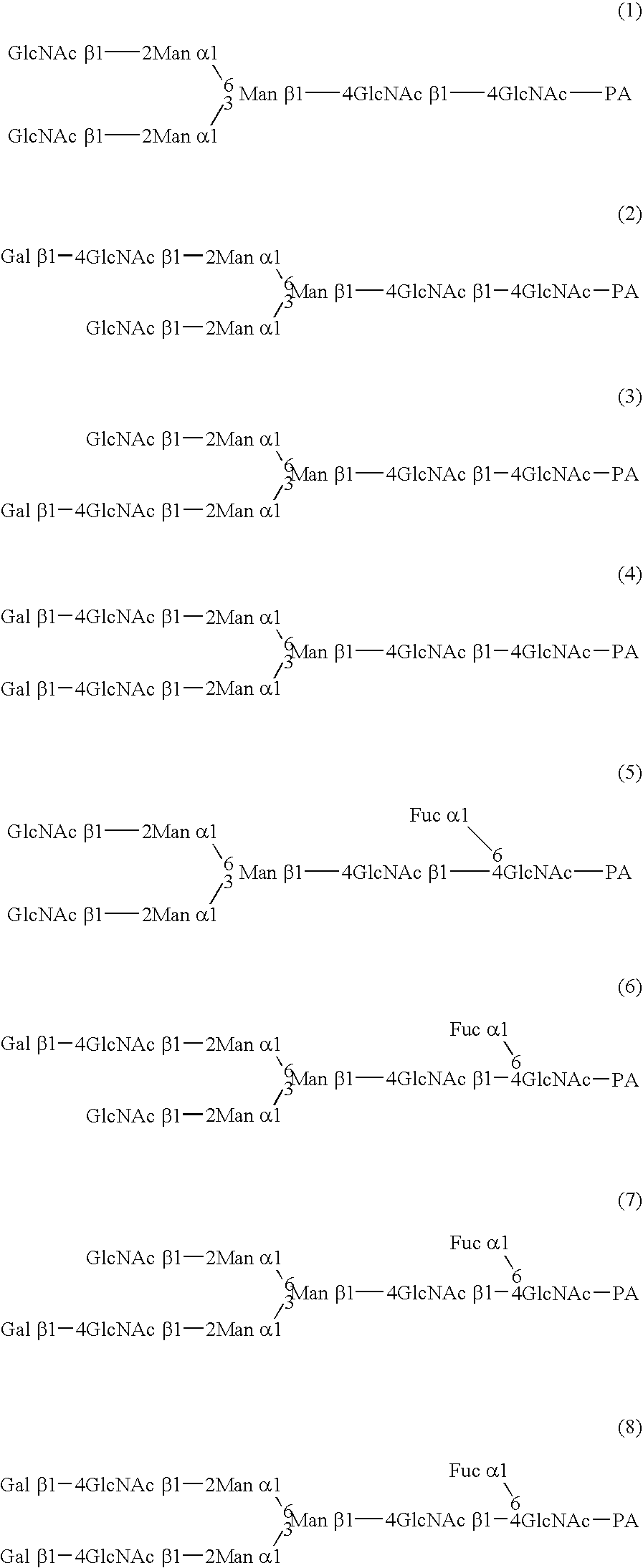Patents
Literature
95689results about "Vector-based foreign material introduction" patented technology
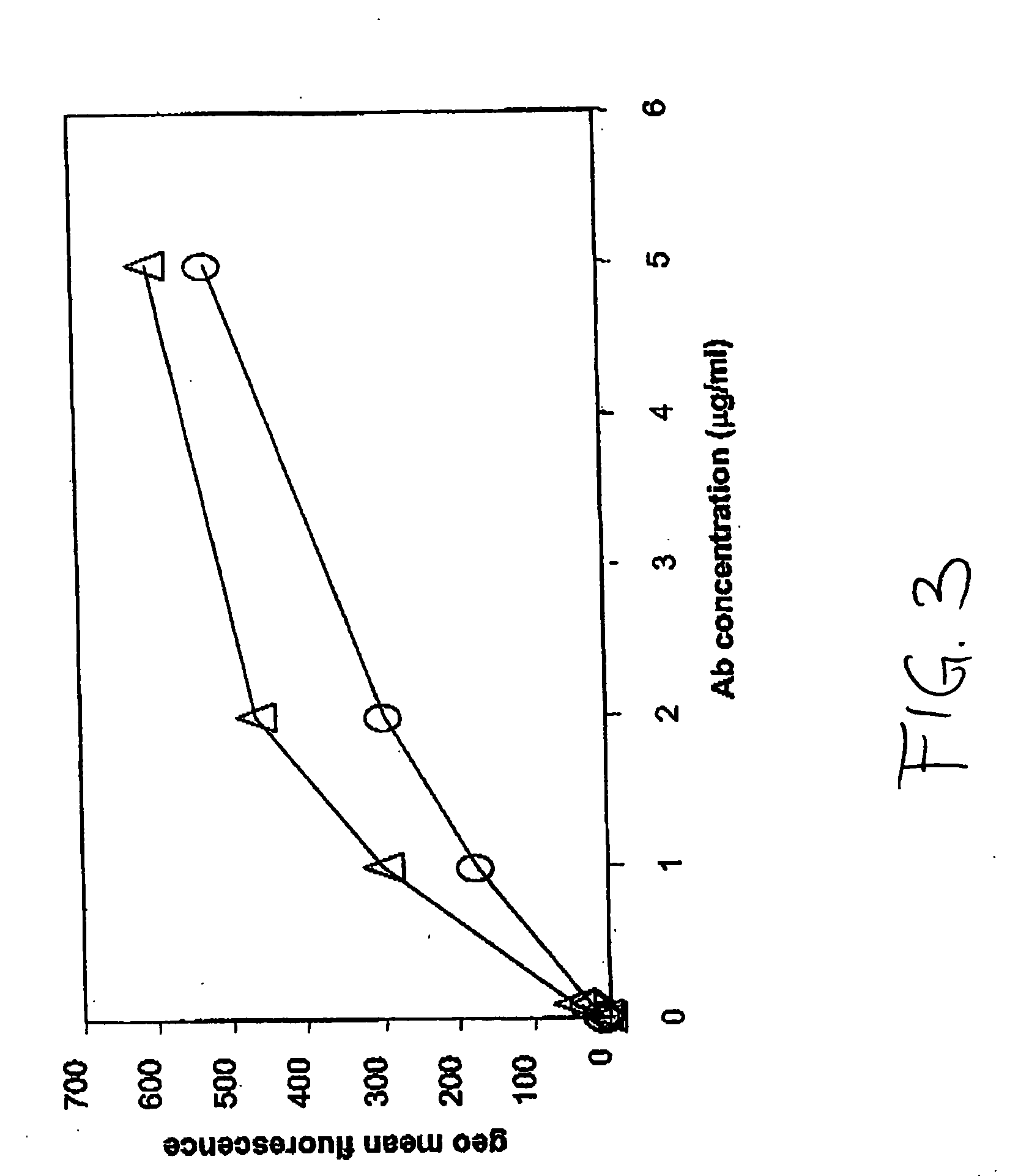
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS6602684B1Increase healing valueEnhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicityNanotechFungiAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
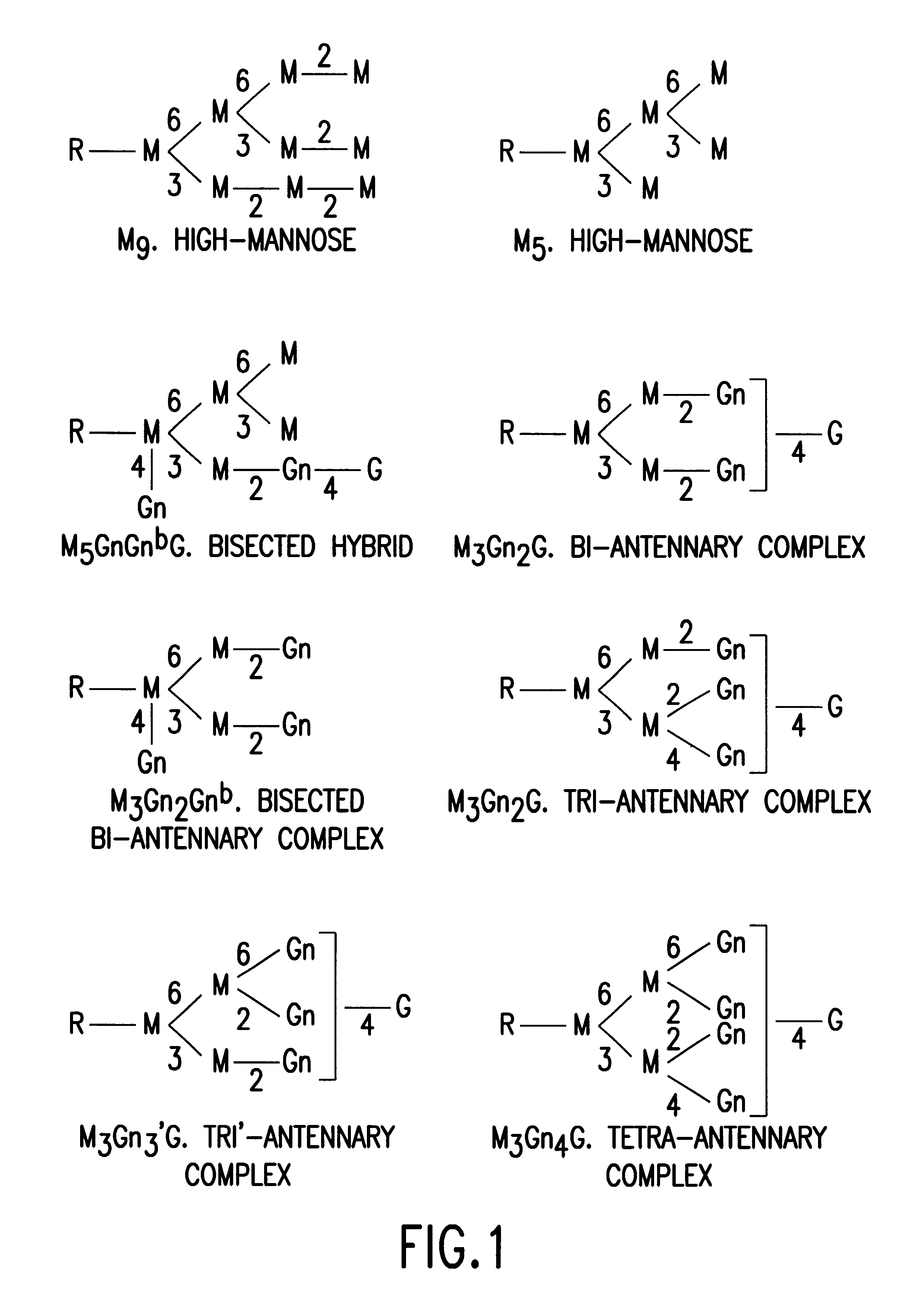
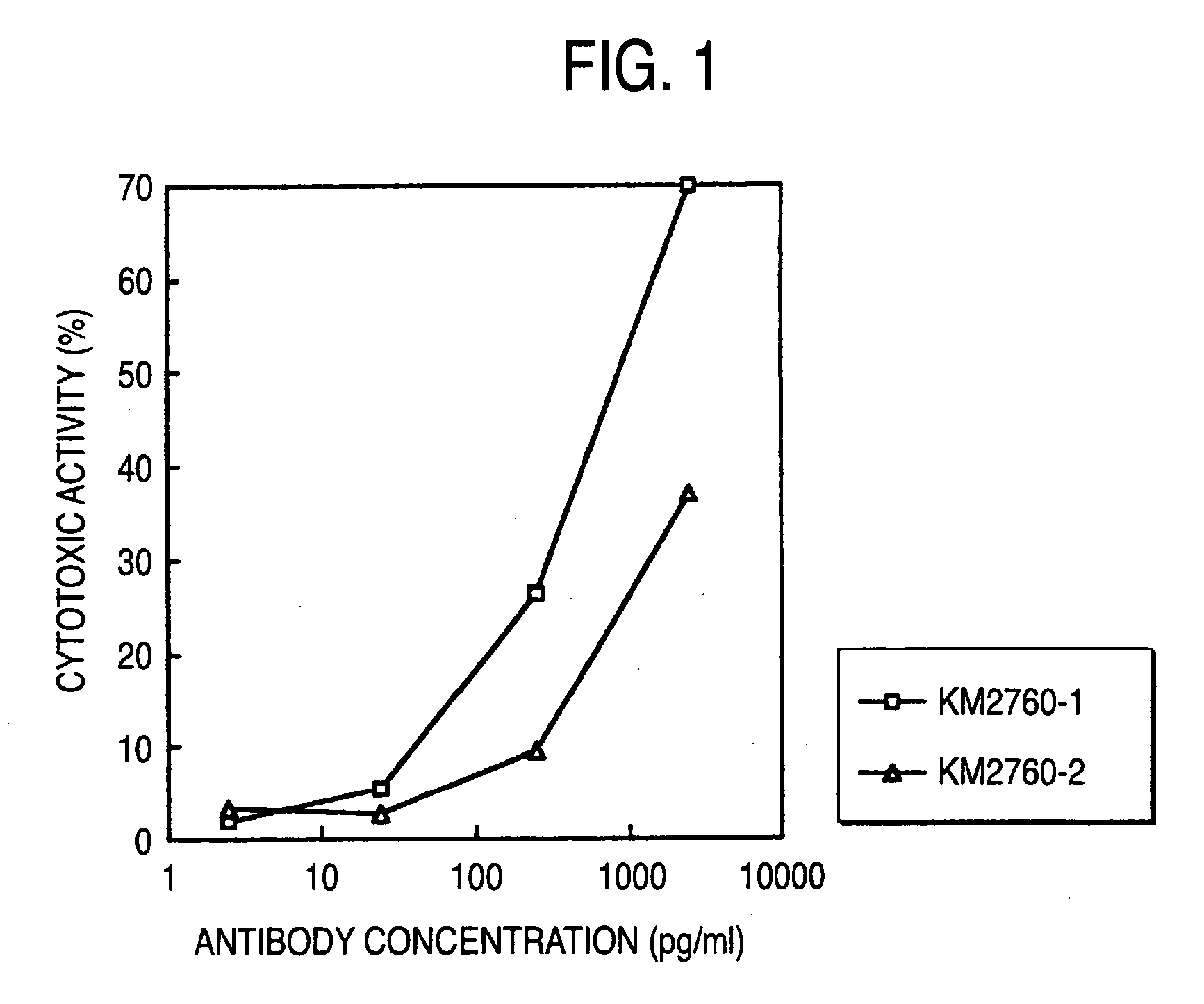
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Cells of which genome is modified
InactiveUS20040110704A1Raise the ratioDecreased and deleted activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticGlycosideN-Acetylglucosamine
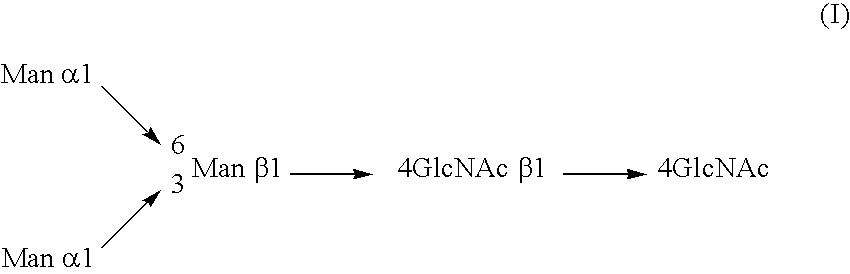
A cell in which genome is modified so as to have a more decreased or deleted activity of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain than its parent cell, and a process for producing an antibody composition using the cell.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Inbred corn line LH283BtMON810
InactiveUS6852915B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
An inbred corn line, designated LH283BtMON810, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of inbred corn line LH283BtMON810, to the plants of inbred corn line LH283BtMON810 and to methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the inbred line LH283BtMON810 with itself or another corn line. The invention further relates to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from the inbred LH283BtMON810.
Owner:HOLDENS FOUND SEEDS
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Promoter for regulating expression of foreign genes
InactiveUS7125978B1Regulate expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesOrganismFhit gene
The present invention relates to a promoter for regulating expression of foreign genes in transgenic organisms, which comprises a promoter having the identifying characteristics of a promoter having a sequence selected from the group consisting of sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOS:1 to 3 and functional fragments or derivatives thereof, wherein said promoter is adapted to be operationally located with respect to said foreign gene for expression of said gene.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
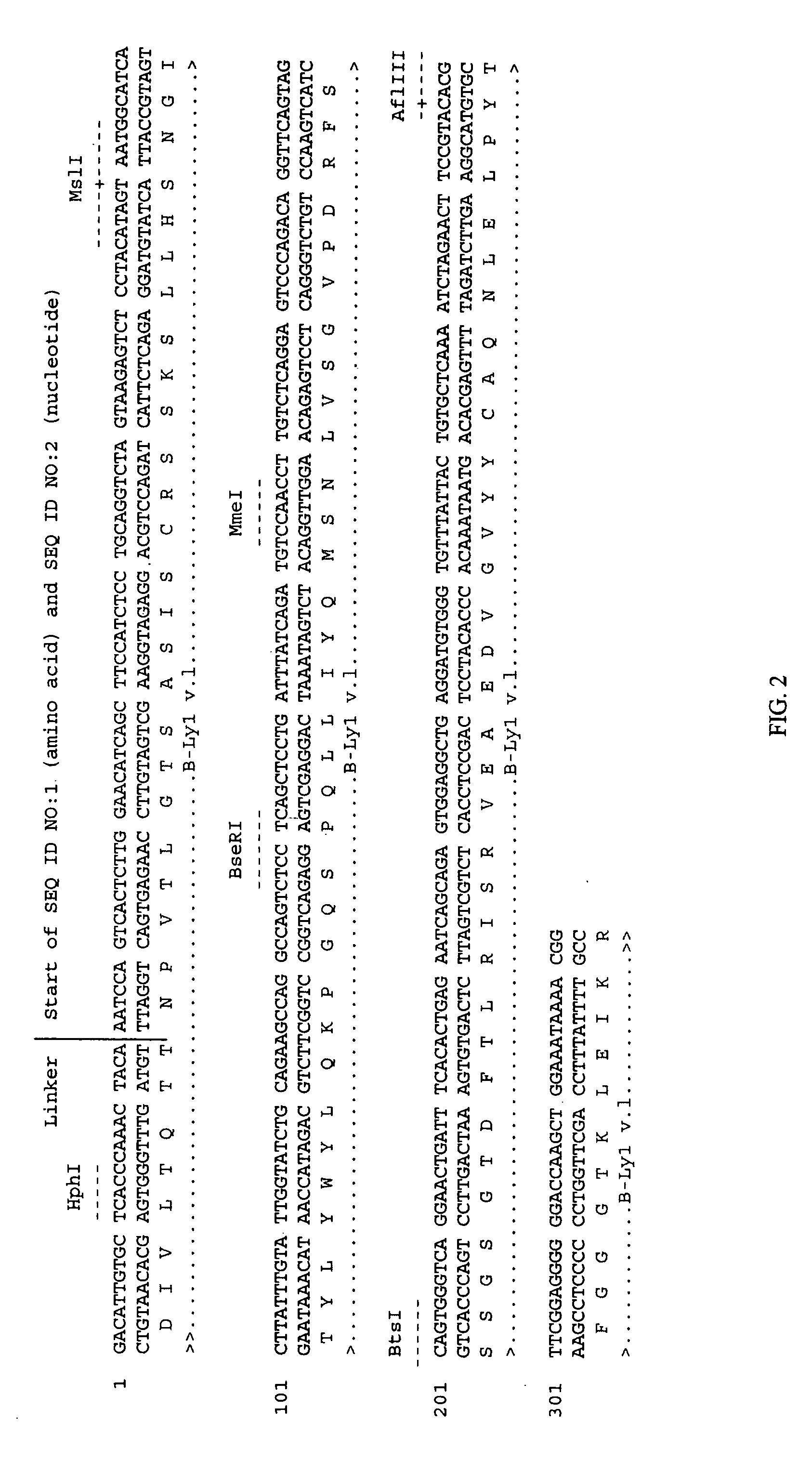
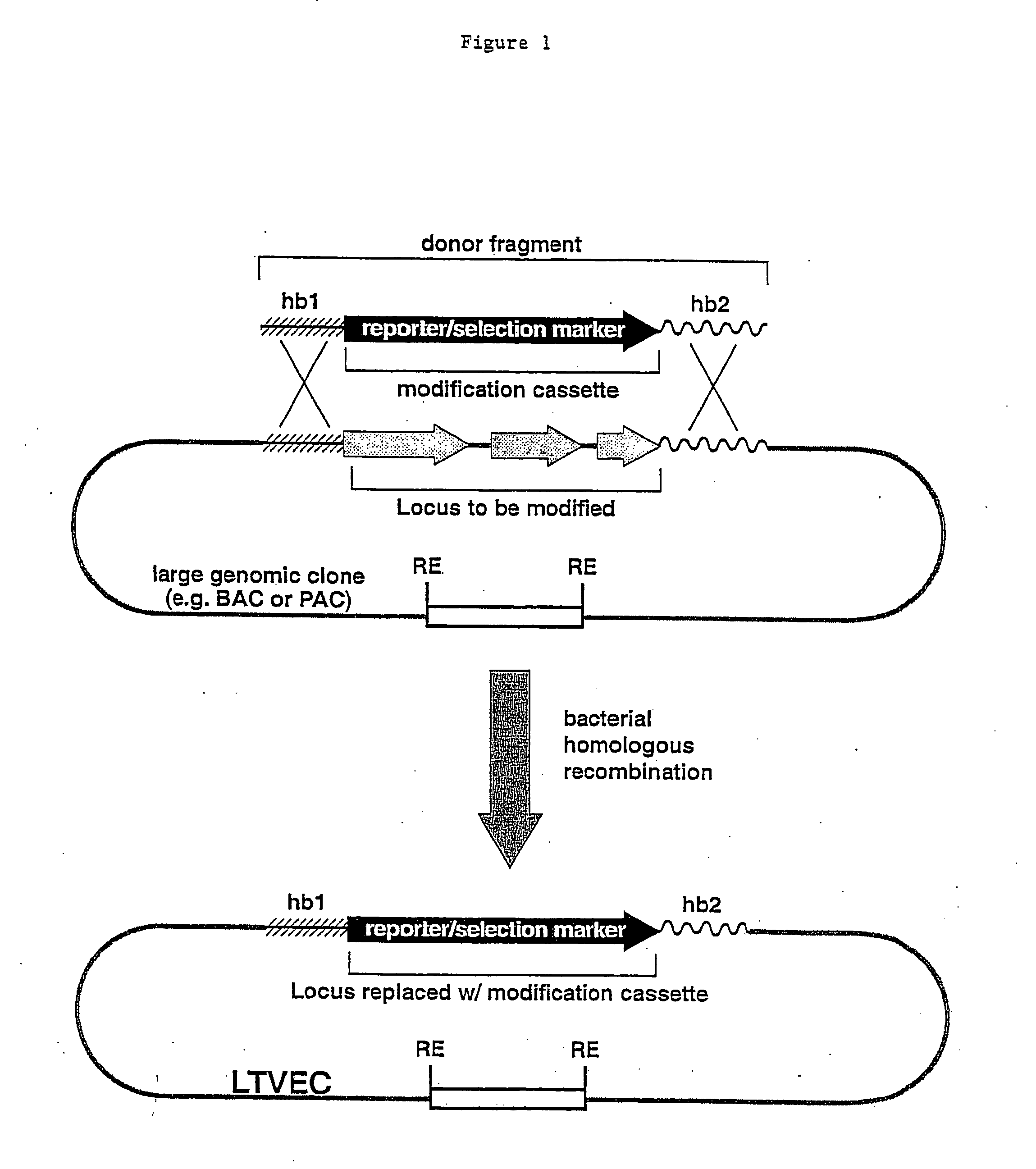
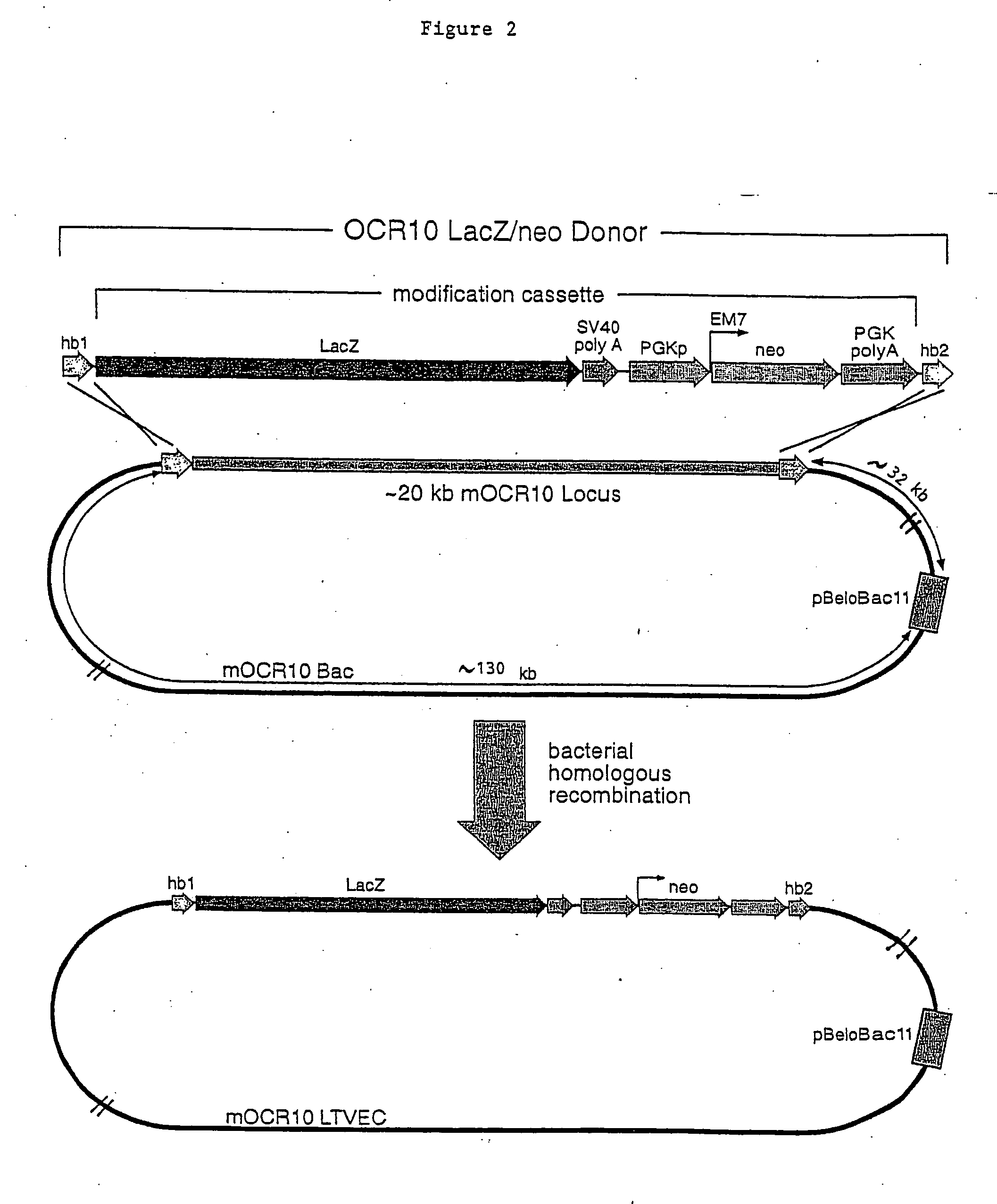
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Soybean cultivar SN79525
InactiveUS6967263B2Improve nutritional qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCultivar
A novel soybean cultivar, designated SN79525, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar SN79525, to the plants of soybean SN79525 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar SN79525 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar SN79525 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean cultivar 0509244
ActiveUS6982367B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivar
Owner:STINE SEED FARM +1
Soybean cultivar S030160
ActiveUS6969787B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetically modified soybeanCultivar
A novel soybean cultivar, designated S030160, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar S030160, to the plants of soybean S030160 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar S030160 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to transgenic soybean plants Produced by transforming a soybean of the cultivar S030160.
Owner:STINE SEED FARM INC AN IOWA +1
Soybean cultivar 0037357
A soybean cultivar, designated 0037357, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar 0037357, to the plants of soybean 0037357 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar 0037357 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar 0037357 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean variety SE90346
InactiveUS6958436B2Improve nutritional qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCultivar
A soybean cultivar, designated SE90346, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar SE90346, to the plants of soybean SE90346 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar SE90346 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar SE90346 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean cultivar S030010
InactiveUS6979760B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivar
A novel soybean cultivar, designated S030010, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar S030010, to the plants of soybean S030010 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar S030010 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar S030010 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:STINE SEED FARM +1
Soybean cultivar 0509245
ActiveUS6972354B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivarSoya bean
A soybean cultivar, designated 0509245, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar 0509245, to the plants of soybean 0509245 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar 0509245 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar 0509245 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:STINE SEED FARM +1
Genetic constructs for delaying or repressing the expression of a target gene
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Soybean cultivar 0491737
InactiveUS6972353B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetically modified soybeanCultivar
A novel soybean cultivar, designated 0491737, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar 0491737, to the plants of soybean 0491737 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar 0491737 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to transgenic soybean plants produced by transforming a soybean of the cultivar 0491737.
Owner:STINE SEED FARM +1
Soybean cultivar 0509240
ActiveUS6972355B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivarSoya bean
Owner:STINE SEED FARM INC IOWA +1
Binding polypeptides with optimized scaffolds
InactiveUS20070292936A1Improve folding stabilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsVariable domainChemistry
The invention provides variant heavy chain variable domains (VH) with increased folding stability. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, compositions and methods of generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
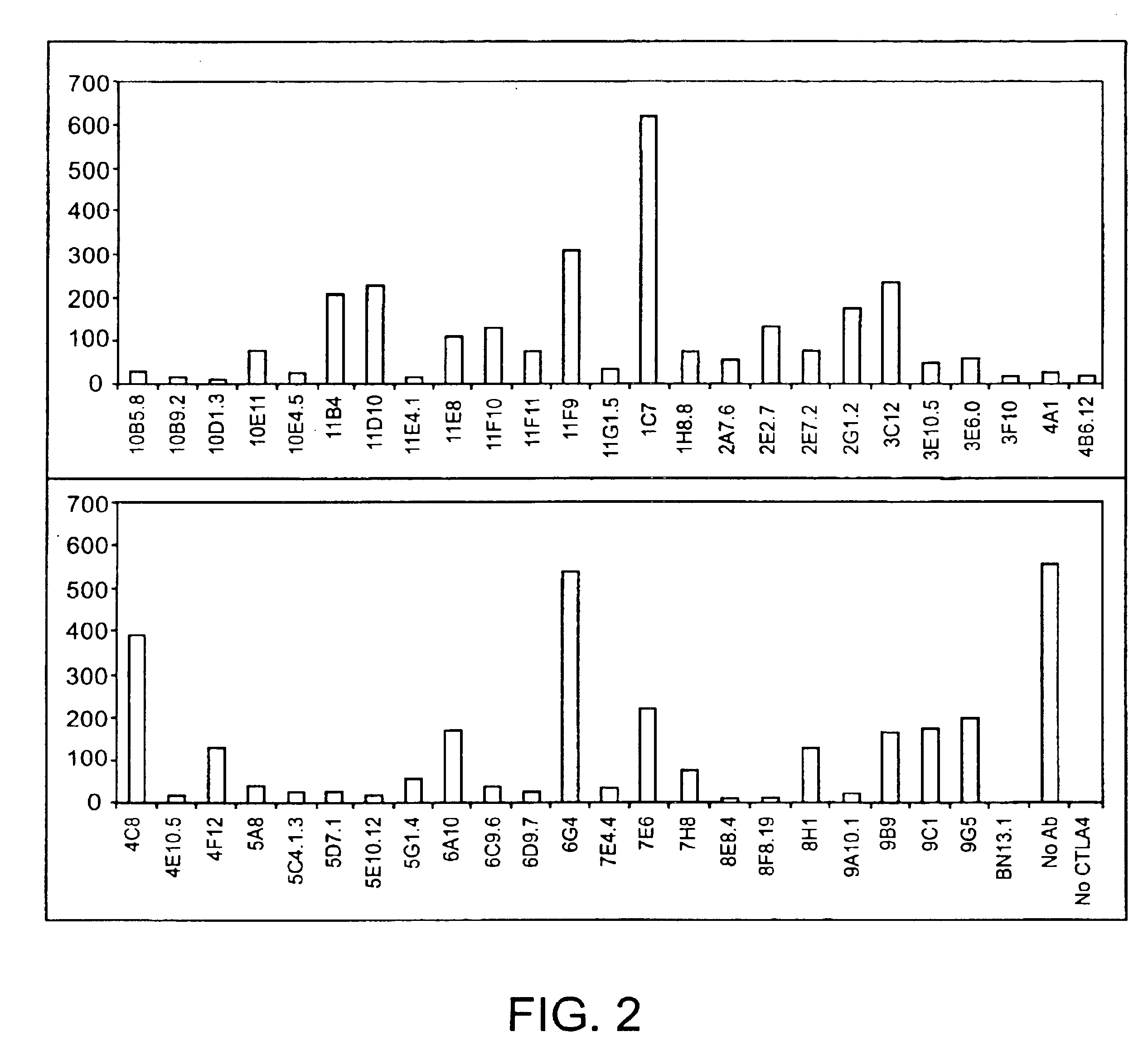
Human CTLA-4 antibodies
The present invention provides human sequence antibodies against CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20070237764A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
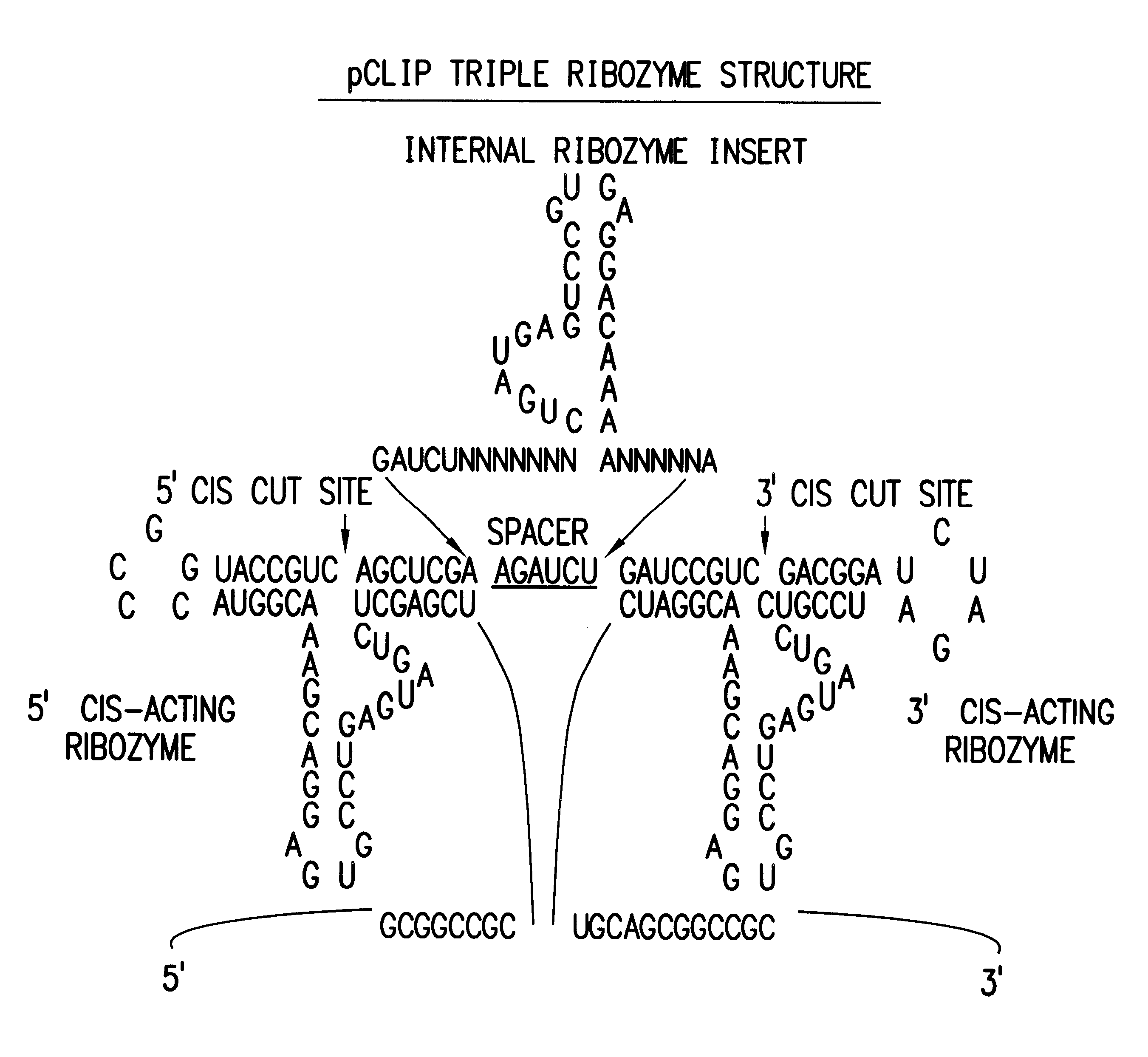
Tissue-specific and pathogen-specific toxic agents and ribozymes
InactiveUS6271359B1Rapidly and effectively expressedImprove stabilityVirusesSugar derivativesCancer cellBiology
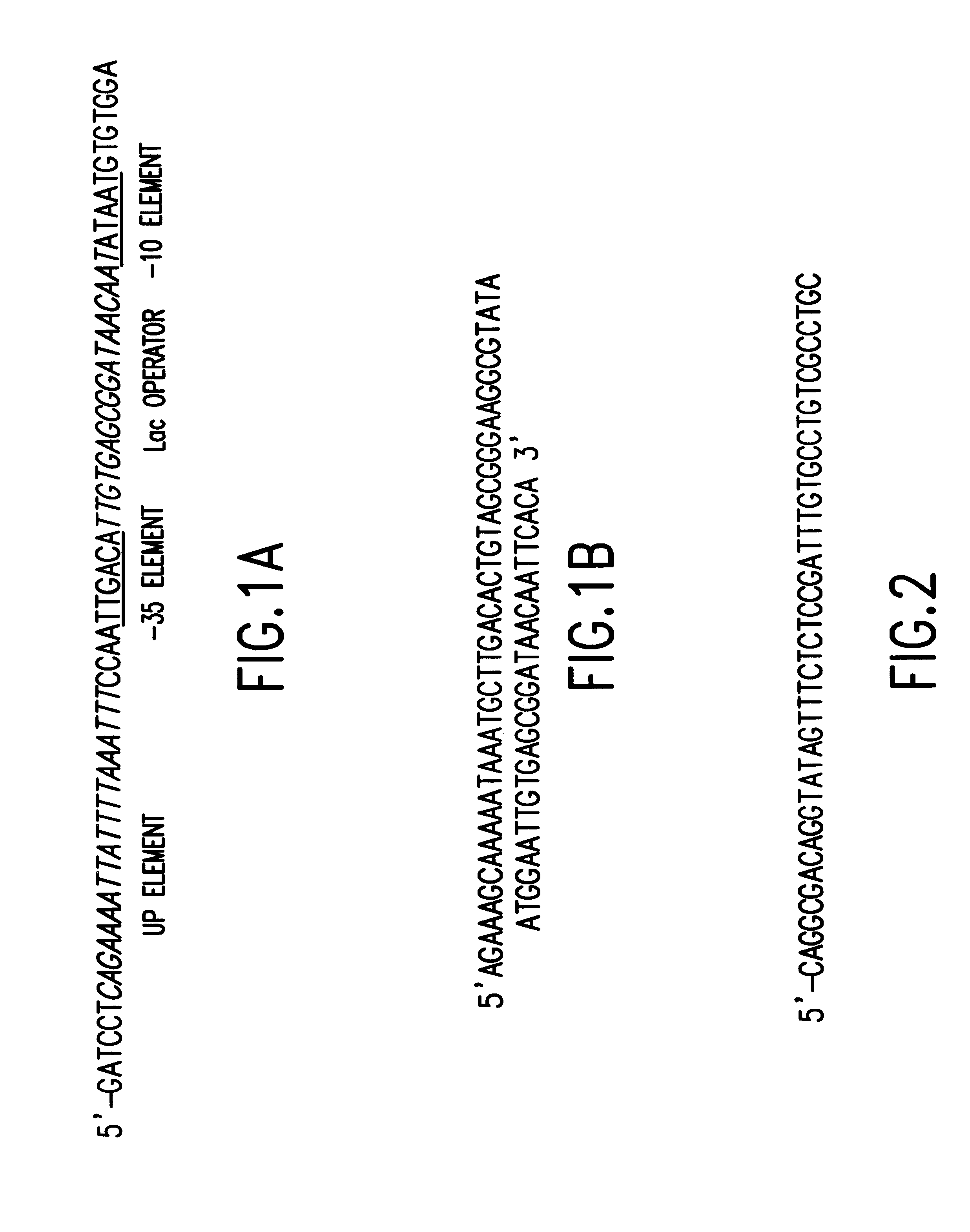
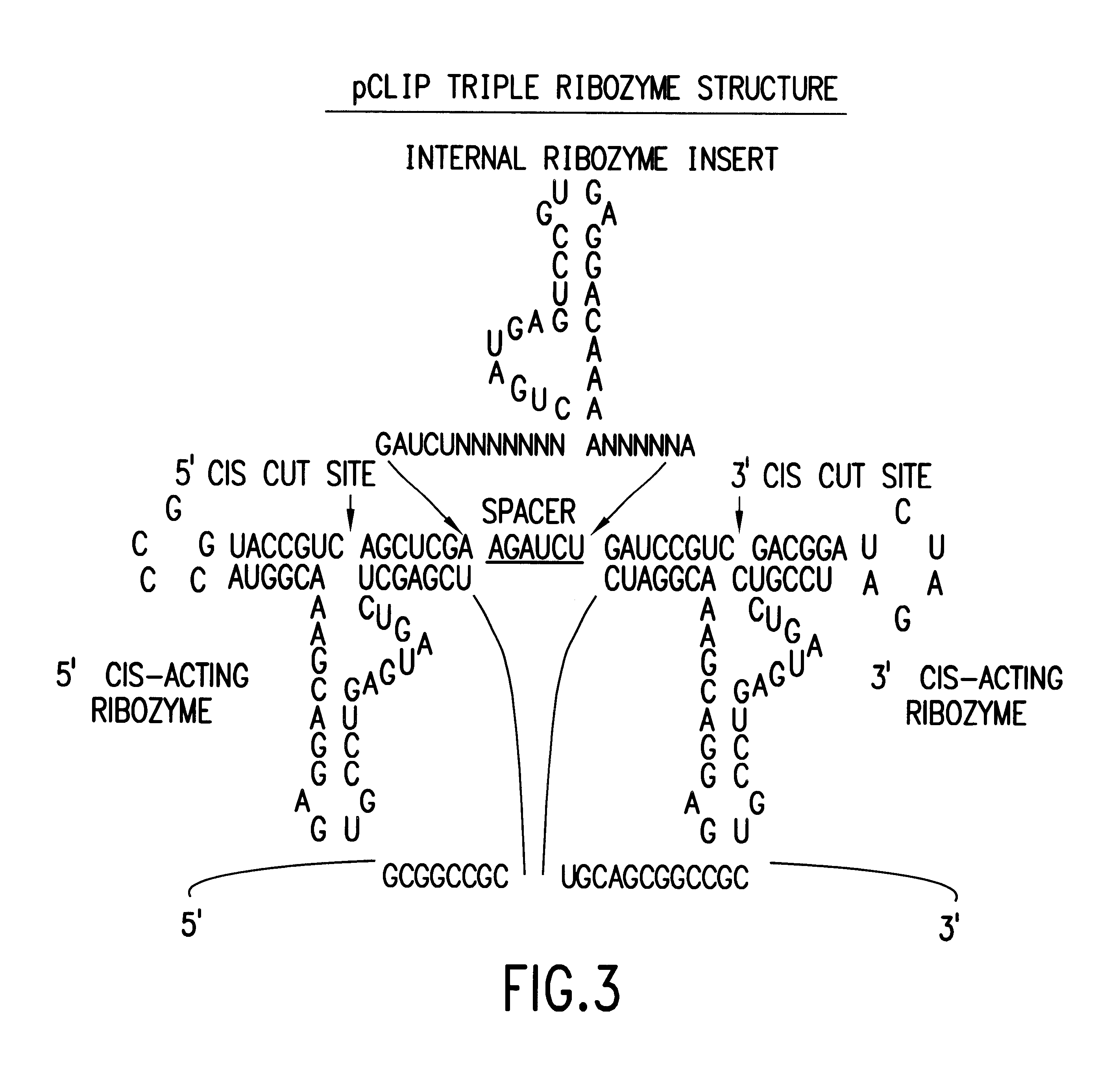
The present invention relates to the discovery, identification and characterization of toxic agents which are lethal to pathogens and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a pathogen or pathogen infected cells in order to treat and / or eradicate the infection. In particular, the present invention relates to toxic agents which target bacteria at different stages of the bacterial life cycle, which are delivered alone or in combination to bacteria or bacteria-infected cells. The invention relates to toxic agents which are lethal to diseased cells and methods for targeting such toxic agents to a diseased cell in order to treat and / or eradicate the disease. The present invention relates to promoter elements which are pathogen-specific or tissue-specific and the use of such promoter elements to achieve pathogen-specific or tissue-specific expression of the toxic agent(s) and / or ribozyme(s) of the present invention. Specifically, the invention relates to the delivery of one or more toxic gene products, antisense RNAs, or ribozymes, or combination thereof. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple pathogenic targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a pathogen, or cell infected with a pathogen. Further, the invention has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant bacterium and bacterial pathogens. The invention provides a novel system by which multiple targets may be simultaneously targeted to cause the death of a diseased cell. The invention also has important implications in the eradication of drug-resistant pathogens and drug-resistant diseased cells (such as cancer cells).
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
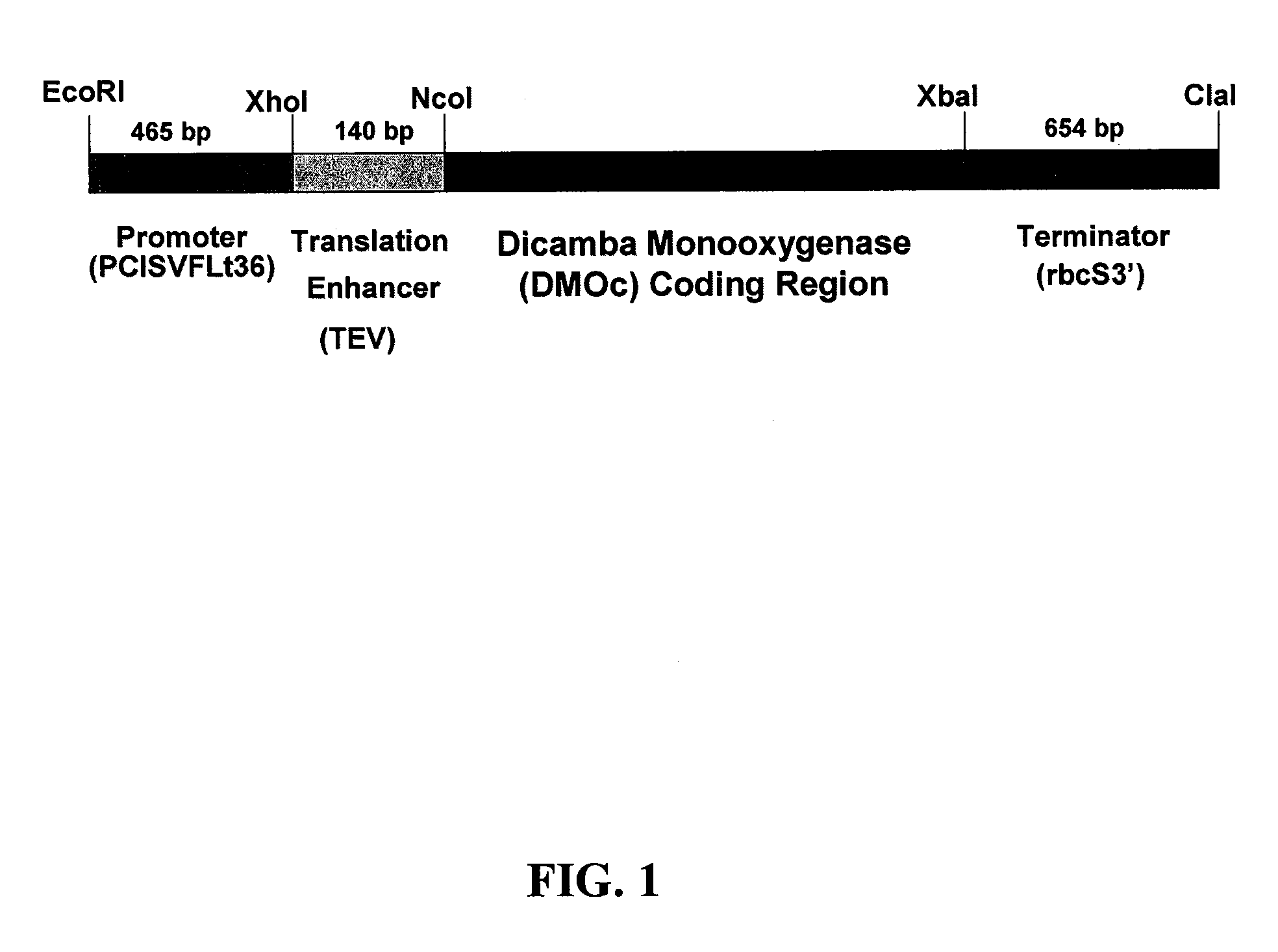
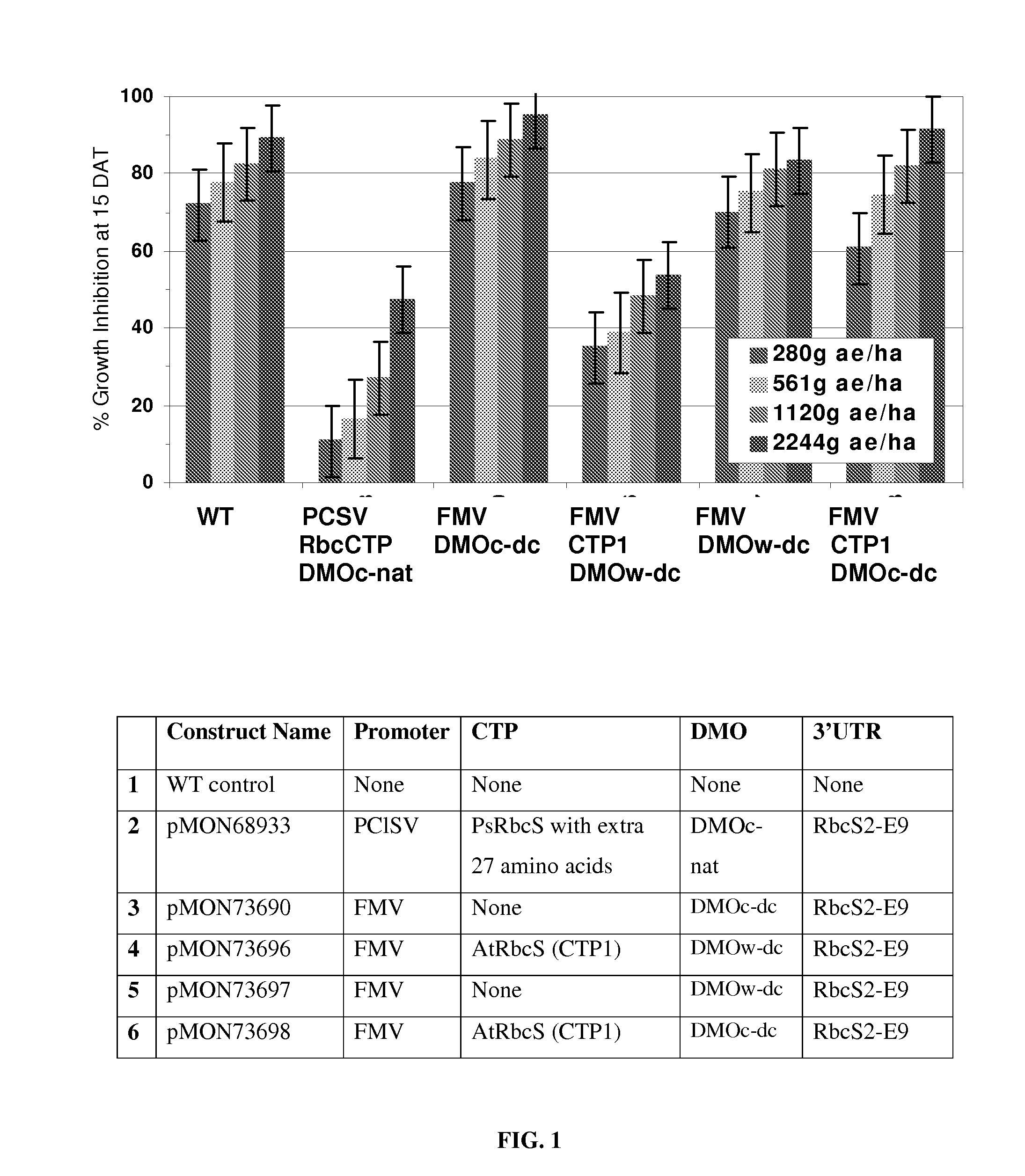
Modified DMO enzyme and methods of its use
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
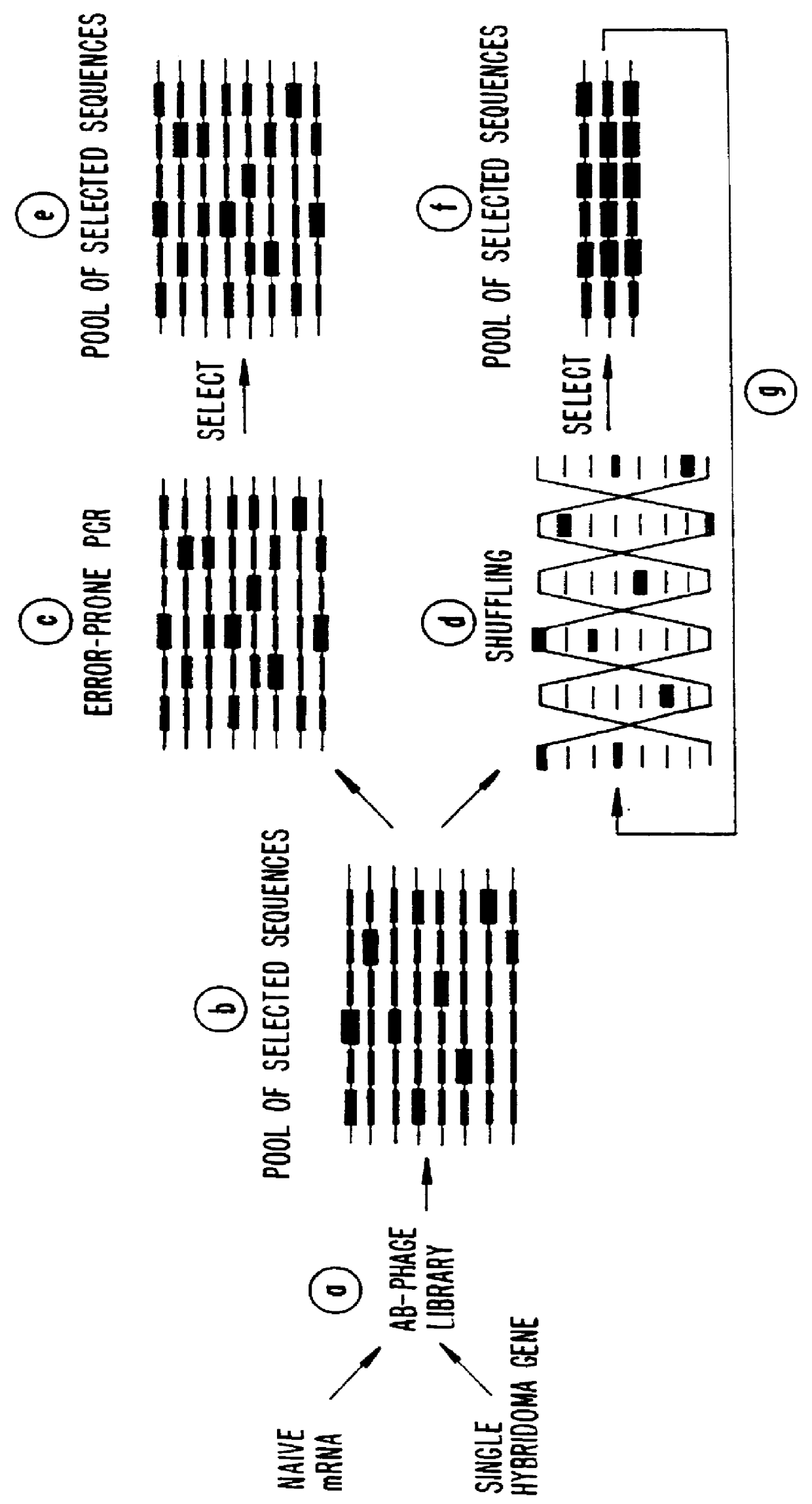
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
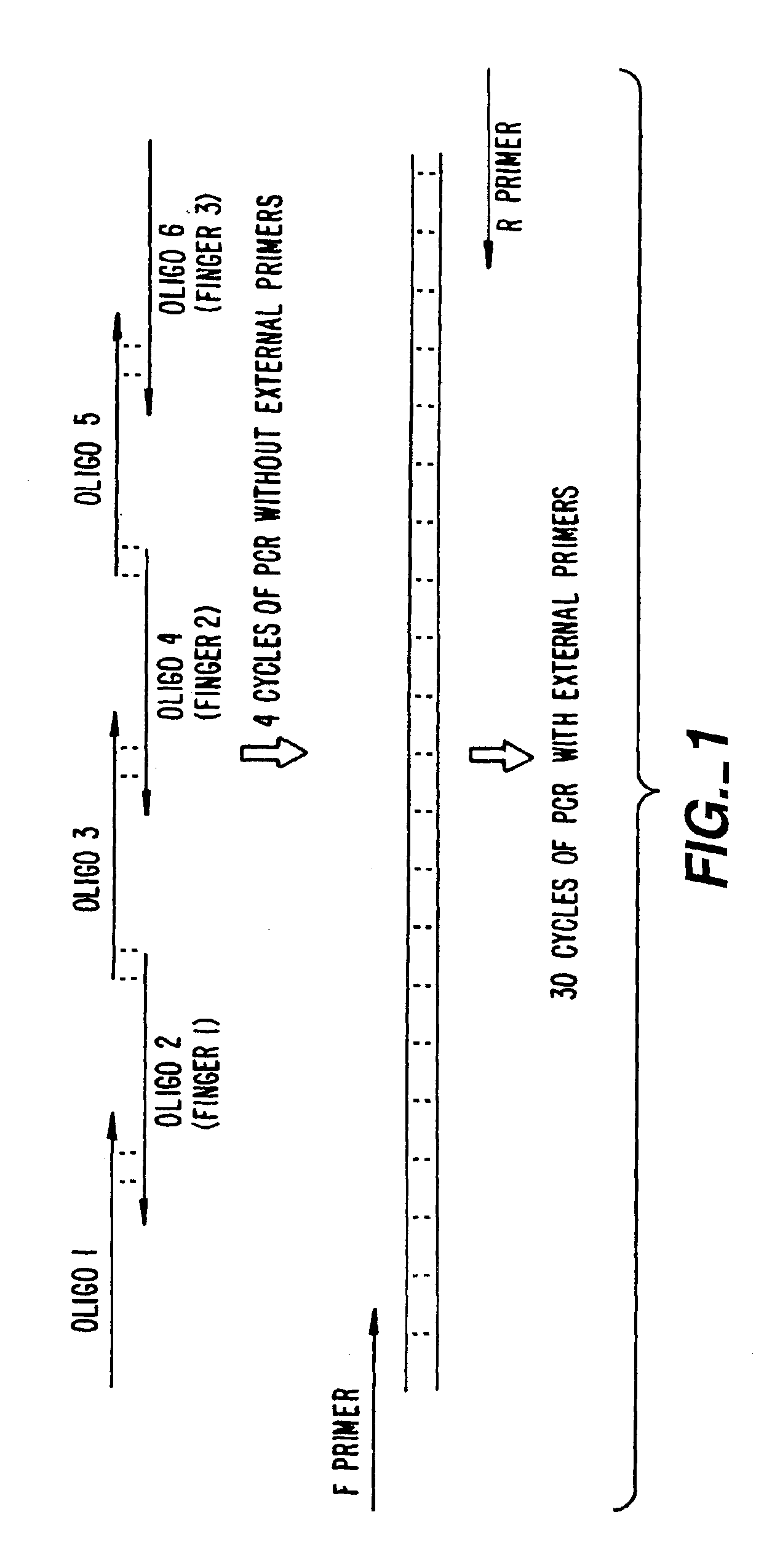
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of DMO and uses thereof
ActiveUS7838729B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMonooxygenaseGMO Plants
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
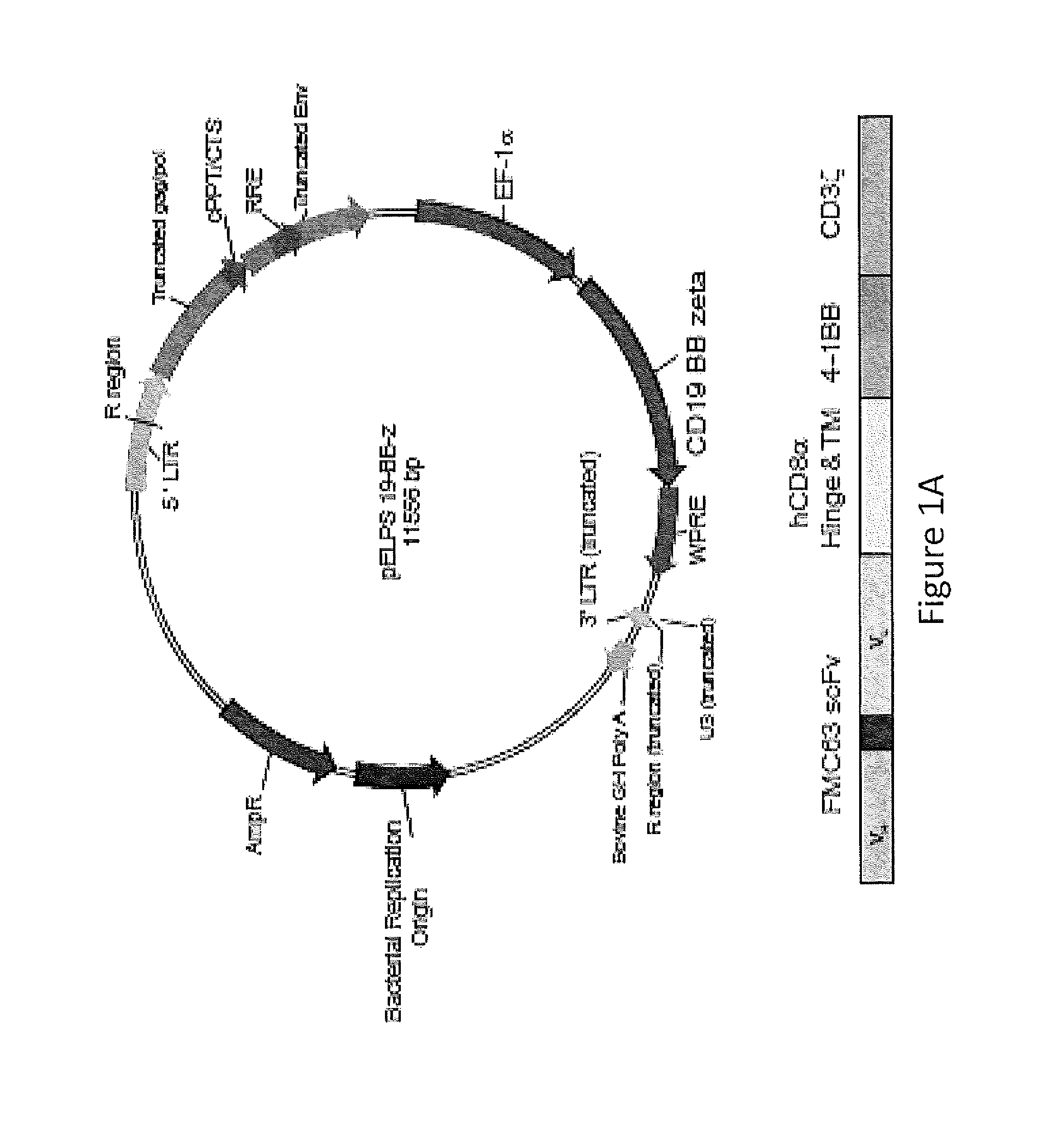
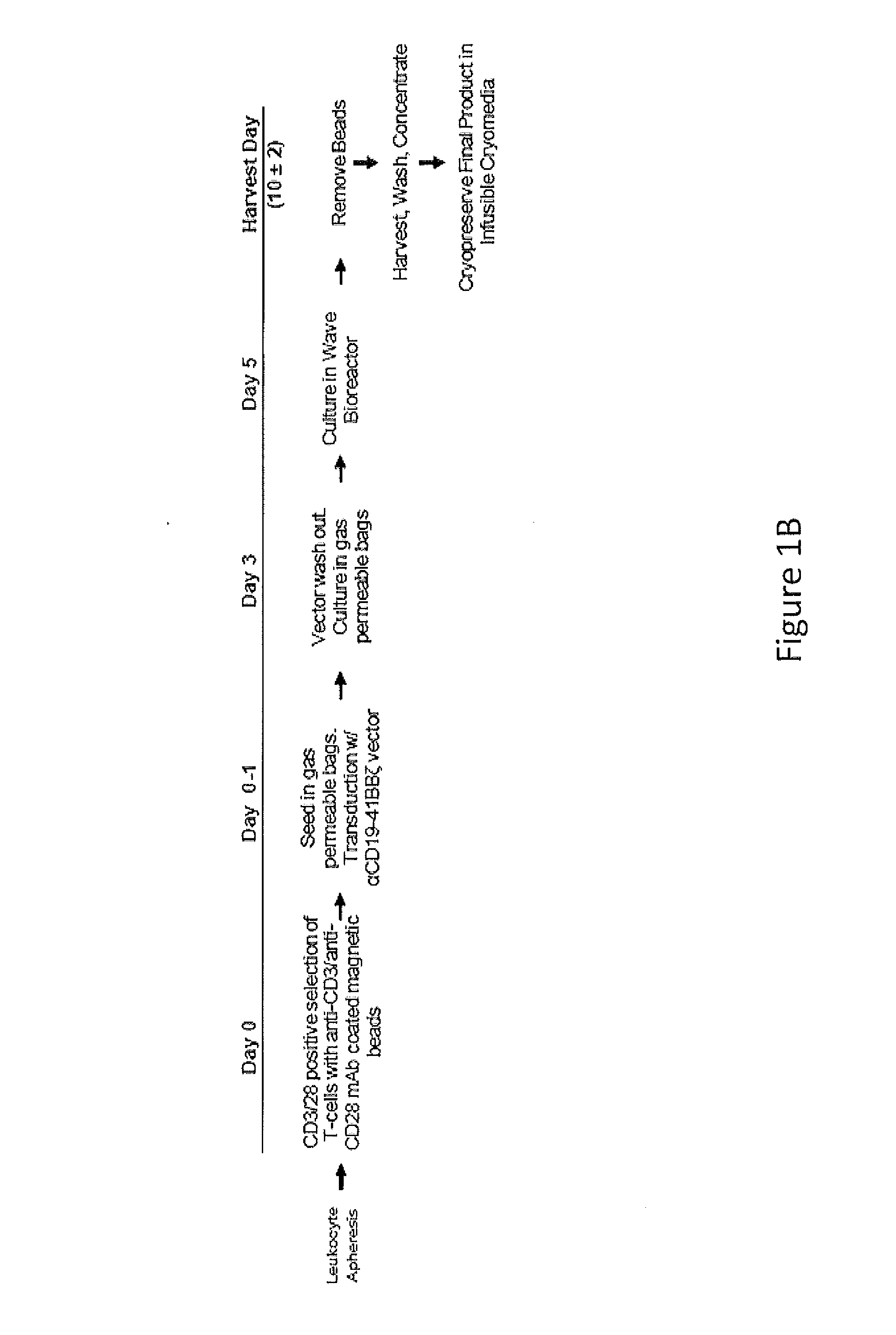
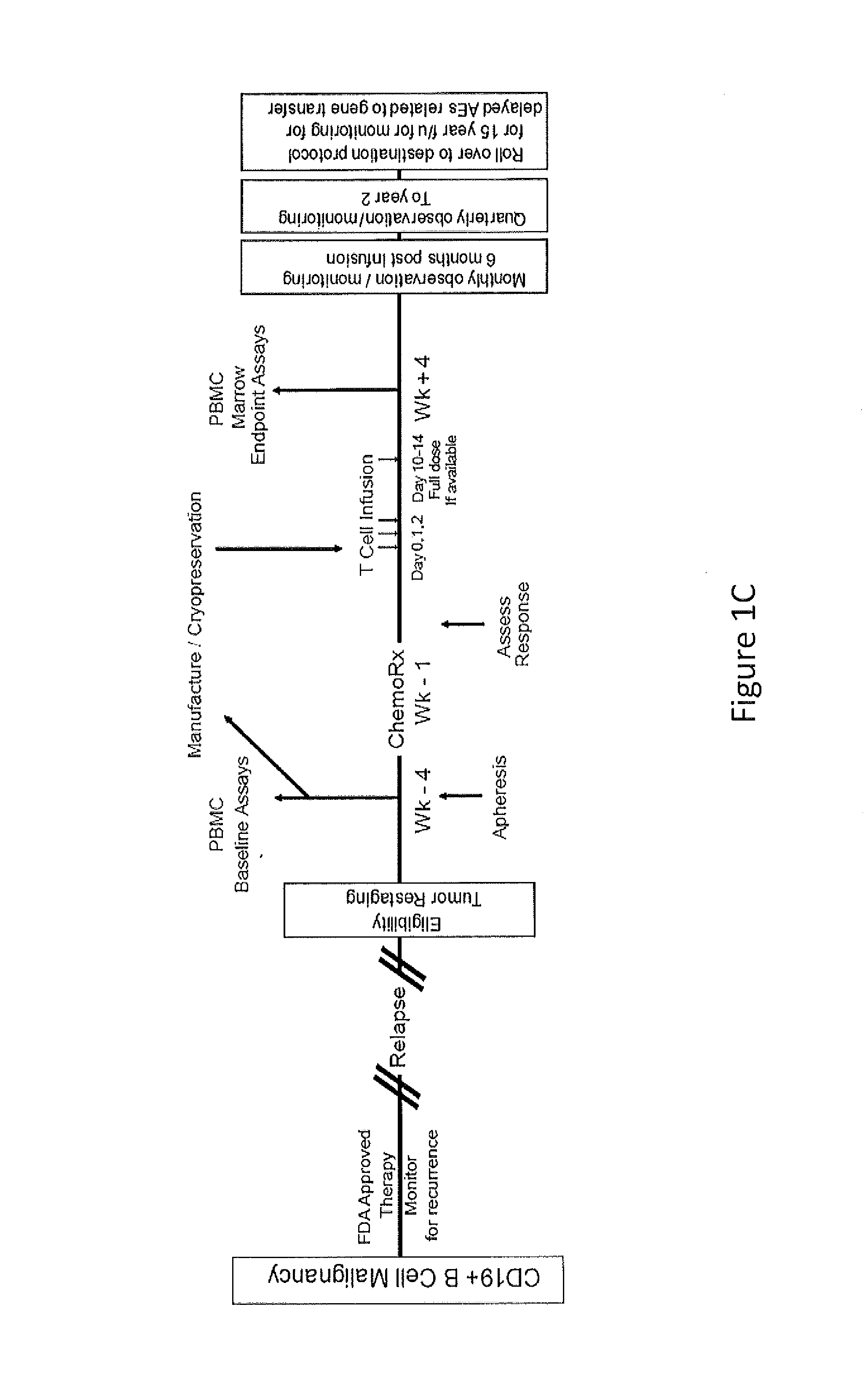
Use of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T-Cells to Treat Cancer
ActiveUS20130287748A1Stimulate immune responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainAntigen binding
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
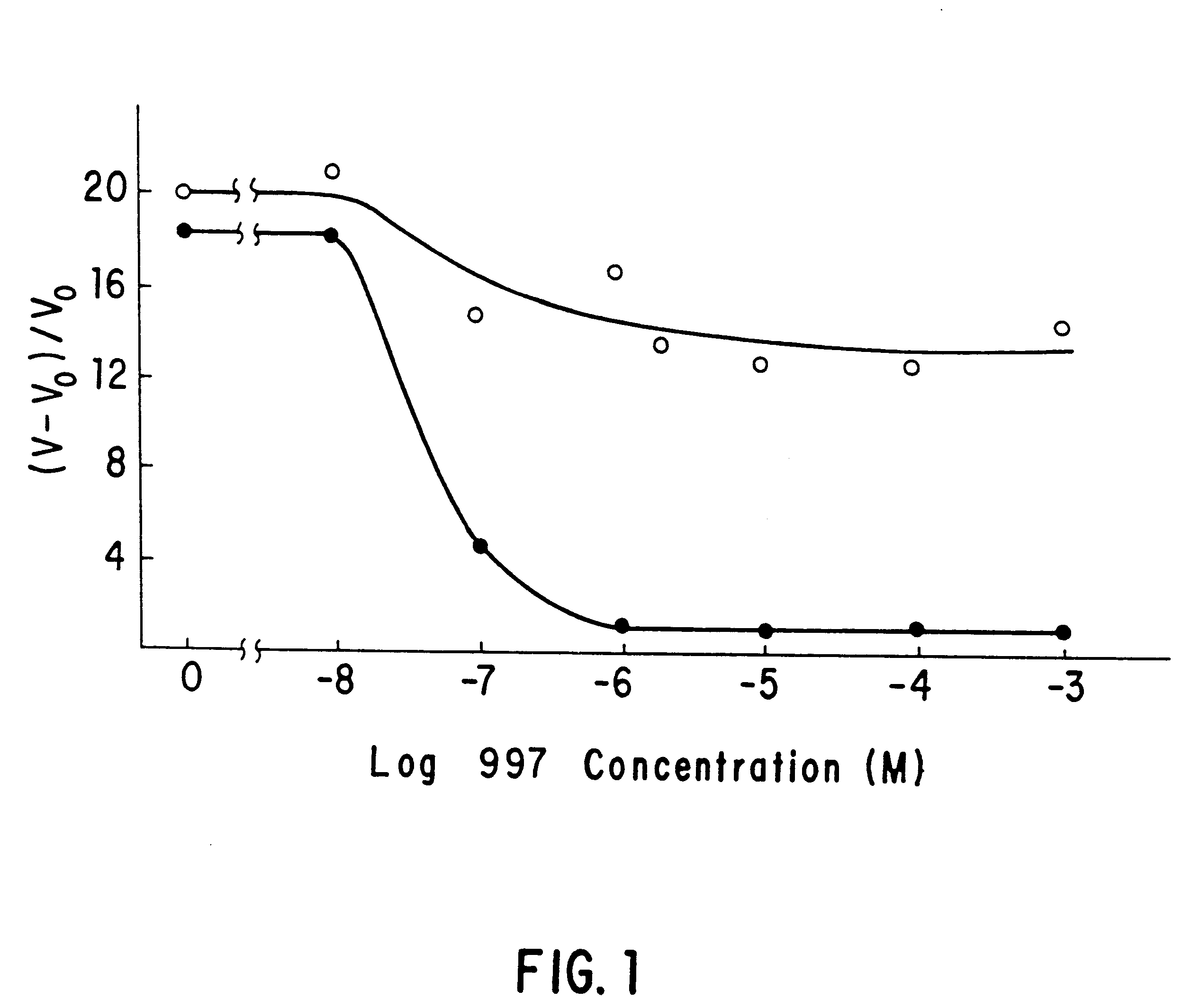
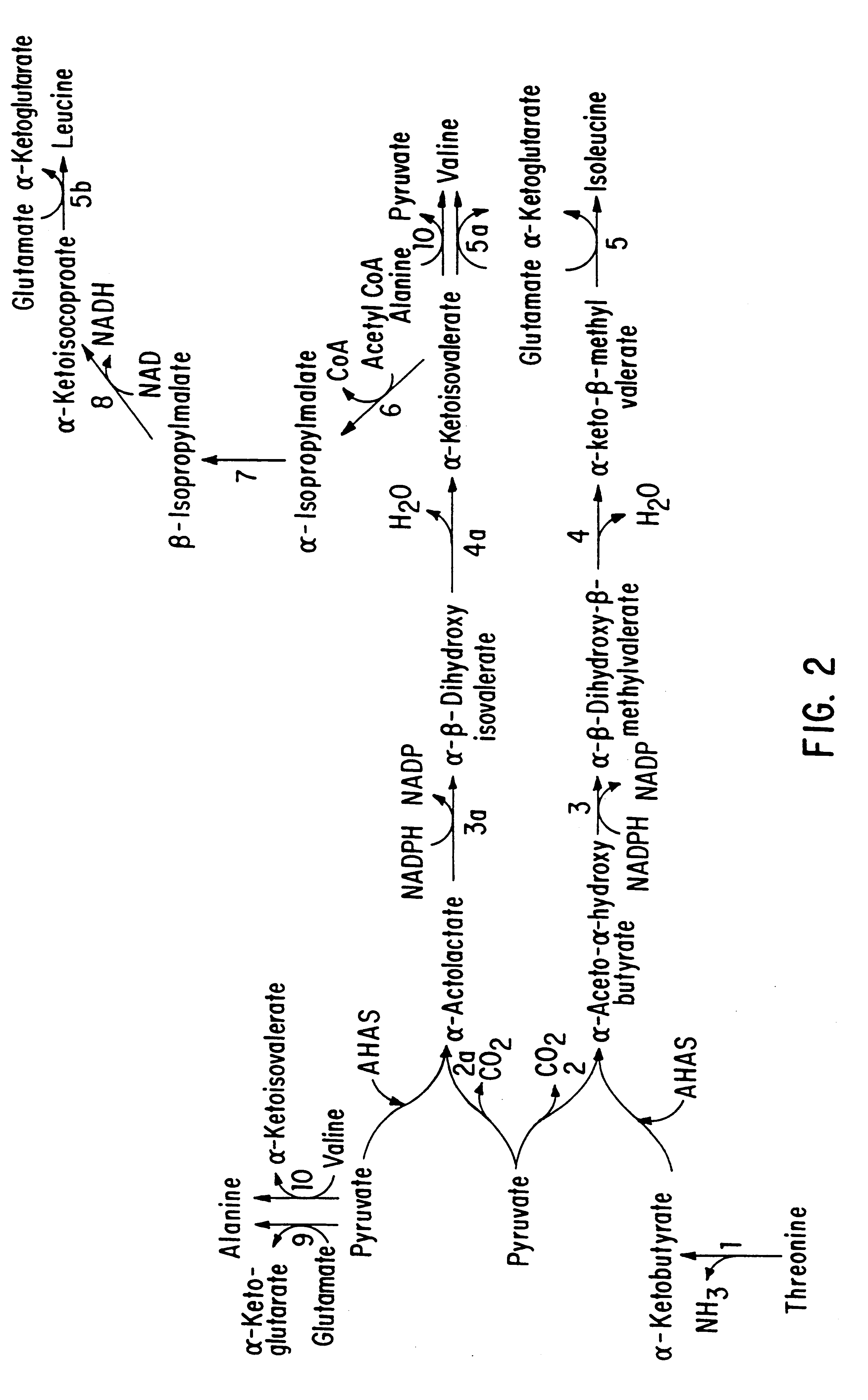
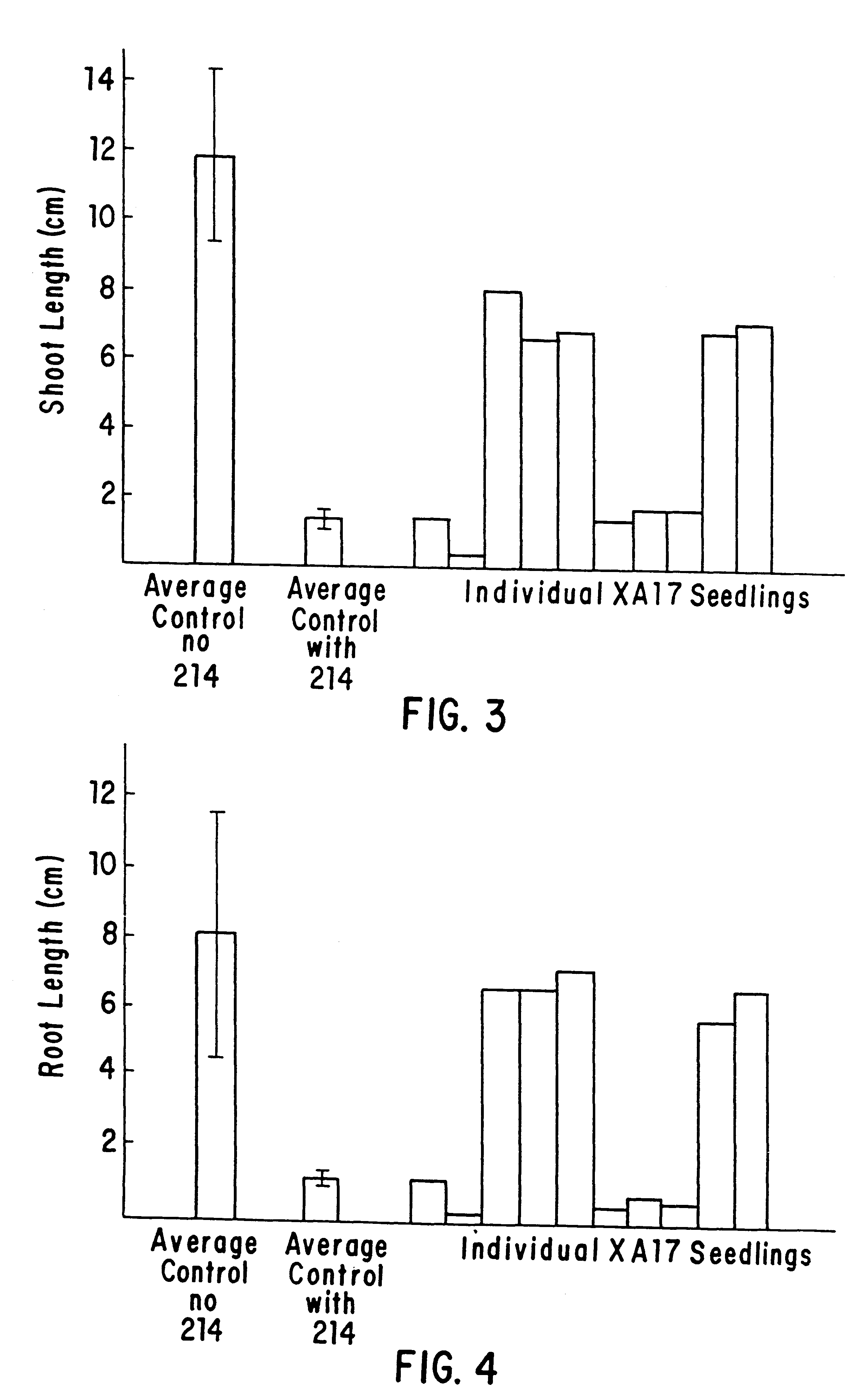
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Regulation of endogenous gene expression in cells using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS7013219B2Fusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZinc fingerGene expression
The present invention provides methods for modulating expression of endogenous cellular genes using engineered zinc finger proteins.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Plants and processes for obtaining them
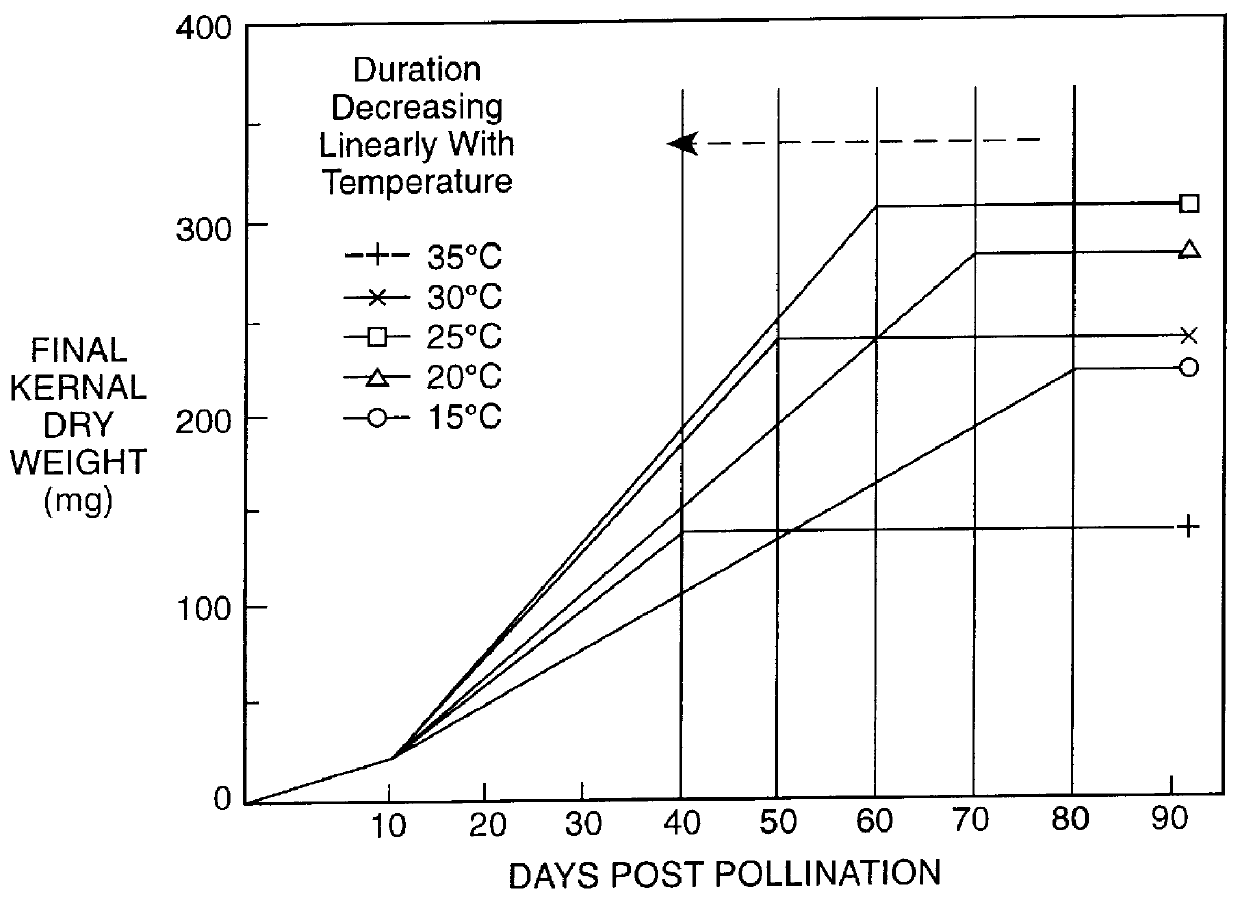
InactiveUS6013861AIncrease depositionAlteration of fine structureOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch synthaseStarch synthesis
Plants, particularly cereal plants, which have improved ability to synthesise starch at elevated or lowered temperatures and / or to synthesise starch with an altered fine structure are produced by inserting into the genome of the plant (i) a gene(s) encoding a form of an enzyme of the starch or glycogen biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which display an activity which continues to increase over a temperature range over which the activity would normally be expected to decrease, and / or (ii) a gene(s) encoding sense and anti-sense constructs of enzymes of the starch biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which alters the natural ratios of expression of the said enzymes or inserts enzymes with special structural characteristics which alter the natural branching pattern in starch.
Owner:ZENECA LTD
Systems for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides
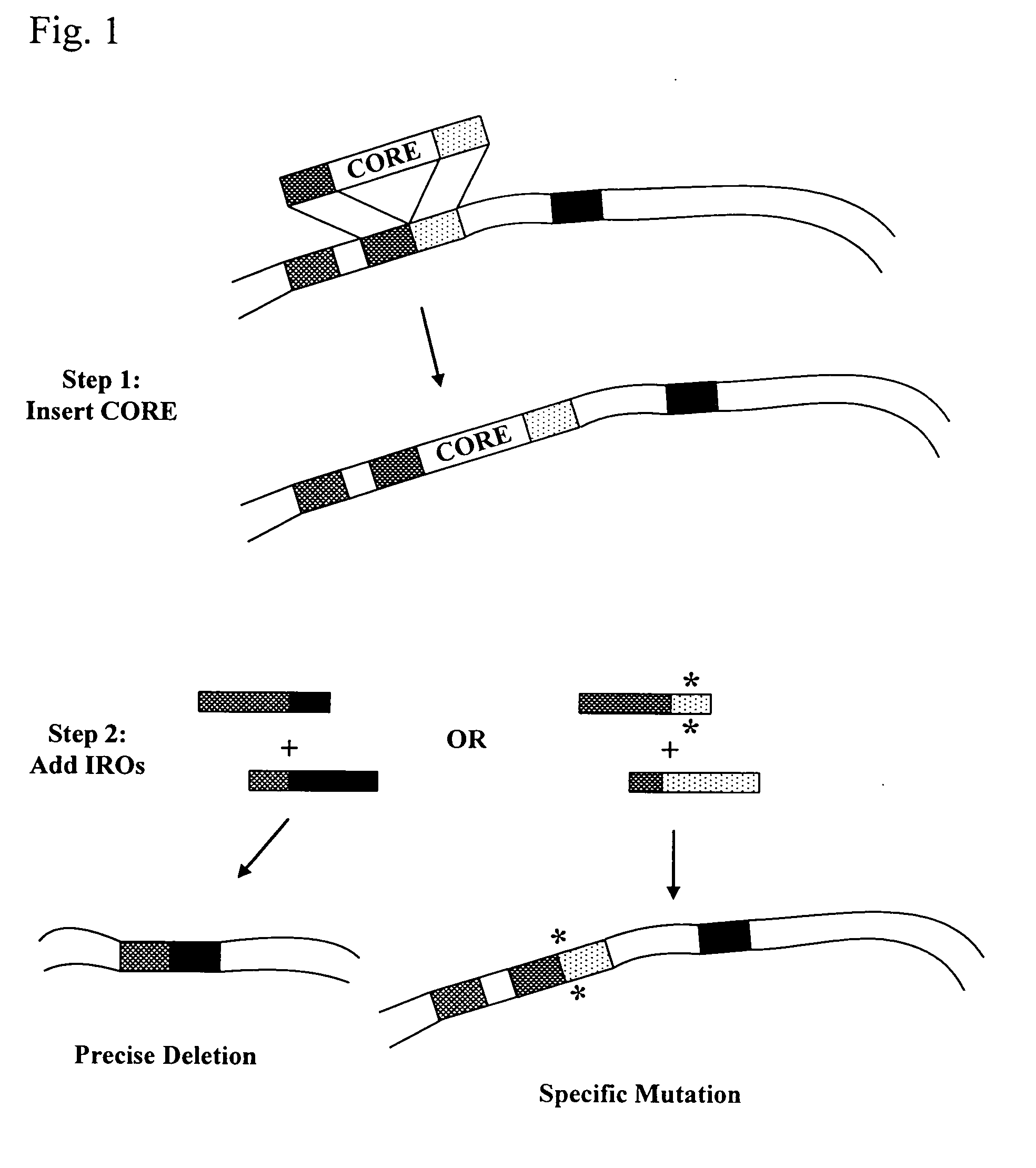
InactiveUS20040171154A1Large deletionImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousSite-directed mutagenesis
This disclosure provides several methods to generate nucleic acid mutations in vivo, for instance in such a way that no heterologous sequence is retained after the mutagenesis is complete. The methods employ integrative recombinant oligonucleotides (IROs). Specific examples of the described mutagenesis methods enable site-specific point mutations, deletions, and insertions. Also provided are methods that enable multiple rounds of mutation and random mutagenesis in a localized region. The described methods are applicable to any organism that has a homologous recombination system.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com