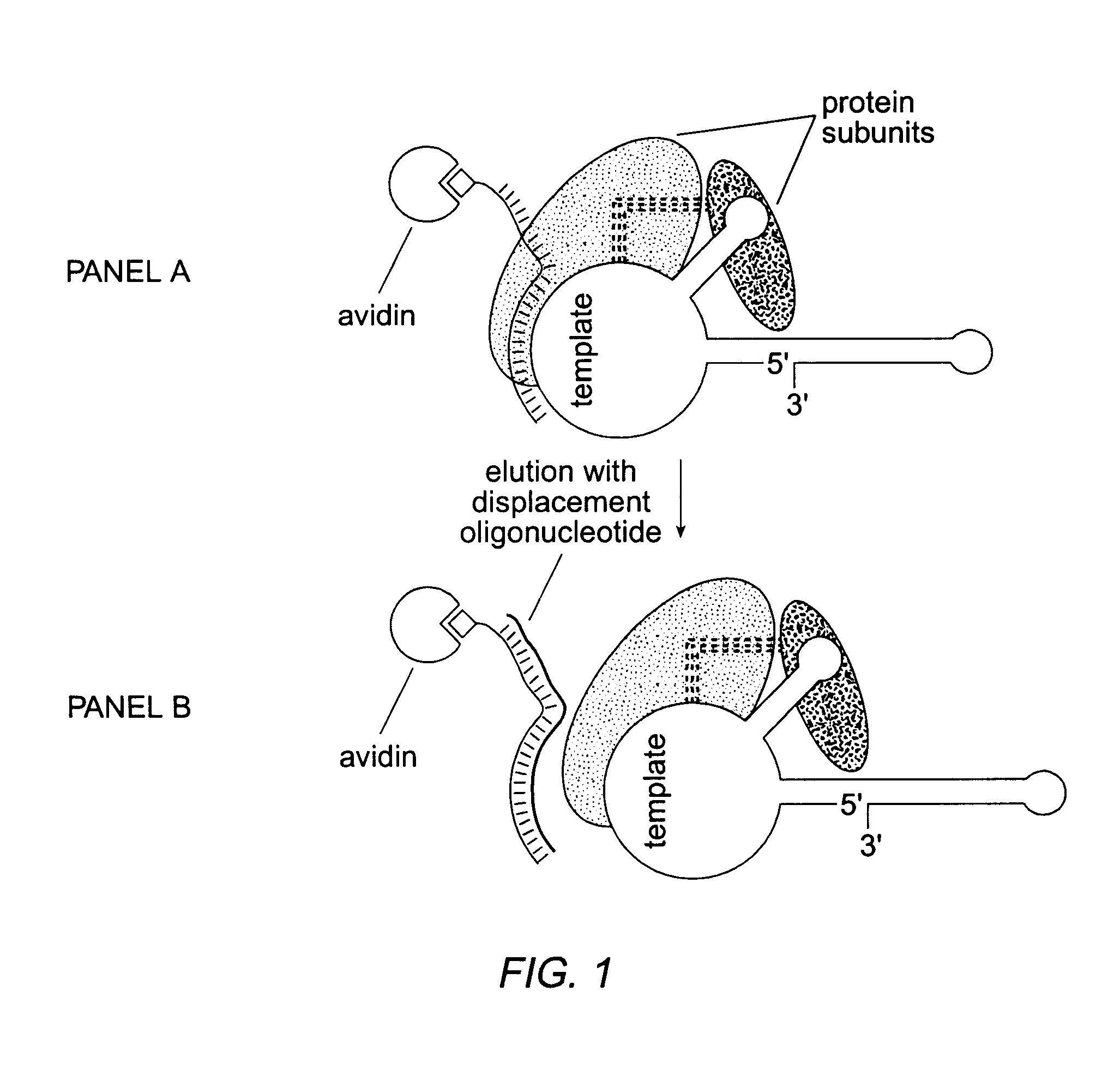
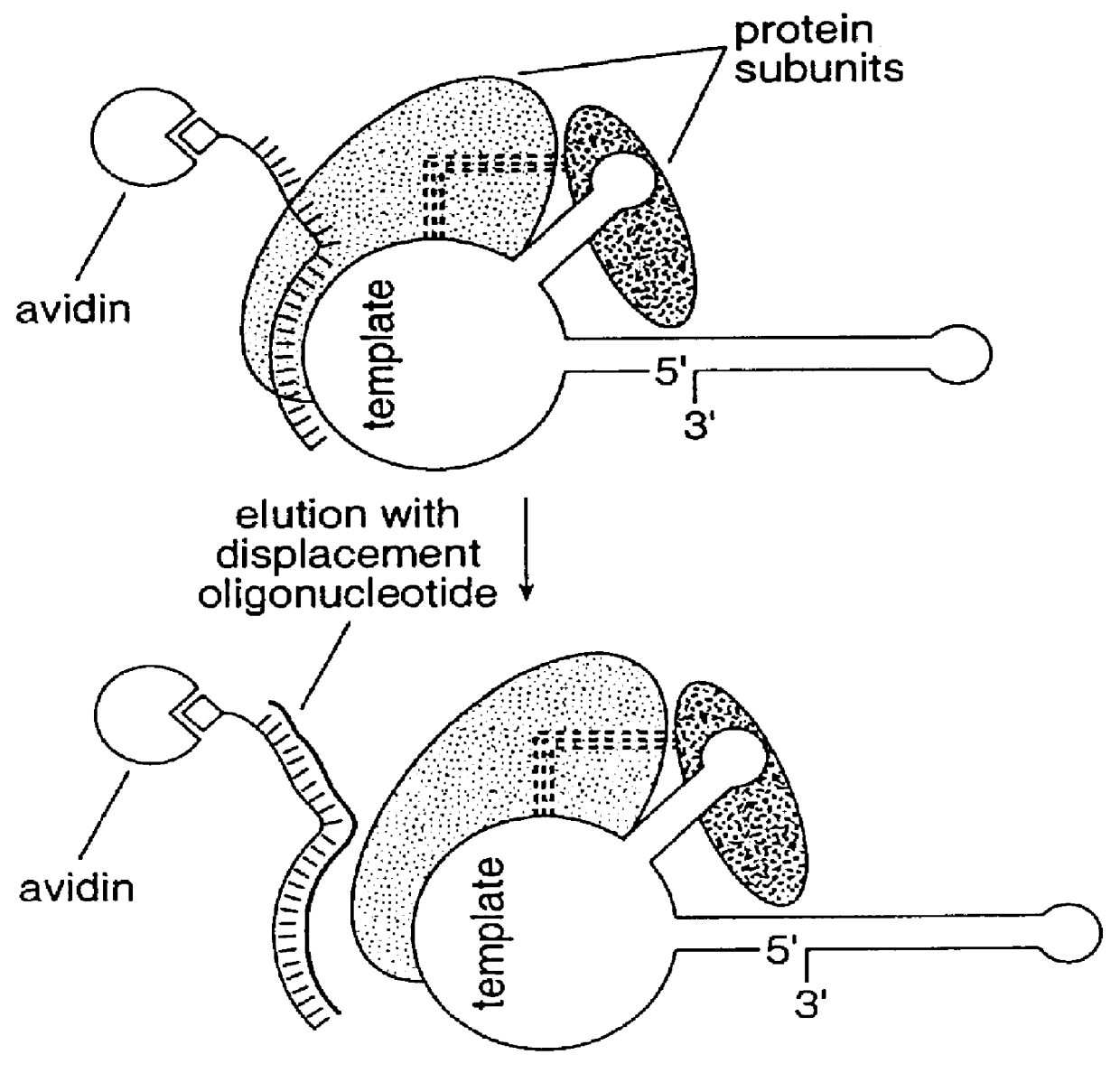
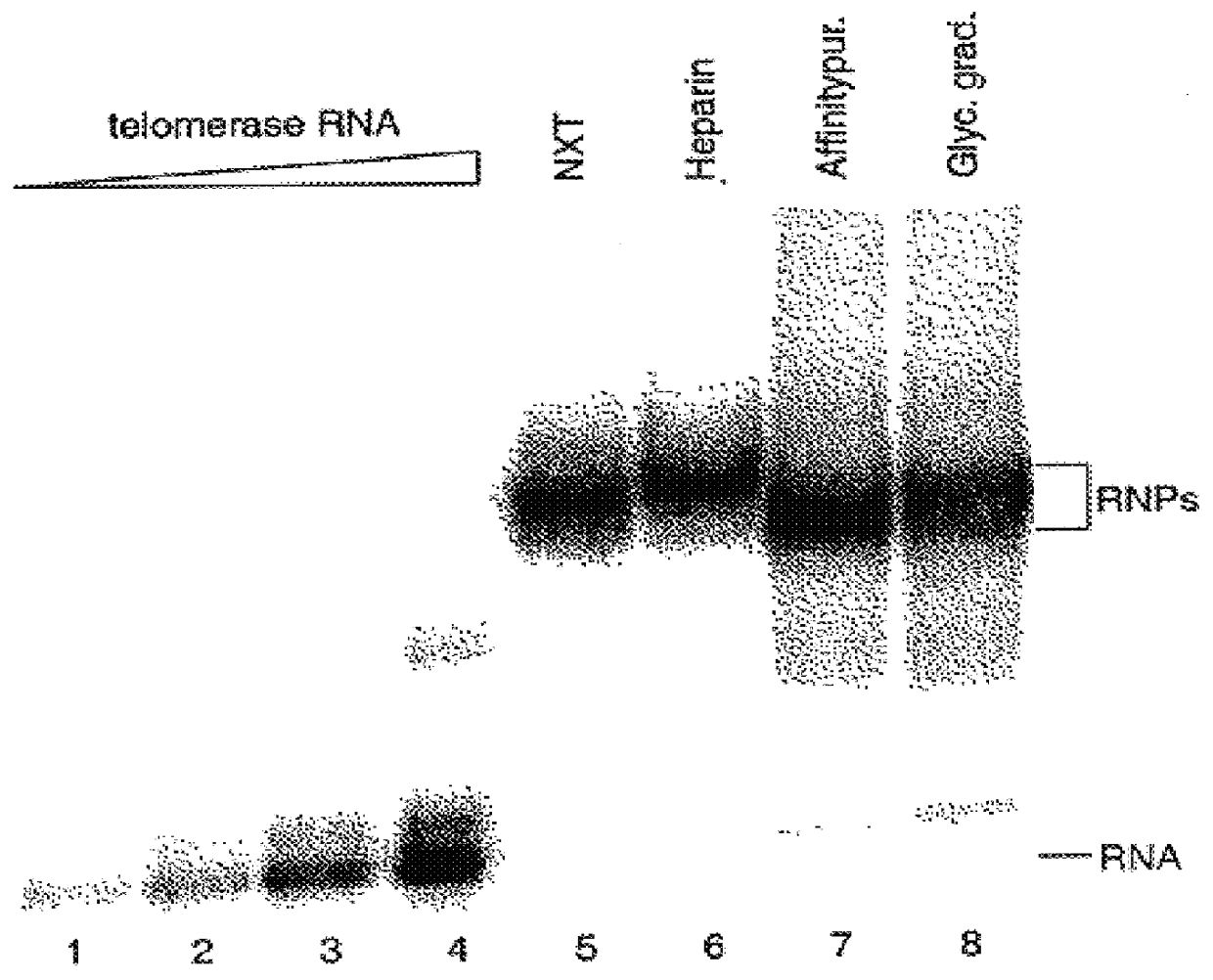
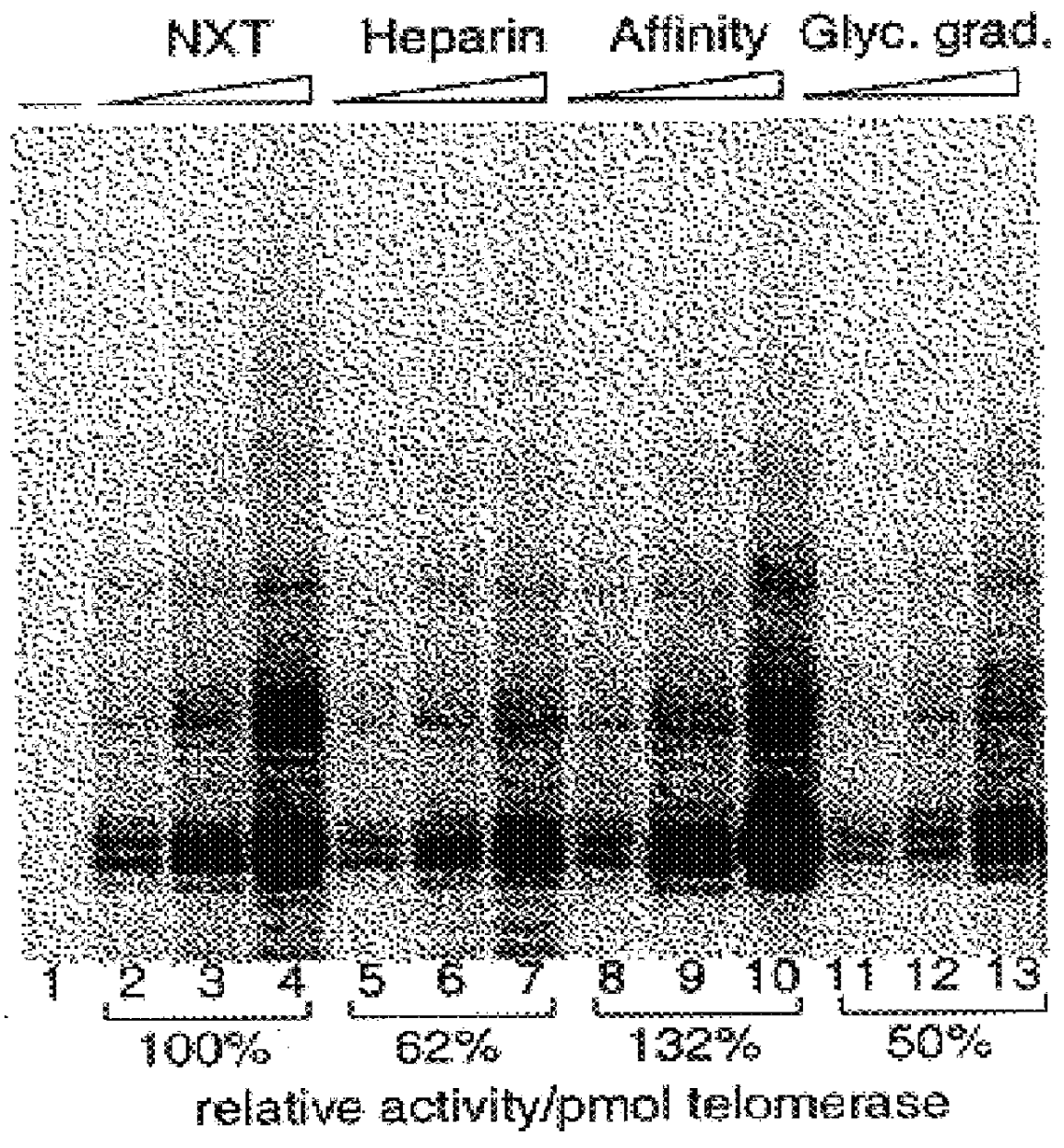
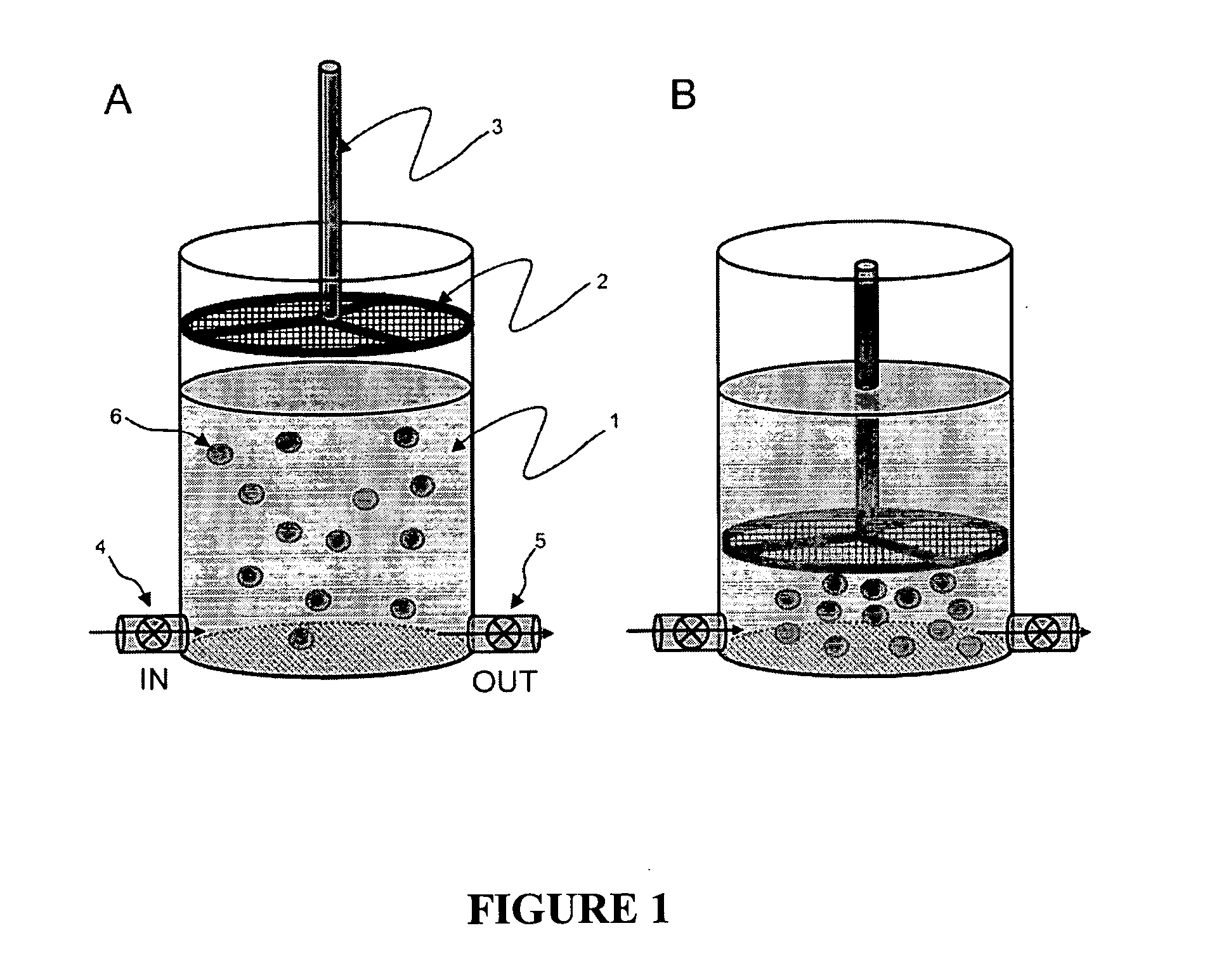
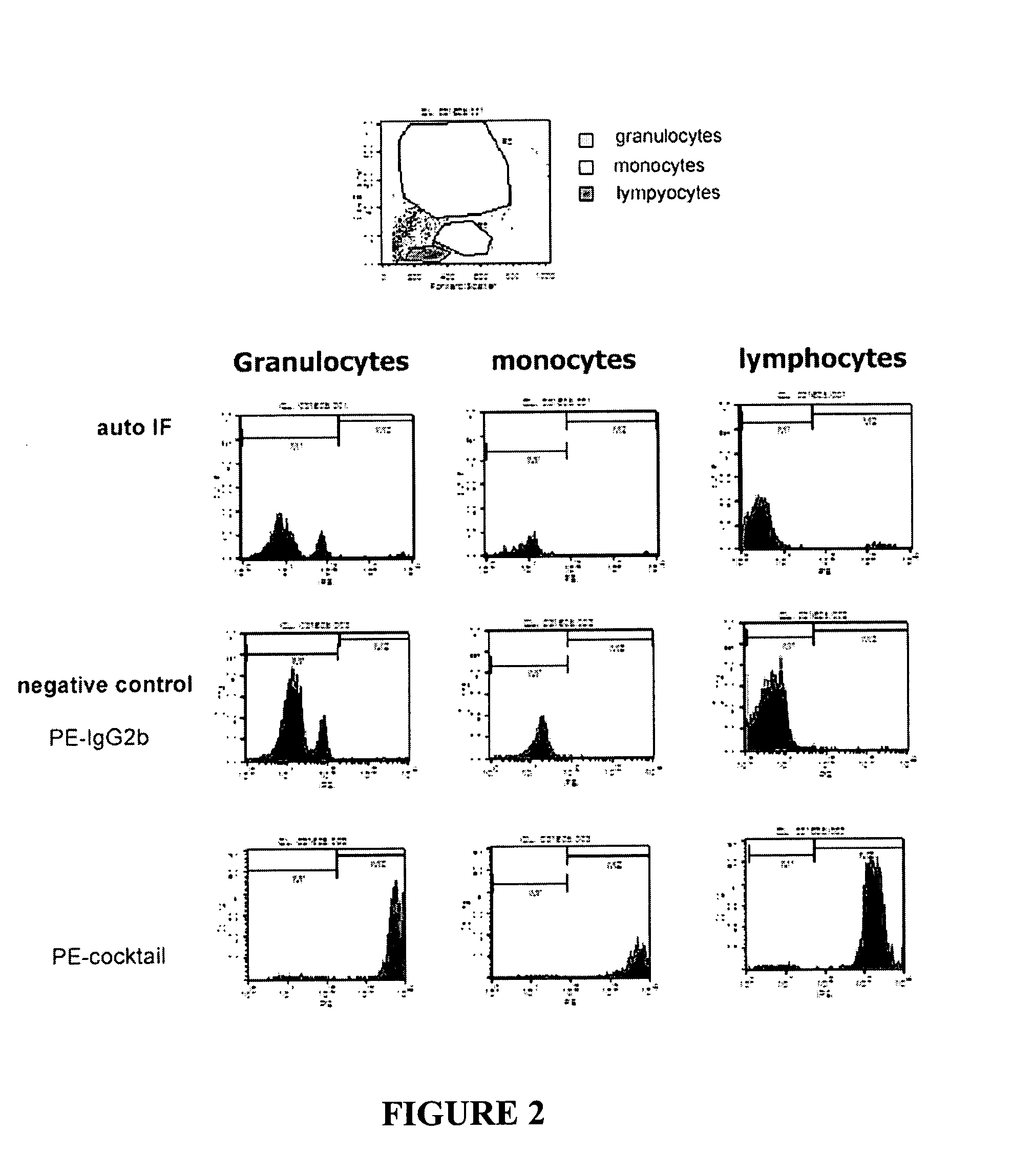
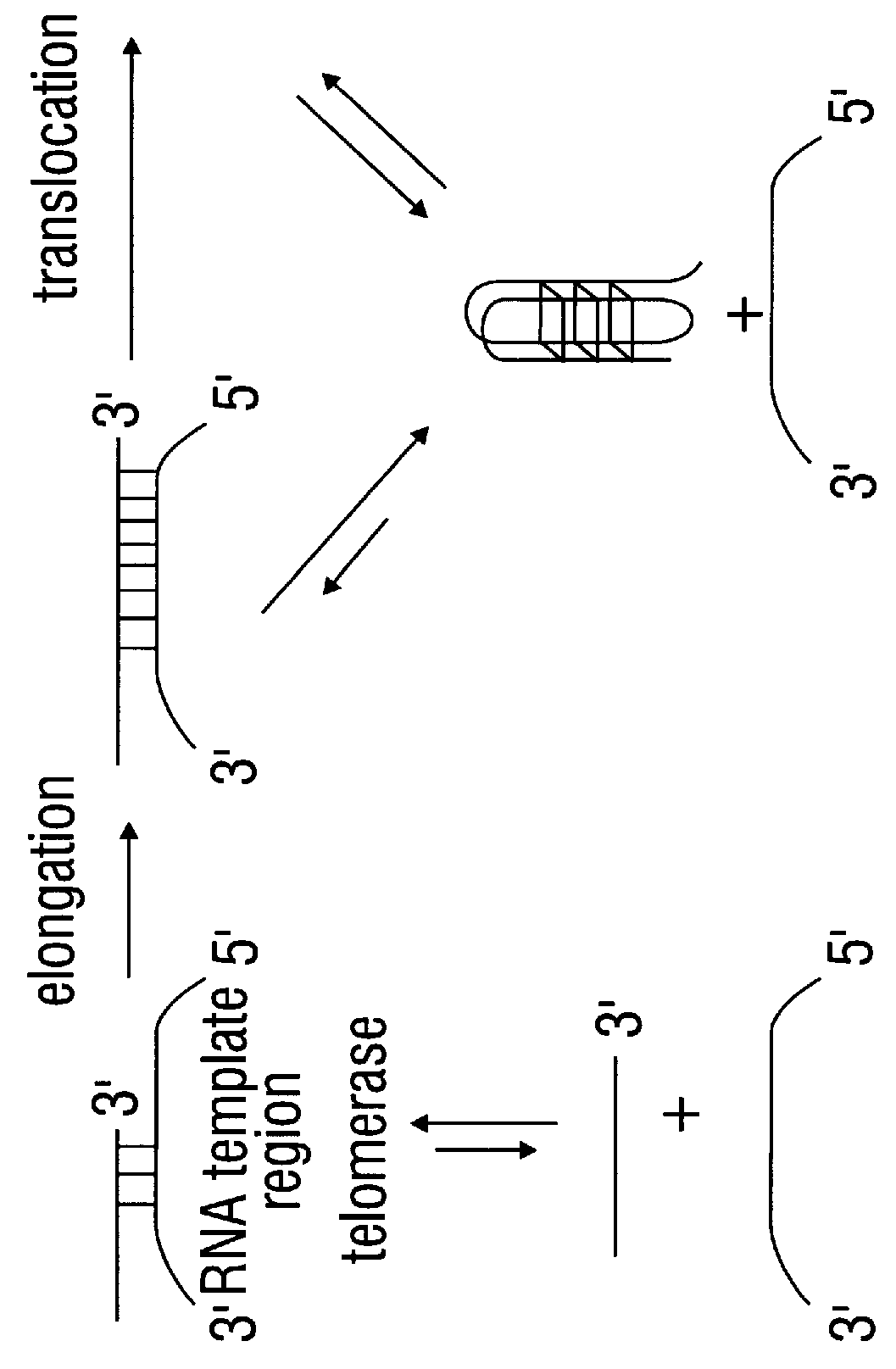
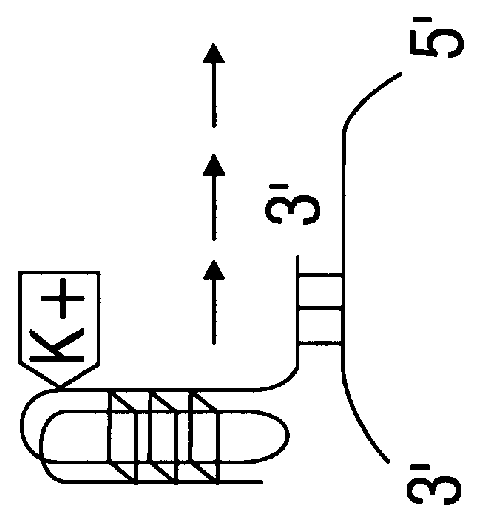
Patents
Literature
559 results about "Telomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of eukaryotic chromosomes in most eukaryotes. Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster lacks telomerase, but instead uses retrotransposons to maintain telomeres.
Telomerase
InactiveUS6261836B1Improve purification effectAvoid the needPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
Telomerase
InactiveUS6093809AImprove purification effectAvoid the needSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
Method for cancer detection, diagnosis and prognosis
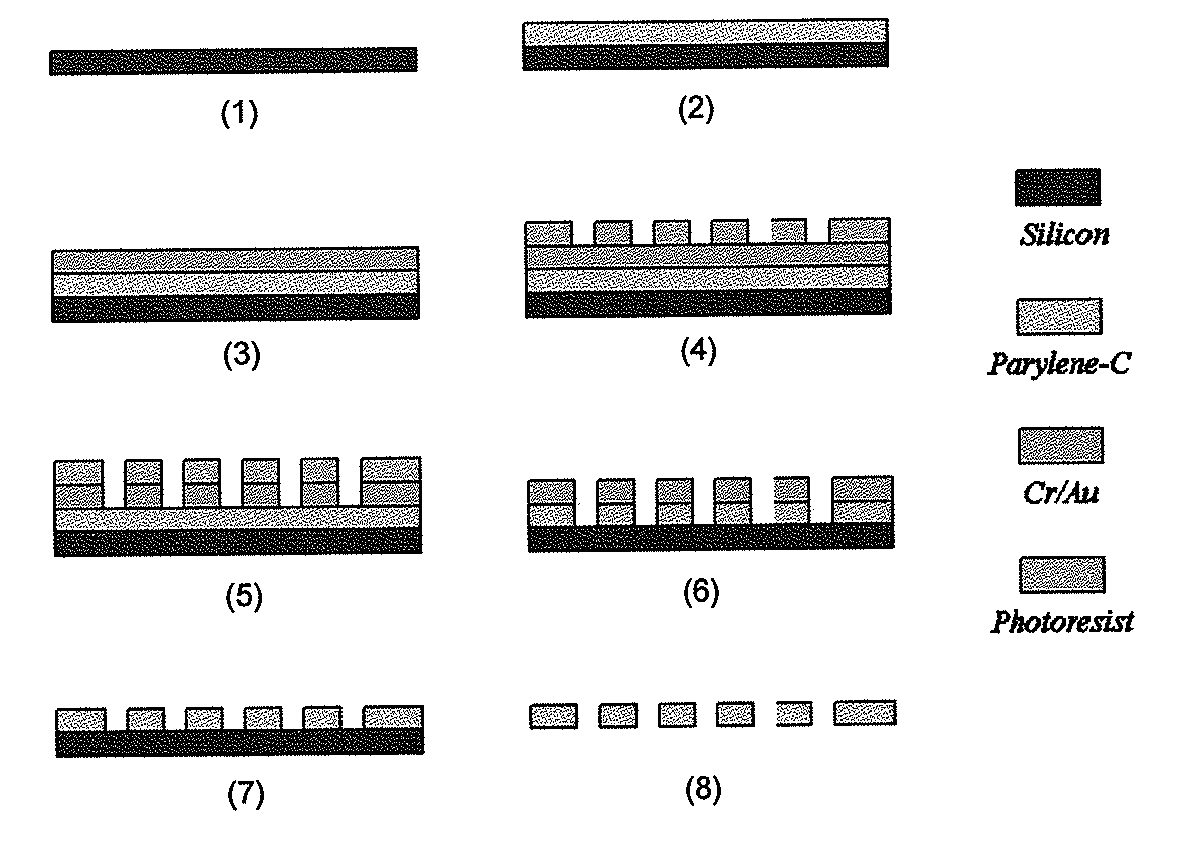
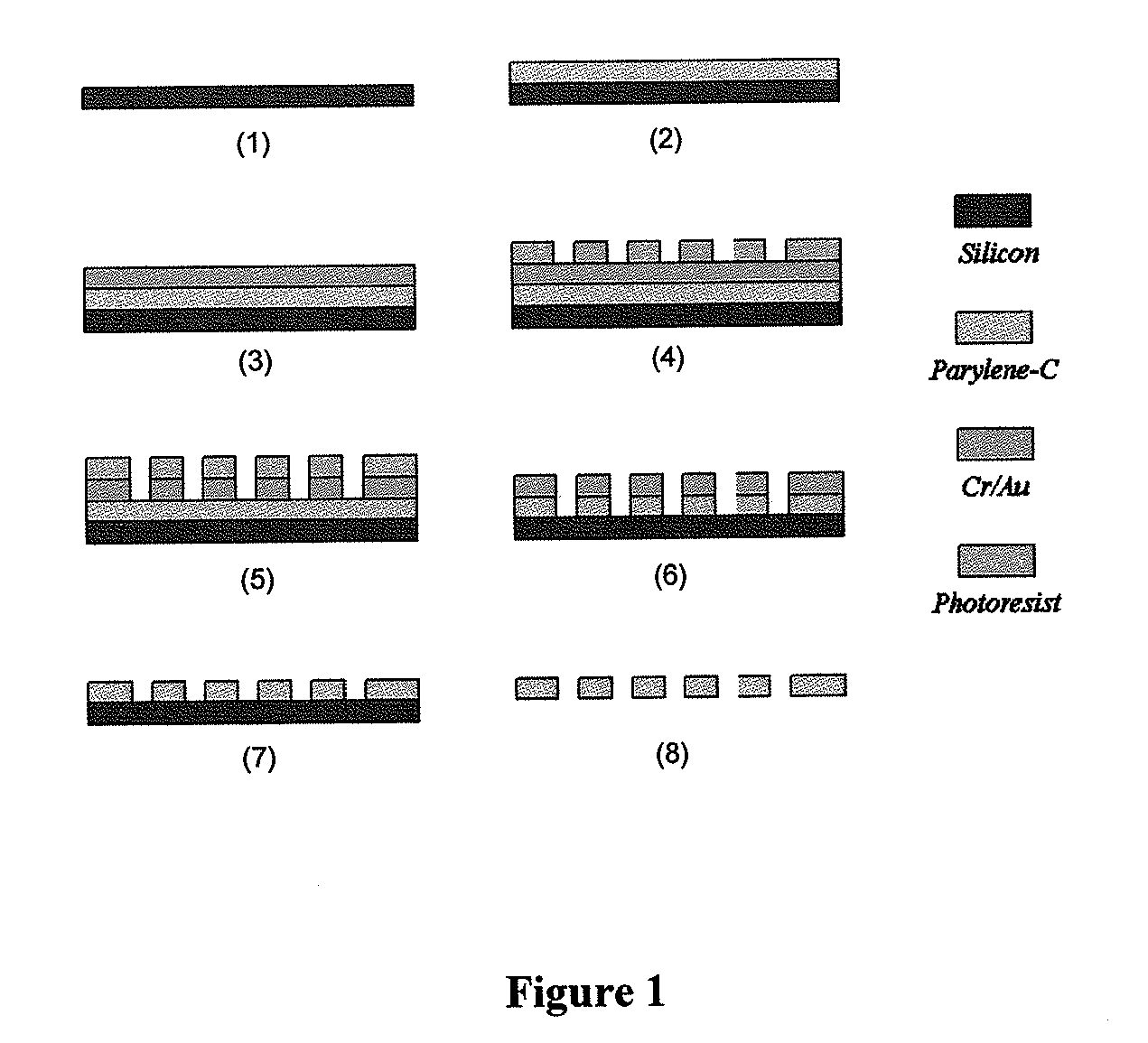
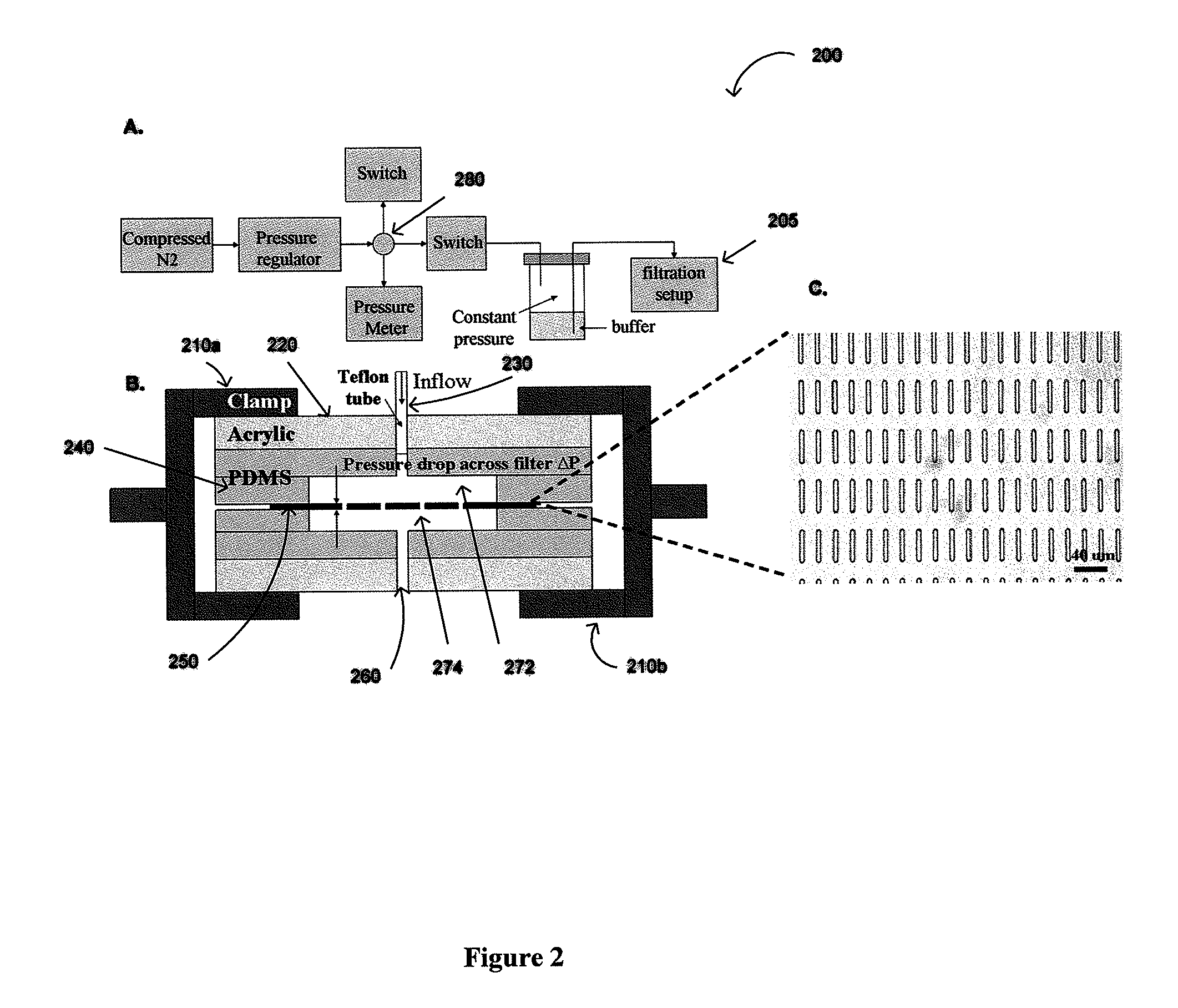
ActiveUS20110053152A1Rapidly and efficiently captureImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTelomeraseParylene
The present invention provides a method for diagnosing cancer, predicting a disease outcome or response to therapy in a patient sample. The method involves isolating a circulating tumor cell (CTC), for example, a viable CTC, from a sample using a parylene microfilter device comprising a membrane filter having or consisting of a parylene substrate, which has an array of holes with a predetermined shape and size; and detecting and quantifying telomerase activity in blood circulating tumor cells. The invention further provides methods of using cells live-captured in various applications.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Methods and compositions for detecting rare cells from a biological sample
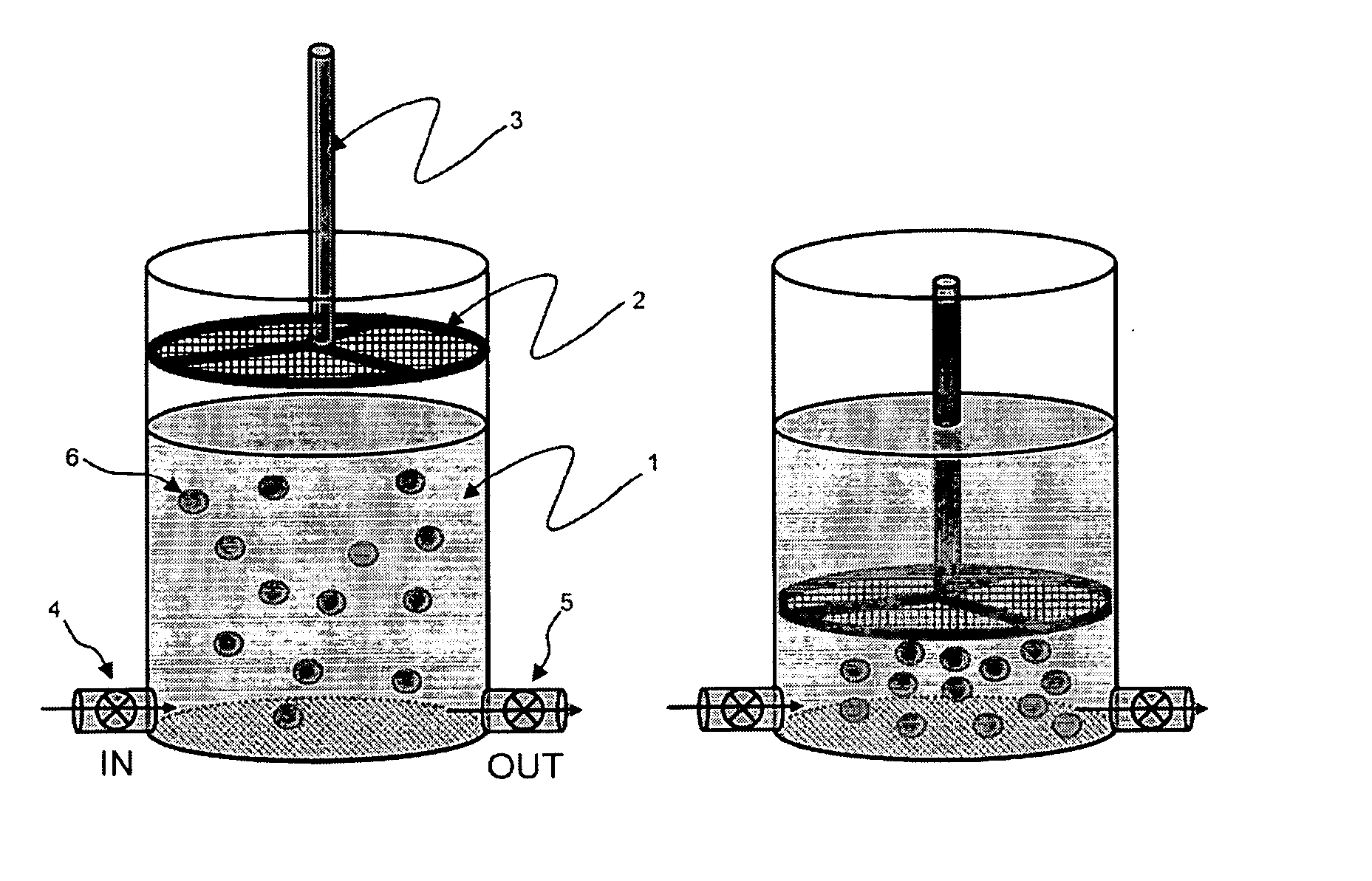
InactiveUS20080057505A1Strong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentHematopoietic cellWhite blood cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for isolating and detecting rare cells from a biological sample containing other types of cells. In particular, the present invention includes a debulking step that uses a microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and the enriched rare cells can be used in a downstream process such as identifies, characterizes or even grown in culture or used in other ways. The invention also include a method of determining the aggressiveness of the tumor or of the number or proportion of cancer cells in the enriched sample by detecting the presence or amount of telomerase activity or telomerase nucleic acid or telomerase expression after enrichment of rare cells. This invention further provides an efficient and rapid method to specifically remove red blood cells as well as white blood cells from a biological sample containing at least one of each of red blood cells and white blood cells, resulting in the enrichment of rare target cells including circulating tumor cells (CTC), stromal cells, mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells, fetal cells, stem cells, non-hematopoietic cells etc from a blood sample. The method is based upon combination of immuno-microparticles (antibody coated microparticles) and density-based separation. The final enriched target cells can be subjected to a variety of analysis and manipulations, such as flowcytometry, PCR, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, image analysis, enzymatic assays, gene expression profiling analysis, efficacy tests of therapeutics, culturing of enriched rare cells, and therapeutic use of enriched rare cells. In addition, depleted plasma protein and white blood cells can be optionally recovered, and subjected to other analysis such as inflammation studies, gene expression profiling, etc.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Porphyrin compounds as telomerase inhibitors
InactiveUS6087493ARegulating telomerase functionModulating tumor proliferation and mortalitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseDna interaction
The present invention has identified compounds with extended aromatic chromophores that bind the G-quadruplex formed by the folding of single-stranded human telomeric DNA. These compounds have been shown to be effective telomerase inhibitors and are contemplated to be useful in developing cancer treatments. A model of cationic porphyrin interaction with quadruplex DNA by intercalation has been established and in combination with structure activity relations has provided novel porphyrin compounds that exhibit discrimination between binding duplex and quadruplex DNA and show improved activity against telomerase.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
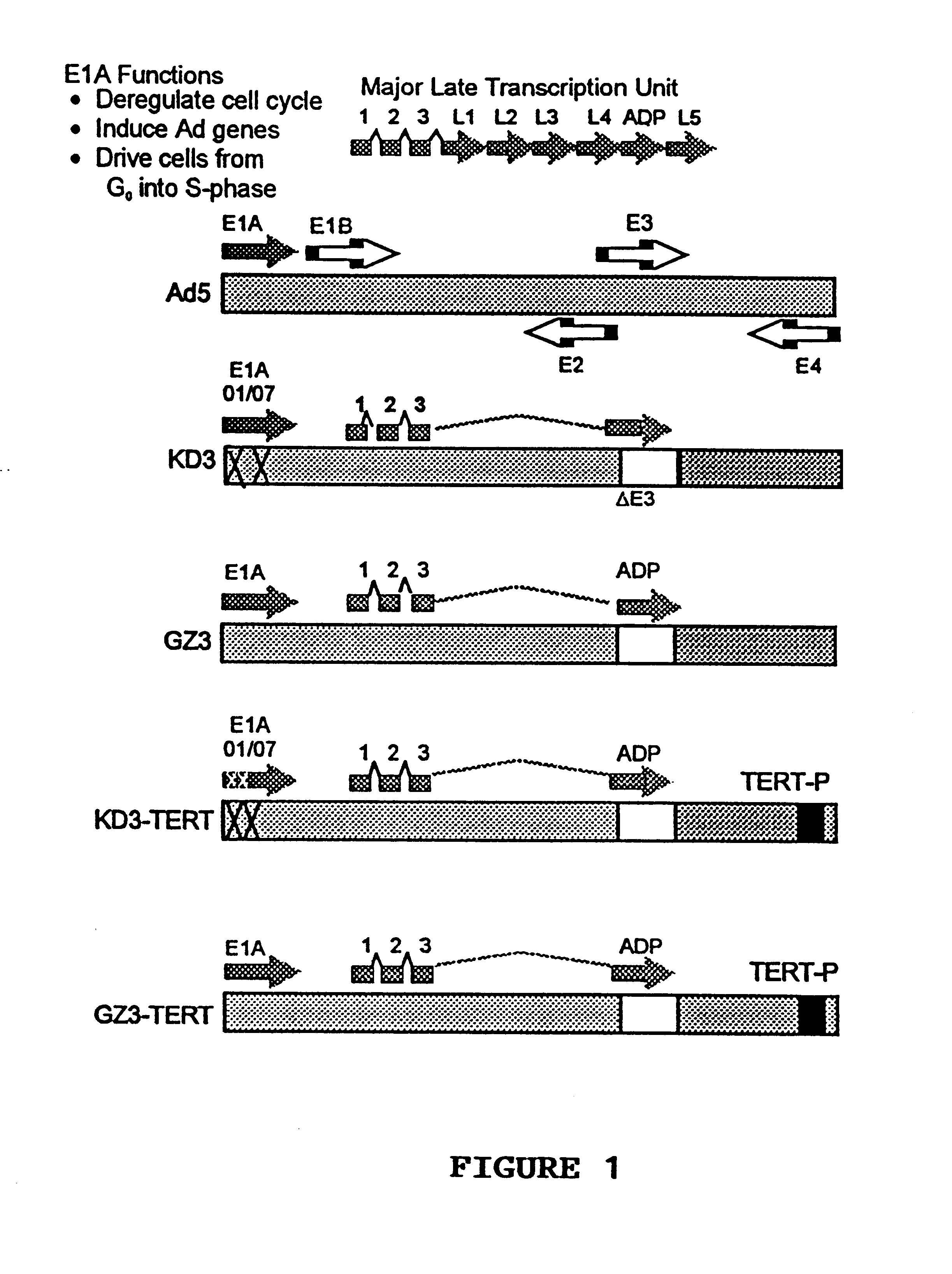
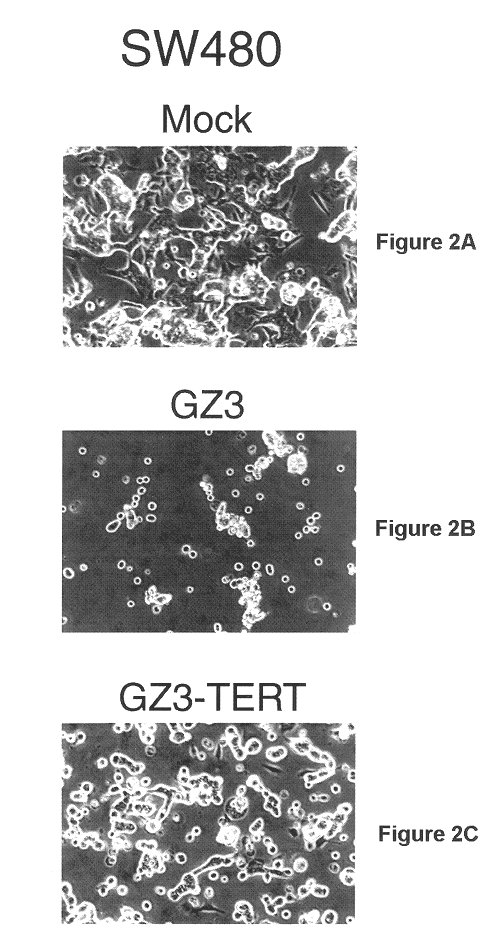
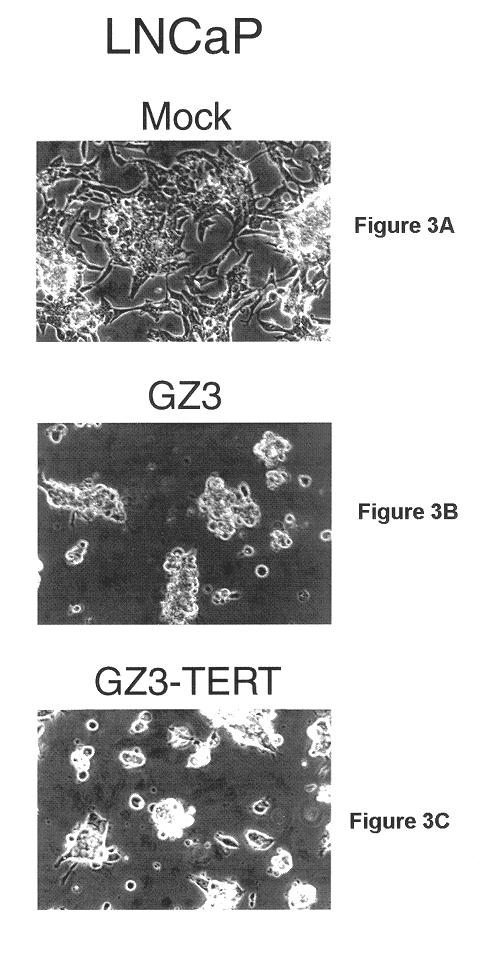
Recombinant adenovirus vectors that are replication-competent in tert-expressing cells
Novel adenovirus vectors which overexpress an adenovirus death protein and which are replication-competent in and, preferably, replication-restricted to cells expressing telomerase. One embodiment provides for efficient destruction and removal of viral-infected host cells expressing telomerase. Still further, another embodiment provides for additional restriction and safety by disrupting E1A's ability to bind p300 and / or members of the Rb family members. Compositions of the novel vectors and methods for promoting death of cells expressing telomerase with these vectors are also disclosed.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
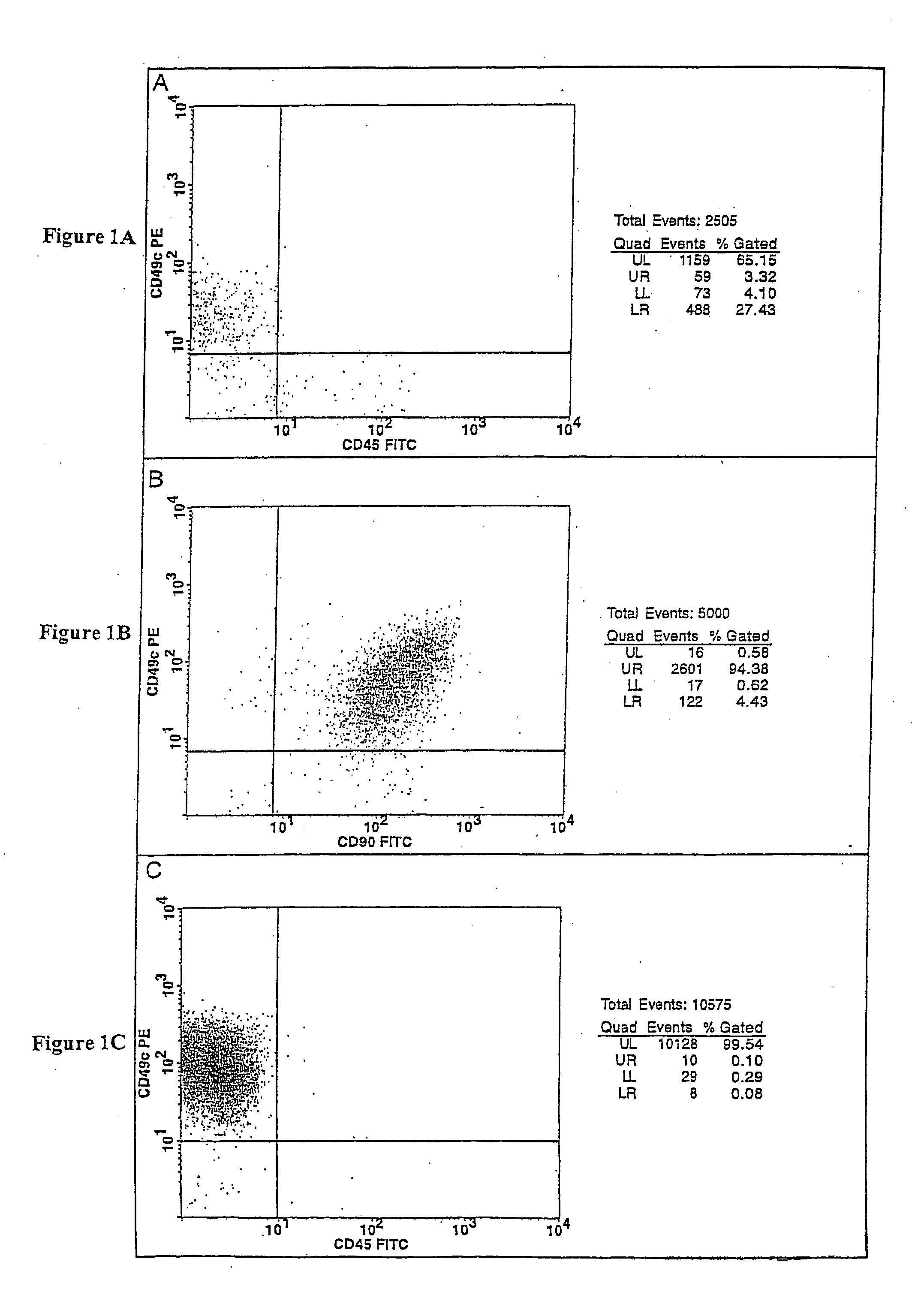
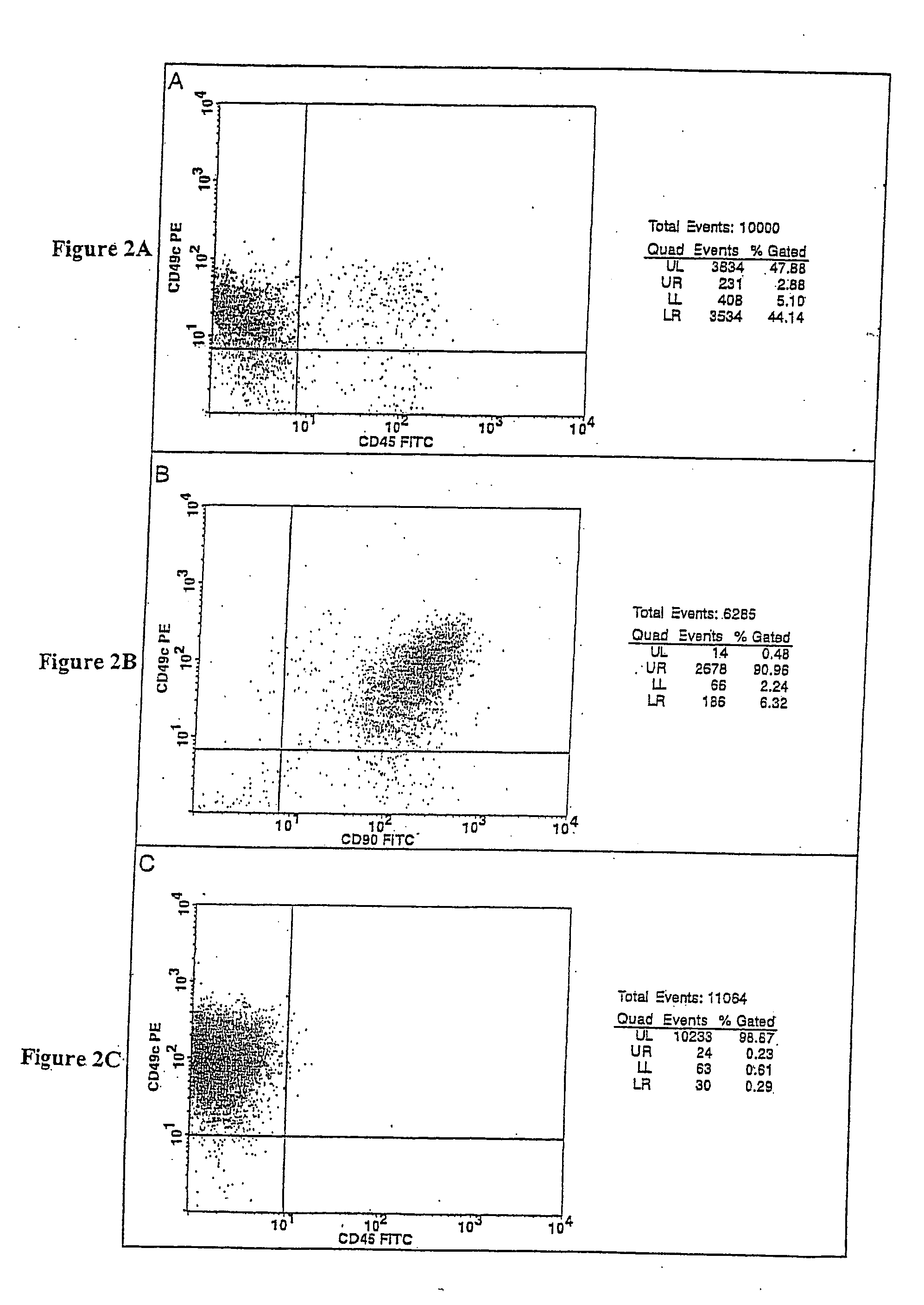
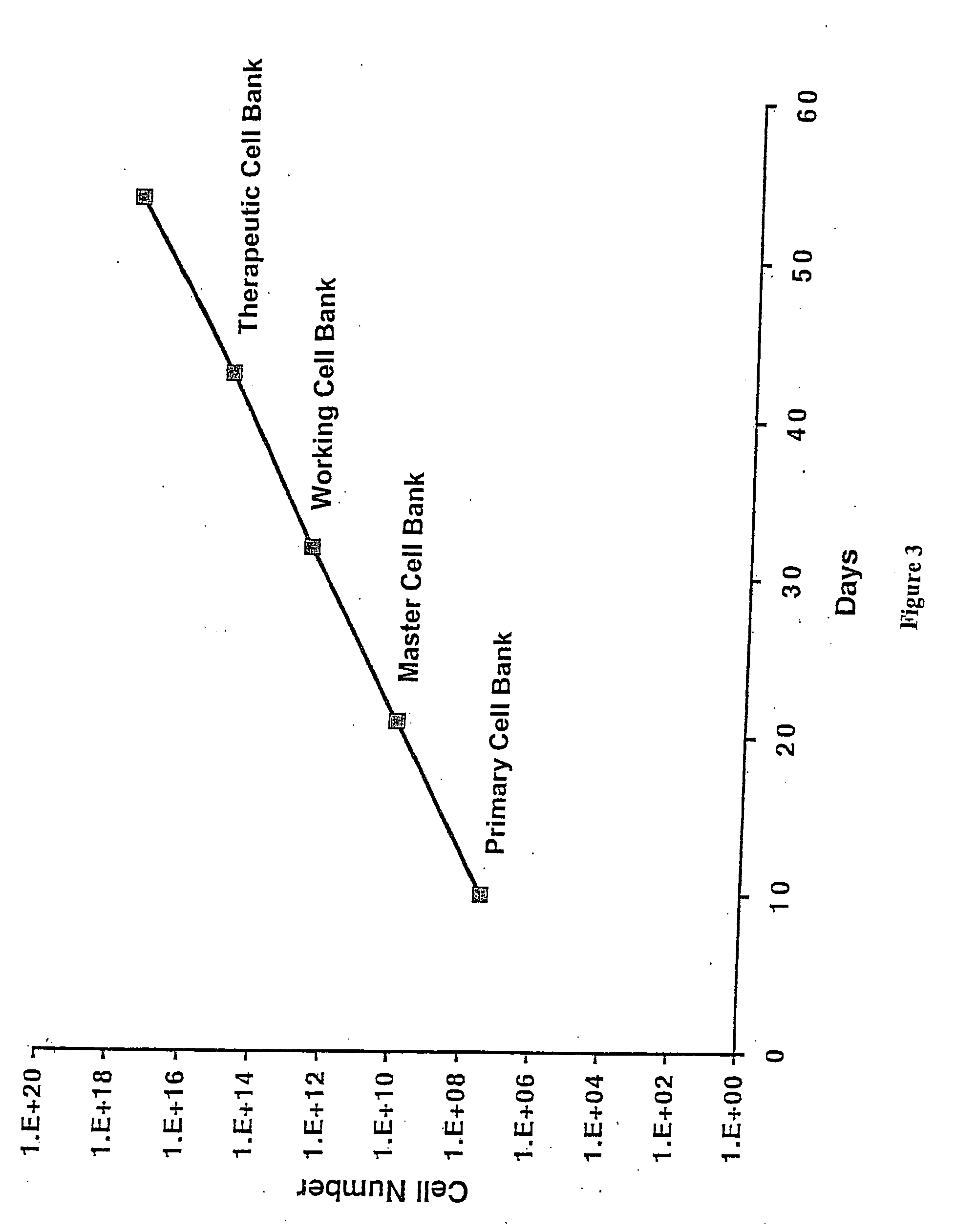
Cell populations which co-express CD49c and CD90
ActiveUS20050233452A1Promote repairIncreasing of life life expectancyBone marrow stroma cellsNervous disorderTelomeraseProgenitor
Substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase are made. In one embodiment, humans suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury, cardiac or neurological condition are treated with the substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase. In another embodiment, committed progenitor cells are made are made by selecting from a cultured source of a cell population which co-express CD49c and CD90 and modifying the cell population. The committed progenitor cells can be employed to treat a human suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury, cardiac or neurological condition and formulate pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:GARNET BIOTHERAPEUTICS
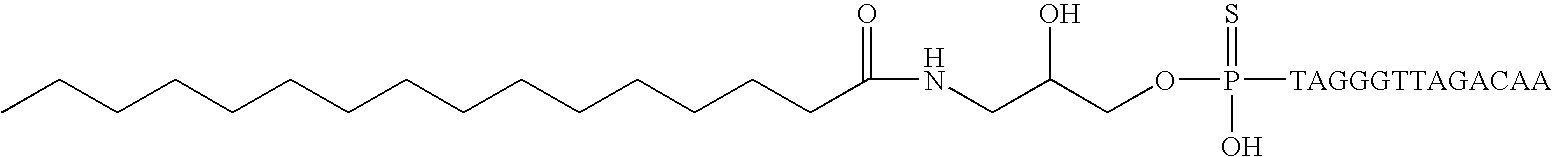
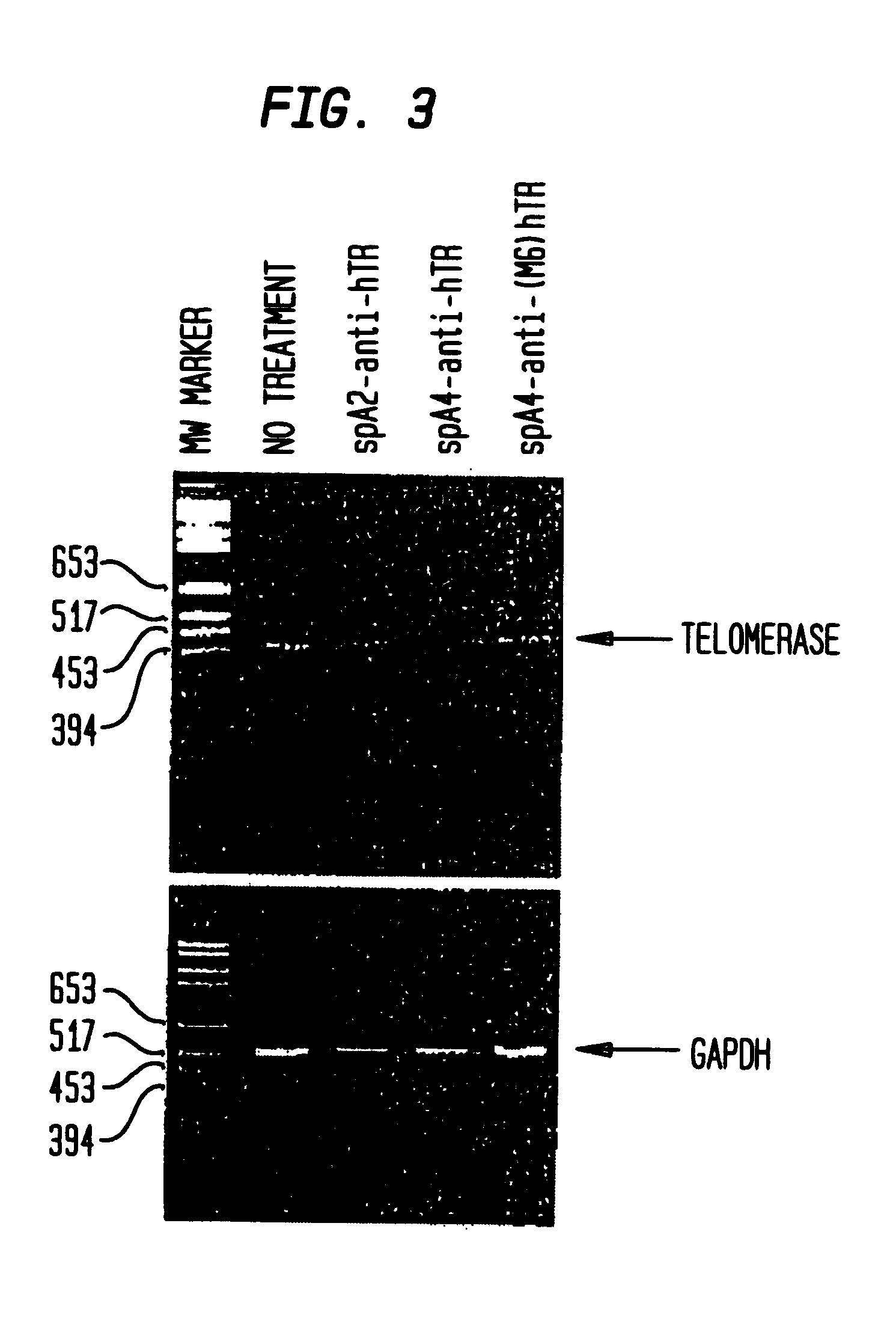
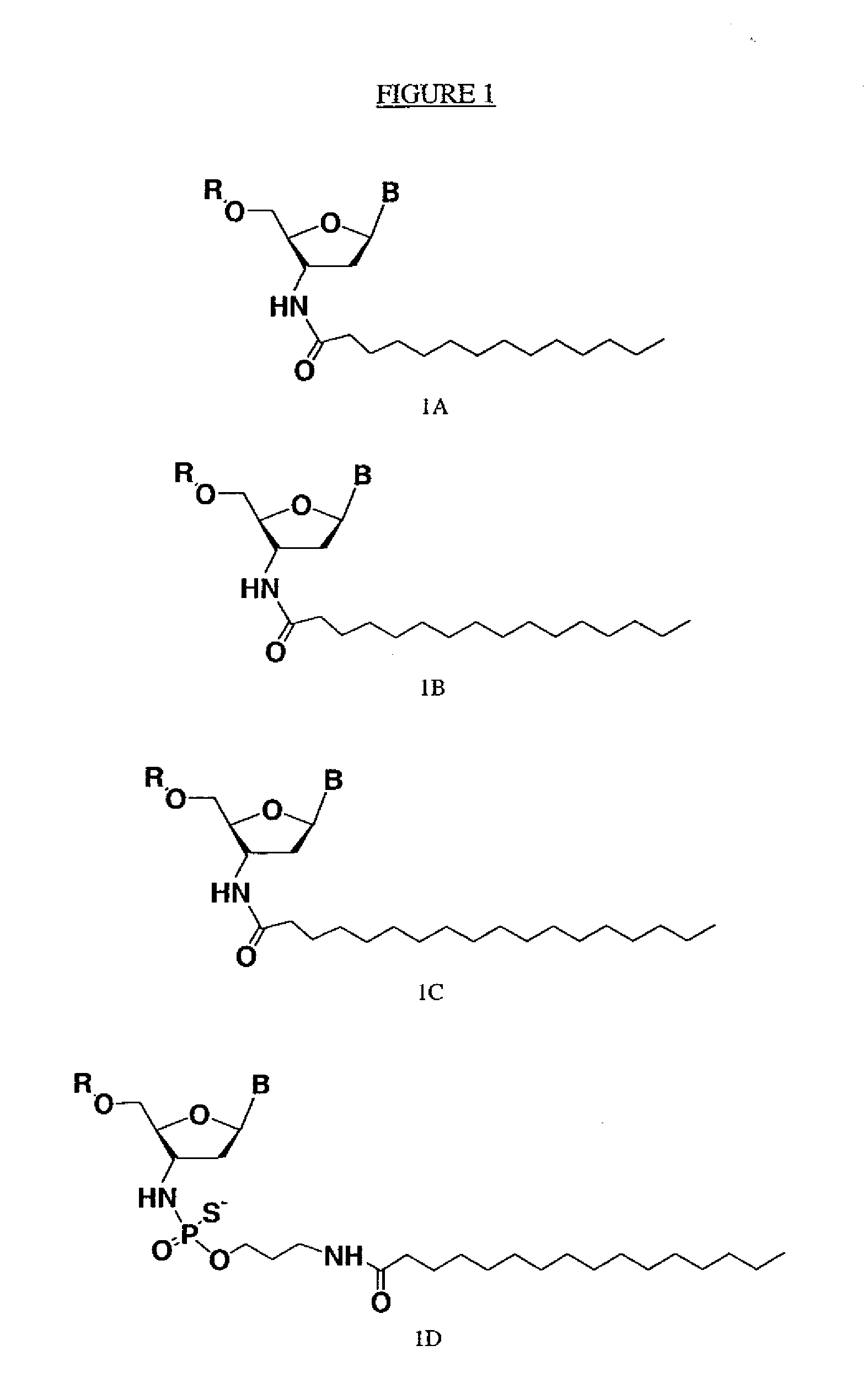
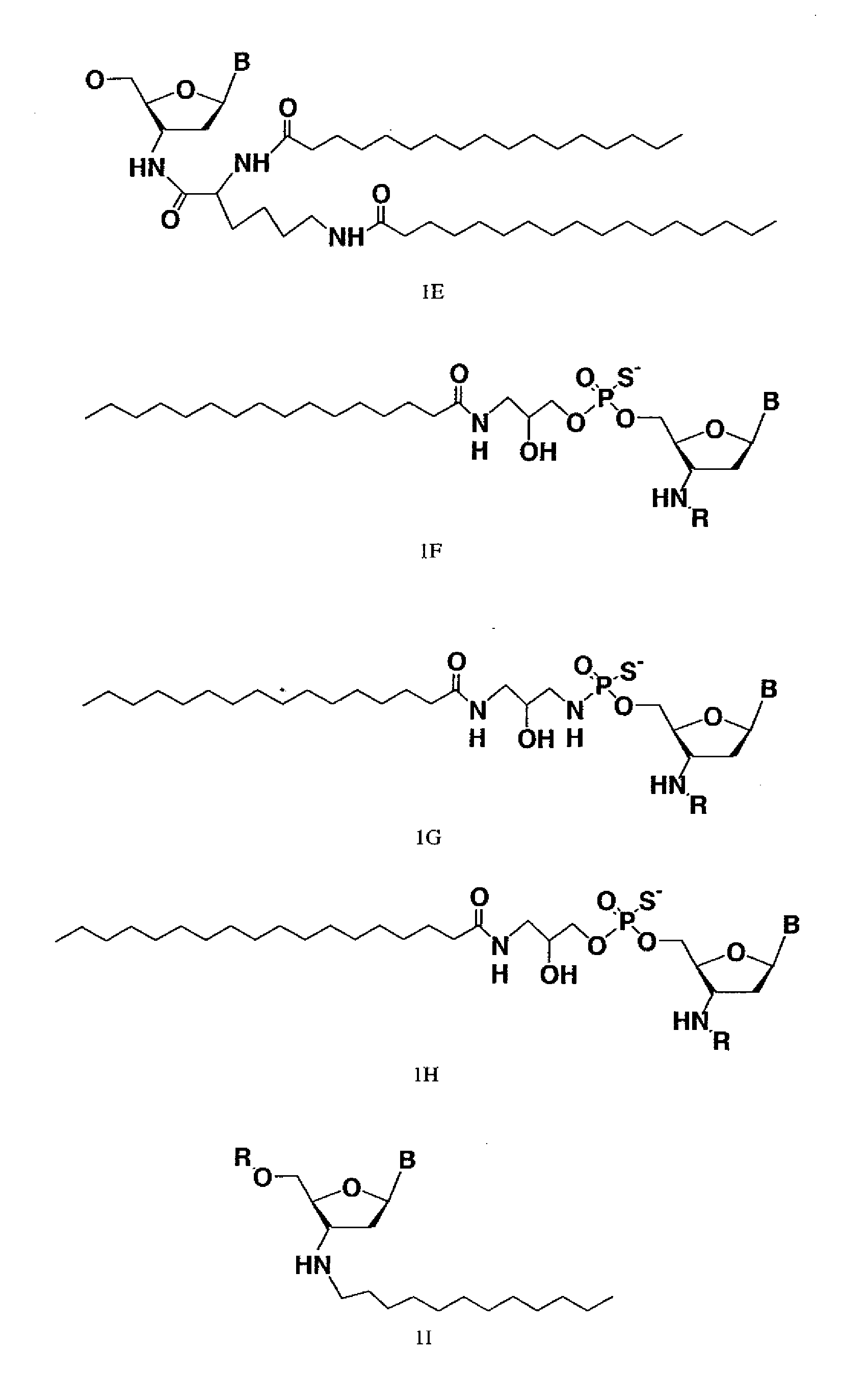
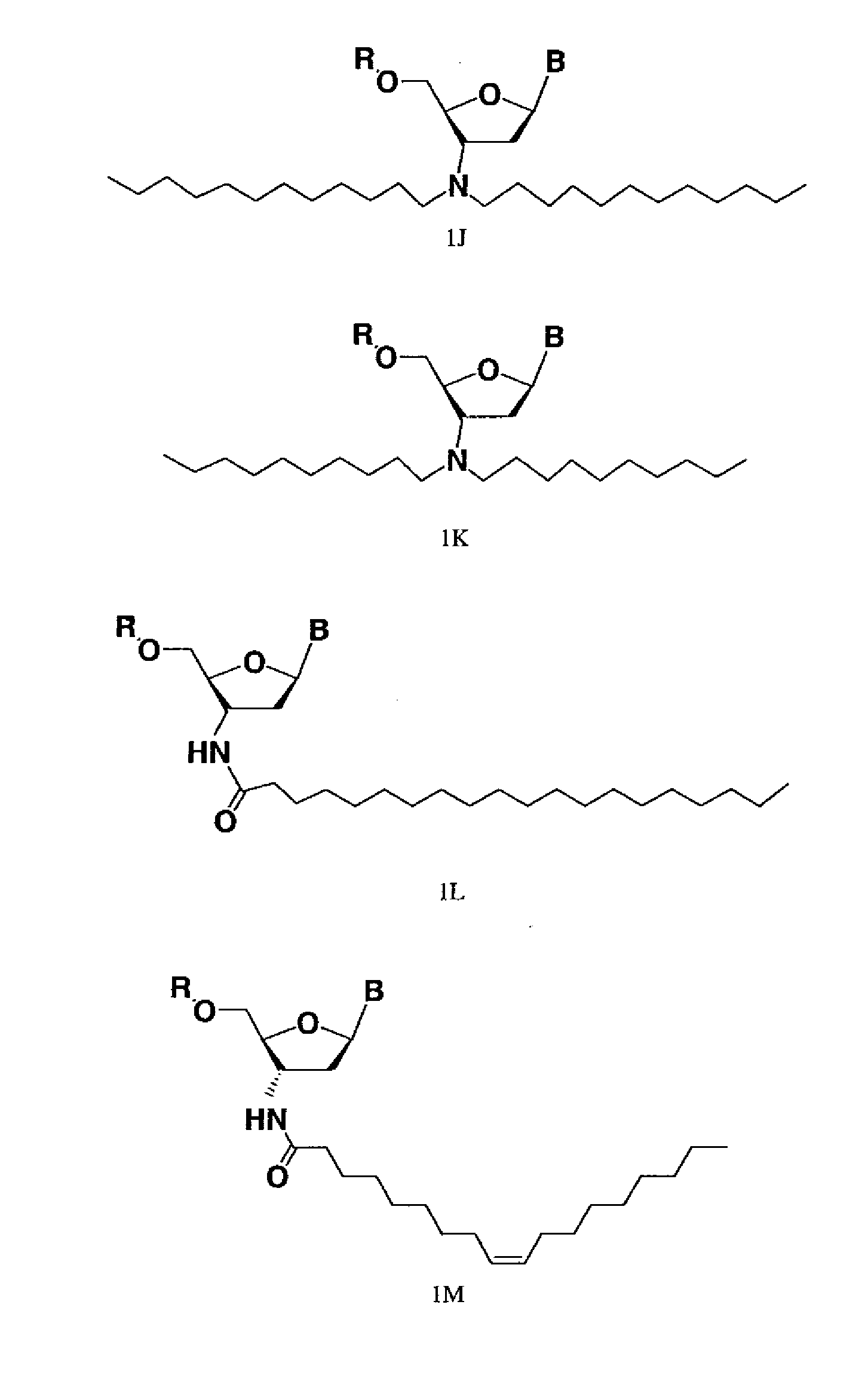
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
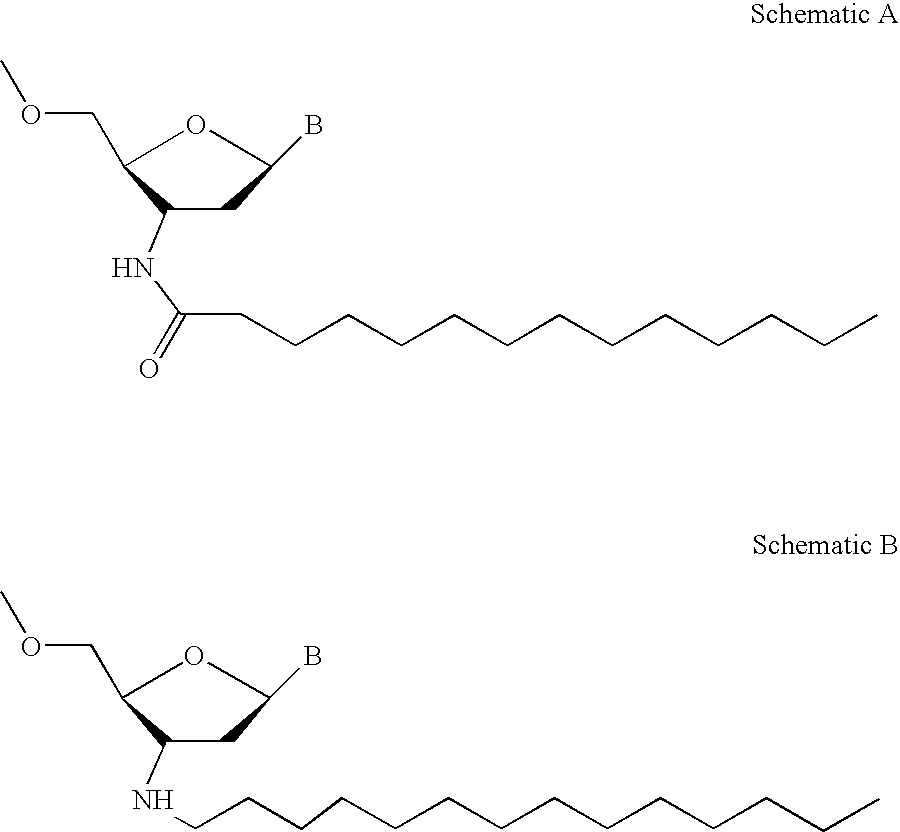
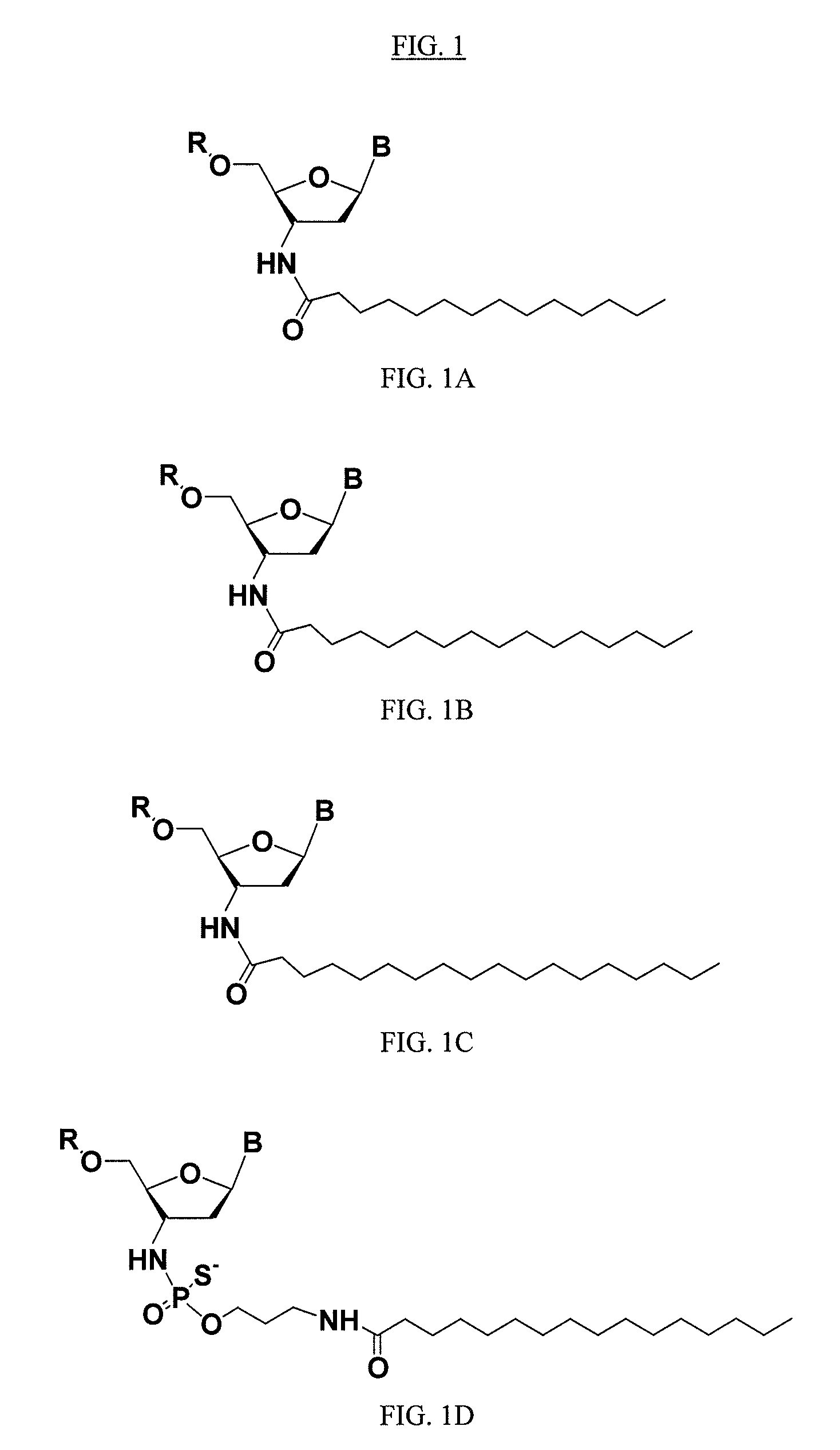
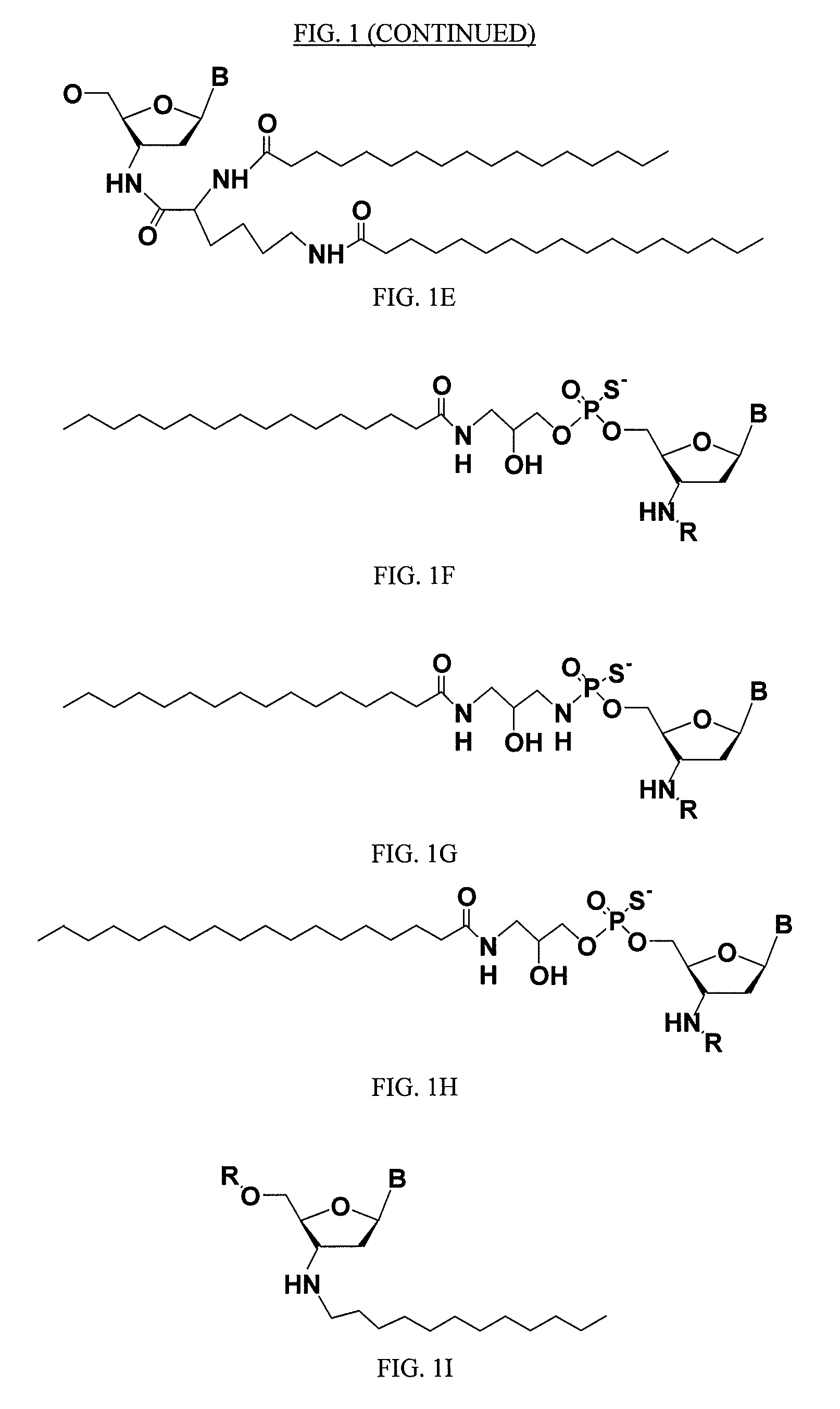
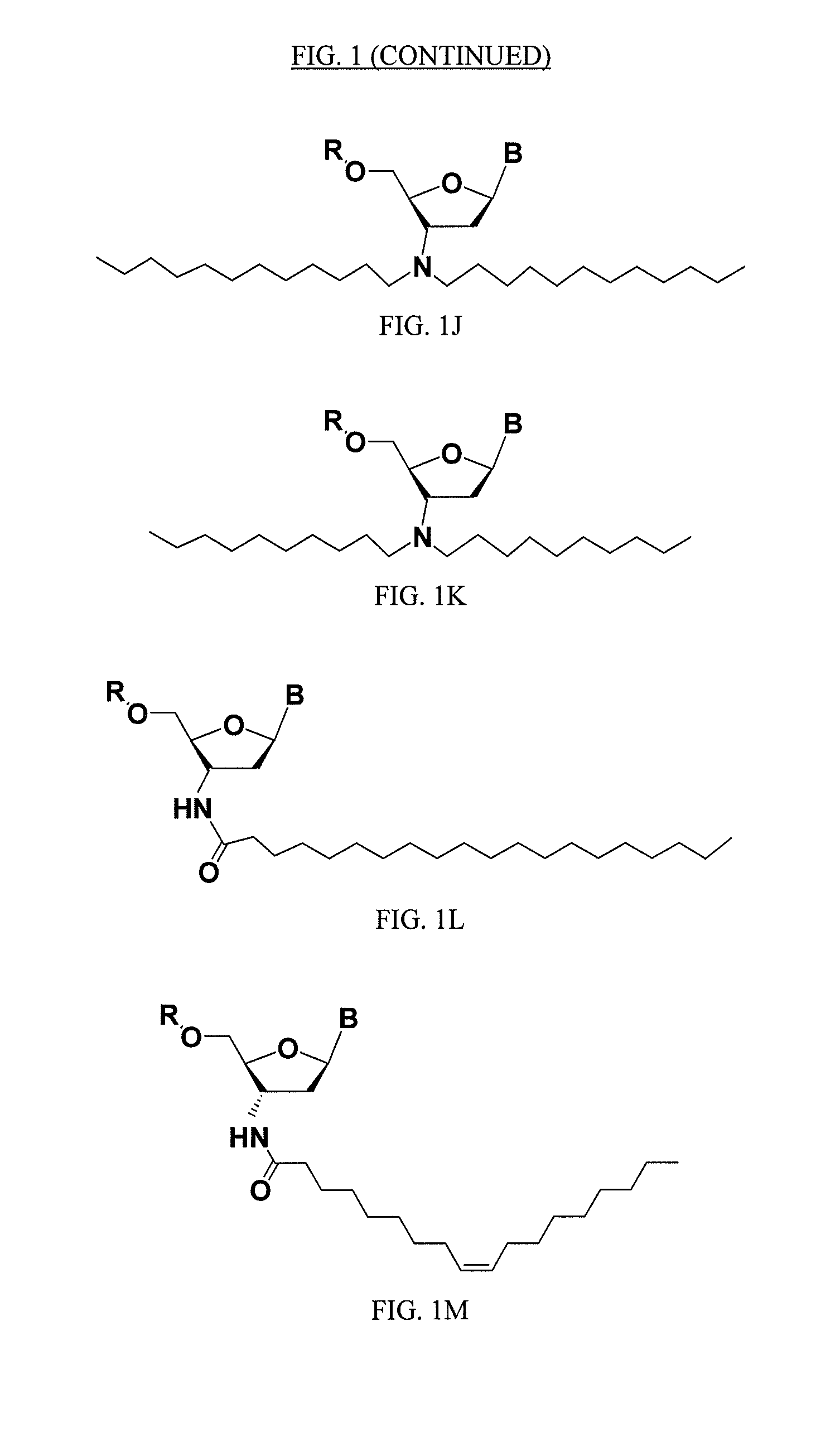
ActiveUS20050113325A1Superior cellular uptake propertyReduce Toxicity RiskBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTelomeraseLipid moiety
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
ActiveUS7494982B2Inhibit telomeraseMaintain good propertiesBiocideSugar derivativesTelomeraseLipid moiety
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
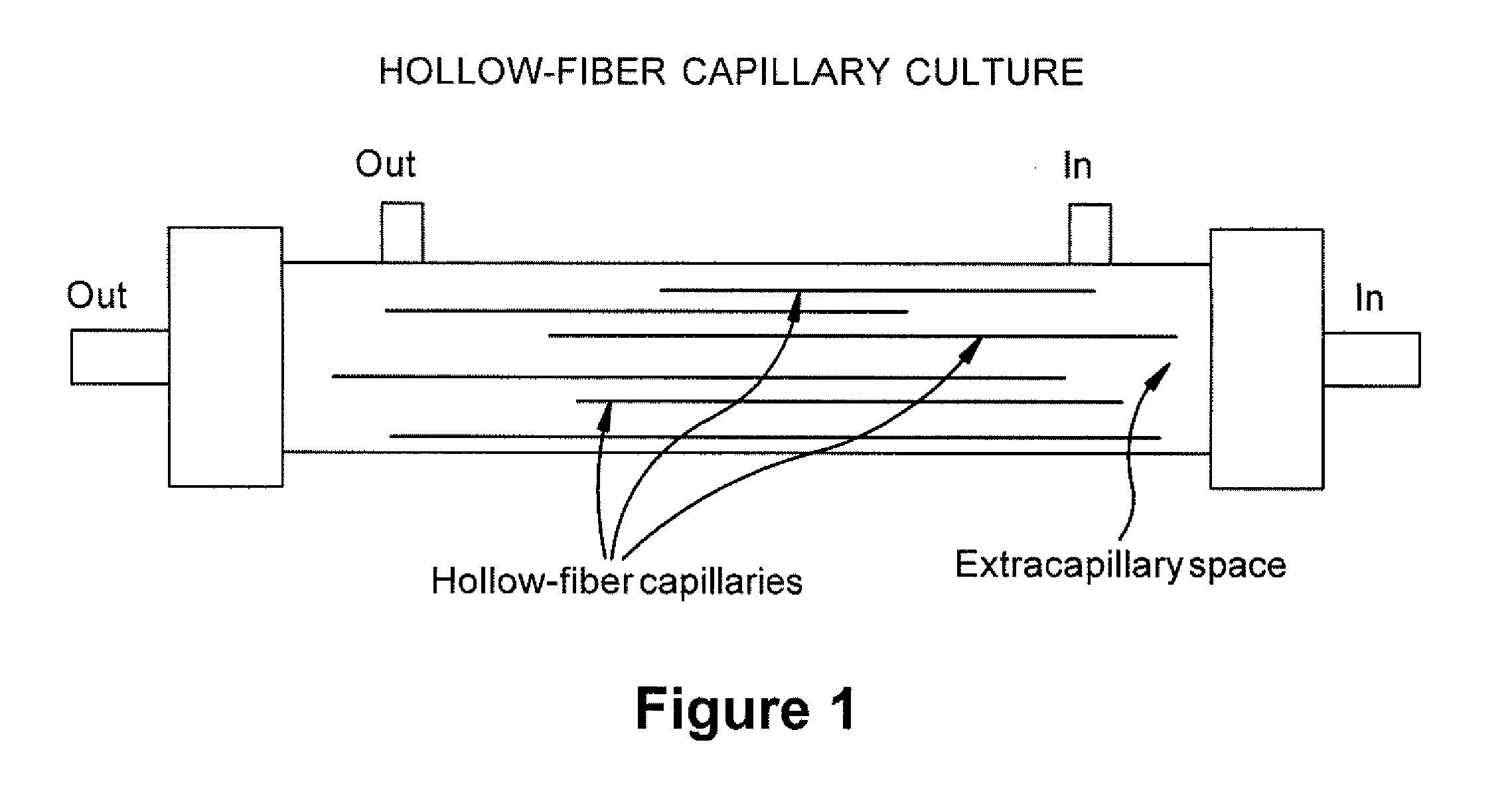
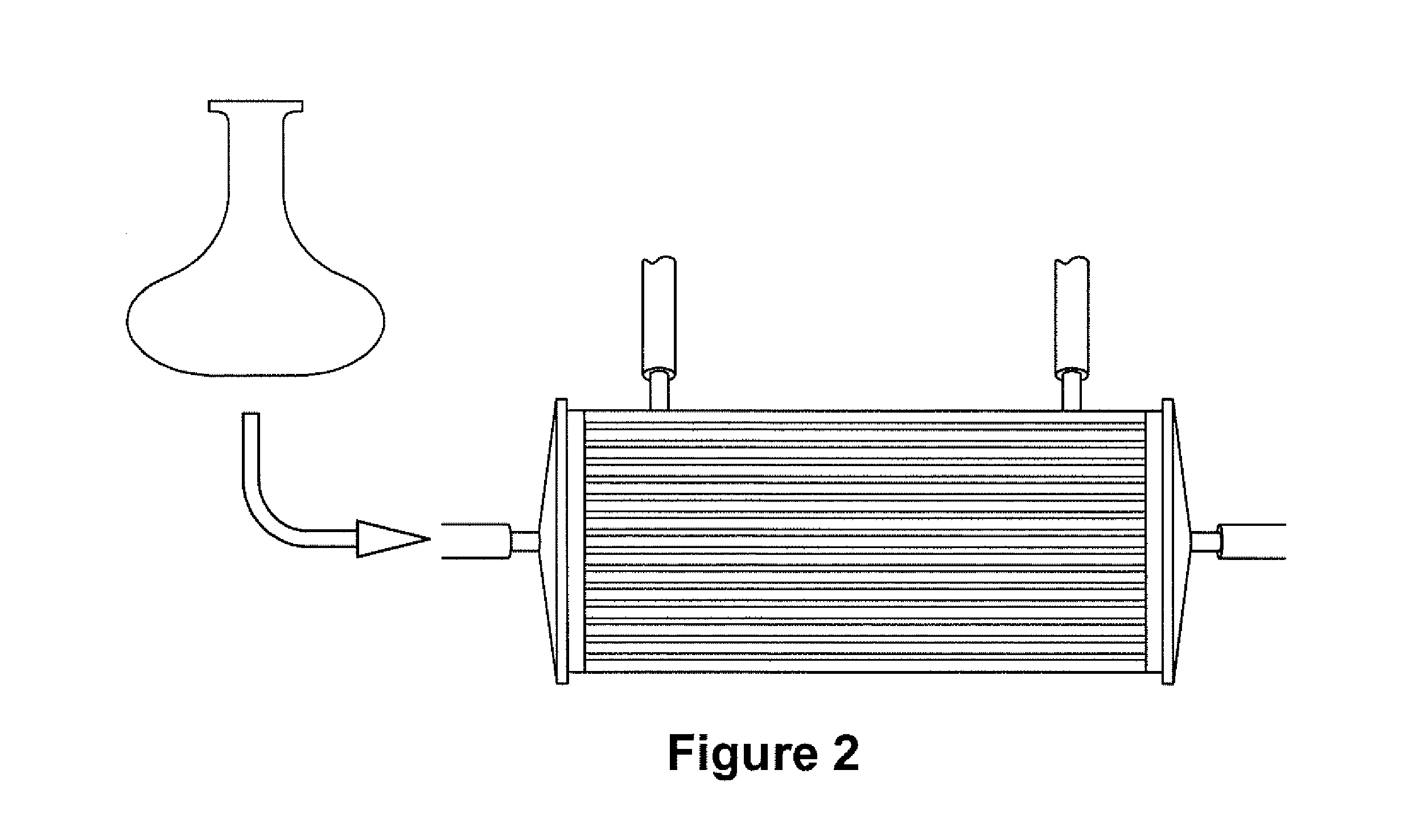
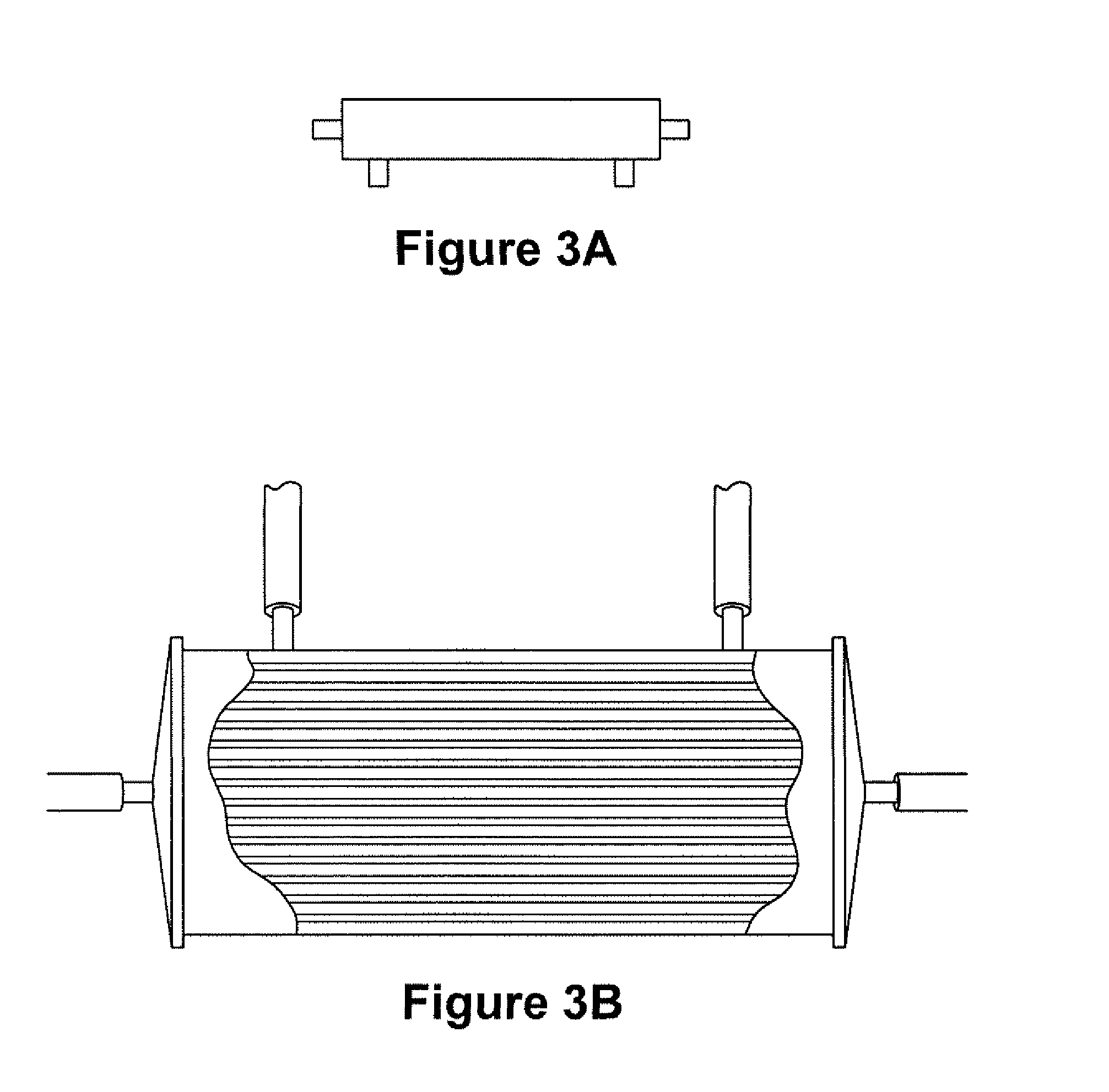
Expansion of Stem Cells in Hollow Fiber Bioreactors
InactiveUS20120308531A1Enhanced cell attachmentEasy to harvestBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsTelomerasePlant Germ Cells
The invention is directed to producing large numbers of cells using hollow fiber bioreactor technology. The cells are non-embryonic stem, non-germ cells that can be characterized by one or more of the following: extended replication in culture and markers of extended replication, such as telomerase, markers of pluripotentiality, and broad differentiation potential, without being transformed.
Owner:REGENESYS
Telomerase
InactiveUS6309867B1Avoid the needEnlarge regionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method for extracting antineoplastic components from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium
InactiveUS20050013879A1Effectively inhibit proliferation of Taxol-resistant tumor cellsEffectively inhibit proliferation of human hepatomaBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTelomeraseCancer cell
A method for extracting antineoplastic component from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium applicable in treating cell proliferative disorder is proposed. The antineoplastic components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium include at least a Y-butyolactone centred heterocyclic compound with a Z configuration or E configuration at its carbon 2(5) position, and molecules, such as Chaihulactone, Isochaihulactone, Chaihulactone analogues or derivatives containing in the heterocyclic compound. From results of cell and molecular biological studies, in vivo animal test, and histological study, it is found that antineoplastic components extracted from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium are effective in suppressing a variety of cancer cell growths, inhibiting telomerase activity, as well as effective in killing with high specificity Taxol-resistant tumor cells at later stage of chemical therapy, making the components a new choice for anti-cancer agent, anti-HIV agent, or synergistic agent.
Owner:BUDDHIST TZU CHI GEN HOSPITAL
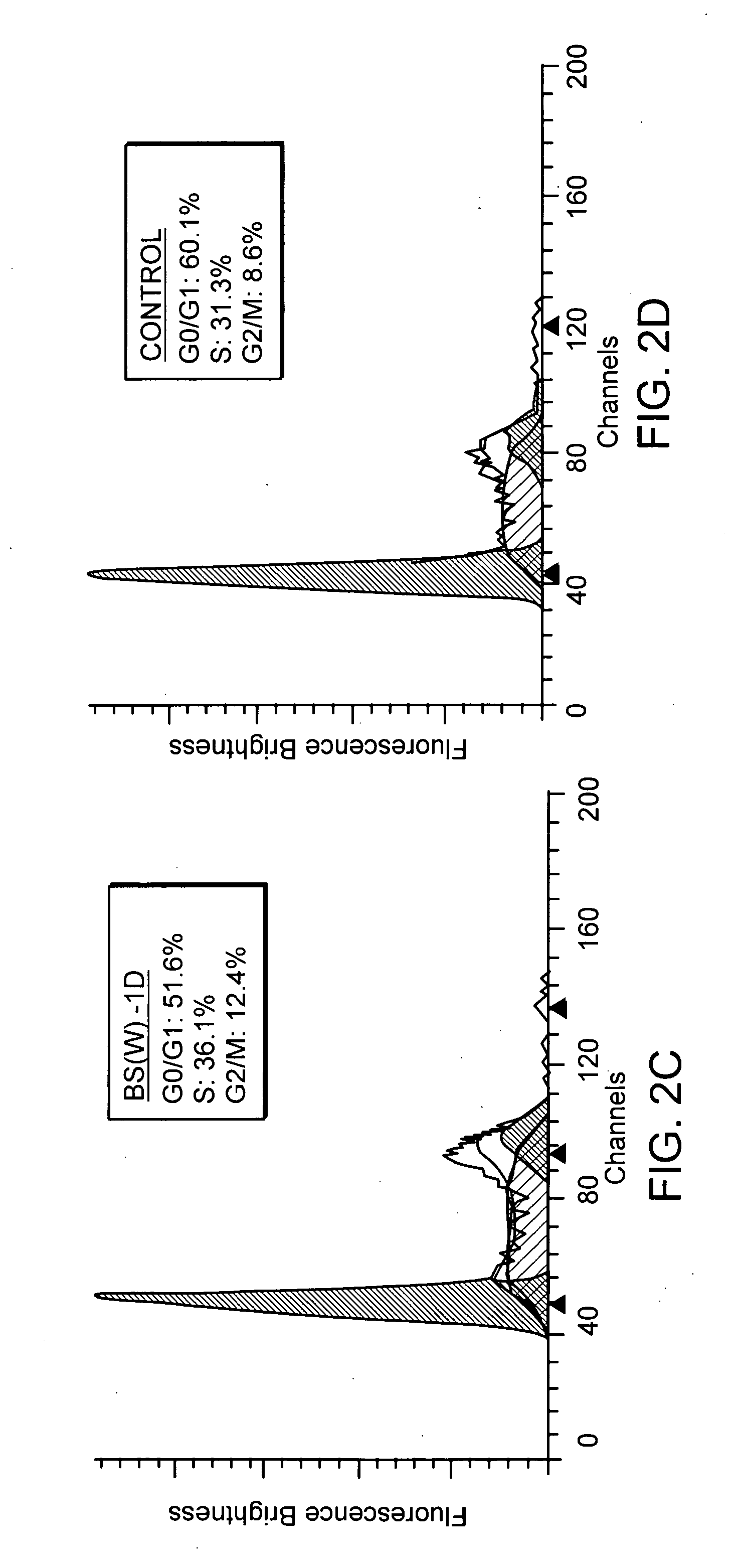
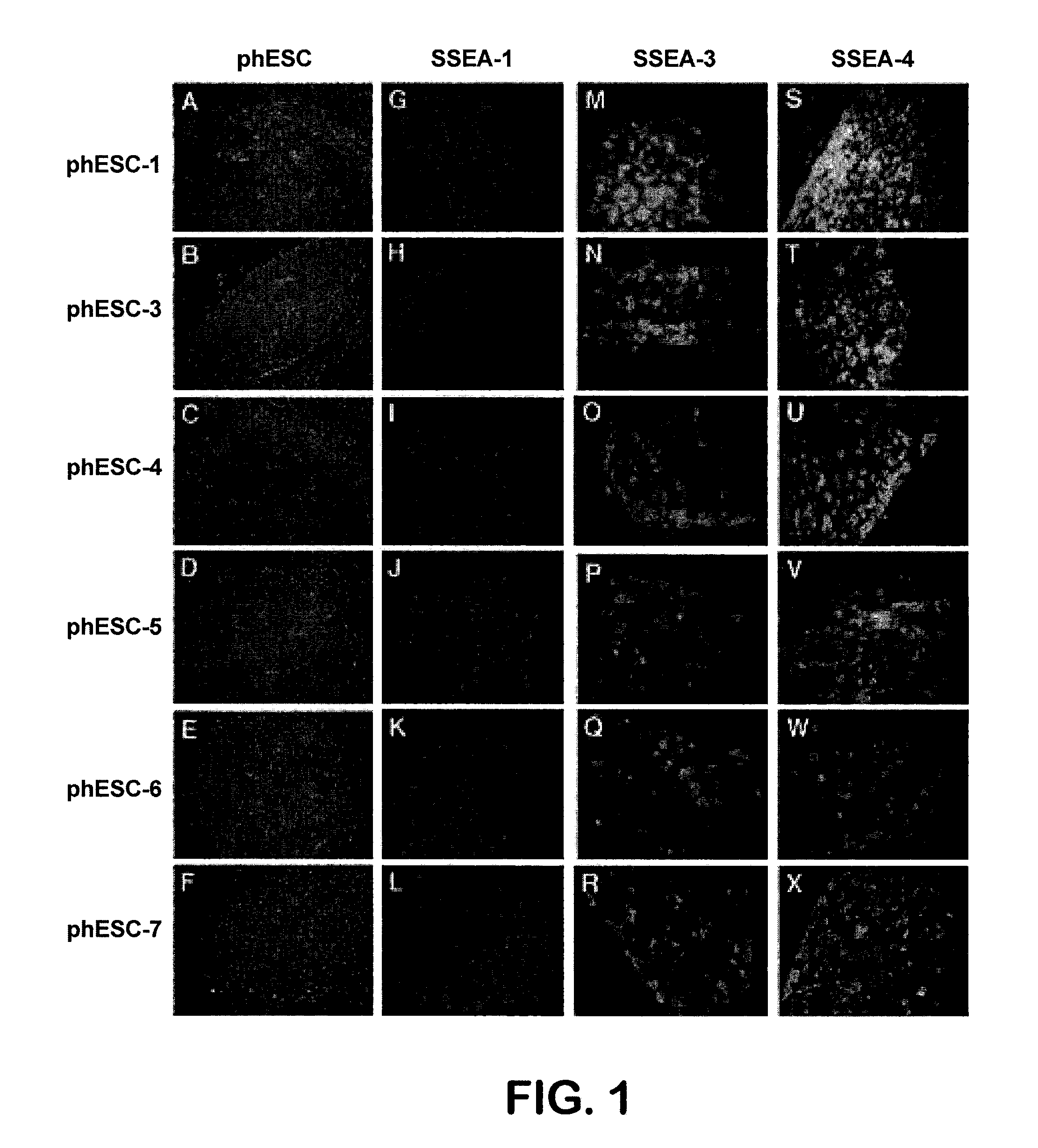
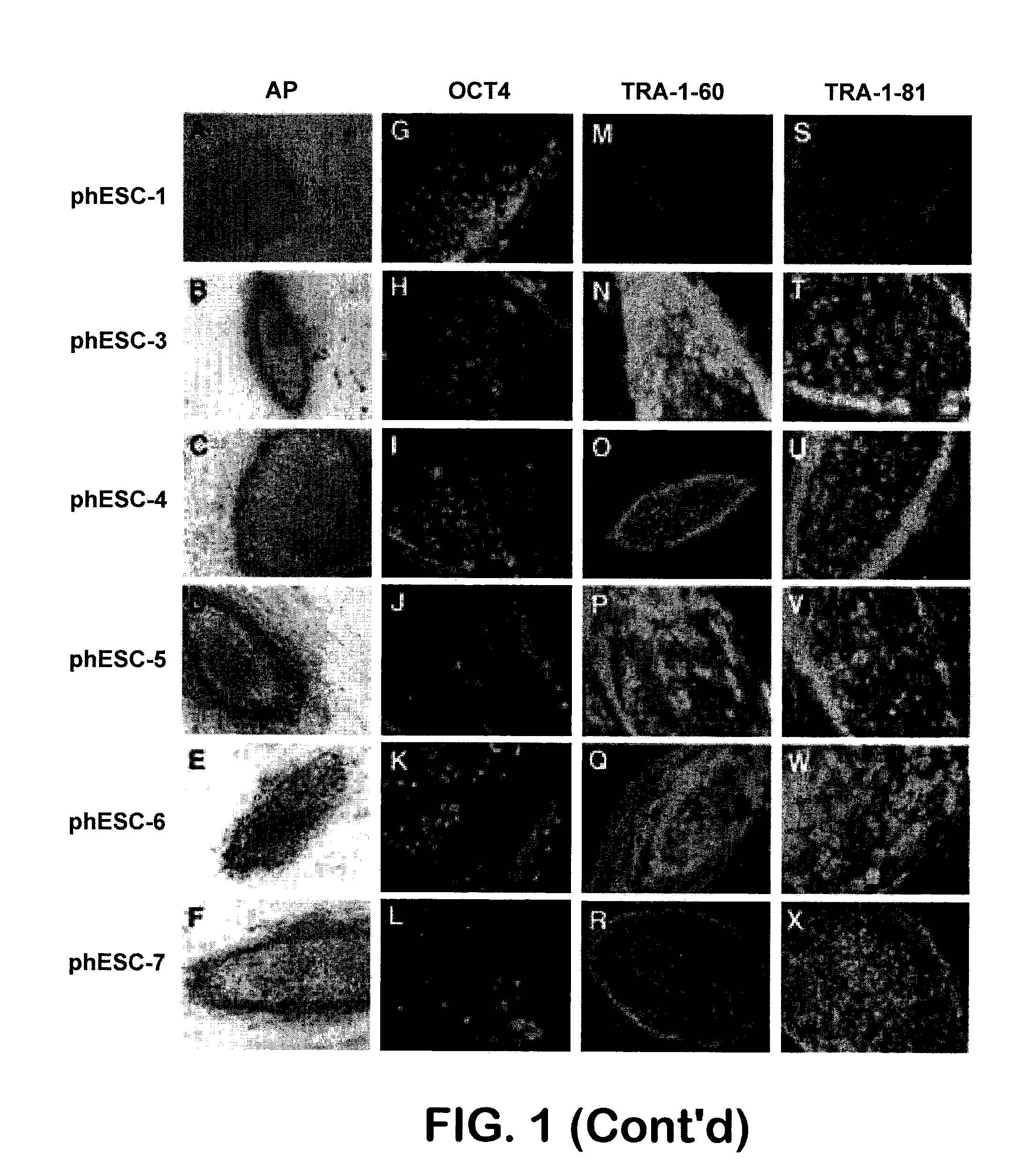
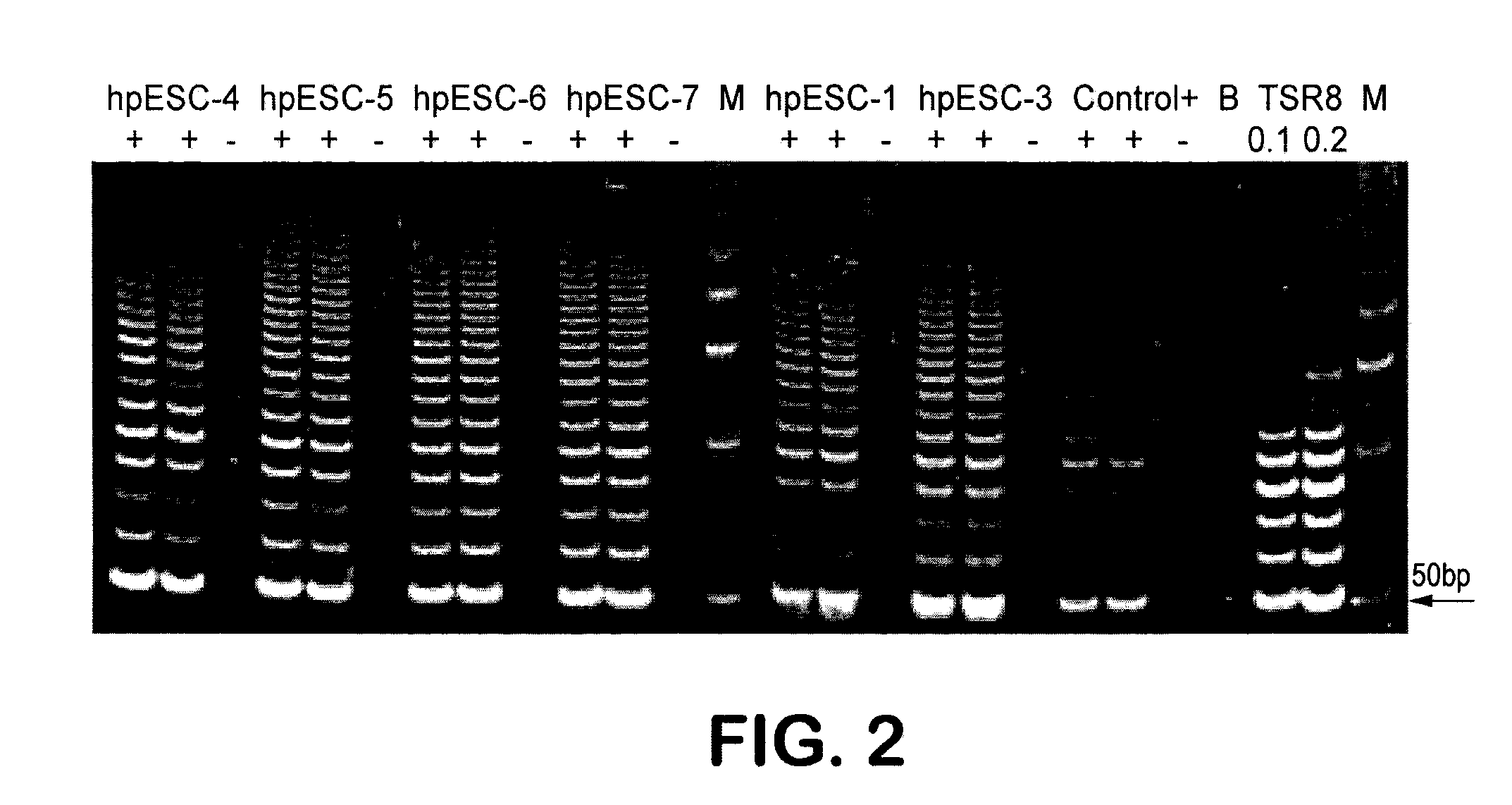
Patient-specific stem cell lines derived from human parthenogenetic blastocysts
InactiveUS20080299091A1Increase alkaline phosphatase activityHigh levelBiocideSenses disorderTelomeraseOocyte donor
Methods are disclosed for generating HLA homozygous parthenogenetic human stem cell (hpSC-Hhom) lines from both HLA homozygous and HLA heterozygous donors. These hpSC-Hhom lines demonstrate typical human embryonic stem cell morphology, expressing appropriate stem cell markers and possessing high levels of alkaline phosphatase and telomerase activity. Additionally, injection of these cell lines into immunodeficient animals leads to teratoma formation. Furthermore, in the case of HLA heterozygous donors, the hpSC-Hhom lines inherit the haplotype from only one of the donor's parents. SNP data analysis suggests that hpSC-Hhom lines derived from HLA heterozygous oocyte donors are homozygous throughout the genome as assessed by single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis. The protocol as disclosed minimizes the use of animal-derived components, which makes the stem cells more practical for clinical application.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Methods and compositions for using suramin, pentosan, polysulfate, telomerase antisense and telomerase inhibitors
InactiveUS20050282893A1Reduce telomere lengthHigh activityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseActive agent
The invention provides methods and compositions for inhibiting telomerase activity and treatment of telomerase mediated conditions or diseases. The methods, compounds, and compositions of the invention may be employed alone, or in combination with other pharmacologically active agents, surgery, or radiation in the treatment of conditions or diseases mediated by telomerase activity, such as in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AU JESSIE +1
Oligonucleotide conjugates
InactiveUS7563618B2Inhibit telomerase enzymatic activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTelomeraseNucleobase
Oligonucleotide conjugates, where an oligonucleotide is covalently attached to an aromatic system, are provided. In particular embodiments the oligonucleotide is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase and is covalently attached to a nucleobase via an optional linker. The conjugates inhibit telomerase enzyme activity.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
RNA interference mediated inhibition of telomerase gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050153916A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryTelomeraseTankyrase Gene
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating telomerase gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of telomerase gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of telomerase genes, such as telomerase template RNA (TERC / TR), or a telomerase protein (TERT).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
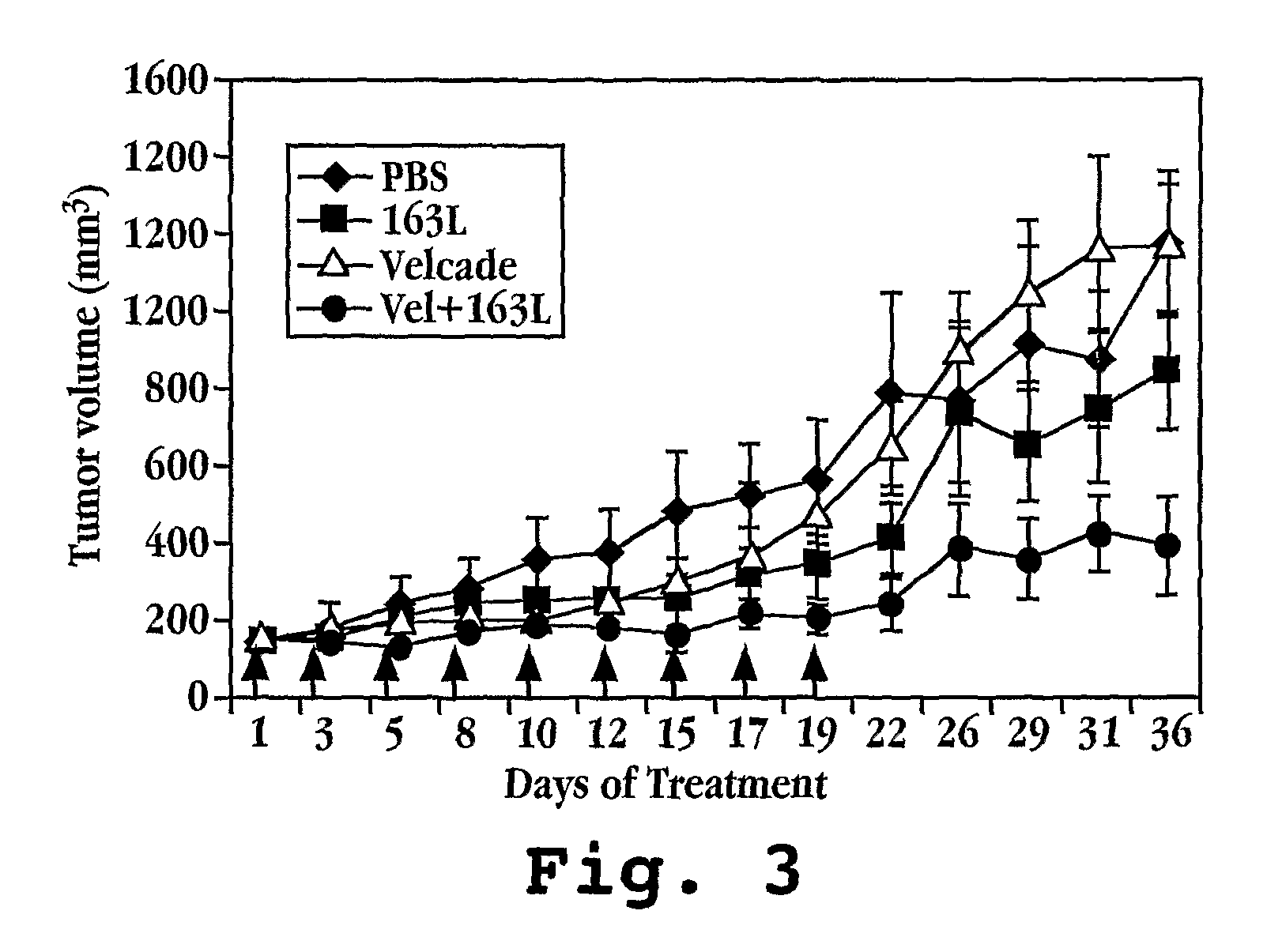
Cancer treatment by combined inhibition of proteasome and telomerase activities
A method and kit for inhibiting the proliferation of cancer cells are disclosed, based on a combination of a proteasome inhibitor and a telomerase inhibitor. When used in cancer therapy, the two compounds in combination enhance the anti-cancer treatment efficacy obtained with the proteasome inhibitor alone or the telomerase inhibitor alone. Preferably, efficacy is supraadditive or synergistic in nature relative to the combined effects of the individual agents, with minimal exacerbation of side effects.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
RNase L activators and antisense oligonucleotides effective to treat telomerase-expressing malignancies
InactiveUS6468983B2Facilitate cellular uptakeSuppressed growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseDisease
The present invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising an oligonucleotide complementary to a region of the ribonucleotide component of telomerase attached to an activator of RNase L ("activator-antisense complex") which specifically cleaves the ribonucleotide portion of a telomerase enzyme. The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting telomerase enzymatic activity with activator-antisense complexes targeted to the RNA component of telomerase. The present invention further relates to methods of treating malignant neoplastic disease, wherein the malignant cells contain a telomerase activity that is necessary for the growth of the malignant cells.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Colorectal cancer biomarker
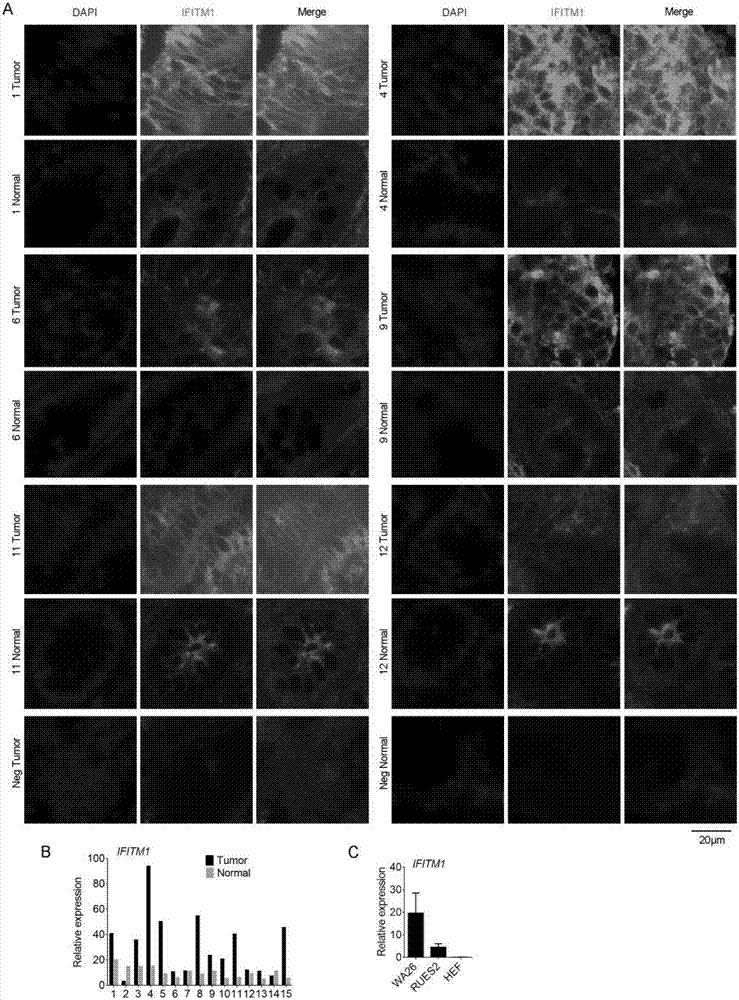
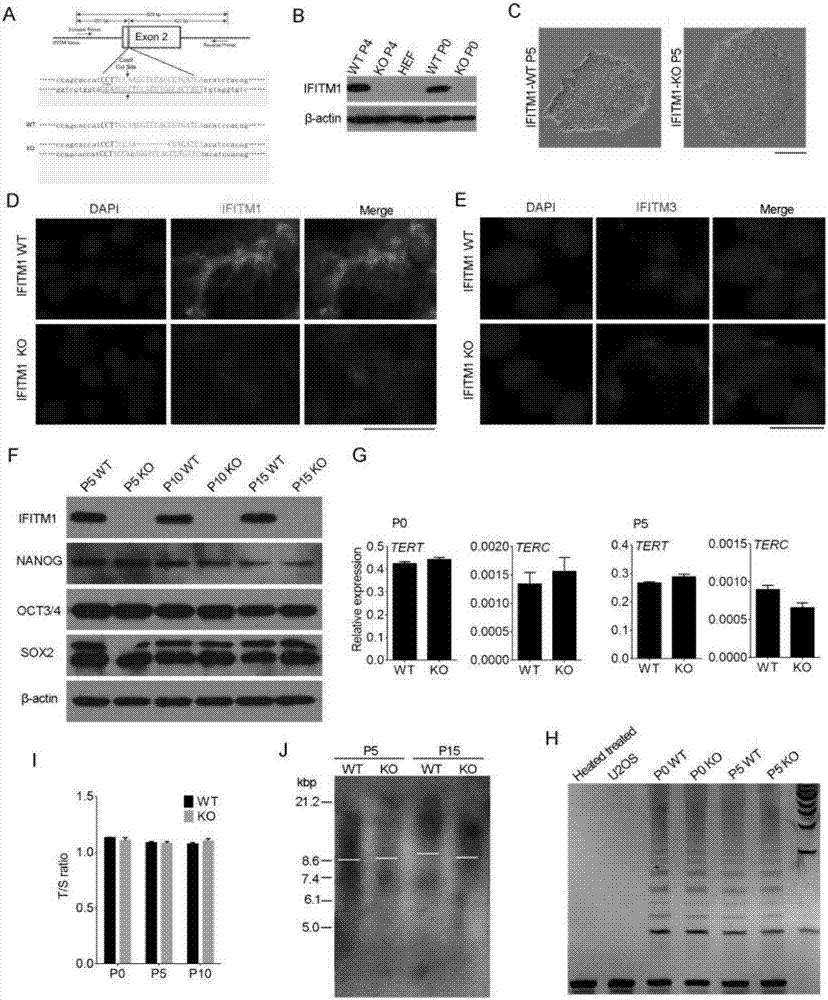
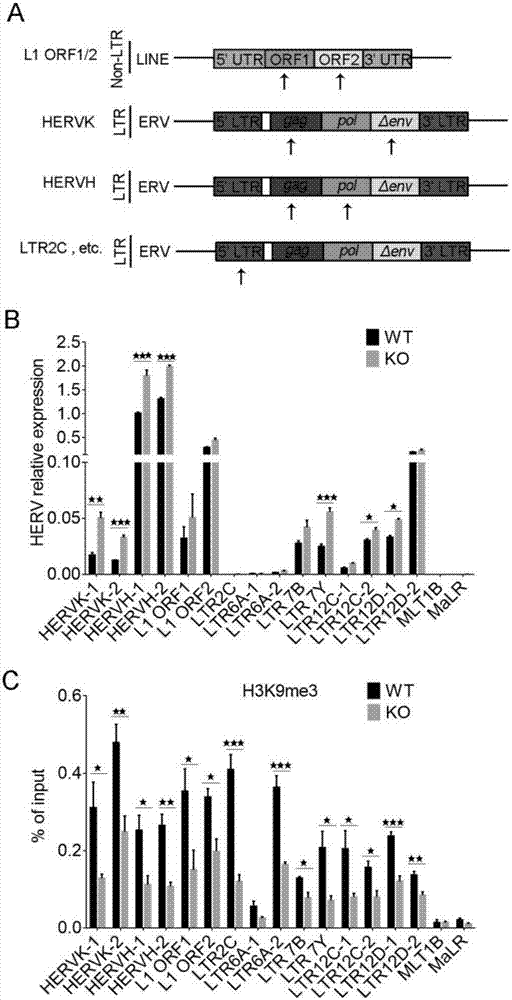
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer biomarker, relating to application of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 in inhibition of endogenous retrovirus in colorectal cancer. The hESCs of IFITM1-KO is constructed by using CRISPR / Cas9 technology so as to study the functions of IFITM1. Studies find that the IFITM1-deleted human embryonic stem cell (hESCs) is identical with IFITM1-WT in the aspects of cell proliferation, cell pluripotency, telomere length, telomerase activity and the like. The expression of human endogenous retrovirus in hESCs of IFITM1-KO increases, and expression in para-carcinoma tissue is higher than that in colorectal carcinoma tissue. ChIP-qPCR detection finds that the enrichment of H3K9me3 in hESCs of IFITM1-KO is reduced at the HERVs site. Data shows that the expression level of IFITM1 in hESCs and colorectal carcinoma is in negative correlation to HERVs expression, and the IFITM1 can inhibit the expression of HERVs by regulating epigenetic inheritance.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
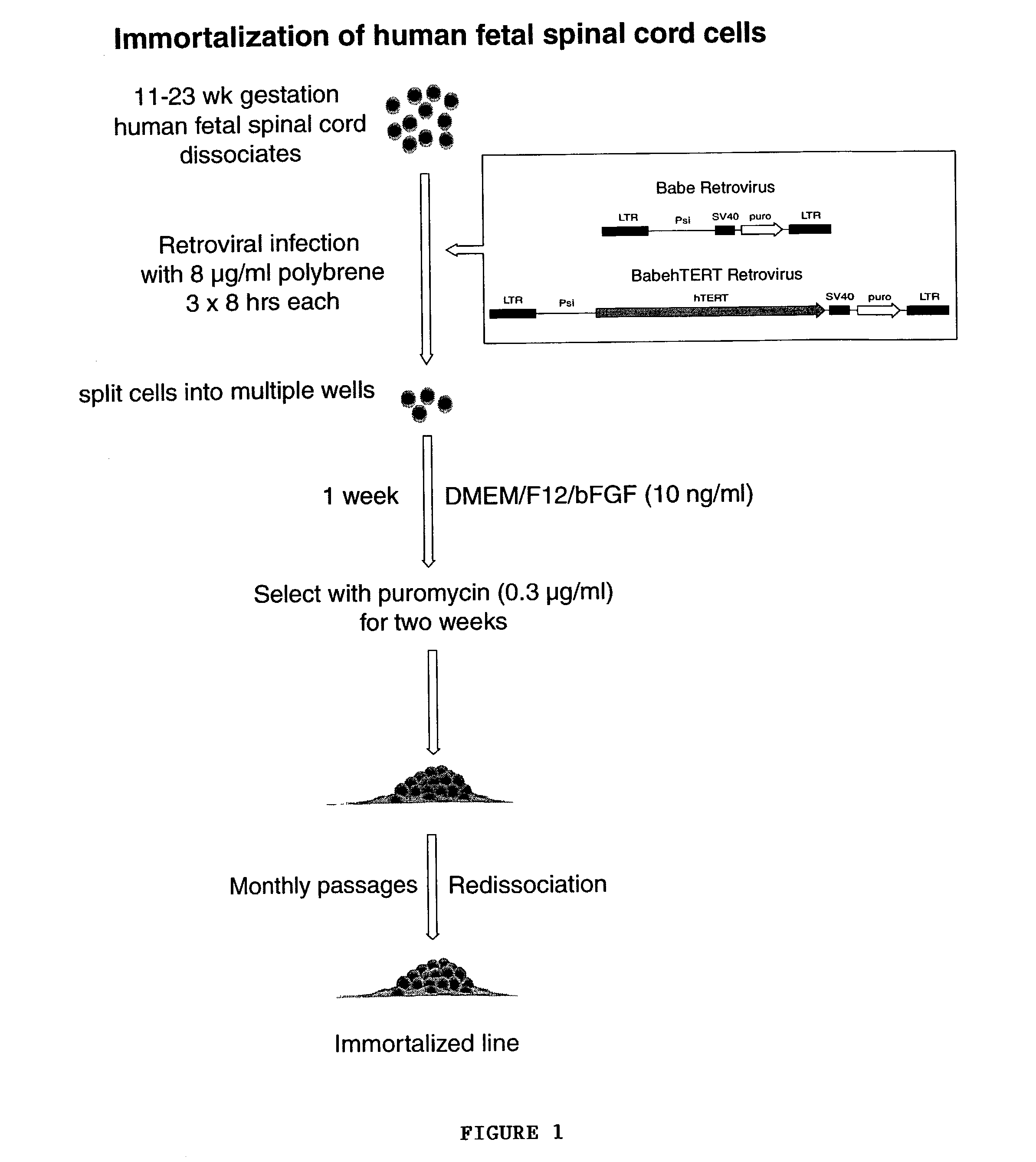
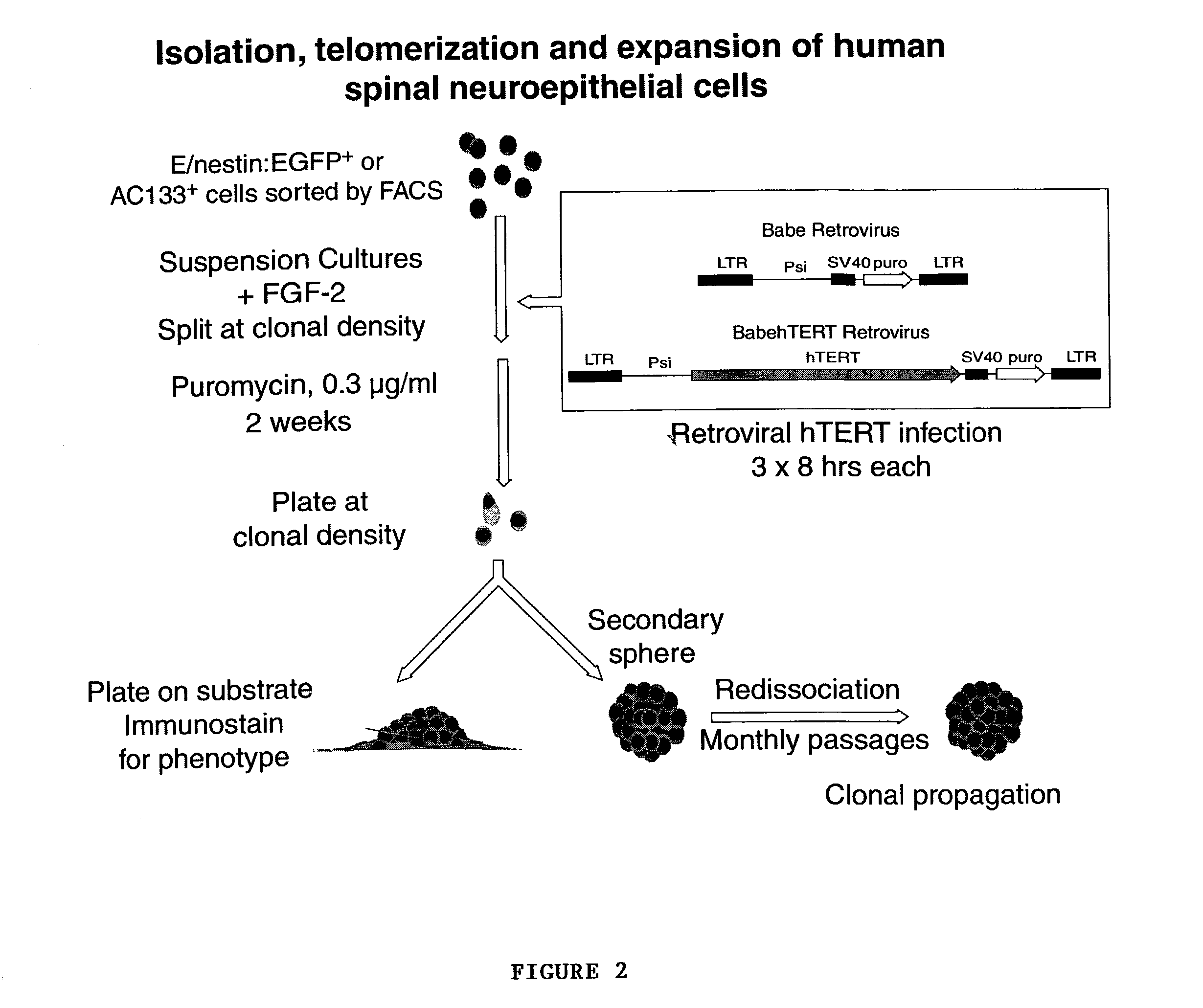
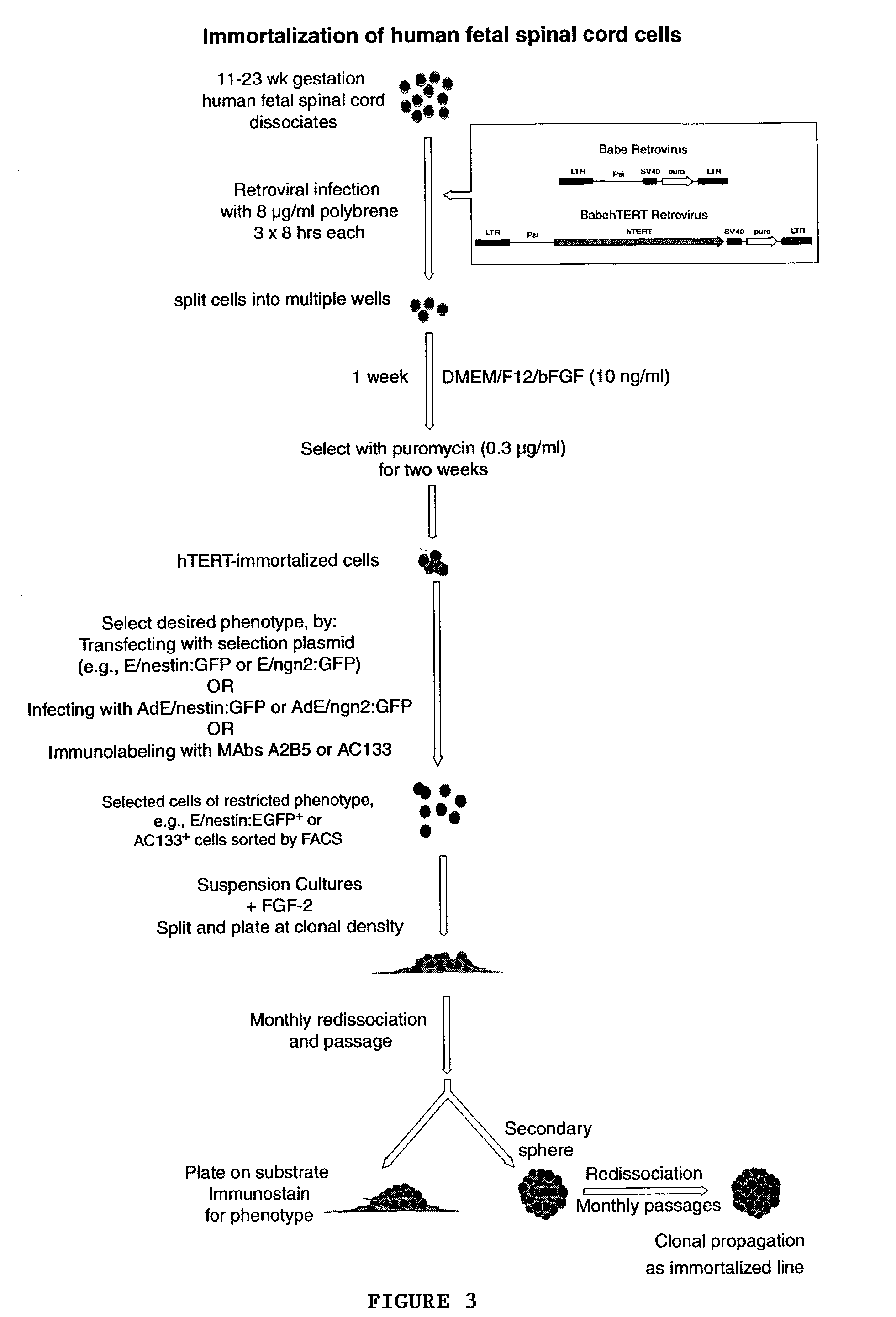
Telomerase immortalized neural progenitor cells
ActiveUS7150989B2Limited clinical utilityLittle expansion capacityVirusesGenetically modified cellsProgenitorTelomerase
The present invention relates to a method of immortalizing progenitor cells by providing a population of progenitor cells (e.g, neural progenitor cells) and immortalizing the progenitor cells either before or after they are enriched or purified. The present invention is also directed to an enriched or purified population of immortalized progenitor cells (e.g., neural progenitor cells).
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
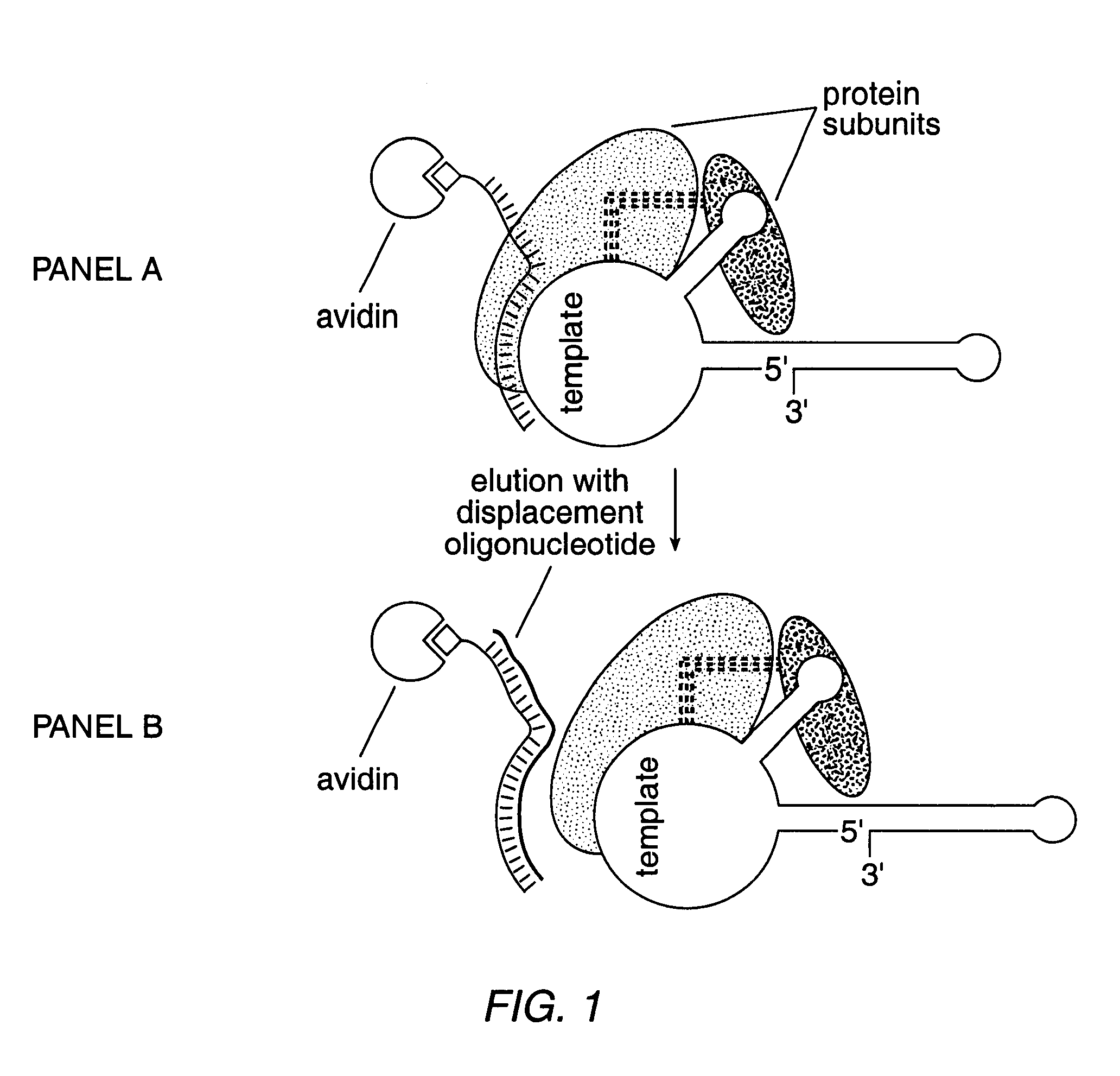
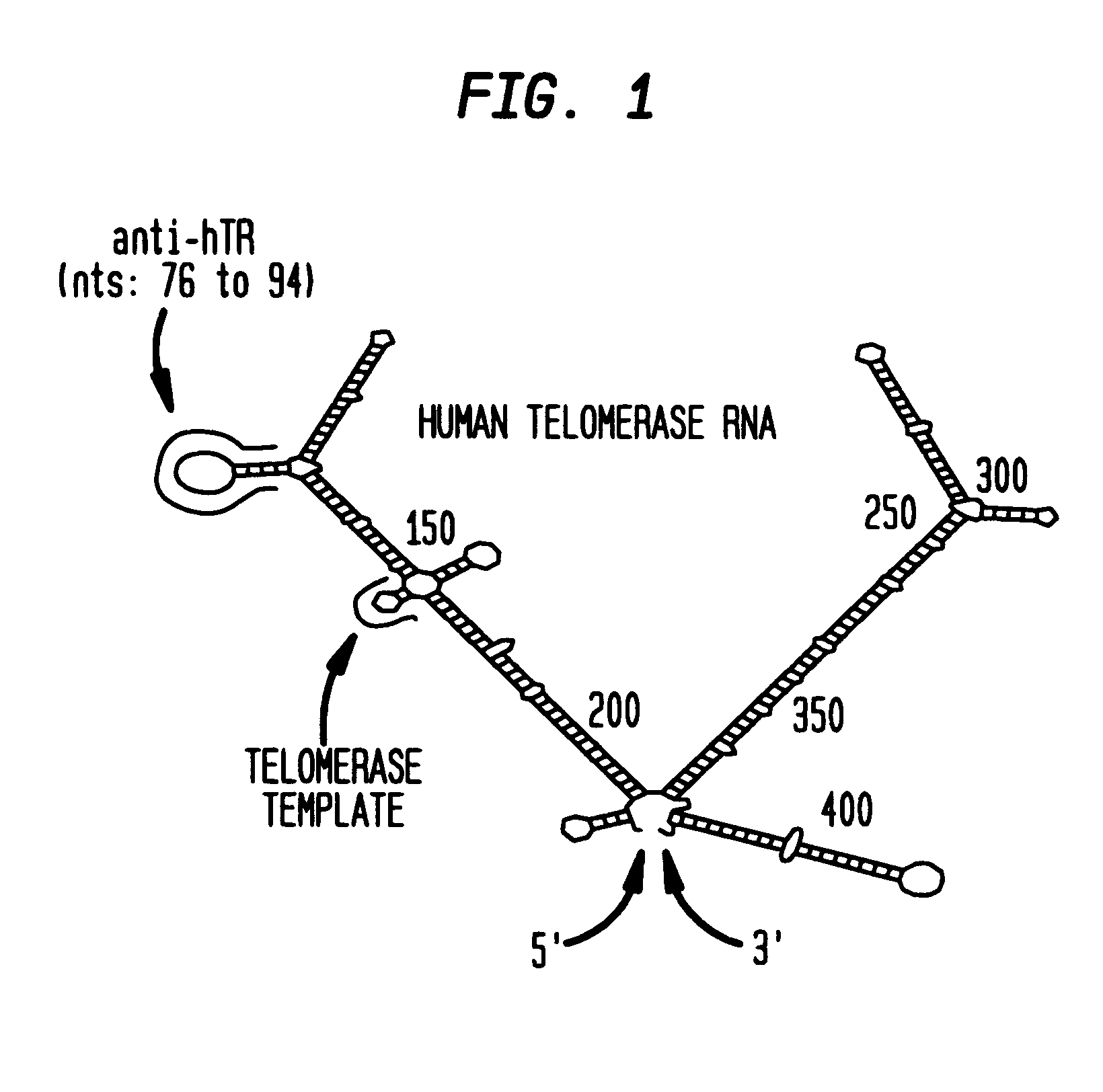
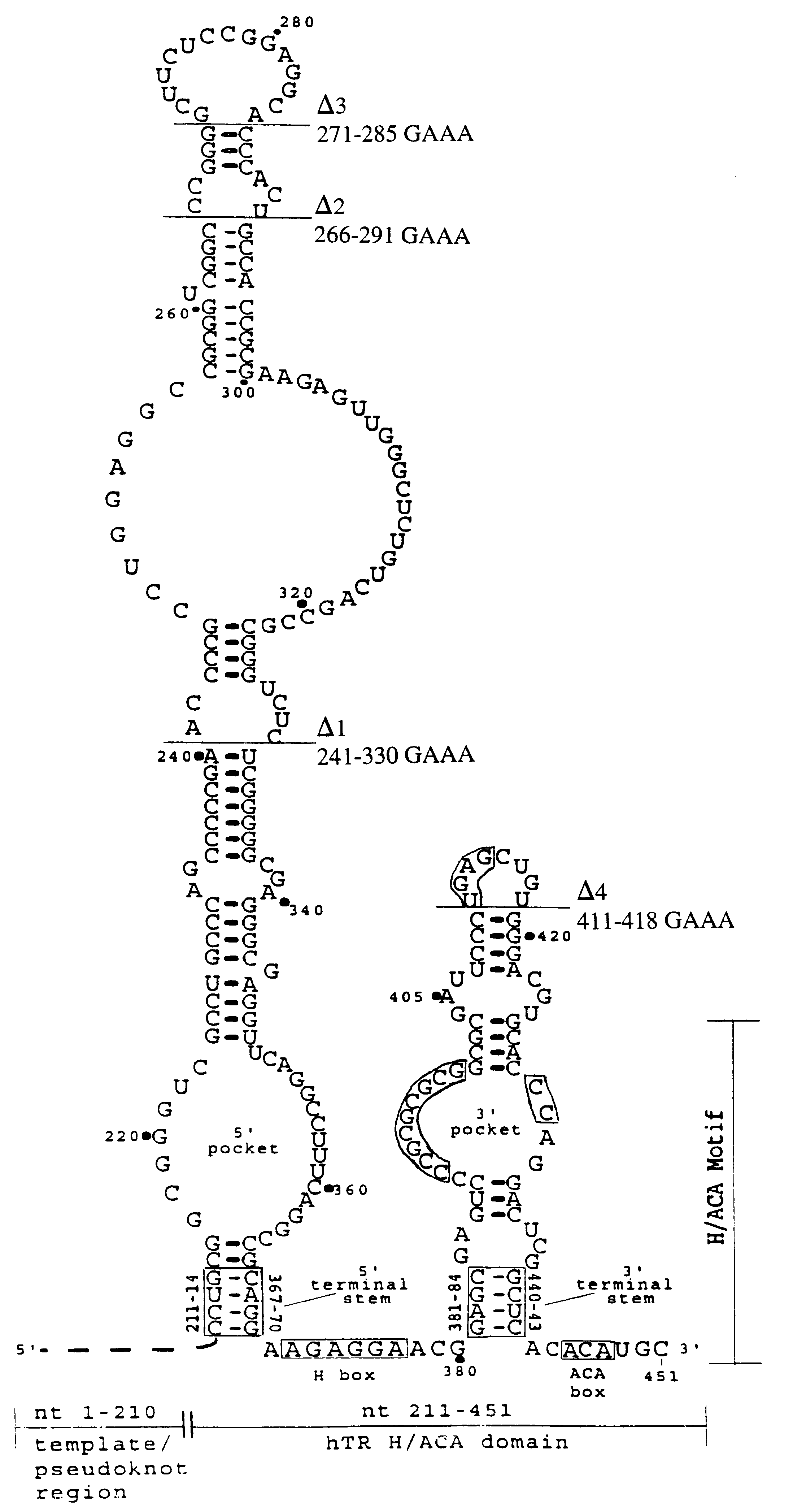
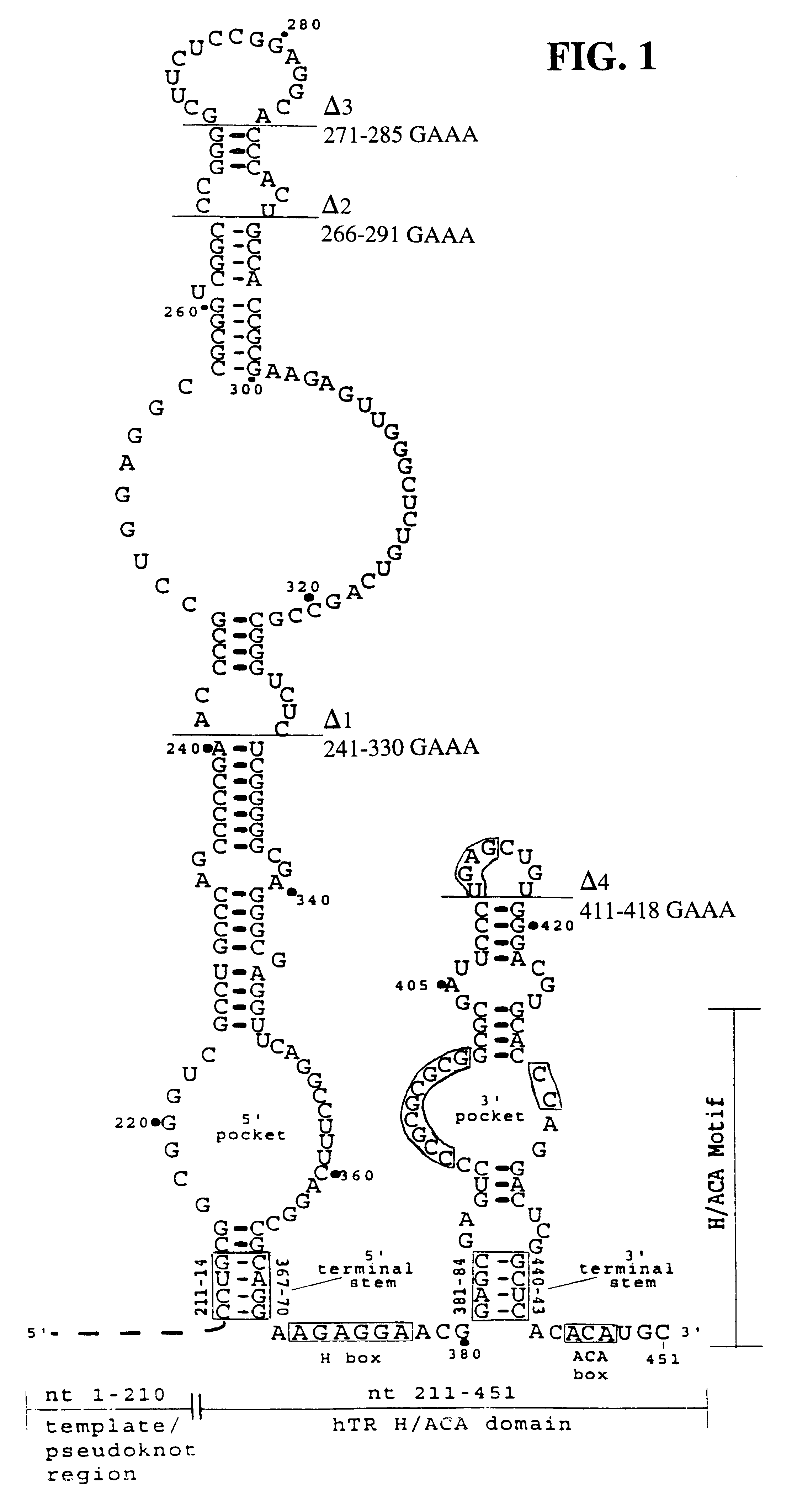
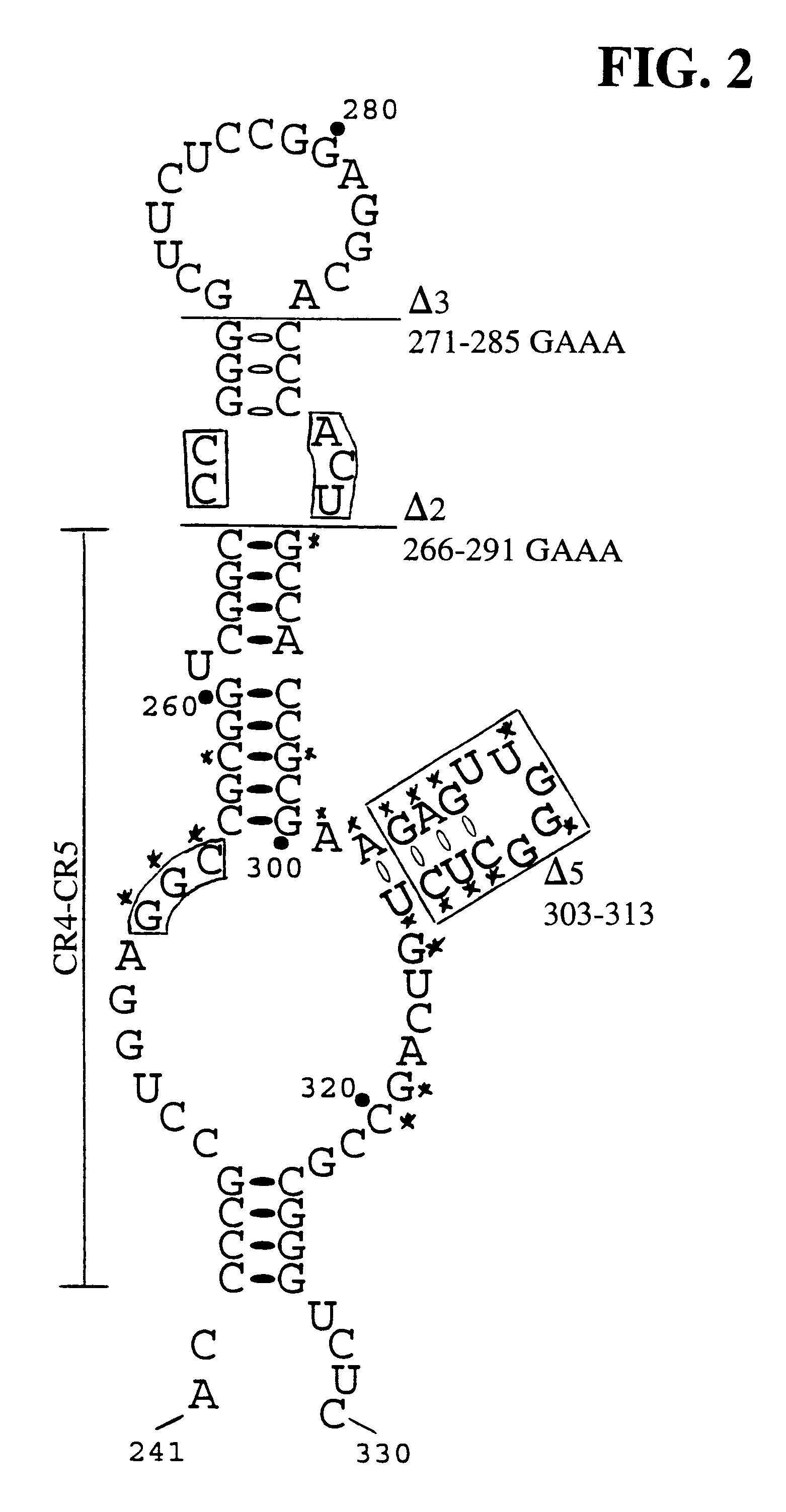
Human telomerase RNA elements
The invention provides methods and compositions relating to discrete elements of human telomerase and human telomerase RNA. In one embodiment, the invention provides a polynucleotide comprising only one element of human telomerase RNA, wherein the element consists of SEQ ID NO:1, residues 241-330. Such human telomerase RNA elements may be employed in mixtures with a human telomerase polypeptide such as TERT or dyskerin, wherein the polypeptide and polynucleotide specifically interact, and such mixtures may be employed in methods for identifying modulators of a human telomerase polypeptide-human telomerase RNA interaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vertebrate telomerase genes and proteins and uses thereof
Nucleic acid molecules encoding vertebrate telomerase are provided. Gene products, expression vectors and host cells suitable for expressing telomerase are also provided. Methods for identifying inhibitors of telomerase activity and inhibitor compositions are disclosed.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
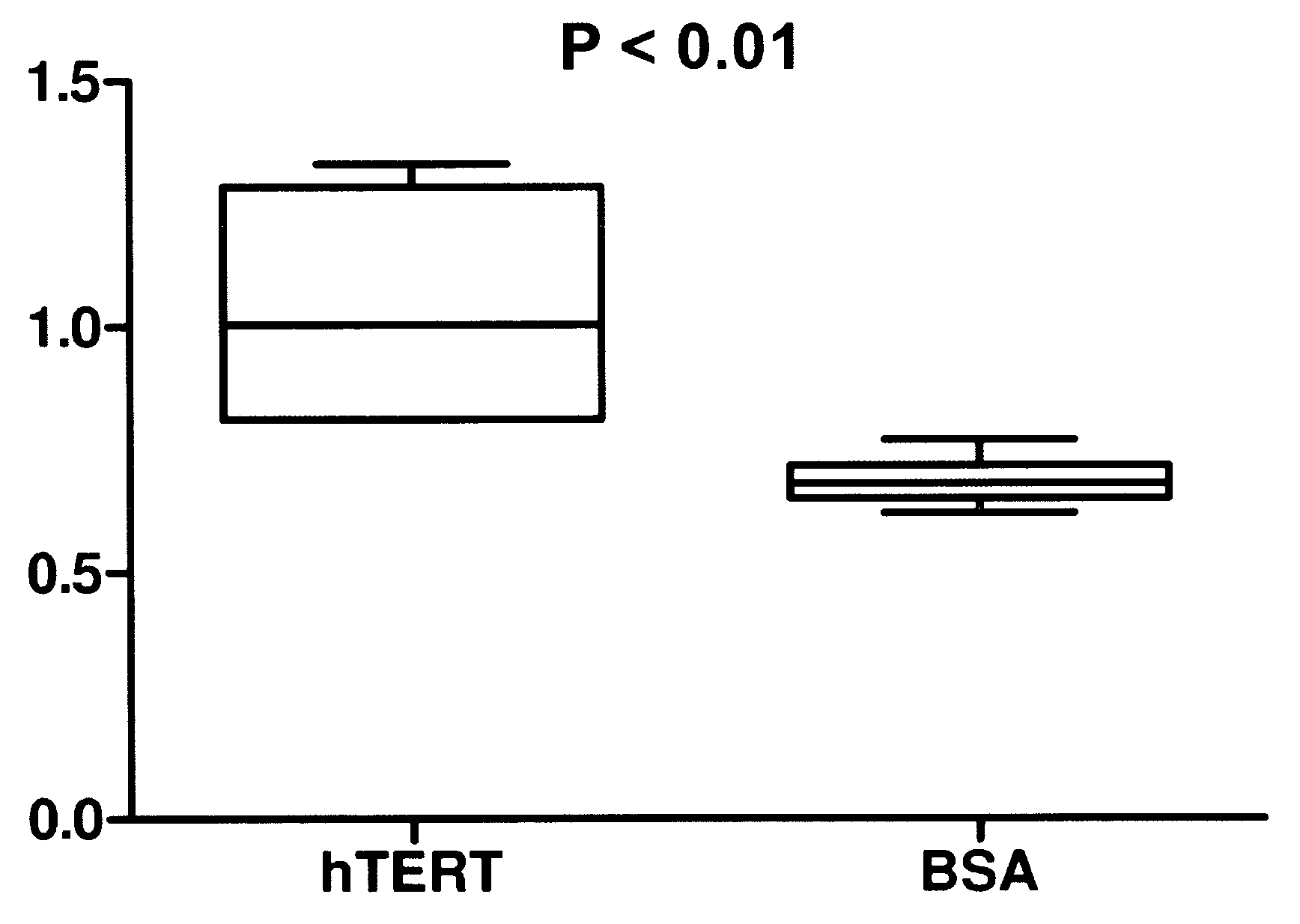
Compositions and methods for increasing telomerase activity
ActiveUS7846904B2Produce a level of telomerase activityEnhancement of replicative capacity and life-spanBiocideSenses disorderTelomeraseMedicine
Owner:TELOMERASE ACTIVATION SCI
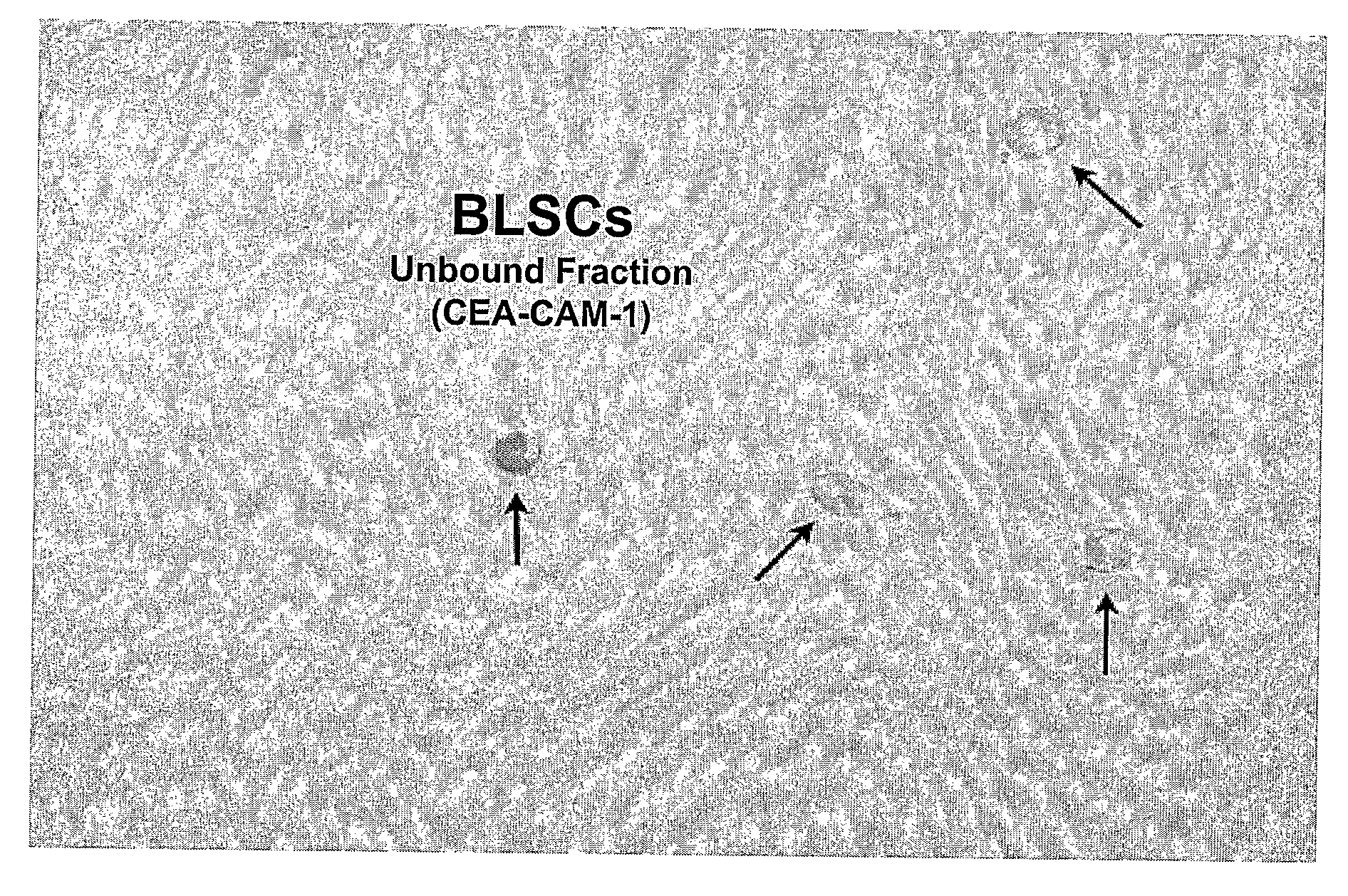
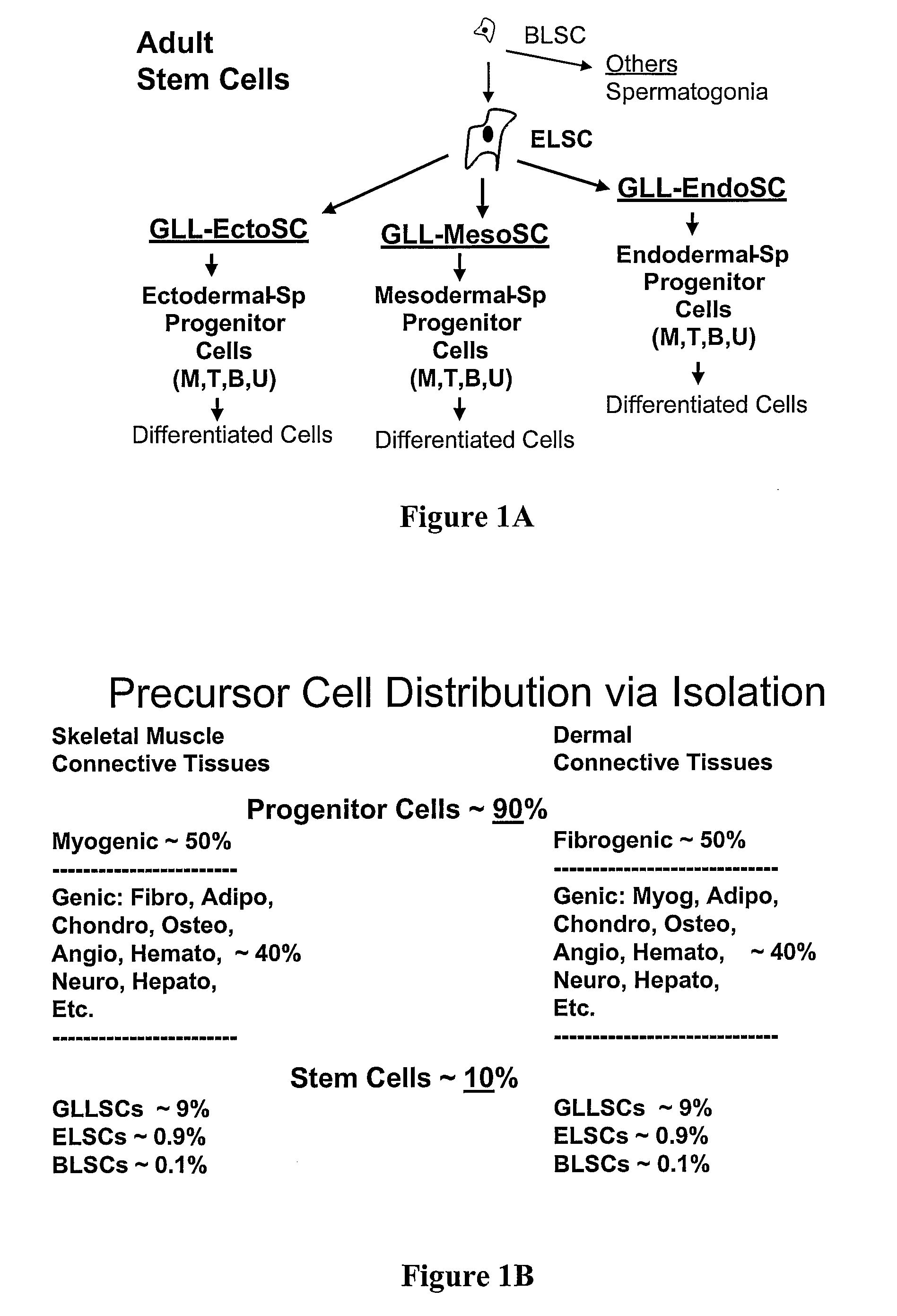
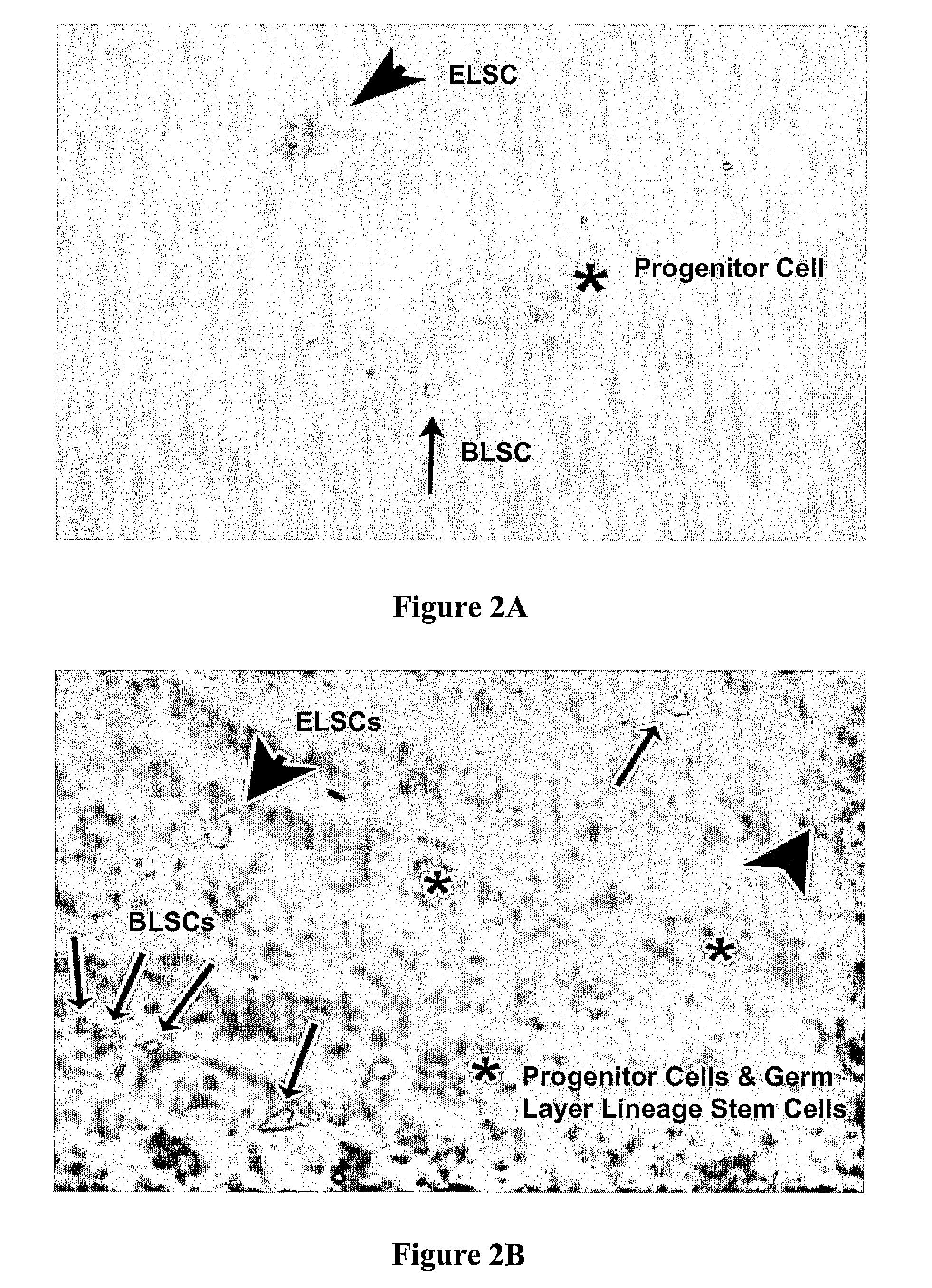
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
Non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells are disclosed. Most preferably, such cells are obtained from various tissues of postnatal mammals (e.g., using tissue biopsied from the mammal), are smaller than 1 μm, have normal karyotype, and do not spontaneously differentiate in serum-free medium without differentiation inhibitors. These non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells typically express CD66e, CEA-CAM-1 and telomerase, but do not typically express CD10, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, and SSEA-4. Such blastomere-like totipotent cells can be differentiated into ectodermal, mesodermal, or endodermal tissues, including placental tissues and germ cells. Moreover, when implanted into a mammal, such cells will not be teratogenic.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
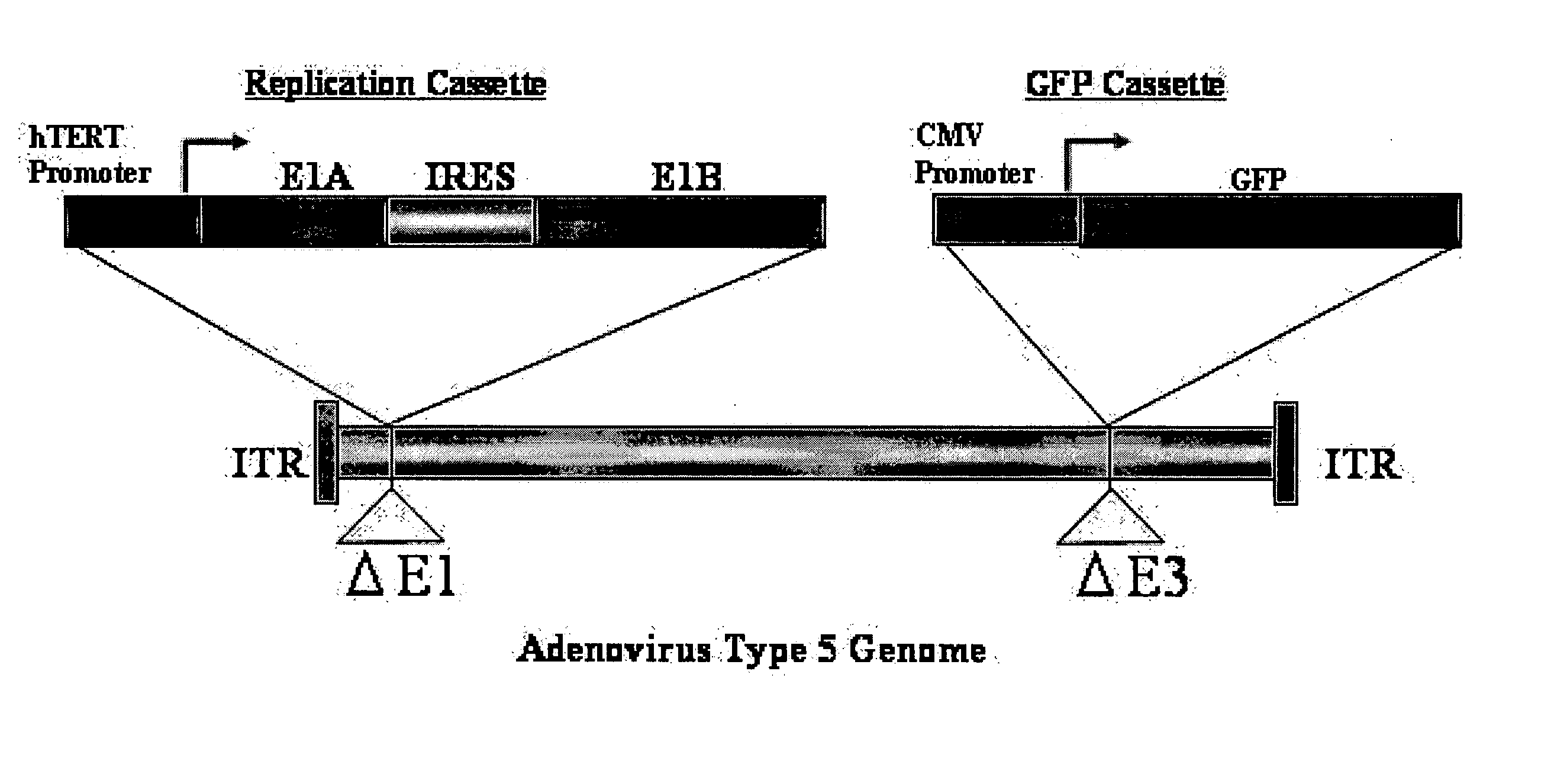
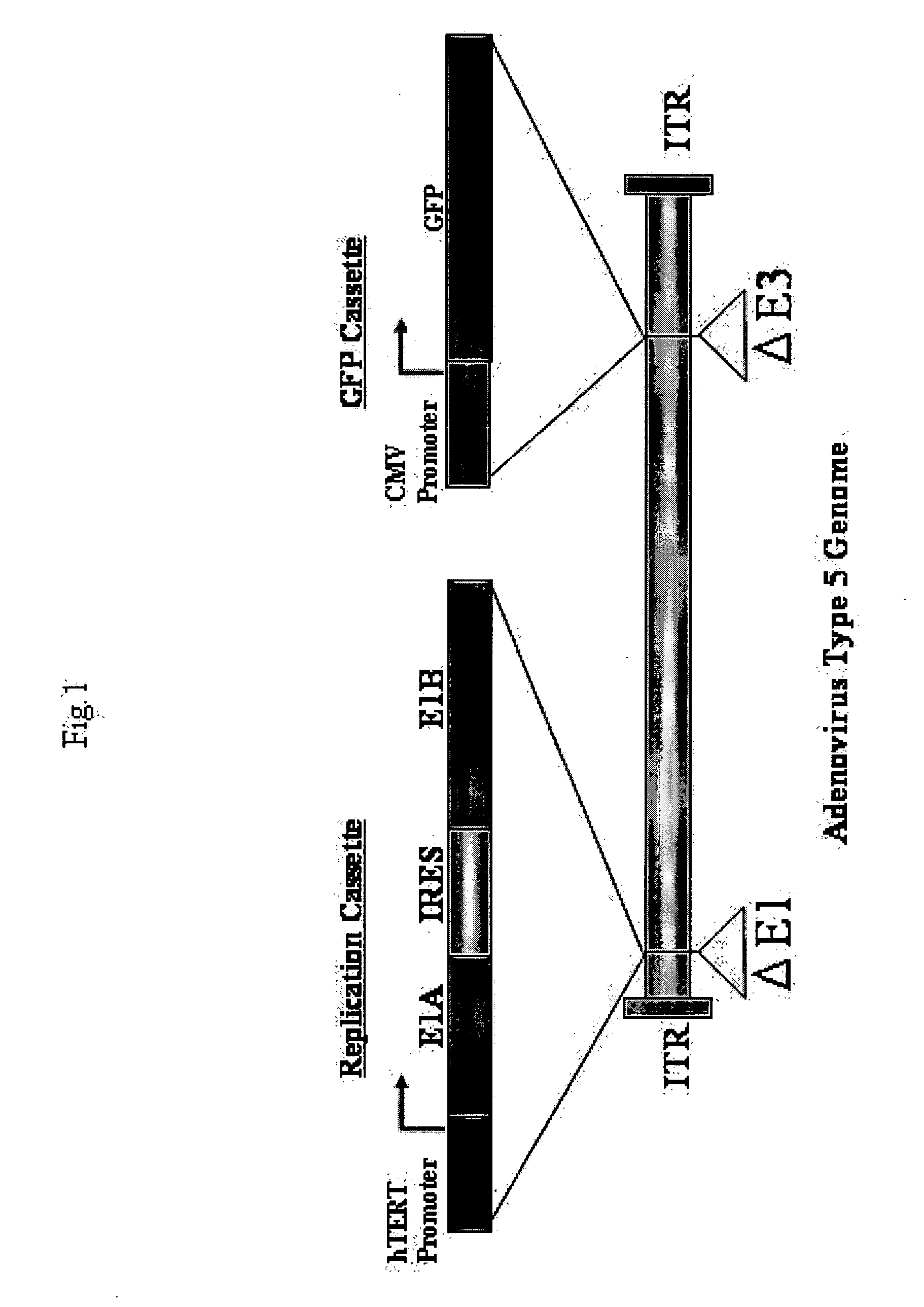
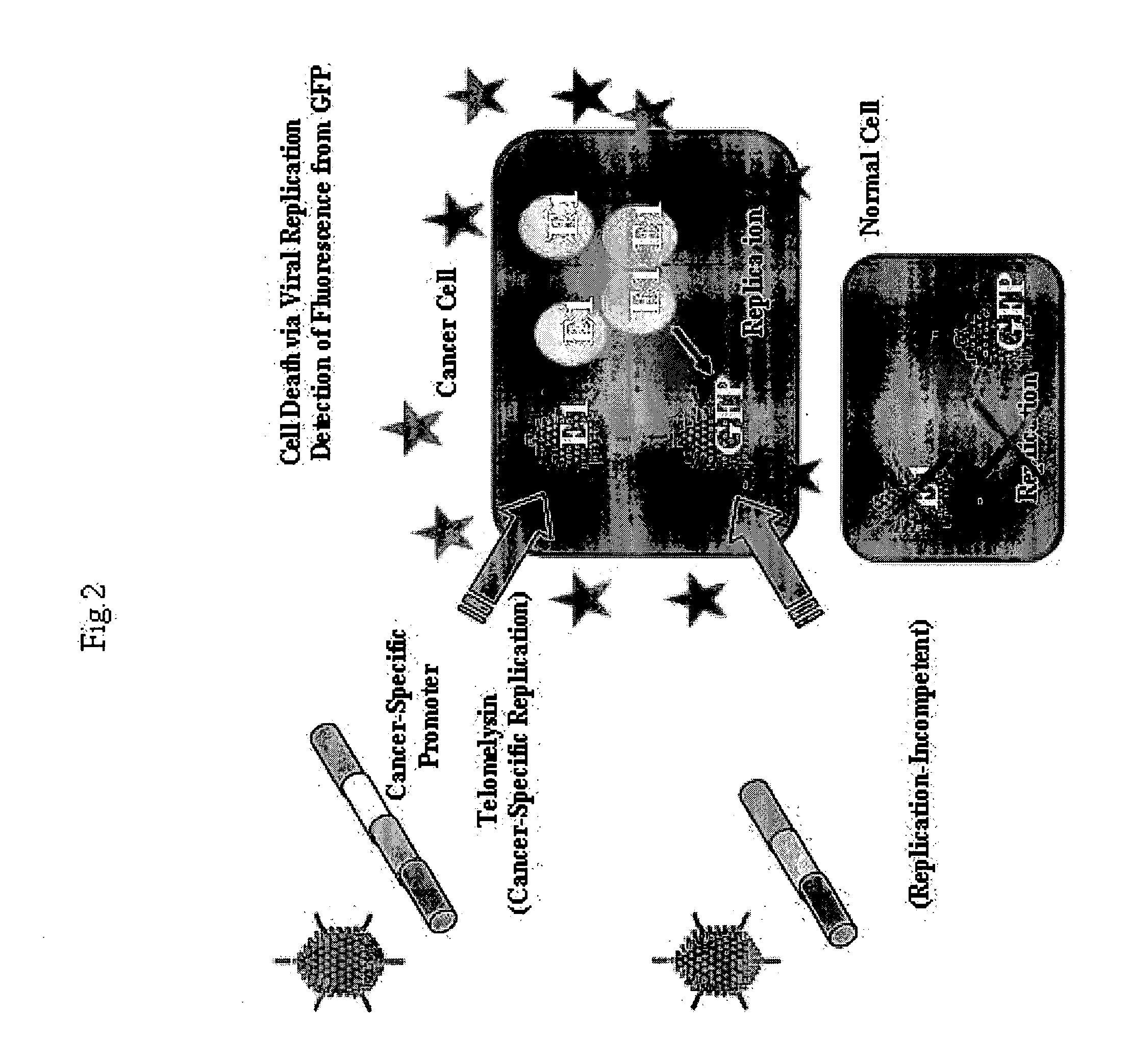
Telomelysin/GFP-expressing recombinant virus
ActiveUS20060067890A1High sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVirusesTelomeraseCancer cell
The present invention provides a reagent for cancer cell detection or cancer diagnosis. The present invention relates to a reagent for cancer cell detection, comprising a recombinant virus where a replication cassette comprising a promoter from human telomerase, an E1A gene, an IRES sequence and an E1B gene in this order is integrated in E1 region of the viral genome and a labeling cassette comprising a gene encoding a labeling protein and a promoter capable of regulating the expression of the gene encoding the labeling protein is integrated in E3 region of the viral genome.
Owner:ONCOLYS BIOPHARMA
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
InactiveUS20120329858A1Superior cellular uptake propertyReduce Toxicity RiskOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseLipid moiety
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
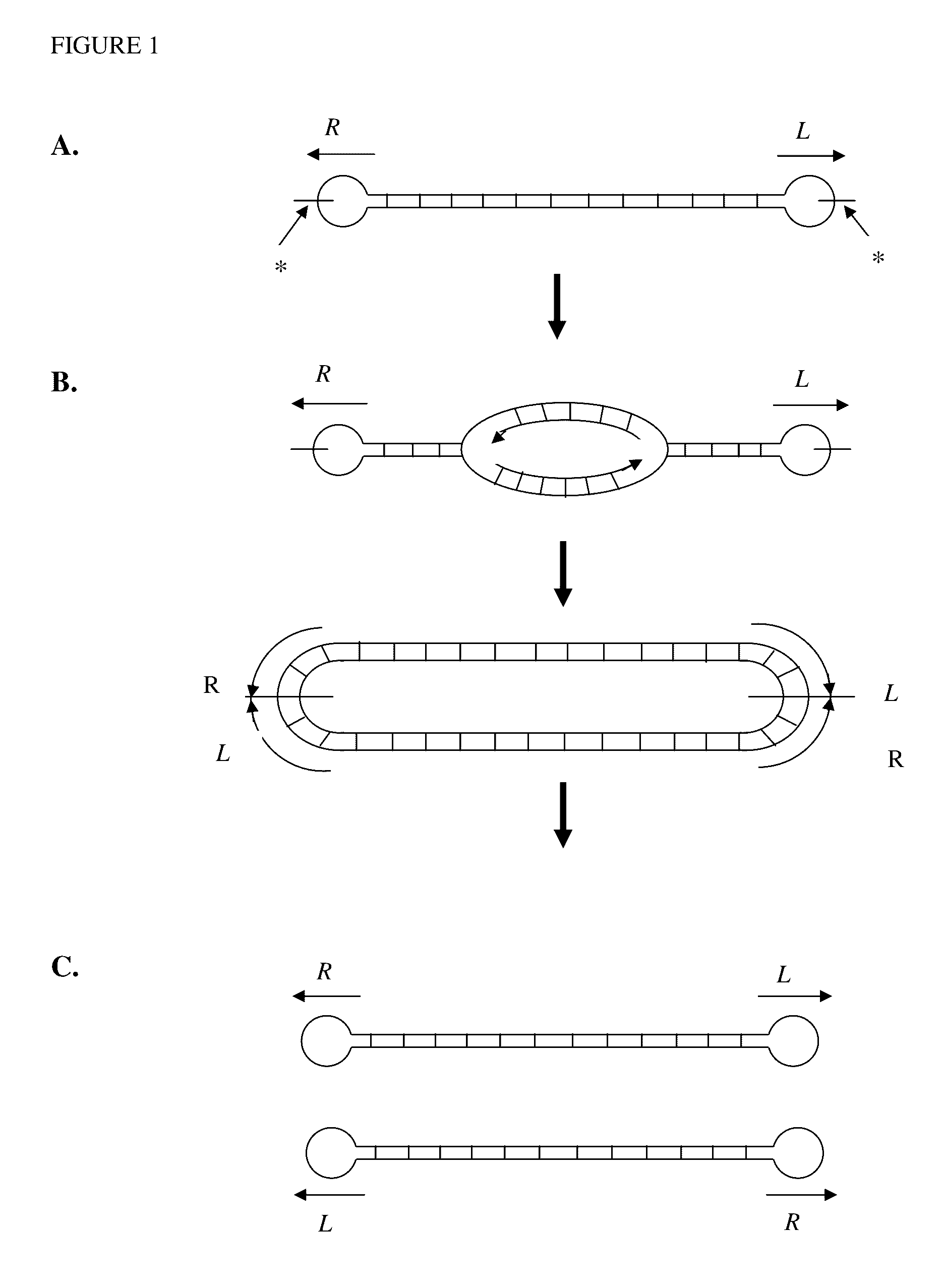
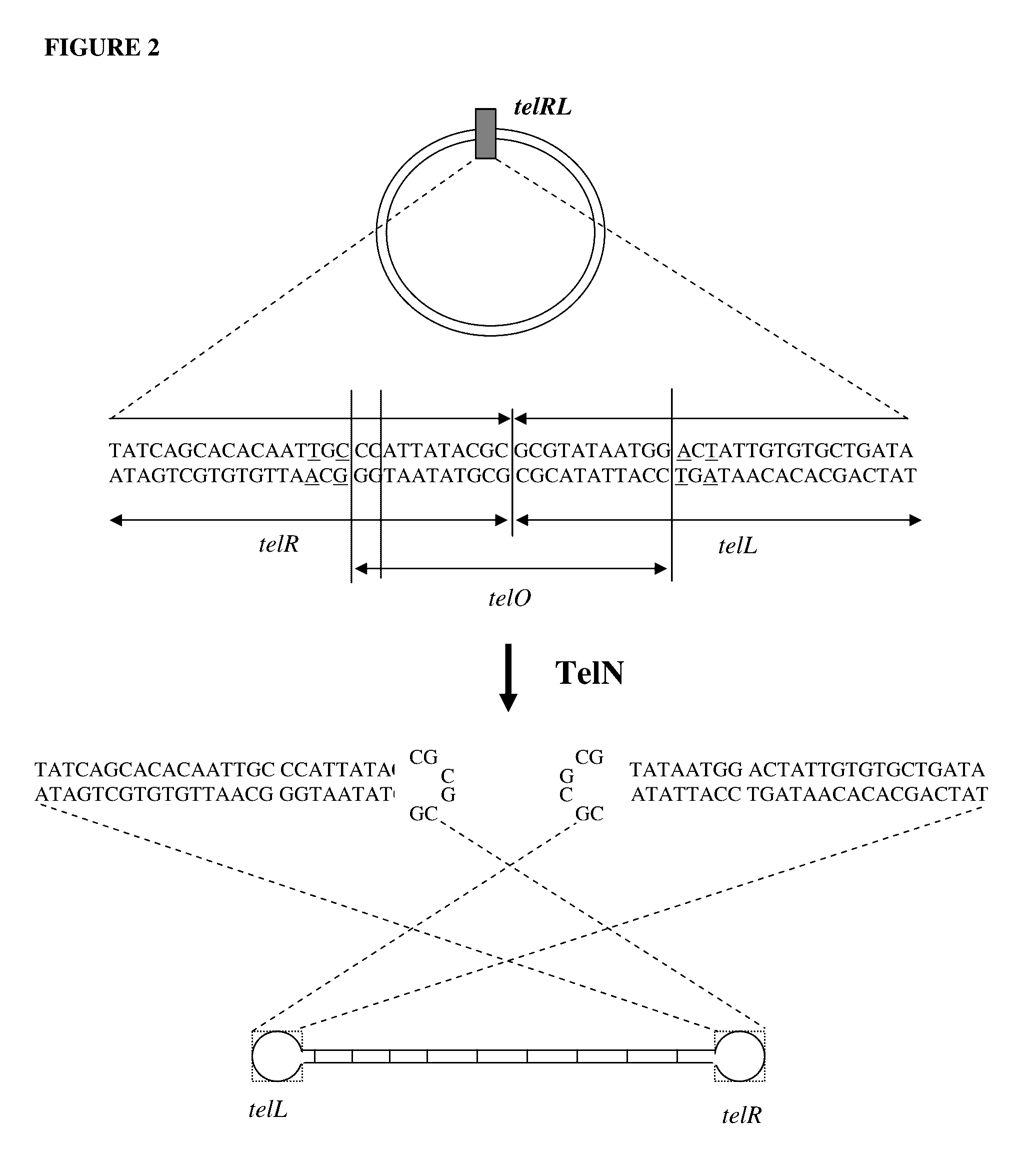
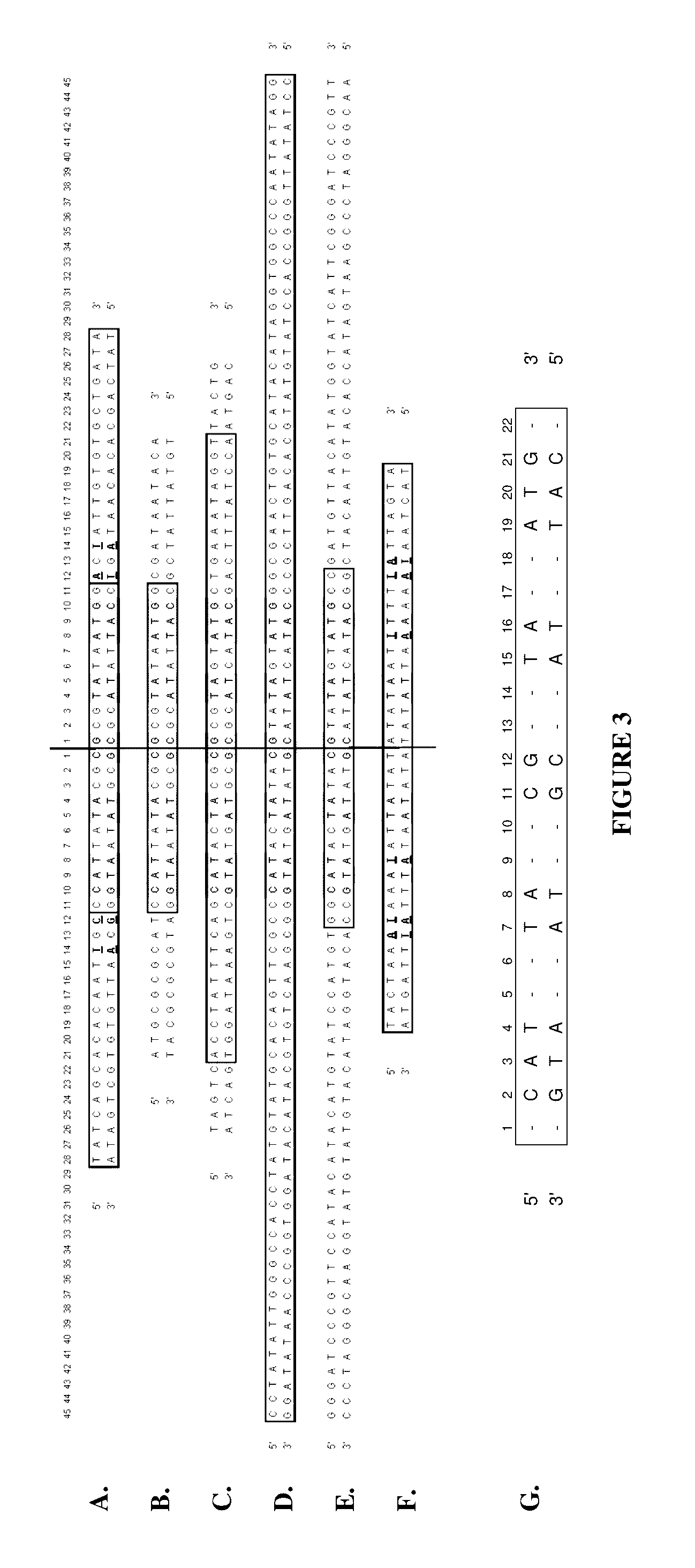
Production of closed linear DNA using a palindromic sequence
A primer for the amplification of a DNA template comprising a protelomerase target sequence, particularly for production of closed linear DNA, which primer is capable of specifically binding to a palindromic sequence within a protelomerase target sequence and priming amplification in both directions.
Owner:TOUCHLIGHT IP LTD
Telomerase delivery by biodegradable Nanoparticle
InactiveUS20090142408A1Effectively crossControl releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAge related diseaseHydrophilic polymers
A therapeutic compound consisting of human telomerase, its catalytic subunit hTert, or a known variant of either, and a biodegradable nanoparticle carrier, which can be administered to cells in a cell culture or in a living animal, is provided herein. The therapeutic compound is envisioned as a method for treating a wide variety of age-related diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, aplastic anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, arteriosclerosis, macular degeneration, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's, diabetes type 2, and any disease that correlates with telomere shortening and may be corrected or ameliorated by lengthening telomeres. The therapeutic compound is also envisioned as method for potentially treating more generic problems of human aging. The nanoparticle carrier is comprised of certain biodegradable biocompatible polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide), poly(lactic acid), poly(alkylene glycol), polybutylcyanoacrylate, poly(methylmethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid), poly-allylamine, polyanhydride, polyhydroxybutyric acid, polycaprolactone, lactide-caprolactone copolymers, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyalkylcyanoacrylates, polyanhydrides, polyorthoester or a combination thereof. The nanoparticle may incorporate a targeting moiety to direct the nanoparticle to a particular tissue type or a location within a cell. The nanoparticle may incorporate a plasticizer to facilitate sustained release of telomerase such as L-tartaric acid dimethyl ester, triethyl citrate, or glyceryl triacetate. A nanoparticle of the present invention can further contain a polymer that affects the charge or lipophilicity or hydrophilicity of the particle. Any biocompatible hydrophilic polymer can be used for this purpose, including but not limited to, poly(vinyl alcohol).
Owner:SARAD MATTHEW
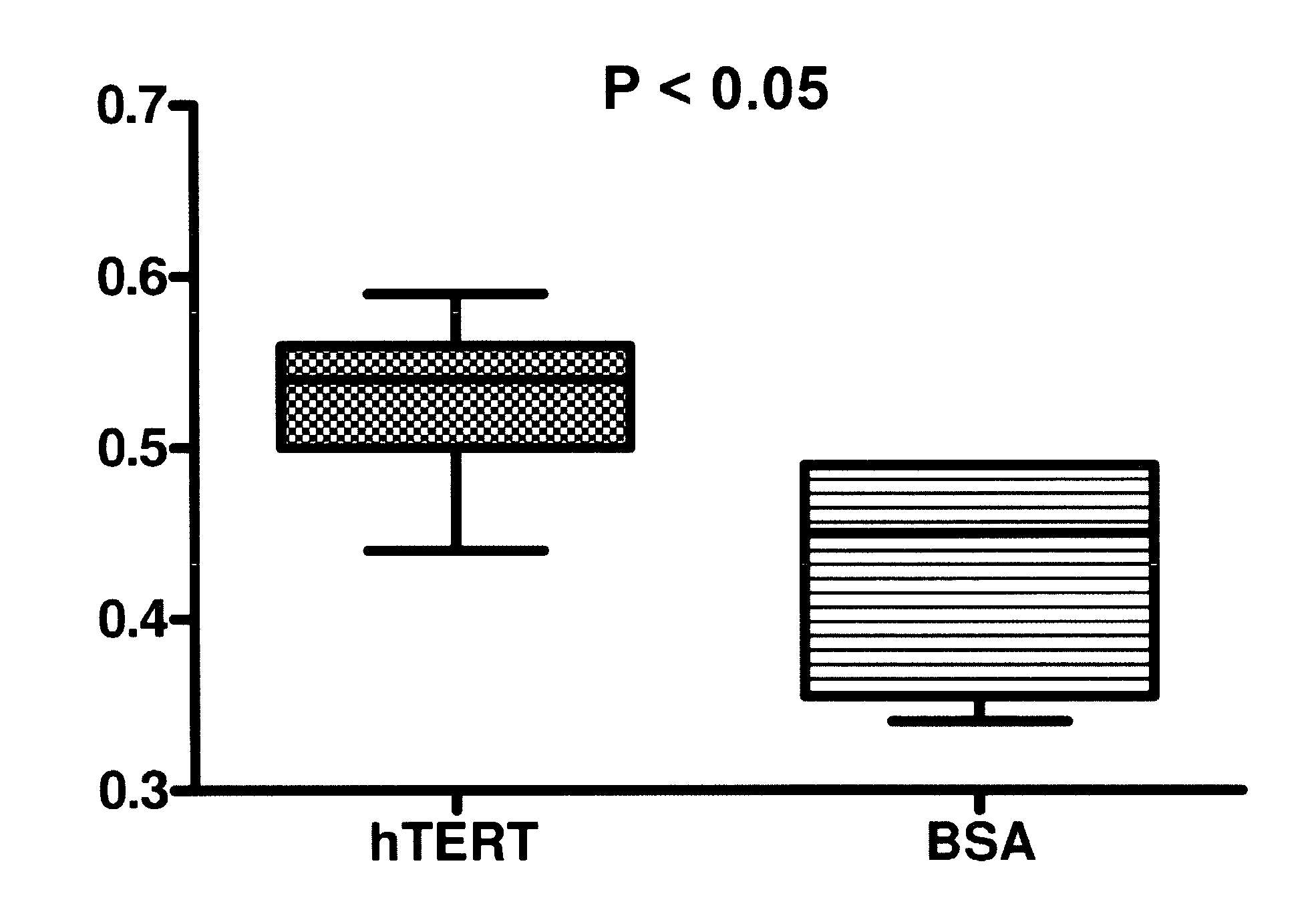
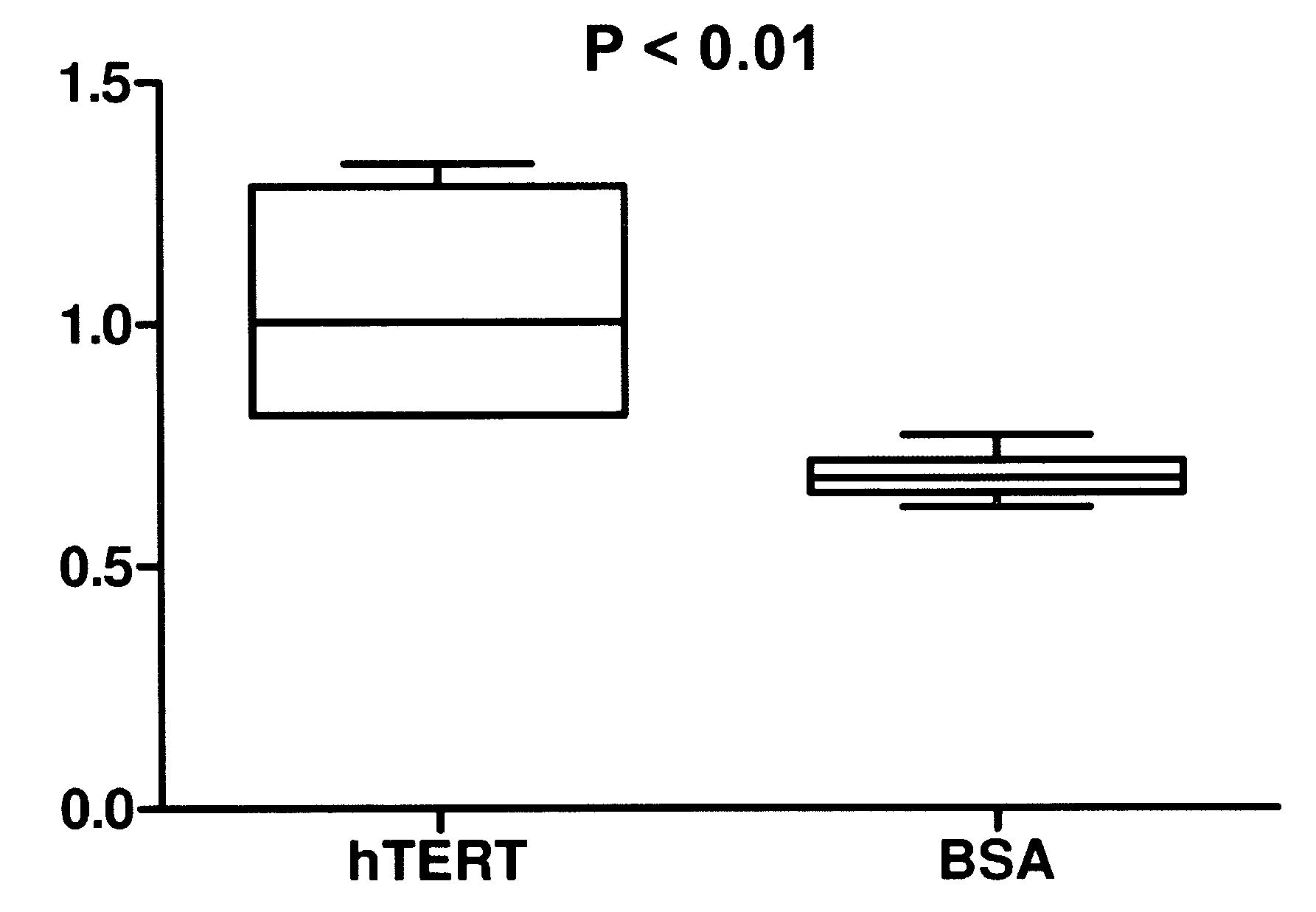
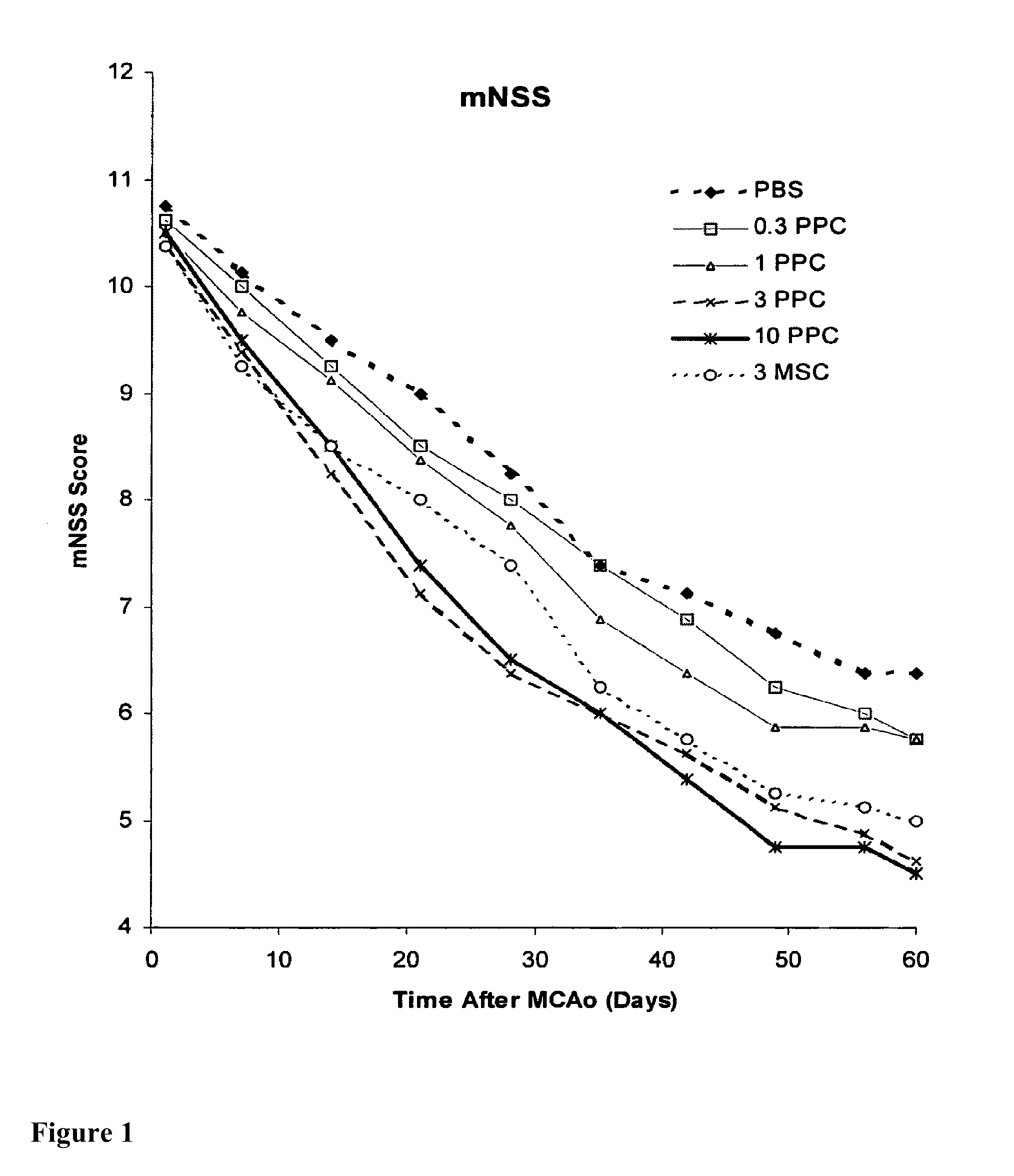
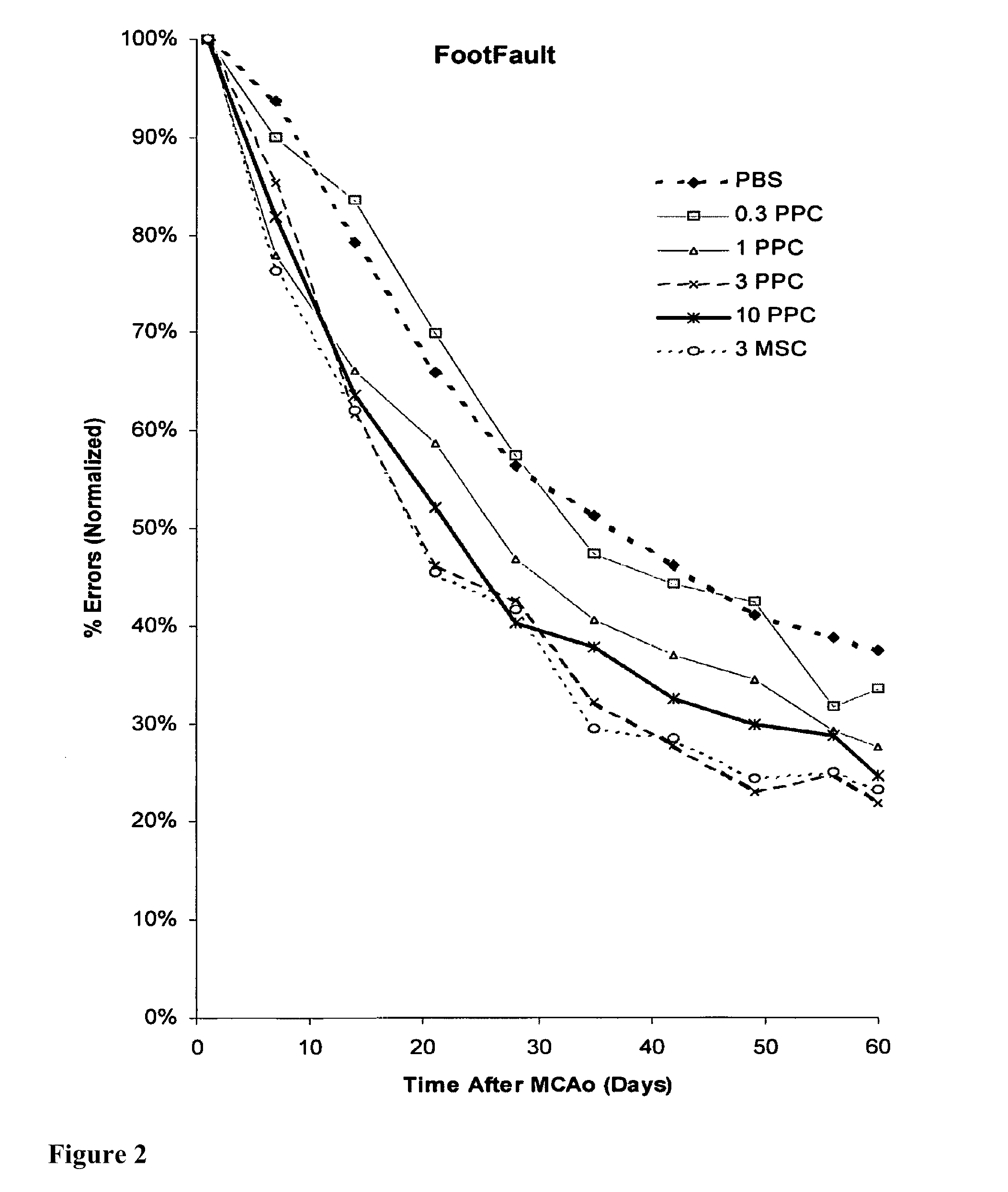
Treatment of stroke and other acute neural degenerative disorders via intranasal administration of umbilical cord-derived cells
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
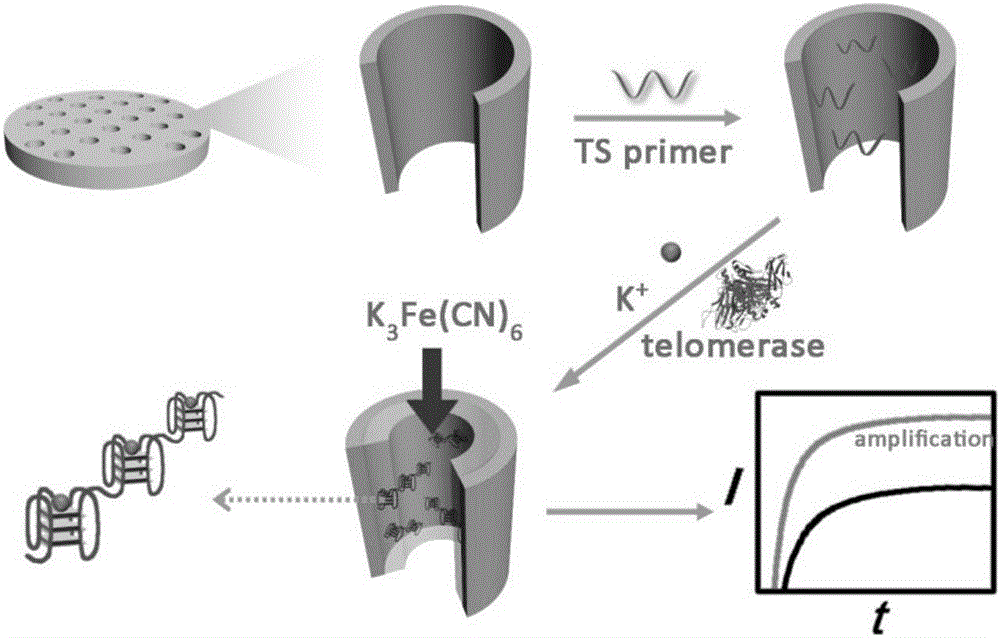
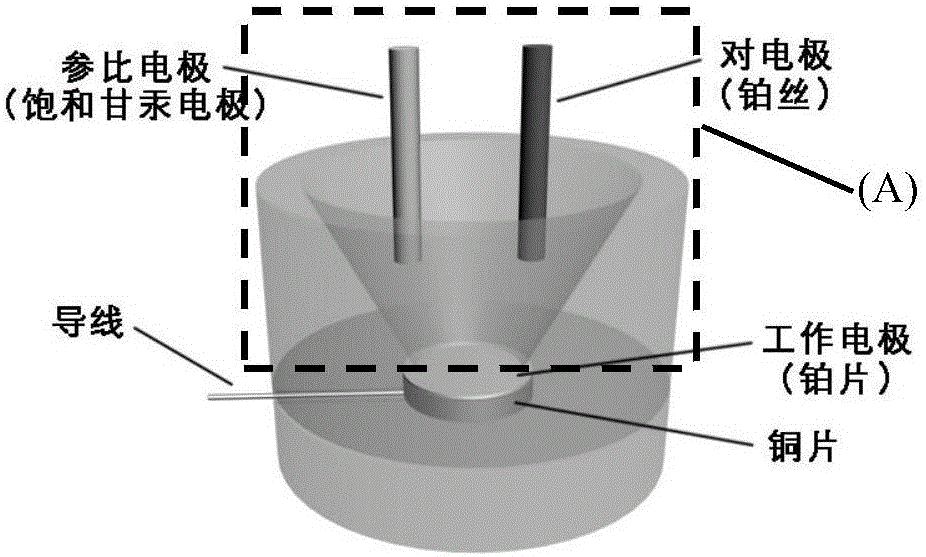
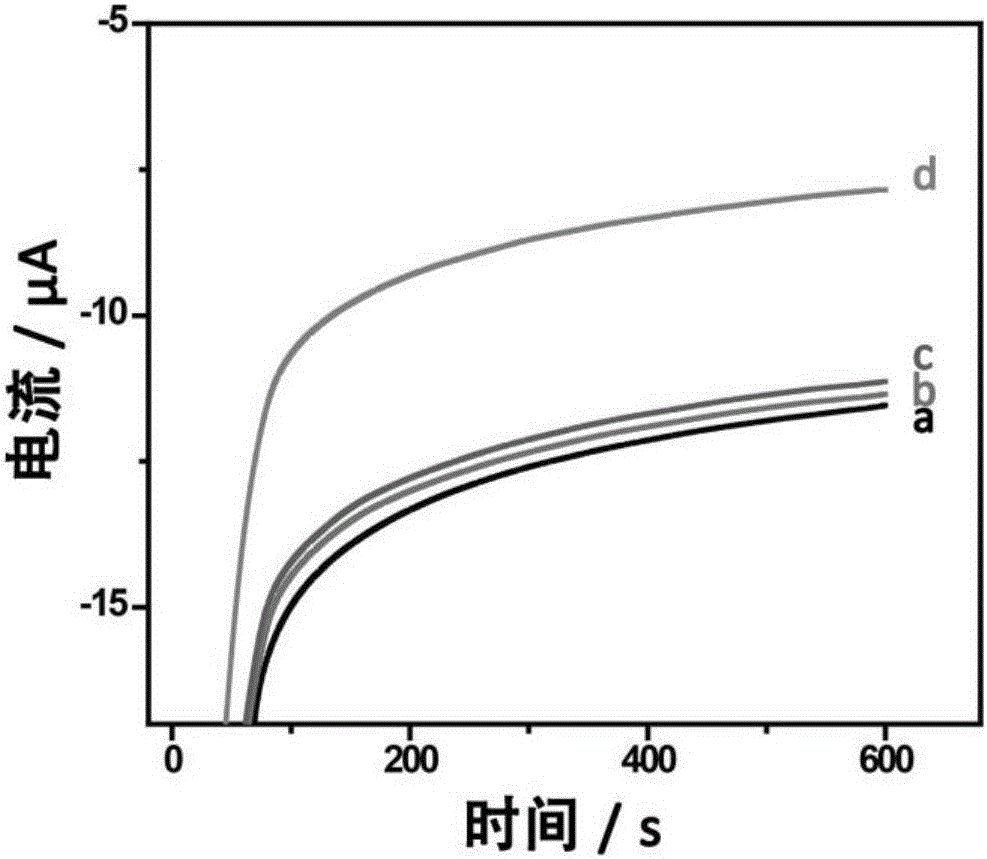
Method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing
ActiveCN105806912AAperture adjustableStable structureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTelomerasePower flow
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on a nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing.The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a telomerase recognition sequence is connected to the inner wall of a porous anodic alumina template or a polyethylene terephthalate film to serve as a primer; secondly, telomerase amplifies the primer to form a G-rich sequence; a G-quadruplex is formed in the presence of potassium ions; electrochemical detection is conducted on the current produced through indicating molecules of the nano pore channel by utilizing an electrochemical workstation.The method does not need complex material preparation and DNA probe marking, and can avoid the defects of high detection cost, complicated operation and poor reproducibility caused by the complex material preparation and DNA probe marking and has the advantages of being low in cost, quick, simple, convenient, high in sensitivity and good in accuracy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com