Patents
Literature
872 results about "Novel gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
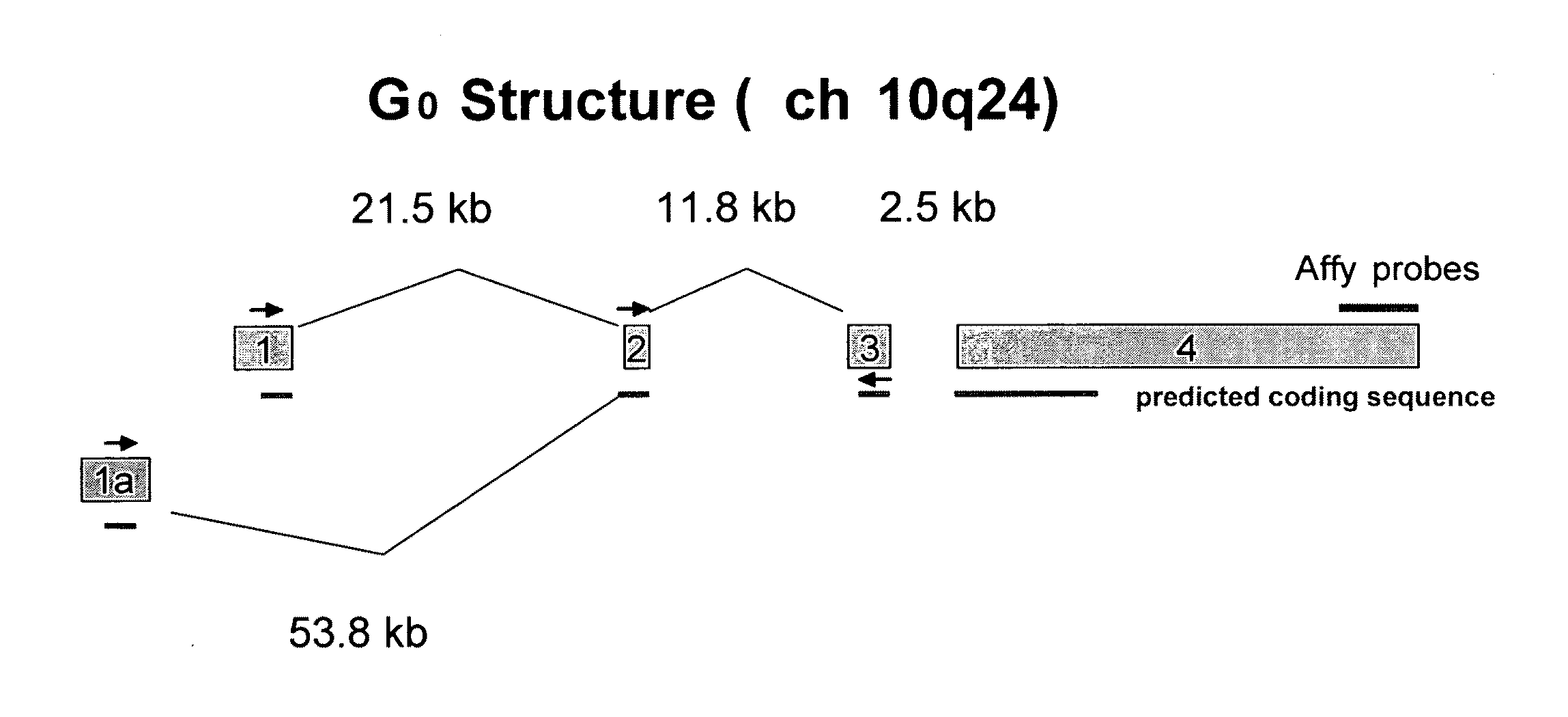
Novel genes are genes that have been predicted by Ensembl on the basis of similarity to protein or cDNA sequences.
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
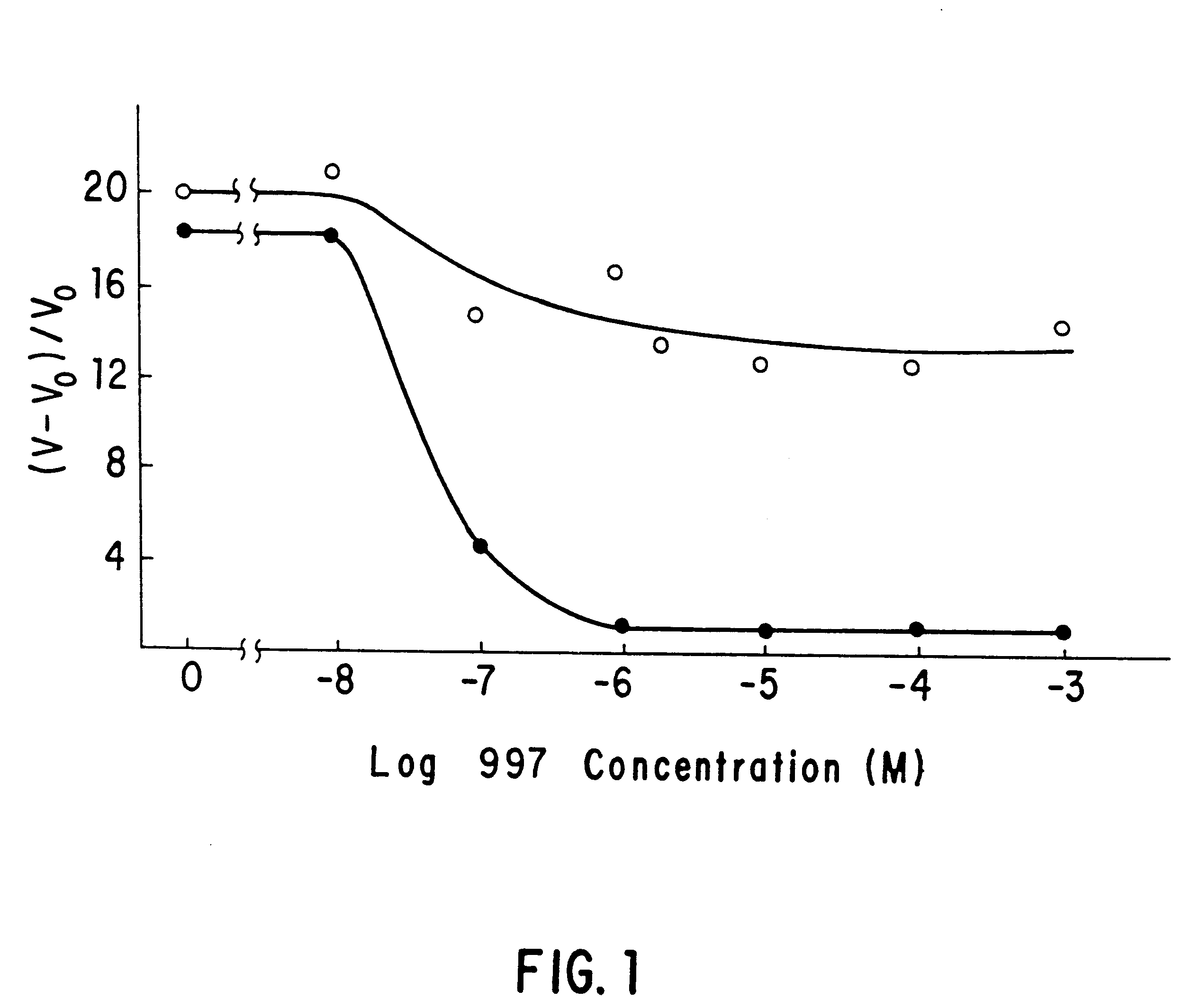
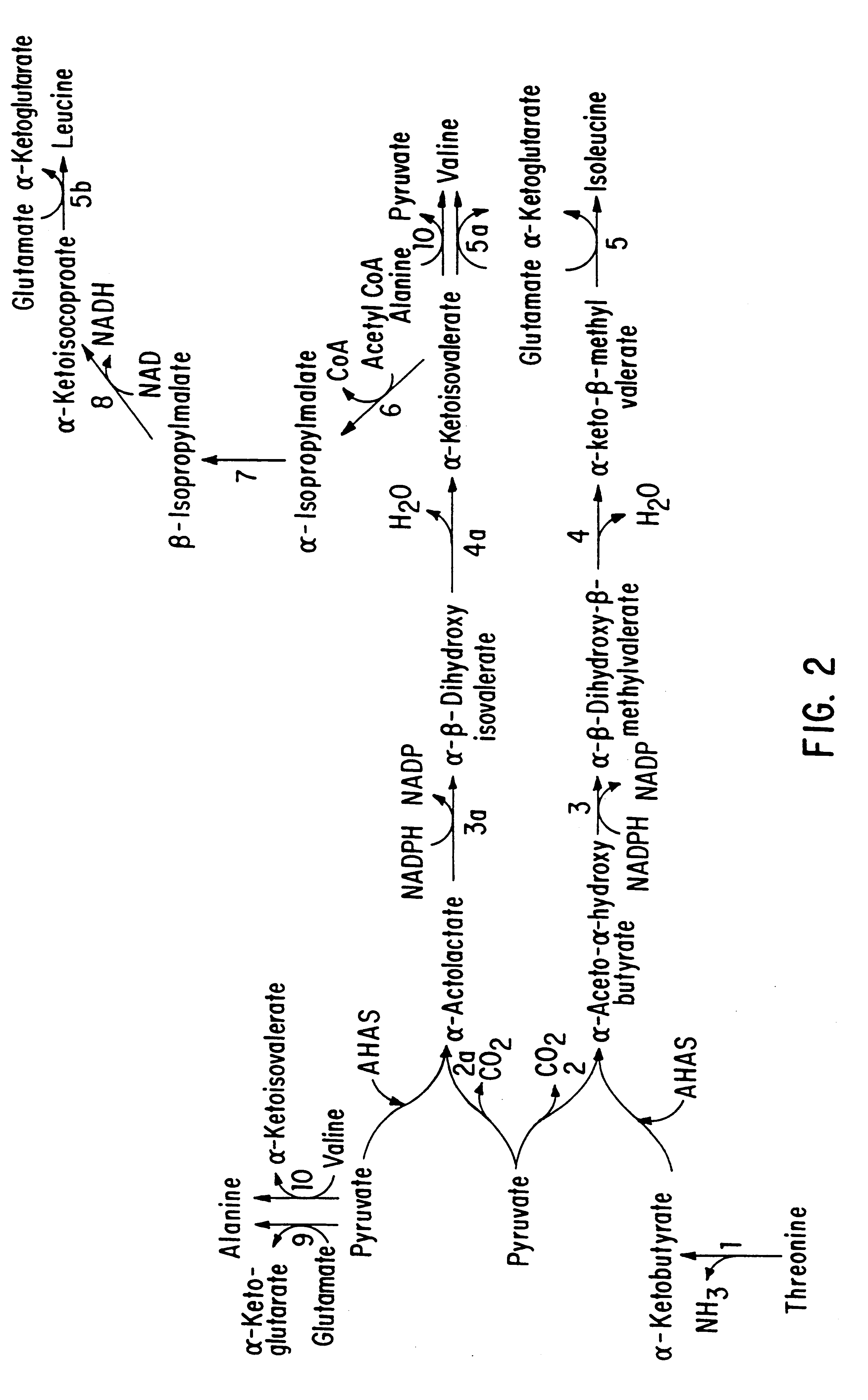
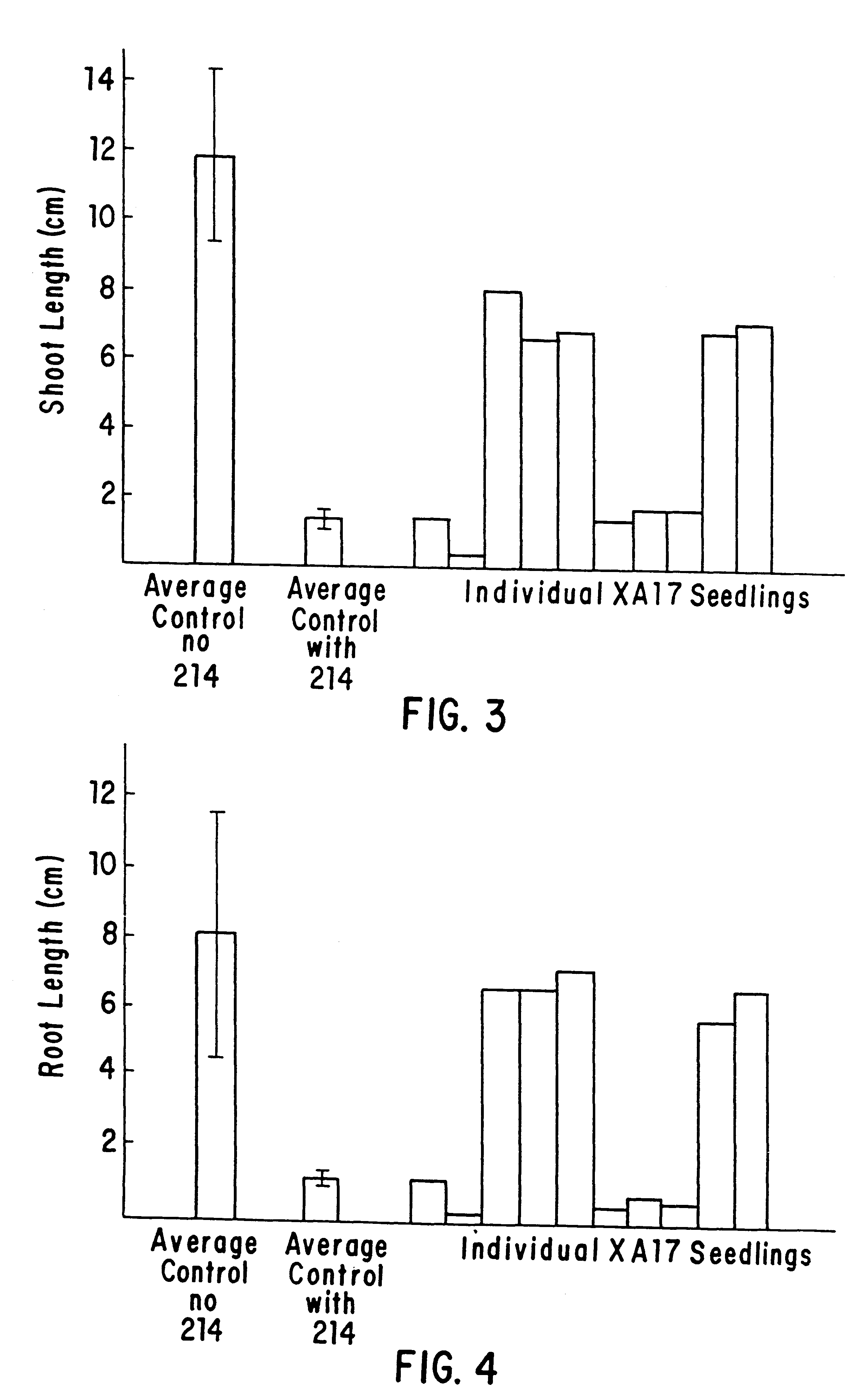
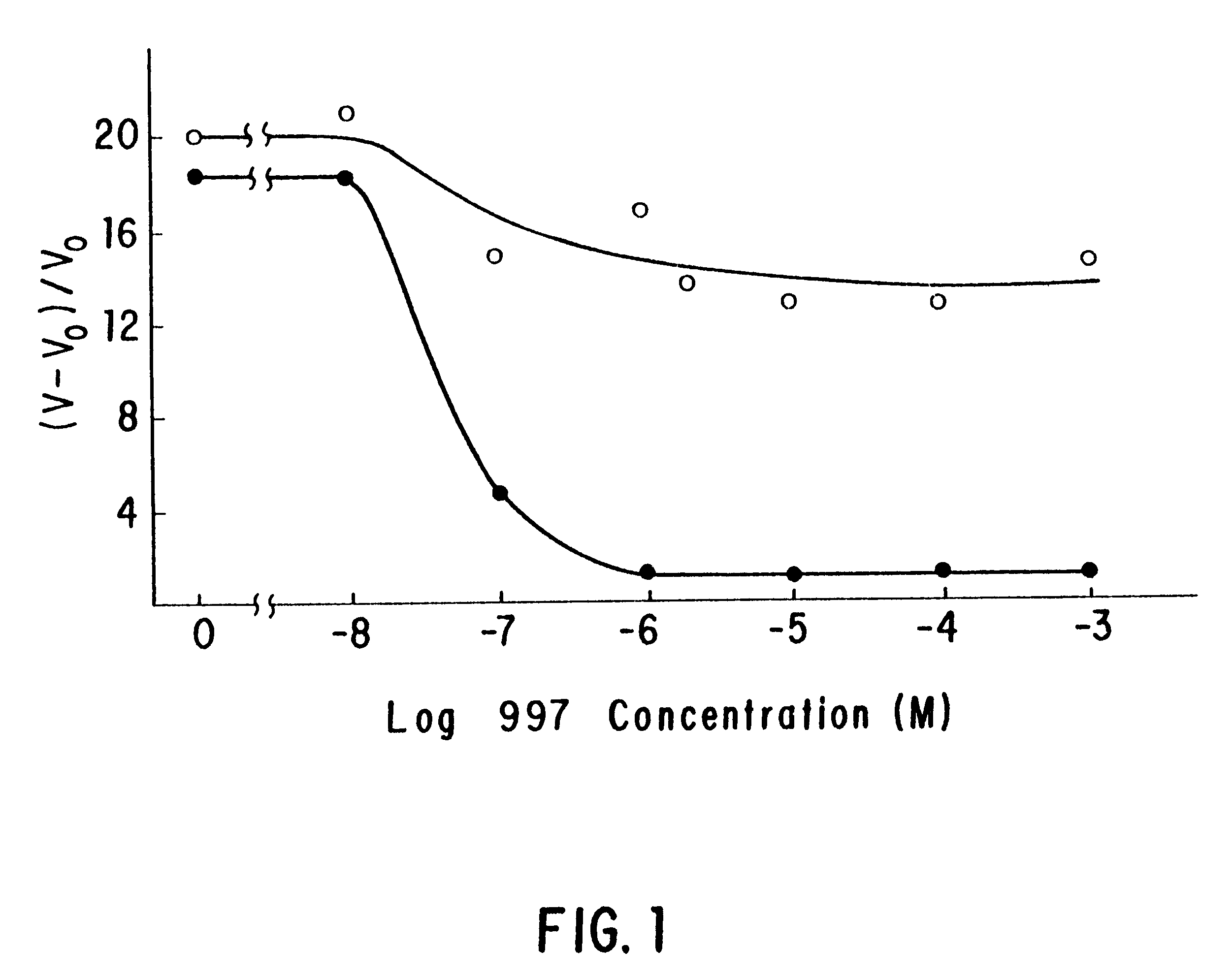
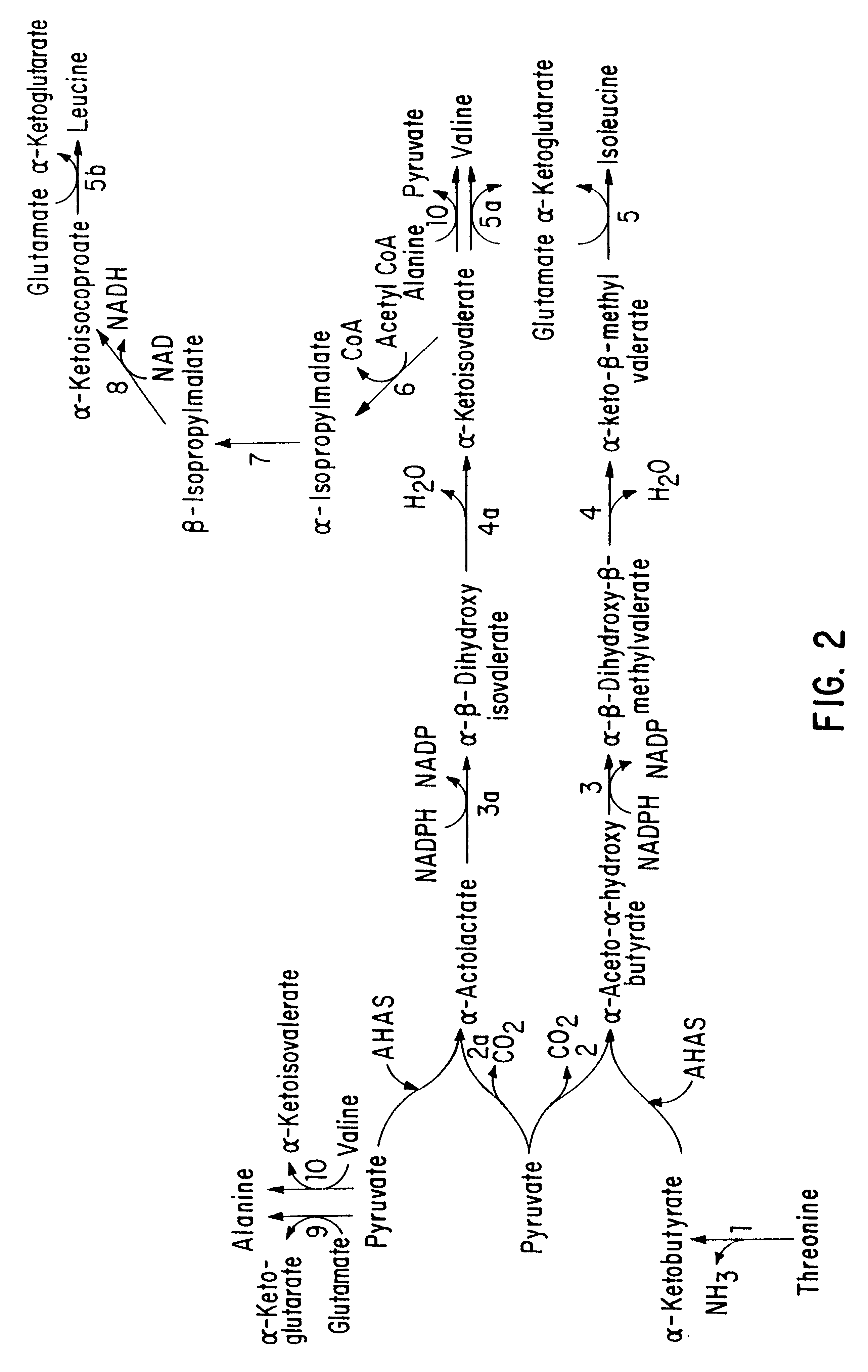
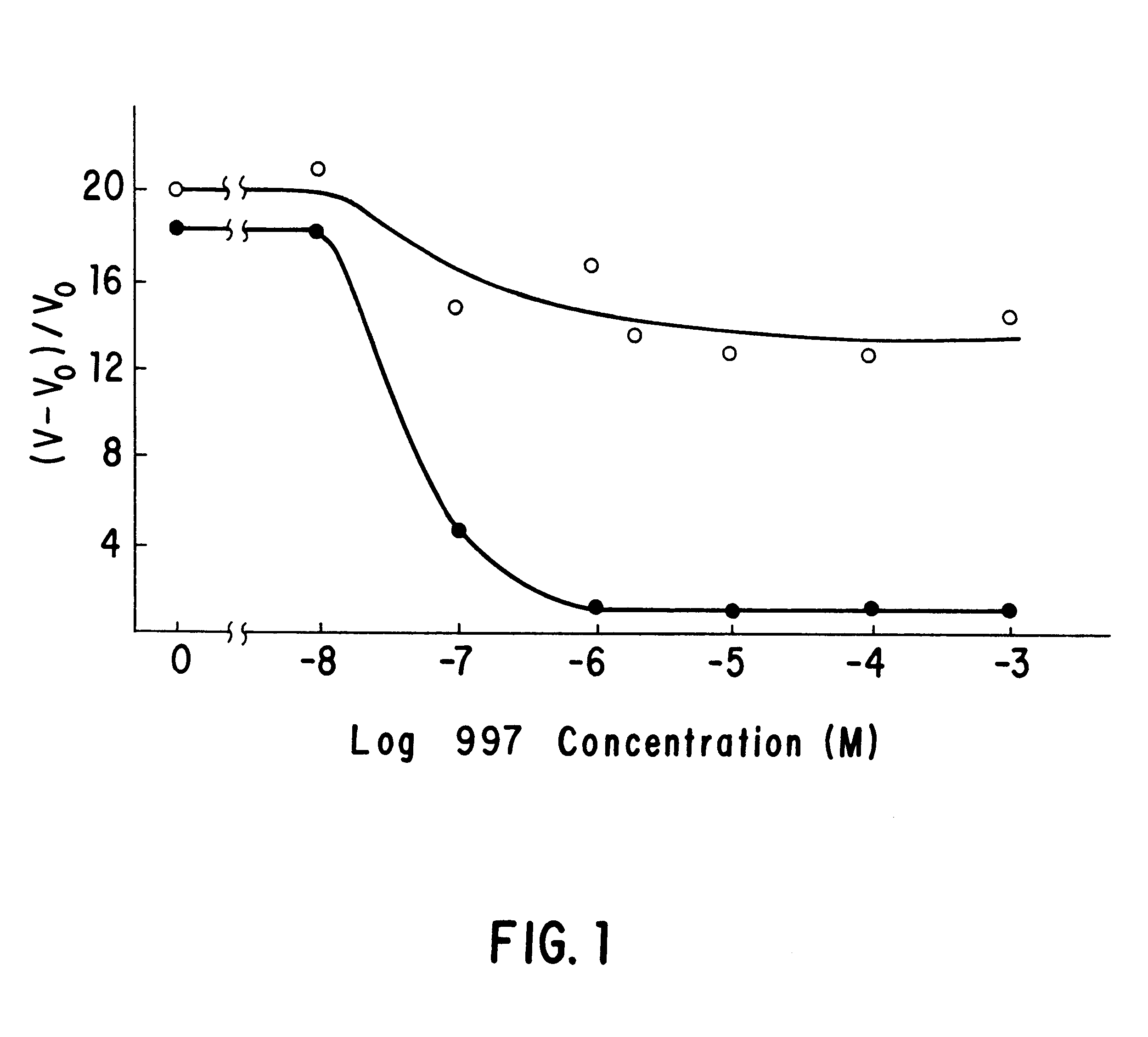
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211438B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemMutant preparationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211439B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemLyasesPlant genotype modificationPlant tissuePlanting seed
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
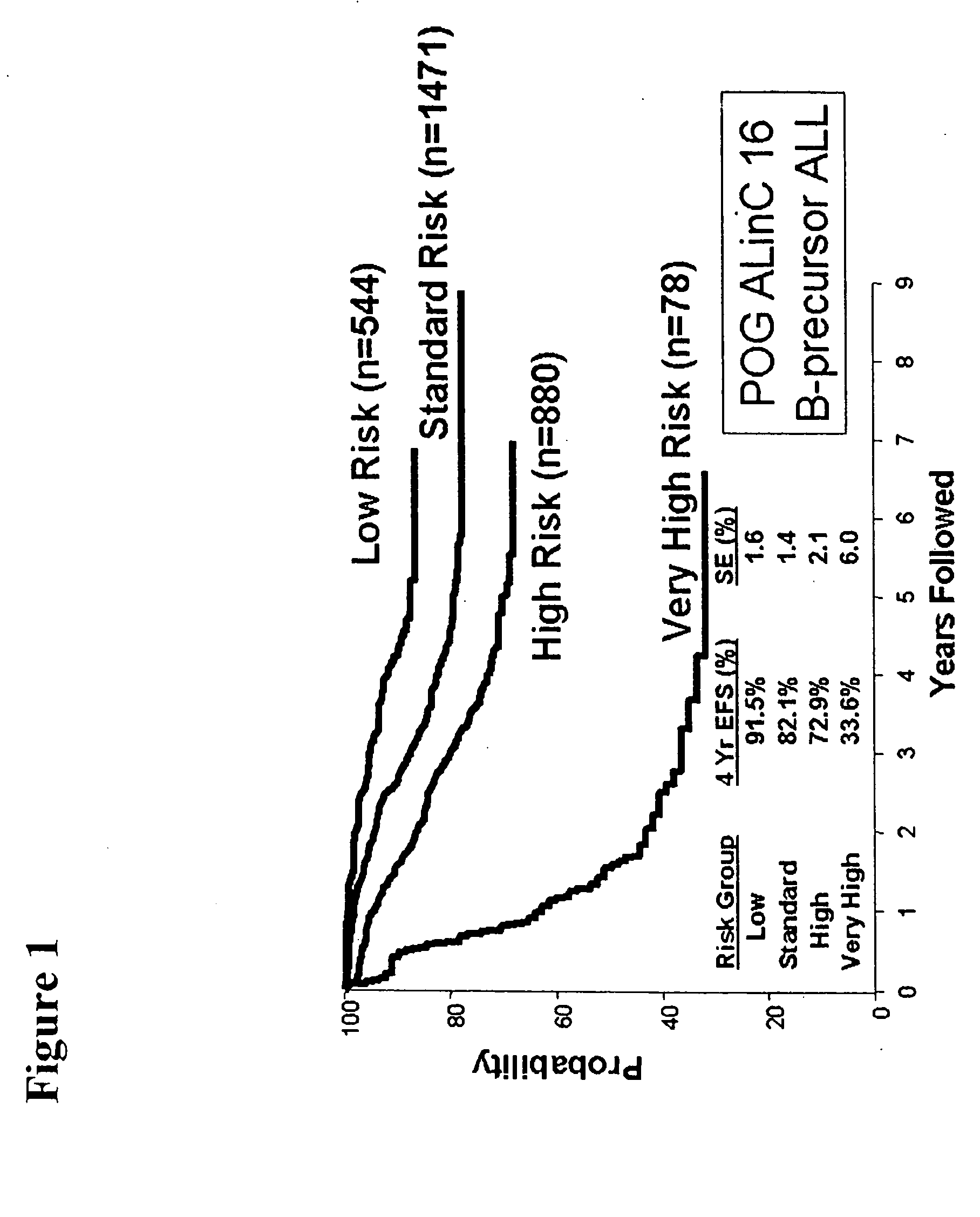
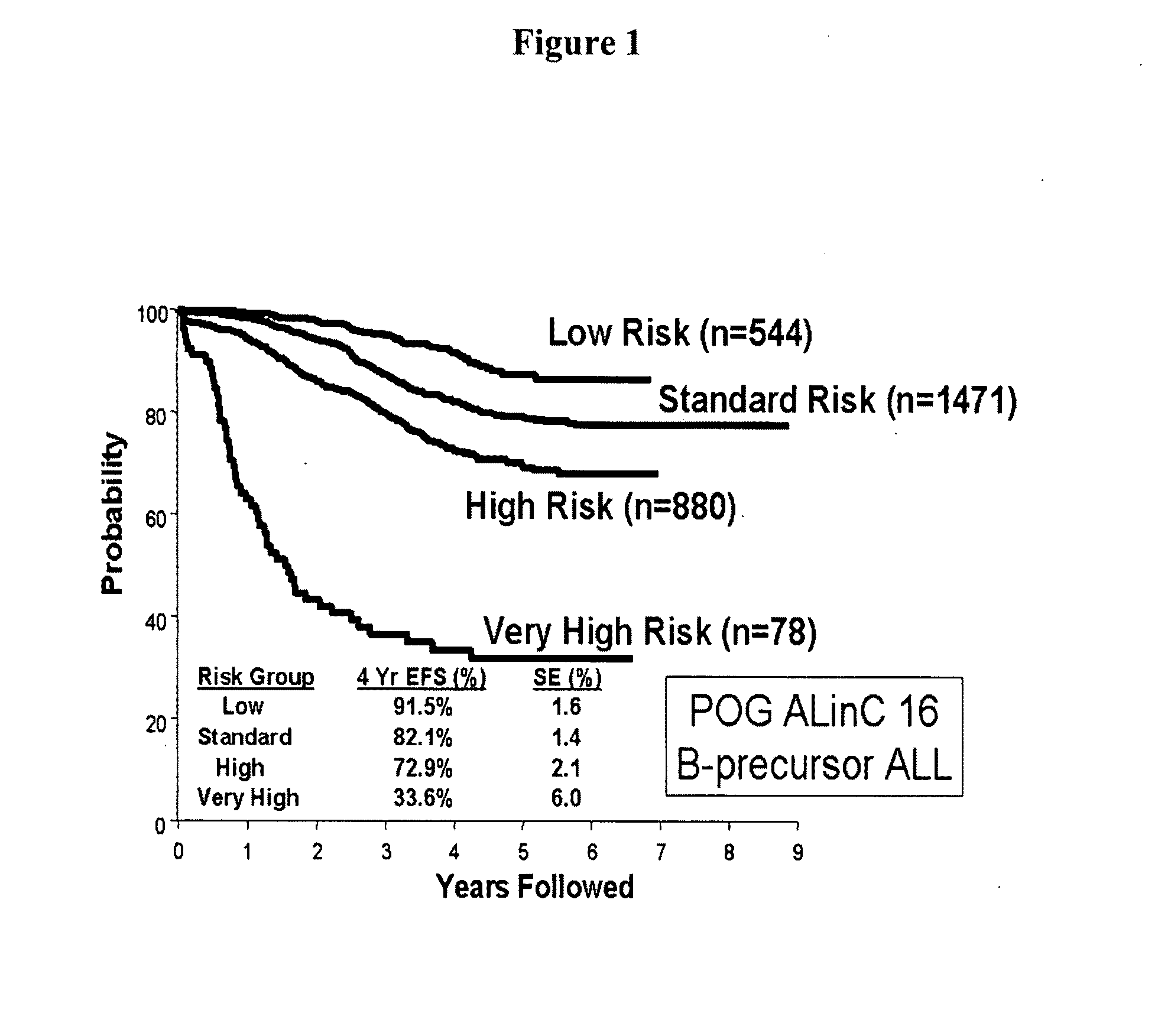
Outcome prediction and risk classification in childhood leukemia
InactiveUS20060063156A1Improve predictive abilityEasy diagnosisCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesEtiologyRisk classification
Genes and gene expression profiles useful for predicting outcome, risk classification, cytogenetics and / or etiology in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). OPAL1 is a novel gene associated with outcome and, along with other newly identified genes, represent a novel therapeutic targets.
Owner:SANDIA
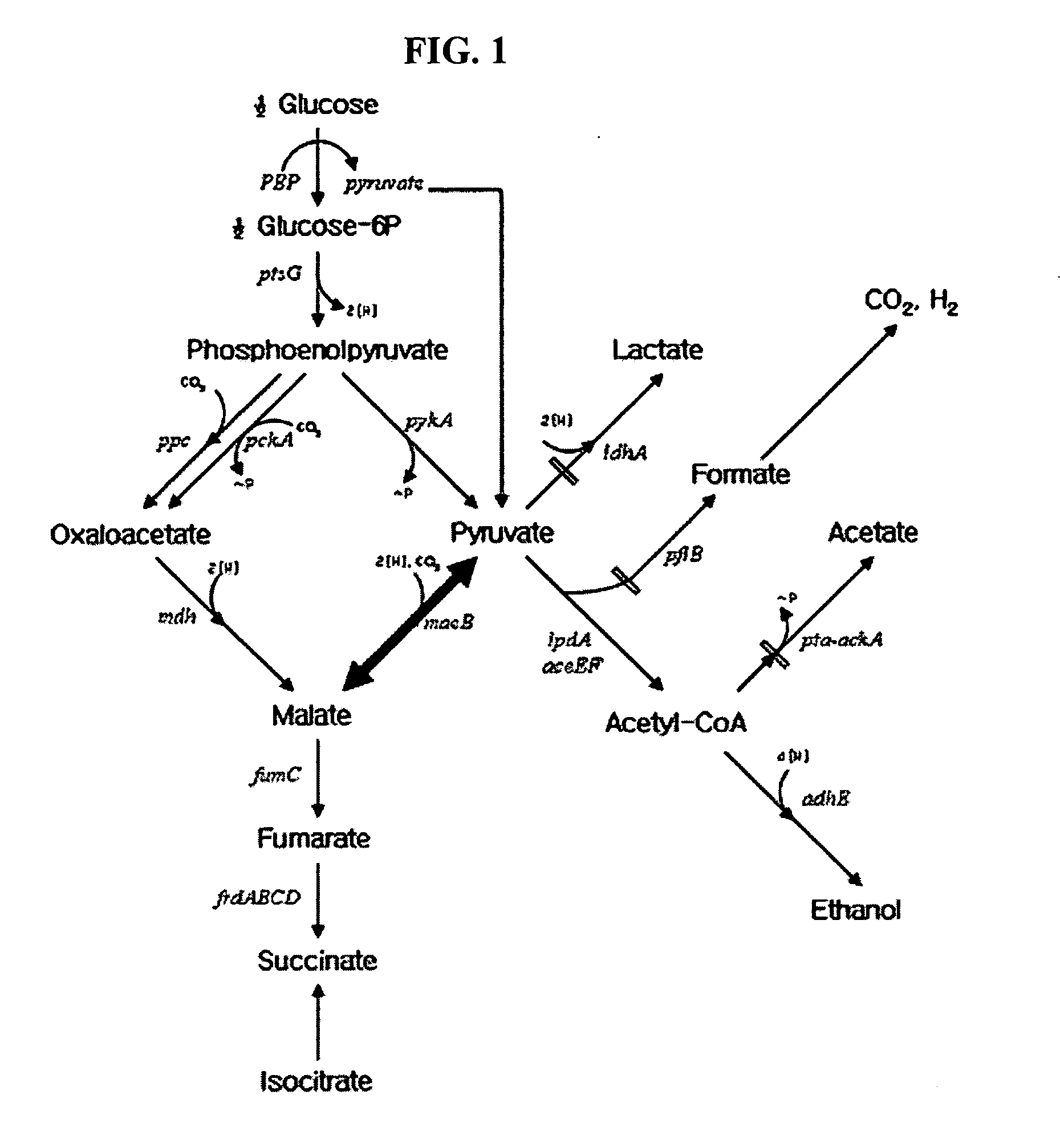
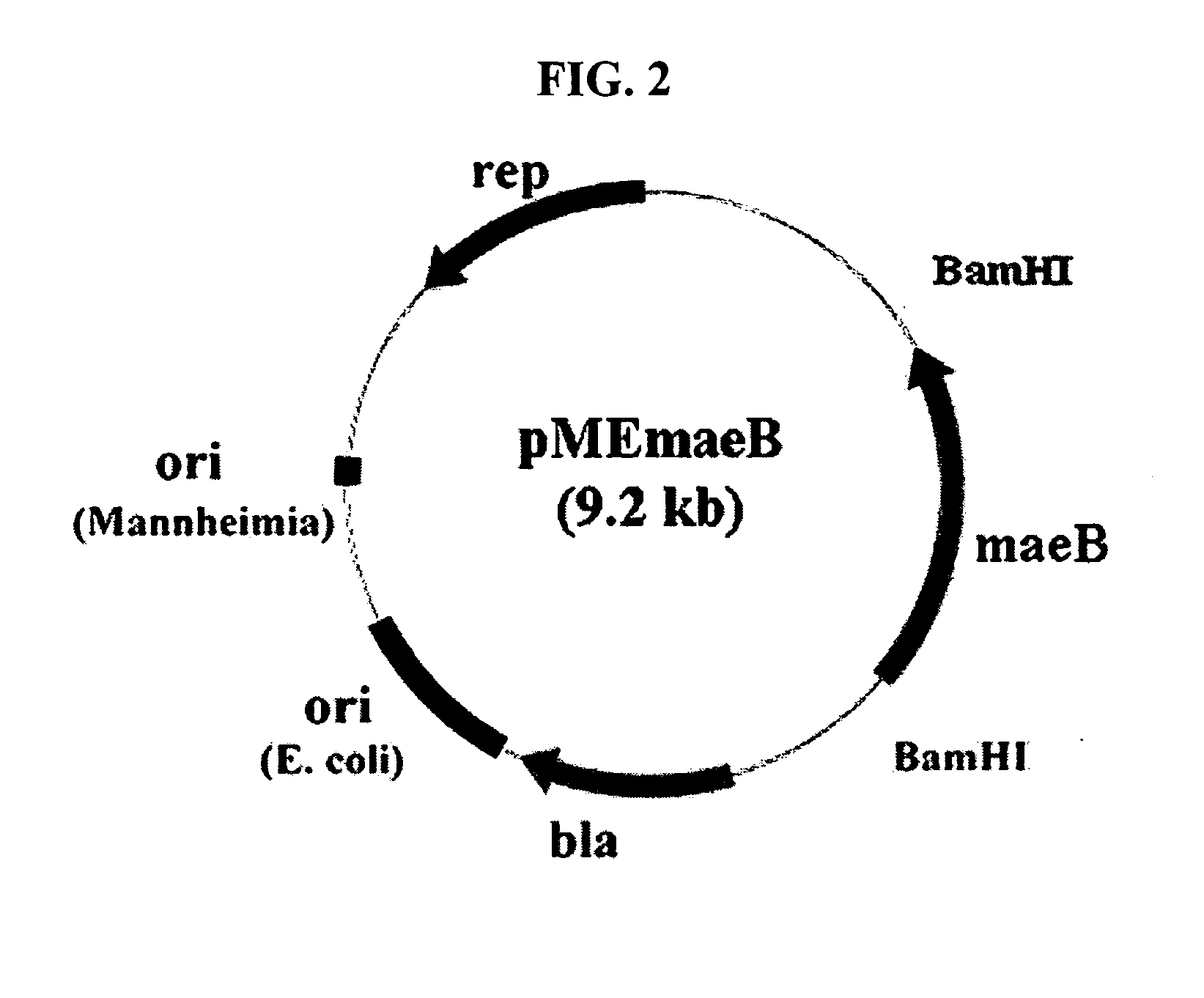
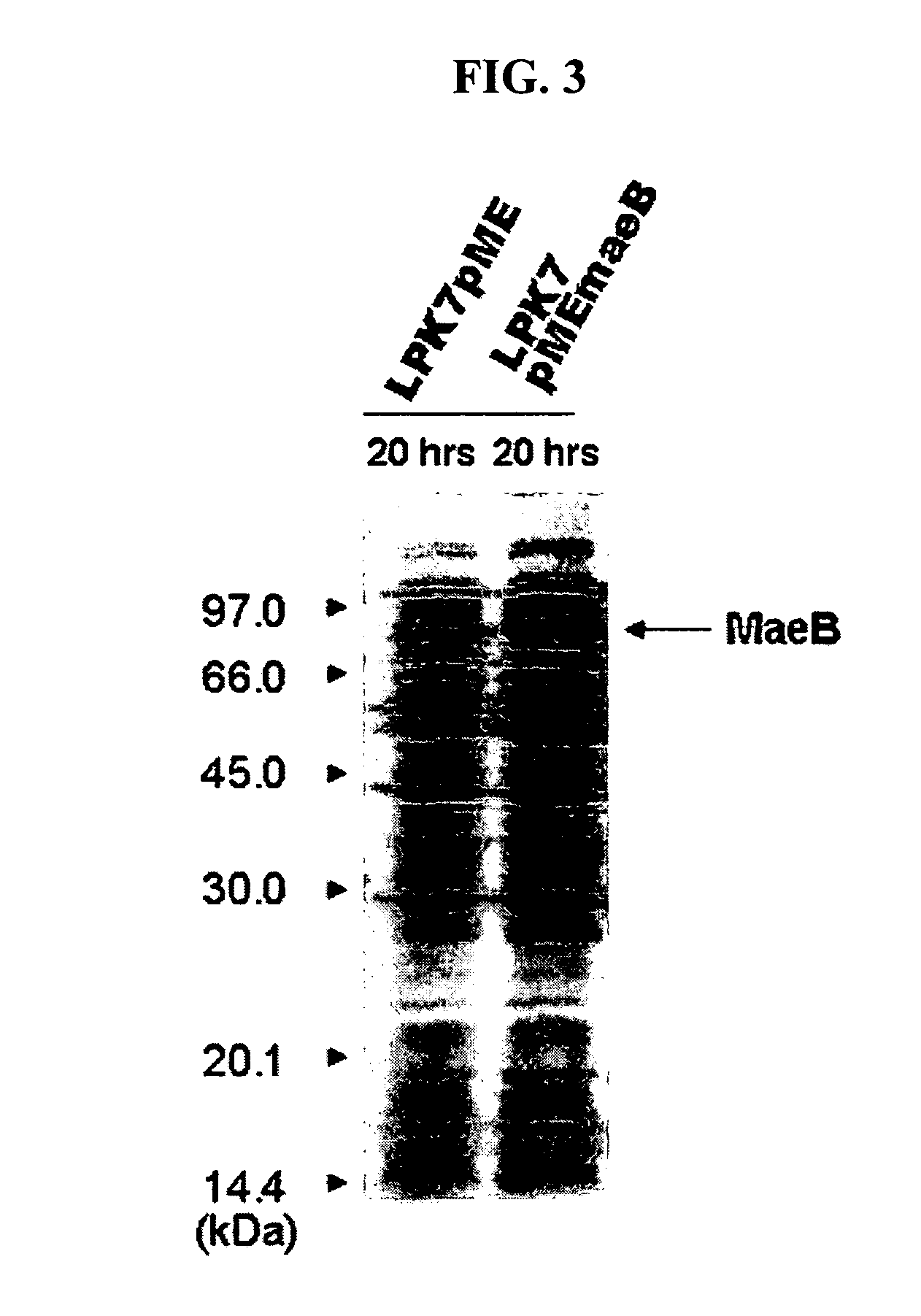
Novel gene encoding malic enzyme and method for preparing succinic acid using the same
ActiveUS20070042476A1Increase productionLightweight productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismNucleotide
A nucleotide sequence encoding a malic enzyme and a method for preparing succinic acid using the same, more particularly, a maeB nucleotide sequence encoding a malic enzyme B having the activity of converting pyruvic acid or pyruvate to malic acid or malate, or vice versa, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a microorganism transformed with the recombinant vector, and a method for preparing succinic acid using the transformed microorganism.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
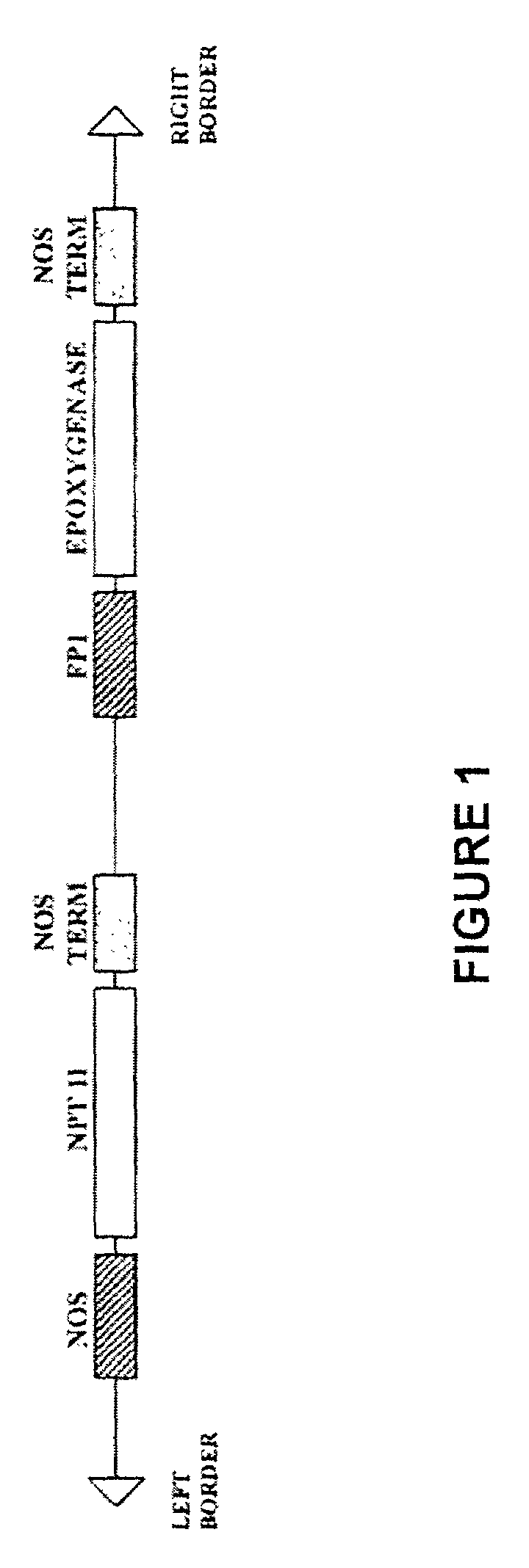
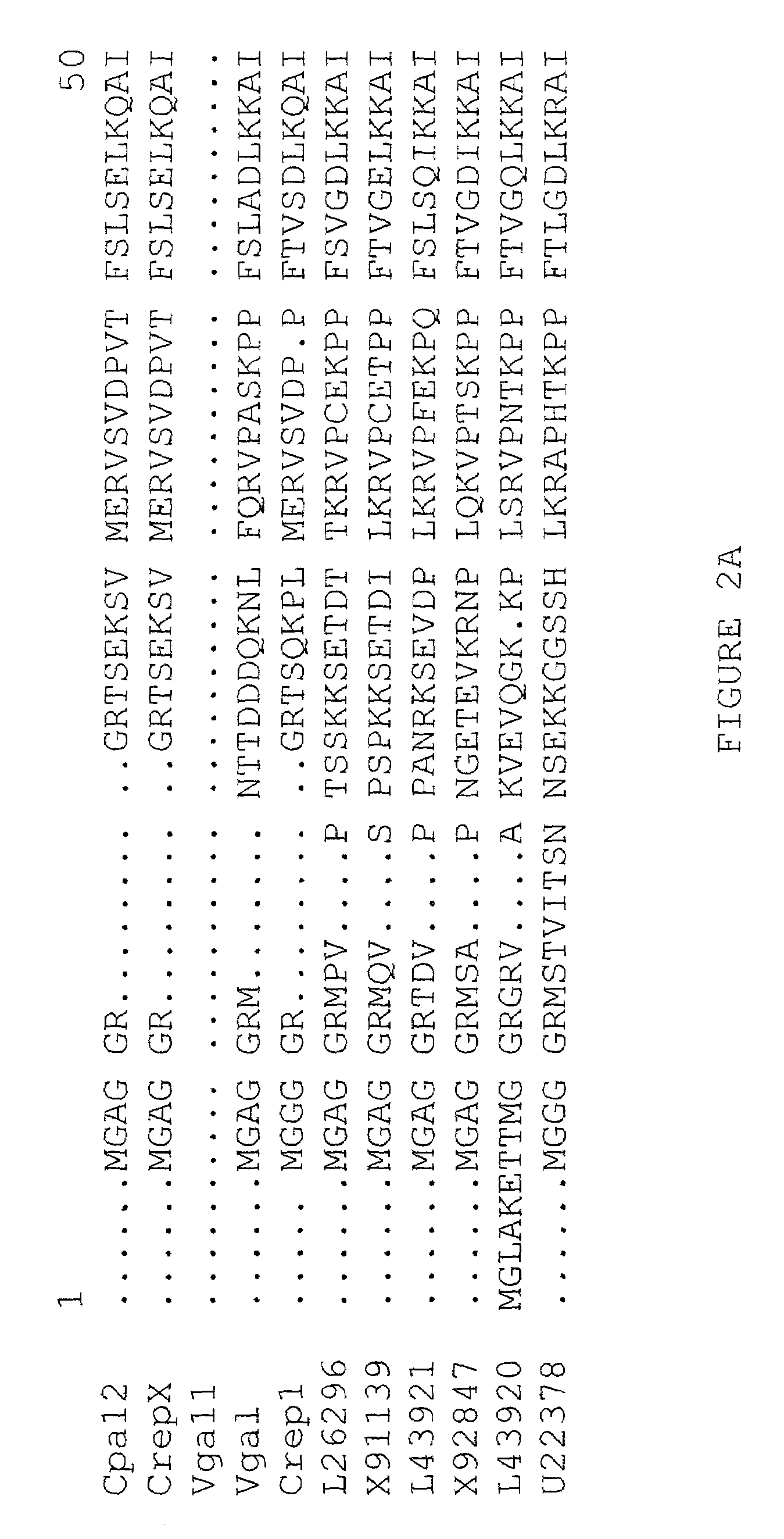
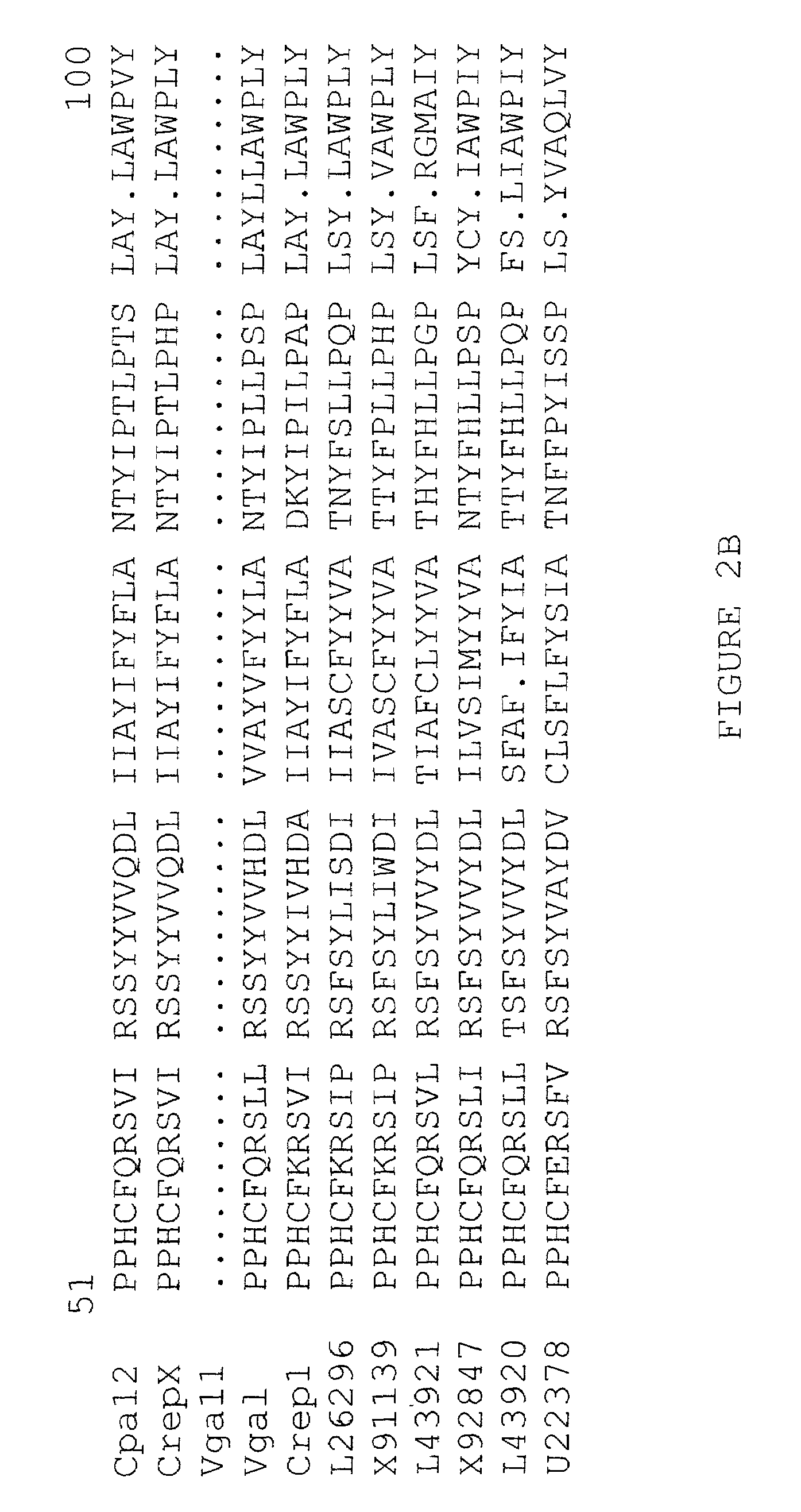
Fatty acid epoxygenase genes from plants and uses therefor in modifying fatty acid metabolism
The present invention relates generally to novel genetic sequences that encode fatty acid epoxygenase enzymes, in particular fatty acid Δ12-epoxygenase enzymes from plants that are mixed function monooxygenase enzymes. More particularly, the present invention exemplifies cDNA sequences from Crepis spp. and Vernonia galamensis that encode fatty acid Δ12-epoxygenases. The genetic sequences of the present invention provide the means by which fatty acid metabolism may be altered or manipulated in organisms, such as, for example, yeasts, moulds, bacteria, insects, birds, mammals and plants, and more particularly in plants. The invention also extends to genetically modified oil-accumulating organisms transformed with the subject genetic sequences and to the oils derived therefrom. The oils thus produced provide the means for the cost-effective raw materials for use in the efficient production of coatings, resins, glues, plastics, surfactants and lubricants.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Angiotensin converting enzyme homolog and therapeutic and diagnostic uses therfor
InactiveUS6194556B1Easy to determineEffectively prescribeSugar derivativesBacteriaAngiotensin-converting enzymeAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme Homolog
The present invention relates to the discovery of novel genes encoding an angiotensin converting enzyme, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2). Therapeutics, diagnostics and screening assays based on these molecules are also disclosed.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Methods for generating and screening novel metabolic pathways
The present invention relates to a novel drug discovery system for generating molecular diversity. The system provides methods for subjecting the genetic materials from a plurality of species of organisms to homologous or homeologous recombination to create novel genes and metabolic pathways. The recombined genetic materials are cloned to form recombined combinatorial gene expression libraries. Methods for screening such gene expression libraries containing recombined genes and metabolic pathways for novel activities and compounds are also provided.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Gene specifically expressed in postmitotic dopaminergic neuron precursor cells
InactiveUS20070122882A1Efficient separationEasy to prepareFungiBacteriaNeuro-degenerative diseaseNovel gene
A novel gene 65B13 expressed specifically and transiently in dopaminergic neuron precursor cells immediately after cell cycle exit was obtained by the present invention. The cellular expression of 65B13 can be used as an index to select cells that are suitable in terms of their safety, survival rate, and network formation ability, for transplant therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Methods of diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS20060269921A1Strong specificityEnhanced and increased and levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOncologyNovel gene
The present invention provides novel genes and proteins for diagnosing pancreatic cancer and / or a likelihood for survival e.g., following surgical resection, wherein the expression of the genes and proteins is up-regulated or down-regulated. The pancreatic cancer-associated genes and proteins of the invention are specifically exemplified by the genes and proteins set forth in Tables 3 to 25 and the Sequence Listing.
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES
Outcome prediction and risk classification in childhood leukemia
InactiveUS20090203588A1Improve predictive abilityEasy diagnosisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEtiologyRisk classification
Genes and gene expression profiles useful for predicting outcome, risk classification, cytogenetics and / or etiology in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). OPAL1 is a novel gene associated with outcome and, along with other newly identified genes, represent a novel therapeutic targets.
Owner:STC UNM
Systems and Methods for Reconstructing Gene Networks in Segregating Populations
ActiveUS20080294403A1Predictive capabilitySimple technologyAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsLiving systemsReconstruction algorithm
The reconstruction of genetic networks in mammalian systems is one of the primary goals in biological research, especially as such reconstructions relate to elucidating not only common, polygenic human disease, but living systems more generally. The present invention provides novel gene network reconstruction algorithms that utilize naturally occurring genetic variations as a source of perturbations to elucidate the networks. The algorithms incorporate relative transcript abundance and genotypic data from segregating populations by employing a generalized scoring function of maximum likelihood commonly used in Bayesian network reconstruction problems. The utility of these novel algorithms can be demonstrated via application to gene expression data from a segregating mouse population. The network derived from such data using the novel network reconstruction algorithm is able to capture causal associations between genes that result in increased predictive power, compared to more classically reconstructed networks derived from the same data.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Acyl-acp thioesterase genes and uses therefor
InactiveUS20110020883A1High activityIncrease volumeSugar derivativesHydrolasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention provides novel genes encoding Class II acyl-ACP thioesterases and variants thereof that are active on C8, C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18 acyl-ACP substrates. The thioesterases can be introduced into transgenic organisms, including microorganisms and photosynthetic organisms, for producing fatty acids and fatty acid products.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Novel Selectable Marker Genes
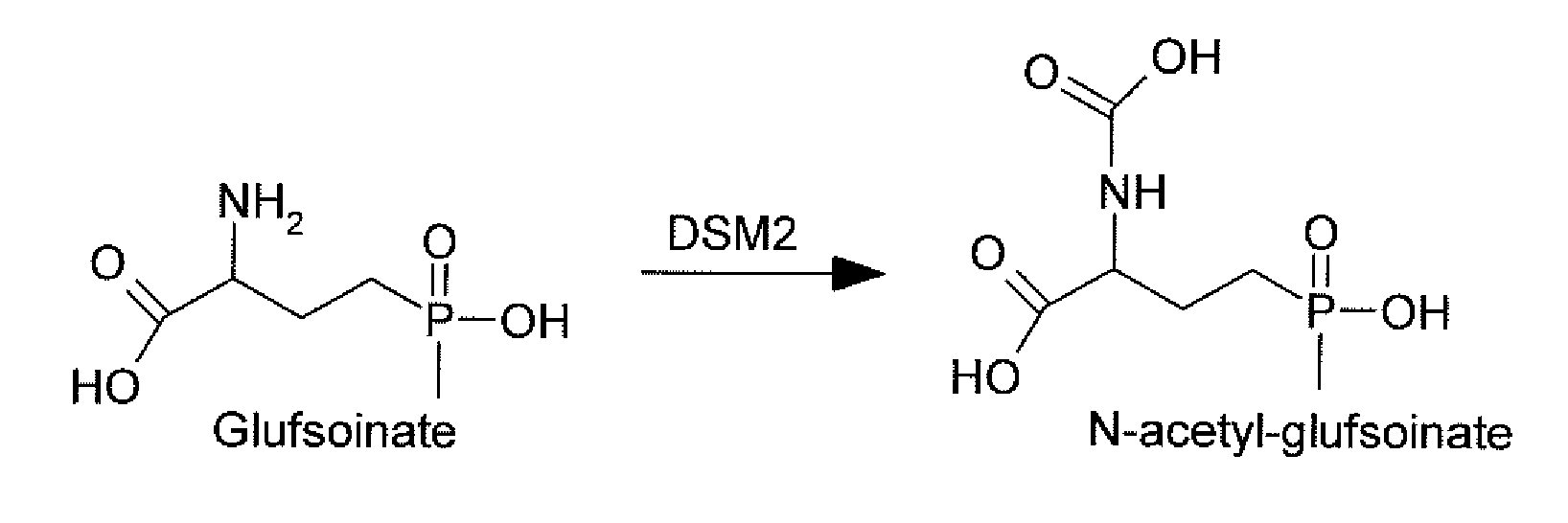
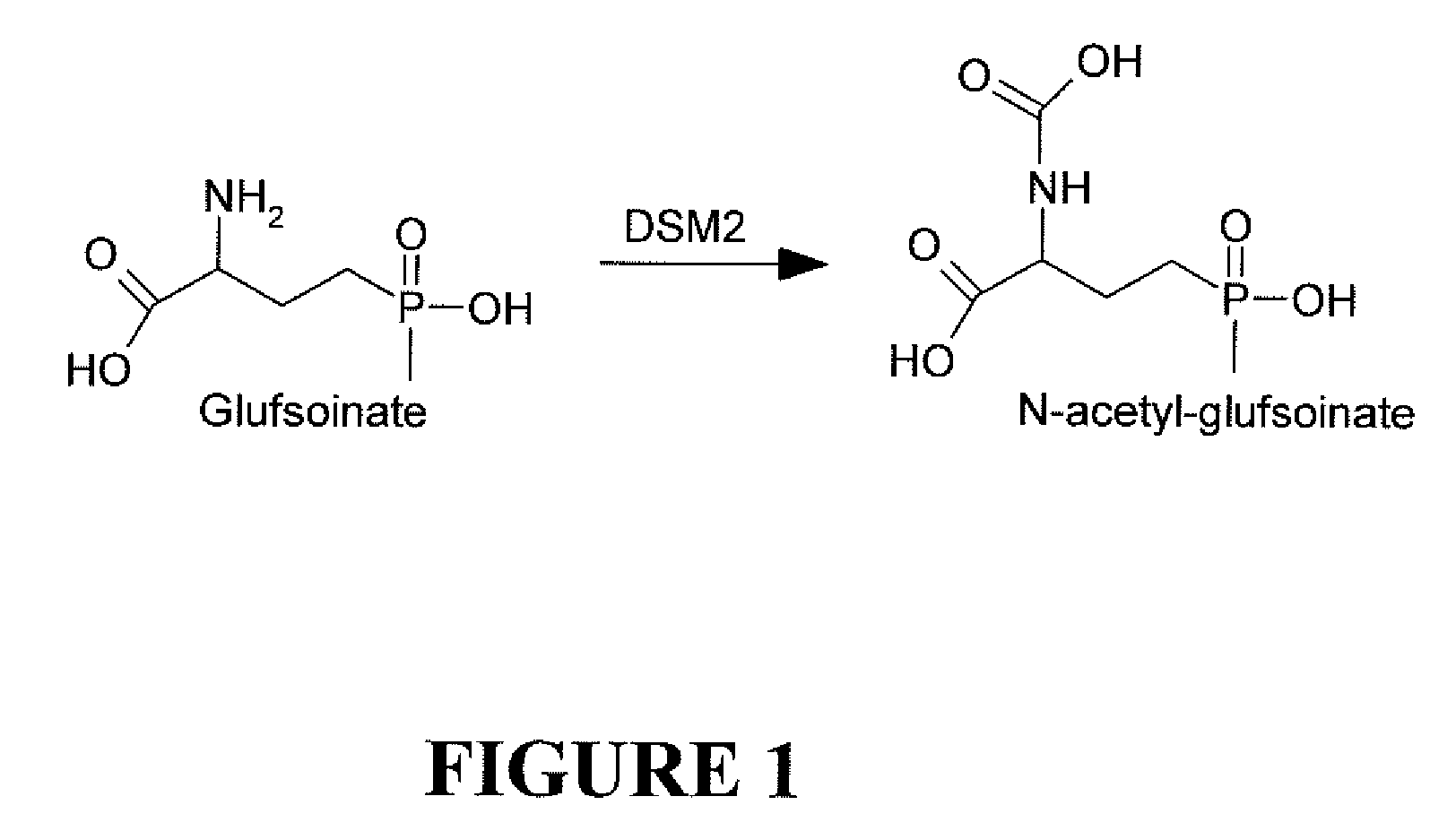
The subject invention relates to a novel gene referred to herein as DSM-2. This gene was identified in Sterptomyces coelicolor A3. The DSM-2 protein is distantly related to PAT and BAR. The subject invention also provides plant-optimized genes encoding DSM-2 proteins, DSM-2 can be used as a transgenic trait to impart tolerance in plants and plant cells to the herbicides glufosinate and bialaphos. One preferred use of the subject genes are as selectable markers. The use of this gene as a selectable marker in a bacterial system can increase efficiency for plant transformations. Use of DSM-2 as the sole selection marker eliminates the need for an additional medicinal antibiotic marker (such as ampicillin resistance) during cloning. Various other uses are also possible according to the subject invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Methods for extracting information on interactions between biological entities from natural language text data
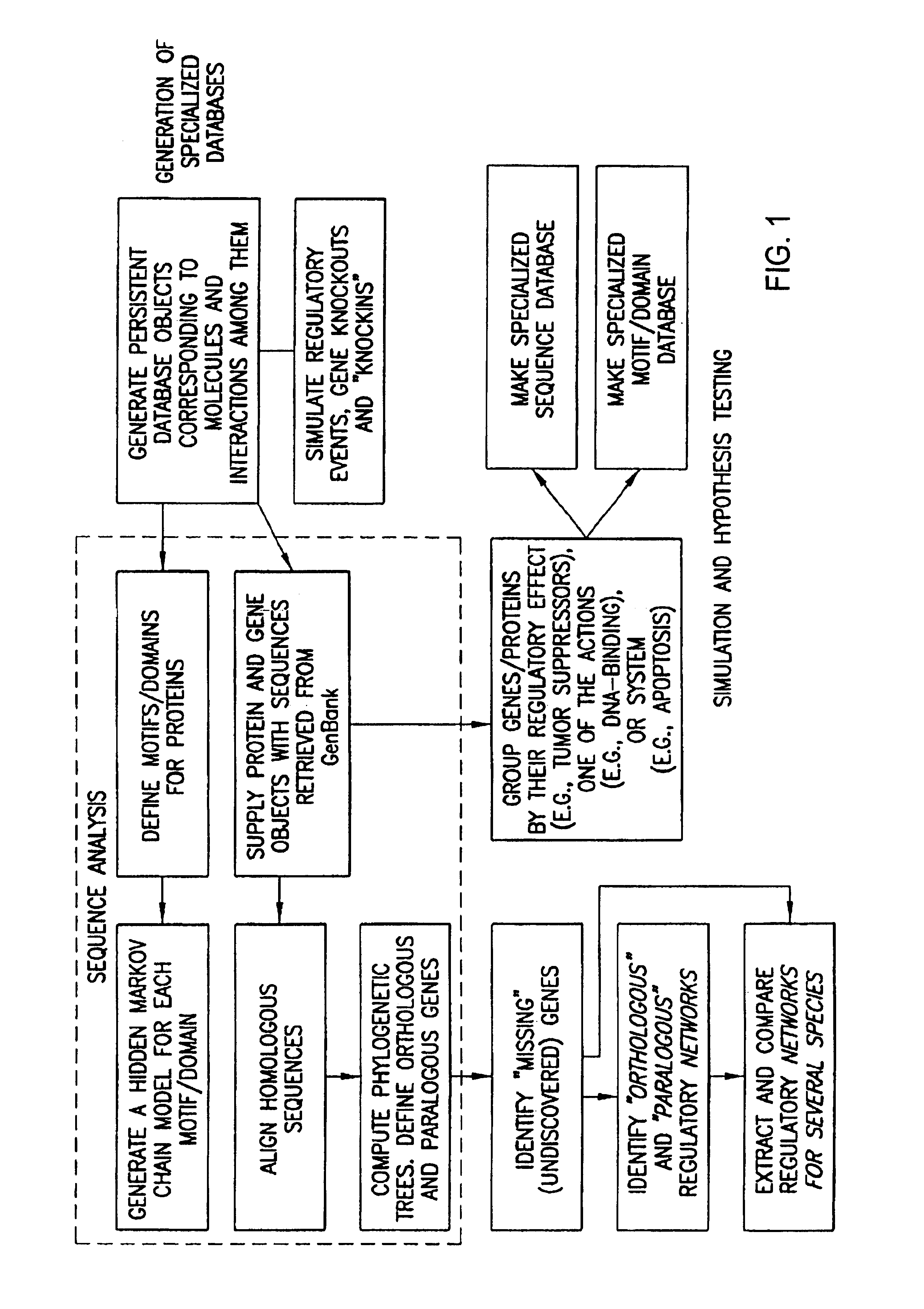
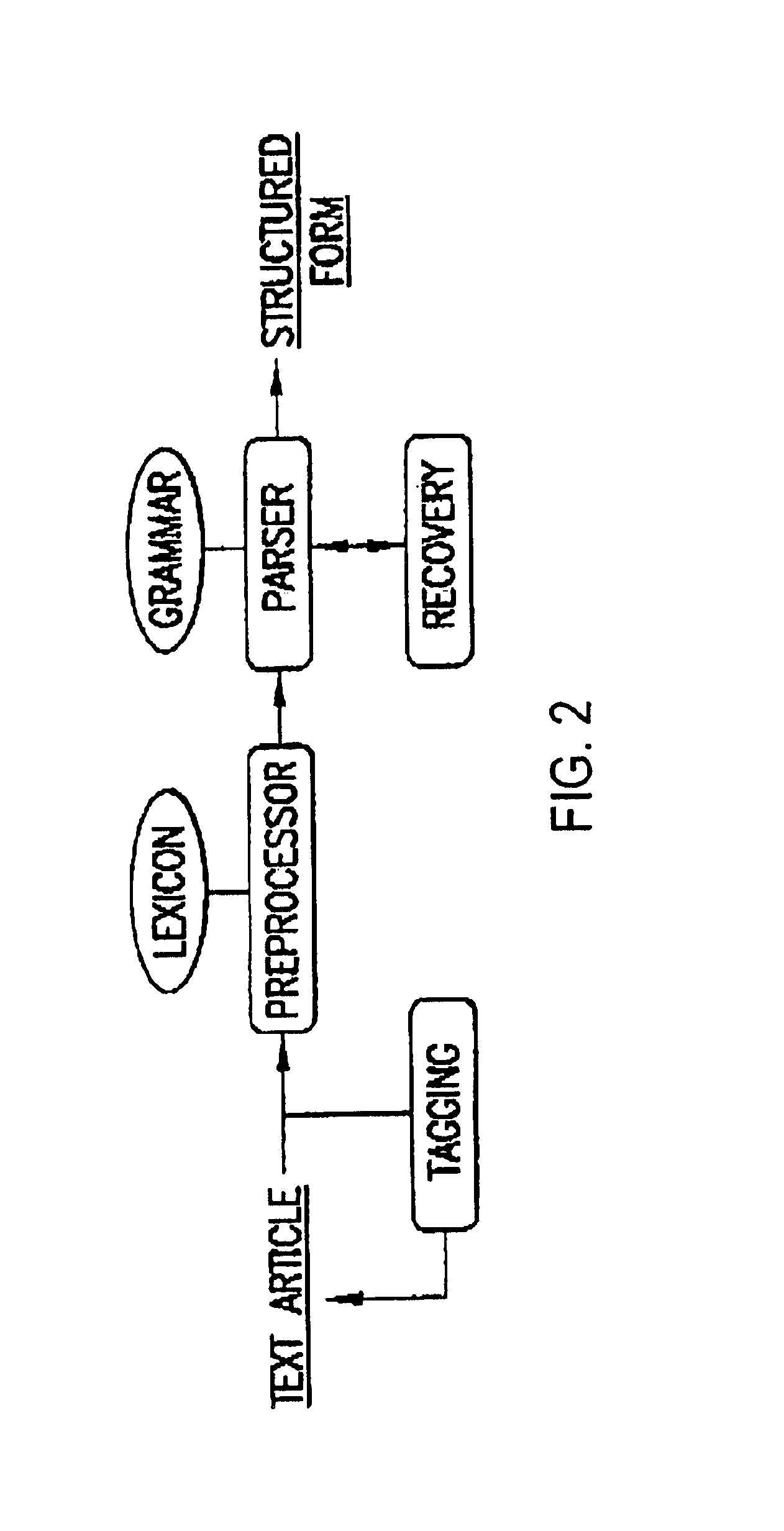
The present invention relates to methods for identifying novel genes comprising: (i) generating one and / or more specialized databases containing information on gene / protein structure, function and / or regulatory interactions; and (ii) searching the specialized databases for homology or for a particular motif and thereby identifying a putative novel gene of interest. The invention may further comprise performing simulation and hypothesis testing to identify or confirm that the putative gene is a novel gene of interest. The present invention also relates to natural language processing and extraction of relational information associated with genes and proteins that are found in genomics journal articles. To enable access to information in textual form, the natural language processing system of the present invention provides a method for extracting and structuring information found in the literature in a form appropriate for subsequent applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for reducing or eliminating alpha-mannosidase resistant glycans for the production of glycoproteins
The present invention provides methods to reduce or eliminate α-mannosidase resistant glycans on glycoproteins in yeast. The reduction or elimination of α-mannosidase resistant glycans on glycoproteins results from the disruption of the newly isolated P. pastoris AMR2 gene encoding β1,2-mannosyltransferase. The present invention also discloses novel genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors and host cells relating to α-mannosidase resistance on glycans.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Gene and its application in treatment of quinoline contaminant
The invention discloses a new gene purE1 which has high degradability on quinoline. Experiment shows that by using the purE1 gene to transform a microbe, the microbe can obtain degradation activity on quinoline, and the maximal degradation concentration of the degradation activity of the microbe provided by the purE1 gene and its coded protein is up to 850 mg / L. The invention has very important practical application value for the treatment of quinoline contaminants.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Recombinant vector for eliminating activity of kanamycin drug resistance gene and building method of recombinant vector
InactiveCN105463003AInhibitory activityHigh copy numberNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionNovel geneOrganism
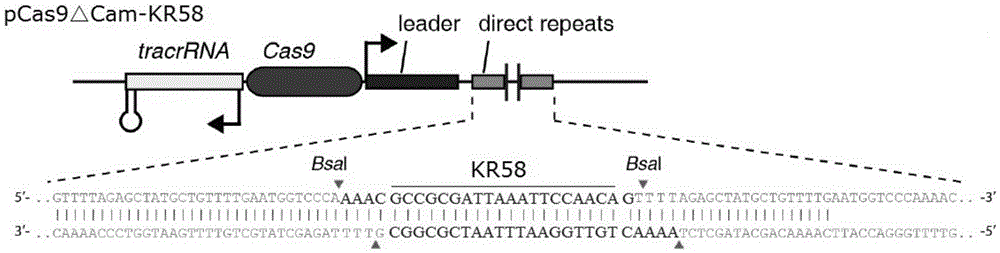
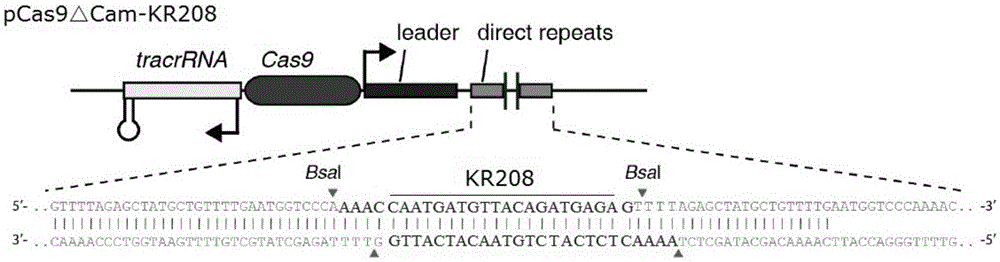
The invention provides a recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of a kanamycin drug resistance gene, and aims at eliminating drug resistance germs in organisms and solving the problem of kanamycin drug resistance of the germs. The recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of the kanamycin drug resistance gene is characterized by comprising a pCas9 vector subjected to chloramphenicol resistance elimination and a gRNA nucleotide sequence KR58 or KR208 aiming at a kanamycin resistance gene kan; the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR58 is GCCGCGAT TAAATTCCAACA, and the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR208 is CAATGATG TTACAGATGAGA. A building method of the recombinant vector mainly comprises the steps of carrying intergenic region nucleic acids by a novel gene editing tool CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system; removing a chloramphenicol resistance gene on the recombinant vector; transforming the gene into vaccine vector bacteria such as attenuated salmonella typhimurium; performing co-culture on the recombinant bacteria and the kanamycin drug resistance gene so that the recombinant vector in the recombinant bacterium cell enters the kanamycin drug resistance bacteria in an engaging mode. The activity of the kanamycin resistance gene kan is effectively inhibited, so that the original drug resistance bacterium cannot grow on a kanamycin culture medium.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Methods of diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer II
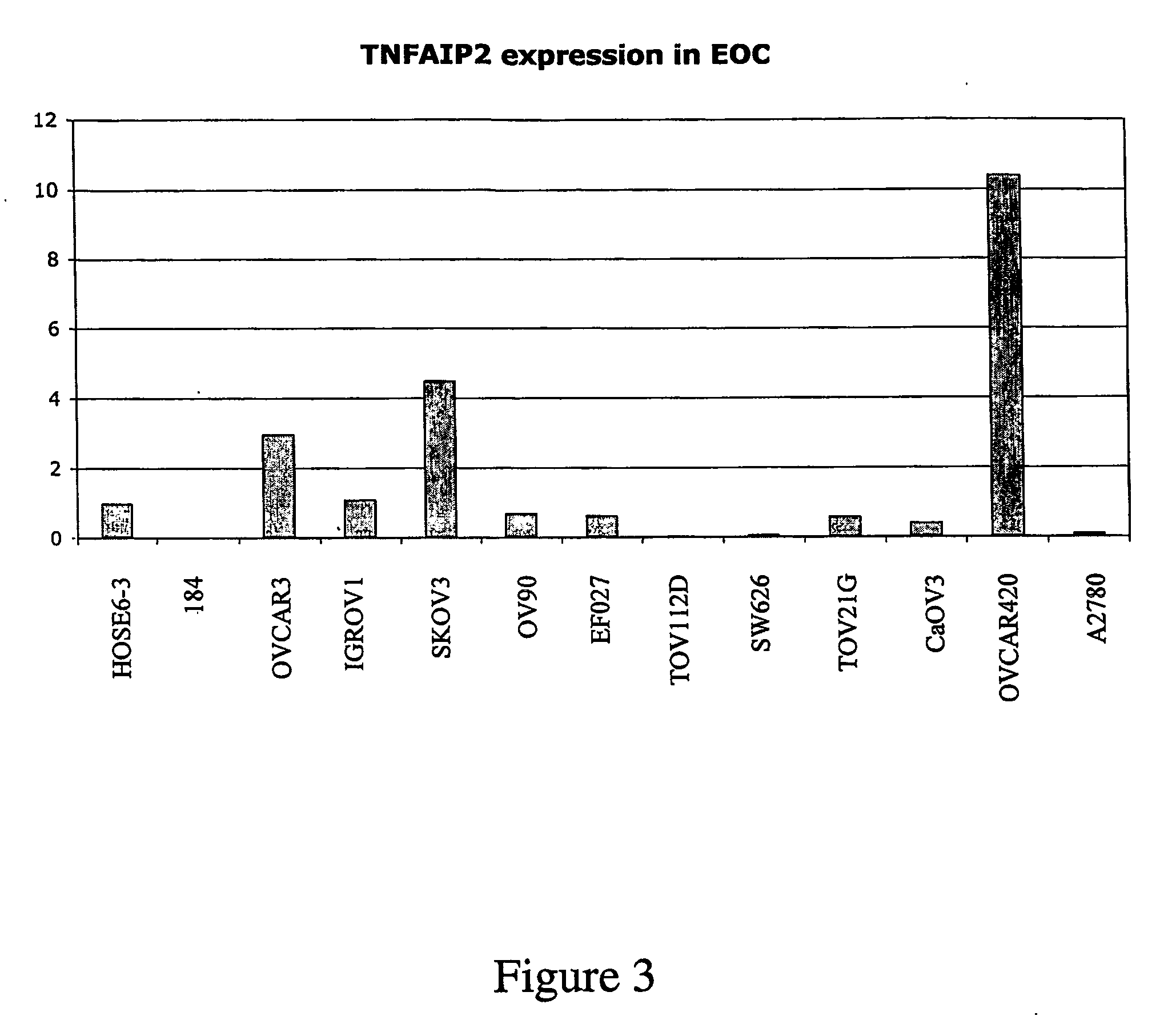
InactiveUS20070178458A1Reduced activityReduce expressionTumor rejection antigen precursorsSugar derivativesDiseaseOncology
The present invention provides novel genes and proteins for diagnosing ovarian cancer and / or a likelihood for survival, or recurrence of disease, wherein the expresson of the genes and proteins is up-regulated or down-regulated or associated with the occurrence or recurrence of a specific cancer sub-type. The ovarian cancer-associated genes and proteins of the invention are specifically exemplified by the genes and proteins set forth in Tables 1 to 5 and the Sequence Listing.
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES
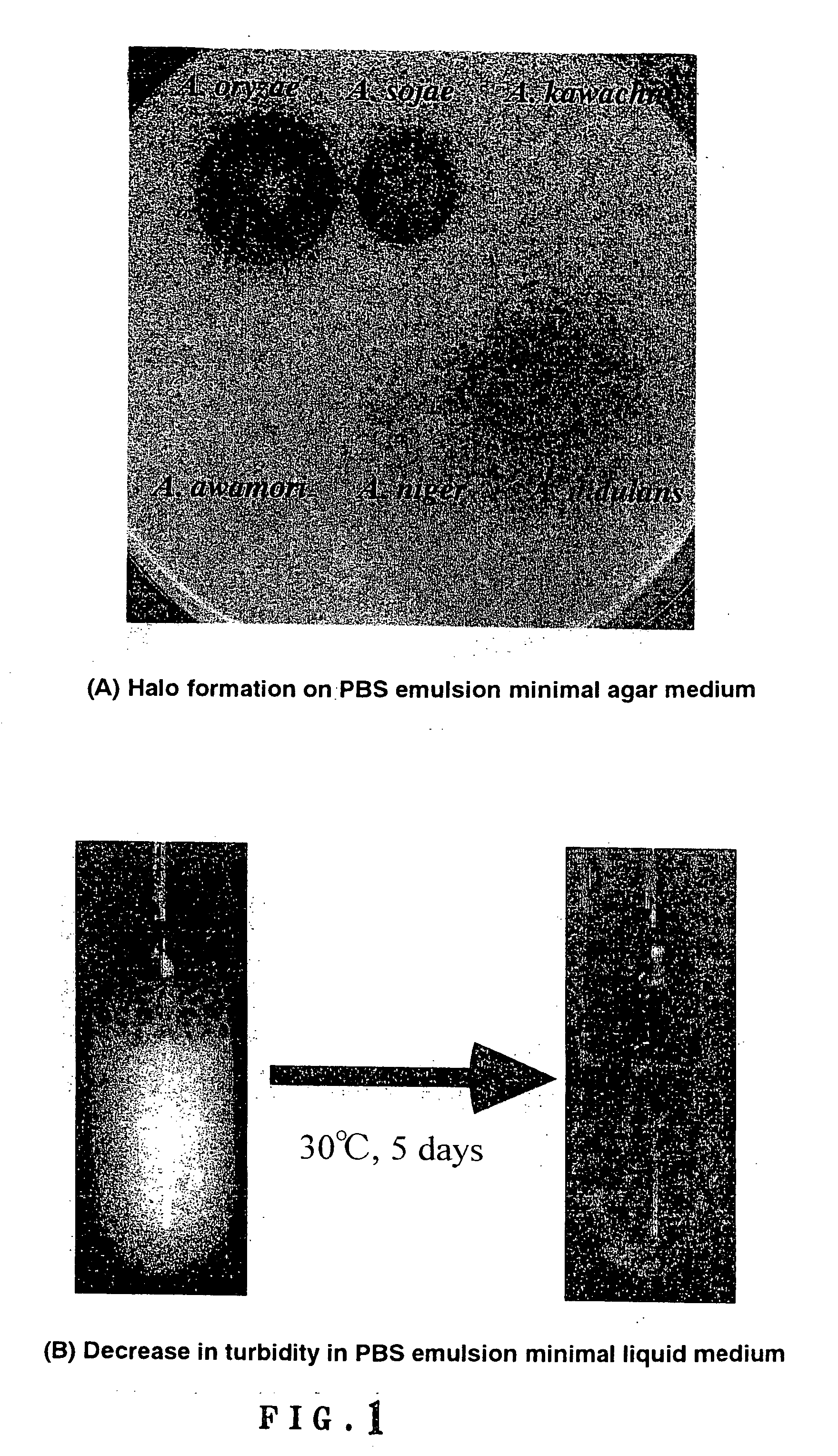
Method of degrading plastic and process for producing useful substance using the same
InactiveUS20060106120A1Lower water activityImprove the degradation problemFungiHydrolasesMicroorganismActive agent
A method of degrading a plastic in the presence of a biosurfactant; a method of degrading a plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism; a process for producing a useful substance from a plastic which comprises degrading the plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism and further converting the components of the thus degraded plastic with the use of a microorganism; a method of degrading a plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism in the coexistence of a biosurfactant and / or a plastic-degrading enzyme and thus degrading the plastic under the action of the microorganism; a transformant microorganism having been recombined with at least one DNA selected from among a DNA containing a gene encoding a surface active substance, a DNA containing a gene encoding a plastic-degrading enzyme and a DNA containing a gene encoding a useful substance; novel genes as described above; and proteins encoded thereby.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD +1
Polypeptide compositions toxic to anthonomus insects, and methods of use
A novel gene encoding a Coleopteran inhibitory Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein is disclosed. The protein, tIC851, is insecticidally active and provides plant protection from at least cotton boll weevil, Anthomomus grandis, when applied to plants in an insecticidally effective composition.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Beta-galactoside-alpha2, 6-sialyltransferase gene
This invention provides to a novel gene encoding a protein aving the activity of beta-galactoside-alpha2,6-sialyltransferase.The gene of the invention encodes a protein which having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, or a protein having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which have been modified by deletion, substitution or addition of at least one amino acid residue in said sequence, while maintaining substantially the same beta-galactoside-alpha2,6-sialyltransferase activity.The present invention uses said gene to further provide a vector for expressing a protein having the beta-galactoside-alpha2,6-sialyltransferase activity, host cells and a recombinant protein. The protein encoded by the gene of the invention does not have any substantial homology with known sialyltransferases, and in addition, the membrane binding region is located in the C-terminal unlike known sialyltransferases.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
InactiveUS6399328B1Control metastatic potentialOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to a novel gene, Di12, that is differentially expressed as a 1.35 kb RNA in breast cancer tissues and cell lines, and in several normal tissues. The full length cDNA encodes a protein of 339 amino acids. Antibodies to the gene product were developed to investigate the expression of Di12 in breast cancer cell-lines and tumors. The Di12 protein was found in tissue sections of infiltrating ductal carcinomas (IDCs), but not in benign or normal breast specimens. Di12 wag also present in IDC-breast cancer patient sera, and its expression level increased markedly if IDC was accompanied by lymph node or distal metastases. As IDC constitutes ~70% of breast cancers seen clinically, the level of Di12 expression is useful for diseases diagnosis predicting disease progression and monitoring a therapeutic treatment.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
C-type lectin transmembrane antigen expressed in human prostate cancer and uses thereof
A novel gene (designated PC-LECTIN) that is highly overexpressed in prostate cancer and its encoded protein is described. PC-LECTIN in normal human tissues is restricted to testis, but is highly expressed in prostate cancer. Consequently, PC-LECTIN provides a diagnostic and / or therapeutic target for prostate cancer.
Owner:AGENSYS
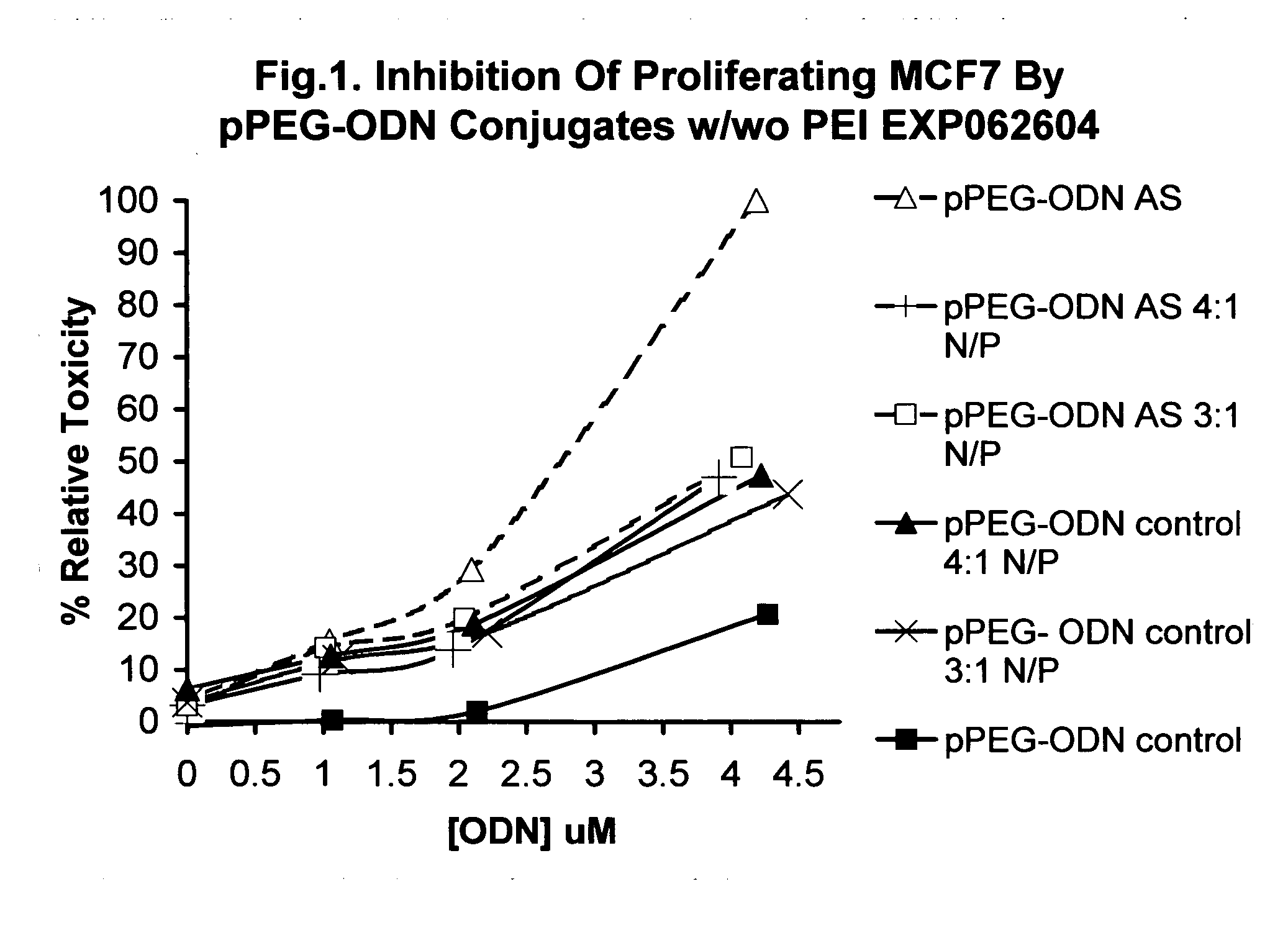
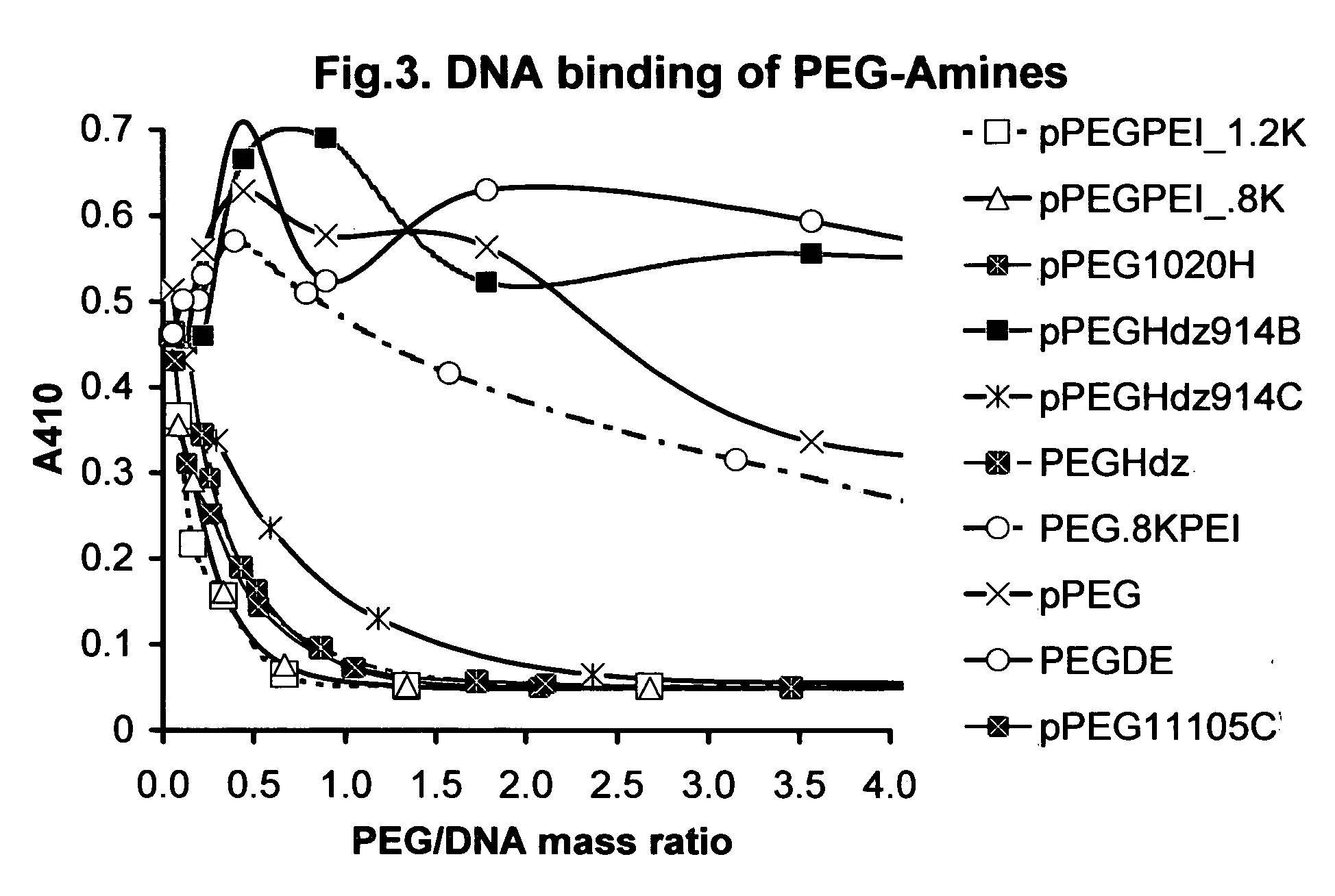
Shielded micelles for polynucleotide delivery
InactiveUS20070141134A1Highly efficient transfection agentLess cytotoxicBiocideSpecial deliverySolubilityCancer cell
The present invention relates to compositions that enhance the intracellular delivery of polynucleotides. The present invention is applicable to the fields of gene therapy and oligonucleotide or DNA therapy. Synthetic methods are disclosed, wherein a polynucleotide can be incorporated into the PEG shielded micelle particle to facilitate the delivery of the polynucleotide across a cellular membrane. Incorporation of the polynucleotide into the shielded micelle particle is provided by covalent and non-covalent means. Other cell targeting agents are provided that may also be covalently coupled to the shielded micelle particle to enhance localization in the body. The compositions herein are suitable for pharmaceutical use but are also suitable as transfection agents for in-vitro or in-vivo research. The PEG shielded polynucleotide micelles can provide favorable pharmacokinetic properties such as enhanced uptake into cancer cells, stability against nucleases, high solubility, and non-binding to serum proteins. The invention comprises a novel gene carrier which is shown to be substantially non-toxic and is suitable for parenteral, oral, pulmonary, and transmucosal delivery of polynucleotides.
Owner:KOSAK MATTHEW K
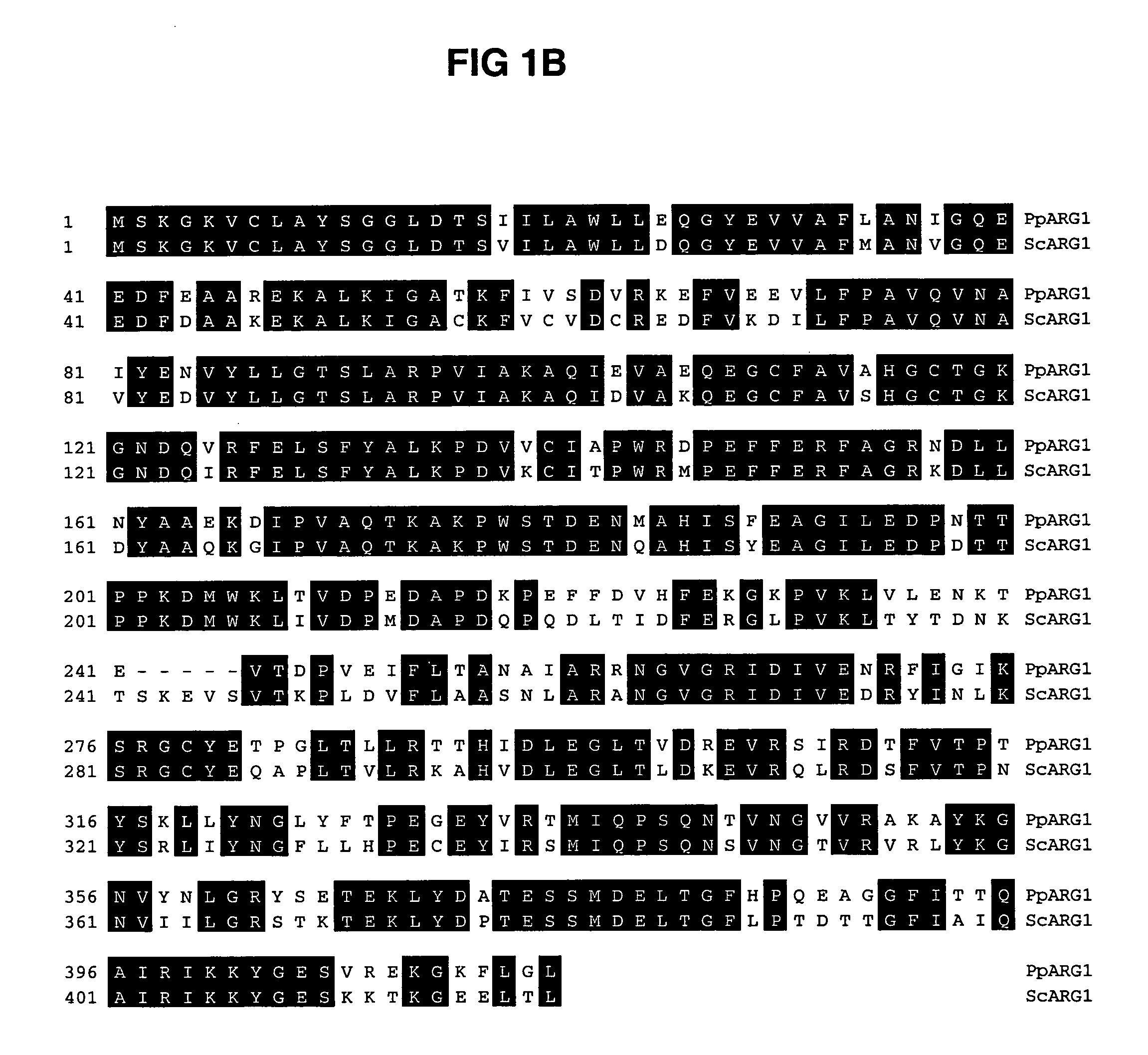
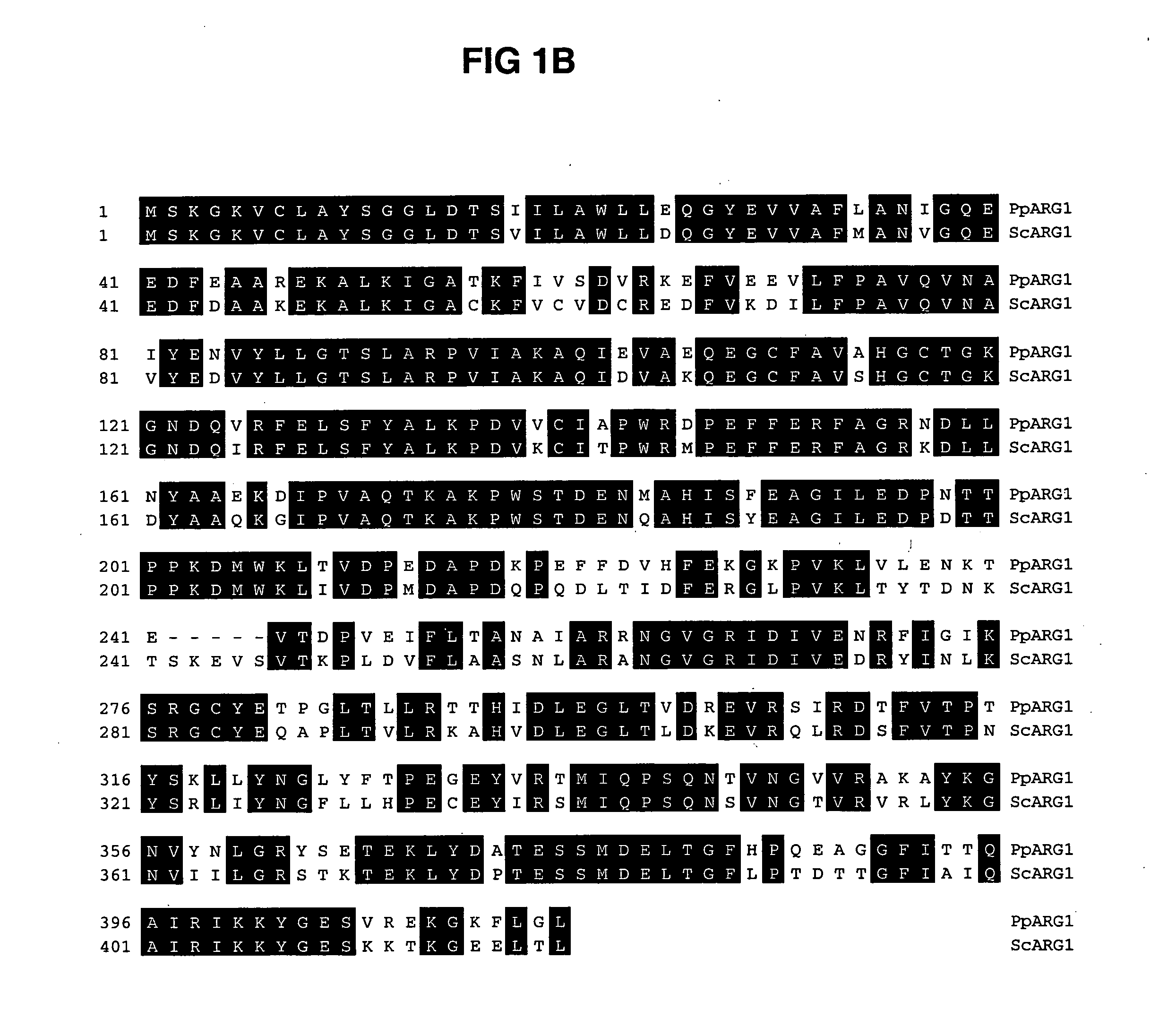
ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, HIS1, HIS2, HIS5, HIS6 genes and methods for stable genetic integration
Novel genes encoding P. pastoris ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, HIS1, HIS2, HIS5 and HIS6 are disclosed. A method for inactivating alternately at least two biosynthetic pathways in a methylotrophic yeast is provided. A method for producing and selecting yeast strains characterized as being capable of genetic integration of heterologous sequences into the host genome using the genes involved in the biosynthetic pathways is also disclosed.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Novel genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20050191673A1Reduced expression levelImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureOncologyNovel gene
The invention relates to newly discovered nucleic acid molecules and proteins associated with prostate cancer including pre-malignant conditions. Compositions, kits, and methods for detecting, characterizing, preventing, and treating human prostate cancers are provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Methods to inhibit growth of prostate cancer cells
InactiveUS7361338B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsProstate cancer cell
A novel gene (designated 101P3A11 or PHOR-1) and its encoded protein, and variants thereof, are described wherein 101P3A11 exhibits tissue specific expression in normal adult tissue, and is aberrantly expressed in the cancers listed in Table I. Consequently, 101P3A11 provides a diagnostic, prognostic, prophylactic and / or therapeutic target for cancer. The 101P3A11 gene or fragment thereof, or its encoded protein, or variants thereof, or a fragment thereof, can be used to elicit a humoral or cellular immune response; antibodies or T cells reactive with 101P3A11 can be used in active or passive immunization.
Owner:AGENSYS INC
ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, HIS1, HIS2, HIS5, HIS6 genes and methods for stable genetic integration
Novel genes encoding P. pastoris ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, HIS1, HIS2, HIS5 and HIS6 are disclosed. A method for inactivating alternately at least two biosynthetic pathways in a methylotrophic yeast is provided. A method for producing and selecting yeast strains characterized as being capable of genetic stable integration of heterologous sequences into the host genome using the genes involved in the biosynthetic pathways is also disclosed.
Owner:GLYCOFI
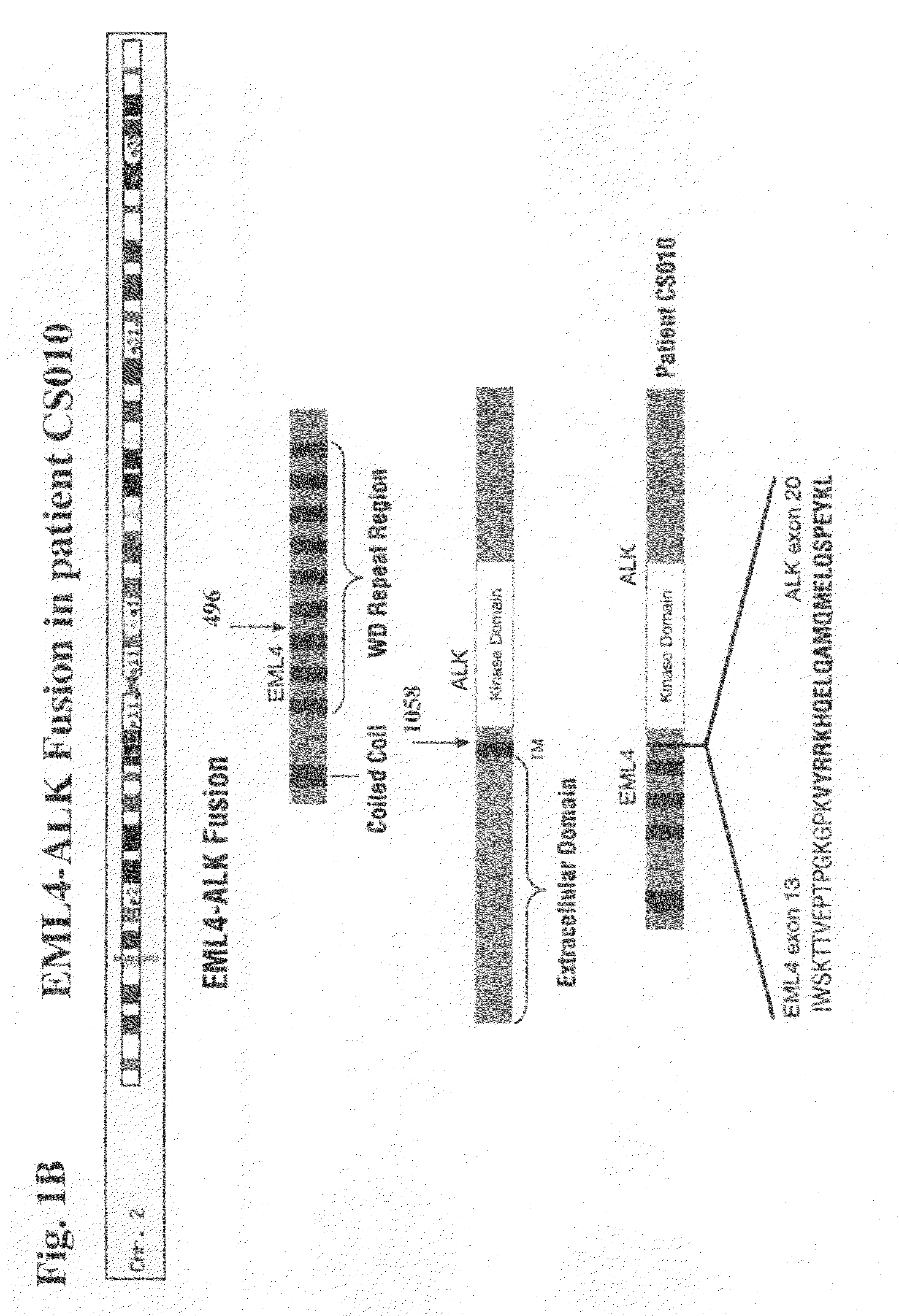
Gene defects and mutant ALK kinase in human solid tumors
In accordance with the invention, novel gene deletions and translocations involving chromosome 2 resulting in fusion proteins combining part of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) kinase with part of a secondary protein have now been identified in human solid tumors, e.g. non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Secondary proteins include Echinoderm Microtubule-Associated Protein-Like 4 (EML-4) and TRK-Fusion Gene (TFG). The EML4-ALK fusion protein, which retains ALK tyrosine kinase activity, was confirmed to drive the proliferation and survival of NSCLC characterized by this mutation. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ALK kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of this new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ALK kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com