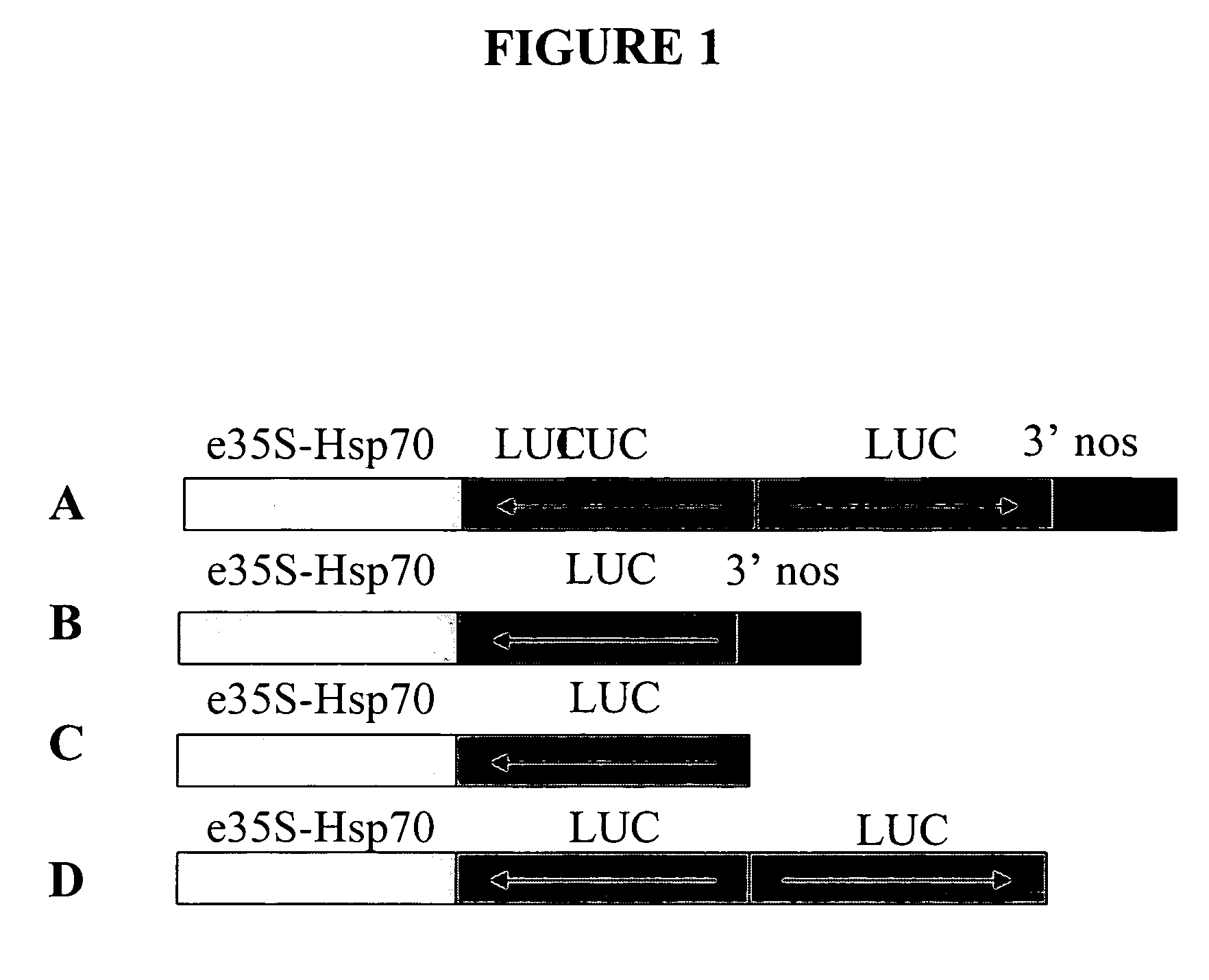
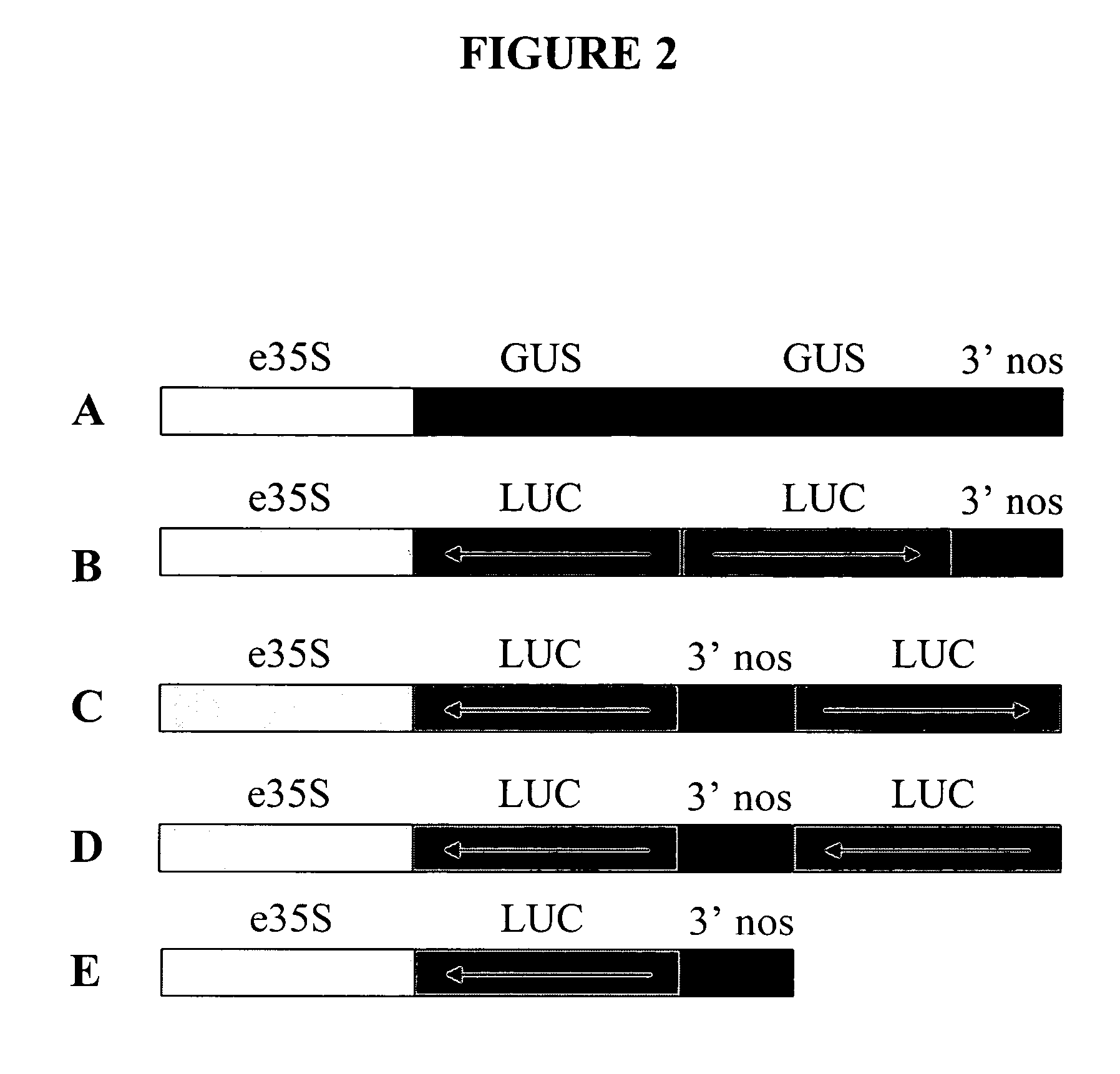
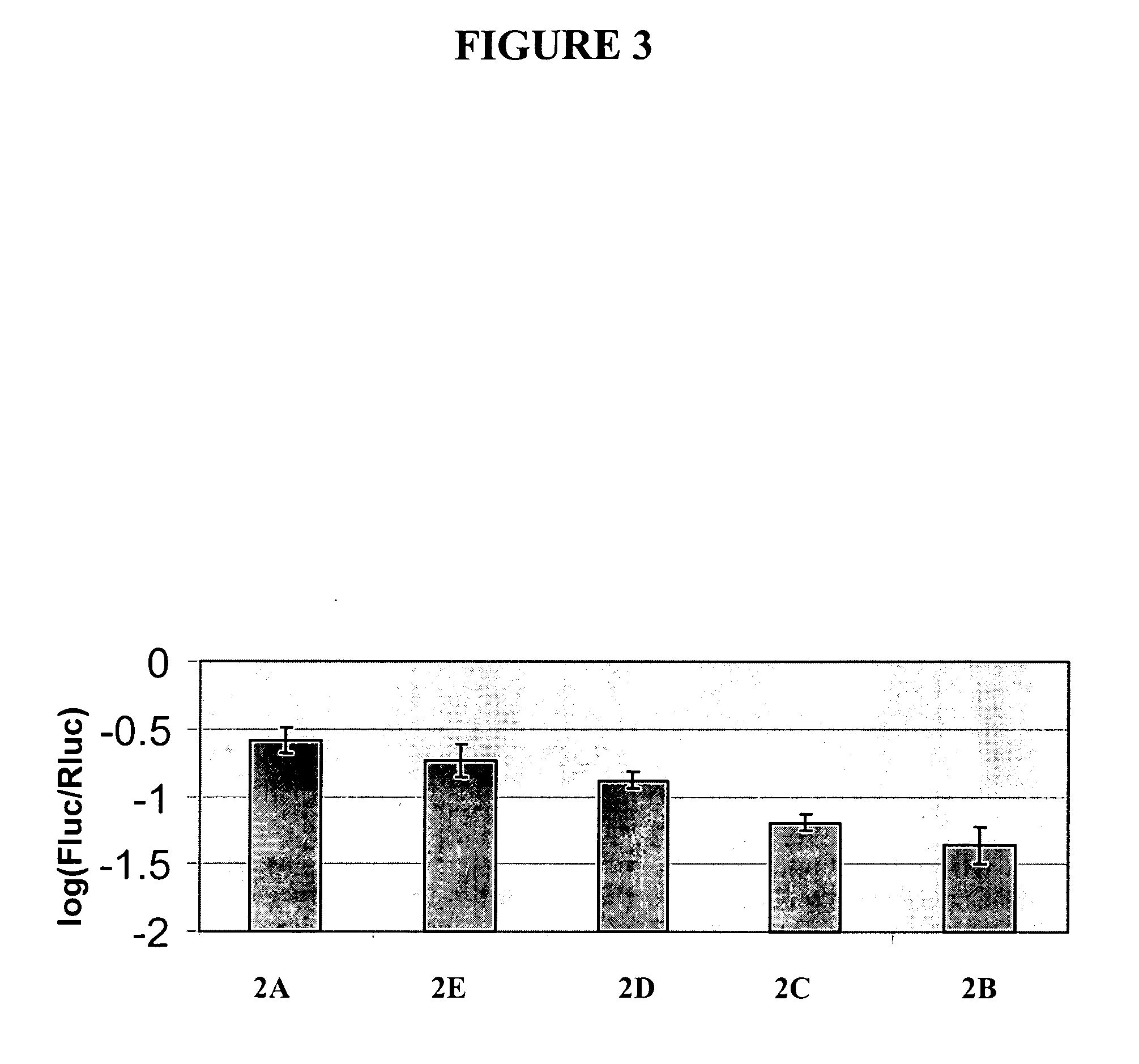
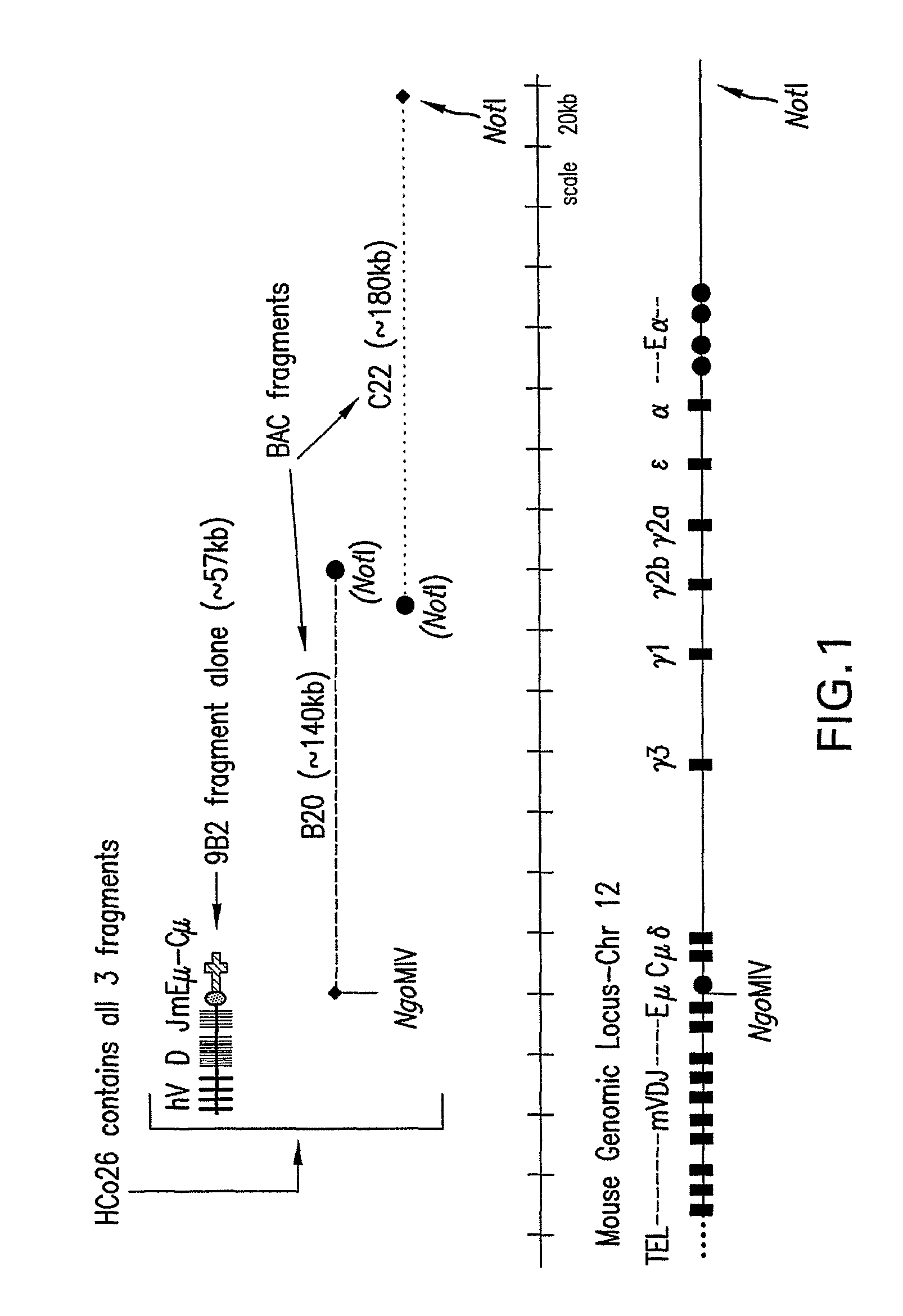
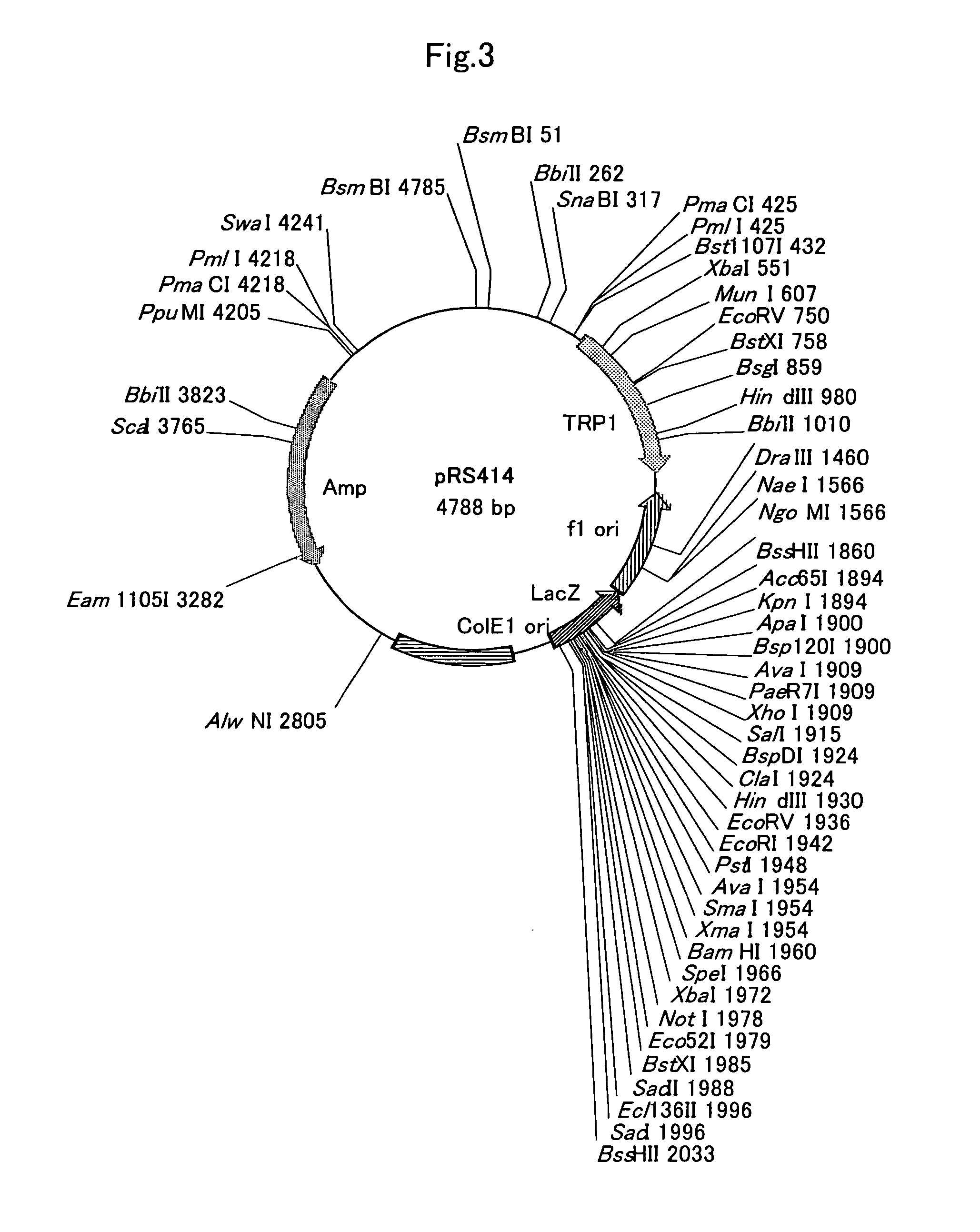
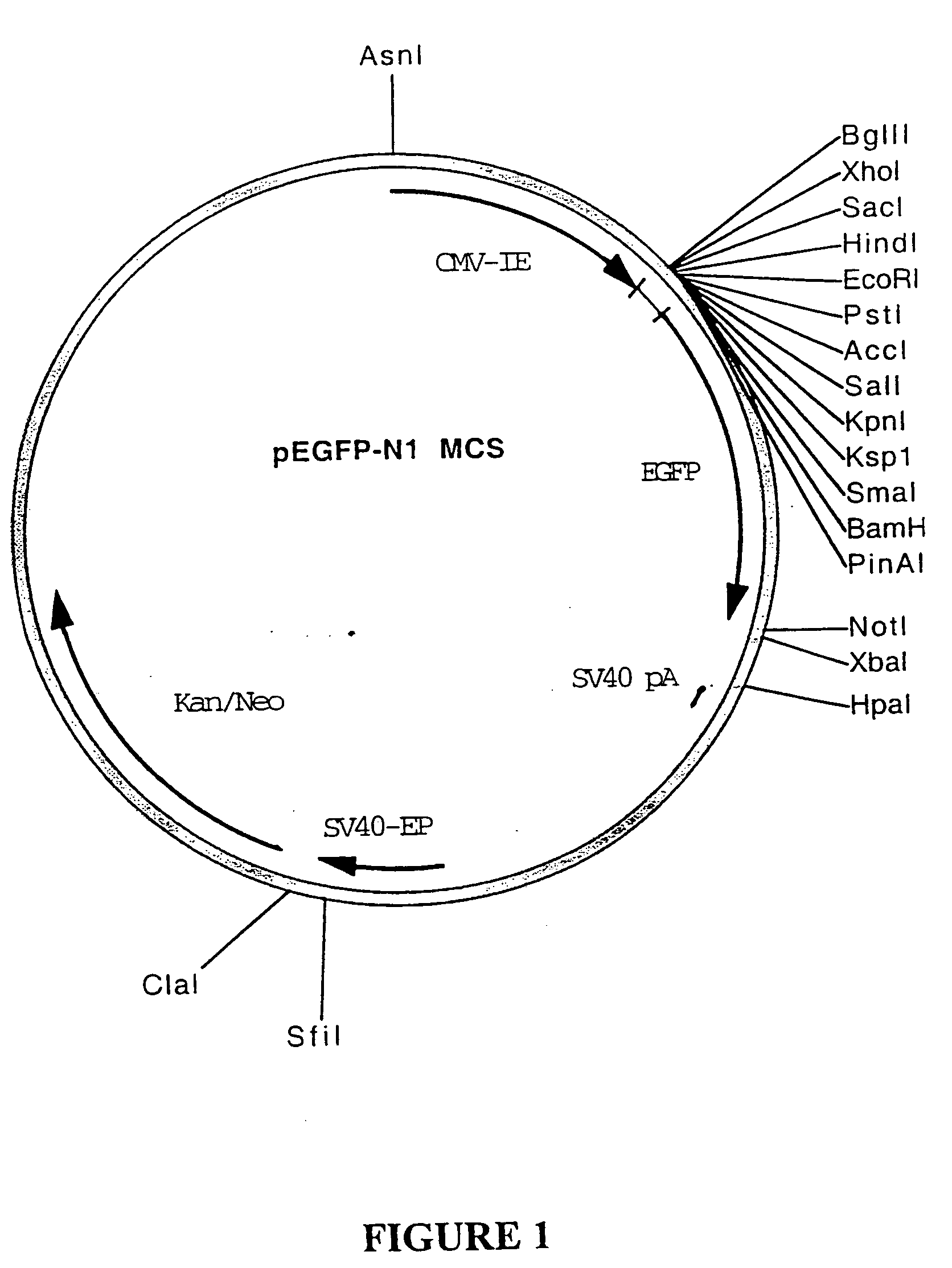
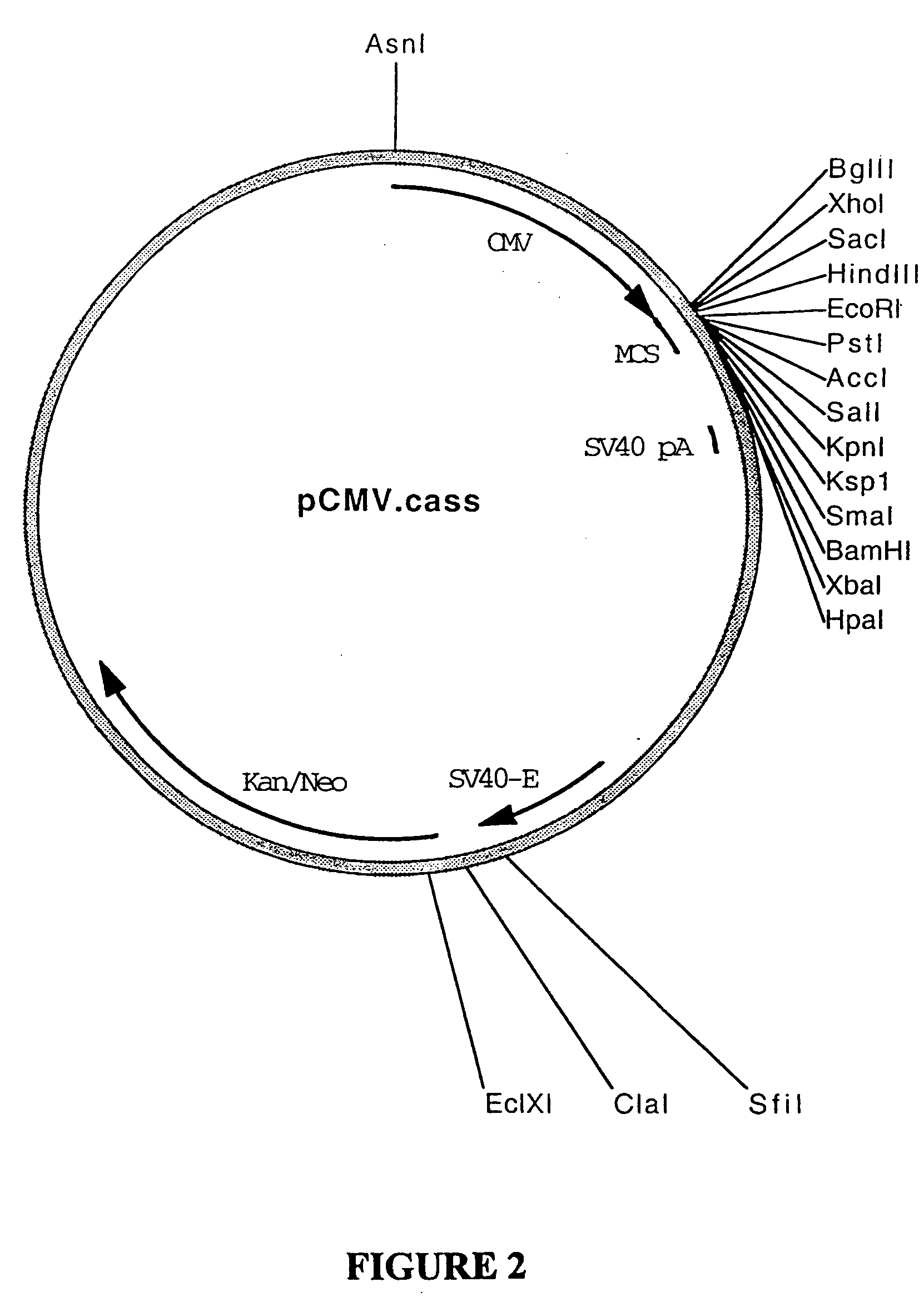
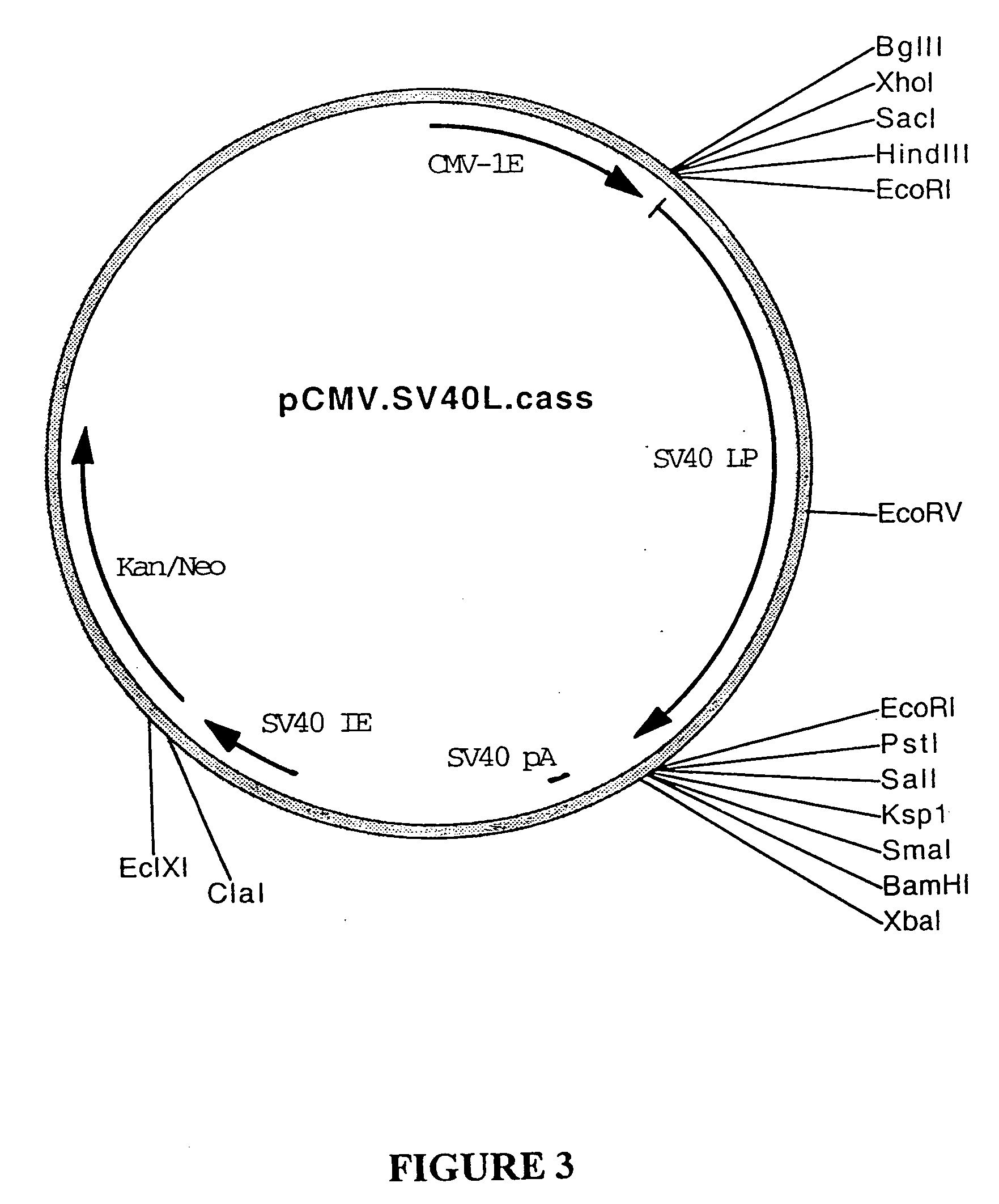
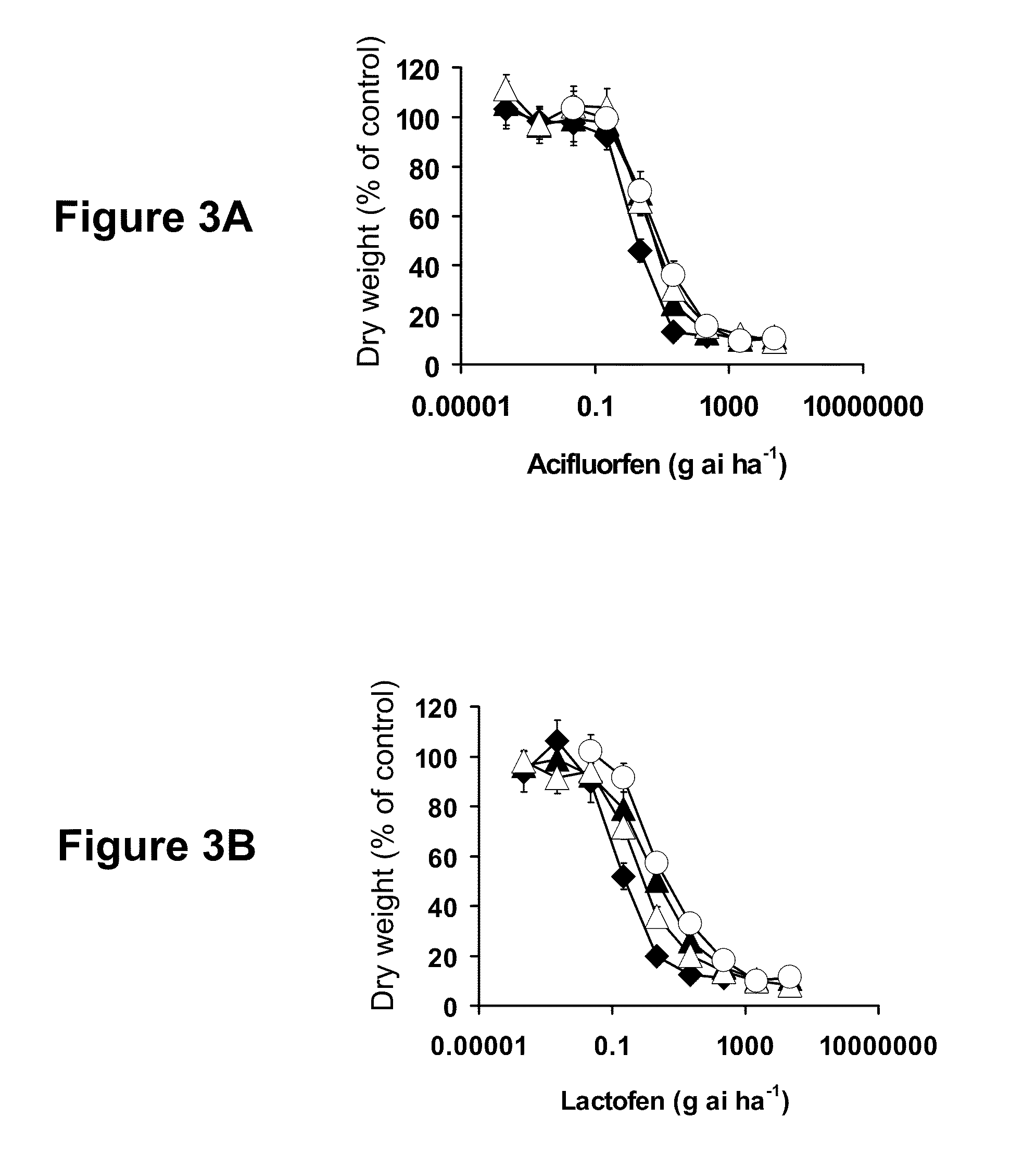
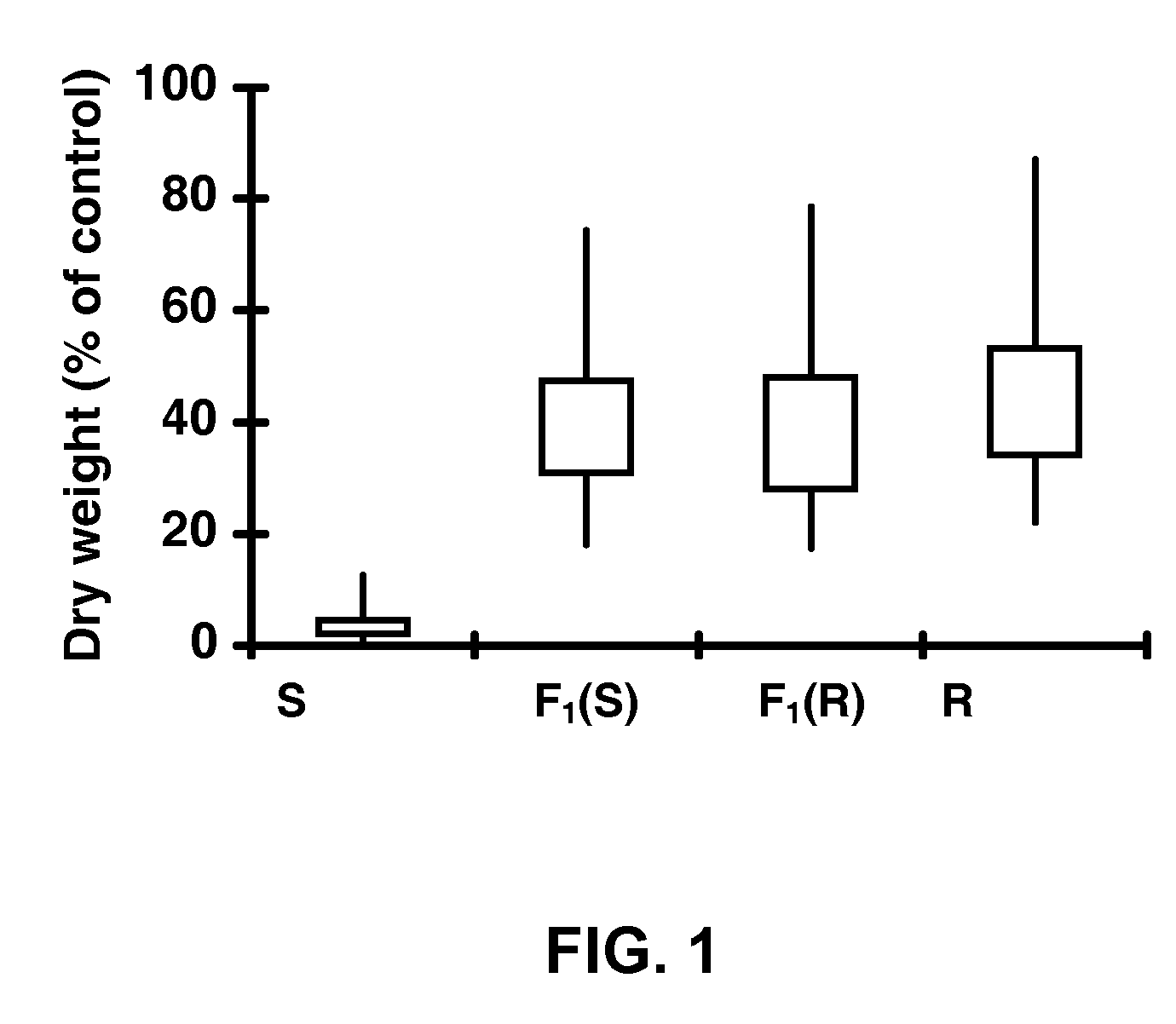
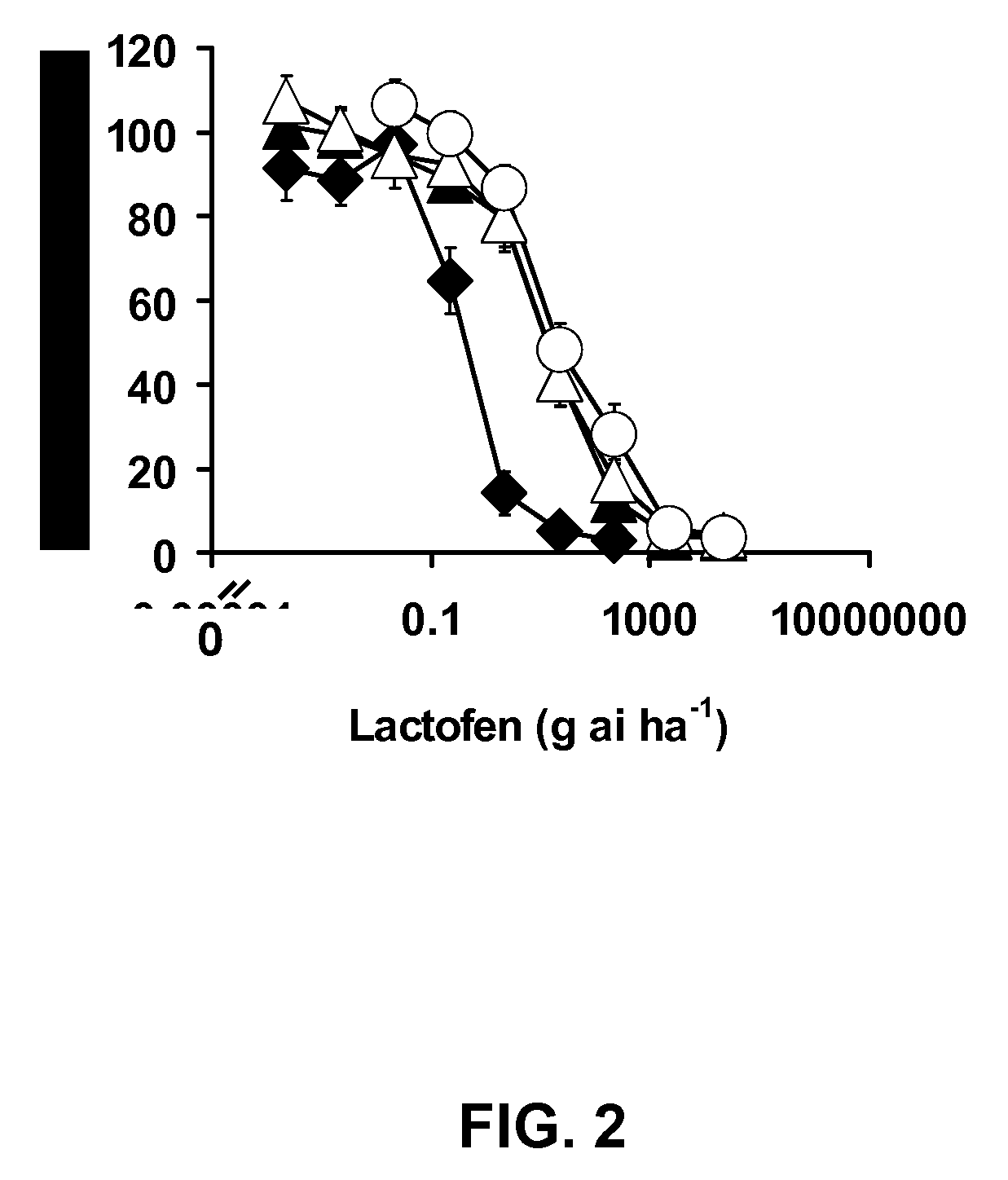
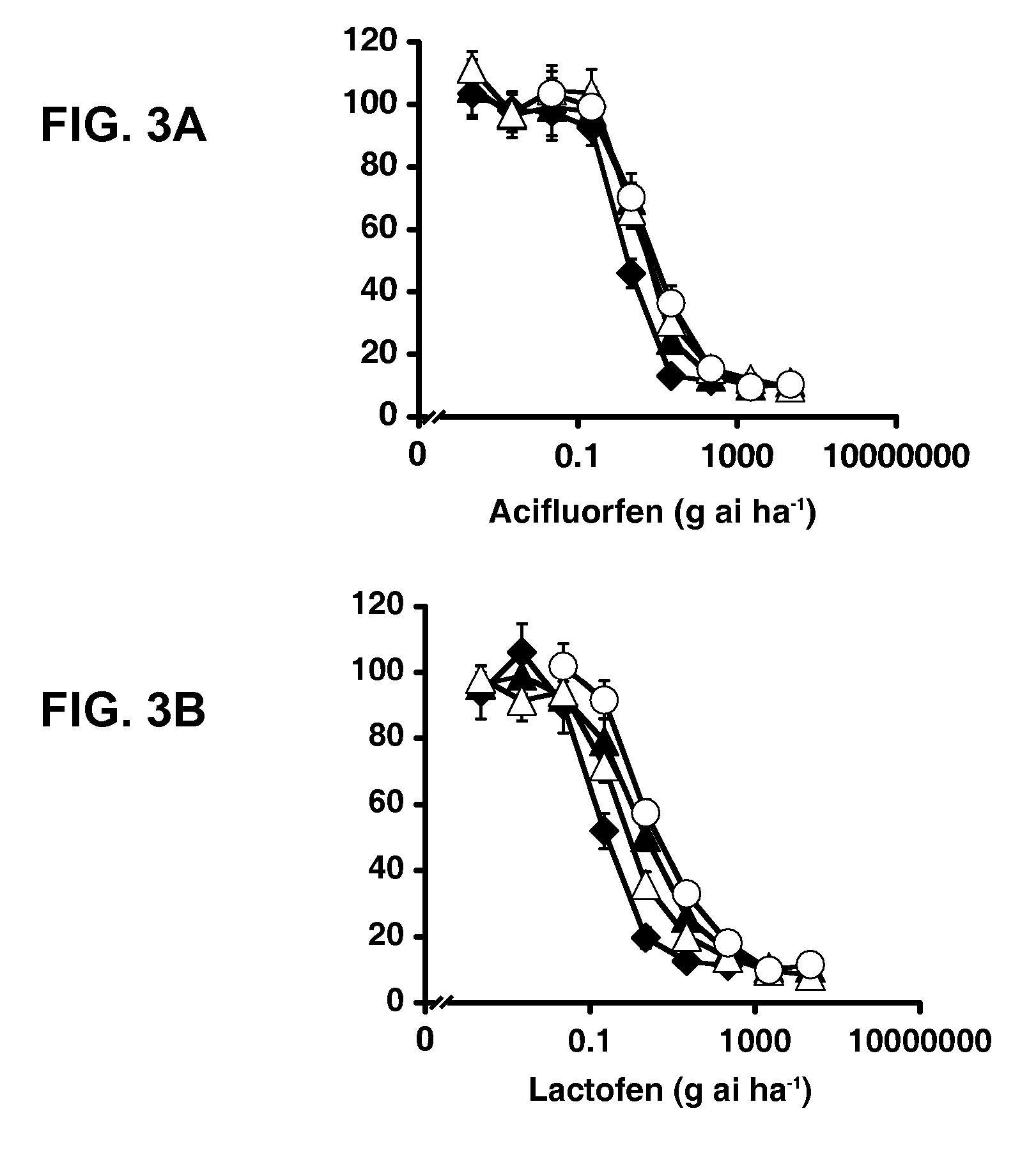
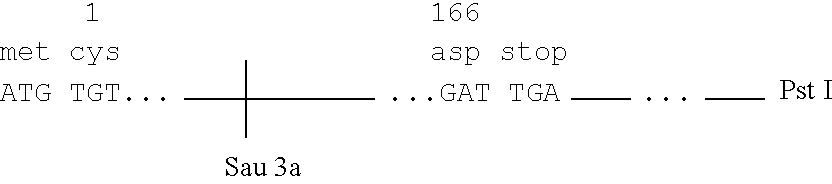Patents
Literature
713 results about "Recombinant DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome.
Recombinant DNA constructs and methods for controlling gene expression
InactiveUS20060200878A1Reduce accumulationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides molecular constructs and methods for use thereof, including constructs including heterologous miRNA recognition sites, constructs for gene suppression including a gene suppression element embedded within an intron flanked on one or on both sides by non-protein-coding sequence, constructs containing engineered miRNA or miRNA precursors, and constructs for suppression of production of mature microRNA in a cell. Also provided are transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing such constructs, and methods for their use. The invention further provides transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing recombinant DNA for the ligand-controlled expression of a target sequence, which may be endogenous or exogenous. Also disclosed are novel miRNAs and miRNA precursors from crop plants including maize and soy.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Transgenic animals expressing chimeric antibodies for use in preparing human antibodies
ActiveUS7910798B2Improved trafficking developmentStrengthen associationSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsTransgenesisIn vivo
The invention provides transgene constructs for expressing chimeric antibodies, and transgenic non-human host animals carrying such constructs, wherein the chimeric antibodies comprise human variable regions and constant regions of the non-human transgenic host animal. The presence of immunoglobulin constant regions of the host animal allows for generation of improved antibodies in such transgenic host animals. Subsequently, the chimeric antibodies can be readily converted to fully human antibodies using recombinant DNA techniques. Thus, the invention provides compositions and methods for generating human antibodies in which chimeric antibodies raised in vivo in transgenic mice are used as intermediates and then converted to fully human antibodies in vitro.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Immunogenic detoxified mutant E. coli LT-A-toxin
InactiveUS7115730B1Maximise adjuvanticityMaximise immunogenicityBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliAdjuvant
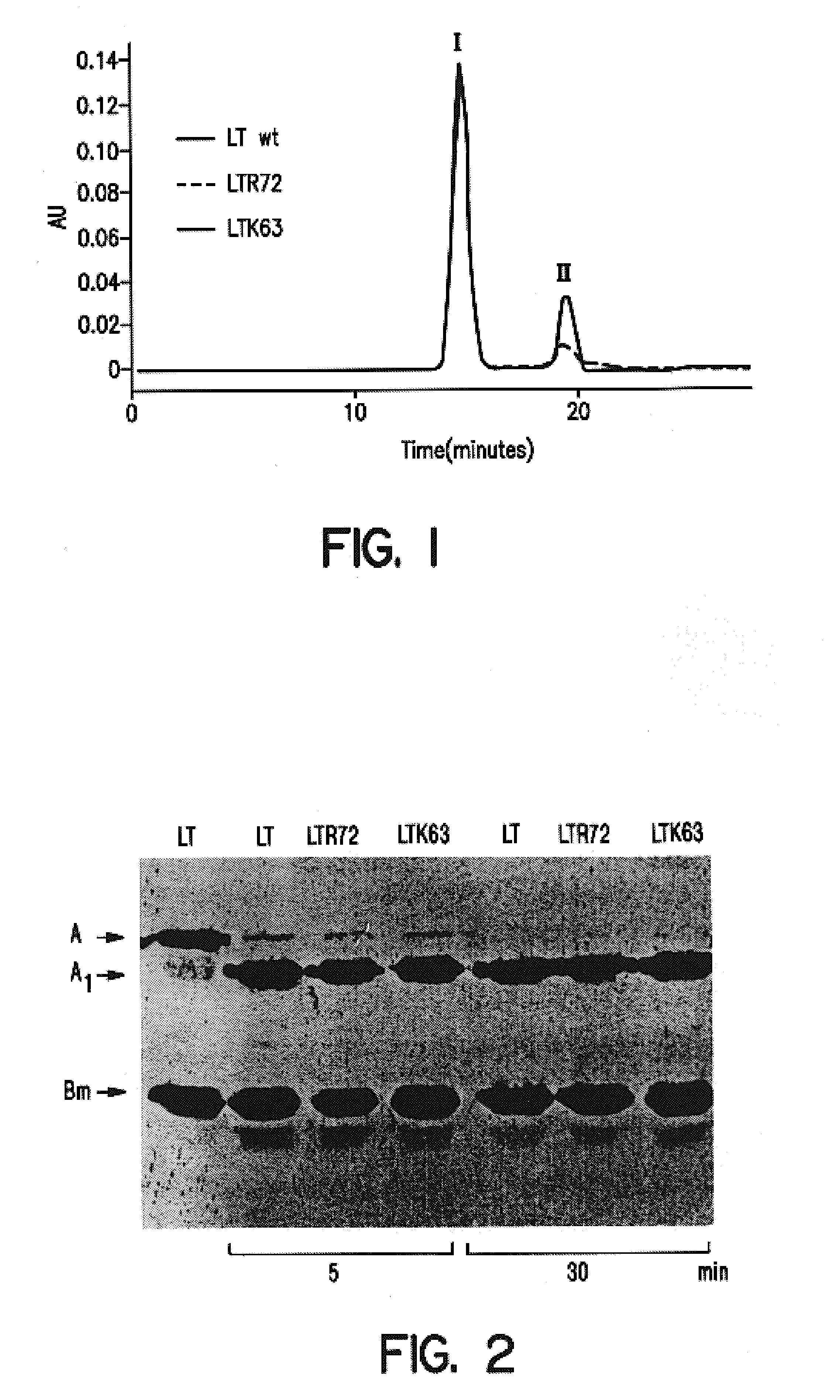
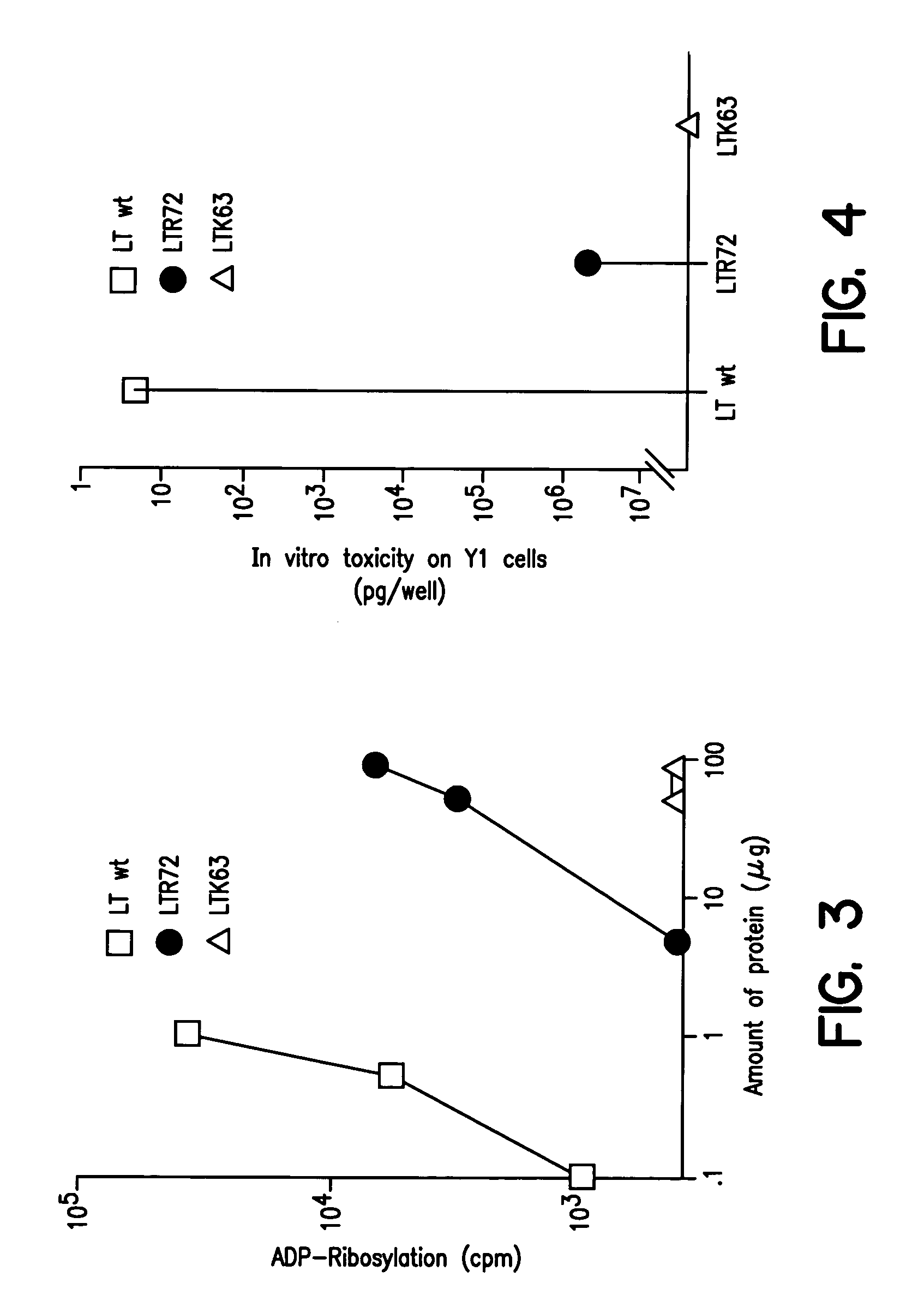
An immunogenic detoxified protein is provided which comprises the amino acid sequence of subunit A of an E. coli heat labile toxin (LT-A) or a fragment thereof in which at least amino acid Ala-72, numbered relative to SEQ ID NO:1, of the A subunits mutated, preferably by substitution with Arg. The toxoid is useful as vaccine against an enterotoxigenic strain of E. coli and is produced by recombinant DNA means by site-directed mutagenesis. It is also an effective adjuvant.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Herbicide Resistance Gene, Compositions and Methods
ActiveUS20100100988A1Improve efficiencyReduce competitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic and genetically engineered plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Methods of producing prenyl alcohols
InactiveUS20070087425A1Efficient cultivationIncrease productivityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiBiotechnologyAlcohol
A method of producing a prenyl alcohol, comprising creating a recombinant by transferring into a host a recombinant DNA for expression or a DNA for genomic integration each comprising a prenyl diphosphate synthase gene or a mutant thereof, culturing the resultant recombinant, and recovering the prenyl alcohol from the resultant culture.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control of gene expression
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Microbial production of mature human leukocyte interferons
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
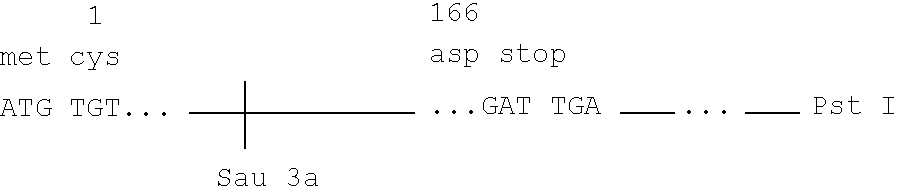
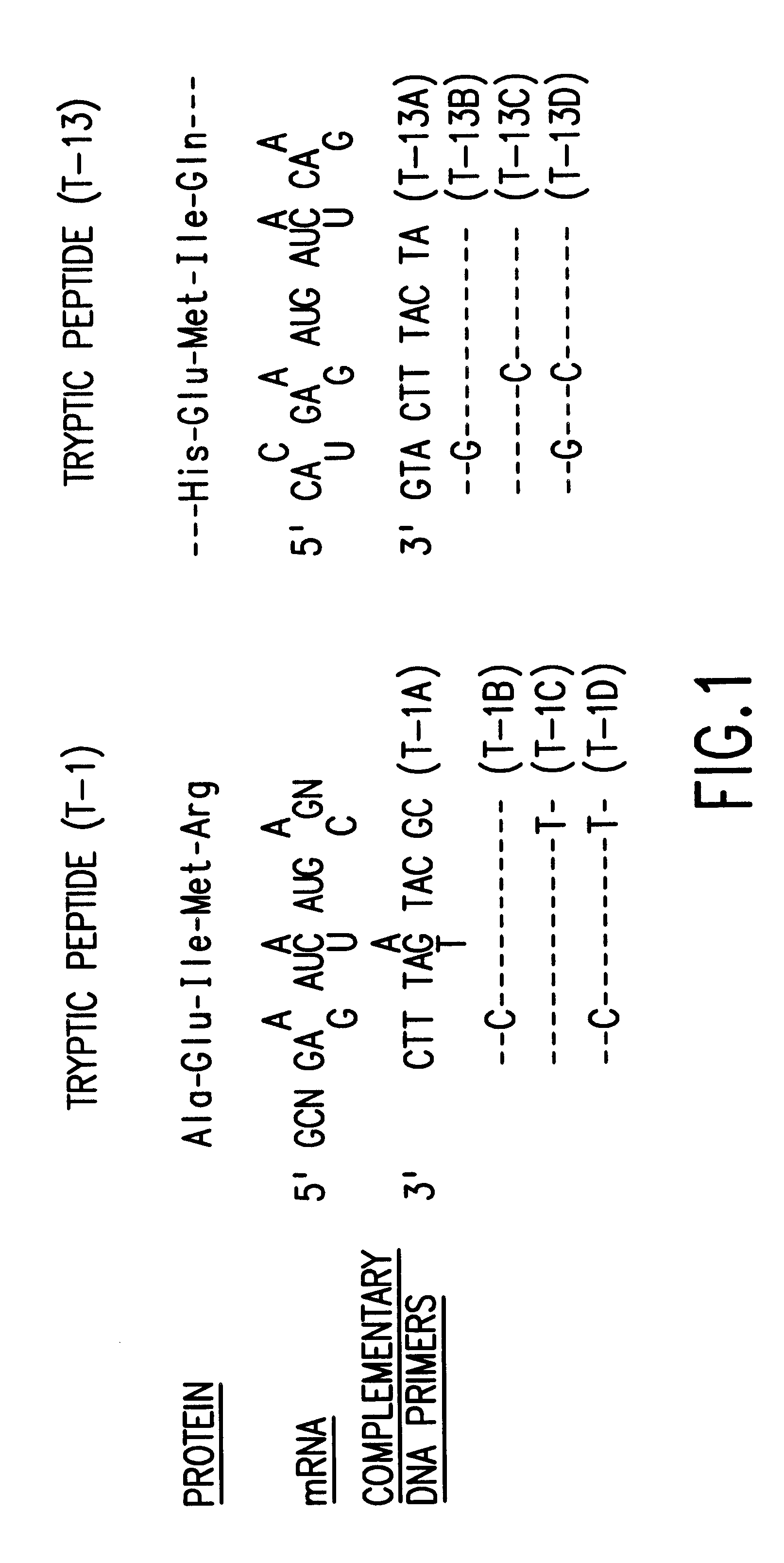
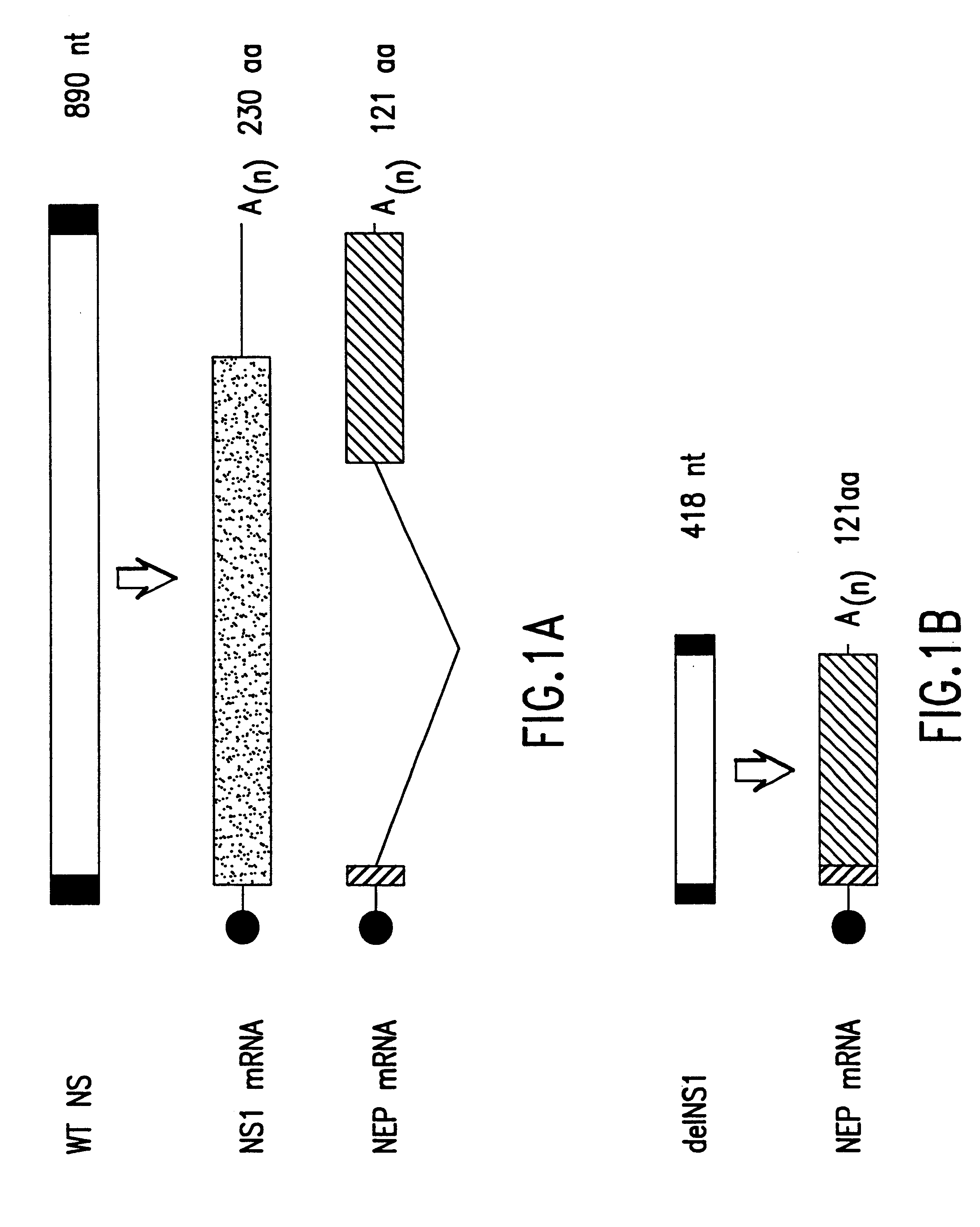
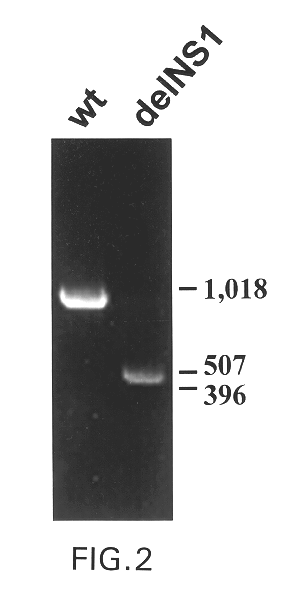
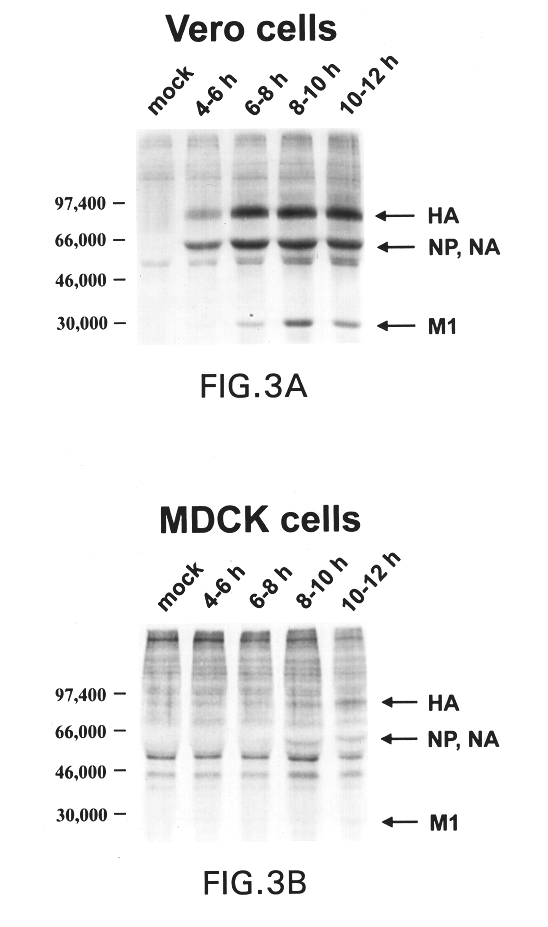
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
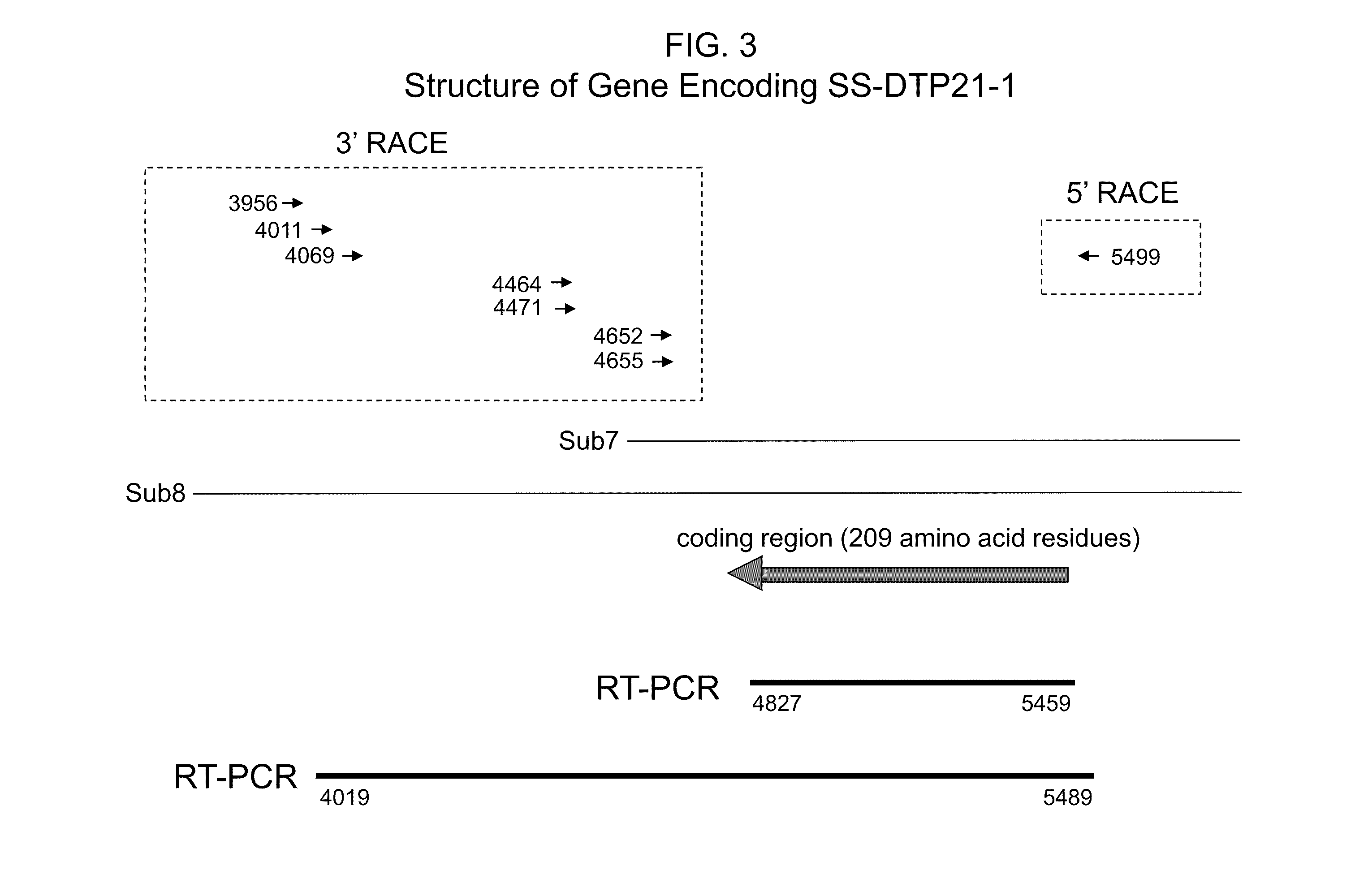
Drought tolerant plants and related constructs and methods involving genes encoding dtp21 polypeptides
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs useful for conferring drought tolerance, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter that is functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a DTP21 polypeptide.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +2
Plants with altered root architecture, related constructs and methods involving genes encoding nucleoside diphosphatase kinase (NDK) polypeptides and homologs thereof
InactiveUS20090064373A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlant rootsNucleotide
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs particularly useful for altering root structure of plants, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide useful for altering plant root architecture.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Methods for generating or increasing revenues from crops
InactiveUS7193128B2Shorten the timeIncrease incomeData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods of doing business and providing services. For example, methods of increasing the revenue of crops are provided. To this end, the method includes the use of a nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and mini chromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
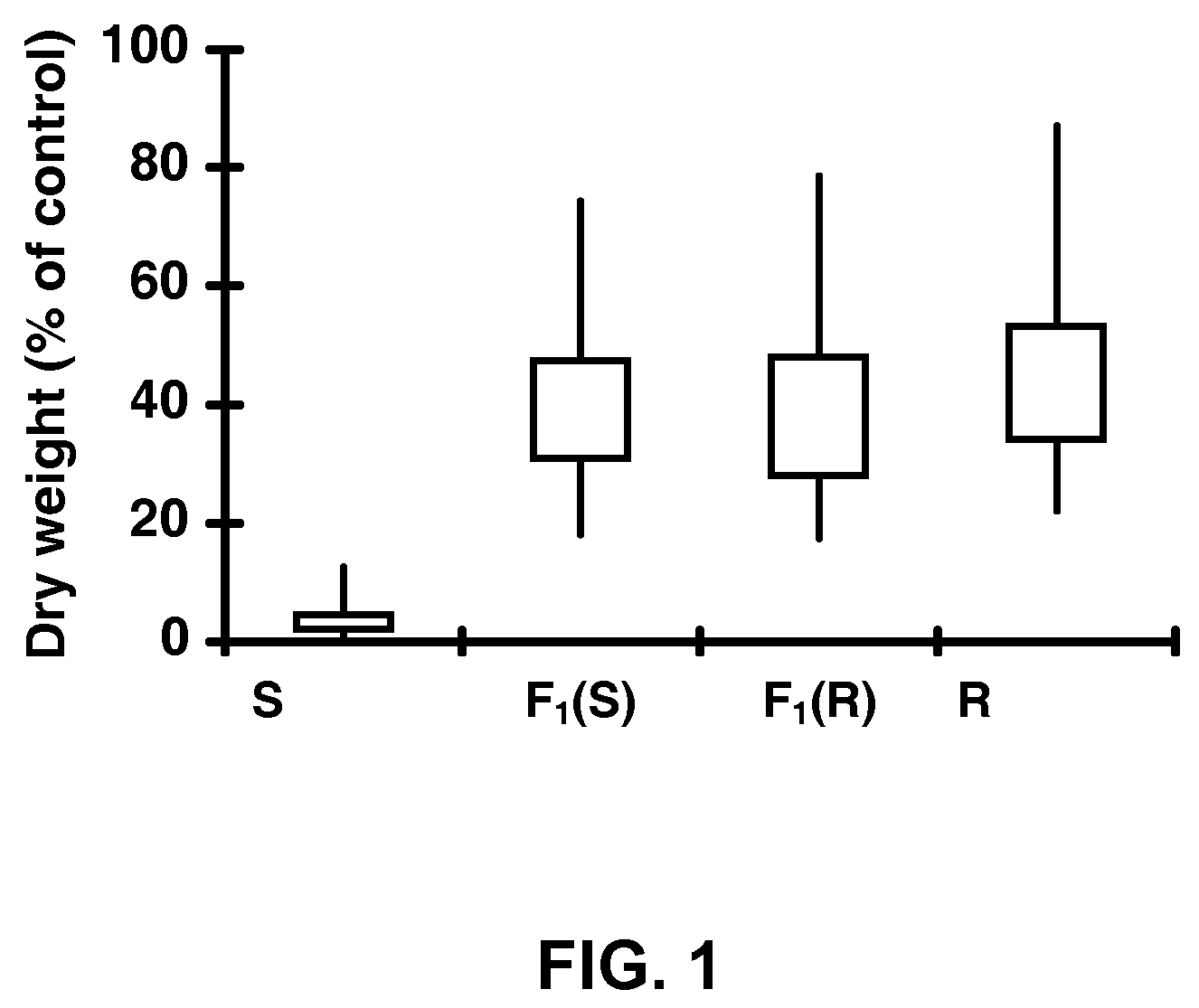
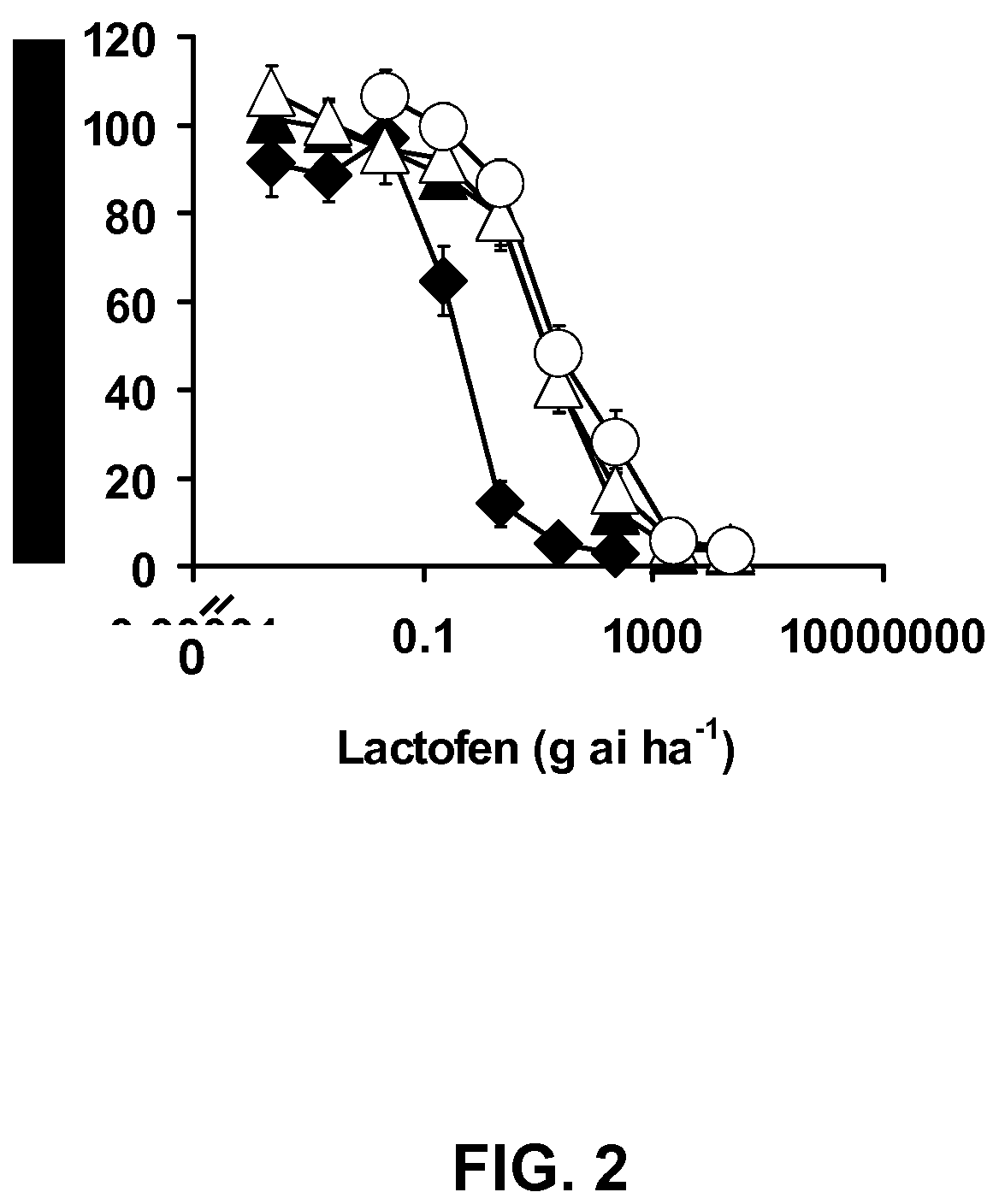
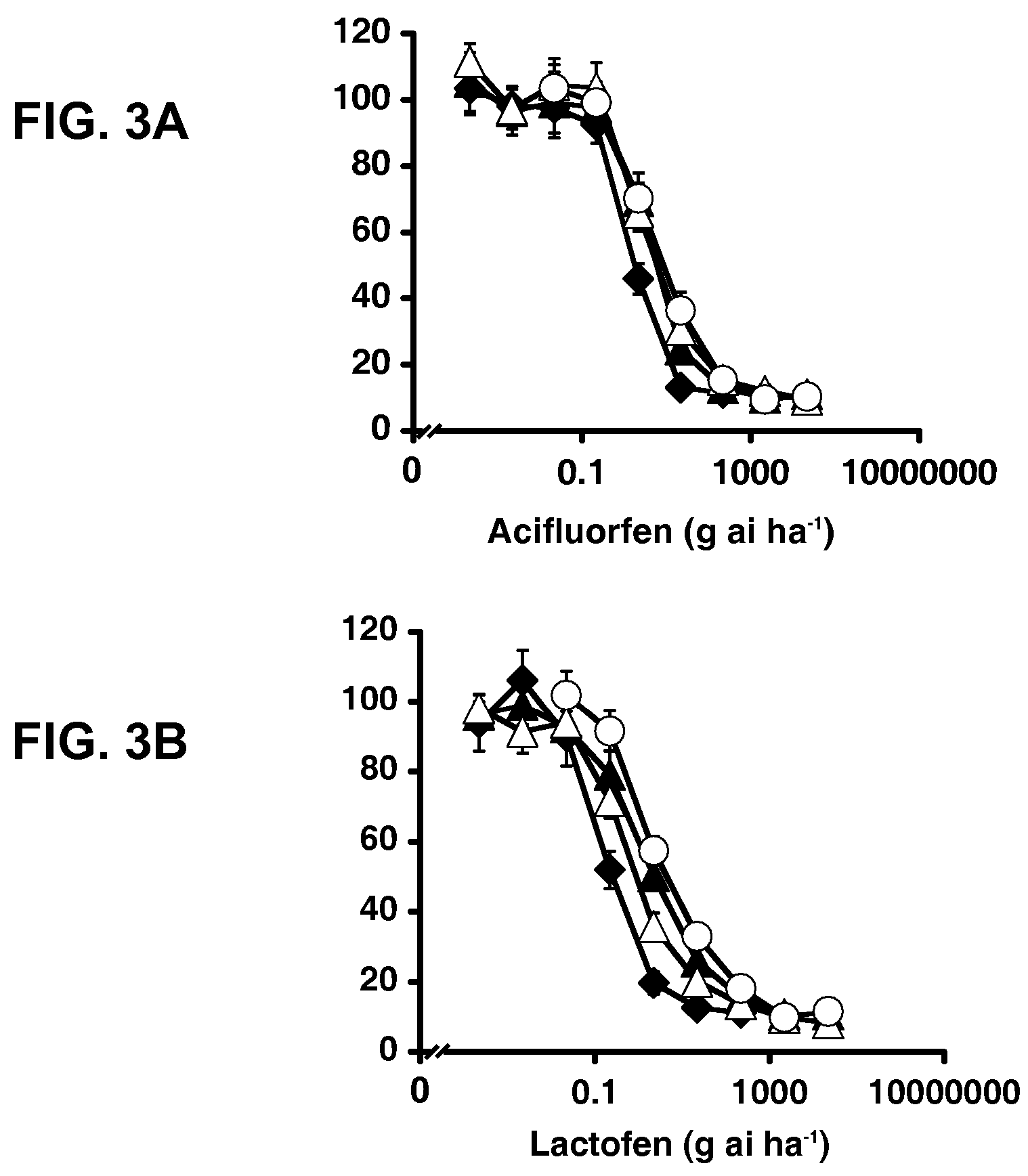
Herbicide resistance gene, compositions and methods
ActiveUS7842856B2Improve efficiencyReduce competitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic and genetically engineered plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Herbicide Resistance Gene, Compositions and Methods
ActiveUS20070050863A1Improve efficiencyReduce competitionImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesPlant cellAdemetionine
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for providing hyaluronic acid
InactiveUSRE37336E1Facilitate easeAbility to controlBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliRecombinant DNA
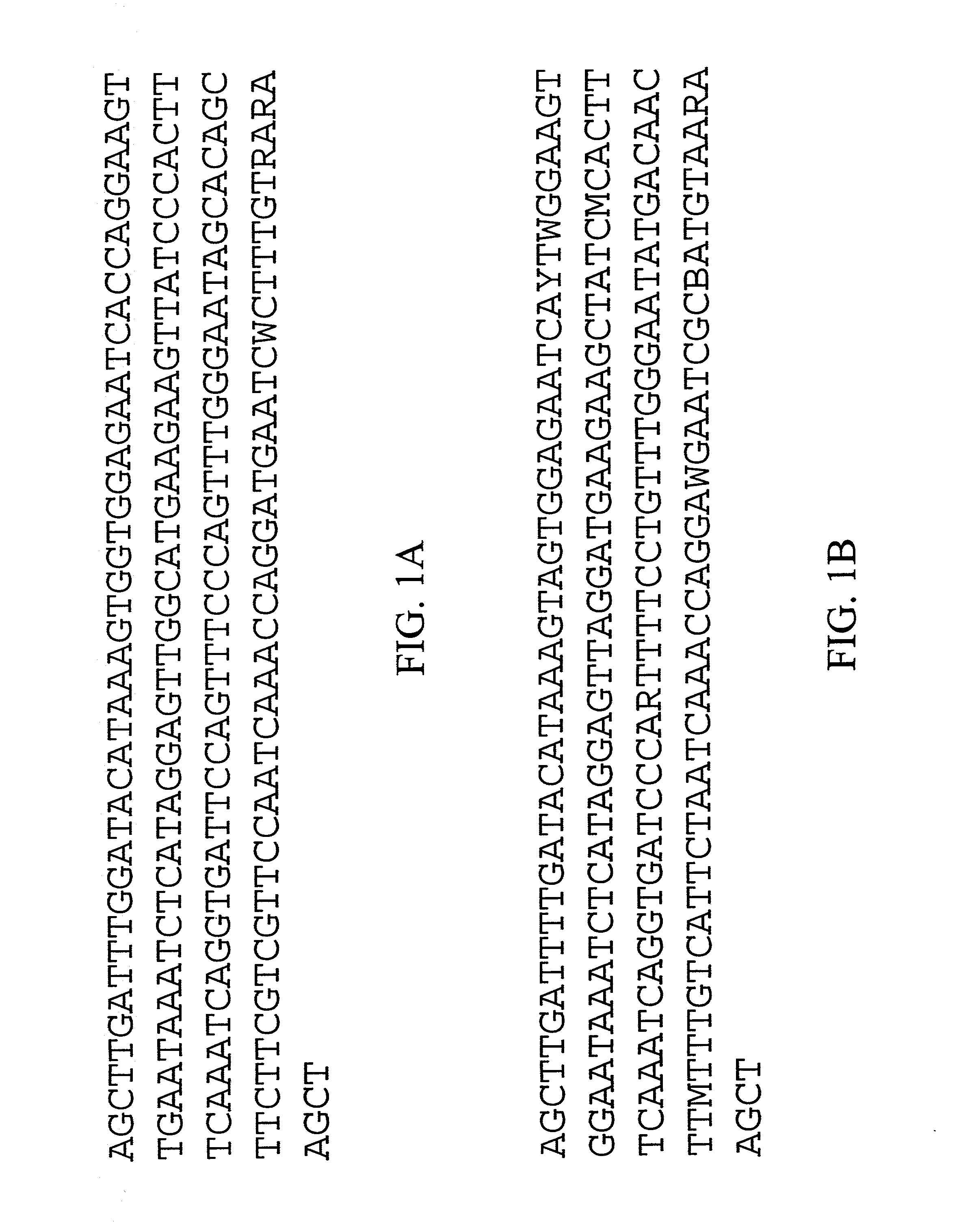
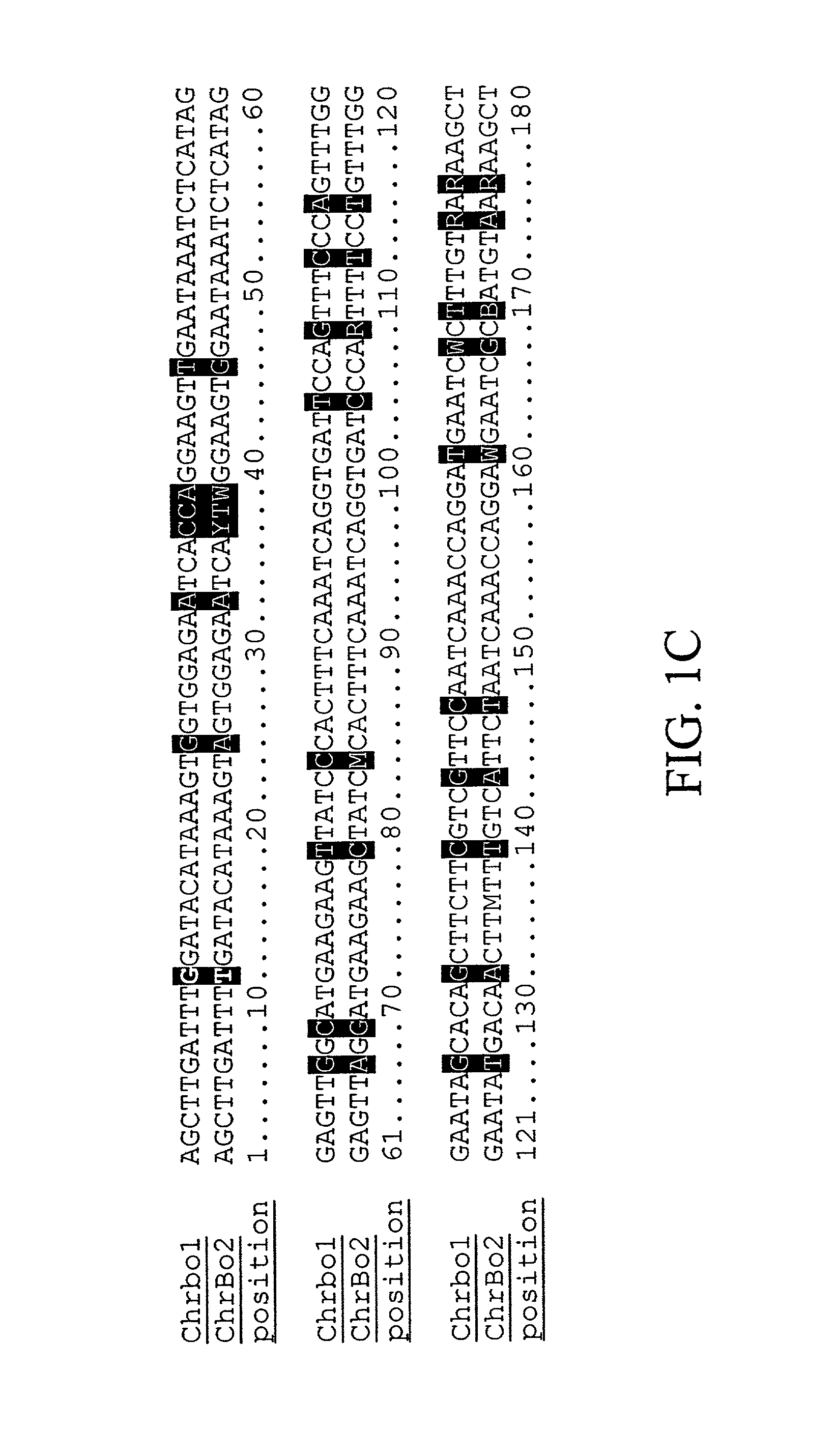
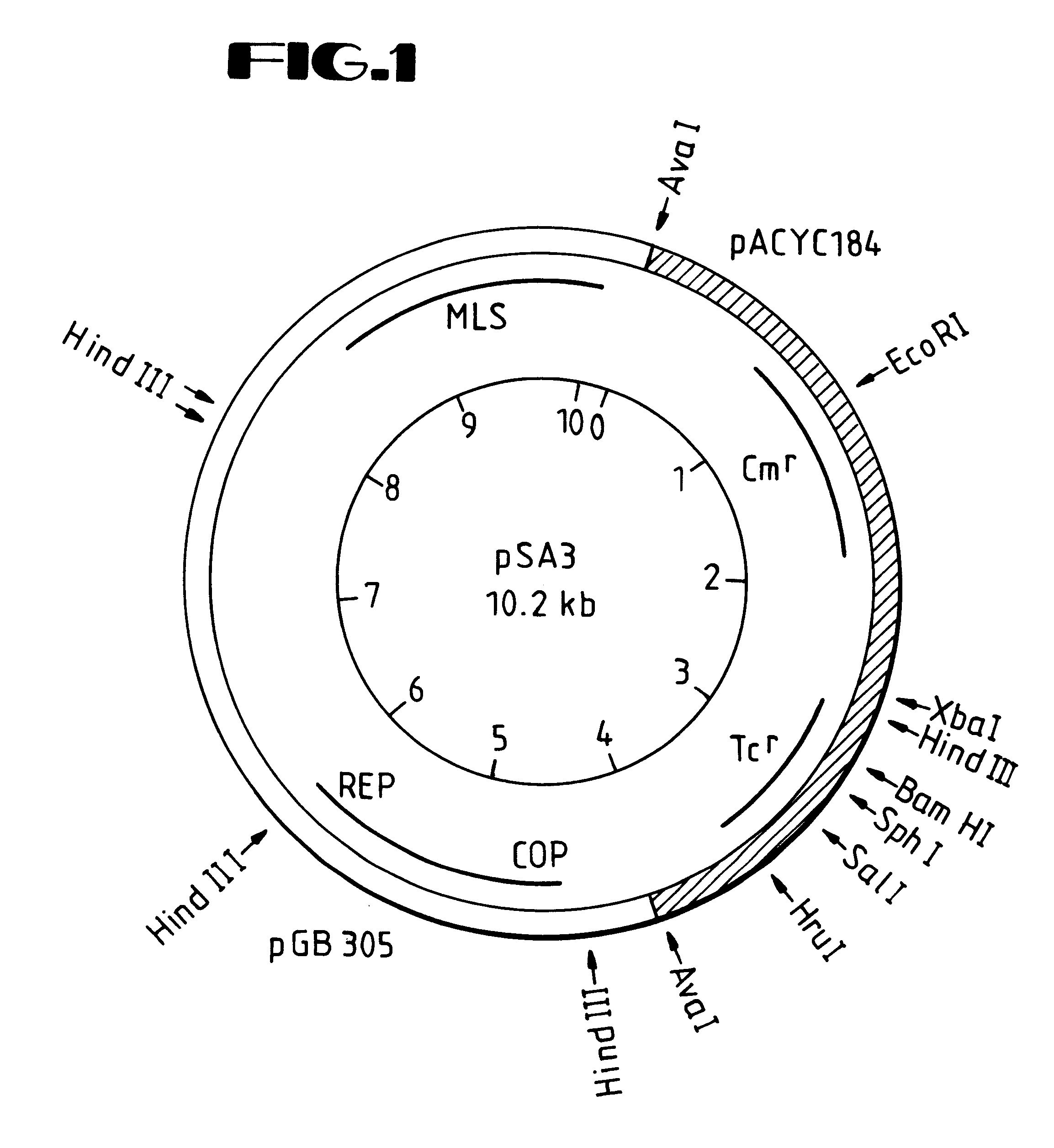
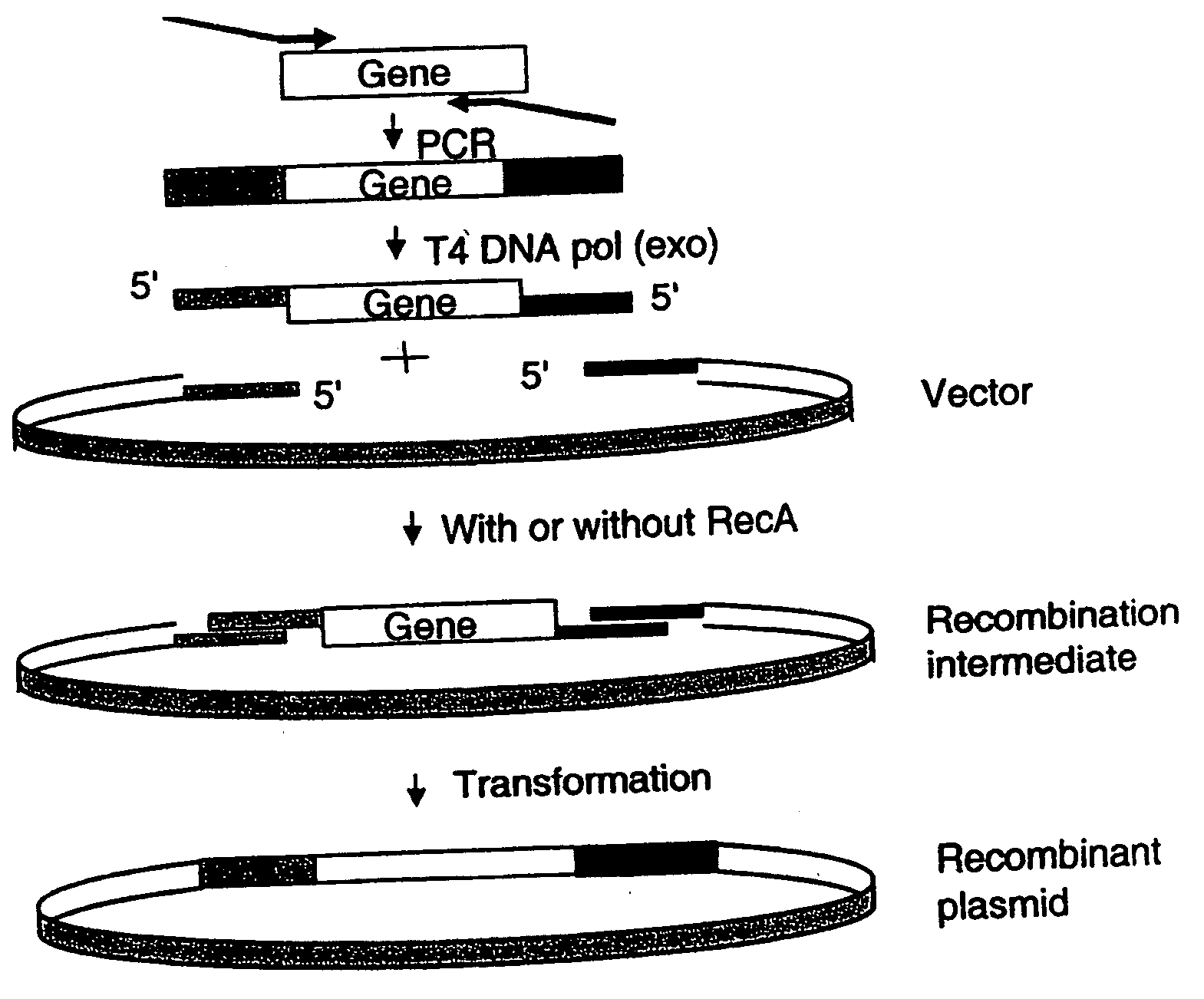
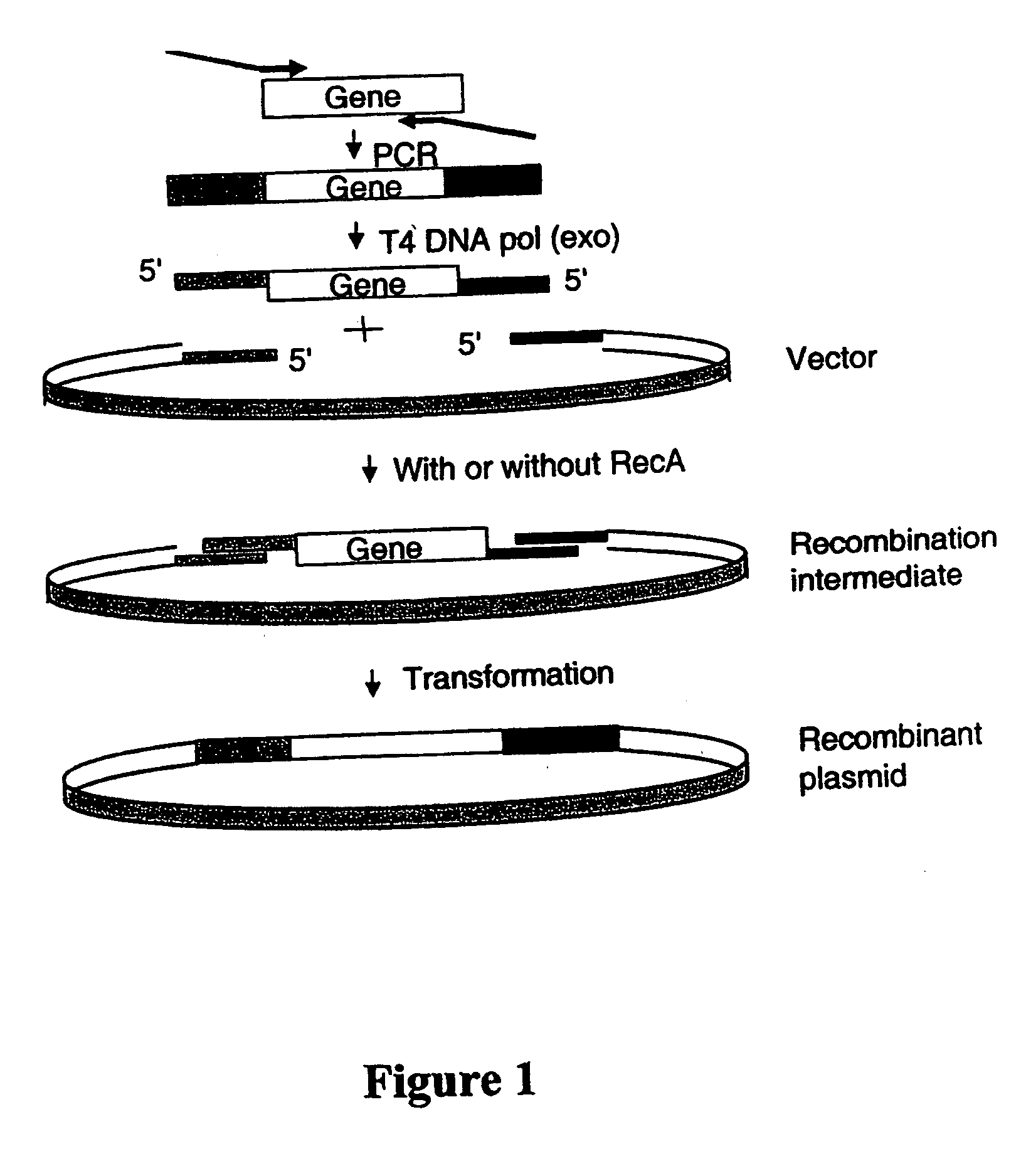
Disclosed are DNA segments encoding <DEL-S DATE="20010821" ID="DEL-S-00001">hyaluronic acid synthase which are employed to construct recombinant cells useful in the production of hyaluronate synthase or hyaluronic acid (HA)<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001"> <INS-S DATE="20010821" ID="INS-S-00001">the recombinant DNA segment identified in FIG. 5. <INS-E ID="INS-S-00001">In preferred aspects, chromosomal DNA from Streptococcus equisimilis is partially digested with EcoRI and the resultant fragments are ligated to form recombinant vectors. These vectors are useful in the transformation of host cells such as E. coli and or Streptococcal hosts. <DEL-S DATE="20010821" ID="DEL-S-00002">Resultant transformants are screened by the novel screening assays to identify colonies which have incorporated HA synthase DNA in a form that is being actively transcribed into the corresponding HA synthase enzyme. These colonies may be selected and employed in the production of the enzyme itself or its product, HA.<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00002"> <INS-S DATE="20010821" ID="INS-S-00002">The recombinant DNA segment identified in FIG. 5 is then inserted into a recombinant Streptococcal host for the production of hyaluronic acid (HA).<INS-E ID="INS-S-00002">
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Microbial production of mature human leukocyte interferons
Disclosed herein are methods and means of microbially producing, via recombinant DNA technology, mature human leukocyte interferons, useful in the treatment of viral and neoplastic diseases.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Herbicide resistance gene, compositions and methods
ActiveUS7671254B2Improve efficiencyReduce competitionImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
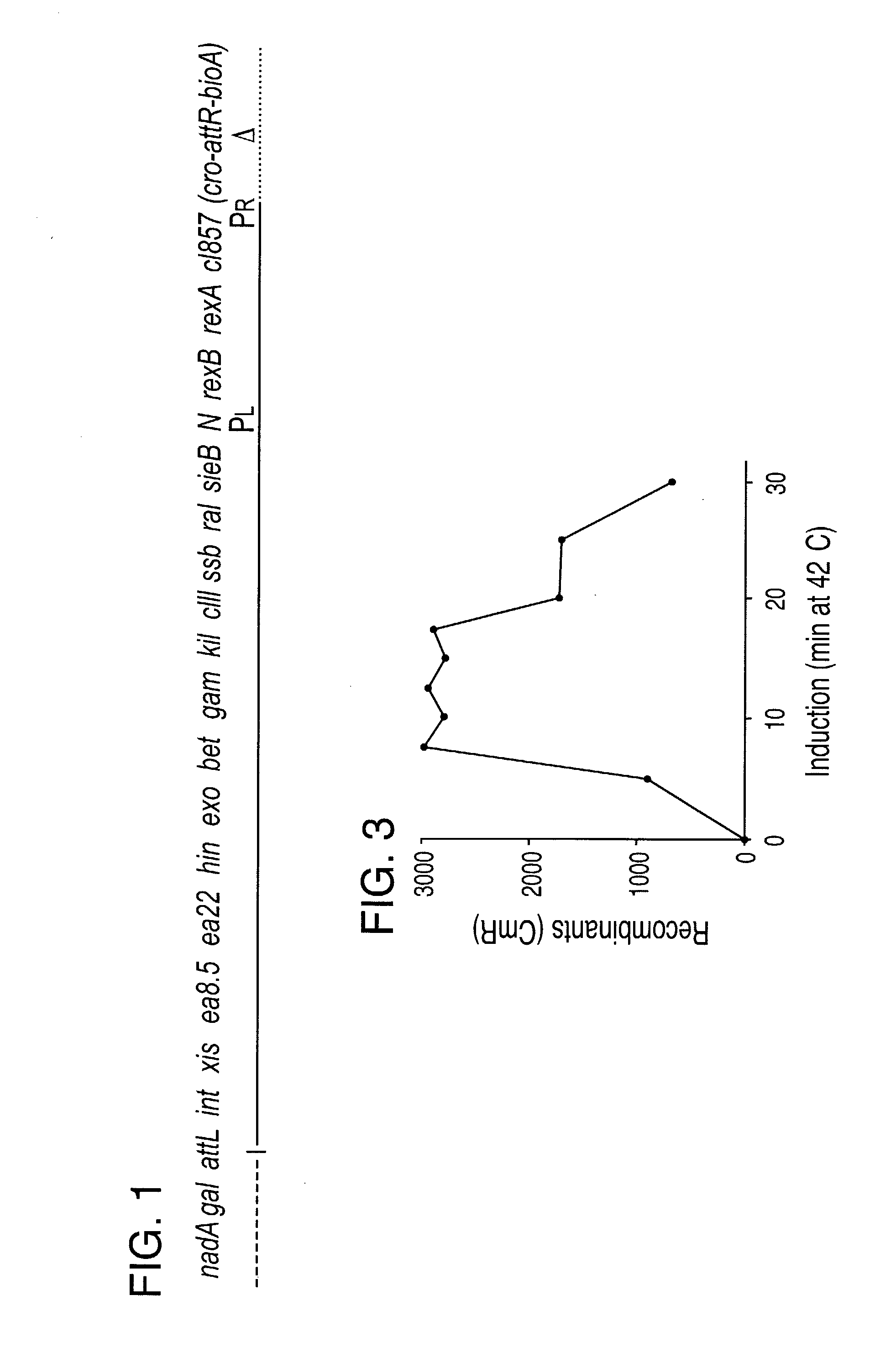
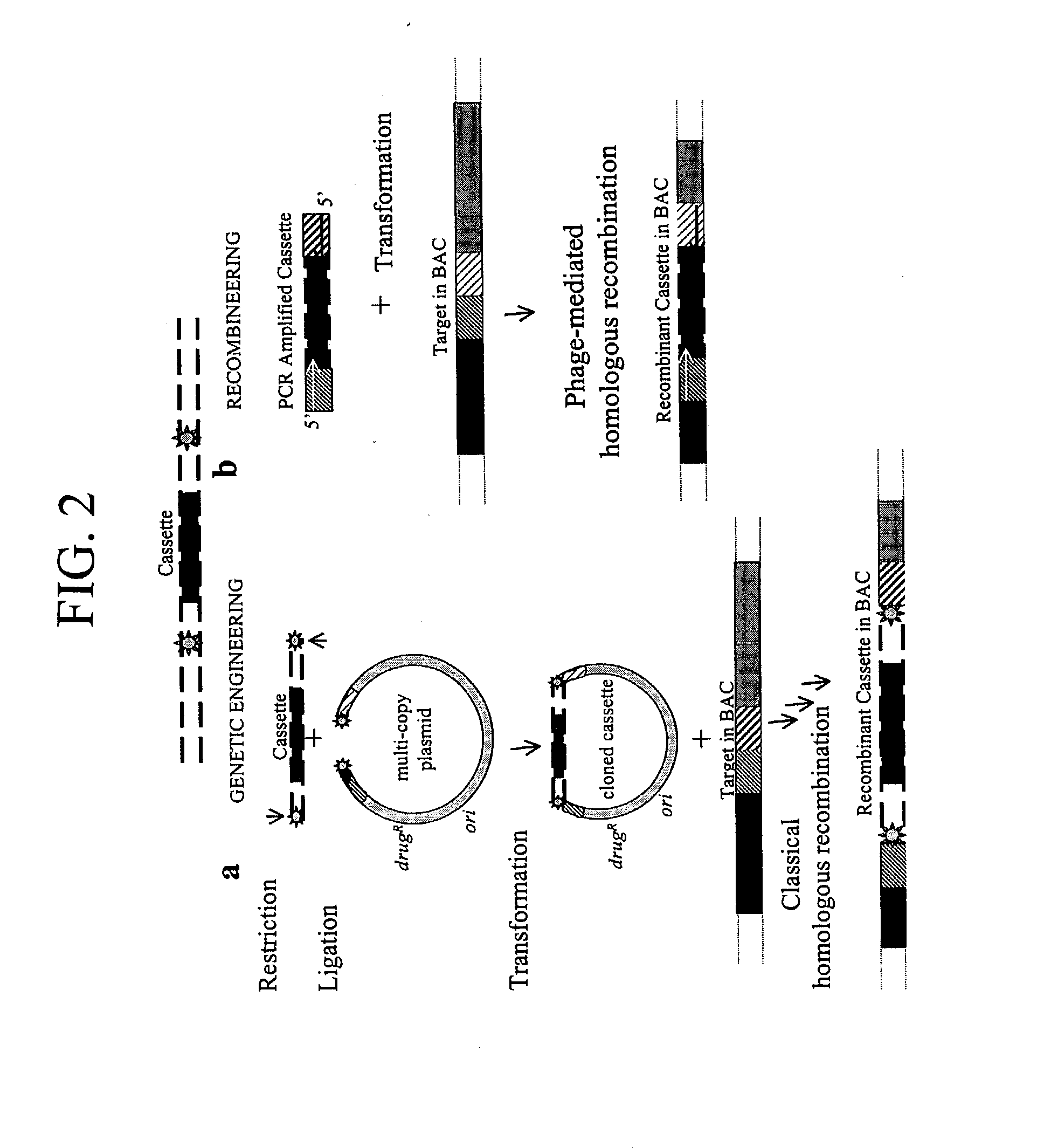
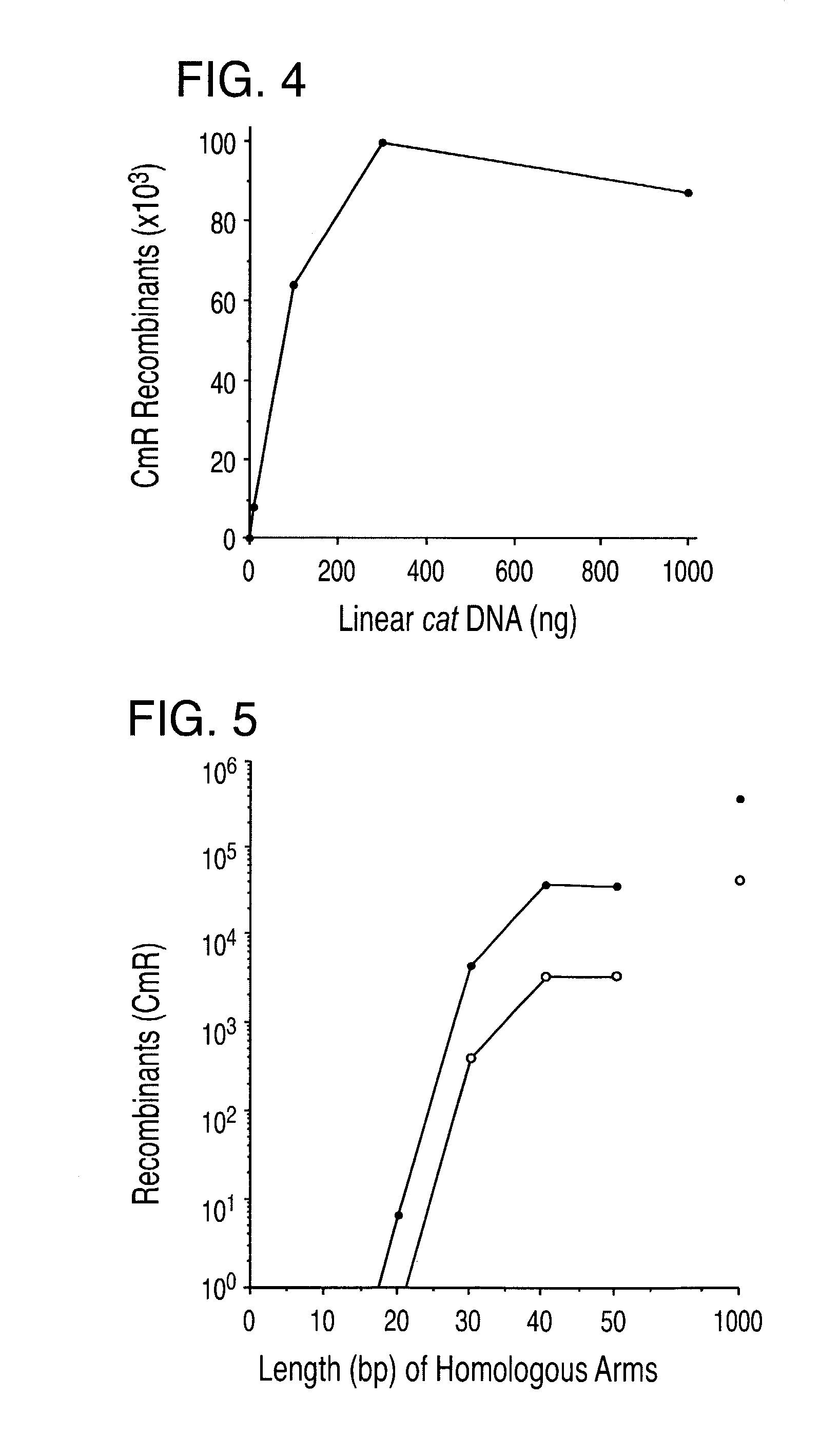
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20030224521A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredFungiBacteriaMammalKnockout animal
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
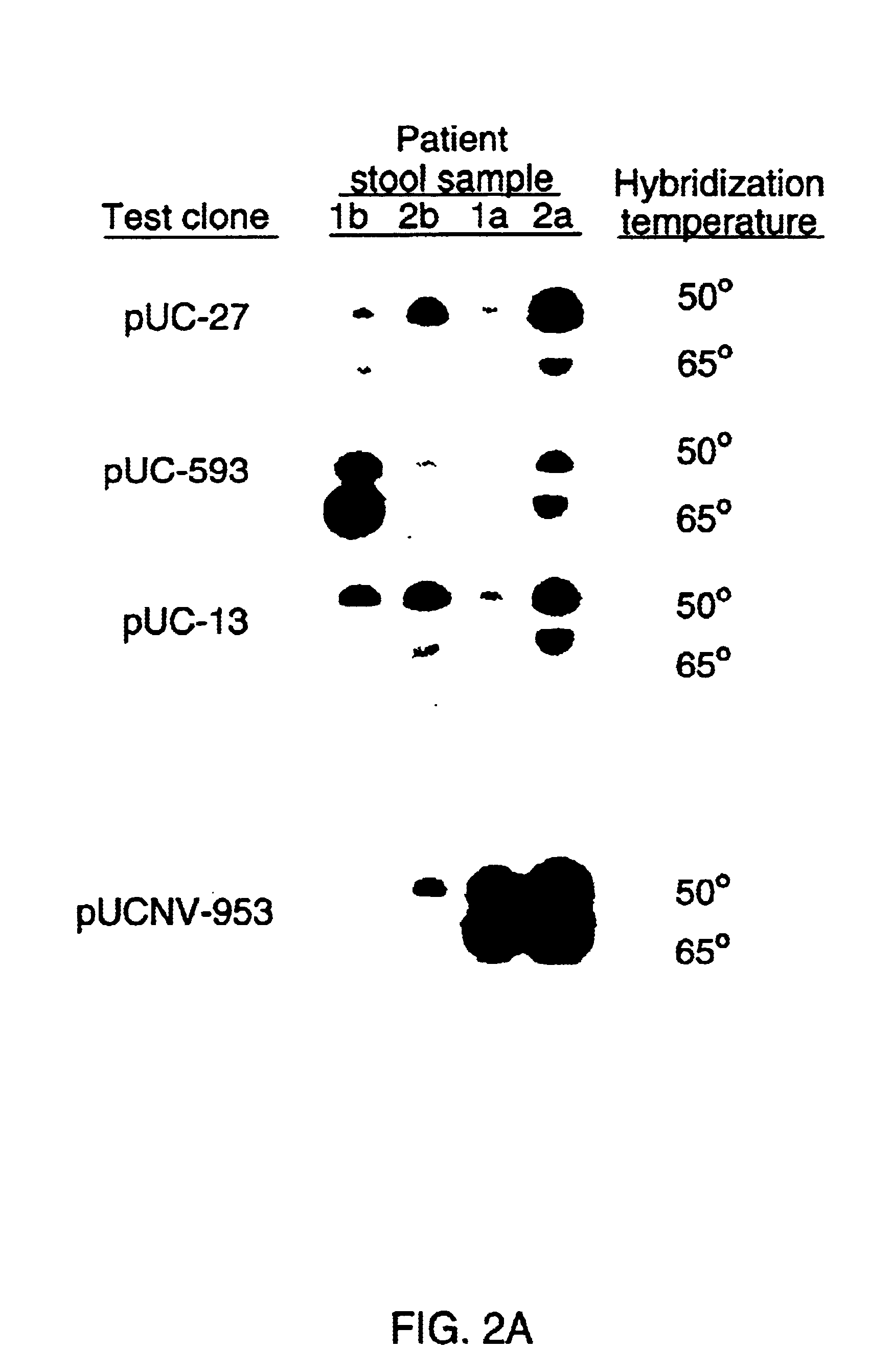
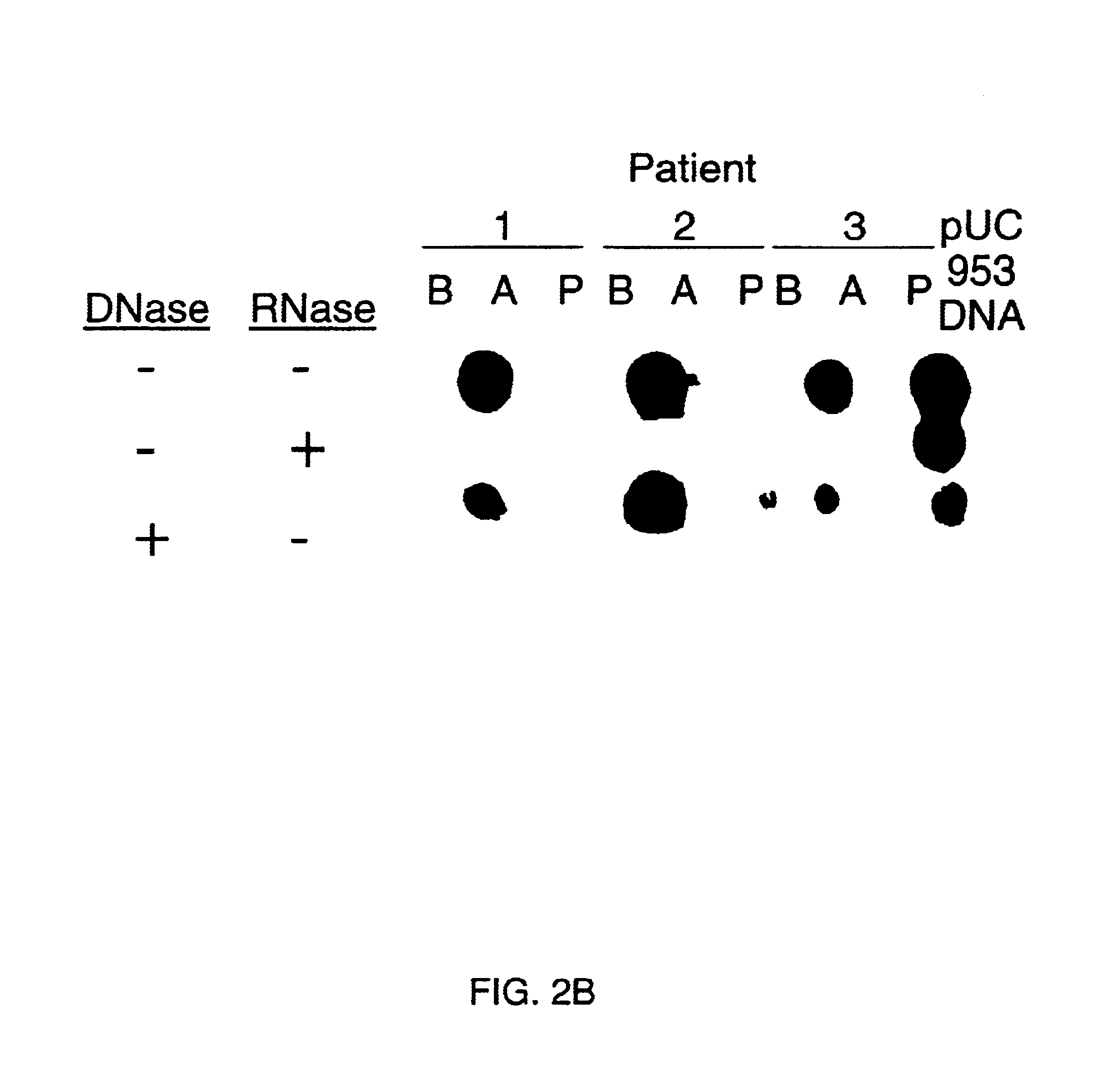
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
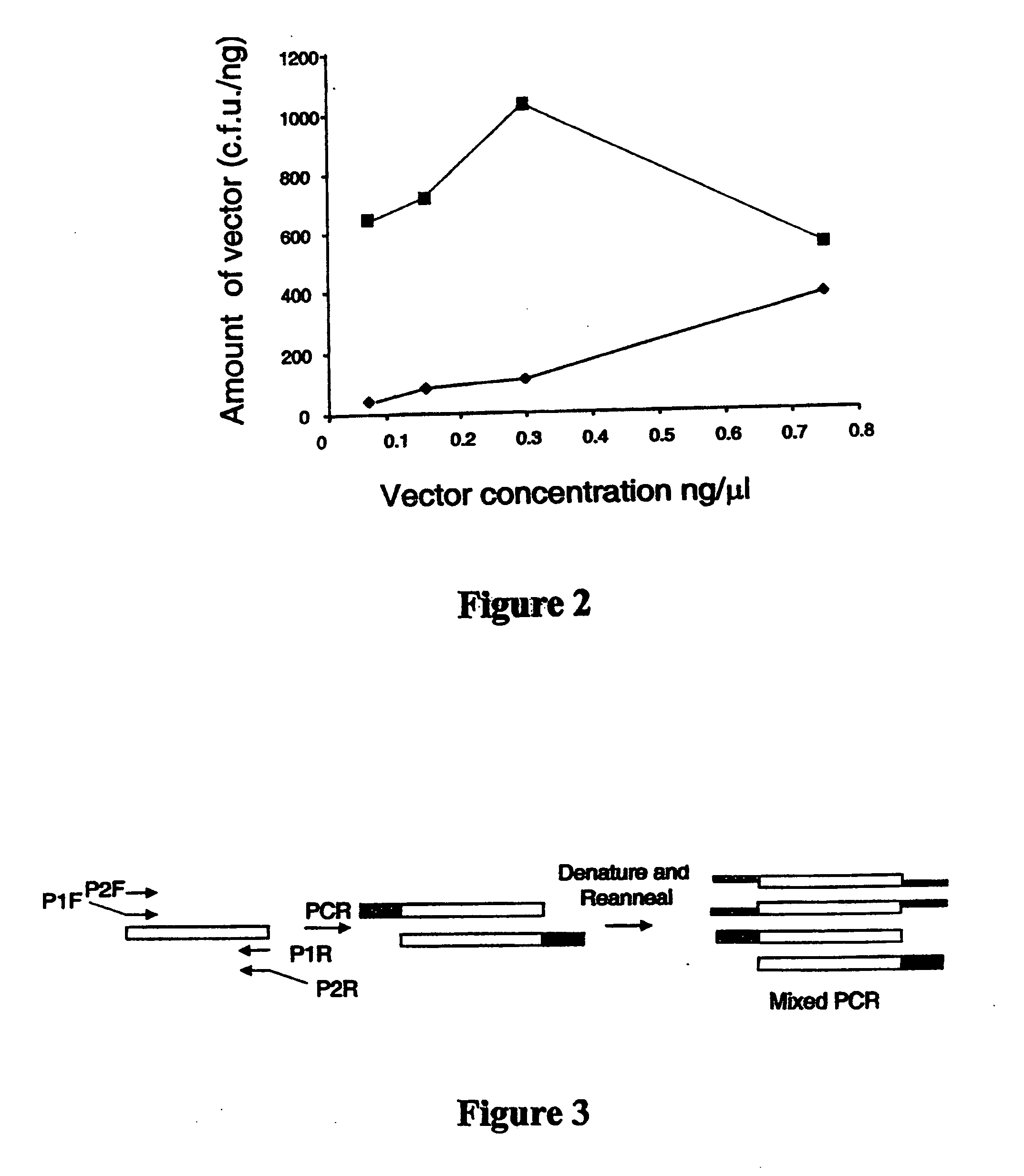
Generation of recombinant DNA by sequence-and ligation-independent cloning
InactiveUS20070292954A1Efficient conversionGenerate efficientlyTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesRecombinant DNAEnzyme
The present invention is directed methods for cloning DNA by homologous recombination. The methods can be used without a need for ligases or restriction enzymes and allow for the rapid alignment of multiple DNA fragments.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Immunogenic compositions derived from poxviruses and methods of using same
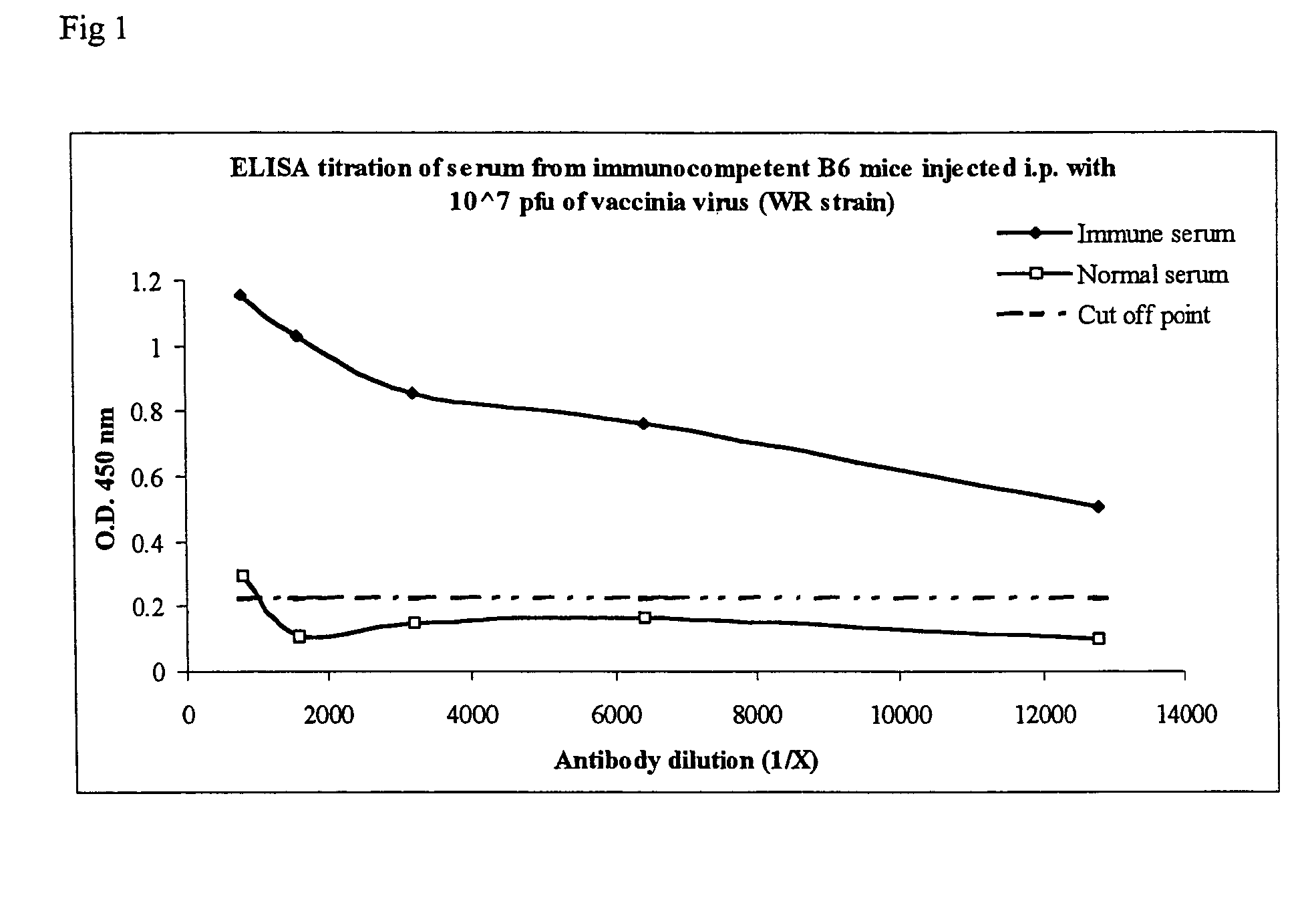
Immunogenic compostions composed of poxvirus immunogens and related methods are disclosed. Specifically, immunogenic compostions useful in eliciting immune responses in animals are disclosed. In one embodiment the immunogenic compostions include viral antigens derived from vaccinia and / or variola that elicit cross-reactive immune responses. The immunogens can be made synthetically, by using recombinant DNA technology or derived from purified virus. Moreover, methods of using the immunogenic compostions are also disclosed.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Thermostable or thermoactive DNA polymerase molecules with attenuated 3′-5′ exonuclease activity
The present invention provides thermostable or thermoactive DNA polymerases with attenuated 3′-5′ exonuclease activity, methods for their synthesis, methods for their use, kits comprising the polymerases, nucleic acids encoding the polymerases and cells comprising such a nucleic acid. The DNA polymerases of the invention are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, such as nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. The DNA polymerases of the invention allow higher fidelity replication and amplification of a template DNA sequence, allow less degradation of primers and / or more efficient use of deoxynucleotide triphosphates and are in general more efficient and less costly to make and use.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
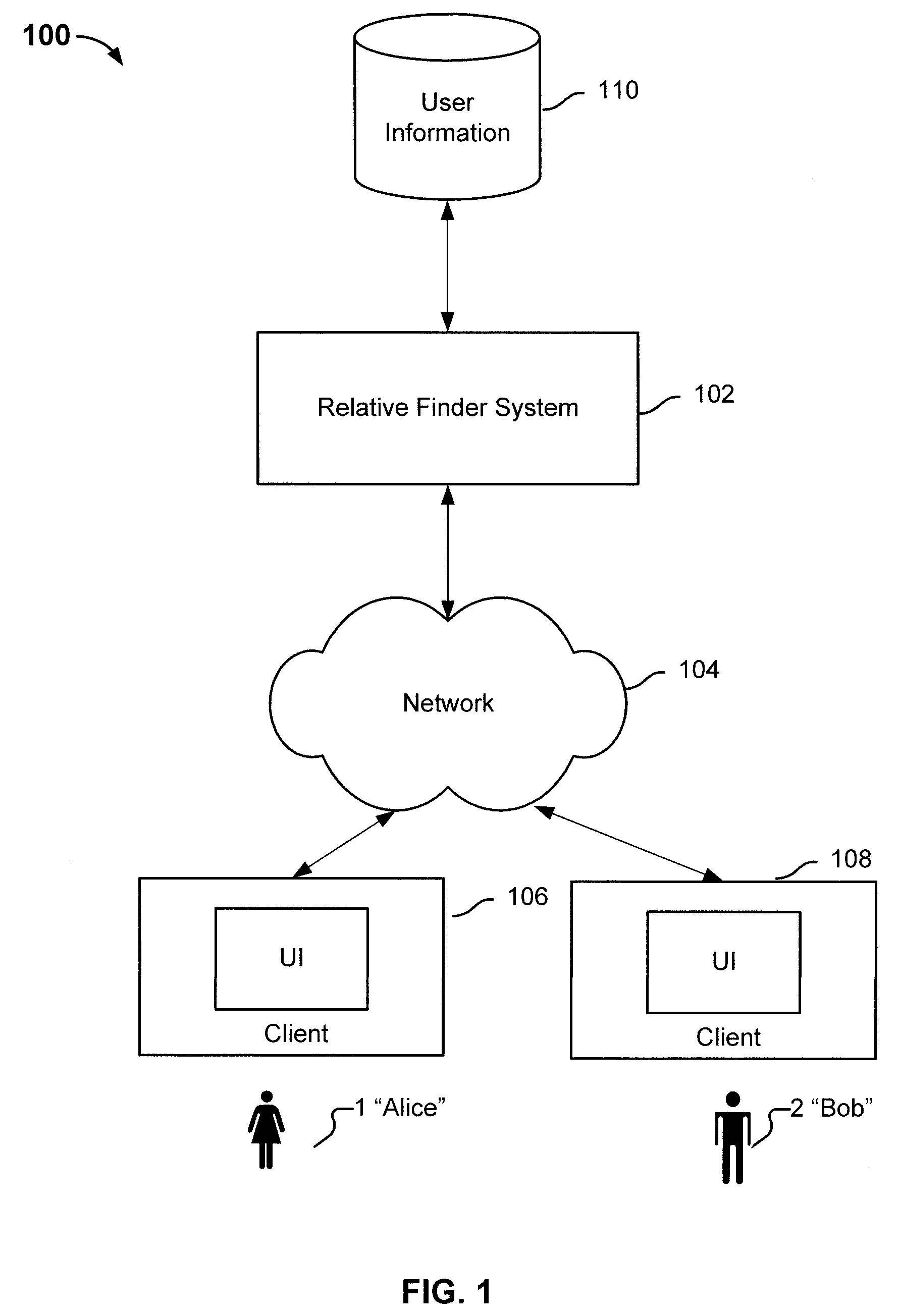
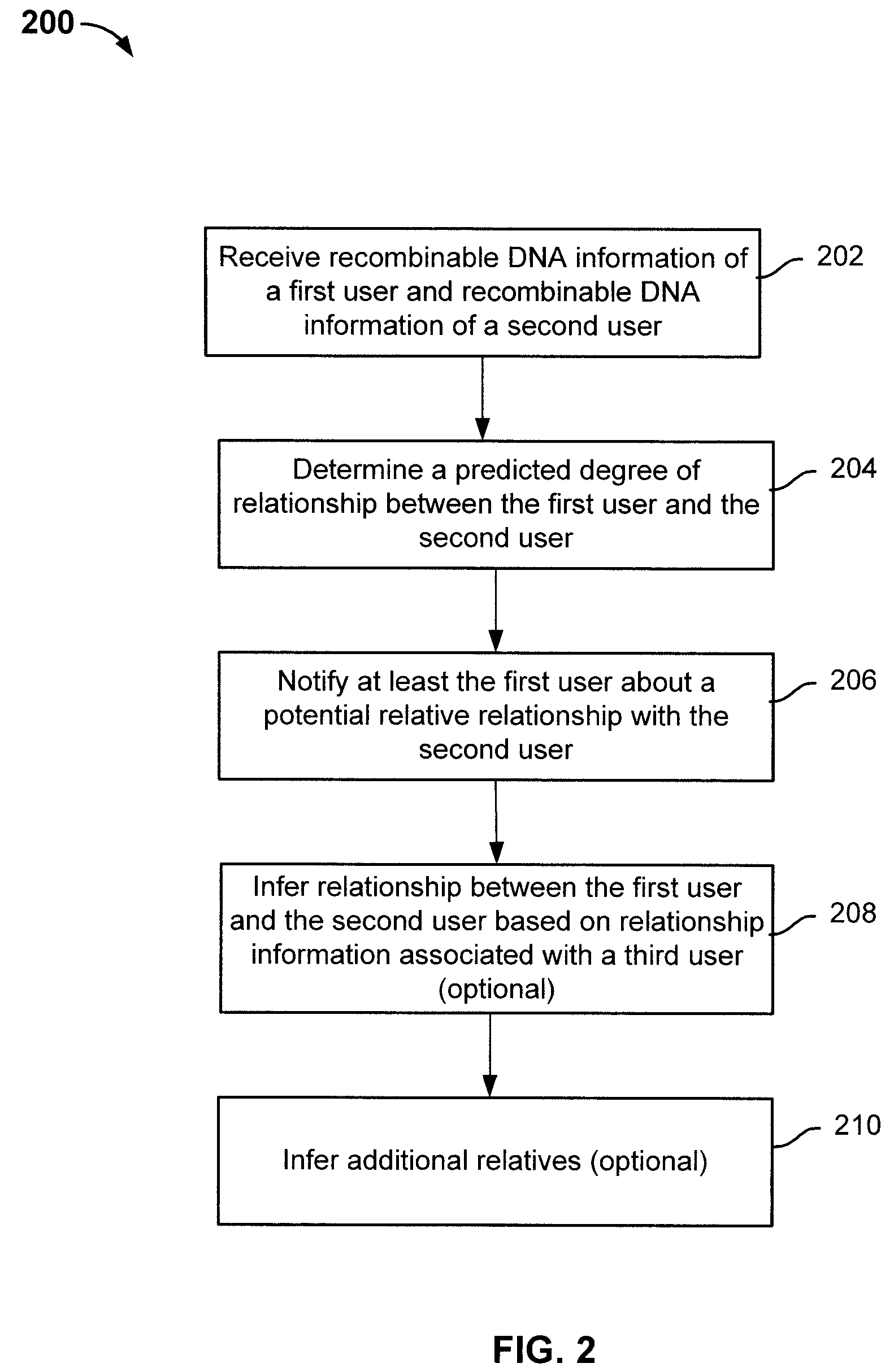
Finding relatives in a database
ActiveUS8463554B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for chemical processesHuman–computer interactionRecombinant DNA
Determining relative relationship includes receiving recombinable deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) information of a first user and recombinable DNA information of a second user, determining, based at least in part on the recombinable DNA information of the first user and recombinable DNA information of the second user, a predicted degree of relationship between the first user and the second user, and in the event that the expected degree of relationship between the first user and the second user at least meets the threshold, notifying at least the first user about a relative relationship with the second user.
Owner:23ANDME
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modifi-cation of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and inser-tion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA pro-duction system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also de-scribed. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intes-tine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
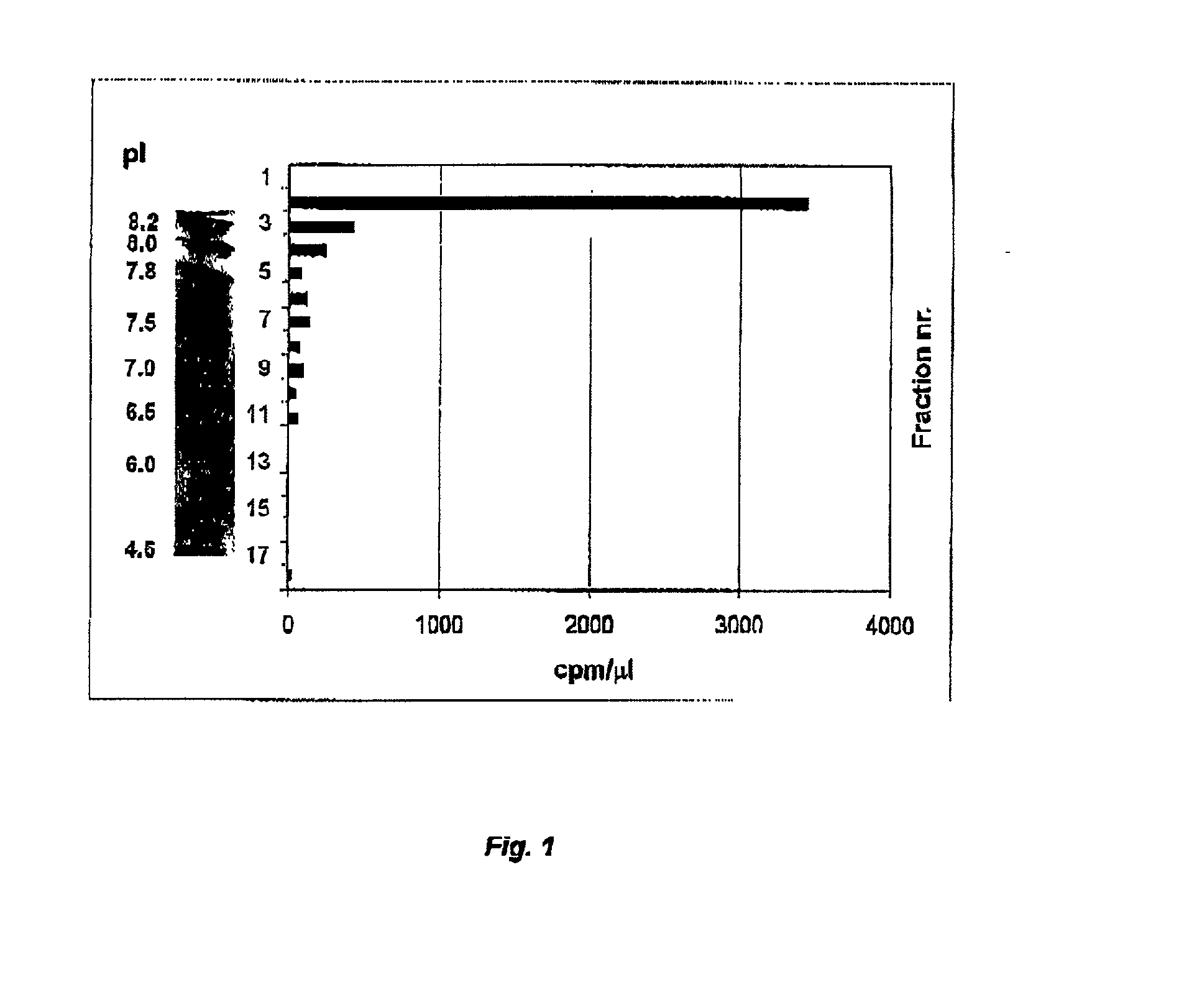
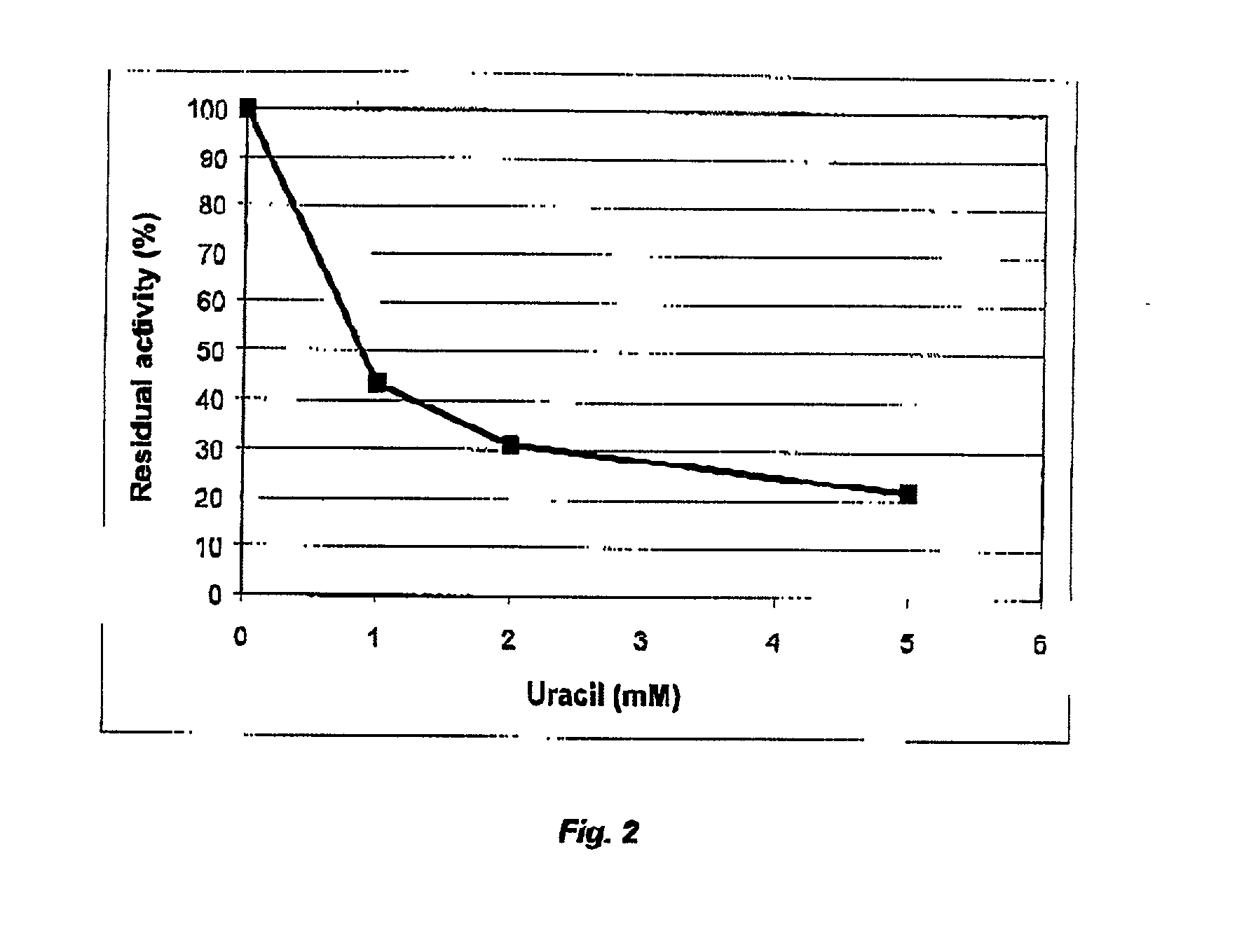
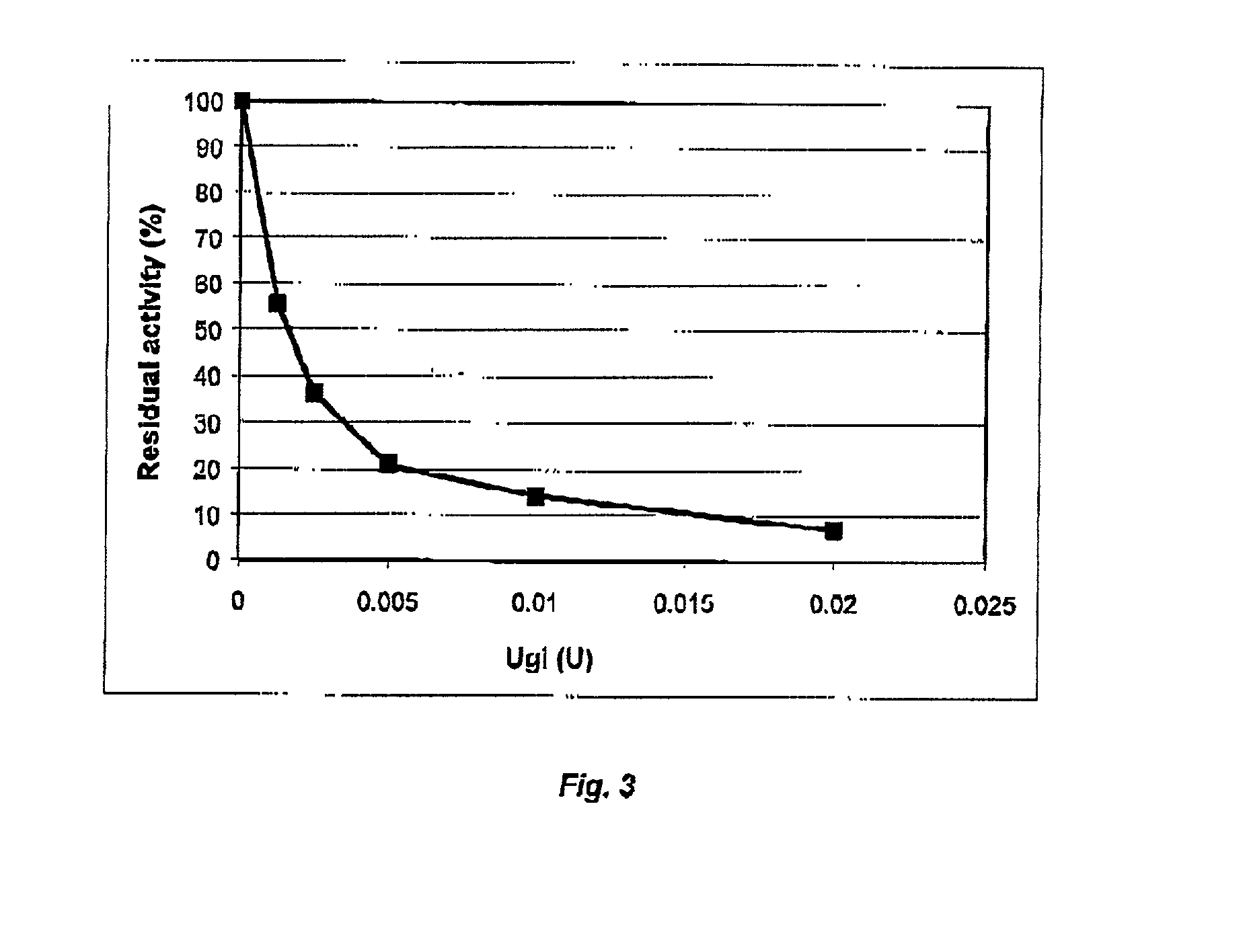
Cod uracil-DNA glycosylase, gene coding therefore, recombinant DNA containing said gene or operative parts thereof, a method for preparing said protein and the use of said protein or said operative parts thereof in monitoring or controlling PCR
InactiveUS20020155573A1Efficient productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyUracil-DNA glycosylase
It is disclosed a novel enzyme present in cod liver, a DNA sequence encoding the enzyme or operative parts or biologically functional parts thereof, a novel recombinant DNA comprising the gene or tho operative or biologically functional parts thereof, a method of preparing the enzyme from cod liver and from bacteria carrying the gene, the bacteria carrying the gene per se, and the use of the protein in monitoring and / or controlling PCR or related reaction systems.
Owner:BIOTEC PHARMACON
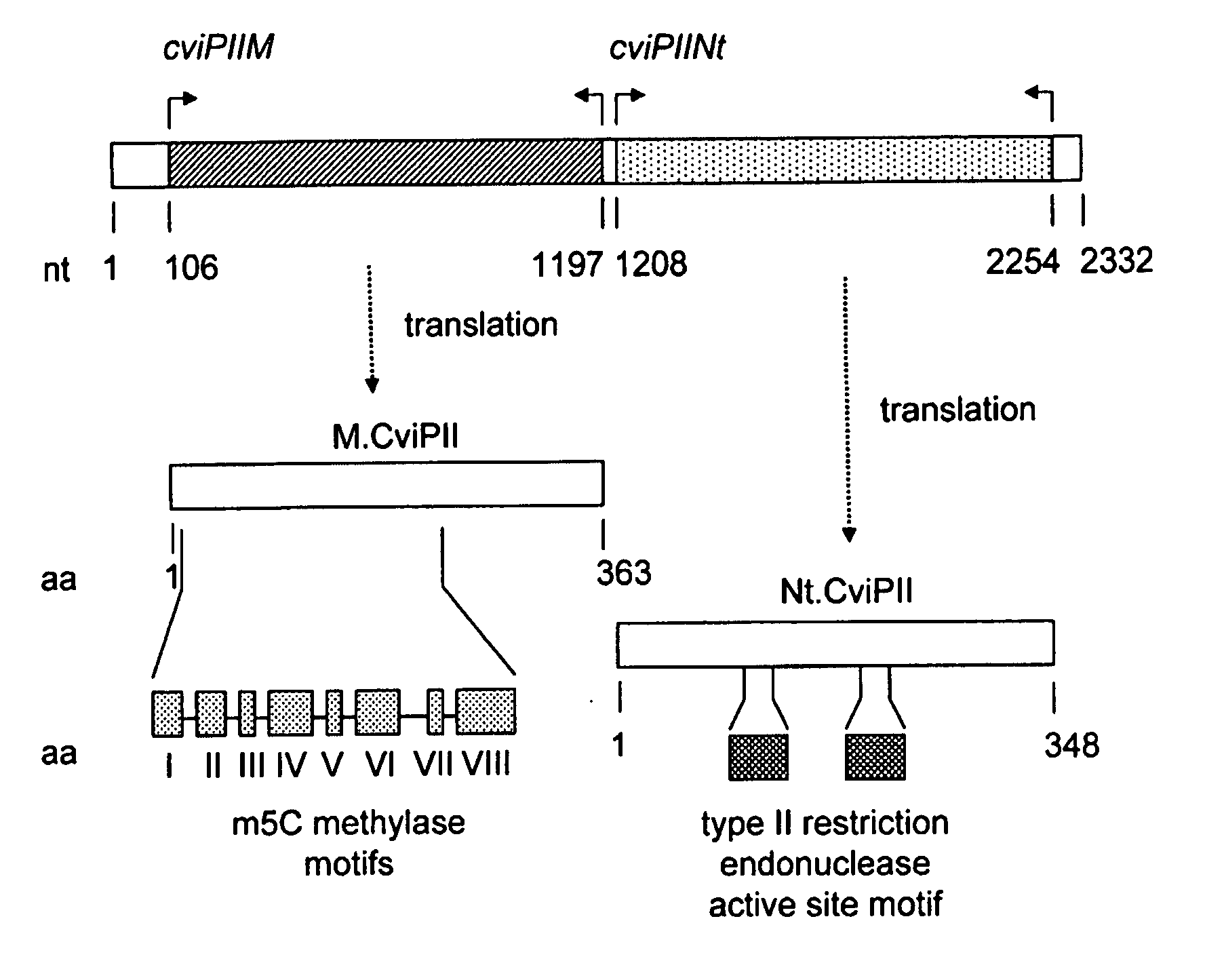
Recombinant Dna Nicking Endonuclease and Uses Thereof
Recombinant nicking endonucleases and associated methylases have been obtained and sequenced and their specificity has been defined. A mutant form of the nicking endonuclease has been cloned where the mutation includes deletion of amino acid sequences at the C-terminal end of the protein. The nicking enzymes have been used for a number of purposes including: amplifying DNA from as few cells as can be found in a single bacterial colony in the presence of a strand displacing polymerase; and for removing genomic DNA in a biological preparation where it is deemed to be a contaminant.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin, insulin, native cholera toxic b submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20030204864A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInsulin-like growth factor
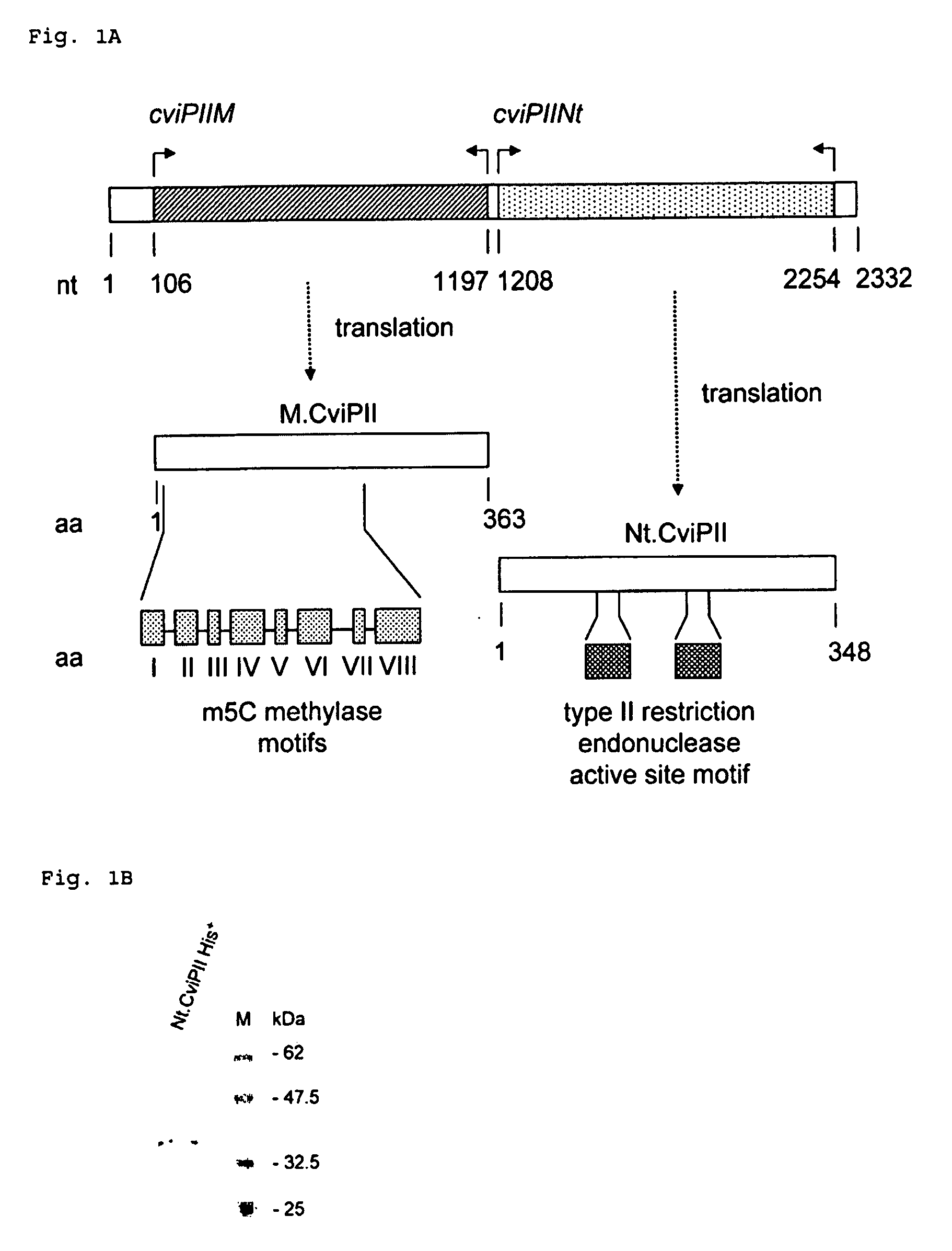
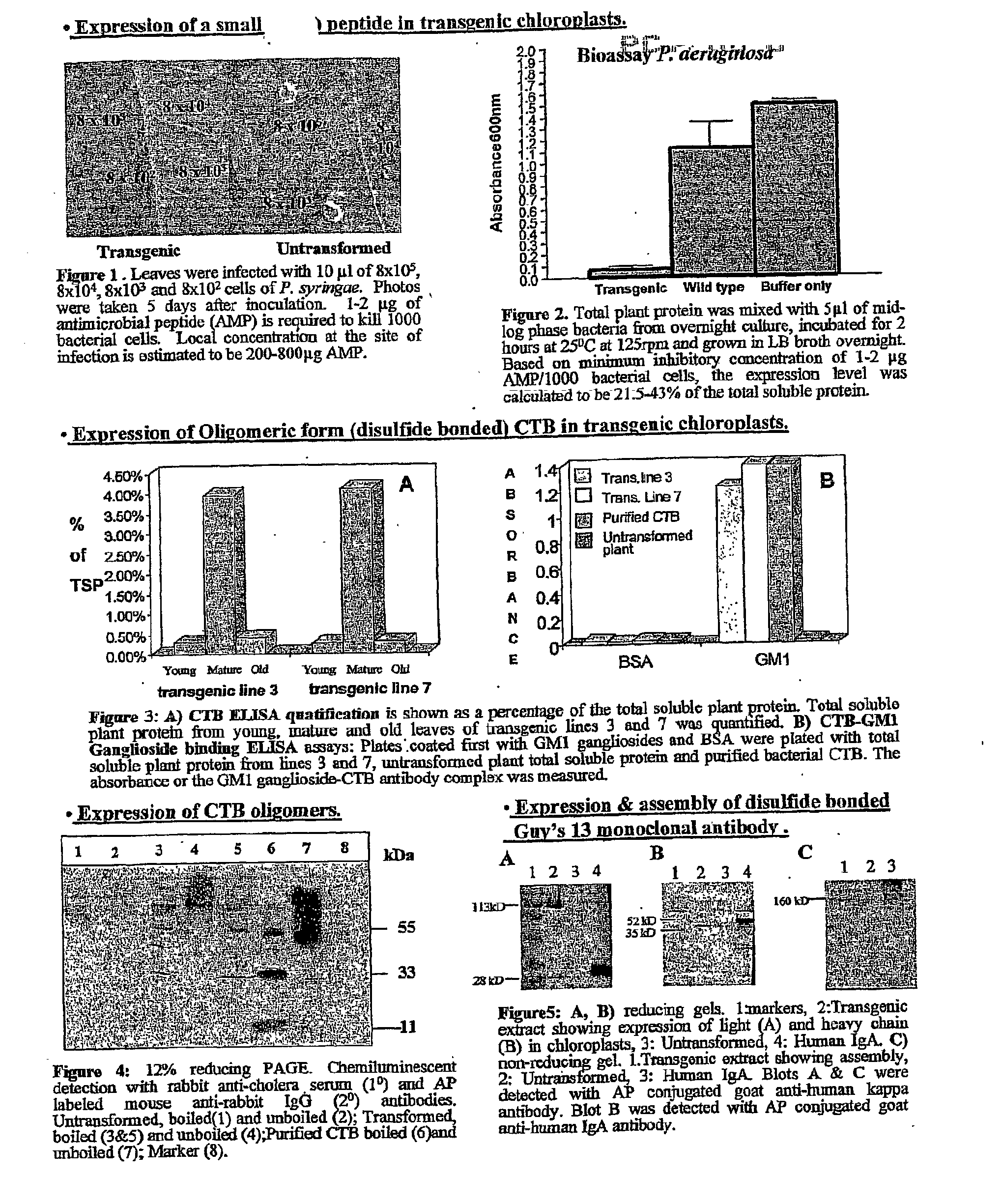
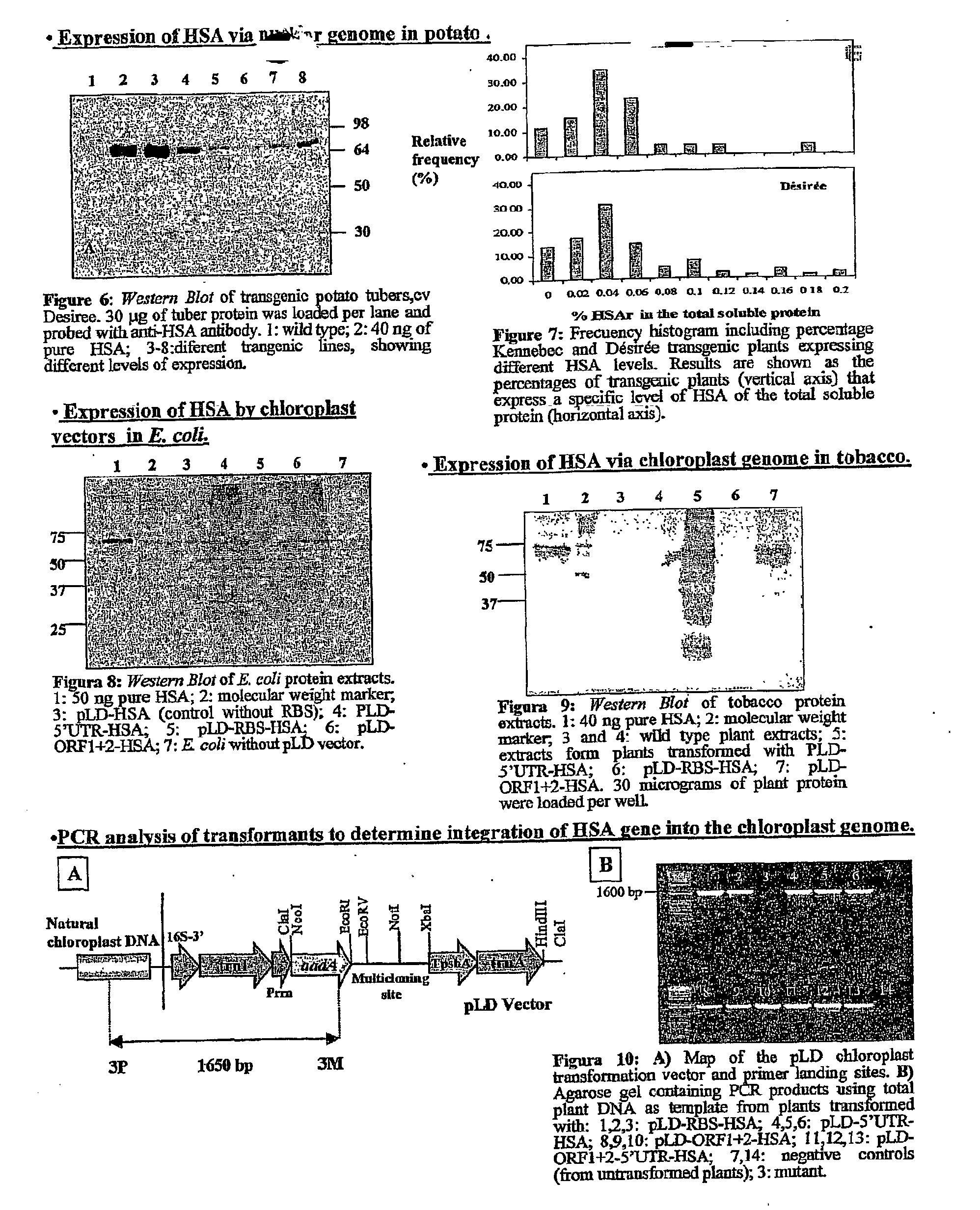
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1,-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS7235716B2Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
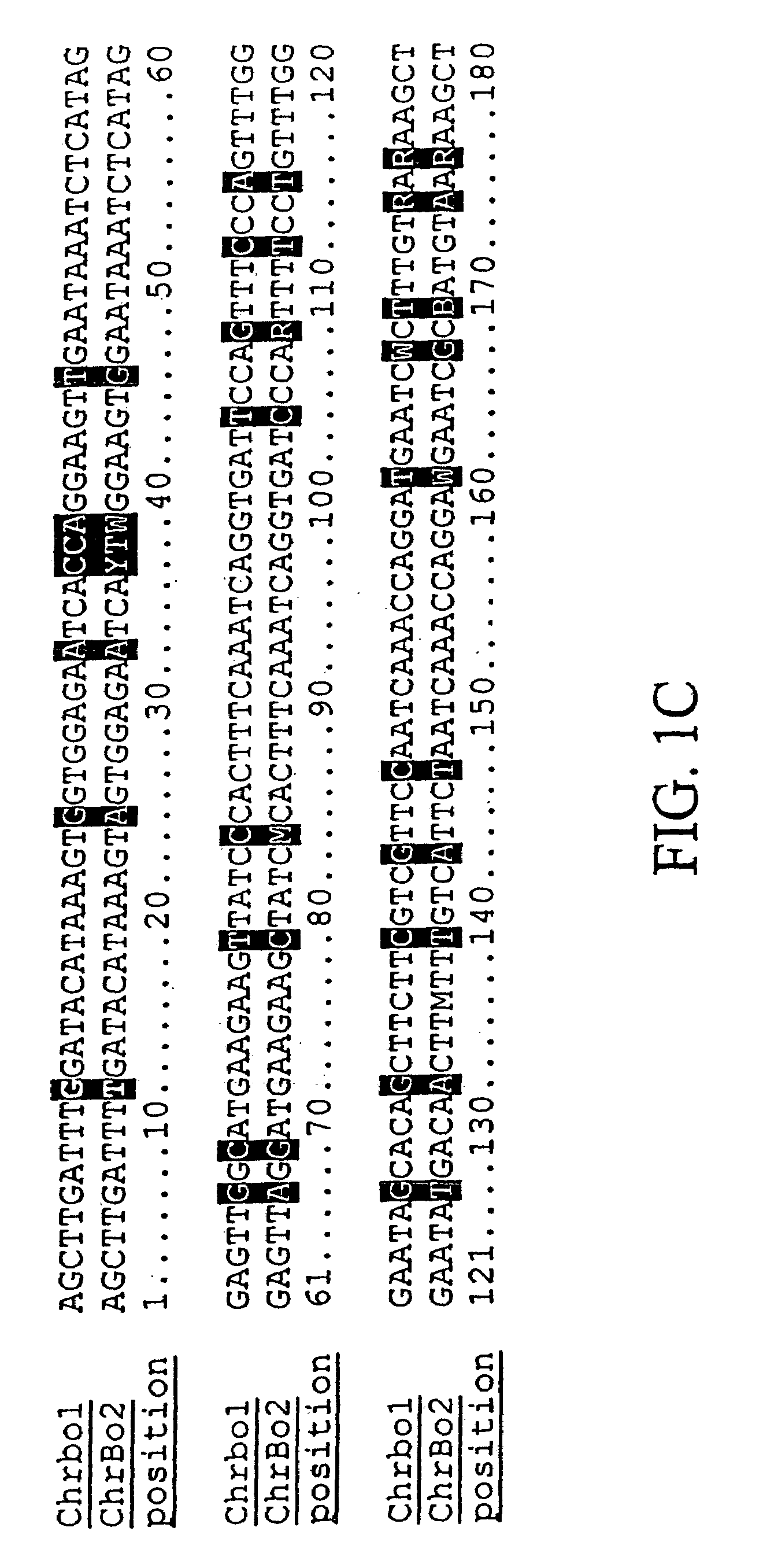
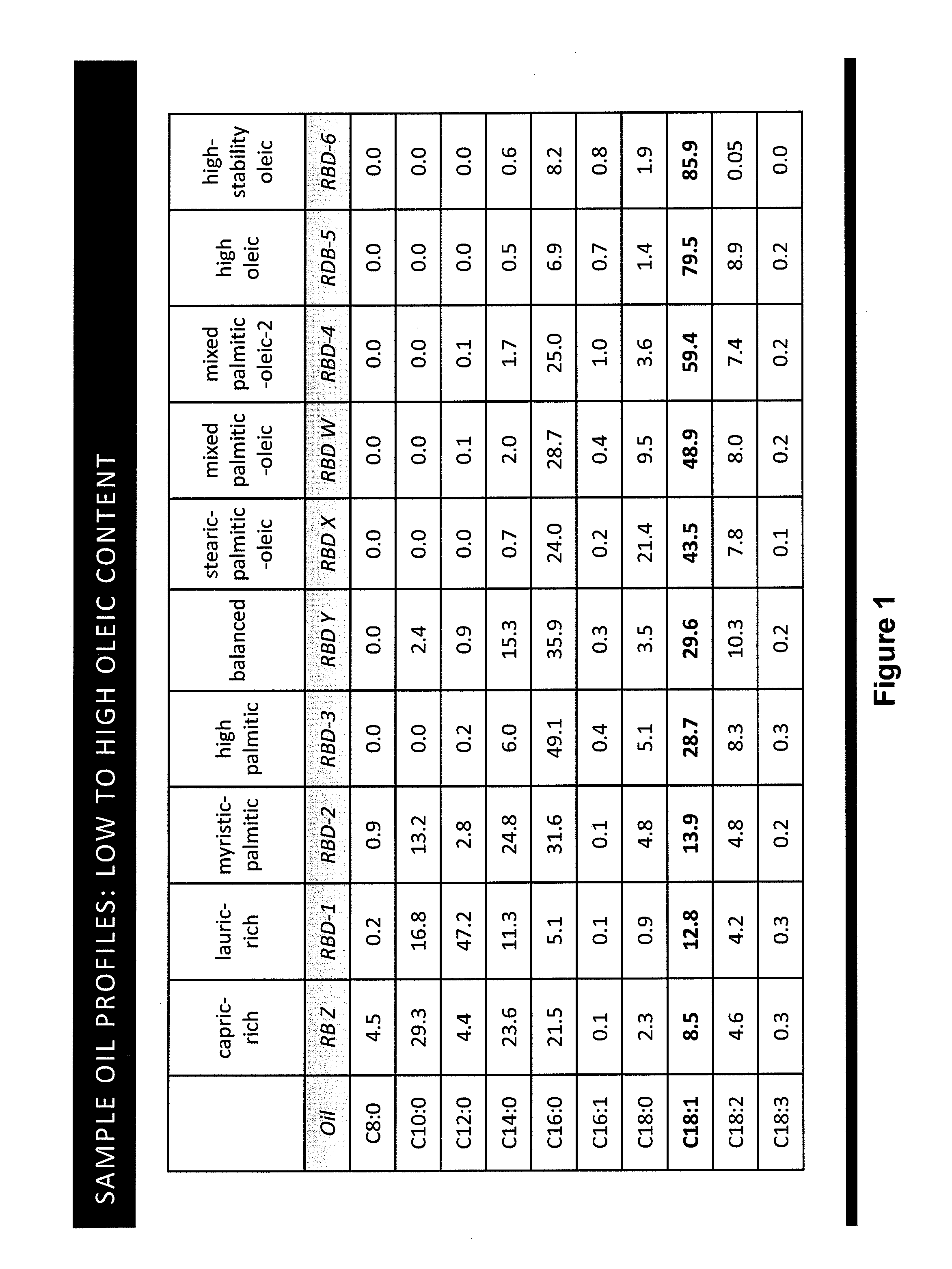
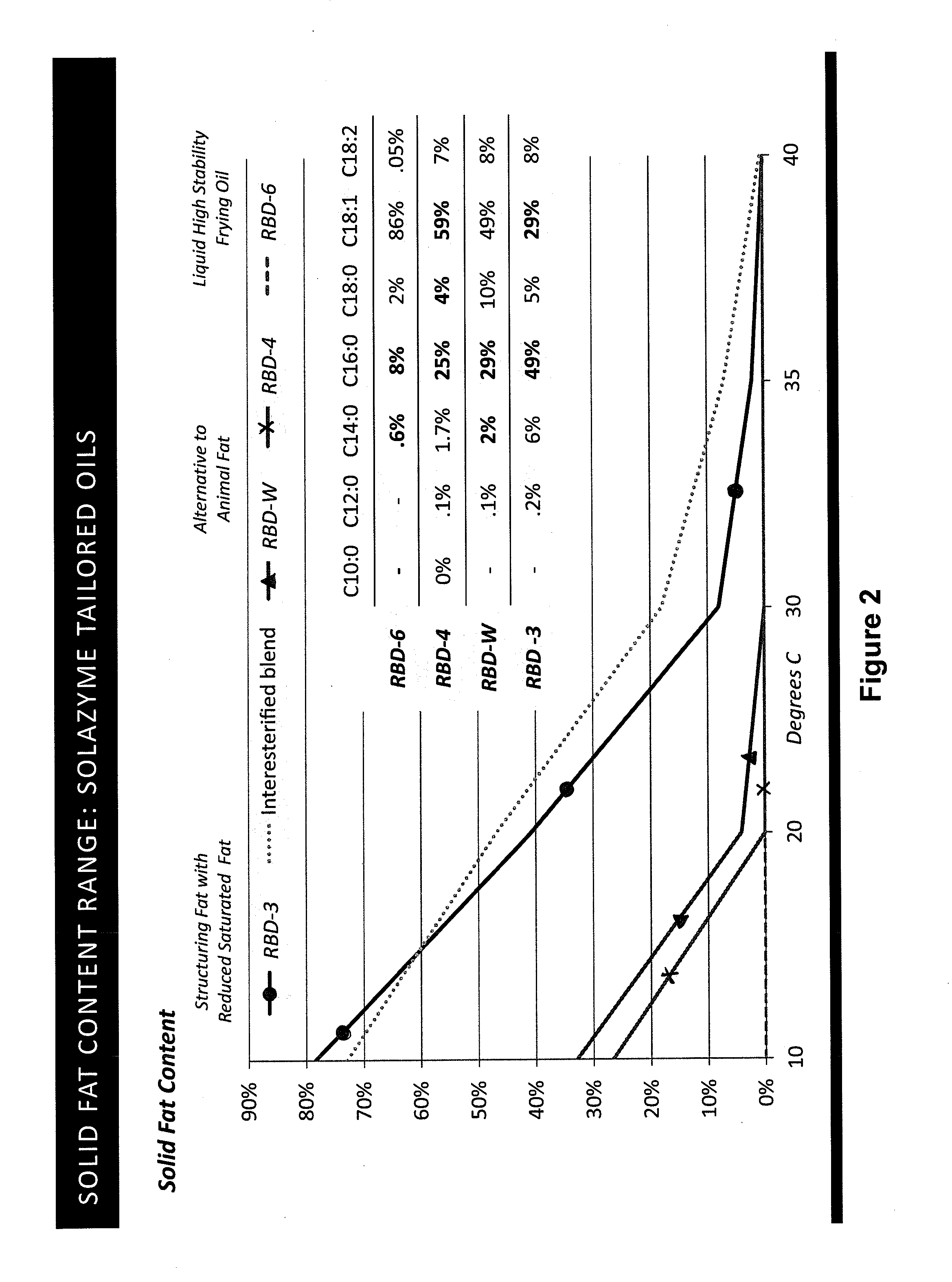
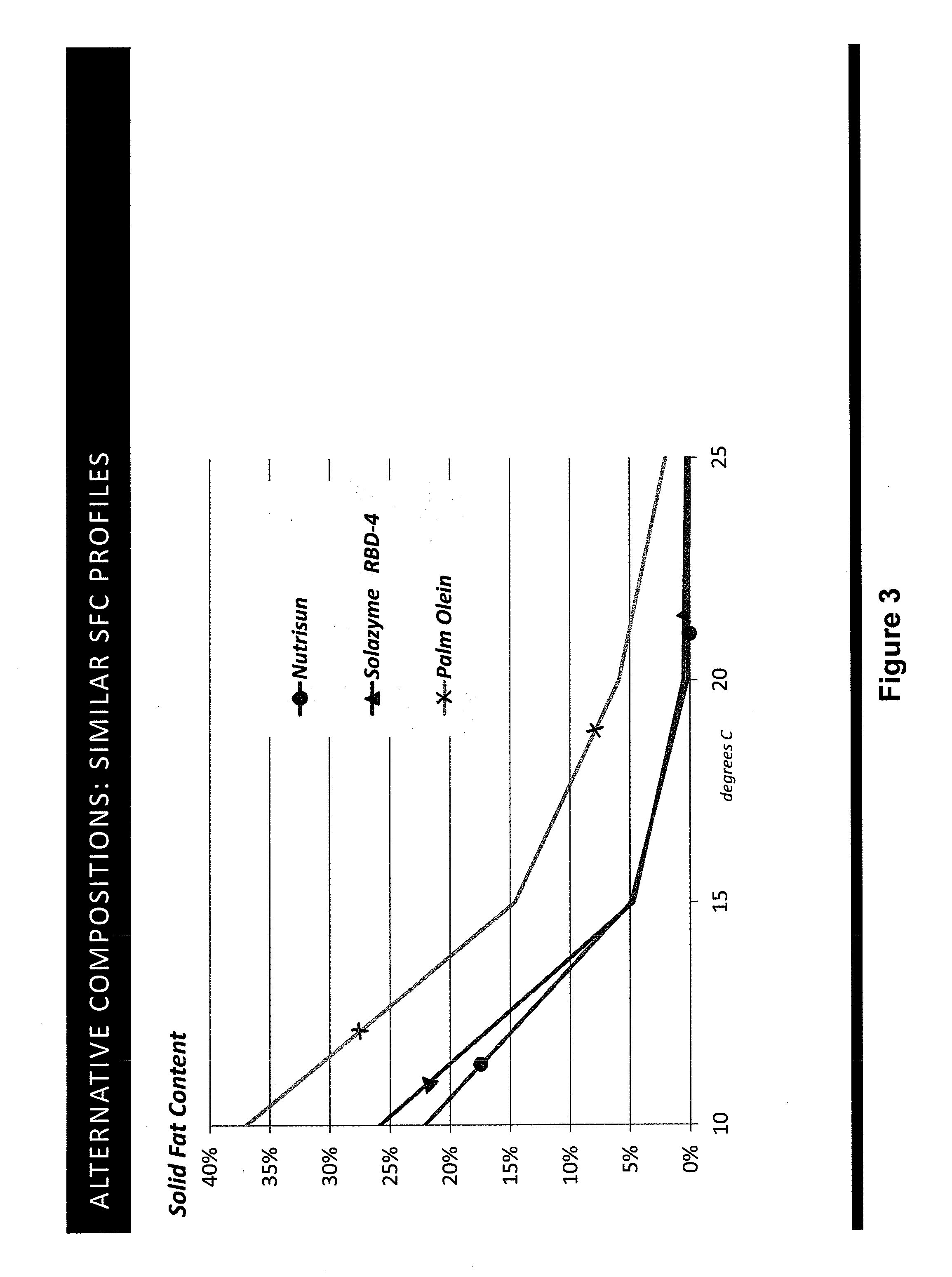
Tailored Oils
ActiveUS20130338385A1Raise the ratioReduced activityOrganic chemistryFatty substance recovery/refiningButter cocoaACP desaturase
Recombinant DNA techniques are used to produce oleaginous recombinant cells that produce triglyceride oils having desired fatty acid profiles and regiospecific or stereospecific profiles. Genes manipulated include those encoding stearoyl-ACP desturase, delta 12 fatty acid desaturase, acyl-ACP thioesterase, ketoacyl-ACP synthase, and lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase. The oil produced can have enhanced oxidative or thermal stability, can be useful as a frying oil, shortening, roll-in shortening, tempering fat, cocoa butter replacement, as a lubricant, or as a feedstock for various chemical processes. The fatty acid profile can be enriched in midchain profiles or the oil can be enriched in triglycerides of the saturated-unsaturated-saturated type.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modification of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and insertion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA production system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also described. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intestine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
Method for recovery of proteins prepared by recombinant DNA procedures
InactiveUS6174704B1Reduced form requirementsDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCellular componentLysis
An improved method is disclosed for the lysis of host cells and extraction of proteins of interest therefrom. The method involves, subsequent to expressing the protein in the host cell by a recombinant DNA procedure, using a reagent solution containing an alkylglycoside or an alkylthioglycoside to lyse the cell to release the protein, and to extract the protein of interest from other host cellular components.
Owner:PIERCE BIOTECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com