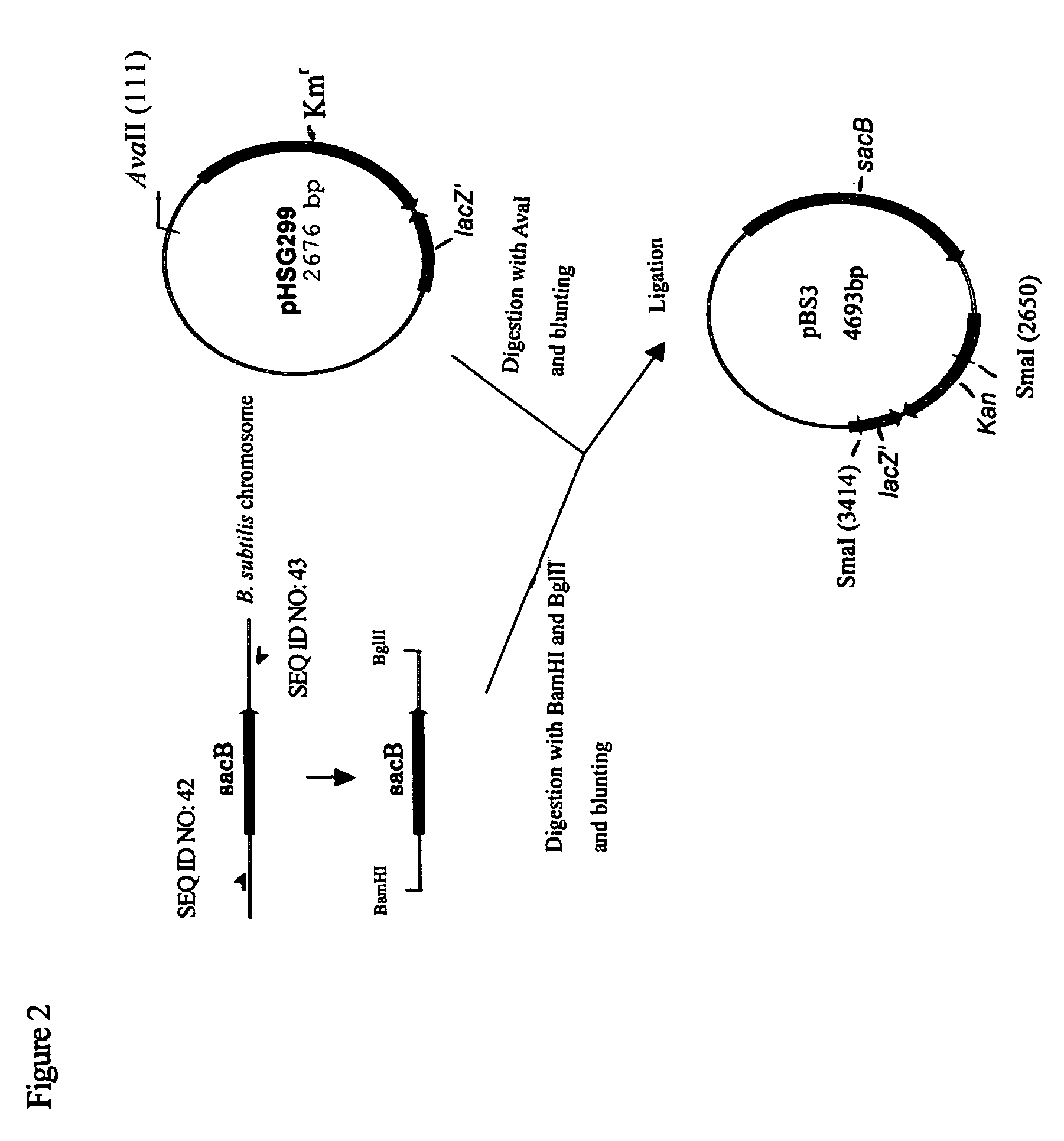
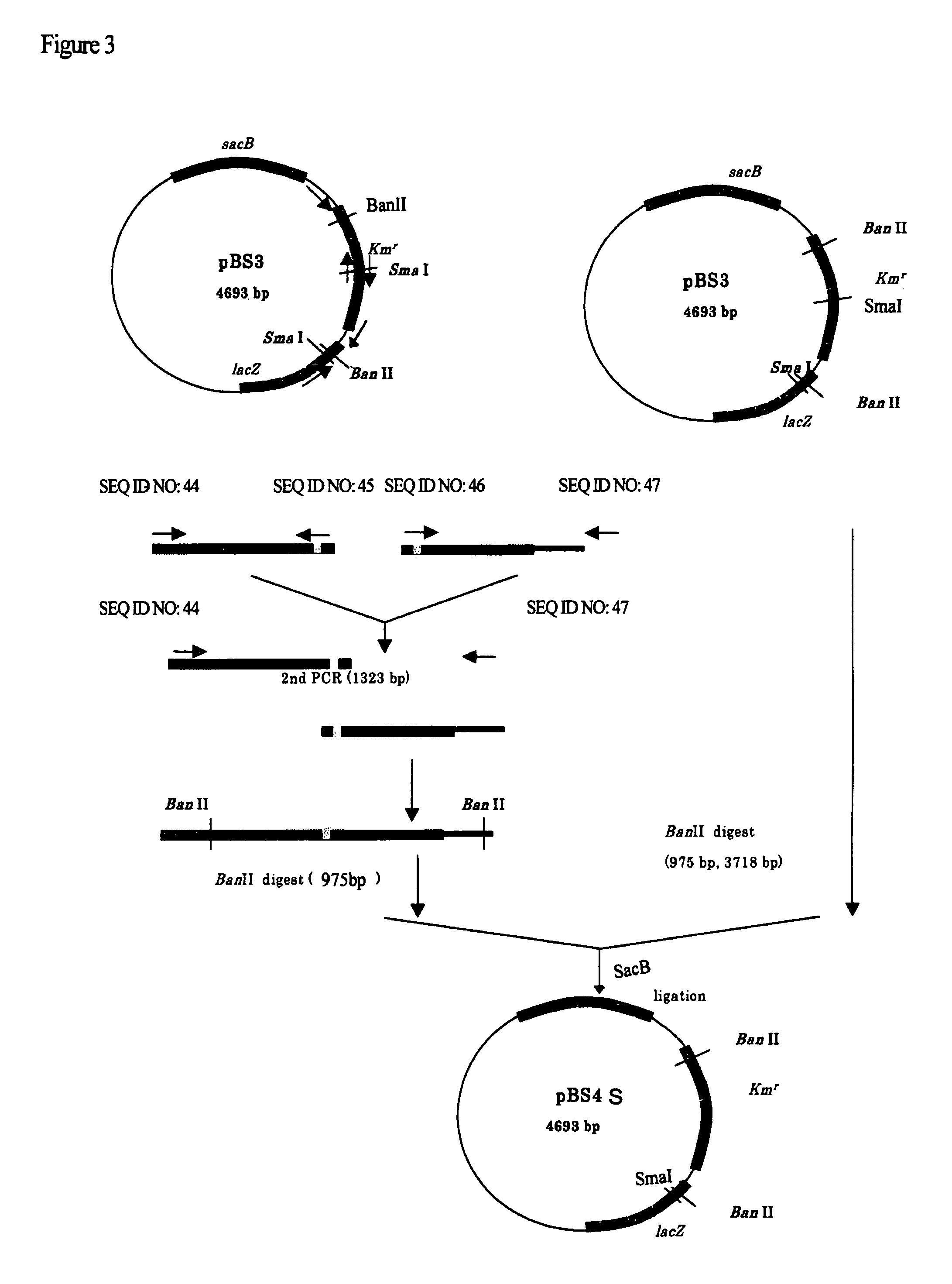
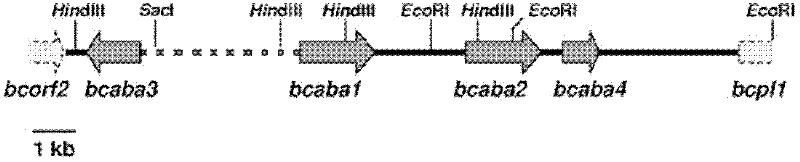
Patents
Literature
210 results about "Acetylcoenzyme A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
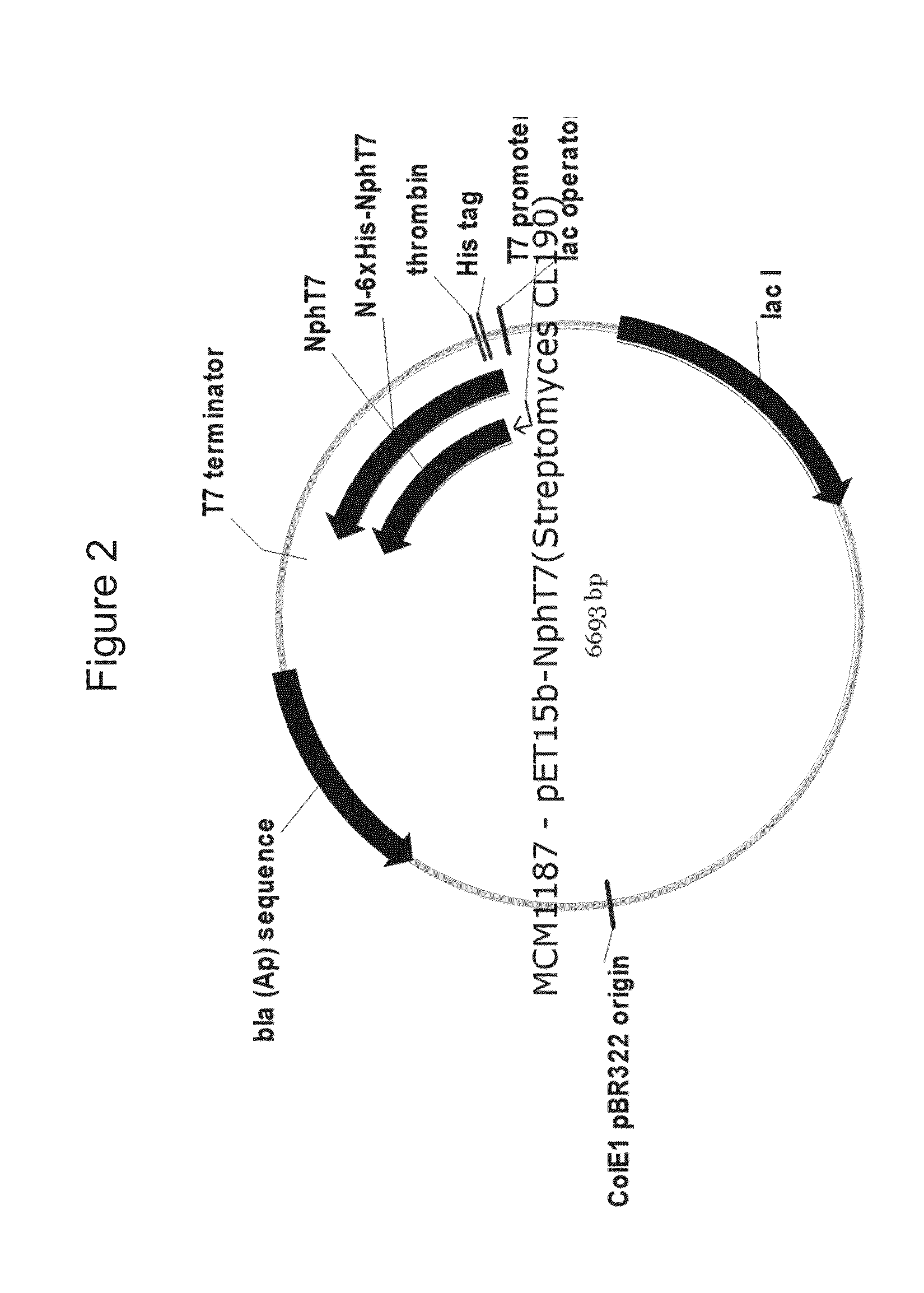
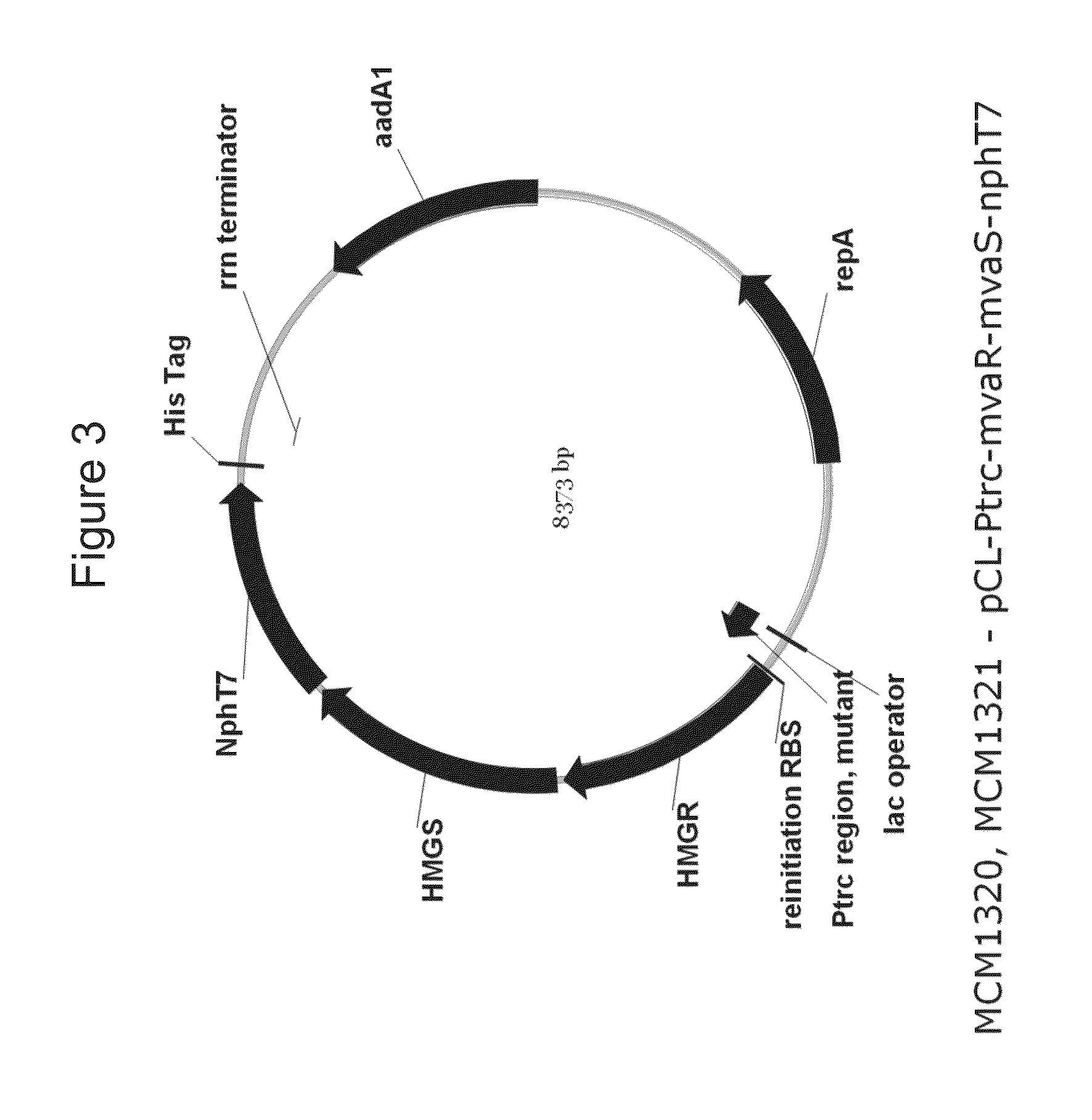
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
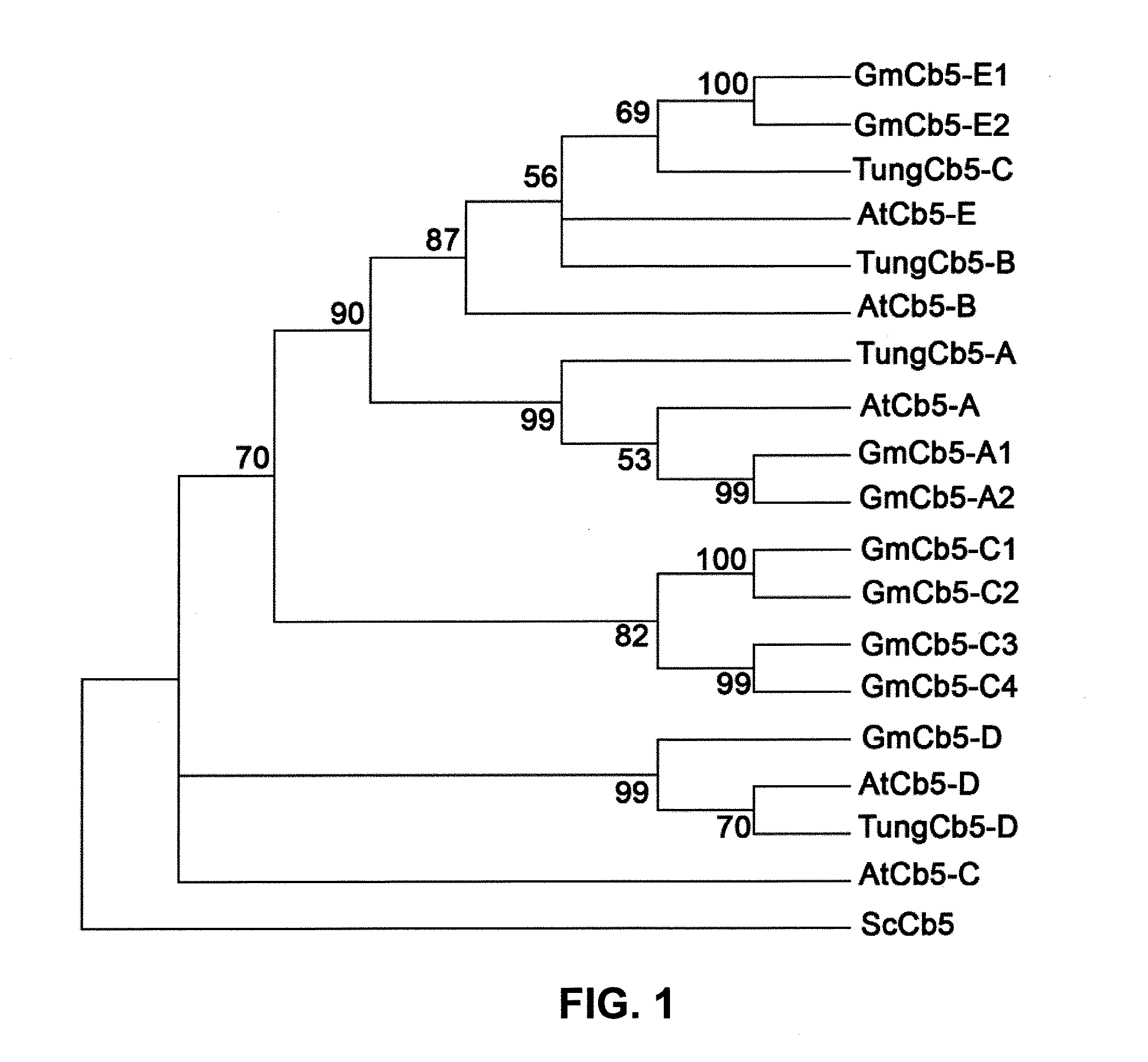
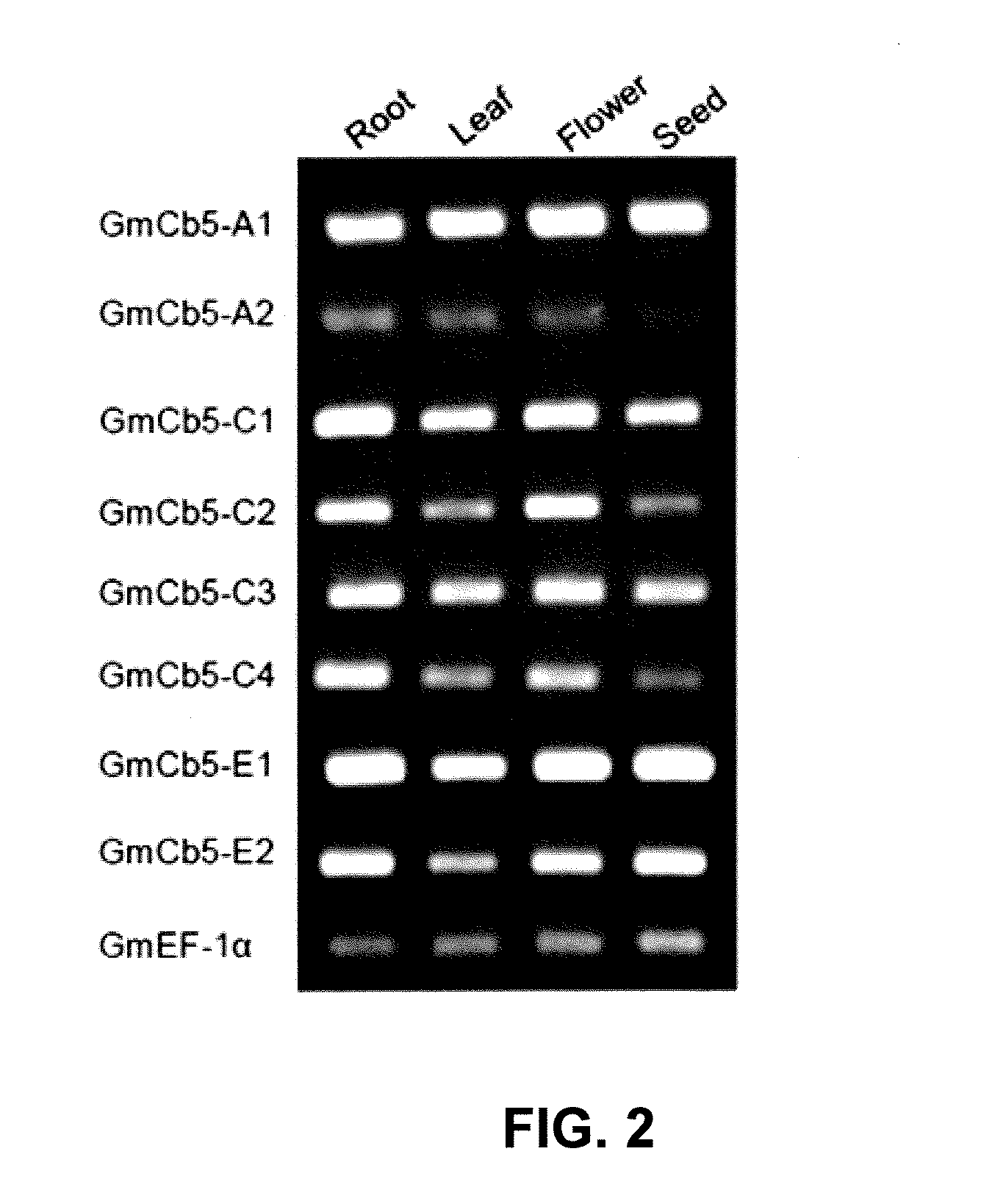
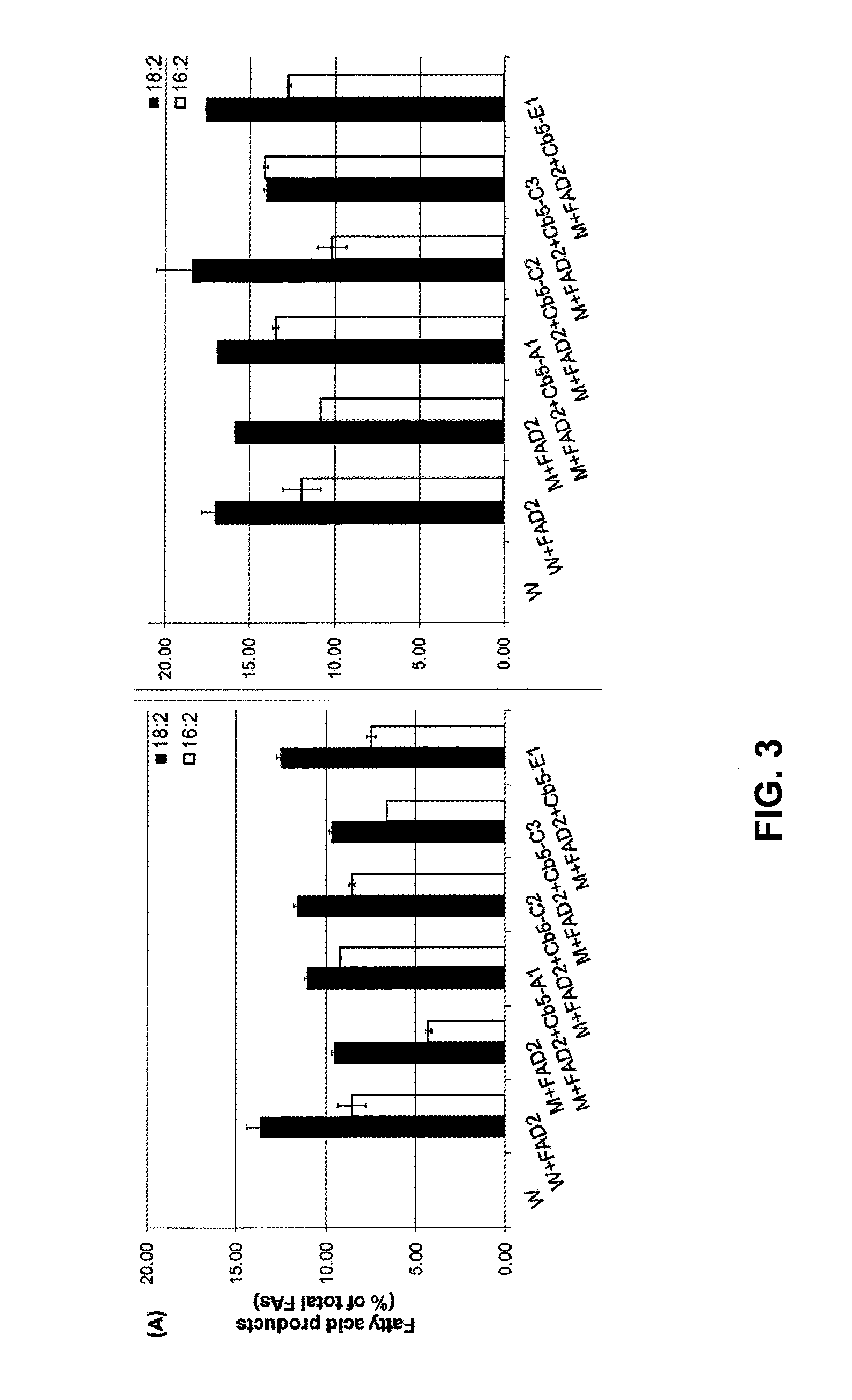
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Methods and organisms for utilizing synthesis gas or other gaseous carbon sources and methanol
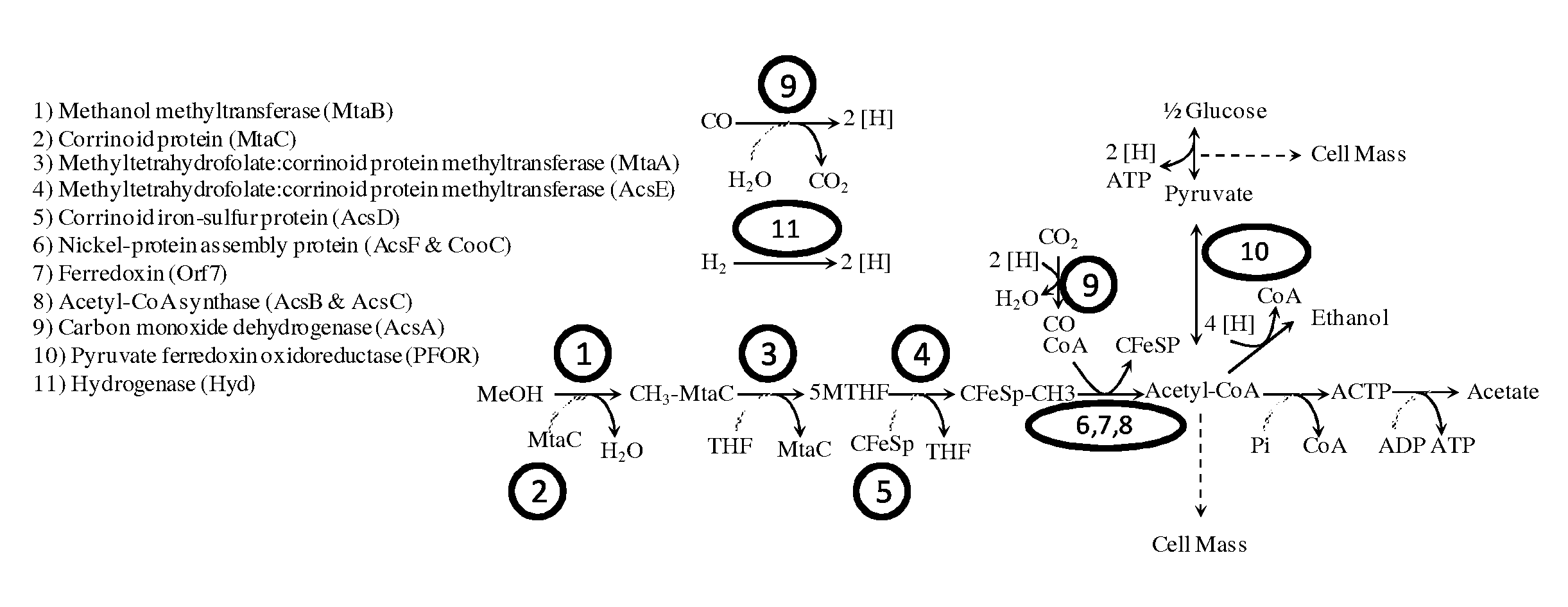
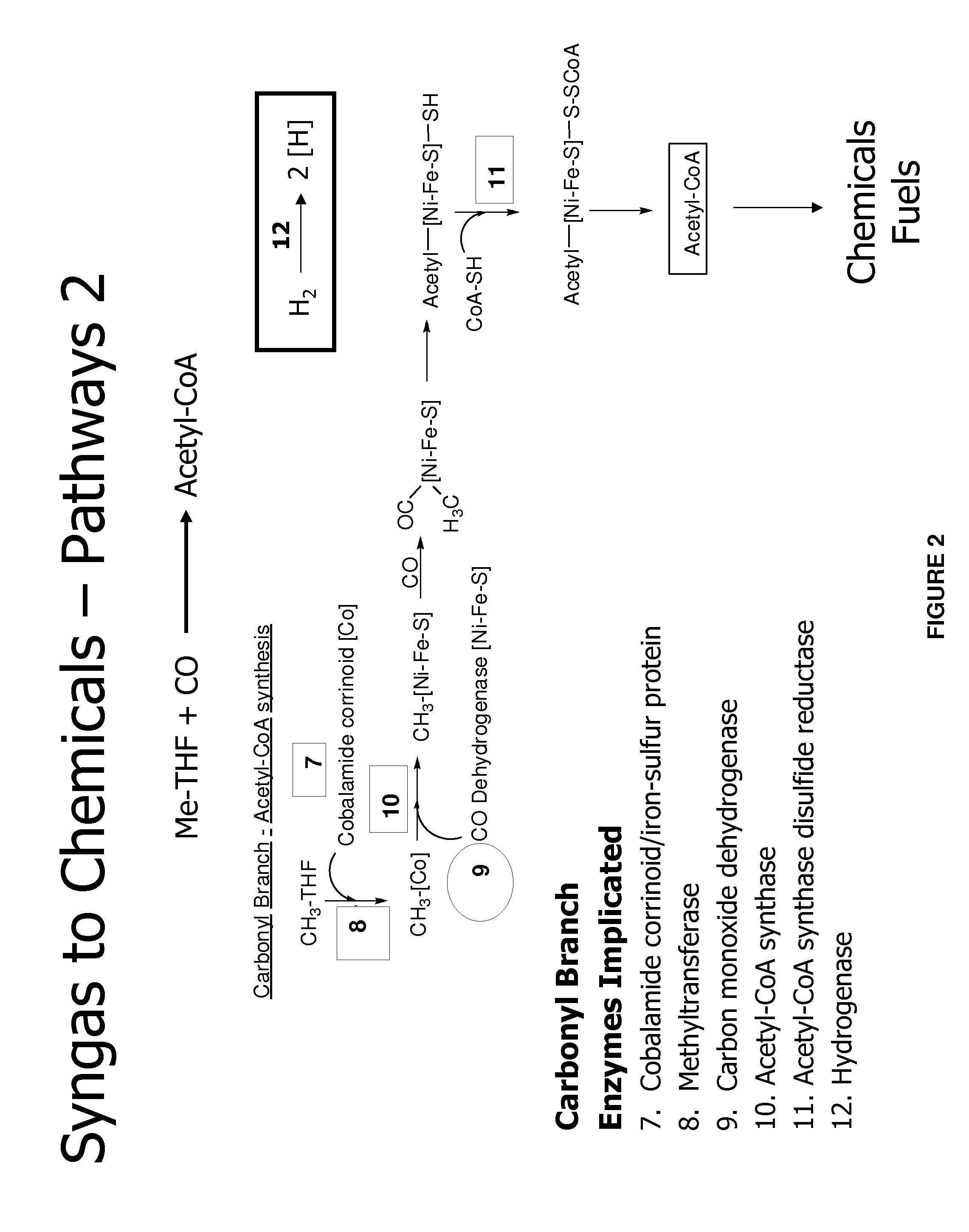
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an acetyl-CoA pathway and the capability of utilizing syngas or syngas and methanol. In one embodiment, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism, comprising one or more exogenous proteins conferring to the microorganism a pathway to convert CO, CO2 and / or H2 to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl-THF) or other desired products, wherein the microorganism lacks the ability to convert CO or CO2 and H2 to acetyl-CoA or methyl-THF in the absence of the one or more exogenous proteins. For example, the microbial organism can contain at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an enzyme or protein in an acetyl-CoA pathway. The microbial organism is capable of utilizing synthesis gases comprising CO, CO2 and / or H2, alone or in combination with methanol, to produce acetyl-CoA. The invention additionally provides a method for producing acetyl-CoA, for example, by culturing an acetyl-CoA producing microbial organism, where the microbial organism expresses at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acetyl-CoA pathway enzyme or protein in a sufficient amount to produce acetyl-CoA, under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce acetyl-CoA.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
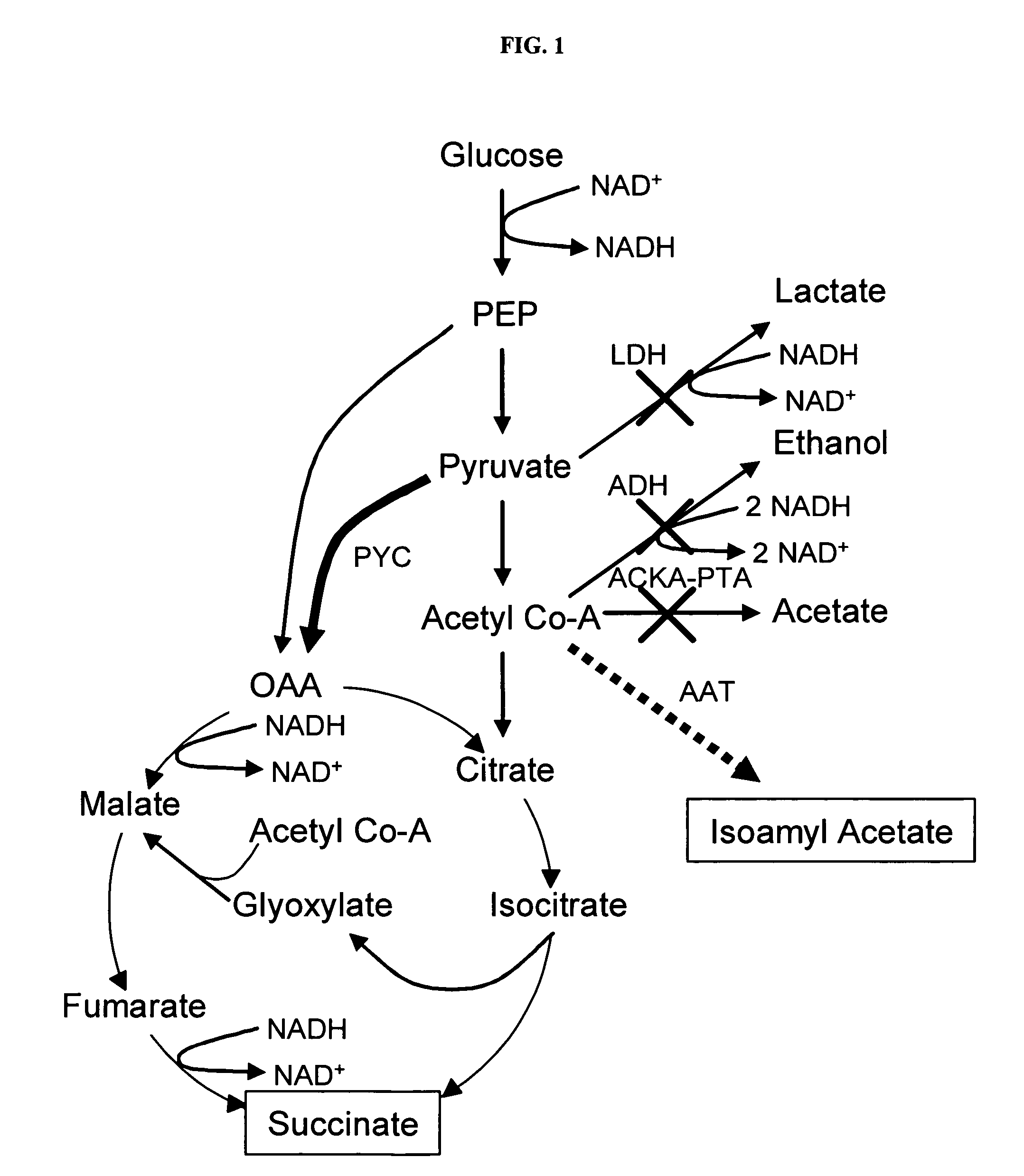
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
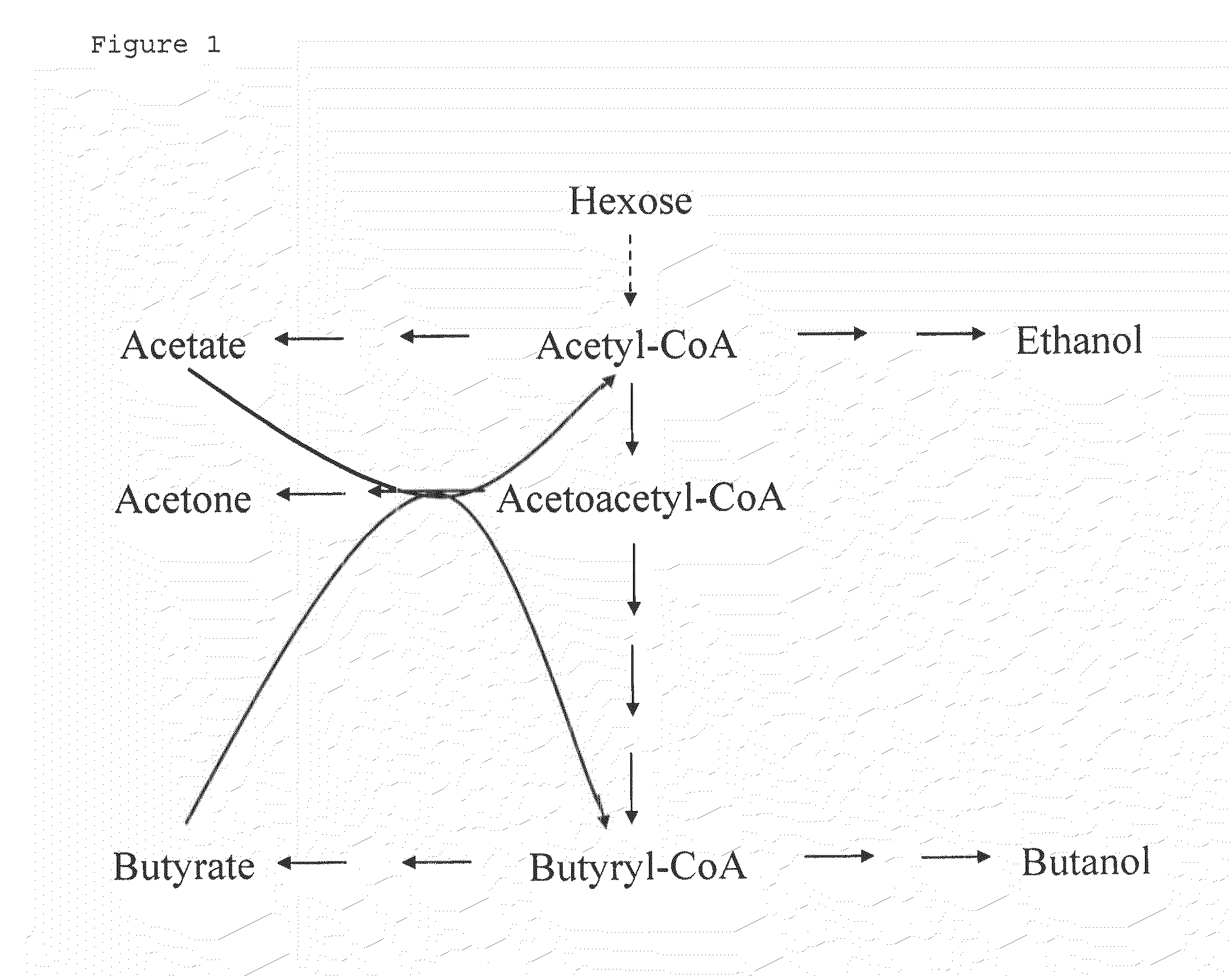
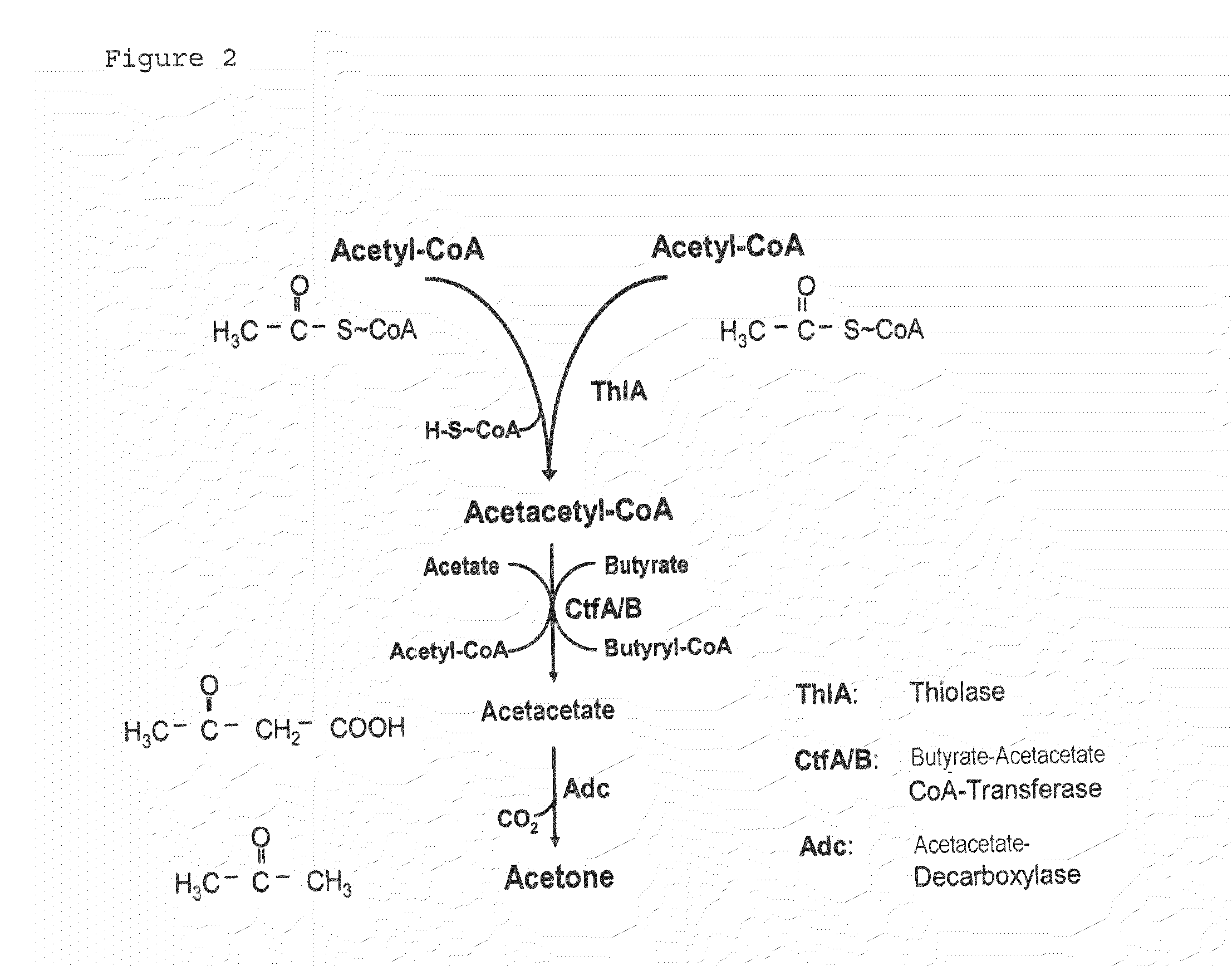
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Genetically modified host cells and use of same for producing isoprenoid compounds
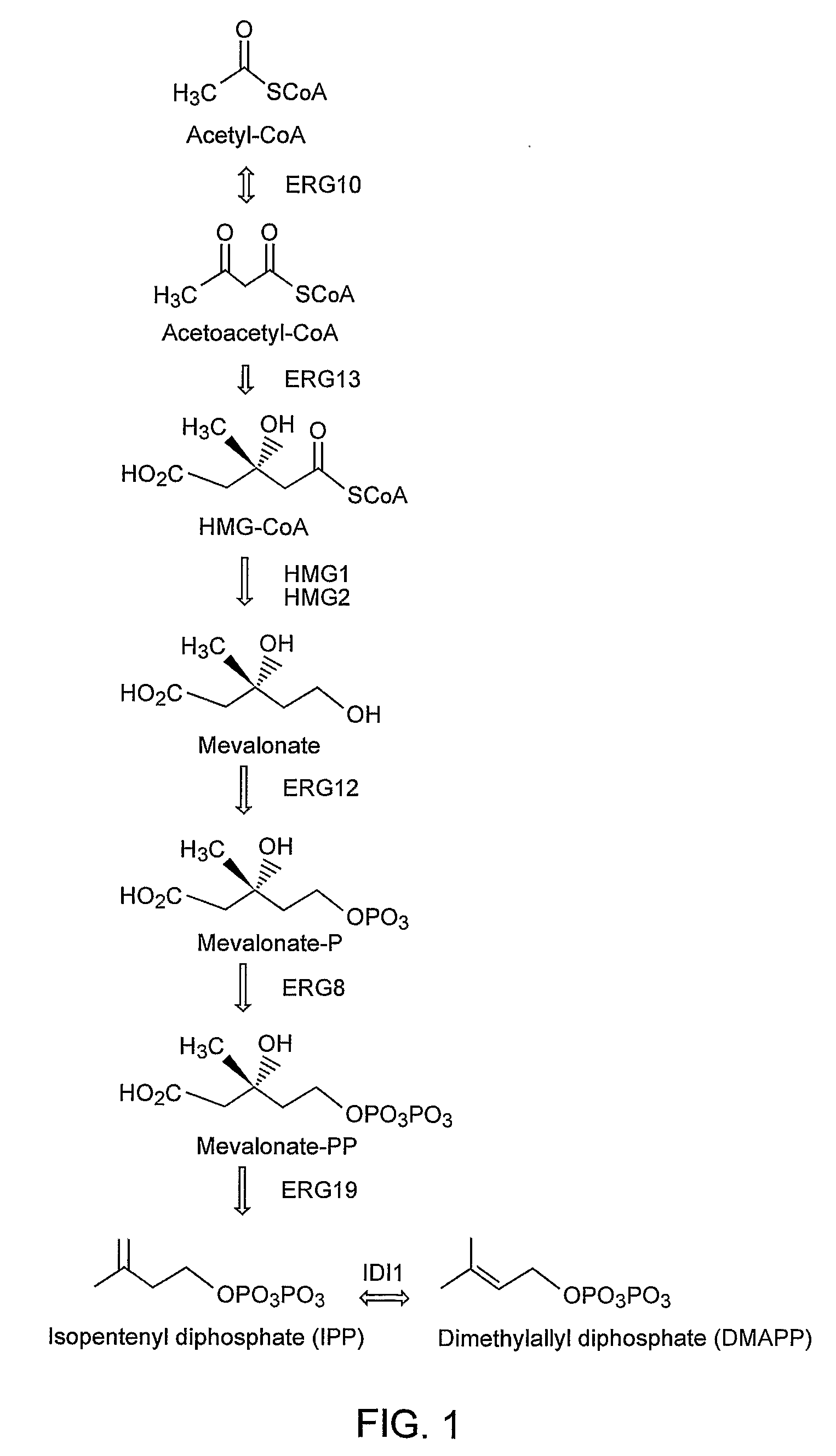
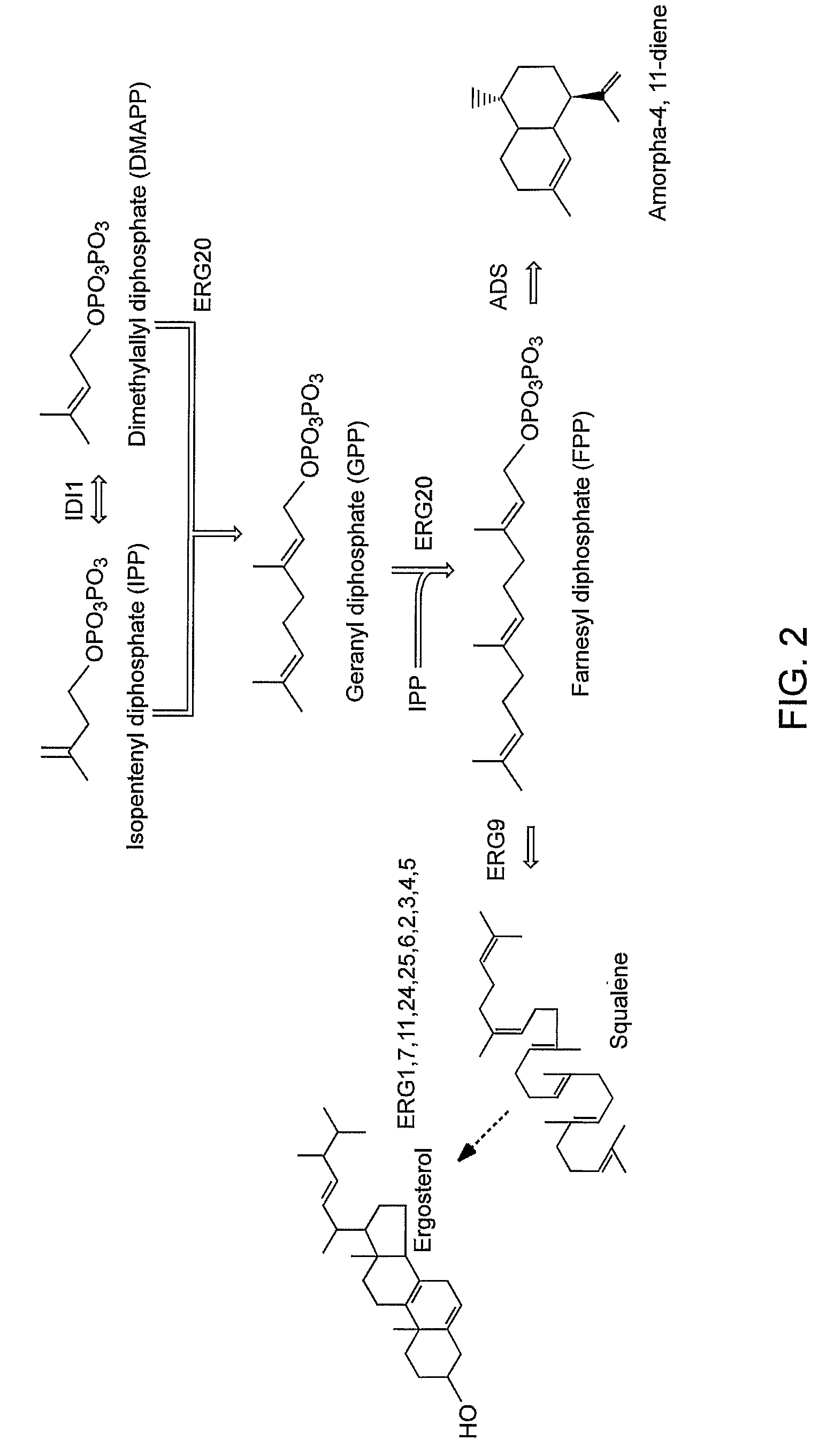
The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells exhibiting increased activity levels of one or more enzymes that generate precursors to be utilized by the mevalonate pathway enzymes, increased activity levels of one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, prenyl transferase, and / or decreased levels of squalene synthase activity; such cells are useful for producing isoprenoid compounds. The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells that produce higher levels of acetyl-CoA than a control cell; such cells are useful for producing a variety of products, including isoprenoid compounds. Methods are provided for the production of an isoprenoid compound or an isoprenoid precursor in a subject genetically modified eukaryotic host cell. The methods generally involve culturing a subject genetically modified host cell under conditions that promote production of high levels of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid precursor compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
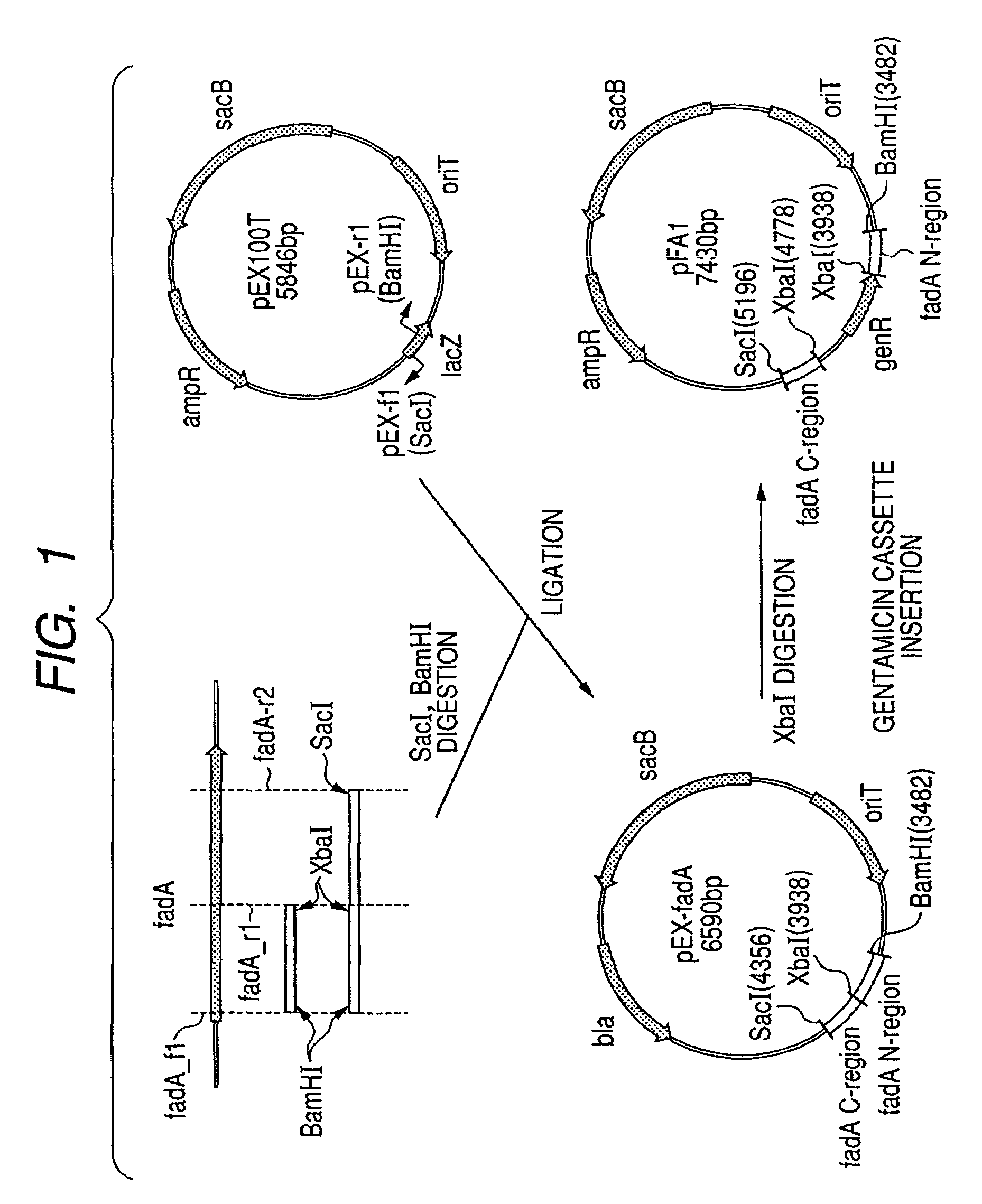
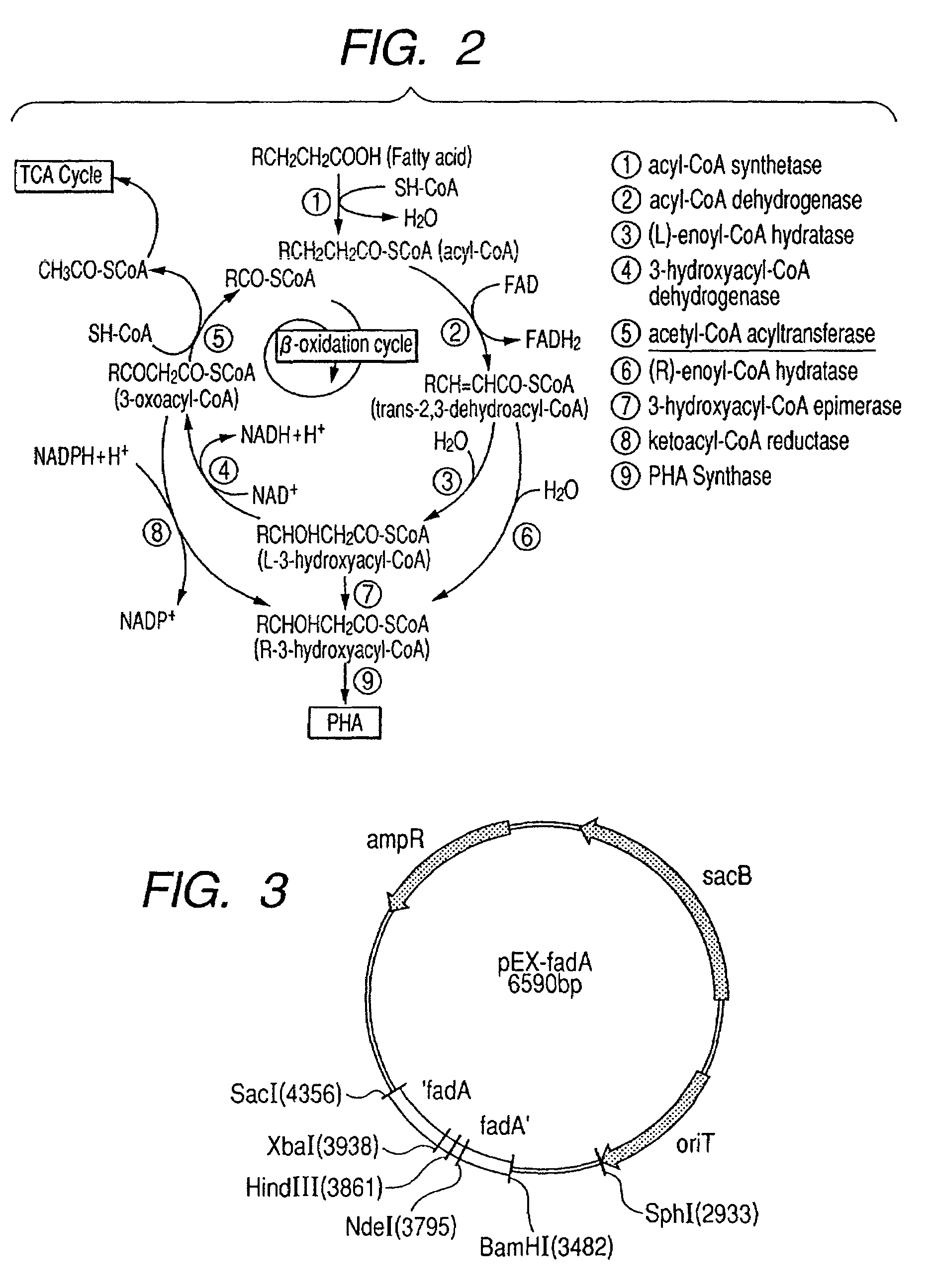
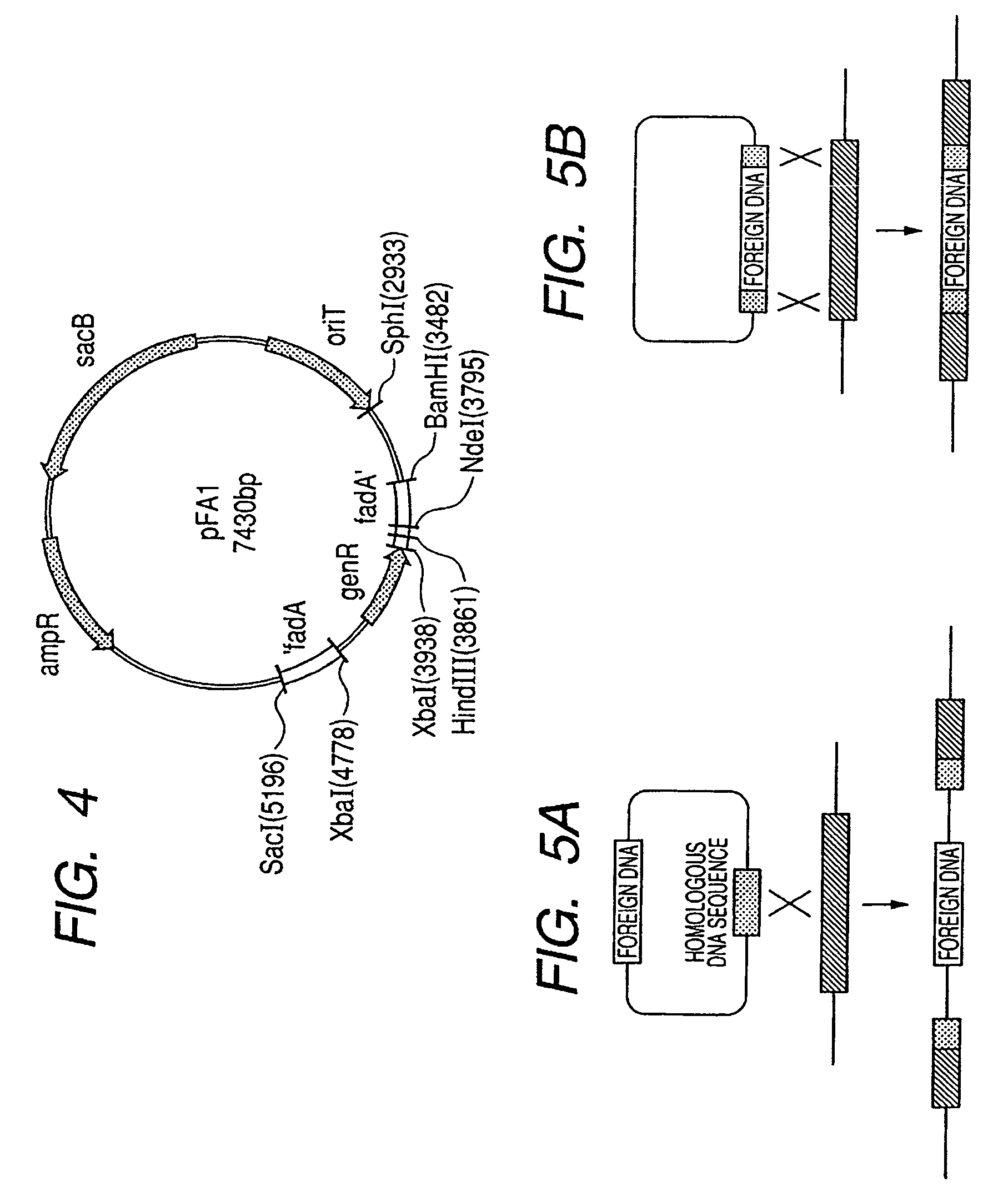
Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene disrupted bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
A method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate with improved productivity and composition is provided. Polyhydroxyalkanoate is produced by a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which a gene encoding acetyl-CoA acyltransferase is disrupted.
Owner:CANON KK
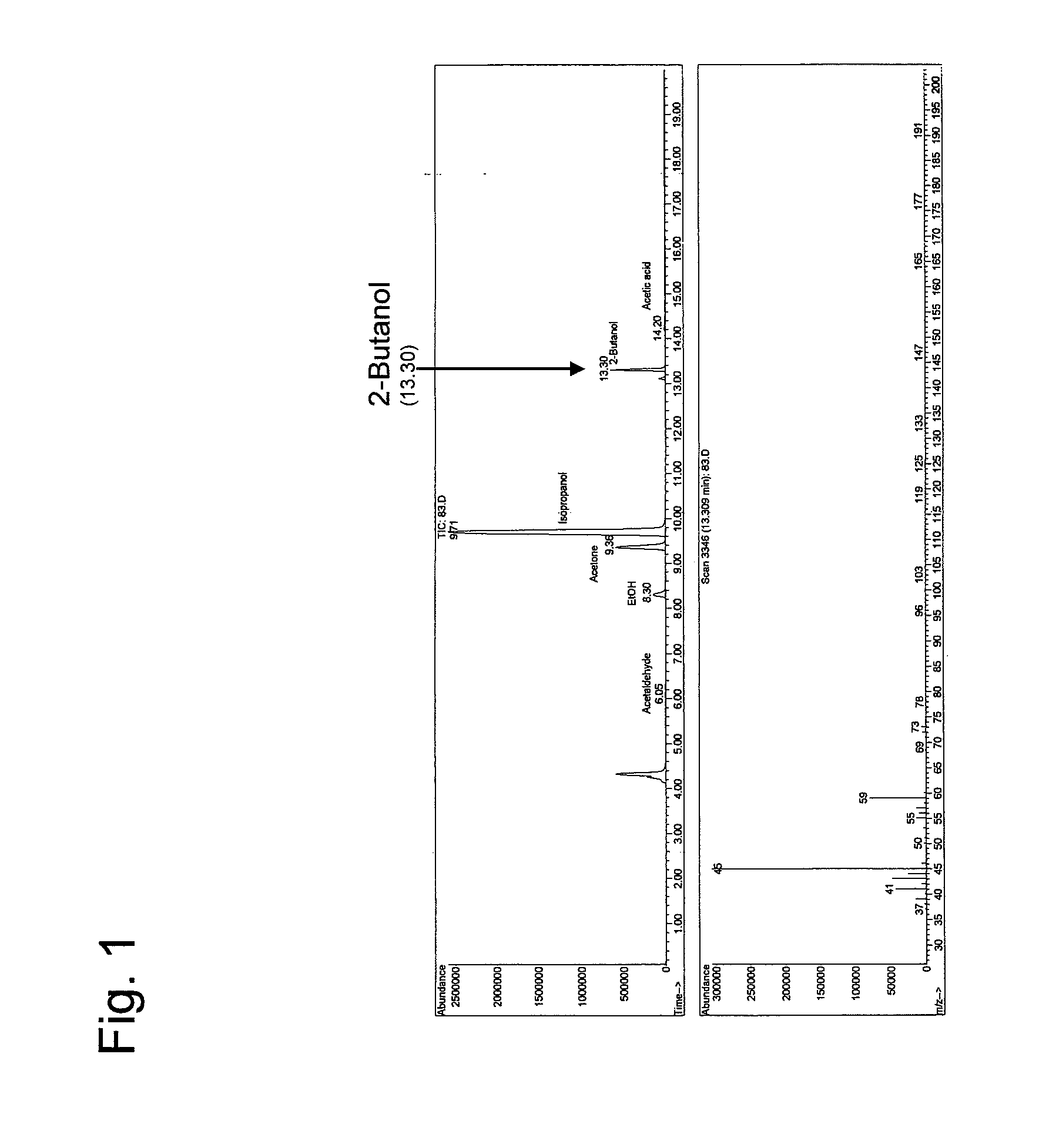
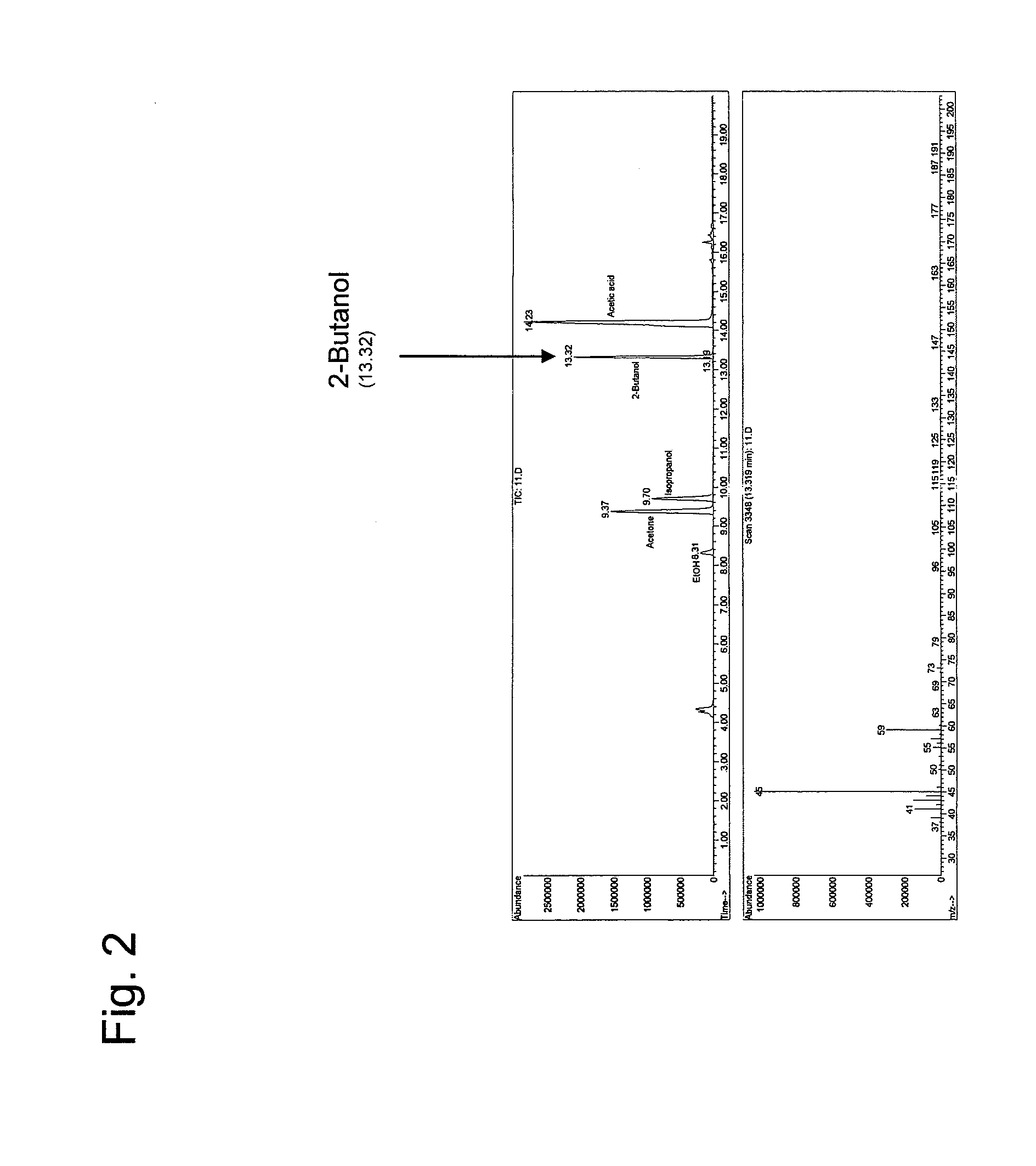
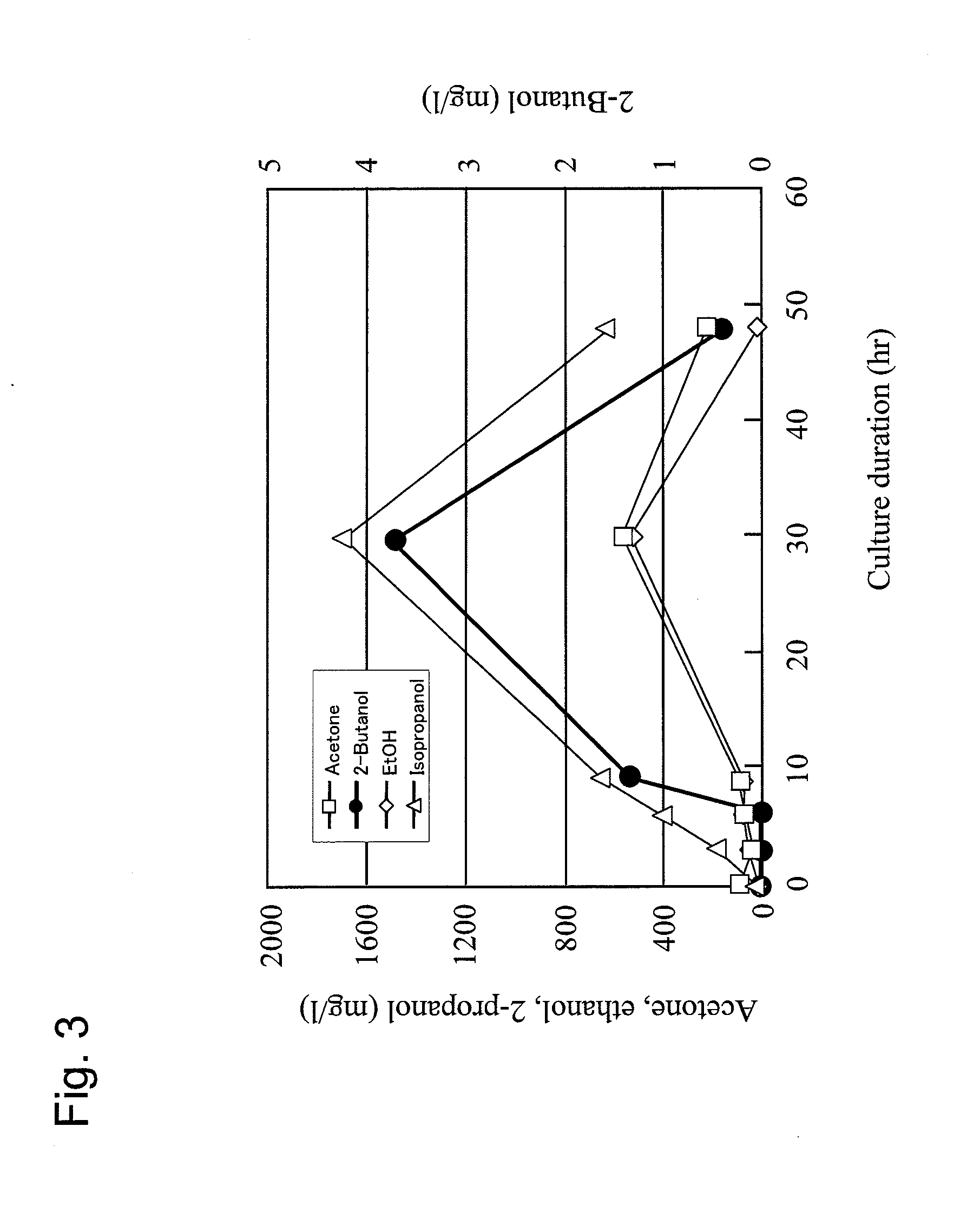
Method for producing 2-butanol and recombinant microorganism having 2-butanol production capacity
ActiveUS20110281315A1Increase production capacitySimple materialBacteriaSugar derivativesPropanolMicroorganism
This invention is intended to produce 2-butanol with excellent productivity via a fermentation process. Recombinant microorganisms into which the acetoacetyl-CoA synthase gene and a group of genes (i.e., genes involved in 2-propanol synthesis) encoding a set of enzymes synthesizing 2-propanol from acetoacetyl-CoA have been introduced are cultured, so that, in addition to 2-propanol, 2-butanol is produced at a high level in a medium.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
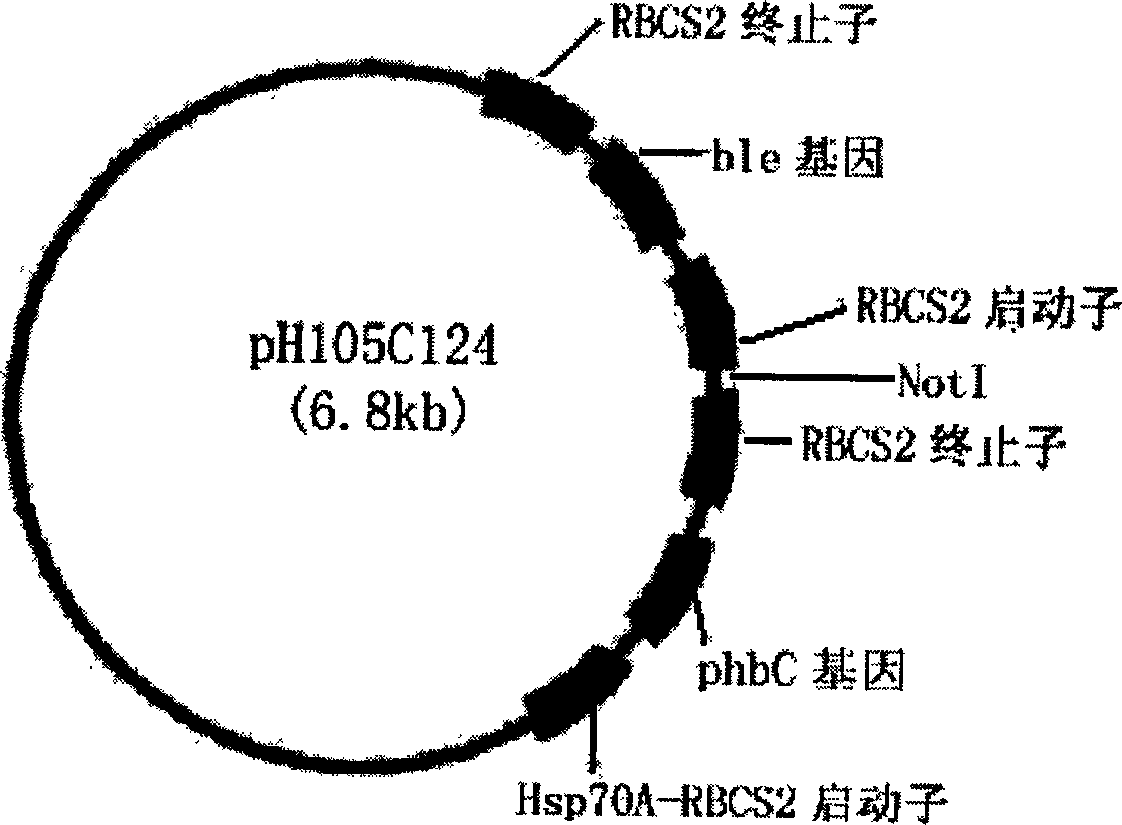
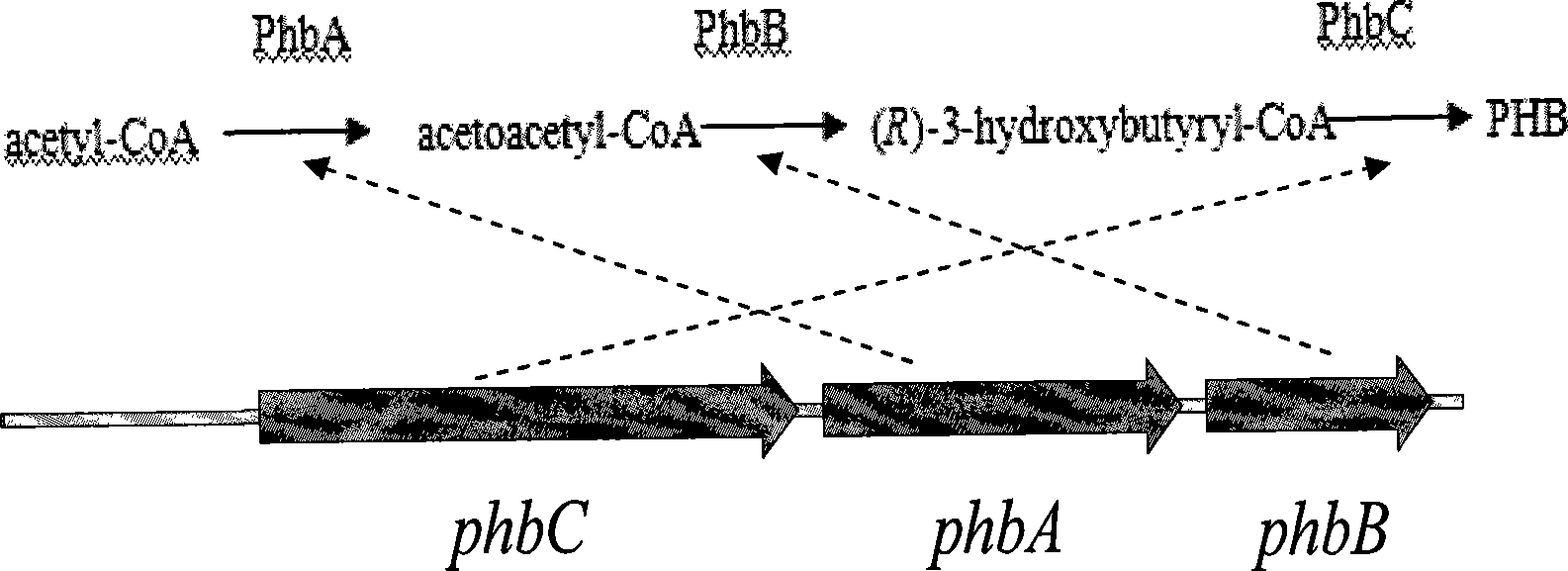
Exogenous gene expression system of Chlamydomonasreinhardtii and method for constructing and producing PHB transgenic algae
ActiveCN1807649AImprove expression efficiencyIncrease productionUnicellular algaeFermentationHydroxybutyric acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses an expression system and constructing PHB transgene algae method of rhine chlamydomonas exogenesis gene, which comprises the following parts: promotor, exogenesis-goal gene, screening badge and rhine chlamydomonas acceptor algae strain, wherein the method comprises the following: A, selecting and cultivating acceptor algae strain; B, cloning key enzyme gene by PHB biosynthesizing; C, expressing carrier of PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme rhine chlamydomonas; D, using PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme to lead in rhine chlamydomonas from fungus Bacillus alcaligenes with bead-milling method, gene-gun method or electrization; obtaining bivalence or transgene Chlamydomonas of producing PHB by screen selecting and molecule detecting. The poly-hydroxybutyric acid is compounded by acting in conjunction of PHB compounding key enzyme of phbA, phbB and phbC gene coding, which uses acetylcoenzyme A as substrate by photosynthesis. The method simplifies the operating, which reduces cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
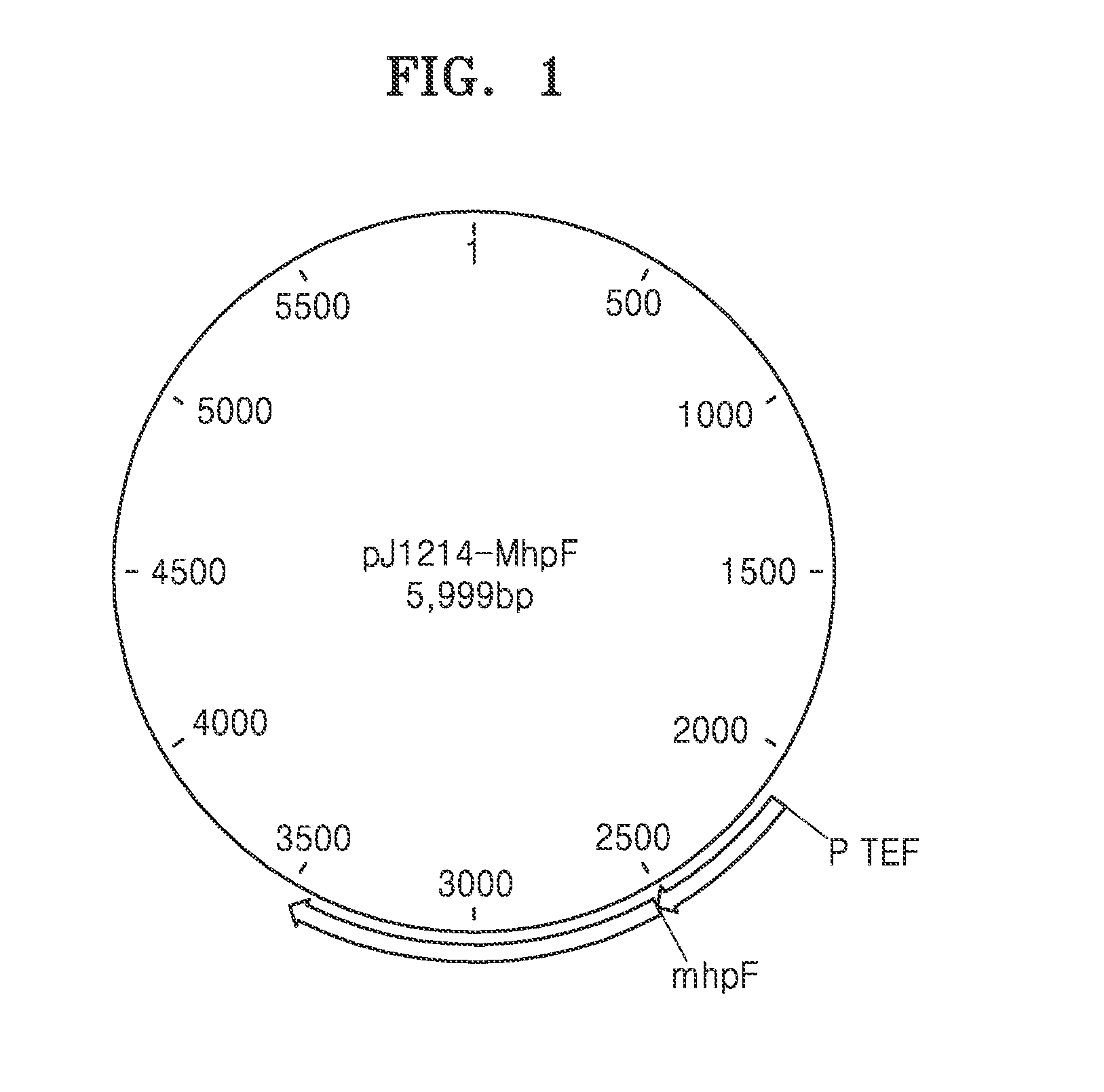
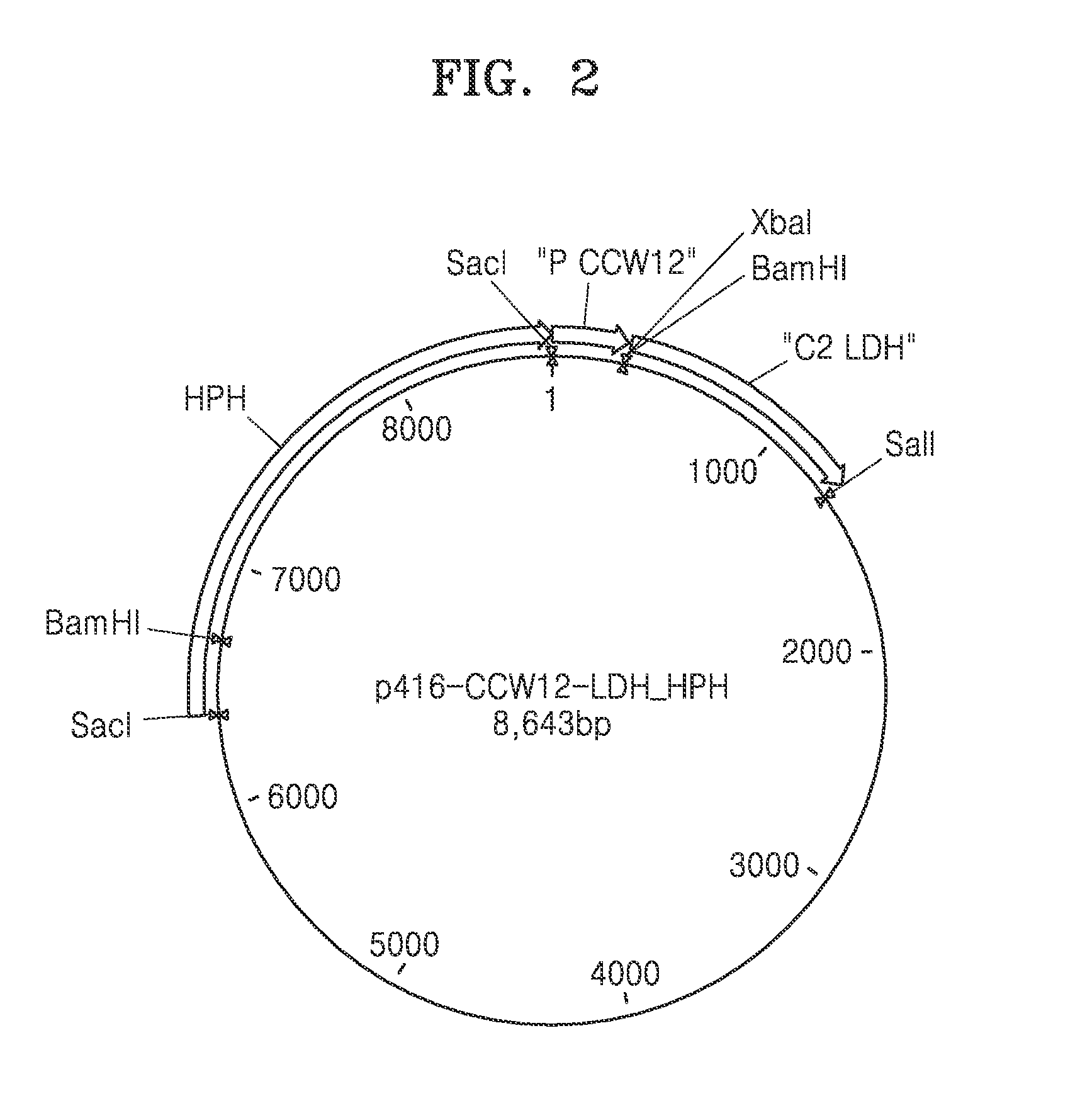
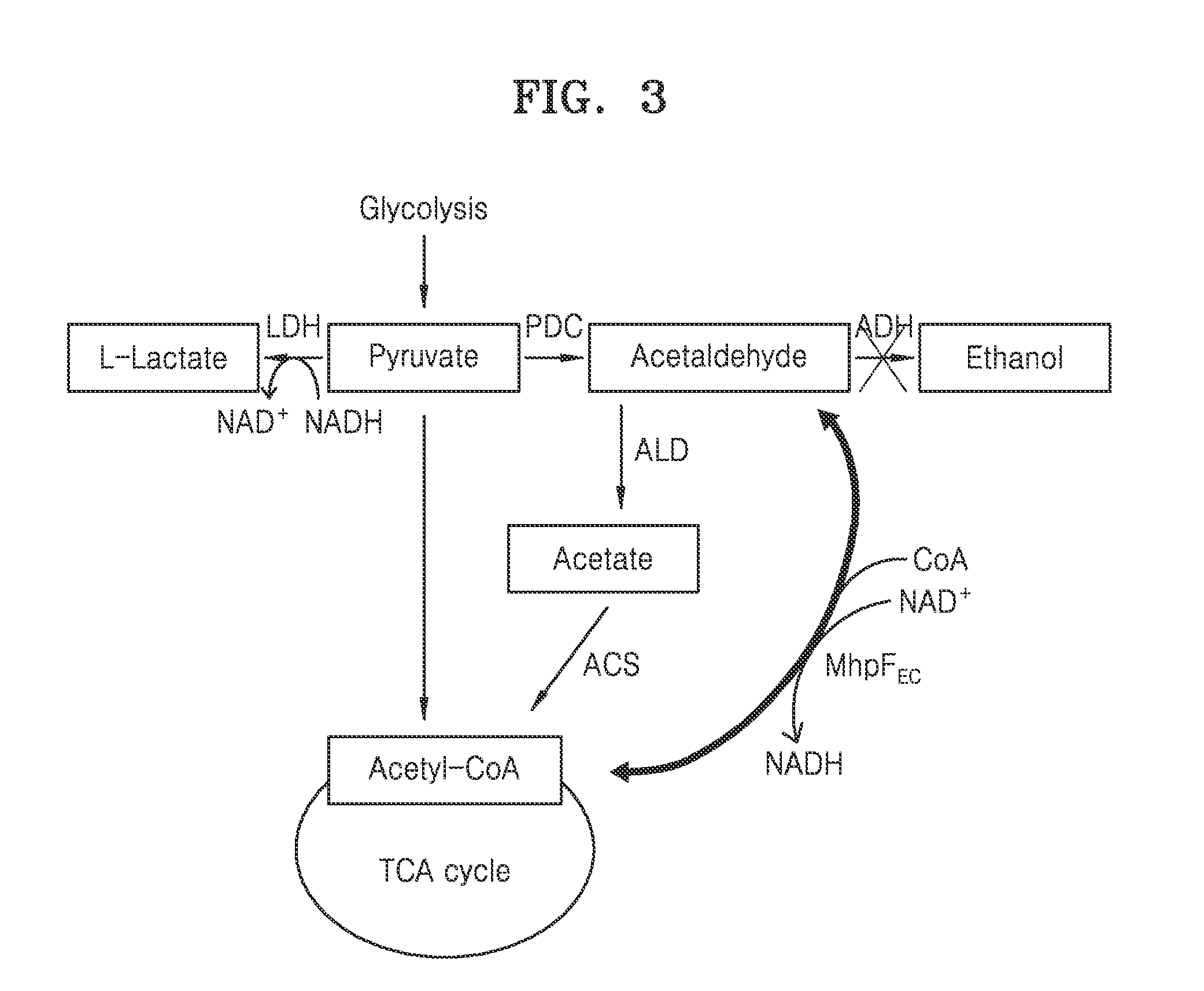
Genetically engineered yeast cell producing lactate including acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, method of producing yeast cell, and method of producing lactate using the same
Provided is a genetically engineered yeast cell with lactate production capacity, including an enzyme that catalyzes conversion of acetaldehyde to acetyl-CoA and an enzyme that catalyzes conversion of pyruvate to lactate, which activities are increased compared to a parent cell of the yeast cell, as well as a method of producing the genetically engineered yeast cell and method of producing lactate using the genetically engineered yeast cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
L-Amino Acid-Producing Bacterium and a Method for Producing L-Amino Acid
ActiveUS20070254345A1Improved ability to produce L-amino acidsEfficient productionBacteriaFermentationArginineL-Glutamin
Coryneform bacteria are described that have an ability to produce L-amino acids and are modified so that acetyl-CoA hydrolase activity is decreased. The bacteria are used to produce L-amino acids generated by a biosynthetic pathway in which pyruvic acid is an intermediate, such as L-glutamic acid, L-arginine, L-glutamine, L-proline, L-alanine, L-valine, and L-lysine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Production of isoprene, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprenoids using acetoacetyl-coa synthase
This invention relates to a recombinant microorganism capable of producing isoprene and isoprene production with the use of such recombinant microorganism with good efficiency. In this invention, the acetoacetyl-CoA synthase gene encoding an enzyme capable of synthesizing acetoacetyl-CoA from malonyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA and one or more genes involved in isoprene biosynthesis that enables synthesis of isoprene from acetoacetyl-CoA are introduced into a host microorganism.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
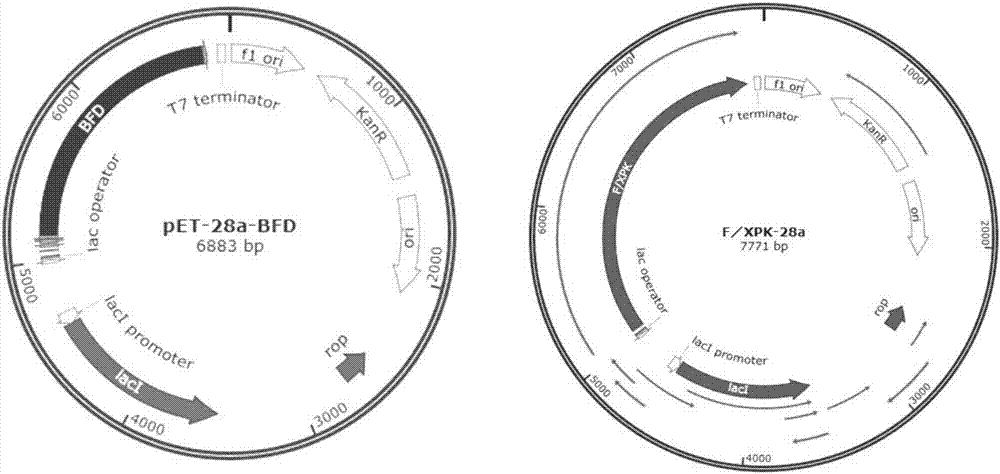
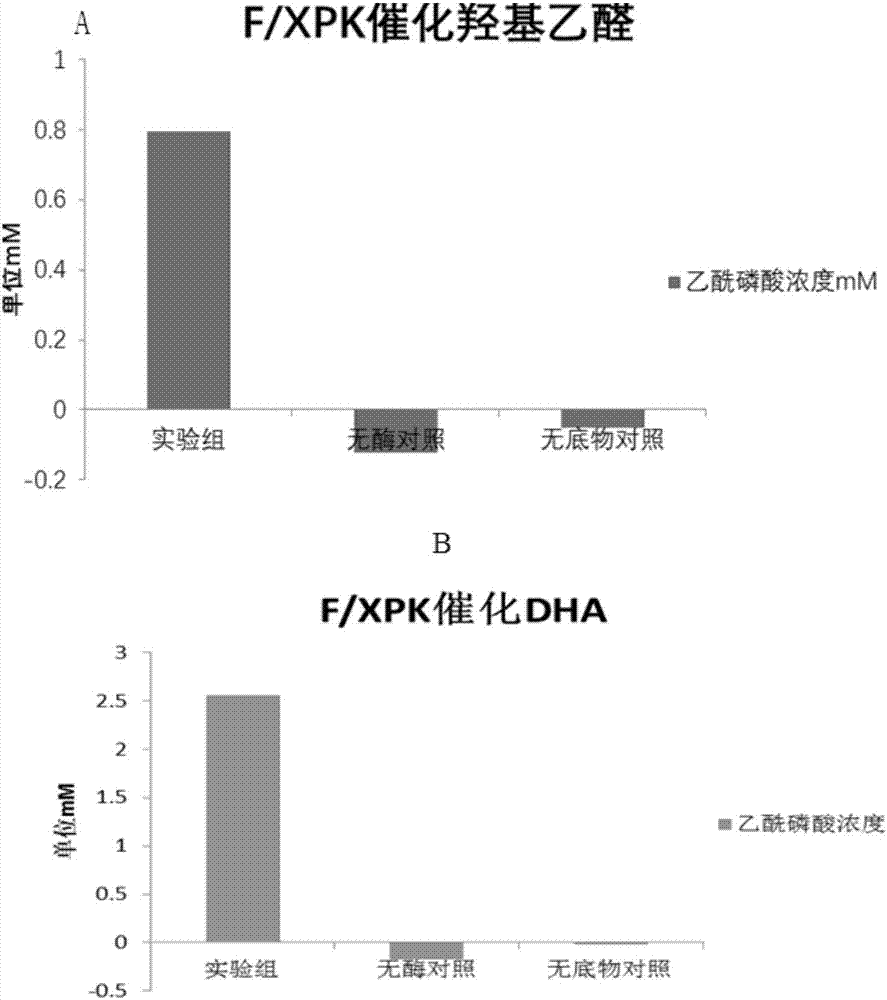
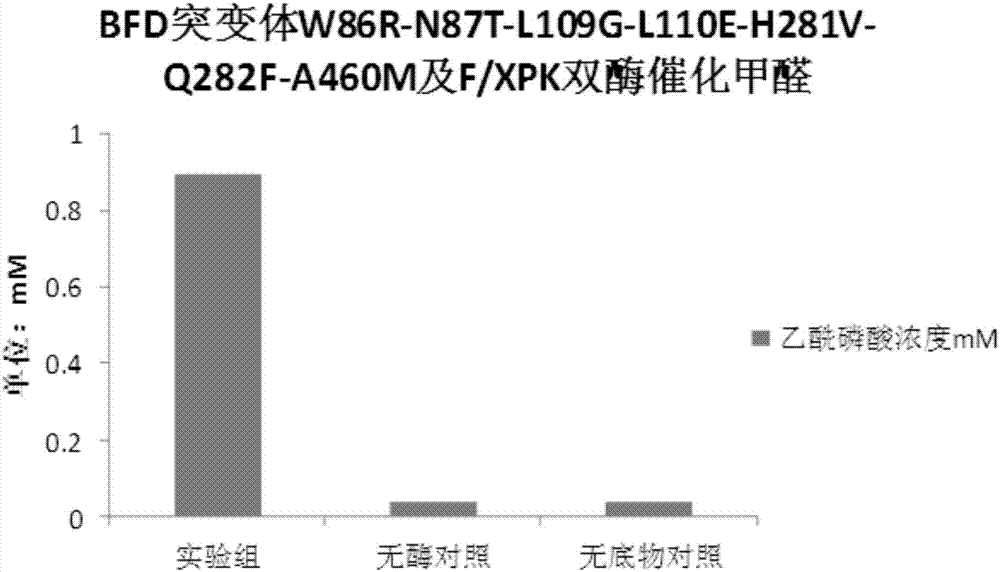
Enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and application thereof
ActiveCN106916794AEfficient aggregationNo inputFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesPhosphate acetyltransferasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and an application thereof. In the invention, through site-directed mutation of BFD, a mutant of the enzyme is found; and by means of the mutant of the enzyme, high-effect polymerization of the formaldehyde is achieved; meanwhile, through F / XPK, generation of acetyl phosphoric acid from the hydroxyl acetaldehyde or 1,3-dihydroxyacetone is achieved; with combination of phosphotransacetylase (Pta), a route from the formaldehyde to acetyl coenzyme A is achieved in three steps with the enzyme, thereby creating a new formaldehyde assimilation route, namely, synthesizing the acetyl coenzyme A from the formaldehyde in three steps. The route is short and is free of carbon loss and ATP input.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
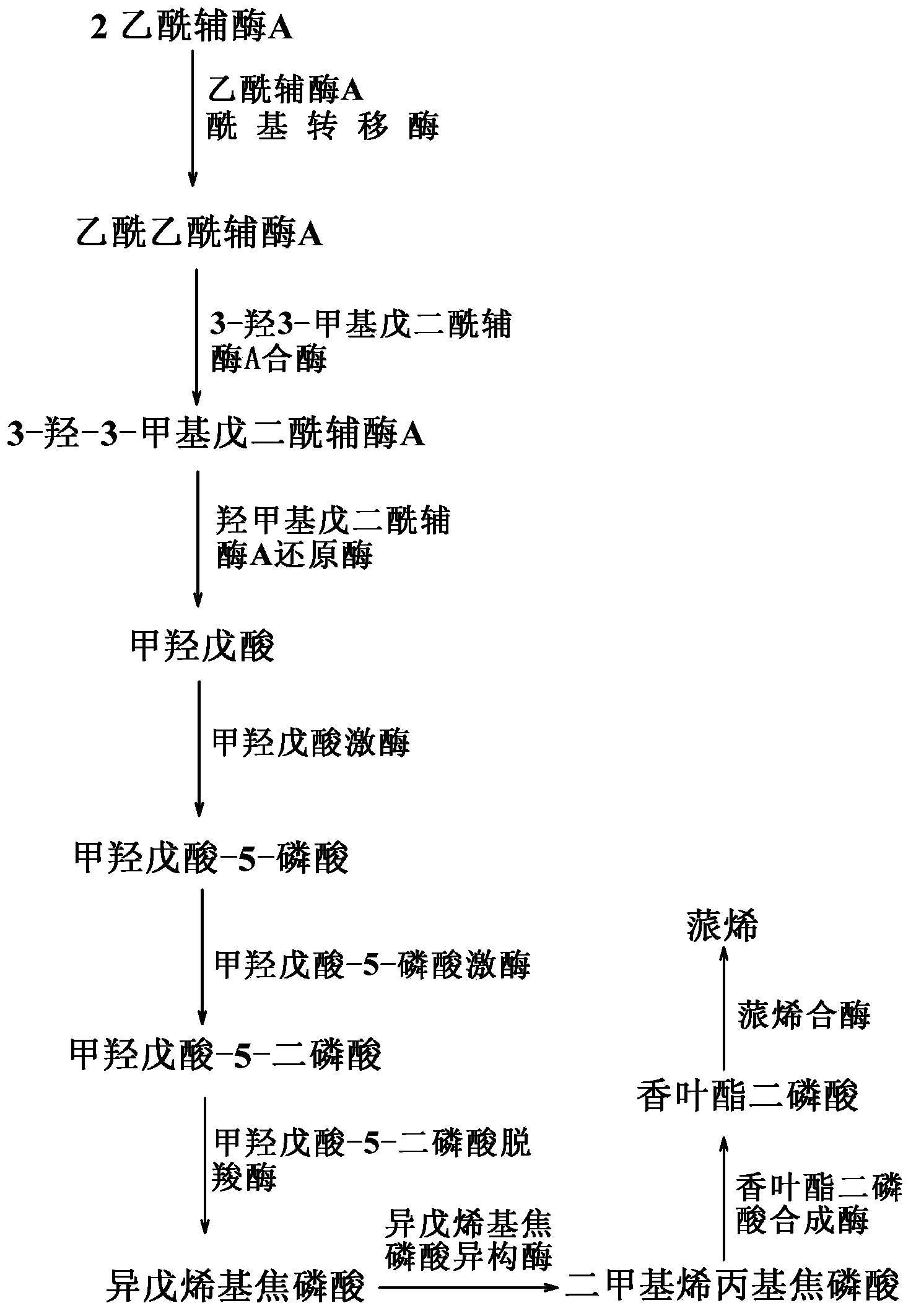
Method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting biological process
InactiveCN104120148AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxy methyl glutarylGlutaryl-coenzyme A
The invention provides a biological method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene from acetyl coenzyme A and a reconstitution cell capable of synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene, wherein the acetyl coenzyme A is obtained from a simple starting material like glucose. The method for synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting a biological process comprises the following steps: transferring acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyldiphosphate synthetase and pinene synthase into an appropriate host cell by adopting metabolic engineering technology, and culturing the obtained reconstitution cell, so that the target product, namely alpha-pinene or beta-pinene can be obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
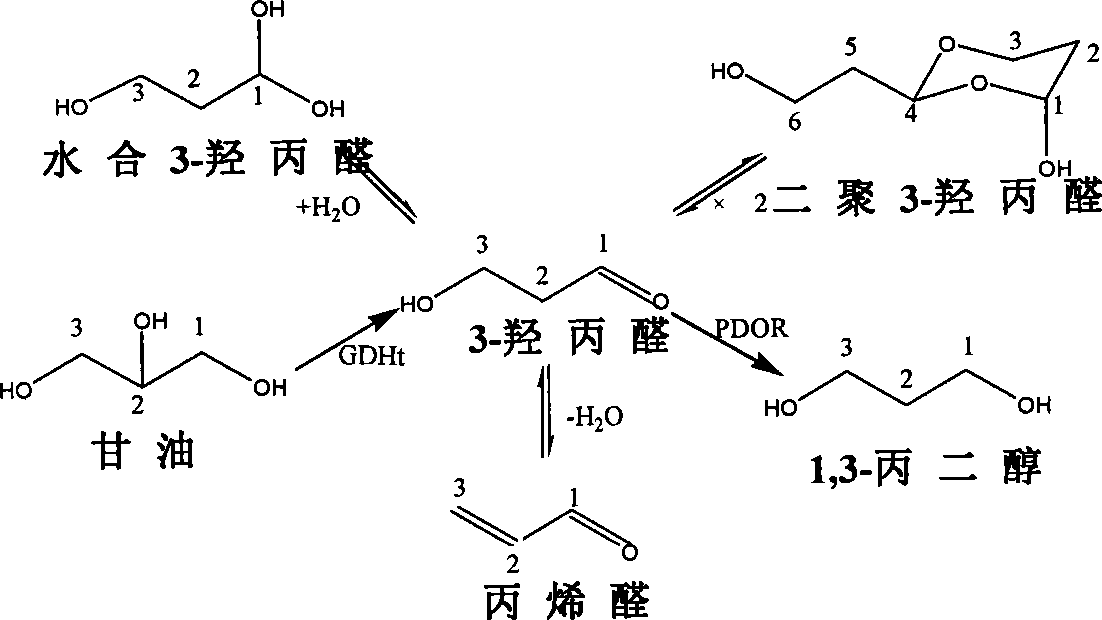
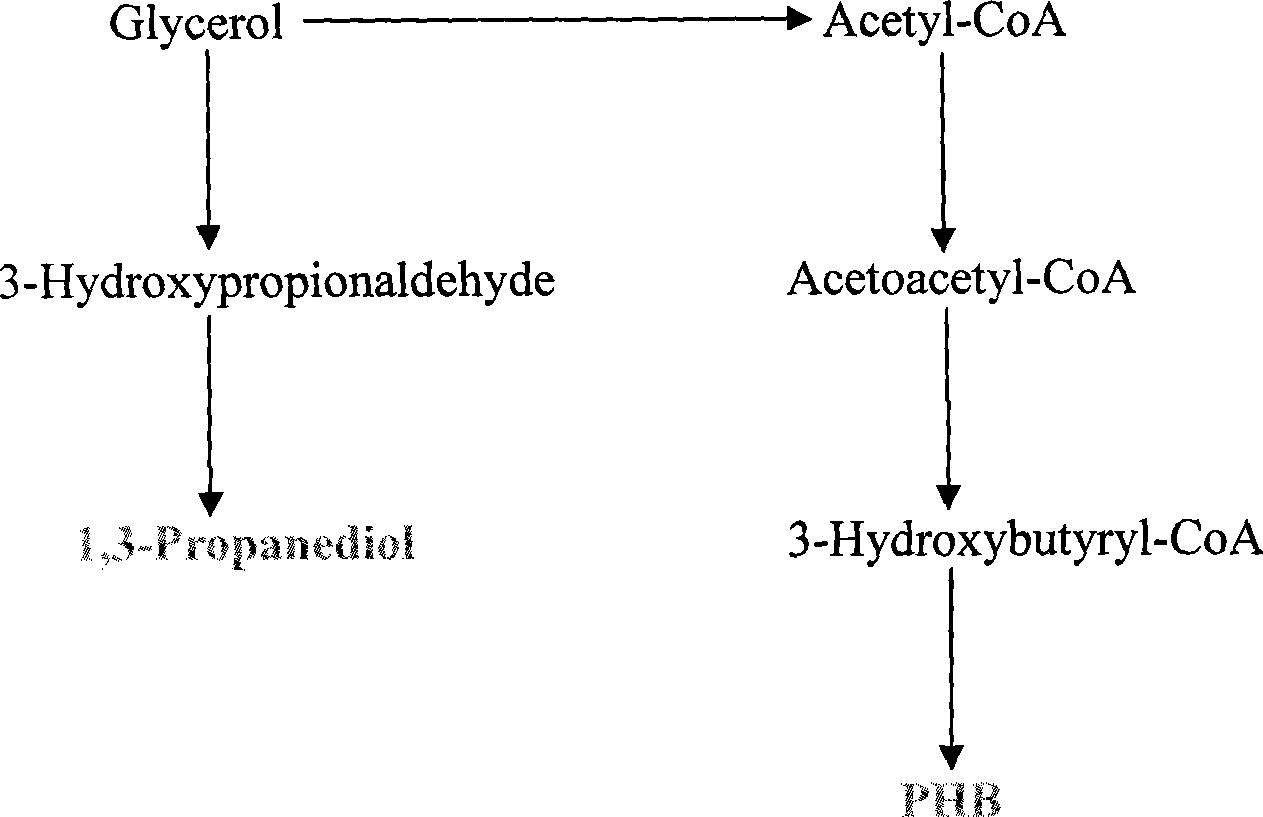
Method for constructing genetic engineering bacteria and enhancing stress resistance of 1,3-propanediol producing strain
InactiveCN101381696AImprove stress resistanceIncrease added valueBacteriaBiofuelsHigh concentrationGlycerol
The invention provides a method for constructing a gene engineering strain to enhance the resistance of a 1, 3-propanediol (PDO) production strain, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering and comprises the step of: introducing Beta-ketothiolase PhbA, NADPH-dependent acetoacetyl CoA, PhbB and polyhydroxyalkanoates synthases, PhbC gene to a wild bacteria which can produce PDO to accumulate high concentration of PHB while the bacterial strain produces PDO so as obviously improve the tolerance of the bacterial strain to glycerol and 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde; the method can also be used to co-produce PHB and PDO. The method has the advantages that the constructed gene engineering strain improves the resistance of the bacterial strain to the high concentration of glycedrol and the intermediate product 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde and reduces the abnormal fermentation in industrial production; in addition, high concentration of PHB can be accumulated while PDO is produced, and PHB can be used as a separated product, thereby promoting the added valve of products and the utilization rate of materials and reducing the production cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
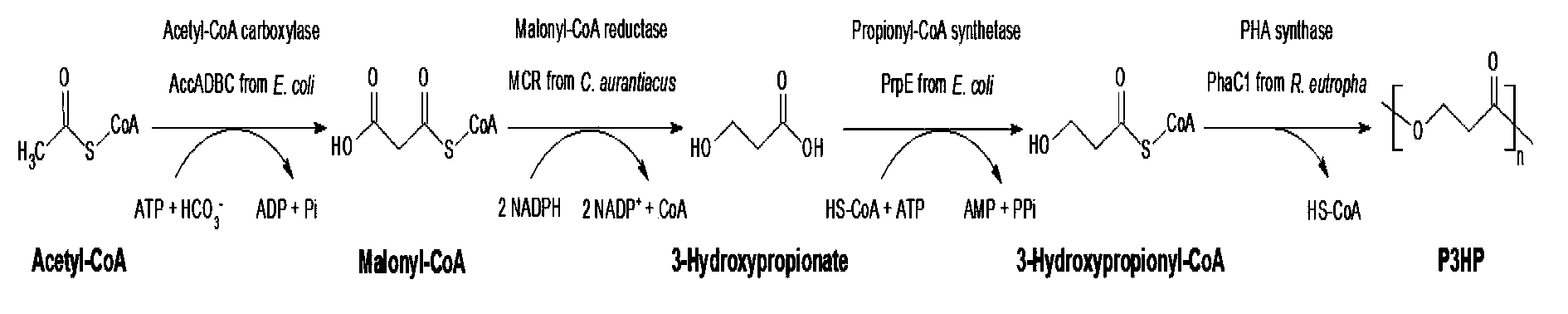
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof
ActiveCN104031872AAvoid the influence of own metabolismShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
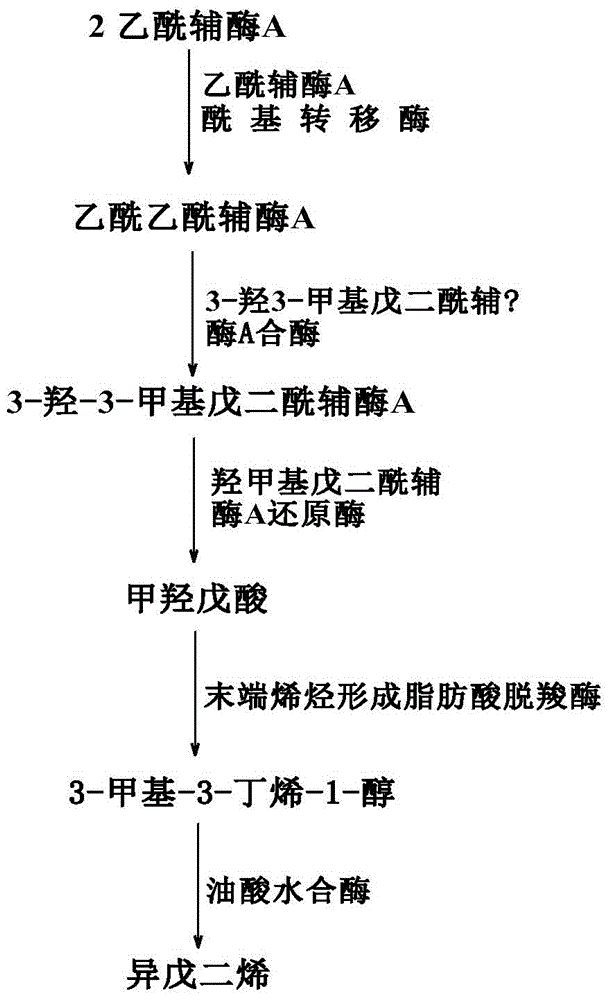
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering technology. According to the invention, a recombinant bacterium is obtained by transforming a gene containing acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, terminal alkene formed fatty acid decarboxylase and oleic acid hydratase into a host bacterium, and is used for fermentation production of isoprene. Such a method substantially shortens reaction process for synthesis of isoprene through an exogenous MVA approach, only five reaction steps are needed for synthesis of isoprene of acetyl-CoA, so influence of excess exogenous gene expression on metabolism of cells is avoided. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of the fermentation product isoprene can reach 39.49 mu g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
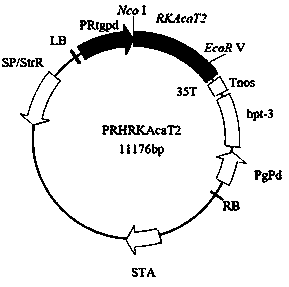
Acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof
ActiveCN109666683AIncreased transcript levelsIncrease contentAcyltransferasesGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the amino acid sequence encoded by thegene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the gene is a key enzyme gene synthesized by carotenoid in Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 and has the functions of the acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase, and the carotenoid produced by the Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 can be controlled; microorganisms are transformed through the genetic engineering means so as to increase the yield of carotenoid inthe microorganisms, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of the carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of Yarrowia lipolytica way
ActiveCN110106209AHigh synthetic yieldImprove the added value of the applicationMicroorganism based processesFermentationHMG-CoA reductaseAlpha-farnesene
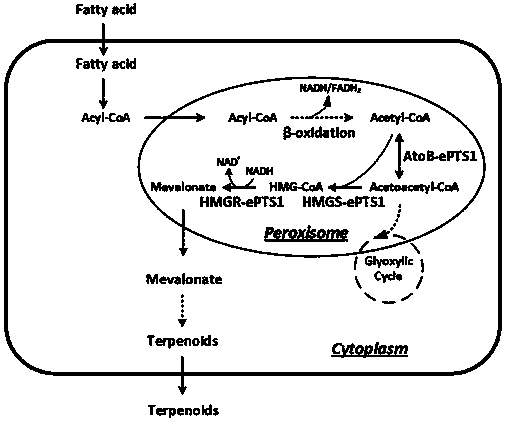
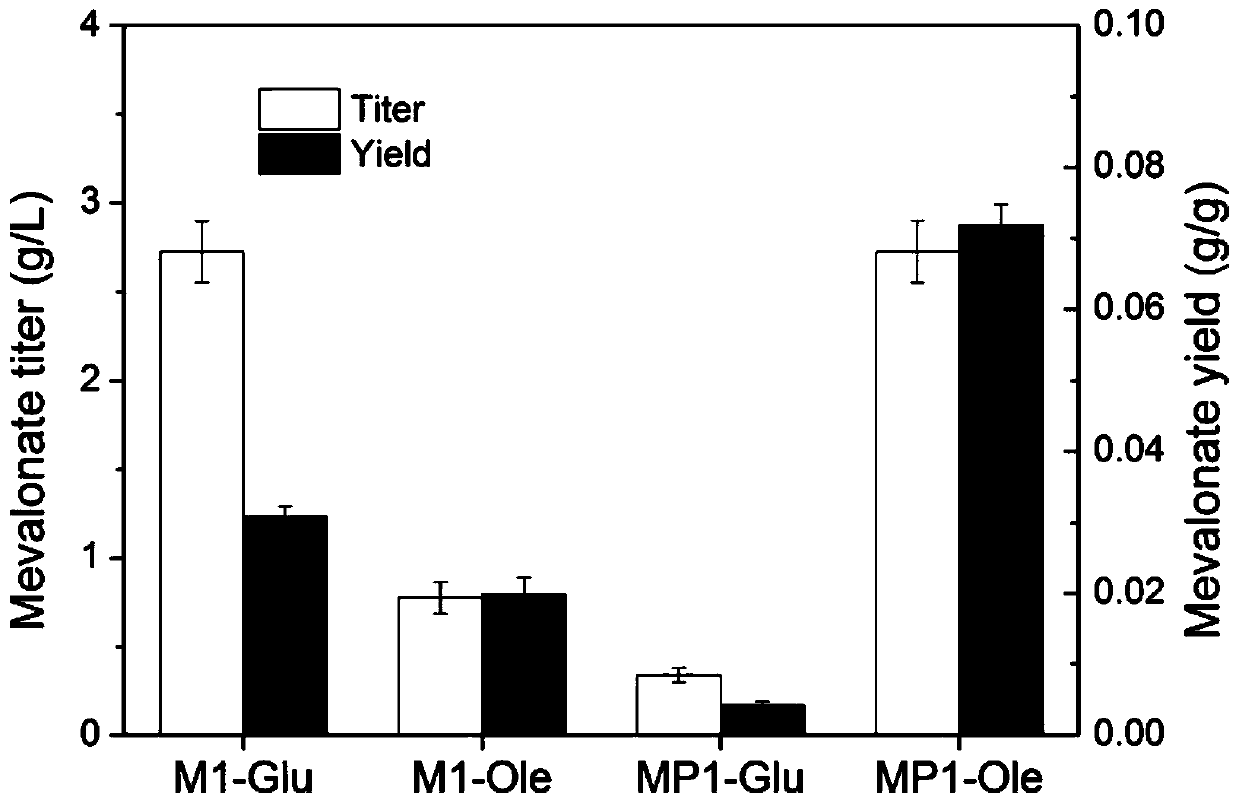
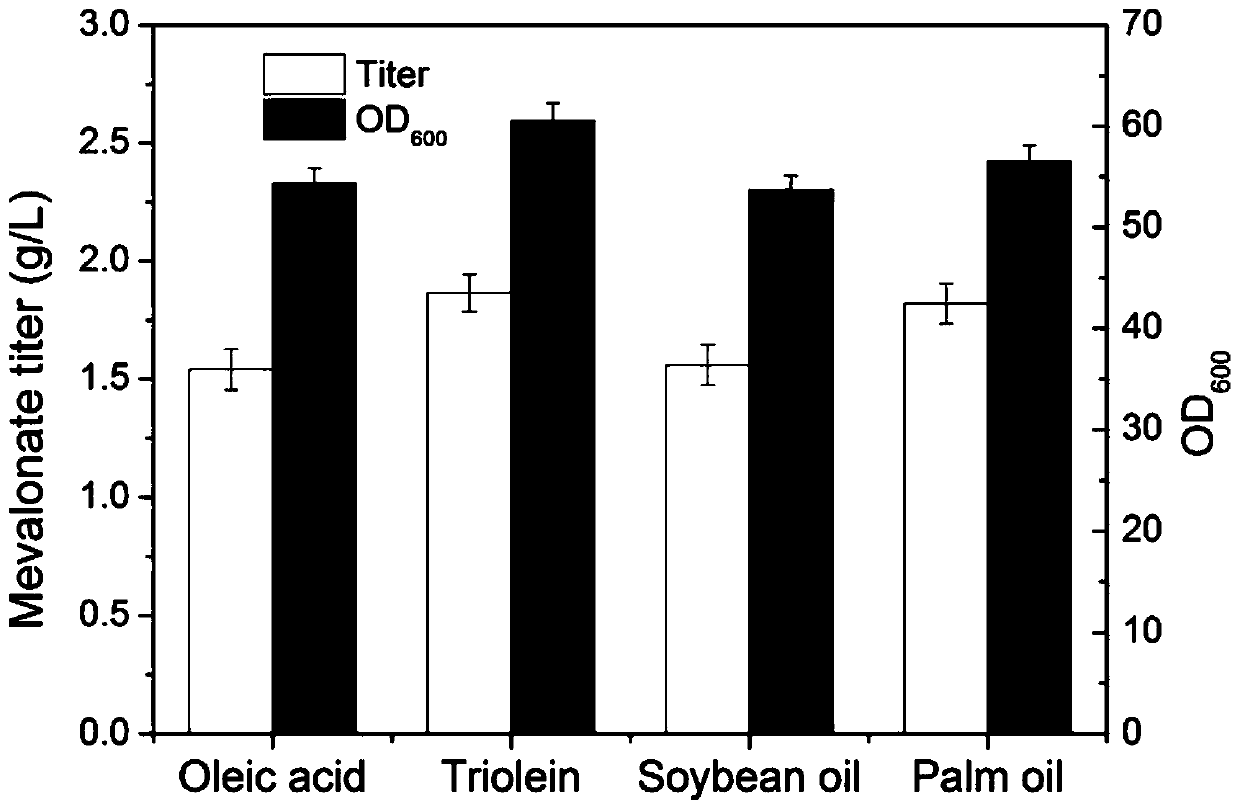
The invention discloses a method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of the Yarrowia lipolytica way. The method comprises the steps that an acetoacetyl coenzyme A thiolase, HMG-CoA synthetase and HMG-CoA reductase in the synthetic route of mevalonic acid in Yarrowia lipolytica are over-expressed and positioned to the peroxisome, and engineering bacteria MP1 are obtained; on the basis of the engineering bacteria MP1, the alpha-farnesene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria FP1 are obtained; or, the beta-carotene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria CP1 are obtained; or, the linalool synthesis way is expressed, engineering bacteria LP1 are obtained; the bacteria FP1 or CP1 or LP1 can synthesize the terpenoids under the aerobatic condition by means of a culture medium containing fatty acid or grease, and the yield of the synthesized terpenoids is higher compared with a traditional method. According to the method, fatty acid, grease and cheap food waste oil can be used for generating mevalonic acid downstream terpenoids, and the considerable application prospect and the economic value are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106086102AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseGlutamate 5-kinase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
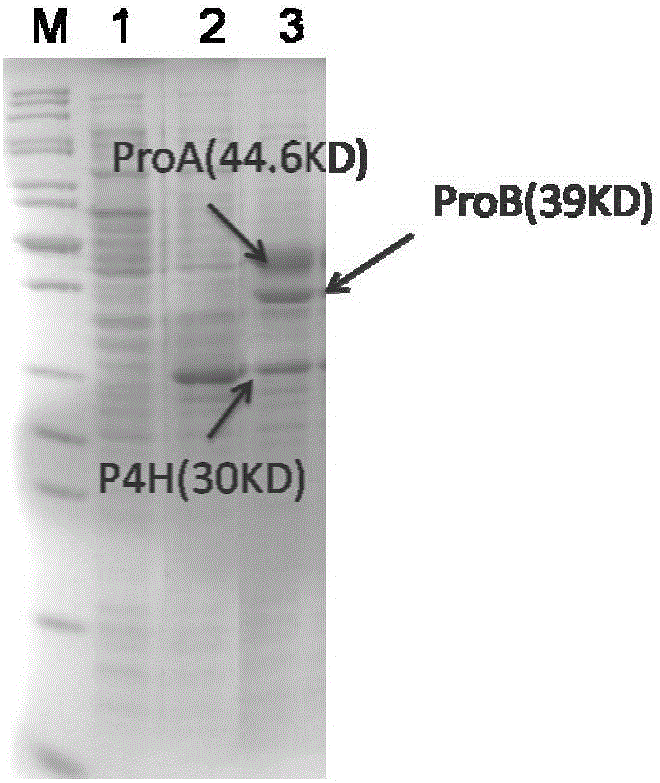
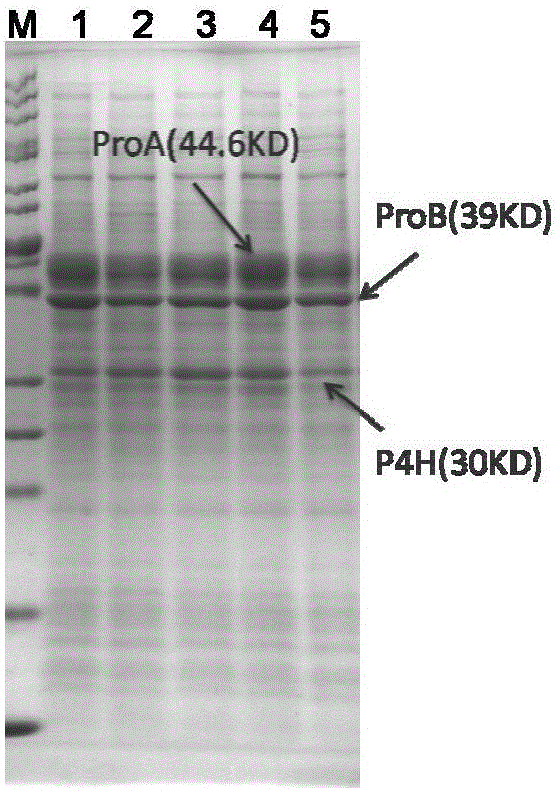
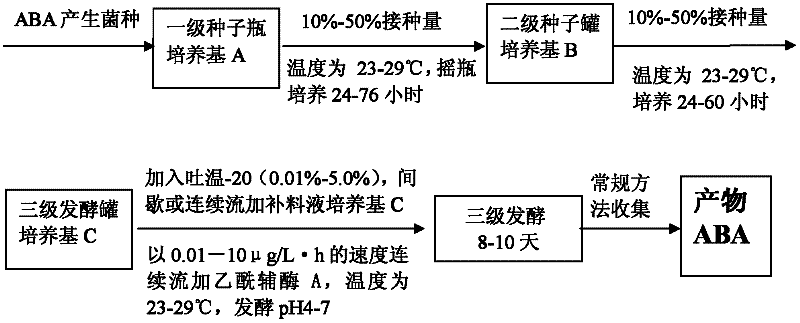
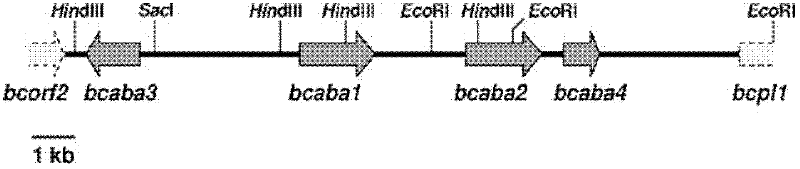
Method for efficiently preparing natural abscisic acid
ActiveCN102399827AImprove utilization efficiencyIncrease acid production rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationAbscisic acidOxygen
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation and relates to a method for efficiently preparing natural abscisic acid through adding acetylcoenzyme A as precursor substances for strains to synthesize the abscisic acid in a flowing way in the fermentation process and simultaneously adding biosurfactant tween-20 for improving the dissolved oxygen condition of the fermentation liquid. The method comprises the following steps that fungi capable of producing the natural abscisic acid are cultured in a first stage liquid culture medium; the cultured first stage seed liquid is inoculated onto a second stage liquid culture medium for culture, supplementing materials are added to a third stage liquid culture medium in the flowing way, simultaneously, the tween-20 is added,and the acetylcoenzyme A is added in the flowing way for fermentation culture; and the obtained abscisic acid is collected from the fermentation culture liquid. The method has the advantages that theoxygen utilization rate of the strains and the acid yield can be improved, so the strains can be used for producing the abscisic acid at higher substrate conversion rate and higher product synthesis velocity, the yield and the production efficiency are improved, the energy consumption is reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Recombinant bacterium of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid, construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention provides a recombinant bacterium of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid, and a construction method and preparation of the recombinant bacterium and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A host bacterium of the recombinant bacterium is escherichia coli, and the recombinant bacterium expresses and codes gene clpP of an ATP (adenosine triphosphate) dependent protease hydrolysis subunit, and codes a gene accABCD of acetylcoenzyme A carboxylase and a gene mcr of malony-coA reductase. A preparation method comprises the steps of obtaining and transforming recombinant vectors pETDuet-clpP-mcr, and pACYCDuet-accADBC into a host competent cell. The recombinant bacterium solves the problem that the increase of a concentration of 3-hydracrylic acid in a microbial fermentation process inhibits microbial growth to influence a yield; a fermentation level is increased by 116% compared with that of strains of the ATP dependent protease hydrolysis subunit without expression and coding; and the level is the highest known shake flask fermentation level.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Free fatty acid determination reagent kit
InactiveCN103207175AStrong specificityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetasePeroxidase
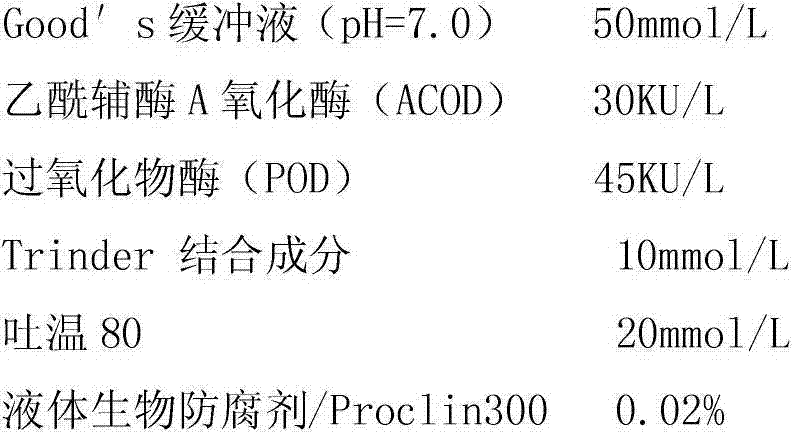
The invention relates to a free fatty acid determination reagent kit which comprises dual reagents. The reagent 1 comprises Good's buffer solution (pH(potential of hydrogen)=7.0), coenzyme A, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, magnesium chloride (MgCL2), Trinder bound constituent, tween 80 and liquid biological preservative / Proclin 300, and the reagent 2 comprises Good's buffer solution (pH=7.0), acetylcoenzyme A oxidase (ACOD), peroxidase (POD), Trinder bound constituent, tween 80 and liquid biological preservative / Proclin 300. The free fatty acid determination reagent kit has the remarkable advantages that the reagent kit is directly used for an automatic biochemical analyzer and is simple; and the adopted automatically separated and purified acetylcoenzyme A synthetase and acetylcoenzyme A oxidase (ACOD) have high specificity on free fatty acid in serum.
Owner:SHAOXING SHENG KANG BIOLOGICAL TECH
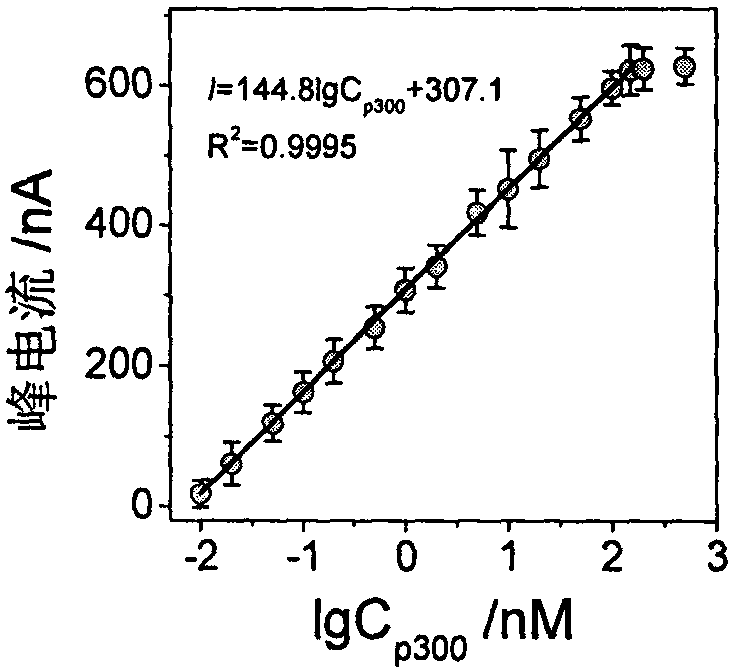
Construction method and application of electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting activity of histone acetyltransferase
ActiveCN108593751AHigh sensitivityAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionMaterial electrochemical variablesWater bathsUltrasonic dispersion
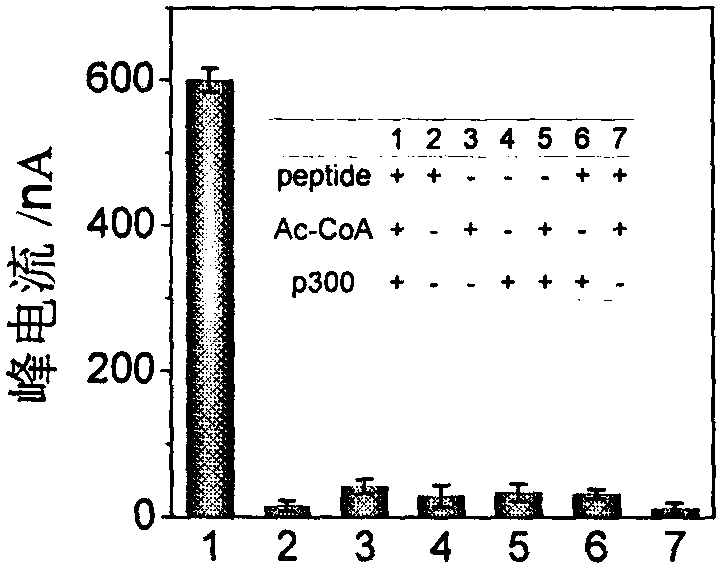
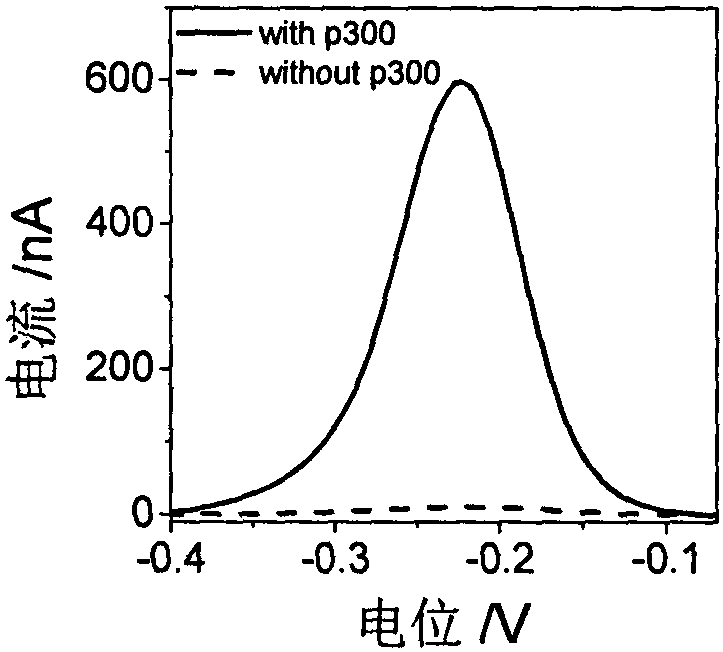
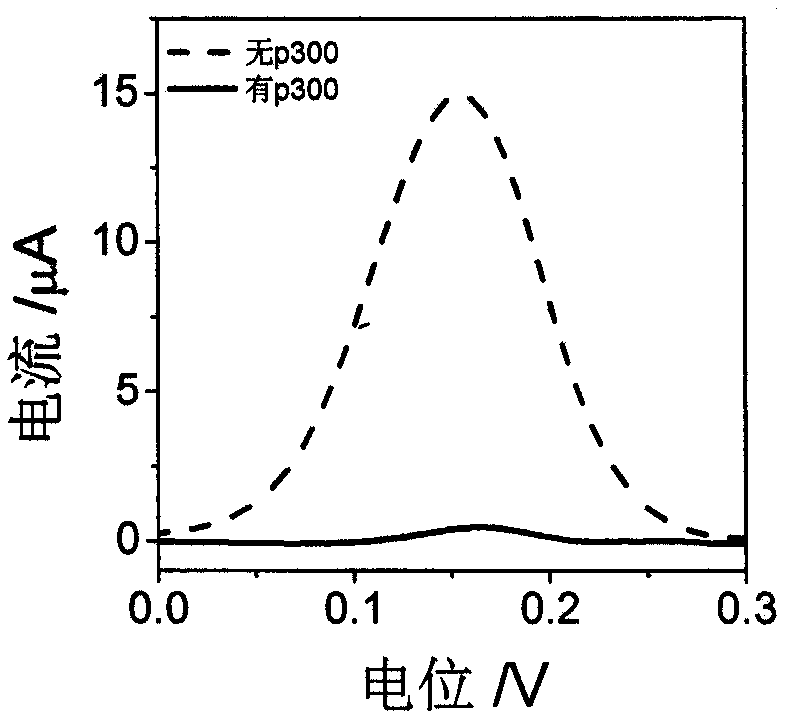
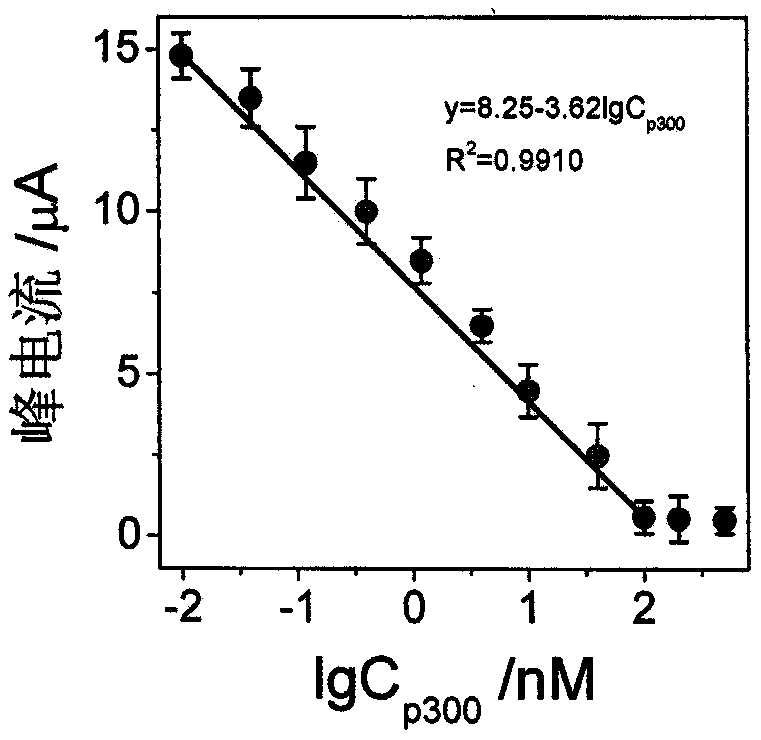
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting the activity of histone acetyltransferase. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing peptide / Au: respectively taking acetyltransferase p300, polypeptide and acetyl-CoA, fully mixing the taken substances in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0), incubating the obtained solution in a constant-temperature water bath, taking and dropwise applying a catalytic reaction to the surface of a gold electrode, and incubating the gold electrode in a 4 DEG C refrigerator; (2) preparing MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab: mixing HAuCl4 and CTAB with water, adding ascorbic acid to the obtained reaction mixture, adding NaOH to obtain CTAB covered AuNPs, centrifuging and purifying the CTAB covered AuNPs, dispersing the purified CTAB covered AuNPs in an equal amount of water, adding GO to the obtained solution, performing ultrasonic dispersion, standing the dispersed solution for later use,adding an acetyl antibody, performing incubation, adding MB, and performing vibration and uniform mixing; and (3) producing the electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor: taking and dropwise applyingthe MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab to the surface of the peptide / Au, performing incubation at room temperature, and placing the produced sensor in the PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0) to carry out electrochemical SWV test.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
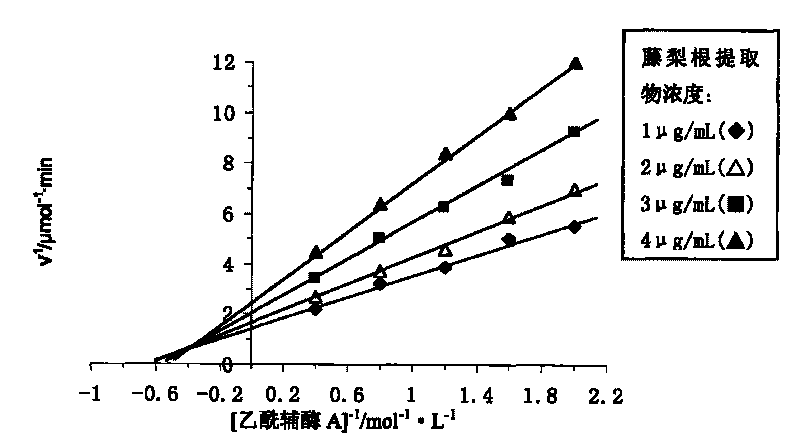
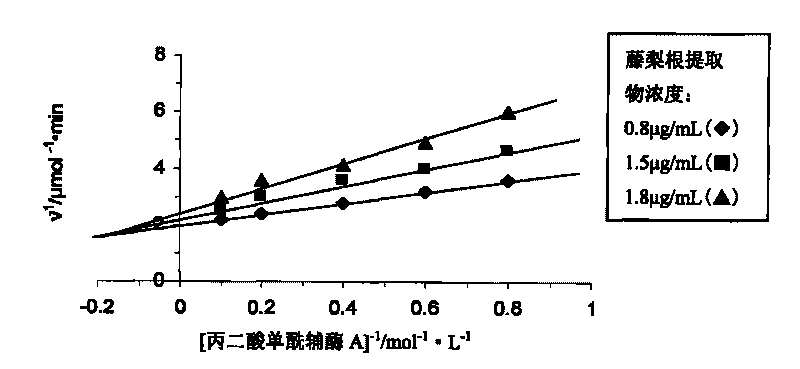
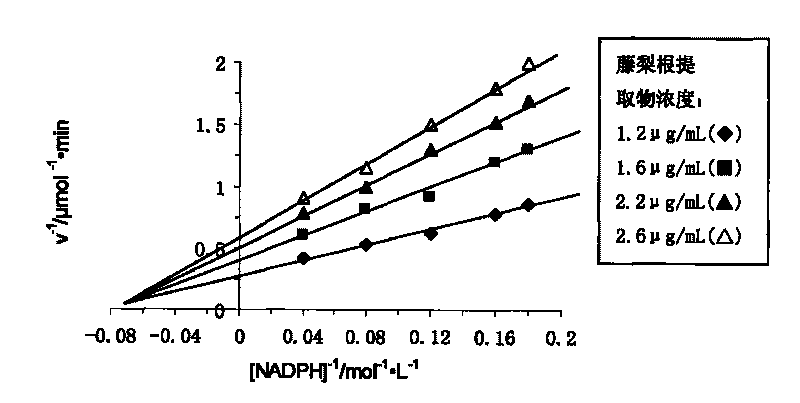
Extract of yangtao actinidia root and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101757056ADon't worry about gaining weightAppetite suppressantMetabolism disorderAntineoplastic agentsOrganic solventActinidia
The invention discloses an extract of yangtao actinidia root and a preparation method and applications thereof. The extract of yangtao actinidia root, which is provided by the invention, is prepared by the following method: using water and / or an organic solvent as an extractant to extract the extract of yangtao actinidia root from yangtao actinidia root. Experiment shows that the extract of yangtao actinidia root can effectively inhibit the activity of fatty acid synthase. The inhibition kinetic analysis shows that the inhibition of the extract of yangtao actinidia root for the fatty acid synthase and the substrates of acetylcoenzyme A and NADPH have a competitive and non-competitive mixed type relationship, but more close to the non-competitive relationship; and the inhibition of the extract of yangtao actinidia root for the fatty acid synthase and the substrate of malonyl coenzyme A have a competitive and non-competitive mixed type relationship. The extract of yangtao actinidia root can be applied to the preparation of weight-reducing medicament and the medicament for preventing and treating cancers, and also can be widely applied as food, health product and daily chemical additive.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Insecticidal and acaricidal composition containing acetyl coenzyme A inhibitor insecticide
ActiveCN104663668ASynergistic effect is obviousImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideAnimal repellantsChemical compositionActive component
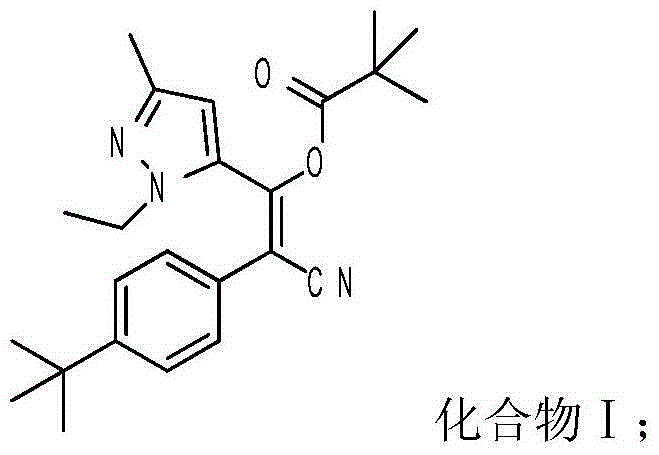
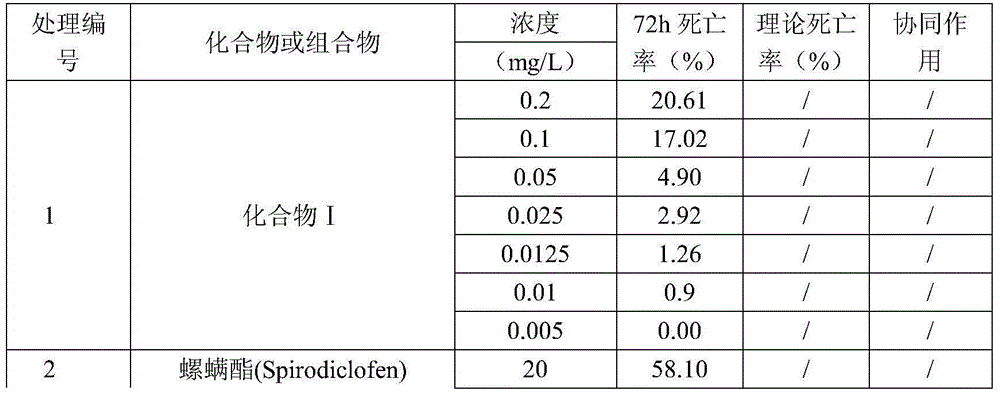
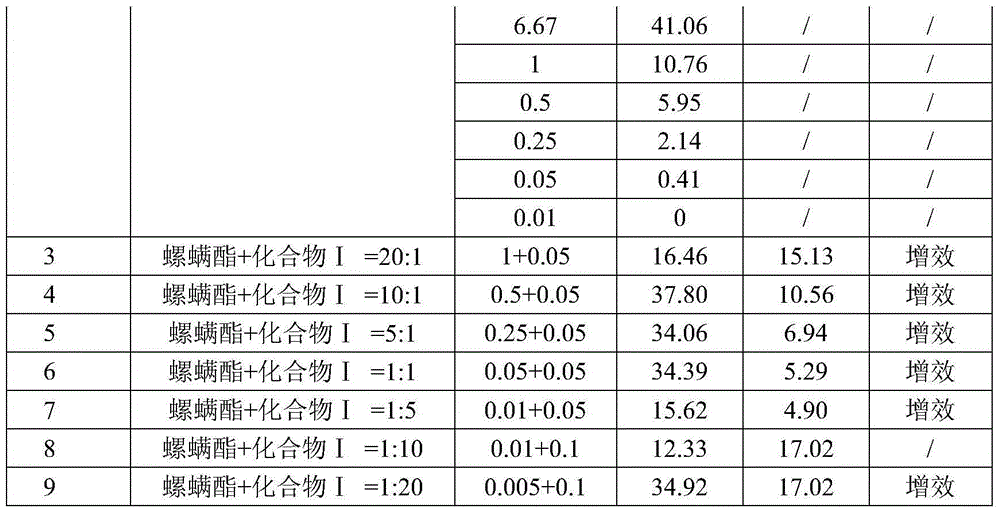
The invention belongs to the field of insecticides, and relates to an insecticidal and acaricidal composition containing an acetyl coenzyme A inhibitor insecticide. The composition contains an active component A and an active component B, a weight part ratio of the component A to the component B is 1:99-99:1, the active component A is a compound I represented by a structural formula shown in the invention, and the active component B is selected from acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase inhibitor insecticides / acaricides. The composition has the advantages of obvious synergy and resistance delaying, and can be used for controlling various insects.
Owner:SHENYANG SINOCHEM AGROCHEMICALS R&D CO LTD
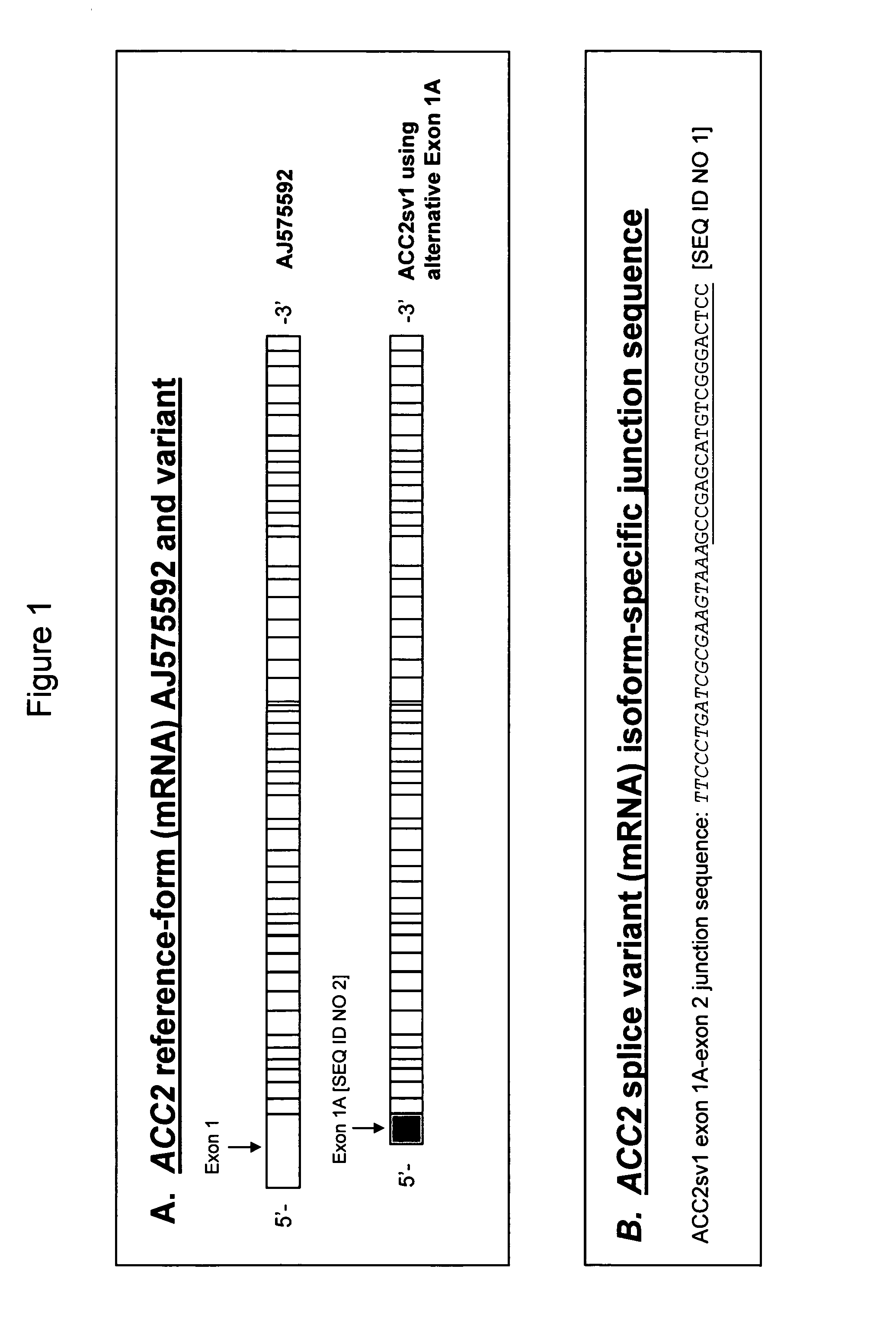
Alternatively spliced isoform of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACC2)
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Preparation method of electrochemical biosensor for simultaneously detecting HAT and TdT and application thereof
ActiveCN109856212ARealize detectionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseElectrochemical biosensor
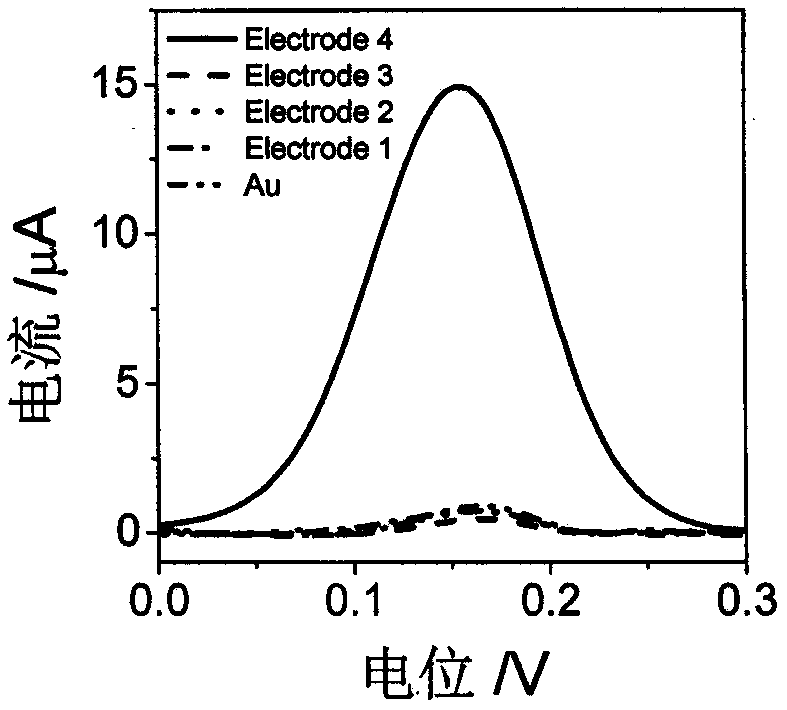
The invention discloses a preparation method of an electrochemical biosensor for simultaneously detecting HAT and TdT and application thereof. The method comprises: step one, adding MCH dropwise ontoa hairpin DNA modified electrode surface induced by Hg<2+> and marking the processed electrode as Electrode 1; step two, taking acetyltransferase p300, polypeptide and acetylcoenzyme A respectively and mixing the acetyltransferase p300, the polypeptide and the acetylcoenzyme A fully in a phosphoric acid buffer solution (PBS, 10 mM, pH 7.0), dropping and coating the mixed solution on the surface ofthe Electrode1, and marking the obtained substance as Electrode2; step three, dropping and coating an Exo I solution on the surface of the Electrode2, carrying out incubation at a room temperature, dropping a TdT reaction solution on the electrode surface, and marking the obtained substance as Electrode3; and step four, adding Cu<2+> on the electrode surface obtained in the step three, dropping an ascorbic acid solution on the electrode surface, marking the obtained substance as Electrode 4, and detecting an electrochemical response in PBS electrolyte solution with parameters of 0.1M and pH7.0. The preparation method has the following advantages: the specificity and sensitivity are high; the detection speed is fast; the activities of two kinds of enzymes can be detected simultaneously; and the result is accurate and reliable and the cost is low.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Serum-free immune cell culture medium and preparation method thereof
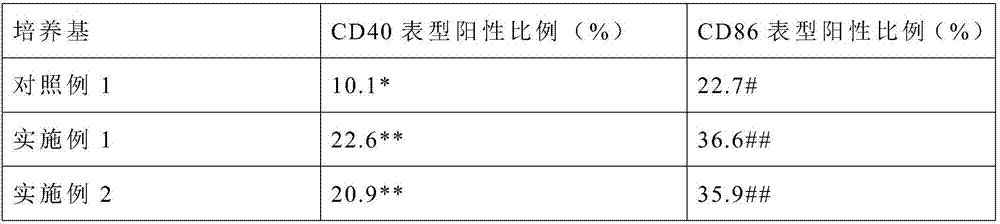
InactiveCN107574150AIncrease the proportion of positive phenotypesHigh positive rateBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeSalidroside
The invention discloses a serum-free immune cell culture medium. The serum-free immune cell culture medium is prepared mainly from amino acids, vitamins, minerals, D-glucose, 4-hydroxyethyl piperazinyl ethanesulfonic acid, insulin, phenol red, sodium pyruvate and transferrin. The invention discloses another serum-free immune cell culture medium which further comprises cofactors including salidroside, luteolin and resveratrol. The invention discloses another serum-free immune cell culture medium which further comprises activators including an acetyl coenzyme A, a coenzyme Q10, glucose 6-phosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. A part of embodiments of the invention can increase the positive ratio of cell phenotypes.
Owner:万向东方生物科技有限公司
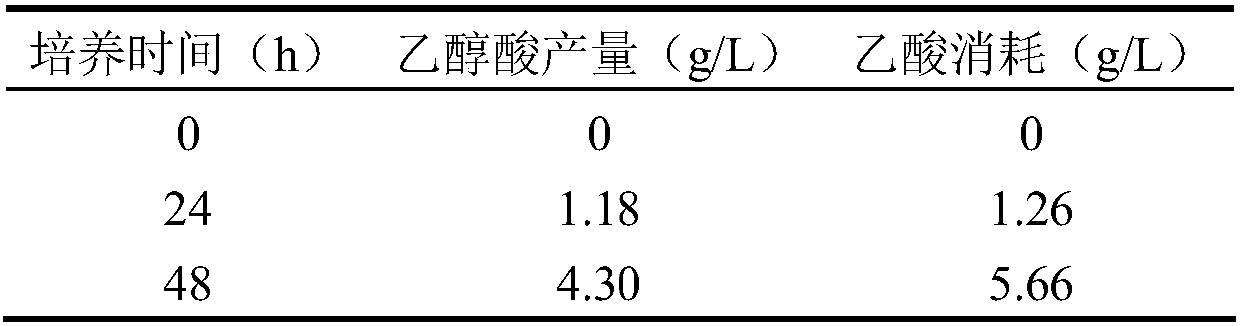
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and building method and application thereof
ActiveCN107603998AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and a building method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid provided by the invention comprises the following steps of improving the expression and / or activity of acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, phosphotransacetylase, acetokinase, citrate synthase, isocitrate lyase, isocitrate dehydrogenase kinase and glyoxylate reductase in the recipient bacterium; reducing the expression and / or the activity of malate synthase, glycolate oxidase and isocitrate lyase repressor protein in the recipient bacterium, so that the engineering bacterium for producing the glycollic acid is obtained. The recipient bacterium is a bacterium capable of using acetic acid as a carbon source for growth. The prepared genetic engineering bacterium uses acetic acid as the carbon source for producing the glycollic acid; in addition, the production quantity and yield of the glycollic acid in shaking culture can reach the relatively high level; relatively good industrial application prospects are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com