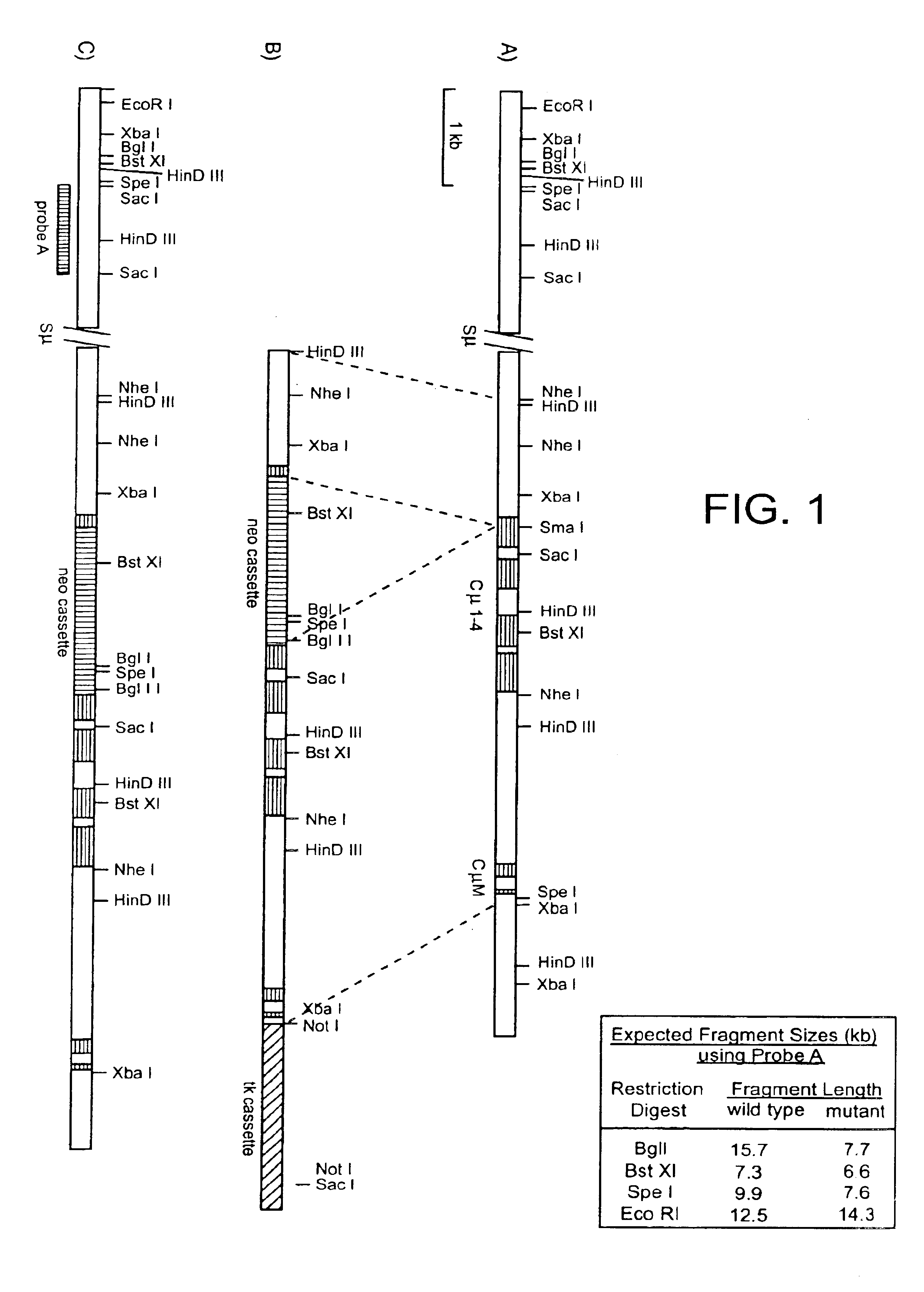
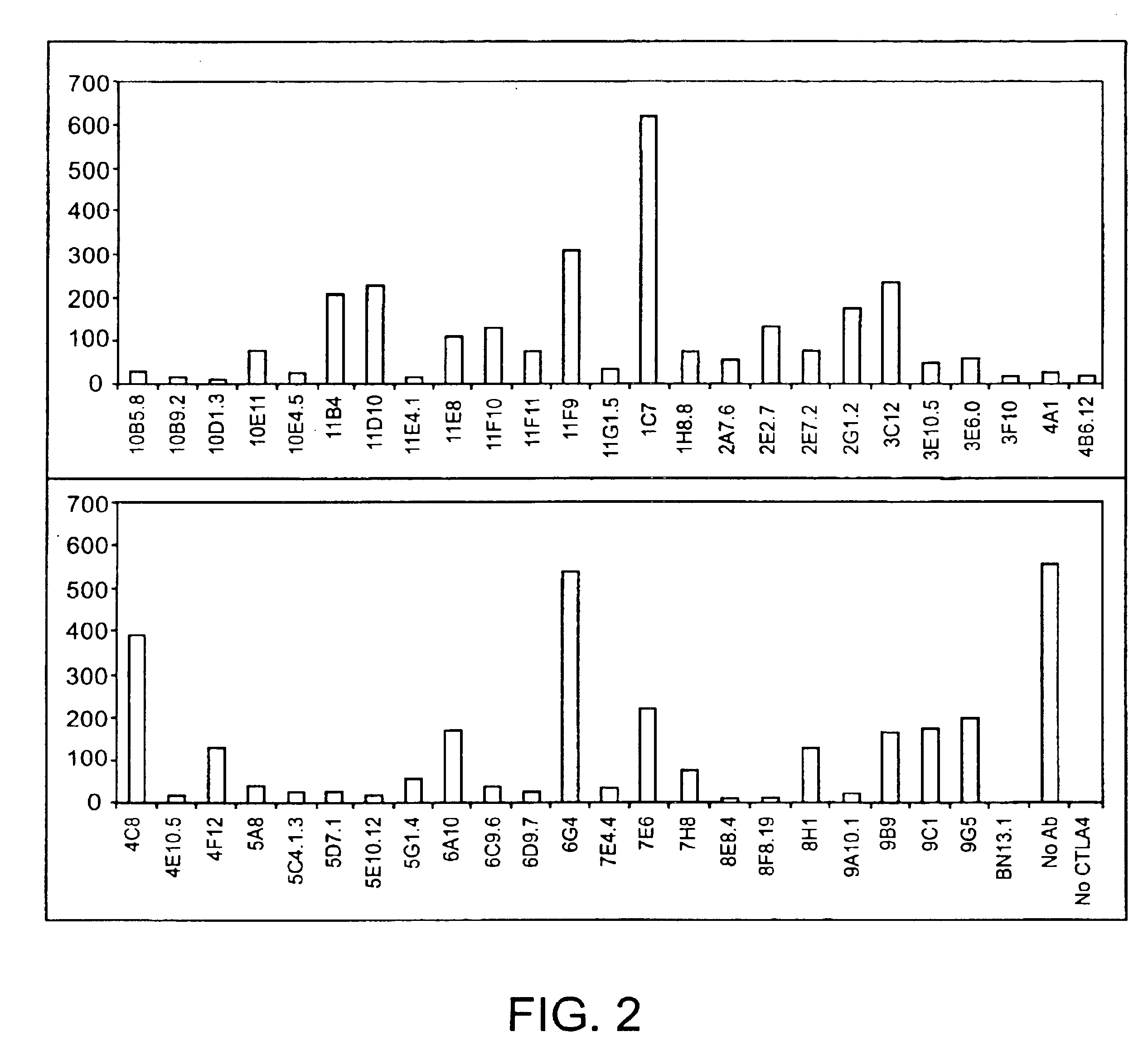
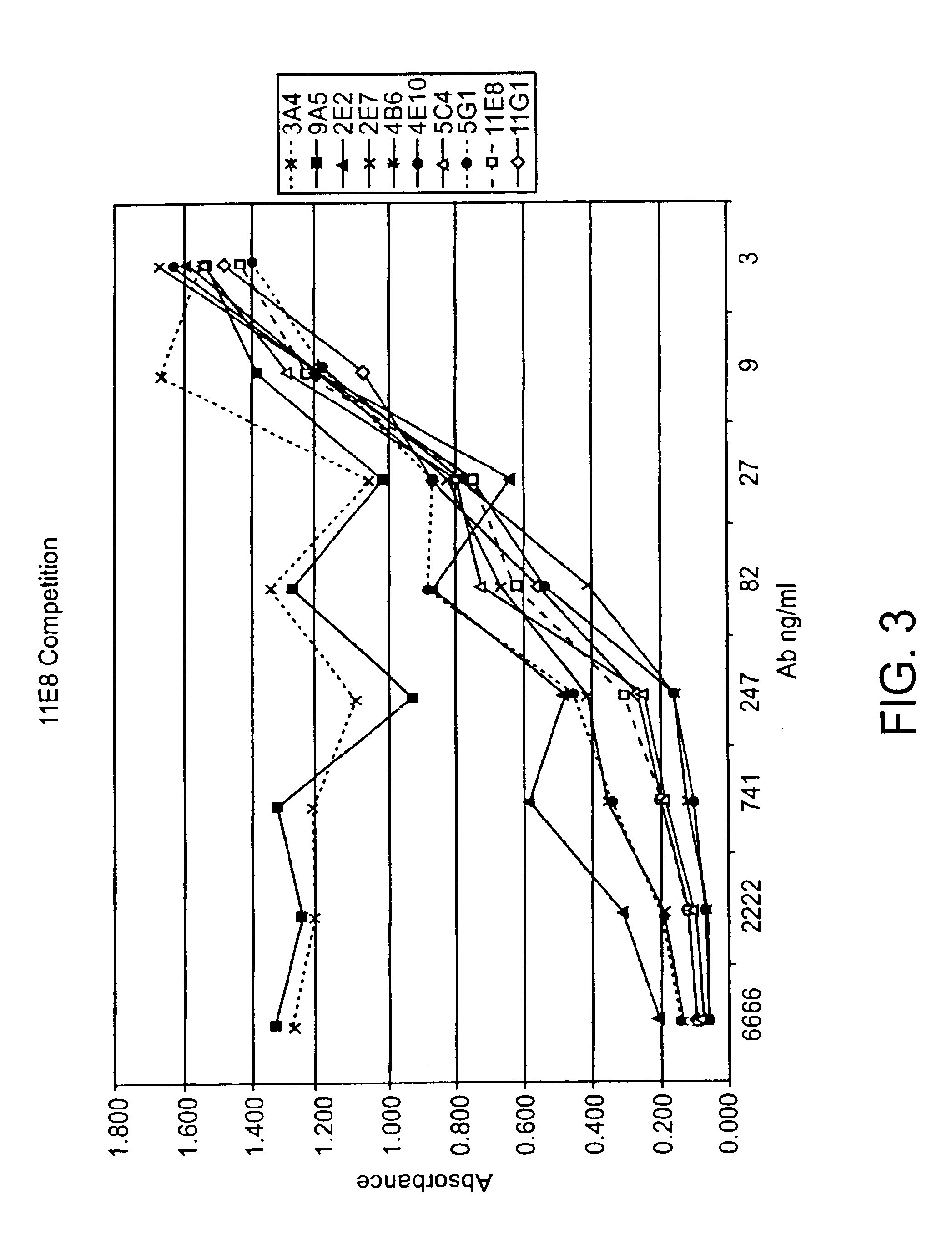
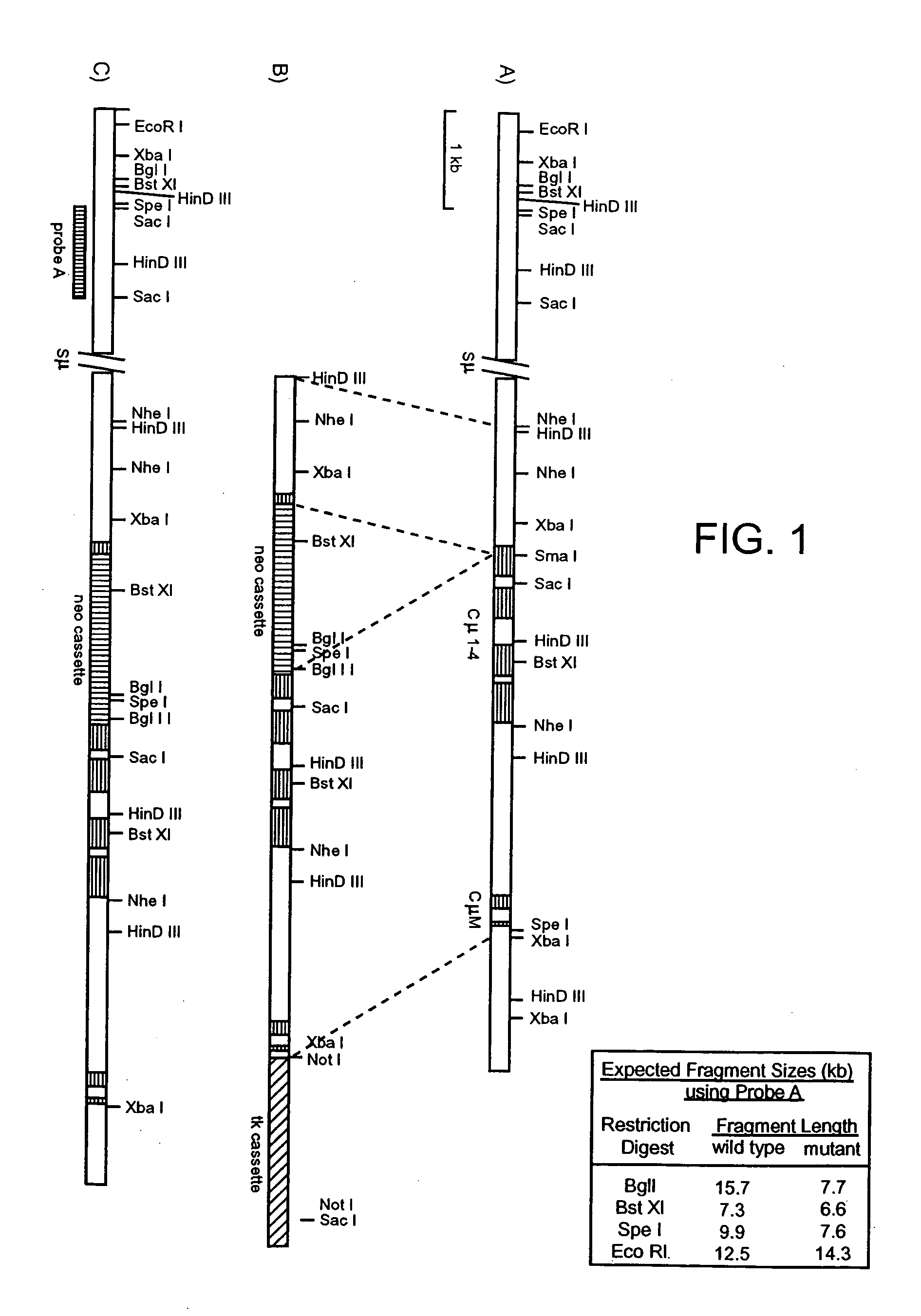
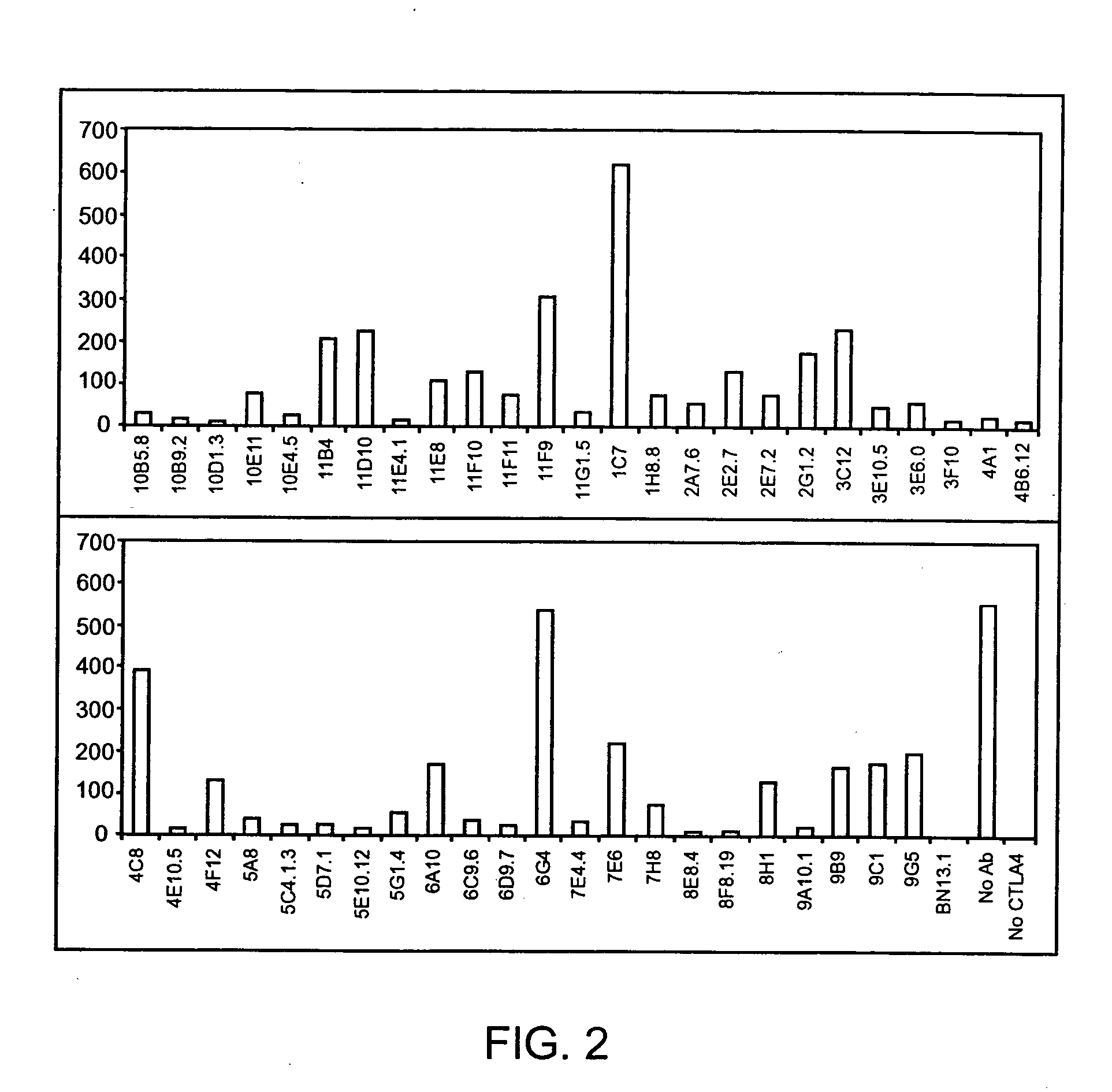
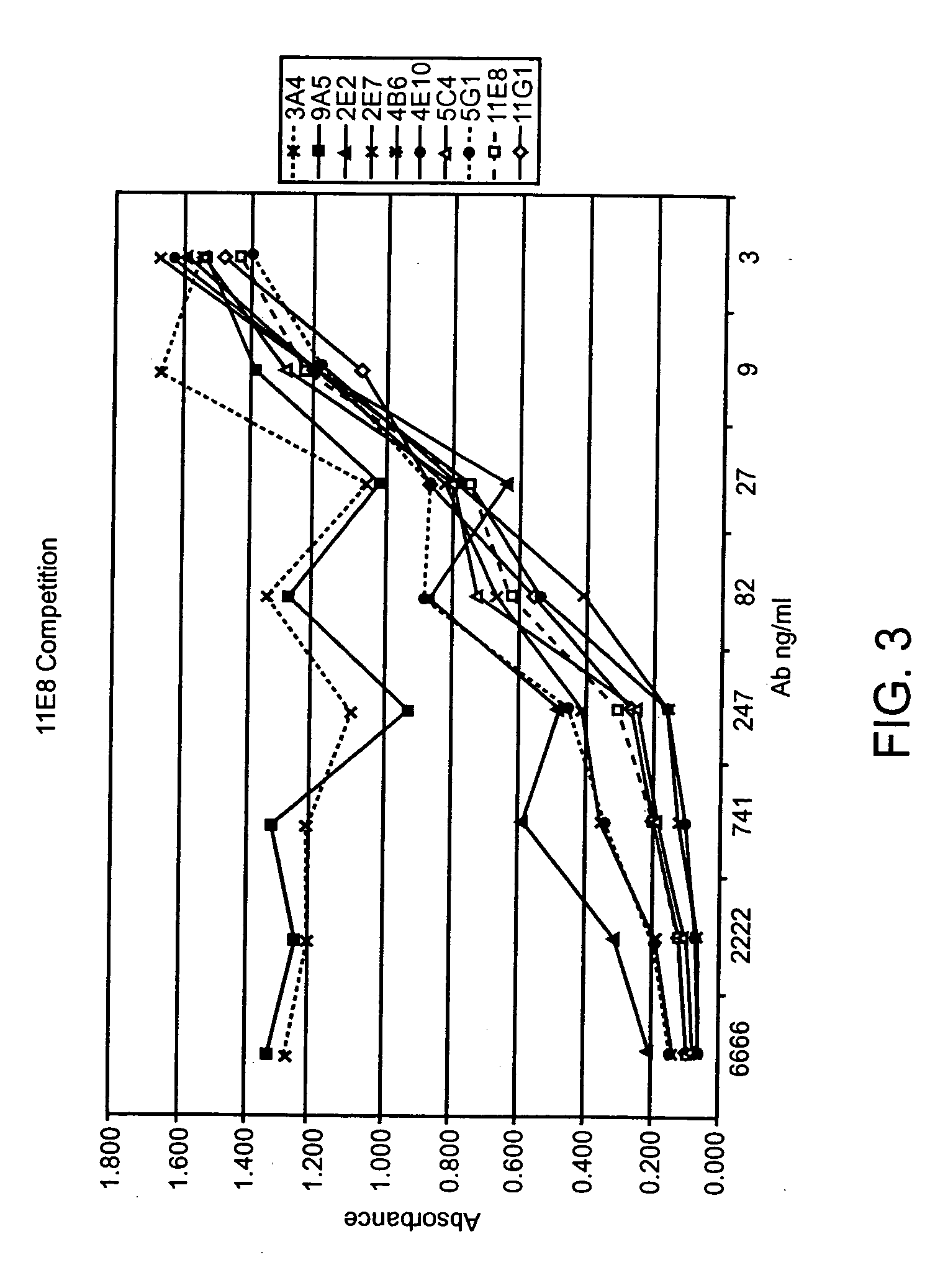
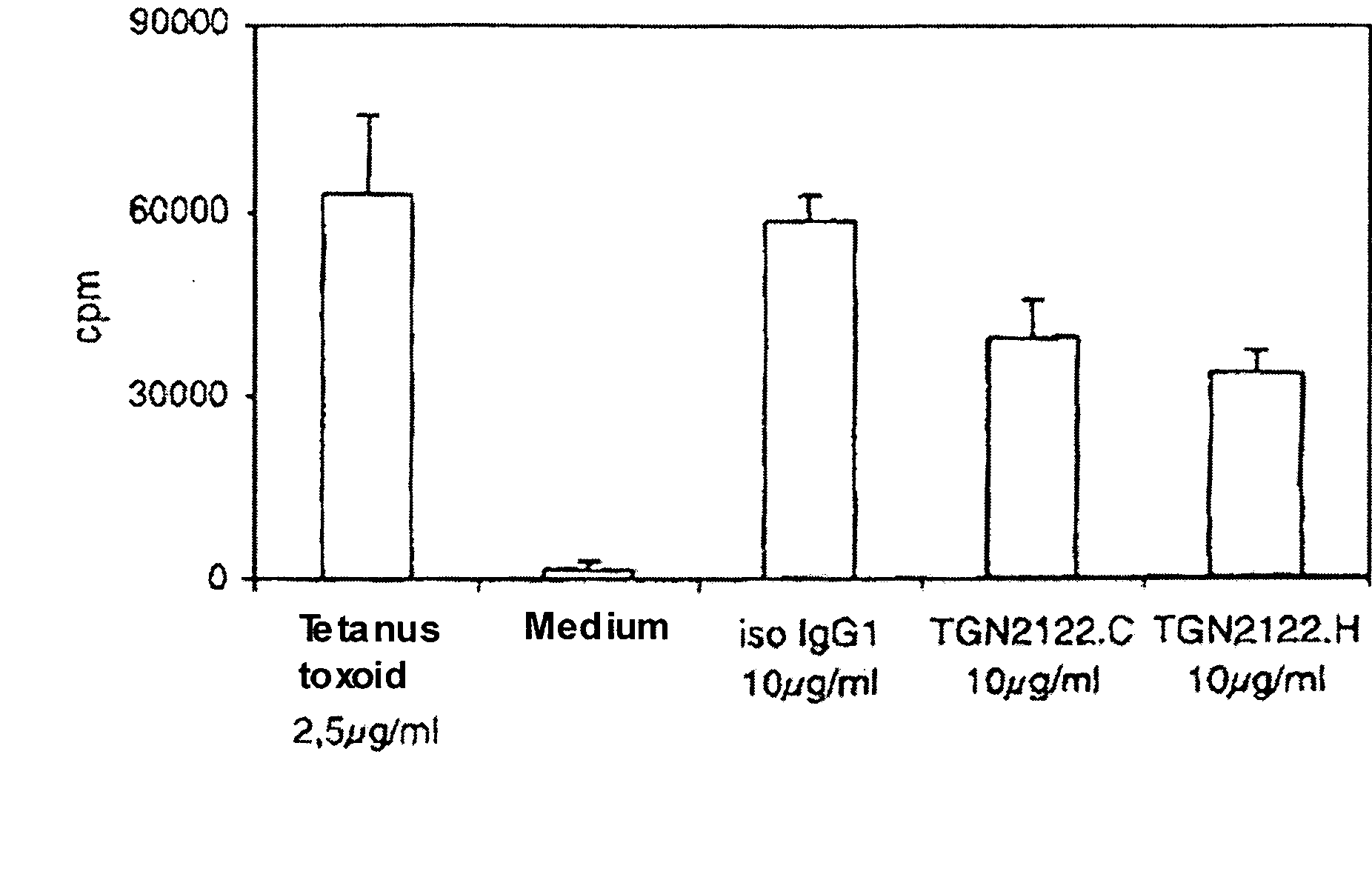
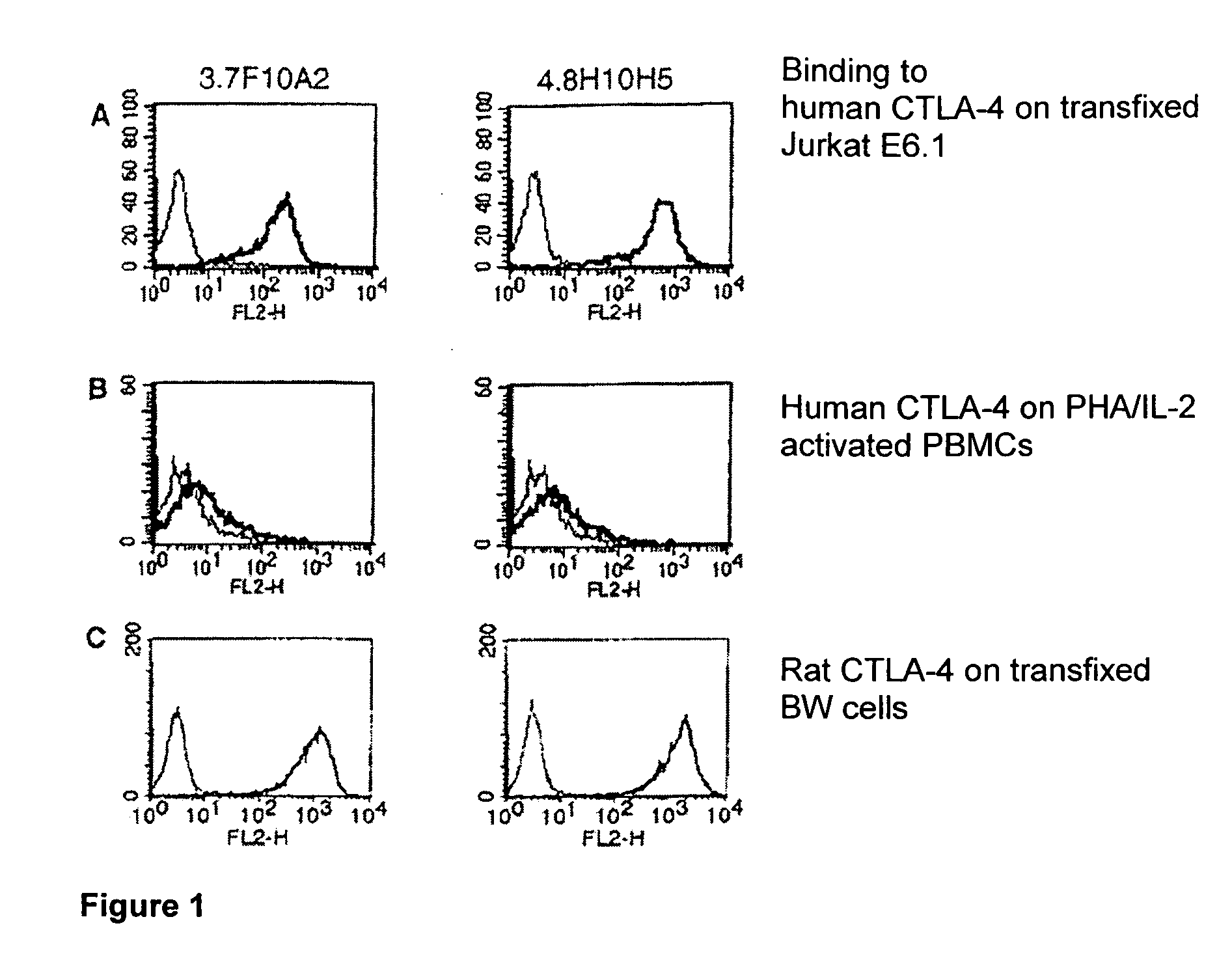
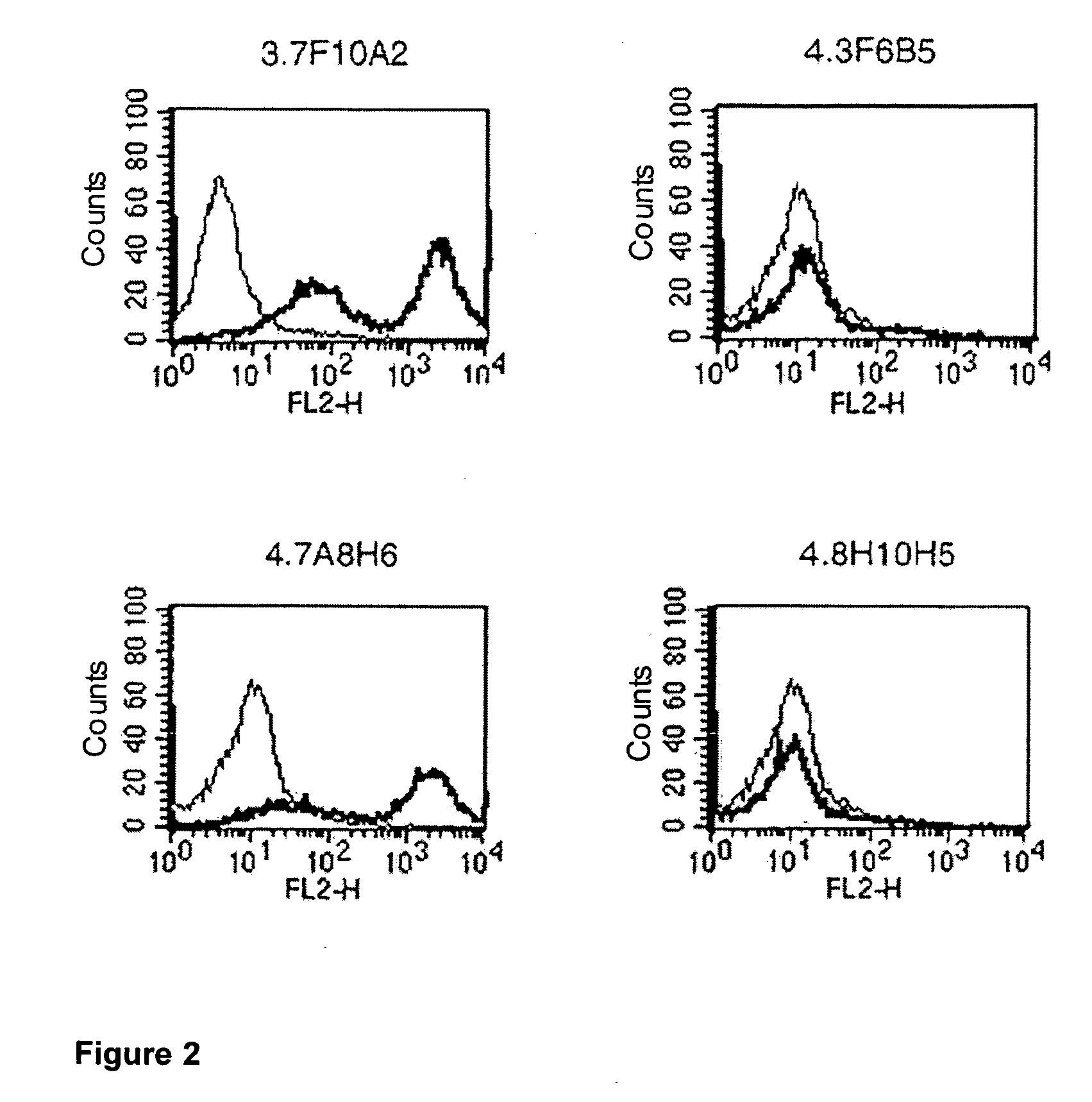
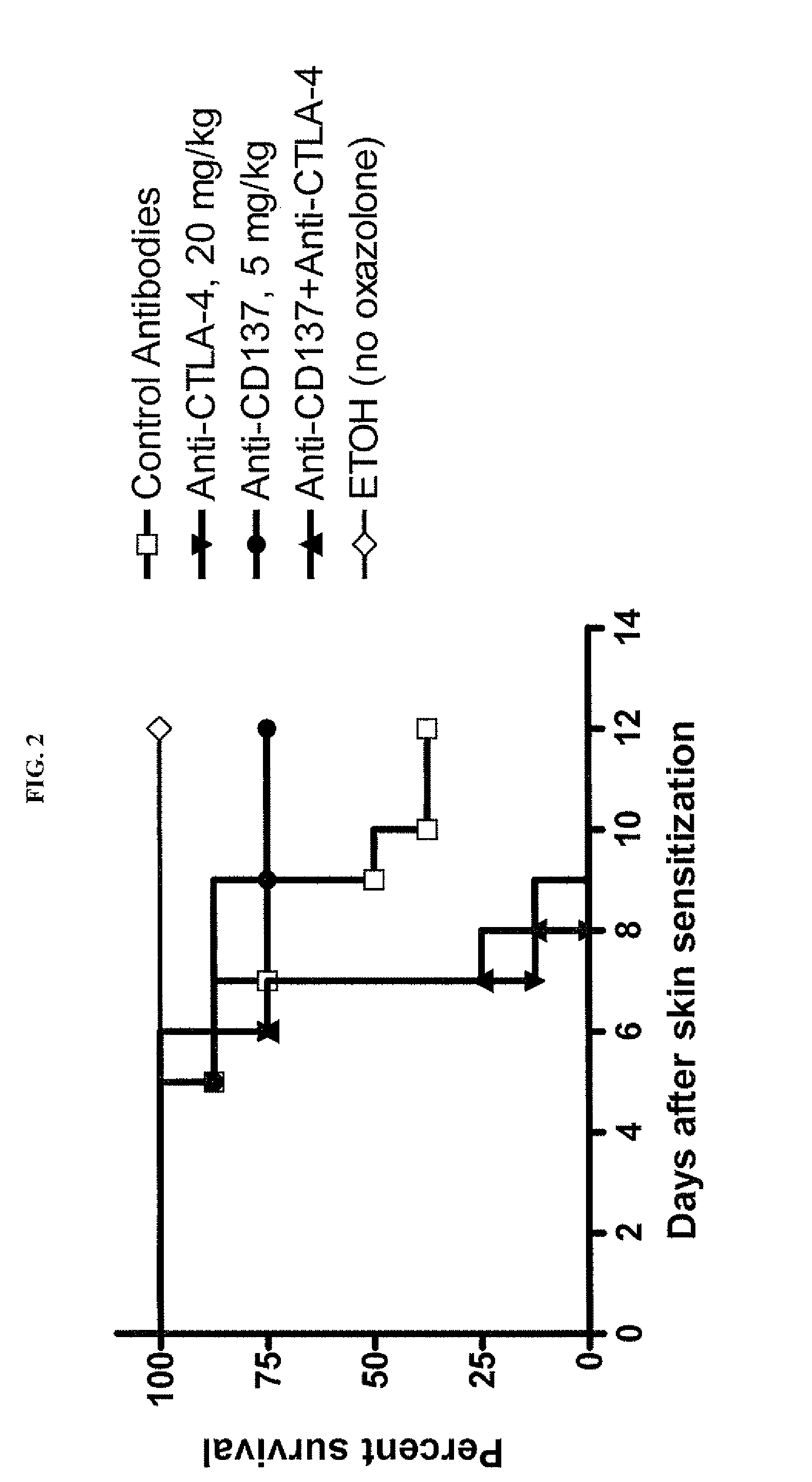
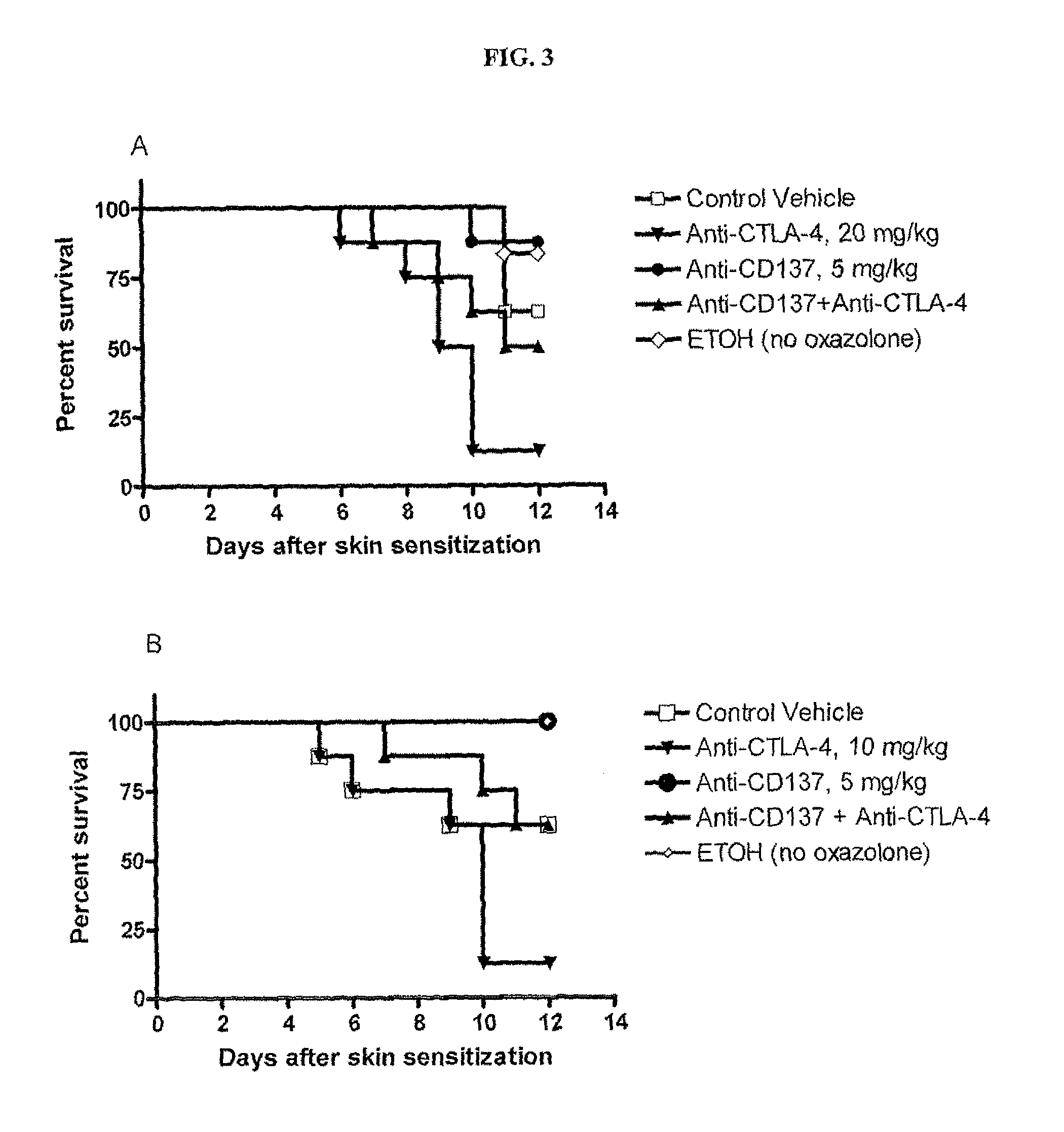
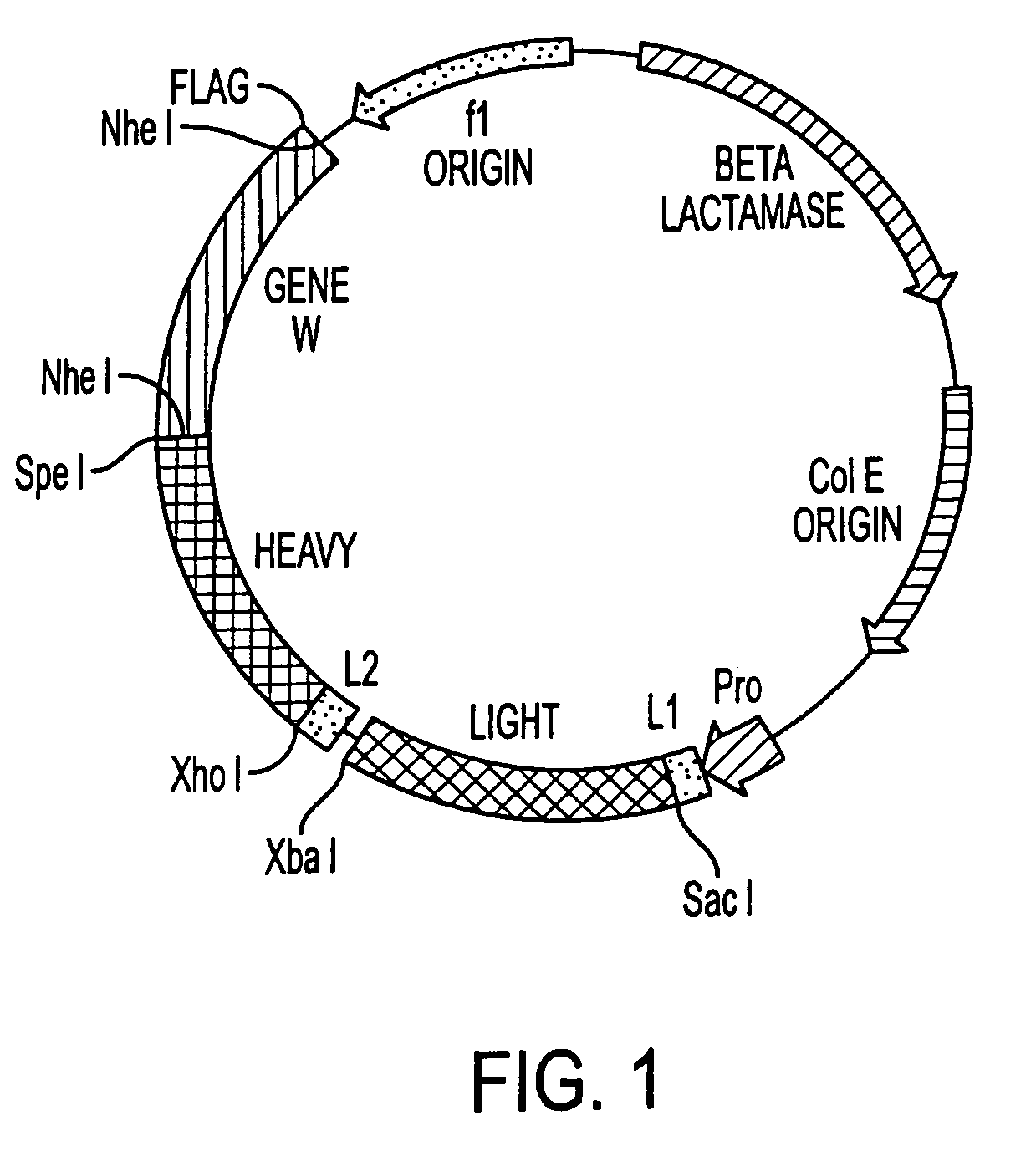
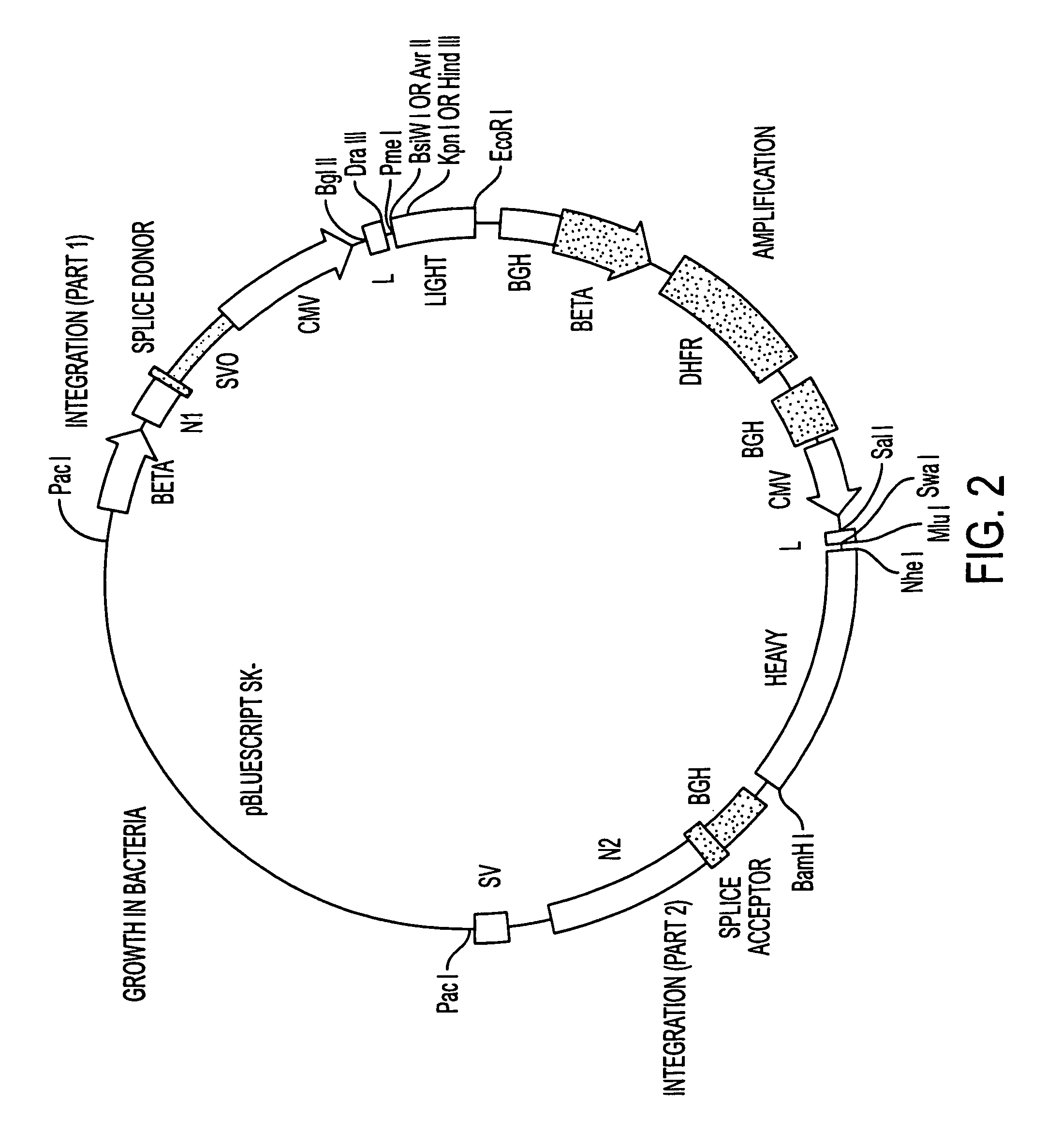
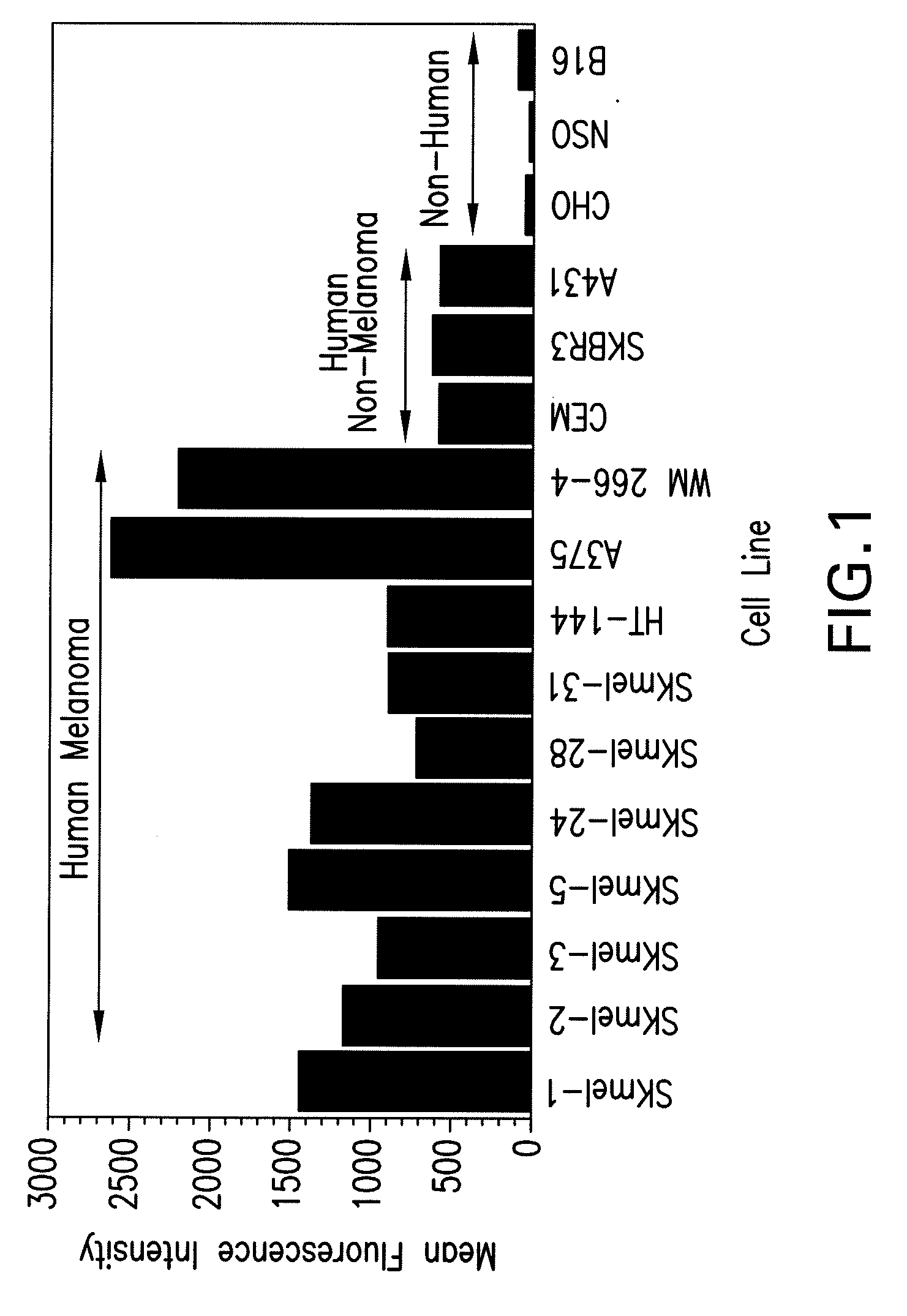
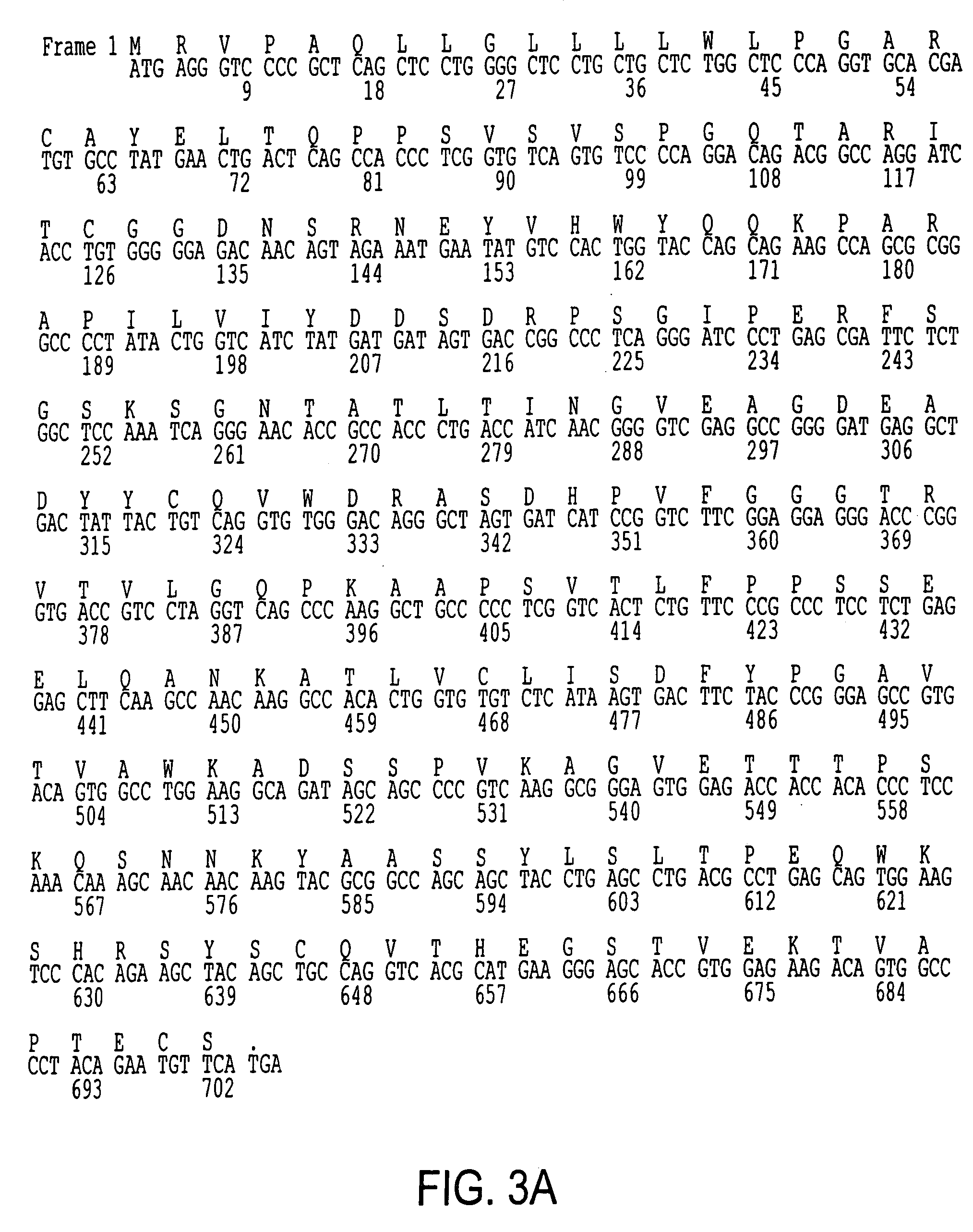Patents
Literature
99 results about "CTLA4 Protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
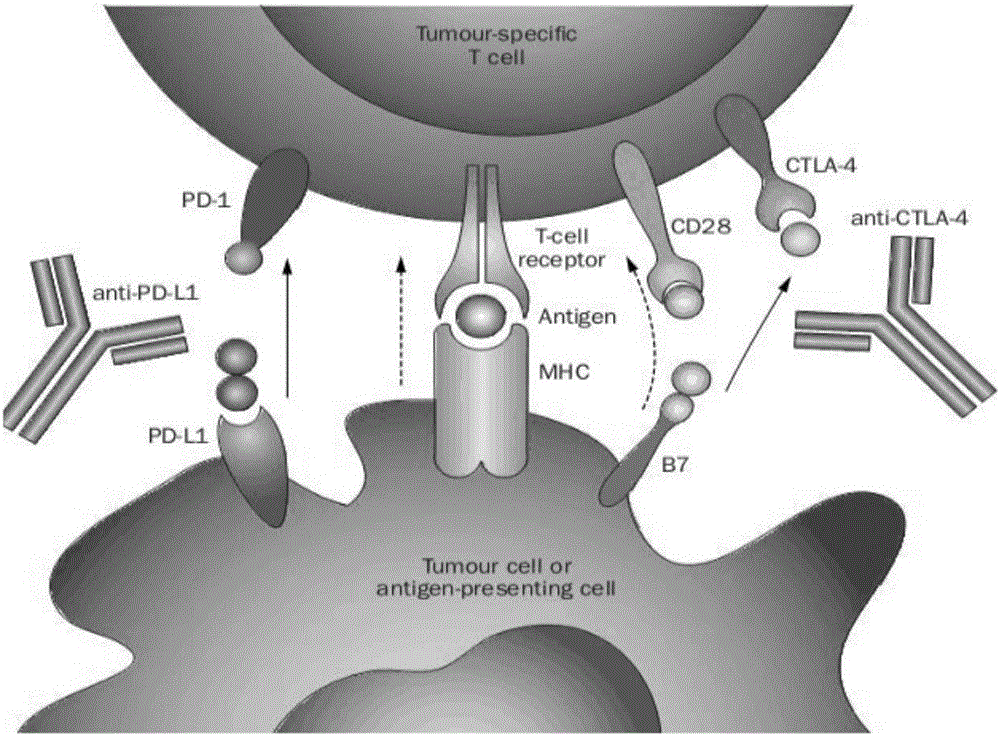
CTLA4 or CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that, functioning as an immune checkpoint, downregulates immune responses.
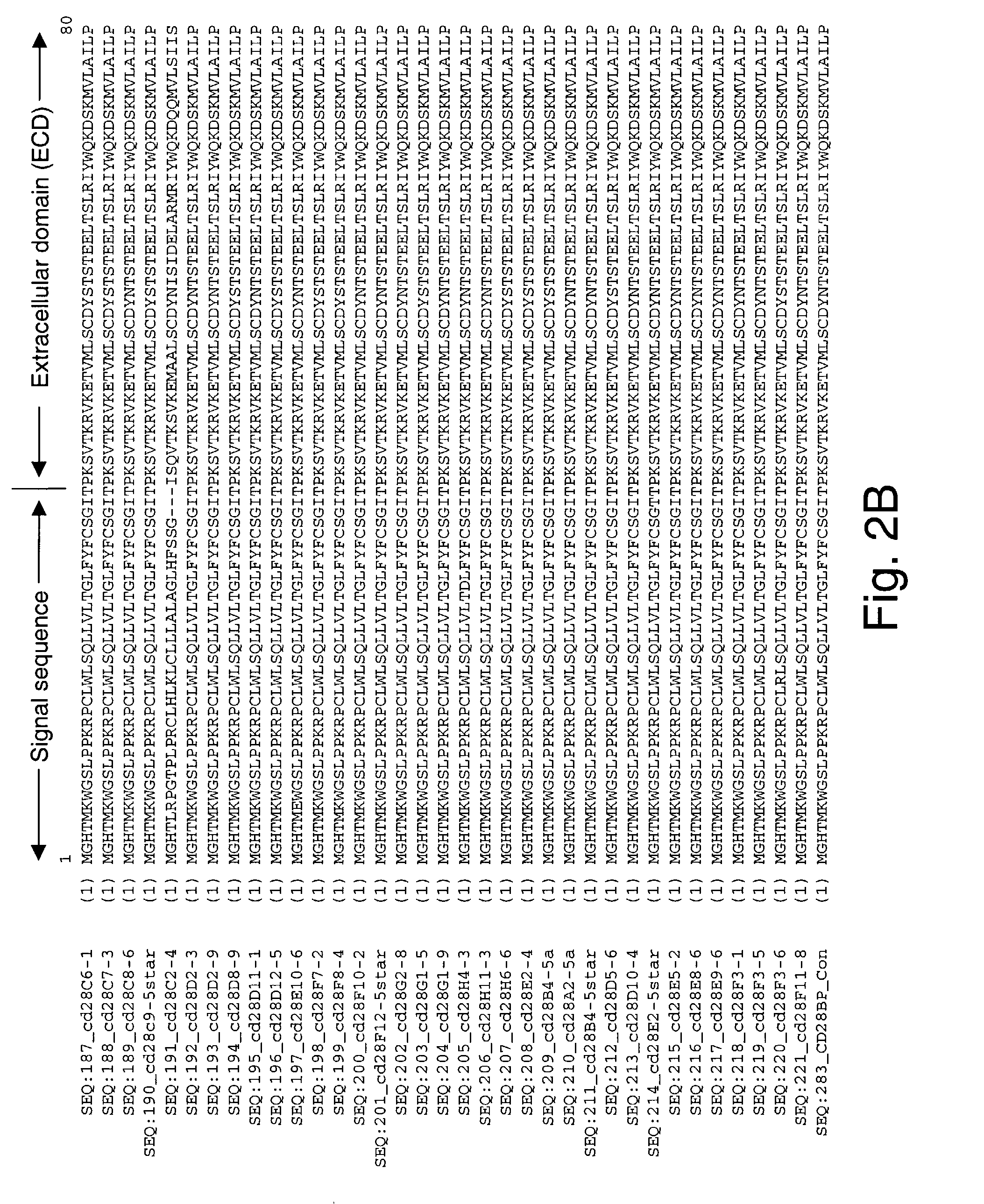
Human CTLA-4 antibodies
The present invention provides human sequence antibodies against CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Human CTLA-4 antibodies and their uses
InactiveUS20050201994A1Augmenting and suppressing and prolonging immune responseBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman sequenceCTLA4 Protein
The present invention provides novel human sequence antibodies against human CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
Antibodies
InactiveUS20090123477A1Sure easyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCTLA4 ProteinMonoclonal antibody
The invention concerns an isolated monoclonal antibody, which is specific and agonistic for CTLA-4, whereby the antibody does not bind to the C″D loop of CTLA-4.
Owner:THERAMAB
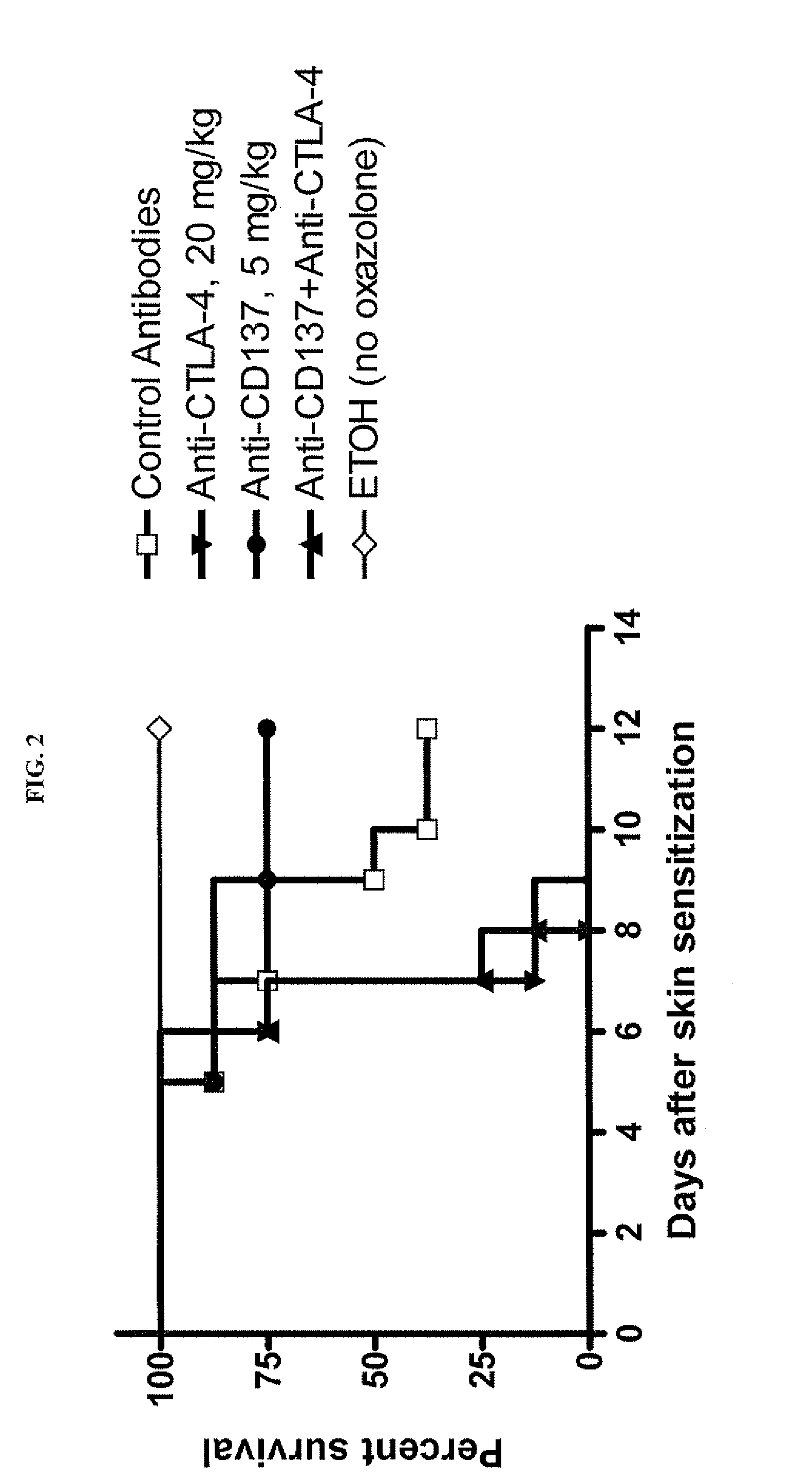
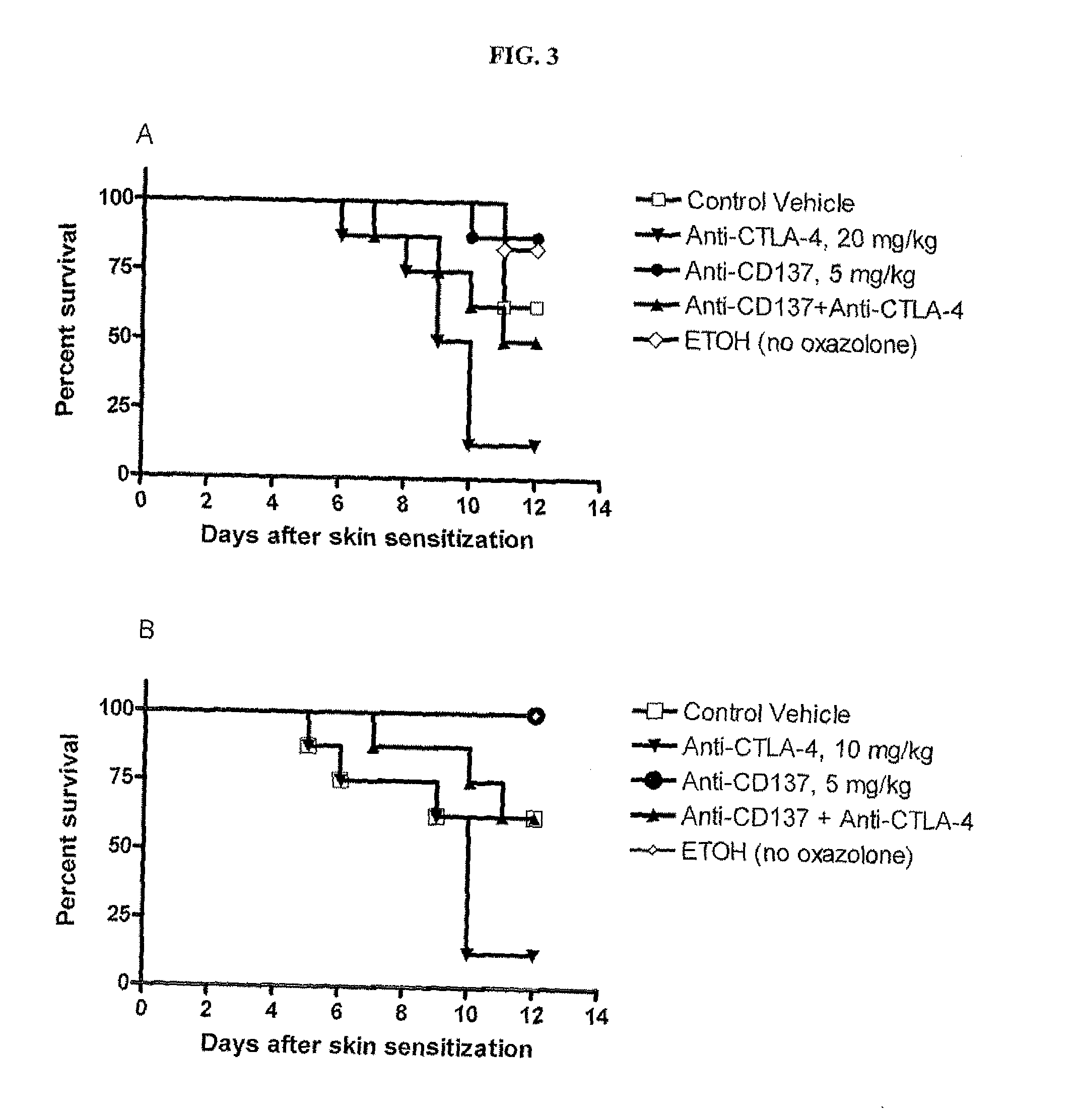
Combination of CD137 antibody and CTLA-4 antibody for the treatment of proliferative diseases
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Blockade of T lymphocyte down-regulation associated with CTLA-4 signaling
InactiveUS7229628B1Lack of responsivenessPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantActivation cells
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
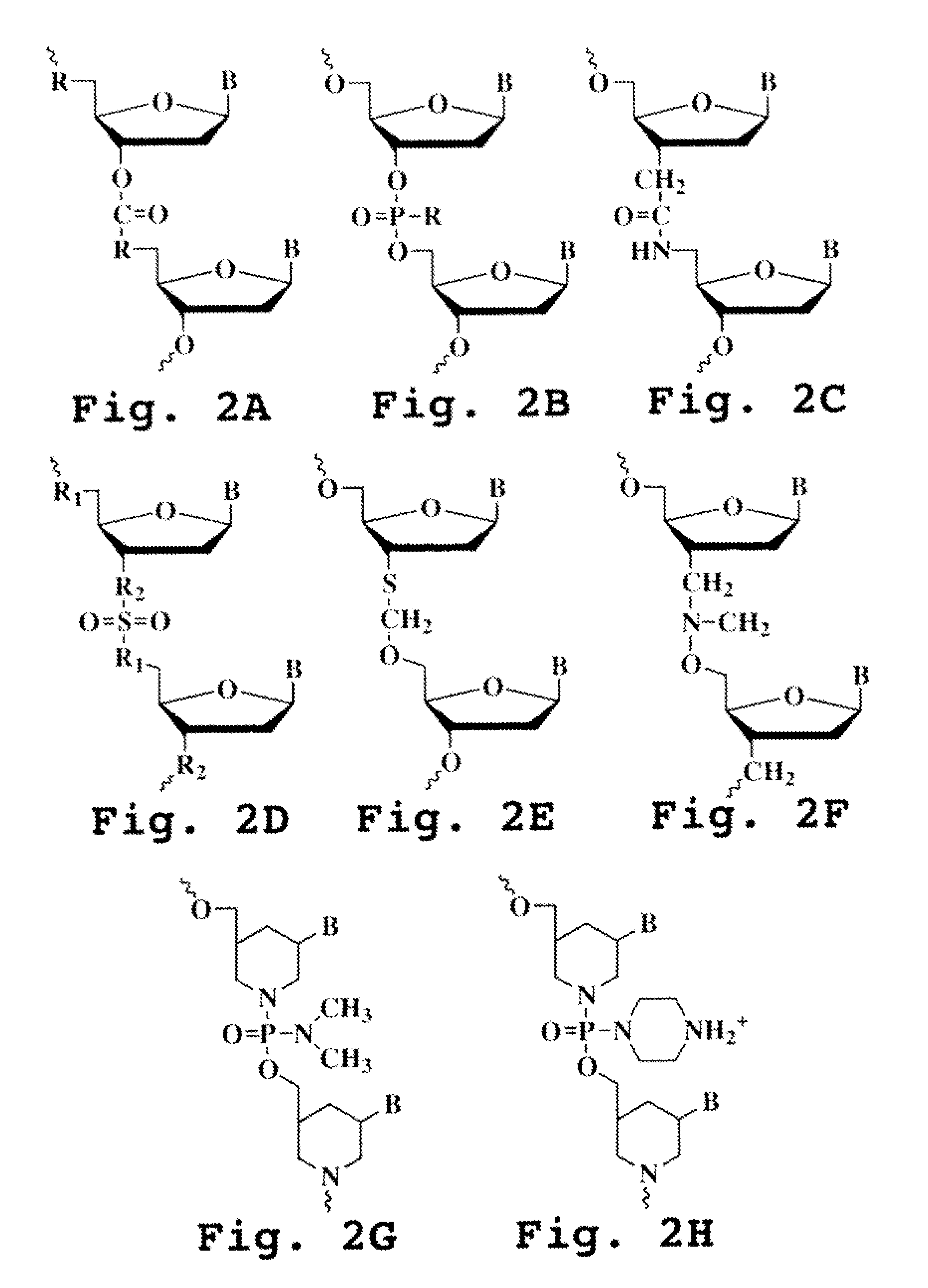
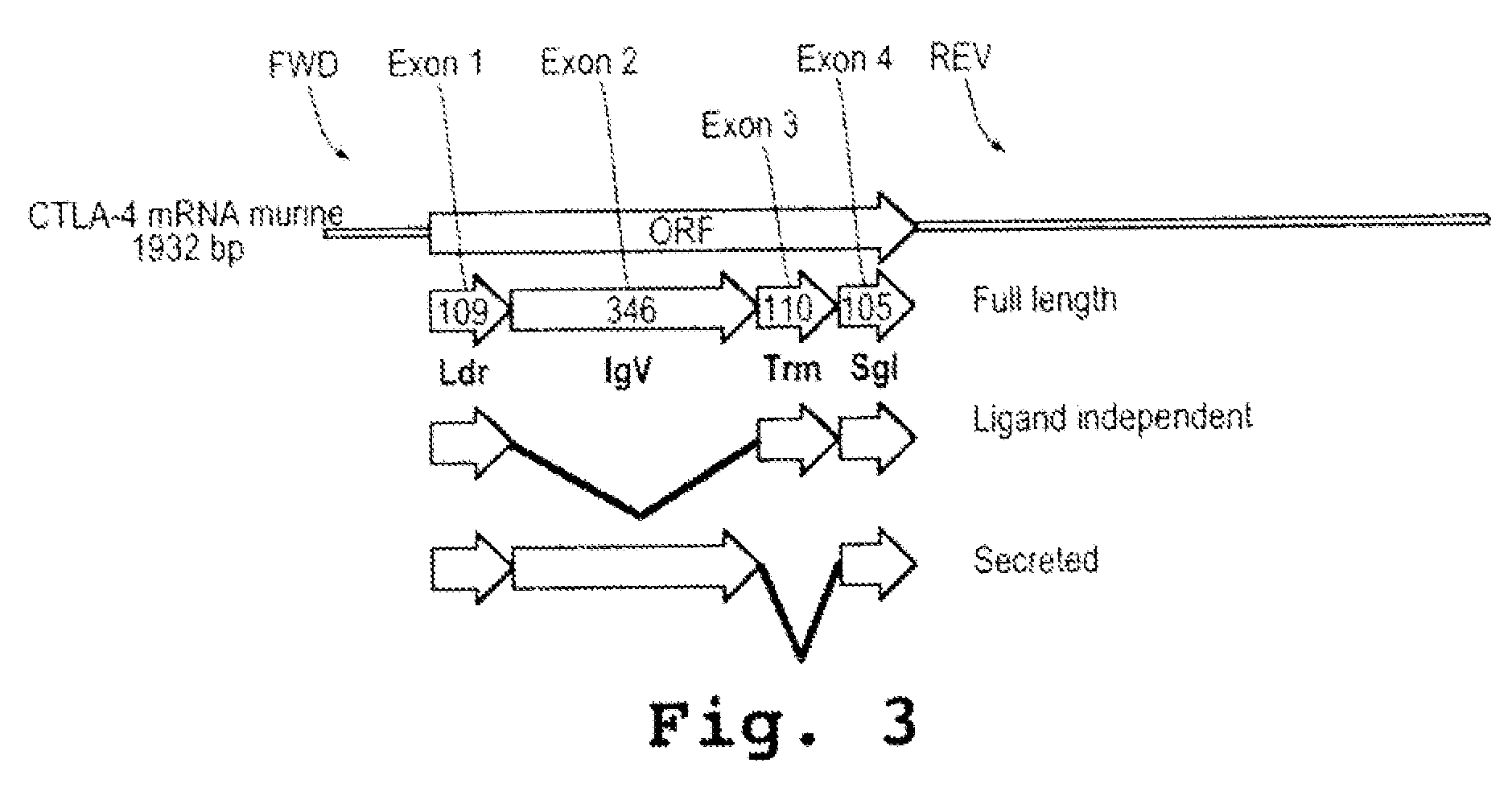
ActiveUS20090110689A1Suppress immune responseSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderHeteroduplexAutoimmune condition
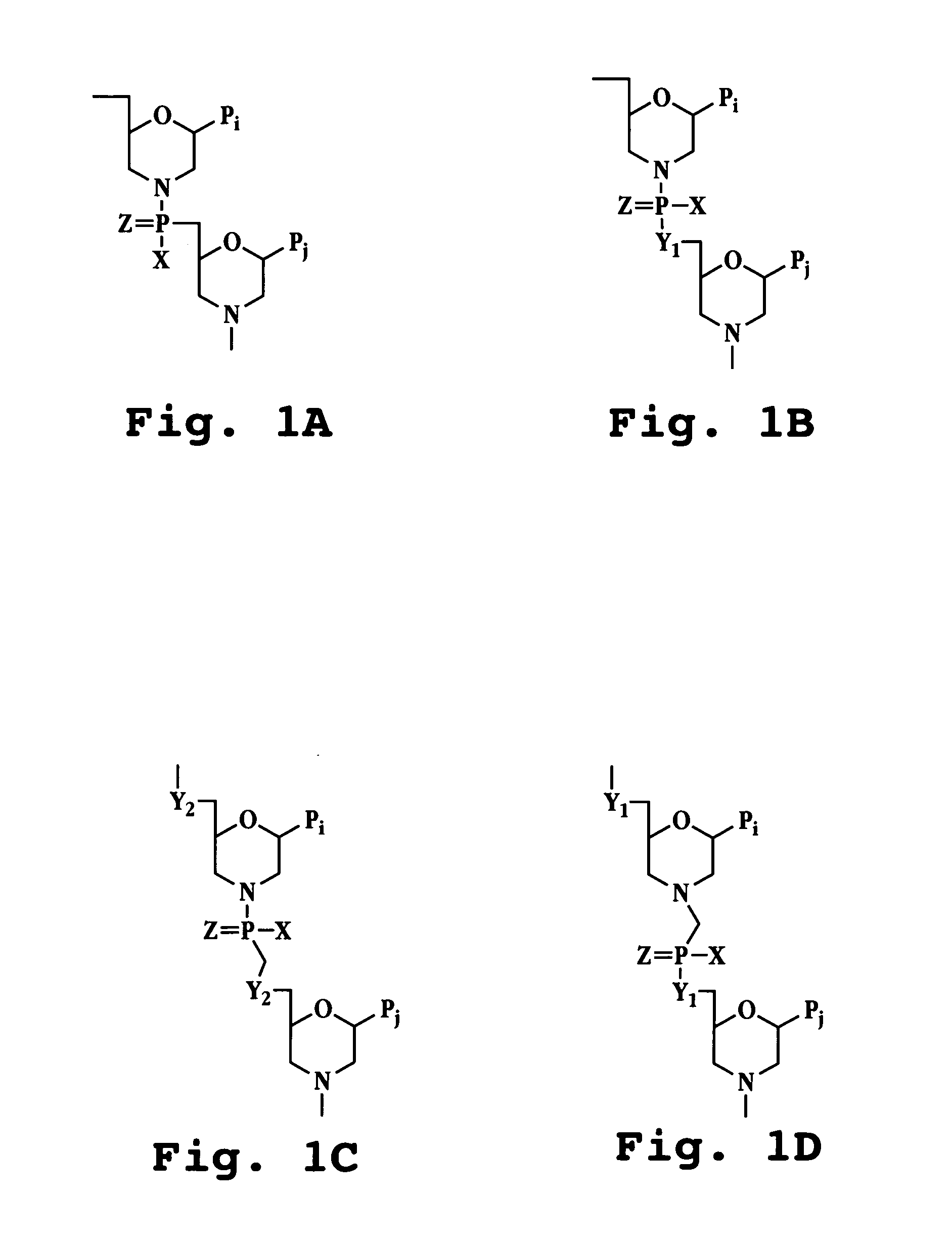
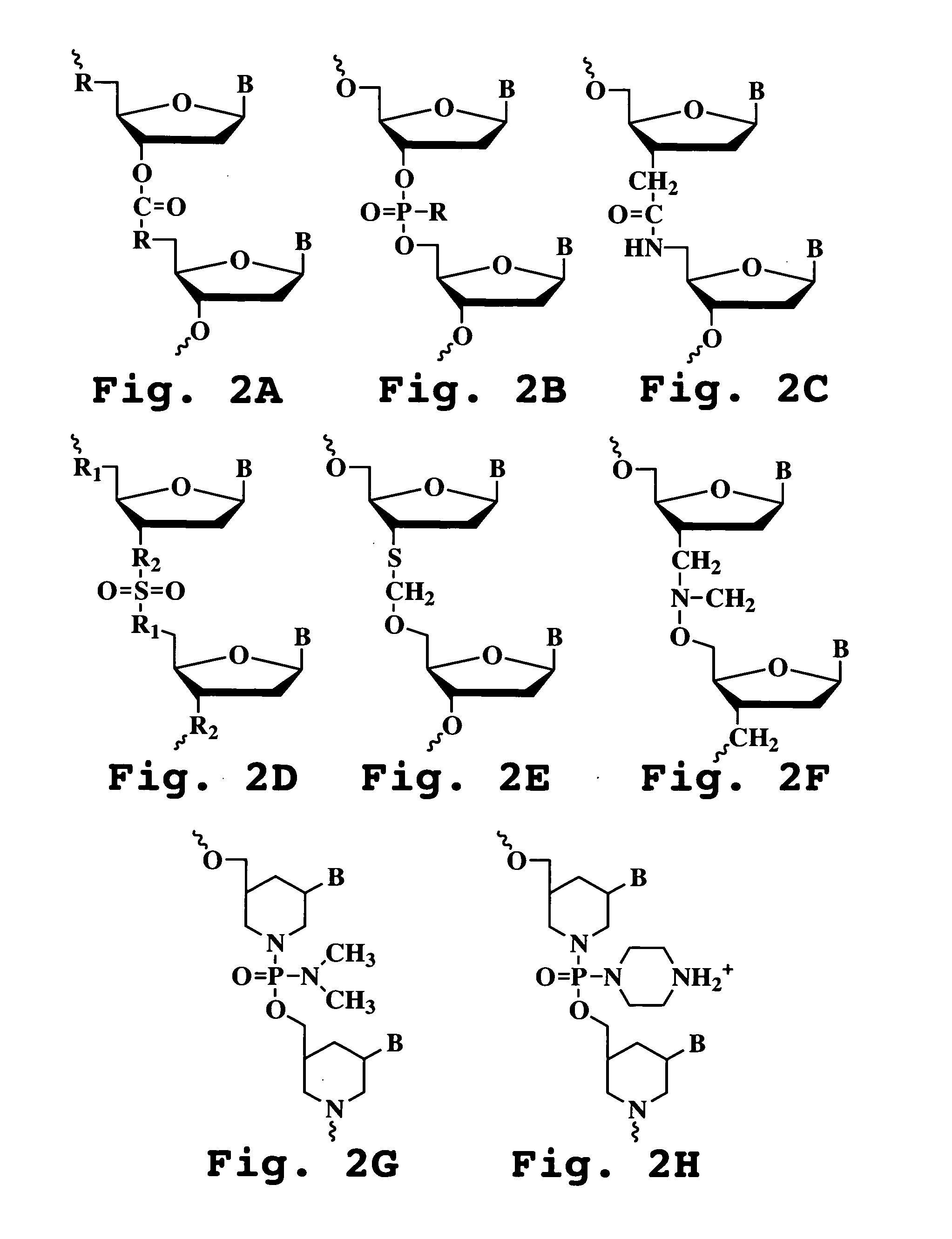
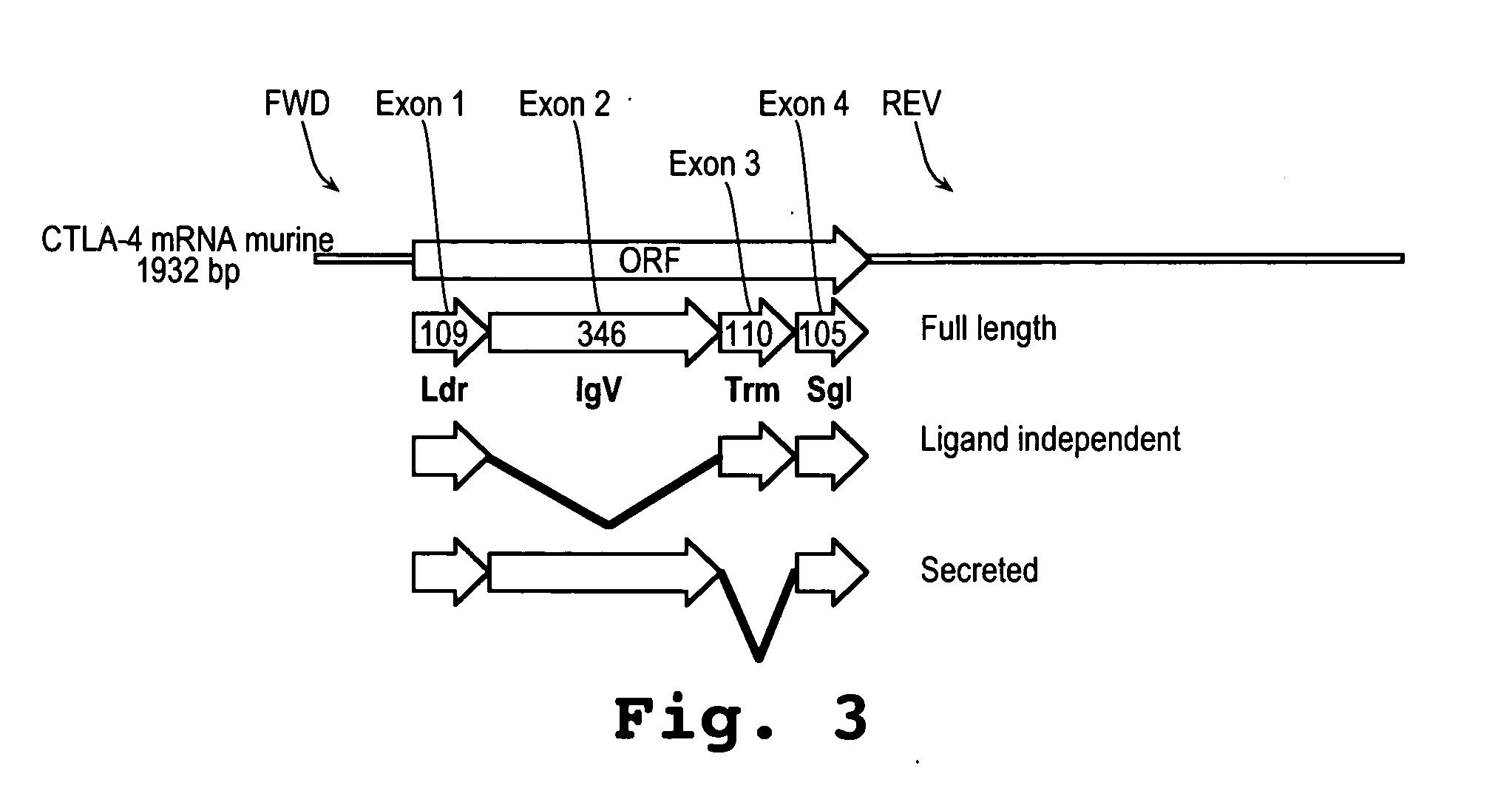
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 22 in SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Treatment of hodgkin's lymphoma using an Anti-pd-1 antibody
InactiveUS20160347836A1Inhibitory activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAnticarcinogenCTLA4 Protein
This disclosure provides methods for treating Hodgkin's lymphoma in a subject comprising administering to the subject an anti-Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) antibody. In some embodiments, this invention relates to methods for treating Hodgkin's lymphoma in a subject comprising administering to the subject a combination of an anti-cancer agent which is an anti-Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) antibody and another anti-cancer agent such as an anti-Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4) antibody.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Altering Gene Expression in CART Cells and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20170335331A1Unlikely can be integratedImmunoglobulin superfamilyHydrolasesAntigenAutoimmune condition
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for generating a modified T cell with a nucleic acid capable of downregulating endogenous gene expression selected from the group consisting of TCR α chain, TCR β chain, beta-2 microglobulin, a HLA molecule, CTLA-4, PD1, and FAS and further comprising a nucleic acid encoding a modified T cell receptor (TCR) comprising affinity for a surface antigen on a target cell or an electroporated nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). Also included are methods and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the modified T cell for adoptive therapy and treating a condition, such as an autoimmune disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
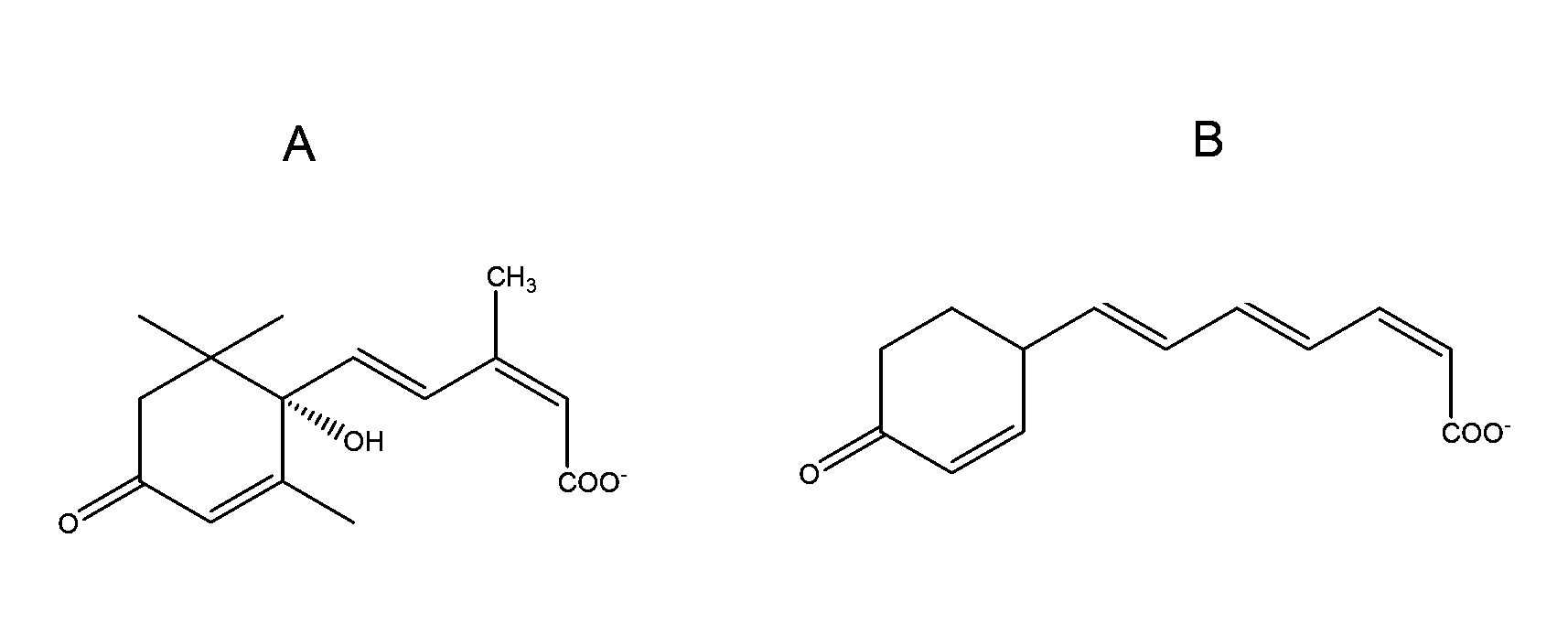
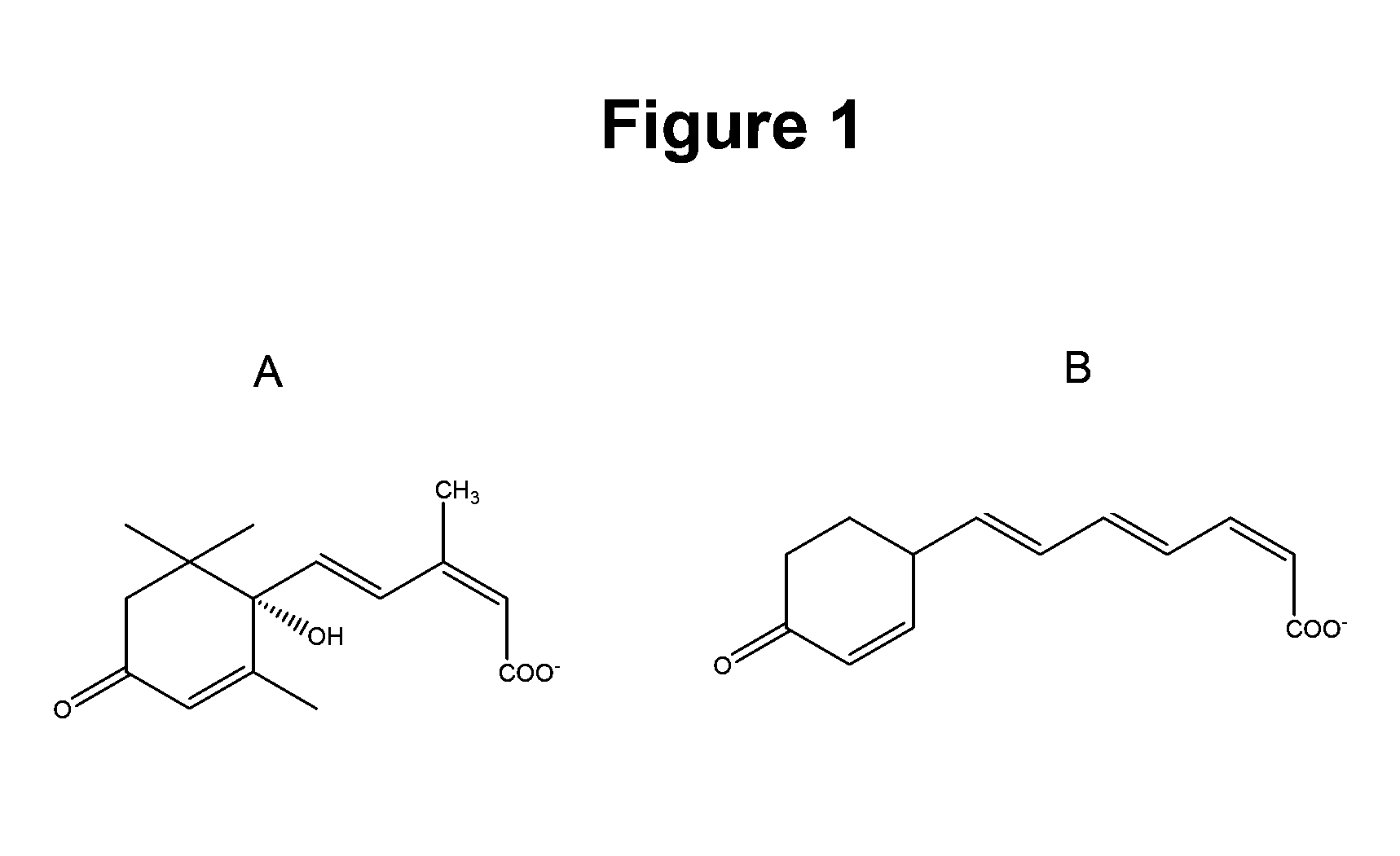
Method of using abscisic acid to treat and prevent diseases and disorders
ActiveUS20100216883A1Increasing CTLA- expressionAlter activityBiocideDigestive systemGastrointestinal inflammationAbscisic acid
Methods and compositions for treating inflammatory bowel disease, gastrointestinal inflammation and maintaining normal gut health are described. These methods of the invention involve the administration of abscisic acid in amounts sufficient to alter the expression or activity of PPAR gamma in a cell. Also described are methods for suppressing the expression of cellular adhesion molecules in the gut and methods for increasing CTLA-4 expression on CD4+ T cells through administration of abscisic acid.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
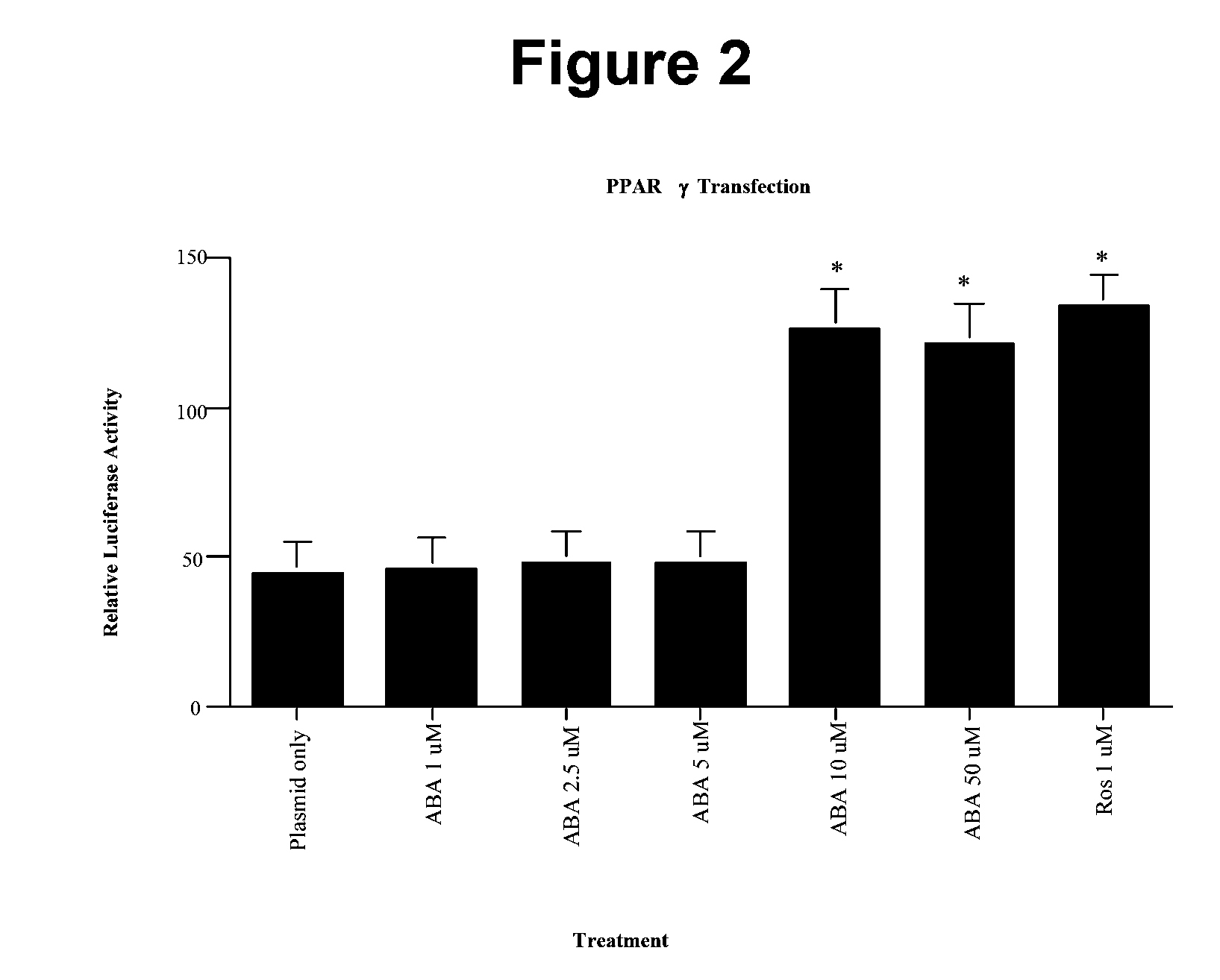
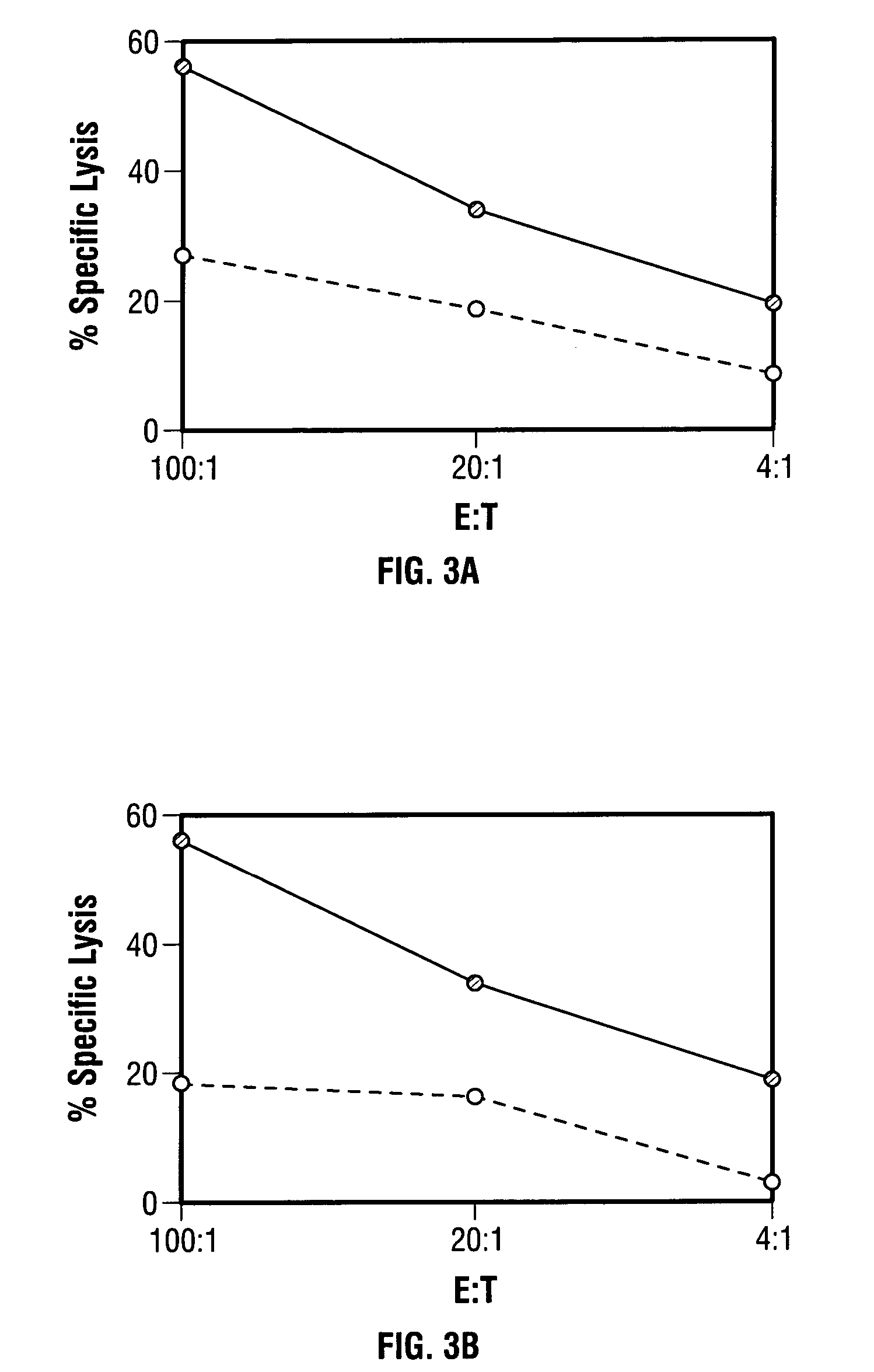
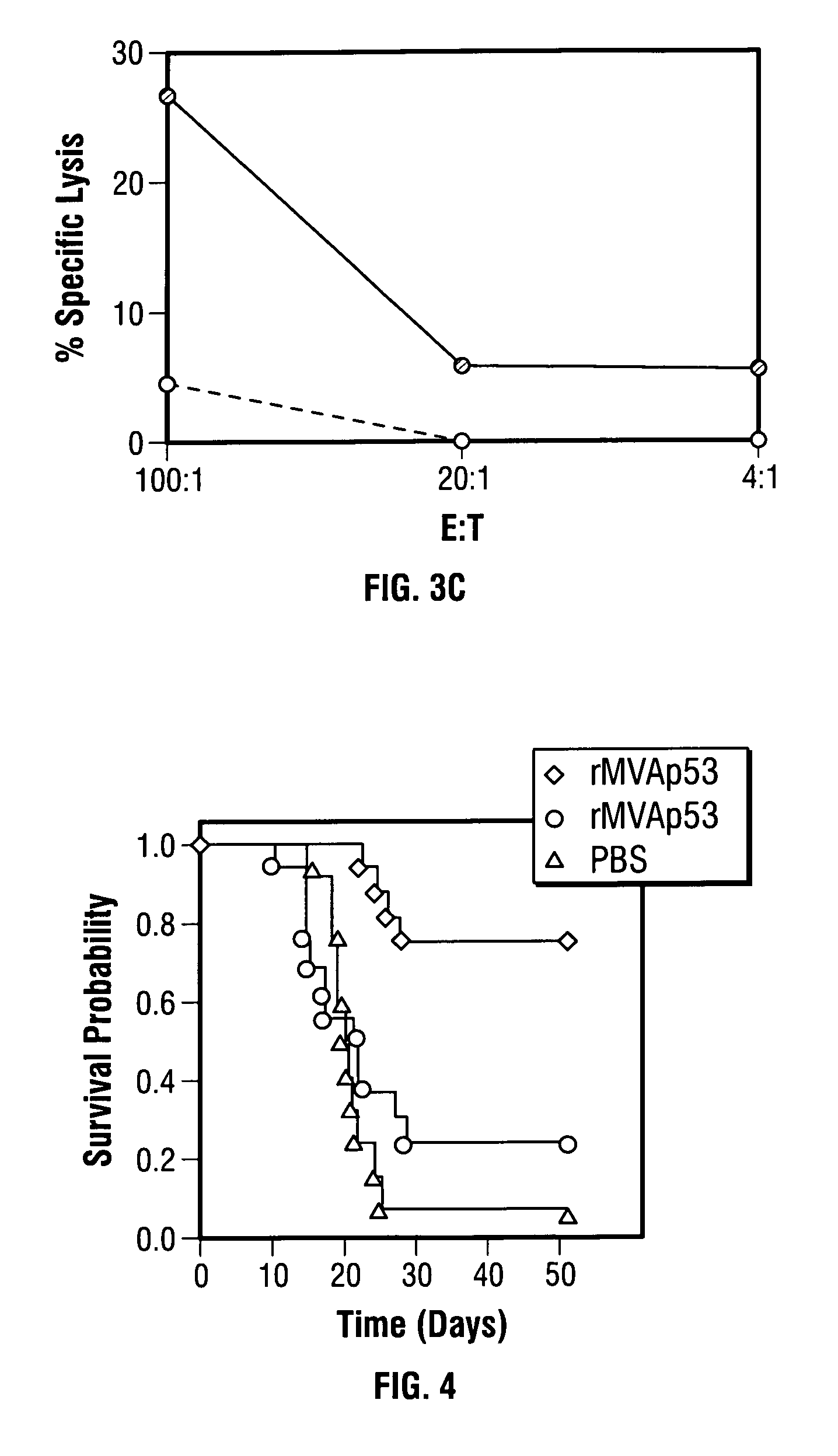
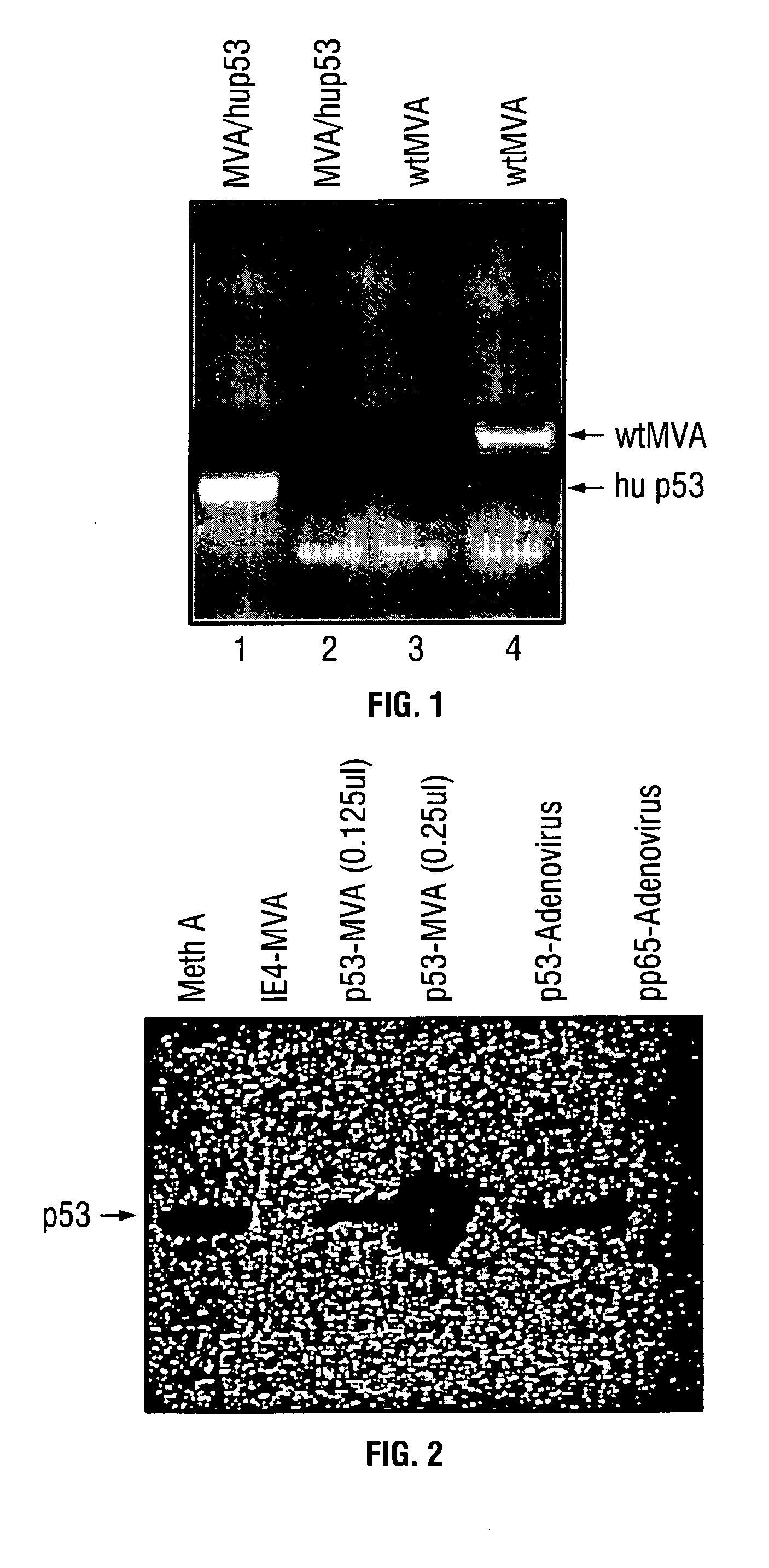
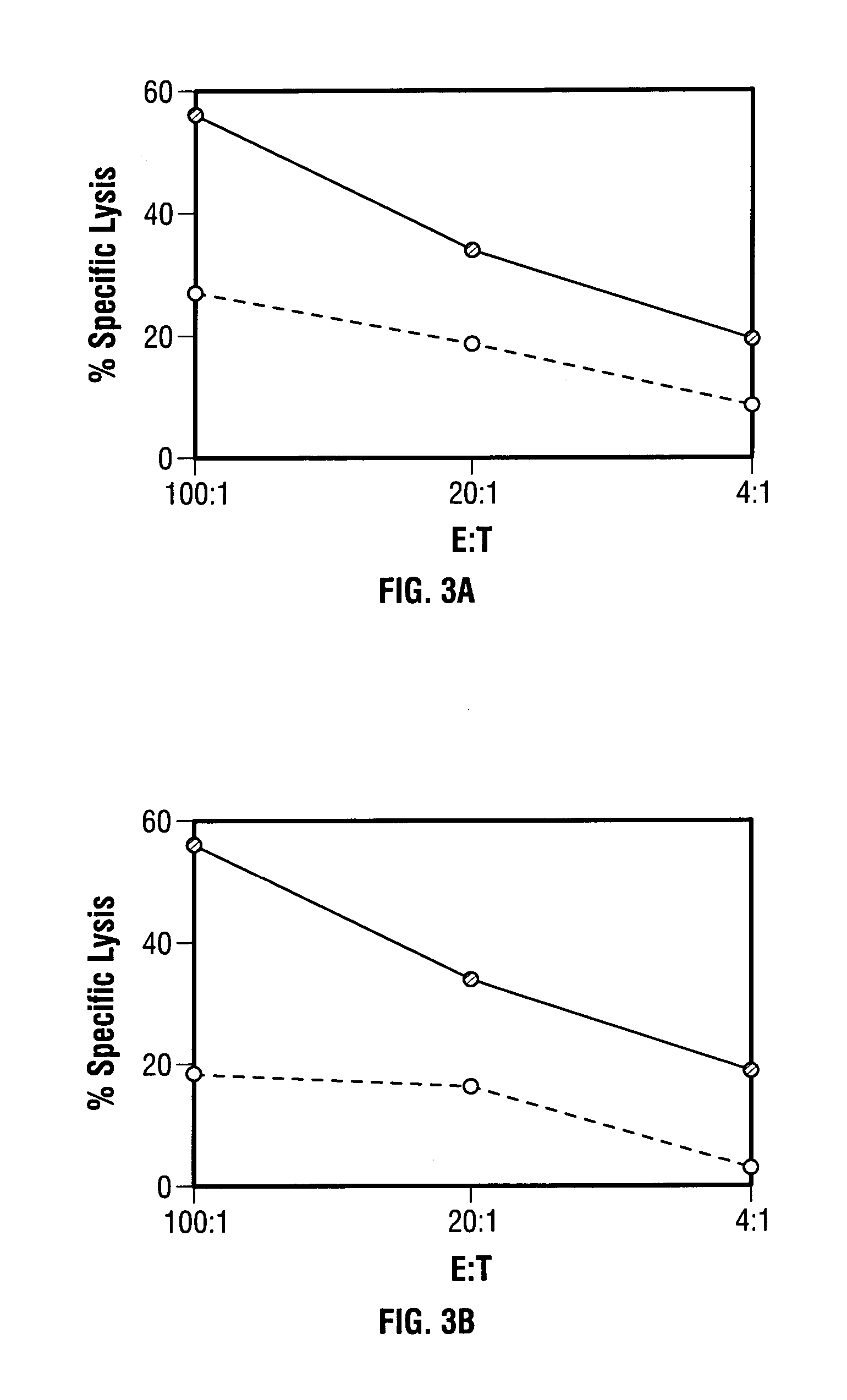
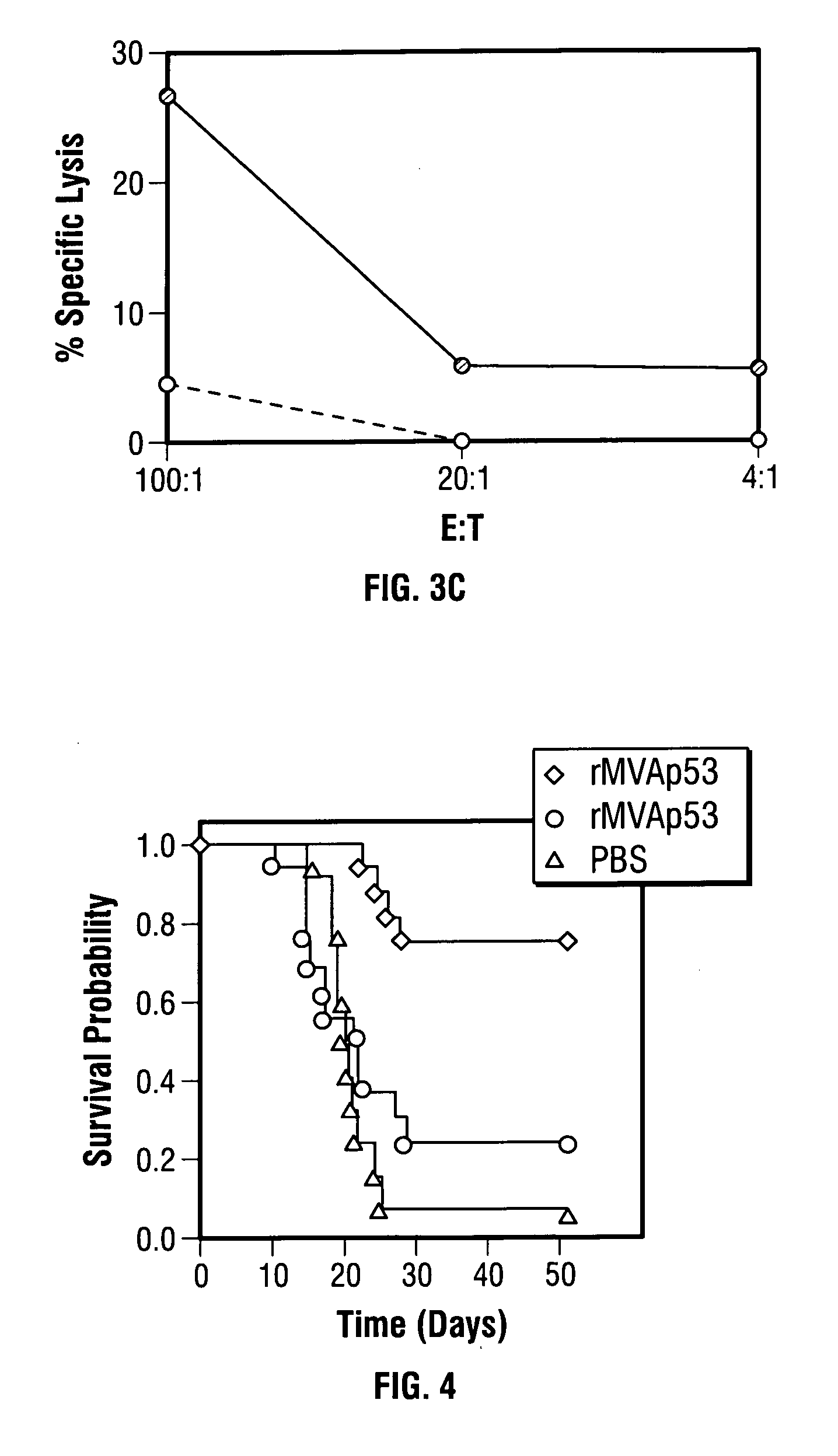
Modified vaccinia Ankara expressing p53 in cancer immunotherapy
ActiveUS7256037B2Limit therapeutic efficacyReduce developmentBiocideGenetic material ingredientsModified vaccinia AnkaraADAMTS Proteins
Mutations to the tumor suppressor protein p53 have been observed in 40-60% of all human cancers. These mutations are often associated with high nuclear and cytoplasmic concentrations of p53. Since many tumors exhibit highly elevated p53 levels, the protein is an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy. Unfortunately, p53 is an autoantigen that is likely to be tolerated as a self-protein by the immune system. The present invention is based on the discovery that this self-tolerance can be overcome by administration of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) containing a nucleic acid that encodes p53 (rMVAp53). The invention discloses a method of generating a p53-specific CTL-response to tumor cells expressing mutated p53 by administering a composition comprising rMVAp53. Administration of rMVAp53 decreases tumor development, tumor growth, and mortality in a variety of malignant cell types. These effects are enhanced by administration of CTLA-4 blocker and / or CpG oligodeoxynucleotide immunomodulators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Modified vaccinia ankara expressing p53 in cancer immunotherapy
Mutations to the tumor suppressor protein p53 have been observed in 40-60% of all human cancers. These mutations are often associated with high nuclear and cytoplasmic concentrations of p53. Since many tumors exhibit highly elevated p53 levels, the protein is an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy. Unfortunately, p53 is an autoantigen that is likely to be tolerated as a self-protein by the immune system. The present invention is based on the discovery that this self-tolerance can be overcome by administration of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) containing a nucleic acid that encodes p53 (rMVAp53). The invention discloses a method of generating a p53-specific CTL-response to tumor cells expressing mutated p53 by administering a composition comprising rMVAp53. Administration of rMVAp53 decreases tumor development, tumor growth, and mortality in a variety of malignant cell types. These effects are enhanced by administration of CTLA-4 blocker and / or CpG oligodeoxynucleotide immunomodulators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Combination of cd137 antibody and ctla-4 antibody for the treatment of proliferative diseases
ActiveUS20110189189A1Significant body weight lossPreventedMetabolism disorderDigestive systemCD137CTLA4 Protein
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
InactiveUS20070111962A1Suppress immune responseRaise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeterologousHeteroduplex
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN101628940AMicroorganismsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainCTLA4 Protein
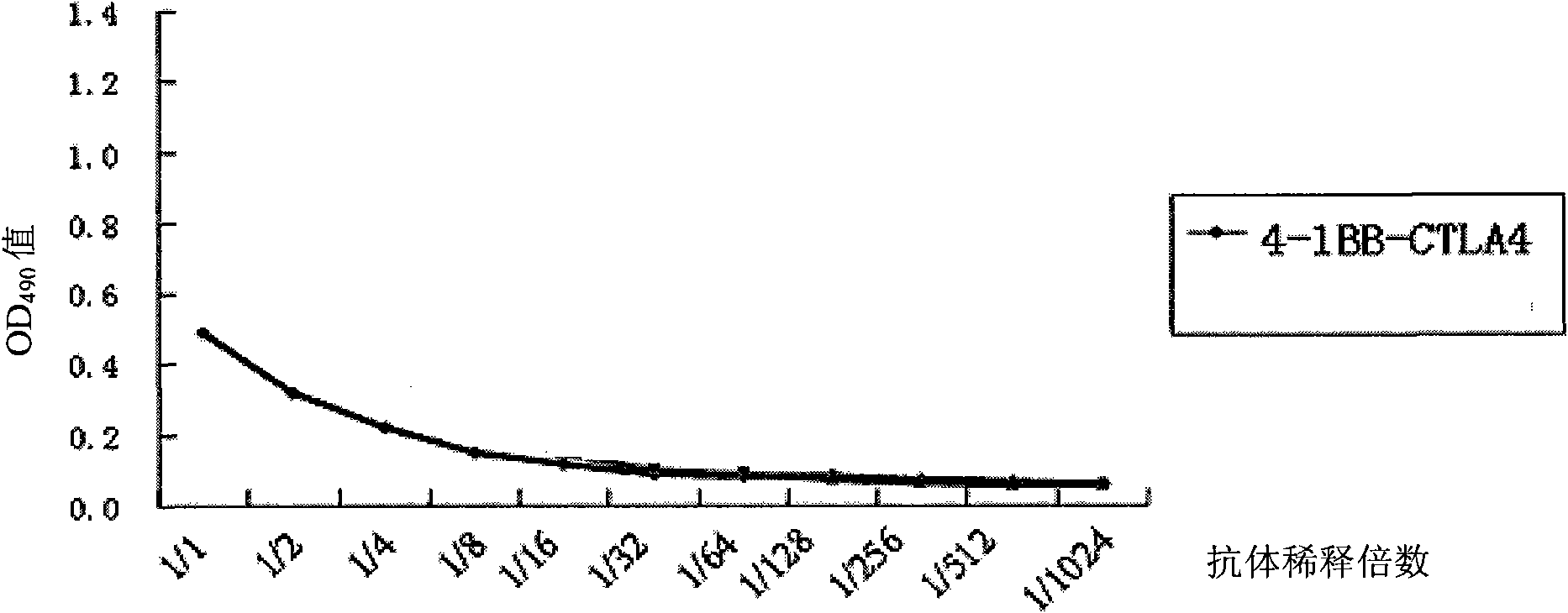
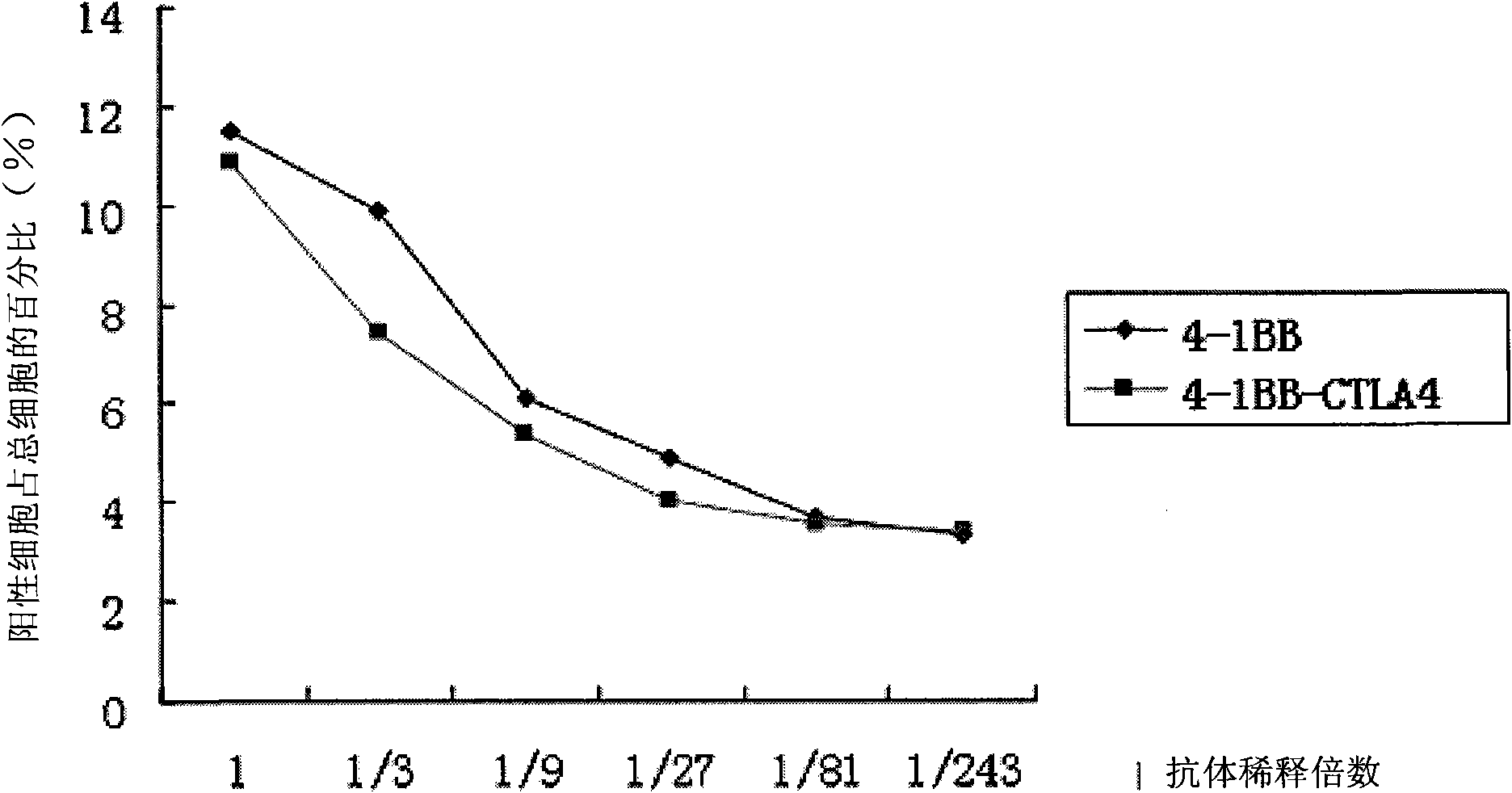
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody and application thereof. The monoclonal antibody consists of light chains and heavy chains, wherein amino acid residue sequences of the variable area of the heavy chains are showed in a sequence 1 in the sequence table, and amino acid residue sequences of the variable area of the light chains are showed in a sequence 2 in the sequence table. The invention combines and constructs anti-CTLA-4 antibodies and anti-4-1BB antibodies to form antihuman 4-1BB and CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies. Experimental result shows that the monoclonal antibody has an antibody structure and can be respectively combined with human 4-1BB and CTLA-4.
Owner:广东云天抗体生物科技有限公司
Treatment of B cell lymphoma using anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit the binding of CD80 to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7153508B2Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Stimulation of T cells against self antigens using CTLA-4 blocking agents
InactiveUS20060034844A1Enhanced T cell responseBreak immune tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsCTLA4 ProteinImmune tolerance
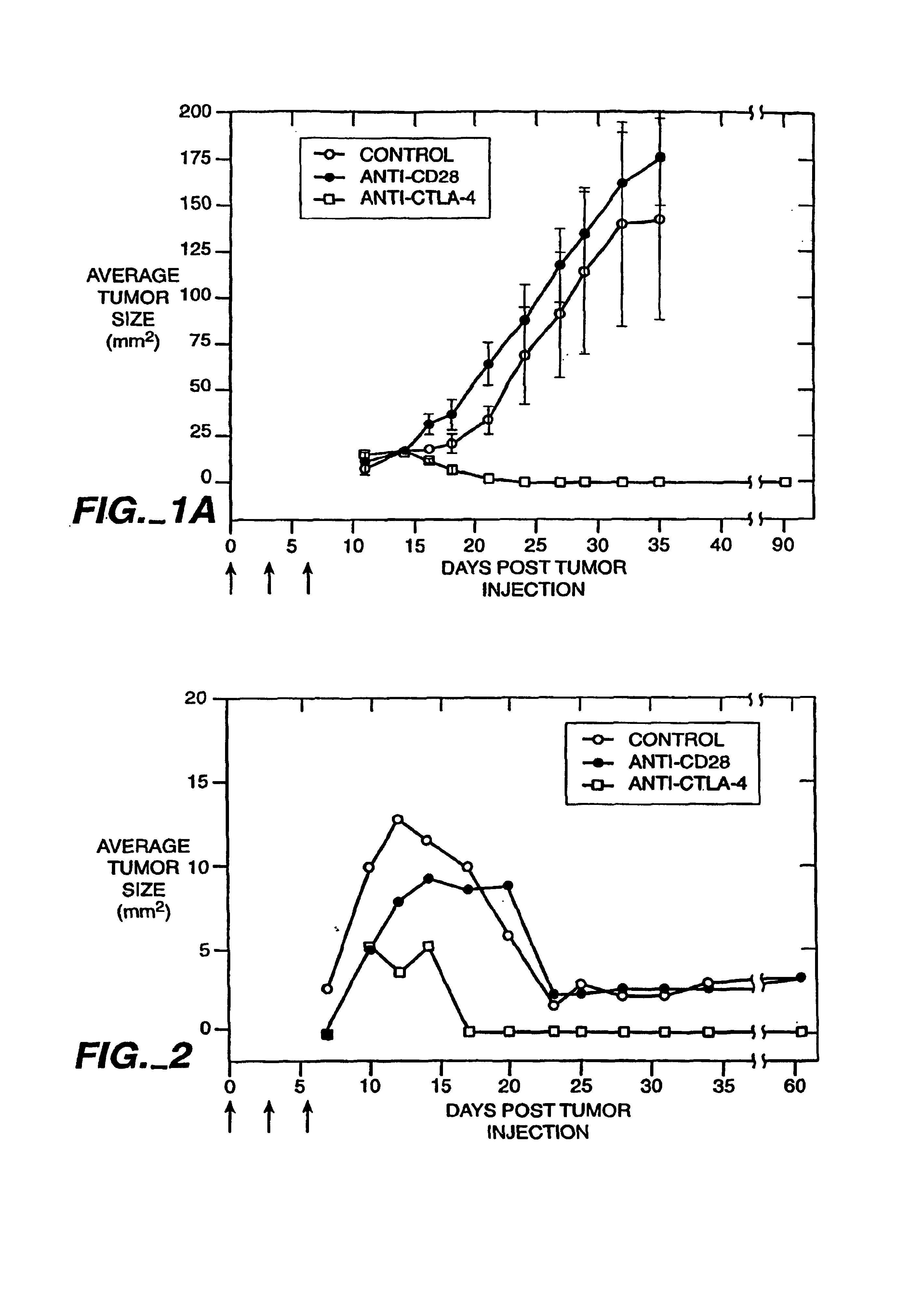
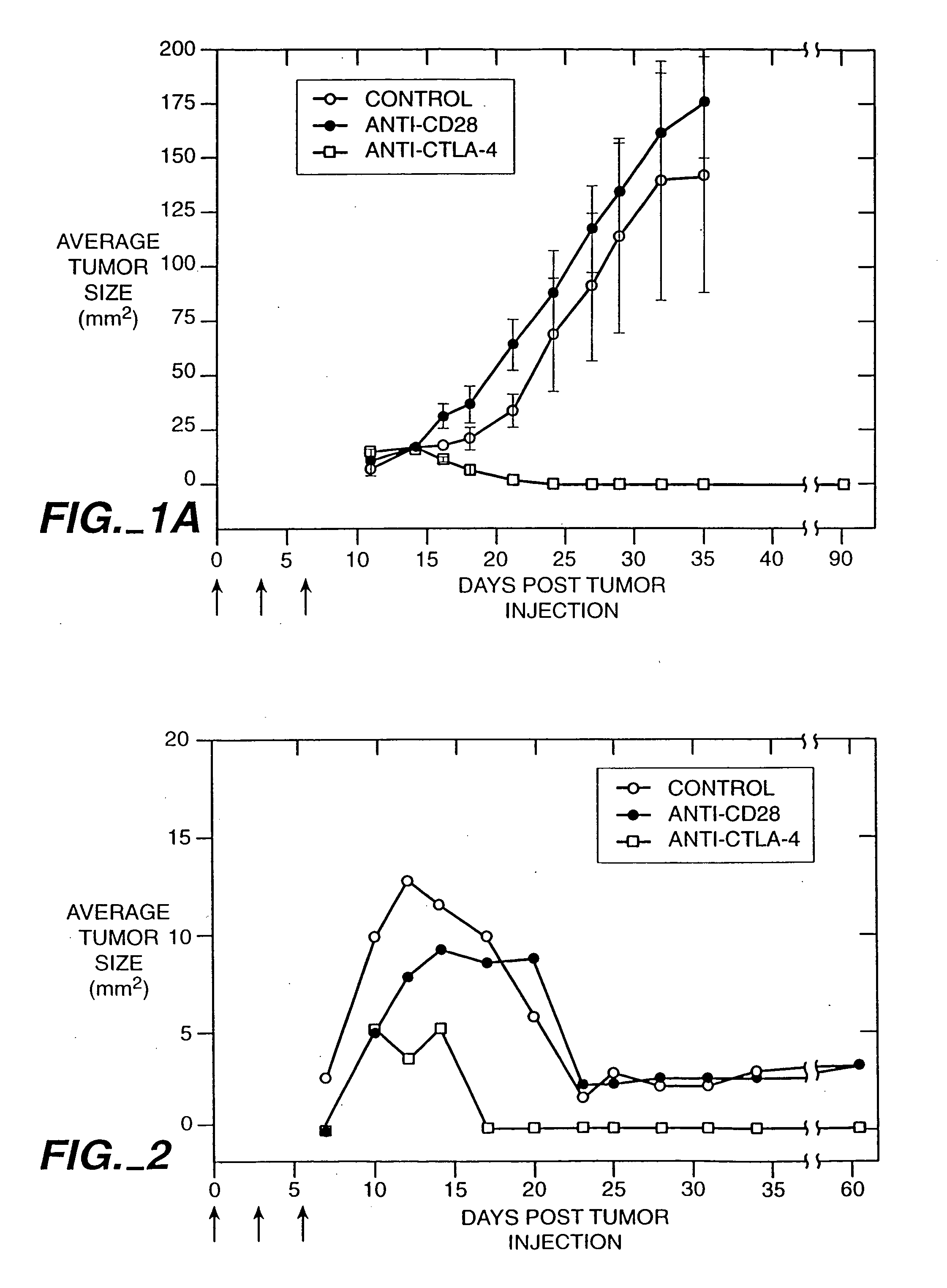
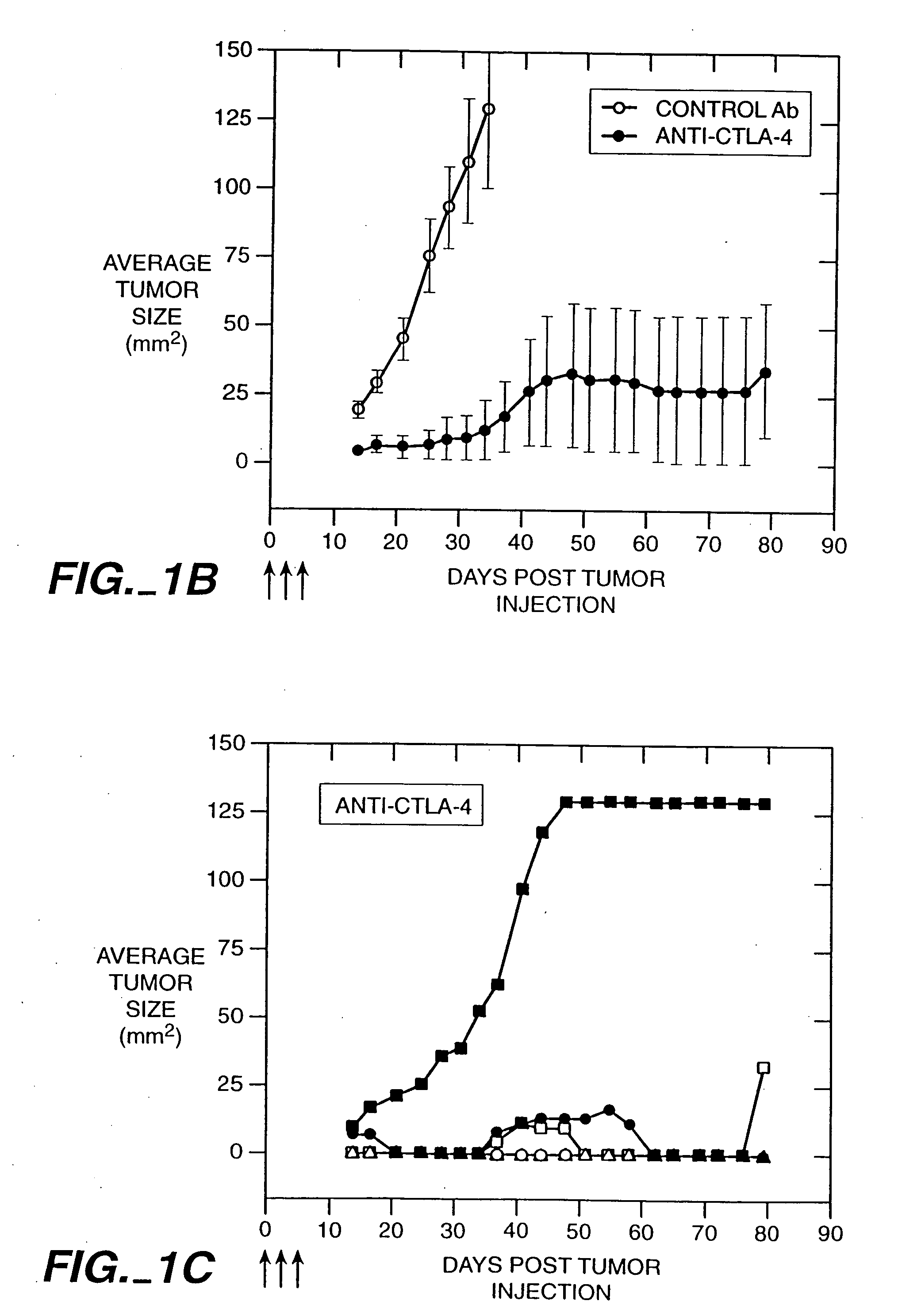
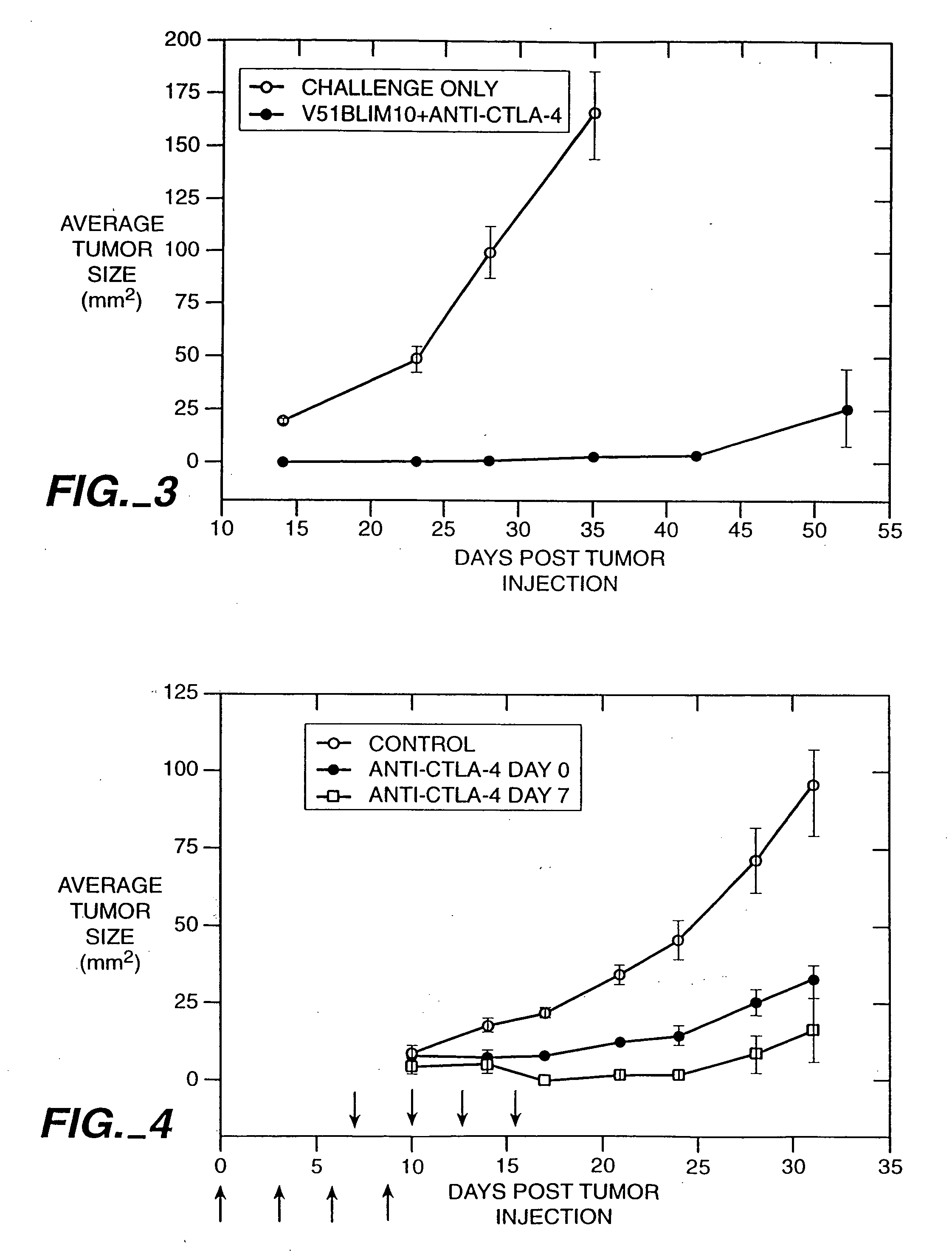
Stimulation of T cells to respond to self antigens is achieved through a blockade of CTLA-4 signaling. CTLA-4 blocking agents are combined with antigen preparations, either alone or with additional immune response stimulating agents, in costimulation strategies to break immune tolerance and stimulate an enhanced T-cell response against self antigens. This enhanced response is useful for the treatment of non-immunogenic and poorly-immunogenic tumors, as well as other medical conditions requiring selective tissue ablation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
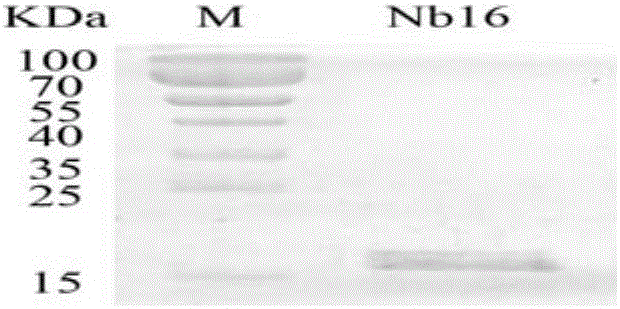
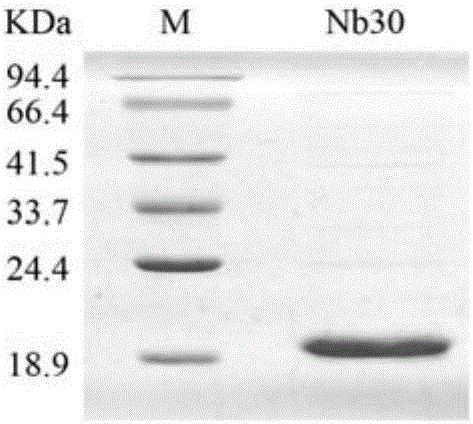
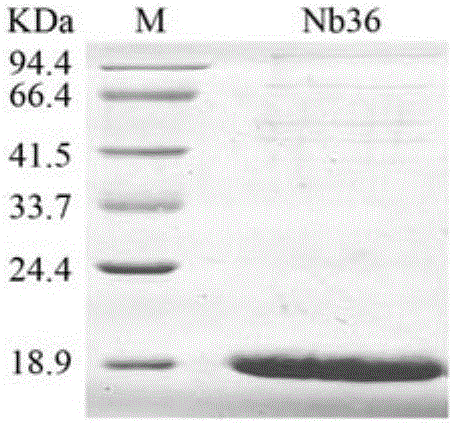
Nanometer antibody Nb16 for anti-CTLA-4 and preparation method and application of nanometer antibody Nb16
ActiveCN106220732AEfficient expressionPromote proliferationMaterial nanotechnologyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCTLA4 ProteinBiology
The invention discloses a nanometer antibody Nb16 for anti-CTLA-4 and a preparation method and application of the nanometer antibody Nb16. The provided nanometer antibody comprises a determinant complementary region and a frame region. The determinant complementary region of the nanometer antibody includes CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein the amino acid sequence of CDR1 is the 26-35 amino acid of SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence list, the amino acid sequence of CDR2 is 51<st>-59 amino acid of SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence list, and the amino acid sequence of CDR3 is 97-106 amino acid of SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence list. The nanometer antibody Nb16 can combine with T cells and CTLA-4, and can be used for researching and developing a CTLA-4 molecular detection agent, preparing a tumor inhibitor or a tumor cell inhibitor, and preparing a medicine for inhibiting activity of CTLA-4 and prompting T cell proliferation.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
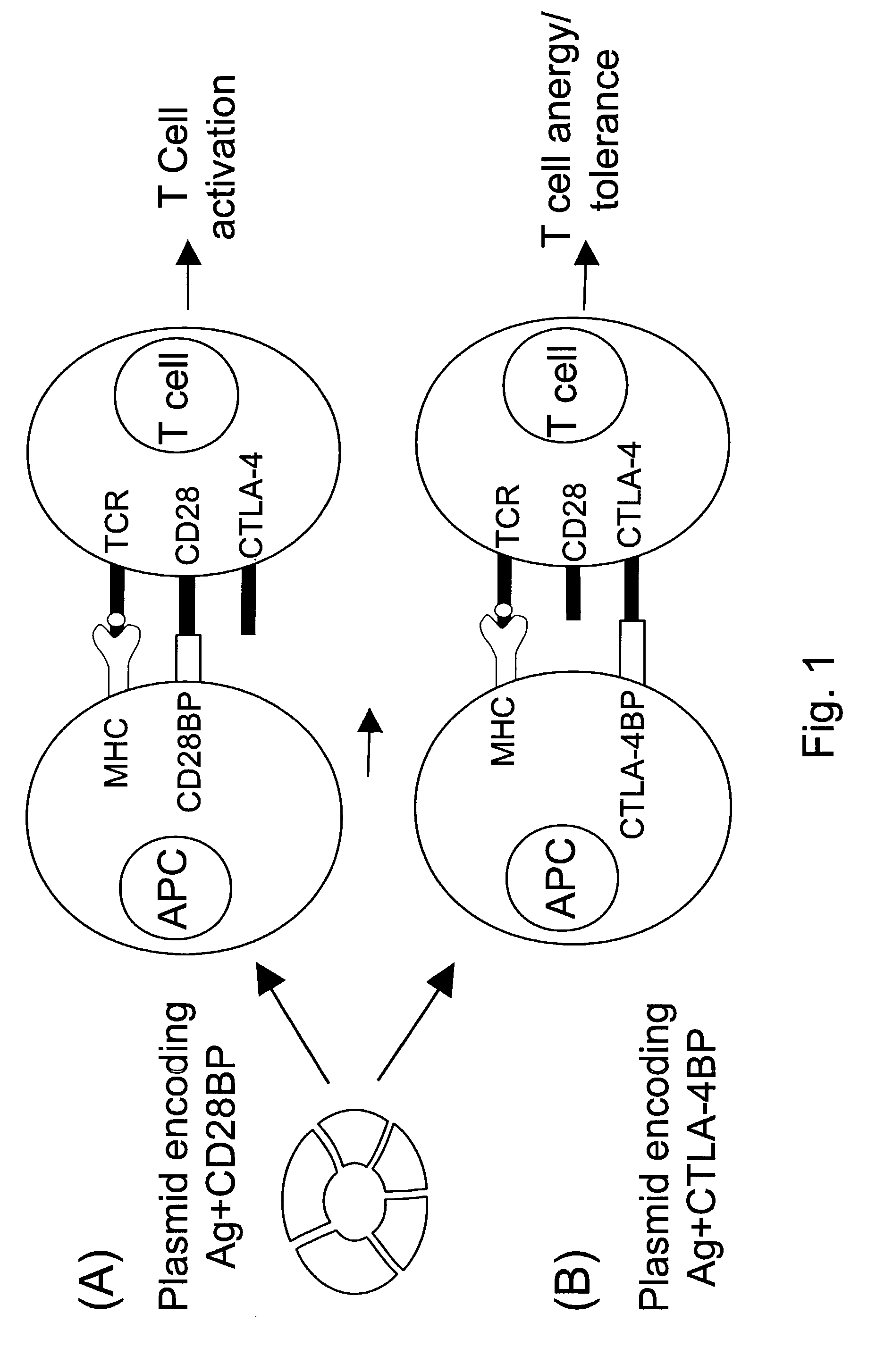
Co-stimulatory polypeptides
InactiveUS7094875B2Enhance and limit cytokine productionImmunoglobulin superfamilySugar derivativesCTLA4 ProteinProphylactic treatment
The invention provides polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded therefrom having advantageous properties, including an ability of the polypeptides to preferentially bind a CD28 or CTLA-4 receptor at a level greater or less than the ability of human B7-1 to bind CD28 or CTLA-4, or to induce or inhibit altered level of T cell proliferation response greater compared to that generated by human B7-1. The polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention are useful in therapeutic and prophylactic treatment methods, gene therapy applications, and vaccines.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Application of CAR-T cell carrying PD-L1 and CTLA-4 antibody genes in tumor immunology
InactiveCN105796597AAvoid inconvenienceEnhance immune responseMammal material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCTLA4 ProteinPD-L1
The invention discloses application of a CAR-T cell carrying PD-L1 and CTLA-4 antibody genes in tumor immunology. The CAR-T cell directly expresses a PD-L1 antibody and a CTLA-4 antibody. Due to the fact that the CAR-T cell directly expresses the PD-L1 antibody and the CTLA-4 antibody, a tumor immunoreaction is enhanced, the defects that exogenous injection of the PD-L1 antibody and the CTLA-4 antibody is inconvenient and expensive are overcome, the CAR-T cell expresses the PD-L1 antibody and the CTLA-4 antibody, and the problems of repeated injection and high price can be solved.
Owner:广东朗源生物科技有限公司
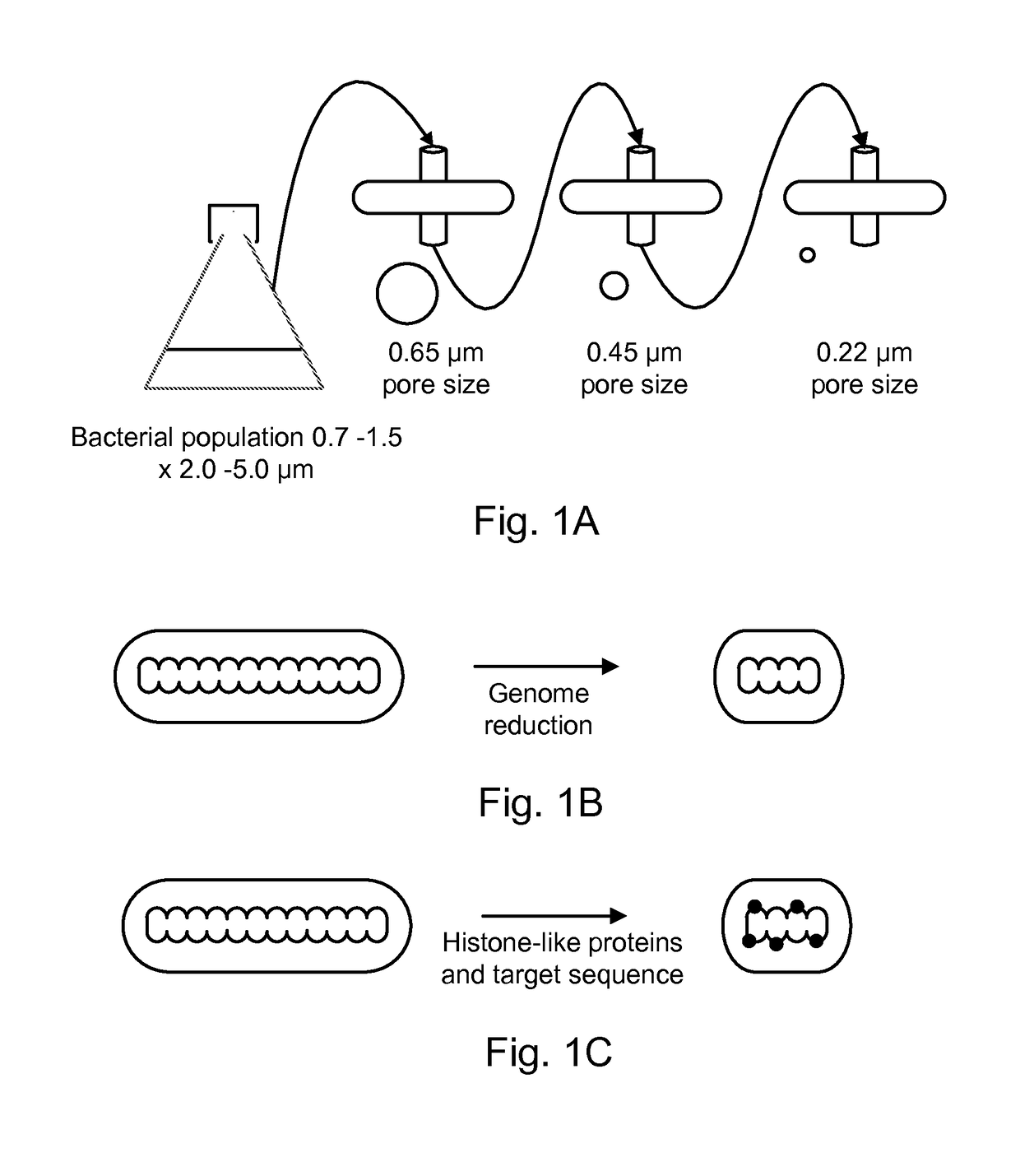
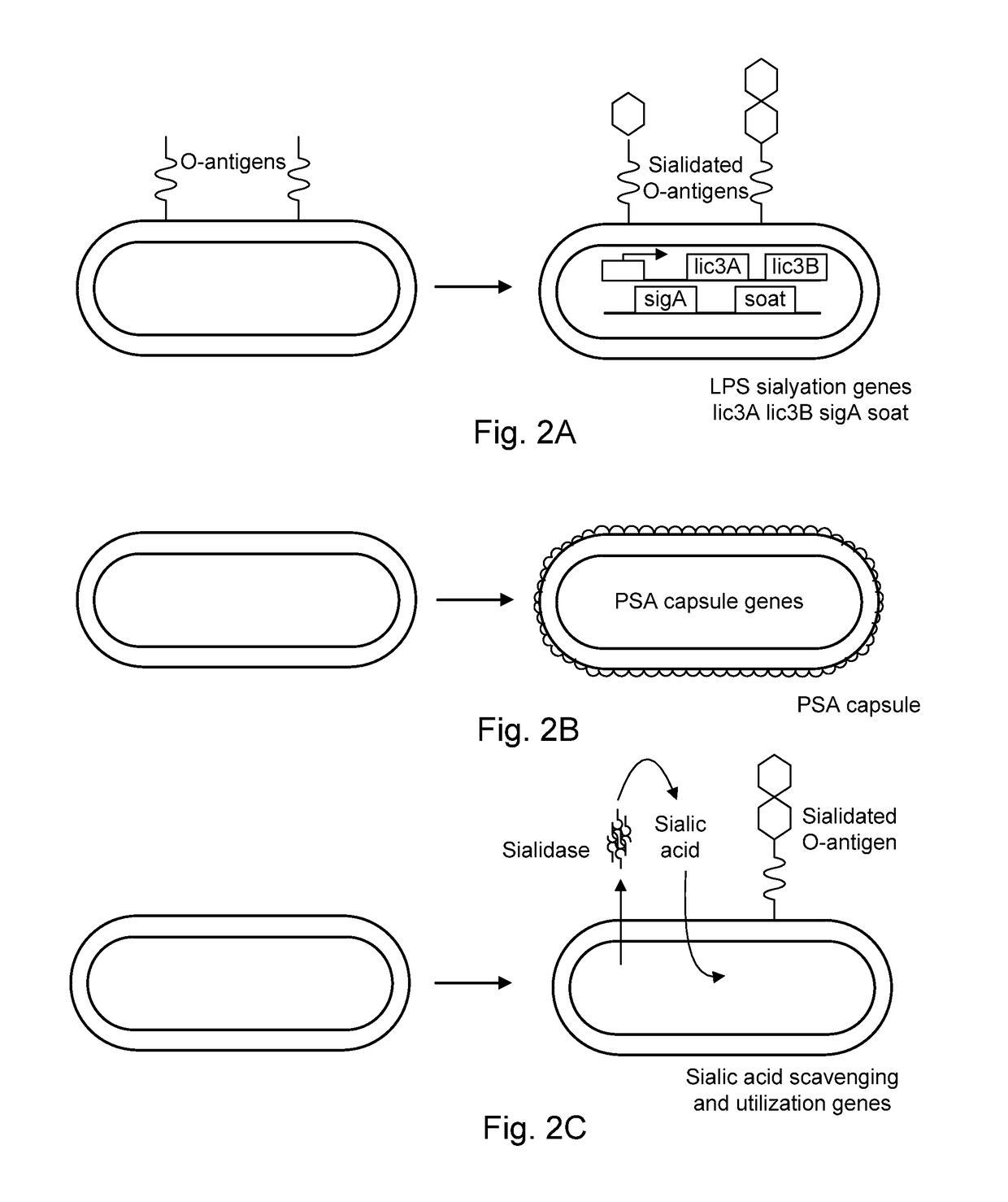
Modified bacteria having improved pharmacokinetics and tumor colonization enhancing antitumor activity
ActiveUS9616114B1Facilitate initiationAvoid host immune response suppressionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsBacteroidesAntigen
Bacterial strains are provided having at least one of a reduced size, a sialic acid coat, inducibly altered surface antigens, and expression of PD-L1 or CTLA-4 agonists and / or tryptophanase. The bacteria may have improved serum half-life, increased penetration into tumors, increased tumor targeting and increased antitumor activity. The bacteria are useful for delivery of therapeutic agents that treat of neoplastic diseases including solid tumors and lymphomas.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Chemical modulators of immune checkpoints and therapeutic use
Compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that down-regulate immune checkpoints such as PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 are provided. Also provided are methods of treating a disease by down-regulating immune checkpoints such as PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4. The methods are useful for treating cancer and viral infection in a subject.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Treating intestinal inflammation with anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit CD80 binding to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7175847B1Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigenCD80
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Methods Of Treatment Using CTLA-4 Antibodies
InactiveUS20090117037A1Induce and enhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiseaseHuman sequence
The present invention provides method of treatment using human sequence antibodies against human CTLA-4 linked to a cytotoxic agent. In particular, methods of treating cancer and autoimmune disease are provided.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Human CTLA-4 Antibodies and Their Uses
InactiveUS20100047244A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHuman sequenceCTLA4 Protein
The present invention provides novel human sequence antibodies against human CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
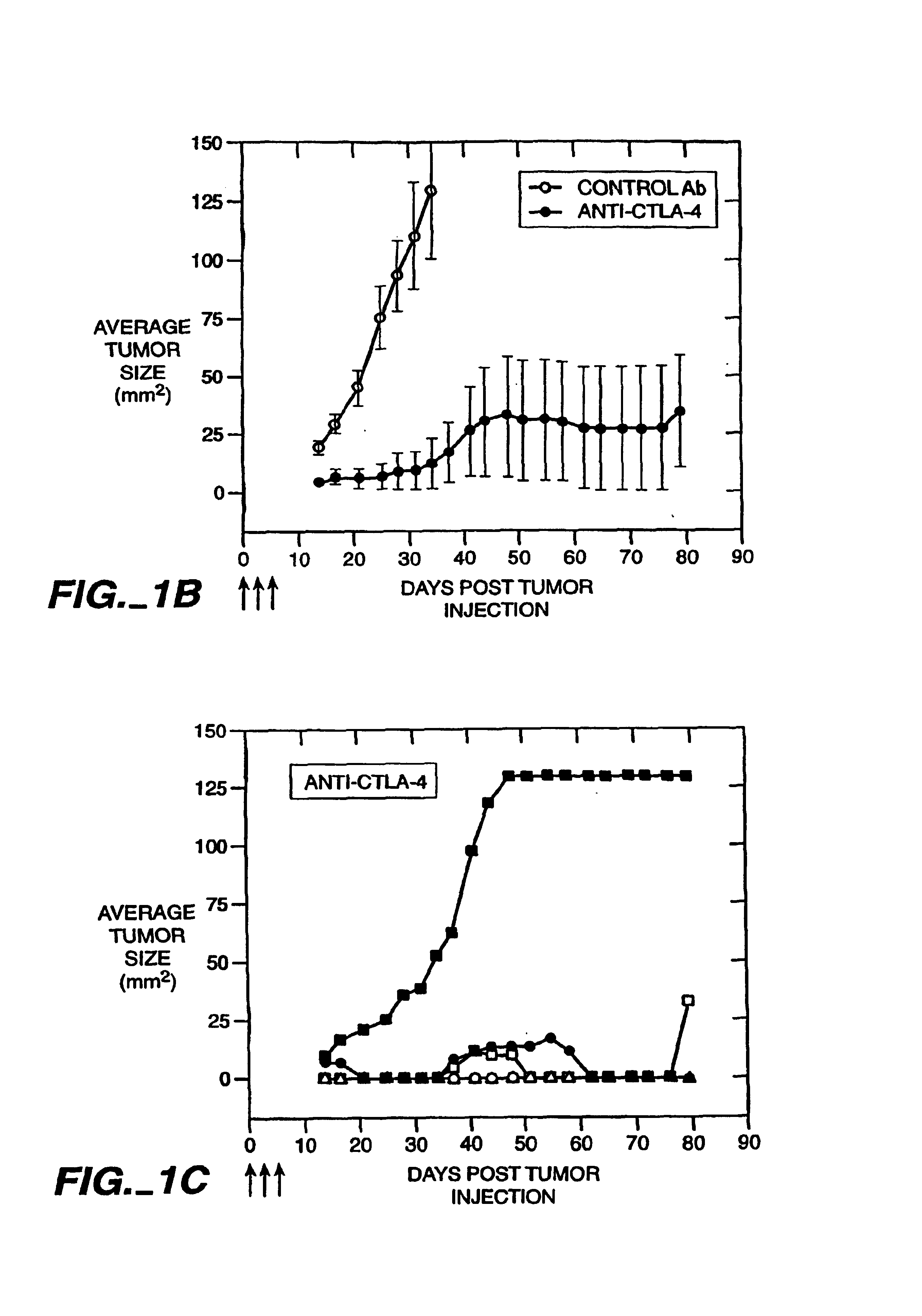
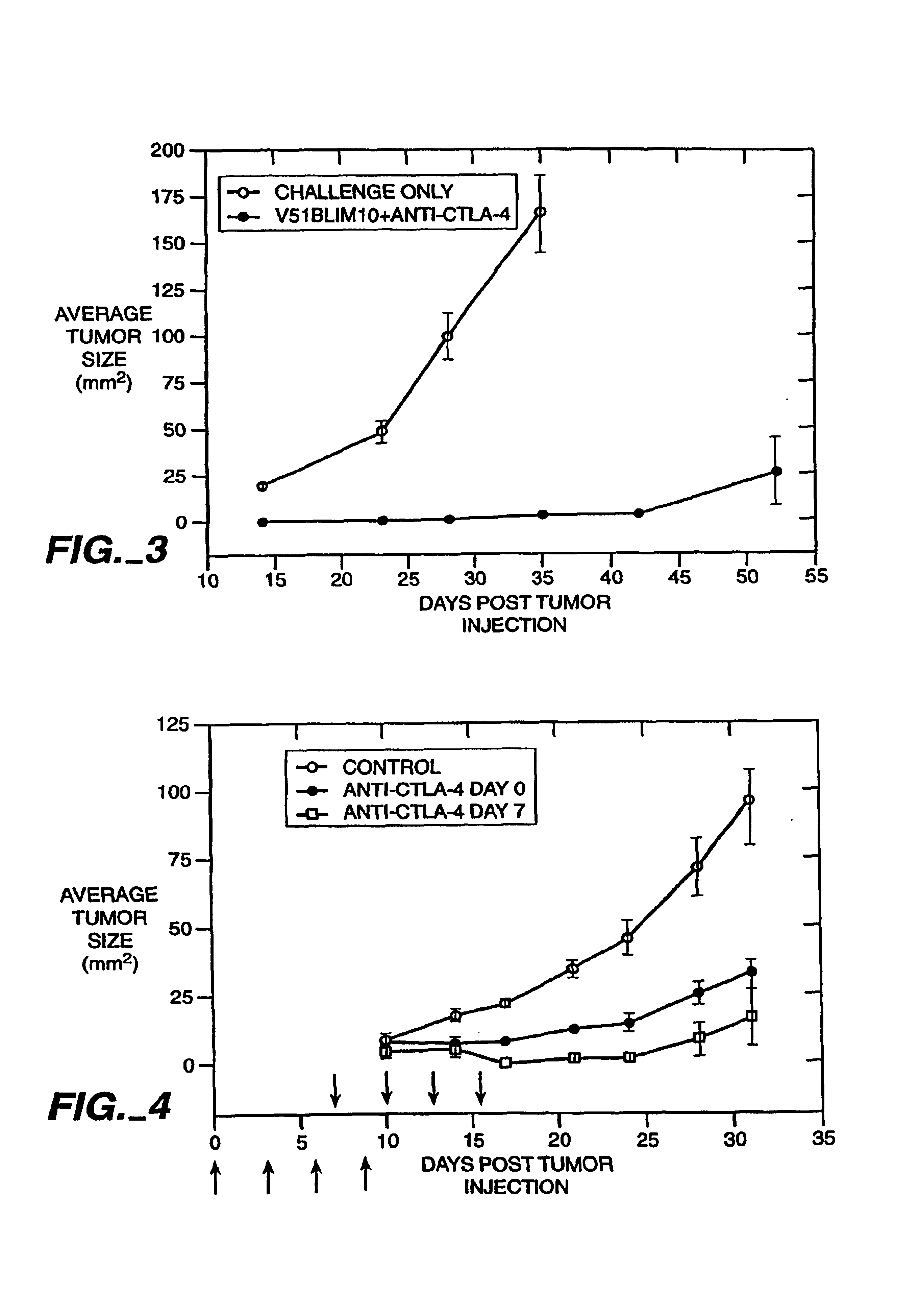
Blockade of T lymphocyte down-regulation associated with CTLA-4 signaling
InactiveUS20050249700A1Increased activationImprove responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAdjuvant
T cell activation in response to antigen is increased by the administration of binding agents that block CTLA-4 signaling. When CTLA-4 signaling is thus blocked, the T cell response to antigen is released from inhibition. Such an enhanced response is useful for the treatment of tumors, chronic viral infections, and as an adjuvant during immunization.
Owner:ALLISON JAMES +2
Application of chlorogenic acid in preparation of drug for treating choriocarcinoma
InactiveCN104586828AEnhance immune responseImprove immunityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsChlorogenic acidCTLA4 Protein
The invention discloses application of chlorogenic acid in preparation of a drug for treating choriocarcinoma, and belongs to the field of biological medicine. The drug is prepared from chlorogenic acid as an active constituent and used for treating choriocarcinoma. The chlorogenic acid has the function of inhibiting tumors, meanwhile is harmless to a human body, and can improve the immunity of the organism, the organism hematopoietic function and the hepatorenal function; furthermore, the chlorogenic acid can block or reduce the inhibiting function of CTLA-4 on T cell immunological competence, so as to stimulate the immune cells to be proliferated in quantity, and further enhance the immunoreaction of the organism to the tumors; meanwhile, the drug can be combined with other anti-tumor drugs to play a more prominent anticancer effect on choriocarcinoma.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHANG BIO TECH CO LTD
Checkpoint Blockade and Microsatellite Instability
InactiveUS20170267760A1High mutational burdenMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemProgrammed deathImmune tolerance
Blockade of immune checkpoints such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) shows promise in patients with cancer. Inhibitory antibodies directed at these receptors have been shown to break immune tolerance and promote anti-tumor immunity. These agents work particularly well in patients with a certain category of tumor. Such tumors may be particularly susceptible to treatment because of the multitude of neoantigens which they produce.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Synergistic Anti-tumor efficacy using alloantigen combination immunotherapy
InactiveUS20130273078A1Increased activationOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsImmunotherapeutic agentPD-L1
Owner:VICAL INC
Anti-ctla4 and Anti-pd-1 bifunctional antibody, pharmaceutical composition thereof and use thereof
ActiveUS20190185569A1Avoid interactionEliminate immunosuppressionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsT lymphocyteAnti ctla4
An anti-CTLA4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4) and anti-PD-1 (programmed cell death 1) bifunctional antibody. a pharmaceutical composition thereof and use thereof. Particularly, the anti-CLTA4 and anti-PD-1 bifunctional antibody comprises a first protein functional domain that targets PD-1 and a second protein functional domain that targets CTLA-4. The bifunctional antibody can bind to CTLA-4 and PD-1 specifically, relieve immunosuppression of CTLA4 and PD-1 on an organism specifically, activate T lymphocytes, and thus has good application prospects.
Owner:AKESO PHARMA INC
Chemical modulators of immune checkpoints and therapeutic use
Compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that down-regulate immune checkpoints such as PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 are provided. Also provided are methods of treating a disease by down-regulating immune checkpoints such as PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4. The methods are useful for treating cancer and viral infection in a subject.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com