Patents
Literature
128 results about "Human telomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Telomerase in Human Development. Telomerase is an enzyme that regulates the lengths of telomeres in the cells of many organisms, and in humans it begins to function int the early stages of embryonic development.
Telomerase
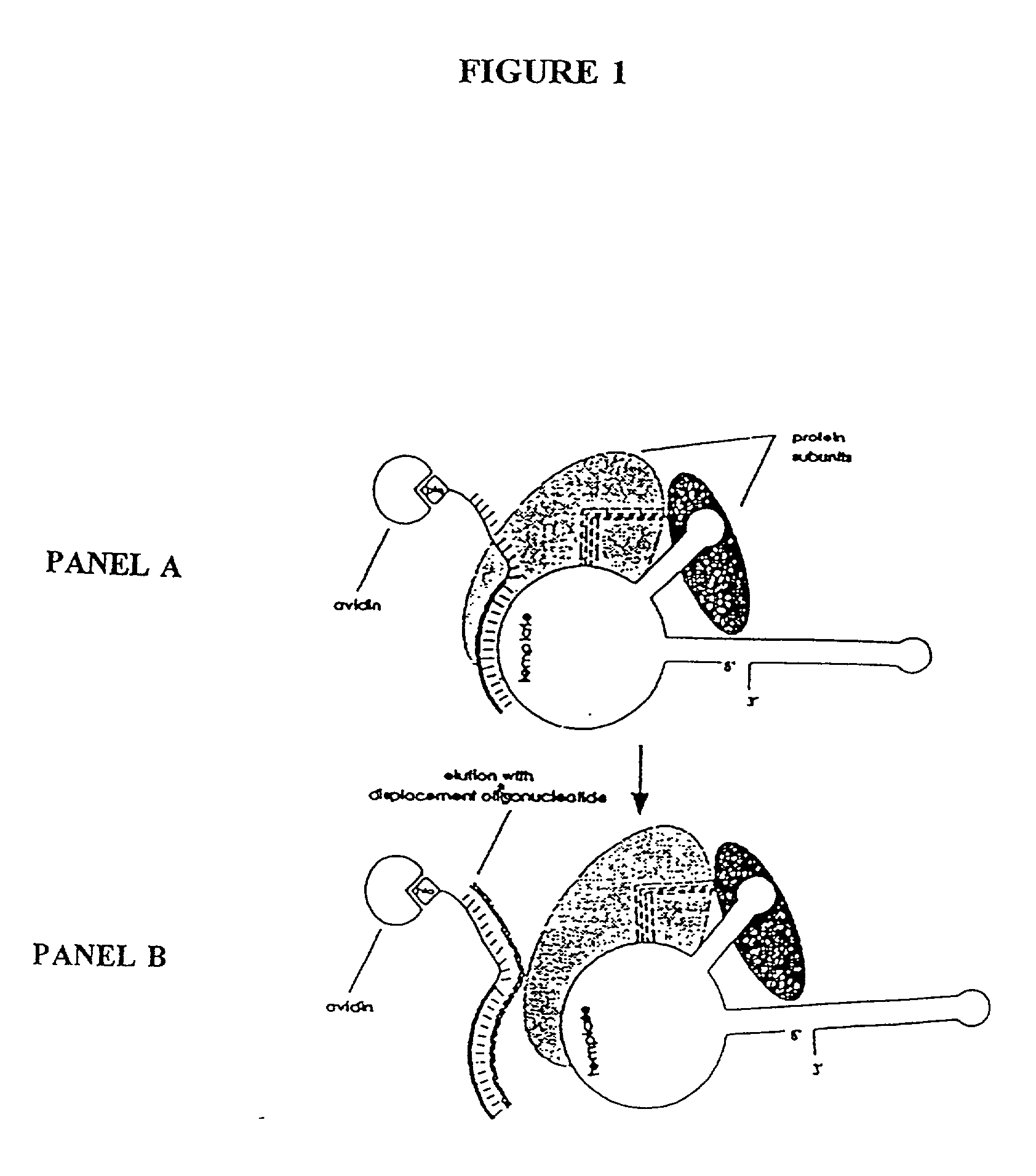
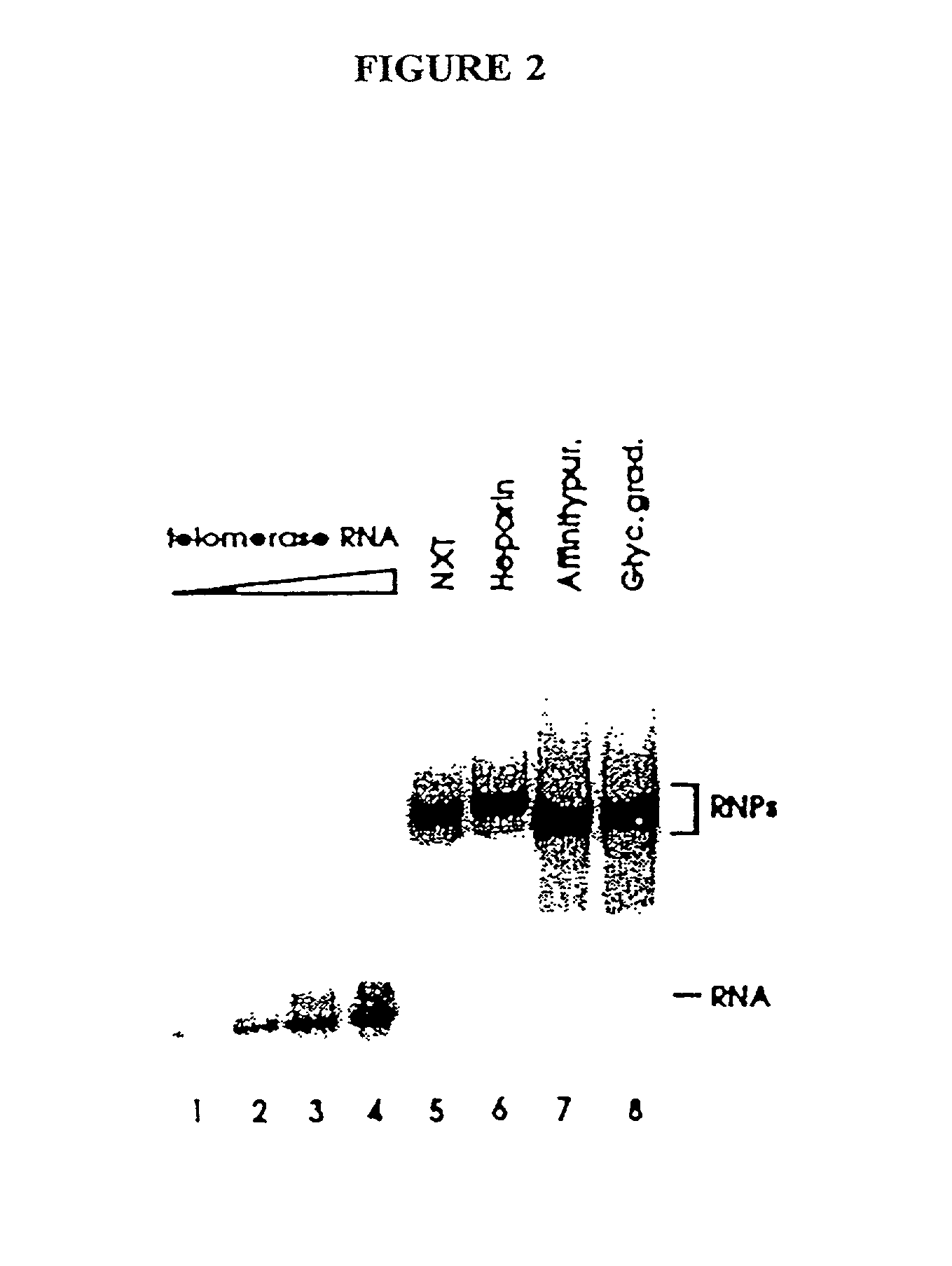
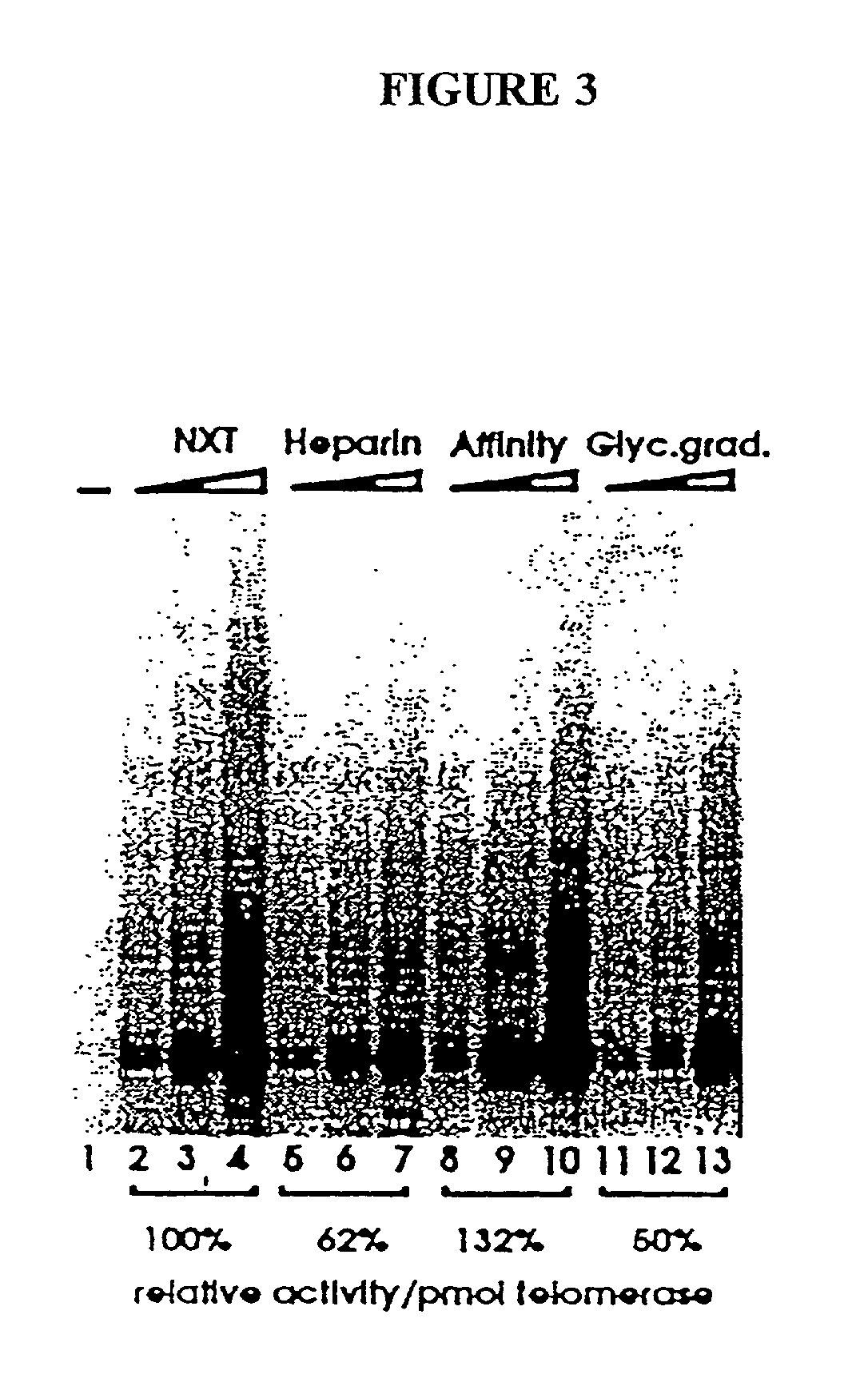
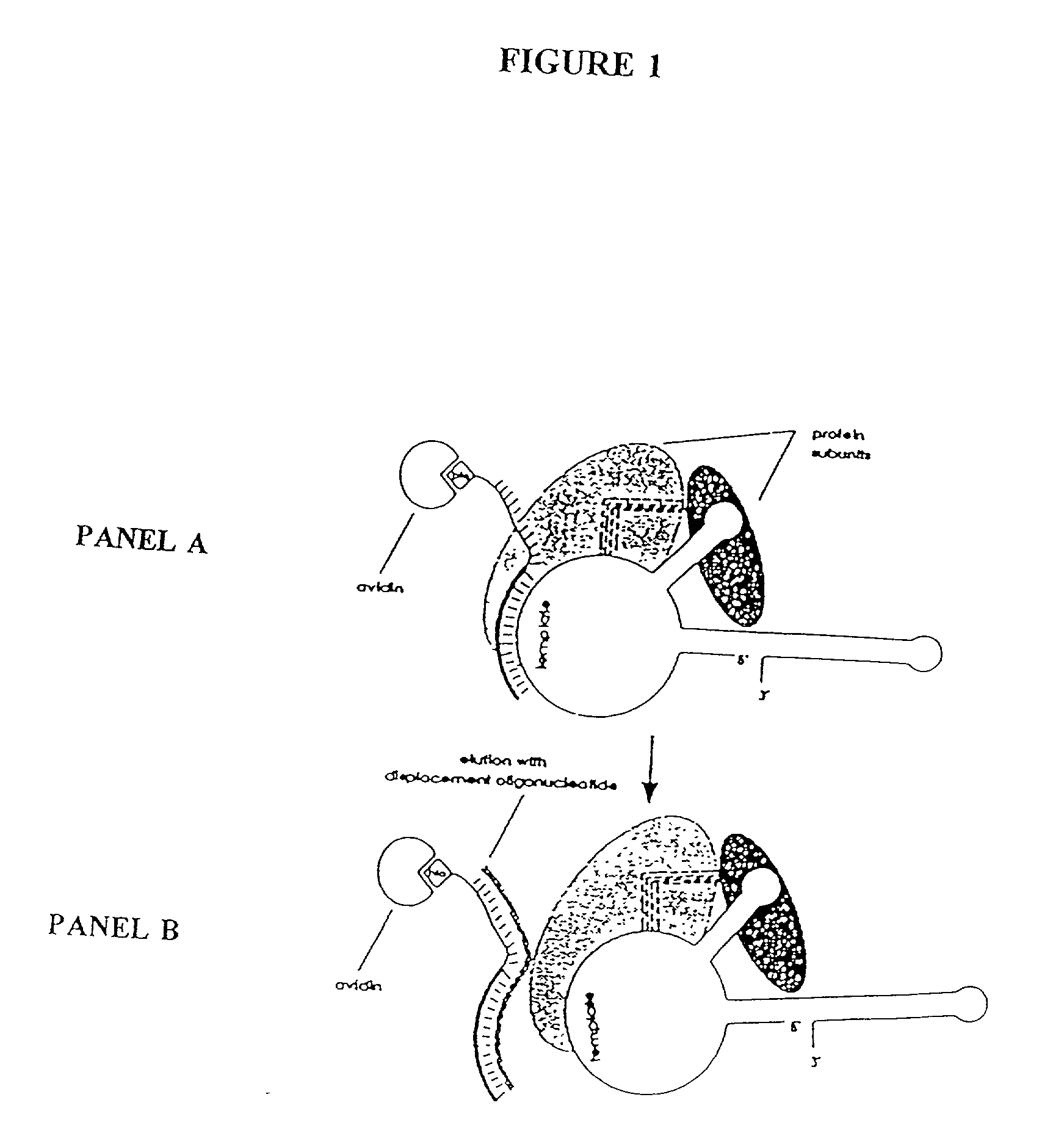
InactiveUS6261836B1Improve purification effectAvoid the needPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
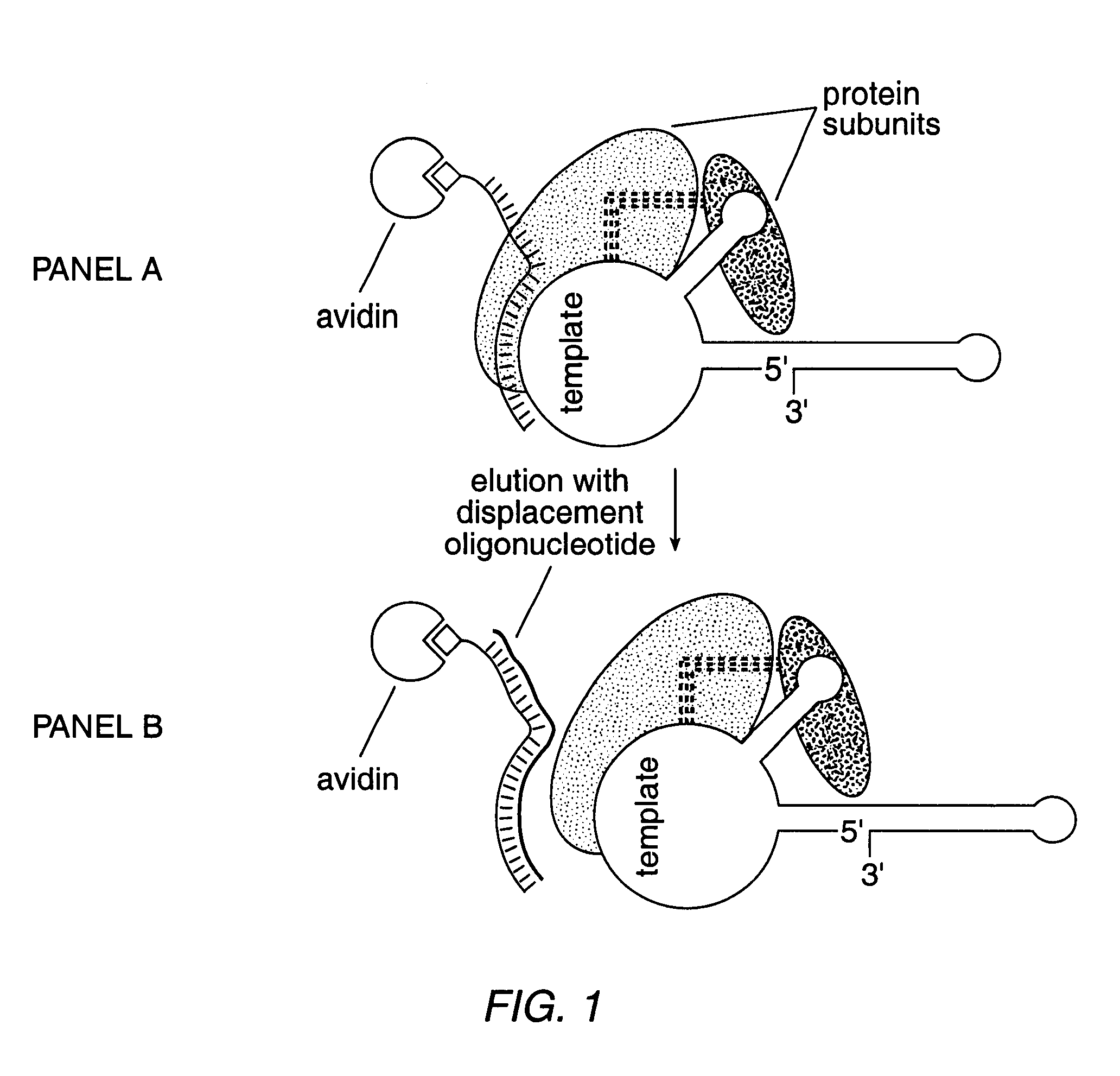
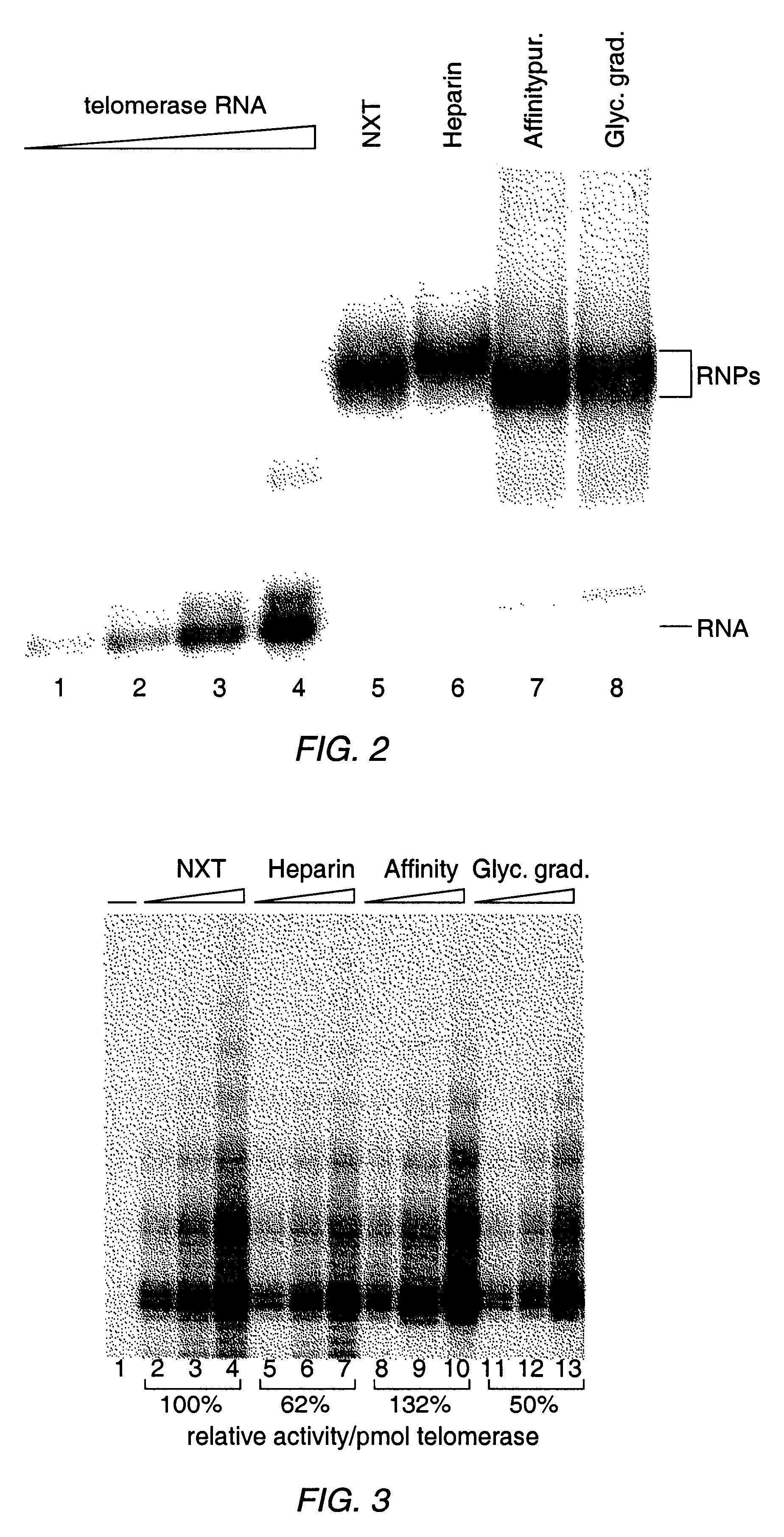
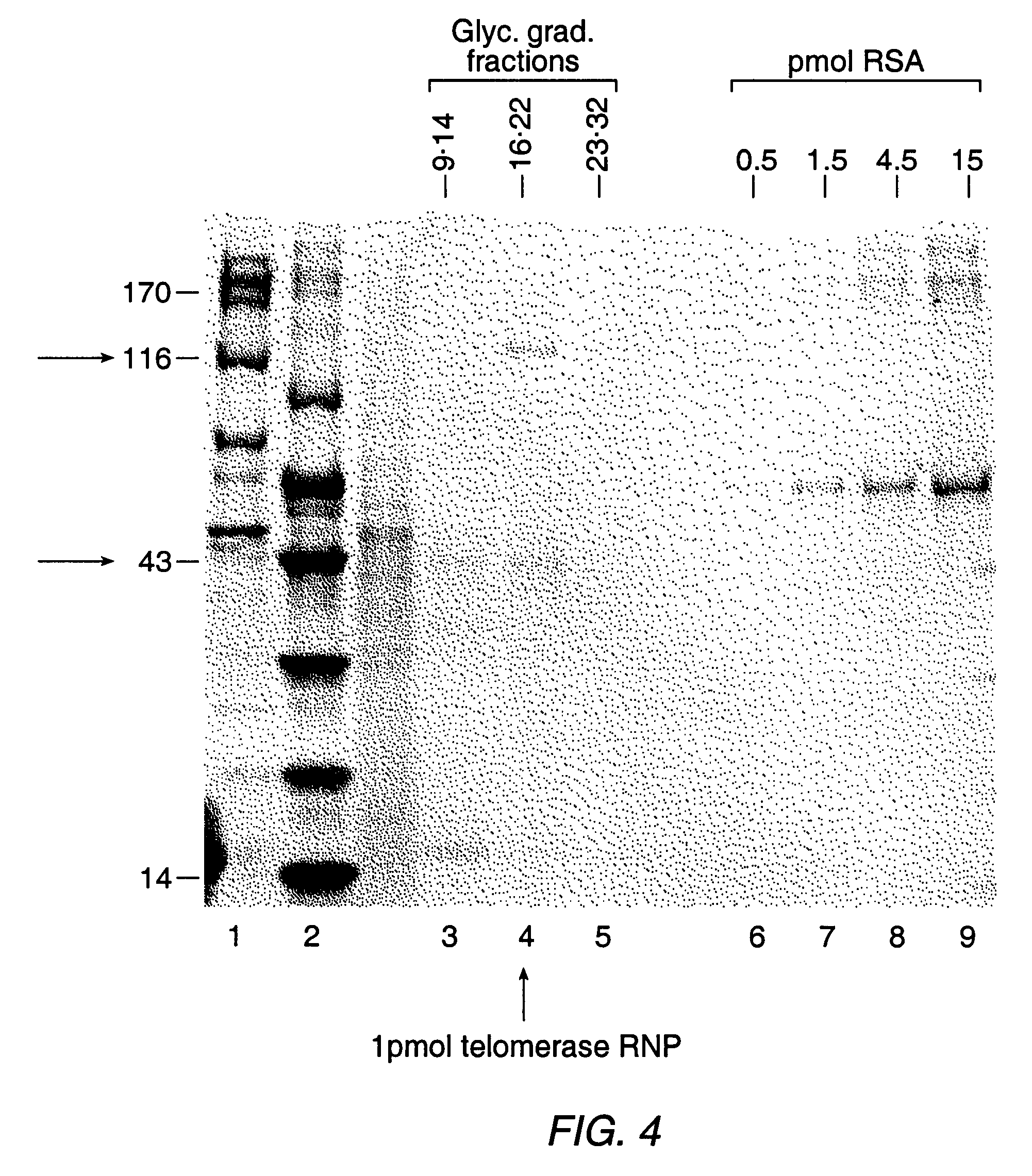
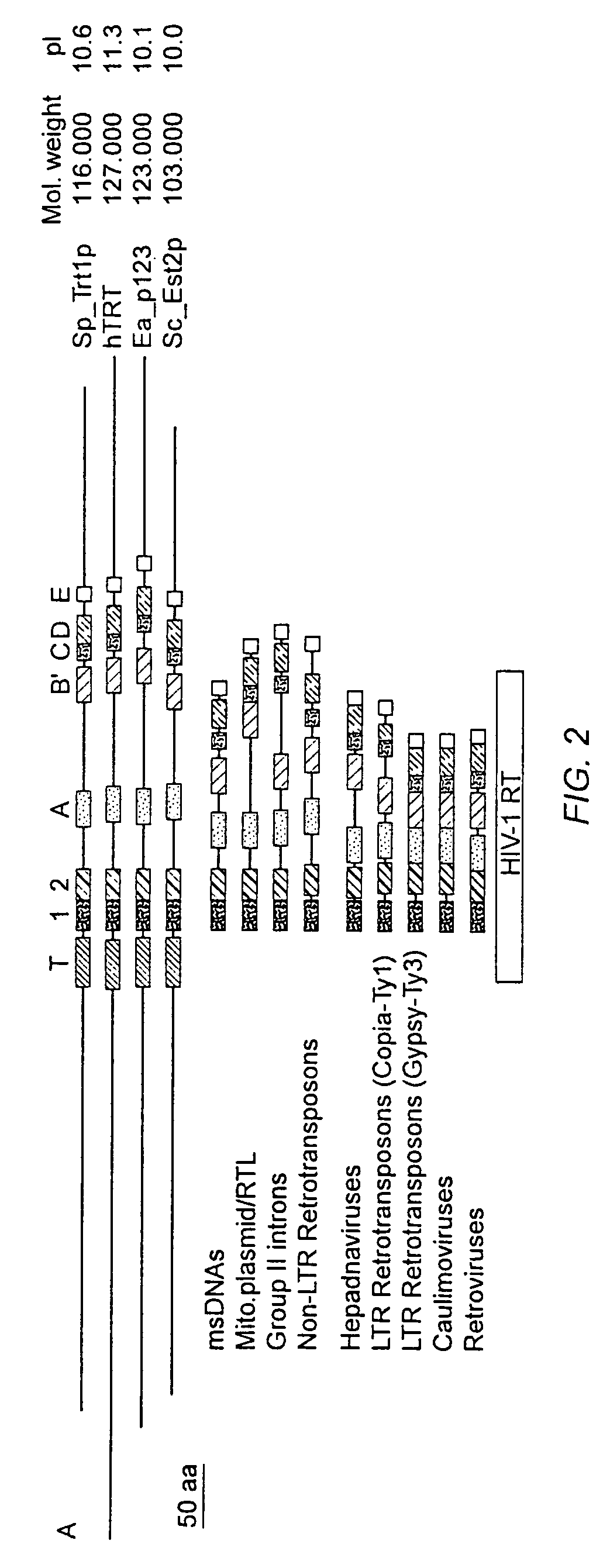
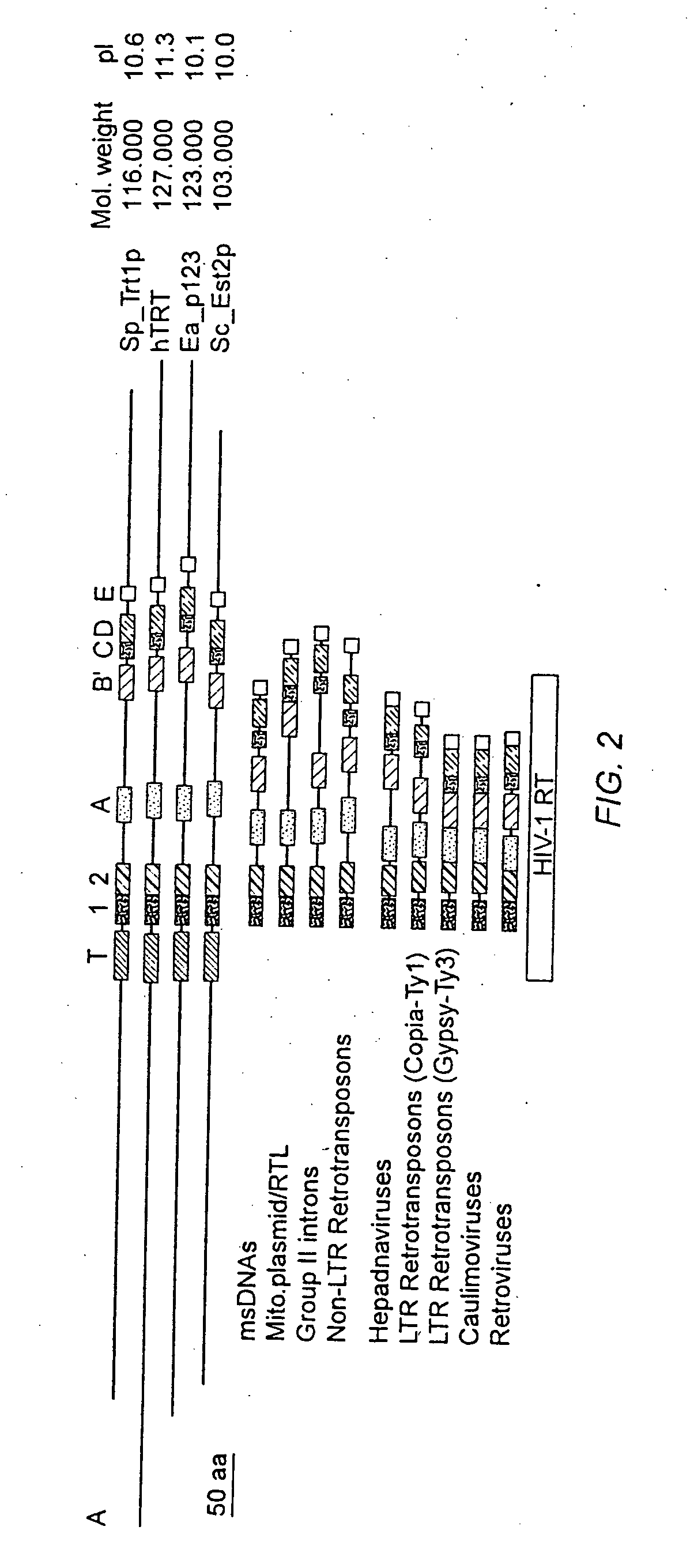
The present invention is directed to telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
Telomerase
InactiveUS6093809AImprove purification effectAvoid the needSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
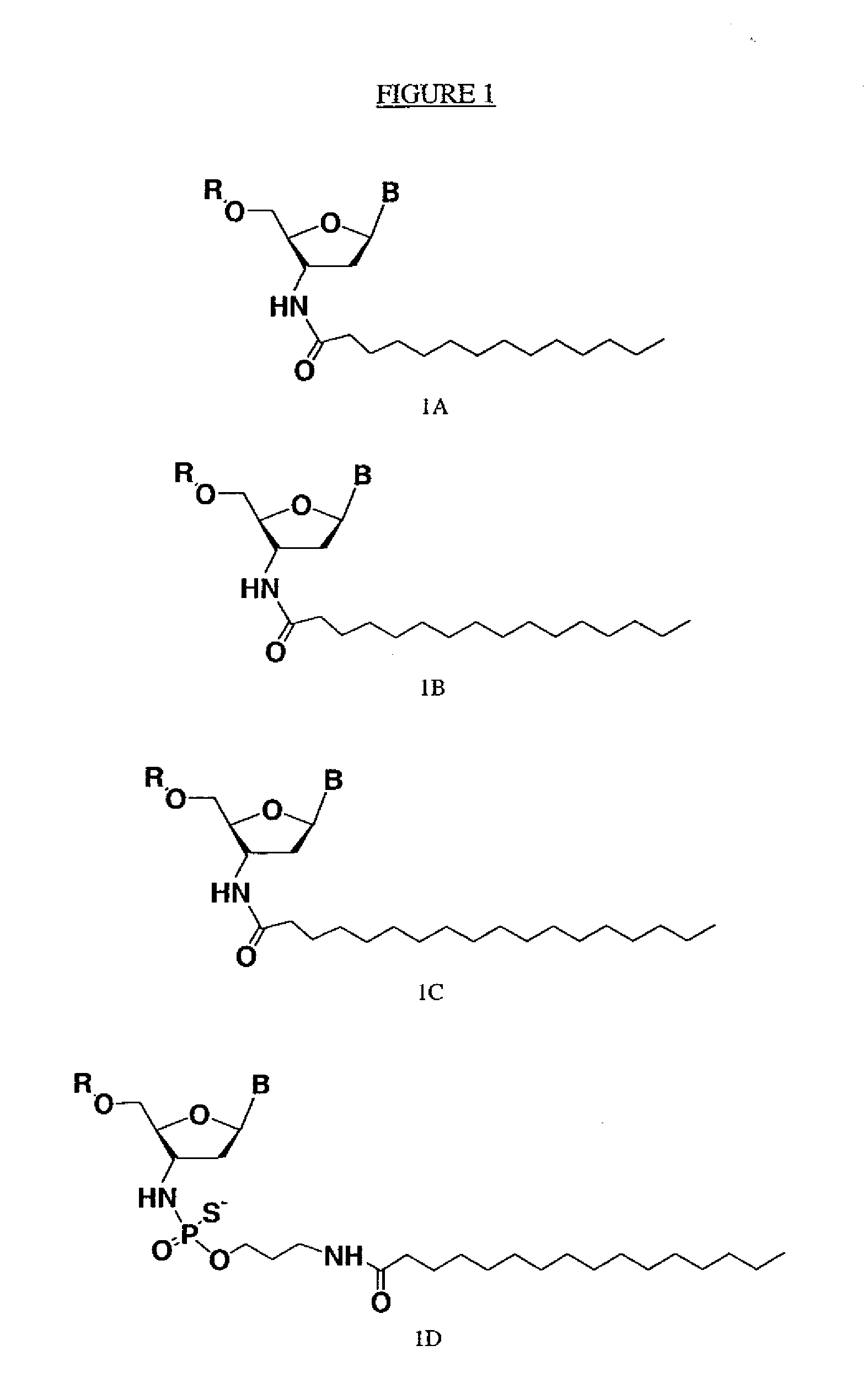
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
ActiveUS20050113325A1Superior cellular uptake propertyReduce Toxicity RiskBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTelomeraseLipid moiety
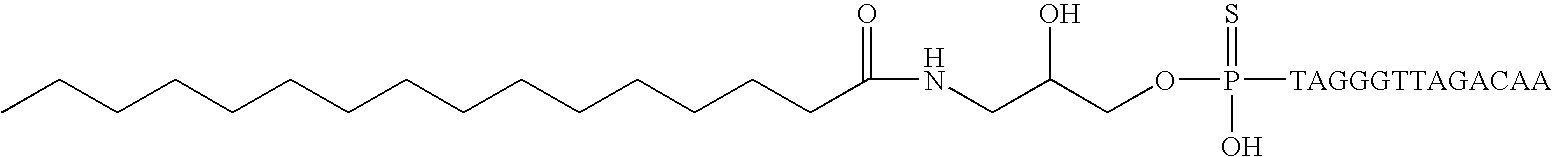
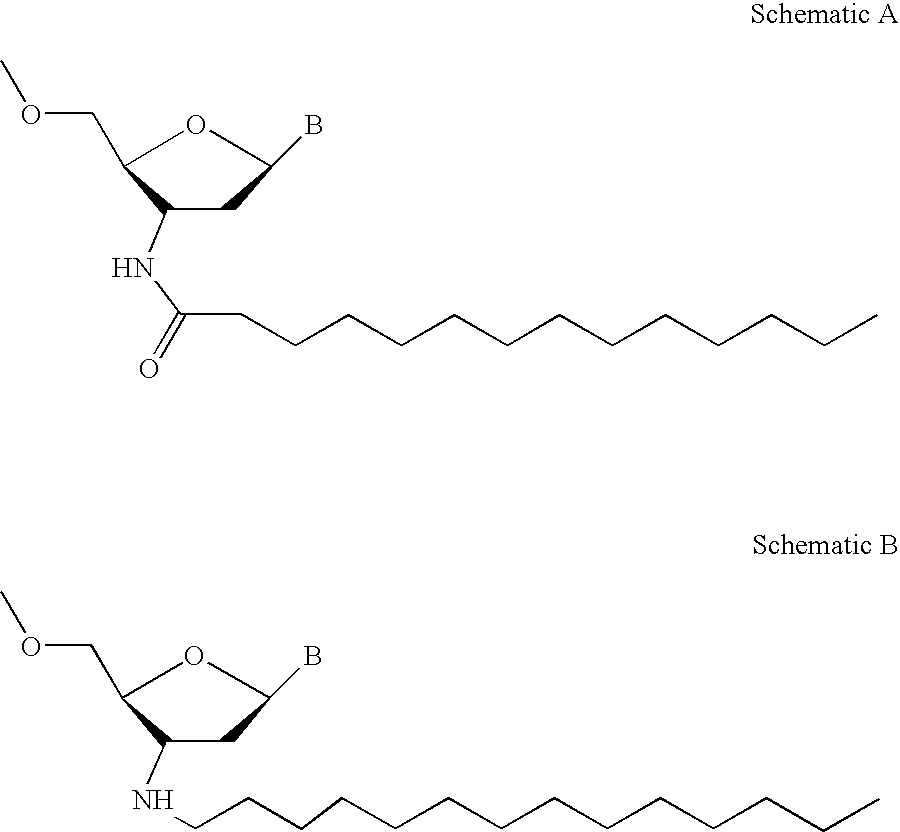
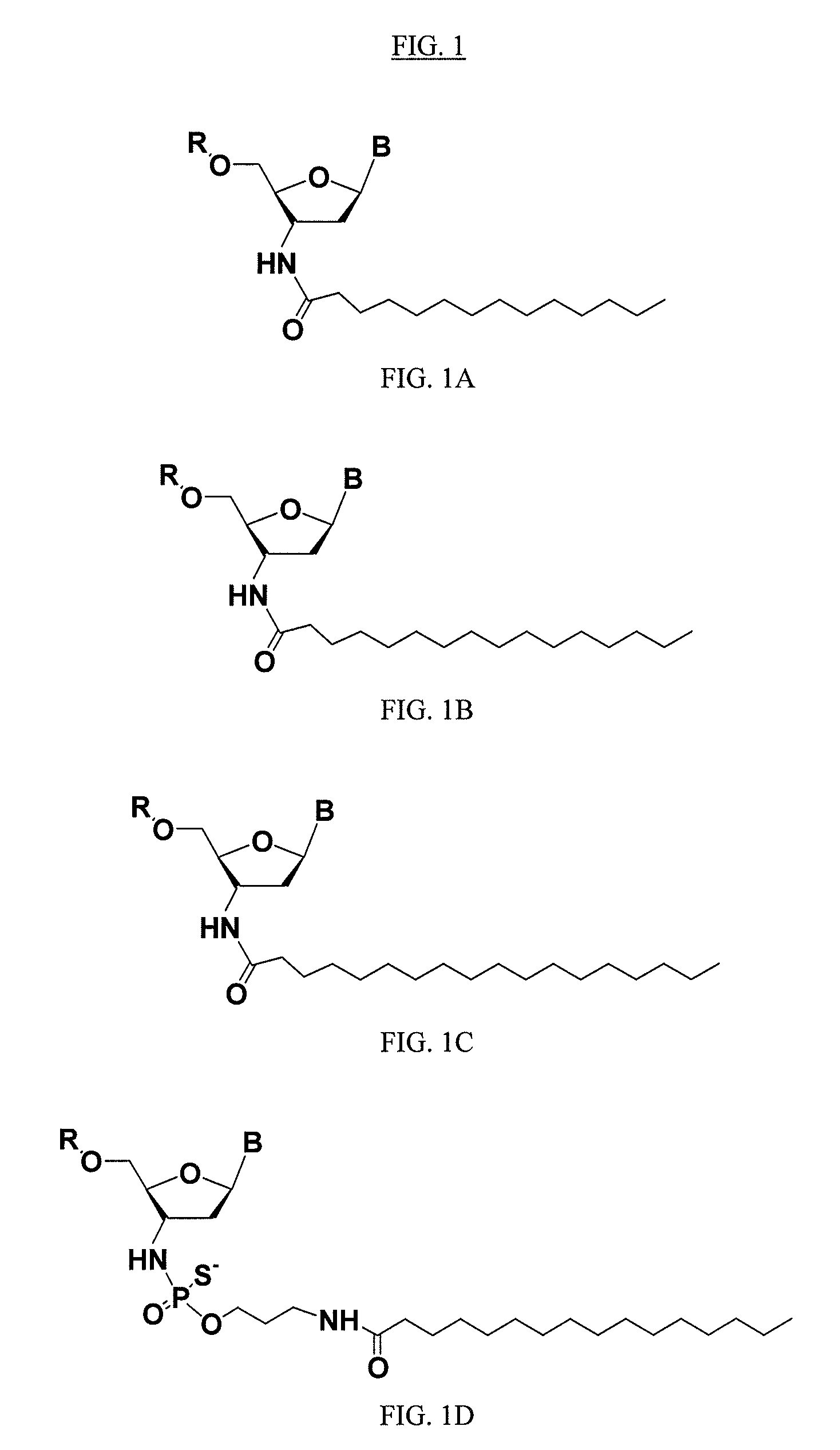
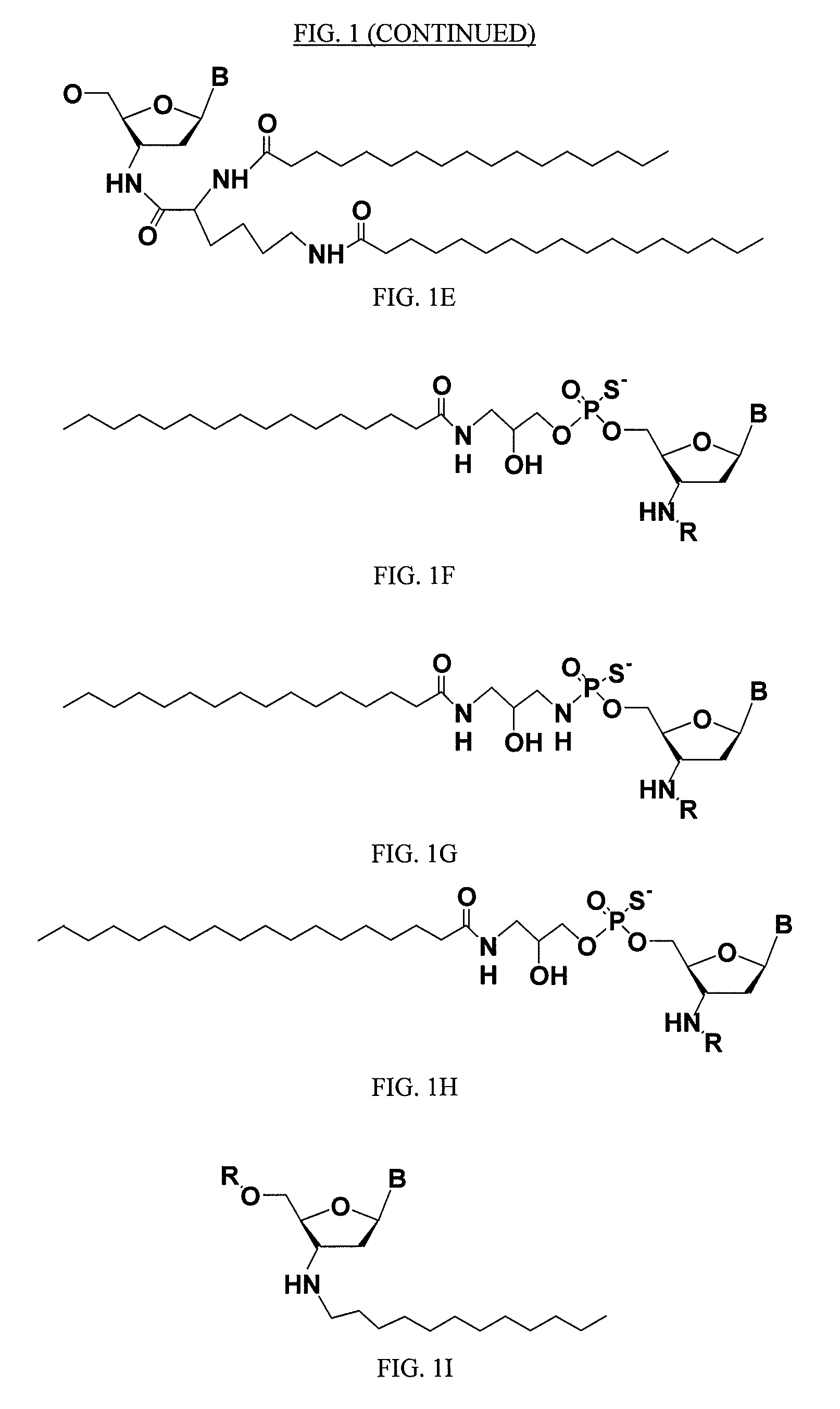
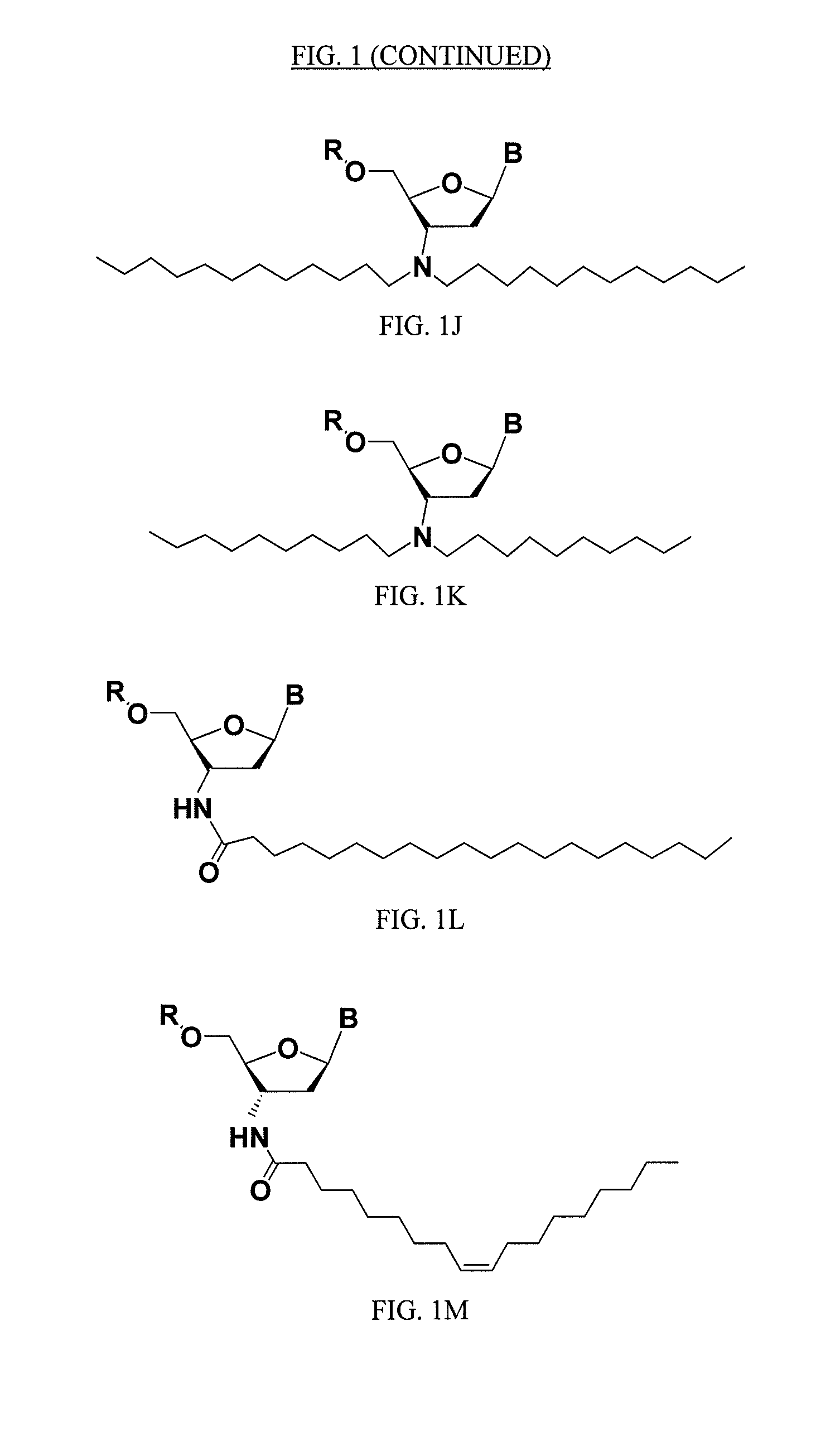
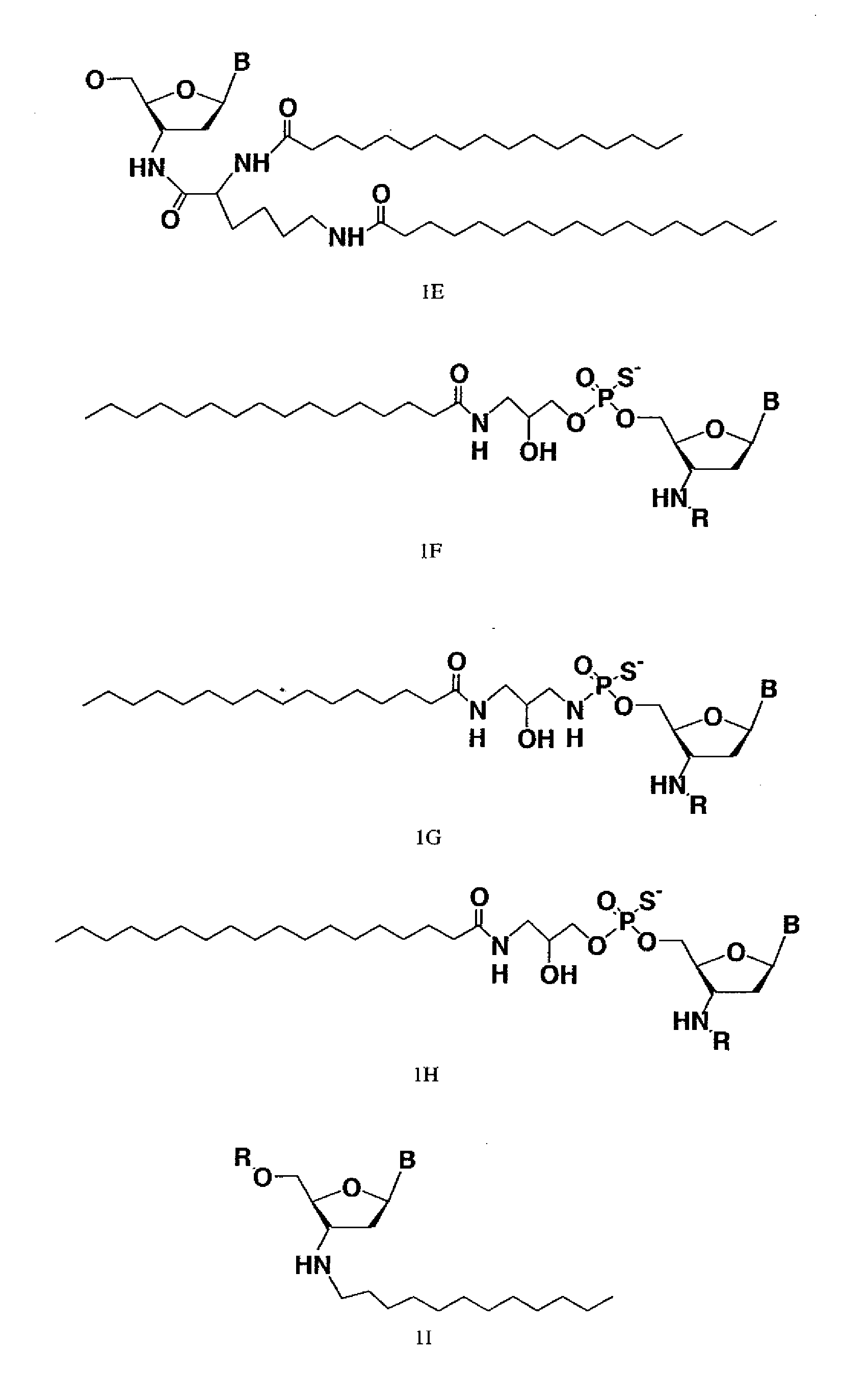
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
ActiveUS7494982B2Inhibit telomeraseMaintain good propertiesBiocideSugar derivativesTelomeraseLipid moiety
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Telomerase
InactiveUS6309867B1Avoid the needEnlarge regionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Nucleic acids encoding human telomerase reverse transcriptase and related homologs
InactiveUS7262288B1Improve proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsFungiBiological bodyReverse transcriptase
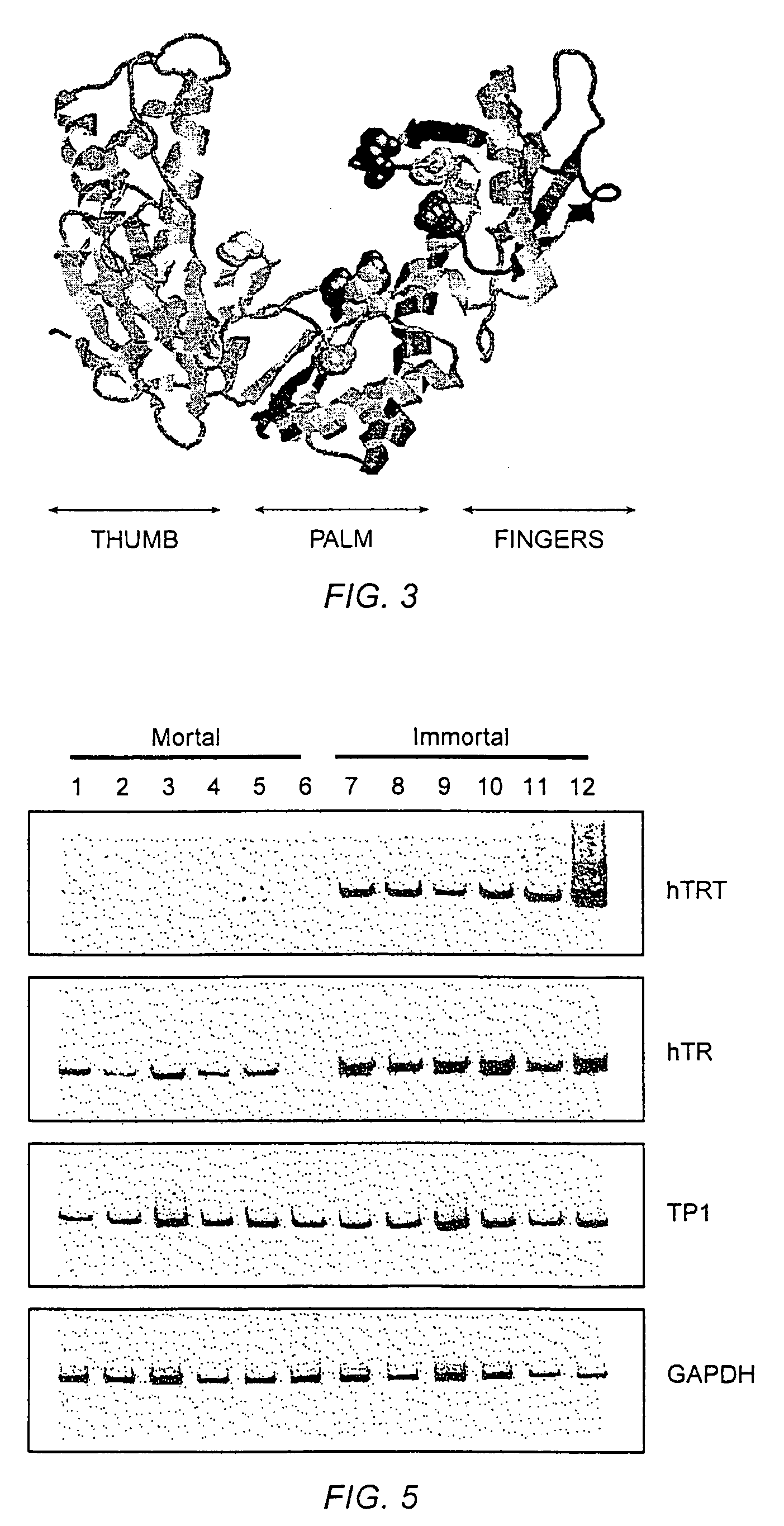
The invention provides compositions and methods related to human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTRT), the catalytic protein subunit of human telomerase. The polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention are useful for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases, for changing the proliferative capacity of cells and organisms, and for identification and screening of compounds and treatments useful for treatment of diseases such as cancers.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Oligonucleotide conjugates
InactiveUS7563618B2Inhibit telomerase enzymatic activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTelomeraseNucleobase
Oligonucleotide conjugates, where an oligonucleotide is covalently attached to an aromatic system, are provided. In particular embodiments the oligonucleotide is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase and is covalently attached to a nucleobase via an optional linker. The conjugates inhibit telomerase enzyme activity.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Nuclear telomerase reverse transcriptase variant
InactiveUS20100003229A1Reverse grayingExtend your lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsReverse transcriptaseWild type
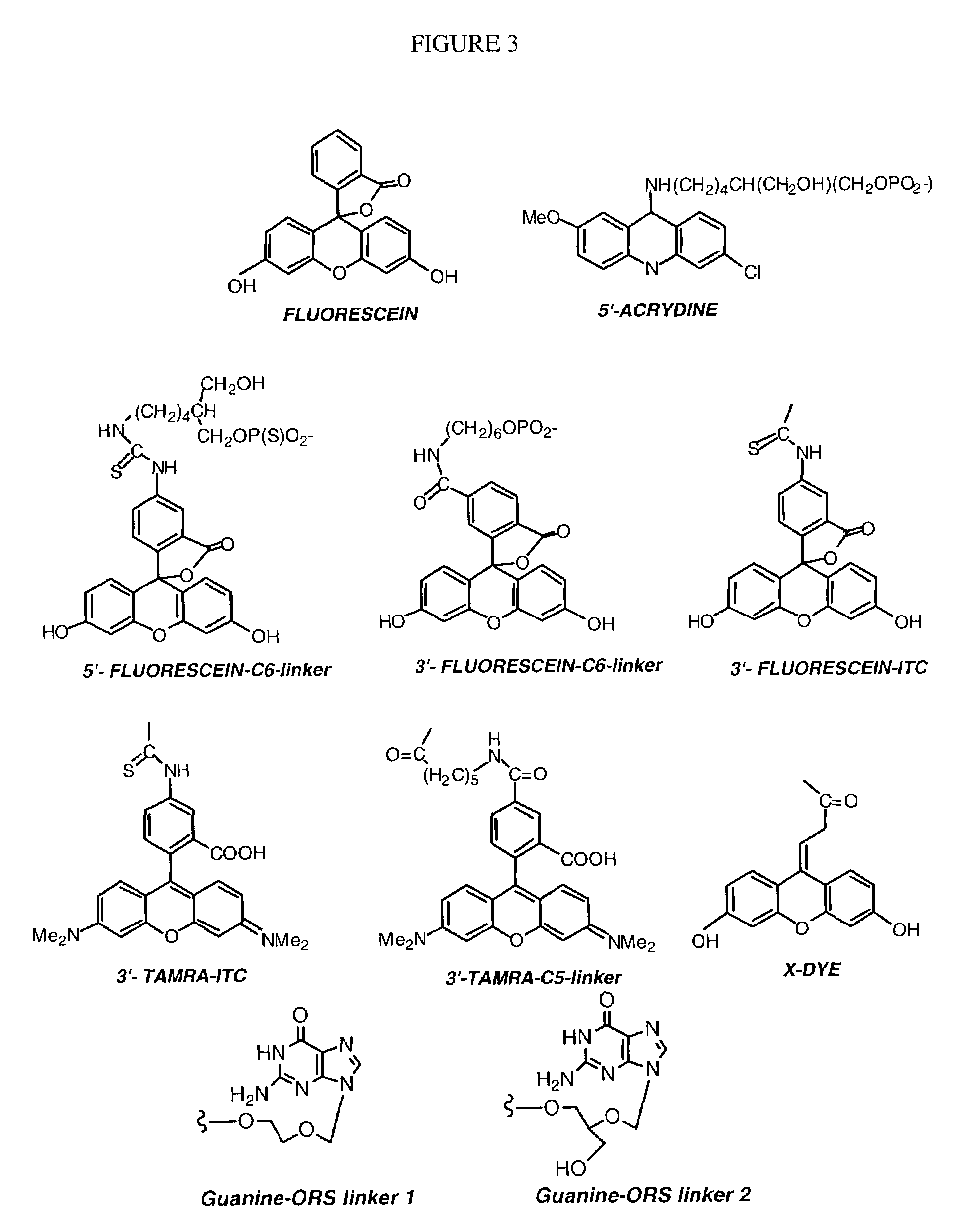
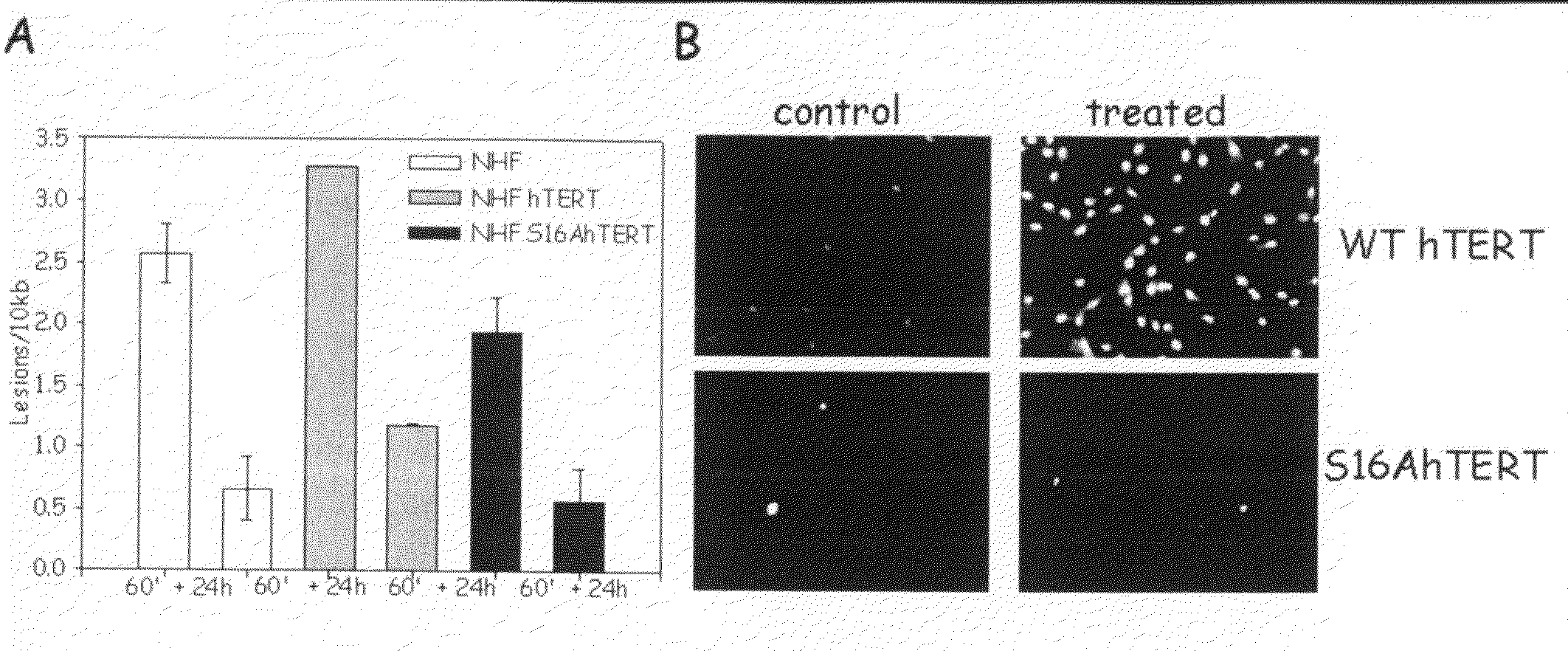
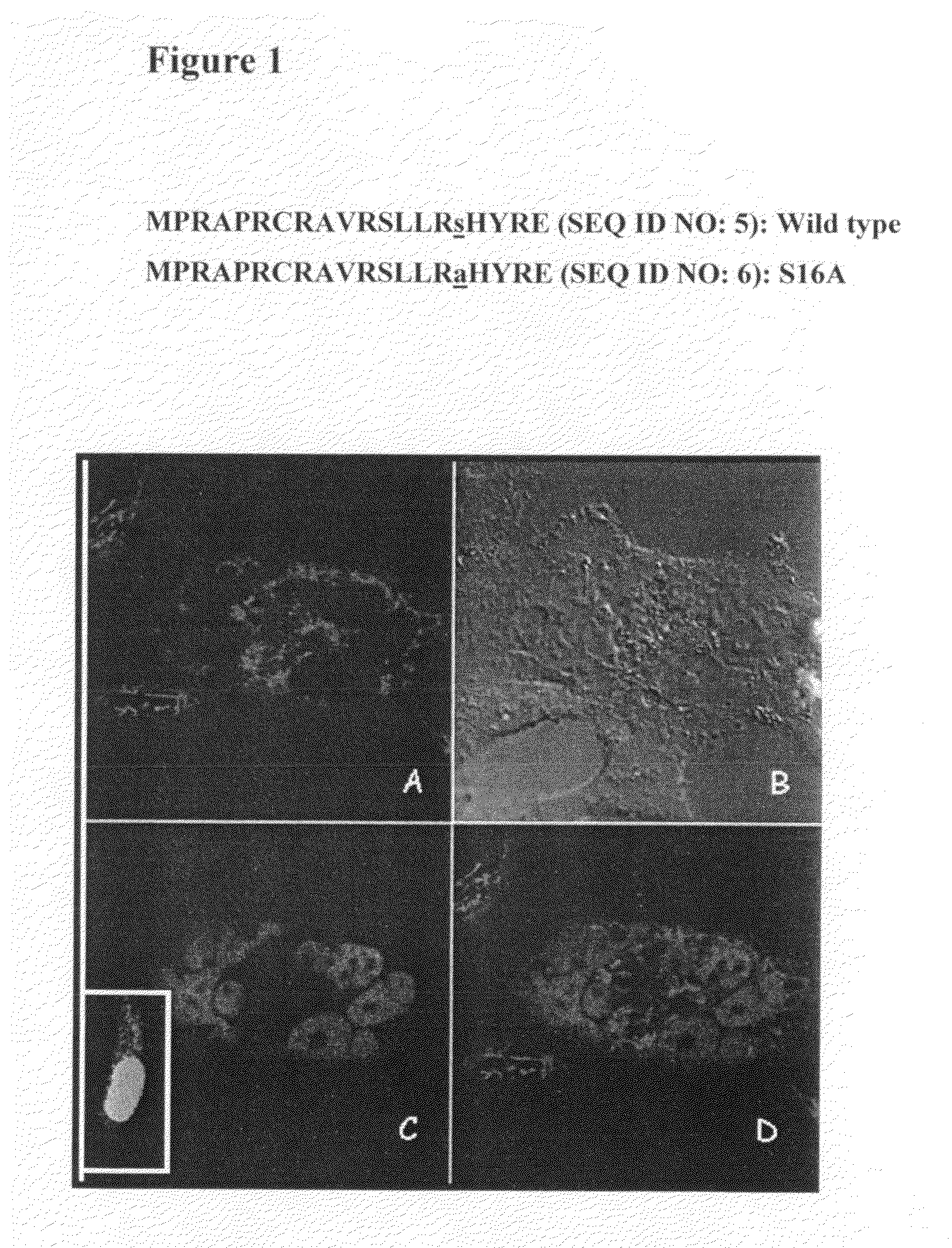
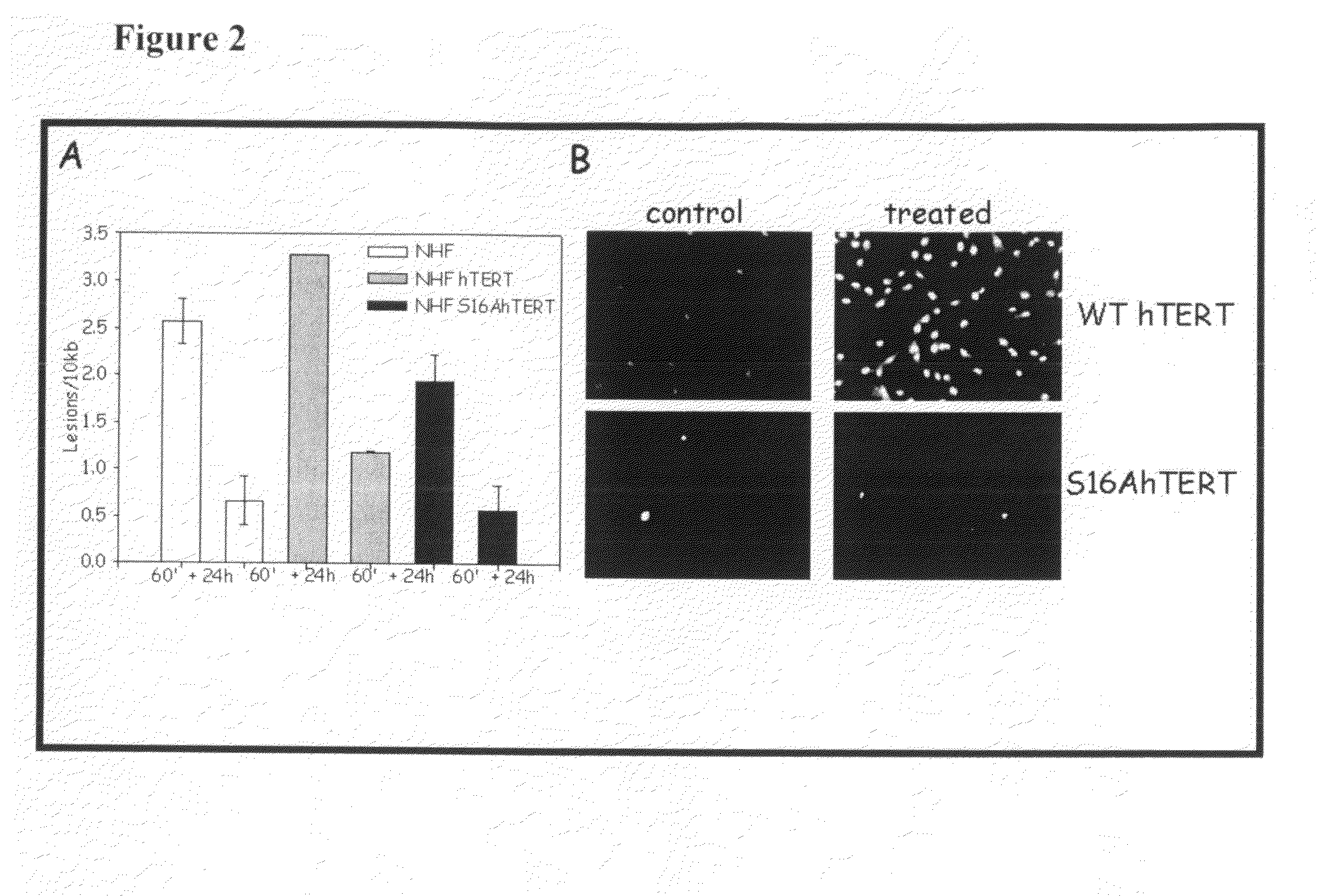
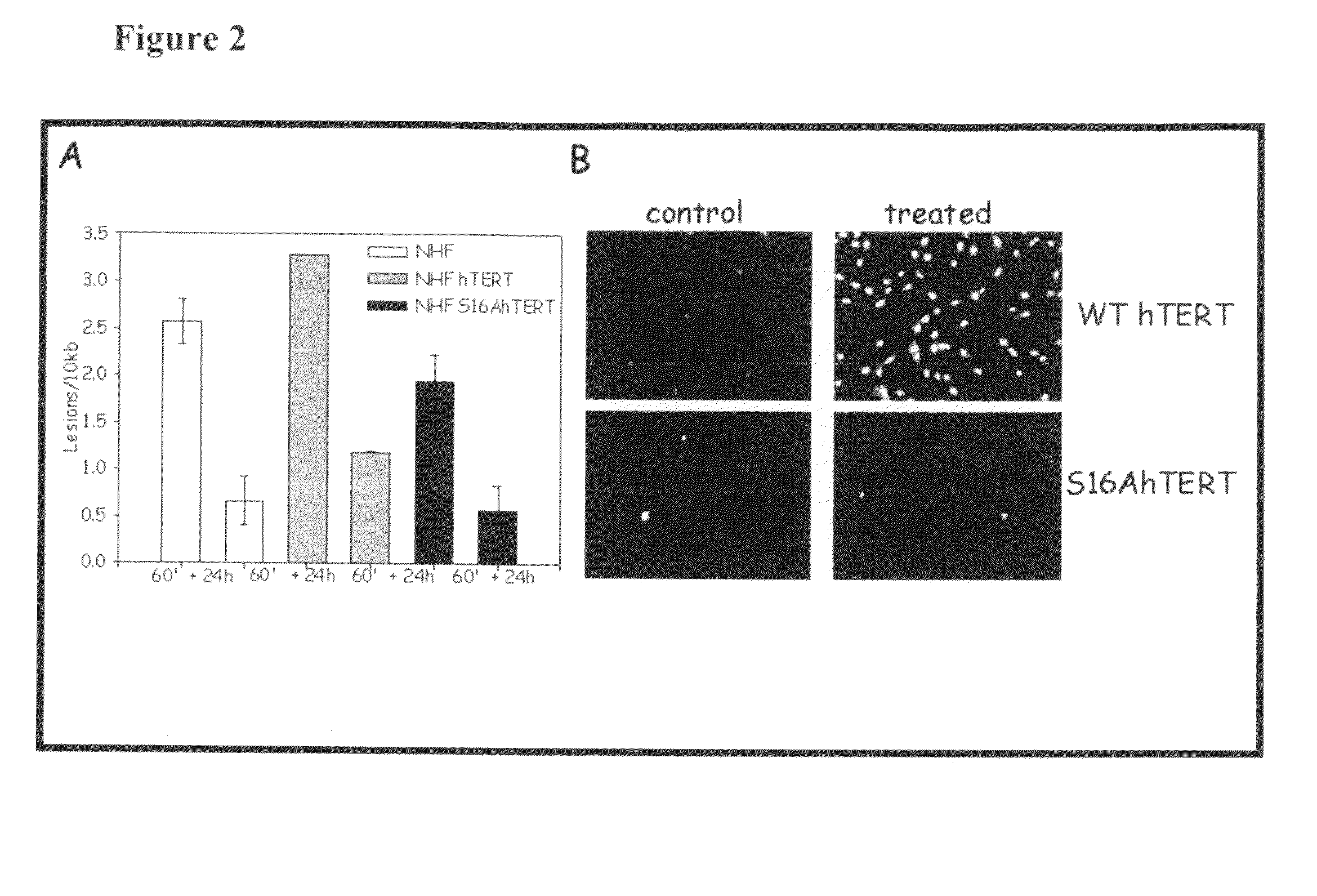
The present invention is directed to a novel variant of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (S16AhTERT), which displays properties distinct from those of wildtype telomerase reverse transcriptase. Accordingly, the amino acid sequence of S16AhTERT and nucleic acid sequences encoding same are presented herein, as are methods of use thereof.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Human telomerase catalytic subunit
InactiveUS20060040307A1Improve proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsFungiTelomerase Catalytic SubunitBiological body
The invention provides compositions and methods related to human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTRT), the catalytic protein subunit of human telomerase. The polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention are useful for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases, for changing the proliferative capacity of cells and organisms, and for identification and screening of compounds and treatments useful for treatment of diseases such as cancers.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Human telomerase RNA elements
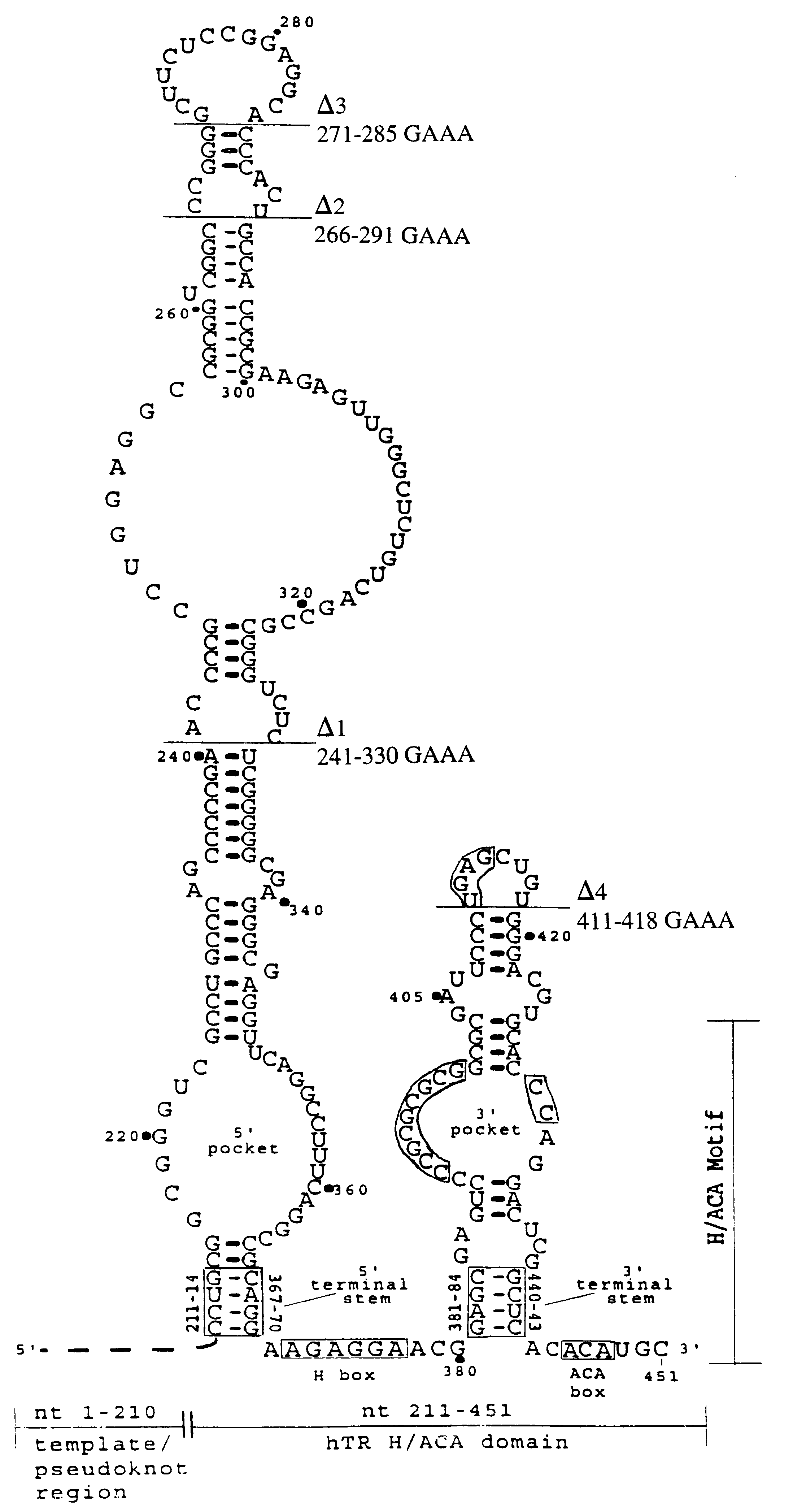
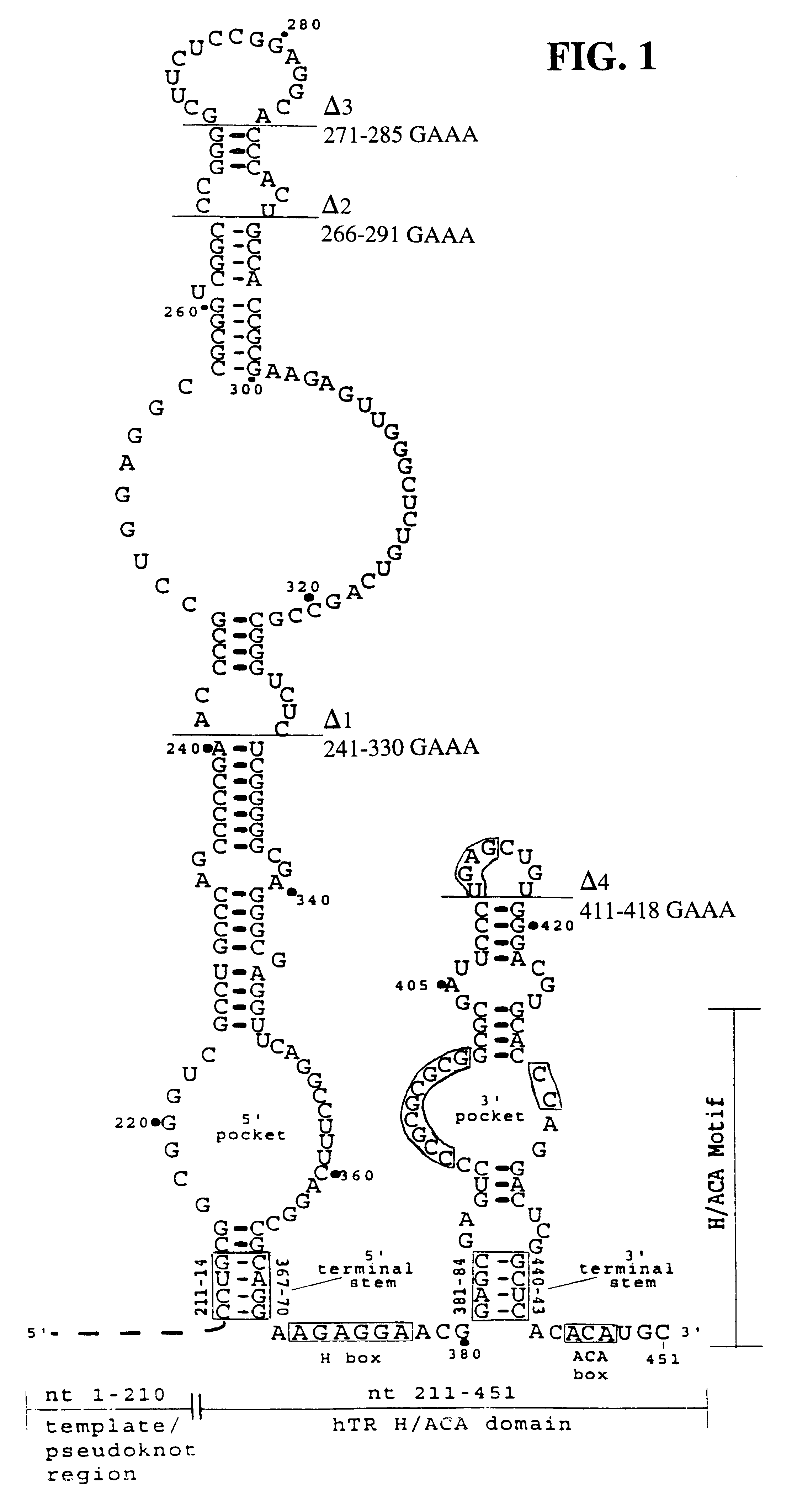
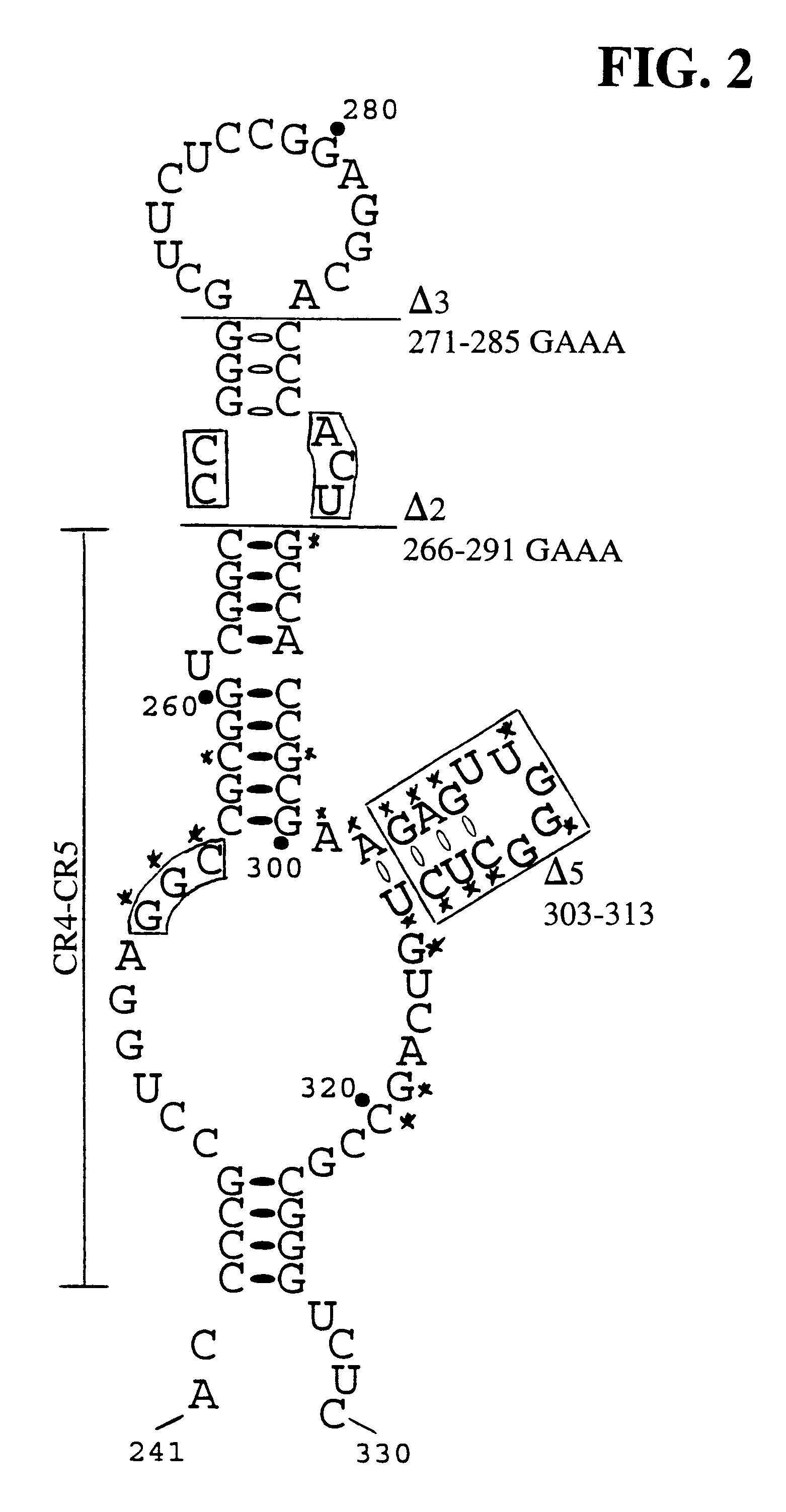
The invention provides methods and compositions relating to discrete elements of human telomerase and human telomerase RNA. In one embodiment, the invention provides a polynucleotide comprising only one element of human telomerase RNA, wherein the element consists of SEQ ID NO:1, residues 241-330. Such human telomerase RNA elements may be employed in mixtures with a human telomerase polypeptide such as TERT or dyskerin, wherein the polypeptide and polynucleotide specifically interact, and such mixtures may be employed in methods for identifying modulators of a human telomerase polypeptide-human telomerase RNA interaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Telomelysin/GFP-expressing recombinant virus
ActiveUS20060067890A1High sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVirusesTelomeraseCancer cell
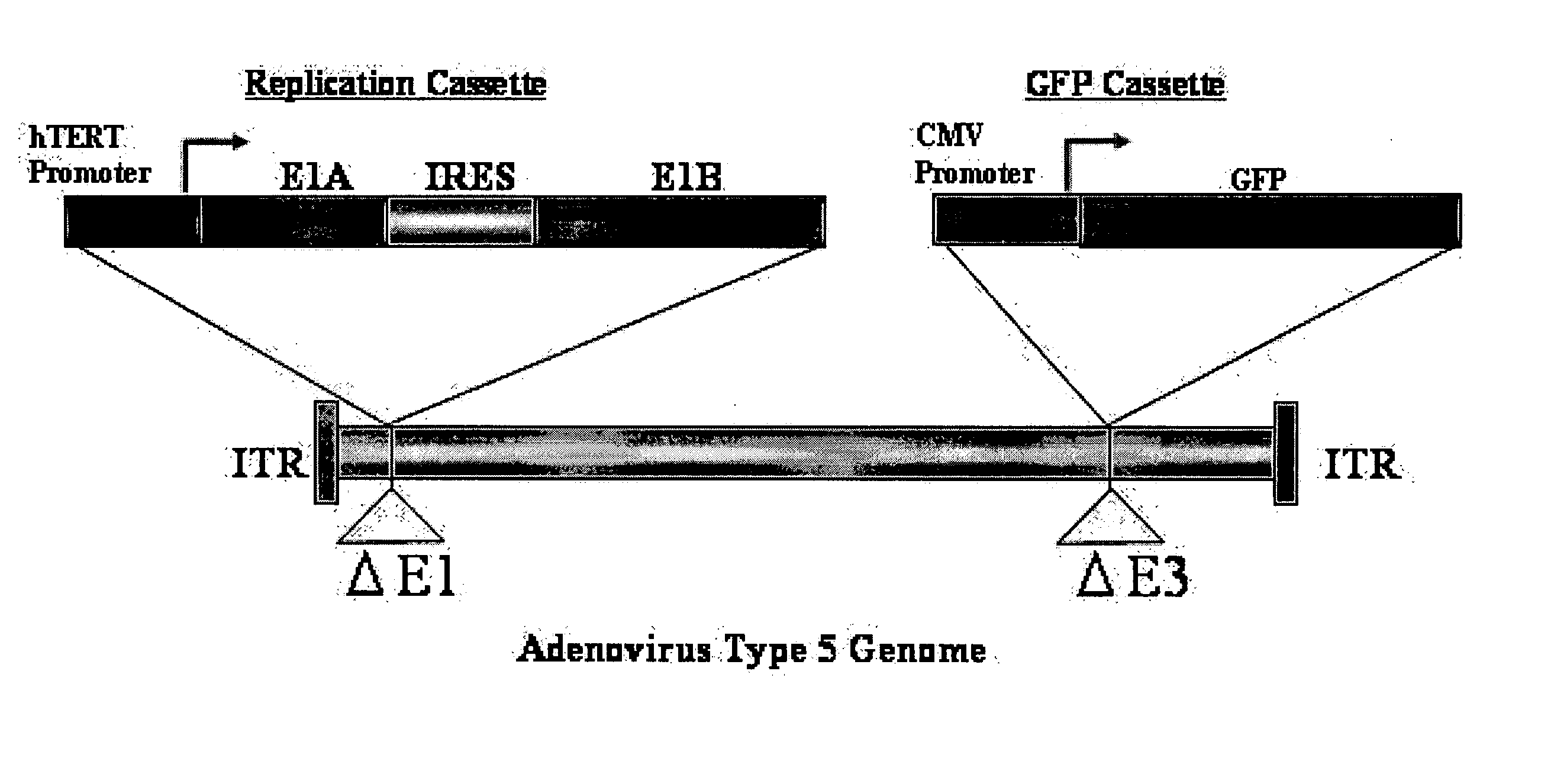
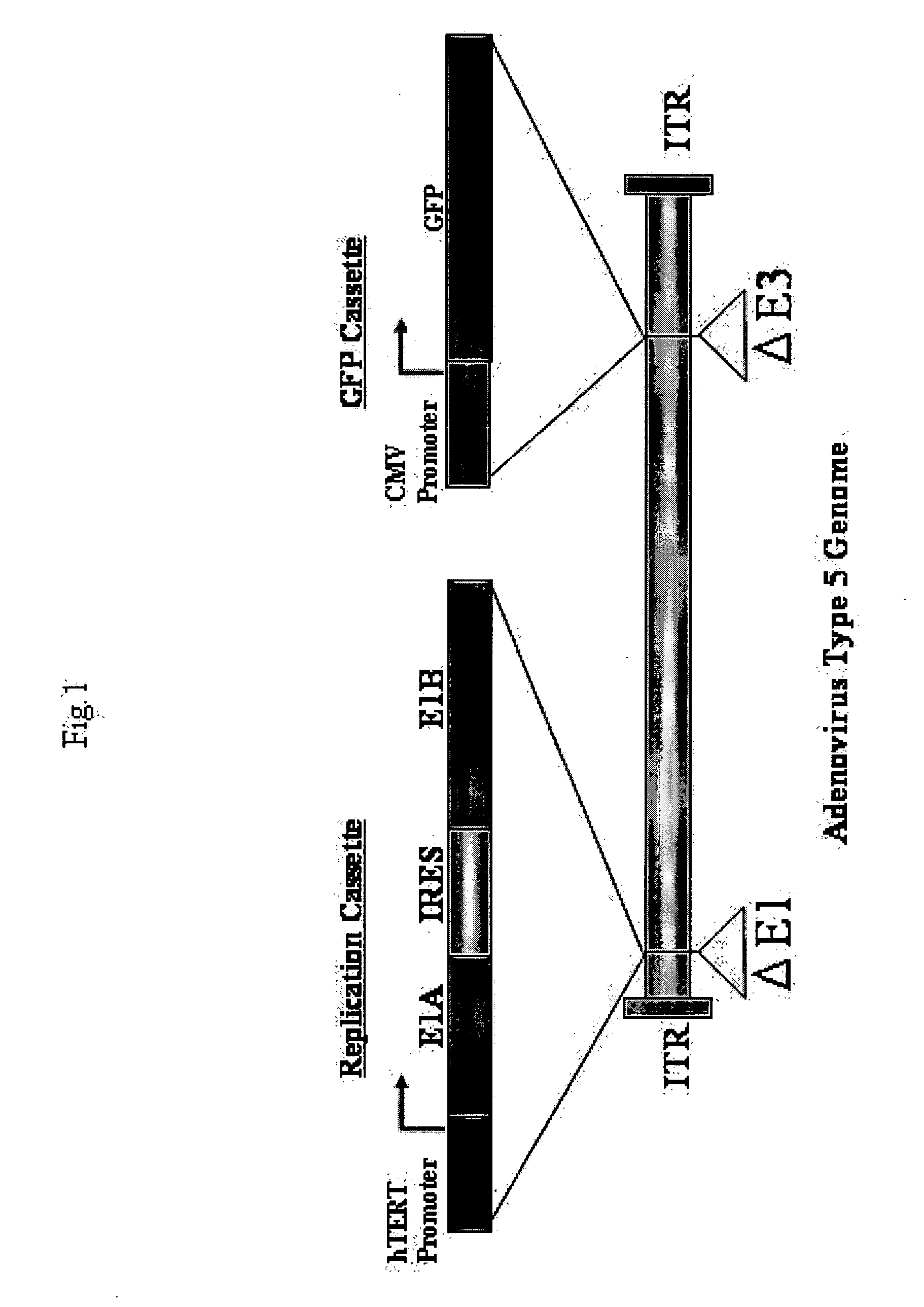
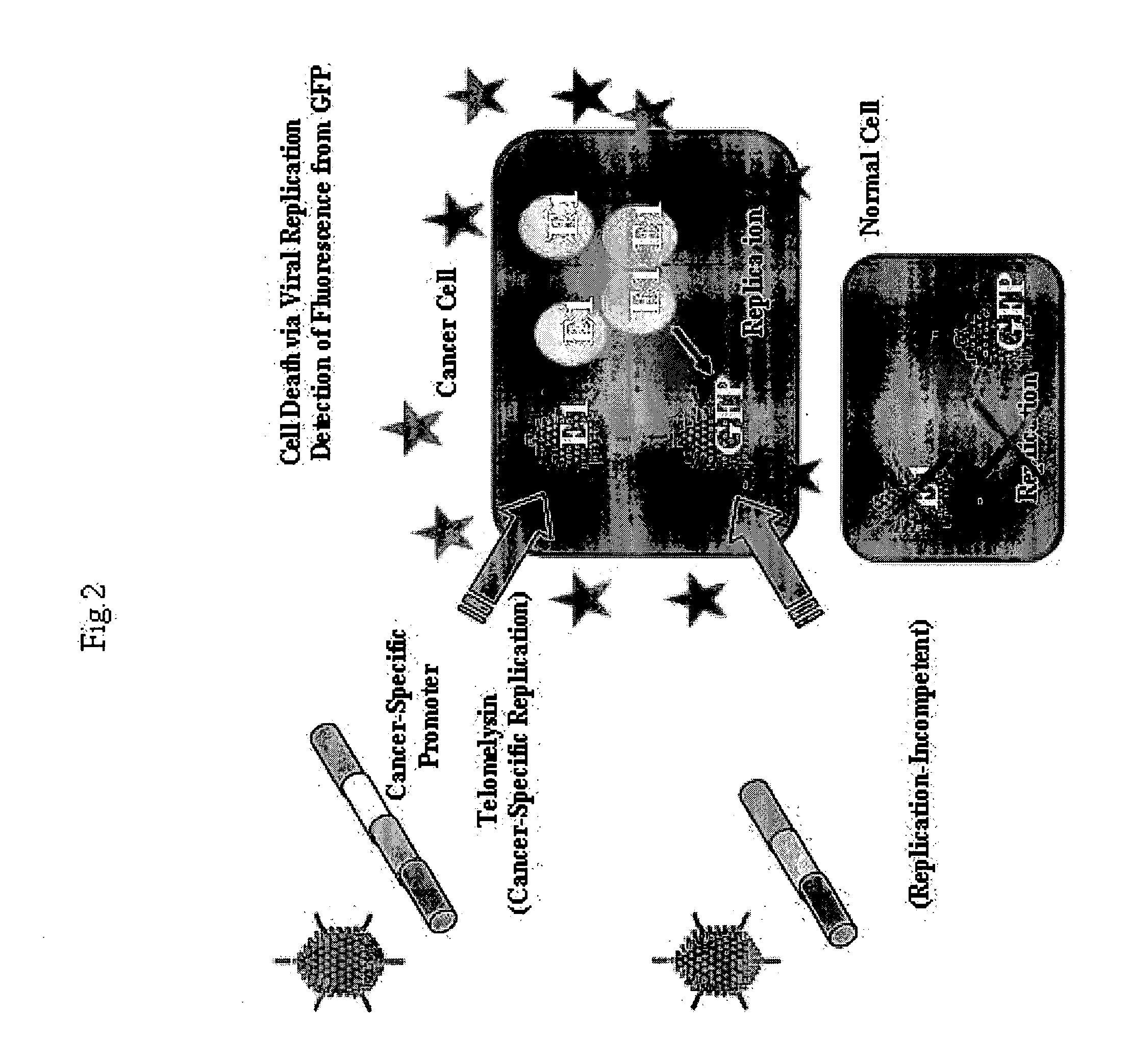
The present invention provides a reagent for cancer cell detection or cancer diagnosis. The present invention relates to a reagent for cancer cell detection, comprising a recombinant virus where a replication cassette comprising a promoter from human telomerase, an E1A gene, an IRES sequence and an E1B gene in this order is integrated in E1 region of the viral genome and a labeling cassette comprising a gene encoding a labeling protein and a promoter capable of regulating the expression of the gene encoding the labeling protein is integrated in E3 region of the viral genome.
Owner:ONCOLYS BIOPHARMA
Modified oligonucleotides for telomerase inhibition
InactiveUS20120329858A1Superior cellular uptake propertyReduce Toxicity RiskOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseLipid moiety
Compounds comprising an oligonucleotide moiety covalently linked to a lipid moiety are disclosed. The oligonucleotide moiety comprises a sequence that is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase. The compounds inhibit telomerase activity in cells with a high potency and have superior cellular uptake characteristics.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
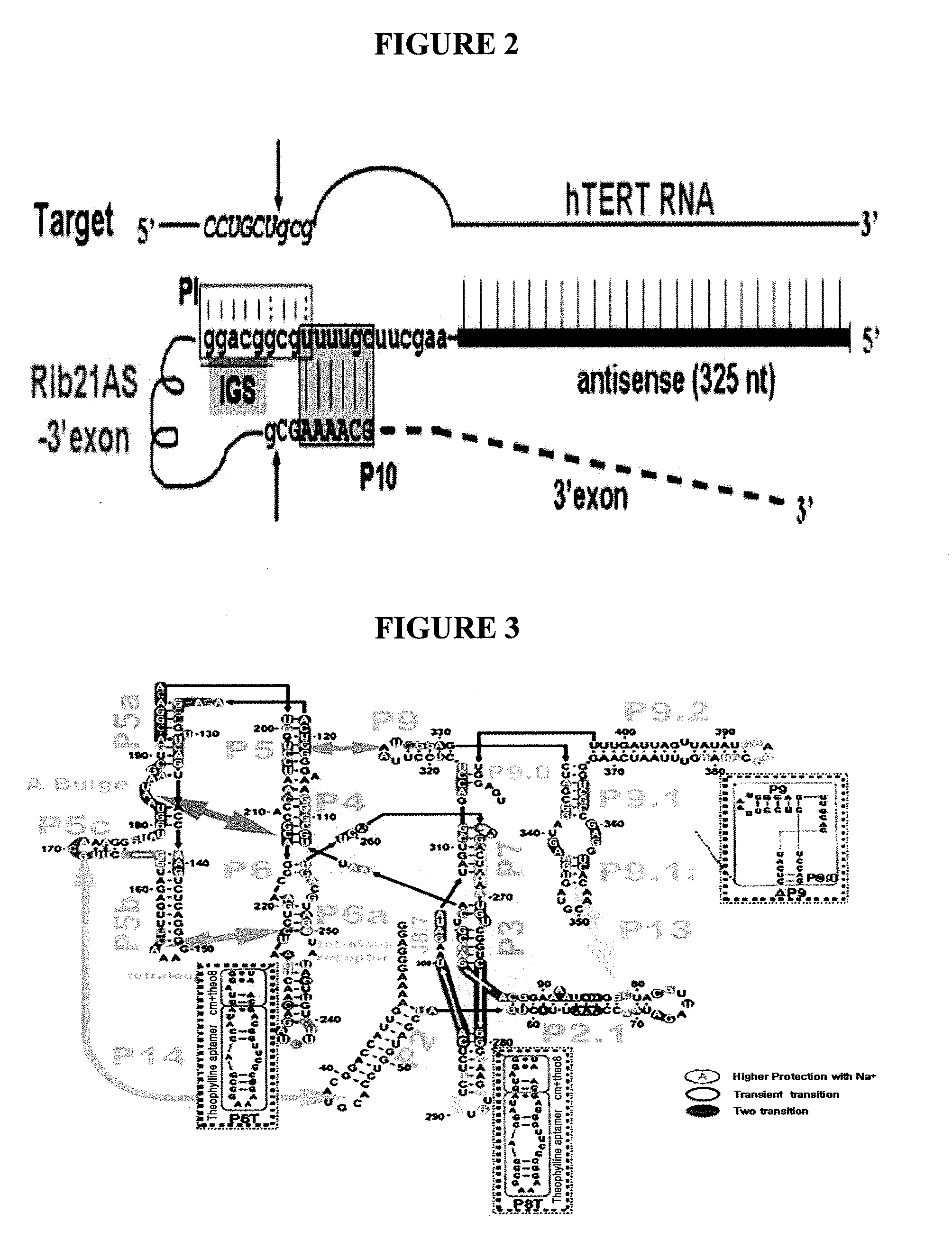
Allosteric trans-splicing group i ribozyme whose activity of target-specific RNA replacement is controlled by theophylline
InactiveUS20110003883A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellReverse transcriptase
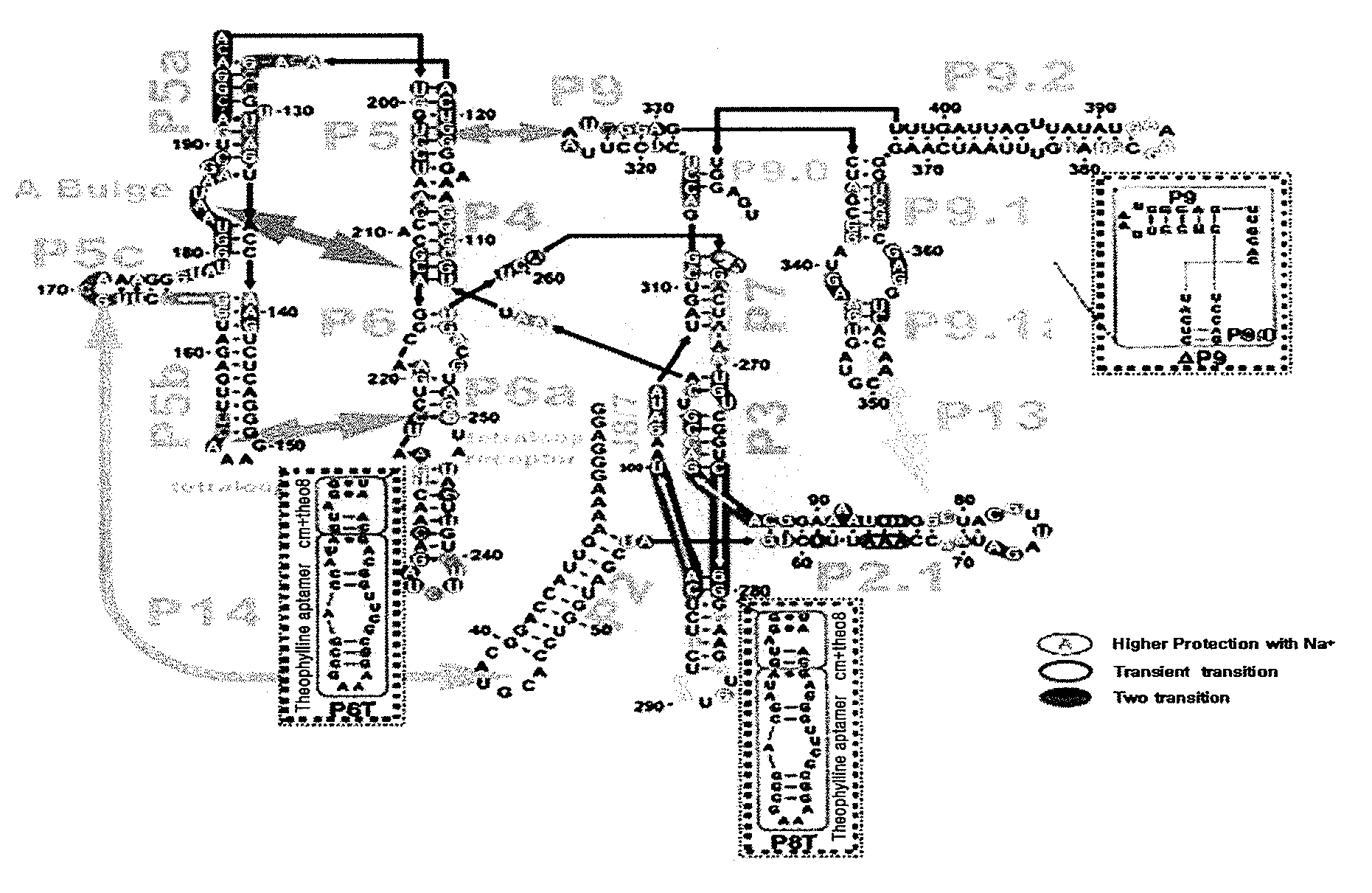
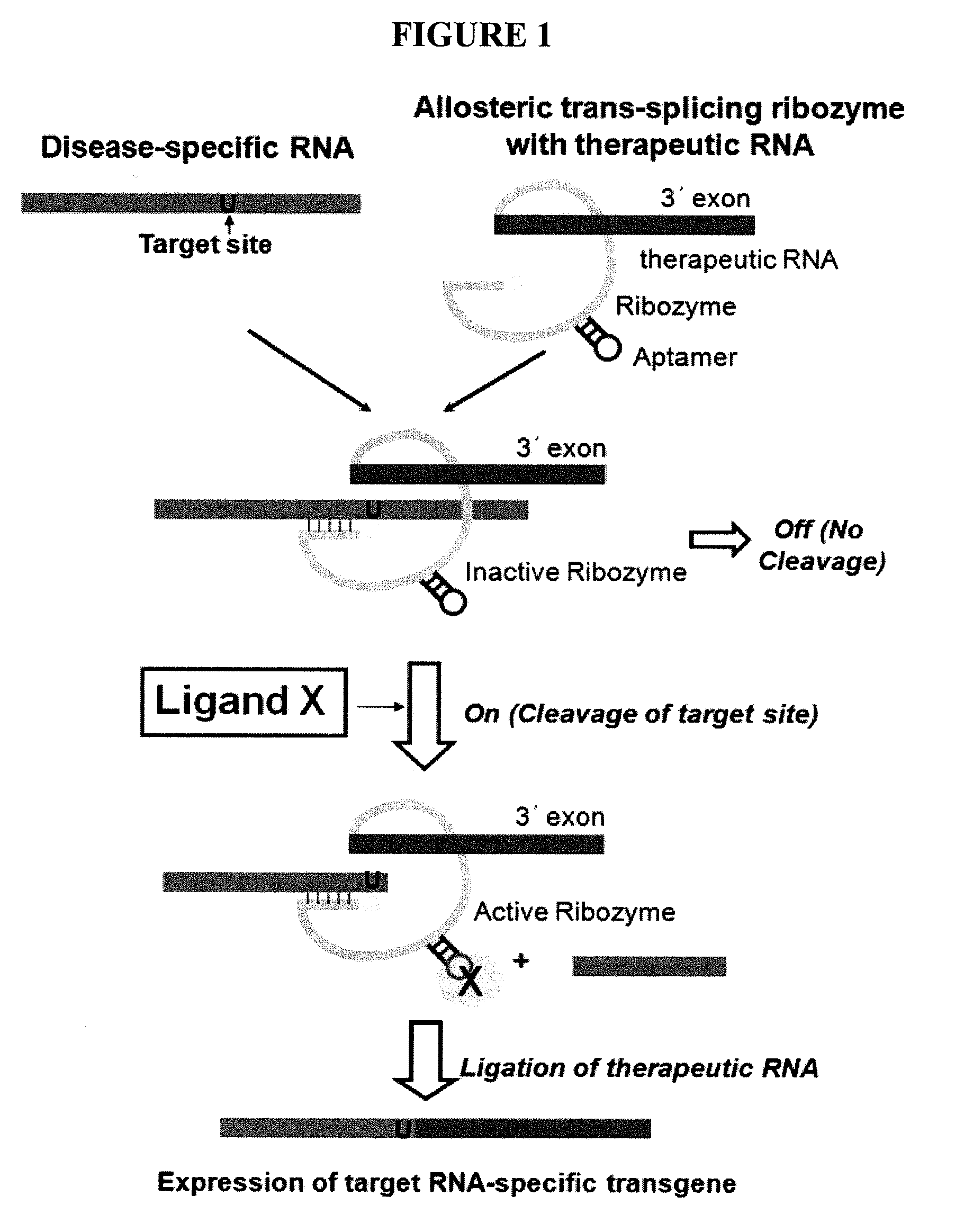
Provided is an allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme whose target-specific RNA replacement activity is controlled by theophylline, wherein the hTERT-targeting trans-splicing ribozyme recognizes mRNA of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) as a cancer-specific RNA transcript to bind a theophylline aptamer to an hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme via a communication module, the hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme having a verified trans-splicing ability. The allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme may be useful to selectively diagnose only cancer cells that express target hTERT RNA, or induce their apoptosis since the activity of the allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme is dependently controlled by theophylline to correct target hTERT RNA by the trans-splicing reaction.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND DANKOOK UNIV
Telomerase delivery by biodegradable Nanoparticle
InactiveUS20090142408A1Effectively crossControl releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAge related diseaseHydrophilic polymers
A therapeutic compound consisting of human telomerase, its catalytic subunit hTert, or a known variant of either, and a biodegradable nanoparticle carrier, which can be administered to cells in a cell culture or in a living animal, is provided herein. The therapeutic compound is envisioned as a method for treating a wide variety of age-related diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, aplastic anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, arteriosclerosis, macular degeneration, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's, diabetes type 2, and any disease that correlates with telomere shortening and may be corrected or ameliorated by lengthening telomeres. The therapeutic compound is also envisioned as method for potentially treating more generic problems of human aging. The nanoparticle carrier is comprised of certain biodegradable biocompatible polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide), poly(lactic acid), poly(alkylene glycol), polybutylcyanoacrylate, poly(methylmethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid), poly-allylamine, polyanhydride, polyhydroxybutyric acid, polycaprolactone, lactide-caprolactone copolymers, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyalkylcyanoacrylates, polyanhydrides, polyorthoester or a combination thereof. The nanoparticle may incorporate a targeting moiety to direct the nanoparticle to a particular tissue type or a location within a cell. The nanoparticle may incorporate a plasticizer to facilitate sustained release of telomerase such as L-tartaric acid dimethyl ester, triethyl citrate, or glyceryl triacetate. A nanoparticle of the present invention can further contain a polymer that affects the charge or lipophilicity or hydrophilicity of the particle. Any biocompatible hydrophilic polymer can be used for this purpose, including but not limited to, poly(vinyl alcohol).
Owner:SARAD MATTHEW
Novel telomerase
InactiveUS20020187471A1Good choiceEarly diagnosisFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Novel telomerase
InactiveUS20030009019A1SpecificallyEfficiently catalyze endonucleolytic cleavageBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTelomeraseRibonucleoprotein complex
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Telomerase inhibitors and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20110257251A1Avoid fluorescence saturationHigh incubation timeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseHuman telomerase
One object of the present invention is to provide methods and compositions for inhibiting human telomerase, by providing inhibitors that bind to the CR4-CR5 or pseudoknot / template domains of the RNA component of human telomerase.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for detecting polynucleotides encoding telomerase
InactiveUS6808880B2Avoid the needEnlarge regionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTelomeraseNucleotide
The present invention is directed to novel telomerase nucleic acids and amino acids. In particular, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding various telomerase protein subunits and motifs, including the 123 kDa and 43 kDa telomerase protein subunits of Euplotes aediculatus, and related sequences from Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomyces sequences, and human telomerase. The present invention is also directed to polypeptides comprising these telomerase protein subunits, as well as functional polypeptides and ribonucleoproteins that contain these subunits.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Telomerase reverse transcriptase fragments and uses thereof
ActiveUS20030225027A1High sensitivityReduce resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesCancer cellReverse transcriptase
The invention provides compositions comprising fragments of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) which can lead to telomere dysfunction in a cell and reduction of growth and tumorigenicity in cancer cells. The invention also relates to uses of the fragments in the treatment of cancer and in drug discovery.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF BIOTECH +1
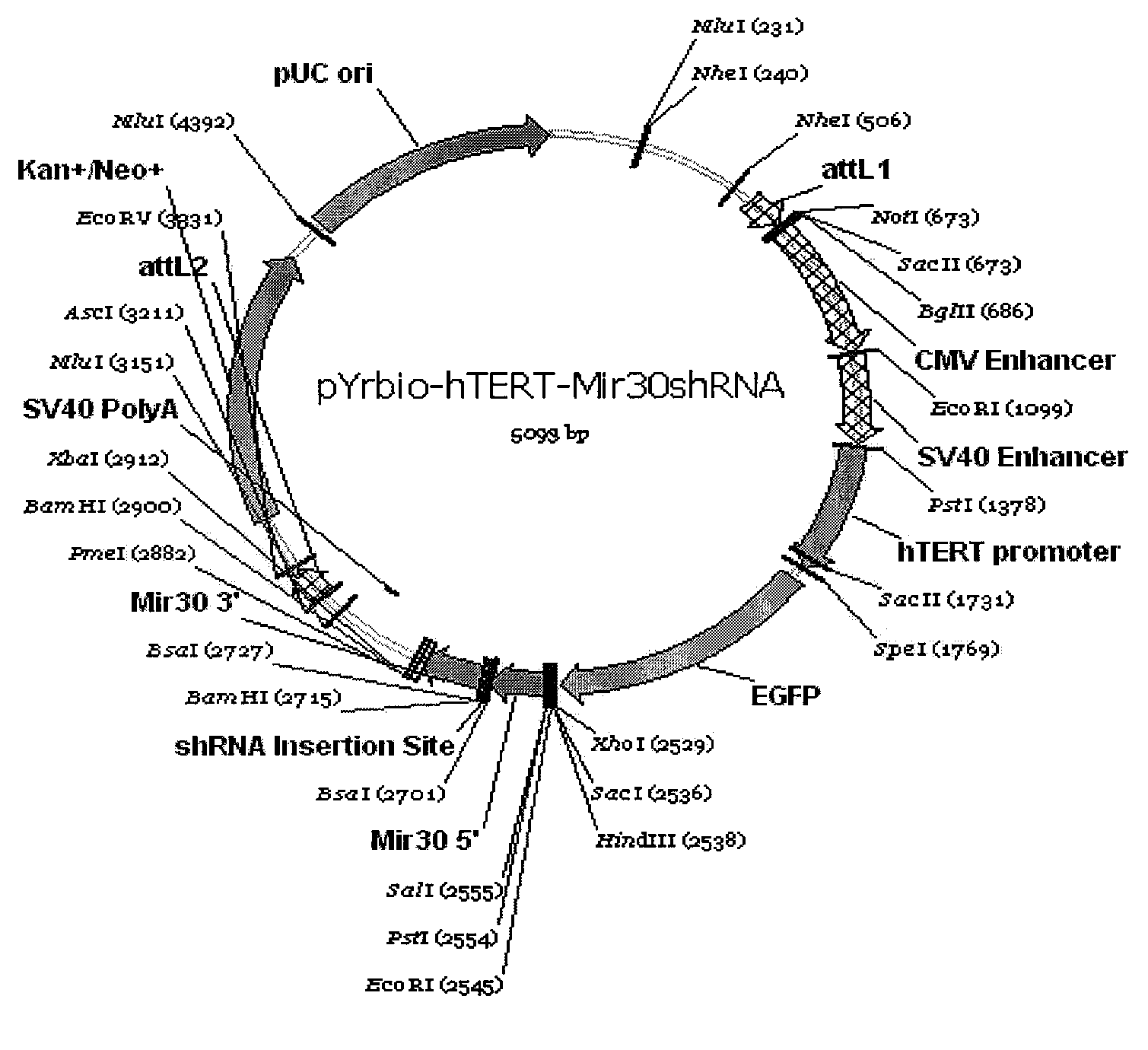
Eukaryotic expression vector for expressing shRNA (short hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) in manner of targeting in cancer cells
InactiveCN101993892ASolve the problem of non-specific interferenceGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesCancer cellReverse transcriptase
The invention provides a eukaryotic expression vector for expressing shRNA (short hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) in manner of targeting in cancer cells, comprising the structure as follows: (1) an expression cassette structure which is driven by a polII-type promoter and connects a fluorescent protein gene and a mirshRNA structure in series together; (2) a hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase) promoter enhanced by a CMV (cytomegalovirus) enhancer and a SV40 (simian virus 40) enhancer; (3) mirshRNA structures based on mir30: mir30 left arm-shRNA-mir30 right arm, and multiple mirshRNA structures can be connected in series; (4) a Kan or Amp resistance selection marker; and (5) LR homologous recombination arms. By utilizing the method to construct the shRNA eukaryotic expression vector, one or more than one shRNA can be specifically expressed in the cancer cells in manner of targeting; normal cells are not influenced while the RNA interference and the gene therapy are carried out on the cancer cells, thereby solving the problem of non-specific interference during carrying out the gene therapy by utilizing the RNA interference and being beneficial to the research and the application of the RNA interference in the cancer gene therapy aspect.
Owner:HUNAN NENGRUN MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS TECH
Tumour-dissolving adenovirus mutant possessing multiple specific anti-tumour mechanism
InactiveCN1884556AGood curative effectPlay a therapeutic roleFermentationGenetic engineeringHuman tumorReverse transcriptase
This invention involved oncolytic adenovirus mutant with the multiple antitumoral Mec. It belongs to the BME field. The adenovirus mutant Elb-55kDa and Elb-19kDa has missing gene, inserts chimeric promoter composed by the human telomerase reverse transcriptase core sequence and human tumor epidermal growth factor receptor enhancer before the replication required gene Ela codons mEla289R and mEla243R. So the virus can specific proliferate in cancer cell. Oncolytic viruses and mEla protein can exert thire influence. It can also increase the sensitivity of cancer cell to chemoradiation and have no influence to normal cell. It inserts the human h-endostatin gene expression cassette in adenovirus mutant gene group; along the replication of virus in cancer cell to amplificate h-endostatin gene and effective expression in tumor so to restrain neovascularization of tumor so to realize the result of restrain the increase and transformation of cancer cell and apoptotic cell. This new oncolytic adenovirus mutant has good clinical prospect in gene curing so to used in curing many kinds of human tumors.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUNTANG BIOENG
Immortalized porcine pancreatic stem cell line and construction and differentiation methods thereof
ActiveCN101974488ASolving activityPromote growthMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionNormal blood glucoseReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses an immortalized porcine pancreatic stem cell line and construction and differentiation methods thereof. In the immortalized porcine pancreatic stem cell line, porcine pancreatic stem cells are taken as host cells and are transfected with a pCI-neo-hTERT eukaryotic expression vector, and the human telomerase reverse transcriptase screened by G418 is expressed and has a transformant with multi-directional differentiation potentiality. The cell line also has higher activity after transferring for over 50 generations in vitro, keeps split proliferation, does not generate aging or apoptosis, and is an immortalized cell line. The cell line can be differentiated to form functional islet cell mass after induction, can reduce the blood glucose concentration after being transplanted into a mouse model suffering from diabetes and can maintain a normal blood glucose level within two weeks.
Owner:陕西九州细胞基因工程有限公司
Nuclear telomerase reverse transcriptase variant
InactiveUS8252282B2Ameliorate signExtend your lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsReverse transcriptaseWild type
The present invention is directed to a novel variant of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (S16AhTERT), which displays properties distinct from those of wildtype telomerase reverse transcriptase. Accordingly, the amino acid sequence of S16AhTERT and nucleic acid sequences encoding same are presented herein, as are methods of use thereof.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Immortalized human liver cell line, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101659941AProlong survival timeEnhance detoxification functionMicrobiological testing/measurementDialysis systemsArtificial liverSupporting system
The invention discloses an immortalized human liver cell line, a preparation method and an application thereof. The immortalized human liver cell line has the main function of primarily cultured humanliver cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: transferring SV40T antigen and human telomerase catalyzed subunit gene into primarily cultured separated human normal liver cell by slow virus carrier; and sieving in a cloning way to obtain the immortalized human liver cell line. The immortalized human liver cell line also can be extrinsically amplified in large scales in a microcarrier way. The immortalized human liver cell line can be used for preparing a biological artificial liver support system and preparing the medicament for curing the liver failure.
Owner:苏州瑞徕生物科技有限公司
Selective binding agents of telomerase
InactiveUS7078491B1Inhibit telomerase activityGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationTelomeraseMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to novel selective binding agents including polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies that recognize and bind to the catalytic subunit of human telomerase (hTERT). The invention also relates to the production, diagnostic use, and therapeutic use of the hTERT antibodies and fragments thereof.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Kit for detection of telomerase reverse transcriptase nucleic acids
InactiveUS20090269739A1Improve proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderBiological bodyReverse transcriptase
The invention provides compositions and methods related to human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTRT), the catalytic protein subunit of human telomerase. The polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention are useful for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases, for changing the proliferative capacity of cells and organisms, and for identification and screening of compounds and treatments useful for treatment of diseases such as cancers.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION +1
Telomerase reverse transcriptase fragments and uses thereof
ActiveUS7294708B2High sensitivityReduce resistanceSugar derivativesHydrolasesCancer cellReverse transcriptase
The invention provides compositions comprising fragments of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) which can lead to telomere dysfunction in a cell and reduction of growth and tumorigenicity in cancer cells. The invention also relates to uses of the fragments in the treatment of cancer and in drug discovery.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF BIOTECH +1
Reversible immortalization of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells
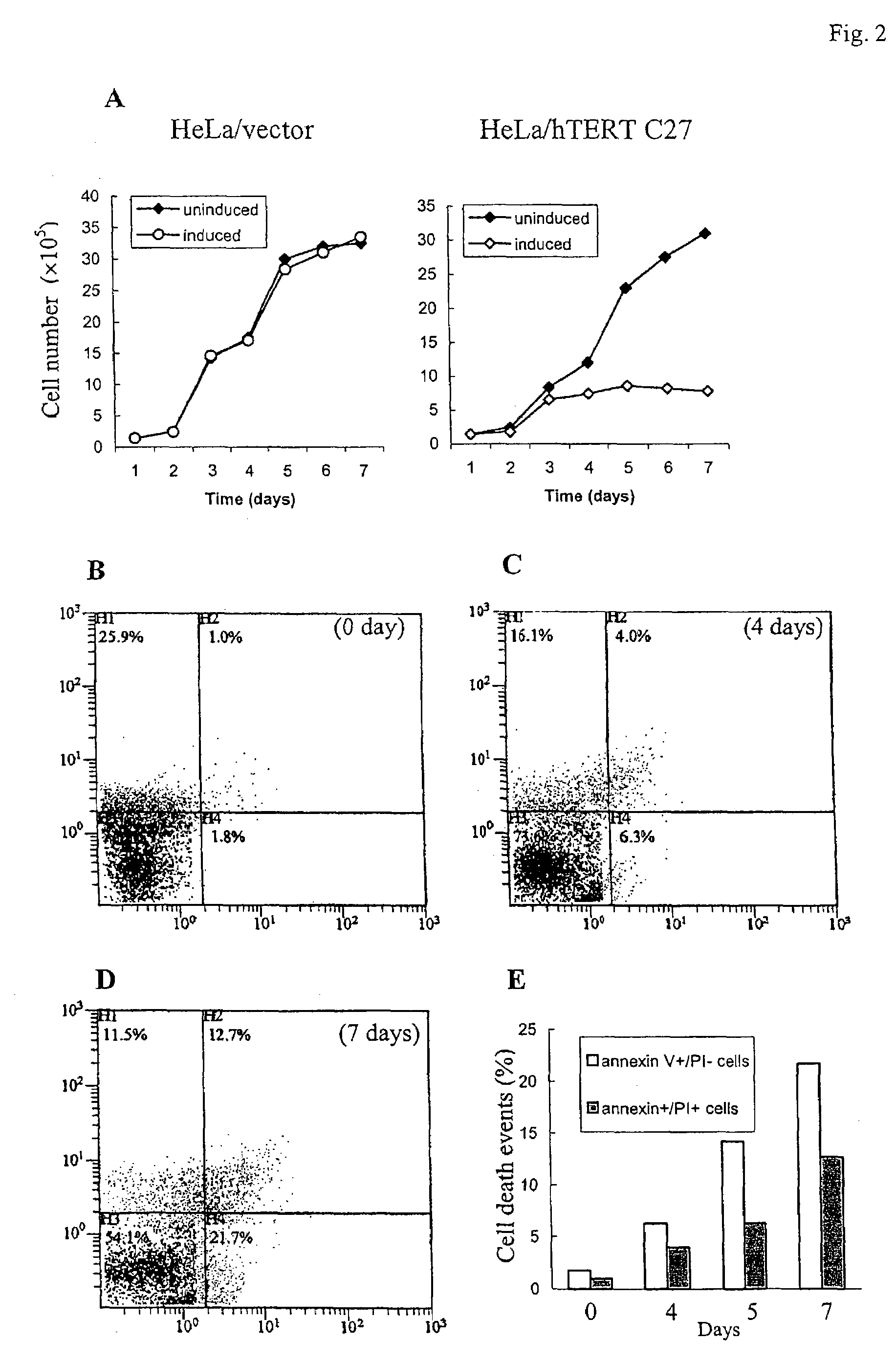
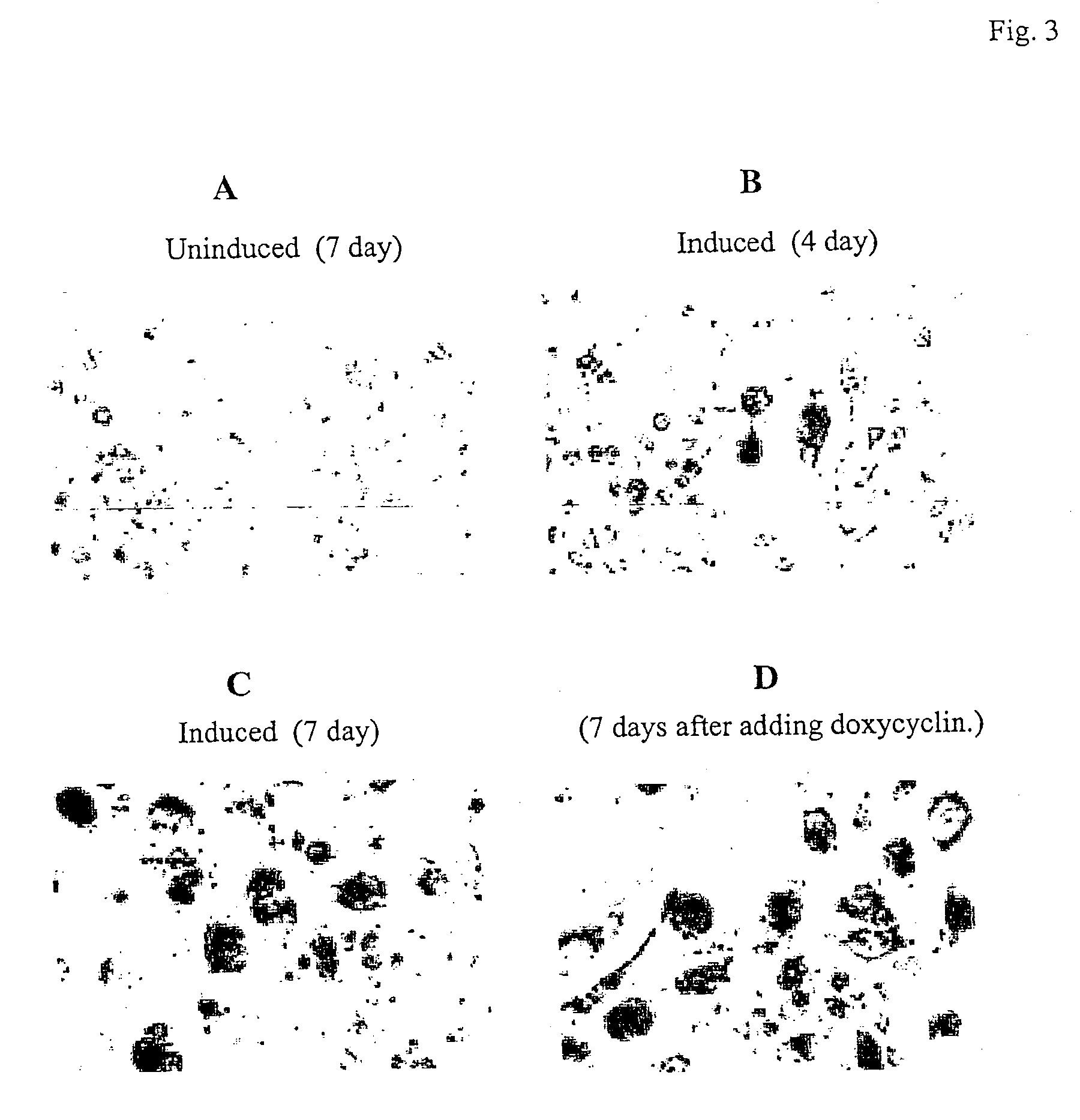
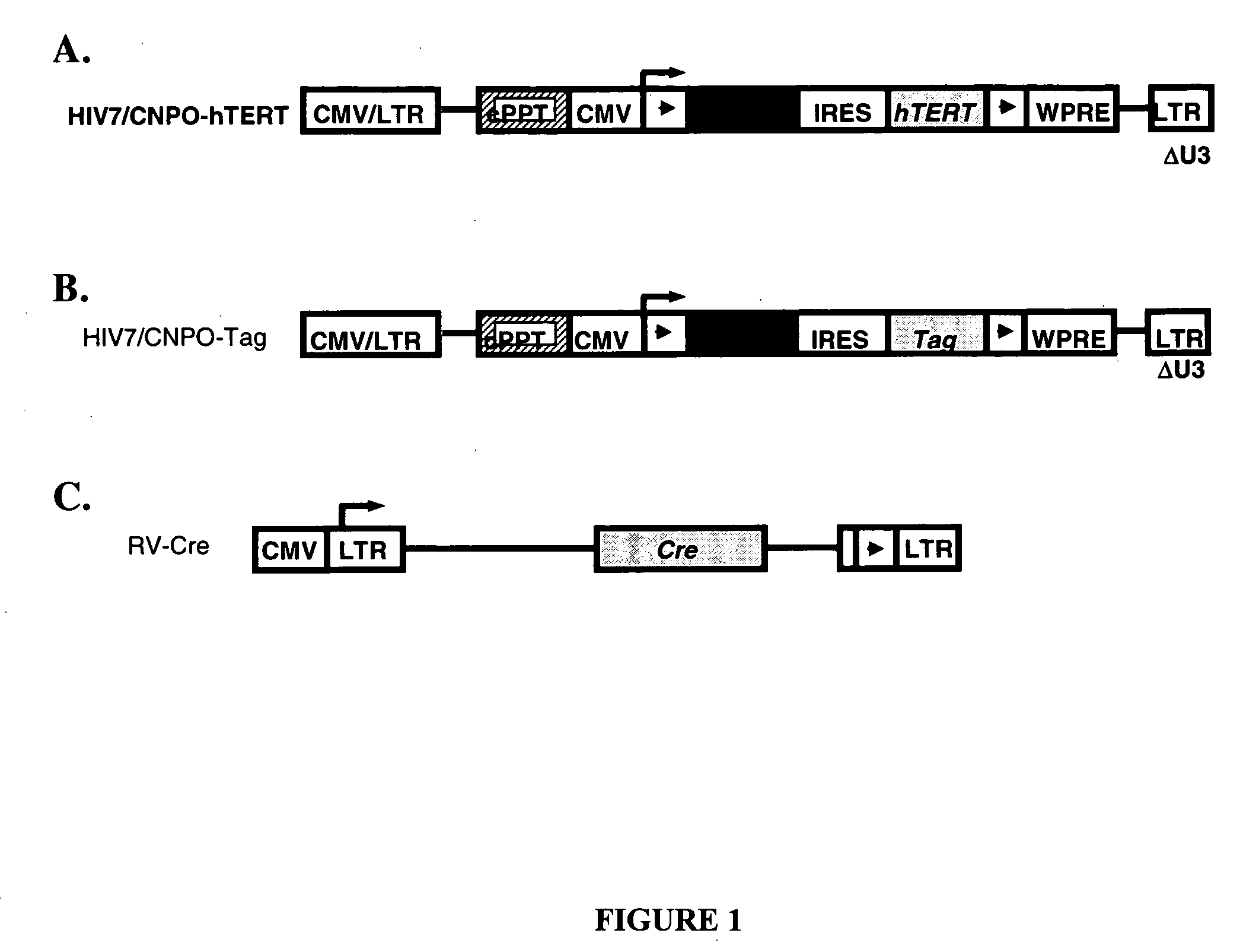
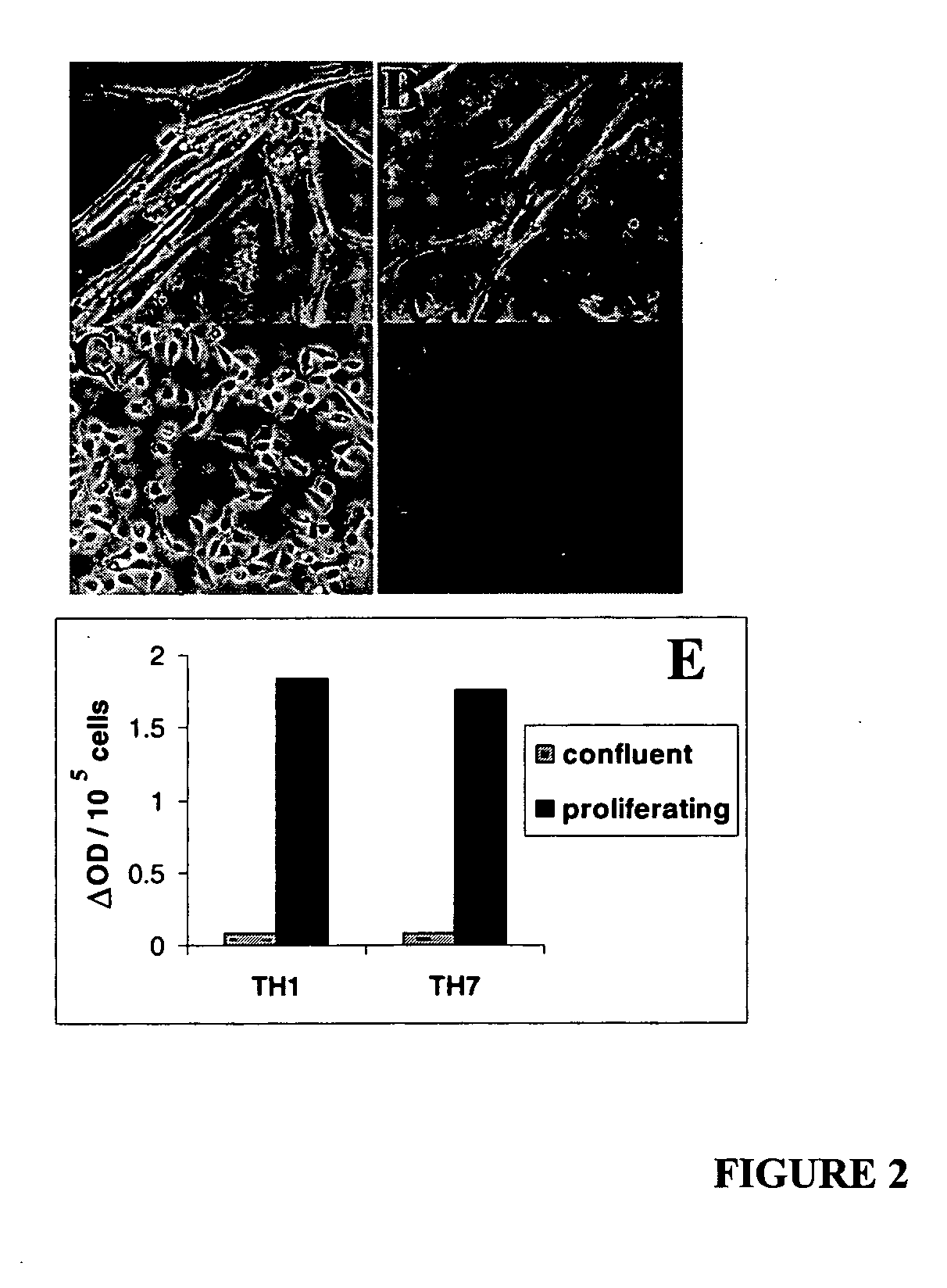
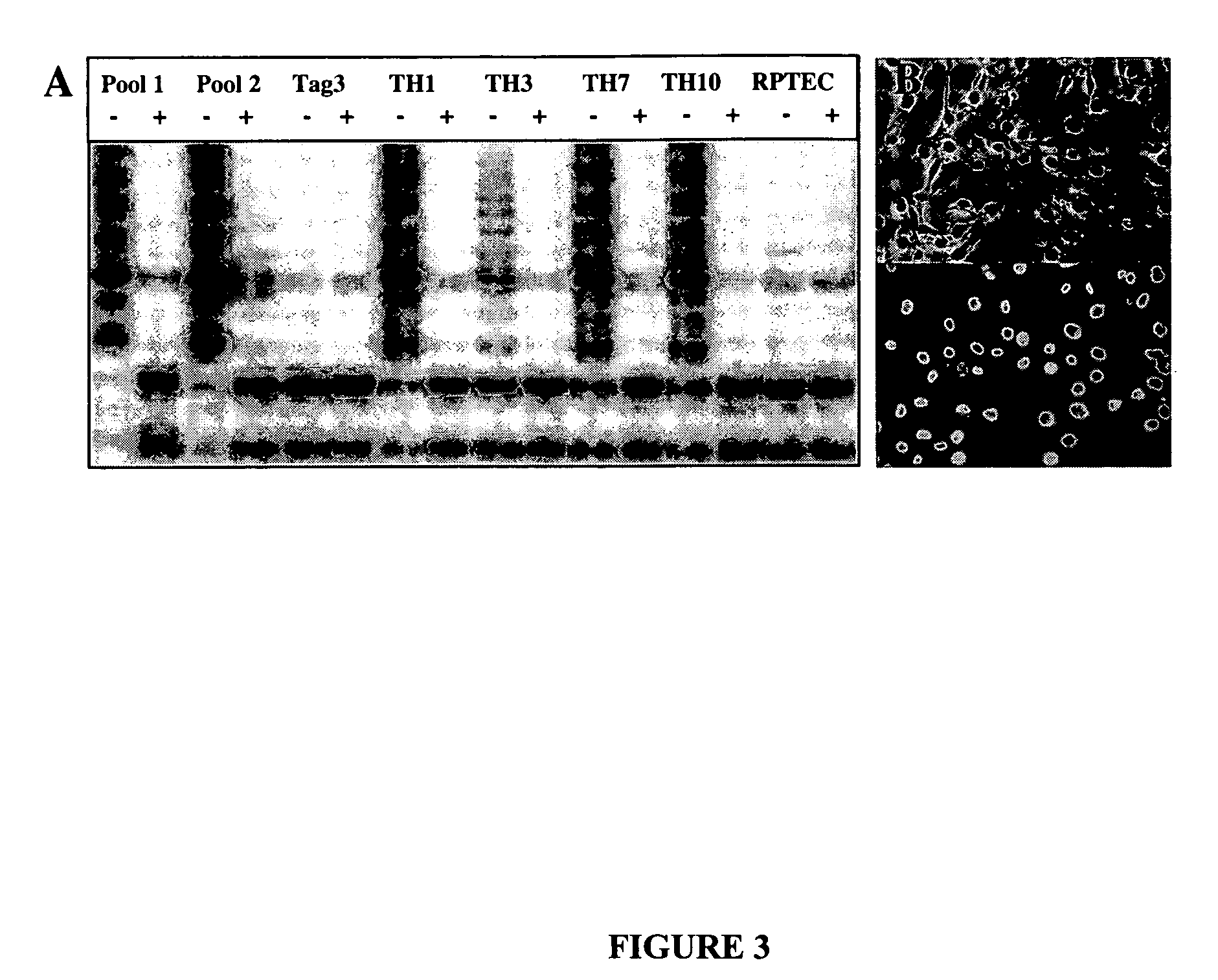
The present provides reversibly immortalized RPTECs and methods for making and utilizing these cells. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of reversibly immortalizing RPTECs by introducing a first vector containing a human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene flanked by loxP sites and a second vector containing an SV40 T antigen (Tag) gene flanked by loxP sites. Immortalization can be reversed by introduction of a third vector containing a Cre recombinase or Cre variant gene. The reversibly immortalized RPTECs generated by this method may be used for a variety of applications, including screening of test agents for the ability to modulate renal toxicity or incorporation into devices designed to mimic the activity of the renal proximal tubules.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Vivo assay for anti angiogenic compounds
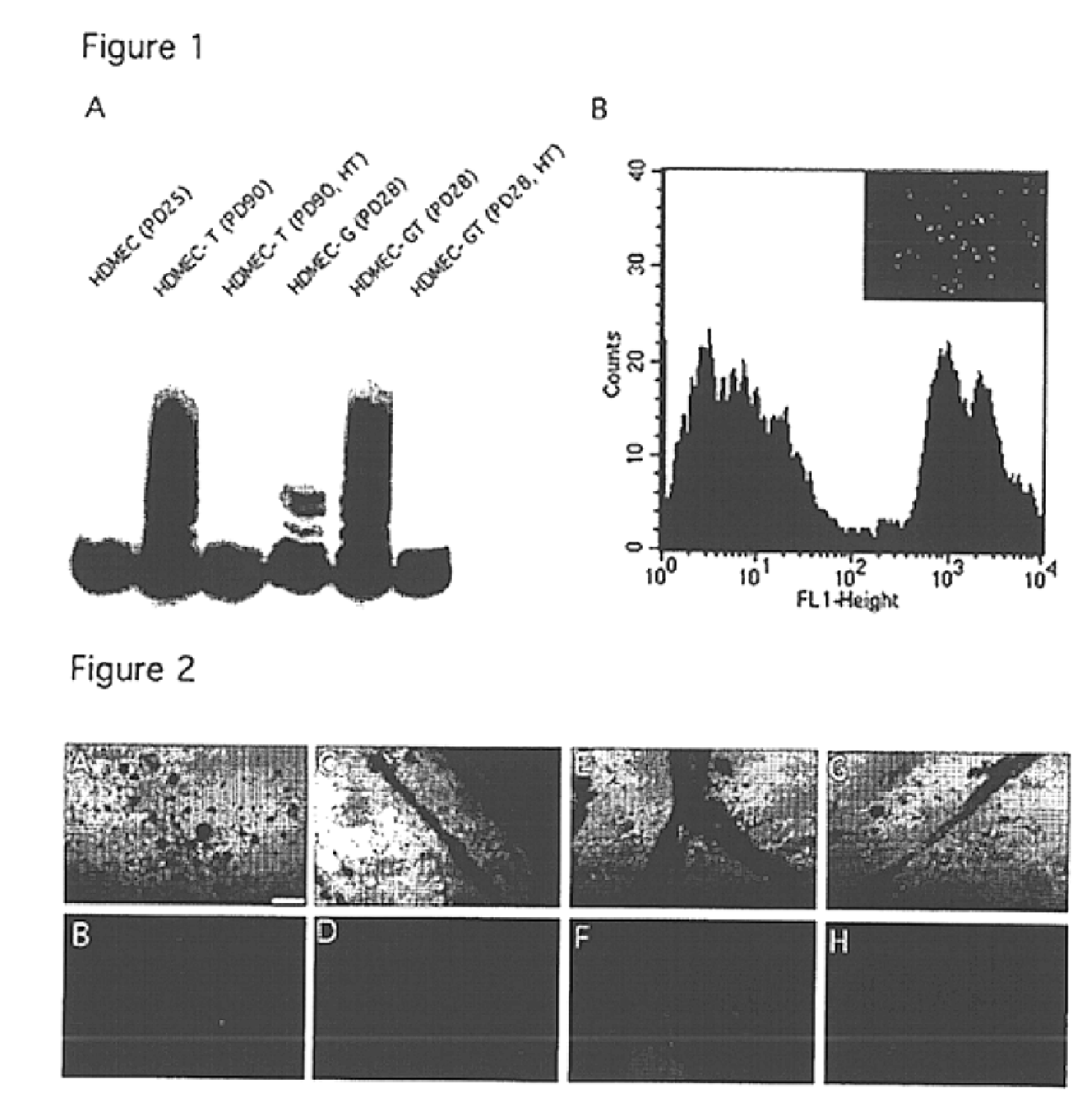
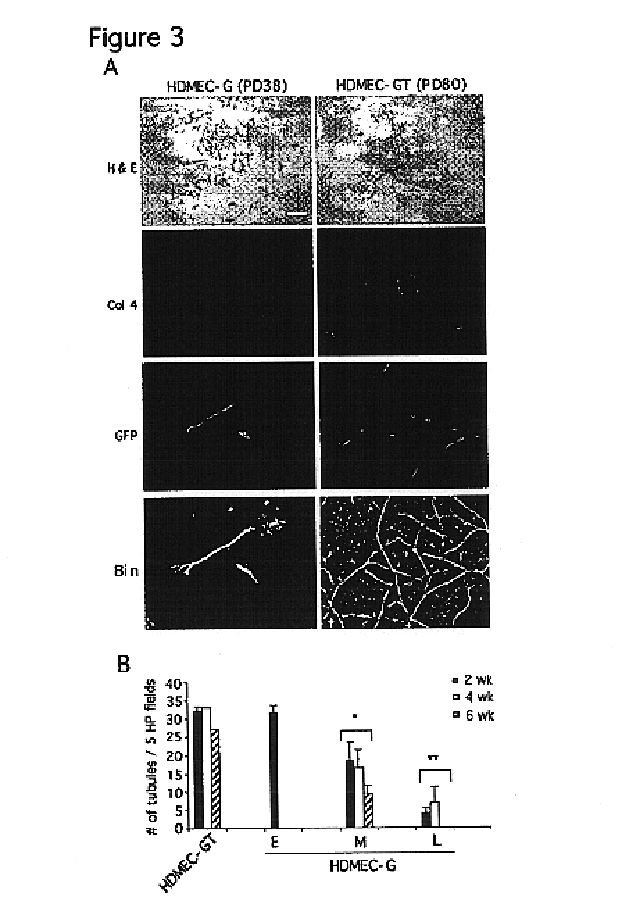
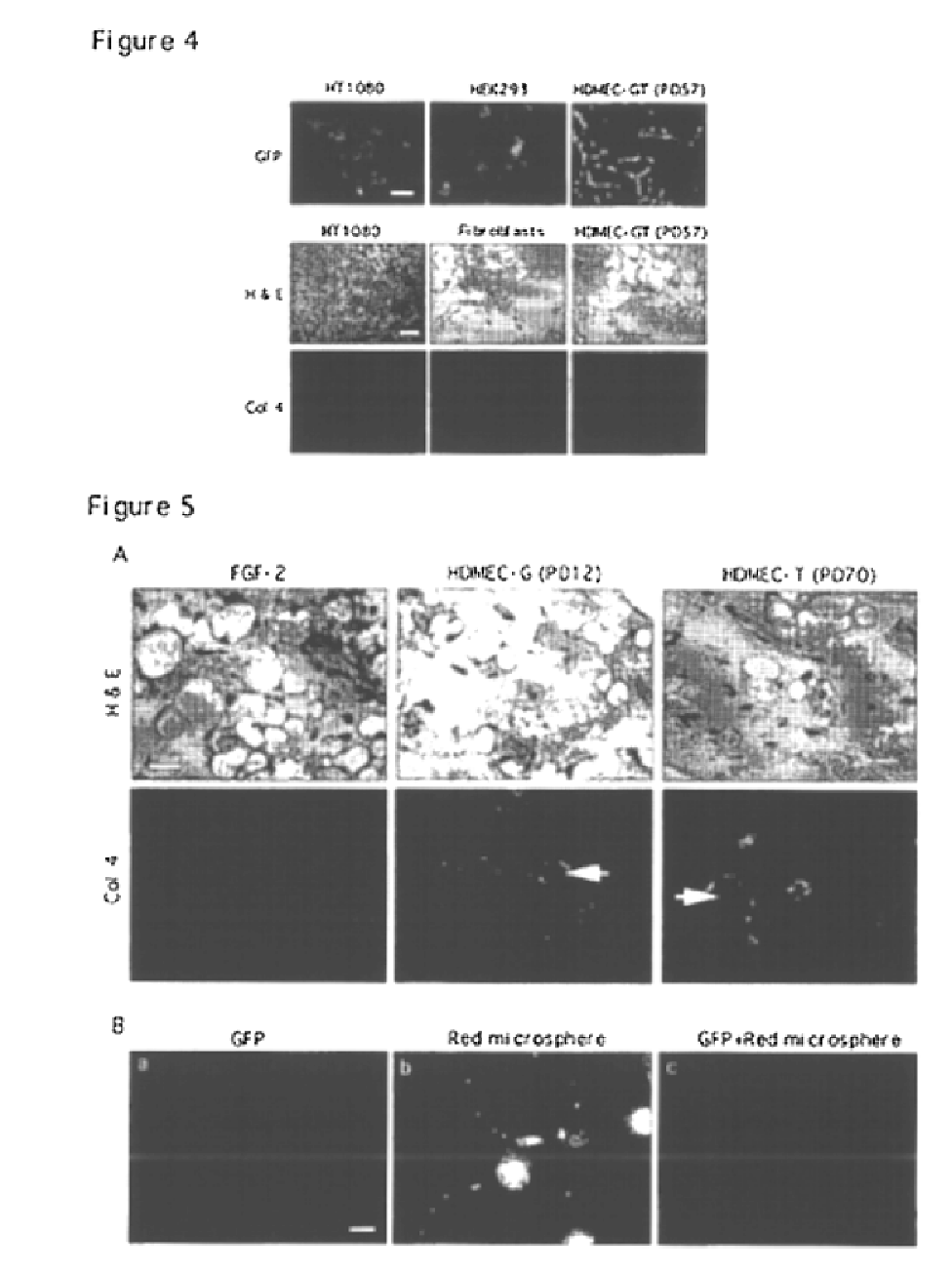
We report the use of telomerase-immortalized human microvascular endothelial cells in the formation of functional capillary blood vessels in vivo. Previously we showed the superior in vitro survival of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT)-transduced human endothelial cells. Here we show that retroviral-mediated transduction of hTERT in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) results in cell lines that form microvascular structures when subcutaneously implanted in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. The human origin of xenografted microvaculature was confirmed both by basement membrane immunoreactivity with anti-human type IV collagen staining and visualization of fluorescent vessels containing HDMEC that were co-transduced with hTERT and green fluorescent protein (eGFP). The lack of human vascular structures after implantation of HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells, 293 human embryonic kidney cells or human skin fibroblasts demonstrated the specificity of HDMEC at forming capillaries. Intravascular red fluorescent microspheres injected into the host circulation were found within green “telomerized” microvessels indicating functional murine-human vessel anastamoses. Whereas primary HDMEC-derived vessel density decreased steadily with time, telomerized HDMEC maintained durable vessels 6 weeks after xenografting. Modulation of implant vessel density by exposure to different angiogenic and angiostatic factors demonstrated the utility of this system for the study of human microvascular remodeling in vivo.
Owner:HERRON G SCOTT
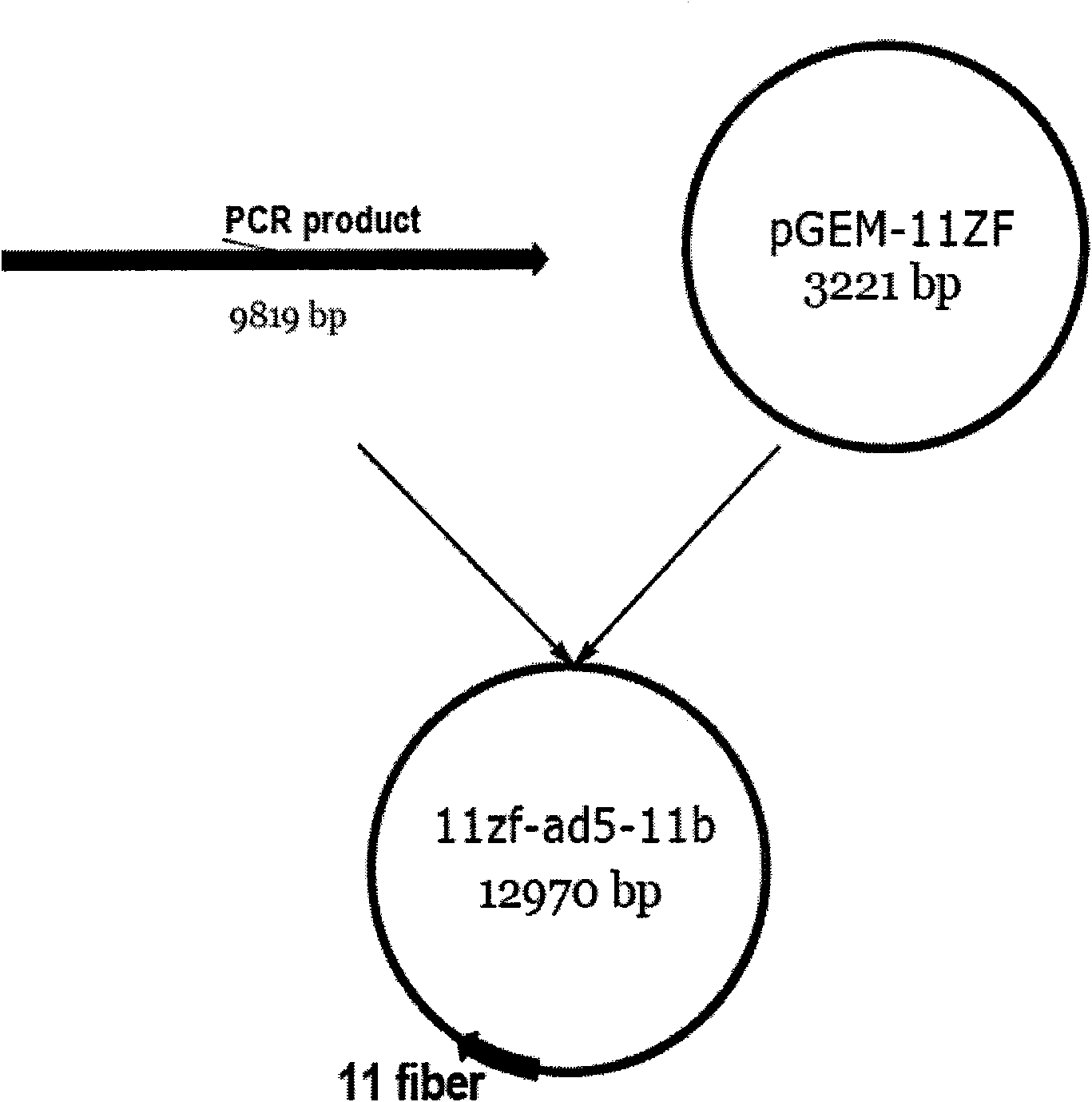
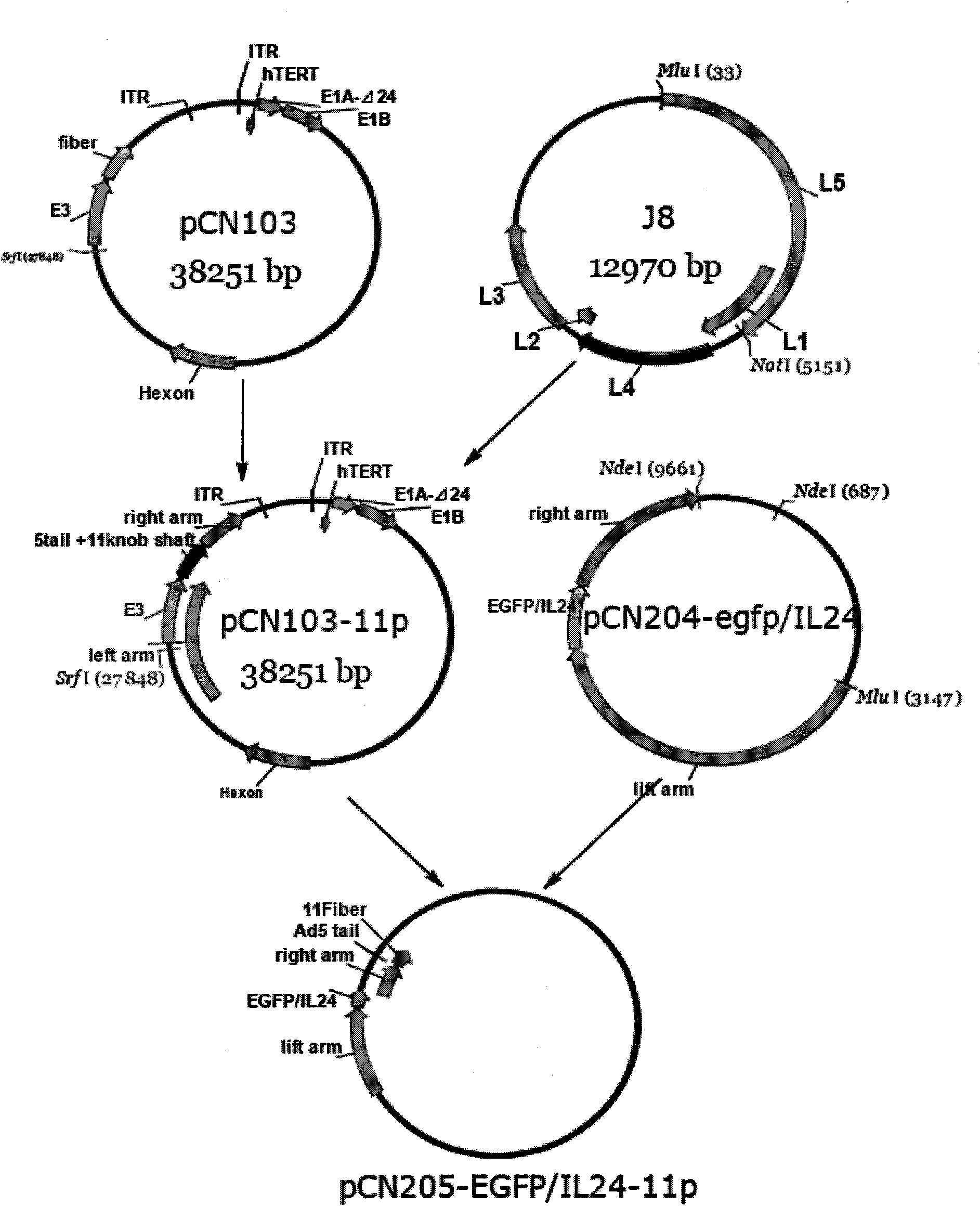
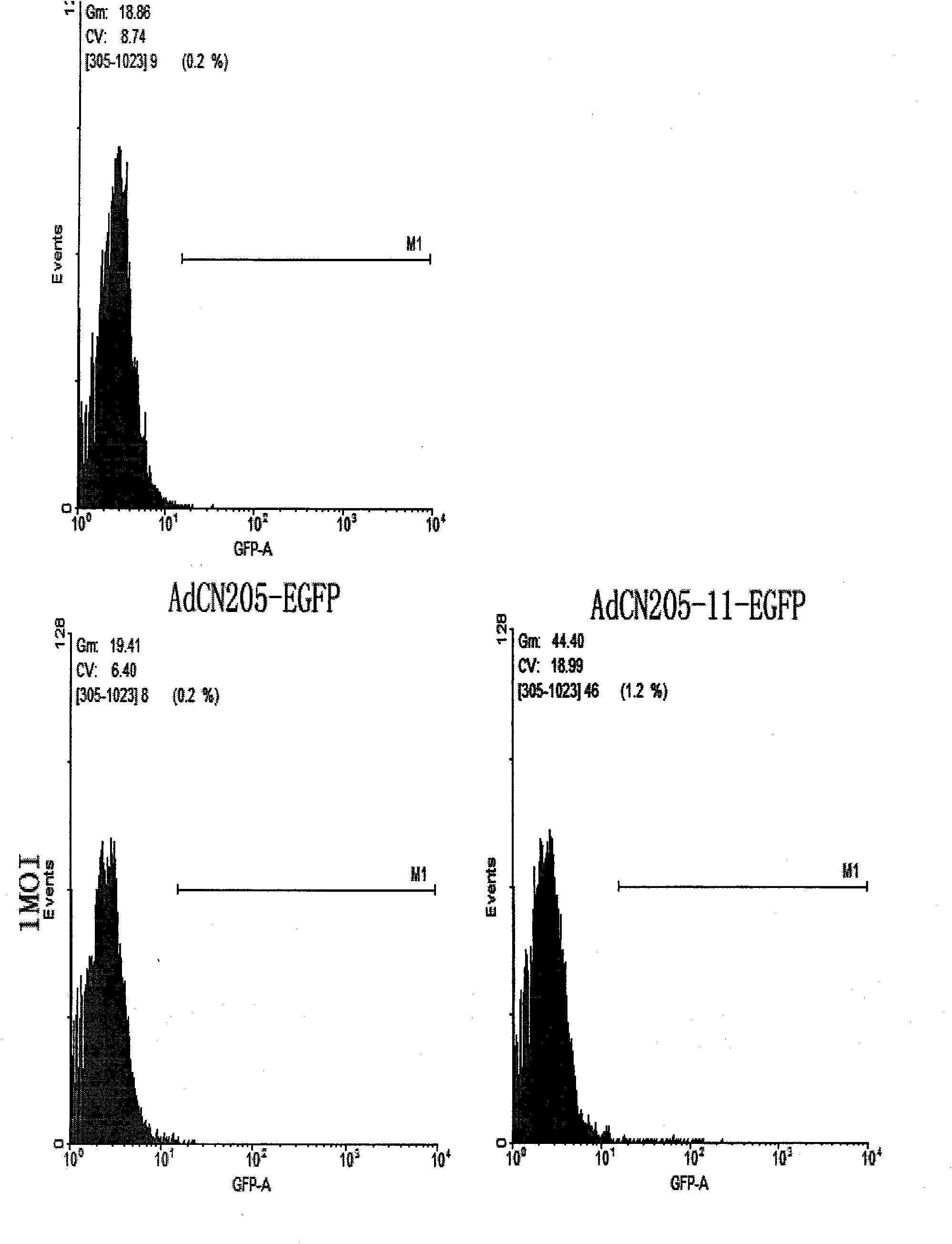
Construction method of three-target mosaic type oncolytic adenovirus Ad5/F11 carrier and use thereof
InactiveCN101565718AIncrease lethalityEffective combinationGenetic material ingredientsFermentationFiberReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a construction method of three-target mosaic type oncolytic adenovirus Ad5 / F11 carrier and use thereof, wherein the carrier uses a double-target oncolytic adenovirus carrier pCN103 and Pcn205 as the basis and the frame of 5 type adenovirus Ad5 is chimeric with the fibrin fiber of human 11 type adenovirus Ad11 and the human telomerase reverse transcriptase hTERT promoter is used for adjusting and controlling the E1A gene deleted with CR2 section and necessary for Rb protein binding and the carrier system is used for controlling the exogenous gene capable of killing and inhibiting various cancers, such as IL-24, TRAIL, SOCS3, cpp-SOCS3, SOCS1, cpp-SOCS1 and the vivo and vitro experiment shows that the carrier has good anti-cancer effect. The three-target mosaic type oncolytic adenovirus, such as AdCN205-11-1l-24, AdCN205-11-TRAIL, AdCN205-11-SOCS3, AdCN205-11-cpp-SOCS3, AdCN205-11-SOCS1 and AdCN205-11-cpp-SOCS1 can be used for treating various cancer and developing new virus-gene anti-cancer medicine capable of effectively treating cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com