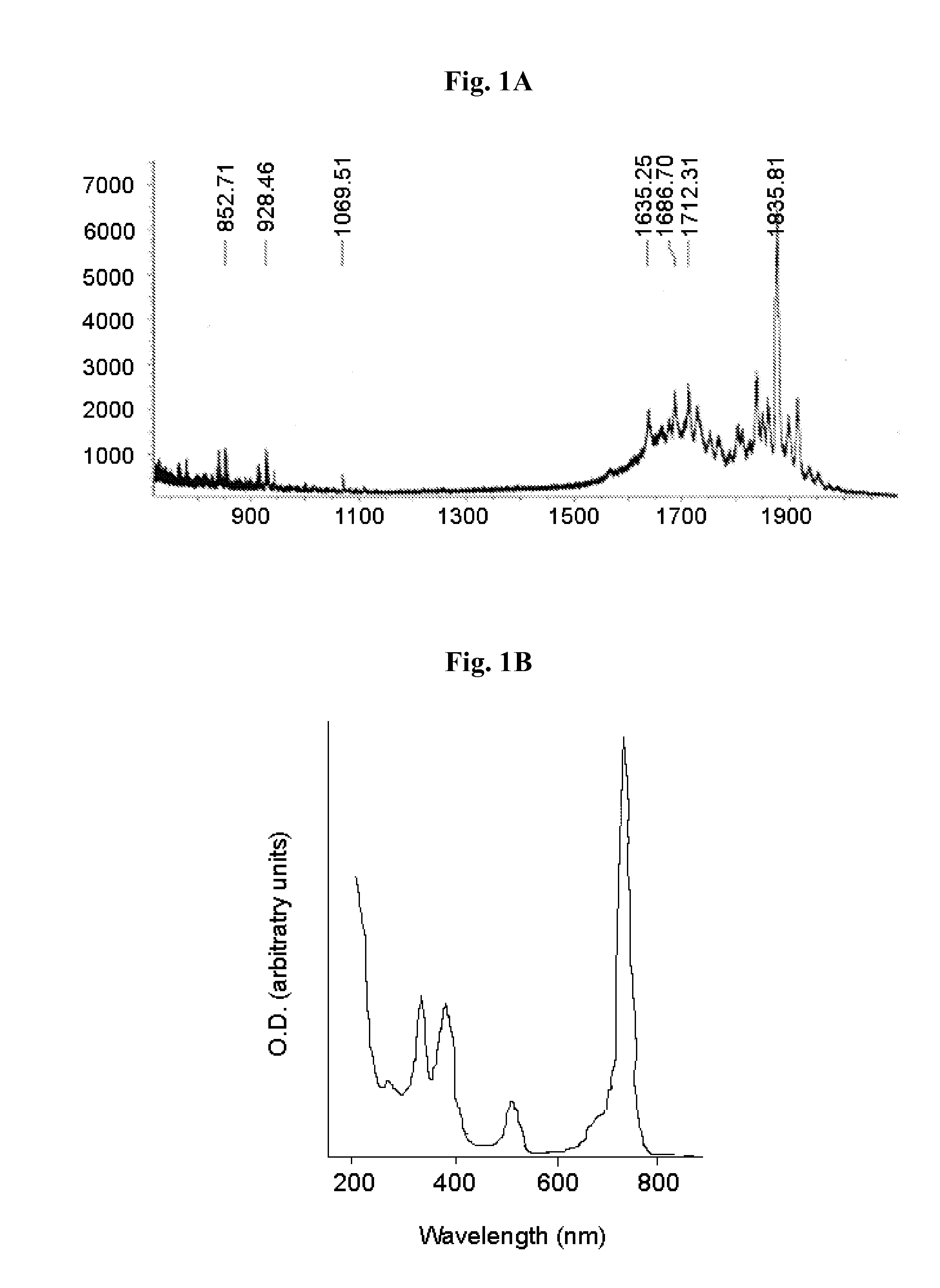
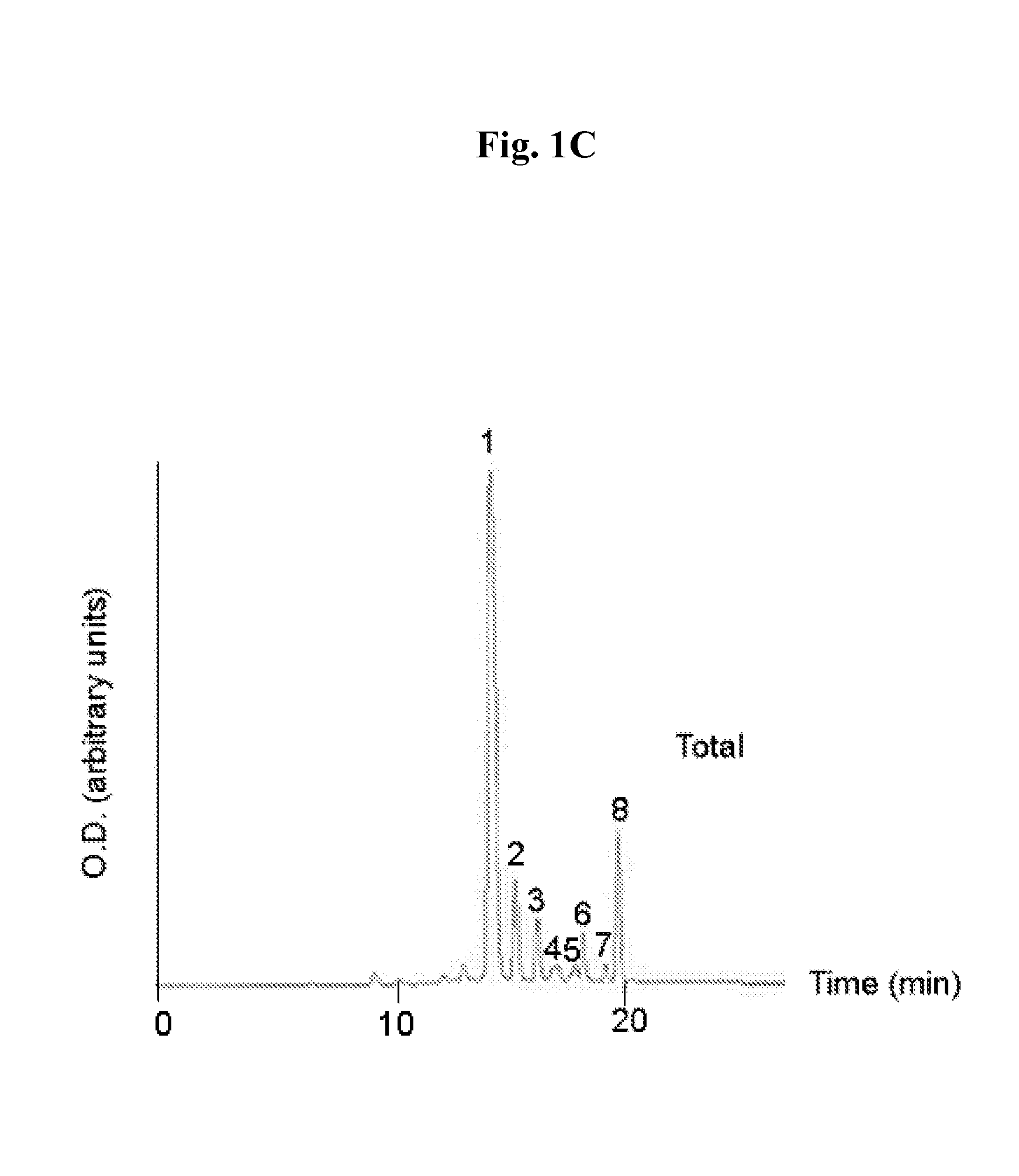
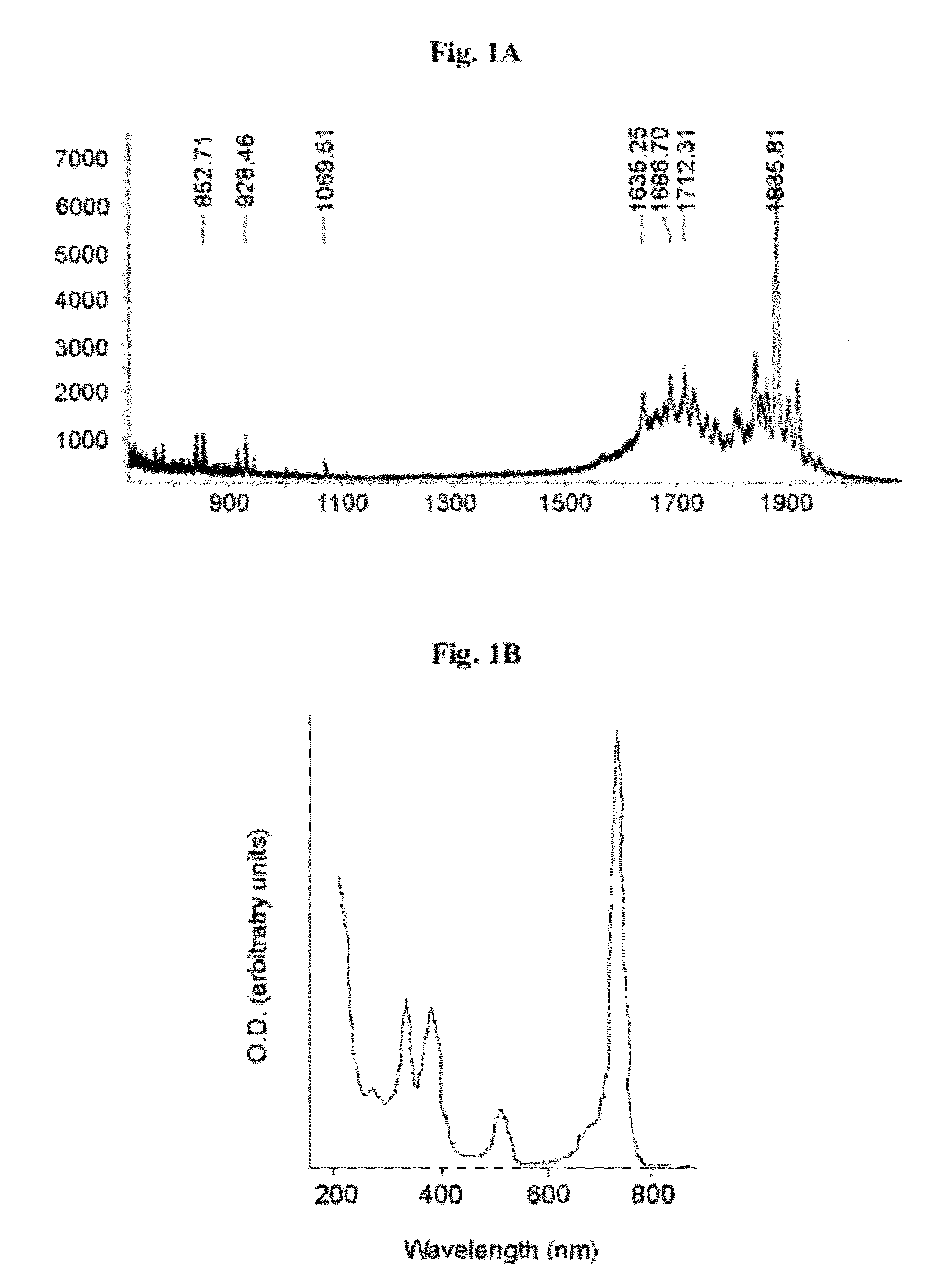
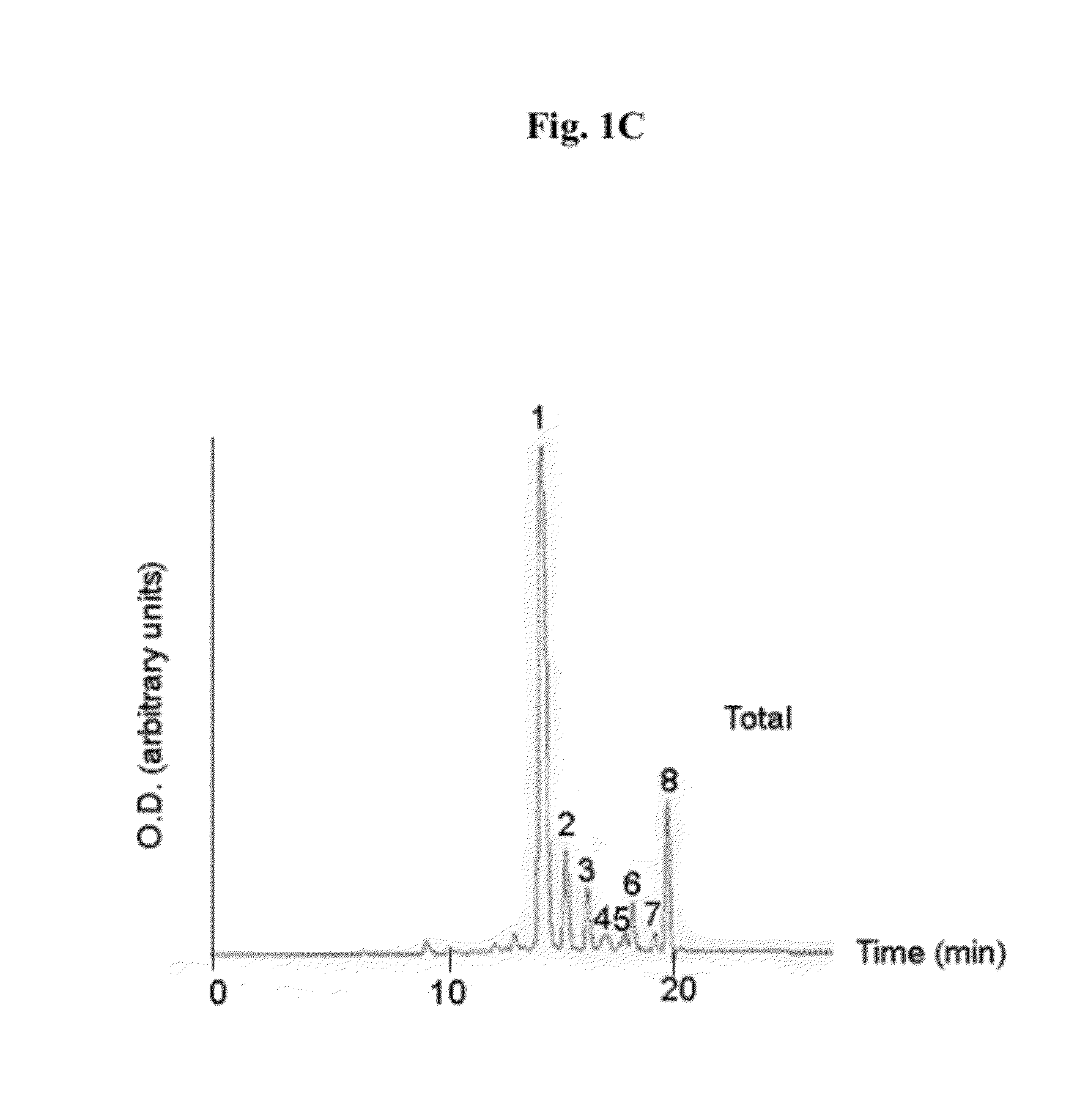
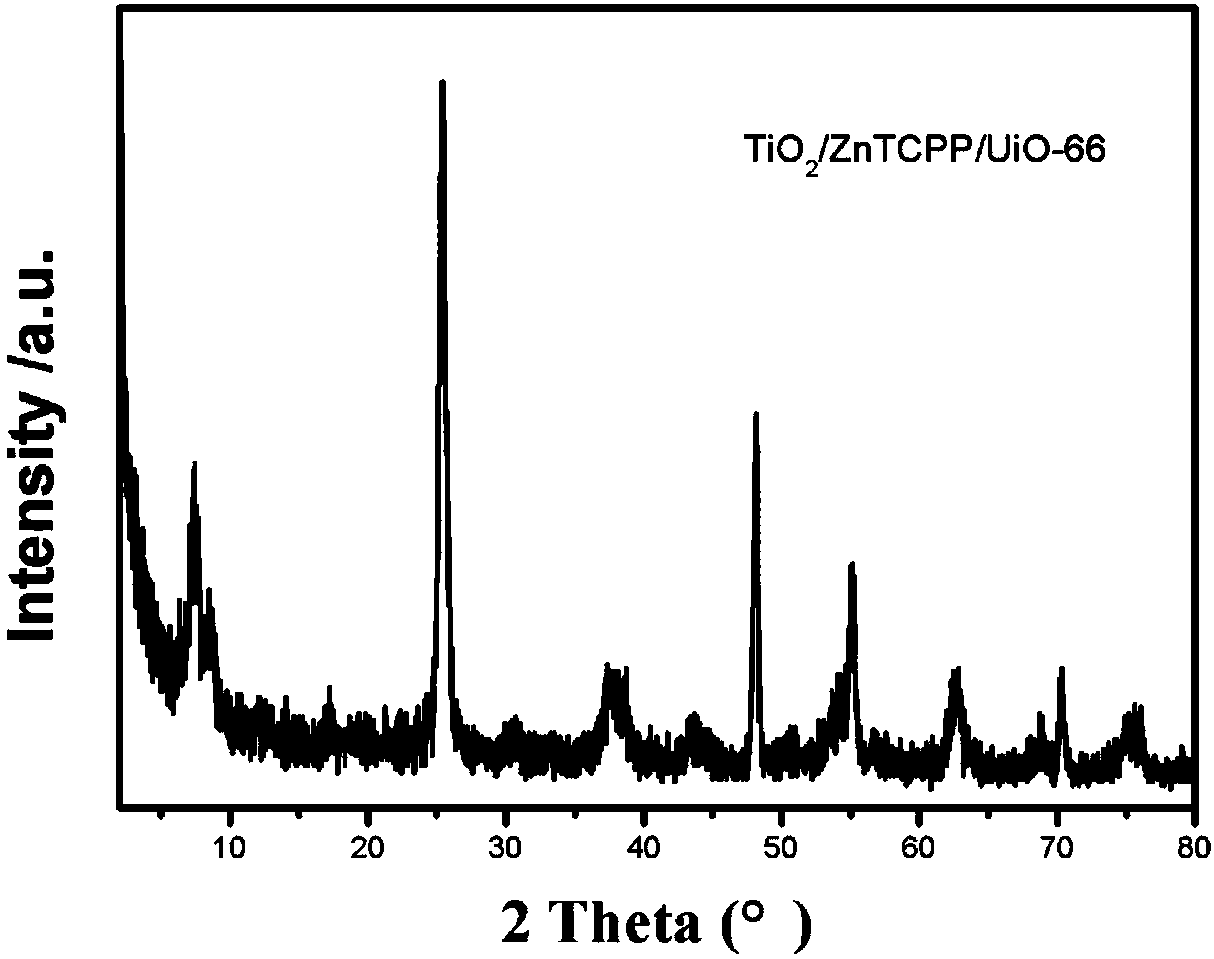
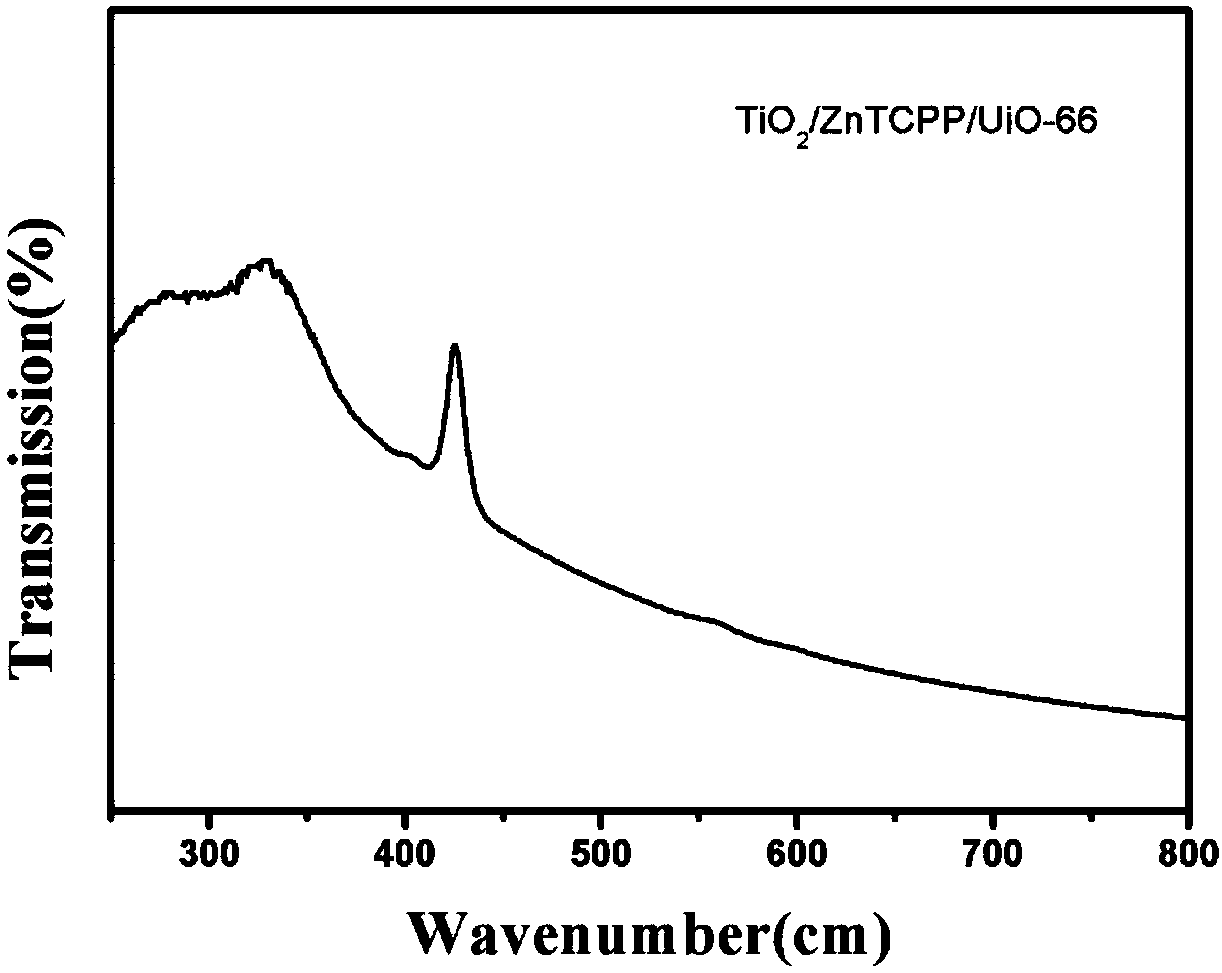
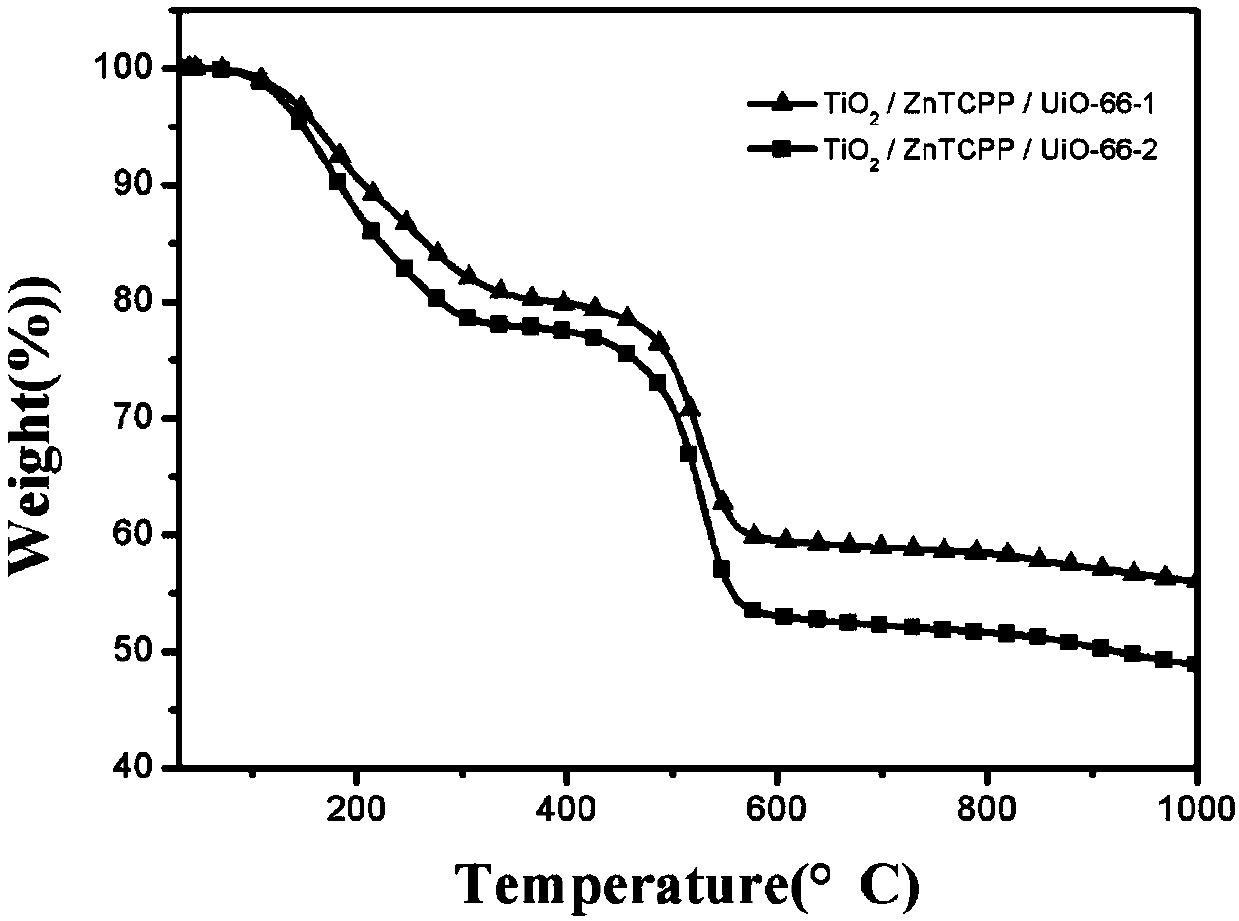
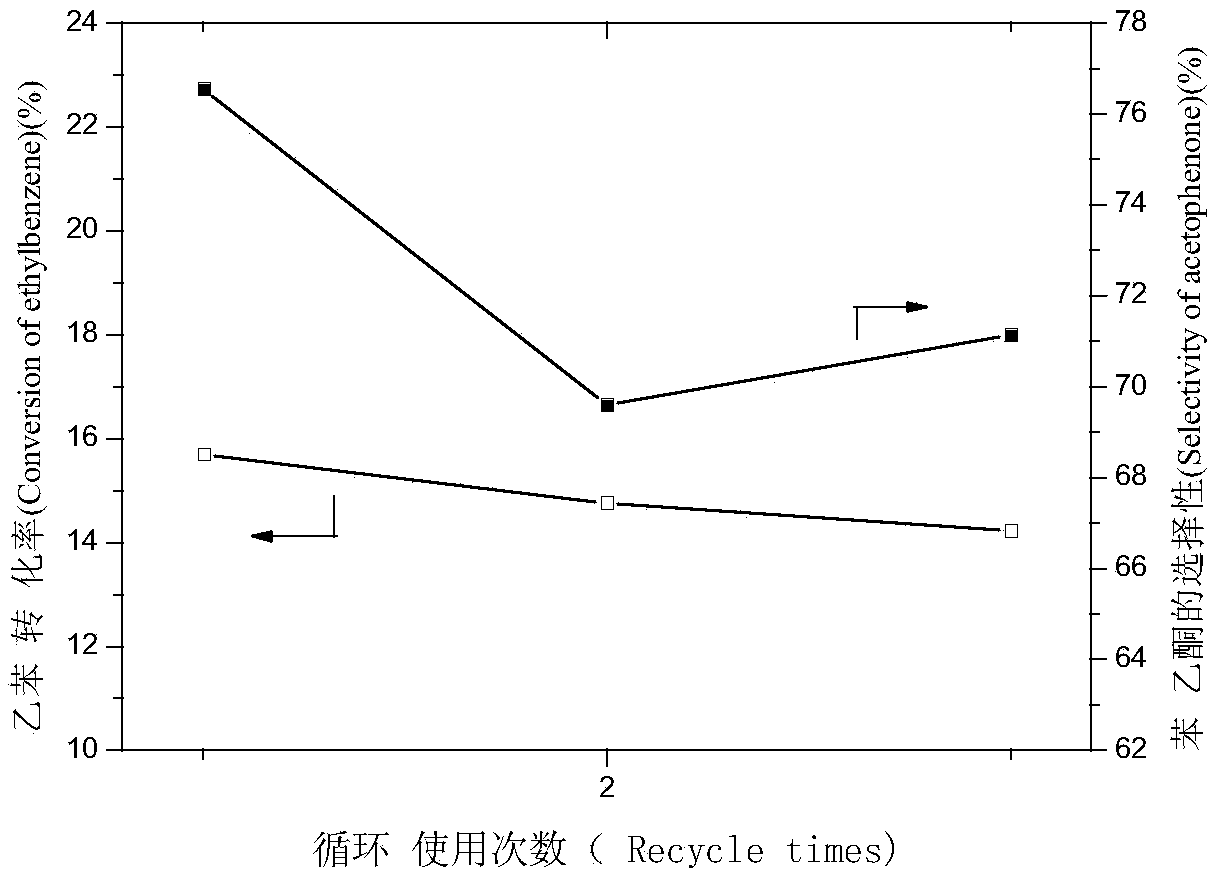Patents
Literature
2314 results about "Porphyrin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
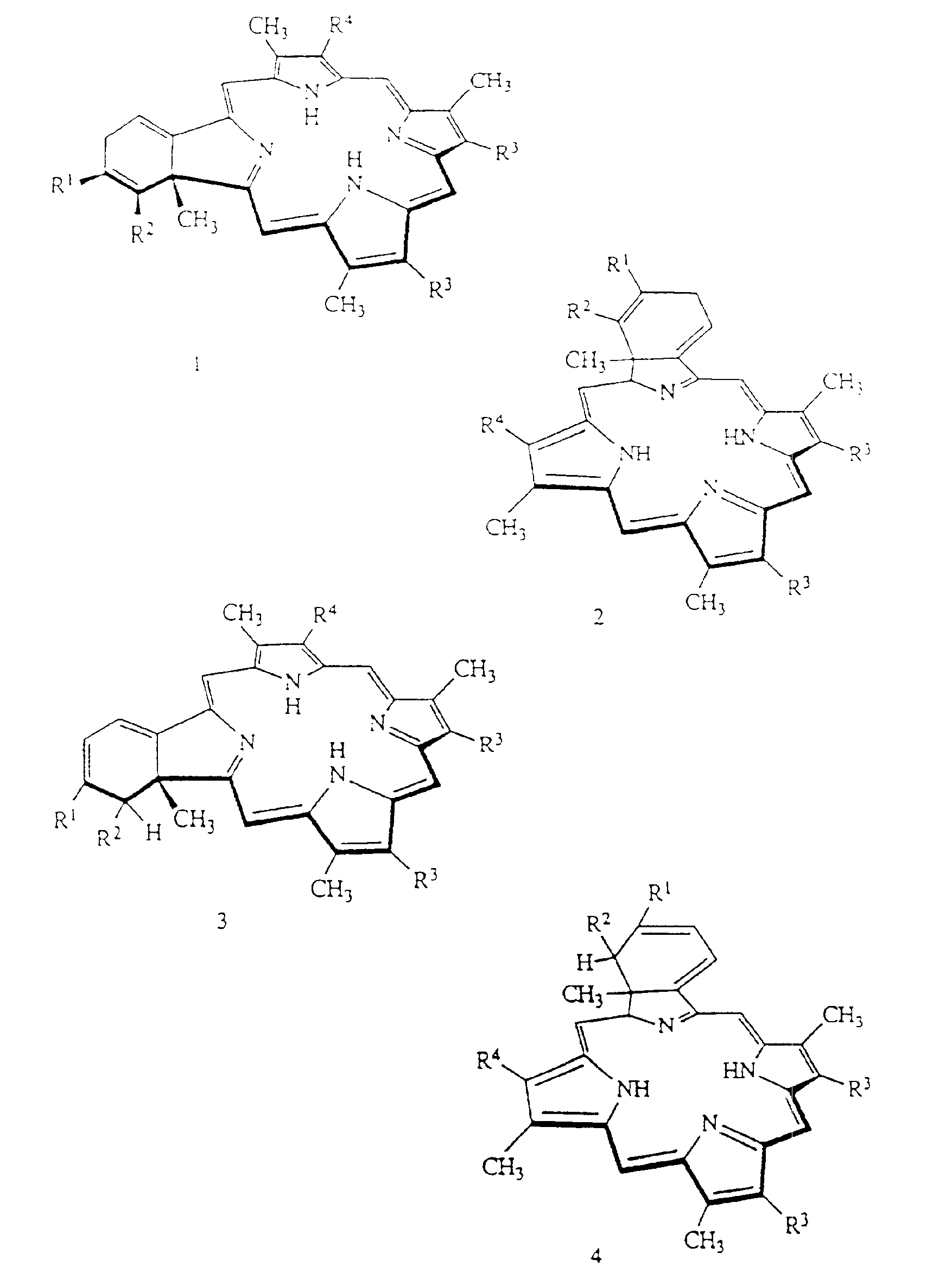
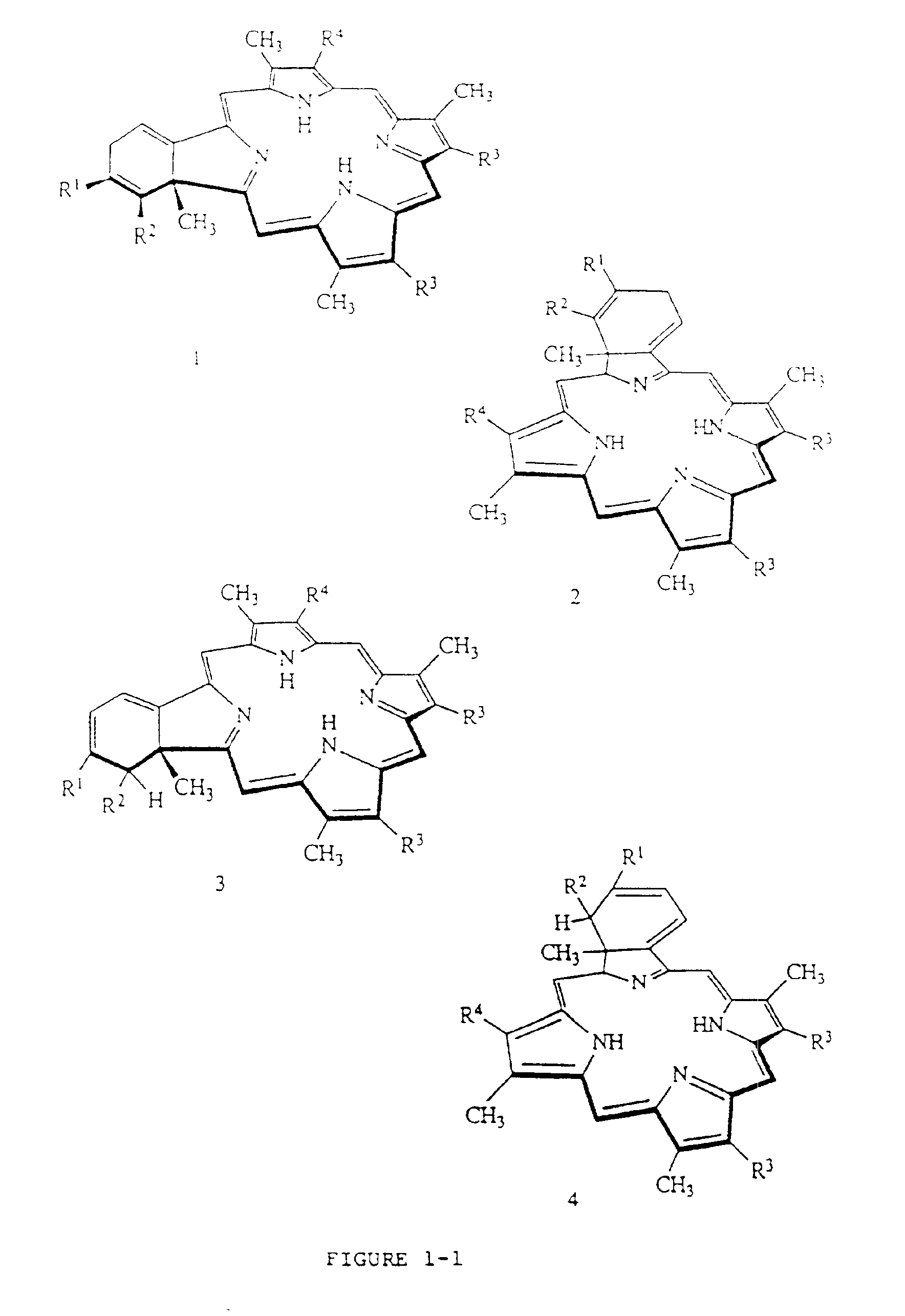
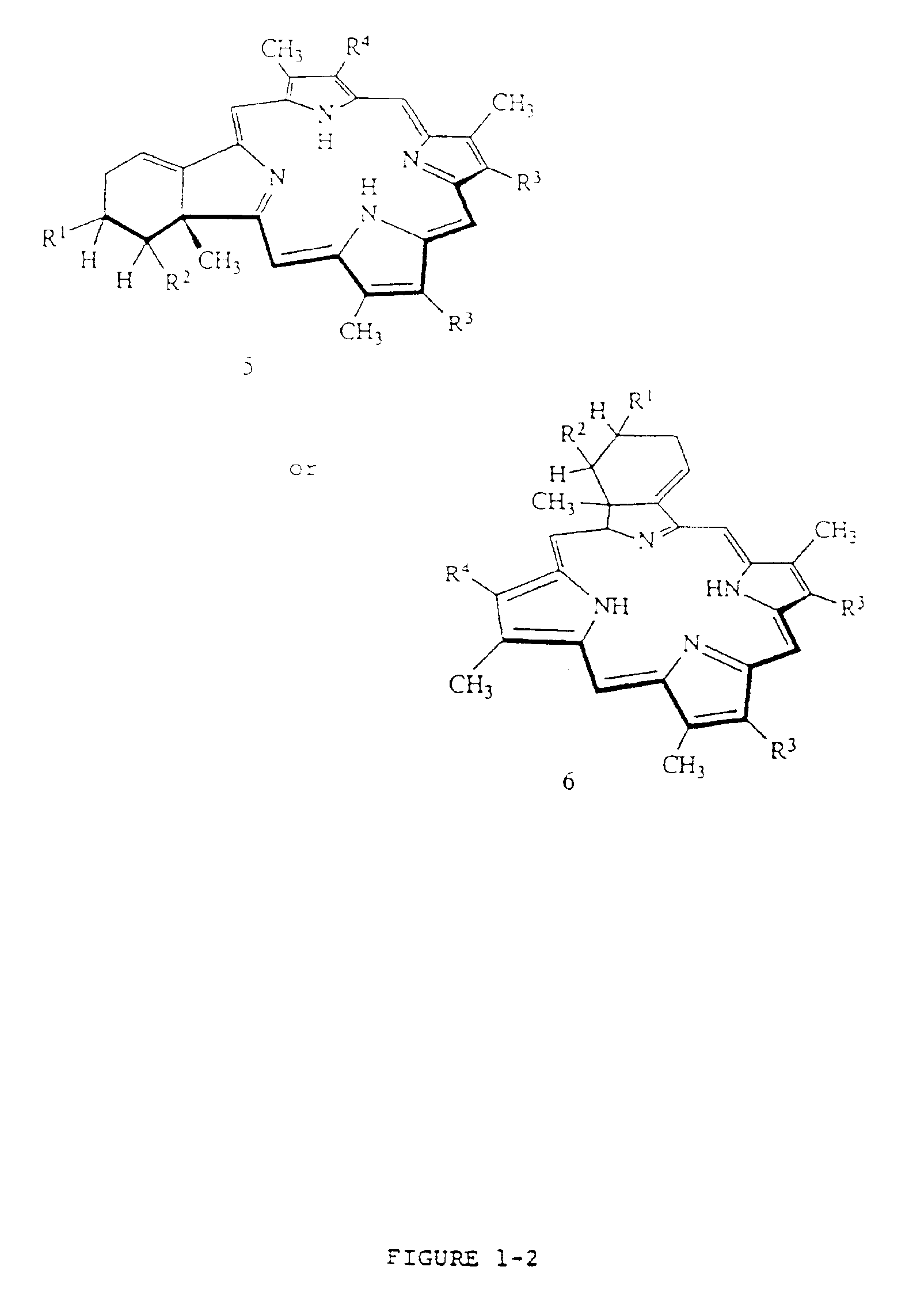
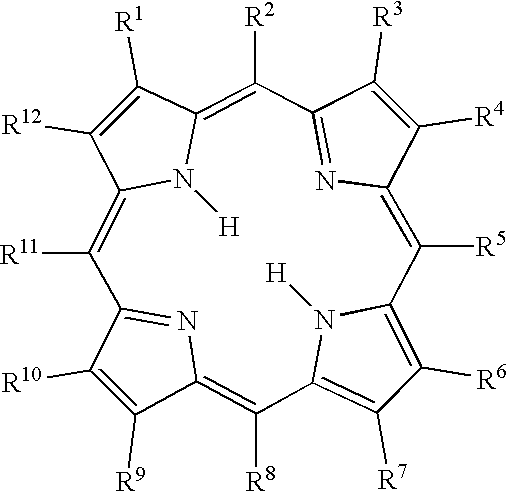
Porphyrins (/ˈpɔːrfərɪn/ POR-fər-in) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (porphyra), meaning purple.
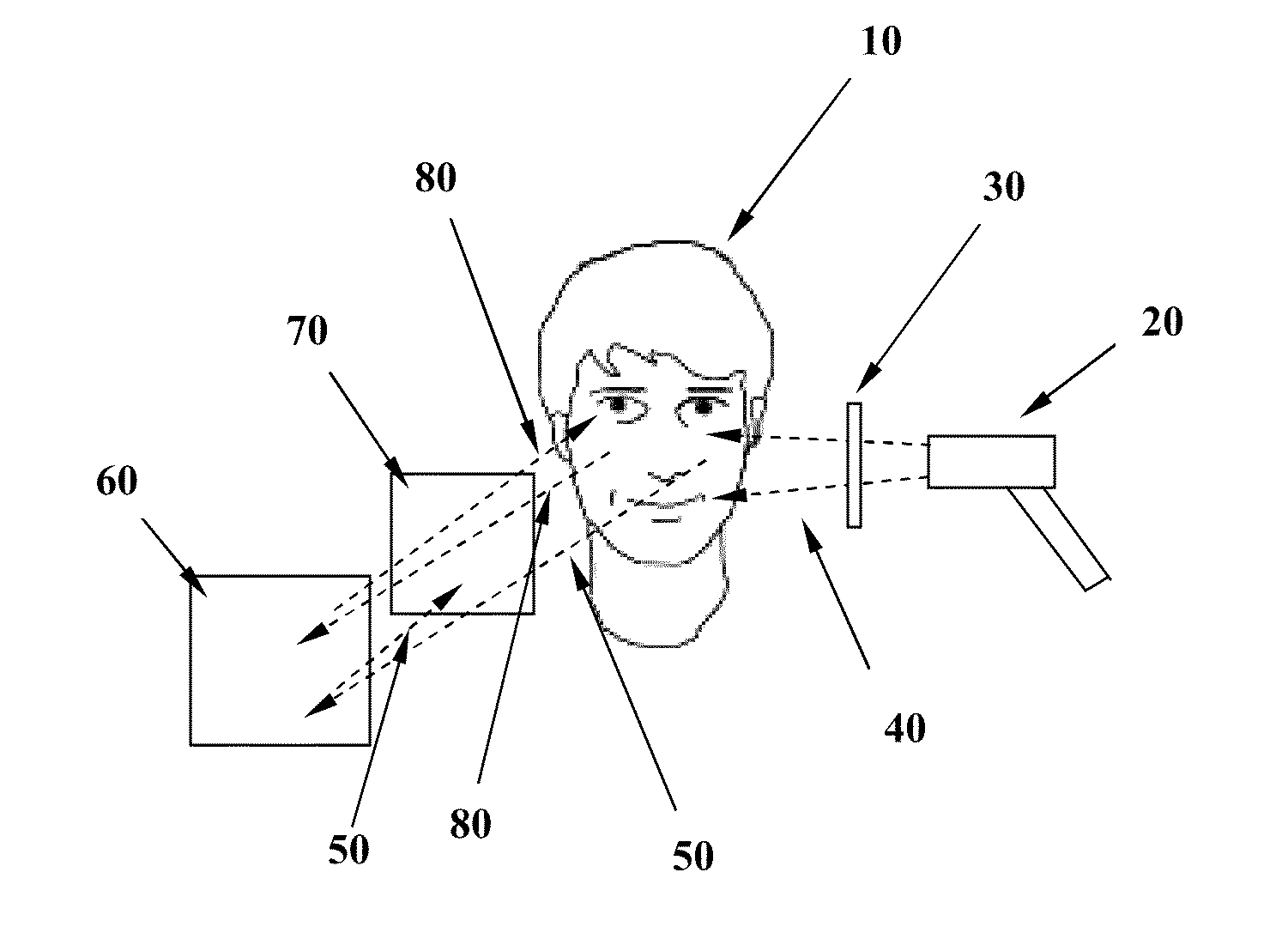
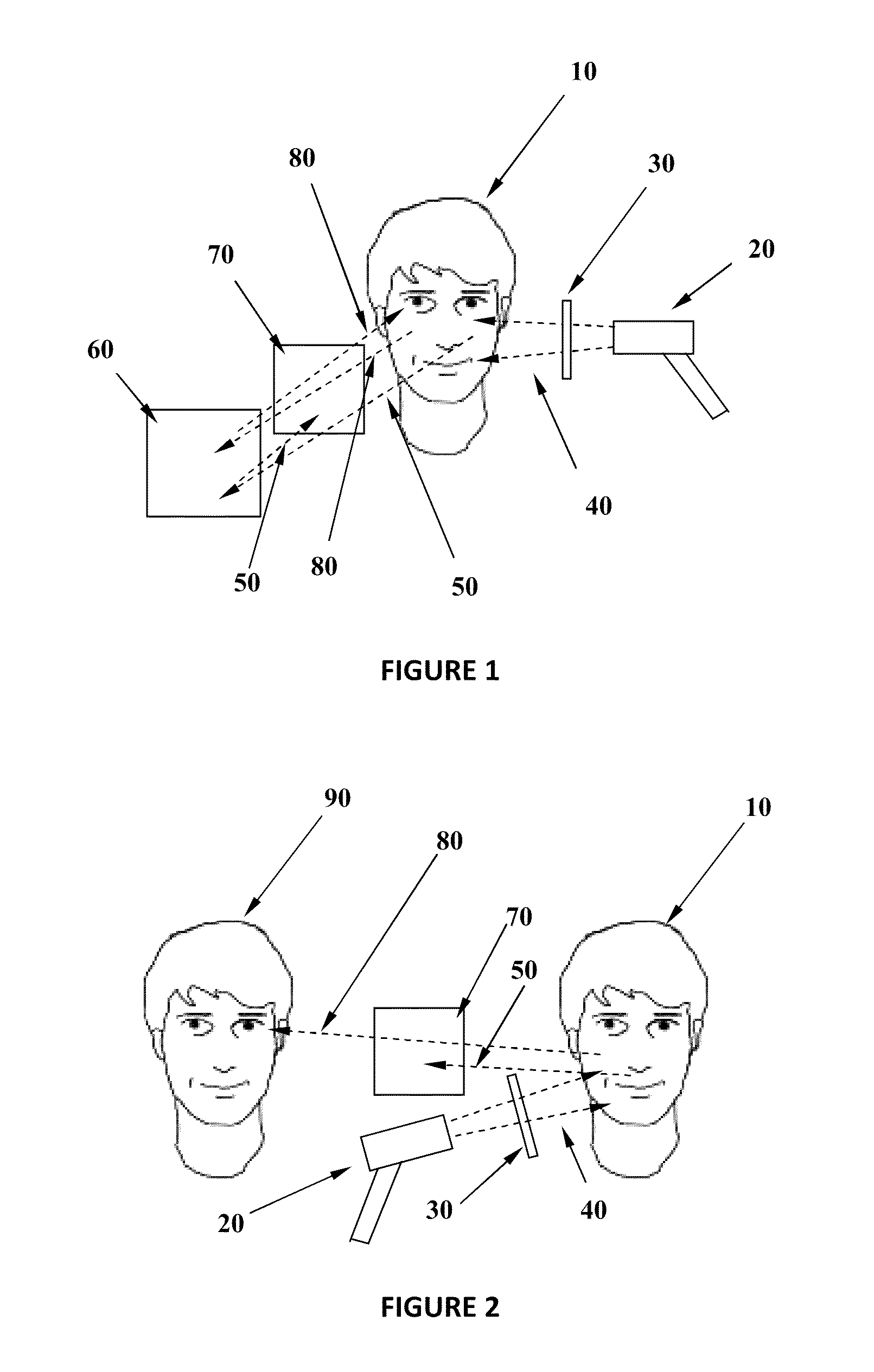
Acne Treatment Method, System and Device
InactiveUS20100069898A1Reduce developmentAvoiding hyperpigmentationDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsBacillus acnesPorphyrin
An acne treatment system, device and method includes optical visualization means for identifying areas of skin colonized by the P. acnes bacteria, and further comprises methods, techniques and apparatus for the reduction or elimination of such colonies through the use of light of a power density and wavelength configured to be absorbed by porphyrins produced by the bacteria, resulting in a quenching. Various alternative embodiments are disclosed, including eye safe embodiments, embodiments in which a treatment regimen is provided on a disposable cartridge, embodiments in which the authenticity of the cartridge is verified to ensure proper operation, as well as others.
Owner:CHANNEL INVESTMENTS LLC
Non-aqueous air battery and catalyst therefor
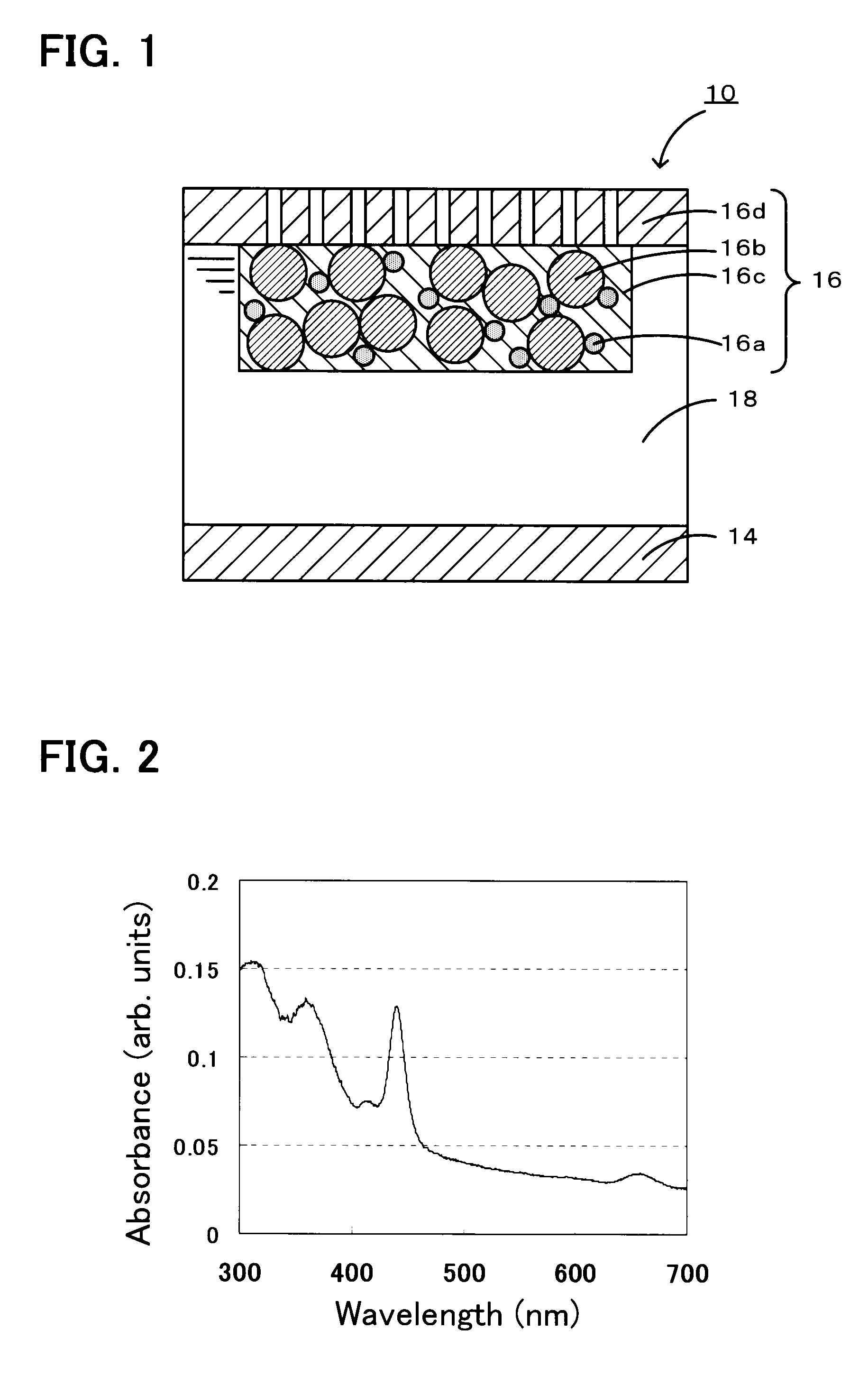
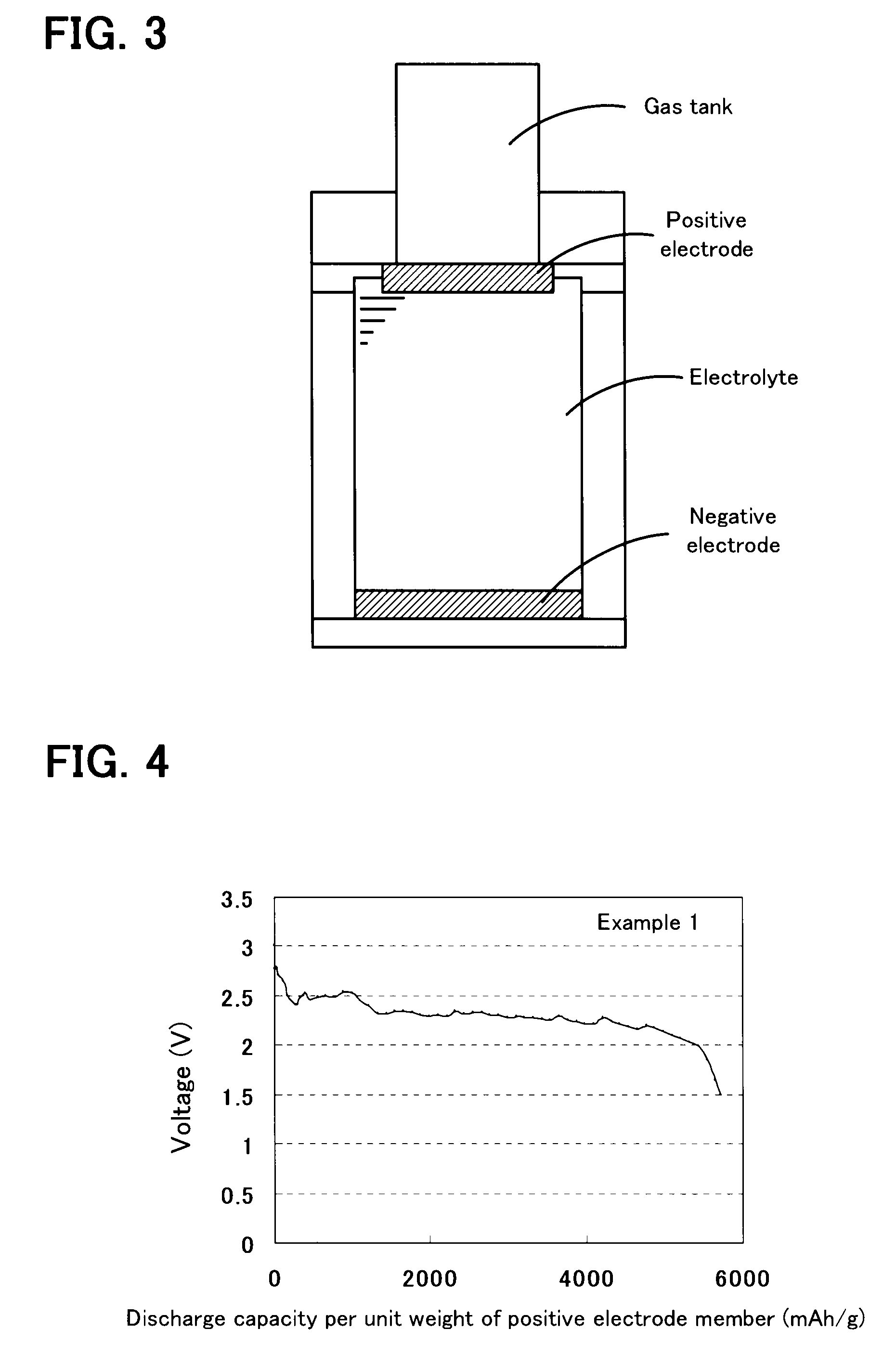
InactiveUS20080299456A1Improve discharge capacityIncrease energy densityFuel and secondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesPorphyrinOxygen
A non-aqueous air battery of the present invention includes a negative electrode for which a material which absorbs and releases lithium ions is used as a negative electrode active material, a positive electrode for which oxygen is used as a positive electrode active material, and a non-aqueous electrolyte disposed between the negative electrode and the positive electrode. The positive electrode contains a donor-acceptor molecule in which an electron-donating donor (D) having a porphyrin ring is connected to an electron-accepting acceptor (A) composed of a fullerene derivative, with a conductive spacer therebetween. An example of the donor-acceptor molecule is triphenylporphyrinyl bithienyl N-methylpyrrolidino[60]fullerene.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Liposome compositions of porphyrin photosensitizers
Liposomal pharmaceutical formulations incorporating porphyrin photosensitizers useful for photodynamic therapy or diagnosis of malignant cells. The liposomal formulations comprise a porphyrin photosensitizer, particularly the hydro-mono benzoporphyrins (BPD) having light absorption maxima in the range of 670-780 nanometers, a disaccharide or polysaccharide and one or more phospholipids.
Owner:QLT INC
Porphyrin compounds as telomerase inhibitors
InactiveUS6087493ARegulating telomerase functionModulating tumor proliferation and mortalitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseDna interaction
The present invention has identified compounds with extended aromatic chromophores that bind the G-quadruplex formed by the folding of single-stranded human telomeric DNA. These compounds have been shown to be effective telomerase inhibitors and are contemplated to be useful in developing cancer treatments. A model of cationic porphyrin interaction with quadruplex DNA by intercalation has been established and in combination with structure activity relations has provided novel porphyrin compounds that exhibit discrimination between binding duplex and quadruplex DNA and show improved activity against telomerase.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and device for detecting freshness of fish based on olfaction visualization
InactiveCN101936912AReduce dosageReduce extractionImage analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSensor arrayTemperature control
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting the freshness of fish based on olfaction visualization, which is characterized in that a computer is connected with a constant temperature control room and a scanner; a visual gas sensor array, the scanner, a reaction room and a sample room are arranged inside the constant temperature control room; detected gas diffused from a detected fish sample is in contact with the visual gas sensor array; the detected gas reacts with a porphyrins sensor, a pH indicator sensor or a solvation chromotropic dye sensor arranged in the visual gas sensor array; images before and after the reaction are collected by the scanner and input into the computer; and the freshness of the detected fish sample is determined according to the correlation between the color change of the three sensors and the variety and the concentration of the detected gas. The invention can ensure that the extraction quantity of characteristic values is reduced by determining the selection of the sensor type and the characteristic values; the synthesis course is simple, and the use quantity of the sensors is less; the gas can be fully contact with the sensors; the detection by human eyes can be utilized; and the use of the device is simple and convenient; the detection time only needs 3 to 5 minutes.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Conjugates of rgd peptides and porphyrin or (bacterio) chlorohyll photosynthesizers and their uses
Conjugates of porphyrin, chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll photosensitizers with RGD-containing peptides or RGD peptidomimetics are provided that are useful for photodynamic therapy (PDT), particularly vascular-targeted PDT (VTP), of tumors and normeoplastic vascular diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, and for diagnosis of tumors by different techniques.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Conjugates of rgd peptides and porphyrin or (bacterio)chlorophyll photosynthesizers and their uses
ActiveUS20120294801A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsPorphyrinWilms' tumor
Conjugates of porphyrin, chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll photosensitizers with RGD-containing peptides or RGD peptidomimetics are provided that are useful for photodynamic therapy (PDT), particularly vascular-targeted PDT (VTP), of tumors and nonneoplastic vascular diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, and for diagnosis of tumors by different techniques.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
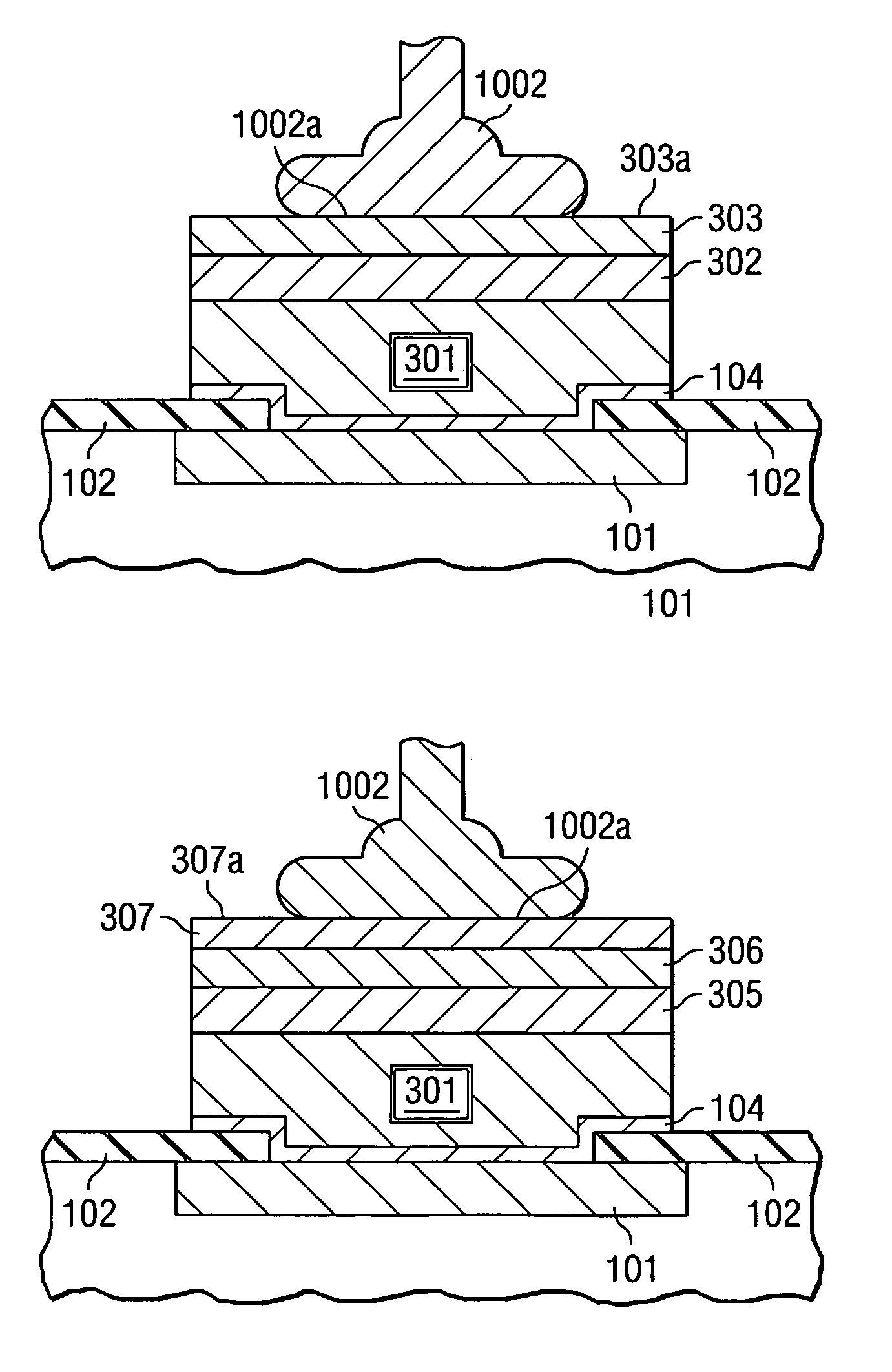
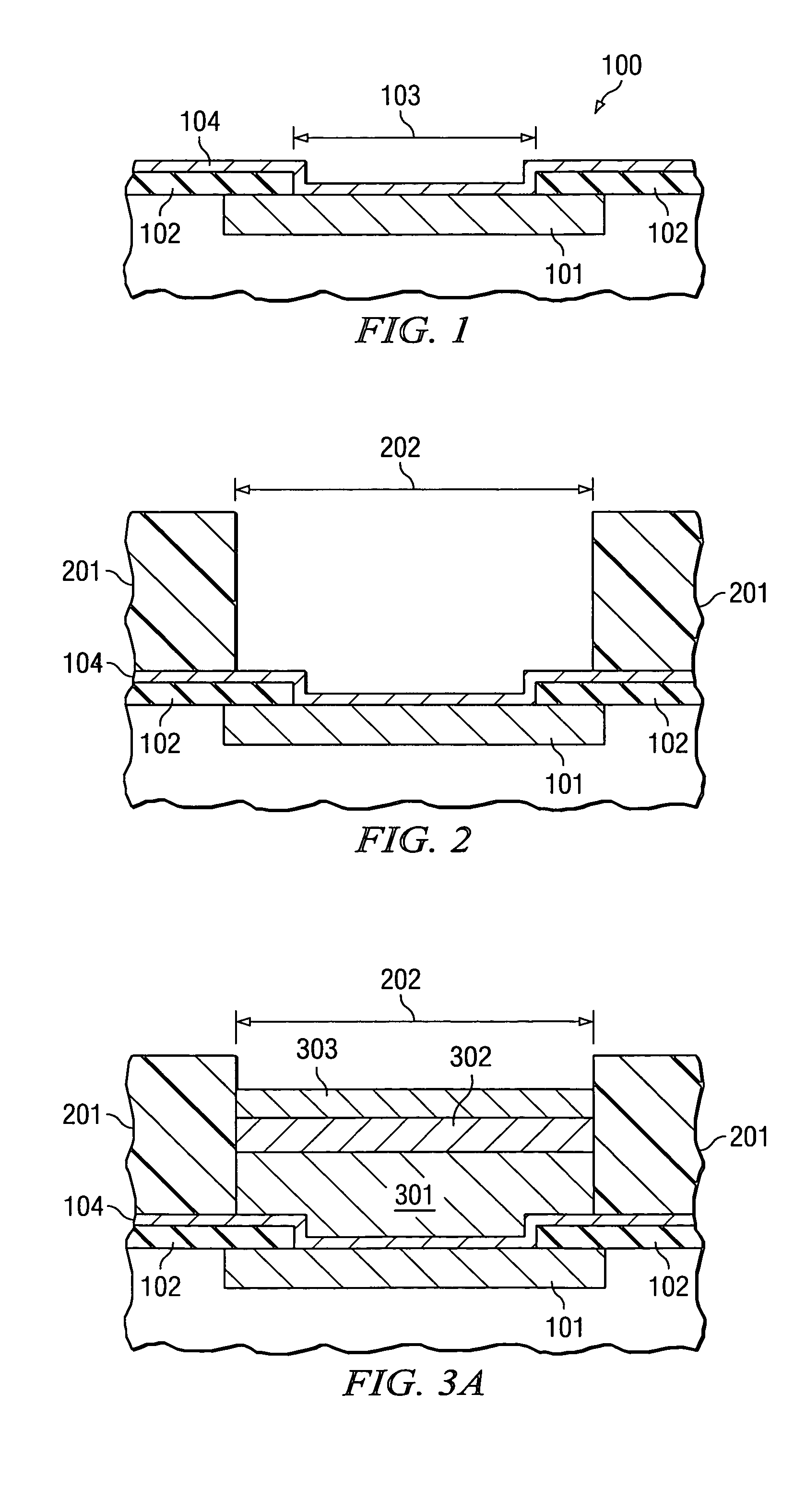
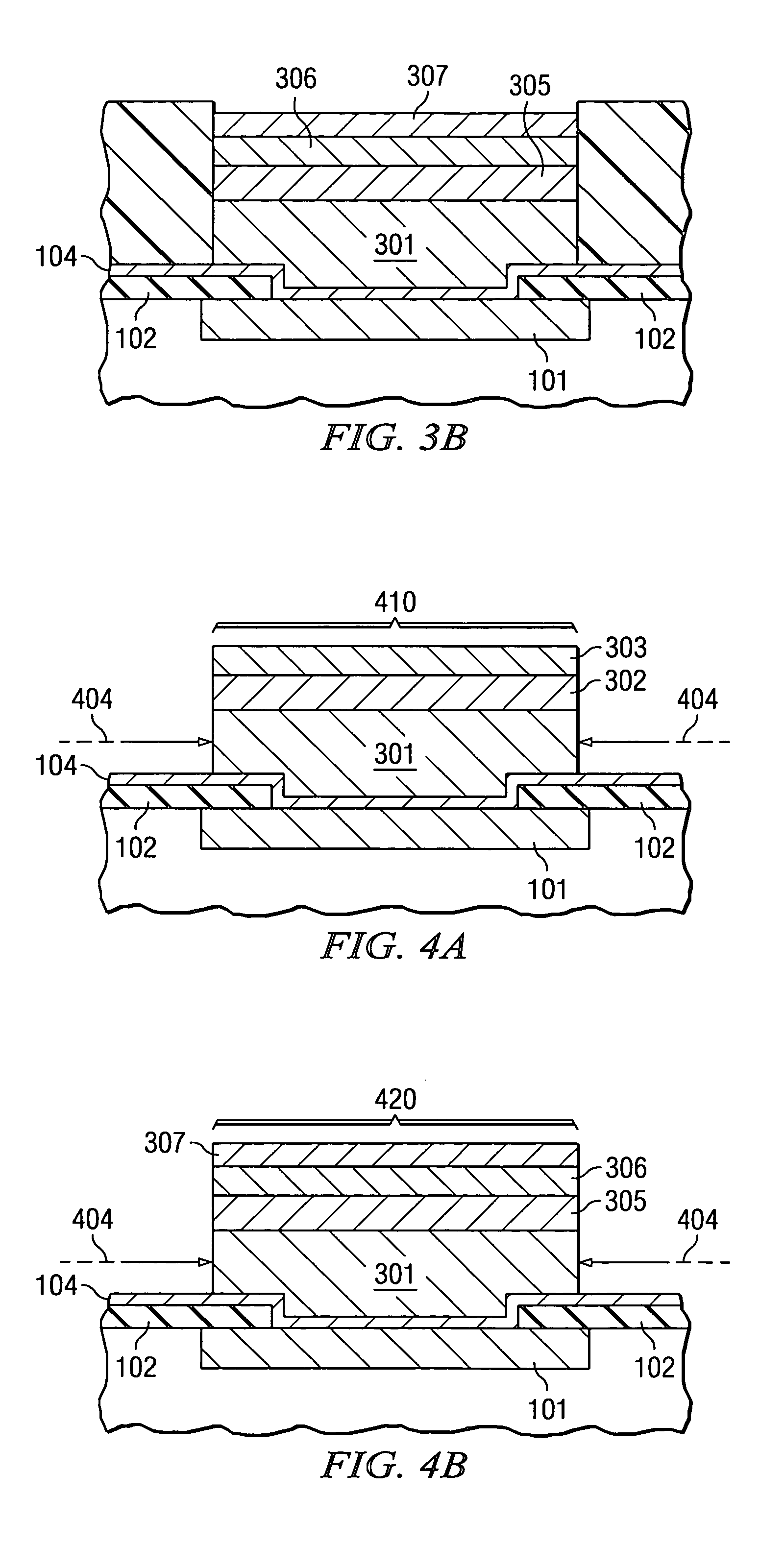
Method for chemical etch control of noble metals in the presence of less noble metals
ActiveUS6979647B2Firmly assembledImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorphyrinQuinoline
A method for preparing a bonding pad on an integrated circuit wafer by the steps of depositing a conductive seed layer (104) on the bonding pad; depositing a metal layer (301, 302, and 303) over a portion of the conductive seed layer; and immersing the wafer in an etchant solution (501) to remove the portion of the seed layer not covered by the metal layer. The etchant solution contains a chelating agent that bonds ions from the seed layer. When the seed layer is copper or a refractory metal, and the metal layer is gold or palladium, the preferred chelating agent is selected from, but is not limited to, but is not limited to, the families of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acids (EDTA), 8-hydroxy-quinolines, including 8-hydroxy-quinoline-5-sulfonic acid, porphyrins, and phthalocyanines.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Liposome compositions of porphyrin photosensitizers
InactiveUS6890555B1Good reproducibilityHydrate fastBiocideEnergy modified materialsPhotodynamic therapyPhotosensitizer
Liposomal pharmaceutical formulations incorporating porphyrin photosensitizers useful for photodynamic therapy or diagnosis of malignant cells. The liposomal formulations comprise a porphyrin photosensitizer, particularly the hydro-mono benzoporphyrine (BPD) having light absorption maxima in the range of 670-780 nanometers, a disaccharide or polysaccharide and one or more phospholipids.
Owner:QLT INC
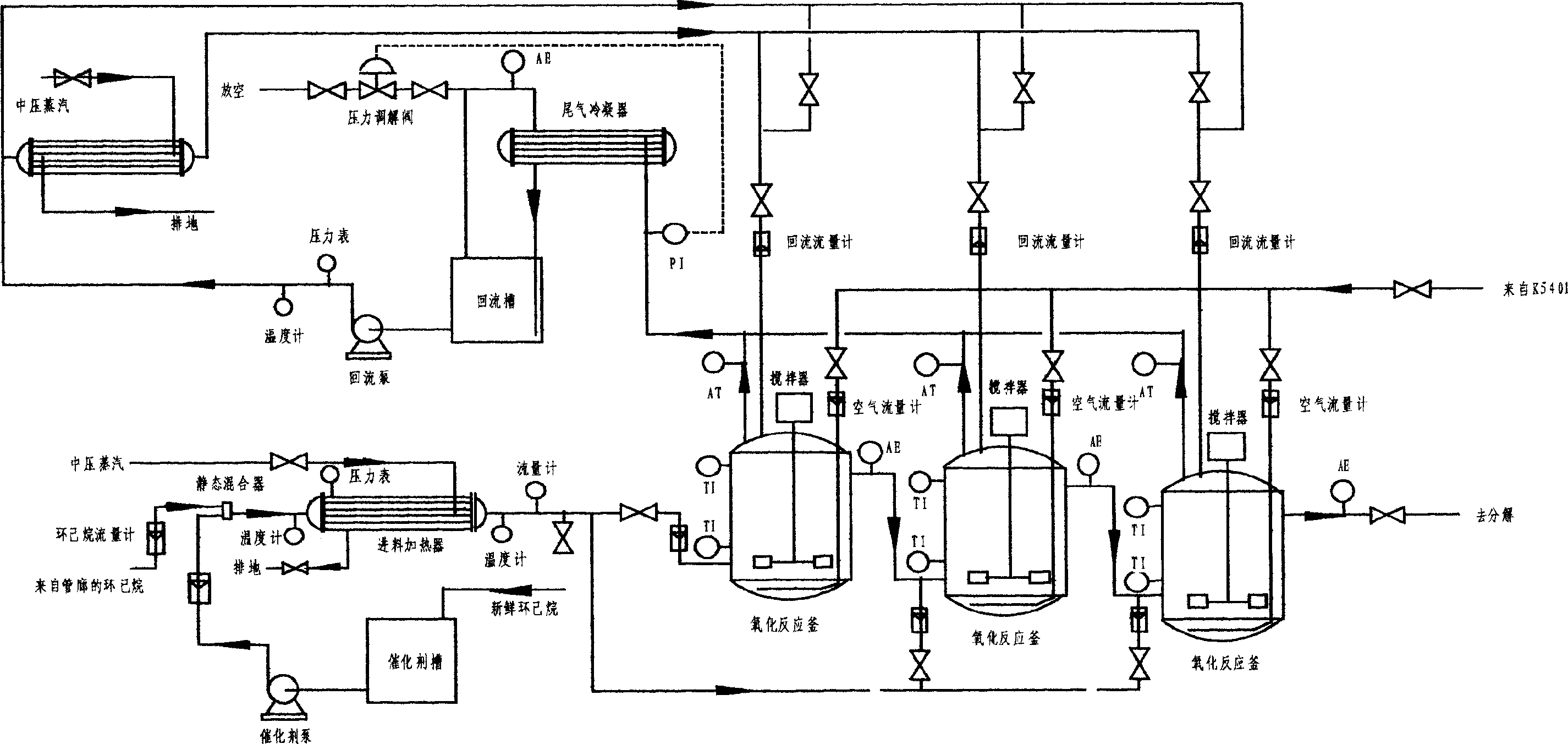
Process and equipment for preparing adipic acid by catalyzing air and oxidizing cyclohexane
InactiveCN101337879AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCyclohexanoneBoiling point
The invention discloses a process and a plant for preparing adipic acid by catalytically aerobically oxidizing cyclohexane. The process comprises the following steps: dissolving 1 to 50 PPM of a catalyst including single metalloporphyrin or mu-oxo bimetallic porphyrin or a mixture of single metalloporphyrin, mu-oxo bimetallic porphyrin and transition metal salt or oxide in cyclohexane; introducing 5 to 12 atm of air or oxygen-rich or oxygen-poor air into a multi-stage oxidation reactor with a gas distributor; controlling the reaction temperature at 140 to 160 DEG C; oxidizing cyclohexane for 45 to 120 min; feeding the mixture of the oxidation reaction into a flash separator to carry out flash evaporation at the temperature of 78 to 155 DEG C and under the pressure of 0.1 to 1.0 atm, so that the low-boiling-point products such as cyclohexane, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone change to gas and are separated from adipic acid with the content above 80%; continuously circularly oxidizing the low-boiling-point products to separate and purify the high-boiling-point oxidation product; and purifying and separating by the existing technique to obtain fine adipic acid product. The process can directly prepare adipic acid by aerobically oxidizing cyclohexane, wherein the conversion rate of cyclohexane is up to 95%, and the yield of adipic acid is up to 70%.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Attachment of organic molecules to group III, IV or V substrates
This invention provides a new procedure for attaching molecules to semiconductor surfaces, in particular silicon. The molecules, which include, but are not limited to porphyrins and ferrocenes, have been previously shown to be attractive candidates for molecular-based information storage. The new attachment procedure is simple, can be completed in short times, requires minimal amounts of material, is compatible with diverse molecular functional groups, and in some instances affords unprecedented attachment motifs. These features greatly enhance the integration of the molecular materials into the processing steps that are needed to create hybrid molecular / semiconductor information storage devices.
Owner:CALIFONRIA UNIV OF RGT +1
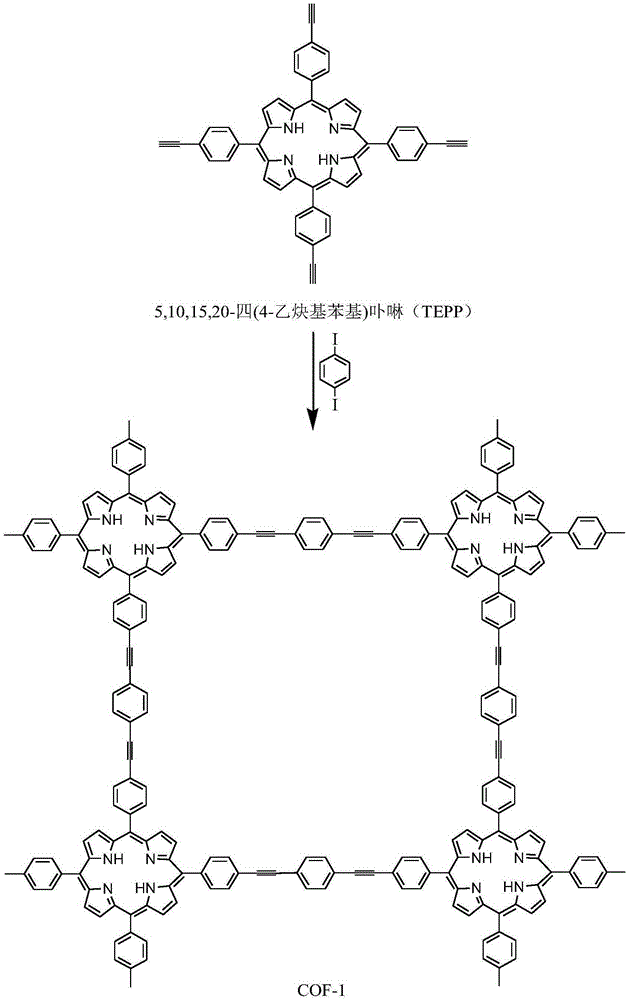
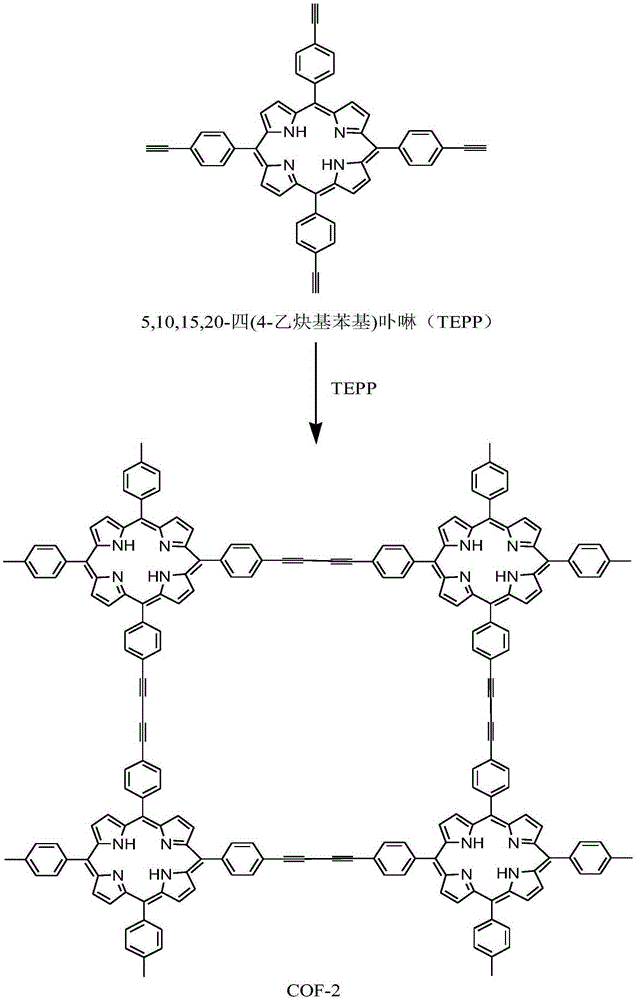
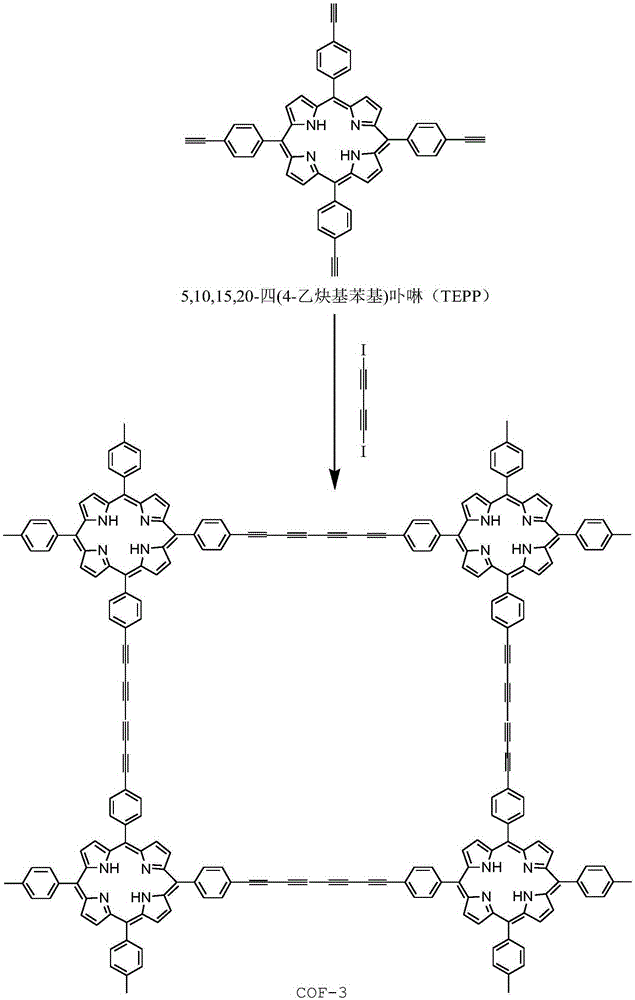
Porphyrin containing covalent organic frameworks and process for the preparation thereof
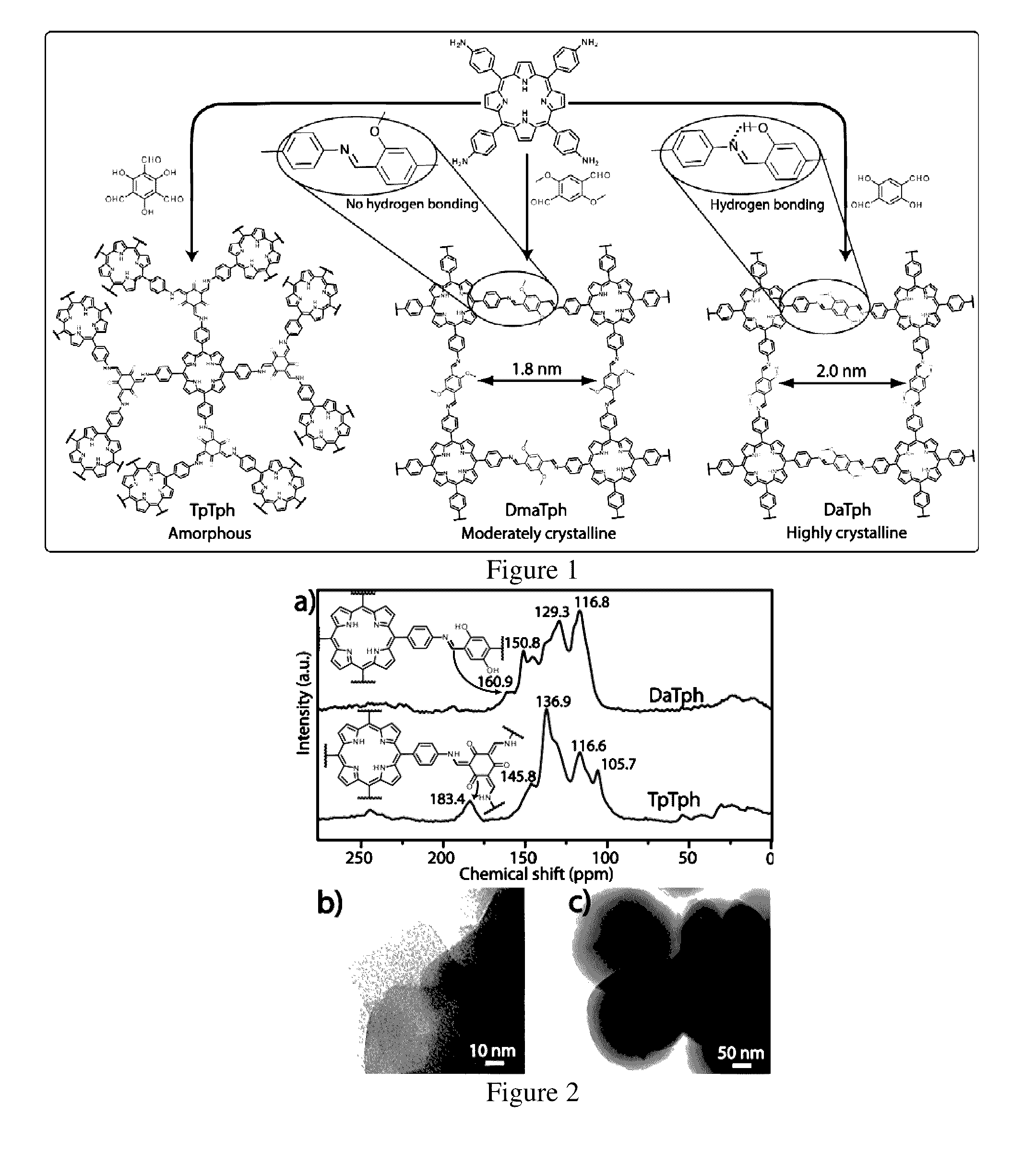
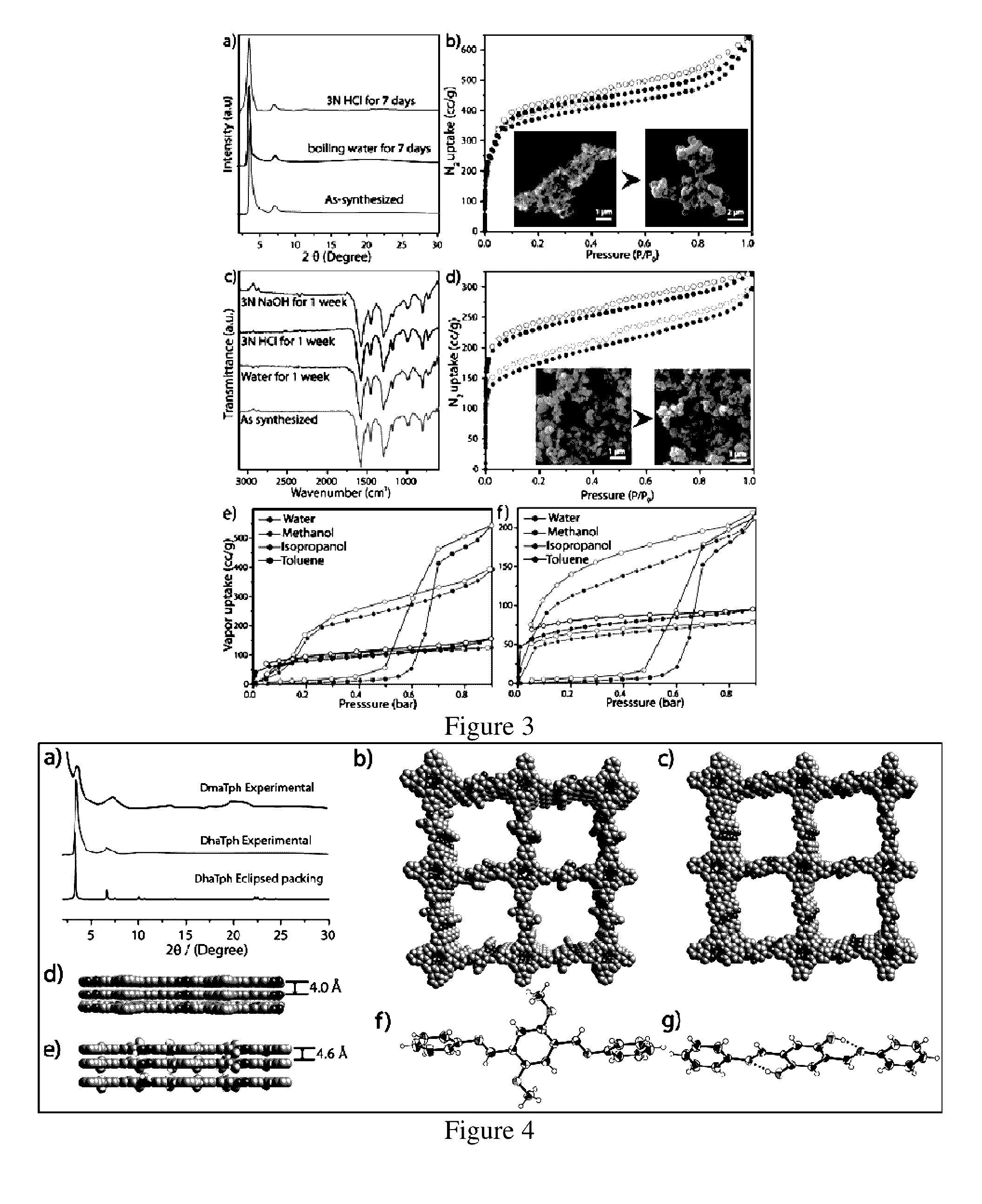
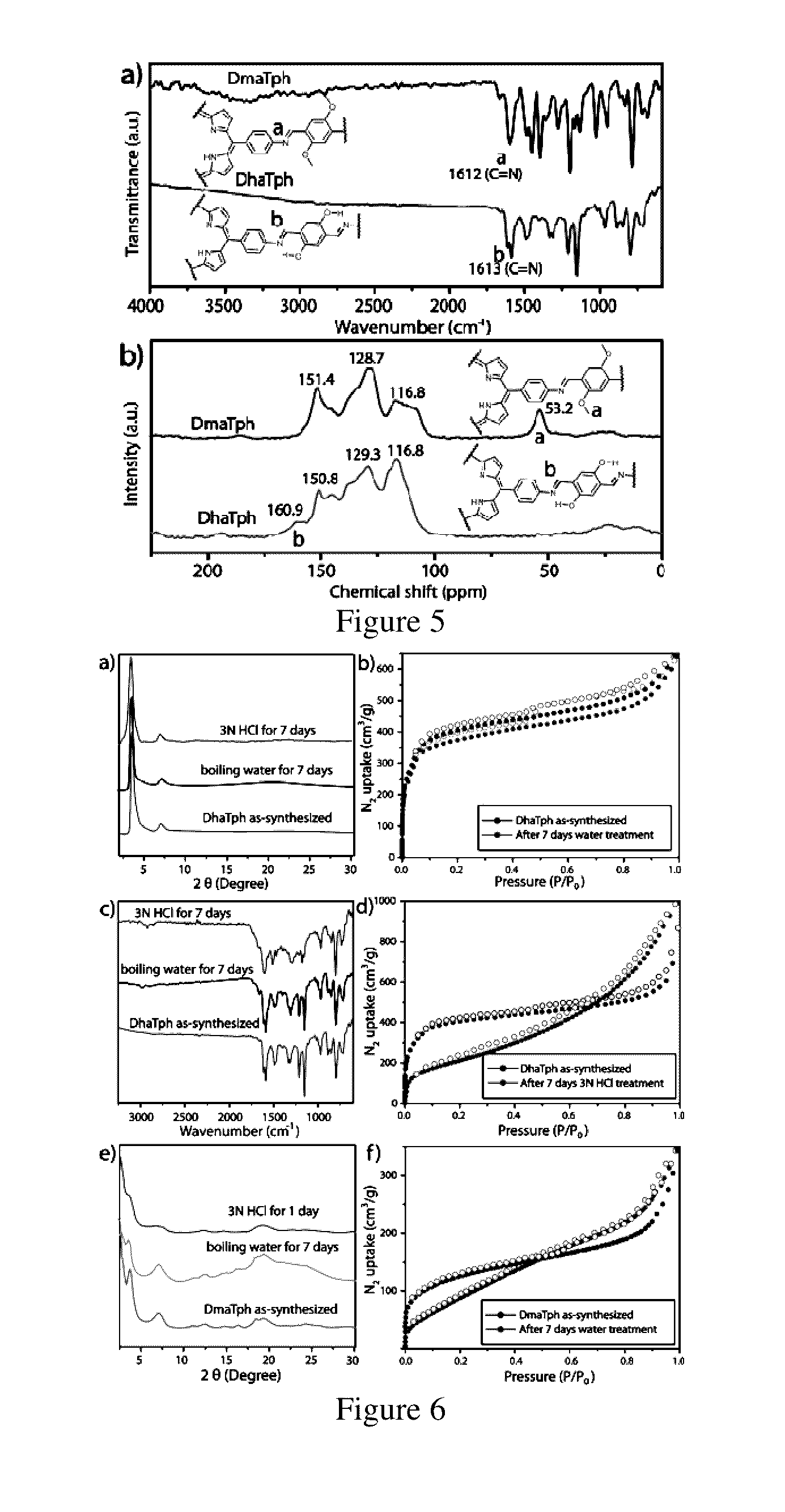
Disclosed herein is novel highly stable, crystalline porphyrin containing covalent organic frameworks and their synthesis using Schiff base reaction which are hydrophobic in nature having good selectivity towards alcohol uptake at low pressure over water. Particularly, present invention provides novel highly stable, porous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) comprising porphyrin linked hydroxyl aromatic compound by intramolecular O—H—N═C bonding; wherein porphyrin is tetra(p-amino-phenyl)porphyrin (Tph) and hydroxyl aromatic compound is selected from group consisting of Triformylphloroglucinol (Tp), 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde (Da).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
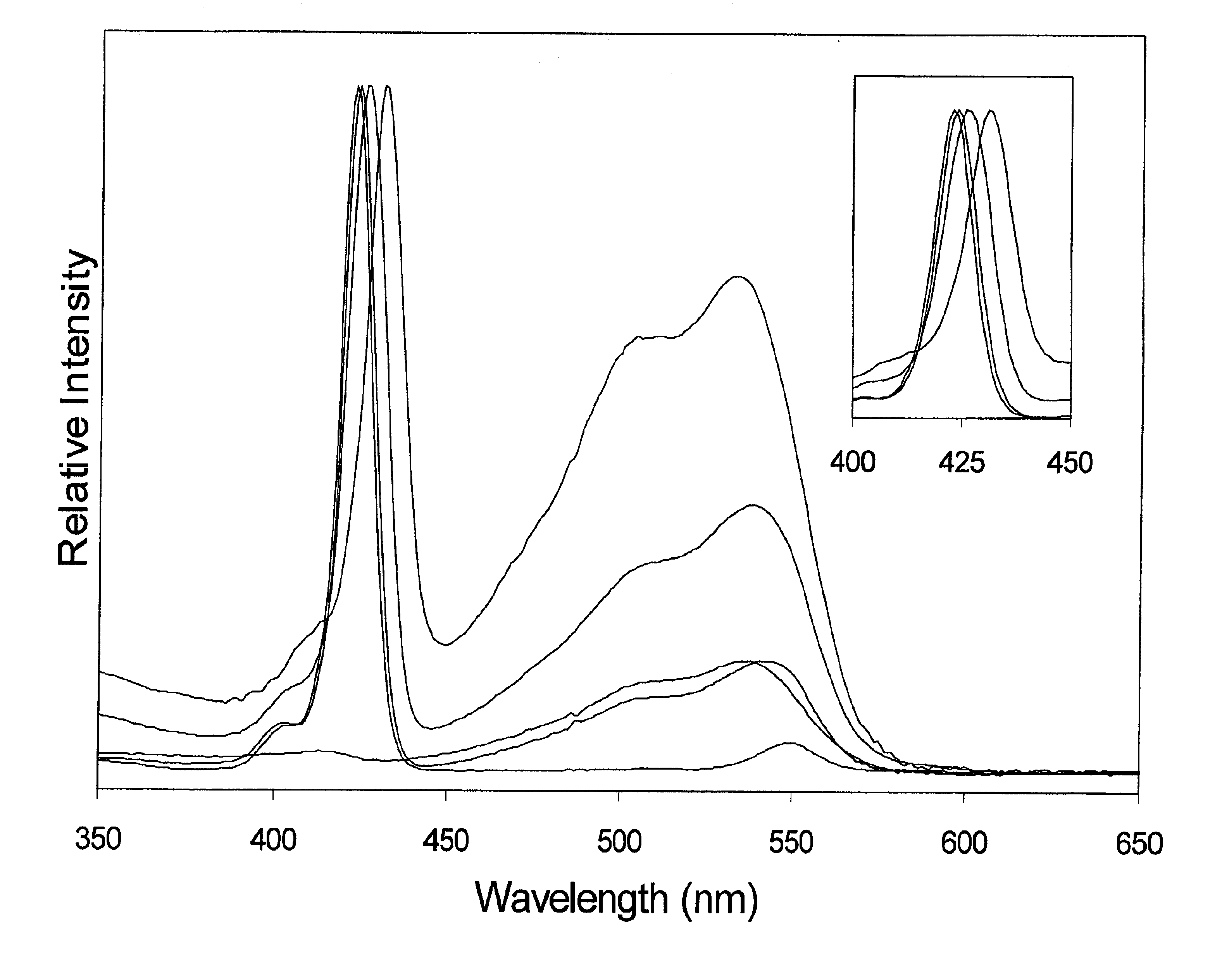
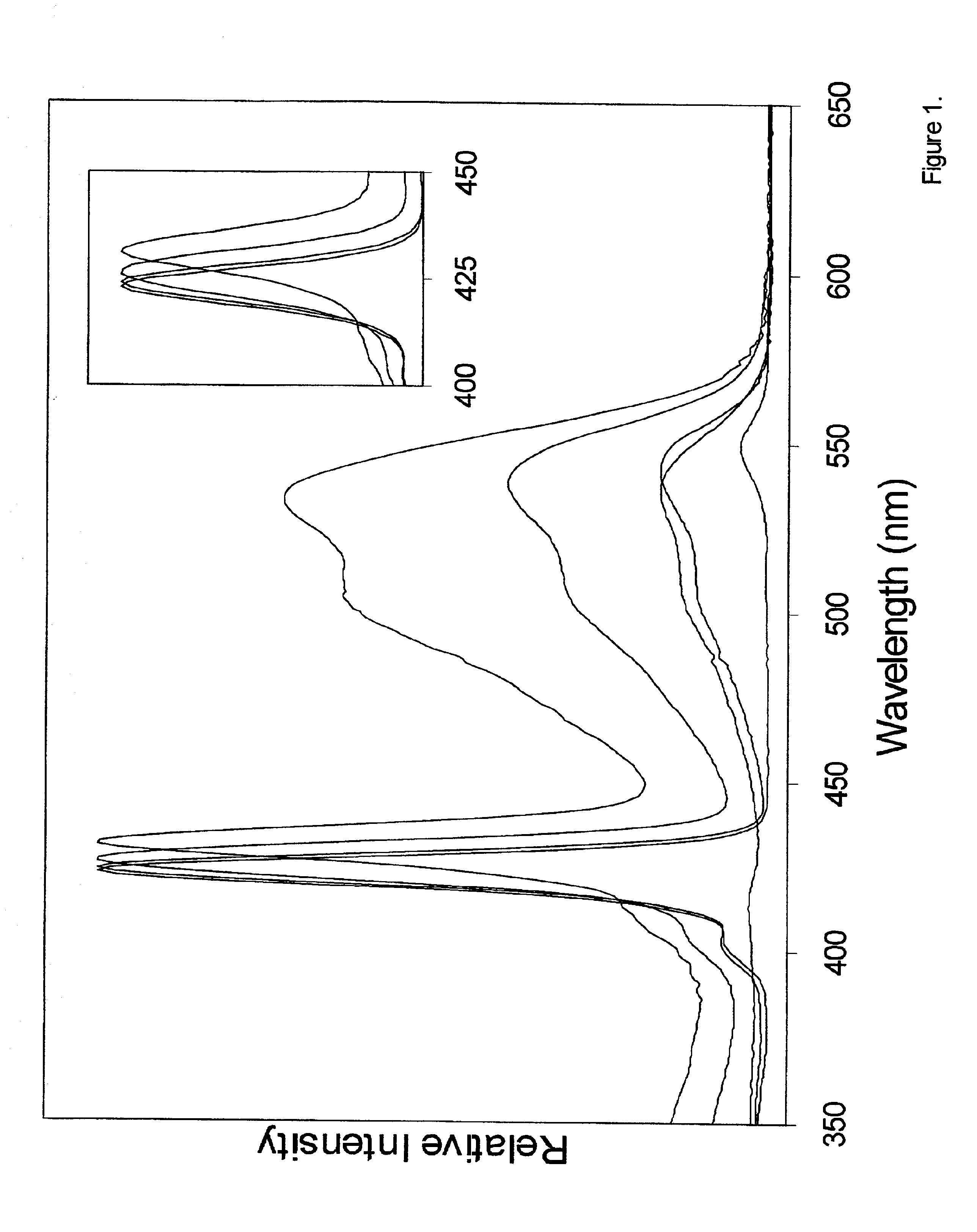
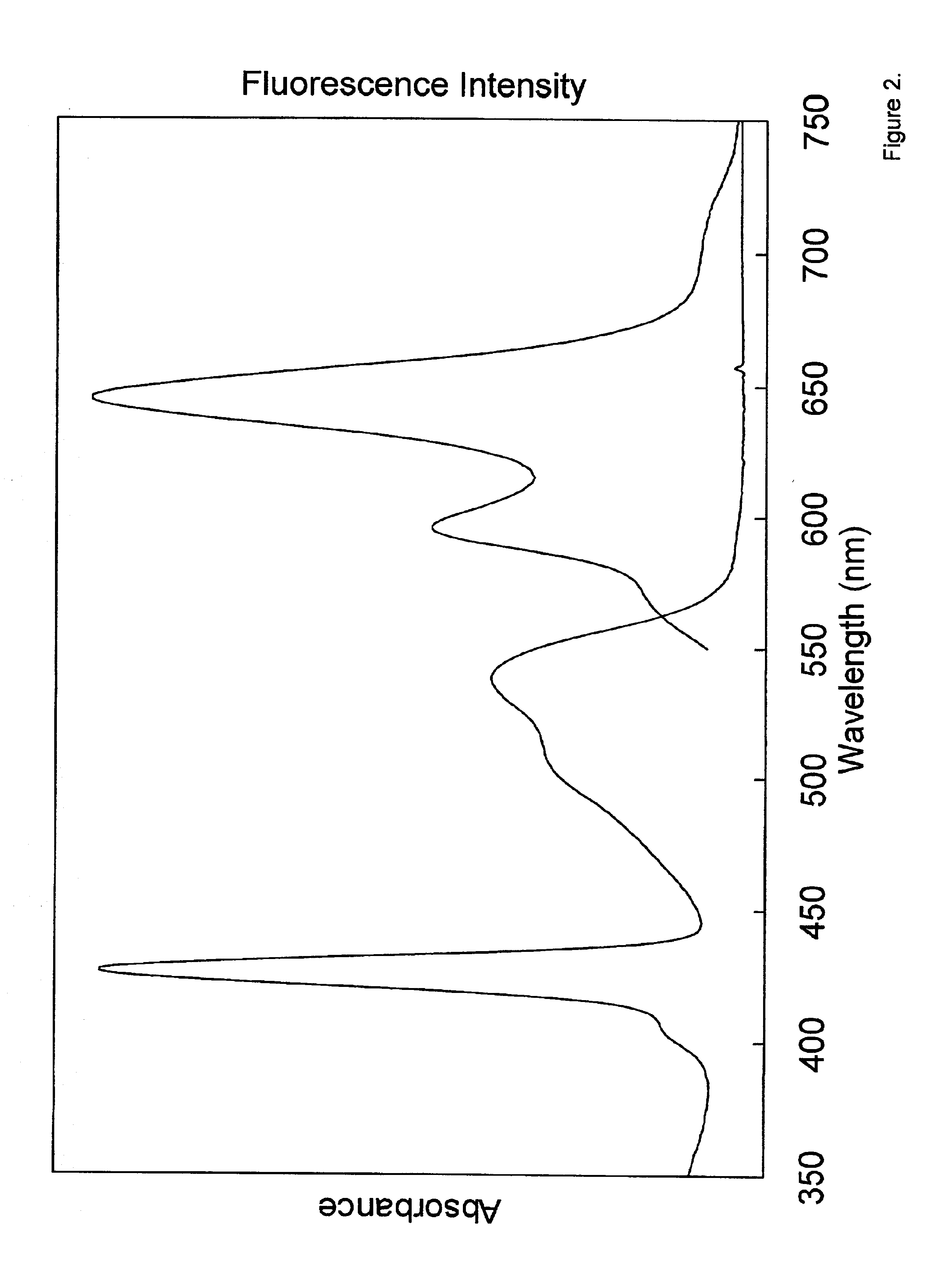
Photodynamic porphyrin antimicrobial agents
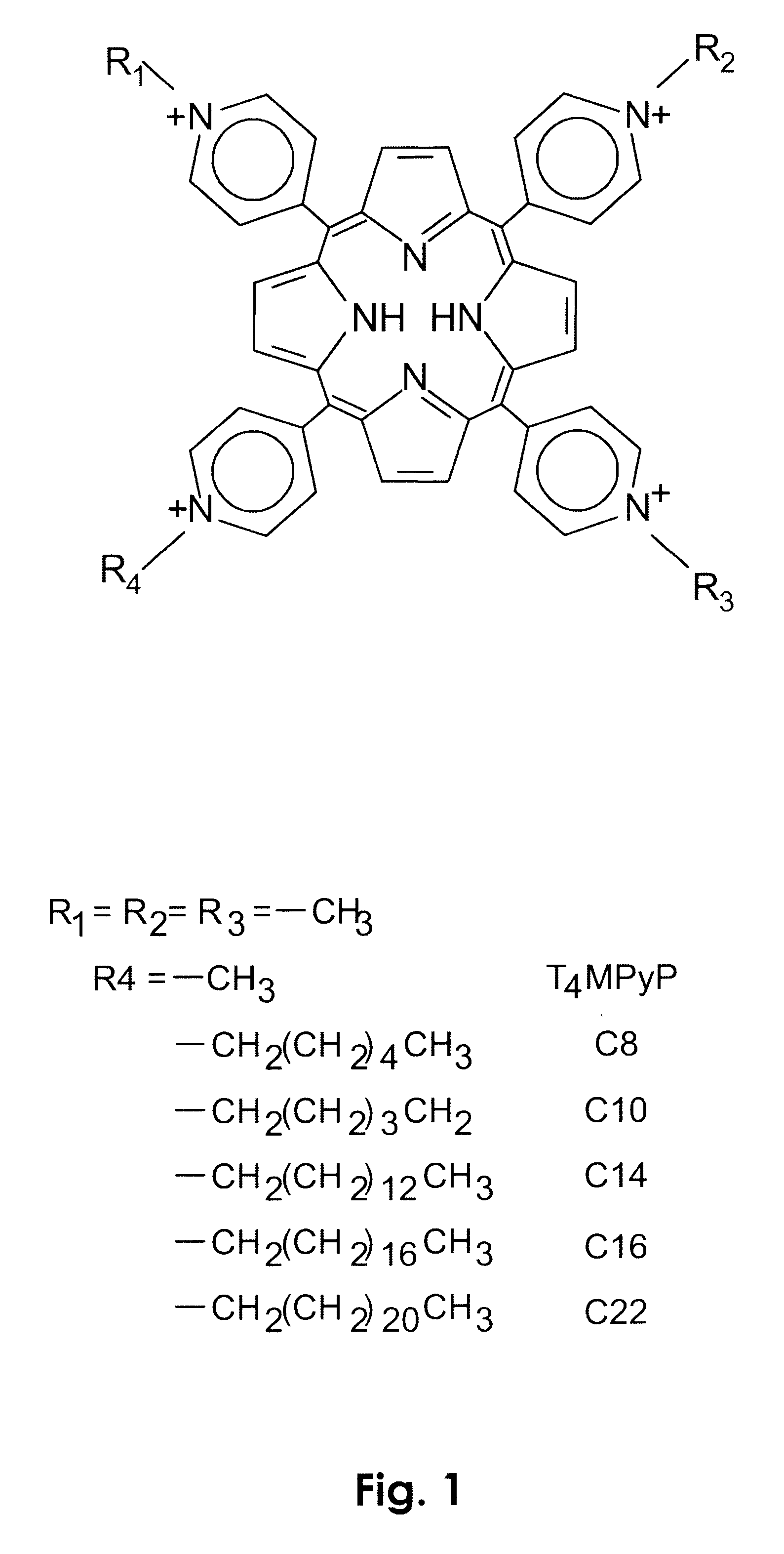
A series of novel positively-charged porphyrins is disclosed which exhibit a markedly increased efficiency in photosensitizing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria to the action of visible light, causing death to such bacteria when present at much lower concentrations and much shorter irradiation times than those porphyrins taught in the prior art. These porphyrins are characterized by the presence of up to four positive charges in the peripheral substituents and at least one hydrophobic tail comprising between 6 and 22 carbons inclusive, originating at one or more of the charged sites.
Owner:FRONTIER SCI INC
Compounds and method for PDT of intimal hyperplasia and other diseases
A broad class of photosensitive compounds having enhanced in vivo target tissue selectivity and versatility in photodynamic therapy. Many furocoumarin compounds, such as psoralens, exhibit cytostatic activity when photoactivated but exhibit little in vivo specificity for selectively accumulating in any particular target tissue such as atheromatous plaques. Reactive Oxygen Producing Photosensitizers ("ROPPs") are photoactivatable compounds having an affinity for hyperproliferating cells (such as atheromatous plaque cells), which when photoactivated, produce cytotoxic reaction products. The photoactivity of a ROPP, such as a porphyrin, may be reduced by metalating the porphyrin while the selective affinity of the metalized ROPP for hyperproliferating tissue remains substantially unchanged. By linking a furocoumarin compound to a ROPP to form a F-ROPP, the cytostatic properties of the furocoumarin portion of the F-ROPP can be exploited while the selective affinity of the ROPP portion of the compound for hyperproliferating cells such as atheromatous plaque provides enhanced tissue selectivity without cytotoxicity. In vivo, certain F-ROPPs may be forced to selectively accumulate in a target tissue by illuminating only the target tissue with light having a wavelength operable for photoactivating the F portion of the F-ROPP thereby causing the F-ROPP to either form a monoadduct with or crosslink the cellular DNA in the target tissue. Light of a second wavelength can then be delivered to the target tissue to photoactivate the ROPP portion causing further interference with cellular activity.
Owner:ADGERO BIOPHARM
Method for atmospheric catalytic oxidation of cyclohexane by metalloporphyrin
InactiveCN1405131APreparation by oxidation reactionsOxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidationCyclohexanoneReaction temperature
The invention relates to a new process in which under the catalytic action of metal porphyrin the cyclohexane can be selectively oxdated by air and made into cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Under the condition of 2-10 atm air, reaction temp. is 125-150 deg.C, it selects and uses micro-oxo double metal porphyrin and single metal porphyrin or their solid carrier as main catalyst, and uses transition metal salt or oxide as co-catalyst, the metal porphyrin can high-effectively and high-selectively catalyze oxidation of cyclohexane by using air in the biological concentratino as biological enzyme. The dose of metal porphyrin is small and said metal porphyrin can be repeatedly used, and said catalyst dose also is small, its catalystic effect is good, said catalyst can be used for making homogeneous catalysis, and after it is solid-carried, it also can be used for making heterogeneous catalysis.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Preparation method of monatomic dispersion catalyst with high catalytic performance
InactiveCN103566935AImprove catalytic performanceImprove stabilityPreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationAlkaneMicrosphere
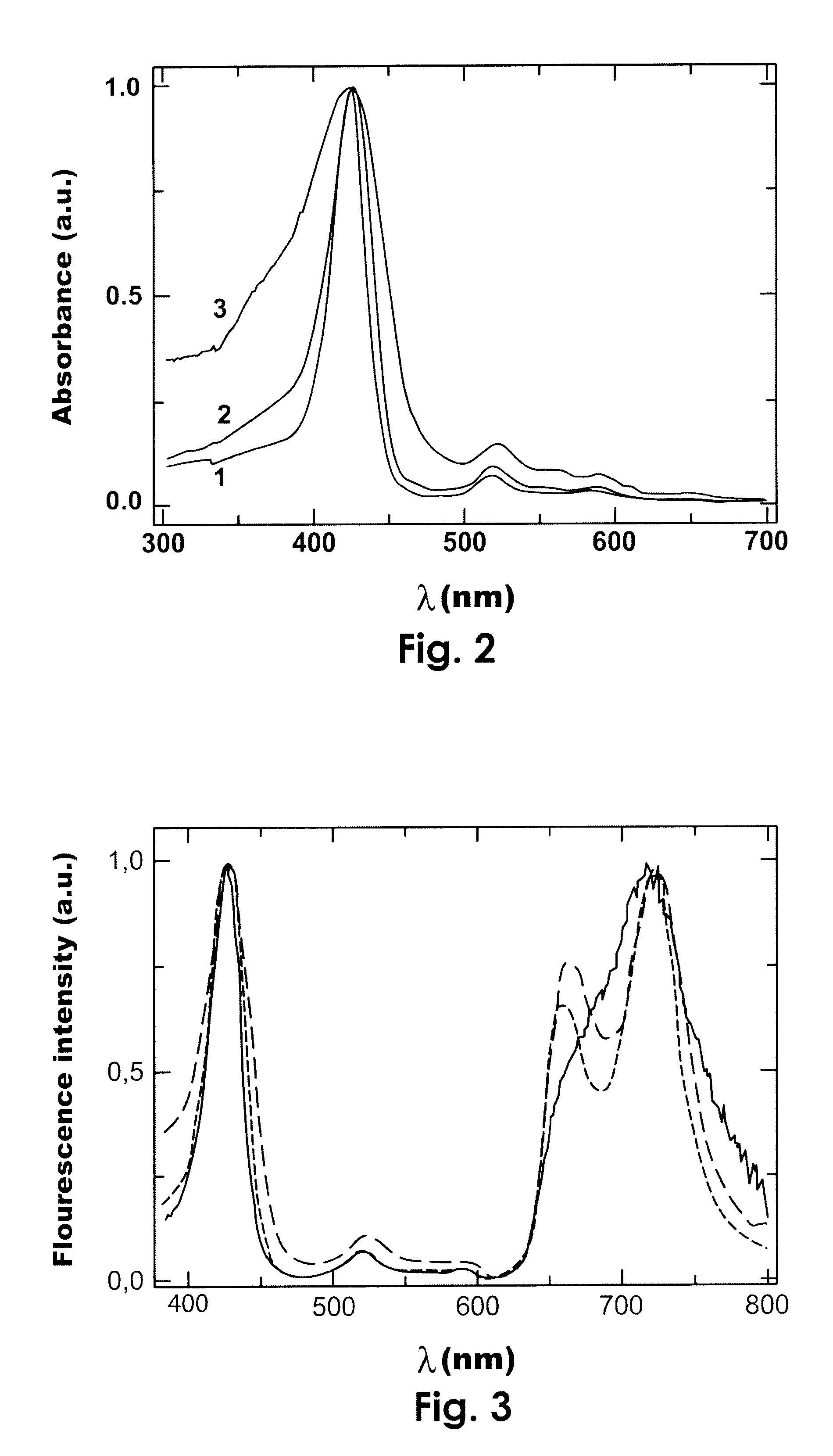
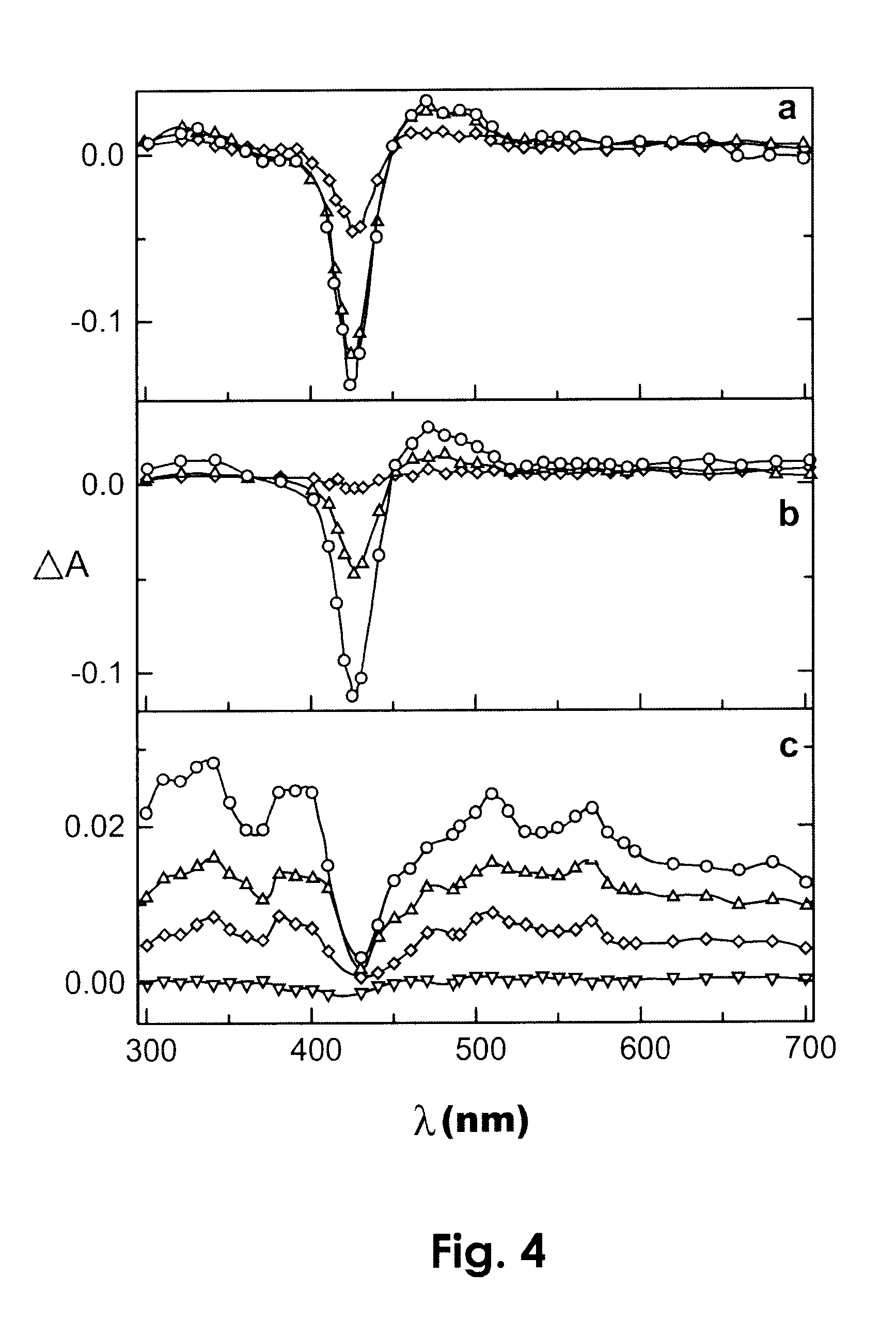
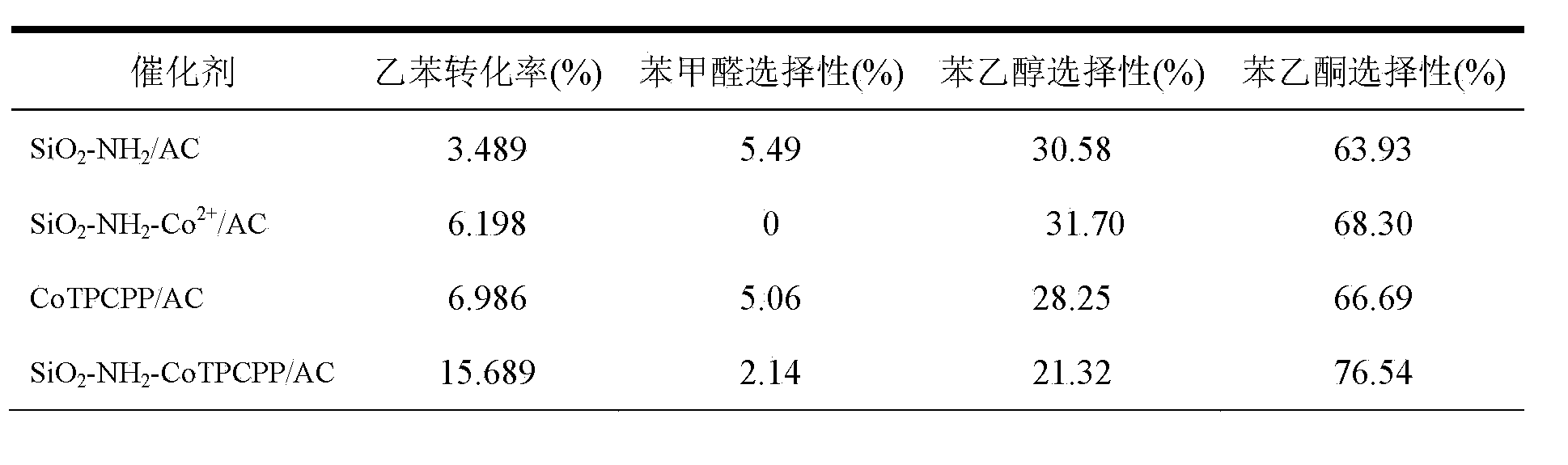
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysis and relates to a method for preparing a monatomic cobalt catalyst by roasting silicon dioxide pellets and immobilizing metalloporphyrin. The method is realized by adopting the following technical scheme: namely stirring and dispersing nano silicon dioxide particles, dropwise adding 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silane, so as to obtain amino modified SiO2 pellets, then linking monocarboxyl metalloporphyrin (CoTPCPP) onto an amino modified SiO2 carrier through organic complexing, carbonizing porphyrin through high-temperature calcination in an inert atmosphere, and loading highly dispersed cobalt atoms onto the amino modified SiO2 pellets, thus an amino modified silicon dioxide pellet loaded monatomic cobalt catalyst is obtained. The monatomic dispersion catalyst has high catalytic activity and stability on a molecular oxygen selective ethylbenzene catalytic oxidation reaction in absence of solvent; meanwhile, a preparation method is simple, and product quality can be easily controlled, so that the monatomic dispersion catalyst is applicable to the fields of alkane selective oxidation reactions and synthesis of medical intermediates.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for preparing metal complex of porphyrin
InactiveUS6420553B1High selectivityIron organic compoundsFunctional group formation/introductionPorphyrinSolvent
A process for producing a metalloporphyrin containing a transition metal inserted into the porphyrin ring which comprises dissolving a porphyrin compound and a transition metal salt each in an independent solvent, combining the solutions, and carrying out the reaction in the presence of a basic substance. By this process a metalloporphyrin containing a transition metal inserted into the porphyrin ring can be synthesized easily under mild conditions and with high selectivity.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Catalyst oxdie cyclohexane process
ActiveCN1530358AIncrease conversion rate per passImprove one-way yieldOxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidationCyclohexanonePorphyrin
A process for preparing cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone and adipic acid by catalytic oxidization of cyclohexane under existance of metallic porphyrin catalyst and a certain temp and pressure through combination of different reactors is disclosed. Its advantages are high single-pass conversion rate of cyclohexane and total output rate, low energy consumption and cost, and no need of cyclohexanol or acetone solvent and cocatalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
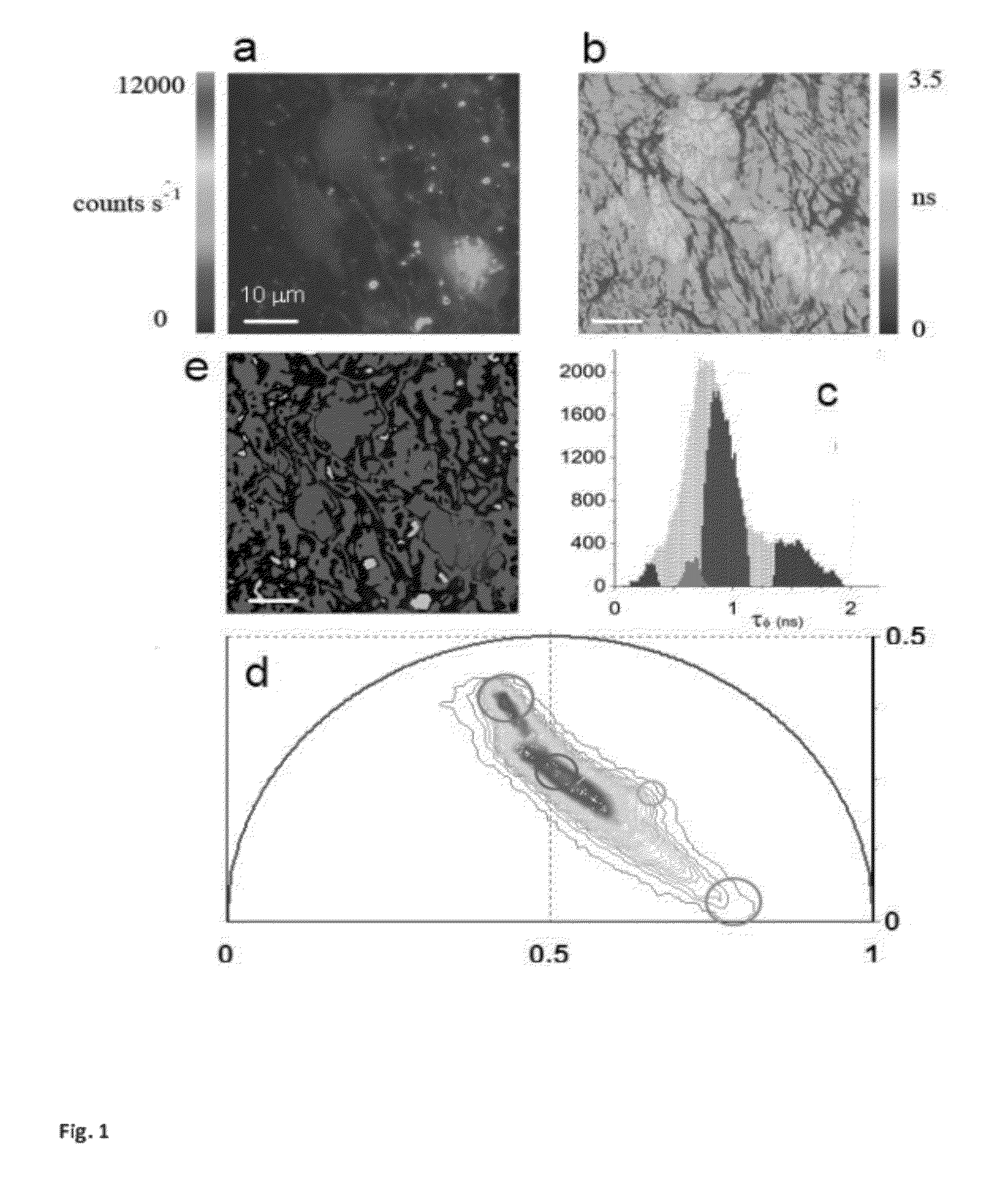
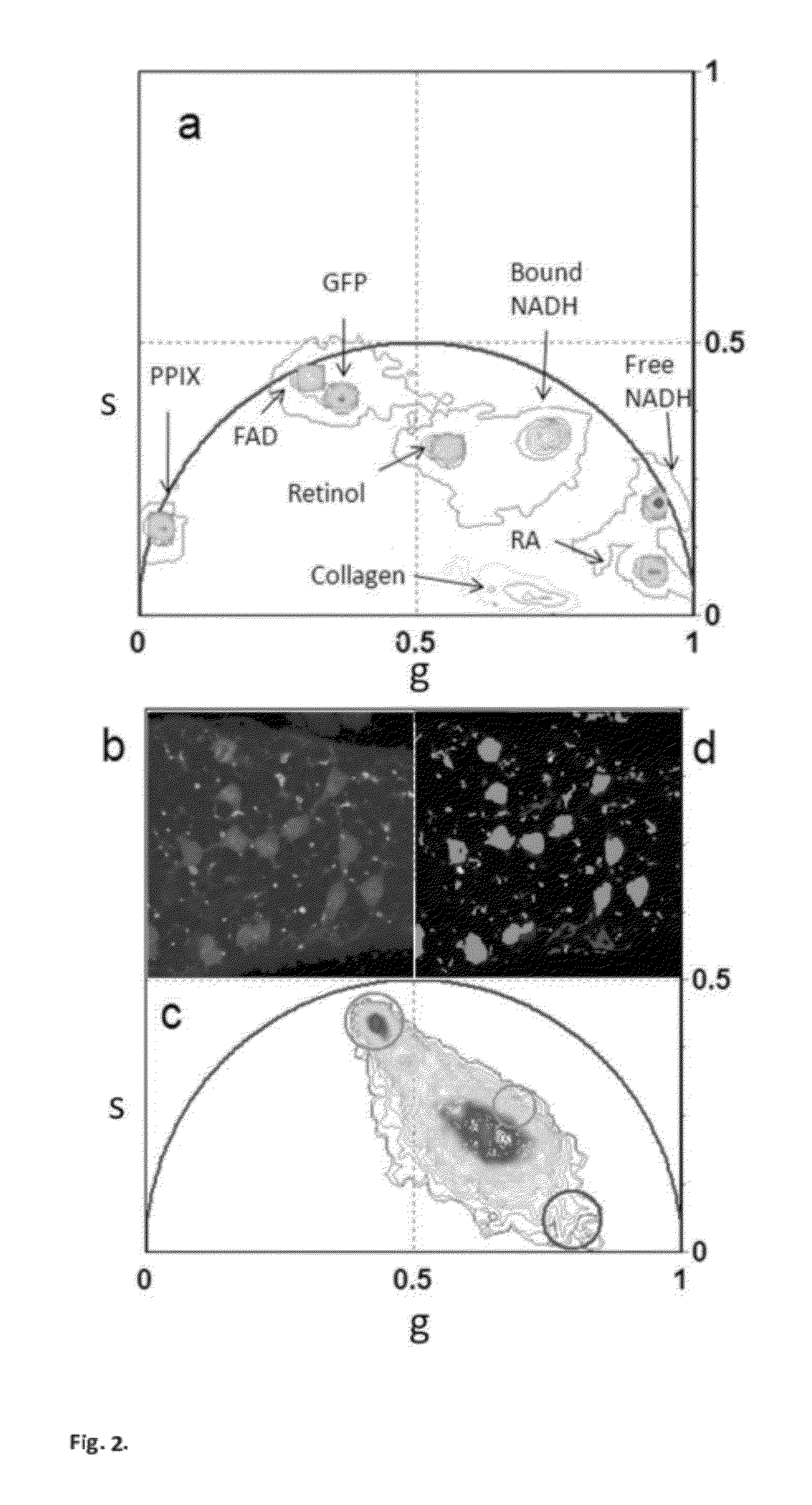
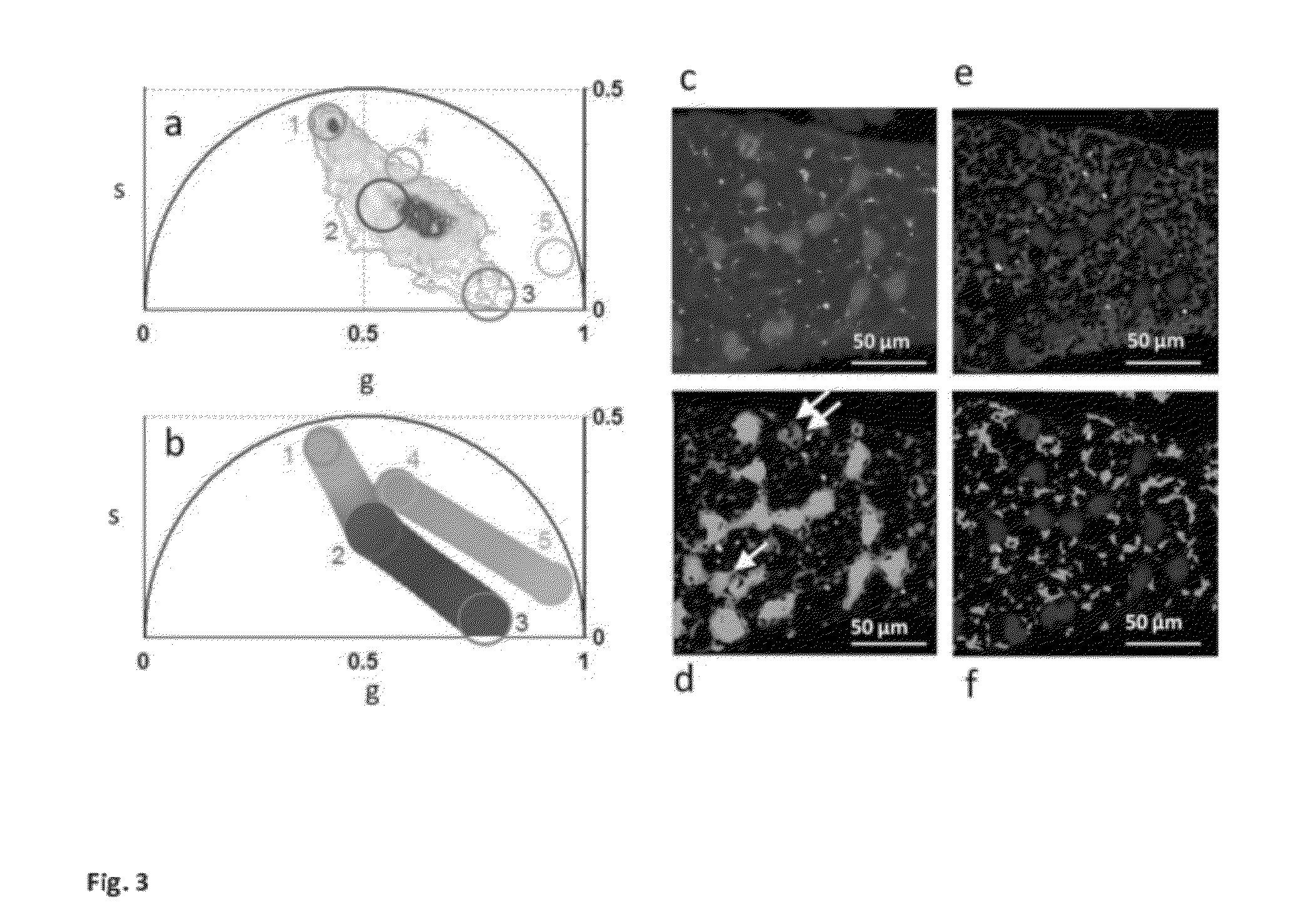
Phasor Method to Fluorescence Lifetime Microscopy to Discriminate Metabolic State of Cells in Living Tissue
ActiveUS20120276578A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant Germ CellsPorphyrin
“A label-free imaging method to monitor stem cell metabolism discriminates different states of stem cell as they differentiate in a living tissues. We use intrinsic fluorescence biomarkers and the phasor approach to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). We identify and map intrinsic fluorophores such as collagen, retinol, retinoic acid, flavins, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and porphyrin. We measure the phasor values of germ cells in C. Elegans germ line. Their metabolic fingerprint cluster according to their differentiation state, reflecting changes in FAD concentration and NADH binding during the differentiation pathway. The phasor approach to lifetime imaging provides a label-free, fit-free and sensitive method to identify different metabolic state of cells during differentiation, to sense small changes in the redox state of cells and may identify symmetric and asymmetric divisions and predict cell fate.”
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
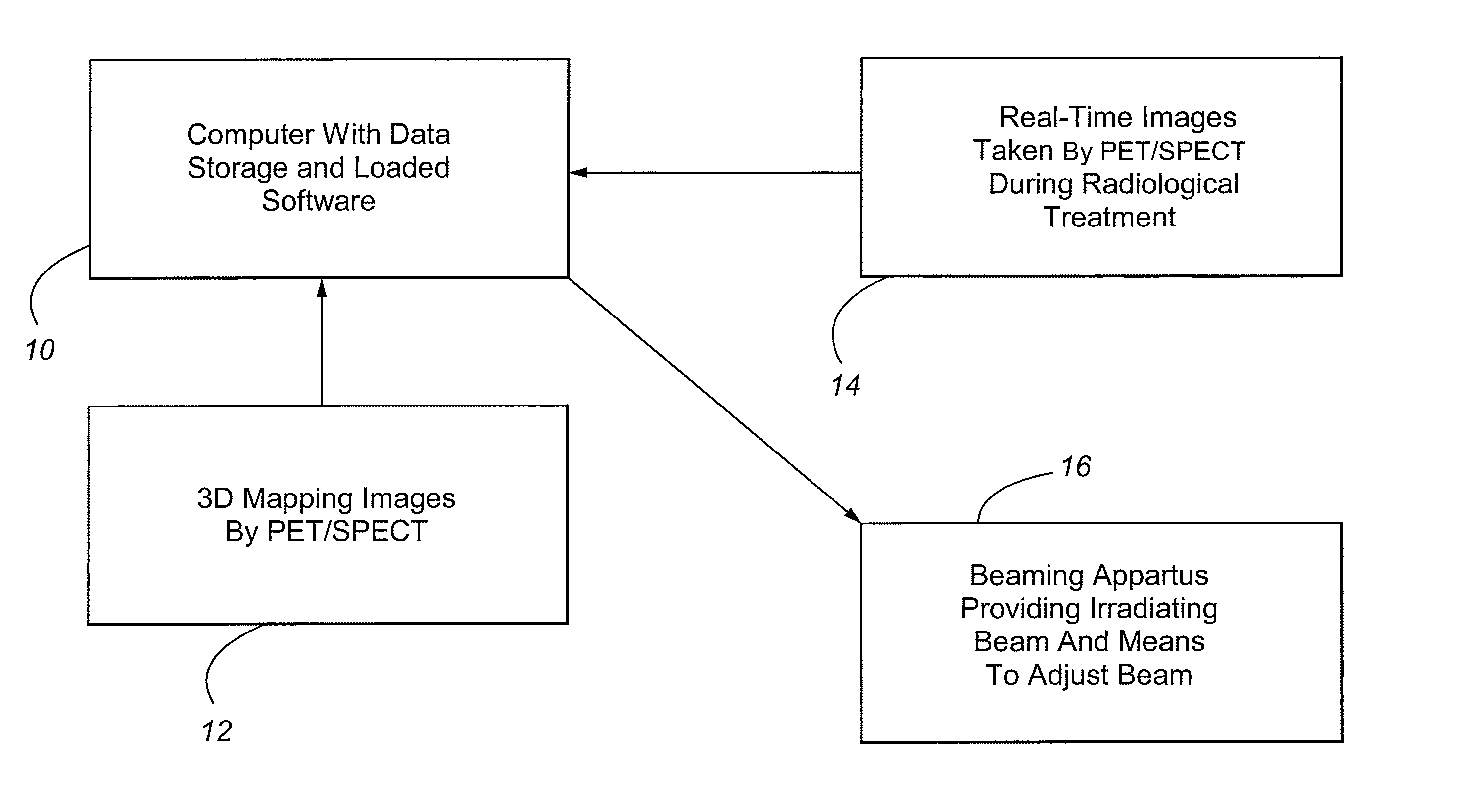
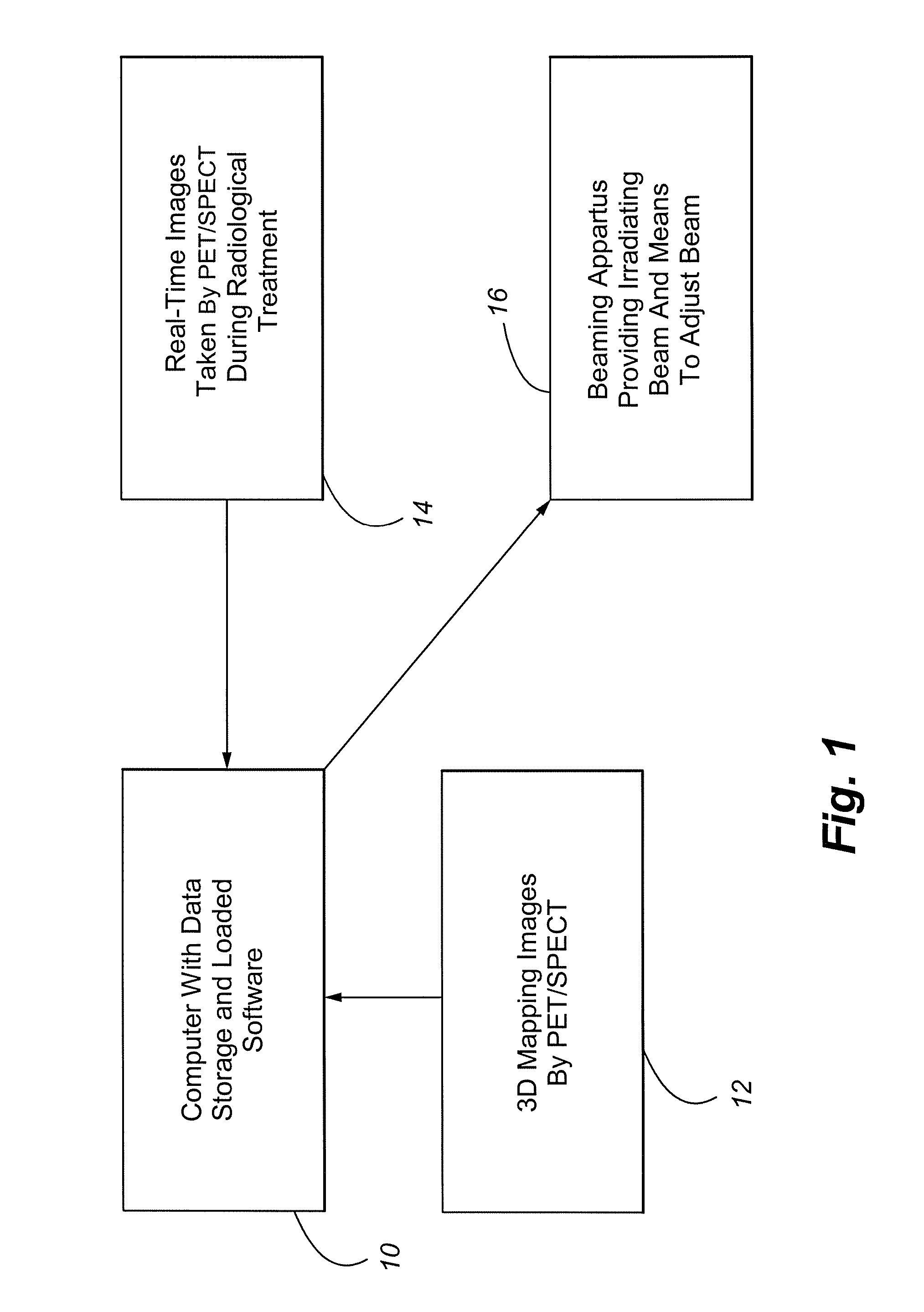
Method and Apparatus Including Use of Metalloporphyrins for Subsequent Optimization of Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy
InactiveUS20070043289A1Selective uptakeEfficient deliveryTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadiosurgeryDual delivery
Owner:ADAIR
Synthesis of perylene-porphyrin building blocks and polymers thereof for the production of light-harvesting arrays
InactiveUS6916982B2Manufactured usingLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufacturePerylenePorphyrin
The present invention provides methods, compounds, and compositions for the synthesis of light harvesting arrays, such arrays comprising: (a) a first substrate comprising a first electrode; and (b) a layer of light harvesting rods electrically coupled to said first electrode, each of said light harvesting rods comprising a polymer of Formula I:X1Xm+1)m (I)wherein m is at least 1; X1 is a charge separation group, and X2 through Xm+1 are chromophores. At least one of X2 through Xm+1 has at least one perylene group coupled thereto.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Method of preparing adipic acid by air-oxidating hexacarbocyclic compound
InactiveCN1535947AReduce dosageHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCyclohexanoneCyclohexene
The present invention relates to a new process for preparing adipic acid by air oxidating cyclohexane, cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone and cyclohexene or mixture of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone under the catalysis of metal porphyrin. Under the condition of 1-20 atm air and reaction temp. is 50-200 deg.C it can select and use mu-oxidized metal porphyrin and monometal porphyrin or their fixed carrier material as catalyst independently, also can select and use metal porphyrin or their fixed carrier material as main catalyst, and use transition metal salt or oxide as co-catalyst. The metal porphyrin like biological-enzyme can high-effectively and high-selectivity catalyze air under the biologicae concentration to directly oxidate the cyclohexane into adipic acid. Said invented dose of metal porphyrin is less, and its catalytic effect is good, it can make homogeneous catalysis, also can make heterogeneous catalysis after the carrier is fixed.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
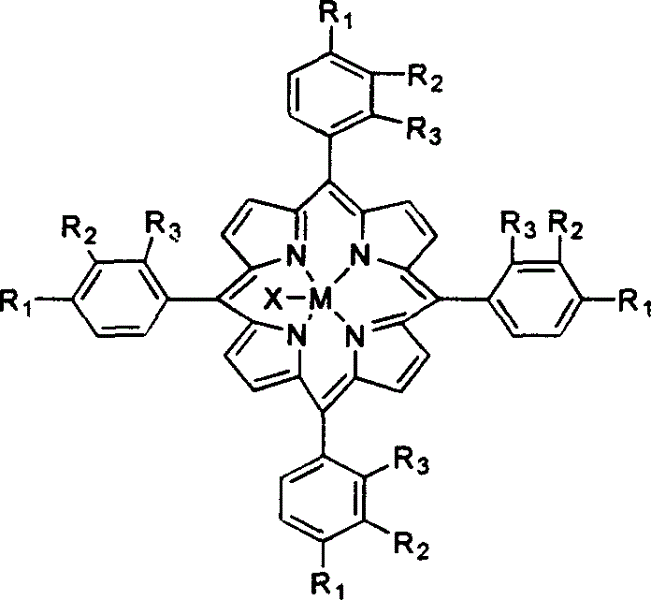
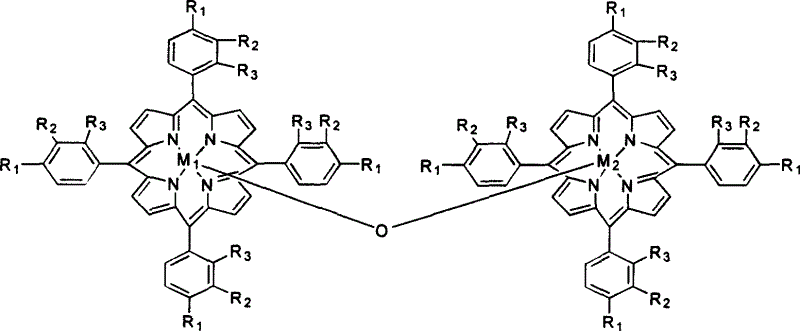
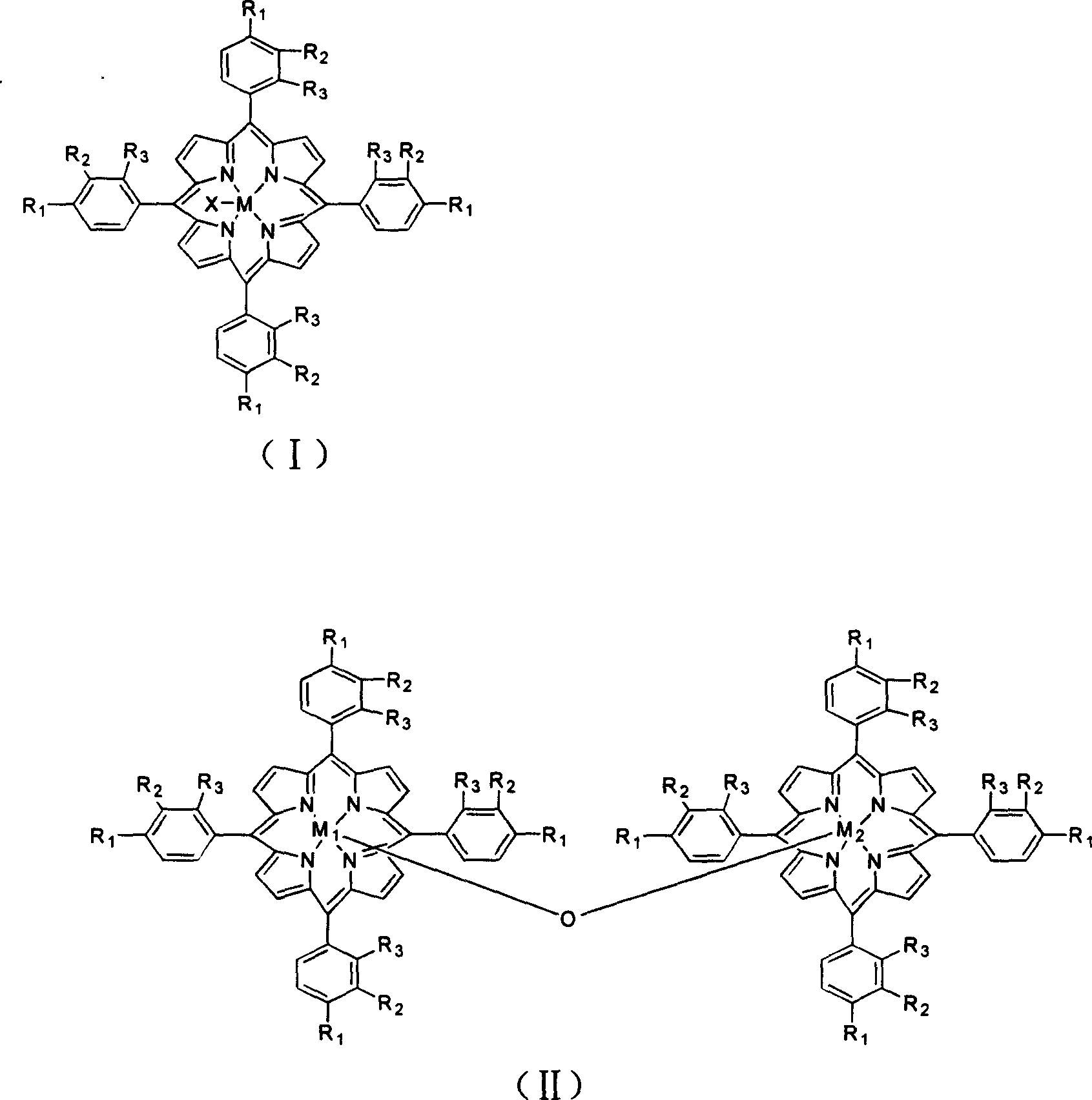
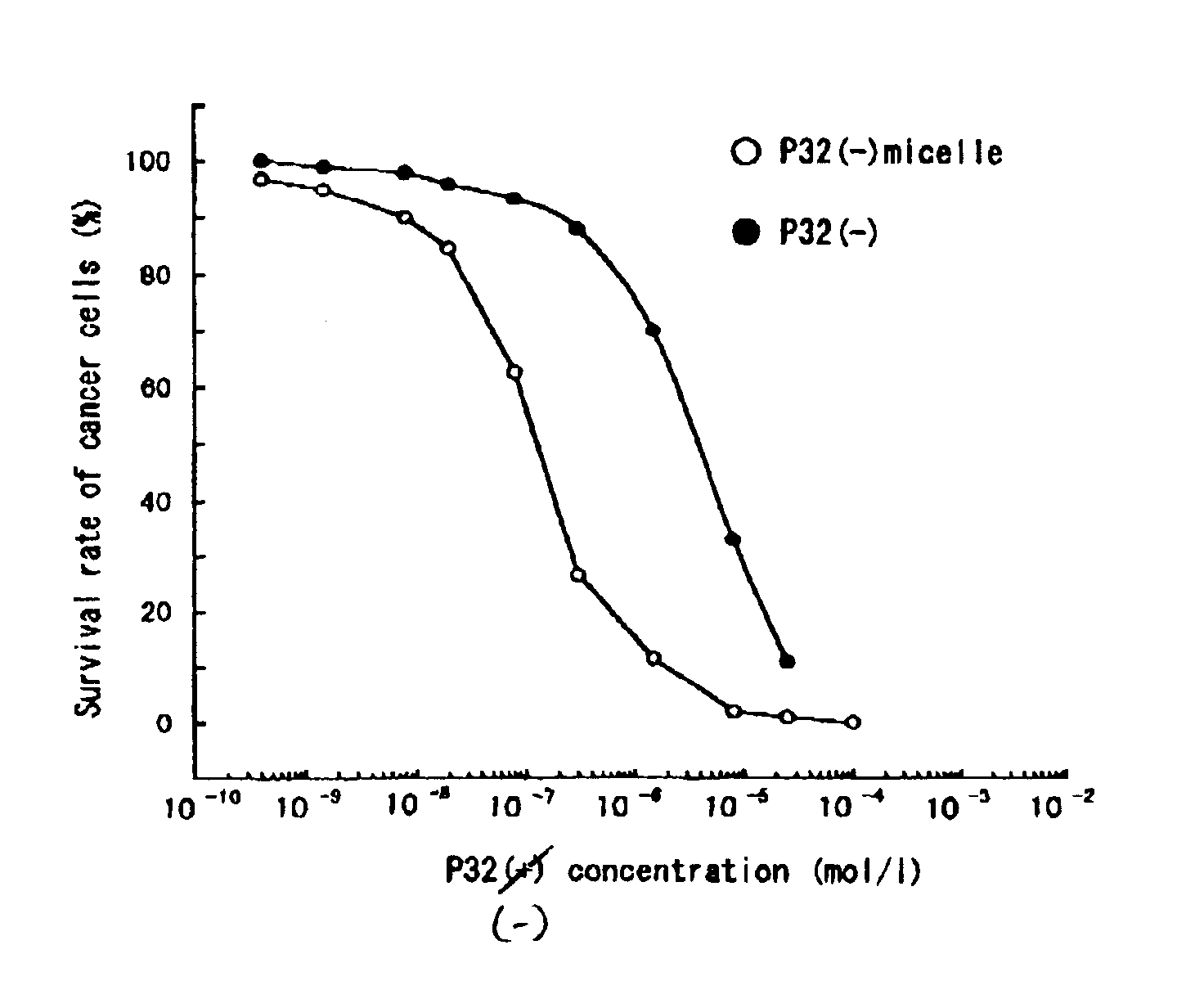
Polymeric micellar structure
The invention relates to a polymeric micellar structure which comprising an ionic porphyrin dendrimer represented by general formula (1): q(c)PM (where q represents the number of charged atoms on the periphery of the dendrimer; c represents a negative (−) or positive (+) charge; and PM is represented by the following general formula (2): wherein M represents two hydrogen atoms or a metal atom, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are the same or different and represents hydrogen or identical or different aryl ether dendrosubunits, provided that at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 represent an aryl ether dendrosubunits and that each aryl ether dendrosubunit has an anionic or cationic group at the end optionally though a spacer molecule chain.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from waste petroleum catalyst
InactiveCN105274344AReduce pollutionAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystPorphyrin
The invention relates to a method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from a waste petroleum catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of petrochemical industry. The method comprises air-burning and ball-removing, ball-milling, soda roasting-water leaching, aluminum removing, molybdenum precipitating and enriching molybdenum by ion exchange. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, igniting sticky oil in the waste catalyst in air to burn carbon and oils in the waste catalyst; then, oxidizing the vanadium and nickel in the forms of porphyrin compounds in the waste catalyst into vanadium oxide and nickel oxide, converting most of the molybdenum into molybdenum oxide, wherein the waste catalyst subjected to air-burning and oil-removing is more beneficial for crushing, and the crushed waste catalyst and a certain proportion of sodium carbonate are mixed, and are roasted at a high temperature; leaching roasted materials by hot water, dissolving sodium salts of the vanadium and the molybdenum into water to obtain a solution, filtering the solution, introducing the filtered solution into a leaching solution, introducing a little aluminum into the leaching solution, regulating the pH value of the solution to remove aluminum; regulating the pH value of the solution to 8-9, adding ammonium chloride, precipitating and separating out the vanadium in the form of ammonium vanadate; and concentrating vanadium-precipitated solution by adopting an ion exchange process and enriching an ammonium molybdate solution.
Owner:刘楚玲
Photochemotherapeutic method using 5-aminolevulinic acid and other precursors of endogenous porphyrins
InactiveUS6710066B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAmino-Levulinic AcidProtoporphyrin IX
Methods of detecting and treating rapidly growing exogenous cells, such as Protista, or parasites, that preferentially accumulate a photoactivatable porphyrin in which 5-aminolevulinic acid or precursor thereof is administered to the patient, or contacted to the exogenous cells, in an amount sufficient to induce synthesis fluorescence and / or photosensitizing concentrations of a protoporphyrin IX in the exogenous cells, followed by exposure of the exogenous cells to light of photoactivating wavelengths.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Method and apparatus for detecting ammonia from exhaled breath
InactiveUS20050171449A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHelicobacterPorphyrin
The present invention is an apparatus for detecting the presence of exhaled ammonia and a method for using the same to detect the present of a Helicobacter in a subject. The apparatus is composed of a breath capture device having a sensor plate with at least one selected Lewis acid dye (e.g., a metal ion-containing dye such as a metalloporphyrin) deposited thereon which produces a detectable spectral, transmission or reflectance response in the presence of ammonia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA--CHAMPAIGN
Preparation method of TiO2/porphyrin/MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) ultra-thin heteroplasmon
ActiveCN107308990APromote conversionImprove adsorption capacityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsMaterials preparationPorphyrin
The invention discloses a preparation method of TiO2 / porphyrin / MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) ultra-thin heteroplasmon, and belongs to the technical field of inorganic-organic composite functional material preparation. A TiO2 ultra-thin nano-sheet serves as a template, a porphyrin compound is anchored on the surface of the TiO2 ultra-thin nano-sheet by functional groups such as carboxyl and hydroxy on the periphery of the porphyrin compound, and MOFs wrap an outer layer of the porphyrin compound by means of metal-organic framework layer-by-layer self-assembly through residual functional groups such as carboxyl and hydroxy on the periphery of the porphyrin compound to obtain the TiO2 / porphyrin / MOFs ultra-thin heteroplasmon with efficient and stable catalytic activity. The preparation method has the advantages that ultra-thin heteroplasmon catalysis area / light absorption area / adsorption area layer construction and functional integration are creatively performed by the aid of TiO2, porphyrin and the MOFs, a novel catalytic material with excellent performance for photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide is developed, and the performance of the TiO2 / porphyrin / MOFs ultra-thin heteroplasmon is optimized based on adjustable structural and functional characteristics of porphyrin and MOFs materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
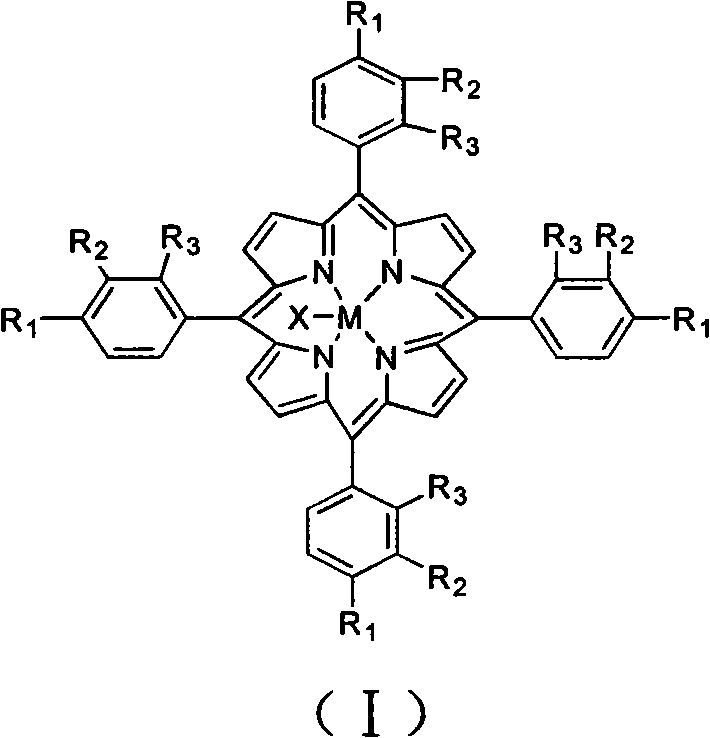
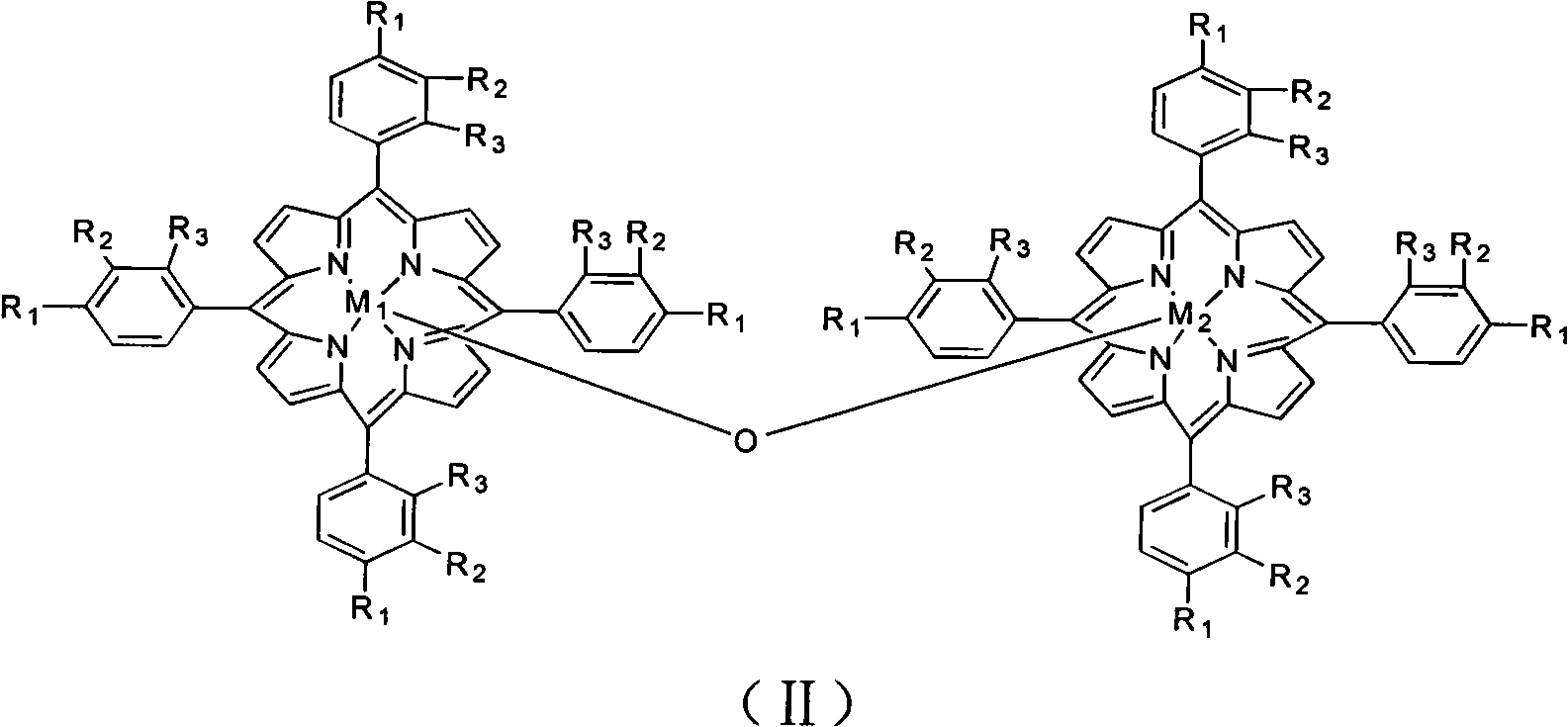
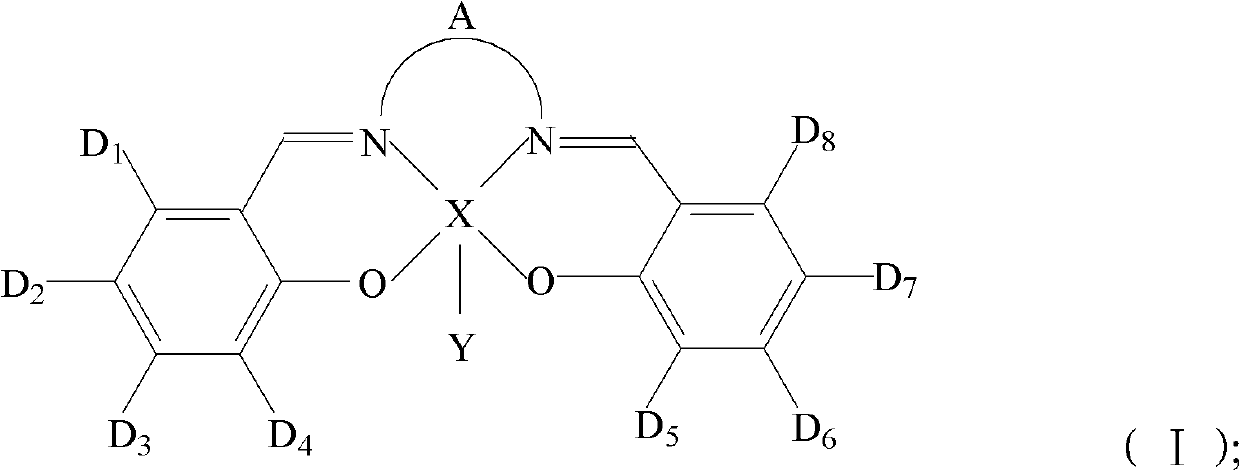
Tetradentate schiff base metal complexes, metal porphyrin complexes and preparing method of polycarbonate
ActiveCN102558199AHigh catalytic activityPrevent the problem of excessive toxic metal contentGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMagnesium organic compoundsQuaternary ammonium cationPorphyrin
The invention provides tetradentate schiff base metal complexes with formula (I) and metal porphyrin complexes with formula (II). The active centers of the two complexes are non-toxic zinc, magnesium, manganese or iron. The invention also provides a method for preparing polycarbonate by using the complexes as a catalyzer. The ligand of the two complexes contain at least one or more quaternary ammonium salt or strong sterically hindered organic base group, so the two complexes have higher catalytic activity, meanwhile the complexes have non-toxic active center metal like zinc, magnesium, manganese or iron, can effectively prevent the problem of the exceeding content of toxic metals in polycarbonate and ensure that the product does not contain toxic metal residues.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
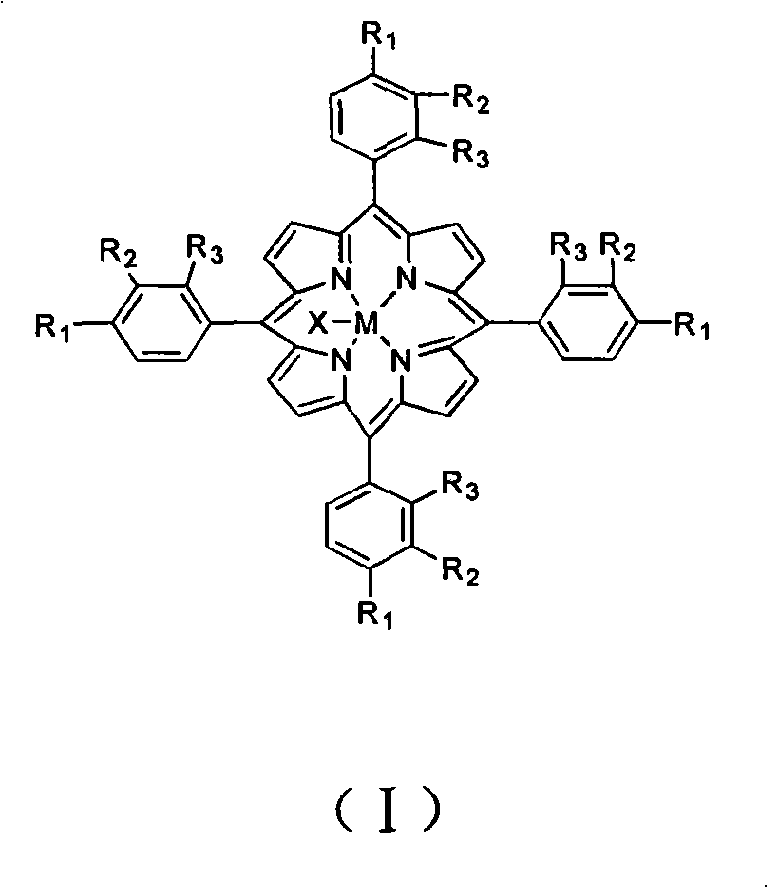
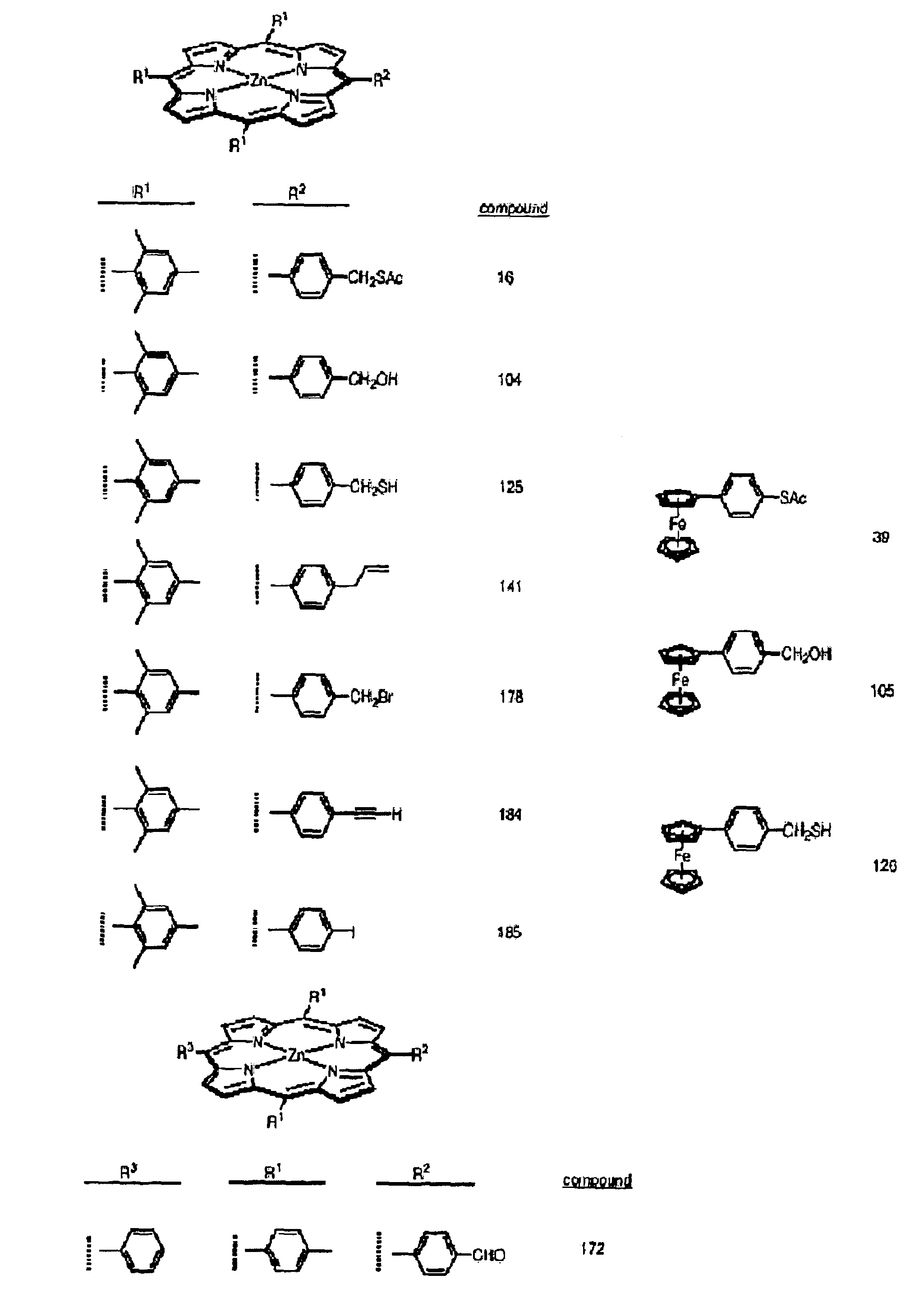
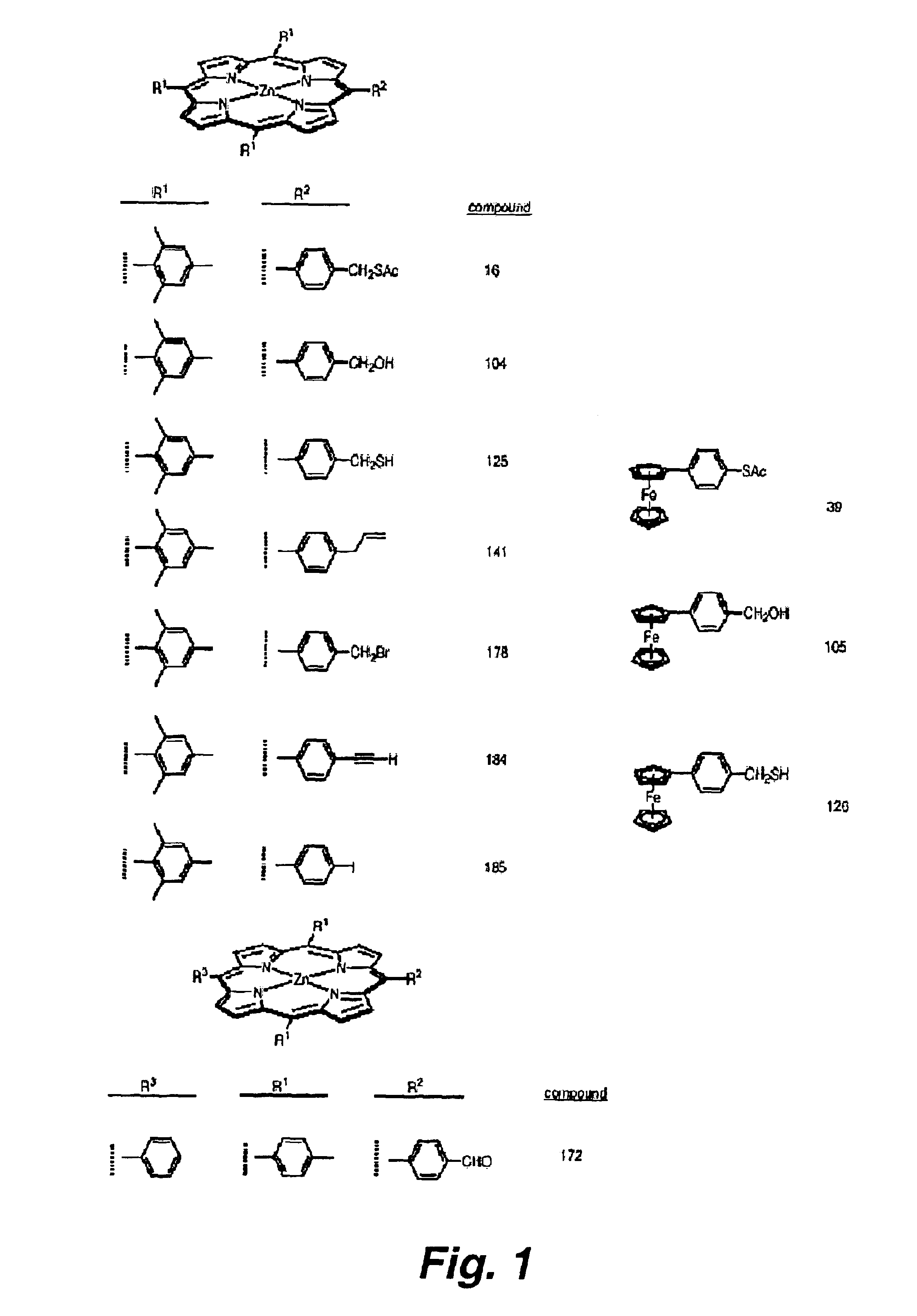
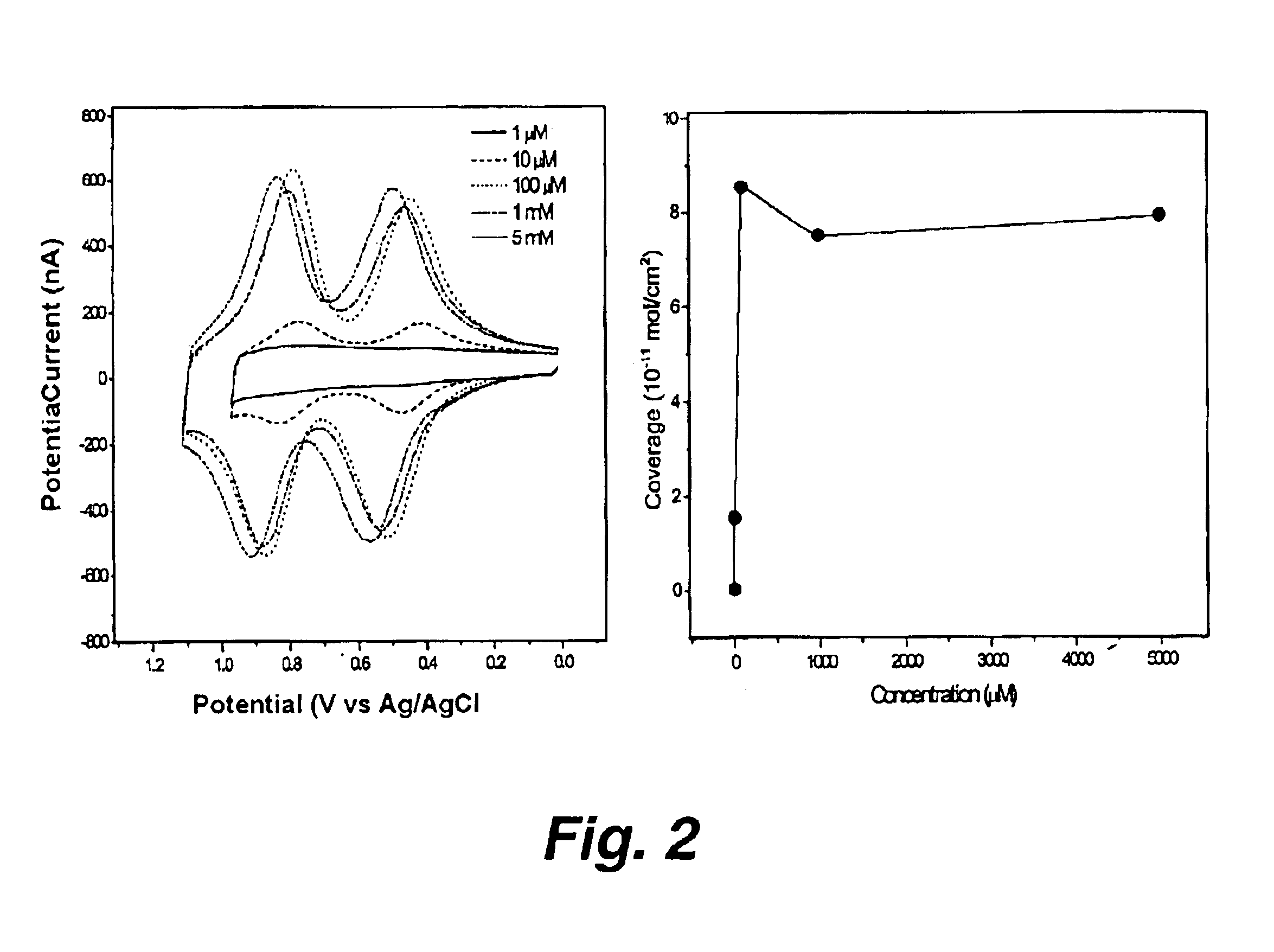
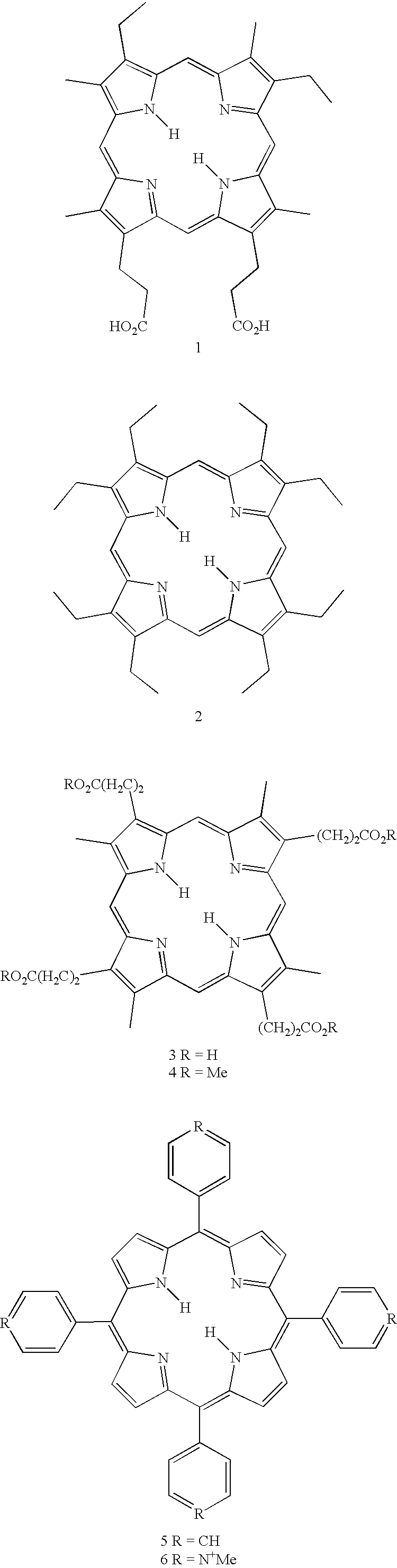
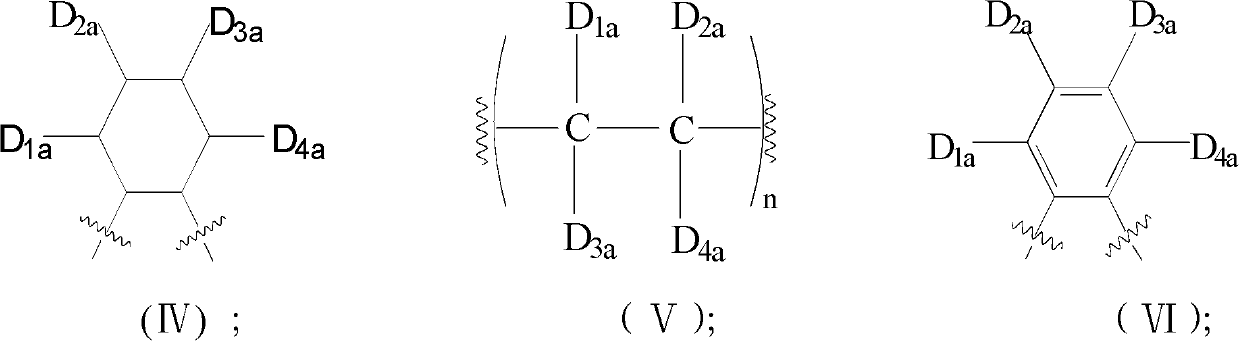
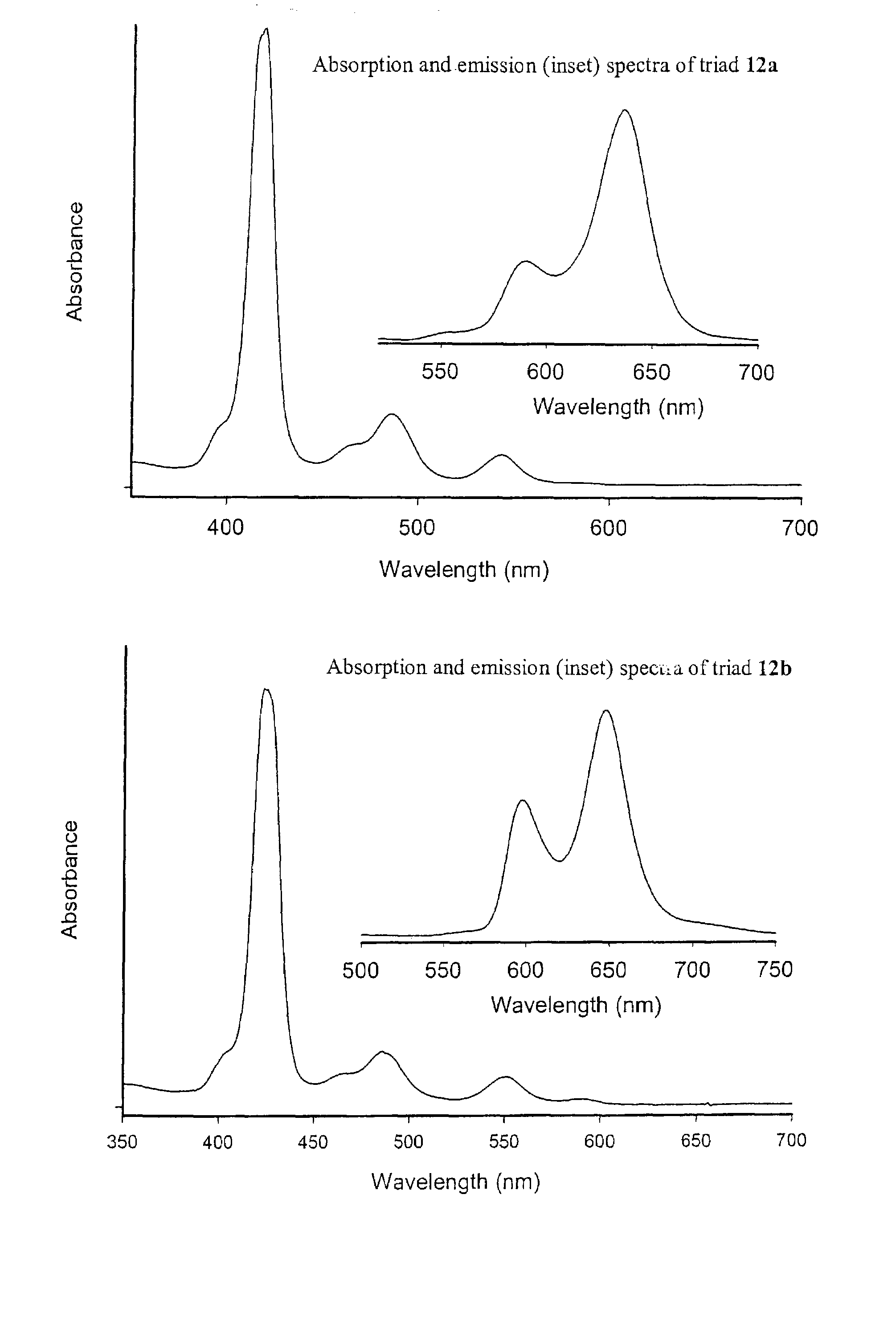
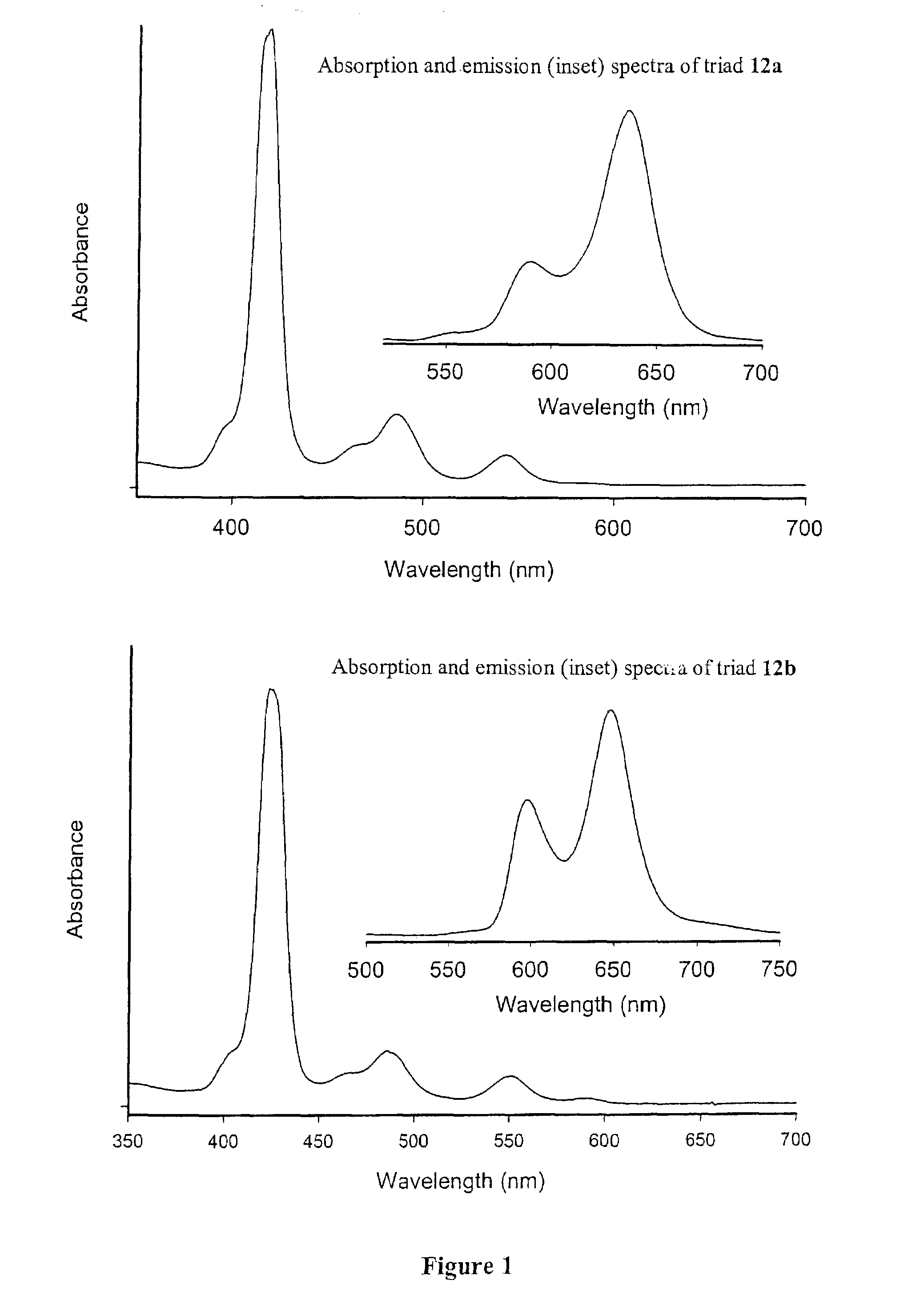
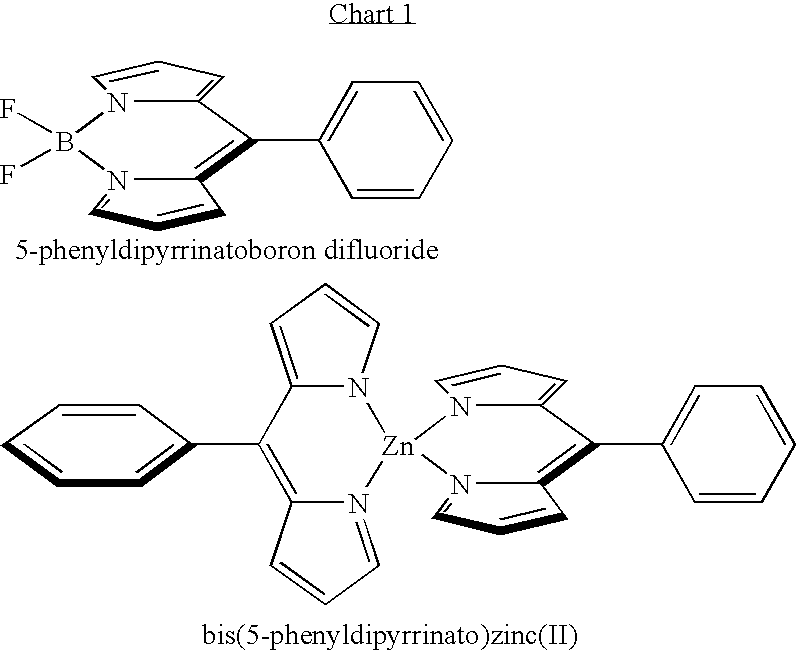
Methods and intermediates for the synthesis of dipyrrin-substituted porphyrinic macrocycles
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105348303AImprove performanceExcellent rate performanceOrganic chemistryHybrid capacitor electrodesPotassiumPorphyrin
The invention belongs to the fields of a metal ion battery and a super capacitor, and concretely relates to a porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer, and a preparation method and an application thereof. A structural formula of the porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer is shown in formula (I), wherein m=0 or 1, n=0 or 1. The porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer can be directly used as a cathode material of the metal ion battery and the super capacitor, so that the cathode material shows excellent properties, which include good cycle performance, high specific capacity and excellent rate capability; the polymer powder also has the same effects and properties, and can be used as a cathode material of other metal ion (sodium, potassium, zinc, nickel, etc.) batteries and super capacitors.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com