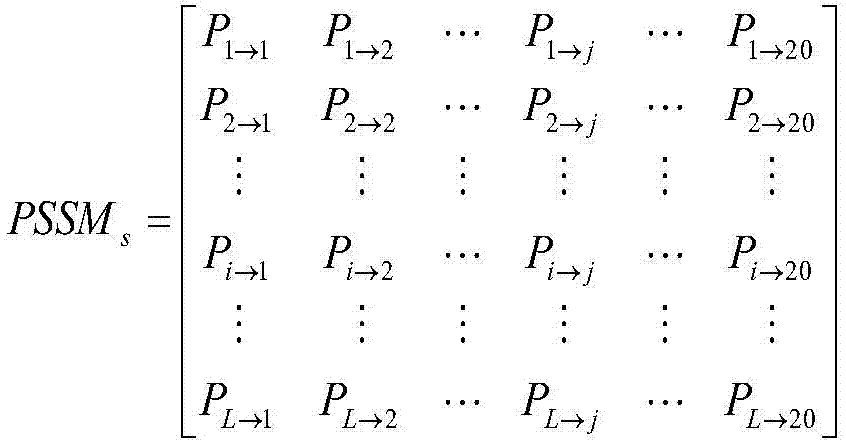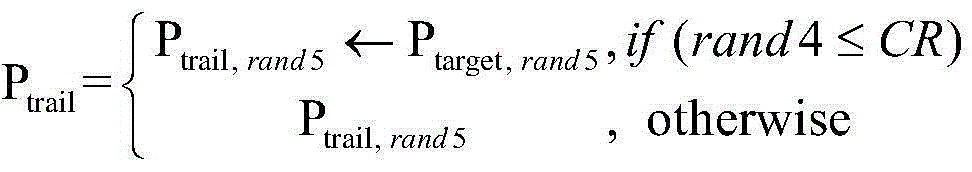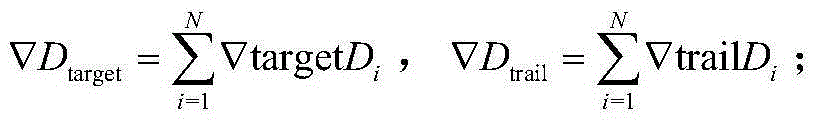Patents
Literature
647 results about "Protein structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a residue indicating a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the topic of the scientific field of structural biology, which employs techniques such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, and dual polarisation interferometry to determine the structure of proteins.
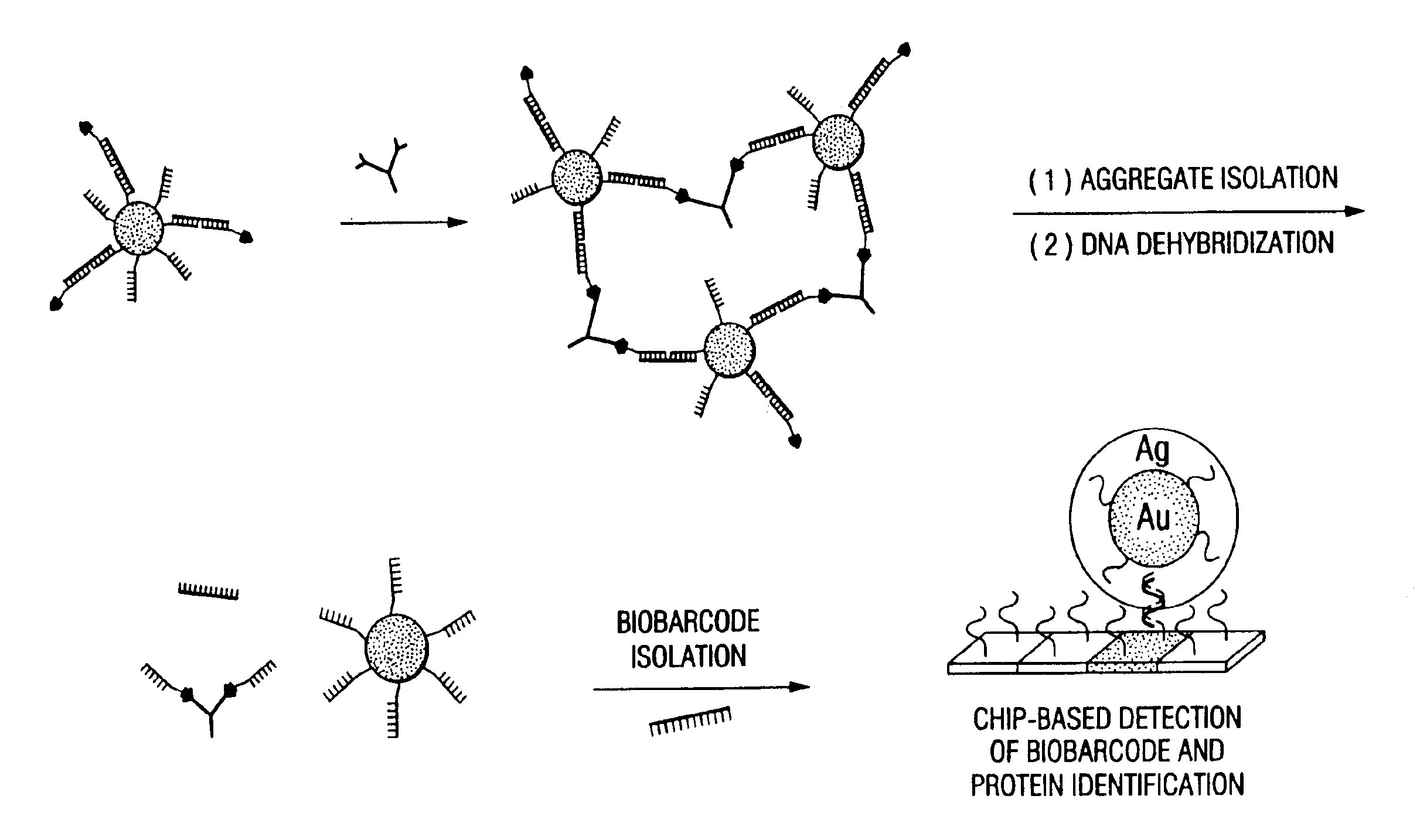
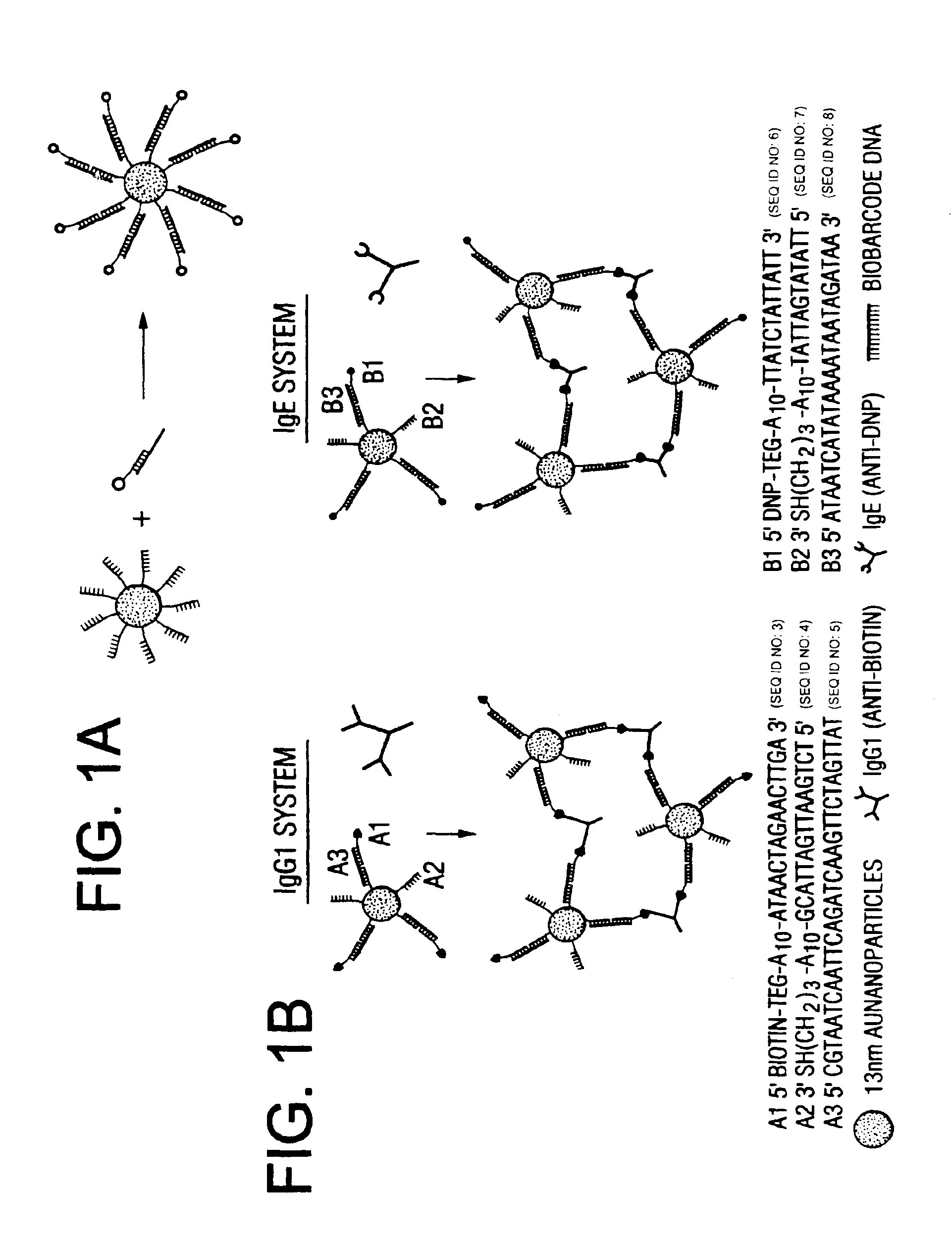
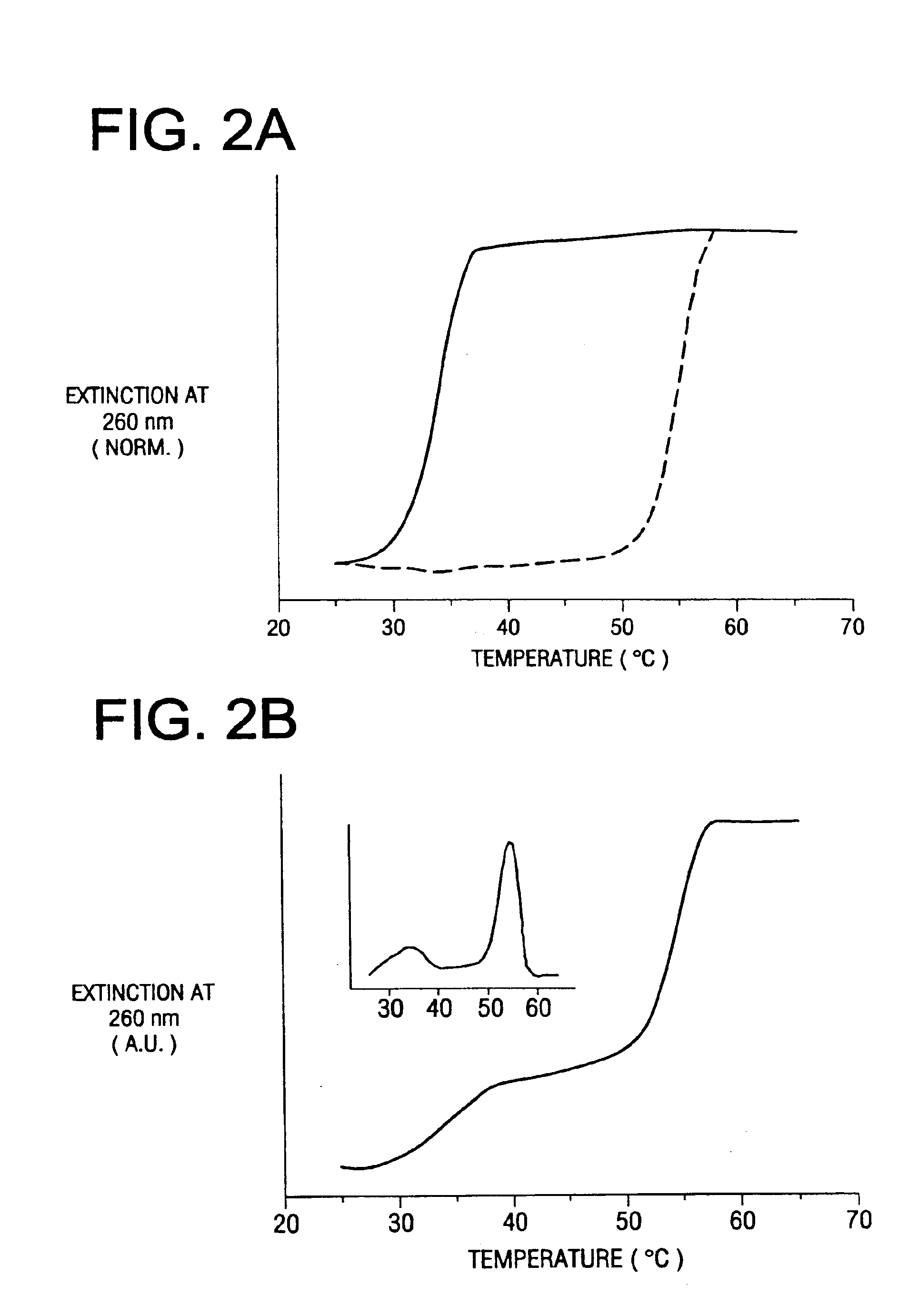
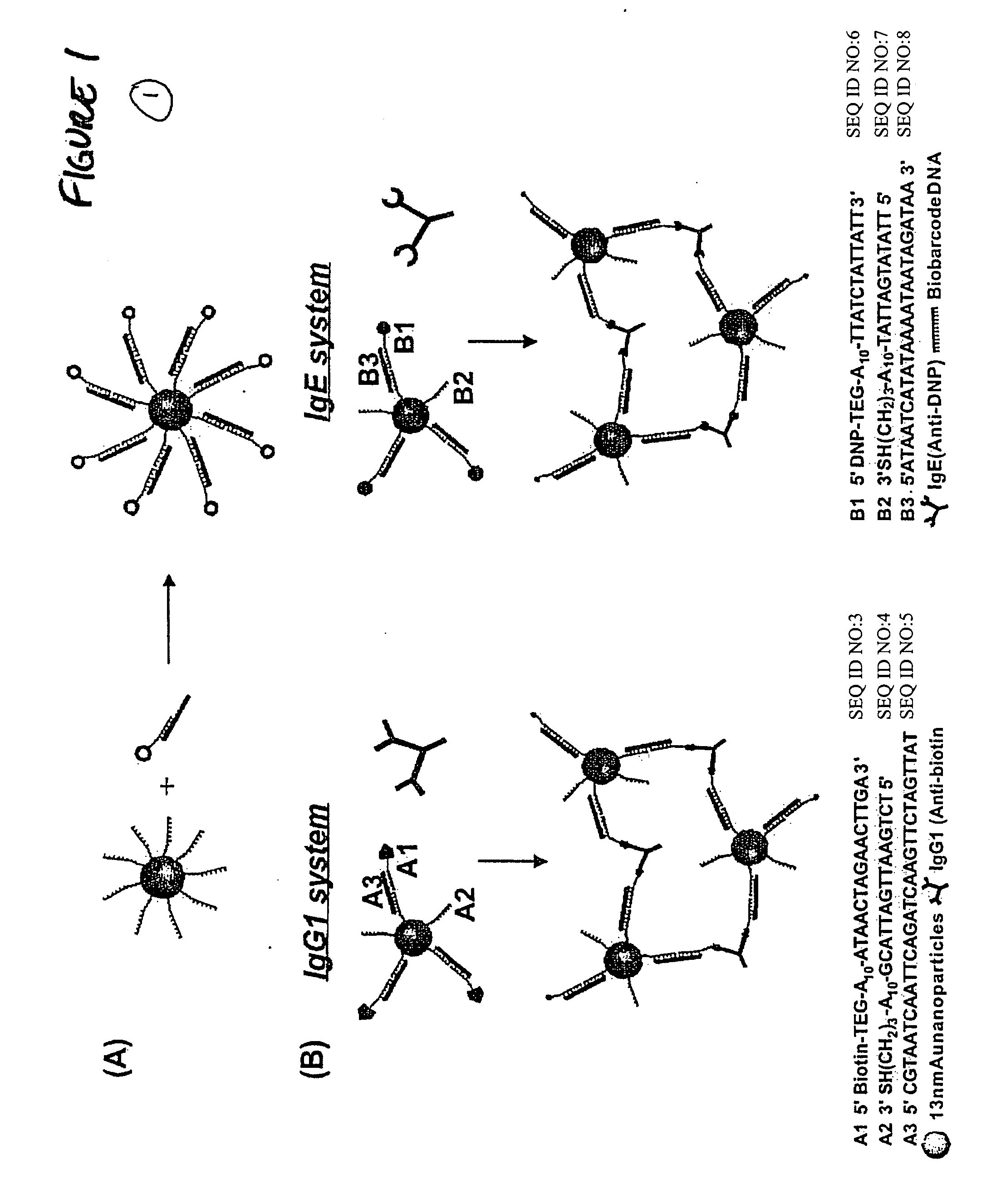
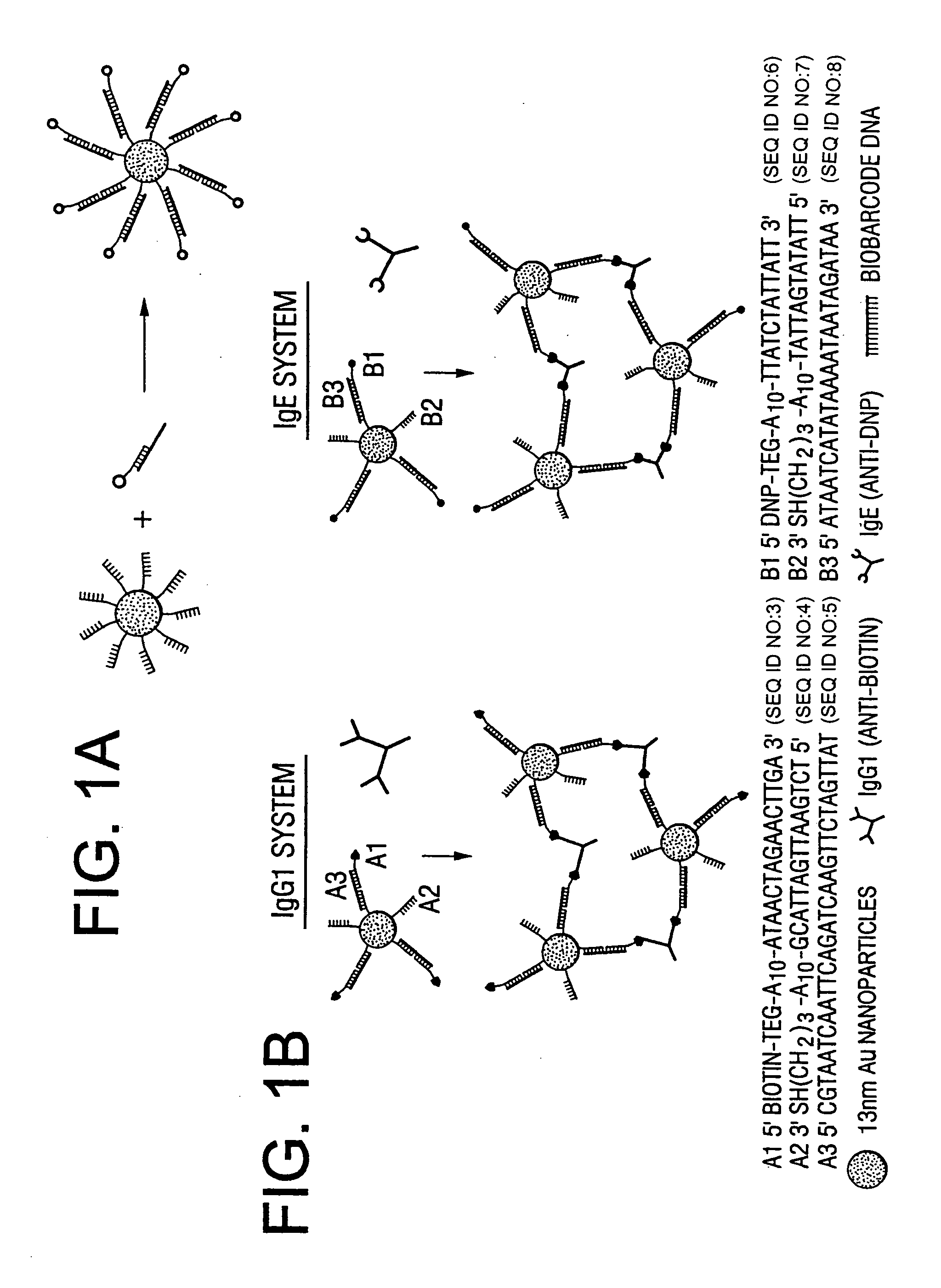
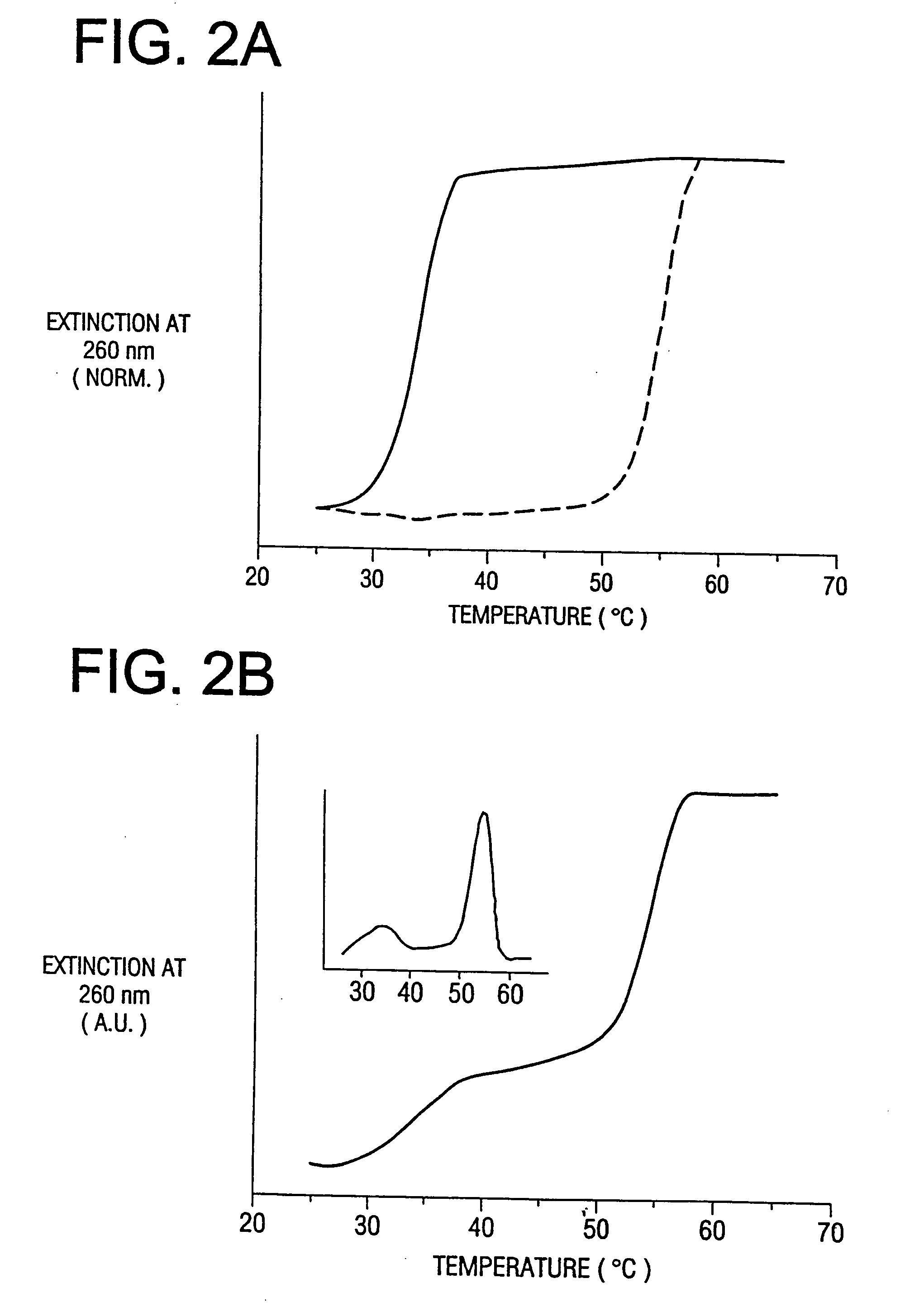
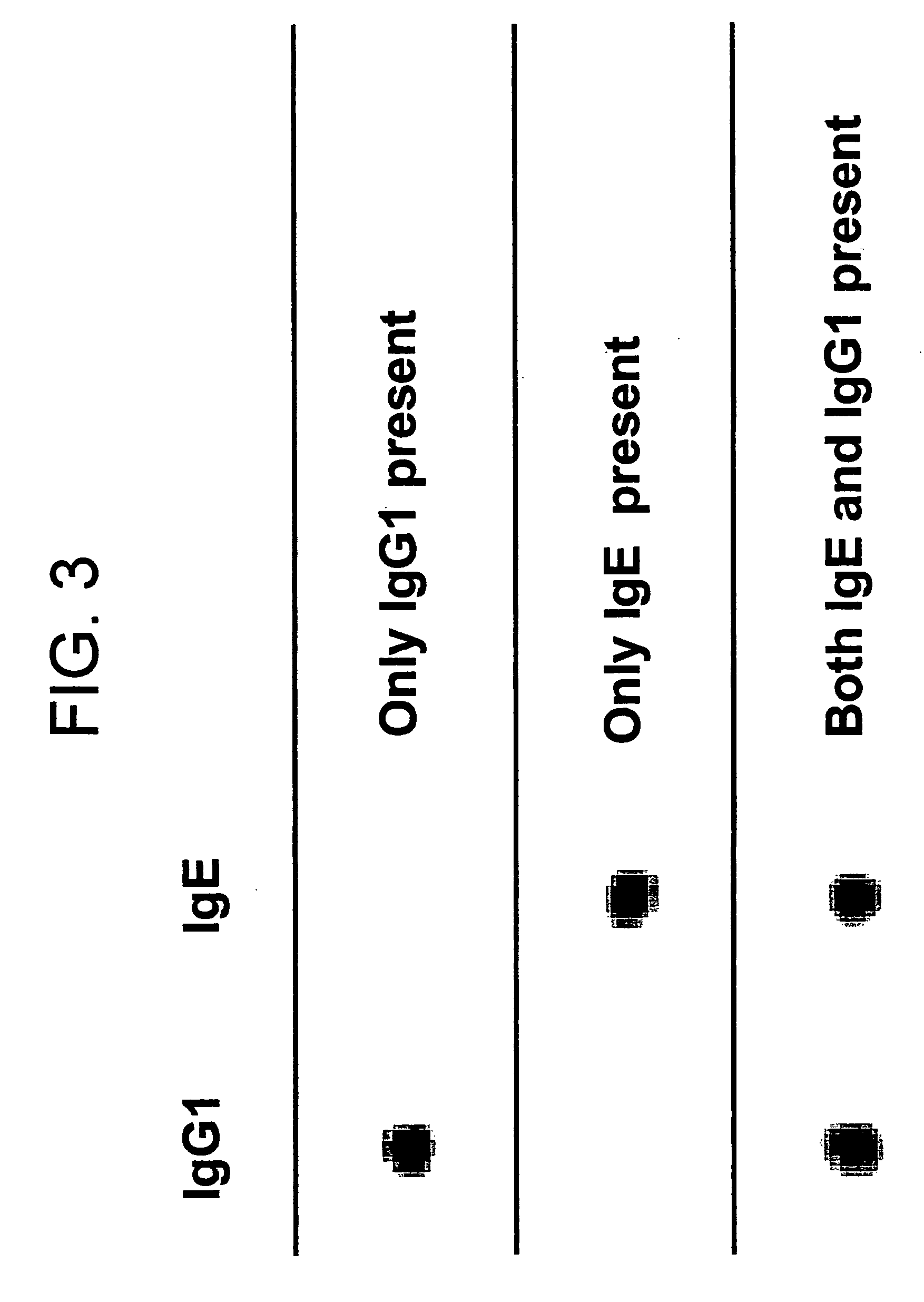
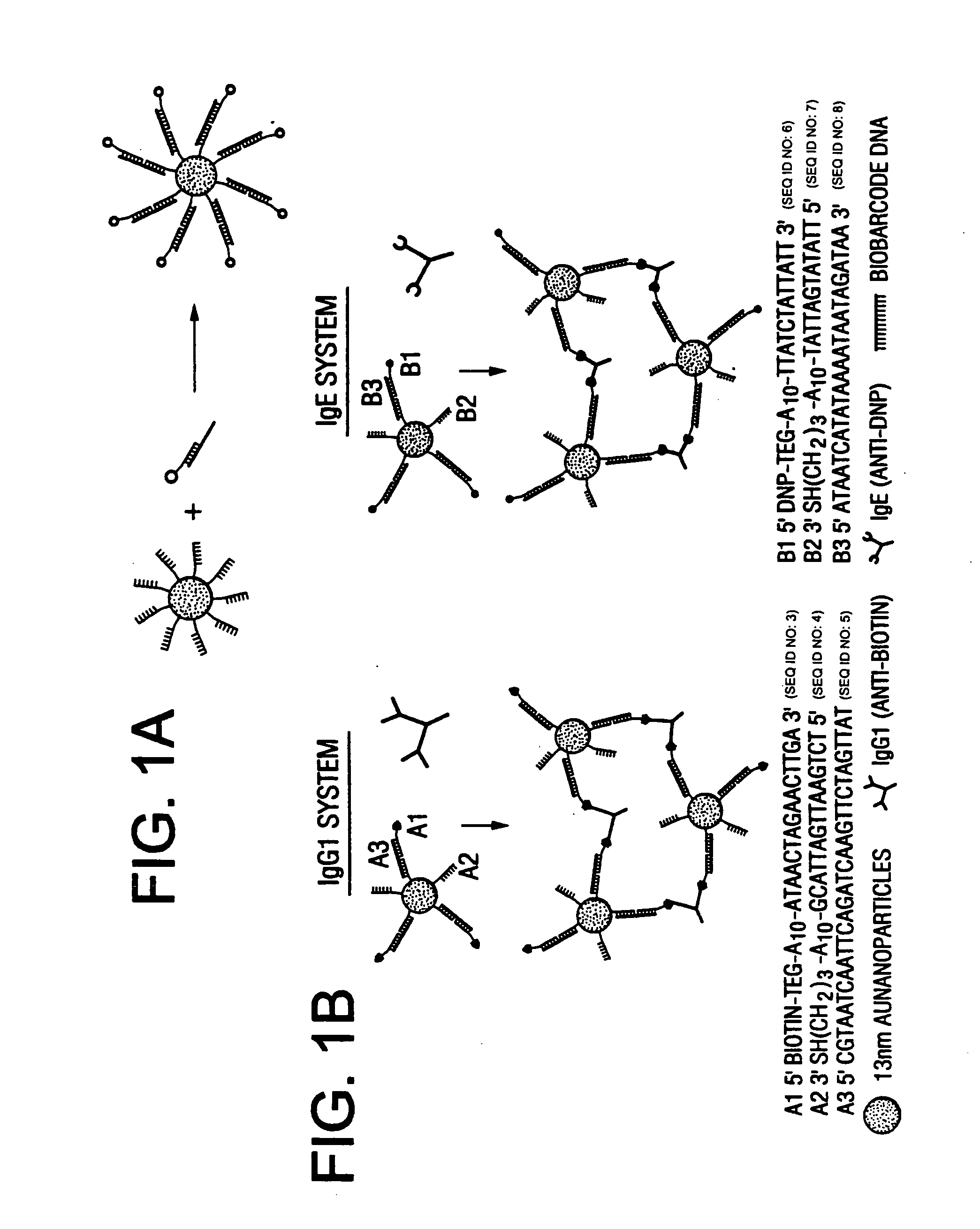
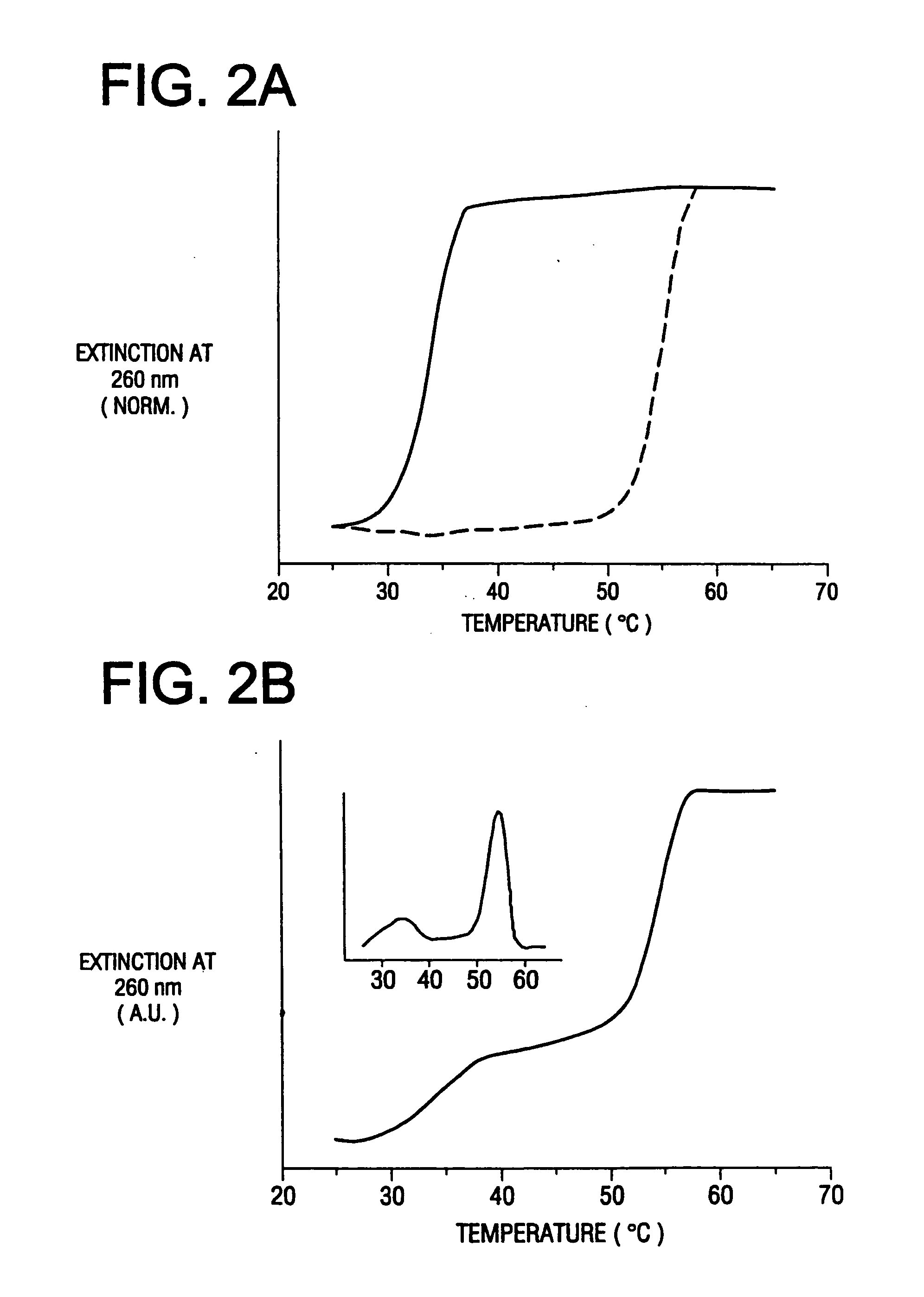
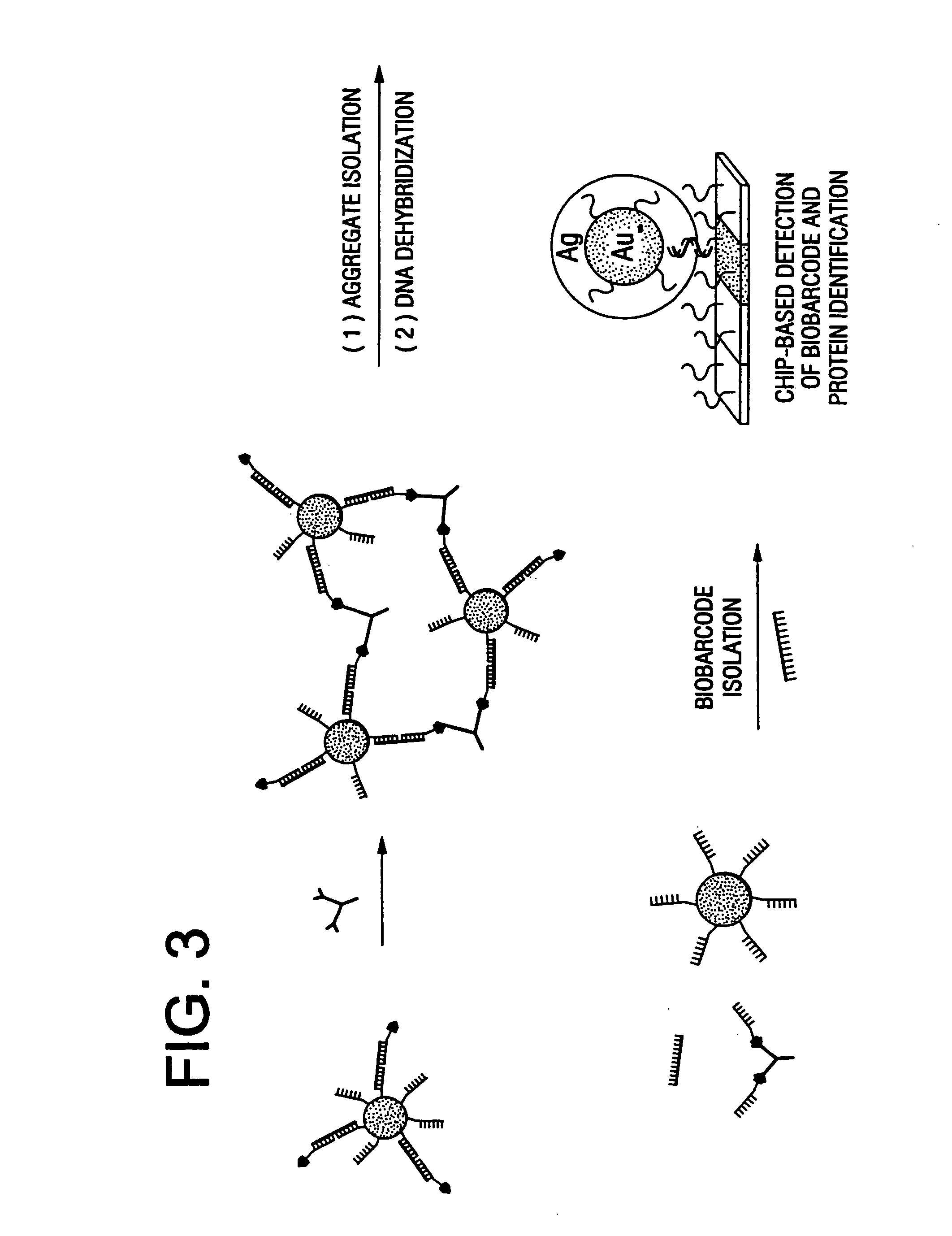
Bio-barcodes based on oligonucleotide-modified nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a screening methods, compositions, and kits for detecting for the presence or absence of one or more target analytes, e.g. proteins such as antibodies, in a sample. In particular, the present invention relates to a method that utilizes reporter oligonucleotides as biochemical barcodes for detecting multiple protein structures or other target analytes in one solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method for predicting the onset or change of a medical condition
InactiveUS20050119534A1Minimizes adverse reactionMaximize therapeutic responseDrug and medicationsSurgeryMedical recordCost effectiveness
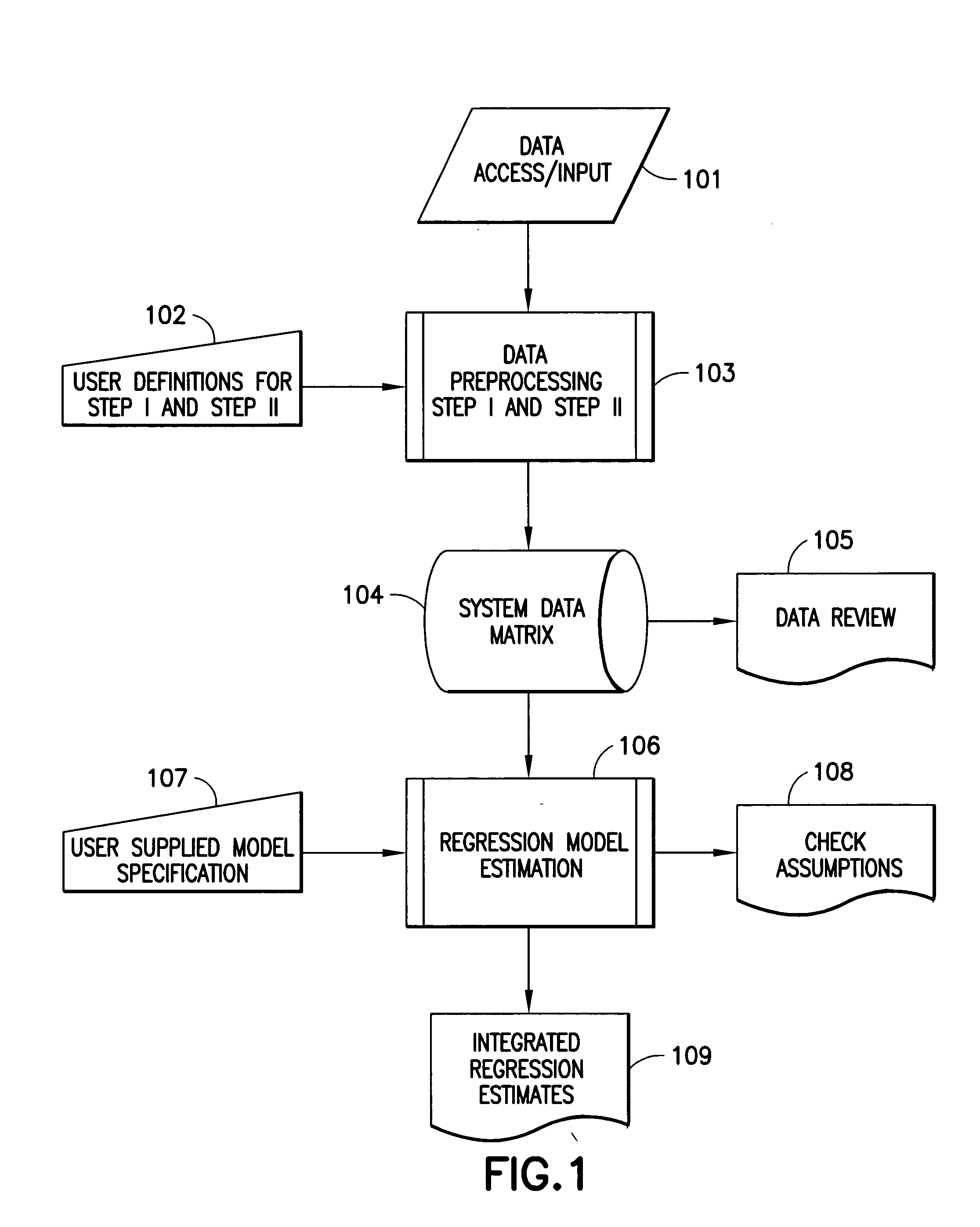
Nonlinear generalized dynamic regression analysis system and method of the present invention preferably uses all available data at all time points and their measured time relationship to each other to predict responses of a single output variable or multiple output variables simultaneously. The present invention, in one aspect, is a system and method for predicting whether an intervention administered to a patient changes the physiological, pharmacological, pathophysiological, or pathopsychological state of the patient with respect to a specific medical condition. The present invention uses the theory of martingales to derive the probabilistic properties for statistical evaluations. The approach uniquely models information in the following domains: (1) analysis of clinical trials and medical records including efficacy, safety, and diagnostic patterns in humans and animals, (2) analysis and prediction of medical treatment cost-effectiveness, (3) the analysis of financial data, (4) the prediction of protein structure, (5) analysis of time dependent physiological, psychological, and pharmacological data, and any other field where ensembles of sampled stochastic processes or their generalizations are accessible. A quantitative medical condition evaluation or medical score provides a statistical determination of the existence or onset of a medical condition.
Owner:PFIZER PROD INC +1
Bio-barcode based detection of target analytes
InactiveUS20060040286A1Long complexityKeep for a long timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention relates to screening methods, compositions, and kits for detecting for the presence or absence of one or more target analytes, e.g. biomolecules, in a sample. In particular, the present invention relates to a method that utilizes reporter oligonucleotides as biochemical barcodes for detecting multiple protein structures or other target analytes in a solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Novel kinases
InactiveUS20050125852A1Prevent hybridizationDecrease in proliferation and growth and differentiationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid kinasesProtein structure
The present invention relates to kinase polypeptides, nucleotide sequences encoding the kinase polypeptides, as well as various products and methods useful for the diagnosis and treatment of various kinase-related diseases and conditions. Through the use of a bioinformatics strategy, mammalian members of protein and lipid kinase families have been identified and their protein structure predicted.
Owner:SUGEN INC
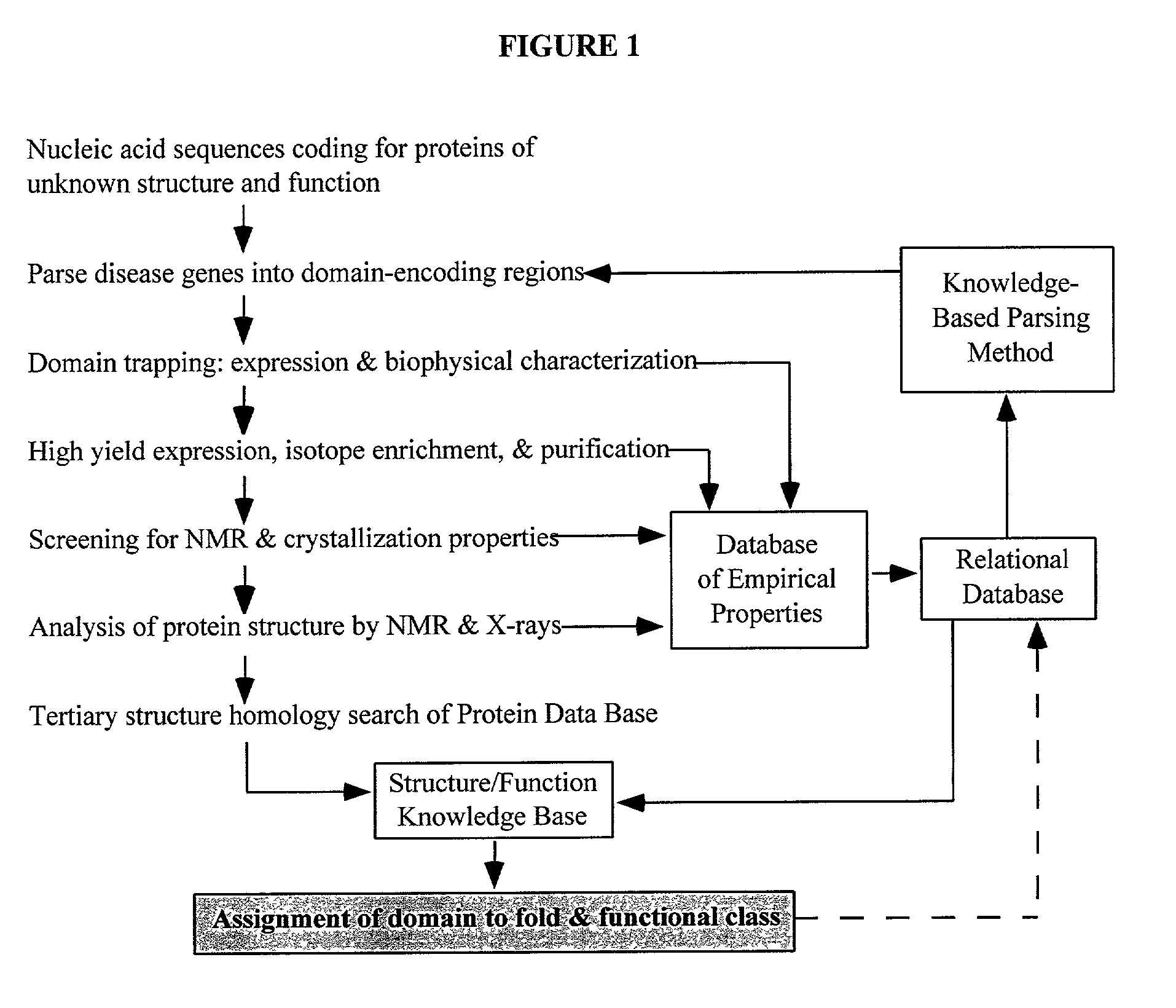
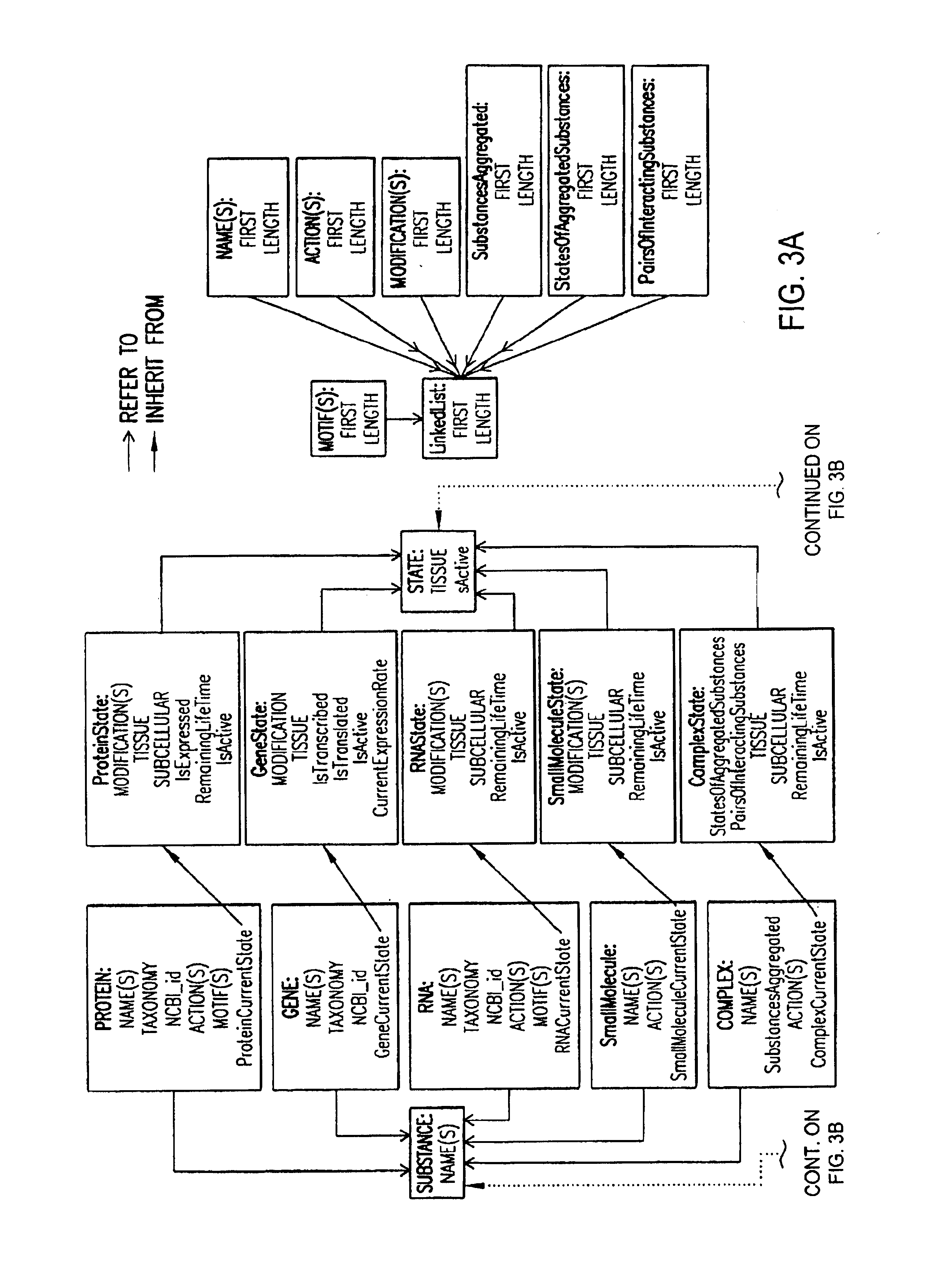
Linking gene sequence to gene function by three dimesional (3D) protein structure determination
InactiveUS20010016314A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional profilingProtein structure
The present invention provides a structure-functional analysis engine for the high-throughput determination of the biochemical function of proteins or protein domains of unknown function. The present invention uses bioinformatics, molecular biology and nuclear magnetic resonance tools for the rapid and automated determination of the three-dimensional structures of proteins and protein domains.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
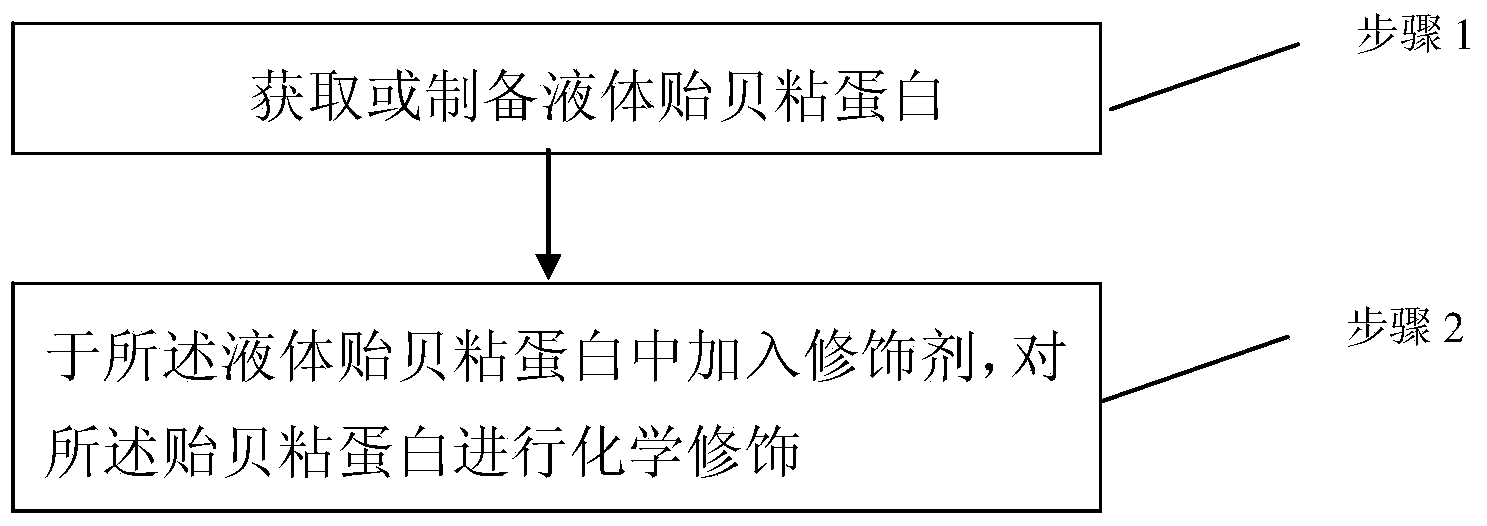
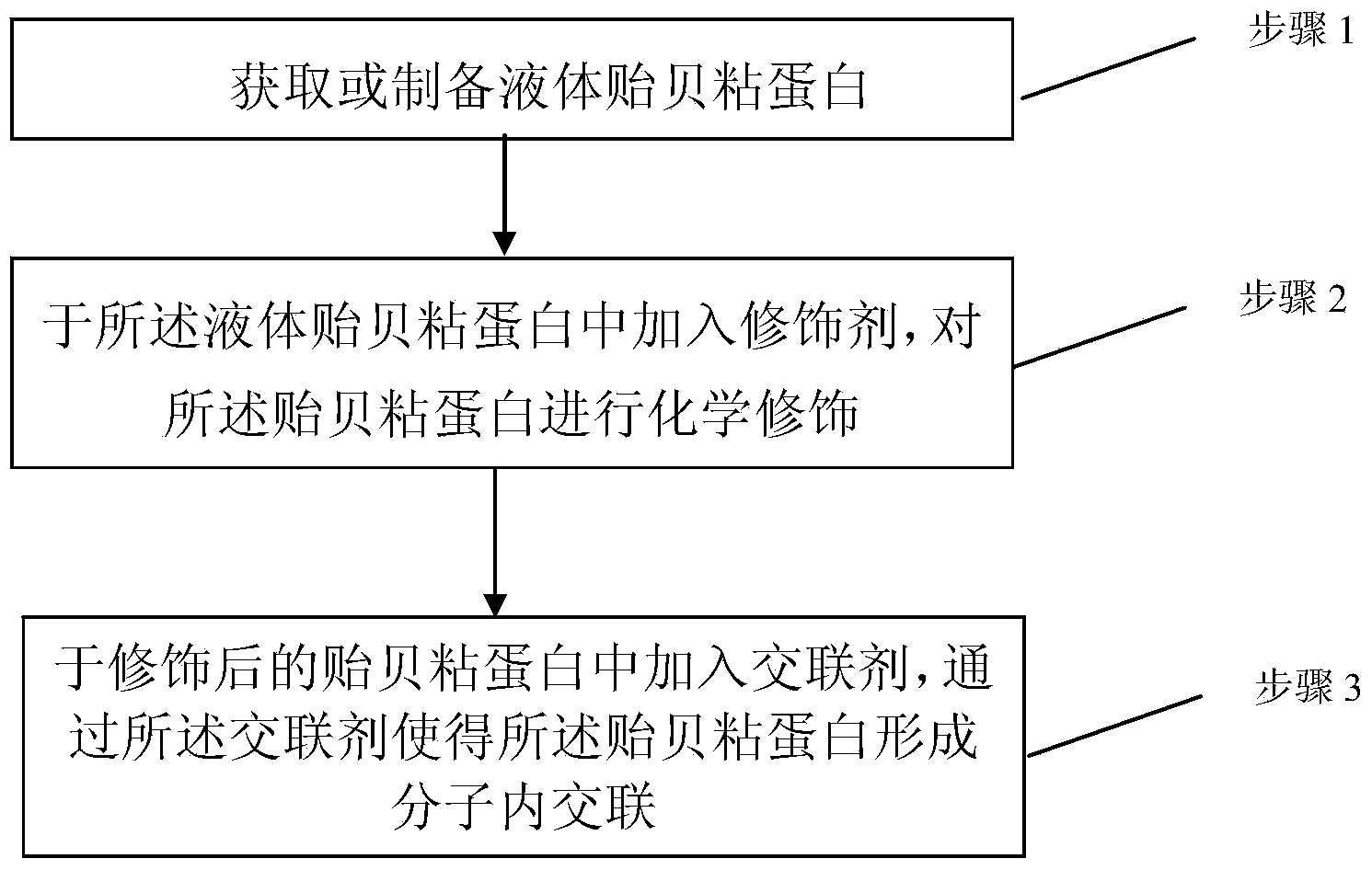
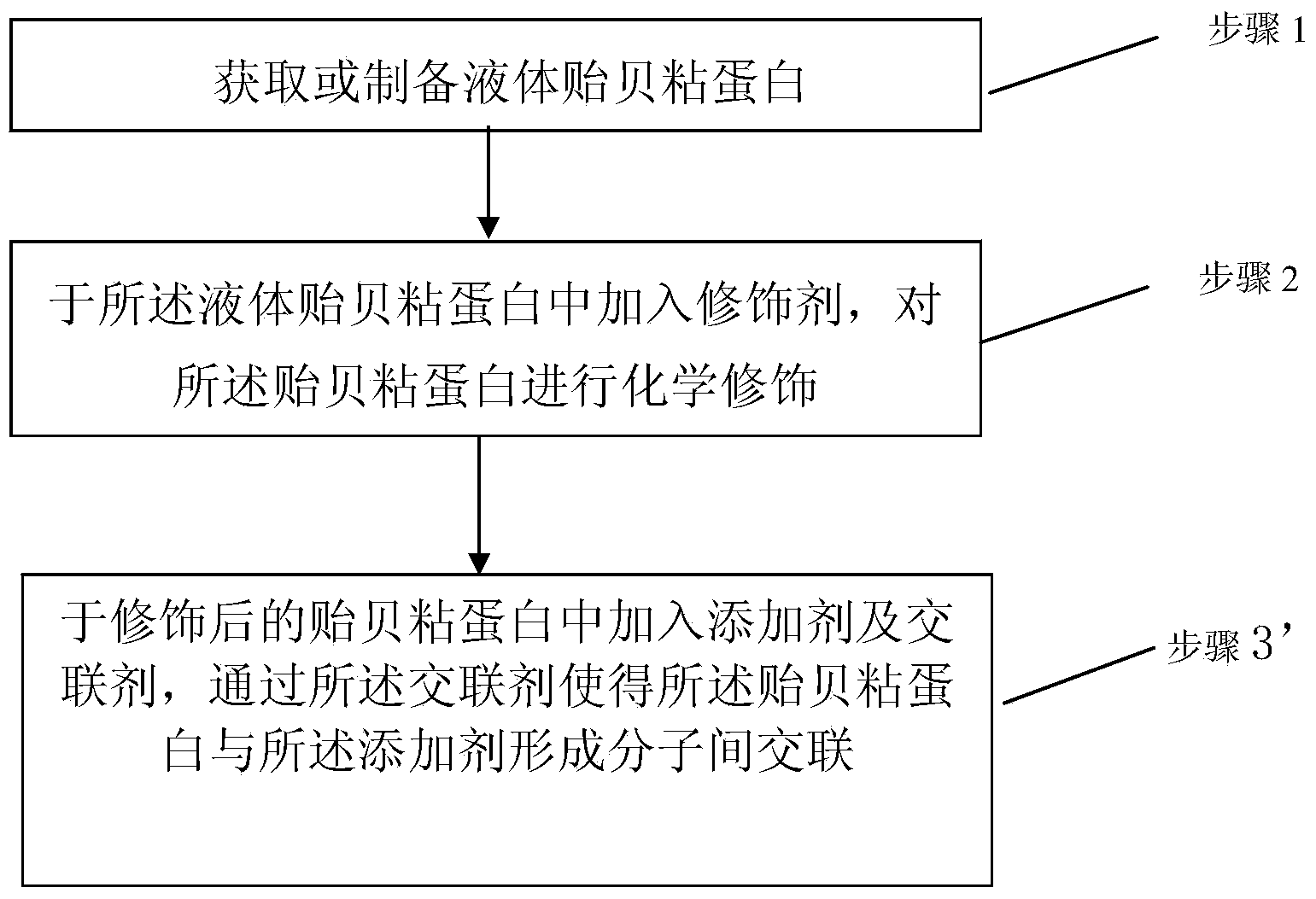
Mussel mucoprotein liquid product as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103520766AImprove stabilityHigh molecular weightSurgical adhesivesPeptide preparation methodsLiquid productProtein molecules
The invention discloses a mussel mucoprotein liquid product as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. One or more of a modifier, an additive and a crosslinker are added into mussel mucoprotein to form a new product which can serve as a wound repair product, a wound protection product, a medical biological bonder product, a medical coating product, an industrial coating product, a biochemical reagent product or the like. According to the mussel mucoprotein liquid product and the preparation method of the mussel mucoprotein liquid product, the modifier, the additive and the crosslinker are added into the mussel mucoprotein, so that the stability of a protein structure is enhanced, the protein molecular weight is increased, and the mussel mucoprotein liquid product is widely applied in various fields.
Owner:高敏
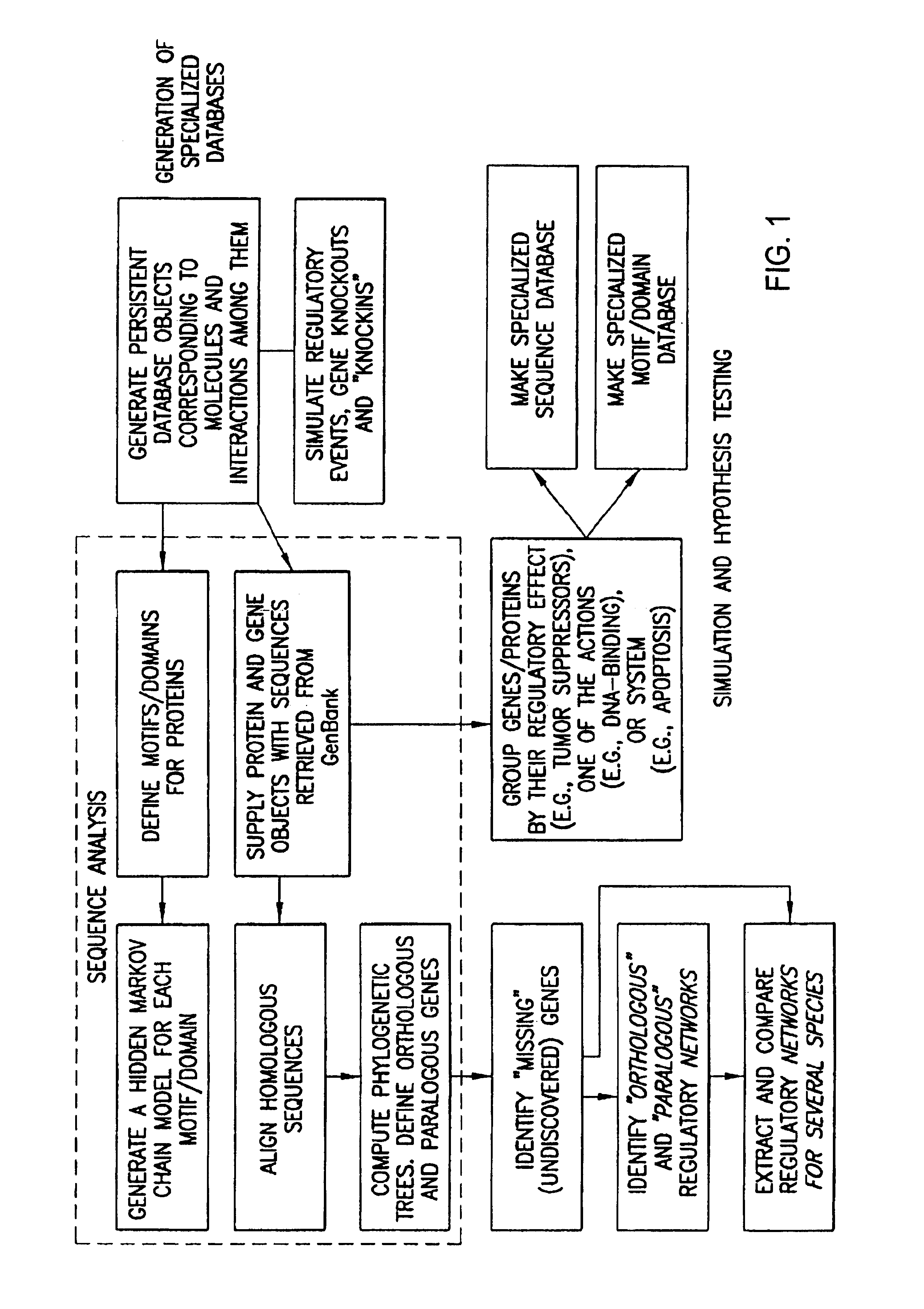
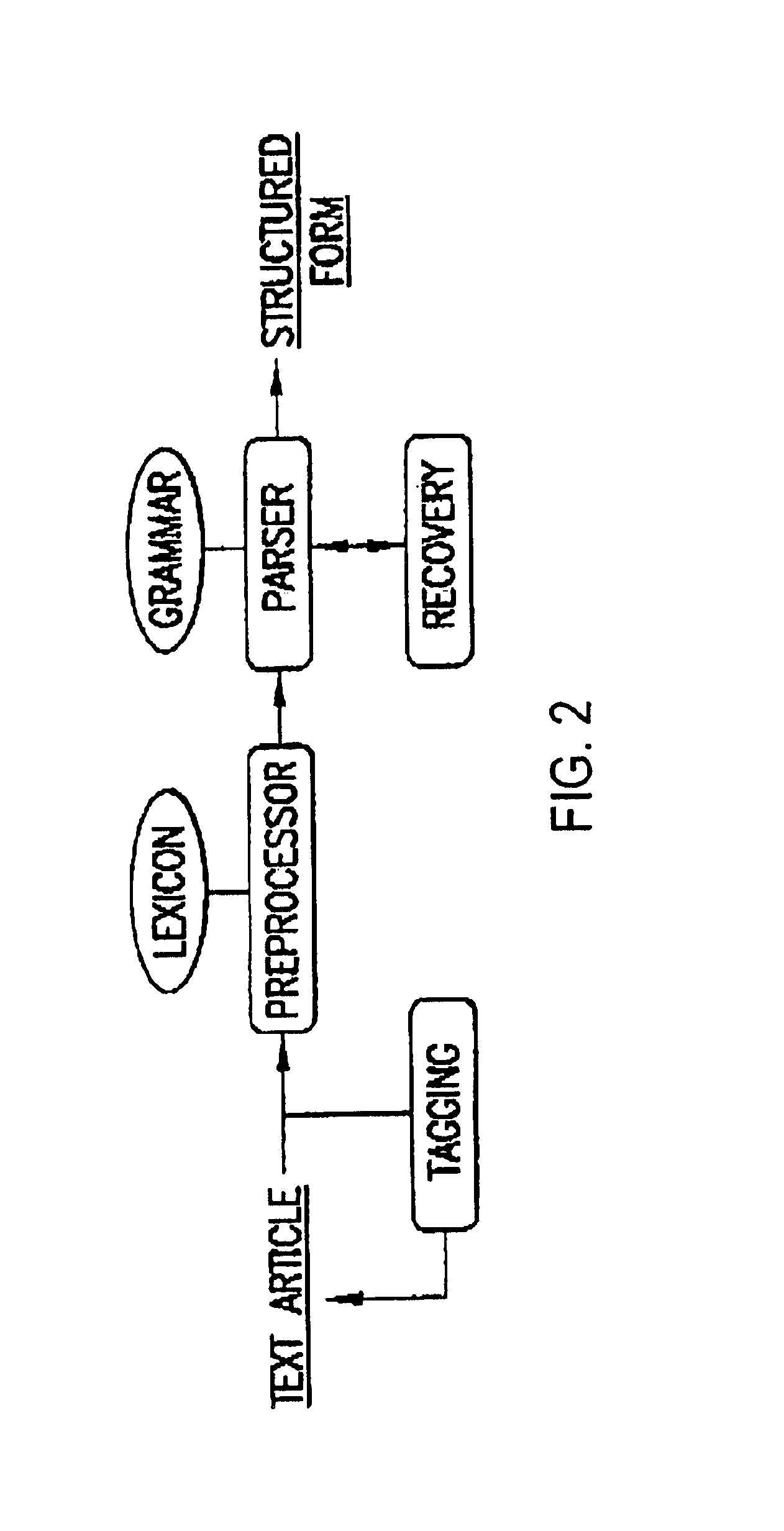
Methods for extracting information on interactions between biological entities from natural language text data
The present invention relates to methods for identifying novel genes comprising: (i) generating one and / or more specialized databases containing information on gene / protein structure, function and / or regulatory interactions; and (ii) searching the specialized databases for homology or for a particular motif and thereby identifying a putative novel gene of interest. The invention may further comprise performing simulation and hypothesis testing to identify or confirm that the putative gene is a novel gene of interest. The present invention also relates to natural language processing and extraction of relational information associated with genes and proteins that are found in genomics journal articles. To enable access to information in textual form, the natural language processing system of the present invention provides a method for extracting and structuring information found in the literature in a form appropriate for subsequent applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Nonlinear optical detection of molecules comprising an unnatural amino acid possessing a hyperpolarizability
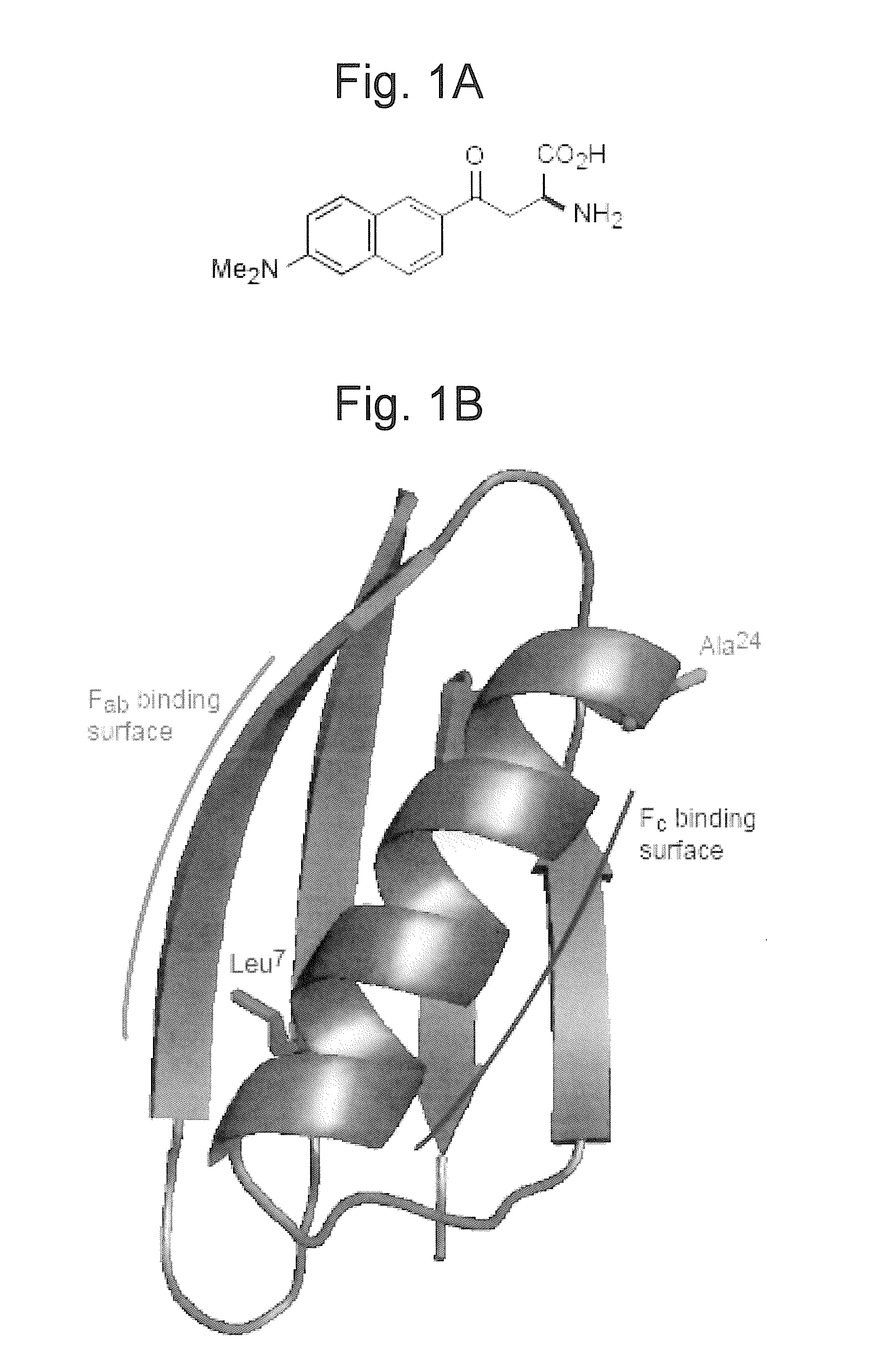
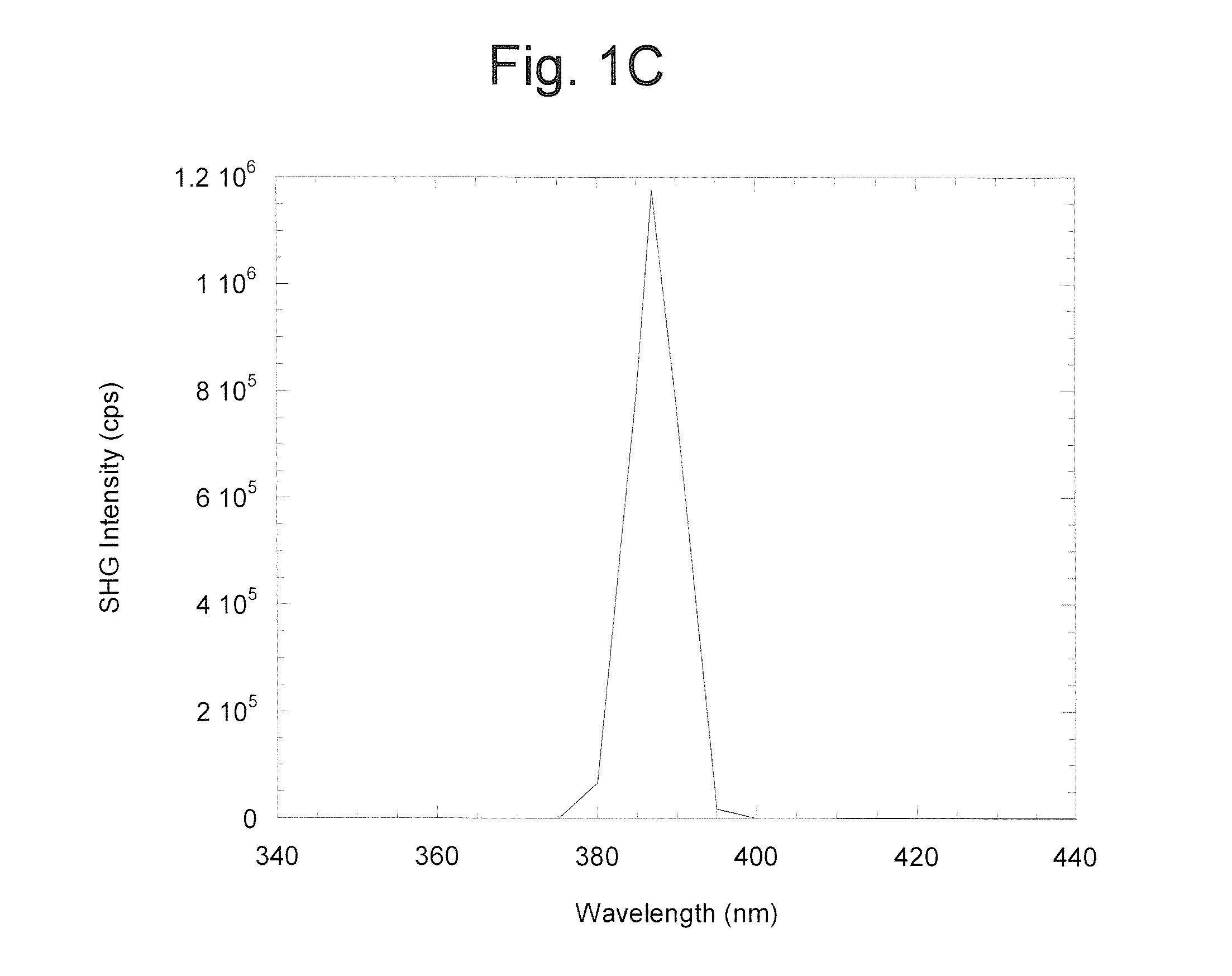
A system for making molecules, and proteins in particular, suitable for detection by a surface-selective nonlinear optical technique. A first use of the invention is for determining a protein's structure in real space and real time. A second use of the invention is to detect a protein or its activity (conformational change). A third use of the invention is for drug screening. A further aspect of the present invention is measuring probe tilt angle orientation in an oriented protein.
Owner:BLUELIGHT THERAPEUTICS INC
Protein modeling tools
InactiveUS20030130797A1Rapid and computationally efficient generationEfficient representationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsProtein modellingSide chain
The invention provides a new, efficient method for the assembly of protein tertiary structure from known, loosely encoded secondary structure constraints and sparse information about exact side chain contacts. The method is based on a new method for the reduced modeling of protein structure and dynamics, where the protein is described by representing side chain centers of mass rather than alpha-carbons. The model has implicit, built-in multi-body correlations that simulate short- and long-range packing preferences, hydrogen bonding cooperativity, and a mean force potential describing hydrophobic interactions. Due to the simplicity of the protein representation and definition of the model force field, the Monte Carlo algorithm is at least an order of magnitude faster than previously published Monte Carlo algorithms for three-dimensional structure assembly. In contrast to existing algorithms, the new method requires a smaller number of tertiary constraints for successful fold assembly; on average, one for every seven residues as compared to one for every four residues. The reliability and robustness of the invention make it useful for routine application in model building protocols based on various (and even very sparse) experimentally-derived structural constraints.
Owner:SKOLNICK JEFFREY +1
Micromolecule walnut peptide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105002247AHigh egg contentLow costPeptide preparation methodsFermentationAlkaline proteaseProtein structure
The invention relates to a micromolecule walnut peptide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method sequentially comprises the following steps of protein extraction, twice enzymolysis, filtering, purification, concentration and drying. In the twice enzymolysis process, alkaline protease with the mass being 1-3% that of the walnut protein is added into a walnut protein extracting solution for once enzymolysis; enzyme deactivation is performed on a once enzymolysis solution after the once enzymolysis is finished; one or more kinds of proteinase including the flavored proteinase, the neutral proteinase and the papain with the mass being 1-3% that of the walnut protein are added after the once enzymolysis solution obtained after enzyme deactivation is performed is cooled for secondary enzymolysis. According to the preparation method, the twice enzymolysis method is adopted, due to the specificity of the structure of the walnut protein structure, sufficient enzymolysis cannot be performed on the walnut protein through enzymolysis of one proteinase, and the twice enzymolysis method is adopted for ensuring that the enzymolysis is brought into play on the most suitable condition of each proteinase, and therefore the obtained walnut peptide content is high.
Owner:BEIJING TIANTAI BIOTECH
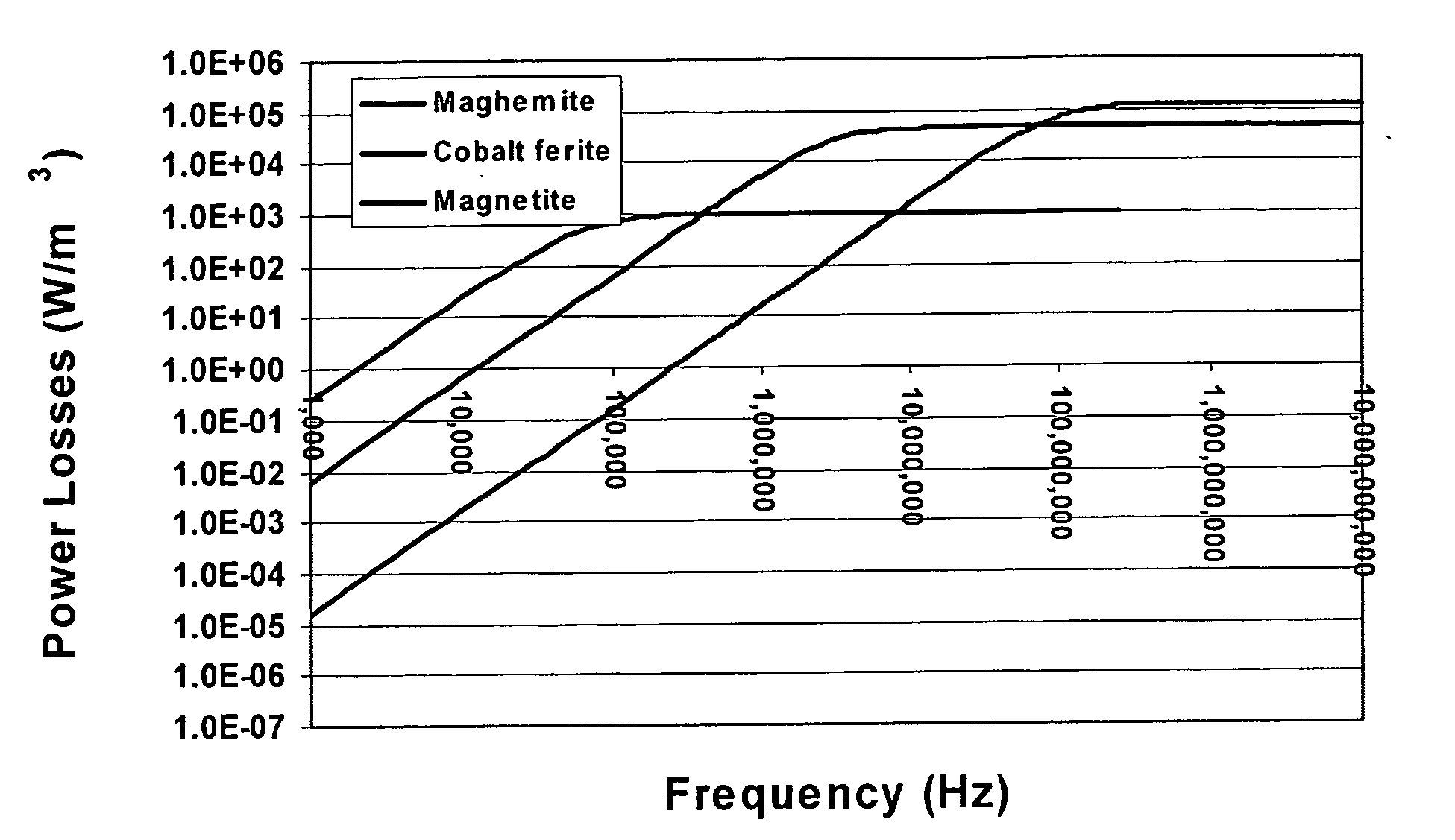
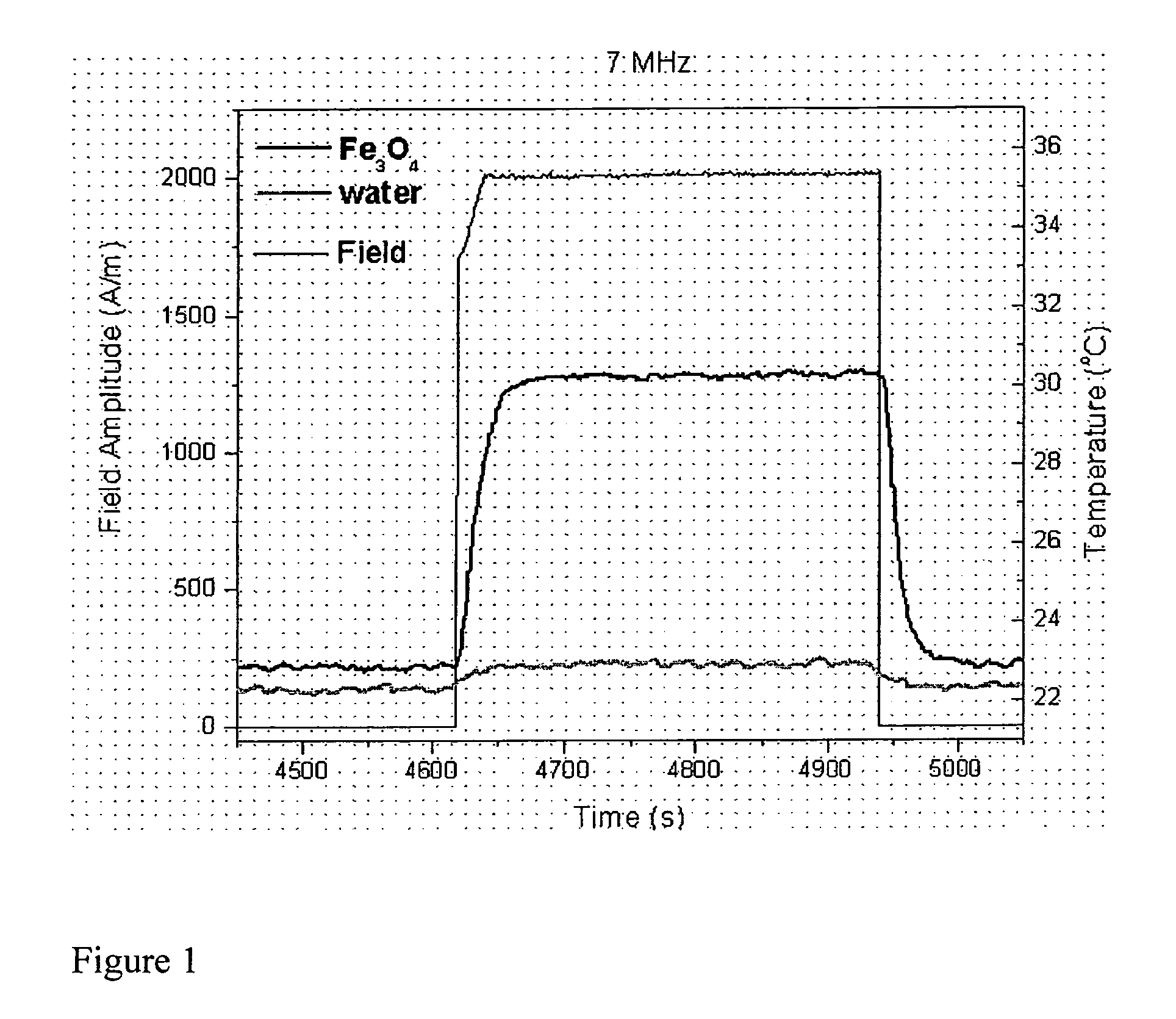
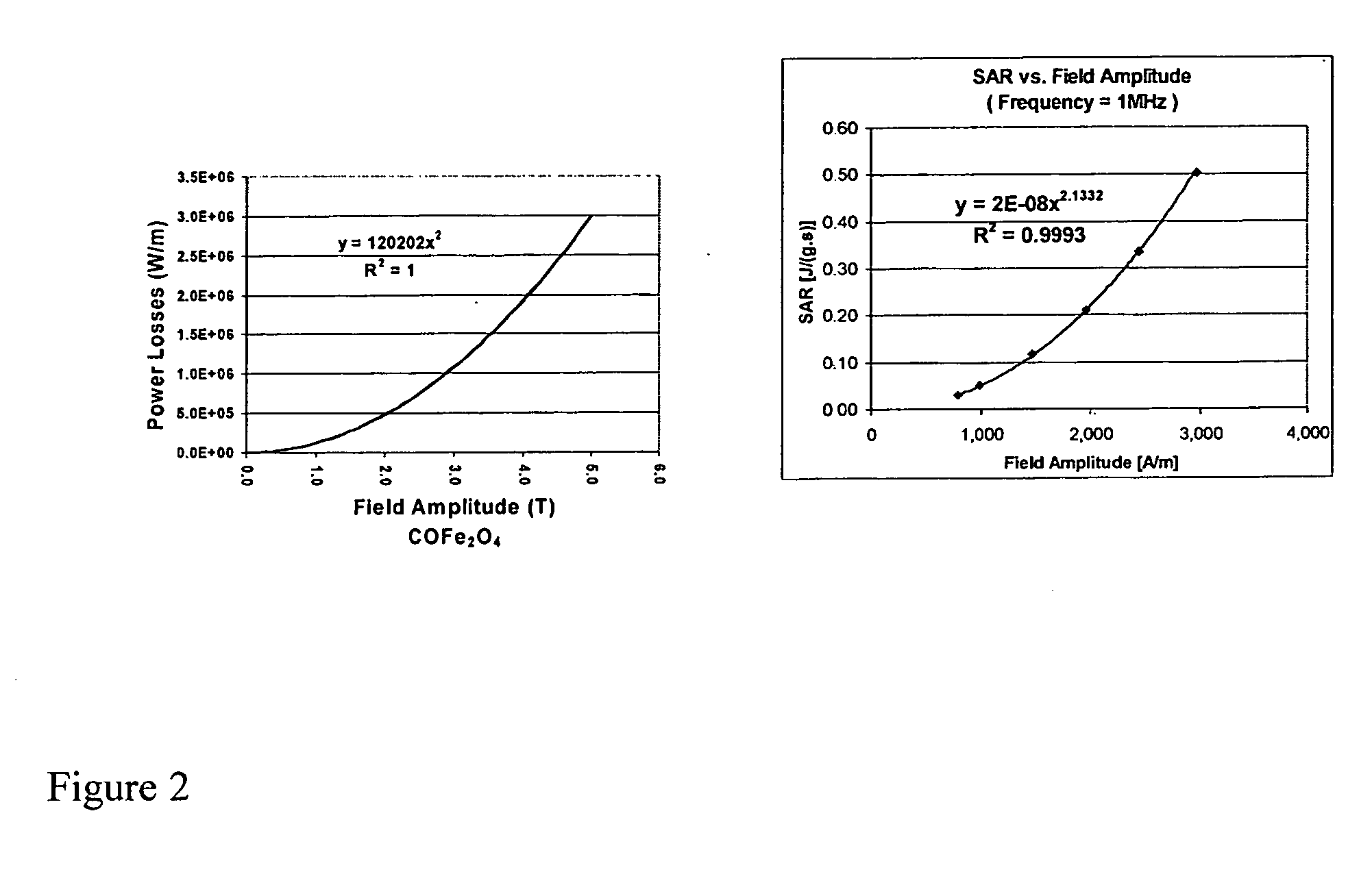
Nanoparticle heating and applications thereof
This invention provides magnetic nanoparticles, which when placed in a magnetic field are selectively heated at a certain frequency of the magnetic field, as a function of their size, composition, or both. The invention also provides for use of such nanoparticles, in applications including, inter alia, selective nanoparticle heating and applications thereof, hyperthermia induction in cells or tissue, remote alteration of protein structure and / or drug delivery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
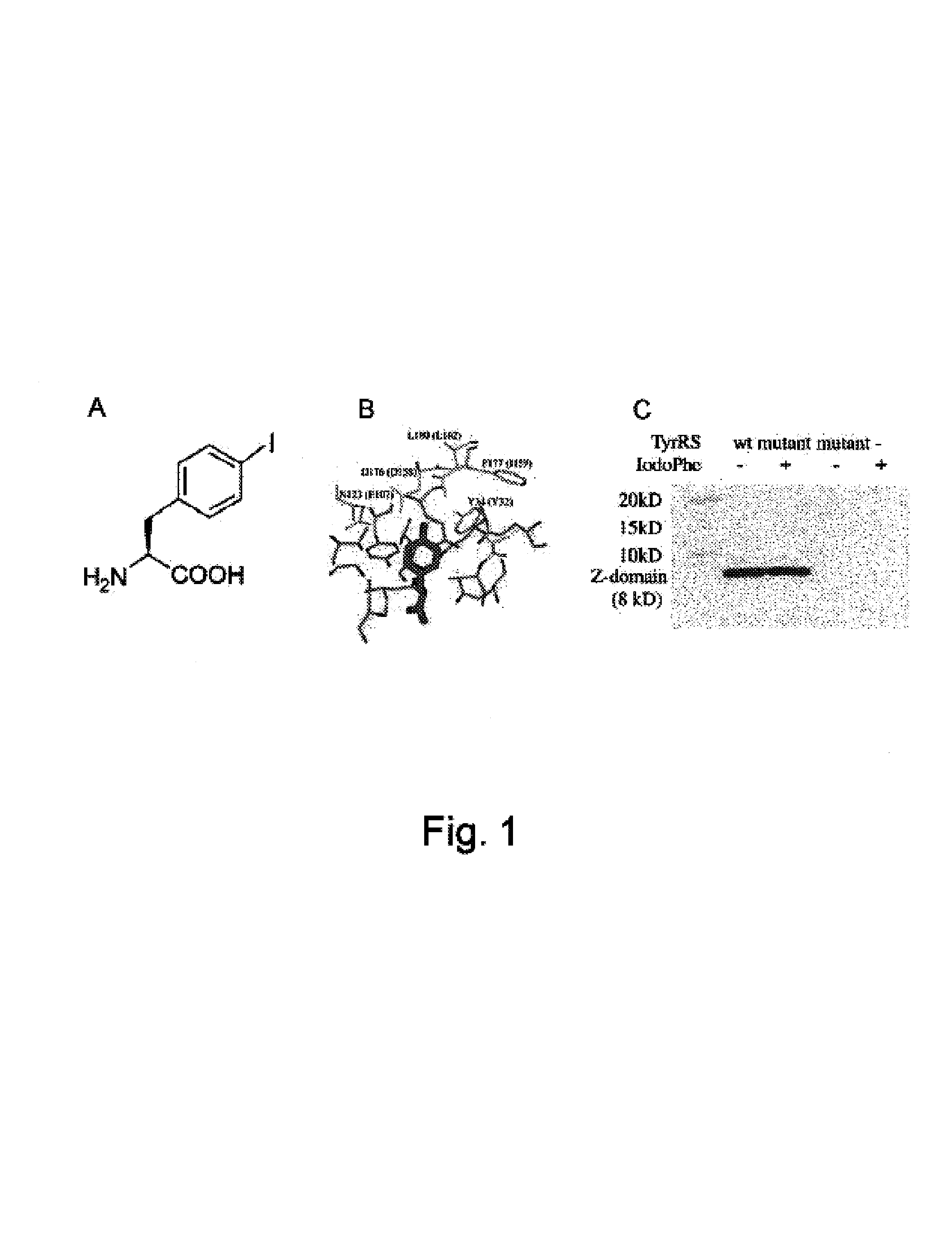
Site specific incorporation of heavy atom-containing unnatural amino acids into proteins for structure determination
Translation systems and other compositions including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA-synthetases that preferentially charge an orthogonal tRNA with an iodinated or brominated amino acid are provided. Nucleic acids encoding such synthetases are also described, as are methods and kits for producing proteins including heavy atom-containing amino acids, e.g., brominated or iodinated amino acids. Methods of determining the structure of a protein, e.g., a protein into which a heavy atom has been site-specifically incorporated through use of an orthogonal tRNA / aminoacyl tRNA-synthetase pair, are also described.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
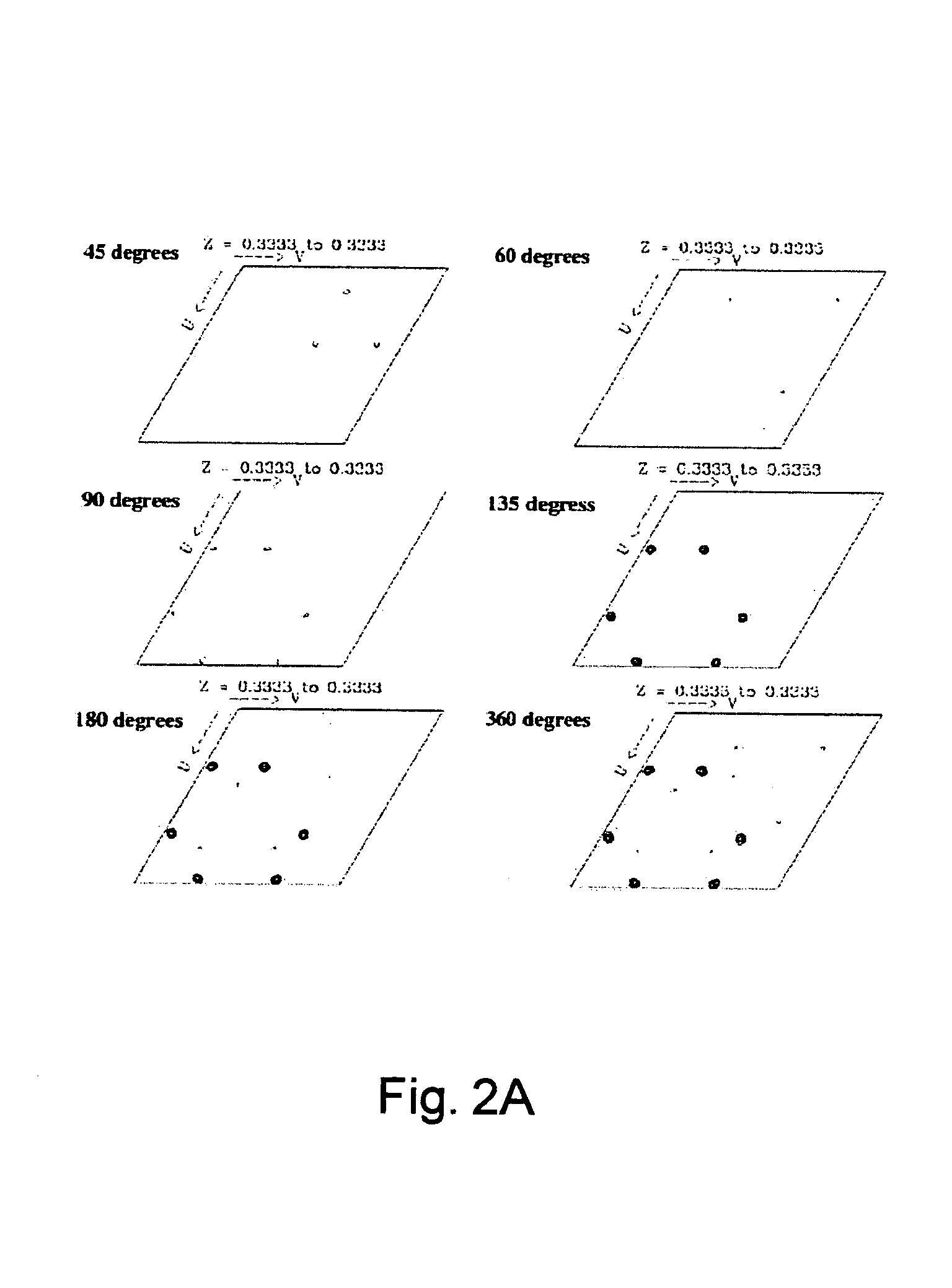
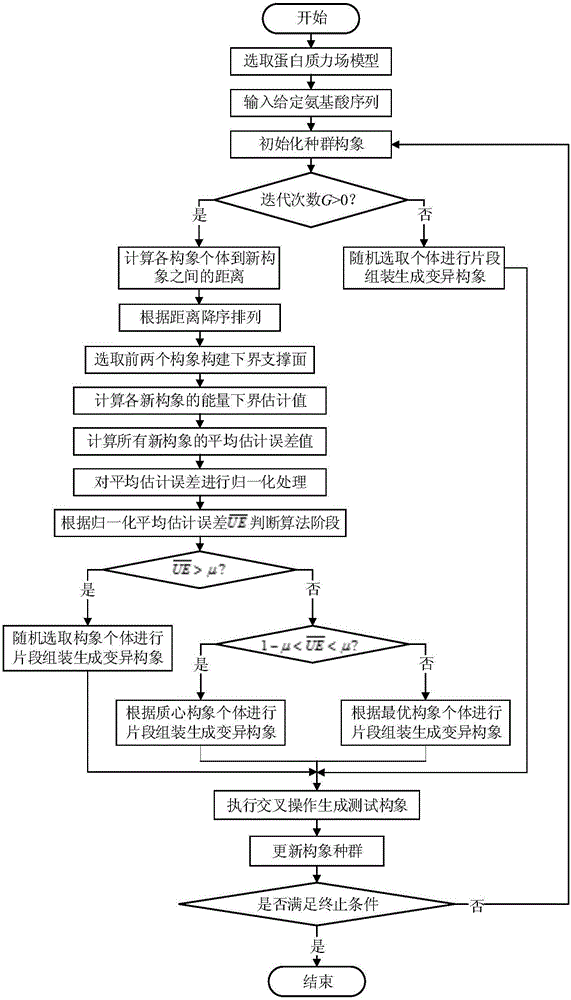
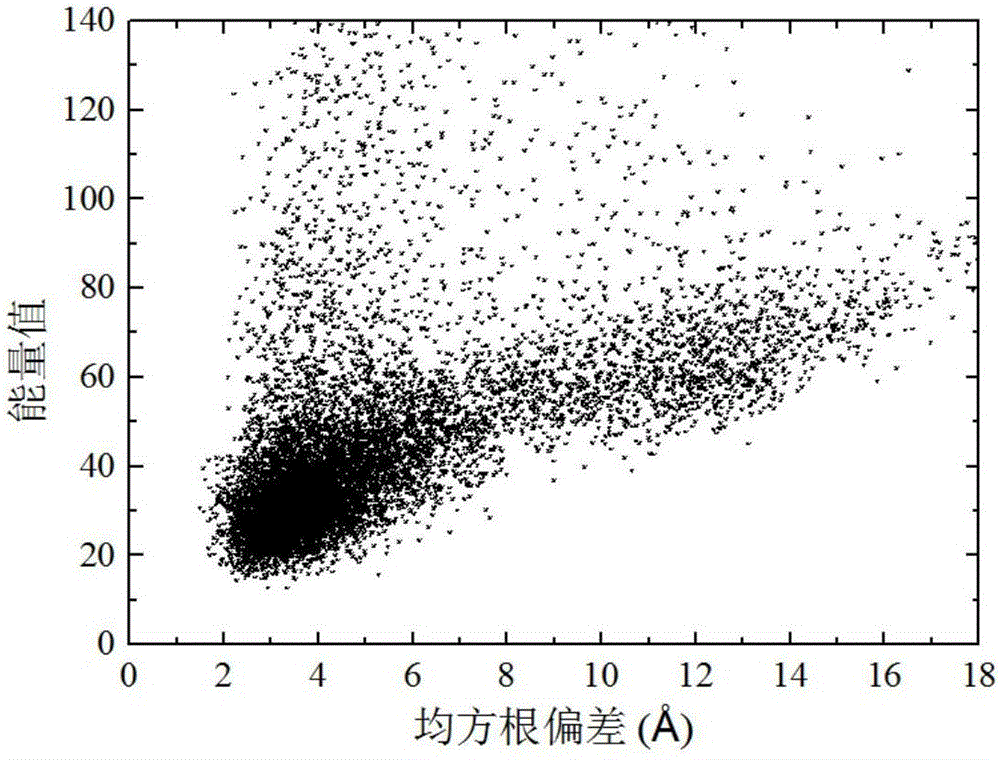
Forecasting method for multi-stage differential evolution protein structure based on abstract bulge estimation
ActiveCN106503484AFast convergenceImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsMolecular structuresLower limitProtein structure
The invention relates to a forecasting method for a multi-stage differential evolution protein structure based on abstract bulge estimation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating the distance from each conformation individual in a current colony to a new conformation and performing ascending sorting according to the distance; then selecting the part of the new conformation individual close to a abstract bulge lower-limit estimation support surface of the conformation individual, thereby acquiring an energy lower-limit estimation value of the new conformation individual; calculating an average estimation error between the energy lower-limit estimation value of all the new conformation individuals and a practical energy value; dividing the whole algorithm into a plurality of optimizing stages according to the change in the average estimation error; judging the stage of the present iteration according to the average estimation error in the last iteration; and designing different strategies for all the stages and generating the new conformation individual. The forecasting method for the multi-stage differential evolution protein structure based on the colony abstract bulge estimation provided by the invention is high in forecasting precision and low in calculation cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102943083AImprove stabilityHigh expressionHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention provides site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and an expression vector and application thereof. Amino acid in a specific area in a phytase amino acid sequence is mutated into praline and arginine so as to enable the phytase to have a special stable protein structure. Simultaneously, a gene sequence is optimized to synthesize a phytase gene according to pichia pastoris codon preference and GC content, recombinant plasmids are built and transferred to pichia pastoris, and positive converters are obtained through screening to conduct induction expression to obtain the high temperature resistant phytase. Experiments prove that the phytase obtained through expression of the pichia pastoris can resist high temperature plasmids with the temperature higher than 85 DEG C, and survival rate reaches 85%. Popularization and application of the high temperature resistant phytase have substantial economical benefit and social benefit on development of feed animal husbandry of our country, and simultaneously great ecological benefit can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN CHIATAI FEED TECH
Latex Adhesives Derived From Ionic Strength Induced Soy Protein Complexes
InactiveUS20080287635A1Easy to operateHigh strengthPeptide preparation methodsFiberProtein molecules
Macro hydrophobic clusters and complexes of soybean globular proteins were observed using TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). Upon unfolding, hydrophobic groups of the proteins became exposed toward the surface of the protein and actively interacted with other hydrophobic groups of other protein molecules, thereby forming hydrophobic bonding. The hydrophobic bonding resulted in hydrophobic protein clusters, the formation of which was affected by the degree of protein unfolding, protein structure, and hydrophobic components. Such hydrophobic clusters followed the global minimum free energy theory and formed spherical like structures with diameters ranging from 100 nm to 3000 nm. Such an understanding lends applicability to many uses in adhesives, molding composites, surfactants for oil-water systems, bio-based interior construction paints and paper coatings, fiber production, and metal powder molding applications.
Owner:SUN XIUZHUI +2
Analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction
ActiveCN107525842ARich varietySimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein containing complexHydrolysate
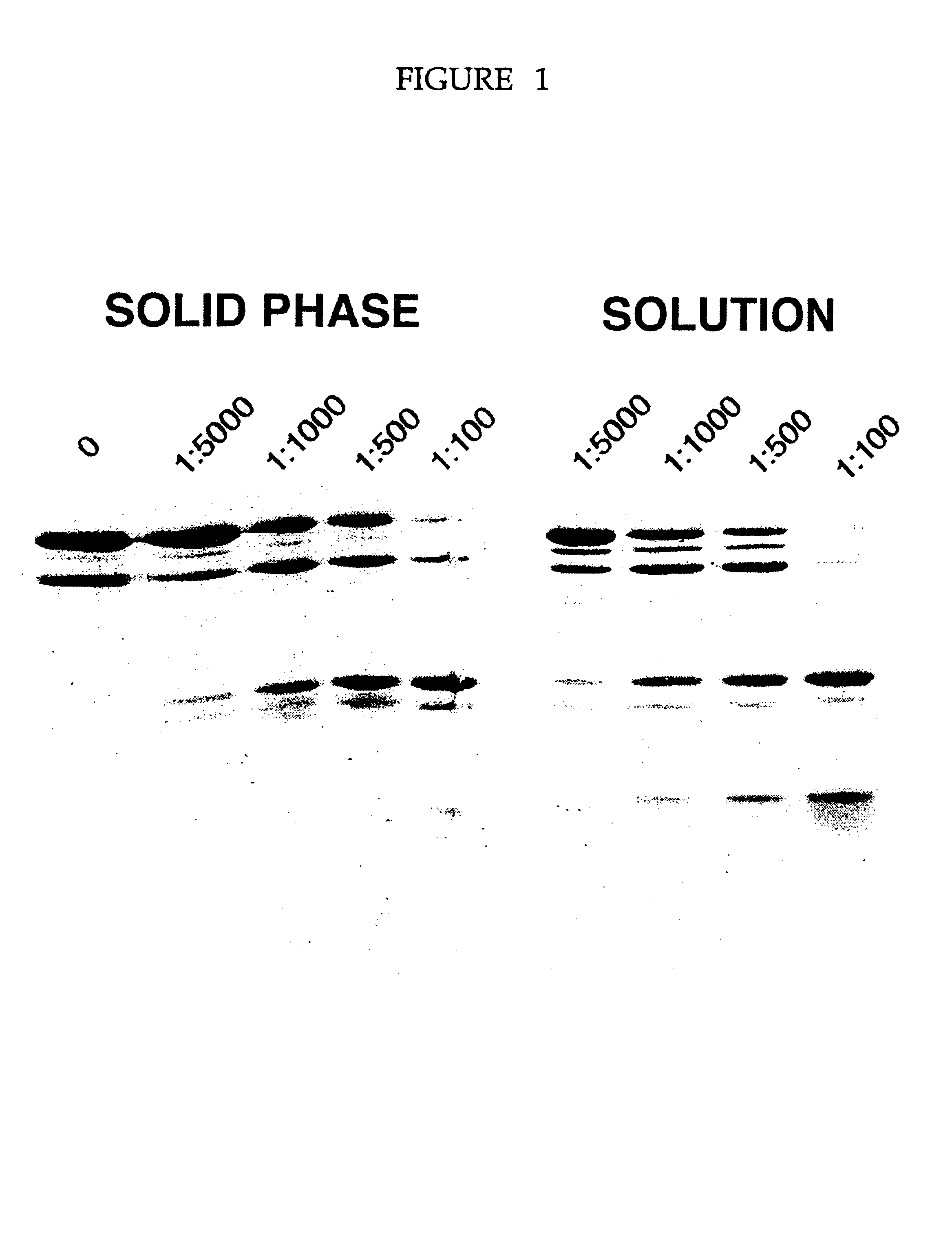
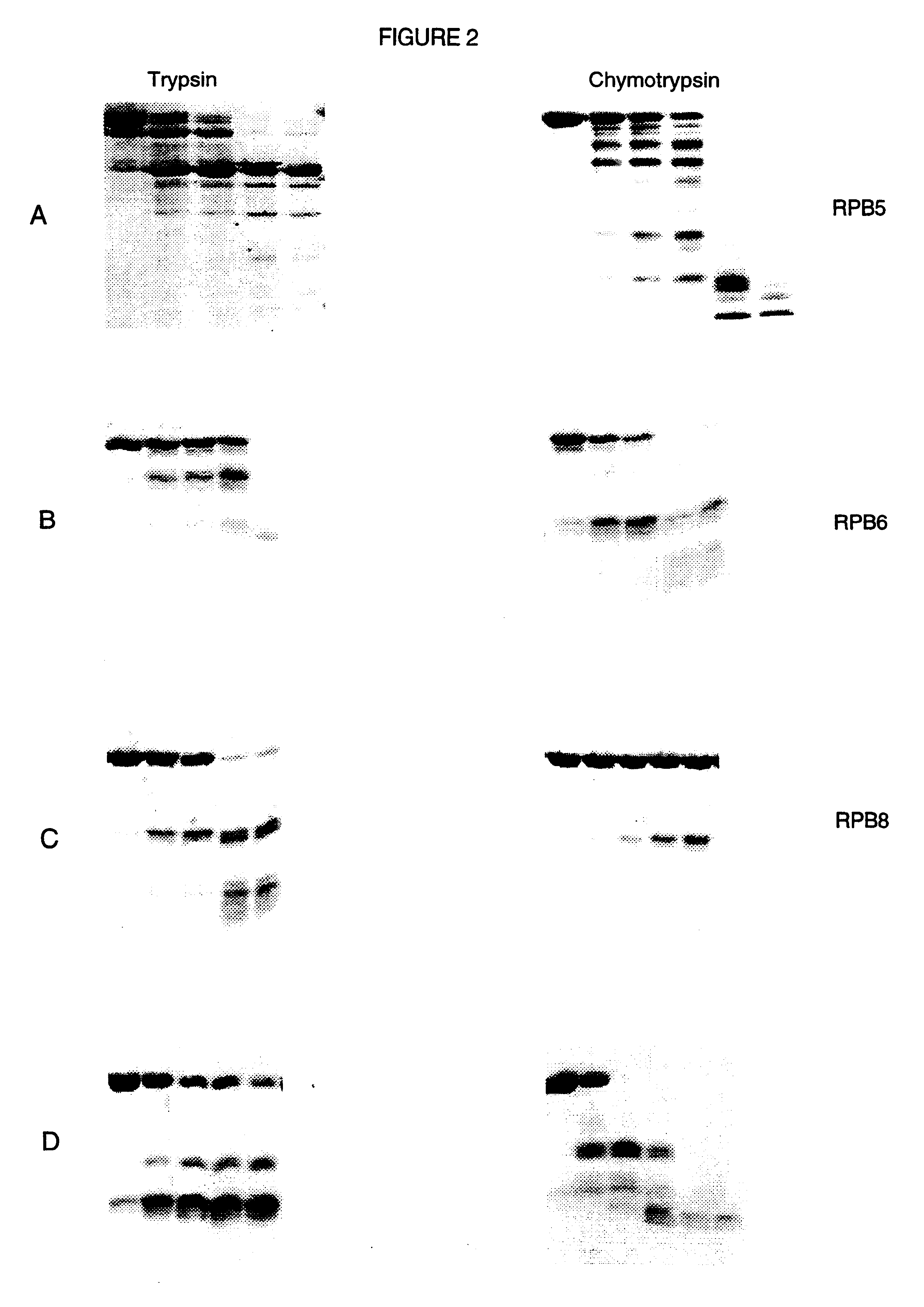
The invention relates to an analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction. The method comprises the following steps: performing crosslinking and enzymolysis on a protein composite in a cell by using a crosslinking agent with reactive groups on two sides and a breakable group, and taking a part of the enzymatic hydrolysate for a derivatization reaction for mass spectrometry; after breaking the crosslinking agent by means of a chemical method for the other part of the enzymatic hydrolysate, enriching peptide sections with an enriching material, and performing mass spectrometry on the enzymatic hydrolysate without the enriched peptide sections; determining the crosslinked peptide sections according to a library searching result so as to establish a peptide section library; finding out a candidate peptide section from the peptide section library according to N-terminal amino acid information of the crosslinked peptide section determined in the mass spectrogram of the crosslinked peptide section; and determining the crosslinked peptide section sequence by combining the mass spectrogram m / z of the crosslinked peptide section and the characteristic ions of the peptide section so as to obtain the protein structure and protein-protein interaction information. The method has the advantage of being simple to operate, and is applied to structural analysis of proteins and analysis of protein-protein composite interaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for the determination of protein domain boundaries
InactiveUS6451591B1Improve throughputSuitable for automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProteinase activityProtein structure
A method and device to assist in the determination of protein domain boundaries is described. In particular the device is designed to provide a high throughput of proteolytic digestion of proteins to identify domains and their boundaries, for use in protein structure determination, in a manner that is amenable to automation. Proteases are immobilized in a convenient format such as a microtitre plate and preferably arranged in a matrix thereby allowing for simultaneous degradation of a protein by a number of proteases at a number of concentrations.
Owner:AFFINIUM PHARMA
Bio-barcode based detection of target analytes
The present invention relates to screening methods, compositions, and kits for detecting for the presence or absence of one or more target analytes, e.g. biomolecules, in a sample. In particular, the present invention relates to a method that utilizes reporter oligonucleotides as biochemical barcodes for detecting multiple protein structures or other target analytes in a solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
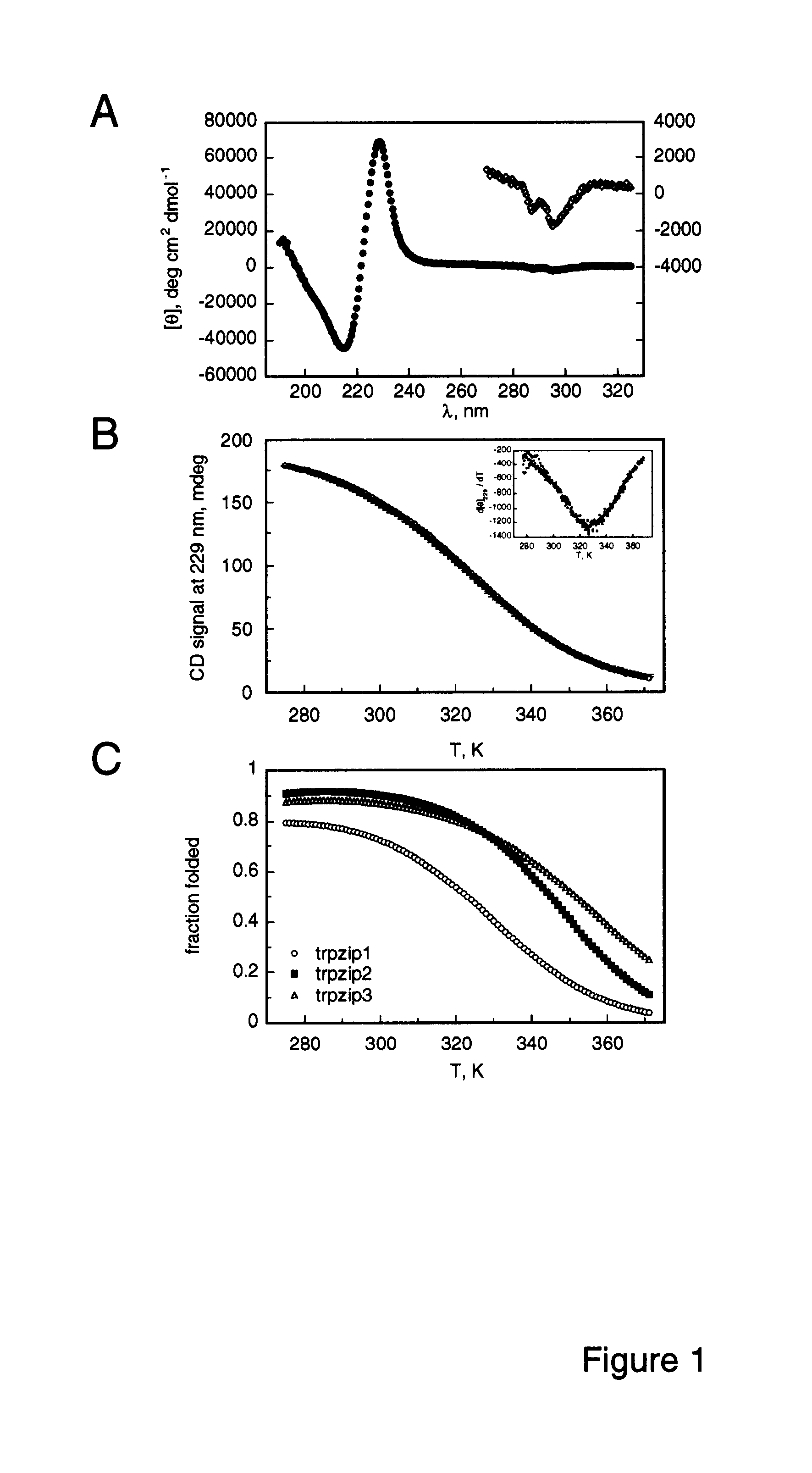
Hairpin peptides with a novel structural motif and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6914123B2Enable stabilizationImprove structural stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein moleculesModel system
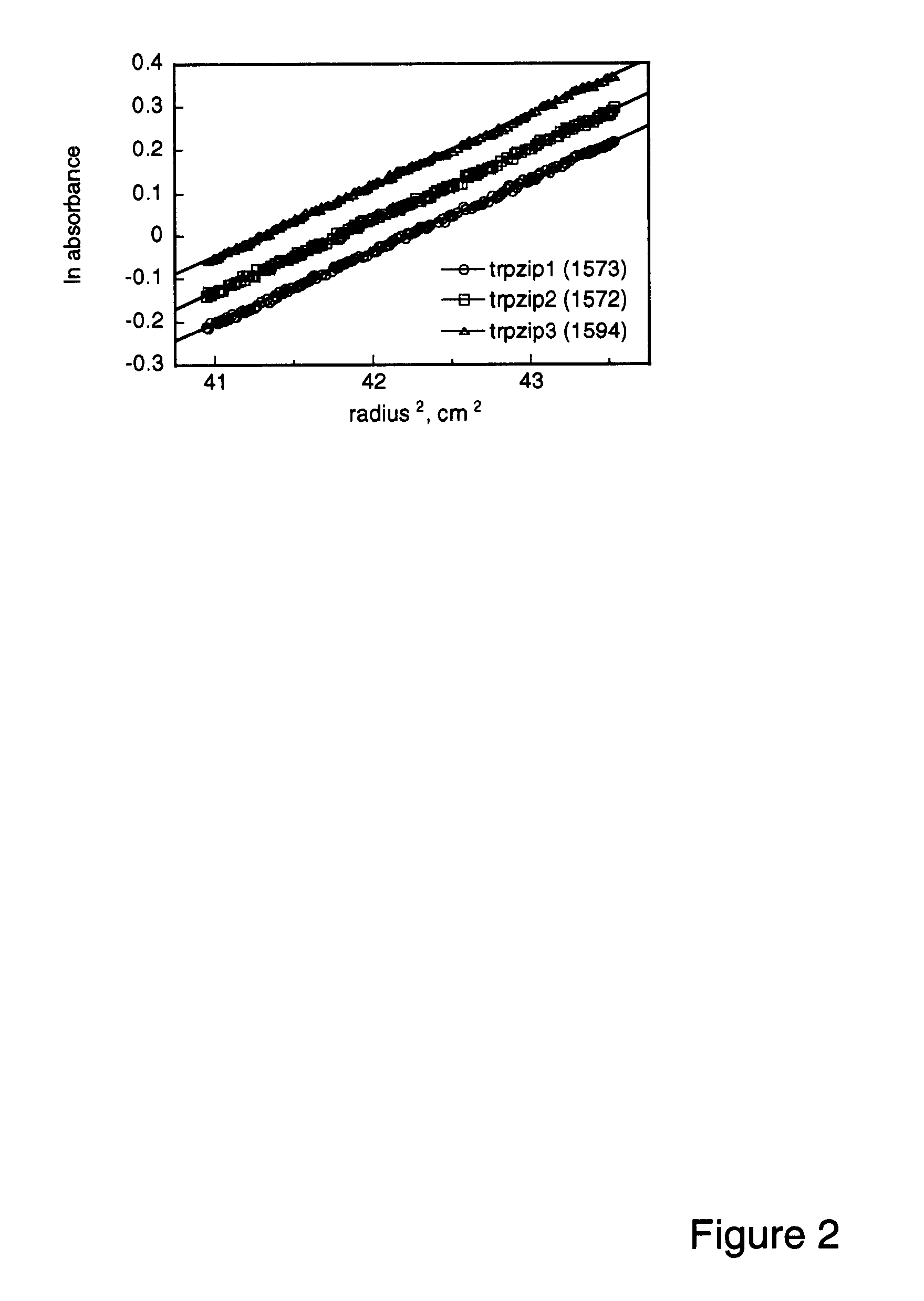
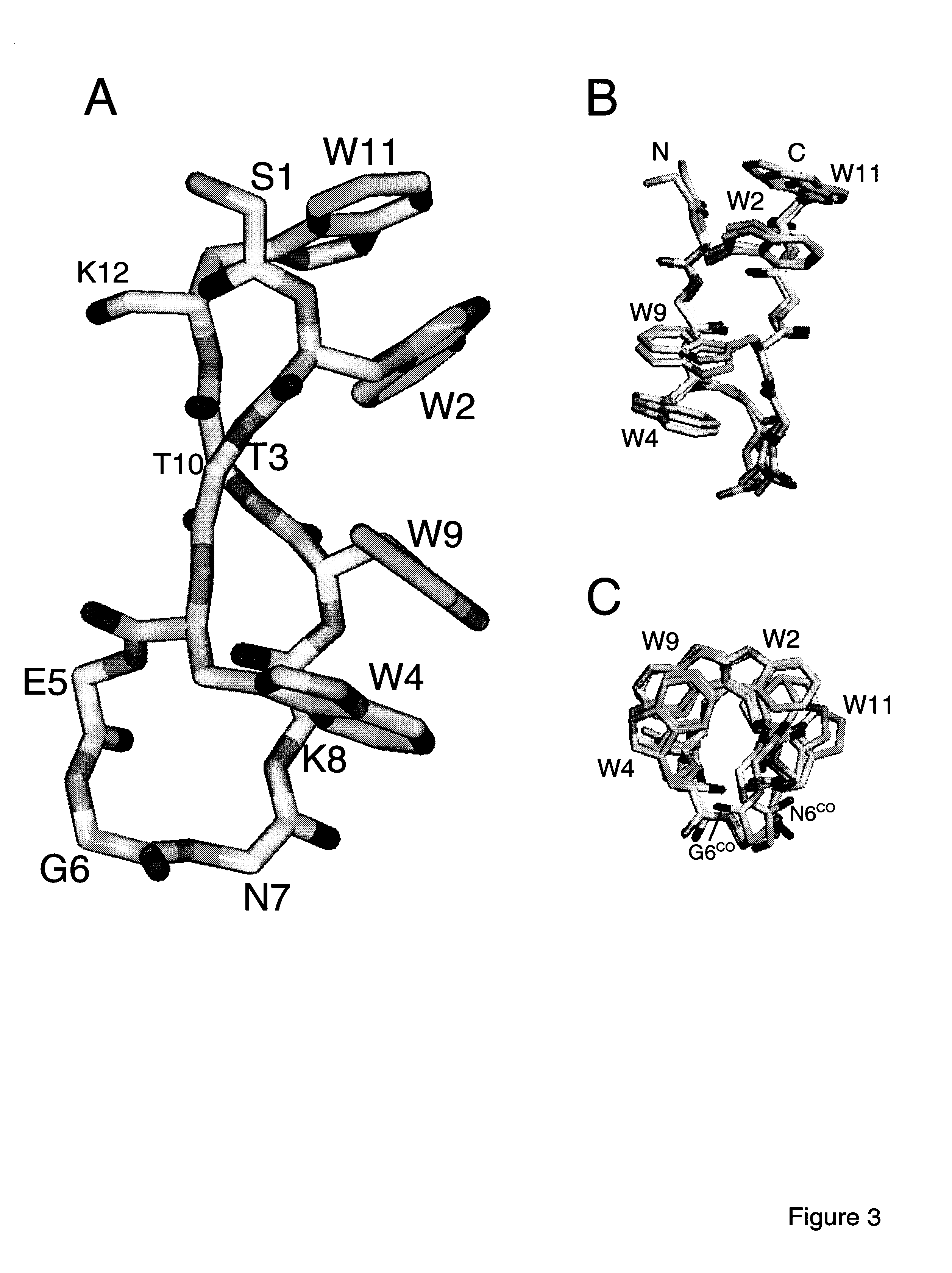
The invention is directed to a model system for structure-activity relationship analysis of peptide or protein molecules involved in important biological processes. Provided by the invention are combinatorial peptide libraries comprising peptides with a novel “tryptophan zipper” scaffold (trpzip) that forms stable β-hairpin structure in solution. Methods of selecting and using such scaffold are provided herein, which are useful for mimicking native protein structures and interactions and designing therapeutic agents. Thus, the invention has profound utility for biological studies and drug development.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
High-throughput, high-precision methods for detecting protein structural changes in living cells
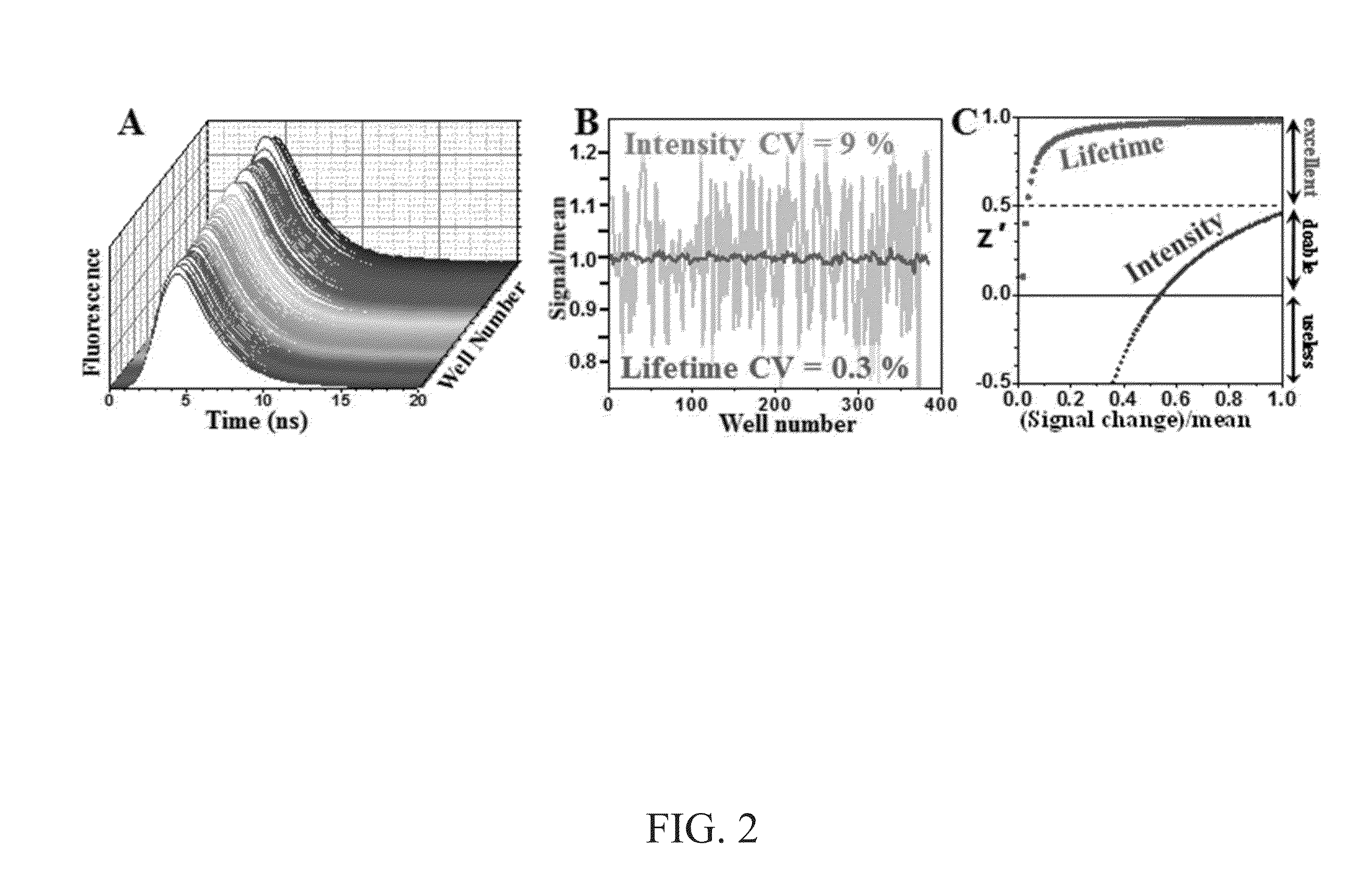
ActiveUS20150204847A1Highly parallel biological researchQuick analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein targetProtein structure
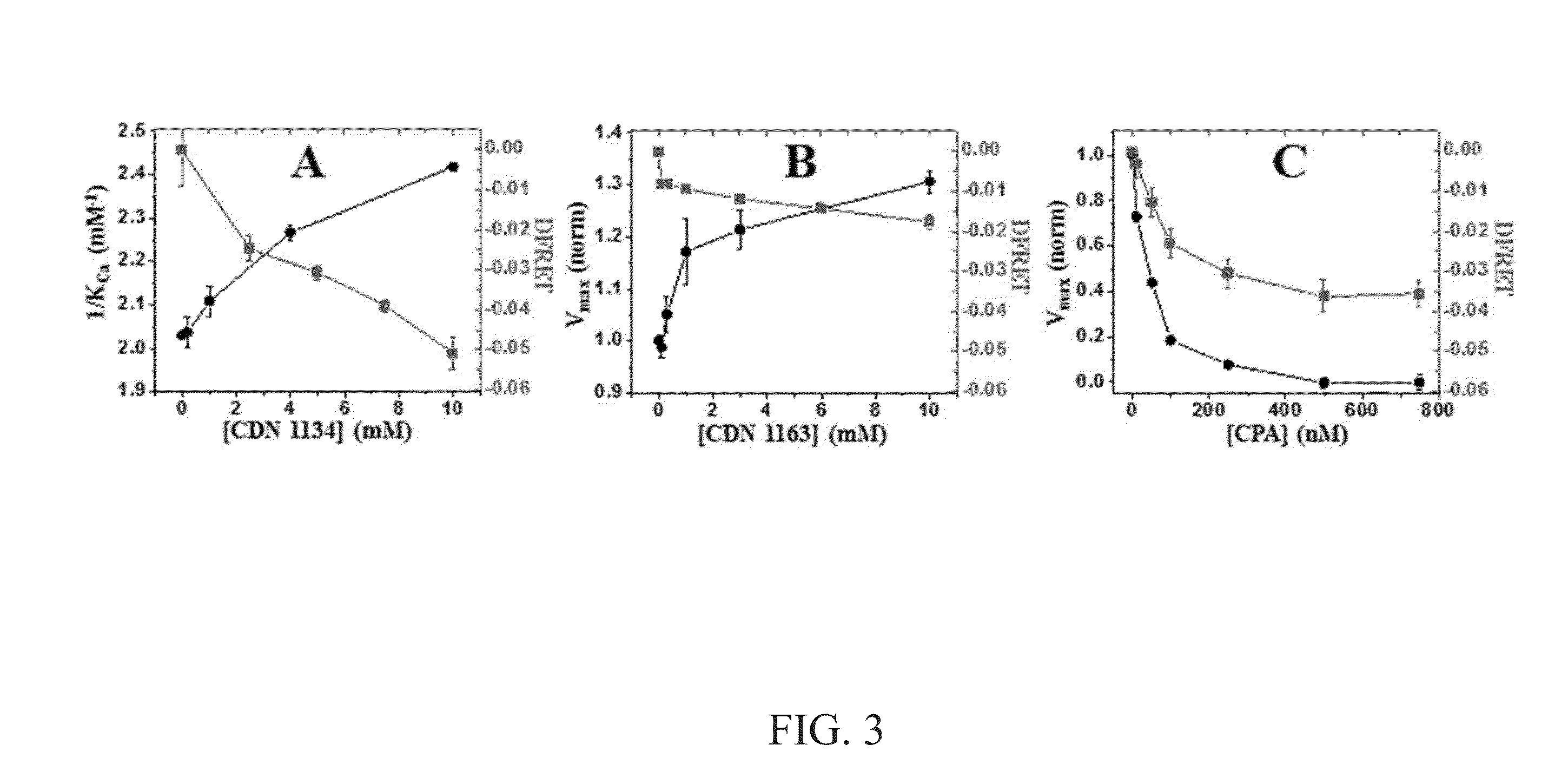
Methods for identifying a compound that alters fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) of a protein. The methods include use of a genetically engineered cell that includes a target protein. The target protein includes one or more heterologous domains. In one embodiment, a target protein includes two heterologous domains, and in another embodiment, the target protein includes a heterologous domain and the cell further includes a second protein that includes a heterologous domain. A heterologous domain may include a chromophore or an amino acid to which a fluorescent dye attaches. The fluorescence lifetime of one or more chromophore, one or more fluorescent dye, or the combination thereof, is measured after contacting the cell with a compound A difference between the fluorescence lifetime in the presence of the test compound and the fluorescence lifetime in the absence of the test compound indicates that the test compound alters the FRET of the target protein.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO +1
Absorbent products with a linked enzyme treatment
InactiveUS7928282B2Improve abilitiesReduce sensitizationSynthetic resin layered productsBaby linensProtein structurePhotochemistry
The present invention provides a substrate treated with an linked enzyme. It has been discovered that a substrate treated with a linked enzyme can be effective in improving the ability of the substrate to absorb viscoelastic materials, such as menses, by cleaving a protein structure present in some viscoelastic materials. In addition, the linked enzyme is less likely to migrate from the treated material onto the user, as compare to an enzyme being placed directly on the substrate, thereby reducing the risk of sensitization to the user of the absorbent product. Also provided by the present invention are absorbent articles which contain at least one surface or layer containing the linked enzyme.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Novel coronavirus antigen epitope and application thereof
ActiveCN111848753AImproving immunogenicityHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen epitopeCoronavirus vaccination
The invention provides a novel coronavirus antigen epitope and application thereof. A super computer is used for simulating S, E, M and N protein structures of the novel coronavirus, and novel coronavirus epitopes SEQ ID NO 1-38 are obtained through calculation. The epitopes have very good immunogenicity; an antibody generated by inducing a part of epitope polypeptide has the effect of neutralizing the novel coronavirus; the antigen epitope can be combined with antibodies in serum of novel coronavirus patients at home and abroad, has the potential of resisting various novel coronavirus strains, and also has the potential of identifying and applying different strains. The epitope provided by the invention can be used for (1) research and development of novel coronavirus vaccines and universal coronavirus vaccines such as MERS viruses and SARS viruses; and (2) preparing a novel coronavirus antibody, and further detecting and typing viruses and treating diseases caused by the viruses. Thenovel coronavirus antigen epitope has a wide application prospect in the aspects of prevention of coronavirus and propagation and outbreak thereof, and detection and diagnosis of virus strains.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bio-barcodes based on oligonucleotide-modified particles
The present invention relates to a screening methods, compositions, and kits for detecting for the presence or absence of one or more target analytes, e.g. proteins such as antibodies, in a sample. In particular, the present invention relates to a method that utilizes reporter oligonucleotides as biochemical barcodes for detecting multiple protein structures or other target analytes in one solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
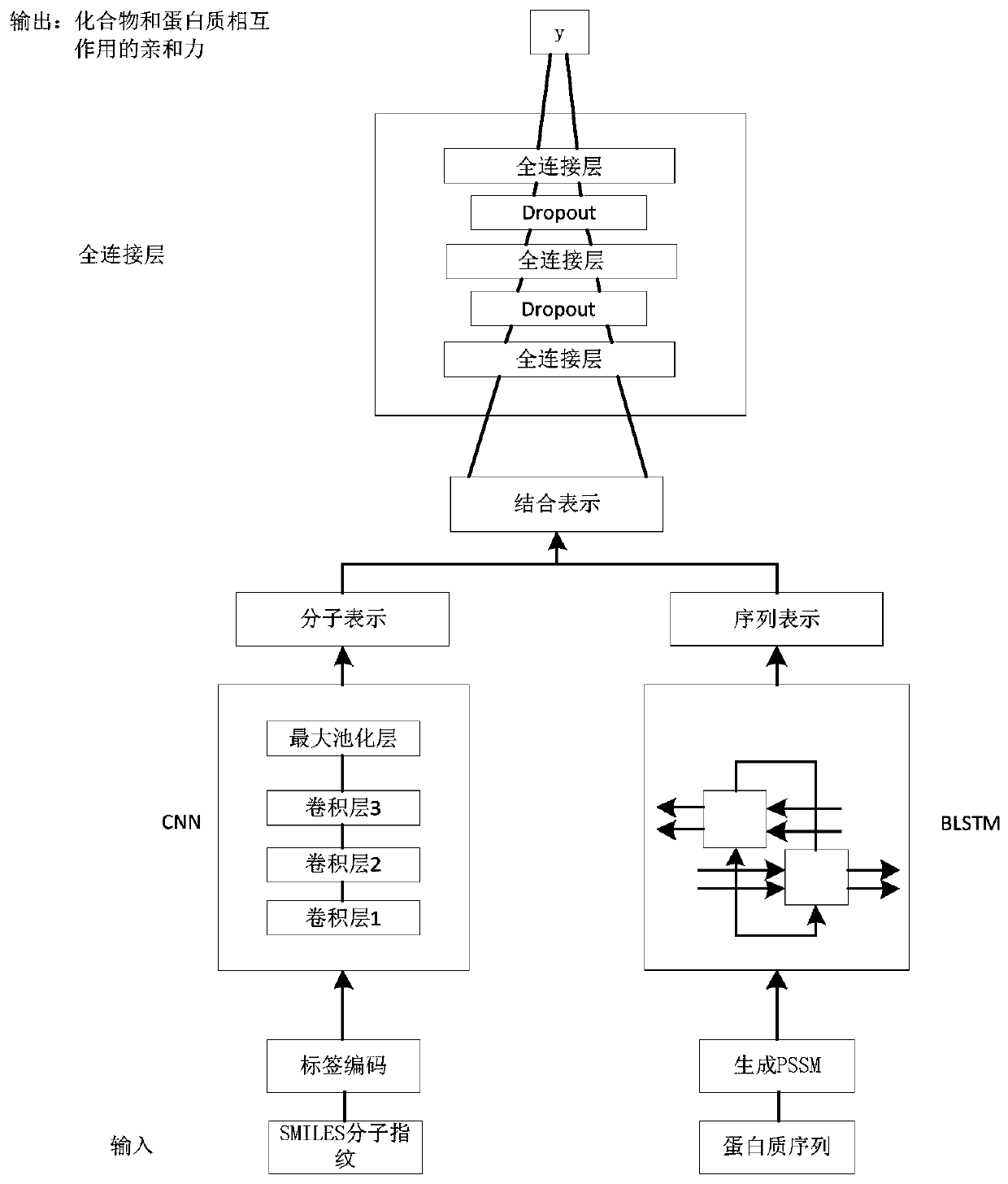
Drug target affinity prediction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN110689965ARepresentative featuresPredicted Affinity RelationshipsDrug referencesNeural architecturesProtein targetDrug compound
The invention discloses a drug target affinity prediction method based on deep learning, and relates to the technical field of drug target affinity prediction. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a drug compound and target protein data from a Davis data set and a KIBA data set; encoding the compound, and representing the protein by using a position specificity scoring matrix; inputting acompound label code into a CNN model, and performing feature extraction on the compound to obtain molecular representation of the compound; inputting the position specificity scoring matrix of the protein into an LSTM model, performing feature extraction on a protein sequence, and learning an order relationship between amino acids in a protein structure and a relationship between residues on the protein sequence to obtain the sequence representation of the protein; and simultaneously inputting the molecular representations of the compounds and the sequence representations of the proteins intoa fully linked layer to predict the affinity of the interaction of the compounds and the proteins. The method can predict the affinity relationship between the drug and the target more accurately.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
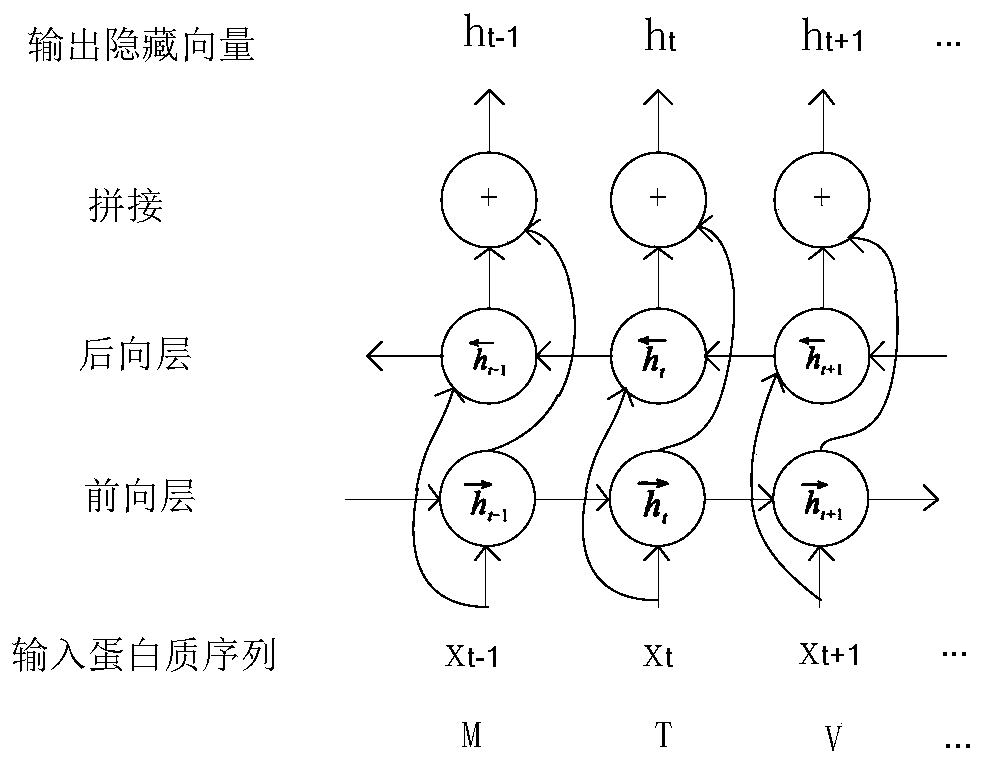
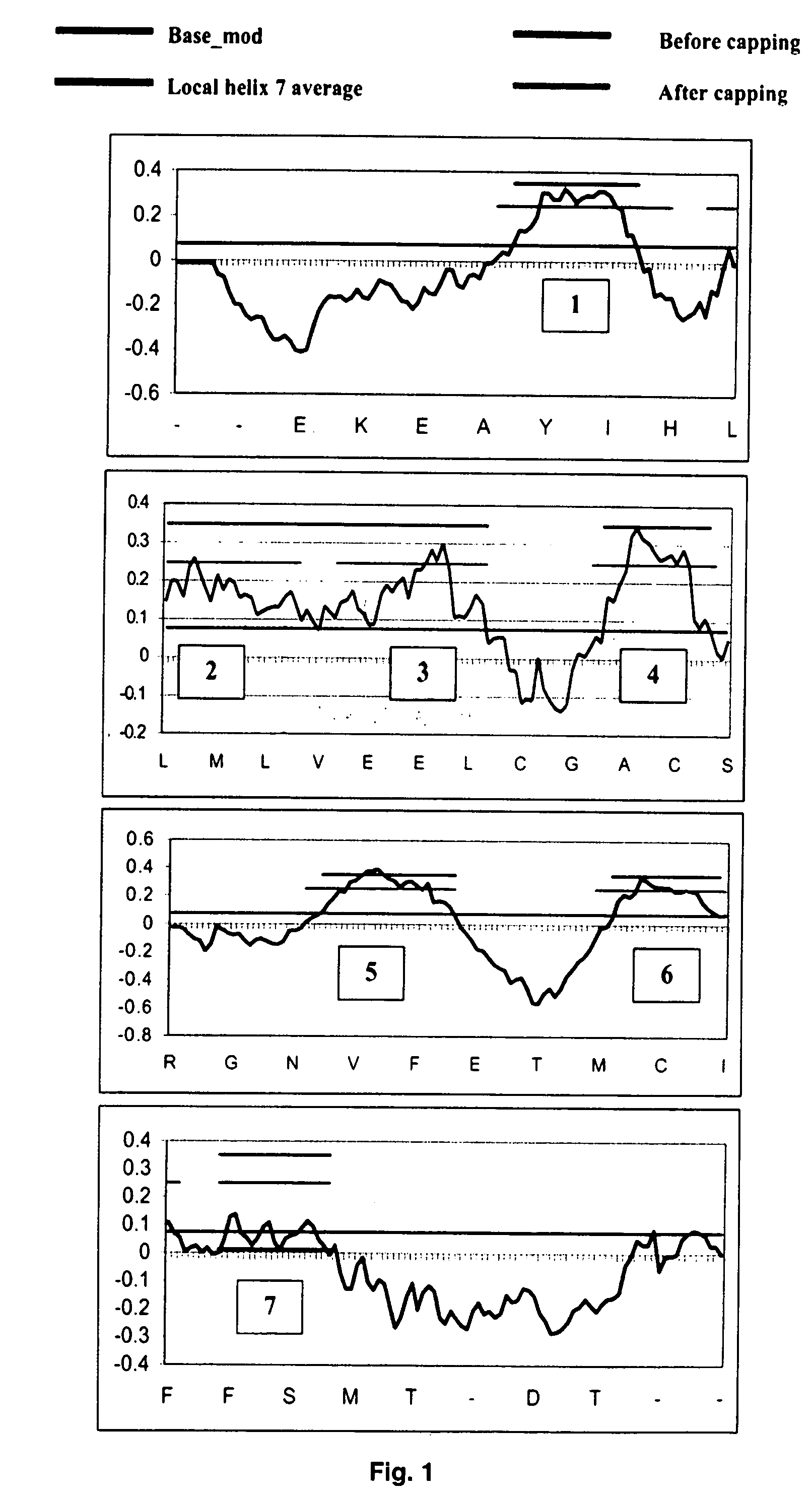
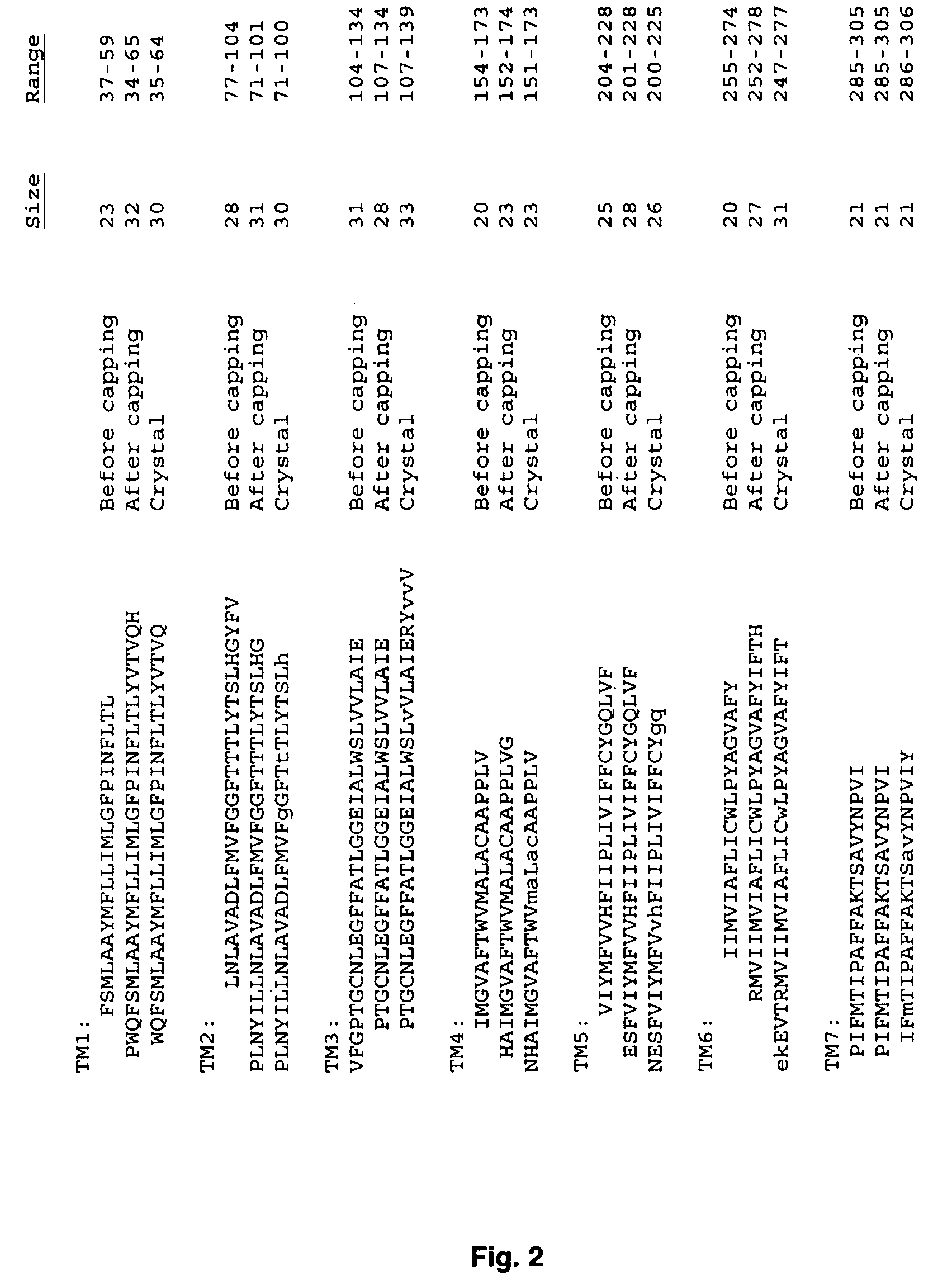
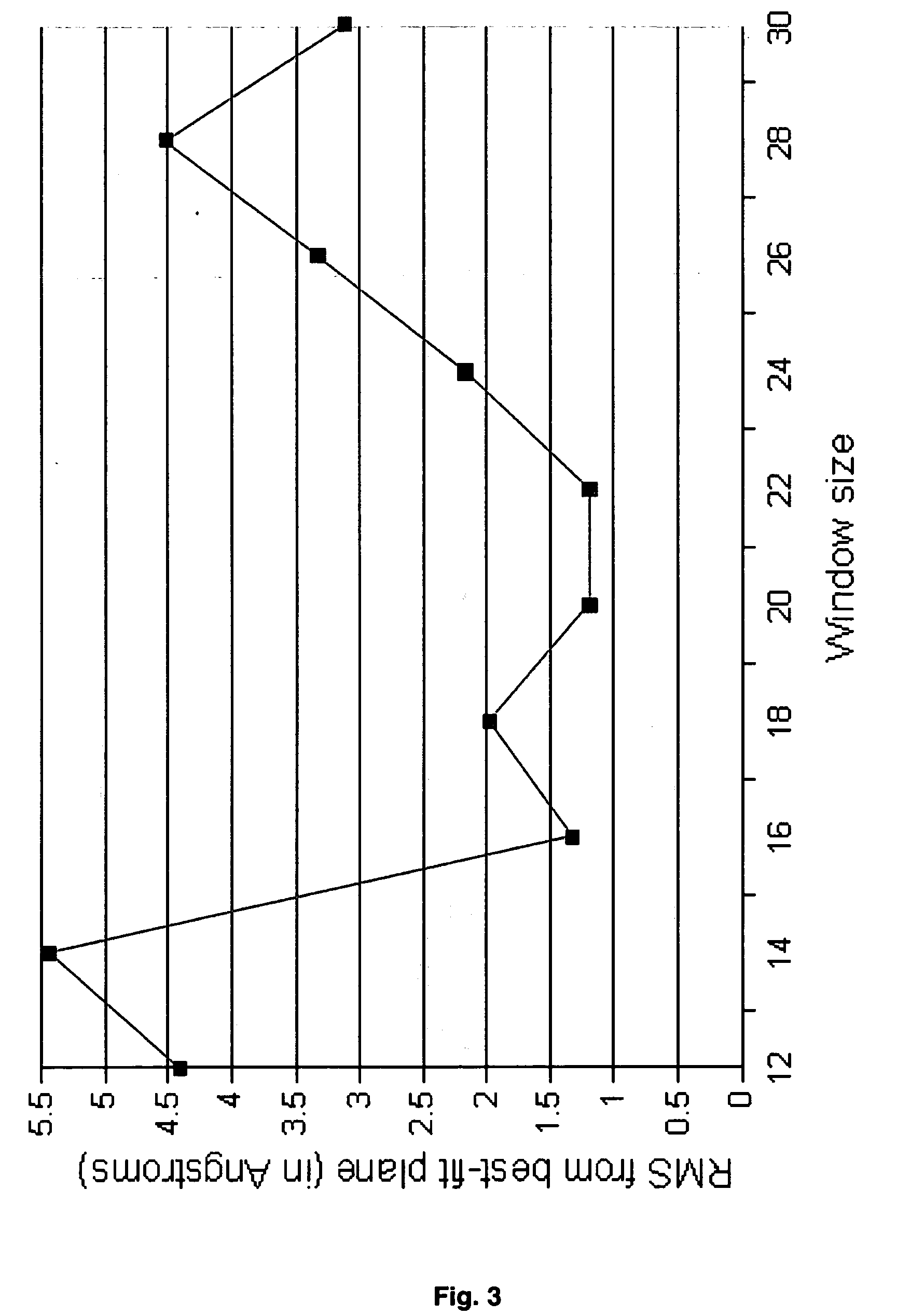
Systems and methods for predicting the structure and function of multipass transmembrane proteins
InactiveUS20050136481A1Fast and accurate procedureMinimizing energyBiological testingSequence analysisProtein structureMolecular modelling
The invention provides computer-implemented methods and apparatus implementing a hierarchical protocol using multiscale molecular dynamics and molecular modeling methods to predict the structure of transmembrane proteins such as G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and protein structural models generated according to the protocol. The protocol features a combination of coarse grain sampling methods, such as hydrophobicity analysis, followed by coarse grain molecular dynamics and atomic level molecular dynamics, including accurate continuum solvation. Also included are energy optimization to determine the rotation of helices in the (seven-helical) TM bundle, and optimization of the helix translations along their axes and rotational optimization using hydrophobic moment of the helices, to provide a fast and accurate procedure for predicting GPCR tertiary structure.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
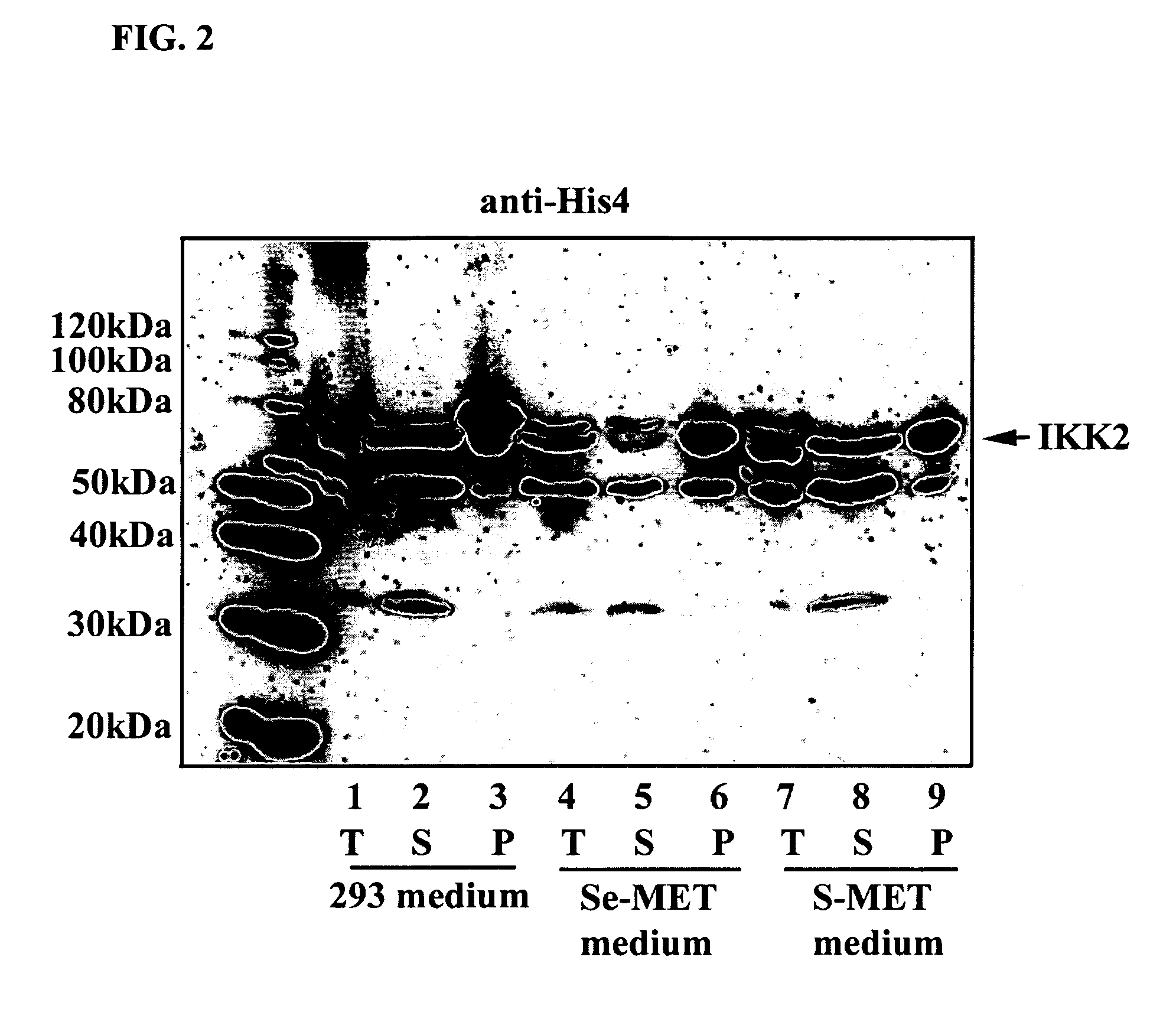
Methods of labeling transiently expressed proteins in large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures
InactiveUS20070161047A1Rapid productionSufficient quantityFungiTransferasesChemical compositionProtein structure
The present invention is based on observations that transiently transfecting large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures with a polynucleotide encoding a protein of interest can be used to rapidly produce the large quantities of labeled proteins required for various biochemical techniques such as spectroscopy, microscopy, and crystallography, and applications including protein structure determination, protein tracing and / or localization, diagnostic and therapeutic applications, and affinity experiments. Thus, the present invention provides methods for rapidly producing large quantities of labeled proteins by using transient transfection of large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures, which are then grown in a chemically defined labeling medium that includes labeled amino acids. The present invention is also directed to methods of using the labeled proteins produced by the novel labeling methods for use in various techniques.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Protein folding parallel predicting method
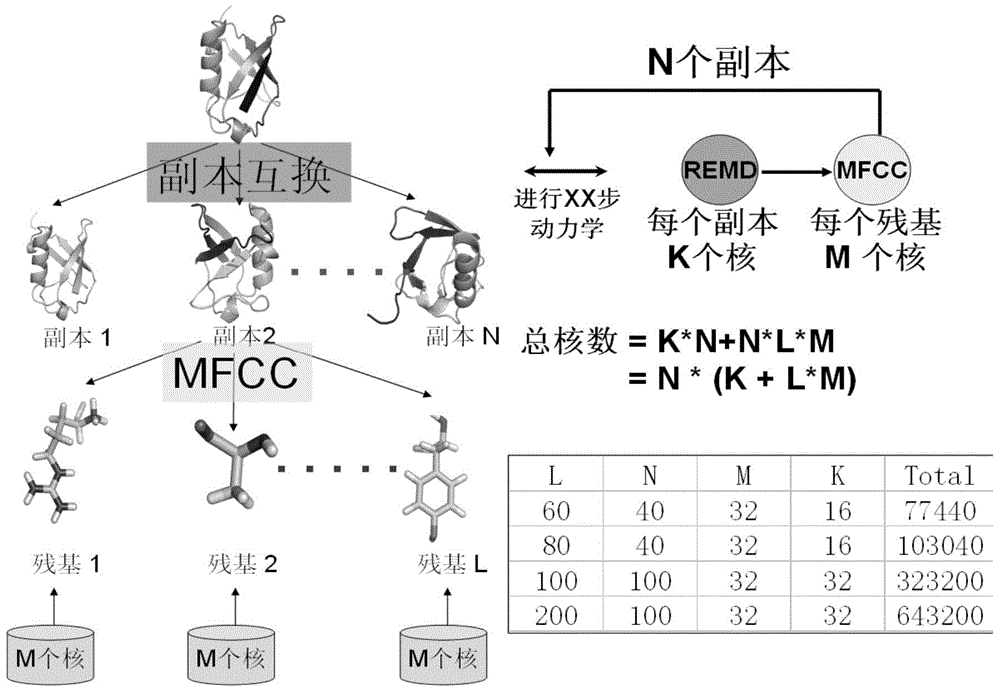
InactiveCN105787292APolarization cannot be ignoredThe result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsProtein structureAmino acid
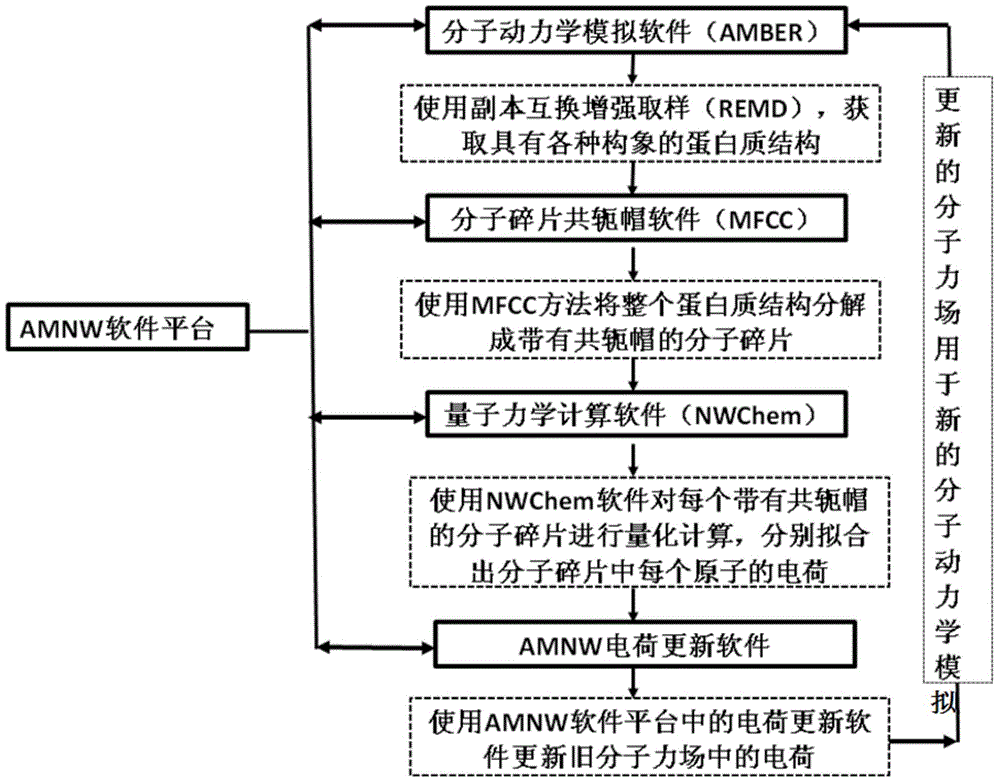
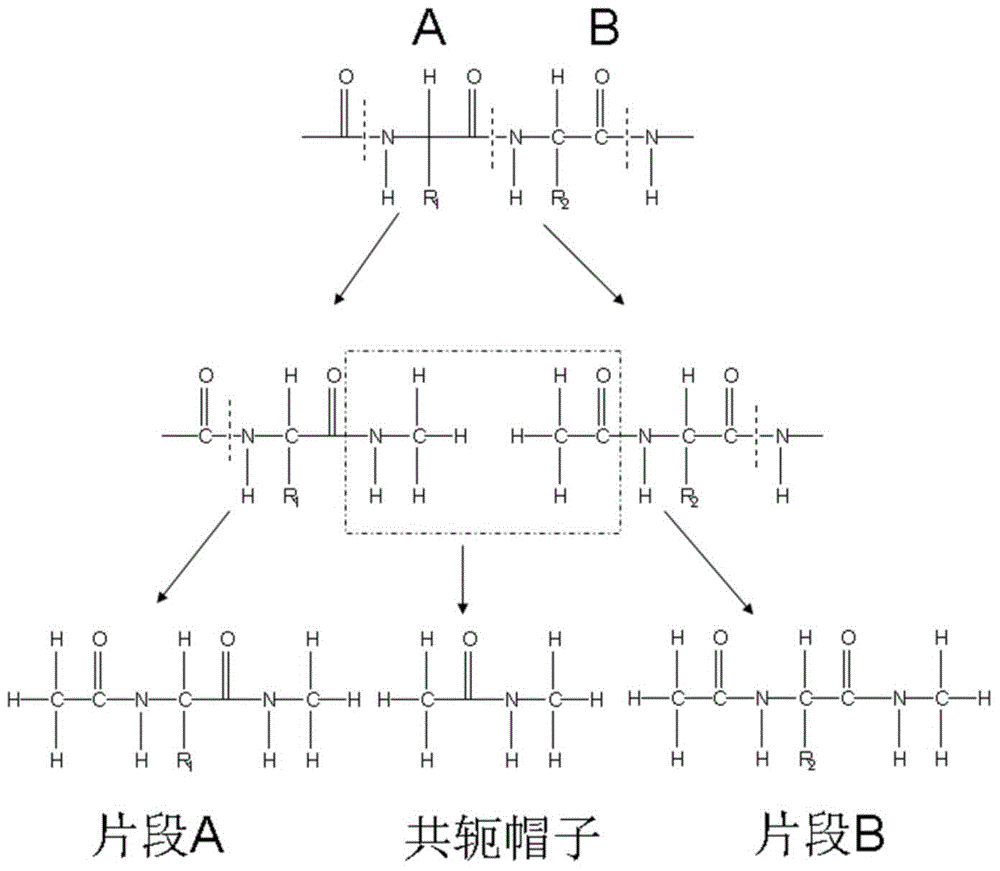
The invention relates to a protein folding parallel predicting method. The method includes the following steps: obtaining different protein structures through molecular dynamics simulation; setting different temperatures, and obtaining more protein structures with different conformations; partitioning the protein structures with different conformations through a conjugate cap molecule partitioning method, decomposing amino acids from proteins, and wearing a conjugate cap on each amino acid; calculating out the electrostatic potential of molecular fragments through quantum mechanics software to fit out the electric charge of each atom in each amino acid molecular fragment, and updating the electric charge of atoms in a molecule force field. To research protein folding, the scheme of considering a protein polarization effect and a copy interchange-based method are organically integrated, and then two difficult problems of atom interaction potential and a sampling technique in dynamics simulation can be overcome in order to achieve a good effect in protein folding simulation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for predicting secondary structure of protein based on multiple evolution matrices
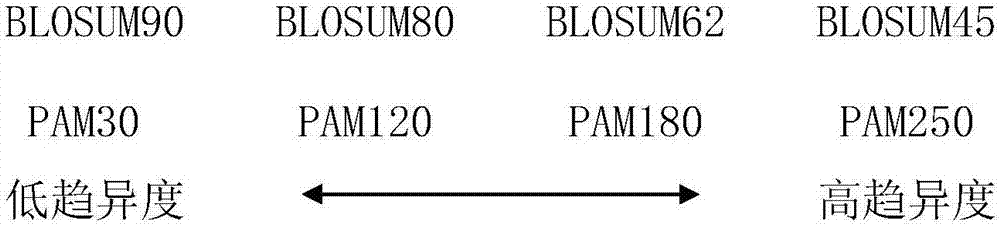
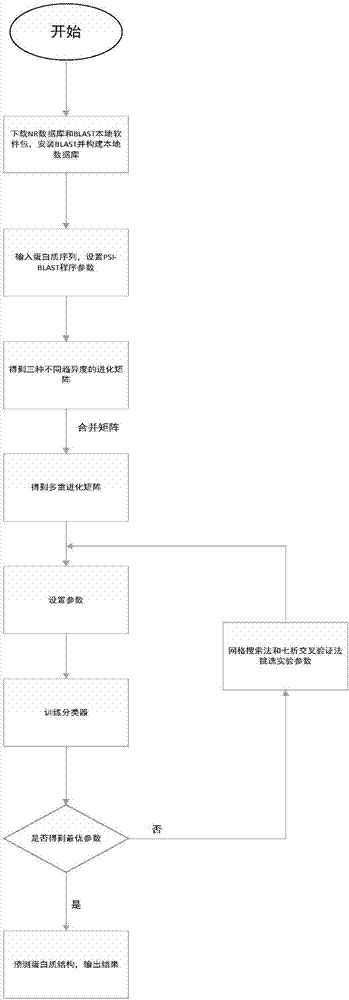
ActiveCN106951736AImprove accuracySimple coding methodSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorProtein insertion
The present invention discloses a method for predicting a secondary structure of the protein based on multiple evolution matrices. The method comprises: downloading a protein NR database and a BLAST program local software package to generate a position-specific scoring matrix PSSM of a given protein sequence, carrying out parameter adjustment on the PSI-BLAST program to obtain evolution matrices of different divergence degrees of the protein sequence; processing all eigenvectors in the evolution matrices to form multiple evolution matrix features; taking the multiple evolution matrix features as input of a classifier and evaluating classification accuracy to obtain an optimization model; and for the protein with an unknown structure, inputting the optimization model, and predicting the secondary structure of the protein. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, for a protein sequence, multiple matrices with different evolutionary divergence degrees are simultaneously used to express the protein sequence, so that the protein structure information is more fully expressed, the possibility of residue replacement is considered more comprehensively, accuracy for predicting the secondary structure of the protein is improved, and the encoding method is simple and effective.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for protein structure alignment
InactiveUS6859736B2Easy to handleHandle protein permutations efficientlyAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingAdditive ingredientField methods
This invention provides a method for protein structure alignment. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for identification, classification and prediction of protein structures. The present invention involves two key ingredients. First, an energy or cost function formulation of the problem simultaneously in terms of binary (Potts) assignment variables and real-valued atomic coordinates. Second, a minimization of the energy or cost function by an iterative method, where in each iteration (1) a mean field method is employed for the assignment variables and (2) exact rotation and / or translation of atomic coordinates is performed, weighted with the corresponding assignment variables.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for colony conformation space optimization based on distance constraint selection strategy
ActiveCN105205348AReduce the search dimensionFast convergenceBiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein structureDistance constraints
A method for colony conformation space optimization based on a distance constraint selection strategy comprises the following steps: under a differential evolution algorithm framework, adopting a Rosetta Score3 coarseness knowledge energy model to effectively reduce a conformation space search dimension number and improve the convergence rate of an algorithm; introducing a fragment packaging technique based on knowledge to effectively improve prediction accuracy; utilizing character constraints of a distance spectrum in protein structure to make more structurally similar protein conformations enter a colony, so as to reduce errors caused by energy function inaccuracy and obtain more excellent local conformations; and performing more effective sampling on conformation space in combination with a high global searching capability of the differential evolution algorithm, so as to obtain conformations highly similar to a natural structure. The Rosetta Score3 coarseness knowledge energy model is adopted to effectively reduce the conformation space search dimension number and improve the convergence rate of the algorithm and prediction accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com