Patents
Literature
6356 results about "Artery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An artery (plural arteries) (from Greek ἀρτηρία (artēria), meaning 'windpipe, artery') is a blood vessel that takes blood away from the heart to all parts of the body (tissues, lungs, etc). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it. The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system.
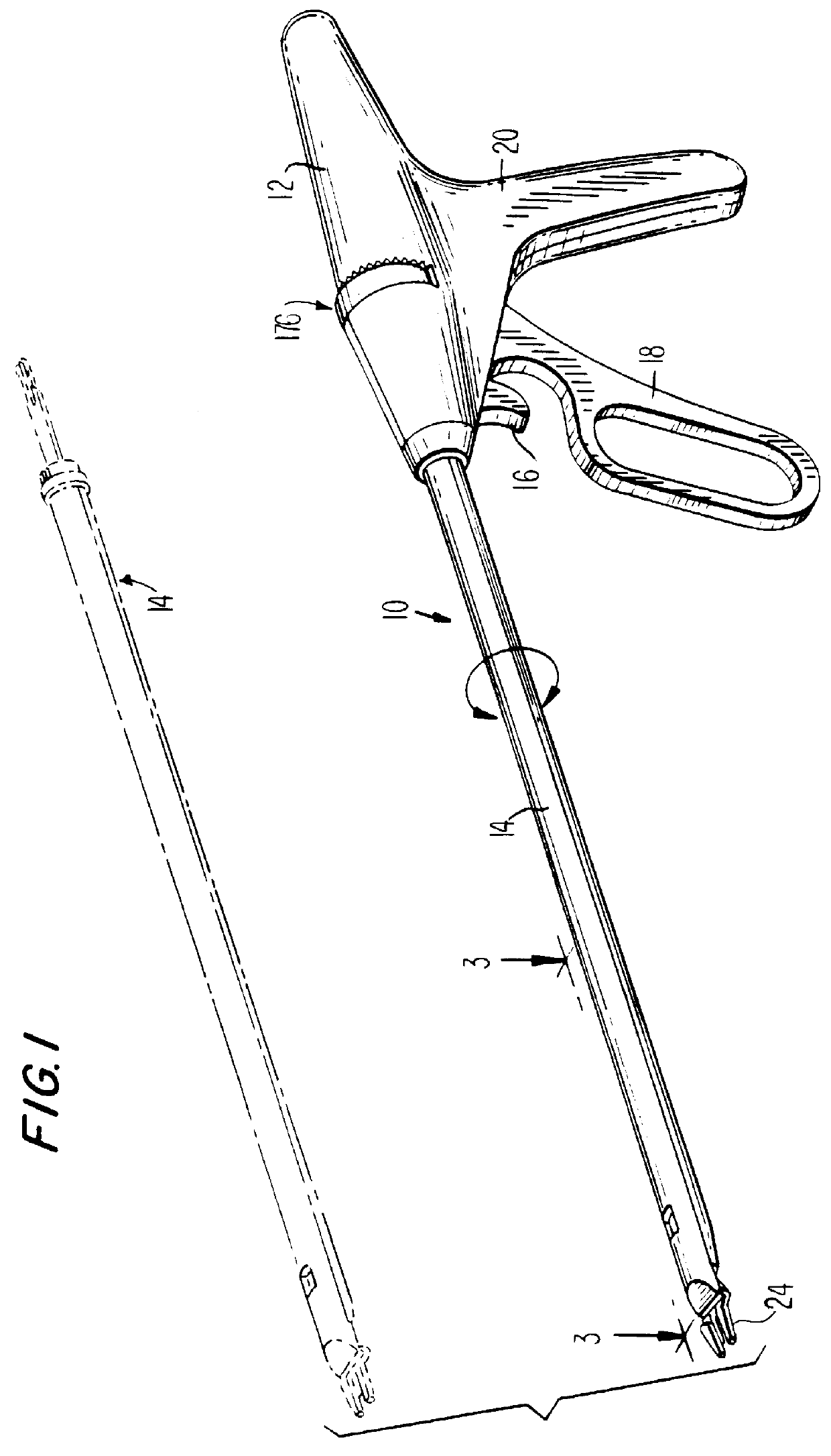
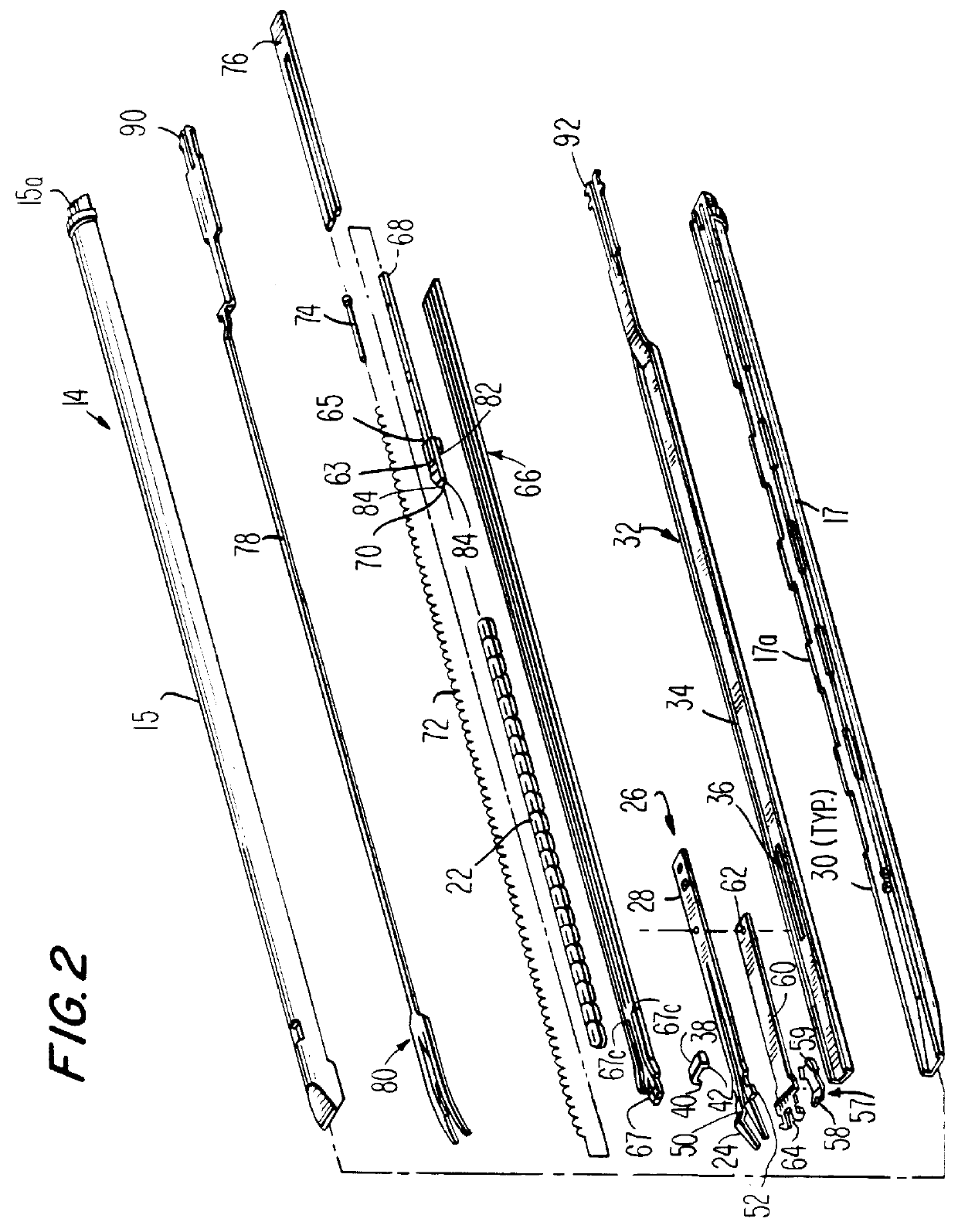
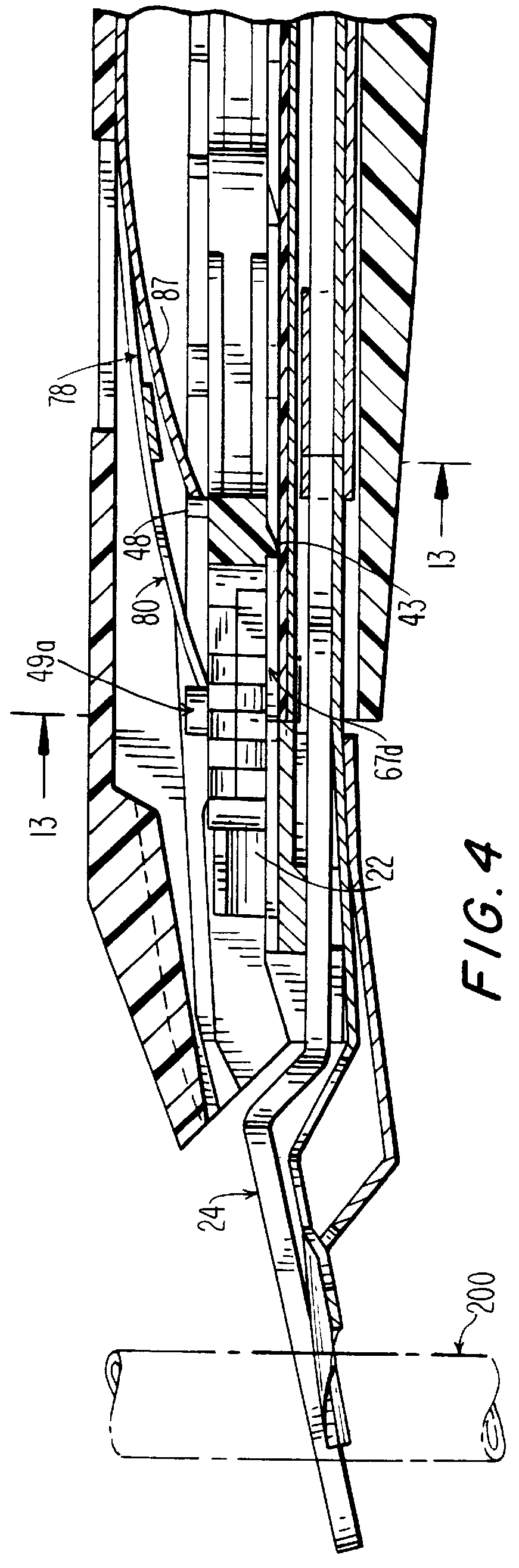
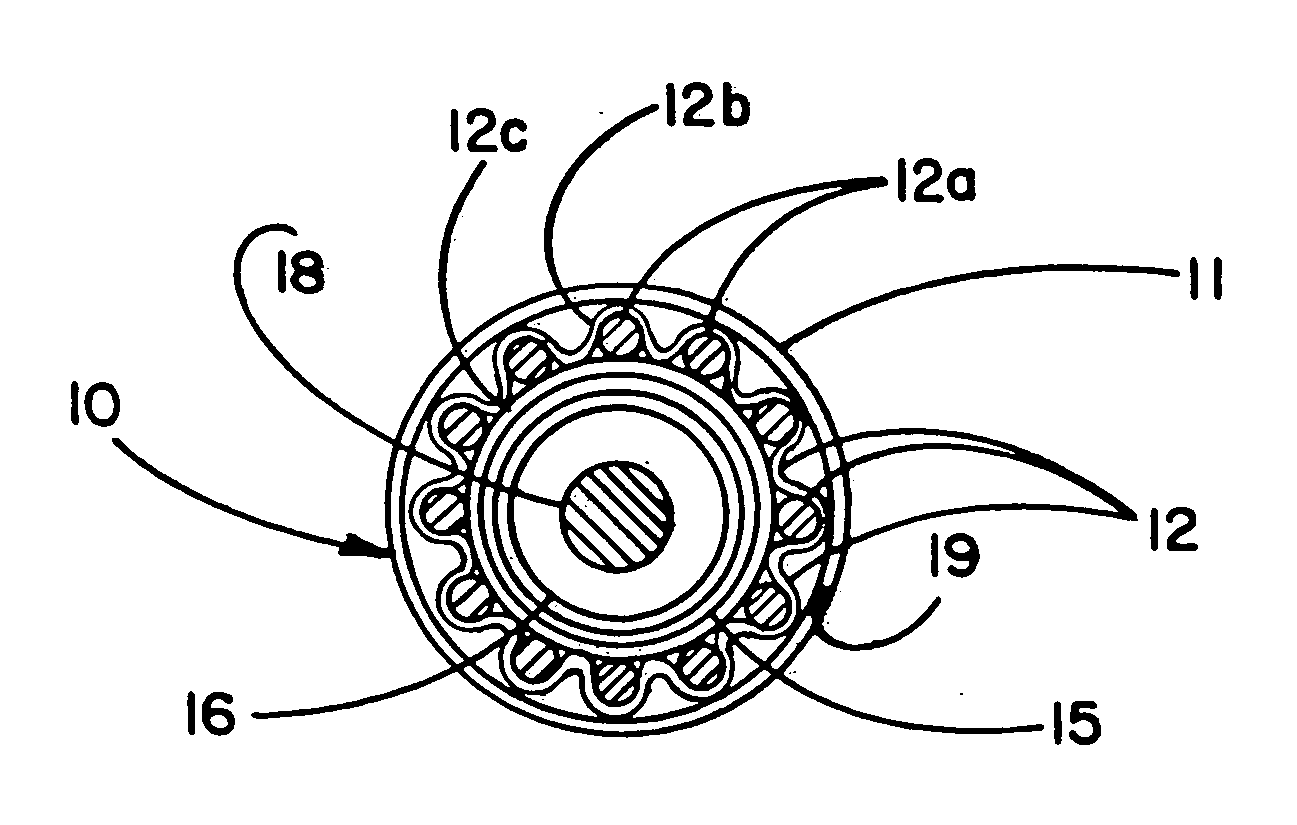
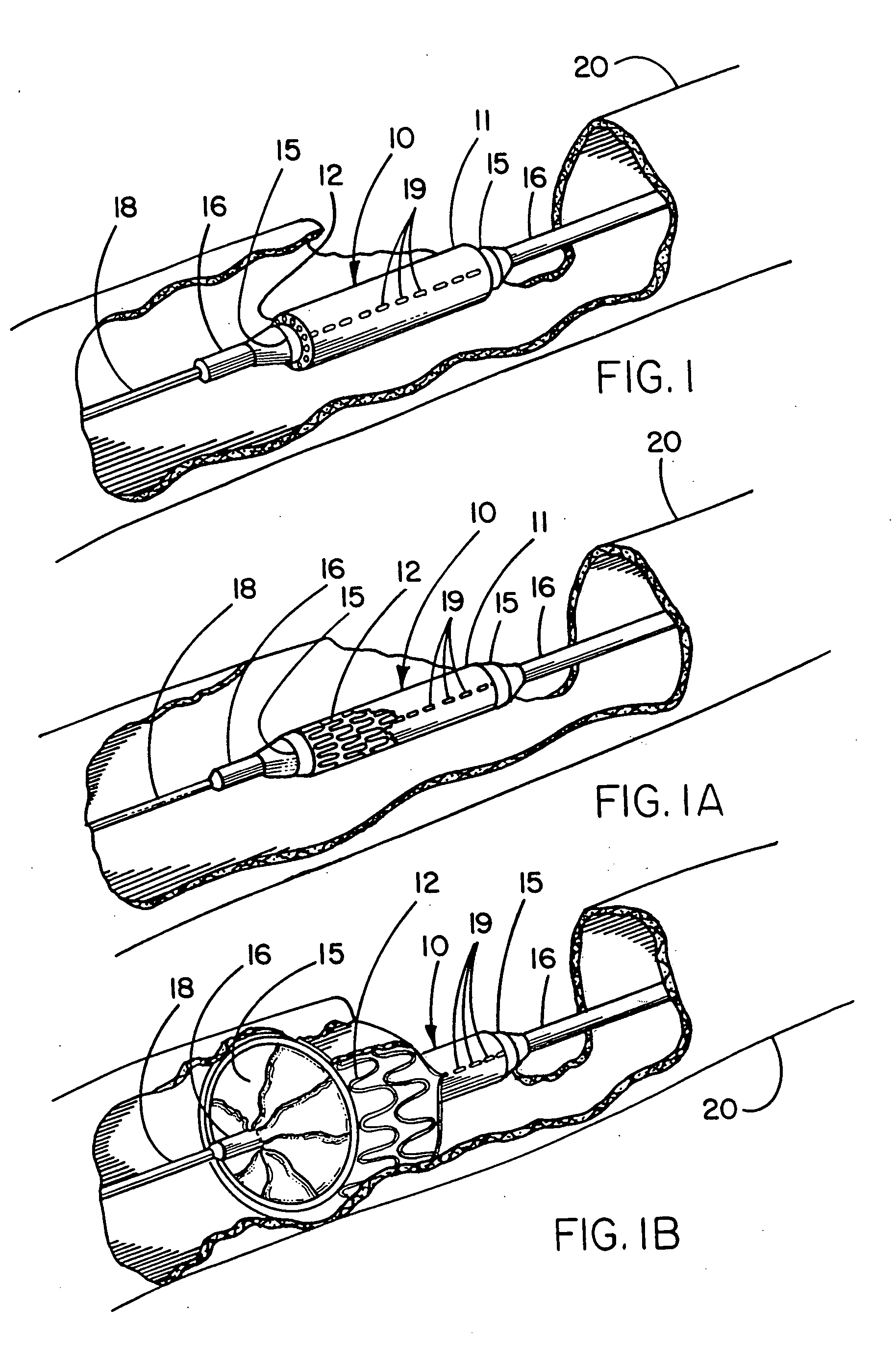
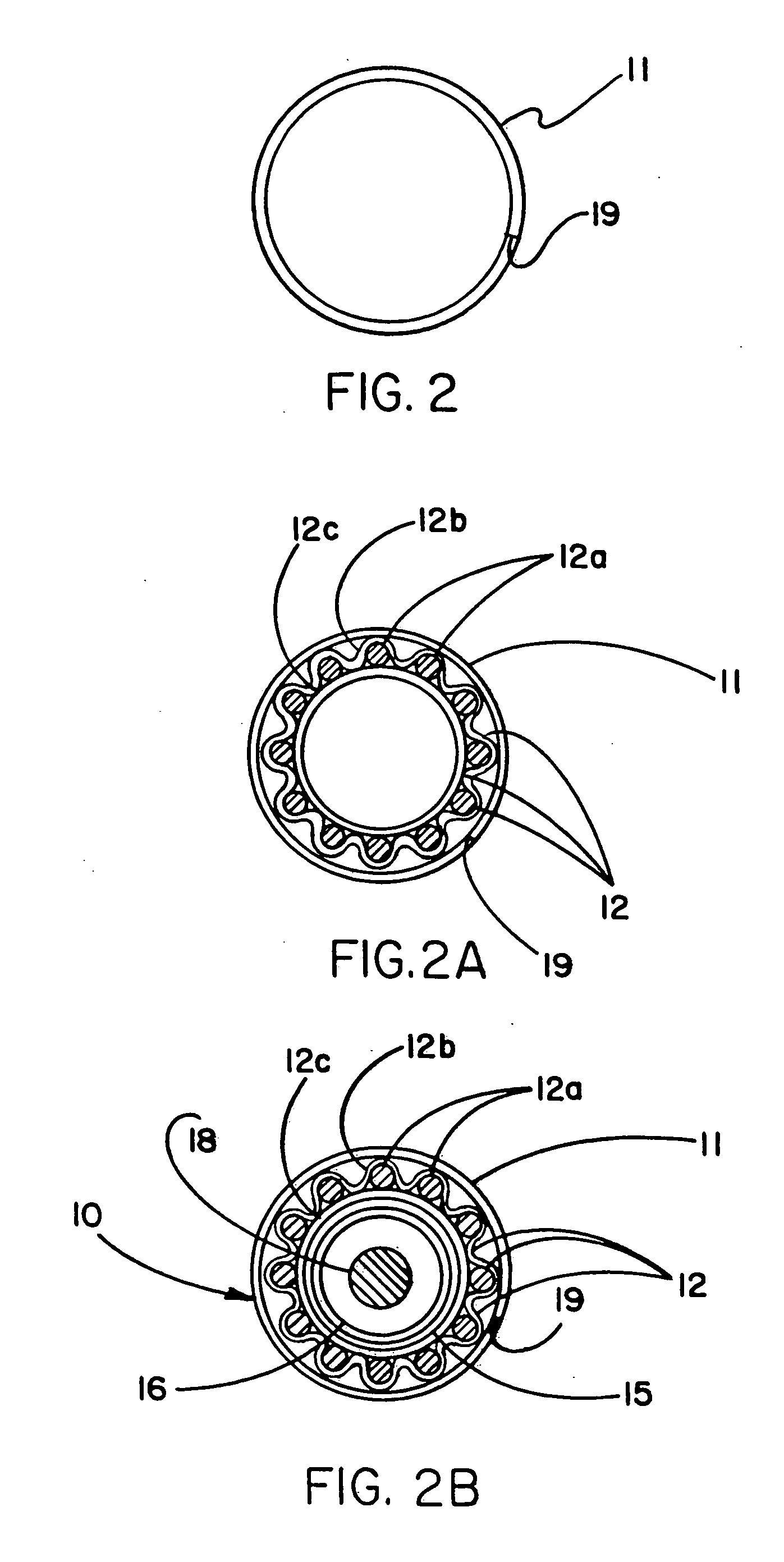
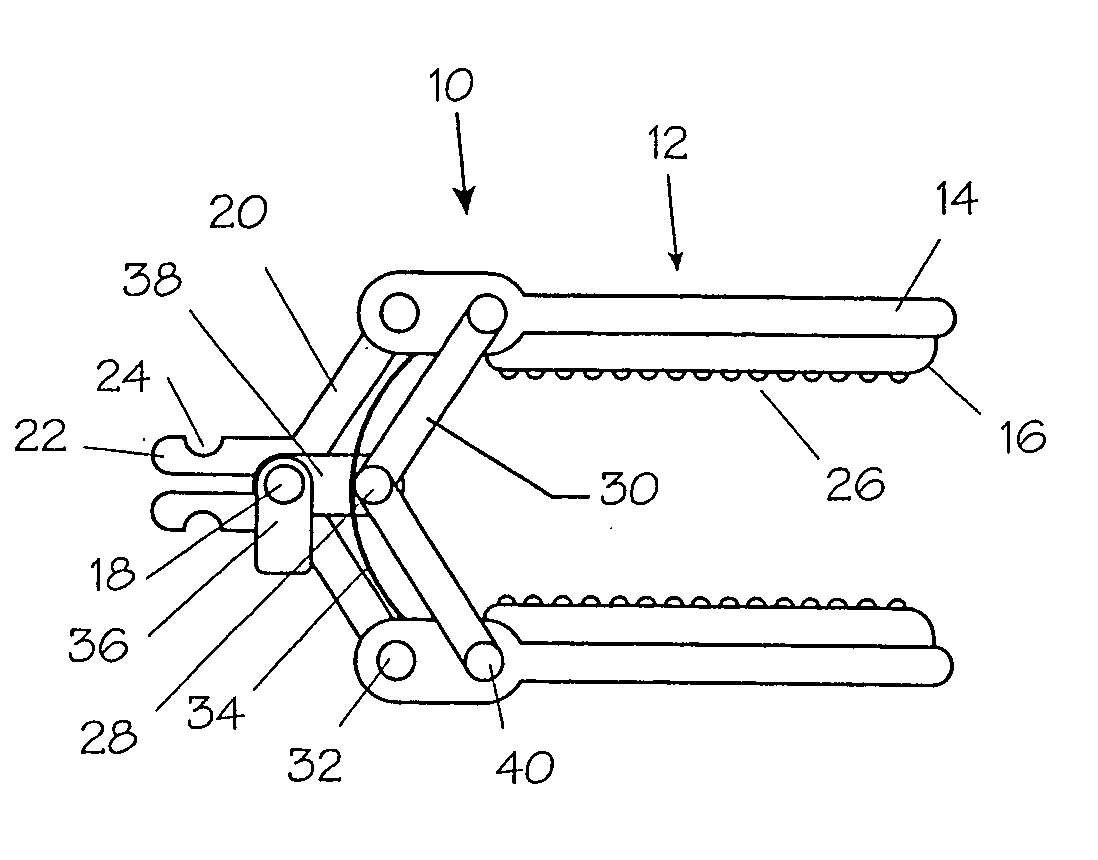
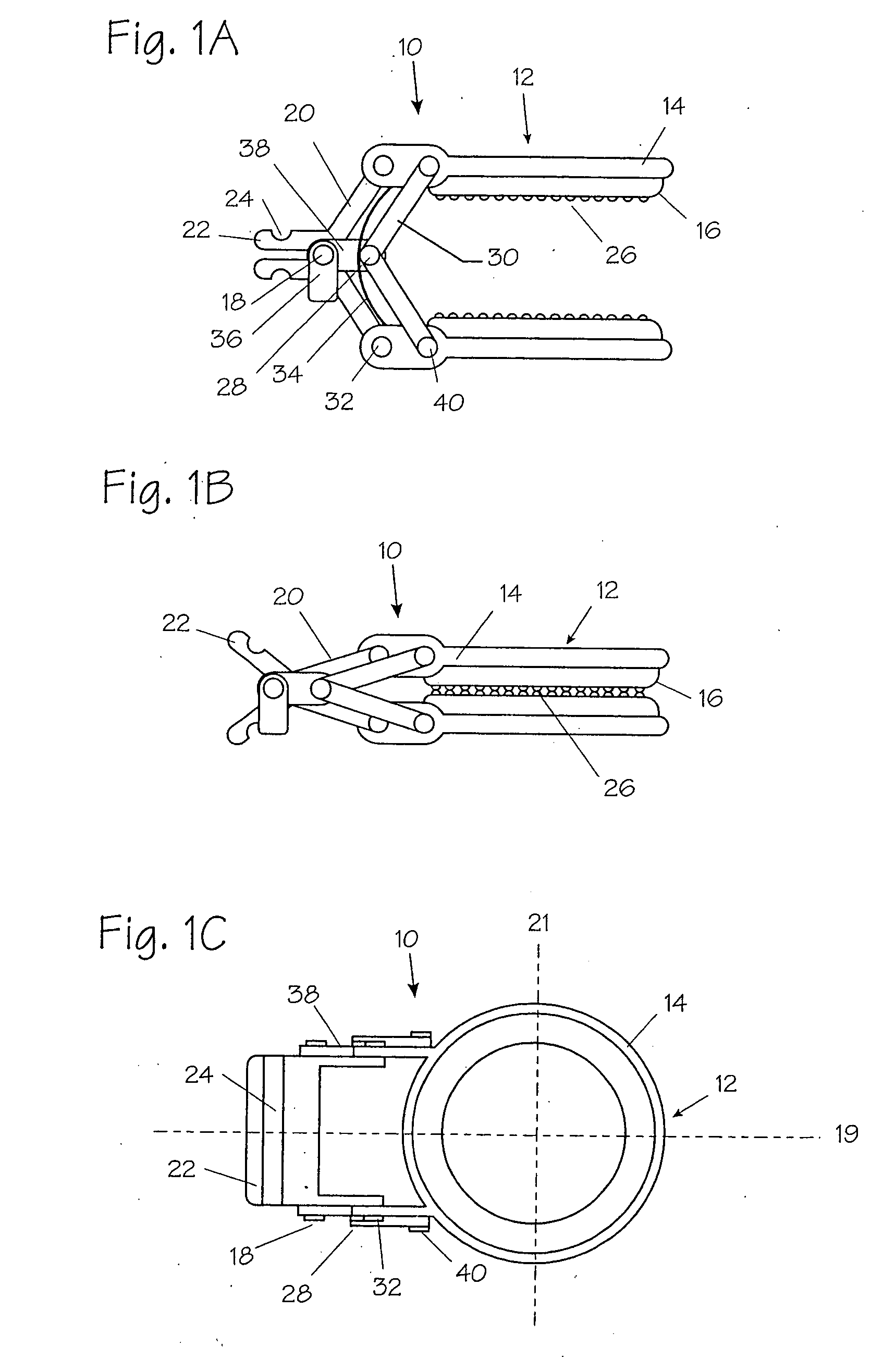
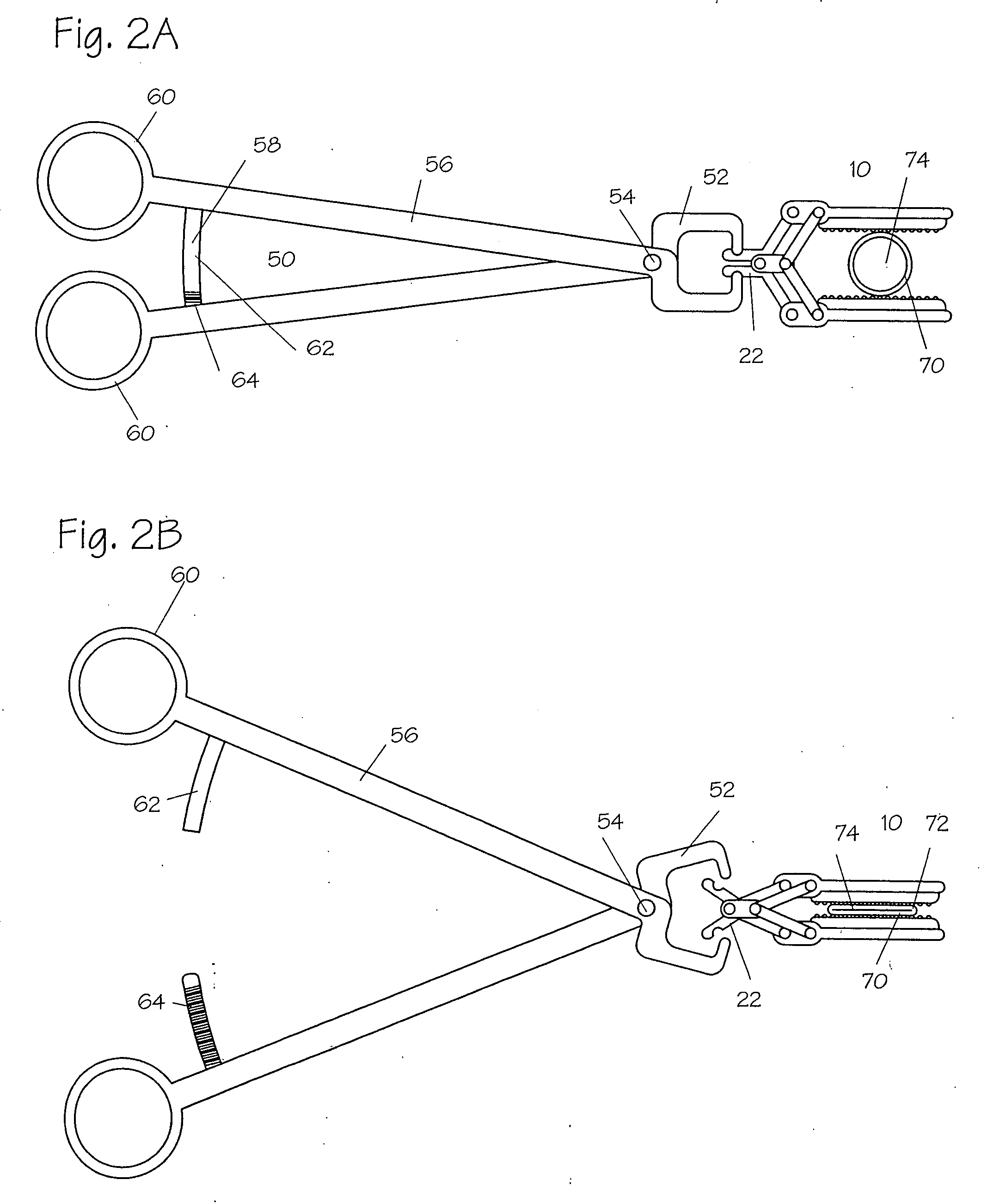
Apparatus and method for applying latchless surgical clips
InactiveUSRE36720E1Completely disposableSuture equipmentsFriction grip releasable fasteningsSurgical ClipsEndoscope
A disposable apparatus is disclosed for applying latchless surgical clips to body tissue in endoscopic surgical procedures. The latchless clips are resiliently biased to a closed configuration. The apparatus includes a frame which is adapted to be gripped by hand, and an endoscopic section connected to the handle and capable of storing surgical clips in preparation for clipping arteries or other body tissue. The apparatus includes means for advancing each clip sequentially, temporarily opening the clip and advancing the clip further to a pair of distal jaws where the clip is positioned around the body tissue and closes around the tissue. Also included are means for closing the jaws about the clip. When the jaws are closed, the clip advancing means is simultaneously positioned to advance the next clip. The present apparatus also makes it possible to partially close a clip without interfering with the sequential movement of the clip advancing mechanism.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
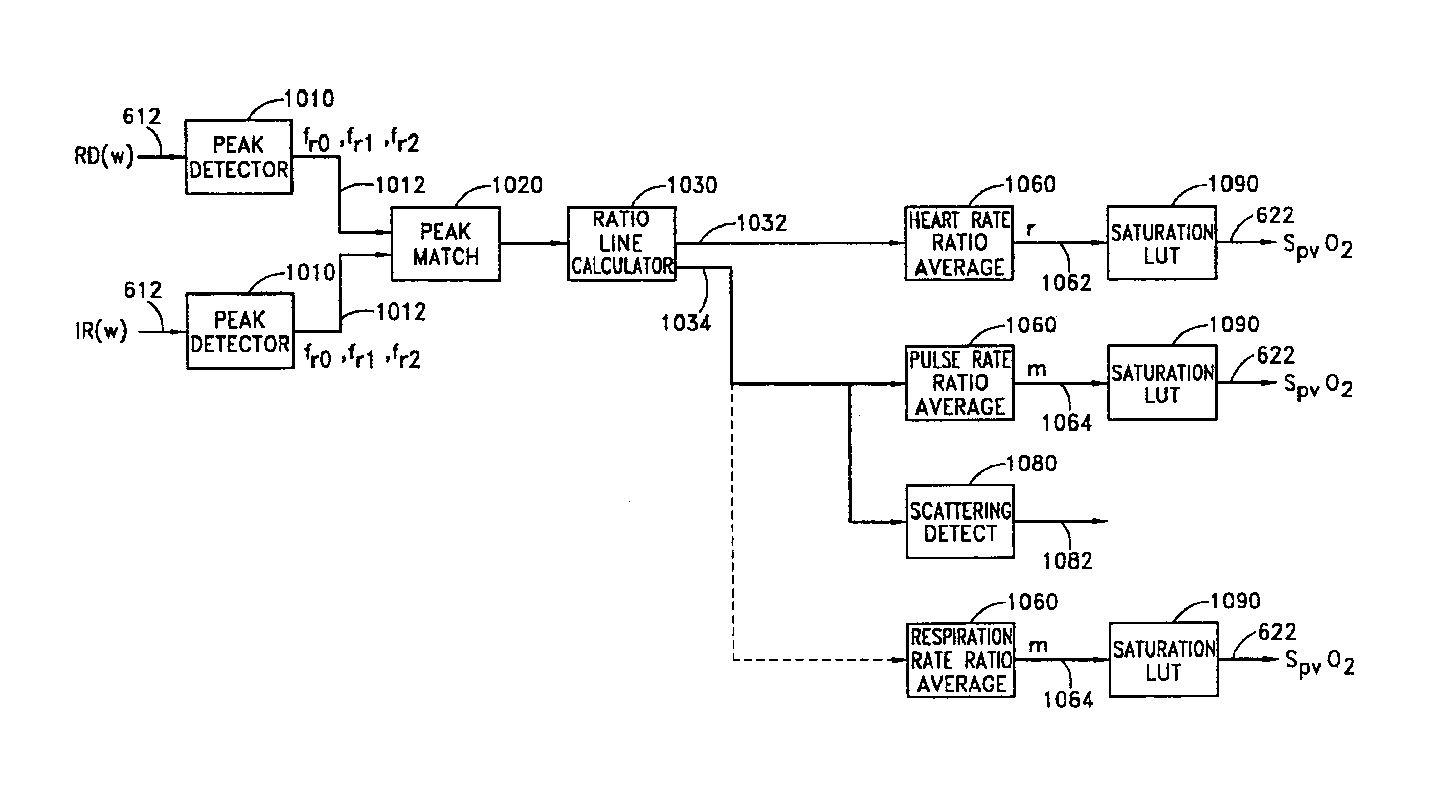
Stereo pulse oximeter
InactiveUS6898452B2Exact reproductionAccurate measurementRespiratorsMedical devicesVenous blood specimenVenous blood
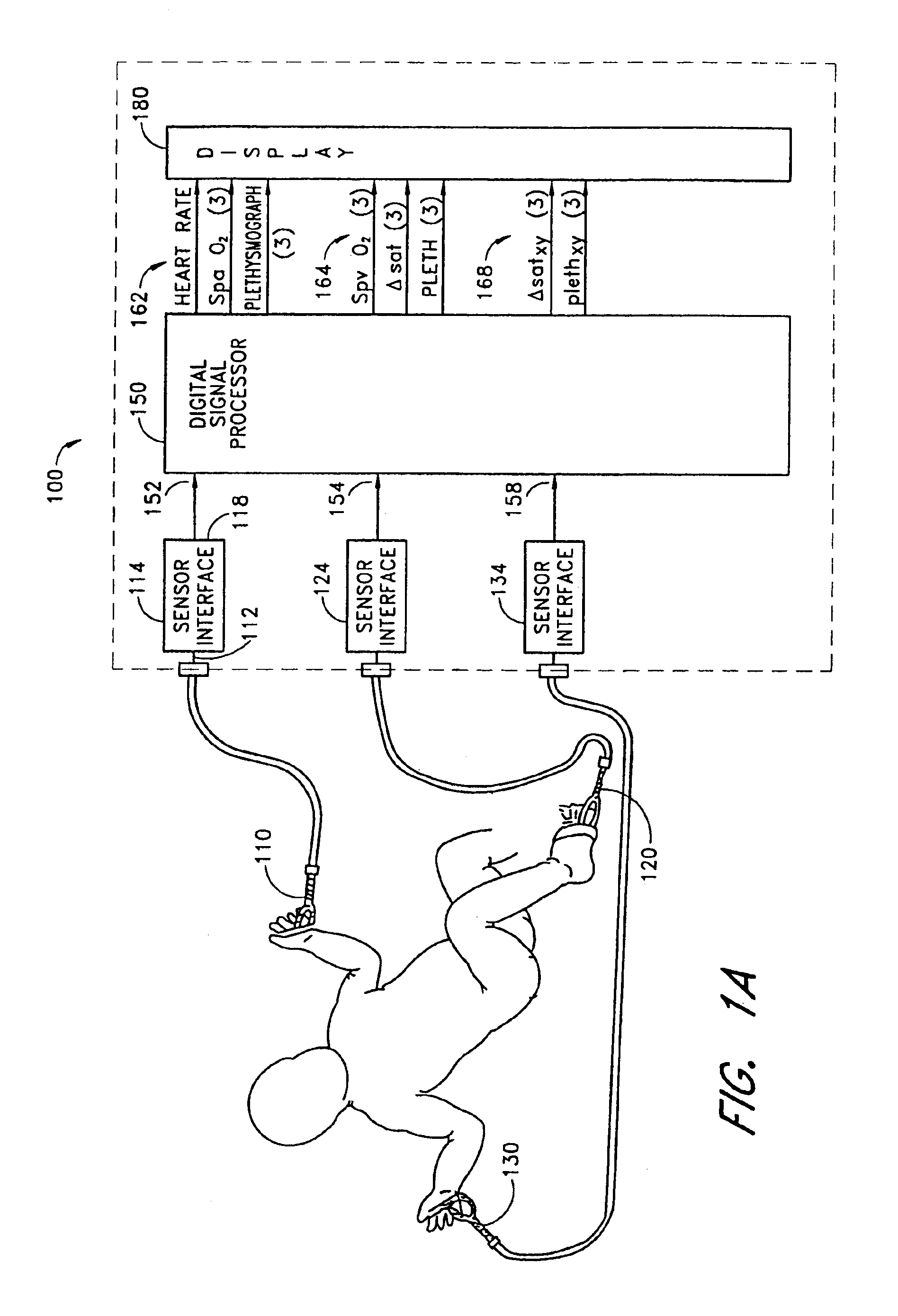
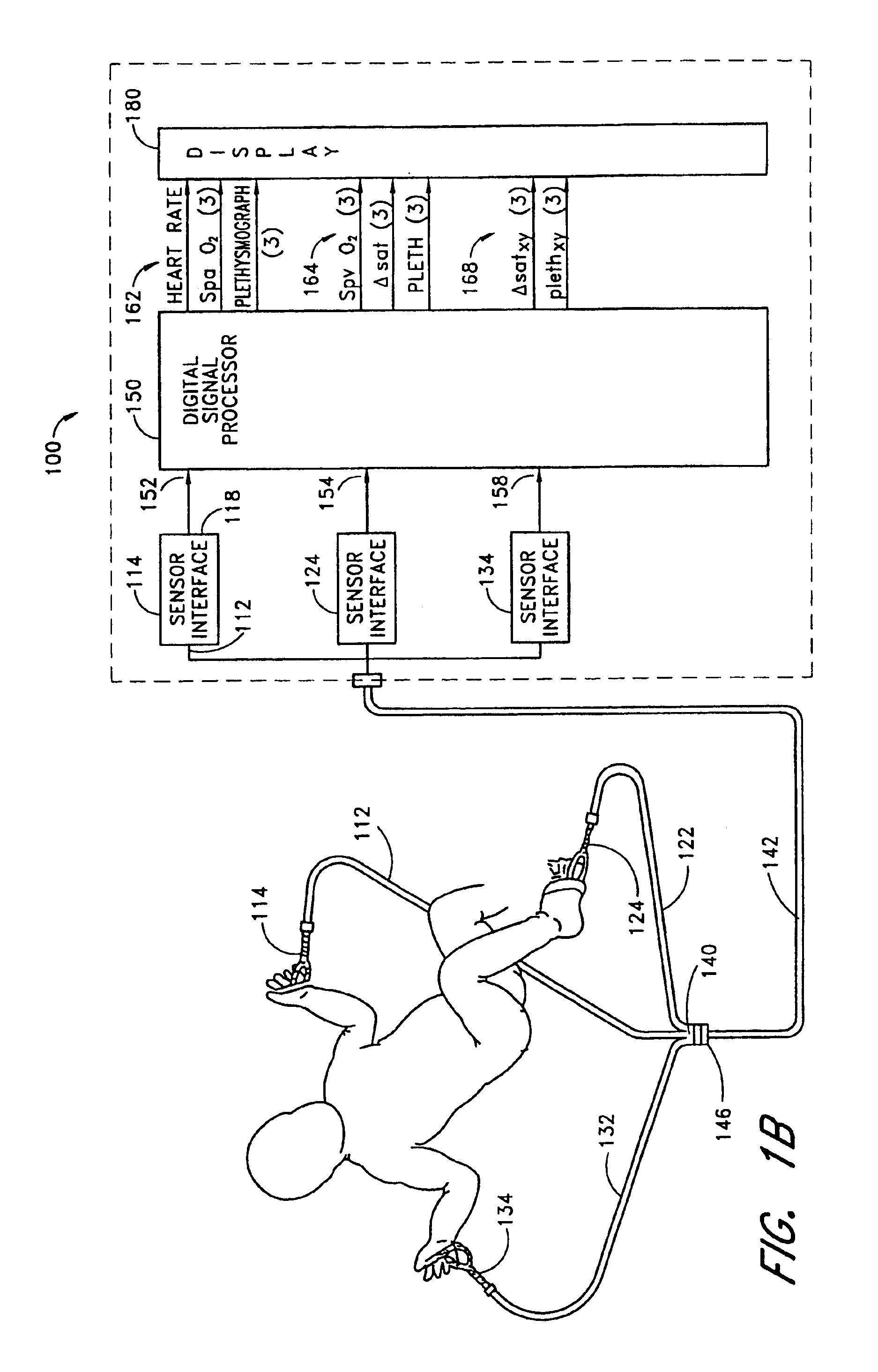
An improved pulse oximeter provides for simultaneous, noninvasive oxygen status and photoplethysmograph measurements at both single and multiple sites. In particular, this multiple-site, multiple-parameter pulse oximeter, or “stereo pulse oximeter” simultaneously measures both arterial and venous oxygen saturation at any specific site and generates a corresponding plethysmograph waveform. A corresponding computation of arterial minus venous oxygen saturation is particularly advantageous for oxygen therapy management. An active pulse-inducing mechanism having a scattering-limited drive generates a consistent pulsatile venous signal utilized for the venous blood measurements. The stereo pulse oximeter also measures arterial oxygen saturation and plethysmograph shape parameters across multiple sites. A corresponding calculation of delta arterial saturation and comparison of plethysmograph shape parameters between multiple sites is particularly advantageous for the detection and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension in neonates (PPHN), a patent ductus arteriosis (PDA), and aortic coarctation.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
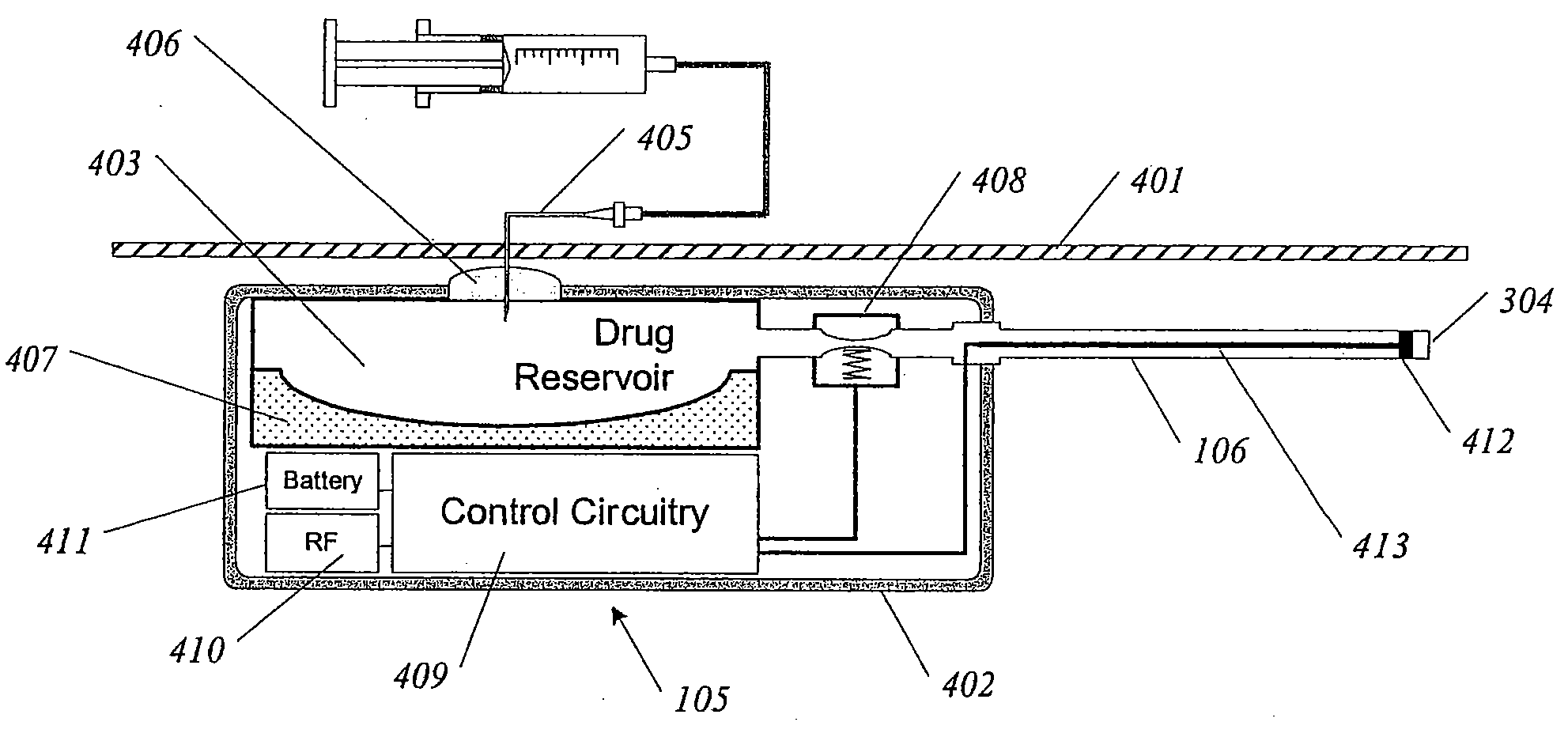
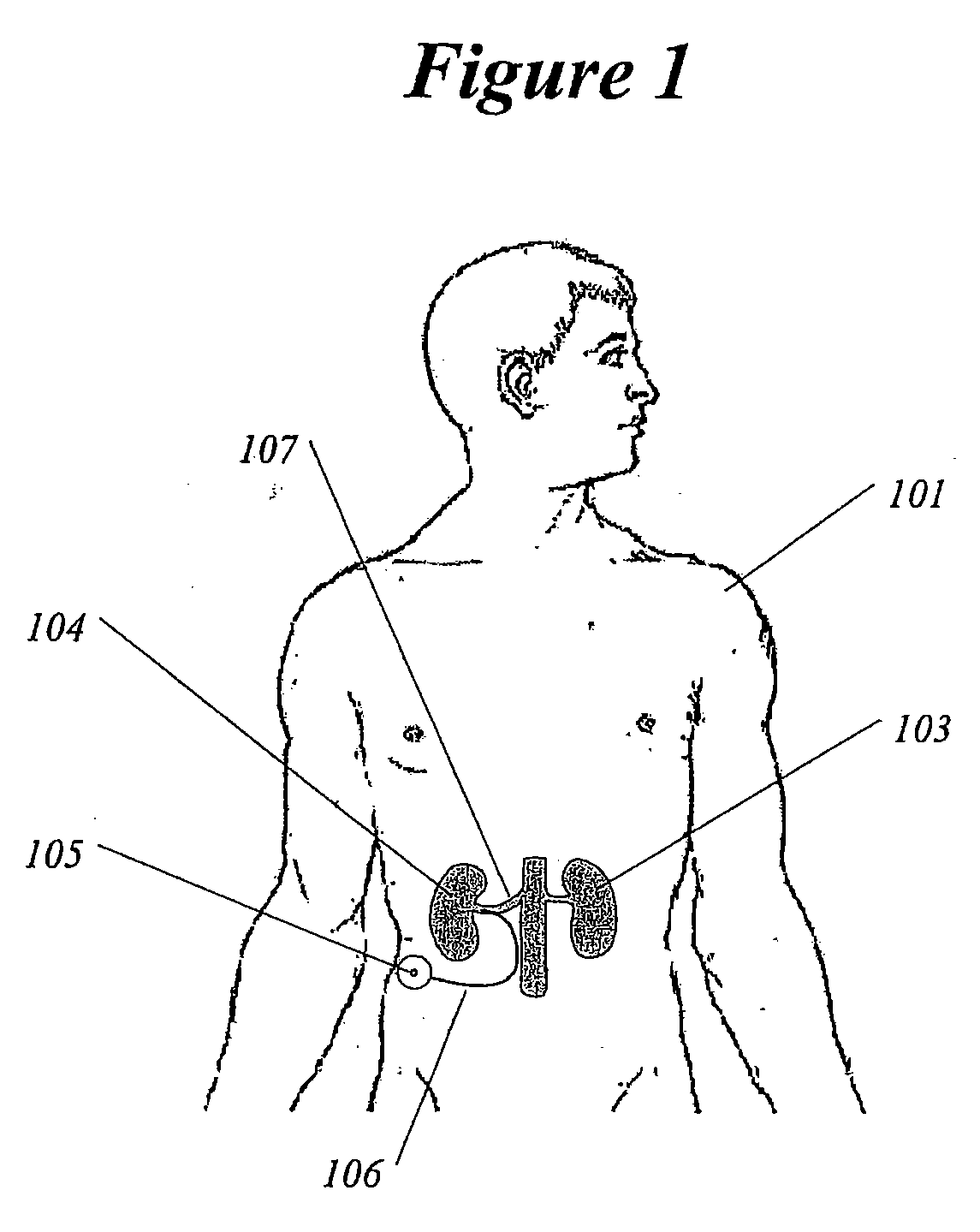
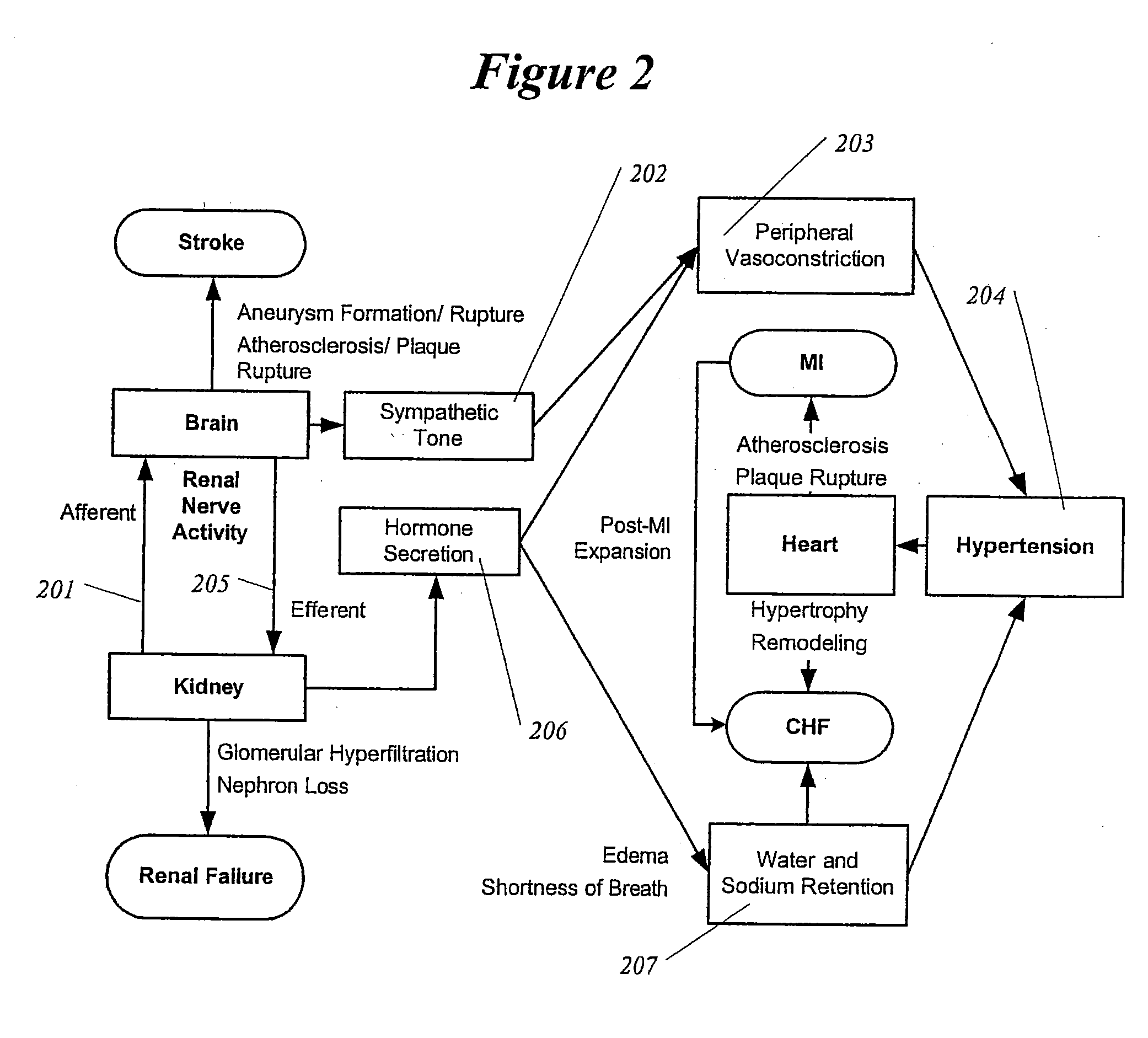
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS6978174B2Shorten the progressResolution of overloadPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseNephropathy
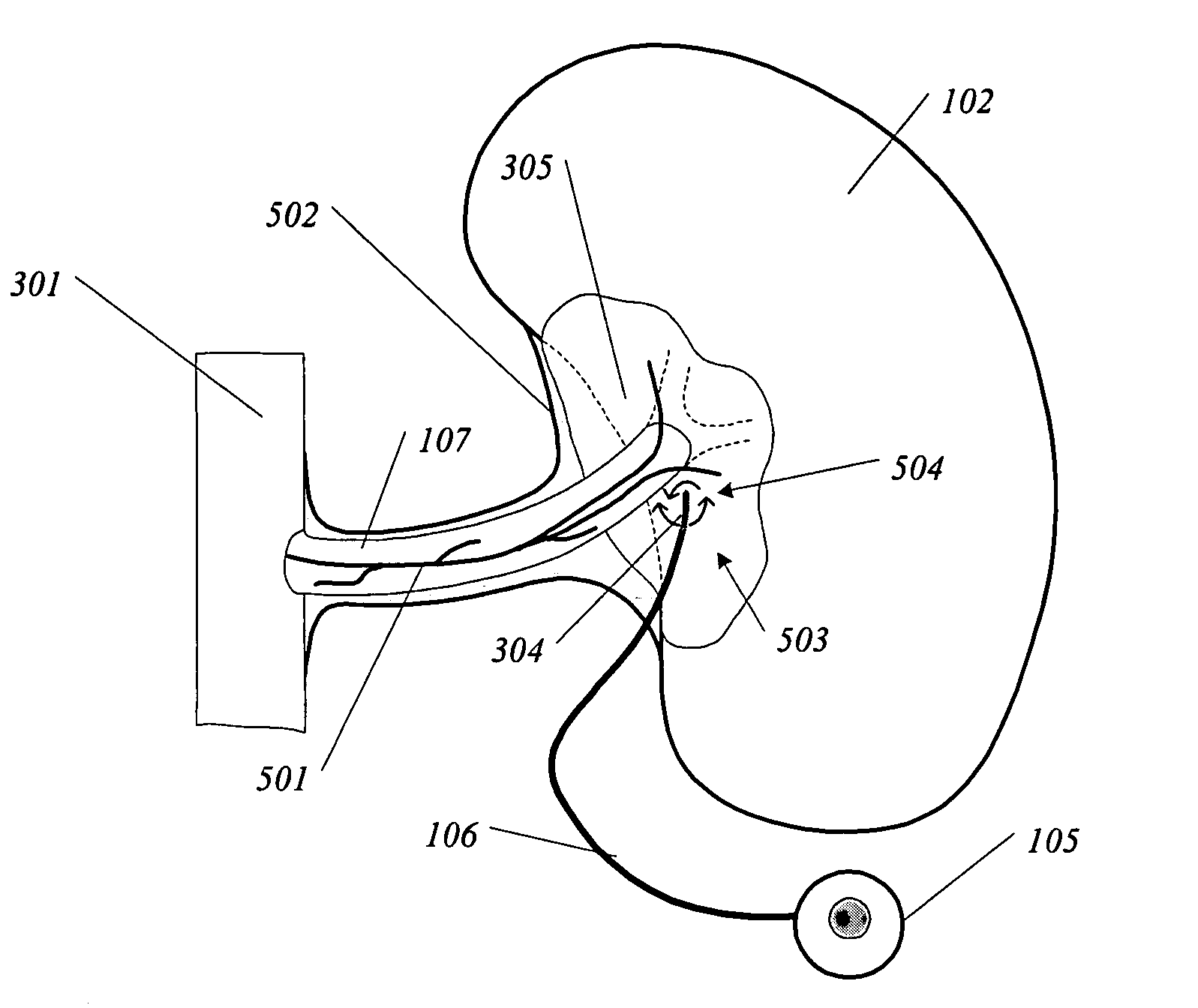
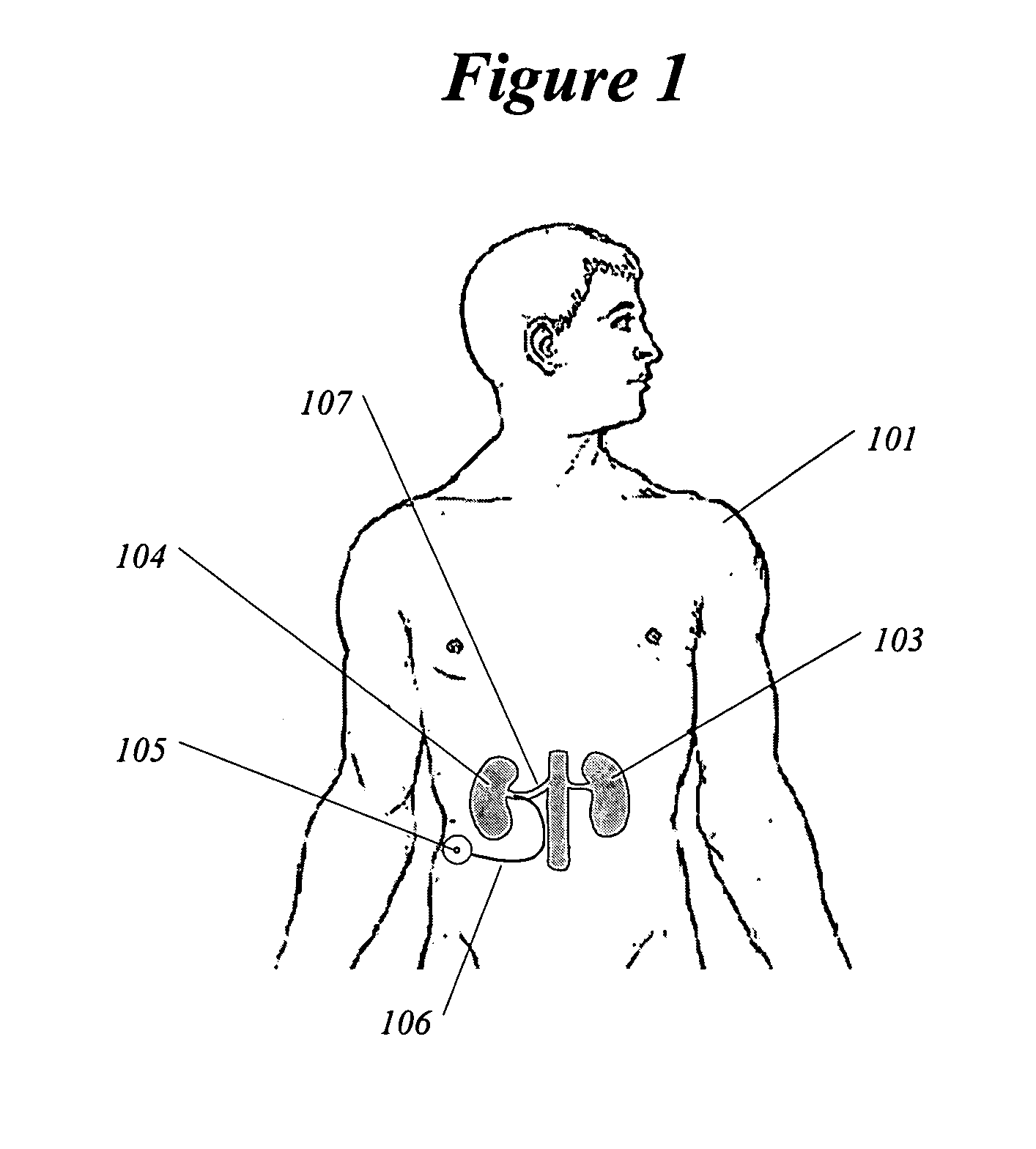
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump eluting implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
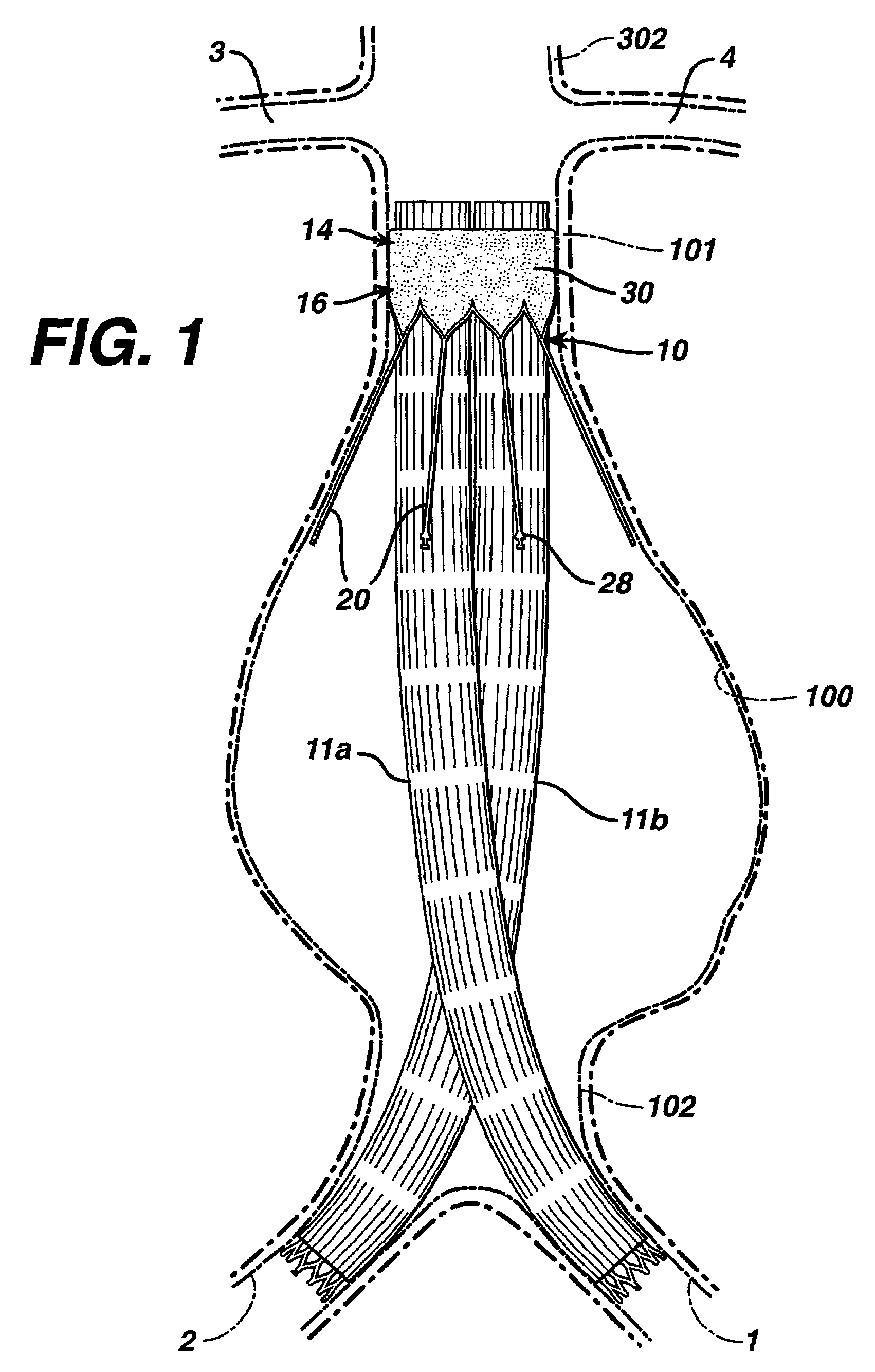
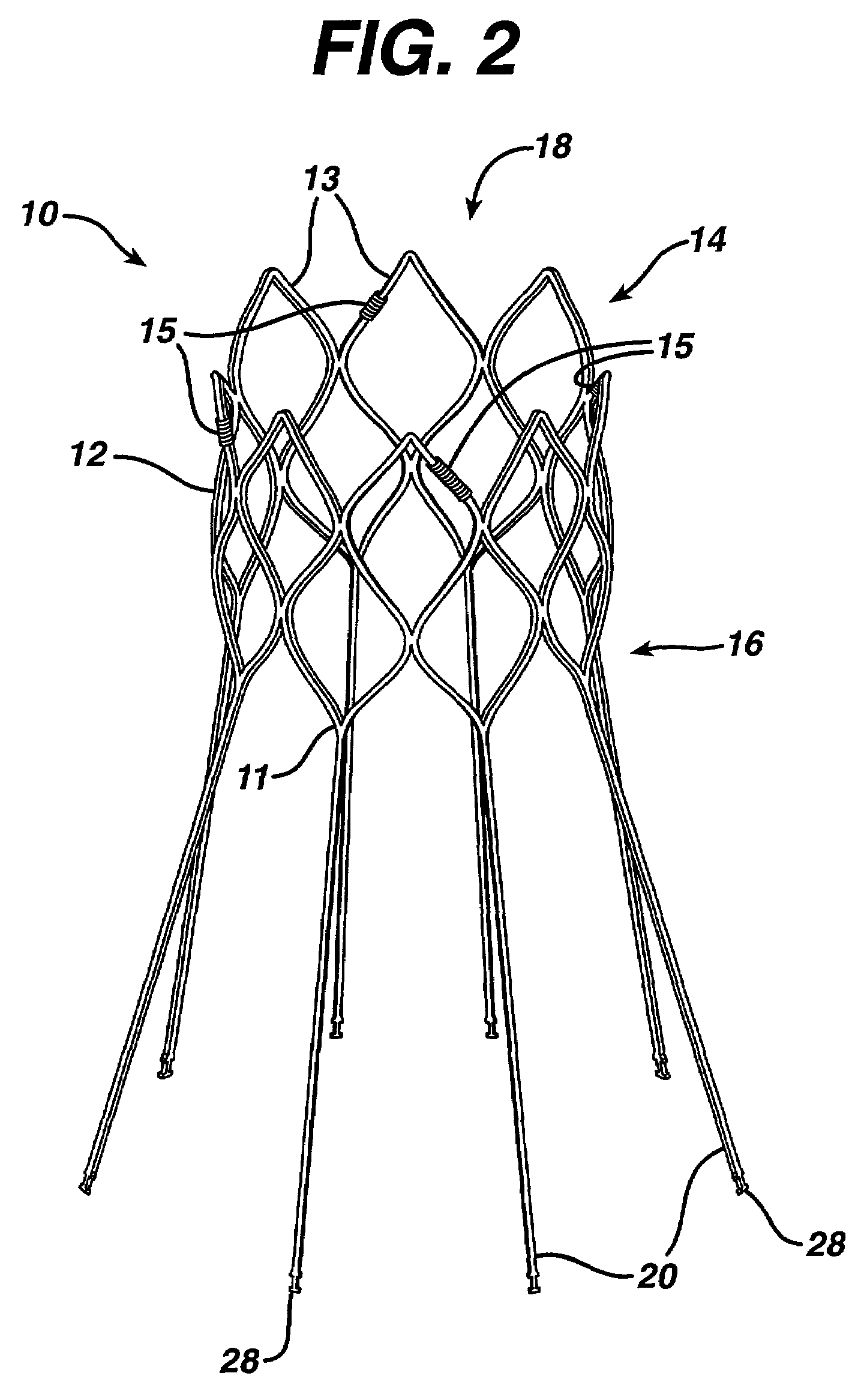
Valve implanting device
ActiveUS6951571B1Easy to replaceIncreased durabilityVenous valvesBlood vesselsImplanted deviceGuide wires
Disclosed is a valve implanting device comprising a collapsible frame, inner and outer guide wires removably connected to the collapsible frame, and a plurality of valve flaps attached to the collapsible frame. The collapsible frame is inserted into a patient's femoral vein or artery, guided to a deployment position using the guide wires, expanded using the guide wires, and stabilized using the guide wires to manipulate fixating hubs on the collapsible frame. The collapsible frame includes a central hub, a plurality of spokes, fixating hubs, gripping members, and a plurality of valve flaps.
Owner:SRIVASTAVA ROHIT
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
Prosthetic Valve for Transluminal Delivery
InactiveUS20100004740A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesVenous accessImplantation Site
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchors may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. A radial restraint, comprising a wire, thread or cuff, may be used to ensure expansion does not exceed the preset diameter. The valve support may optionally comprise a drug elution component. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. A blood pump may be inserted into the catheter to ensure continued blood flow across the implantation site during implantation procedure. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. Insertion of the catheter may optionally be performed over a transseptally delivered guidewire that has been externalized through the arterial vasculature. Such a guidewire provide dual venous and arterial access to the implantation site and allows additional manipulation of the implantation site after arterial implantation of the prosthetic valve. Additional expansion stents may be delivered by venous access to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Device for the implantation and fixation of prosthetic valves
ActiveUS20070100440A1High positioning accuracyImprove mobilityStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveProsthetic heart
A device for the transvascular implantation and fixation of prosthetic heart valves having a self-expanding heart valve stent (10) with a prosthetic heart valve (11) at its proximal end is introducible into a patient's main artery. With the objective of optimizing such a device to the extent that the prosthetic heart valve (11) can be implanted into a patient in a minimally-invasive procedure, to ensure optimal positioning accuracy of the prosthesis (11) in the patient's ventricle, the device includes a self-expanding positioning stent (20) introducible into an aortic valve positioned within a patient. The positioning stent is configured separately from the heart valve stent (10) so that the two stents respectively interact in their expanded states such that the heart valve stent (10) is held by the positioning stent (20) in a position in the patient's aorta relative the heart valve predefinable by the positioning stent (20).
Owner:JENAVALVE TECH INC
Electrosurgical instrument with minimally invasive jaws
A surgical instrument useful in harvesting blood vessels such as veins and arteries and for manipulating and grasping tissue. The instrument has a pair of jaws and a closing tube to open and close the jaws.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS20080213331A1Shorten the progressResolution of overloadSpinal electrodesMedical devicesDiseaseRenal nerve
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump or a drug eluding implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:ARDIAN
Devices and methods for controlling expandable prostheses during deployment
InactiveUS20050288766A1Reduce deliveryPrevents excessive spacing and overlapStentsBlood vesselsStenotic lesionProsthesis
Prosthesis delivery devices and methods are provided that enable precise control of prosthesis position during deployment. The prosthesis delivery devices may carry multiple prostheses and include deployment mechanisms for delivery of a selectable number of prostheses. Control mechanisms are provided in the prosthesis delivery devices that control either or both of the axial and rotational positions of the prostheses during deployment. This enables the deployment of multiple prostheses at a target site with precision and predictability, eliminating excessive spacing or overlap between prostheses. In particular embodiments, the prostheses of the invention are deployed in stenotic lesions in coronary or peripheral arteries or in other vascular locations.
Owner:XTENT INC
Laser ablation process and apparatus
InactiveUS20020045811A1Reduce Fresnel reflectionMaximize transmitted lightControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostics using spectroscopyFiberLaser light
A laser catheter is disclosed wherein optical fibers carrying laser light are mounted in a catheter for insertion into an artery to provide controlled delivery of a laser beam for percutaneous intravascular laser treatment of atherosclerotic disease. A transparent protective shield is provided at the distal end of the catheter for mechanically diplacing intravascular blood and protecting the fibers from the intravascular contents, as well as protecting the patient in the event of failure of the fiber optics. Multiple optical fibers allow the selection of tissue that is to be removed. A computer controlled system automatically aligns fibers with the laser and controls exposure time. Spectroscopic diagnostics determine what tissue is to be removed.
Owner:KITTRELL CARTER +2
Electrode designs and methods of use for cardiovascular reflex control devices
InactiveUS7158832B2RemissionReduce pressureInternal electrodesExternal electrodesNervous systemBaroreceptor function
Devices, systems and methods by which the blood pressure, nervous system activity, and neurohornonal activity may be selectively and controllably reduced by activating baroreceptors. A baroreceptor activation device is positioned near a baroreceptor, preferably in the carotid sinus. The baroreceptor activation device may utilize electrodes to activate the baroreceptors. The electrodes may be adapted for connection to the carotid arteries at or near the carotid sinus, and may be designed to minimize extraneous tissue stimulation.
Owner:CVRX
Method and apparatuses for treating an intravascular occlusion
InactiveUS20060200191A1Minimize timeReduce amountBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterThree vesselsExternal carotid artery
Methods for an intravascular occlusion are provided. A guidewire having an occlusive device such as balloon or a filter at one end is advanced across the occlusion using a guide catheter, and the occlusive device is expanded distal to the occlusion to occlude the blood vessel. The guide catheter may also have an occlusive device to occlude the vessel proximal to the occlusion. In a treatment method for the carotid arteries, occlusive devices may be provided in the external carotid artery, in the internal carotid artery, and in the common carotid artery.
Owner:ZADNO AZIZI GHOLAM REZA
Methods and apparatus for perfusion of isolated tissue structure
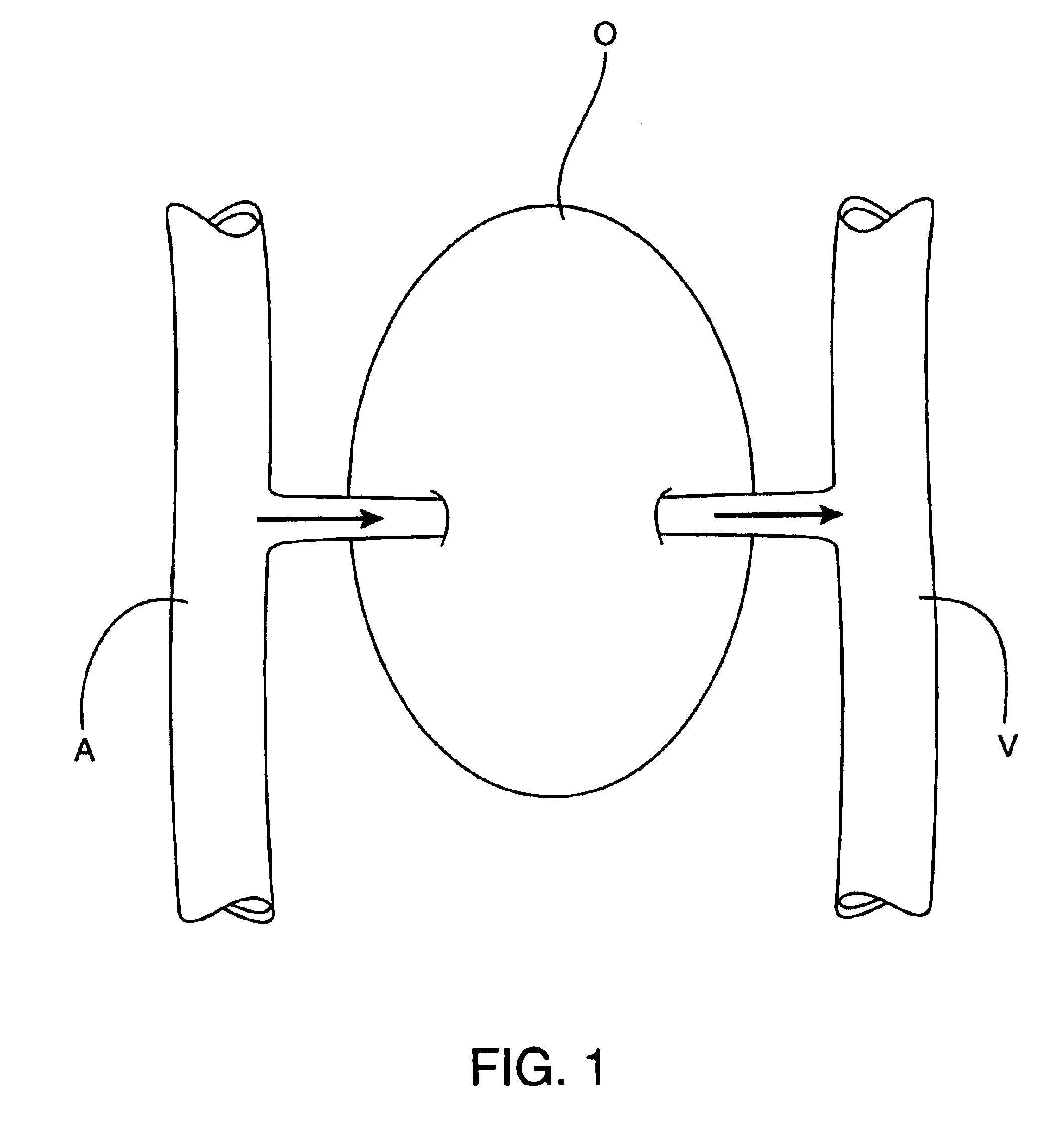
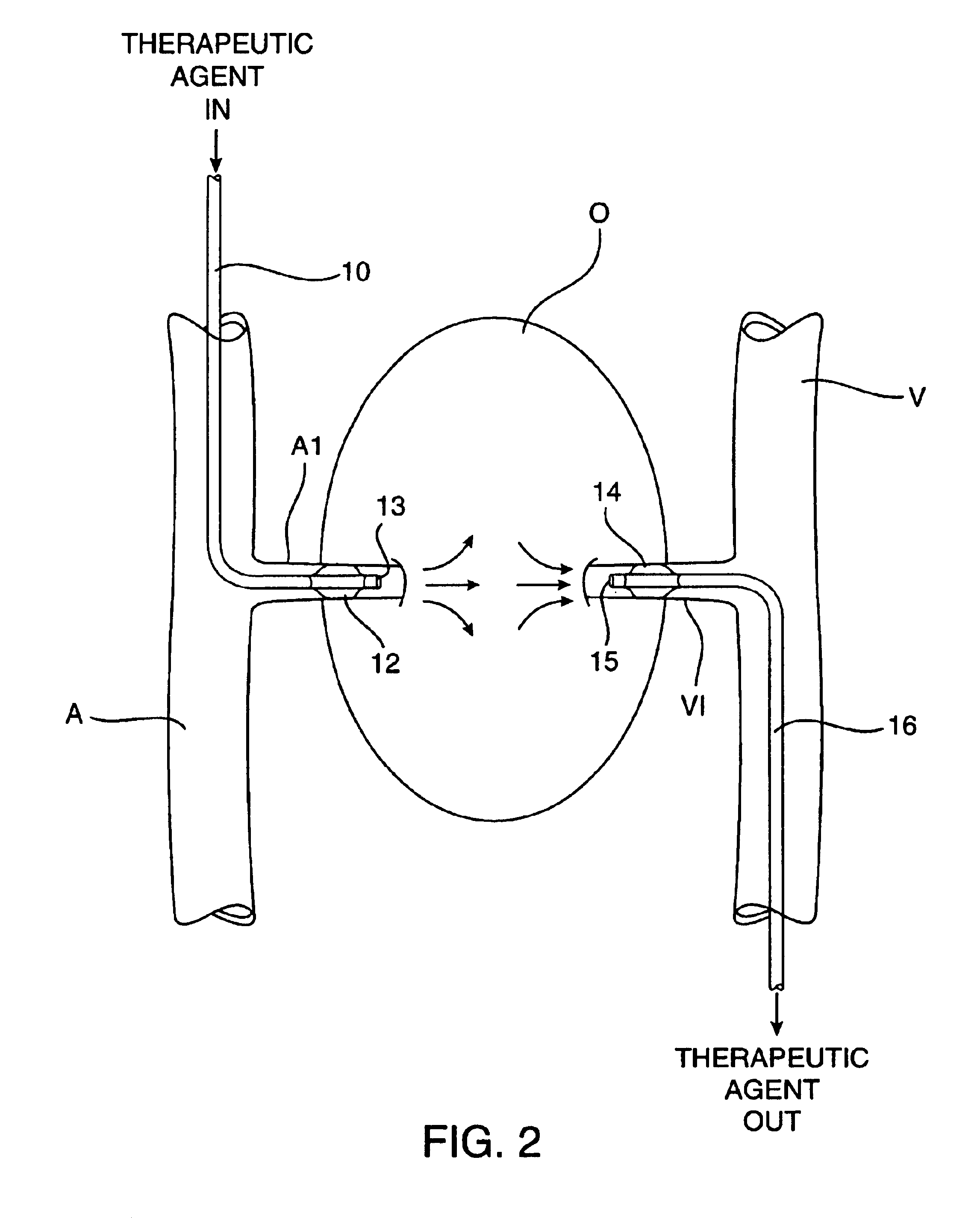
Organs and other tissue structures are isolated and perfused with a therapeutic agent. Isolation is effected by endovascularly positioning catheters having occlusion balloons within the arteries or other blood vessels which supply blood to the organ. Similarly, blood flow from the organ back to the patient's circulatory system is blocked by endovascularly positioning one or more catheters carrying occlusion members within the veins or other blood vessels leading from the organ. The therapeutic agent may then be perfused through the organ in either an antegrade or retrograde fashion using the endovascularly positioned catheters while maintaining isolation.
Owner:PINPOINT THERAPEUTICS
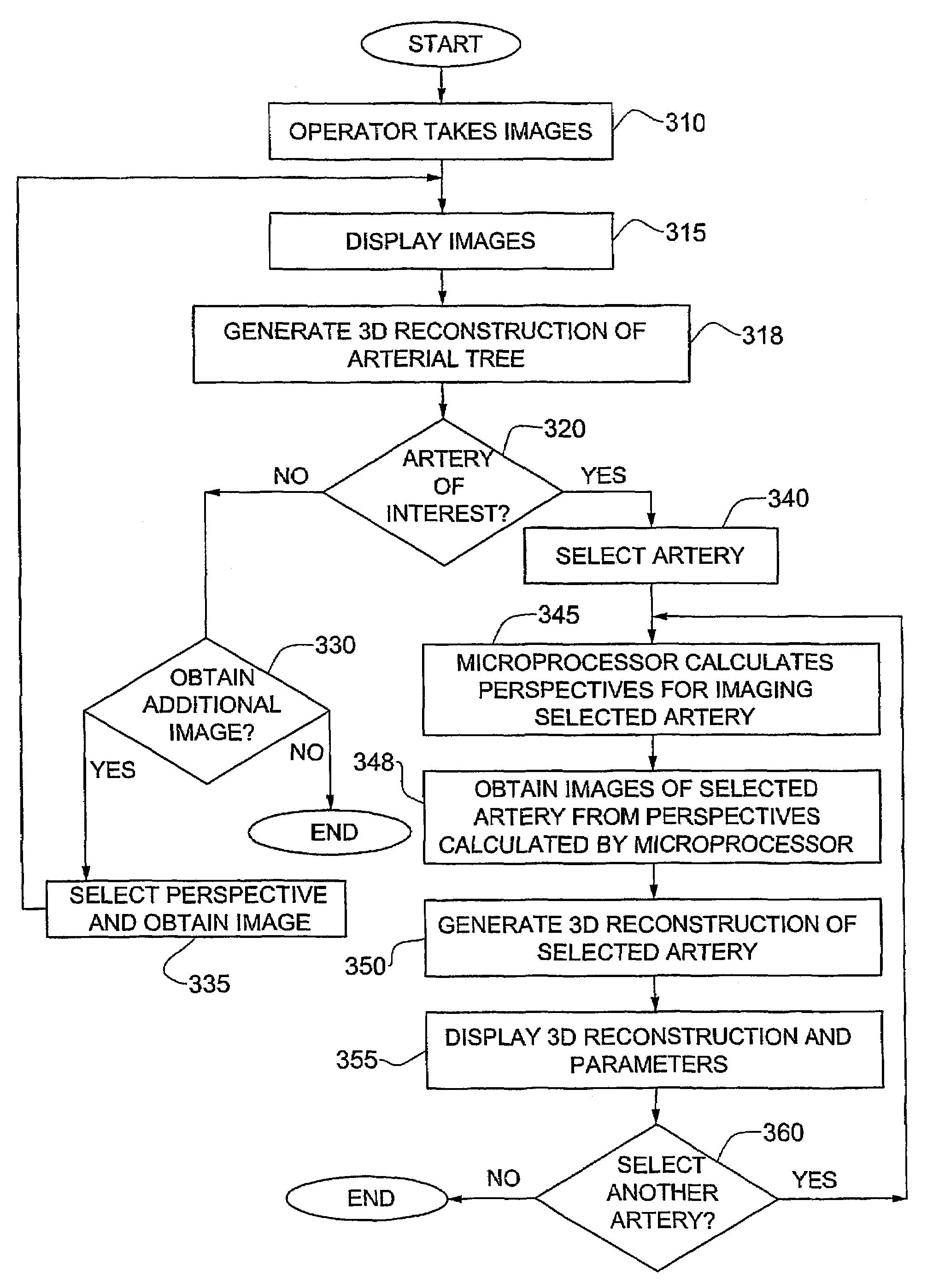
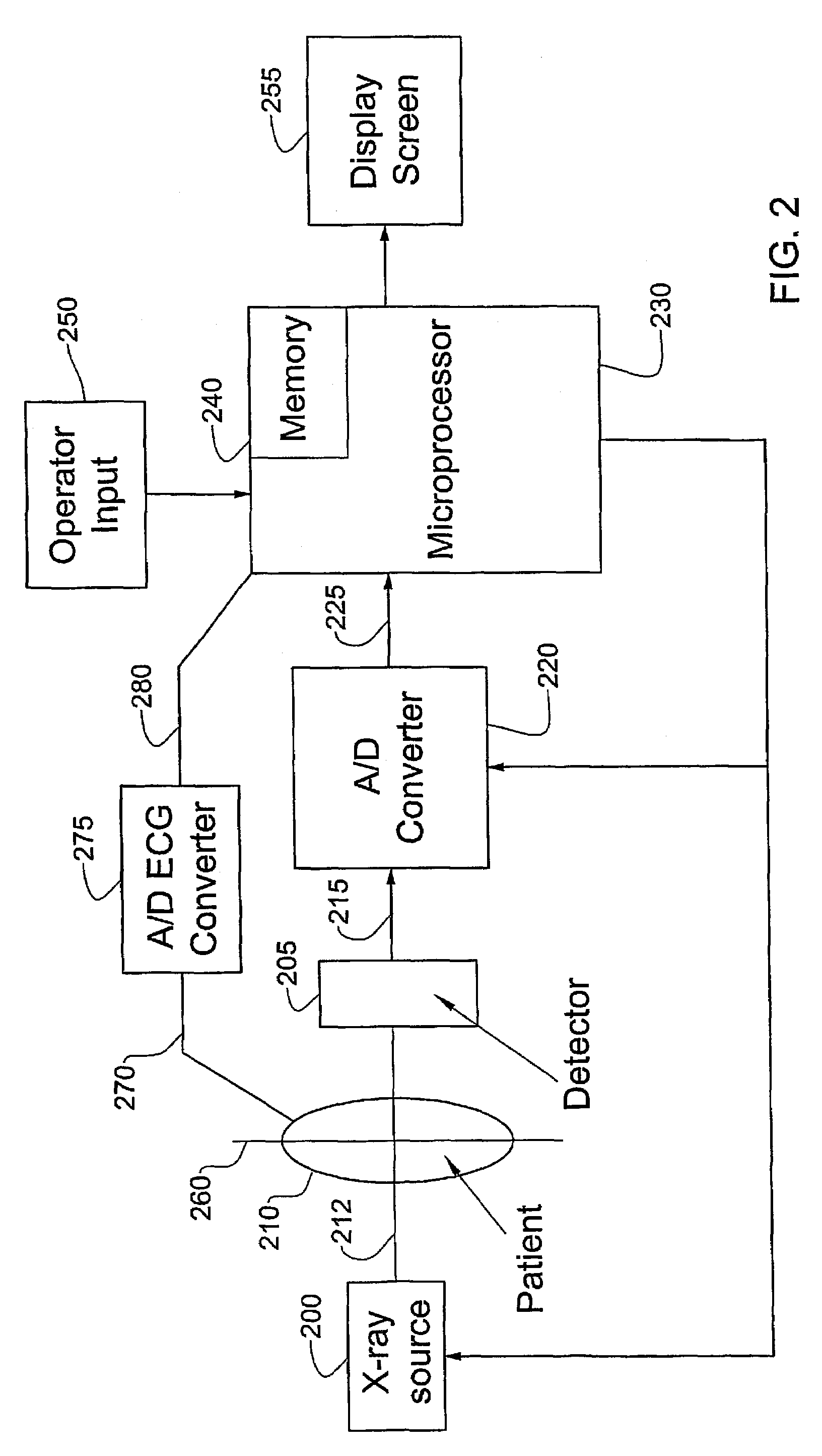
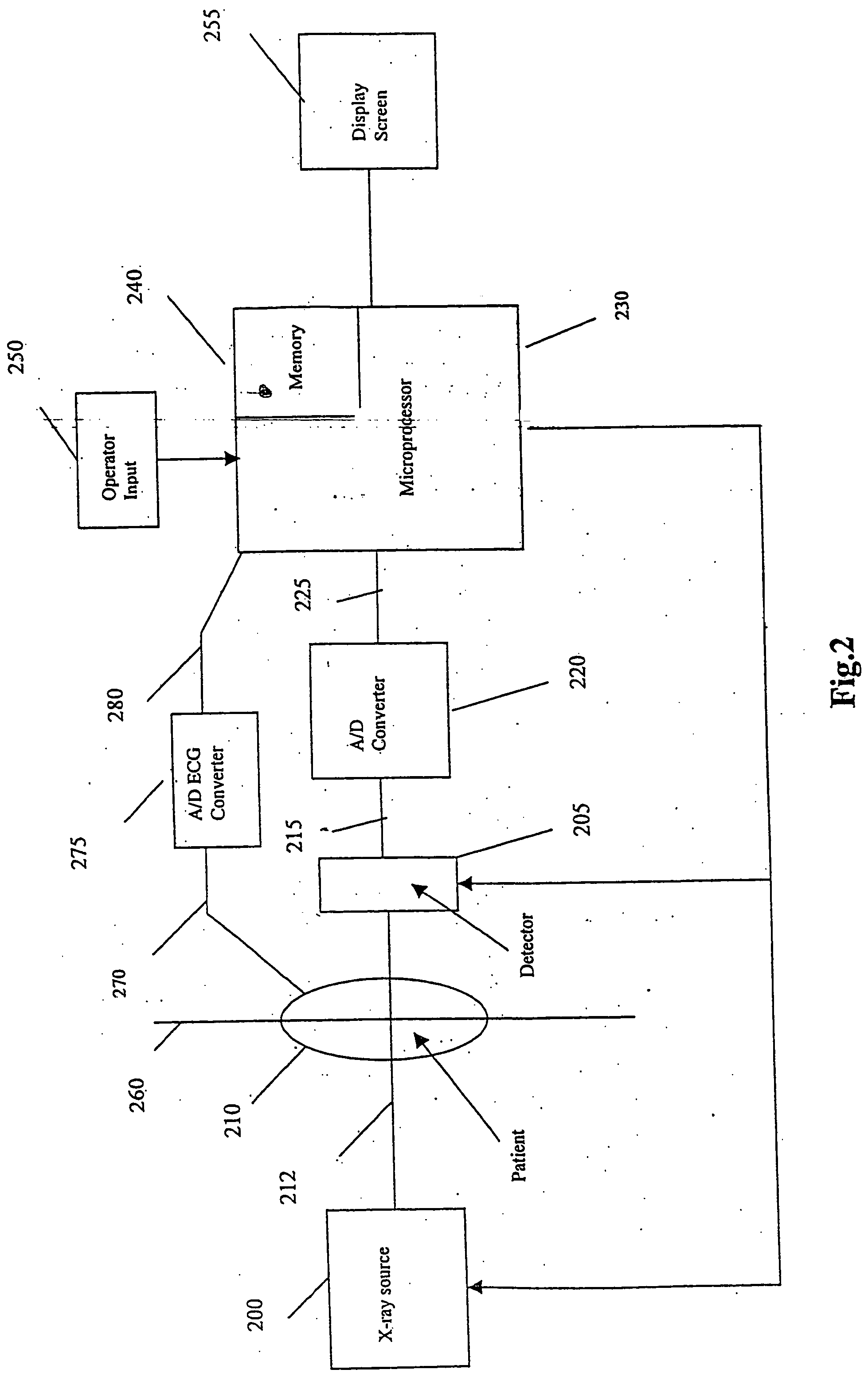
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS7321677B2Reduce exposureEasy accessBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
A method and system for imaging an artery contained in an arterial tree. A microprocessor generates a three-dimensional reconstruction of the arterial tree from two or more angiographic images obtained from different perspectives. The orientation of the axis of the artery in the arterial tree is then determined, and a perspective of the artery perpendicular to the axis of the artery is determined. A three dimensional reconstruction of the artery from angiographic images obtained from the determined perspective is then generated.
Owner:PAIEON INC
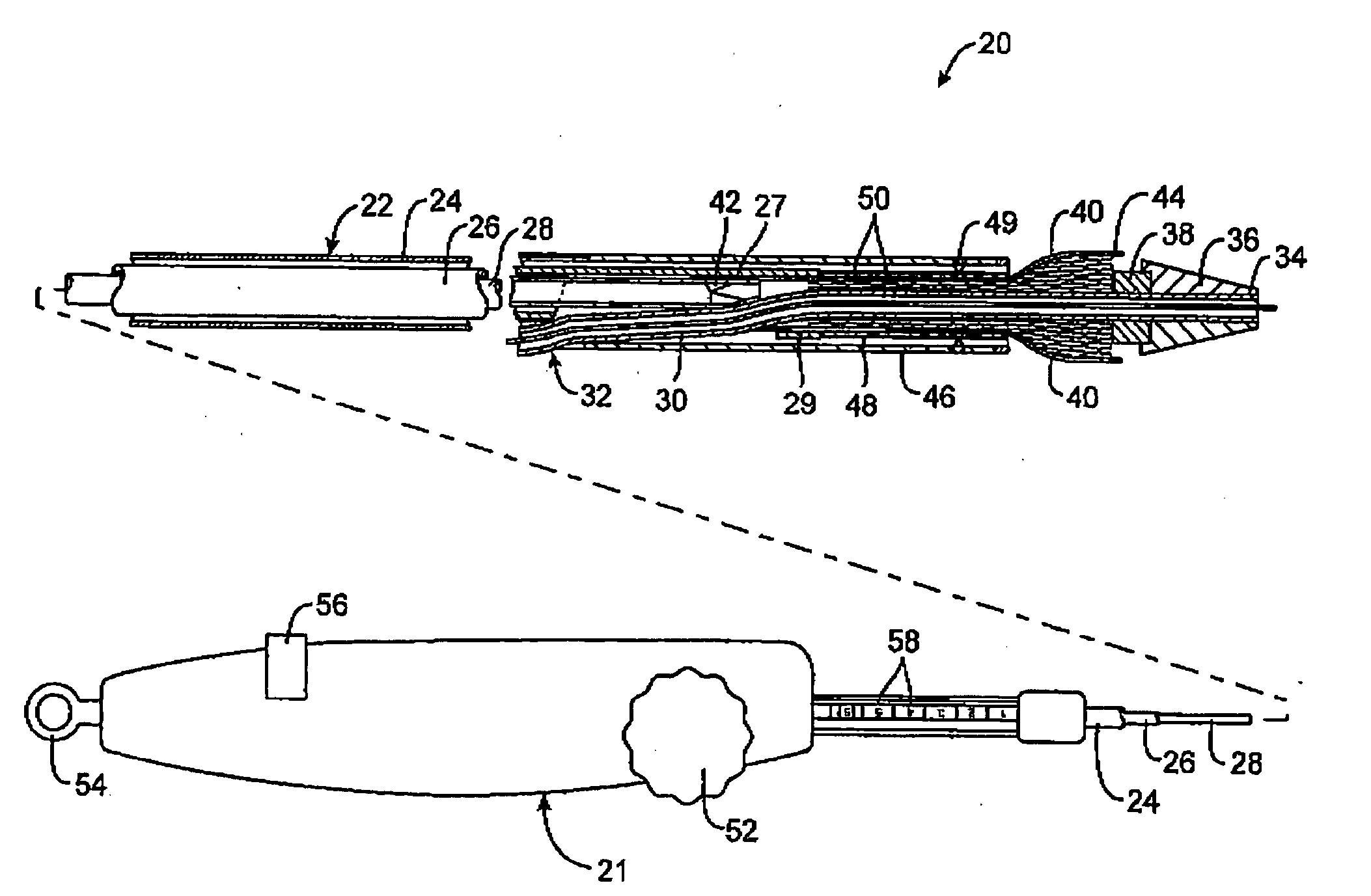
Deployment system for intraluminal devices
ActiveUS20060015171A1Short working lengthRisk minimizationStentsDiagnosticsProsthesisBiomedical engineering
A constraining sheath for use around an endoprosthesis (e.g., a stent device, with or without a graft covering), which may be a balloon expandable endoprosthesis but more preferably is a self-expanding prosthesis. The endoprosthesis is coaxially enclosed within and substantially covered by the constraining sheath, which is an outer, removable tubular sheath, preferably made of ePTFE. The sheath is preferably corrugated circumferentially along at least a portion of the length of the endoprosthesis. The constraining sheath and endoprosthesis are preferably mounted together as an assembly at the distal end of a delivery means such as a catheter shaft, for delivery of the endoprosthesis to a desired location within a body conduit such as an artery. The constraining sheath is removed by the application of tension to a tensile member such as a tether to cause sequential pulling out of the corrugations followed by release and deployment of the endoprosthesis. The use of a corrugated constraining sheath in comparison to a non-corrugated sheath results in a more smoothly applied tensile force to effect the endoprosthesis release as well as requiring less maximum force.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Method and apparatus for performing a procedure on a cardiac valve
InactiveUS20050055088A1Risk minimizationWithout riskHeart valvesBlood vesselsLeft atriumValvular prosthesis
The present invention comprises a method for deploying an aortic valve prosthesis. This valve prosthesis may include any of the known aortic valves including, but not limited to, stented and unstented bioprosthetic valves, stented mechanical valves, and expandable or self-expanding valves, whether biological or artificial. The method involves the steps of: making a first opening leading to the left atrium; passing a valve prosthesis through the opening and into a cardiac chamber of the left side of the heart using a first manipulation instrument; making a second opening in the arterial system and advancing one end of a second manipulation instrument through the arterial opening and into the aforementioned cardiac chamber; securing the second manipulation instrument to the valve prosthesis; and using the second manipulation instrument to retract at least some portion of the valve prosthesis out of the aforementioned cardiac chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
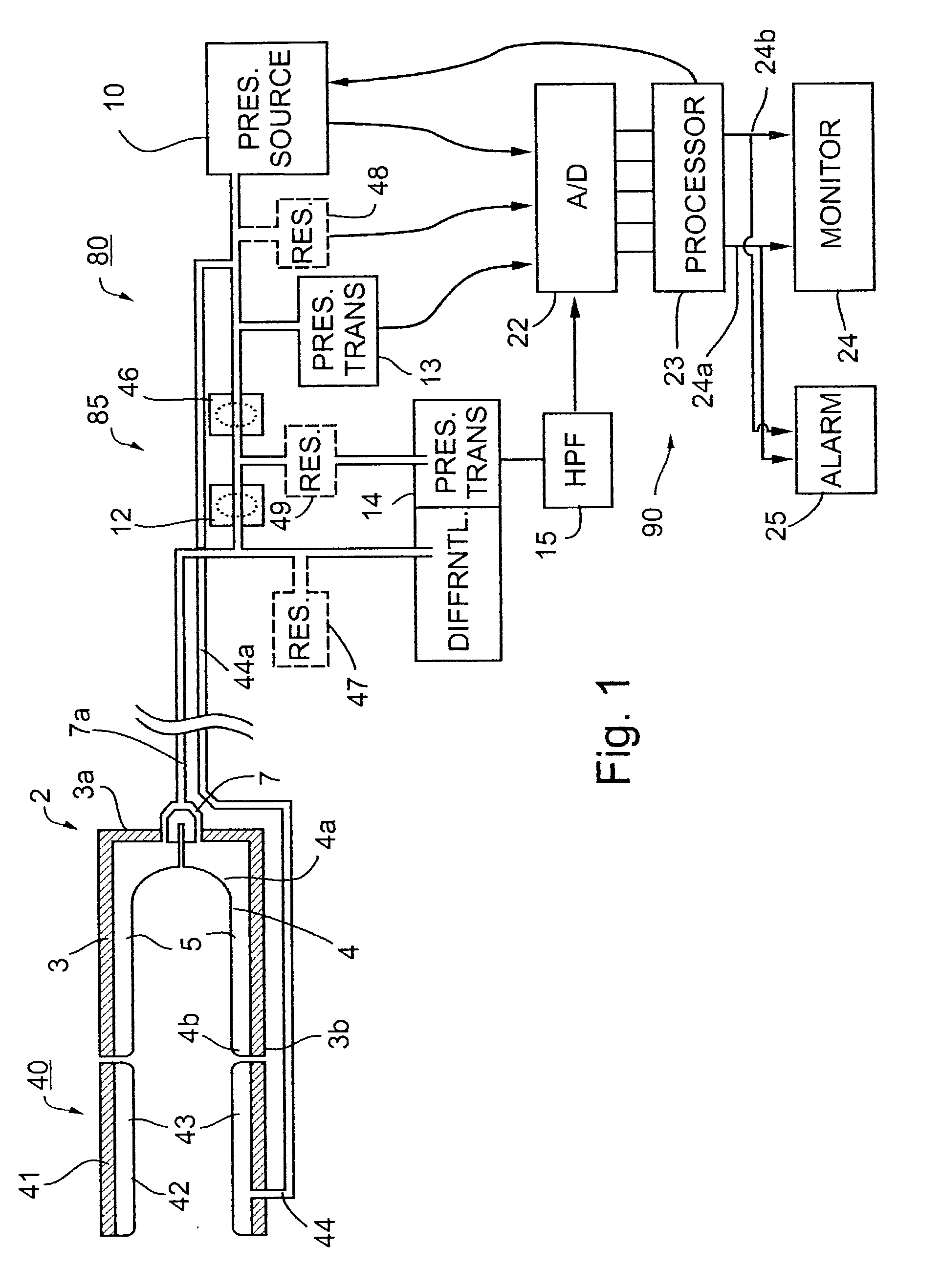
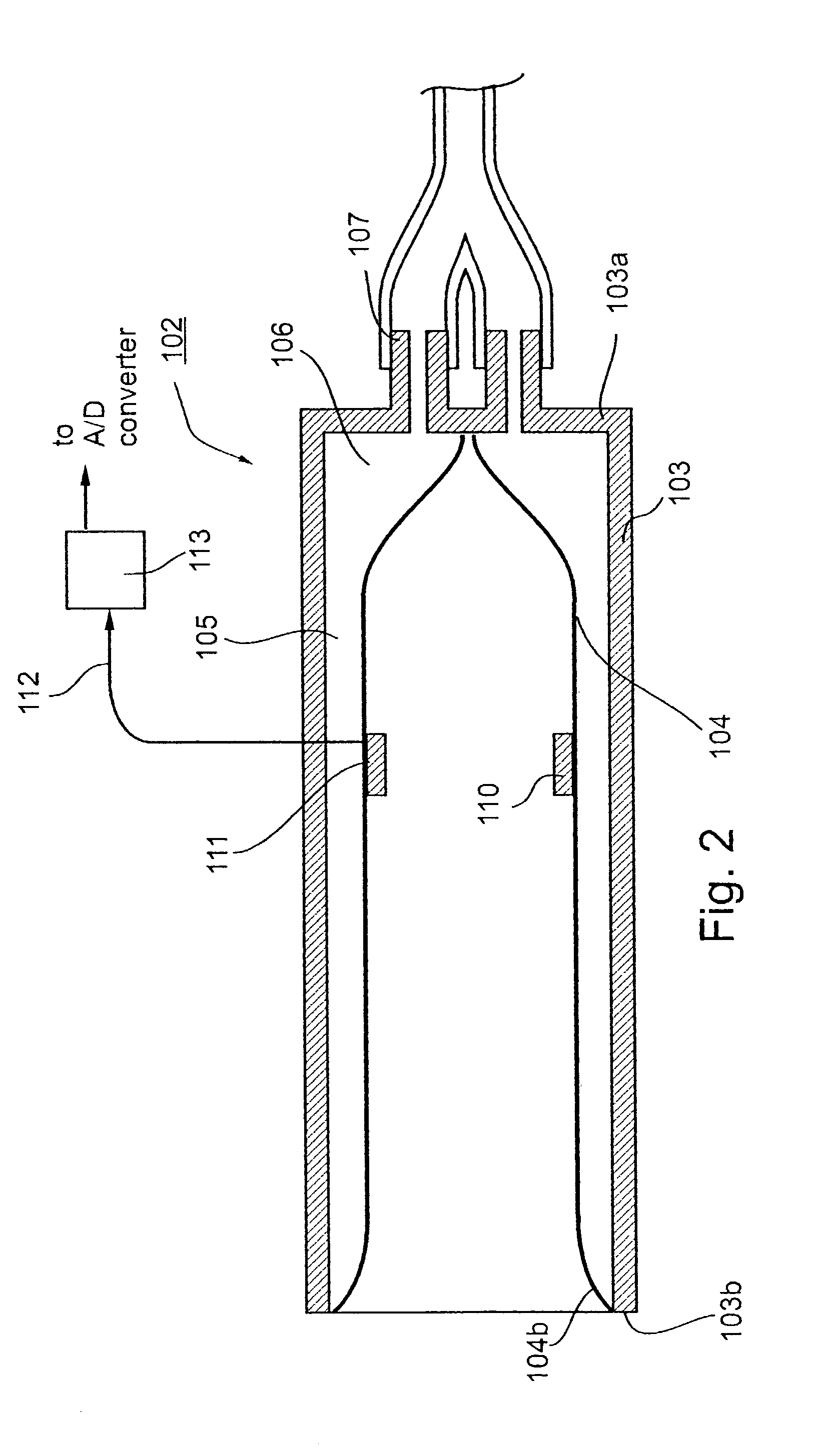
Method and apparatus for the non-invasive detection of particular sleep-state conditions by monitoring the peripheral vascular system
ActiveUS20030004423A1Avoid it happening againReduce pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterVeinDiabetes mellitus
Method and apparatus for monitoring the sleep state condition of an individual by using an external probe applied to a peripheral body location, such as the individual's finger or toe, for detecting changes in the peripheral vascular bed volume of the individual. A predetermined pressure field is applied to the distal end of the peripheral body location, including its distal-most extremity, to prevent the occurrence of venous pooling within and distal to the peripheral body location. The probe produces an output corresponding to changes in the peripheral arterial bed volume at the peripheral body location, which output provides an indication of the sleep state condition of the individual. Such information is useful in diagnosing and / or in treating, a number of sleep disorders as well as other conditions, such as impotence, diabetes, and various disorders in children.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
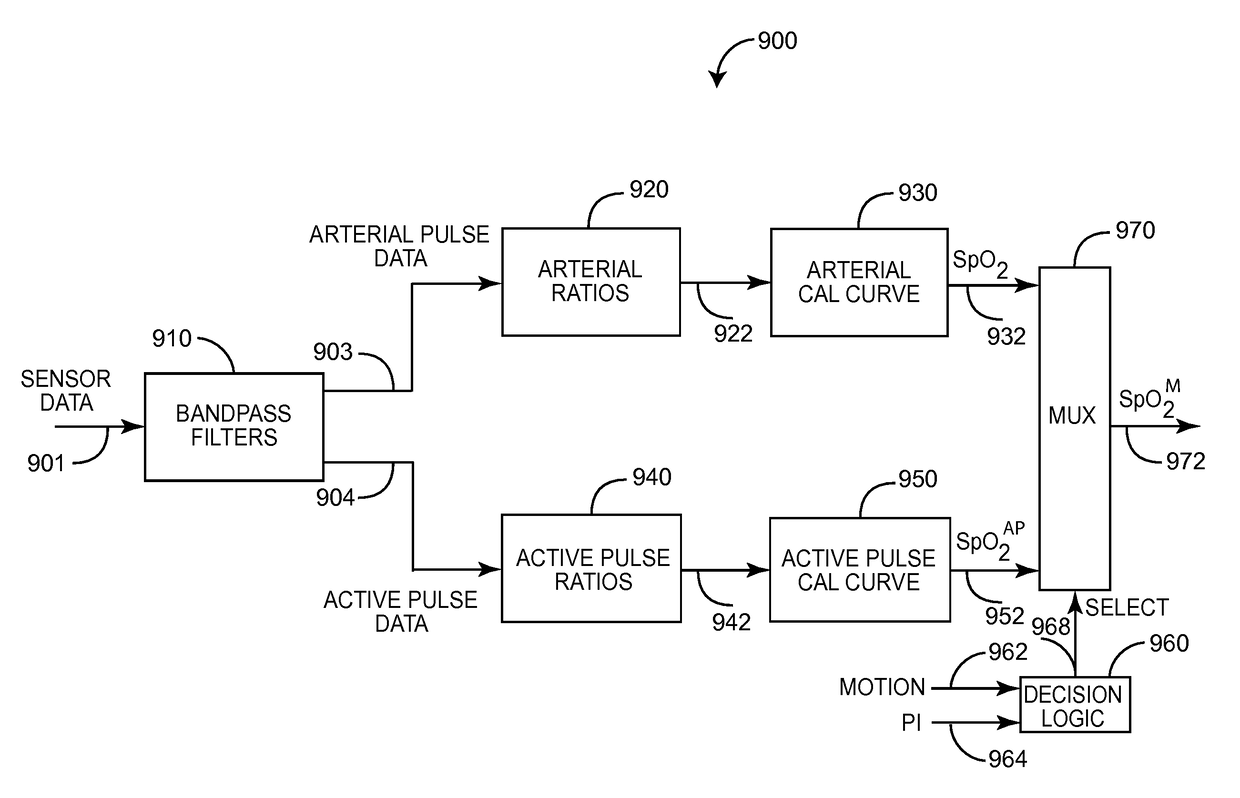
Active-pulse blood analysis system
An active-pulse blood analysis system has an optical sensor that illuminates a tissue site with multiple wavelengths of optical radiation and outputs sensor signals responsive to the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flow within the tissue site. A monitor communicates with the sensor signals and is responsive to arterial pulses within a first bandwidth and active pulses within a second bandwidth so as to generate arterial pulse ratios and active pulse ratios according to the wavelengths. An arterial calibration curve relates the arterial pulse ratios to a first arterial oxygen saturation value and an active pulse calibration curve relates the active pulse ratios to a second arterial oxygen saturation value. Decision logic outputs one of the first and second arterial oxygen saturation values based upon perfusion and signal quality.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Mated main and collateral stent and method for treatment of arterial disease
The present invention is directed to the use of a stented graft having predetermined and sized lateral openings for the treatment of arterial disease at or around the intersection of multiple arteries, thereby ensuring blood flow through such arteries to collateral organs. In particular, the lateral opening of a main stent supporting a main artery has a collar with either at least two detents or inlets spaced about the annular extent thereof. The main collar mates with a collateral collar provided at the proximal end of the collateral stent having the other of at least two detents or inlets spaced about the annular extent thereof at intervals coincident with the inlets or detents on the main collar to mate and lock the main stent to the collateral stent supporting a collateral artery.
Owner:TAHERI SYDE A
Techniques for applying, configuring, and coordinating nerve fiber stimulation
ActiveUS20050267542A1Decreased heart rateEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bilateral extension prosthesis and method of delivery
The invention is a system, apparatus, and method for treating, and / or repairing an aneurysm, preferably an aortic aneurysm, and most preferably, an abdominal aortic aneurysm. The systems, devices, and methods of the present invention include a prosthesis assembly for establishing a fluid flow path between an upstream portion of an artery and at least one bifurcated downstream portion of the artery.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
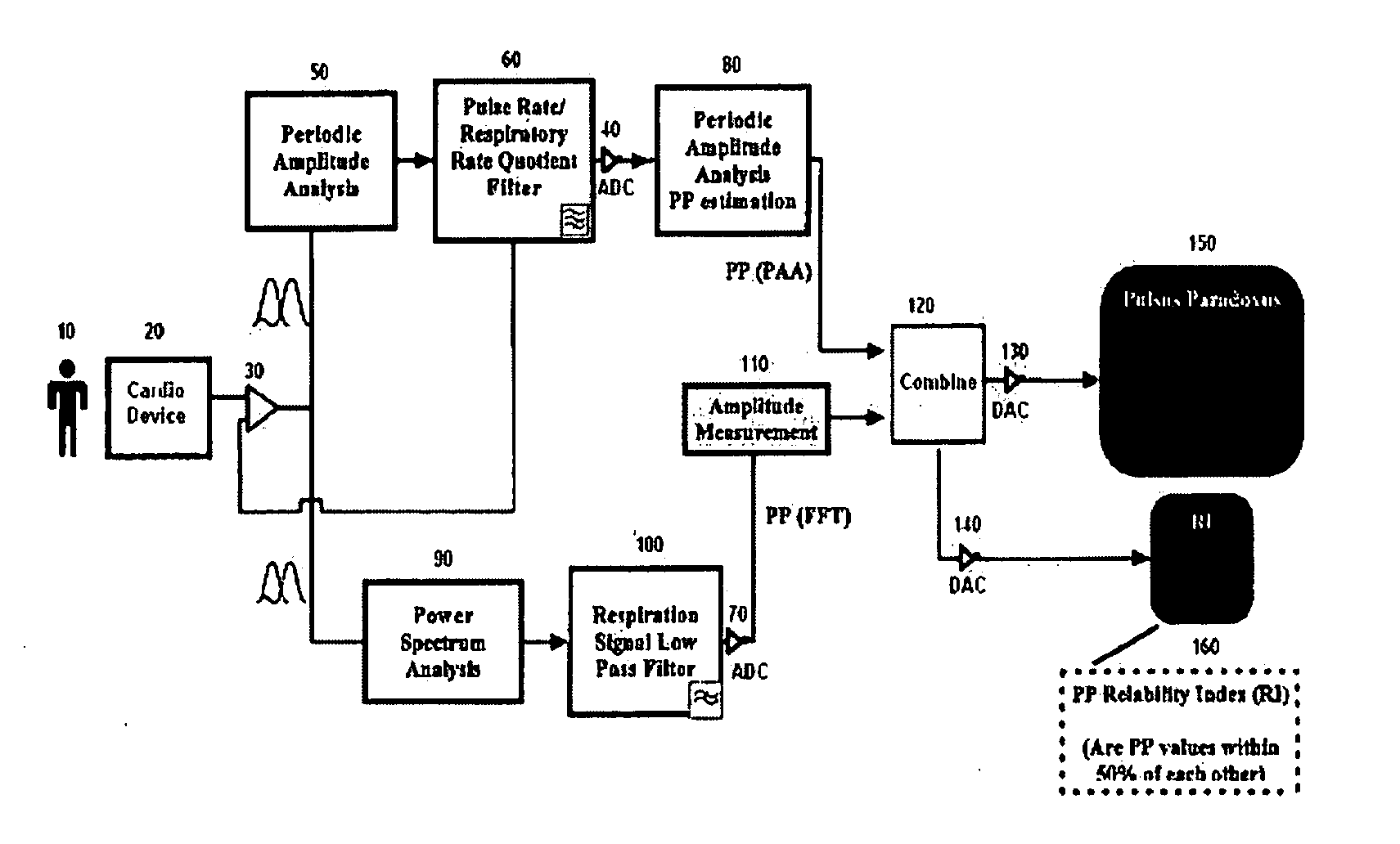
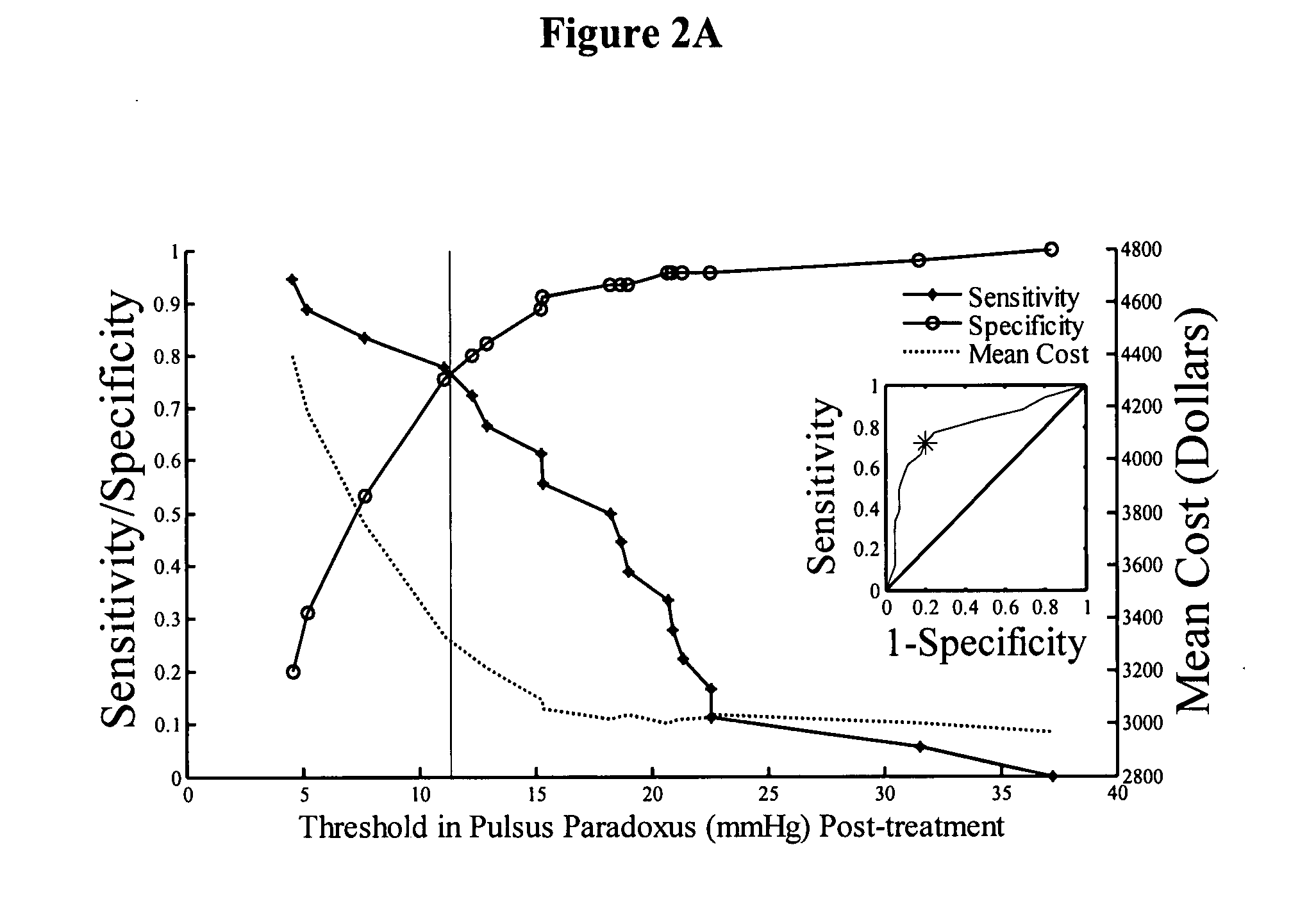
Devices and methods for measuring pulsus paradoxus
The invention relates to methods and devices for measuring pulsus paradoxus. The methods herein employ a combination of one or more forms of waveform analysis for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus and diagnosing respiratory distress. The methods also combine measurements of pulsus paradoxus and physician assessments to diagnose respiratory distress. The methods also combine measurements of pulsus paradoxus and percentage oxygenated hemoglobin to diagnose respiratory distress. The devices of this invention employ pulse oximeters, arterial tonometers, finometers, or processors for the purpose of implementing the methods of the invention.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS20050251183A1Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryLarge intestine
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS7144363B2Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Owner:BAY INNOVATION GROUP
Pressure applicator devices particularly useful for non-invasive detection of medical conditions
InactiveUS6461305B1Low mobilityEasy constructionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterVeinBlood arterial
A probe for application to a body part particularly a finger of a patient to detect a change in the physical condition of the patient includes a housing defining a compartment closed at one end and open at the opposite end for receiving the distal end of the patient's finger and a medium wholly self-contained within the probe for applying a static pressure field substantially uniformly around the distal end of the patient's finger, of a predetermined magnitude sufficient to substantially prevent distention of the venous vasculature, uncontrolled venous backflow, and retrognade shockwave propagation into the distal end, and to partially unload the wall tension of, but not to occlude, the arteries in the distal end when at heart level or below. A sensor senses changes in the distal end of the patient's finger related to changes in arterial blood volume therein.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS20050008210A1Precise processingReduce exposureBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
Owner:PAIEON INC
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149173A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
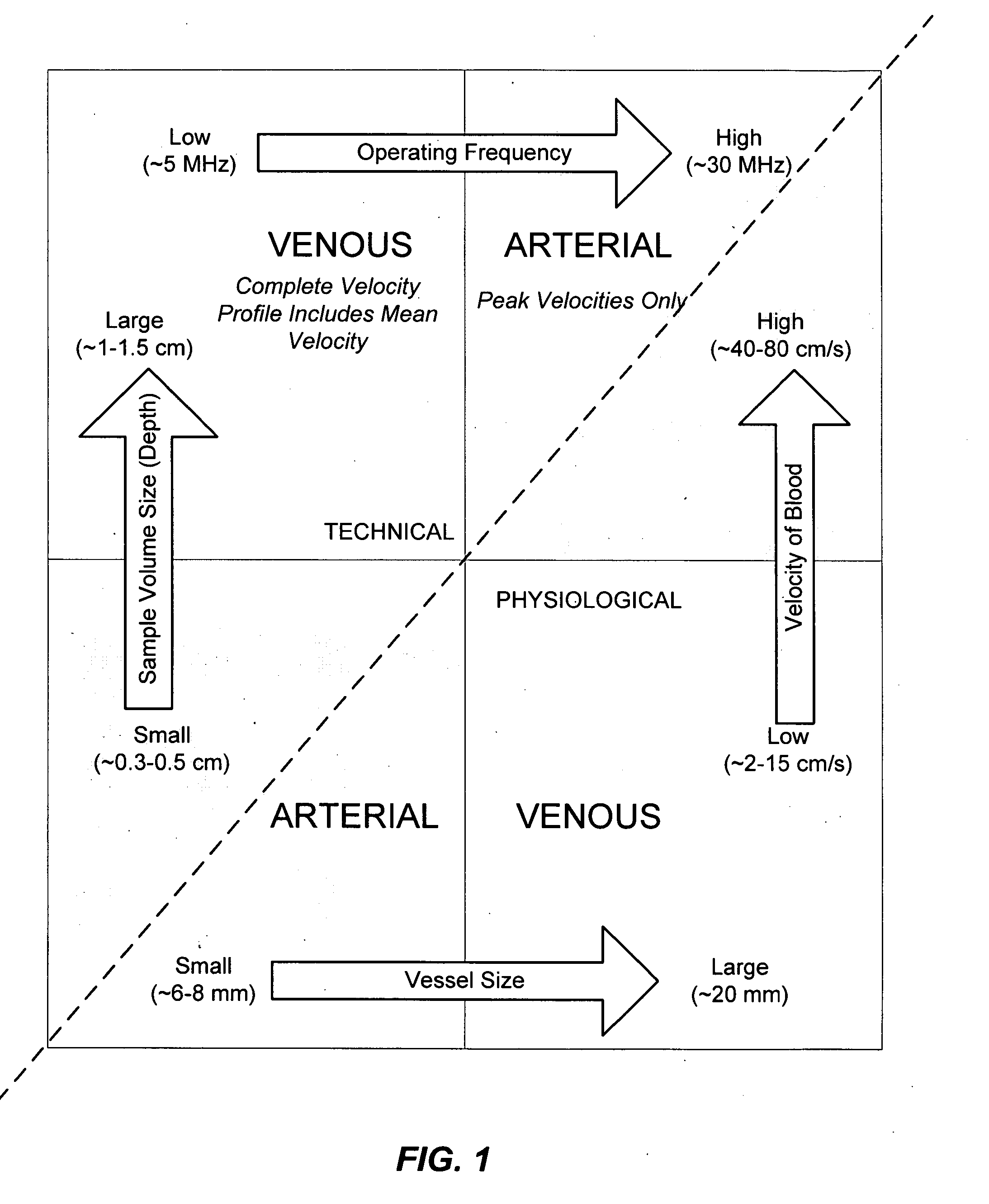
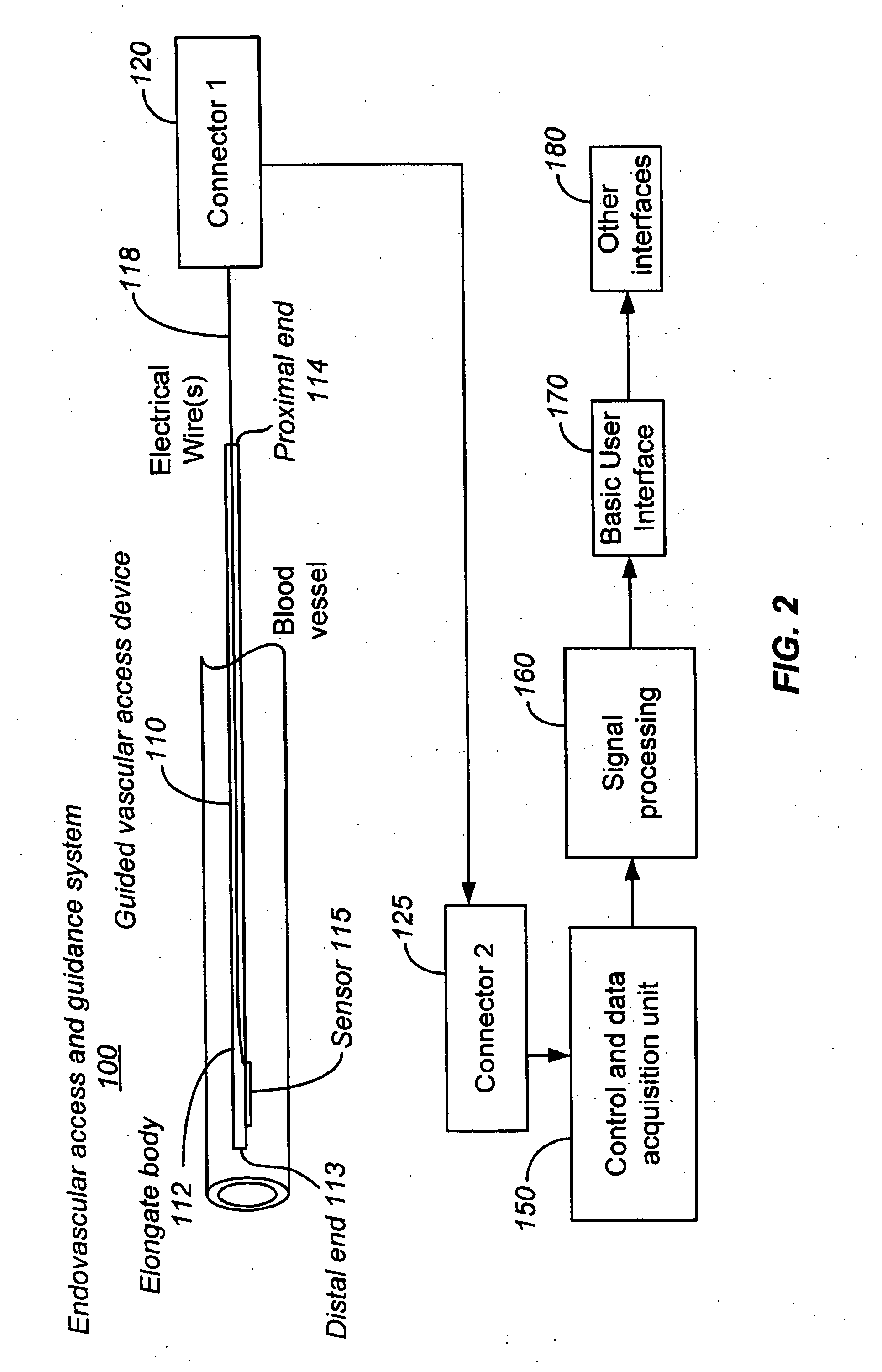
Ultrasound methods of positioning guided vascular access devices in the venous system
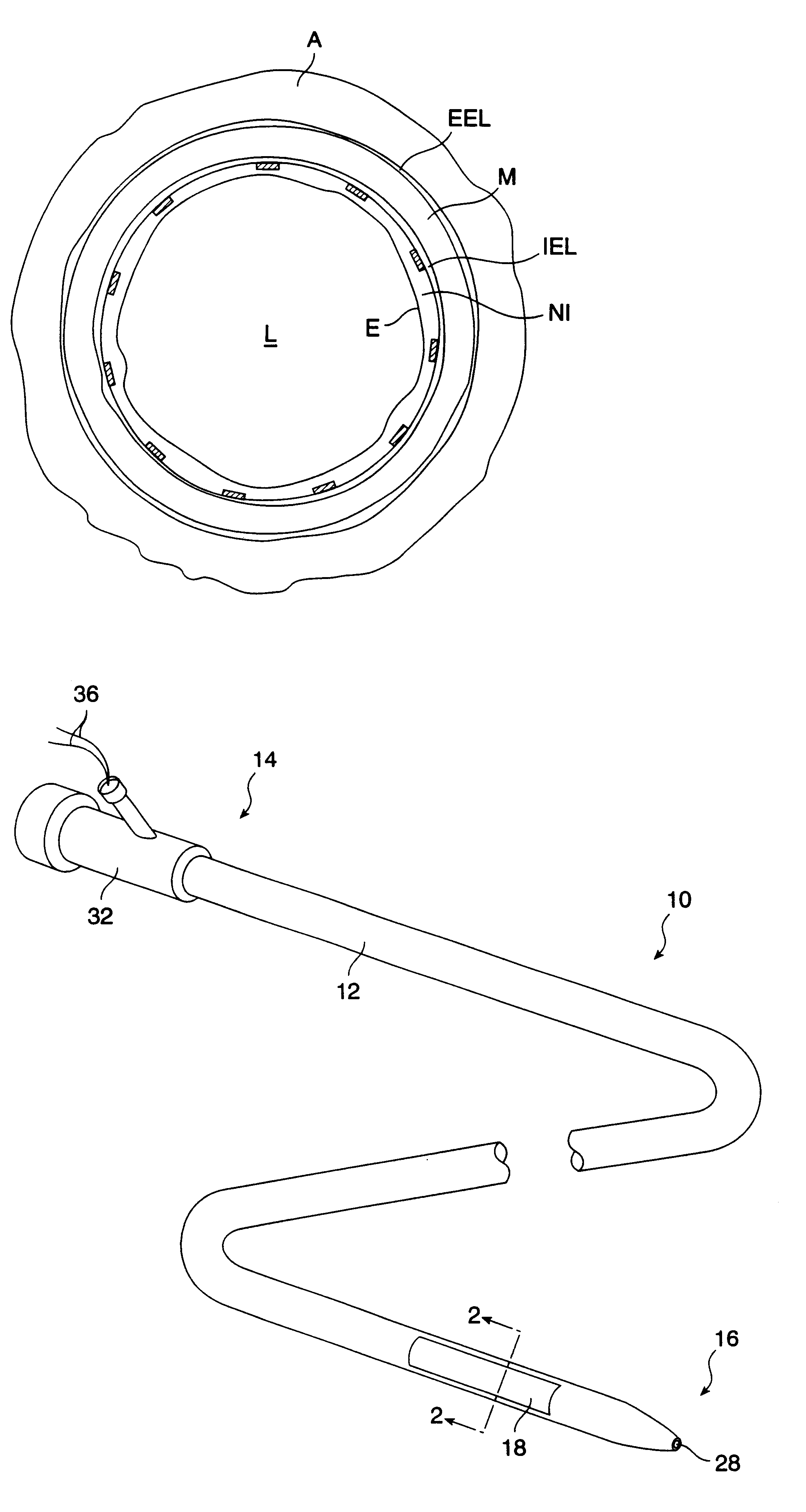
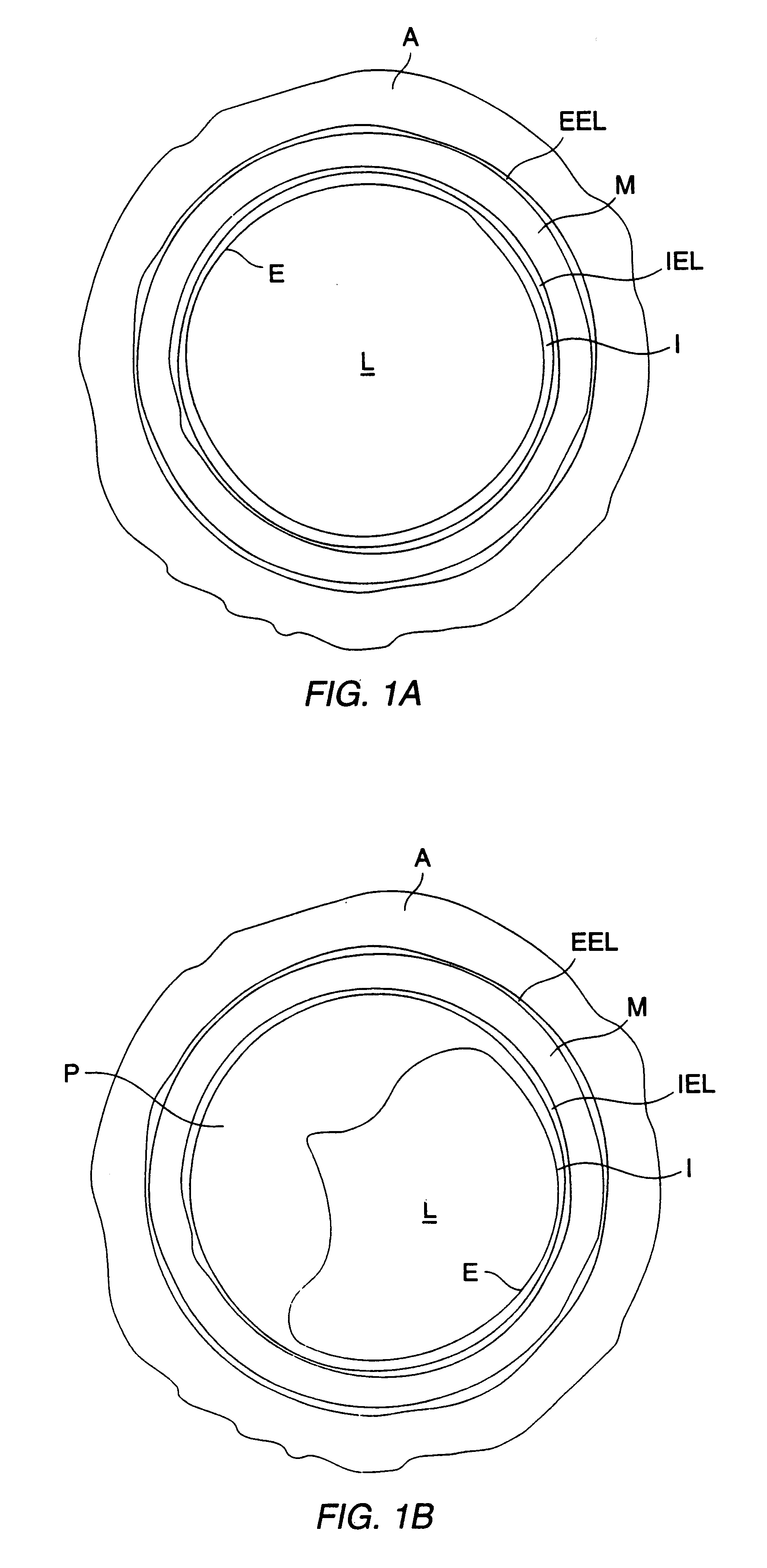
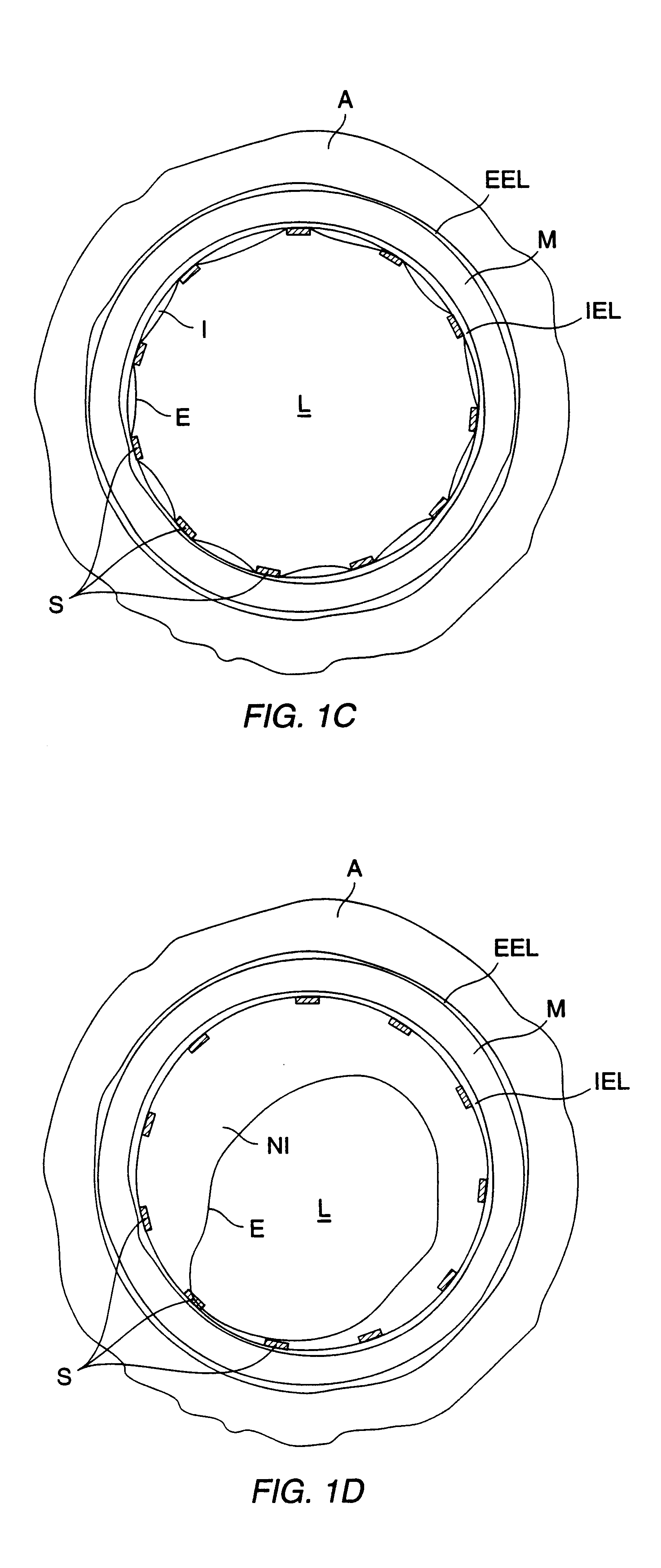
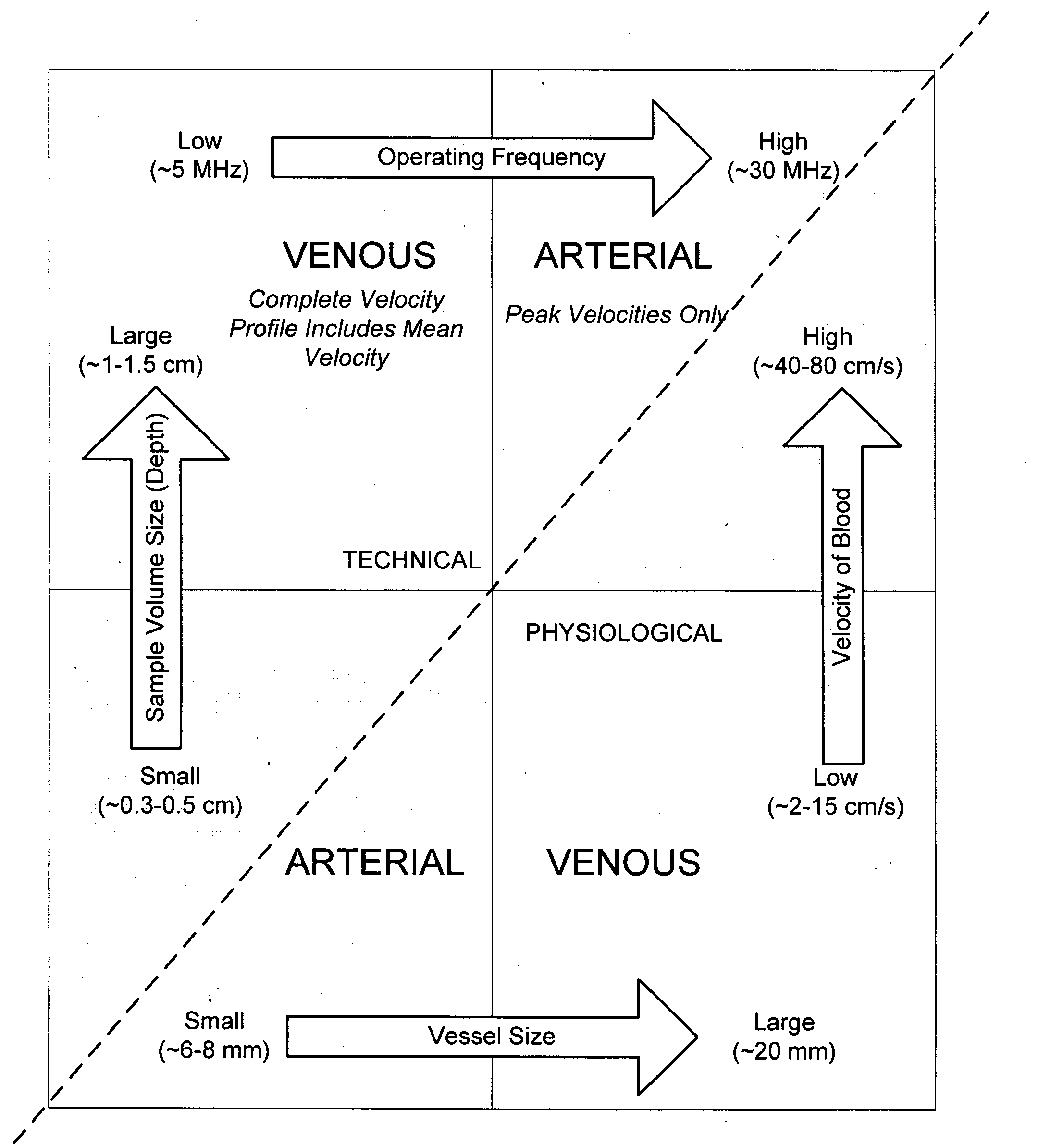
ActiveUS20070016068A1Diagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesGuidance systemVascular Access Devices
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com