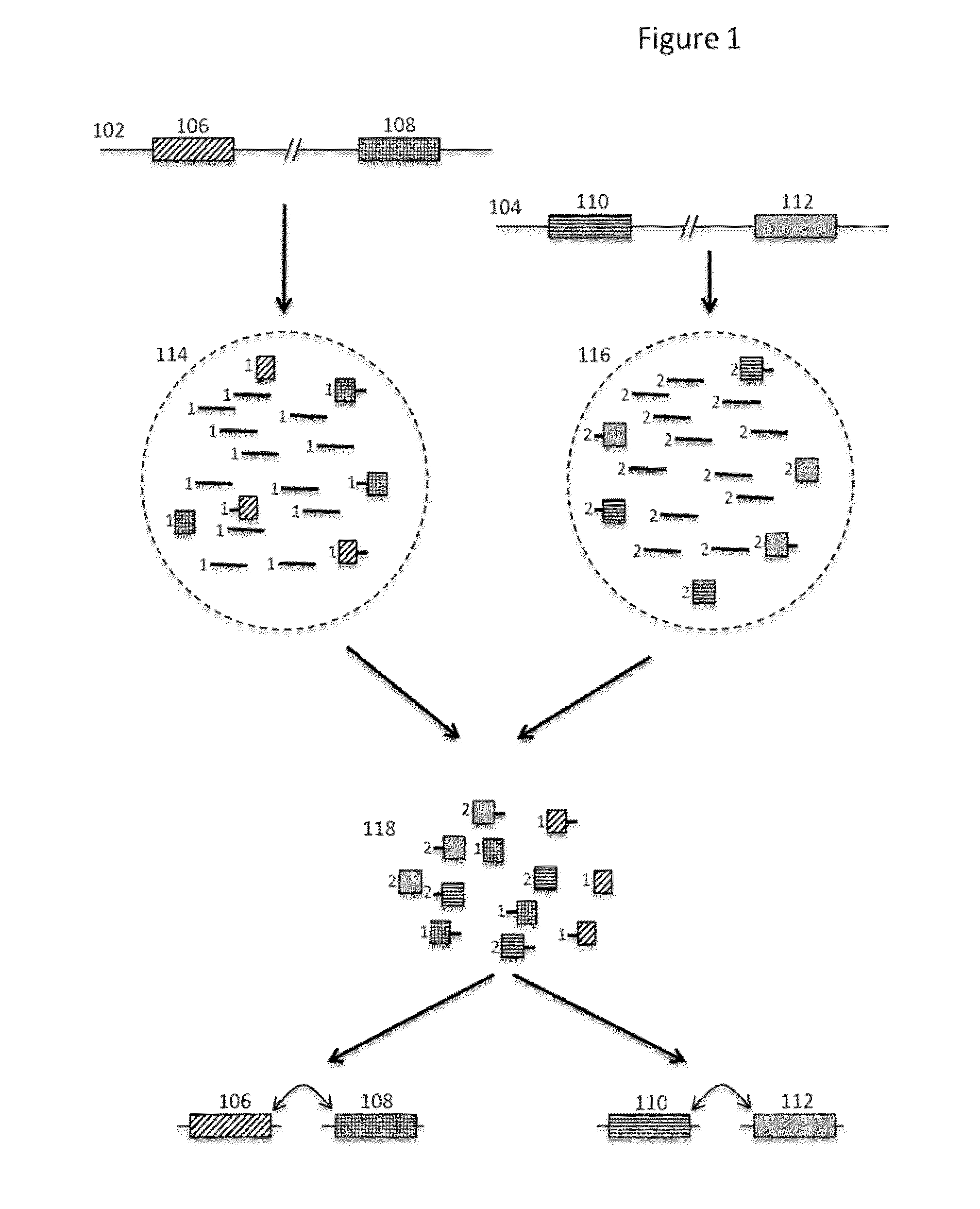
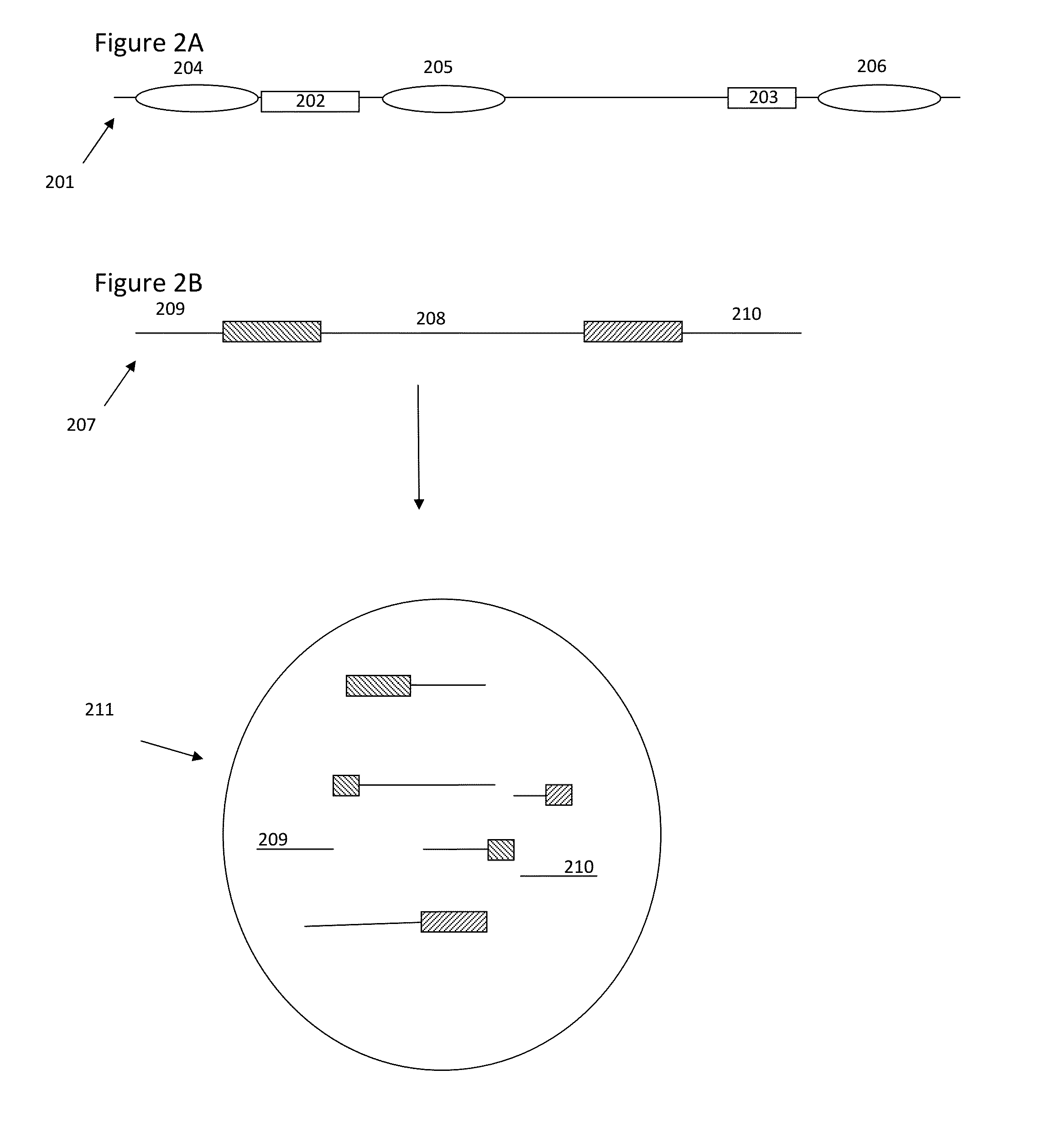
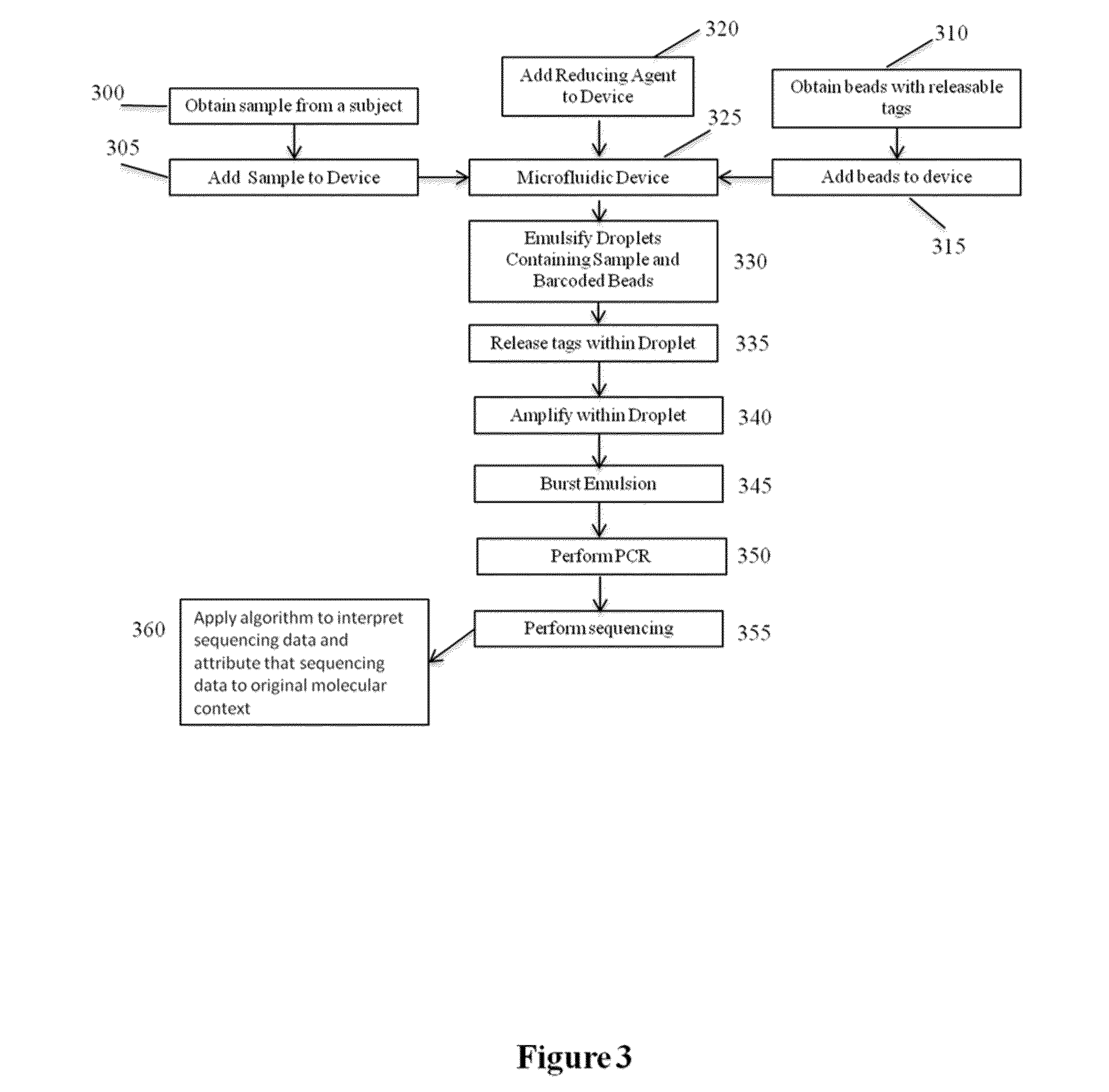
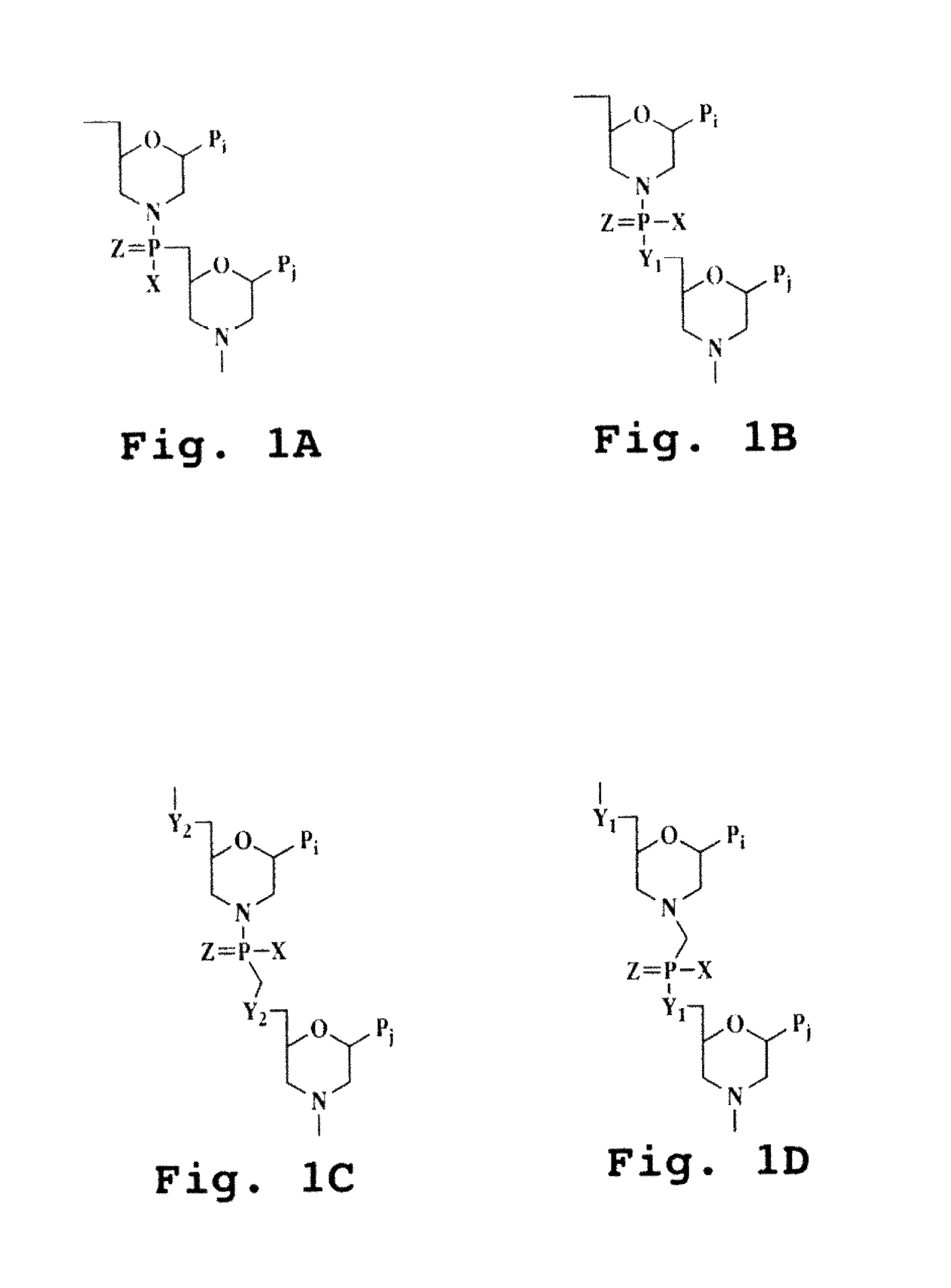
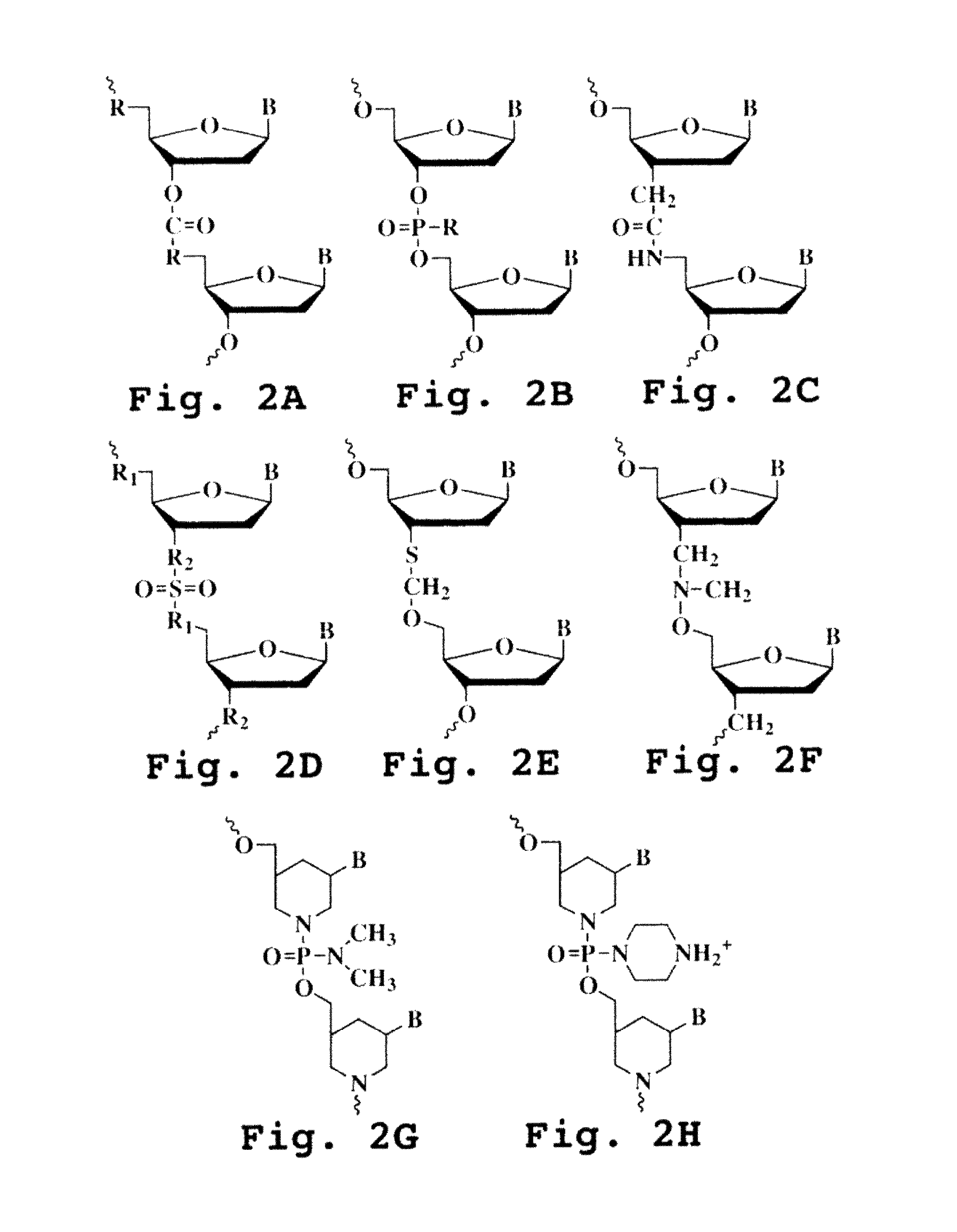
Patents
Literature
593 results about "Intein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
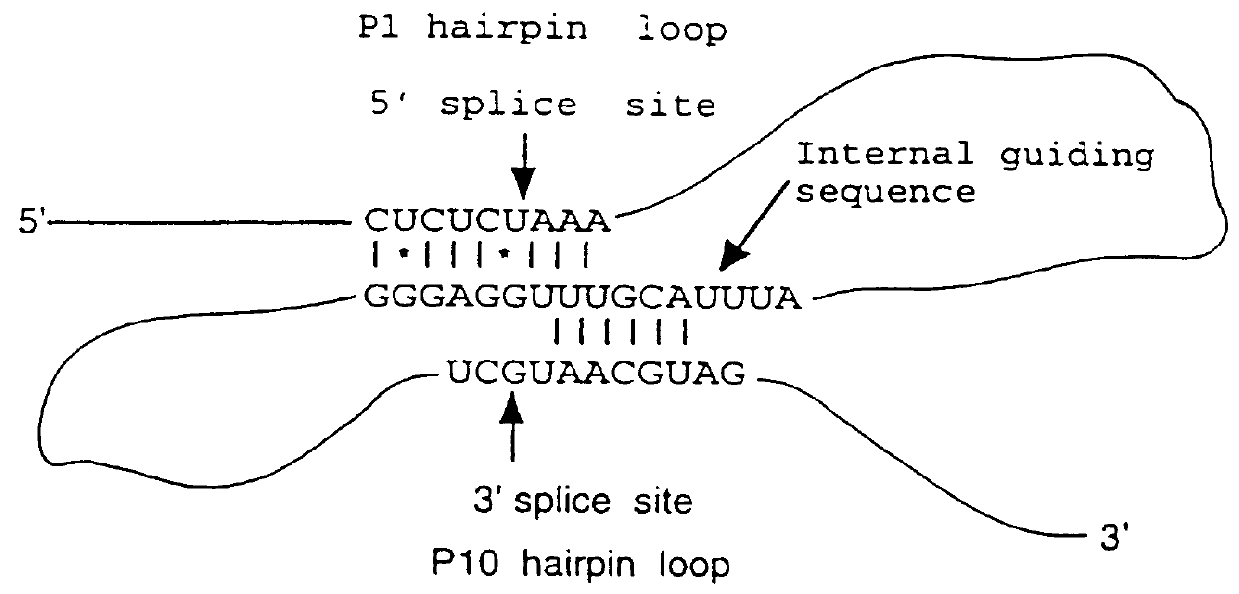
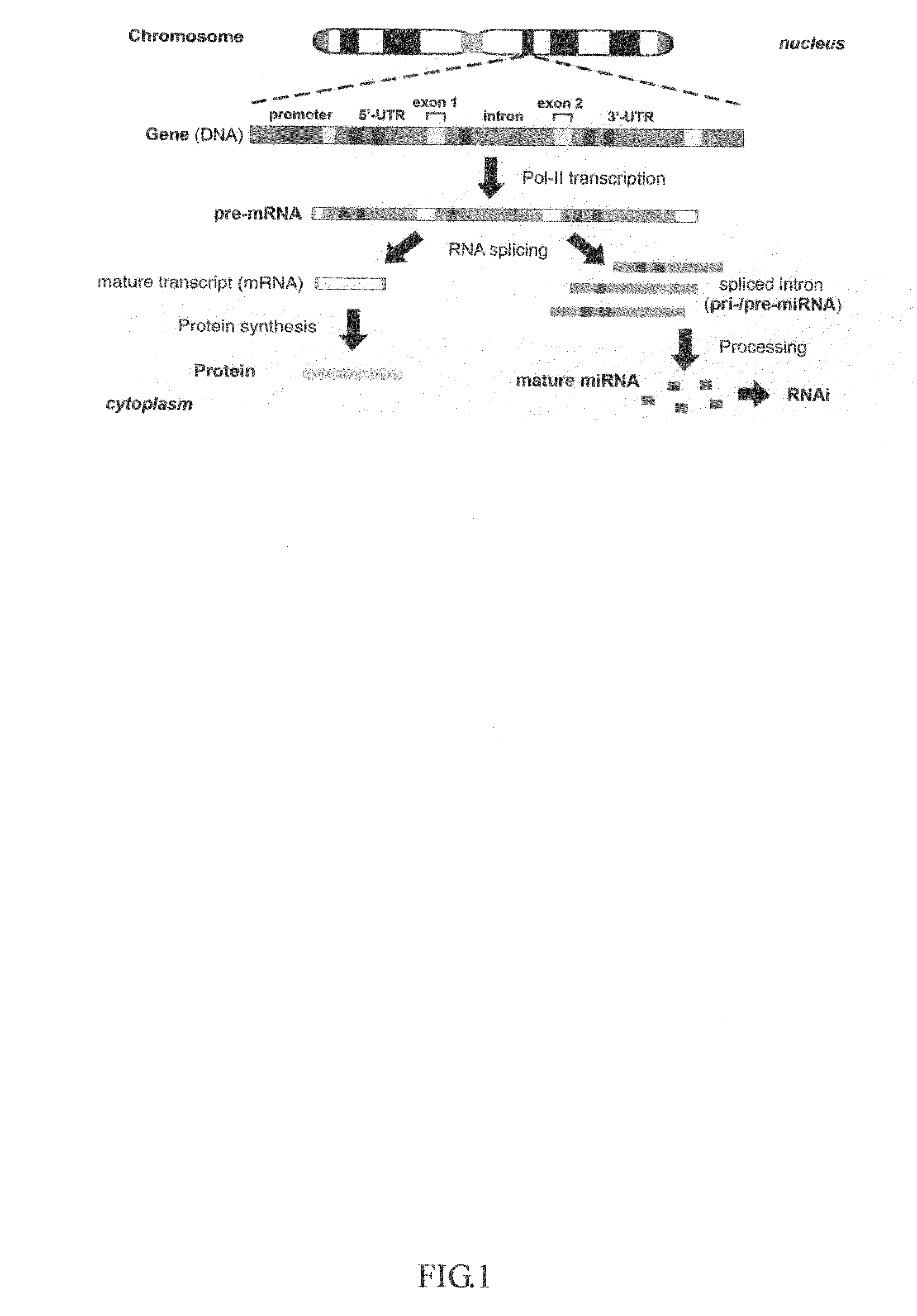
An intein is a segment of a protein that is able to excise itself and join the remaining portions (the exteins) with a peptide bond in a process termed protein splicing. Inteins have also been called "protein introns".
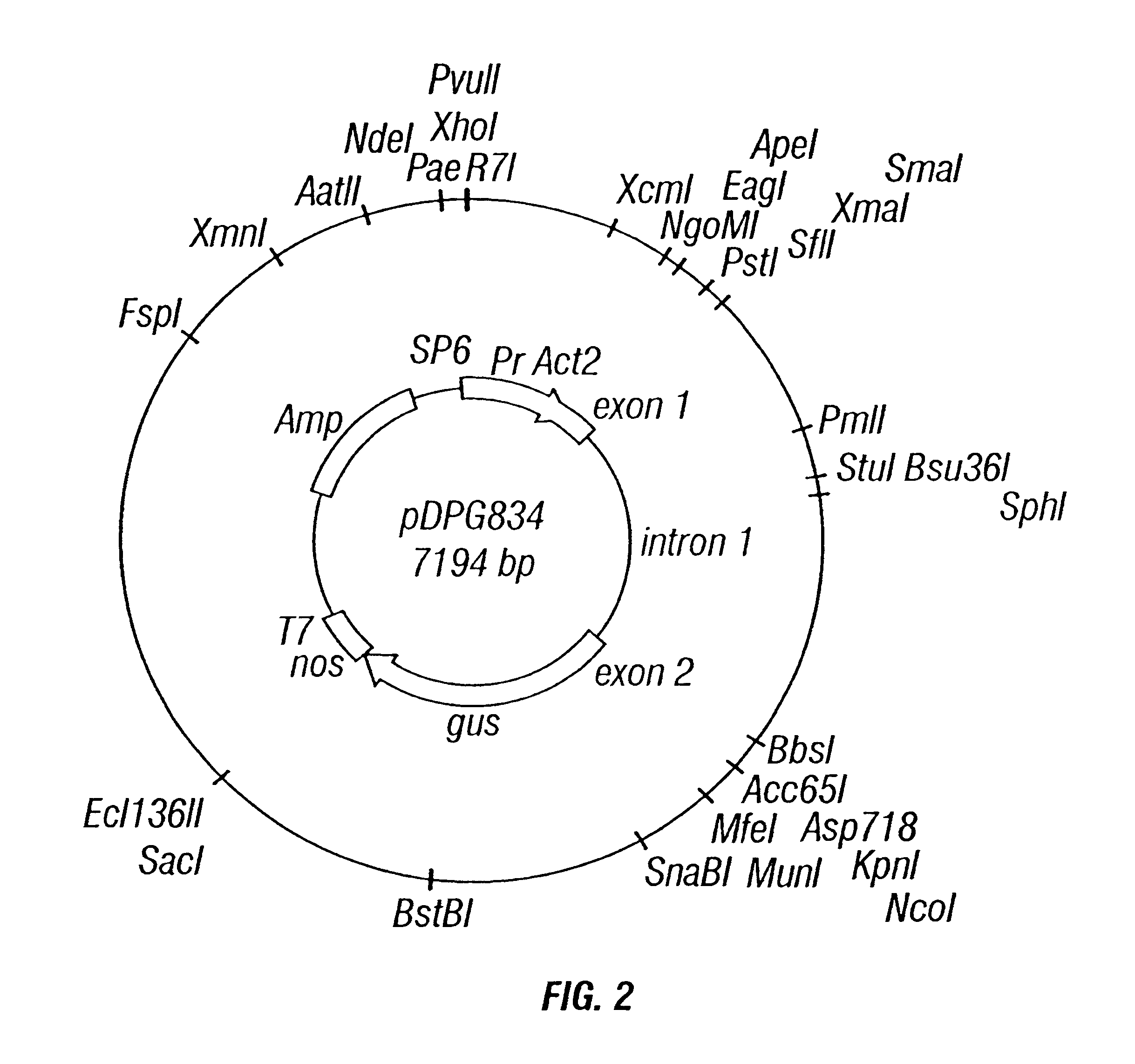
Rice actin 2 promoter and intron and methods for use thereof
The current invention provides regulatory regions from the rice actin 2 gene. In particular, the current invention provides the rice actin 2 promoter and actin 2 intron. Compositions comprising these sequences are described, as well as transformation constructs derived therefrom. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the rice actin 2 intron and / or promoter directly by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The actin 2 sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
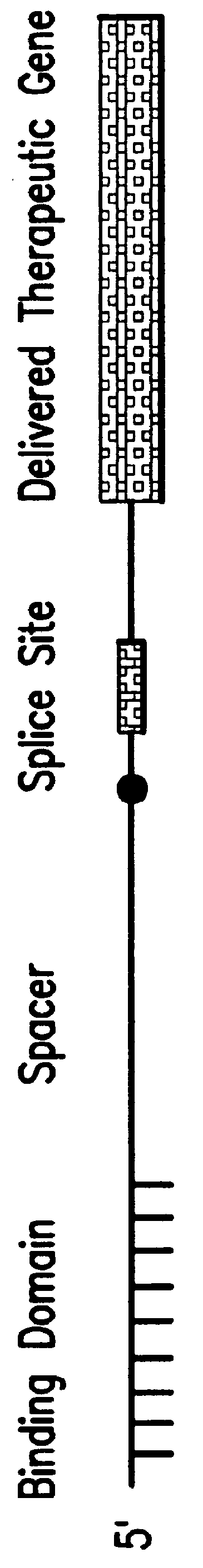
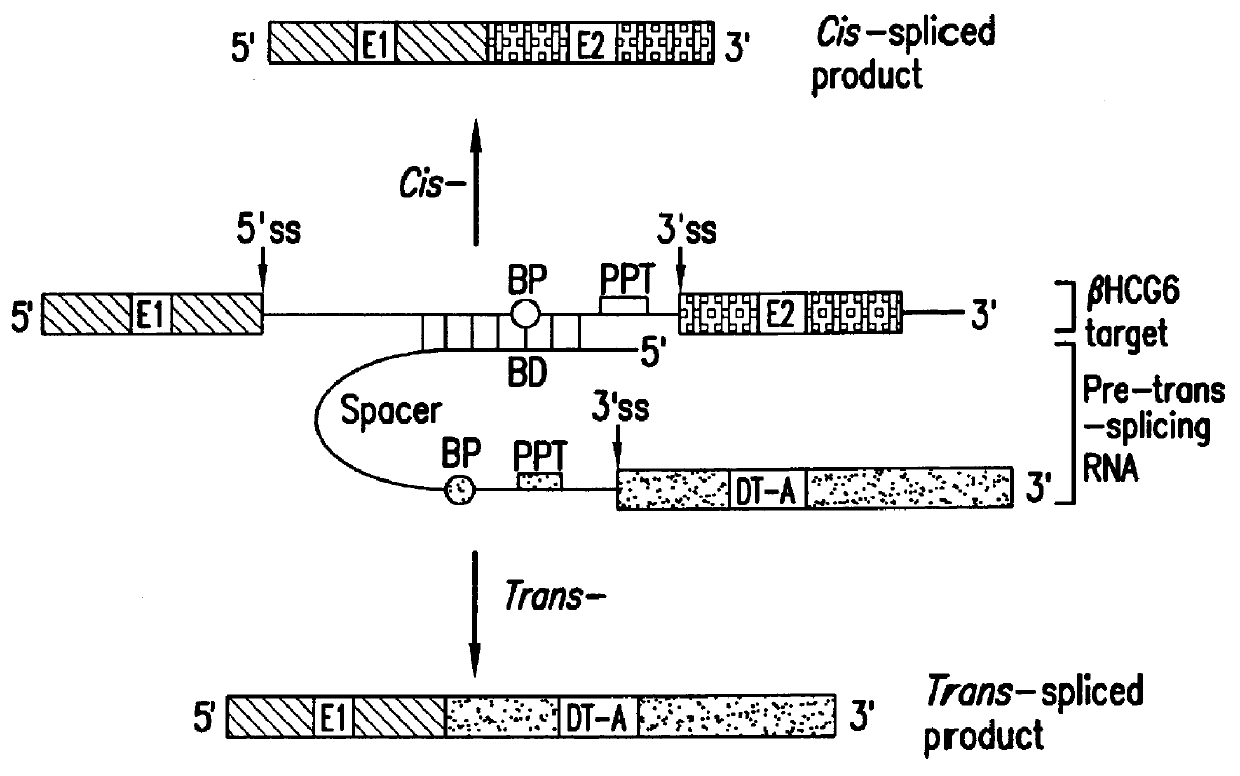
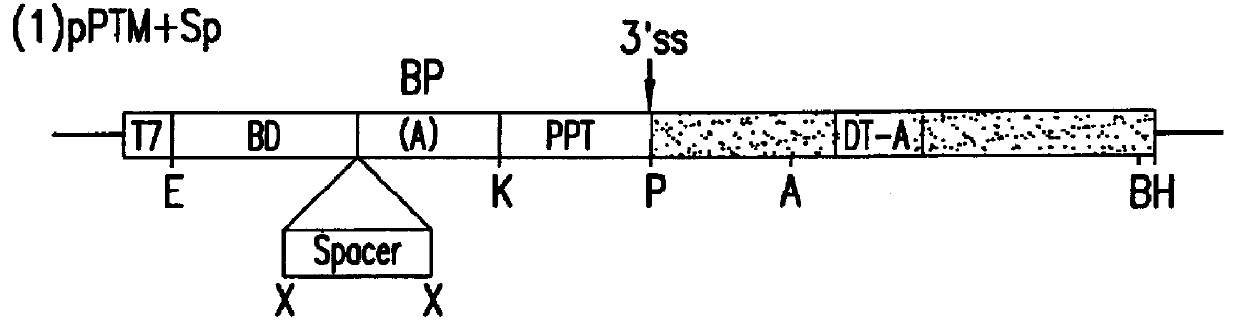
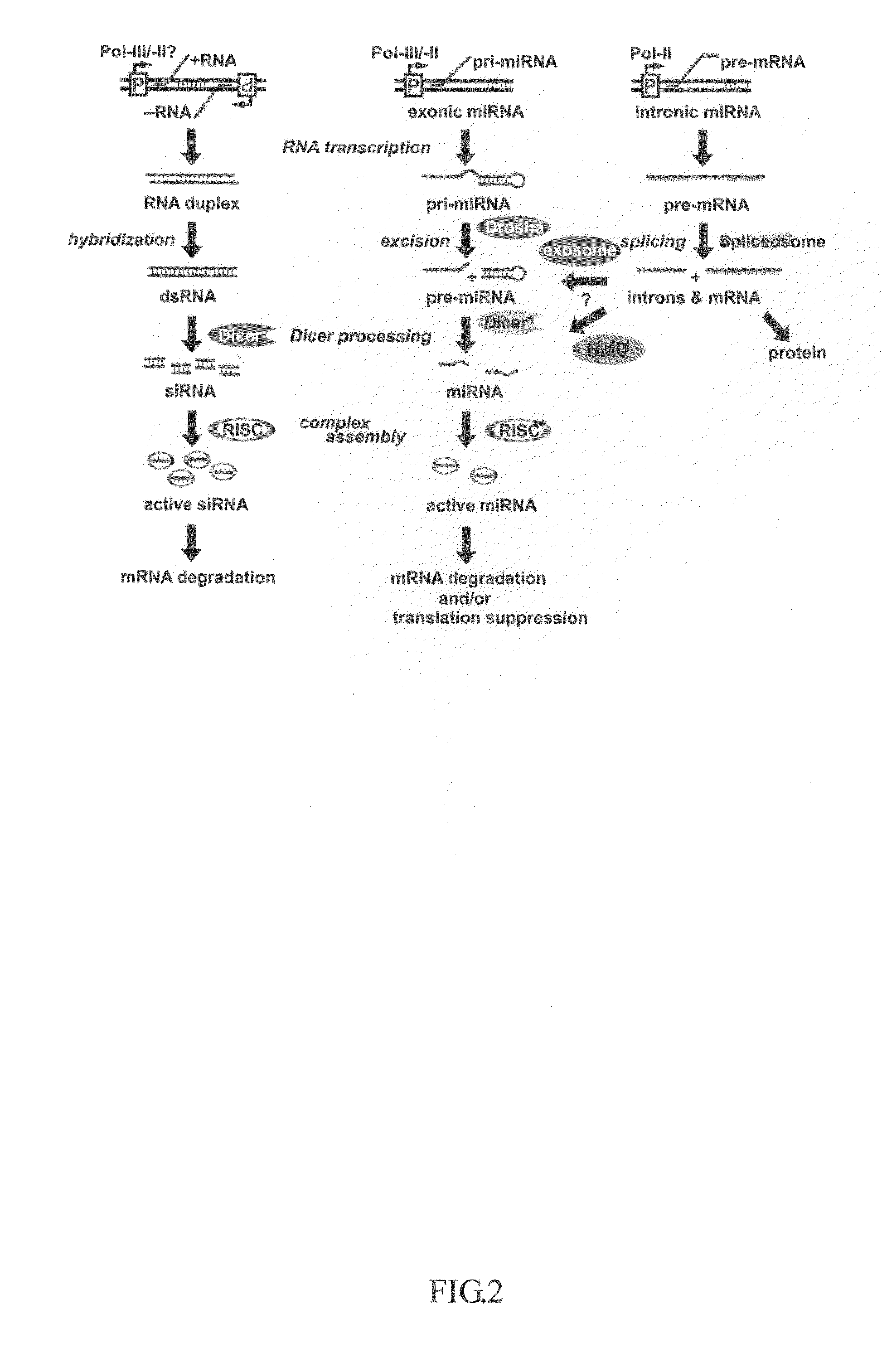
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
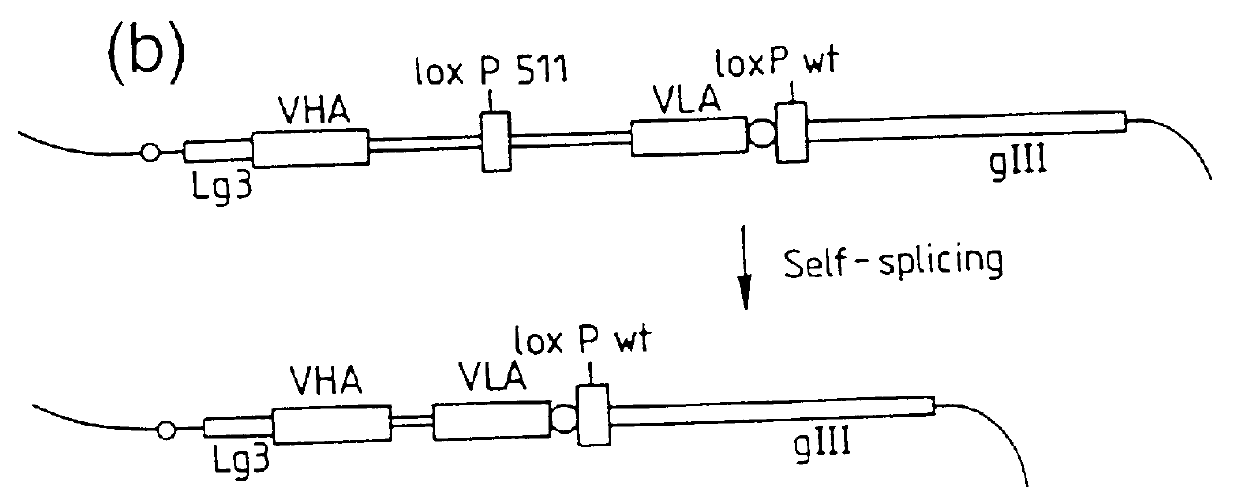
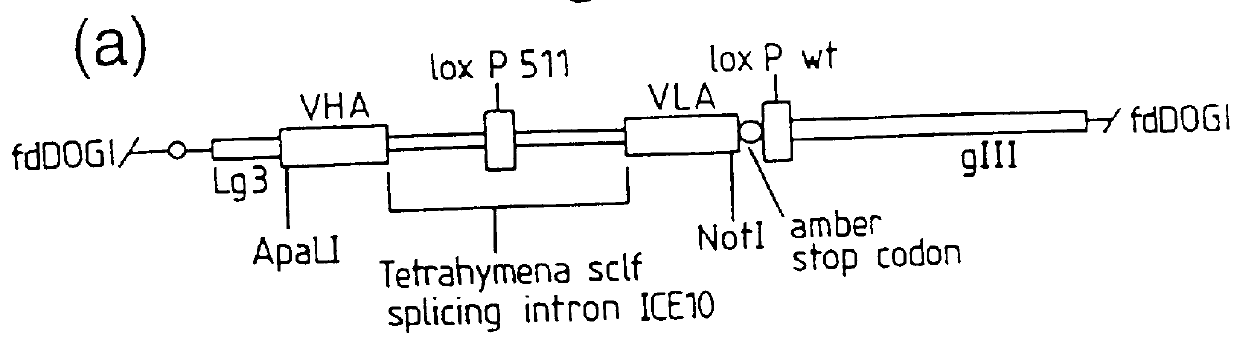
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
ActiveUS20100293625A1Increase transgene expressionImprove stabilityVectorsSugar derivativesReticulum cellIntein
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20160122817A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationInteinNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for capturing and analyzing sequence information contained in targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include exomes, partial exomes, introns, combinations of exonic and intronic regions, genes, panels of genes, and any other subsets of a whole genome that may be of interest.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Generation of human embryonc stem-like cells using intronic RNA
ActiveUS20080293143A1Stable and relatively long-term effectDelivery stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentReprogrammingMammal
This invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting human embryonic stem (hES)-like pluripotent cells using transgenic expression of intronic microRNA-like RNA agents. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its intronic components capable of being processed into mir-302-like RNA molecules in mammalian cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on differentiation-related and fate-determinant genes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into a pluripotent embryonic stem (ES)-cell-like state. The ES-like cells so obtained are strongly express hES cell markers, such as Oct3 / 4, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, and can be guided into various tissue cell types by treating certain hormones and / or growth factors under a feeder-free cell culture condition in vitro, which may be used for transplantation and gene therapies. Therefore, the present invention offers a simple, effective and safe gene manipulation approach for not only reprogramming somatic cells into ES-like pluripotent cells but also facilitating the maintenance of pluripotent and renewal properties of ES cells under a feeder-free cell culture condition, preventing the tedious retroviral insertion of four large transcription factor genes into one single cell as used in the previous iPS methods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
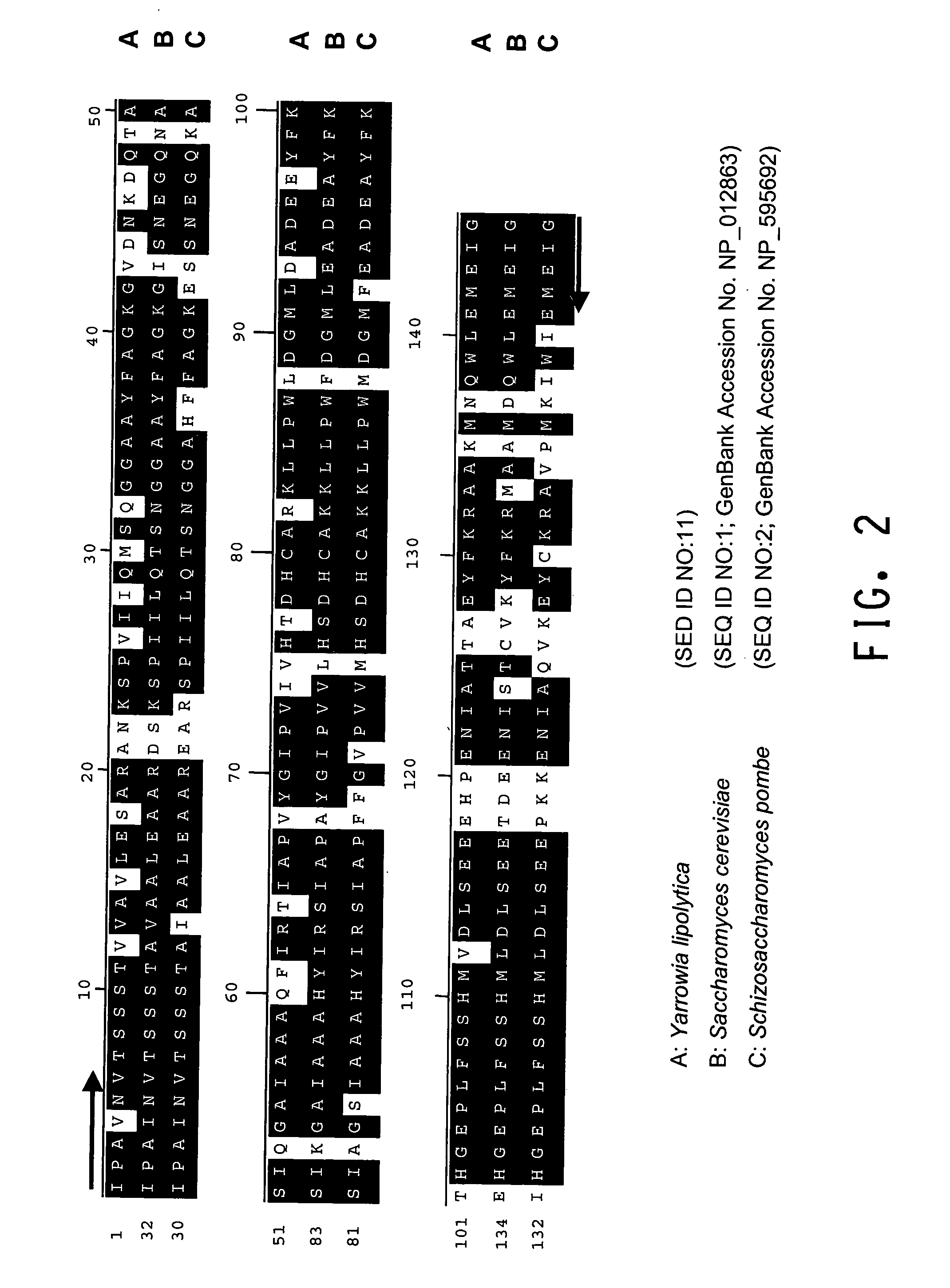
The regulatory sequences (i.e., promoter regions, introns and enhancers) associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica gene encoding fructose bis-phospate aldolase (FBA1) have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologus genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Expression Enhancing Intron Sequences
The invention relates to methods for the identification and use of introns with gene expression enhancing properties. The teaching of this invention enables the identification of introns causing intron-mediated enhancement (IME) of gene expression. The invention furthermore relates to recombinant expression construct and vectors comprising said IME-introns operably linked with a promoter sequence and a nucleic acid sequence. The present invention also relates to transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with these recombinant expression constructs or vectors, to cultures, parts or propagation material derived there from, and to the use of same for the preparation of foodstuffs, animal feeds, seed, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals, to improve plant biomass, yield, or provide desirable phenotypes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
ActiveUS7112439B2Maintaining their functionalityEasy to identifyAnimal cellsBacteriaAntigenBacteroides
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
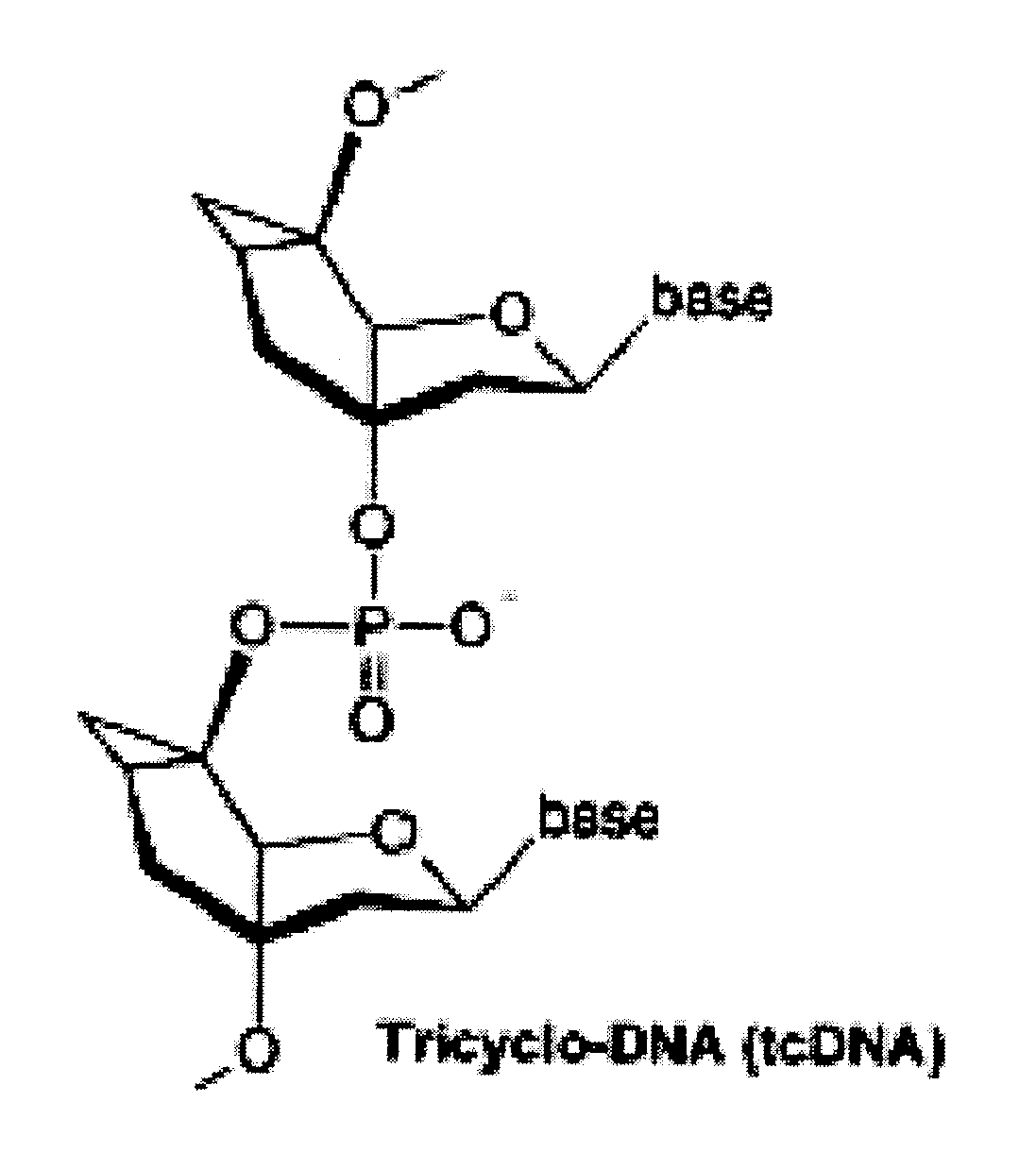
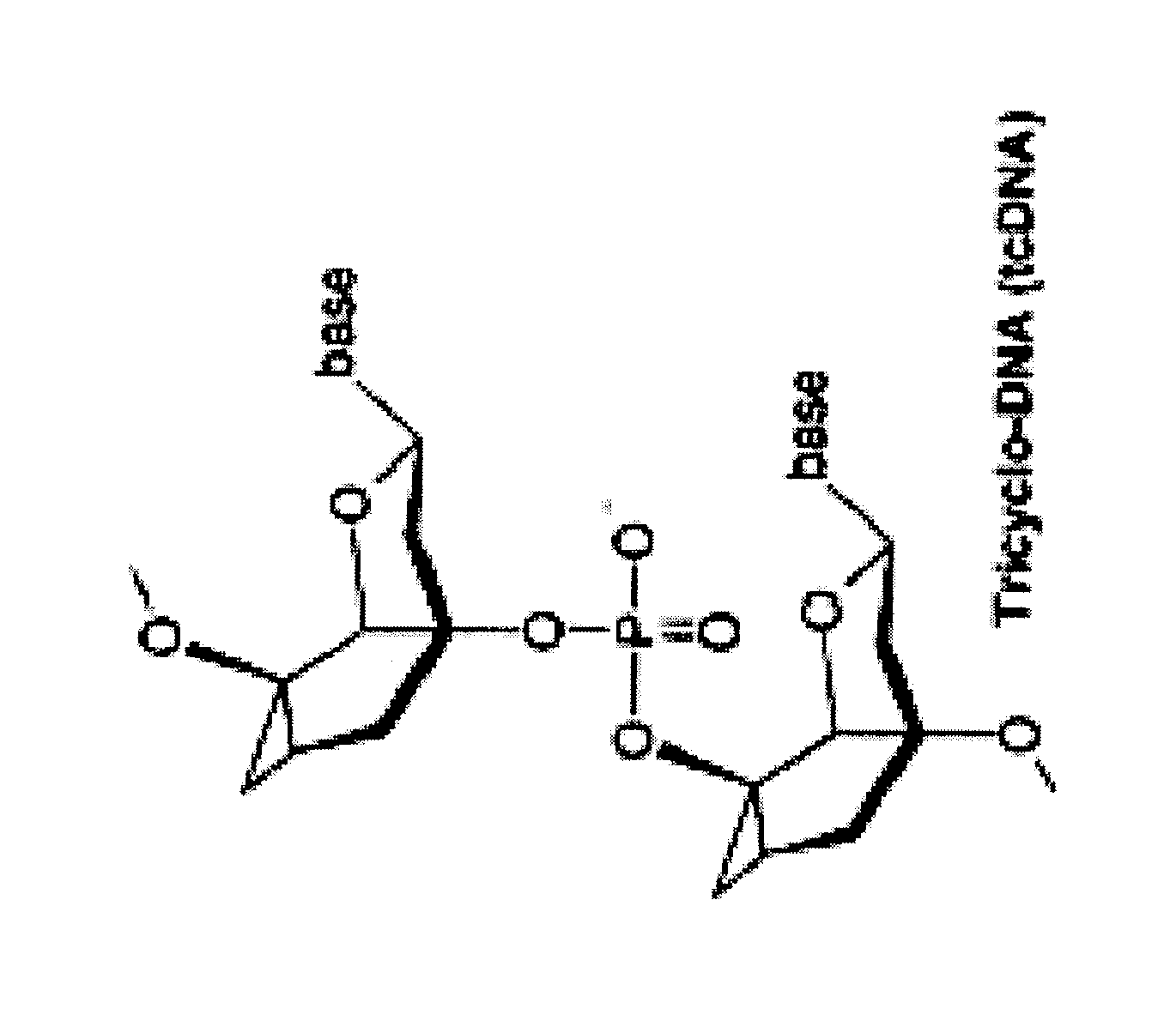
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
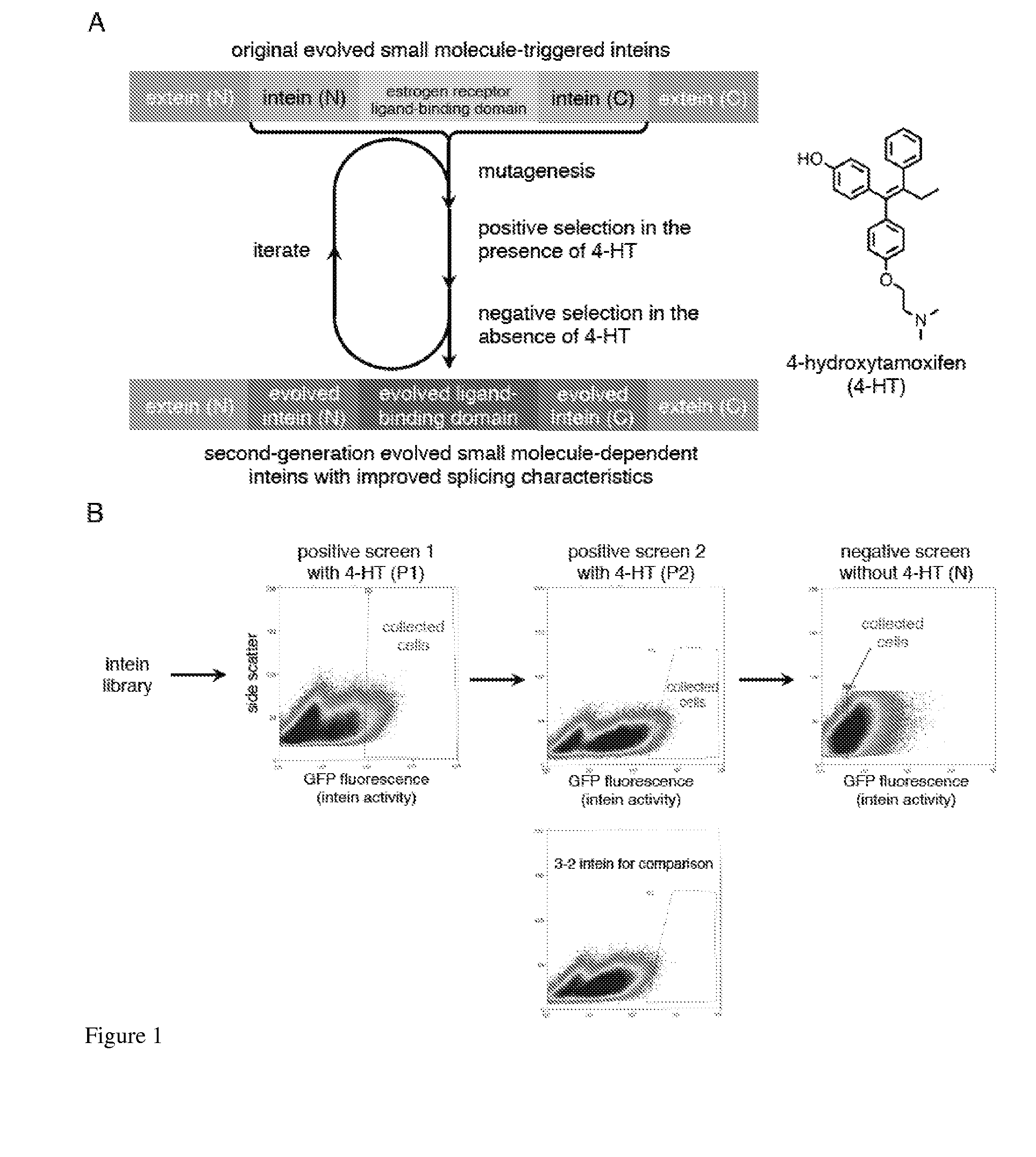
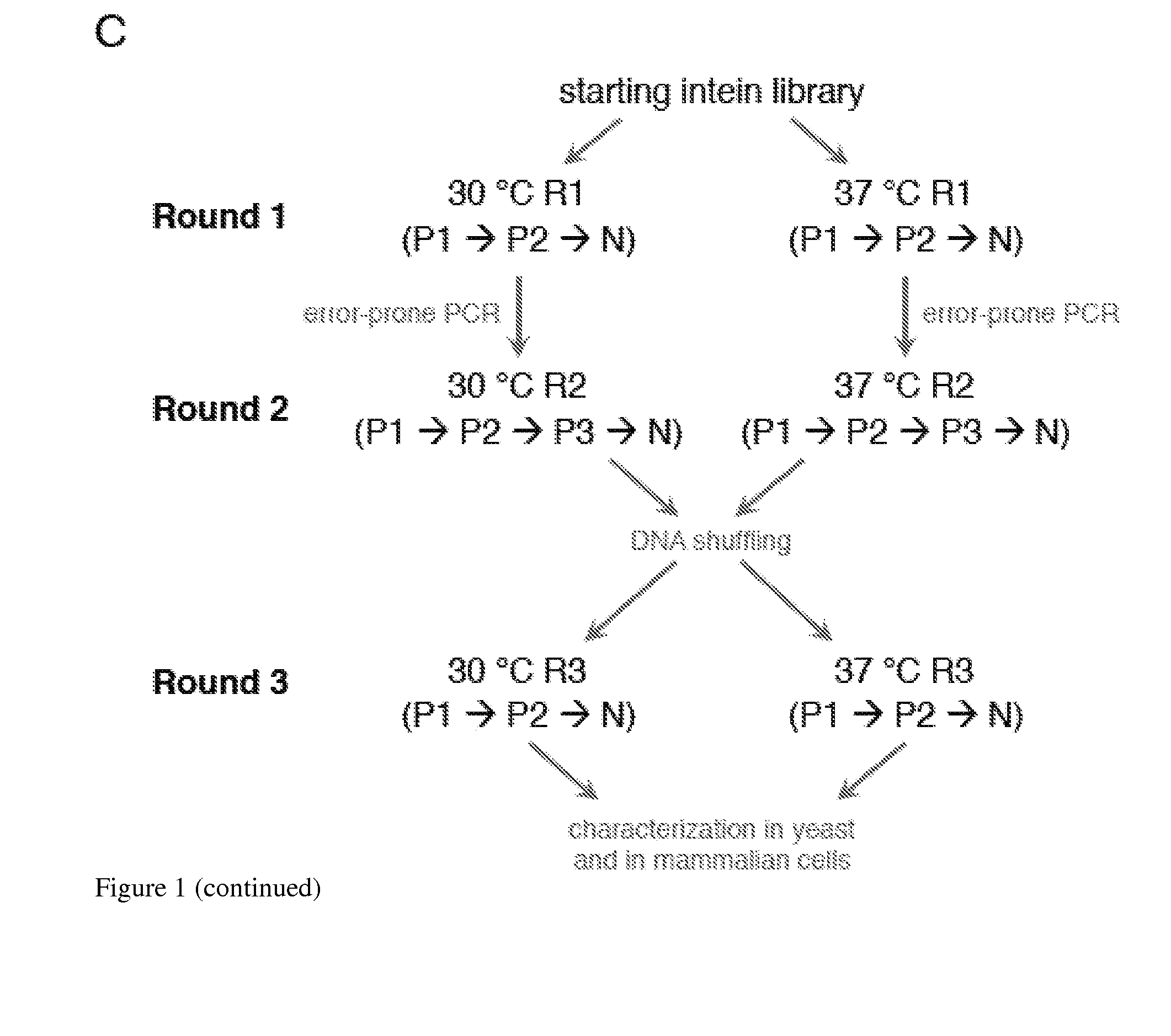
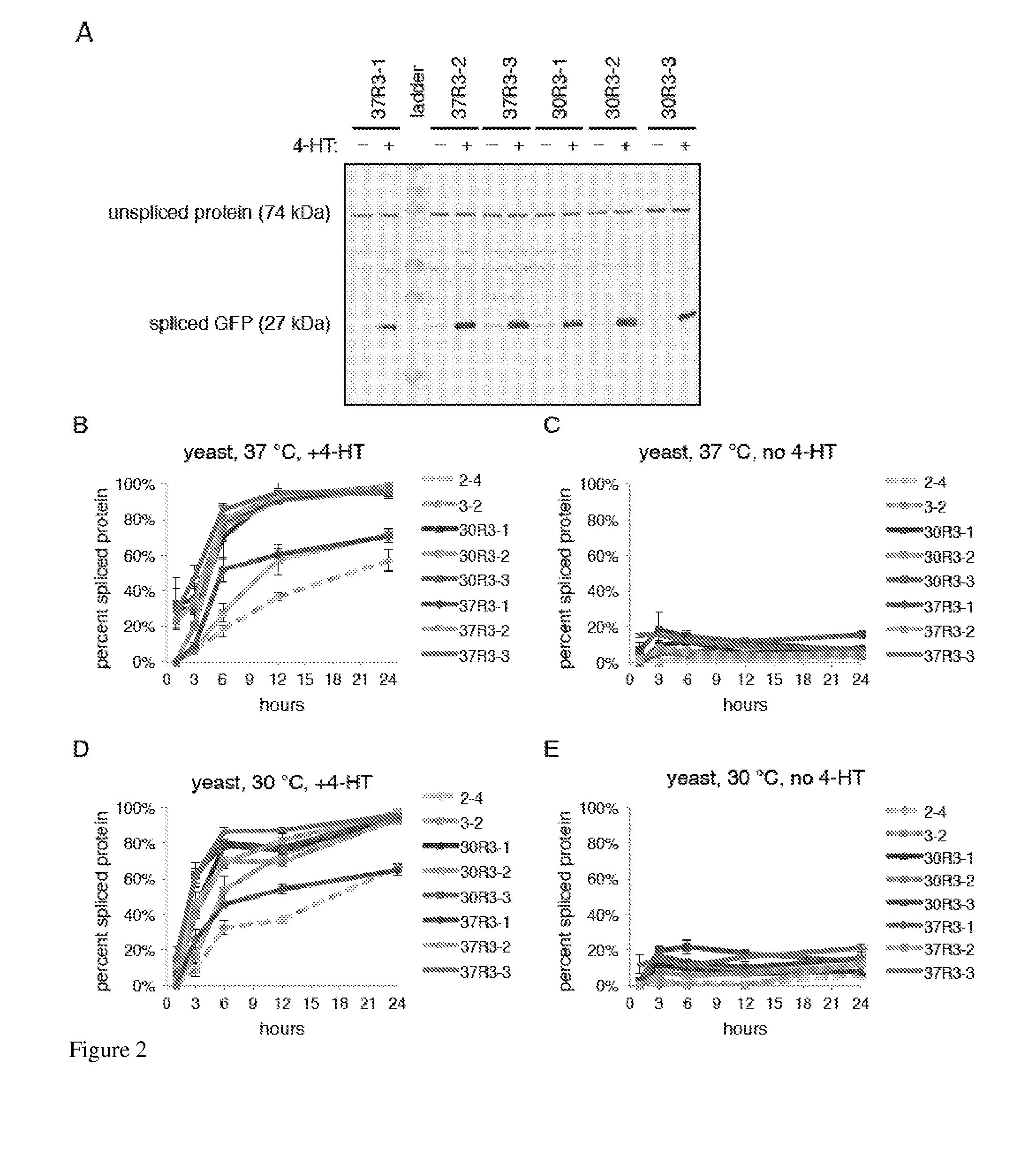
Small molecule-dependent inteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140065711A1Low splicing efficiencySlow splicingHydrolasesFusion with post-translational modification motifInteinNatural state
Elucidating the function of proteins in mammalian cells is particularly challenging due to the inherent complexity of these systems. Methods to study protein function in living cells ideally perturb the activity of only the protein of interest but otherwise maintain the natural state of the host cell or organism. Ligand-dependent inteins offer single-protein specificity and other desirable features as an approach to control protein function in cells post-translationally. Some aspects of this invention provide second-generation ligand-dependent inteins that splice to substantially higher yields and with faster kinetics in the presence of the cell-permeable small molecule 4-HT, especially at 37° C., while exhibiting comparable or improved low levels of background splicing in the absence of 4-HT, as compared to the parental inteins. These improvements were observed in four protein contexts tested in mammalian cells at 37° C., as well as in yeast cells assayed at 30° C. or 37° C. The newly evolved inteins described herein are therefore promising tools as conditional modulators of protein structure and function in yeast and mammalian cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
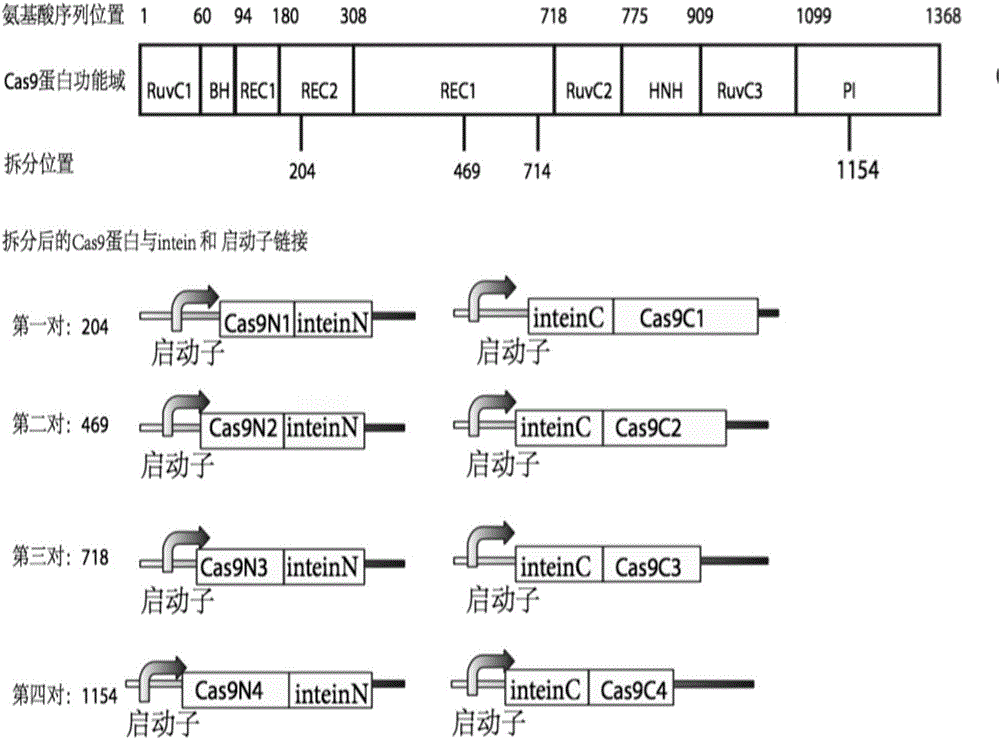
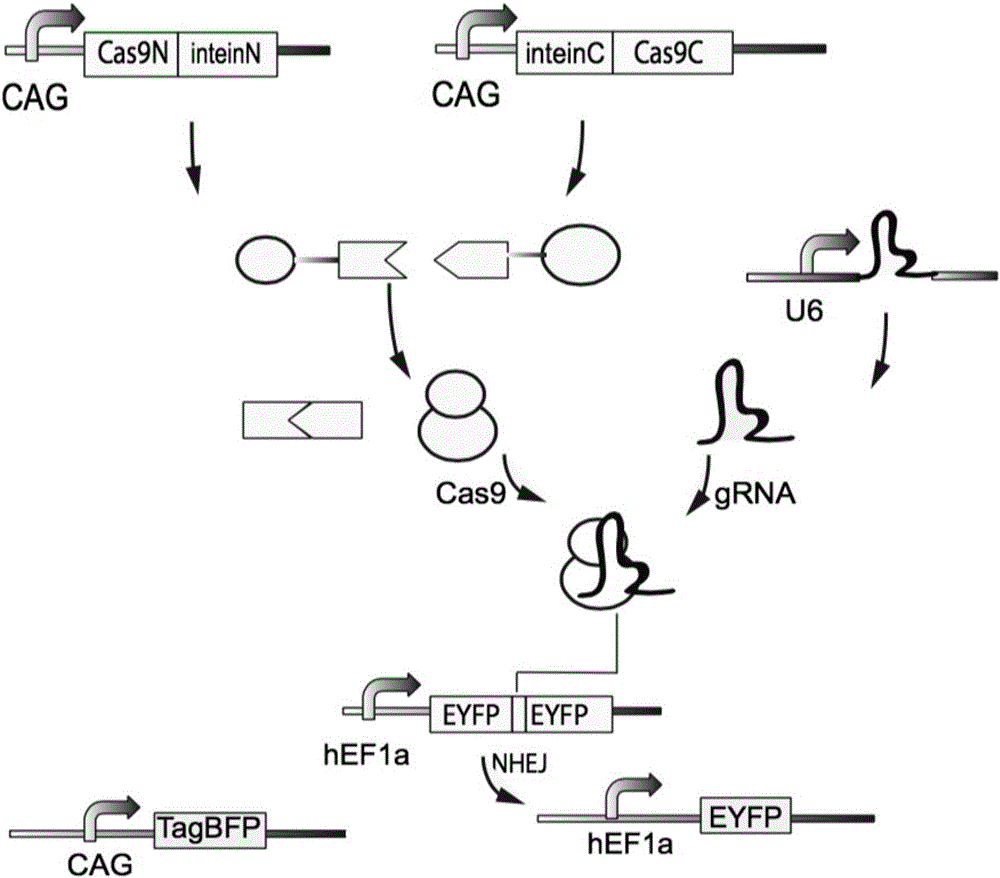
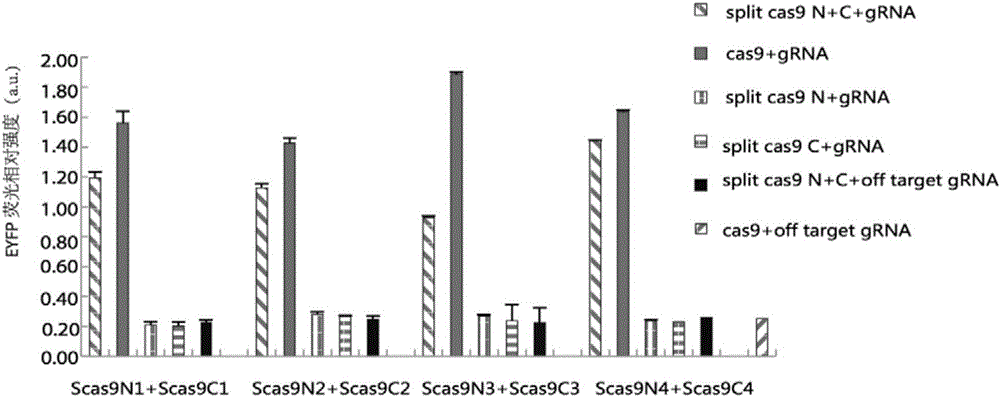
Method for carrying out gene editing and expression regulation by utilizing Cas splitting system
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
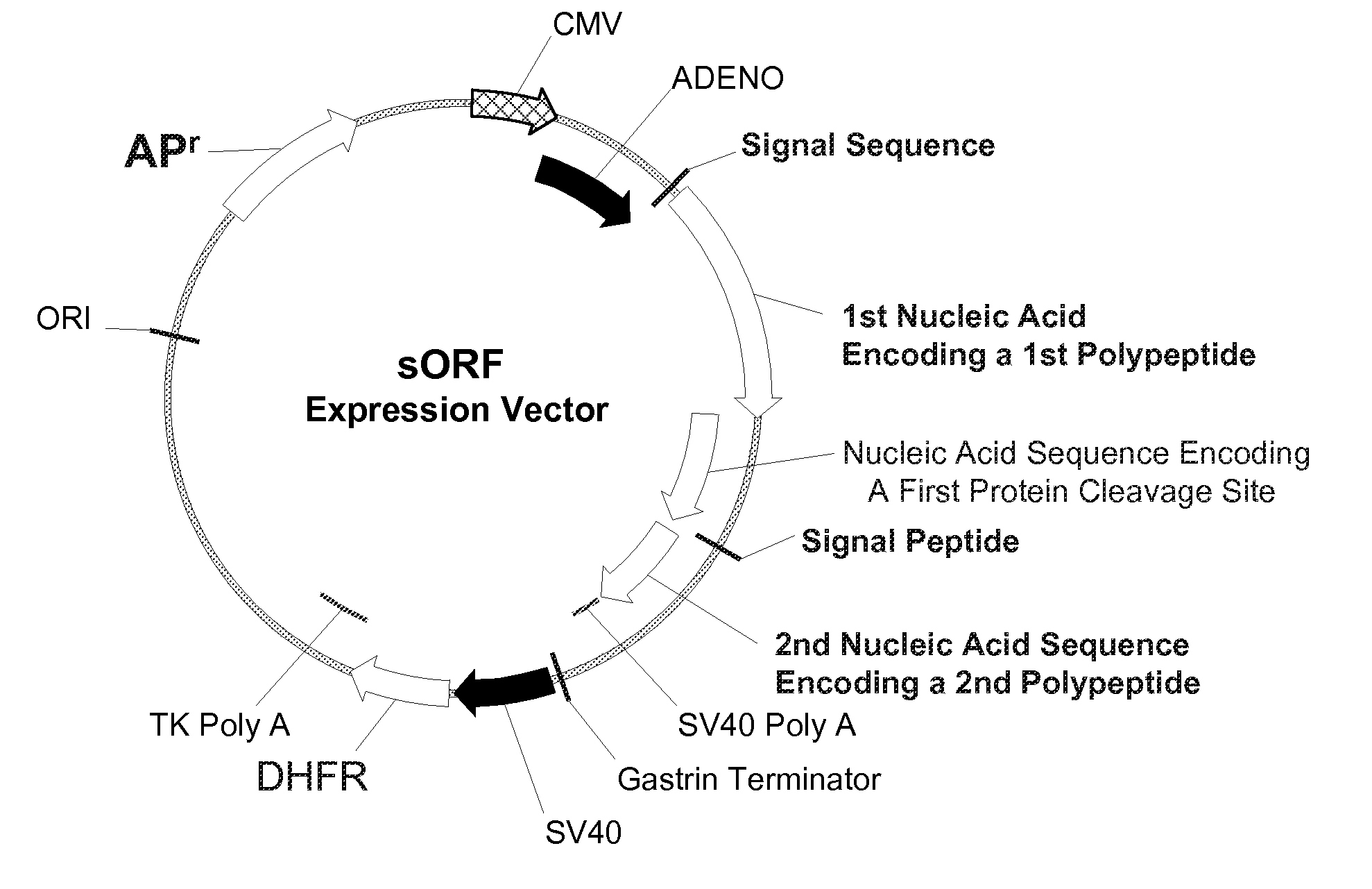
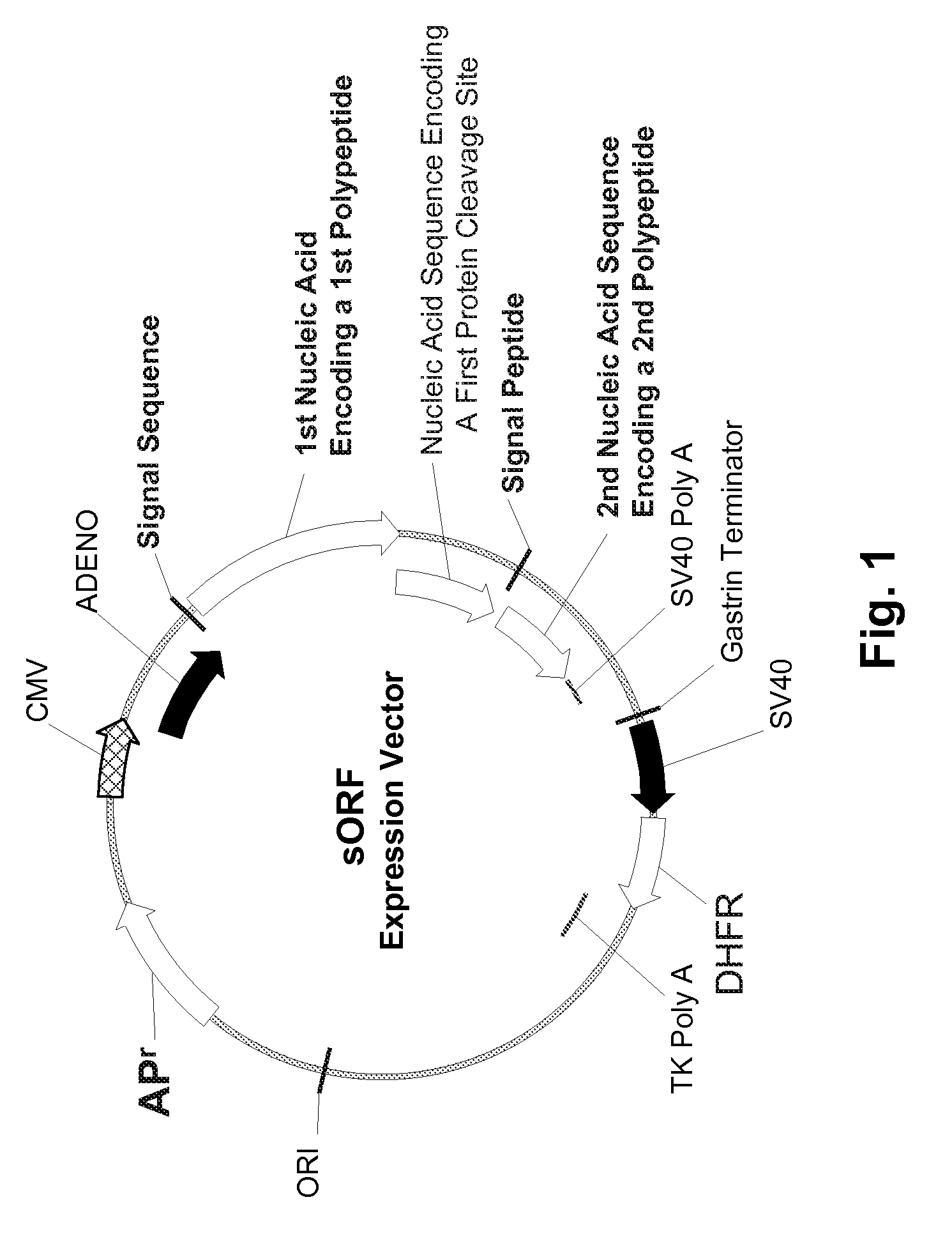
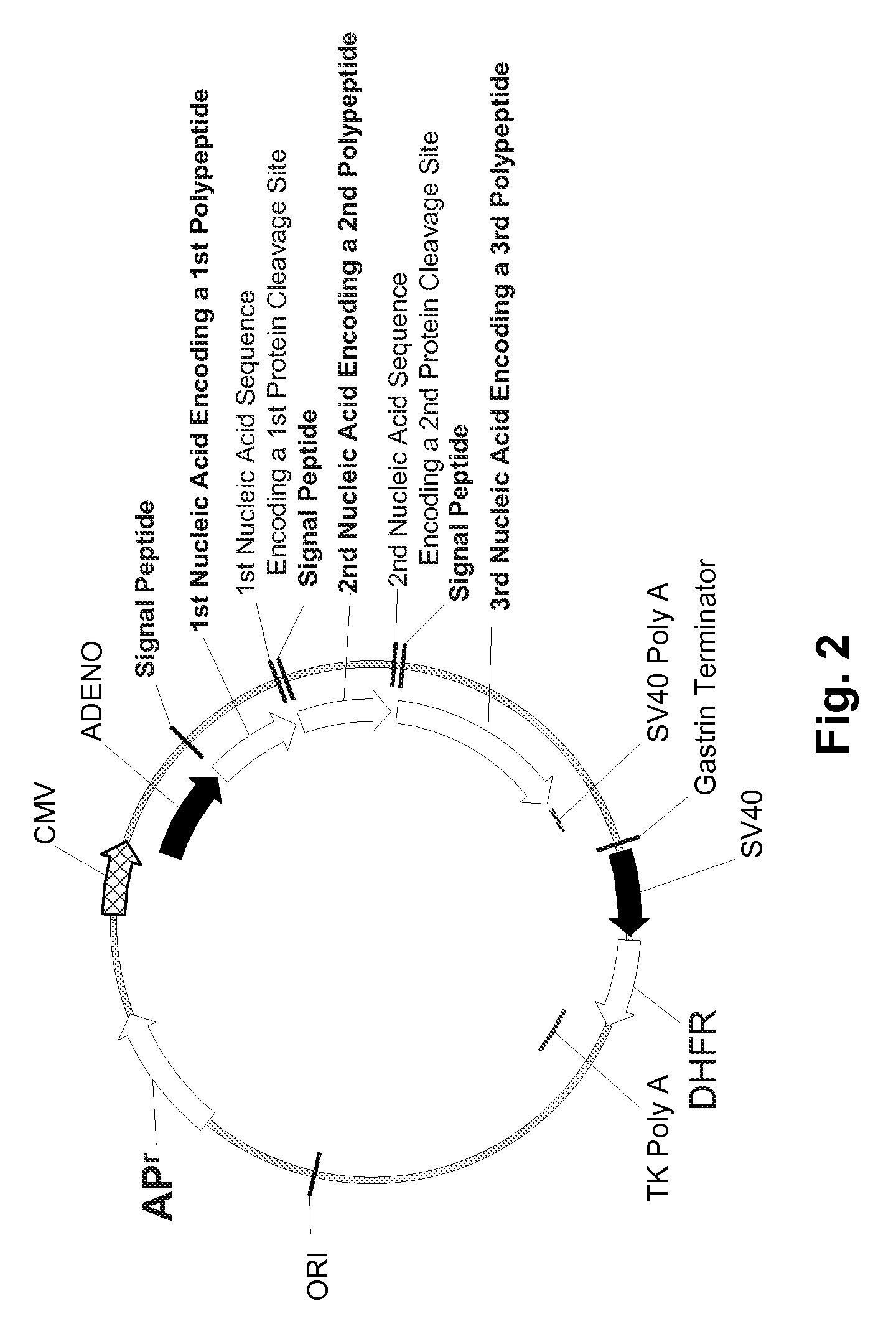
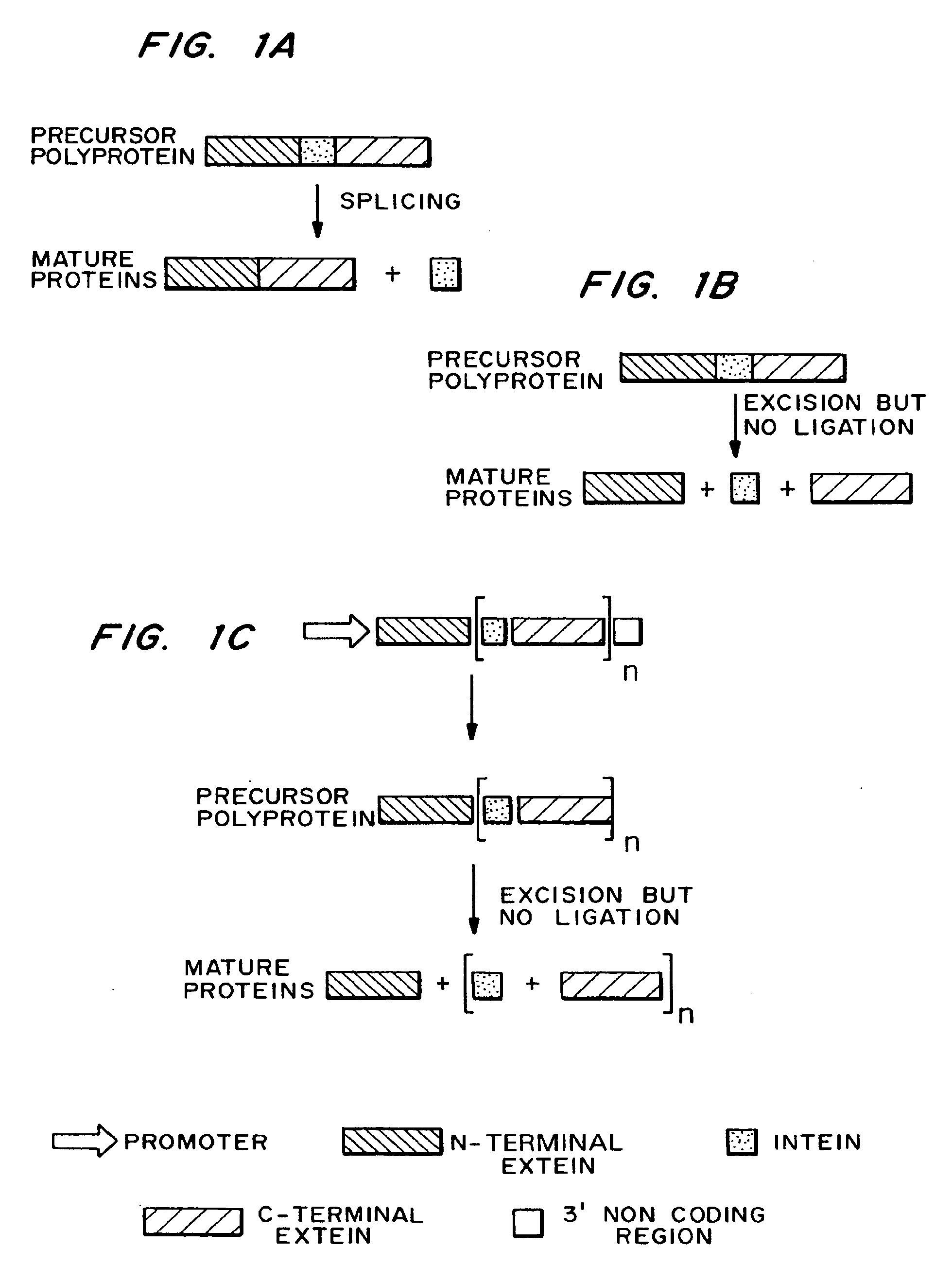
Multiple Gene Expression including sORF Constructs and Methods with Polyproteins, Pro-Proteins, and Proteolysis
InactiveUS20070065912A1Efficient expressionImprove economyFungiFusion with post-translational modification motifOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
Disclosed are useful constructs and methods for the expression of proteins using primary translation products that are processed within a recombinant host cell. Constructs comprising a single open reading frame (sORF) are described for protein expression including expression of multiple polypeptides. A primary translation product (a pro-protein or a polyprotein) contains polypeptides such as inteins or hedgehog family auto-processing domains, or variants thereof, inserted in frame between multiple protein subunits of interest. The primary product can also contain cleavage sequences such as other proteolytic cleavage or protease recognition sites, or signal peptides which contain recognition sequences for signal peptidases, separating at least two of the multiple protein subunits. The sequences of the inserted auto-processing polypeptides or cleavage sites can be manipulated to enhance the efficiency of expression of the separate multiple protein subunits. Also disclosed are independent aspects of conducting efficient expression, secretion, and / or multimeric assembly of proteins such as immunoglobulins. Where the polyprotein contains immunoglobulin heavy and light chain segments or fragments capable of antigen recognition, in an embodiment a selectable stoichiometric ratio is at least two copies of a light chain segment per heavy chain segment, with the result that the production of properly folded and assembled functional antibody is made. Modified signal peptides, including such from immunoglobulin light chains, are described.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
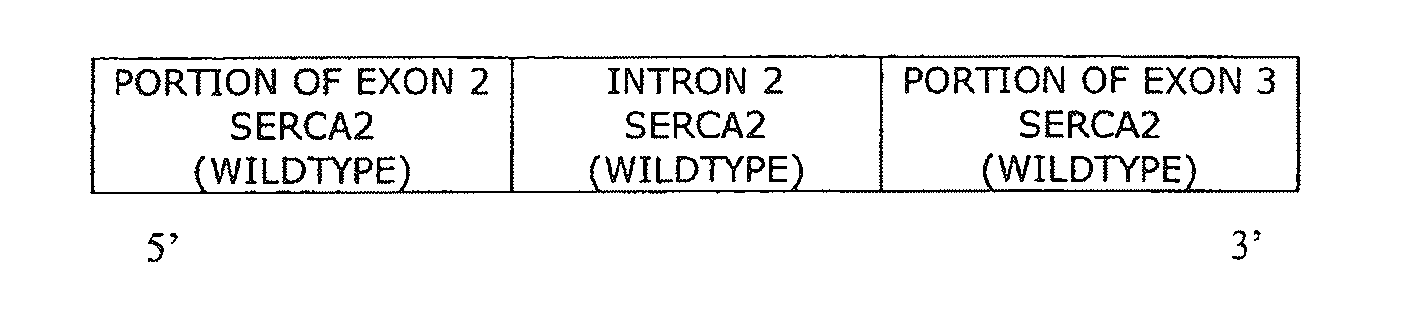
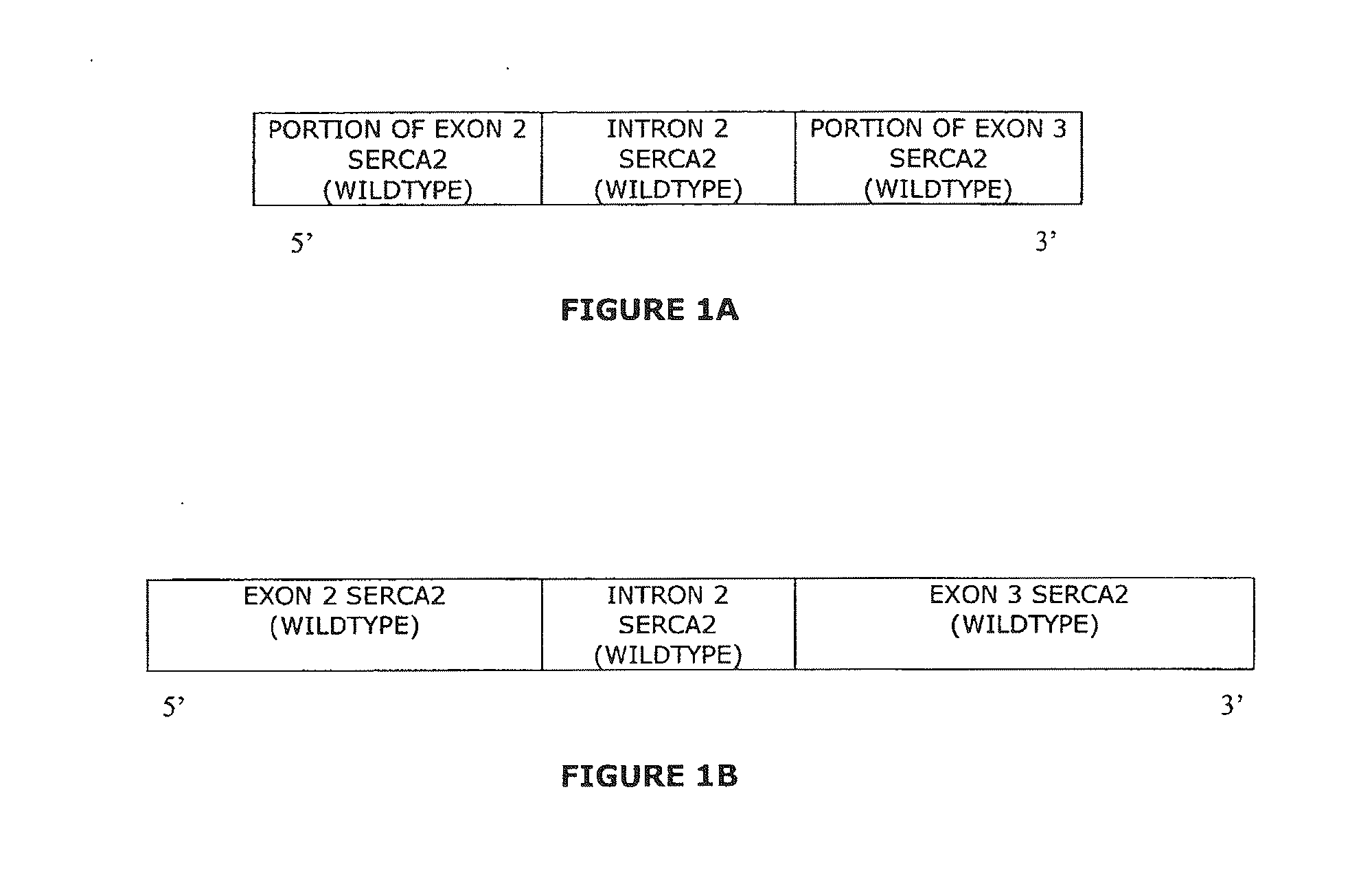
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
InactiveUS20110247090A1High expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideReticulum cell
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
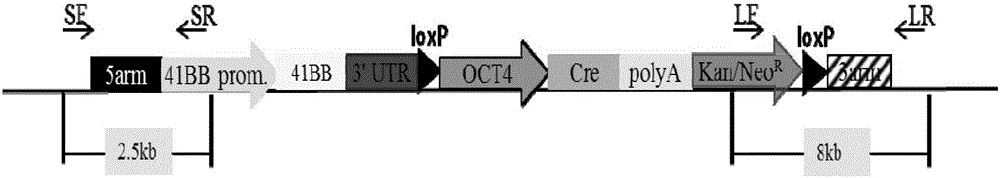
Overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105087620AHigh copy numberLower activation thresholdVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInteinEmbryo
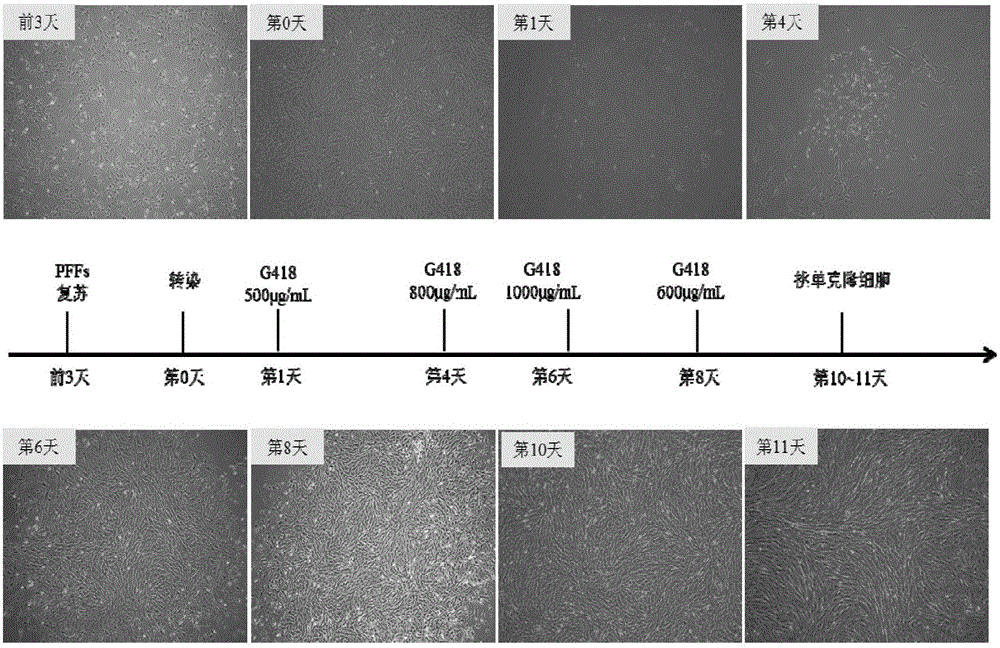
The invention provides an overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of an intron 1 of a rosa26 gene, a 4-1BB regulatory sequence and an OCT4 specific promoter; the left homologous arm, a 4-1BB expression cassette, LoxP locus-contained Cre and Neo expression cassettes, the right homologous arm and negative selection DTA diphtheria toxin are connected in sequence to obtain a 4-1BB homologous recombinant vector p4BOCNDR; the vector and a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated) targeting vector of sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid) containing the intron 1 of the specific targeting porcine rosa26 gene are transferred together into a porcine fetus fibroblast; by taking a positive cell as a donor cell and an oocyte as a recipient cell, a cloned embryo is obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique; the cloned embryo is transplanted into a porcine uterus for fetation to obtain a transgenic pig integrating a 4-1BB gene at the fixed point of a first intron of the rosa26 gene and automatically deleting a marker gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
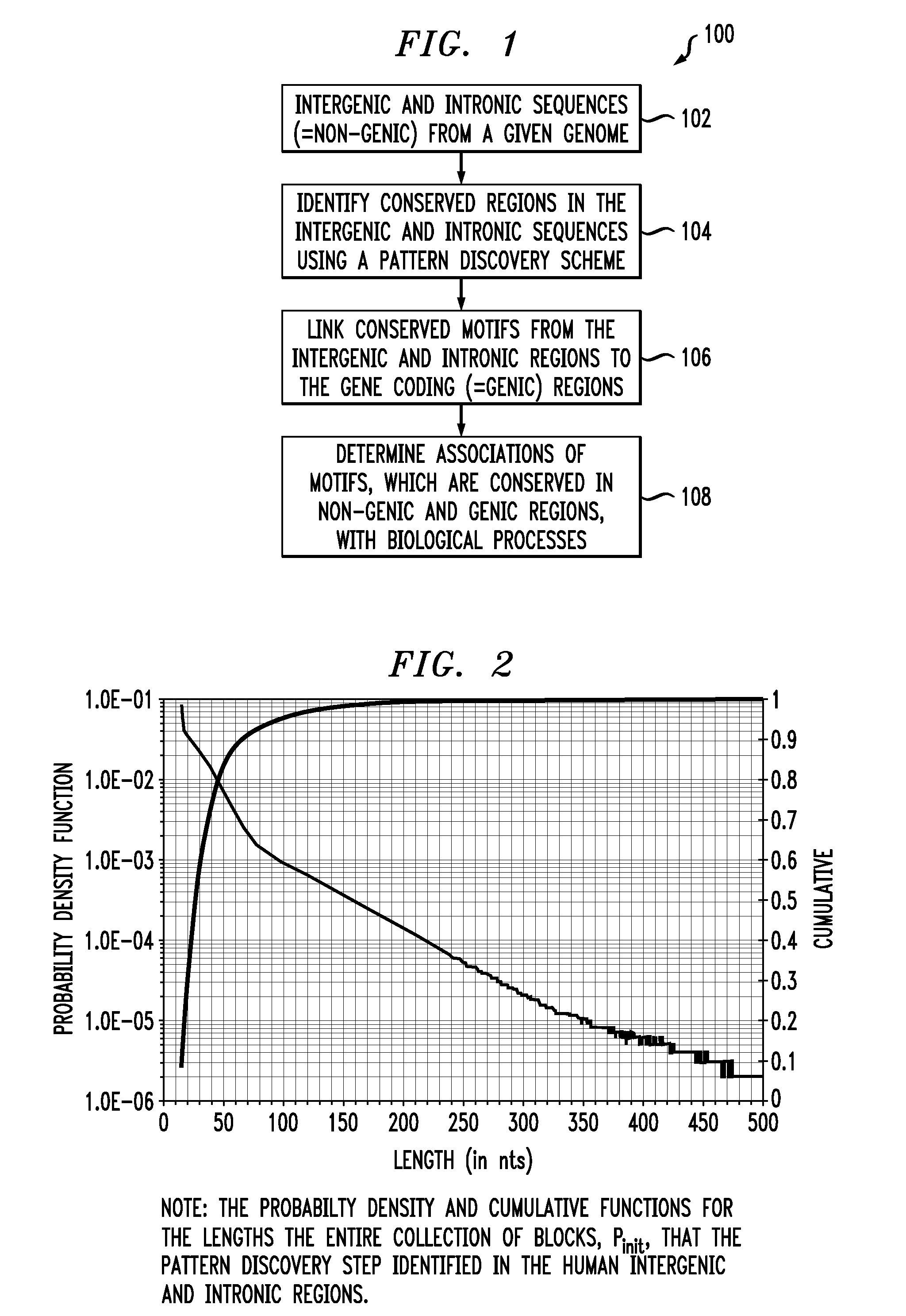
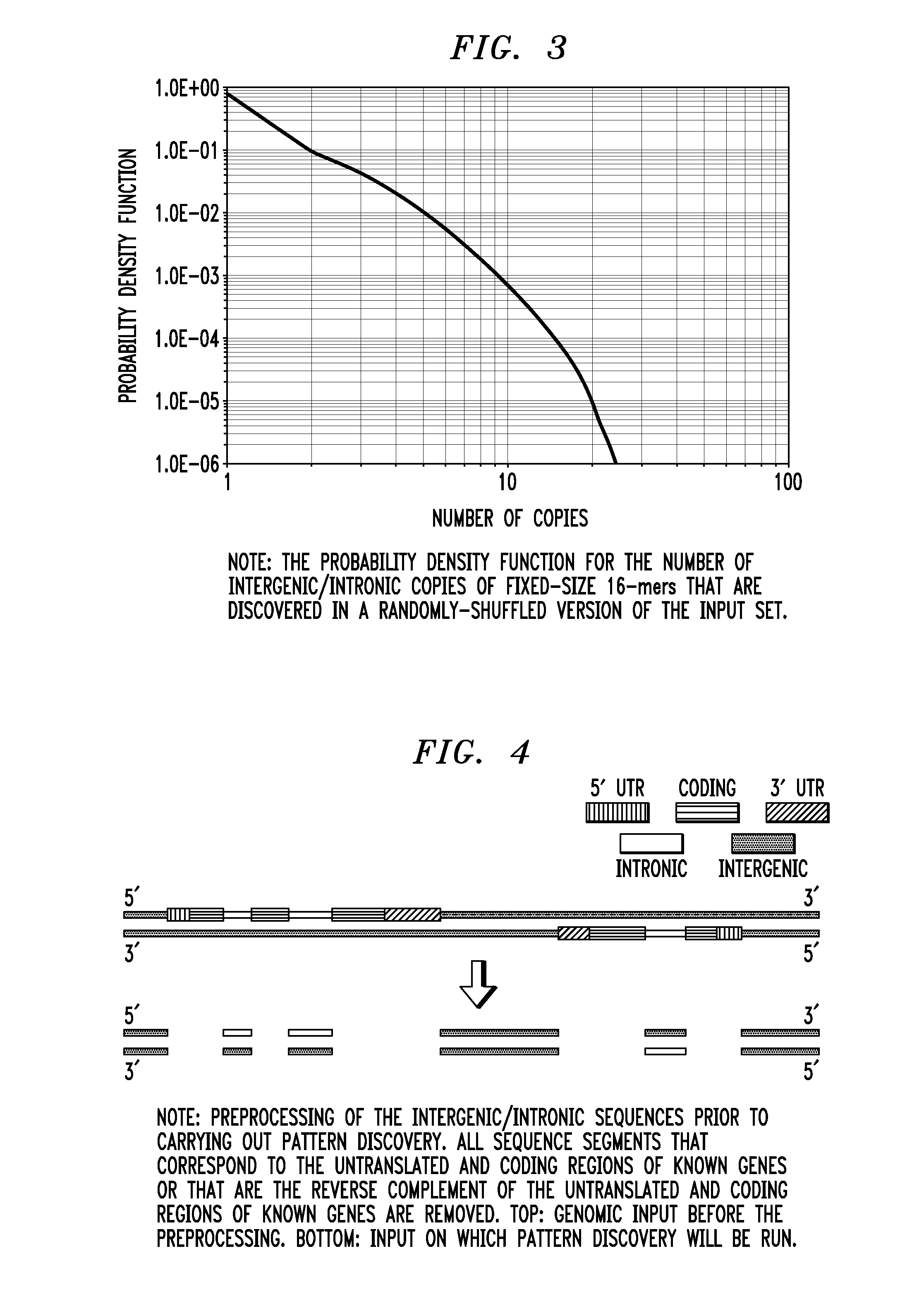
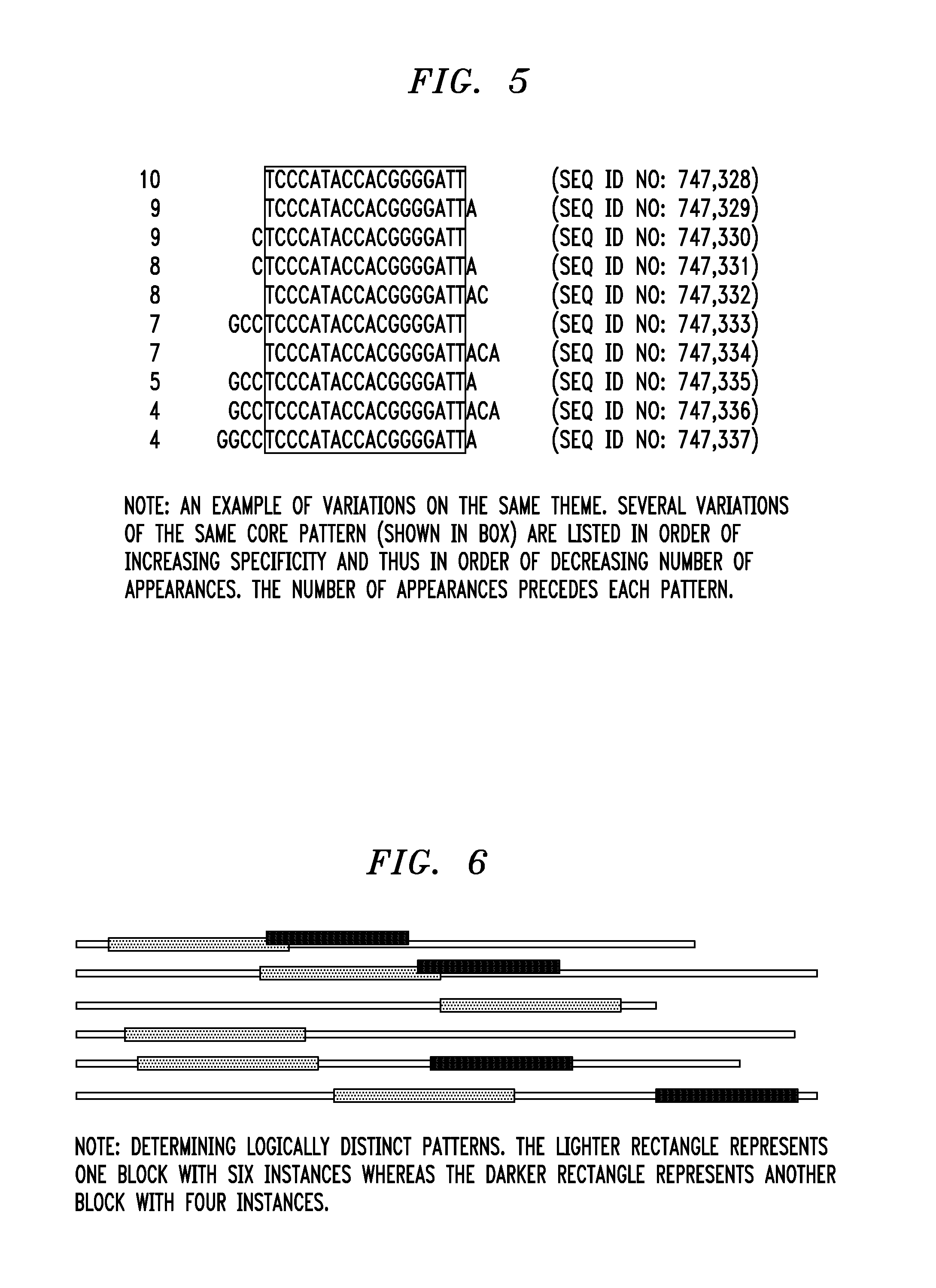
Ribonucleic acid interference molecules and binding sites derived by analyzing intergenic and intronic regions of genomes
In one aspect of the invention, a method for regulating the expression of a transcript comprises using at least one interfering RNA molecule that binds to an area of transcript containing a region that corresponds to at least one sequence having SEQ ID NO: 1, the interfering RNA molecule regulating the expression of the transcript through post-transcriptional silencing. In another aspect, a method for regulating the expression of a transcript comprises at least one of the provided sequences having SEQ ID NO: 1 being used to design an interfering RNA molecule that contains a region that corresponds to the reverse complement of one or more sequences having SEQ ID NO: 1, the interfering molecule regulating, through post-transcriptional silencing, transcripts that contain the sequence having SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
ActiveUS20090110689A1Suppress immune responseSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderHeteroduplexAutoimmune condition
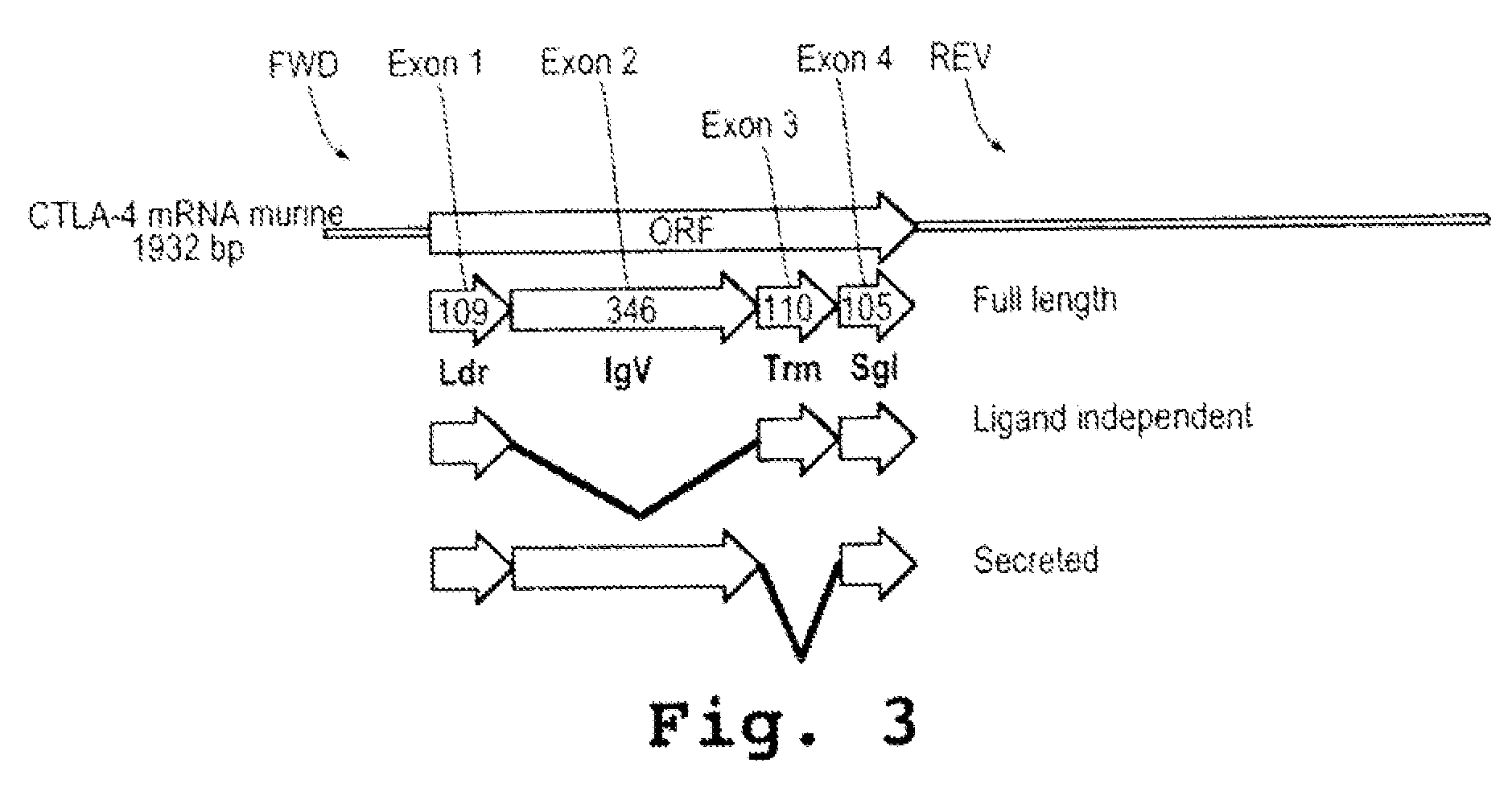
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 22 in SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
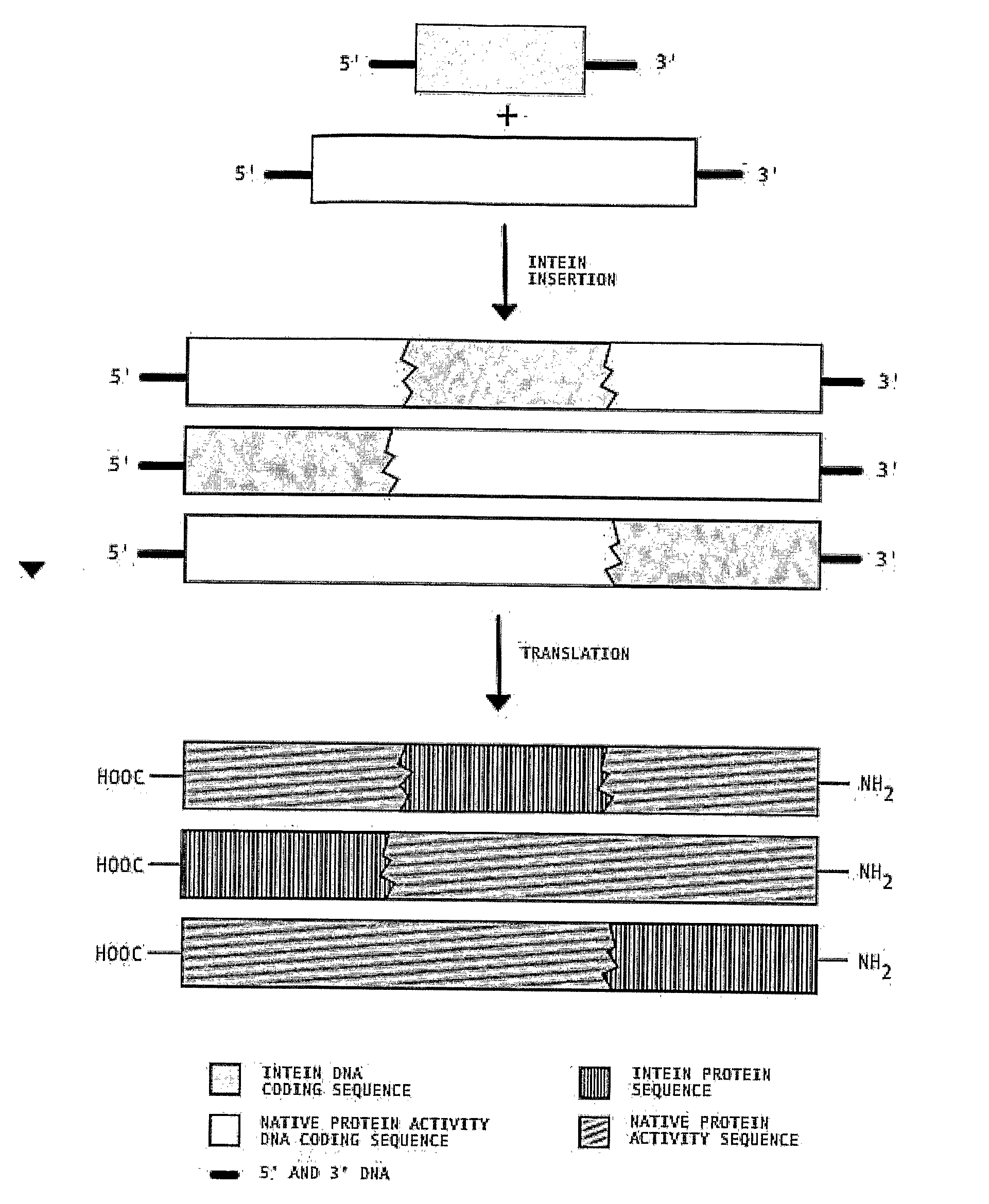
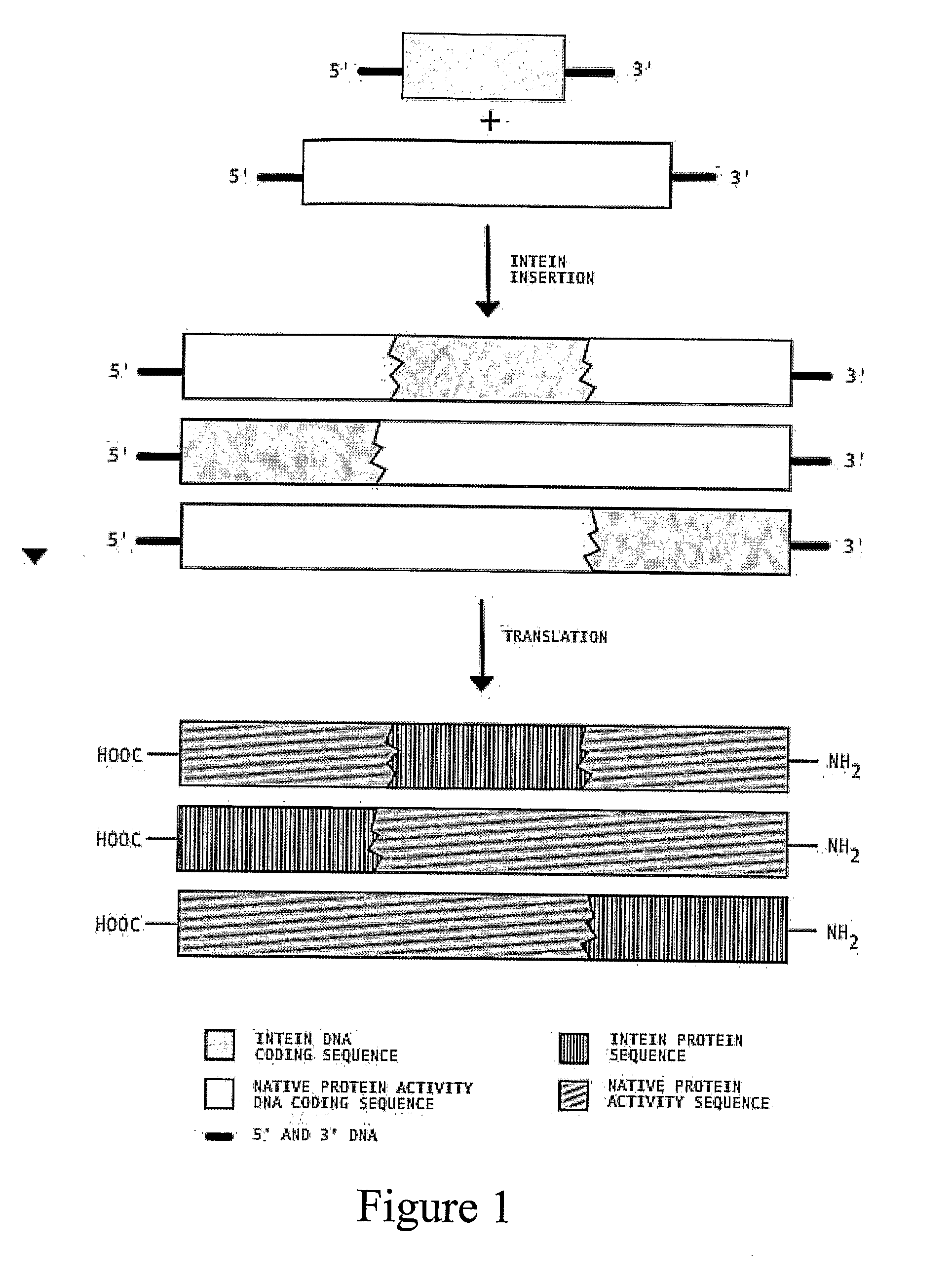
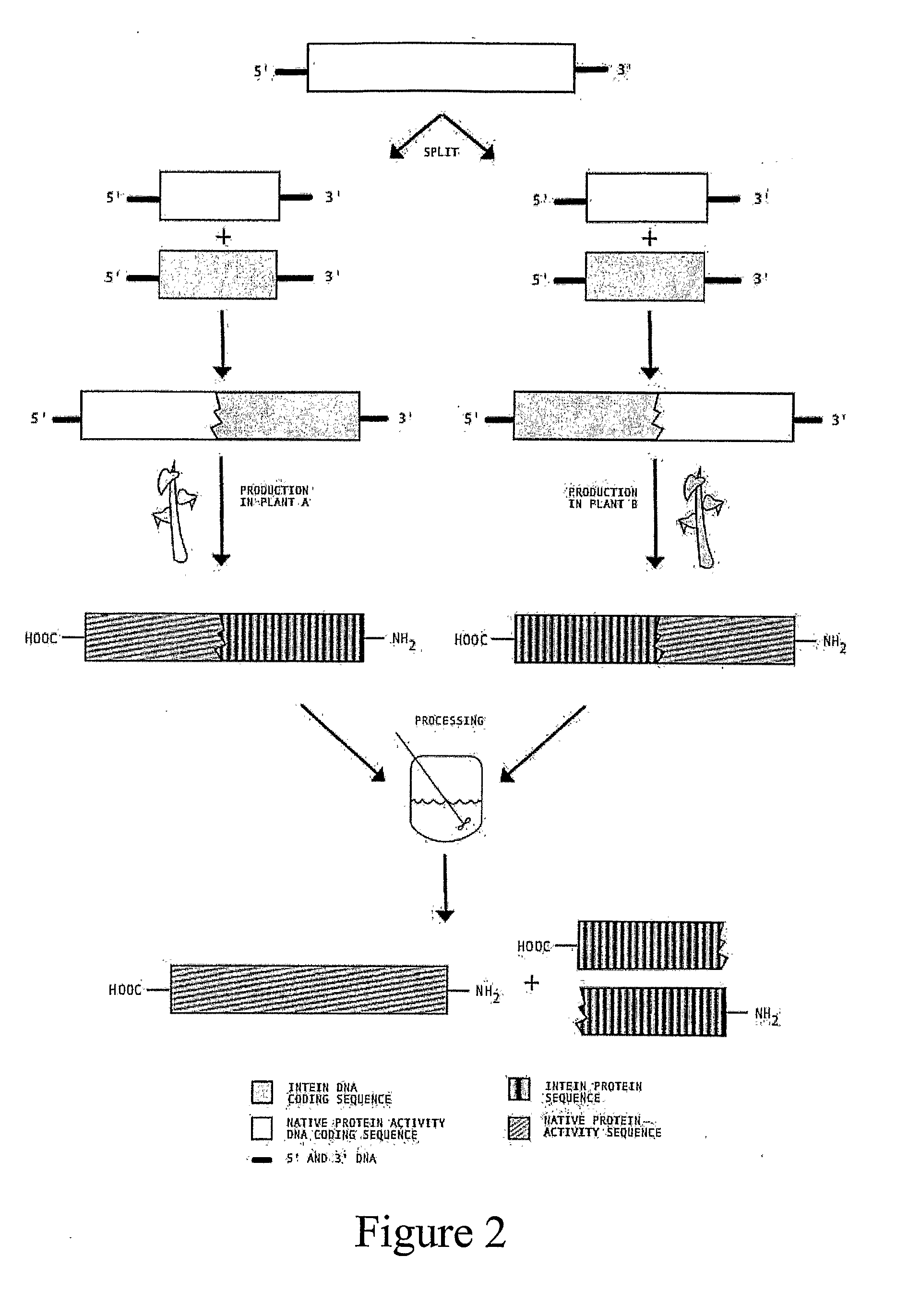
Transgenic Plants Expressing Intein Modified Proteins and Associated Processes for Bio-Pharmaceutical Production
InactiveUS20080115243A1Other foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureBiotechnologyTherapeutic protein
Transgenic plants that express CIVPS or intein modified therapeutic proteins, compositions of matter comprising them, therapeutic proteins made from the transgenic plants, methods to construct the transgenic plants containing CIVPS or intein modified therapeutic genes, methods to express CIVPS or intein modified therapeutic proteins in plants, and methods of using the transgenic plants.
Owner:AGRIVIDA
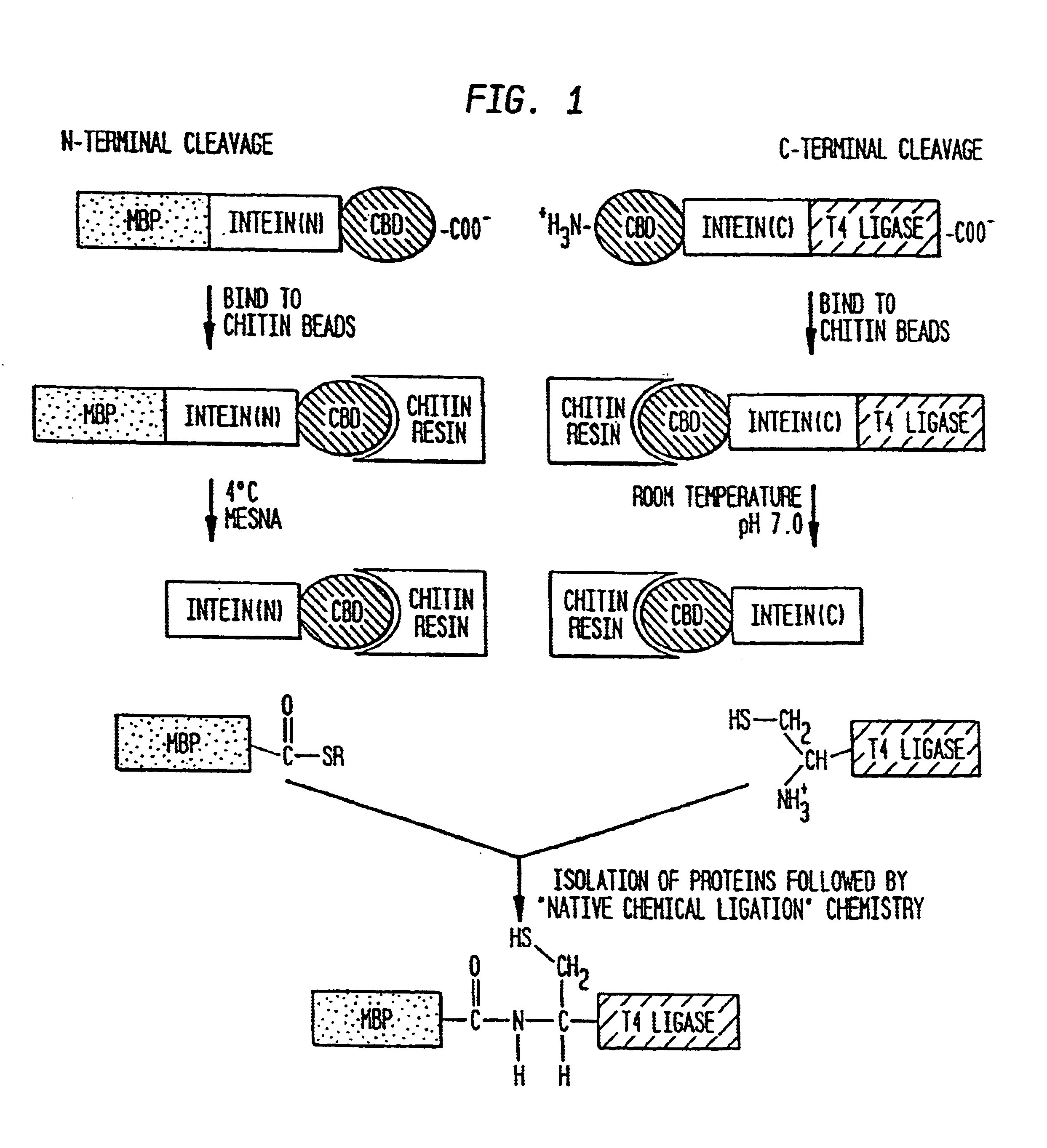
Genetic system and self-cleaving inteins derived therefrom, bioseparations and protein purification employing same, and methods for determining critical, generalizable amino acid residues for varying intein activity
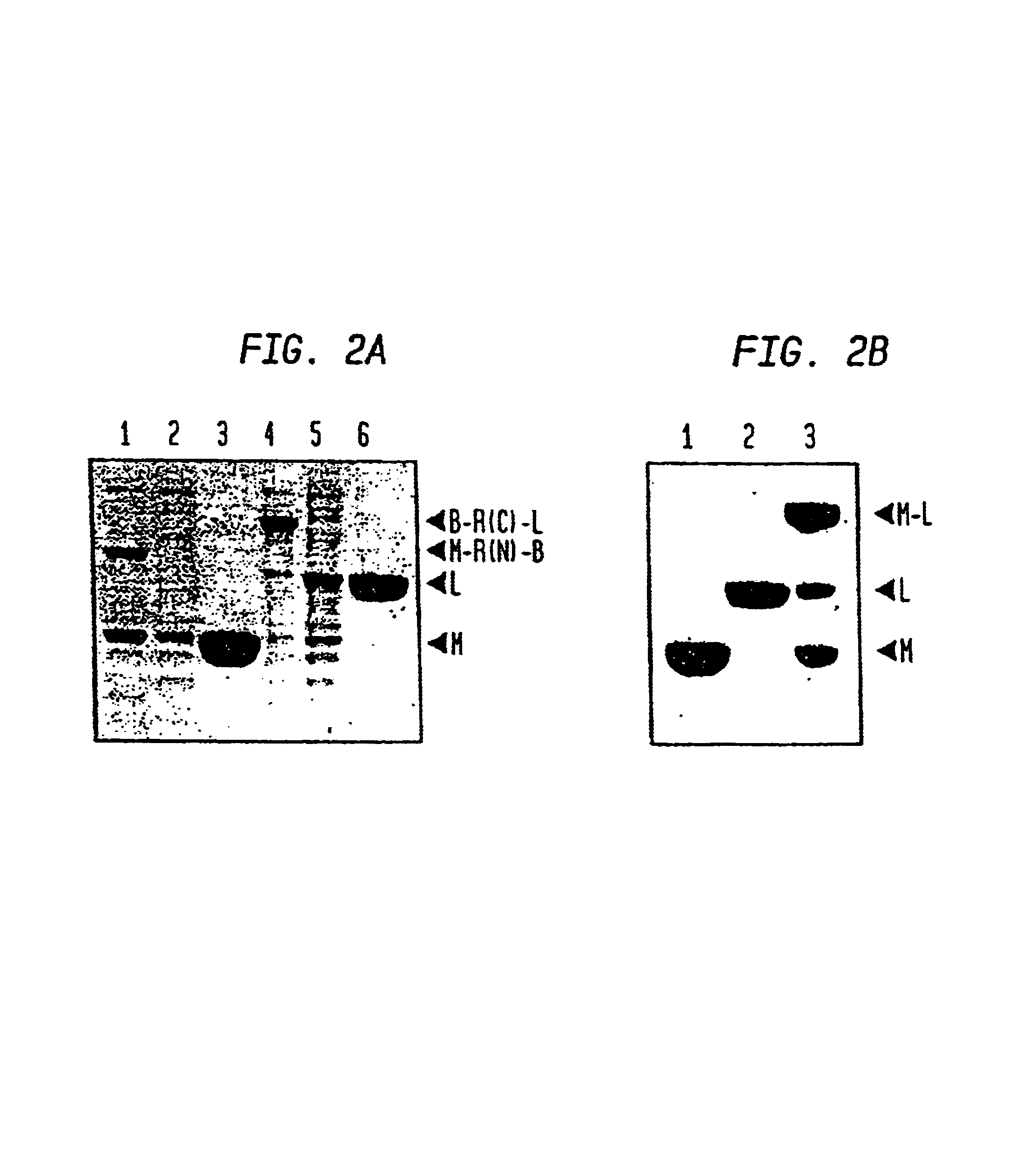
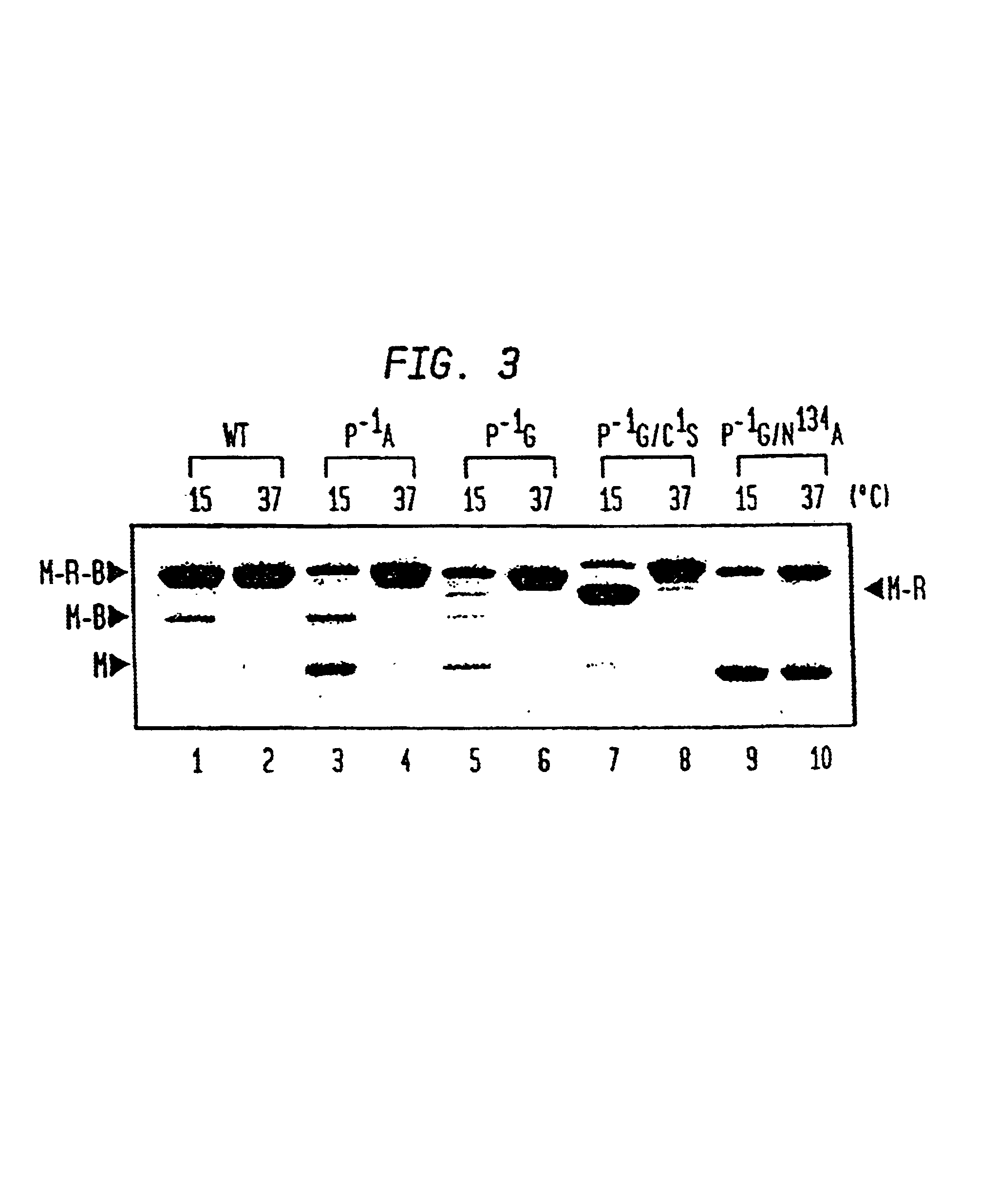
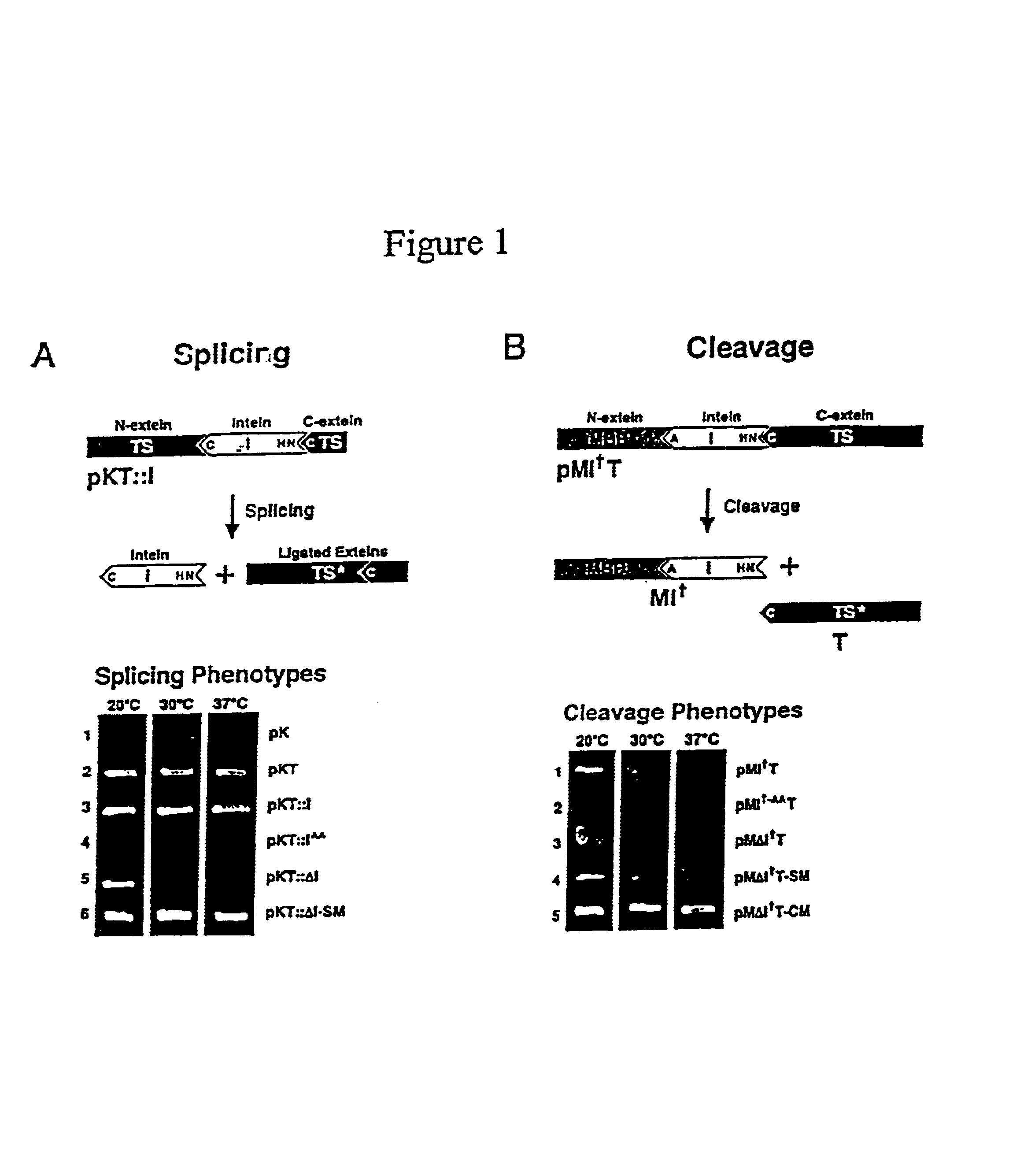
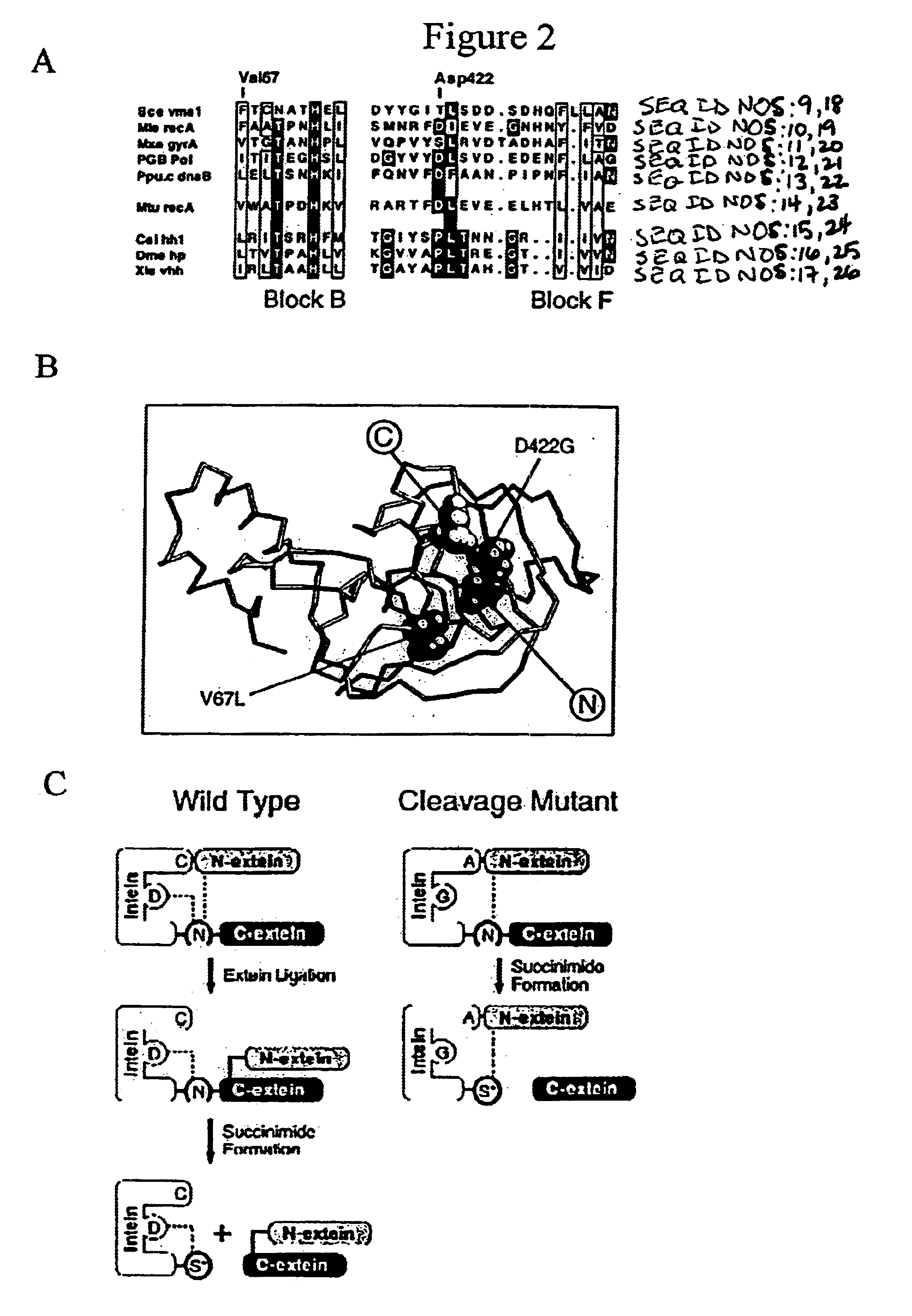
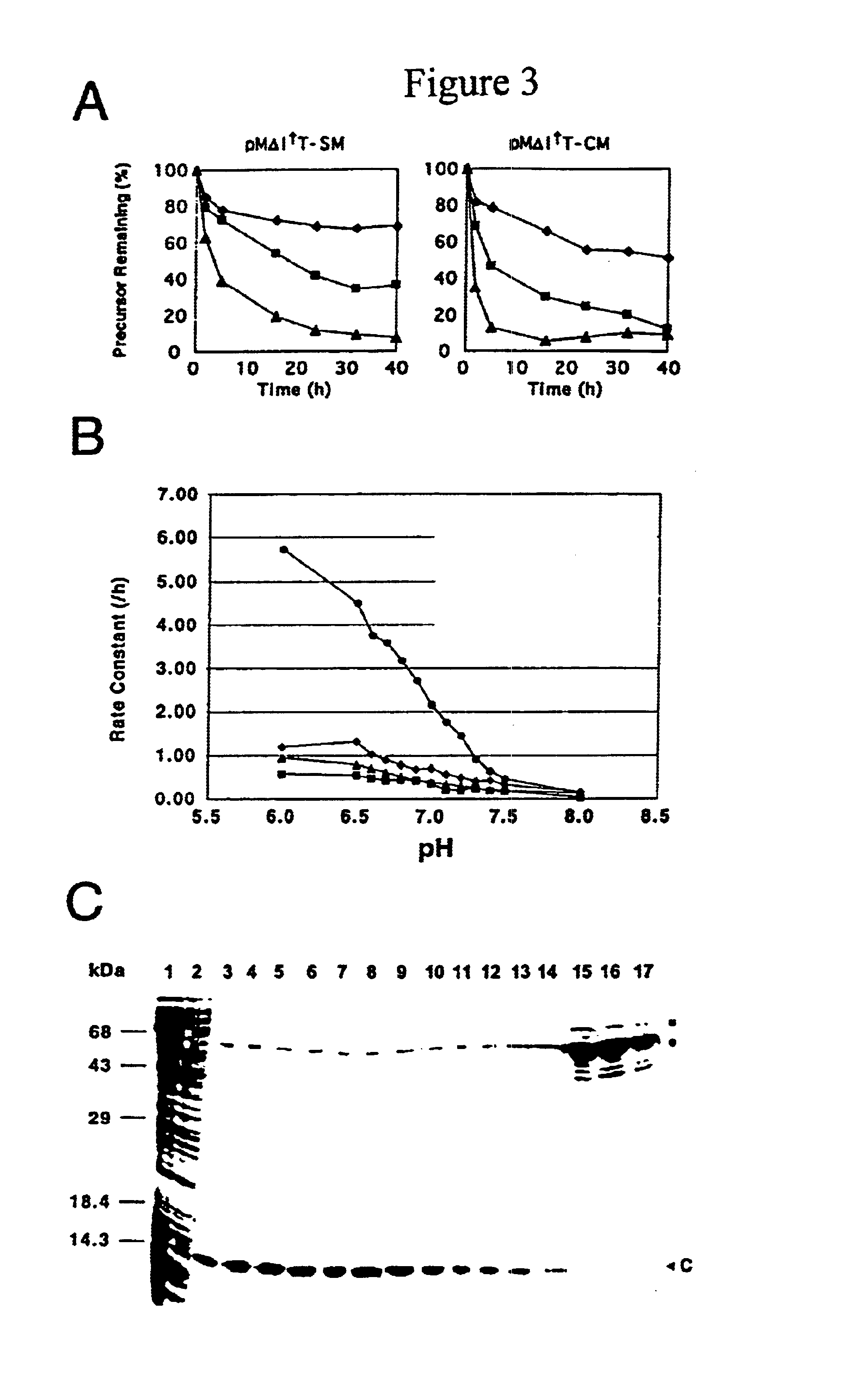
A self-cleaving element for use in bioseparations has been derived from a naturally occurring, 43 kDa protein splicing element (intein) through a combination of protein engineering and random mutagenesis. A mini-intein (18 kDa) previously engineered for reduced size had compromised activity and was therefore subjected to random mutagenesis and genetic selection. In one selection a mini-intein was isolated with restored splicing activity, while in another, a mutant was isolated with enhanced, pH-sensitive C-terminal cleavage activity. The enhanced cleavage mutant has utility in affinity fusion-based protein purification. The enhanced splicing mutant has utility in purification of proteins such as toxic proteins, for example, by inactivation with the intein in a specific region and controllable splicing. These mutants also provide new insights into the structural and functional roles of some conserved residues in protein splicing. Thus, disclosed and claimed are: a genetic system and self-cleaving inteins therefrom; bioseparations employing same; protein purification by inactivation with inteins in specific regions and controllable intein splicing; methods for determining critical, generalizable residues for varying intein activity; and products.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
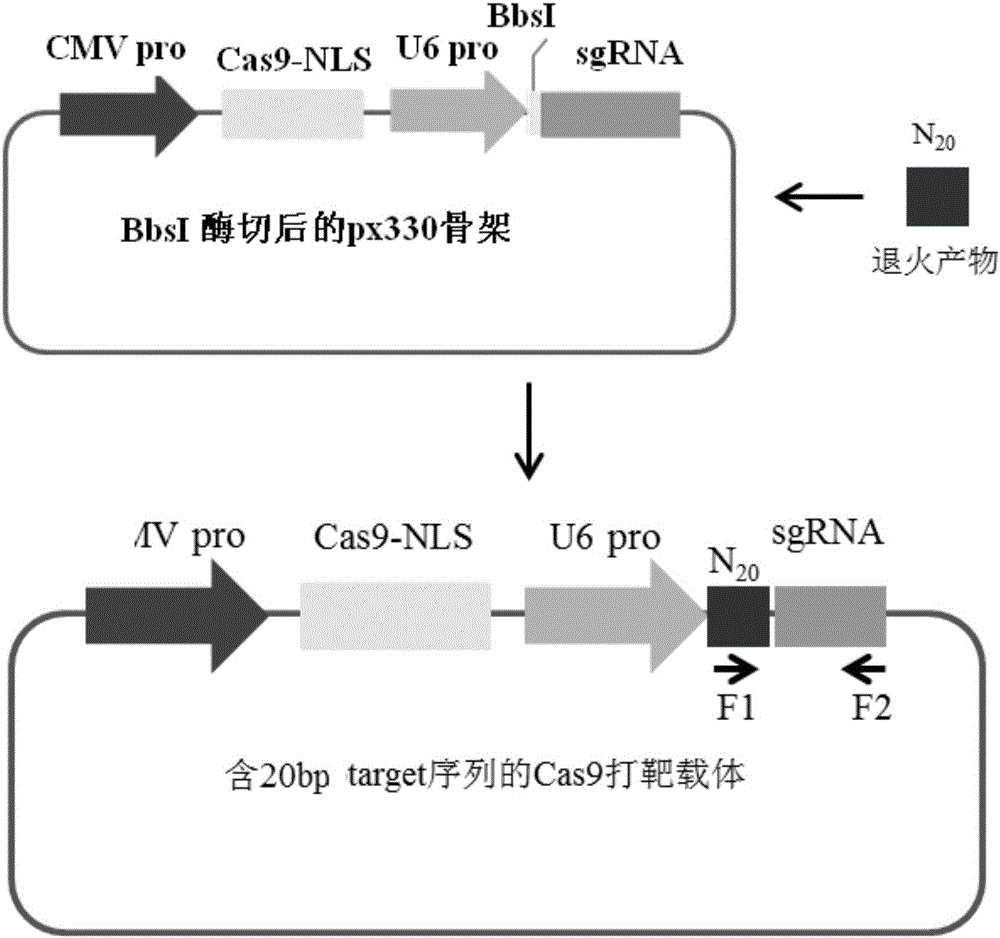
Method for pig CMAH gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specially targeting CMAH gene
The invention discloses a method for pig CMAH gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specially targeting a CMAH gene. A target sequence of the sgRNA for specially targeting the CMAH gene on the CMAH gene meets a 5'-N(20)NGG-3' sequence arrangement rule, wherein the N(20) represents 20 continuous bases, and each N represents A, T, C or G; the target sequence on the CMAH gene locates at a 5-exon coding area or a junction position of adjacent introns of an N end of the CMAH gene; and the target sequence on the CMAH gene is unique. The sgRNA is used in a method for pig CMAH gene specific knockout through the CRISPR-Cas9, the pig CMAH gene can be rapidly, accurately, efficiently and specifically knocked out, and the problems of the long period and high cost of construction of a CMAH gene knockout pig are effectively solved.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
CRISPR-Cas9 specificity pig SLA-1 gene knockout method and sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene
The present invention discloses a pig SLA-1 gene knockout method using CRISPR-Cas9 specificity and sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene. The target sequence of the sgRNA used for specific targeting SLA-1 gene in the SLA-1 gene complies with a 5'-N (20) NGG-3' sequence arrangement rule, wherein N (20) represents 20 consecutive basic groups, wherein each N represents a A or T or C or G; the target sequence in the SLA-1 gene is located at the four exon coding regions of the N-terminal of the SLA-1 gene or the junction of adjacent introns; and the target sequence in the SLA-1 gene is unique. The sgRNA used in the pig SLA-1 gene knockout method using CRISPR-Cas9 specificity, may fast, accurately, efficiently, and specifically knockout pig SLA-1 gene, effectively solve long cycle and high cost in construction of SLA-1 gene knockout pig.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Nucleic acid sequences and methods of use for the production of plants with modified polyunsaturated fatty acid levels
InactiveUS7148336B2Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIntein
By this invention, novel nucleic acid sequences are provided, wherein said nucleic acid sequence is a genomic sequence of a plant desaturase encoding sequence. Also provided in the present invention are the promoter and intron sequences of the desaturase genomic sequences. Furthermore, recombinant DNA constructs employing the polynucleotide sequences are provided. The instant invention also provides methods for the modification of fatty acid compositions in host plant cells.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Method for CRISPR-Cas9 specific knockout of pig GGTA1 gene and sgRNA for specific targeted GGTA1 gene
The invention discloses a method for CRISPR-Cas9 specific knockout of a pig GGTA1 gene and sgRNA for a specific targeted GGTA1 gene. The target sequence of the sgRNA for the specific targeted GGTA1 gene on the GGTA1 gene is in accordance with the sequence arrangement rule of 5'-N(20)NGG-3', wherein N(20) represents 20 continuous bases, and each N represents A or T ot C or G; the target sequence on the GGTA1 gene is positioned at a junction of 5 exon coding areas and / or adjacent introns of the N-end of the GGTA1 gene; and the target sequence on the GGTA1 gene is unique. According to the method for CRISPR-Cas9 specific knockout of the pig GGTA1 gene via sgRNA, specific knockout of the pig GGTA1 gene can be rapidly and accurately realized with high efficiency, and the problems of long period and high cost for constructing the knockout of the pig GGTA1 gene can be effectively solved.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Method for specifically removing pig SALL1 gene by CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA used for specific targeting SALL1 gene
ActiveCN105518137AKnockout fastKnockout precisionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionInteinExon
The invention discloses a method for specifically removing a pig SALL1 gene by CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA used for the specific targeting SALL1 gene. The sgRNA of the specific targeting SALL1 gene has a target sequence on the SALL1 gene which accords with a sequence arrangement rule of 5'-N(20)NGG-3', wherein N(20) represents 20 continuous basic groups, each N represents A or T or C or G. The target sequence on the SALL1 gene is positioned in the three exon code areas at the N end of the SALL1 gene or at the junction of the exons and the adjacent intrones. The target sequence on the SALL1 gene is unique. The sgRNA is used in the method for specifically removing the pig SALL1 gene by the CRISPR-Cas9, the pig SALL1 gene can be removed, and the problems if long period and high cost for SALL1 gene removal are effectively solved.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
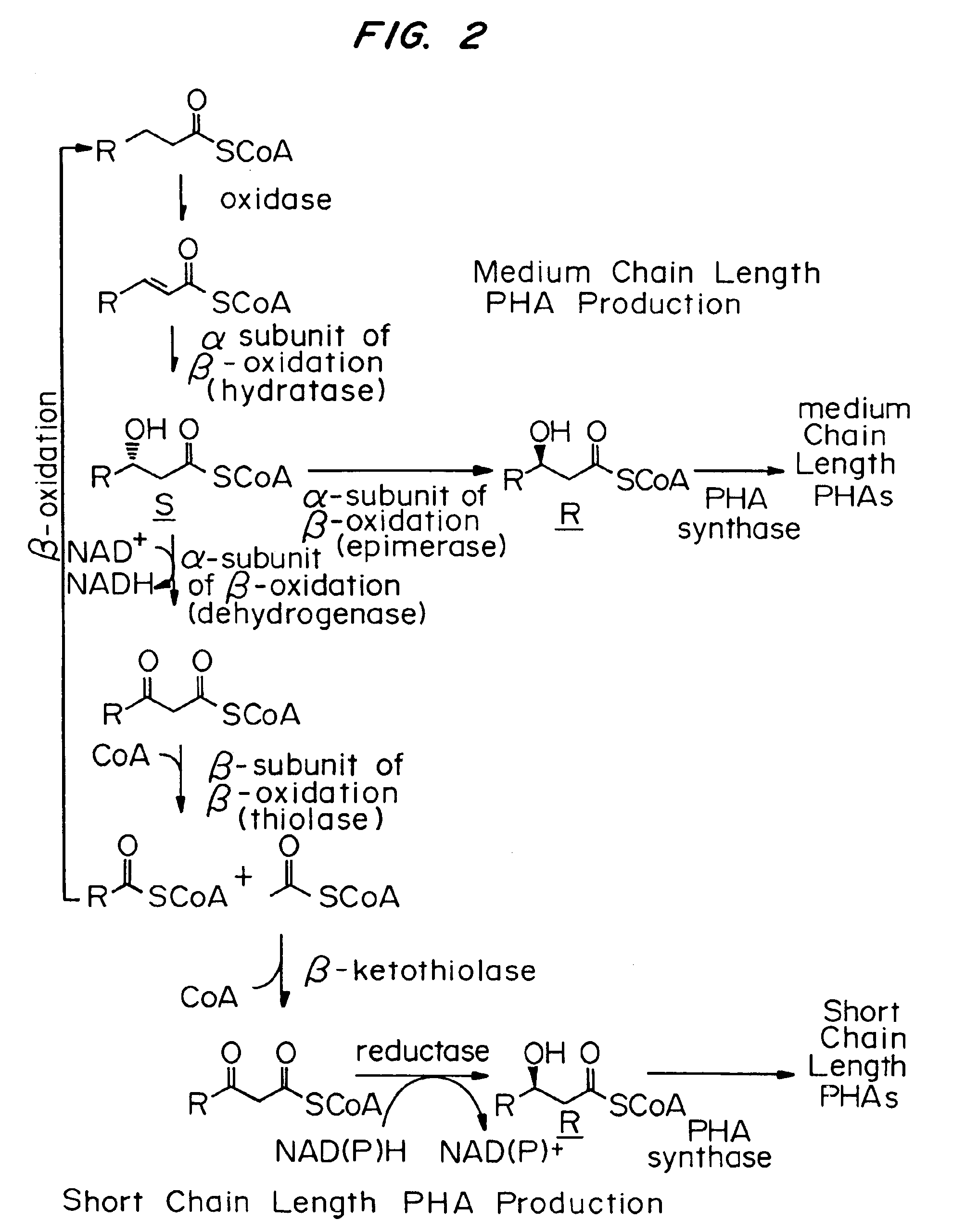
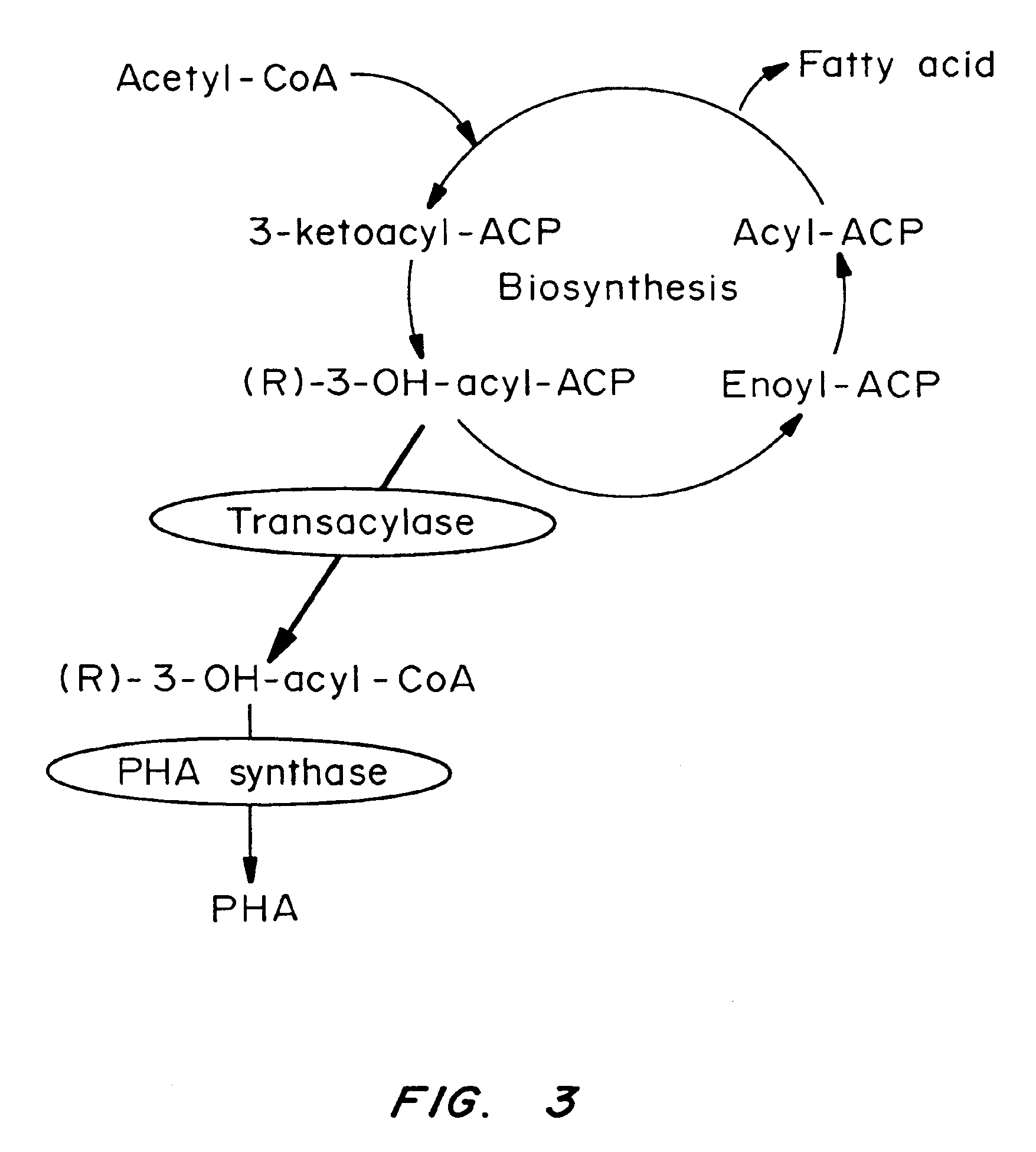
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
Method for producing tagged genes, transcripts and proteins
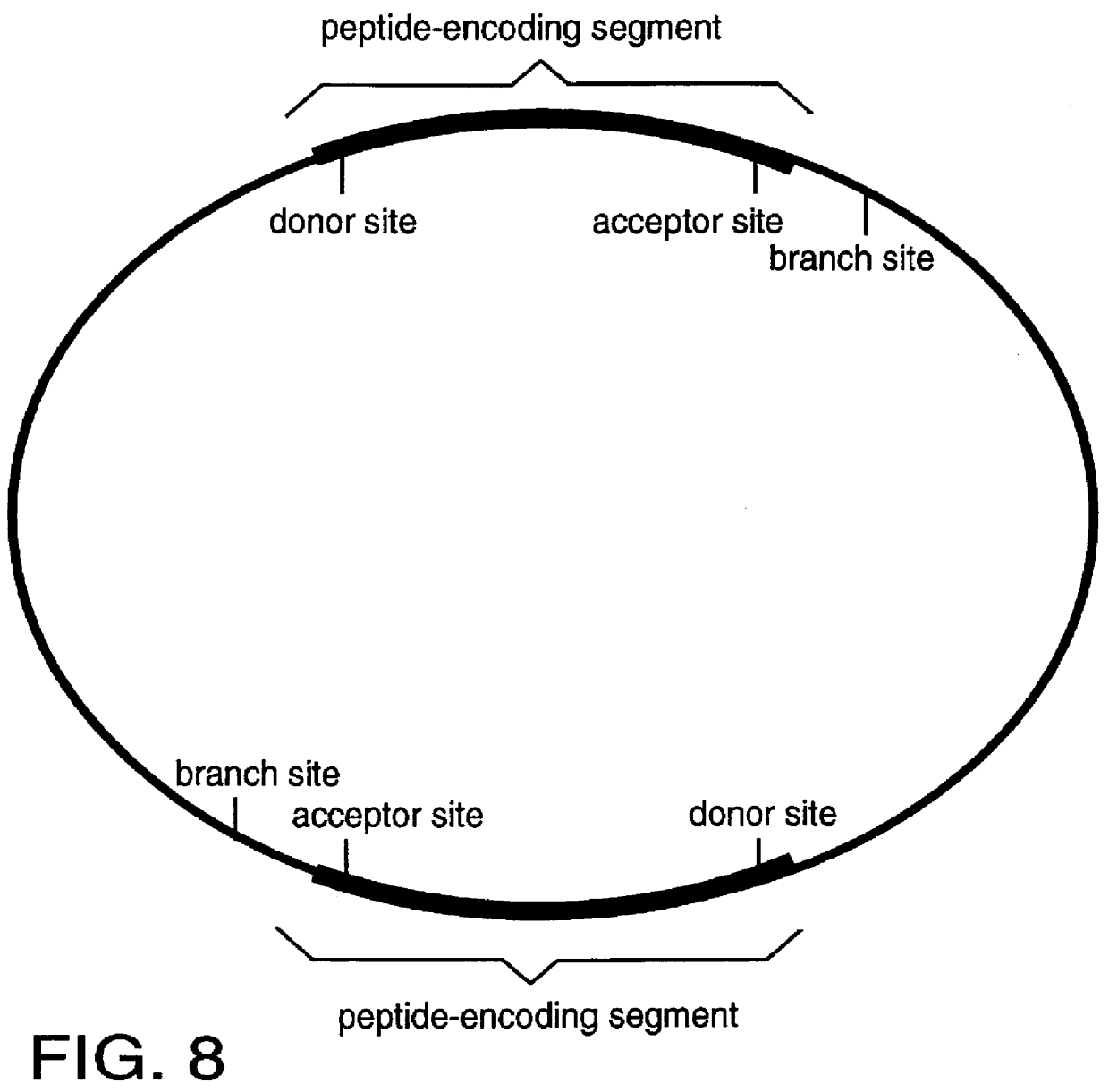
The invention described here is a method whereby a molecular tag is put on a gene, transcript and protein in a single recombinational event. The protein tag takes the form of a unique peptide that can be recognized by an antibody or other specific reagent, the transcript tag takes the form of the sequence of nucleotides encoding the peptide that can be recognized by a specific polynucleotide probe, and the gene tag takes the form of a larger sequence of nucleotides that includes the peptide-encoding sequence and other associated nucleotide sequences. The central feature of the invention in its essential form is that the tag-creating DNA has a structure such that when it is inserted into an intron within a gene it creates two hybrid introns separated by a new exon encoding the protein tag. A major virtue of the method is that it allows one to identify new proteins or protein-containing structures, and, having done so, to readily identify and analyze the genes encoding those proteins.
Owner:JARVIK JONATHAN W
Method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting
The invention discloses a method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting. The target sequence of sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting on PDX1 gene is accord with the sequence alignment rule of 5'-N(20)NGG-3', wherein N(20) represents 20 continuous bases, and each N represent A, T, C or G; the target sequence of PDX1 gene is arranged in the first exon coding region on the N terminal of PDX1 gene or a junction between the coding region and neighbored intron, and the target sequence of PDX1 gene is unique. The provided method can rapidly, precisely, efficiently and specifically knock off PDX1 gene of pigs, and solves the problems of long period and high cost of pig PDX1 gene knocking.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Genome editing method based on CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat) system and application thereof
ActiveCN107937432AImprove editing efficiencyImprove editing abilityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionInteinFusion gene
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
Provided are methods and antisense oligonucleotide analogs for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection. The oligonucleotide analogs provided herein comprise a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region that spans the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA. Also provided are methods of use, in which the oligonucleotides are effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com