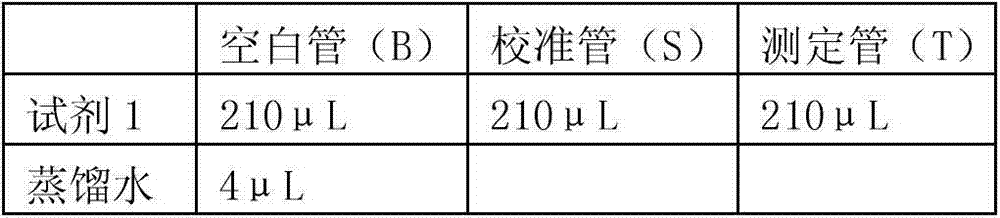
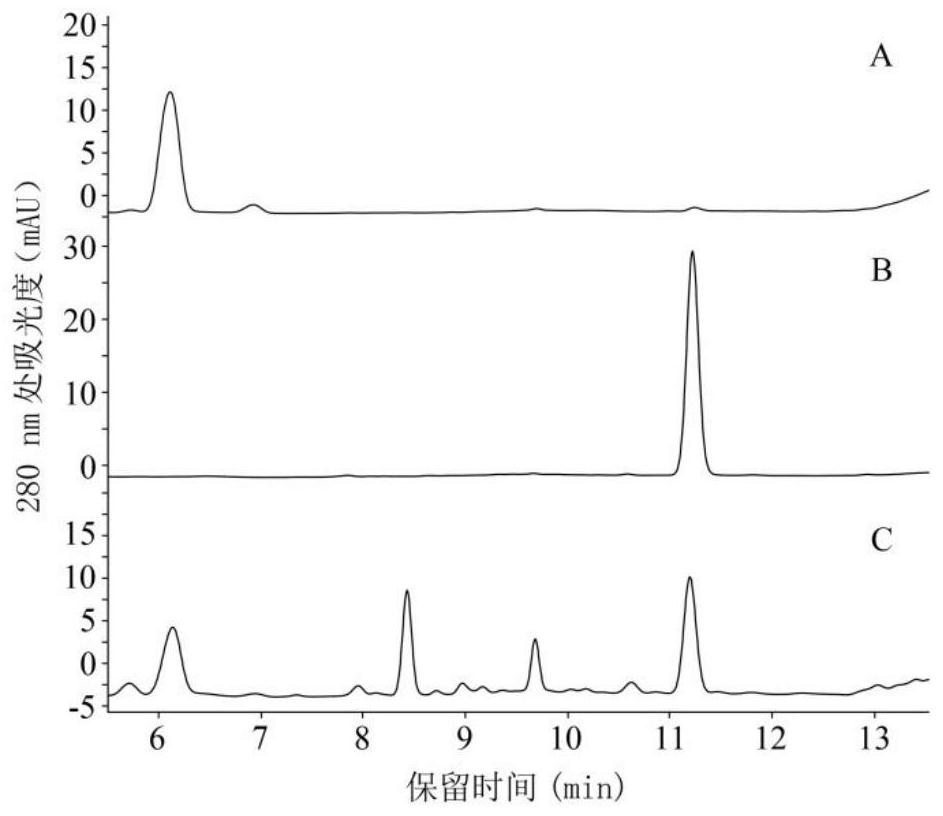
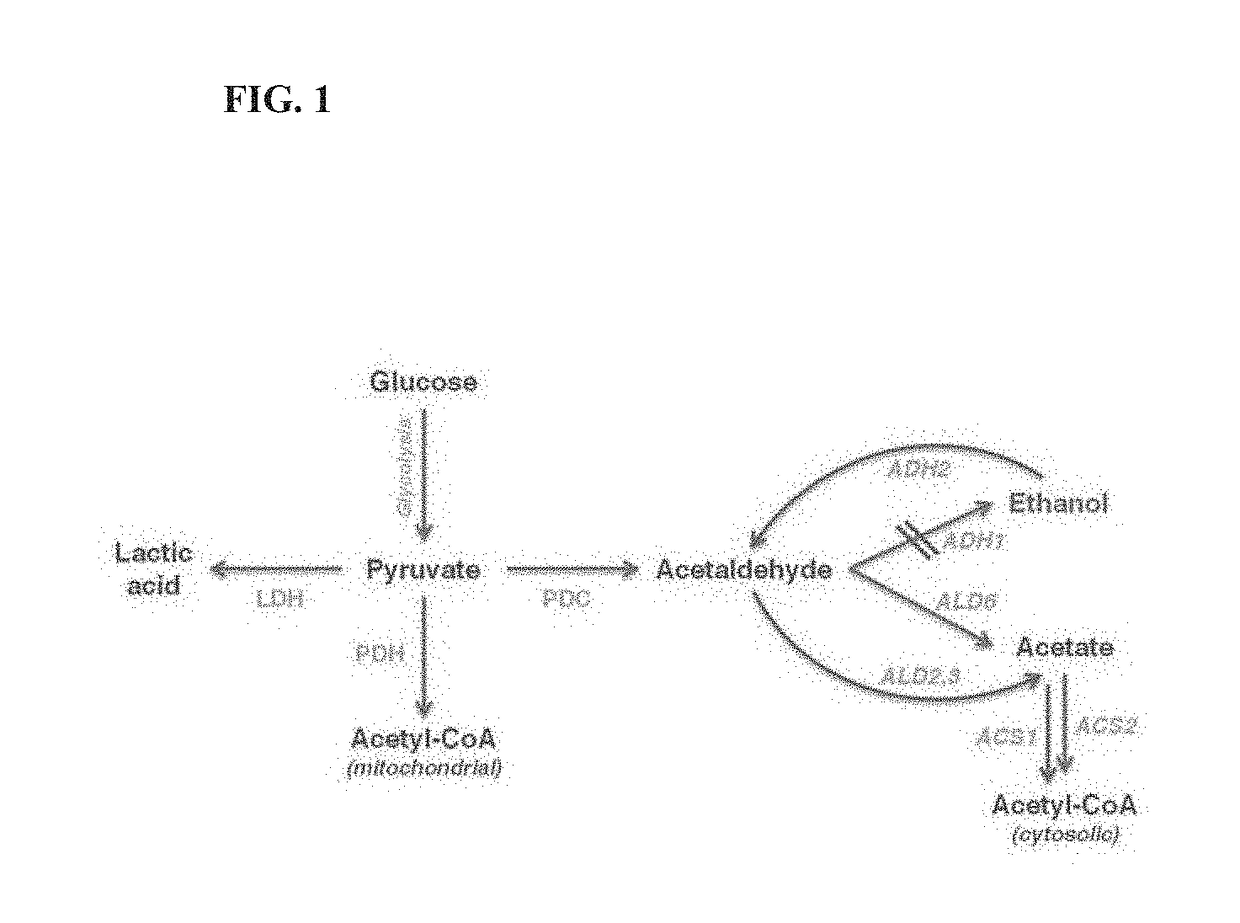
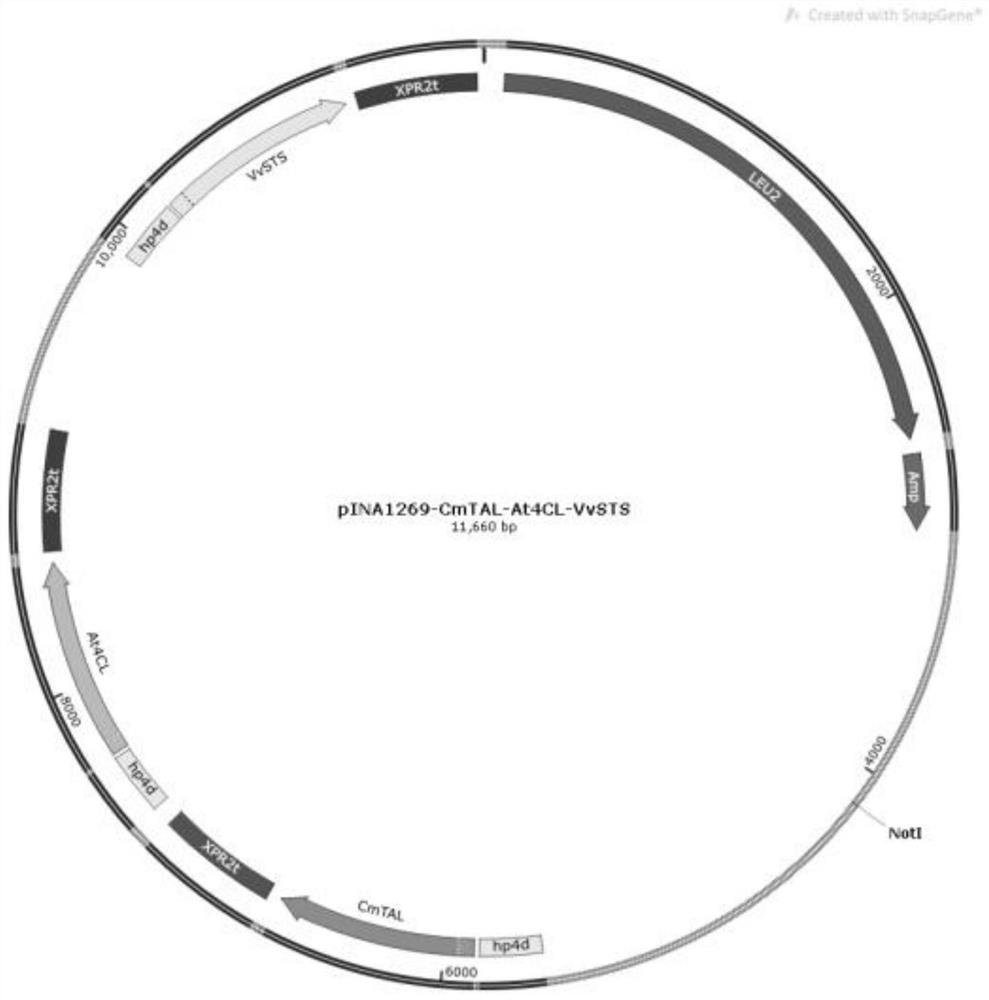
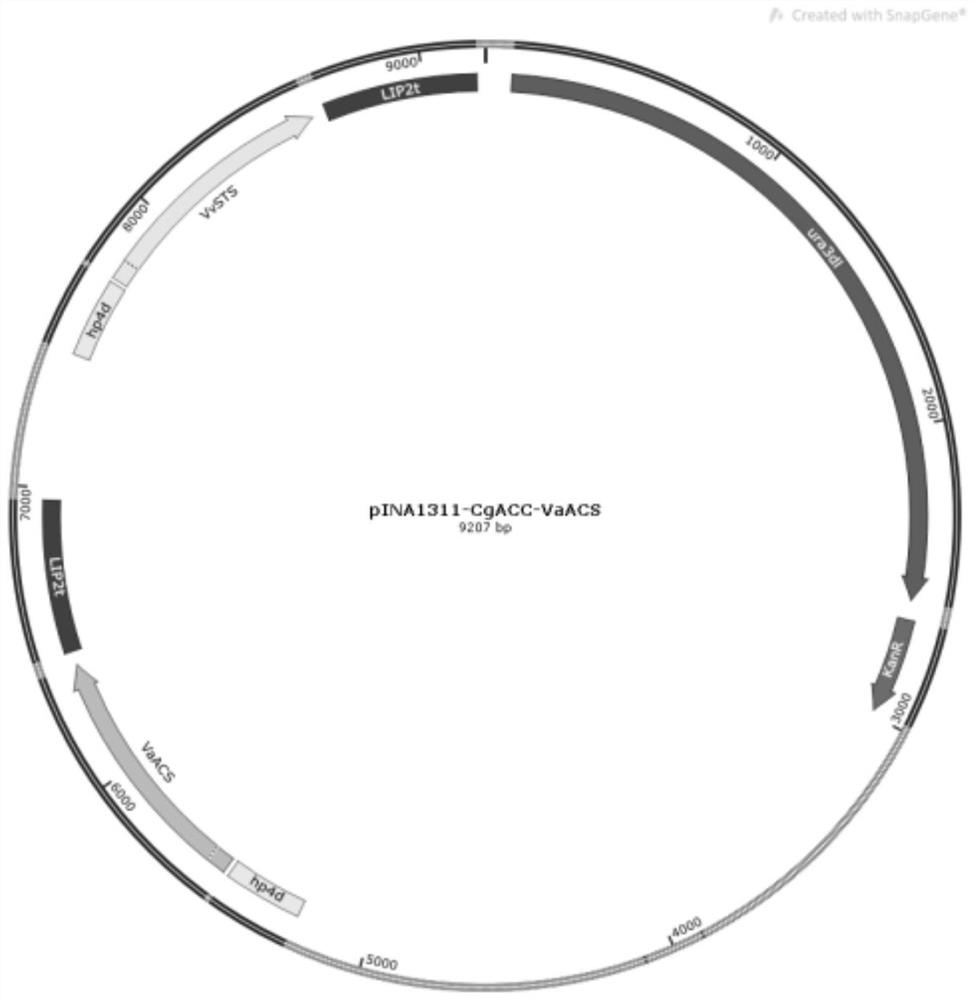
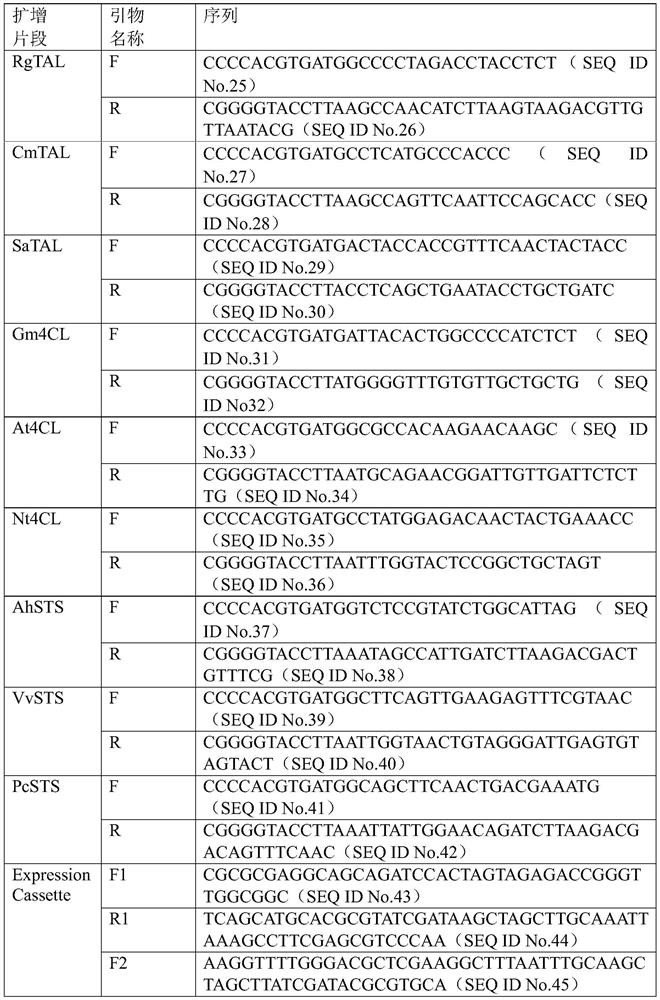
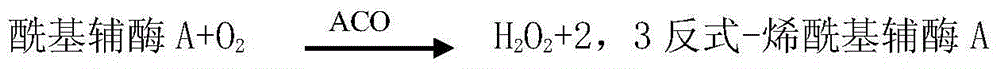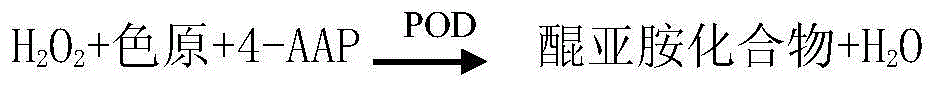Patents
Literature
39 results about "Acetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
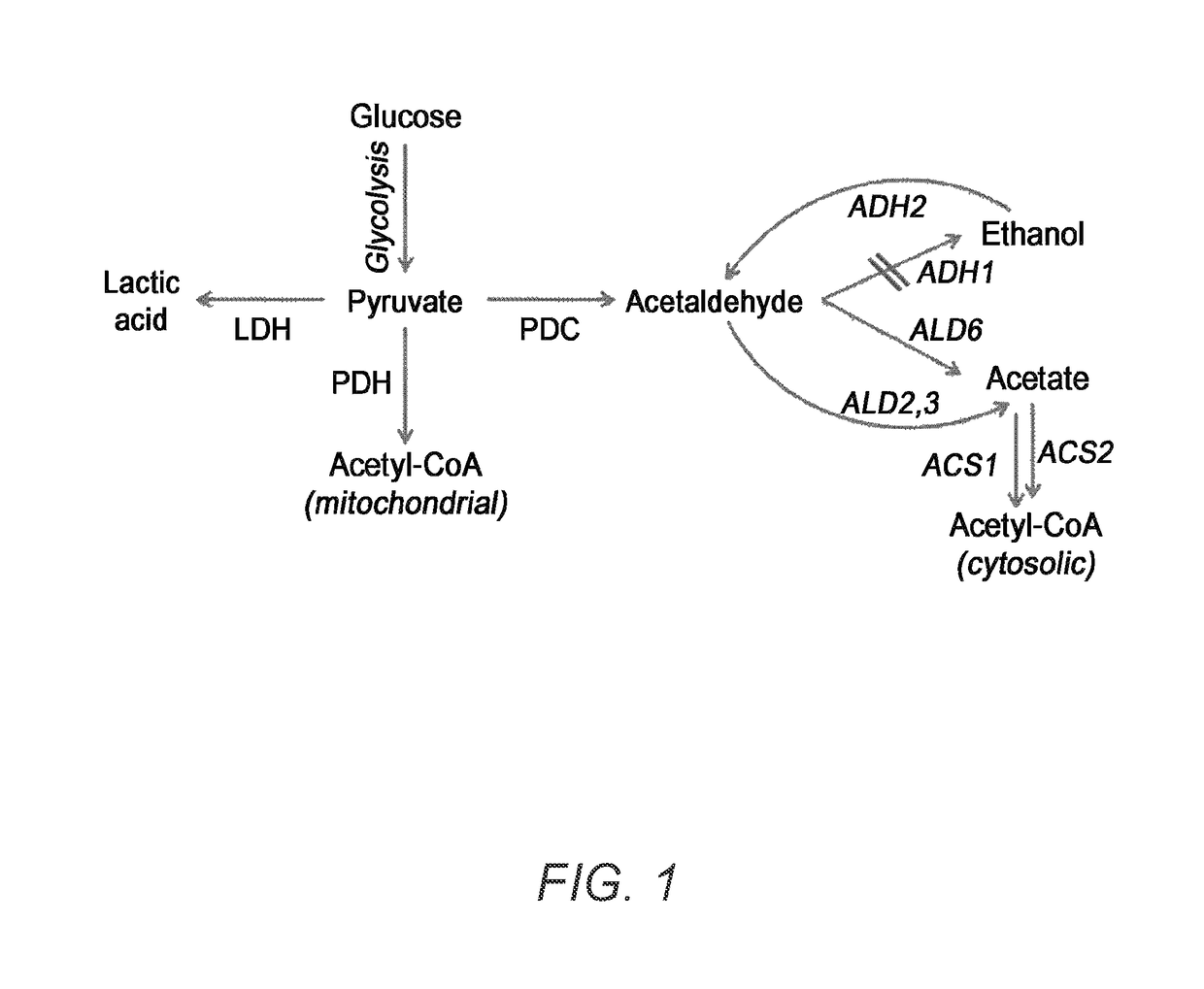
Acetyl-coa producing enzymes in yeast
InactiveUS20100248233A1Increase productionFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
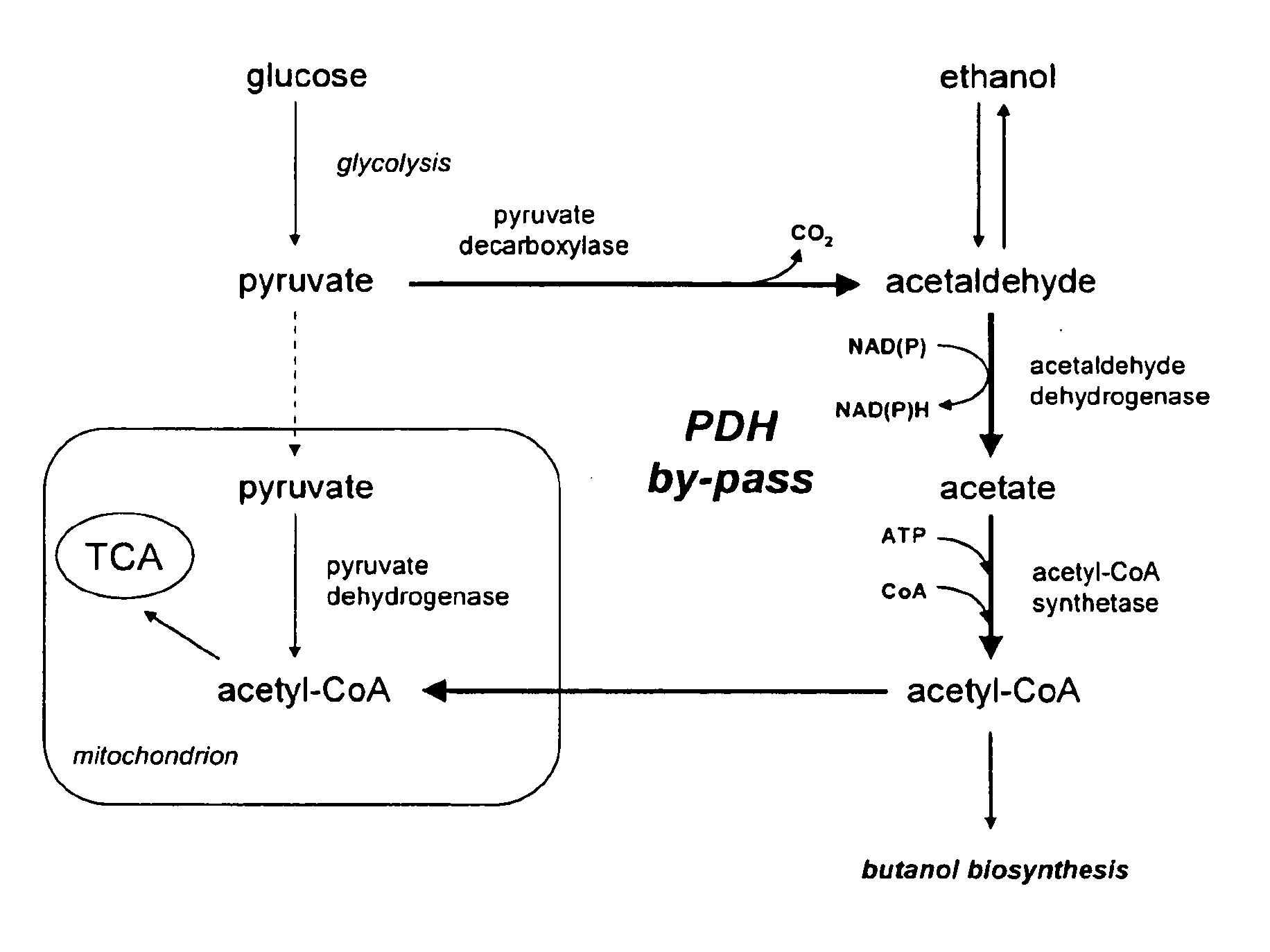
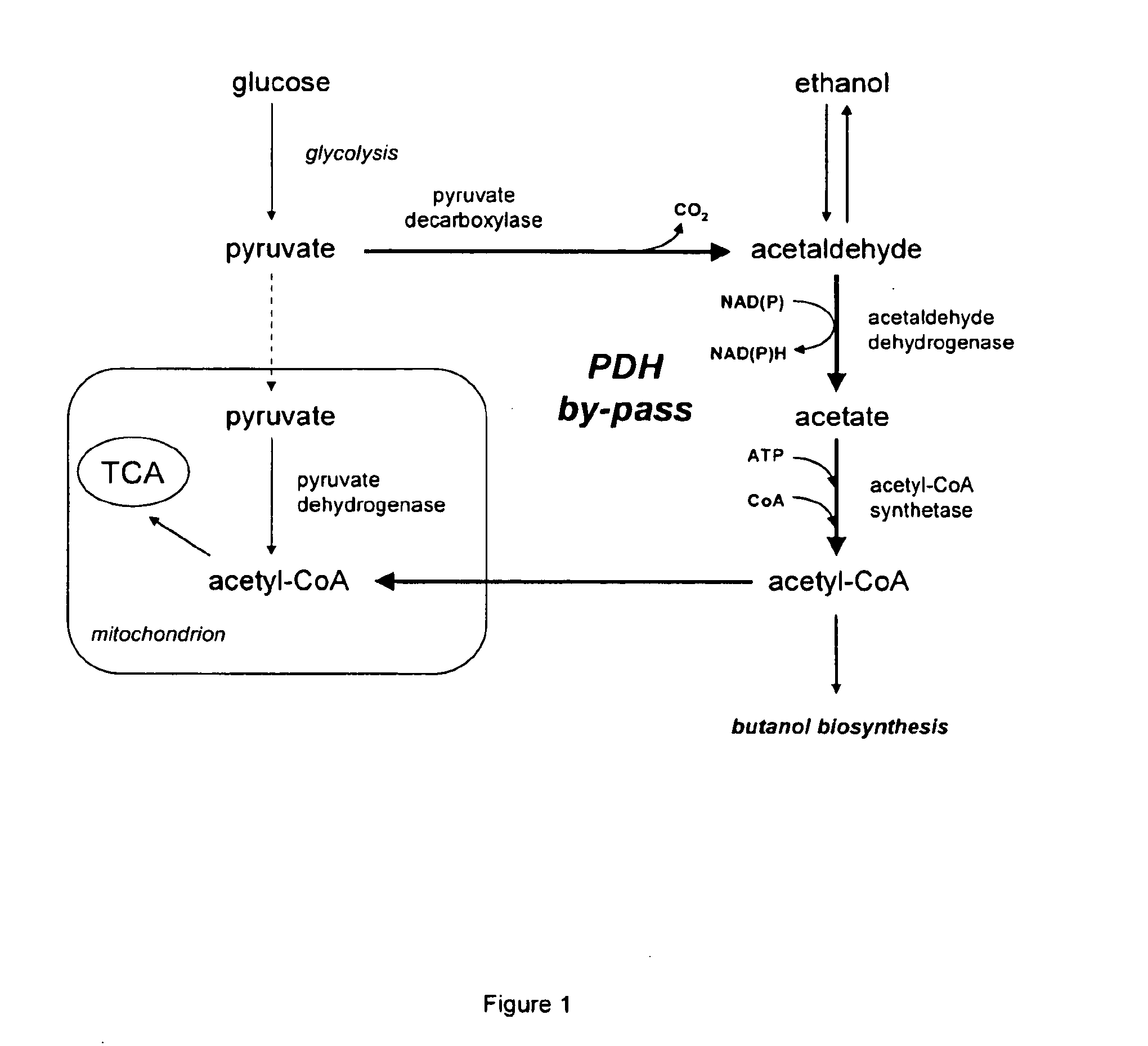
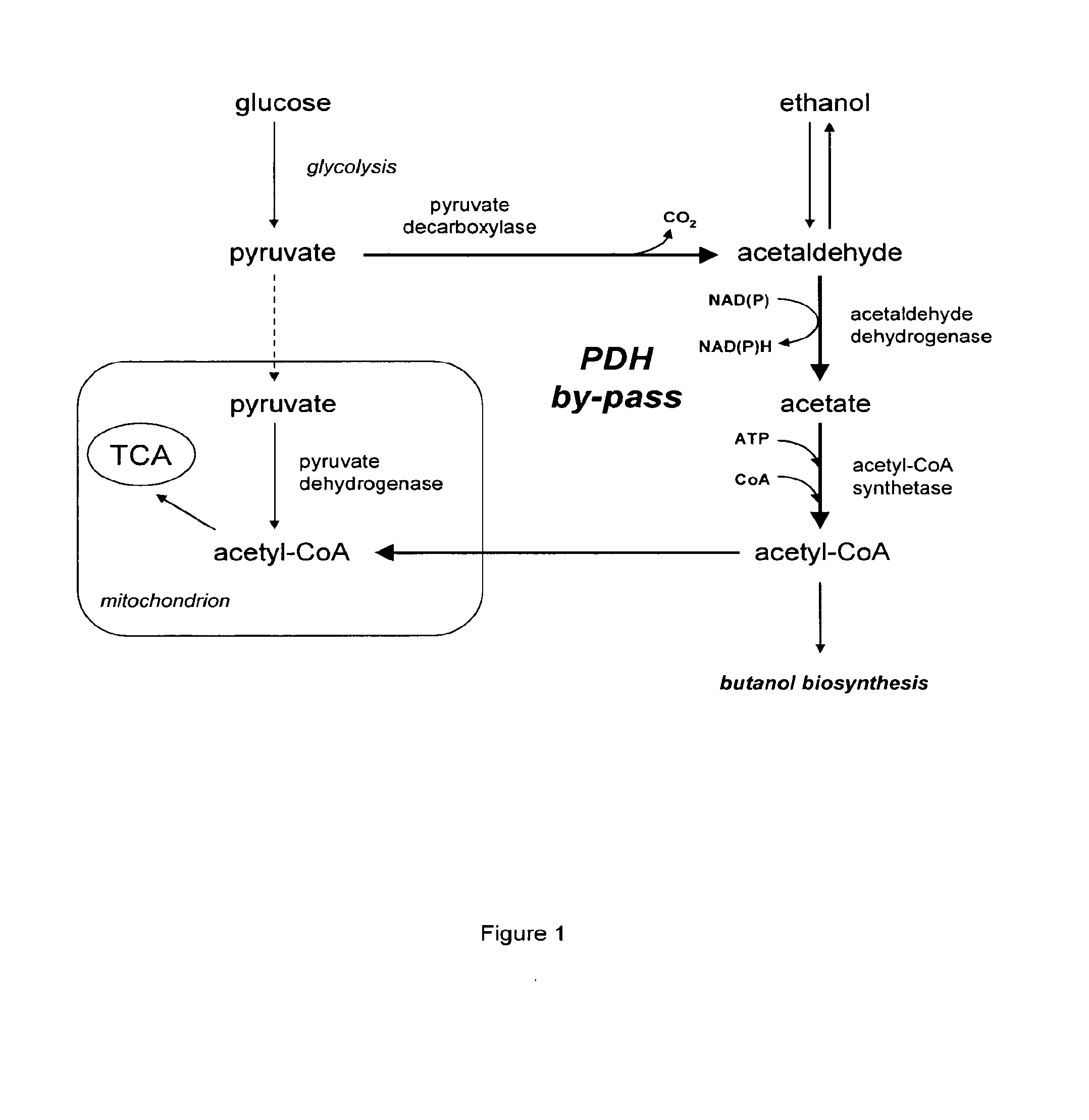
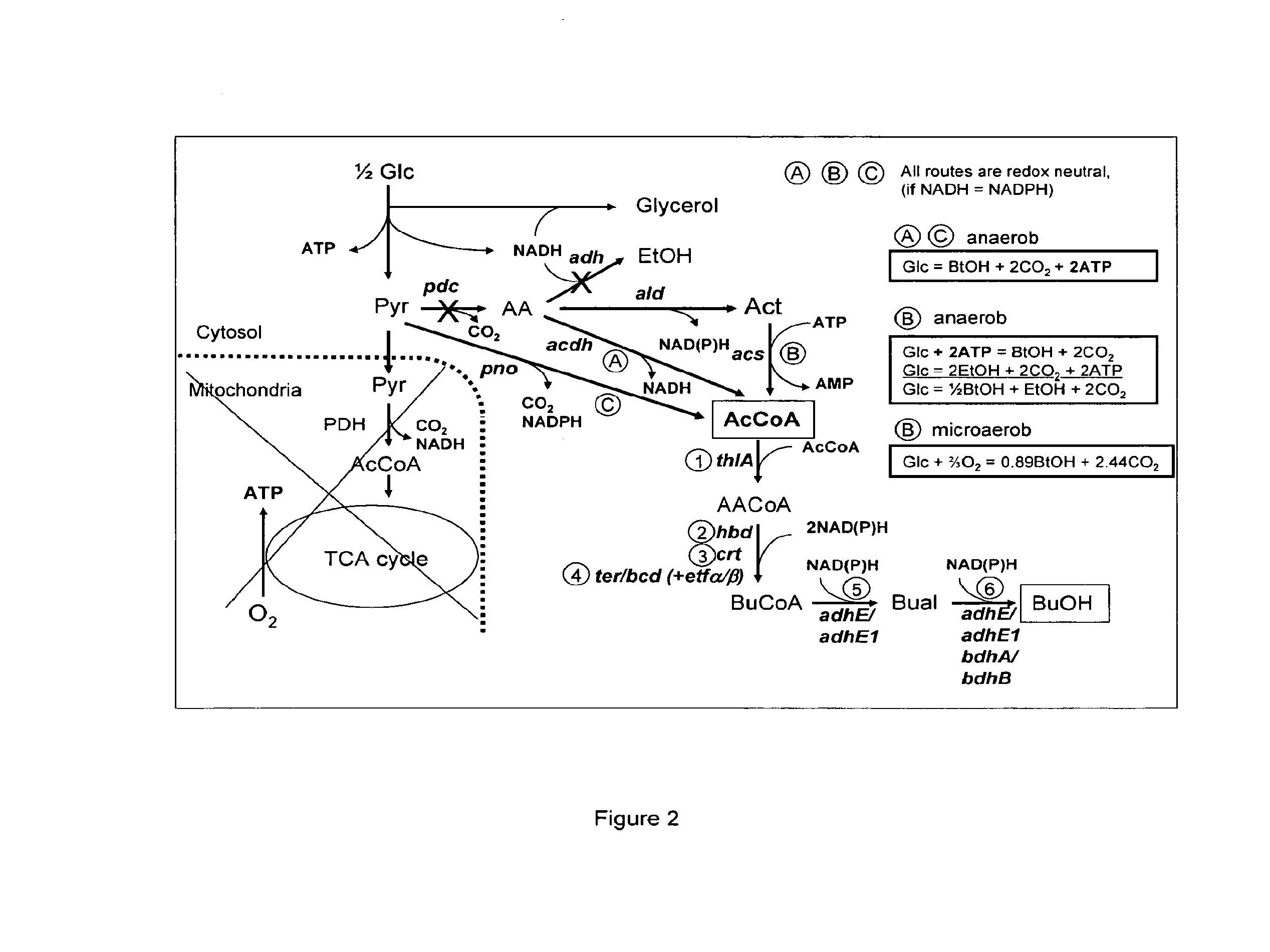
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) a yeast cell comprising: a) providing a mutated yeast cell comprising a deletion of at least one gene of the (PDH) by-pass, selected from the genes encoding the enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC), acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALD), and acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS); b) transforming said mutated yeast cell with an expression vector comprising a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a candidate polypeptide having potential enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA; c) testing said recombinant mutated yeast cell for its ability to grow on minimal medium containing glucose as sole carbon source, and d) identifying said candidate polypeptide as a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) said yeast cell when growth of said cell is observed. The invention further relates to a method of producing a fermentation production such as butanol.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
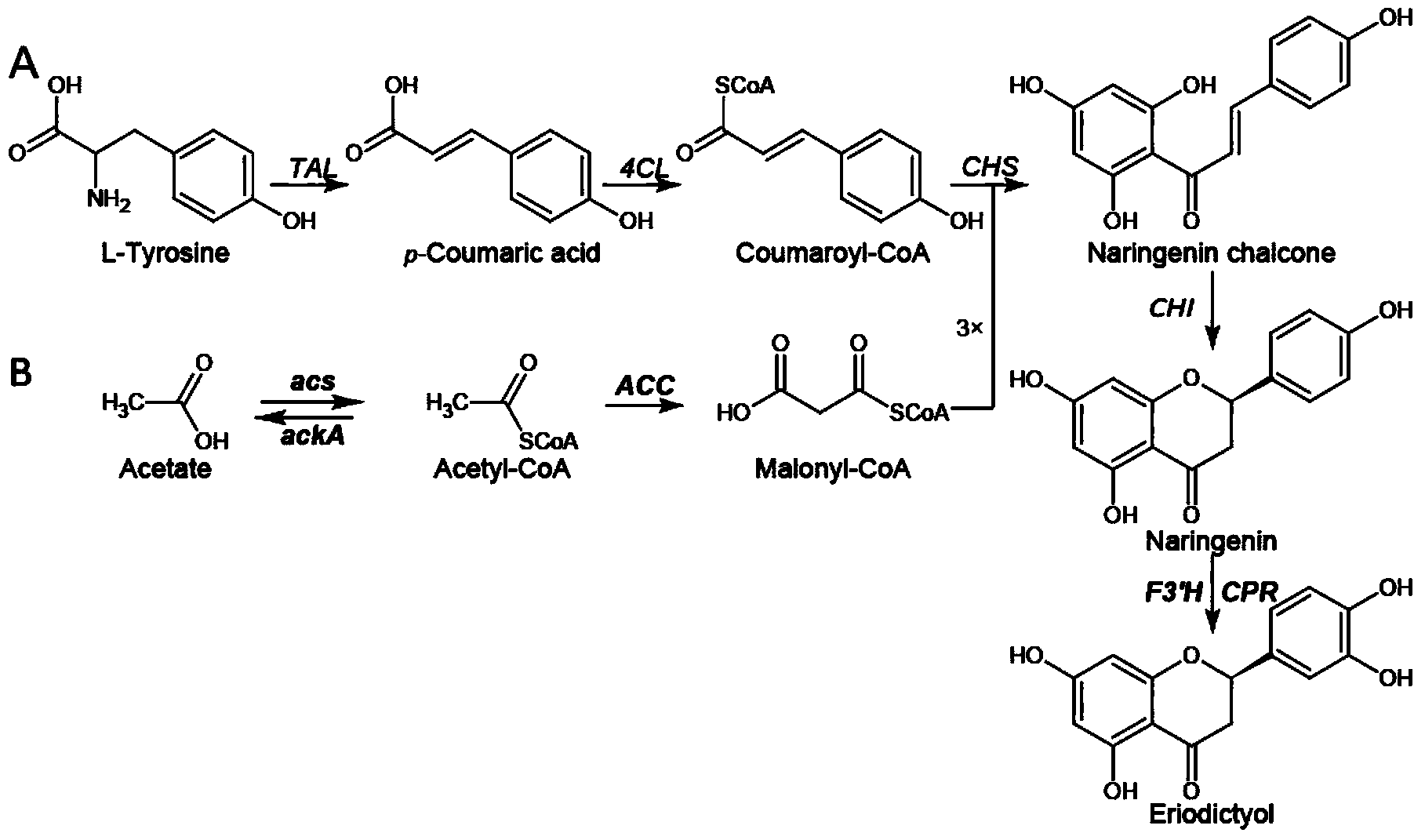
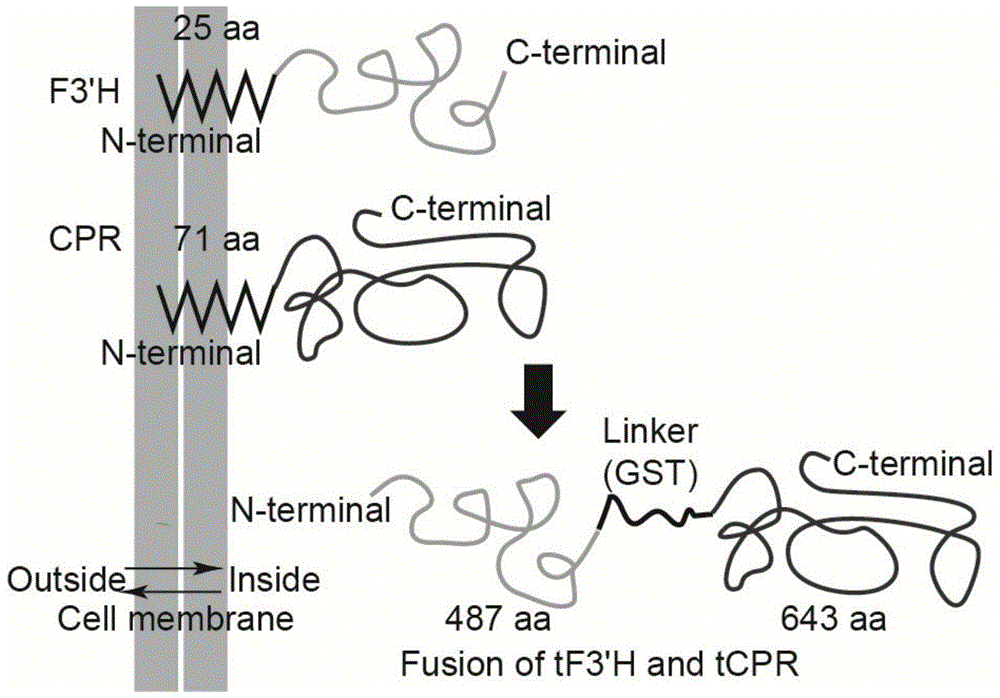
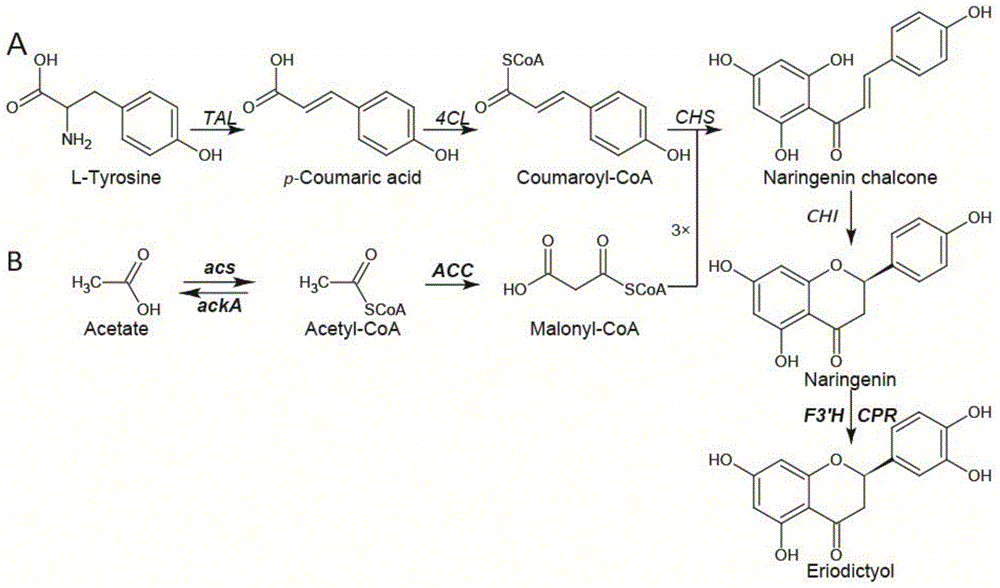
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
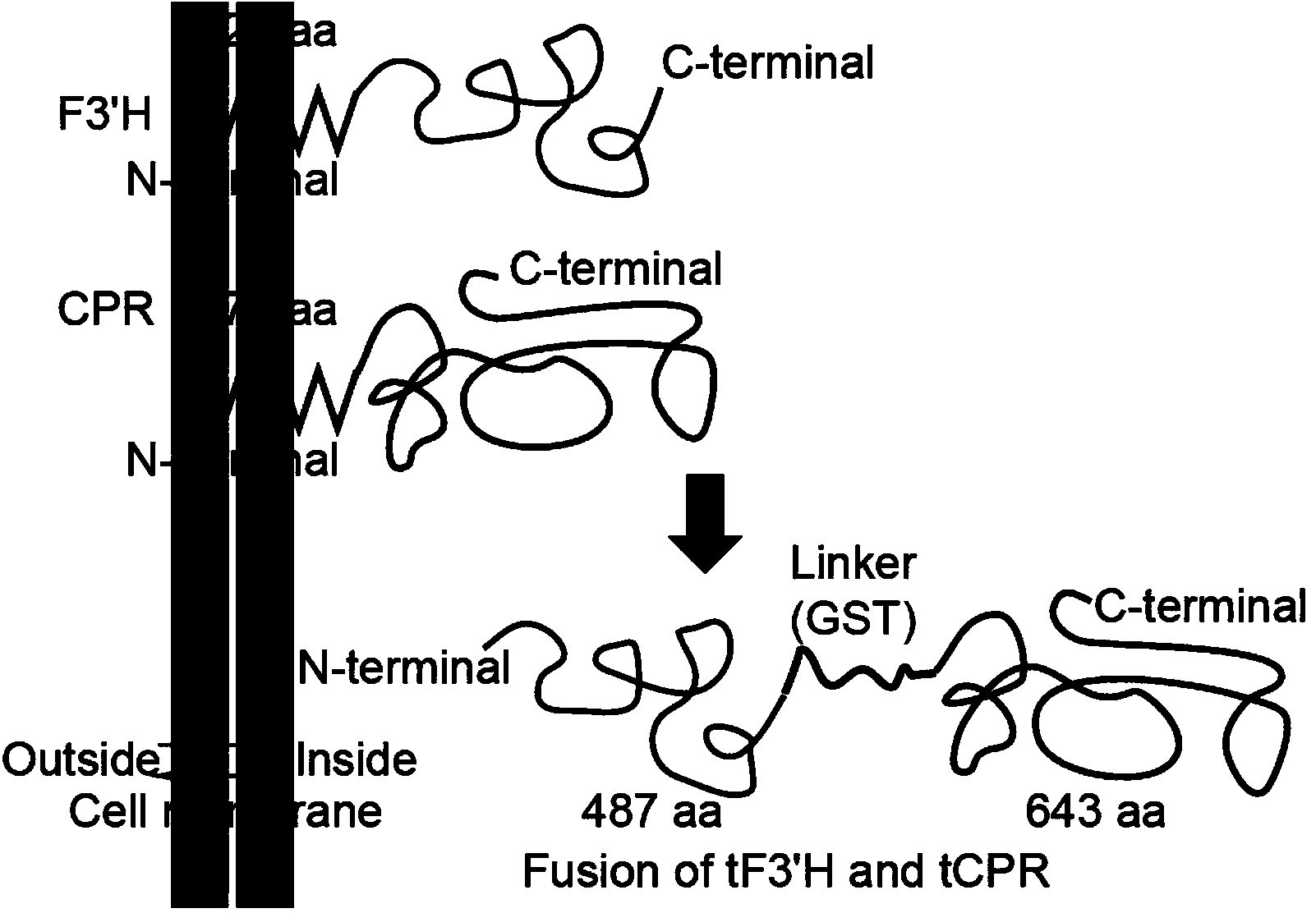
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106086102AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseGlutamate 5-kinase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
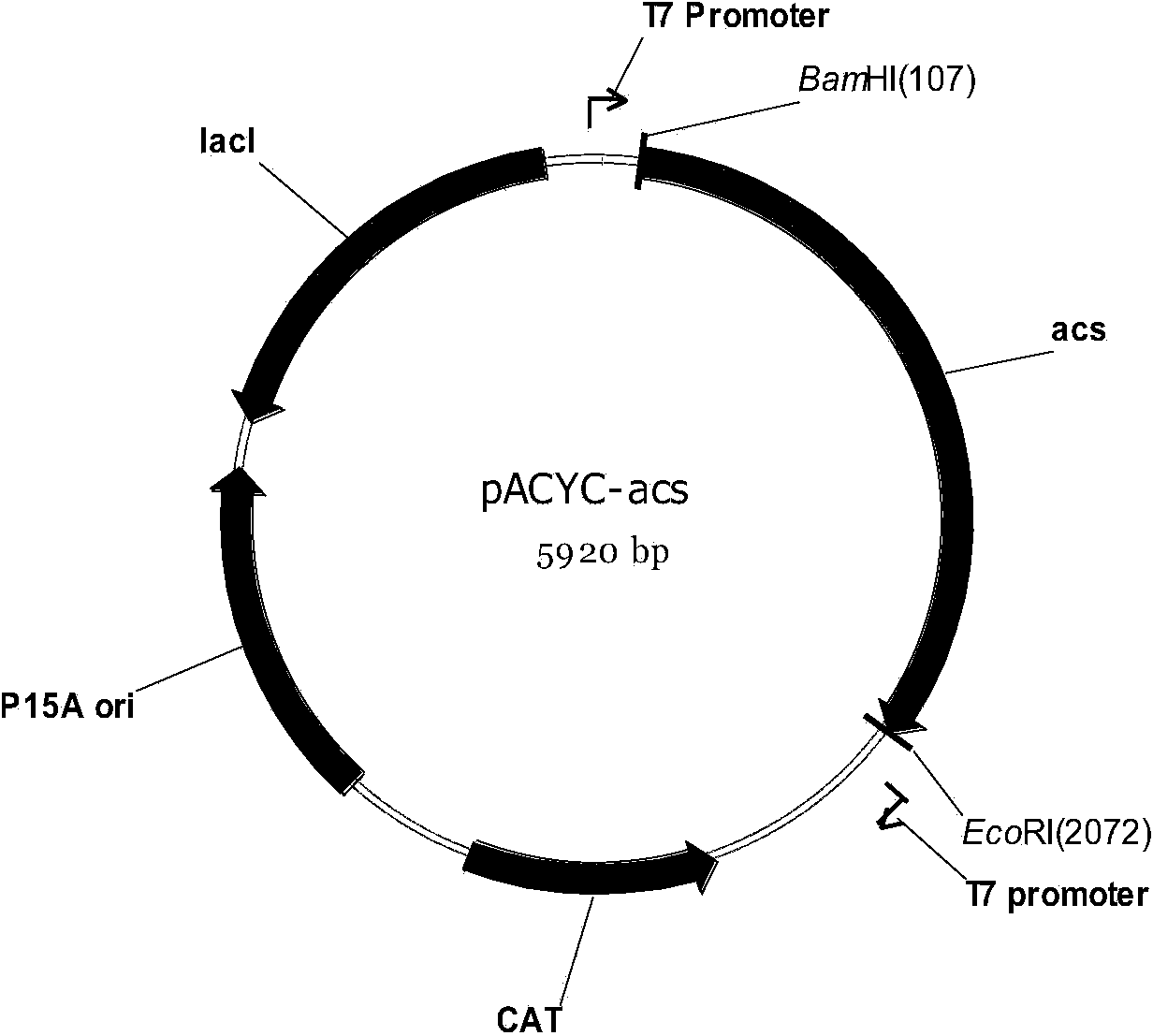
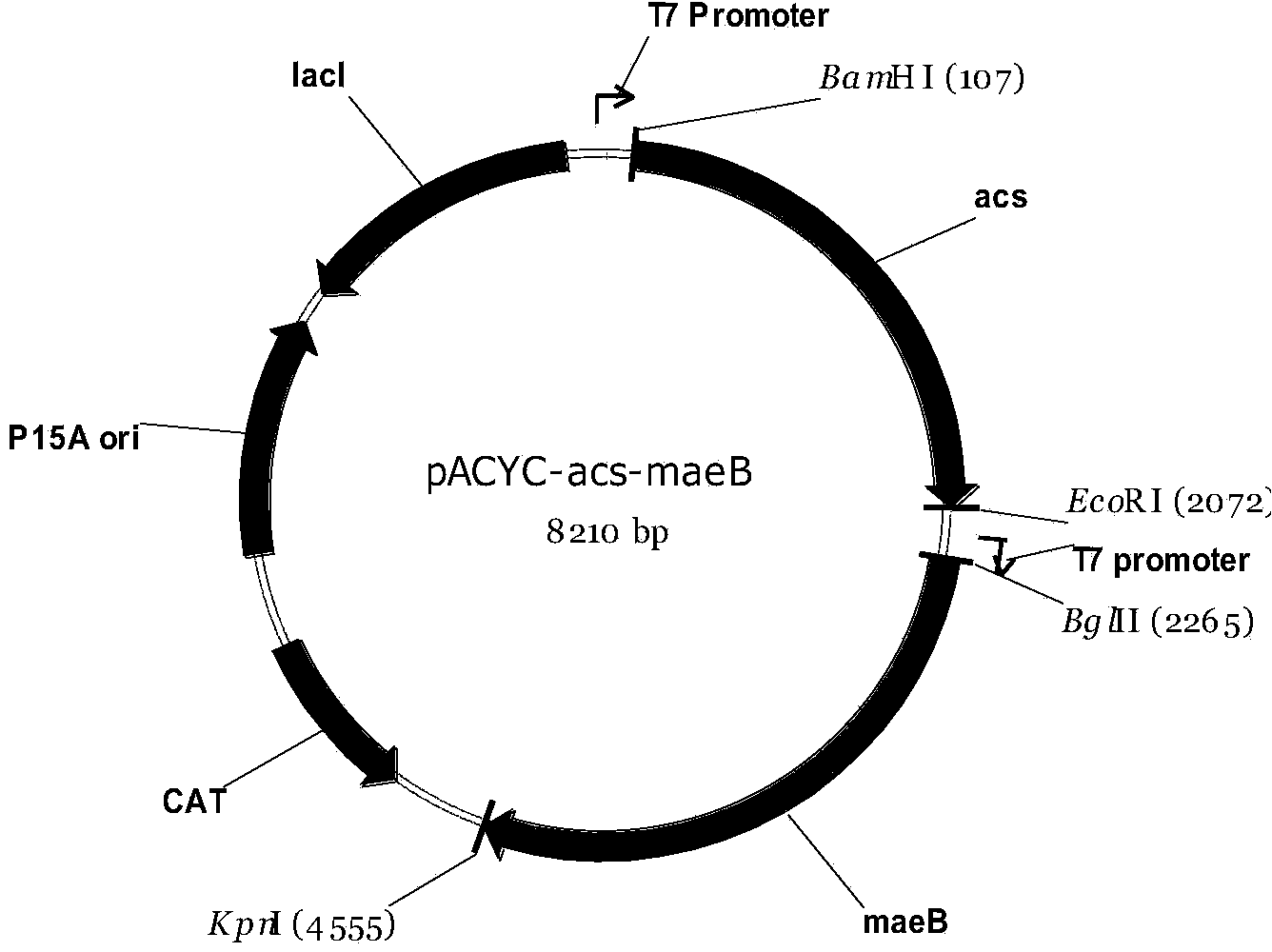
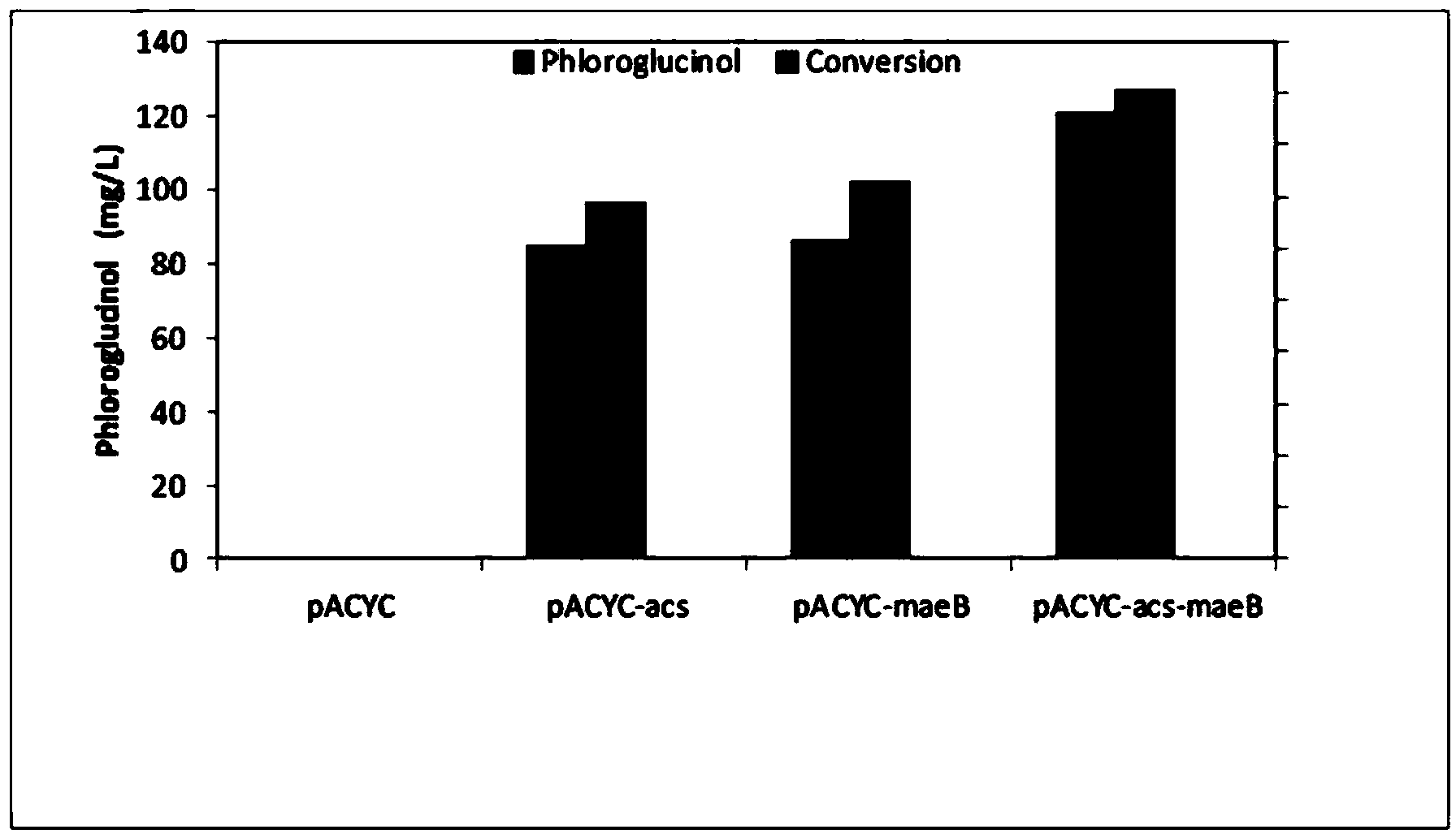
Gene engineering strain capable of synthesizing phloroglucinol from acetic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene engineering strain capable of synthesizing phloroglucinol from acetic acid and a construction method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The gene engineering strain disclosed by the invention co-expresses an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs, a malate dehydrogenase gene maeB, a polyketene anhydride synthetase gene phlD and a multi-resistance factor gene marA. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a construction method of the gene engineering strain. The gene engineering strain disclosed by the invention can be used for synthesizing phloroglucinol from acetic acid and has the characteristics of low production cost and high yield, the yield can reach over 1.2g / L, and the maximum output can reach 30% and is 52% of the theoretical yield, so that the gene engineering strain is suitable for industrialized popularization.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Free fatty acid determination reagent kit
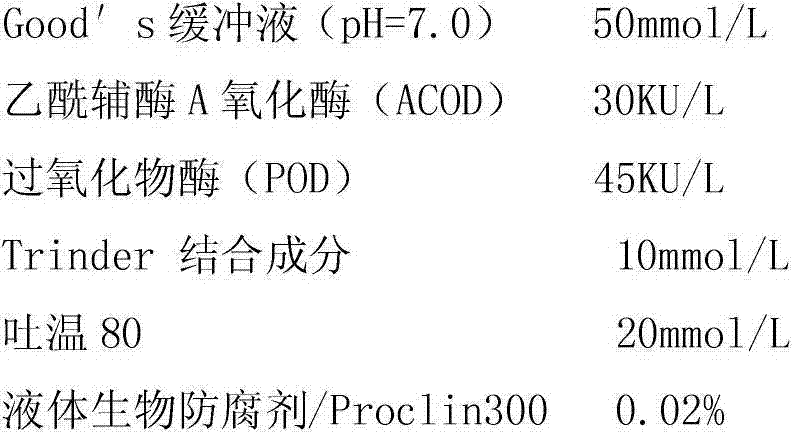
InactiveCN103207175AStrong specificityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetasePeroxidase
The invention relates to a free fatty acid determination reagent kit which comprises dual reagents. The reagent 1 comprises Good's buffer solution (pH(potential of hydrogen)=7.0), coenzyme A, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, magnesium chloride (MgCL2), Trinder bound constituent, tween 80 and liquid biological preservative / Proclin 300, and the reagent 2 comprises Good's buffer solution (pH=7.0), acetylcoenzyme A oxidase (ACOD), peroxidase (POD), Trinder bound constituent, tween 80 and liquid biological preservative / Proclin 300. The free fatty acid determination reagent kit has the remarkable advantages that the reagent kit is directly used for an automatic biochemical analyzer and is simple; and the adopted automatically separated and purified acetylcoenzyme A synthetase and acetylcoenzyme A oxidase (ACOD) have high specificity on free fatty acid in serum.
Owner:SHAOXING SHENG KANG BIOLOGICAL TECH
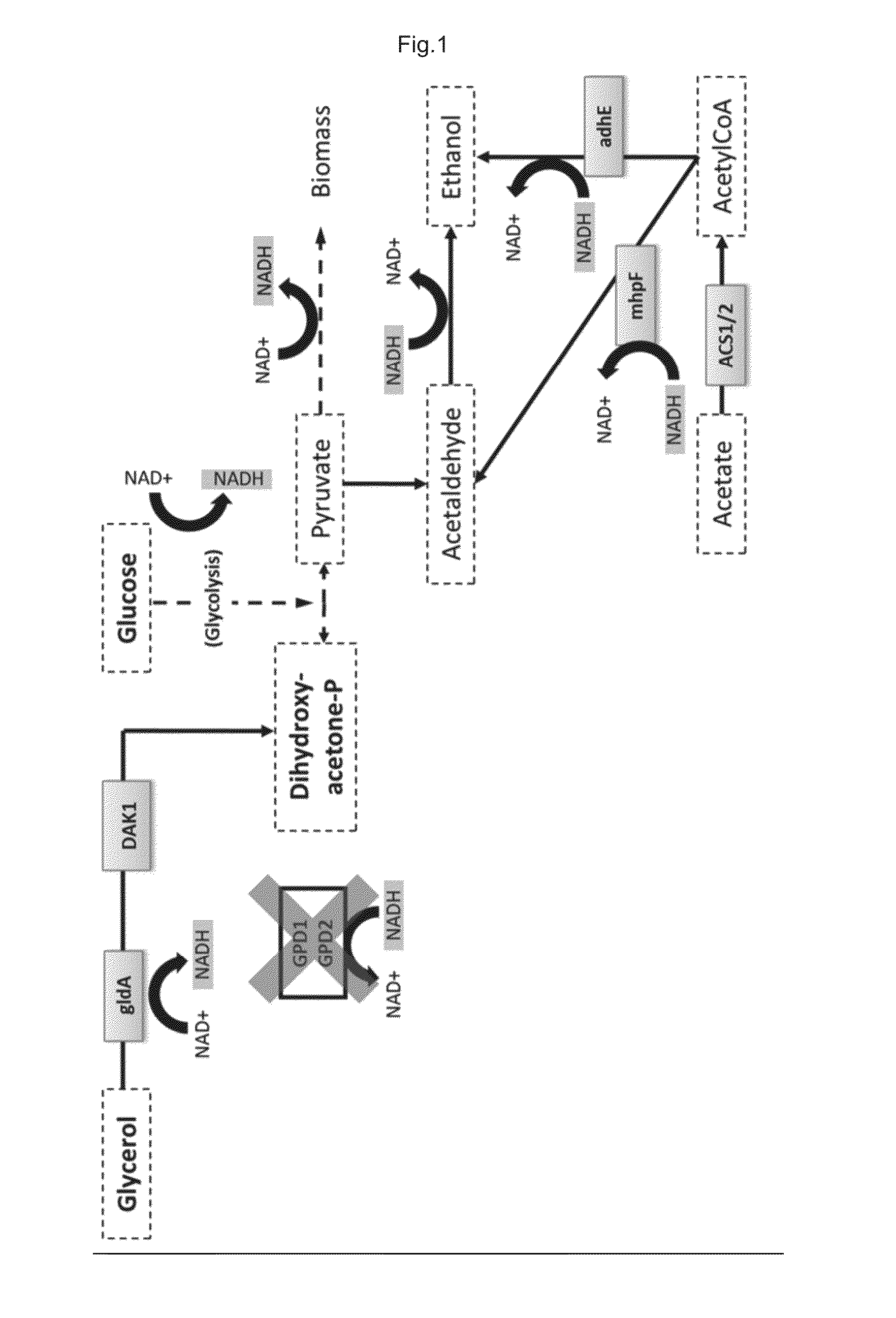
Glycerol and acetic acid converting yeast cells with improved acetic acid conversion
Cell that is genetically modified comprising:a) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a NAD+-dependent acetylating acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.2.1.10);b) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a acetyl-CoA synthetase (E.C. 6.2.1.1);c) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a glycerol dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.1.1.6); andd) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a dihydroxyacetone kinase (E.C. 2.7.1.28 or E.C. 2.7.1.29).
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid
ActiveCN110951660APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPhosphorous acid
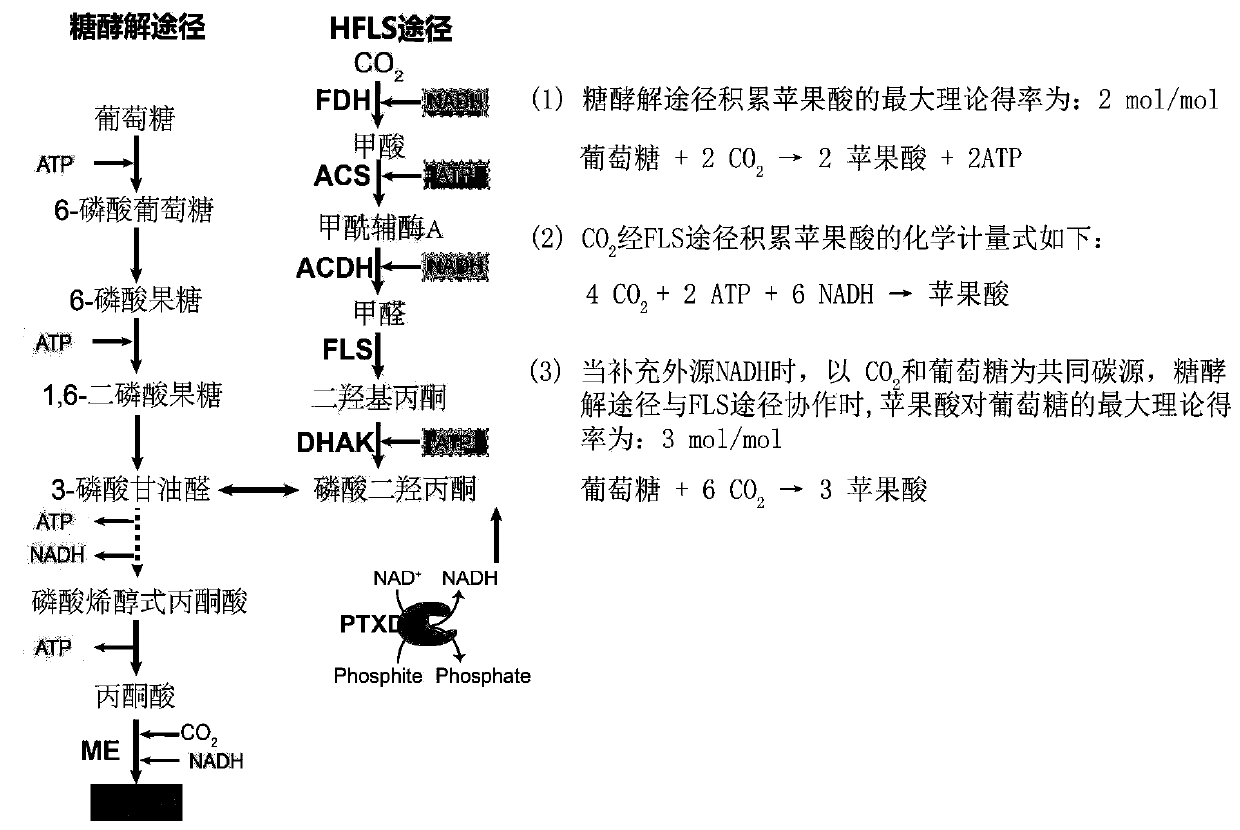
The invention discloses construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation. The engineeringbacterium is a strain obtained by carrying out gene engineering modification on Escherichia coli MG1655. The genetic engineering transformation is as follows: 1, knocking out a fumarate reductase gene, a fumarase gene, a lactic dehydrogenase gene and an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, and carrying out free over-expression on formate dehydrogenase, acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, acylated acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, formaldehyde lyase, dihydroxyacetone kinase, malic enzyme and phosphorous acid oxidordeuctase so as to obtain a strain GH0407. The strain is used for fermentation production of malic acid, CO2 and glucose are used as co-substrates for anaerobic fermentation for 72 h, the malic acid yield reaches 39 g / L, the yield is 1.53 mol / mol, and malic acid is not accumulated in an original starting strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Acetyl-coa producing enzymes in yeast
ActiveUS20140030730A1Increase productionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseFermentation
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) a yeast cell comprising: a) providing a mutated yeast cell comprising a deletion of at least one gene of the (PDH) by-pass, selected from the genes encoding the enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC), acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALD), and acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS); b) transforming said mutated yeast cell with an expression vector comprising a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a candidate polypeptide having potential enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA; c) testing said recombinant mutated yeast cell for its ability to grow on minimal medium containing glucose as sole carbon source, and d) identifying said candidate polypeptide as a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) said yeast cell when growth of said cell is observed. The invention further relates to a method of producing a fermentation production such as butanol.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for producing L-amino acid
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing an L-amino acid-producing bacterium which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and which has been modified so that the acetyl-CoA synthetase activity is increased.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and building method and application thereof
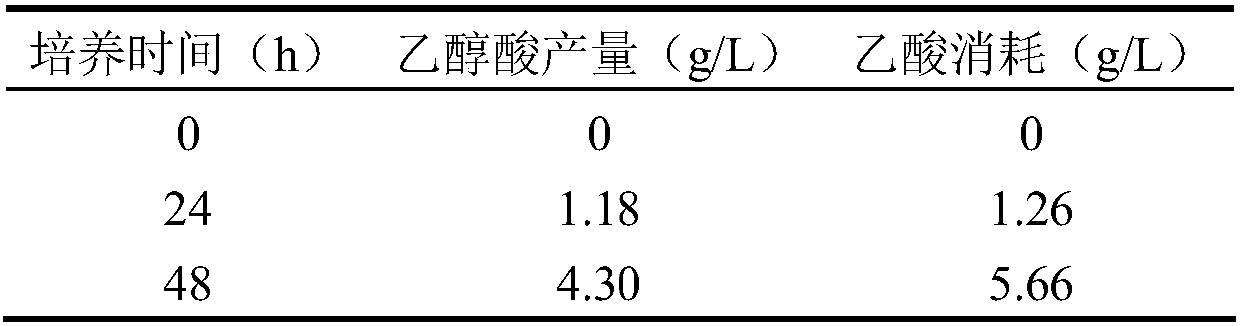
ActiveCN107603998AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and a building method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid provided by the invention comprises the following steps of improving the expression and / or activity of acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, phosphotransacetylase, acetokinase, citrate synthase, isocitrate lyase, isocitrate dehydrogenase kinase and glyoxylate reductase in the recipient bacterium; reducing the expression and / or the activity of malate synthase, glycolate oxidase and isocitrate lyase repressor protein in the recipient bacterium, so that the engineering bacterium for producing the glycollic acid is obtained. The recipient bacterium is a bacterium capable of using acetic acid as a carbon source for growth. The prepared genetic engineering bacterium uses acetic acid as the carbon source for producing the glycollic acid; in addition, the production quantity and yield of the glycollic acid in shaking culture can reach the relatively high level; relatively good industrial application prospects are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Construction method and application of high-yield phloroglucinol gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104988172AIncrease productionImprove circulatory activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a high-yield phloroglucinol gene engineering bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out transcription control factor iclR gene of an original strain to obtain a mutant strain, converting the mutant strain to obtain competence cells, and inducing the competence cells into a recombinant plasmid containing polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activation factor marA, acetyl CoA carboxylase gene Accase and acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs in order to obtain recombinant cells. The method realizes improvement of the output of phloroglucinol through improving the cycle activity of glyoxalic acid and promoting acetic acid assimilation metabolism for the first time, and has high industrial application values.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
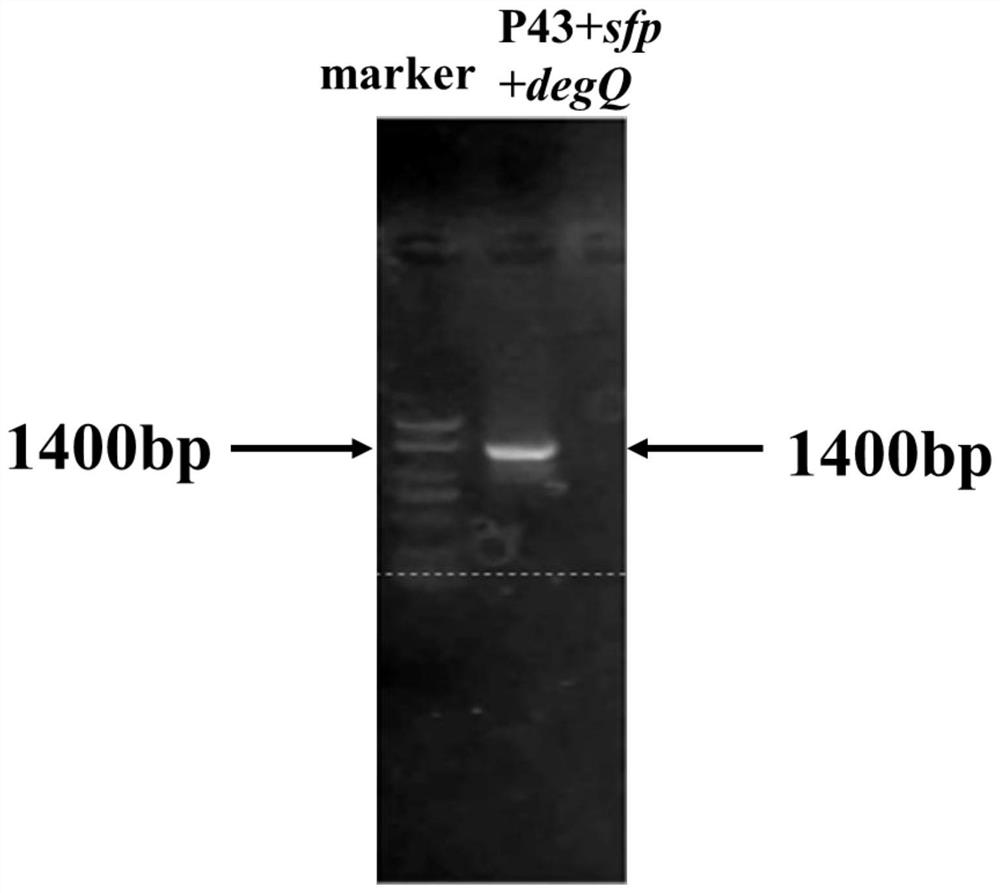
Construction and fermentation method of artificial strain with high yield of fengycin
The invention provides a construction and fermentation method of an artificial strain with high yield of fengycin. The 4'-phosphoric acid pantetheinyl transferase gene sfp from bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, a multi-effect factor gene degQ from bacillus subtilis 168 and a strong promoter P43 are integrated in series onto a genome of the bacillus subtilis 168 by utilizing CRISPR gene editing to construct a strain B.subtilis ds; an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs of Escherichia coli BL21, an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene accACD of Salmonella enterica and a biotin ligase gene bisA of Corynebacterium glutamicum are connected in series to an expression vector pHT43, and the expression vector pHT43 is introduced into a fengycin synthesis strain B.subtilis ds, so that a fengycin high-yield strain B.subtilis dspabacd is constructed; the constructed engineering strain is fermented and cultured in a shake flask to produce the fengycin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of palmitoyl coenzyme A
ActiveCN103074400ALow costGet rid of the useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a palmitoyl coenzyme A. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, carrying out clone coding of an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene, transforming the acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene into an escherichia coli cell, and carrying out expression to obtain a gene engineering strain for expression of an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, 2, inoculating a fermentation initial medium with the gene engineering strain, and carrying out initial culture, 3, after the initial culture, adding an induction feed-supplement medium into the culture products, and carrying out induction culture to obtain the acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, and 4, after the induction culture, adding SDS into the culture products, carrying out pre-conversion culture, carrying out fed-batch of a conversion feed-supplement medium into the culture products, and carrying out conversion culture to obtain the palmitoyl coenzyme A. The preparation method utilizes acetylcoenzyme A synthetase recombinant bacteria to realize conversion of ATP and coenzyme A produced by organisms into the palmitoyl coenzyme A having a high additional value under mild conditions, and has a cost greatly lower than a cost of the existing enzymatic conversion method for preparation of the palmitoyl coenzyme A.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
Recombinant Escherichia coli having enhanced acetyl-coenzyme a synthetase activity for producing glyerol and glycerol-derived products
Recombinant Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria that have enhanced acetyl-CoA synthetase activity and the ability to produce glycerol and glycerol-derived products, such as 3-hydroxypropionic acid, methylglyoxal, 1,2-propanediol, and 1,3-propanediol, are described. The recombinant E. coli comprise a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having acetyl-CoA synthetase enzyme activity, wherein the promoter and nucleotide sequence are each independently either native or non-native.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
A method for metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce eriodictyol
ActiveCN103865864BReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
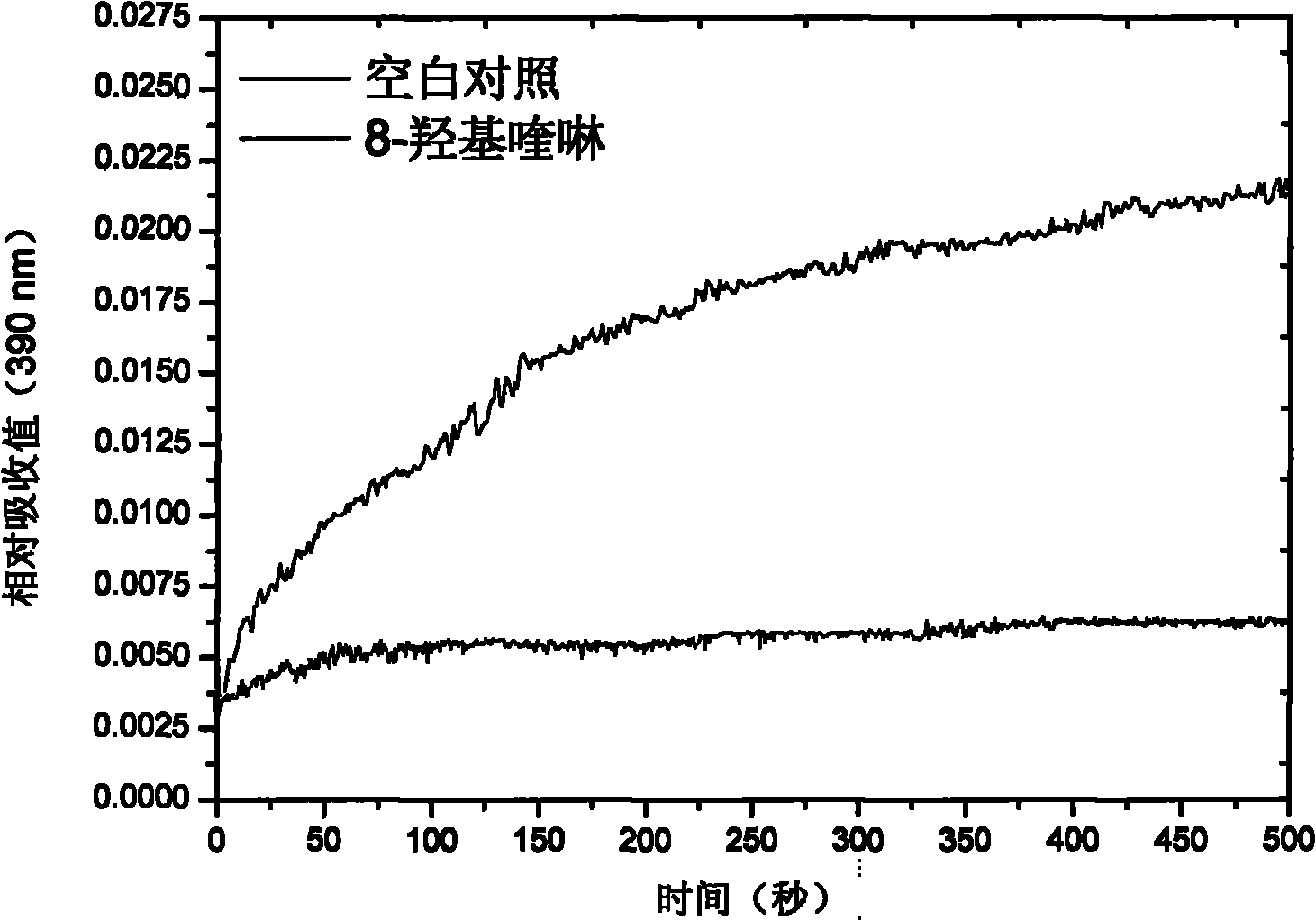
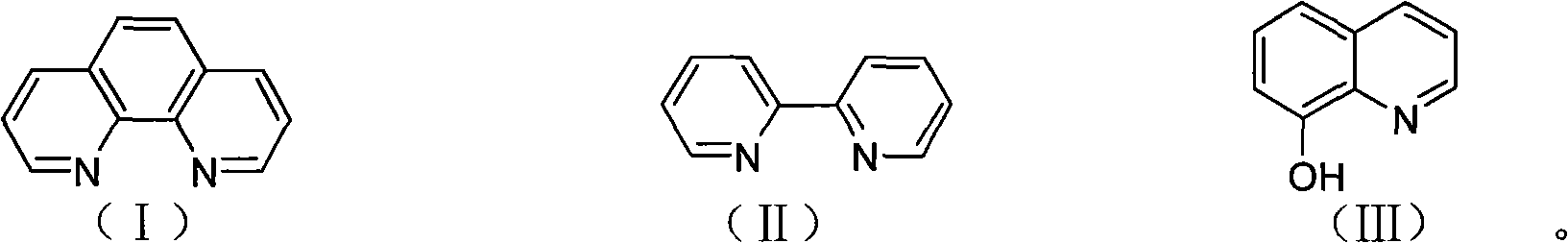
Inhibitor for acetylcoenzyme A synthetase in human pathogen clostridium difficile
InactiveCN101797251AAntibacterial agentsColor/spectral properties measurementsAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseClostridium difficile (bacteria)
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicine, and specifically provides a human pathogen clostridium difficile inhibitor taking acetylcoenzyme A synthetase (ACS) as a target. This invention utilizes a fast reaction kinetics technique to successfully find an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase inhibitor with high inhibitory activity, which comprises 1,10-o-phenanthroline, 2,2-bipyridyl and 8-hydroxyquinoline, wherein the conventional clinically applied medicament, namely 8-hydroxyquinoline, can inhibit methyl transfer activity of acetylcoenzyme A nearly by 100 percent in a low concentration. A method of the invention is the only reported method at present for an efficient inhibitor of human pathogen clostridium difficile acetylcoenzyme A synthetase. The inhibitor is of important application value in the field of biological medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Gene engineering bacteria with high-yield malonyl coenzyme A and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110713962AIncrease contentIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
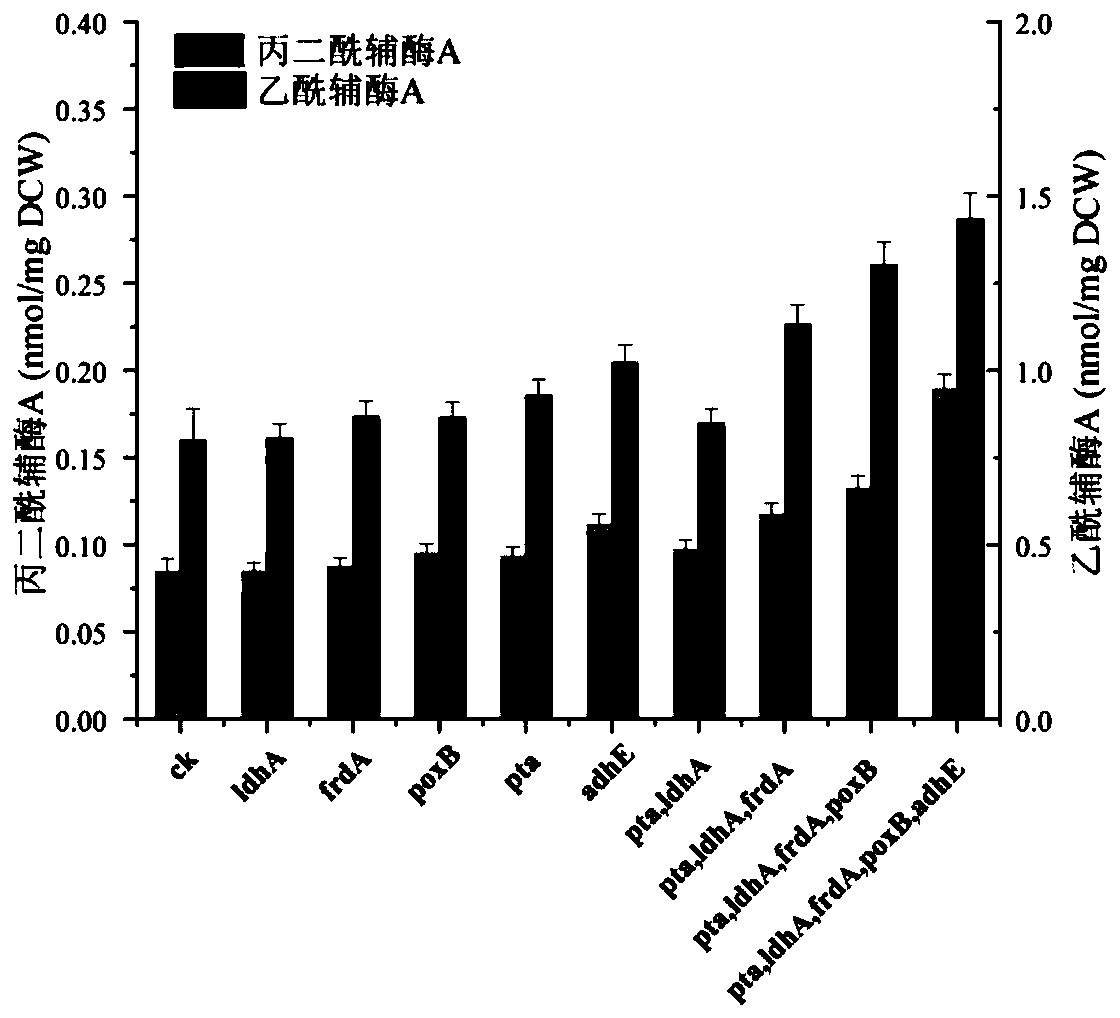
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacteria with high-yield malonyl coenzyme A and a construction method and application thereof. The gene engineering bacteria is constructed by: knocking outfive genes (ldhA, pta, frdA, poxB and adhE) in the Escherichia coli genome, and then introducing malonyl coenzyme A synthesis pathway genes including acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene of the Escherichia coli, acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene of Salmonella enteritidis and biotin ligase gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum. According to the gene engineering bacteria of the invention, a highly-efficient accumulation of the malonyl coenzyme A can be realized by inhibiting internal acetyl coenzyme A outflow pathways of the engineering bacteria and constructing malonyl coenzyme A synthesis pathwaysinto different expression vectors to be transferred into the engineering bacteria; the engineering bacteria can efficiently synthesize a precursor, malonyl coenzyme A, of flavonoid compounds by takingacetic acid, a metabolite by-product of the Escherichia coli, as a substrate; and the engineering bacteria can be used to increase the yield of naringenin, a skeleton precursor of the flavonoid compounds, synthesized by a microbiological method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Naringenin in-vitro enzymatic synthesis method based on malonyl coenzyme A regeneration
ActiveCN113621629ASimple ingredientsIncrease productionLigasesAcyltransferasesEnzymatic synthesisEscherichia coli
The invention designs a naringenin in-vitro enzymatic synthesis method based on malonyl coenzyme A regeneration. On the basis of constructing recombinant expression plasmids of an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase ACS gene and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase ACC1 gene, the recombinant plasmids are respectively transformed into escherichia coli and yeast cells to express a target protein, and the purified ACS and ACC1 recombinant proteins are added into a naringenin in-vitro enzymatic synthesis system to realize the regeneration of malonyl coenzyme A and the in-vitro low-cost enzymatic synthesis of naringenin by using 4-coumaric acid as a substrate. The invention designs a new reaction system, which can be regenerated and utilized without adding expensive malonyl coenzyme A and finally generates naringenin.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Microorganism having enhanced productivity of lactic acid and a process for producing lactic acid using the same
InactiveUS20170175150A1Improve productivityHigh activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesProduction rateMicroorganism
The present invention relates to Saccharomyces sp. capable of producing lactic acid with a decreased activity of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) and increased activities of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALD) and acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS), and a method of producing lactic acid from the culture medium obtained by culturing the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase
ActiveCN104480077AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseNucleotide
The invention discloses recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase. The amino acid sequence of therecombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is shown in SEQ ID No.2 and the nucleotide sequence of the recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.The recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase has the characteristics of high thermal stability and high activity; the retaining rate of enzyme activity is 59.6% after the recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is treated for 30 min at the temperature of 60 DEG C and is much improved compared with constitutive enzyme; an apparent Km value of a catalyzed oleic acid acetylation reaction is 1.2*10<-5>M; the thermal stability of enzyme in a kit can be improved, and temperature influences can be avoided or reduced in the transportation and utilization processes of the kit.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Construction method and application of a high-yielding phloroglucinol genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN104988172BIncrease productionImprove circulatory activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a high-yielding phloroglucinol genetic engineering bacterium, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method provided by the present invention is to knock out the transcription control factor iclR gene of the starting strain to obtain a mutant strain, and then transfer the mutant strain to a competent state and then introduce polyketide synthase gene phlD, multiple resistance activator marA, and acetyl CoA carboxylation Enzyme gene Accase, acetyl-CoA synthetase gene acs recombinant plasmid to obtain recombinant cells. The present invention realizes for the first time the production of phloroglucinol by improving the glyoxylic acid cycle activity and promoting the assimilation of acetic acid in a metabolic transformation mode, and has high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for enhancing utilization of acetic acid and improving L-arginine produced by escherichia coli fermentation
PendingCN114854658AReduce the impactEfficient use ofBacteriaBiofuelsEscherichia coliAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention discloses a method for enhancing utilization of acetic acid and improving L-arginine produced by escherichia coli fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Acetobacter pasteurianus sourced acetyl coenzyme A synthetase ACS is successfully expressed on a pET28a carrier, and then a recombinant plasmid is transferred into modified escherichia coli ARG-4. The recombinant escherichia coli is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium containing glucose and is subjected to shake flask fermentation for 48 hours, so that the yield of the L-arginine in the fermentation liquid can reach 7.51 g / L, and meanwhile, the content of a byproduct acetic acid is 2.53 g / L. The recombinant Escherichia coli is inoculated into a fermentation medium containing glucose and is fermented in a fermentation tank for 48 hours, so that the yield of L-arginine in fermentation liquor can reach 15.07 g / L, meanwhile, the content of byproduct acetic acid is only 0.41 g / L. In the whole fermentation process, acetic acid can be effectively utilized to generate acetyl coenzyme A, and the recombinant Escherichia coli has the advantages of low raw material cost, few byproducts and easiness in operation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacterium for biosynthesizing resveratrol by taking L-tyrosine as substrate, construction and application
PendingCN113930349AIncrease contentThe implementation method is simpleCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for biosynthesizing resveratrol by taking L-tyrosine as a substrate, construction and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the invention, a simple and effective implementation method is provided for safe biotransformation of the resveratrol; biosynthesis from the L-tyrosine to the resveratrol is implemented in cells by adopting co-expression on TAL, 4CL and STS modules; the content of the product resveratrol is remarkably increased by expressing an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene and an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene; and the yield of the resveratrol biotransformed by the engineering bacterium is as high as 5.5-6 g / L.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
Method for improving bacitracin produced by bacillus licheniformis
ActiveCN114874950AReduce growth toxicityEfficient use ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a method for improving bacitracin produced by bacillus licheniformis and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The bacillus licheniformis ATH with high yield of bacitracin is screened from a feed sample, the acetyl coenzyme A synthetase Bsacs gene derived from bacillus subtilis is expressed in the bacillus licheniformis ATH through a genetic engineering method, supply of amino acid formed by intracellular bacitracin is increased, and the titer of bacitracin is improved. After the obtained recombinant bacillus licheniformis is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium containing soybean meal for fermentation culture for 42 hours, the titer of the obtained bacitracin is 1928 IU / mL and is improved by 46.16% compared with that of the bacitracin of an original strain ATH, and meanwhile, the content of bacitracin A is 1081 IU / mL and is improved by 37.2% compared with that of the original strain. The bacitracin production efficiency in the whole fermentation process is high, the raw material cost is low, and the method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing acetylcoenzyme A synthetase in human pathogen clostridium difficile
InactiveCN101798580BHigh purityEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesEnzymesEscherichia coliAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and specifically provides a method for preparing acetylcoenzyme A synthetase (ACS) in human pathogen clostridium difficile. The invention utilizes gene engineering technology to successfully get expression plasmid of acetylcoenzyme A synthetase target gene in human pathogen clostridium difficile 630, shifts the plasmid into escherichia coli host bacteria for culture and fermentation, and establishes an efficient expression-purification method for acetylcoenzyme A synthetase target gene in human pathogen clostridium difficile 630 for the first time. The method can obtain clostridium difficile 630 acetylcoenzyme A synthetase protein of which the purity is up to over 90 percent and the yield is up to over 10 mg / L, and is the only expression method reported at present. The inhibitor is of important application value in the field of biological medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis/determination kit and method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101620102AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetasePhosphate
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis / determination kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of test and determination of medical science, food, and environment. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, adenoside, bisphosphate, acetyl coenzyme A, pyruvic acid, 5'nucleotidase, acetyl-coA-synthetase, pyruvate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Mateirals and methods for alteration of enzyme and acetyl coA levels in plants
InactiveCN1268749CIncreased or decreased enzyme levelsLevel up or downHydrolasesTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetasePlant cell
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
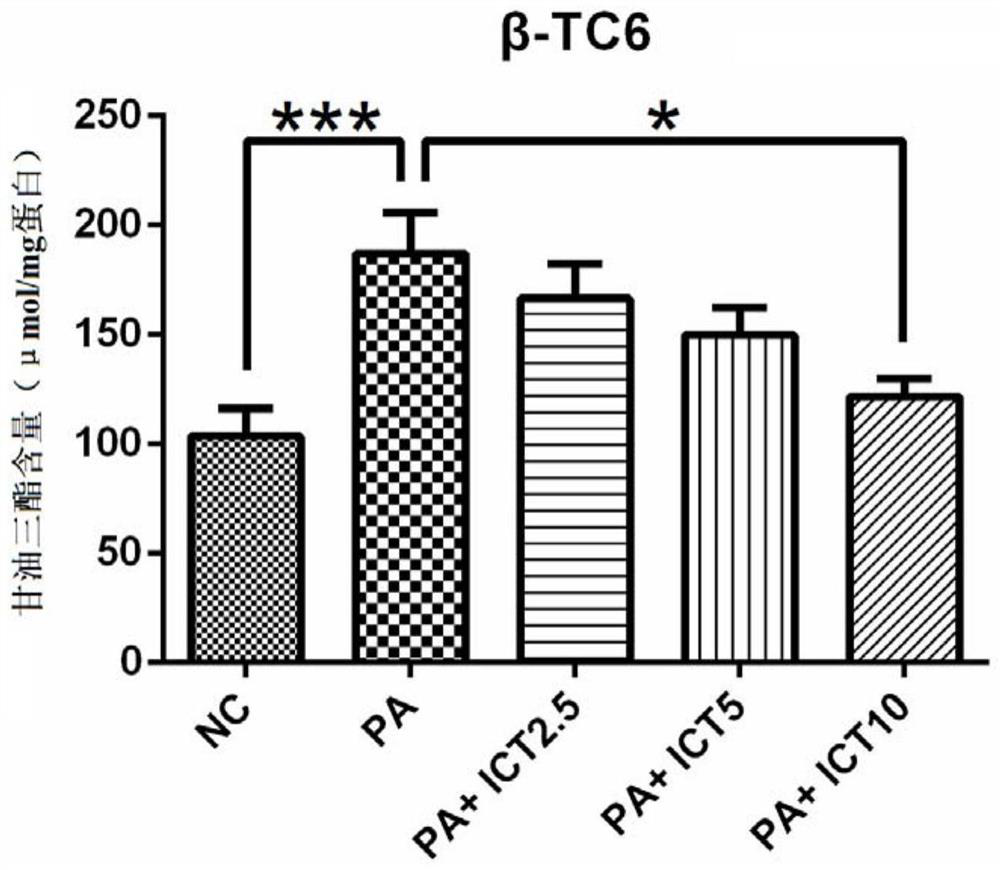
Human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activator and application thereof
PendingCN112451515AInhibit synthetase activityEasy to synthesizeOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderGlycolipid metabolismAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
The invention relates to a human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) activator and application thereof. The human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activator comprises a compound shown in a formula I which is described in the specification or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound, and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are respectively and independently selected from any one of H, C1-C4 alkyl, sulfydryl, phosphate group, vinyl or acetyl. It is found for the first time that the compound shown in the formula I or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can improve glycolipid metabolism of whole-body tissue cells, enhance oxidative degradation of lipid molecules, inhibit expression of adipogenic genes, inhibit activity of acetyl coenzyme A synthetase and reduce synthesis of triglyceride, glucose-induced insulin synthesis and secretion are improved, insulin antagonism is relieved, compensatory amplification of pancreatic beta cells is relieved, and the survival rate and functions of pancreatic cells in the II-type diabetes mellitus-like state are improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microorganism having enhanced productivity of lactic acid and a process for producing lactic acid using the same
The present invention relates to Saccharomyces sp. capable of producing lactic acid with a decreased activity of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) and increased activities of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALD) and acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS), and a method of producing lactic acid from the culture medium obtained by culturing the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis/determination kit and method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101620101AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetasePhosphate
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis / determination kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of test and determination of medical science, food, and environment. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, adenoside, bisphosphate, acetyl coenzyme A, 5'nucleotidase, acetyl-coA-synthetase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, alcohol dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the descending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com