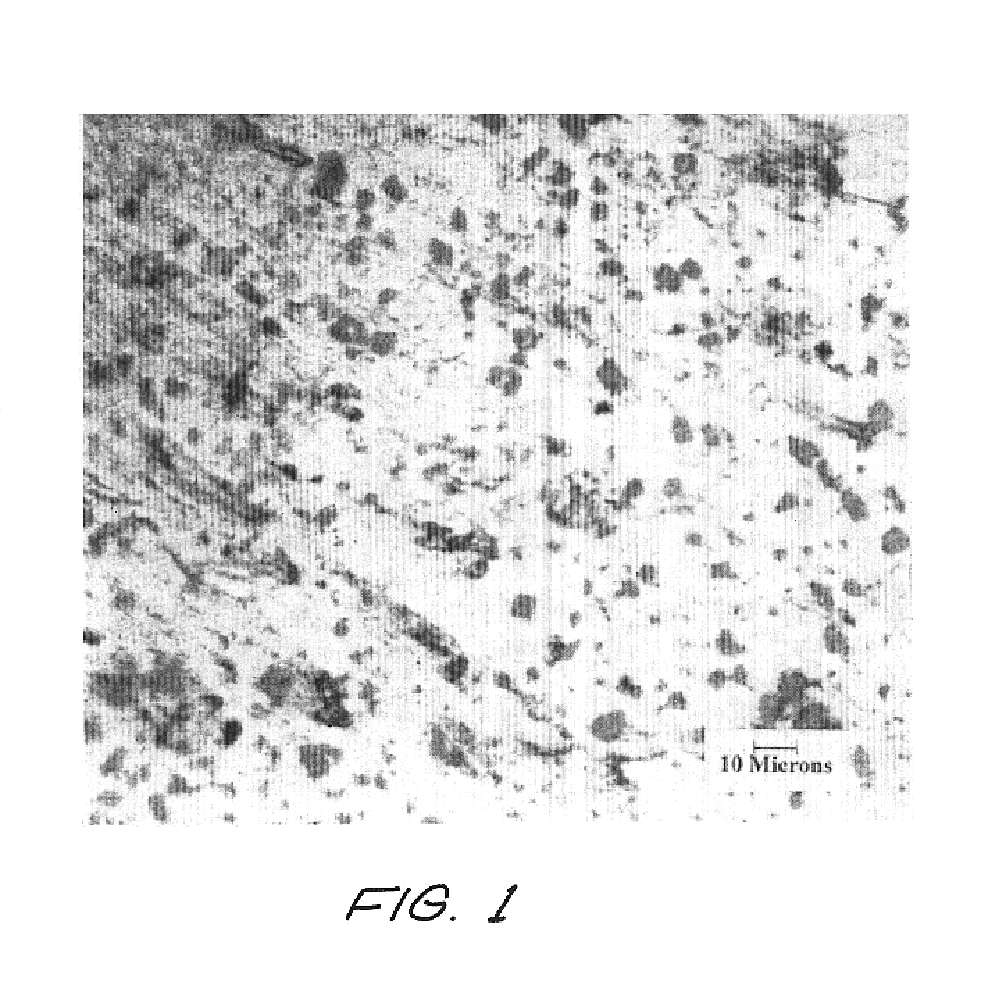
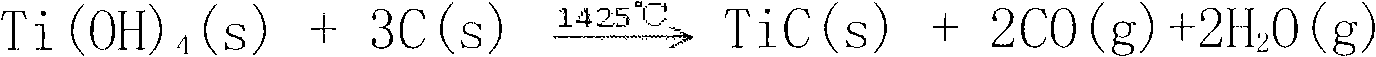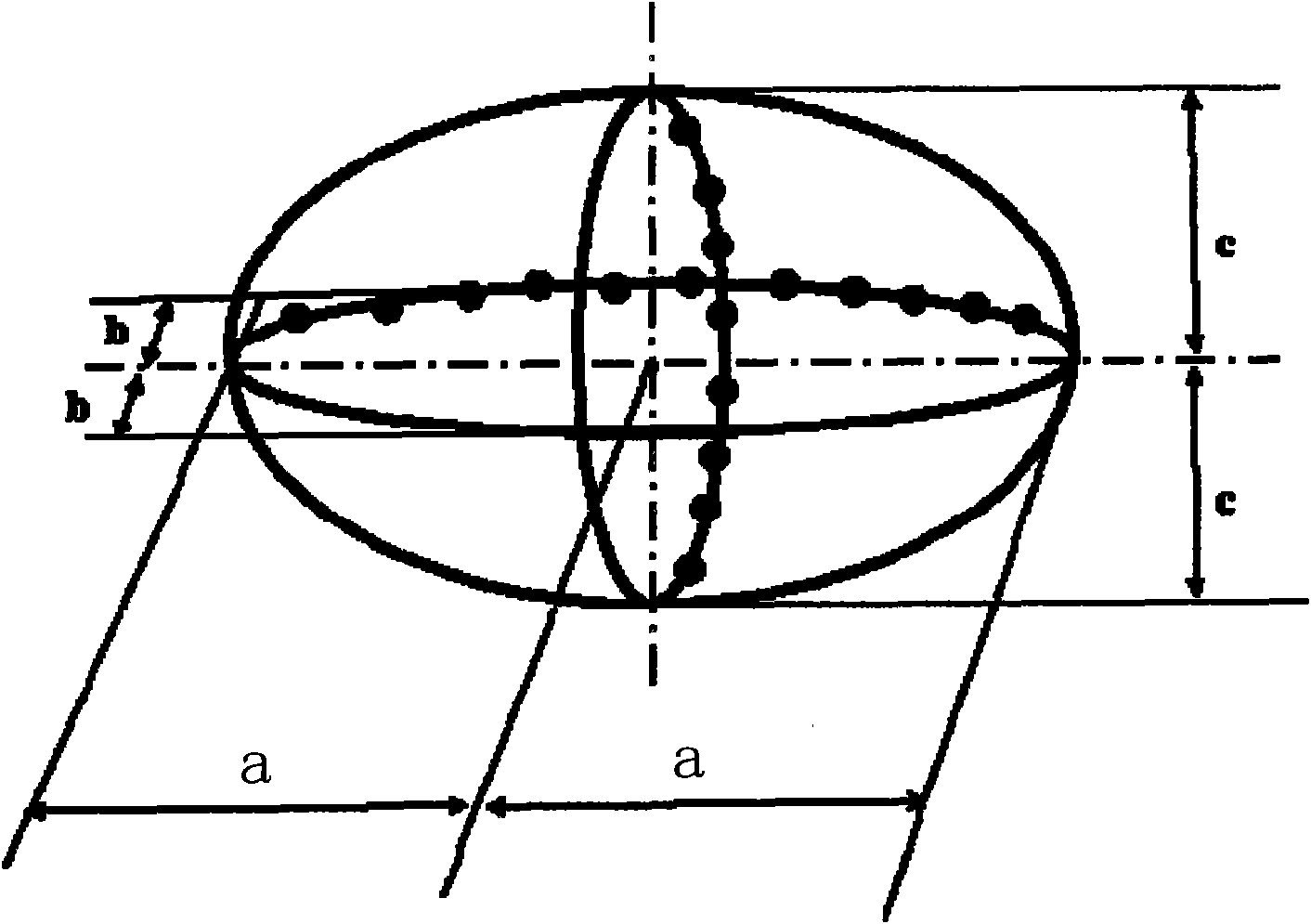Patents
Literature
2538 results about "Titanium carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
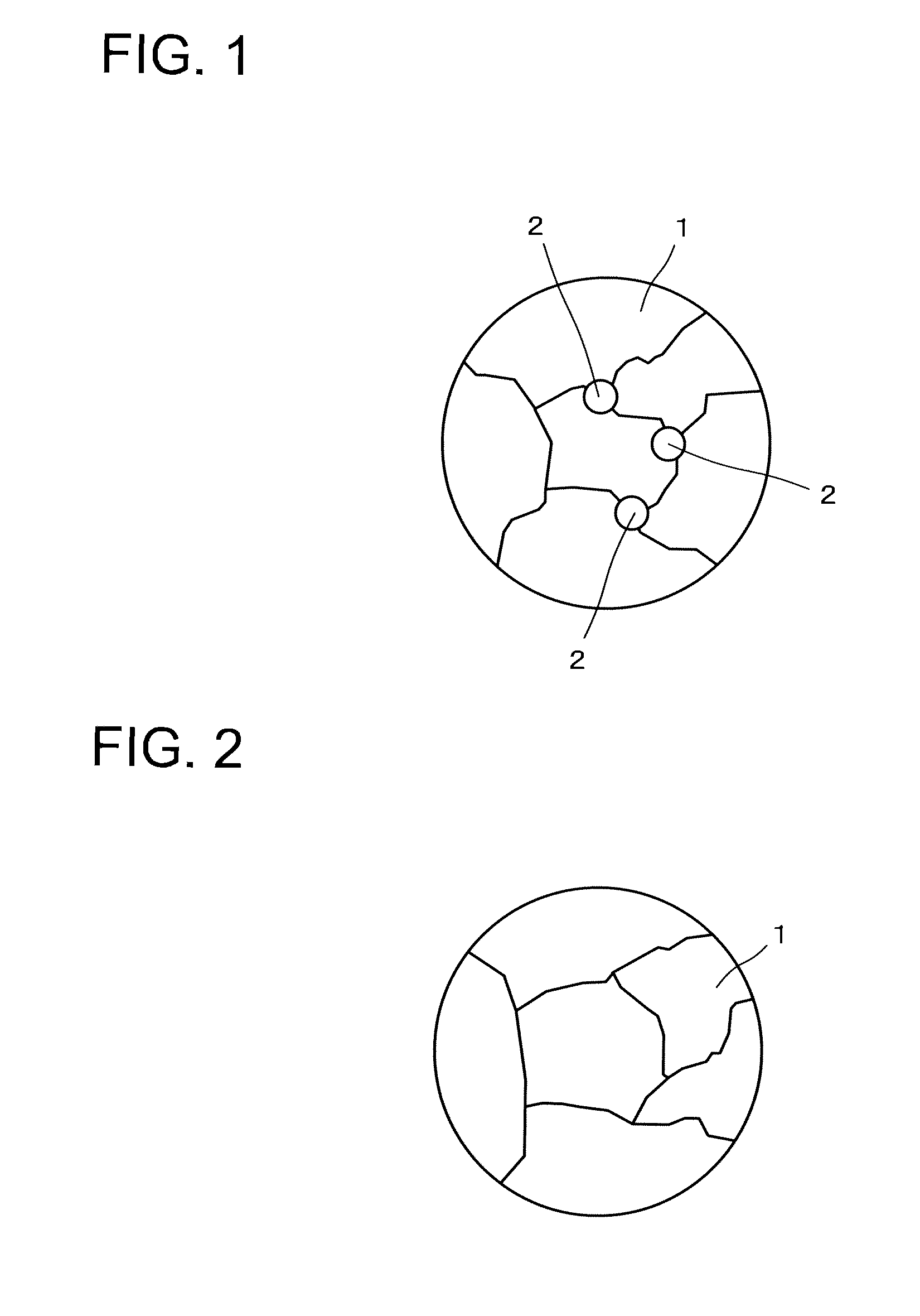
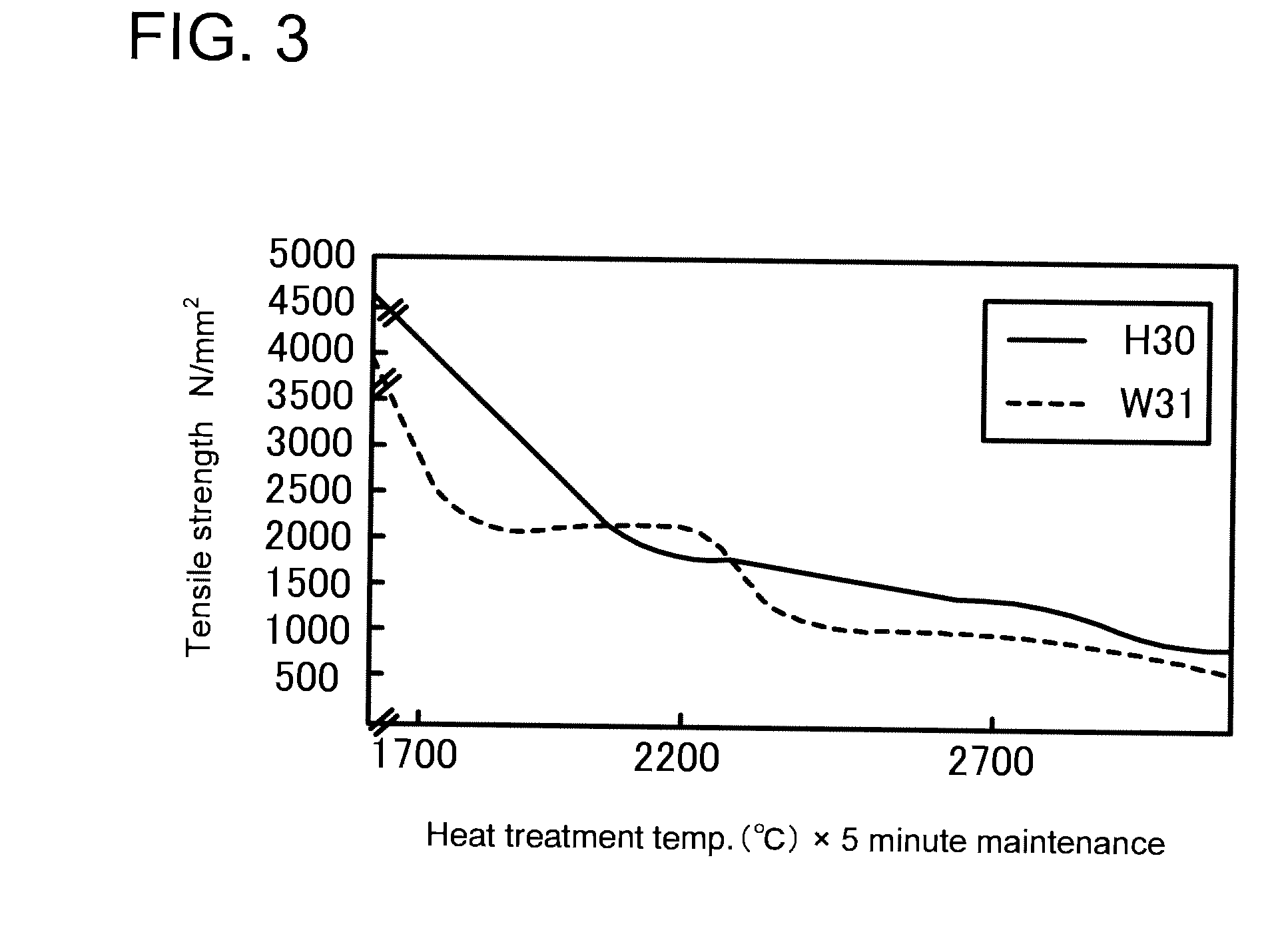
Titanium carbide, TiC, is an extremely hard (Mohs 9–9.5) refractory ceramic material, similar to tungsten carbide. It has the appearance of black powder with the sodium chloride (face-centered cubic) crystal structure. As found in nature its crystals range in size from 0.1 to 0.3mm.
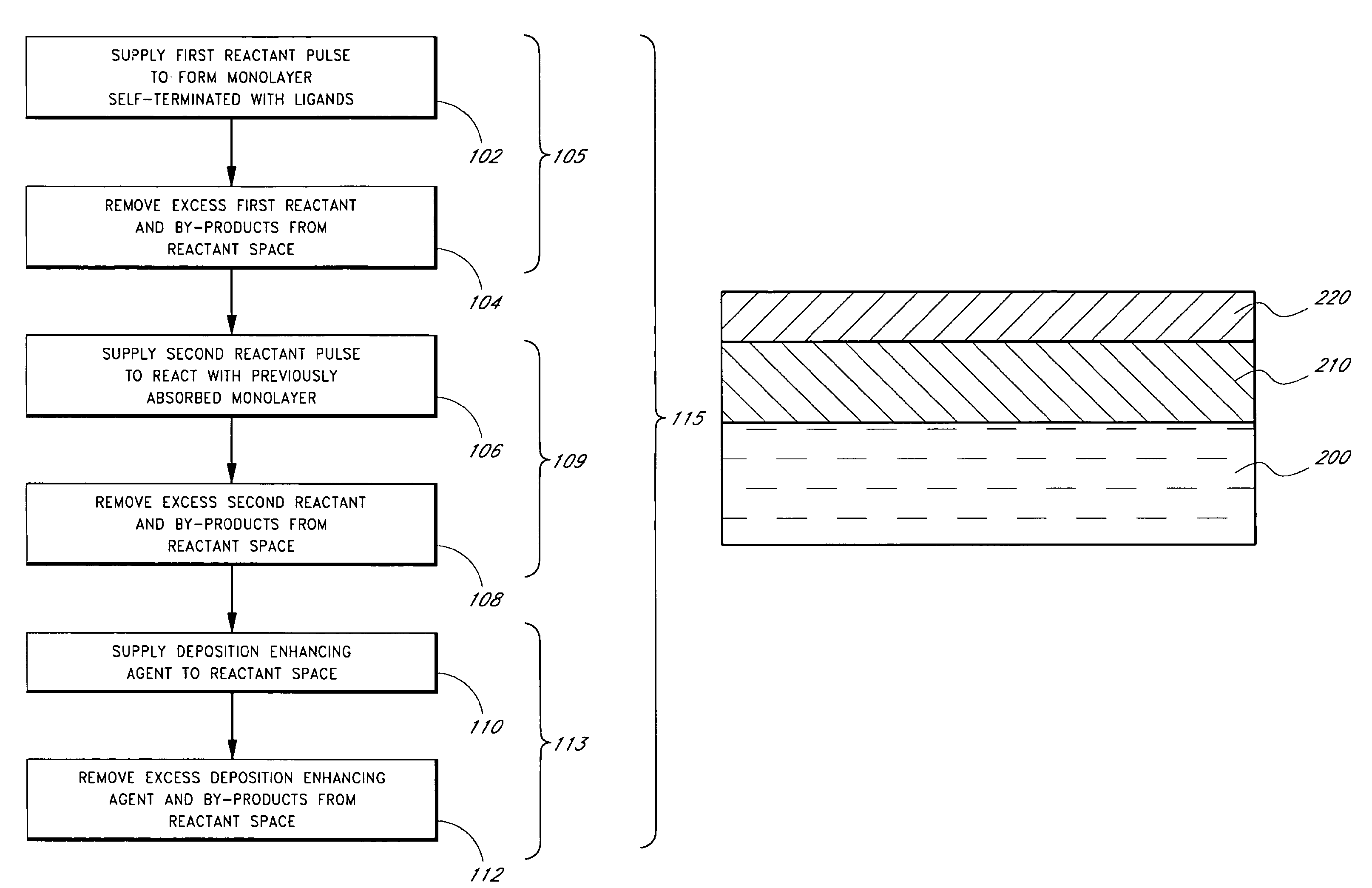
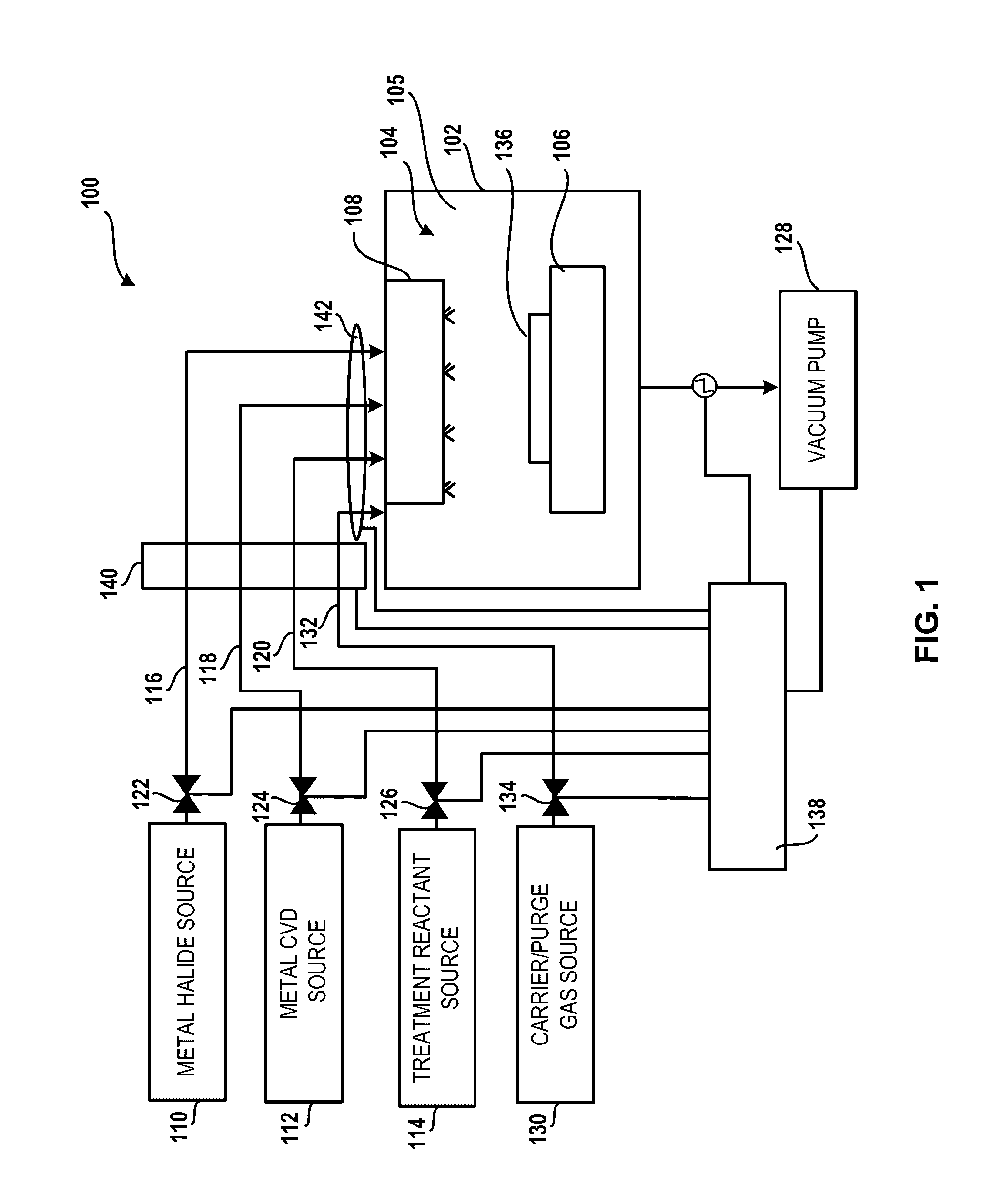
Silane and borane treatments for titanium carbide films
ActiveUS8841182B1Reduce oxidized portionPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesCompound (substance)
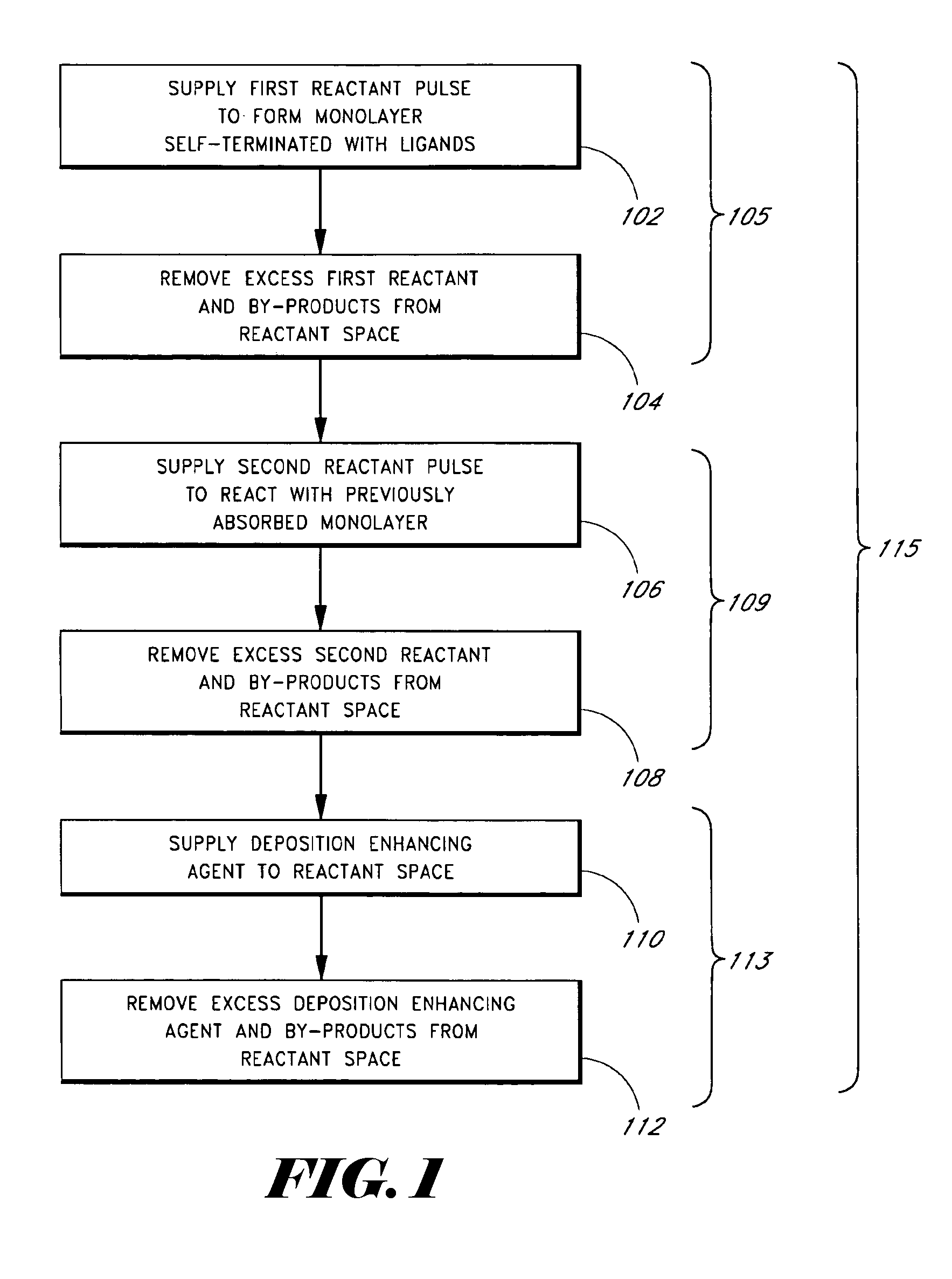
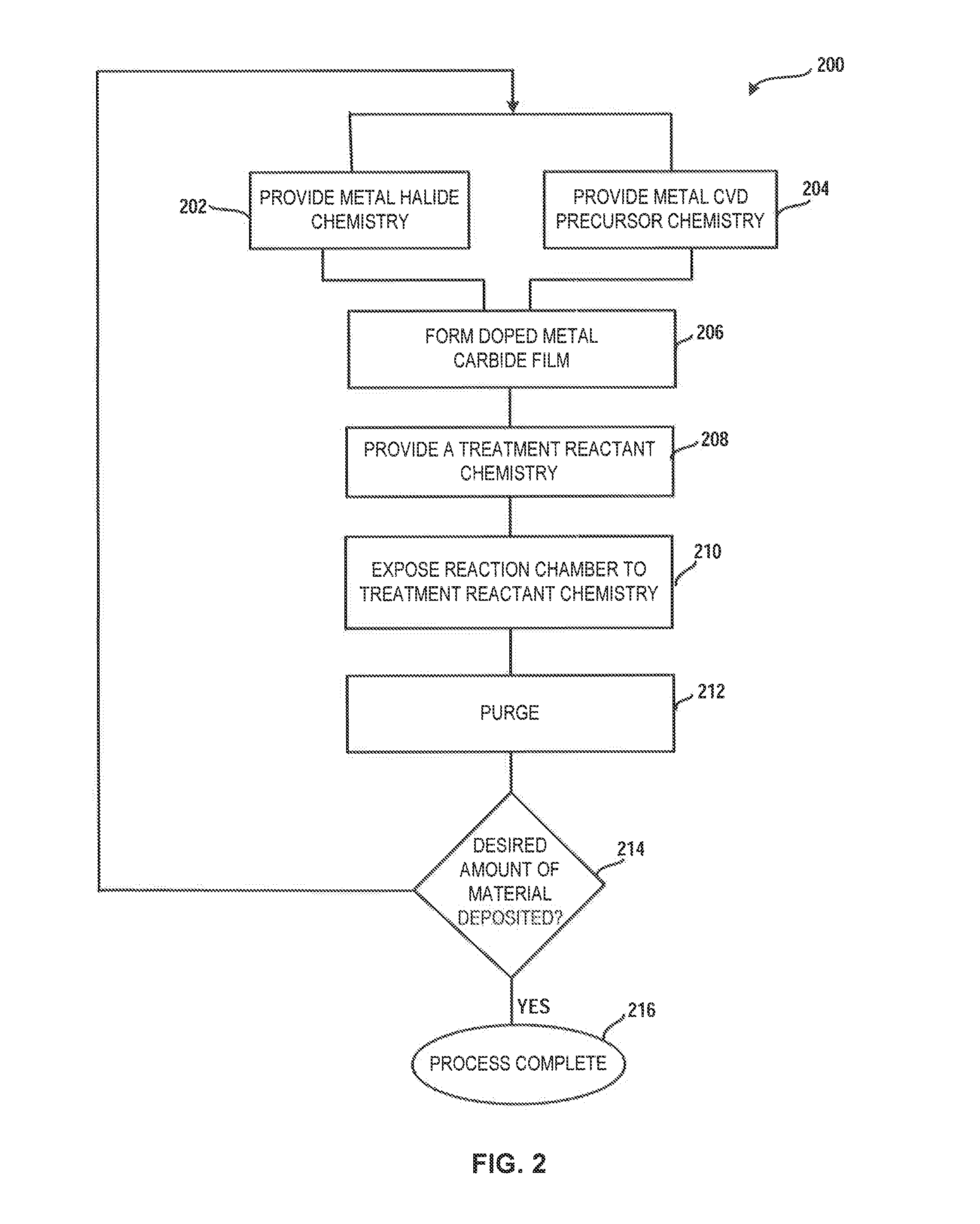
Methods of treating metal-containing thin films, such as films comprising titanium carbide, with a silane / borane agent are provided. In some embodiments a film including titanium carbide is deposited on a substrate by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The process may include a plurality of deposition cycles involving alternating and sequential pulses of a first source chemical that includes titanium and at least one halide ligand, a second source chemical that includes metal and carbon, where the metal and the carbon from the second source chemical are incorporated into the thin film, and a third source chemical, where the third source chemical is a silane or borane that at least partially reduces oxidized portions of the titanium carbide layer formed by the first and second source chemicals. The treatment can form a capping layer on the metal carbide film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
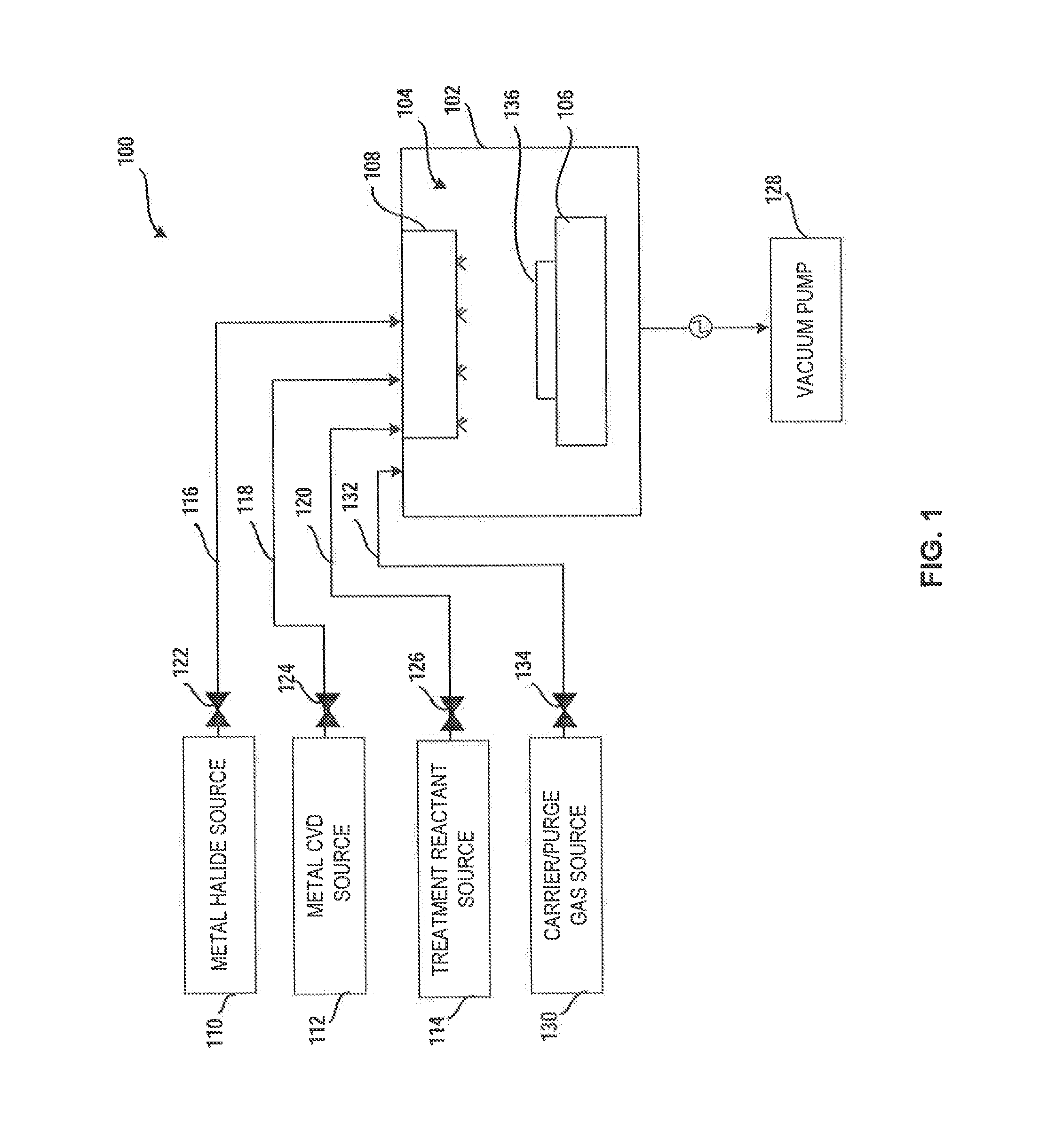
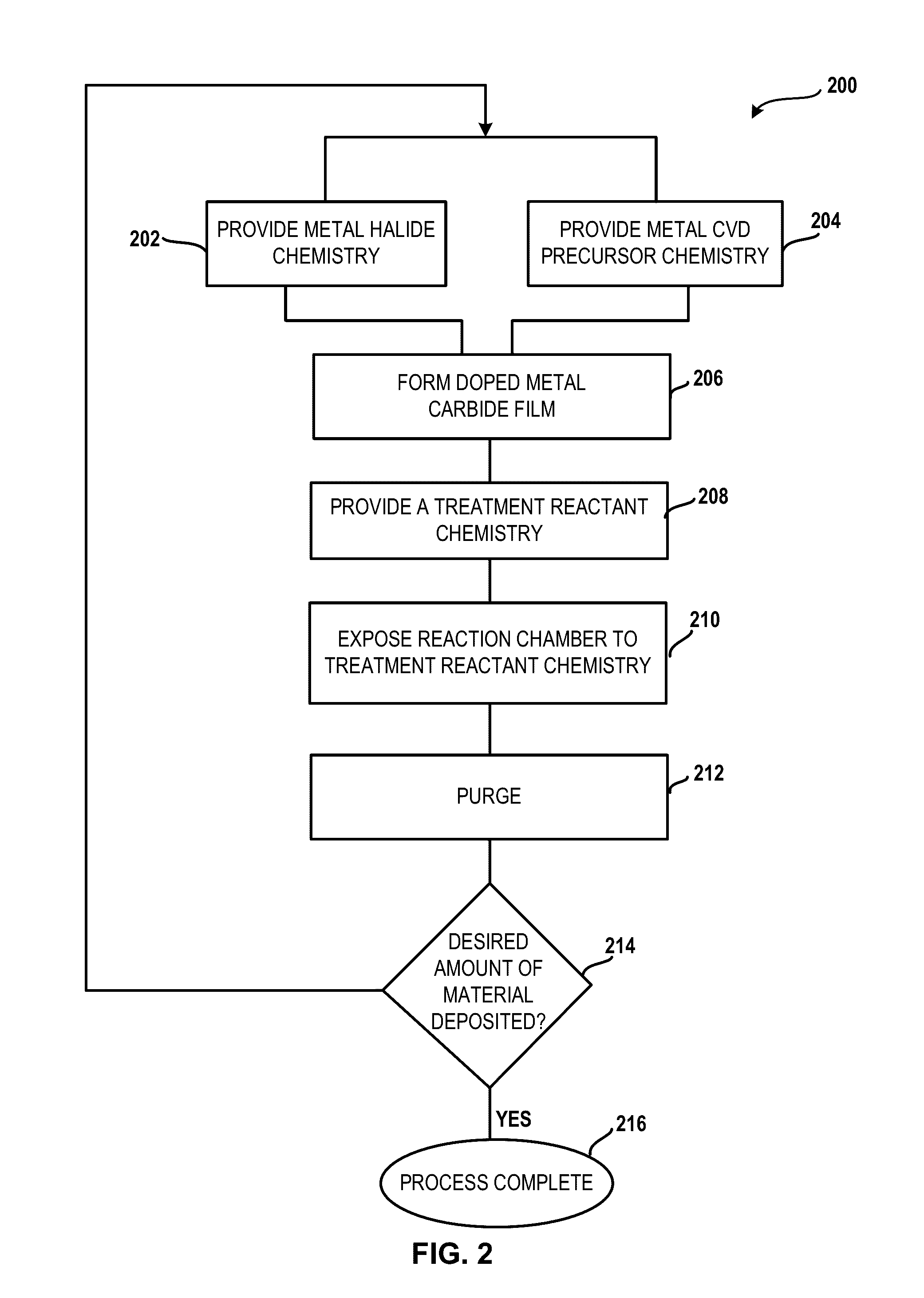
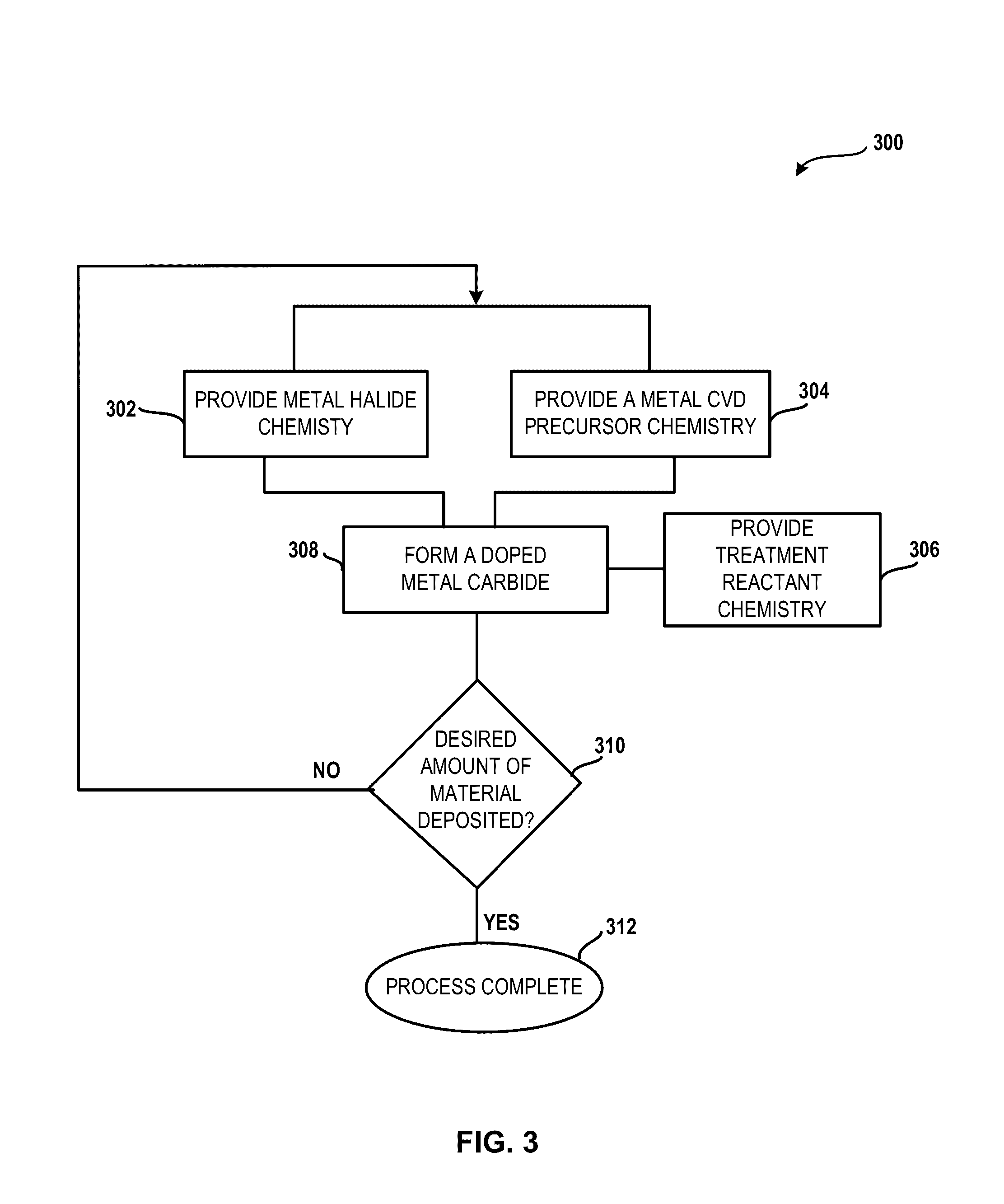
Method and system for treatment of deposition reactor
ActiveUS20140220247A1Substrate throughput can be increasedReduce operating costsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium carbideMetal membrane
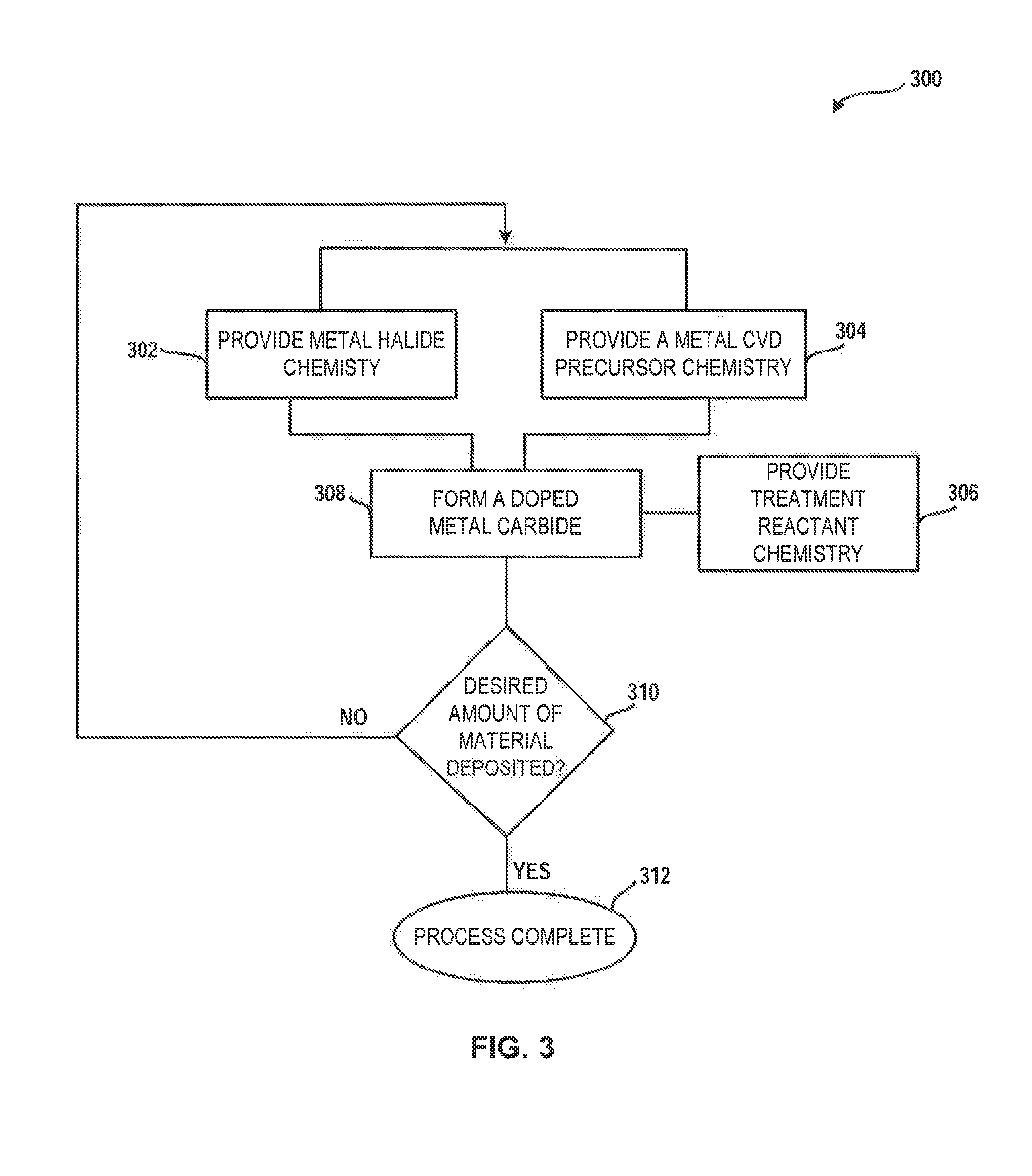
A system and method for treating a deposition reactor are disclosed. The system and method remove or mitigate formation of residue in a gas-phase reactor used to deposit doped metal films, such as aluminum-doped titanium carbide films or aluminum-doped tantalum carbide films. The method includes a step of exposing a reaction chamber to a treatment reactant that mitigates formation of species that lead to residue formation.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for producing carbon surface films by plasma exposure of a carbide compound
InactiveUS20060068125A1Reduce frictionEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingFlexible microstructural devicesCarbon filmCarbon coating
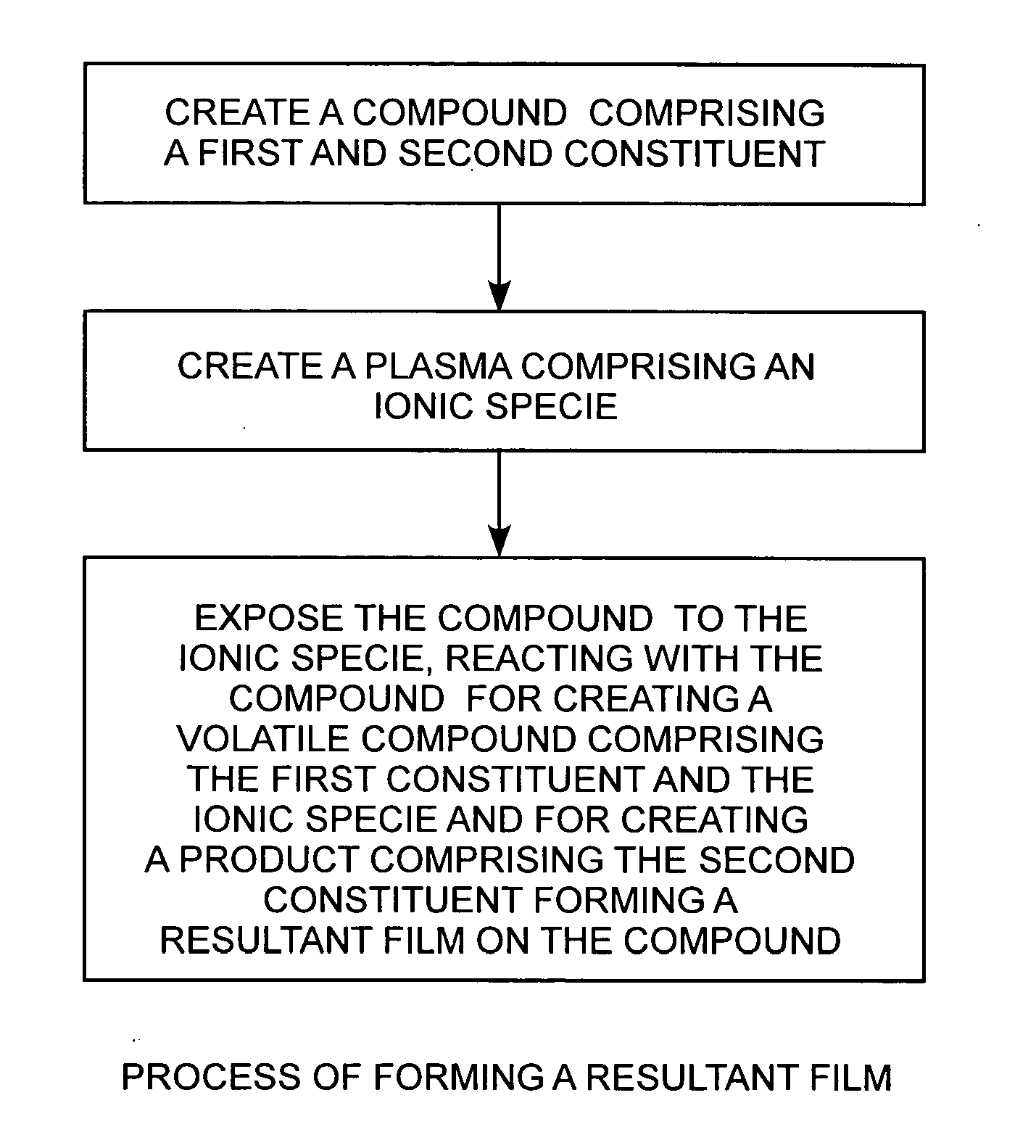
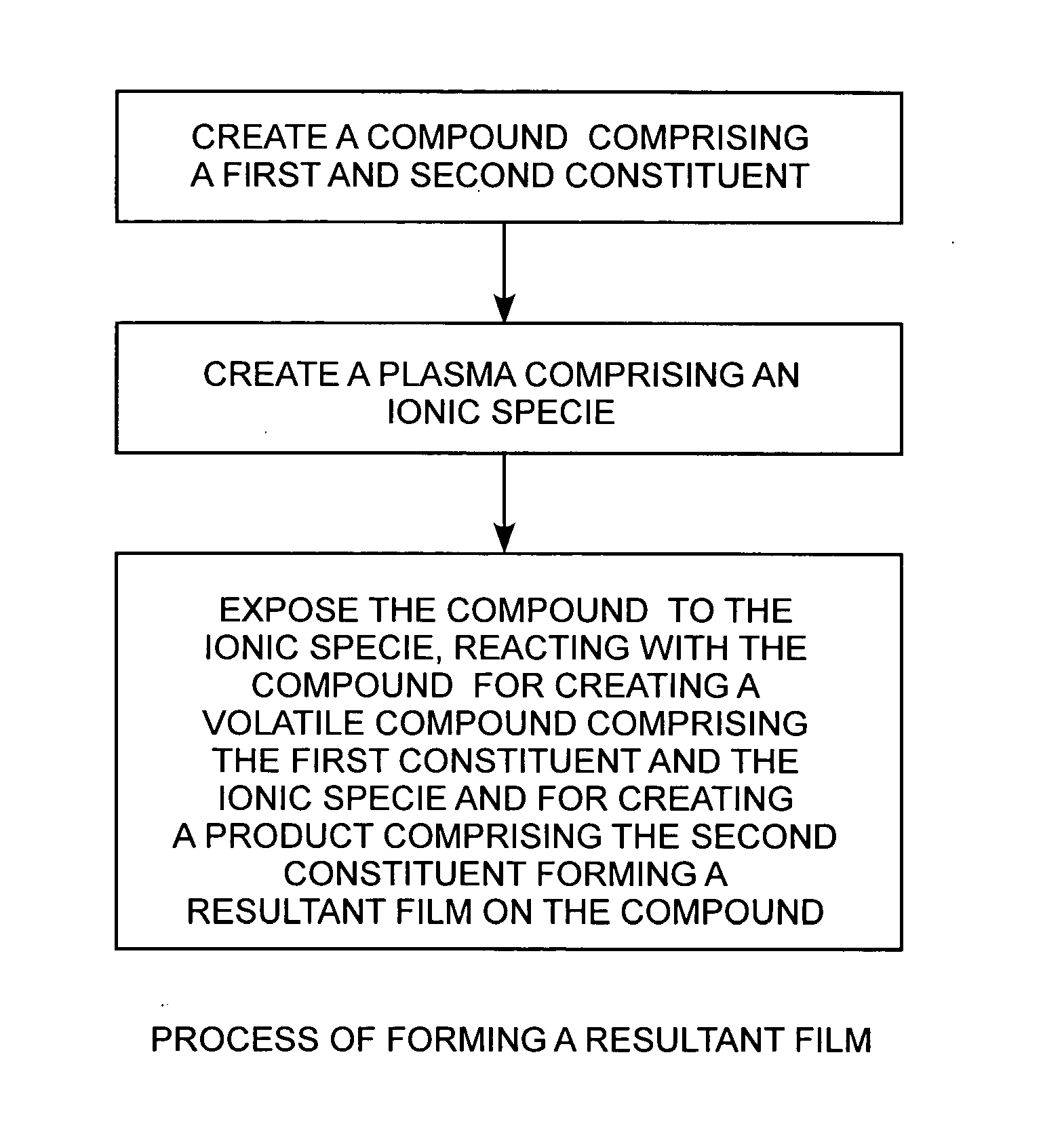
Reactive halogen-ion plasmas, having for example, generating chloride ions, generated from low-pressure halogen gases using a radio-frequency plasma are employed for producing low-friction carbon coatings, such as a pure carbon film, at or near room temperature on a bulk or thin film of a compound, such as titanium carbide.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
System for treatment of deposition reactor
InactiveUS20160376700A1Improve throughputReduce operating costsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseTitanium carbide
A system and method for treating a deposition reactor are disclosed. The system and method remove or mitigate formation of residue in a gas-phase reactor used to deposit doped metal films, such as aluminum-doped titanium carbide films or aluminum-doped tantalum carbide films. The method includes a step of exposing a reaction chamber to a treatment reactant that mitigates formation of species that lead to residue formation.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
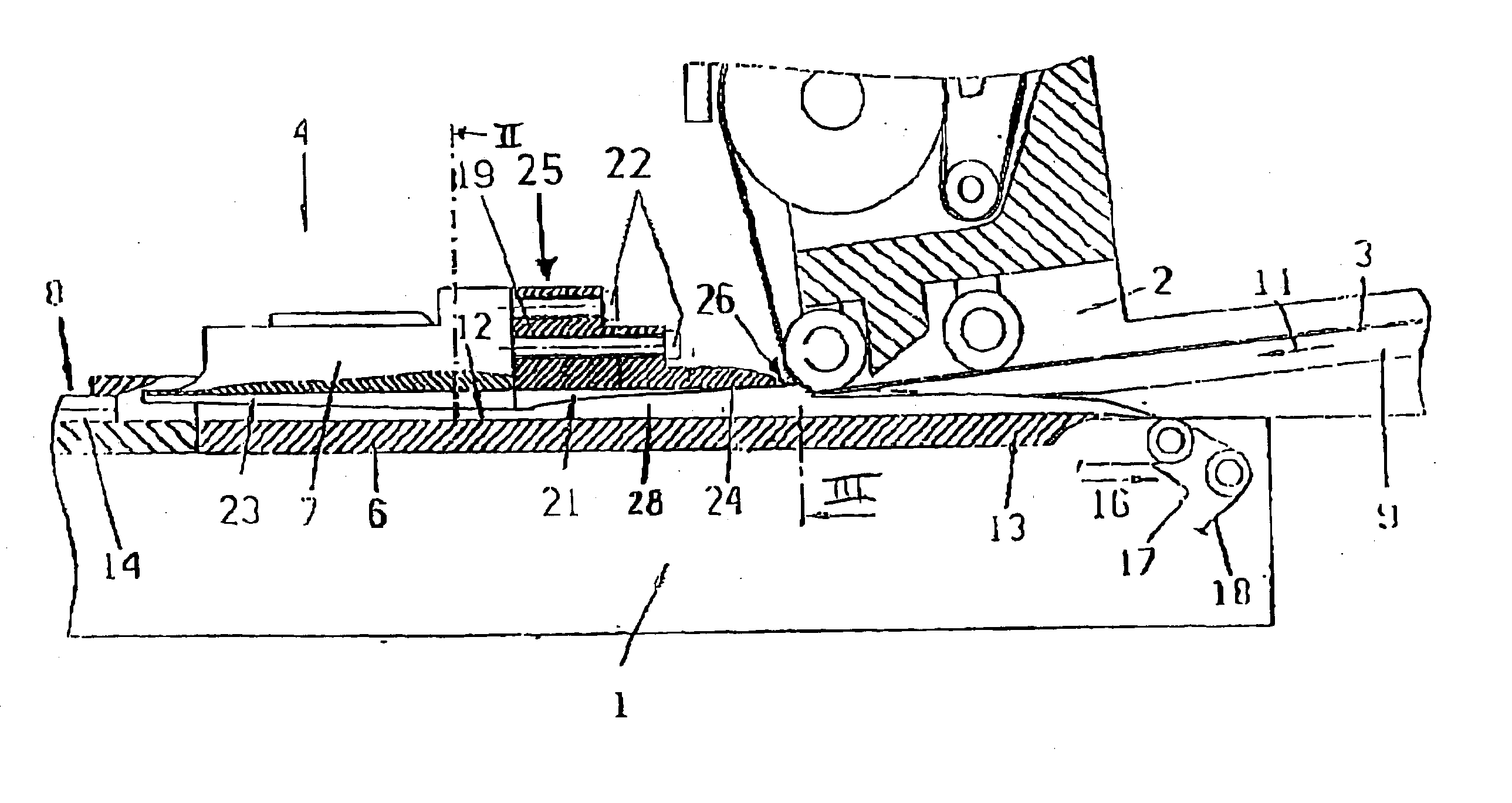
Garniture tongue of a garniture device
InactiveUS20030136419A1Reduce coefficient of frictionEasy to slideCigarette manufactureAlloyTitanium carbide
Garniture tongue of a garniture device of a rod machine arranged for compressing a material. The garniture tongue includes a rod guide surface and the garniture tongue being composed at least in part of a steel alloy with high titanium carbide content. The instant abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
Golf club and other structures, and novel methods for making such structures
InactiveUS6723279B1Overcome deficienciesImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingFiberHeavy particle
Golf club structures, including club heads and shafts, composed of composites comprised of a matrix of metal, such as an aluminum alloy, or a plastic material and a fiber such as graphite or a ceramic, which may be whiskerized, and which may also be selectively weighted as in the toe and heel of a club head, with heavy particles such as tungsten metal. The club structure may also be surface hardened by applying a coating of fullerenes to a metal club structure and heat treating it to produce a hard coating of metal carbide, preferably by coating a titanium golf club structure with fullerenes and heat treating the coated structure to produce a titanium carbide surface.
Owner:MATERIALS & ELECTROCHEM RES
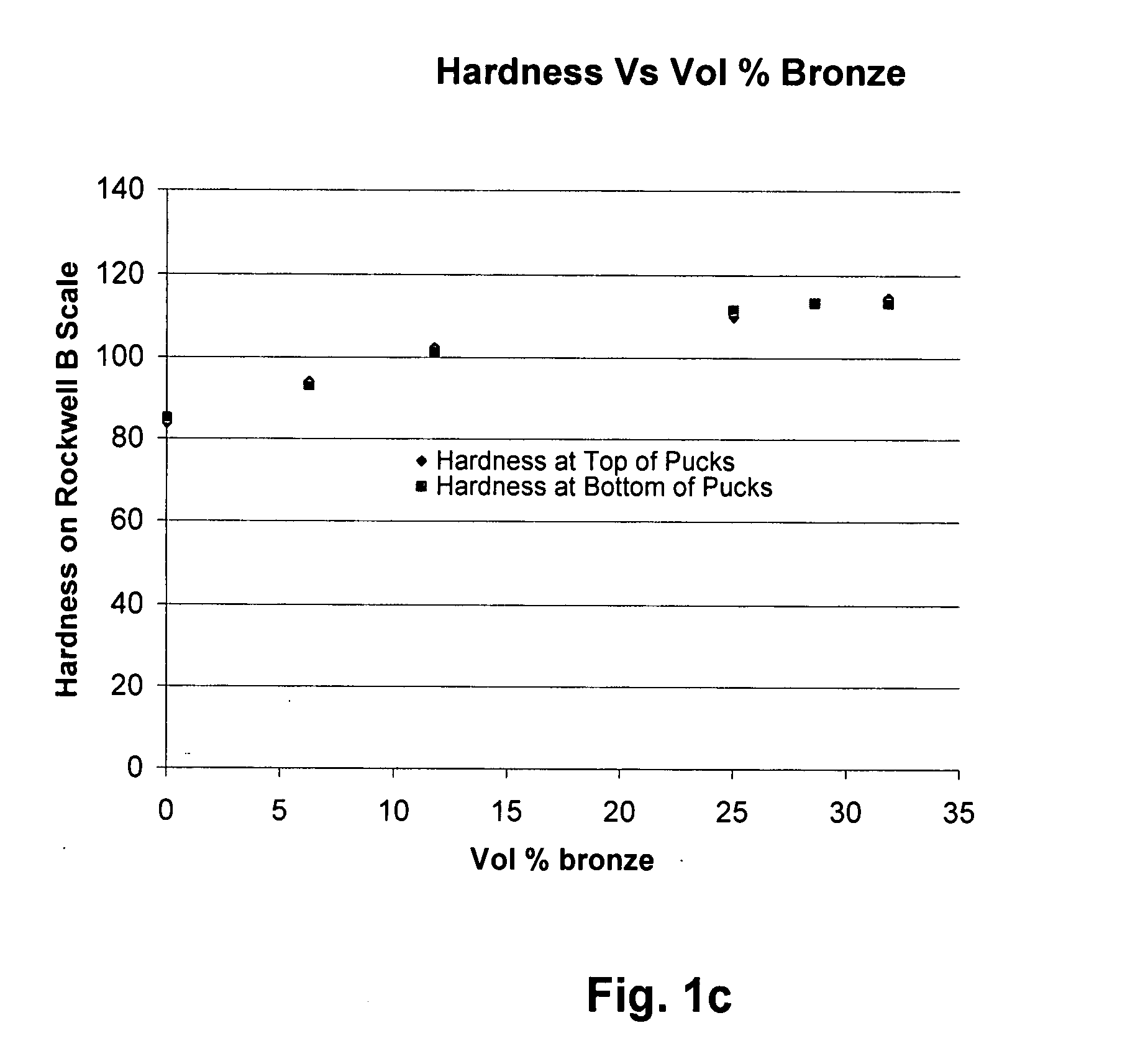
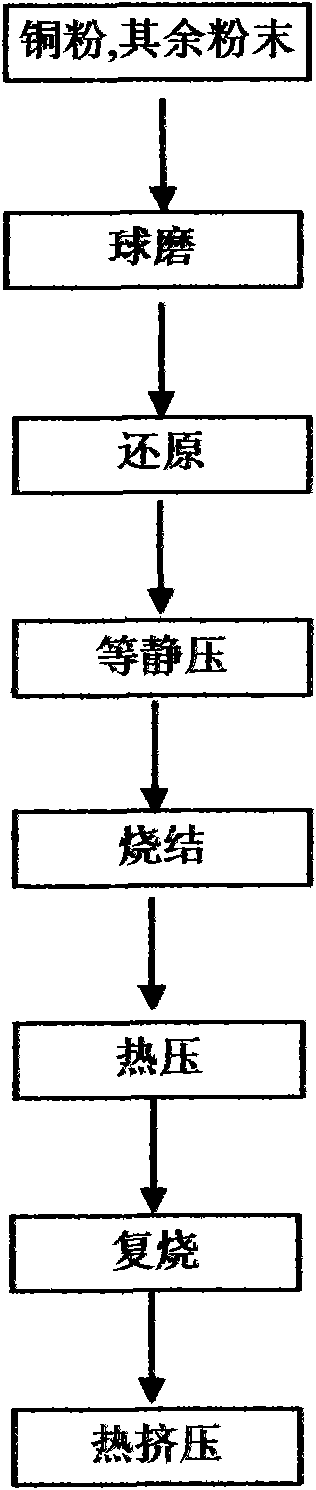
Short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a copper-based composite material, and particularly relates to a short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material which is prepared through powder metallurgy. Short fibers and particles are used as reinforced phases, the content of the short fiber is 0.1-0.1 wt%, and the content of reinforcement particles is 0.1-10 wt%. The short fibers can be carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, ceramic short fibers, and the like, and the particles used as reinforced phases can be aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, magnesium oxide, titanium dioxide, silicon carbide, titanium carbide, tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, titanium nitride, titanium diboride, Ti3SiC2, and the like. The composite material is prepared through the steps of mixing, forming, sintering and processing, and the room temperature and the high temperature strength of the composite material can be increased by more than 3 times in comparison with those of pure copper; the electrical conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 80% of that of pure copper; the thermal conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 70% of that of pure copper; the coefficient of friction of the composite material can be reduced to be below 70% of that of pure copper; and the wear rate of the composite material can be reduced to be below 50% of that of pure copper.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing graphene-like two-dimensional laminar titanium carbide nanoplate
InactiveCN104016345AHigh purityHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium carbideSem micrographsCrystallinity
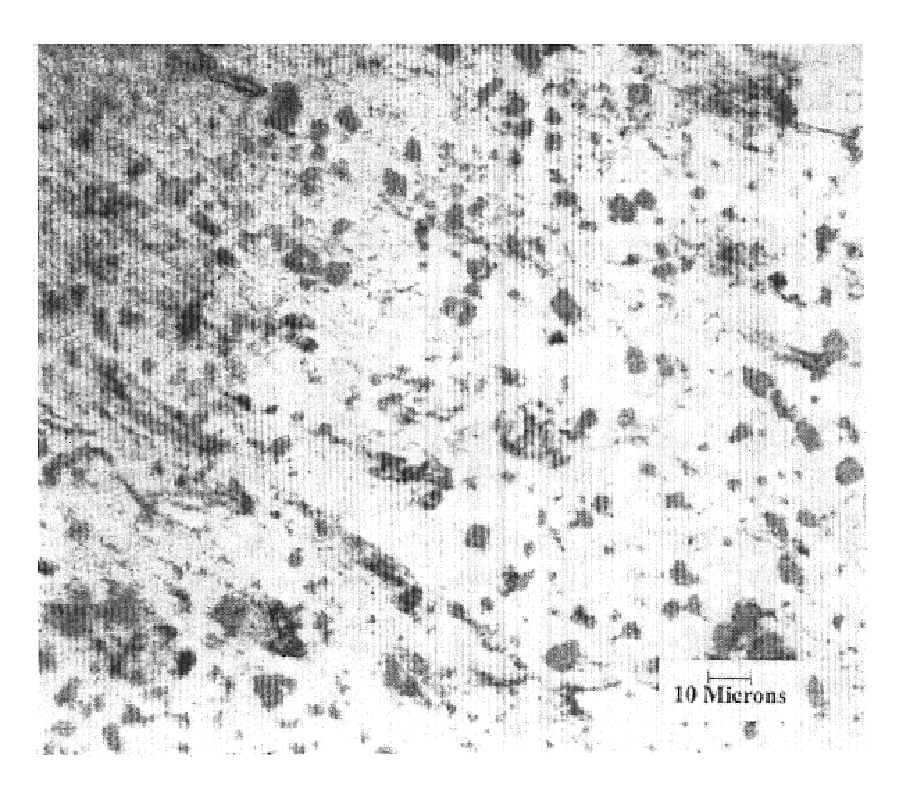
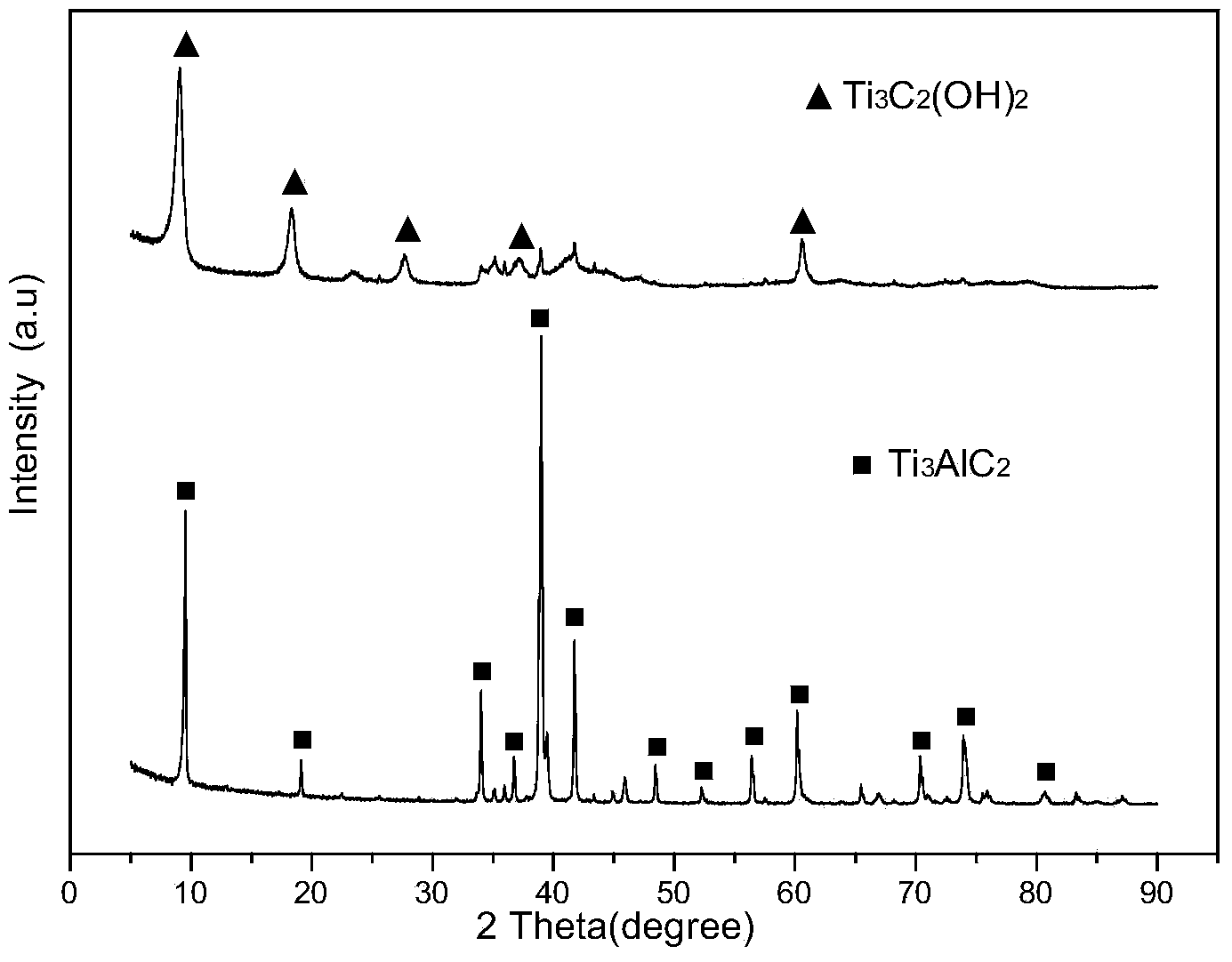
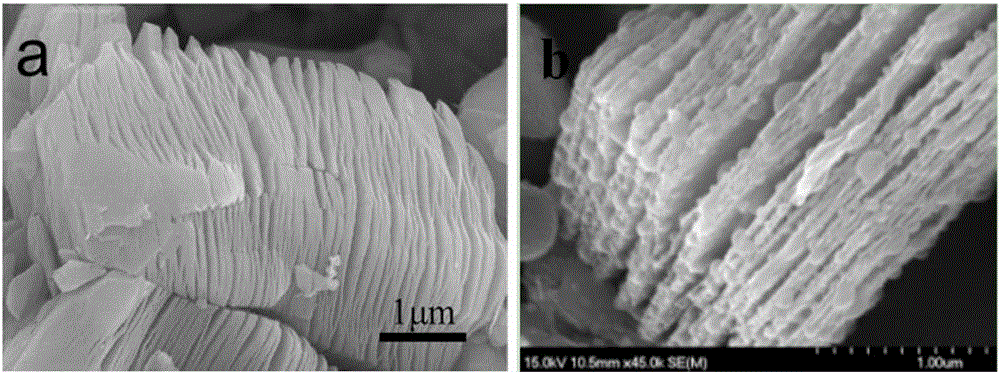
The invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene-like two-dimensional laminar titanium carbide nanoplate. The method comprises the following steps: preparing Ti3AlC2 powder by an in-situ hot-pressing solid-liquid reaction; preparing two-dimensional titanium carbide by a chemical liquid phase reaction; performing vacuum calcination post-treatment, and the like. The method can be used for preparing a Ti3AlC2 precursor with excellent crystallinity and high purity under simple process flow, stable process parameters, controllable process, high efficiency, low cost, short time and low pressure; the information that the transverse size of the two dimensional Ti3AlC2 nanoplate prepared by the method can be 5-10 microns, the average thickness of a single layer is about 10-20 nanometers can be found from an SEM picture, the inter-laminar spacing is remarkably enlarged after calcination treatment, and the laminar surface is regular and smooth.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Refractory high-entropy alloy/titanium carbide composite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite. A refractory high-entropy alloy serves as a matrix phase, and titanium carbide serves as a wild phase; and elements in the refractory high-entropy alloy are selected from at least four kinds of elements of W, Mo, Ta, Nb, V, Ti, Zr, Hf and Cr. A preparation method of the refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite comprises the steps that at least four kinds of carbonization metal powder in tungsten carbide, molybdenum carbide, tantalum carbide, niobium carbide, vanadium carbide, the titanium carbide, hafnium carbide, zirconium carbide and chromium carbide are selected and mixed according to the equal molar ratio or the ratio close to the equal molar ratio to form high-entropy matrix powder; and after the high-entropy matrix powder and titanium powder are mixed, alloy mechanization is carried out, then spark plasma sintering or hot-press sintering is carried out, and the refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite is obtained. The density and cost of the composite are reduced while the hardness of the composite is improved, excellent high-temperature performance is achieved, and the requirement for manufacturing a high-temperature structural component is met.
Owner:江西咏泰粉末冶金有限公司
Method for making a semiconductor device having a high-k gate dielectric and a titanium carbide gate electrode
InactiveUS7064066B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSufficient time
A method for making a titanium carbide layer is described. That method comprises alternately introducing a carbon containing precursor and a titanium containing precursor into a chemical vapor deposition reactor, while a substrate is maintained at a selected temperature. The reactor is operated for a sufficient time, and pulse times are selected for the carbon containing precursor and the titanium containing precursor, to form a titanium carbide layer of a desired thickness and workfunction on the substrate.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Pure titanium production from titanium monoxide/titanium carbide soluble solid anode electrolysis
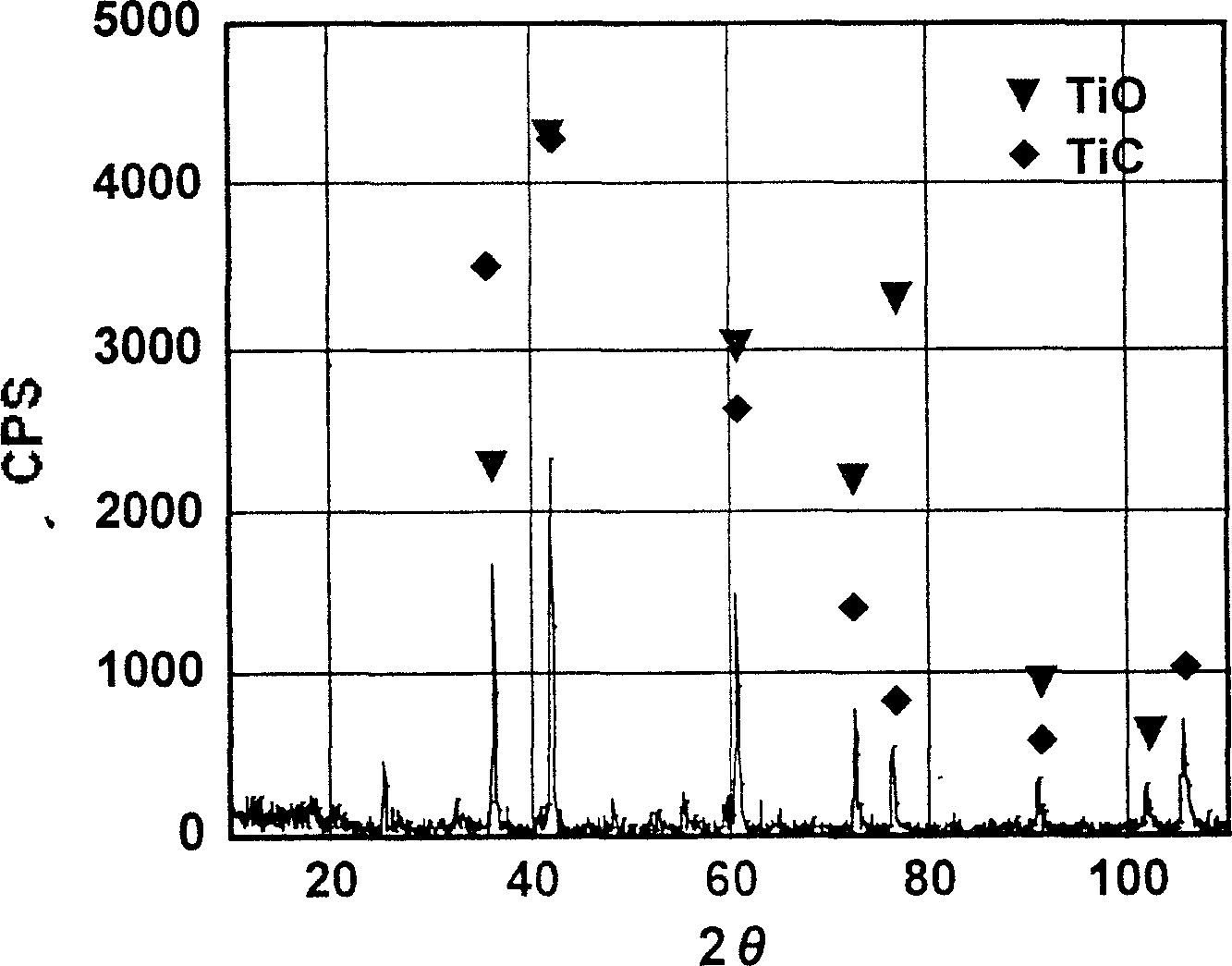
A process of preparing purified Ti by the way of electrolysis directly from sosoloid positive pole, TiO?mTiC. Mix the powder of C and TiO2 or TiC as measurement of chemical reaction. Then press to be certain size to make positive pole, TiO?mTiC in airvoid at 600-1600íµ. Electrolyte is halide fused salt of alkali. Electrolysis at 400-1000íµ. C and O in the positive pole form CO, CO2 and O2. Purified Ti is obtained from negative pole.
Owner:鸿钛(北京)科技有限公司
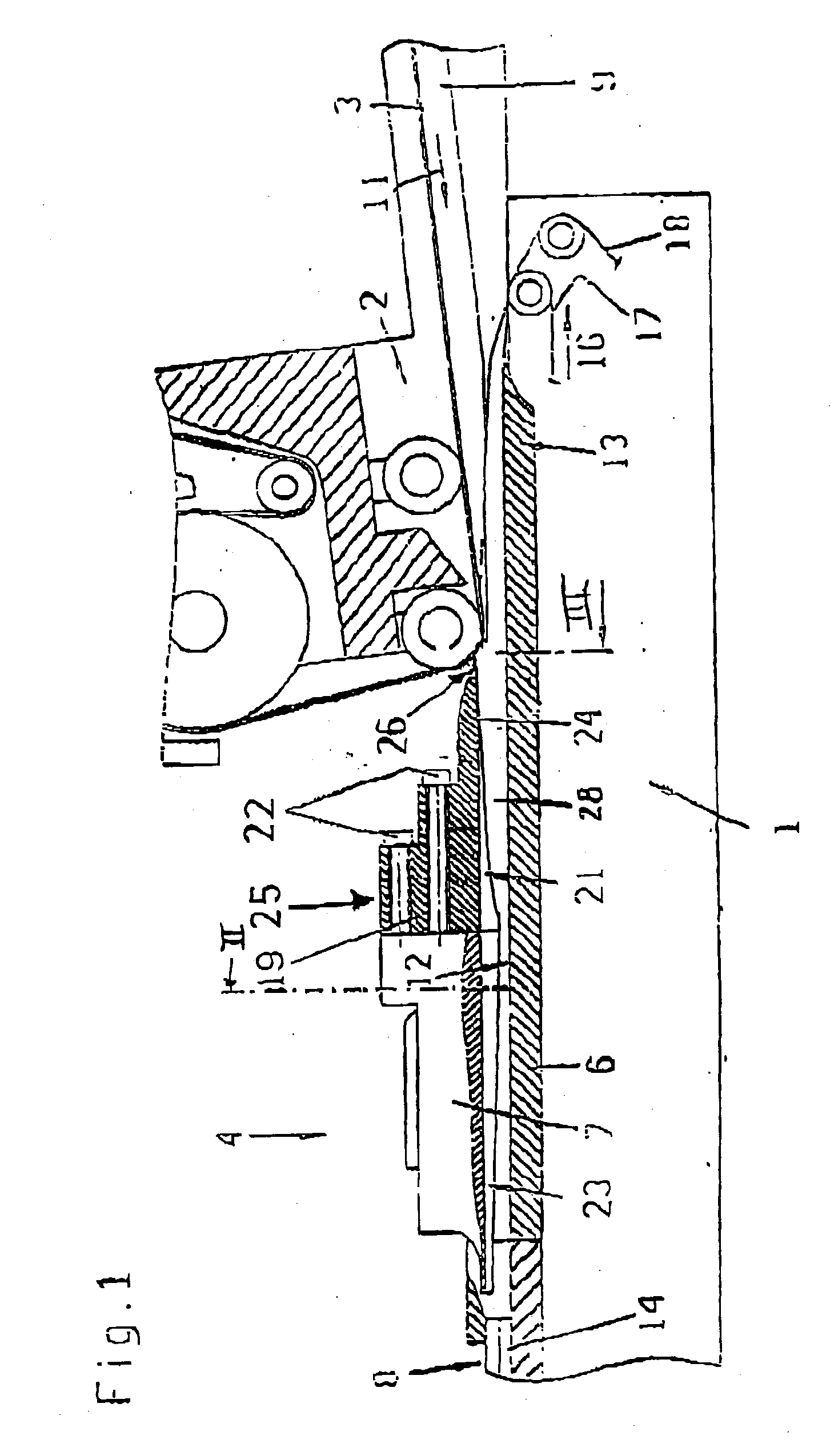
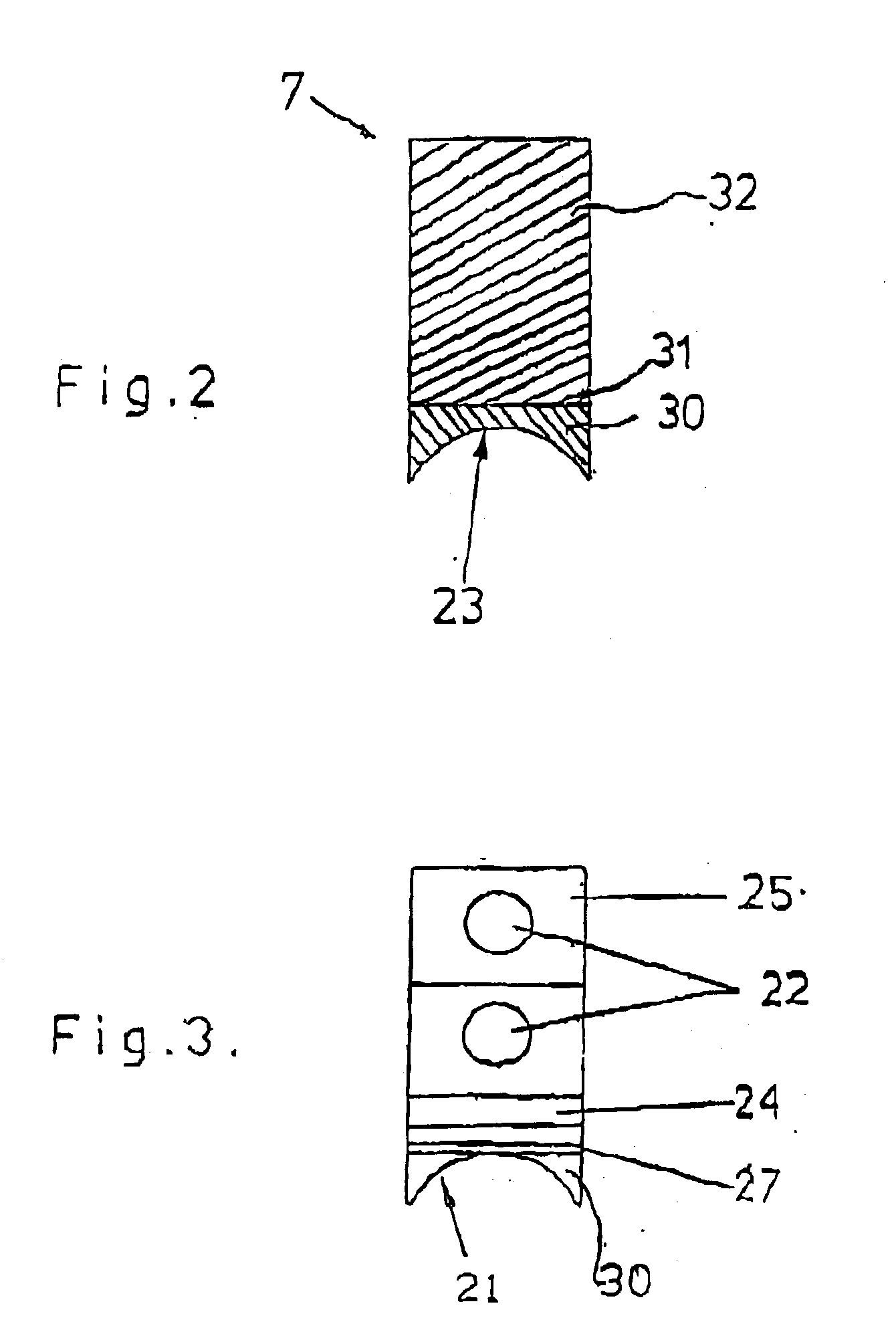
Friction stir welding tool
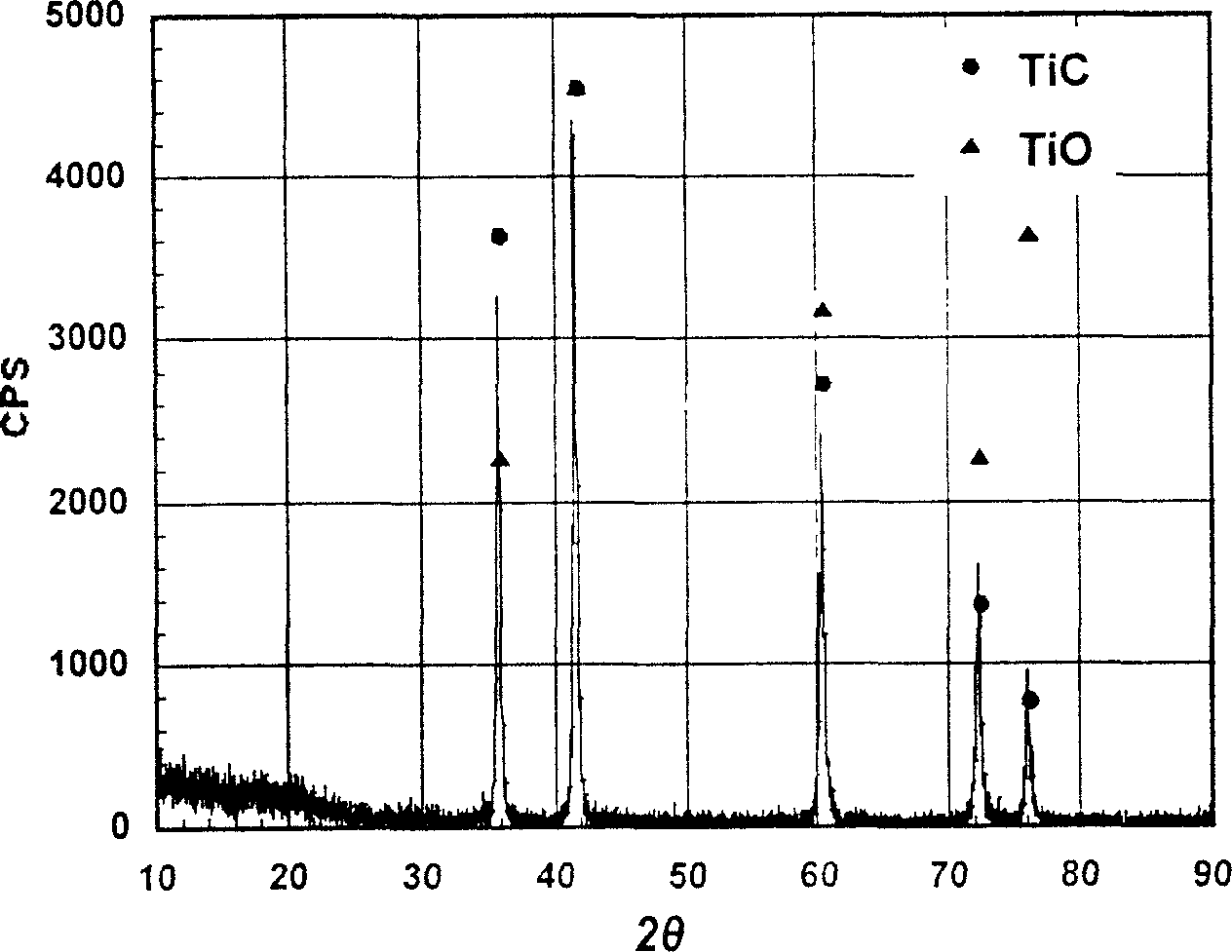
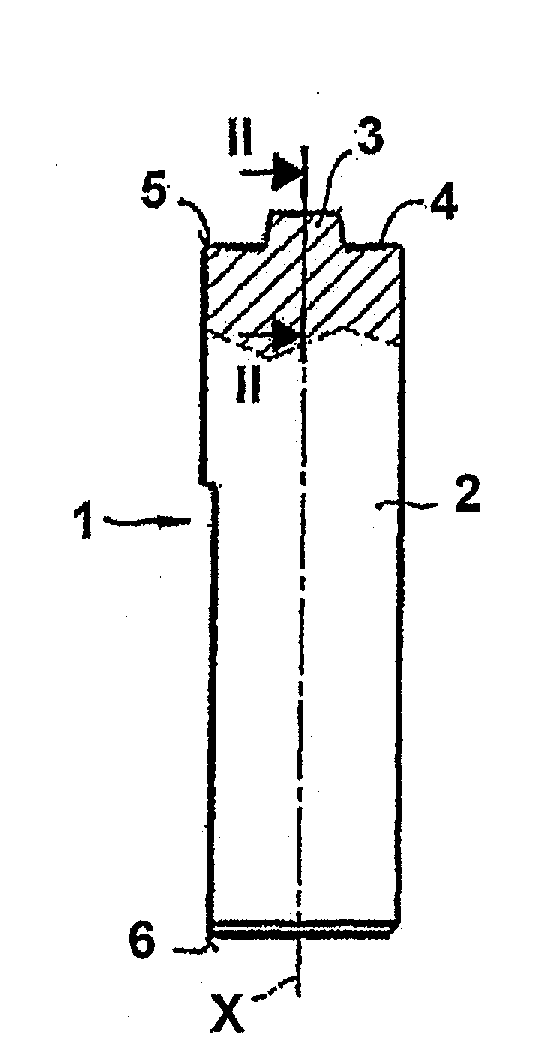
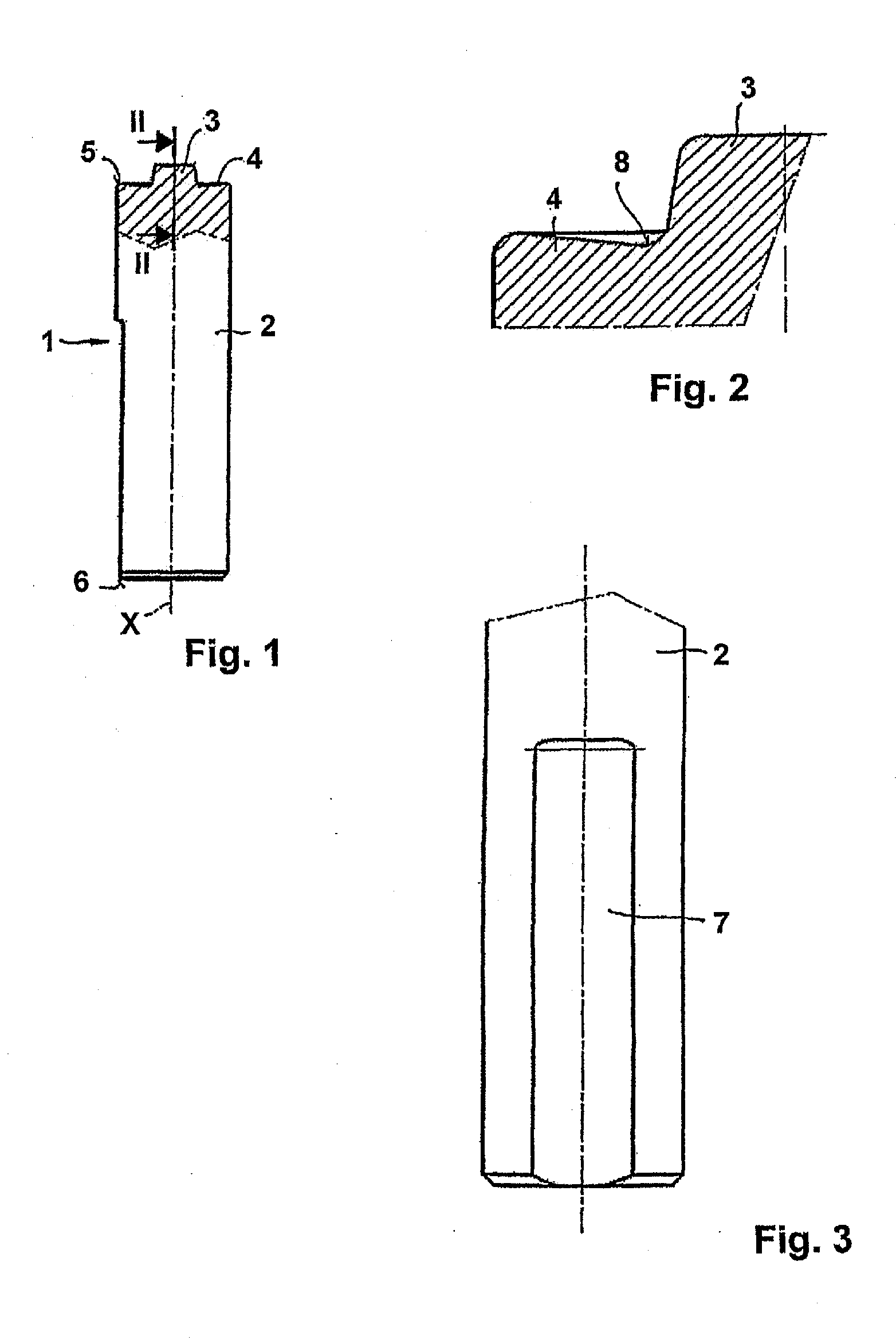
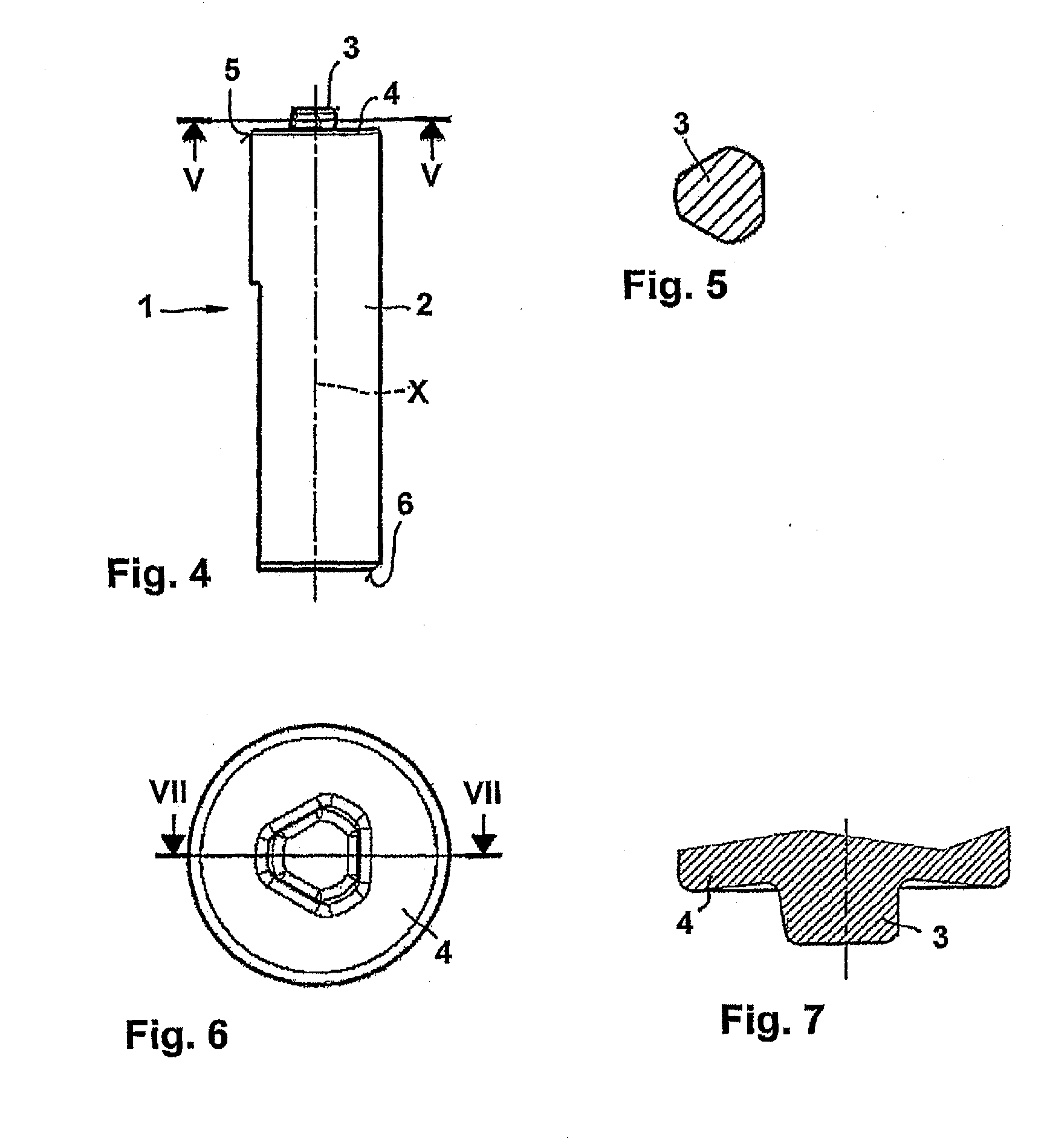
InactiveUS20100258612A1Easy to useReduce sensitivityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesHard metalTitanium carbide
The invention relates to a friction stir welding tool (1) with an essentially cylindrical shank (2), which has a peg (3) with a smaller diameter projecting on one end (5) starting from a shoulder region (4) of the shank (2). According to the invention it is provided in order to create a friction stir welding tool (1) for welding steel, that the friction stir welding tool (1), at least in the region of the peg (3) and in the shoulder region (4), is made of a hard metal containing 80% by weight to 98% by weight tungsten carbide with an average grain size of more than 1 μm and up to 20% by weight cobalt as well as optionally a total of up to 18% by weight titanium carbide, tantalum carbide, niobium carbide and / or mixed carbides thereof and at least in one of the referenced regions has a coating of one or more layers.
Owner:BOEHLERIT GMBH & CO KG
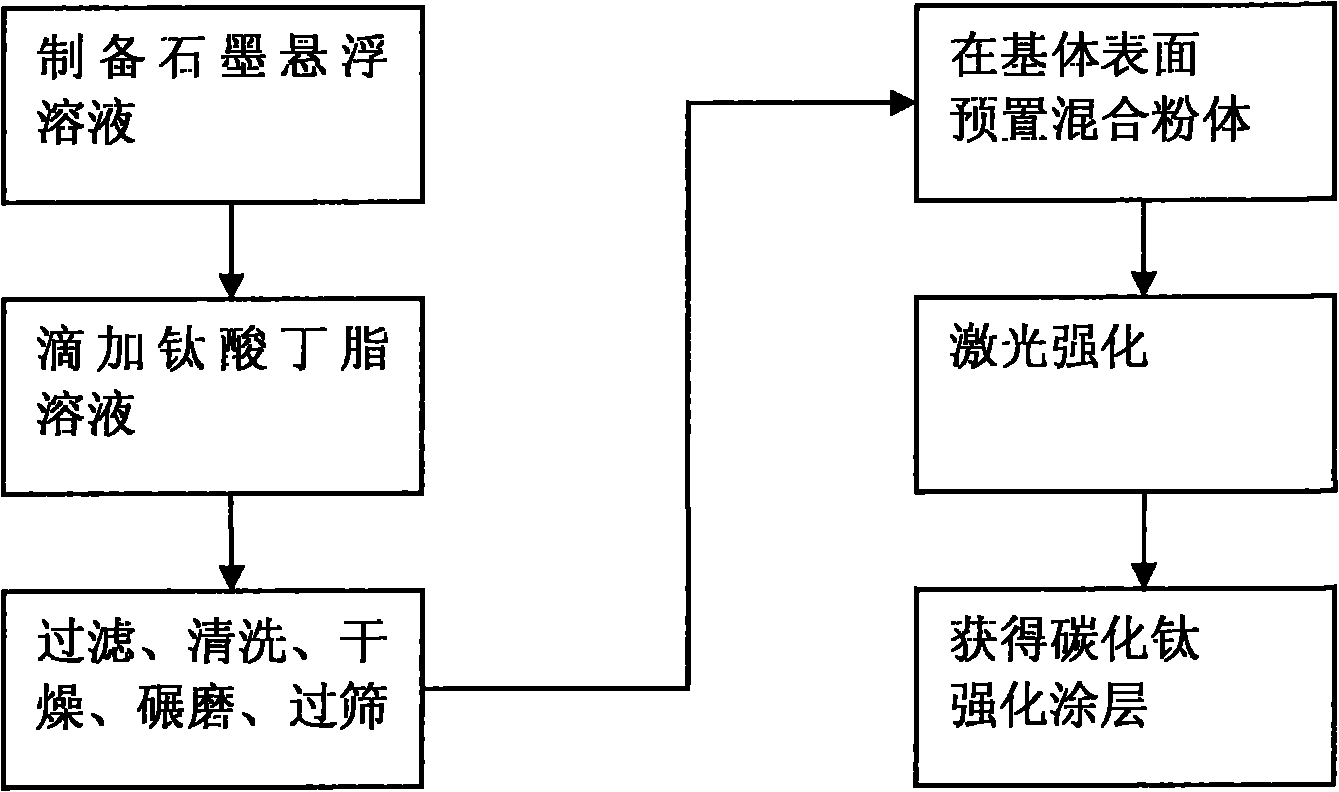
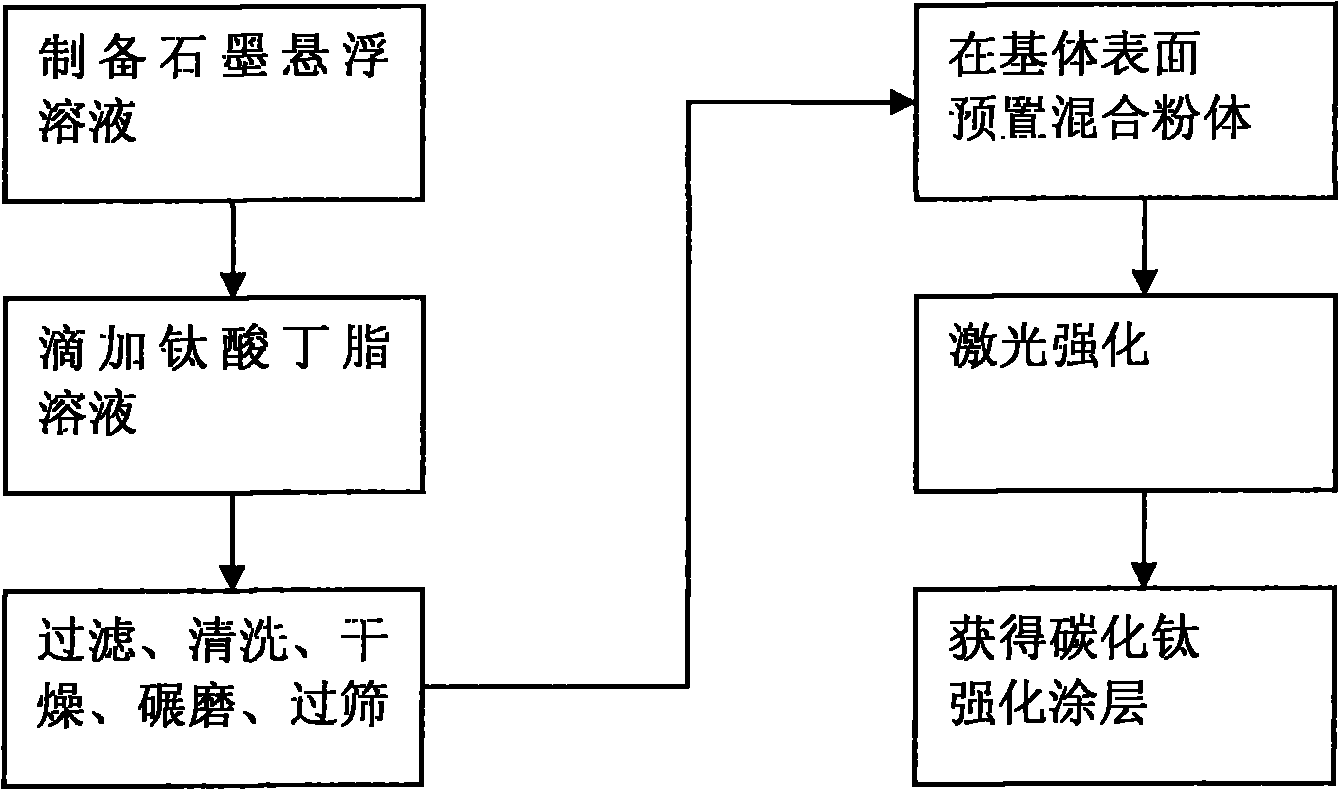
Method for preparing metal surface laser strengthened coat
InactiveCN101812684AIncrease profitImprove the strengthening effectMetallic material coating processesChemical reactionArgon atmosphere
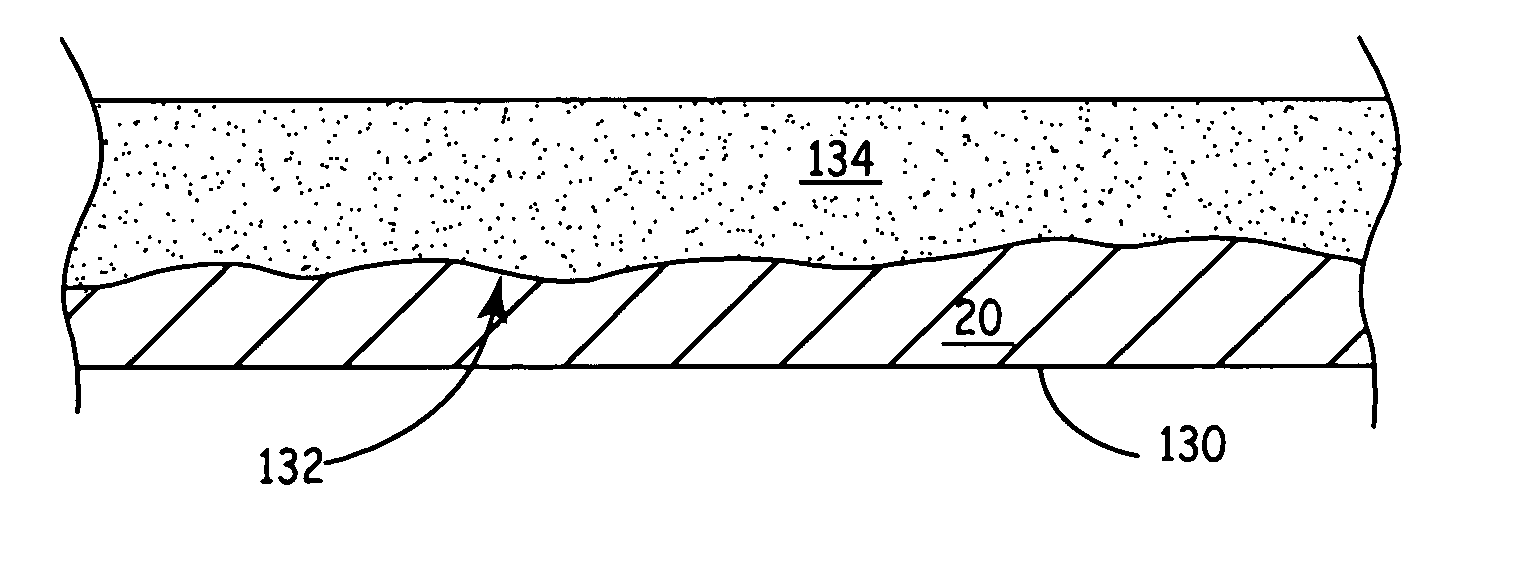
The invention discloses a method for preparing a metal surface laser strengthened coat, which comprises the following steps: preparing uniformly mixed powder of titanium dioxide hydrate and graphite powder by using a wet chemistry method; pre-placing the mixed powder on the surface of a basal body; and irradiating the surface of the basal body by using laser as a heat source under an argon atmosphere to form a molten pool, performing a carbon-thermal chemical reaction on the pre-placed mixed powder under a high-temperature environment to generate titanium carbide, and finally forming a titanium carbide composite coat on the surface of the basal body. In the same way, the method is also suitable for preparing a TiN enhanced composite coat by mixing hydrated oxide thereof and graphite by the wet chemistry method, then mixing the mixture and urea to form pre-placed powder and cladding the pre-placed powder on the basal body by laser. The surface of the enhanced coat prepared by the technical scheme is smooth, and has no cracks or pores; enhancing particles are uniformly distributed in the coat; the enhanced coat and the basal body are metallurgically combined; and the mixed powder prepared by adopting the wet chemistry method is uniformly mixed, ensures complete reaction, and is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:姚建华
Abrasive processing of hard and /or brittle materials
ActiveUS20090084042A1Slow feed ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesManufacturing technologyTitanium carbide
Abrasive articles possessing a highly open (porous) structure and uniform abrasive grit distribution are disclosed. The abrasive articles are fabricated using a metal matrix (e.g., fine nickel, tin, bronze and abrasives). The open structure is controlled with a porosity scheme, including interconnected porosity (e.g., formed by leaching of dispersoid), closed porosity (e.g., induced by adding a hollow micro-spheres and / or sacrificial pore-forming additives), and / or intrinsic porosity (e.g., controlled via matrix component selection to provide desired densification). In some cases, manufacturing process temperatures for achieving near full density of metal bond with fillers and abrasives, are below the melting point of the filler used, although sacrificial fillers may be used as well. The resulting abrasive articles are useful in high performance cutting and grinding operations, such as back-grinding silicon, alumina titanium carbide, and silicon carbide wafers to very fine surface finish values. Techniques of use and manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
Multiple dispersion strengthening copper-base composite material prepared in situ and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101613816APromote generationImprove organizational structureTitanium carbideSelf generation
The invention discloses a multiple dispersion strengthening copper-base composite material produced in situ and a preparation method thereof; the reinforced phase comprises at least three of the following substances: titanium carbide, zirconium carbide, alumina, titanium boride, aluminum carbide, chromium oxide, zirconia, graphite and copper; wherein, the contents of titanium carbide, zirconium carbide, alumina, titanium boride, chromium oxide and zirconia are not less than 0.3% and not more than 5%, the content of aluminum carbide is not less than 0.1% and not more than 5%, the content of graphite is not less than 0.1% and not more than 1% and the balance is copper. The particle size of the reinforced phase is between 10nm to 10mu m. The preparation method adopts ball milling; pressing, sintering and squeezing processes and the technological parameters are optimized and controlled properly to obtain the multiple dispersion strengthening copper-base composite material. Because the in situ self-generation technology is adopted and various reinforced phase methods are combined, the material of the invention has higher high-temperature strength and better electroconductibility and anti-creep property compared with the traditional ceramic particle strengthening copper-base composite material.
Owner:WENZHOU HONGFENG ELECTRICAL ALLOY
Method of in situ synthetic steel bond hard alloy casting composite hammerhead and hammerhead
A method of an in situ synthetic steel bond hard alloy casting composite hammerhead adopts a vacuum lost foam casting technology, wherein Ti powder, graphite powder, W powder and metal powder are mixed, and are added with an adhesion agent to produce a powder coating paste, the powder coating paste is filled in a reinforcement groove or a hole of a working part of an expanded poly styrol (EPS) foaming plastic modal of a hammerhead casting, during the pouring process, the high temperature of liquid steel is utilized to initiate the self propagating synthesis reaction, the reactions of Ti plus C->TiC and W plus C->WC are carried out, so the TiC and WC-based hard alloy phases are formed, the liquid steel is filled into the clearance of a hard phase, so an in situ synthetic titanium carbide and tungsten carbide steel bond hard alloy is obtained, and the hard alloy is embedded in the steel base body of the working part of the hammerhead. When the hammerhead which is produced through the method of the in situ synthetic steel bond hard alloy casting composite hammerhead is used, because the hard alloy and the casting are completely, metallurgically and firmly combined together, the hammerhead has high wear resistance and impact resistance during the use, has a simple technological process, low production cost, and is applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:KING STRONG MATERIAL ENG LTD
Ceramic cladding powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101423398AThere will be no phenomenon of grain aggregation and growthEvenly distributedCeramic coatingTitanium nitride
The invention relates to ceramic coating powder the ceramic phase of which is coated by a metallic phase cobalt or / and a metallic phase nickel. The metallic phase cobalt and the metallic phase nickel are obtained by means of a liquid phase reduction method; and the ceramic phase is at least one of titanium carbonitride, titanium carbide, titanium nitride, tungsten carbide, silicon carbide, niobium carbide, tantalum carbide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, magnesium oxide, boron nitride and silicon nitride. A method for preparing the ceramic coating powder is the liquid phase reduction method to carry out a reduction reaction between cobalt or / and nickel ions in a plating solution to generate the metallic phase cobalt or / and nickel which is deposited on the surface of a ceramic core to form the ceramic coating powder; and the process steps are as follows: (1) pre-treatment of the ceramic powder; (2) preparation of the plating solution; (3) liquid-phase reduction reaction; and (4) plating post treatment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in refractory metals and refractory metal carbides coated graphite molds under vacuum
InactiveUS20050016706A1Quality improvementImprove mechanical propertiesCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsSuperalloyTitanium carbide
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with a refractory metal such as W or Re or a refractory metal carbide such as TaC or HfC. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with titanium carbide via either chemical deposition or plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition, magnetron sputtering or sputtering. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU AMERICA
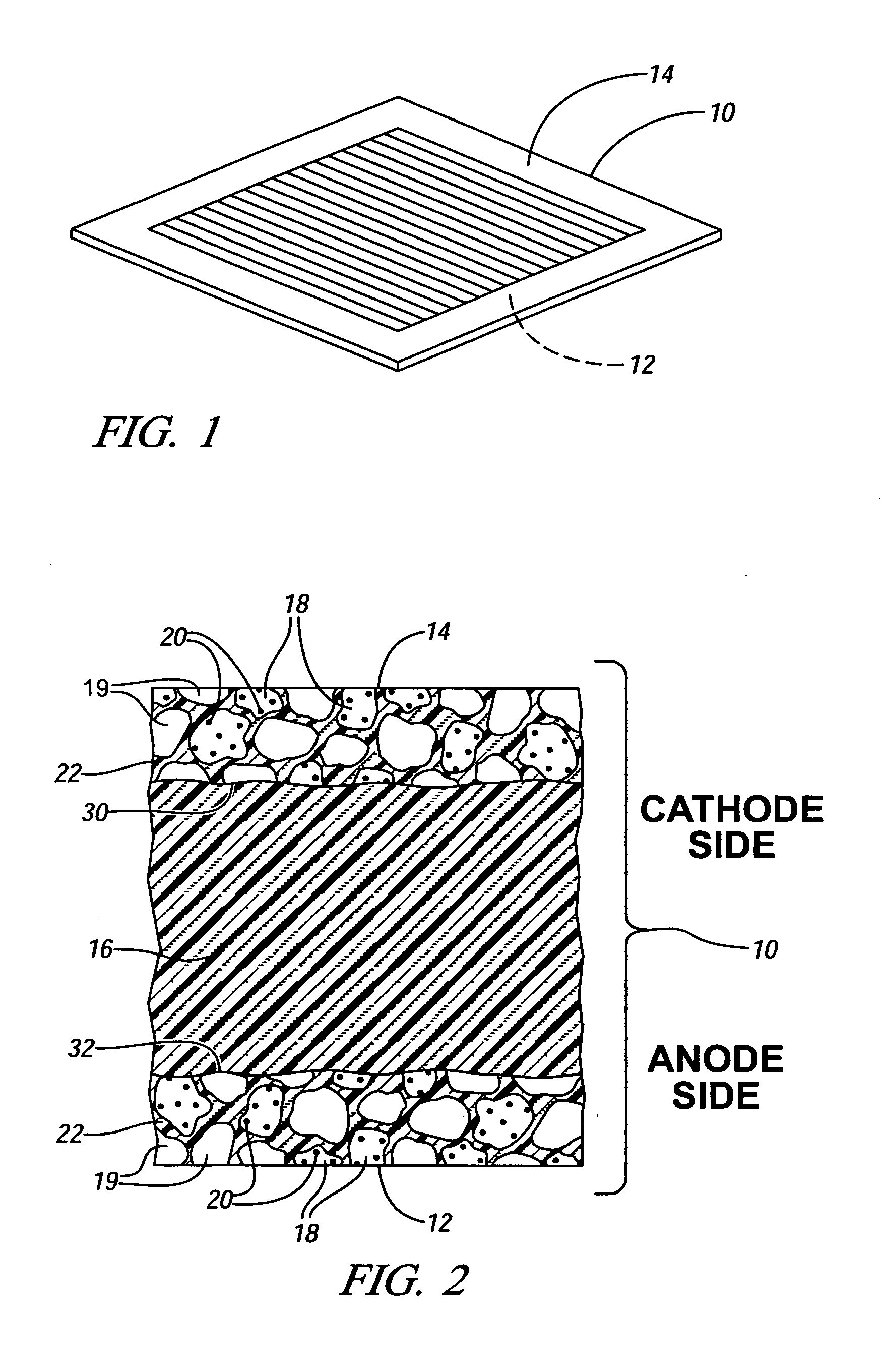
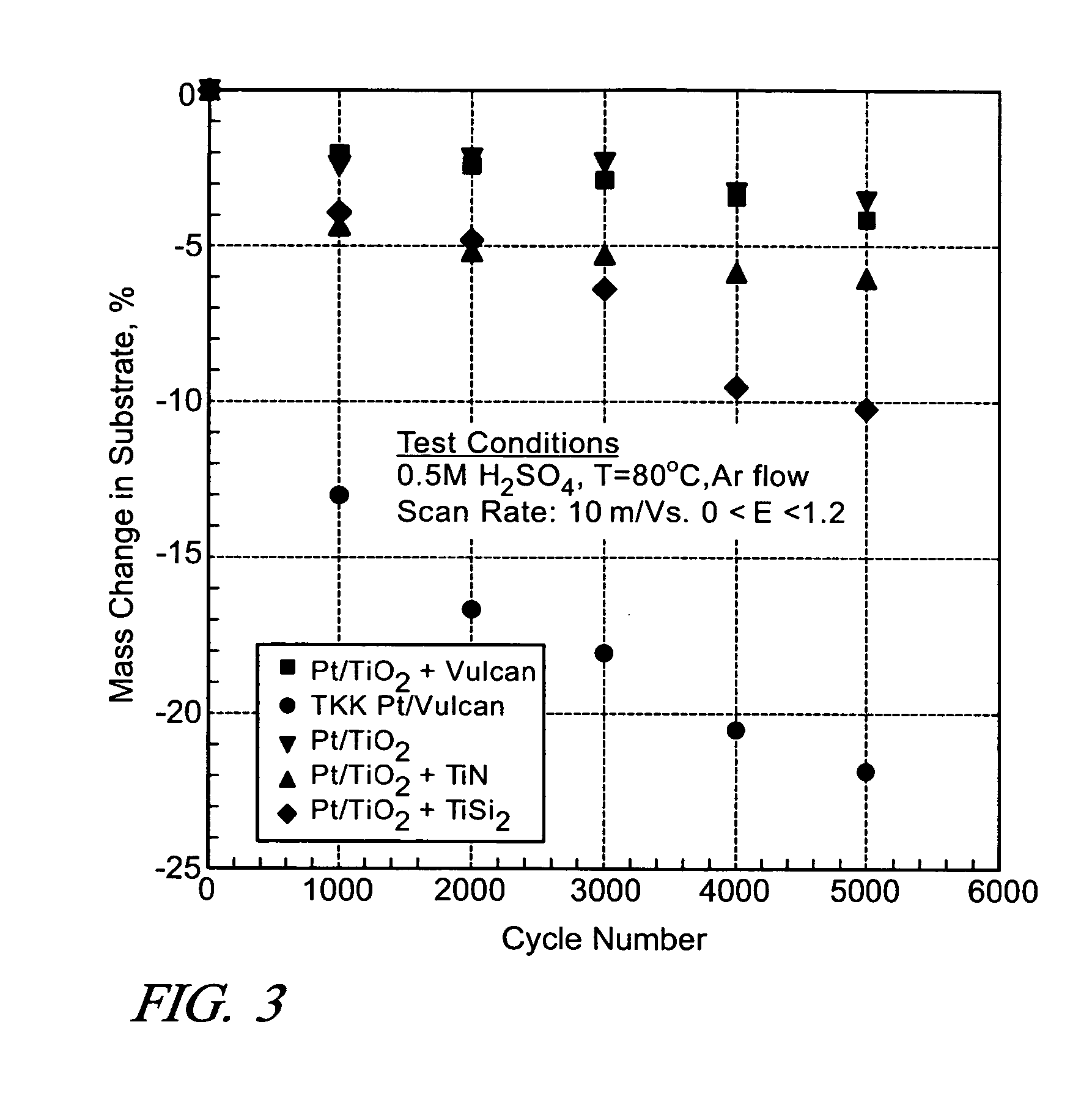
Conductive matrices for fuel cell electrodes
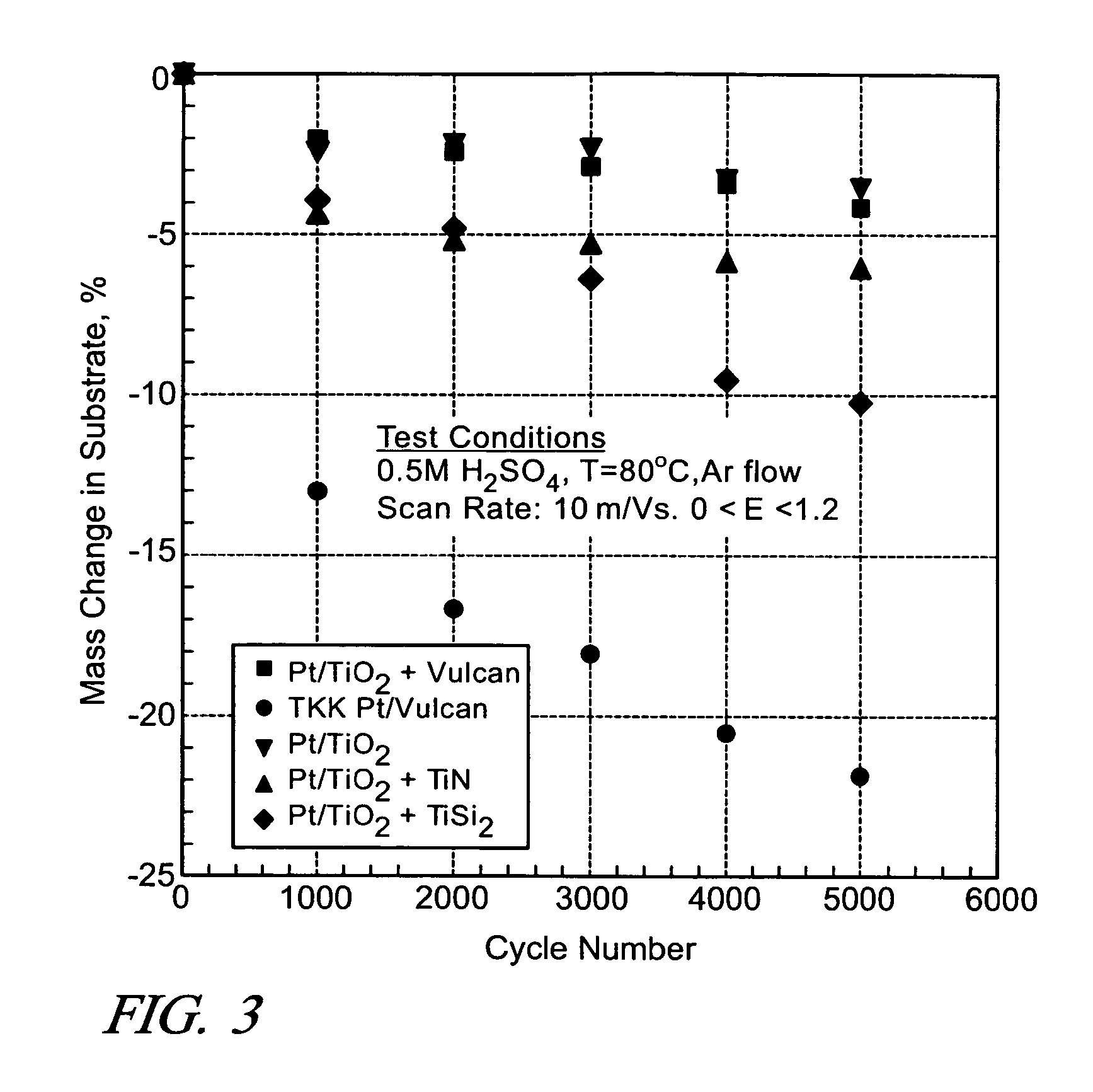
InactiveUS20060251954A1Enhanced catalytic behaviorIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyActive material electrodesTungstenTitanium carbide
The durability of a fuel cell having a polymer electrolyte membrane with an anode on one surface and an oxygen-reducing cathode on the other surface is improved by replacing conductive carbon matrix materials in an electrode with a matrix of electrically conductive metal compound particles. The electrode includes a catalyst supported on a nanosize metal oxides and electrically conductive nanosize matrix particles of a metal compound. One or more metal compounds such as a boride, carbide, nitride, silicide, carbonitride, oxyboride, oxycarbide, or oxynitride of a metal such as cobalt, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, neodymium niobium, tantalum, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zirconium is suitable. For example, the combination of platinum particles deposited on titanium dioxide support particles mixed in a conductive matrix of titanium carbide particles provides an electrode with good oxygen reduction capability and corrosion resistance in an acid environment.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Antimicrobial ceramic cutting tool and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN101269961AImprove antibacterial propertiesGood antibacterial effectTitanium nitrideUltra fine
The present invention provides an antibacterial ceramic cutting tool and belongs to the technological field of fine ceramics. The present invention comprises ingredients and is characterized in that the ceramic cutting tool is essentially made of fine ceramic material that is used as the main raw material, and 1.5 to 5 weight percent of antibacterial material. The fine ceramic material can be selected from ultra-fine zirconia powder, ceylon ceramic materials, alumina or silicon nitride that is used for plasticizing the ceramic materials, and metal ceramic materials such as titanium carbide or titanium nitride. The application of antibacterial ingredients in the fine ceramic material has resulted in the antibacterial and bacteriostatic properties of fine ceramic products. Further the ceramic cutting tool of the antibacterial function can be prepared.
Owner:淄博博纳科技发展有限公司
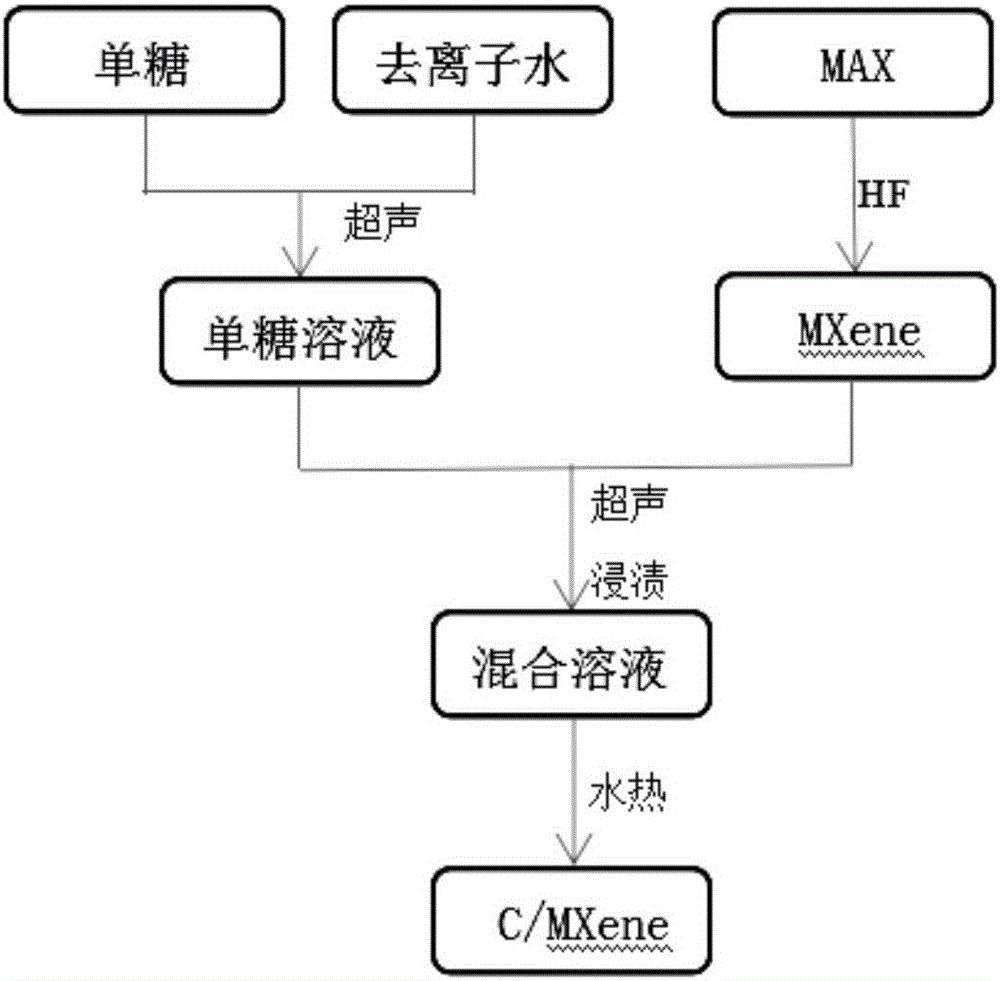
Method for preparing carbon nanoparticle/two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material
InactiveCN106185937AImprove mechanical propertiesSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologyHydrofluoric acidSupercapacitor
The invention relates to a method for preparing a carbon nanoparticle / two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material. The method includes the steps that a two-dimensional layered titanium carbide nano material MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) is prepared through hydrofluoric acid corrosion; the material MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) and monosaccharide are processed through ultrasonic treatment, vacuum impregnation, hydrothermal treatment and other steps, so carbon nanoparticles are generated between layers and on the surface of the MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) material, and the carbon nanoparticle / two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material is obtained. Raw materials which are not toxic and easy to obtain are adopted, the preparation process is simple, the technology is controllable, cost is low, repeatability is good, the layered structure of the prepared two-dimensional layered MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) is uniform and complete, the carbon nanoparticles are evenly distributed between the layers and on the surface of the MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) material, and the prepared composite material has the advantages of being large in specific surface area, good in conductivity, good in hydrophilic property and the like and can be used in the fields such as functional ceramic, wave-absorbing materials, supercapacitors and ion batteries.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
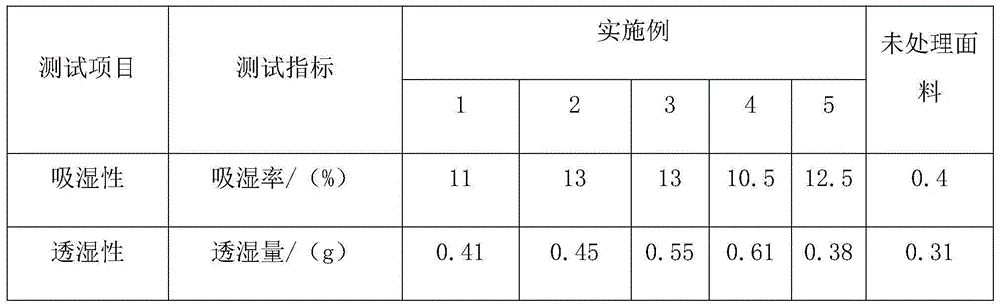
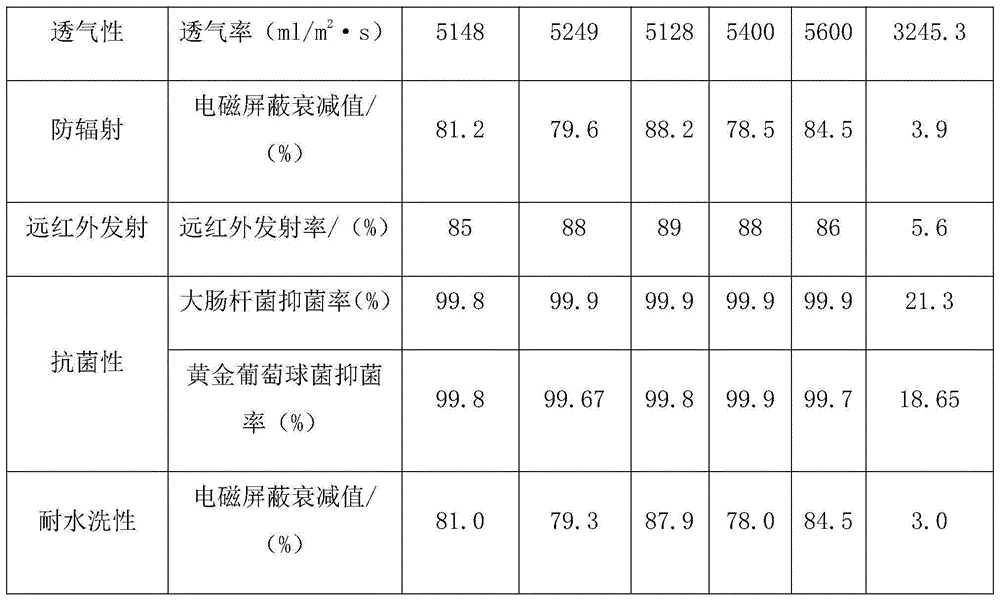
Antibacterial warming anti-electromagnetic radiation textile fabric and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105040426ADiversified functions of antibacterial, radiation protection and warmth preservationVersatileFibre treatmentCarbon nanotubeTitanium carbide
The invention discloses an antibacterial warming anti-electromagnetic radiation textile fabric and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of multifunctional fabrics. The preparation method mainly comprises multifunctional impregnation liquid preparation and fabric impregnation. The impregnation liquid mainly comprises deionized water, nanometer titanium dioxide, nanometer cerium oxide, nanometer silicon carbide, metal-loaded carbon nanotubes and nanometer titanium carbide. Through a vacuum-high pressure repeated impregnation technology, effective components in the impregnation liquid can be fast bonded to a textile fabric and the textile fabric subjected to impregnation has washing resistance and retains effective functions. The textile fabric functionalization method is simple and is free of repeated impregnation treatment in impregnation liquids with different functions. The preparation method reduces a production cost and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
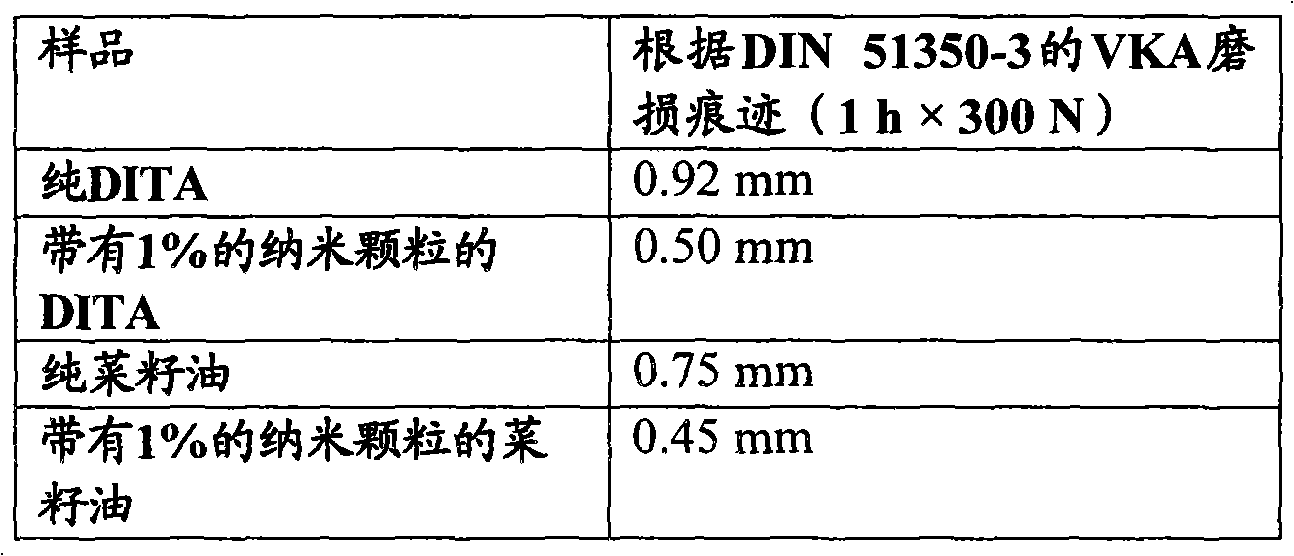
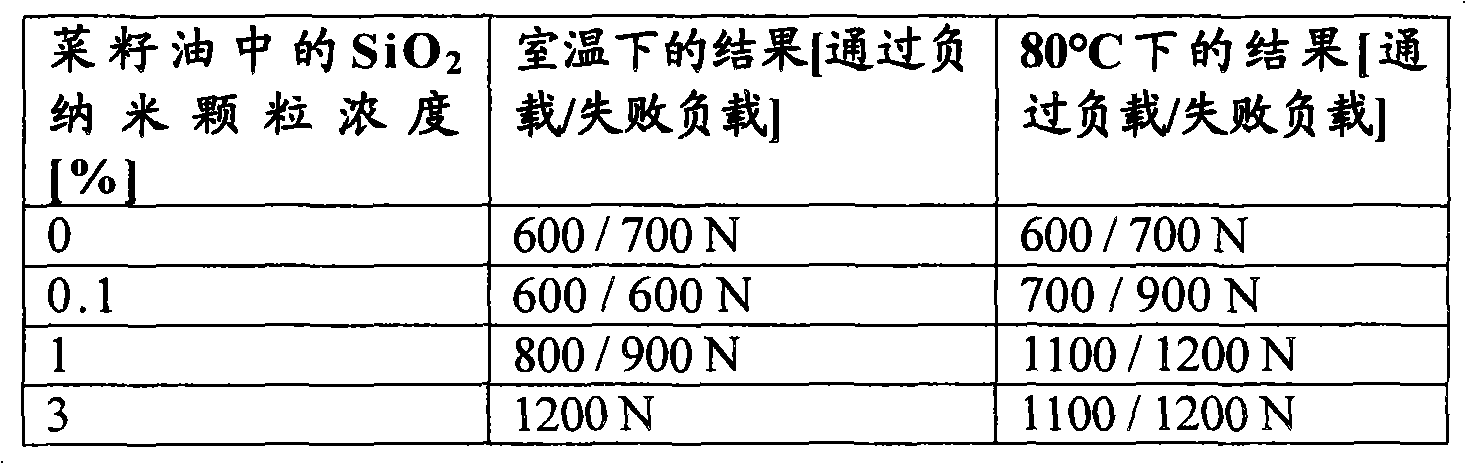
Additive for lubricant for improving the tribologic properties, a method for its production and application
The present invention relates to novel lubricant additives for improving the tribological properties, novel lubricants containing these additives, processes for the preparation thereof and the use thereof. Lubricant comprises ceramic nanoparticles as additives comprising aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, zirconium oxide, yttrium oxide, tungsten oxide, tantalum pentoxide, vanadium pentoxide, niobium pentoxide, cerium dioxide, boron carbide, aluminum titanate, boron nitride, molybdenum disilicide, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, titanium carbide, titanium nitride, zirconium diboride and / or clay minerals, and thermally stable carbonates and / or sulfates. The nanoparticles represent an ellipsoid with three semi-axes a, b and c, which are not equal to each other, or equal to each other. The ratio of a and b is 1-100, a and c is 1-1000, and b and c is 1:100.
Owner:แลนด์เซสส์ ดอยช์แลนด์ จีเอ็มบีเอช
Composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to a composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to a wear-resistant coating and a preparation process thereof. The composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating consists of adhesive coated tungsten carbide and other carbides, wherein the adhesive coated tungsten carbide has the grain size of WC-Co or WC-Ni; and the other carbides comprise chromium carbide, vanadium carbide, iron carbide, titanium carbide and the like. The preparation process comprises the following steps of: mixing the adhesive coated tungsten carbide and one or more kinds of the carbide powder; and performing spray coating (welding) or plasma spray coating (welding) on the surface of a medium-carbon steel part through supersonic flame to form the wear-resistant coating, wherein the carbon content of the medium-carbon steel is 0.35 to 0.55 weight percent (wt); the medium-carbon steel is subjected to the thermal refining state of quenching and high-temperature tempering; and the supersonic flame spray coating (welding) or plasma spray coating (welding) process sequentially comprises steps of performing sand blasting and rust removal on the surface of the medium-carbon steel, spraying a Ni-5 percent Al alloy adhesive coating and spraying a composite carbide wear-resistant coating. The composite carbide wear-resistant coating has Vickers hardness (HV) of 1,200 to 1,800, bonding force of more than 60 Mpa, and high mechanical property, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Method for preparing metallic titanium
The invention provides a method for preparing metallic titanium. The method comprises the following steps of: in the process of melting titanium slag by using titanium concentrate, directly adding excessive carbon-containing reducing agents to obtain titanium carbide or introducing nitrogen while directly adding the excessive carbon-containing reducing agents to prepare titanium nitride or titanium carbonitride in the melting process of the titanium slag; electrolyzing molten salts containing low-valence chloride of titanium to obtain metallic titanium powder by taking the prepared titanium carbide, the titanium nitride or the titanium carbonitride as a soluble anode and a metal material as a cathode; in addition, further electrolyzing and refining products obtained in the later period of the electrolysis to obtain high-purity titanium. The method has the advantages of simple process, low raw material cost, low energy consumption, small investment in permanent assets and the like. In addition, the prepared metallic titanium has high purity and ferrotitanium can be prepared by further electrolyzing residual anode titanium powder remained by the anode.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +2
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in refractory metals and refractory metal carbides coated graphite molds under vacuum
InactiveUS6986381B2Quality improvementImprove mechanical propertiesCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsTitanium carbideSuperalloy
Owner:SANTOKU AMERICA
Preparation of aluminium titanium carbide intermediate alloy grain refiner in the ultrasonic field
The invention relates to the composition, structure characteristics and preparation method of a new type of aluminum-titanium-carbon master alloy grain refiner and its application to aluminum and aluminum alloy grain refinement methods and effects. The present invention proposes a composition of an aluminum-titanium-carbon master alloy refiner prepared under the action of an ultrasonic field, which is characterized in that the main component of this type of refiner only needs to include aluminum (Al) , Titanium (Ti), carbon (C) without the need for other additional components. The method for preparing an aluminum-titanium-carbon master alloy under the action of an ultrasonic field proposed by the present invention is characterized in that raw materials such as pure aluminum ingot, potassium fluorotitanate, and graphite carbon are prepared according to the pre-designed master alloy composition; The aluminum ingot is melted by internal heating, and then various raw materials are added; ultrasonic waves are added to the melt that starts to react; after the reaction is completed, the temperature is raised, kept warm, left still, and slag is removed, and then cast into ingots or continuously cast and rolled into wire rods, thereby Get the required master alloy refiner with various components and shapes.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High capacitance electrode and methods of producing same
The present invention provides improved cathodes and methods for producing such cathodes for ultimate use in conjunction with valve metal capacitors. A family of titanium carbide cathodes according to the present invention can be produced so that they inhabit a pre-existing metallic surface such as an inner surface of a titanium casing adjacent but insulated from direct electrical communication from an anode. Foil-type valve metal anodes as well as porous valve metal anodes formed from metallic powders may be used in conjunction with the titanium cathodes of the present invention.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Probe needle material, probe needle and probe card each using the same, and inspection process
ActiveUS20100194415A1Maintain contact stabilityNot abraded heavilyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingProbe cardHafnium
Disclosed is a probe needle material used for producing a probe needle which is used in contact with an inspection object to inspect electrical characteristics of the inspection object, comprising not less than 0.1% by volume but not more than 3.5% by volume of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of titanium boride, zirconium boride, hafnium boride, niobium boride, tantalum boride, chromium boride, titanium carbide, zirconium carbide, hafnium carbide, vanadium carbide, niobium carbide, tantalum carbide, zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and chromium oxide and the balance of a tungsten alloy mainly consisting of tungsten.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Conductive matrices for fuel cell electrodes
InactiveUS7767330B2Suitable conductivity and durabilityIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyActive material electrodesTitanium carbideCobalt
The durability of a fuel cell having a polymer electrolyte membrane with an anode on one surface and an oxygen-reducing cathode on the other surface is improved by replacing conductive carbon matrix materials in an electrode with a matrix of electrically conductive metal compound particles. The electrode includes a catalyst supported on a nanosize metal oxides and electrically conductive nanosize matrix particles of a metal compound. One or more metal compounds such as a boride, carbide, nitride, silicide, carbonitride, oxyboride, oxycarbide, or oxynitride of a metal such as cobalt, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, neodymium niobium, tantalum, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zirconium is suitable. For example, the combination of platinum particles deposited on titanium dioxide support particles mixed in a conductive matrix of titanium carbide particles provides an electrode with good oxygen reduction capability and corrosion resistance in an acid environment.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com