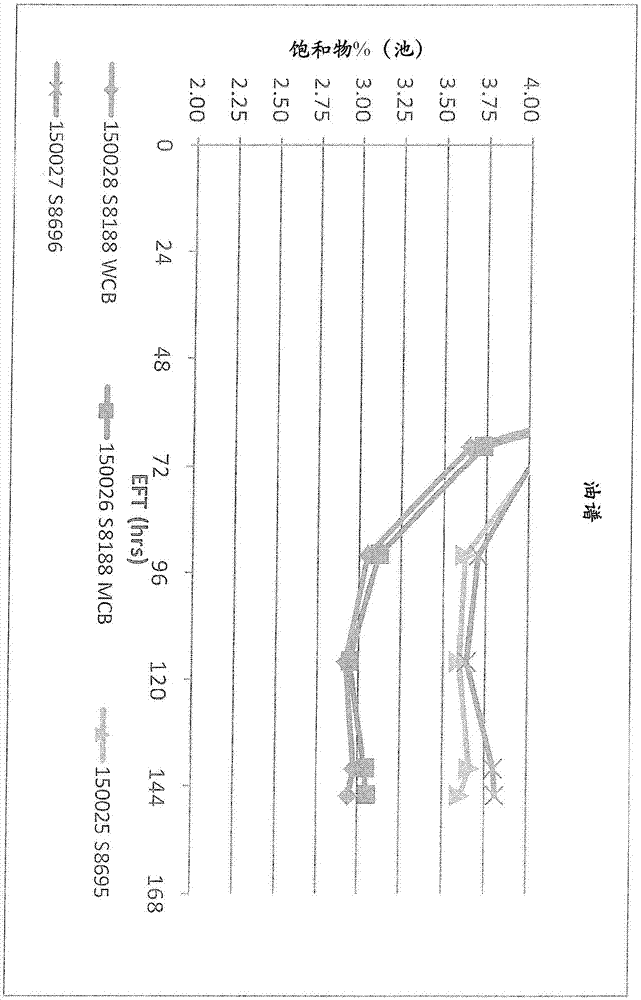
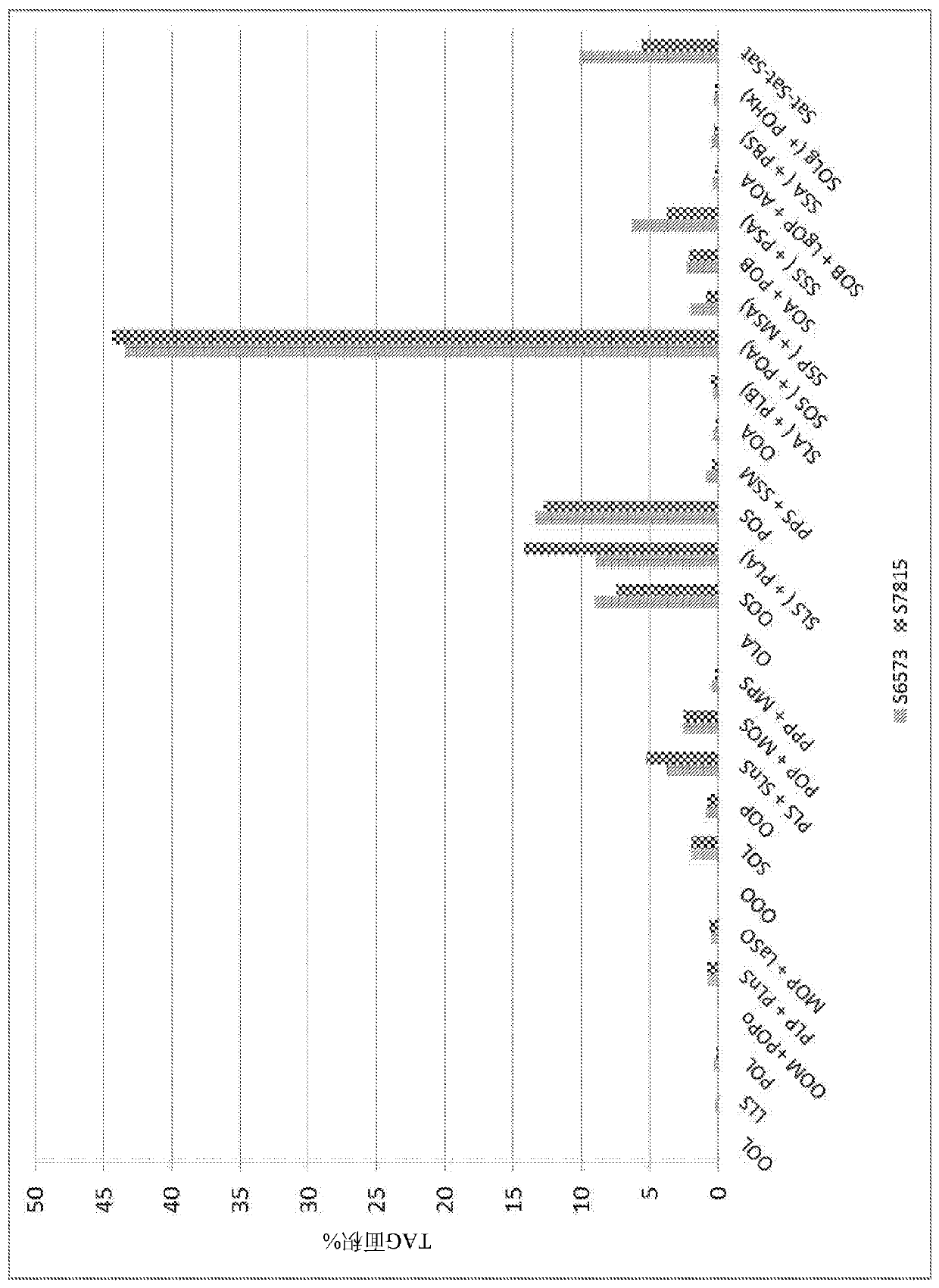
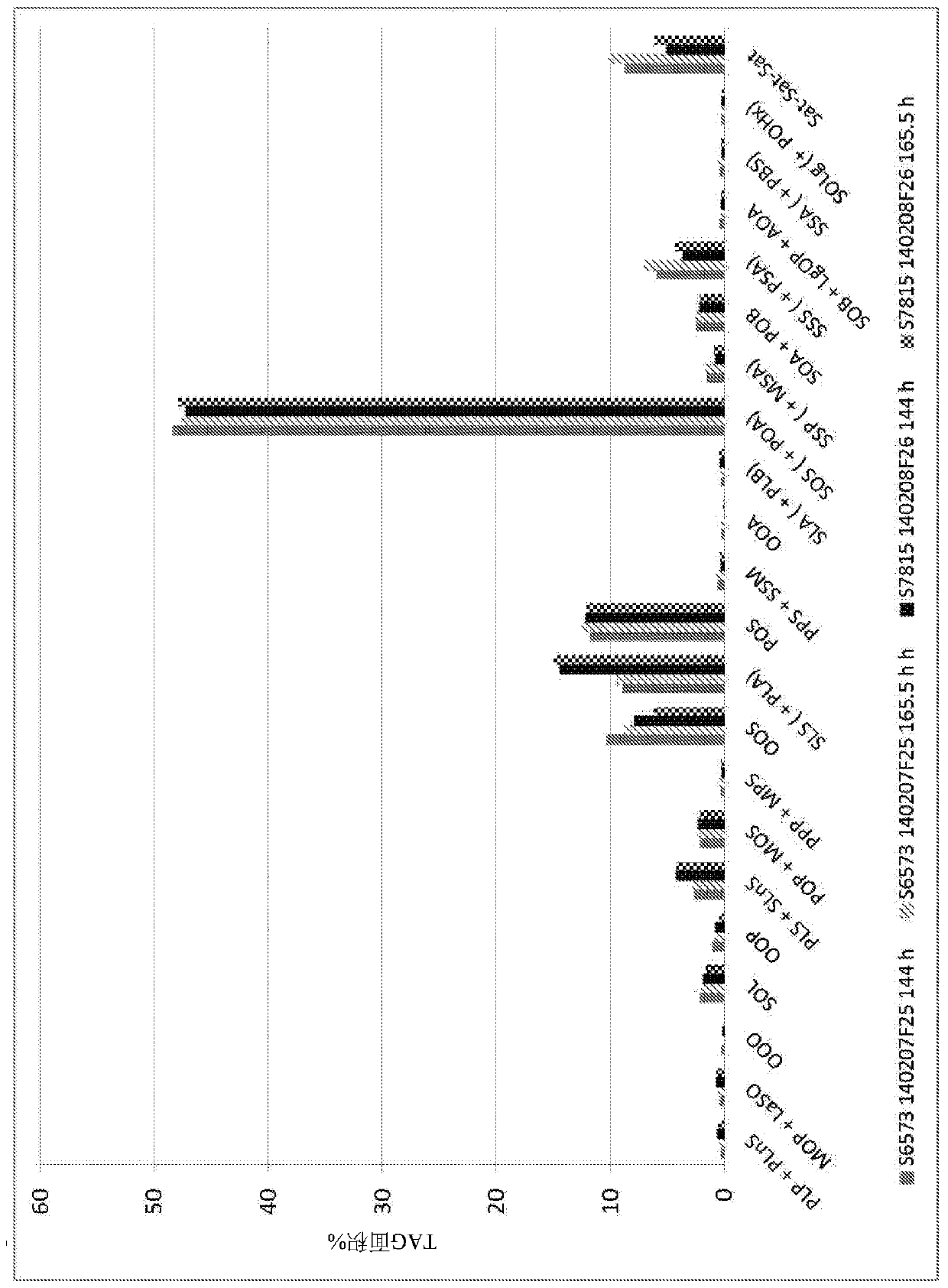
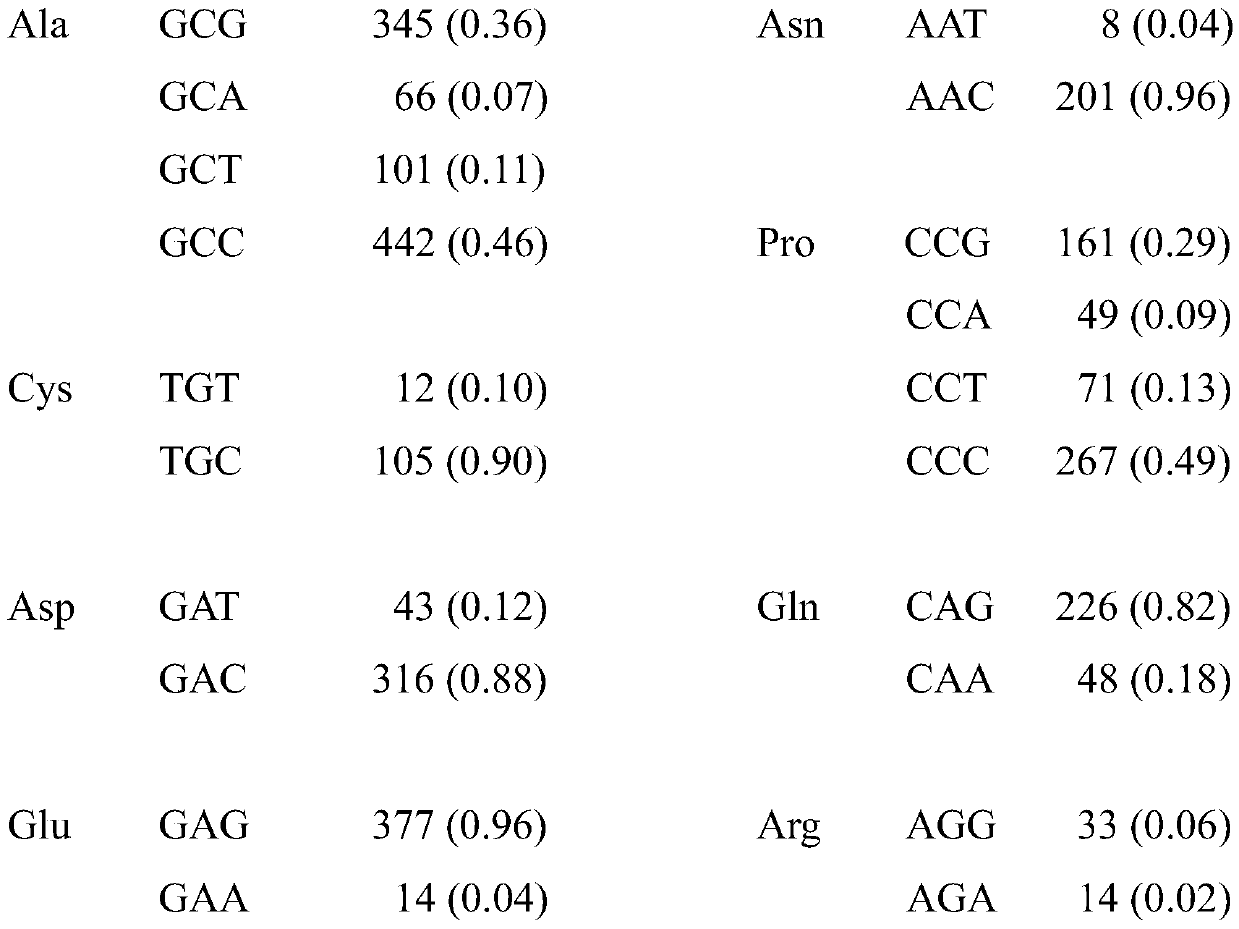
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Thioesterase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
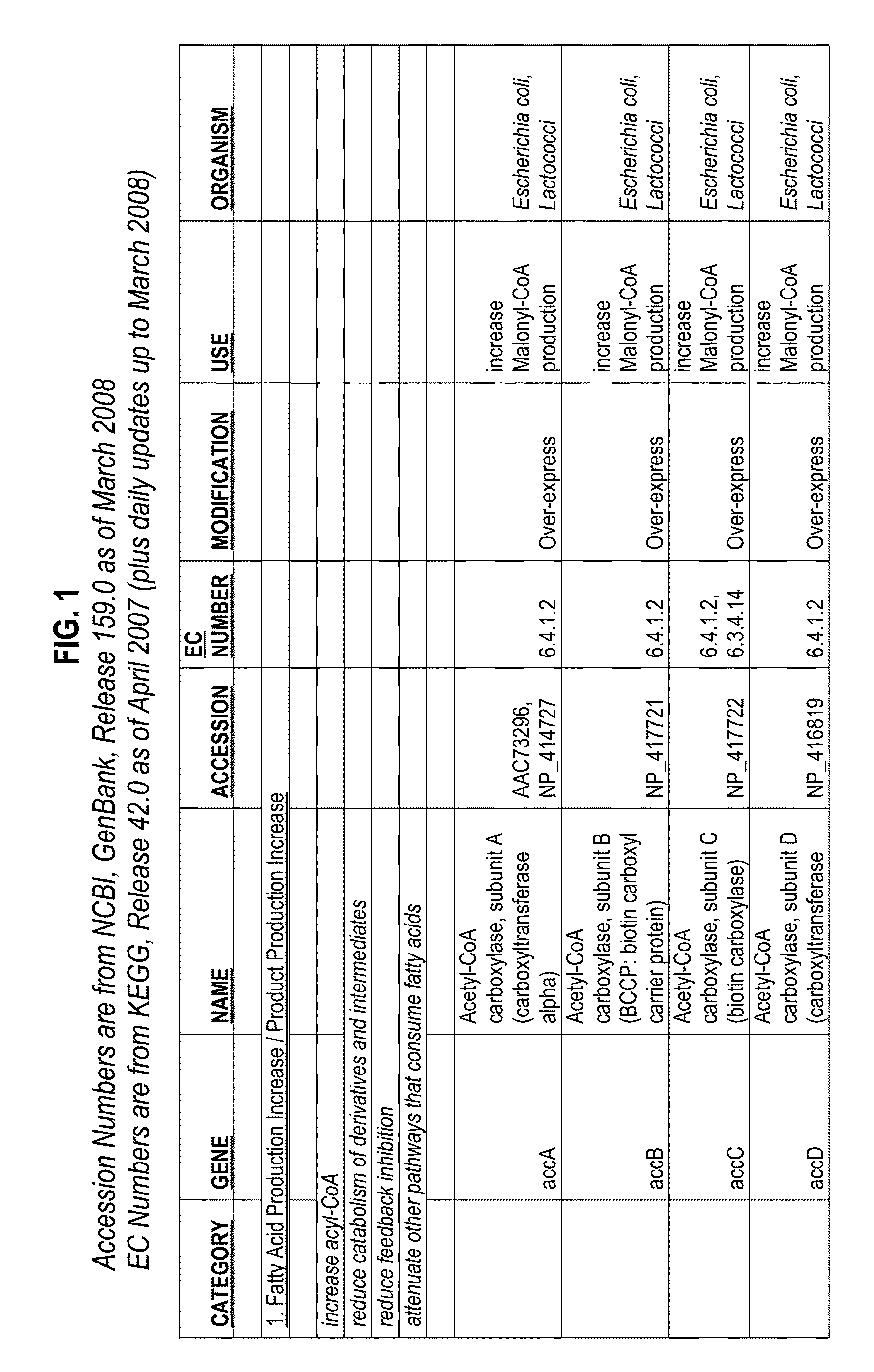
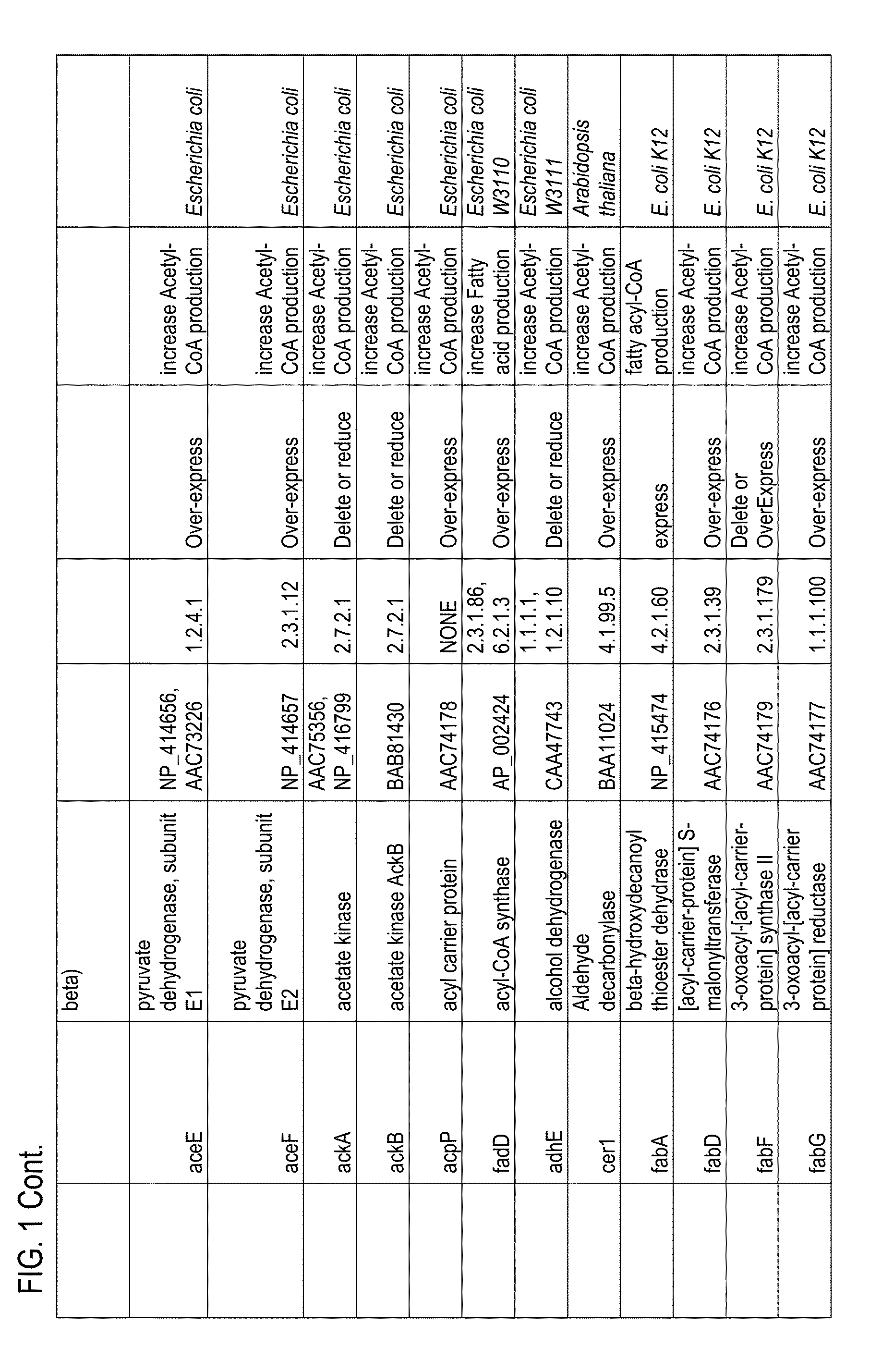
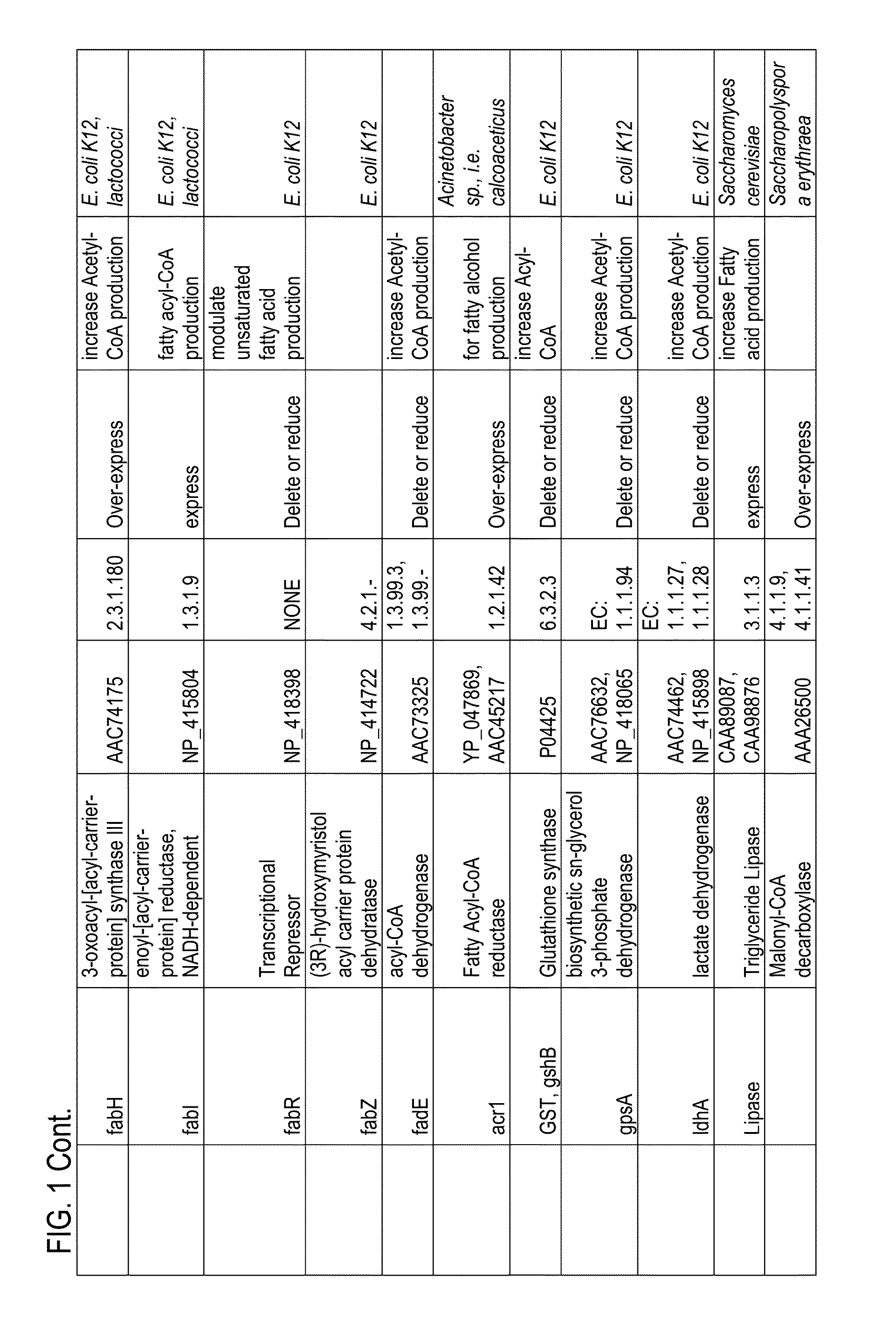
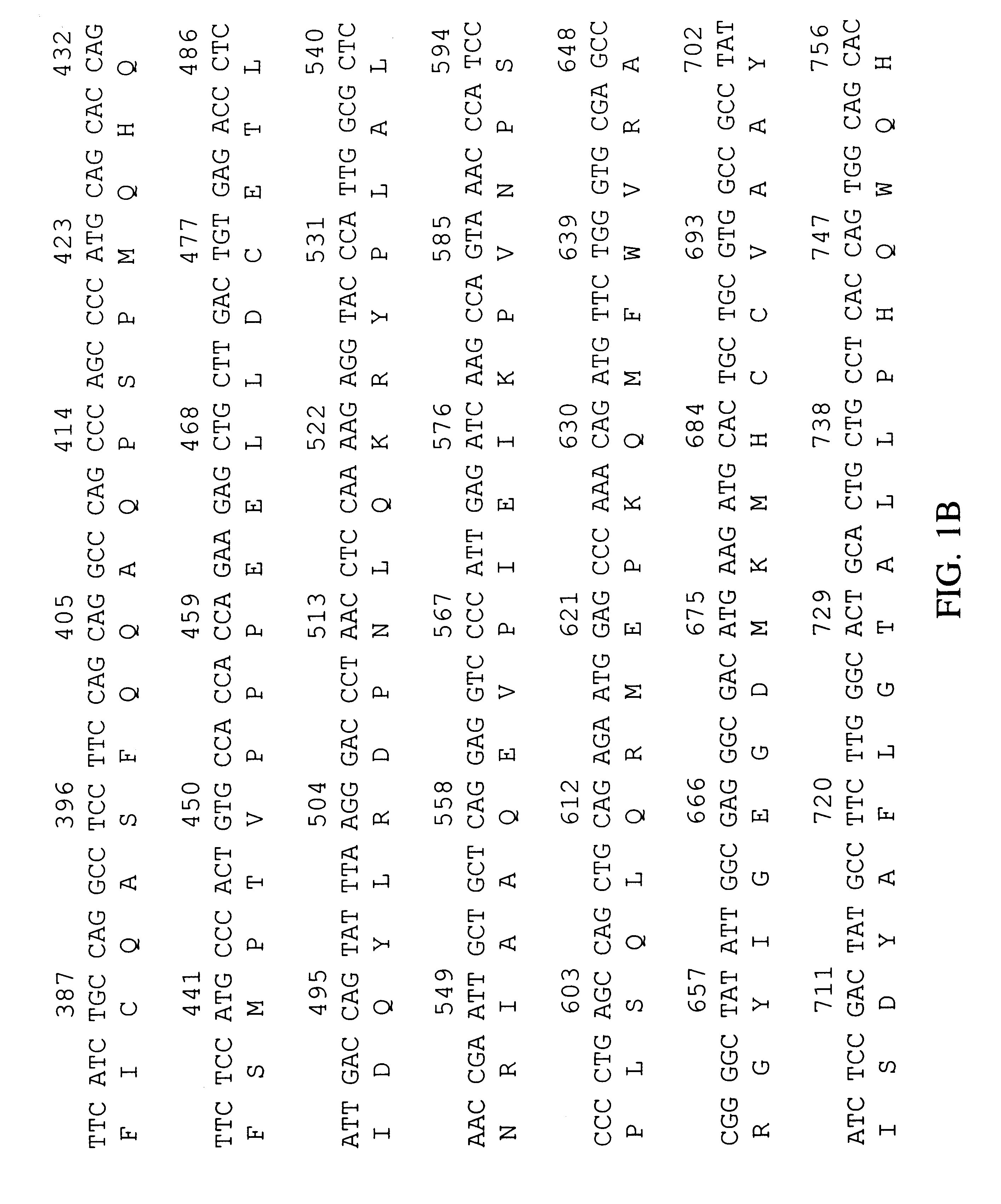
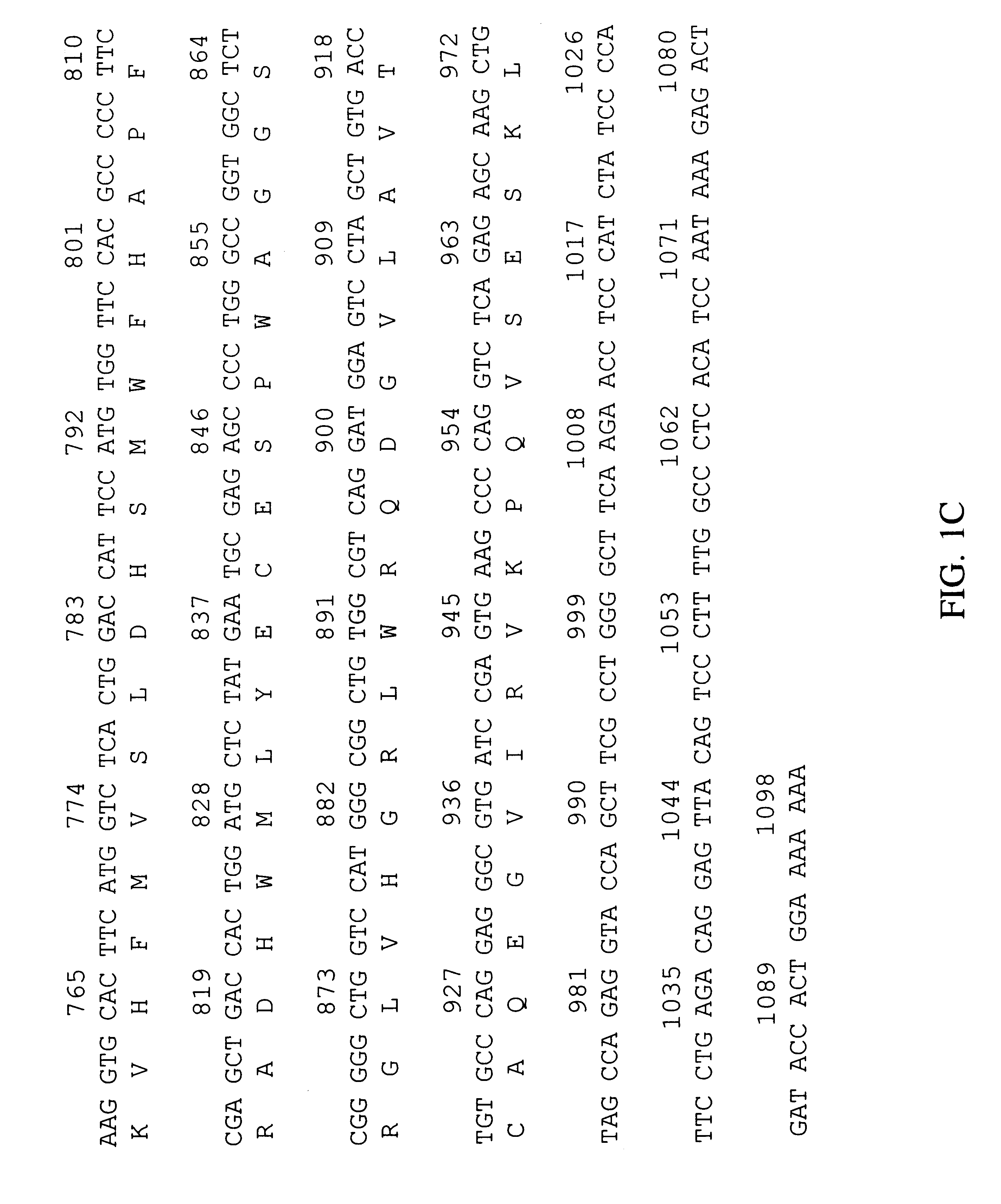
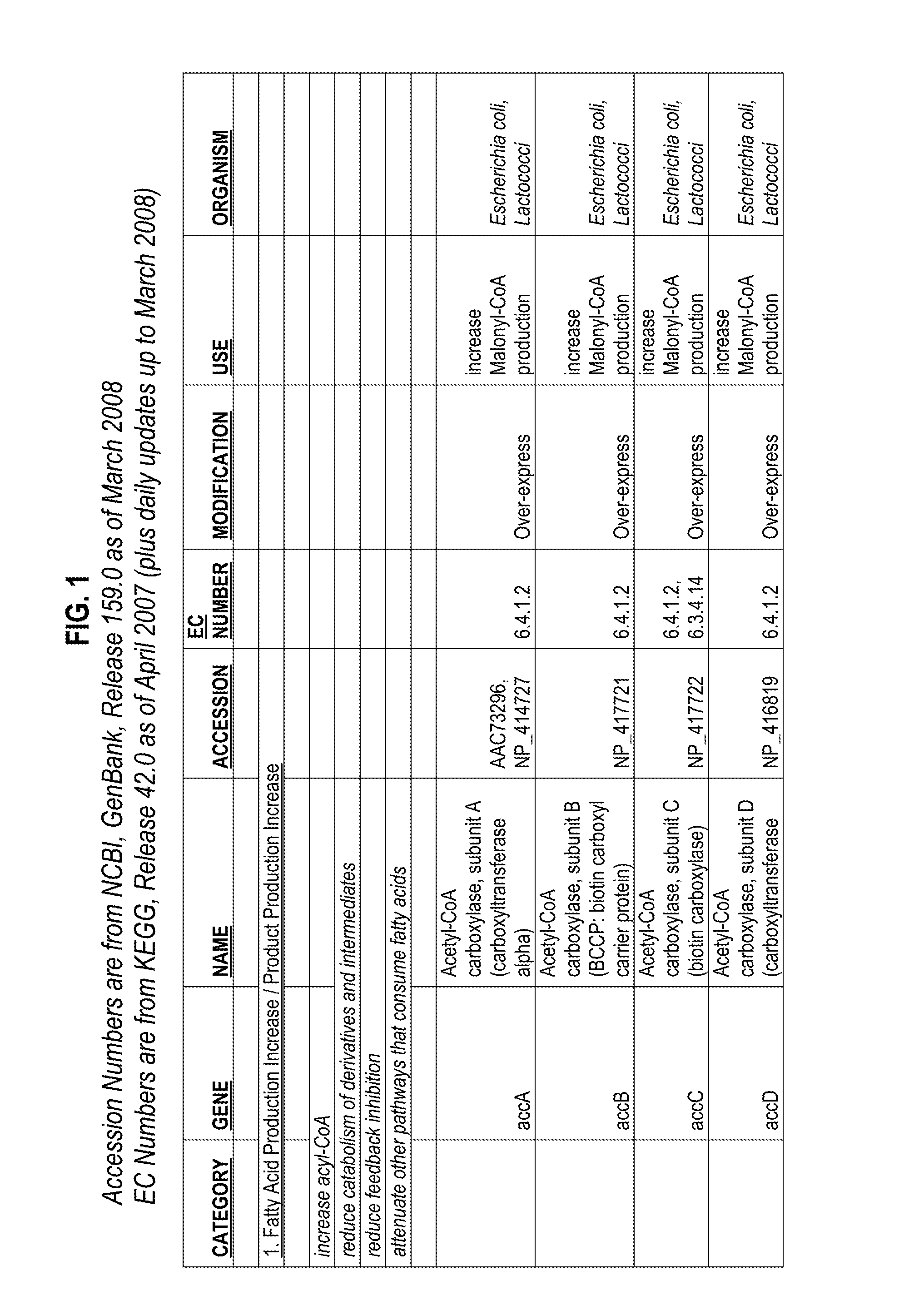
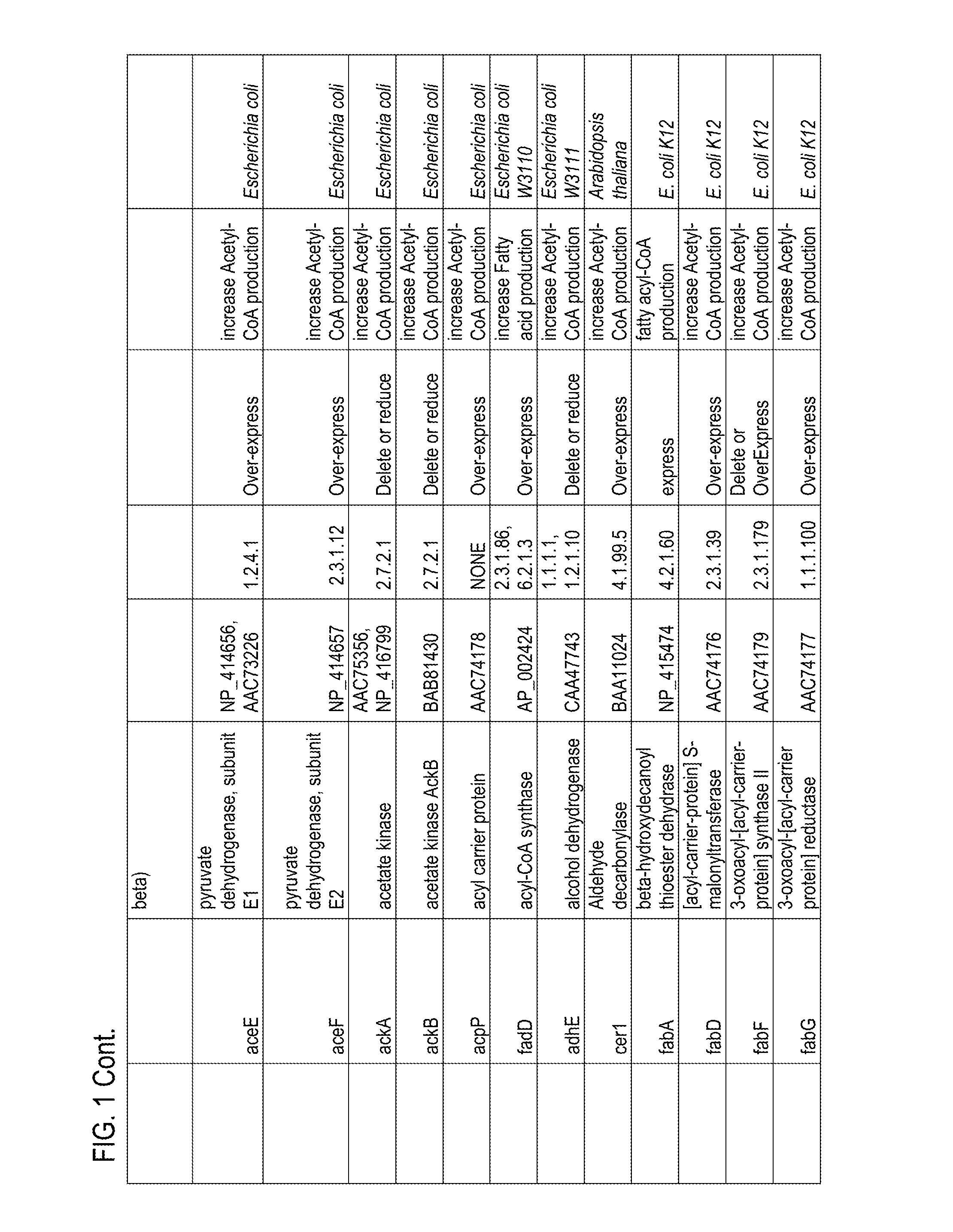
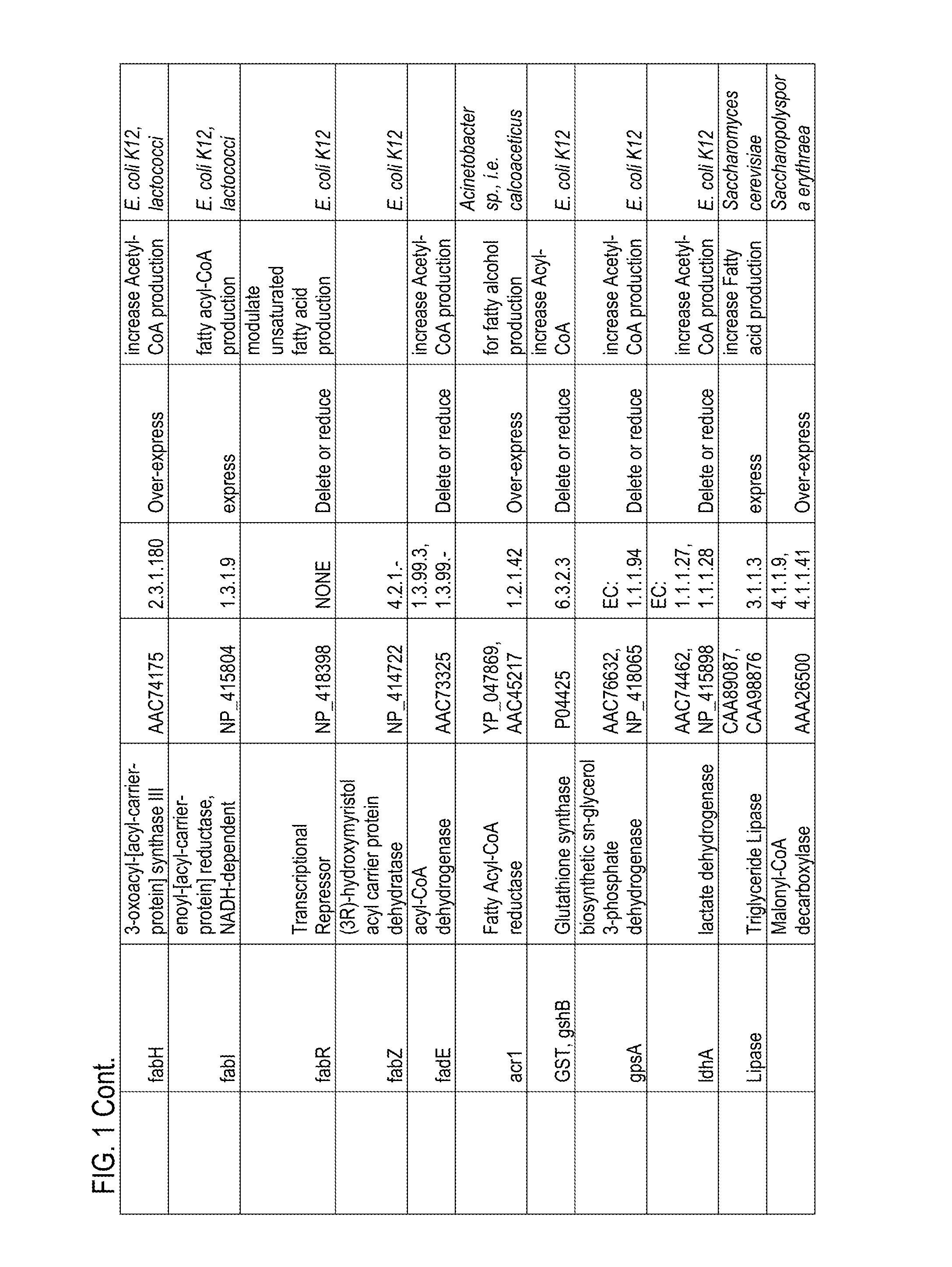
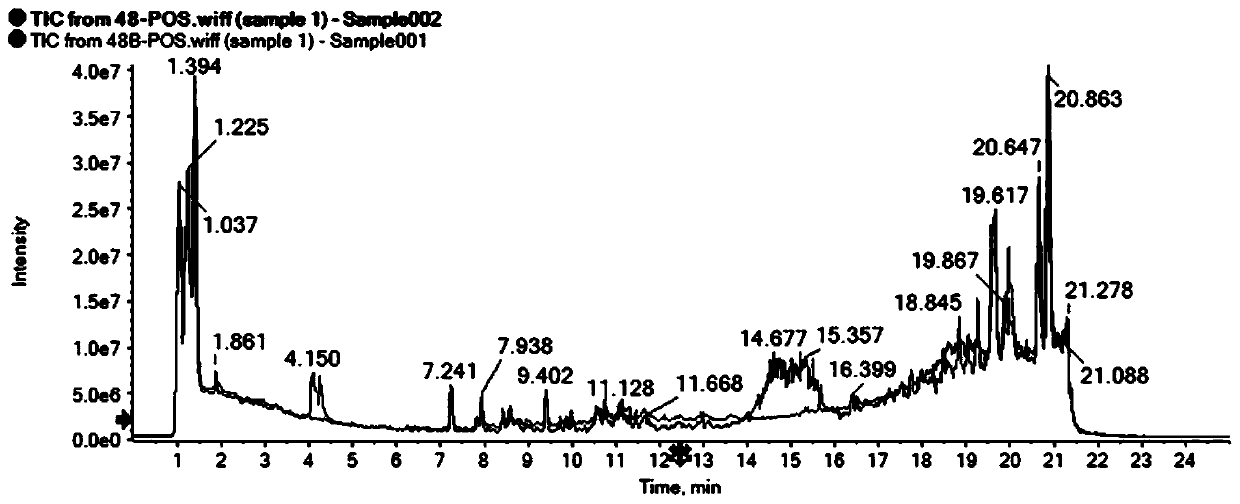
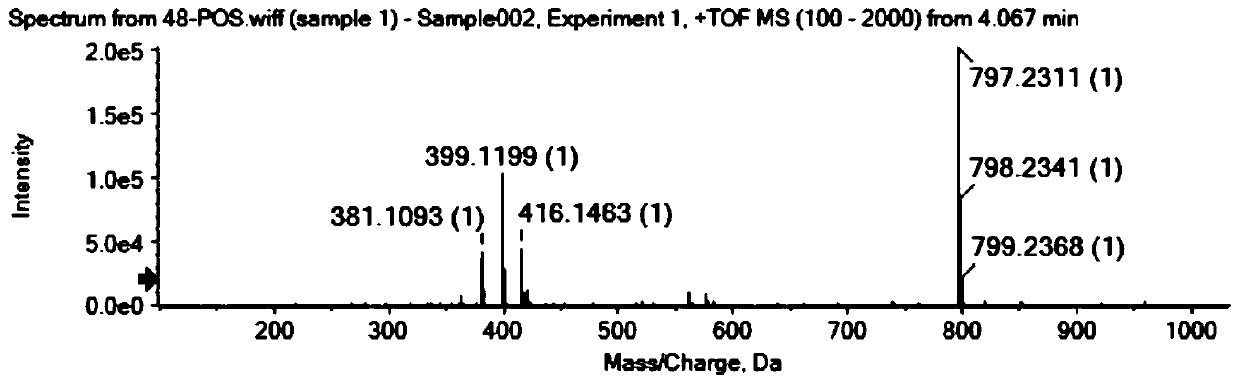
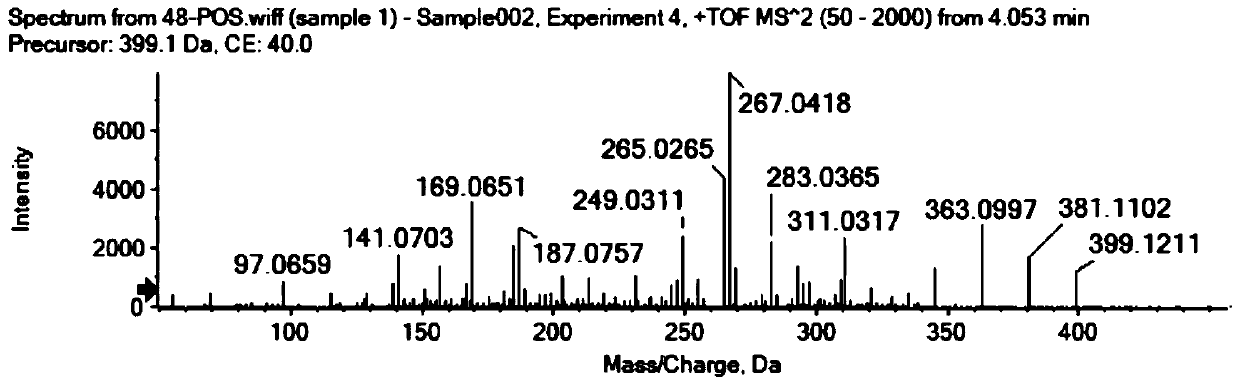
Thioesterases are enzymes which belong to the esterase family. Esterases, in turn, are one type of the several hydrolases known. Thioesterases exhibit Esterase activity (splitting of an ester into acid and alcohol, in the presence of water) specifically at a thiol group.
Methods and compositions related to thioesterase enzymes
ActiveUS20100154293A1Improved fuel characteristicGood suitSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleotidePolynucleotide
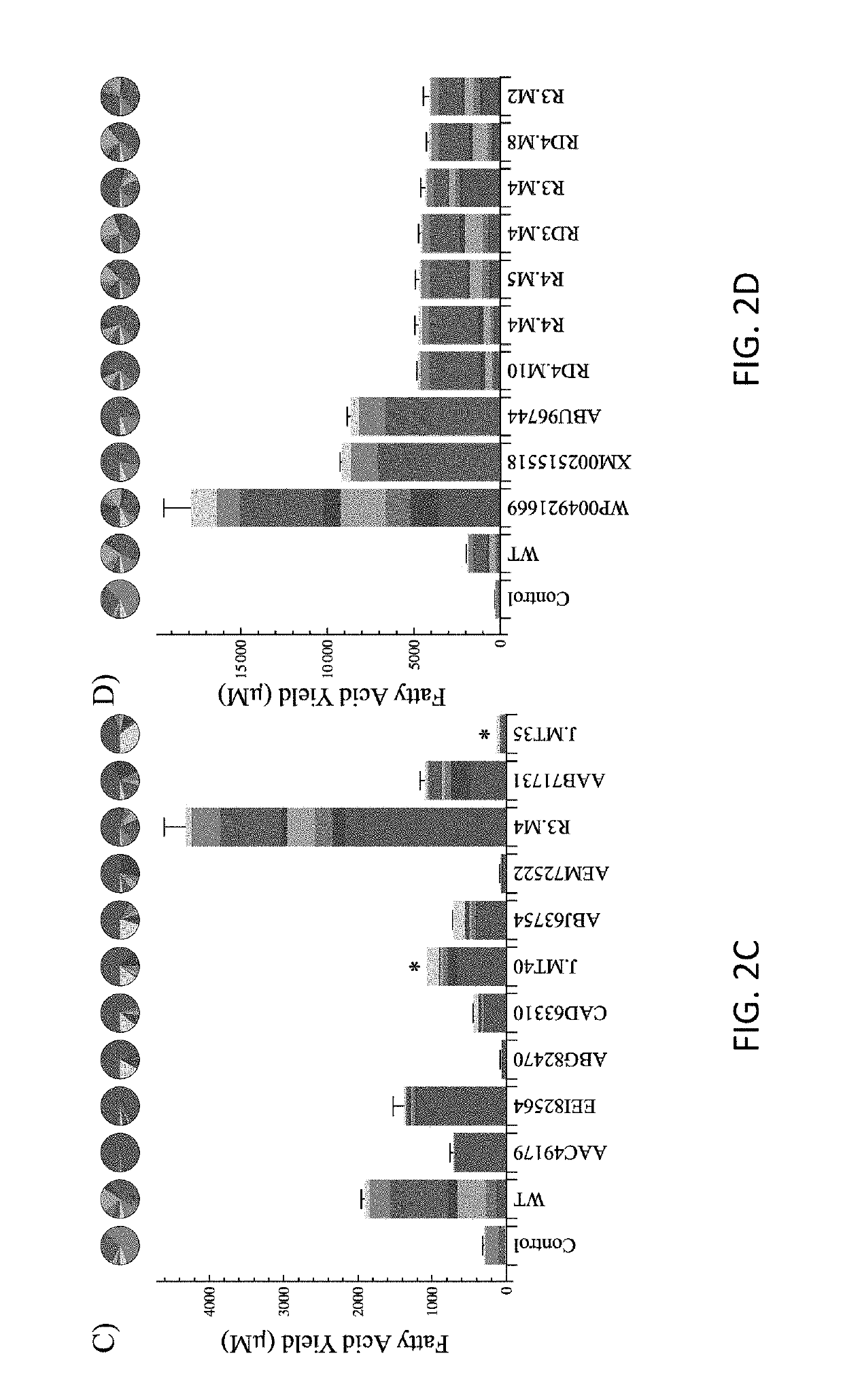
The present invention relates to novel mutant thioesterase enzymes and naturally-occurring equivalents thereof, compositions made from such enzymes and uses of thioesterase enzymes. In particular, the present invention provides mutant thioesterase enzymes that have altered properties, for example, altered substrate specificity, altered activity, altered selectivity, and / or altered proportional yields in the product mixtures. The present invention also provides polynucleotides encoding such mutant thioesterase enzymes, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further provides for novel uses of thioesterases in the production of various fatty acid derivatives, which are useful as, or as components of, industrial chemicals and fuels.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
Novel antagonists of the human fatty acid synthase thioesterase
InactiveUS20070203236A1Inhibit tumor cell growthBiocideOrganic chemistryMetaboliteCompound (substance)
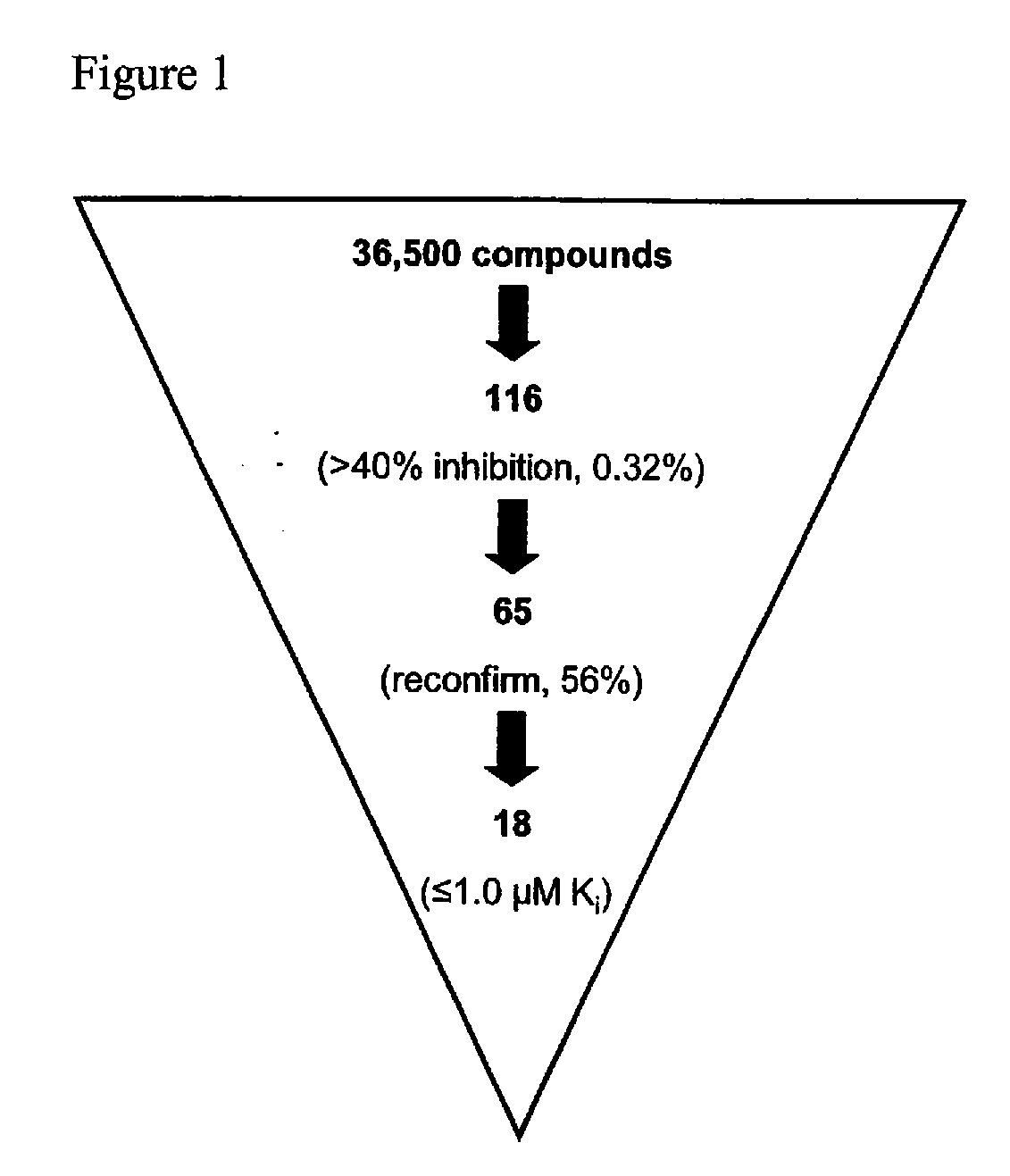
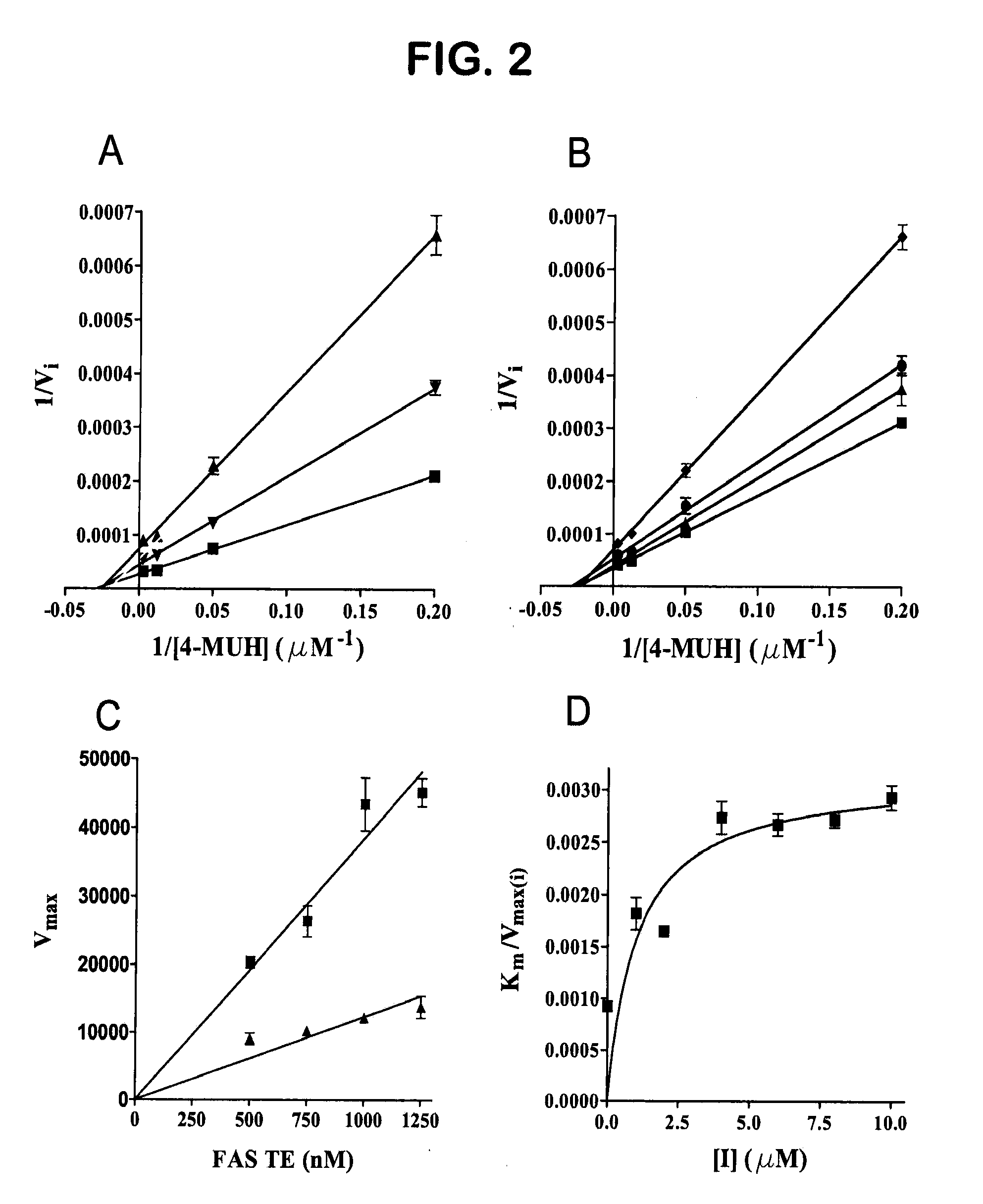
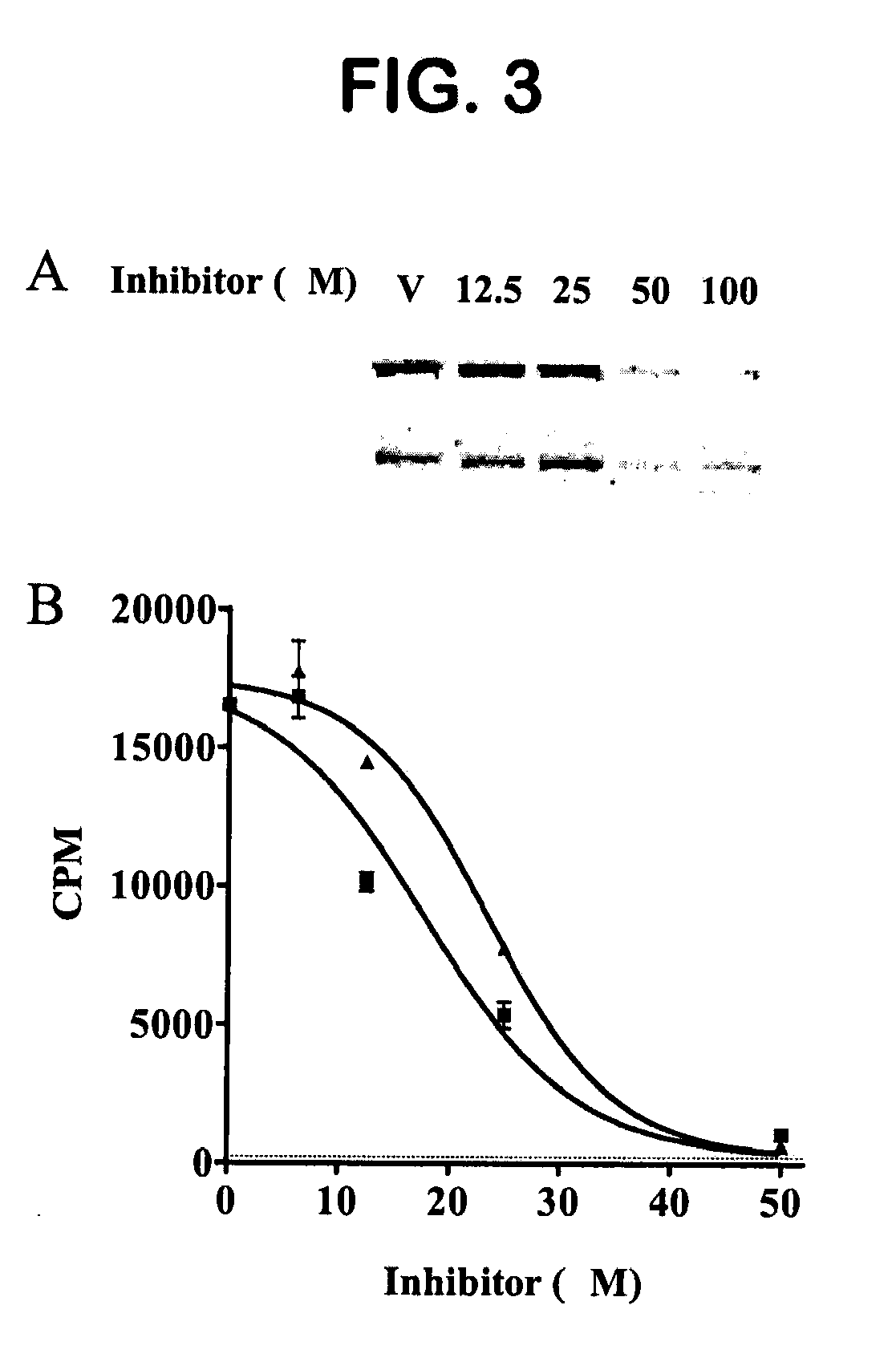
The present invention provides for compounds of formula (I)-(XIII), as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, metabolites thereof, pro-drugs thereof, and pharmaceutical kits that include such compounds. The present invention also provides for the compounds of formula (I)-(XIII) for use in medical therapy or diagnosis. The present invention also provides for the use of the compounds of formula (I)-(XIII) in treating cancer in mammals (e.g., humans), as well inhibiting tumor cell growth in such mammals. The present invention also provides for methods of inhibiting FAS. The methods include contacting FAS with an effective amount of a compound of formula (I)-(XIII). The present invention also provides for methods of inhibiting the TE domain of the FAS. The methods include contacting the thioesterase TE domain of the FAS with an effective amount of a compound of formula (I)-(XIII). The present invention also provides for methods of treating cancer in mammals, as well as methods of inhibiting tumor cell growth in such mammals. The methods include administering a compound of formula (I)-(XIII) to a mammal in need of such treatment.
Owner:BURNHAM INST THE
Thioesterase-related nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified fatty acid composition
InactiveUS20050262588A1HydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesFatty acid biosynthesisNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid constructs, and other agents associated with fatty acid synthesis, particularly the ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. Moreover, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered ratios of saturated and unsaturated fats. In particular, the present invention is directed to plants incorporating such agents where the plants exhibit altered levels of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
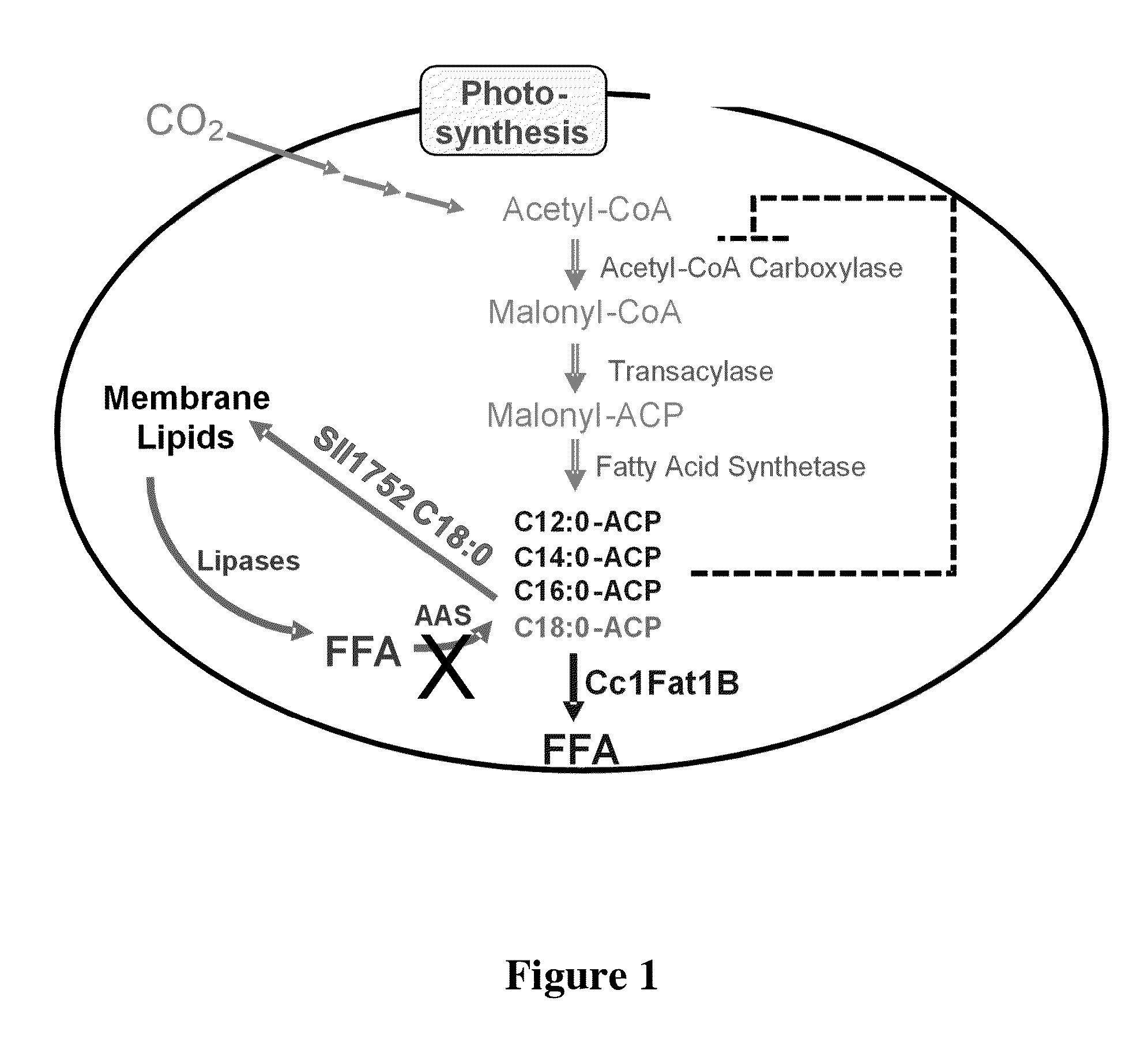
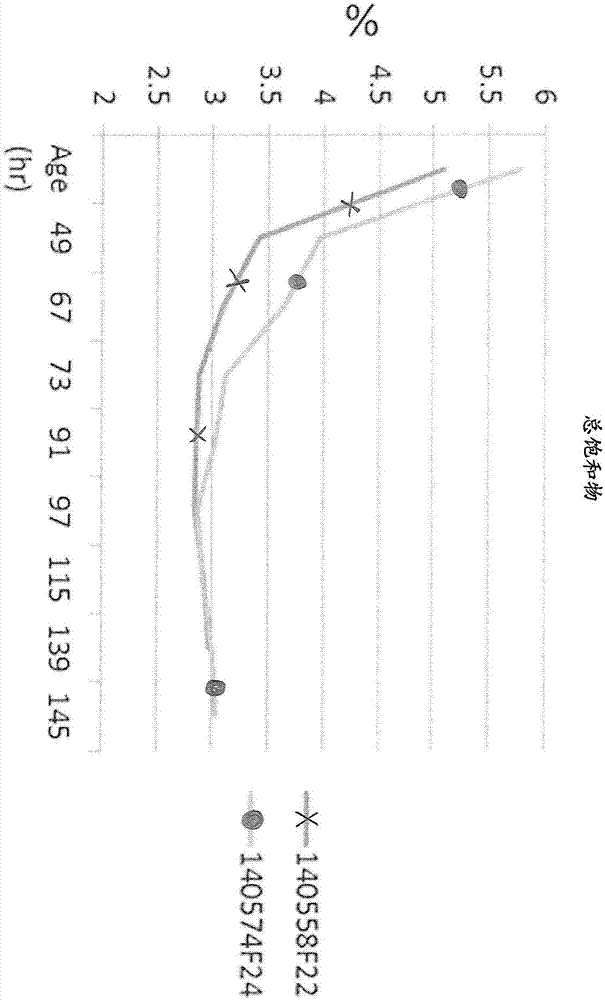
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Novel antagonists of the human fatty acid synthase thioesterase
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Method for the poduction of cyclic molecules
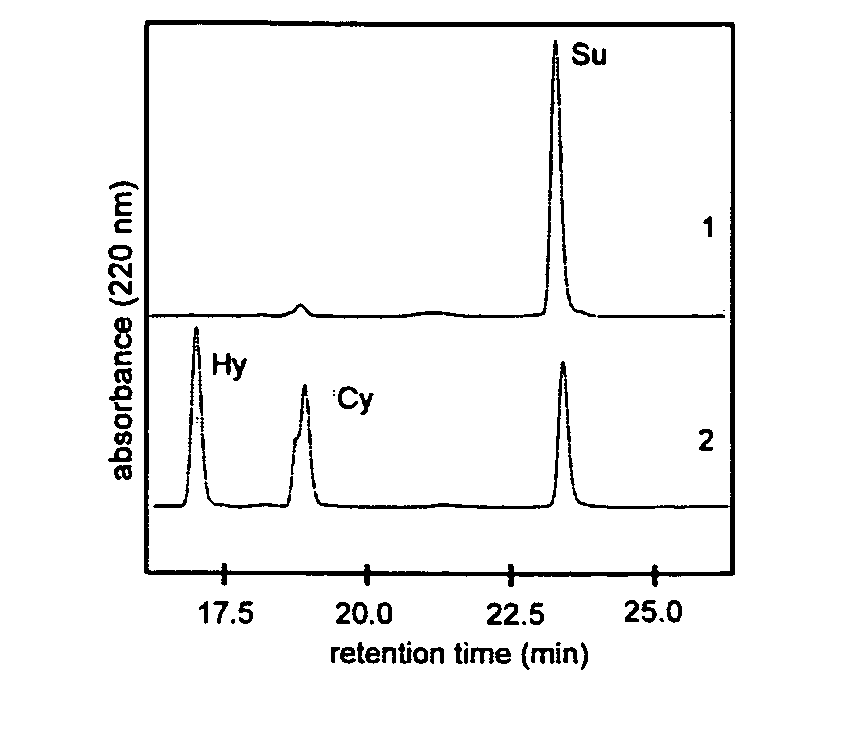
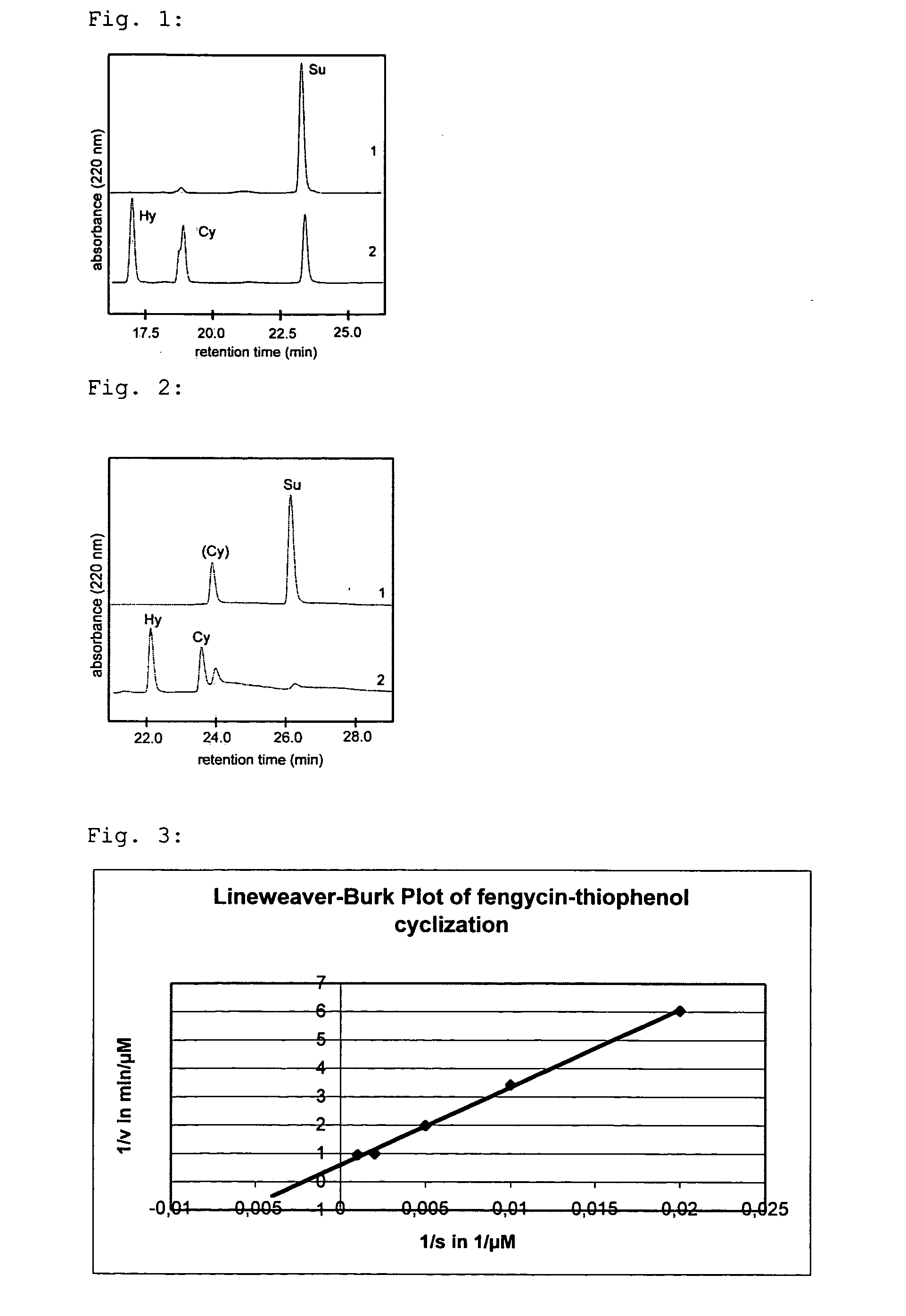
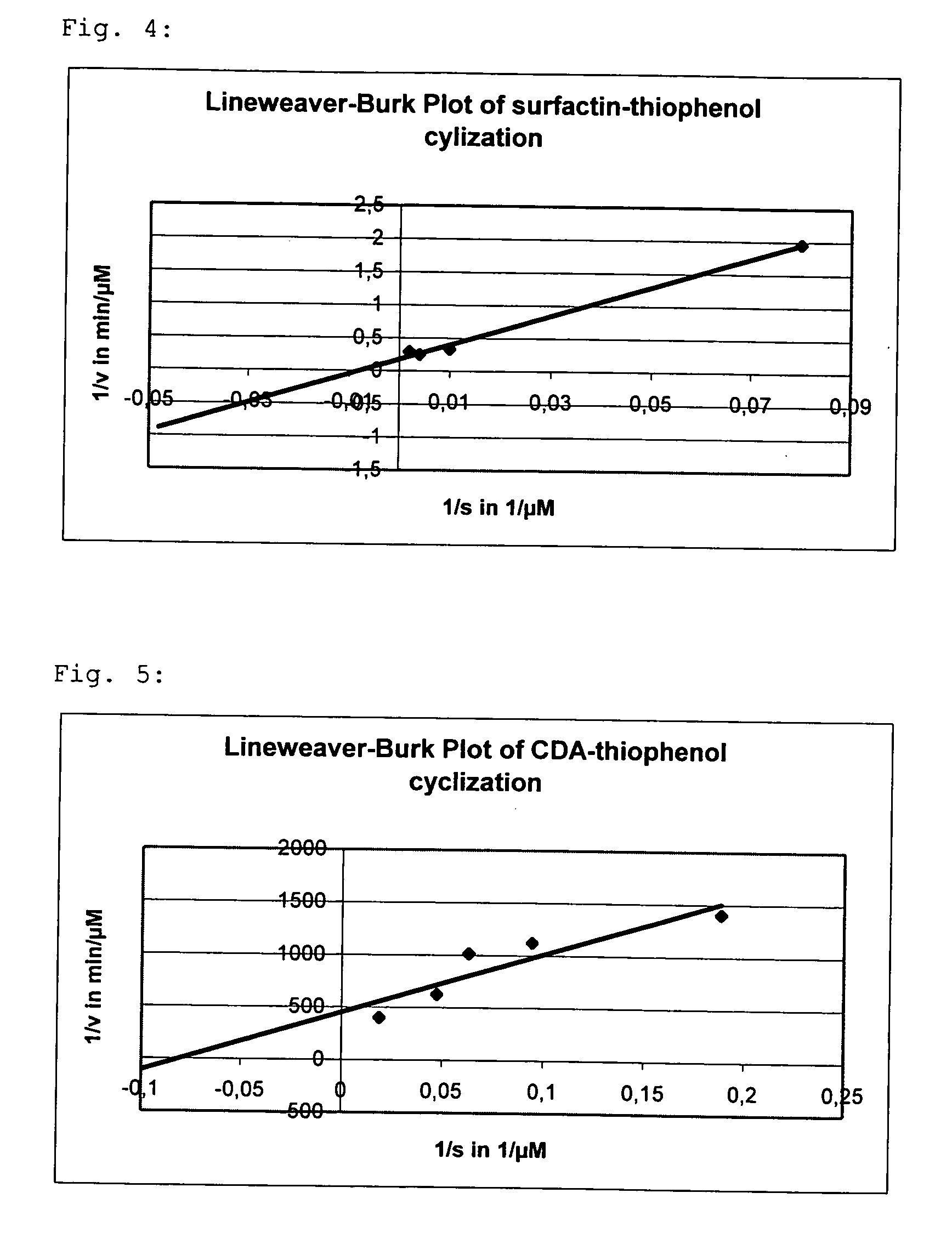
InactiveUS20070184516A1High yieldImprove reaction speedPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclaseThioester synthesis
The invention at hand describes a method for the cyclization of peptides and proteins in which linear thioesters serve as substrates. The cyclization is catalyzed by thioesterase domains of NRPS or PKS cyclases. The substrates according to the present invention are composed of one linear peptide on which a charge-stabilized aromatic, heteroaromatic or araliphatic leaving group is bound. These substrates lead to higher yields and reaction rates than linear peptides able to be cyclized with methods known so far and, furthermore, allow the cyclization of such peptides which were previously not able to be cyclized.
Owner:ZYRUS BET GMBH & CO PATENTE I KG
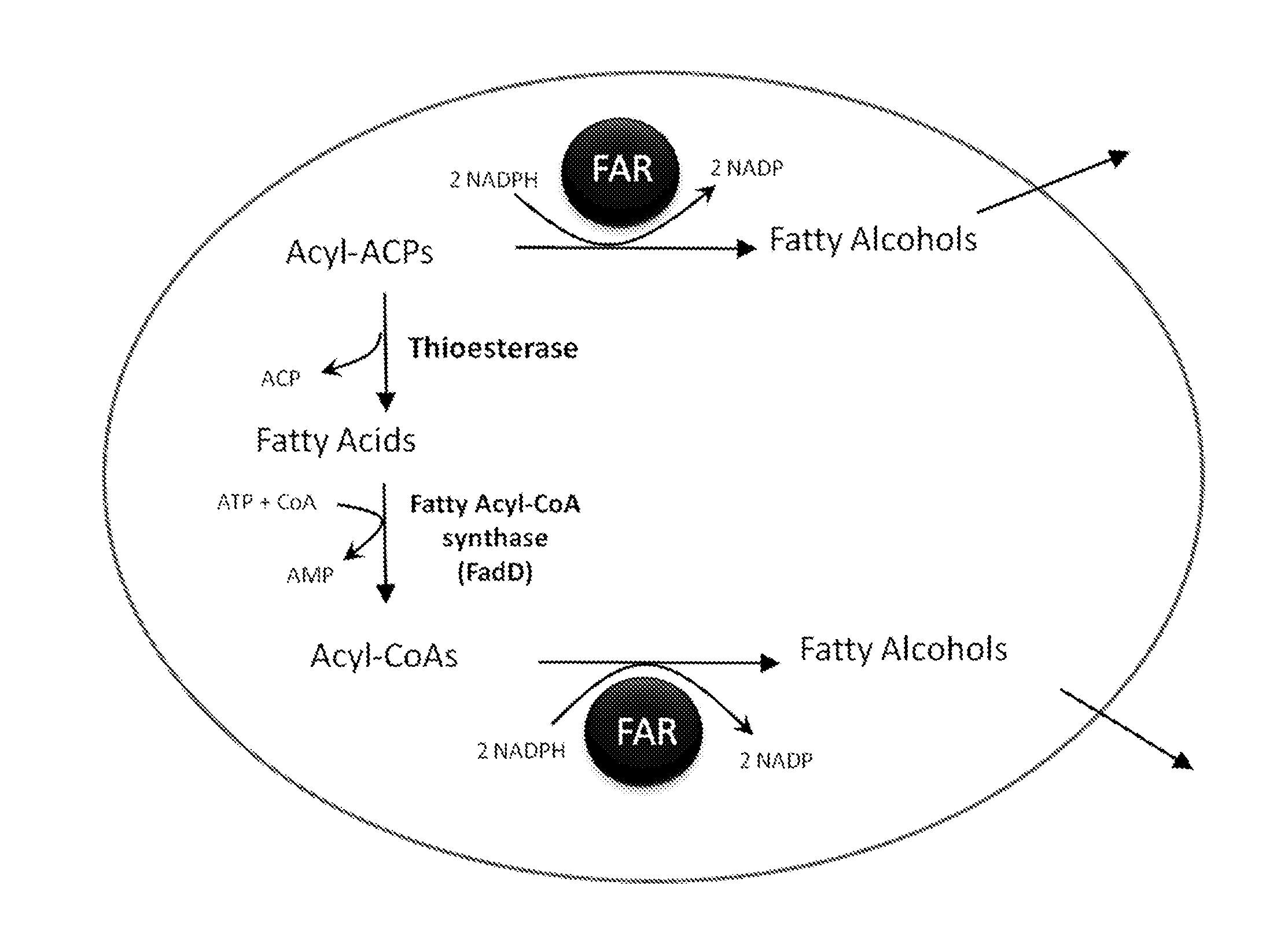
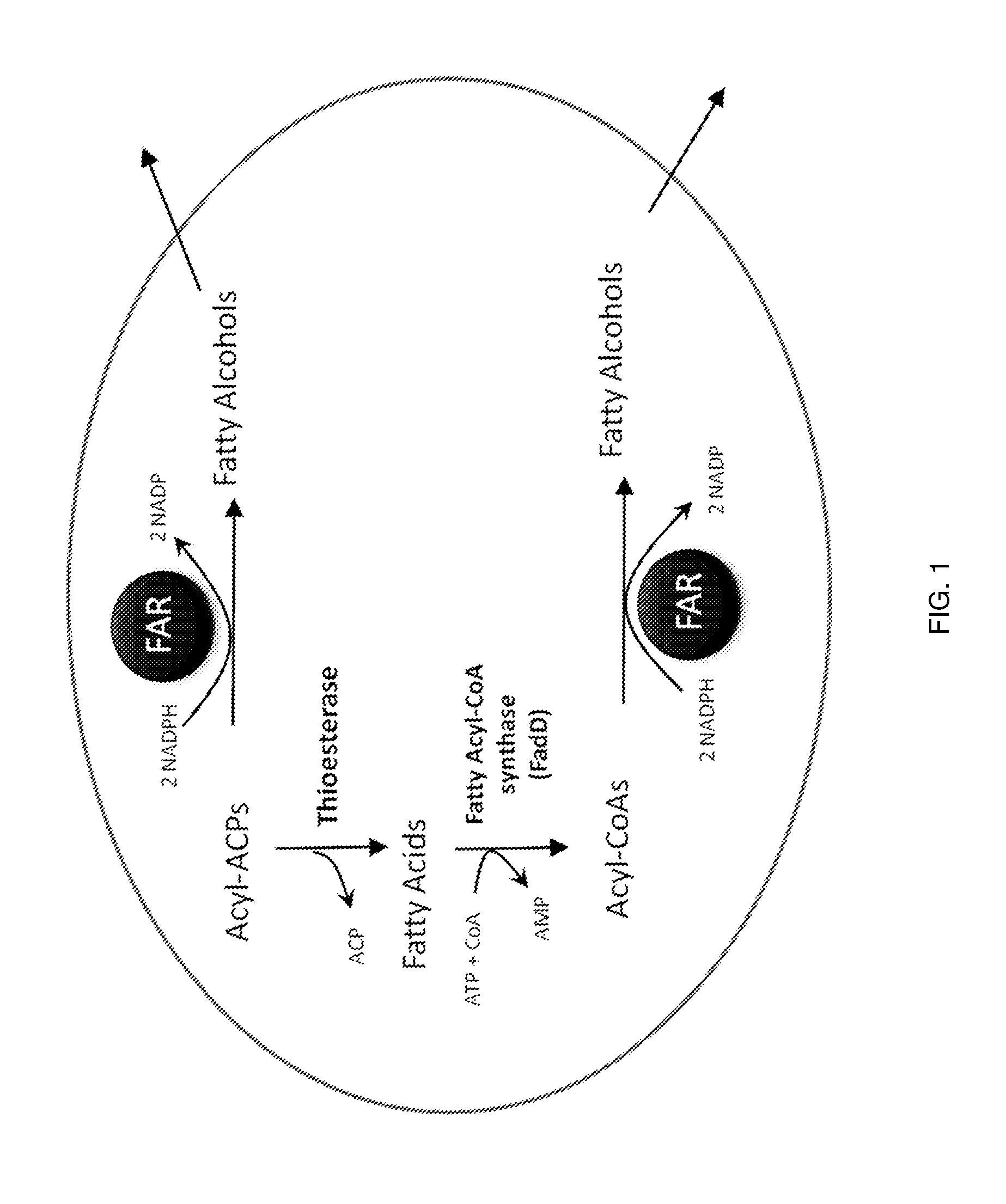
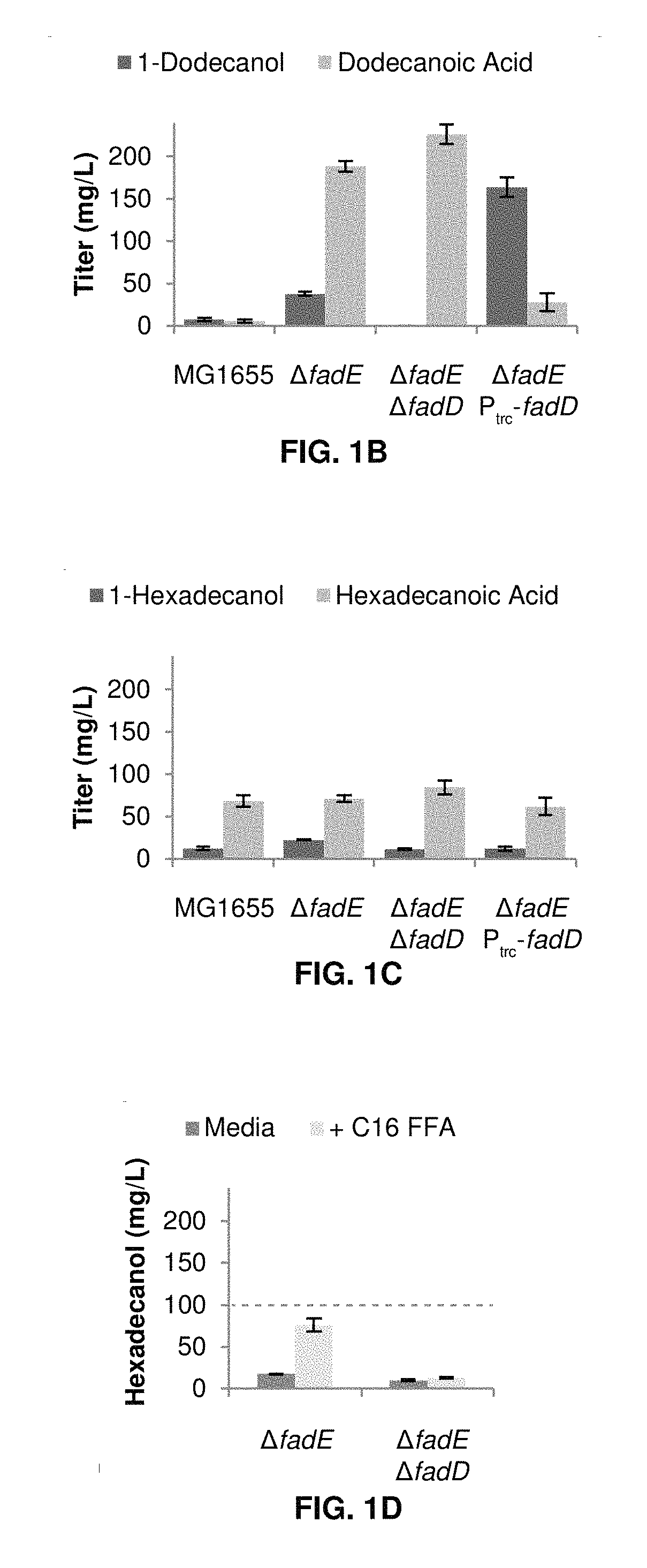
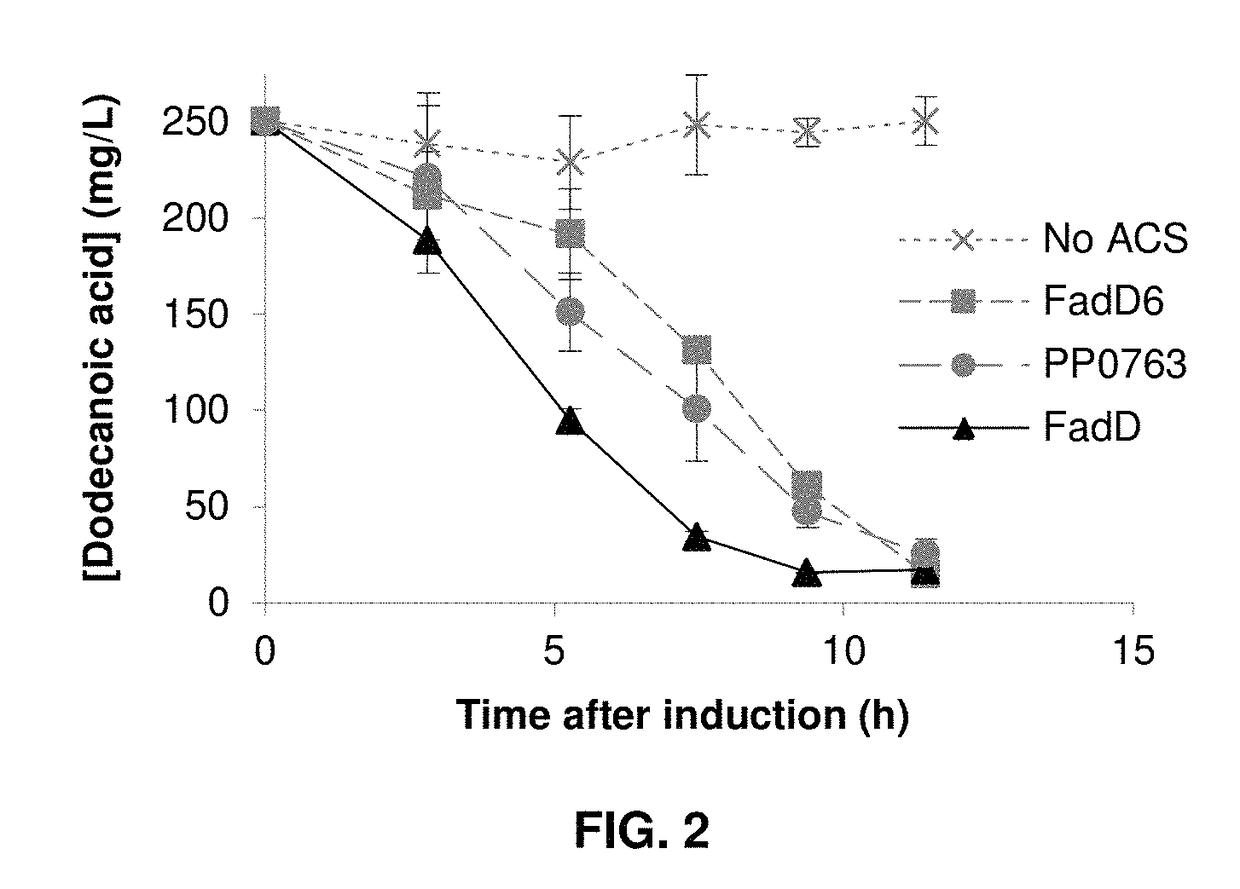
Production of fatty alcohols from engineered microorganisms
The invention generally relates to the production of a fatty alcohol composition from recombinant microbial cells. The fatty alcohols are produced by expressing a gene encoding a heterologous fatty alcohol forming acyl-CoA reductase (“FAR”); a gene encoding a heterologous thioesterase (“TE”) gene and a gene encoding an acyl-CoA synthetase (“ACS”).
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Production method for C8:0/C10:0/C12:0/C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof
InactiveCN102586350AImprove low temperature performanceSimple extraction processMicroorganism based processesFermentationCupheaThiogalactosides
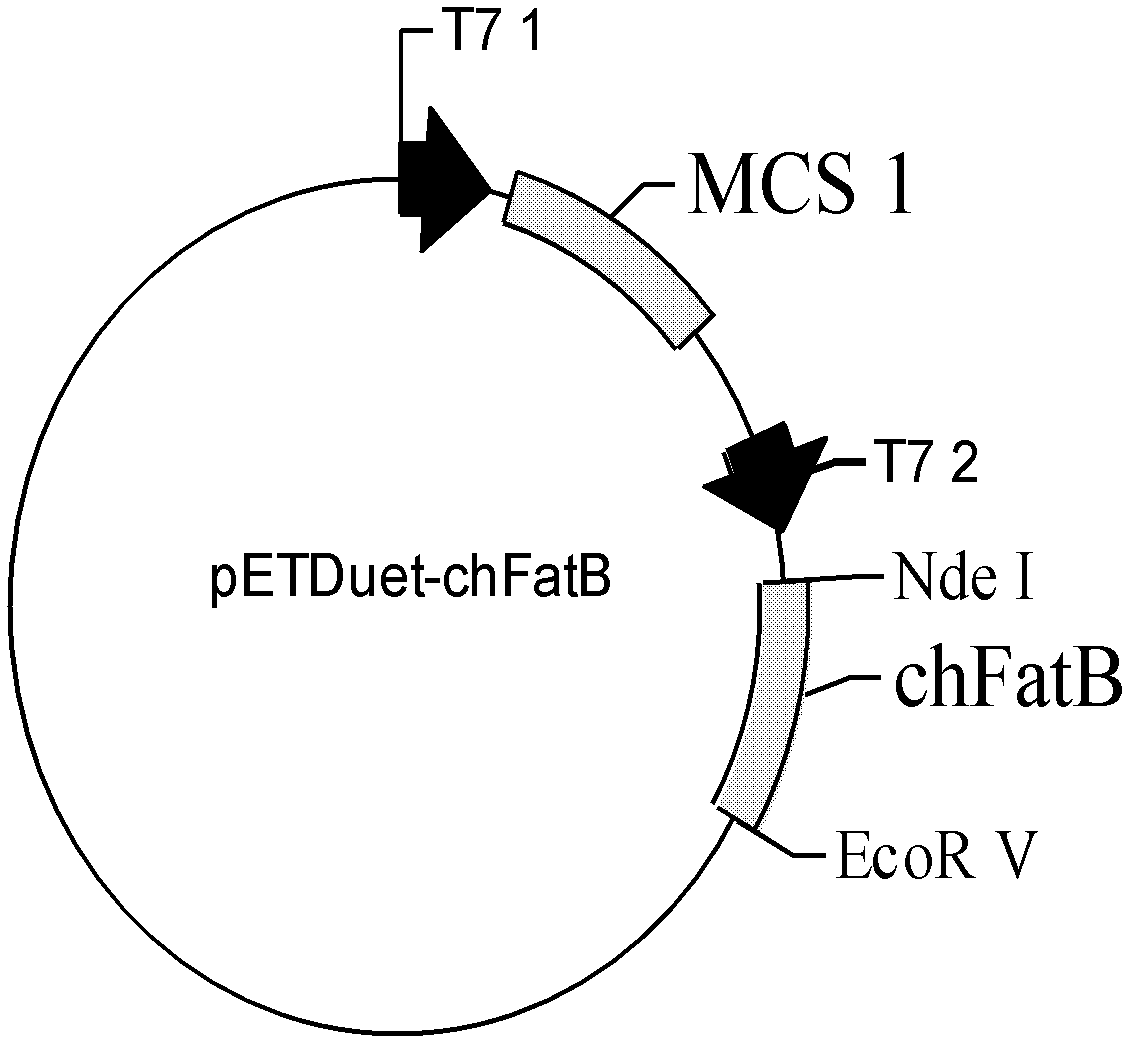
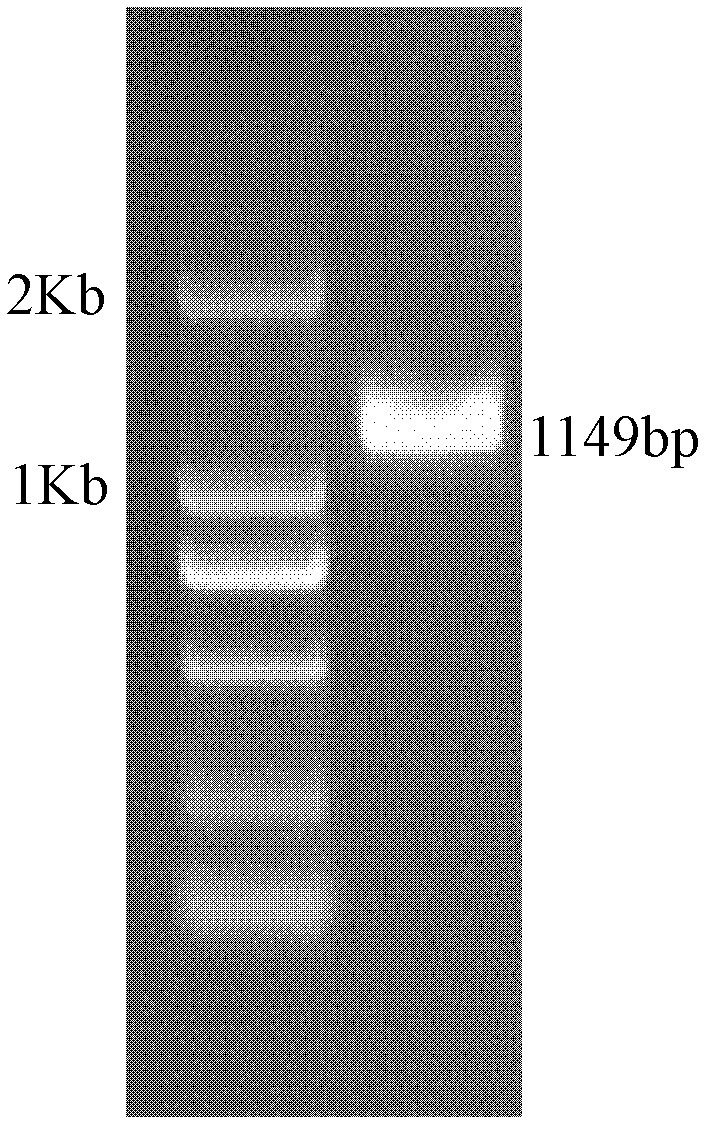
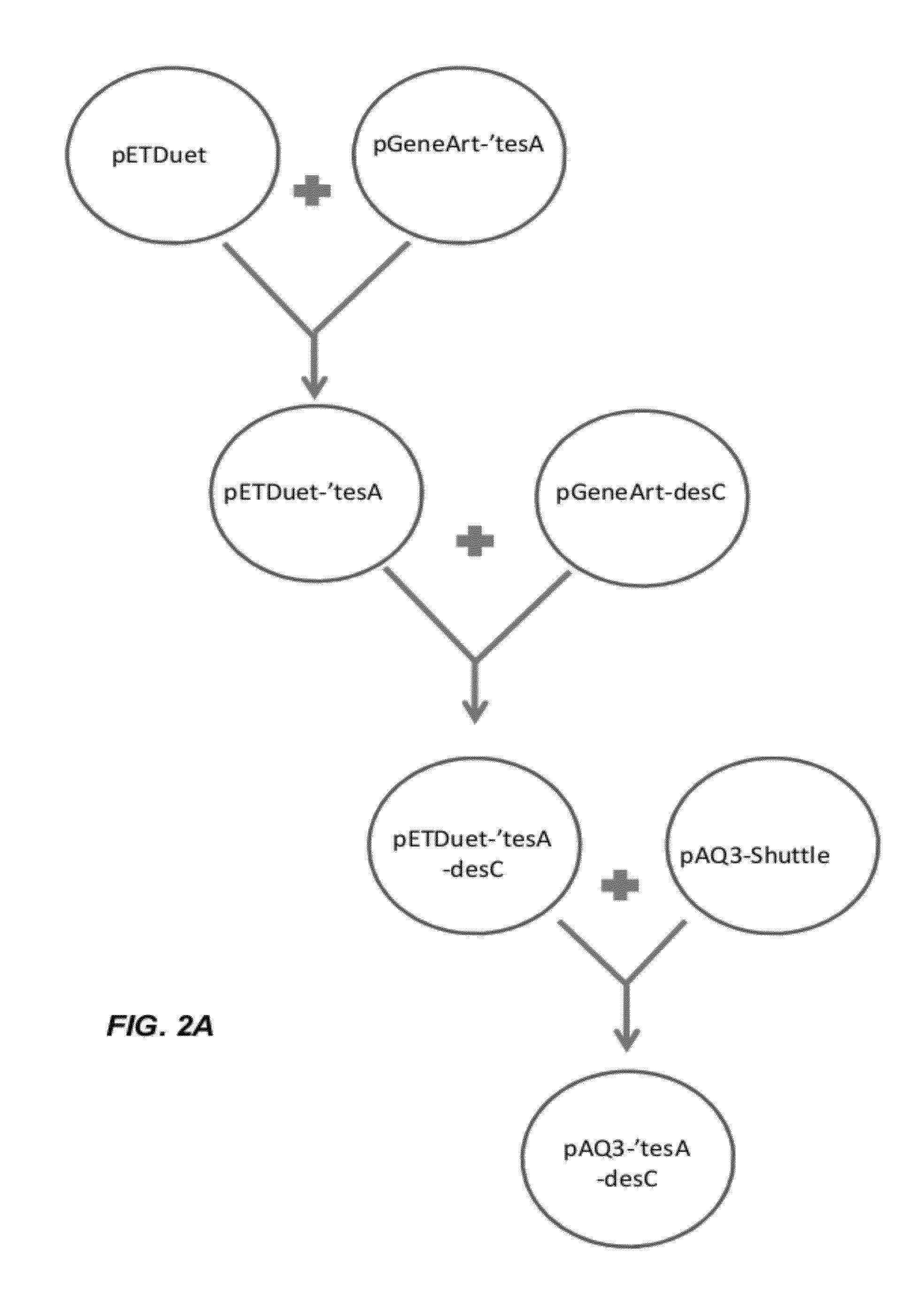
The invention relates to a production method for synthesizing C8:0 / C10:0 / C12:0 / C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof by using engineering Escherichia coli. The production method comprises the following steps of: cloning thioesterase genes with different specificities chFatB / ucFatB / ccFatB in cuphea / laurel / camphorwood into an expression vector pETDuet-1 to obtain a corresponding recombinant plasmid; transferring the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21, performing isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPDT) induction expression, and specifically hydrolyzing acyl carrier protein (ACP) with specific chain length by using the expressed thioesterase to obtain medium-chain fatty acid; cloning acyltransferase gene (atfA) in acinetobacter into expression vectors pETDuet-chFatB / pETDuet-ucFatB / pETDuet-ccFatB to obtain corresponding recombinant plasmids; and transferring the recombinant plasmids into the Escherichia coli BL21, performing IPTG induction expression, performing acyl transfer reaction on exogenously fed ethanol and acyl-CoA formed by the medium-chain fatty acid intracellularly by using the co-expressed acyltransferase to obtain fatty acid ethyl ester.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Microorganisms and methods for producing unsaturated fatty acids
ActiveUS20120116108A1Increase productionIncrease secretionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyAcyl group
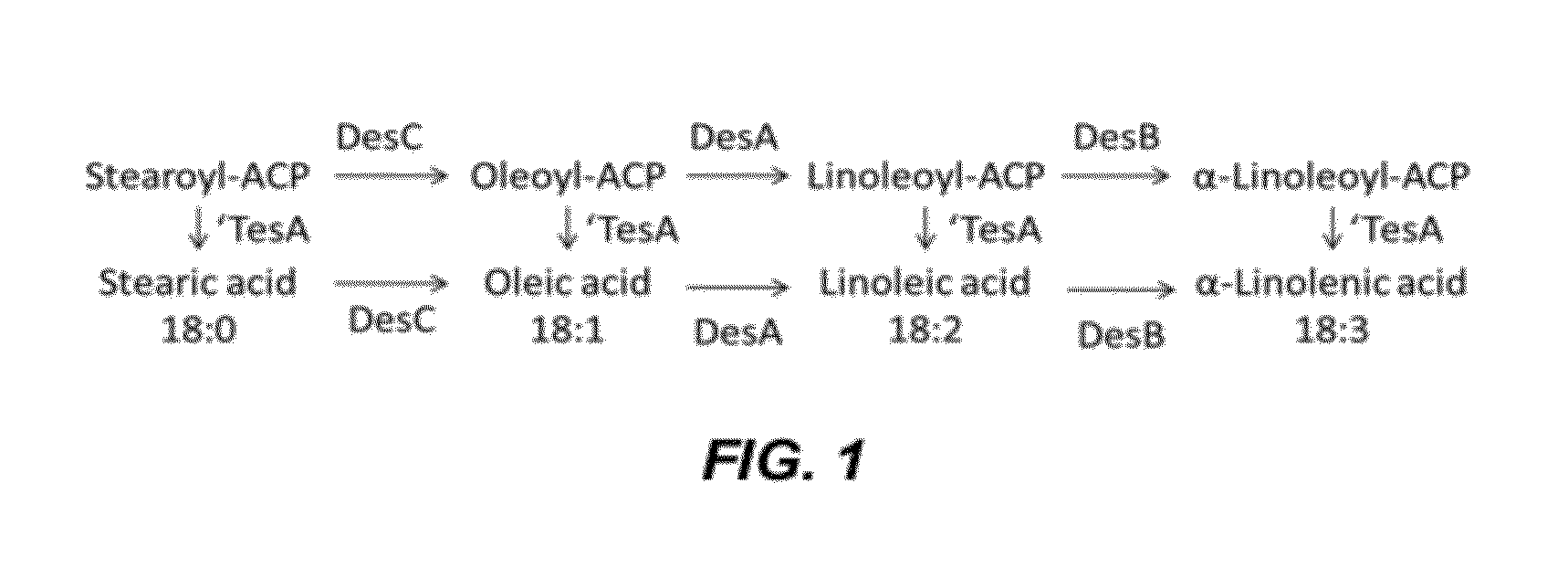
Methods of producing an unsaturated free fatty acid comprising at least 18 carbon atoms are provided. In some embodiments, the methods comprise culturing an engineered microorganism in a culture medium, wherein the engineered microorganism comprises at least one recombinant enzyme selected from acyl-lipid desaturase delta-9 (EC:1.14.19.1), acyl-lipid desaturase delta-12 (EC:1.14.19.6), acyl-lipid desaturase delta-15 (EC:1.14.19.-), and thioesterase (EC:3.1.2.14). Engineered microorganisms comprising at least one of those recombinant enzymes are also provided. The methods and organisms can be used to produce at least one free fatty acid selected from oleic acid, linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid.
Owner:AXCELLA HEALTH INC
BFIT compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20030220238A1Ameliorate any conditionIncrease cell efficiencySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBROWN FAT-INDUCIBLE THIOESTERASENucleotide
Isolated polynucleotides encoding brown fat inducible thioesterase (BFIT) polypeptides and the polypeptides are provided. Methods of using these polynucleotides and polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
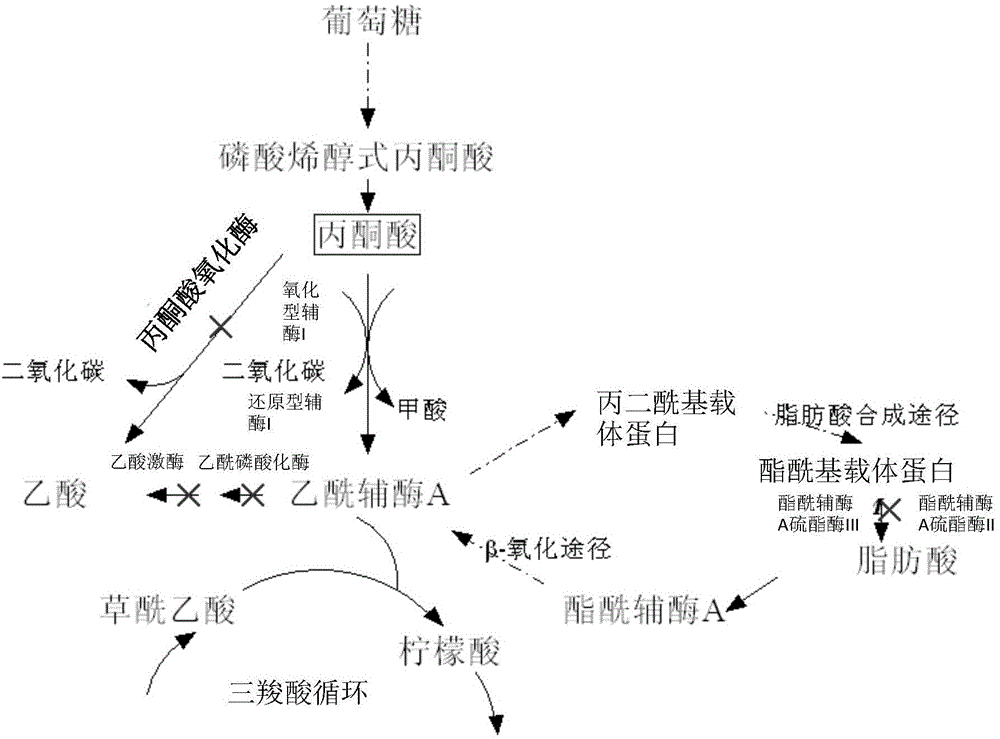
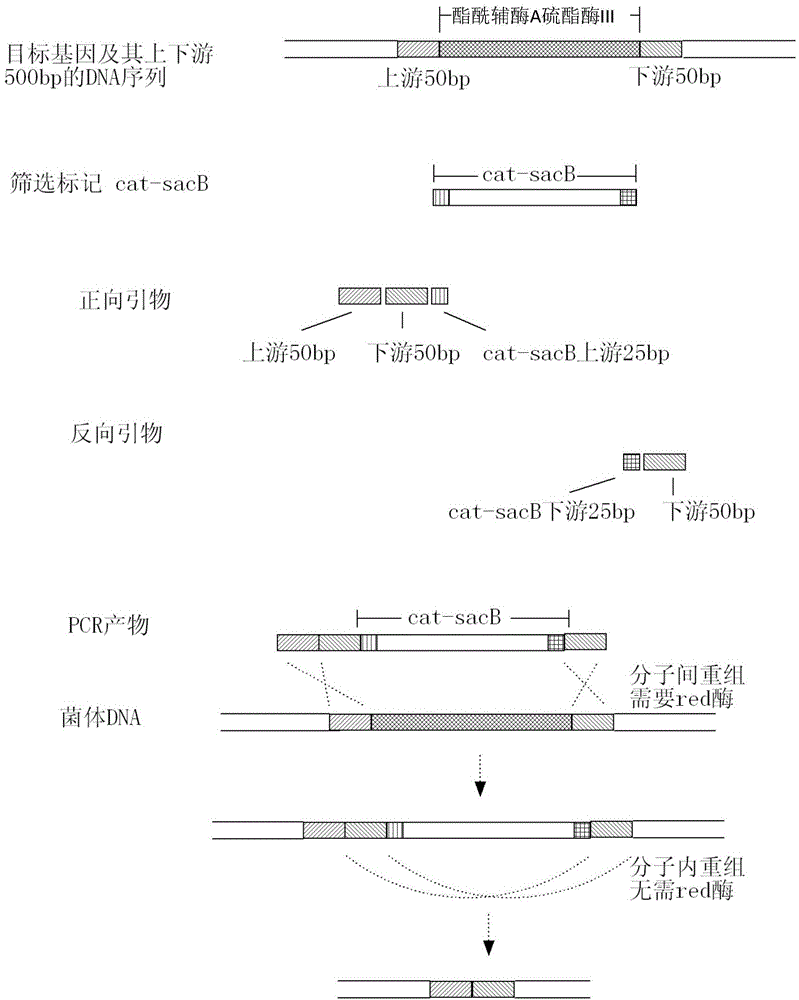
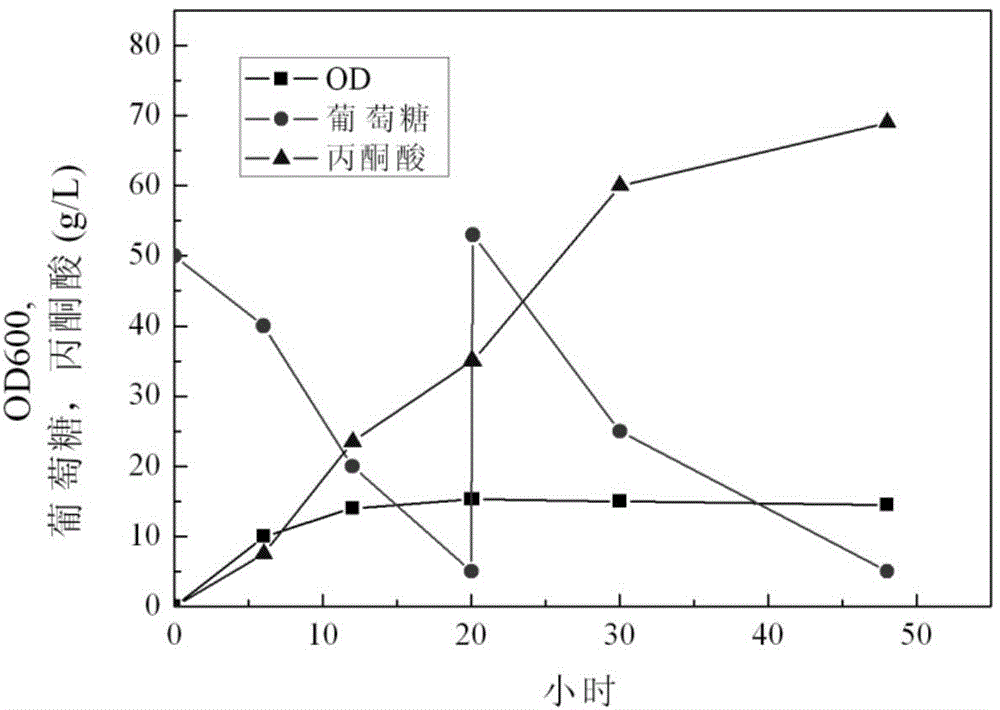
Escherichia coli gene engineering strain and construction method thereof, and application of strain in pyruvic acid production
ActiveCN104946576ACurb consumptionWeakening cycleBacteriaStable introduction of DNAInorganic saltsAcetic acid
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli gene engineering strain, and a construction method an application thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: lowering or inhibiting thioesterase activity in initial Escherichia coli, and inactivating the acetic acid synthesis pathway to obtain the Escherichia coli gene engineering strain YP01. The Escherichia coli gene engineering strain YP01 can convert 95 g / L glucose into 69 g / L pyruvic acid when being fermented in an inorganic salt culture medium under aerobic conditions for 48 hours, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human peroxisomal thioesterase
InactiveUS6210890B1Avoid developmentPreventing further progressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAgonistENCODE
The invention provides a human peroxisomal thioesterase (PxTE) and polynucleotides which identify and encode PxTE. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, agonists, antibodies and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for treating disorders associated with expression of PxTE.
Owner:INCYTE
Methods and compositions related to thioesterase enzymes
The present invention relates to novel mutant thioesterase enzymes and naturally-occurring equivalents thereof, compositions made from such enzymes and uses of thioesterase enzymes. In particular, the present invention provides mutant thioesterase enzymes that have altered properties, for example, altered substrate specificity, altered activity, altered selectivity, and / or altered proportional yields in the product mixtures. The present invention also provides polynucleotides encoding such mutant thioesterase enzymes, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further provides for novel uses of thioesterases in the production of various fatty acid derivatives, which are useful as, or as components of, industrial chemicals and fuels.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
Plants producing modified levels of medium chain fatty acids
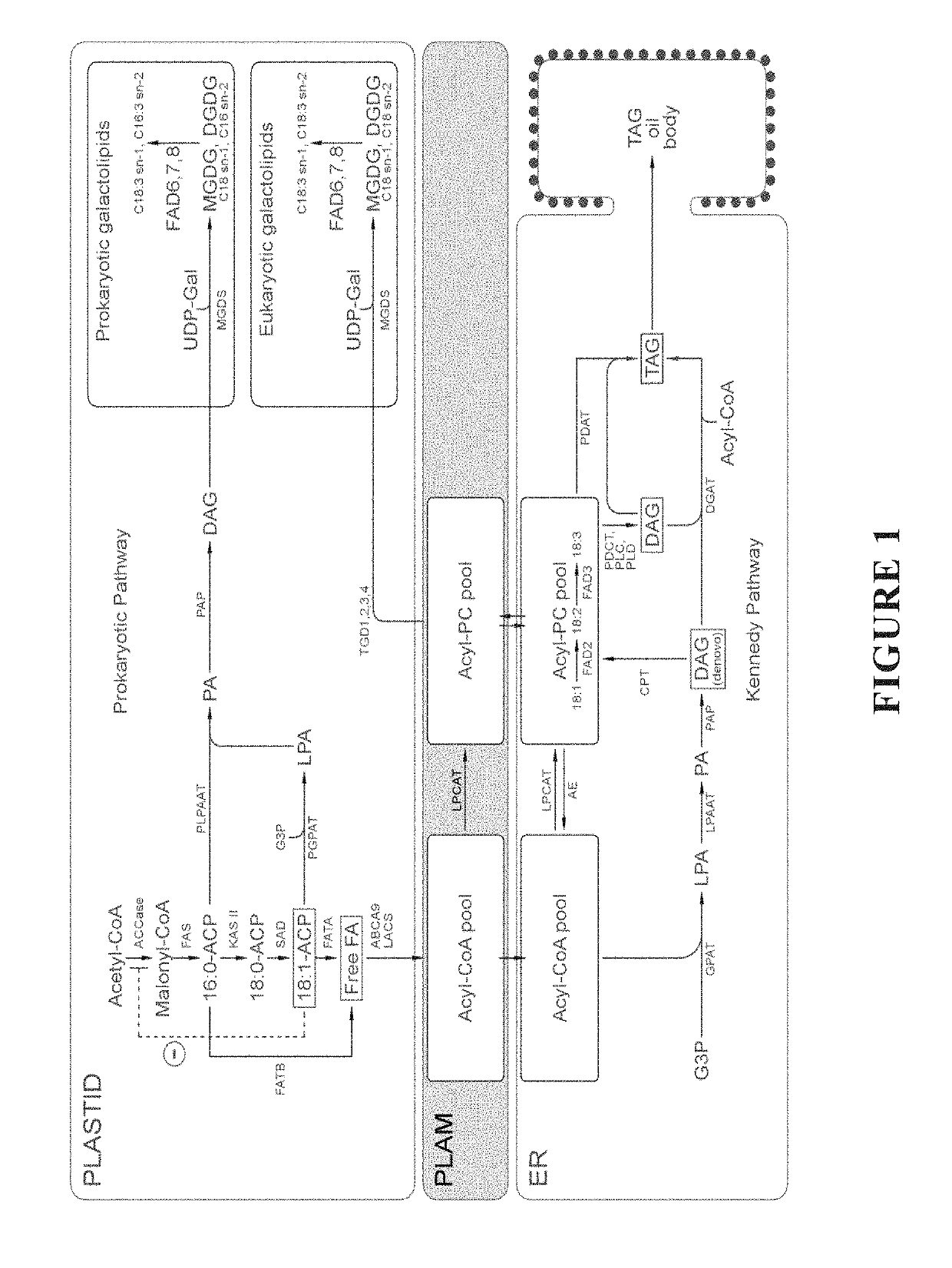
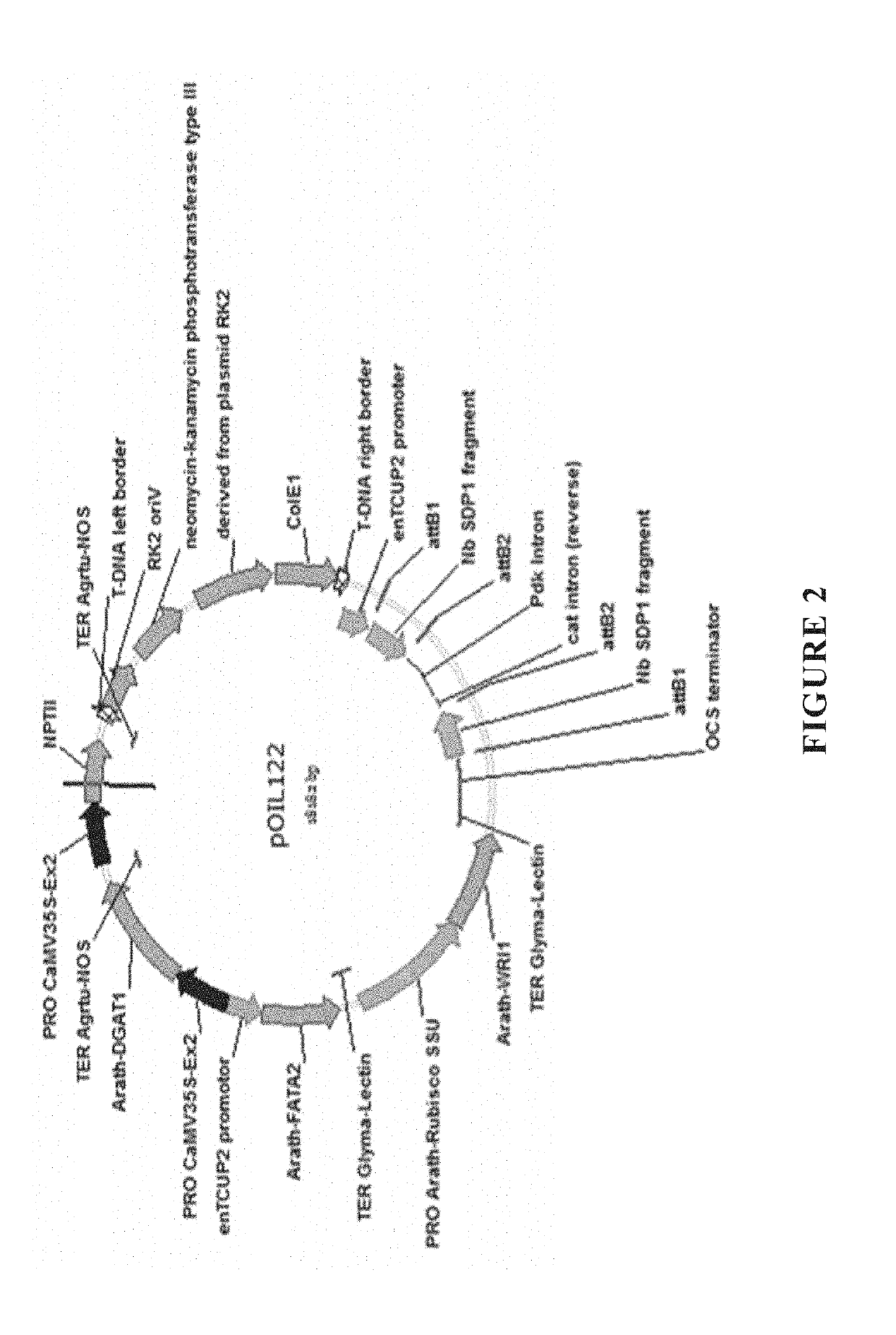
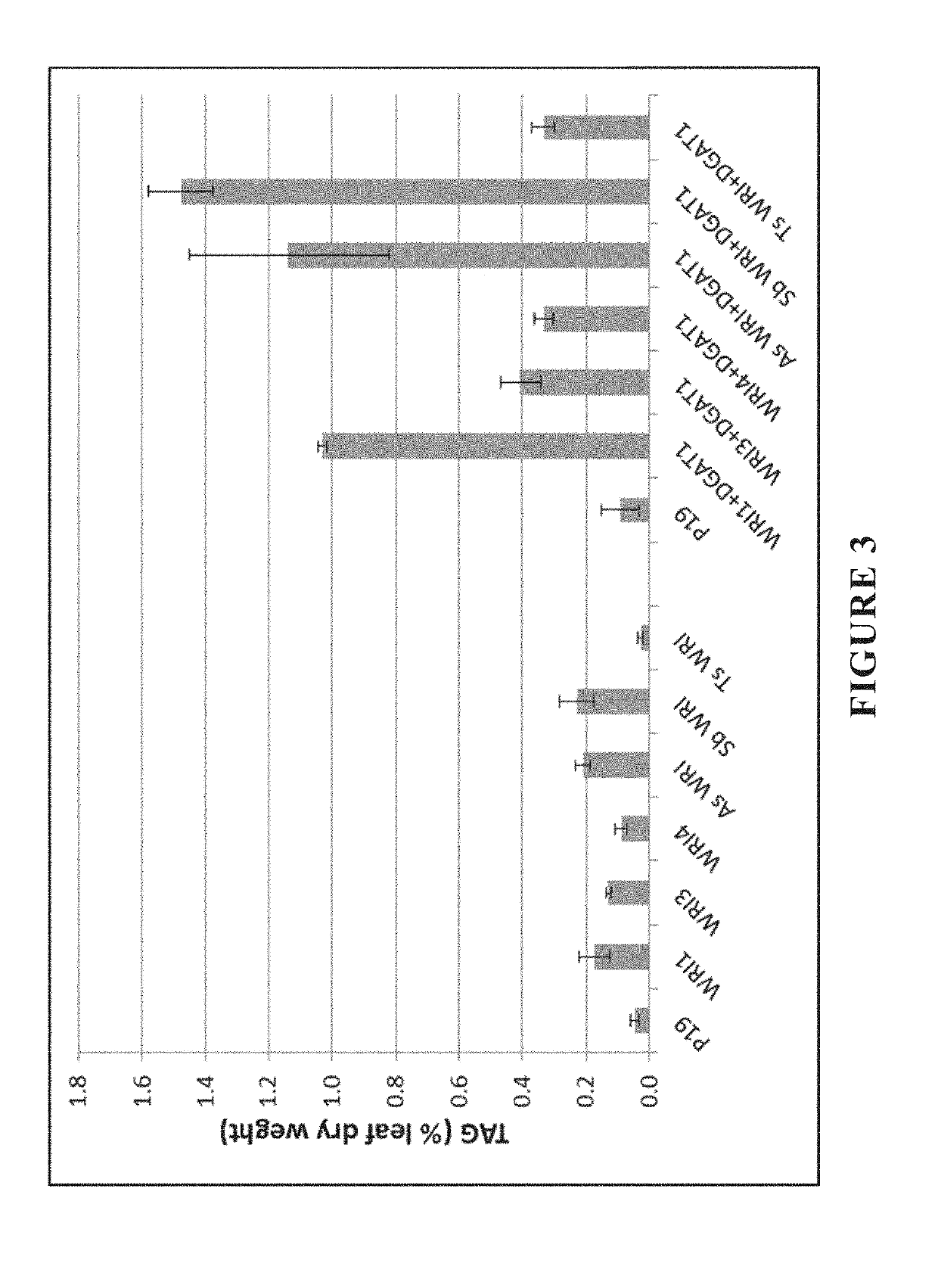
The present invention relates to methods of producing industrial products from plant lipids, particularly from vegetative parts of plants. In particular, the present invention provides oil products such as biofuel, and processes for producing these products, as well as plants having an increased level medium chain fatty acids such as lauric acid and myristic acid. In one particular embodiment, the present invention relates to combinations of modifications in a fatty acid thioesterase and one or more acyltransferases. In an embodiment, the present invention relates to a process for extracting lipids. In another embodiment, the lipid is converted to one or more hydrocarbon products in harvested plant vegetative parts to produce alkyl esters of the fatty acids which are suitable for use as a renewable biofuel.
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
A method of selectively producing male or female sterile plants
A method of producing male or female sterile plants comprising the steps of transforming plant material with a polynucleotide which encodes at least one enzyme which reacts with a non-phytotoxic substance to produce a phytotoxic one, and regenerating the thus transformed material into a plant, wherein the said non-phytotoxic substance is applied to the plant up to the time of male or female gamete formation and / or maturation, so that the non-phytotoxic substance provides for the production of a phytotoxic one which selectively prevents the formation of or otherwise renders the said gametes non-functional, wherein the enzyme is expressed preferentially in either male or female reproductive structures, characterised in that (i) the non-phytotoxic substance is selected from the group consisting of ester derivatives of non-phosphonate herbicides which herbicides are directly phytotoxic to non-green tissue, D-alpha amino acids, peptide derivatives of non-protein D-alpha amino acids, S-enantiomers of aryloxyphenoxypropionates and S-enantiomers of ester derivatives of aryloxyphcnoxypropionatcs and (ii) the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of carboxylesterases, D-amino acid oxidases, D-amino acid dehydrogenases, D-amino acid racemases, 2-arylpropionyl-CoA epimerases, alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemases, thioesterases and acyl-CoA synthetases.
Owner:SYNGENTA BIO TECH CHINA
Plant C18:1 preferring thioesterases
This invention relates to plant thioesterases, means to identify such proteins, amino acid and nucleic acid sequences associated with such protein, methods to obtain, make and / or use such plant thioesterases. Also, by this invention, the existence of a heretofore unproven factor critical to the biosynthesis of medium-chain fatty acids in plants is demonstrated.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Method for preparing 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid through escherichia coli engineering bacteria resting cells
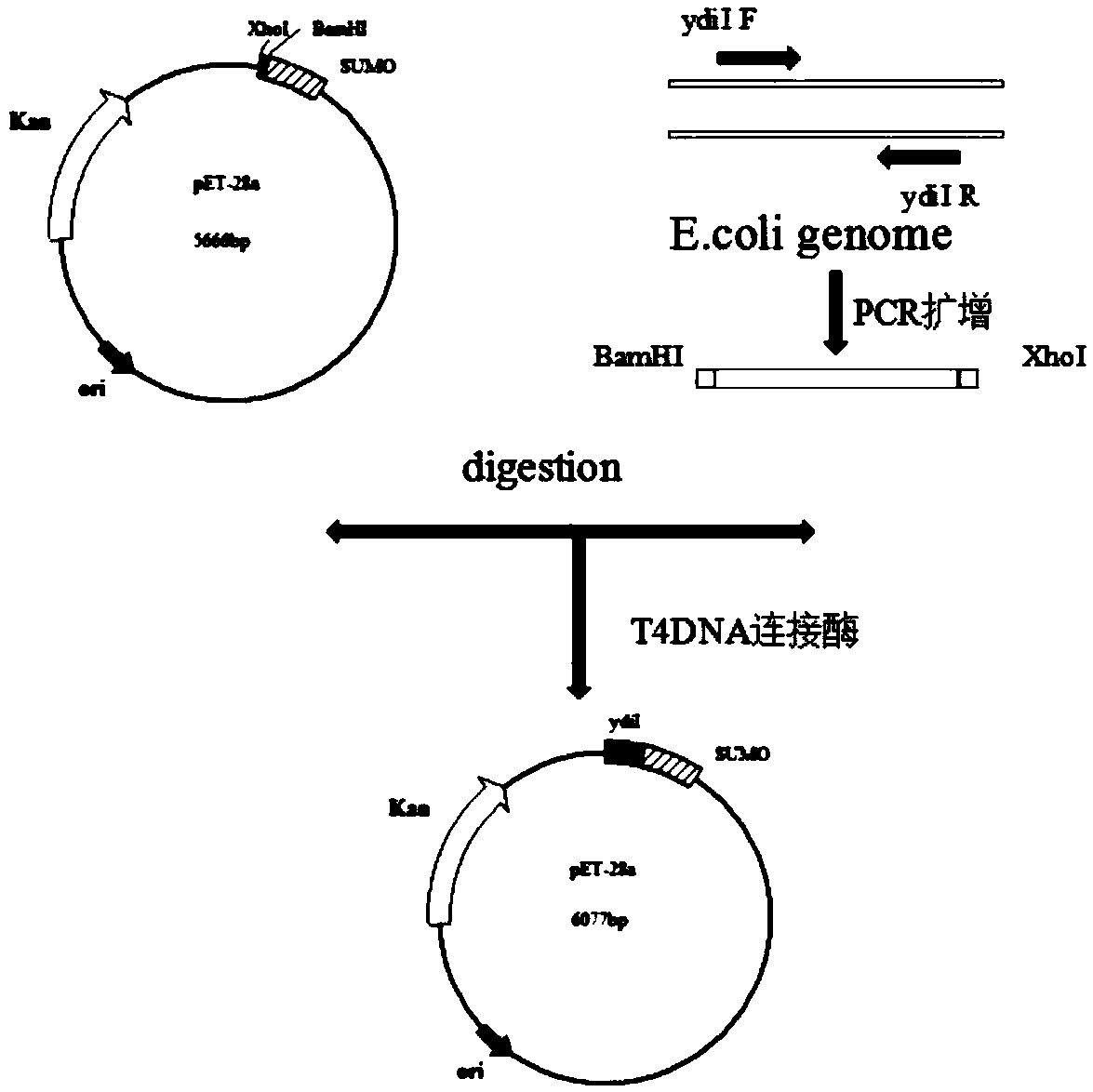
ActiveCN109402182AAchieve biosynthesisImprove conversion rateBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliINDUCTION TREATMENT
The invention relates to a method for preparing 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid through escherichia coli engineering bacteria resting cells. The method includes the following steps that (1) escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing recombinant plasmids pET-28a-ydiI is constructed; (2) the escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing the recombinant plasmids pET-28a-ydiI is taken to prepareinduced cells; and (3) the induced cells are cultured in a transformed culture medium to obtain the resting cells, and 10-hydroxy capric acid is then added into the culture medium to prepare the 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid. According to the method for preparing the 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid through the escherichia coli engineering bacteria resting cells, positive recombinant escherichia coli, containing thioesterase, modified through genetic engineering is disclosed for the first time, after special induction treatment, the 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid can be produced by fermentation throughthe resting cells, and a large quantity of biosynthesis of the 10-hydroxy-2-caproleic acid is realized.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Engineering strain and application thereof to production of long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acid
ActiveCN102952774AIncrease productionHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidPHA synthase
The invention discloses an engineering strain and application thereof to production of long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acid. The engineering strain provided by the invention is a recombinant strain obtained by conducting the following modification on a starting strain: (a) inactivation of a PHA synthase gene; and (b) introduction of a thioesterase gene. The starting strain is bacteria producing polyhydroxyalkanoates. hen the engineering strain provided by the invention is used, and a middle to long-chain fatty acid is used as a single carbon source, a 3-hydroxy fatty acid product with high yield, high purity, and a structure highly consistent with that of the provided fatty acid carbon source can be obtained in a fermentation liquid. The method provided by the invention can be used for production of 3-hydroxy fatty acid with high yield and high purity, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Bacteria and method for synthesizing fatty acids
ActiveUS20140093921A1Increasing production of fatty acidIncrease synthesisBacteriaSugar derivativesTricarboxylic acidAcyl group
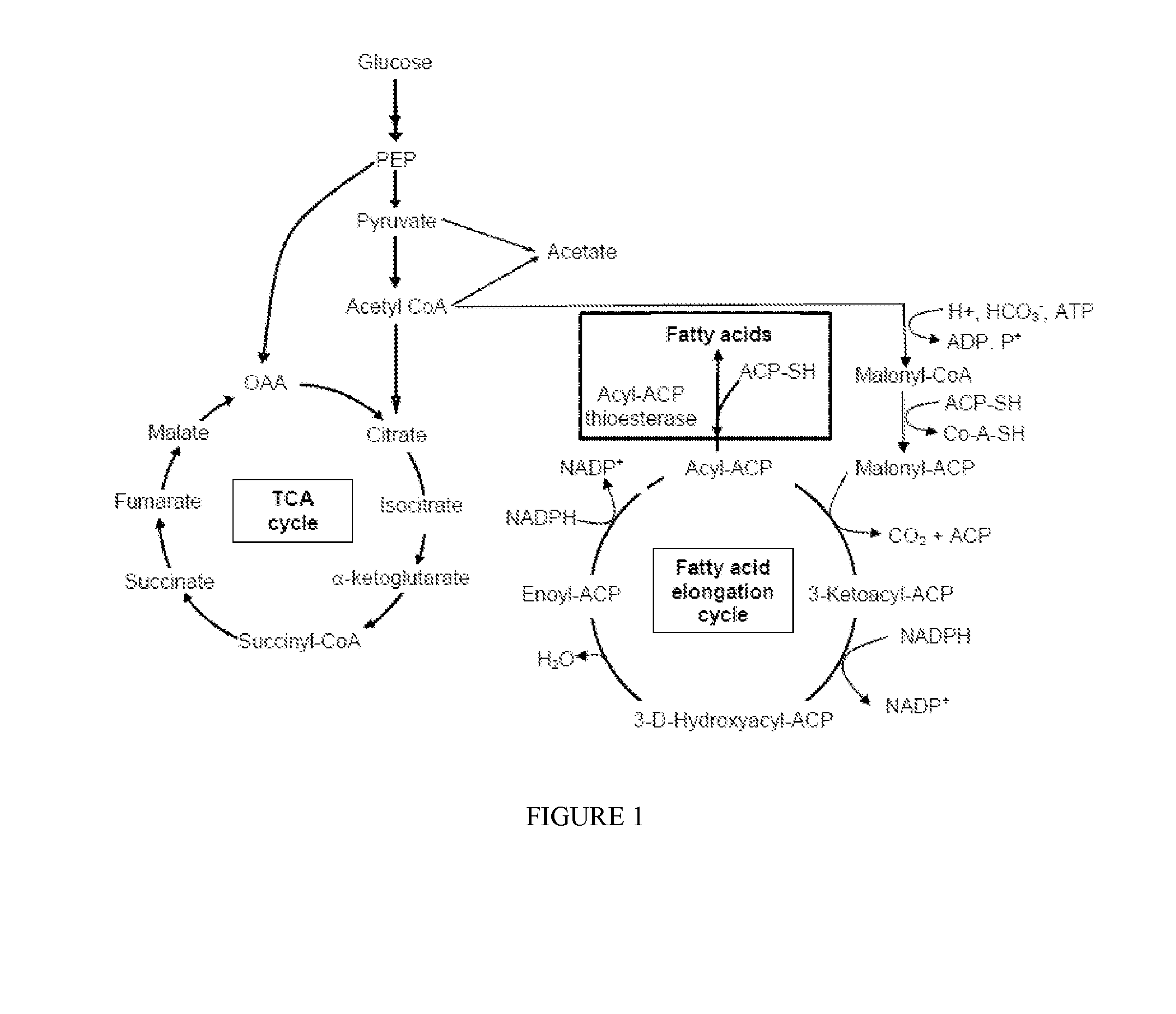
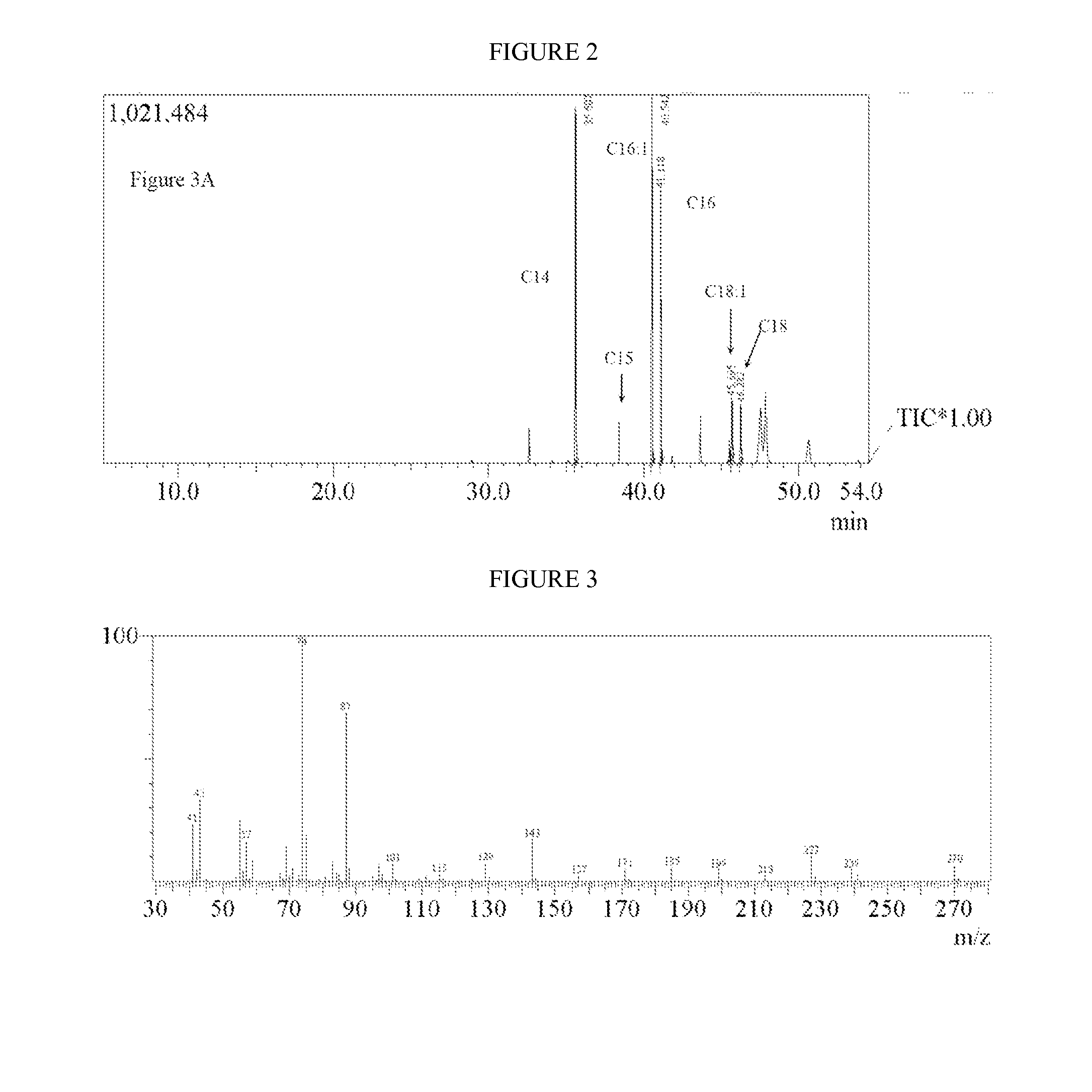
There is provided a recombinant bacterium comprising at least one overexpressed acyl-ACP thioesterase gene, and wherein at least one gene from the tricarboxylic acid cycle or glycolysis or both is inactivated. There is also provided a method for producing fatty acids, said method comprising culturing bacteria comprising at least one overexpressed acyl-ACP thioesterase gene in a growth medium in a container having walls; allowing said bacteria to secrete fatty acids; and collecting said fatty acids. Acid supplementation is also shown to increase productivity.
Owner:RICE UNIV
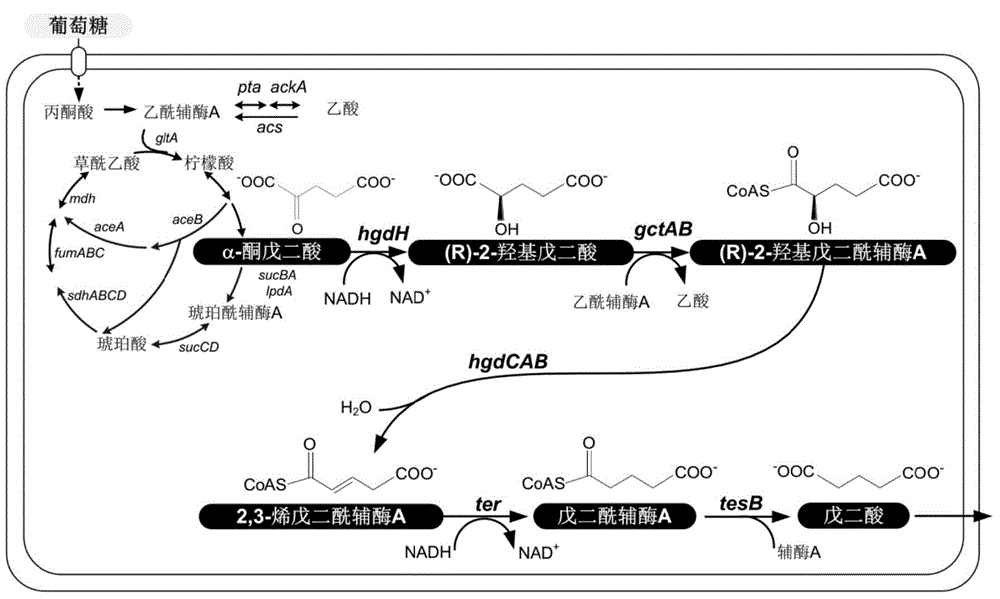
Biological improvement synthesis method of glutaric acid
The invention relates to a biological improvement synthesis method of glutaric acid. According to the present invention, the method is achieved by expressing 2-hydroxyglutaric acid dehydrogenase, glutaryl-coenzyme A transferase, 2-hydroxyglutaryl coenzyme A dehydratase, trans-CoA reductase and thioesterase in a recombinant host Escherichia coli, the recombinant Escherichia coli expressing the genes is subjected to fermentation production, and the generation of the target product glutaric acid and the by-products such as glutaconic acid and 2-hydroxyglutaric acid is successfully detected in the fermentation broth; and the constructed biological synthesis approach provides the new method for the utilization of the renewable resources to synthesize the glutaric acid.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Gene construct encoding mutant thioesterase, mutant thioesterase encoded thereby, transformed host cell containing the gene construct, and method of using them to produce medium-chain fatty acids
Unnatural, mutated thioesterases having an amino acid sequence that is at least 80% identical to SEQ. ID. NO: 1 and having substitutions at one or more of amino acid positions I107, R108, L109, S122, M141, E142, Y145, and L146, gene constructs encoding and configured to express the mutated thioesterases in a transformed host cell and host cells transformed to contain the gene constructs.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Acyl coenzyme A thioesterase, application of gene thereof in degradation of zearalenone and preparation for degrading zearalenone
The invention relates to application of acyl coenzyme A thioesterase and gene thereof in degradation of zearalenone, and a preparation for degrading the zearalenone, and belongs to the technical fieldof biodegradation of mycotoxins. According to microbial transcriptome sequencing analysis, it discovers that the acyl- coenzyme A thioesterase gene of the YBGC / FADM family in a bacillus amyloliquefaciens H6 strain is a key gene for degrading the zearalenone, the acyl coenzyme A thioesterase gene is expressed in escherichia coli, the protein is found to be soluble, and recombinant protein is obtained after purification. A zearalenone ELISA detection kit detects that the recombinant protein has the biological activity of efficiently degrading ZEN. Therefore, the acyl coenzyme A thioesterase andthe coding gene thereof can be used for degrading the zearalenone, and the acyl coenzyme A thioesterase can be used for preparing an enzyme preparation or a complex enzyme preparation for degrading the zearalenone.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enhanced production of fatty acids and fatty acid derivatives by recombinant microorganisms
The present invention provides for the improved production of fatty acid products in a recombinant microorganism or host cell engineered to express a non-native gene encoding a thioesterase and a non-native gene encoding a lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT), in which the LPAAT is overexpressed in the recombinant microorganism compared to an otherwise identical microorganism that does not include the non-native LPAAT gene. The invention also provides methods of producing fatty acid products using such recombinant microorganisms.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Hot-pickled mustard tuber production wastewater treating agent and wastewater treating method
InactiveCN105254036AReduce SS contentHigh removal rateMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from food industryPectinaseCellulose
The invention belongs to the field of food enterprise wastewater treatment and particularly relates to a hot-pickled mustard tuber production wastewater treating agent and a hot-pickled mustard tuber production wastewater treating method. The hot-pickled mustard tuber production wastewater treating agent is prepared from, by weight, a physical water purifying agent, a composite microbial agent and an enzymic preparation. The physical water purifying agent is prepared from, by weight, 1-5 parts of activated carbon, 1-5 parts of organic modified zeolite and 1-5 parts of polyacrylamide. The composite microbial agent is prepared from, by weight, 0.02-0.1 part of halophilic pseudomonas powder, 0.05-0.2 part of aspergillus flavus powder, 0.05-0.2 part of bacillus licheniformis powder and 0.04-0.2 part of paracoccus aminovorans powder. The enzymic preparation is prepared from, by weight, 0.05-0.1 part of cellulose, 0.04-0.09 part of pectinase and 0.01-0.06 part of thioesterase. By means of the wastewater treating agent and the wastewater treating method, organic matter which is complex, difficult to degrade and large in particle is hydrolyzed into simple organic matter easy to degrade, the SS content in wastewater is greatly reduced, the BOD and COD removal rate of the treated wastewater is high, and the wastewater reaches the regulated emission standard.
Owner:JINAN HAOZE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Oleaginous microalgae having an LPAAT ablation
Recombinant DNA techniques are used to produce oleaginous recombinant cells that produce triglyceride oils having desired fatty acid profiles and regiospecific or stereospecific profiles. Genes manipulated include those encoding stearoyl-ACP desaturase, delta 12 fatty acid desaturase, acyl-ACP thioesterase, ketoacyl-ACP synthase, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, ketoacyl-CoA reductase, hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase, and / or enoyl-CoA reductase. The oil produced can have enhanced oxidative or thermal stability, or can be useful as a frying oil, shortening, roll-in shortening, tempering fat,cocoa butter replacement, as a lubricant, or as a feedstock for various chemical processes. The fatty acid profile can be enriched in midchain profiles or the oil can be enriched in triglycerides of the saturated-unsaturated-saturated type.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Novel acyltransferases, variant thioesterases, and uses thereof
Recombinant nucleic acids and vector constructs encoding acyltransferases and variant thioesterases, and the acyltransferases and variant thioesterases encoded by the nucleic acids are provided. The acyltransferases and variant thioesterases are useful in fatty acid synthesis and triacylglycerol production. Host cells that express the recombinant nucleic acids as well as methods of cultivating thehost cells, methods of producing oils from the host cells are provided. The recombinant host cells and the oils produced therefrom have altered fatty acid profiles and / or triacylglycerols with altered regiospecificity.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with a defined composition from an unrelated carbon source
Cells and methods for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates. The cells comprise one or more recombinant genes selected from an R-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a PHA polymerase gene, a thioesterase gene, and an acyl-CoA-synthetase gene. The cells further have one or more genes functionally deleted. The functionally deleted genes include such genes as an enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene. The recombinant cells are capable of using producing polyhydroxyalkanoates with a high proportion of monomers having the same carbon length from non-lipid substrates, such as carbohydrates.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cells and methods for producing fatty alcohols
Recombinant cells and methods for improved yield of fatty alcohols. The recombinant cells harbor a recombinant thioesterase gene, a recombinant acyl-CoA synthetase gene, and a recombinant acyl-CoA reductase gene. In addition, a gene product from one or more of an acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene, an enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene, and a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene in the recombinant cells is functionally deleted. Culturing the recombinant cells produces fatty alcohols at high yields.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
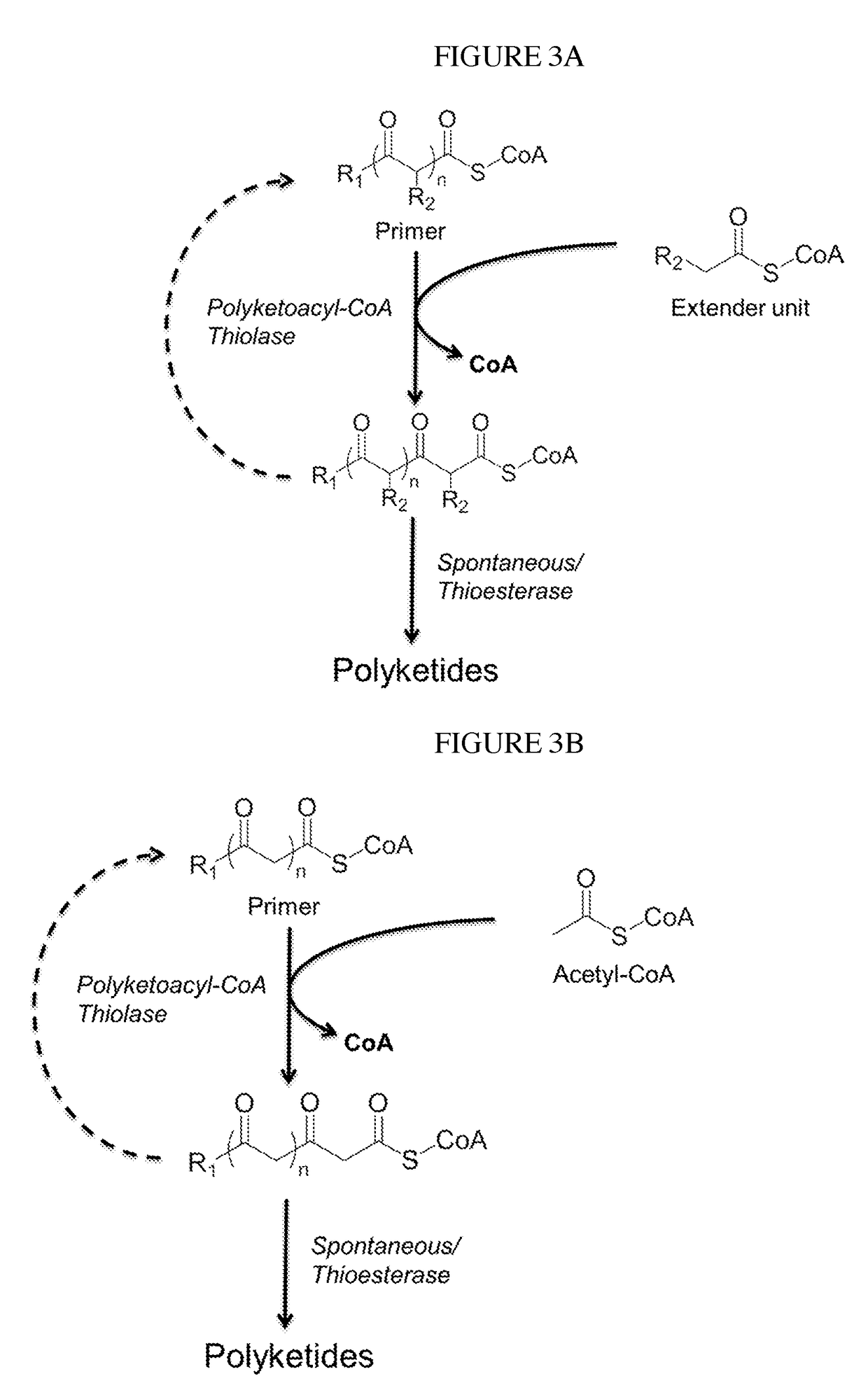
Biosynthesis of polyketides
InactiveUS20190002848A1Increase diversityWide-ranging product diversityAcyltransferasesFermentationClaisen condensationPolyketide biosynthesis
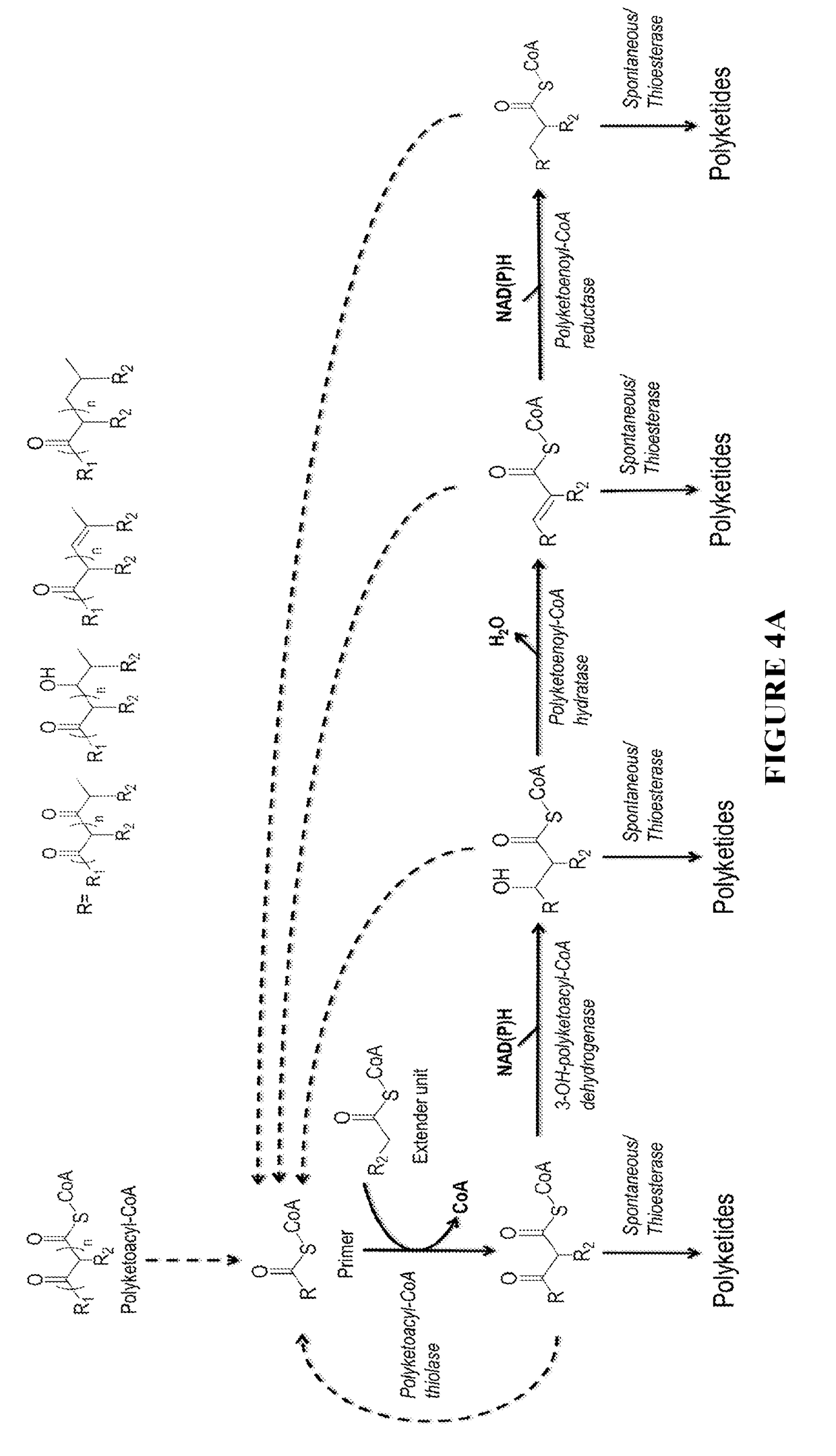
This disclosure generally relates to the use of microorganisms to make various functionalized polyketides through polyketoacyl-CoA thiolase-catalyzed non-decarboxylative condensation reactions instead of decarboxylative reactions catalyzed by polyketide synthases. Native or engineered polyketoacyl-CoA thiolases catalyze the non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation in an iterative manner (i.e. multiple rounds) between two either unsubstituted or functionalized ketoacyl-CoAs (and polyketoacyl-CoAs) serving as the primers and acyl-CoAs serving as the extender unit to generate (and elongate) polyketoacyl-CoAs. Before the next round of polyketoacyl-CoA thiolase reaction, the β-keto group of the polyketide chain of polyketoacyl-CoA can be reduced and modified step-wise by 3-OH-polyketoacyl-CoA dehydrogenase or polyketoenoyl-CoA hydratase or polyketoenoyl-CoA reductase. Dehydrogenase converts the β-keto group to β-hydroxy group. Hydratase converts the β-hydroxy group to α-β-double-bond. Reductase converts the α-β-double-bond to single bond. Spontaneous or thioesterase catalyzed termination reaction terminates the elongation of polyketide chain of polyketoacyl-CoA at any point through CoA removal and spontaneous reactions rearrange the structure, generating the final functional polyketide products.
Owner:GONZALEZ RAMON
A kind of engineering bacteria and its application in the production of medium and long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids
The invention discloses an engineering strain and application thereof to production of long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acid. The engineering strain provided by the invention is a recombinant strain obtained by conducting the following modification on a starting strain: (a) inactivation of a PHA synthase gene; and (b) introduction of a thioesterase gene. The starting strain is bacteria producing polyhydroxyalkanoates. hen the engineering strain provided by the invention is used, and a middle to long-chain fatty acid is used as a single carbon source, a 3-hydroxy fatty acid product with high yield, high purity, and a structure highly consistent with that of the provided fatty acid carbon source can be obtained in a fermentation liquid. The method provided by the invention can be used for production of 3-hydroxy fatty acid with high yield and high purity, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com