Gene specifically expressed in postmitotic dopaminergic neuron precursor cells
a dopaminergic neuron and gene technology, applied in the field of new 65b13 gene expressed in postmitotic dopaminergic neurons, to achieve the effect of high therapeutic efficacy, convenient preparation, and efficient separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Sequence Analysis of a Gene Specific for Dopaminergic Neuron Precursor Cells
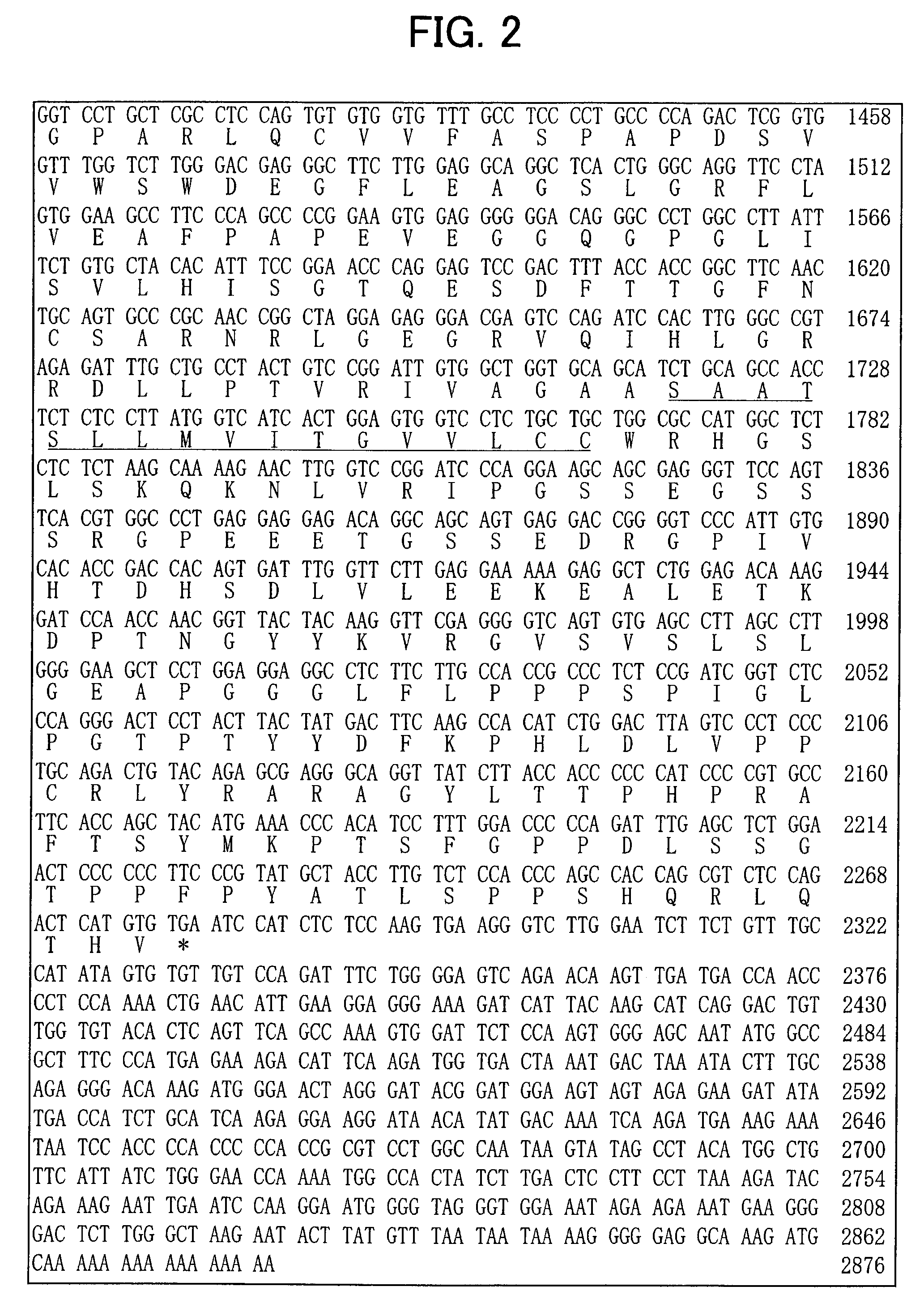
[0123] To isolate a gene specific to dopaminergic neuron precursor cells, genes with differences in expression were amplified by the subtraction (N-RDA) method using RNA from ventral and dorsal midbrain of E12.5 mice, and sequences of the resulting genes were analyzed.
1. N-RDA Method
1-1. Adapter Preparation
[0124] The following oligonucleotides were annealed to each other, and prepared at 100 μM. (ad2: ad2S+ad2A, ad3: ad3S+ad3A, ad4: ad4S+ad4A, ad5: ad5S+ad5A, ad13: ad13S+ad13A)
ad2S:cagctccacaacctacatcattccgt(SEQ ID NO:11)ad2A:acggaatgatgt(SEQ ID NO:12)ad3S:gtccatcttctctctgagactctggt(SEQ ID NO:13)ad3A:accagagtctca(SEQ ID NO:14)ad4S:ctgatgggtgtcttctgtgagtgtgt(SEQ ID NO:15)ad4A:acacacteacag(SEQ ID NO:16)ad5S:ccagcatcgagaatcagtgtgacagt(SEQ ID NO:17)ad5A:actgtcacactg(SEQ ID NO:18)ad13S:gtcgatgaacttcgactgtcgatcgt(SEQ ID NO:19)ad13A:acgatcgacagt.(SEQ ID NO:20)
1-2. cDNA Synthesis
[0125] Total ...
example 2
Expression Analysis of the 65B13 Genes
[0164] Next, an expression analysis of these genes by in situ hybridization was carried out according to the following protocol.
[0165] First, E12.5 mouse embryos were embedded in O.C.T., and fresh frozen sections of 16 μm thickness were prepared. After drying on a slide glass, the sections were fixed in 4% PFA at room temperature for 30 minutes. After washing with PBS, hybridization was carried out at 65° C. for 40 hours (1 μg / ml DIG-labeled RNA probe, 50% formamide, 5×SSC, 1% SDS, 50 μg / ml yeast RNA, 50 μg / ml Heparin). Subsequently, the sections were washed at 65° C. (50% formamide, 5×SSC, 1% SDS) and then treated with RNase (5 μg / ml RNase) at room temperature for 5 minutes. After washing with 0.2×SSC at 65° C. and washing with 1×TBST at room temperature, blocking was carried out (Blocking reagent: Roche). The sections were then reacted with alkaline phosphatase-labeled anti-DIG antibody (DAKO), washed (1×TBST, 2 mM Levamisole), and color dev...
example 3
Expression Analysis of the 65B13 Proteins
[0168] Next, a portion of the 65B13 gene sequence that encodes the extracellular region was used to generate an anti-65B13 antibody to be used for expression analysis by immunohistochemical staining.
[0169] First, a partial sequence of the 65B13 gene that encodes the extracellular region was introduced into 293E cells, and the extracellular region of the 65B13 protein was expressed and recovered. After immunizing hamsters with the recovered protein, lymphocytes were extracted and fused with myeloma cells. The fused cells were then transplanted into the abdominal cavities of mice, ascites was obtained, and an anti-65B13 monoclonal antibody was purified. Next, E12.5 mouse embryos were fixed in 4% PFA / PBS(−) at 4° C. for 2 hours, and then stood overnight at 4° C. in 20% sucrose / PBS(−), followed by O.C.T. embedding. Sections of 12 um thickness were produced. After affixing to slide glasses, the sections were dried for 30 minutes at room temperat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heterogeneous | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com