Patents
Literature
100 results about "Ventricular assist device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
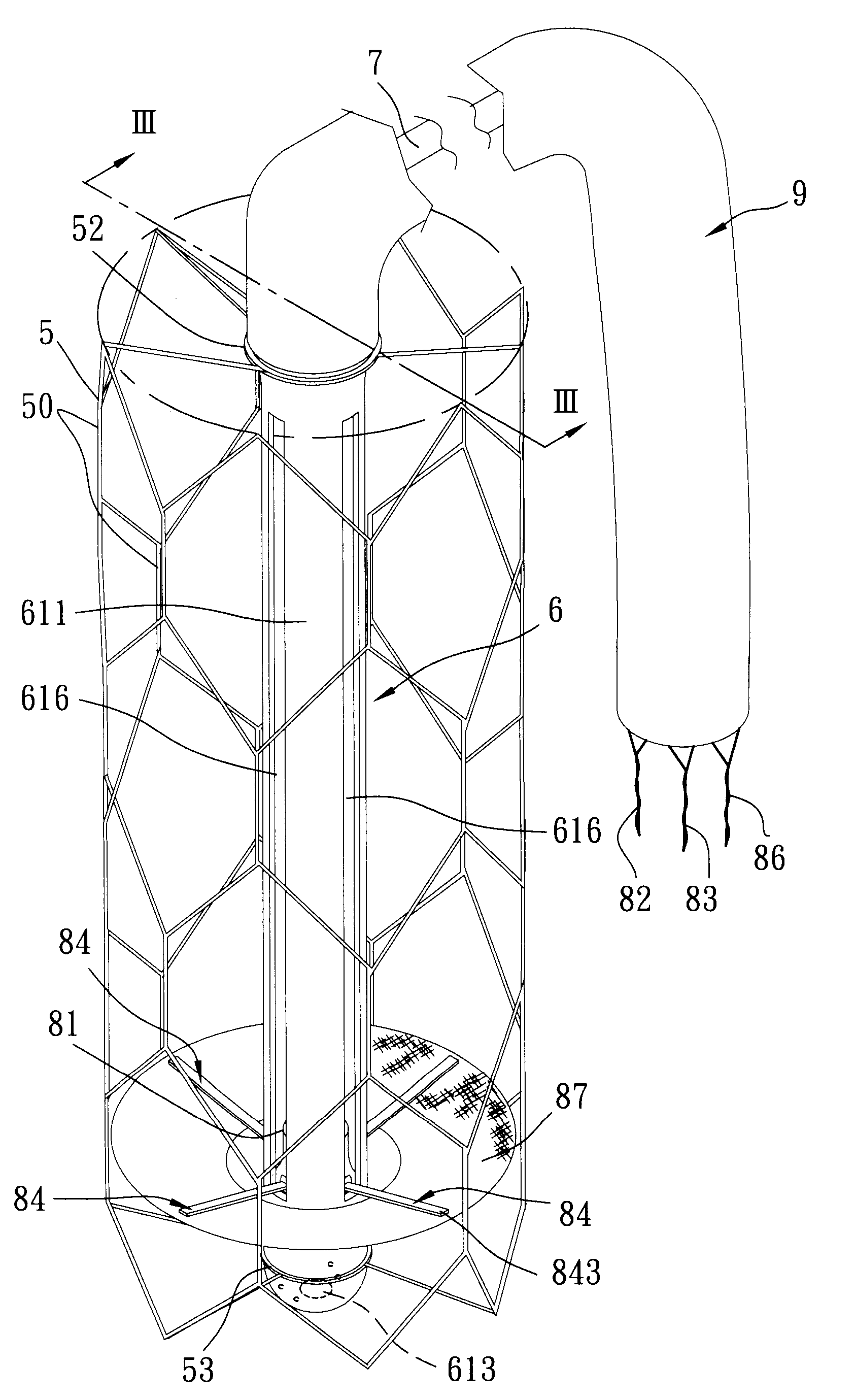
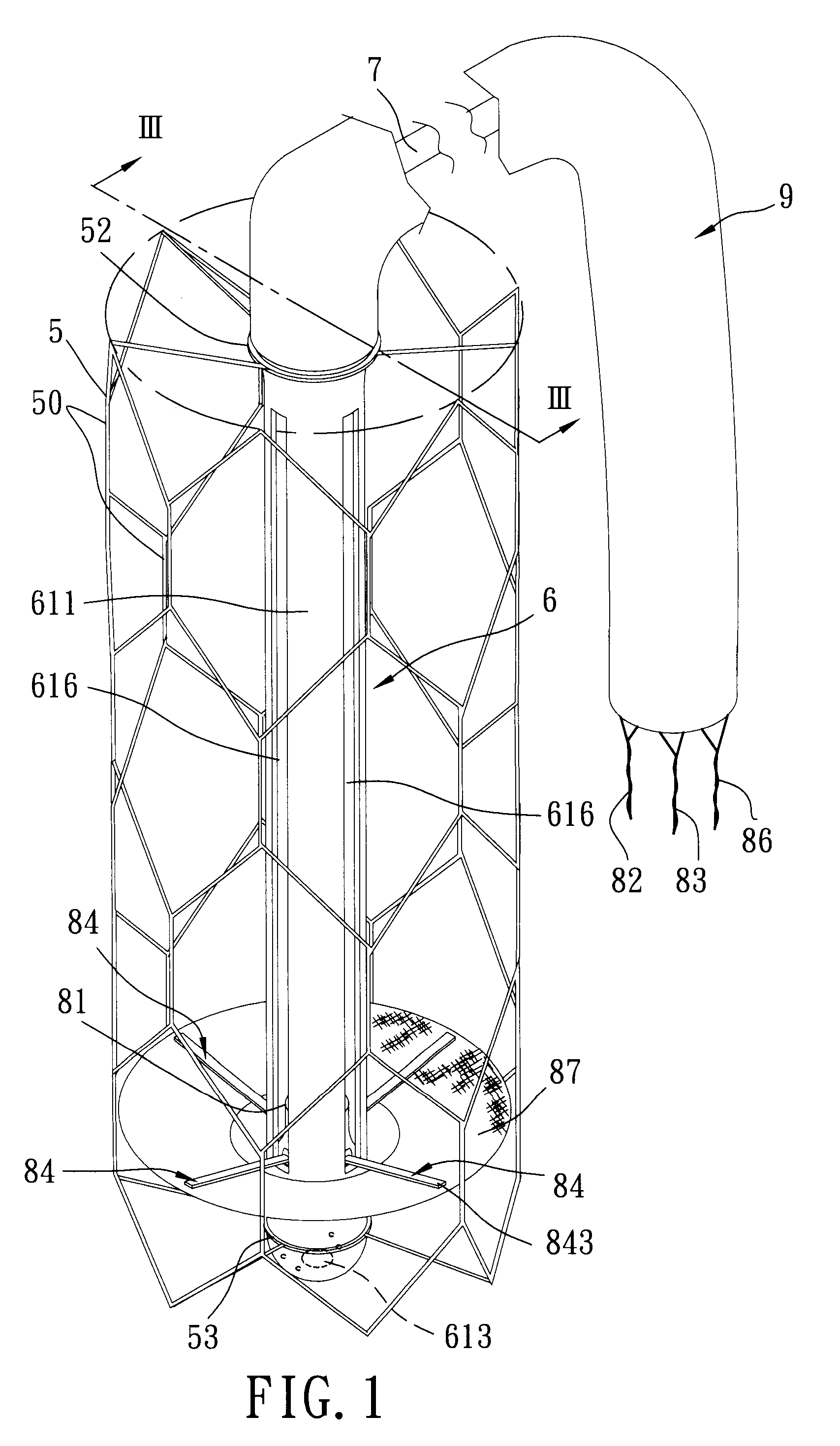
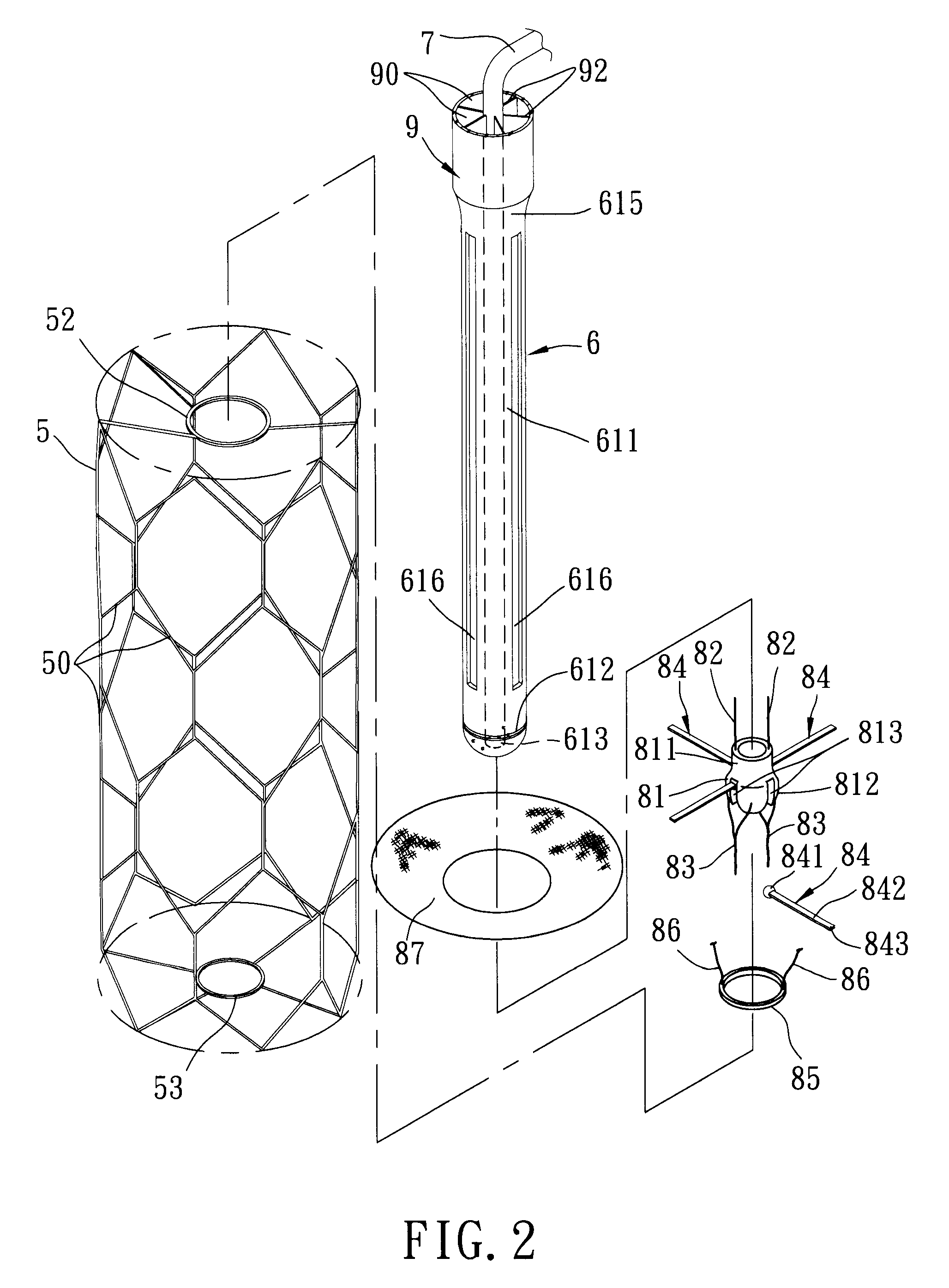
A ventricular assist device (VAD) is an electromechanical device for assisting cardiac circulation, which is used either to partially or to completely replace the function of a failing heart. The function of VADs is different from that of artificial cardiac pacemakers; some are for short-term use, typically for patients recovering from myocardial infarction (heart attack) and for patients recovering from cardiac surgery; some are for long-term use (months to years to perpetuity), typically for patients suffering from advanced heart failure.
Fluid pump
ActiveUS7238165B2ElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesEngineeringCardiopulmonary bypass time
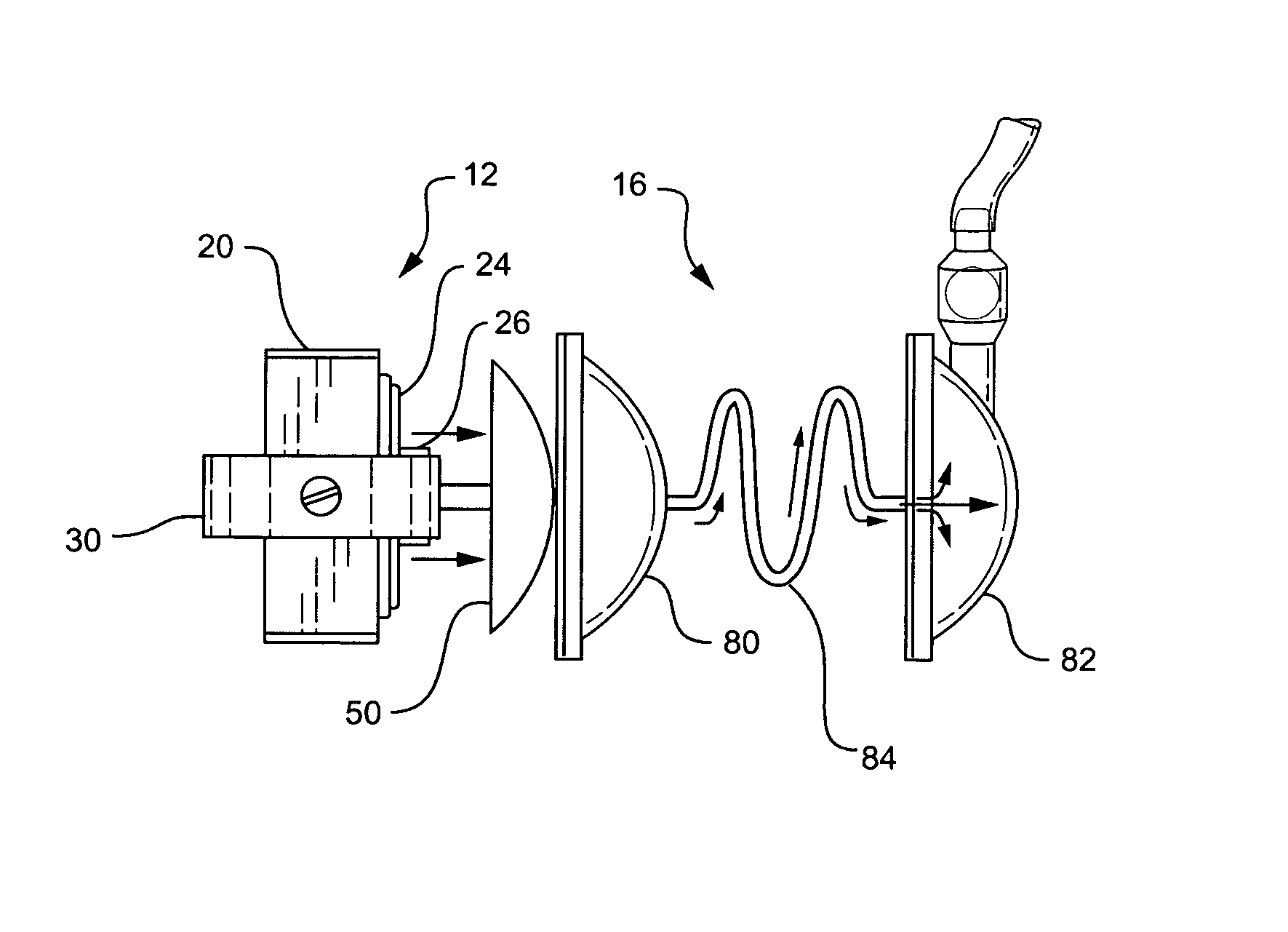
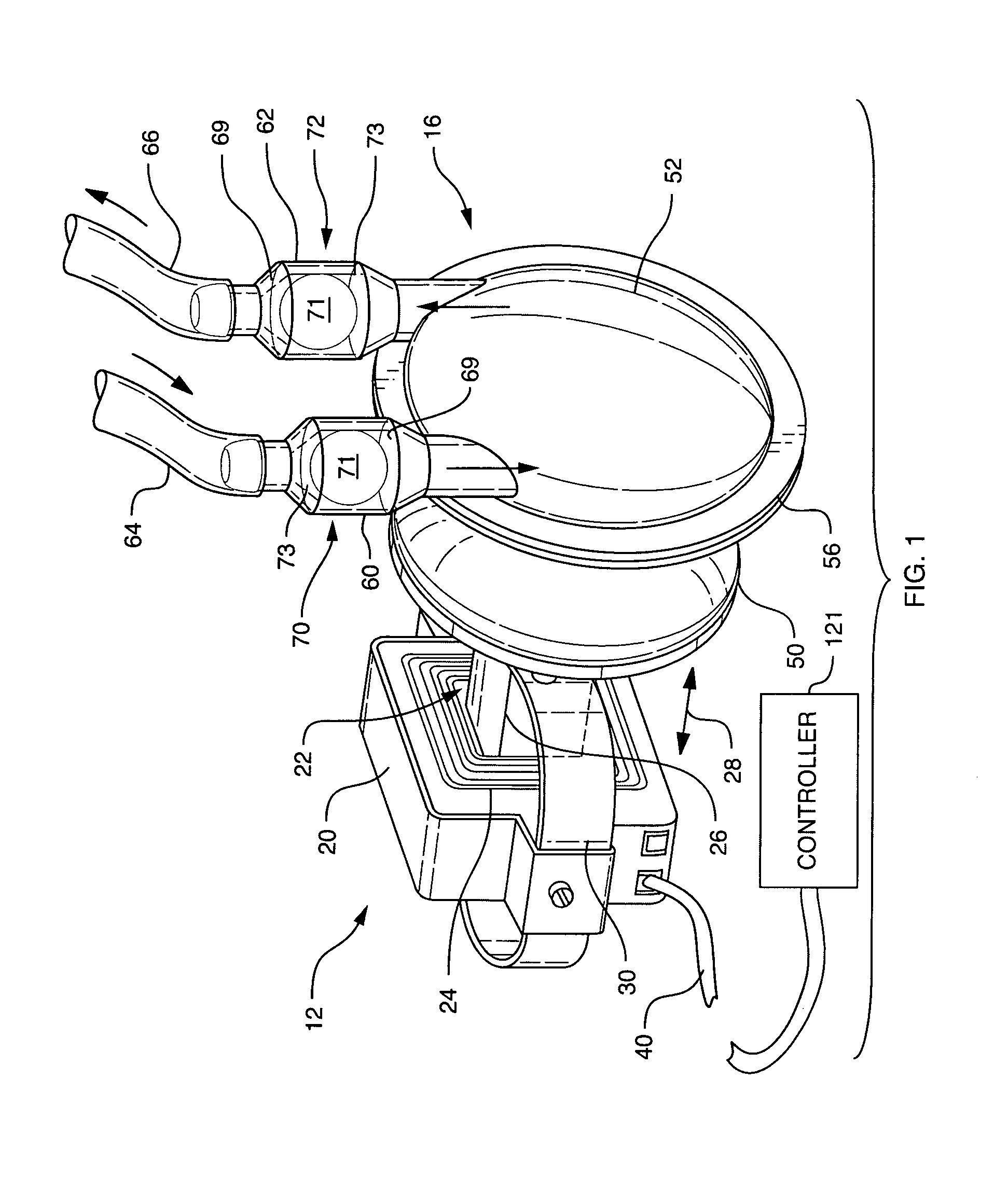
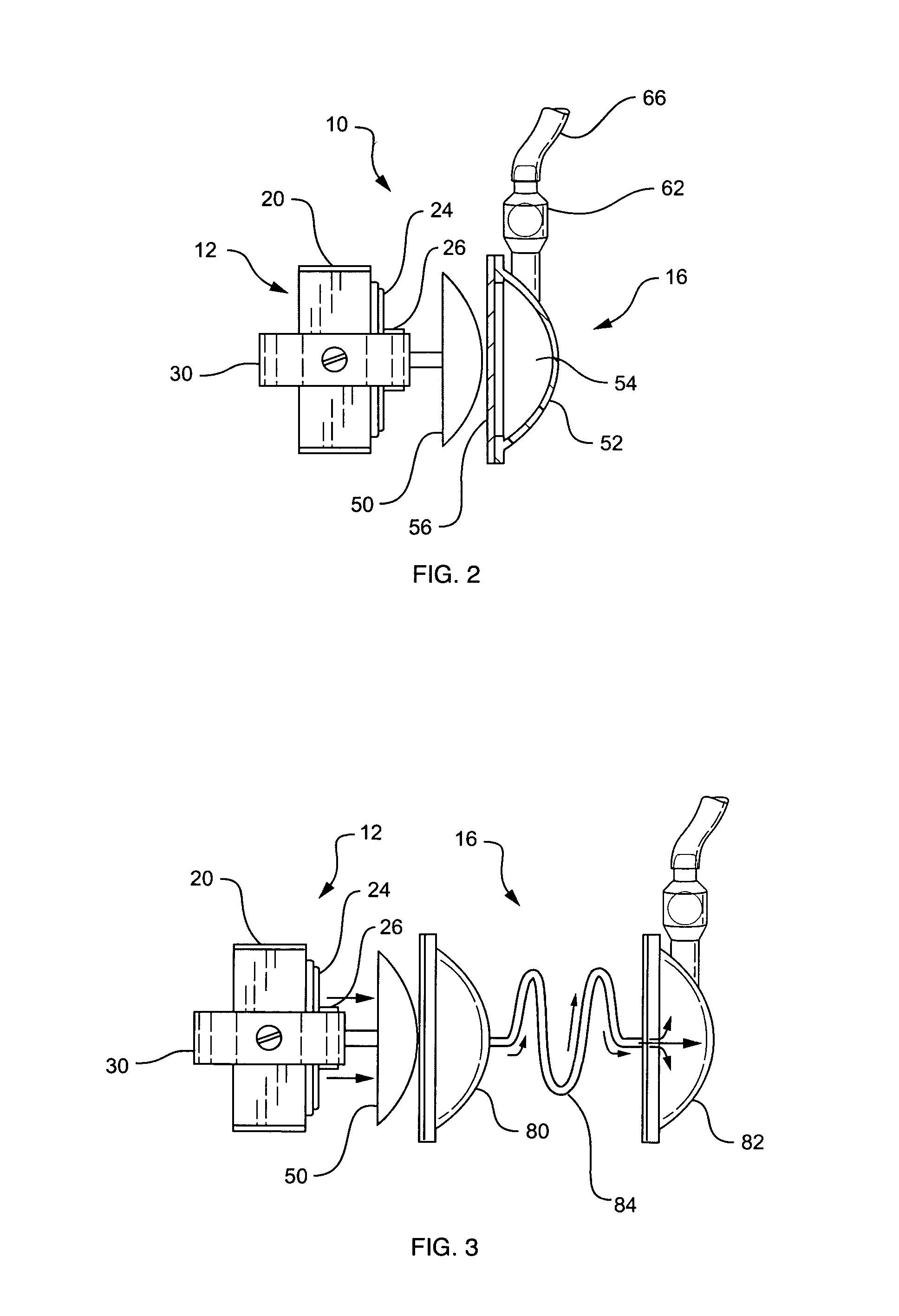
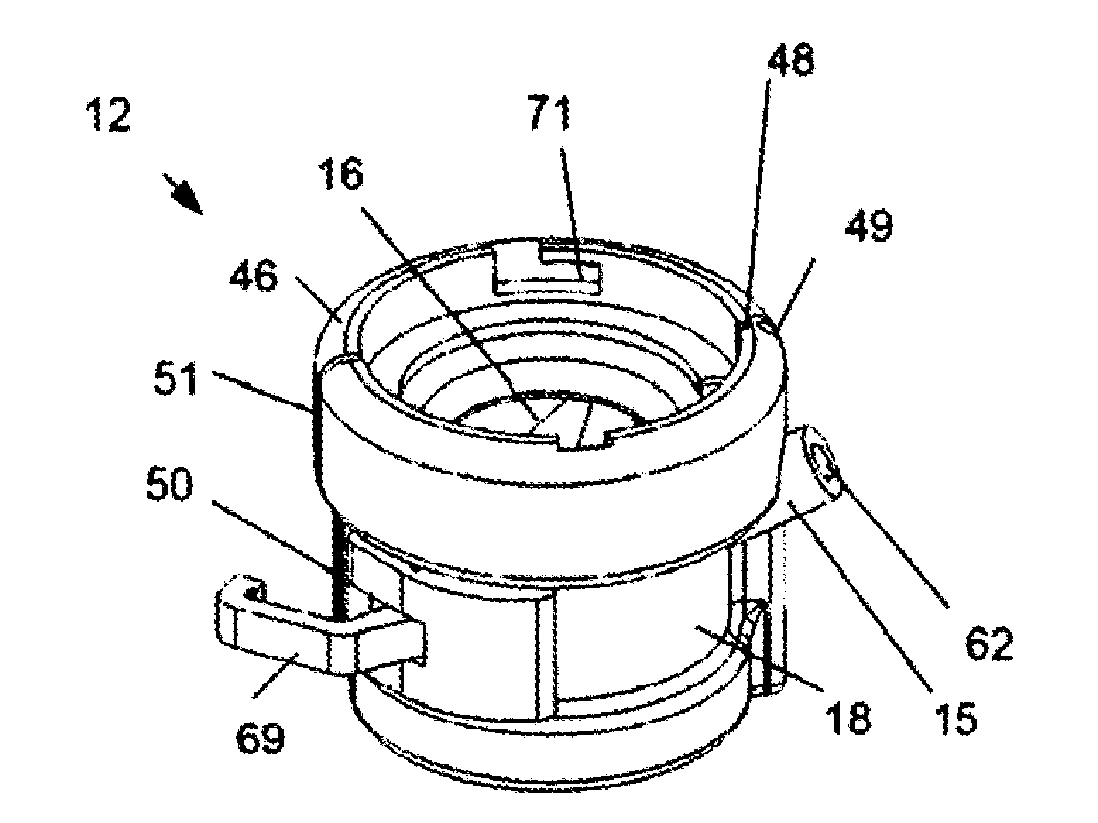
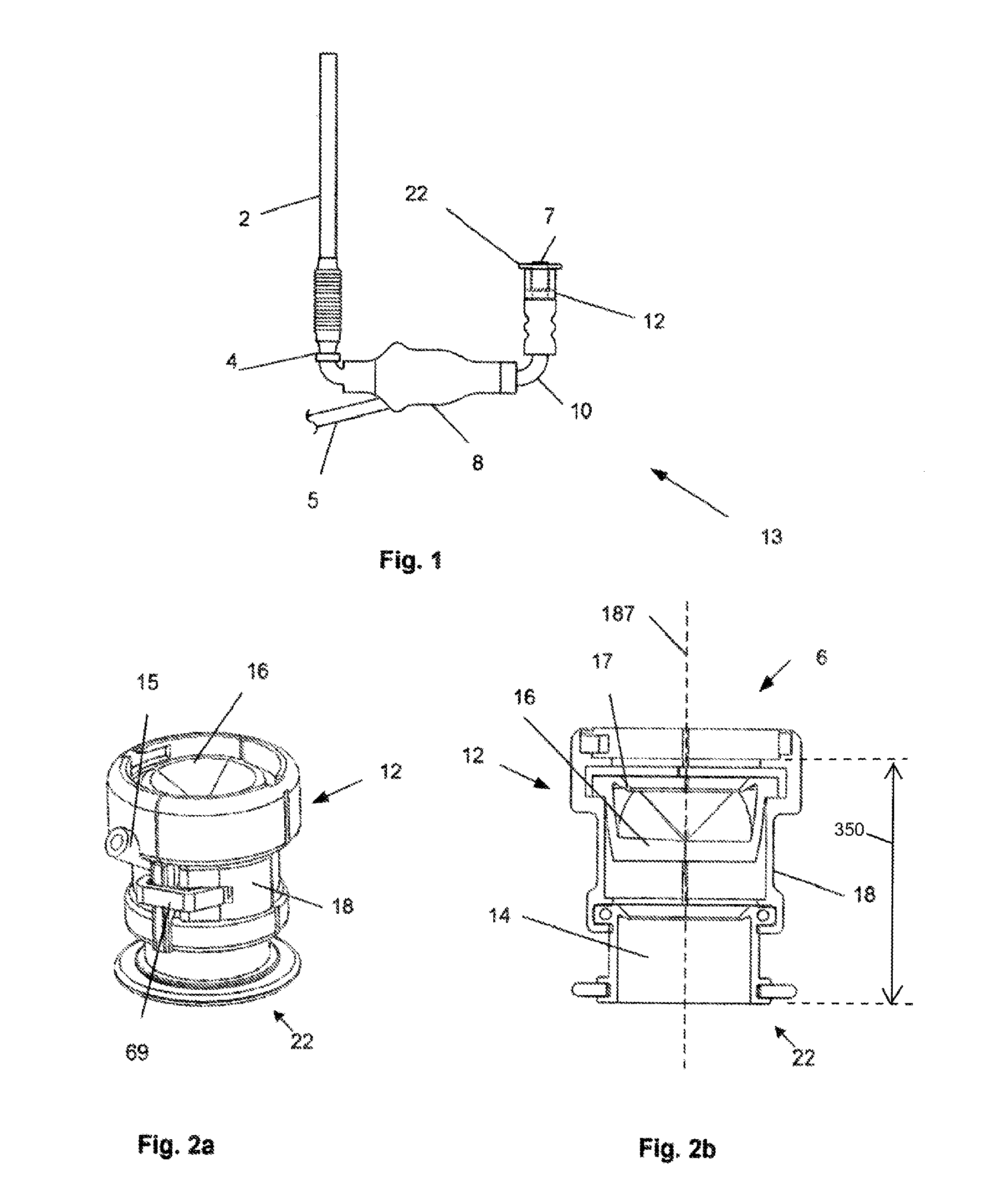
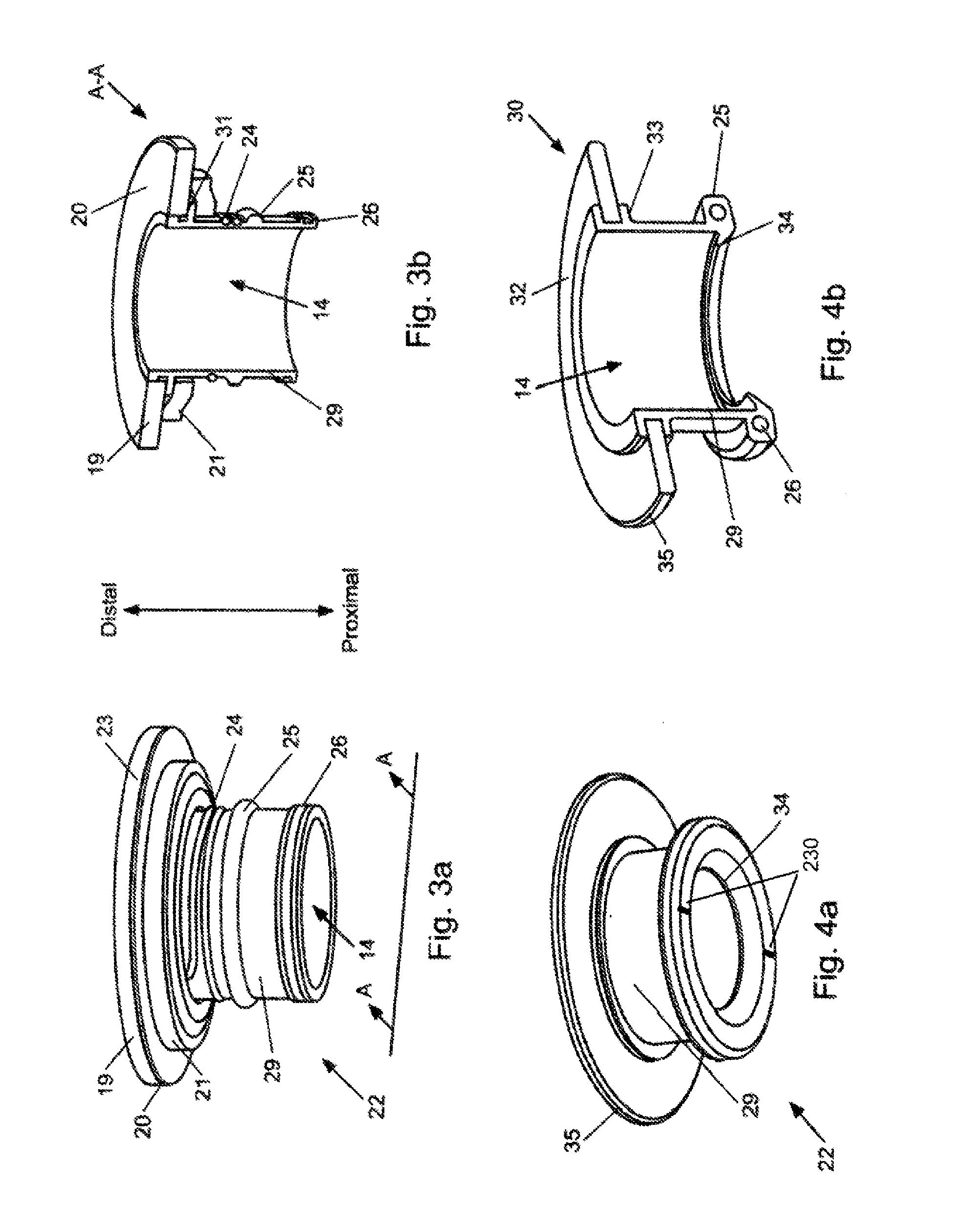
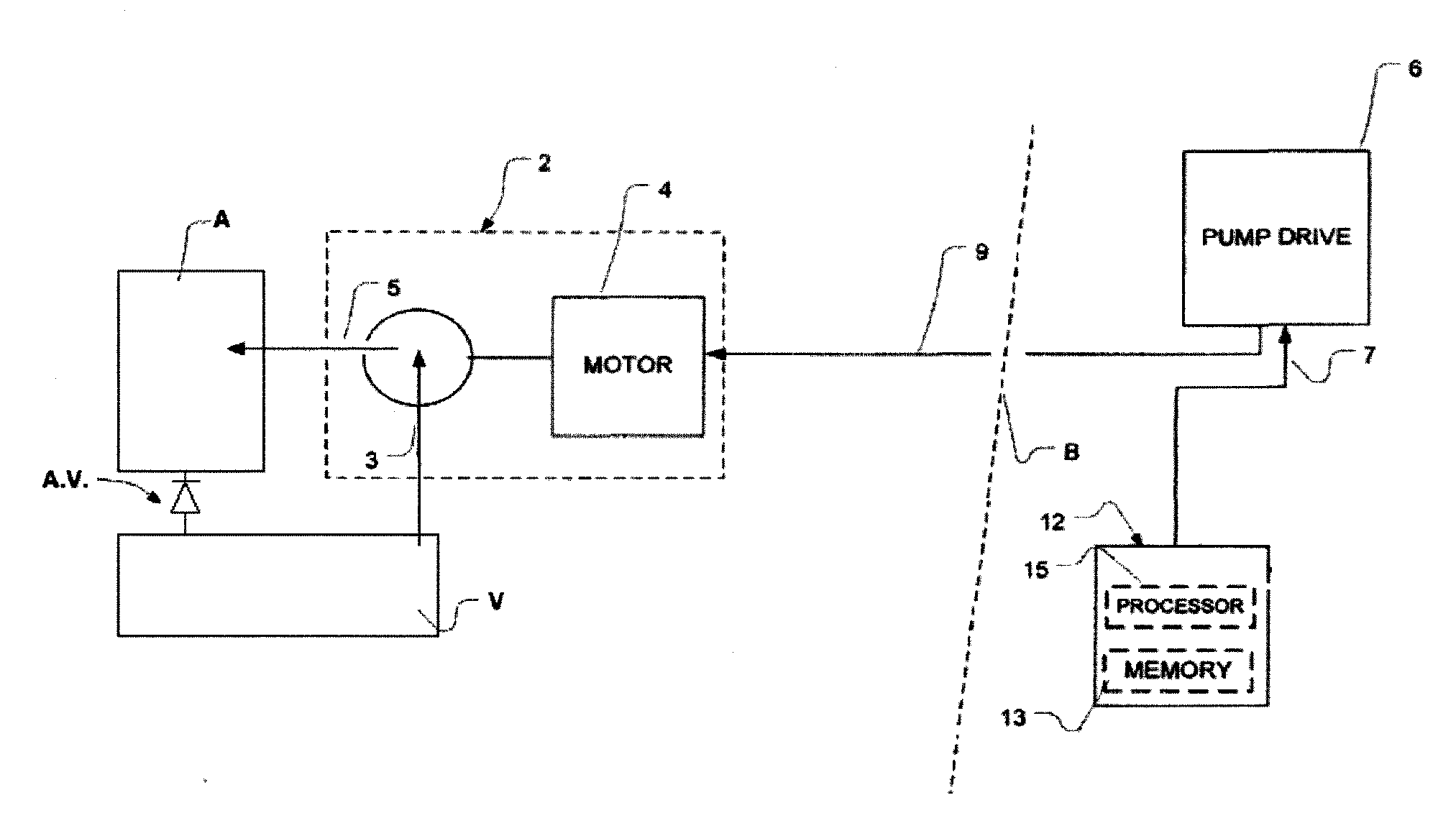
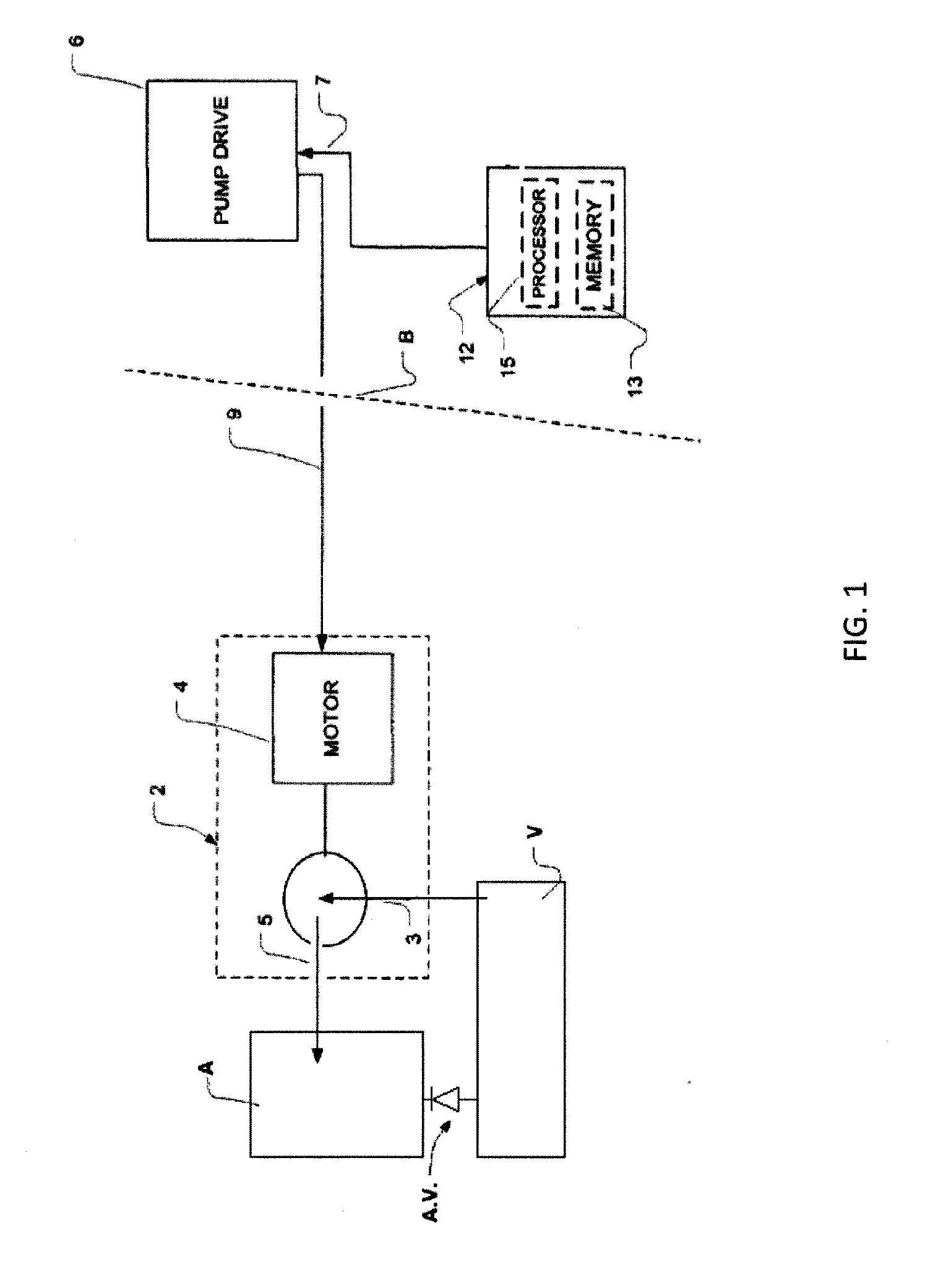
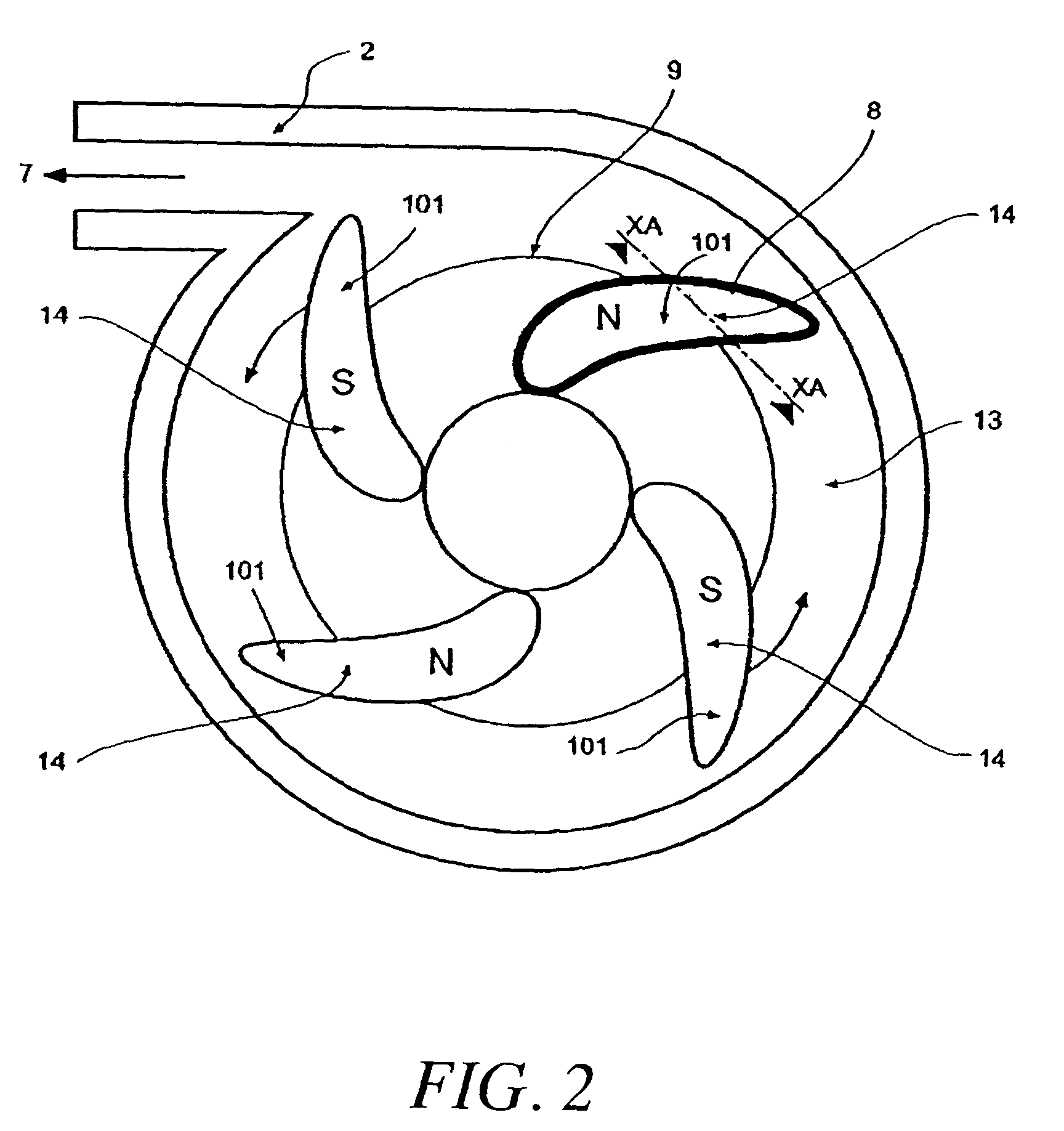
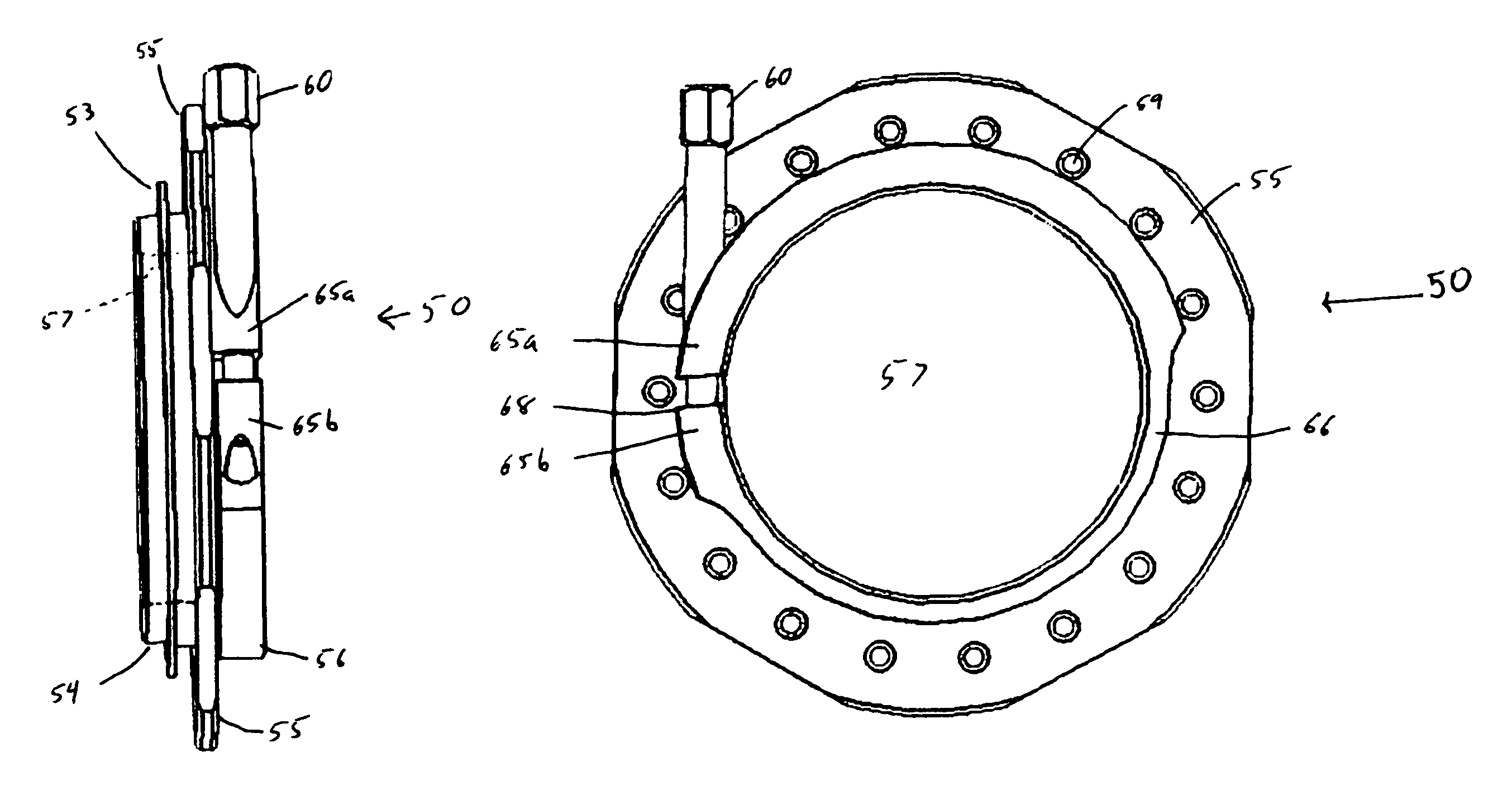
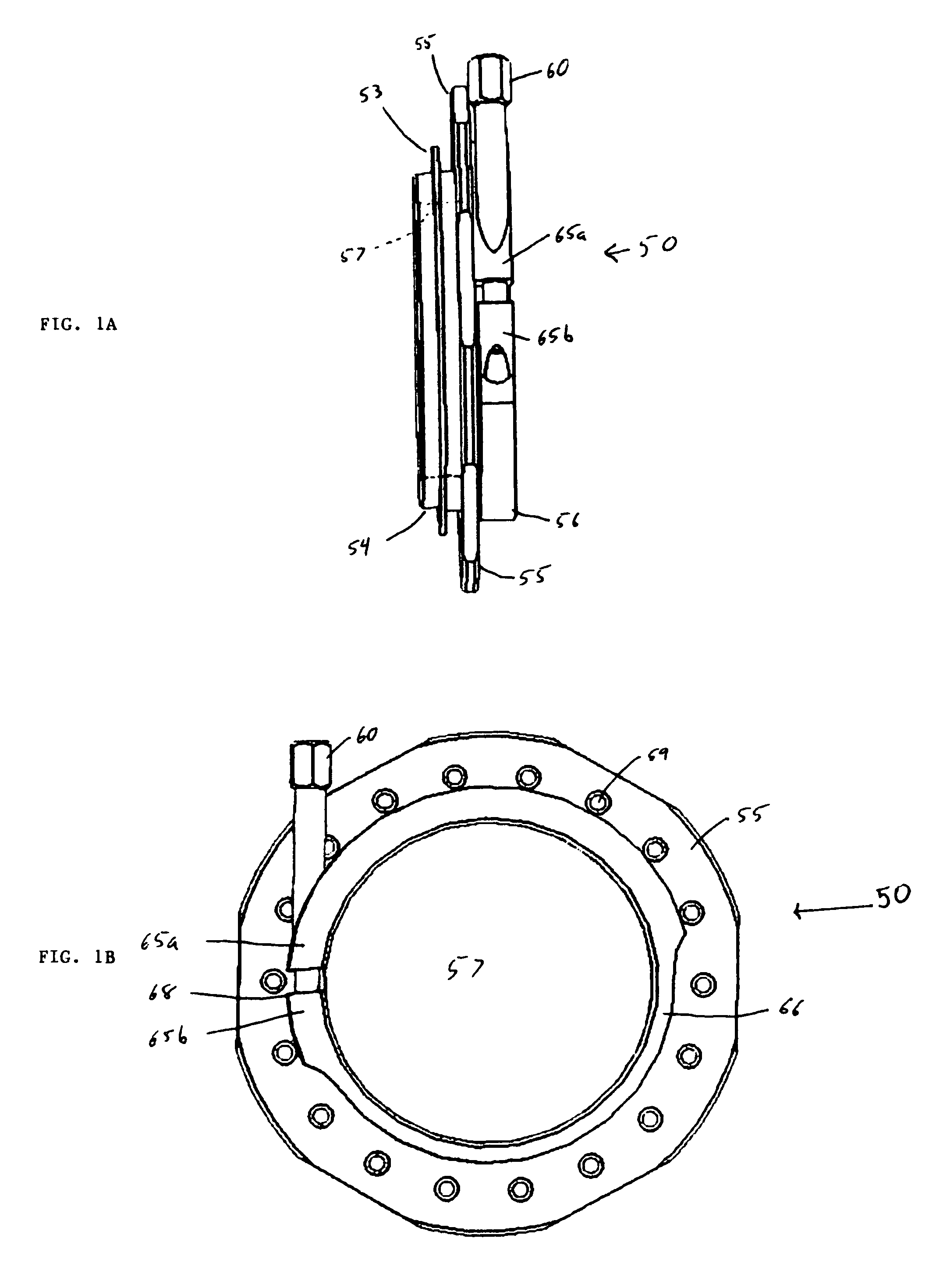
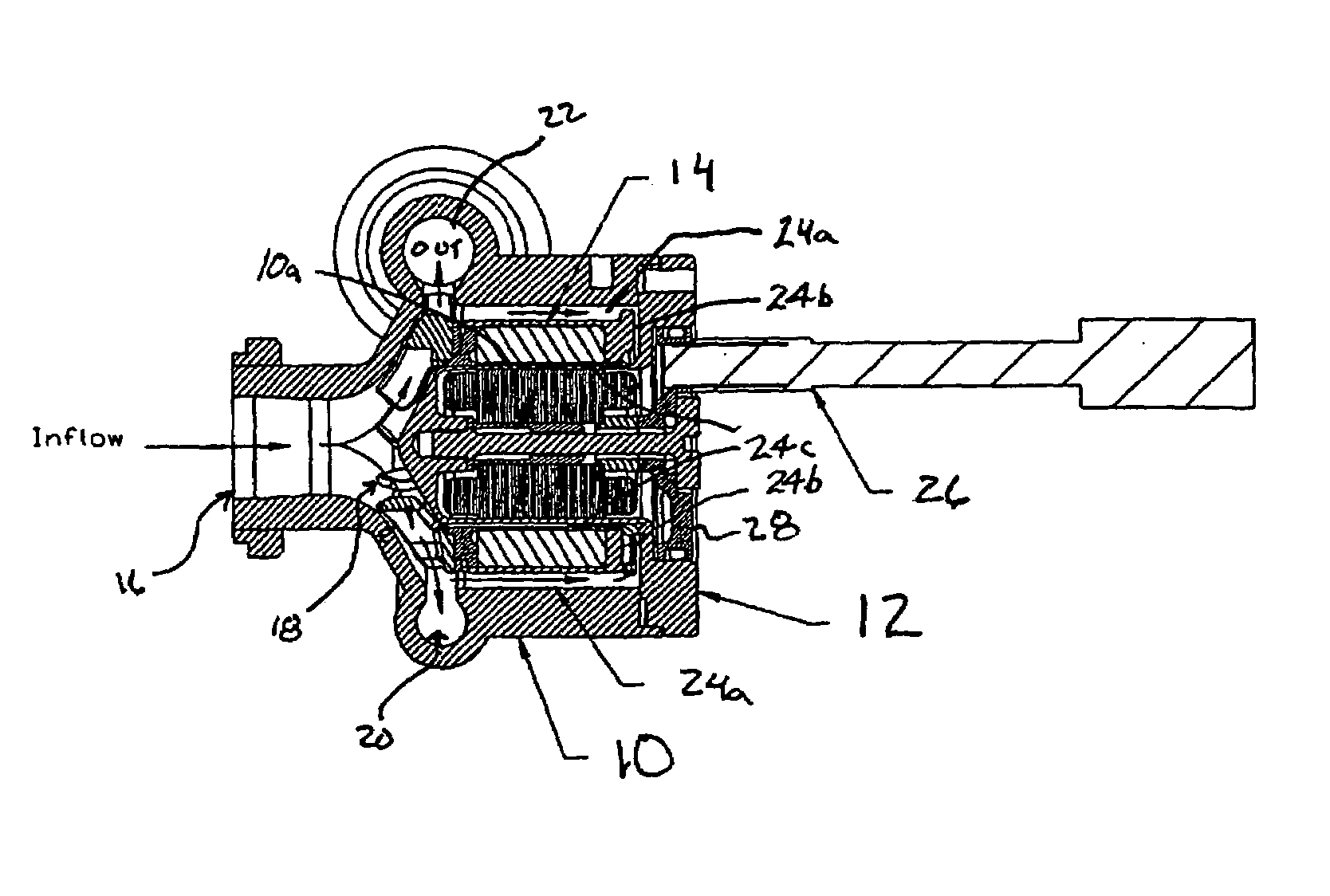
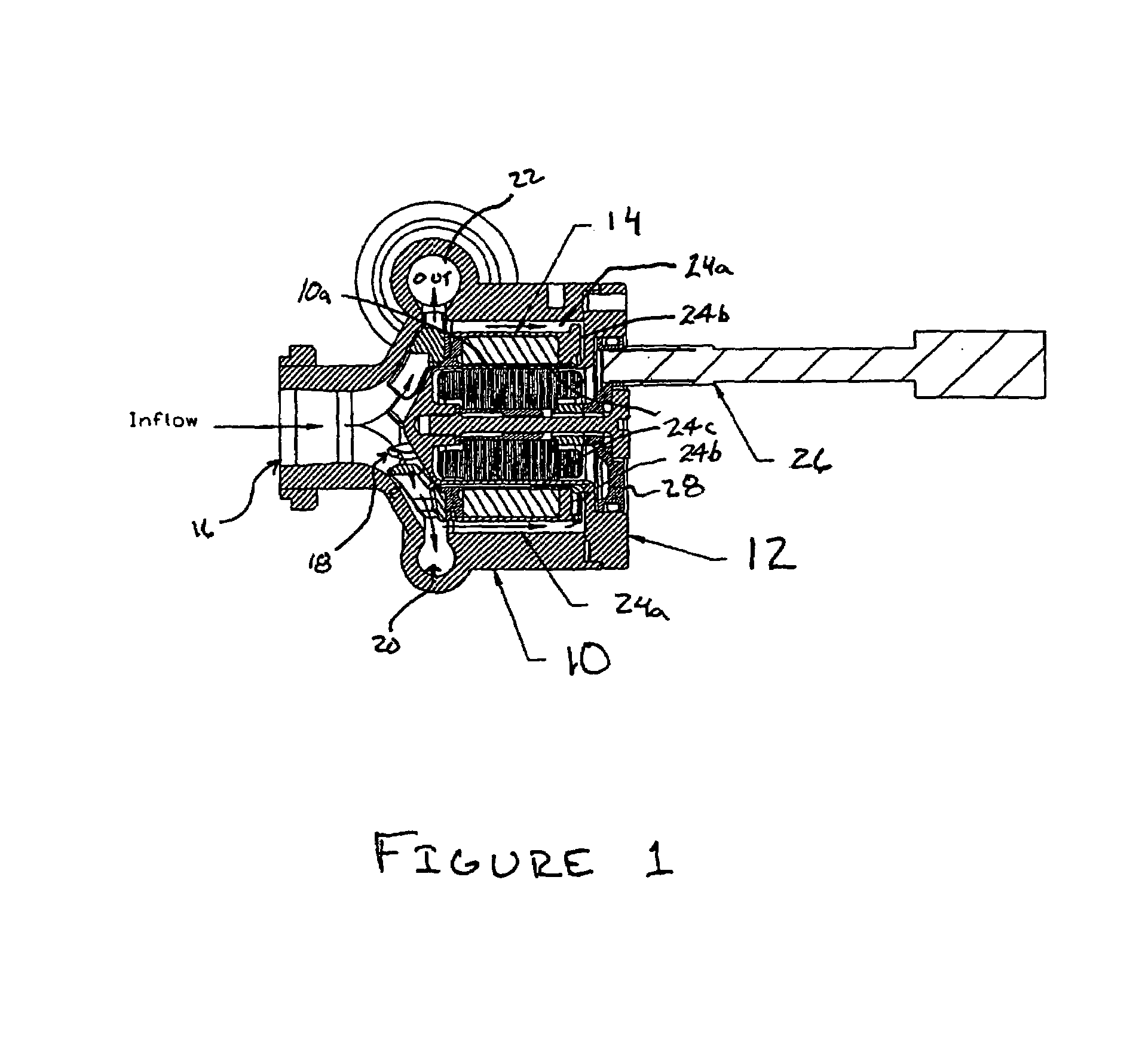
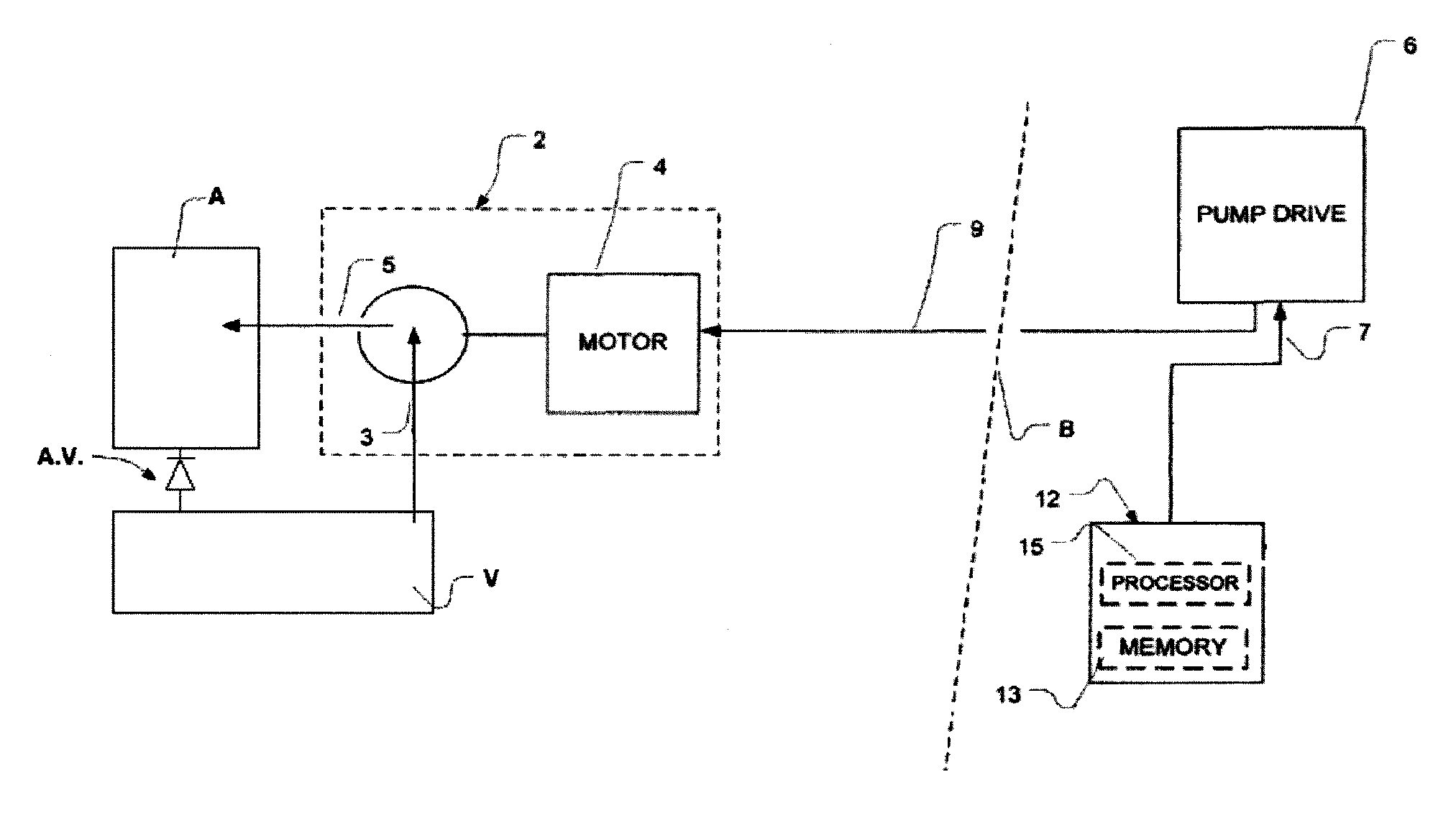
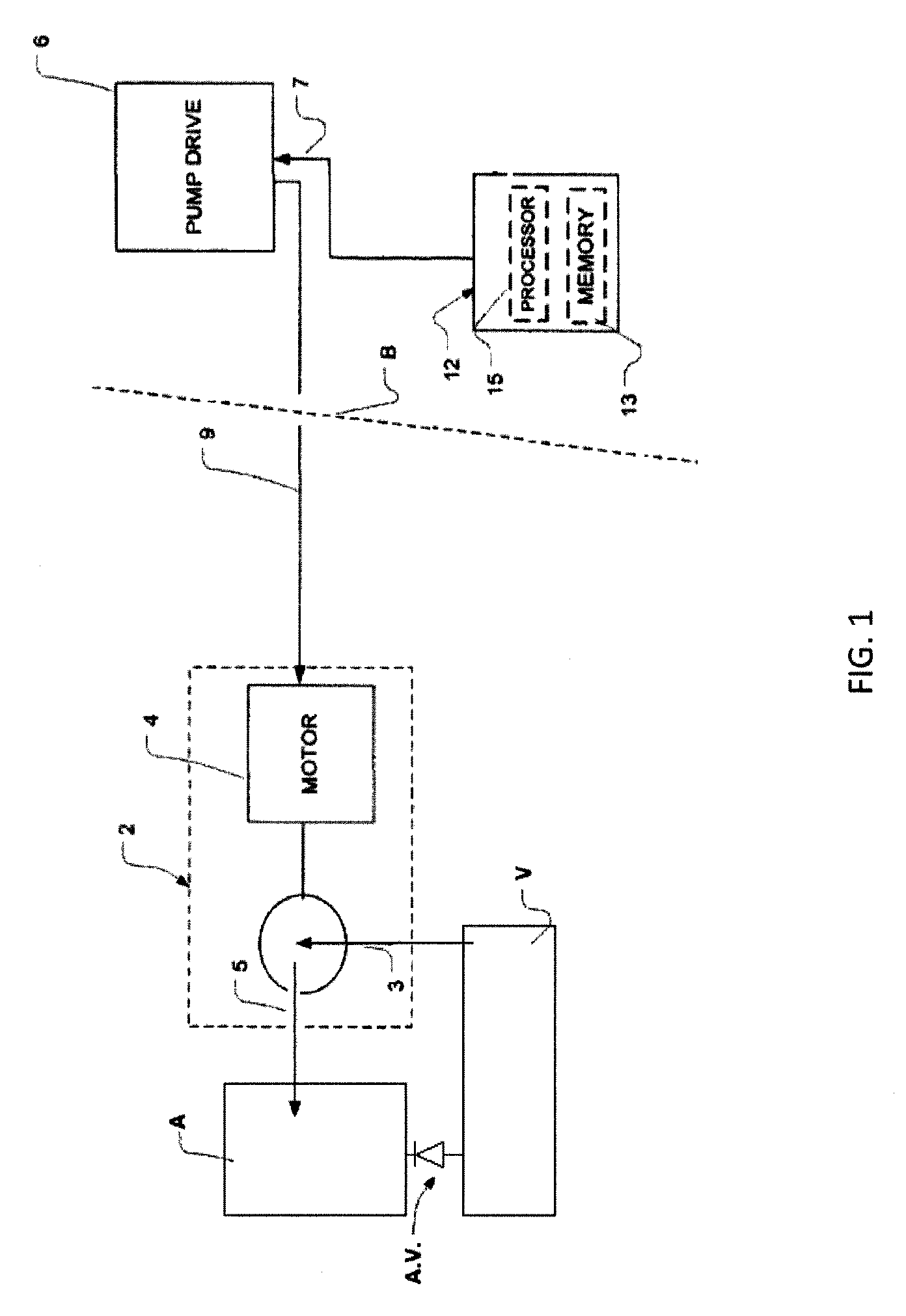
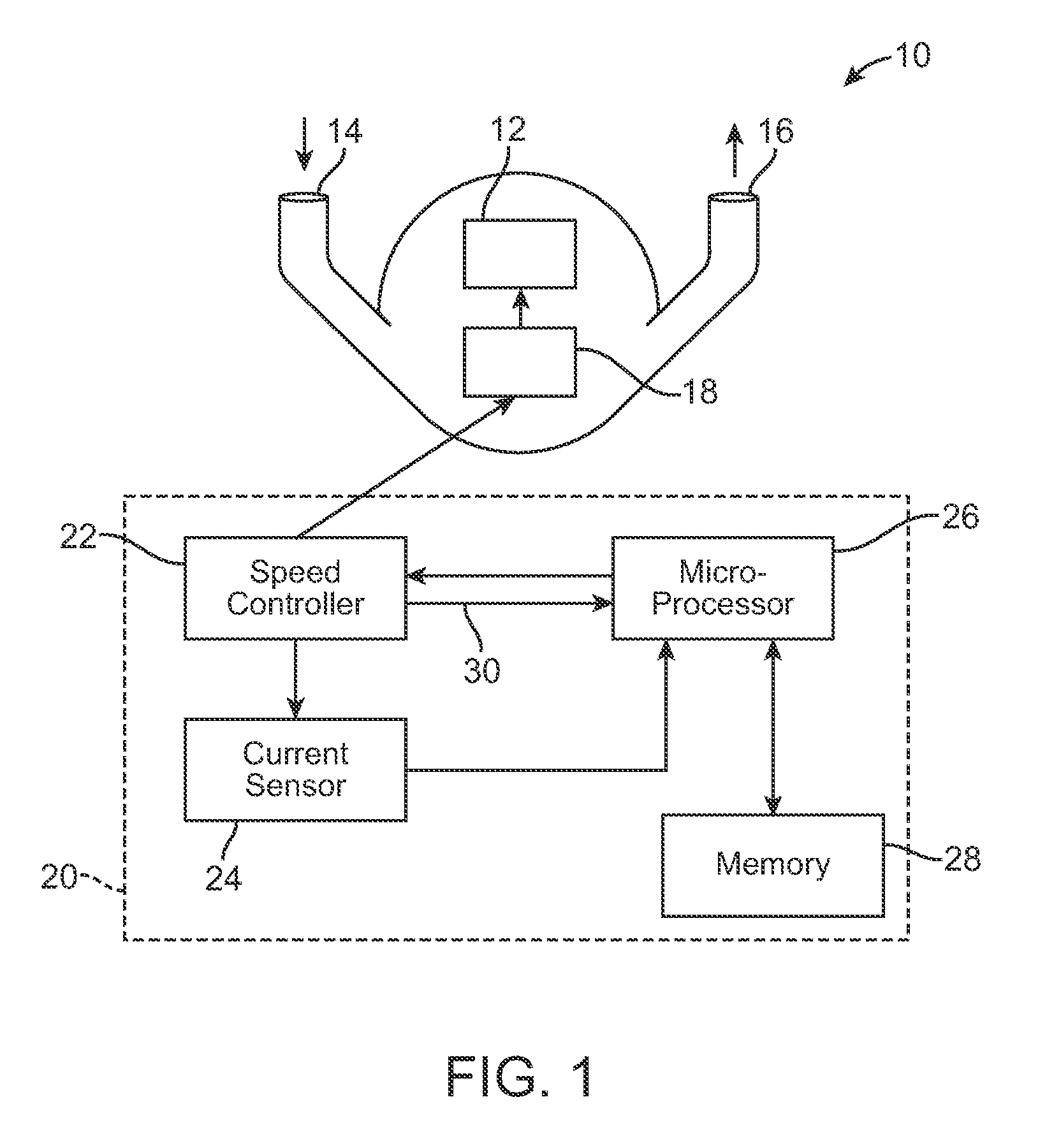
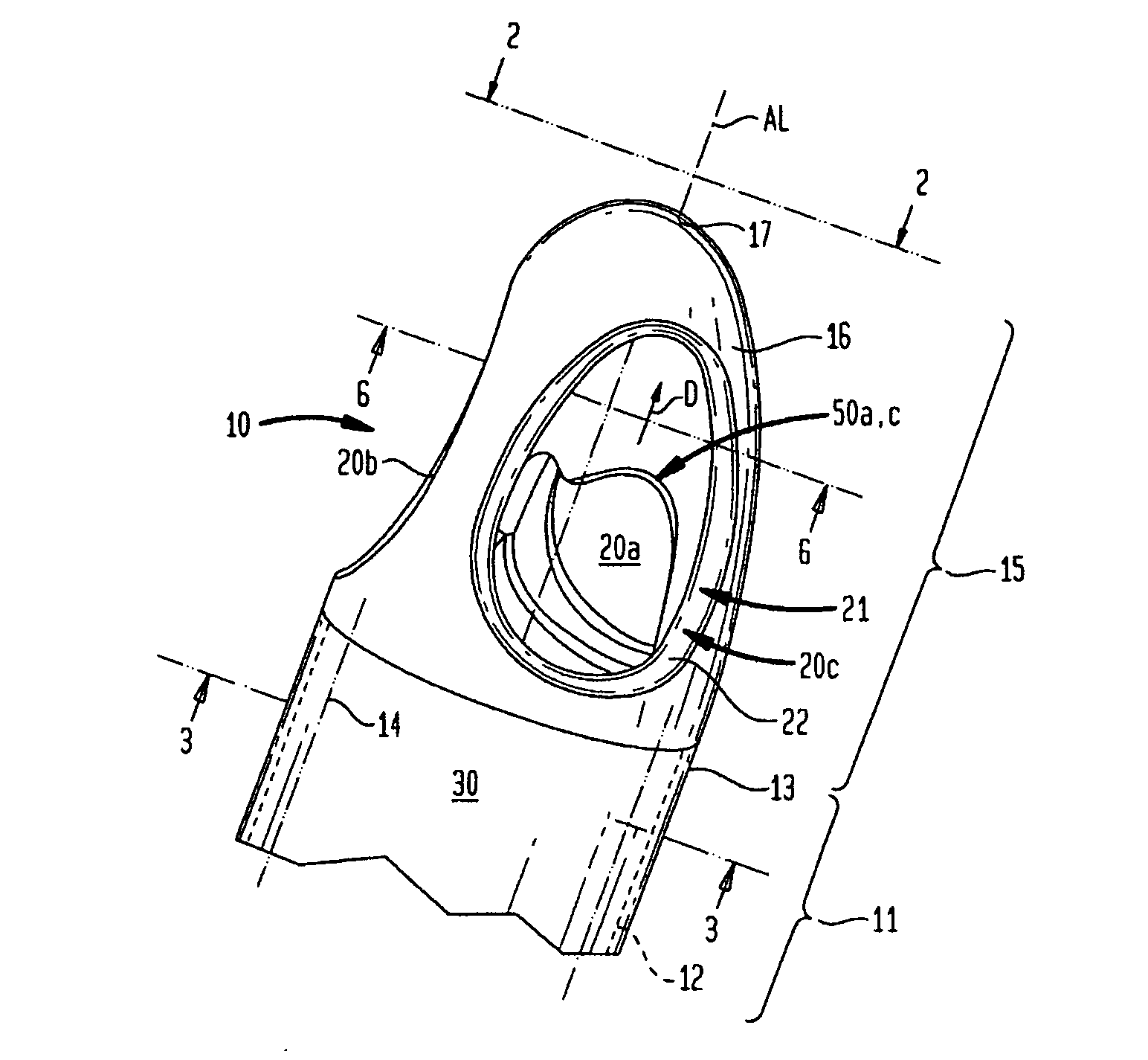
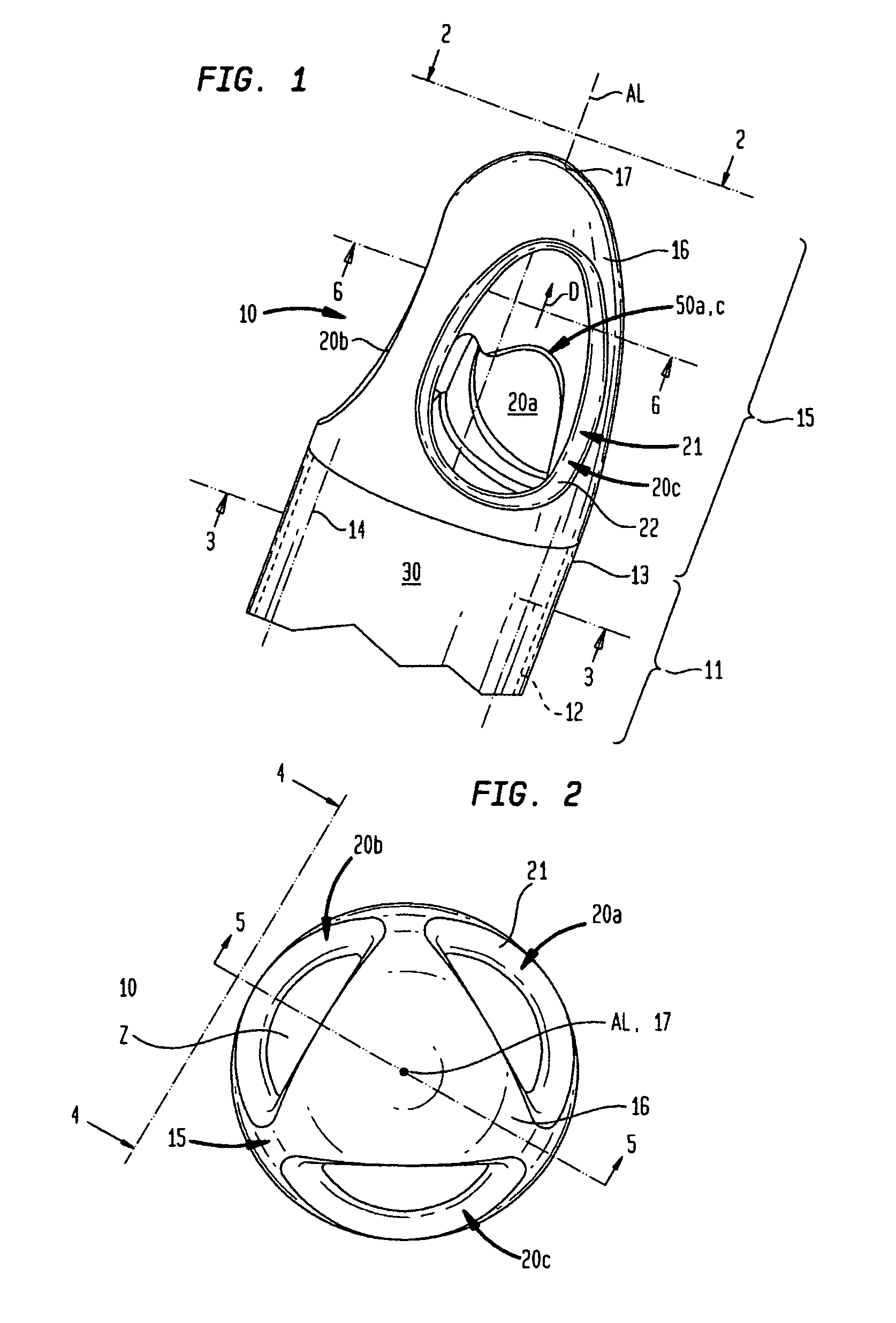
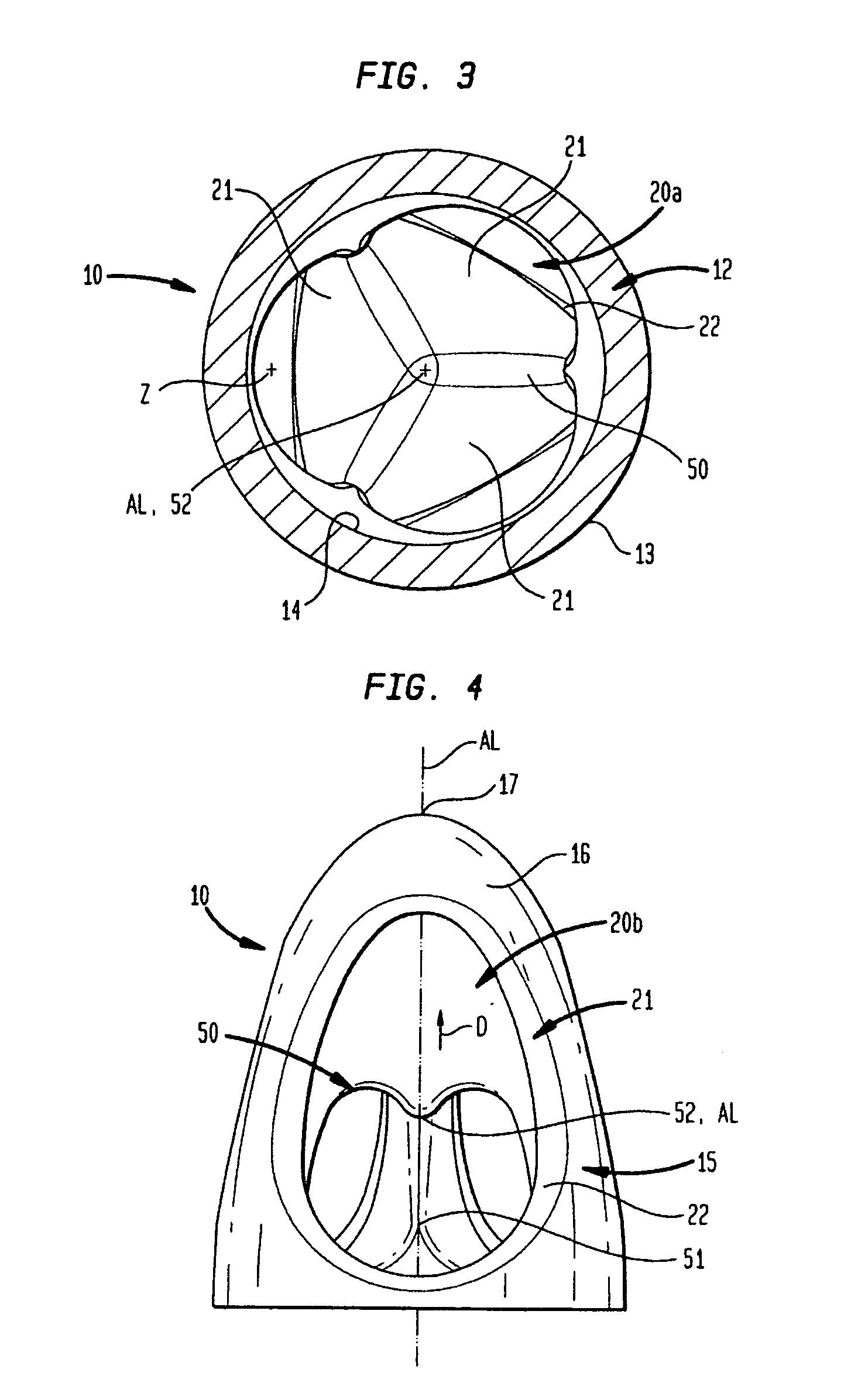
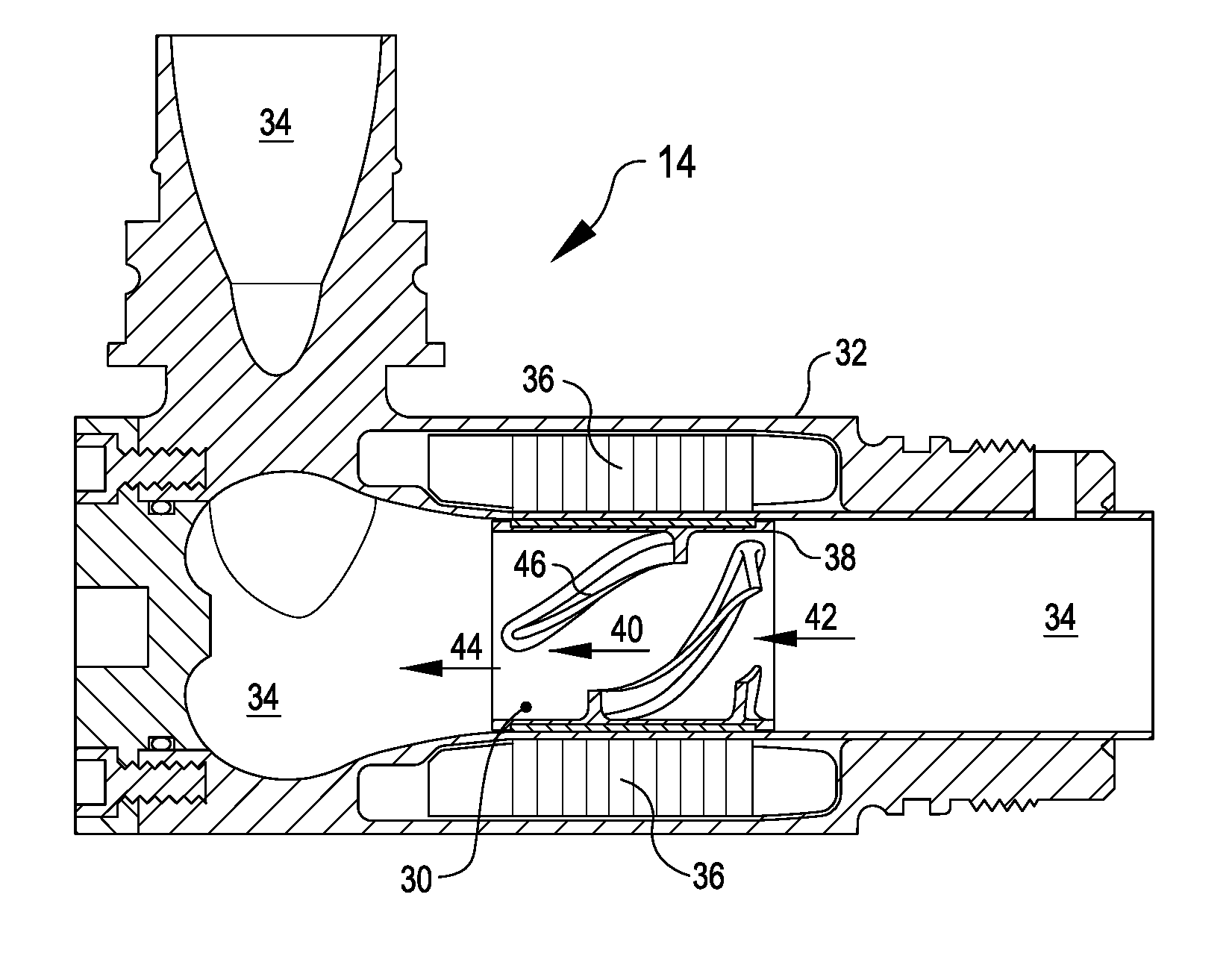
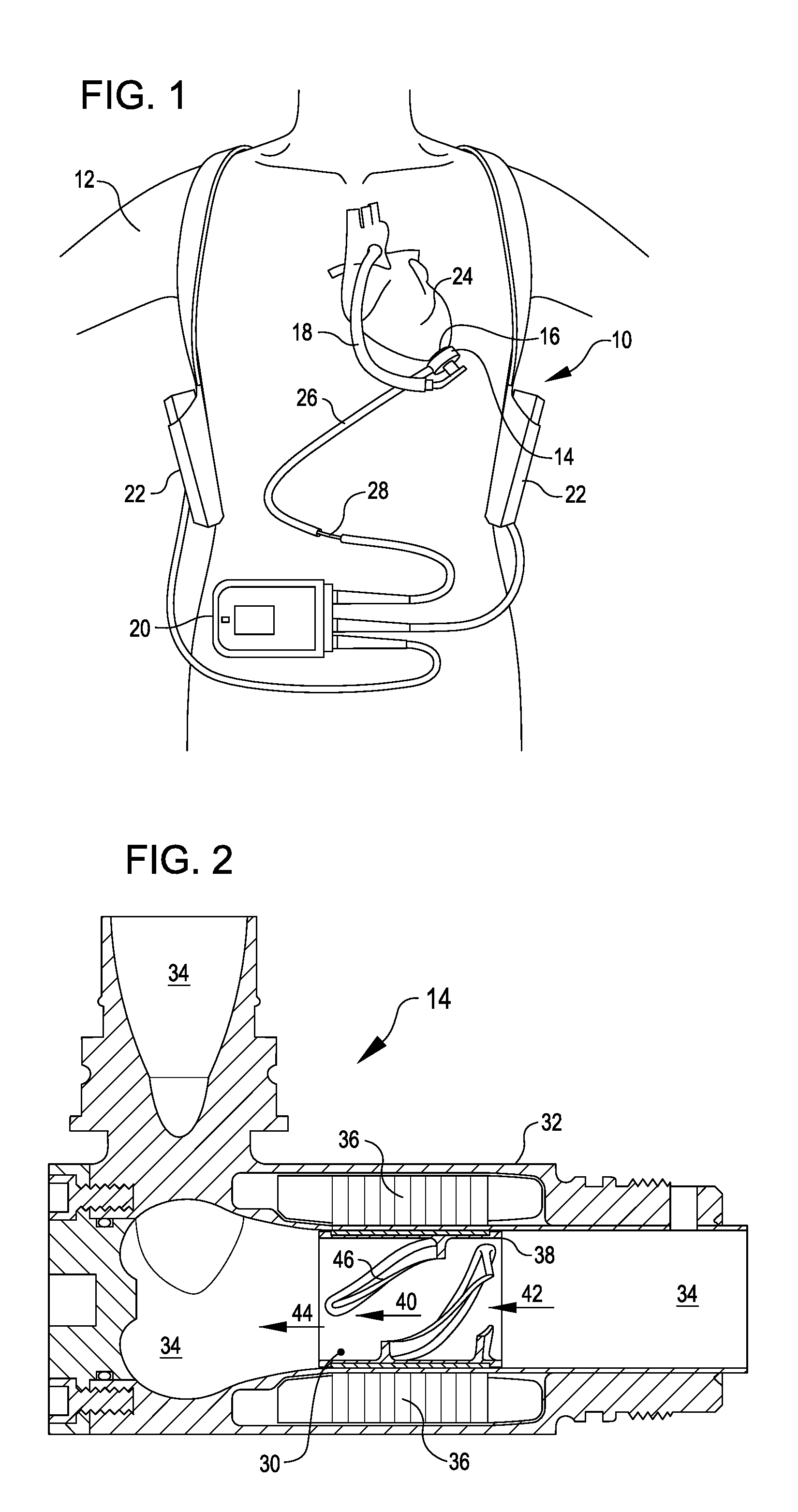
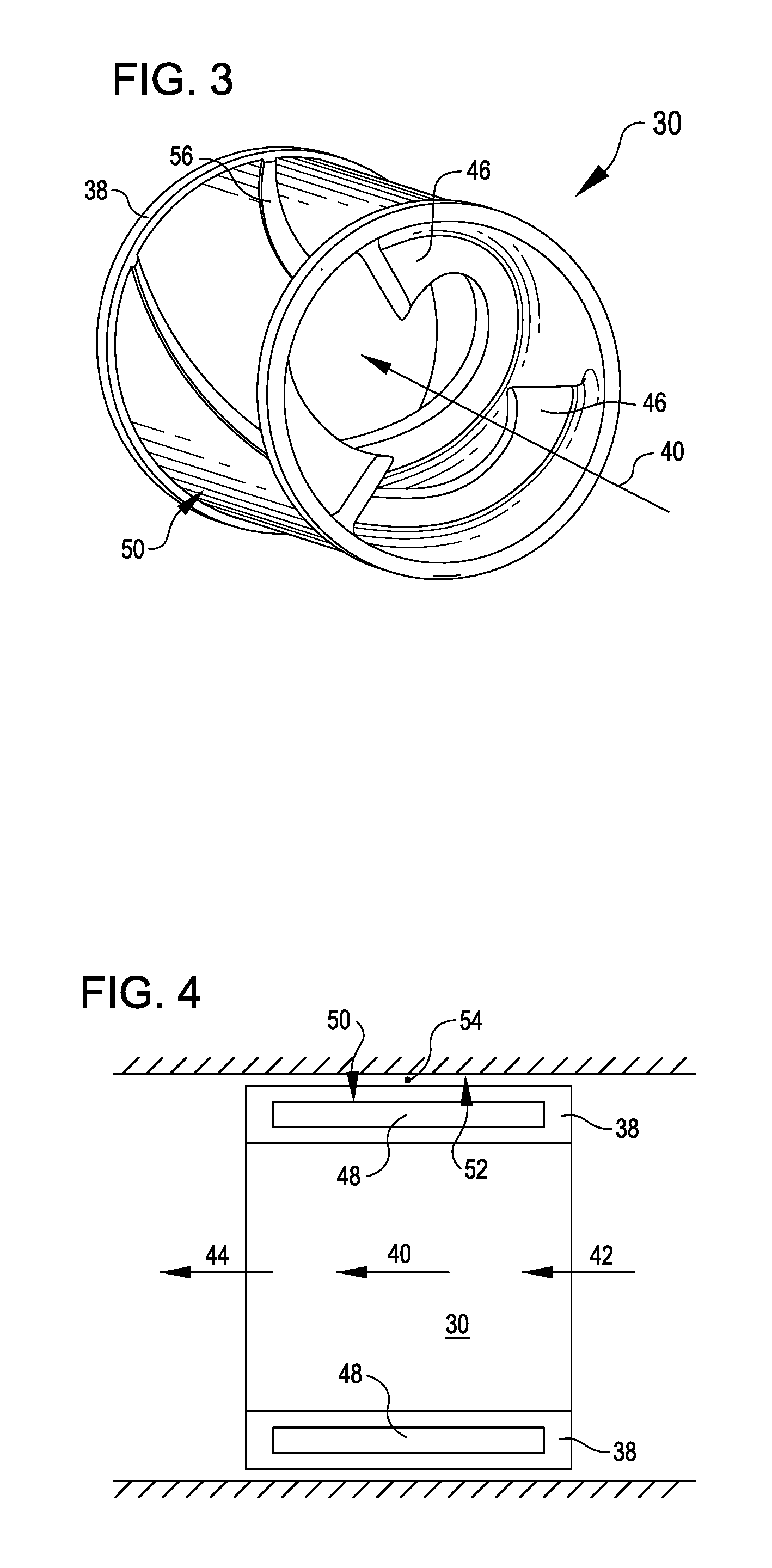
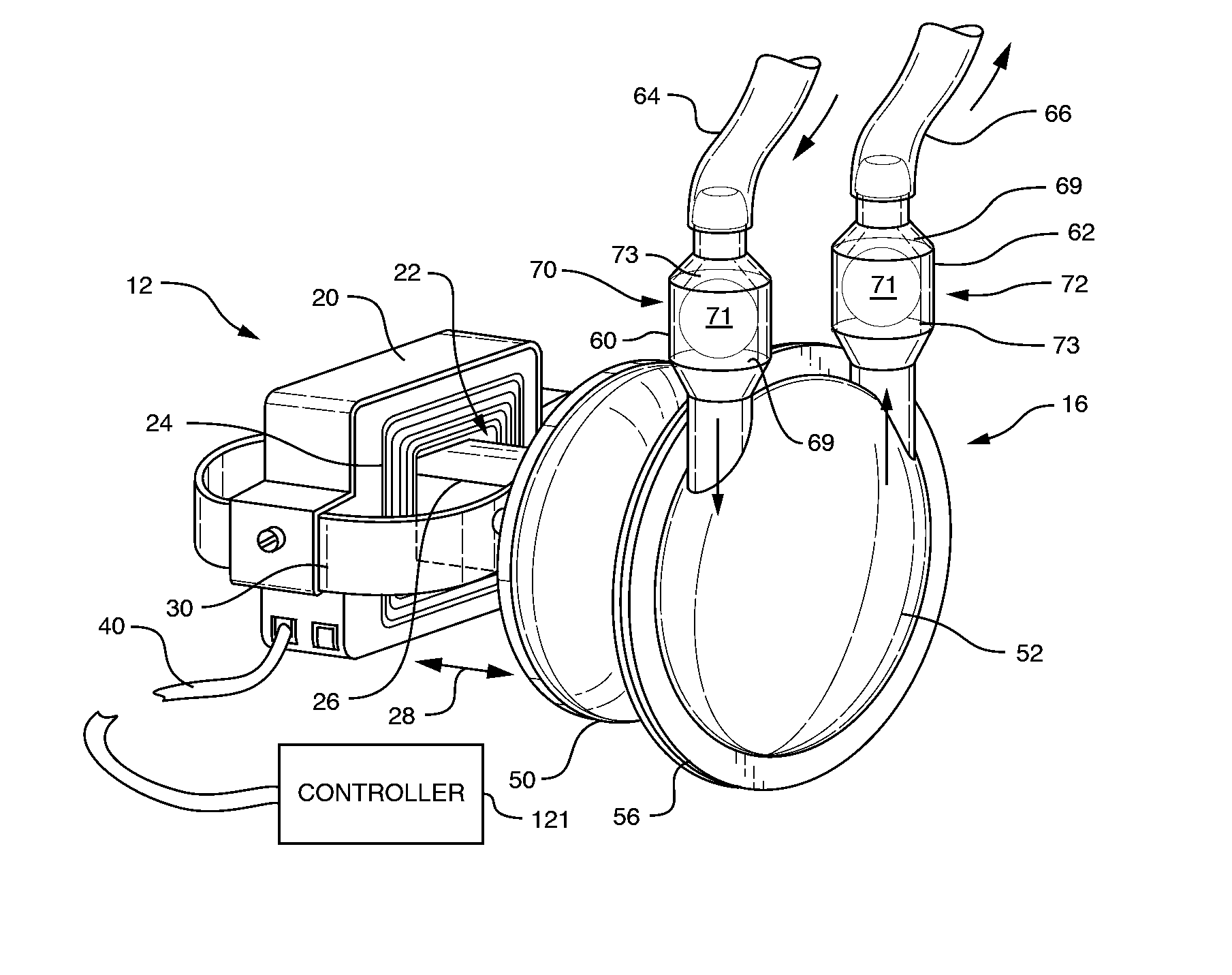
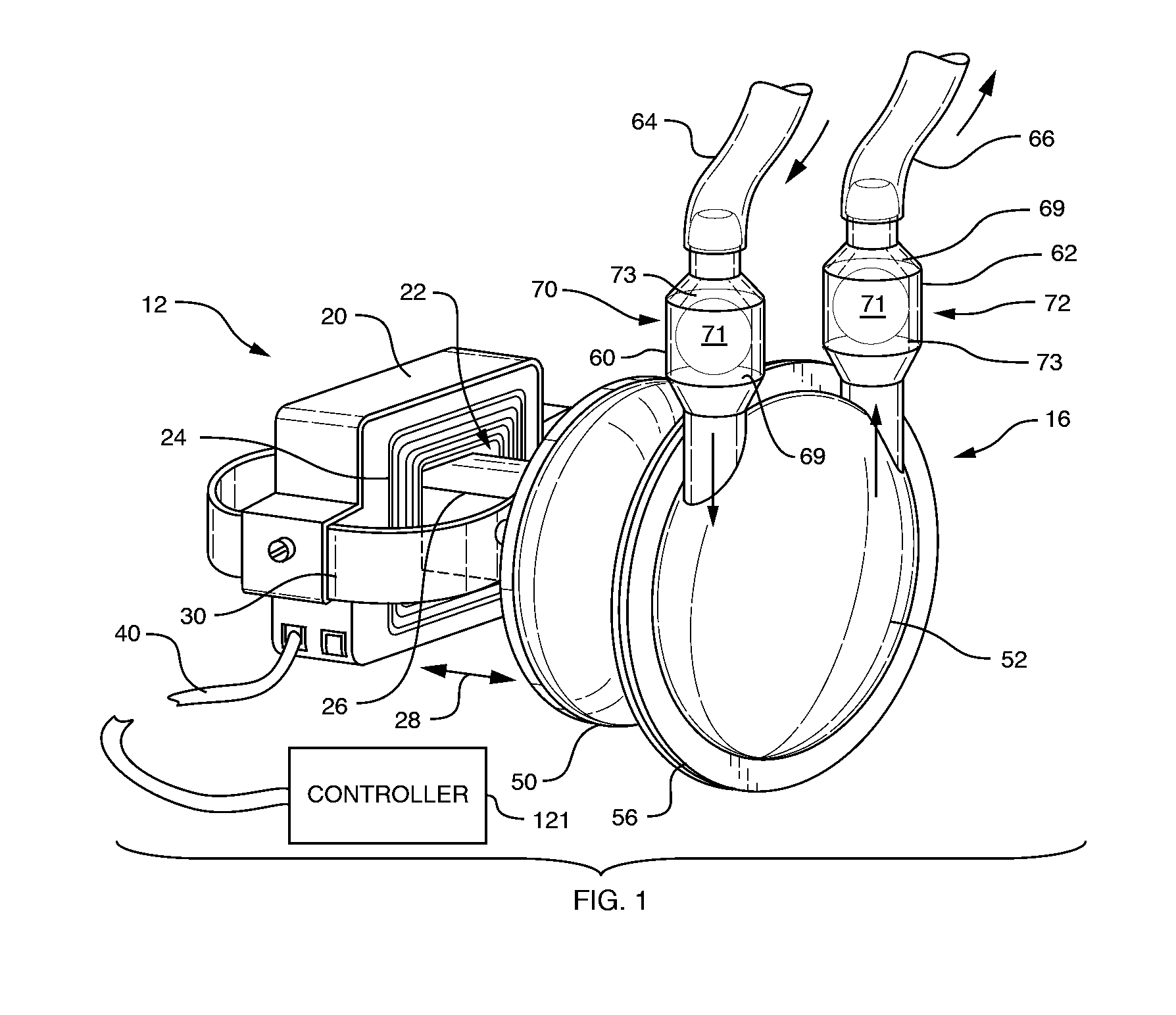
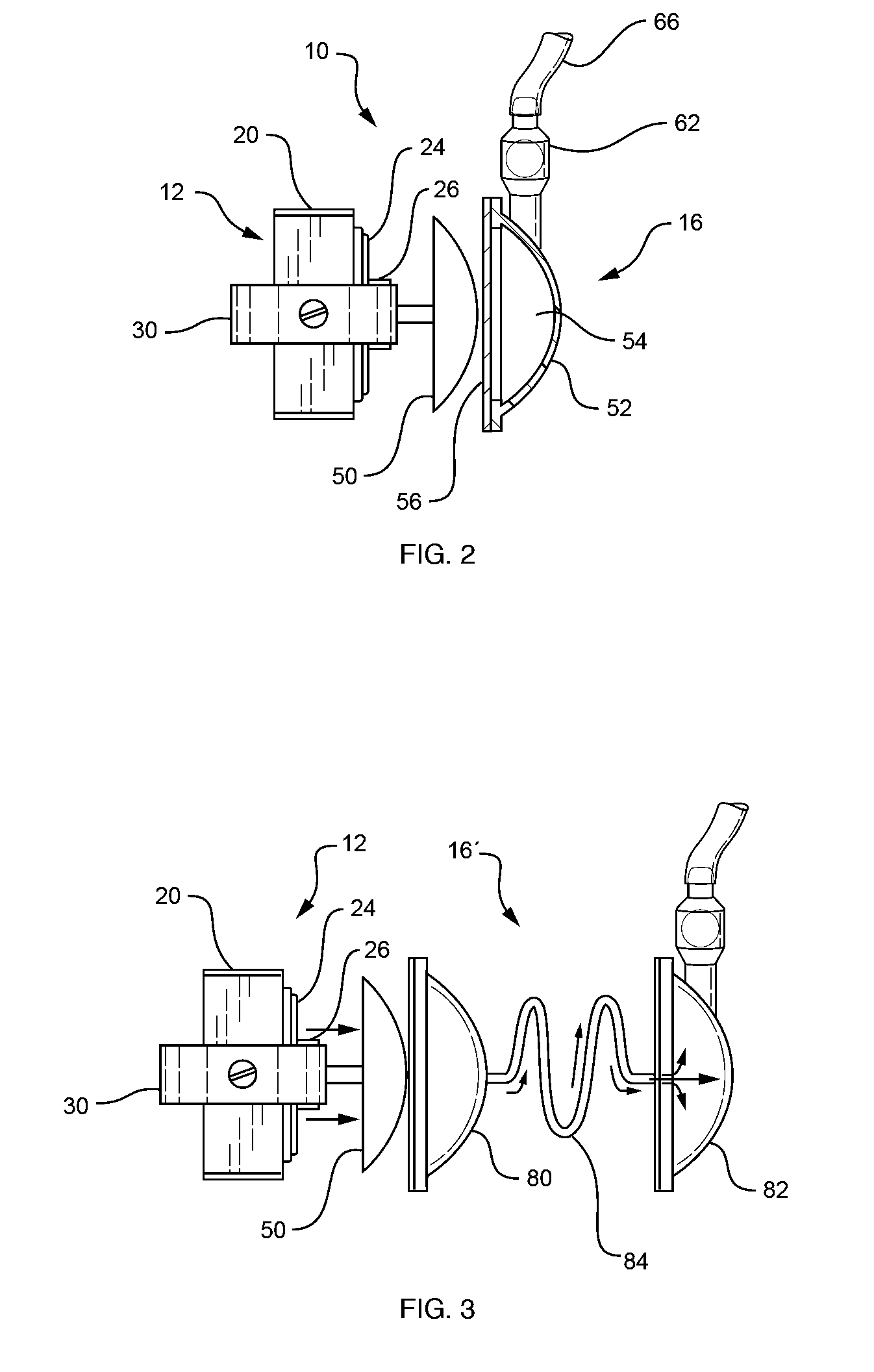
A pumping system 10 provides a physiological pulsatile flow and includes controller 121, a pump drive head 50 coupled to a motor 12 and a fluid housing 52 having at least one port 60. The port 60 includes a ball valve retainer region 69, a valve seat 73, and an occluder ball 71 disposed in the ball valve retainer region 69. During operation, the motor 12 forces the fluid in and out the fluid housing 52 and causes the occluder ball 71 to move from a first position whereby the fluid cannot pass through the port 60, to a second position whereby the fluid moves annular to and generally around the occluder ball 71. This movement creates a slight flow reversal that “breaks up” any blood clots that may form. The pumping system may be used as part of a cardiopulmonary bypass system, a ventricular assist device (VAD) and / or a heart pump.
Owner:DESIGN MENTOR
Intravascular ventricular assist device
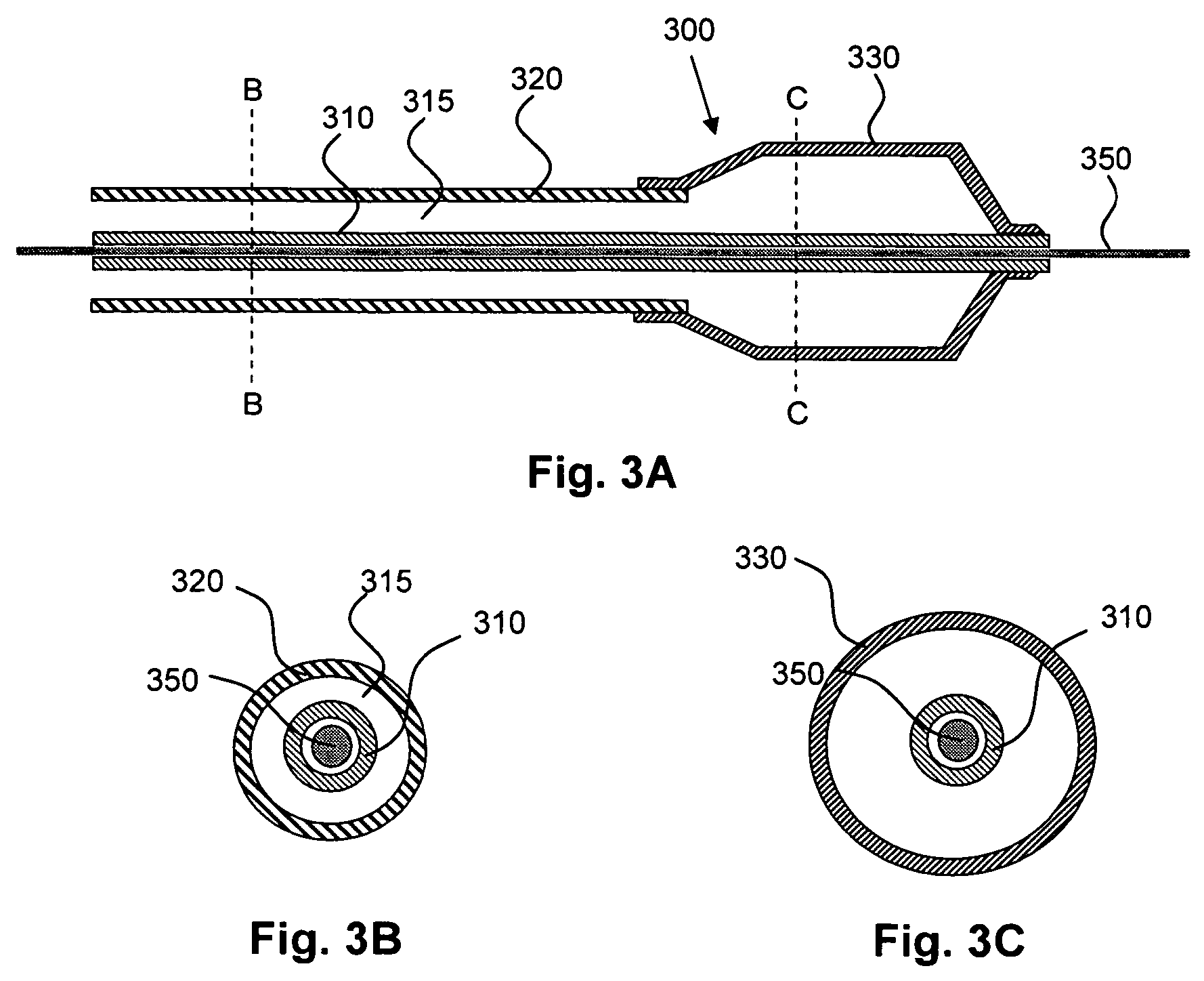
One aspect of an intravascular ventricular assist device is an implantable blood pump where the pump includes a housing defining a bore having an axis, one or more rotors disposed within the bore, each rotor including a plurality of magnetic poles, and one or more stators surrounding the bore for providing a magnetic field within the bore to induce rotation of each of the one or more rotors. Another aspect of the invention includes methods of providing cardiac assistance to a mammalian subject as, for example, a human. Further aspects of the invention include rotor bodies having helical channels formed longitudinally along the length of the body of the rotor where each helical channel is formed between peripheral support surface areas facing radially outwardly and extending generally in circumferential directions around the rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Medical devices having superhydrophobic surfaces, superhydrophilic surfaces, or both
InactiveUS20070005024A1Reduce frictionLower resistanceMedical devicesCatheterUrinary catheterLeft ventricular size
According to an aspect of the invention, medical devices are provided, which have the following (a) one or more superhydrophobic surface regions, (b) one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A, or (c) a combination of one or more superhydrophobic surface regions and one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A. Such surfaces are created, for example, to provide reduced resistance to the movement of adjacent materials, including adjacent fluids and solids. Examples of medical device surface regions benefiting from the present invention include, for example, outside and / or inside (luminal) surfaces of the following: vascular catheters, urinary catheters, hydrolyser catheters, guide wires, pullback sheaths, left ventricular assist devices, endoscopes, airway tubes and injection needles, among many other devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Permanent ventricular assist device for treating heart failure
The invention is a kit for a permanent ventricular assist device that can be permanently implanted into the circulatory system of a patient. The kit comprises one or more passive cores (Pcore), a stator, a power supply, and a controller unit. The inventors have realized that major open heart surgery, generally used for implementing a magnetic blood pump in the circulatory system, can be wholly avoided if the rotor and the stator are physically separated and are implanted respectively inside and around the blood vessel at the location of interest. Therefore the kit is characterized in that the one or more Pcores are configured to allow them to be implanted inside a blood vessel and the stator is configure to enable it to be placed outside of the blood vessel surrounding the Pcores. Also described are illustrative medical procedures for implanting the components of the kit at different locations in the body.
Owner:LEVITICUS CARDIO
Attachment System, Device and Method
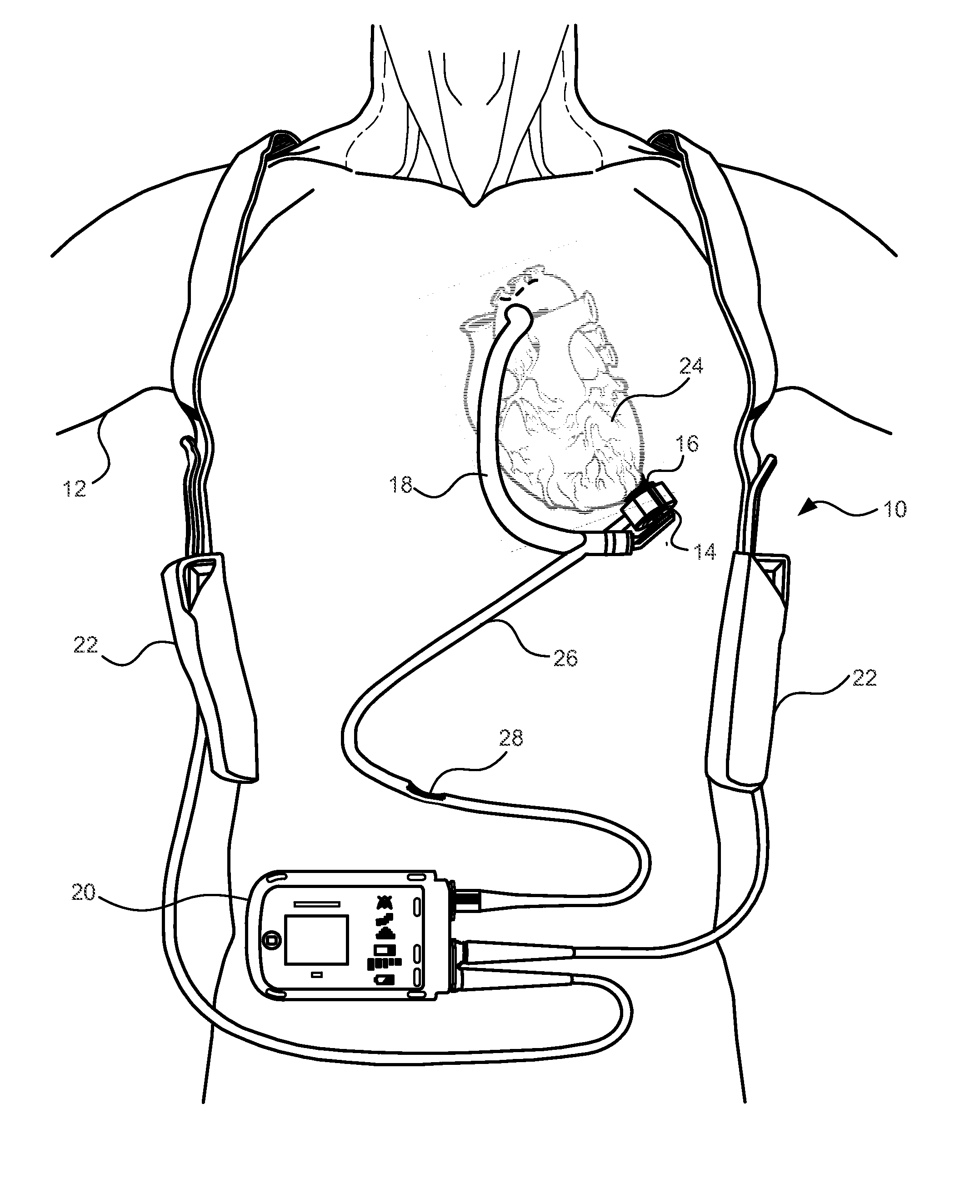
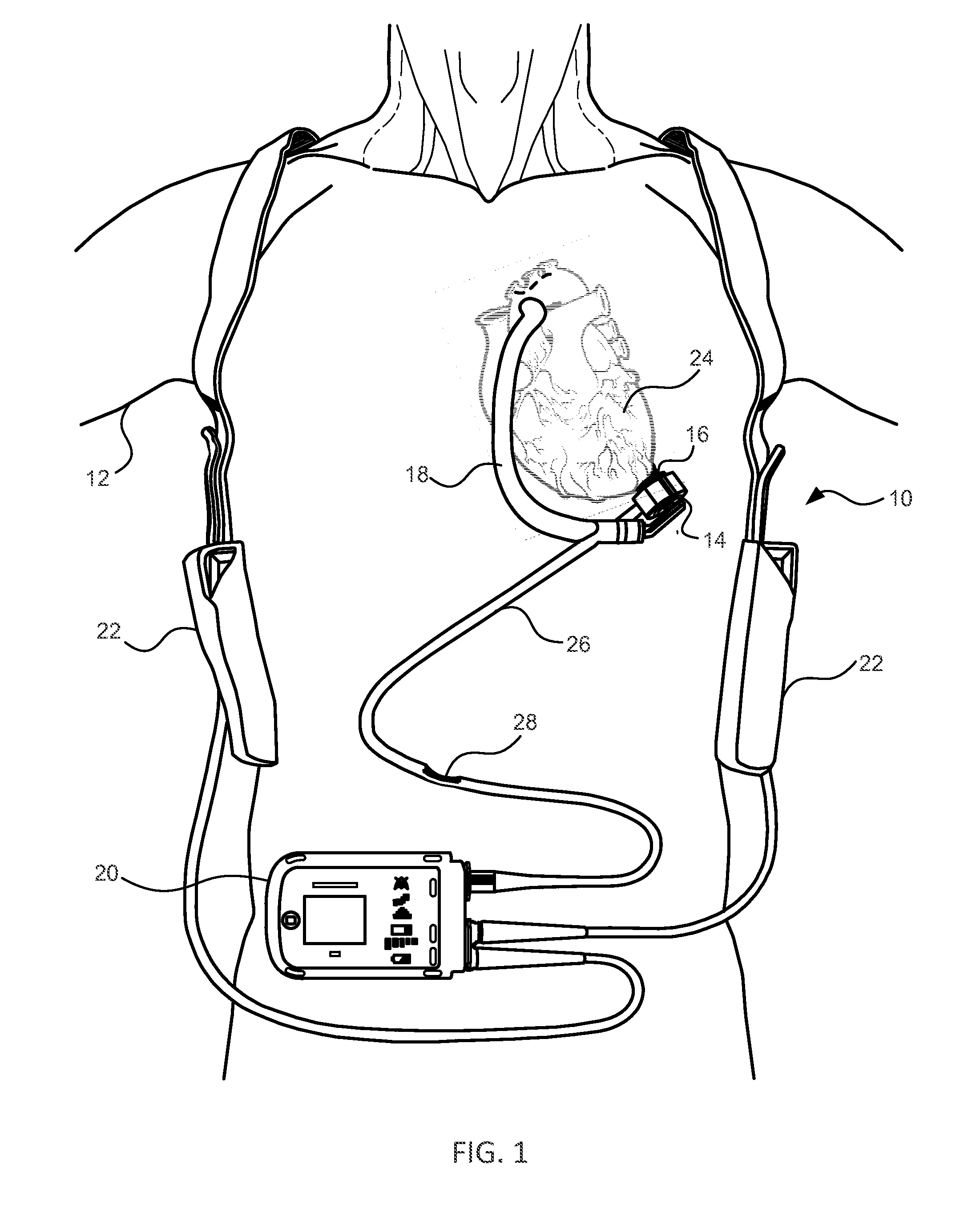
A ventricular assist system and a method of implanting the system are disclosed. The system can have a pump, an inflow conduit, an outflow conduit, attachment ring, ring clamp, and a valvular structure. The attachment ring can be attached to the apex of the heart. The valvular structure can have a flexible, one-way valve in a rigid housing. The inflow conduit can be passed through the valvular structure and the attachment ring into a beating heart with minimal loss of blood. Devices such as slitting tool, coring knife, and / or C-clamp and use of the devices can form part of the system and method for implanting the ventricular assist device.
Owner:TC1 LLC
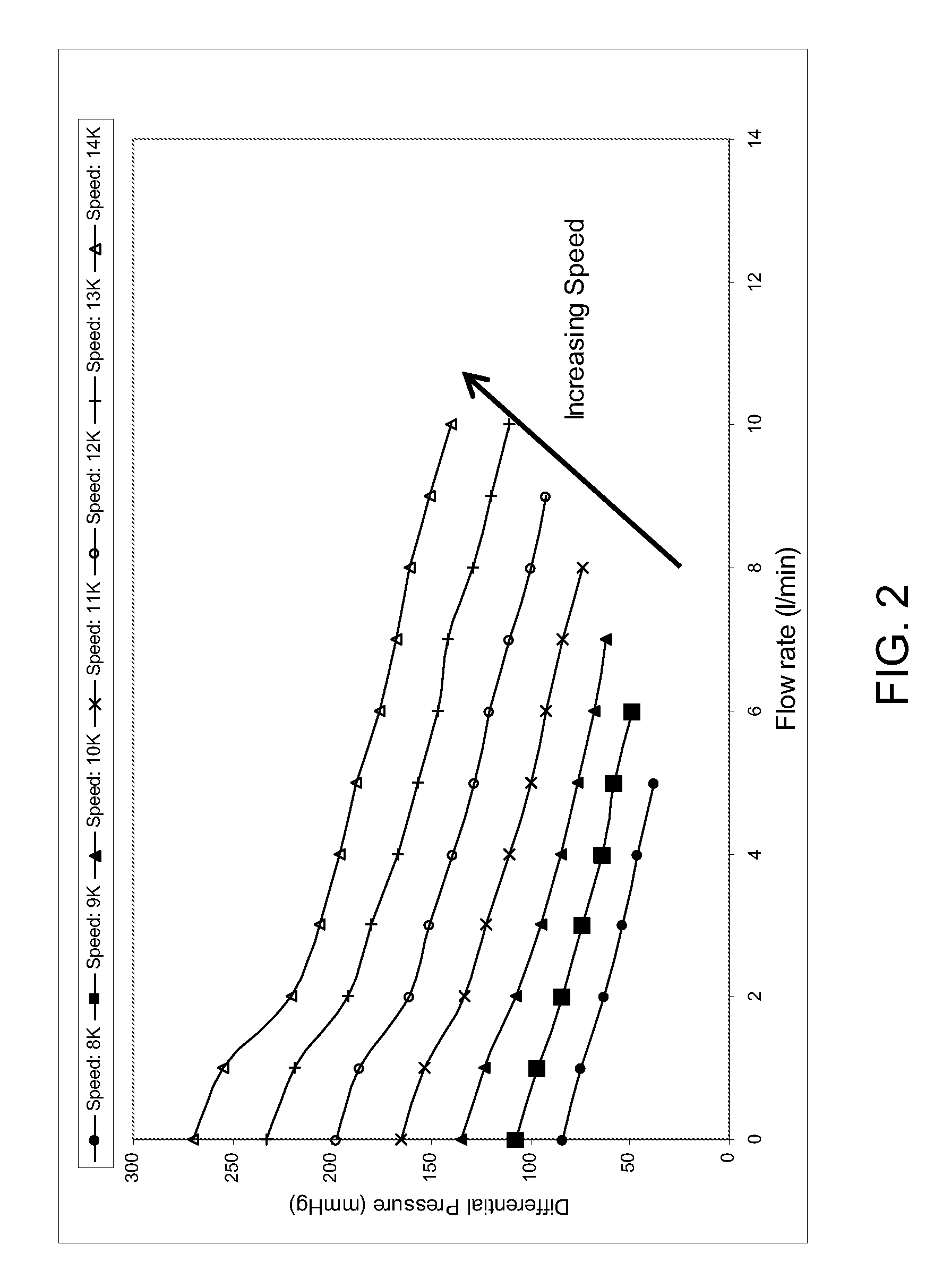
Speed change algorithim for a continuous flow blood pump
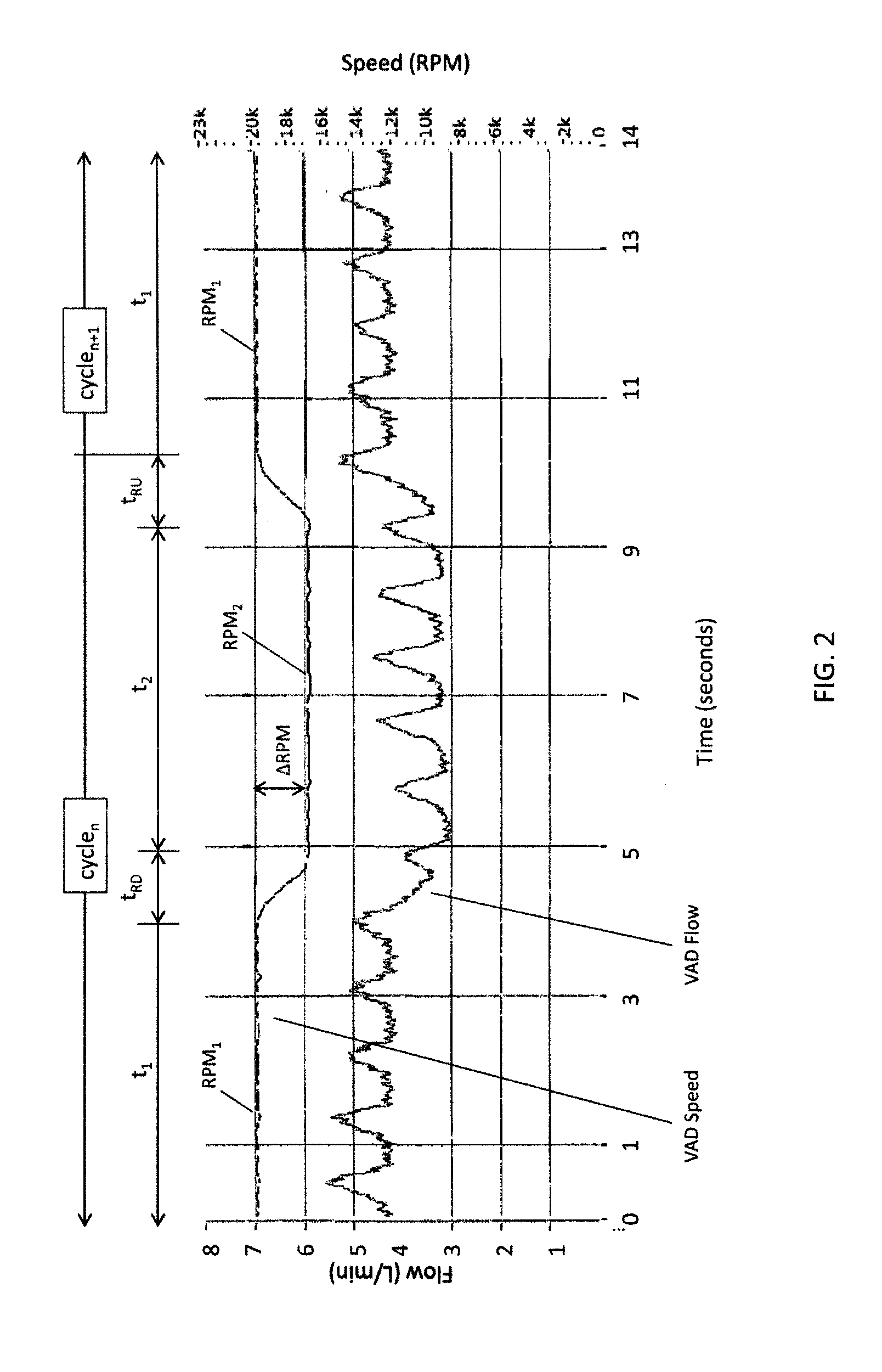
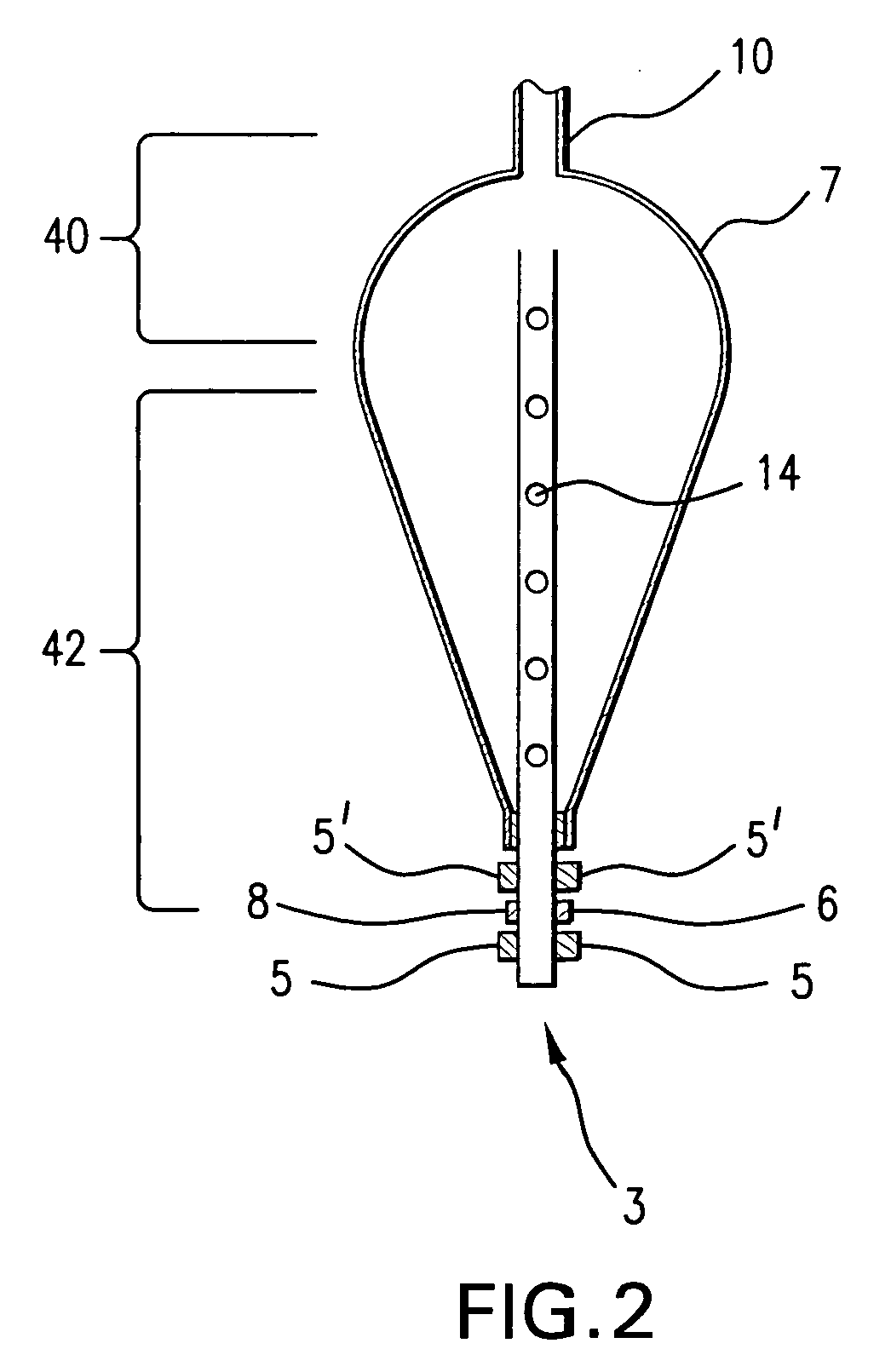
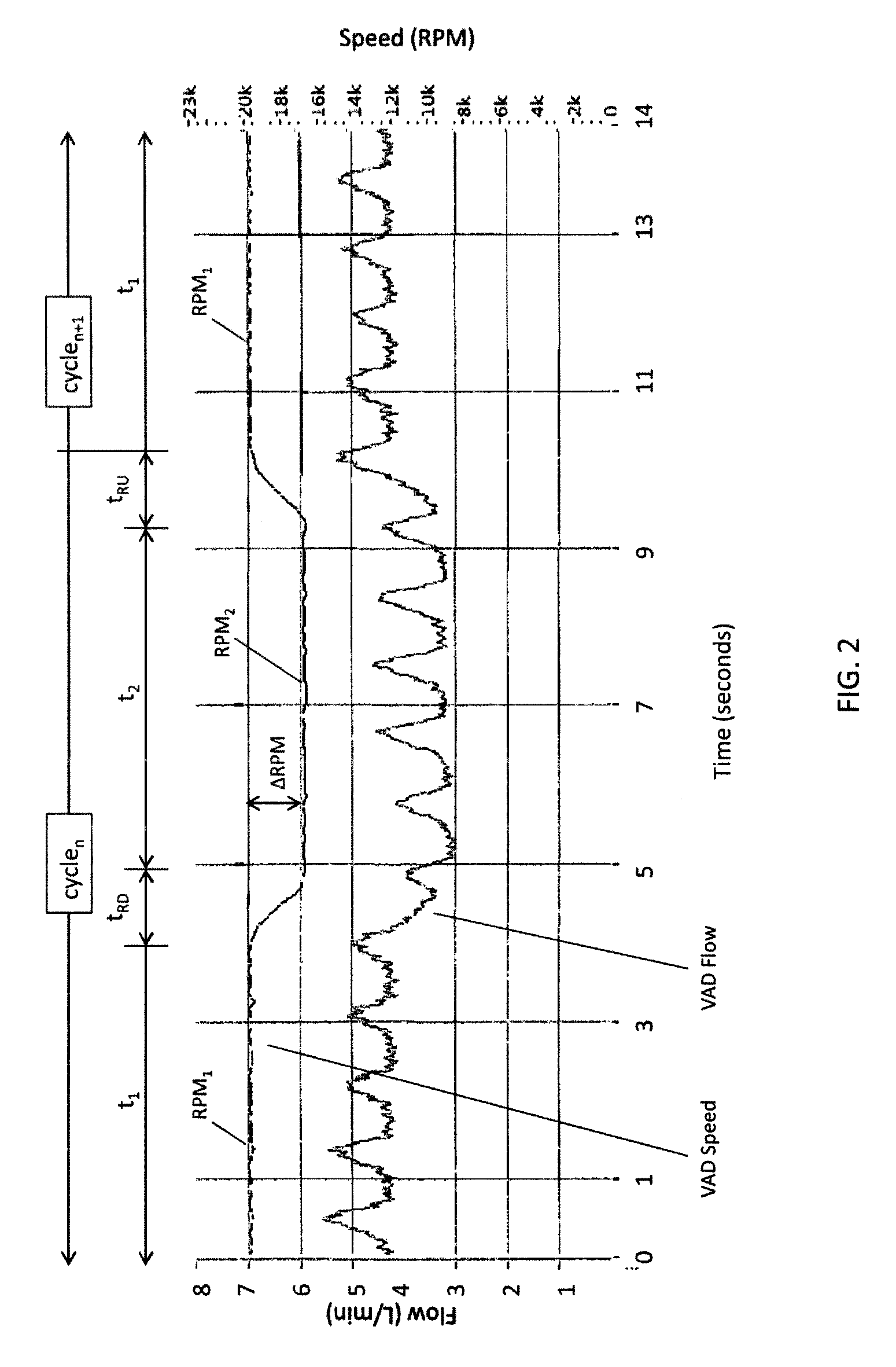
A ventricular assist device (“VAD”) includes a continuous-flow pump (2) implantable in fluid communication with a ventricle (V) and an artery (A) of a patient to assist blood flow from the ventricle to the artery. The VAD also includes a control circuit (12) connected to the pump, the control circuit being configured to direct the pump to operate in a series of cycles. Each cycle may include (i) pumping blood at a first speed (RPM1) and at a first flow rate during a first period (t1); then (ii) decreasing the speed of the pump from the first speed to a second speed (RPM2) during a ramp-down period (tRD); then (iii) pumping blood at the second speed and at a second flow rate during a second period (t2); and then (iv) increasing the speed of the pump from the second speed to the first speed during a ramp-up period (tRU).
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Percutaneous intra-aortic ventricular assist device
A percutaneous intra-aortic ventricular assist device is adapted for implantation in an aorta that has a luminal wall, and includes a tubular stent body, an inner tubular body, a vane member, a carrier member, a rib unit, a first pulled string, a second pulled string, an alternately pulling mechanism, and a synchronizing member.
Owner:KANG WEI CHANG +1
Intravascular ventricular assist device
One aspect of an intravascular ventricular assist device is an implantable blood pump where the pump includes a housing defining a bore having an axis, one or more rotors disposed within the bore, each rotor including a plurality of magnetic poles, and one or more stators surrounding the bore for providing a magnetic field within the bore to induce rotation of each of the one or more rotors. Another aspect of the invention includes methods of providing cardiac assistance to a mammalian subject as, for example, a human. Further aspects of the invention include rotor bodies having helical channels formed longitudinally along the length of the body of the rotor where each helical channel is formed between peripheral support surface areas facing radially outwardly and extending generally in circumferential directions around the rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Percutaneous Intra-Aortic Ventricular Assist Device
A percutaneous intra-aortic ventricular assist device is adapted for implantation in an aorta that has a luminal wall, and includes a tubular stent body, an inner tubular body, a vane member, a carrier member, a rib unit, a first pulled string, a second pulled string, an alternately pulling mechanism, and a synchronizing member.
Owner:KANG WEI CHANG +1
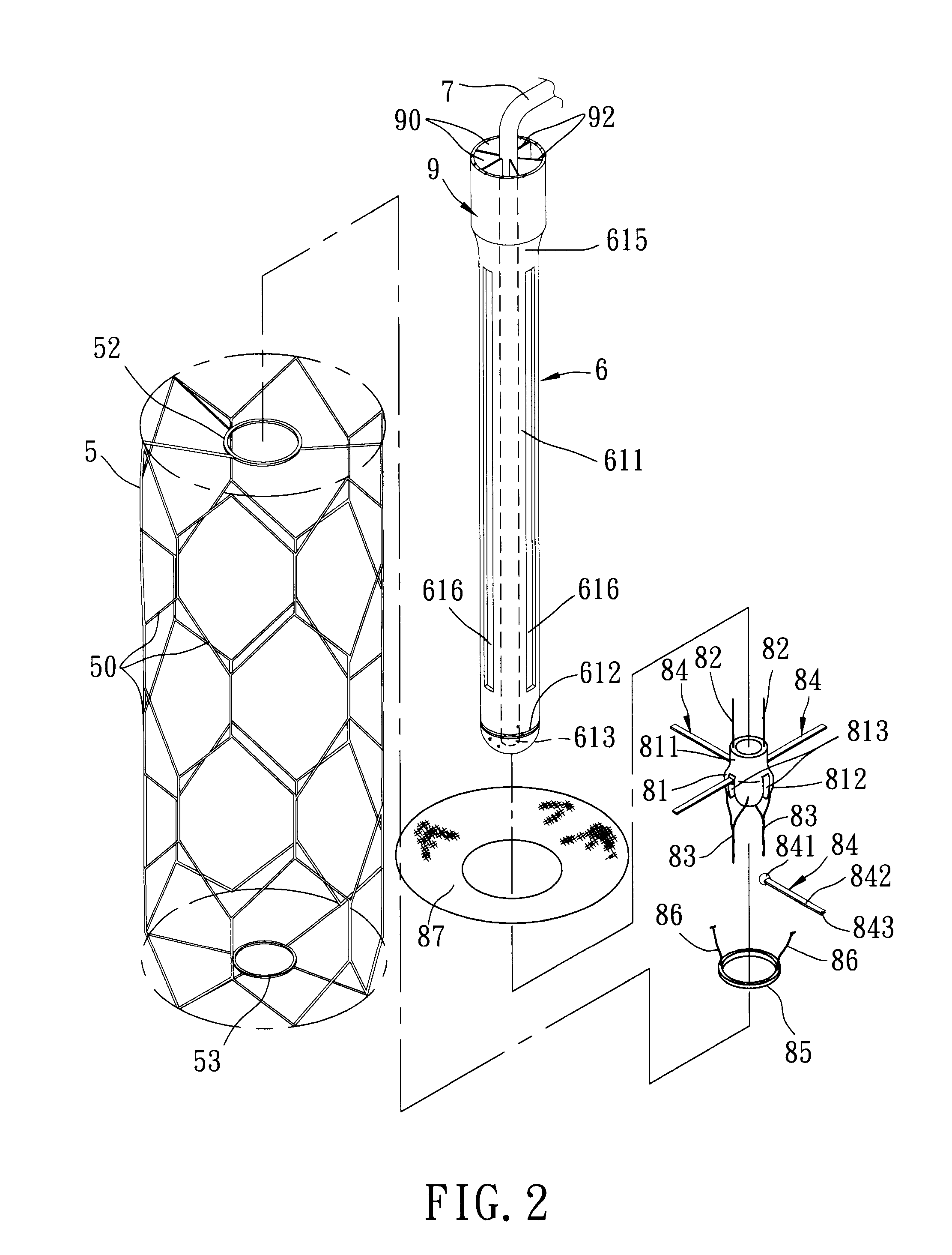
Conduit device for use with a ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20120059212A1Simplified noninvasive approachBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesCatheterHeart walls
The present invention is a conduit device designed to be placed within a wall of a heart, such as through a prepared opening or hole in the heart wall. The conduit is hollow and extends to form a sleeve over a portion of the heart pump, such as a VAD, which traverses the heart wall and enters a chamber of the heart. The conduit provides for a simplified and noninvasive approach to removal and / or replacement of the heart pump.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Rotary pump with hydrodynamically suspended impeller
InactiveUS7156802B2Increase thrustReduce thrustPump componentsRotary piston pumpsImpellerRotary pump
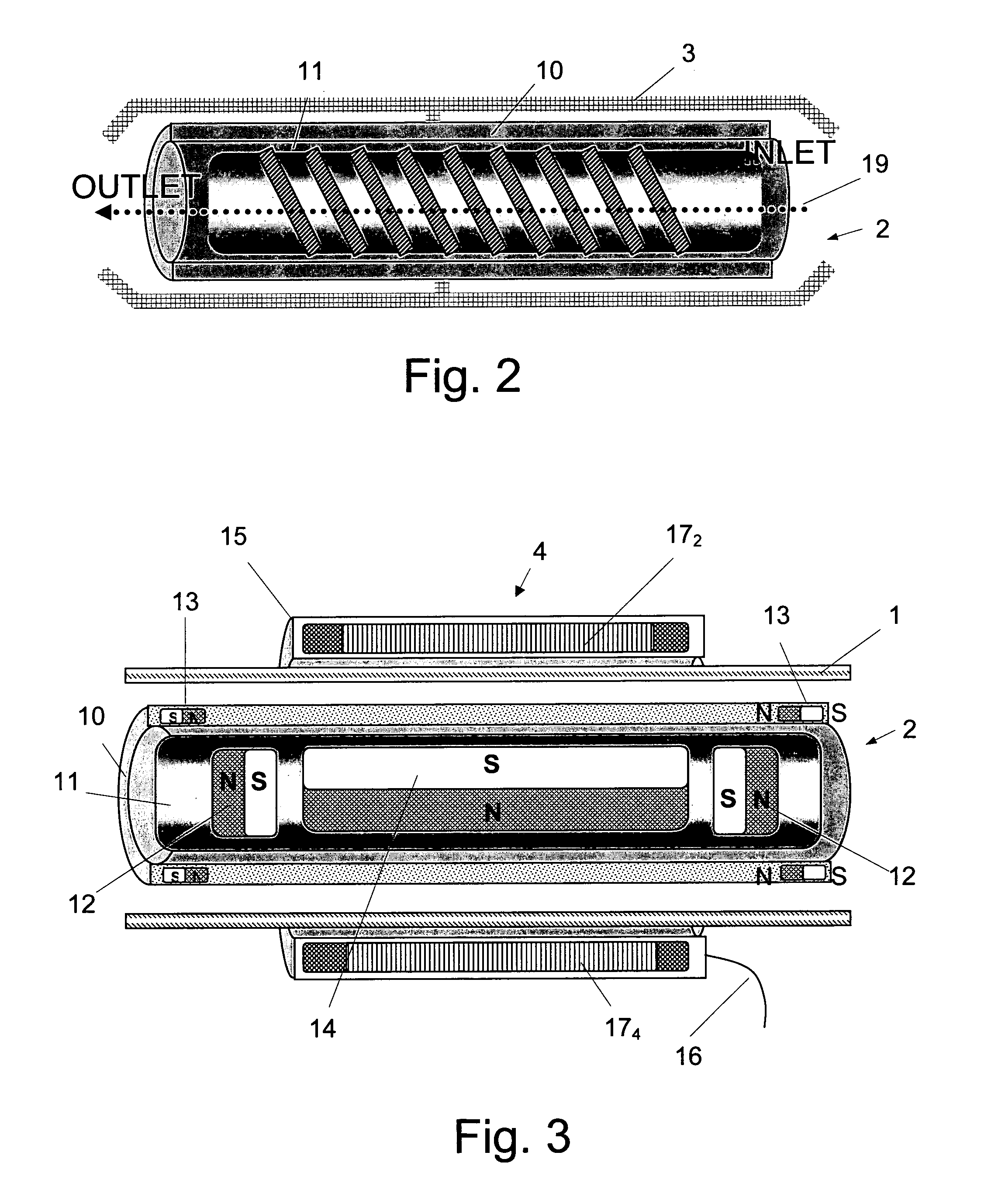
This invention relates to rotary pumps adapted, but not exclusively, for use as artificial hearts or ventricular assist devices and, in particular, discloses in preferred forms a seal-less shaft-less pump featuring open or closed (shrouded) impeller blades with the edges of the blades used as hydrodynamic thrust bearings and with electromagnetic torque provided by the interaction between magnets embedded in the blades and a rotating current pattern generated in coils fixed relative to the pump housing.
Owner:TECH SYDNEY UNIV OF +2
Implantable bi-ventricular stimulation device and system, and bi-ventricular stimulation and sensing method
InactiveUS6961613B2Overcome problemsEasy to implementHeart stimulatorsControl circuitBiventricular stimulation
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device has a control circuit that within a time cycle, delivers pacing pulses with both first and second pacing circuits with a time gap between a pacing pulse delivered by these pacing circuits. The time gap can be such that a pacing pulse delivered by the second pacing circuits falls substantially within a first time interval in which an evoked response can be expected to a pacing pulse delivered by the first pacing circuit. The control circuit performs a temporary modification of the operation of the device such that during at least one time cycle no pacing pulse is delivered by the second pacing circuit during the first time interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Anchored mounting ring
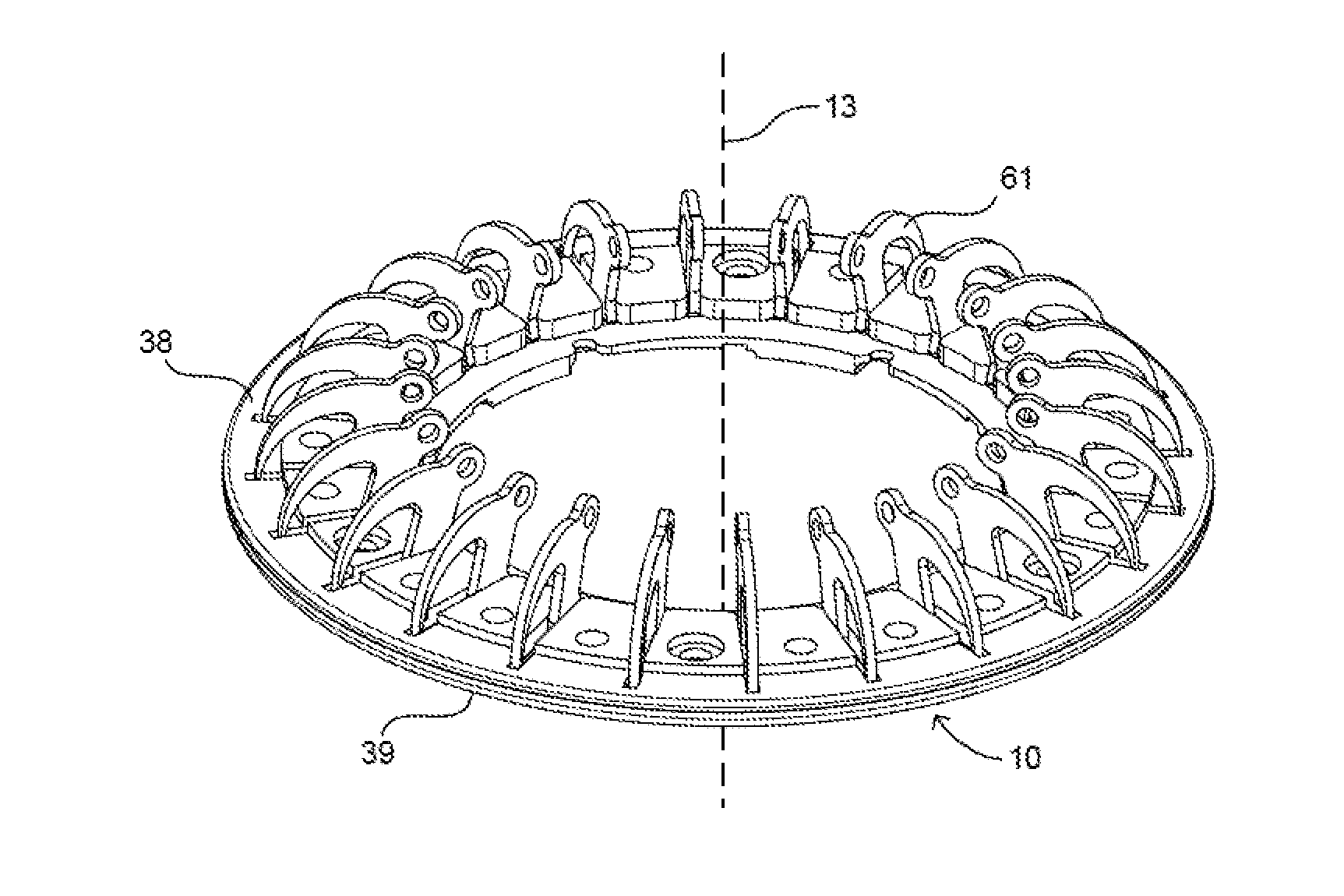
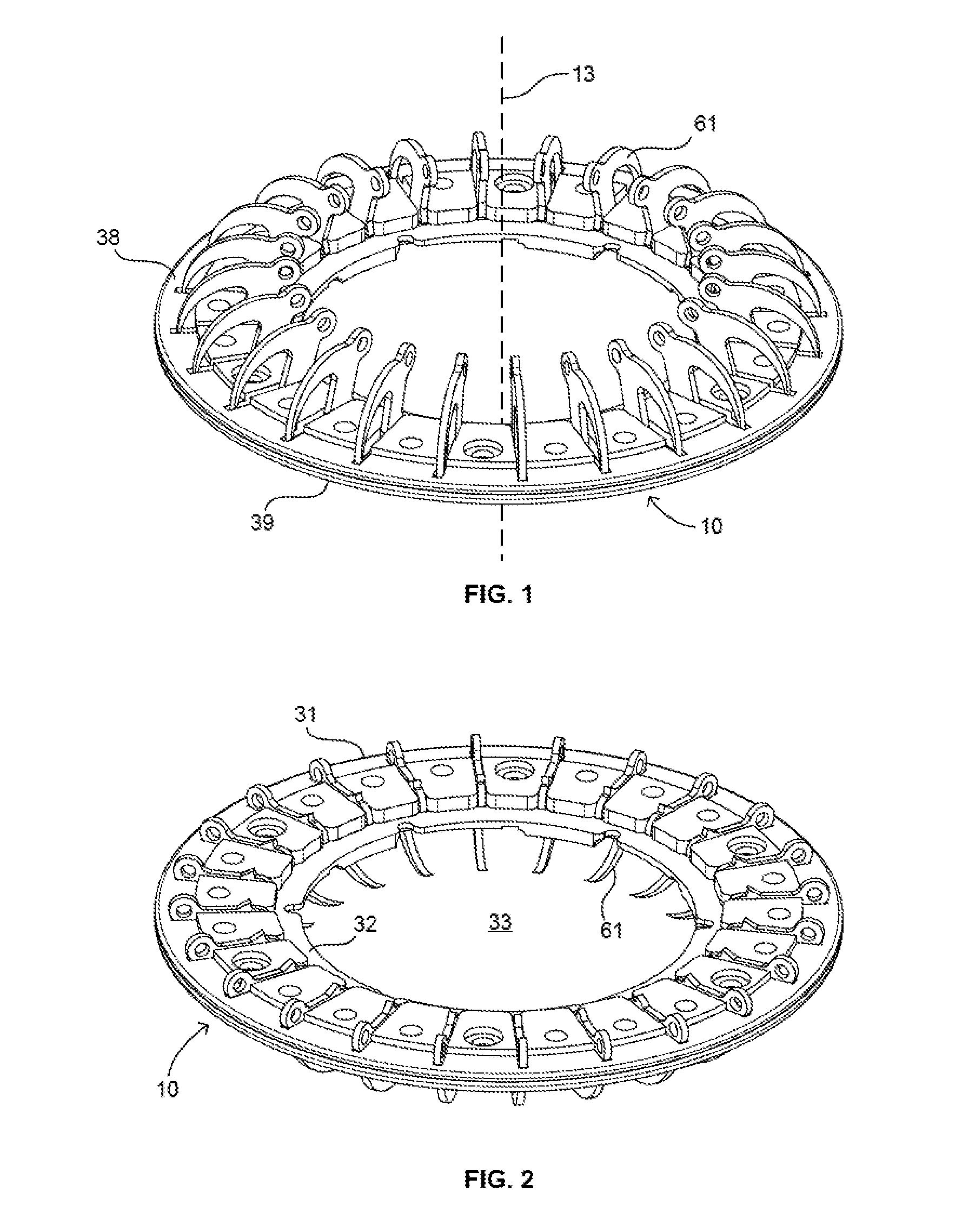
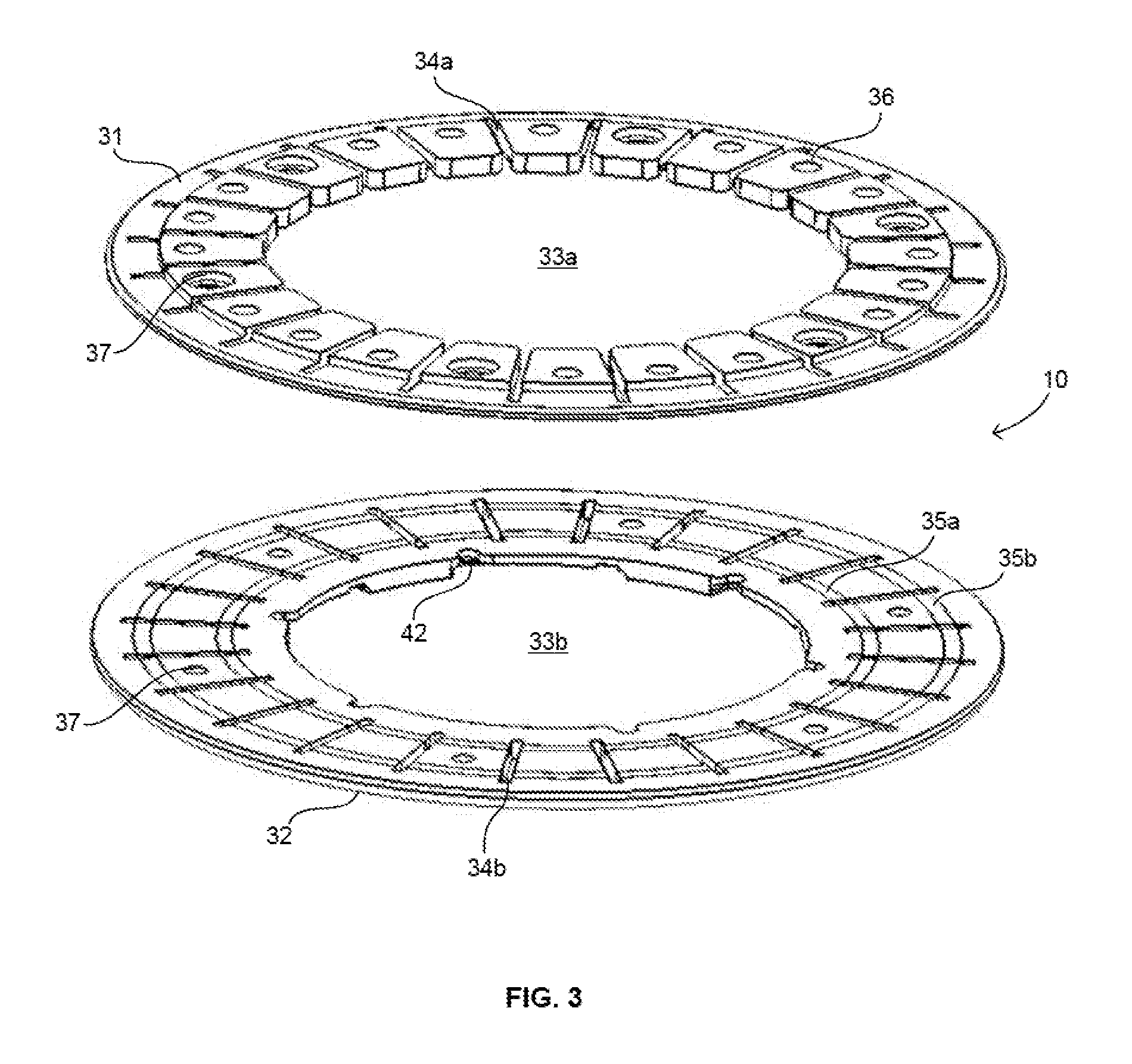
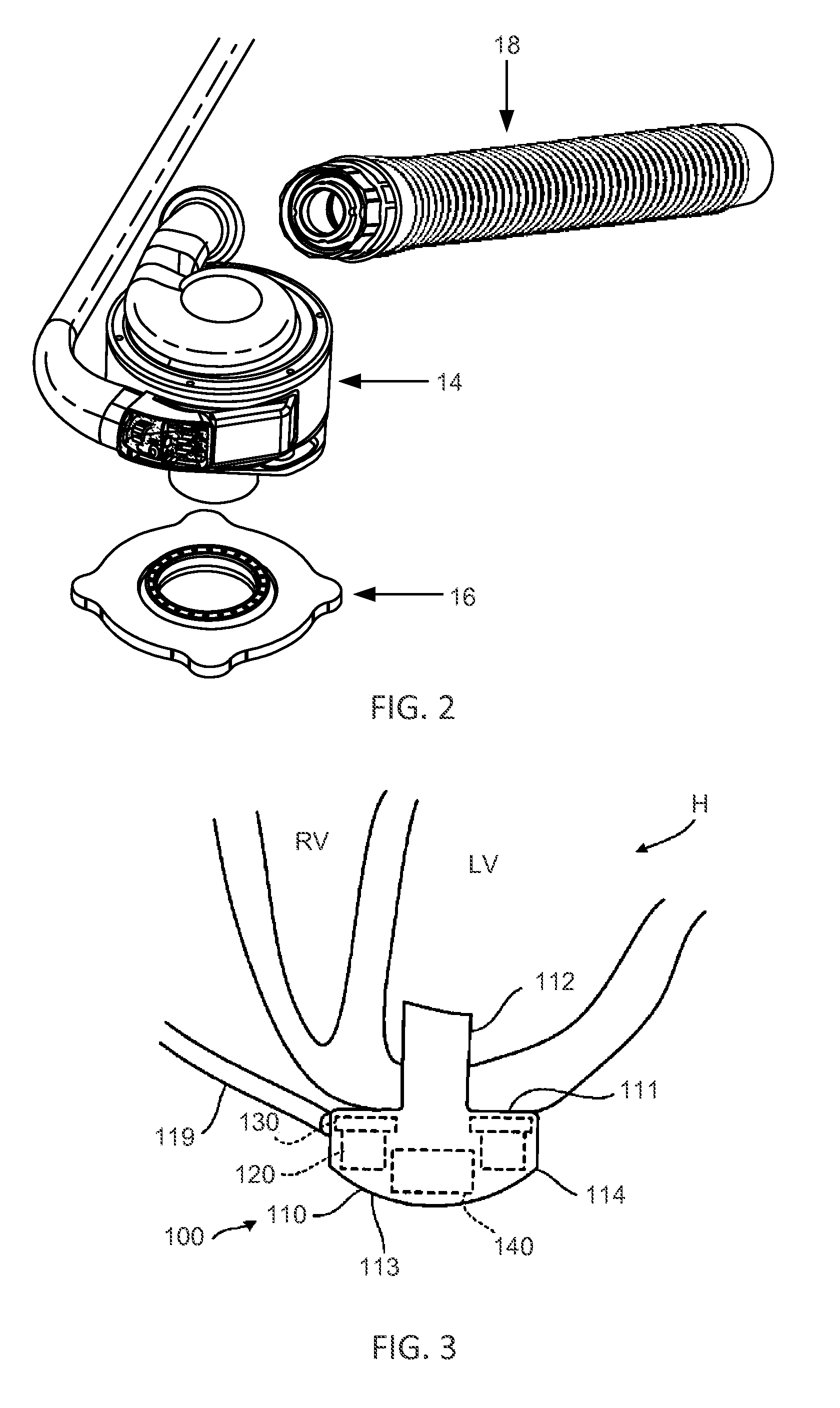
A mounting ring for a ventricular assist device or other device used in the heart includes a plate adapted to be secured to the exterior of the heart by rigid anchors such as hook, pin, or screw. When hooks are used, they can be pivotally mounted to the plate so that the hooks can rotate from retracted positions to advanced positions. A tool can be included in a mounting ring kit to move the hooks from their retracted positions to their advanced positions so that the hooks secure the plate to the heart. Preferably, all of the hooks are advanced simultaneously. The VAD or other device is then secured to the plate. The plate can be mounted to the heart in less time than required to install a traditional mounting ring by suturing to the heart.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Vehicular drive assist device, and vehicular drive assist method
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
VAD connector plug
A plug which may be positioned in place of a Ventricular Assist Device (“VAD”) within a VAD connector mounted to the heart. The VAD connector may have at least one VAD-engaging feature and may define an opening. The plug may have a body adapted to fill the opening of the VAD connector and may engage the VAD connector. The plug may be installed in place of a VAD when the heart heals, and then removed and replaced by a VAD if the patient's condition deteriorates.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Smart Tip LVAD Inlet Cannula
ActiveUS20150306290A1Reduce morbidityMinimize the possibilityElectrocardiographyControl devicesAutomatic controlVentricular volume
Embodiments of the invention provide a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) cannula that includes multiple independent sensors may help decrease the incidence of ventricular collapse and provide automatic speed control. A cannula may include two or more independent sensors. One sensor may measure ventricular pressure, while another may measure ventricular volume and / or ventricular wall location. With this information an automatic control system may be configured to adjust pump speed to minimize the likelihood of ventricular collapse and maximize LVAD flow in response to physiologic demand. Typically the volume sensors are conductance sensors. Further embodiments provide LVADs that are powered by RF energy.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Methods and Systems for Controlling a Blood Pump
ActiveUS20150290374A1Advantageously sustain VAD operationExtended durationControl devicesBlood pumpsBlood pumpEngineering
The present invention generally relates to ventricular assist device power monitoring and conservation. In some embodiments, a pump controller may transition the pump to operate in a power-saving operational mode when a power source and / or a power source condition indicate a need to conserve power. In some embodiments, when the power source is an emergency battery and when the emergency battery has powered the pump for an extended period of time, the controller may signal the pump to operate in the power saving-operational mode. In some embodiments, when a low power hazard condition is triggered by signals from one or more external power sources, the controller may signal the pump to transition to the power-saving operational mode if the condition lasts for an extended period of time. In some embodiments, the controller may trigger the power-saving mode when the emergency backup battery is below a voltage threshold.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Ventricular assist system secondary impeller
InactiveUS7189260B2Avoid problemsInhibition formationSpecific fluid pumpsPump componentsImpellerLeft ventricular size
In a centrifugal flow blood pump, usable in left ventricular assist applications, blood is pumped from an inlet (16) to an outlet (22) by a primary impeller (18). A portion of the blood that enters the pump follows a secondary channel (24) where a secondary impeller (70) routes the blood to lubricate a bearing between an impeller assembly (14) and a post formed by a component of the pump housing. The unique shape of the secondary impeller (70) prevents blood stagnation and provides for a well-washed fluid bearing.
Owner:HORVATH DAVID +2
Intra-ventricular cardiac assist device and related method of use
InactiveUS20070287880A1Reduce loadRaise aortic pressureTransvascular endocardial electrodesControl devicesCardiac cycleT wave
A system and method for cardiac assist of a heart. The system comprises a catheter on which is mounted an inflatable balloon configured for inflation inside a ventricle. The system preferably includes a fluid pump and a processor configured to activate the pump to inflate the intra-ventricular balloon in the ventricle during a predetermined first phase of the cardiac cycle and to deflate the balloon during a predetermined second phase of the cardiac cycle. The predetermined first phase may be the end of the slow ejection phase corresponding to the ascending part of the T wave, and the predetermined second phase may begin at the peak of systolic augmentation resulting from inflation of the balloon which corresponds to the descending part of the T-wave. The method of the invention includes delivering the balloon to a ventricle of the heart and transiently inflating the balloon to achieve a predetermined intra-ventricular systolic pressure
Owner:OVIL YOEL +2
Speed change algorithm for a continuous flow blood pump
A ventricular assist device (“VAD”) includes a continuous-flow pump (2) implantable in fluid communication with a ventricle (V) and an artery (A) of a patient to assist blood flow from the ventricle to the artery. The VAD also includes a control circuit (12) connected to the pump, the control circuit being configured to direct the pump to operate in a series of cycles. Each cycle may include (i) pumping blood at a first speed (RPM1) and at a first flow rate during a first period (t1); then (ii) decreasing the speed of the pump from the first speed to a second speed (RPM2) during a ramp-down period (tRD); then (iii) pumping blood at the second speed and at a second flow rate during a second period (t2); and then (iv) increasing the speed of the pump from the second speed to the first speed during a ramp-up period (tRU).
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Implantable bi-ventricular stimulation device and system, and bi-ventricular stimulation and sensing method
ActiveUS20040116971A1Shorten the time intervalImprove reliabilityHeart stimulatorsControl circuitBiventricular stimulation
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device has a control circuit that within a time cycle, delivers pacing pulses with both first and second pacing circuits with a time gap between a pacing pulse delivered by these pacing circuits. The time gap can be such that a pacing pulse delivered by the second pacing circuits falls substantially within a first time interval in which an evoked response can be expected to a pacing pulse delivered by the first pacing circuit. The control circuit performs a temporary modification of the operation of the device such that during at least one time cycle no pacing pulse is delivered by the second pacing circuit during the first time interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
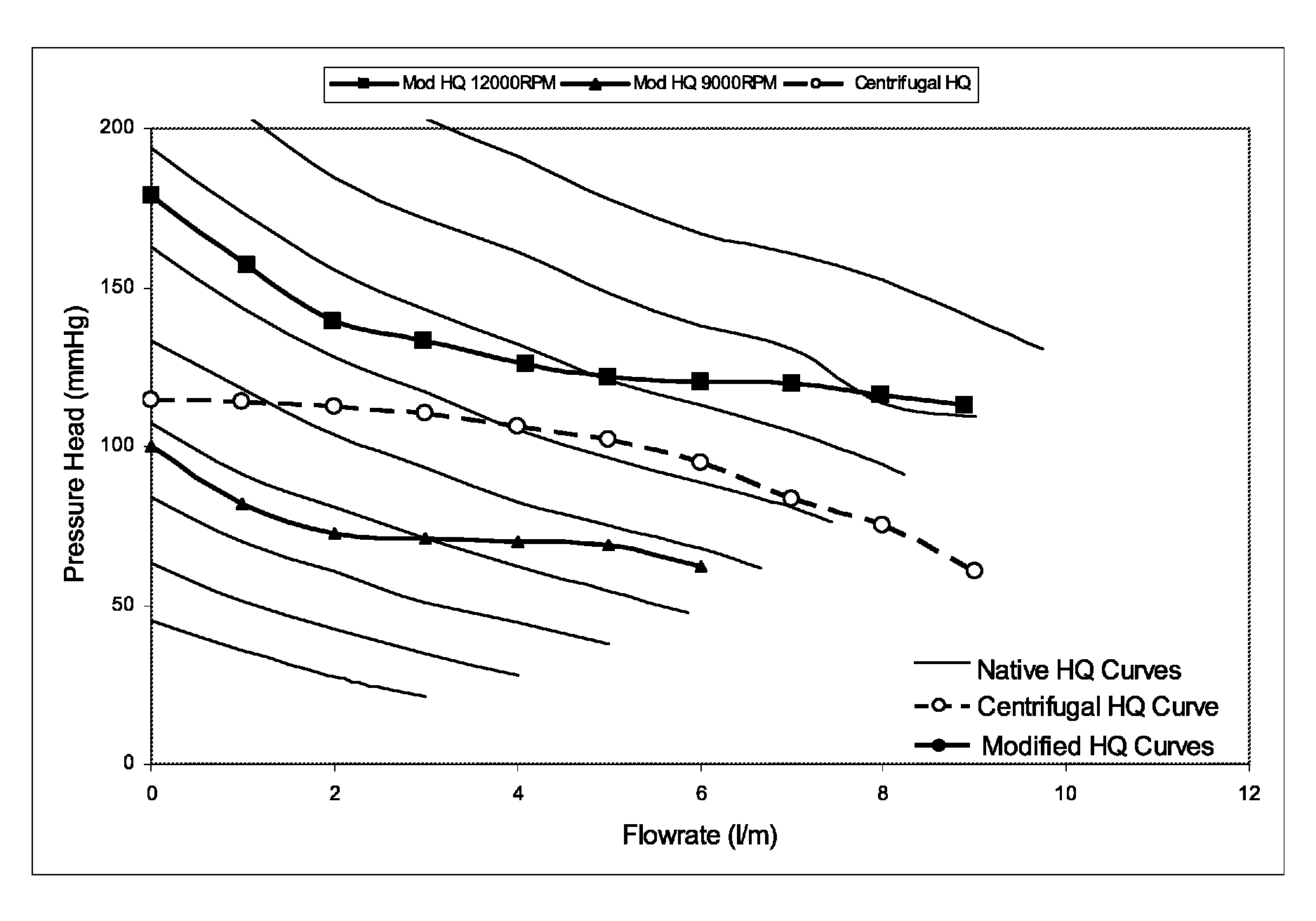
Apparatus and method for modifying pressure-flow characteristics of a pump
A method for modifying a pump of a ventricular assist device includes the step of modifying pressure-flow characteristics of a pump of a ventricular assist device to simulate different pressure-flow characteristics or to make the flow rate of the pump more responsive to changes in the pressure differential of the pump. The step of modifying the pressure-flow characteristics of the pump may includes one or both of the steps of (1) estimating a flow rate of the pump from the speed of an electric motor of the ventricular assist device and from the current or power consumption of the electric motor, wherein the electric motor drives the pump, and (2) adjusting the speed of the electric motor as a function of the estimated flow rate of the pump and a set speed of the electric motor to simulate the different pressure-flow characteristics or to make the flow rate of the pump more responsive to changes in the pressure differential of the pump.
Owner:TC1 LLC
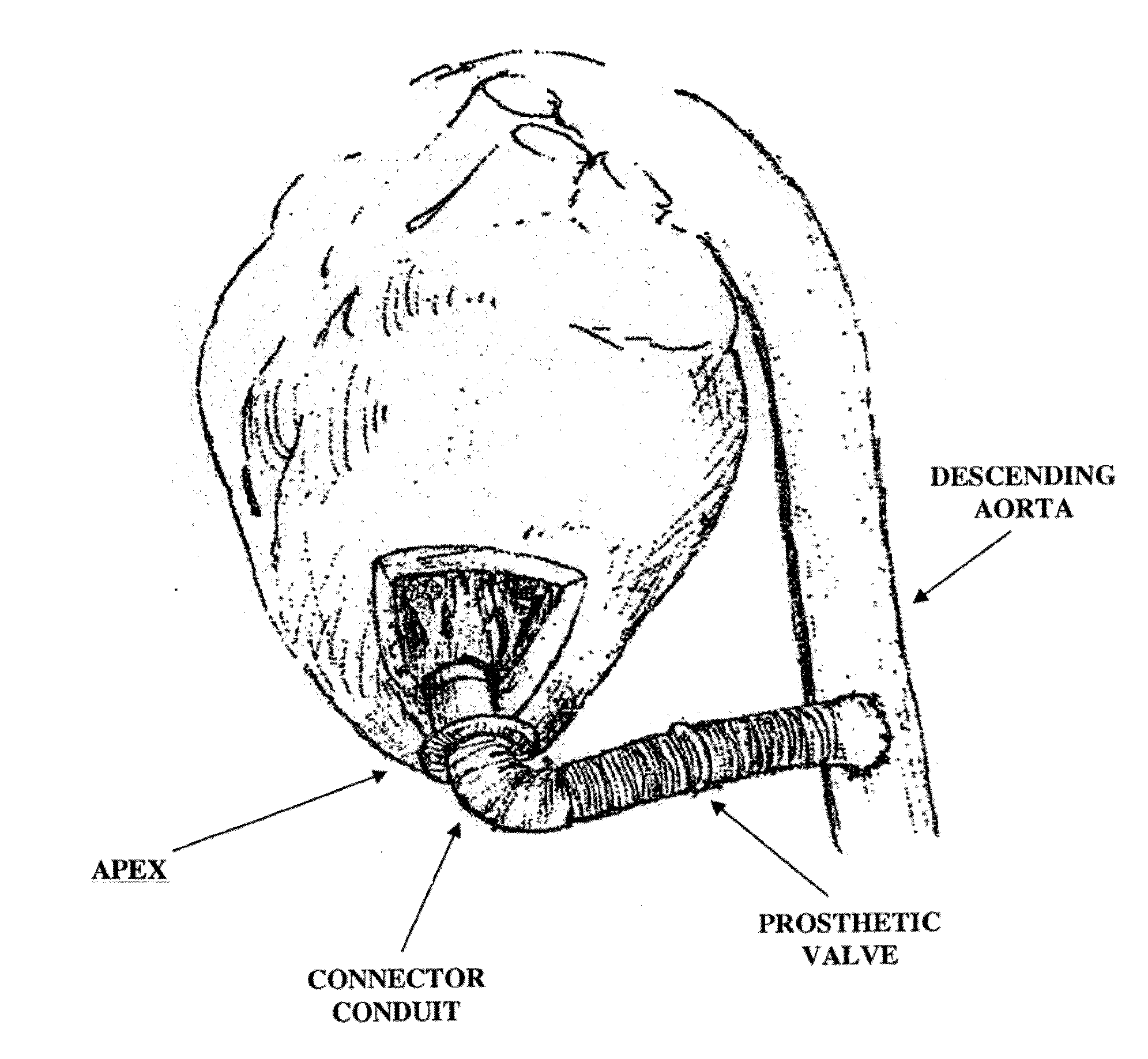
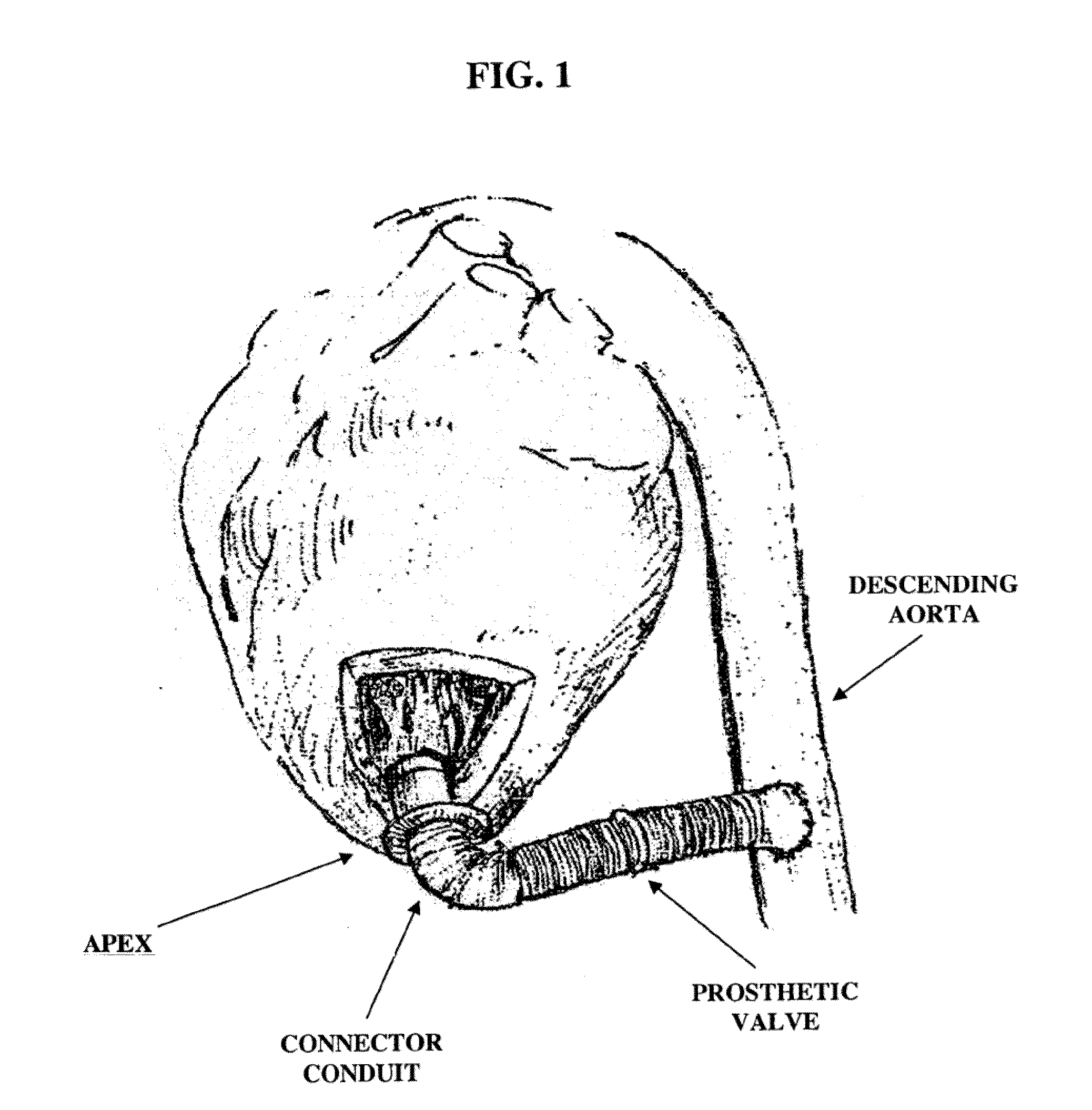
Apparatus and method for forming a hole in a hollow organ, connecting a conduit to the hollow organ and connecting a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) to the hollow organ
InactiveUS20150290370A1Easy procedureReduce the possibilityBlood pumpsMedical devicesCardiac wallLeft ventricular size
Apparatus for attaching a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) to a heart, the apparatus comprising: a connector conduit comprising: a distal end, a proximal end and a lumen extending between the distal end and the proximal end, wherein the distal end is configured to be inserted into a wall of the heart, and the proximal end is configured to receive the LVAD, whereby hemostasis is maintained during insertion of the connector conduit into the wall of the heart and during insertion of the LVAD into the proximal end of the connector conduit.
Owner:CORREX
Removable left ventricular assist device with an aortic support apparatus
InactiveUS6228018B1Prevent the collapse of the walls of the aortaProlonged ejectionStentsControl devicesSystoleThumb opposition
An apparatus and method of temporarily replacing the function of the left ventricle in a patient whose heart is severely injured and is unable to maintain a systemic arterial pressure adequate to support the inside walls of patient's aorta, the method comprising a removable pressurizable support means having an external profile which is expandable to fit firmly against the inside wall of the aorta of a patient, wherein the external profile of the pressurizable support means presents a central opening that allows blood to flow through the aorta. The pressurizable support means can both support and expand the aorta under low blood pressure to assist the drawing of blood from the left ventricle. The central opening also allows for the placement of a blood flow control means. The blood flow control means can comprise a pumping balloon and a proximal blocking balloon, the two members pressurized and depressurized in opposition within the aorta of a patient to simulate systole and diastole of a healthy heart. The pumping balloon has a pressurized pumping position that is engaged while the proximal blocking balloon is in a depressurized deflated position.
Owner:NORTH TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER AT FORT WORTH THE UNIVERSITY OF
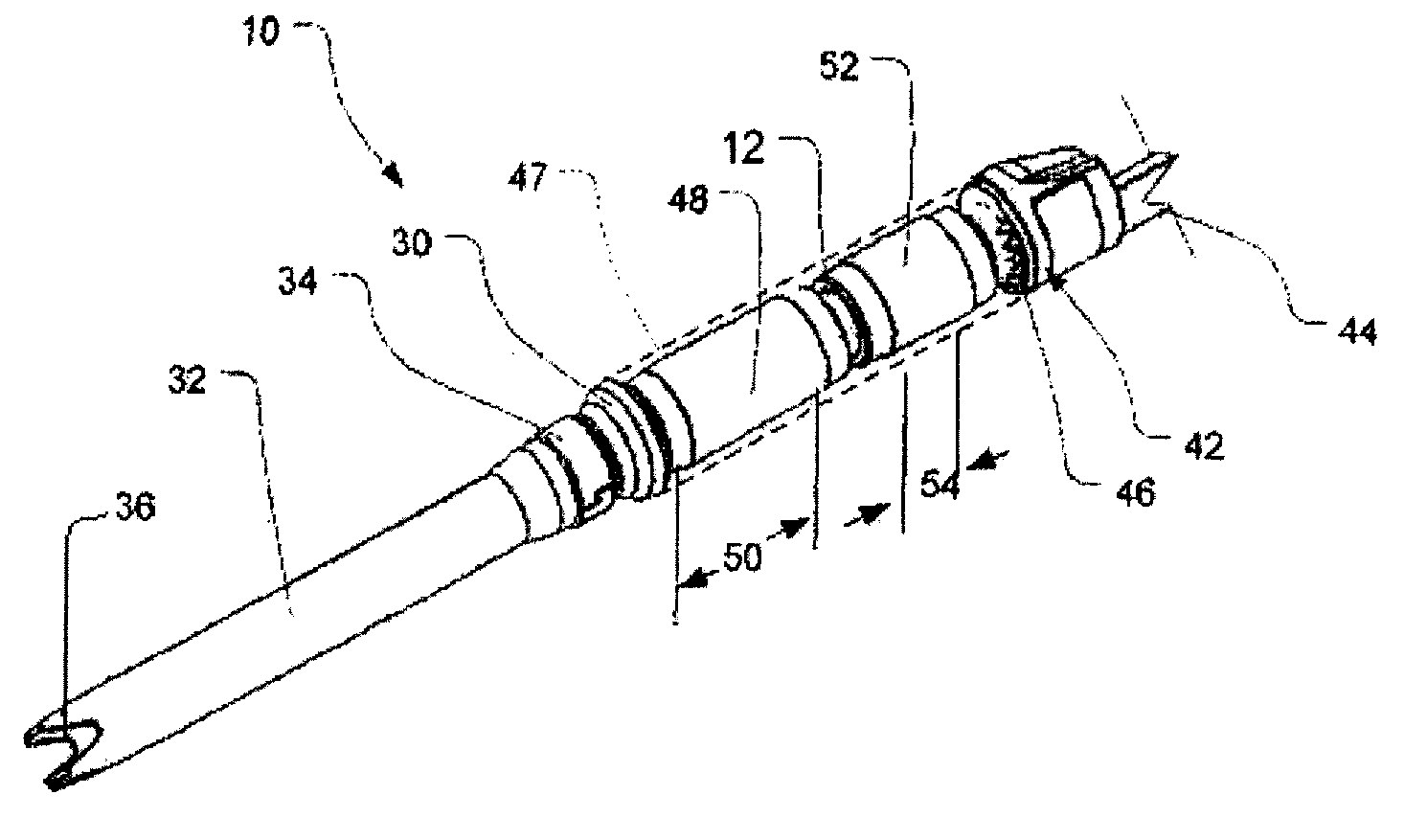
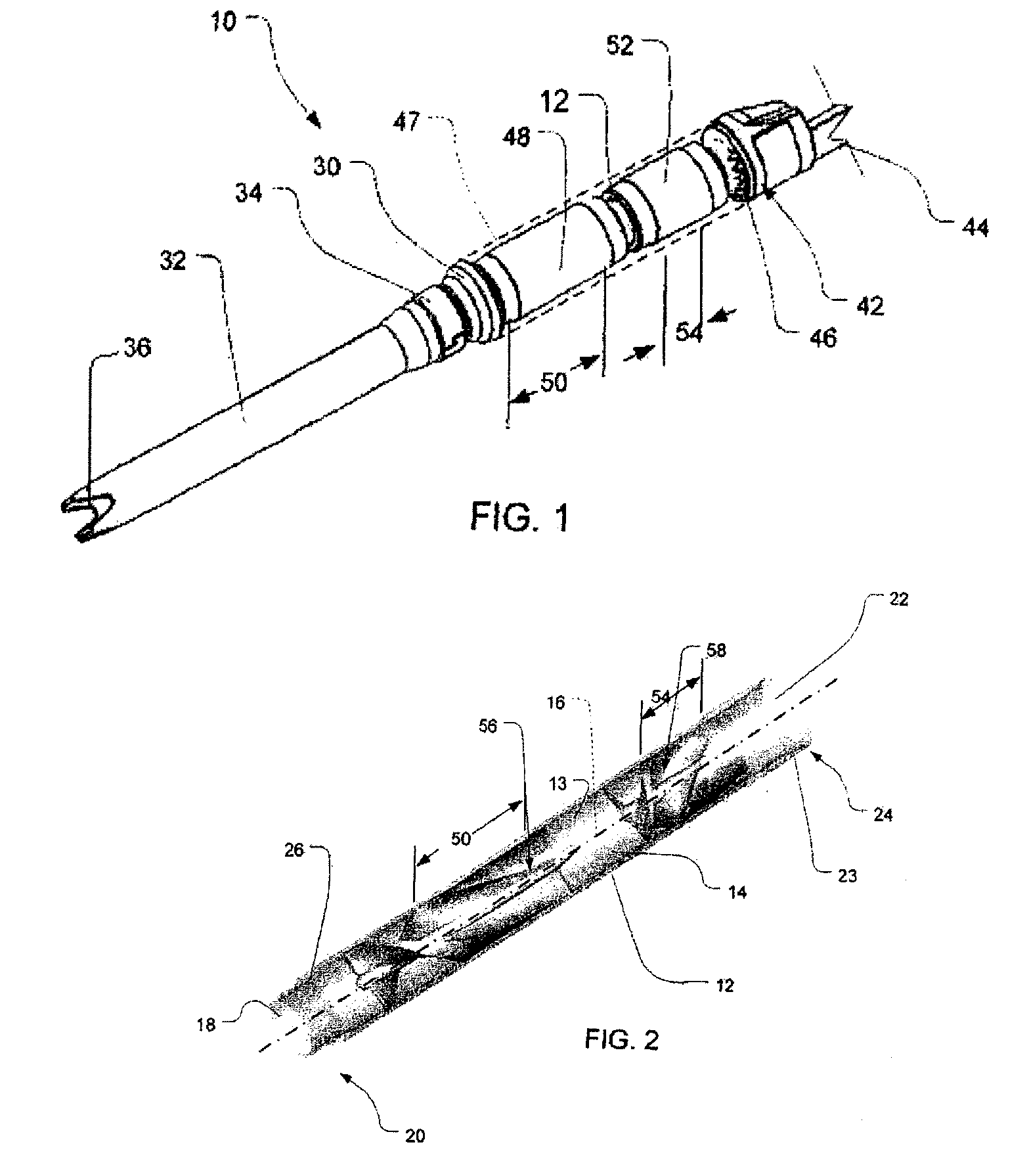
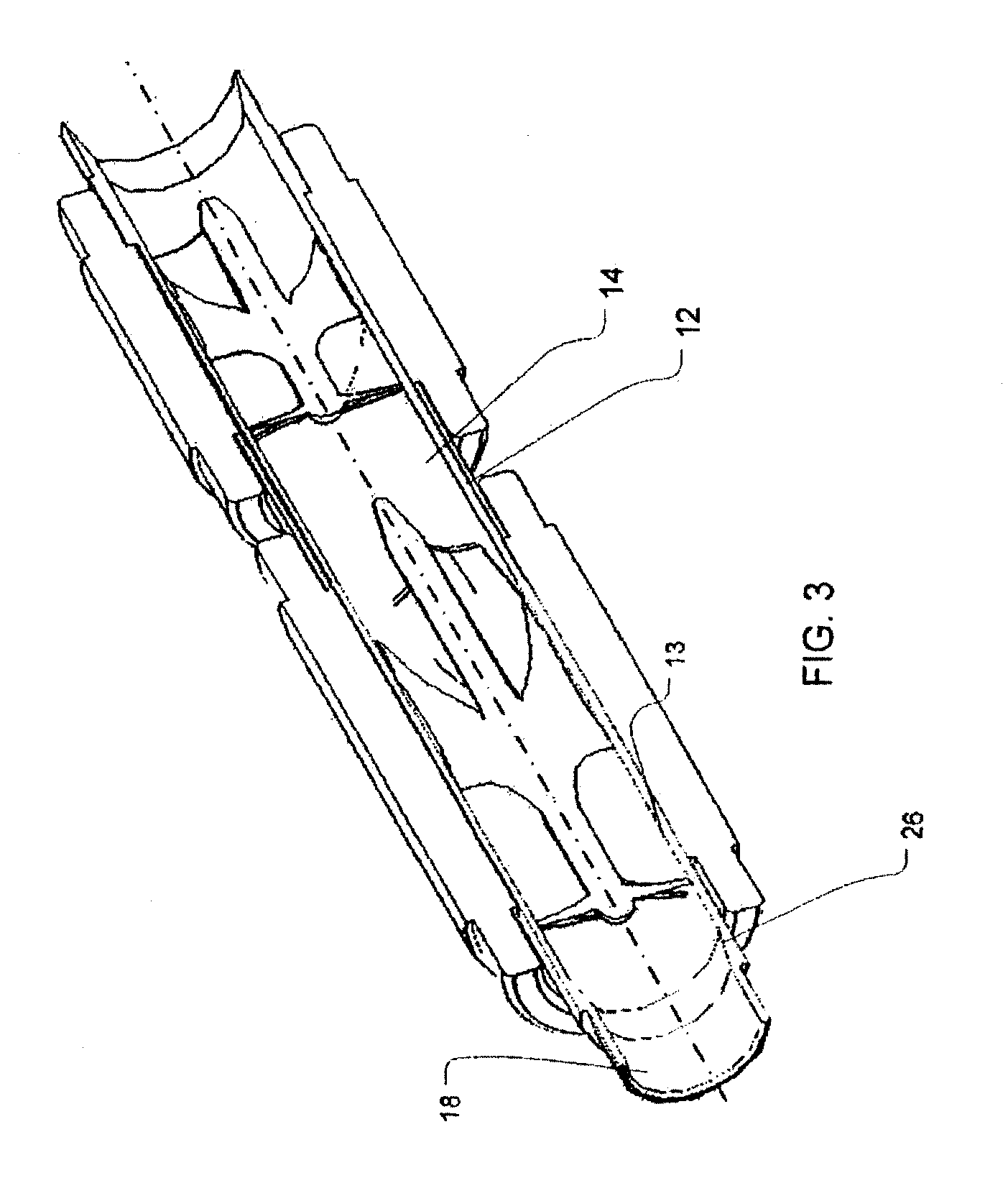
Cannula tip for use with a VAD
InactiveUS9050418B2Efficient use ofMinimal damageOther blood circulation devicesSurgical needlesDistal portionCannula tip
In one embodiment of the present invention, a cannula for use with a blood circulation device may include the cannula having a longitudinal axis and proximal and distal directions along the longitudinal axis. The cannula may also include a proximal portion having a wall extending around the longitudinal axis and having outer and inner faces, the inner face may define a bore, the proximal portion may have dimensions transverse to the longitudinal axis, and the dimensions may be constant in the proximal and distal directions. Also, the cannula may have a distal portion having an outer face, continuous with the outer face of the proximal portion. The outer face of the distal portion may extend around and along the longitudinal axis, and the outer face of the distal portion may taper distally toward the longitudinal axis. The distal portion may include at least two openings extending from the outer face of the distal portion, which may merge with one another within the distal portion. Then, the openings may communicate with the bore of the proximal portion. One type of blood circulation device may be a ventricular assist device.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Ventricular assist devices having a hollow rotor and methods of use
ActiveUS20160375187A1Improve hydraulic performanceHemolysis rateControl devicesBlood pumpsBlood pumpEngineering
Blood pumps for ventricular assist devices employ a hollow rotor to impel blood through the blood pump. A blood pump includes a housing having a housing inlet, a housing outlet, and a housing blood flow channel through which the housing inlet and the housing outlet are in fluid communication. A motor stator is disposed around the housing blood flow channel and operable to generate a rotating magnetic field. A hollow rotor is disposed within the housing blood flow channel and rotated via the rotating magnetic field. The hollow rotor has a rotor circumferential wall enclosing a rotor blood flow channel. The hollow rotor has at least one rotor blade extending inwardly from the rotor circumferential wall. The at least one rotor blade is configured to impel blood through the rotor blood flow channel when the hollow rotor is rotated via the rotating magnetic field.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Fluid pump
ActiveUS20070255089A1ElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesEngineeringCardiopulmonary bypass time
A pumping system 10, FIG. 1, provides a physiological pulsatile flow and includes controller 121, a pump drive head 50 coupled to a motor 12 and a fluid housing 52 having at least one port 60. The port 60 includes a ball valve retainer region 69, a valve seat 73, and an occluder ball 71 disposed in the ball valve retainer region 69. During operation, the motor 12 forces the fluid in and out the fluid housing 52 and causes the occluder ball 71 to move from a first position whereby the fluid cannot pass through the port 60, to a second position whereby the fluid moves annular to and generally around the occluder ball 71. This movement creates a slight flow reversal that “breaks up” any blood clots that may form. The pumping system may be used as part of a cardiopulmonary bypass system, a ventricular assist device (VAD) and / or a heart pump.
Owner:VENTRIFLO INC
Cannula tip for use with a vad
InactiveUS20100022939A1Efficient use ofMinimal damageSurgical needlesMedical devicesDistal portionMedicine
In one embodiment of the present invention, a cannula for use with a blood circulation device may include the cannula having a longitudinal axis and proximal and distal directions along the longitudinal axis. The cannula may also include a proximal portion having a wall extending around the longitudinal axis and having outer and inner faces, the inner face may define a bore, the proximal portion may have dimensions transverse to the longitudinal axis, and the dimensions may be constant in the proximal and distal directions. Also, the cannula may have a distal portion having an outer face, continuous with the outer face of the proximal portion. The outer face of the distal portion may extend around and along the longitudinal axis, and the outer face of the distal portion may taper distally toward the longitudinal axis. The distal portion may include at least two openings extending from the outer face of the distal portion, which may merge with one another within the distal portion. Then, the openings may communicate with the bore of the proximal portion. One type of blood circulation device may be a ventricular assist device.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
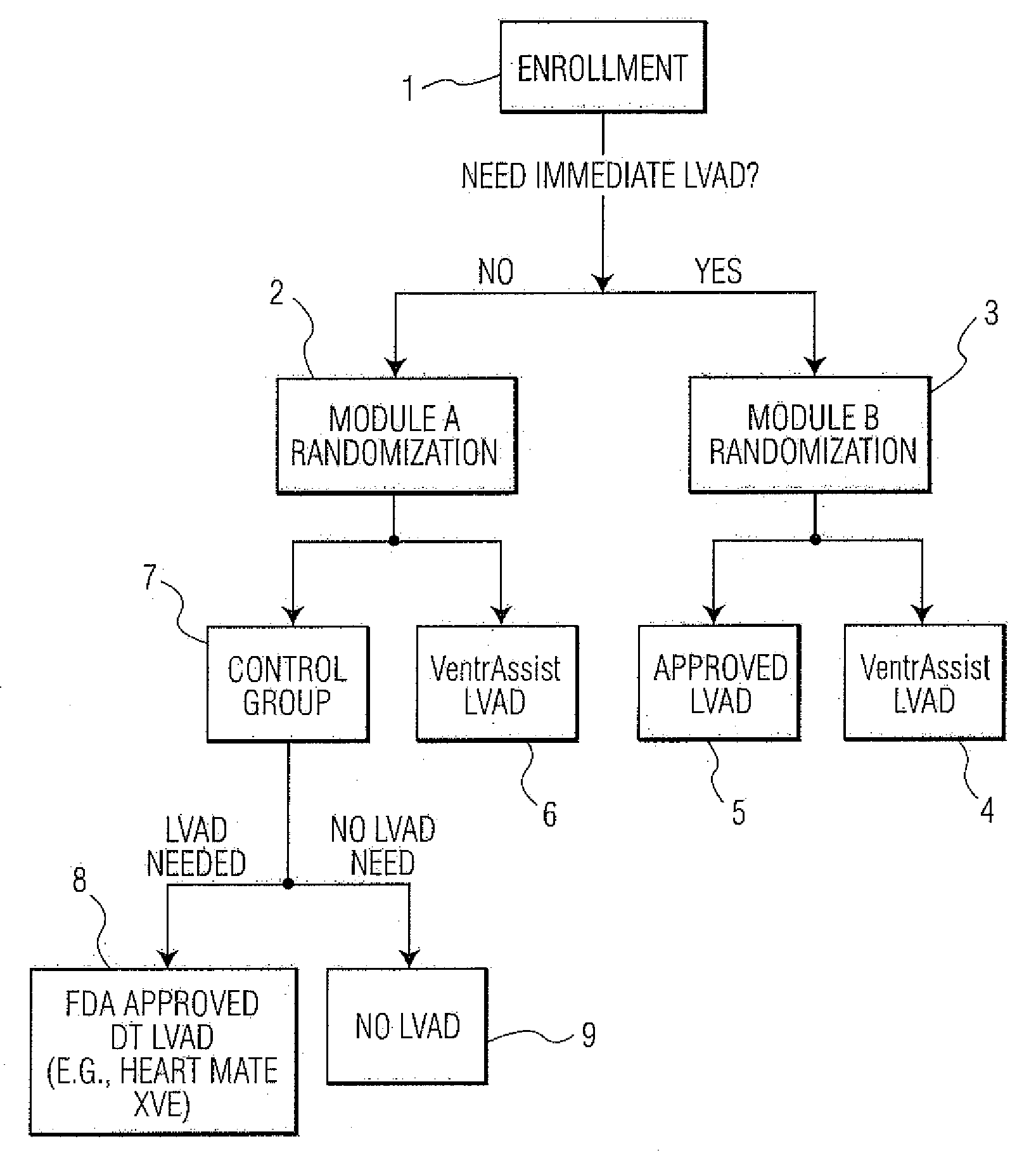
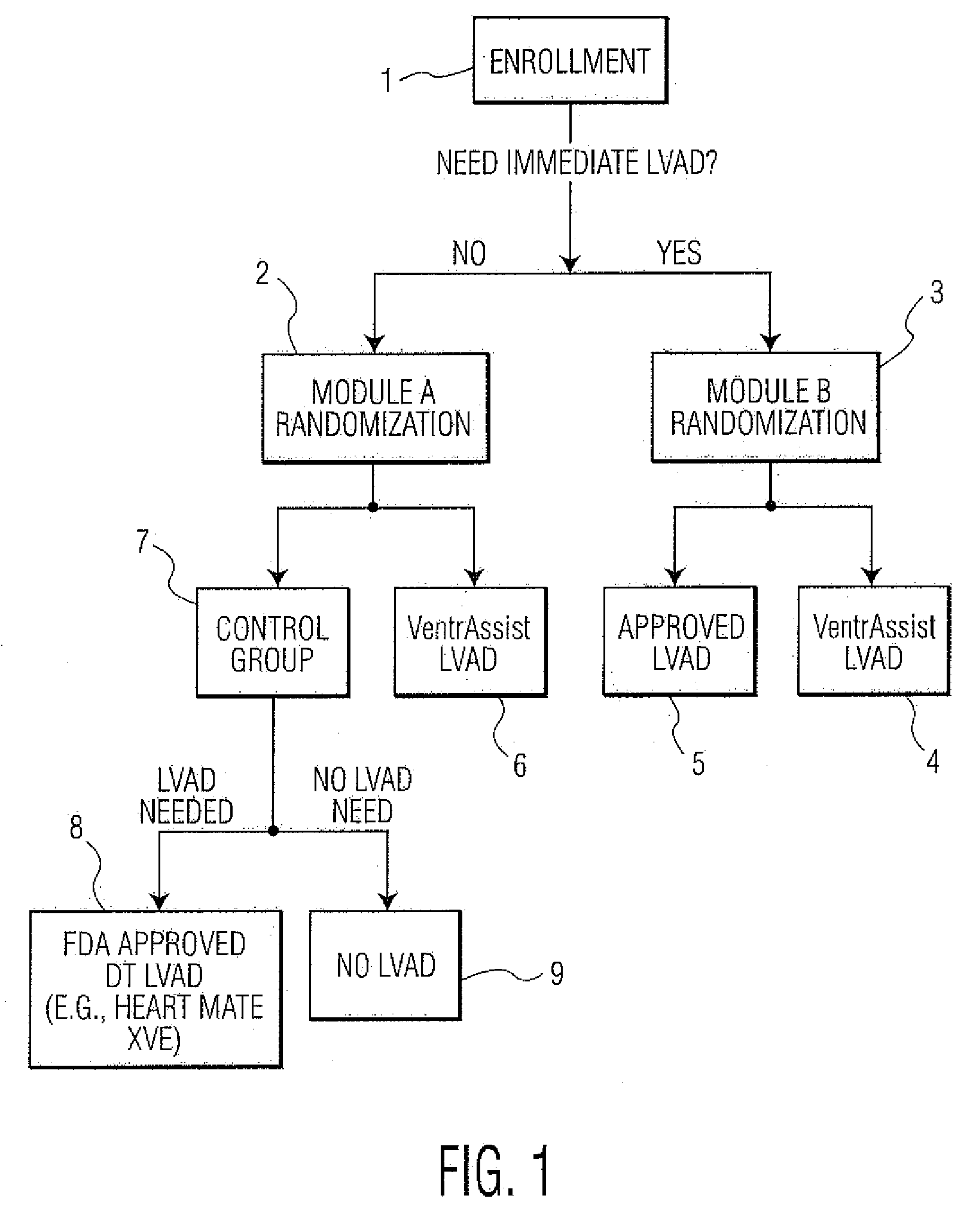
Method of conducting a clinical trial
InactiveUS20080221921A1Data processing applicationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLeft ventricular sizeClinical trial
Disclosed are methods of conducting and assessing the outcomes of a randomized controlled clinical trial. The method comprises the steps of: trialing, with respect to a first group of patients as an experimental group, an experimental treatment; and trialing, with respect to a second group of patients as a control group, at least first and second control therapies. The control therapies will have been previously validated or are a known standard of care. This method is described in relation to trialing and assessing implantable medical devices such as left ventricular assist devices (LVAD) but may be used for trialing and assessing other medical devices.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
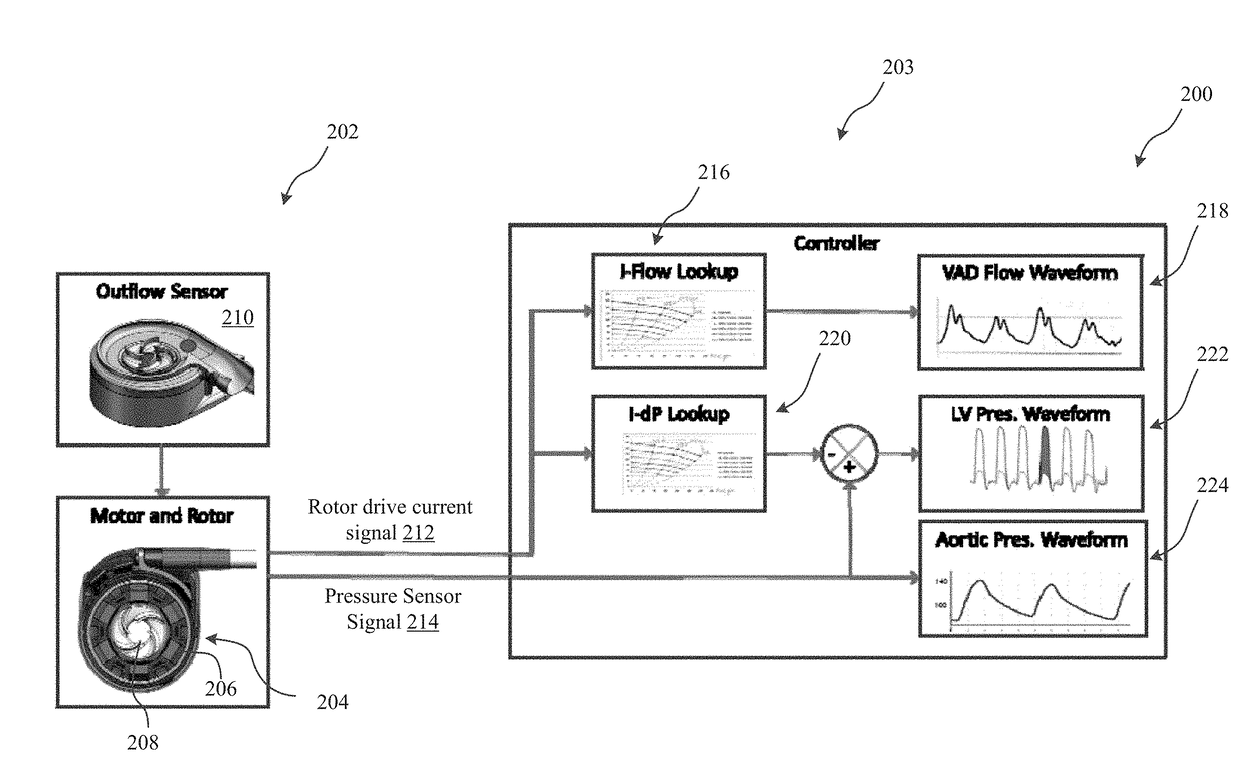
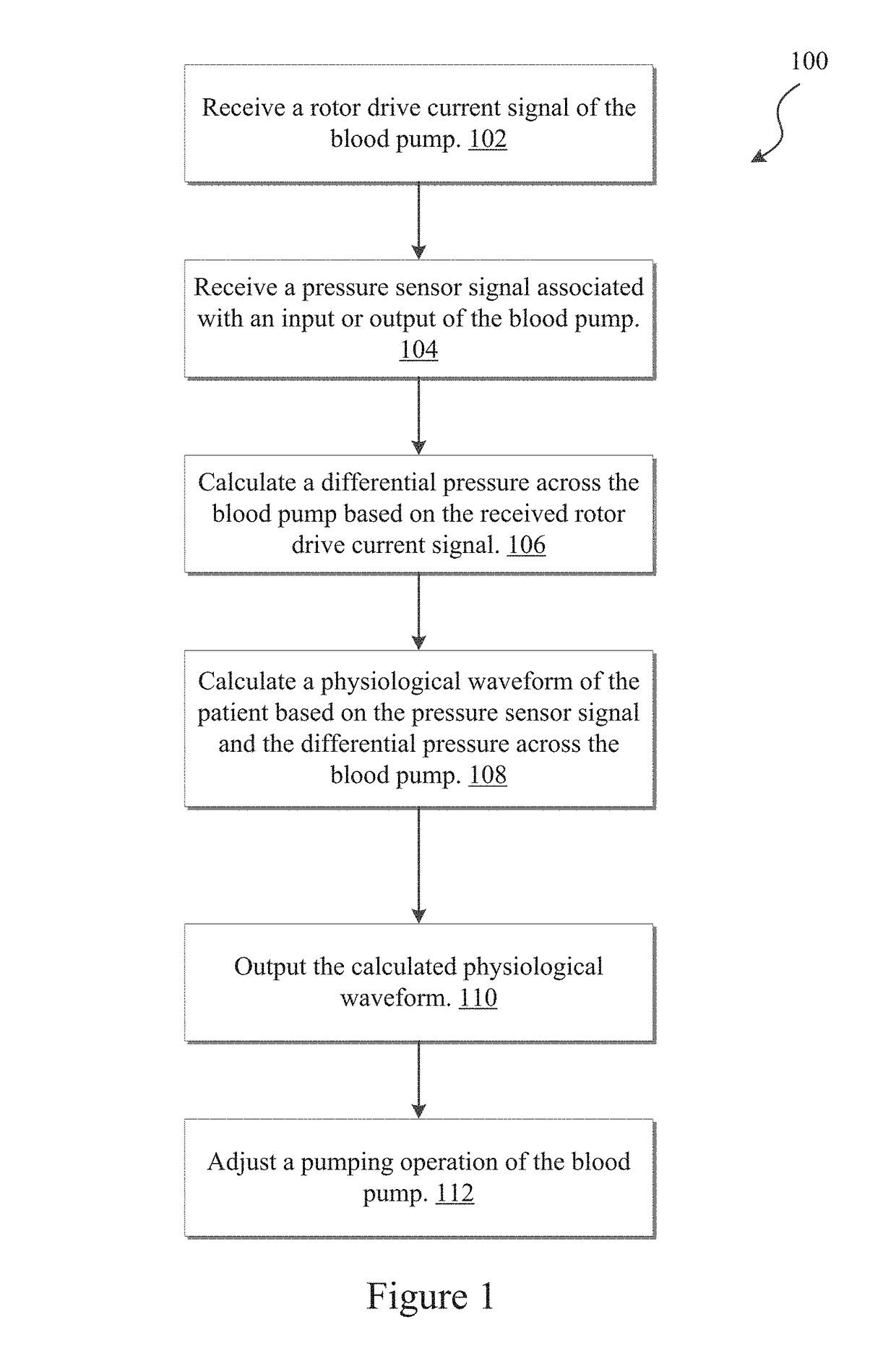
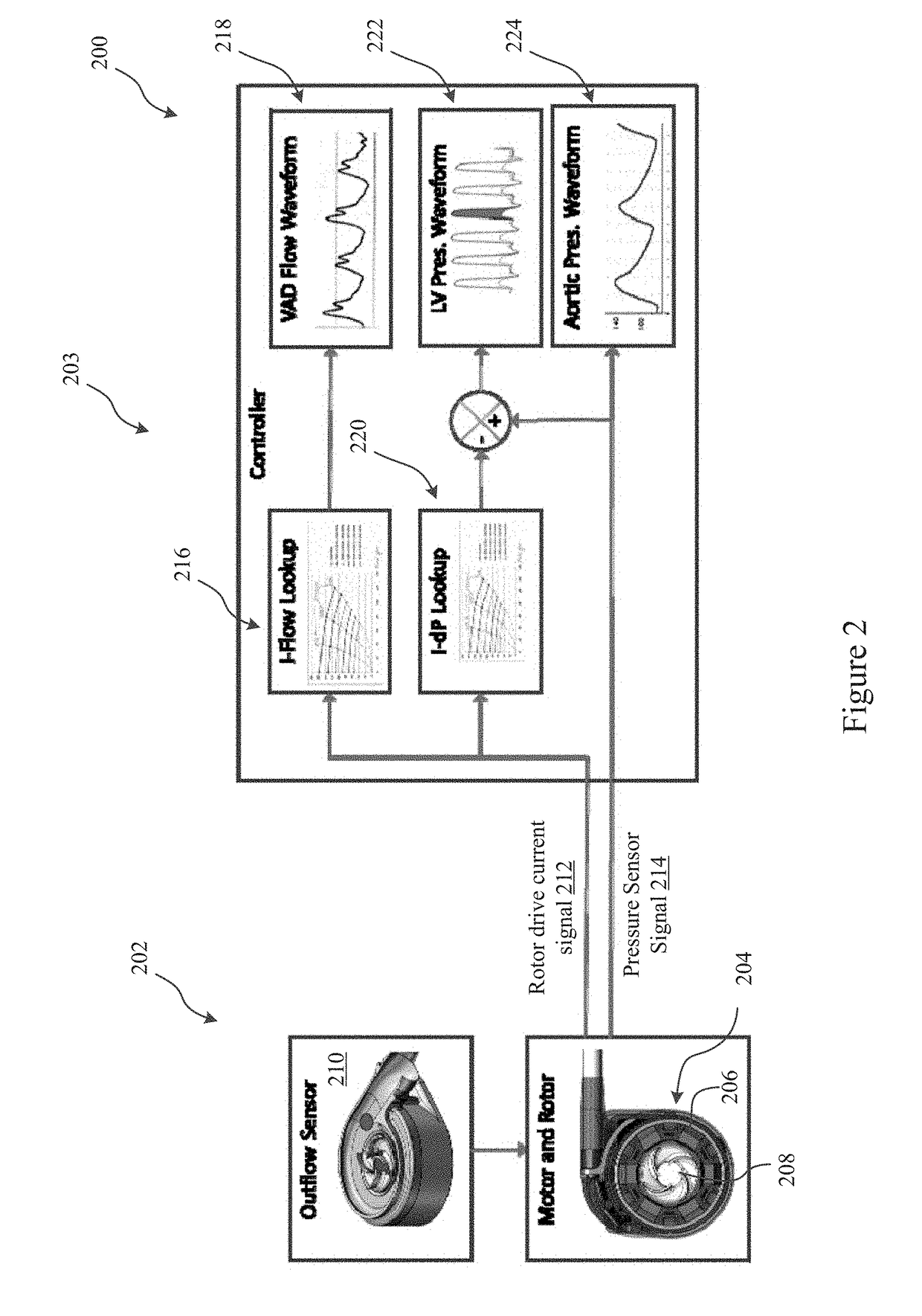
Pressure sensing ventricular assist devices and methods of use
The invention generally relates to heart pump systems. In some embodiments, a pressure sensor is provided with a heart pump, either at the inflow or the outflow of the blood pump. The heart pump may further include a flow estimator based on a rotor drive current signal delivered to the rotor. Based on the rotor drive current signal, a differential pressure across the pump may be calculated. The differential pressure in combination with the pressure measurements from the pressure sensor may be used to calculate pressure on the opposite side of the pump from the pressure sensor. In some embodiments, the pressure sensor is located at the outflow of the pump and the pump is coupled with the left ventricle. The differential pressure and pressure measurement may be used to calculate a left ventricular pressure waveform of the patient. With such a measurement, other physiological parameters may be derived.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com