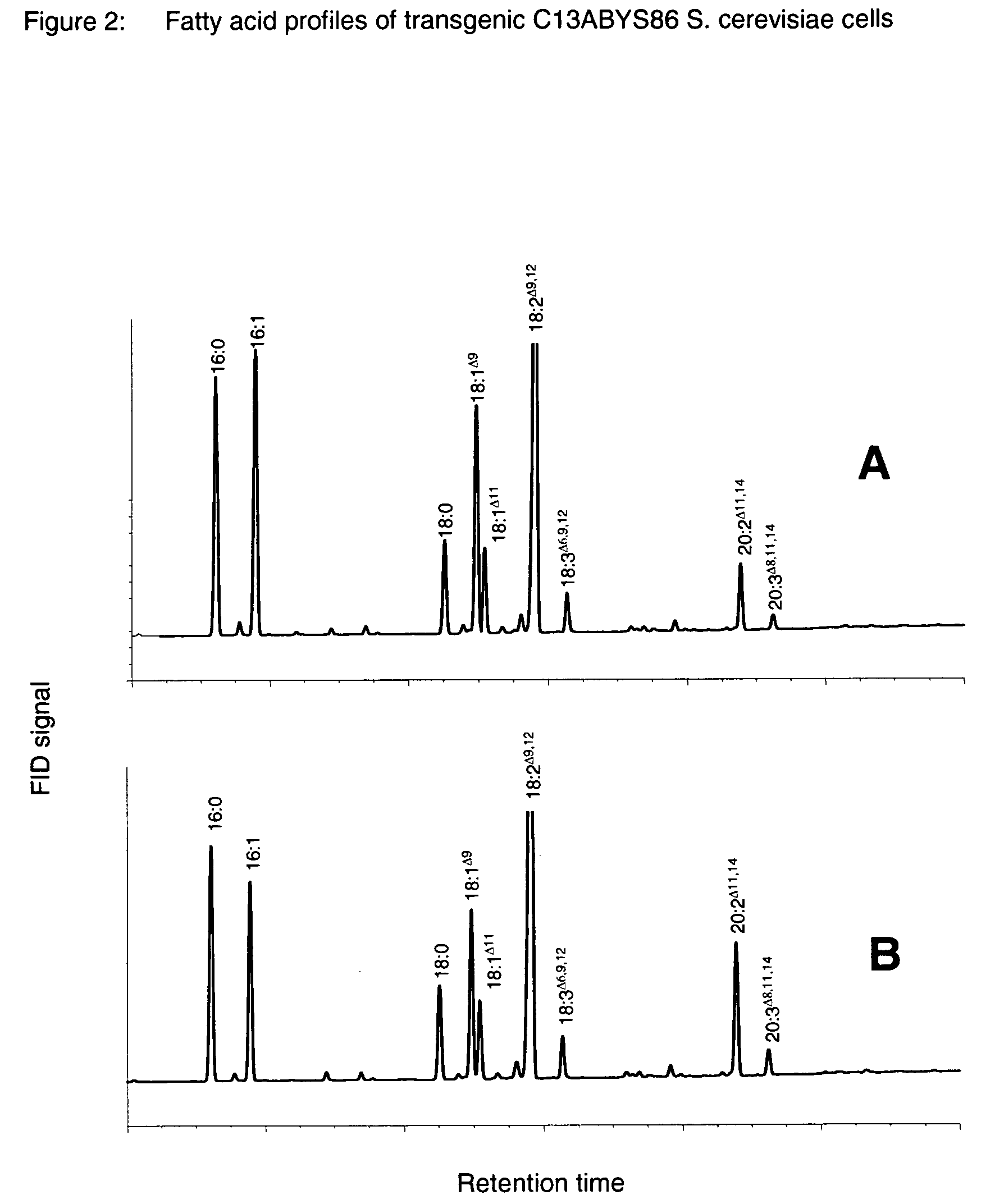
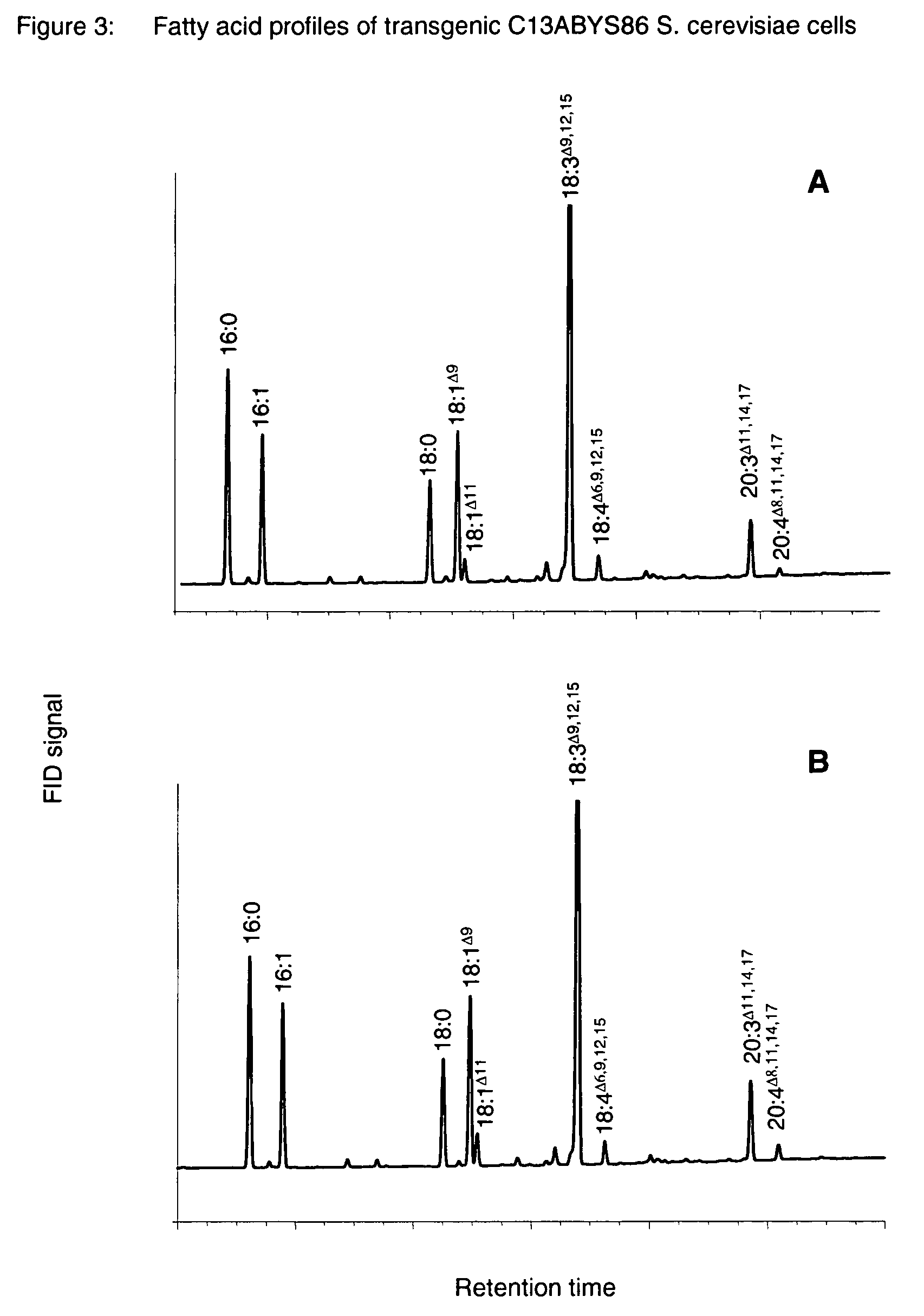
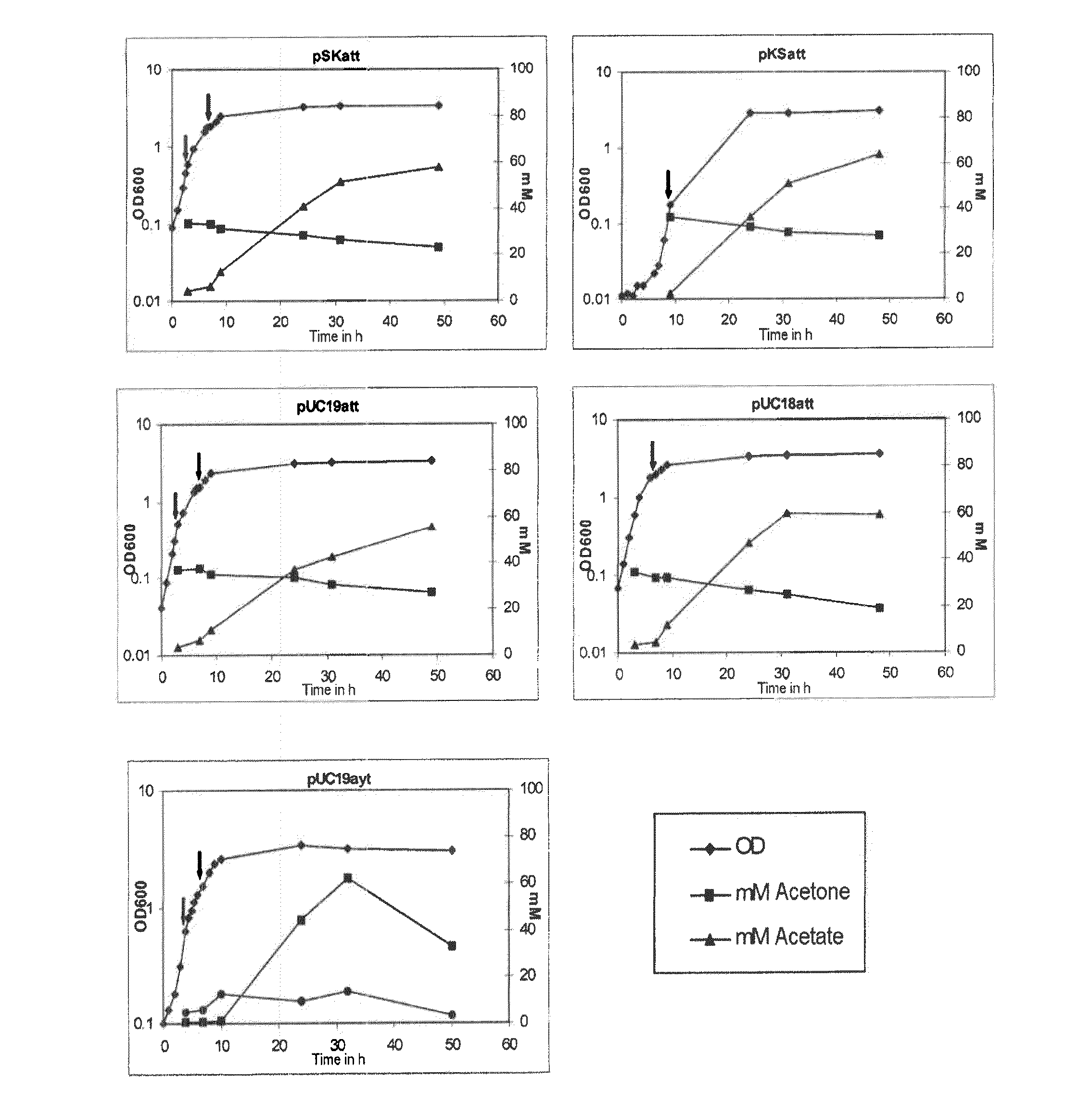
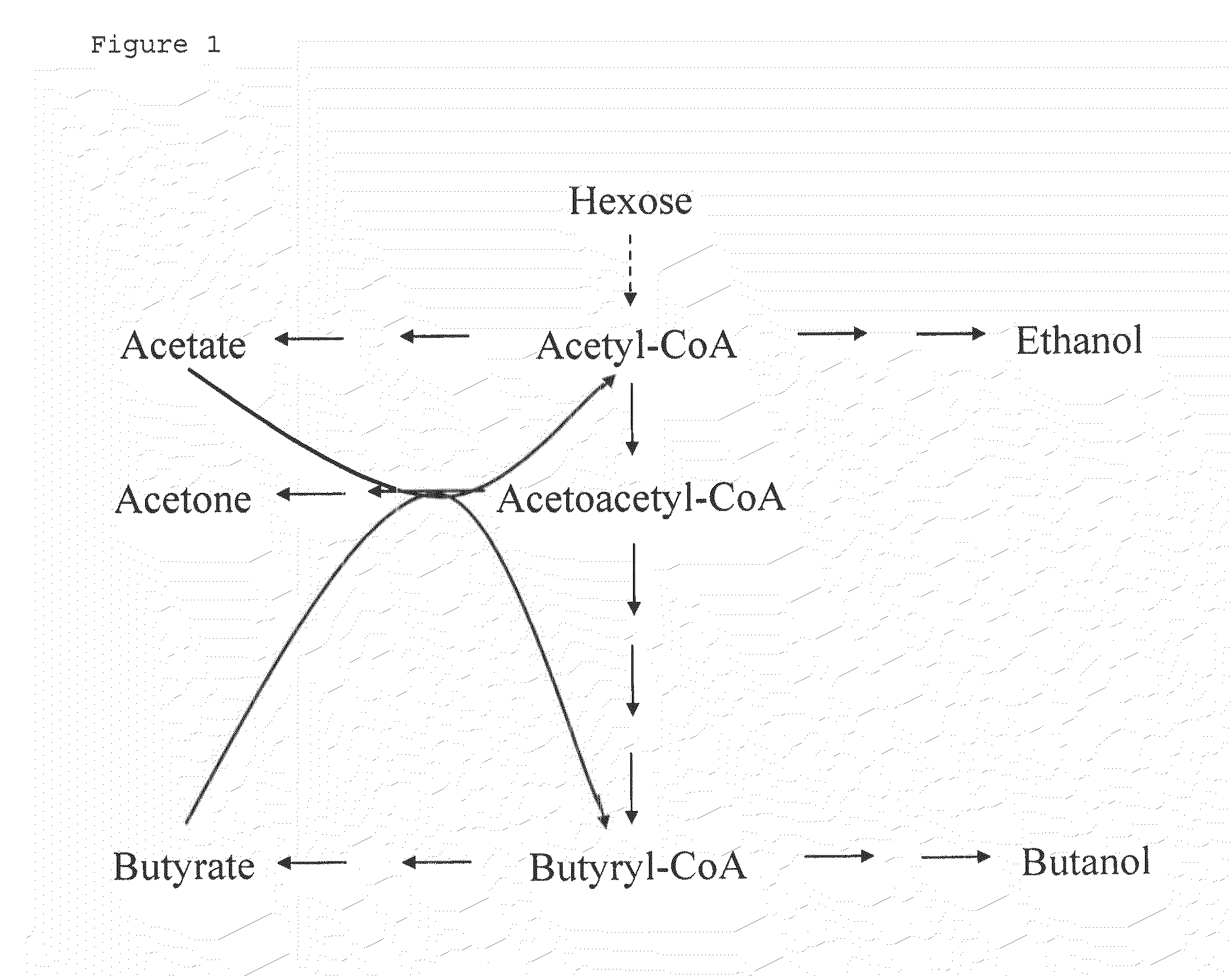
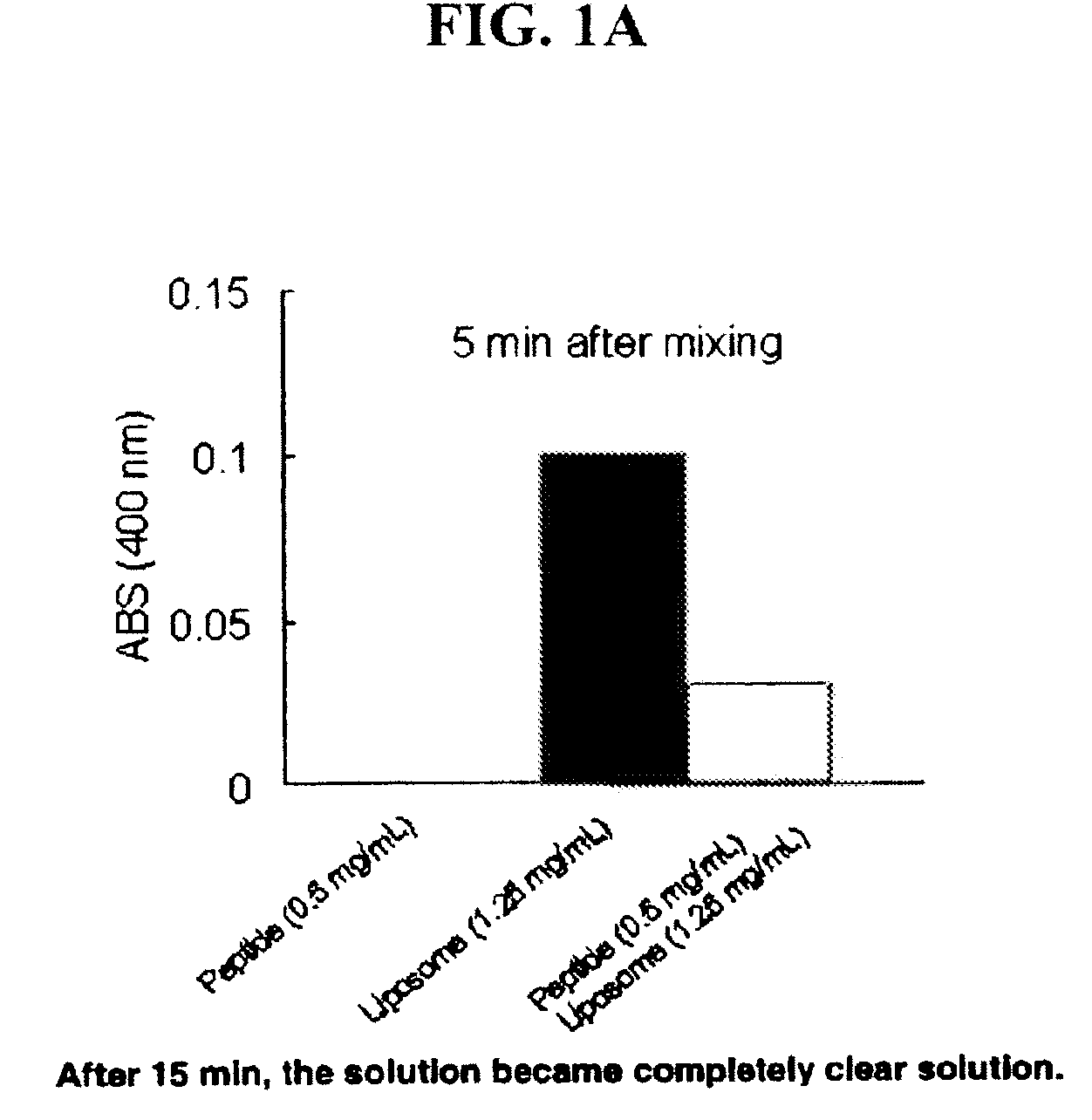
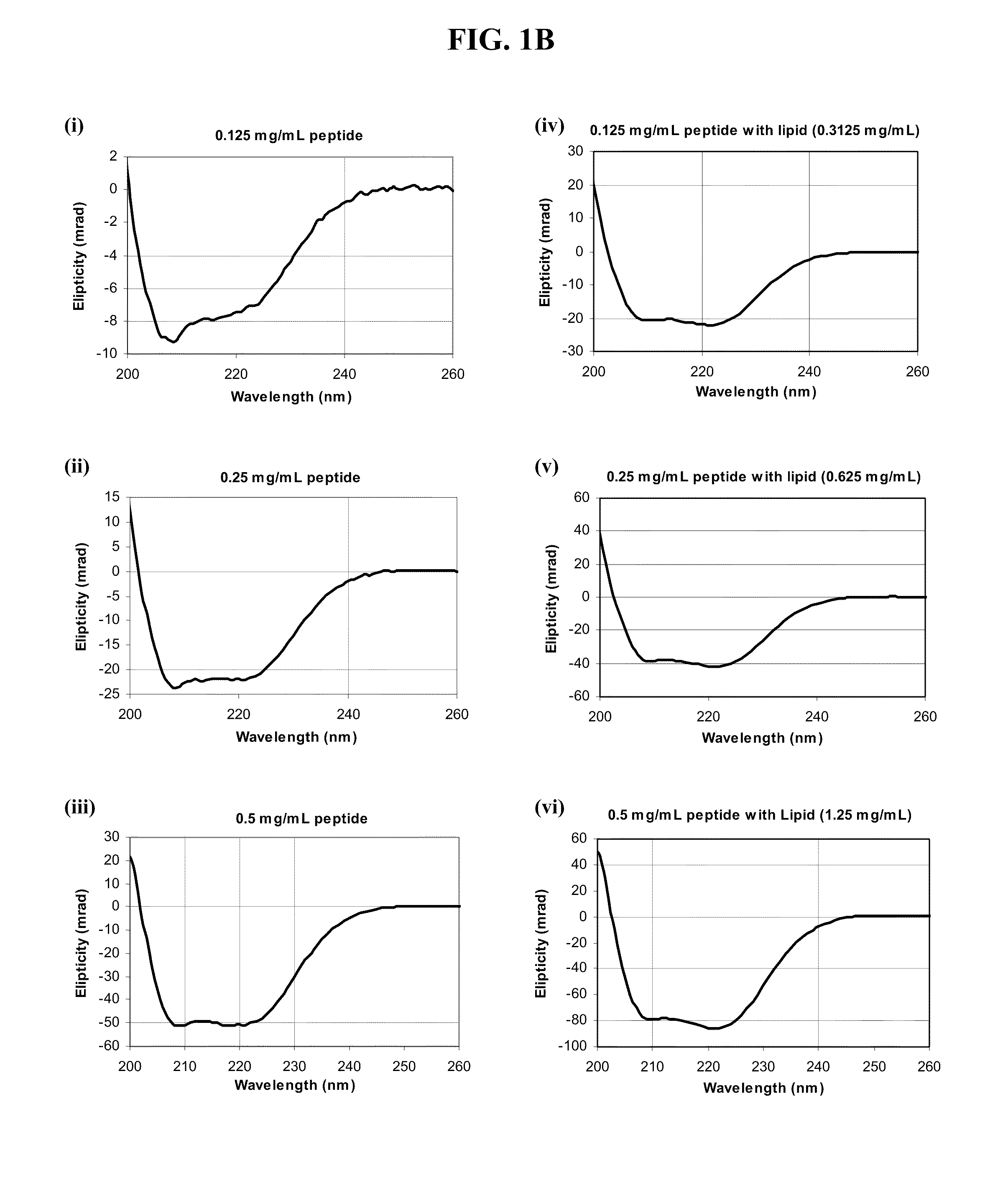
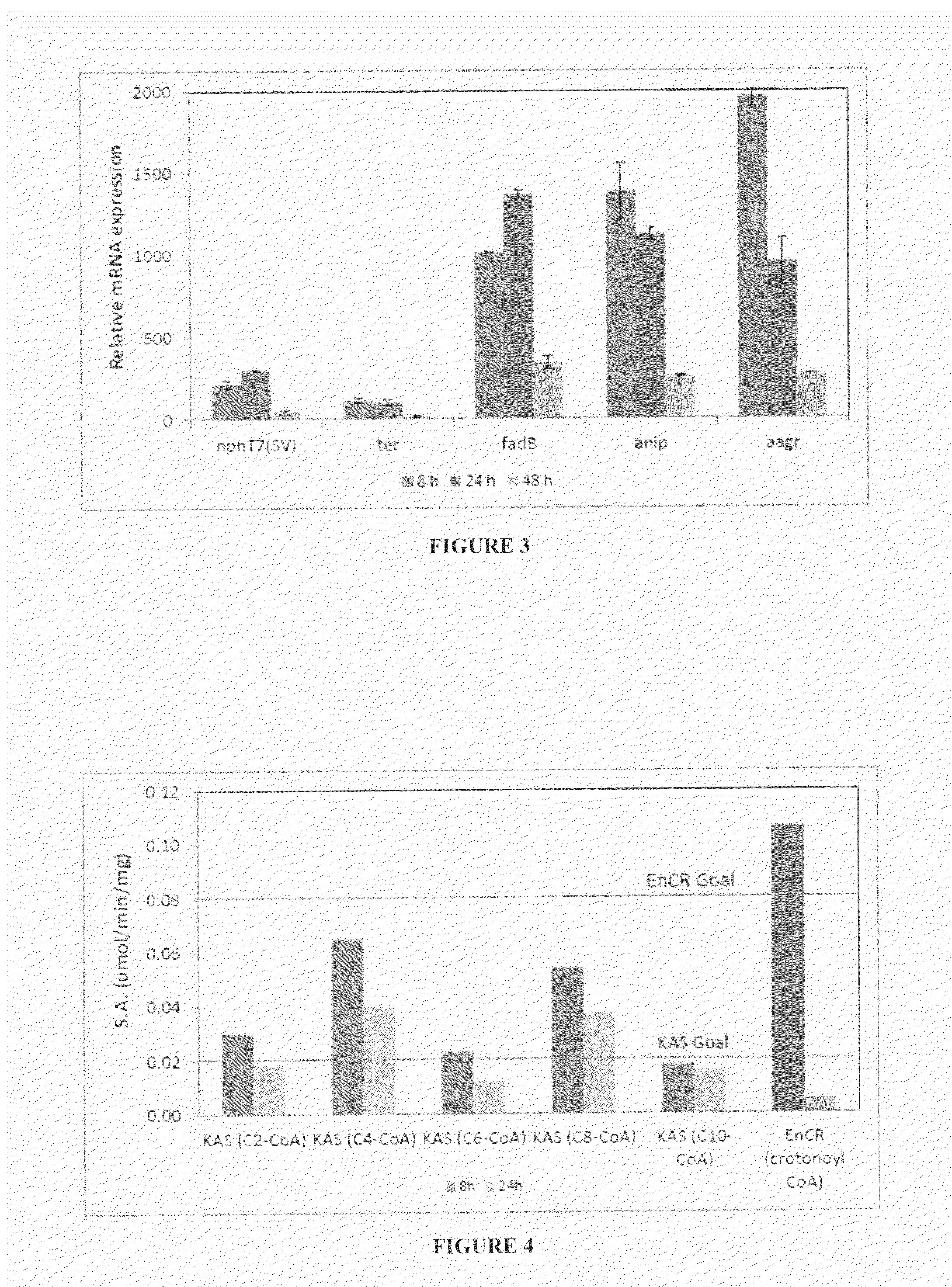
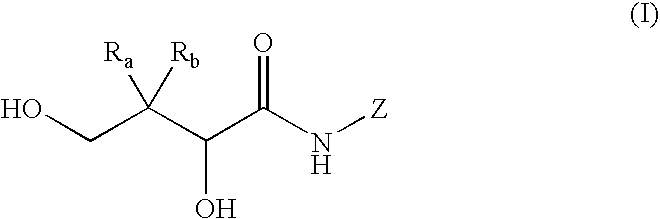
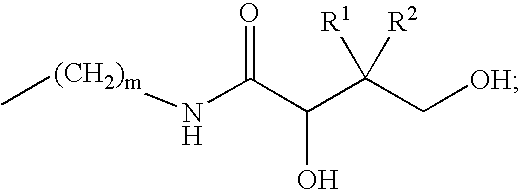
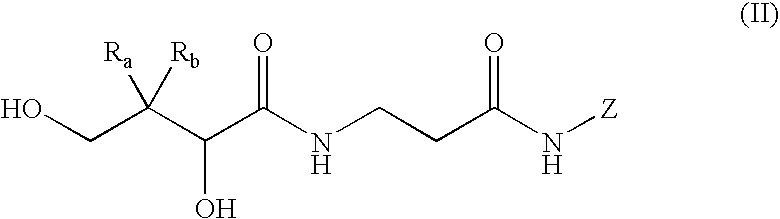
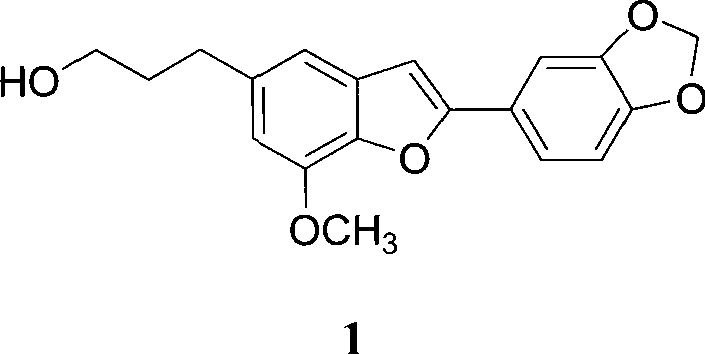
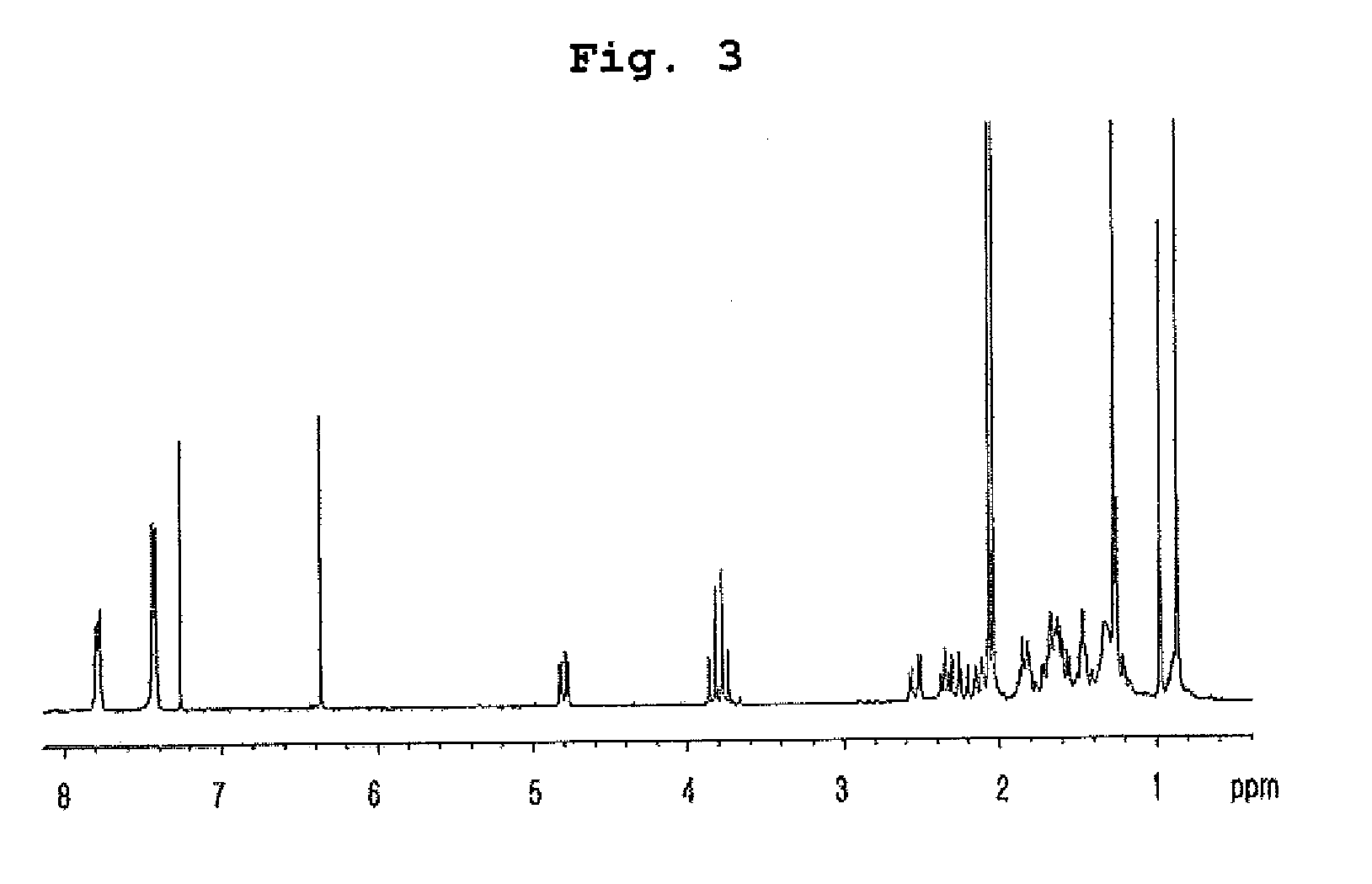
Patents
Literature
128 results about "Acyl coenzyme A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
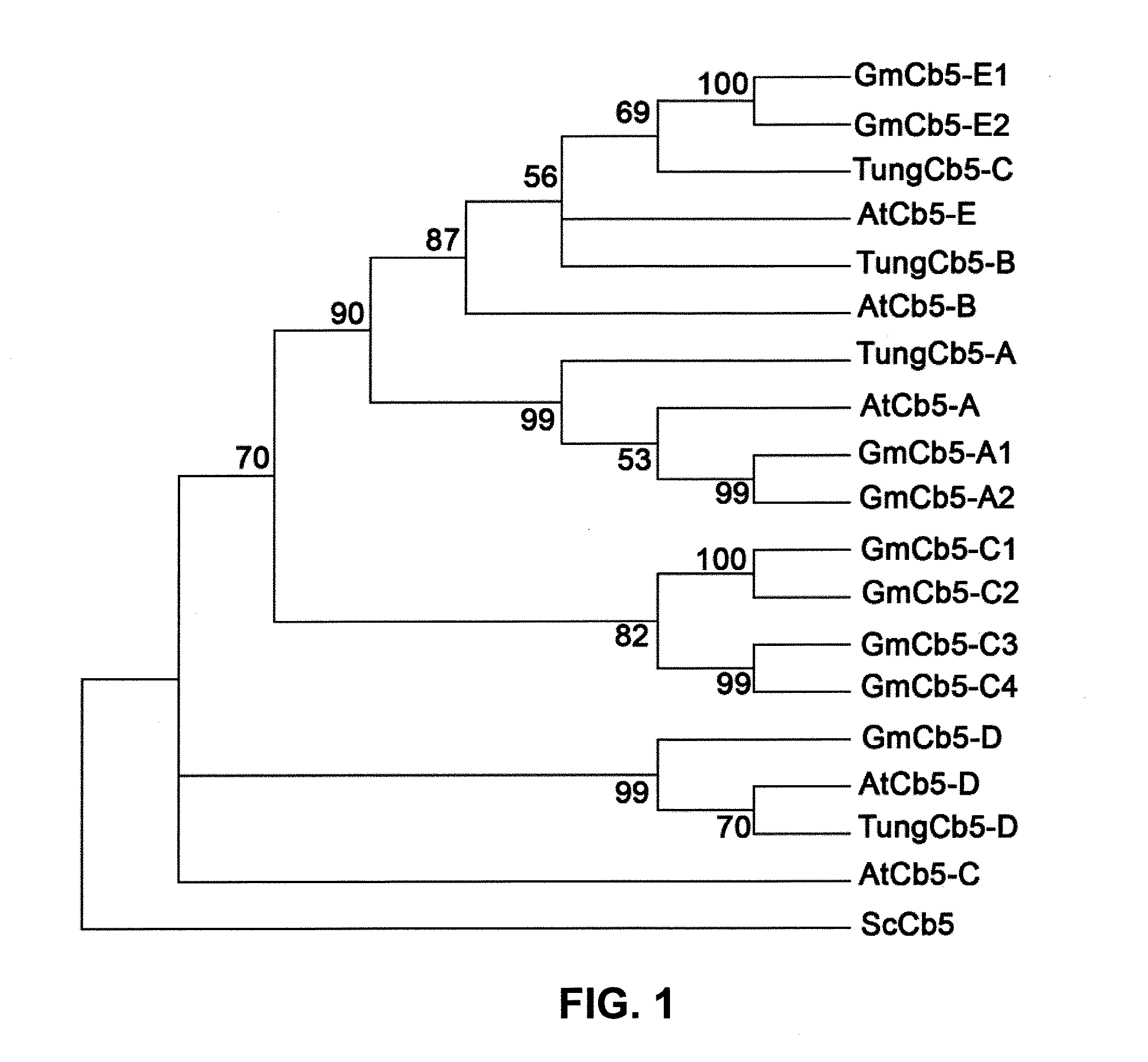
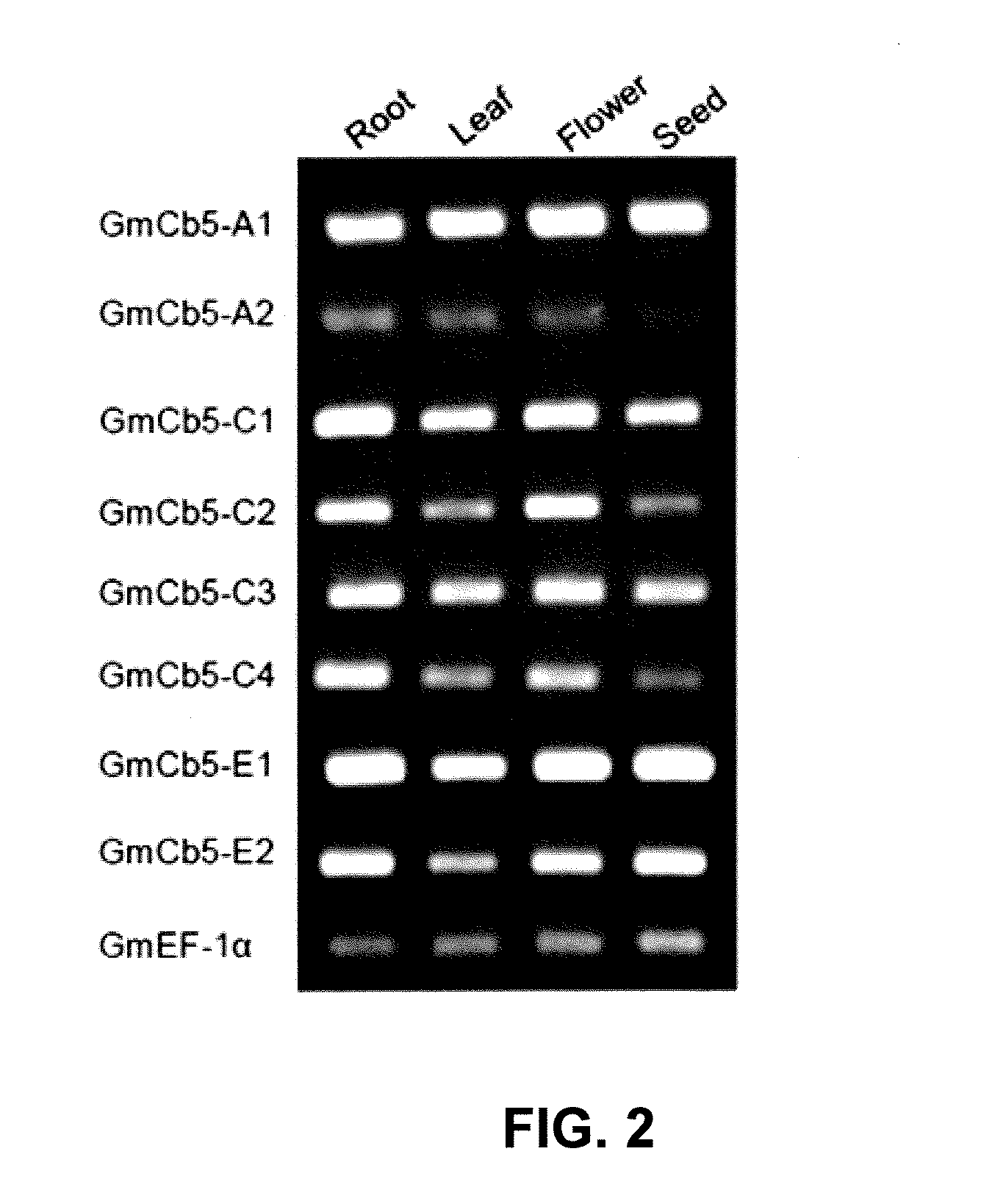
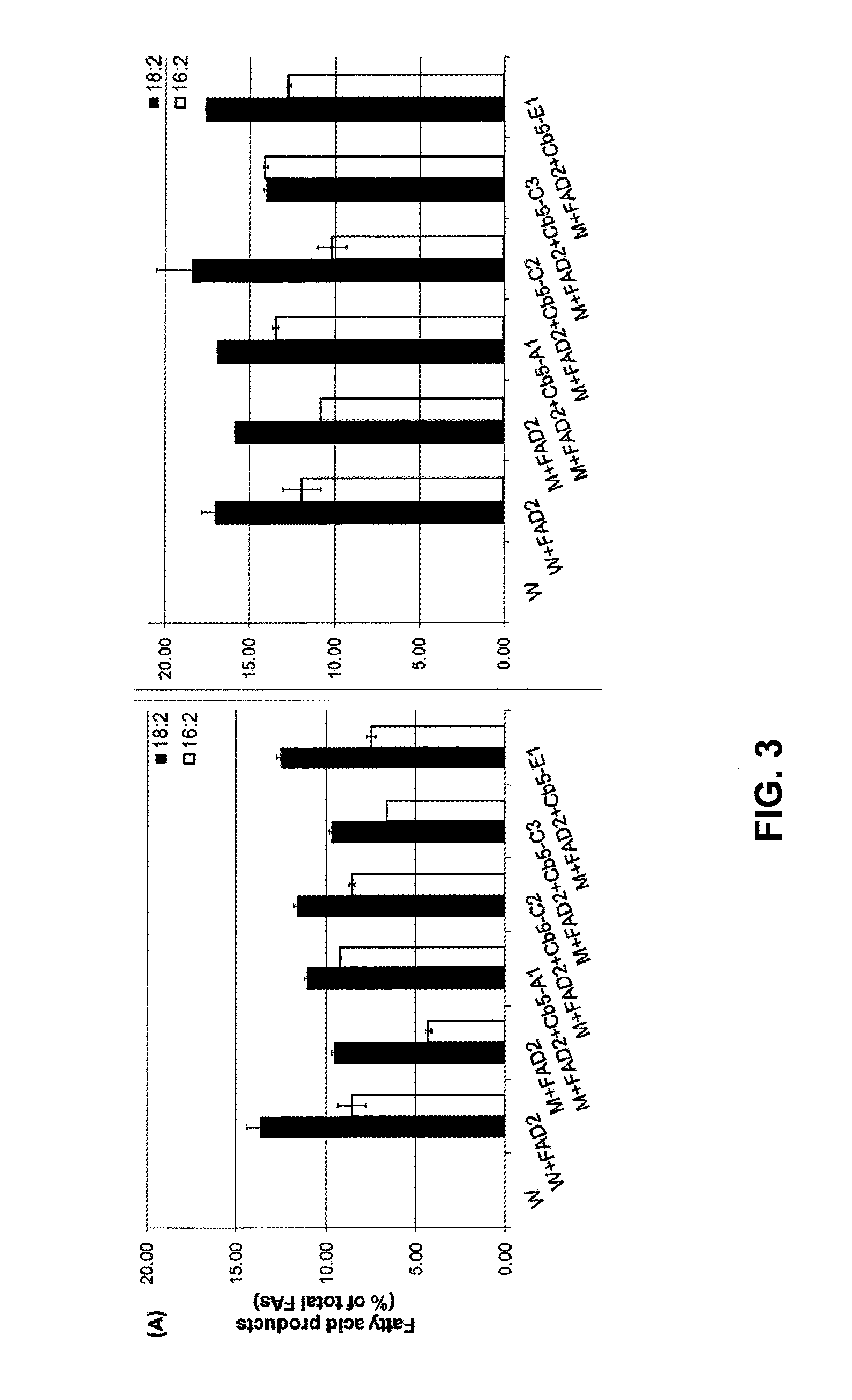
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
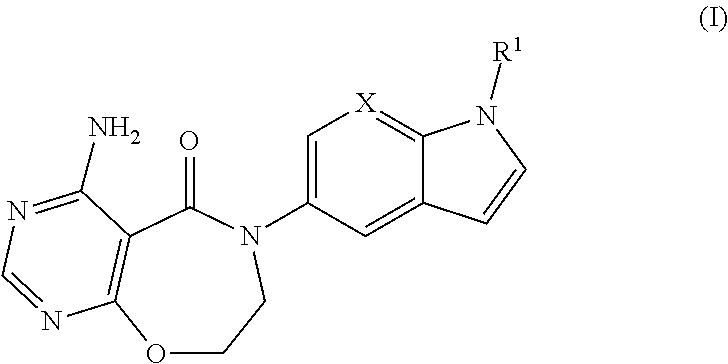
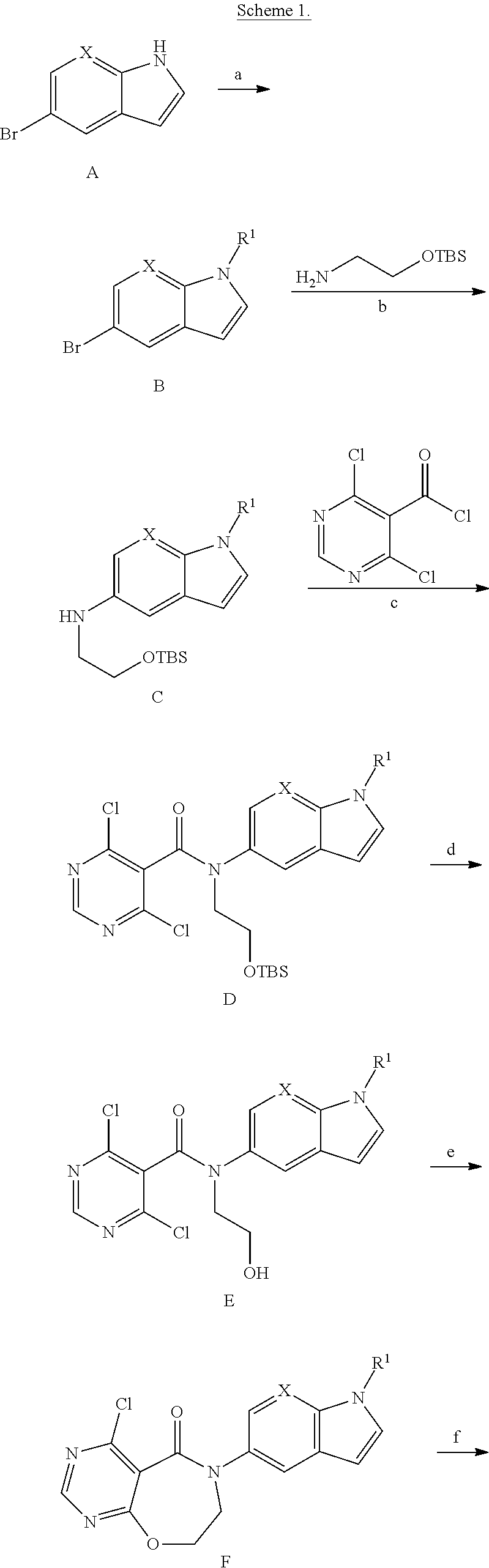
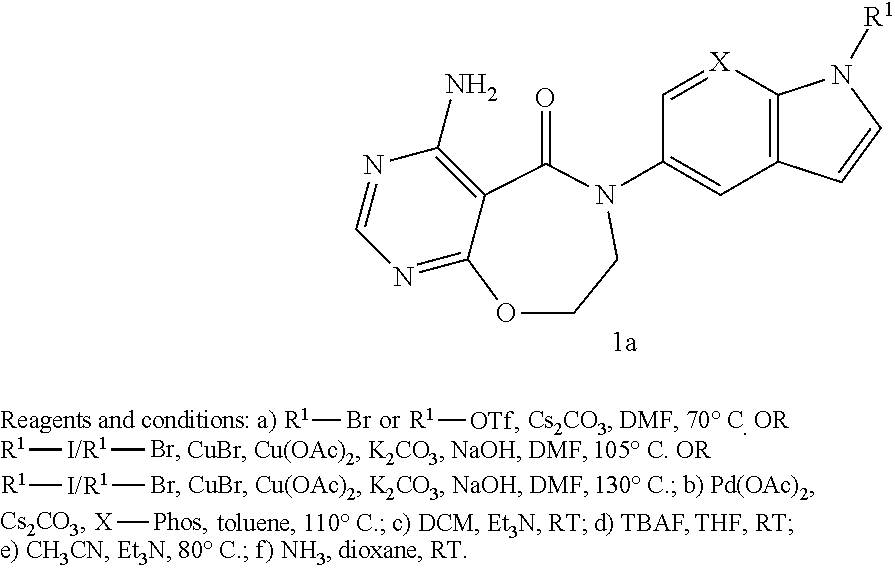
Urea derivatives having ACAT inhibitory activity, their preparation and their therapeutic and prophylactic use
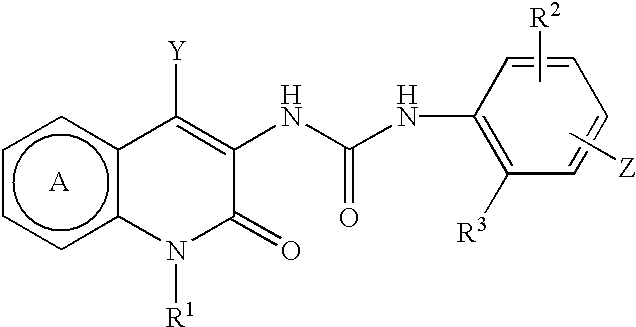
Compounds of formula (I): wherein: R1 is alkyl; R2a, R2b, R2c and R2d are the same or different and each is hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl or various other organic groups; R3 is alkyl; R4 is a group of formula (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII) or (IX): wherein: A1 is a single bond, alkylene or alkenylene; A2 is or alkenylene; A3 is a single bond, alkyleneor alkenylene; R5a and R5b are the same or different and each is hydrogen, alkyl or various other groups; R6 is alkyl or phenyl; R7 is hydrogen or alkyl; R8 is alkyl or various other groups; and n is 0 and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof have valuable inhibitory activity against acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Method for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids
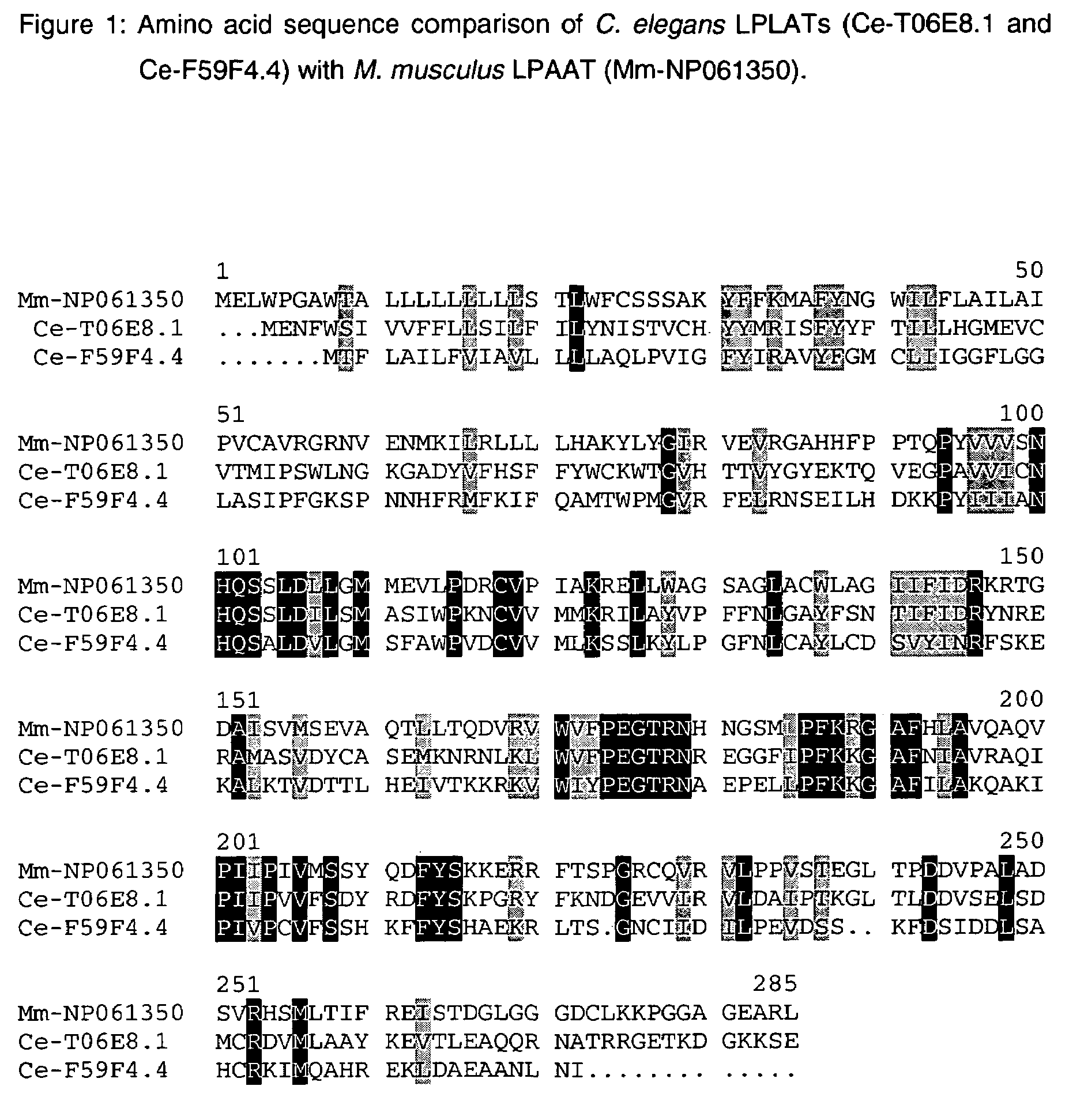
The present invention relates to a process for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids in an organism by introducing nucleic acids into the organism which code for polypeptides having acyl-CoA:lysophospholipid a cyltransferase activity. Advantageously, these nucleic acid sequences may, if appropriate together with further nucleic acid sequences coding for biosynthesis polypeptides of the fatty acid or lipid metabolism, be expressed in the transgenic organism. The invention furthermore relates to the nucleic acid sequences, to nucleic acid constructs comprising the nucleic acid sequences of the invention, to vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences and / or the nucleic acid constructs and to transgenic organisms comprising the abovementioned nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs and / or vectors. A further part of the invention relates to oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced by the process of the invention and to their use.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI
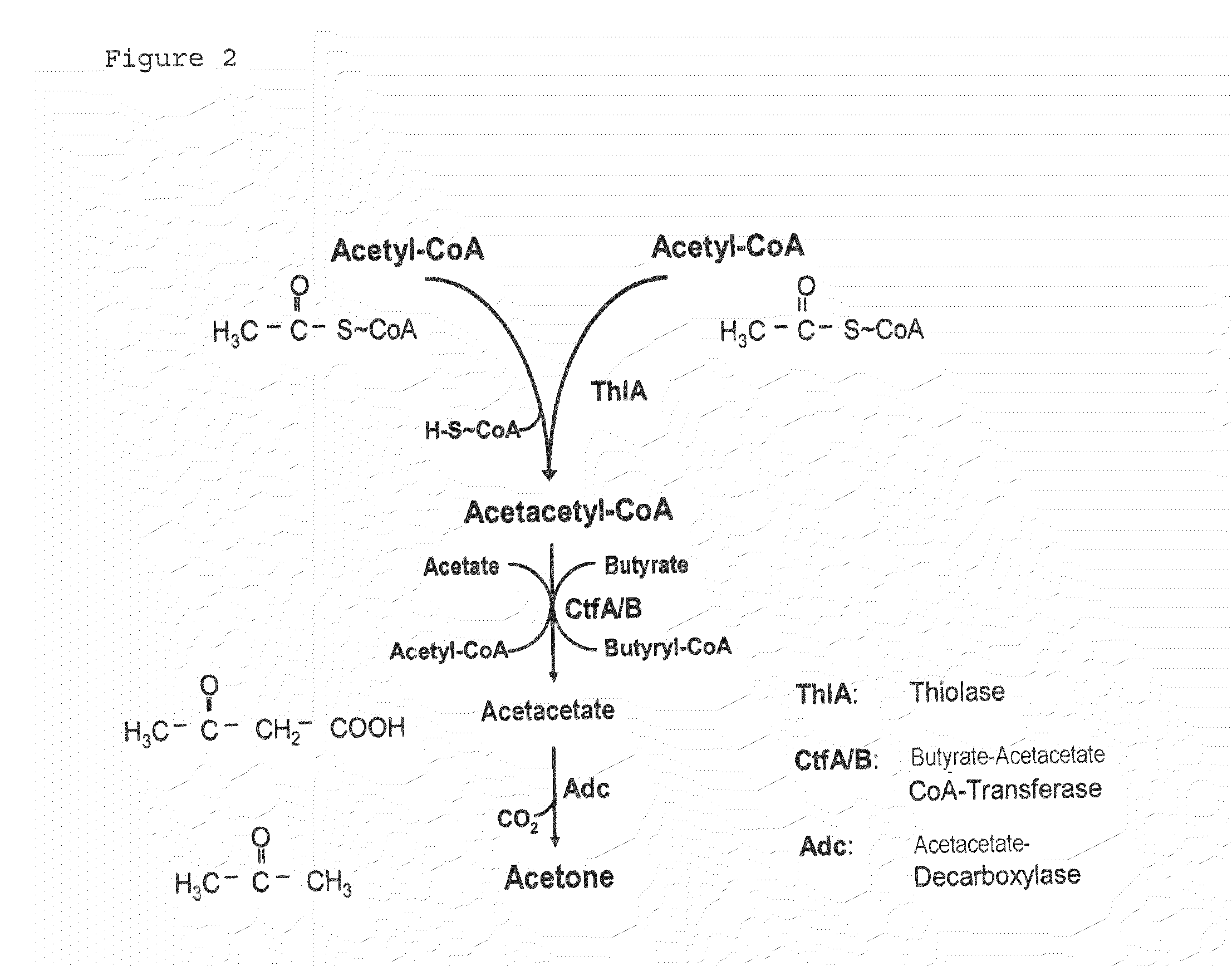
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
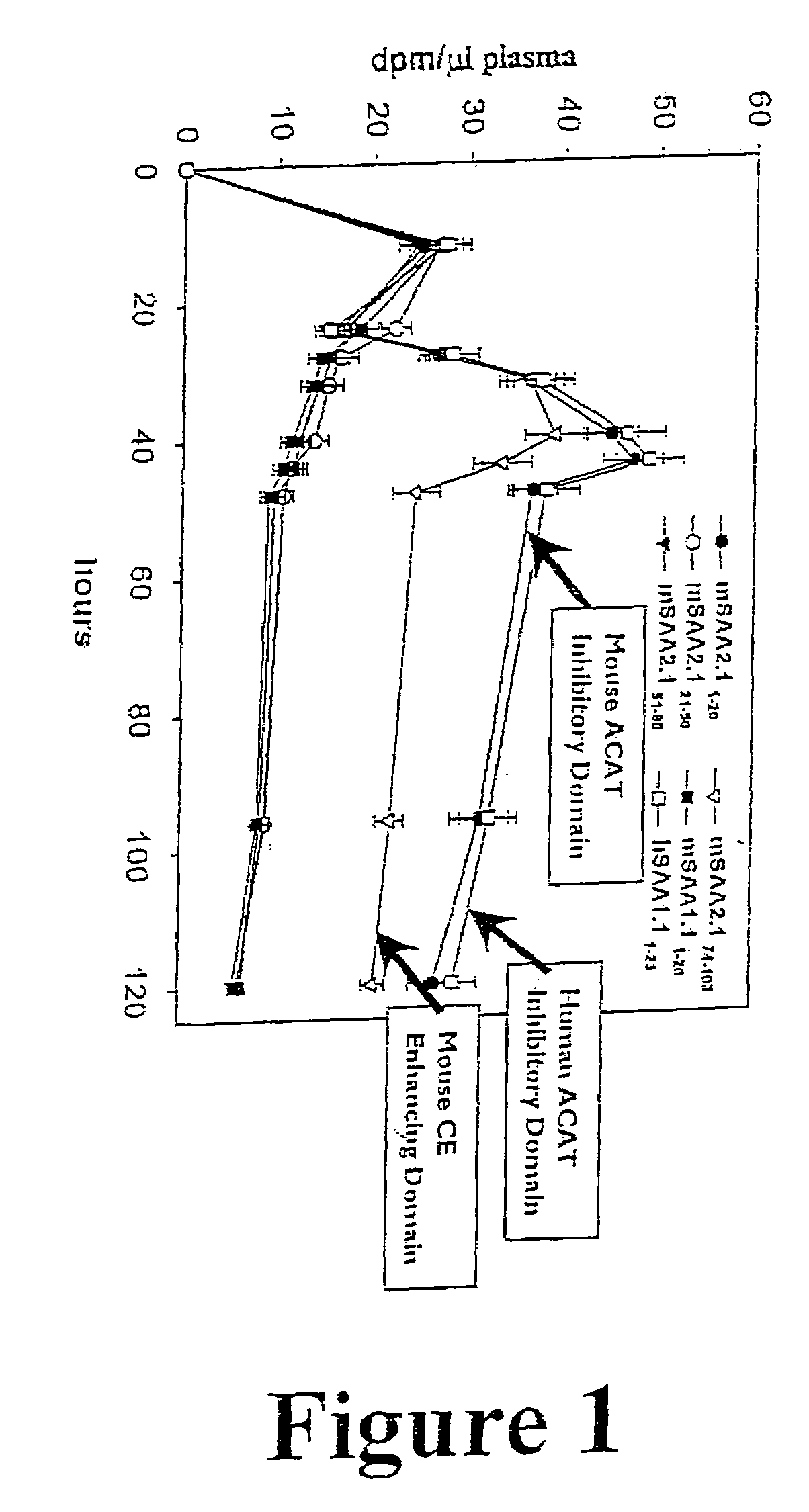
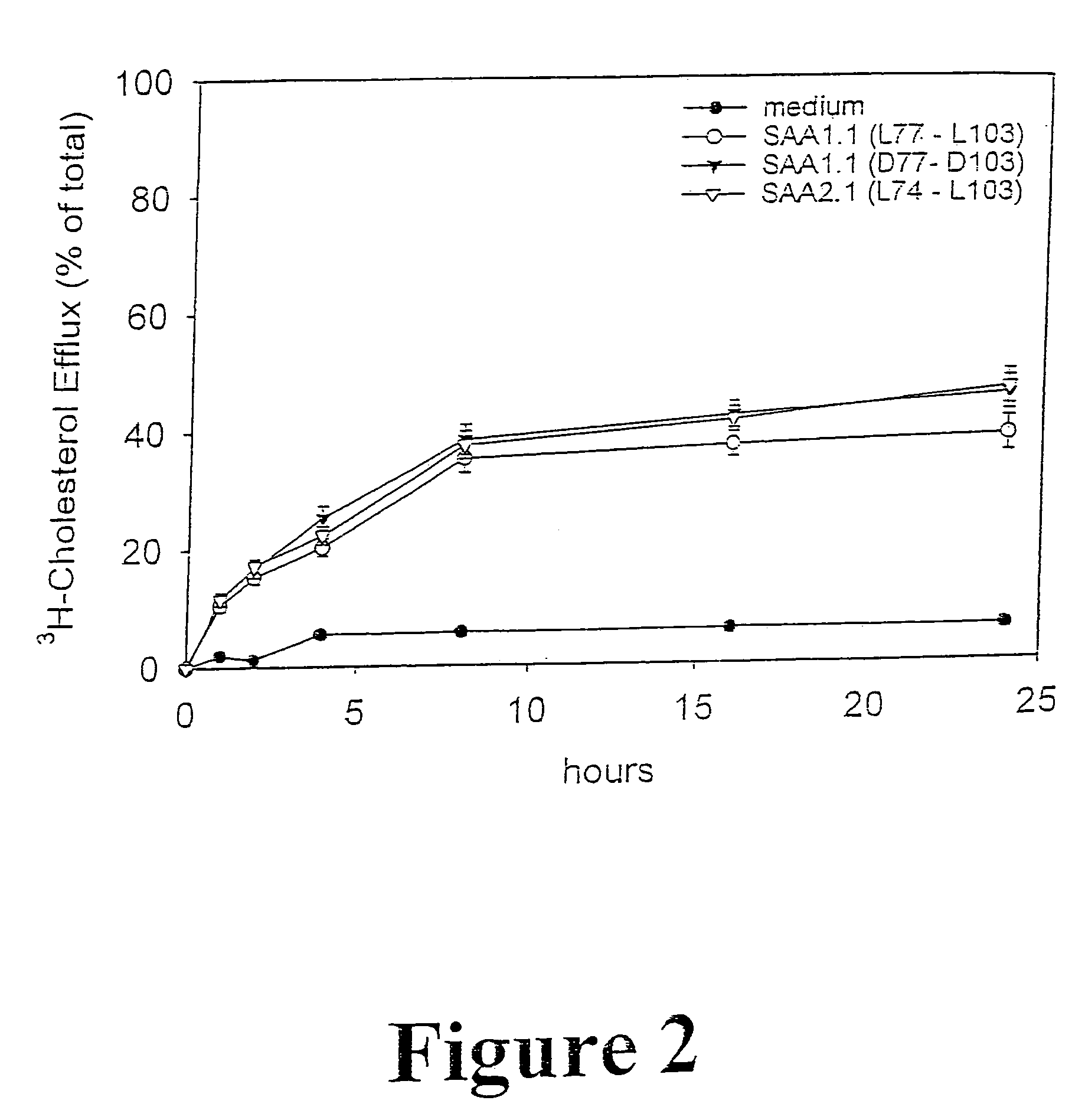
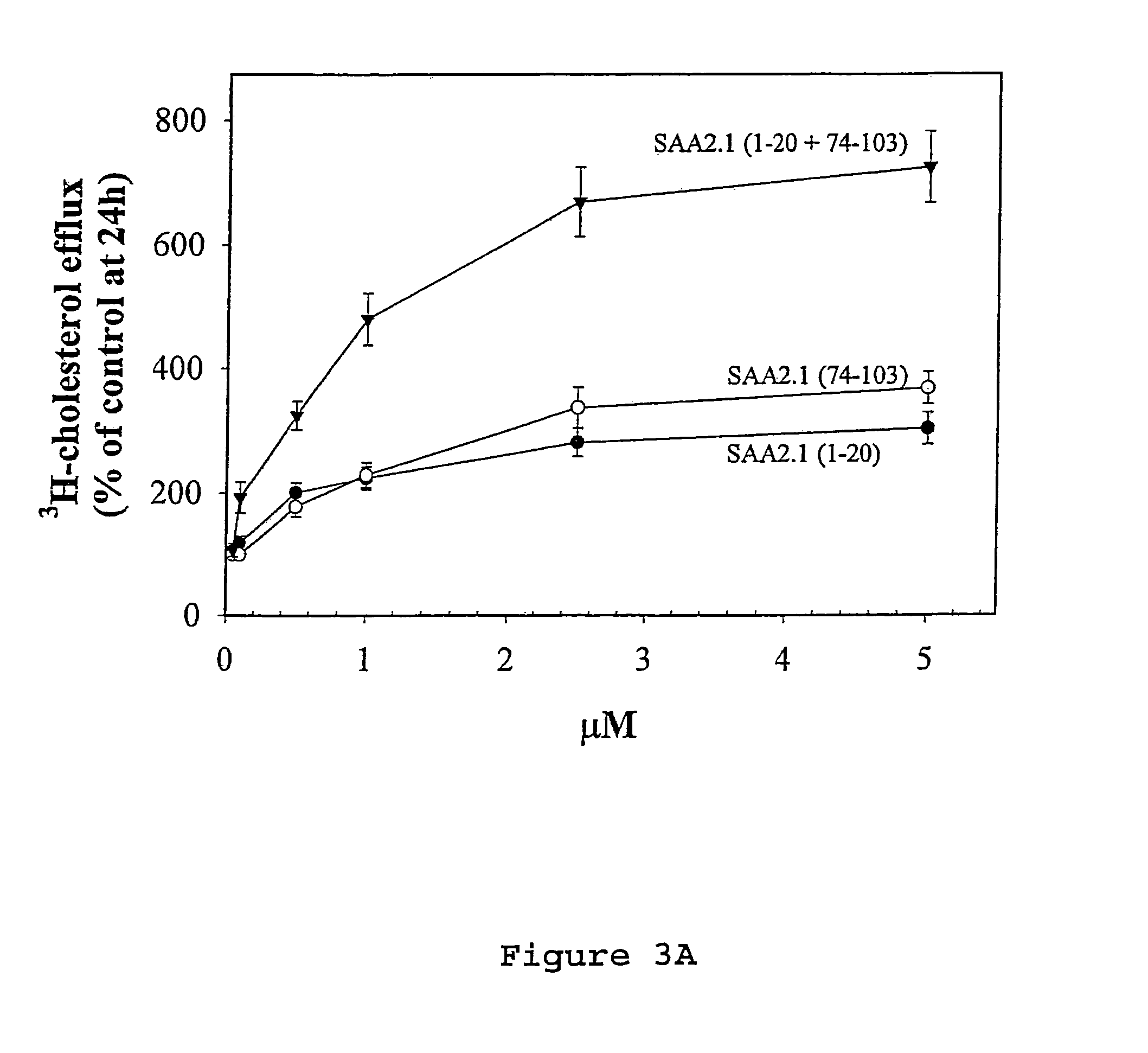
Compositions and methods for treating atherosclerosis
InactiveUS7291590B2Inhibition effectInhibiting the storage of cholesterolHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCholesterol acyl transferaseMedicine
Peptides and mimetics of selected domains of mammalian serum amyloid A isoform 2.1 (SAA2.1) and compounds and compositions thereof are provided that enhance the effect on macrophage cholesterol ester hydrolase activity and / or inhibit acyl CoA:cholesterol acyl transferase activity. Methods of using these compositions in the treatment and / or prevention of atherosclerosis as well as coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Methods for treating ACAT-related diseases
InactiveUS20050118226A1Inhibition is effectiveEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAcyl coenzyme ACholesterol acyltransferase
The invention relates to methods for administering inhibitors of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) activity, and for treating Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, and other ACAT-related diseases. The invention also relates to sustained release delivery systems.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
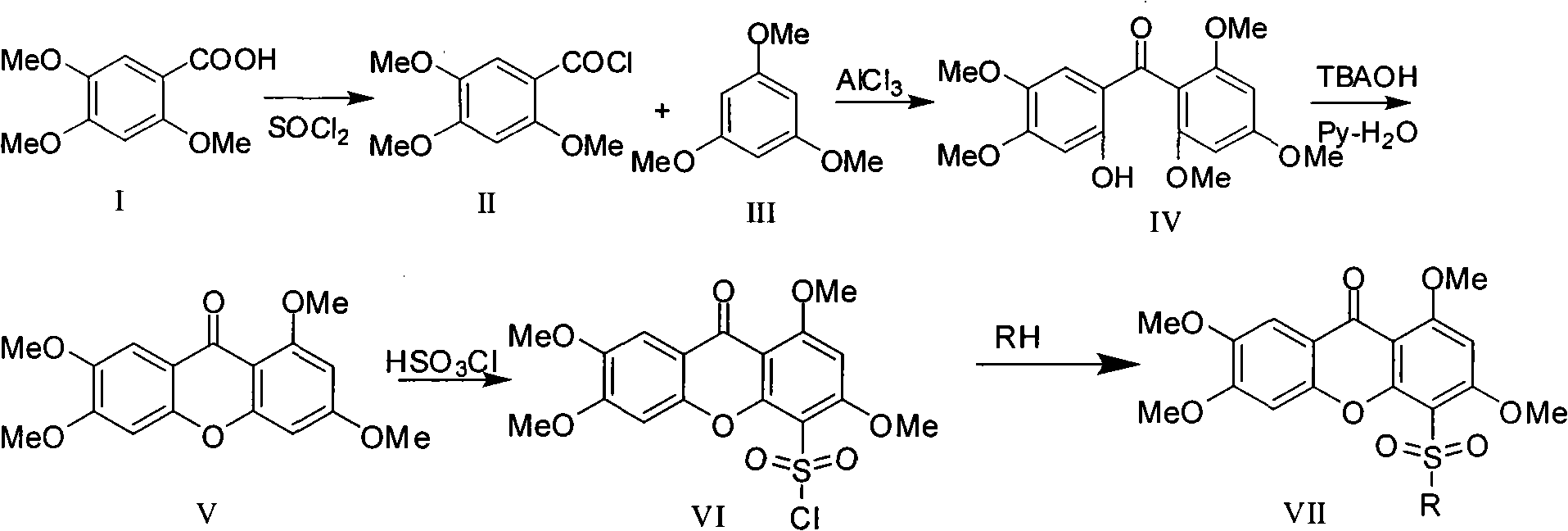
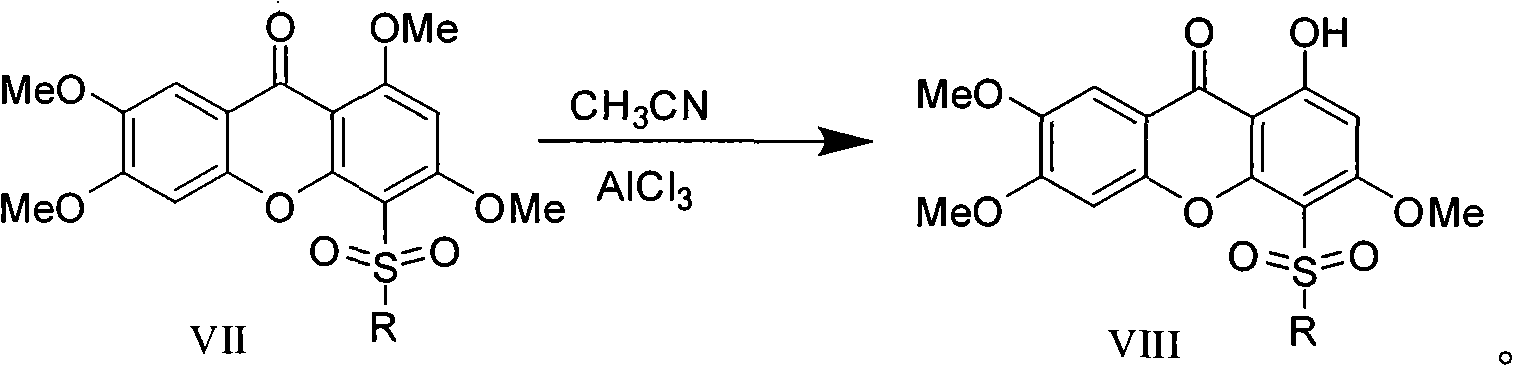
Novel sulfonyl substituted benzophenone oxide compounds, prepraring method and application thereof
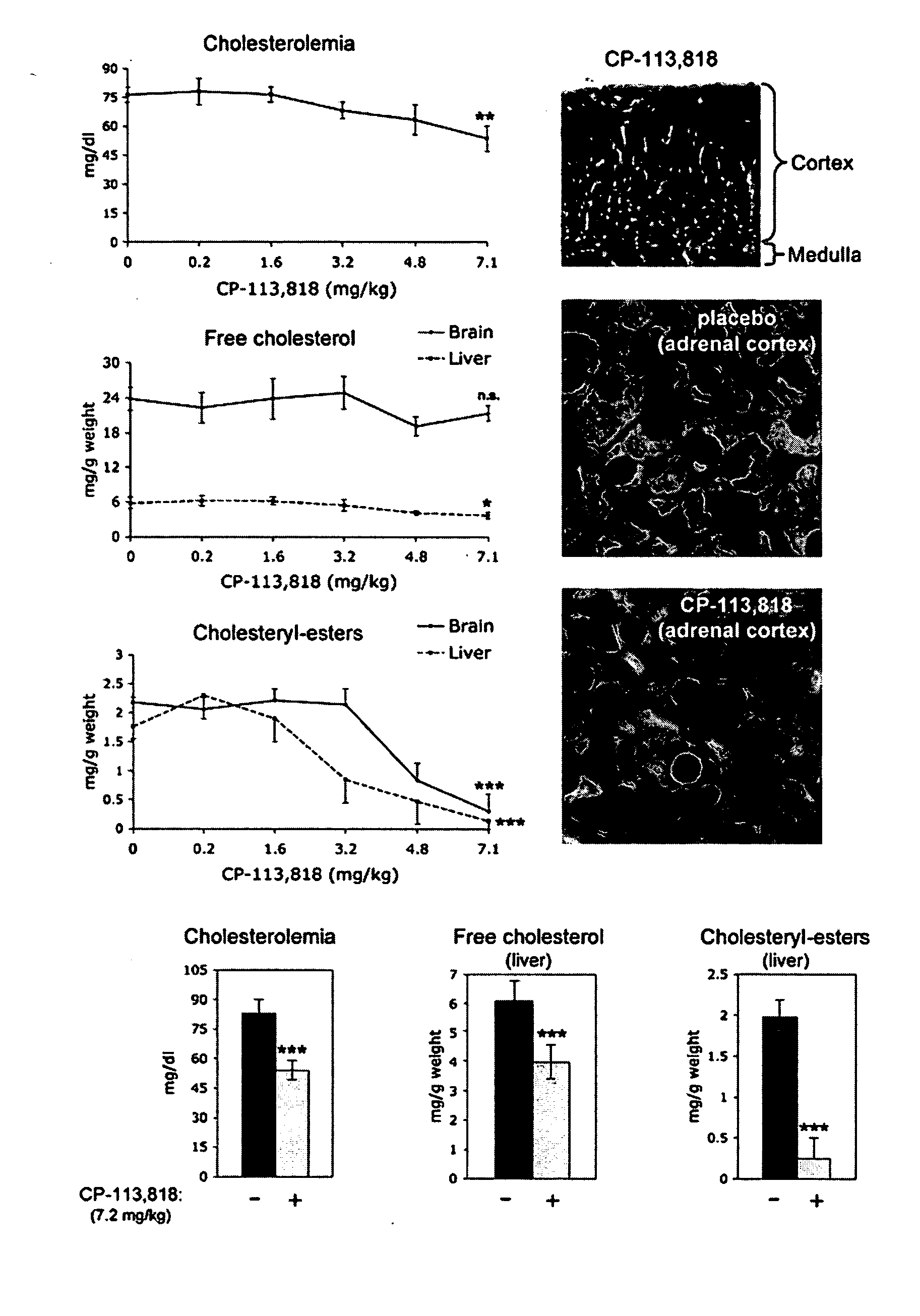
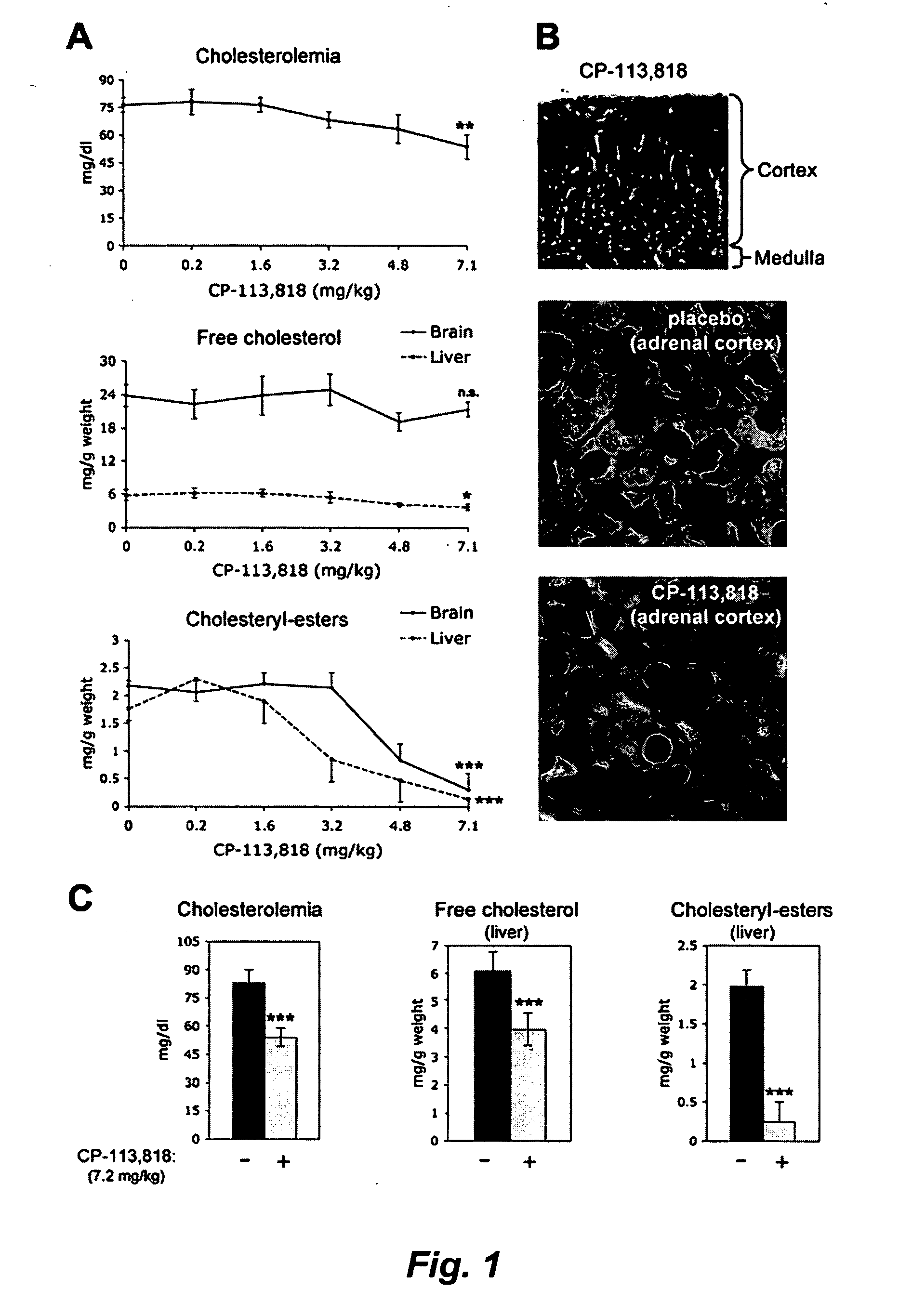
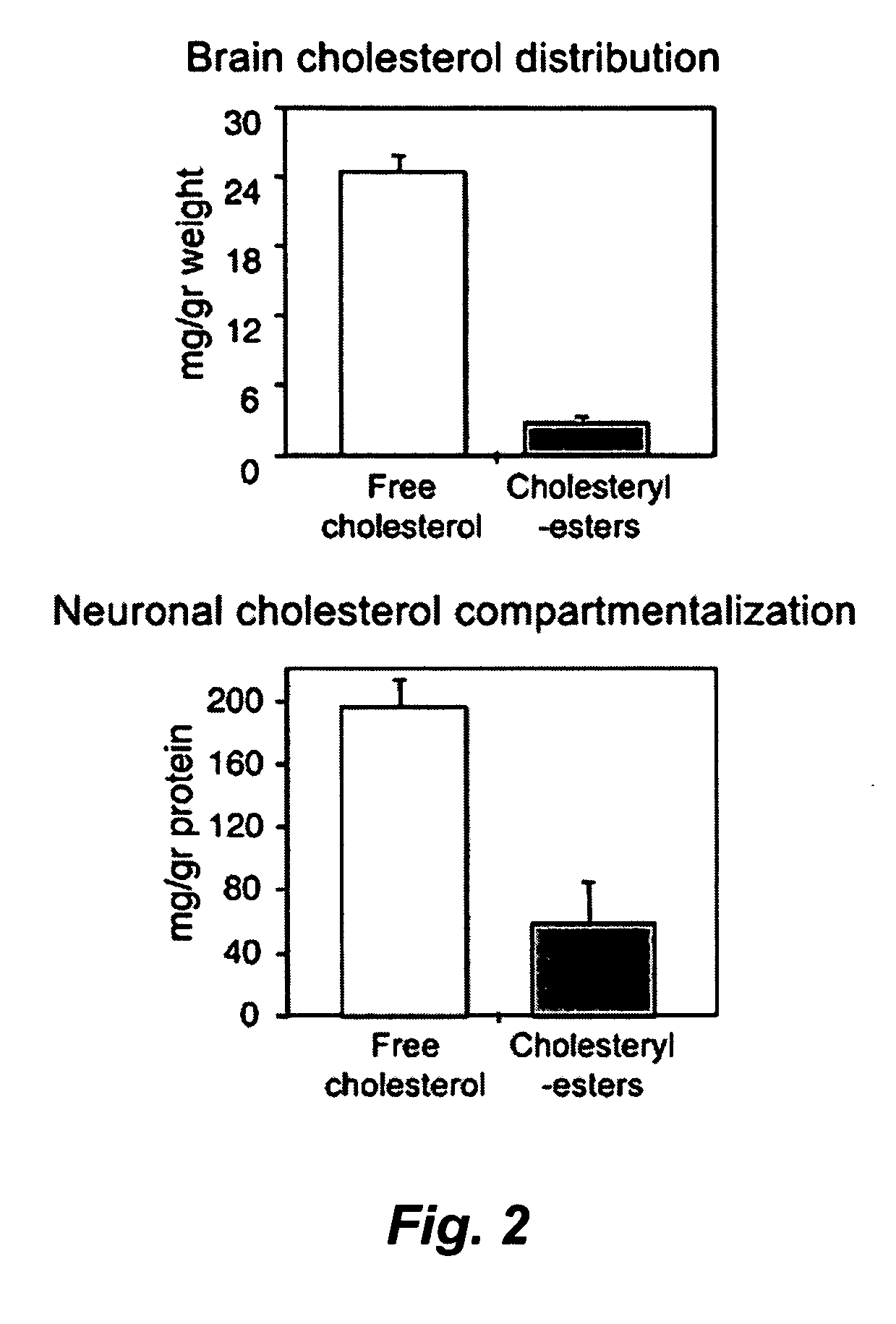
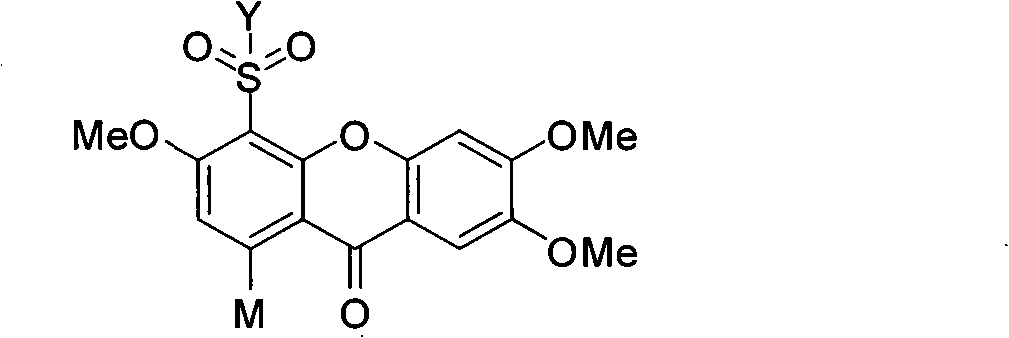
InactiveCN101270110AGood inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAcylcoenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase
The present invention relates to the field of medical technology, and in particular relates to a category of novel sulphonyl substituted xanthene ketone compounds that have a structural formula as shown in the right, a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has high inhibitory activity for ACAT1 / ACAT2; most of the compounds have high inhibitory activity for acyl coenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). The compounds can be used for preparing anti-atherosclerosis drug combination. Furthermore, the compounds can be used as a preventive or a treating agent of such diseases as angina, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, apoplexy, Alzheimer's disease, acute coronary syndrome, PTCA or restenosis of coronary artery after a bracket is arranged. The compounds can be used as a treating agent to adjust the function of sebaceous glands of the skin and inhibit the excessive generation of sebum. And the compounds can be used for treating such diseases as acne-like damage caused by oily skin, acne, seborrhea and corticosteroids.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
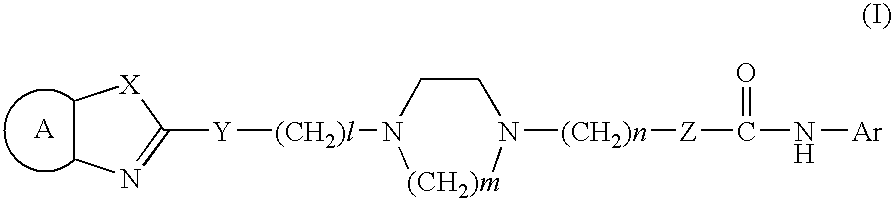
Cyclic diamine compounds and medicine containing the same
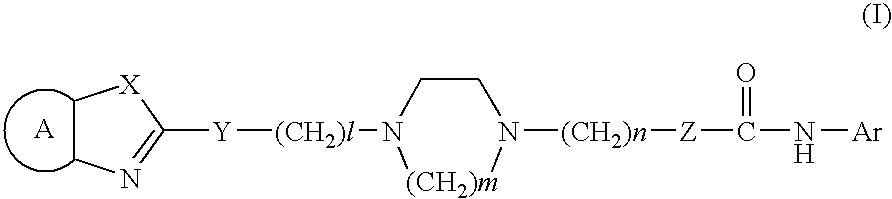
InactiveUS6969711B2Highly soluble in waterImprove biological activityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAcylcoenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferaseSilylene
The present invention offers novel cyclic diamine compounds and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same.The present invention relates to a compound represented by the formula (I) or salt(s) or solvate(s) thereof. (In the formula, is an optionally substituted divalent residue of benzene, pyridine, cyclohexane or naphthalene or is a vinylene group whereAr is an optionally substituted aryl group;X is —NH—, oxygen atom or sulfur atom;Y is —NR1—, oxygen atom, sulfur atom, sulfoxide or sulfone;Z is a single bond or —NR2—;R1 is hydrogen atom, optionally substituted lower alkyl group, optionally substituted aryl group or optionally substituted silyl lower alkyl group;R2 is hydrogen atom, optionally substituted lower alkyl group, optionally substituted aryl group or optionally substituted silyl lower alkyl group;l is an integer of from 0 to 15;m is an integer of 2 or 3; andn is an integer of from 0 to 3).The compound of the present invention is useful as a pharmaceutical composition, particuarly as an inhibitor of acyl coenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT).
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Plant sterol acyltransferases
InactiveUS7157619B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant sterol
The present invention is directed to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-like polypeptides (LCAT) and acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferases-like polypeptides (ACAT). The invention provides polynucleotides encoding such cholesterol:acyltansferases-like polypeptides, polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides, and the use of such polynucleotides to alter sterol composition and oil production in plants and host cells. Also provided are oils produced by the plants and host cells containing the polynucleotides and food products, nutritional supplements, and pharmaceutical composition containing plants or oils of the present invention. The polynucleotides of the present invention include those derived from plant sources.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081299A1Improve concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
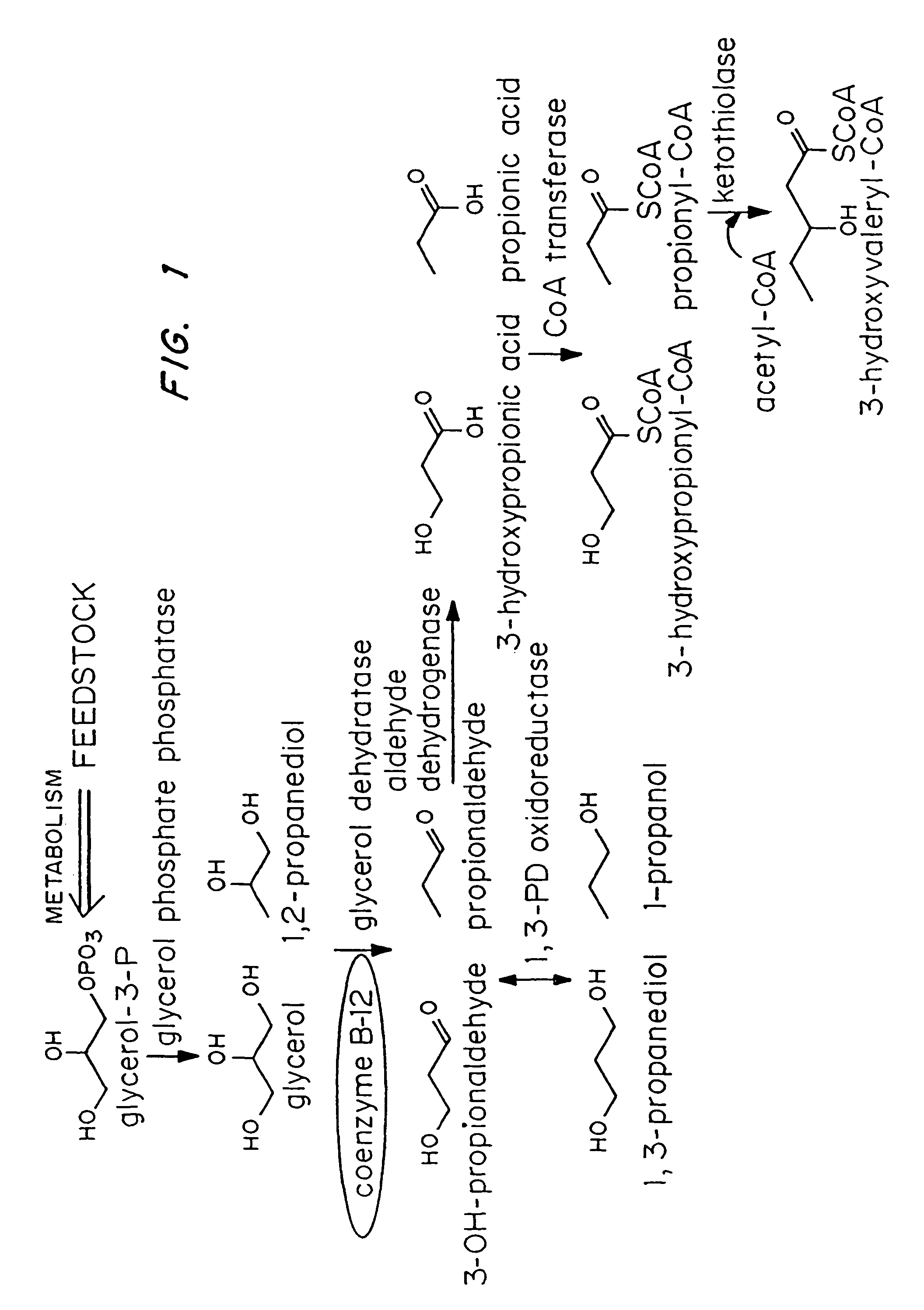
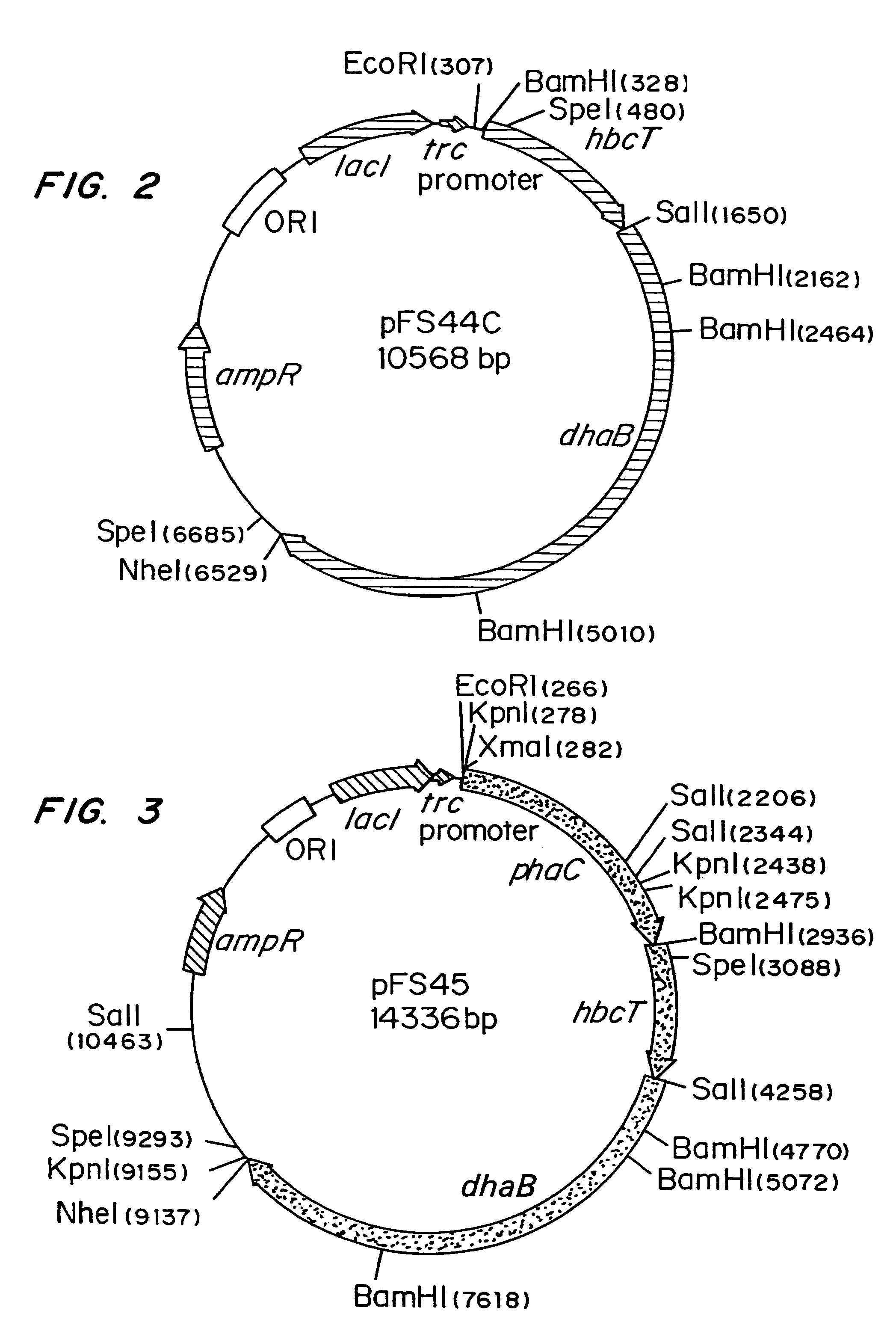
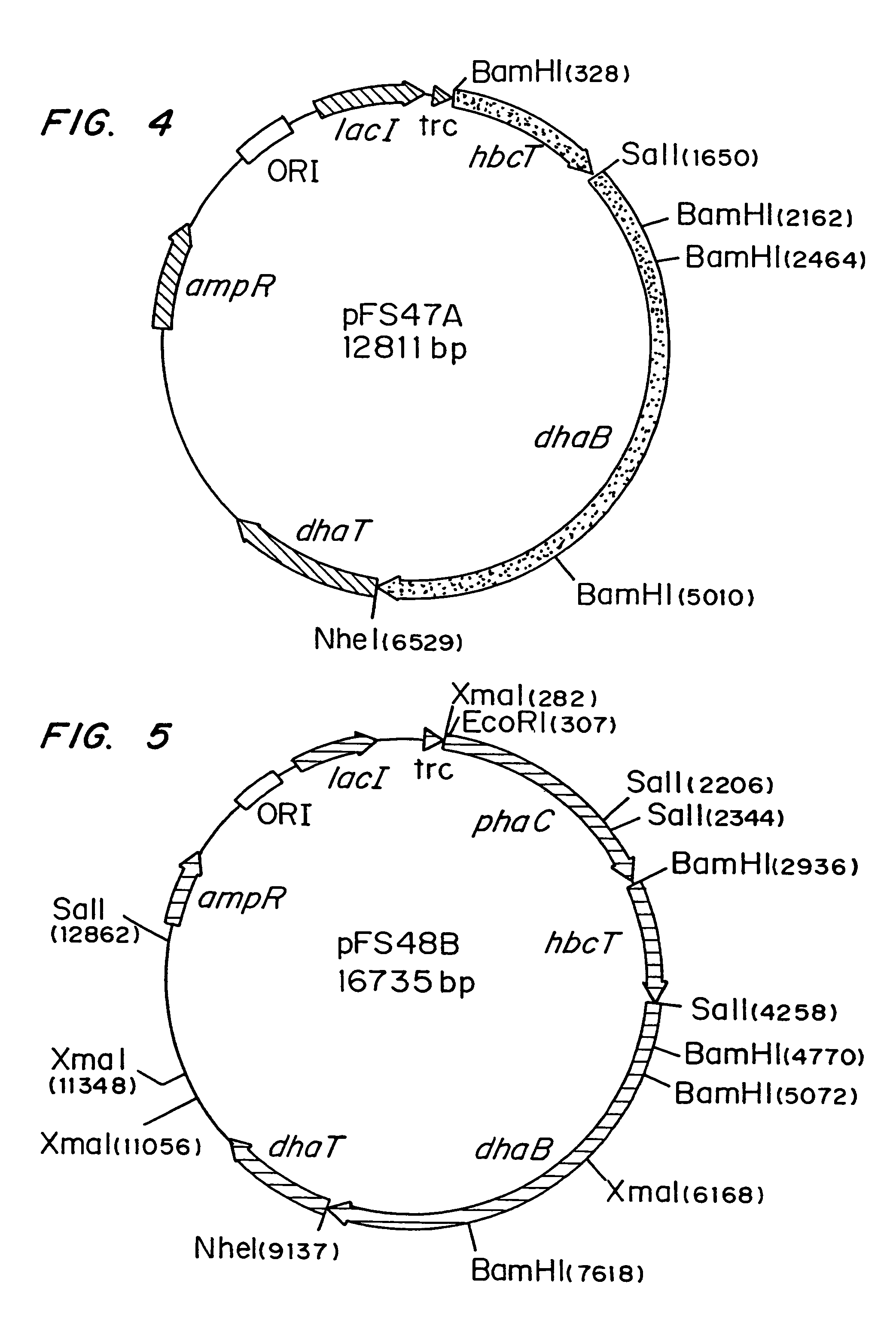
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalerate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Novel compounds as diacylglycerol acyltransferase inhibitors
This invention relates to novel compounds which are inhibitors of acyl coenzyme A: diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT-1), to pharmaceutical compositions containing them, to processes for their preparation, and to their use in therapy, alone or in combination with weight management therapies or other triglyceride lowering therapy for the prevention or treatment of diseases related to DGAT-1 dysfunction or where modulation of DGAT-1 activity may have therapeutic benefit including but not limited to obesity, obesity related disorders, genetic (Type 1, Type 5 hyperlipidemia) and acquired forms of hypertriglyceridemia or hyperlipoproteinemia-related disorders, caused by but not limited to lipodystrophy, hypothyroidism, medications (beta blockers, thiazides, estrogen, glucocorticoids, transplant) and other factors (pregnancy, alcohol intake), hyperlipoproteinemia, chylomicronemia, dyslipidemia, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, diabetes, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular outcomes, angina, excess hair growth (including syndromes associated with hirsutism), nephrotic syndrome, fibrosis such as myocardial, renal and liver fibrosis, hepatitis C virus infection and acne or other skin disorders.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
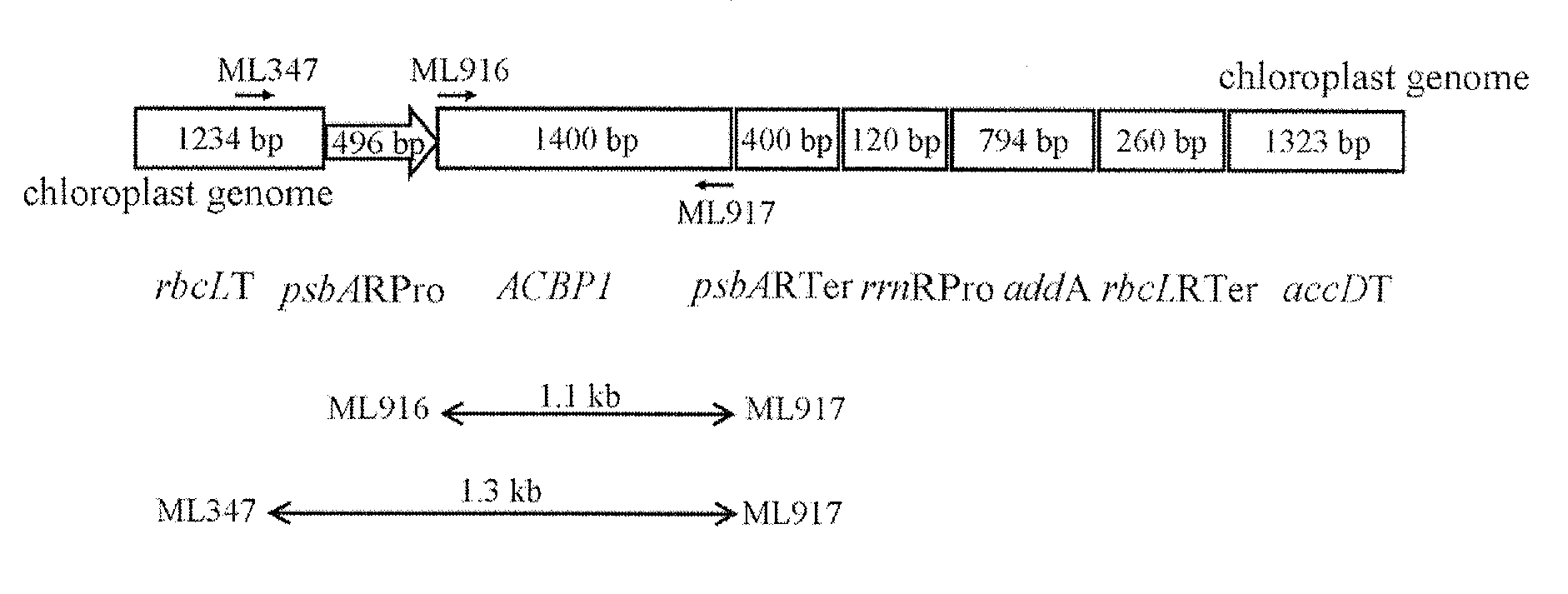
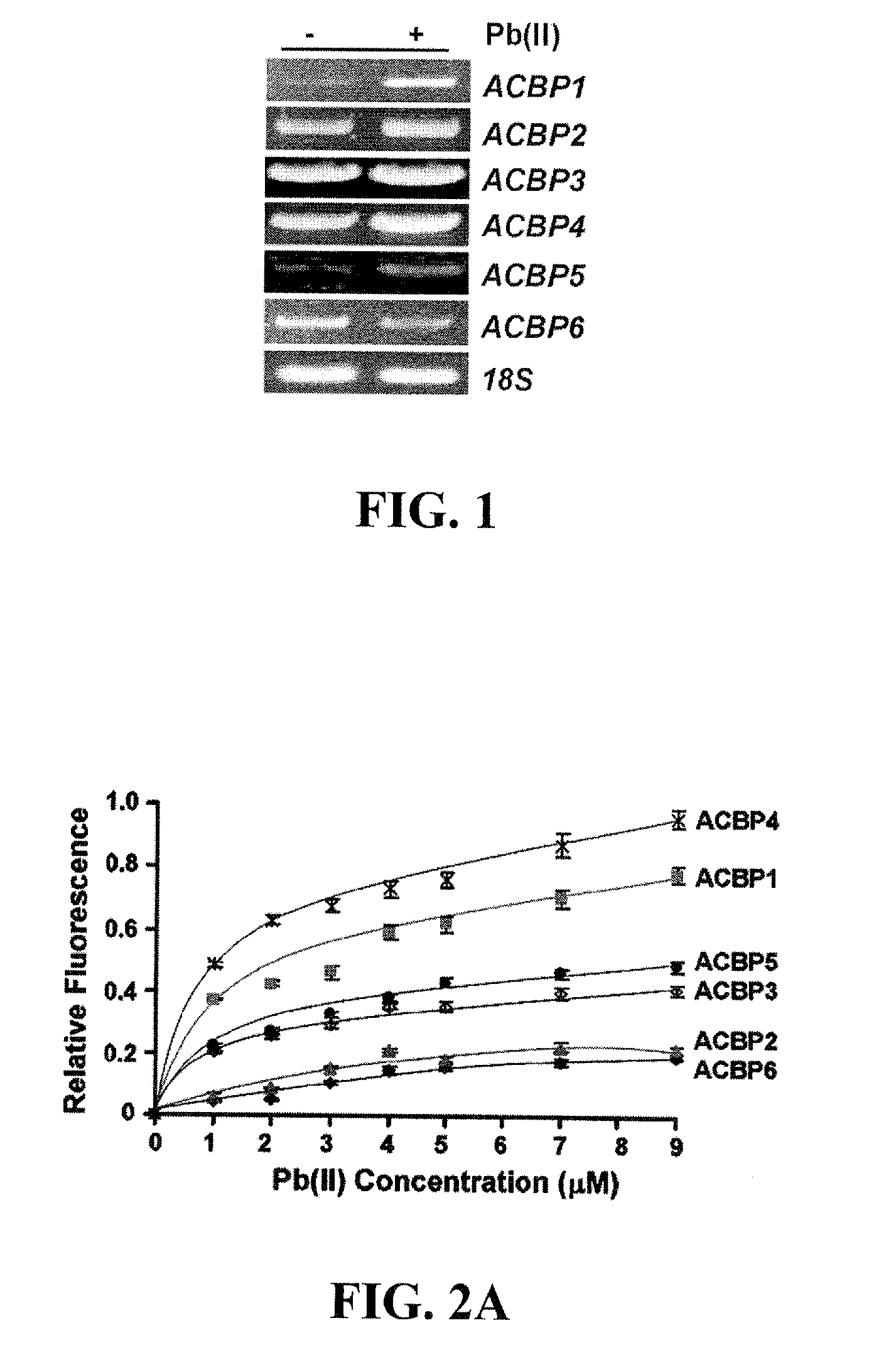
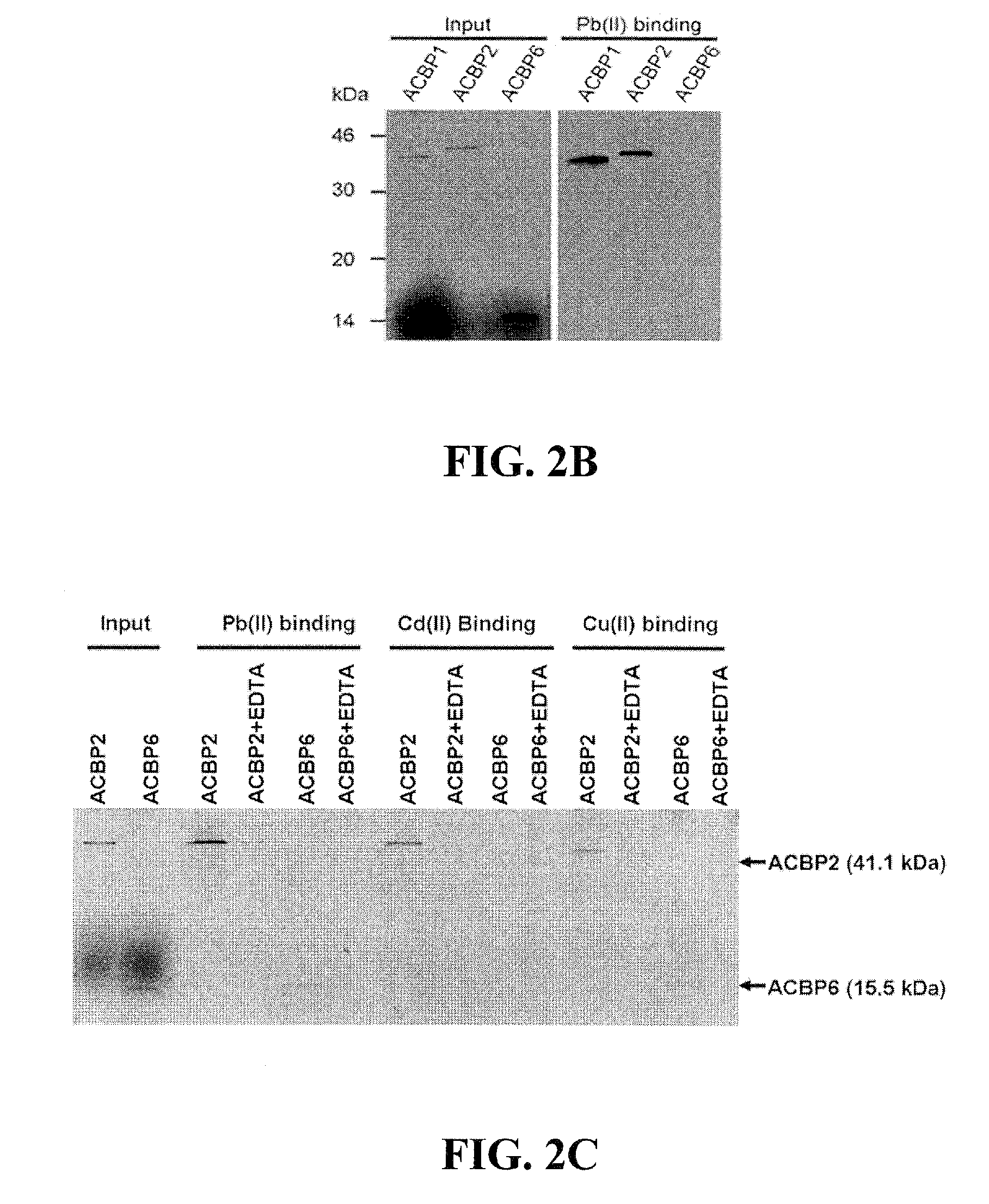
Methods of Using Transformed Plants Expressing Plant-Derived Acyl-CoEnzyme-A-Binding Proteins in Phytoremediation
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-2)
Nucleic acid compositions encoding novel ACAT proteins, as well as the novel ACAT-2 proteins, (ACAT-2) are provided. Also provided are methods of producing the subject nucleic acid and protein compositions. The subject polypeptide and nucleic acid compositions find use in a variety of applications, including research, diagnostic, and therapeutic agent screening applications, as well as in treatment therapies for disease conditions associated with ACAT-2 activity.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS +1
Production of fatty acids esters
A microbial cell is used for producing at least one fatty acid ester, wherein the cell is genetically modified to contain (i) at least one first genetic mutation that enables the cell to produce at least one fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A (CoA) thereof by increased enzymatic activity in the cell relative to the wild type cell of malonyl-CoA dependent and malonyl-ACP independent fatty acyl-CoA metabolic pathway, wherein the fatty acid contains at least 5 carbon atoms; and (ii) a second genetic mutation that increases the activity of at least one wax ester synthase in the cell relative to the wild type cell and the wax ester synthase has sequence identity of at least 50% to a polypeptide of SEQ ID NO: 1-8 and combinations thereof or to a functional fragment of any of the polypeptides for catalyzing the conversion of fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A thereof to the fatty acid ester.
Owner:CARGILL INC
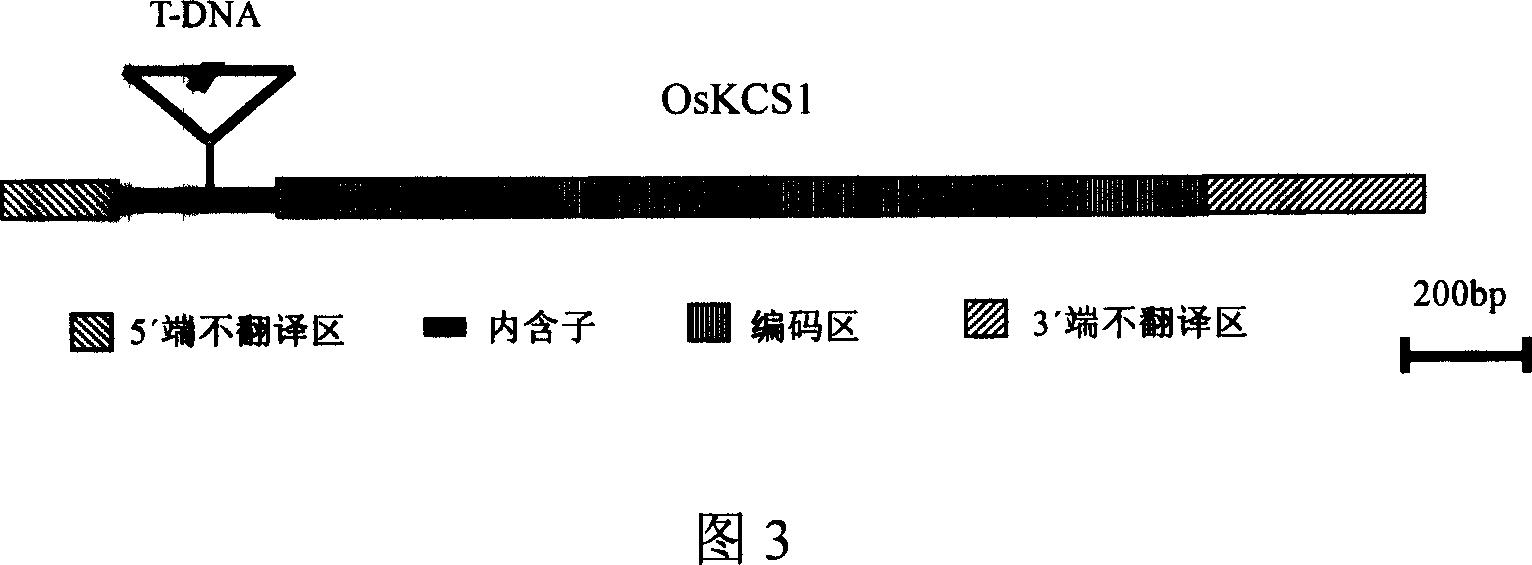
Paddy rice gene of synthetase of coded beta - keto acyl coenzyme A
This invention provides a rice gene coding beta-keto co A synthetase, OsKCS1, which comprises 2186bp and 1560bp coding zones at the upstream of the start codon with promoter function, codes 519 amino acid, and contains typical FAE1 CUT1 RppA domain. The function-deficient mutant P1424 obtained by inserting T-DNA into rice OsKCS1 gene has short plants, occasionally curled leaves, and low fruiting rate. Further research shows that the wax at the surfaces of the mutant gas-generating organs is obviously reduced, and the draught resistance is seriously influenced. The expression of OsKCS1 gene in the mutant can recover its wild phenotype, thus can confirm the direction relationship between OsKCS1 gene and synthesis and growth of wax on rice surfaces. The identification of the gene is important to research on synthesis of wax on rice surfaces, and breeding of draught-resistant rice or other monocotyledon crops.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Naphthyridine derivatives
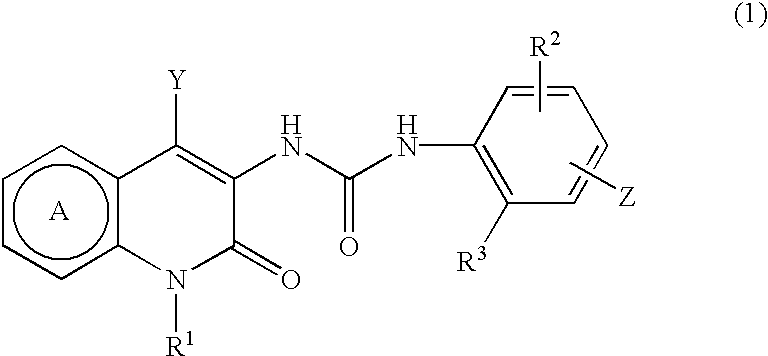
A compound of the formula (I):wherein Ring A is substituted or unsubstituted pyridine ring, Y is substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, etc., R1 is hydrogen, or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, etc., R2 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, R3 is lower alkyl, Z is1) -D1-Q [D1 is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., Q is hydroxy, carboxyl, etc.], or2) -D2M-E-W [D2 is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., M is oxygen, sulfur, etc., E is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., W is hydroxyl, carboxyl, etc.],or a prodrug thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the same, which exhibits acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT) inhibitory activity, and is useful as an agent for treatment of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Combined medication combination for tumor immnuotherapy
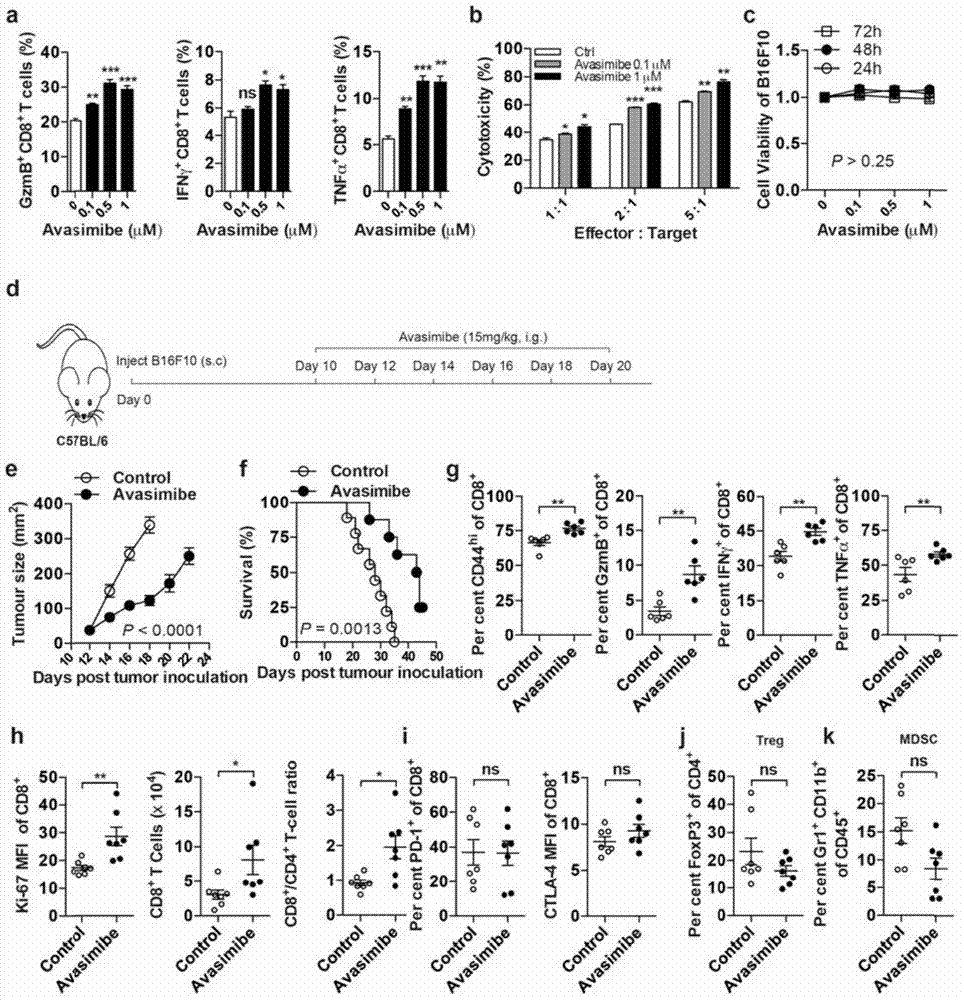
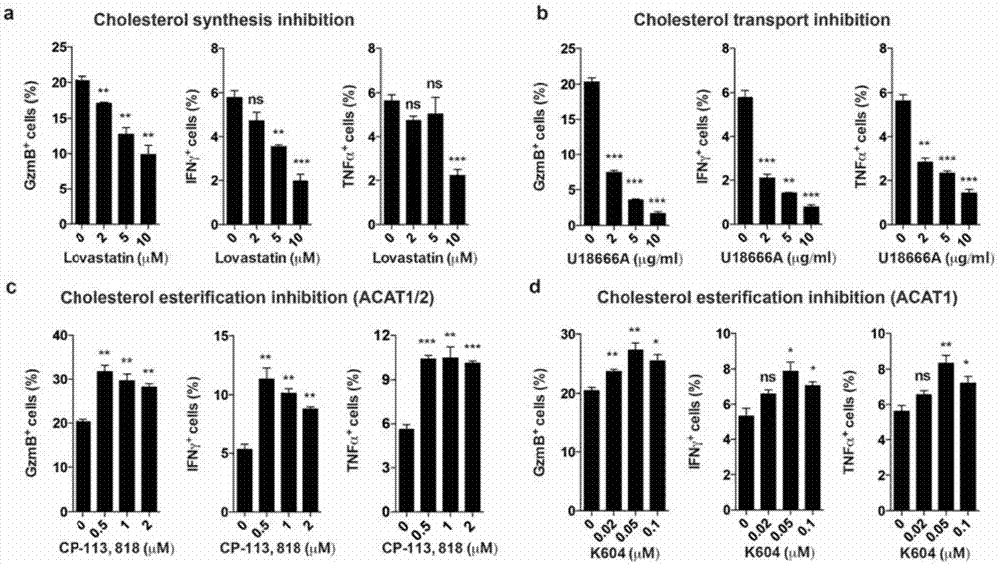
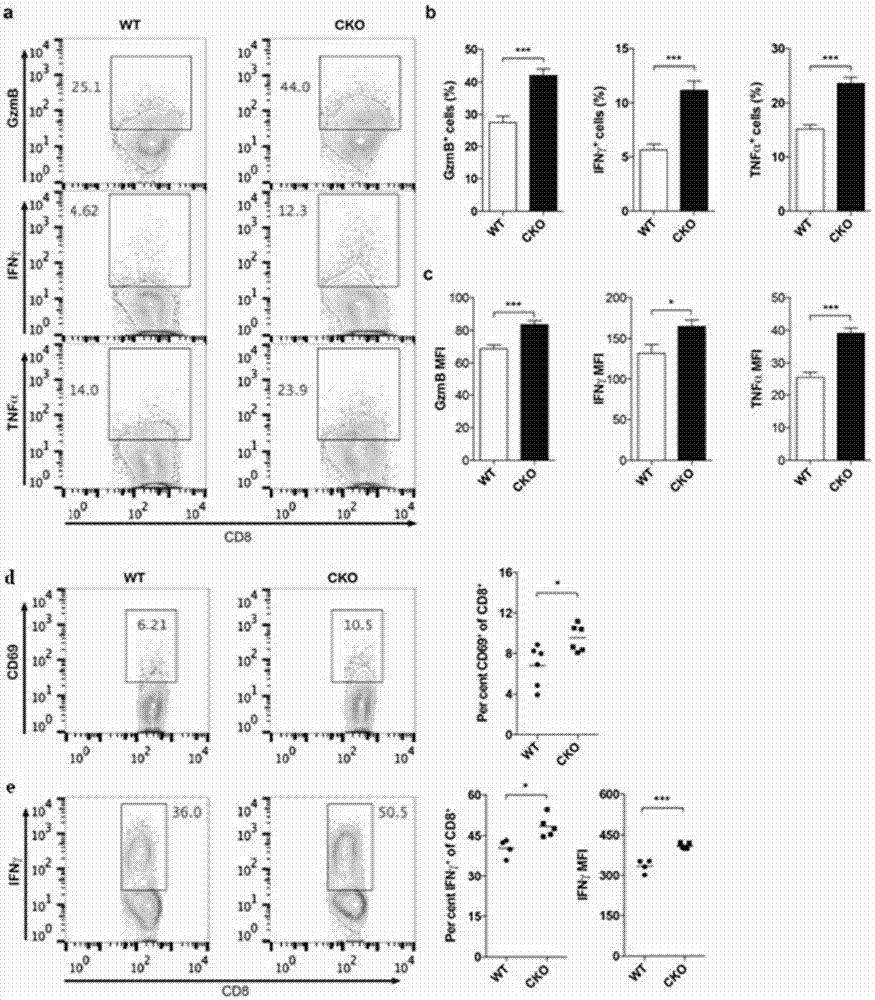
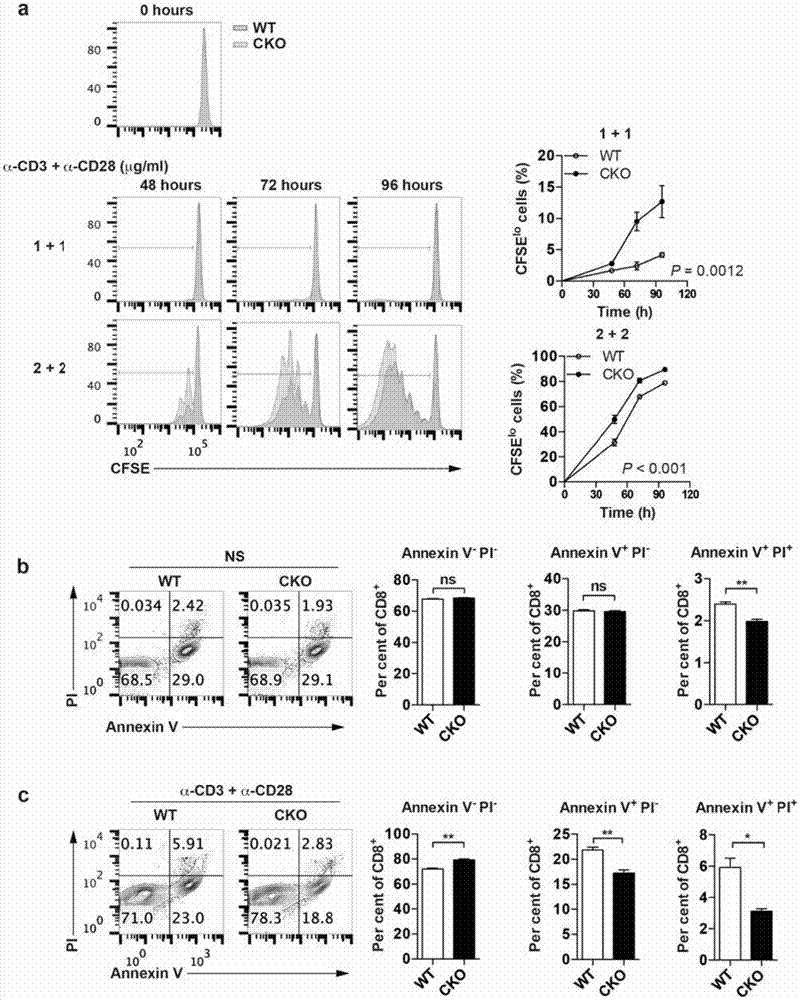
ActiveCN106955354AInhibitory activityEnhance antigen-specific immune responseAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCD8Acyl coenzyme A
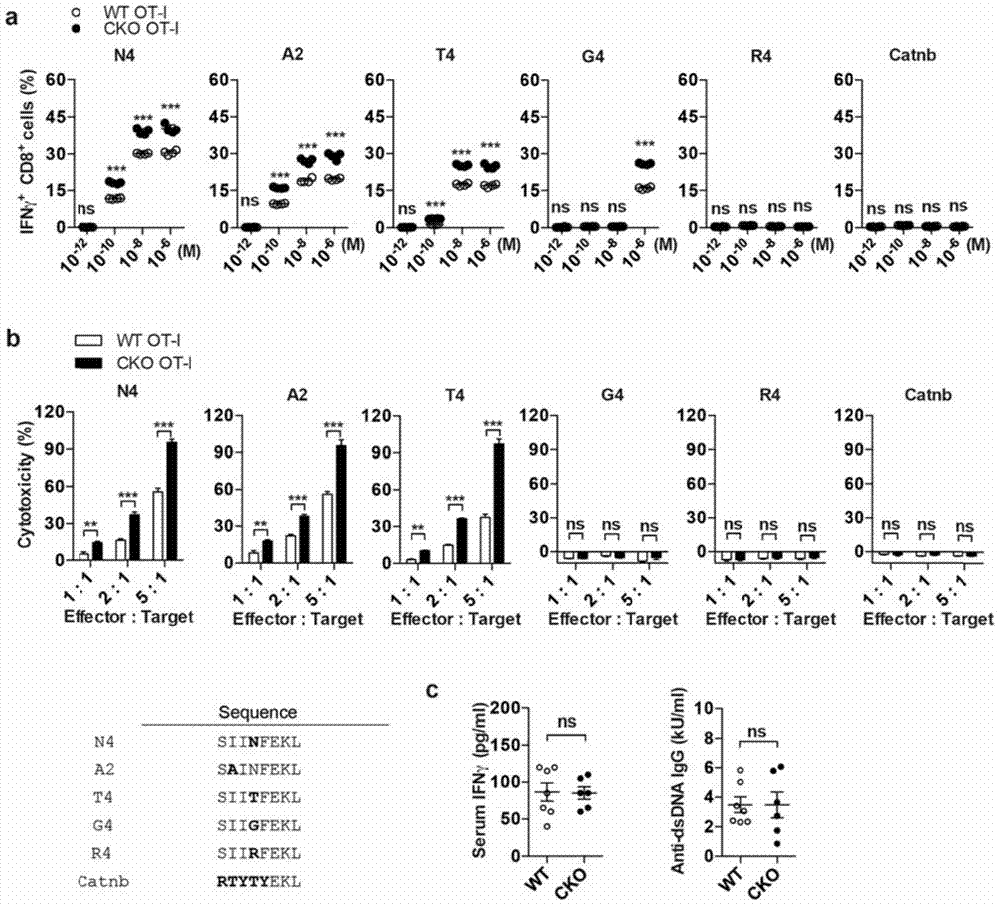
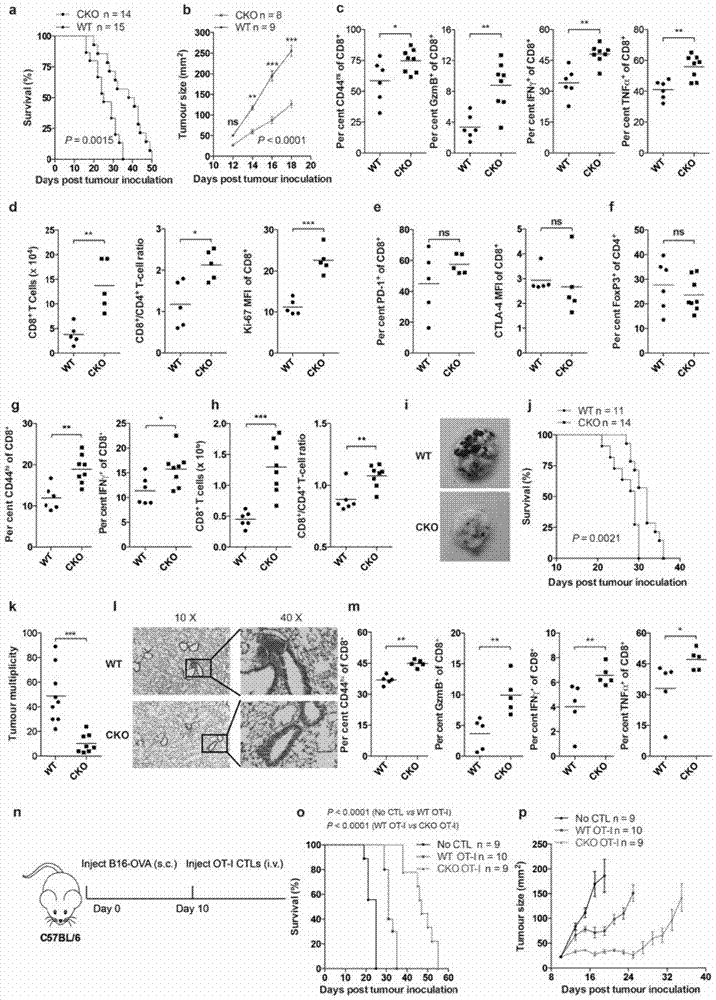
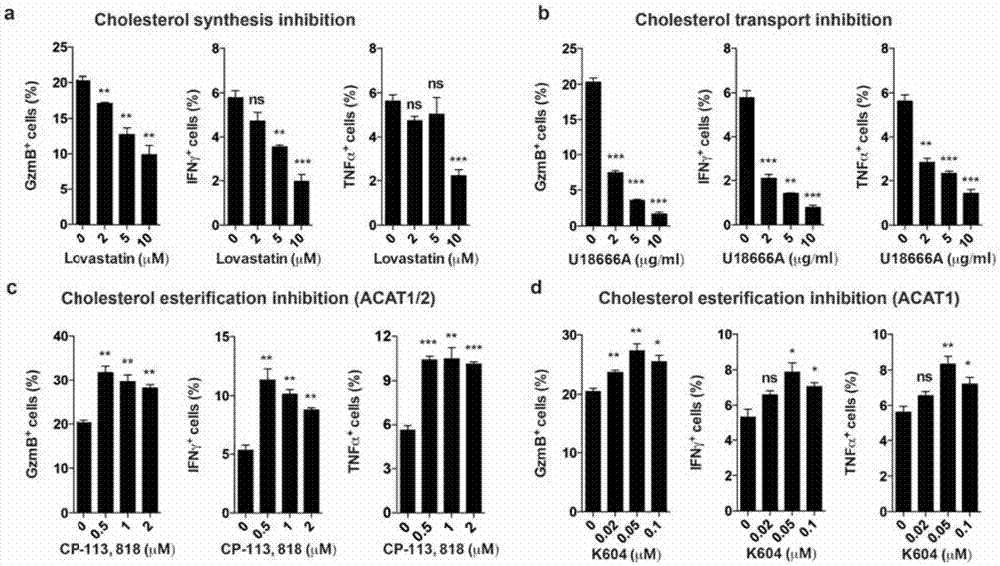
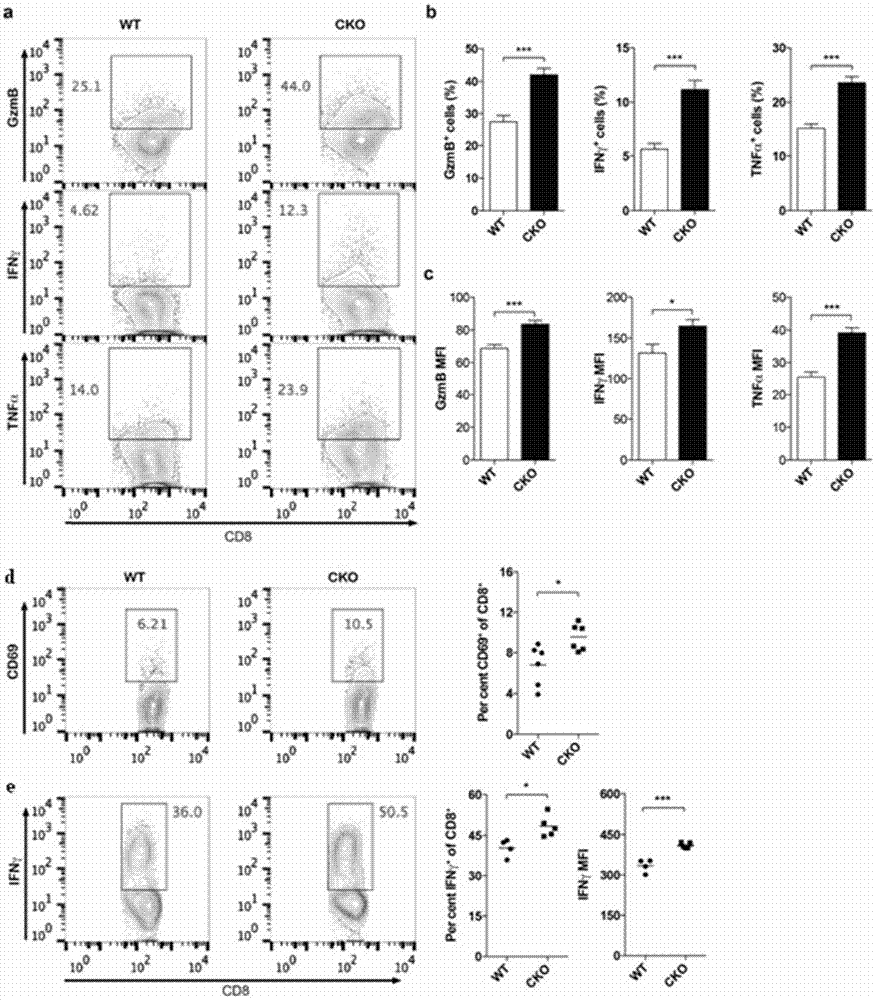
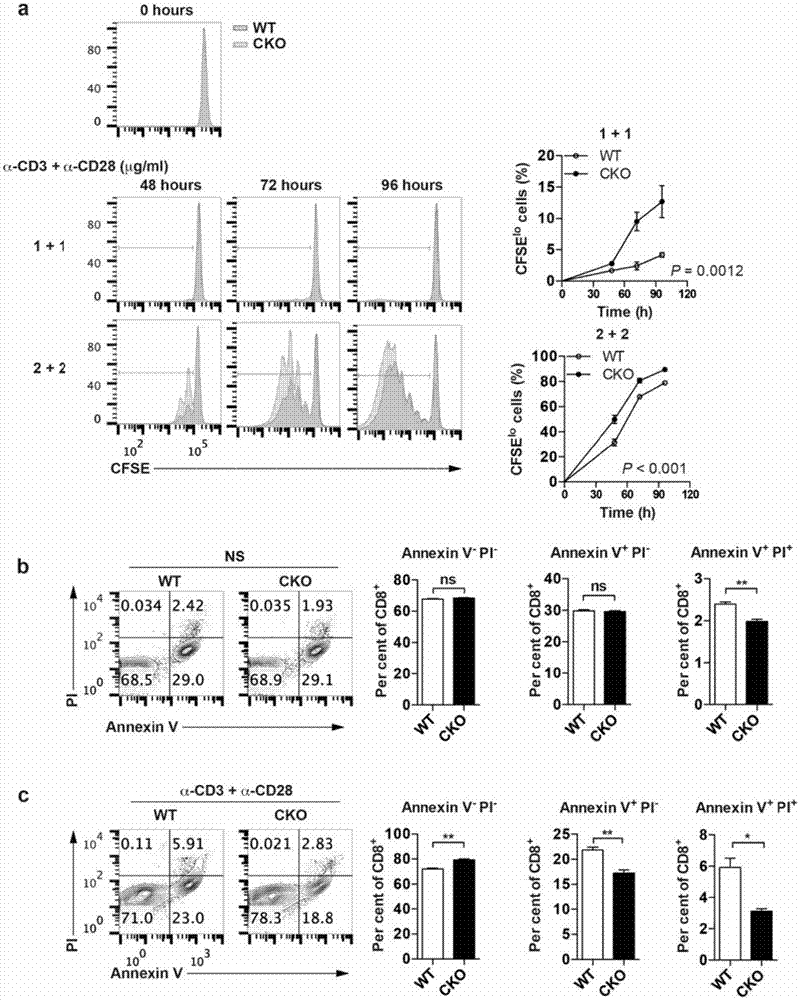
The invention provides a combined medication combination for tumor immunotherapy. The combined medication combination contains an effective dose of an acyl coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor and an effective dose of an immune detection point blocking antibody. The invention further provides a combined medication method for the tumor immunotherapy. By inhibiting the acyl coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1, the killing activity of CD8 T cells to tumors can be enhanced, and the acyl coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 and the immune detection point blocking antibody can generate a synergic effect in combined medication, so that the inhibition to the tumors can be further enhanced.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tumor immunotherapy drug target and application thereof
ActiveCN106957893AInhibitory activityEnhance antigen-specific immune responseMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPrimary screeningAcyl coenzyme A
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, relates to a tumor immunotherapy drug target and application thereof, discloses application of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 serving as a drug target on one hand, and provides a method for in-vitro screening a tumor immunotherapy drug on the other hand, According to the method, a gene of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 or acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 serving as a drug object is used for selecting the inhibitor of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 as a tumor immunotherapy candidate primary screening medicine. A new target is provided to the tumor immunotherapy drug, and a new platform is provided to screening of tumor immunotherapy drugs.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
New application of acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor
ActiveCN106955353AInhibitory activityEnhance antigen-specific immune responseAntibody ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsEffect functionImmunocompetence
The invention provides a new application of an acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor. The invention discloses the acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor. The acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the immune response capacity of CD8 T cells can be enhanced; the killing activity of the CD8 T cells for tumors can be enhanced; the effect function of the CD8 T cells can be enhanced; the multiplication of the CD8 T cells can be promoted; the apoptosis of the CD8 T cells can be reduced; the clustering of T-cell antigen receptors (TCR) on plasma membranes of the CD8 T cells can be promoted; the directional release of cytotoxic particles from the CD8 T cells can be promoted; and the formation of immunological synapses of the CD8 T cells can be promoted. The acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase ACAT1 inhibitor can be used for immunotherapy of the tumors or improving the immunocompetence to the tumors.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Increased Phytosterol Content Through Overexpression of an Acyl-CoA Sterol Acyl-Transferase
InactiveUS20100064381A1Low and reduce cholesterol contentImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsFermentationSterol esterAcyl coenzyme A
The present invention relates to the use of genetic engineering to produce sterol esters. In certain embodiments, an isolated or recombinant nucleic acid molecule encoding a sterol acyltransferase is disclosed. In certain other embodiments, a cell transformed with the isolated or recombinant nucleic acid molecule encoding a sterol acyltransferase is disclosed. A process for producing sterol esters using the transformed cell is also disclosed. In a further embodiment, an isolated or recombinant sterol acyltransferase is disclosed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Genetically modified organism for the production of lipids
InactiveUS8841114B2Increased level and yieldIncrease storage spaceCosmetic preparationsBacteriaSterol O-acyltransferaseWax
The invention provides an isolated genetically modified non-mammalian organism, wherein the activity of acyl-CoA: sterol acyltransferase / sterol O-acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.26) and / or diacylglycerol acyltransferase / diacylglycerol O-acyltranferase (EC 2.3.1.20) and / or lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase / phospholipid: diacylglycerol acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.158) and / or acyl CoA-wax alcohol acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.75) is reduced or abolished in comparison with a corresponding wildtype organism, methods of use of such an organism, shuttle vehicles for making such an organism and methods for producing such an organism.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
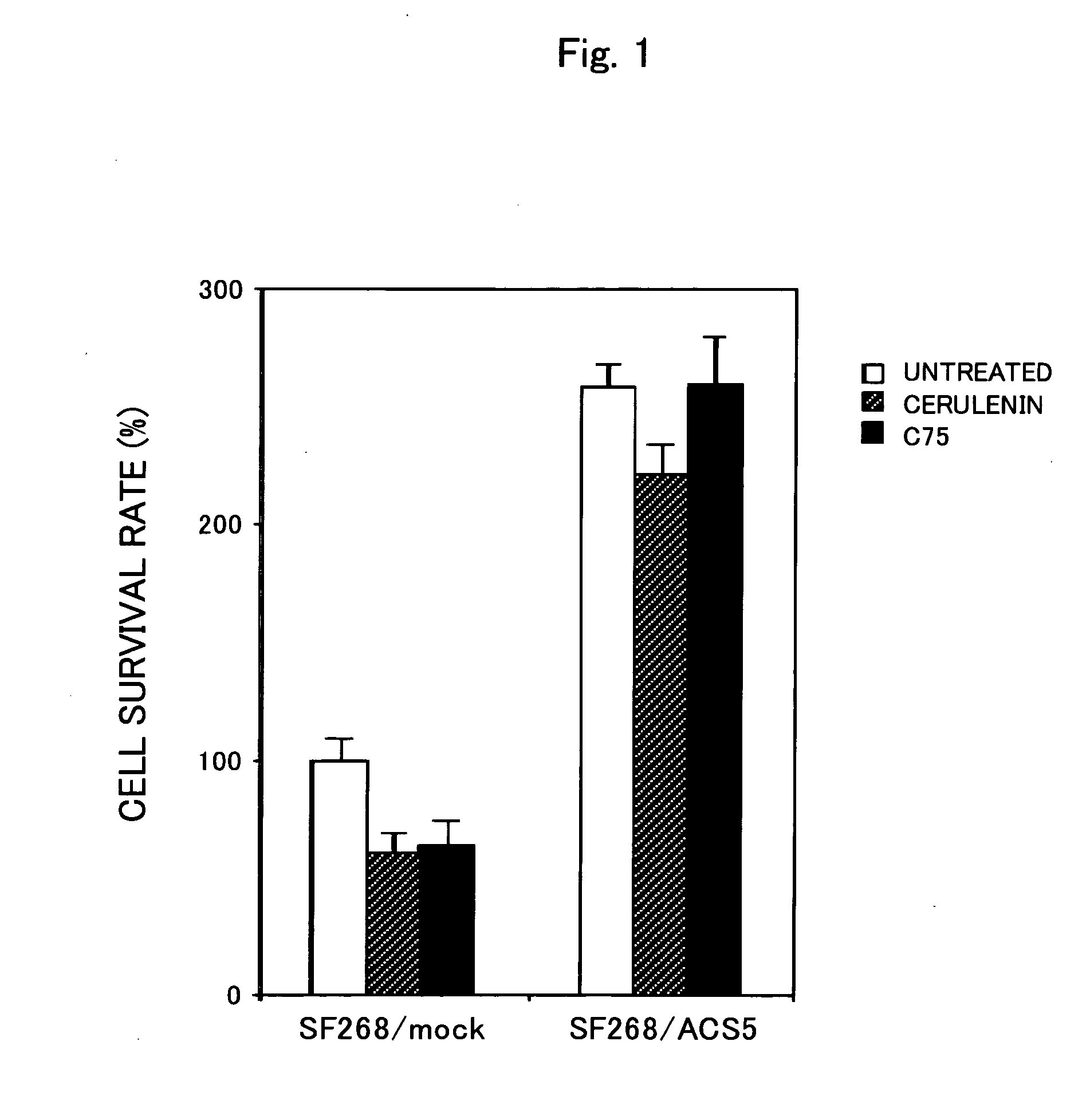
Prophylactic/Therapeutic Agent for Cancer
The present invention provides a preventative / therapeutic agent for cancer capable of selectively and effectively killing cancer cells. A medicament of the present invention prepared by combining at least one selected from a substance that inhibits the activity of an enzyme belonging to the acyl-CoA synthase family and a substance that inhibits expression of a gene for an enzyme belonging to the acyl-CoA synthase family, with at least one selected from a substance that inhibits the activity of fatty acid synthase and a substance that inhibits expression of a fatty acid synthase gene and the like can be used as a preventative / therapeutic agent for cancer capable of selectively and effectively killing cancer cells.
Owner:JAPANESE FOUND FOR CANCER RES +1
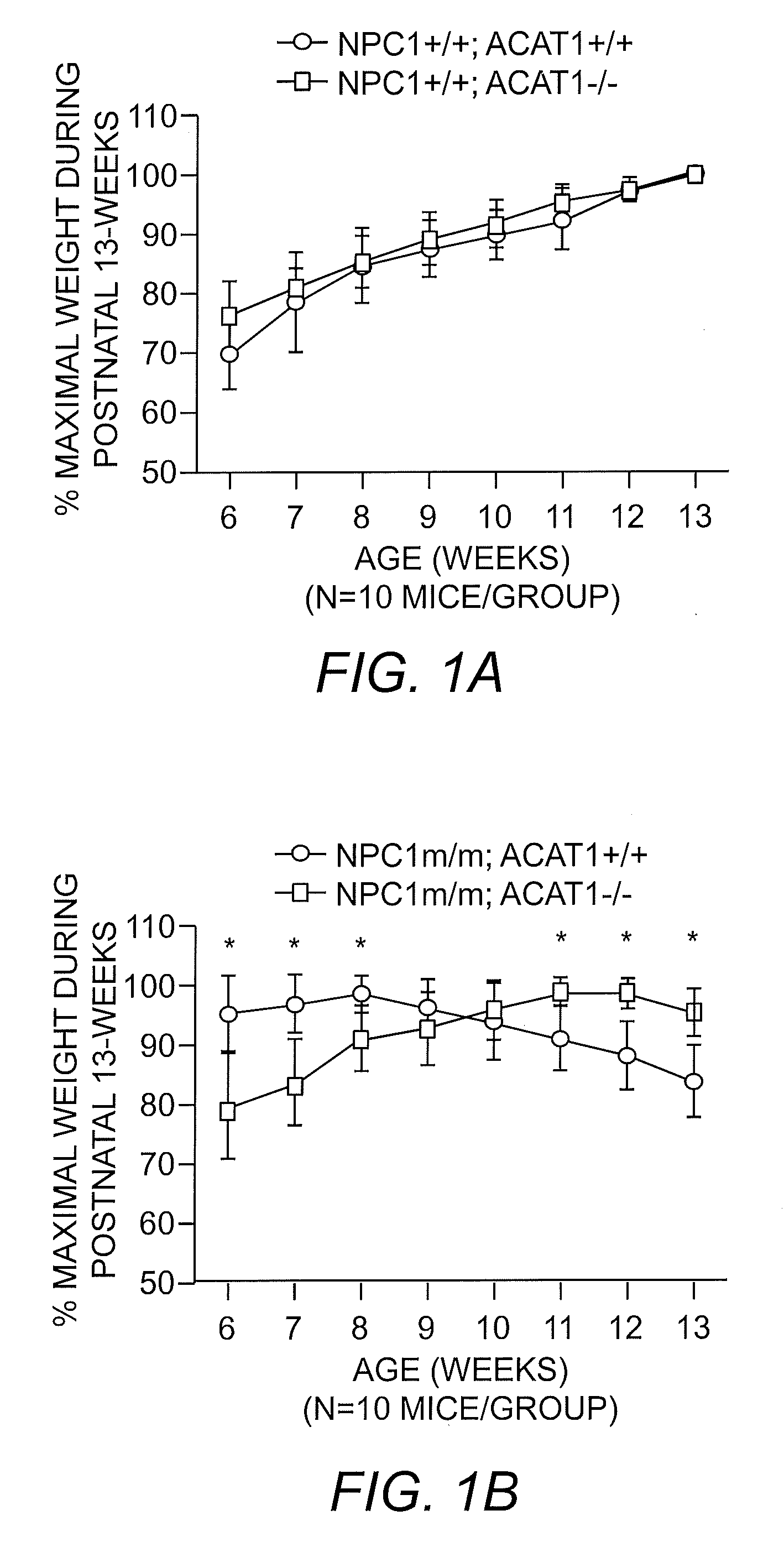
Methods for treating Niemann-Pick type C disease
ActiveUS9206425B2Organic active ingredientsAcyltransferasesAcyl coenzyme ANiemann-pick type c disease
The present invention includes methods for treating Niemann-Pick Type C disease through administration of inhibitors of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (ACAT1). ACAT inhibitors are used to treat symptoms of Niemann-Pick Type C disease and prolong survival of patients with the disease, either alone or in combination with other treatments.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
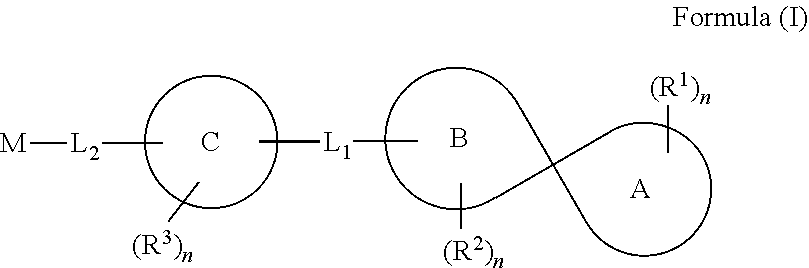
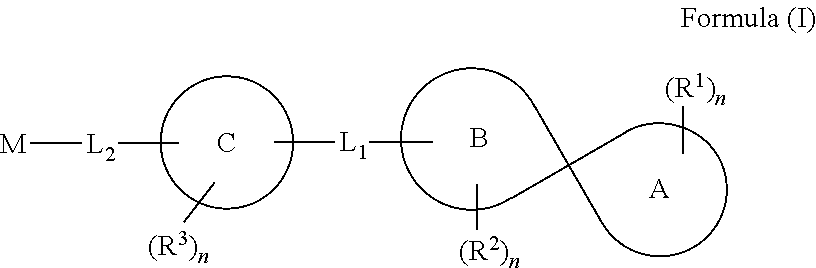
Spirocyclic compounds, compositions and medicinal applications thereof
The present disclosure relates to a series of spirocyclic compounds of formula (I), their stereoisomers, tautomers, prodrugs, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, solvates, hydrates, N-Oxides, Co crystals and formulations thereof. The disclosure also relates to process of preparation of these spirocyclic compounds.These compounds are useful in the treatment, prevention, prophylaxis, management, or adjunct treatment of all medical conditions related to inhibition of acyl CoA diacyl glycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1).
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
Sustained release of apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS8044021B2Organic active ingredientsPowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Mimics of acyl coenzyme-A comprising pantolactone and pantothenic acid derivatives, compositions thereof, and methods of cholesterol management and related uses
InactiveUS20030236213A1Increase level of HDL cholesterolDecrease level of LDL-cholesterolAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDyslipidemiaKetone
The invention relates to novel Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions comprising ketone compounds, and methods useful for treating and preventing cardiovascular diseases, dyslipidemias, dysproteinemias, and glucose metabolism disorders comprising administering a composition comprising a ketone compound. The Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions, and methods of the invention are also useful for treating and preventing Alzheimer's Disease, Syndrome X, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-related disorders, septicemia, thrombotic disorders, obesity, pancreatitis, hypertension, renal disease, cancer, inflammation, bacterial infection and impotence. In certain embodiments, the Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions, and methods of the invention are useful in combination therapy with other therapeutics, such as hypocholesterolemic and hypoglycemic agents.
Owner:ESPERION THERAPEUTICS
Styrax plant and use of extract thereof
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical use of styrax. The invention particularly relates to use of the styrax in the preparation of acyl coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor, and the styrax can be prepared into injections, oral tablets, capsules and a variety of preparations for being applicable to preventing and treating atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia and other diseases. Furthermore, the styrax can be used as a preventive drug or a therapeutic agent for angina, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, Alzheimer's disease, acute coronary syndrome, PTCA or posterior coronary artery re-stenosis with stent and other diseases. The styrax can also be used as the therapeutic agent for regulating the functions of sebaceous glands and inhibiting excessive production of sebum, thereby being used for treating oily skin, acne, seborrhea, acne-like injuries caused by corticosteroids and other diseases.
Owner:CHENGDU DIAO JIUHONG PHARMA FAB
Insecticidal compositions comprising compounds having inhibitory activity versus acyl coa: cholesterol acyltransferase or salts thereof as effective ingredients
The present invention relates to insecticidal compositions comprising compounds having an inhibitory activity versus acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) or salts thereof as effective ingredients. The compounds having inhibitory activity versus ACAT have an excellent insecticidal effect by inhibiting sterol metabolism in noxious insects. Therefore, the compounds of the present invention can be used as safe and effective insecticides.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
New application of acyl coenzyme A/cholesterol acyltransferase-1 inhibitor
InactiveCN109125324APrevention and/or treatment of metastasesOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisAcyl coenzyme A
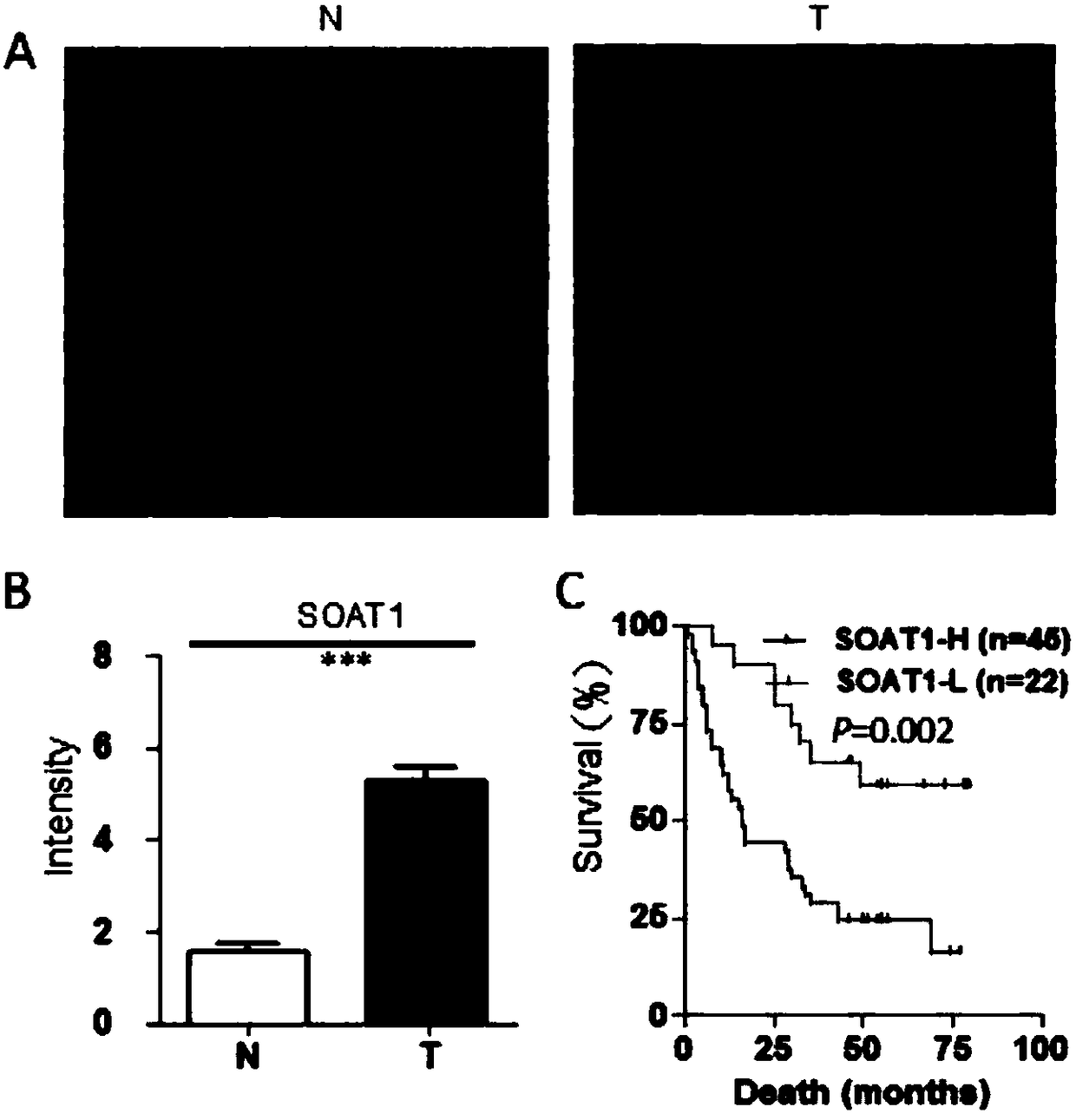
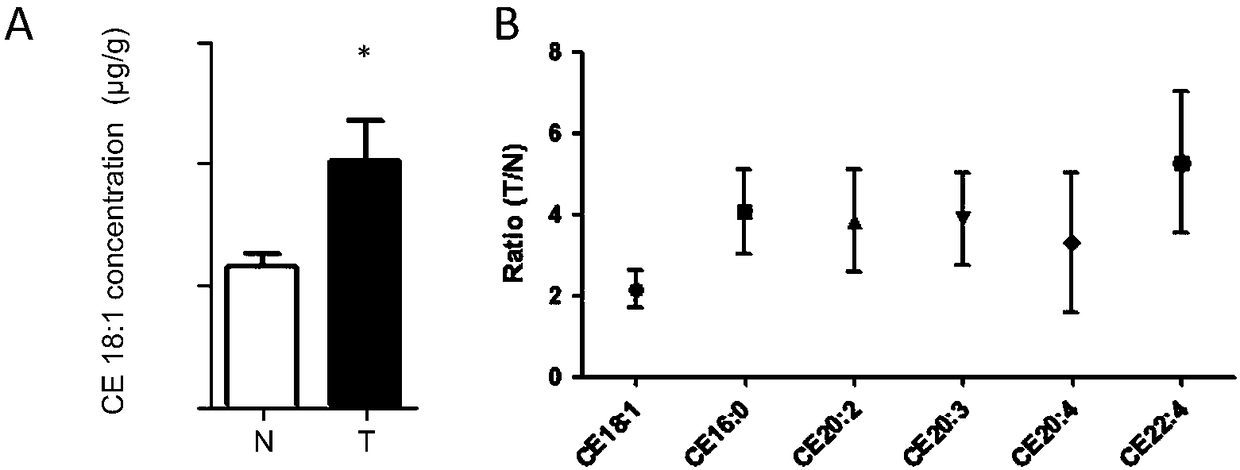
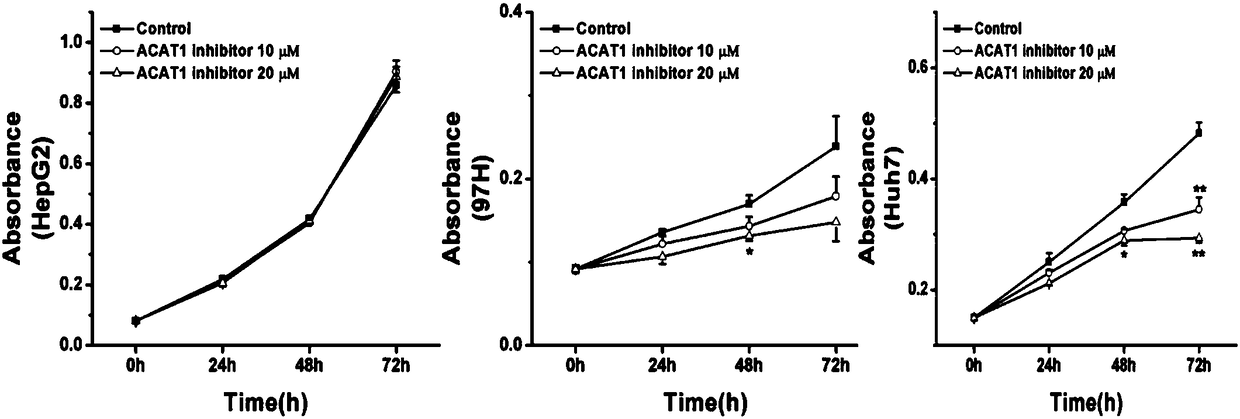
The invention discloses new application of a substance for inhibiting genetic expression and / or protein activity of acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1. According to the application, the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / or treating cancer; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / treating cancer spreading and metastasis; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for promoting apoptosis of cancer cells; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for inhibiting cancer cells from being transformed into cancer; the inhibitor canbe used for preparing drugs for inhibiting in vitro proliferation growth of the cancer cells. Through experiments, the inventor proves that the acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (ACAT1 / SOAT1) is obviously highly expressed in liver cancer tissue, and the high enrichment value of the acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1 shows that prognosis of a liver cancer patient is poor. TheACAT1 / SOAT1 inhibitor can effectively inhibit growth of human liver cancer cells and other cancer cells in the cellular level, and the inhibitor can used as a candidate drug target of cancers, especially the liver cancer.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com