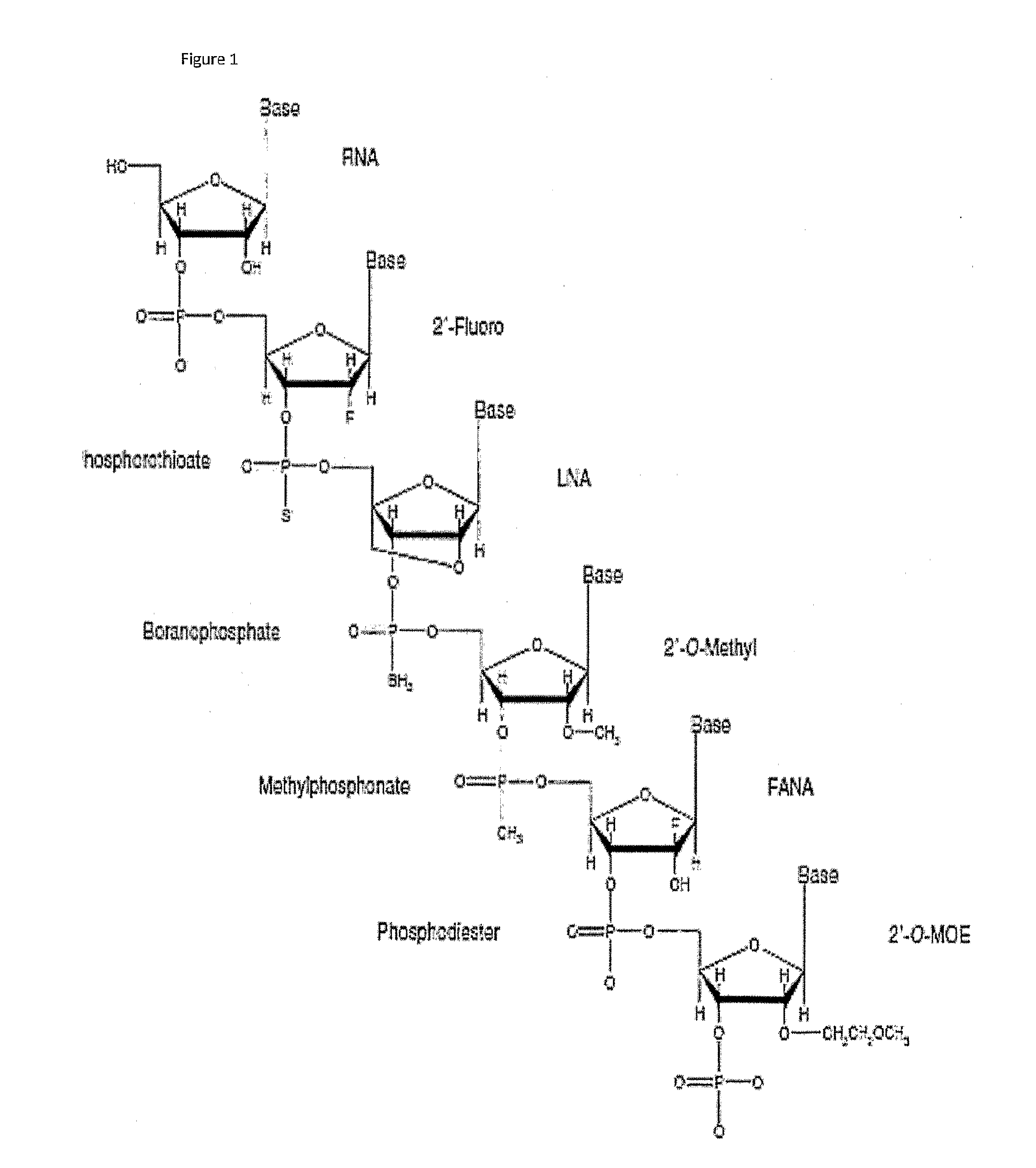
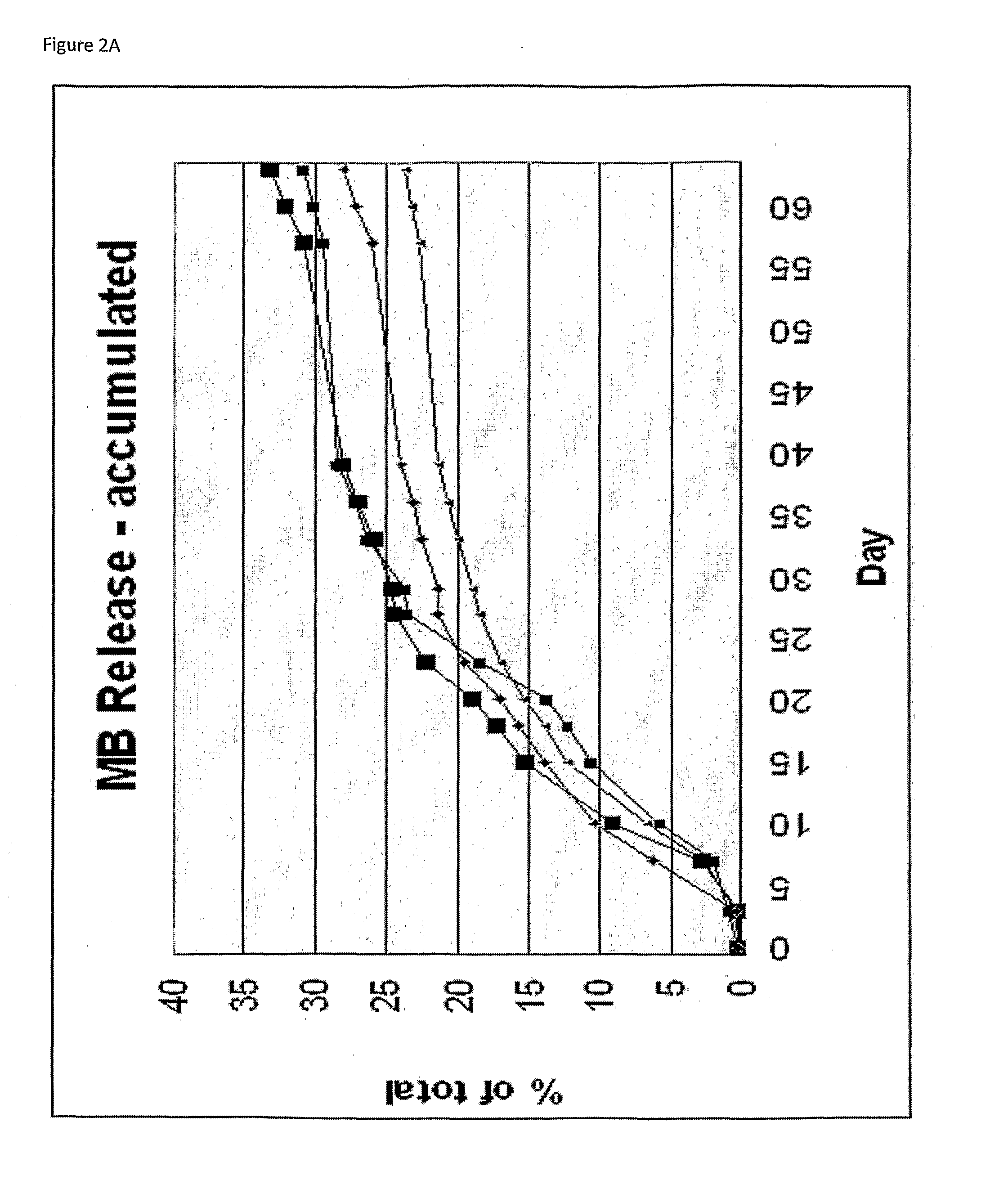
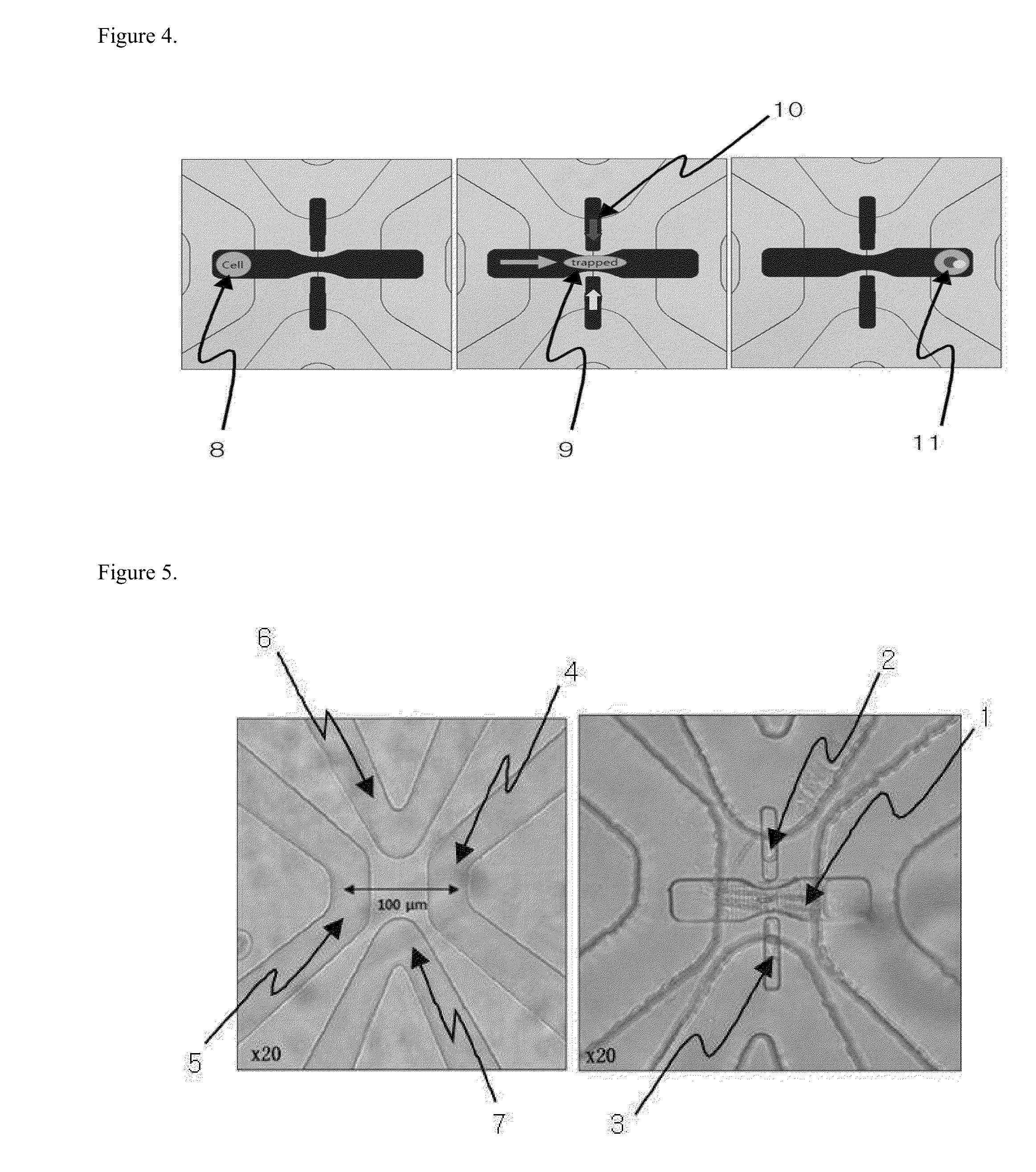
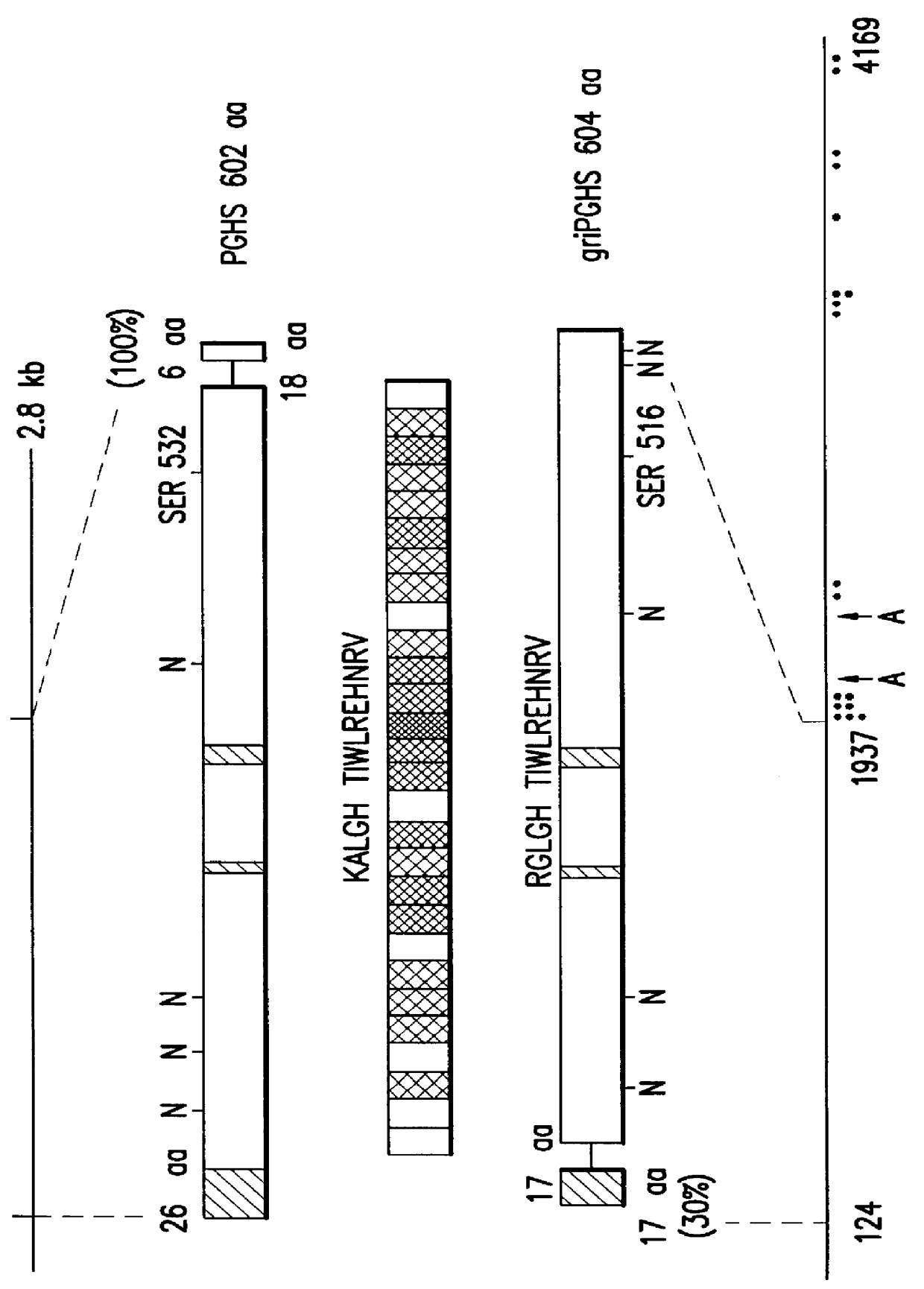
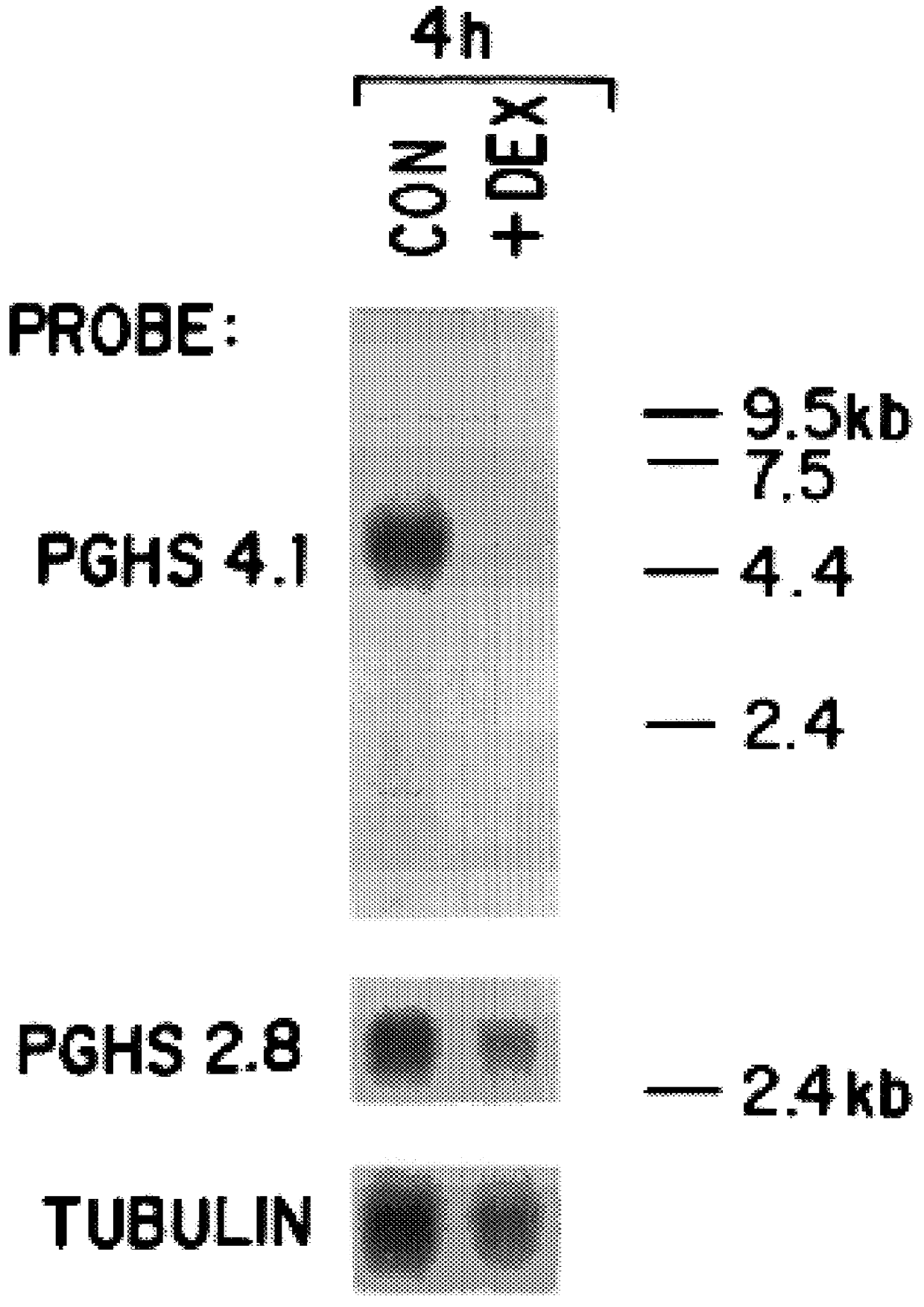
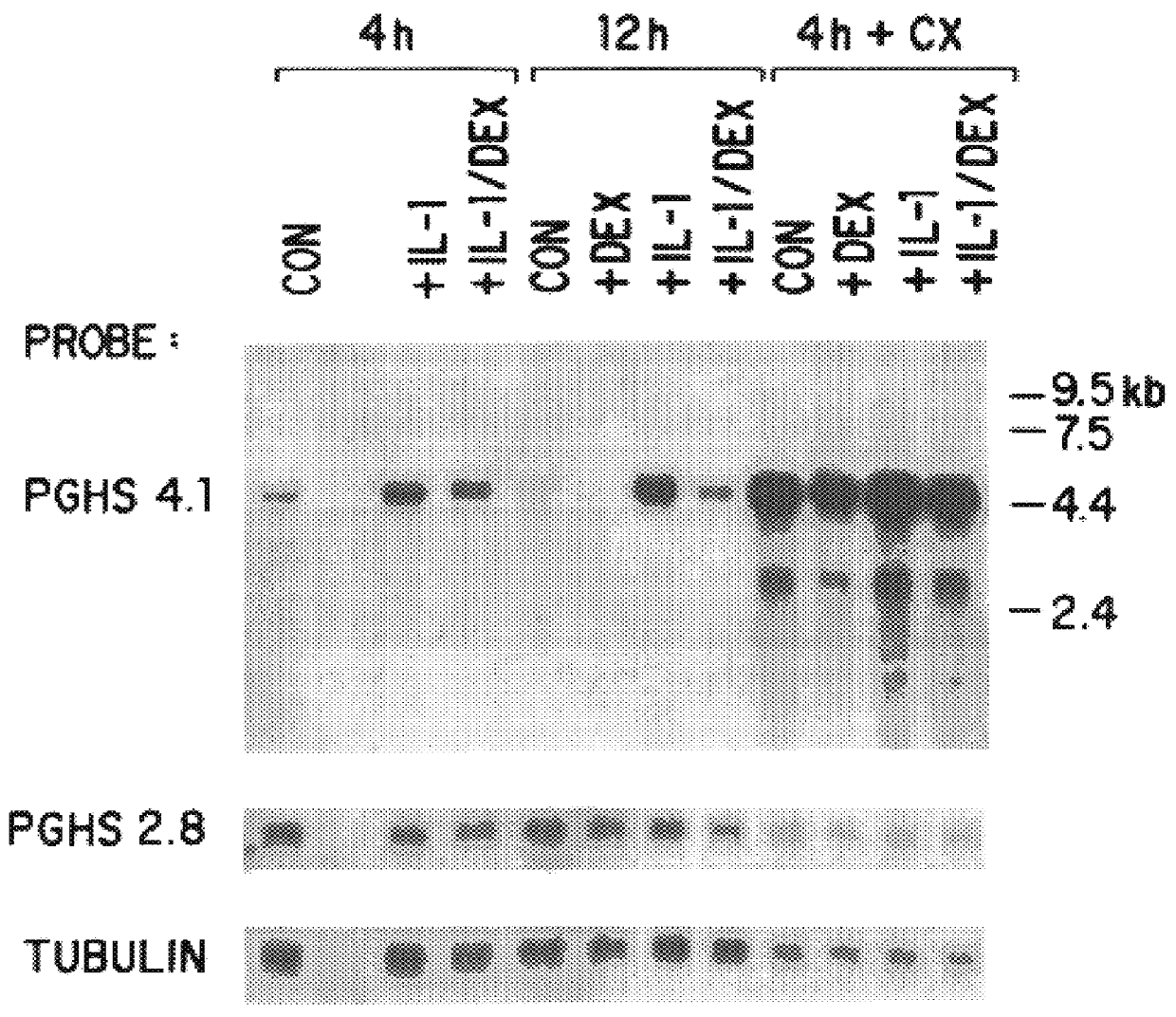
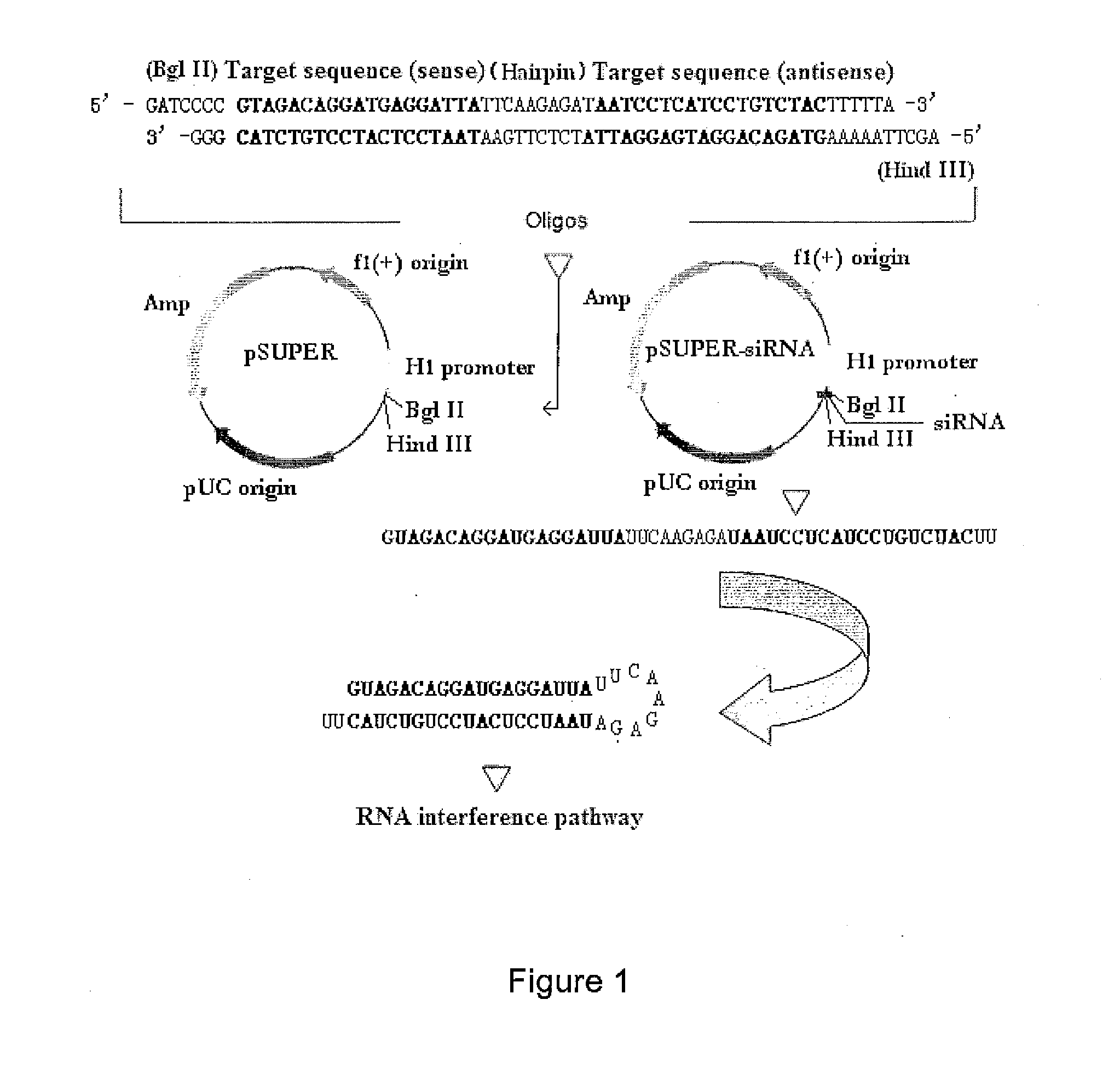
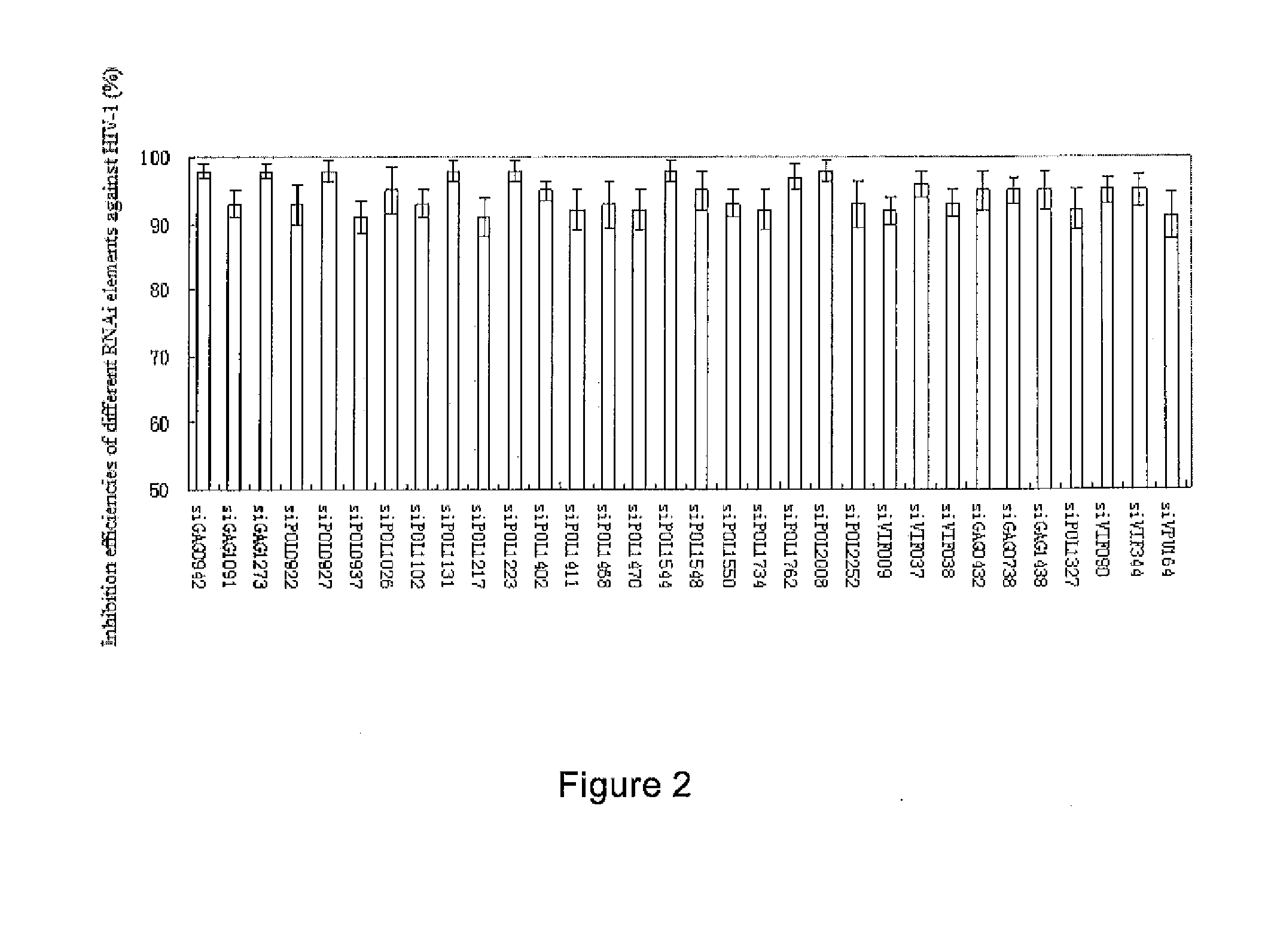
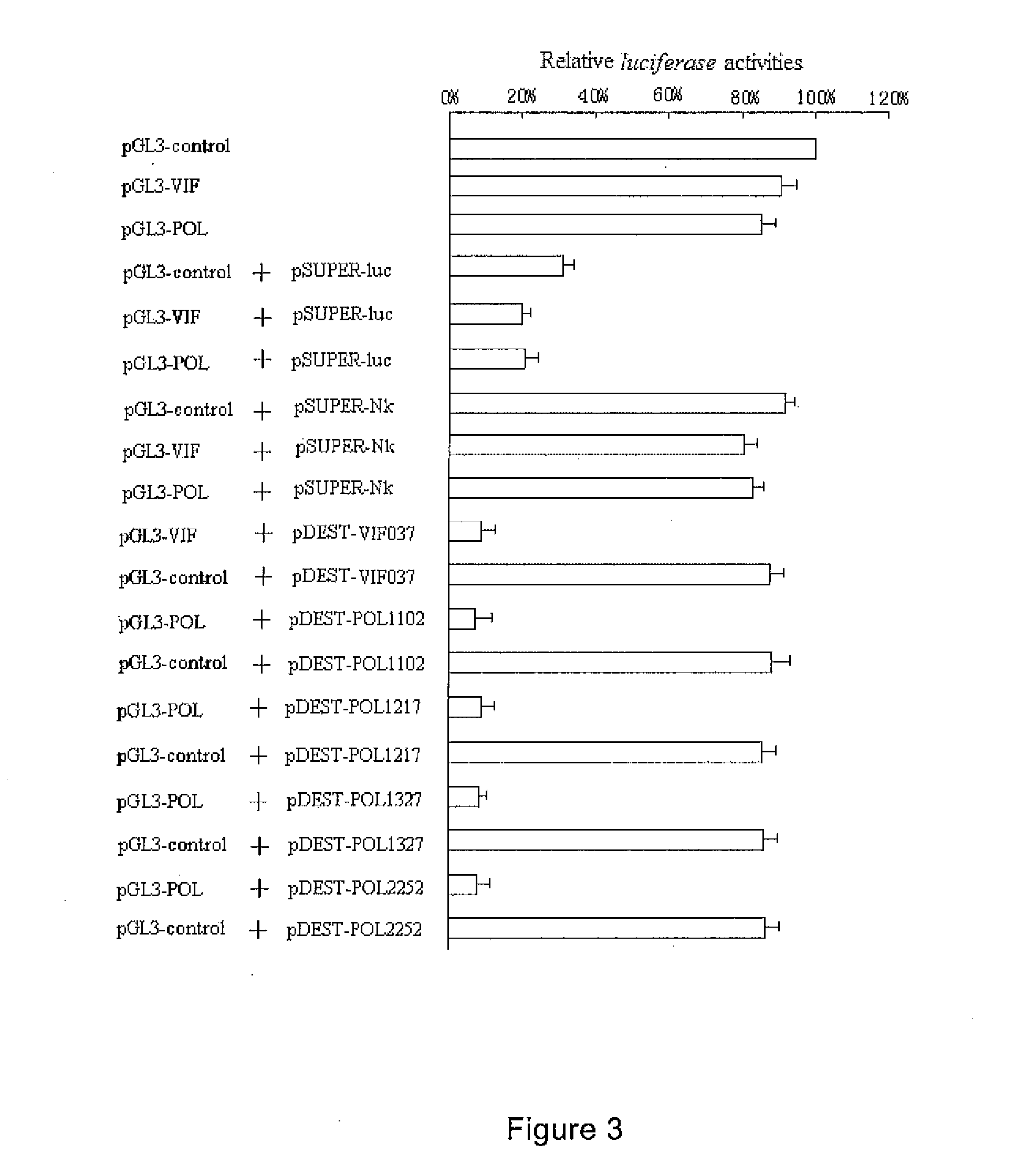
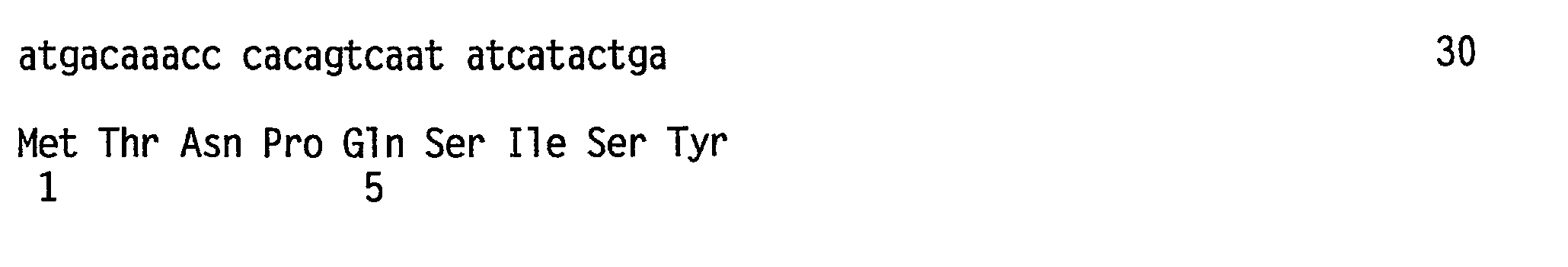Patents
Literature
426 results about "Ribozyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that are capable of catalyzing specific biochemical reactions, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or in vitro-evolved ribozymes are the cleavage or ligation of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during protein synthesis. They also participate in a variety of RNA processing reactions, including RNA splicing, viral replication, and transfer RNA biosynthesis. Examples of ribozymes include the hammerhead ribozyme, the VS ribozyme, Leadzyme and the hairpin ribozyme.
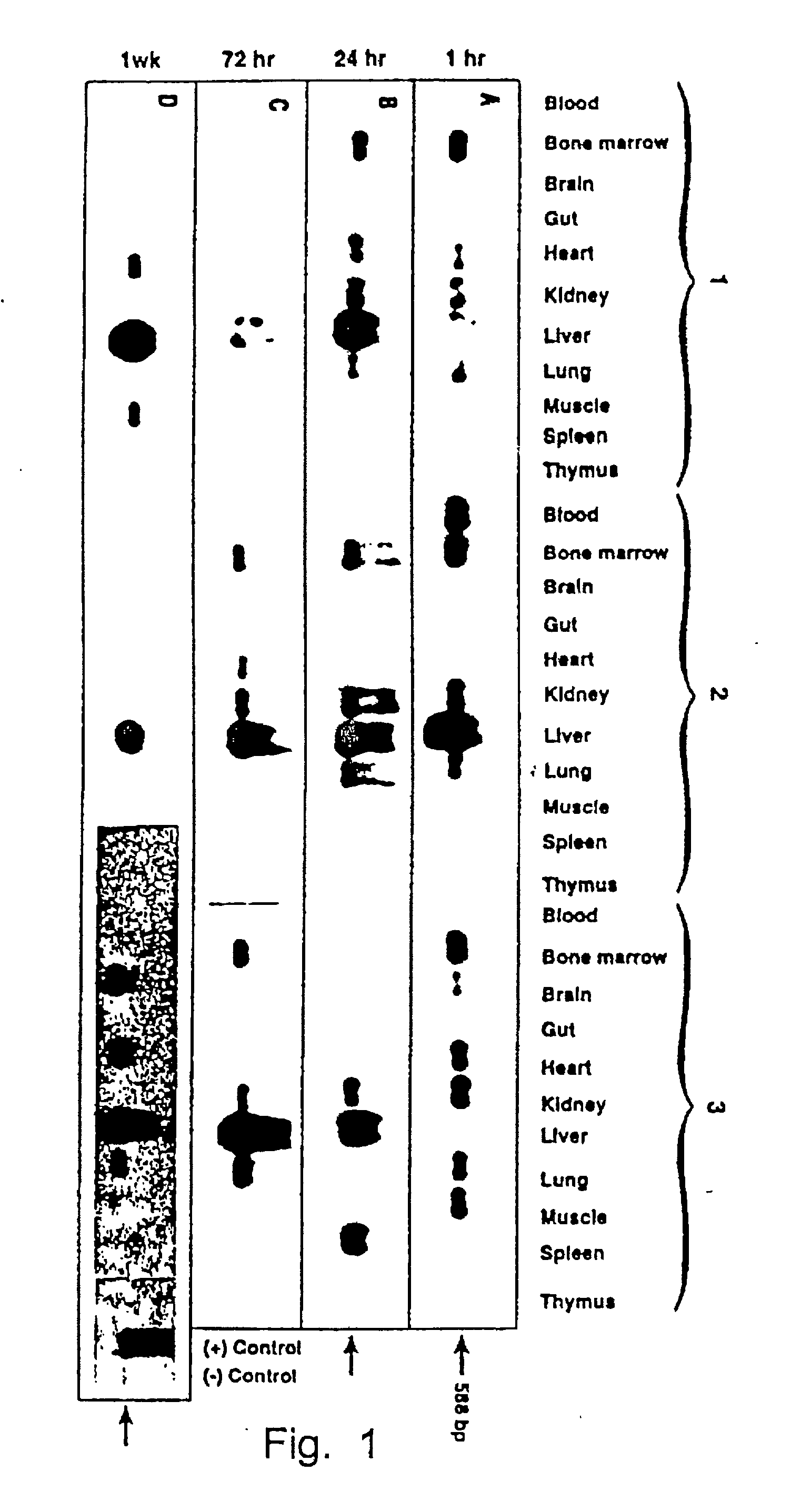
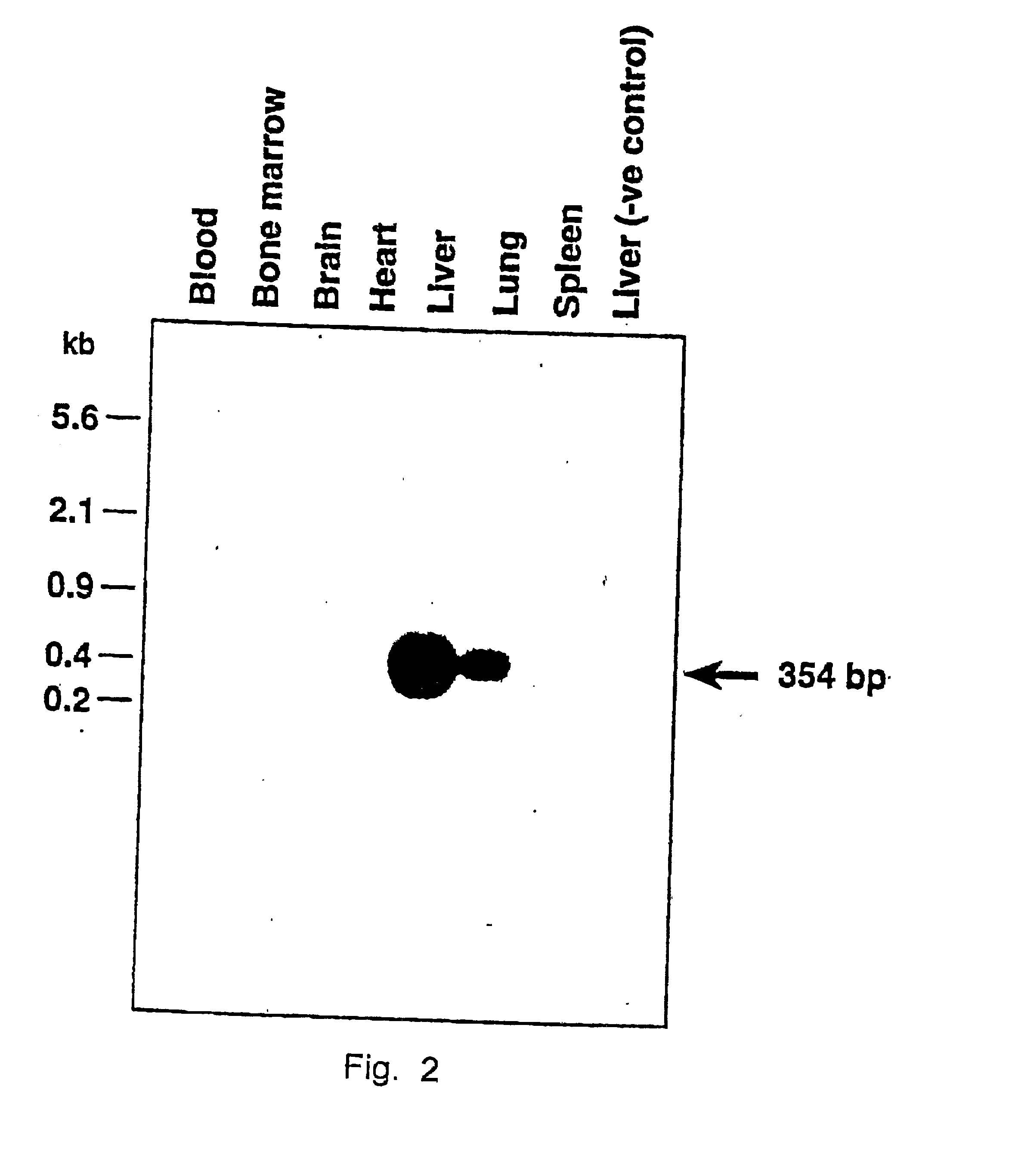
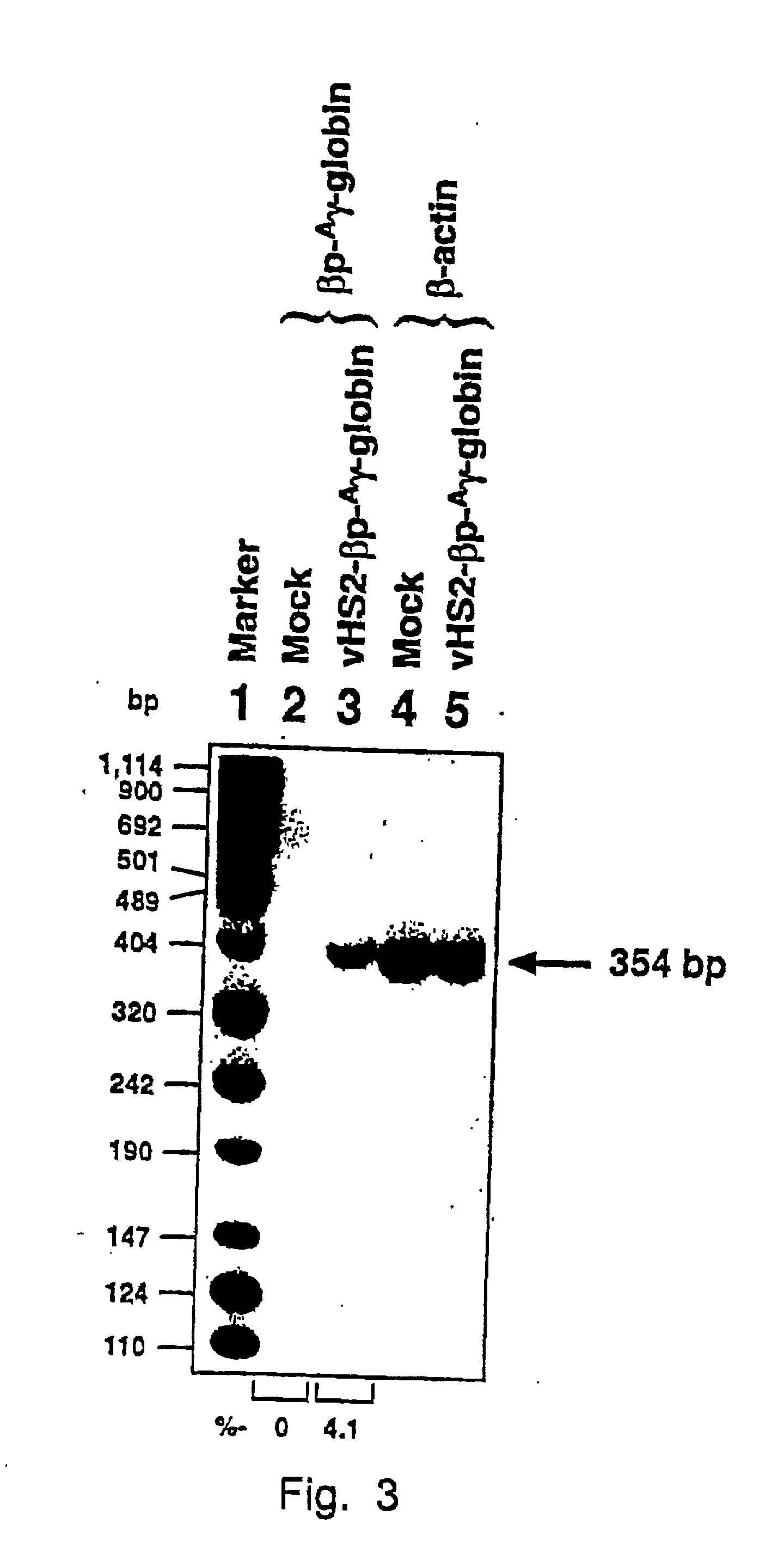
Tissue-specific and pathogen-specific toxic agents and ribozymes
InactiveUS6271359B1Rapidly and effectively expressedImprove stabilityVirusesSugar derivativesCancer cellBiology
The present invention relates to the discovery, identification and characterization of toxic agents which are lethal to pathogens and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a pathogen or pathogen infected cells in order to treat and / or eradicate the infection. In particular, the present invention relates to toxic agents which target bacteria at different stages of the bacterial life cycle, which are delivered alone or in combination to bacteria or bacteria-infected cells. The invention relates to toxic agents which are lethal to diseased cells and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a diseased cell in order to treat and / or eradicate the disease. The present invention relates to promoter elements which are pathogen-specific or tissue-specific and the use of such promoter elements to achieve pathogen-specific or tissue-specific expression of the toxic agent(s) and / or ribozyme(s) of the present invention. Specifically, the invention relates to the delivery of one or more toxic gene products, antisense RNAs, or ribozymes, or combination thereof. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple pathogenic targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a pathogen, or cell infected with a pathogen. Further, the invention has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant bacterium and bacterial pathogens. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a diseased cell. The invention also has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant pathogens and drug-resistant diseased cells (such as cancer cells).
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Methods, compositions and systems for local delivery of drugs
ActiveUS20110195123A1Reduce degradationImprove permeabilityBiocidePowder deliveryCell-Extracellular MatrixBrachytherapy
Implantable medical device eluting drug locally and in prolonged period is provided, including several types of such a device, the treatment modes of implementation and methods of implantation. The device comprising of polymeric substrate, such as a matrix for example, that is used as the device body, and drugs, and in some cases additional scaffolding materials, such as metals or additional polymers, and materials to enhance visibility and imaging. The selection of drug is based on the advantageous of releasing drug locally and in prolonged period, where drug is released directly to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of the diseased area such as tumor, inflammation, degeneration or for symptomatic objectives, or to injured smooth muscle cells, or for prevention. One kind of drug is the gene silencing drugs based on RNA interference (RNAi), including but not limited to si RNA, sh RNA, or antisense RNA / DNA, ribozyme and nucleoside analogs. The modes of implantation in some embodiments are existing implantation procedures that are developed and used today for other treatments, including brachytherapy and needle biopsy. In such cases the dimensions of the new implant described in this invention are similar to the original implant. Typically a few devices are implanted during the same treatment procedure.
Owner:SILENSEED LTD
Transgenic organism
InactiveUS20090007284A1Efficient productionEfficiency advantageAnimal cellsVectorsNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
A method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a non-primate lentiviral expression vector comprising a nucleotide of interest (NOI). Also described is a method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a lentiviral expression vector comprising a NOI capable of generating an antisense oligonucleotide, a ribozyme, an siRNA, a short hairpin RNA, a micro-RNA or a group 1 intron. Also described is a viral vector comprising a first nucleotide sequence, wherein said first nucleotide sequence comprises: (a) a second nucleotide sequence comprising an aptazyme; and (b) a third nucleotide sequence capable of generating a polynucleotide; wherein (a) and (b) are operably linked and wherein the aptazyme is activatable to cleave a transcript of the first nucleotide sequence such that said polynucleotide is generated.
Owner:RADCLIFFE PHILIPPA +2
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors 1,2,3, and 4 as Targets for Therapeutic Intervention
InactiveUS20070248605A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAbnormal tissue growthAntibody
A composition is provided that contains a polypeptide and a modulator or a cell comprising the polypeptide and a modulator, where the modulator specifically interferes with the activity of the polypeptide, and the polypeptide is either FGFR3 or FGFR4, inclusive of all polymorphic forms and variants thereof. The modulator can be an antibody or active fragments thereof, a small molecule drug, an RNAi molecule, an antisense molecule or a ribozyme. A method of treatment of tumors in a subject is also provided where an antagonist of FGFR3 or FGFR4 is administered to the subject.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
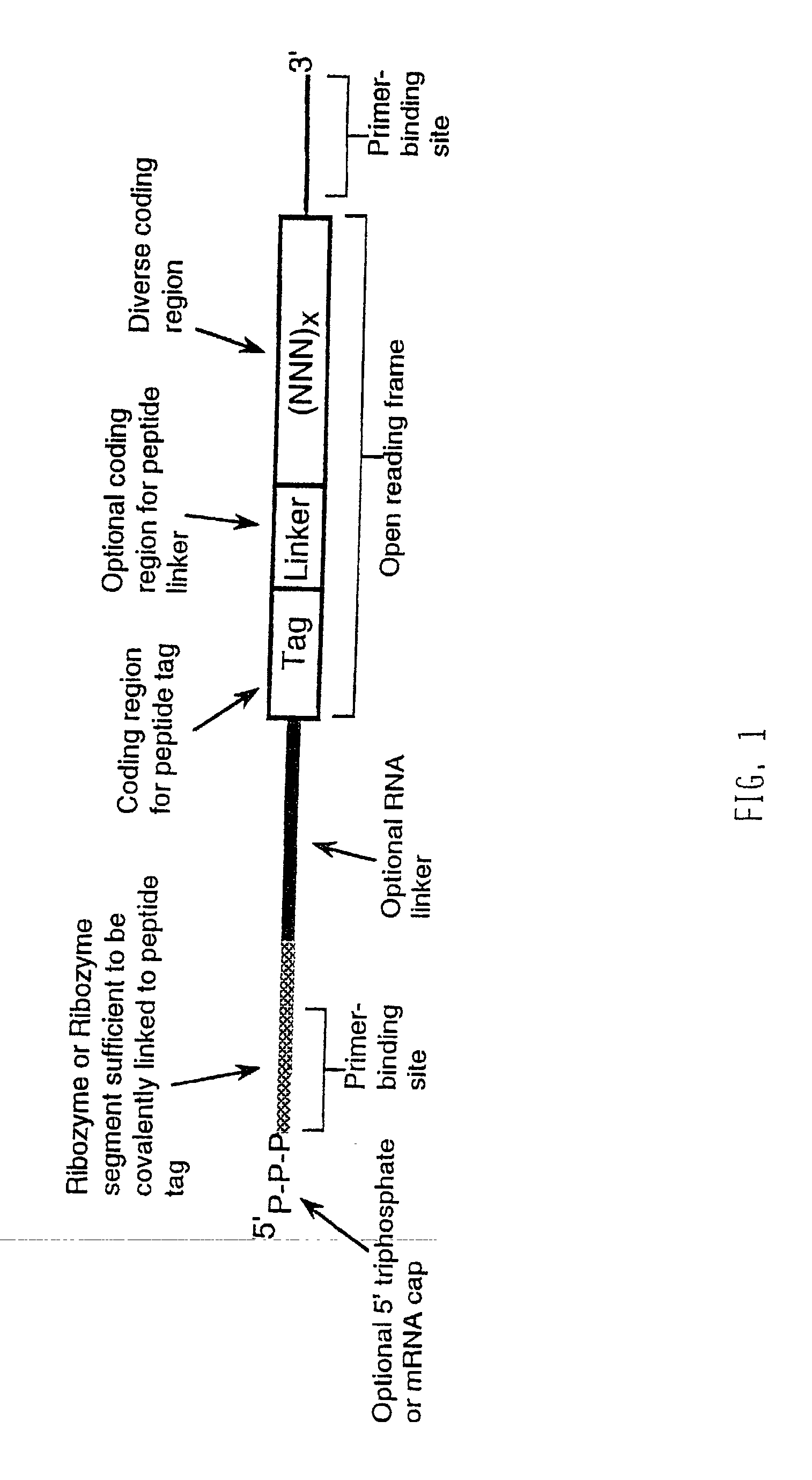
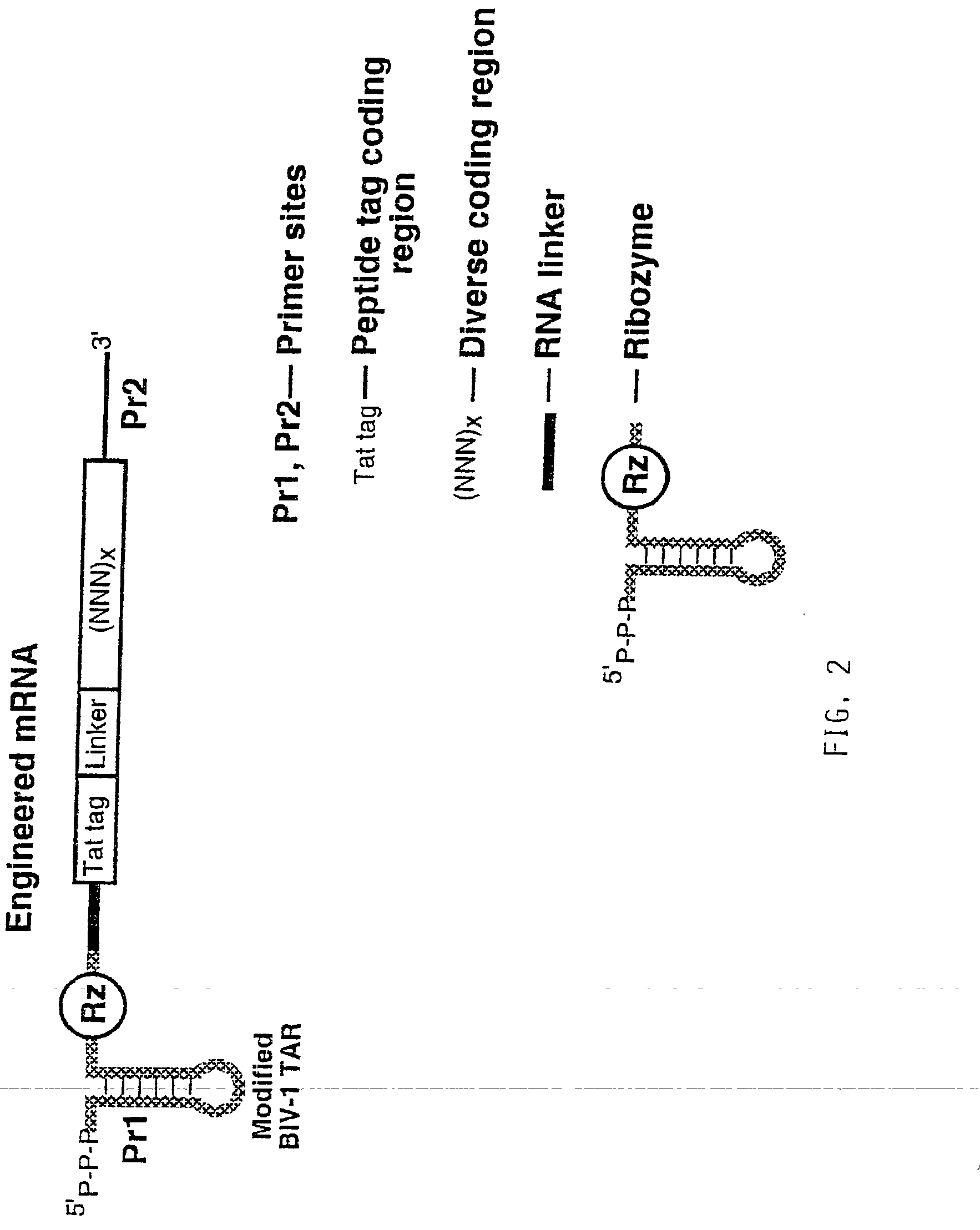
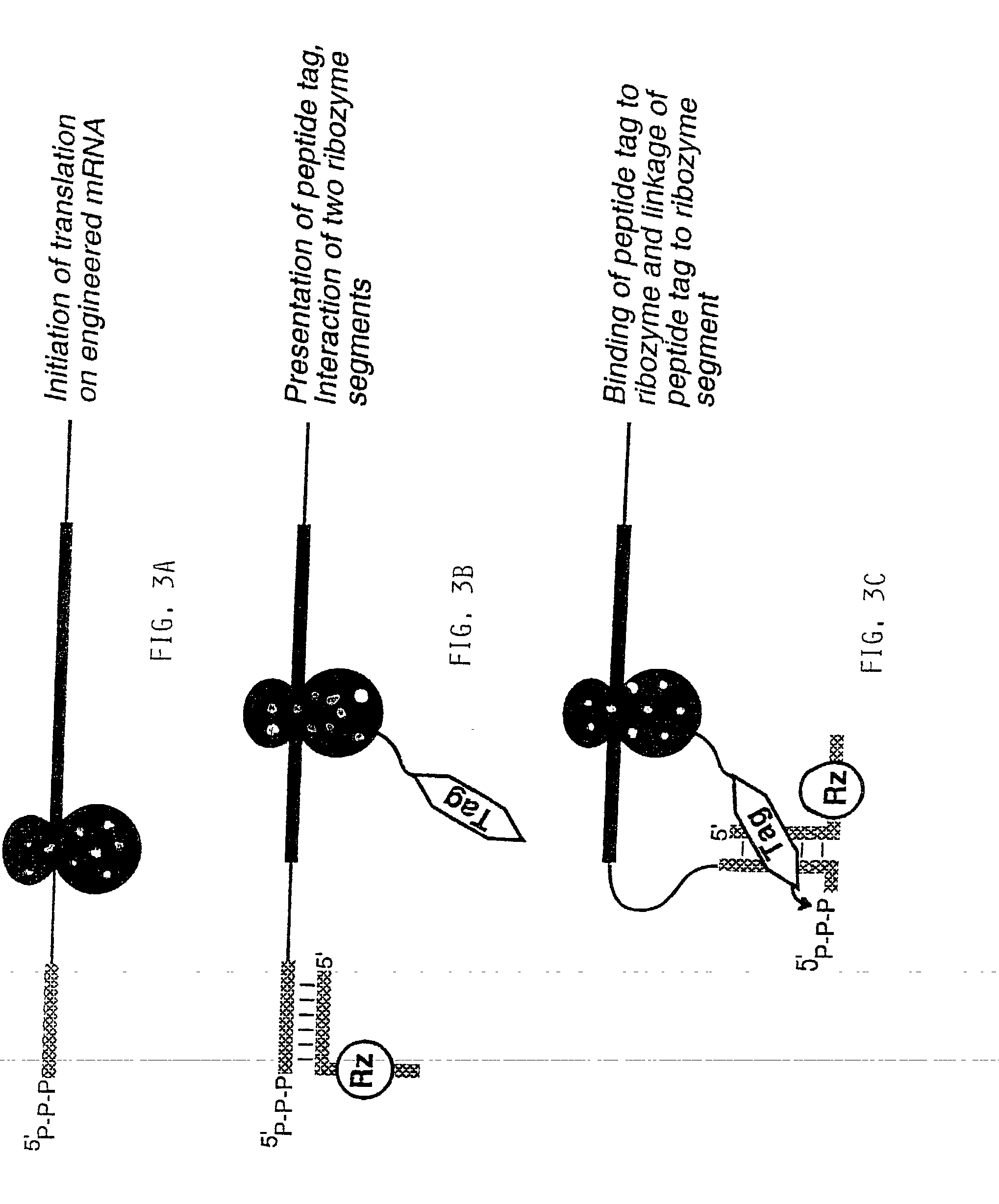
Use of a ribozyme to join nucleic acids and peptides
InactiveUS20030082768A1Good linkageImprove efficiencySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptideRibozyme
Engineered mRNA useful in producing libraries of engineered mRNAs, polypeptide-engineered mRNA conjugates and diverse encoded polypeptide libraries, as well as novel ribozyes that join an mRNA to the translation product of the mRNA and methods of identifying members of diverse encoded polypeptide libraries which exhibit a desired activity. Also described are polypeptide-nucleic acid tag conjugates, methods of producing the conjugates and uses therefor.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Process for modifying a cell by putting material into the cell
InactiveUS20160272961A1Maximize freedomPerformance maximizationOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentDevice formNanoparticle
The present invention relates to a process for modifying a cell by putting material into the cell. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process for modifying a cell by putting material, such as protein, DNA, RNA, ribozyme, various compounds, collagen, cell nucleus, mitochondria or nanoparticle into the cell, by using a sealing-less device formed within one solid and comprises a first passage on which the cell passes; a second passage on which said material passes and connected to the first passage at a position randomly selected between both ends of the first passage; and an apparatus which applies pressure difference or electric potential difference on the first passage and the second passage.
Owner:FEMTOBIOMED INC
Method of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in a human host
The invention relates to the gene encoding the mammalian prostaglandin H synthase-2 and its product. More specifically, the invention relates to the diagnosis of aberrant PGHS-2 gene or gene product; the identification, production, and use of compounds which modulate PGHS-2 gene expression or the activity of the PGHS-2 gene product including but not limited to nucleic acid encoding PGHS-12 and homologues, analogues, and deletions thereof, as well as antisense, ribozyme, triple helix, antibody, and polypeptide molecules as well as small inorganic molecules; and pharmaceutical formulations and routes of administration for such compounds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
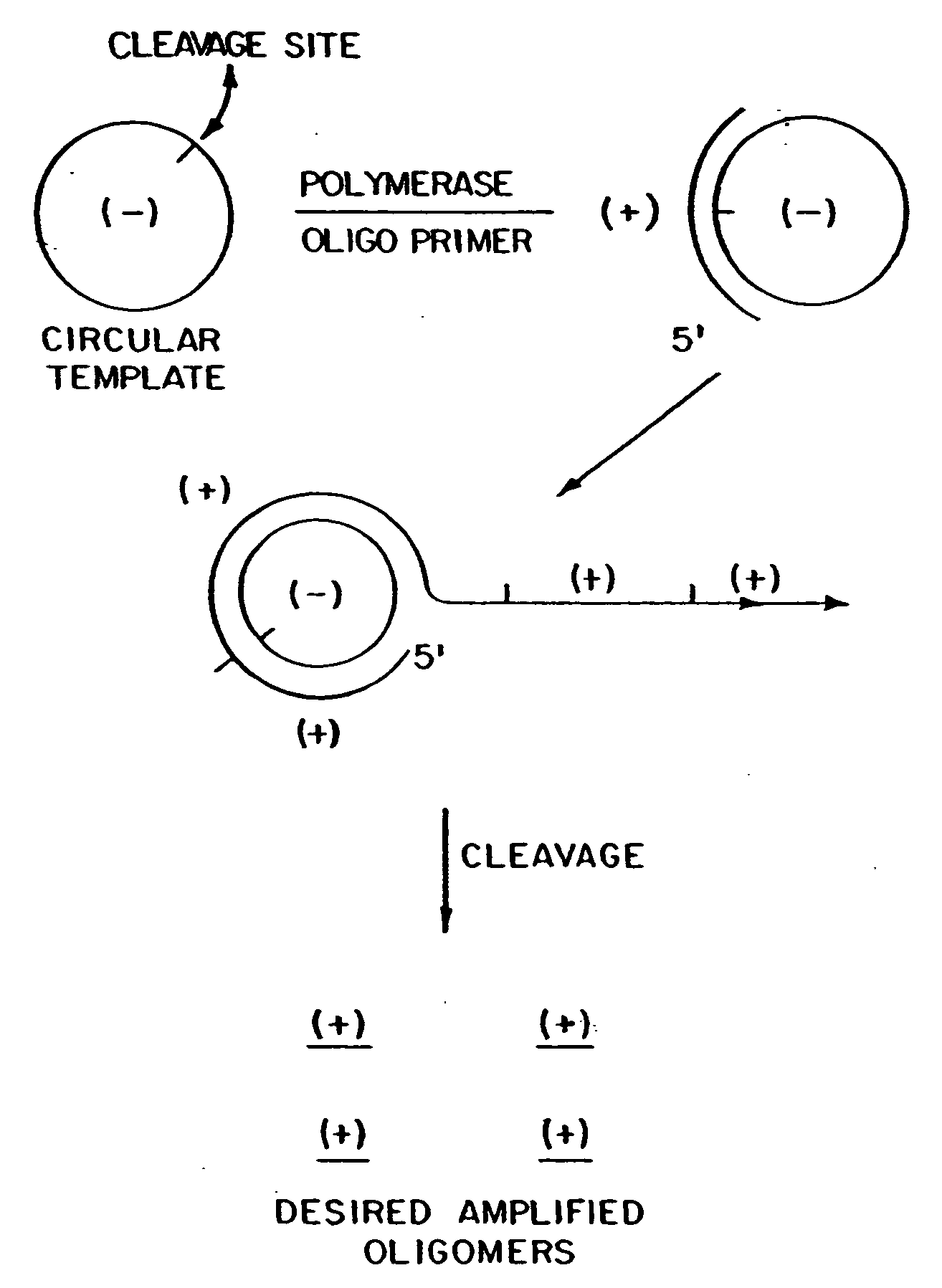
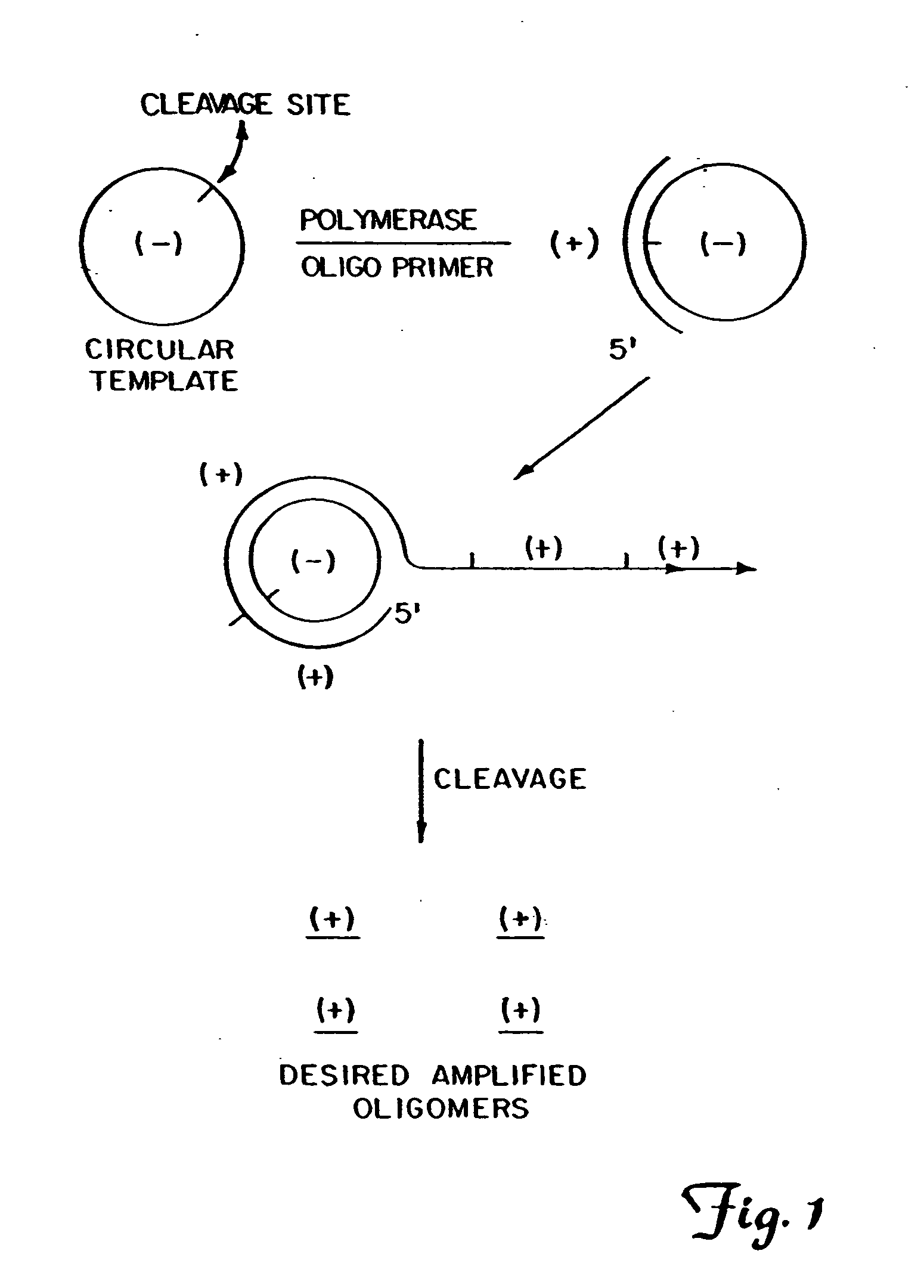
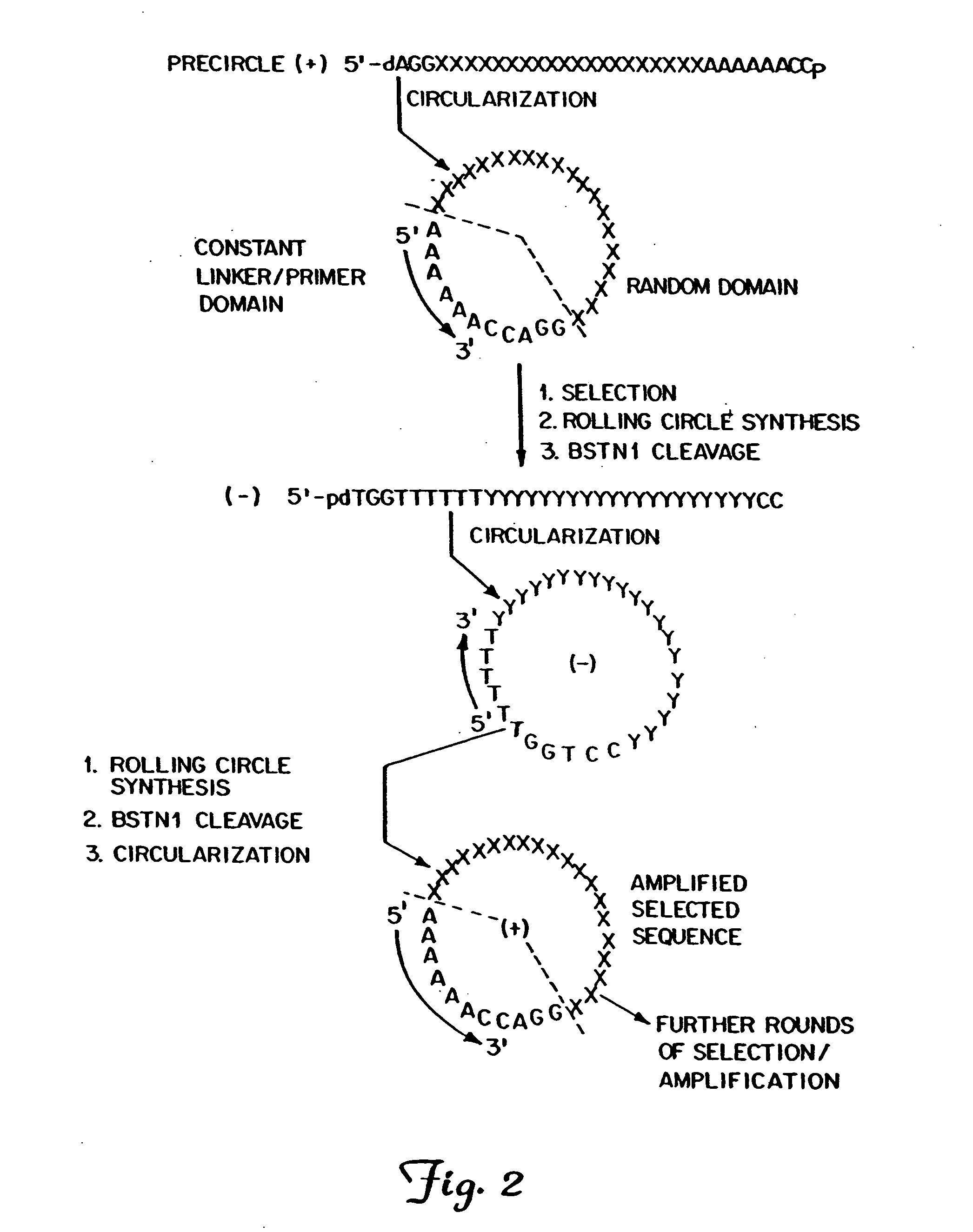
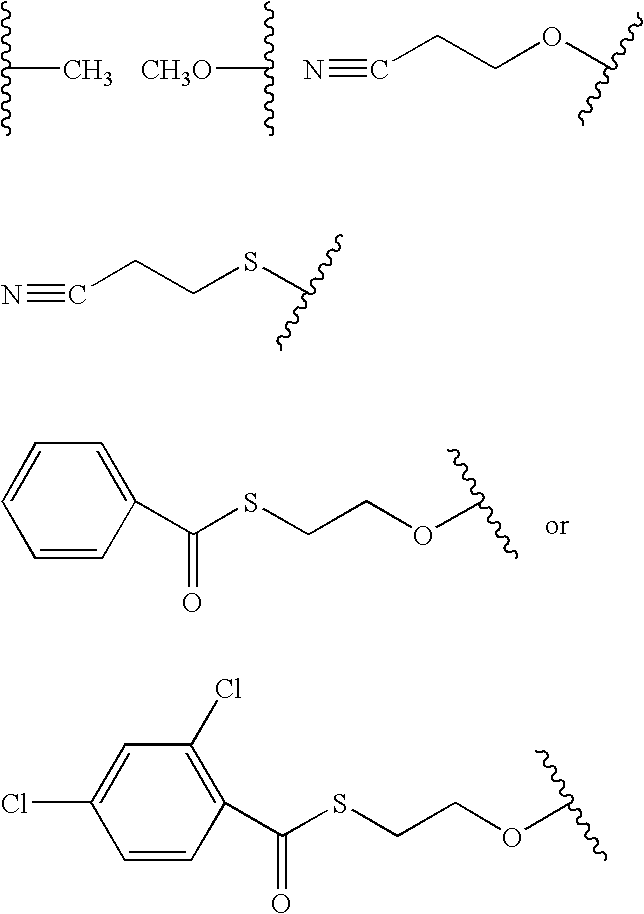
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Fluoroalkoxy, nucleosides, nucleotides, and polynucleotides
InactiveUS20050266422A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunitySugar derivativesActivity regulationDiseaseDecoy
The present invention related to fluoroalkoxy (“—OCF3”) nucleosides, nucleotides, and polynucleotides comprising fluoroalkoxy nucleotides. The present invention also relates to methods of synthesizing fluoroalkoxy nucleosides, nucleotides, and polynucleotides comprising fluoroalkoxy nucleotides. The present invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity. The invention also relates to fluoroalkoxy modified nucleic acid molecules, such as ribozymes, antisense, aptamers, decoys, triplex forming oligonucleotides (TFO), immune stimulatory oligonucleotides (ISO), immune modulatory oligonucleotides (IMO), and small nucleic acid molecules, including short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against polynucloetide targets. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions to treat, prevent, inhibit, or reduce diseases, traits, or conditions in a subject or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Particle delivery techniques
InactiveUS20050271733A1Reduce deliveryPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsPresent methodBiology
A method is provided for in vivo or ex vivo delivery of a preparation of powdered nucleic acid molecules into vertebrate tissue for transformation of cells in the tissue using needleless injection techniques. The method can be used to deliver therapeutically relevant nucleotide sequences to cells in mammalian tissue to provide gene therapy, elicit immunity or to provide antisense or ribozyme functions. A method for providing densified processed pharmaceutical compositions is also described. The method is used to convert non-dense pharmaceutical powders or particulate formulations into densified particles optimally suited for transdermal delivery using a needleless syringe. The method is also used to optimize the density and particle size of powders and particulate formulations for subsequent transdermal delivery thereof. Densified pharmaceutical compositions formed by the present methods are also provided.
Owner:POWDERJECT RES LTD OXFORD (GB)
RNA interference target for treating hepatitis B virus infection
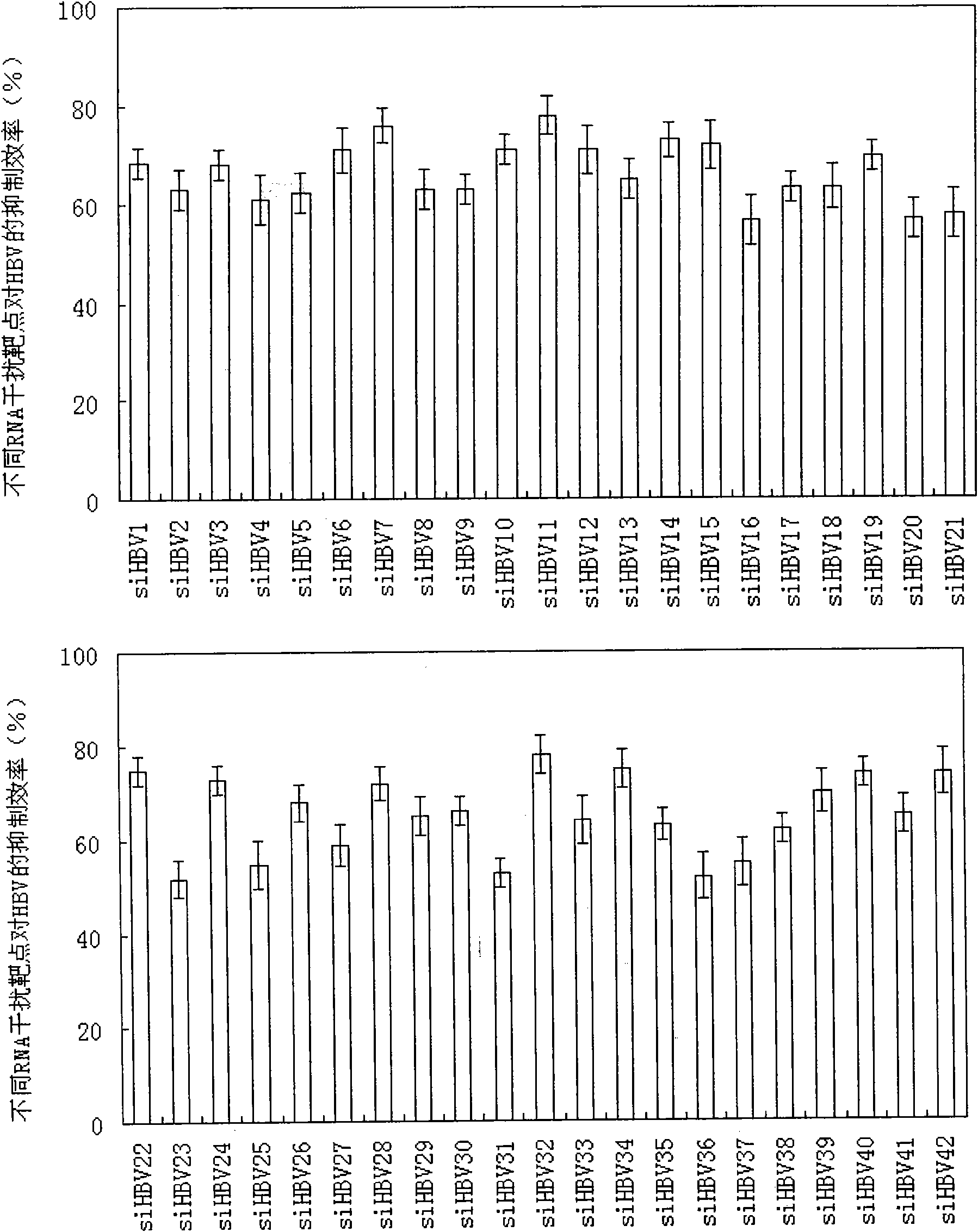
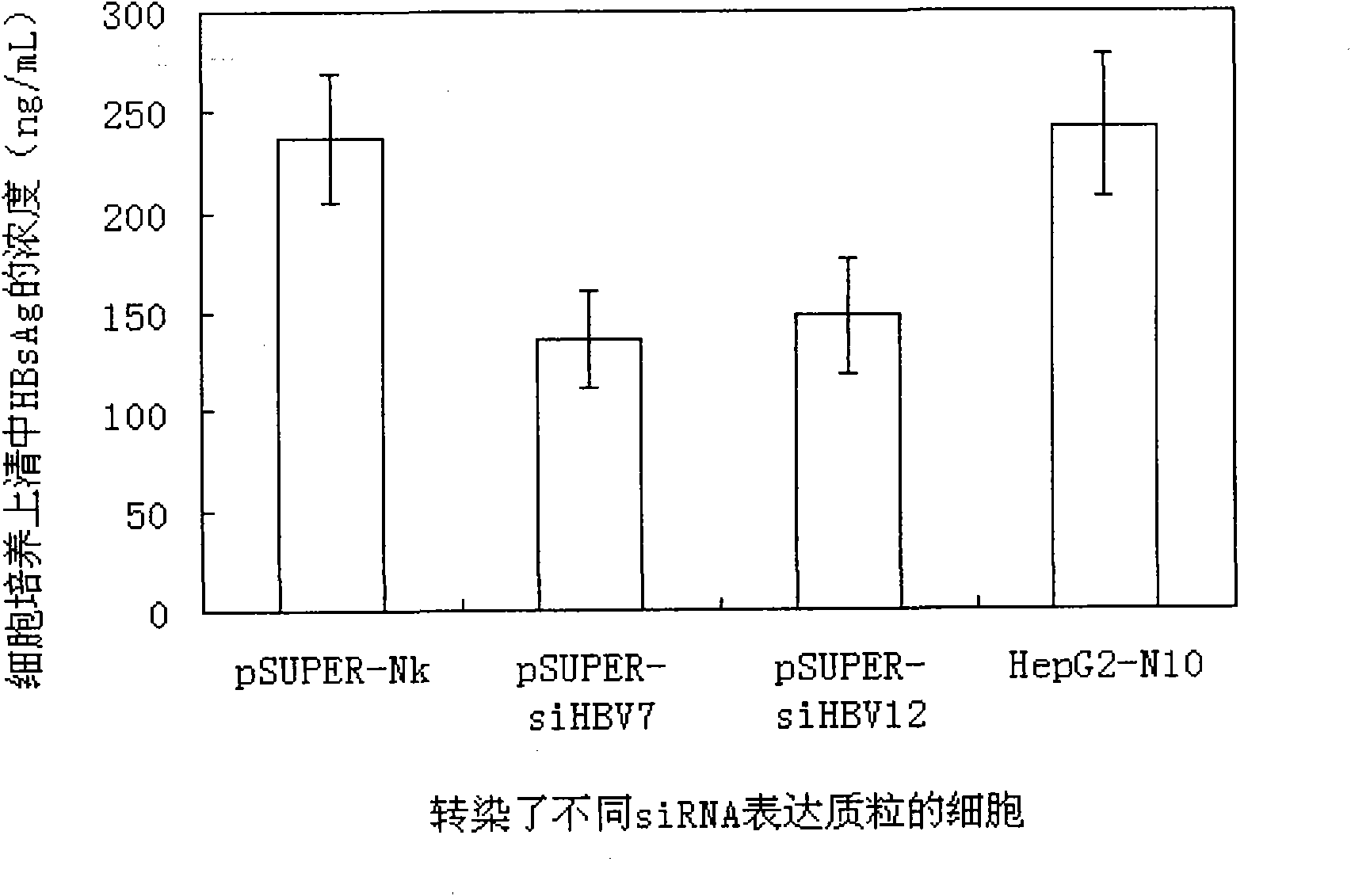
The invention relates to an RNA interference target for treating hepatitis B virus infection with 42 different targeting hepatitis B viruses (HBV), which can be used for preparing a medicament for treating the hepatitis B virus infection. The invention provides a recombinant expression vector of siRNA and / or miRNA and / or ribozyme and / or antisense oligonucleotide, which can be used for expressing targeting HBV. The invention relates to a cell which has the function of inhibiting the expression of HBV virus gene and can express and / or is induced with the siRNA and / or the miRNA and / or the ribozyme and / or the antisense oligonucleotide and / or the medication obtained according to the RNA interference target.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
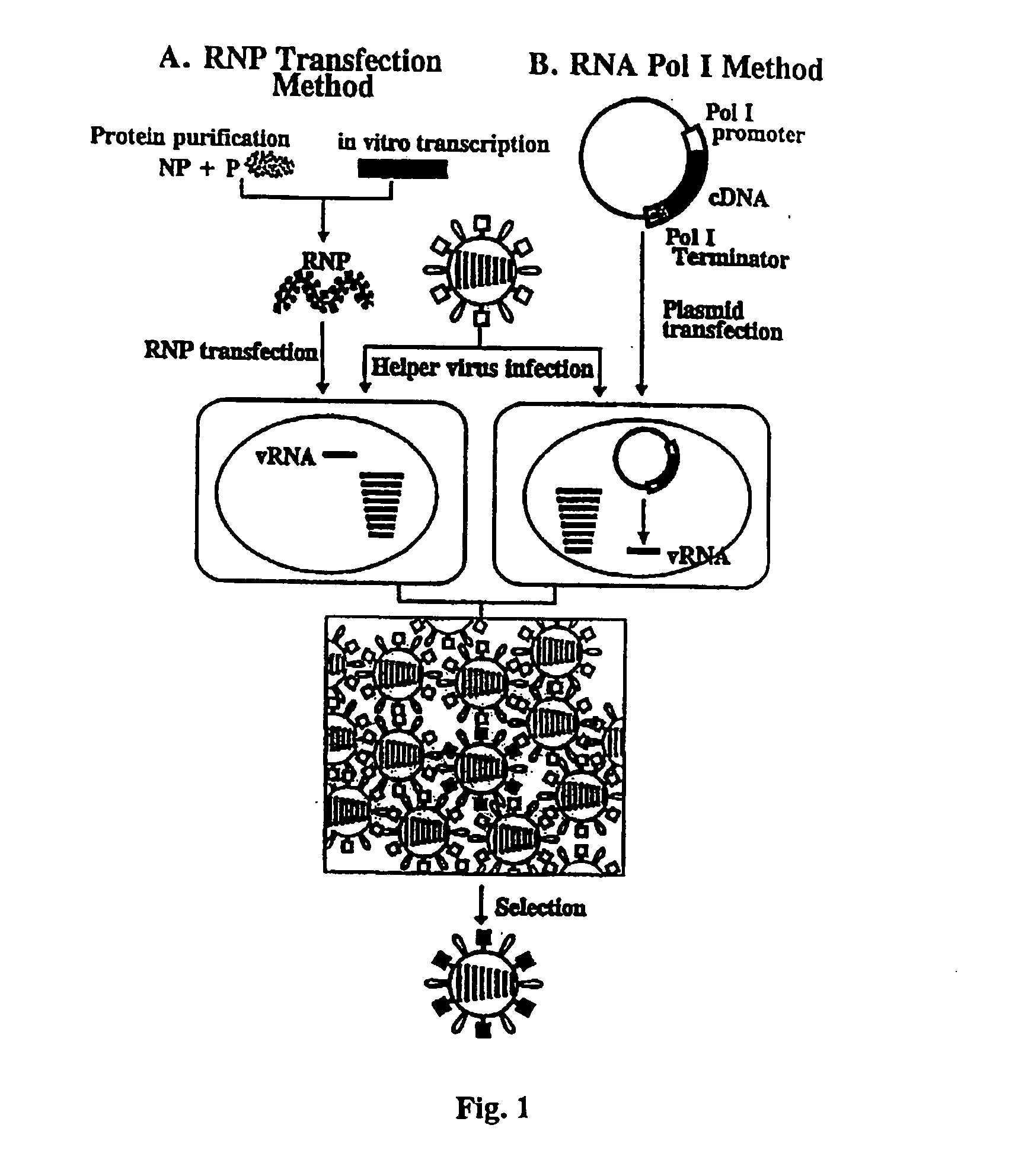
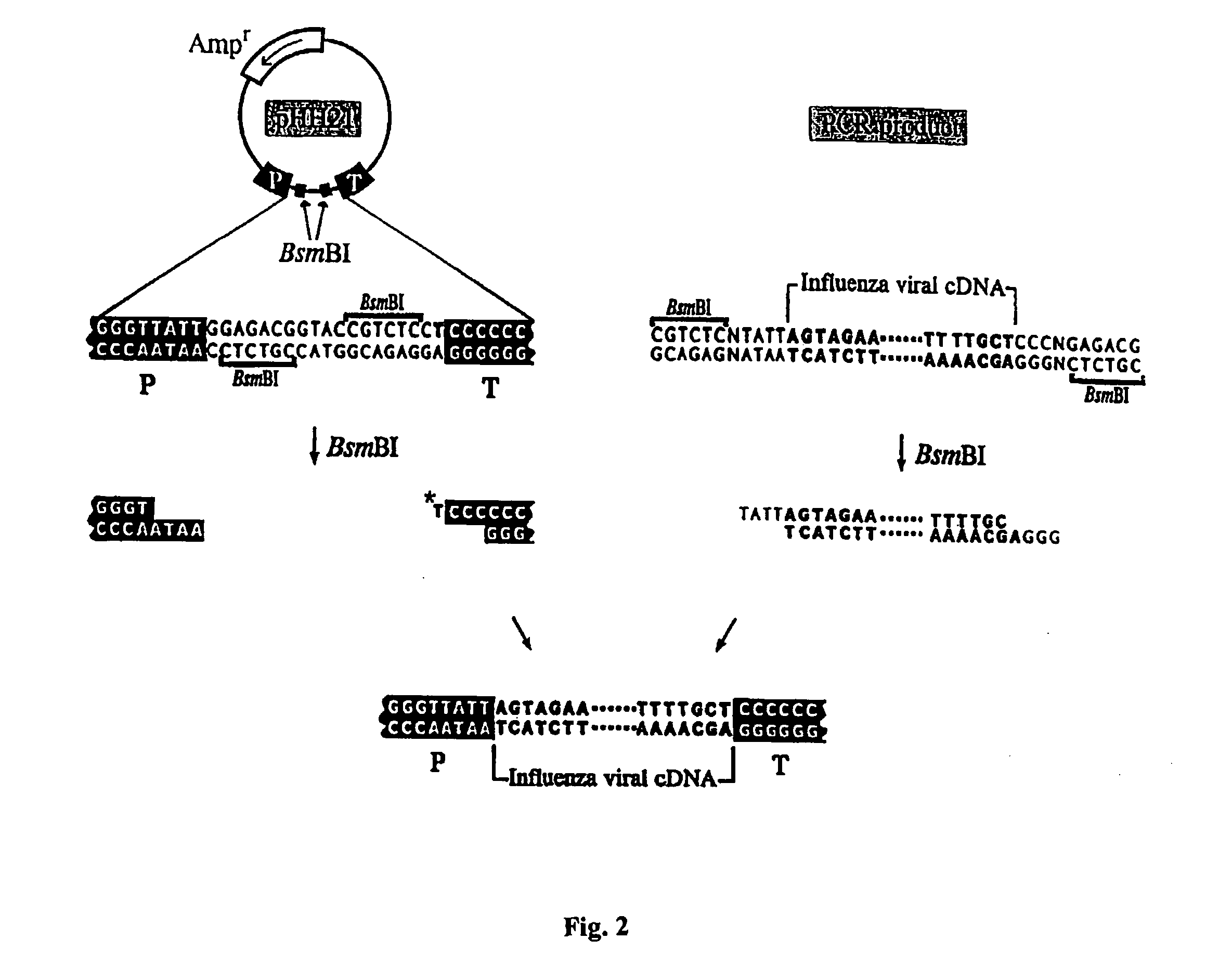
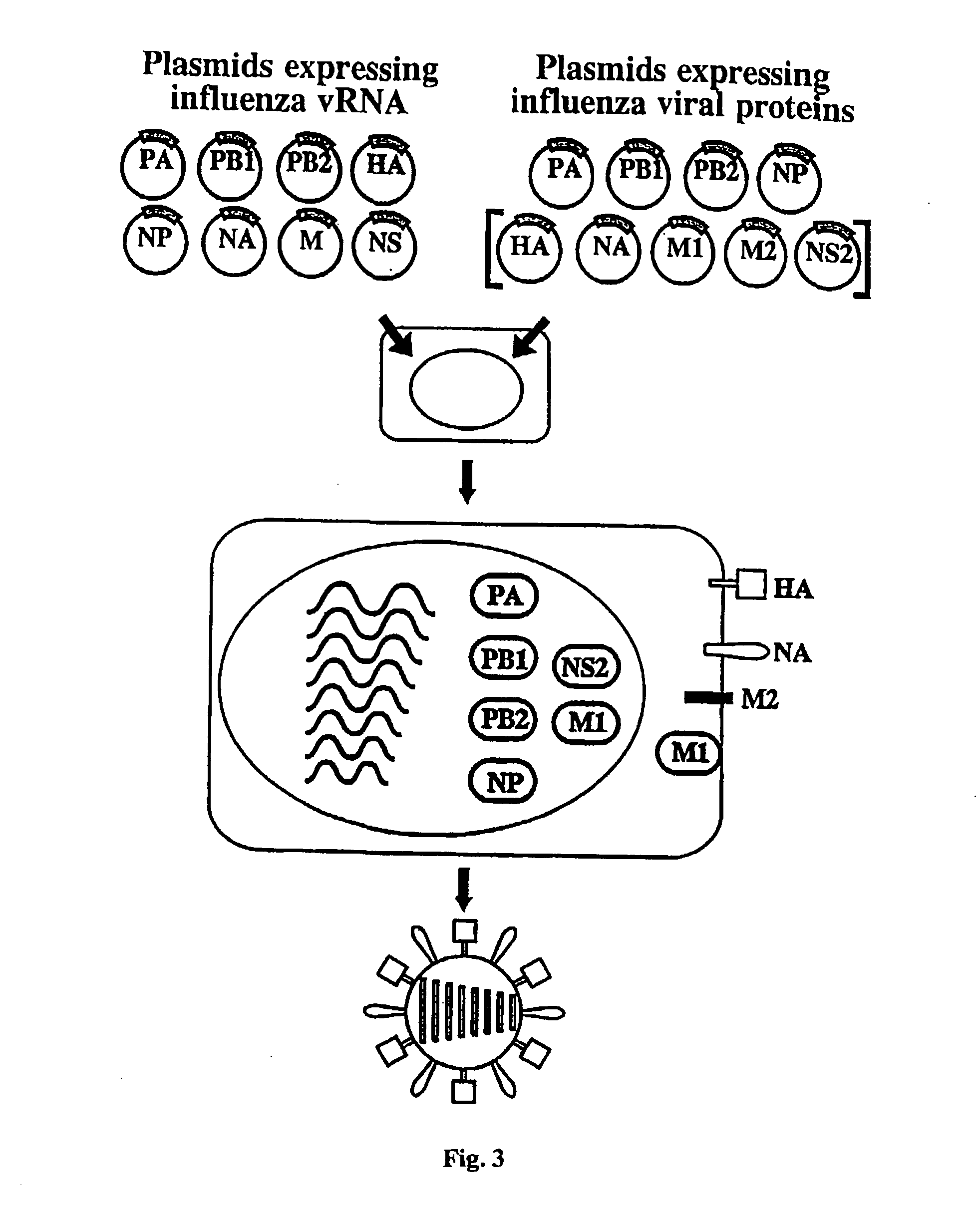
Recombinant influenza vectors with a PolII promoter and ribozymes for vaccines and gene therapy
InactiveUS20050037487A1Easy to operateEnhances these viruses as vaccine vectorsSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHelper virusViral vector
The invention provides a composition useful to prepare influenza viruses, e.g., in the absence of helper virus, using vectors which include Po1II promoters and multiple ribozyme sequences.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
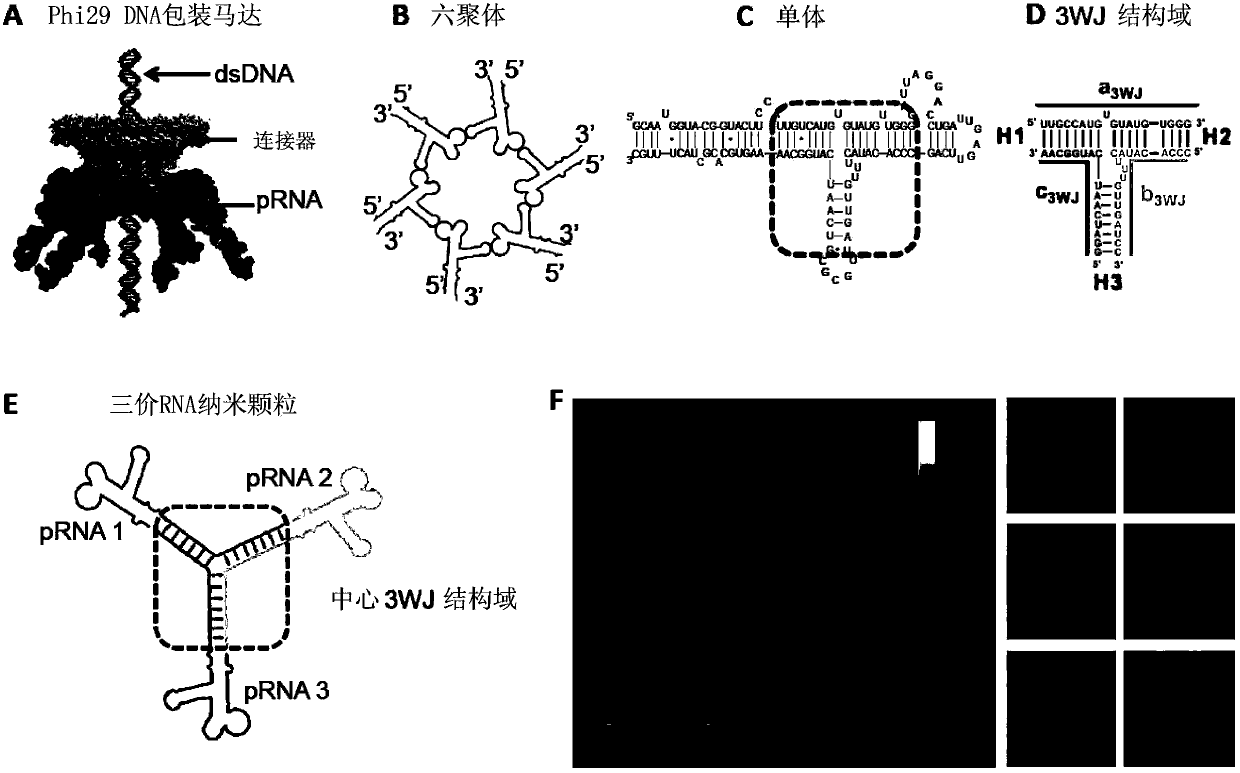
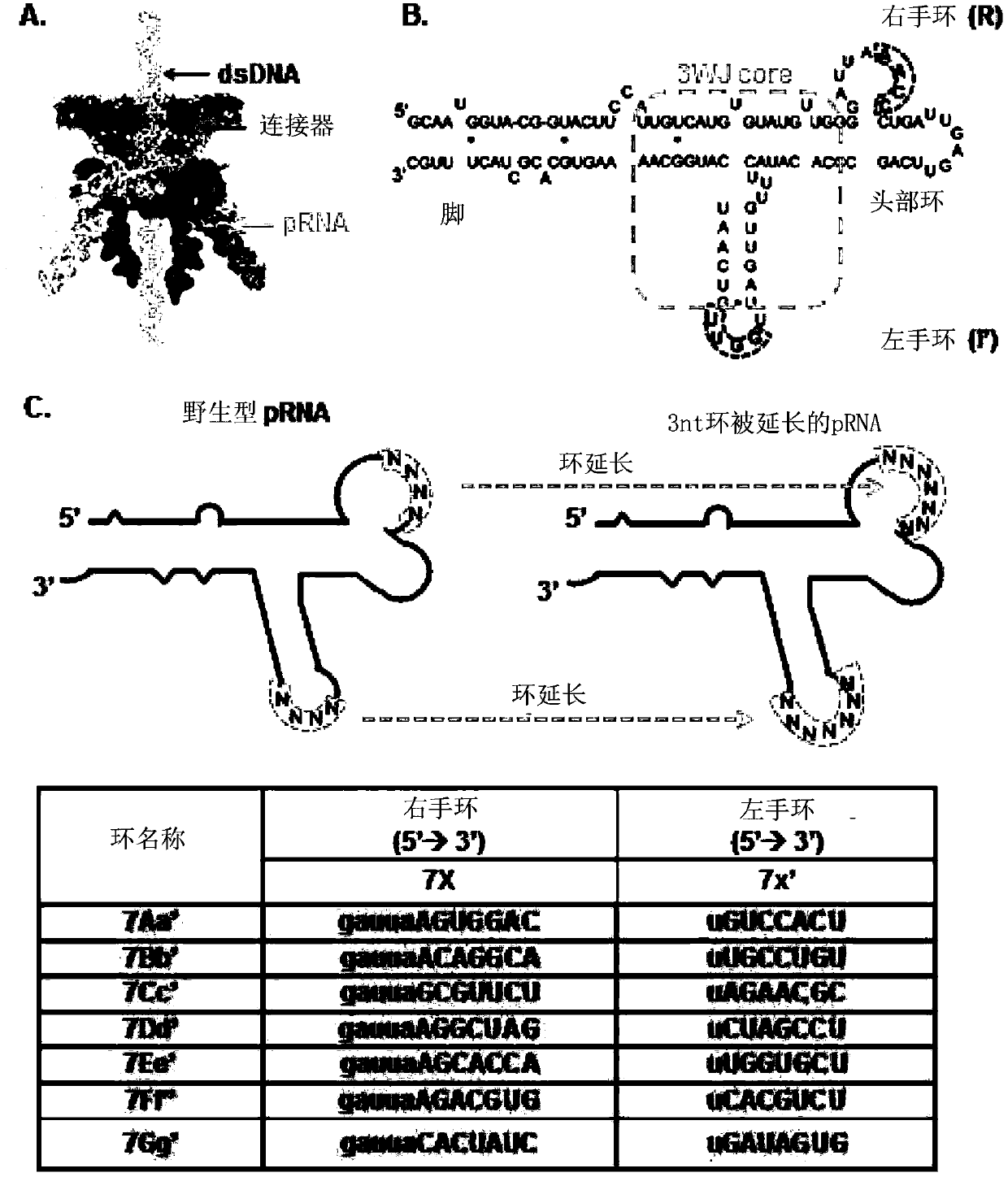
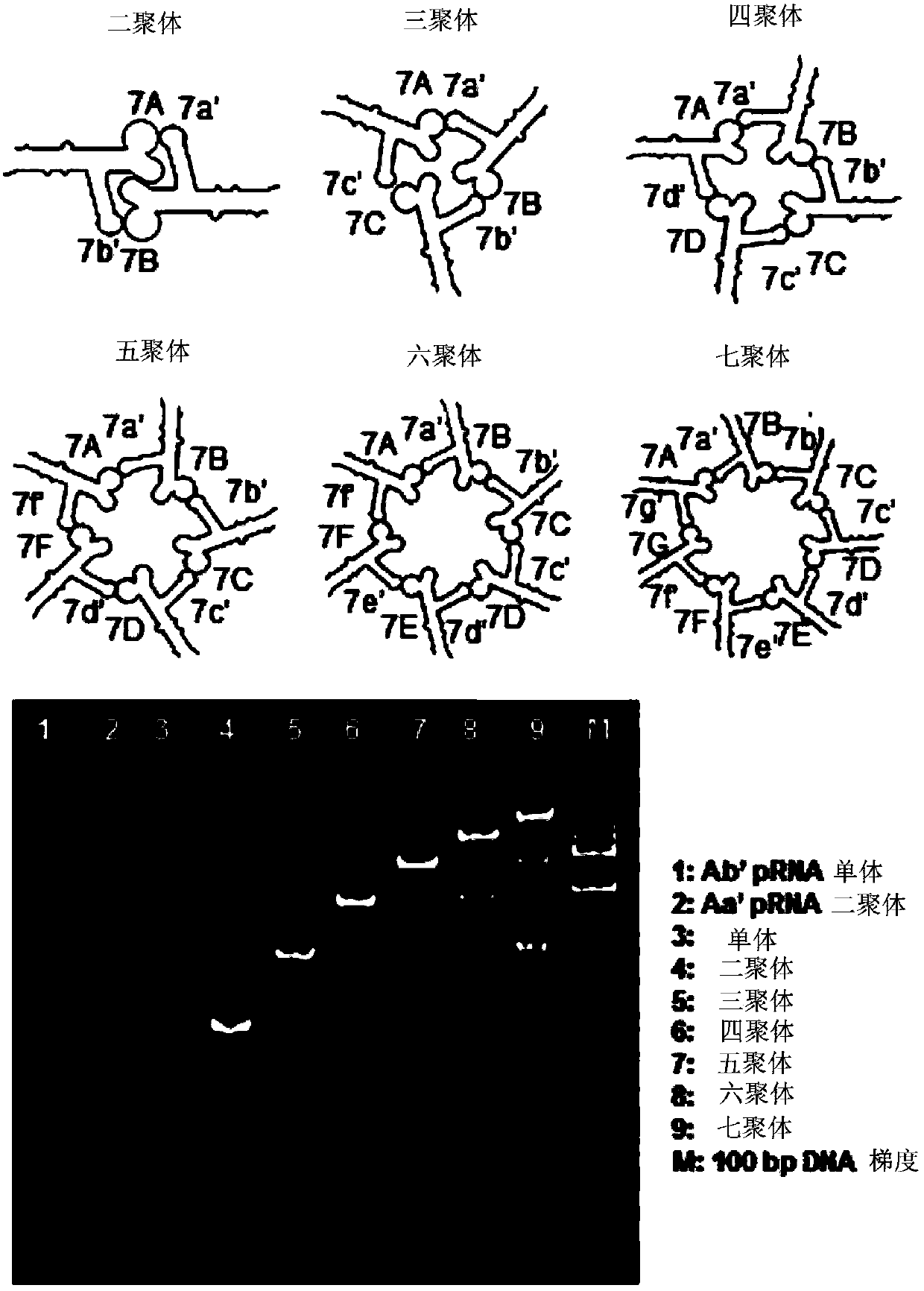
PRNA mutlivalent junction domain for use in stable multivalent RNA nanoparticles
ActiveCN103403189AStrong specificityImprove targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiagnostic agentNanoparticle
Trifurcate RNA junction domains derived from phi29 pRNA are described that assemble with high affinity and that are stable in vitro and in vivo. Further expansion of trifurcated RNA domains to multiple way junction scaffolds via creative designs enable an array of toolkit to construct nanoparticle architectures with diverse shapes and angles. The scaffolds can be used to form RNA nanoparticles having a wide variety of uses, including promotion of RNA crystallization, creation of RNA aptamer with high affinity to mimic antibody, delivery of therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents such as biologically active RNA-based moieties, including siRNA, ribozymes, aptamers, and others.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
RNA interference target for treating aids
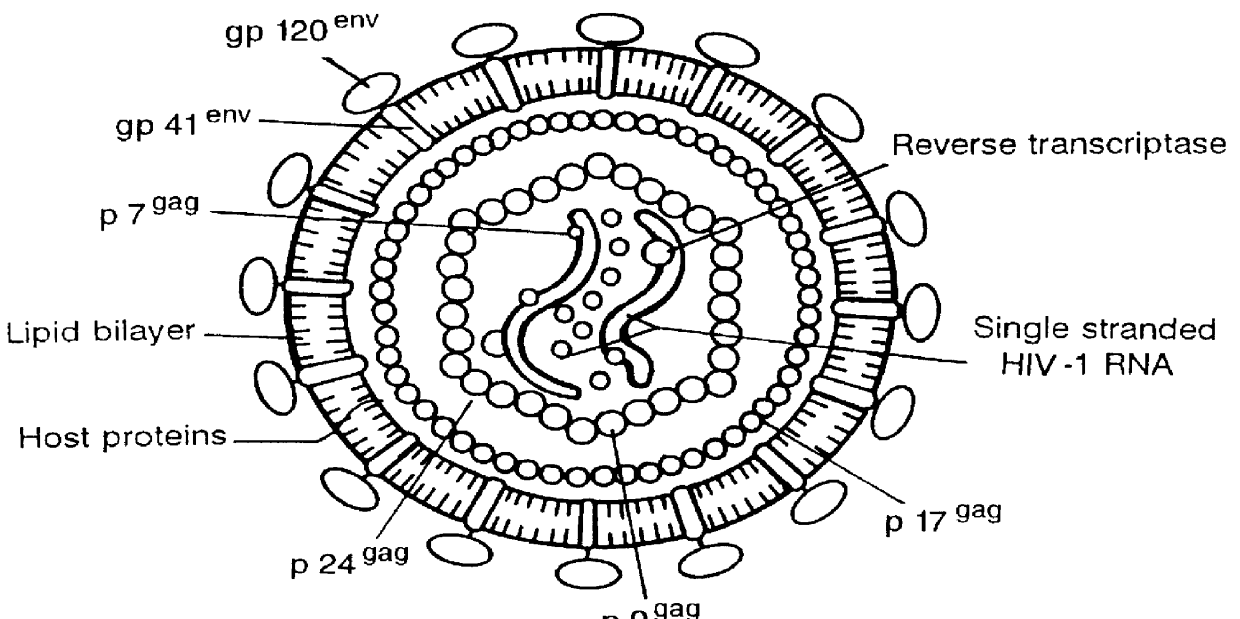
The present invention relates to RNA interference target sequence targeting HIV for the treatment of AIDS. Based on the target sequence, recombinant expression vectors, packaging vectors and cells were constructed, which express a siRNA and / or a miRNA and / or a ribozyme and / or an antisense oligonucleotide targeting HIV. Also provided is the use of the recombinant expression vectors, packaging vectors and recombinant cells in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of AIDS.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment and diagnosis of conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death. The invention encompasses protective nucleic acids which, when introduced into a cell predisposed to undergo cell death or in the process of undergoing cell death, prevent, delay, or rescue the cell from death relative to a corresponding cell into which no exogenous nucleic acids have been introduced. The invention encompasses nucleic acids of the protective sequence, host cell expression systems of the protective sequence, and hosts that have been transformed by these expression systems, including transgenic animals. The invention also encompasses novel protective sequence products, including proteins, polypeptides and peptides containing amino acid sequences of the proteins, fusion proteins of proteins, polypeptides and peptides, and antibodies directed against such gene products. The invention further relates to target sequences, including upstream and downstream regulatory sequences or complete gene sequences, antibodies, antisense molecules or sequences, ribozyme molecules, and other inhibitors or modulators directed against such protective sequences, protective sequence products, genes, gene products, and / or their regulatory elements involved in cell death. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases, involving cell death, including, but not limited to, treatment of the types of conditions, disorders, or diseases, which can be prevented, delayed or rescued from cell death and include, but are not limited to, those associated with the central nervous system, including neurological and psychiatric conditions, disorders, or diseases, and those of the peripheral nervous system. Further, the invention relates to methods of using the protective sequence, protective sequence products, and / or their regulatory elements for the identification of compounds that modulate the expression of the protective sequence and / or the activity of the protective sequence product. Such compounds can be useful as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various conditions, disorders, or diseases involving cell death.
Owner:COGENT NEUROSCI
System and method for loading a beneficial agent into a medical device
A system for delivery of a beneficial agent in the form of a viscous liquid or paste allows holes in a medical device to be loaded in a single step process. The loading of a beneficial agent in a paste form also provides the ability to deliver large and potentially sensitive molecules including proteins, enzymes, antibodies, antisense, ribozymes, gene / vector constructs, and cells including endothelial cells.
Owner:INNOVATIONAL HLDG LLC
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS7138565B2Reduce expressionFused cellsOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
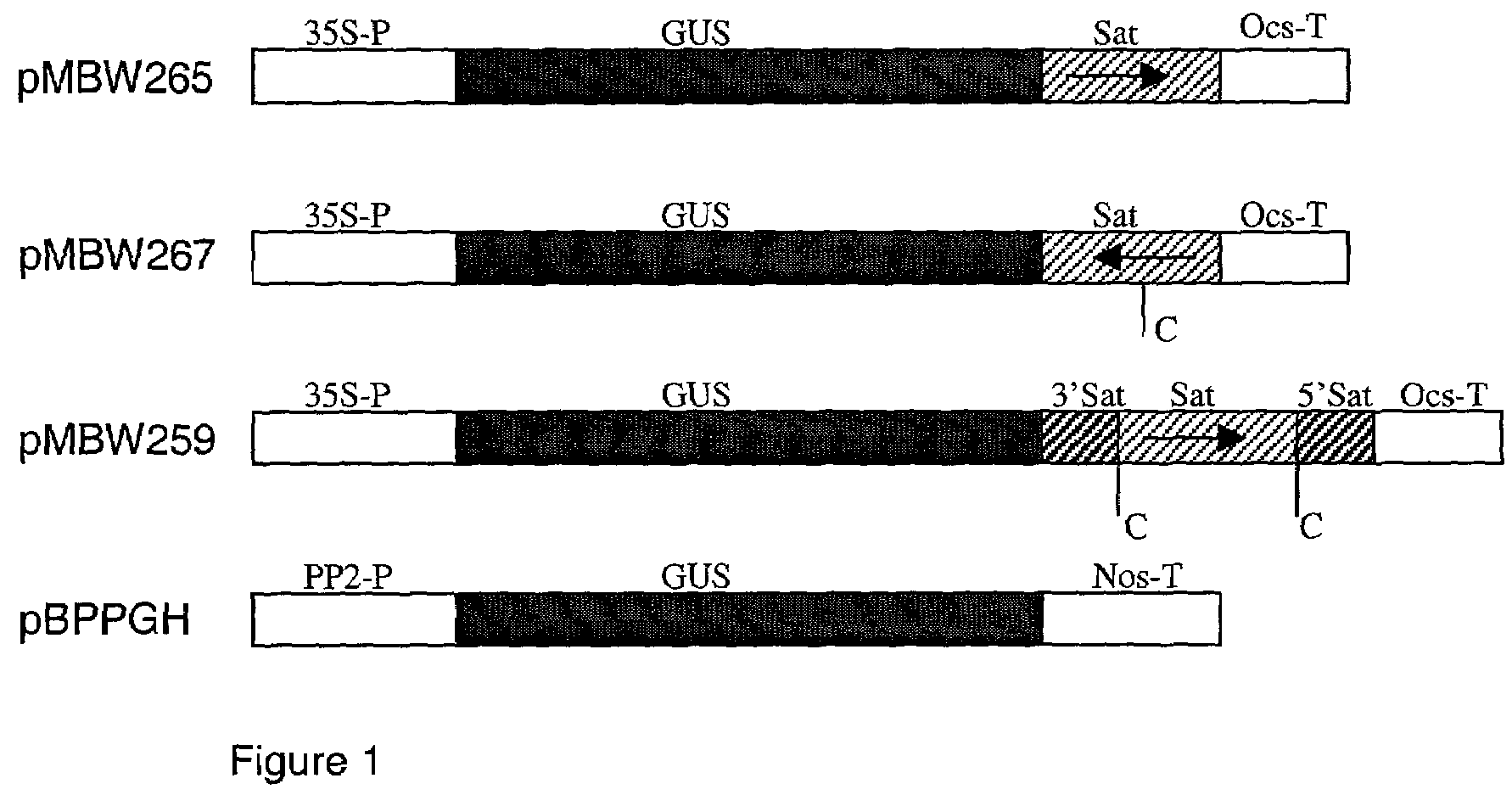
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specific RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
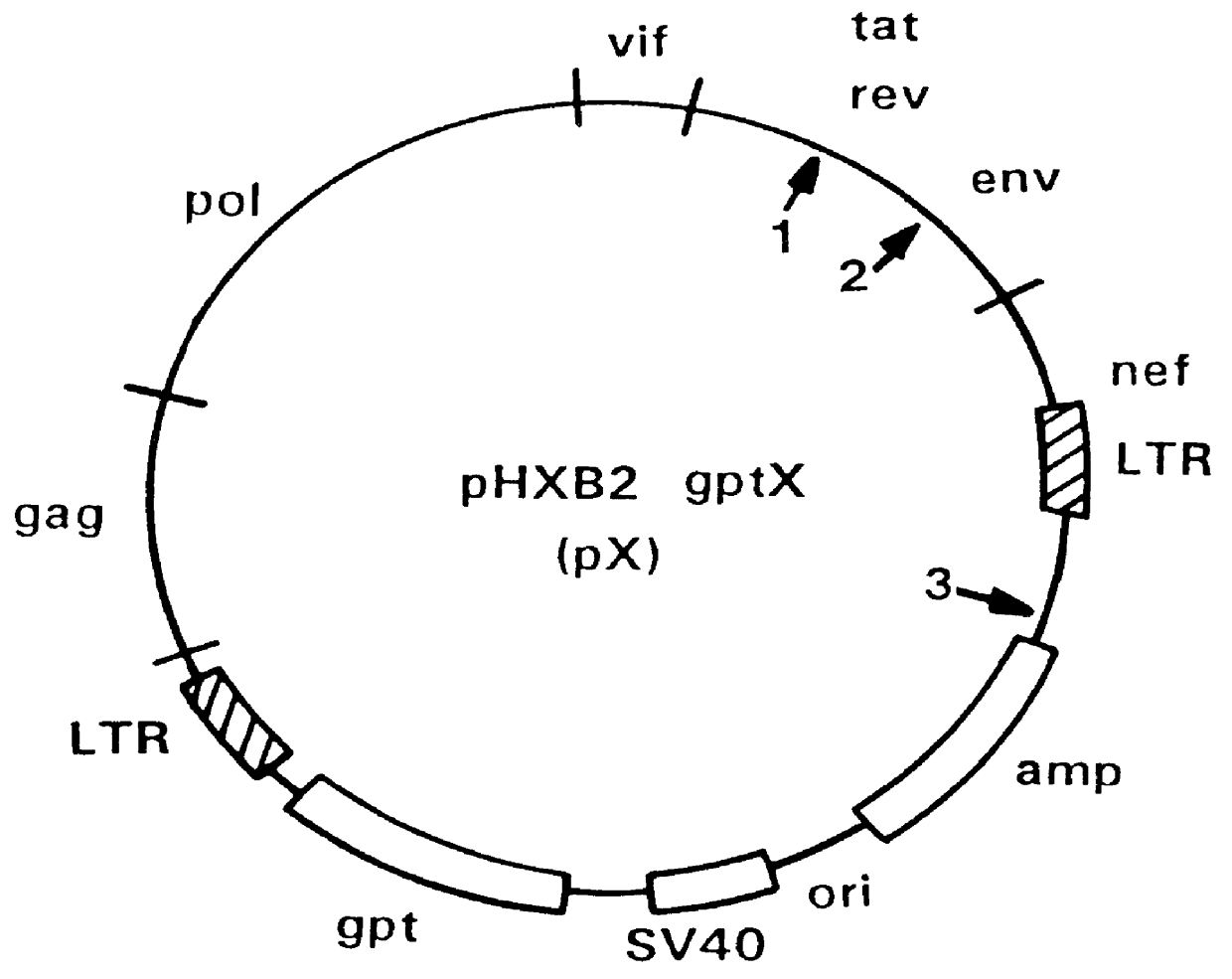
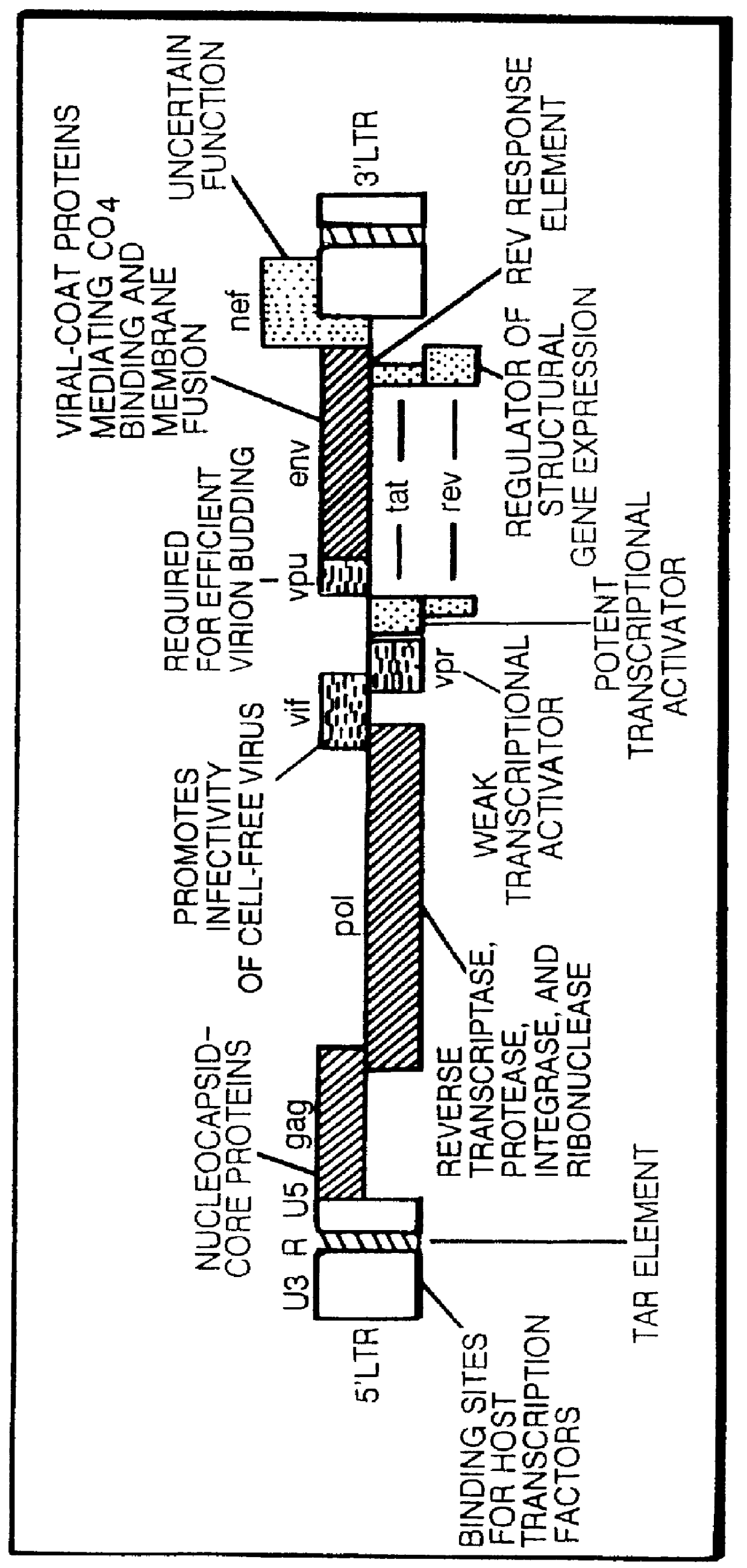
Antisense viruses and antisense-ribozyme viruses
InactiveUS6107062AFacilitating recombinant clone screeningGood compensationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsViral infectionRibozyme
Antisense viruses and antisense ribozyme viruses are disclosed. The novel artificial viruses, their synthesis and their use in preventing and treating viral infections are presented.
Owner:INPAX
Methods and compositions for liver specific delivery of therapeutic molecules using recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS20010051611A1Prevent and limit expressionPrevents terminal glycosylationOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseHepatic Diseases
Provided are methods for selectively expressing therapeutic molecules, such as secretory proteins, antisense molecules and ribozymes, in the liver. The methods find use in treating hepatic diseases or conditions. The methods also find use in treating any disease or condition in which systemic administration of the therapeutic substance, for example, a secretory protein, is desired. The methods involve administering to a mammalian patient having a need for liver expression of a therapeutic molecule an AAV vector containing a therapeutically effective amount of the therapeutic molecule. Also provided are novel vectors employable in these methods.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
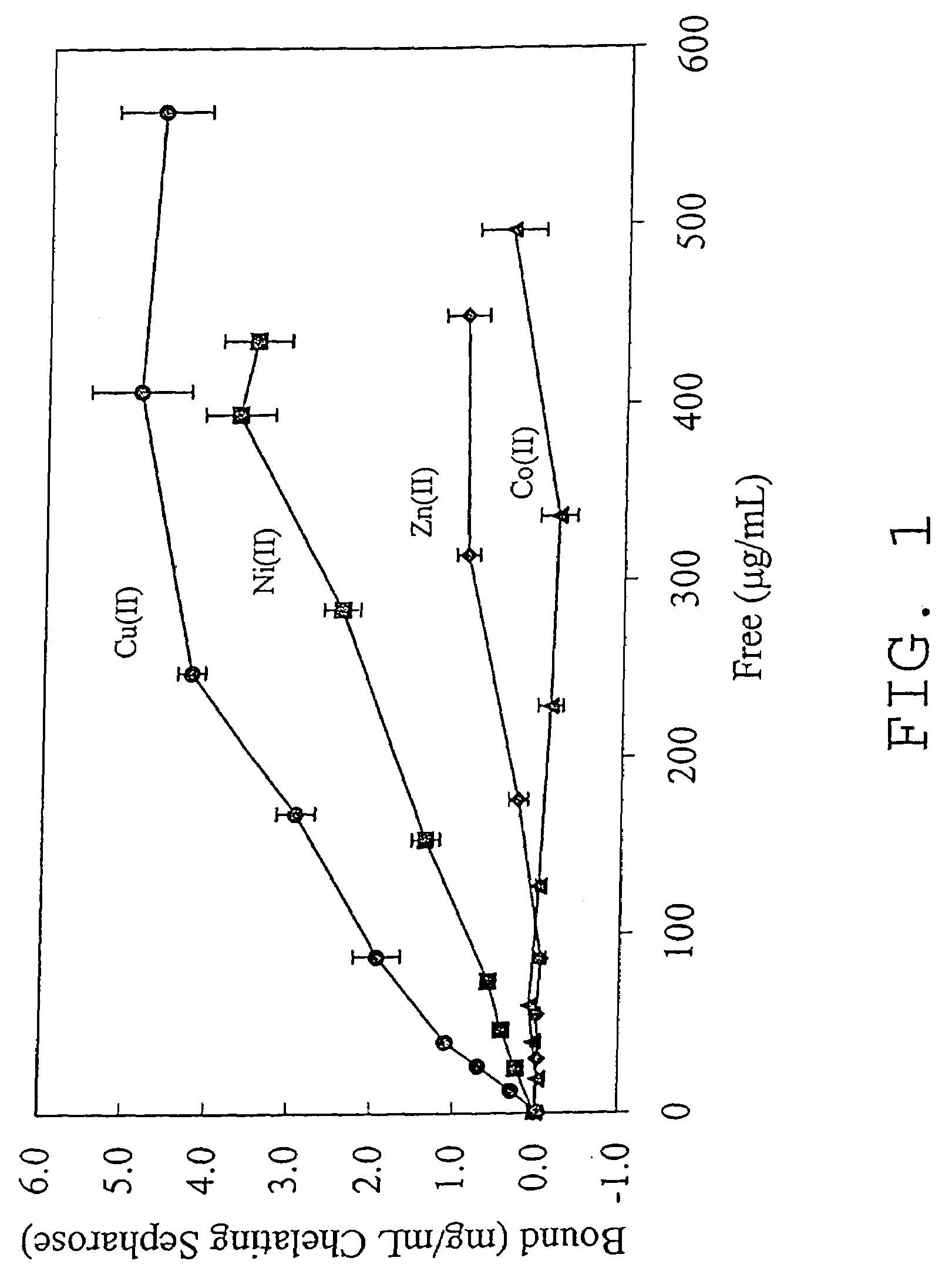
Nucleic acid separation using immobilized metal affinity chromatography
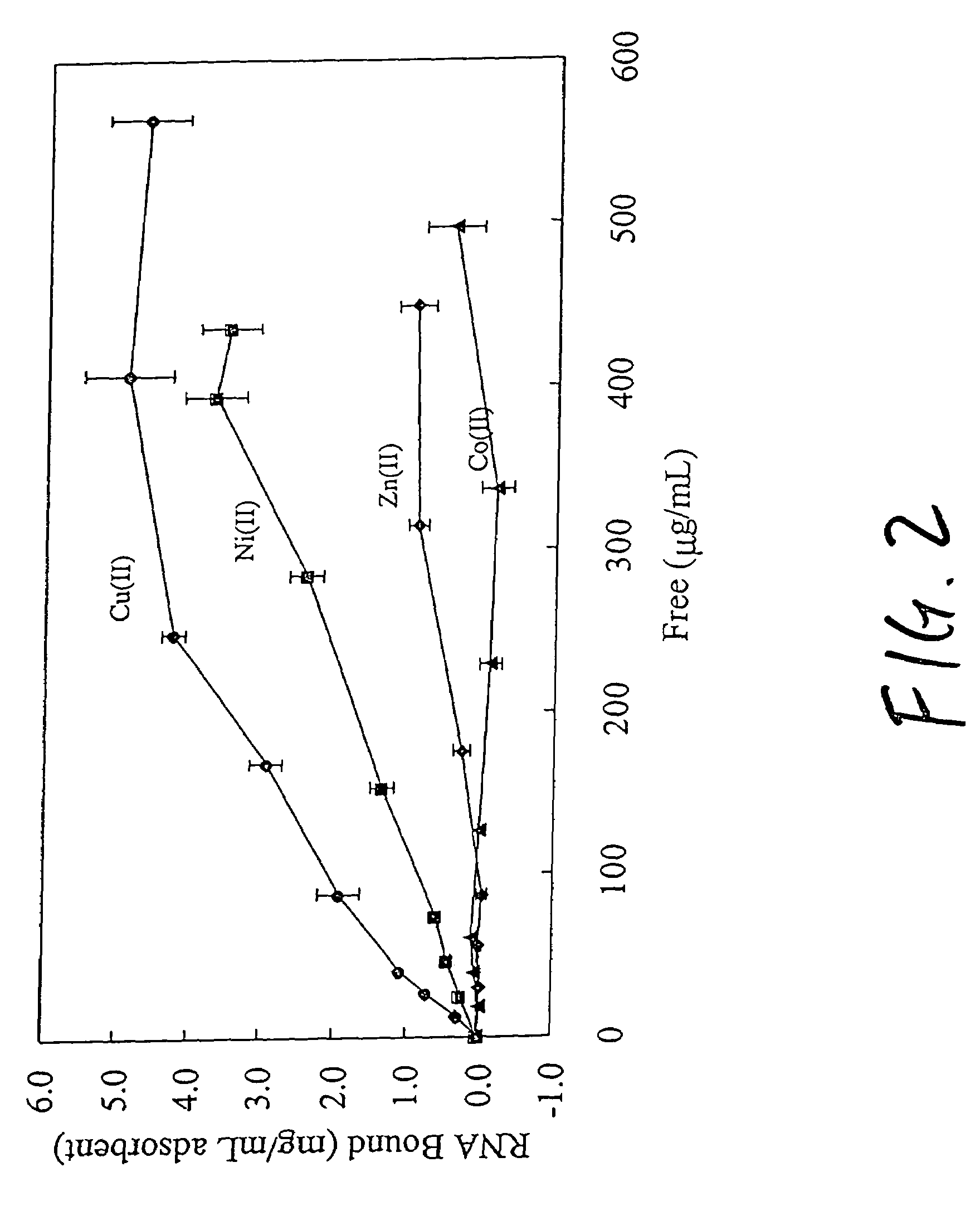
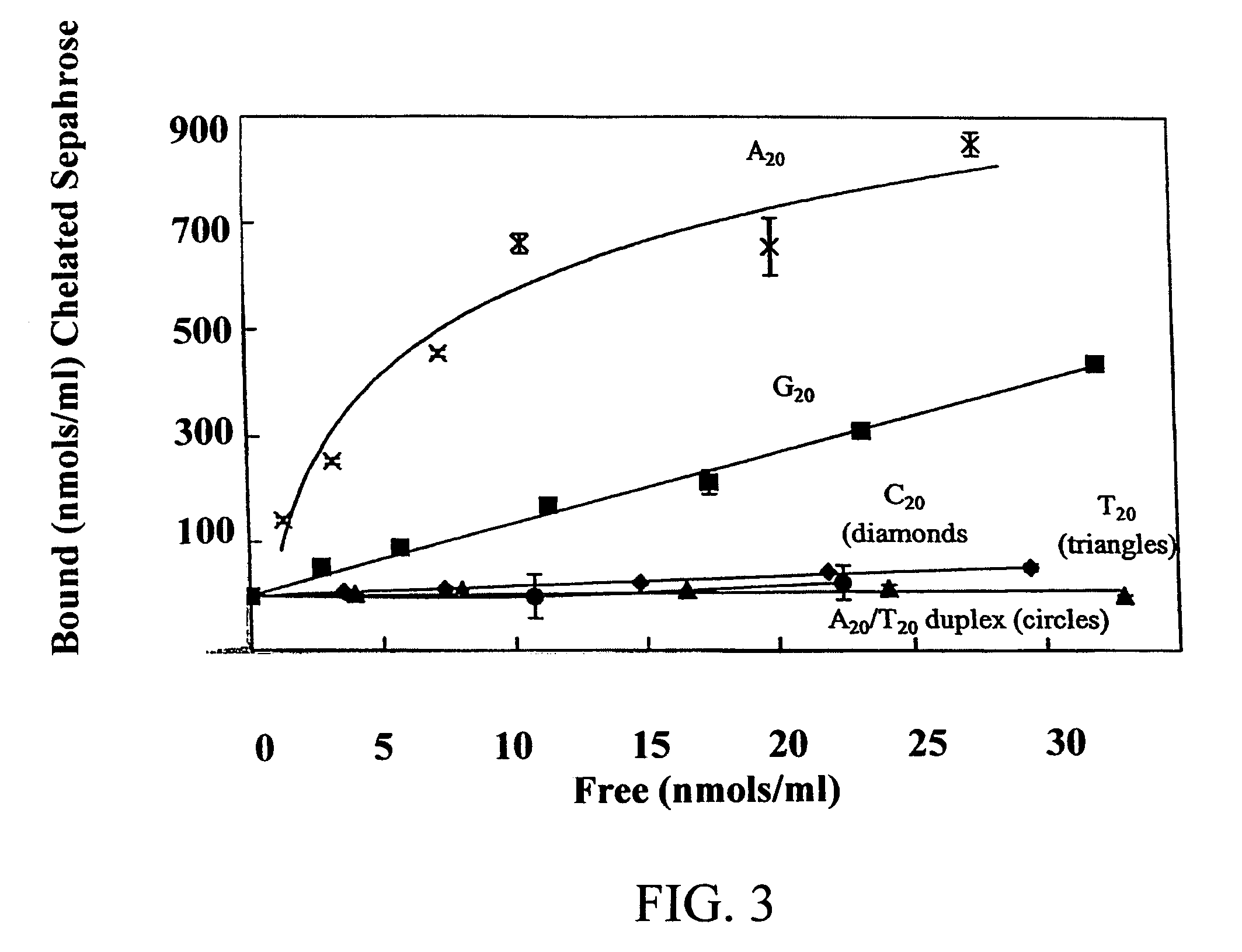
An immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) method for separating and / or purifying compounds containing a non-shielded purine or pyrimidine moiety or group such as nucleic acid, presumably through interaction with the abundant aromatic nitrogen atoms in the purine or pyrimidine moiety. The method can also be used to purify compounds containing purine or pyrimidine moieties where the purine and pyrimidine moieties are shielded from interaction with the column matrix from compounds containing a non-shielded purine or pyrimidine moiety or group. Thus, double-stranded plasmid and genomic DNA, which has no low binding affinity can be easily separated from RNA and / or oligonucleotides which bind strongly to metal-charged chelating matrices. IMAC columns clarify plasmid DNA from bacterial alkaline lysates, purify a ribozyme, and remove primers and other contaminants from PCR reactions. The metal ion affinity of yeast RNA decreases in the order: copper (II), nickel (II), zinc (II), and cobalt (II).
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Adeno-associated virus-delivered ribozyme compositions and methods for the treatment of retinal diseases
InactiveUS20050096282A1Shorten the progressDecreasing the amount of mRNA encodingSenses disorderVirusesRetinalVirus
Disclosed are ribozymes, as well as compositions, vectors, virus particles, host cells, and therapeutic kits comprising them useful in the treatment of diseases of the eye, including retinopathy and macular degeneration, and the amelioration of symptoms of such diseases including loss of vision, retinitis, and blindness.
Owner:FLORIDA RES FOUND UNIV OF
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20070056057A1Reduce expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specific RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Detection of oligonucleotides by dual hybridization
The invention provides methods and compositions for detecting and / or quantifying modified nucleic acid oligonucleotides. These methods and compositions are useful for detecting and quantifying diagnostic and / or therapeutic synthetic modified oligonucleotides, such as aptamers, RNAi, siRNA, antisense oligonucleotides or ribozymes in a biological sample.
Owner:EYETECH
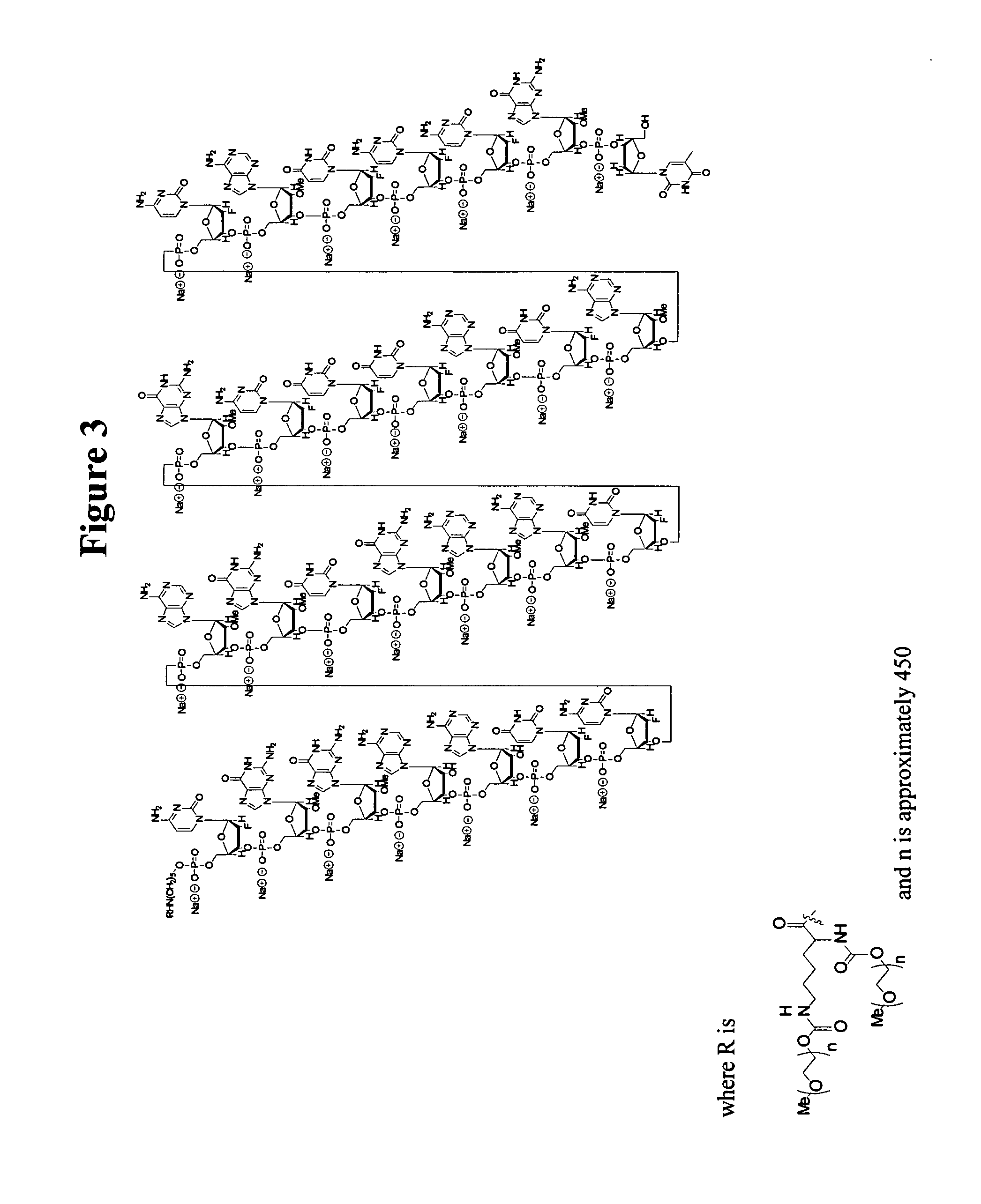
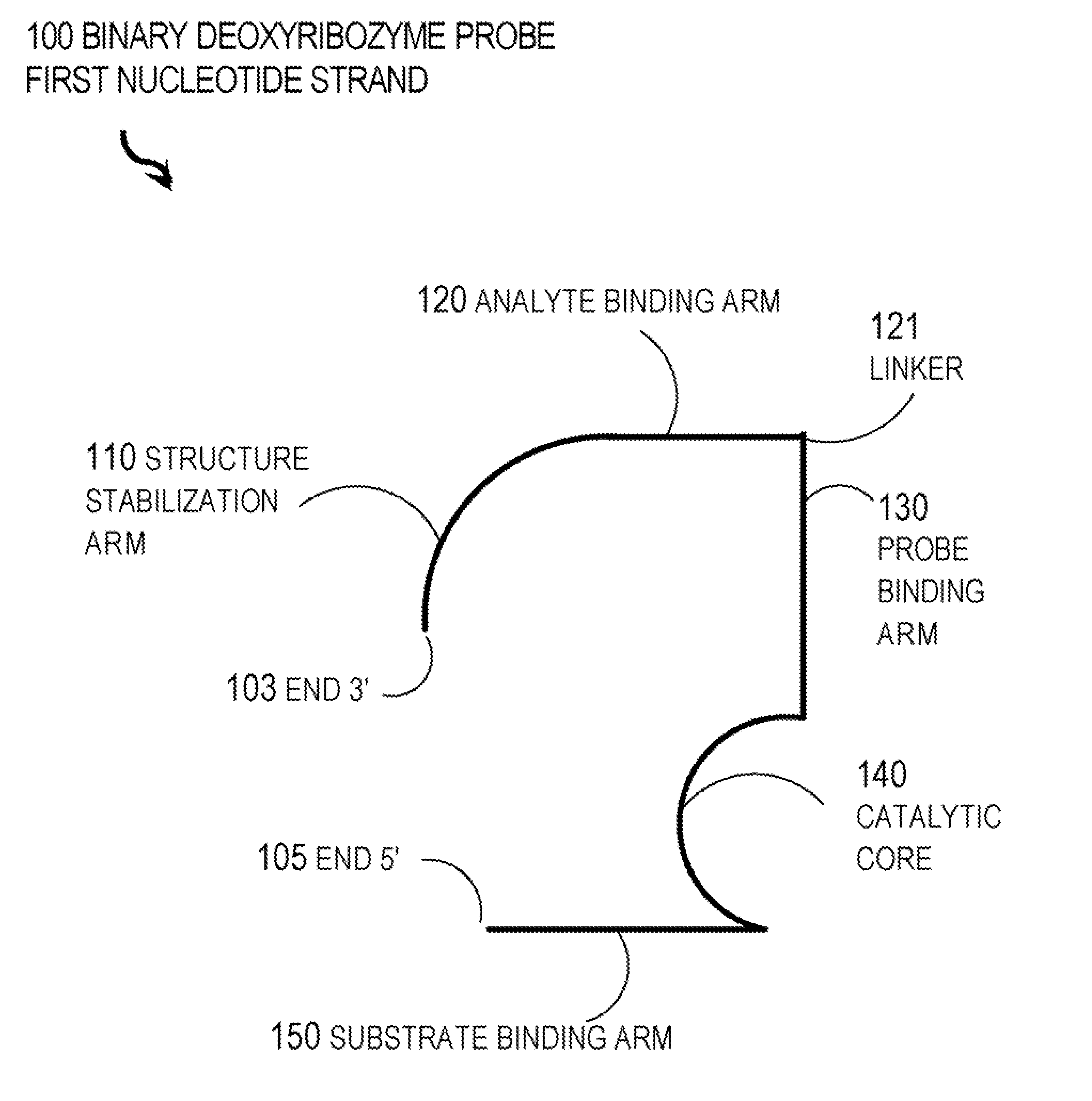
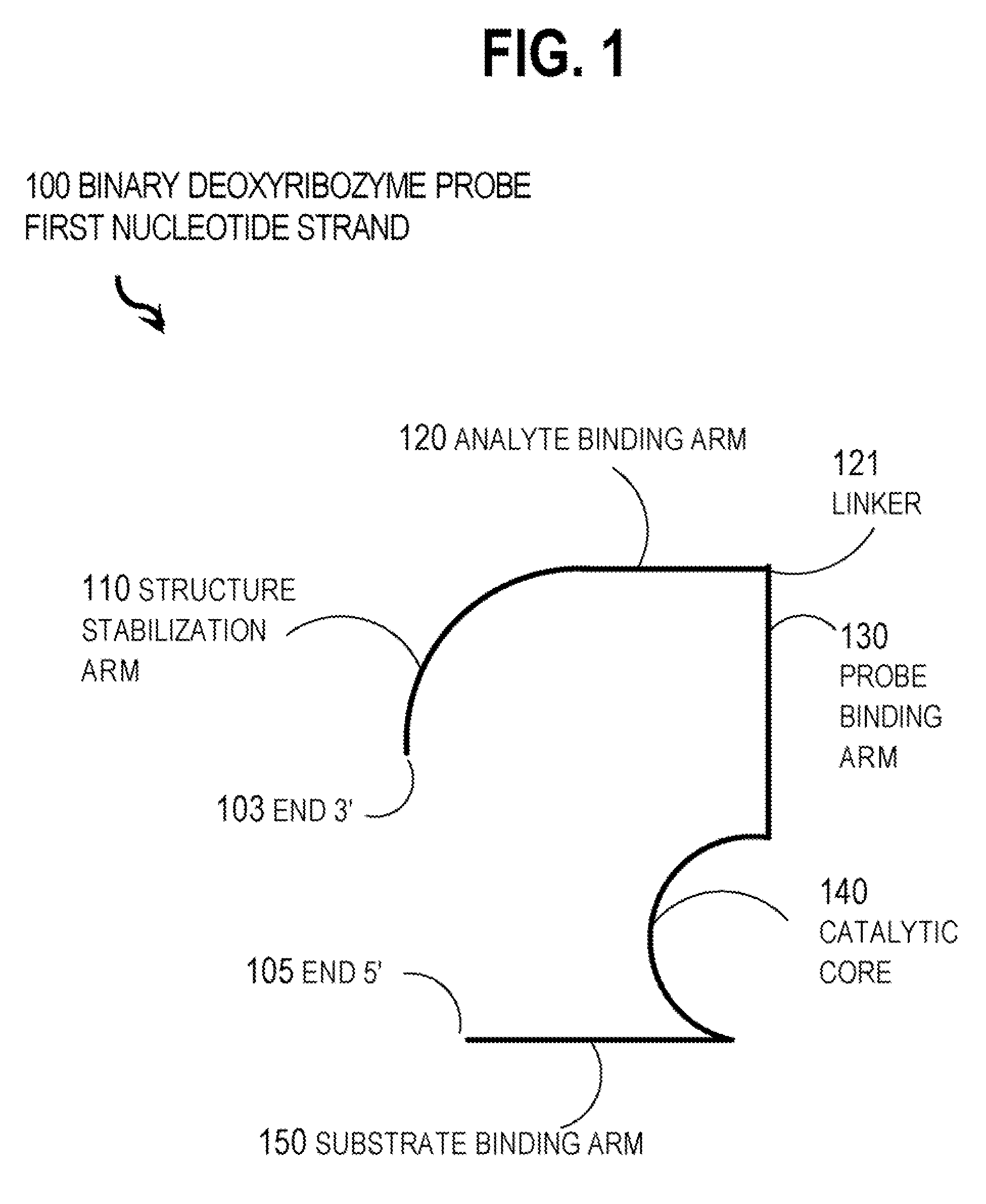
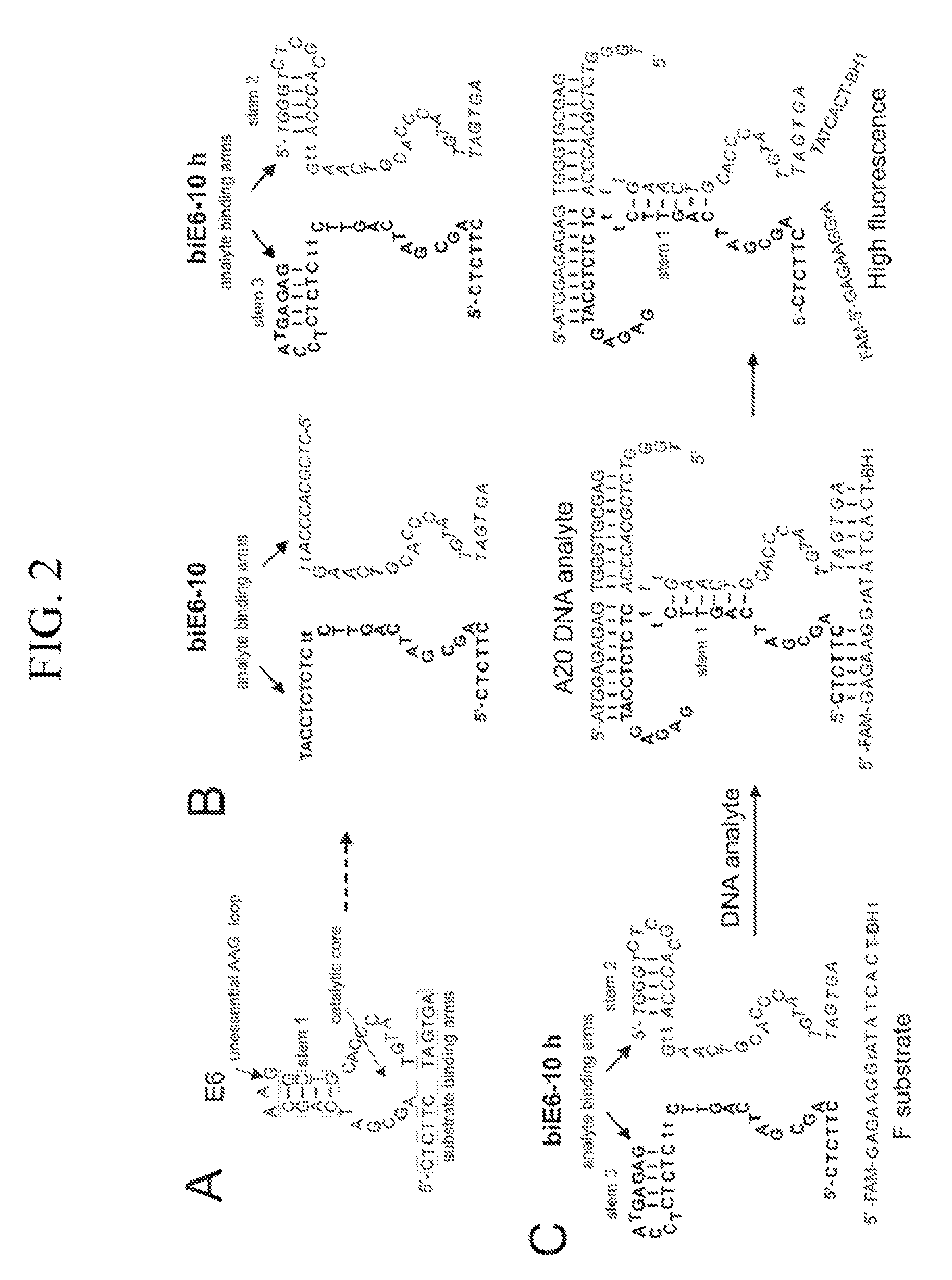
Binary deoxyribozyme probes for nucleic acid analysis
New binary deoxyribozyme or ribozyme probes and methods are described for nucleic acid analysis, which allows the detection of nucleic acids under mild physiologic conditions with extraordinary specificity and high sensitivity to single nucleotide mismatches without PCR amplification.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Medicine-carrying nanometer polymer particle and its prepn and use
InactiveCN1608675AGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsWater insolublePolyethylene glycol
The present invention discloses one medicinal polymer (PELGE / PELGA) nanometer particle carrier and its preparation process and use. The carrier material is PELGE material of different molecular weights, different LA / GA ratios and different PEG contents, and the nanometer PELGE / PELGA carrier particle is prepared through evaporation process. The said copolymer is self-assembled in water into nanometer particle or micelle, and its hydrophobic PLGA segment coagulates into the core while the hydrophilic polyglycol forms hydrophilic shell. The carrier may be used for the nanometer preparation of plasmid, nucleic acid vaccine, antisense oligodeoxynucleotide or ribozyme for genetic treatment; the nanometer preparation of various chemical medicines; and the nanometer preparation of polypeptide and protein medicines.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
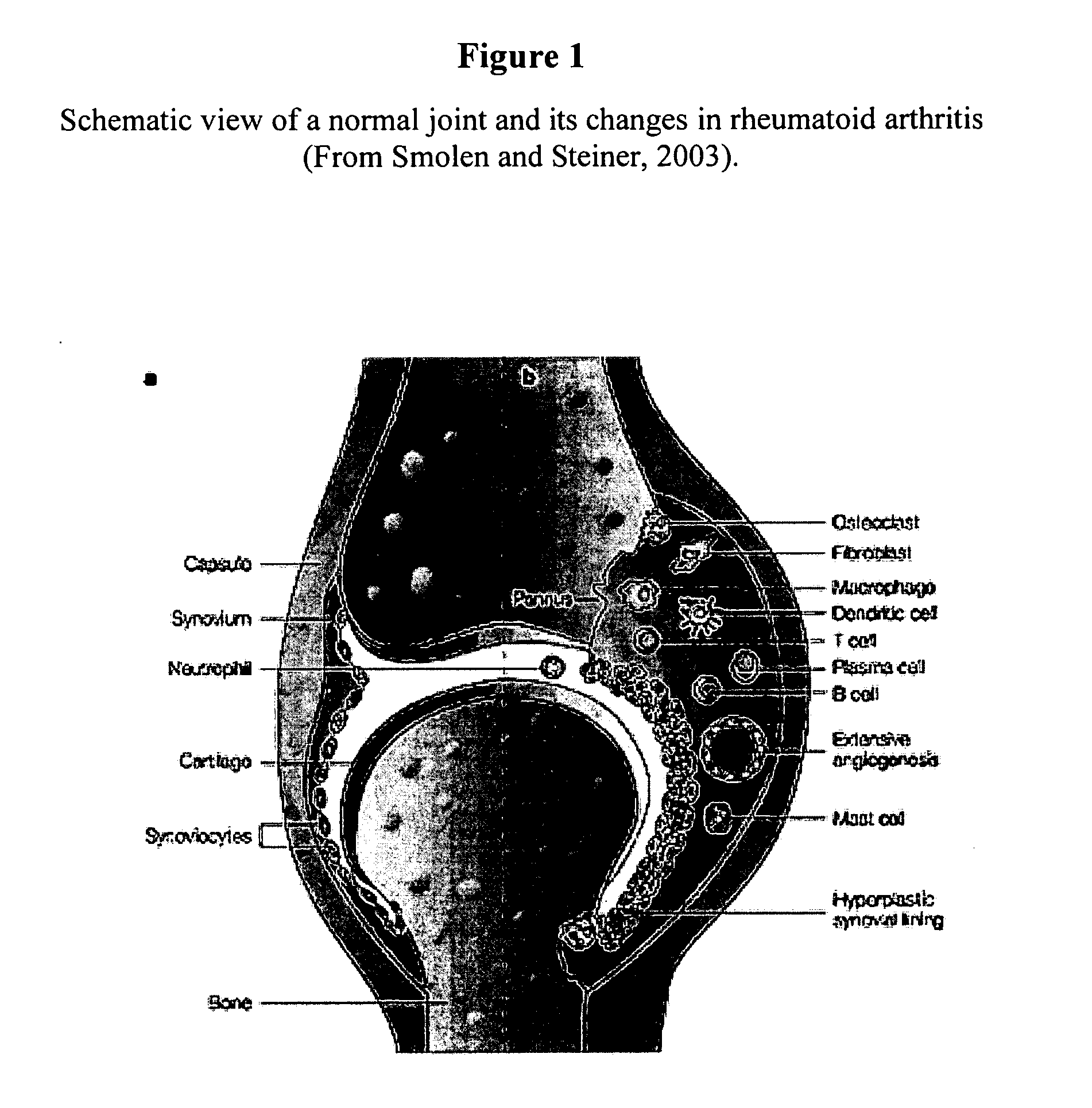
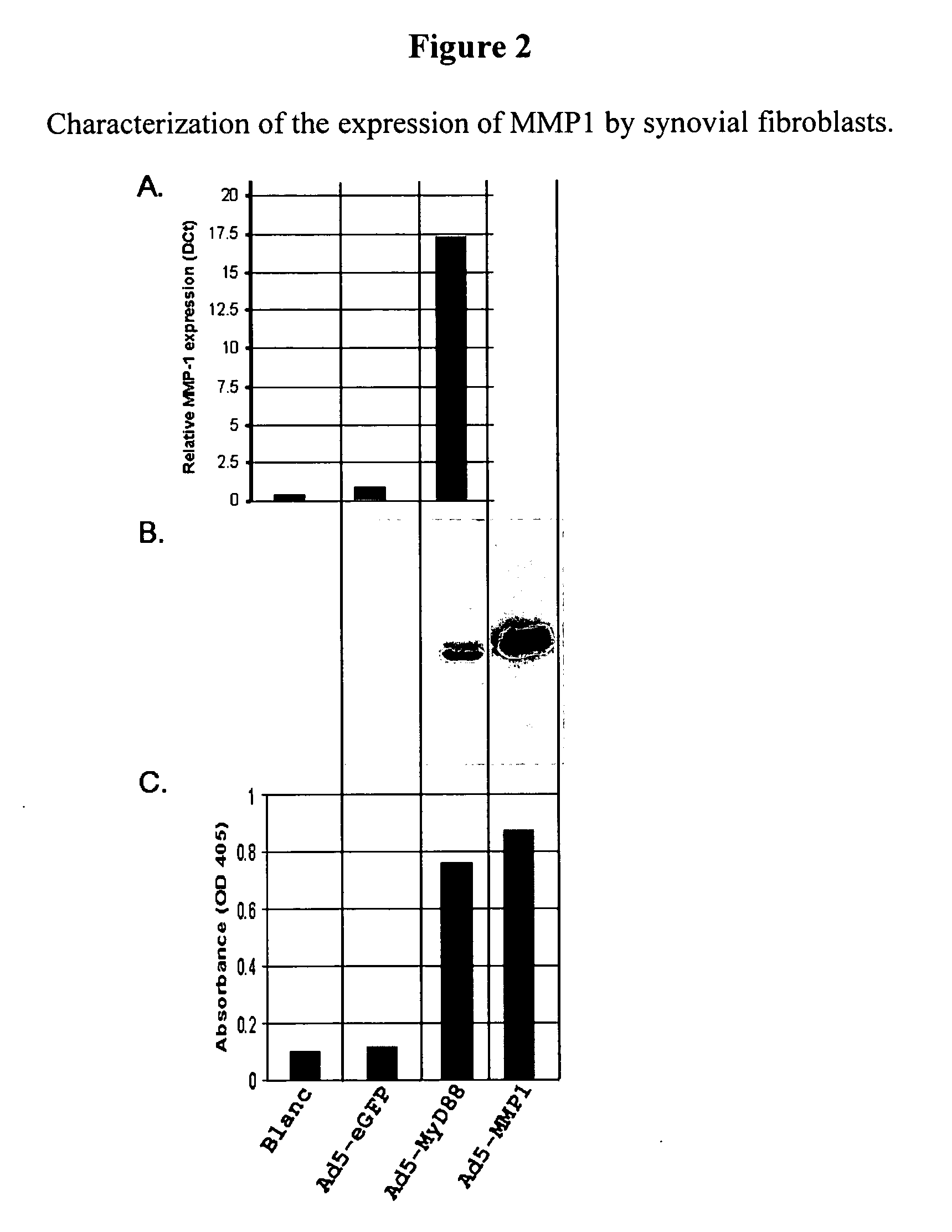
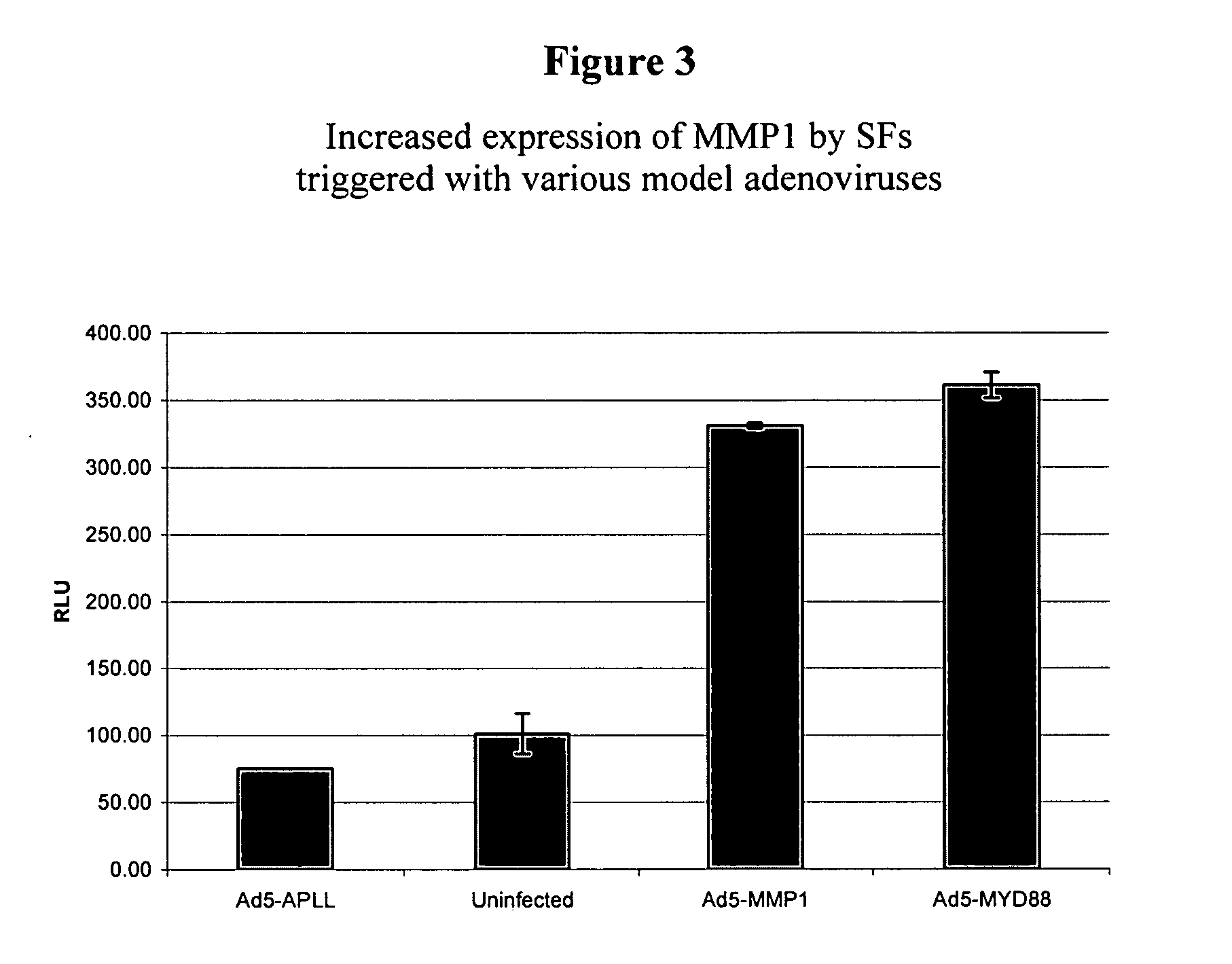
Molecular targets and compounds, and methods to identify the same, useful in the treatment of joint degenerative and inflammatory diseases
The application discloses methods for identifying and using compounds that inhibit extra-cellular matrix (ECM) degradation and inflammation, using a polypeptide sequence including SEQ ID NO: 17-127 (hereinafter “TARGETS”) and fragments thereof, expression inhibitory agents such as antisense polynucleotide, a ribozyme, and a small interfering RNA (siRNA), comprising a nucleic acid sequence complementary to, or engineered from, a naturally occurring polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide of SEQ ID NO: 17-127, useful in pharmaceutical compositions comprising said agent, for the treatment, or prevention, of chronic joint degenerative and / or inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:GALAPAGOS NV
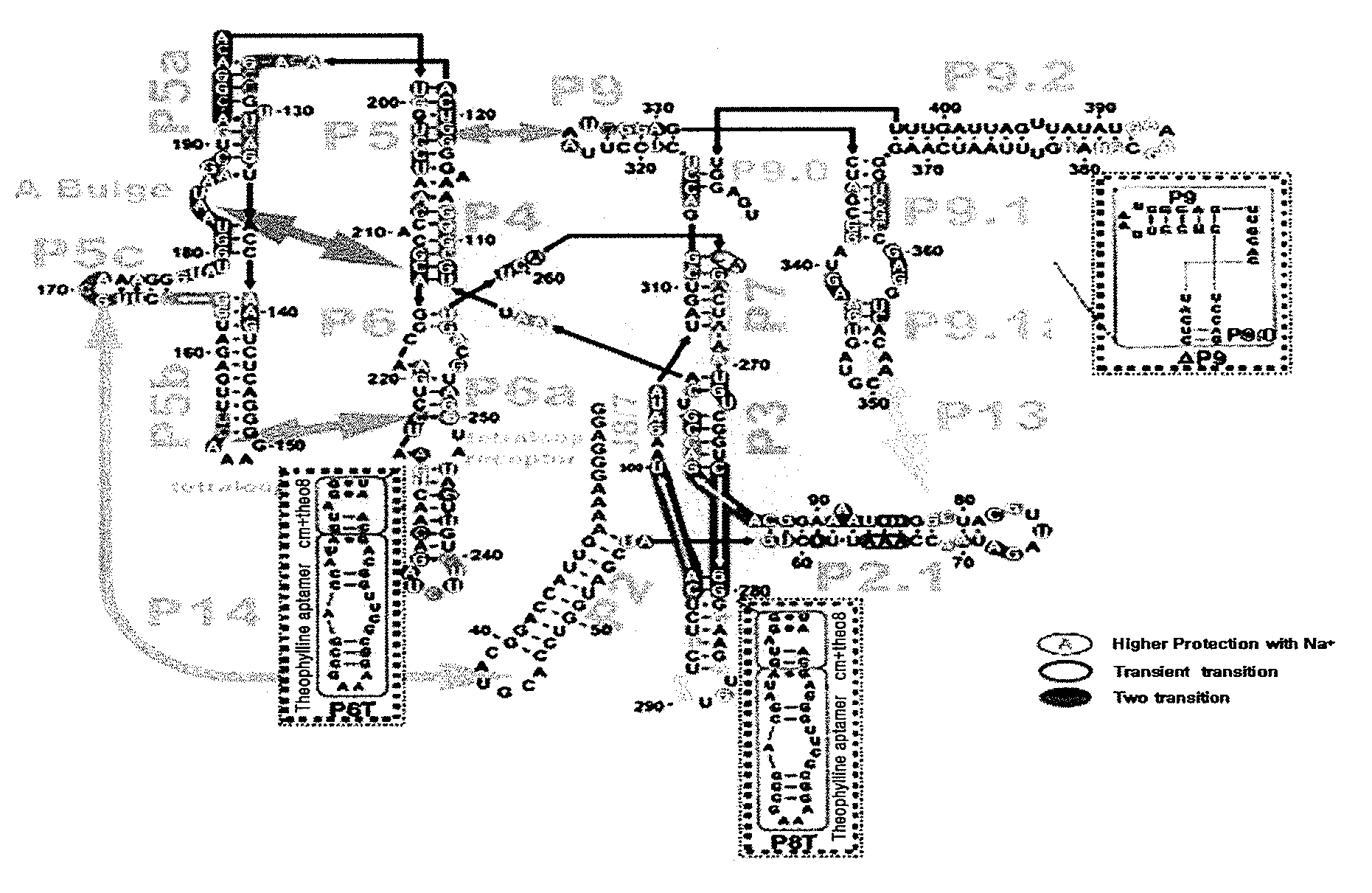
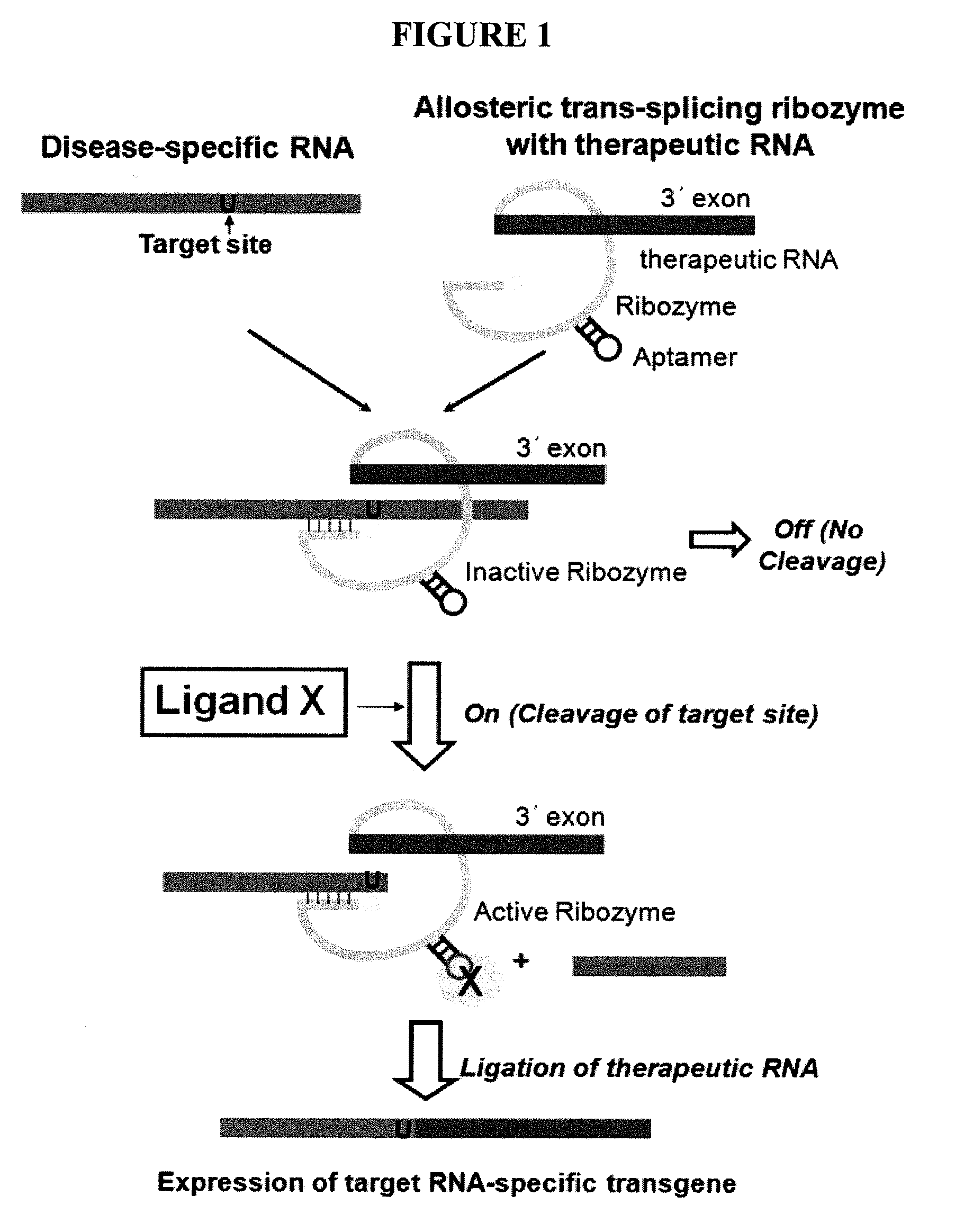
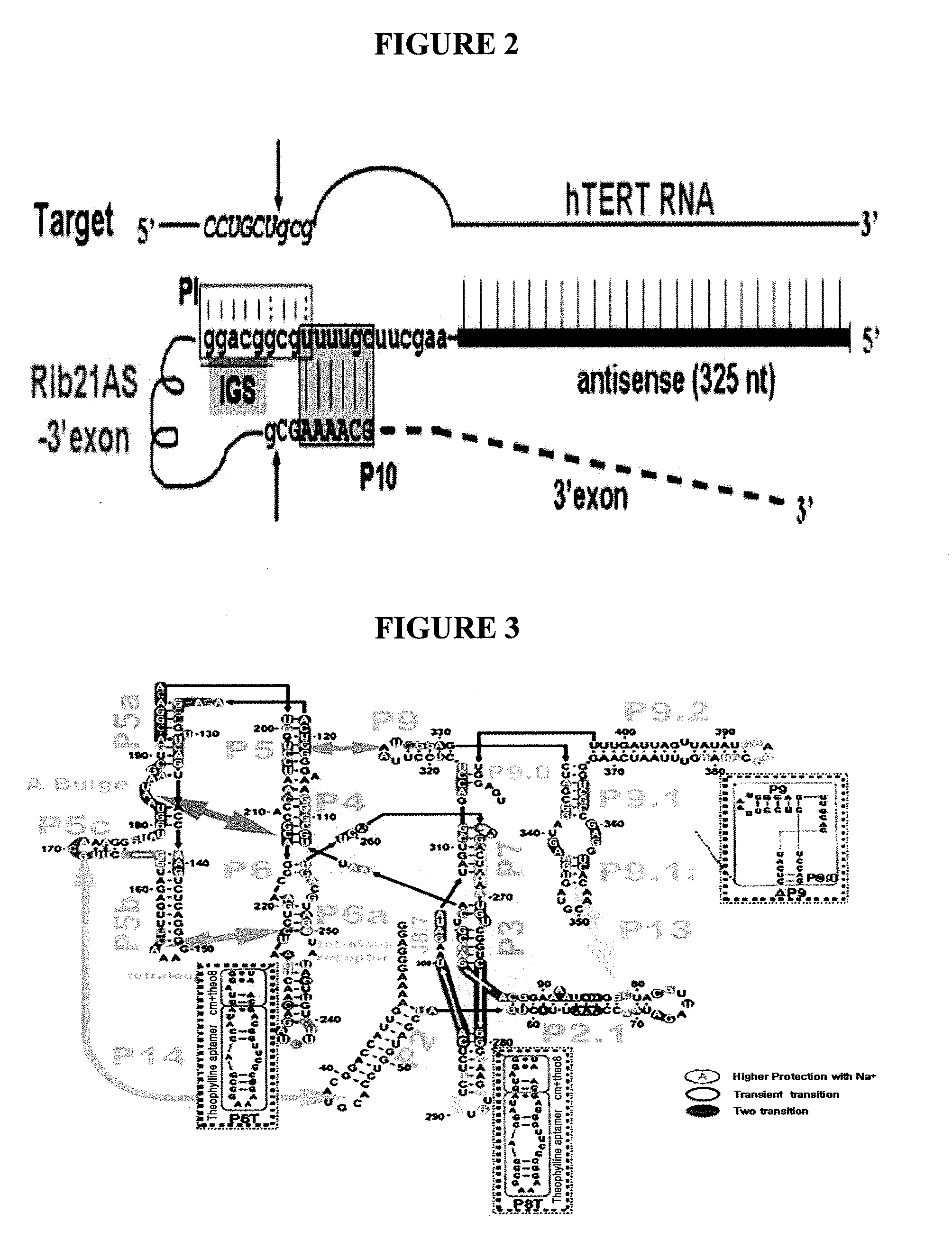
Allosteric trans-splicing group i ribozyme whose activity of target-specific RNA replacement is controlled by theophylline
InactiveUS20110003883A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellReverse transcriptase
Provided is an allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme whose target-specific RNA replacement activity is controlled by theophylline, wherein the hTERT-targeting trans-splicing ribozyme recognizes mRNA of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) as a cancer-specific RNA transcript to bind a theophylline aptamer to an hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme via a communication module, the hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme having a verified trans-splicing ability. The allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme may be useful to selectively diagnose only cancer cells that express target hTERT RNA, or induce their apoptosis since the activity of the allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme is dependently controlled by theophylline to correct target hTERT RNA by the trans-splicing reaction.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND DANKOOK UNIV
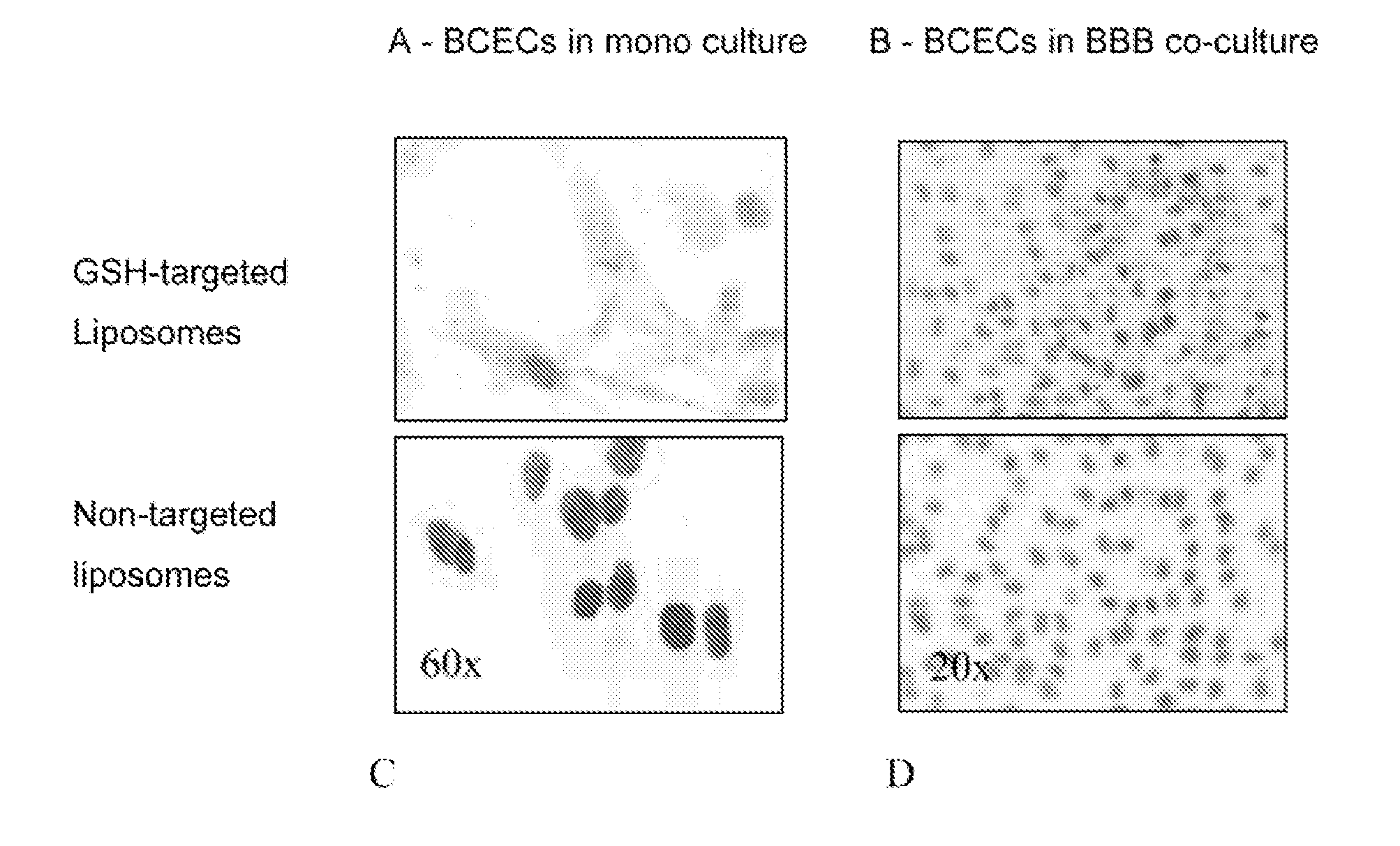
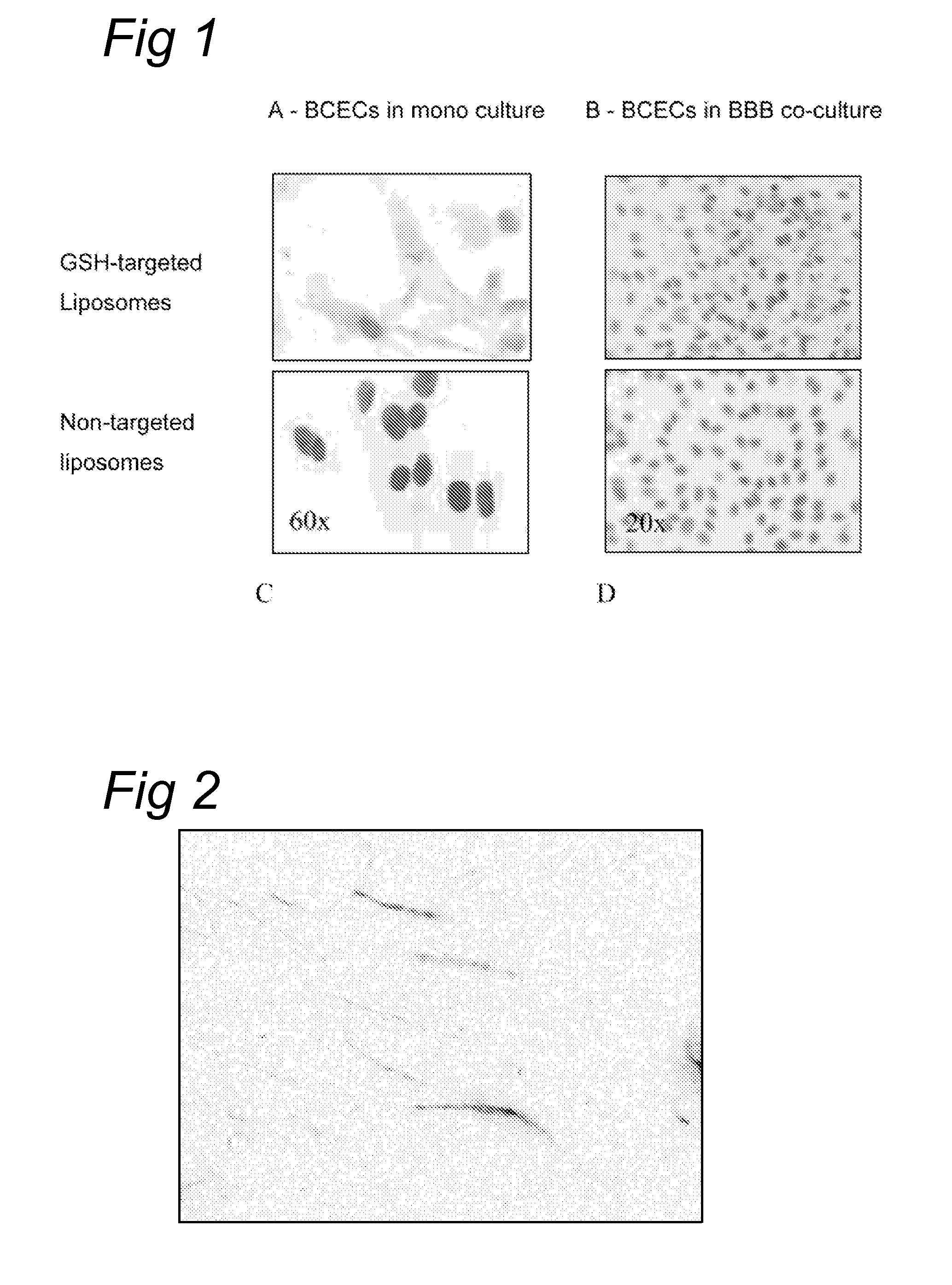
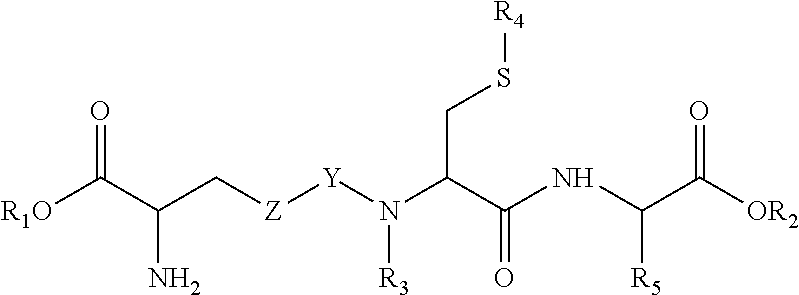
Glutathione-based drug delivery system
InactiveUS20110305751A1High affinitySpecificity of bindingAntibacterial agentsCompounds screening/testingEukaryotic plasmidsInternalization
The invention relates to methods of targeted drug delivery of compounds, including, chemical agents, (poly)peptides and nucleic acid based drugs (like DNA vaccines, antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, catalytic DNA (DNAzymes) or RNA molecules, siRNAs or plasmids encoding thereof). Furthermore, the invention relates to targeted drug delivery of compounds to extravascular and intracellular target sites within cells, tissues and organs, in particular to target sites within the central nervous system (CNS), into and across the blood-brain barrier, by targeting to glutathione transporters present on these cells, tissues and organs. Thereto, the compounds, or the pharmaceutical acceptable carrier thereof, are conjugated to glutathione-based ligands that facilitate the specific binding to and internalization by these glutathione transporters.
Owner:TO BBB HLDG
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20050251877A1Reducing phenotypic expressionReduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specifc RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
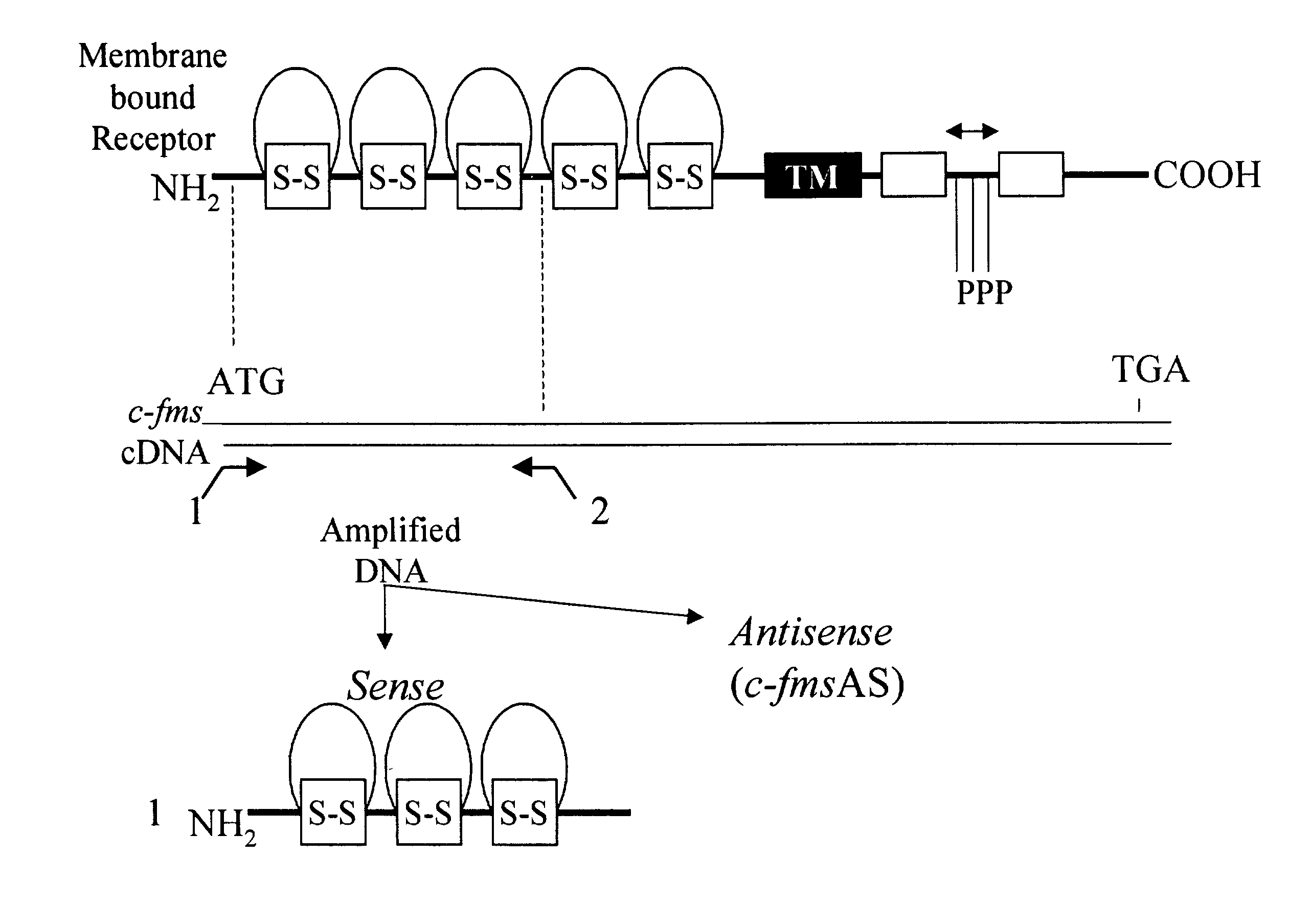
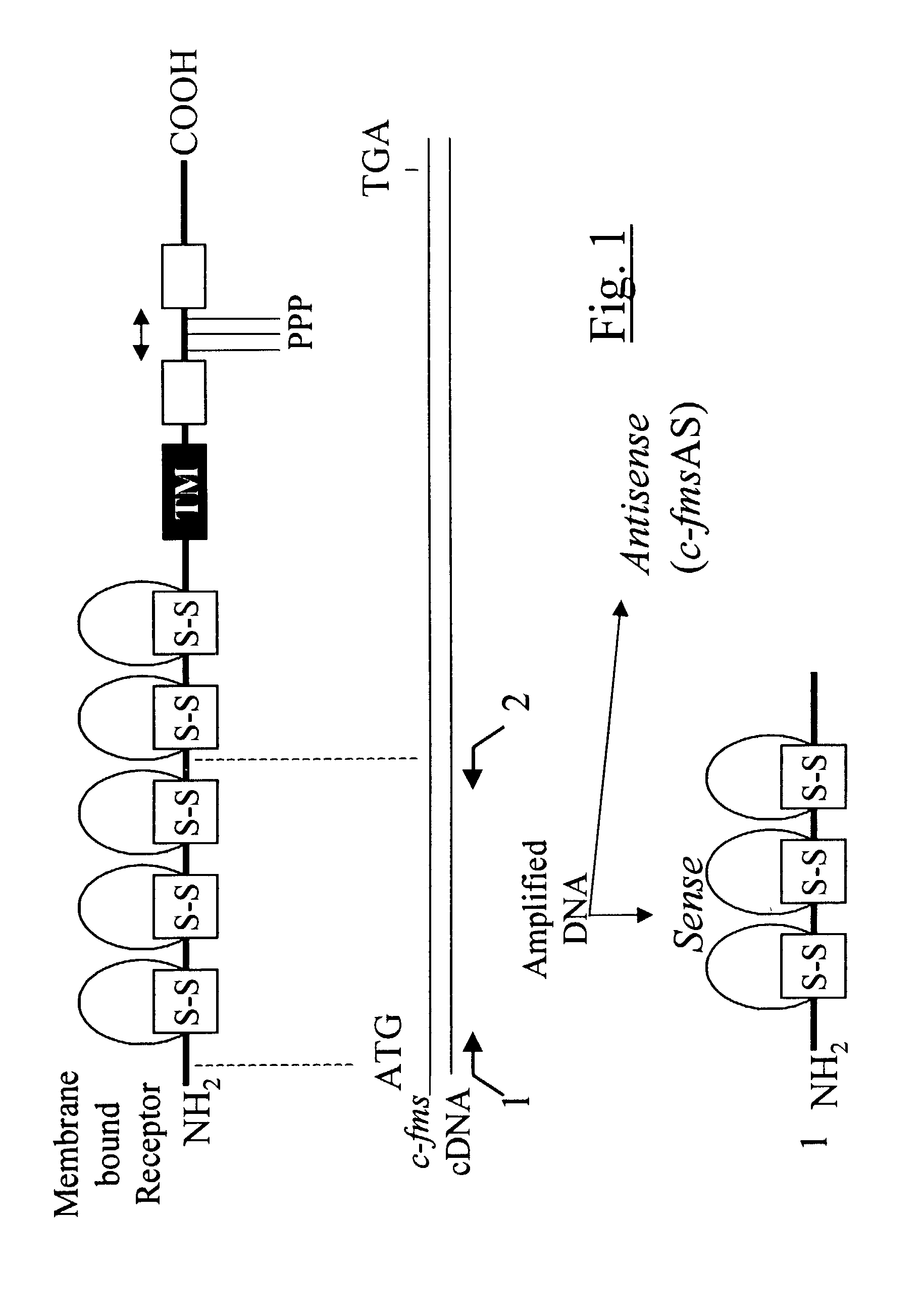
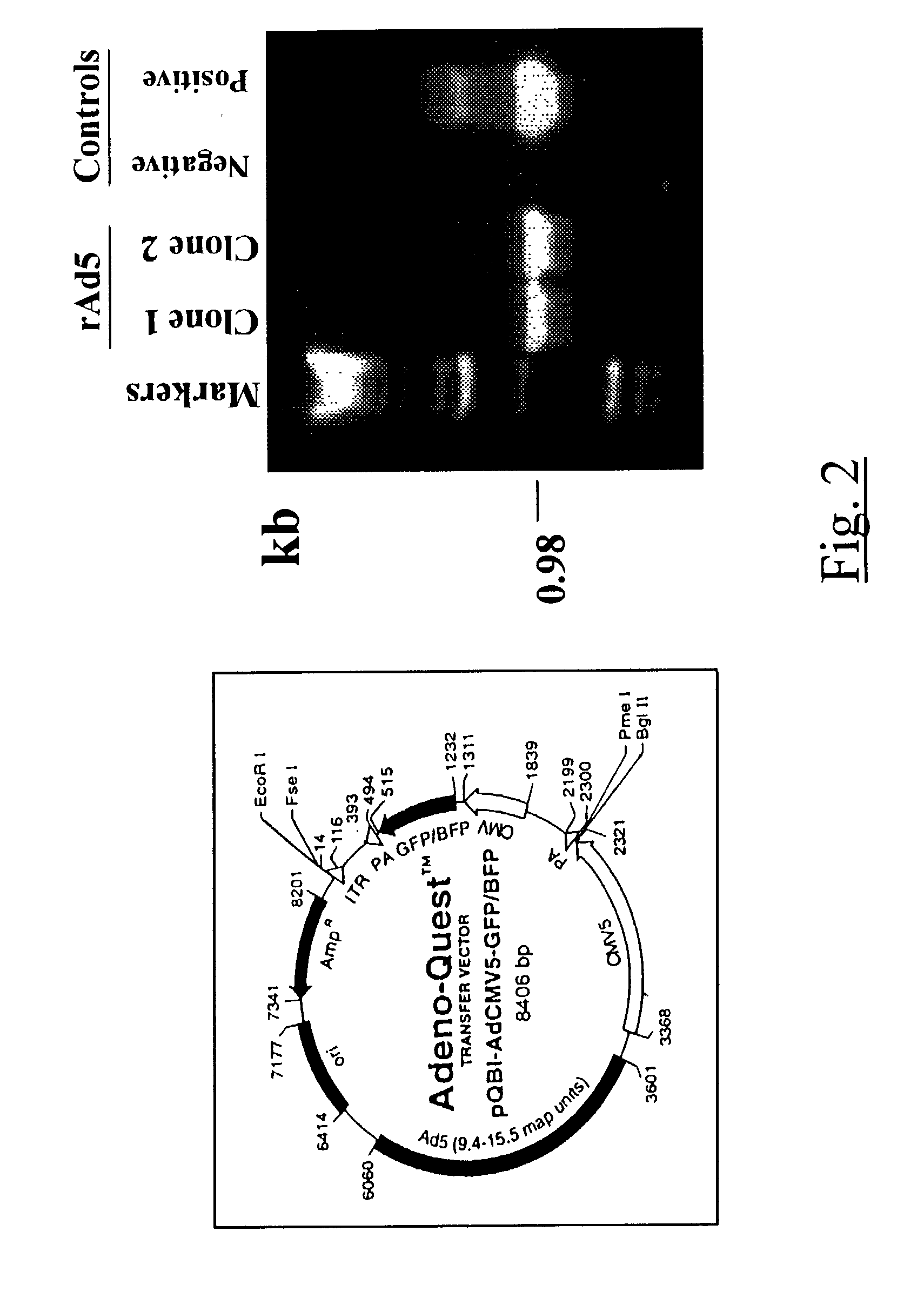
Methods for inhibiting macrophage colony stimulating factor and c-FMS-dependent cell signaling
Owner:RAJAVASHISTH TRIPATHI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com