Patents
Literature
4647results about "Other blood circulation devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
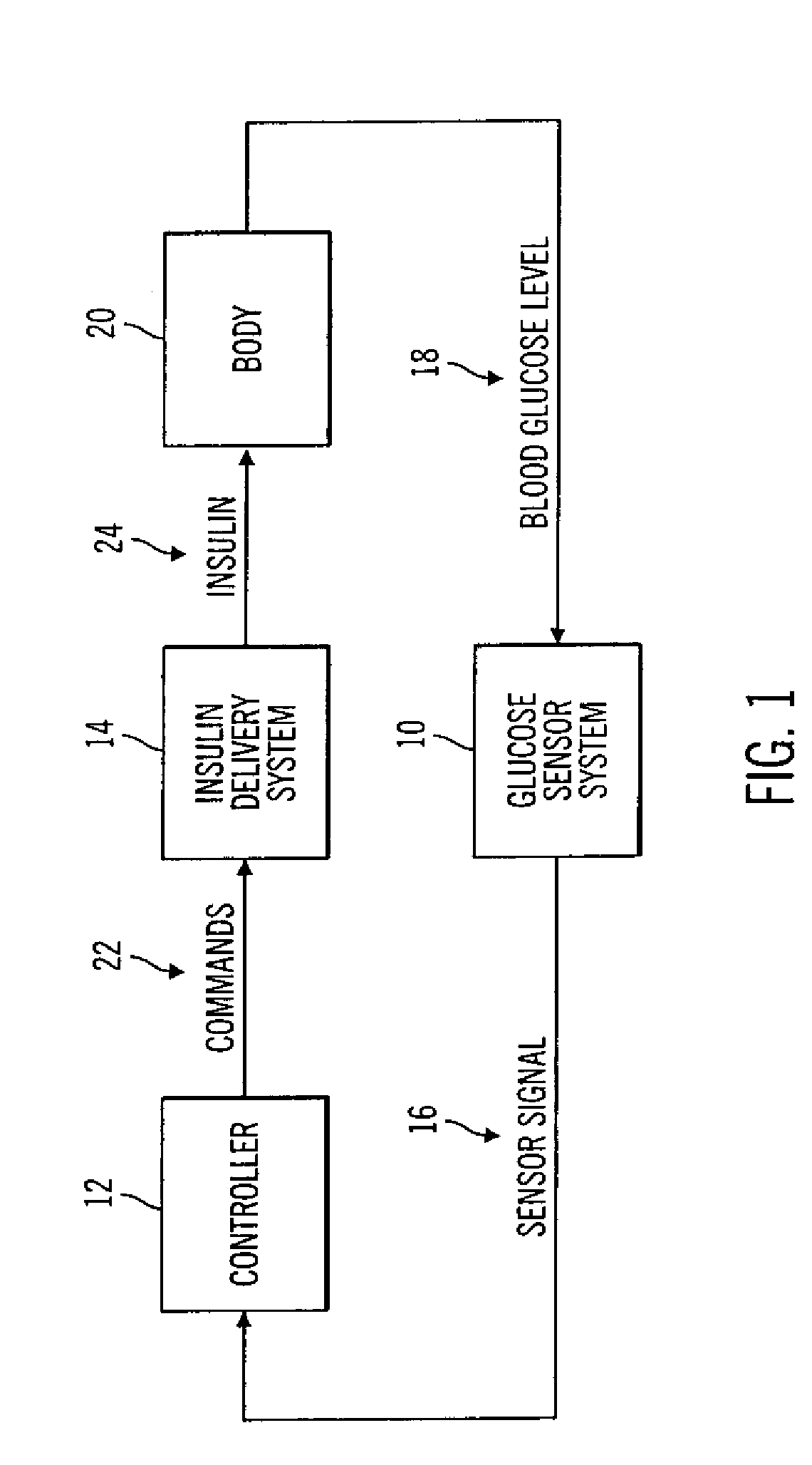
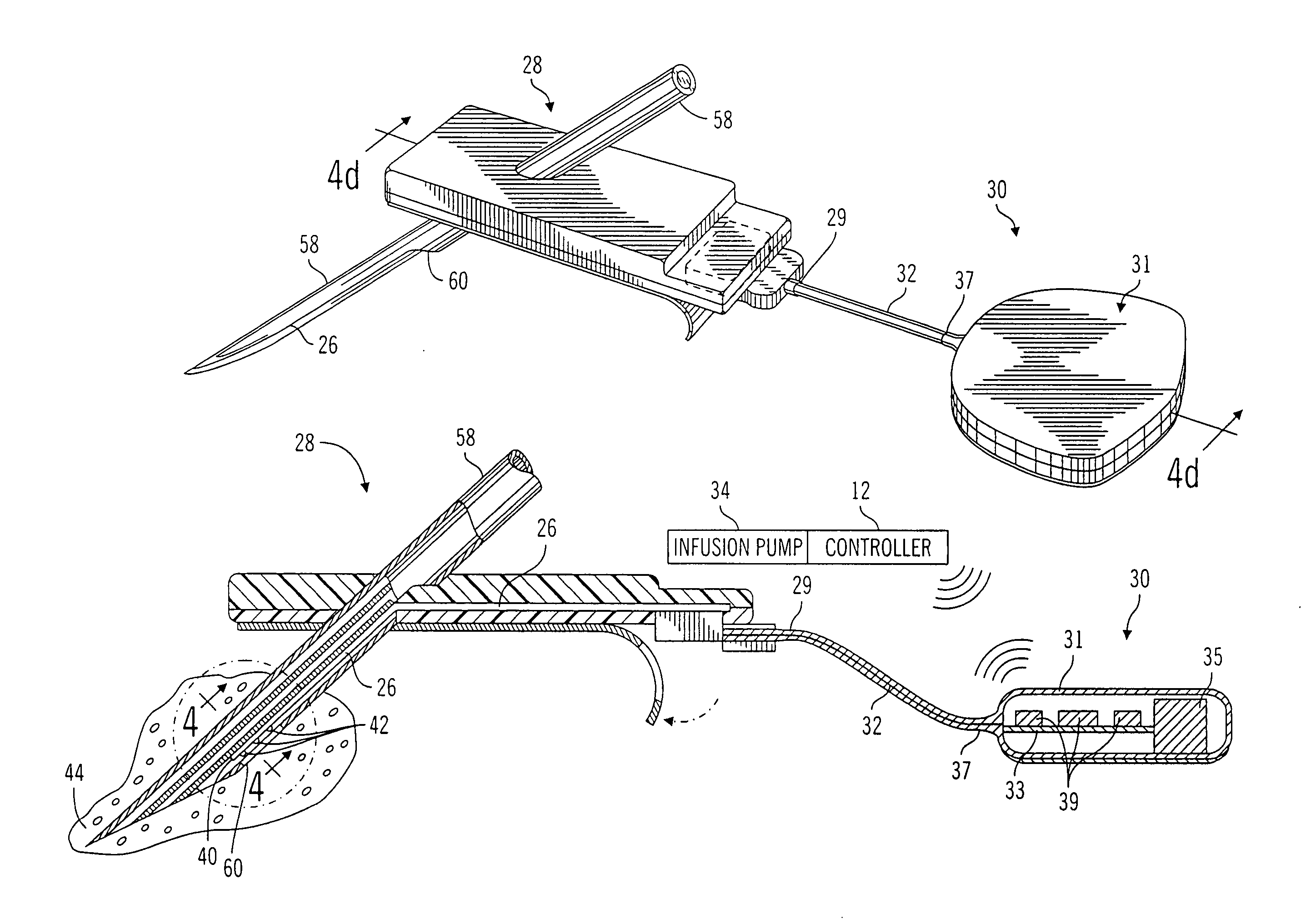
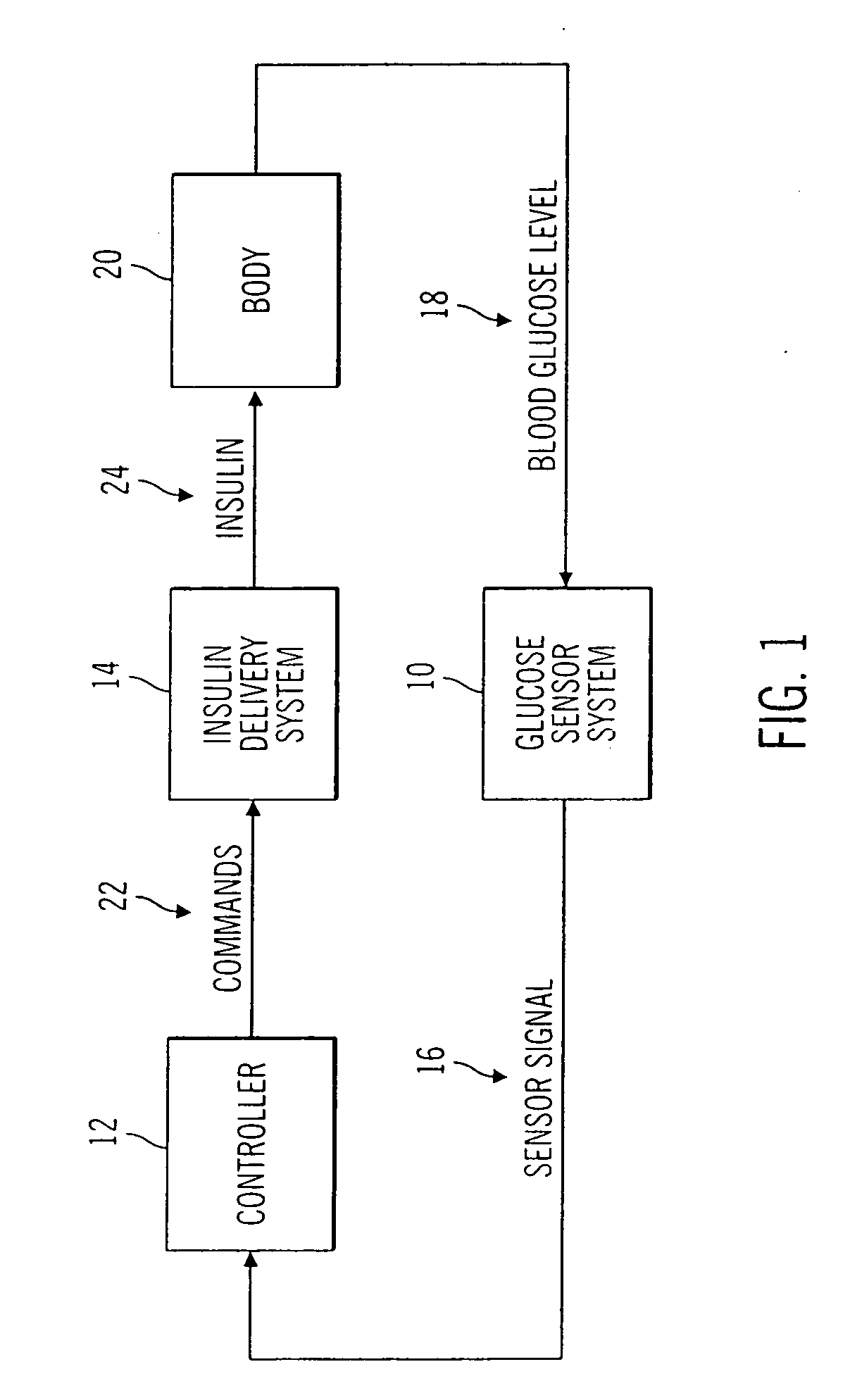
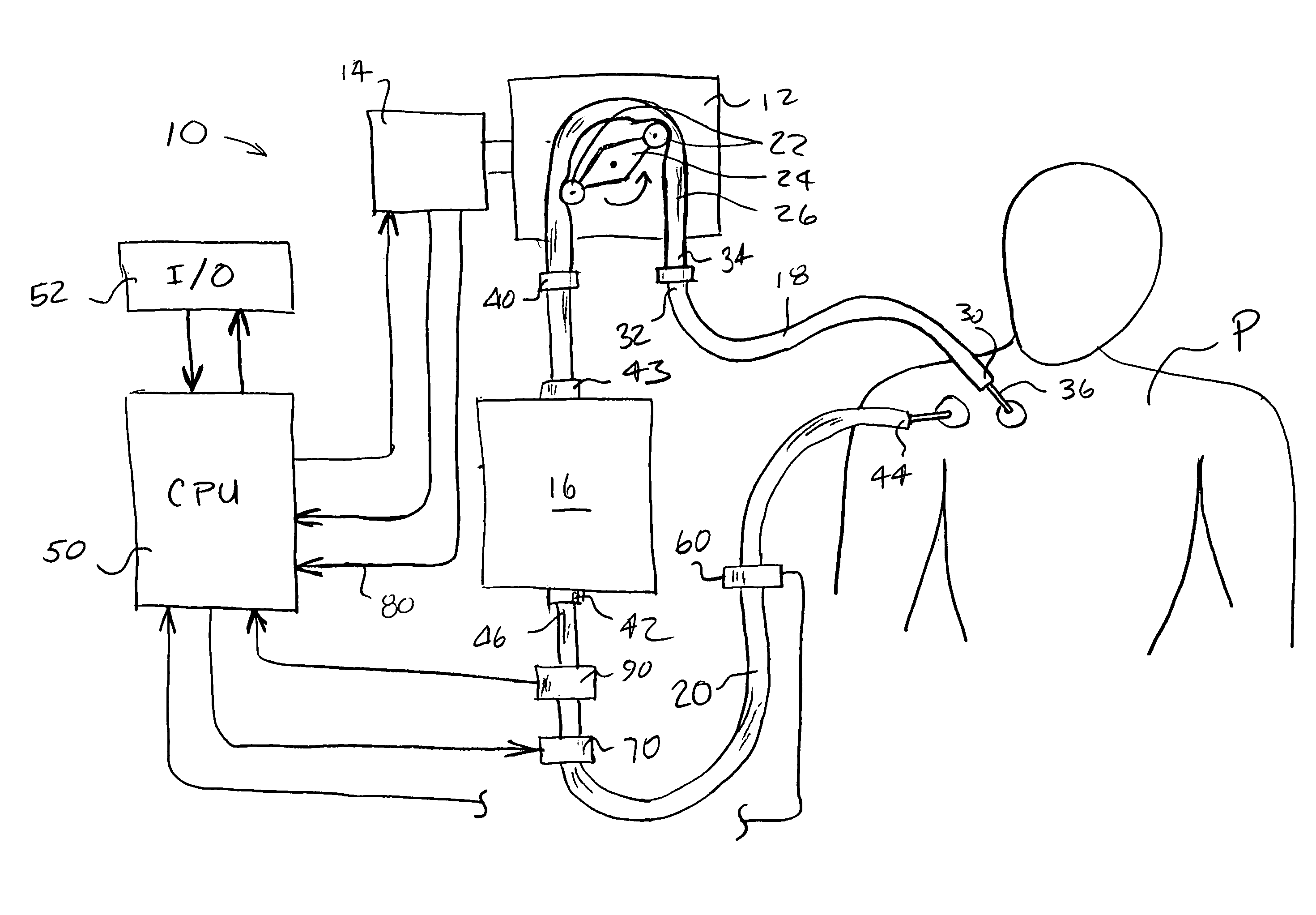
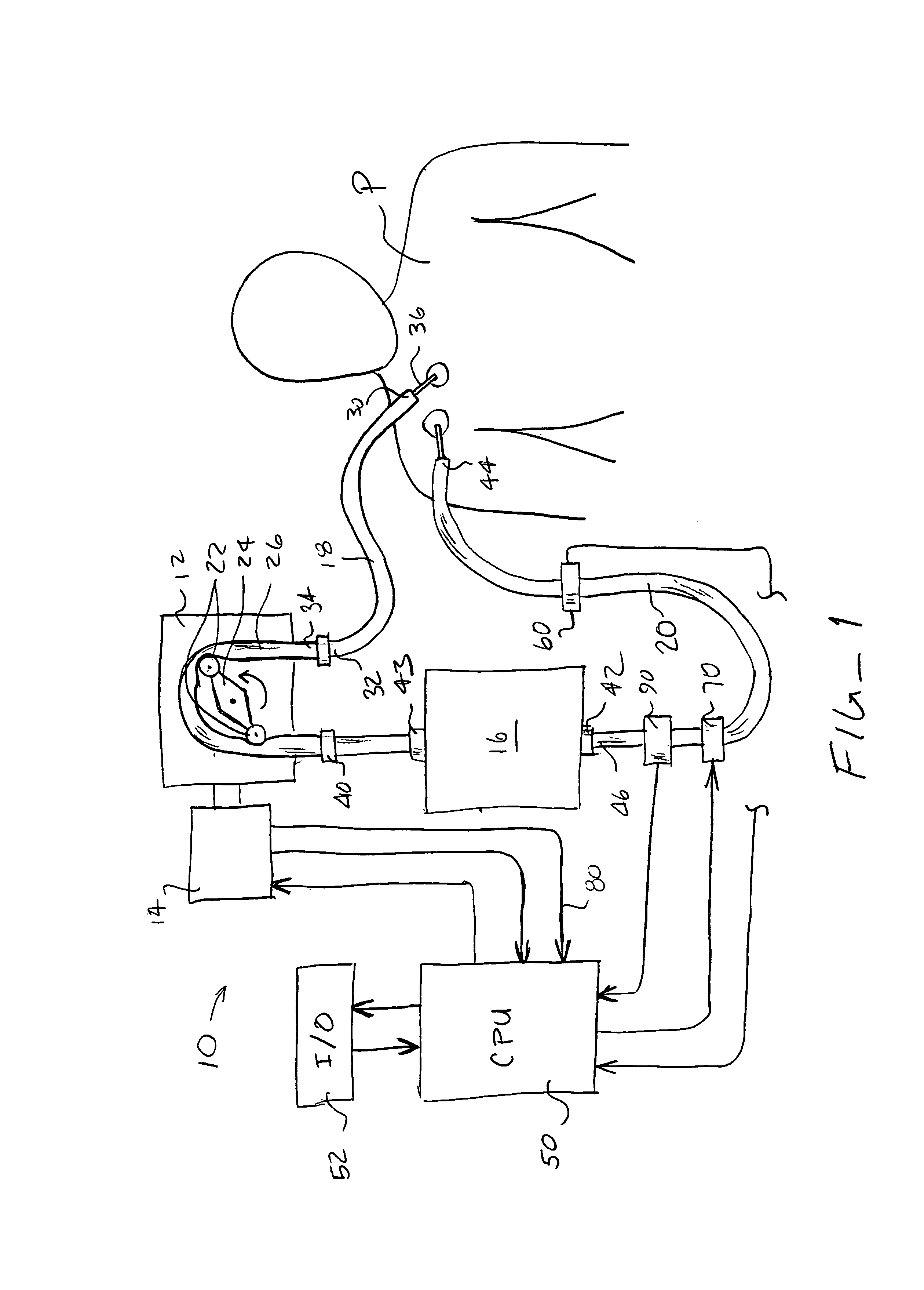
Closed loop system for controlling insulin infusion
InactiveUS7267665B2Other blood circulation devicesMedical devicesInsulin infusionConcentrations glucose
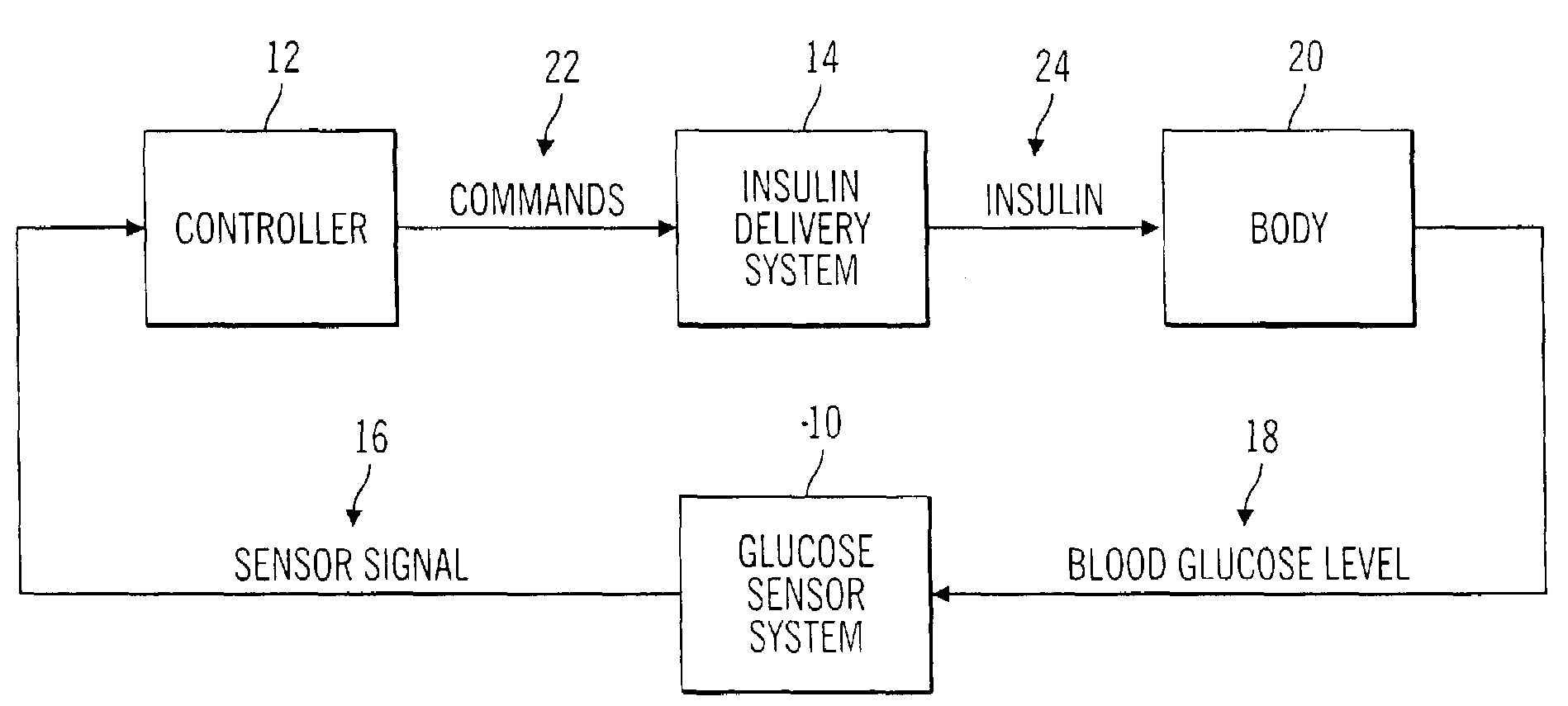
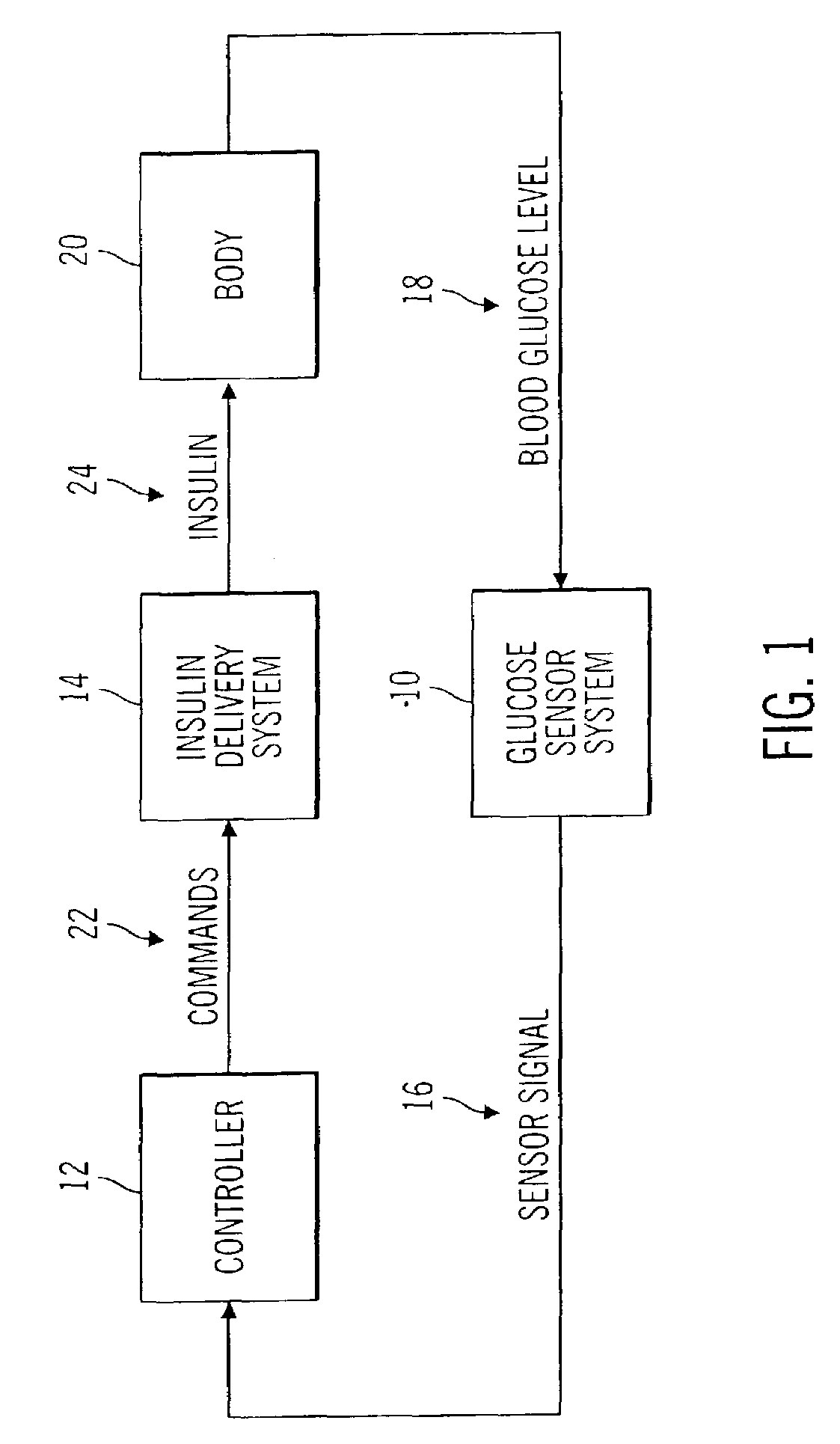
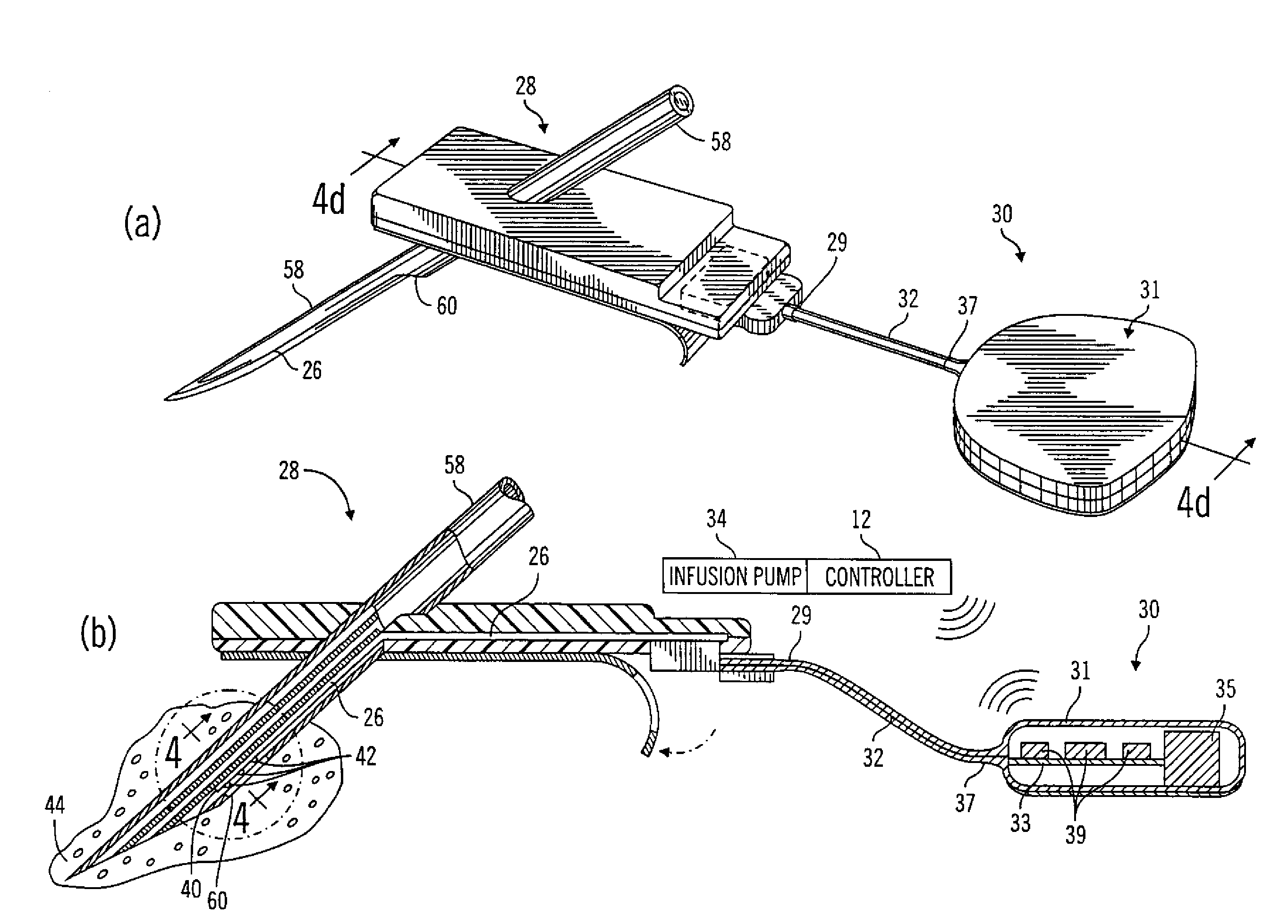
A closed loop infusion system controls the rate that fluid is infused into the body of a user. The closed loop infusion system includes a sensor system, a controller, and a delivery system. The sensor system includes a sensor for monitoring a condition of the user. The sensor produces a sensor signal, which is representative of the condition of the user. The sensor signal is used to generate a controller input. The controller uses the controller input to generate commands to operate the delivery system. The delivery system infuses a liquid into the user at a rate dictated by the commands from the controller. Preferably, the sensor system monitors the glucose concentration in the body of the user, and the liquid infused by the delivery system into the body of the user includes insulin.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Closed-Loop Method for Controlling Insulin Infusion
InactiveUS20080188796A1Other blood circulation devicesDrug and medicationsInsulin infusionConcentrations glucose
A closed loop infusion system controls the rate that fluid is infused into the body of a user. The closed loop infusion system includes a sensor system, a controller, and a delivery system. The sensor system includes a sensor for monitoring a condition of the user. The sensor produces a sensor signal, which is representative of the condition of the user. The sensor signal is used to generate a controller input. The controller uses the controller input to generate commands to operate the delivery system. The delivery system infuses a liquid into the user at a rate dictated by the commands from the controller. Preferably, the sensor system monitors the glucose concentration in the body of the user, and the liquid infused by the delivery system into the body of the user includes insulin.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Closed loop system for controlling insulin infusion
InactiveUS20060224109A1Limit accuracy of signalOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesInsulin infusionConcentrations glucose
A closed loop infusion system controls the rate that fluid is infused into the body of a user. The closed loop infusion system includes a sensor system, a controller, and a delivery system. The sensor system includes a sensor for monitoring a condition of the user. The sensor produces a sensor signal, which is representative of the condition of the user. The sensor signal is used to generate a controller input. The controller uses the controller input to generate commands to operate the delivery system. The delivery system infuses a liquid into the user at a rate dictated by the commands from the controller. Preferably, the sensor system monitors the glucose concentration in the body of the user, and the liquid infused by the delivery system into the body of the user includes insulin.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include hollow fibers which are adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. The hollow fibers enhance the surface area of contact, as well as the mixing of both the heat exchange fluid and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body or alternatively positioned to systemically cool the entire body system.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
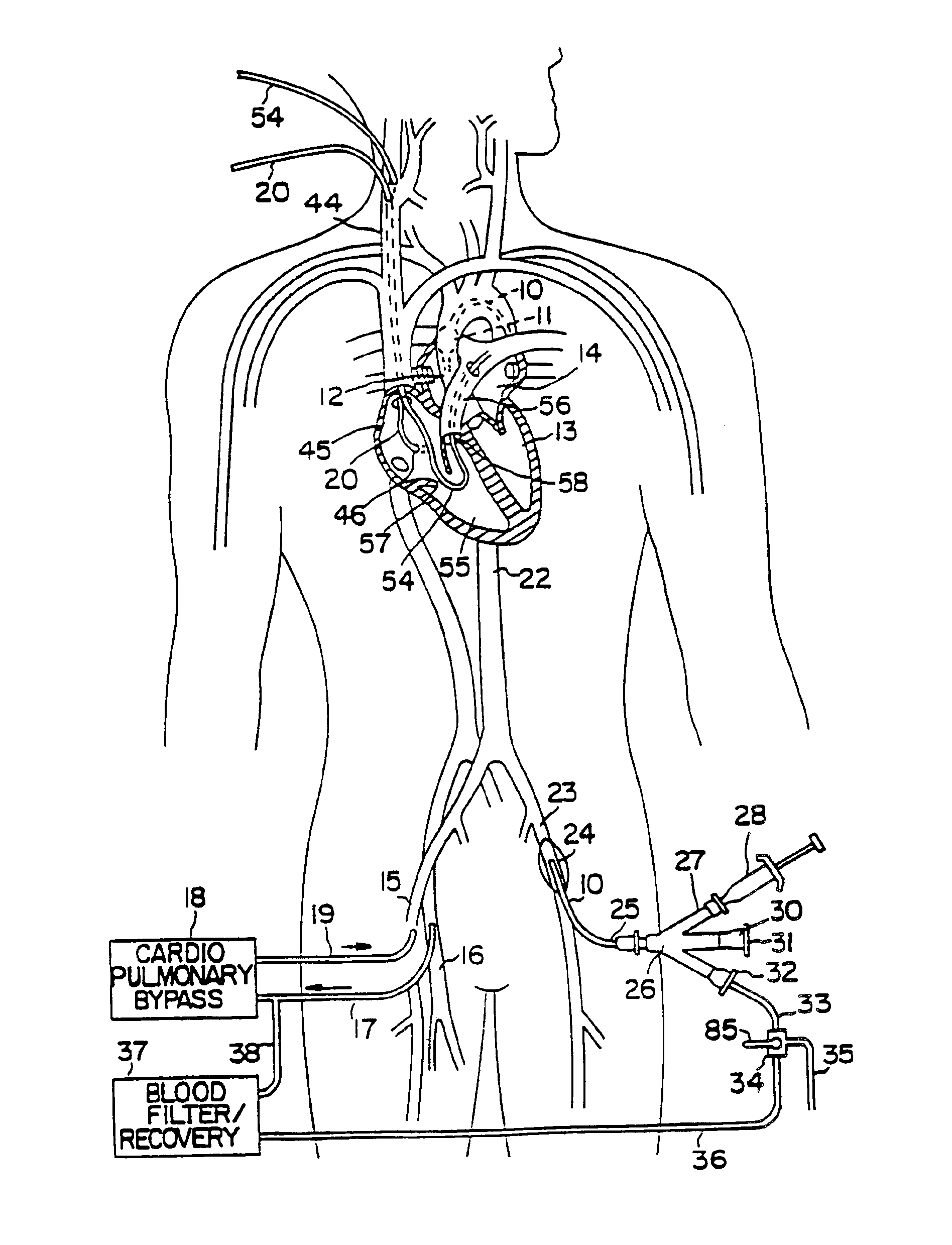
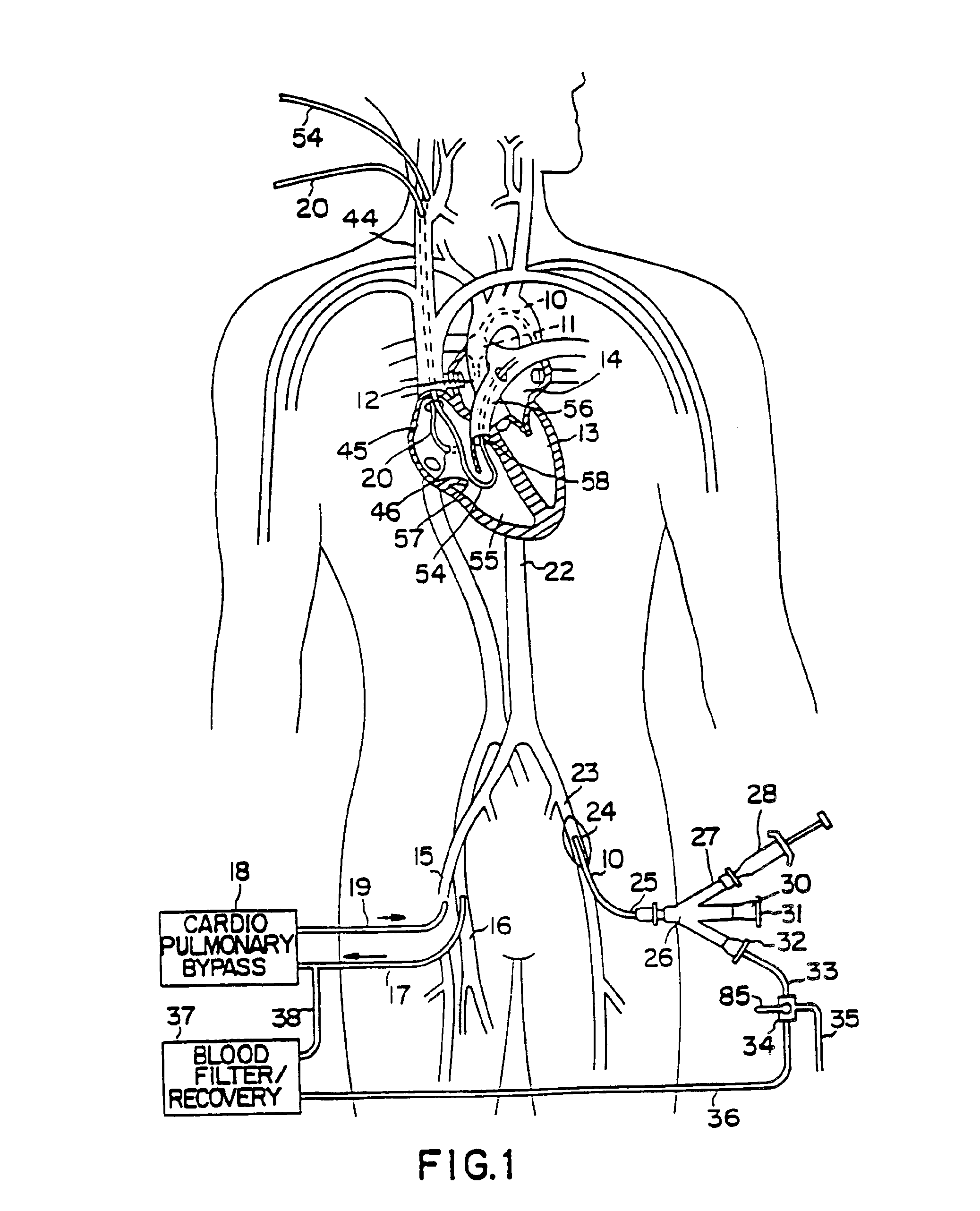
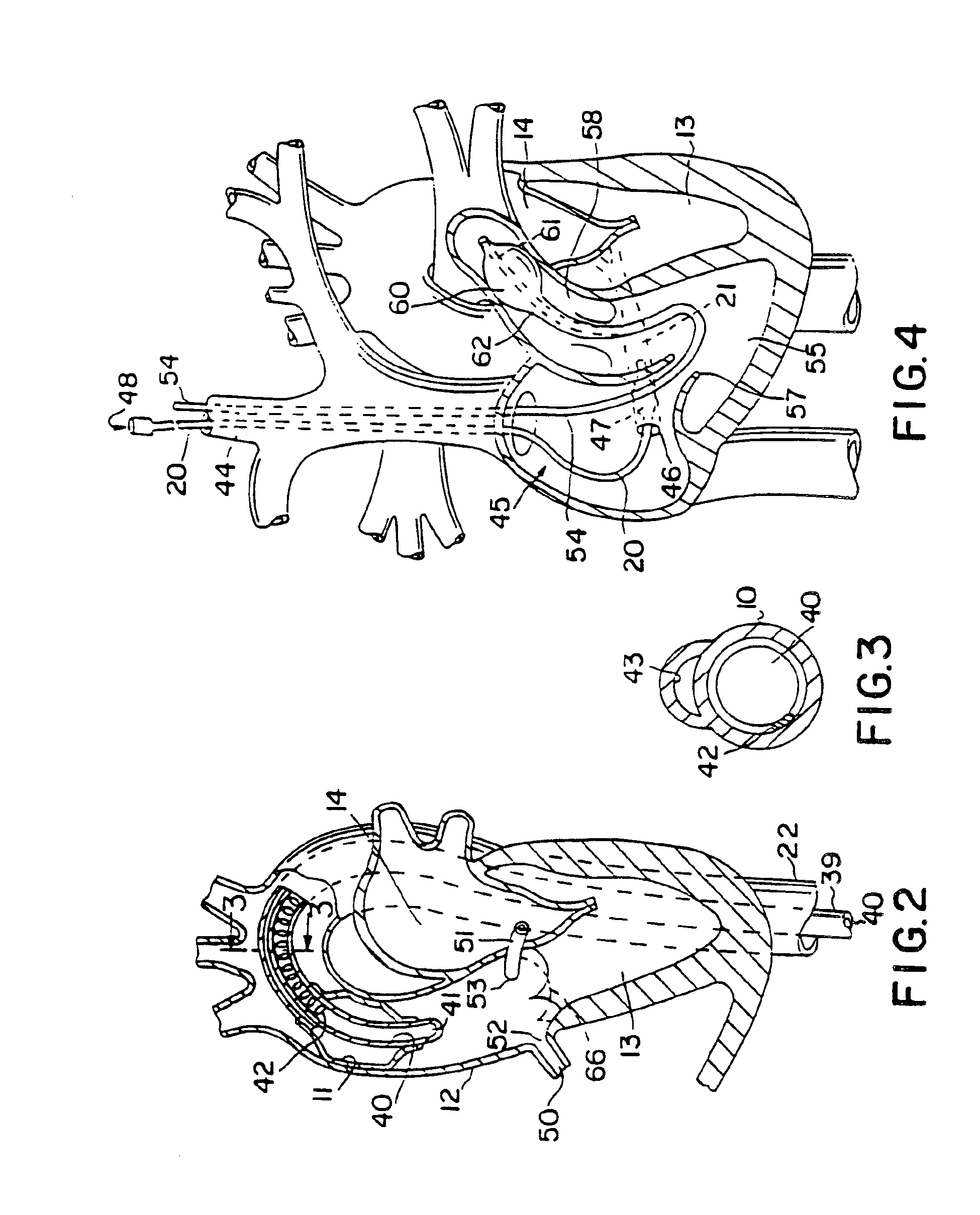
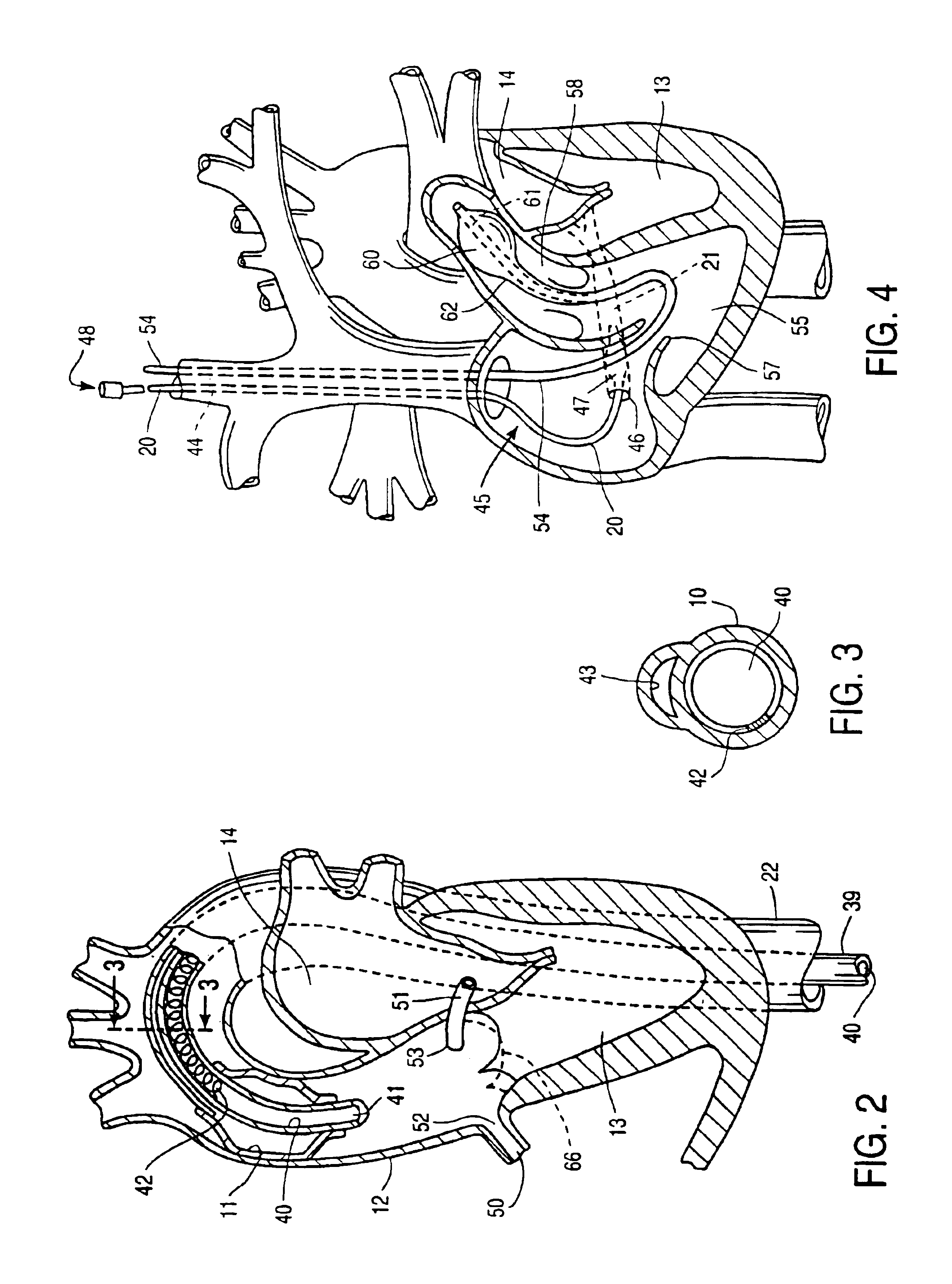
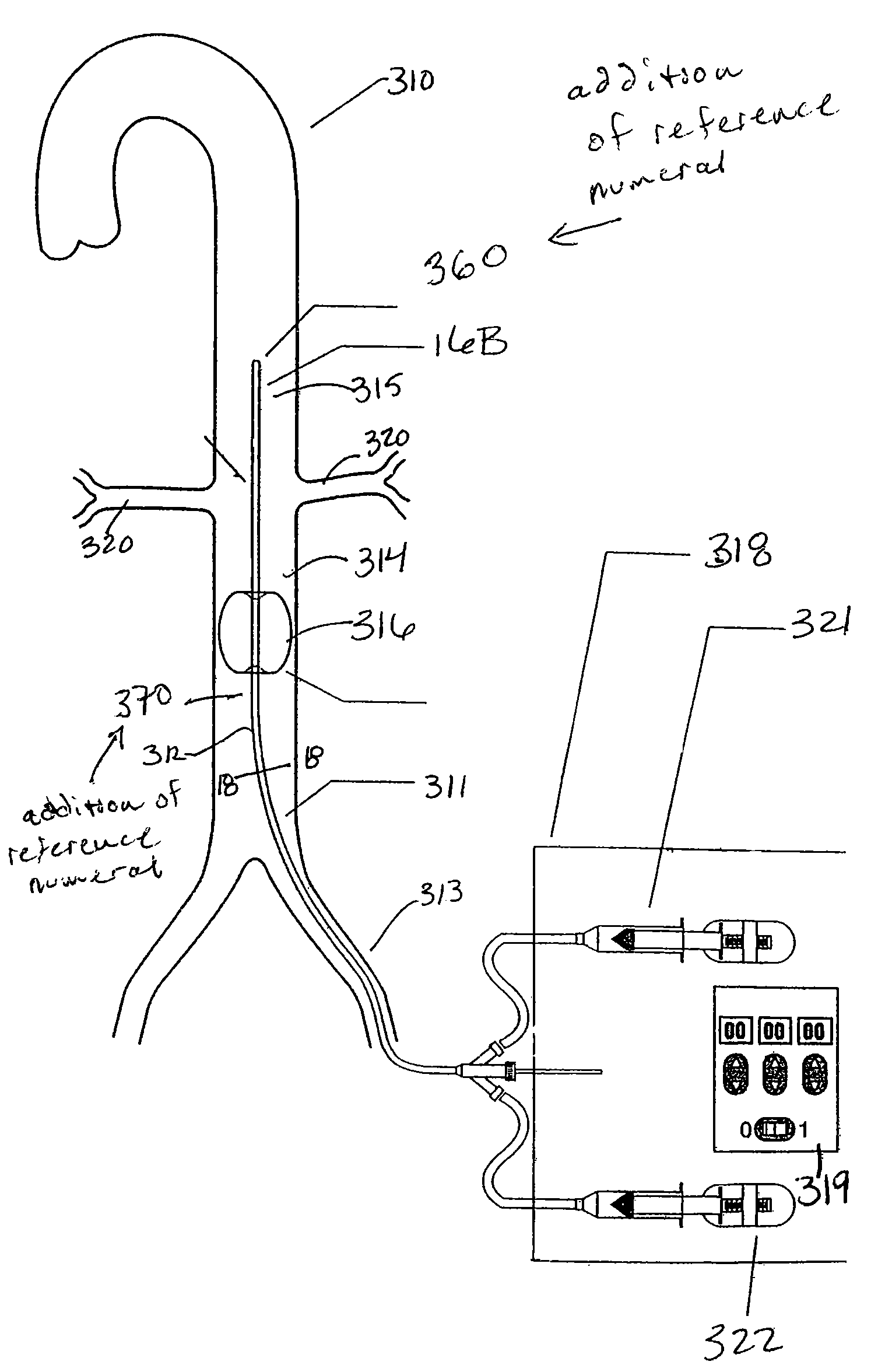
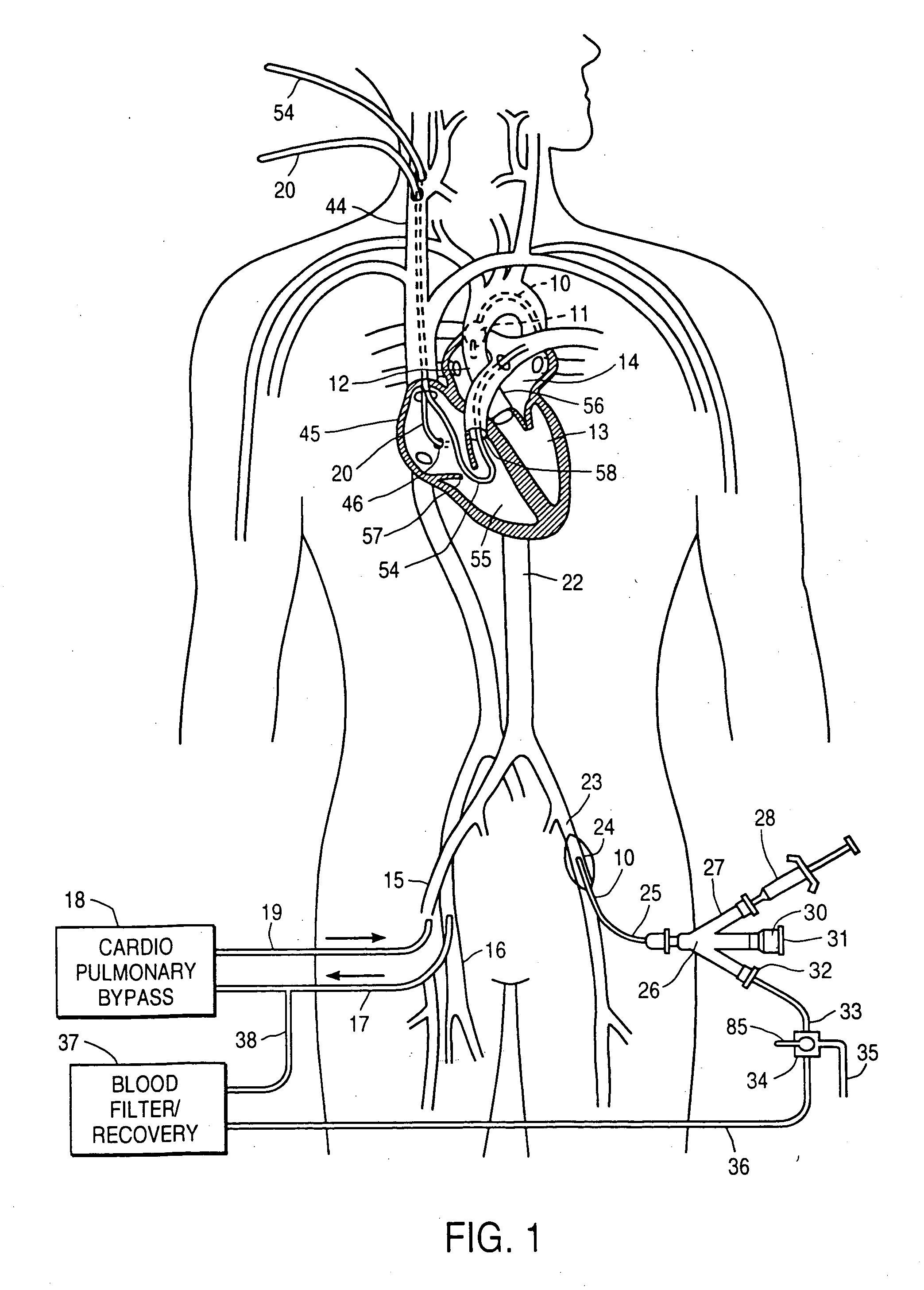
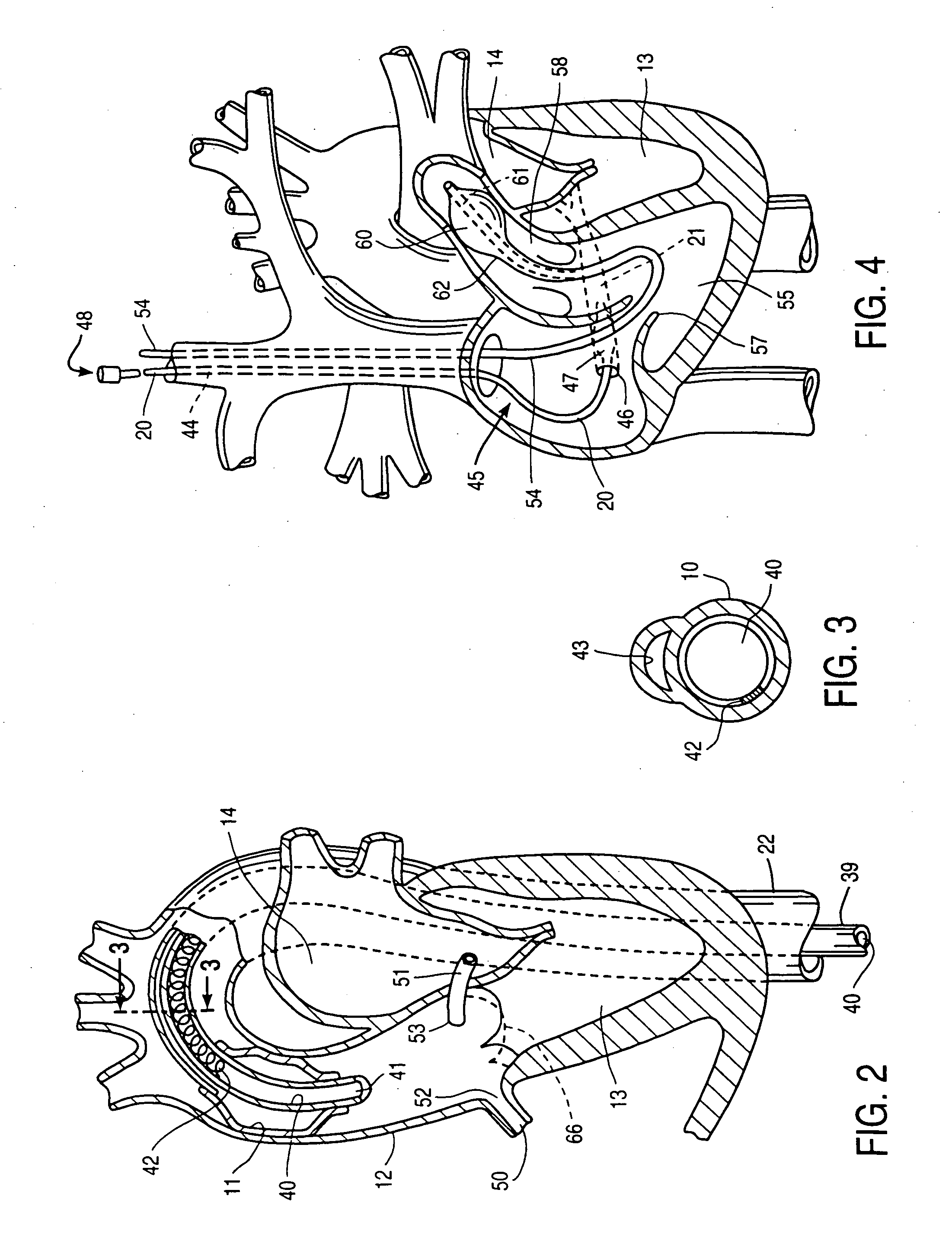
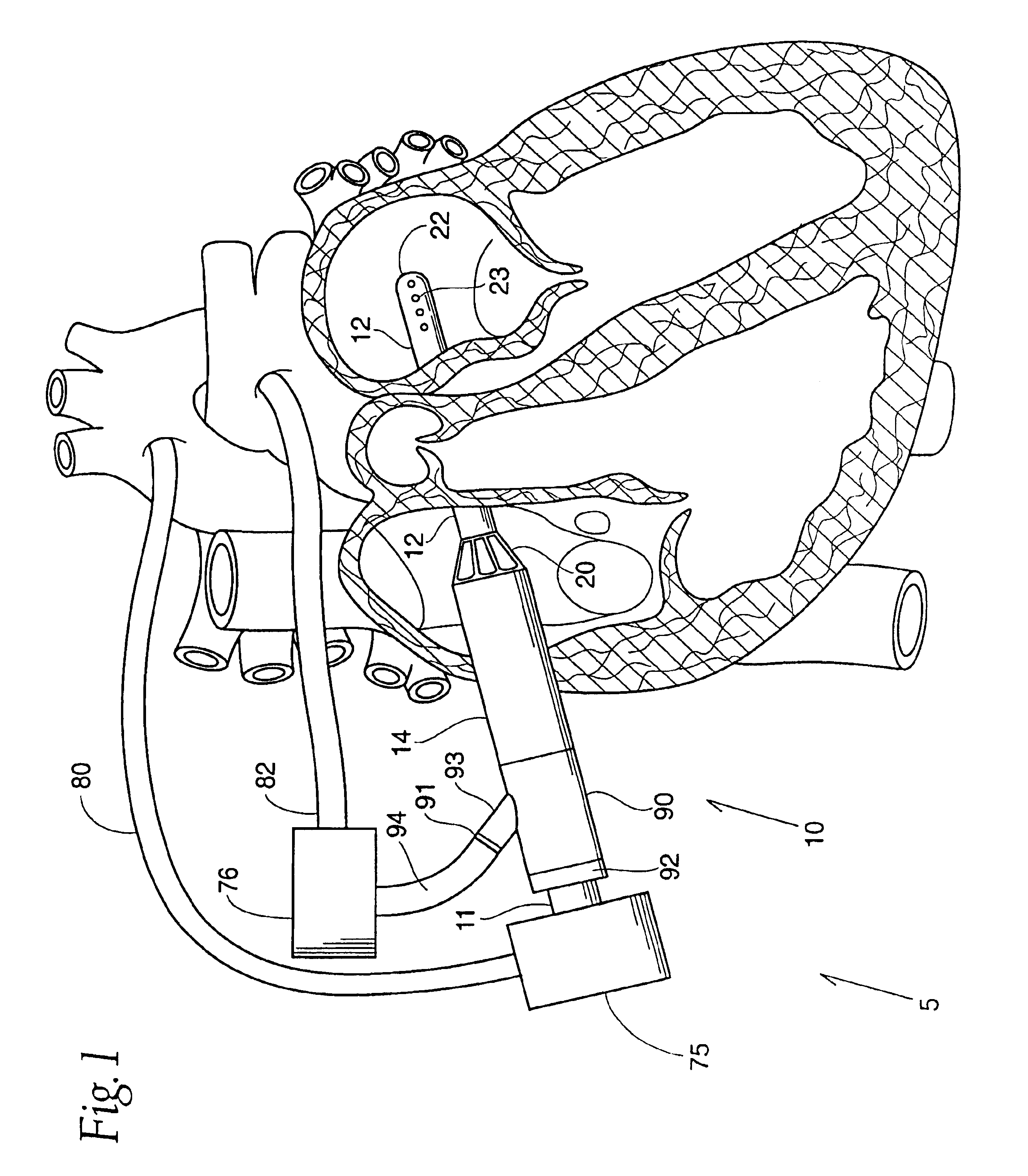
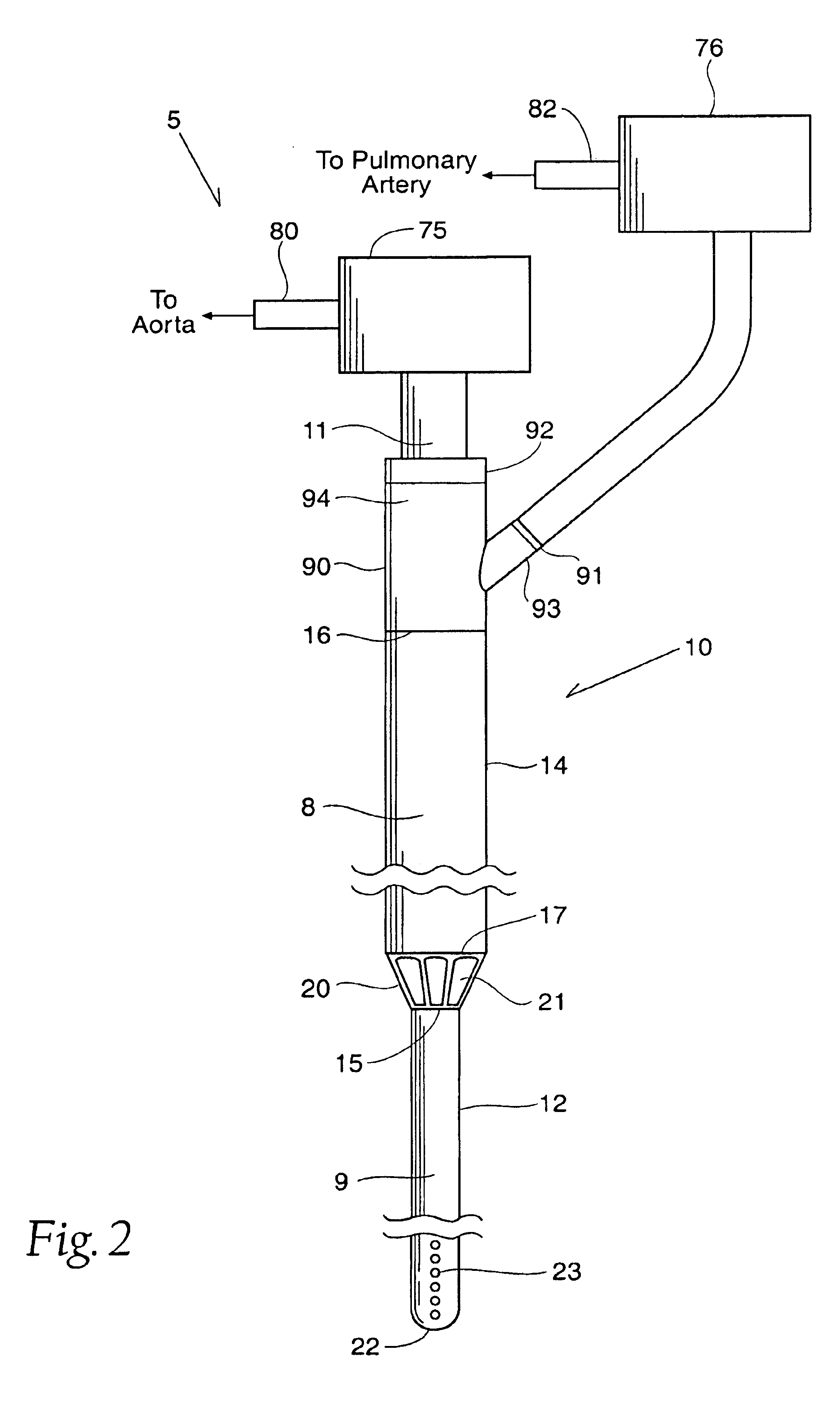
System for cardiac procedures
A system for accessing a patient's cardiac anatomy which includes an endovascular aortic partitioning device that separates the coronary arteries and the heart from the rest of the patient's arterial system. The endovascular device for partitioning a patient's ascending aorta comprises a flexible shaft having a distal end, a proximal end, and a first inner lumen therebetween with an opening at the distal end. The shaft may have a preshaped distal portion with a curvature generally corresponding to the curvature of the patient's aortic arch. An expandable means, e.g. a balloon, is disposed near the distal end of the shaft proximal to the opening in the first inner lumen for occluding the ascending aorta so as to block substantially all blood flow therethrough for a plurality of cardiac cycles, while the patient is supported by cardiopulmonary bypass. The endovascular aortic partitioning device may be coupled to an arterial bypass cannula for delivering oxygenated blood to the patient's arterial system. The heart muscle or myocardium is paralyzed by the retrograde delivery of a cardioplegic fluid to the myocardium through patient's coronary sinus and coronary veins, or by antegrade delivery of cardioplegic fluid through a lumen in the endovascular aortic partitioning device to infuse cardioplegic fluid into the coronary arteries. The pulmonary trunk may be vented by withdrawing liquid from the trunk through an inner lumen of an elongated catheter. The cardiac accessing system is particularly suitable for removing the aortic valve and replacing the removed valve with a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
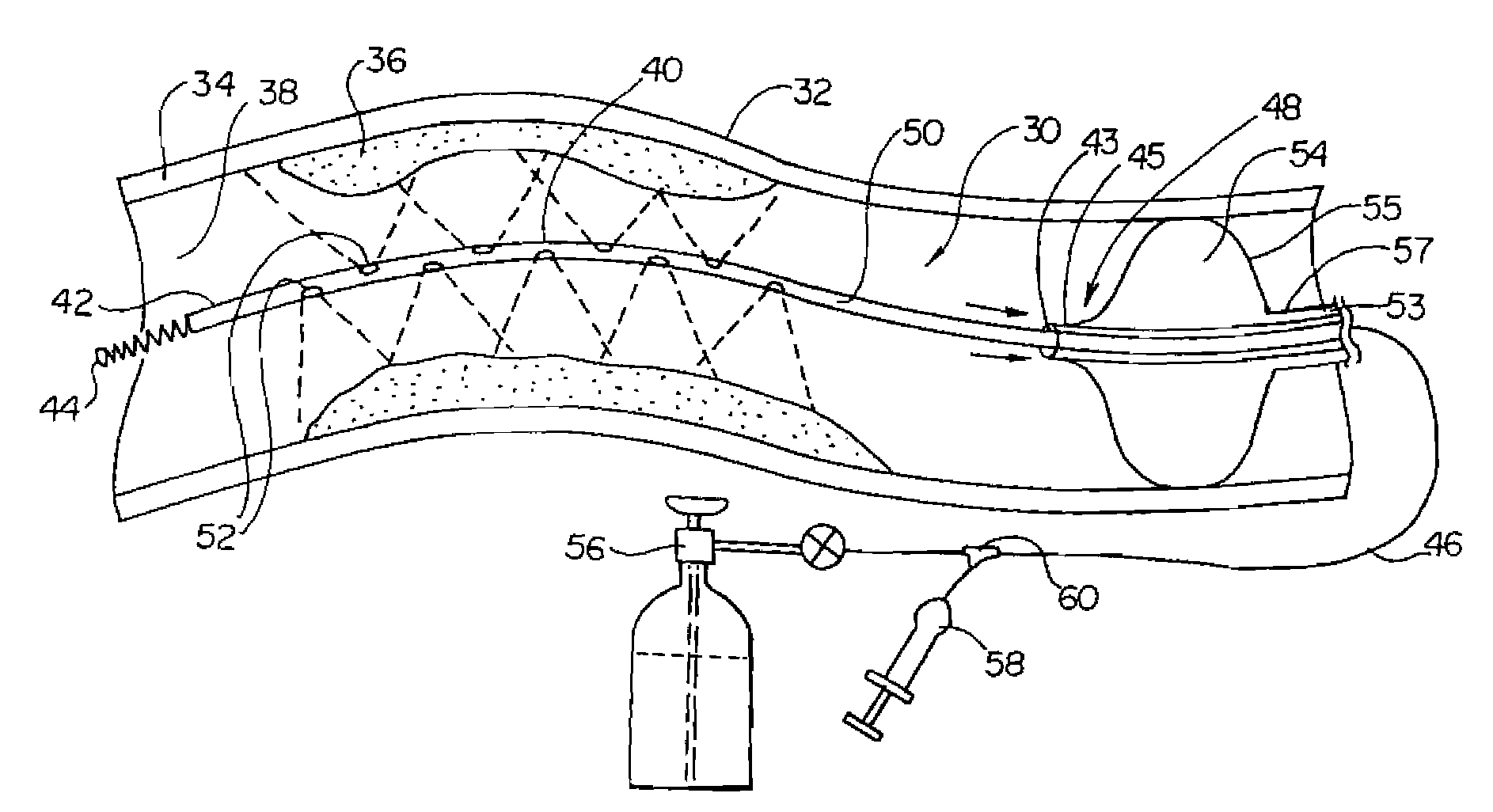
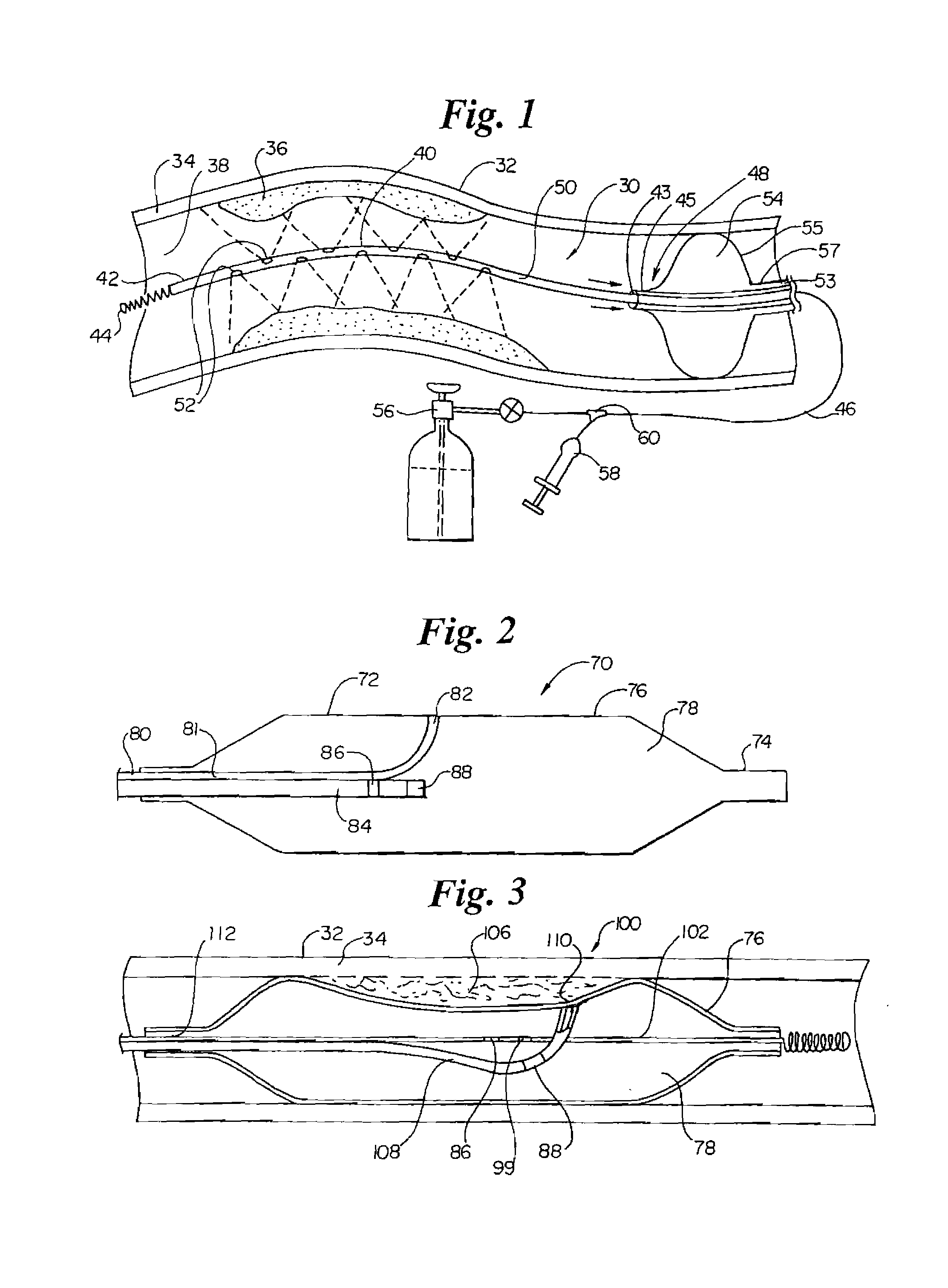
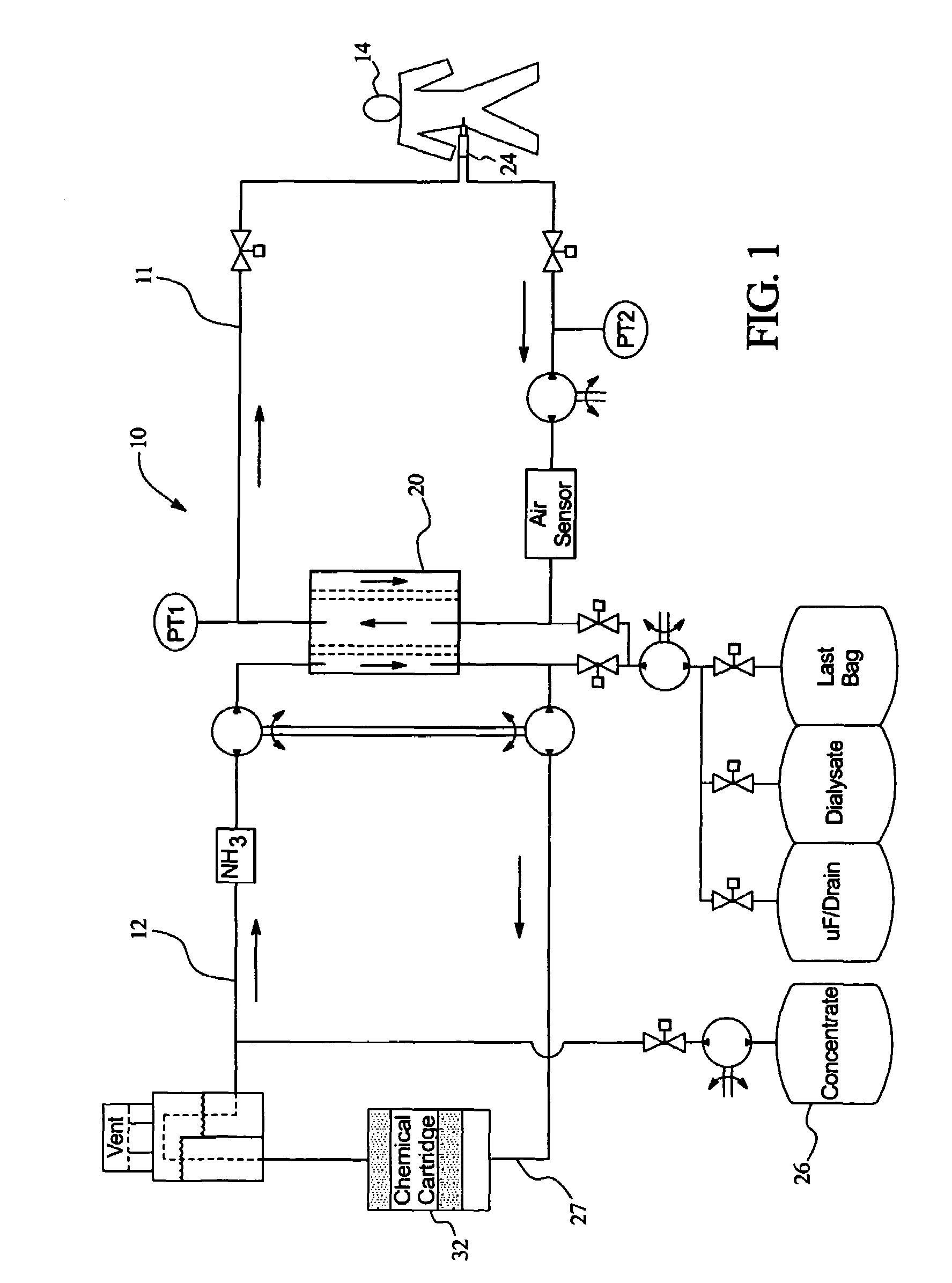
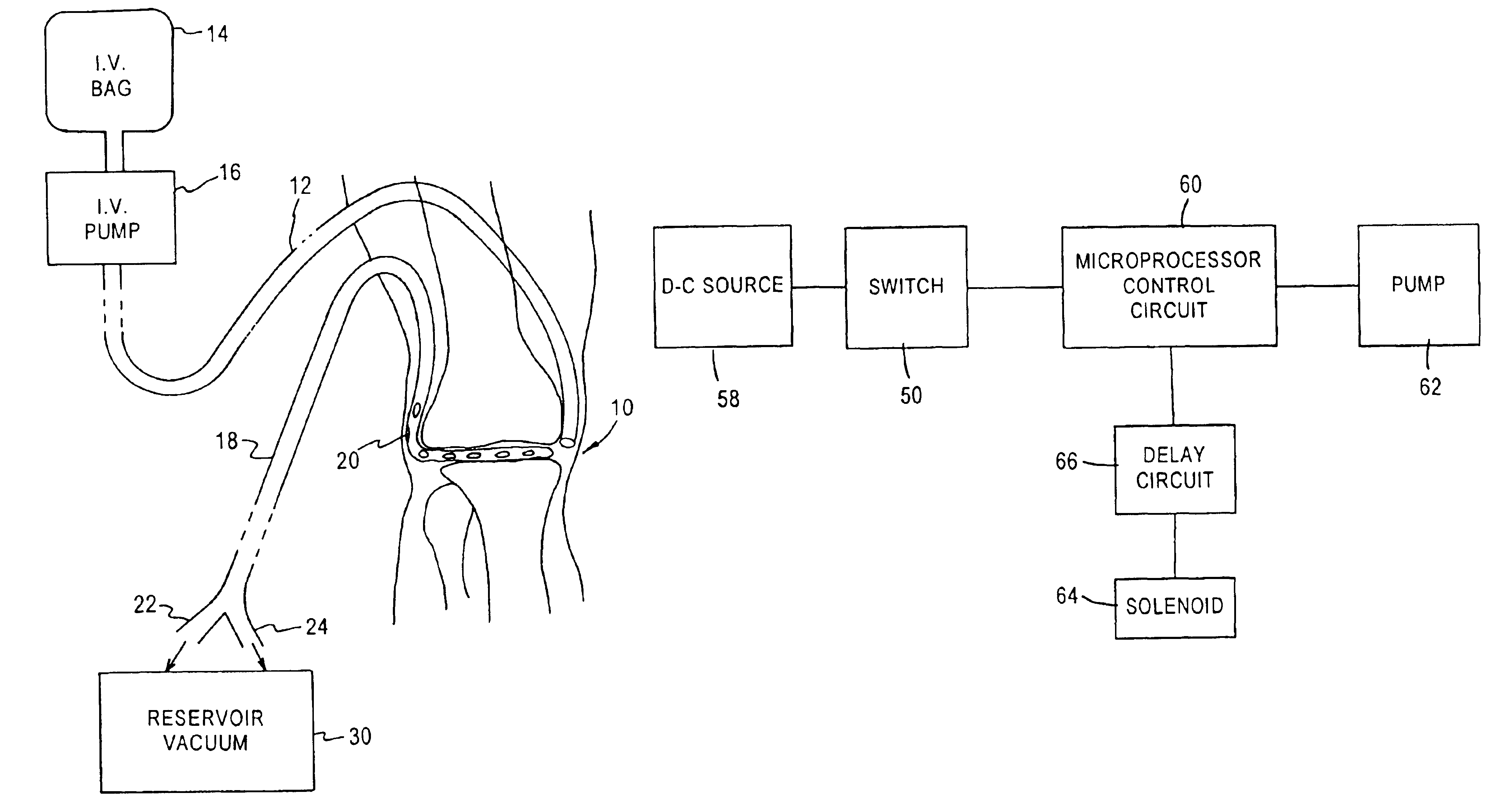
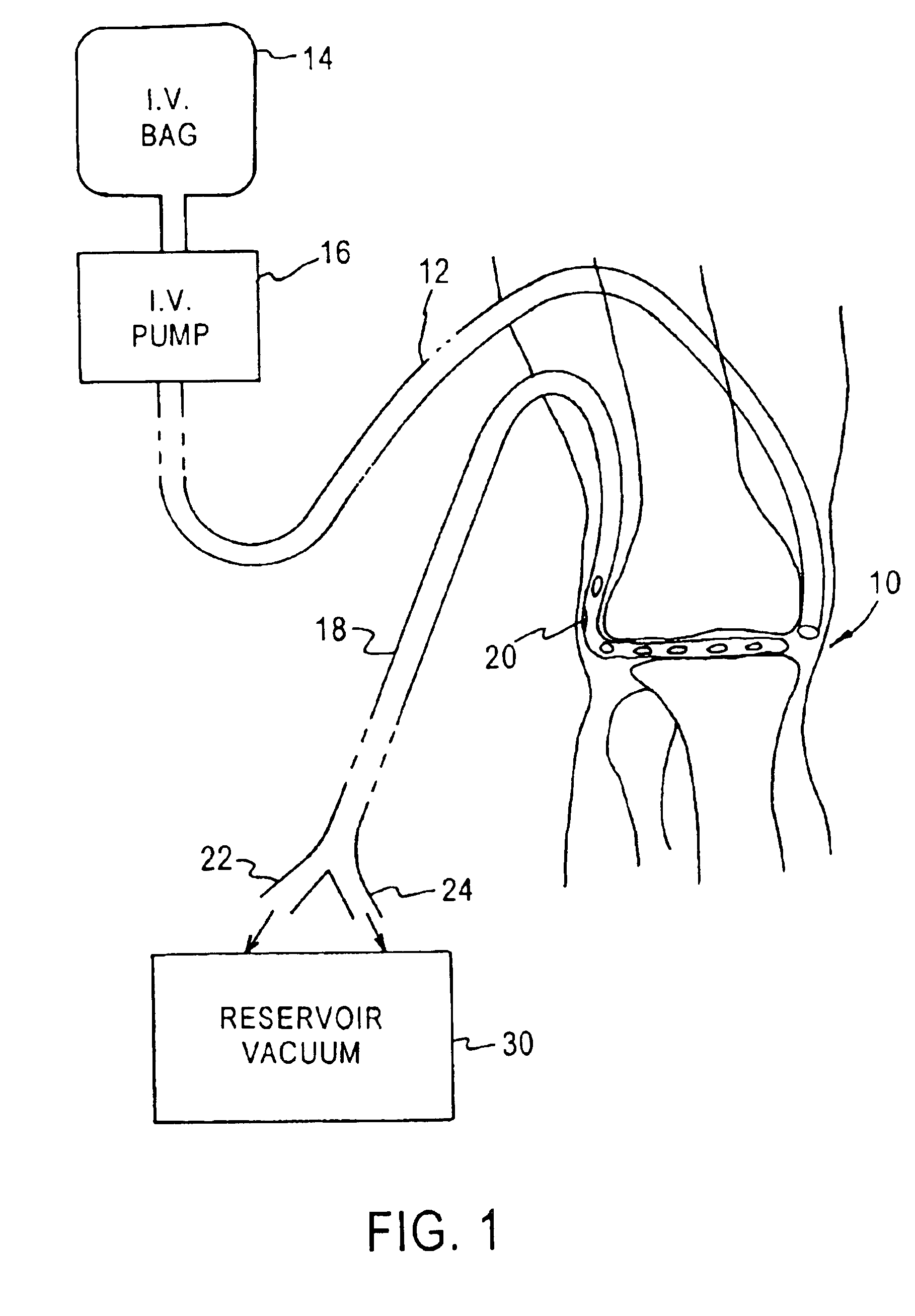
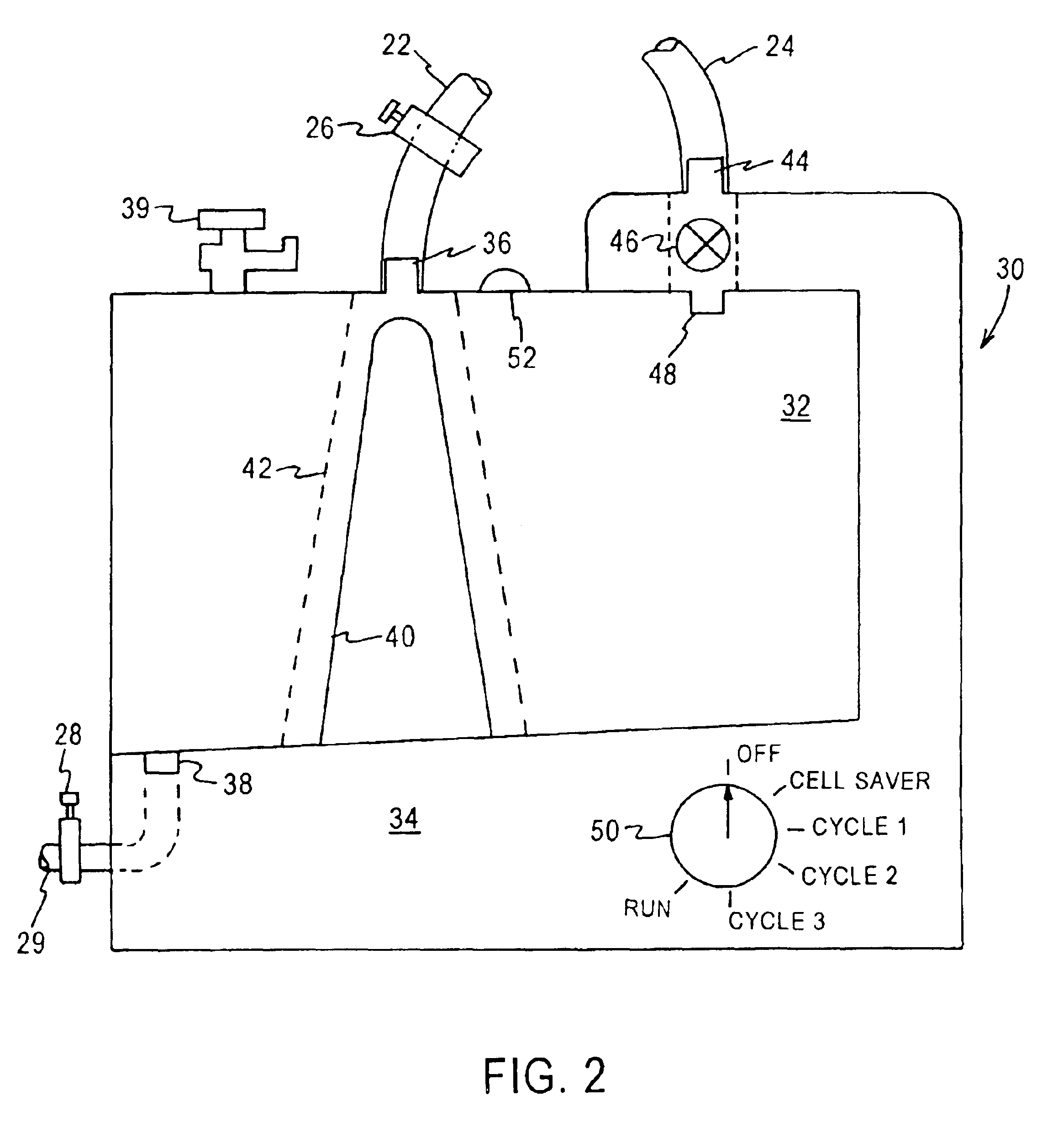
Method and device for monitoring loss of body fluid and dislodgment of medical instrument from body
InactiveUS20050038325A1Unobstructed viewOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesFistula needlesHaemodialysis machine
A method of alerting medical personnel of a problem during hemodialysis includes providing an active, fail-to-safe site sensor for a fistula needle at an access site during hemodialysis; and automatically alerting medical personnel of a problem during hemodialysis using the active, fail-to-safe site sensor during at least the following: failing of the active, fail-to-safe site sensor; insufficient powering to the active, fail-to-safe site sensor; partial fistula needle dislodging from the access site; and complete needle dislodging from the access site.
Owner:BRADLEY JON MOLL RODNEY L MOLL & ANN E MOLL FAMILY TRUST
Endovascular system for arresting the heart
InactiveUS6913600B2Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypass timeSurgical department
Devices and methods are provided for temporarily inducing cardioplegic arrest in the heart of a patient and for establishing cardiopulmonary bypass in order to facilitate surgical procedures on the heart and its related blood vessels. Specifically, a catheter based system is provided for isolating the heart and coronary blood vessels of a patient from the remainder of the arterial system and for infusing a cardioplegic agent into the patient's coronary arteries to induce cardioplegic arrest in the heart. The system includes an endoaortic partitioning catheter having an expandable balloon at its distal end which is expanded within the ascending aorta to occlude the aortic lumen between the coronary ostia and the brachiocephalic artery. Means for centering the catheter tip within the ascending aorta include specially curved shaft configurations, eccentric or shaped occlusion balloons and a steerable catheter tip, which may be used separately or in combination. The shaft of the catheter may have a coaxial or multilumen construction. The catheter may further include piezoelectric pressure transducers at the distal tip of the catheter and within the occlusion balloon. Means to facilitate nonfluoroscopic placement of the catheter include fiberoptic transillumination of the aorta and a secondary balloon at the distal tip of the catheter for atraumatically contacting the aortic valve. The system further includes a dual purpose arterial bypass cannula and introducer sheath for introducing the catheter into a peripheral artery of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
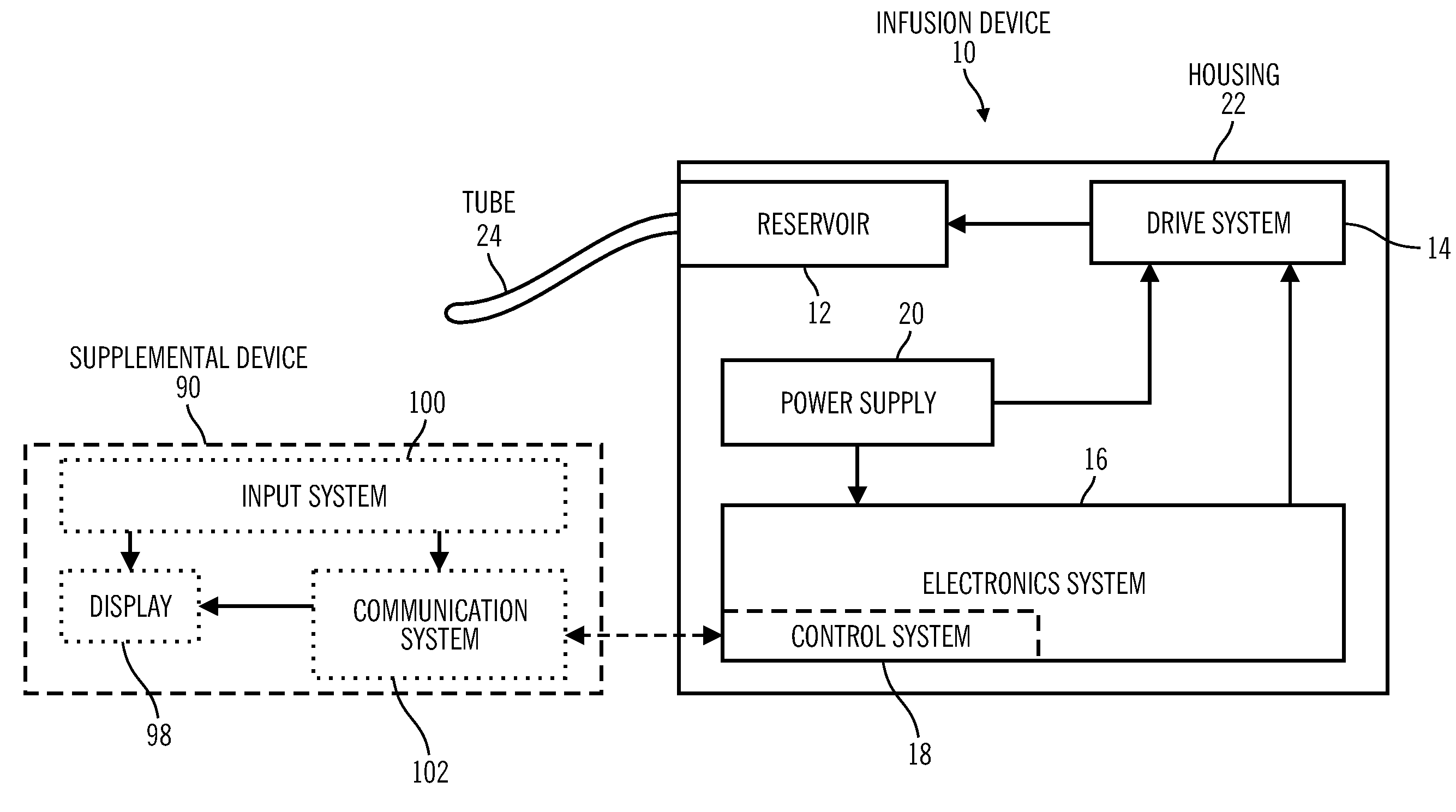
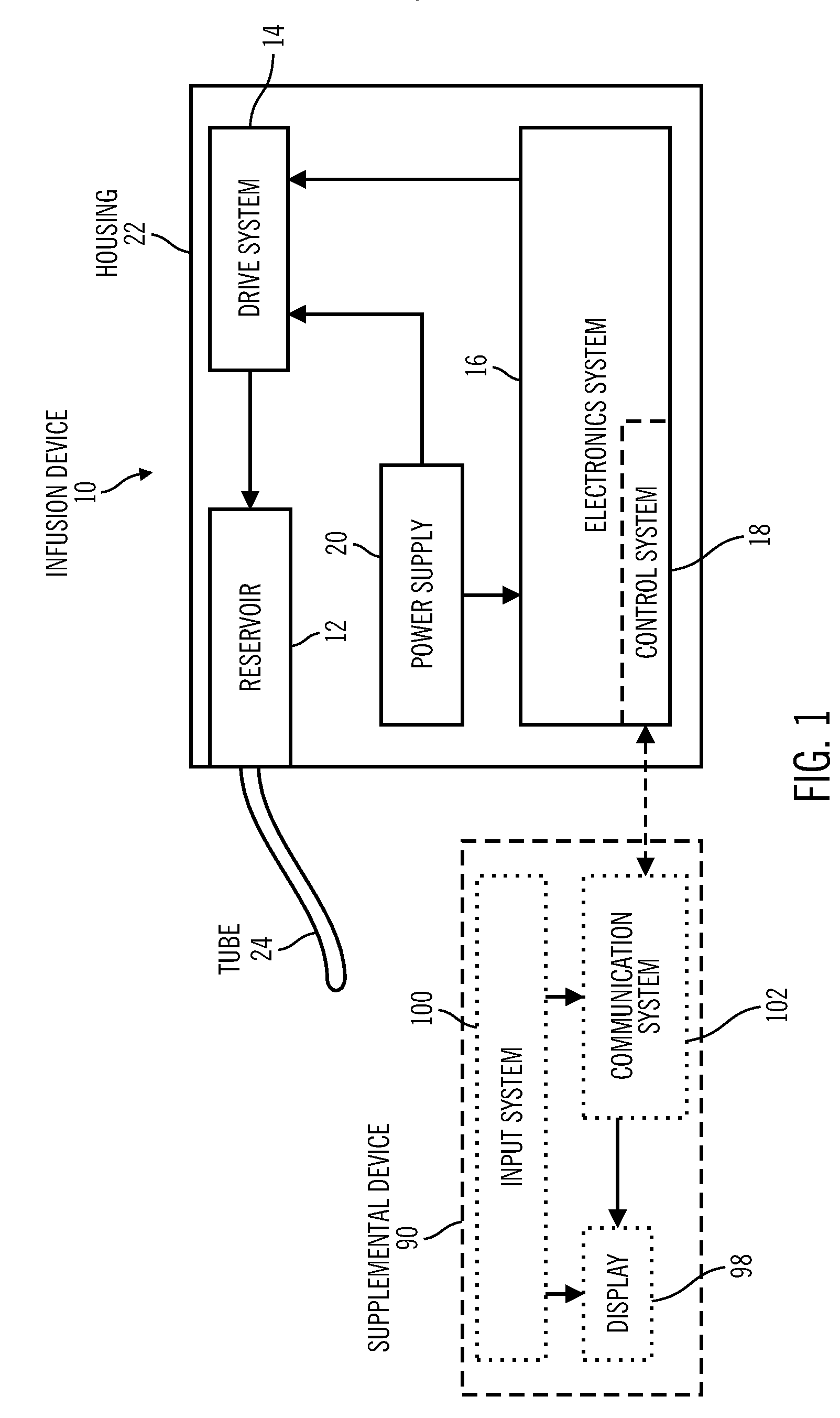
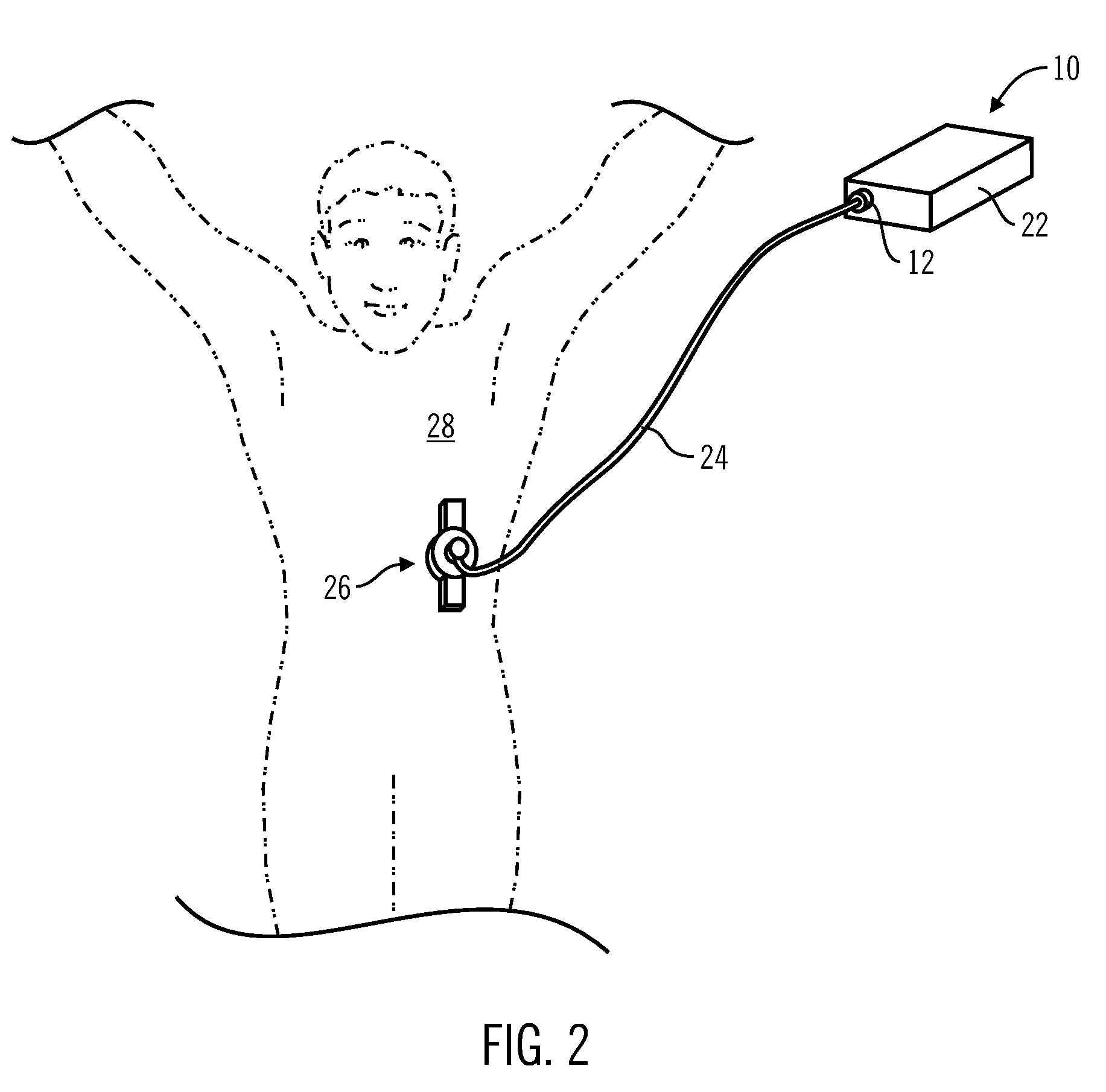
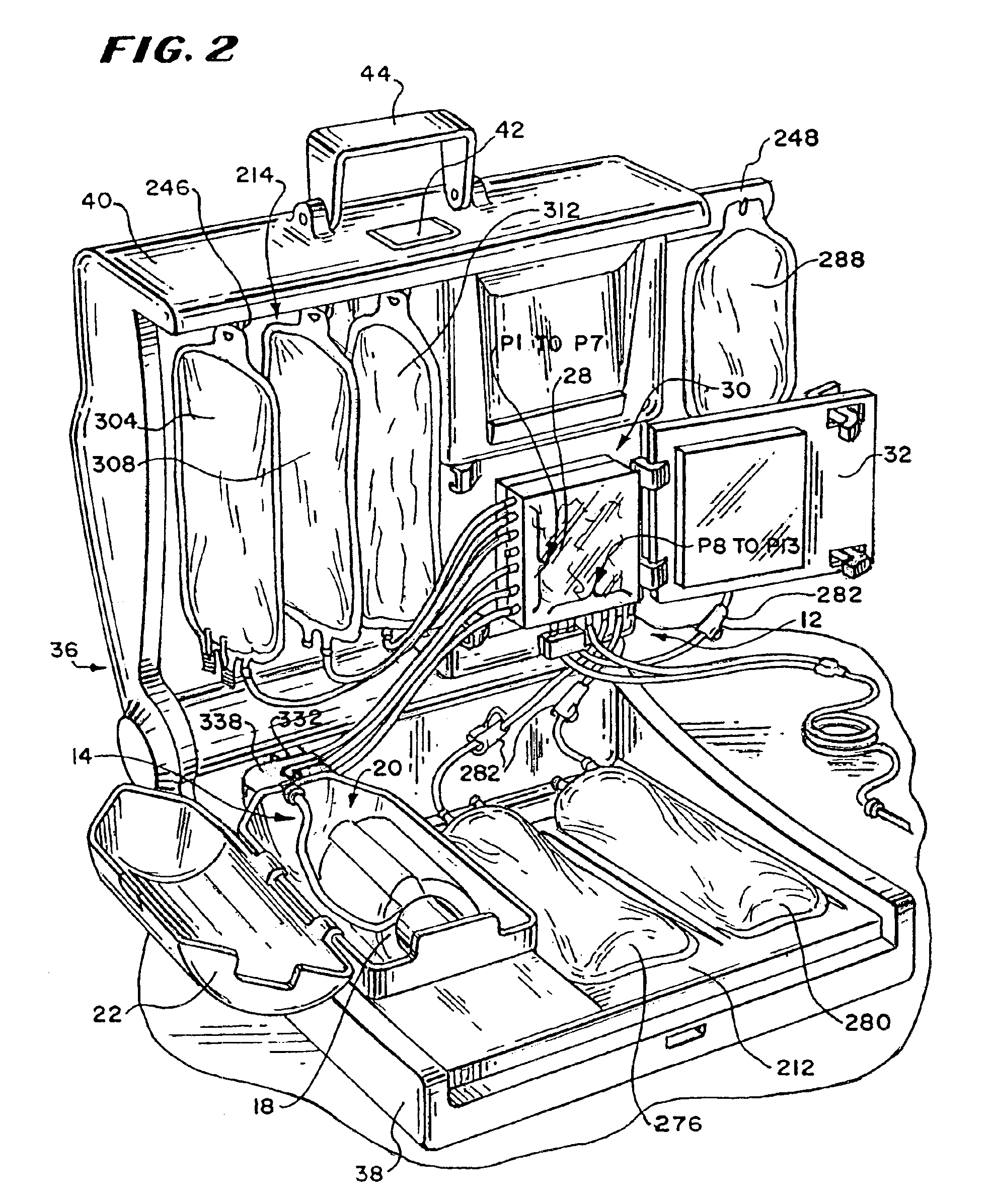
Control Tabs for Infusion Devices and Methods of Using the Same
InactiveUS20100160861A1Improve water resistanceImprove the immunityOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringElectrical element
An external infusion device that infuses a fluid into an individual's body includes a housing, a reservoir, a drive system, a power supply, electrical elements, and a tab. The reservoir contains the fluid, and the drive system forces the fluid from the reservoir. The electrical elements control the power to the drive system to regulate the rate that fluid is forced from the reservoir. The tab mates with the housing, and contains at least one electrical element. The tab is removable, and may be replaced with a different tab. The different tab may change the rate fluid is forced from the reservoir. A tab may be removed from one external infusion device and installed in a different external infusion device. The tab may be limited to use in a predetermined number of external infusion devices and may include a power supply.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart disease
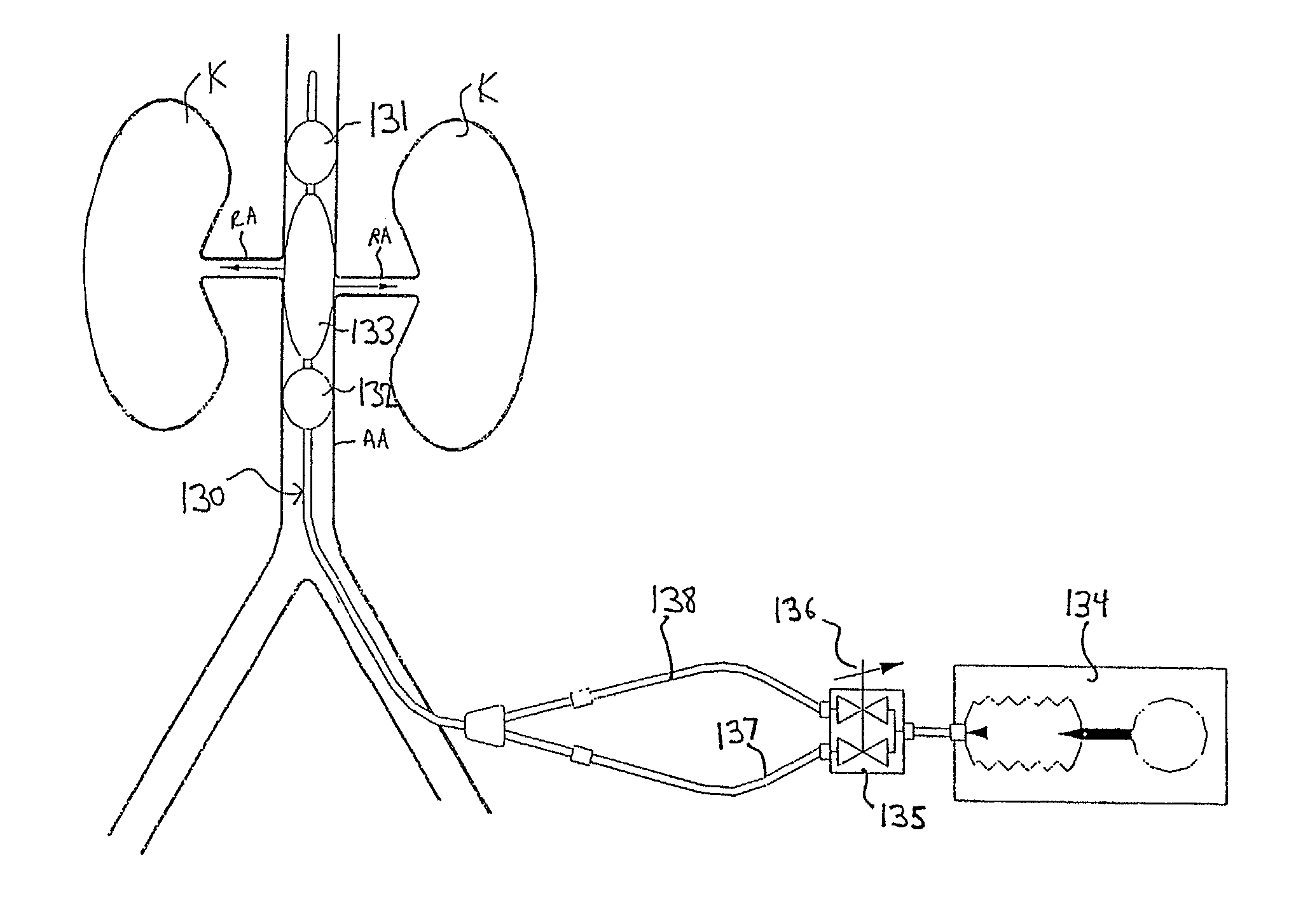
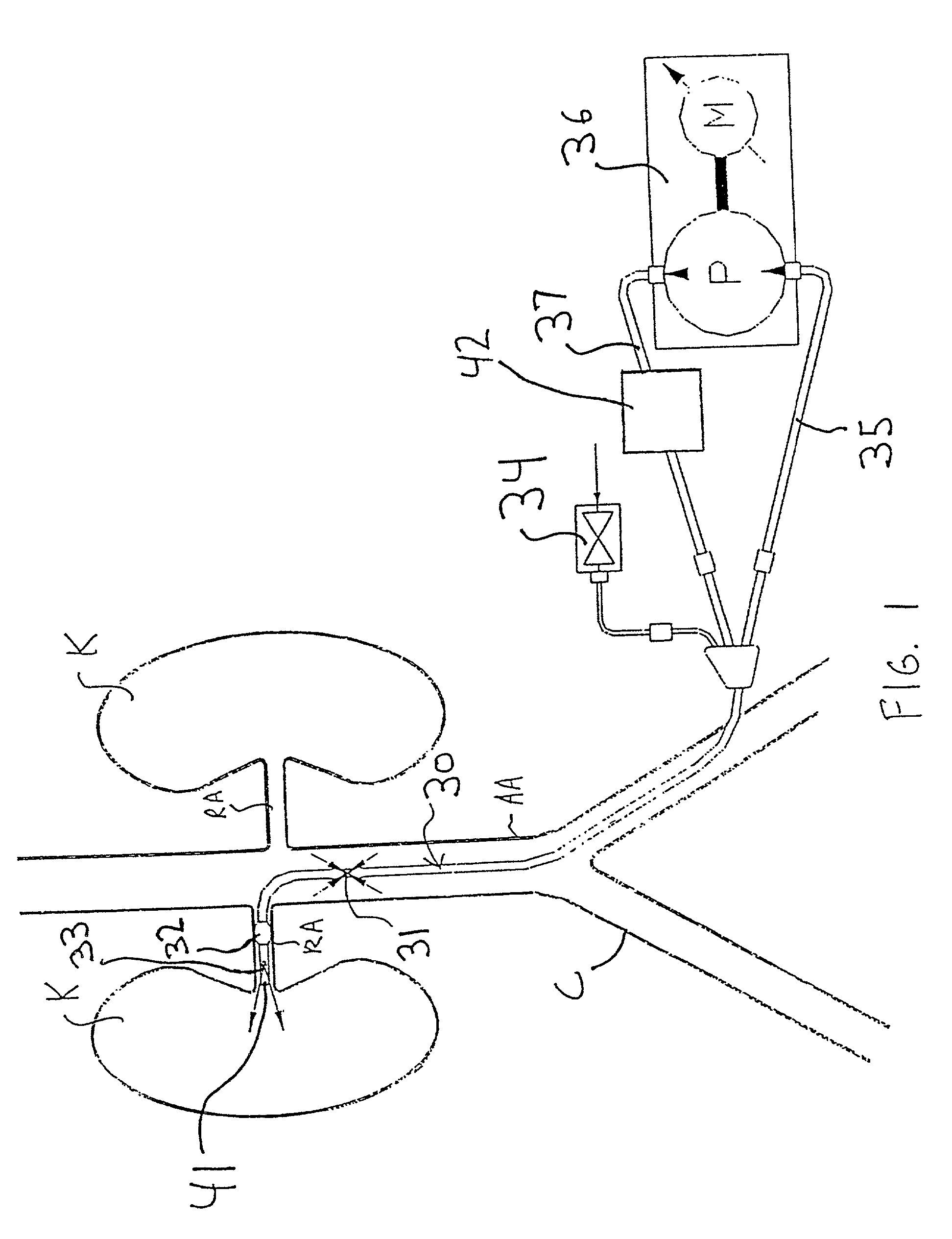
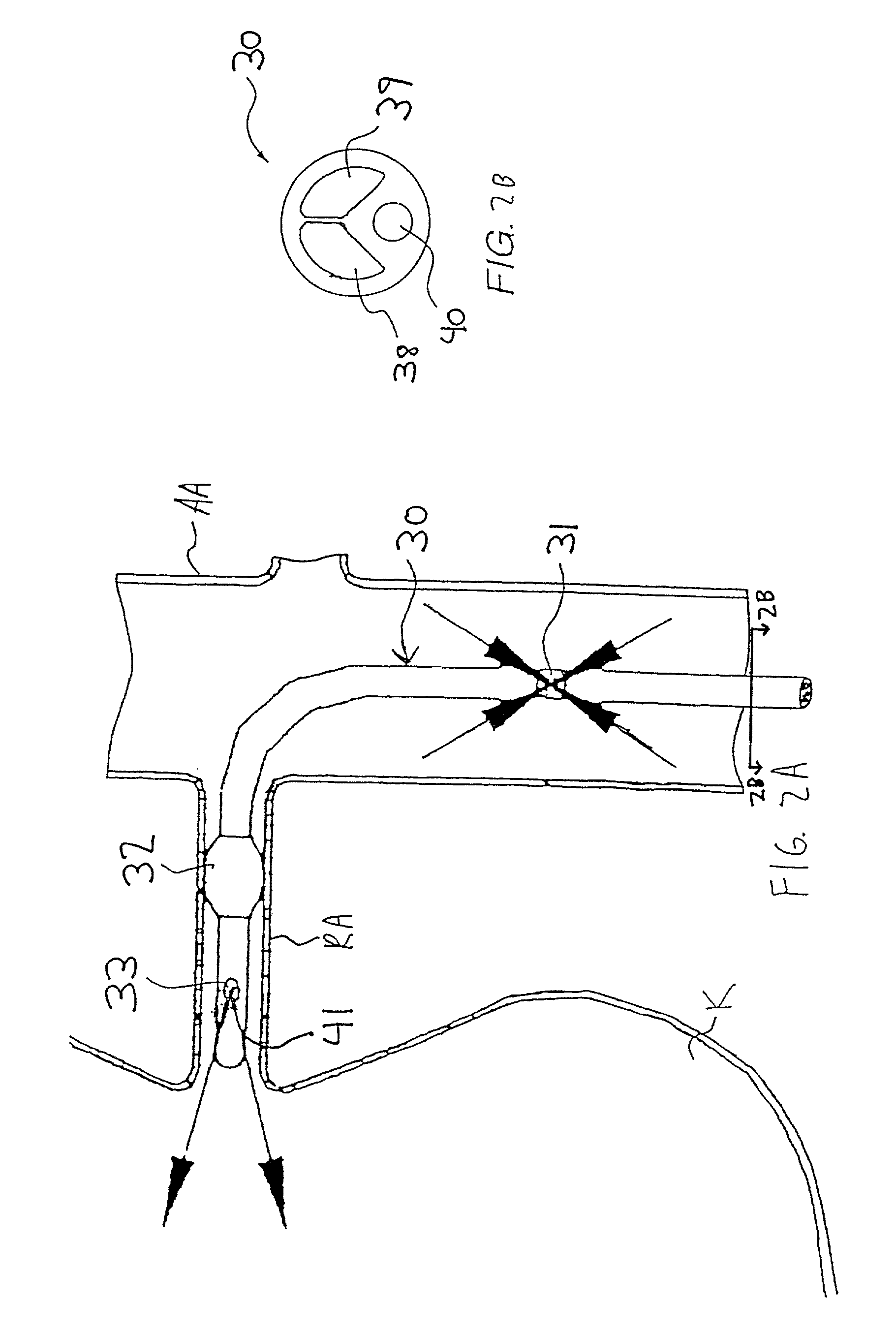
InactiveUS7335192B2Increase blood flowImprove kidney functionBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentPeri-aortic
Methods and apparatus are provided for treating congestive heart by actively or passively enhancing perfusion to the renal arteries. A first embodiment comprises a specially configured balloon catheter and extracorporeal pump, wherein the pump operates in a “once-through” fashion or alternating volume displacement mode. In another embodiment the catheter includes a pair of balloons to isolate a region of the aorta, and a third balloon that directs flow into the renal arteries. In still further embodiments, a stent or cuff having a constricted region is deployed in or around the aorta, respectively, to create a backpressure upstream of the stent or cuff. Methods of enhancing renal perfusion also are provided.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Methods and apparatus for anchoring an occluding member
Pressure is measured on both sides of an occluding member for determining when pressure forces on the occluding member may cause migration of the occluding member. An alarm indicates when the pressure force on the balloon exceed a predetermined threshold. In another aspect of the invention, a pressure monitor determines when a rate of pressure increase with respect to the fluid volume in the balloon reaches a predetermined threshold when inflating the occluding member. A predetermined amount of fluid is then added to the balloon so that the balloon is not under inflated or over inflated.
Owner:VALLEY KIRSTEN L +3
Methods, systems, and kits for the extracorporeal processing of blood
InactiveUS7004924B1Easy to detectOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesExtracorporeal circulationLine tubing
Methods, systems, and kits for extracorporeally circulating and processing blood are described. The systems include a pump, a processing unit, and blood drawn return lines for accessing a patient's vasculature. Blood flow through the return line is measured and pump speed controlled to maintain a desired blood flow rate. Alarm conditions can be initiated when expected pump performance differs from that needed to maintain the control point flow rate. By using a ultrasonic flow detector, gas bubbles in the blood flow can be detected.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
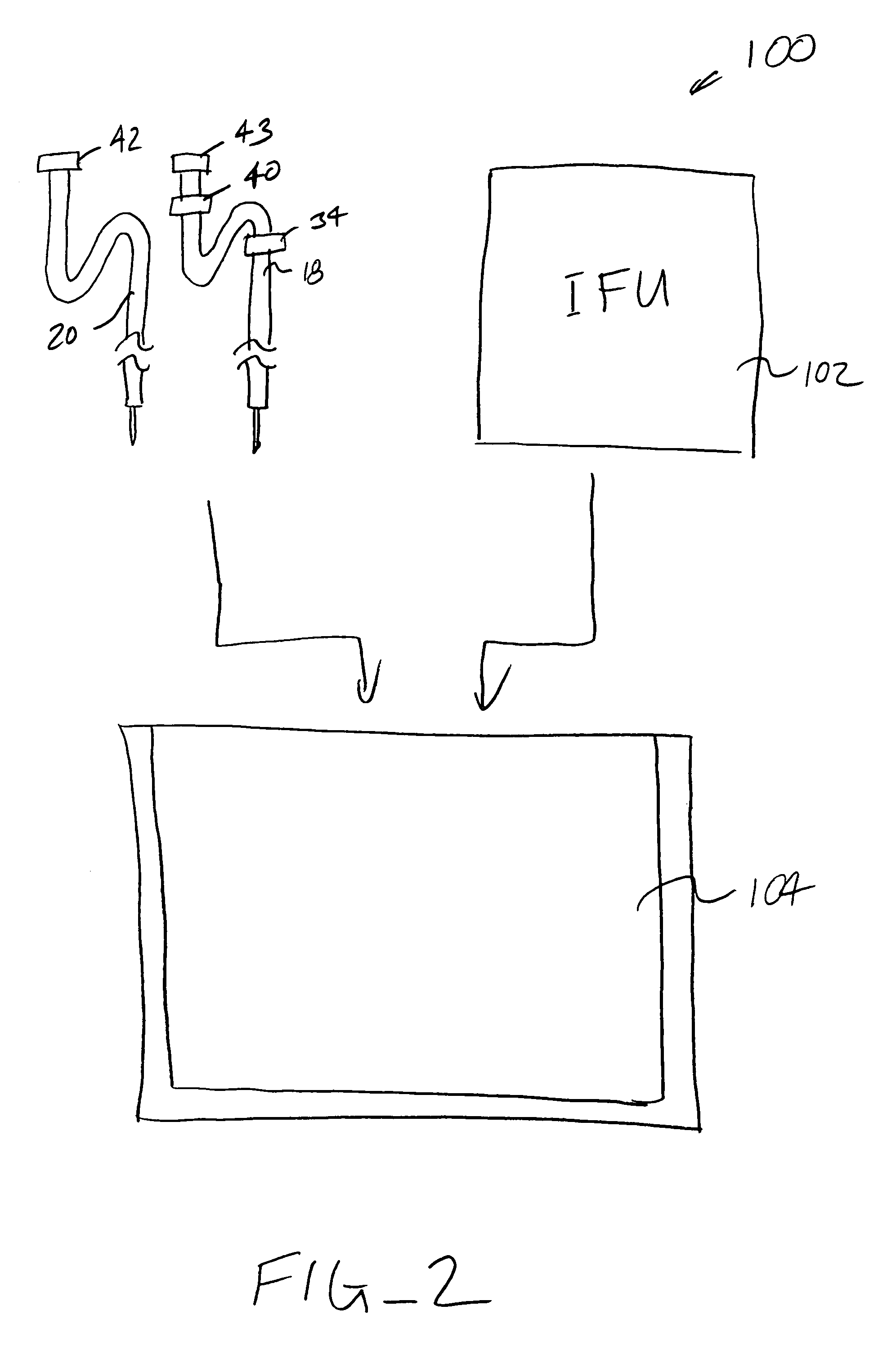
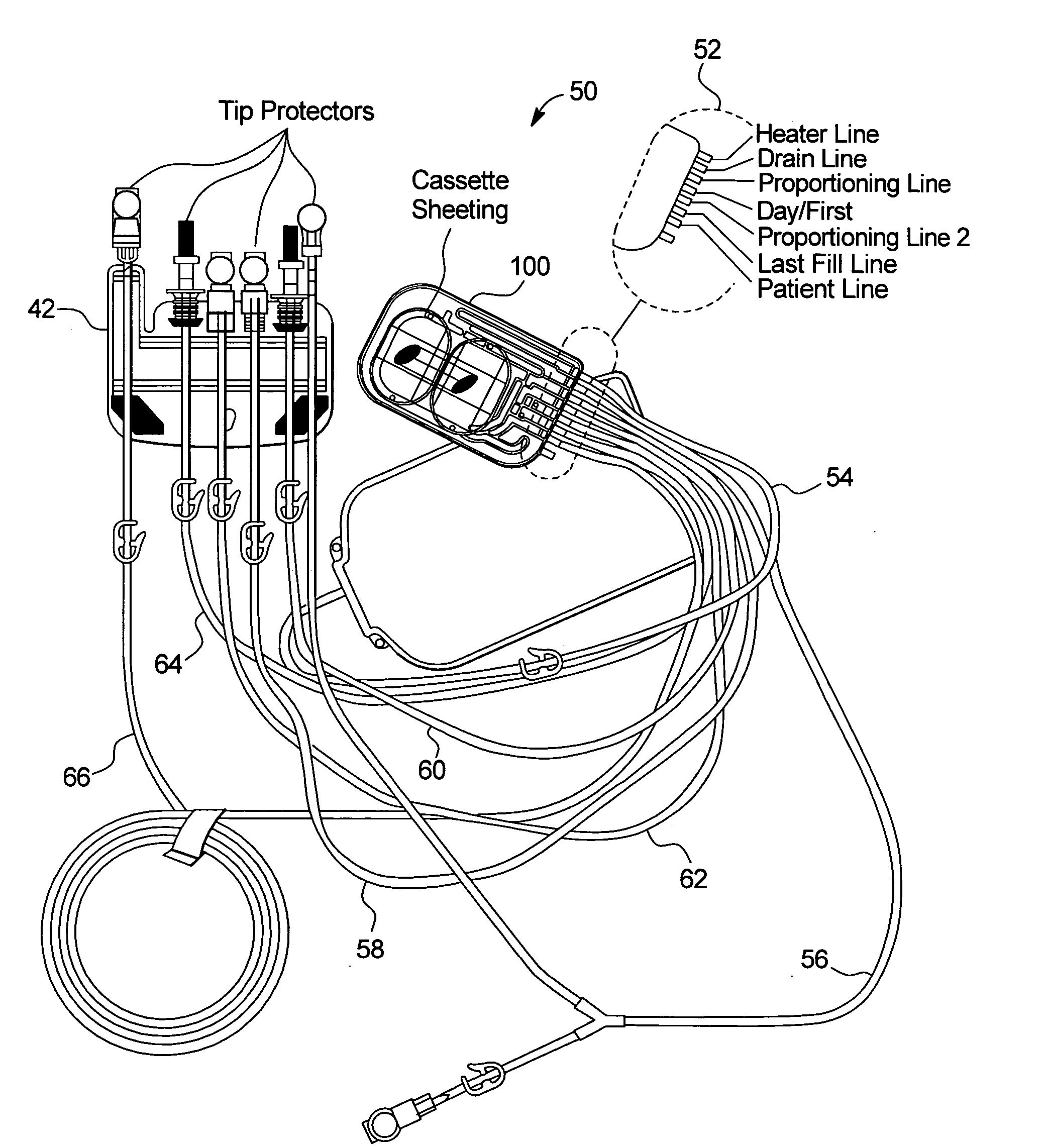
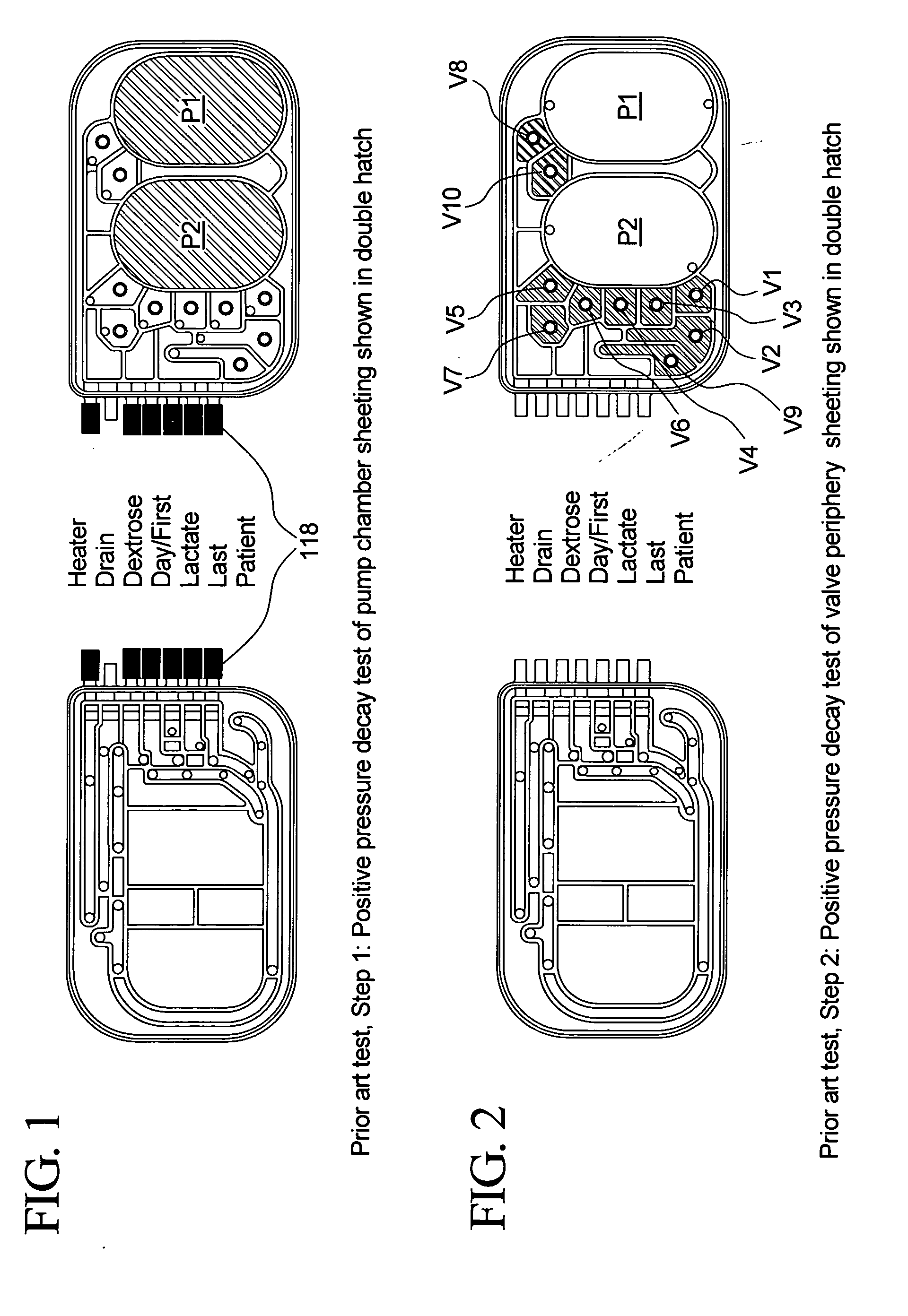
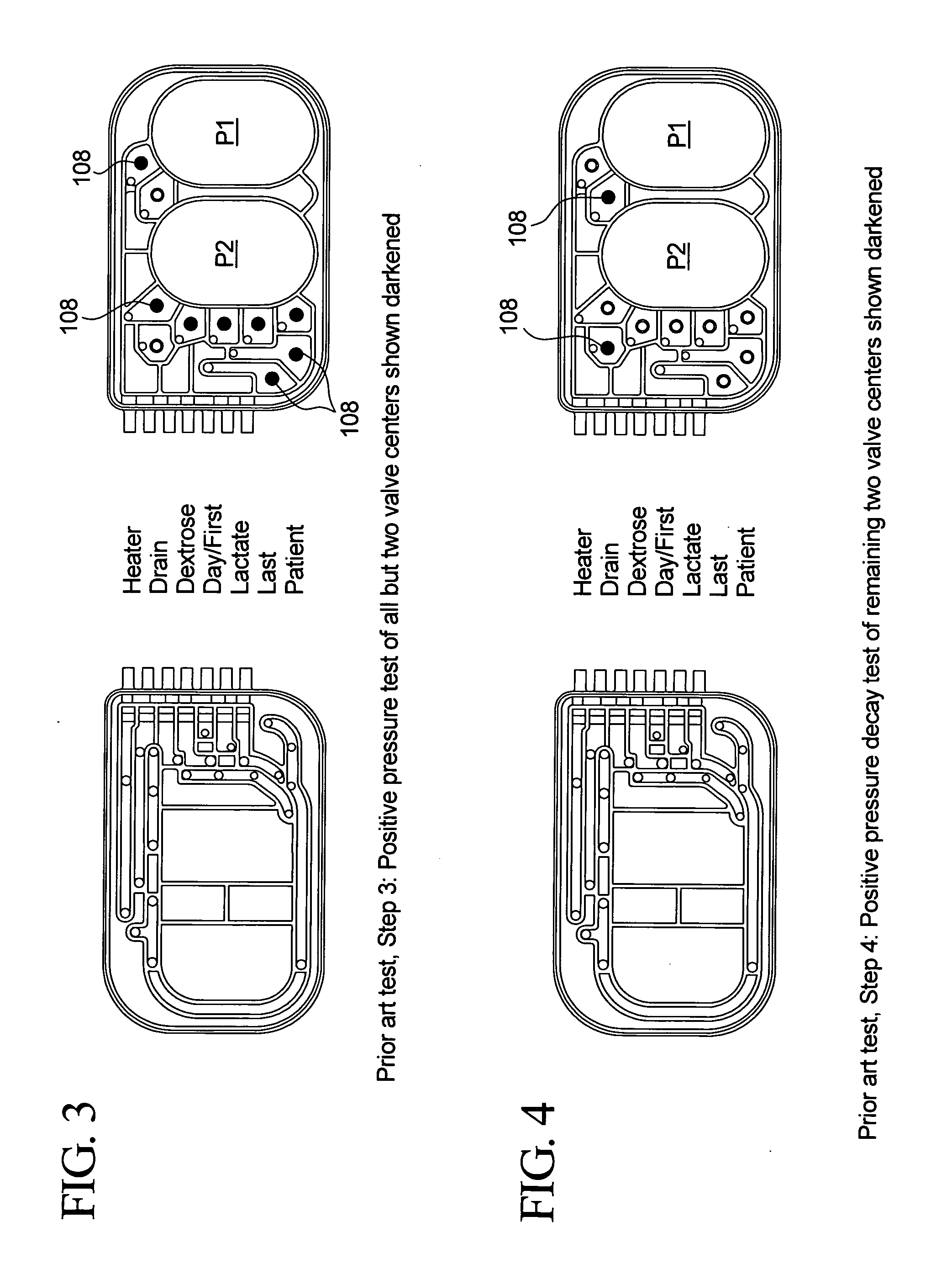
Priming, integrity and head height methods and apparatuses for medical fluid systems
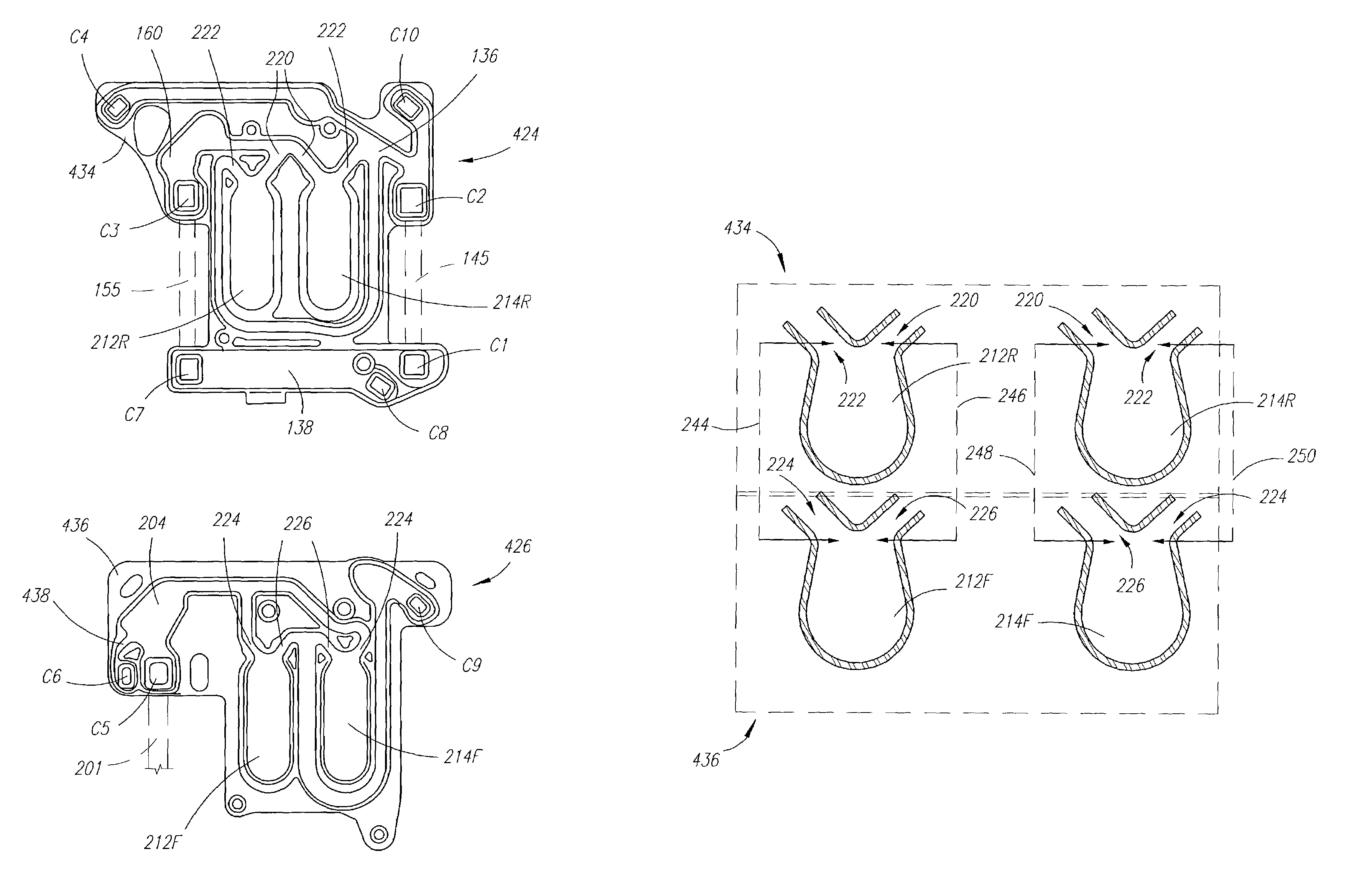
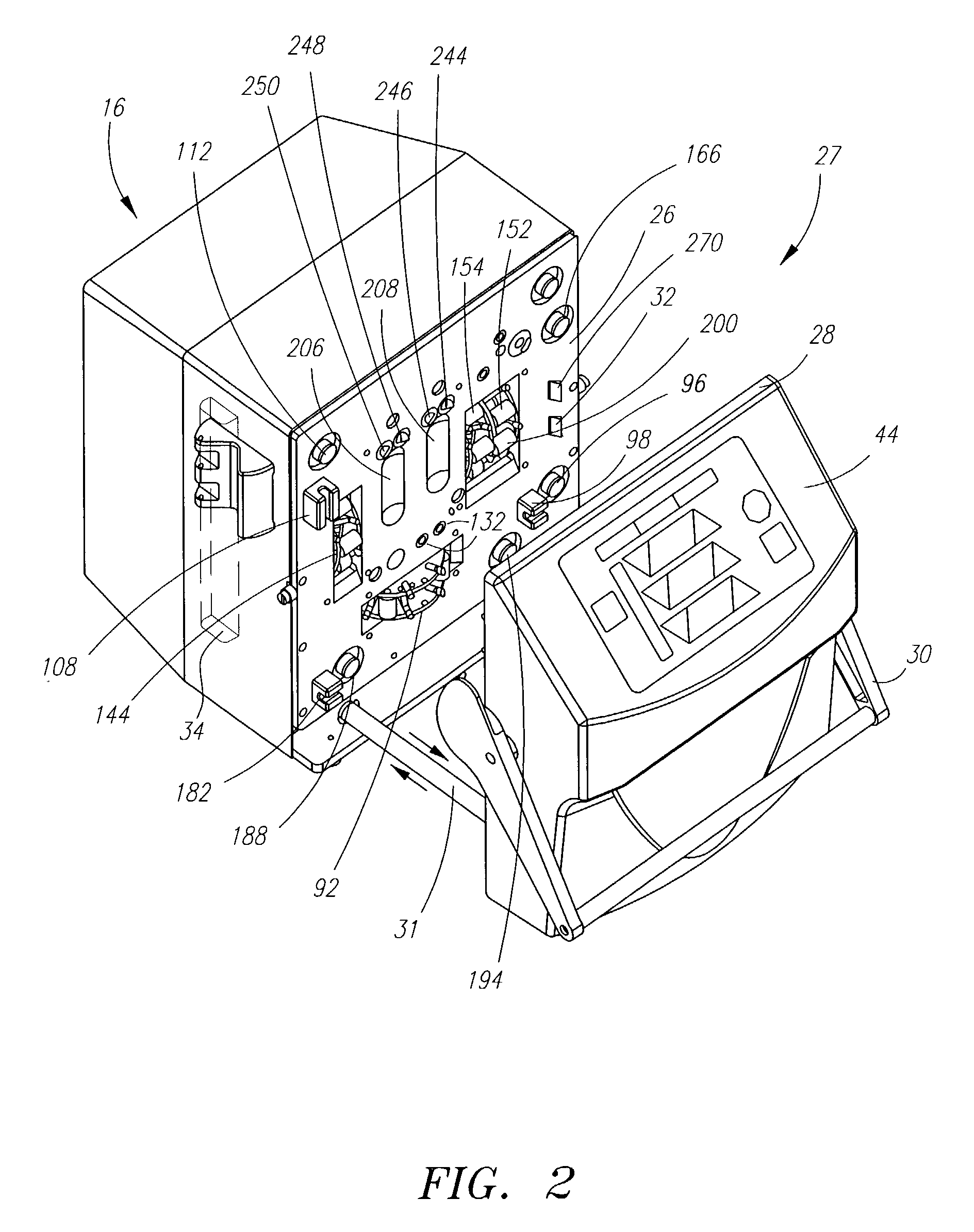
ActiveUS20050126998A1Less timeLeakage is detectedDetection of fluid at leakage pointOther blood circulation devicesDelivery systemFluid system
Improved integrity test, priming sequence and bag height detection tests, apparatuses and methods for a medical fluid delivery system are provided. The integrity test includes a plurality of air pressure decay tests, using positive and negative pressure. The priming sequence includes pumping fluid through a portion of a patient line to be primed to overcome air in the line and other potential obstacles. The head height test measures a pressure build-up or drop-off within a pump chamber of a membrane pump. The measured pressure corresponds to a head height between a fluid supply and the pump or between the pump and a fluid drain. A determination is made whether the corresponding head height is acceptable.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Pumping cartridge having an integrated filter and method for filtering a fluid with the cartridge
InactiveUS6905479B1Positive displacement pump componentsOther blood circulation devicesParticulatesEngineering
The present invention involves, in some embodiments, reusable pump drive systems, which are coupled to removable, and preferably disposable, pumping cartridges. The invention provides, in some embodiments, novel pumping cartridges for use in pumping systems. One such cartridge includes an integrated filter element therein for filtering fluids, for example fluids pumped to the body of a patient in a medical procedure. In some embodiments, the integrated filter is utilized as a blood clot removal filter and in other embodiments is used to remove particulates liquids infused to a patient. The filter element includes a filter with pores therein that are preferably sized to permit essentially unrestricted flow of individual human blood cells therethrough and to block or collect blood clots, cell clumps, particulates etc. with sizes substantially larger than the average size of a human blood cell.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
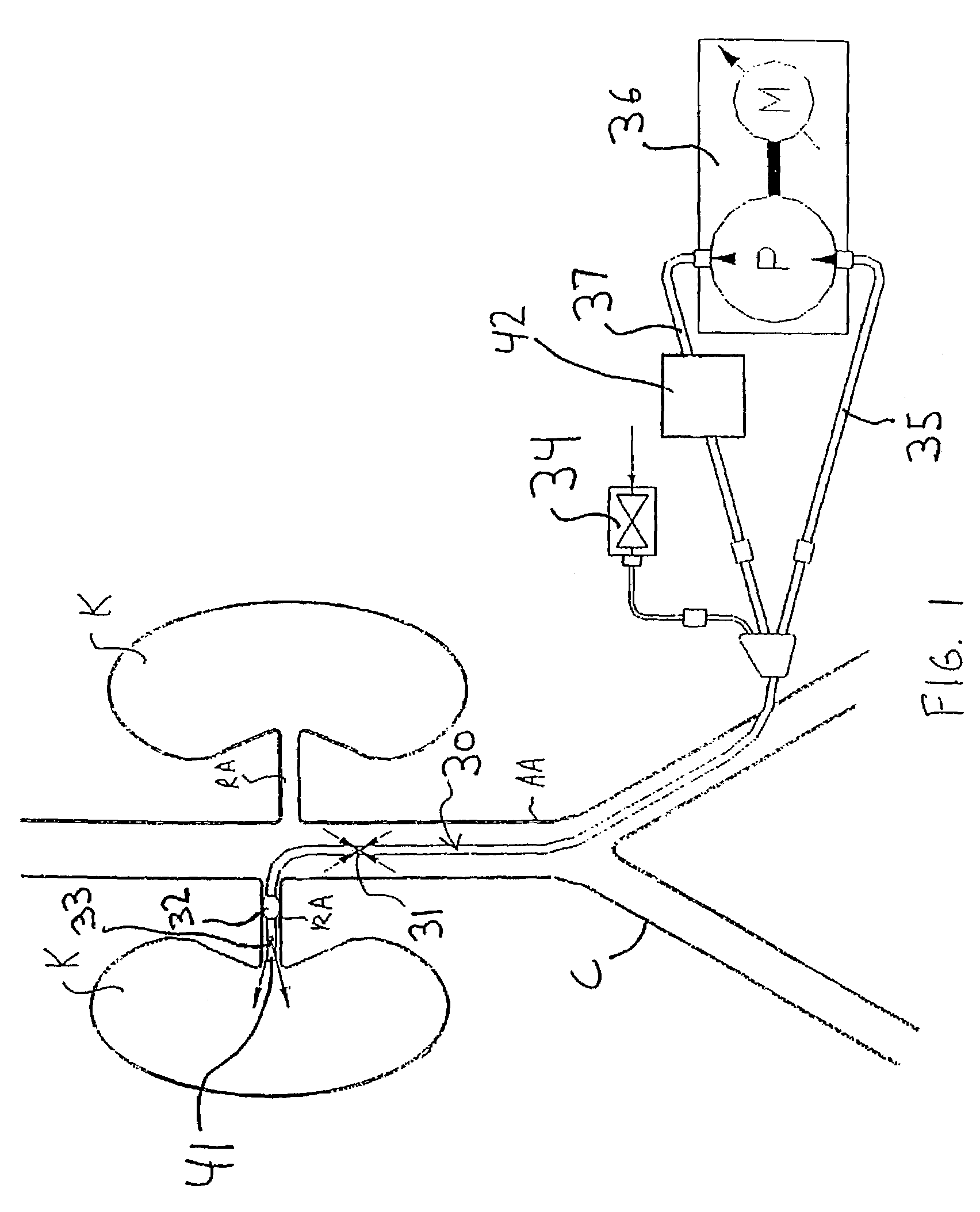
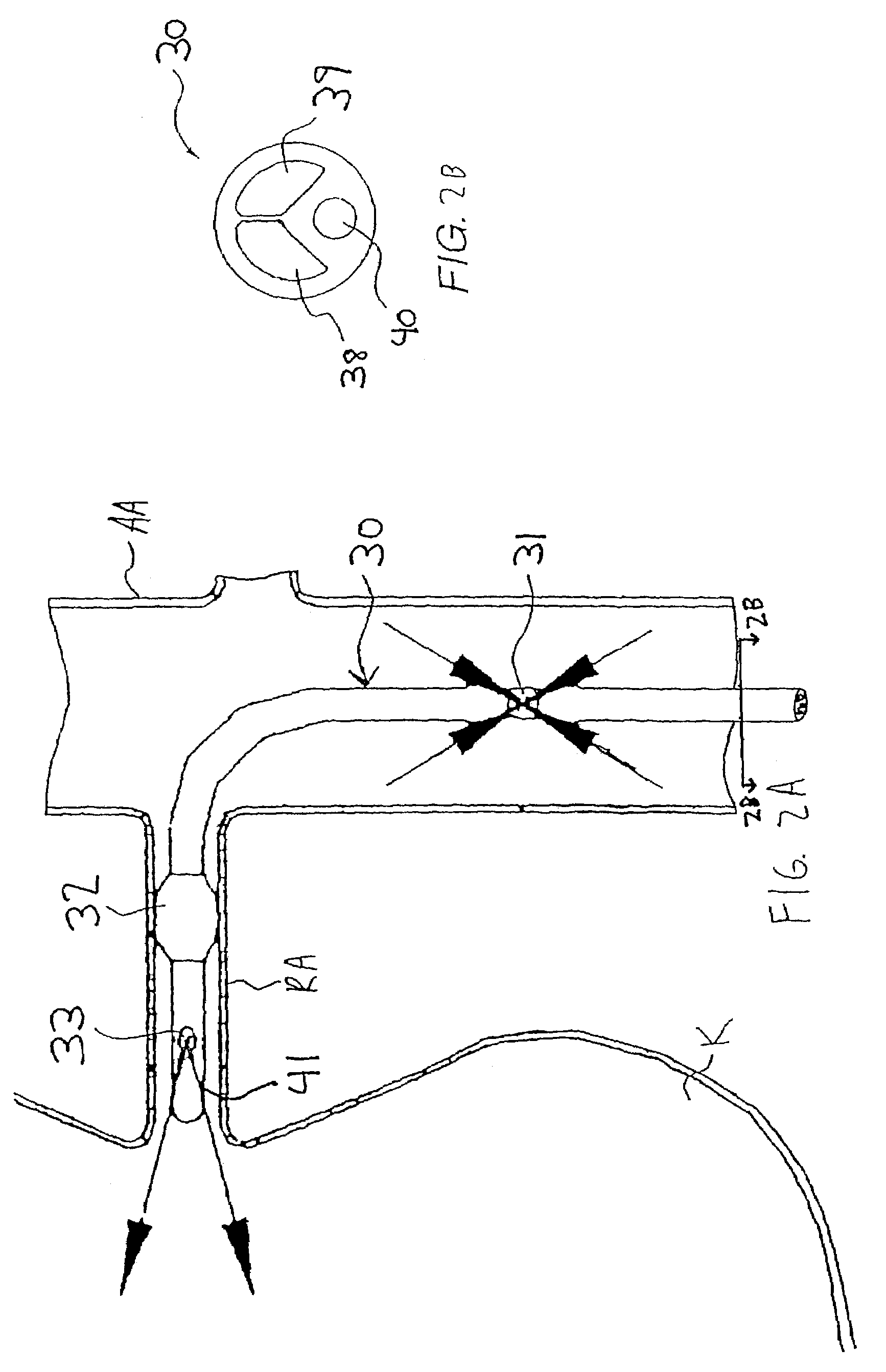
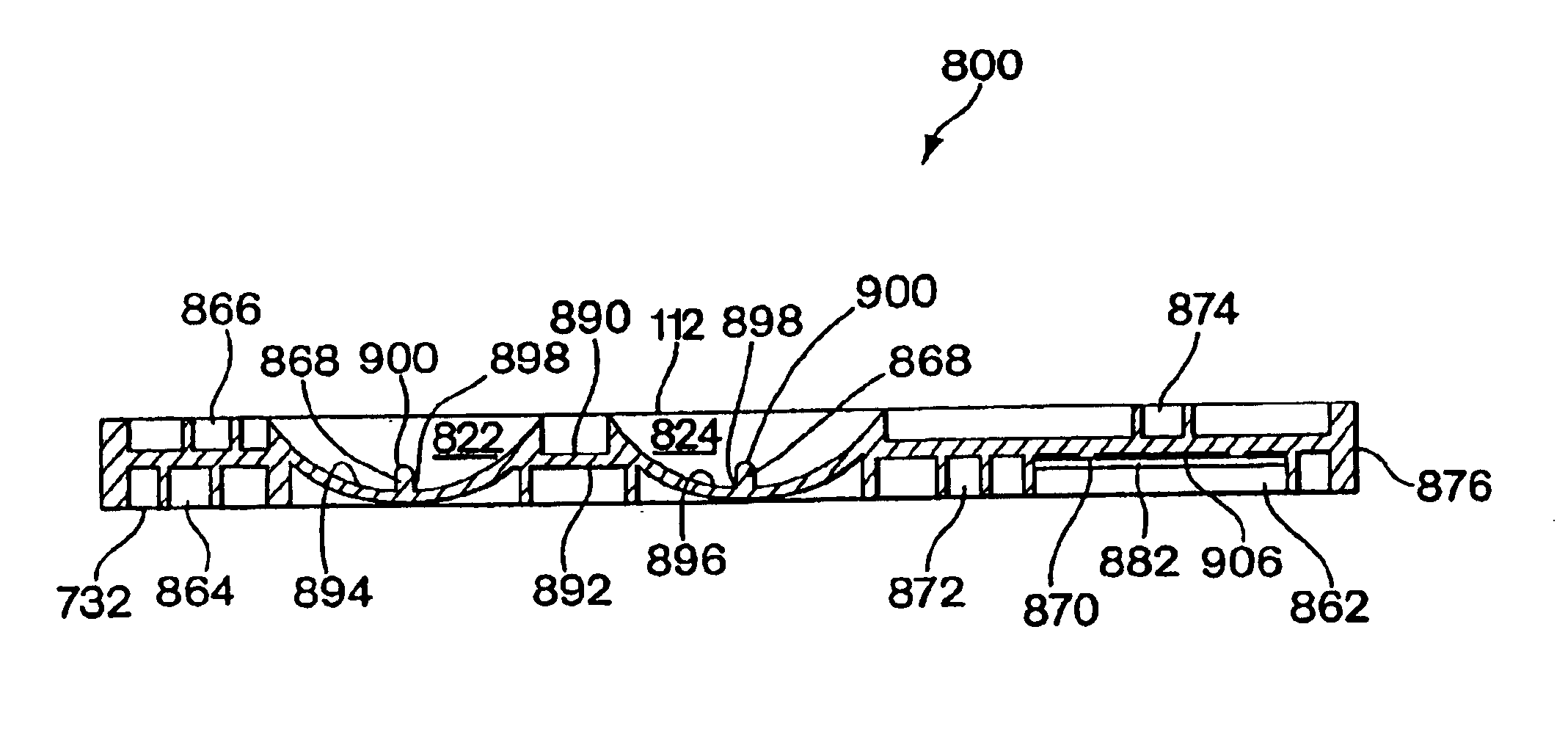
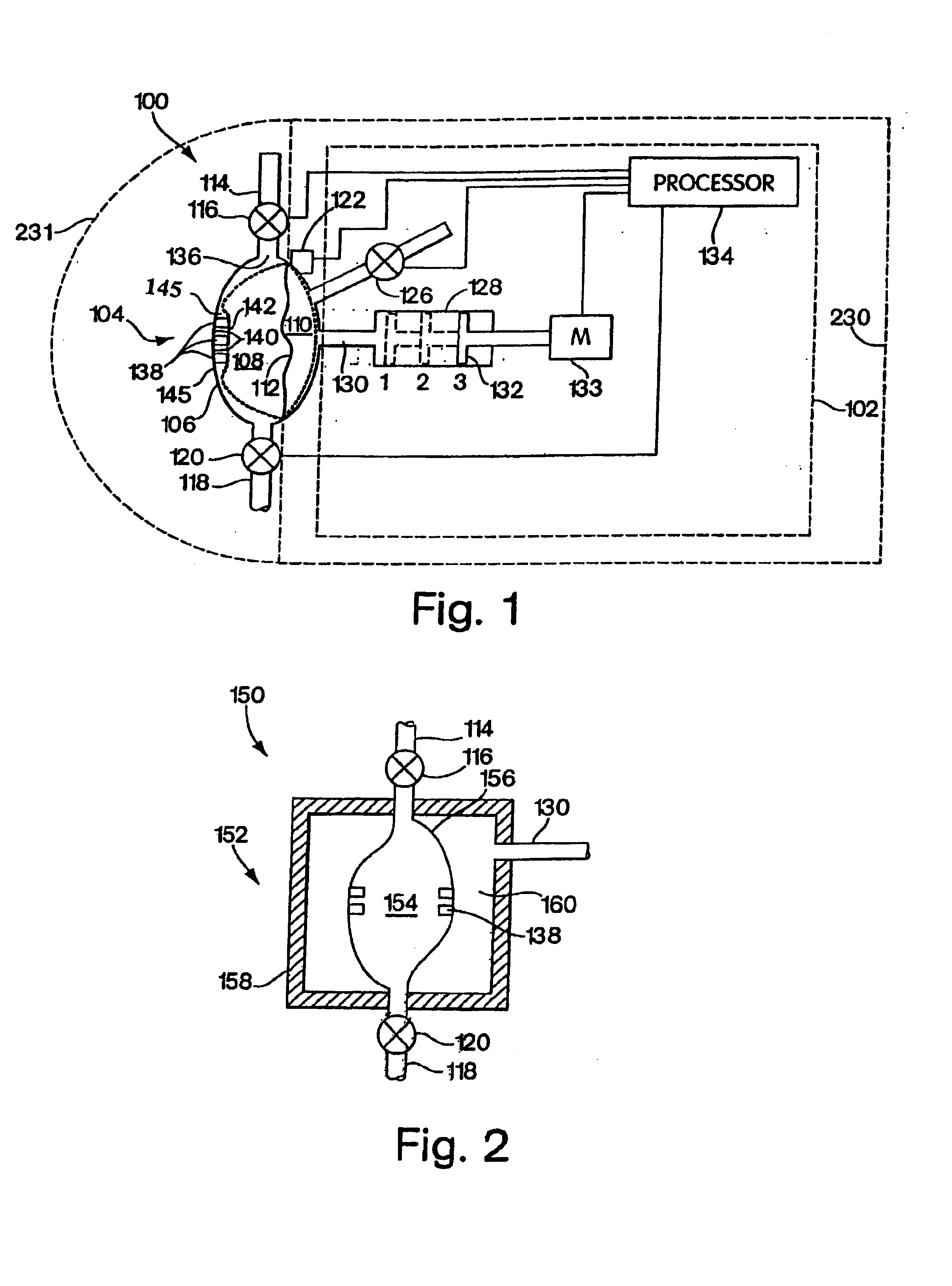
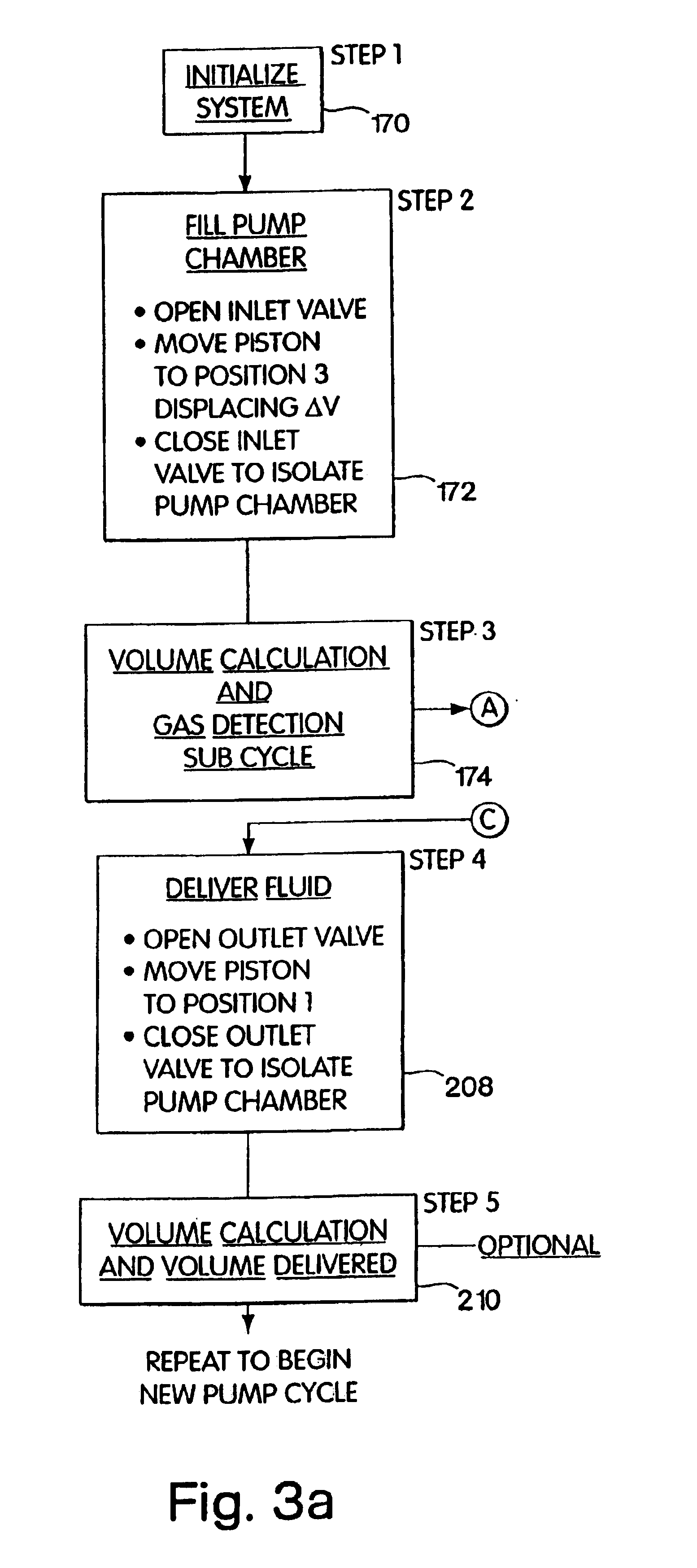
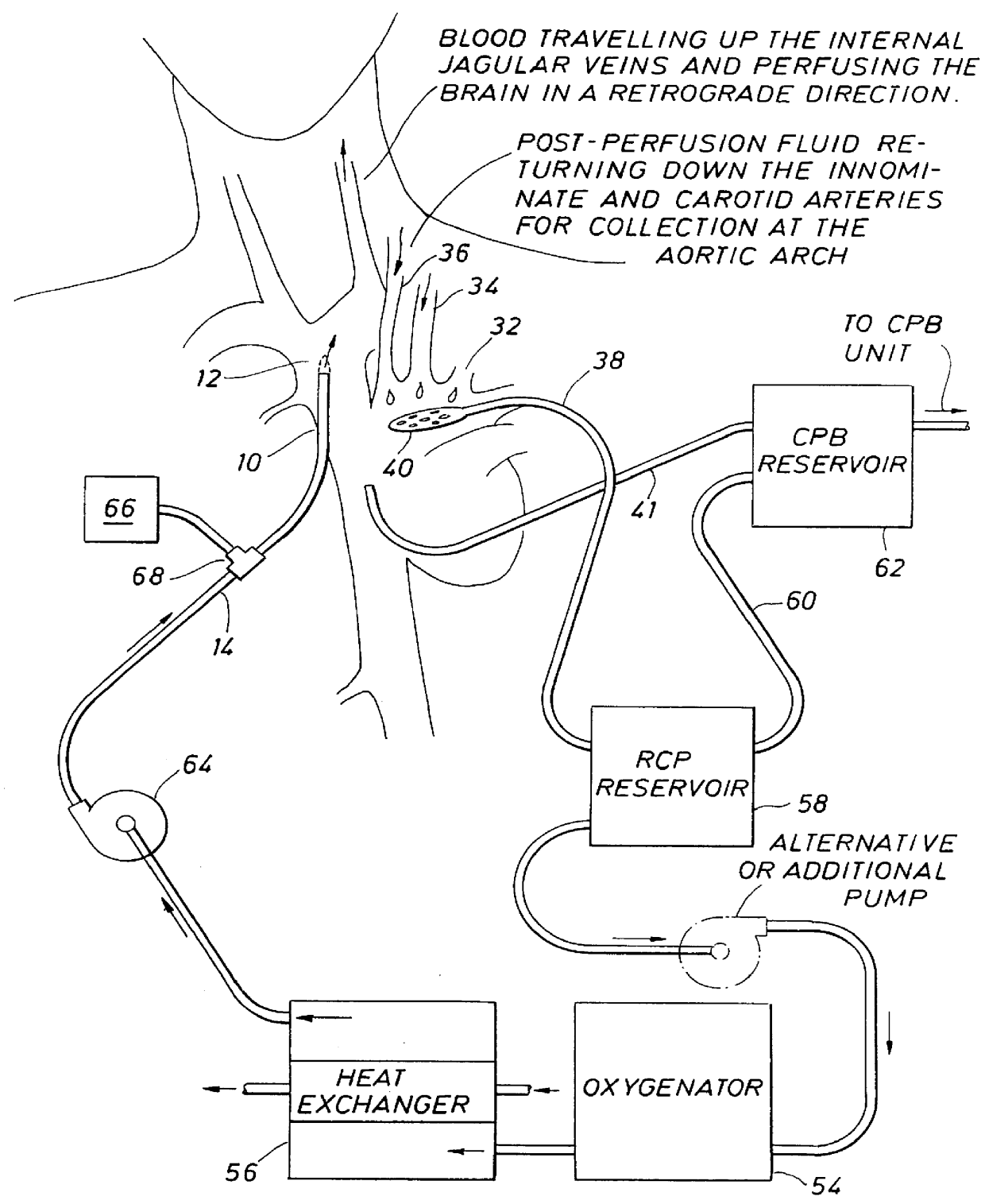
Retrograde perfusion monitoring and control system
InactiveUS6110139AOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsOrgan systemCardiopulmonary bypass time
Apparatus and methods for performing retrograde perfusion, especially during cardiopulmonary bypass operations, including dedicated pediatric scaled apparatus for retrograde perfusion of an adult human organ, organ system, or limb, especially the brain, employing small scale oxygenators and heat exchangers such as are designed for pediatric surgery; also including methods and apparatus for retrograde cerebral perfusion, using nonselective infravalvular cannulation of the superior vena cava, estimating the efficacy of cerebral perfusion by monitoring fluid flow across a valve of an internal jugular vein, modification of inflow pressure and administration of pharmacologic agents, and increasing fluid flow into a brain by occlusion of an inferior vena cava distal to its junction with an azygos vein.
Owner:LOUBSER PAUL GERHARD
Programmable, fluid pressure actuated blood processing systems and methods
InactiveUS6949079B1Solvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesBlood separation deviceEngineering
Owner:FENWAL
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart disease
InactiveUS7766892B2Improve kidney functionIncrease blood flowBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentPeri-aortic
Methods and apparatus are provided for treating congestive heart by actively or passively enhancing perfusion to the renal arteries. A first embodiment comprises a specially configured balloon catheter and extracorporeal pump, wherein the pump operates in a “once-through” fashion or alternating volume displacement mode. In another embodiment the catheter includes a pair of balloons to isolate a region of the aorta, and a third balloon that directs flow into the renal arteries. In still further embodiments, a stent or cuff having a constricted region is deployed in or around the aorta, respectively, to create a backpressure upstream of the stent or cuff. Methods of enhancing renal perfusion also are provided.
Owner:LIBRA MEDICAL SYST
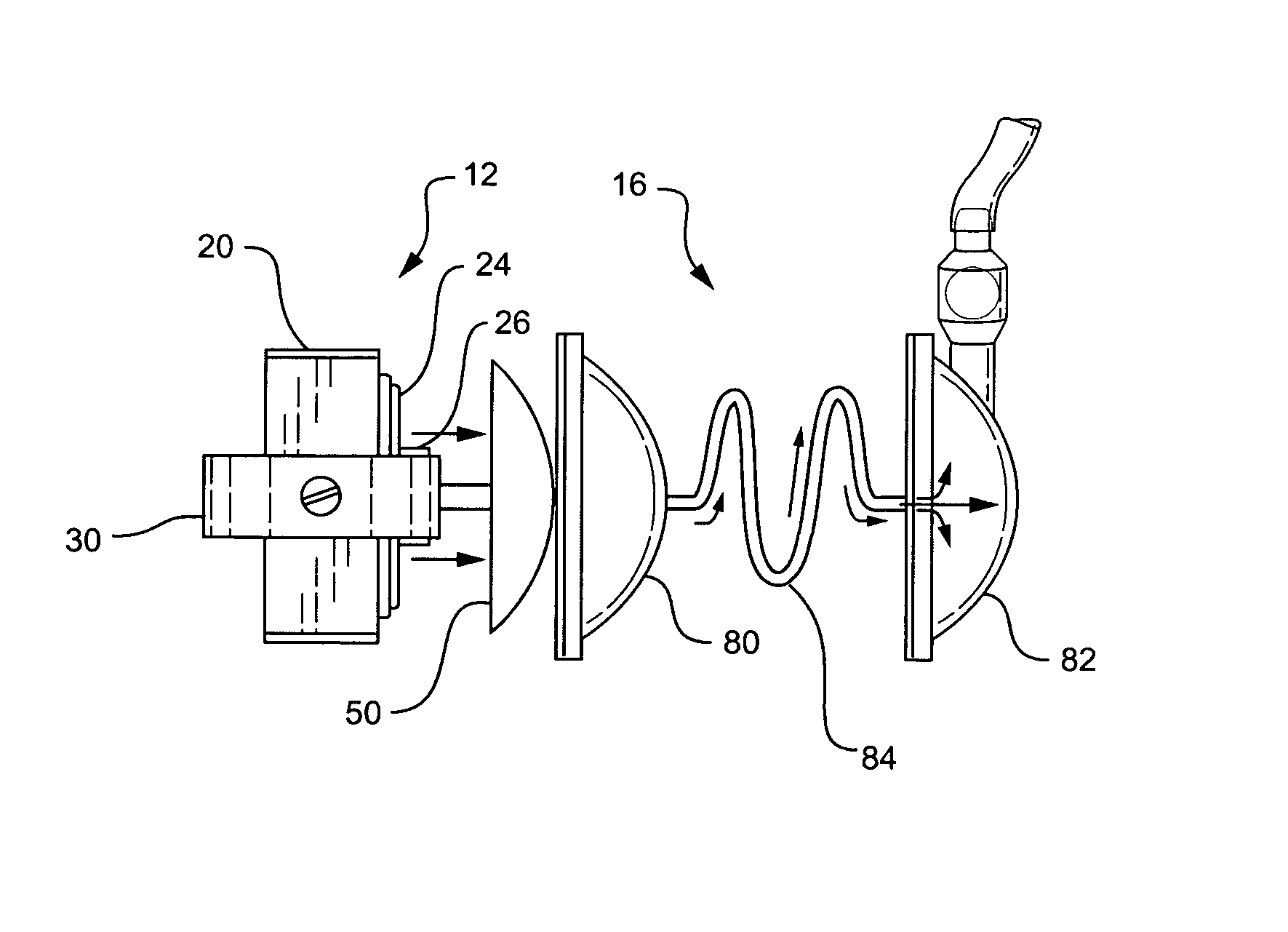
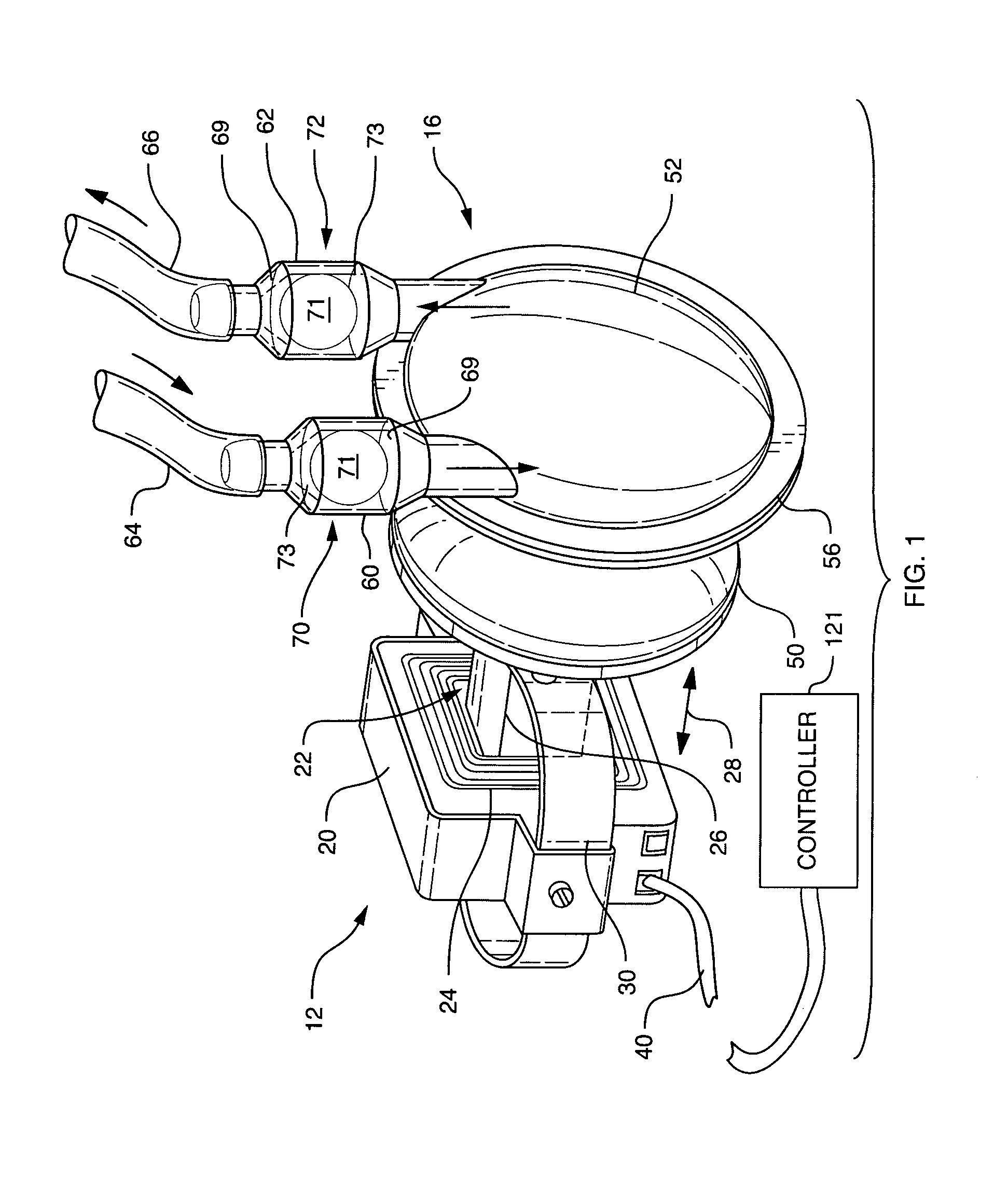
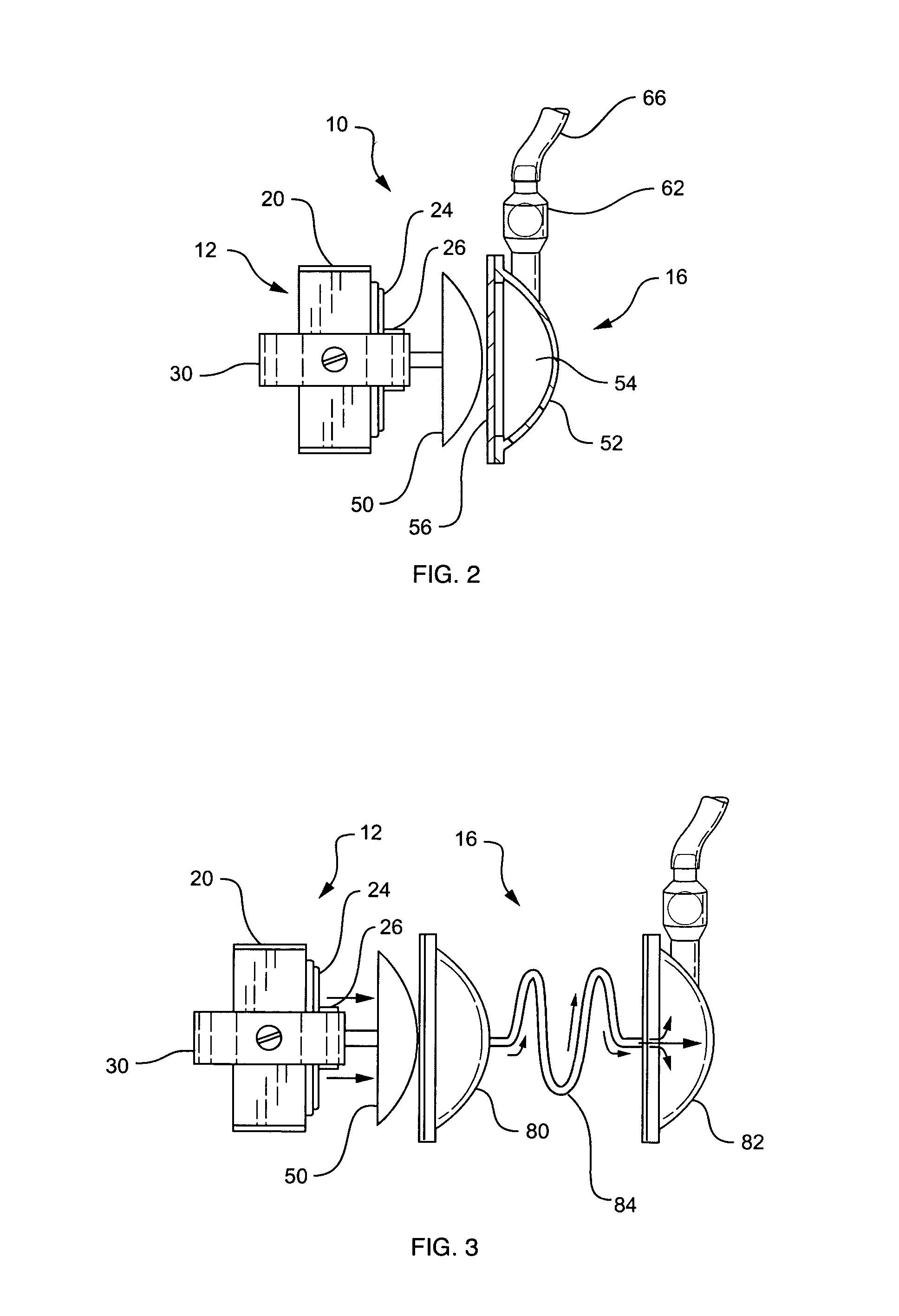
Fluid pump
ActiveUS7238165B2ElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesEngineeringCardiopulmonary bypass time
A pumping system 10 provides a physiological pulsatile flow and includes controller 121, a pump drive head 50 coupled to a motor 12 and a fluid housing 52 having at least one port 60. The port 60 includes a ball valve retainer region 69, a valve seat 73, and an occluder ball 71 disposed in the ball valve retainer region 69. During operation, the motor 12 forces the fluid in and out the fluid housing 52 and causes the occluder ball 71 to move from a first position whereby the fluid cannot pass through the port 60, to a second position whereby the fluid moves annular to and generally around the occluder ball 71. This movement creates a slight flow reversal that “breaks up” any blood clots that may form. The pumping system may be used as part of a cardiopulmonary bypass system, a ventricular assist device (VAD) and / or a heart pump.
Owner:DESIGN MENTOR
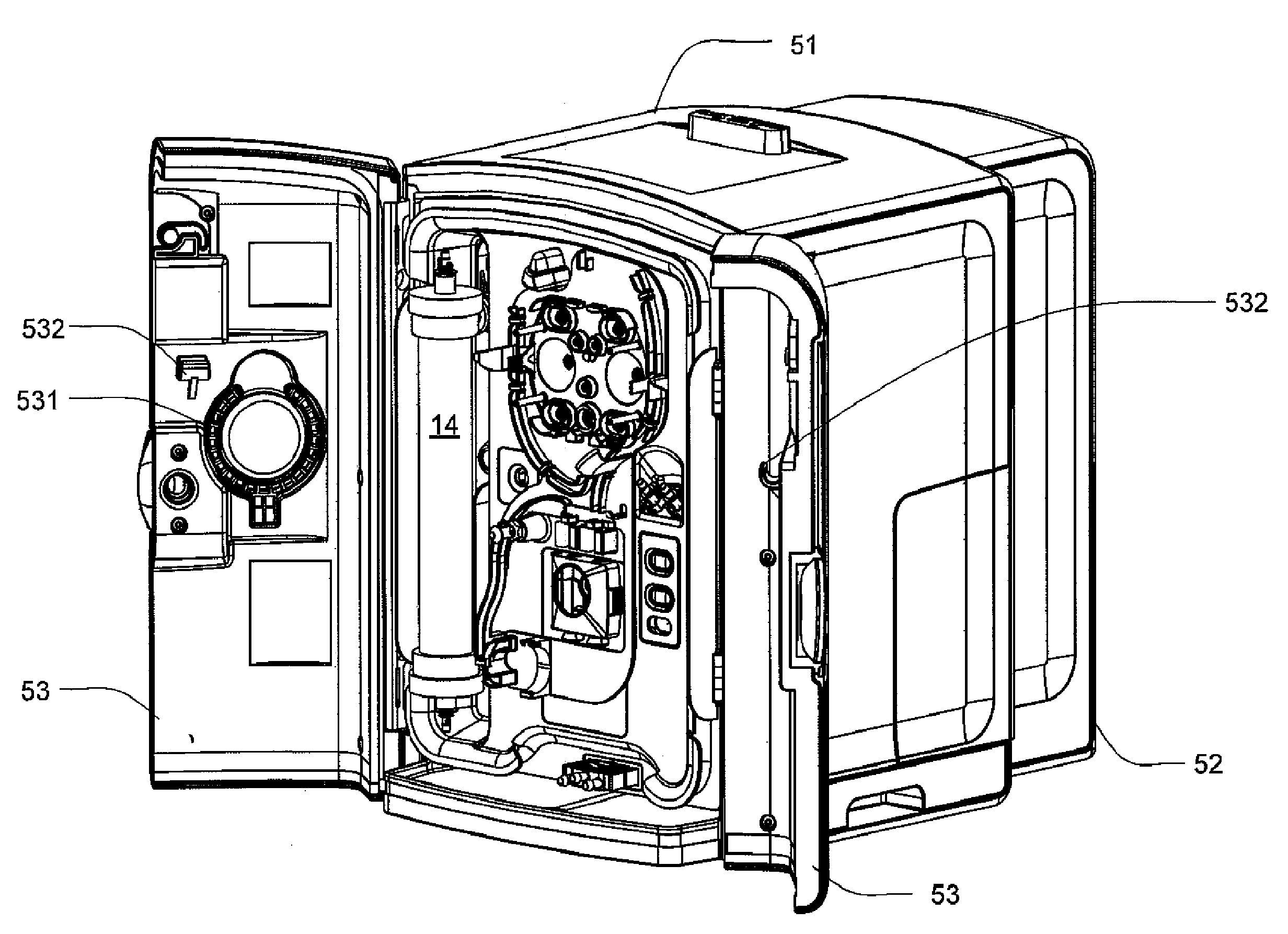
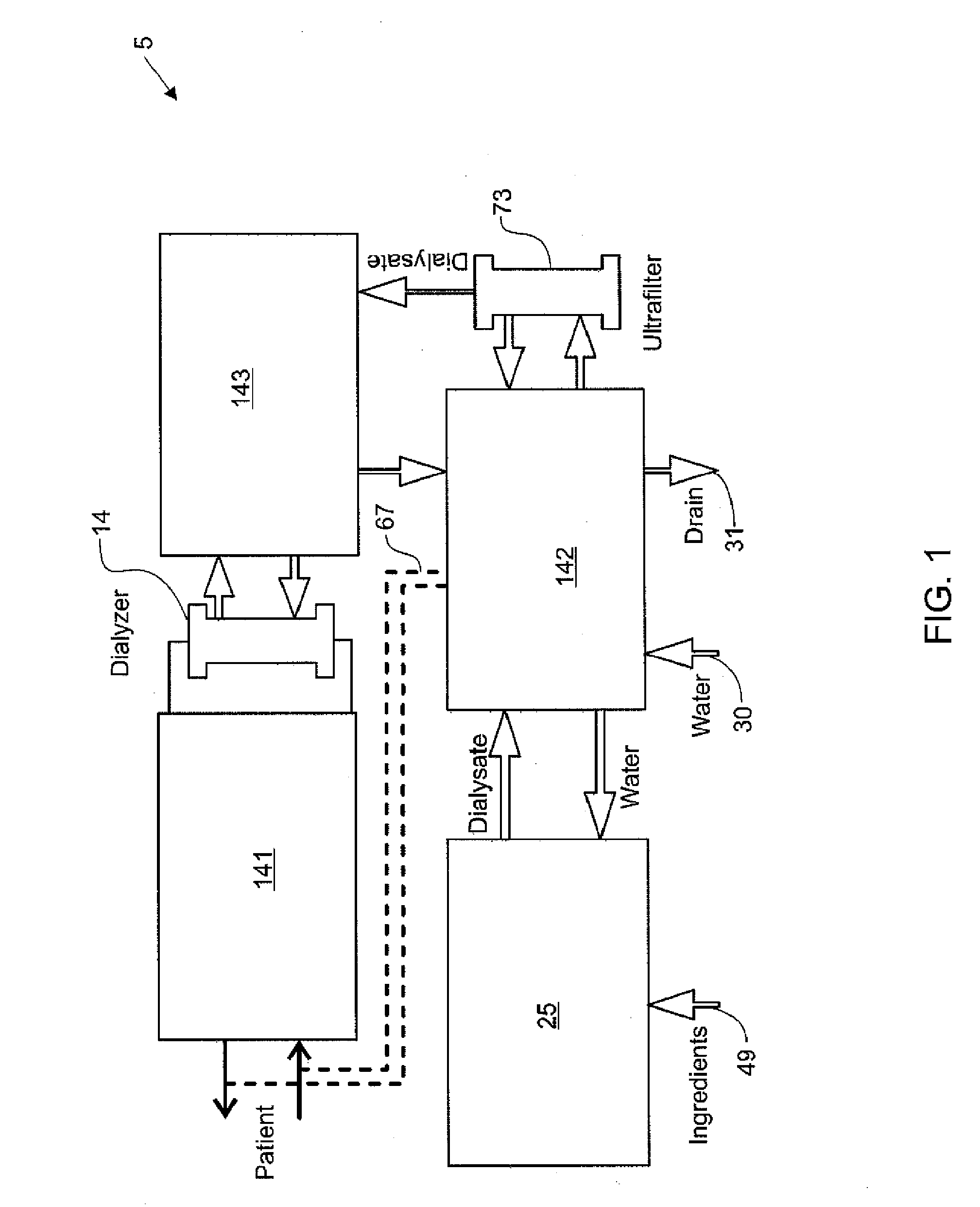
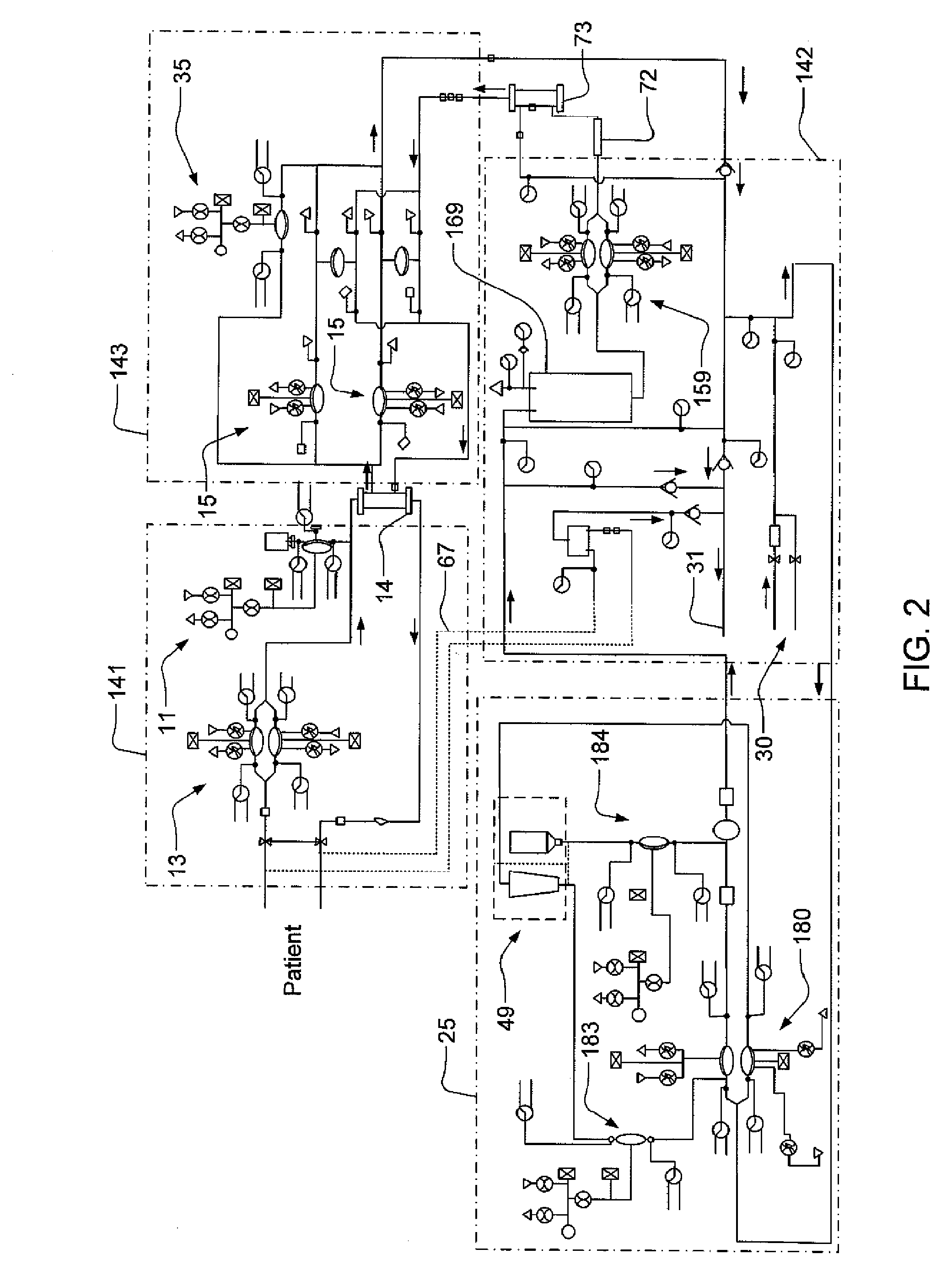
Modular assembly for a portable hemodialysis system
ActiveUS20090101549A1Easy to useOptimize locationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesHaemodialysis machineModularity
A modular assembly for a portable hemodialysis system may include a dialysis unit, e.g., that contains suitable components for performing hemodialysis, such as a dialyzer, one or more pumps to circulate blood through the dialyzer, a source of dialysate, and one or more pumps to circulate the dialysate through the dialyzer, and a power unit having a housing that contains suitable components for providing operating power to the pumps of the dialysis unit. The power unit may be selectively connected to the dialysis unit and provide power (e.g., pneumatic power in the form of pressure and / or vacuum) to the dialysis unit for the pumps when connected to the dialysis unit, but may be incapable of providing power to the dialysis unit when disconnected from the dialysis unit. The dialysis unit and the power unit are sized and weighted to each be carried by hand by a human.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
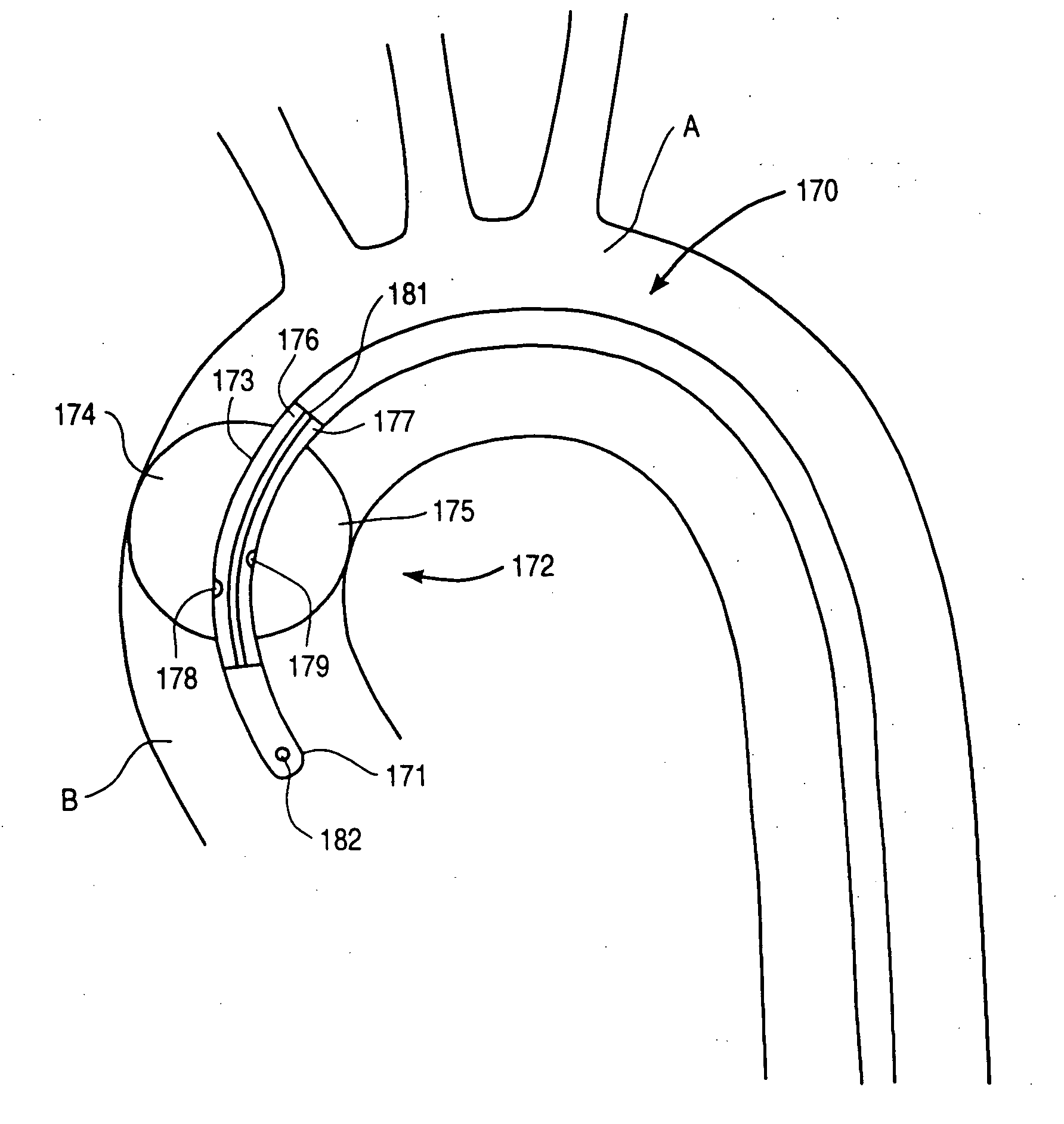
Single port cardiac support apparatus
A reverse flow pump comprising two concentric passageways and an interior compartment having cut out portions in communication with a pump passageway for the directional flow of fluid relative to the pump, and a rotor positioned within the interior compartment for reversing the directional flow of fluid through a region in communication with another pump passageway. A reverse flow pump and cannula system is further provided comprising an inner cannula adjoining a pump passageway, and an outer conduit adjoining another pump passageway for the reverse flow of fluid relative to the pump. A method of transporting fluid between body cavities is also provided comprising the steps of selecting a reverse flow pump and cannula system, forming an opening in a body passageway, positioning the outer conduit through the opening, inserting the inner cannula into the outer conduit so that the distal openings of the inner cannula and the outer conduit are positioned in separated portions of the body, connecting the inlet and the outlet passageways of the pump to the proximal ends of the inner cannula and the outer conduit, and activating the pump to transport fluid between the separated portions of the body.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
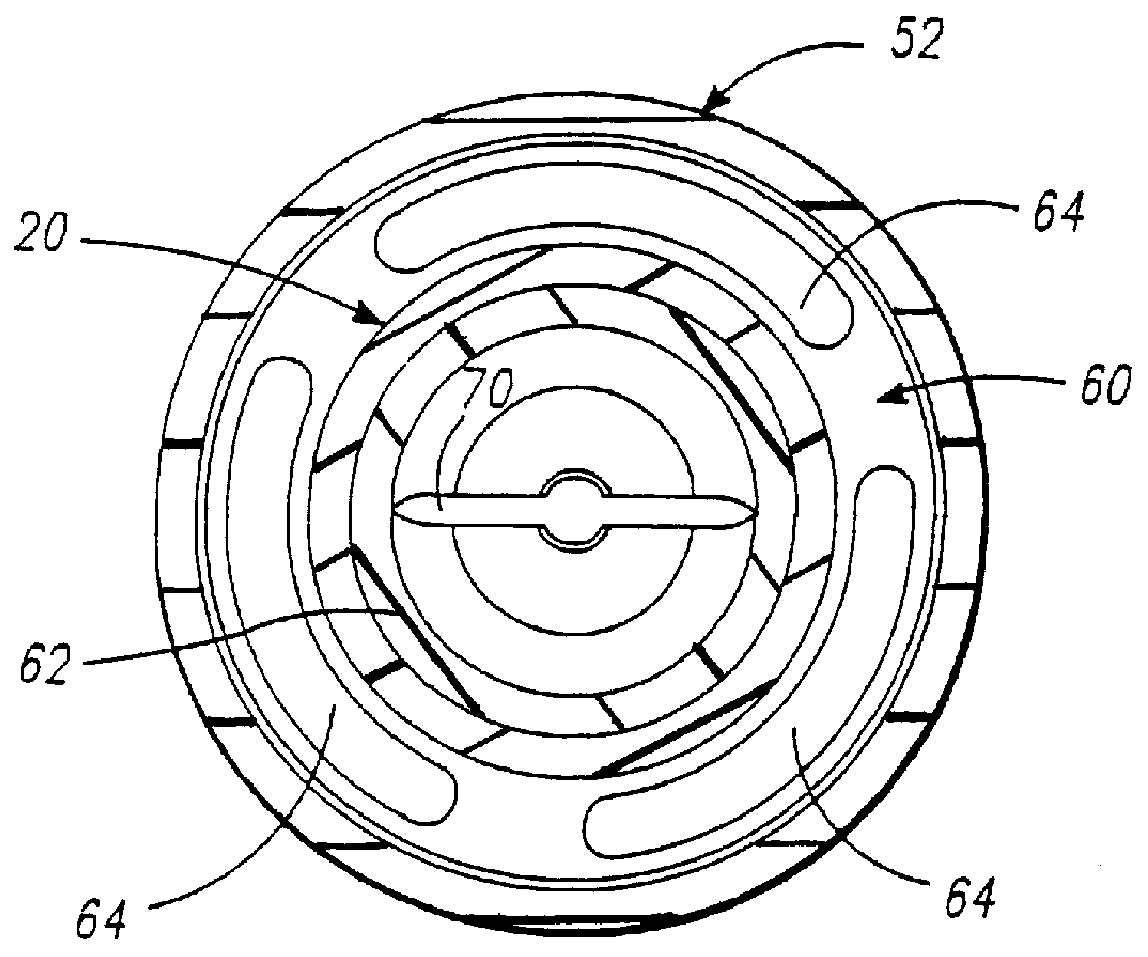
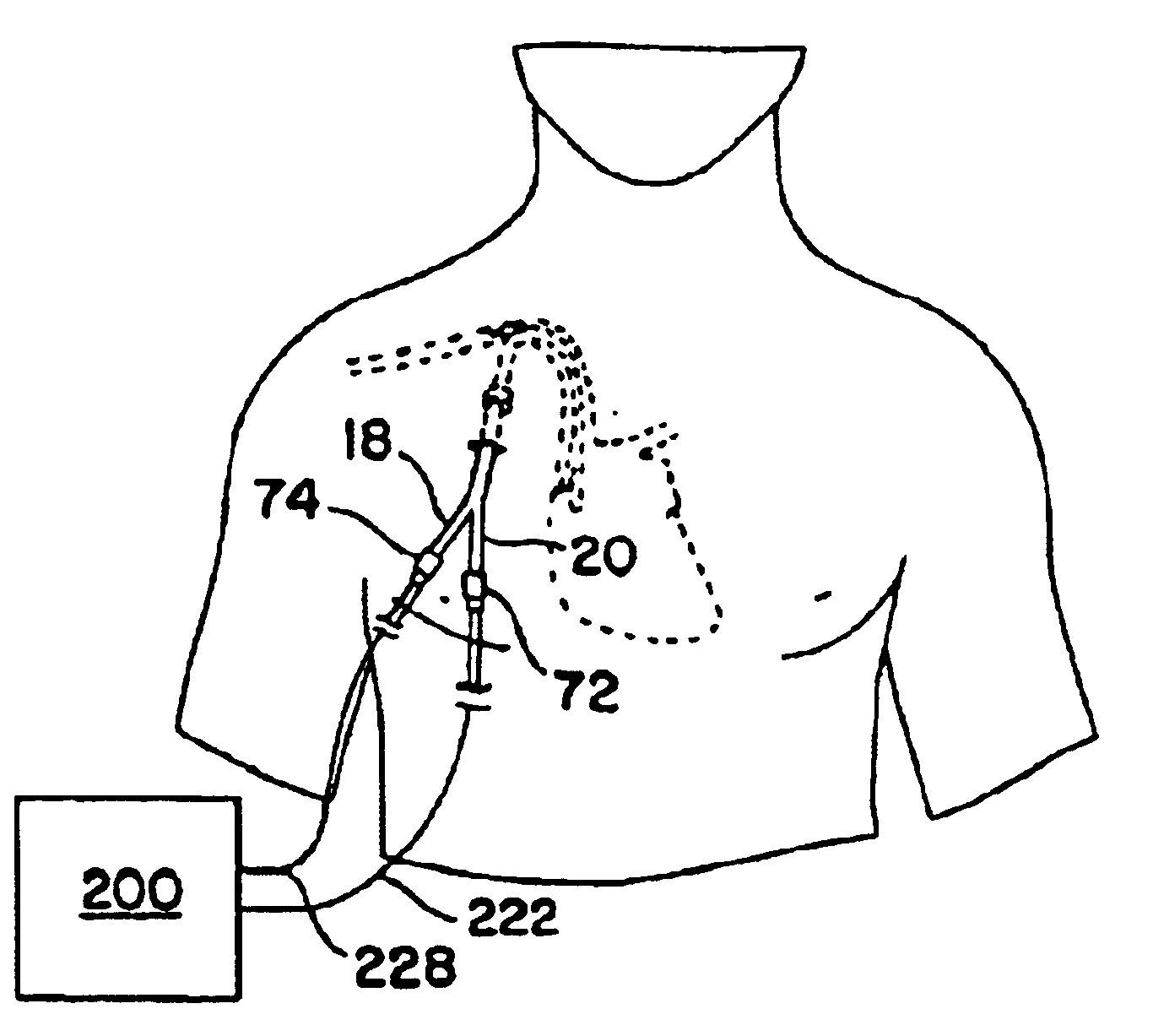
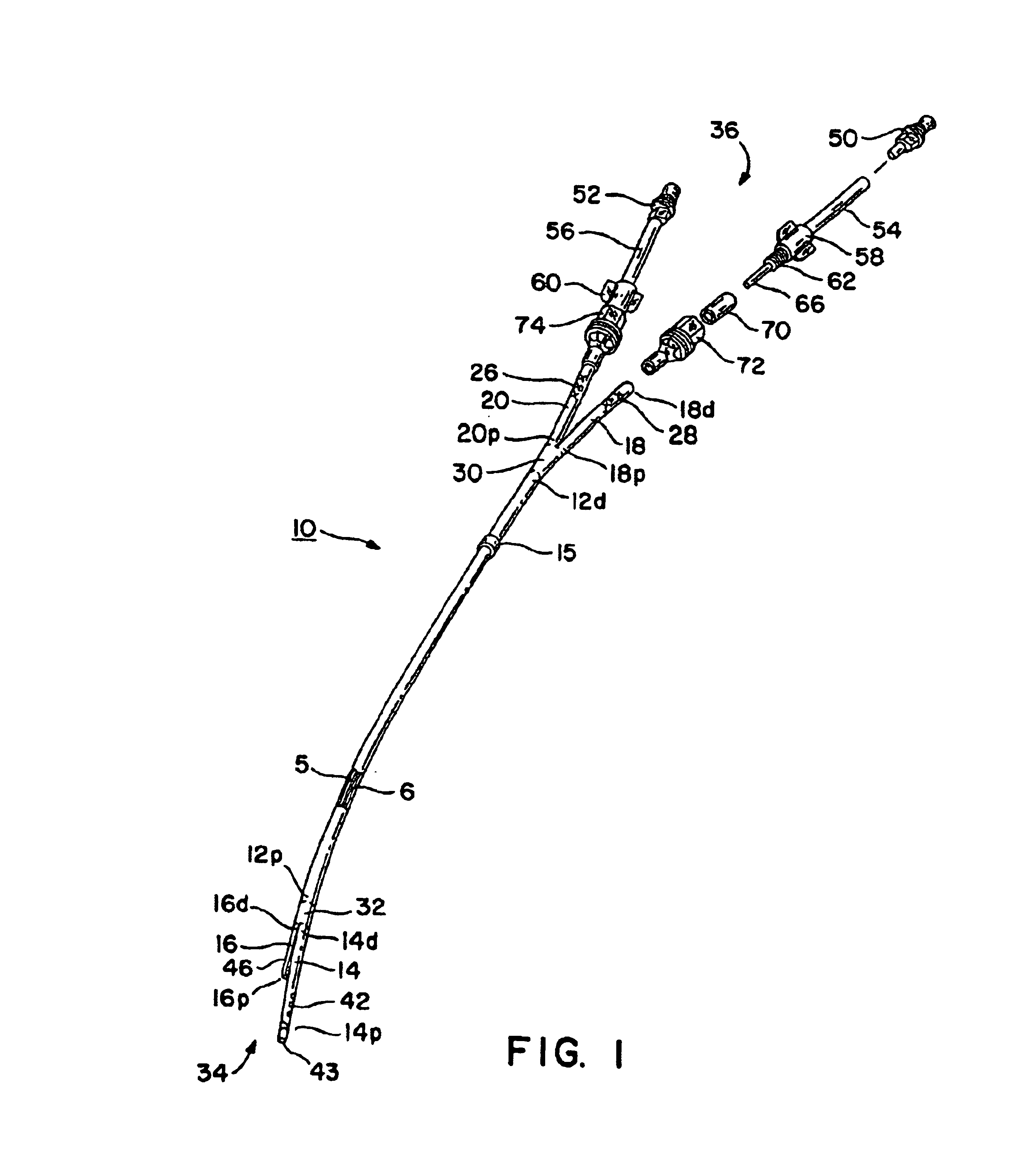
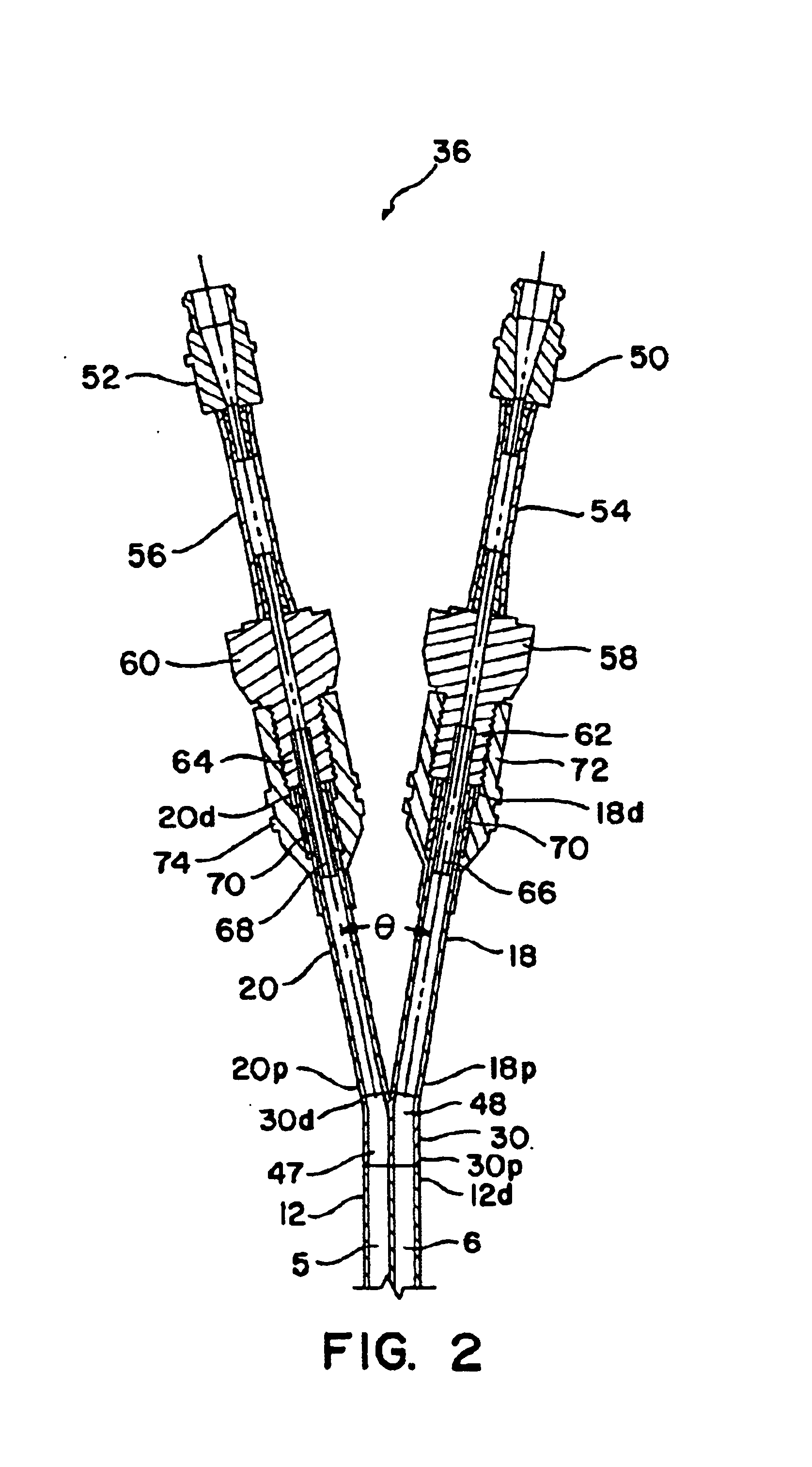
Double-y-shaped multi-lumen catheter with selectively attachable hubs
A multi-lumen catheter and method for inserting same in a patient is disclosed. The catheter includes an elongated, central, multi-lumen tube portion having a proximal end and a distal end. The central tube portion has a substantially cylindrical outer shape and is internally segmented into a plurality of lumens. A distal branch portion includes a plurality of single-lumen distal extension tubes. A proximal branch portion includes a plurality of single-lumen proximal extension tubes. Each proximal extension tube has a distal first end and a proximal second end. The distal first end of each proximal extension tube is connected to the proximal end of the central tube portion such that the single lumen of each distal extension tube is in fluid communication with one of the plurality of lumens of the central tube portion. Each lumen of the central tube portion and the lumens of the distal and proximal extension tubes in fluid communication therewith define a flow path through the catheter. Selectively attachable hub connectors are provided for selective attachment to the distal extension tubes and connection of the catheter to a fluid exchange device.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Device for administering an injectable product in doses
InactiveUS6878132B2Avoid spendingIncrease expensesAmpoule syringesOther blood circulation devicesEngineeringAlarm signal
The present invention provides a device for administering an injectable product in doses, the device including a casing, a container accommodated by the casing, a delivering appliance for delivering the product from the container, a drive for the delivering appliance, and a means for determining a malfunction of the device, wherein a vibrator motor is accommodated by the casing, the vibrator motor being triggered by the means for determining a malfunction such that it generates a vibrating alarm signal when a malfunction is determined.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Dose setting limiter
InactiveUS6524280B2Easy to manufactureImprove gripOther blood circulation devicesInfusion syringesMedicineBiomedical engineering
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Left and right side heart support
InactiveUS6926662B1Lower the volumeReduce the amount requiredOther blood circulation devicesBlood pumpsOuter CannulaRight atrium
A cannulation system for cardiac support uses an inner cannula disposed within an outer cannula. The outer cannula includes a fluid inlet for placement within the right atrium of a heart. The inner cannula includes a fluid inlet extending through the fluid inlet of the outer cannula and the atrial septum for placement within at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. The cannulation system also employs a pumping assembly coupled to the inner and outer cannulas to withdraw blood from the right atrium for delivery to the pulmonary artery to provide right heart support, or to withdraw blood from at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle for delivery into the aorta to provide left heart support, or both.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Cryotreatment device and method
InactiveUS7220257B1Reduce adverse reactionsReduced responseStentsOther blood circulation devicesCoronary artery angioplastyPercent Diameter Stenosis
Devices and methods for cooling vessel walls to inhibit restenosis in conjunction with medical procedures such as coronary artery angioplasty. Stenosed vessel walls can be cooled prior to angioplasty, after angioplasty, or both. The invention is believed to inhibit restenosis through cooling to a temperature near freezing, preferably without causing substantial vessel wall cell death. One catheter device includes a distal tube region having coolant delivery holes radially and longitudinally distributed along the distal region. In some devices, holes spray coolant directly onto the vessel walls, with the coolant absorbed into the blood stream. In other embodiments, a balloon or envelope is interposed between the coolant and the vessel walls and the coolant returned out of the catheter through a coolant return lumen. Some direct spray devices include an occlusion device to restrict blood flow past the region being cooled. Pressure, temperature, and ultrasonic probes are included in some cooling catheters. Pressure control valves are included in some devices to regulate balloon interior pressure within acceptable limits. In applications using liquid carbon dioxide as coolant, the balloon interior pressure can be maintained above the triple point of carbon dioxide to inhibit dry ice formation. Some cooling catheters are coiled perfusion catheters supporting longer cooling periods by allowing perfusing blood flow simultaneously with vessel wall cooling. One coiled catheter is biased to assume a coiled shape when unconstrained and can be introduced into the body in a relatively straight shape, having a stiffening wire inserted through the coil strands.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device and method for vascular access
ActiveUS20060064159A1Reduce kinksReduce kinking in said catheter portionOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryVeinGraft portion
Vascular access systems for performing hemodialysis are disclosed. The vascular access system contemplates a catheter section adapted for insertion into a vein and a graft section adapted for attachment to an artery. The catheter section may have metal or polymer wall reinforcements that allow the use of thin-walled, small outer diameter conduits for the vascular access system. One or more of the adhered, embedded or bonded conduit reinforcement structures may be removable without significant damage to the conduit sections to facilitate attachment of the sections, or to a connector between the sections. Various self-sealing materials are provided for use in the vascular access system, as well as temporary access sites and flow control / sensor systems.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Systems and methods for performing blood processing and/or fluid exchange procedures
InactiveUS6979309B2Fast and convenient and one step process for loading processingPotent inhibitionSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBlood treatmentsEngineering
A flow management system for extracorporeal blood treatment application helps to ensure proper balance of incoming and outgoing fluids by precise balancing of relatively small balance chambers. The invention employs combinations of features that help to ensure accuracy including underfilling of the waste flow side of a fixed volume chamber and mechanical connections to synchronize valves and pumps.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
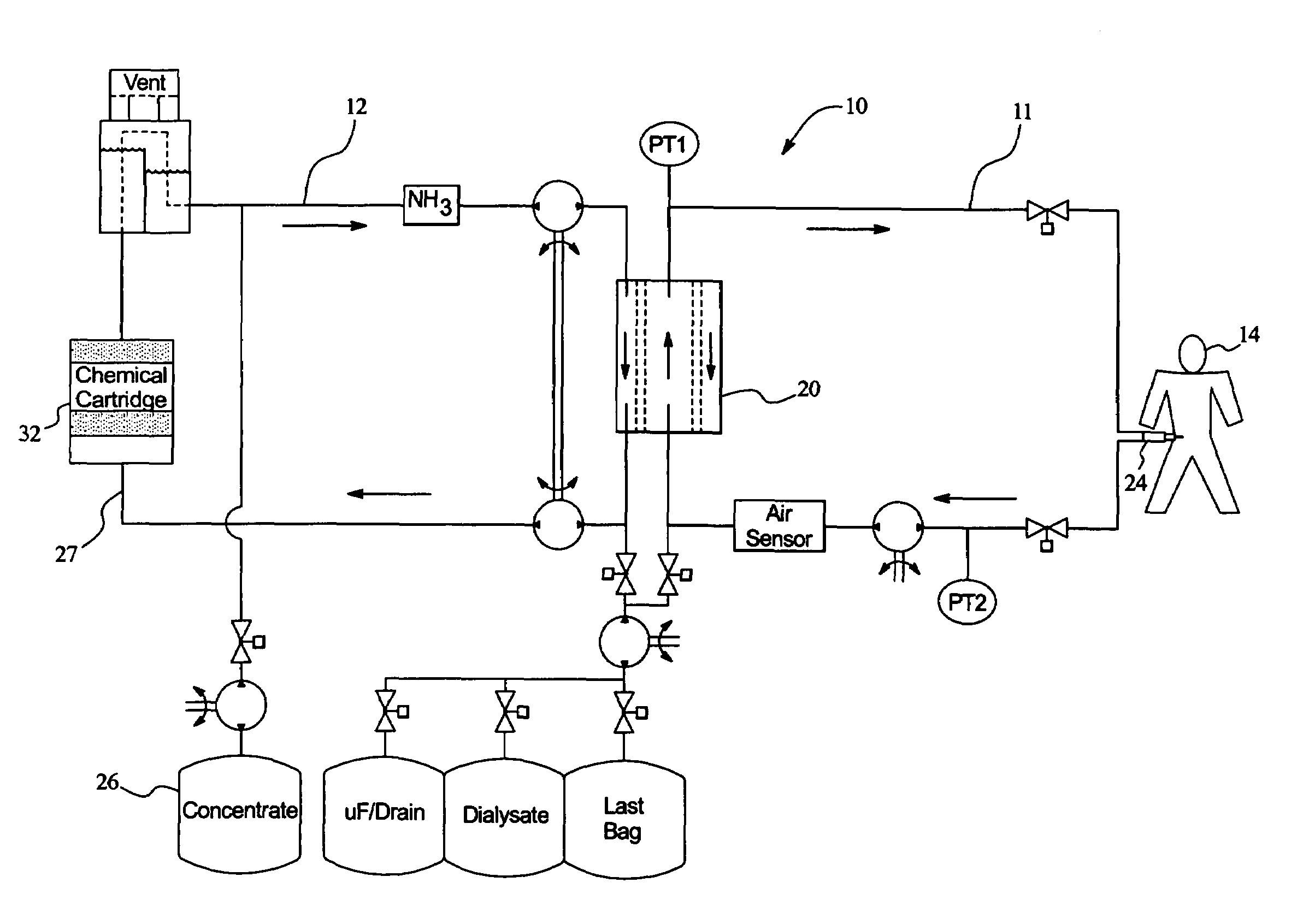
Method and composition for removing uremic toxins in dialysis processes
ActiveUS7241272B2Improved dialysis procedureReduce impurityOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesToxinUrease
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS7166443B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients. The invention includes microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and methods of enriching rare cells of fluid samples using microfabricated filters of the present invention. The invention also includes solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample and methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample. Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that includes a microfabricated filter; automated means for directing fluid flow through at least one filtration chamber of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples. Preferred fluid samples are blood, effusion, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
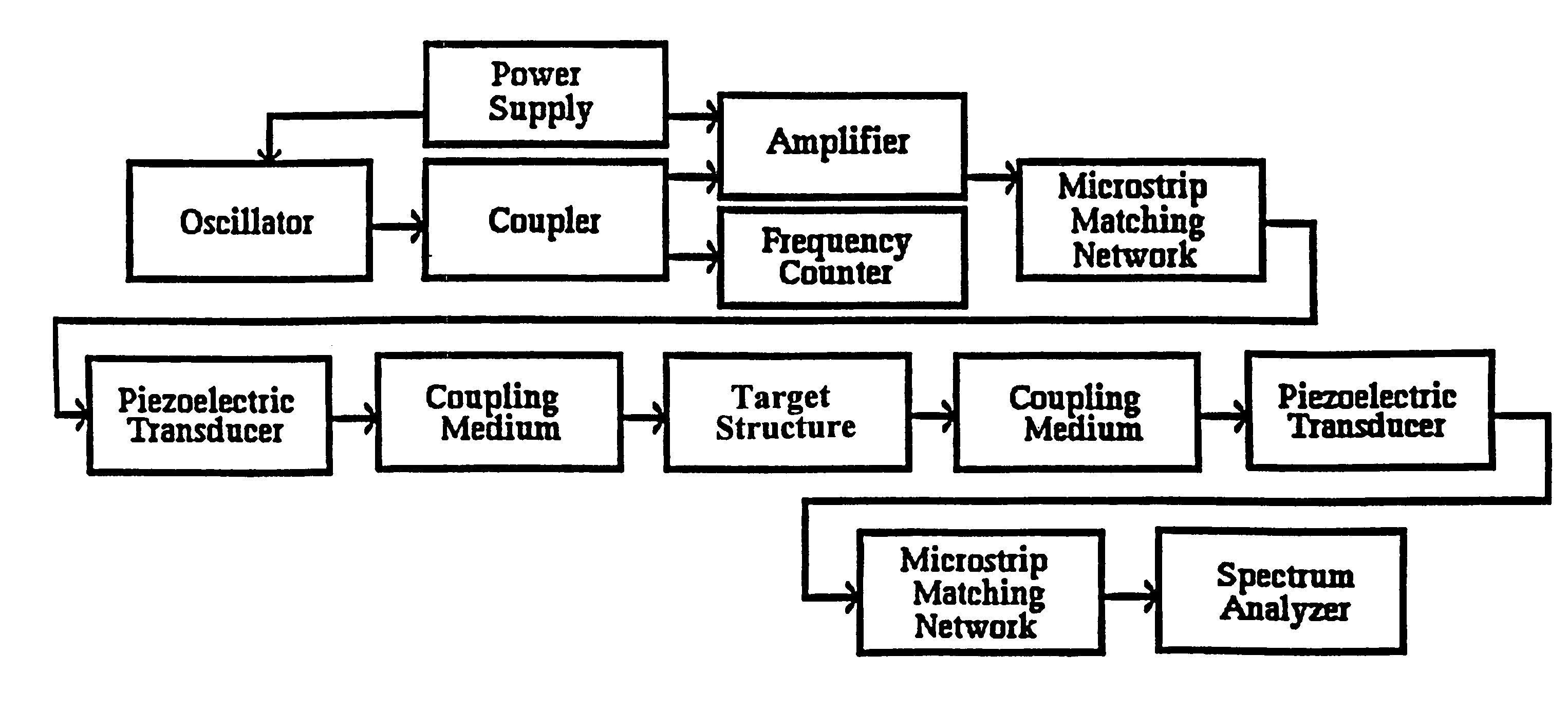
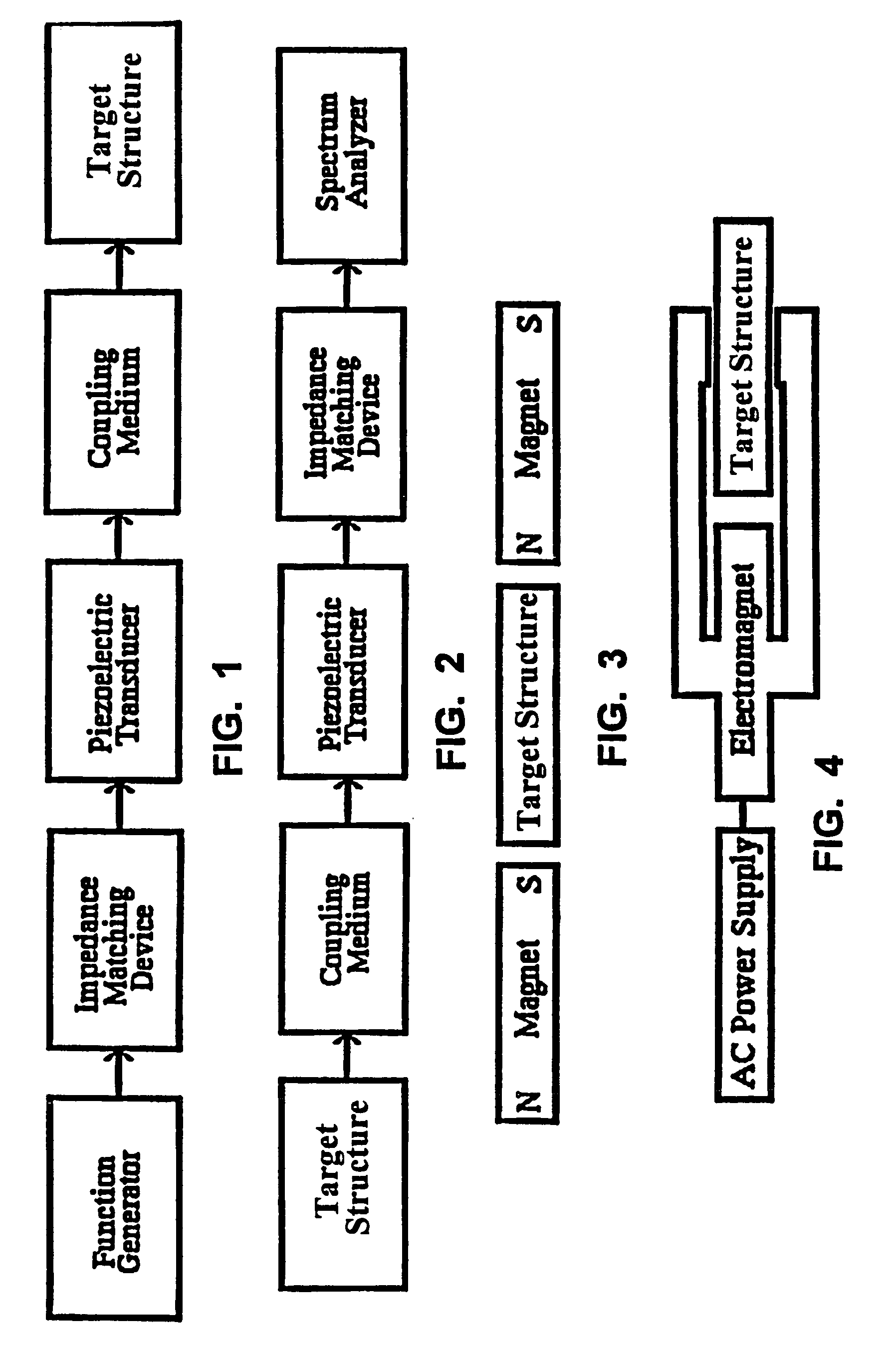
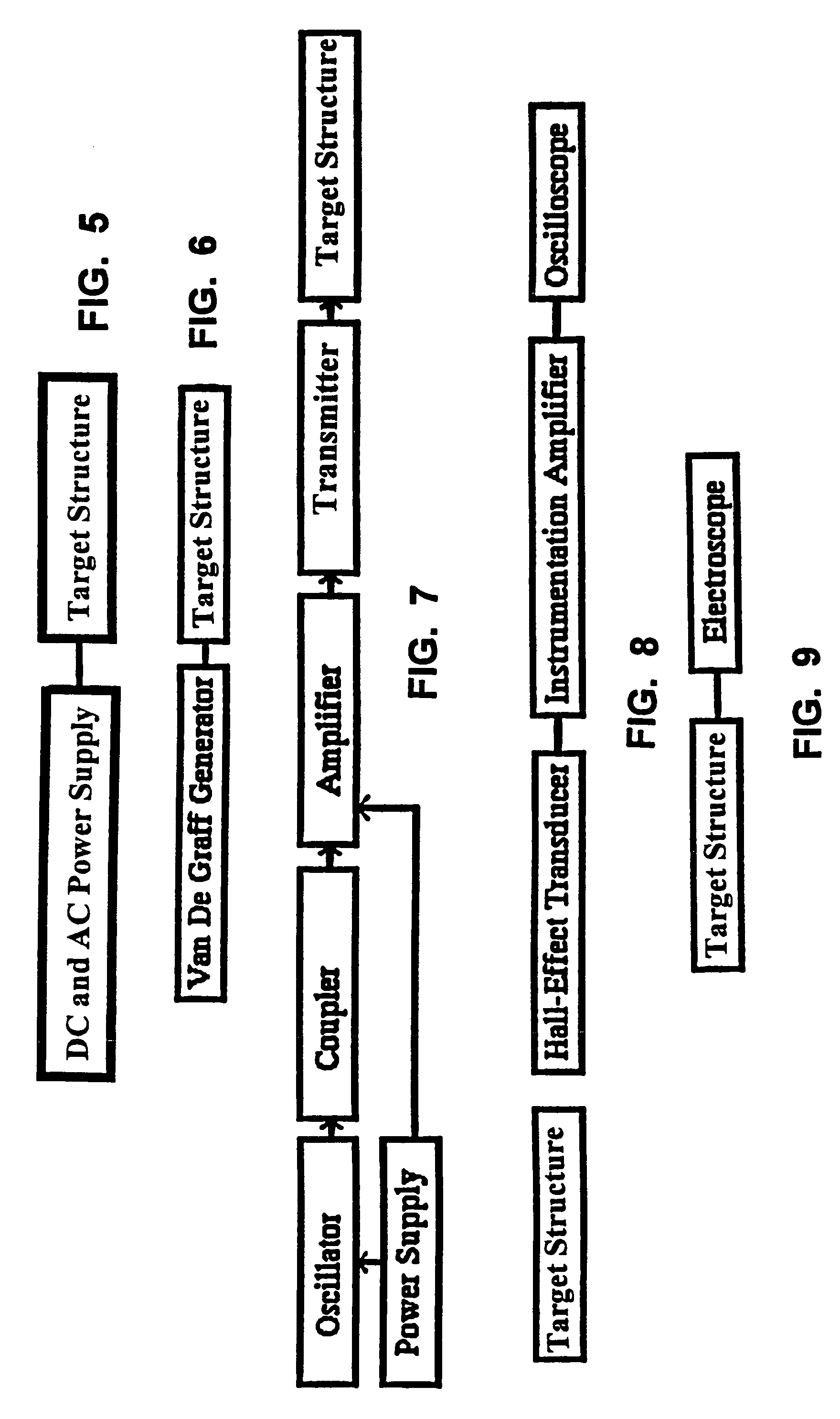
Methods for using resonant acoustic and/or resonant acousto-EM energy to detect and/or effect structures
InactiveUS7165451B1Avoid damageAccurate detectionVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
Treatment of wound or joint for relief of pain and promotion of healing
InactiveUS6887228B2Relieve painPromote healingOther blood circulation devicesEnemata/irrigatorsBody jointsBiomedical engineering
Owner:MCKAY DOUGLAS WILLIAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com