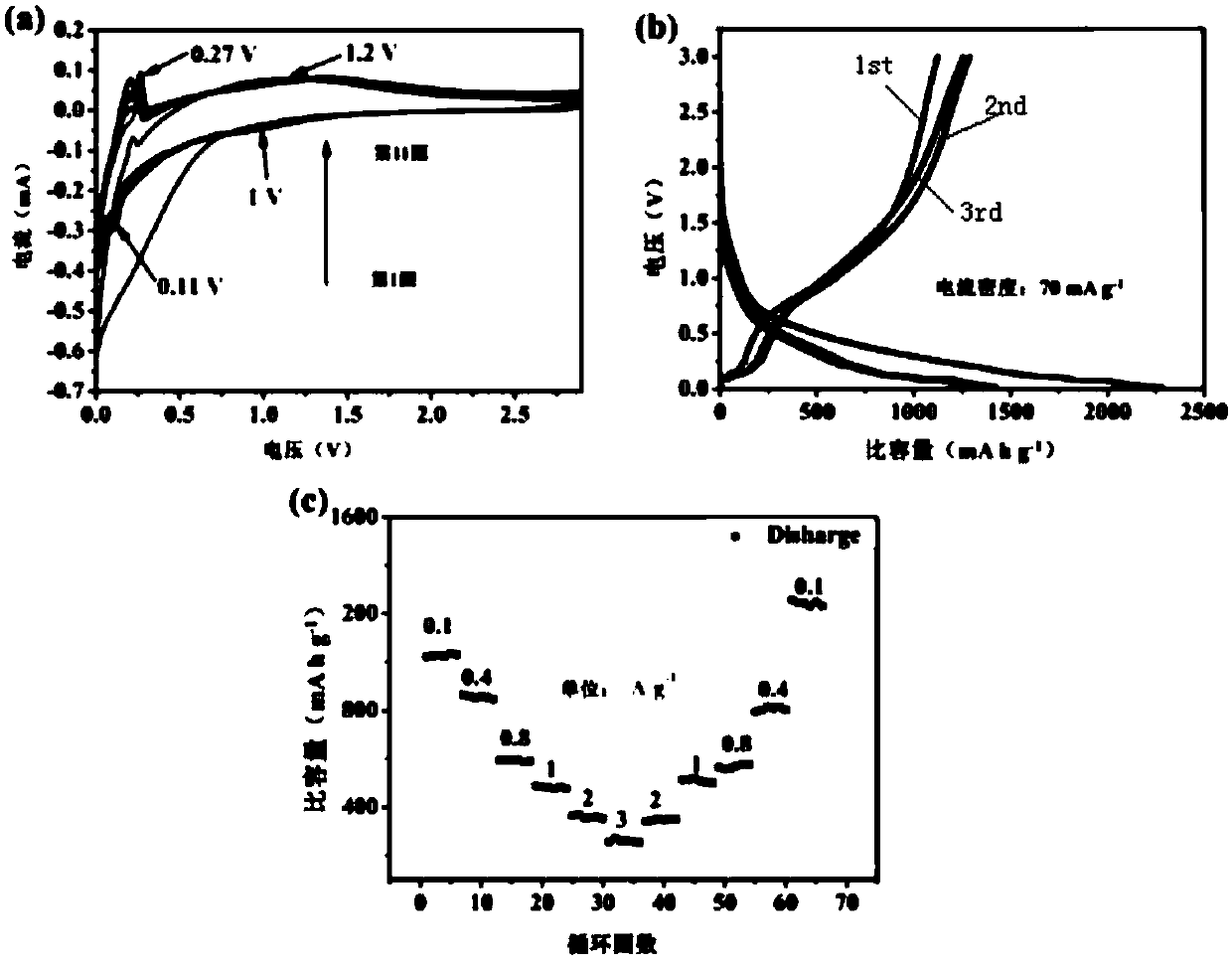
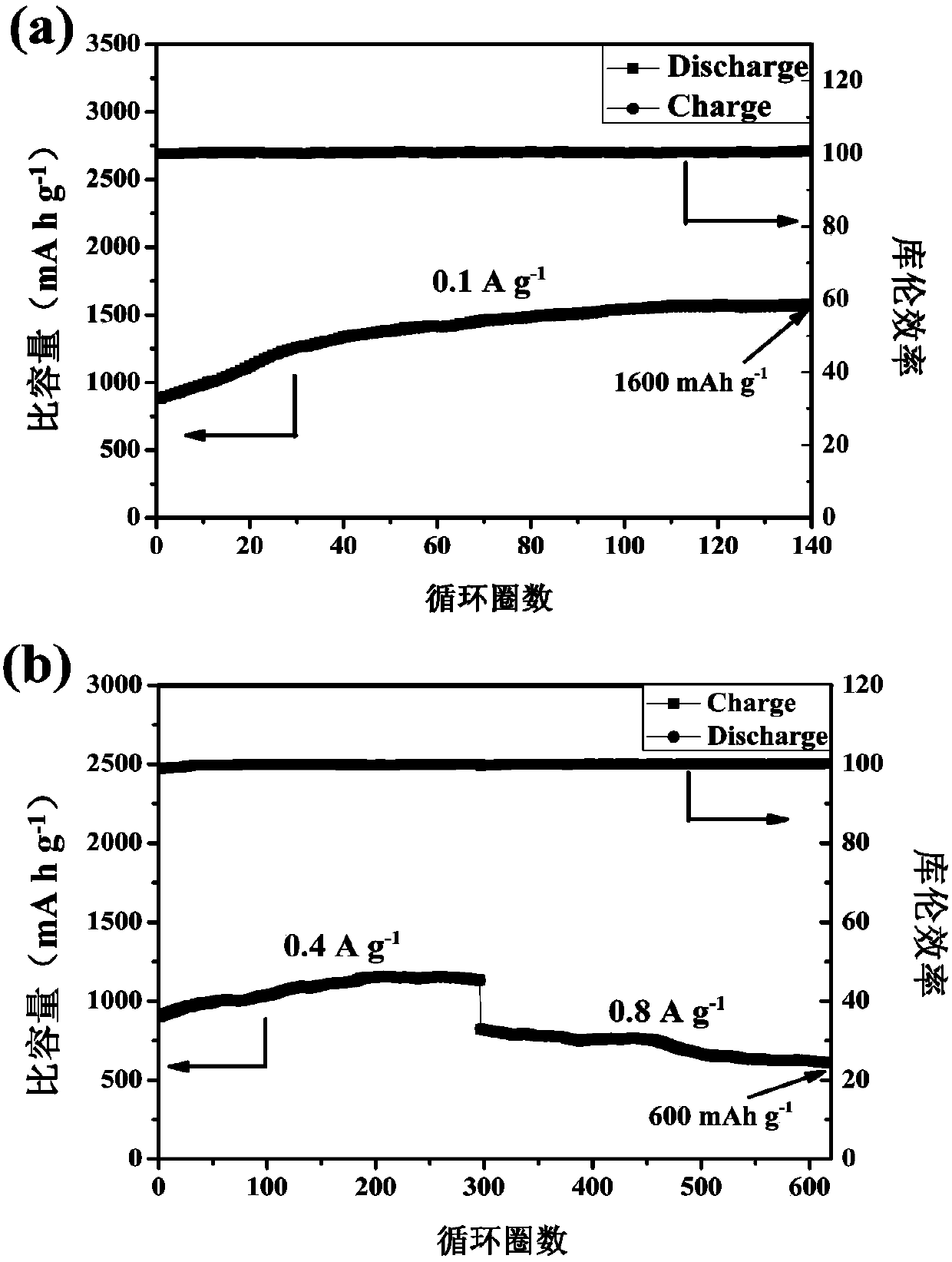
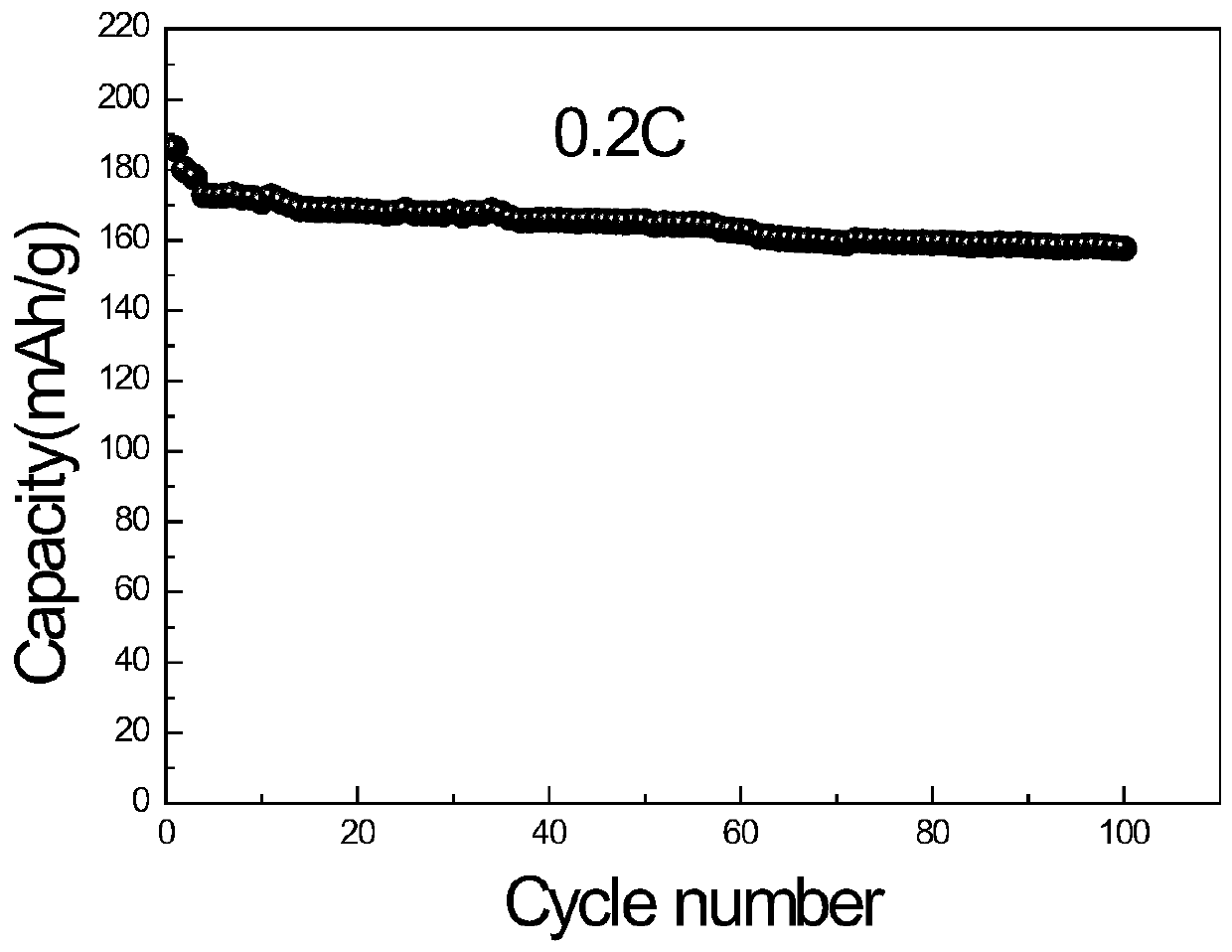
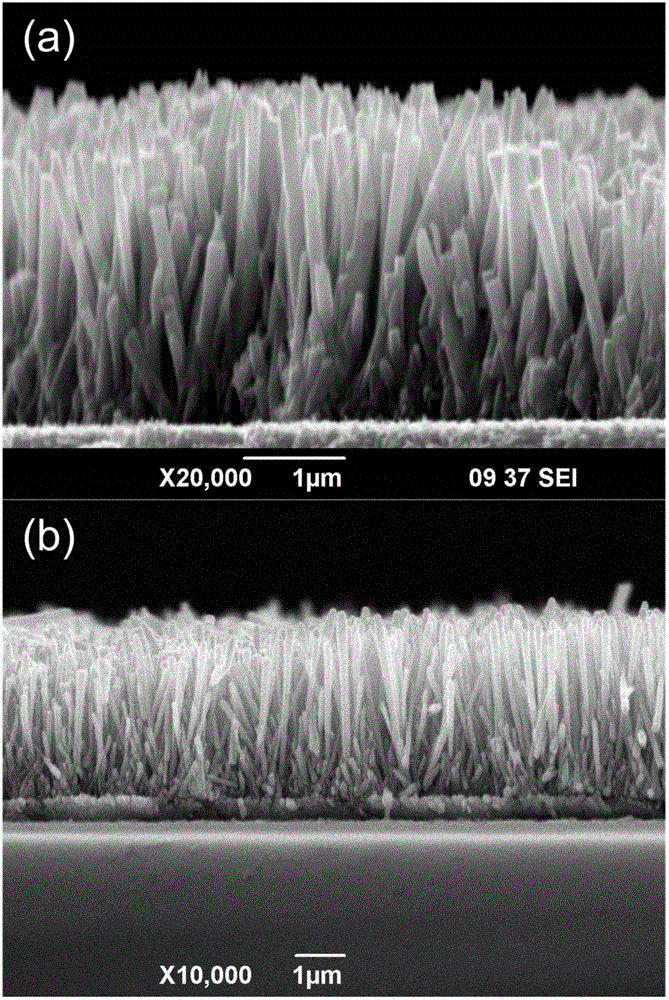
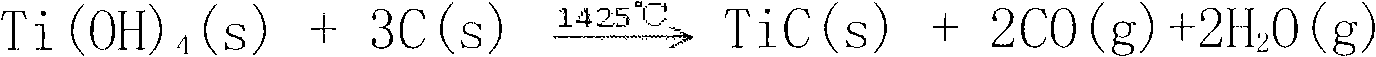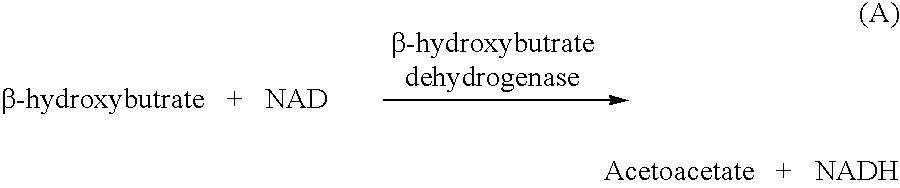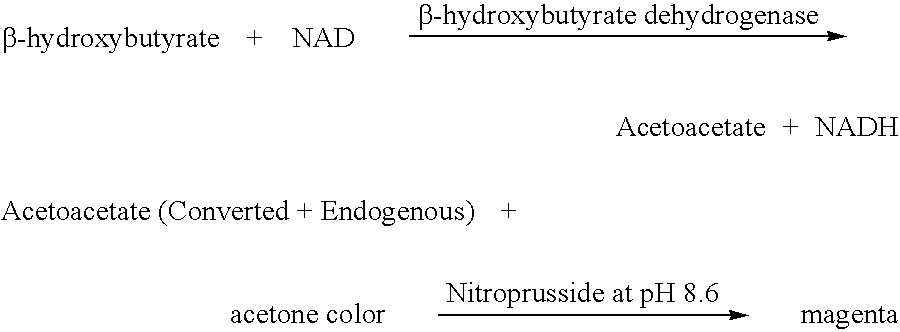Patents
Literature
185 results about "Wet chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
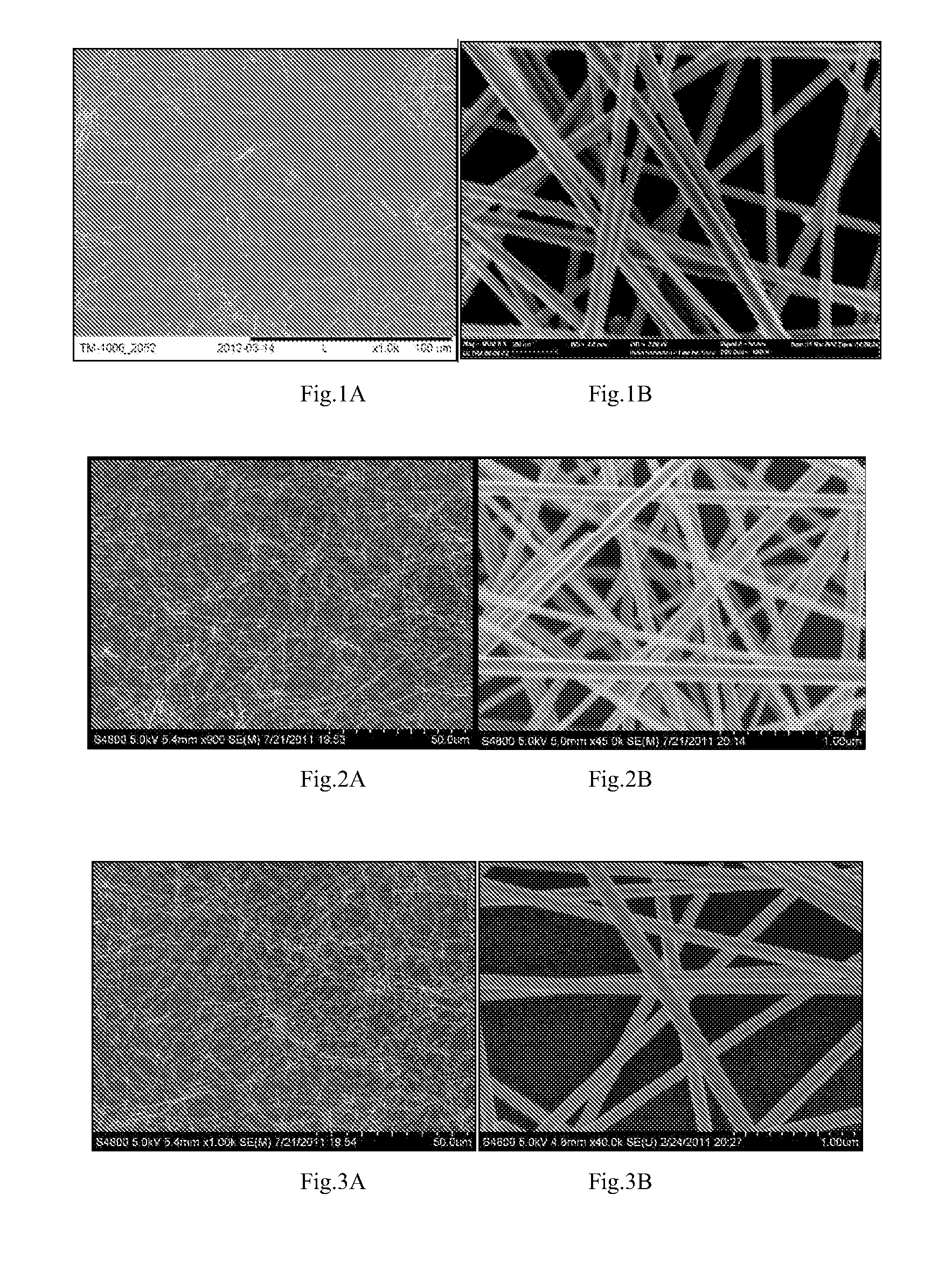
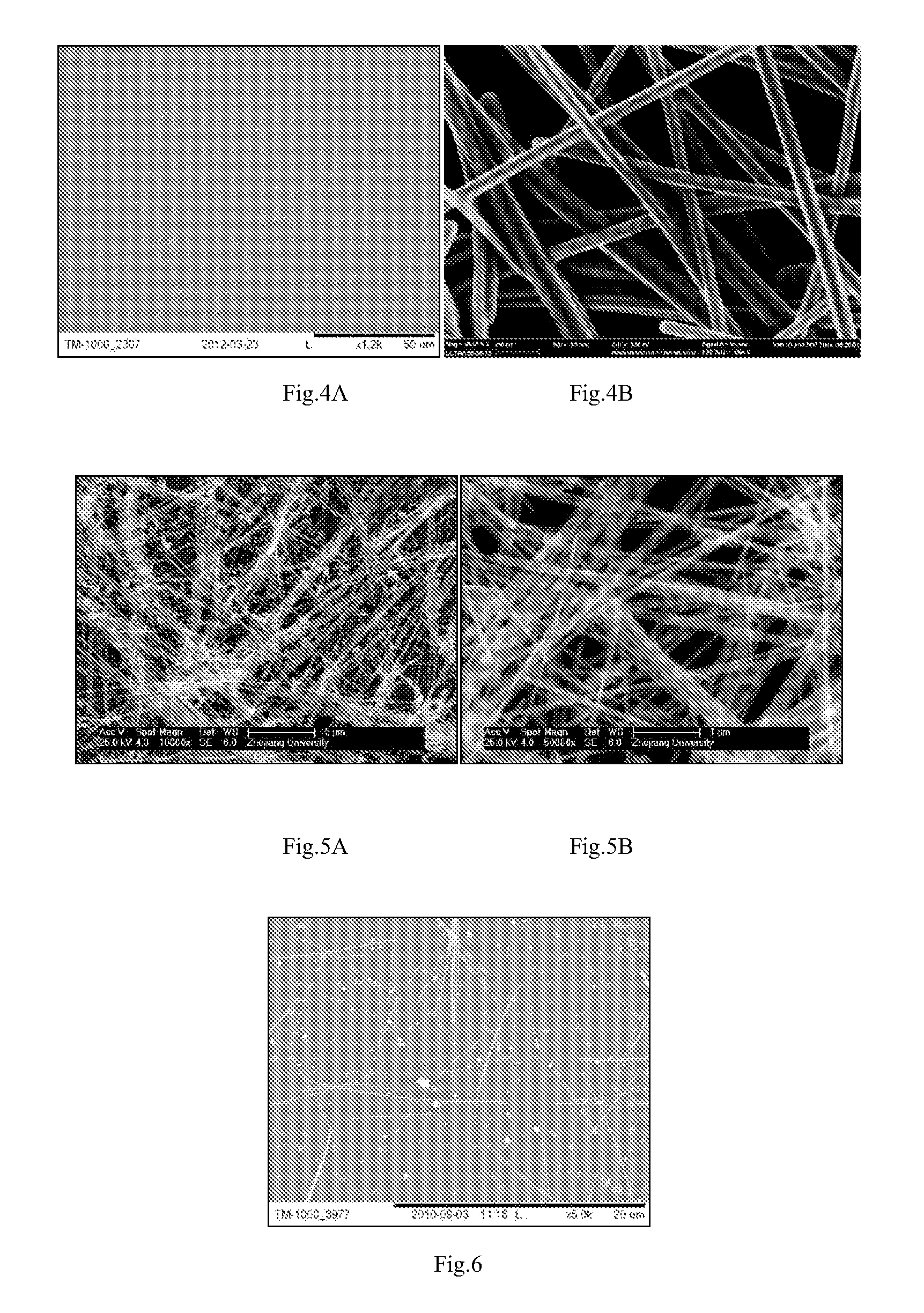
Wet chemistry is a form of analytical chemistry that uses classical methods such as observation to analyze materials. It is called wet chemistry since most analyzing is done in the liquid phase. Wet chemistry is also called bench chemistry since many tests are performed at lab benches.
Wet chemistry method for preparing lithium iron phosphate
InactiveCN1431147AEasy to controlEvenly distributedElectrode thermal treatmentLi-accumulatorsChemical compositionLithium iron phosphate
A wet chemical process for preparing iron lithium phosphate includes mixing the solution or suspensions of Li source compound, Fe source compound, P source compound, doping element compound or electric conducting agent, and precipitant, reaction at 5-120 deg.C for 0.5-24 hr while stirring, filtering, washing, baking to obtain nano precursor, quickly heating to 500-800 deg.C in non-air or non-oxidizing atmosphere, calcining for 5-48 hr, and cooling. Its advantages are easy control, high uniformity and electric conductivity.
Owner:郑绵平
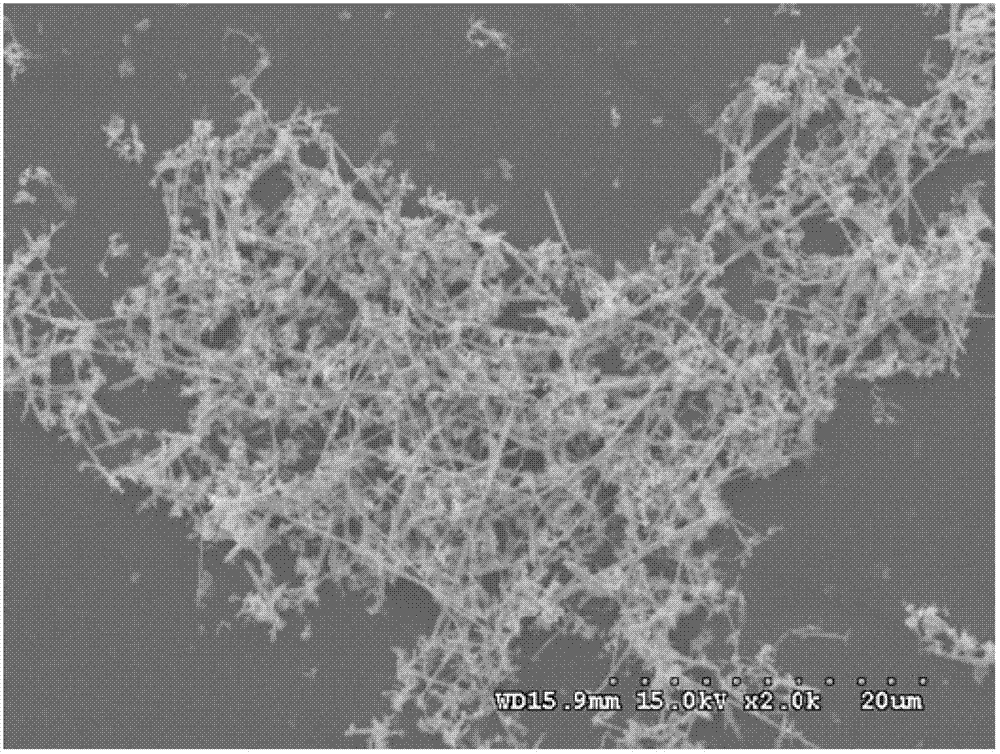
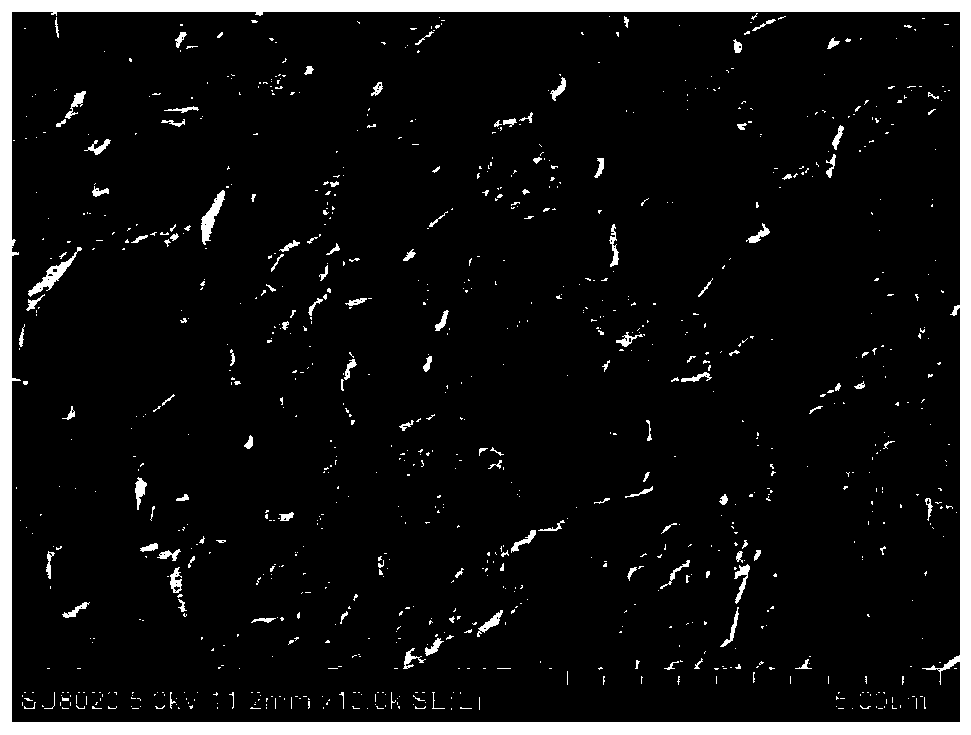
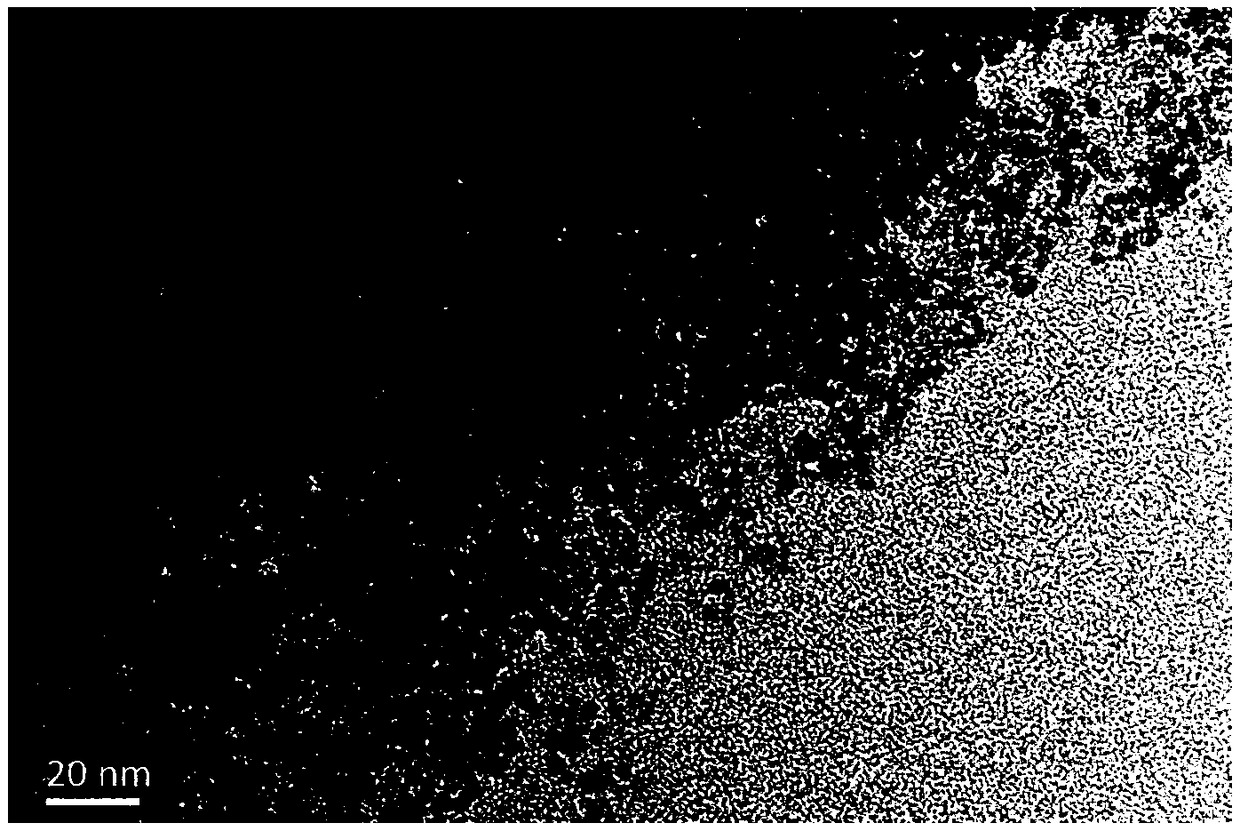
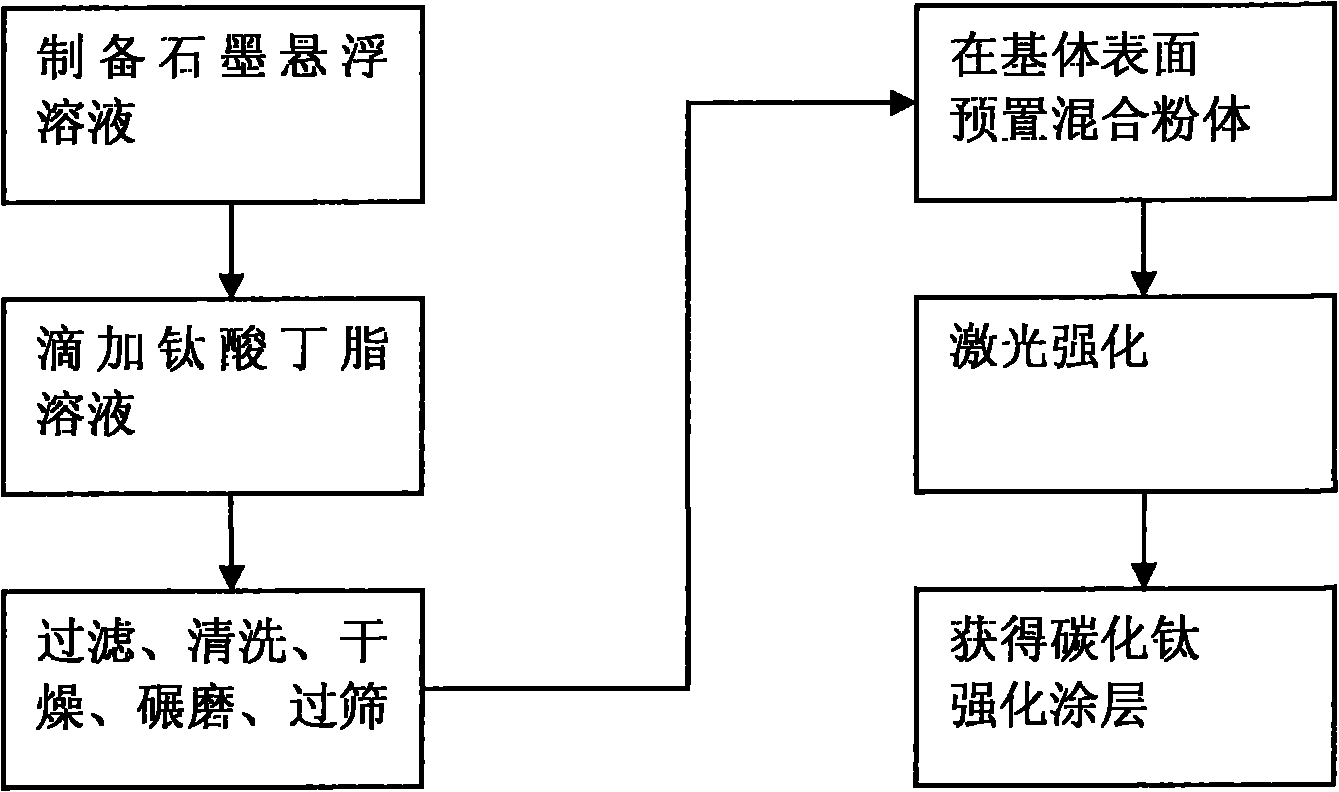
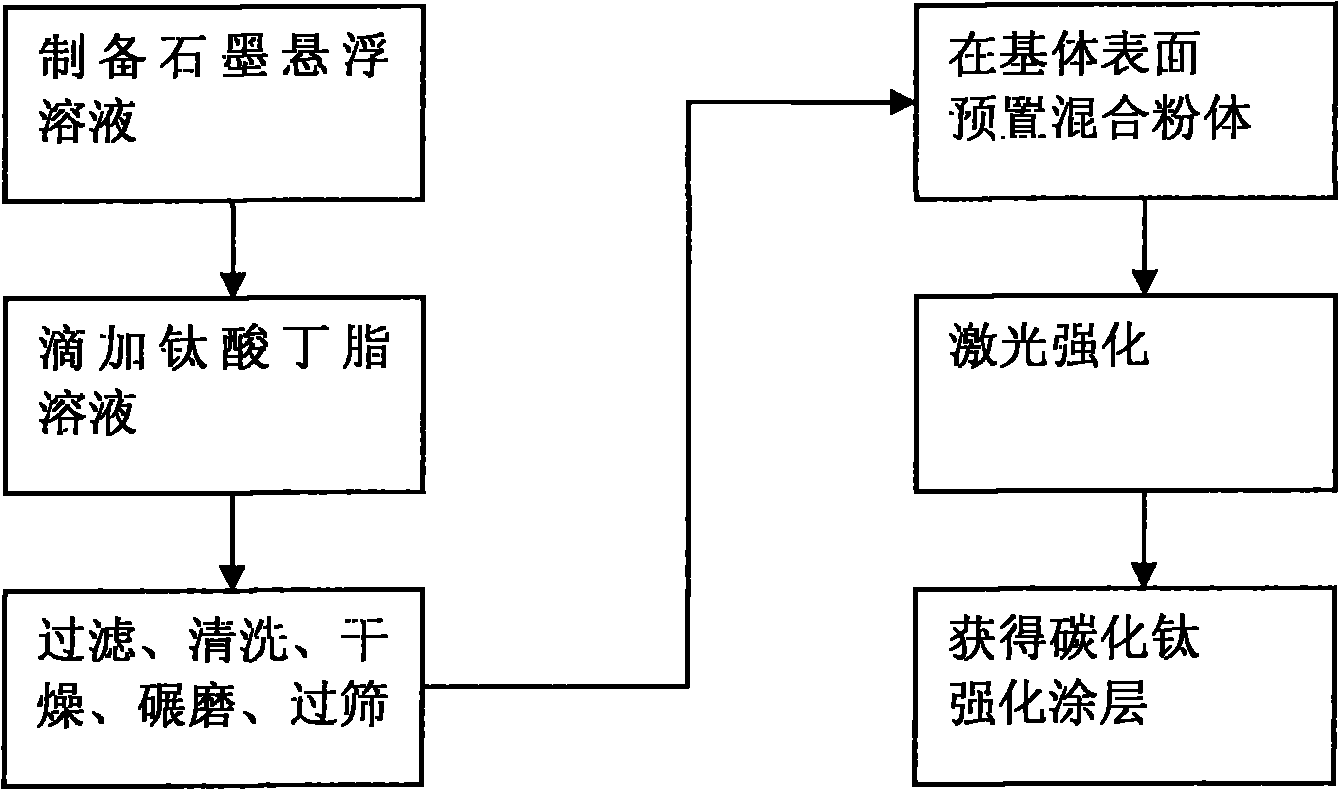
Method for preparing metal surface laser strengthened coat
InactiveCN101812684AIncrease profitImprove the strengthening effectMetallic material coating processesChemical reactionArgon atmosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing a metal surface laser strengthened coat, which comprises the following steps: preparing uniformly mixed powder of titanium dioxide hydrate and graphite powder by using a wet chemistry method; pre-placing the mixed powder on the surface of a basal body; and irradiating the surface of the basal body by using laser as a heat source under an argon atmosphere to form a molten pool, performing a carbon-thermal chemical reaction on the pre-placed mixed powder under a high-temperature environment to generate titanium carbide, and finally forming a titanium carbide composite coat on the surface of the basal body. In the same way, the method is also suitable for preparing a TiN enhanced composite coat by mixing hydrated oxide thereof and graphite by the wet chemistry method, then mixing the mixture and urea to form pre-placed powder and cladding the pre-placed powder on the basal body by laser. The surface of the enhanced coat prepared by the technical scheme is smooth, and has no cracks or pores; enhancing particles are uniformly distributed in the coat; the enhanced coat and the basal body are metallurgically combined; and the mixed powder prepared by adopting the wet chemistry method is uniformly mixed, ensures complete reaction, and is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:姚建华
Noninvasive transdermal systems for detecting an analyte in a biological fluid and methods
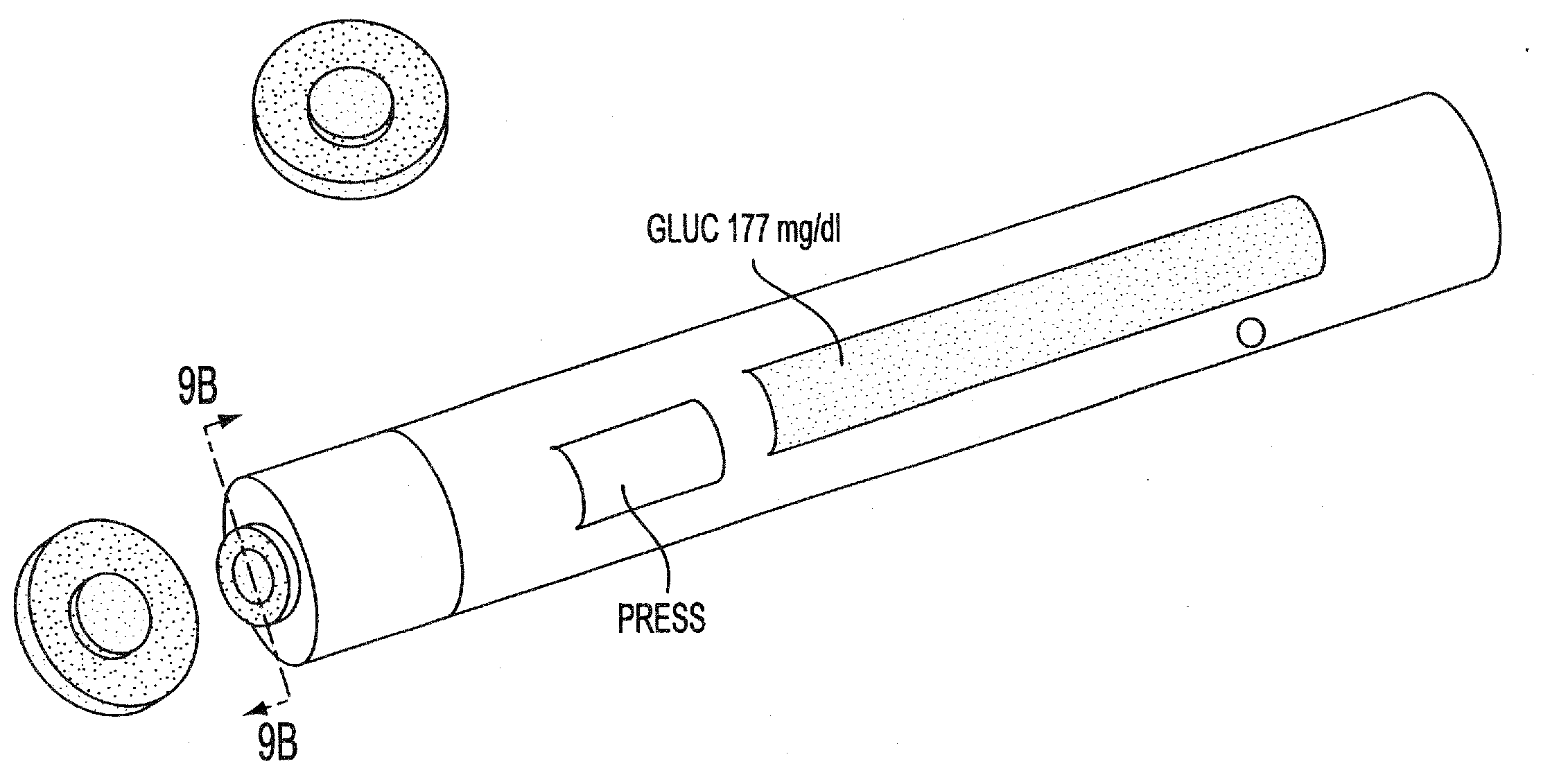
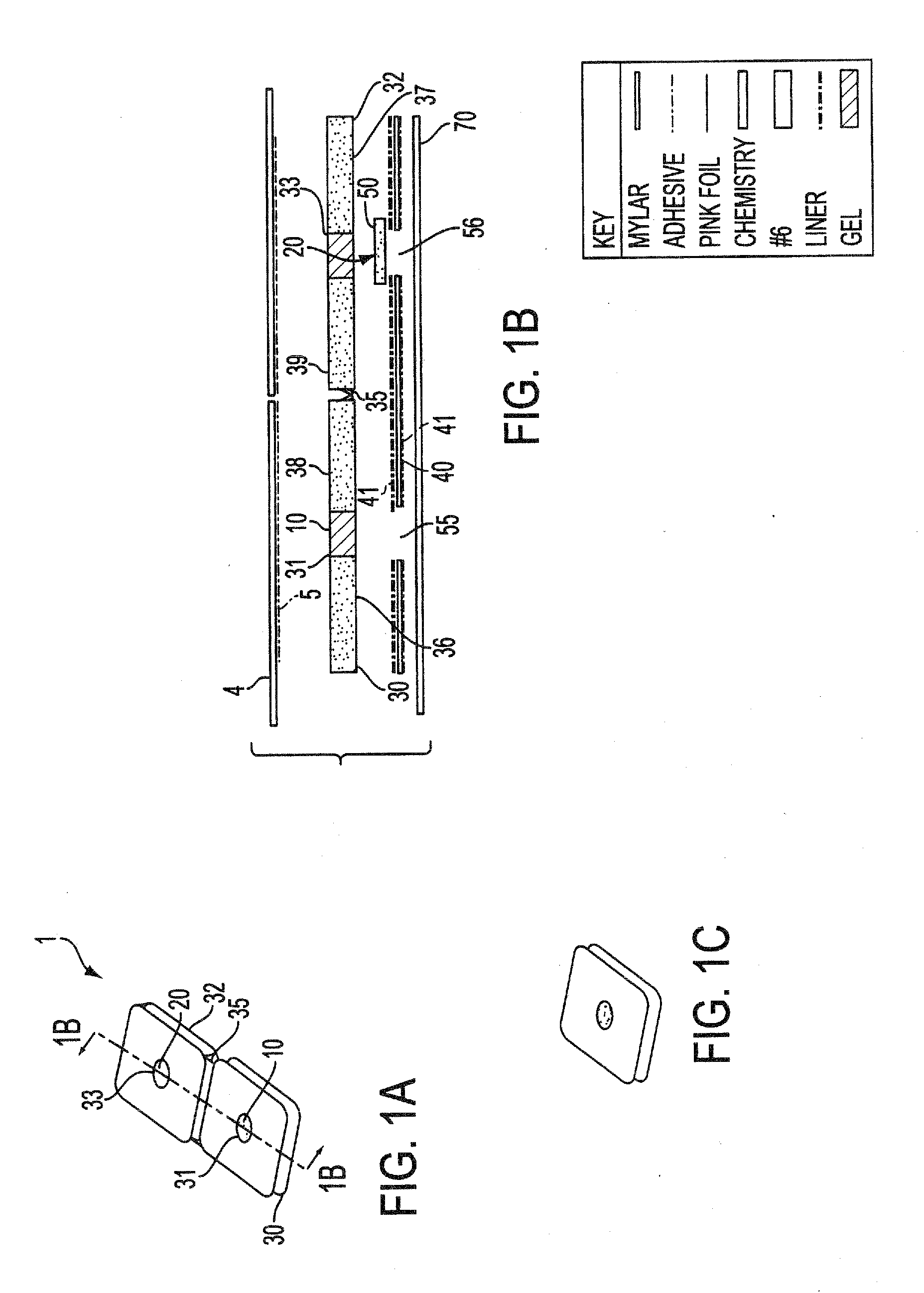
InactiveUS7577469B1Easy to useImprove complianceInvestigating moving sheetsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransdermal patchColor changes
The present invention relates to noninvasive transdermal systems comprised of a noninvasive transdermal patch and a reflectometer. The noninvasive transdermal patches are comprised of a wet chemistry component and a dry chemistry component. The wet chemistry component is a liquid transfer medium in the form of a gel layer for the extraction and liquid bridge transfer of the analyte of interest from the biological fluid within or beneath the skin to the dry chemistry component. The dry chemistry component is a reagent system for interacting with the analyte of interest (glucose) to generate a color change. The reflectometers include a modulated light source for emitting light to illuminate a target surface which possesses a certain color and shade of color for detection by an optical detector. The output signal is processed for determining a corresponding quantity or quality measurement.
Owner:PLDHC ACQUISITIONS LLC
WET CHEMICAL METHOD OF FORMING STABLE PiPd DIESEL OXIDATION
InactiveUS20120214666A1Minimizing and eliminating mobilityMinimizing and eliminating and agglomerationMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationNanoparticleCopper
A nano-particle comprising: an interior region comprising a mixed-metal oxide; and an exterior surface comprising a pure metal. In some embodiments, the mixed-metal oxide comprises aluminum oxide and a metallic pinning agent, such as palladium, copper, molybdenum, or cobalt. In some embodiments, the pure metal at the exterior surface is the same as the metallic pinning agent in the mixed-metal oxide in the interior region. In some embodiments, a catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal at the exterior surface. In some embodiments, the interior region and the exterior surface are formed using a plasma gun. In some embodiments, the interior region and the exterior surface are formed using a wet chemistry process. In some embodiments, the catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal using a plasma gun. In some embodiments, the catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal using a wet chemistry process.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
A method for rapid and large-scale preparation of silver nanowires with high aspect ratio
InactiveCN102259190AQuality improvementEasy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthWater solubleMaterials science
Disclosed is a method suitable for efficiently producing silver nanowires with high aspect ratio. In this method, silver nanowires with aspect ratio of more than 300 and purity of more than 80% are produced through an acid compound mediated microwave-assisted wet chemistry method. Such silver nanowires are especially suitable for the application in the flexible transparent electrodes, as they can simultaneously improve the electrical conductivity and transparency.
Owner:JIANGSU NANOWELL ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI&TECH
Wet chemical and plasma methods of forming stable PtPd catalysts
InactiveUS8669202B2Minimizing and eliminating mobility and agglomerationArea maximizationMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesCobaltInterior design
A nano-particle comprising: an interior region comprising a mixed-metal oxide; and an exterior surface comprising a pure metal. In some embodiments, the mixed-metal oxide comprises aluminum oxide and a metallic pinning agent, such as palladium, copper, molybdenum, or cobalt. In some embodiments, the pure metal at the exterior surface is the same as the metallic pinning agent in the mixed-metal oxide in the interior region. In some embodiments, a catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal at the exterior surface. In some embodiments, the interior region and the exterior surface are formed using a plasma gun. In some embodiments, the interior region and the exterior surface are formed using a wet chemistry process. In some embodiments, the catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal using a plasma gun. In some embodiments, the catalytic nano-particle is bonded to the pure metal using a wet chemistry process.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Particulate nanoparticles and nanowires of silver and method for large scale producing the same
ActiveUS20100148132A1Good dispersionLow filling concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthParticulatesMean diameter
Disclosed is a method suitable for large-scale producing silver nanostructures including nanoparticles and nanowires with high crystallization and purity in a short period of time. In this method, silver particles with mean diameter less than 200 nm and silver nanowires with length in micrometers are produced through a microwave-assisted wet chemistry method. Tens to hundreds grams of silver nanoparticles and nanowires are obtained in minutes by microwave irradiation treatment to a precursor pre-made by highly concentrated silver salt solution and other additives. These silver nanoparticles and nanowires have good dispersibility and are ideal for forming conductive adhesives.
Owner:JIANGSU NANOWELL ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI&TECH
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
InactiveUS20040241779A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific enzymeAssay
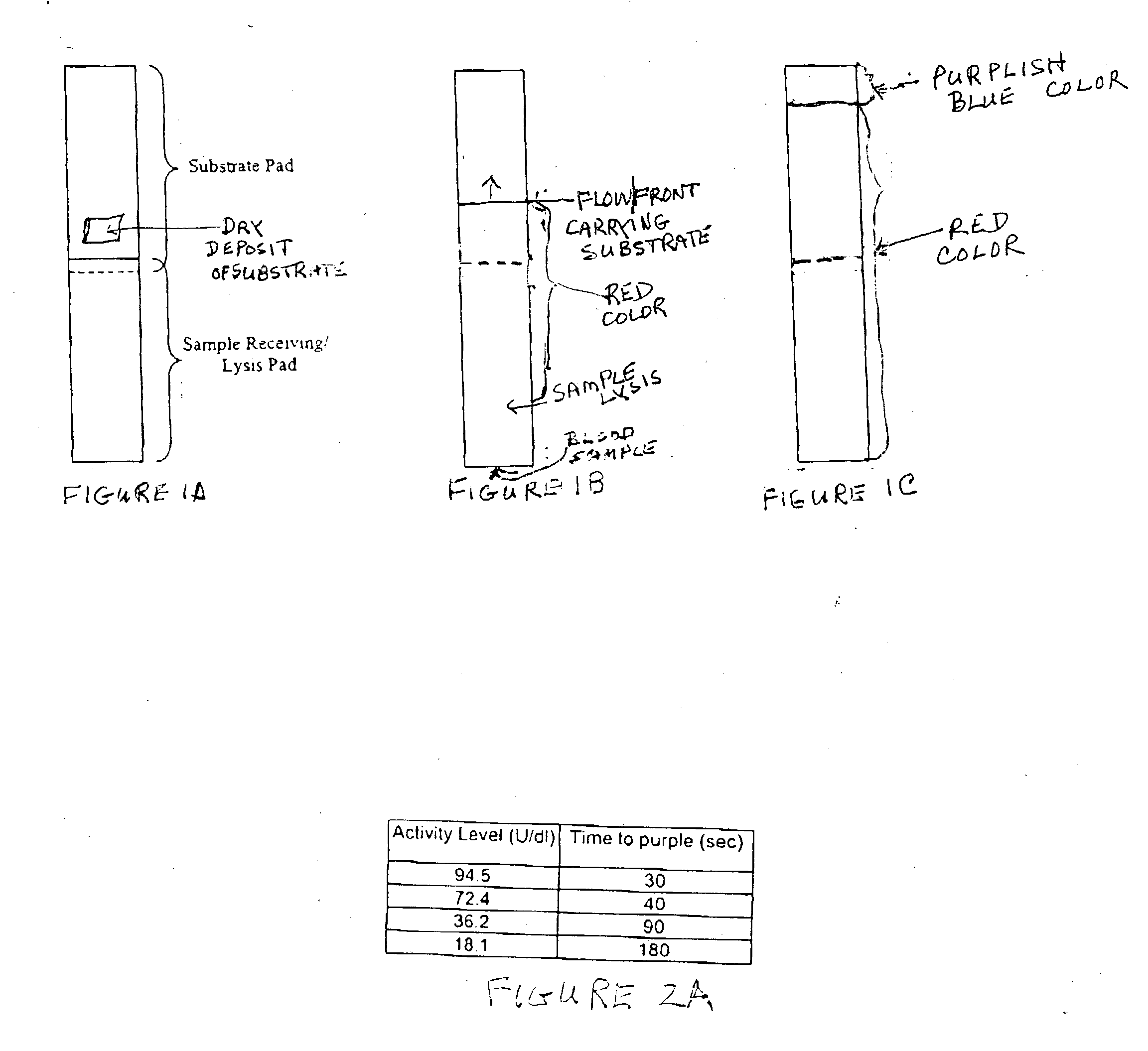
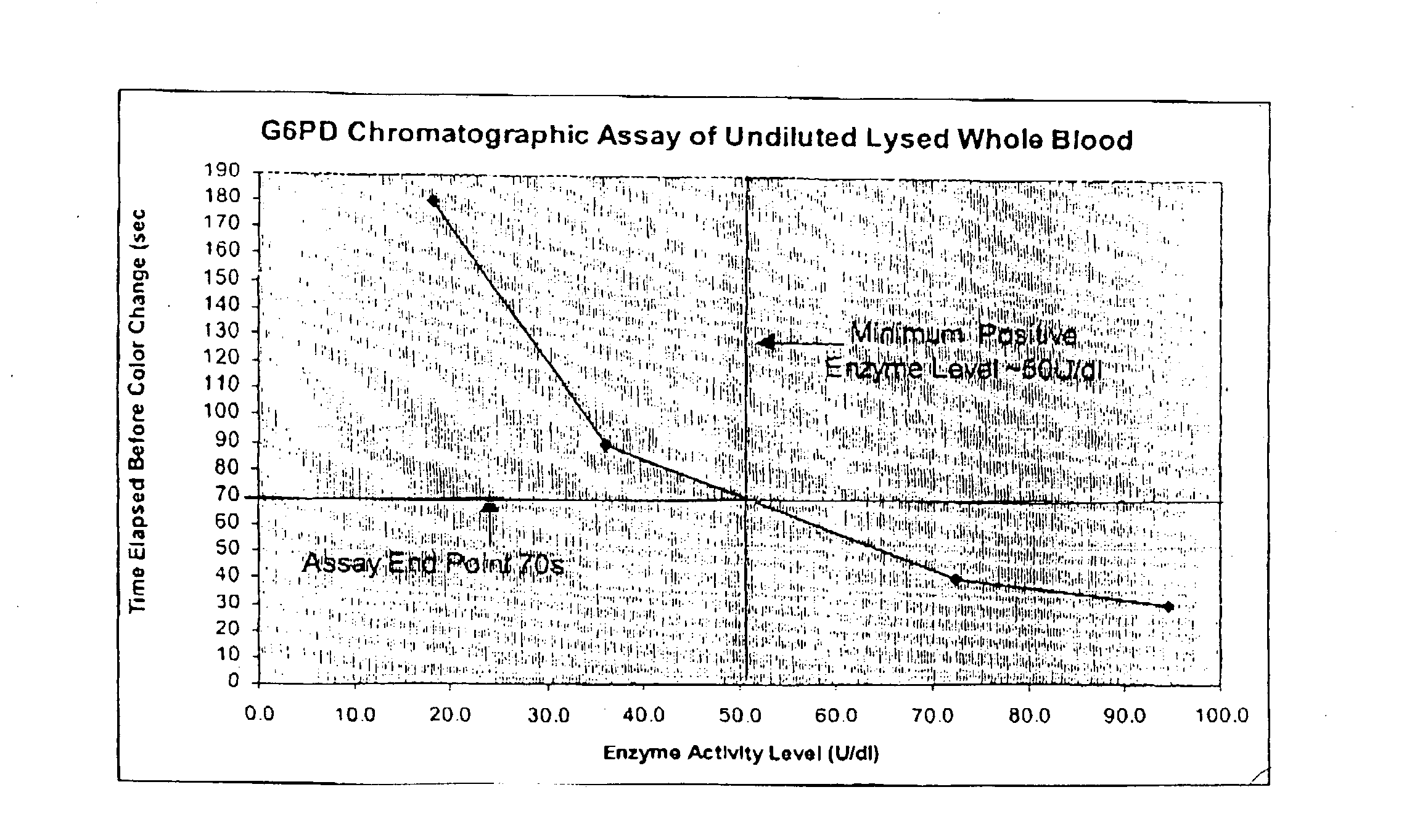
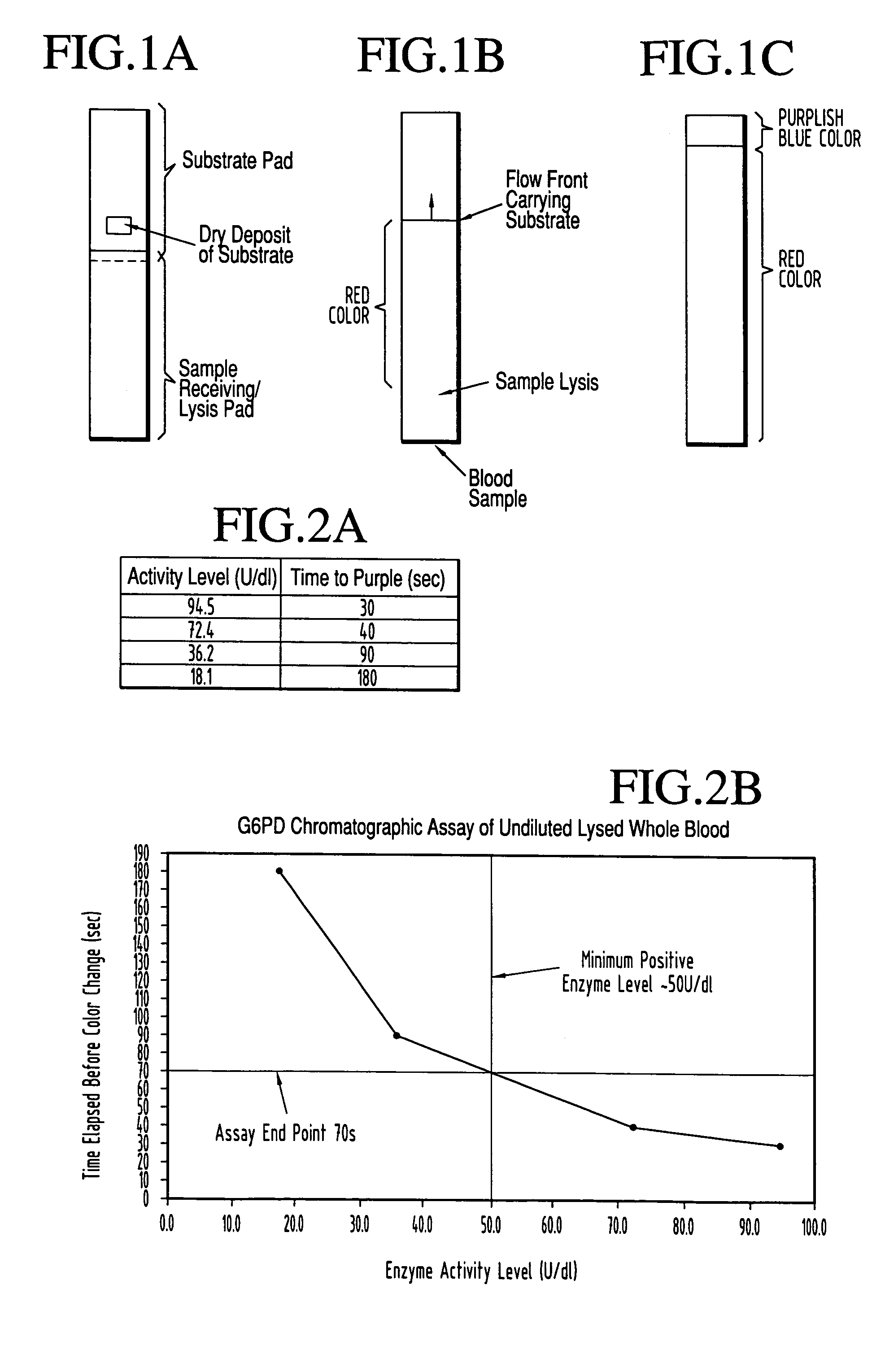
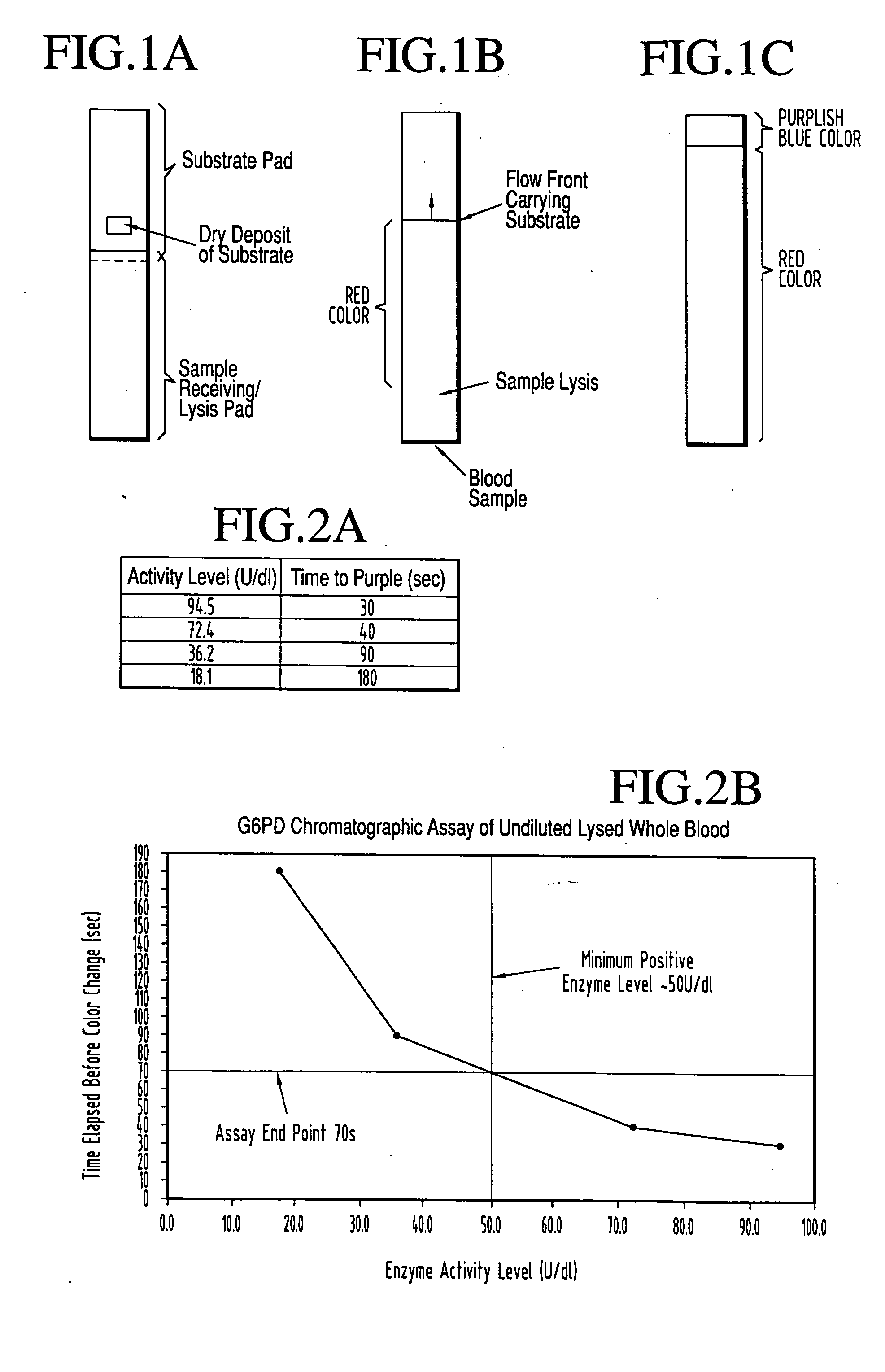
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final "read zone" wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays. A specific assay for glucose-phosphate dehydrogenase ("G-6PD") in this format is disclosed.
Owner:BINAX INC
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
InactiveUS7425302B2Easy to observeHigh detection sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAdditive ingredientPeroxidase
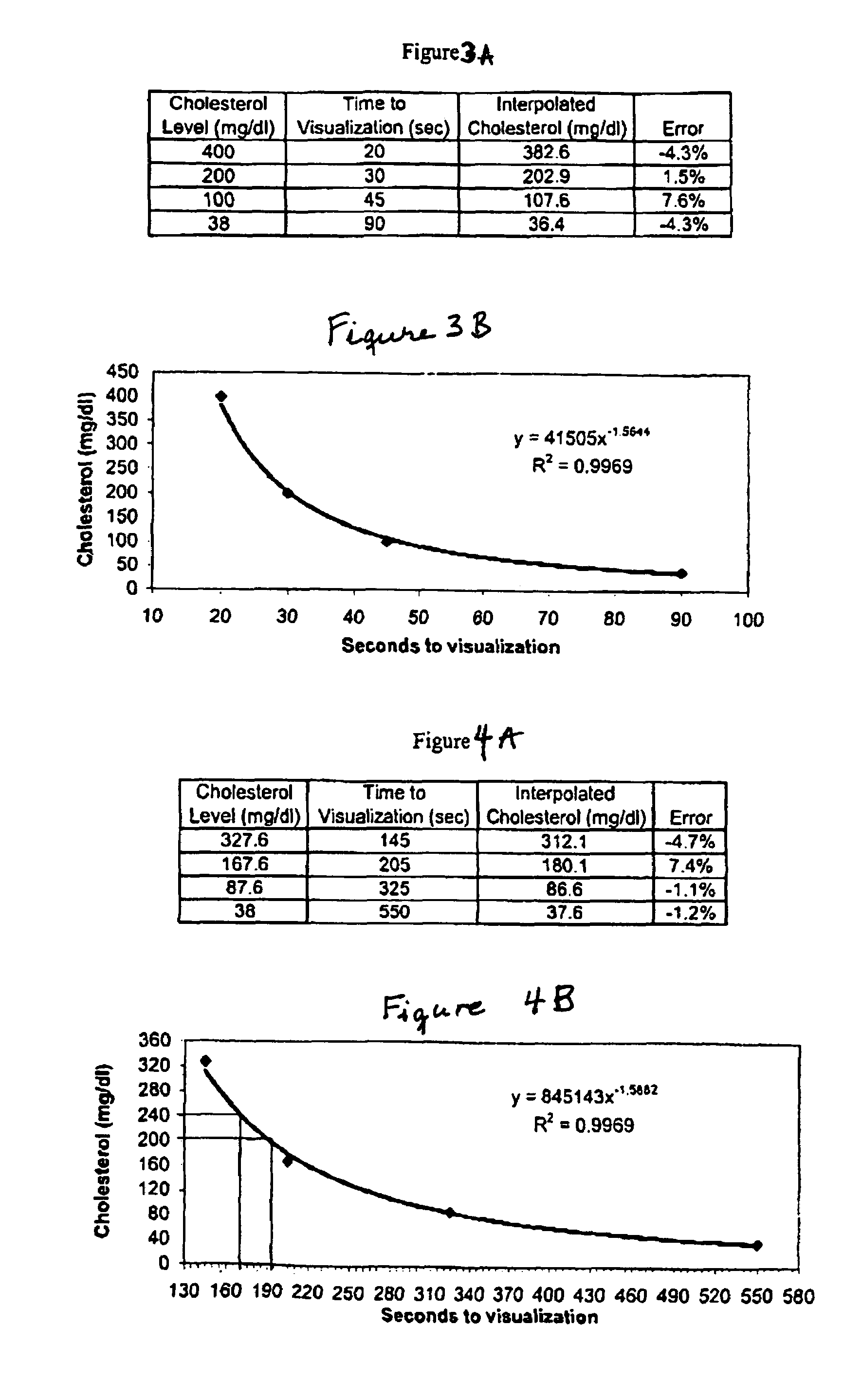
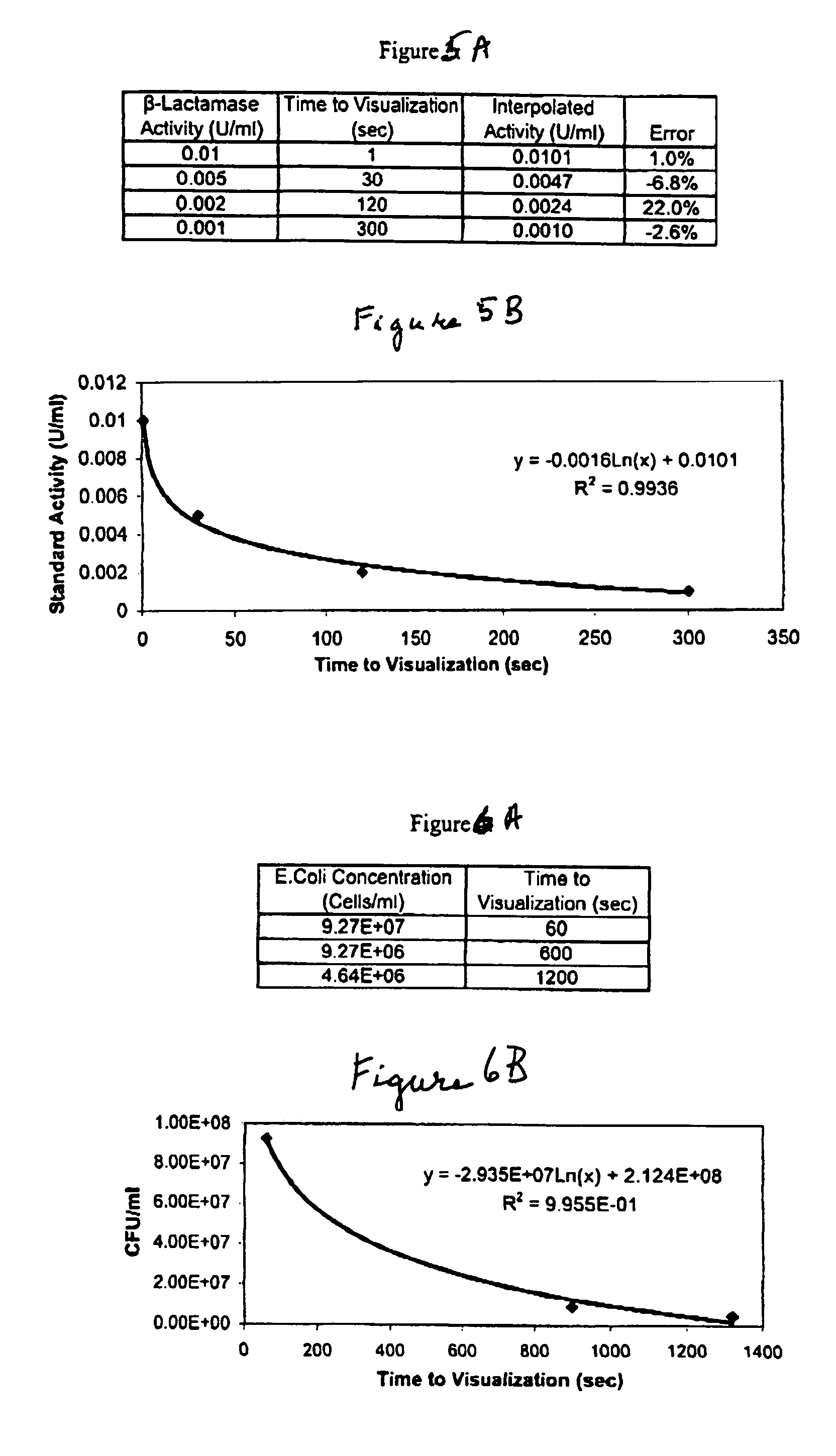
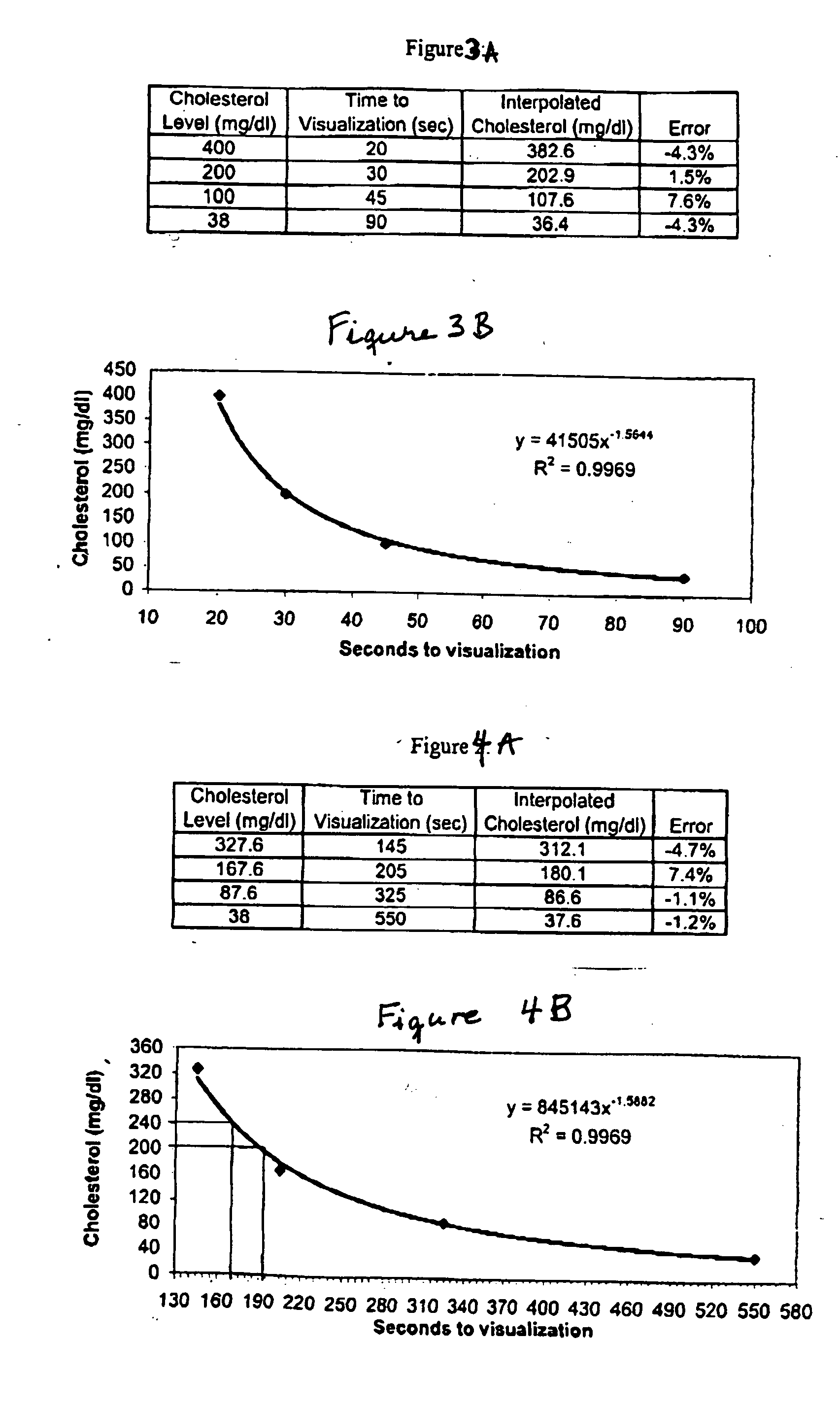
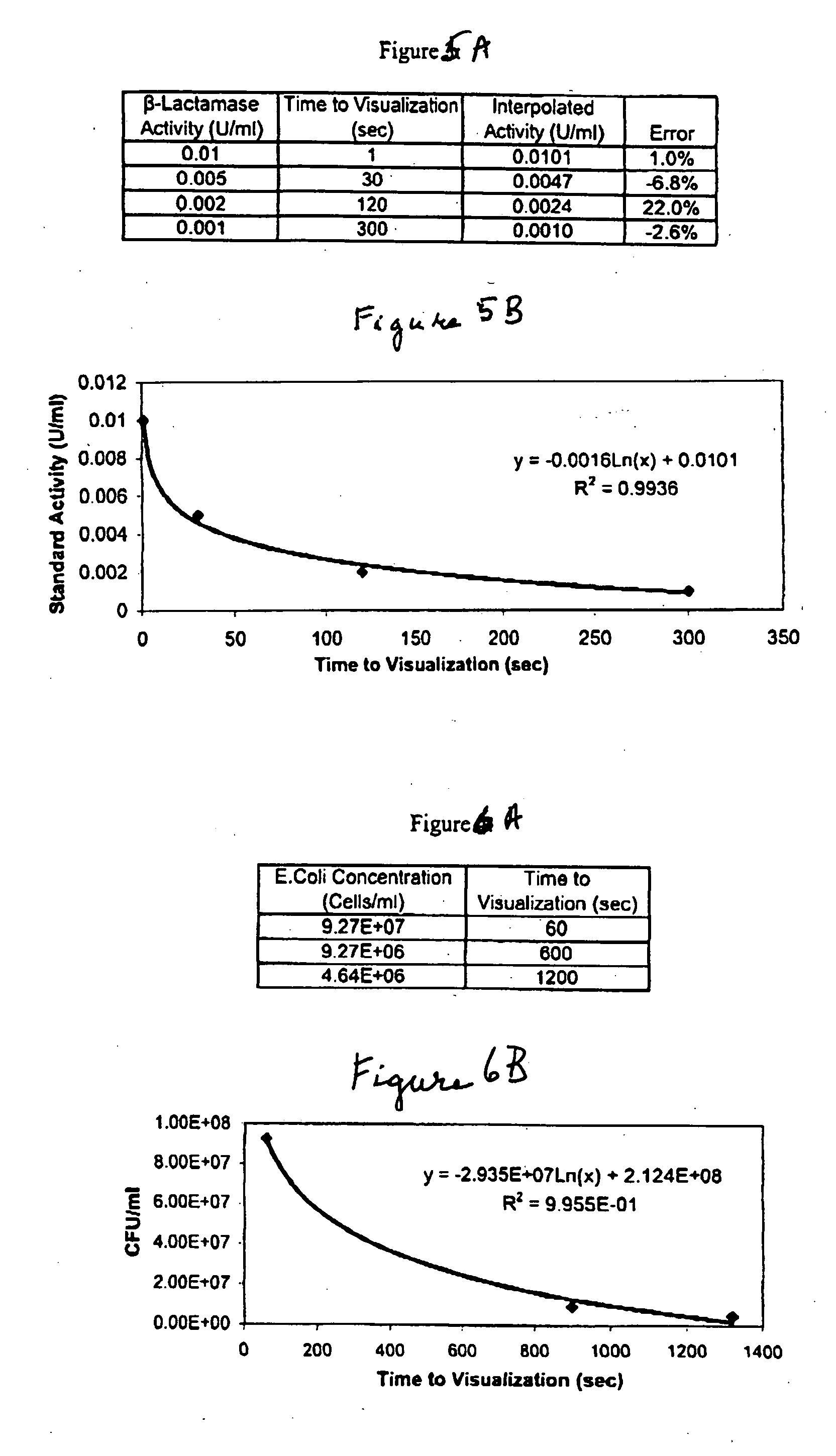
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final “read zone” wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays.Specific assays for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (“G-6PD”), total serum cholesterol, β-lactamase activity and peroxidase activity are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Quantitative analysis of surface-derived samples using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070259445A1Reduce riskFast and accurate analysisParticle separator tubesBiological testingAnalyteInternal standard
A substrate incorporating an internal standard facilitates quantitating analytes in a sample by surface-interrogating mass spectrometry techniques without wet chemistry sample preparation. The user disposes a sample to be analyzed onto the surface of the pretreated substrate. Then the sample-bearing solid substrate, which incorporates an internal standard for each analyte to be quantitated, is ready for interrogation.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Methods of rapid preparation of silver nanowires with high aspect ratio
InactiveUS20140102254A1High aspect ratioHigh manufacturing requirementsMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMaterials scienceSilver nanowires
Disclosed is a method suitable for efficiently producing silver nanowires with high aspect ratio. In this method, silver nanowires with aspect ratio of more than 300 and purity of more than 80% are produced through an acid compound mediated microwave-assisted wet chemistry method. Such silver nanowires are especially suitable for the application in the flexible transparent electrodes, as they can simultaneously improve the electrical conductivity and transparency.
Owner:JIANGSU NANOWELL ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI&TECH
Noninvasive Transdermal Systems for Detecting an Analyte in a Biological Fluid and Methods
InactiveUS20100049016A1Low costEasy to useInvestigating moving sheetsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransdermal patchColor changes
The present invention relates to noninvasive transdermal systems comprised of a noninvasive transdermal patch and a reflectometer. The noninvasive transdermal patches are comprised of a wet chemistry component and a dry chemistry component. The wet chemistry component is a liquid transfer medium in the form of a gel layer for the extraction and liquid bridge transfer of the analyte of interest from the biological fluid within or beneath the skin to the dry chemistry component. The dry chemistry component is a reagent system for interacting with the analyte of interest (glucose) to generate a color change. The reflectometers include a modulated light source for emitting light to illuminate a target surface which possesses a certain color and shade of color for detection by an optical detector. The output signal is processed for determining a corresponding quantity of quality measurement.
Owner:ARONOWITZ JACK L +3
Method and test strips for the measurement of fat loss during weight loss programs
InactiveUS20040043376A1Great advantageEasy to manufactureMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
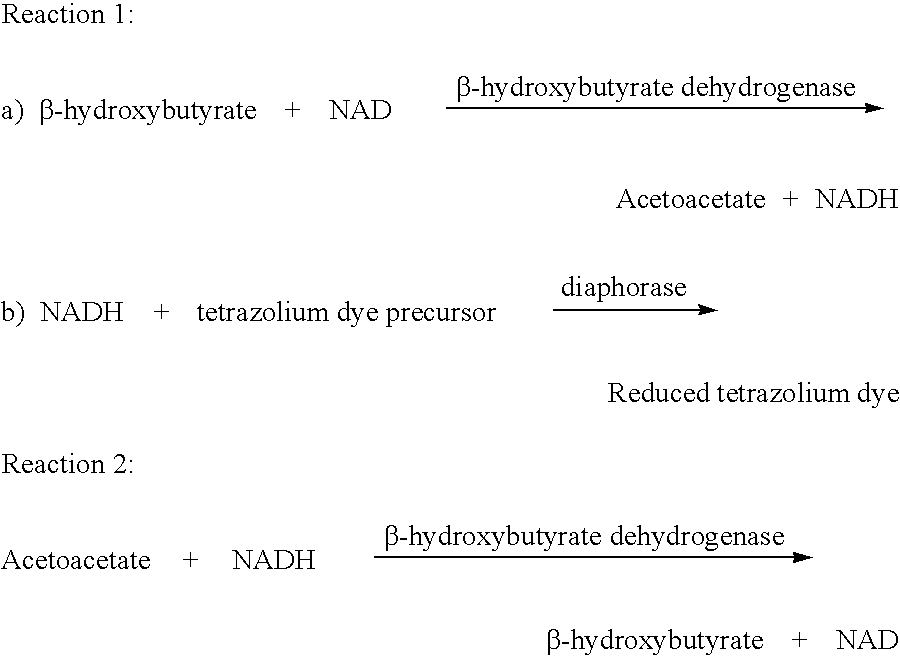
Disposable test strips and a wet chemistry method for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate or total ketone bodies (i.e., beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) in human bodily fluid samples, including but not limited to urine, saliva or sweat are described. The test strips need only be dipped in the sample and can be used by anyone in almost any milieu. Measurement can be made electrochemically, spectrophotometrically, fluorometrically or by comparision to a color standard. Combined acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate which account for 97-98% of total ketone bodies and may be measured in a cyclic reaction that occurs at pH about 7.0 to about 8.3 with beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (beta-HBD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a tetrazolium dye precursor and an electron mediator. Using this reaction, false positive results obtained from urine samples taken from patients on sulfhydryl drugs are avoided. beta-HBD from some sources was found to cause false negative results in samples (e.g. urine) containing high chloride content due to chloride inhibition of beta-HBD. Using a simple test for chloride inhibition, it was found that beta-HBD from Alcaligenes is not so inhibited. Using either beta-HBD that is not inhibited by chloride or using 10-20 times the normal concentration of this enzyme eliminates false negatives in samples having substantial chloride content, such as urine, both in the reaction described above and in other reactions disclosed for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and total ketone bodies, all of which reactions occur in the pH range of about 8.6 to about 9.5.
Owner:GUPTA SURENDRA
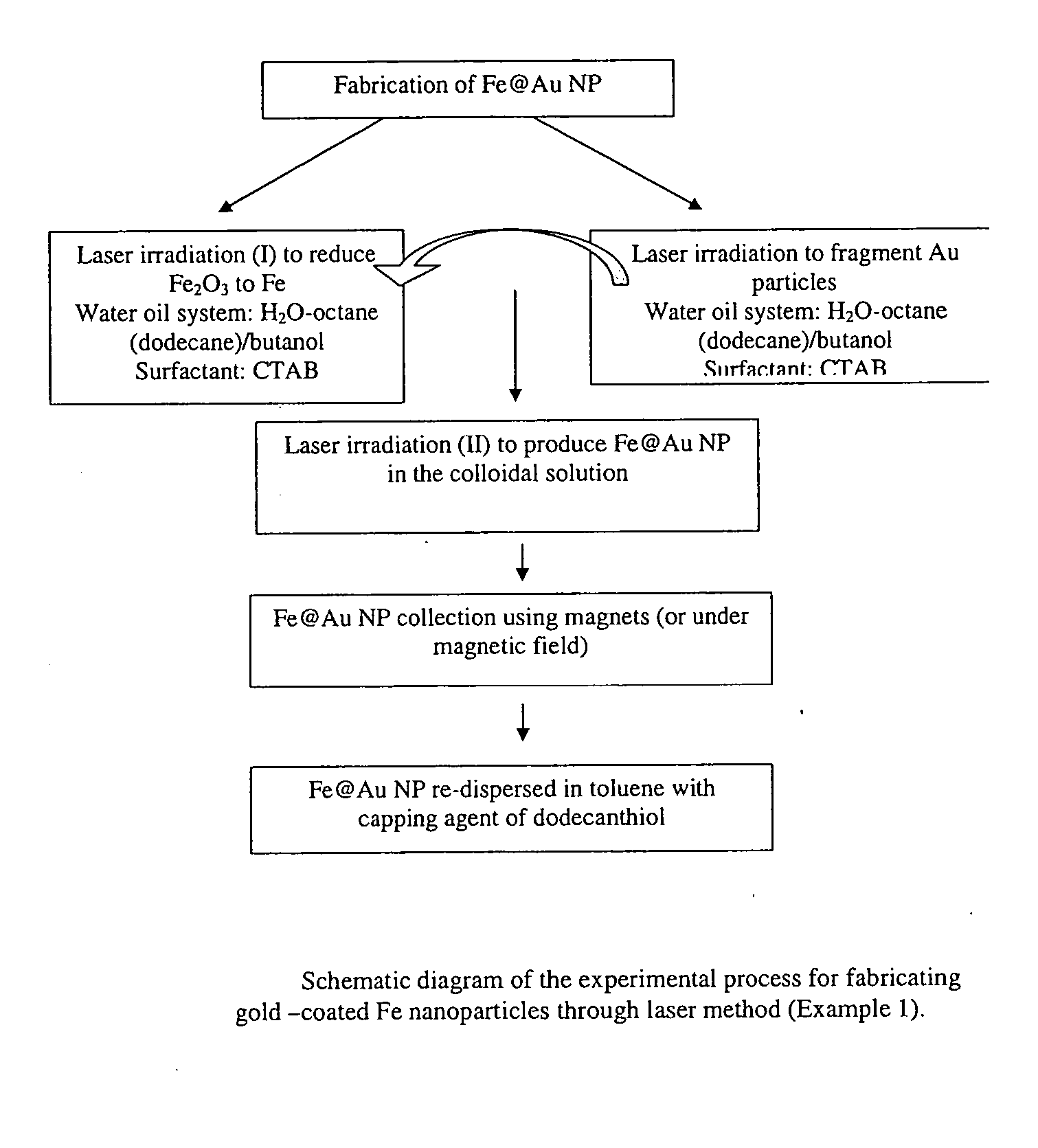
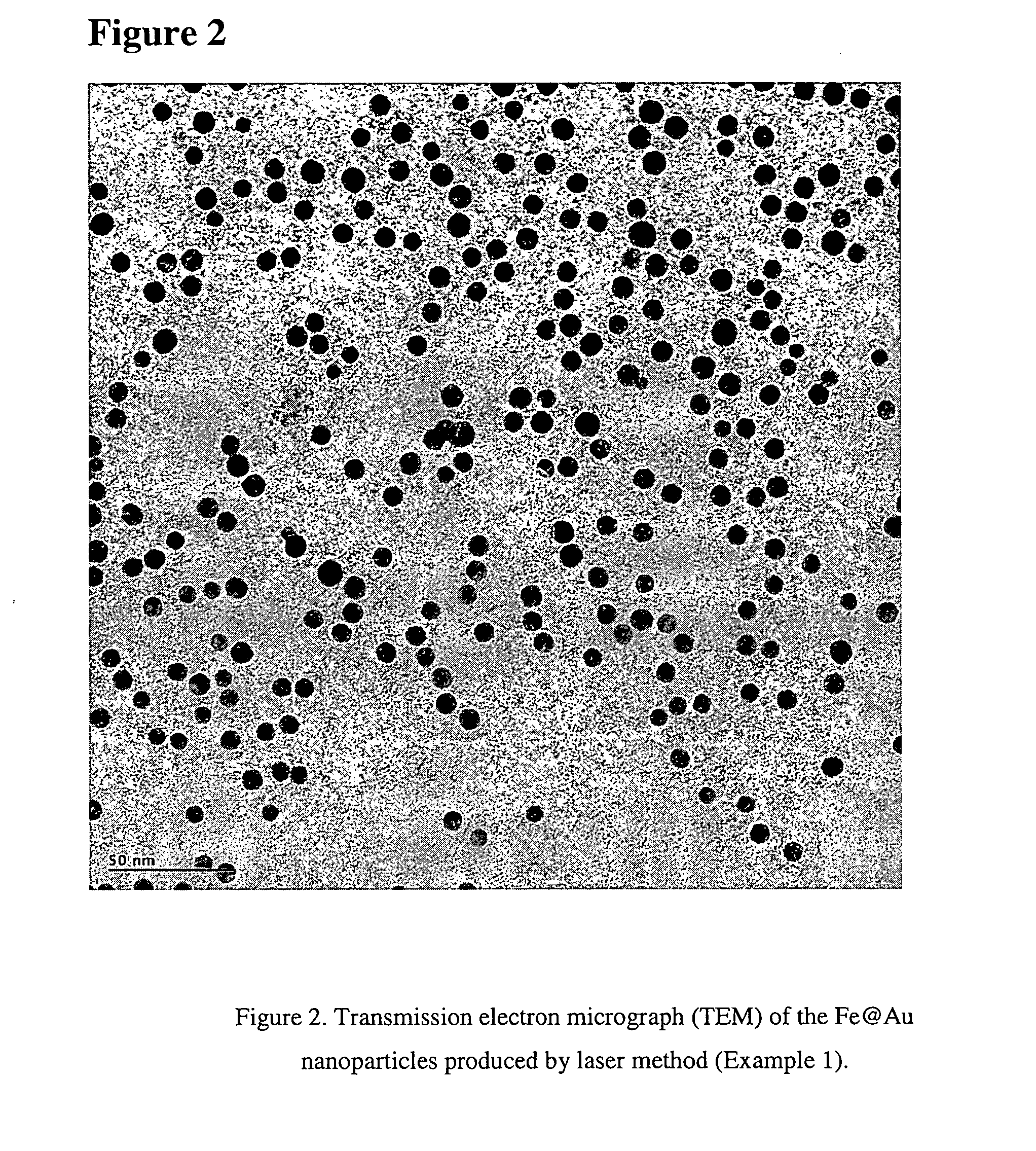
Methods for the fabrication of gold-covered magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060057384A1Reduce oxidationMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsGold ColloidMagnetite Nanoparticles
There is disclosed an approach for the gold-coating of cores, such as magnetic nanoparticles. In some instances, the core and gold colloids can be fabricated first through irradiation, such as laser irradiation, and then mixed together for further laser irradiation. Alternatively, the cores may be fabricated using wet chemistry and subsequently coated using an irradiation method. Also disclosed is a two phase aqueous:oil system and its use in coating a material present in one phase with a second material present in the second phase.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Ultraviolet detector manufacturing method
InactiveCN103441186AReduce thermal effectsExtended UV Photoelectric ResponseFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsHorizontal distributionExtreme ultraviolet
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric detection, and particularly discloses an ultraviolet detector manufacturing method which is achieved by gradient assembly of multi-size zinc oxide quantum dots in multiple layers of graphene. According to the ultraviolet detector manufacturing method, structure and performance advantages of the ZnO quantum dots and the graphene are combined, and collochemistry is adopted as the basic method to obtain the ZnO quantum dots with different sizes, and the band gaps of the ZnO quantum dots vary from the near ultraviolet area to the deep ultraviolet area; wet chemistry is adopted to prepare single-layer oxidized graphene, carboxyl functional group modification is then carried out on the surface of the single-layer oxidized graphene so that ZnO quantum dots with a single size can be suitable for being assembled on the surface of the single-layer oxidized graphene, and then the ZnO quantum dots (QD) with different sizes are used as active materials of ultraviolet response to construct a multi-layer sandwich type structure. According to the ultraviolet detector manufacturing method, gold, or platinum or ITO is used as electrode materials, a horizontal distribution type strip-shaped or itnerdigital electrode structure is designed, and then an ultraviolet detector is obtained and inter-band absorption response from near ultraviolet to deep ultraviolet is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Dry chemistry, lateral flow-reconstituted chromatographic enzyme-driven assays
ActiveUS20040203086A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeroxidaseAdditive ingredient
A lateral flow chromatographic assay format for the performance of rapid enzyme-driven assays is described. A combination of components necessary to elicit a specific enzyme reaction, which are either absent from the intended sample or insufficiently present therein to permit completion of the desired reaction, are predeposited as substrate in dry form together with ingredients necessary to produce a desired color upon occurrence of the desired reaction. The strip is equipped with a sample pad placed ahead of the substrate deposit in the flowstream, to which liquid sample is applied. The sample flows from the sample pad into the substrate zone where it immediately reconstitutes the dried ingredients while also intimately mixing with them and reacting with them at the fluid front. The fluid front moves rapidly into the final "read zone" wherein the color developed is read against predetermined color standards for the desired reaction. Pretreatment pads for the sample, as needed, (e.g. a lysing pad for lysing red blood cells in whole blood) are placed in front of the sample pad in the flow path as appropriate. The assay in the format of the invention is faster and easier to perform than analogous wet chemistry assays. Specific assays for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ("G-6PD"), total serum cholesterol, beta-lactamase activity and peroxidase activity are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Lithium ion battery negative electrode MOF material and application thereof
ActiveCN107732248AHigh lithium storage capacityWith lithium storage performanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithiumHigh energy
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery negative electrode MOF material. The MOF material disclosed by the invention is prepared by reacting porphyrin or porphyrin derivative of the porphyrin with transition metal or a transition metal cluster through a solvent thermal or wet chemistry method. When the MOF material is utilized as a lithium ion battery negative electrode material, the MOF material has a series of advantages of high specific capacity, long cycle life, outstanding rate capability and the like. Theoretical calculation proves that an active site of the action between the MOFmaterial disclosed by the invention and metal lithium has excellent performance, and the MOF material can be applied to developing high energy density lithium ion batteries.
Owner:南京铁鸣能源科技有限公司
Surface modification method of high-nickel ternary material lithium nickel cobalt manganate
PendingCN109920993AUniform particle size distributionGrain boundaries are clearCell electrodesSecondary cellsAir atmosphereHigh rate
The invention discloses a surface modification method of a high-nickel ternary material lithium nickel cobalt manganate. The surface modification method comprises the following steps of (1) accordingto a preset coating material and a coating amount, weighing nitrate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate based on stoichiometric ratio, and dissolving nitrate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in a proper amount of absolute ethyl alcohol; (2) weighing a certain amount of main material, slowly adding into the mixed solution, and performing stirring for a certain time until the absolute ethyl alcohol is completely volatilized; and (3) carrying out drying on the prepared product at a certain temperature for several hours, and putting the dried product into a tubular furnace, and carrying out calcining for several hours at a certain temperature in an air atmosphere, and then carrying out grinding and sieving treatment to obtain the product. According to the surface modification method provided bythe invention, absolute ethyl alcohol is used as a solvent, and phosphate coating is carried out on NCM622 by adopting a wet chemistry method, so that the prepared lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material is uniform in particle size distribution, clear in particle boundary, and relatively high in secondary particle spherical structure, and has high rate performance and cycling stability.
Owner:四川纳创时代新能源科技有限公司
Preparation method of composite nanowire array with one-dimensional ZnO(zinc oxide)-TiO2(titanium dioxide) core-shell structure
InactiveCN102723208AImprove efficiencyLow environmental requirementsLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationAtomic layer depositionZno nanowires
A preparation method of a composite nanowire array with a one-dimensional ZnO(zinc oxide)-TiO2(titanium dioxide) core-shell structure. In the whole preparation process, a wet chemistry method is adopted. The preparation method comprises the following steps: at first, a ZnO seed layer is prepared on conductive glass in a sol-gel method, then a ZnO nanowire array is grown on the seed layer in a liquid-phase deposition method, and next a TiO2 shell layer is prepared on a ZnO nanowire array in a circulating adsorption reaction method, so as to obtain the composite nanowire array with the one-dimensional ZnO-TiO2 core-shell structure. The preparation method has the advantages that (1) compared with the other methods (such as a chemical meteorology deposition method, an atom layer deposition method and a magnetron sputtering method), the preparation method has a simple process, does not require complex equipment and severe environments, and is low in cost; (2) the preparation method can control the diameter and the length of the ZnO nanowire and the thickness of the TiO2 shell layer conveniently; and (3) the preparation method can be combined with a photoanode preparation method of a quantum dot dye-sensitized solar cell conveniently to facilitate the research of the cell performance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
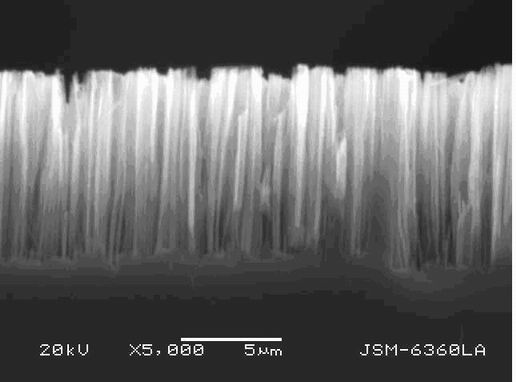
Micro hollow silicon needle and preparation method thereof
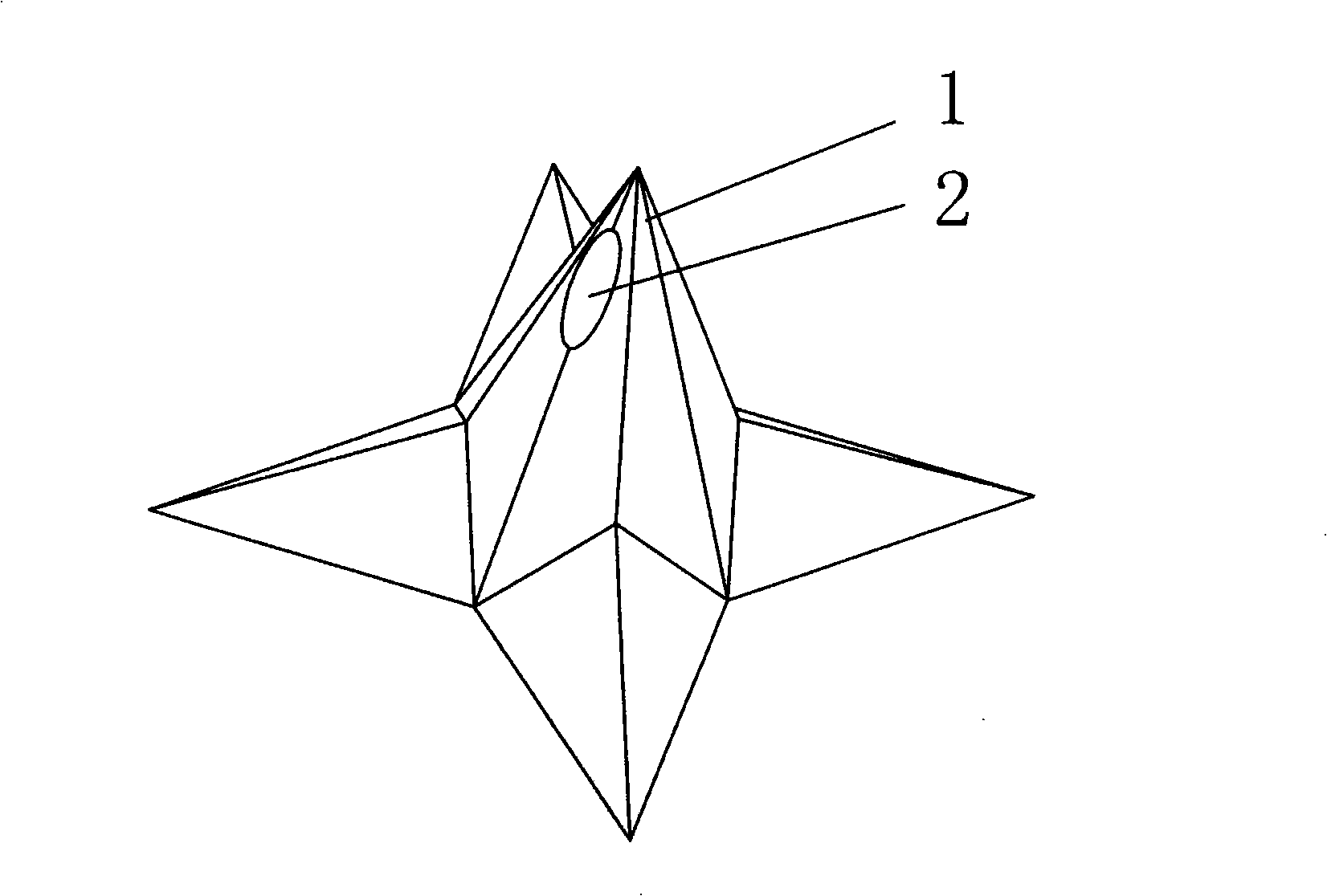
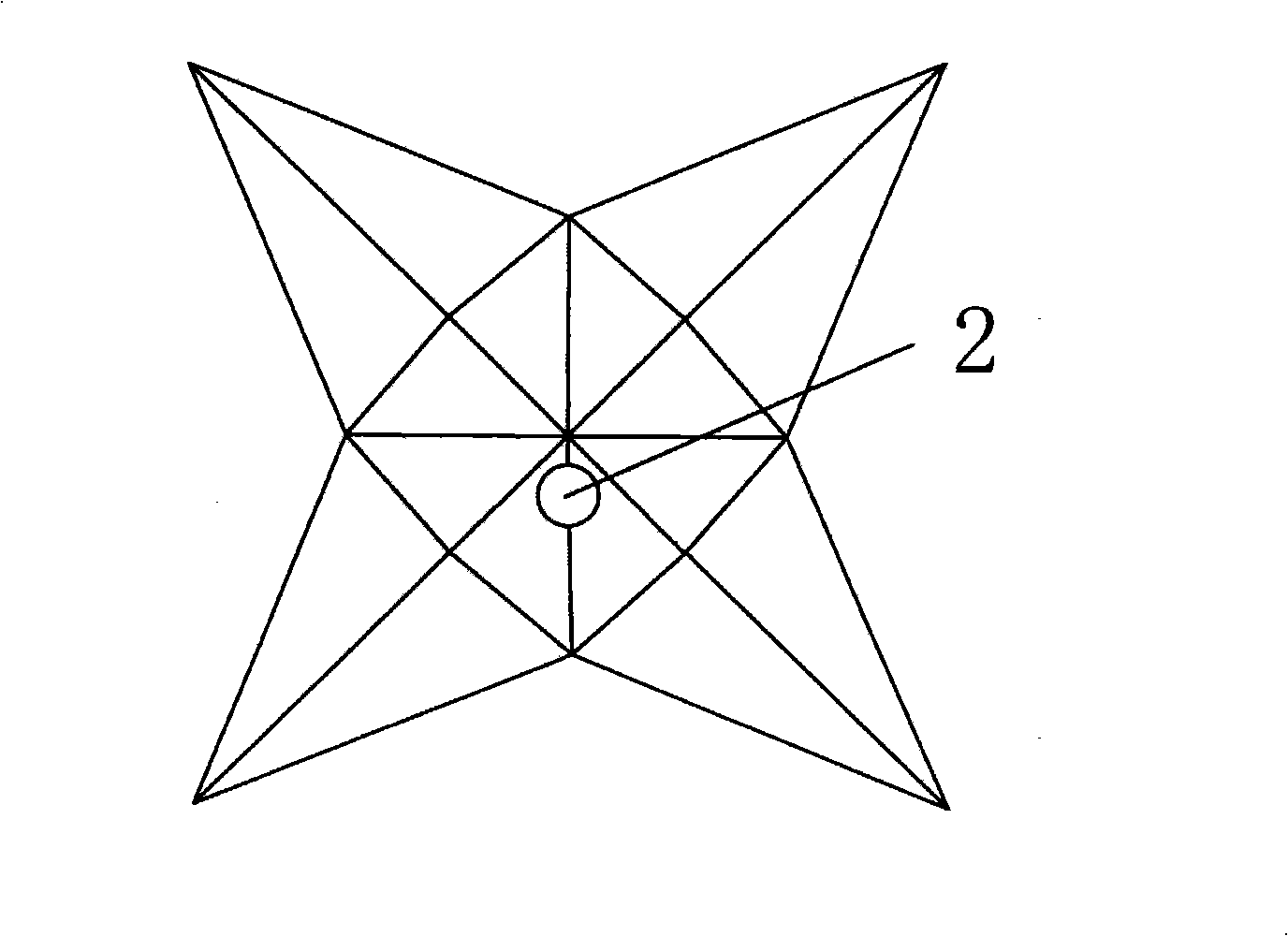
InactiveCN101332327AStable structureSimple preparation processDecorative surface effectsMicroneedlesManufacturing technologyCrystal orientation
The invention discloses a tiny hollow silicon probe, the needle of which takes the shape of a pyramid. A needlepoint or the side wall of a microneedle has a through hole which is vertical to a silicon substrate. The height of the tiny hollow silicon probe is 100-600 micron. The diameter of the through hole is larger than 5 micron. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the tiny hollow silicon probe which comprises that: a hole or hole arrays with the depth reaching or being close to the thickness of the silicon are processed through a method of anisotropy chemical etch on the reverse side of monocrystalline silicon chips on crystal orientation; on the positive side of the silicon, by adopting an anisotropy wet chemistry etch method, a pyramid-shaped tiny silicon probe is processed and the through hole which is connected with the reverse side of the silicon is exposed. The tiny hollow silicon probe array prepared by the invention not only has stable structure, but also is simple in manufacture technology, short in manufacture cycle, low in cost, high in the rate of finished products and good in repetitiveness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method and application for ternary composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN105688899ASimple processImprove photocatalytic activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsOctahedronMaterial synthesis
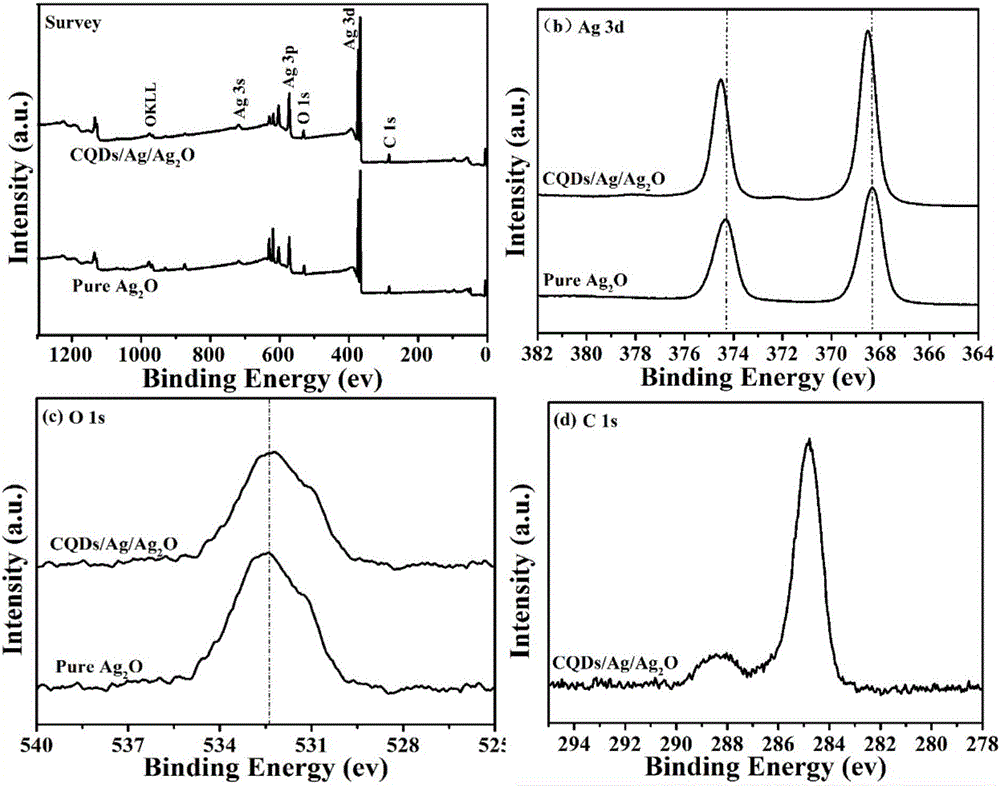
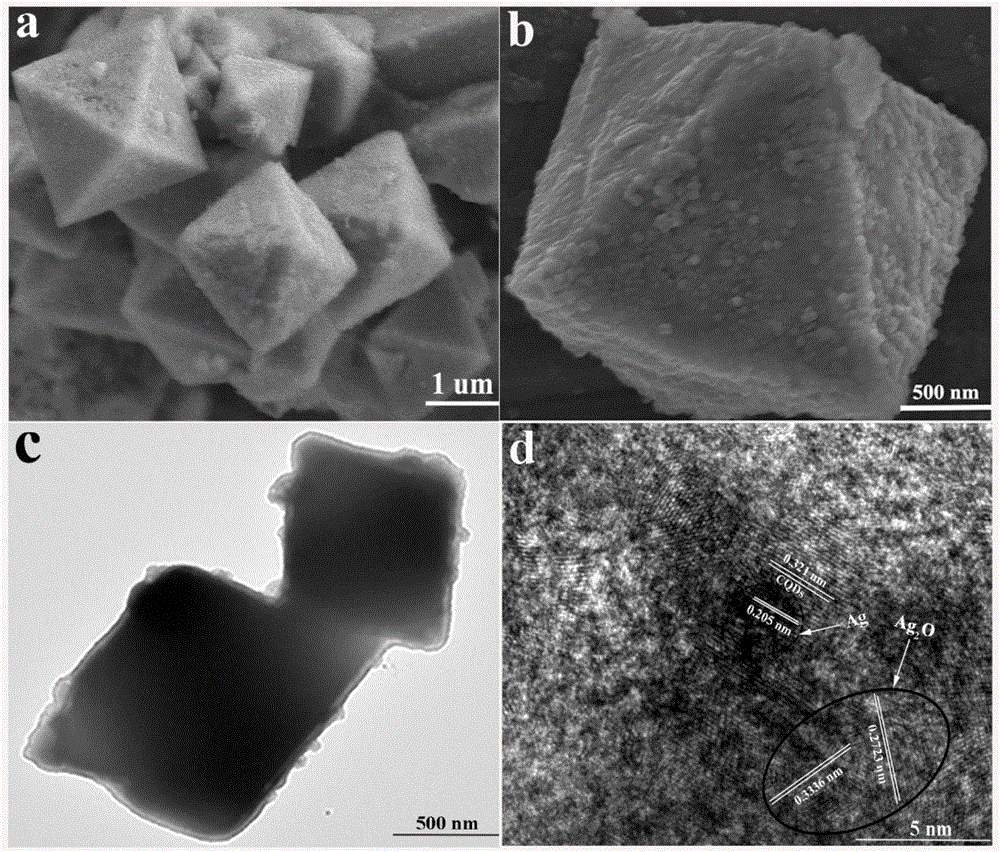
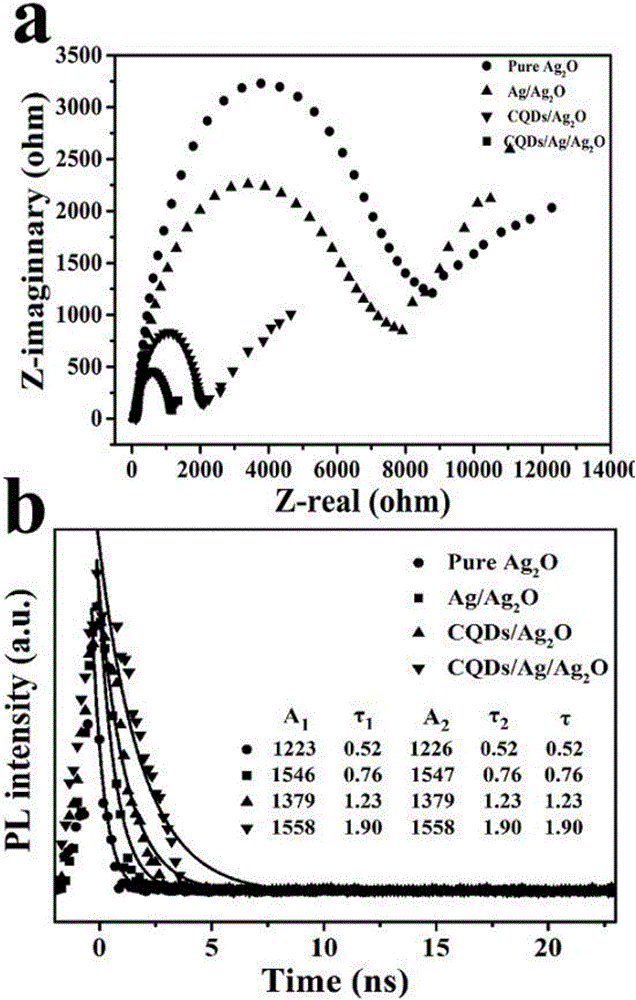
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano-material synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method and the application of a ternary composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first, synthesizing CQDs (Carbon Quantum Dots) with a remarkable up-conversion fluorescence effect by utilizing a simple one-step alkali auxiliary ultrasonic processing method; then, generating silver oxide (Ag2O) with an octahedral structure in CQDs solution by a wet-chemical method to obtain a CQDs / Ag2O compound with a CQDs coating layer; finally, loading silver (Ag) nano-particles on the surface of the CQDs / Ag2O by using chemical deposition and photo-deposition methods. The ternary composite photocatalyst can be used for degrading organic pollutants, such as rhodamine B, under full spectrum.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
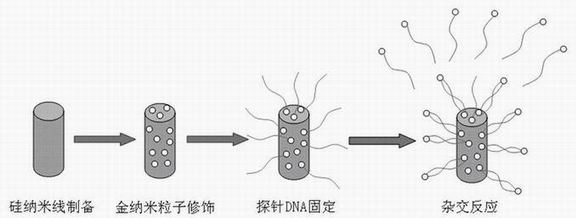
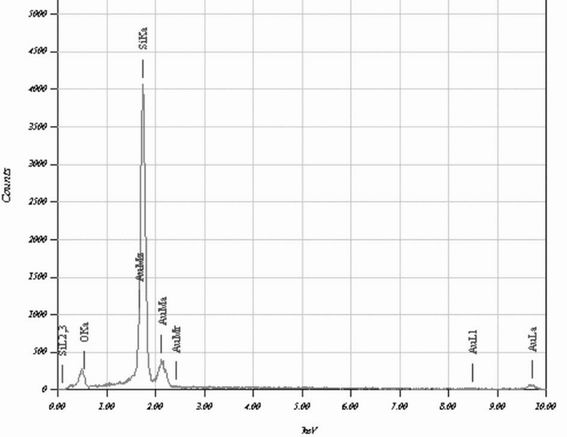
Method for preparing biosensor based on silicon nanowires and application of biosensor to detecting DNA
InactiveCN102072931AImprove conductivityGood biocompatibilityNanosensorsMaterial electrochemical variablesBiocompatibility TestingIntegrated circuit
The invention discloses a method for preparing a biosensor based on silicon nanowires and application of the biosensor to detecting DNA. The method is characterized by preparing the silicon nanowires by a wet chemical method, modifying gold nanoparticles on the silicon nanowires via a silane coupling agent and grafting a probe DNA on the silicon nanowires through binding of chemical bonds betweenthe gold nanoparticles and the DNA to prepare a sensor probe. The sensor is applied to detecting the unknown DNA sequences in the target solution to be detected. The detecting results are mainly obtained by analyzing the data measured by cyclic voltammetry. The invention has the following advantages: (1) mass production can be carried out through simple microprocessing technology, the cost is lowand the microprocessing technic is compatible with the large scale integration technology; (2) the biosensor mainly utilizes the specificity and biocompatibility among the silicon nanowires, the goldnanoparticles and the DNA, is easy to realize and has wide applicability; and (3) the biosensor is simple and convenient to manufacture, has good repeatability and high sensibility, is easy to realize microminiaturization and can realize real-time monitoring.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
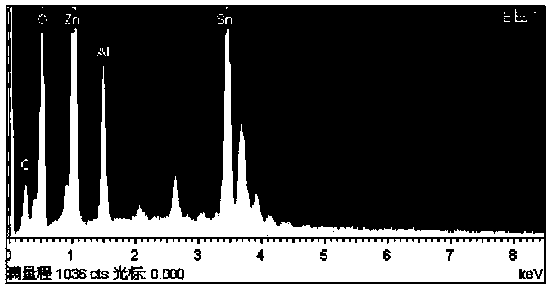
Preparation method for zinc oxide/stannic oxide composite microsphere
InactiveCN103566843ALarge specific surface areaUniform particle size distributionZinc oxides/hydroxidesMicroballoon preparationTin dioxideMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method for a zinc oxide / stannic oxide composite microsphere. According to the method, a wet chemistry method is utilized; a block polymer is used as a template in an organic solvent; a water-soluble zinc salt and a stannum salt are used as precursors; the size of particles is controlled through an ordered composition of the template in the mesoscopic size, and through hydrophilic characteristic, lipophilic characteristic, and the like; and a metal oxide microsphere is obtained by removing the template. The method has advantages of simple technology, low cost, and easily controllable and adjustable size, components, and other characteristics of the microsphere. The zinc oxide / stannic oxide composite microsphere prepared by the method can be used for photocatalysis and hydrolysis of water or polymers, solar cell light anodes, gas-sensitive sensors, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Preparation method and application of photoelectrochemical aptamer sensing electrode
InactiveCN105403603ASimple preparation processHigh selectivityMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerIndium
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectrochemical sensing, and relates to a preparation method of a photoelectrochemical aptamer sensing electrode and an application of the photoelectrochemical aptamer sensing electrode to detection of microcystins. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, BiOBr-NG nano-composites are prepared with a wet chemical method; then ITO (indium tin oxide) electrode surfaces are modified with the BiOBr-NG nano-composites, the pi-pi stacking action of NG and aptamers is further utilized for fixation of the aptamers and construction of a photoelectrochemical platform, and then the photoelectrochemical platform is applied to detection of the microcystins. The invention aims to invent the preparation method of the photoelectrochemical aptamer sensing electrode which adopts the simple preparation technology and has the good selectivity, the high sensitivity and the low detection cost.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Wet-chemical preparation method for silver micro/nanowires
ActiveCN102699341AImprove securityLower operating temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyNanowireChemical preparation
The invention relates to a preparation method for silver micro / nanowires, which comprises the following steps: adding a templating agent into the aqueous solution of silver salt under the condition of low temperature, adding a reducing agent dropwise, washing and drying to obtain the silver micro / nanowires. The preparation method for the silver micro / nanowires needs low operation temperature, no polymer protecting agent is added, and the materials react in an aqueous medium completely. The preparation method for the silver micro / nanowires is easy to operate and control and has environmental friendly reaction process and low cost.
Owner:武汉一封材料科技有限公司
Method for improving sintering compactness of W-Y2O3 composite material
The invention discloses a method for improving the sintering compactness of a W-Y2O3 composite material. The method comprises the steps that a second phase Y2O3 is added into a tungsten-based materialby adopting a wet chemistry method, and meanwhile, a surfactant is added so as to obtain the W-Y2O3 composite material. According to the method, based on the actual situation that tungsten is taken as PFMs, based on the consideration that the grain boundary density needs to be improved, and the second phase Y2O3 is added into the tungsten-based material by using the wet chemical method, so that the grain boundary strength is improved, and the problem that crystal grain distribution is not uniform due to traditional mechanical alloying is solved; and in order to further improve the density ofa tungsten-based alloy, the surfactant is added in the process of preparing W-Y2O3 composite powder, the grain refinement is further promoted, the distribution is uniform, the sintering density and heat conduction performance of the W-Y2O3 composite material are improved, so that the brittleness problem is effectively relieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Straw plate and preparing method thereof
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Wet chemistry method for preparing lithium iron phosphate
InactiveCN1208241CEasy to controlEvenly distributedElectrode thermal treatmentLi-accumulatorsLithium iron phosphateLITHIUM PHOSPHATE
A wet chemical process for preparing iron lithium phosphate includes mixing the solution or suspensions of Li source compound, Fe source compound, P source compound, doping element compound or electric conducting agent, and precipitant, reaction at 5-120 deg.C for 0.5-24 hr while stirring, filtering, washing, baking to obtain nano precursor, quickly heating to 500-800 deg.C in non-air or non-oxidizing atmosphere, calcining for 5-48 hr, and cooling. Its advantages are easy control, high uniformity and electric conductivity.
Owner:郑绵平
Platinum Adlayered Ruthenium Nanoparticles, Method for Preparing, and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110256469A1Superior and industrially scalableHigh activityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufacturePlatinumFuel cells
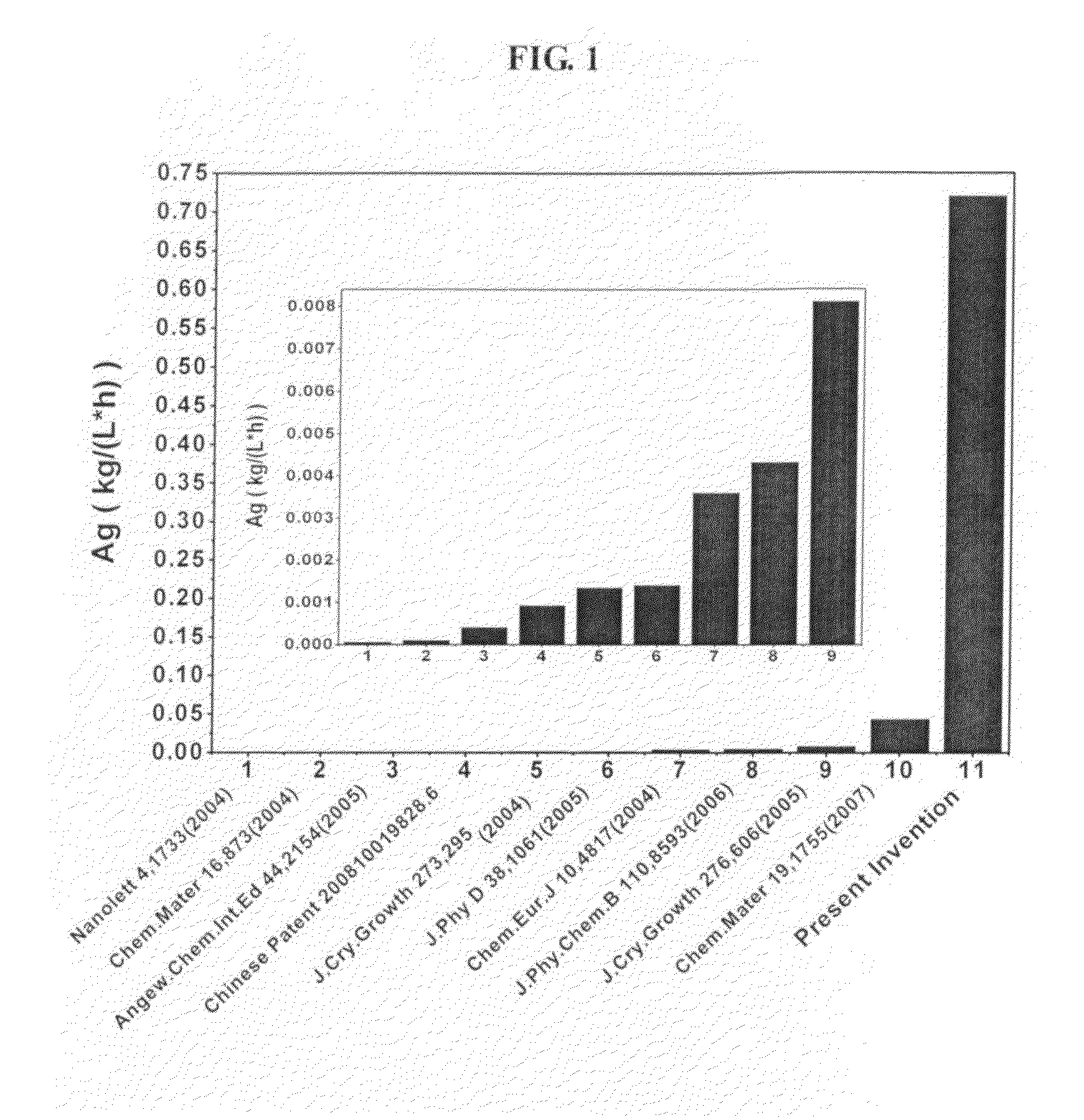
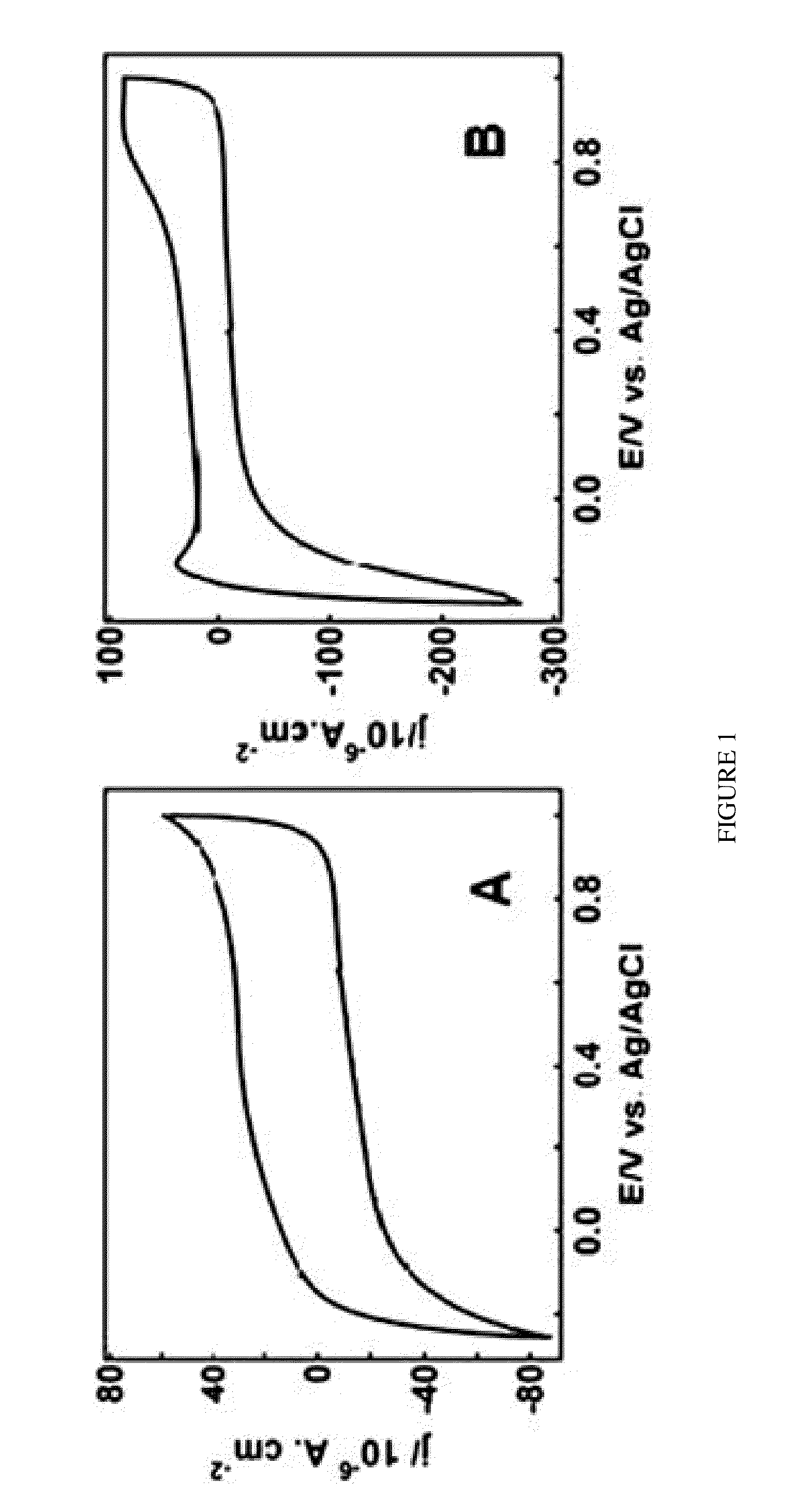
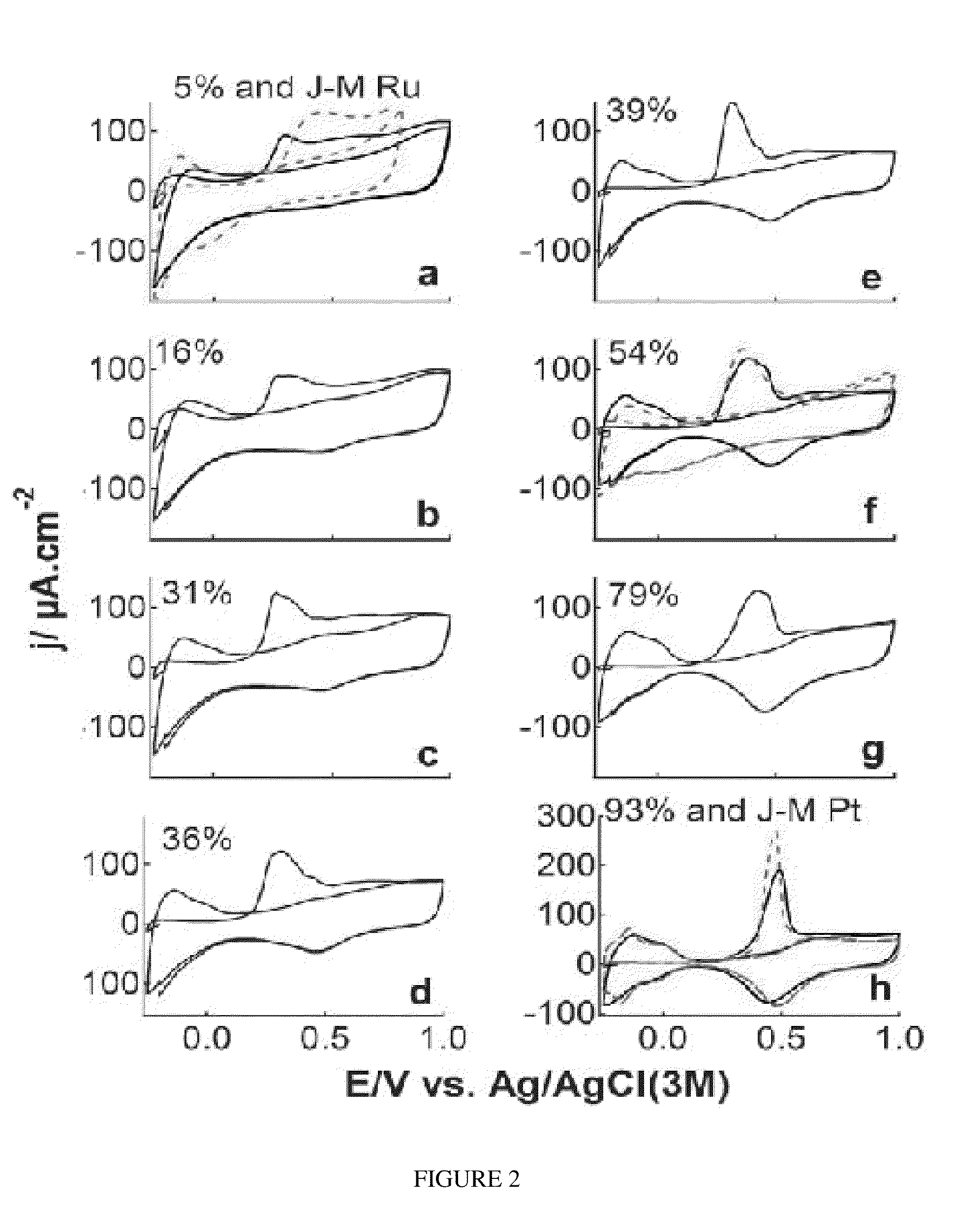
A superior, industrially scalable one-pot ethylene glycol-based wet chemistry method to prepare platinum-adlayered ruthenium nanoparticles has been developed that offers an exquisite control of the platinum packing density of the adlayers and effectively prevents sintering of the nanoparticles during the deposition process. The wet chemistry based method for the controlled deposition of submonolayer platinum is advantageous in terms of processing and maximizing the use of platinum and can, in principle, be scaled up straightforwardly to an industrial level. The reactivity of the Pt(31)-Ru sample was about 150% higher than that of the industrial benchmark PtRu (1:1) alloy sample but with 3.5 times less platinum loading. Using the Pt(31)-Ru nanoparticles would lower the electrode material cost compared to using the industrial benchmark alloy nanoparticles for direct methanol fuel cell applications.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com