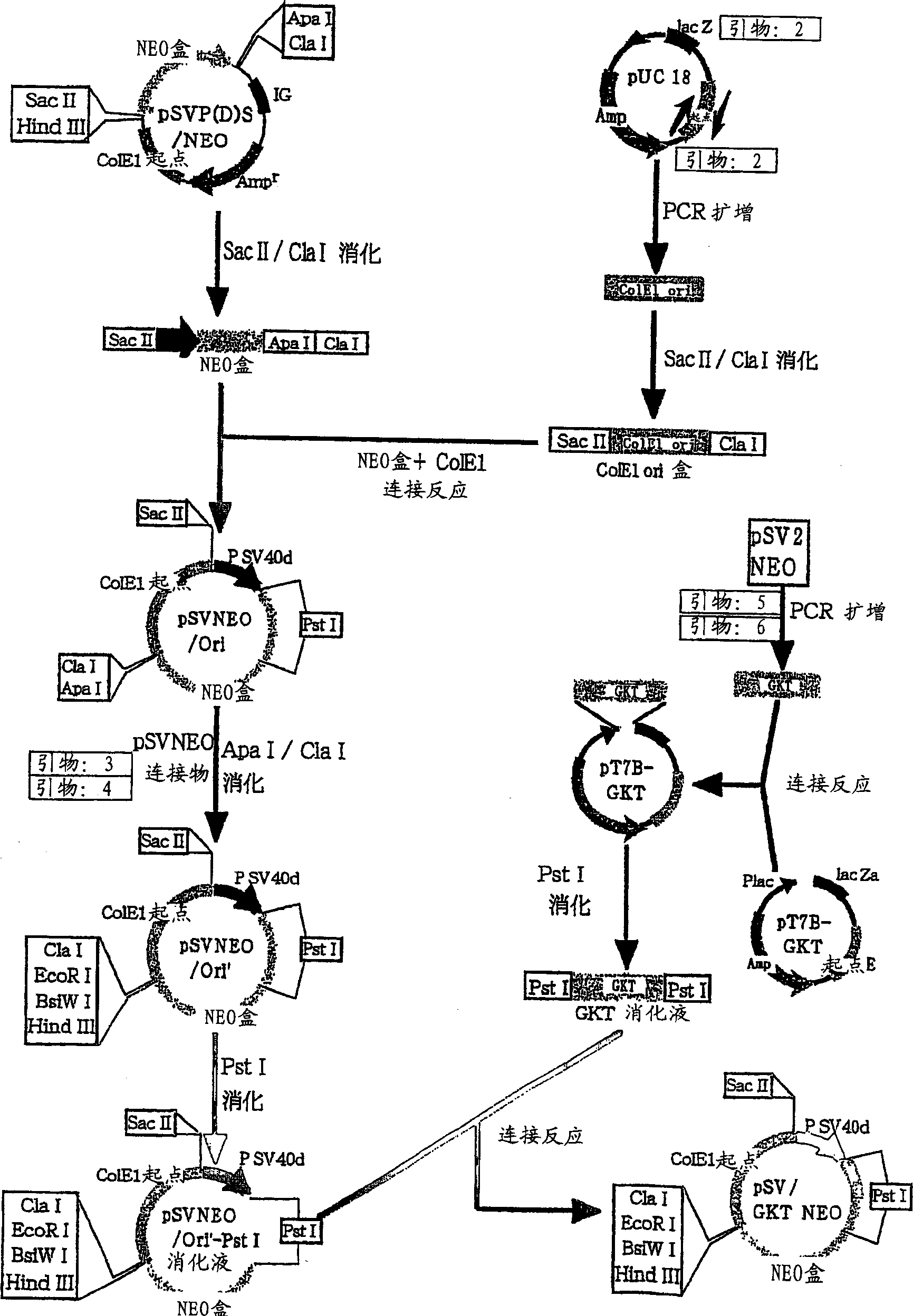
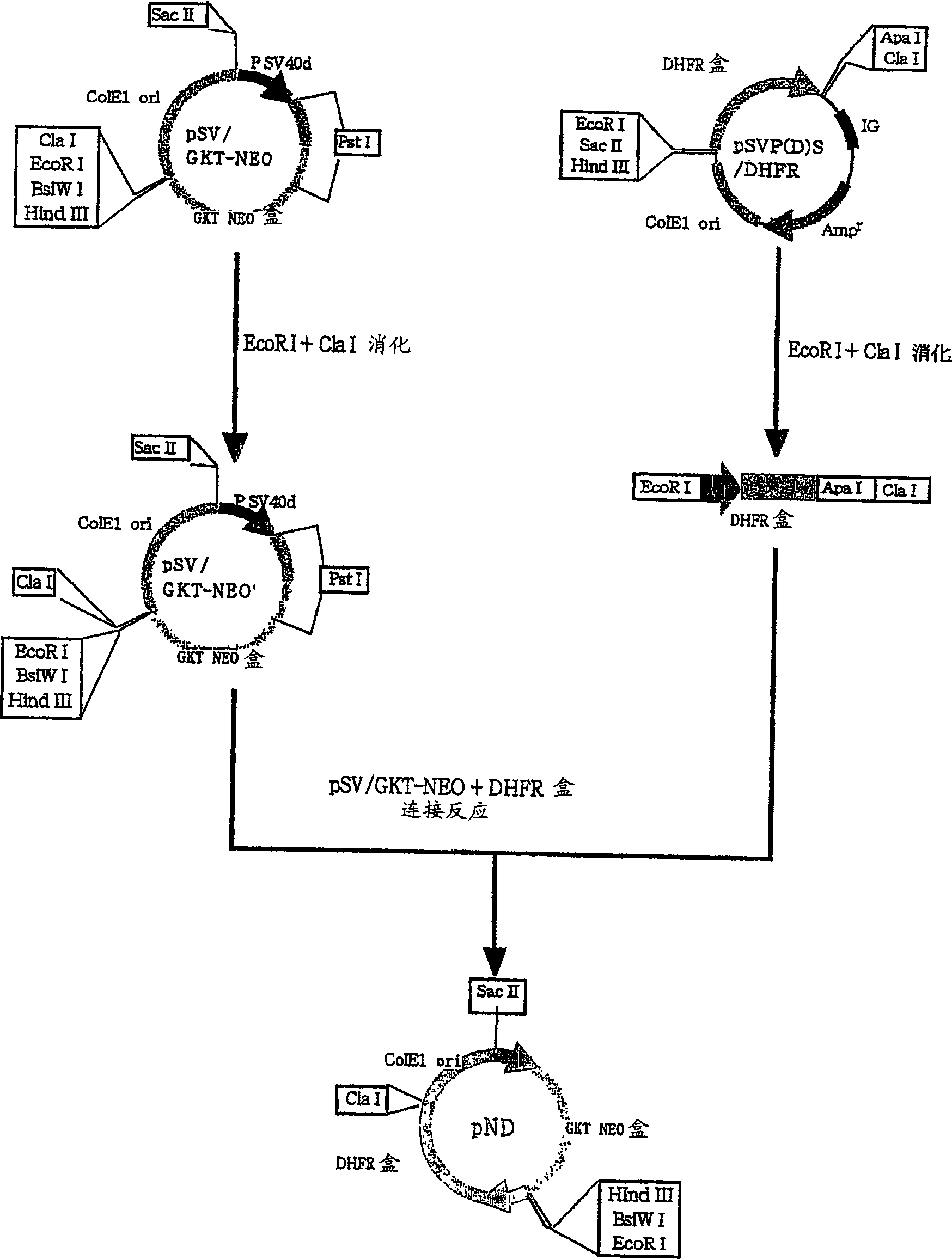
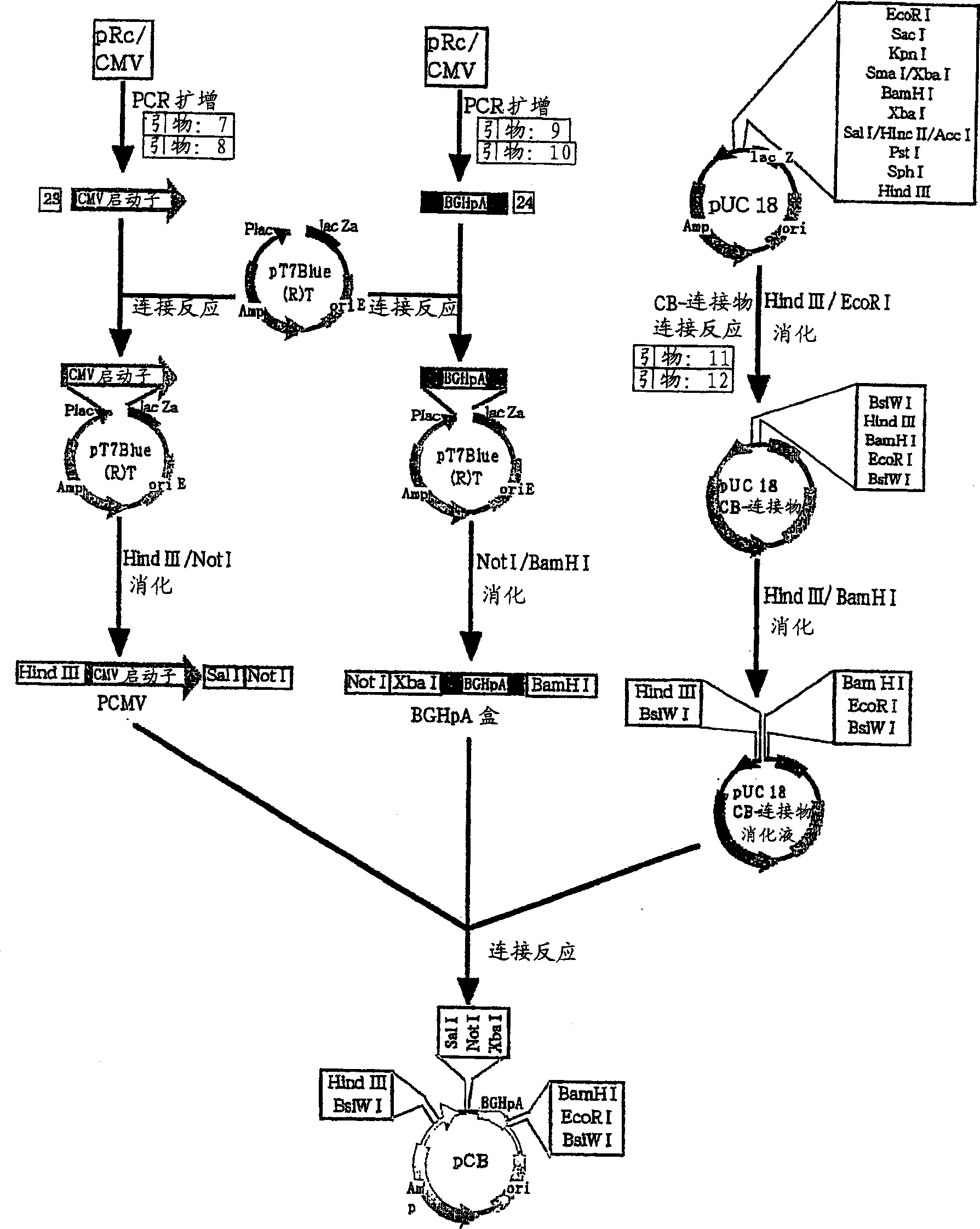
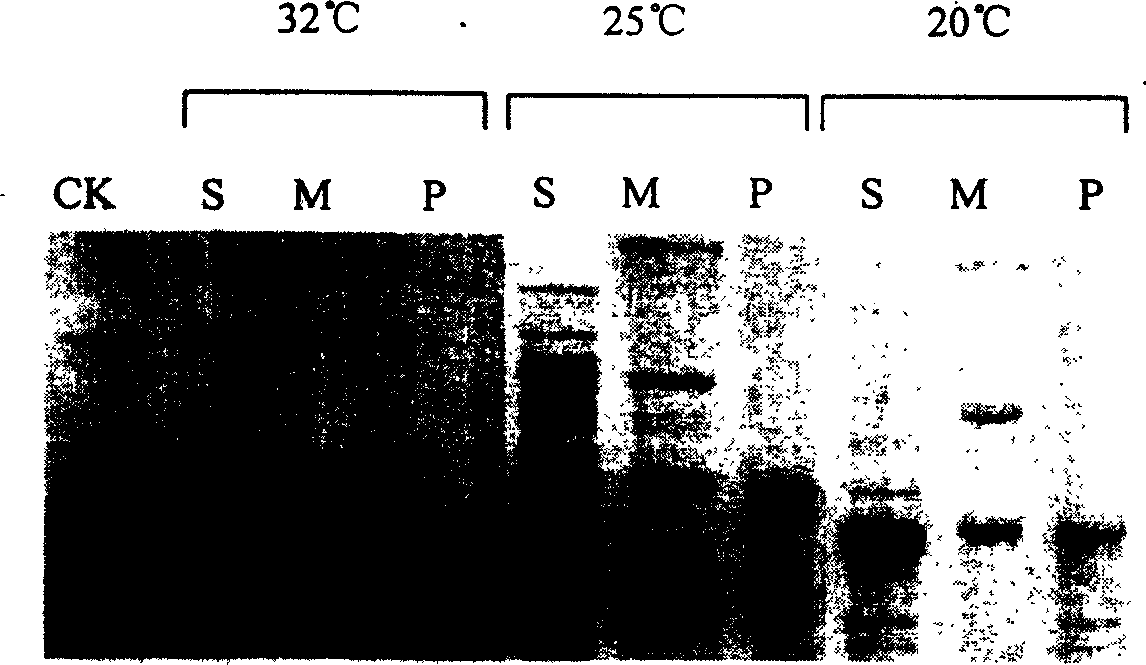
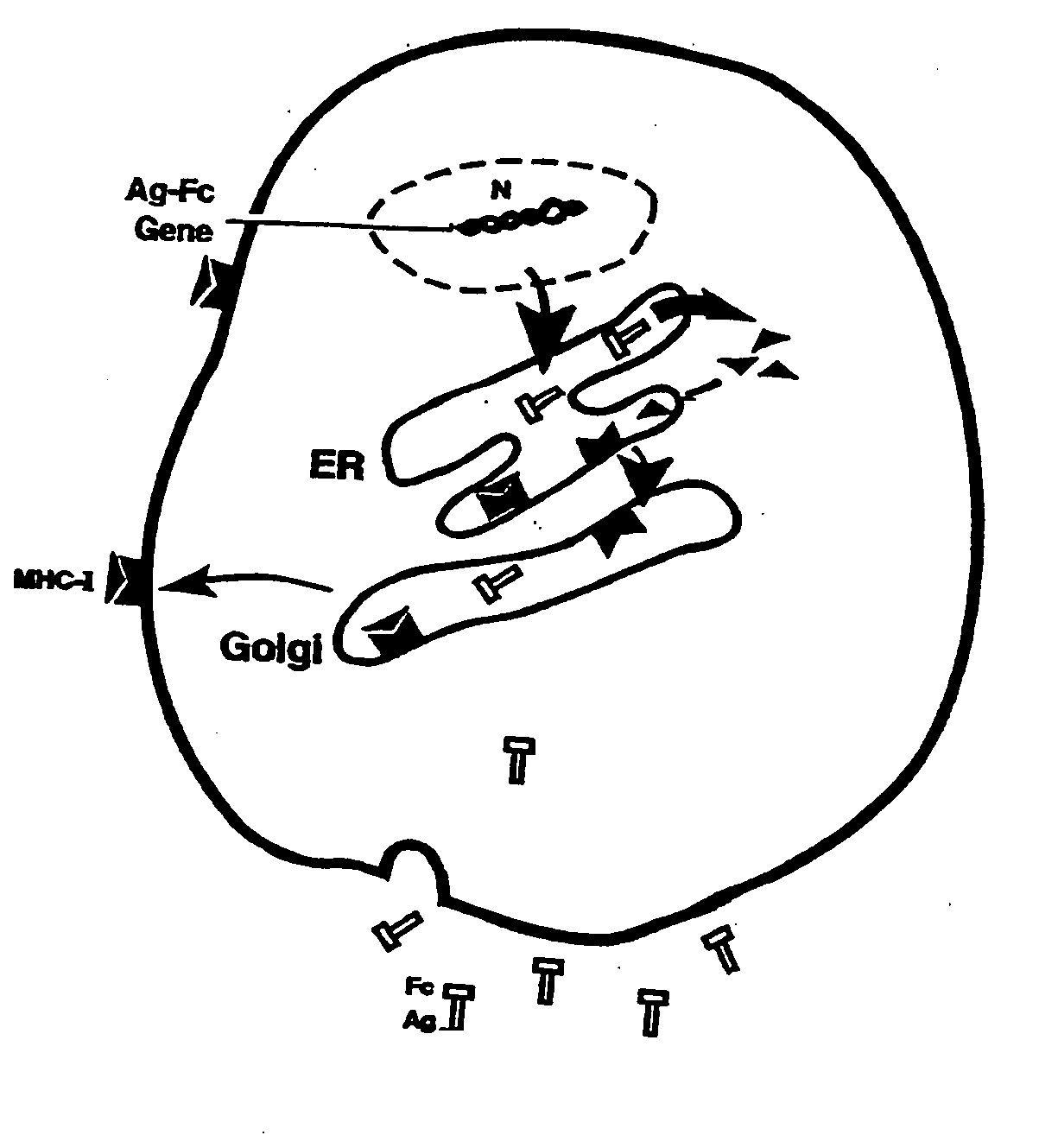
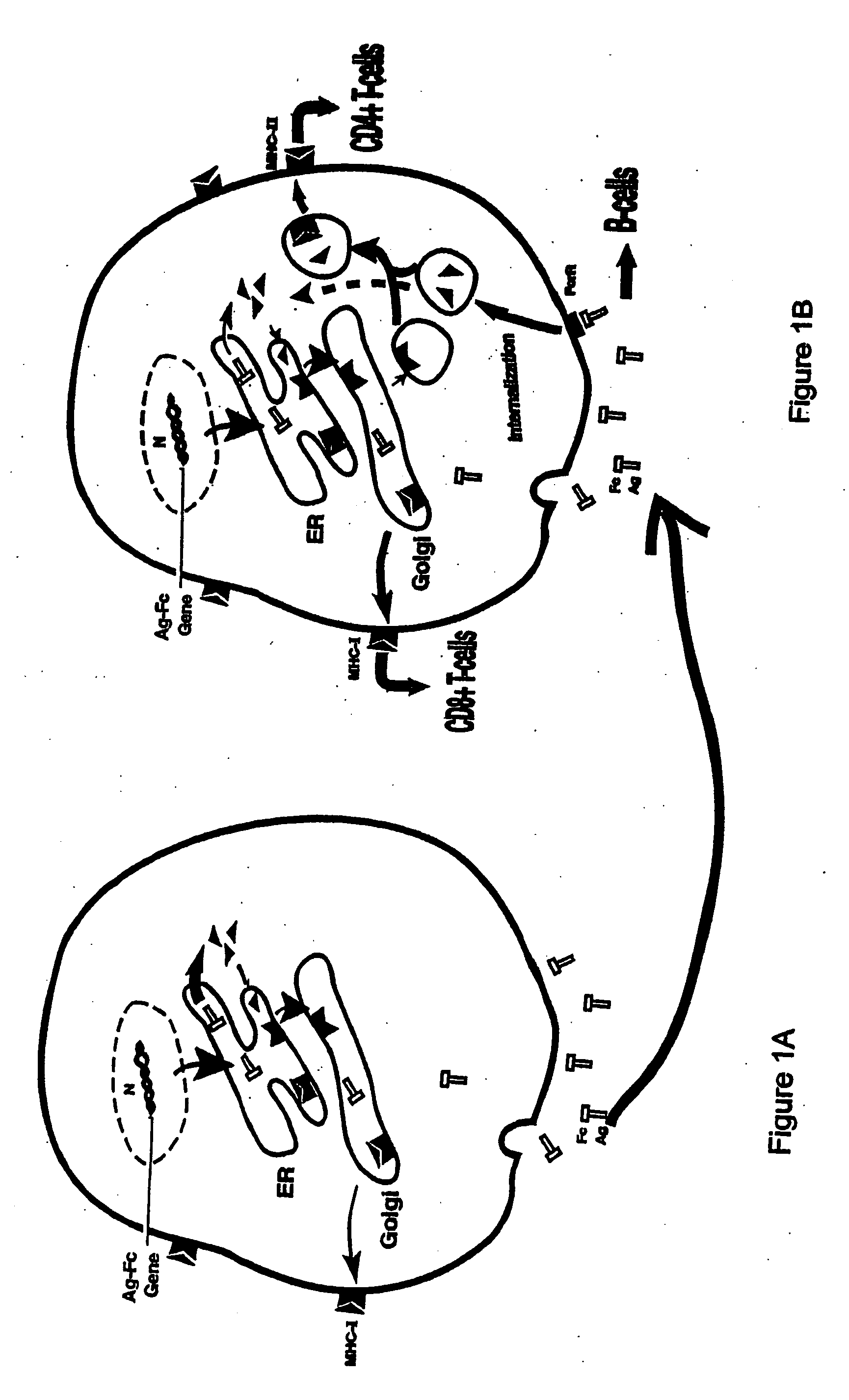
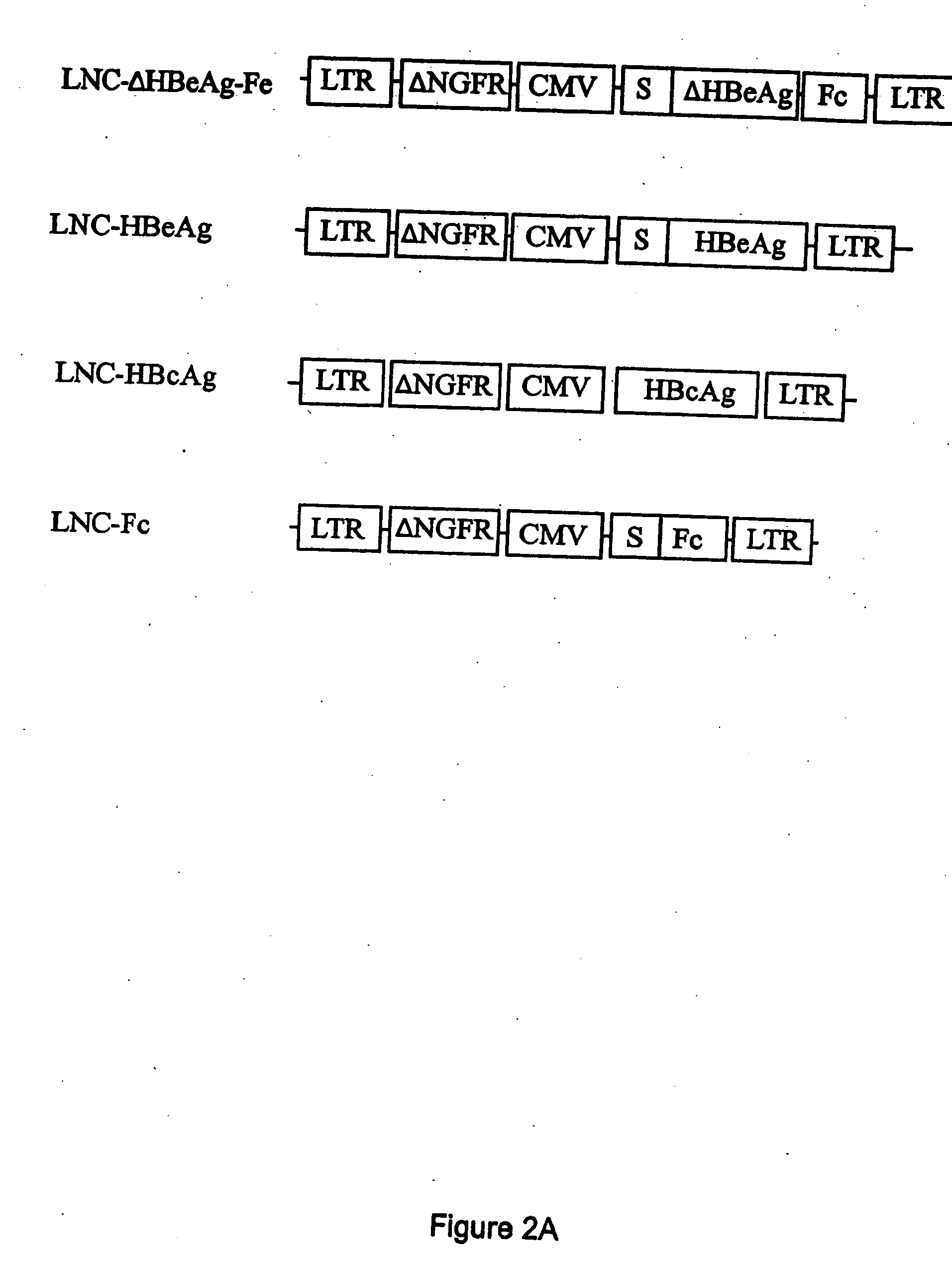
Patents
Literature
145 results about "Polyadenylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA. The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.
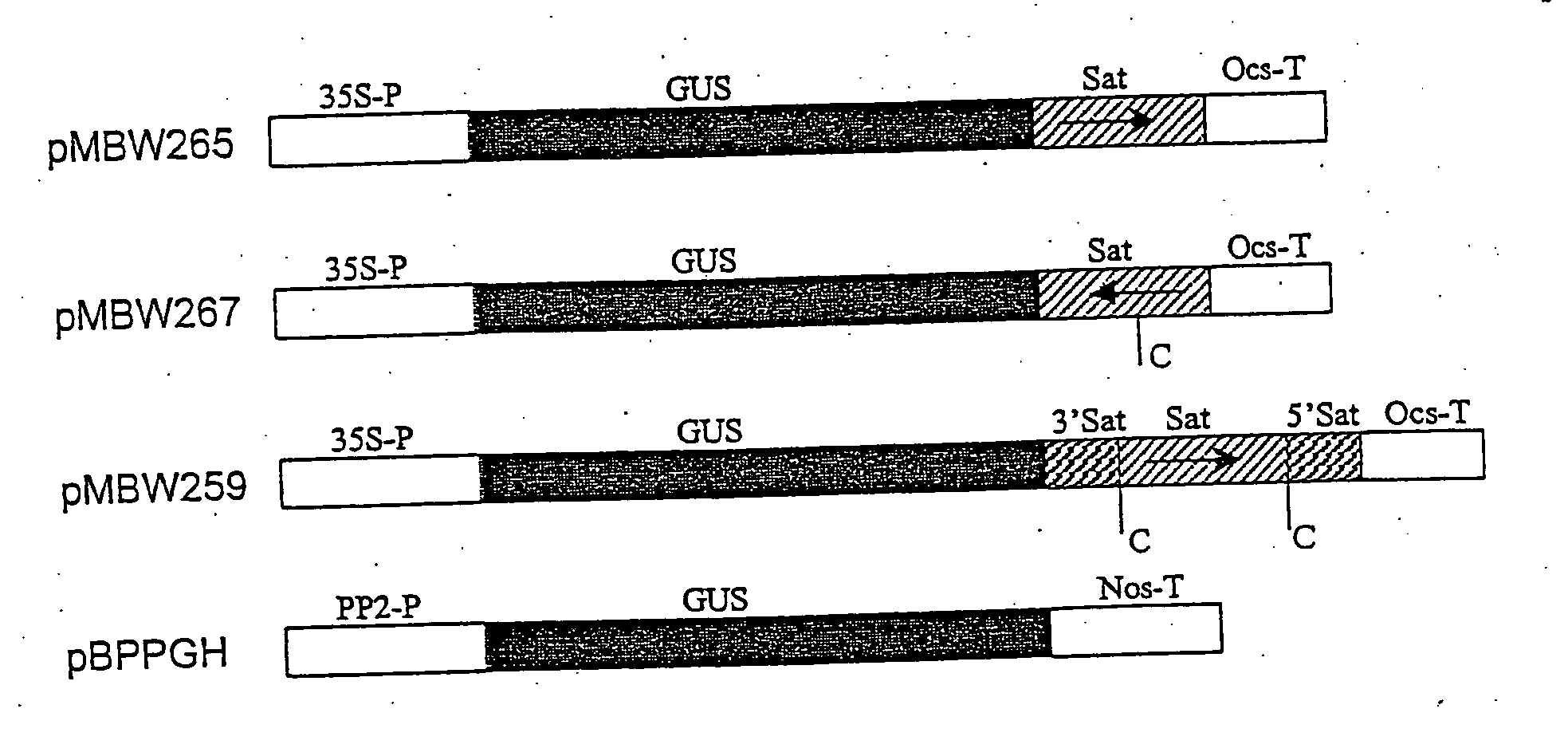
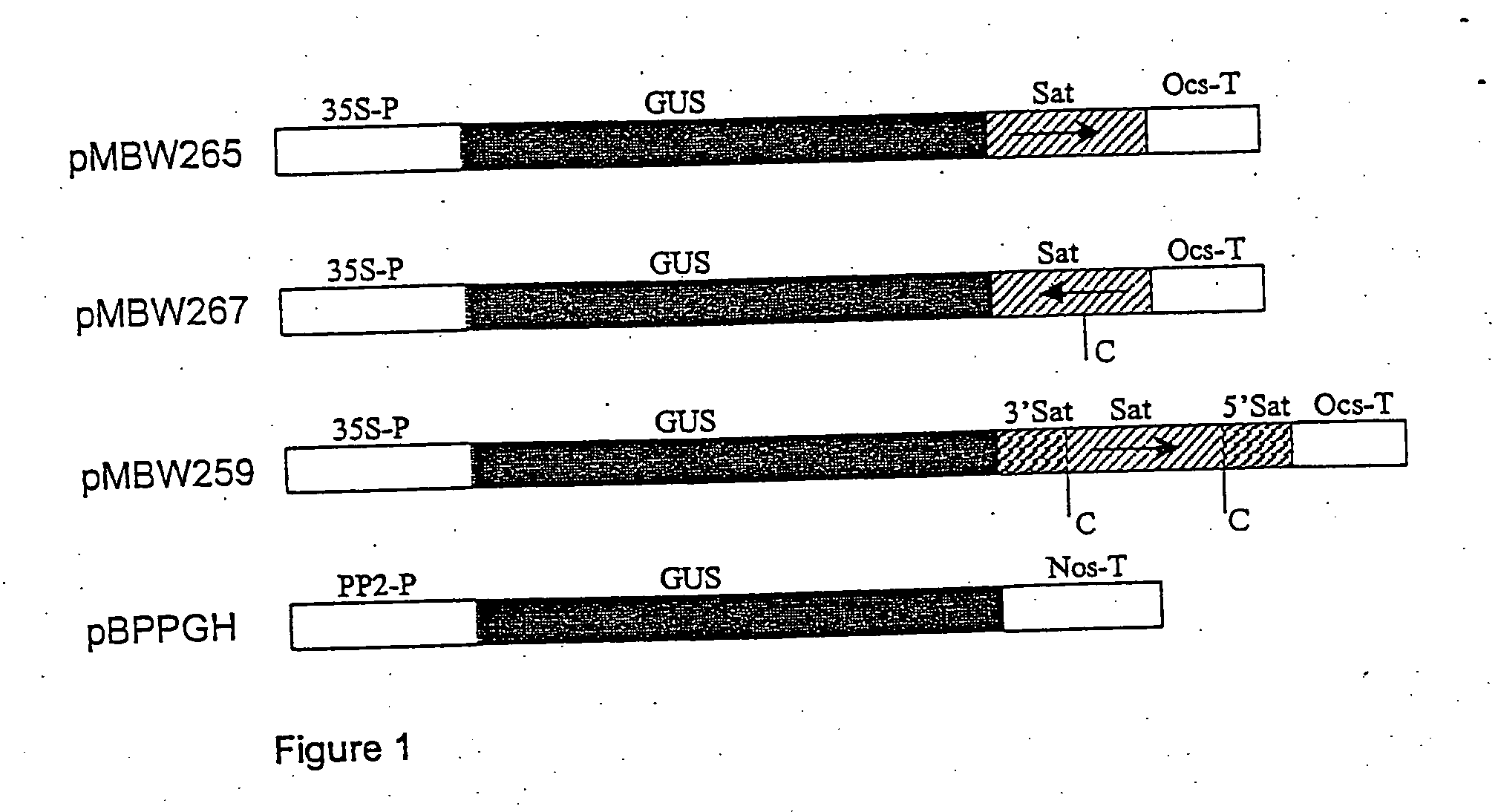
Chimeric gene for the transformation of plants
InactiveUSRE37287E1Most efficientPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationIncreased tolerance
Chimeric gene for conferring to plants an increased tolerance to a herbicide having as its target EPSPS comprises, in the direction of transcription, a promoter region, a transit peptide region, a coding sequence for glyphosate tolerance and a polyandenylation signal region, wherein the transit peptide region comprises, in the direction of translation, at least one transit peptide of a plant gene encoding a plastid-localized enzyme and then a second transit peptide of a plant gene encoding, a plastid-localized enzyme. Production of glyphosate-tolerant plants is disclosed.
Owner:BAYER SAS
DNA sequences comprising dystrophin minigenes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7001761B2Small sizeEfficient and stable correctionVirusesSugar derivativesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
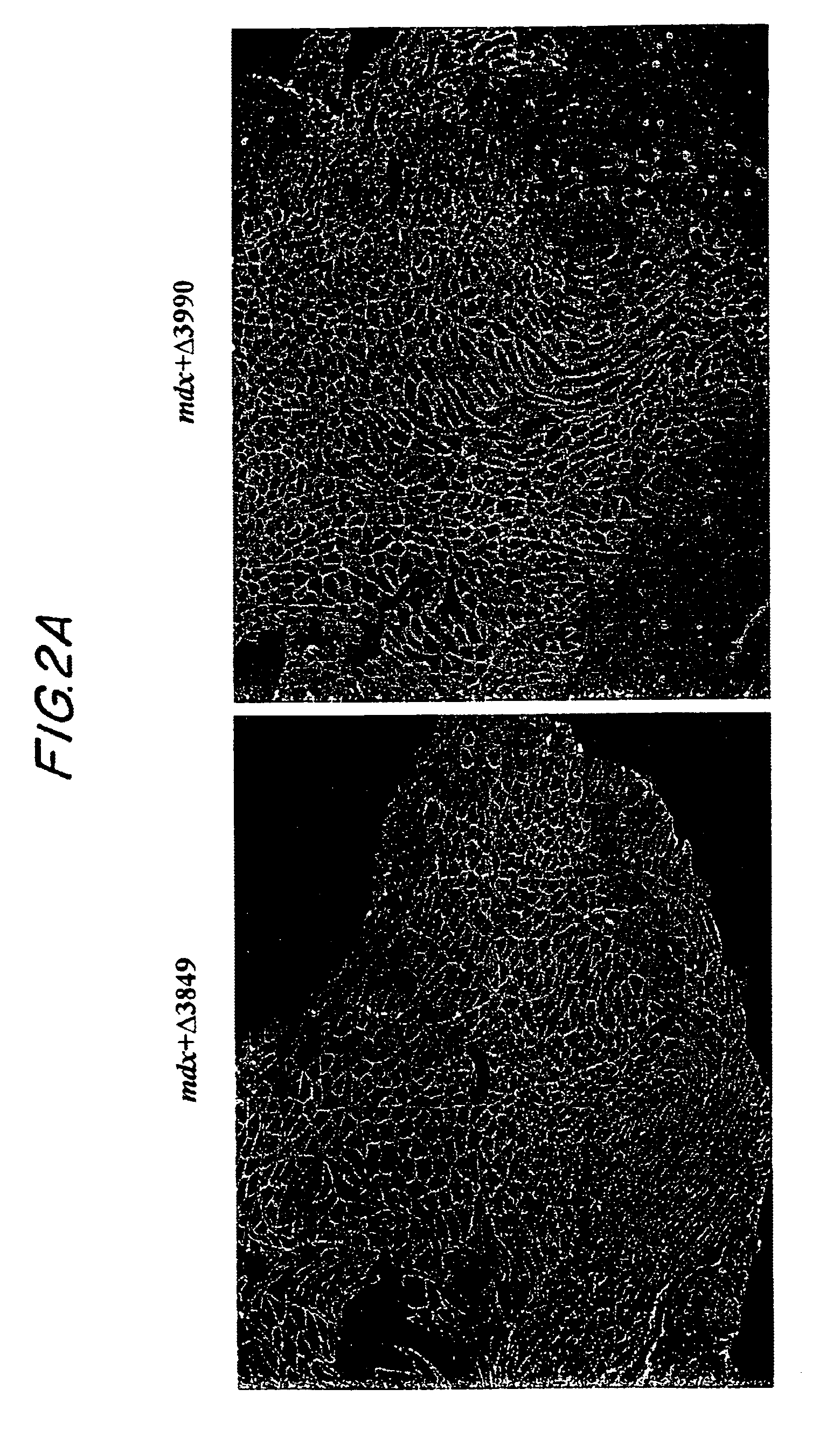
The present invention provides a series of novel dystrophin minigenes that retain the essential biological functions. The expression of the dystrophin minigenes may be controlled by a regulatory element along with a small polyadenylation signal. The entire gene expression cassettes may be readily packaged into a viral vector, preferably an AAV vector. The present invention further defines the minimal functional domains of dystrophin and provides ways to optimize and create new versions of dystrophin minigenes. Finally, the present invention provides a method of treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD).
Owner:ASKLEPIOS BIOPHARMACEUTICAL INC
Artificial nucleic acid molecules for improved protein expression
ActiveUS20180044687A1Strong attackAdaptableSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsPolyadenylationOpen reading frame
The invention relates to an artificial nucleic acid molecule comprising an open reading frame and a 3′-UTR comprising at least one poly(A) sequence or a polyadenylation signal. The invention further relates to a vector comprising the artificial nucleic acid molecule comprising an open reading frame and a 3′-UTR comprising at least one poly(A) sequence or a polyadenylation signal, to a cell comprising the artificial nucleic acid molecule or the vector, to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the artificial nucleic acid molecule or the vector and to a kit comprising the artificial nucleic acid molecule, the vector and / or the pharmaceutical composition. The invention also relates to a method for increasing protein production from an artificial nucleic acid molecule and to the use of a 3′-UTR for a method for increasing protein production from an artificial nucleic acid molecule. Moreover, the invention concerns the use of the artificial nucleic acid molecule, the vector, the kit or the pharmaceutical composition as a medicament, as a vaccine or in gene therapy.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS7138565B2Reduce expressionFused cellsOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specific RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
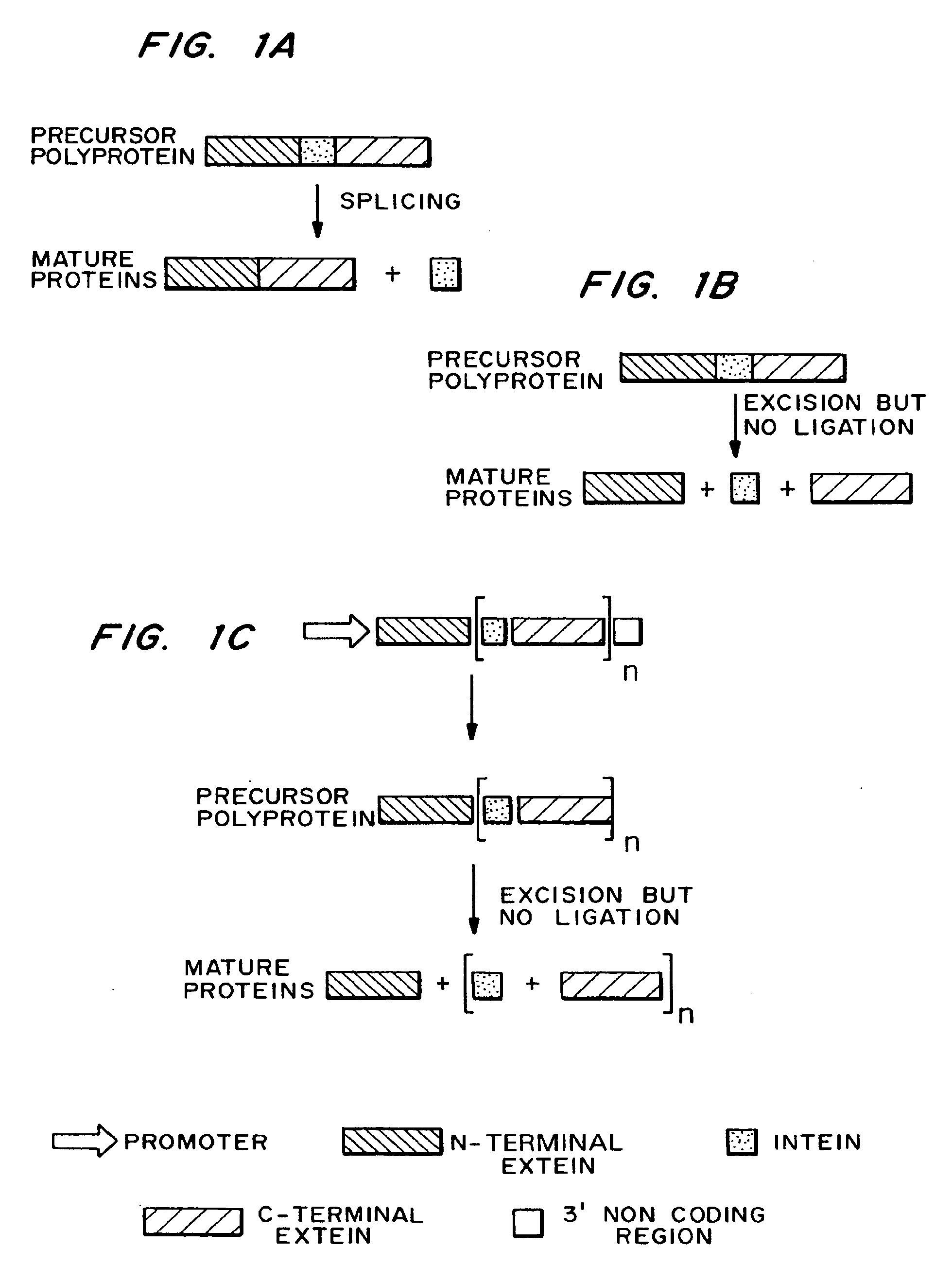
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
Identifying and quantifying small RNAs
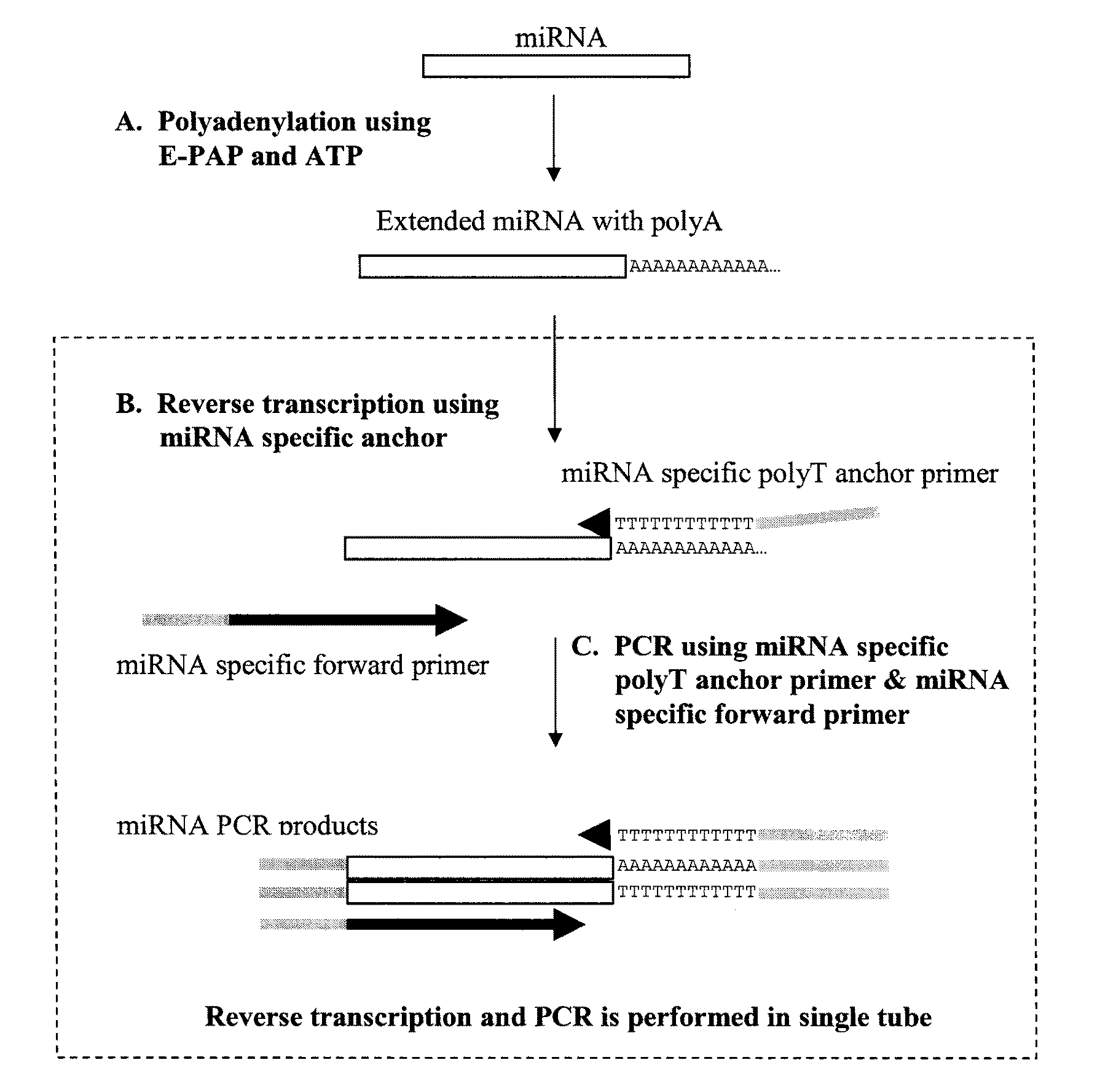
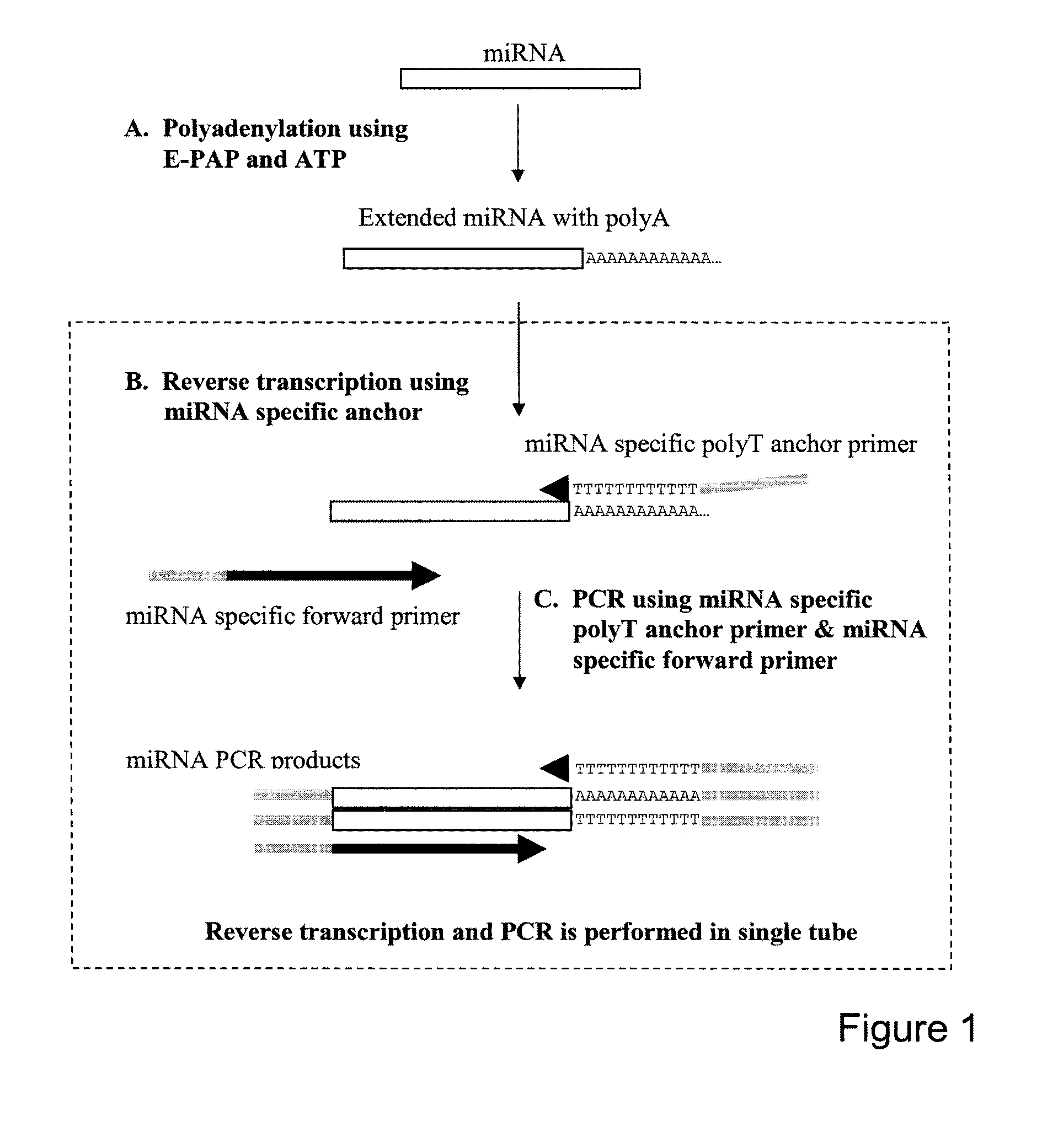
One-step RT-PCR methods, compositions and kits for the detection and quantification of small RNAs in a sample are disclosed. The one-step RT-PCR approach involves polyadenylation of a small RNA followed by reverse transcription with a first primer containing a poly(T) sequence and at least two 3′ nucleotides complementary to the 3′ terminal end nucleotides of the small RNA, to produce a cDNA. This may be followed by PCR amplification using the same first primer as the revere primer and a second, forward primer in which a portion of its sequence is complementary to the 3′ terminal end of the cDNA. This may be then followed by detection and / or quantification of the amplified product.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
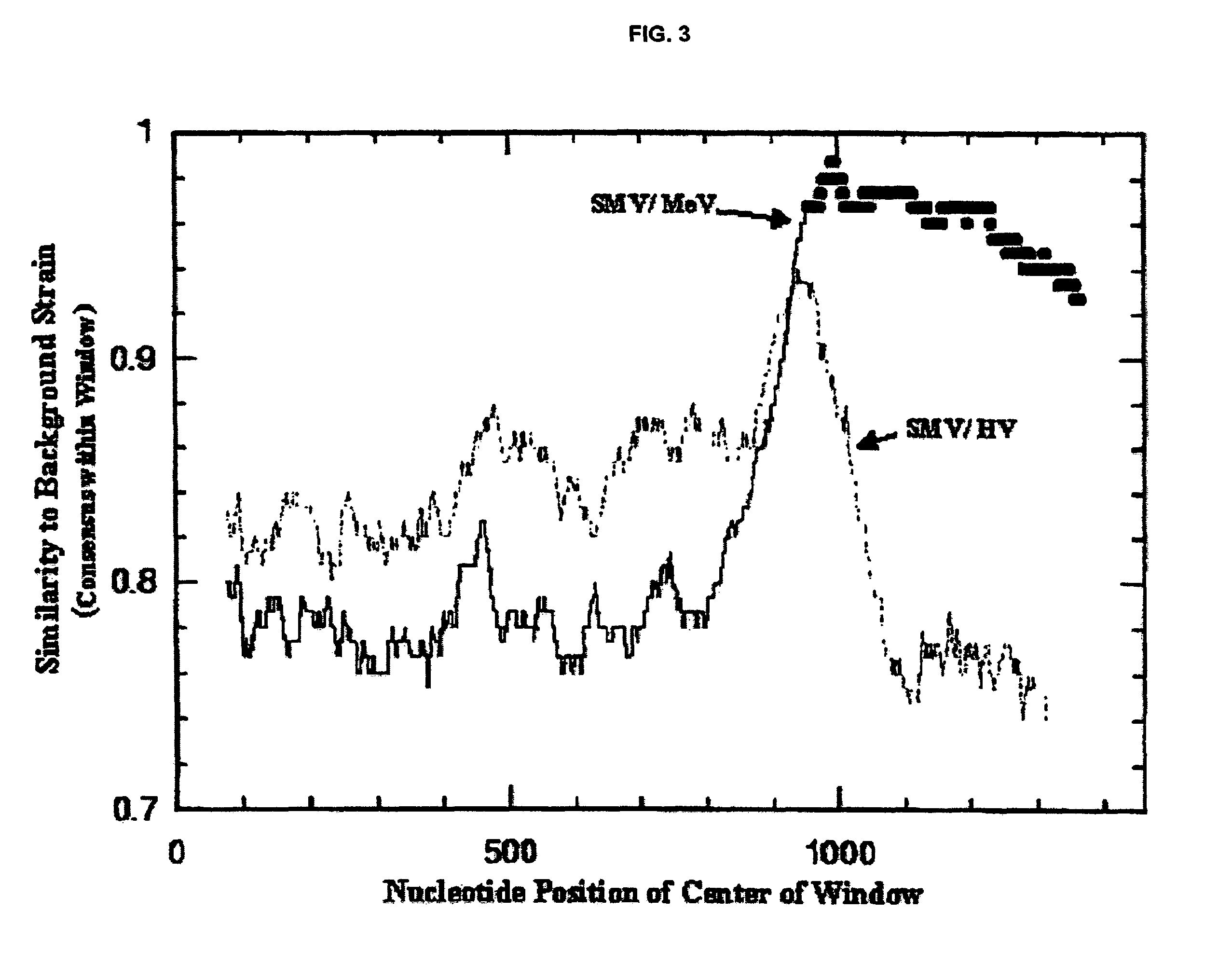
Snow mountain virus genome sequence, virus-like particles and methods of use
Snow Mountain Virus (SMV) belongs to the Norovirus genus of the Caliciviridae family. SMV is a genogroup II (GII) reference strain of human enteric caliciviruses associated with epidemic gastroenteritis. The positive sense RNA genome sequence of SMV was determined to be 7,537 nucleotides in length excluding the 3′ polyadenylated tract. The genome is organized into three open reading frames. Pairwise sequence alignments showed SMV ORF1 is highly conserved with other GII noroviruses, and most closely related to GII strains Melksham and Hawaii viruses. Comparative sequence analyses showed the SMV is a recombinant norovirus. VP1 / NP2 proteins assembled into virus-like particles (VLPs) when expressed in insect cells by a recombinant baculovirus. Characterization of one clone that expressed VP1 but failed to assemble into VLPs, identified histidine residue 91 as important for particle assembly.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods and systems for detection and isolation of a nucleotide sequence
InactiveUS20050053942A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPolyadenylationRna degradation
A method for isolating nucleic acid molecules having a repeating nucleotide sequence or a homopolymeric nucleotide sequence, e.g. a poly A stretch, is described. In particular, the method uses oligomeric capture probes spiked with various amounts of locked nucleic acid (LNA). The invention further describes methods for the isolation of RNA molecules, for example polyadenylated mRNA molecules, which overcome the problems of rapid RNA degradation during isolation and analysis of such nucleic acid molecules. This is of major clinical and diagnostic importance, especially when dealing with RNA viruses, such as retroviruses or when analyzing rare or low-abundant mRNAs or mRNAs from biopsies or tissues enriched with RNases.
Owner:EXIQON AS
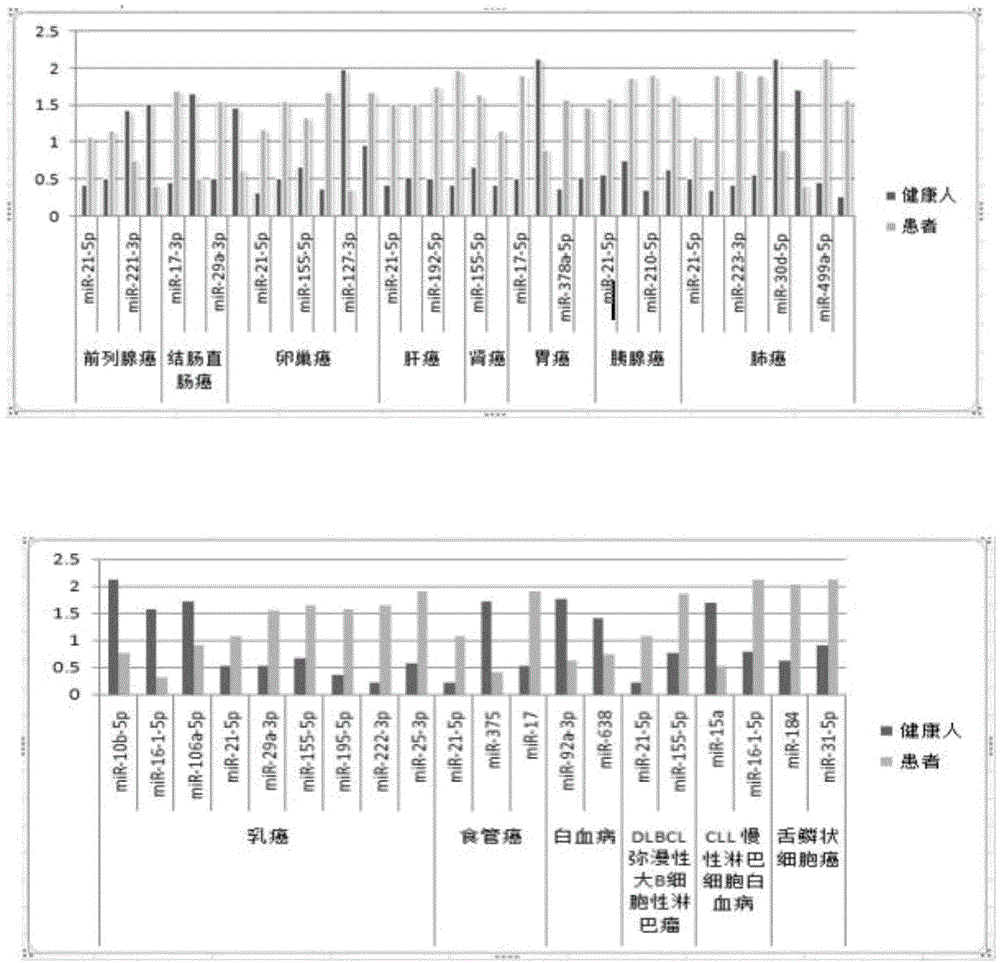
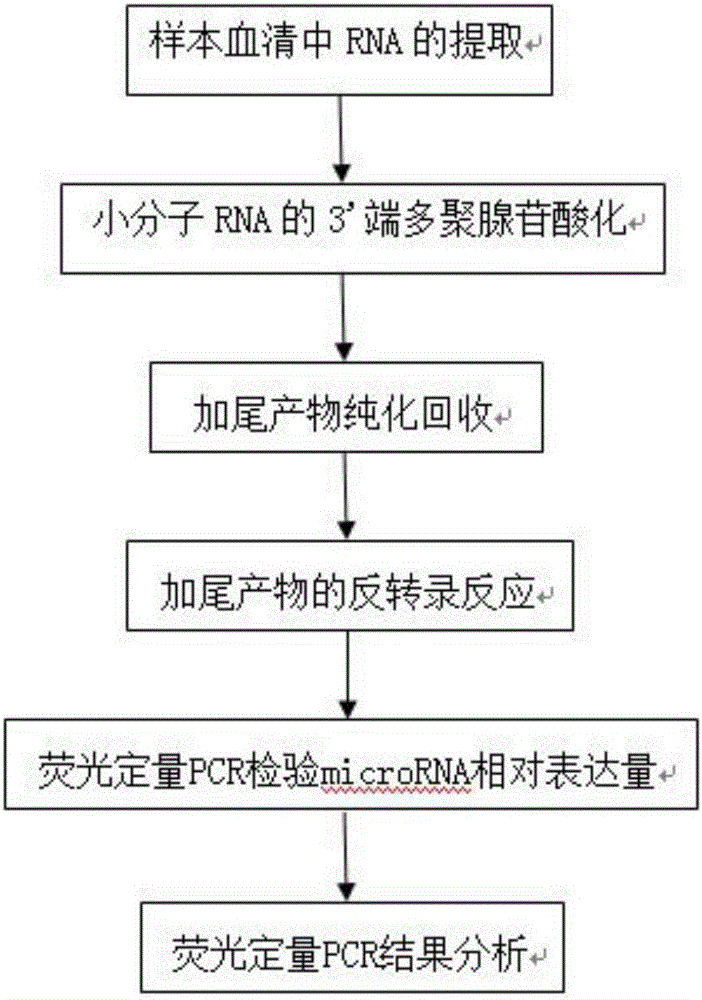
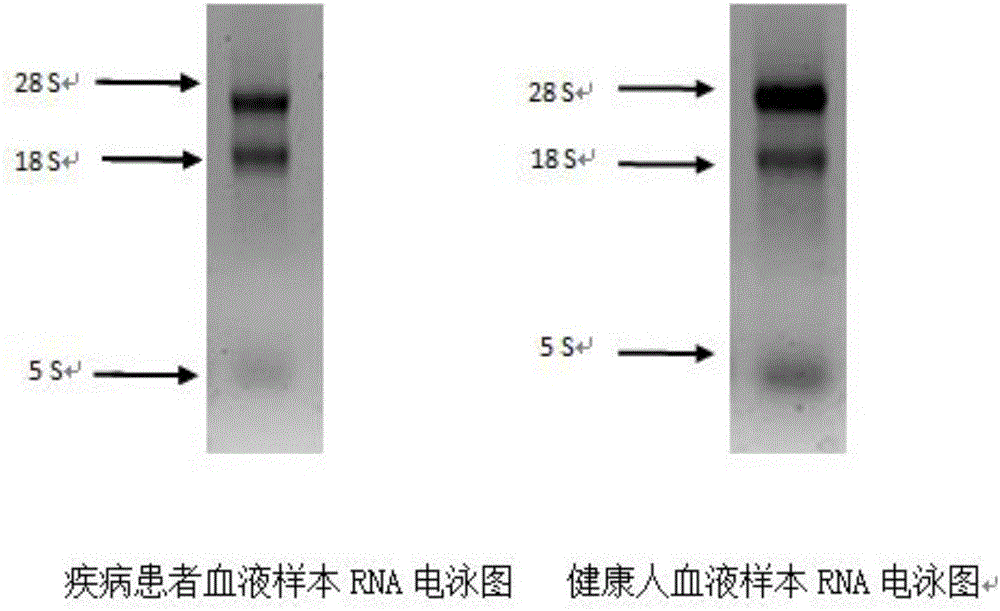
Kit for auxiliary diagnosis of multiple tumors by taking micro ribonucleic acid (RNA) combination as tumor marker, and detection method of kit
PendingCN105950768AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPoly-A RNAIndividualized treatment
The invention relates to a kit for auxiliary diagnosis of multiple tumors by taking a micro ribonucleic acid (RNA) combination as a tumor marker, and a detection method of the kit. The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and oncology. The detection method comprises the steps of (1) extracting RNA from serum; (2) carrying out polyadenylation on the 3' end of micro RNA; (3) purifying and recovering a tailing product; (4) carrying out an inverse transcription reaction on the tailing product; (5) testing the relative expression of the micro RNA by means of a fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction); (6) analyzing the result of the fluorescent quantitative PCR. The kit has the characteristics of high conservative property, space-time specificity, stability, tissue specificity and the like, and plays an important role in the aspects such as disease pathogenesis research, early diagnosis, individualized treatment and prognosis; furthermore, the kit is simple to operate, convenient in material obtaining, safe and noninvasive, and is conveniently used for screening of a great deal of diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU YINUOWAN CELL CLINIC CO LTD
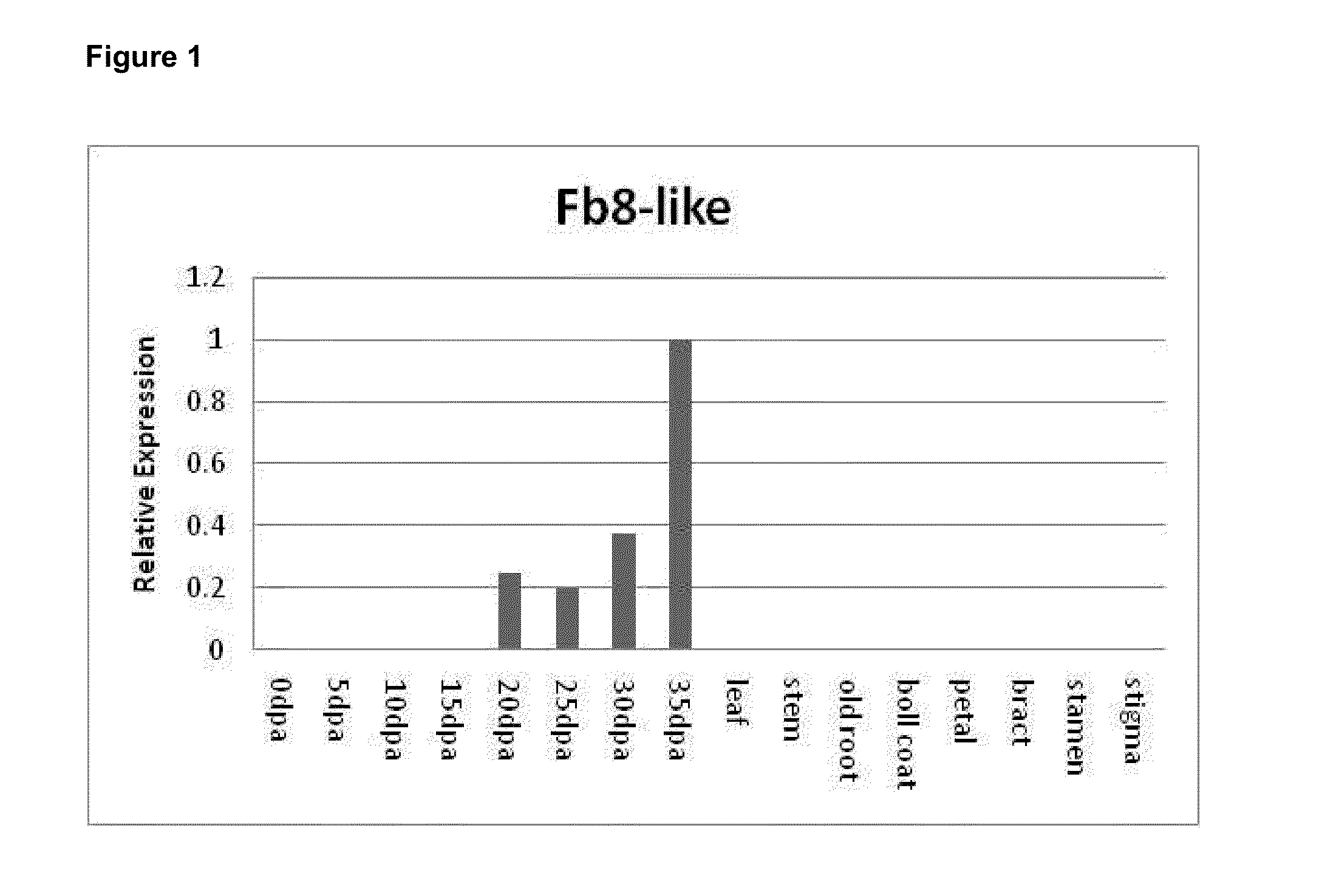
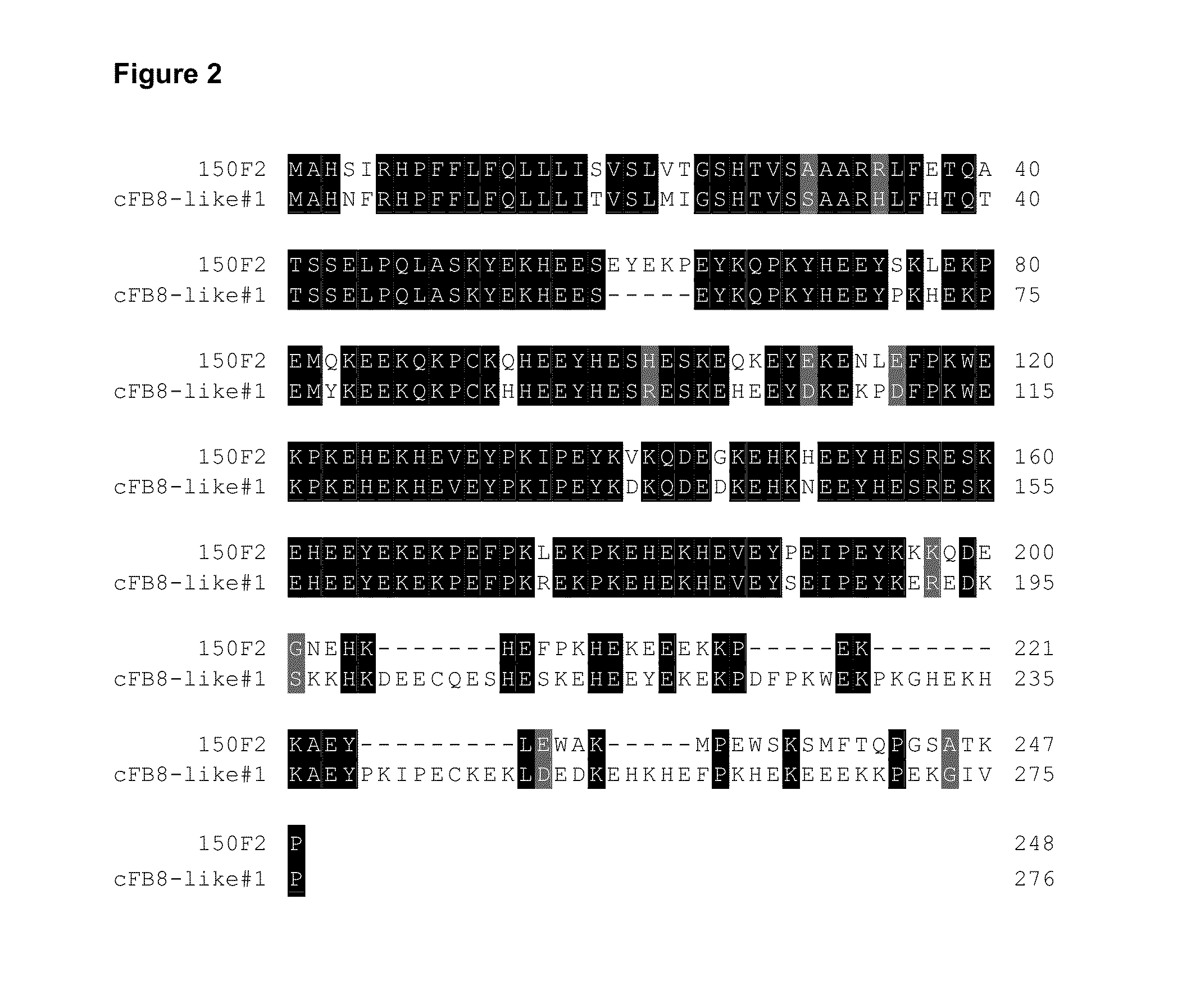
Novel fiber-preferential promoter in cotton
The present application discloses an isolated nucleic acid sequence comprising (a) at least 700 consecutive nucleotides of SEQ ID NO: 1; (b) a nucleotide sequence with at least 80% sequence identity to the nucleotide sequence of (a); (c) a nucleotide sequence hybridizing under stringent conditions to the nucleotide sequence of (a) or (b); and (d) a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of any one of (a) to (c). Further disclosed herein is a chimeric gene comprising the isolated nucleic acid described herein operably linked to a nucleic acid coding for an expression product of interest, and a transcription termination and polyadenylation sequence. Also disclosed herein are a vector, a transgenic plant cell, a transgenic plant and a seed as characterized in the claims. Methods disclosed herein relate to the production of a transgenic plant, growing cotton, producing a seed, effecting fiber-preferential expression of a product in cotton and of altering fiber properties in a cotton plant as characterized in the claims.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC +1
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20070056057A1Reduce expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specific RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
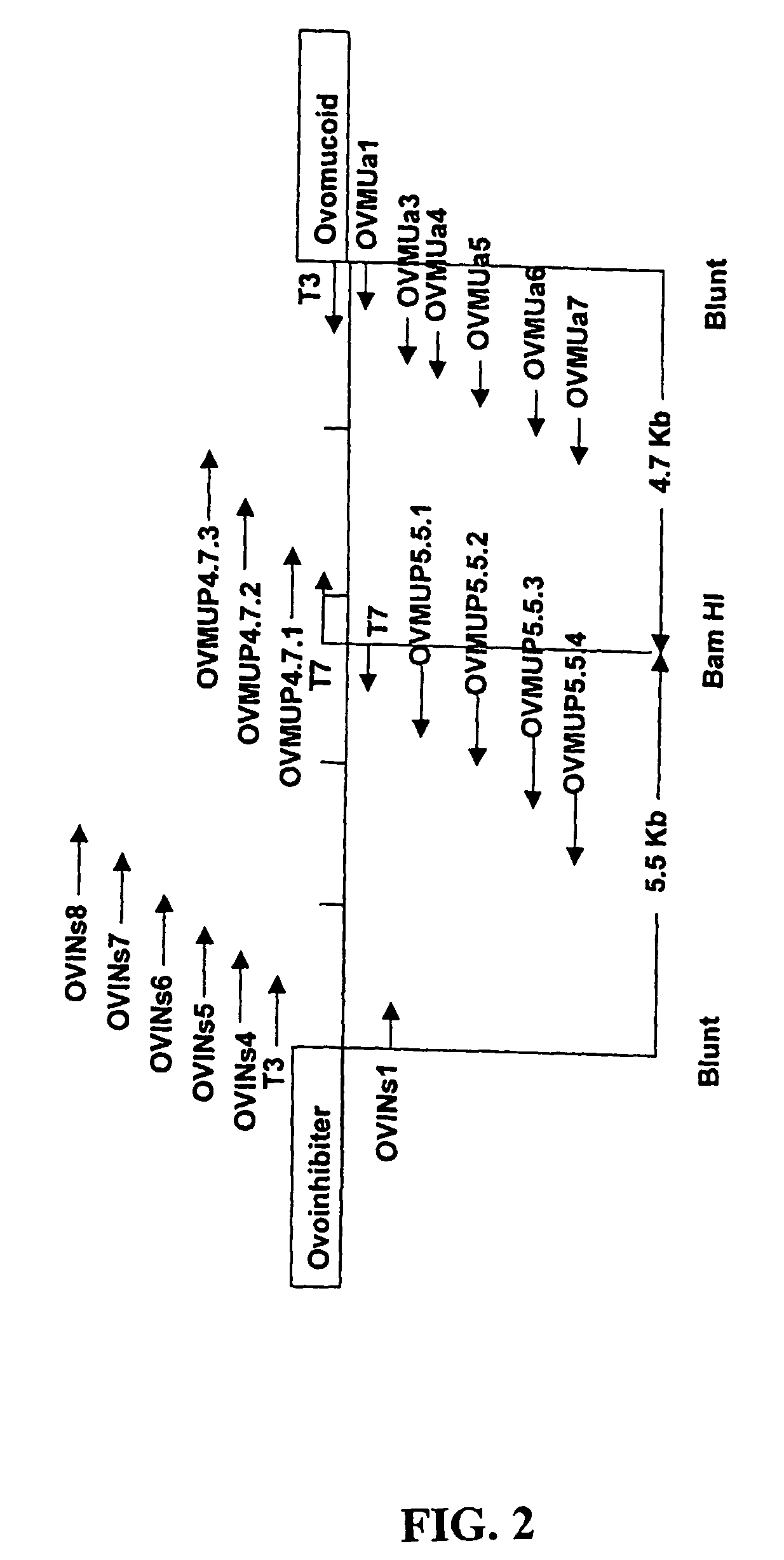
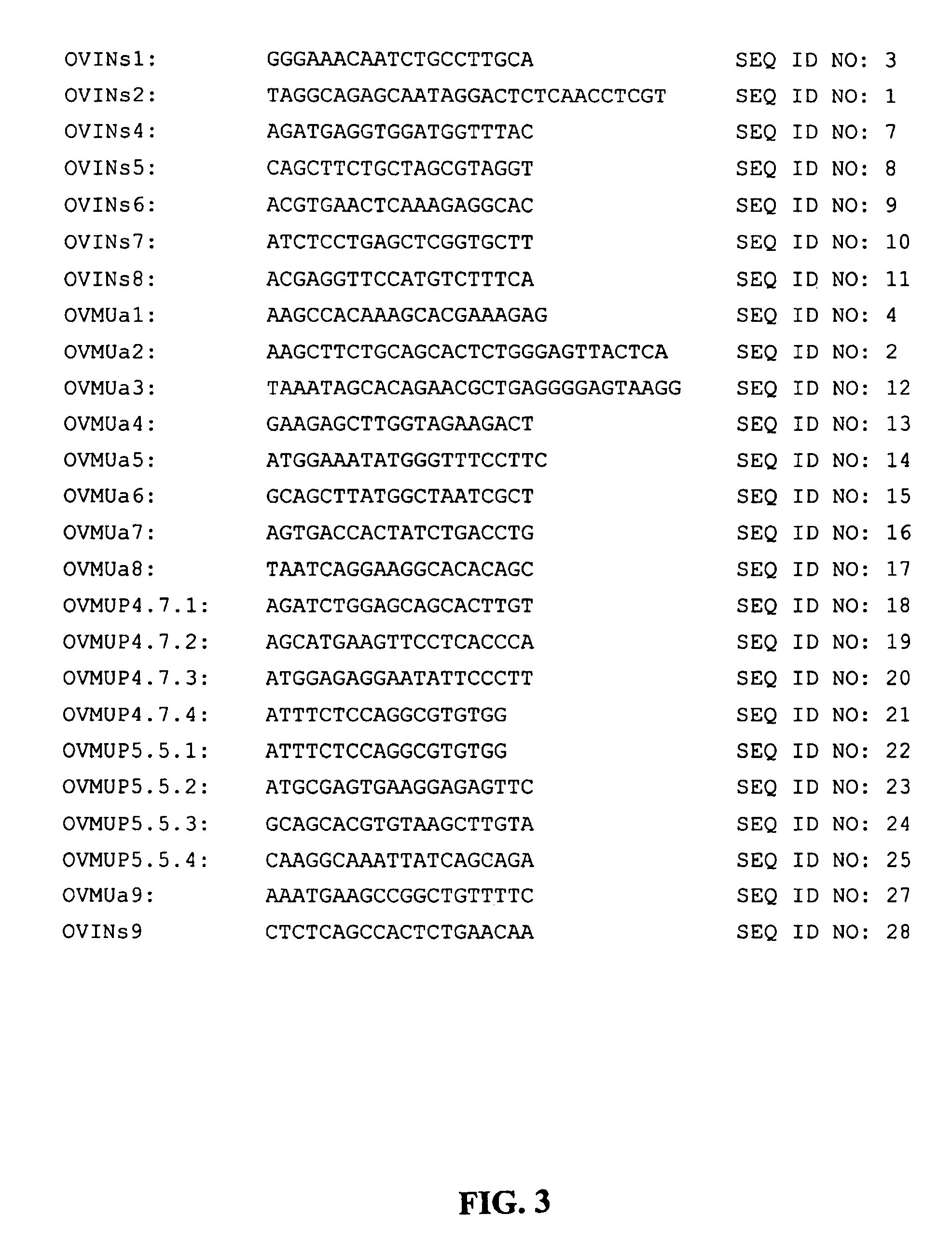
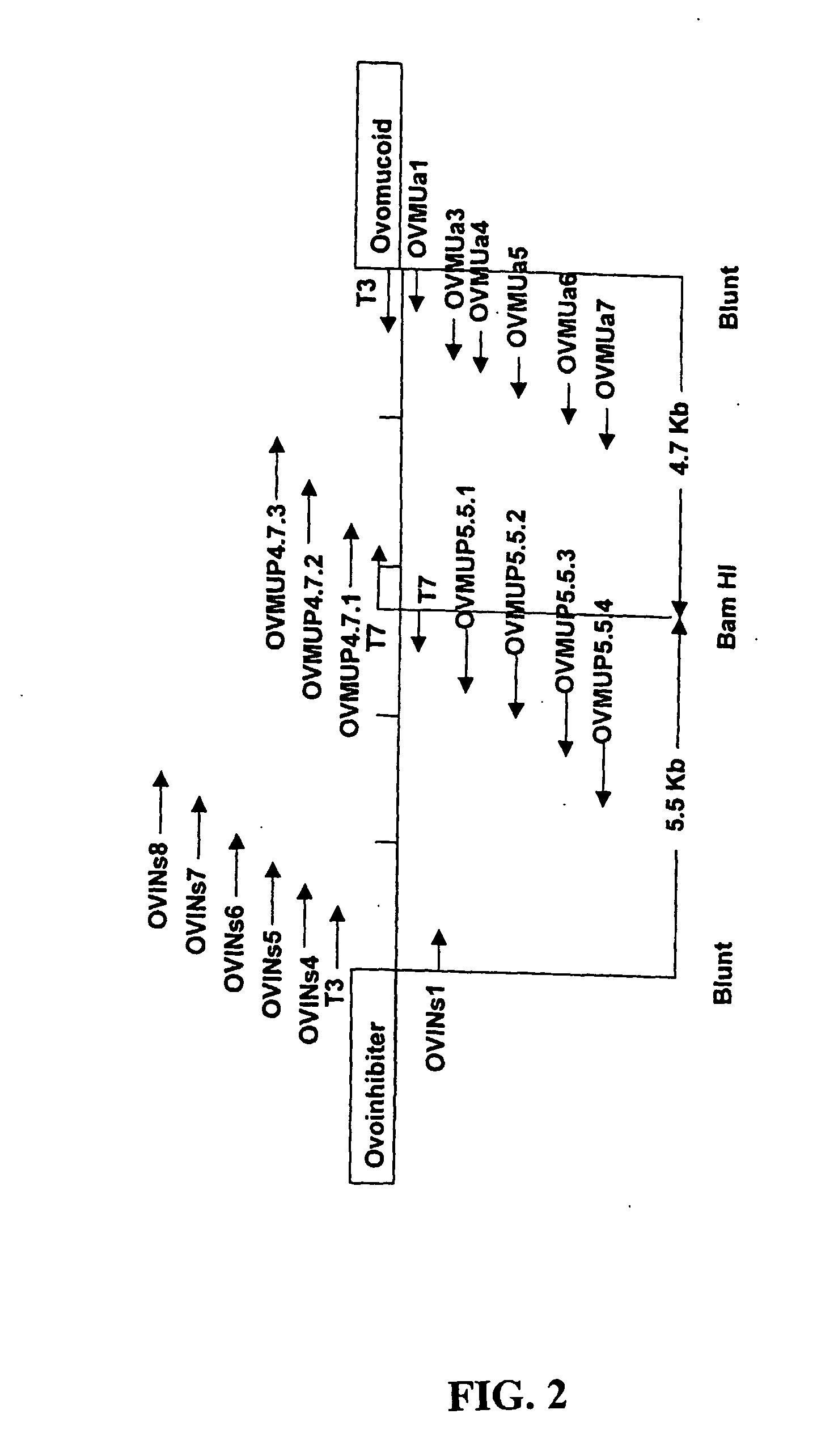
Transgenic avians with an ovomucoid gene expression control region linked to a nucleotide sequence encoding a heterologous polypeptide
The present invention provides novel isolated nucleic acids that comprise an avian nucleic acid sequence comprising a ovomucoid gene expression control region. The ovomucoid promoter region of the present invention will allow expression of an operably linked heterologous nucleic acid insert in a transfected avian cell such as, for example, an oviduct cell. The isolated avian ovomucoid of the present invention may be operably linked with a selected nucleic acid insert, wherein the nucleic acid insert encodes a polypeptide desired to be expressed in a transfected cell. The recombinant DNA of the present invention may further comprise a polyadenylation signal sequence. The present invention further includes expression vectors comprising an isolated avian ovomucoid gene expression control region of the present invention, and transfected cells and transgenic avians comprising the expression vectors.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20050251877A1Reducing phenotypic expressionReduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eukaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by providing aberrant, preferably unpolyadenylated, target-specific RNA to the nucleus of the host cell. Preferably, the unpolyadenylated target-specifc RNA is provided by transcription of a chimeric gene comprising a promoter, a DNA region encoding the target-specific RNA, a self-splicing ribozyme and a DNA region involved in 3′ end formation and polyadenylation.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
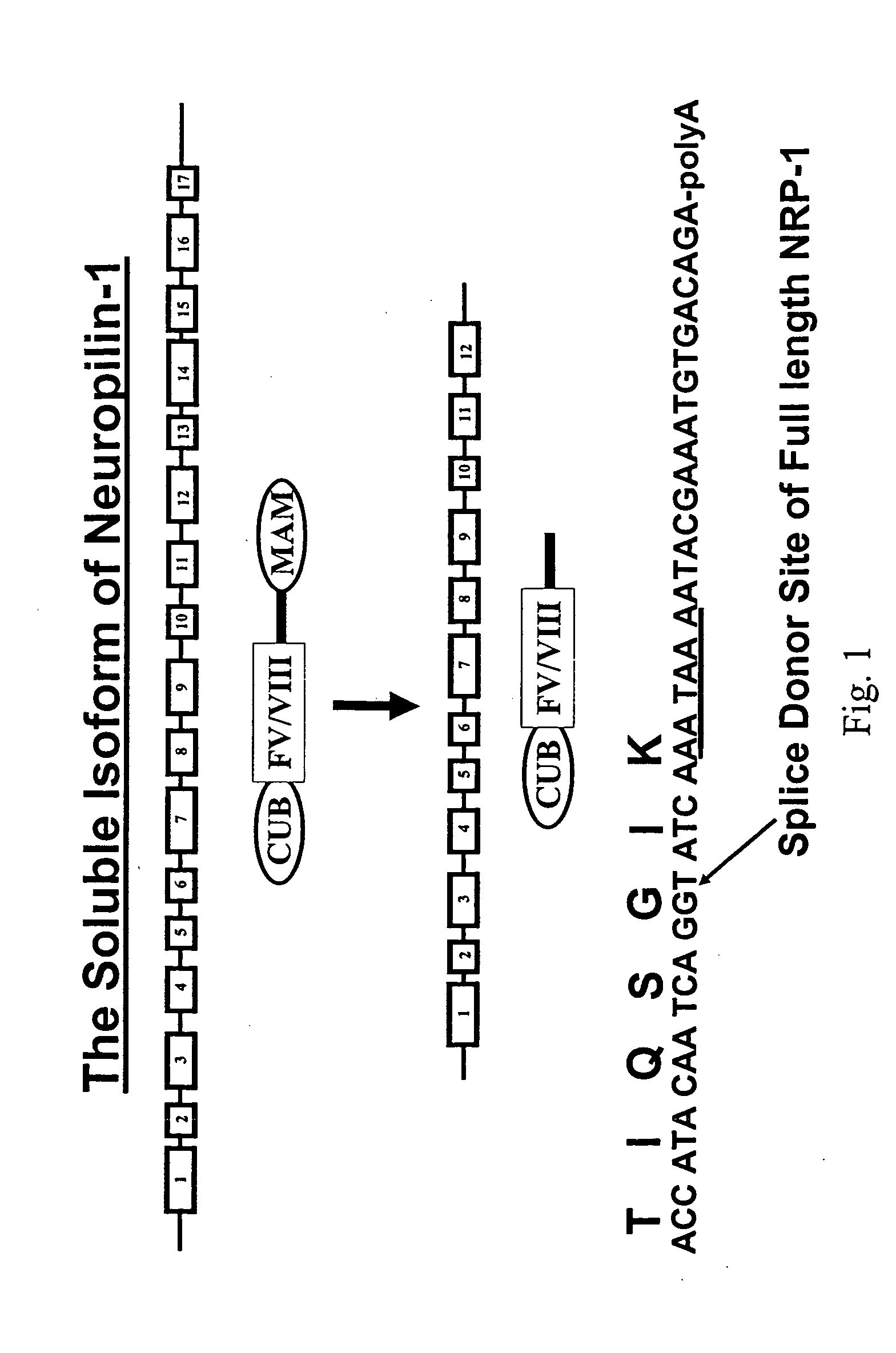
Human soluble neuropilin-1 primary polyadenylation signal and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050175591A1Easy to transportImprove translationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPoly-A RNANucleotide
The human soluble neuropilin-1 (sNRP) polyadenylation signal (sNRP-poly(A)), situated downstream of the GT splice donor site of intron 12 of the full-length neuropilin-1 gene, also functions as the termination codon for sNRP. This 17 nucleotide sequence efficiently facilitates addition of poly(A) tails to RNAs expressed in cells. The present invention shows that this optimally succinct sequence has similar activity to the SV40 polyadenylation signal that is currently used in expression vectors. By using this shorter dual termination / polyadenylation signal and avoiding the need for large and cumbersome polyadenylation signals, expression vectors may be engineered to carry considerably larger genes.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Ovomucoid promoters and methods of use
The present invention provides novel isolated nucleic acids that comprise an avian nucleic acid sequence comprising a ovomucoid gene expression control region. The ovomucoid promoter region of the present invention will allow expression of an operably linked heterologous nucleic acid insert in a transfected avian cell such as, for example, an oviduct cell. The isolated avian ovomucoid of the present invention may be operably linked with a selected nucleic acid insert, wherein the nucleic acid insert encodes a polypeptide desired to be expressed in a transfected cell. The recombinant DNA of the present invention may further comprise a polyadenylation signal sequence. The present invention further includes expression vectors comprising an isolated avian ovomucoid gene expression control region of the present invention, and transfected cells and transgenic avians comprising the expression vectors.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
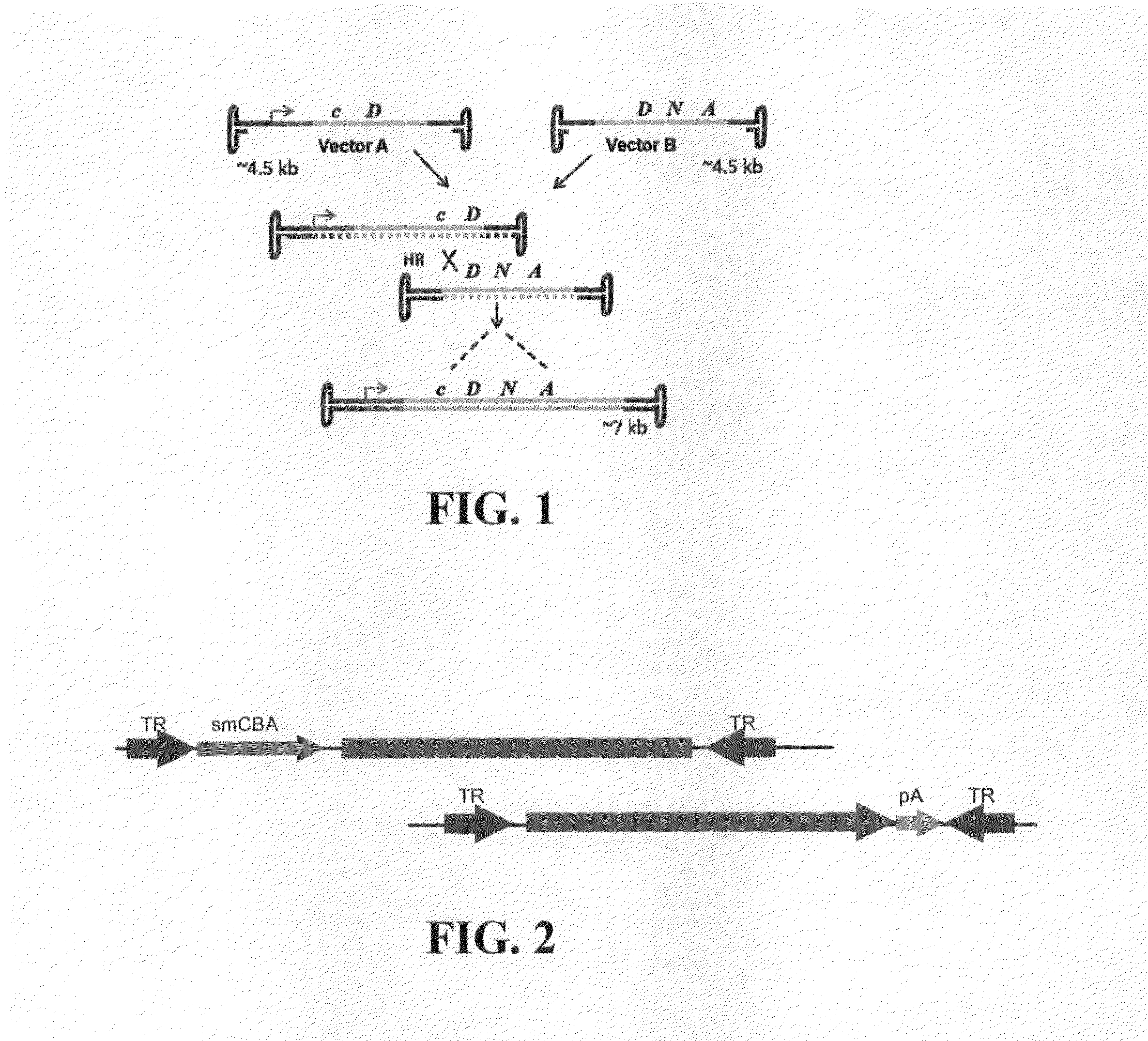
Dual-AAV Vector-Based Systems and Methods for Delivering Oversized Genes to Mammalian Cells
Disclosed are materials and methods for treating diseases of the mammalian eye, and in particular, Usher syndrome 1B (USH1B). The invention provides AAV-based, dual-vector systems that facilitate the expression of full-length proteins whose coding sequences exceed that of the polynucleotide packaging capacity of an individual AAV vector. In one embodiment, vector systems are provided that include i) a first AAV vector polynucleotide that includes an inverted terminal repeat at each end of the polynucleotide and a suitable promoter followed by a partial coding sequence that encodes an N-terminal portion of a full-length polypeptide; and ii) a second AAV vector polynucleotide that includes an inverted terminal repeat at each end of the polynucleotide and a partial coding sequence that encodes a C-terminal portion of a full-length polypeptide, optionally followed by a polyadenylation (pA) signal sequence. In another embodiment, the vector system includes i) a first AAV vector polynucleotide comprising an inverted terminal repeat at each end, a suitable promoter followed by a partial coding sequence that encodes an N-terminal portion of a full-length polypeptide followed by a splice donor site and intron and ii) a second AAV vector polynucleotide comprising an inverted terminal repeat at each end, followed by an intron and a splice-acceptor site for the intron, followed by a partial coding sequence that encodes a C-terminal portion of a full-length polypeptide, optionally followed by a polyadenylation (pA) signal sequence. The coding sequence or the intron sequence in the first and second AAV vectors preferably includes a sequence region that overlaps.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
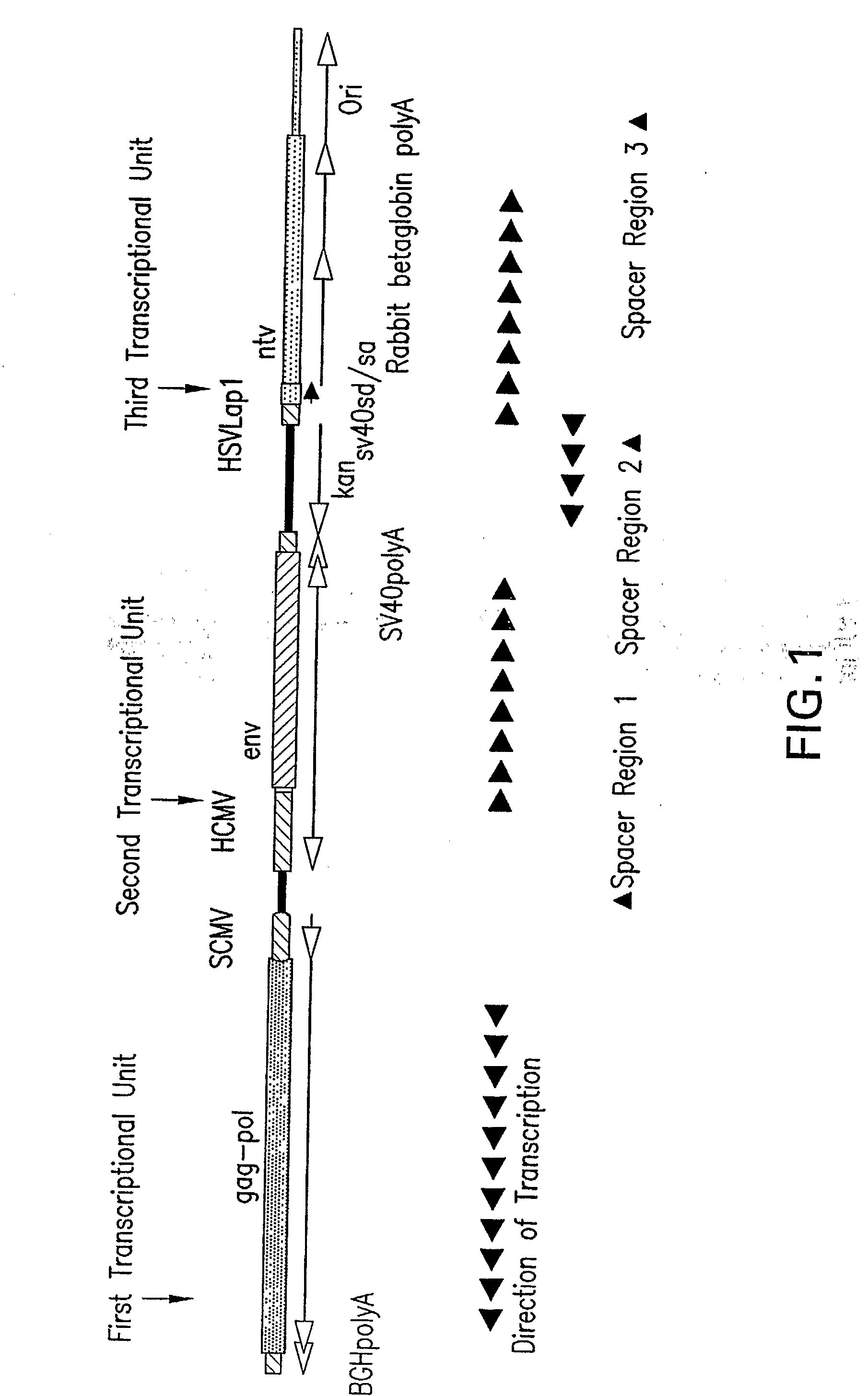
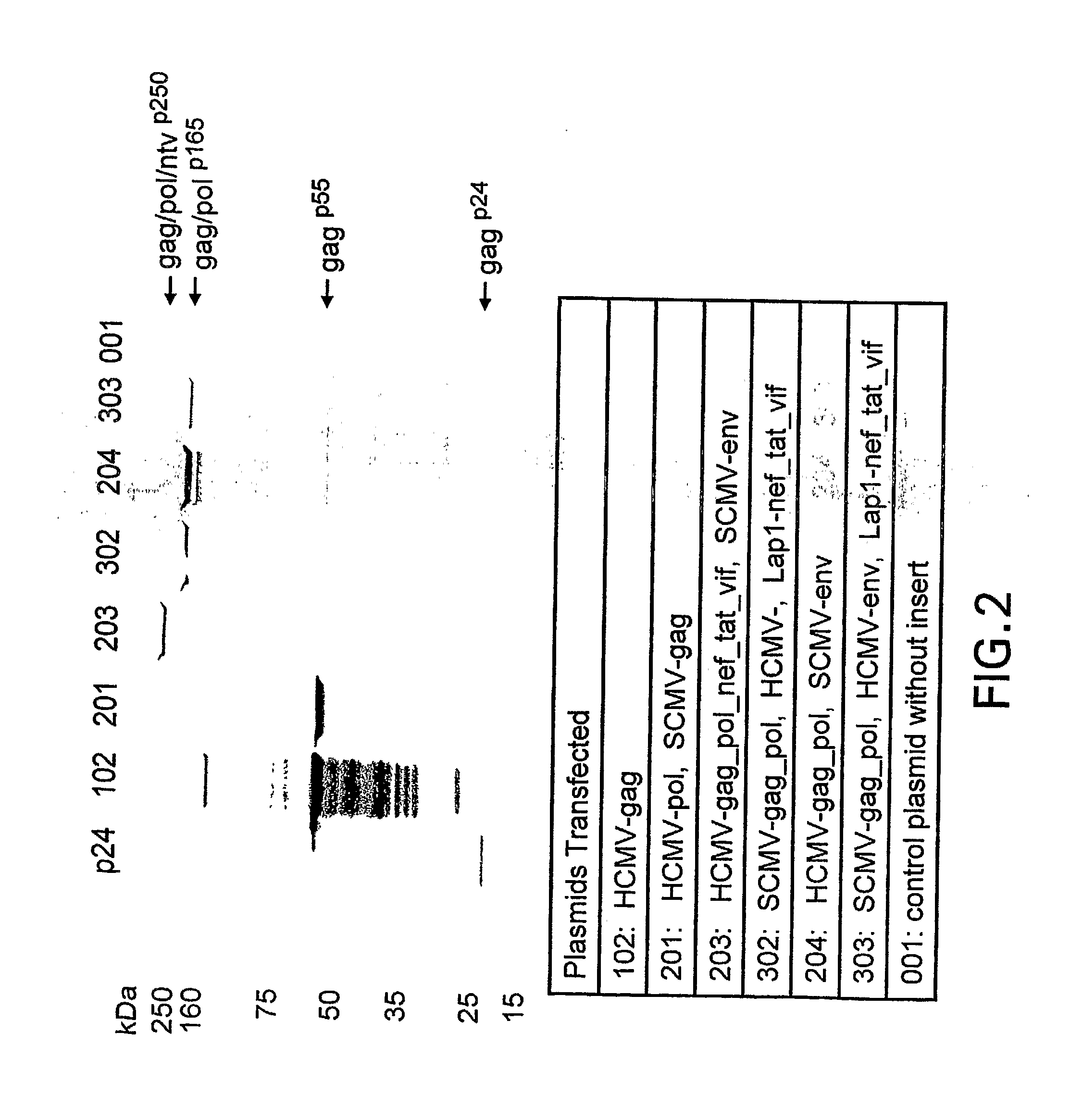
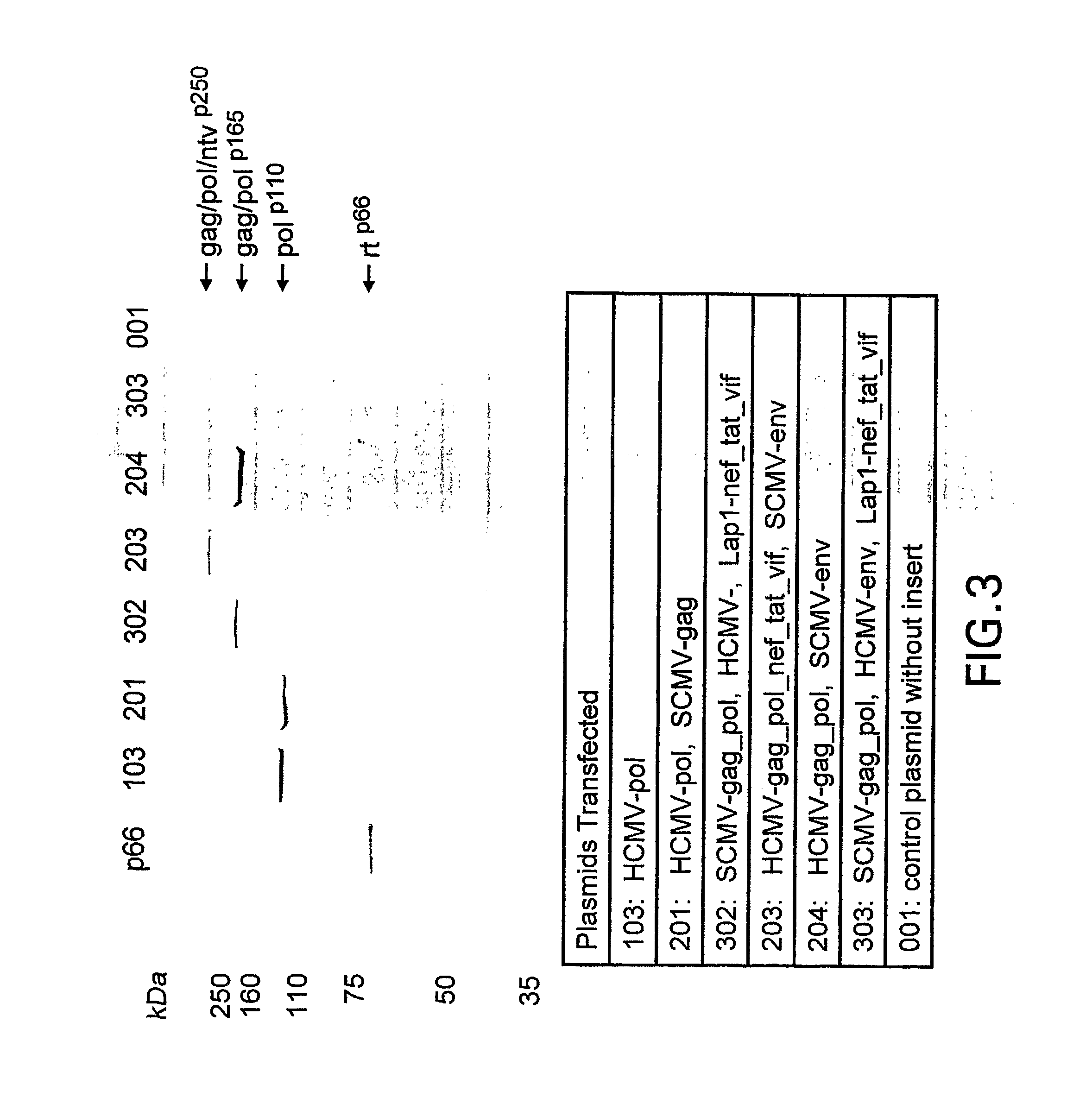
Plasmid having three complete transcriptional units and immunogenic compositions for inducing an immune response to hiv
The invention provides a DNA plasmid comprising: (a) a first transcriptional unit comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes a first polypeptide operably linked to regulatory elements including a first promoter and a first polyadenylation signal; (b) a second transcriptional unit comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes a second polypeptide operably linked to regulatory elements including a second promoter and a second polyadenylation signal; (c) a third transcriptional unit comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes a third polypeptide operably linked to regulatory elements including a third promoter and a third polyadenylation signal; and wherein said first, said second and said third promoters are each derived from different transcriptional units; and wherein said first, said second and said third polyadenylation signals are each derived from different transcriptional units. The invention further relates to immunogenic compositions for inducing an immune response to HIV comprising combinations of two, three, or four plasmids, where each plasmid is expressing a defined antigen, which may be a single antigen or a fusion of two or three antigens.
Owner:WYETH LLC
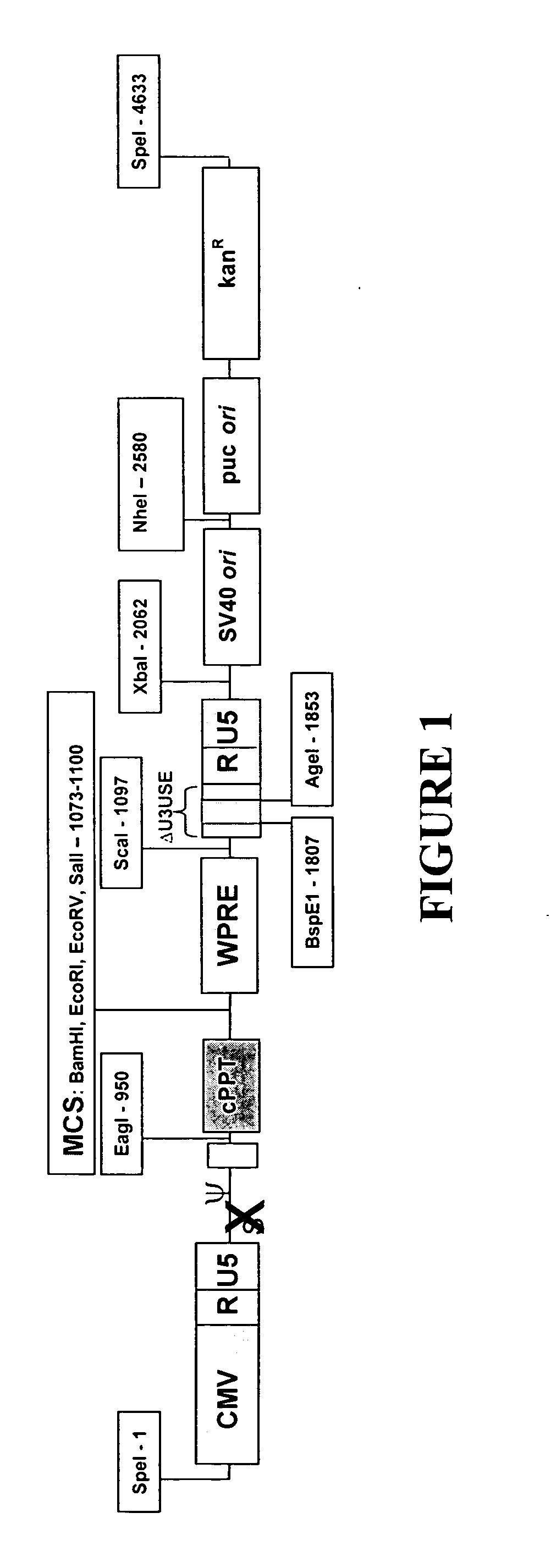
Minimal lentiviral vector system
InactiveUS20060019393A1High potencyMaximize preferenceGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesPoly-A RNAUpstream Enhancer
A lentiviral vector system is described. The system comprises a lentiviral transfer vector and a packaging construct. The transfer vector comprises (a) a 5′ LTR; (b) a 3′ LTR comprising a polyadenylation signal; (c) a minimal packaging signal, (d) (i) at least one heterologous upstream enhancer (UE) sequences, and / or (ii) at least one additional copy of endogenous UE sequences operatively associated with said polyadenylation signal; and (e) a PRE. The packaging construct comprises a nucleic acid encoding and expressing a lentiviral Gag nucleic acid (preferably Gag and Pol). Preferably the lentiviral Gag nucleic acid is a mutated Gag nucleic acid containing one or more substitution mutations, wherein said mutated Gag nucleic acid encodes the same amino acid sequence as the corresponding unmutated Gag nucleic acid, but differs from the nucleic acid sequence of said corresponding unmutated Gag nucleic acid sequence due to the degeneracy of the genetic code. Preferably the packaging construct further comprises a heterologous nucleic acid encoding and expressing an adenovirus VA RNA. The transfer vector and packaging construct can be used together in a producer cell to produce viral particles.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
3'-Based sequencing approach for microarray manufacture
InactiveUS20090082218A1Easy to detectReduce false positiveNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
Methods are described to derive design sequences for the production of nucleic acid microarrays. The present methods use high throughput 3′ sequencing of transcripts in a tissue sample or diseased state to design probes for nucleic acid microarrays. Also described are nucleic acid microarrays that possess probes directed to the extreme 3′ end of transcripts in a tissue. These microarrays preferably represent alternate polyadenylation sequences that are specific to the tissue from which the transcripts are derived. Also described are methods of using the microarrays directed to the extreme 3′ end of the transcript for evaluating gene expression in a tissue where there are reduced false positive and false negative results.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS LIMITED
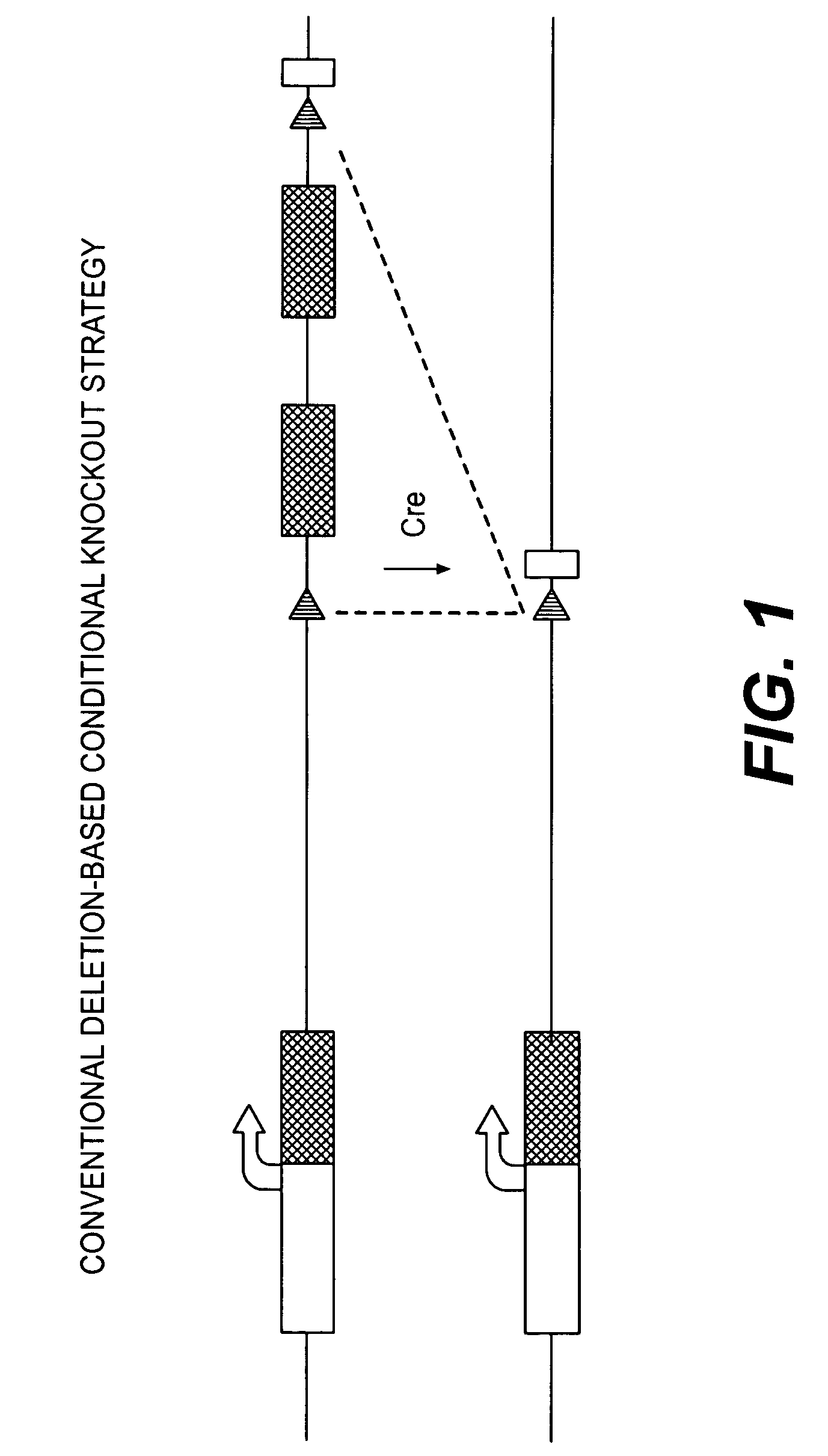
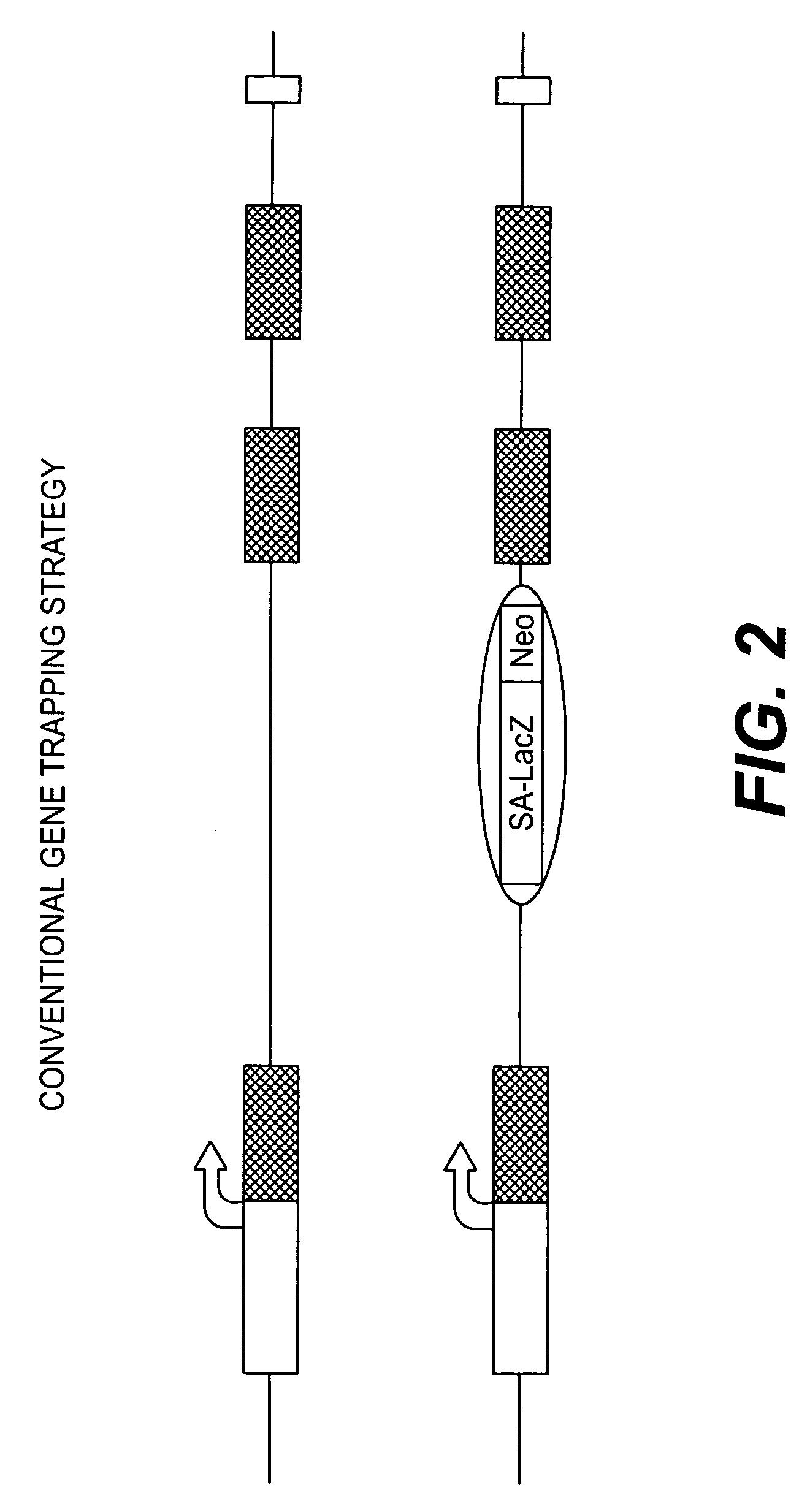
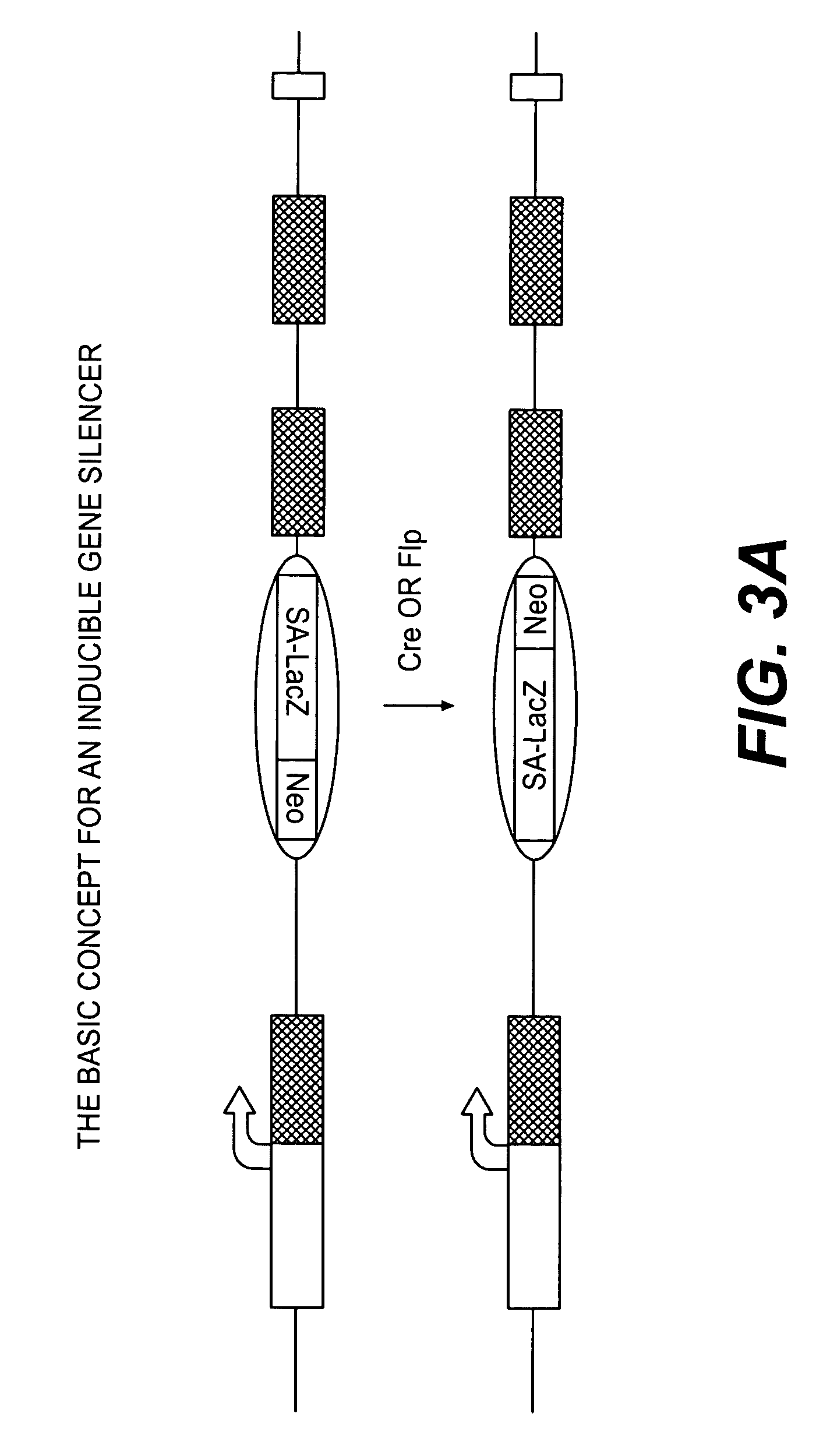
Conditional knockout method for gene trapping and gene targeting using an inducible gene silencer
InactiveUS7625755B2Less genetic manipulationEasy constructionSugar derivativesNucleic acid vectorPoly-A RNANucleotide
A method for conditionally knocking out and altering gene function and genetic sequences that can be used in such methods, for use in gene trapping and gene targeting. Specifically, the genetic sequence is a inducible gene silencer comprising: (a) a splice acceptor sequence; (b) an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) sequence; (c) a nucleotide sequence coding for a reporter protein; (d) a polyadenylation sequence; and (e) a pair of oppositely oriented recombination site sequences, which cause single cycle inversions in the presence of a suitable recombinase enzyme, flanking elements (a) through (d).
Owner:WYETH
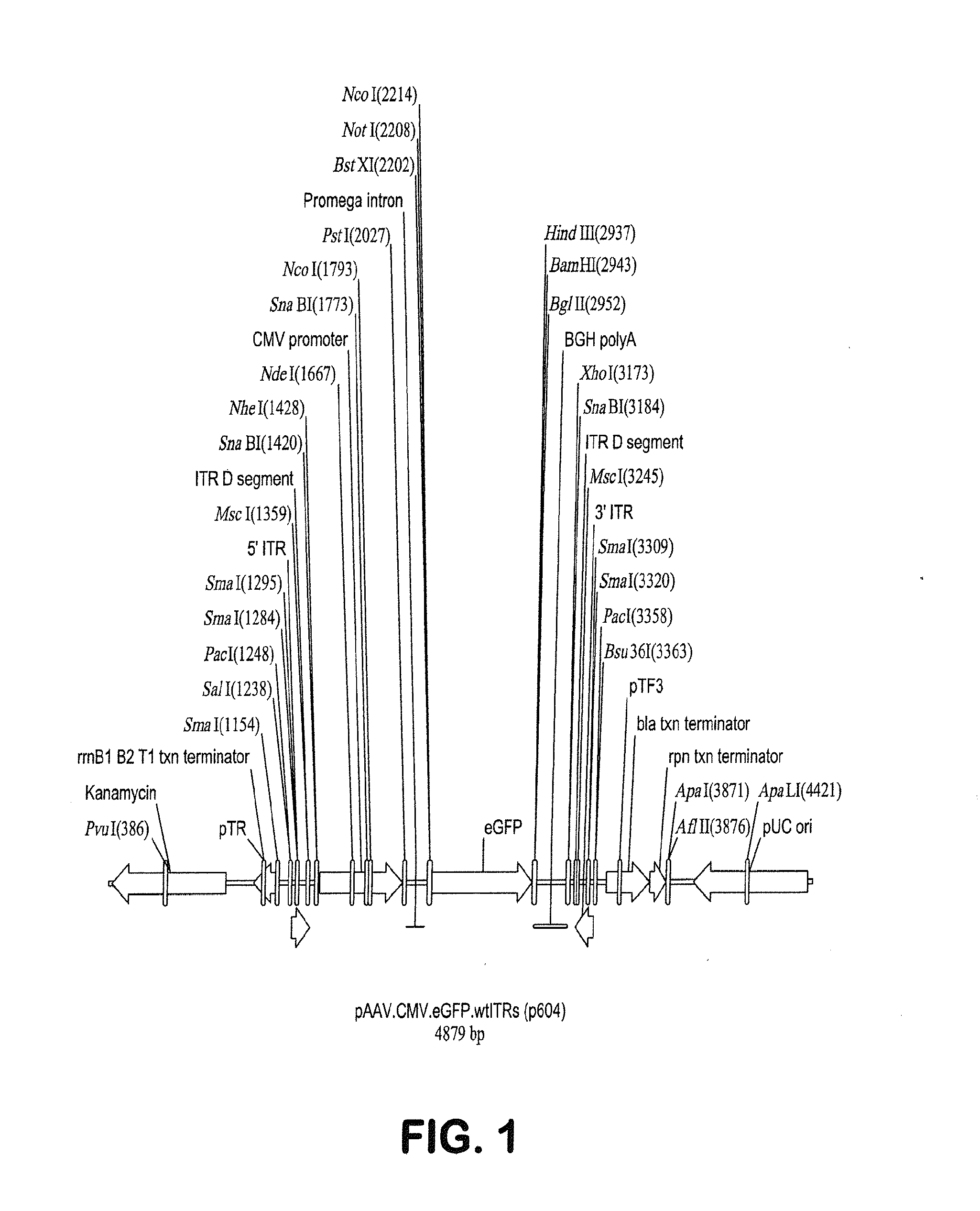
Proviral Plasmids and Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus
ActiveUS20140087444A1Facilitate ready substitutionImprove efficiencyAnimal cellsBacteriaPoly-A RNARestriction site
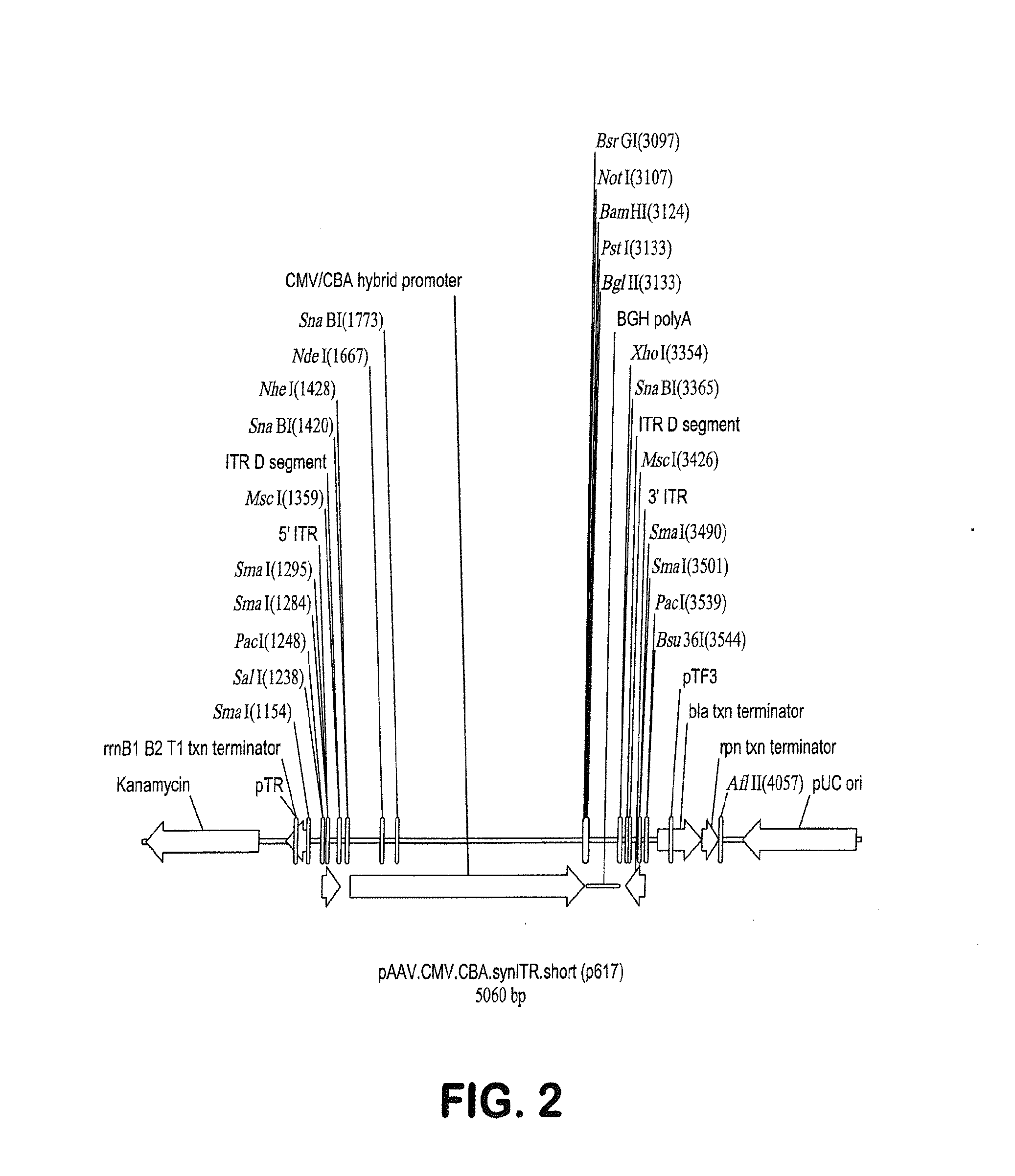
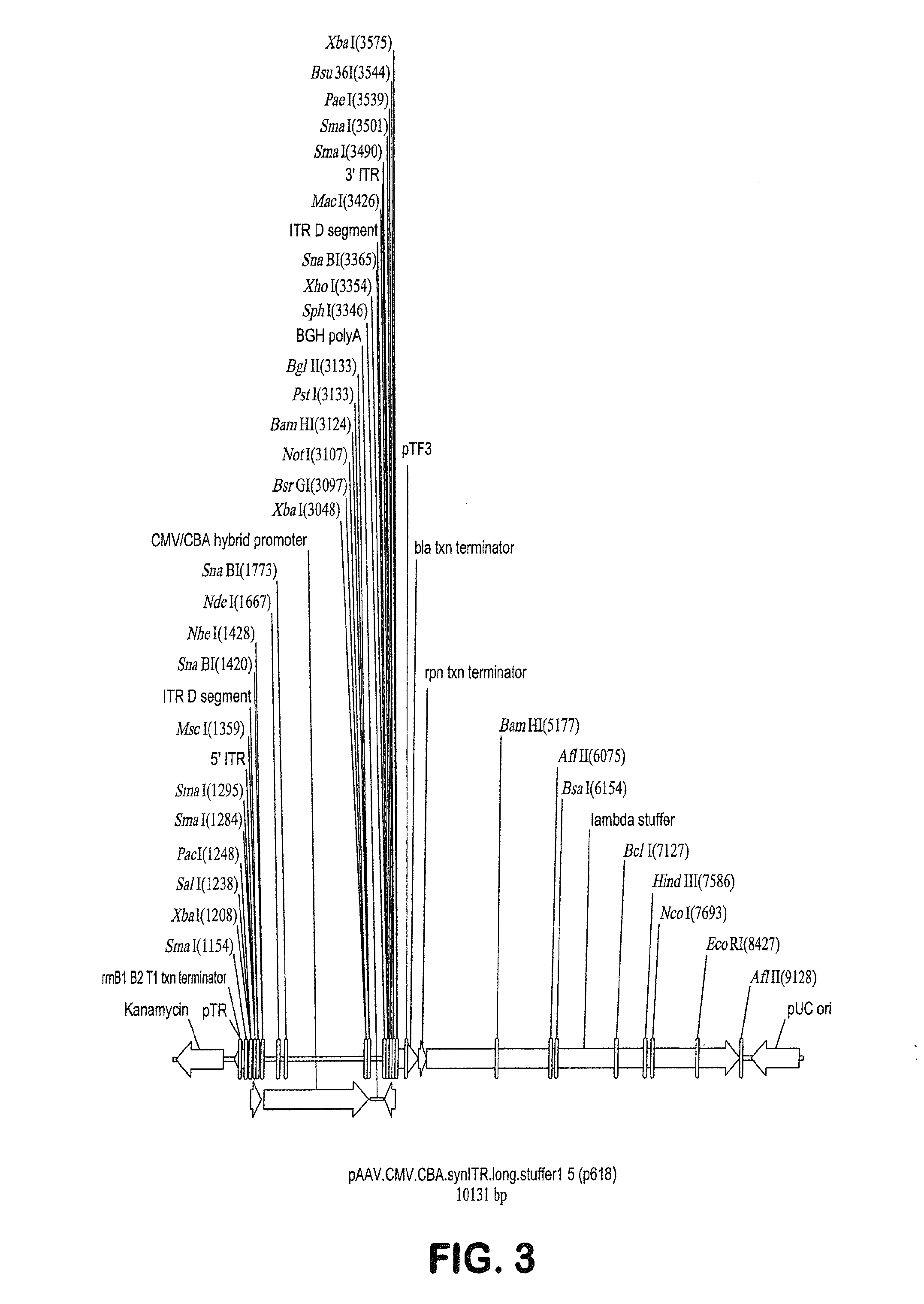
Proviral plasmids contain a modular gene expression cassette with one or a combination of (i) a wildtype 5′ AAV2 ITR sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of said ITR; (ii) a promoter flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of the entire promoter sequence; (iii) a polylinker sequence that permits insertion of a gene coding sequence without modification thereof, wherein the gene is operatively linked to, and under the regulatory control of, the aforementioned promoter; (iv) a bovine growth hormone polyadenylation sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of said polyA sequence; and (v) a wildtype 3′ AAV2 ITR sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of the 3′ ITR. These plasmids enable rapid manipulation of the components of the cassette, e.g., rapid mutation and / or replacement of any component, and thereby increase the efficiency of recombinant viral vector, e.g., rAAV, production.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
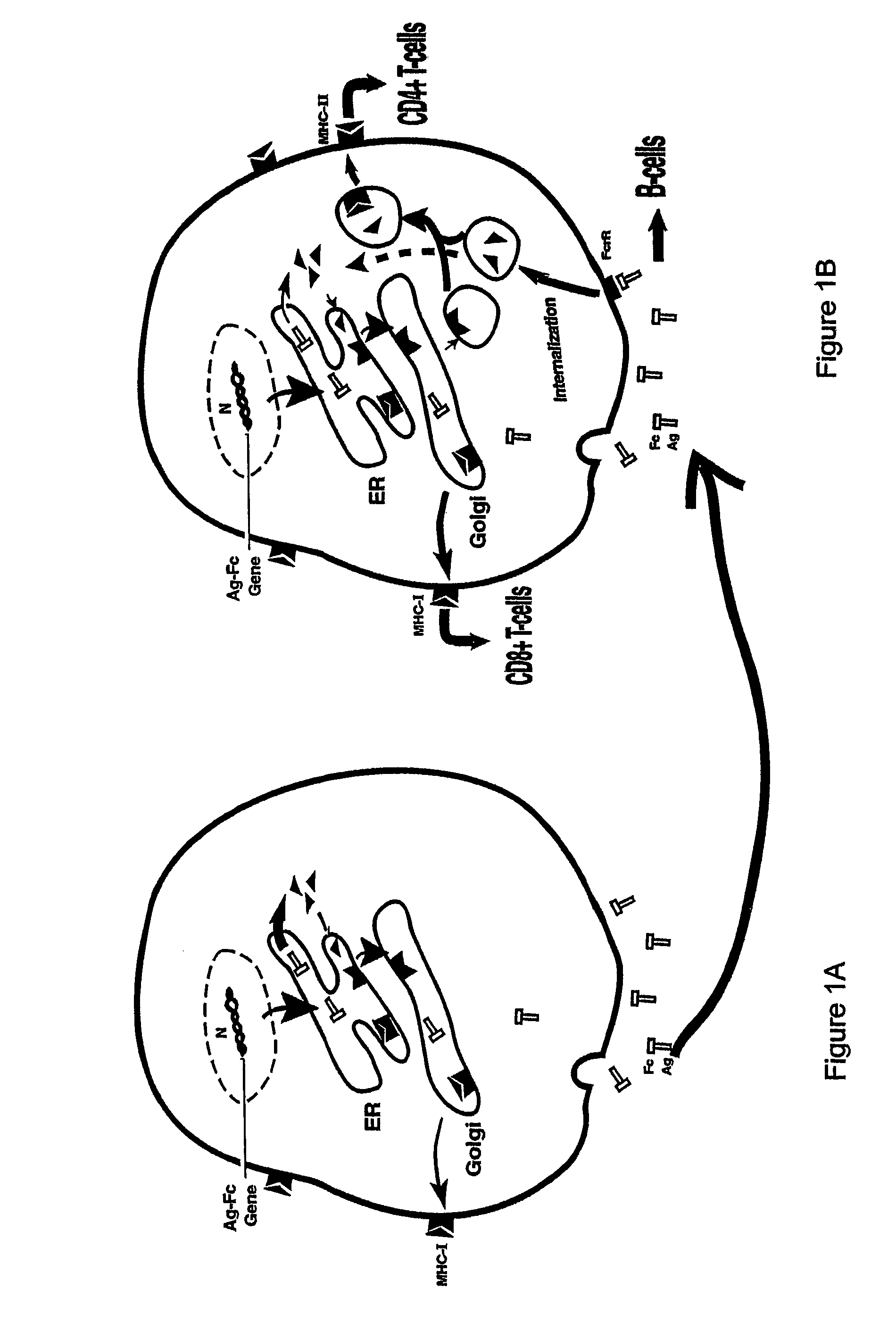
Compositions and methods for identifying antigens which elicit an immune response
This invention relates to an expression vector wherein said expression vector comprises a polynucleotide promoter sequence, a polynucleotide encoding a signal sequence, a polynucleotide encoding an antigen protein or peptide, a polynucleotide encoding a cell binding element, and a polynucleotide polyadenylation sequence all operatively linked. More particularly, it relates to the method of eliciting an immune response directed against an antigen in a mammal comprising the steps of introducing the expression vector into a cell, expressing the vector to produce an antigen under conditions wherein the antigen is secreted from the cell, endocytosing the secreted antigen into the cell, processing the antigen, and presenting fragments to a receptor to elicit a T-cell response. In addition, this invention relates to a vaccine and a method of use. The invention also relates to the method of identifying MHC-II restricted epitopes.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Influenza a virus vaccines and inhibitors
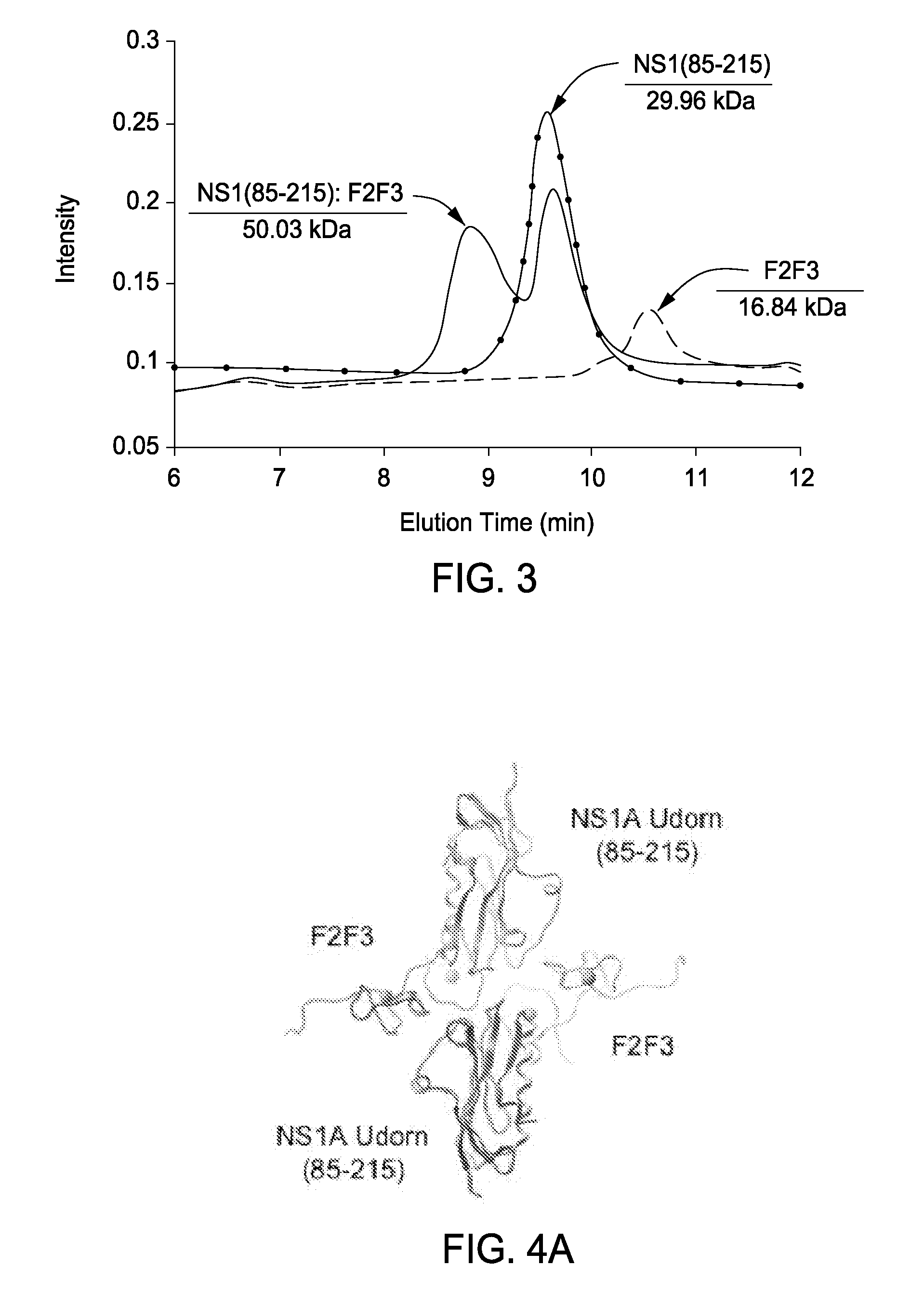
ActiveUS20080108050A1Decreases CPSF3 binding abilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSurgical furniturePoly-A RNABinding site
The present invention includes compositions and methods related to the structure and function of the cellular polyadenylation and specificity factor 30 (CPSF30) binding site on the surface of the influenza A non-structural protein 1 (NS1). Specifically, critical biochemical reagents, conditions for crystallization and NMR analysis, assays, and general processes are described for (i) discovering, designing, and optimizing small molecule inhibitors of influenza A (avian flu) viruses and (ii) creating attenuated influenza virus strains suitable for avian and human flu vaccine development.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Methods and compositions for use of a coccidiosis vaccine
InactiveCN102333877ASuitable for mass vaccinationViruses/bacteriophagesAntiparasitic agentsAntigenHeterologous
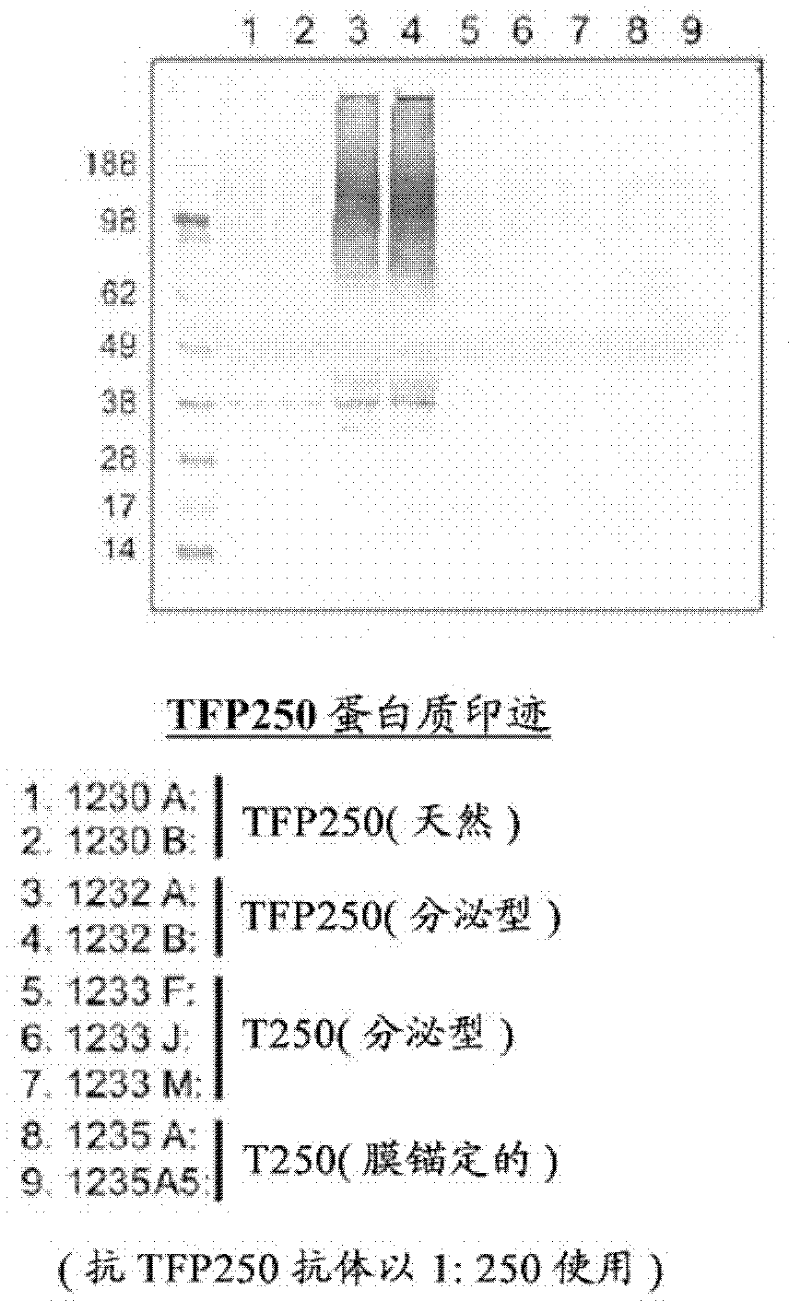
The present invention relates to a coccidiosis vaccine to protect poultry against Eimeria infection, comprising a recombinant avian adenovirus vector comprising in frame a (heterologous) promoter linked to a hydrophobic signal sequence for membrane anchoring, or linked to an hydrophobic secretion signal and a cleavage site to allow secretion; a multiple cloning site for in frame insertion of an Eimeria antigen ORF such as derived from the r56, 82 kDa, and / or TFP250 antigens; a polyadenylation signal; and an avian adenovirus genome.
Owner:VECTOGEN
Wheat plants with immunity to wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV)
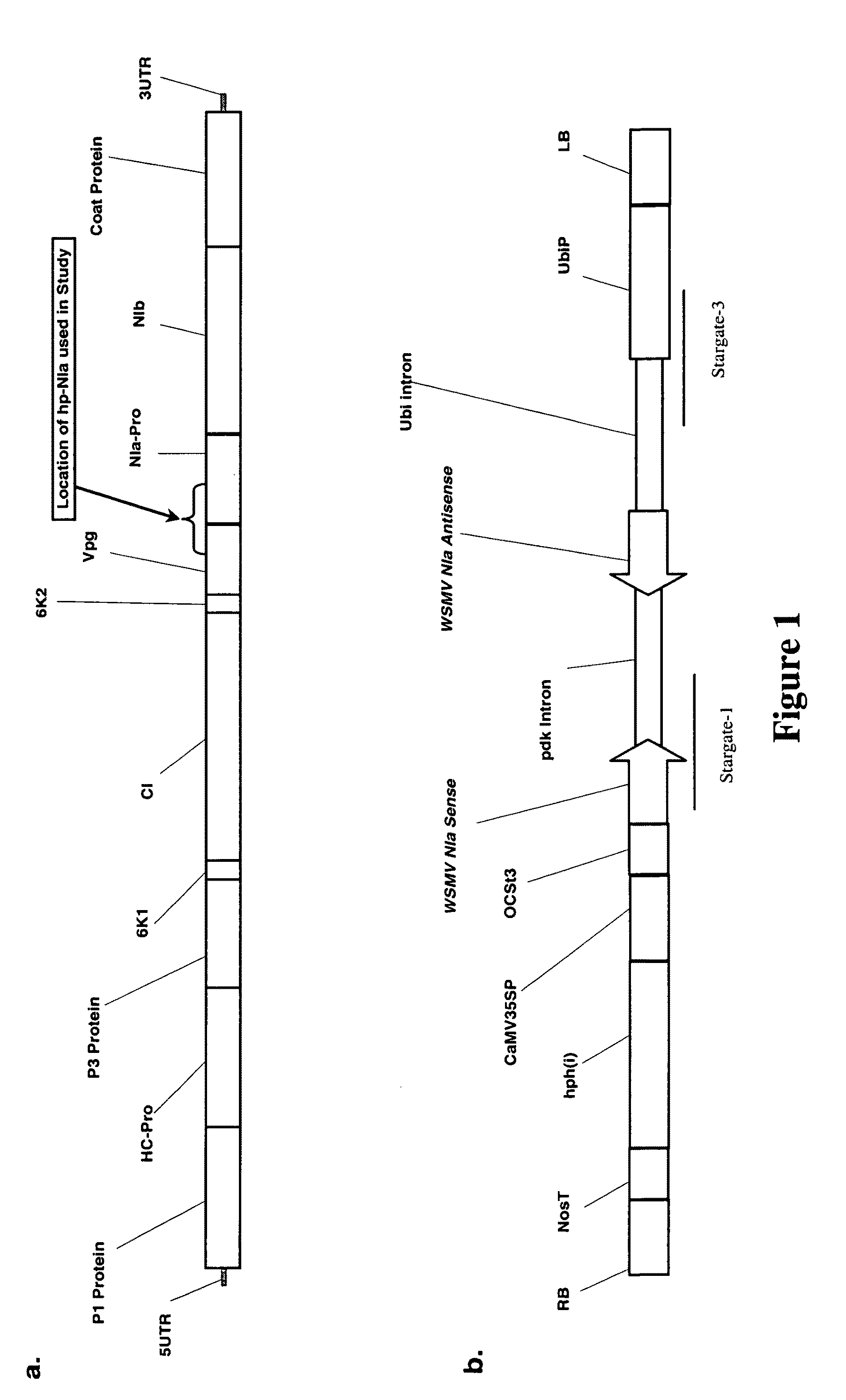
The present invention provides a transgenic wheat cell or wheat plant, the wheat cell or wheat plant comprising a chimeric DNA molecule which encodes a dsRNA molecule which is capable of inhibiting wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) replication, wherein the wheat cell or plant is immune to WSMV. The present invention also provides a chimeric DNA, the chimeric DNA comprising (i) a wheat expressible promoter; (ii) a region which encodes a dsRNA which is capable of inhibiting WSMV replication; and (iii) a transcription termination and polyadenylation signal. Finally, the present invention provides a process for producing the aforementioned transgenic wheat cell or plant, comprising (i) introducing a chimeric DNA molecule comprising (a) a wheat expressible promoter; (b) a region which encodes a dsRNA which is capable of inhibiting WSMV replication; and (c) a transcription termination and polyadenylation signal into a parental wheat cell; and optionally (ii) regenerating a wheat plant from the wheat cell comprising the chimeric DNA molecule; and (iii) identifying and / or selecting a plant which is immune to WSMV.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
High-expression vector for animal cells
It is intended to provide an overexpression vector which makes it possible to easily acquire a high-level producing strain with the use of mammalian cells, in particular, Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO cells) as a host. Namely, an expression vector capable of inducing high productivity of a genetically modified protein in animal host cells which comprises a promoter strongly inducing expression, a multicloning site for gene integration and a polyadenylation signal sequence, in this order starting from the upstream, and a drug-resistance gene having no promoter functioning in animal cells in the downstream thereof.
Owner:IMMUNO JAPAN
Artificial synthetic Bt antiinsect gene used for transgene antiinsect plant and its development method
InactiveCN1513868AHigh expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPolyadenylationPoly-A RNA
An artificially synthetic insecticiding gene Bt used for insect-resisting transgenic plant is prepared from the high-toxic Bt CryIIe protein of lepidopterous pest through insecticiding activity deficiency, amplifying the termination-deficient gene fragment, configuring expression carrier, transforming it to obtain recombinant engineered bacteria, inducing expression analyzing insecticiding activity, determining the minimal terminal active region and active region, reinforming polyadenylation signal sequence and ATTTA sequence, optimiizng plant prefaverable codon, and artificial synthesis.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compositions and methods for identifying antigens which elicit an immune response
This invention relates to an expression vector wherein said expression vector comprises a polynucleotide promoter sequence, a polynucleotide encoding a signal sequence, a polynucleotide encoding an antigen protein or peptide, a polynucleotide encoding a cell binding element, and a polynucleotide polyadenylation sequence all operatively linked. More particularly, it relates to the method of eliciting an immune response directed against an antigen in a mammal comprising the steps of introducing the expression vector into a cell, expressing the vector to produce an antigen under conditions wherein the antigen is secreted from the cell, endocytosing the secreted antigen into the cell, processing the antigen, and presenting fragments to a receptor to elicit a T-cell response. In addition, this invention relates to a vaccine and a method of use. The invention also relates to the method of identifying MHC-II restricted epitopes.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Expression vector for producing protein derived from foreign gene in large quantity using animal cells, and use thereof
ActiveUS9096878B2Increase probabilityImprove the level ofVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyadenylationMammal
The present inventors conducted dedicated studies and successfully constructed expression vectors that enable high-level production of foreign gene-derived proteins in mammalian host cells, which comprise a translation-impaired dihydrofolate reductase gene cistron whose expression has been attenuated by altering the codons to the least frequently used codons in mammals; and a gene cassette which has a cloning site for incorporation of a foreign gene between a highly transcriptionally active promoter and a highly stable polyadenylation signal.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
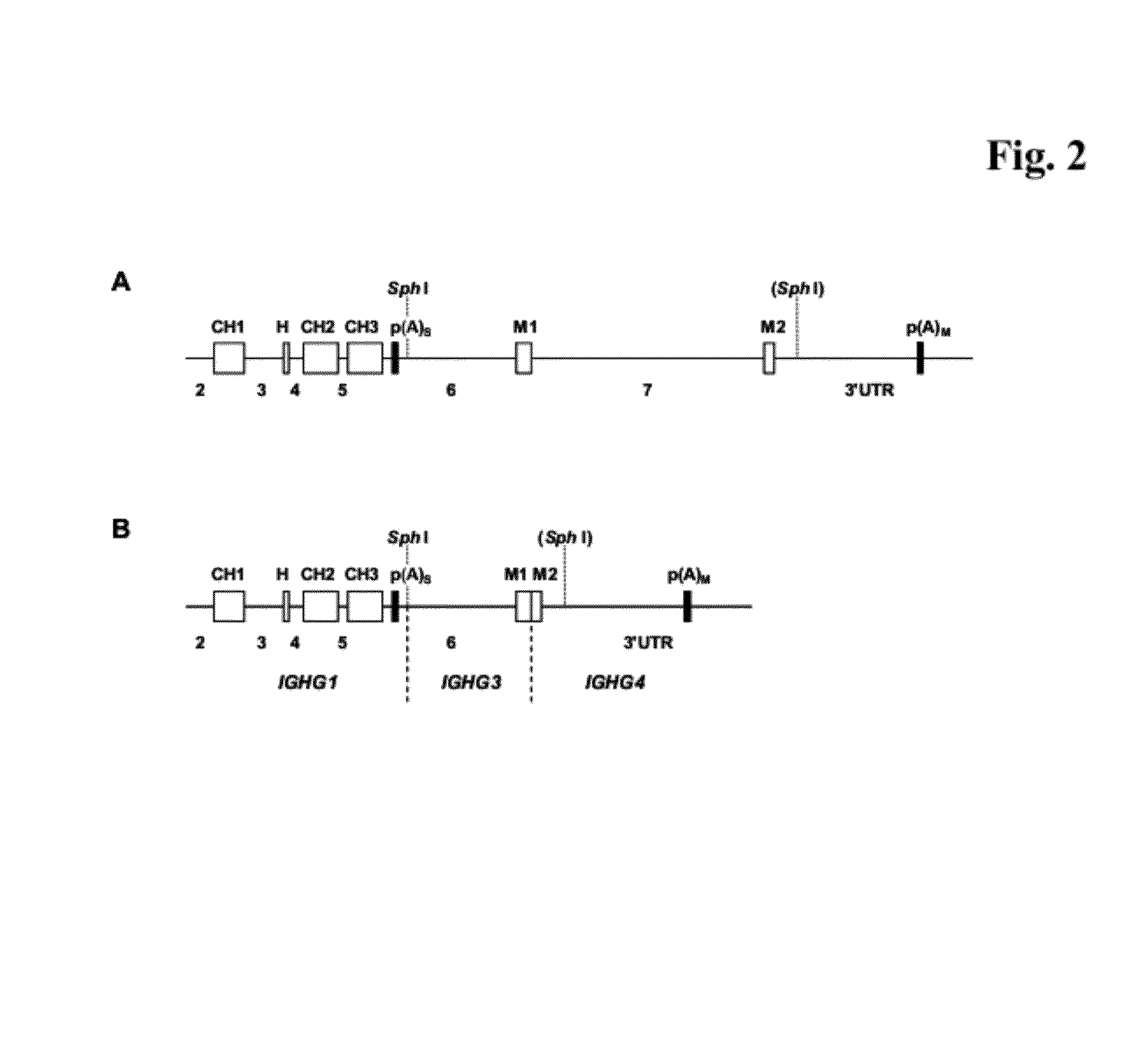
Polypeptide producing cells
ActiveUS8354516B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationPoly-A RNA
The current invention describes a nucleic acid comprising in a 5′ to 3′ direction a) a first nucleic acid encoding a heterologous polypeptide without an in frame stop codon, b) a second nucleic acid beginning with a 5′ splice donor site and terminated by a 3′ splice acceptor site comprising an in frame translational stop codon and a polyadenylation signal, and c) a nucleic acid encoding i) at least a fragment of a transmembrane domain, or ii) a signal peptide for a GPI-anchor.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com