Gene engineering bacteria with high-yield malonyl coenzyme A and construction method and application thereof
A technology of malonyl coenzyme and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of genetically engineered bacteria producing high malonyl coenzyme A and its construction, can solve the problems of lack of in-depth excavation of related genes, lack of integration of multiple pathways, etc., to achieve improved synthesis efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
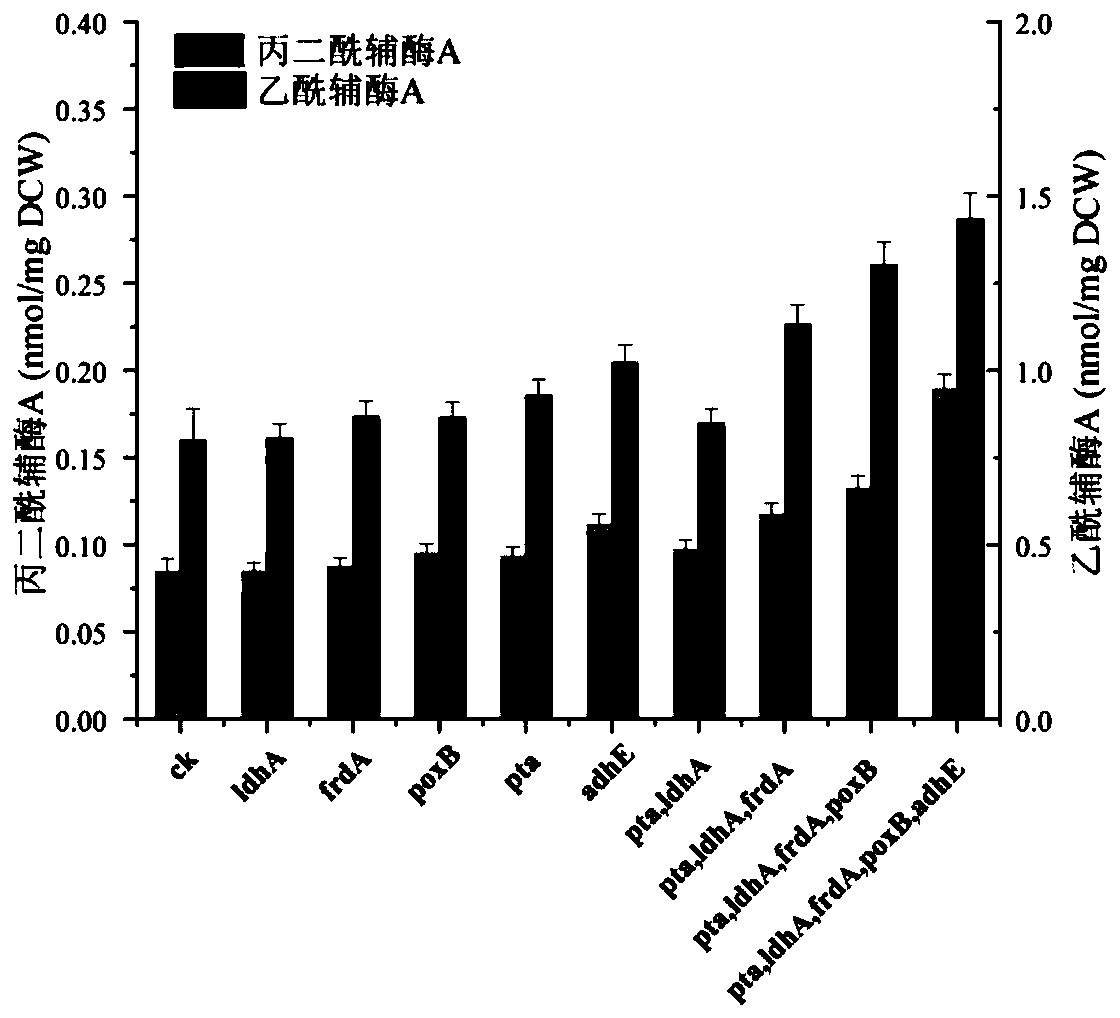
[0046] Base cell construction for knockout of five acetyl-CoA efflux pathway genes
[0047] Strains and plasmids
[0048] Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli JM109) was used for the replication of the plasmid, and Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) was used for the expression of the pathway plasmid and strain fermentation. The strains were purchased from Novagen (Darmstadt, Germany). Plasmids pCDFDuet-1, pETDuet-1, pCOLADuet-1, pACYCDuet-1 were purchased from Novagen (Darmstadt, Germany).
[0049] Enzymes and other reagents
[0050] Various antibiotics including ampicillin and chloramphenicol were purchased from Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd. All chemical reagents were of analytical grade and purchased from Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd. Various restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases were purchased from Thermo. 1kb DNA Ladder, Plasmid Small Extraction Kit, Gel Recovery Kit, and Bacterial Genome Extraction Kit were purchased from Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd.
[0051] Plasmid extraction w...
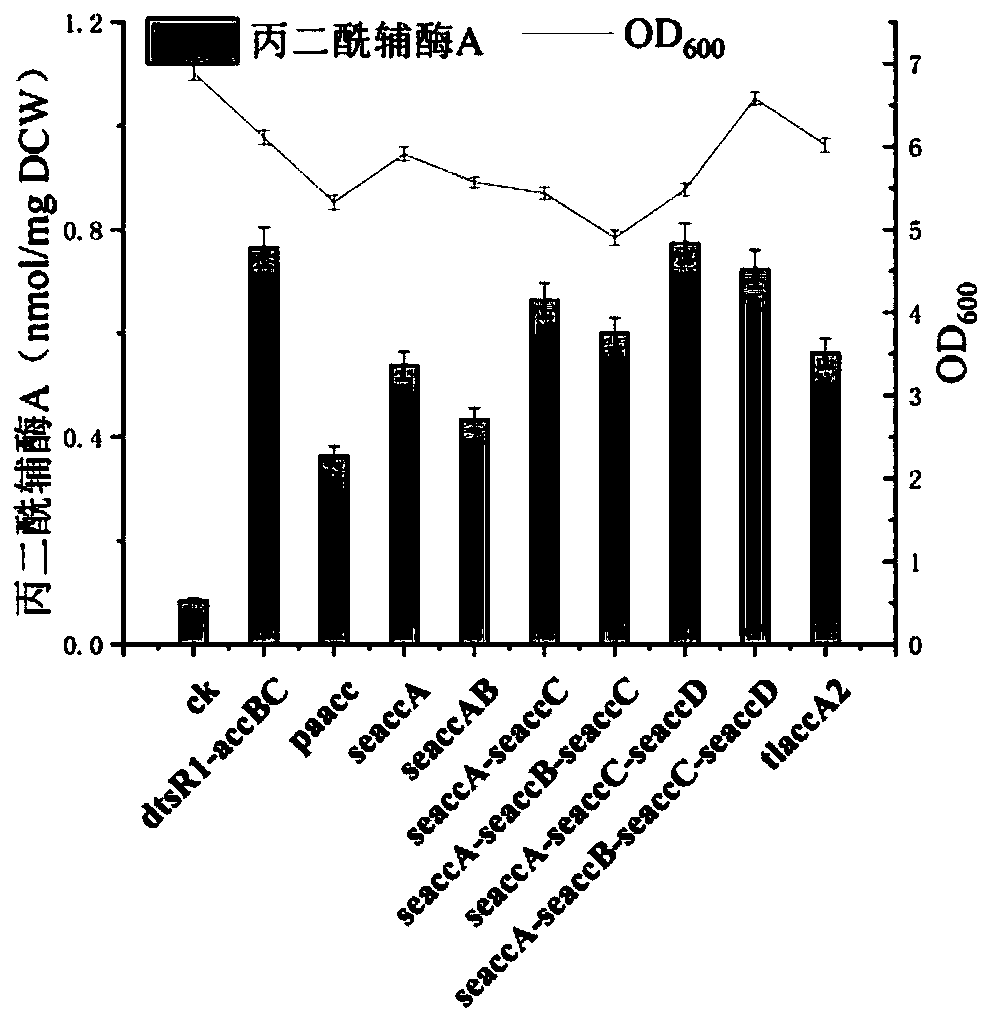
Embodiment 2-4
[0079] Fermentation:
[0080] The engineered bacteria were first cultivated in LB medium on a shaker (37°C, 200rpm) overnight, and then the initial OD 600 The inoculum size of 0.1 was retransferred to fresh MOPS fermentation medium, and carbon source glucose with a final concentration of 5g / L was added to the fermentation system at the same time, and the shaker culture (37°C, 200rpm) until the OD600 was 0.5. At this moment, induce with the IPTG (Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside) final concentration of 1mmol / L, and carry out the feed feeding that final concentration is 5g / L glucose, final concentration is the substrate sodium acetate of 1g / L and final concentration is 2.5 g / L substrate tyrosine was fed and fermented for 52 hours in a shaker culture (30° C., 200 rpm).
[0081] Acetyl-CoA content detection
[0082]Take 1 mL of the fermentation broth, centrifuge at 13,000 rpm, 4°C for 10 min, and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the lysed cells with 1 mL of 6% perchloric a...
Embodiment 2
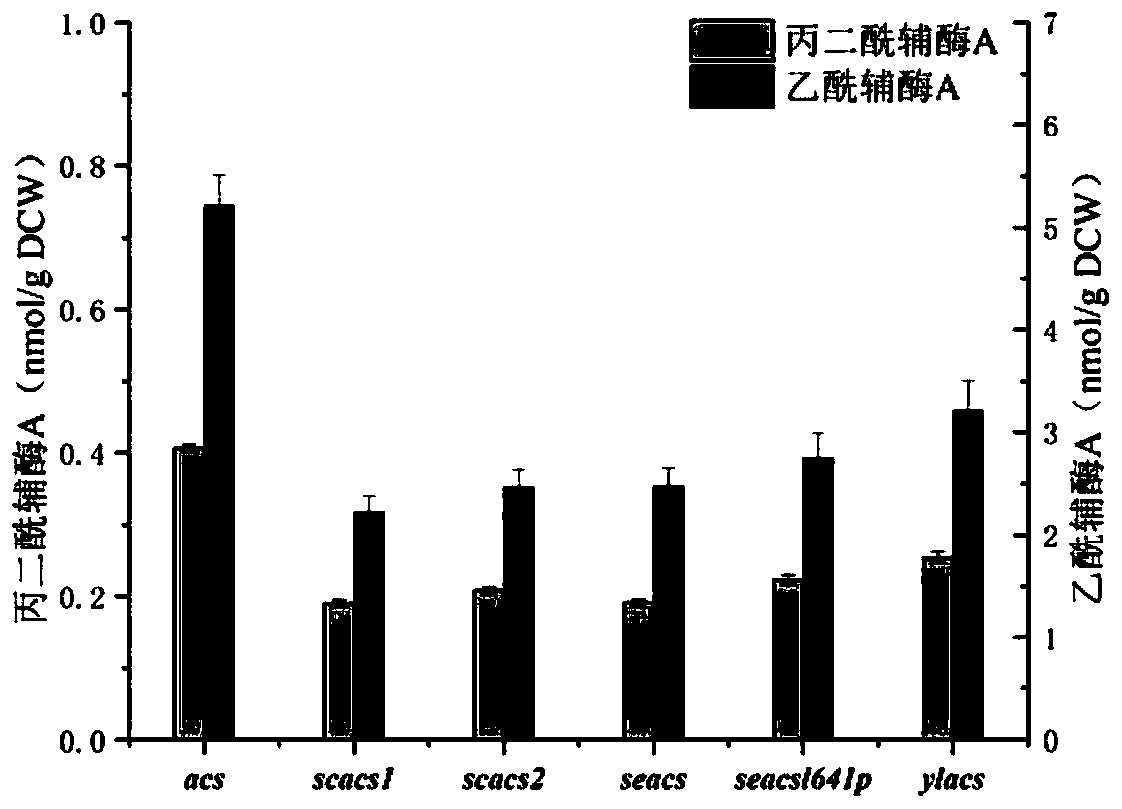
[0086] Overexpression of acetyl-CoA synthetases from different sources
[0087] Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli JM109) was used for the replication of the plasmid, and Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) was used for the expression of the pathway plasmid and strain fermentation. The strains were purchased from Novagen (Darmstadt, Germany). Plasmids pCDFDuet-1, pETDuet-1, pCOLADuet-1, pACYCDuet-1 were purchased from Novagen (Darmstadt, Germany). Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC9080 was purchased from Shanghai Qincheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Yarrowia lipolytica ATCC9773 was purchased from Shanghai Kewei Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Salmonella enterica ATCC10723 was purchased from Beijing Biobowell Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 was purchased from Beijing Qiangxin Borui Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 was purchased from Shanghai Hengfei Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0088] In order to obtain the acs gene (Gene ID: 948572) encodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com