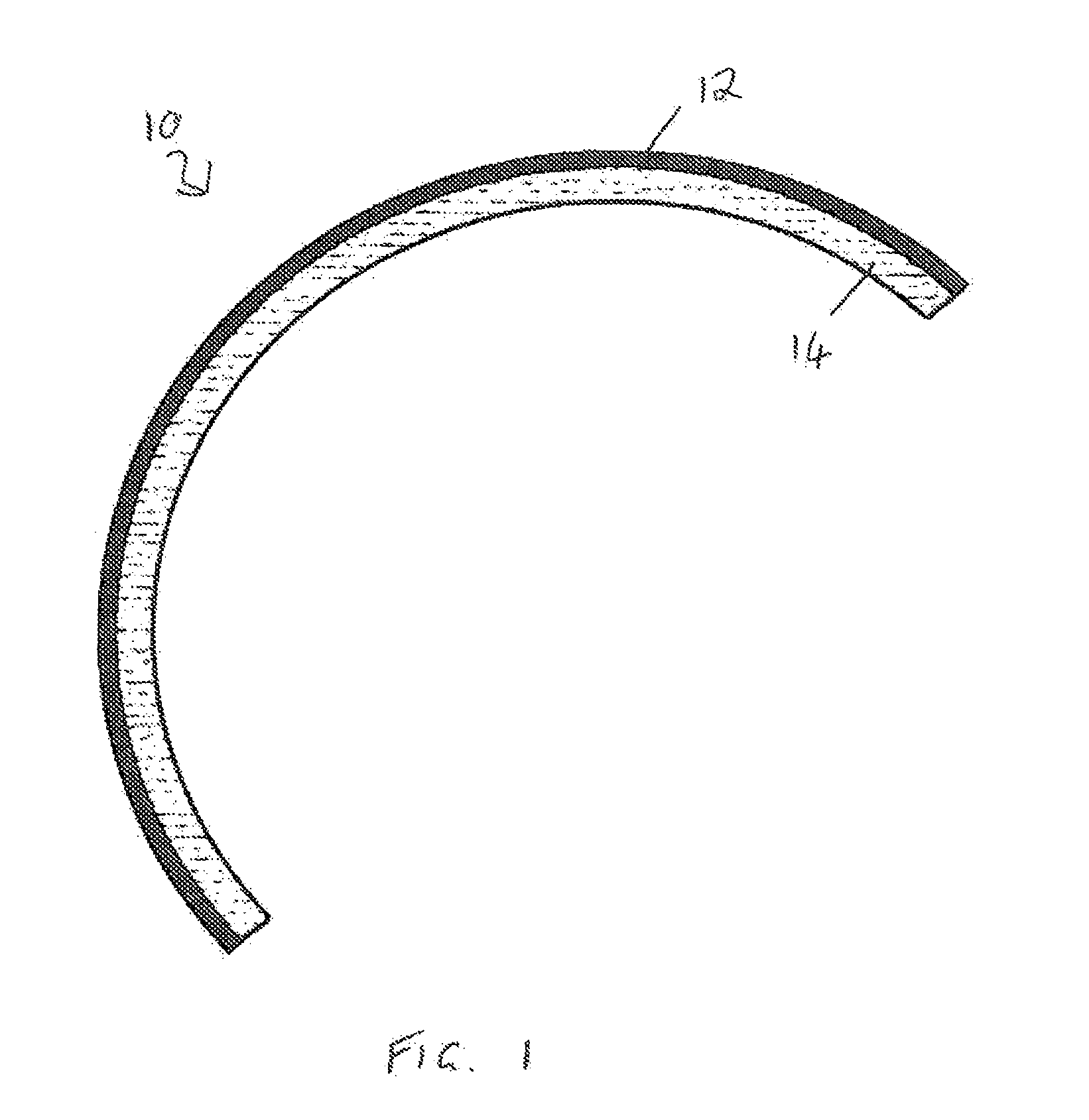
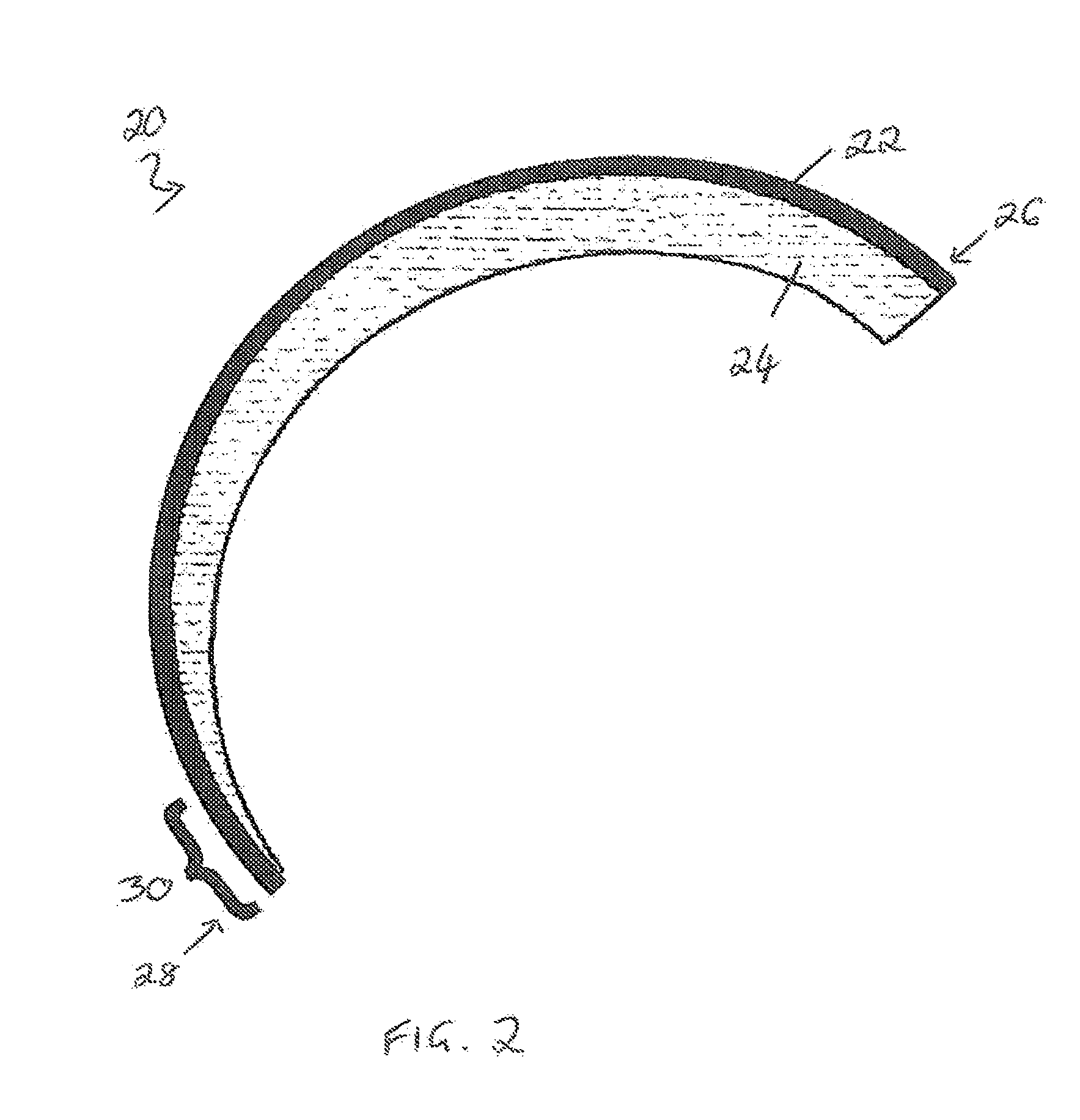
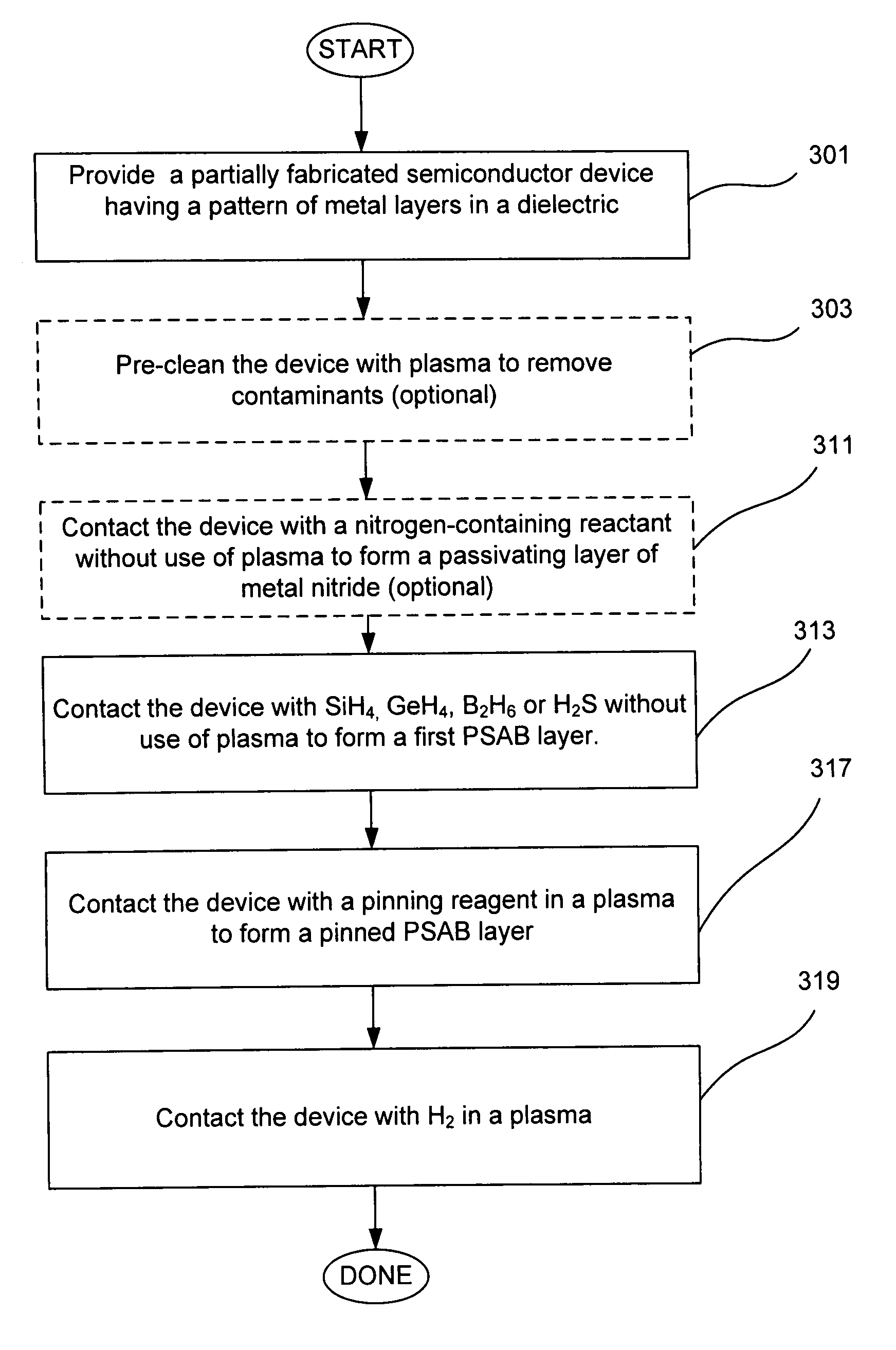
Protective self-aligned buffer layers for damascene interconnects
ActiveUS7727880B1Improving several propertyDecrease in metal electromigrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSalicideMetal silicide
Protective self aligned buffer (PSAB) layers are layers of material that are selectively formed at the surface of metal layers in a partially fabricated semiconductor device. In a Damascene interconnect, PSAB layer typically resides at an interface between the metal layer and a dielectric diffusion barrier layer. PSAB layers promote improved adhesion between a metal layer and an adjacent dielectric diffusion barrier layer. Further, PSAB layers can protect metal surfaces from inadvertent oxidation during fabrication process. A PSAB layer may be formed entirely within the top portion of a metal layer, by, for example, chemically converting metal surface to a thin layer of metal silicide. Thickness of PSAB layers, and, consequently resistance of interconnects can be controlled by partially passivating metal surface prior to formation of PSAB layer. Such passivation can be accomplished by controllably treating metal surface with a nitrogen-containing compound to convert metal to metal nitride.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
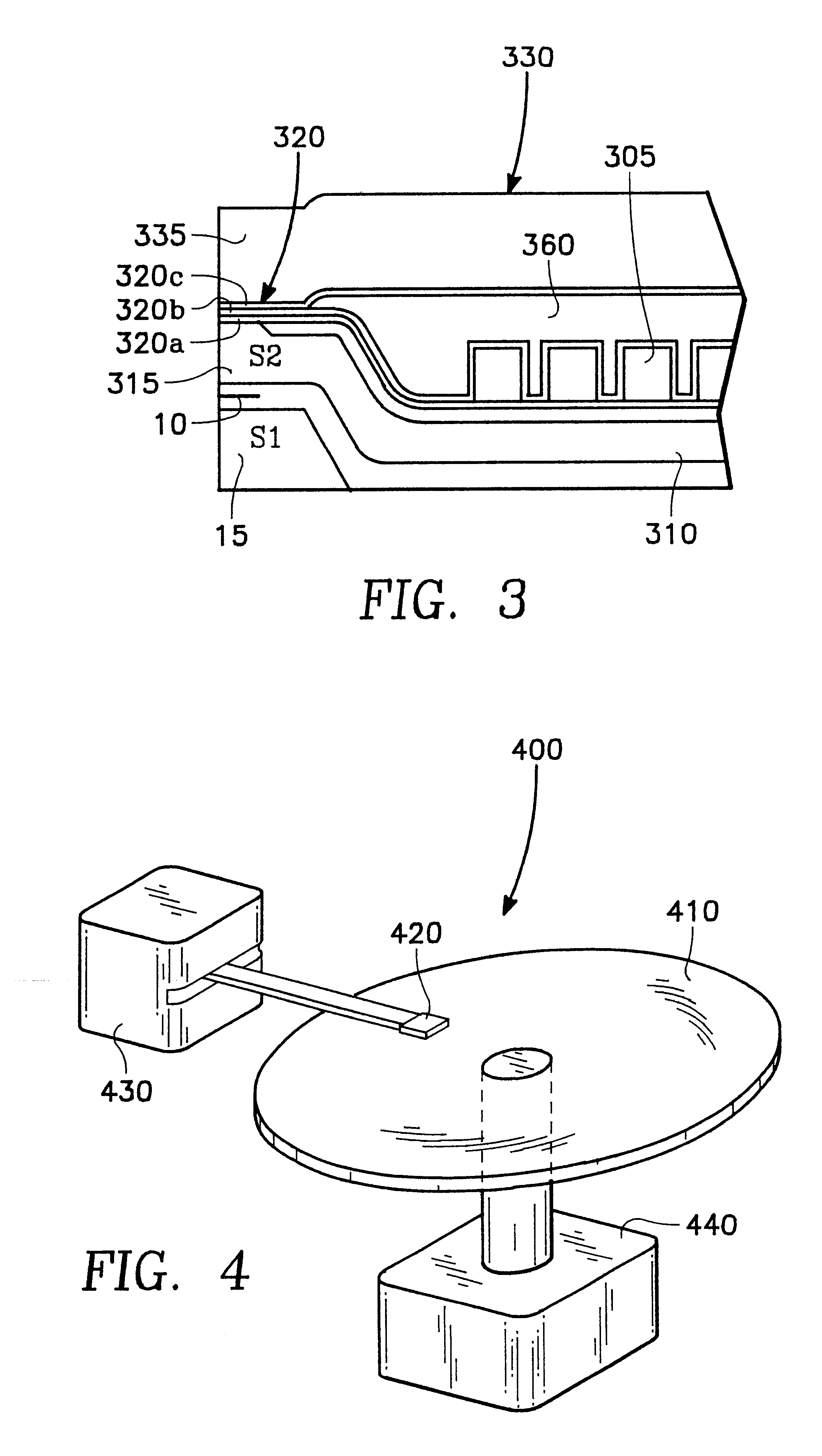
Thin film writer with multiplayer write gap
InactiveUS6724569B1Easy to controlControl performanceConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceElectrical conductorLower pole
Embodiments in accordance with the thin film write head of the present invention have a lower pole structure, an upper pole structure, and a multilayer write gap extending from an air bearing surface between the upper and lower pole structures. In preferred embodiments, the write gap comprises at least two of: (a) a first layer covering a lower pole tip portion of the lower pole structure, (b) a second layer covering turns of a semiconductor winding, or (c) a third layer covering a winding insulation stack. In more preferred embodiments, the write gap is formed of the first, the second, and the third write gap layers. An advantage of a write head with a multilayer write gap is that it allows better control of write gap thickness. As such, loss of write gap thickness can be compensated for by deposition of the second write gap layers, or by deposition of the third write gap layer. Some embodiments have one or more additional advantages in providing increased corrosion prevention, improving the integrity of conductor insulation, and / or improving the top pole magnetic material characteristics.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
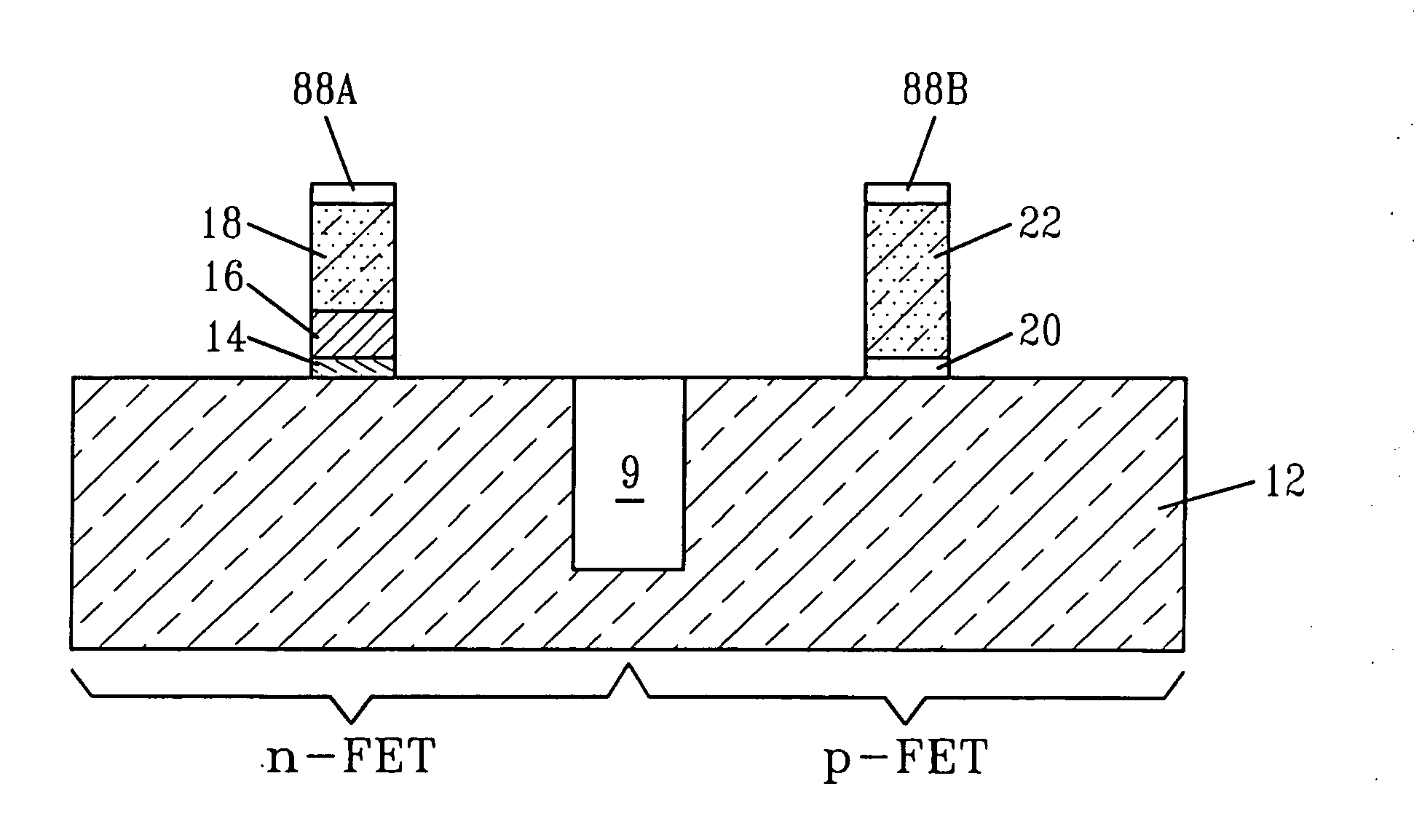
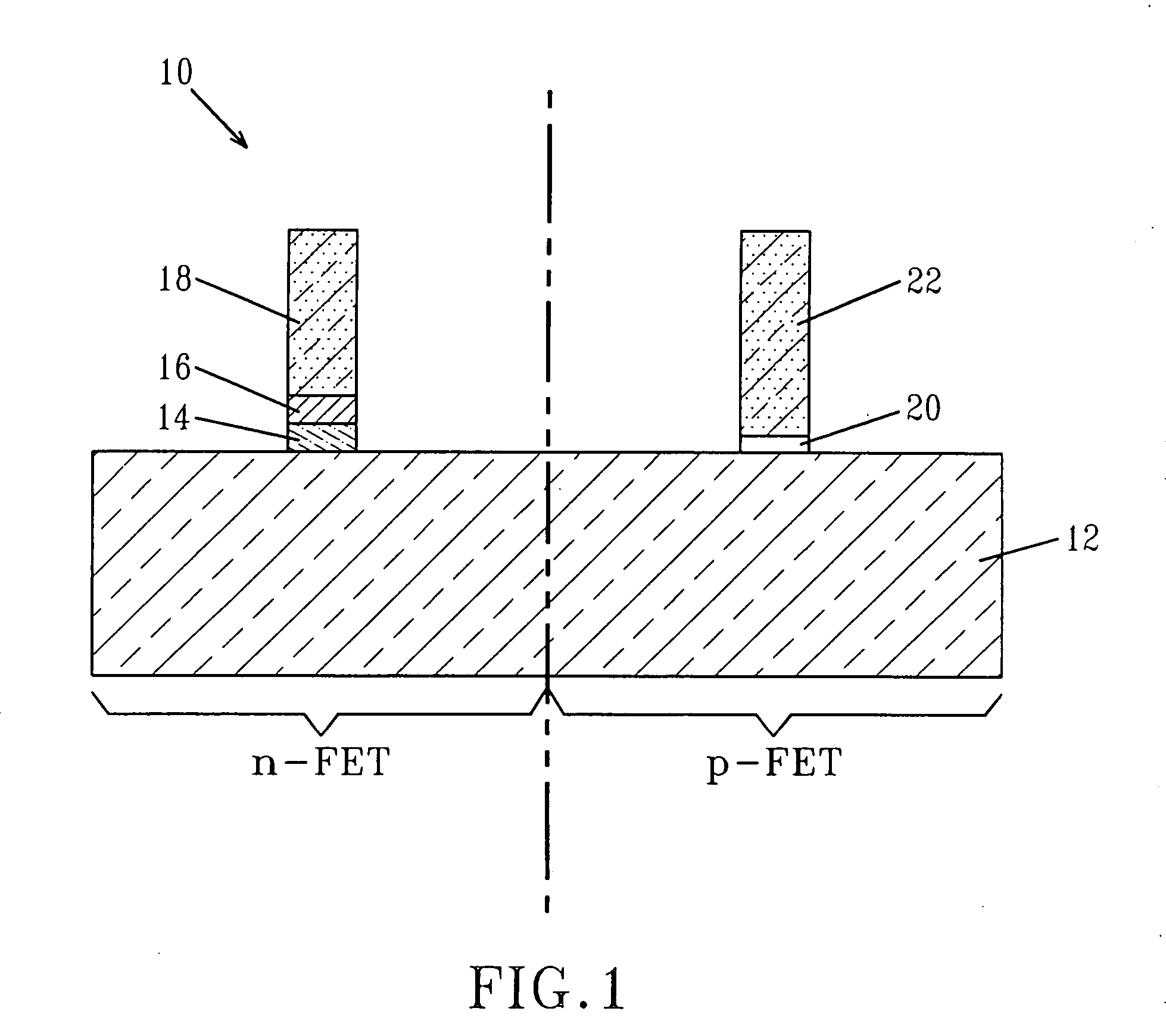
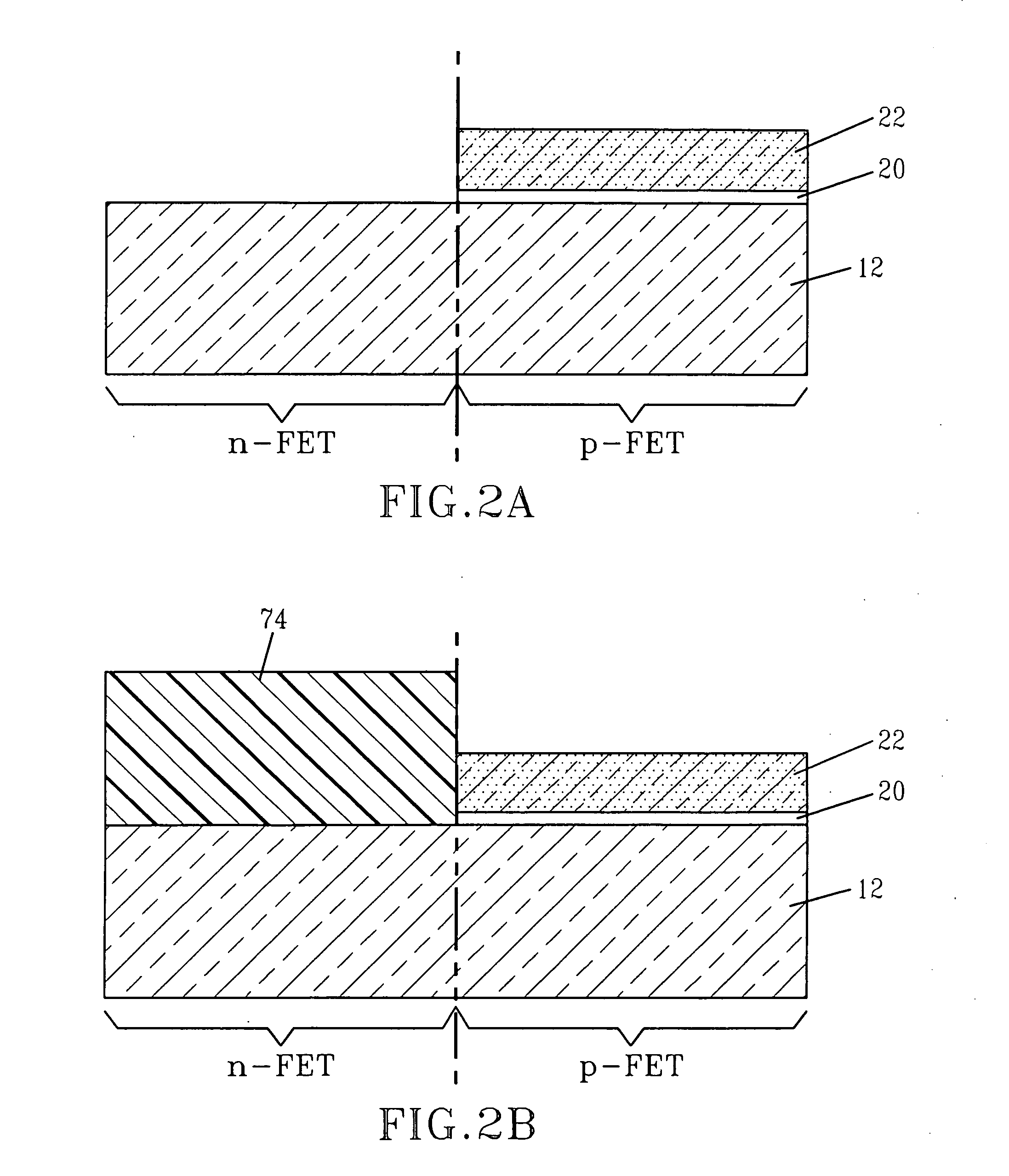
High performance CMOS circuits, and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070152276A1Improve manufacturabilityImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSGate dielectric
The present invention relates to complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) circuits that each contains at least a first and a second gate stacks. The first gate stack is located over a first device region (e.g., an n-FET device region) in a semiconductor substrate and comprises at least, from bottom to top, a gate dielectric layer, a metallic gate conductor, and a silicon-containing gate conductor. The second gate stack is located over a second device region (e.g., a p-FET device region) in the semiconductor substrate and comprises at least, from bottom to top, a gate dielectric layer and a silicon-containing gate conductor. The first and second gate stacks can be formed over the semiconductor substrate in an integrated manner by various methods of the present invention.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Electronic device and manufacturing method thereof
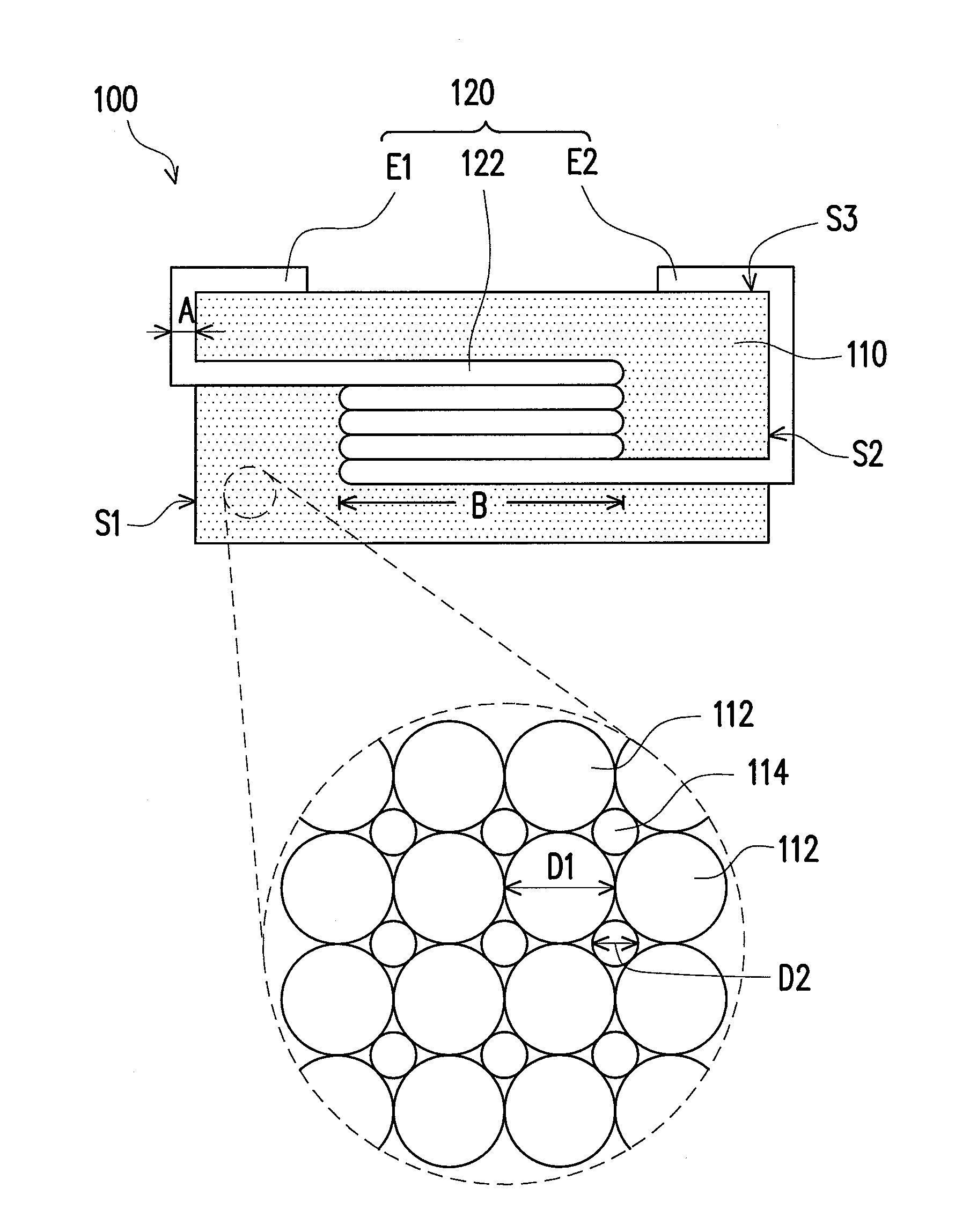
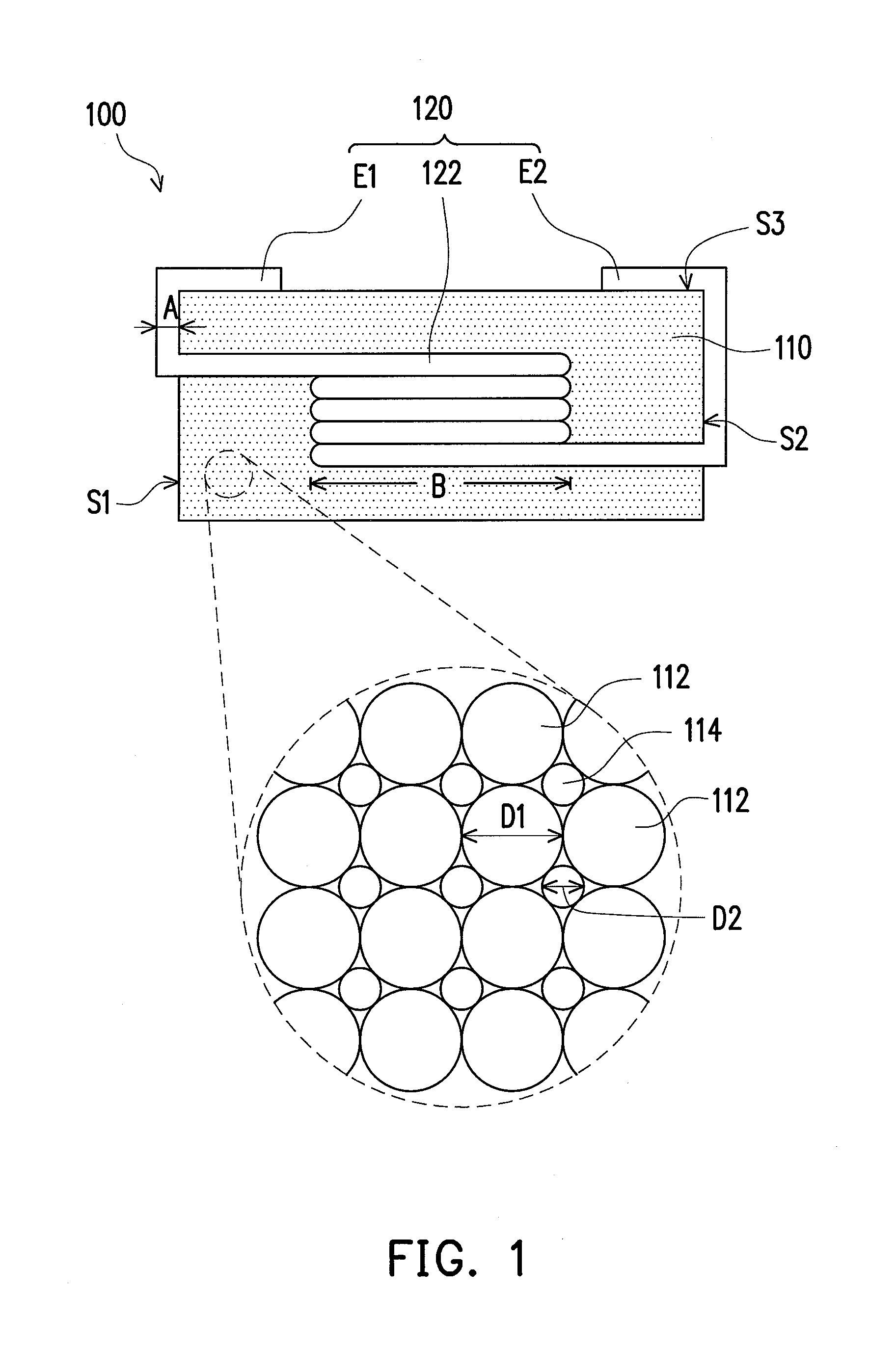
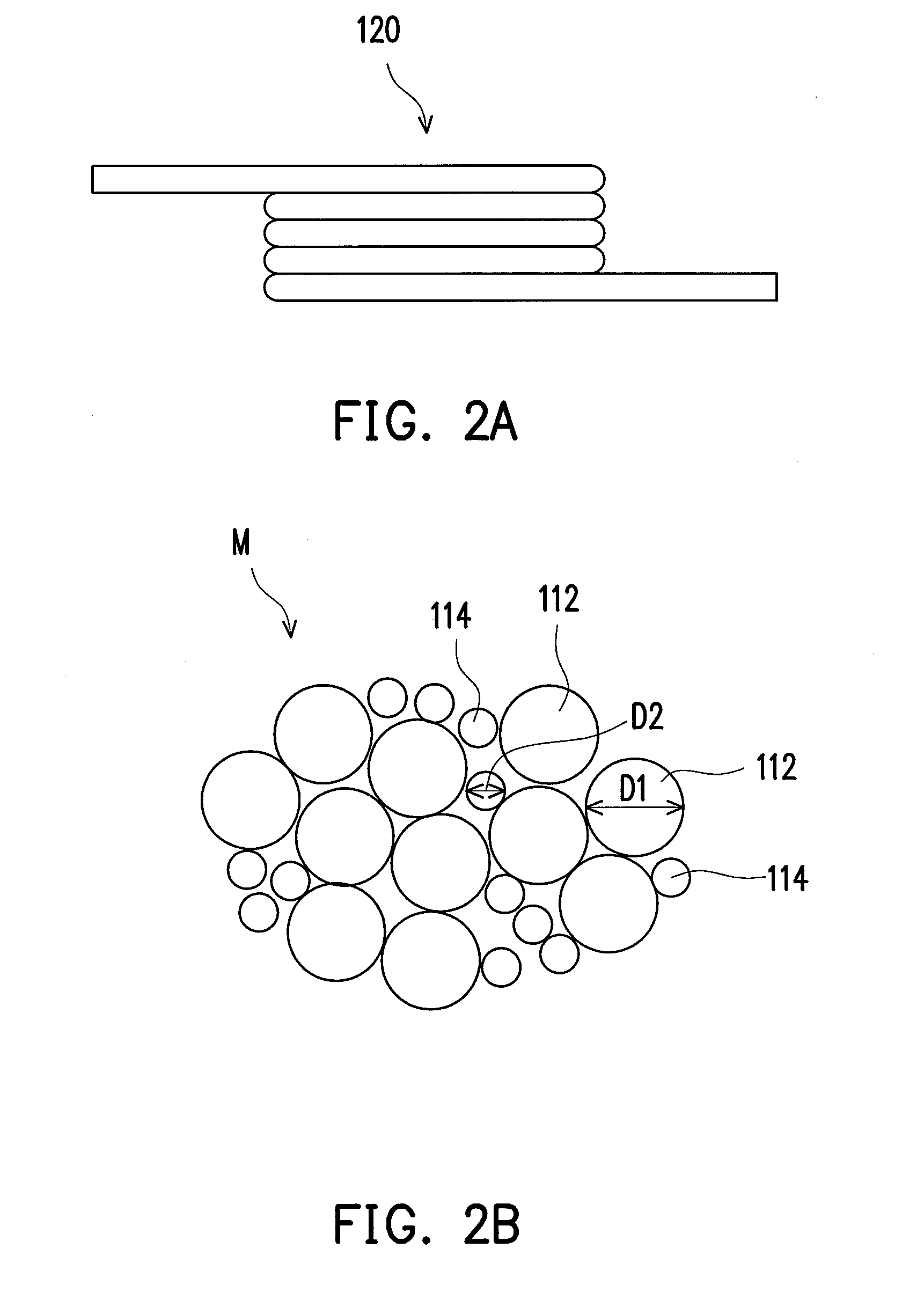
ActiveUS20100289609A1Improve breathabilityPrevent oxidationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic powderHardness
An electronic device including a magnetic body and a wire is provided. The magnetic body has a first magnetic powder and a second magnetic powder mixed with the first magnetic powder. The Vicker's Hardness of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder and the mean particle diameter of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder.
Owner:CYNTEC
Mg-Zn oxide tunnel barriers and method of formation
ActiveUS7252852B1Not diminishing spin polarizationImprove performanceNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsOxygenZinc
ZnMg oxide tunnel barriers are grown which, when sandwiched between ferri- or ferromagnetic layers, form magnetic tunnel junctions exhibiting high tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR). The TMR may be increased by annealing the magnetic tunnel junctions. The zinc-magnesium oxide tunnel barriers may be incorporated into a variety of other devices, such as magnetic tunneling transistors and spin injector devices. The ZnMg oxide tunnel barriers are grown by first depositing a zinc and / or magnesium layer onto an underlying substrate in oxygen-poor (or oxygen-free) conditions, and subsequently depositing zinc and / or magnesium onto this layer in the presence of reactive oxygen.
Owner:IBM CORP
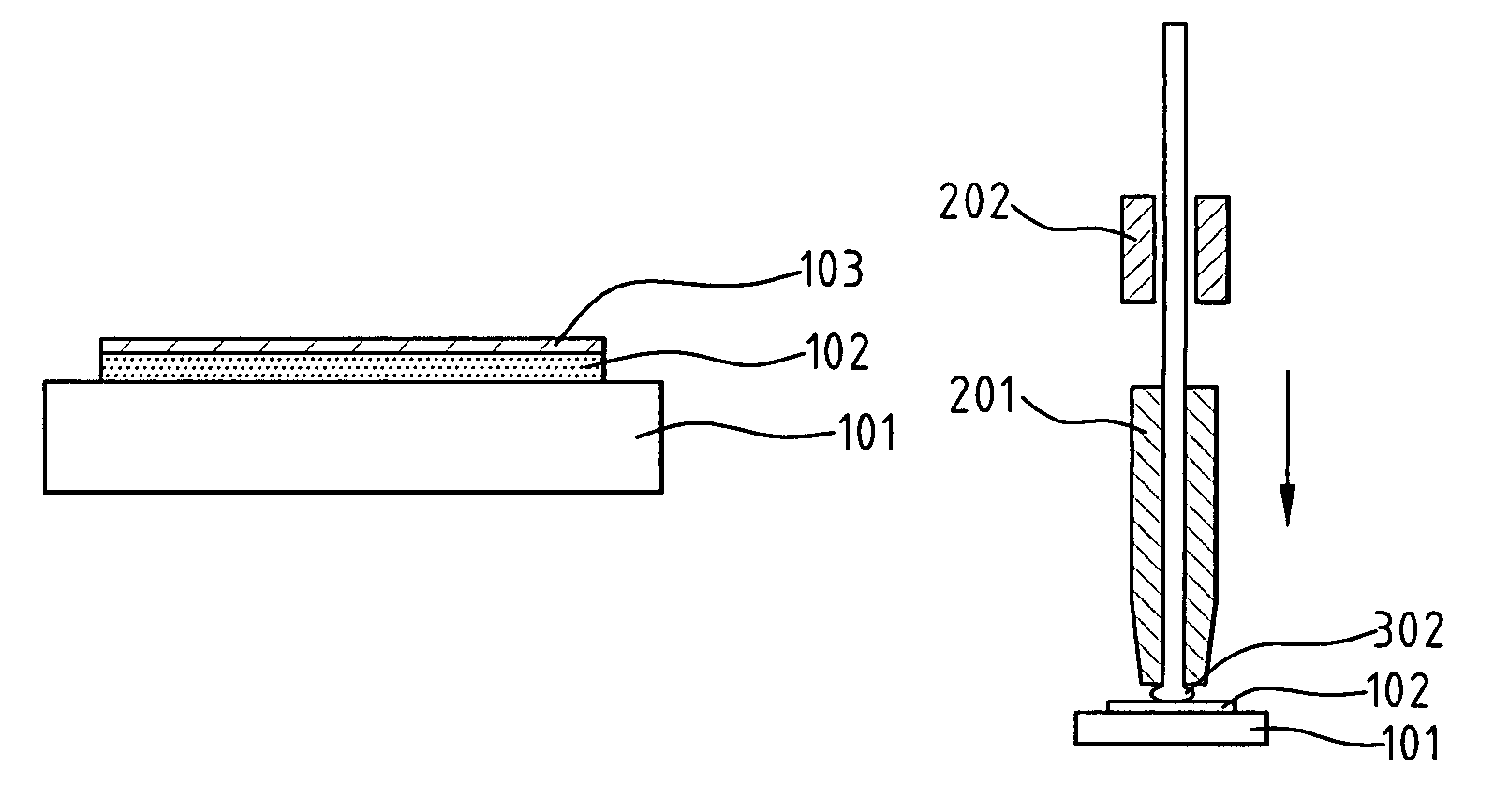
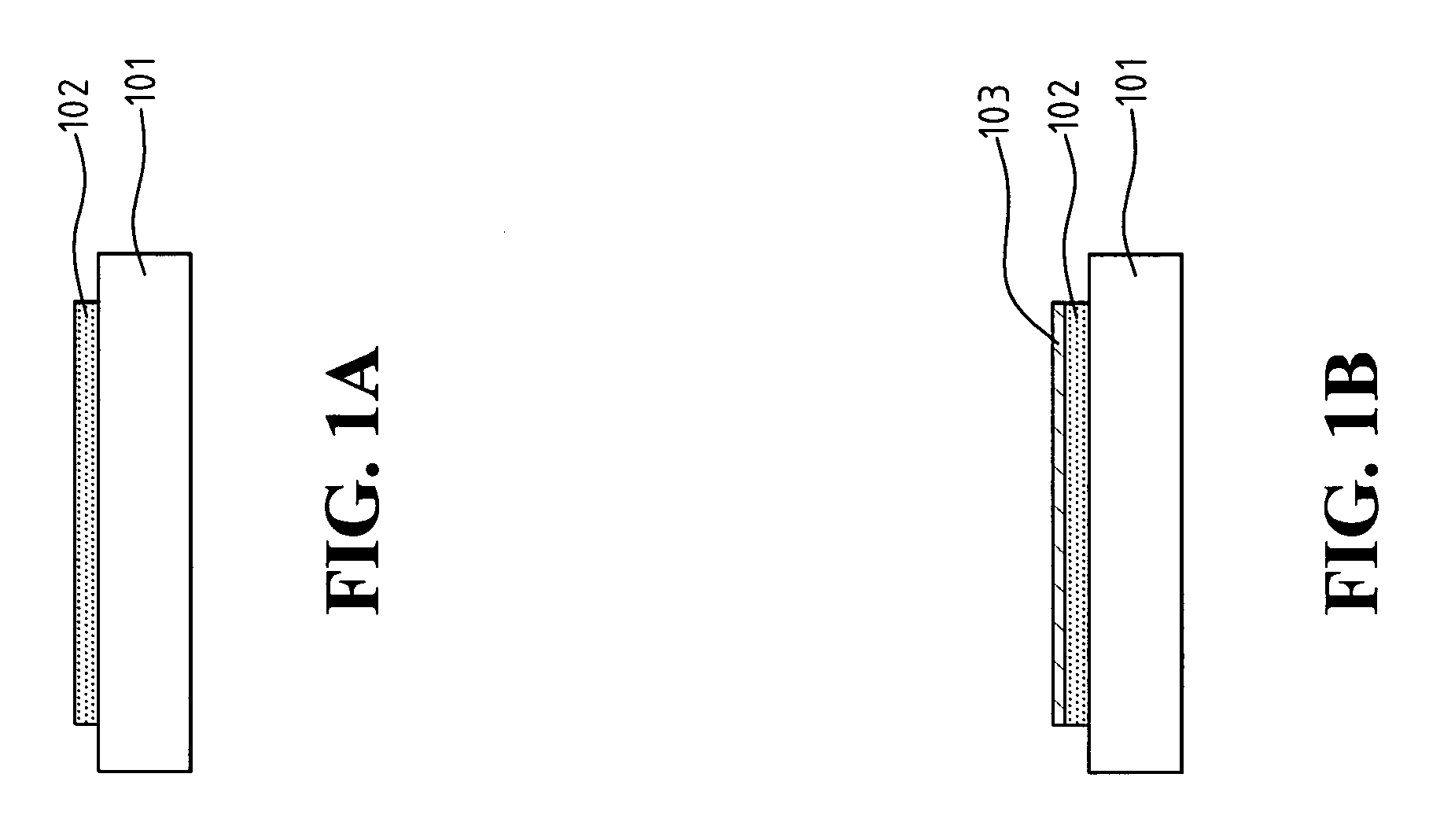
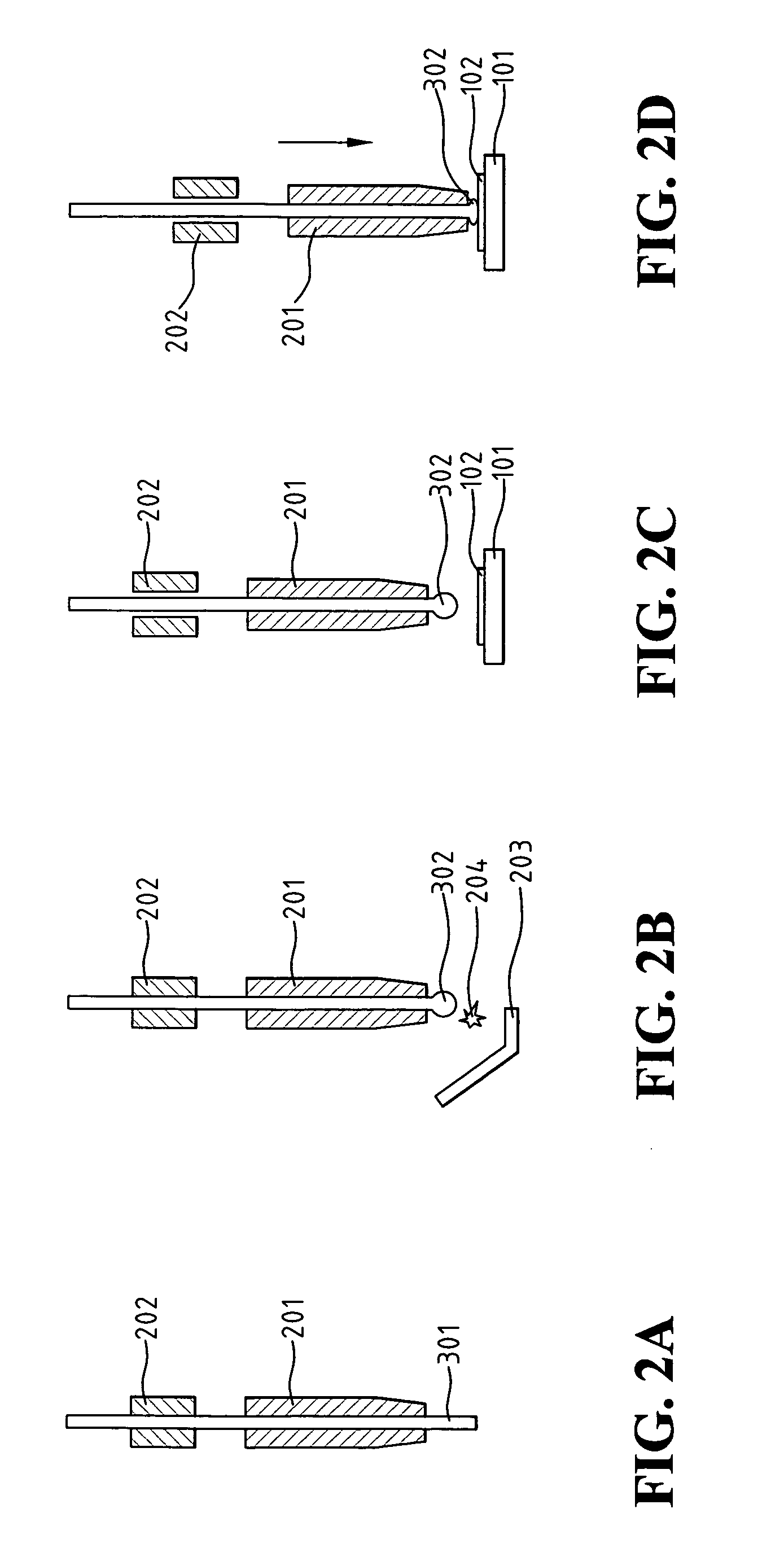
Sheet-shaped heat and light source, method for making the same and method for heating object adopting the same
ActiveUS20090085461A1Prevent oxidationLow efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensIncandescent ignitionCarbon nanotubeLight source
The present invention relates to a sheet-shaped heat and light source. The sheet-shaped heat and light source includes a carbon nanotube layer and at least two electrodes. The at least two electrodes are separately disposed on the carbon nanotube layer and electrically connected thereto. Moreover, a method for making the sheet-shaped heat and light source and a method for heating an object adopting the same are also included.
Owner:BEIJING FUNATE INNOVATION TECH +1
Method for the fabrication of conductive electronic features
InactiveUS20100112195A1Reduce settlementGood dispersionPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronMaterials science
Owner:CABOT CORP
Wire-bonding method for chips with copper interconnects by introducing a thin layer
InactiveUS6962864B1Prevented being oxidizedPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThin layerAqueous solution
A wire-bonding method for chips with copper interconnects by introducing a thin layer is provided for solving the problem of oxidizing a copper bonding-pad during bonding processing in order not to deteriorate the bonding strength and yield rate thereof. The wire-bonding method of the present invention comprises: a step for providing a chip with a copper bonding-pad; another step for providing an aqueous solution to form a Cuprous oxide thin layer on the copper bonding-pad; and yet another step for setting a plurality of copper interconnects on the copper bonding-pad and providing an ultrasonic power for removing the Cuprous oxide layer to have the interconnects bonded on the copper bonding-pad.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Heavy polymer coated slow-release fertilizer with sulfide as bottom coat
InactiveCN1569774AStrong impact resistanceImprove wear resistanceFertiliser formsUrea compound fertilisersControl releaseCoated urea
The invention relates to an enveloped controlled release fertilizer and method for preparation which consists of, preheating the urea particles to a predetermined temperature, spraying the molten liquid state sulfur to the urea particles, forming a layer of smooth and compact sulfur-coated urea, charging hot-curing resin component on the sulfur-coated urea for even distribution onto the urea particle surface and fast formation.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com