Patents
Literature
547results about How to "Minimizing chance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
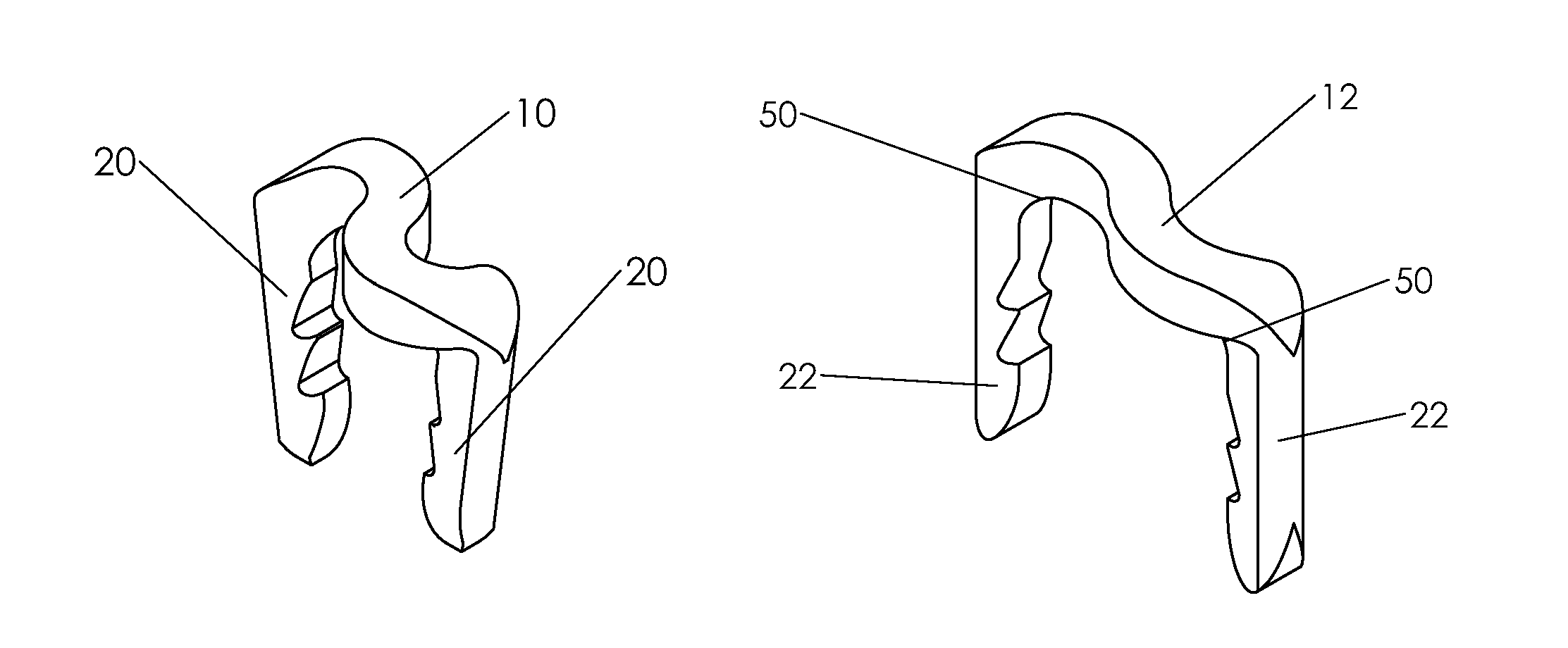
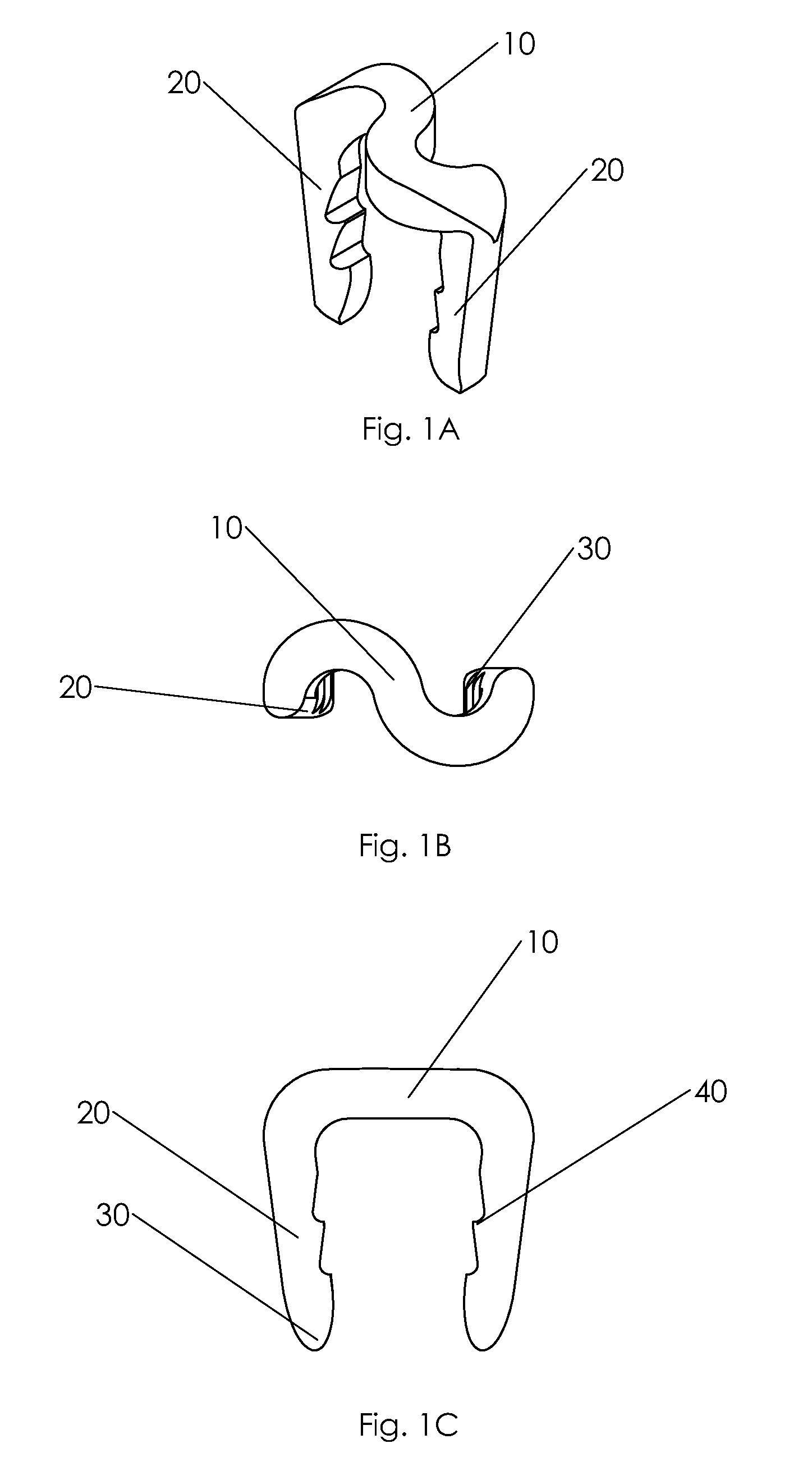
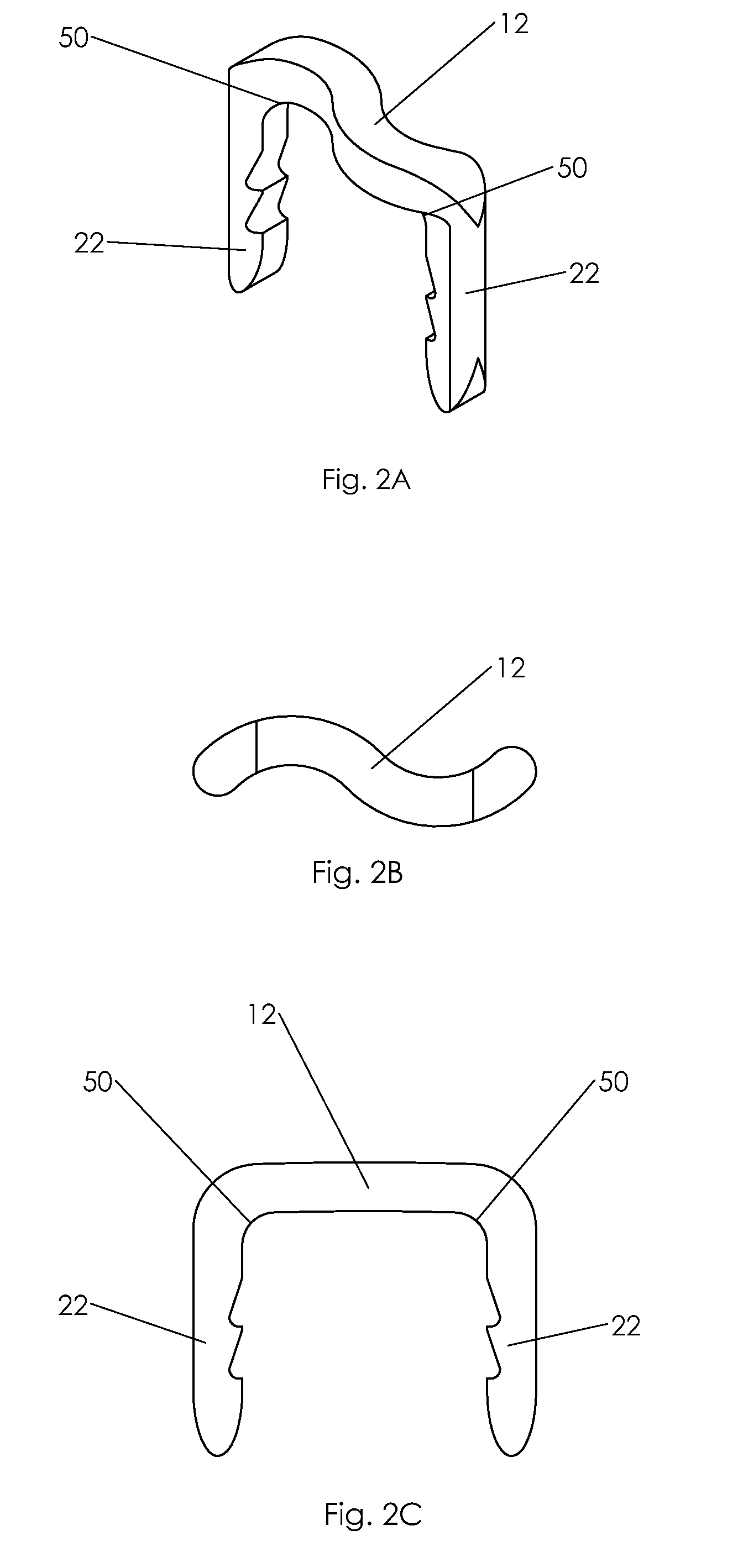
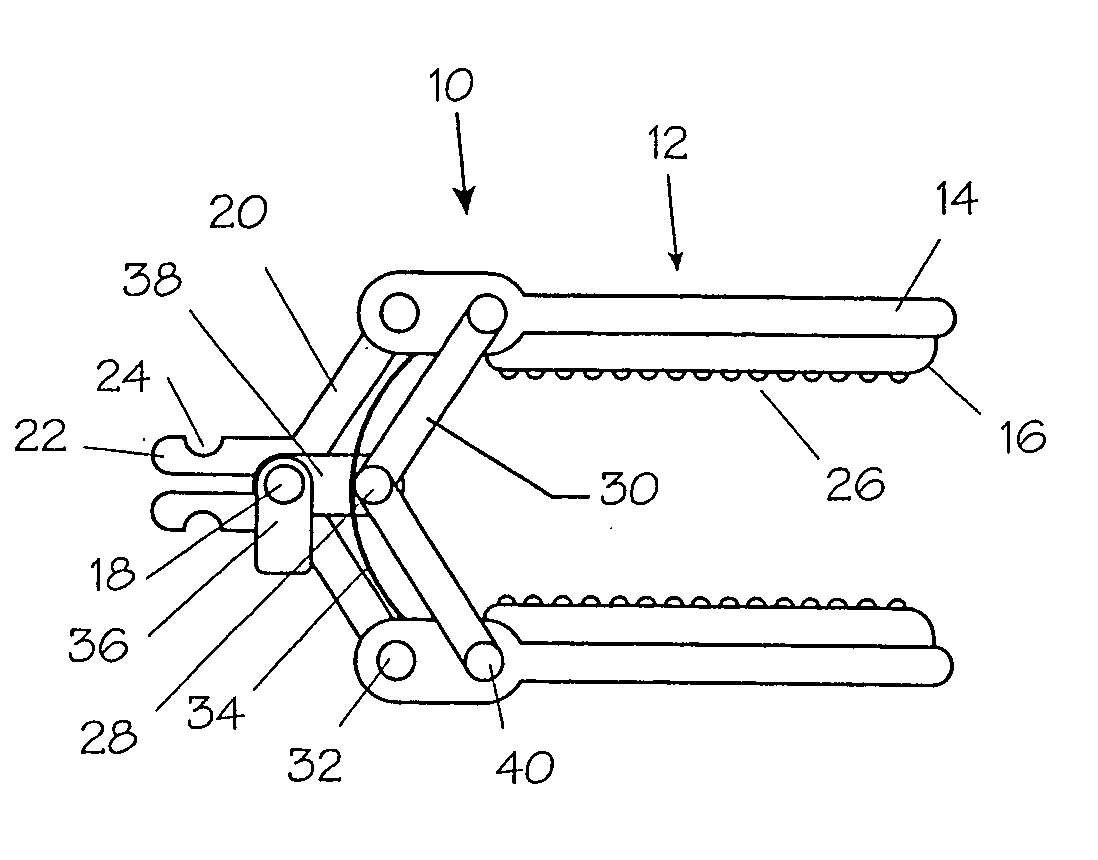
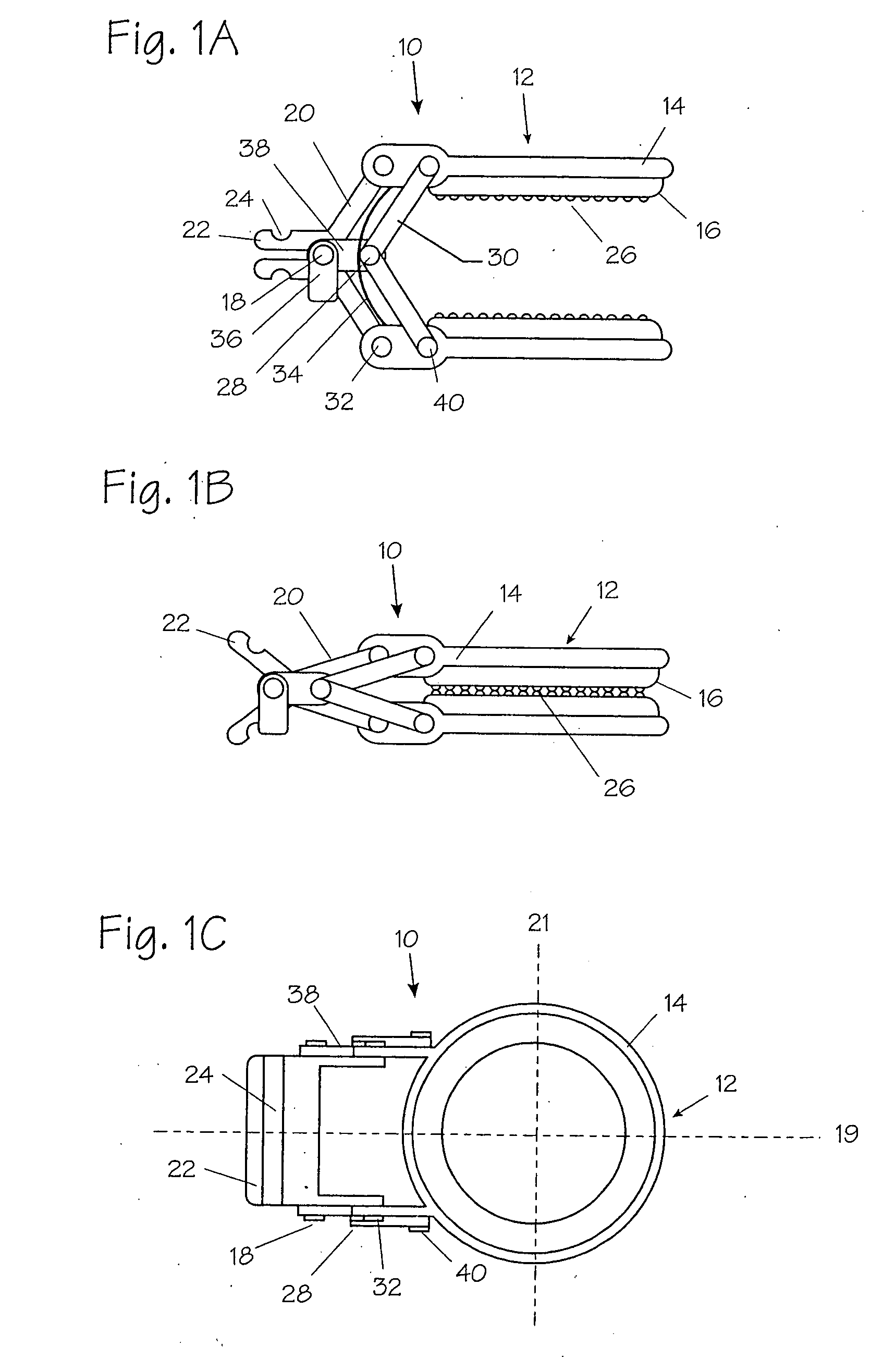
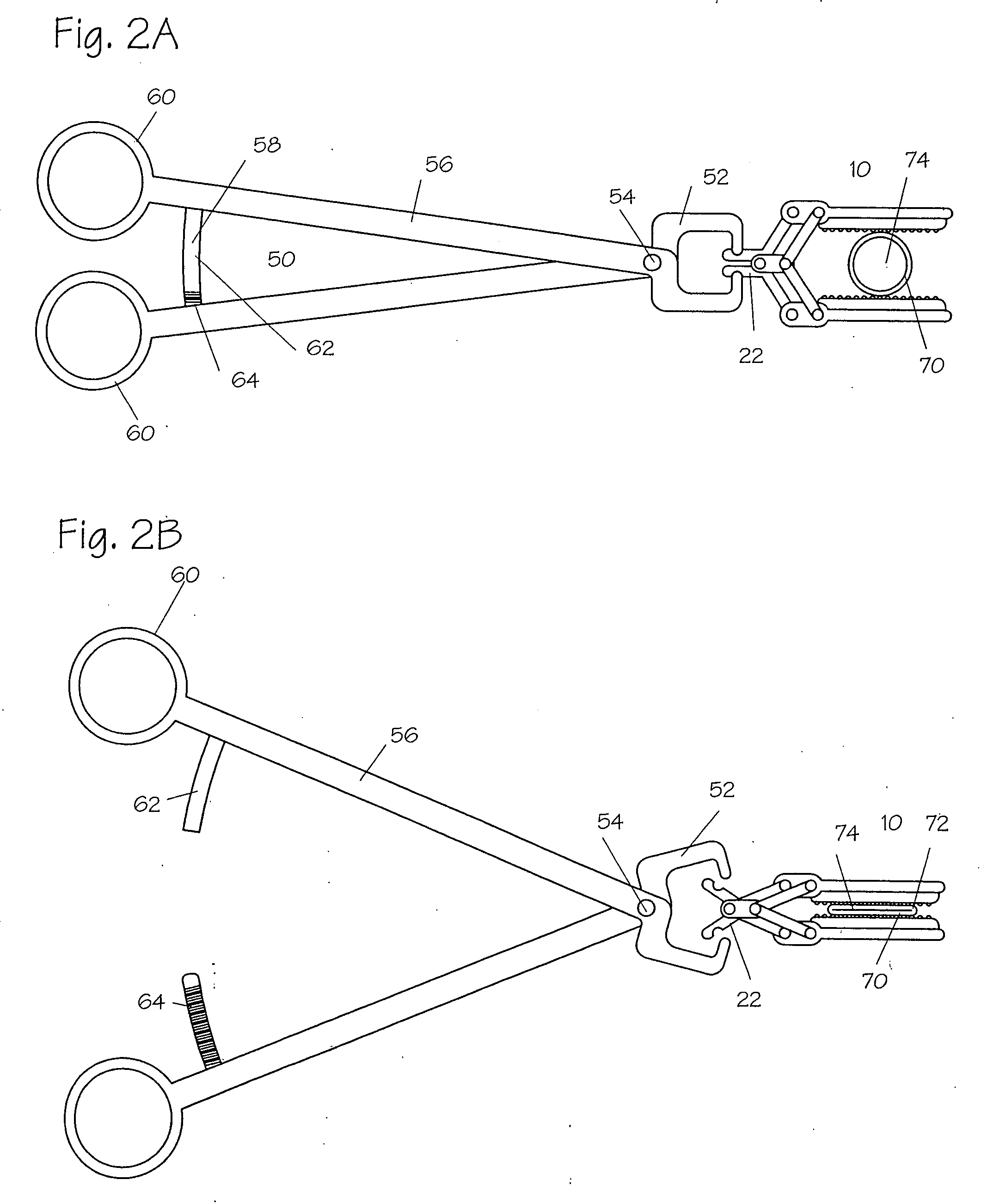
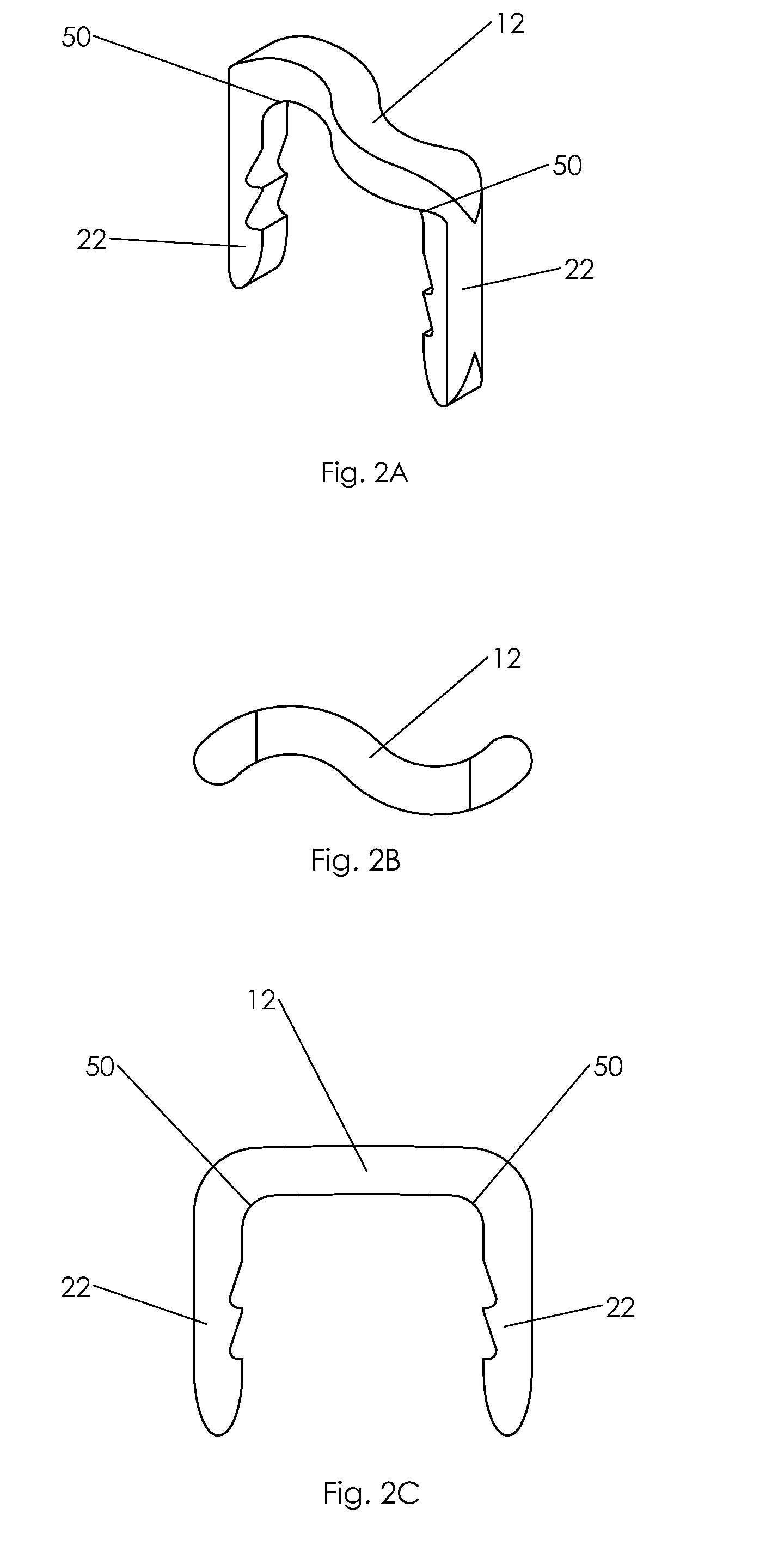
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS9017331B2Stores recoverable mechanical energyEasy to implantPinsInternal osteosythesisShape changeMechanical energy
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
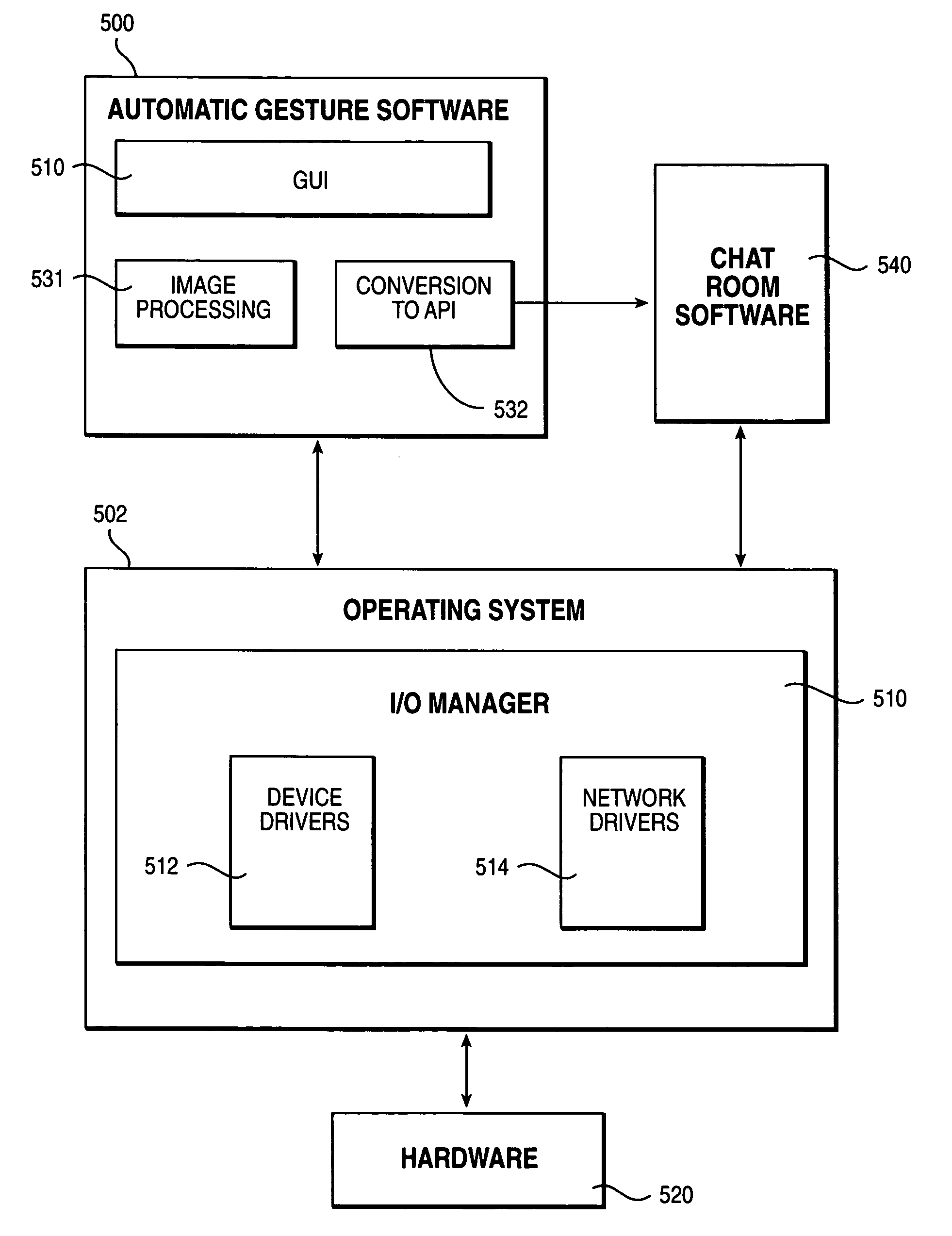
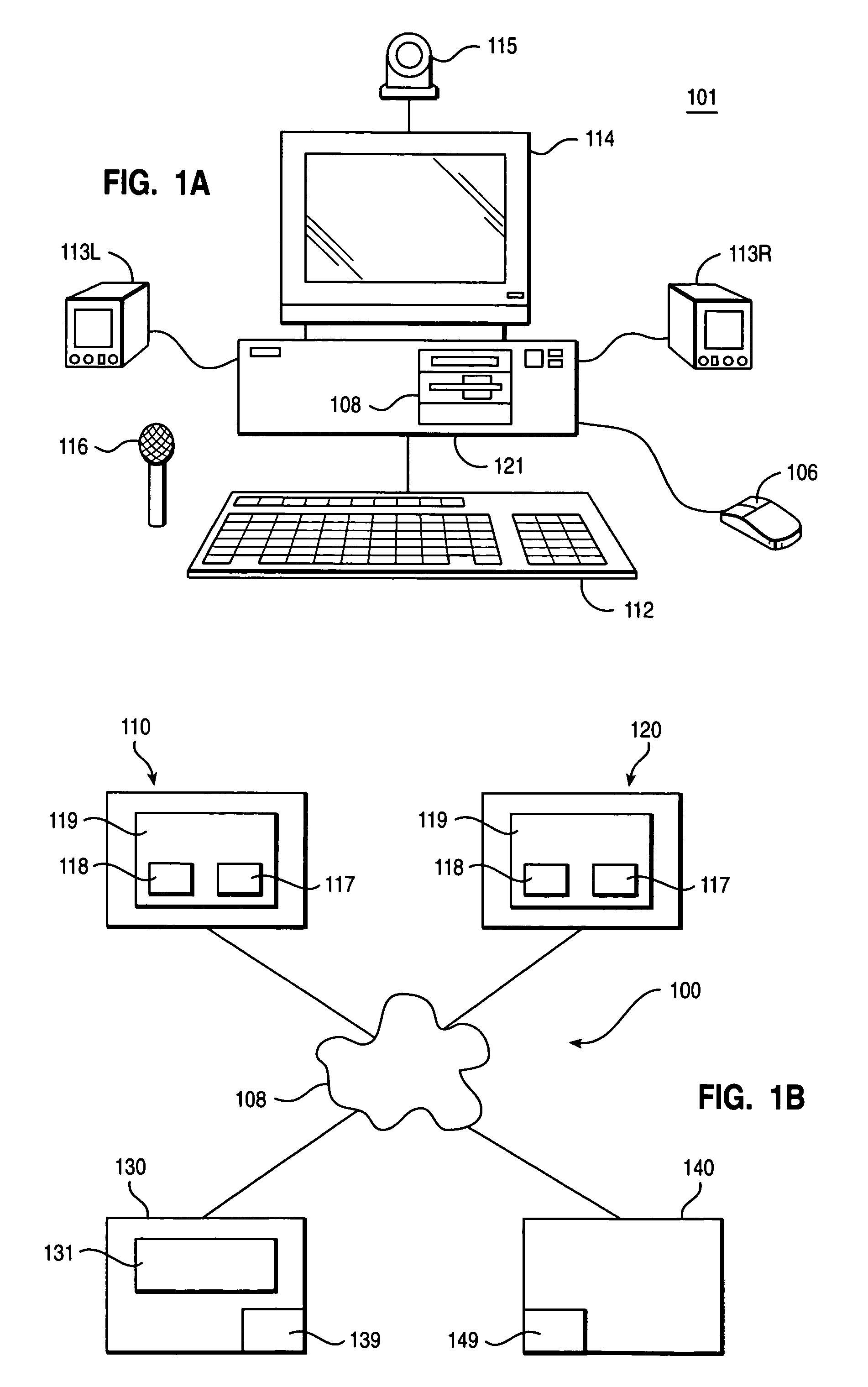
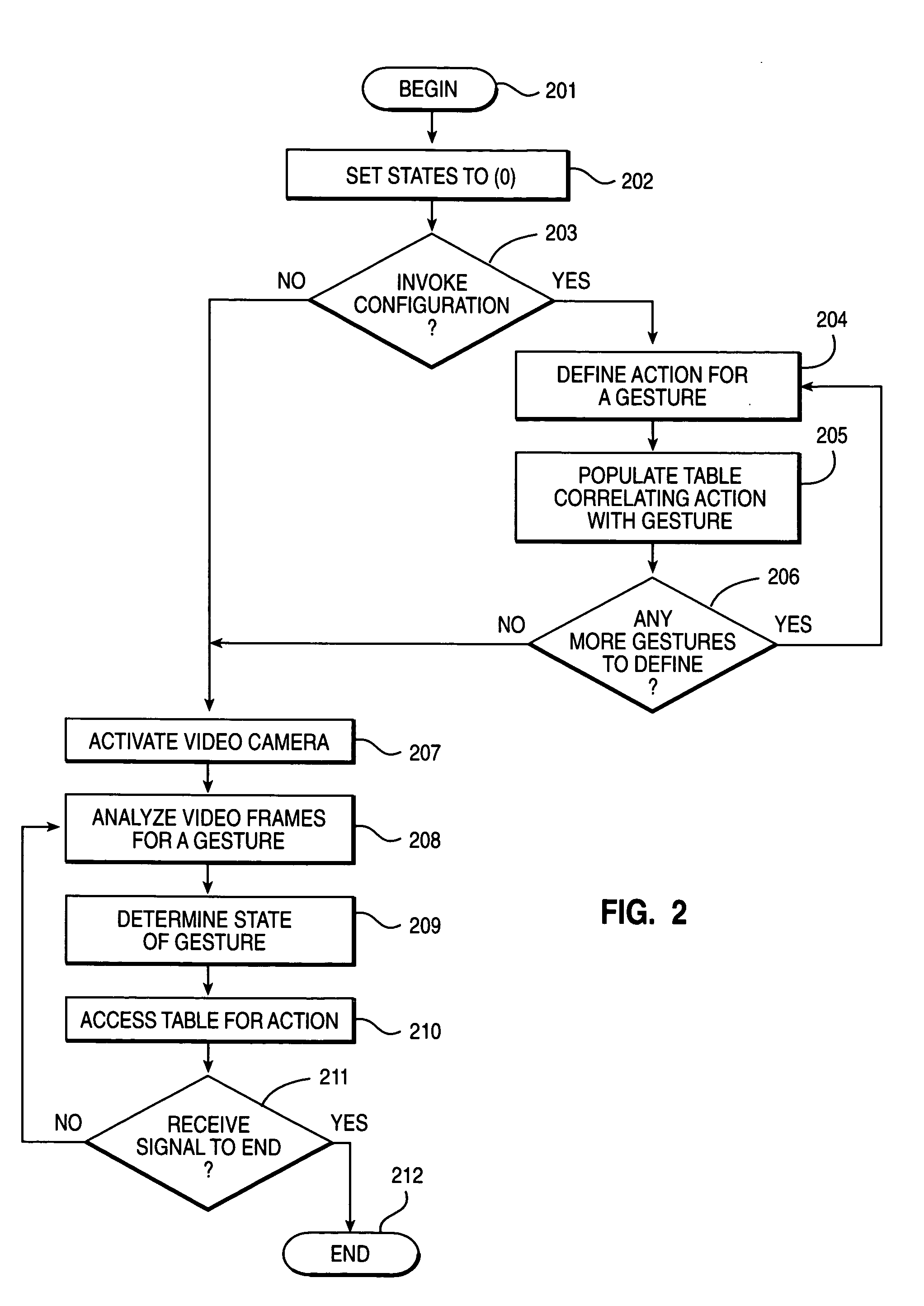
Using video image analysis to automatically transmit gestures over a network in a chat or instant messaging session
InactiveUS7039676B1Minimizing chanceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionChat roomImage processing software
The system, method, and program of the invention captures actual physical gestures made by a participant during a chat room or instant messaging session or other real time communication session between participants over a network and automatically transmits a representation of the gestures to the other participants. Image processing software analyzes successive video images, received as input from a video camera, for an actual physical gesture made by a participant. When a physical gesture is analyzed as being made, the state of the gesture is also determined. The state of the gesture identifies whether it is a first occurrence of the gesture or a subsequent occurrence. An action, and a parameter for the action, is determined for the gesture and the particular state of the gesture. A command to the API of the communication software, such as chat room software, is automatically generated which transmits a representation of the gesture to the participants through the communication software.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for identifying infected networks and systems from unknown attacks
ActiveUS20150128274A1Fast transferMinimizing chanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer scienceData library
Systems and method of the present disclosure are directed to a network security monitor. The monitor can receive logs of a second computer network indicative of a status of the second computer network determined by a monitoring agent executing on the second computer network. The monitor can generate indexed logs from the logs based on log format. The monitor can retrieving a list of threat indicators from a database based on a schema from a plurality of threat indicators received from a plurality of heterogeneous repositories via the first computer network. The monitor can compare the list of threat indicators with the indexed logs. The monitor can generate a report based on the comparing to identify a threat.
Owner:CRYPTEIA NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS20050251183A1Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryLarge intestine
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Apparatuses and methods for forming electronic assemblies
InactiveUS6863219B1Minimizing chanceInformation retrieval from punched cardsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureDisplay device
Apparatuses and methods for forming displays are claimed. One embodiment of the invention includes a contact smart card wherein fluidic self assembly is used to build the microelectronic structures on the display such that a contact smart data is transmitted unidirectionally. A contact smart card is inserted directly into a device that transfers data to a display coupled to the smart card. Another embodiment of the invention relates to a contactless smart card in which fluidic self assembly is also used here to build the display. Data is transmitted to an antenna that is embedded in the contactless card in which a plurality of blocks were deposited thereon.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Active needle devices with integrated functionality
InactiveUS20040176732A1Facilitate biochemical and optical and electrical and physical measurementMinimizing chanceMicroneedlesMedical devicesActive componentActuator
An active needle device (10) for fluid injection or extraction includes at least one hollow elongated shaft (11) defining at least one channel (12). The channel (12) provides communication between at least one input port (15) and at least one output port (16) of the needle device (10). At least one active component (17) such as a sensor or actuator is placed or integrated into the elongated shaft (1 1). The needle device (10) can include a macroneedle, a microneedle (21), or an array of macroneedles or microneedles (25a). The microneedles (21) can be fabricated on a substrate (26) which can remain attached to the microneedles (21) or be subsequently removed. The active component can facilitate biochemical, optical, electrical, or physical measurements of a fluid injected or extracted by the needle device (10).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS7322995B2Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryChest region
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
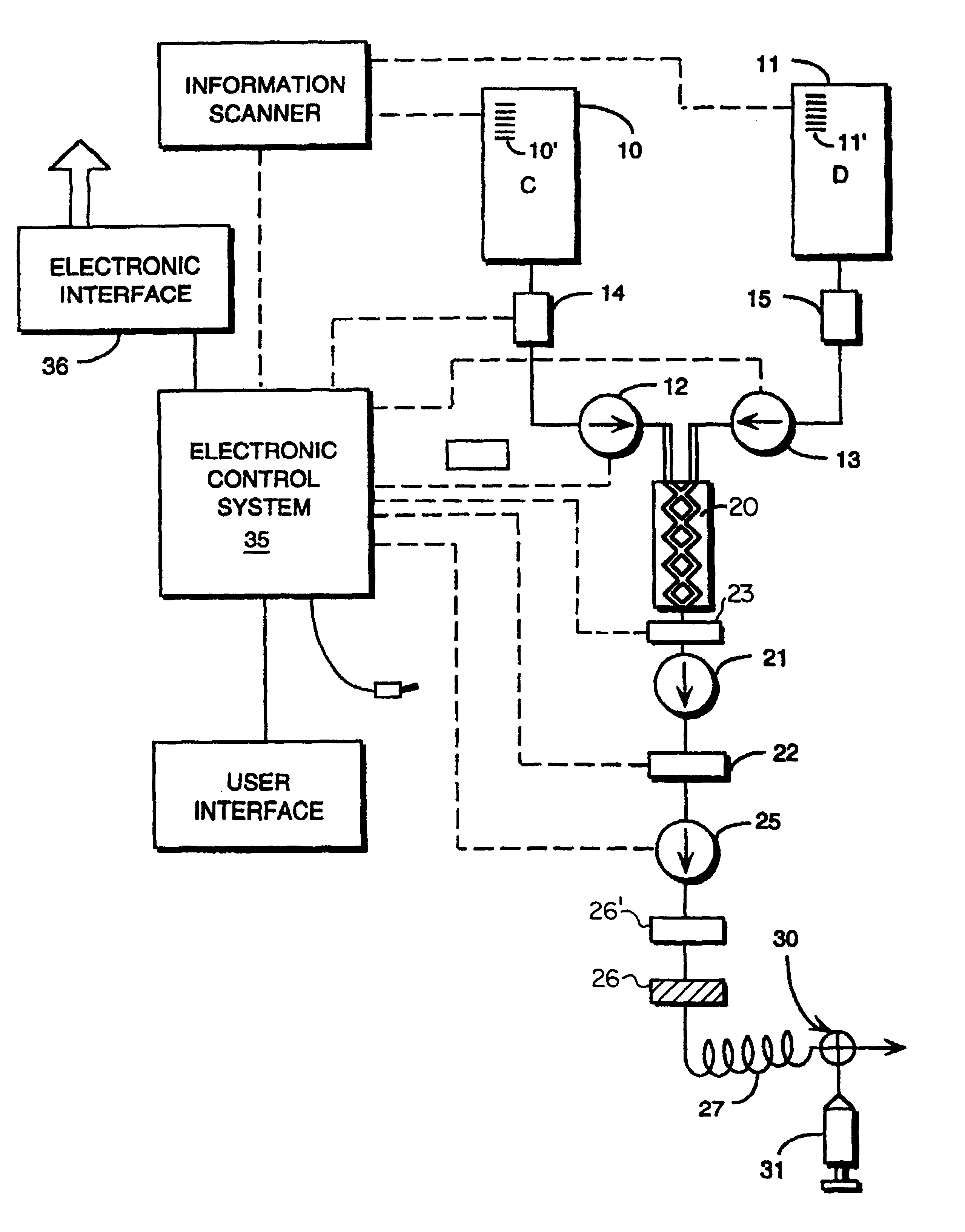
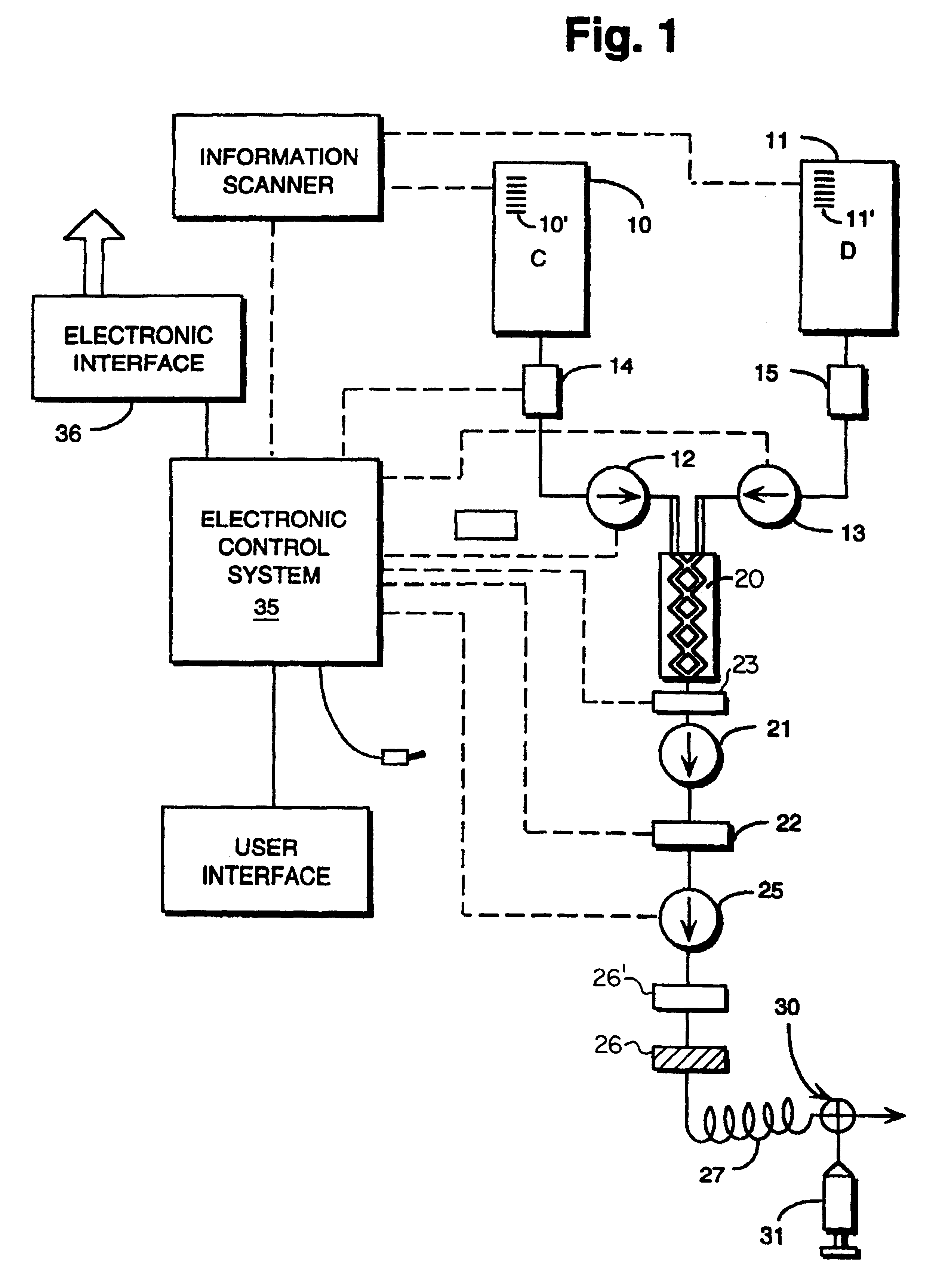
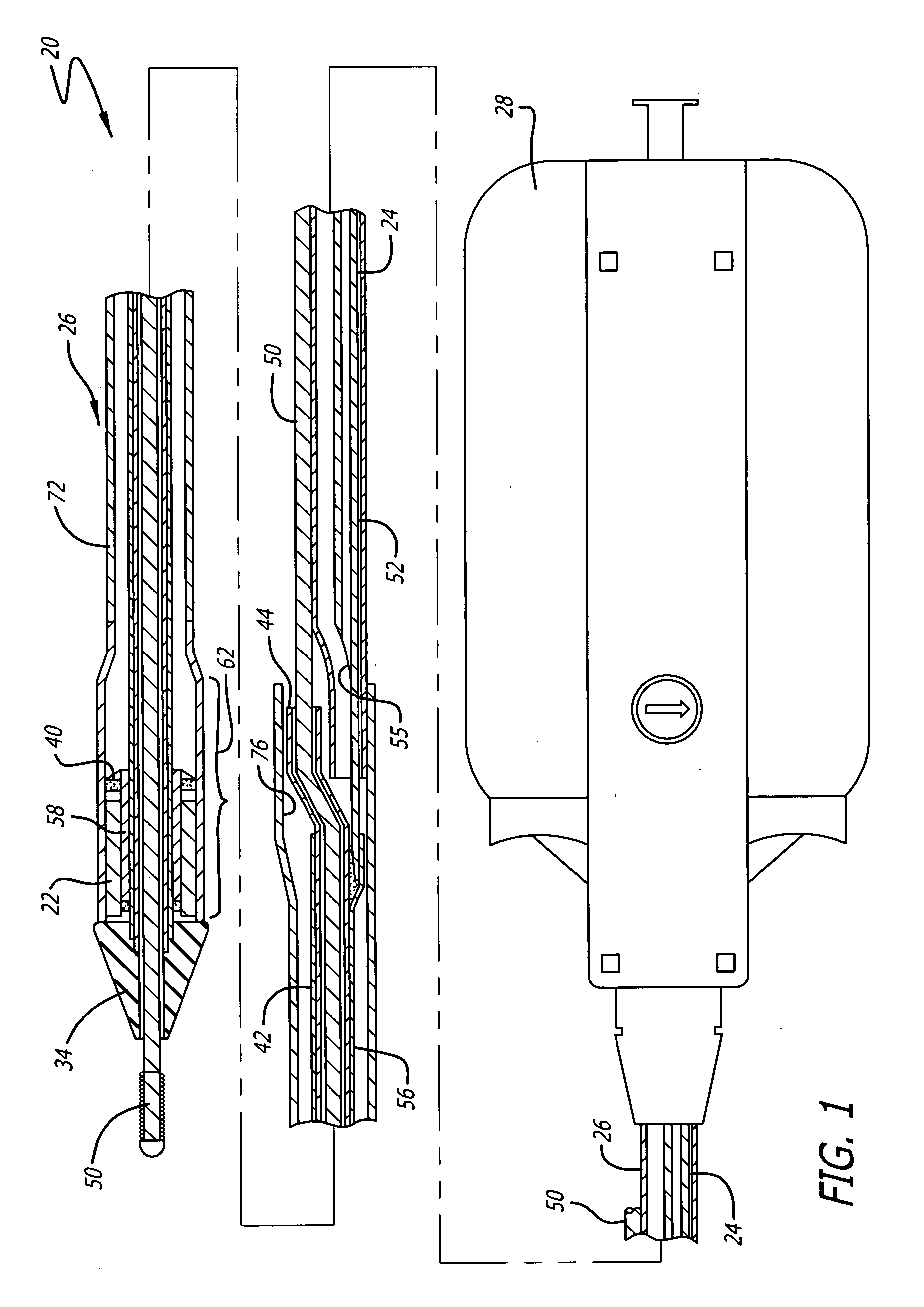
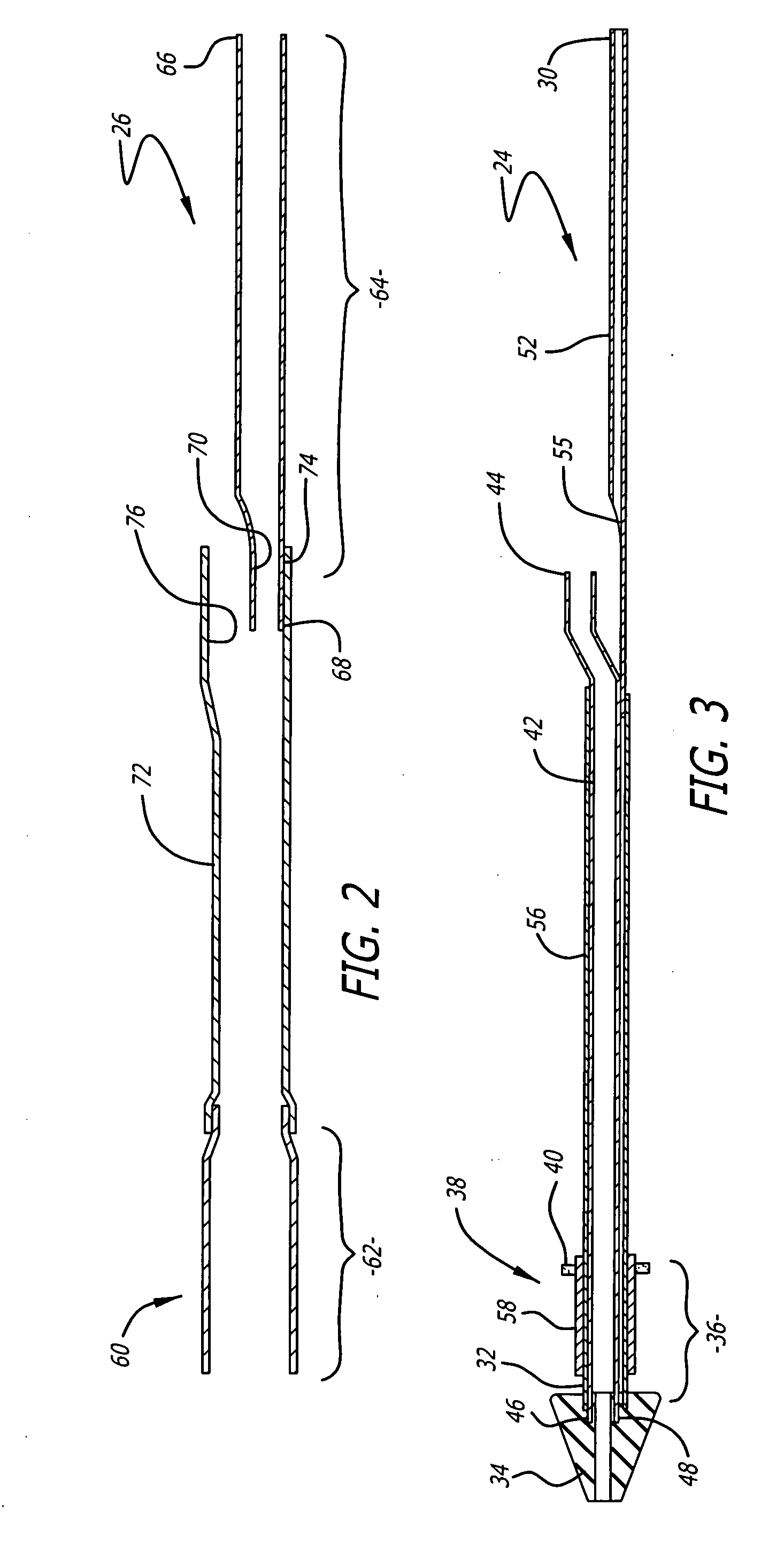
Total system for contrast delivery
InactiveUS6442418B1Minimizing chanceConstant solutionSurgeryMedical devicesIntensive care medicineContamination
A disposable unit for delivering fluid medium to one of a plurality of patients includes a sterile patient supply tube, and structure for receiving pressurized fluid medium into the patient supply tube. One or more devices is provided for precluding backflow of material from the patient to the fluid medium receiving structure, for preventing contamination of the fluid medium receiving structure and / or for preventing cross-contamination between patients.
Owner:BAJER MEDIKAL KEHA INK
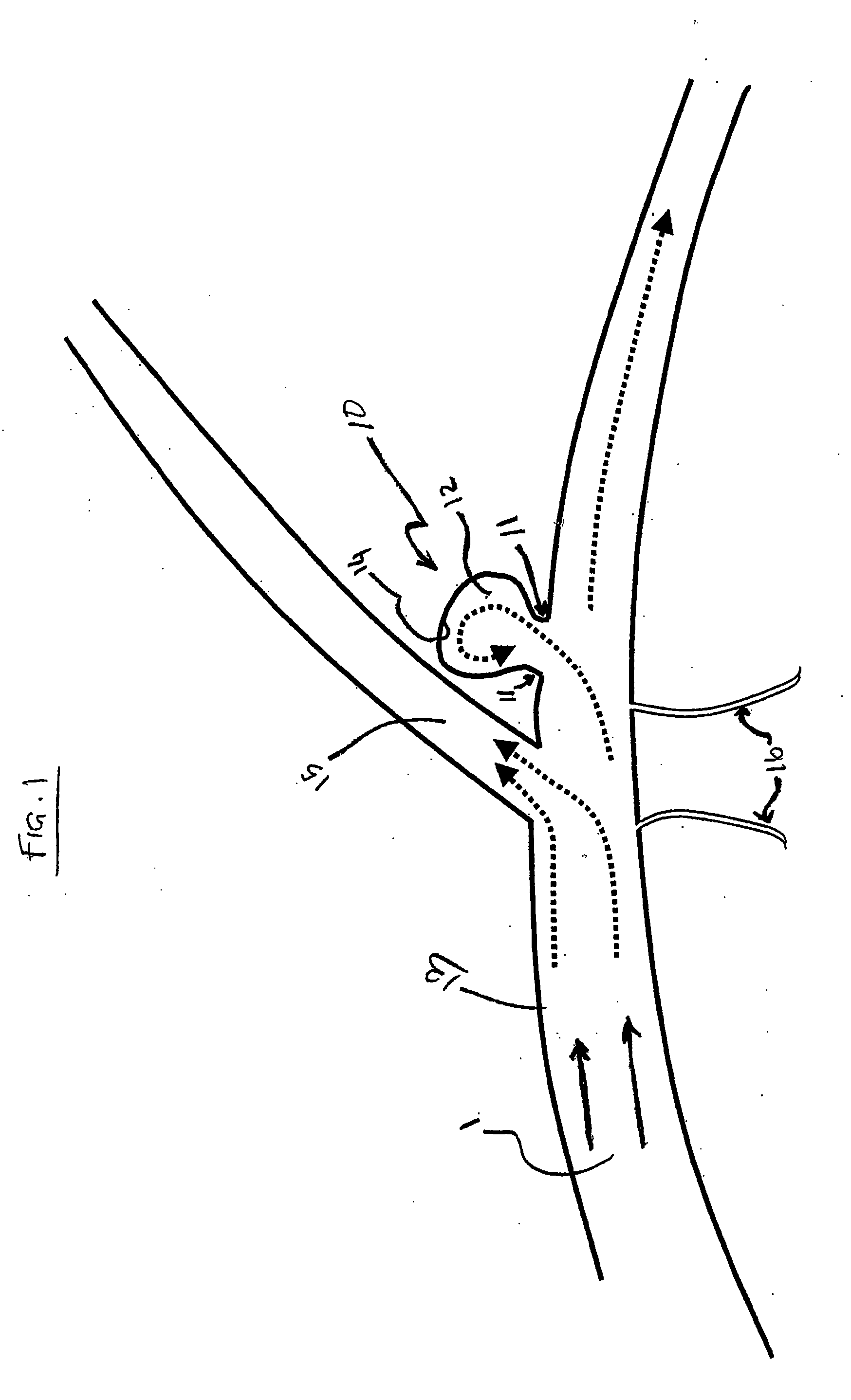
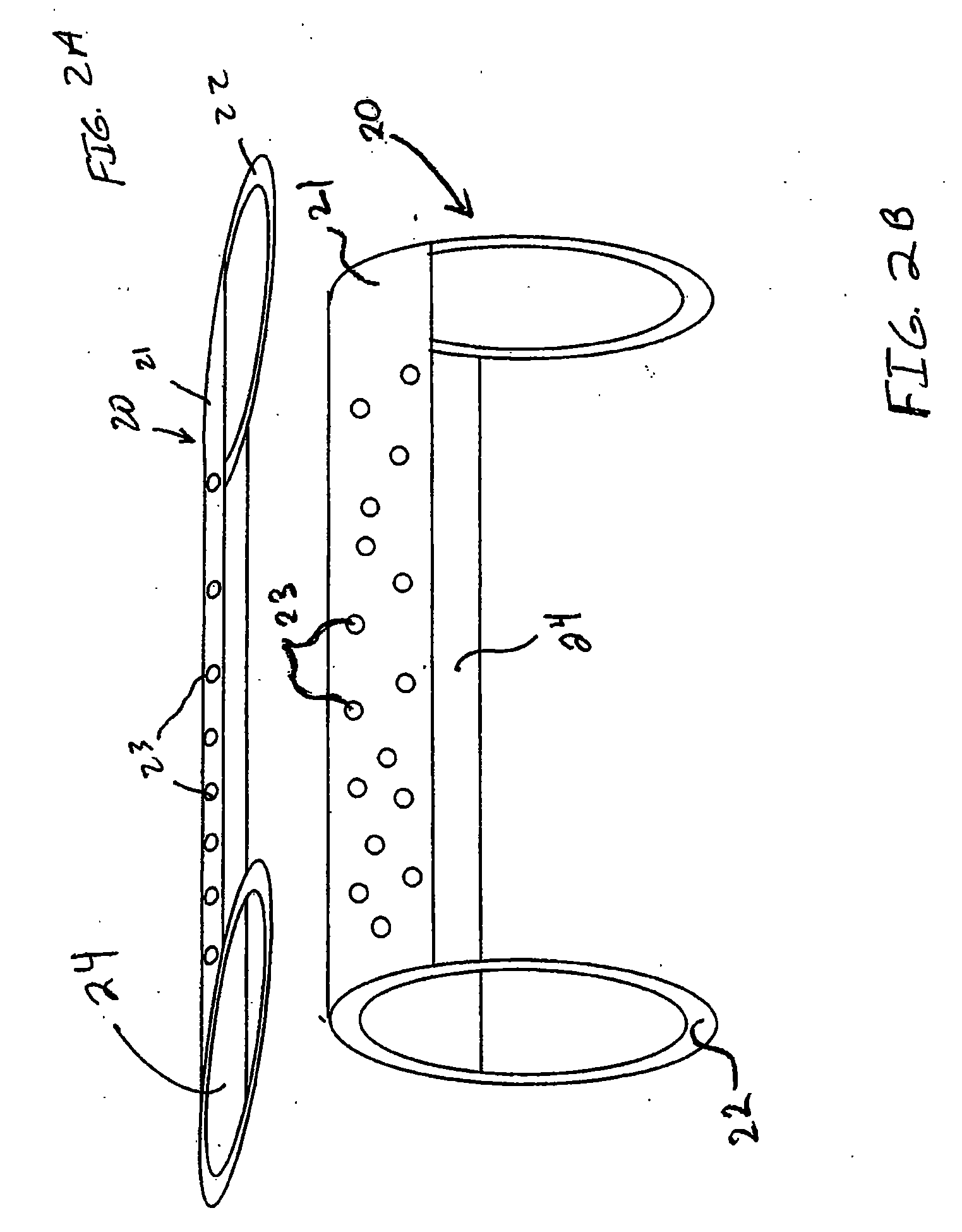
Flexible vascular occluding device
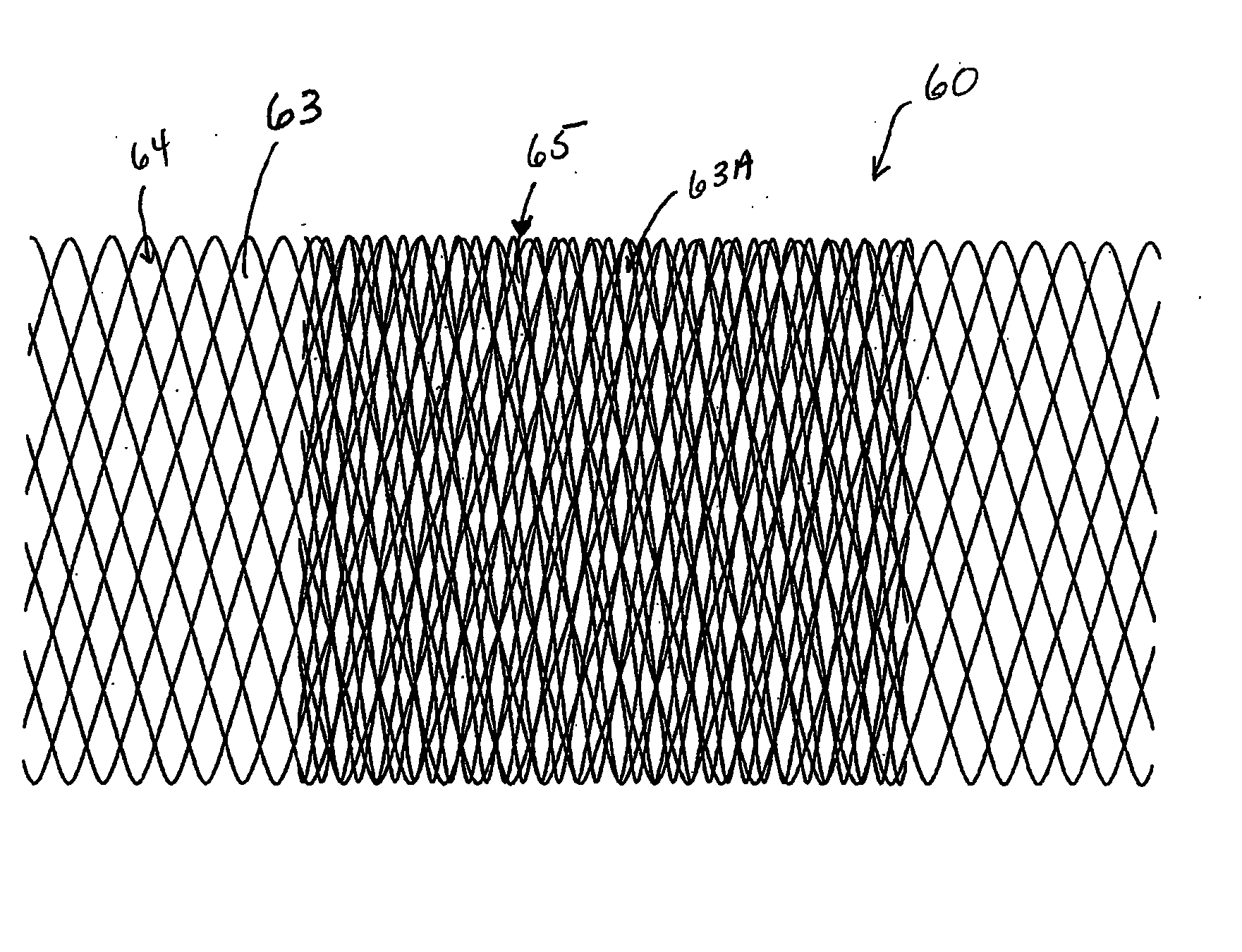
A vascular occluding device for modifying blood flow in a vessel, while maintaining blood flow to the surrounding tissue. The occluding device includes a flexible, easily compressible and bendable occluding device that is particularly suited for treating aneurysms in the brain. The neurovascular occluding device can be deployed using a micro-catheter. The occluding device can be formed by braiding wires in a helical fashion and can have varying lattice densities along the length of the occluding device. The occluding device could also have different lattice densities for surfaces on the same radial plane.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Flexible vascular occluding device
A vascular occluding device for modifying blood flow in a vessel, while maintaining blood flow to the surrounding tissue. The occluding device includes a flexible, easily compressible and bendable occluding device that is particularly suited for treating aneurysms in the brain. The neurovascular occluding device can be deployed using a micro-catheter. The occluding device can be formed by braiding wires in a helical fashion and can have varying lattice densities along the length of the occluding device. The occluding device could also have different lattice densities for surfaces on the same radial plane.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
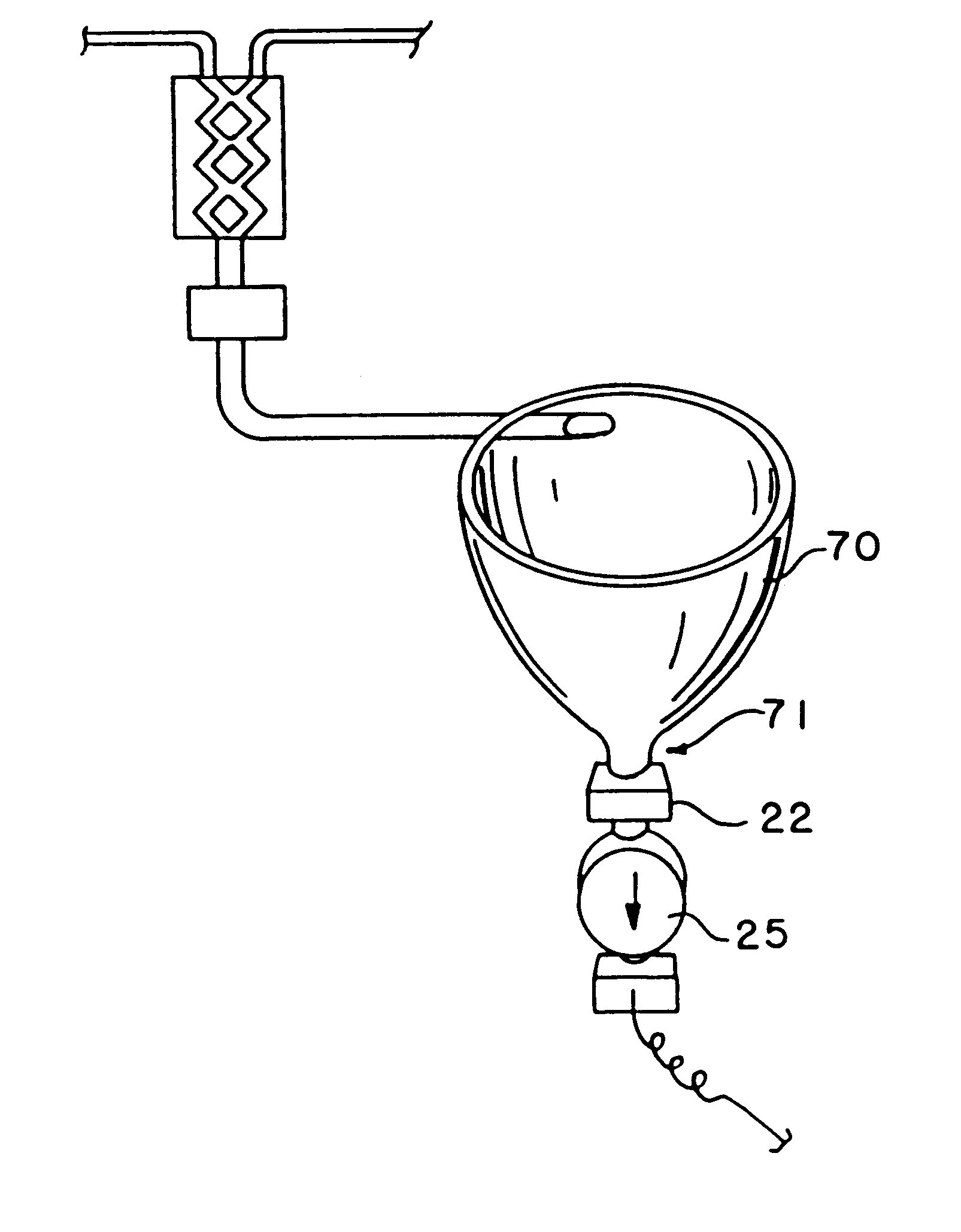
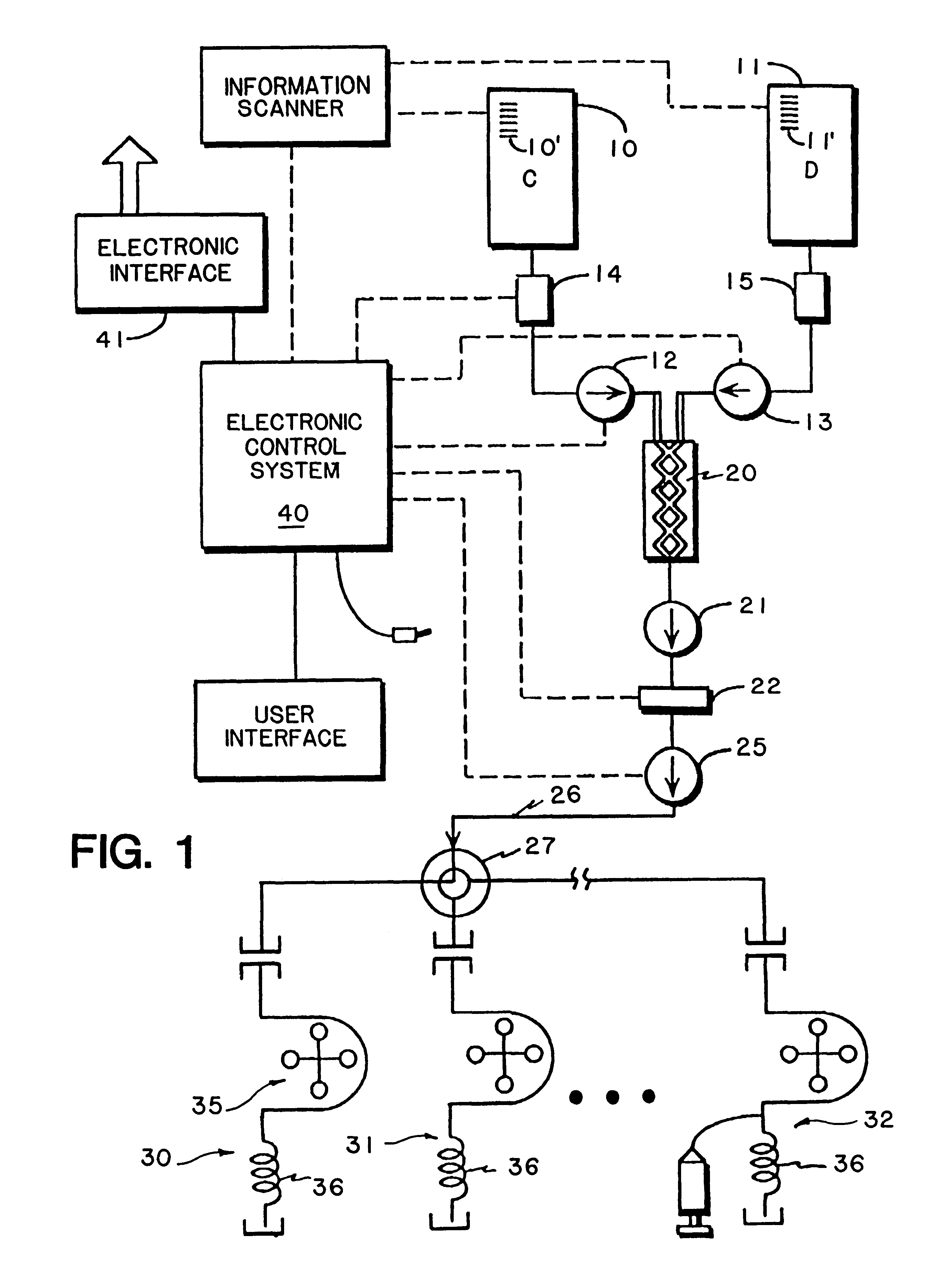
Fluid delivery system including a reusable flow path and a per-patient disposable fluid path
InactiveUS6731971B2Minimizing chanceConstant solutionSurgeryMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringDelivery system
An apparatus and method enabling the injection of fluid media into a plurality of patients is provided, including a fluid supply source providing multiple doses, a metering device for measuring the doses, a pressurizing device to effect injection, a contamination prevention device disposed between the fluid source and the patient and, when desired, an electronic control device to integrate operation of the apparatus and process.
Owner:BAJER MEDIKAL KEHA INK
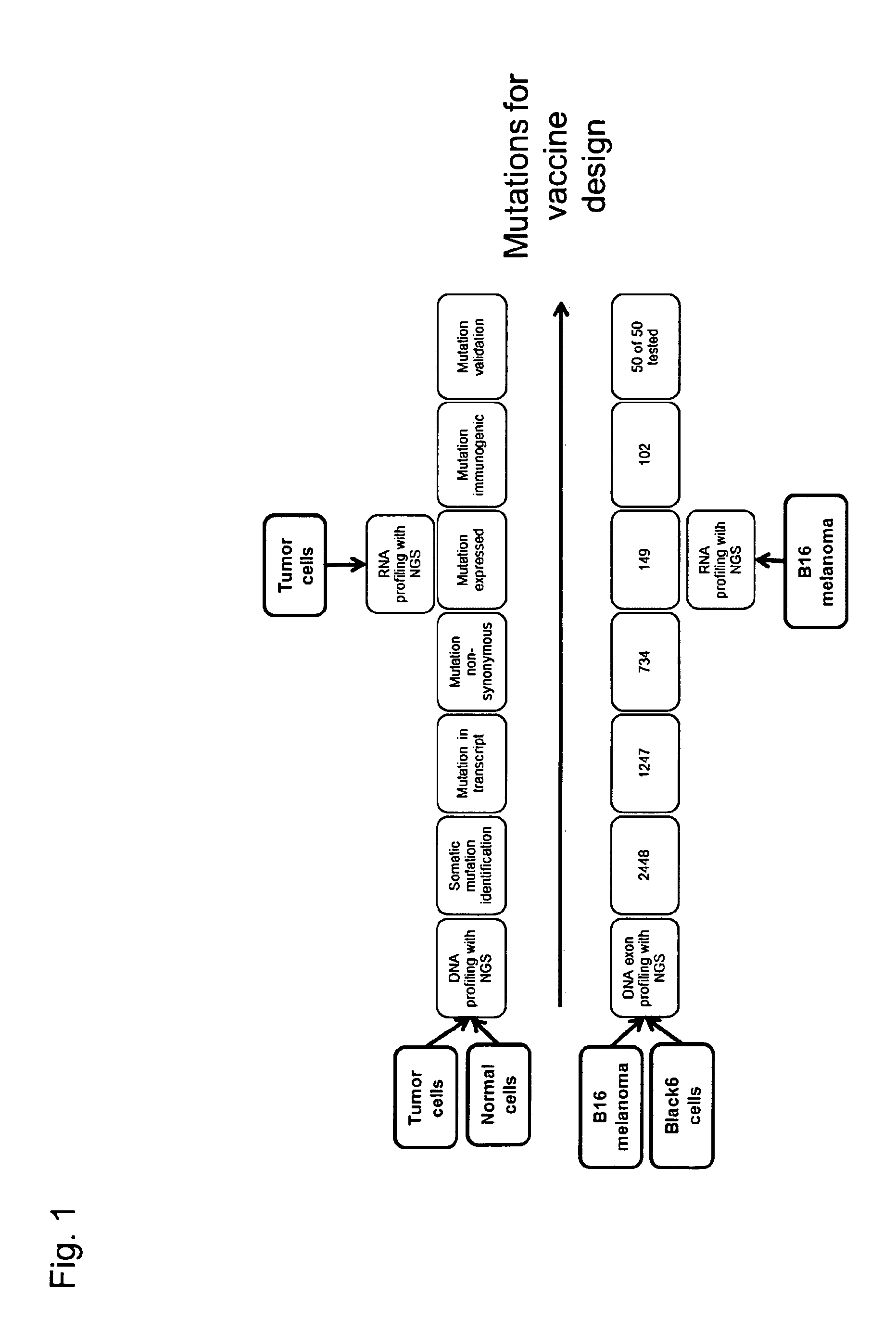
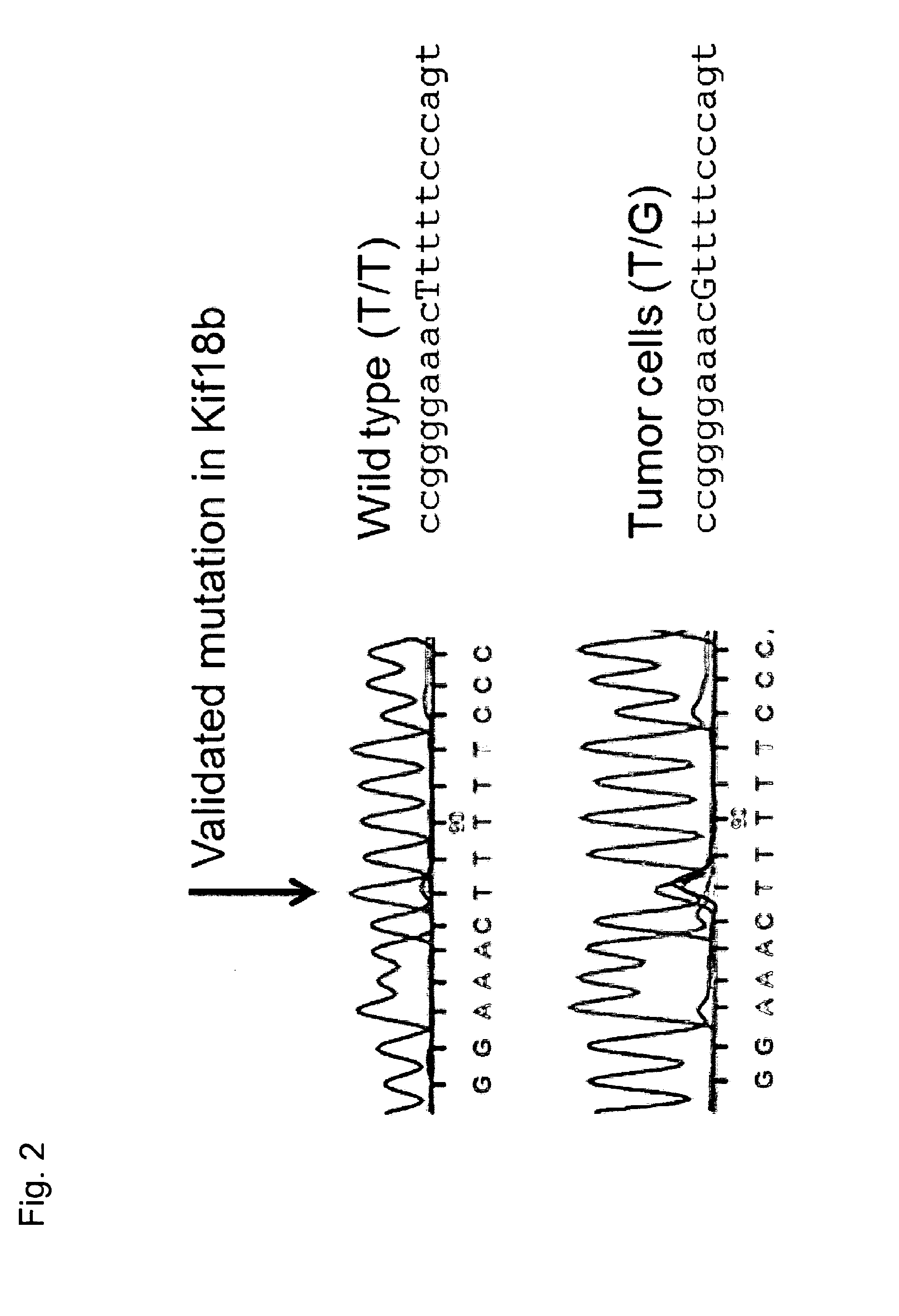
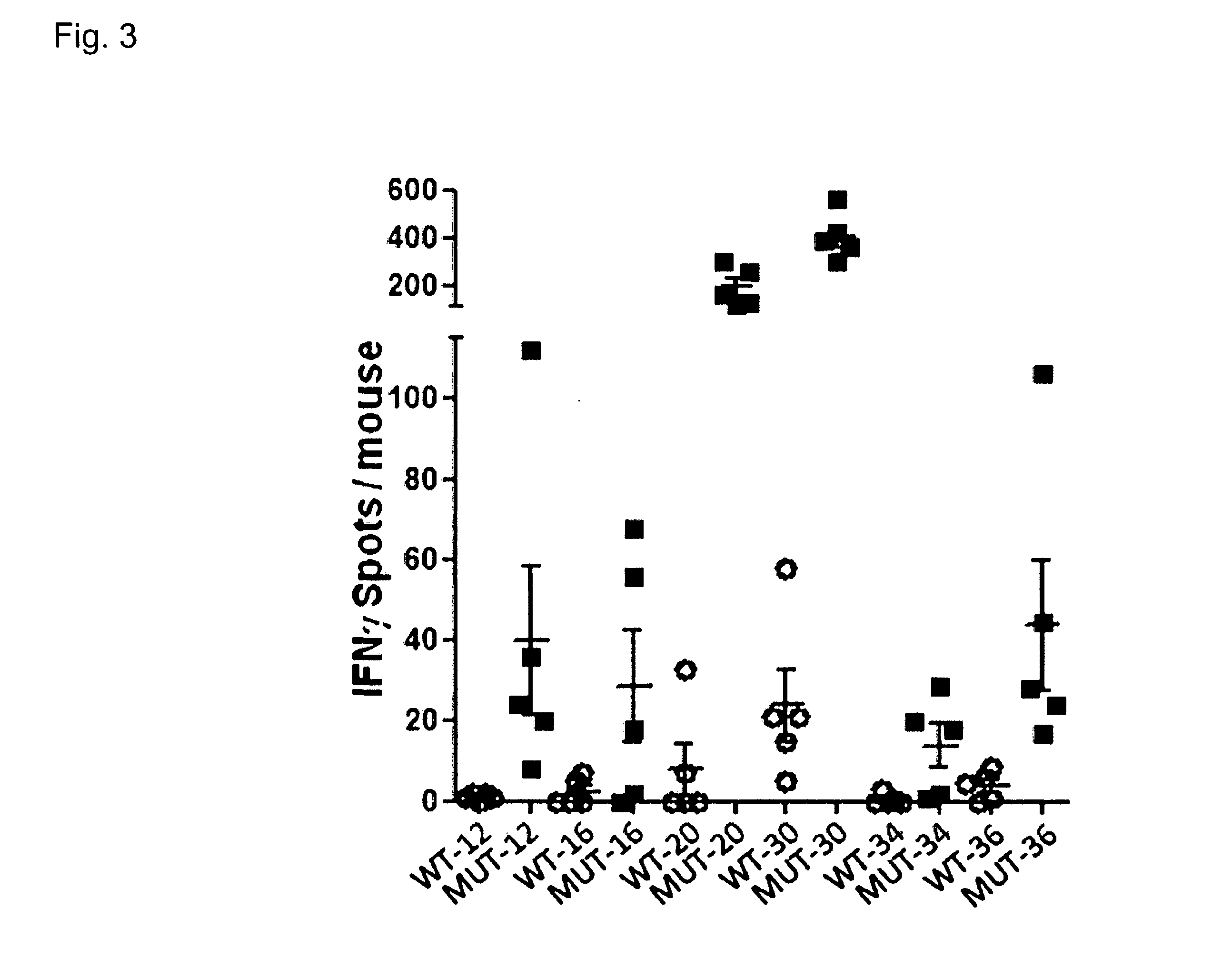
Individualized vaccines for cancer
ActiveUS20140178438A1Reduces steric hindranceImprove translationVaccinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
The present invention relates to the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and are potentially useful for immunotherapy of the primary tumor as well as tumor metastases. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for providing an individualized cancer vaccine comprising the steps: (a) identifying cancer specific somatic mutations in a tumor specimen of a cancer patient to provide a cancer mutation signature of the patient; and (b) providing a vaccine featuring the cancer mutation signature obtained in step (a). In a further aspect, the present invention relates to vaccines which are obtainable by said method.
Owner:TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GGMBH +1
Flexible vascular occluding device
A vascular occluding device for modifying blood flow in a vessel, while maintaining blood flow to the surrounding tissue. The occluding device includes a flexible, easily compressible and bendable occluding device that is particularly suited for treating aneurysms in the brain. The neurovascular occluding device can be deployed using a micro-catheter. The occluding device can be formed by braiding wires in a helical fashion and can have varying lattice densities along the length of the occluding device. The occluding device could also have different lattice densities for surfaces on the same radial plane.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
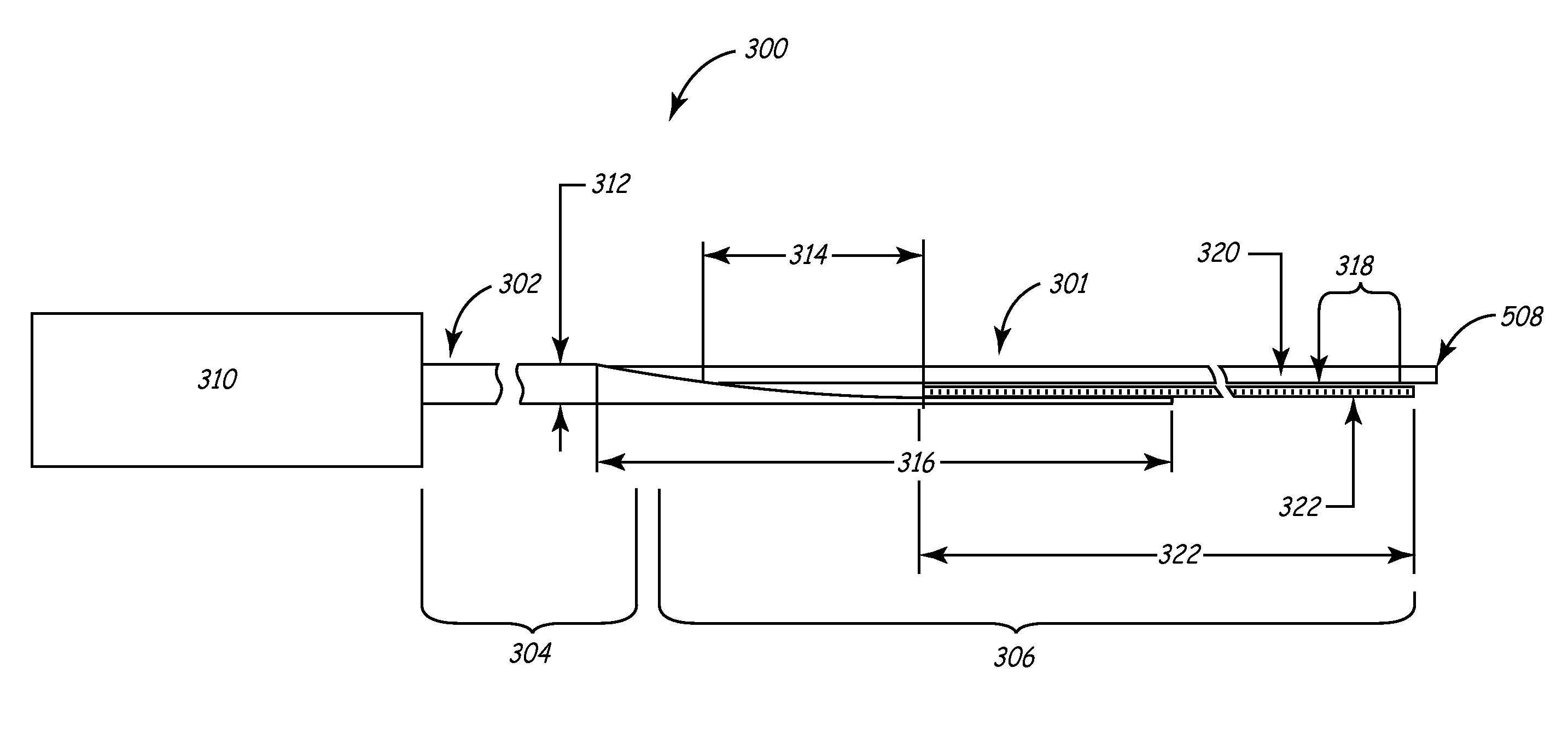
Rapid-exchange delivery systems for self-expanding stents
A catheter assembly is provided having an inner member and an outer member extending along a longitudinal axis, the inner member and the outer member having a coaxial configuration and dimensioned for relative axial movement. The outer member may include an anti rotation member adapted to engage with a longitudinal slot formed on the inner member so as to maintain rotational alignment between inner member and outer member. The inner member can be made with a proximal portion made from a tubing such as hypotubing or a coil tubing. The inner member also may be made with a proximal portion made with a support mandrel. A coil tubing can be utilized to form the guide wire receiving member which is attached to the inner member.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Multi-patient fluid dispensing
InactiveUS6306117B1Minimizing chanceIntravenous devicesFlow controlContaminationBiomedical engineering
A system for delivering sterile fluid to a patient, while preventing cross-contamination, in which flow interrupting means are provided which basically create regions where no fluid exists in the comprehensive or over-all quality of material that is flowing from a fluid source to a patient.
Owner:BAJER MEDIKAL KEHA INK
Flexible vascular occluding device
A vascular occluding device for modifying blood flow in a vessel, while maintaining blood flow to the surrounding tissue. The occluding device includes a flexible, easily compressible and bendable occluding device that is particularly suited for treating aneurysms in the brain. The neurovascular occluding device can be deployed using a micro-catheter. The occluding device can be formed by braiding wires in a helical fashion and can have varying lattice densities along the length of the occluding device. The occluding device could also have different lattice densities for surfaces on the same radial plane.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Particles with improved solubilization capacity
A particle is disclosed that comprises a first volume of hydrophobe-rich material with tunable dissolution and solubilization characteristics and a distinct second volume of nanostructured nonlamellar liquid crystalline material, said second volume containing said first domain and being capable of being in equilibrium with said first volume. Preferably, the nanostructured nonlamellar liquid crystalline material is capable of being in equilibrium with a polar solvent or a water-immiscible solvent or both.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Automatic card shuffler and dealer
An automatic system for shuffling and distributing cards includes two embodiments. One embodiment includes fixed and rotating plates on which a deck of cards is supported. The device according to this embodiment, can be placed on the table. Shuffling is achieved by a plurality of card magazines and delivery trays located on the rotating plate. The fixed plate includes fixed card ejection devices which operate during and in response to rotation of the rotating plate, which eject cards at a plurality of locations about the system. The device is electrically powered and includes means to automatically stop its rotation after the last card in the deck has been distributed. In another embodiment, a hand-hold device is designed so the user can hold it in one hand and by pressing on switch the topmost card is automatically ejected to the location aimed by the user.
Owner:MOTI SHAI
Method and apparatus for measuring catheter contact force during a medical procedure
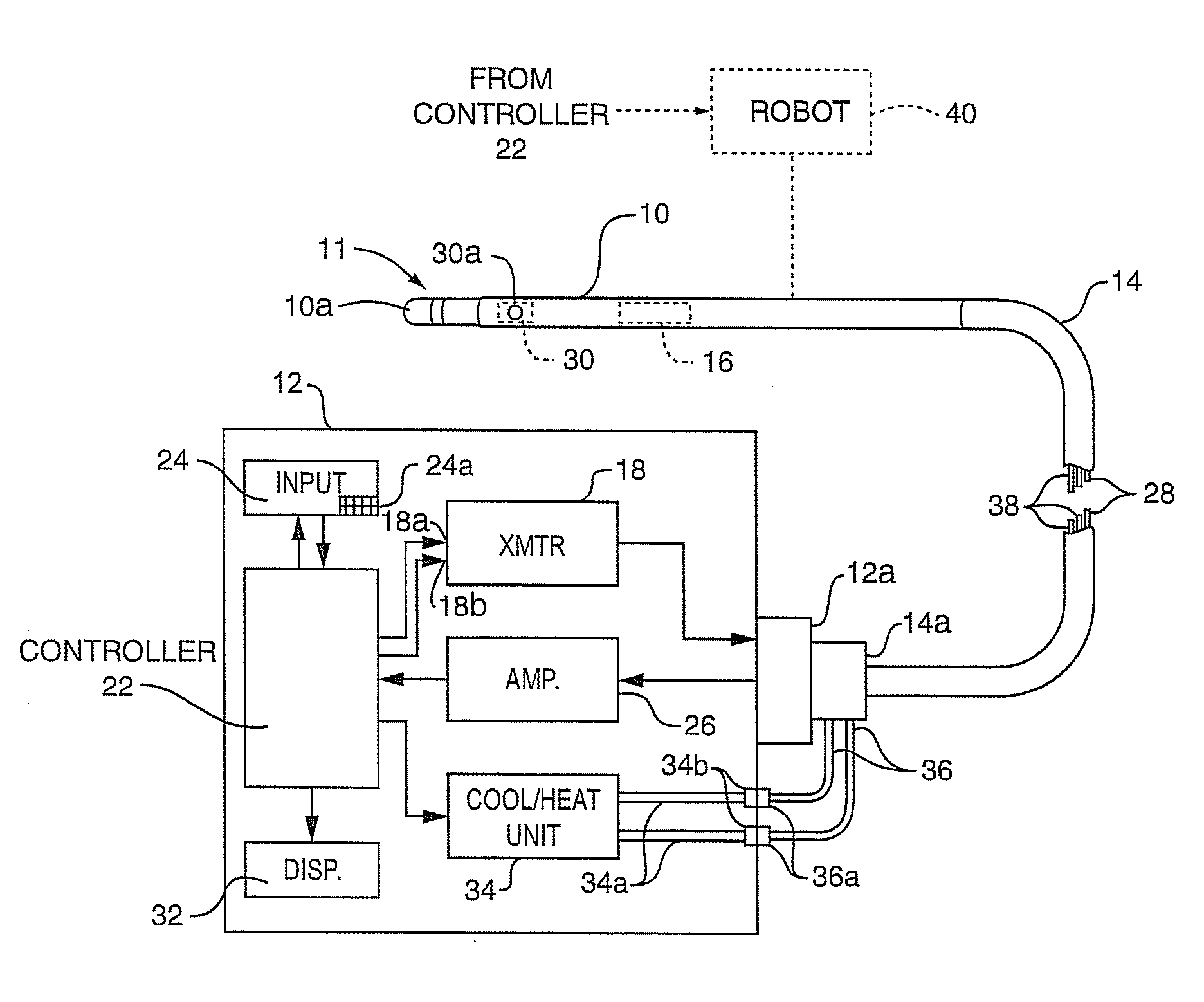
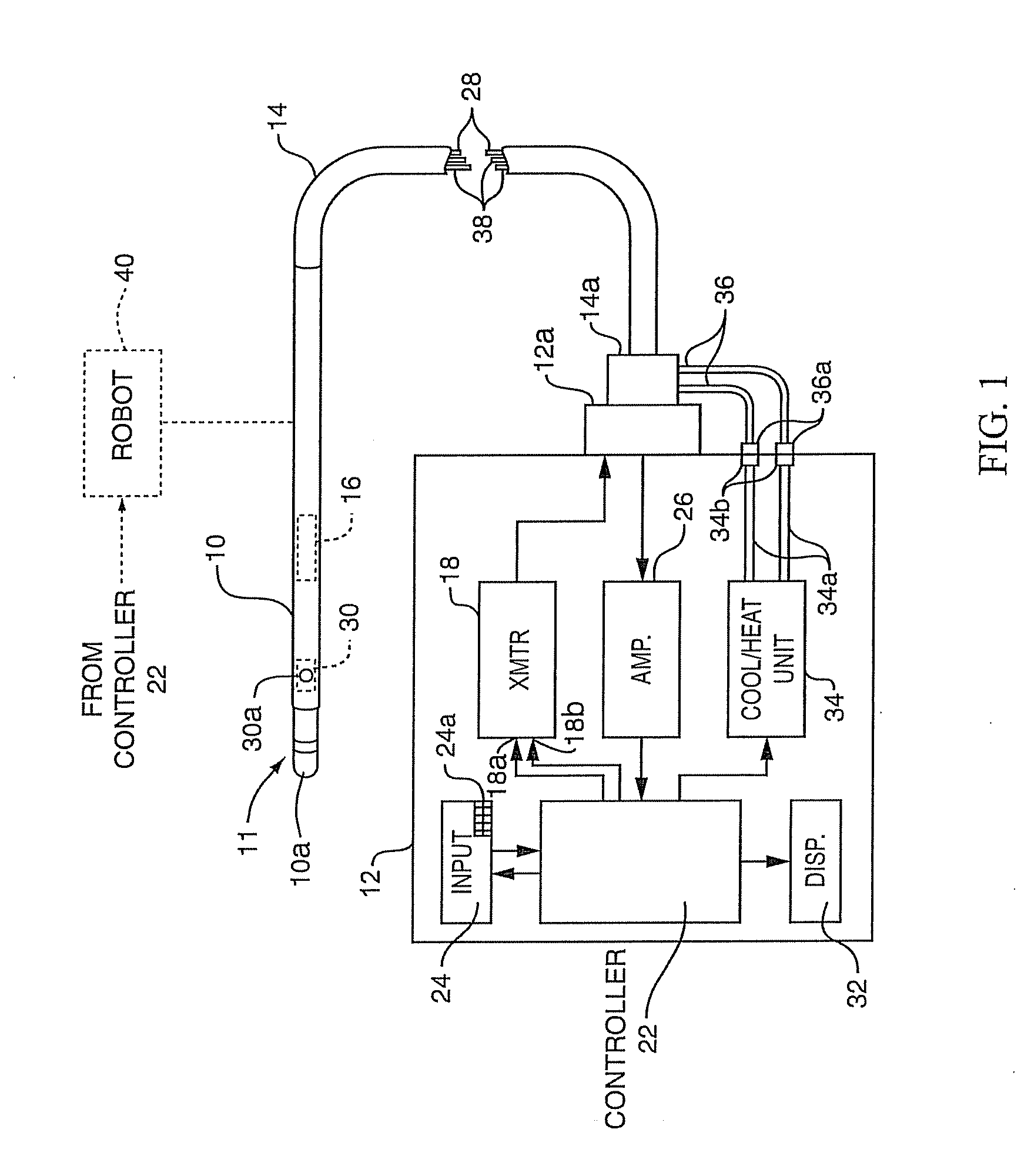
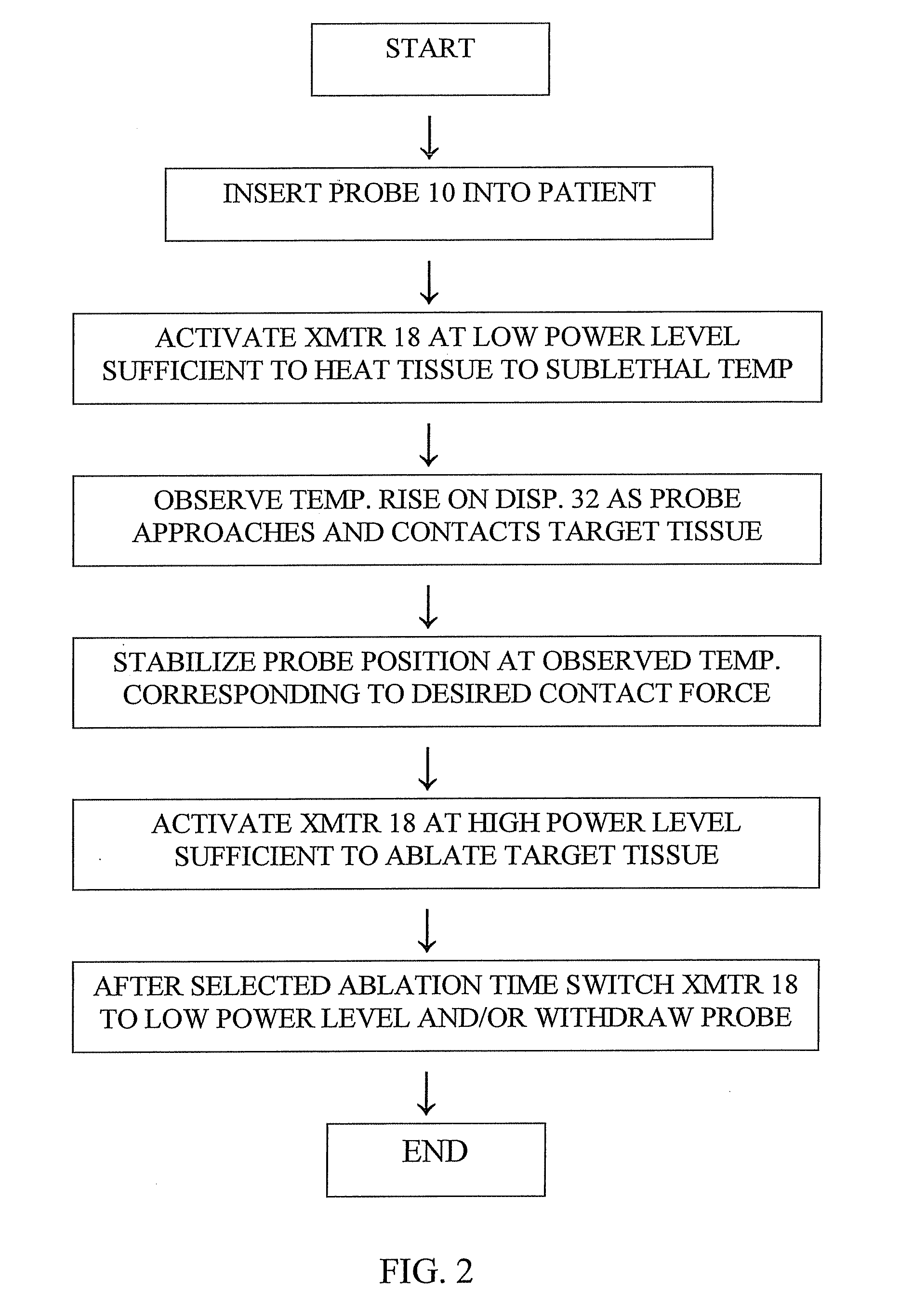
ActiveUS20090312754A1Precise positioningAccurate measurementDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingRadiometerSufficient time
A method for measuring the contact force exerted on tissue by a probe for heating the tissue and containing an antenna which is connected to a radiometer whose output reading indicates the temperature at depth of the tissue contacted by the probe comprises displaying the output reading of the radiometer, applying sufficient power to the probe to heat the tissue to a selected first temperature that is not lethal to the tissue, moving the probe into contact with the tissue, observing the increase in the displayed temperature reading that occurs when the probe contacts the tissue, and advancing the probe toward the tissue until the displayed temperature reading reaches a value corresponding to a selected tissue contact force. After the probe position in the tissue has stabilized, the applied power to the probe may be increased to heat the tissue to a selected second temperature that is lethal to tissue for a sufficient time to ablate the tissue followed by lowering the tissue heating to a sub-lethal temperature. Apparatus for practicing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED CARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
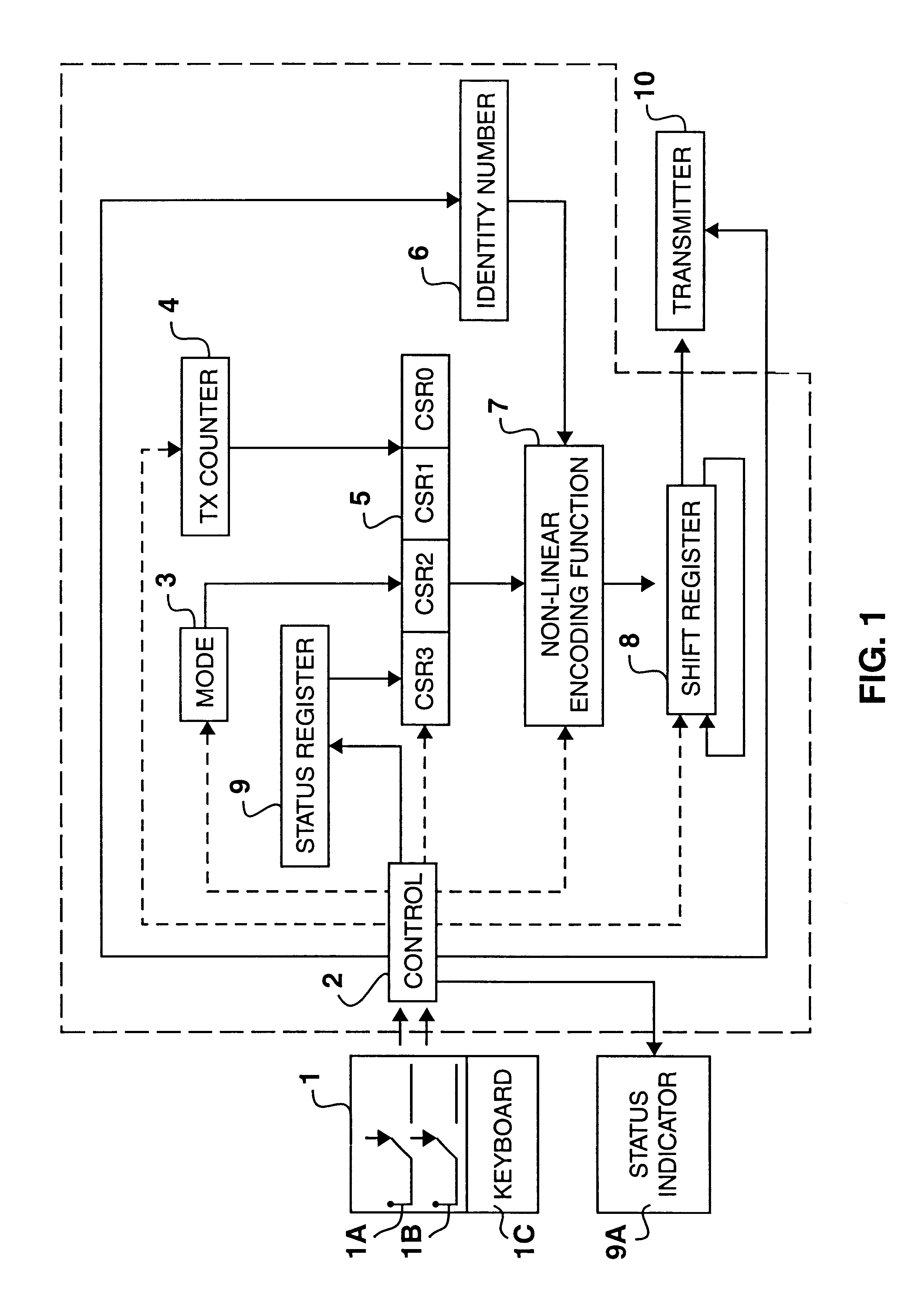
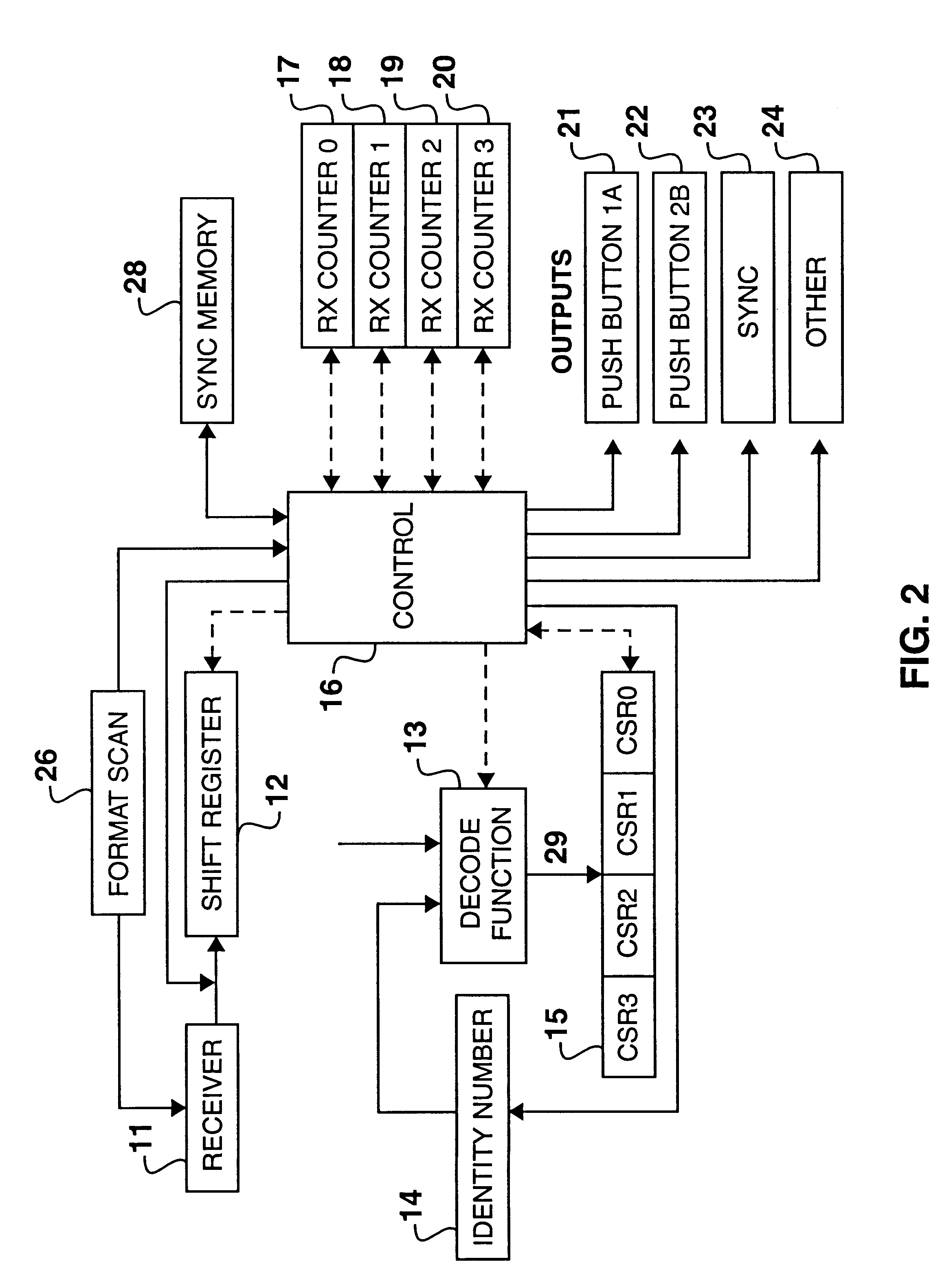
Encoder and decoder microchips and remote control devices for secure unidirectional communication
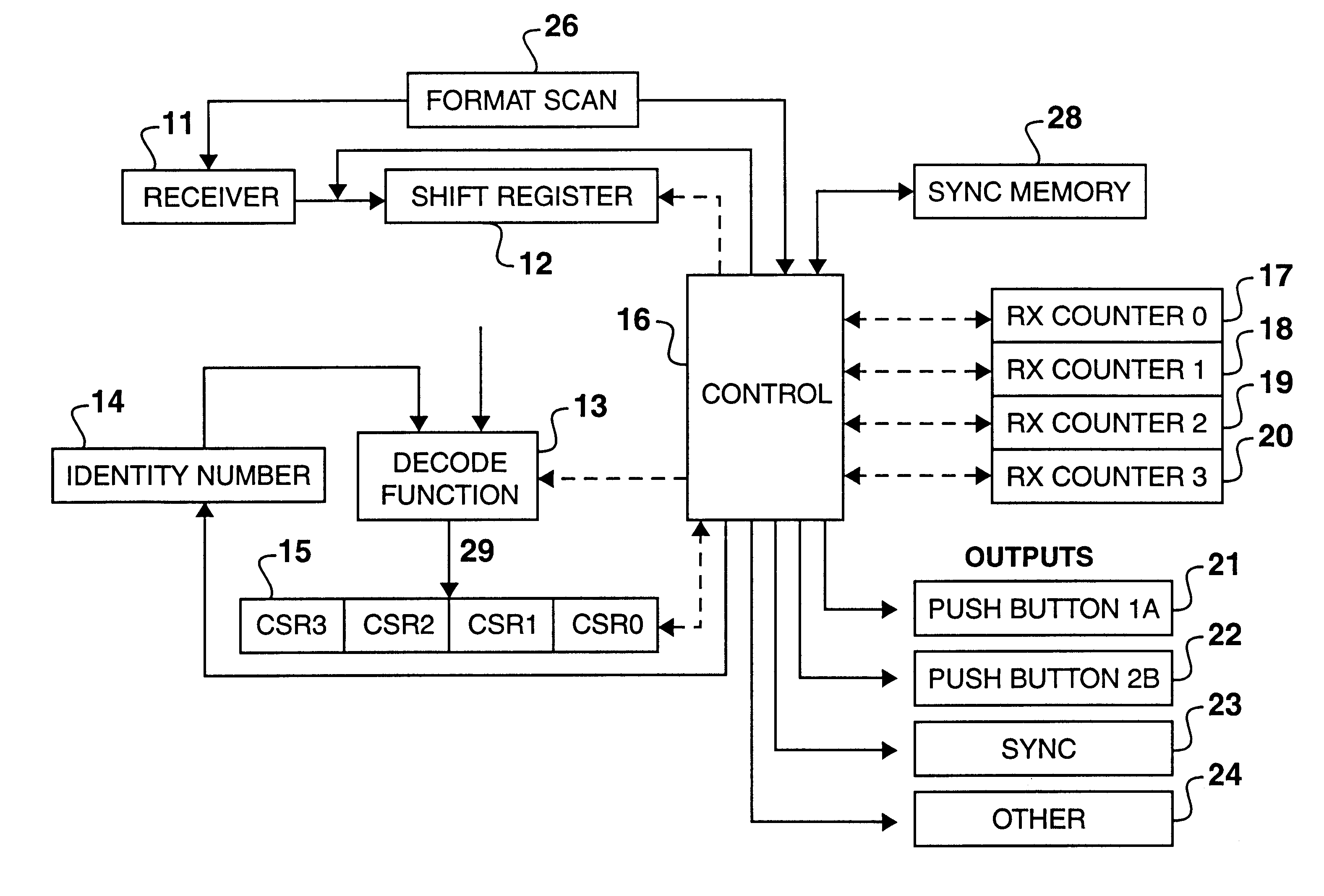
InactiveUS6175312B1Improve securityMinimizing chanceElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareRemote control
Encoder and decoder microchips suitable for use in secure unidirectional remote control devices. The encoder microchip includes circuits for performing and encoding function on an identification number embedded in the microchip and a combination of a characterization number and a stepping counter value, so as to generate a transmission value which is only decidable by a related decoding function having access to the same identification number. The decoder microchip includes circuits for decoding the transmission value into a decoded characterization number and a decoded counter value and circuits for comparing the decoded counter value with a decoded counter value range. The encoder and decoder microchips are also provided with means for synchronizing the decoder microchip with a particular encoder microchip which has generated a synchronization command.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH CORP
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS20130030438A1Simple and reliable processLow costInternal osteosythesisPinsShape changeBone tissue
A new shape changing staple and instrument for the fixation of structures to include bone tissue and industrial materials. This new staple stores elastic mechanical energy to exert force on fixated structures to enhance their security and in bone affect its healing response. This staple once placed changes shape in response to geometric changes in the materials structure, including healing bone tissue. The staple is advanced over prior staples due to its: 1) method of operation, 2) high strength, 3) method of insertion, 4) compressive force temperature independence, 5) energy storing staple retention and delivery system, 6) compatibility with reusable or single use product configuration, 7) efficient and cost effective manufacturing methods, and 8) reduction in the steps required to place the device. In addition to the staple's industrial application an embodiment for use in the fixation of the musculoskeletal system is shown with staple, cartridge, and extrusion handle.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
System and method for positioning implantable medical devices within coronary veins
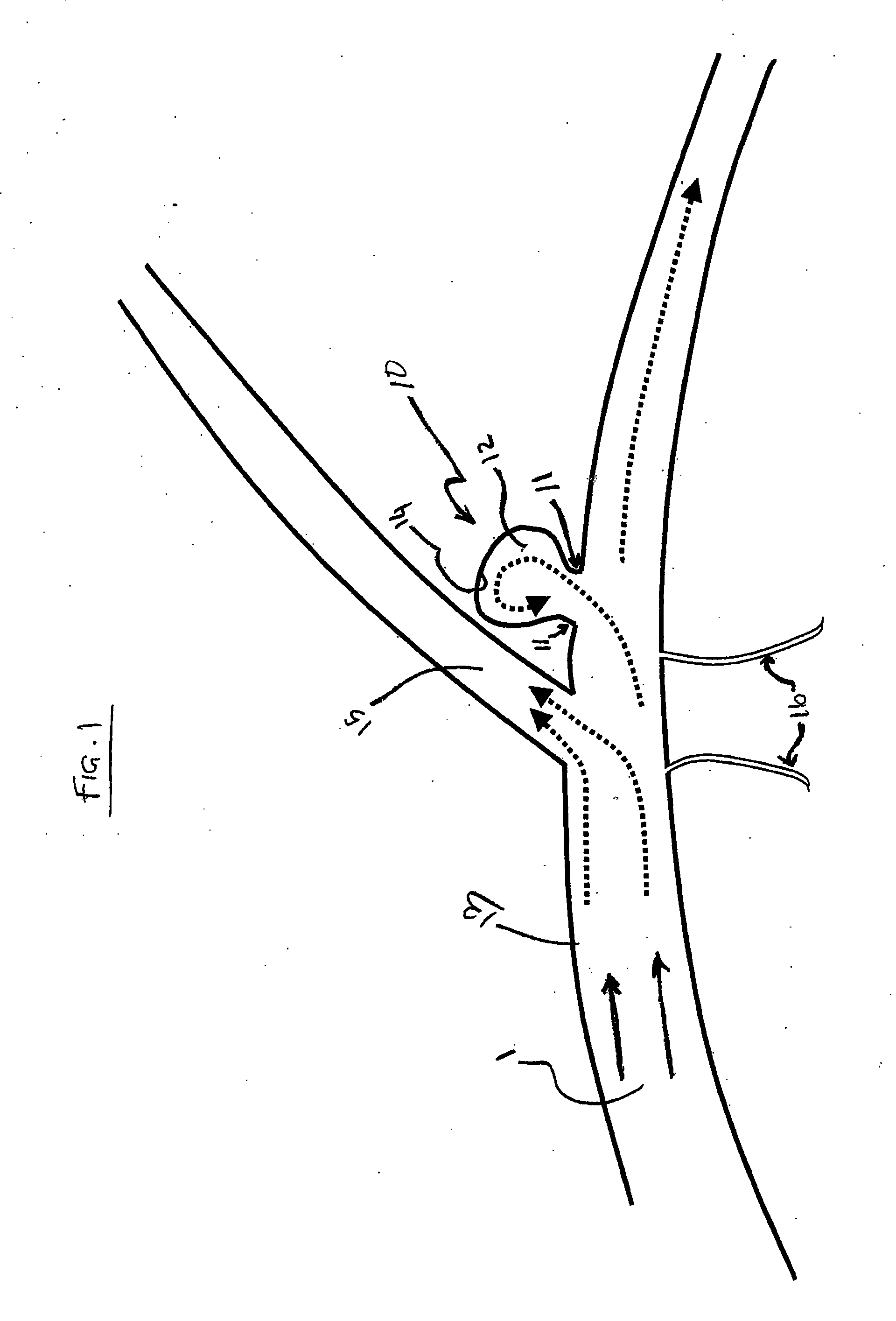
An improved system and method for placing implantable medical devices (IMDs) such as leads within the coronary sinus and branch veins is disclosed. In one embodiment, a slittable delivery sheath and a method of using the sheath are provided. The sheath includes a slittable hub, and a substantially straight body defining an inner lumen. The body comprises a shaft section and a distal section that is distal to, and softer than, the shaft section. A slittable braid extends adjacent to at least a portion of one of the shaft section and the distal section. In one embodiment of the invention, the sheath further includes a transition section that is distal to the shaft section, and proximal to the distal section. The transition section is softer than the shaft section, but stiffer than the distal section.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
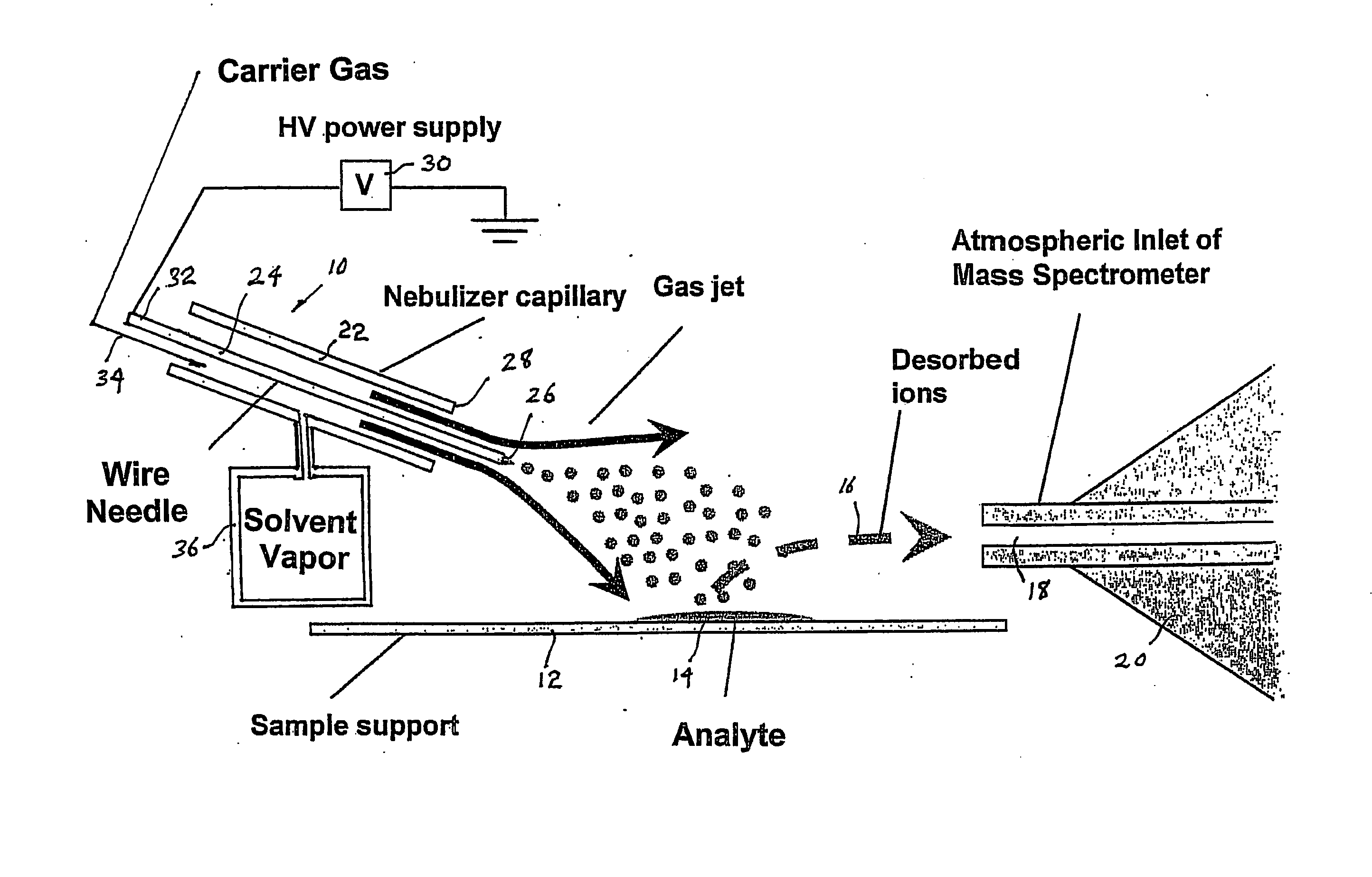
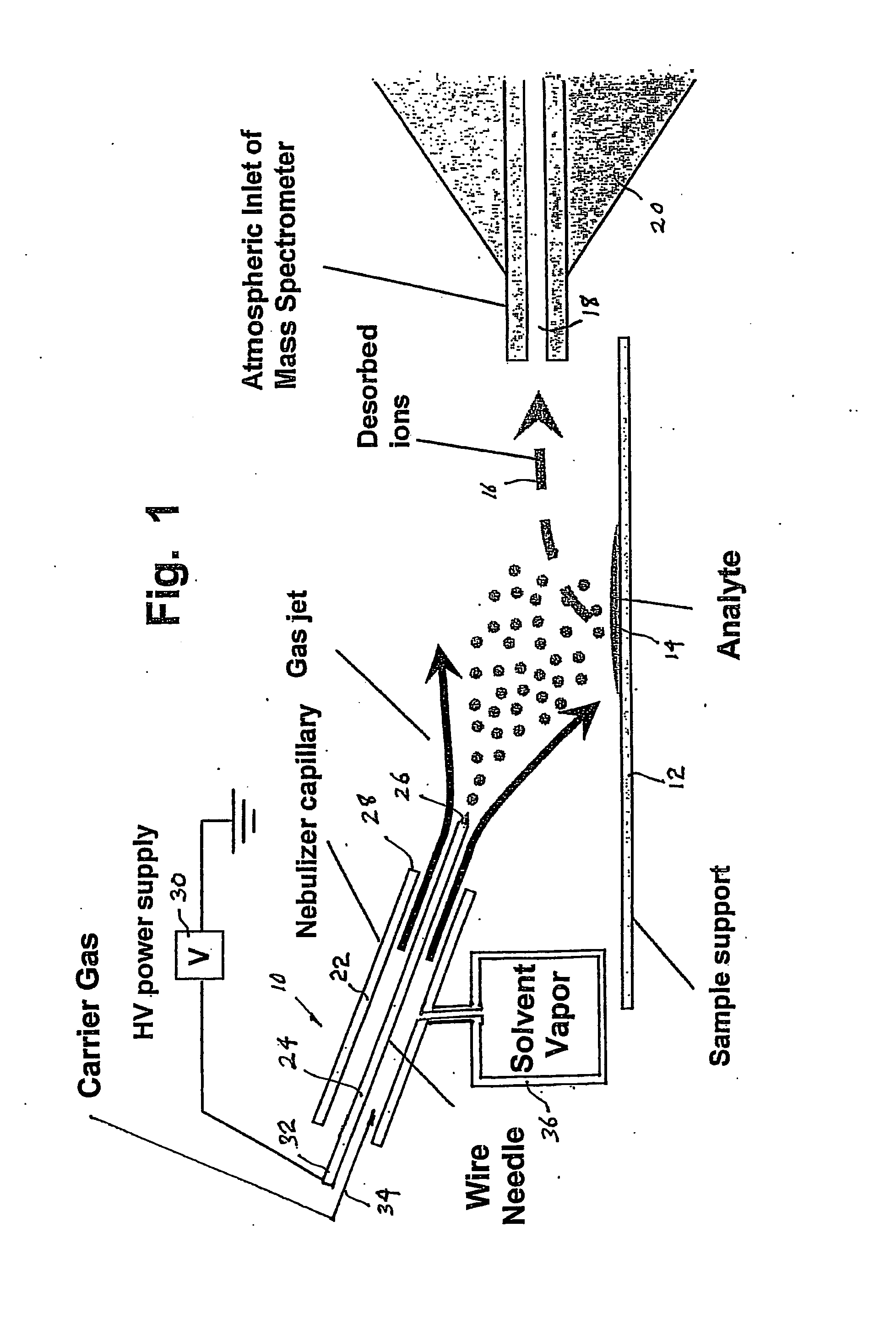
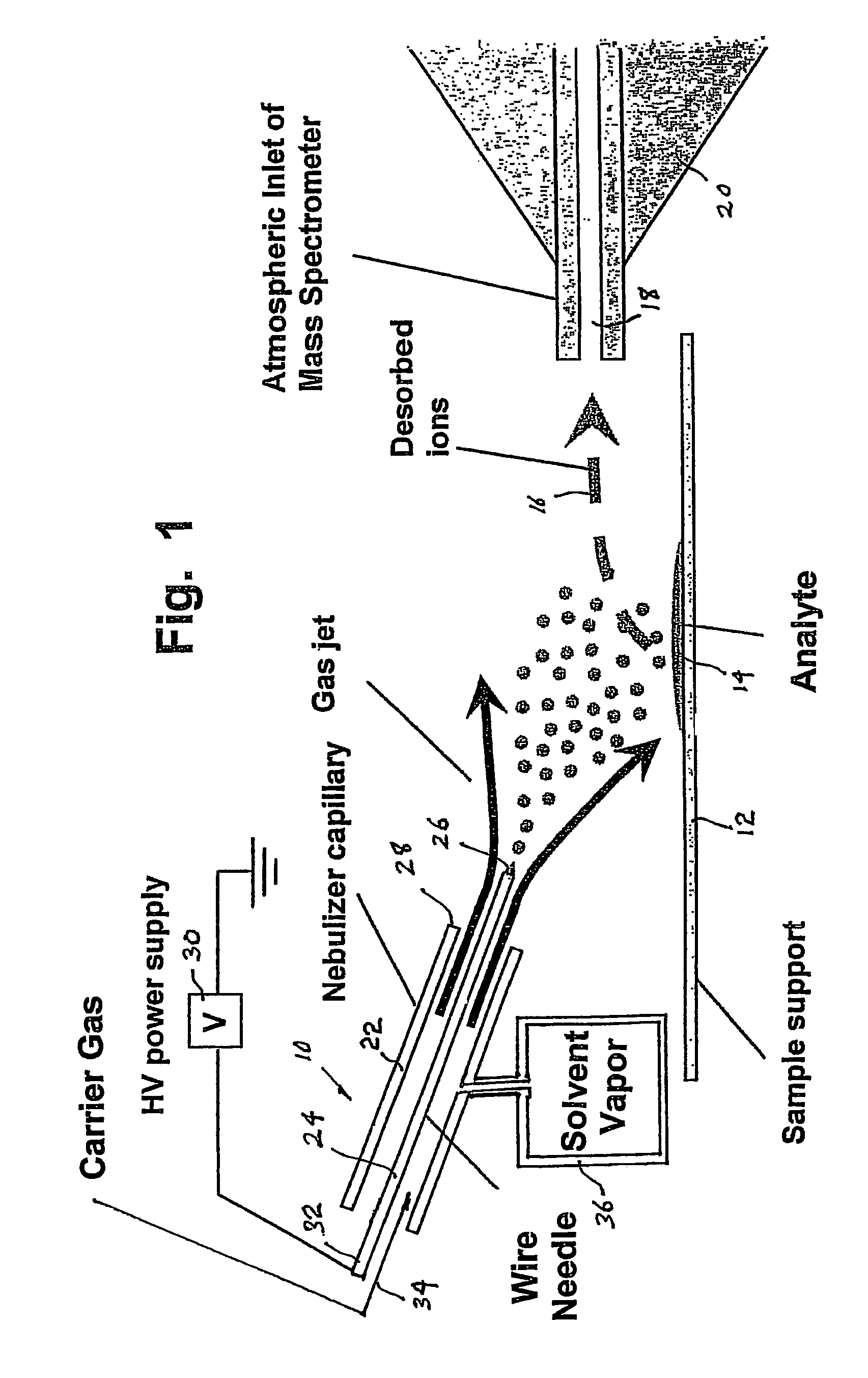
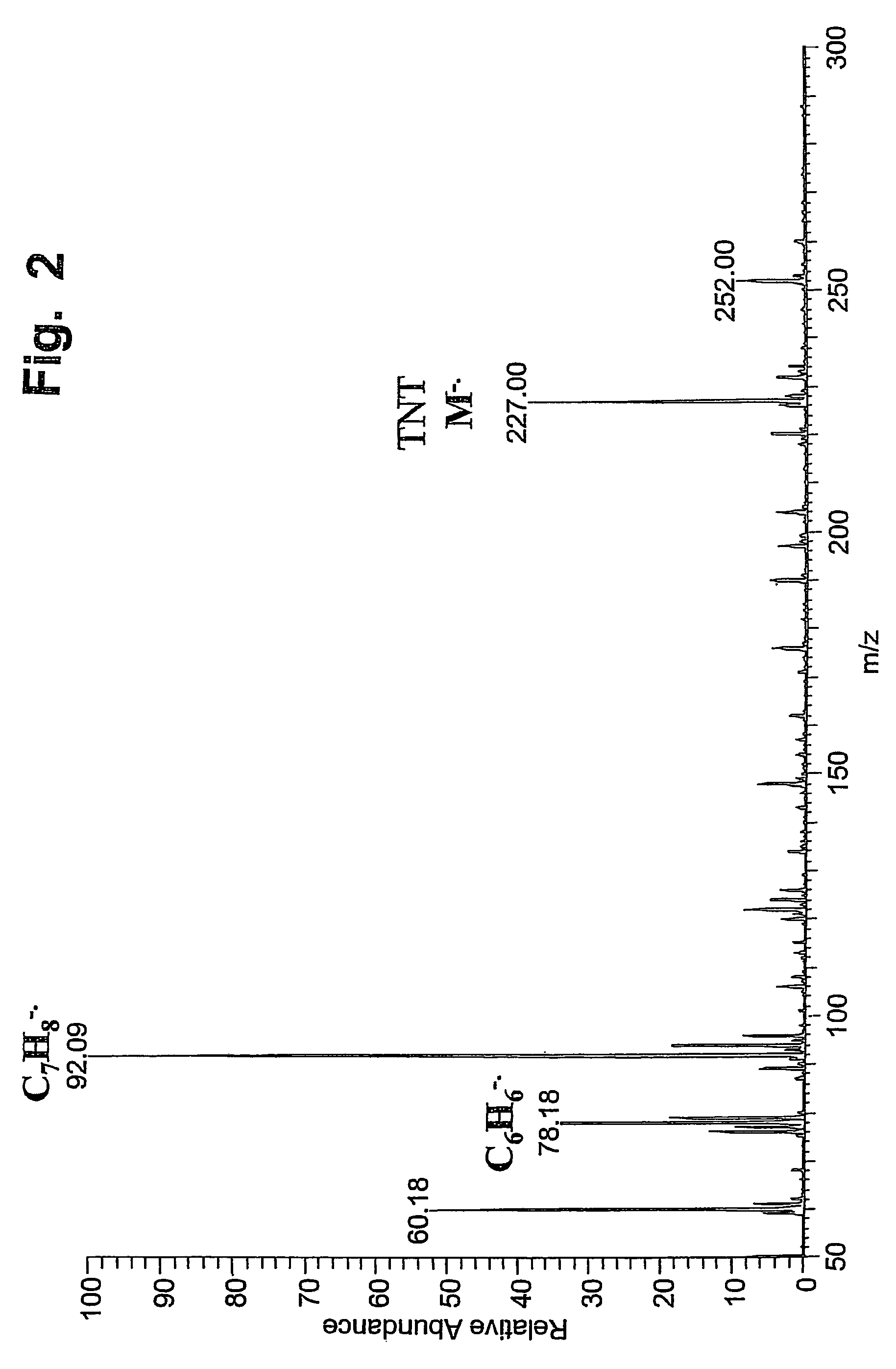
ActiveUS20070187589A1High sensitivityMinimizing chanceMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsIonizationAdduct
A desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI) system delivers a primary ion beam composed of an inert, high velocity gas and solvent ions to a surface to effect desorption and ionization of both volatile and non-volatile species present on surfaces. A electrode having a tapered tip is connected to a high voltage power supply. The tapered tip projects outward from a capillary carrying a high-speed flow of gas. A vapor of a solvent is mixed into the annular gas flow surrounding the needle. The gaseous solvent vapor is ionized in close proximity to the tapered tip by virtue of the high voltage applied to the electrode. The high-speed flow of gas and solvent vapor ions extending outward from the capillary is directed toward a substrate on which an analyte of interest may have been deposited. The solvent vapor ions can blanket the surface of the analyte causing a static charge build up that facilitates ion desorption and additionally can provide positive ion adducts of the analyte freed from the substrate surface that can be directed toward an atmospheric intake of a mass spectrometer or other instrument capable of studying the analyte.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and system for desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
ActiveUS7544933B2Minimizing chanceHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsSolvent vaporDesorption
A desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI) system delivers a primary ion beam composed of an inert, high velocity gas and solvent ions to a surface to effect desorption and ionization of both volatile and non-volatile species present on surfaces. A electrode having a tapered tip is connected to a high voltage power supply. The tapered tip projects outward from a capillary carrying a high-speed flow of gas. A vapor of a solvent is mixed into the annular gas flow surrounding the needle. The gaseous solvent vapor is ionized in close proximity to the tapered tip by virtue of the high voltage applied to the electrode. The high-speed flow of gas and solvent vapor ions extending outward from the capillary is directed toward a substrate on which an analyte of interest may have been deposited. The solvent vapor ions can blanket the surface of the analyte causing a static charge build up that facilitates ion desorption and additionally can provide positive ion adducts of the analyte freed from the substrate surface that can be directed toward an atmospheric intake of a mass spectrometer or other instrument capable of studying the analyte.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
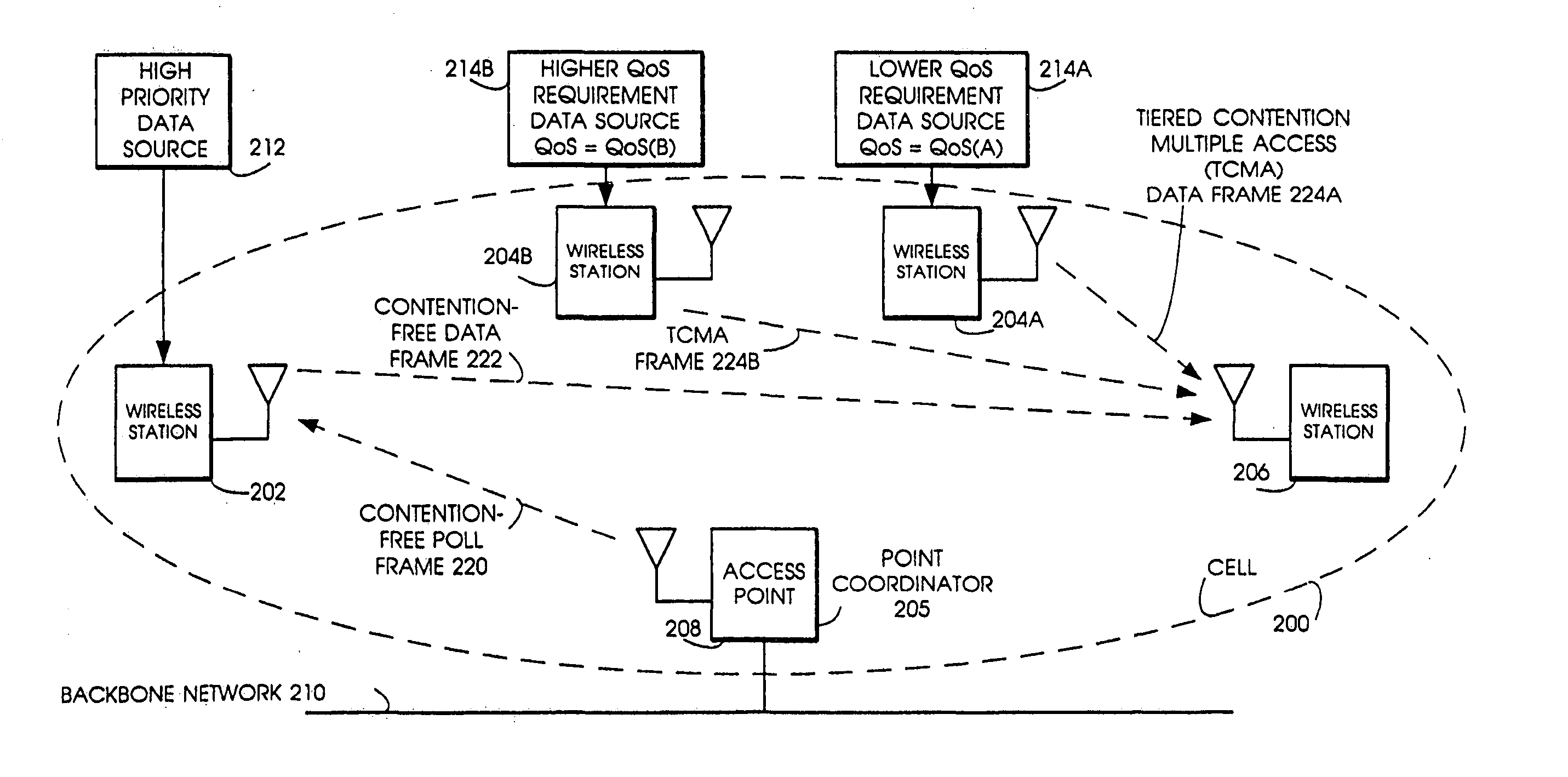
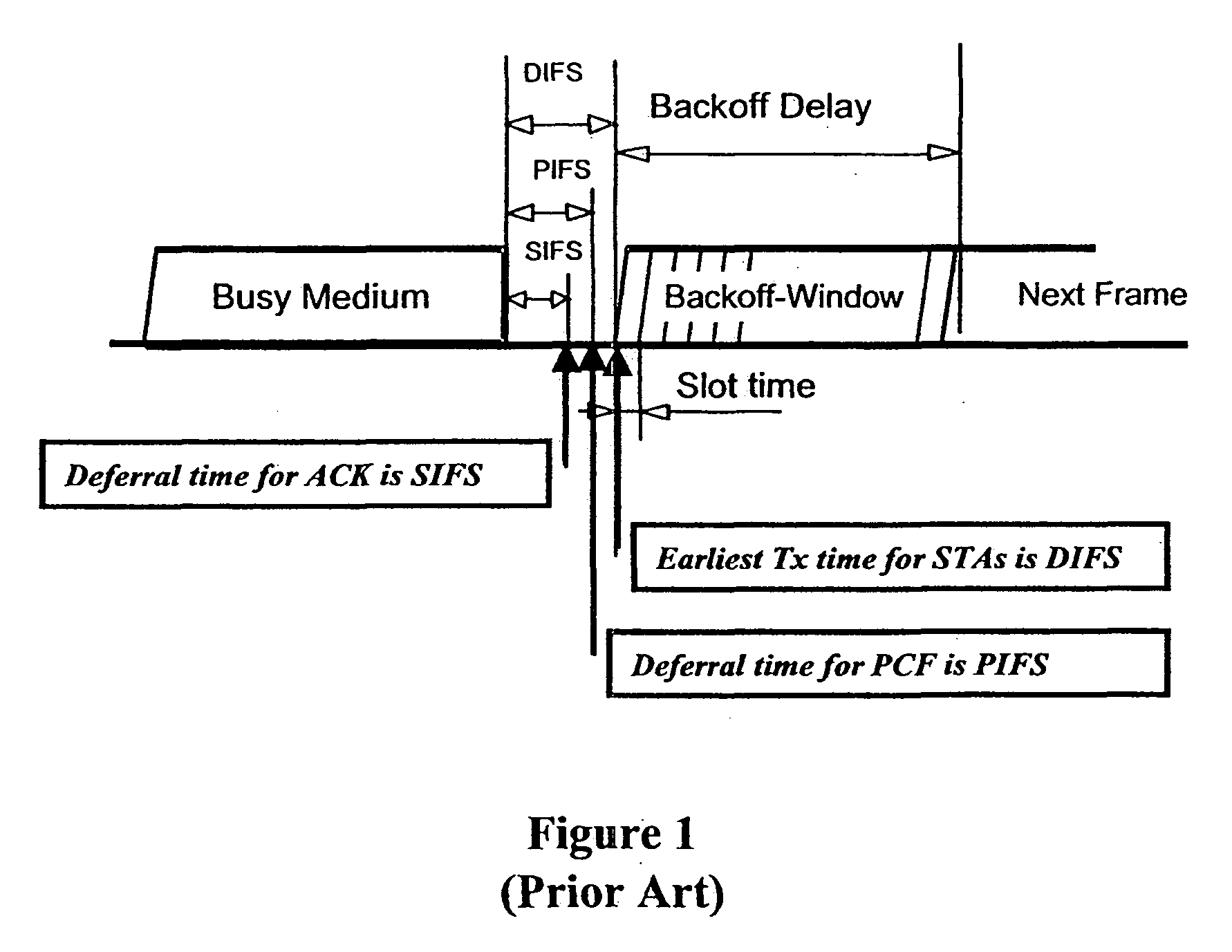
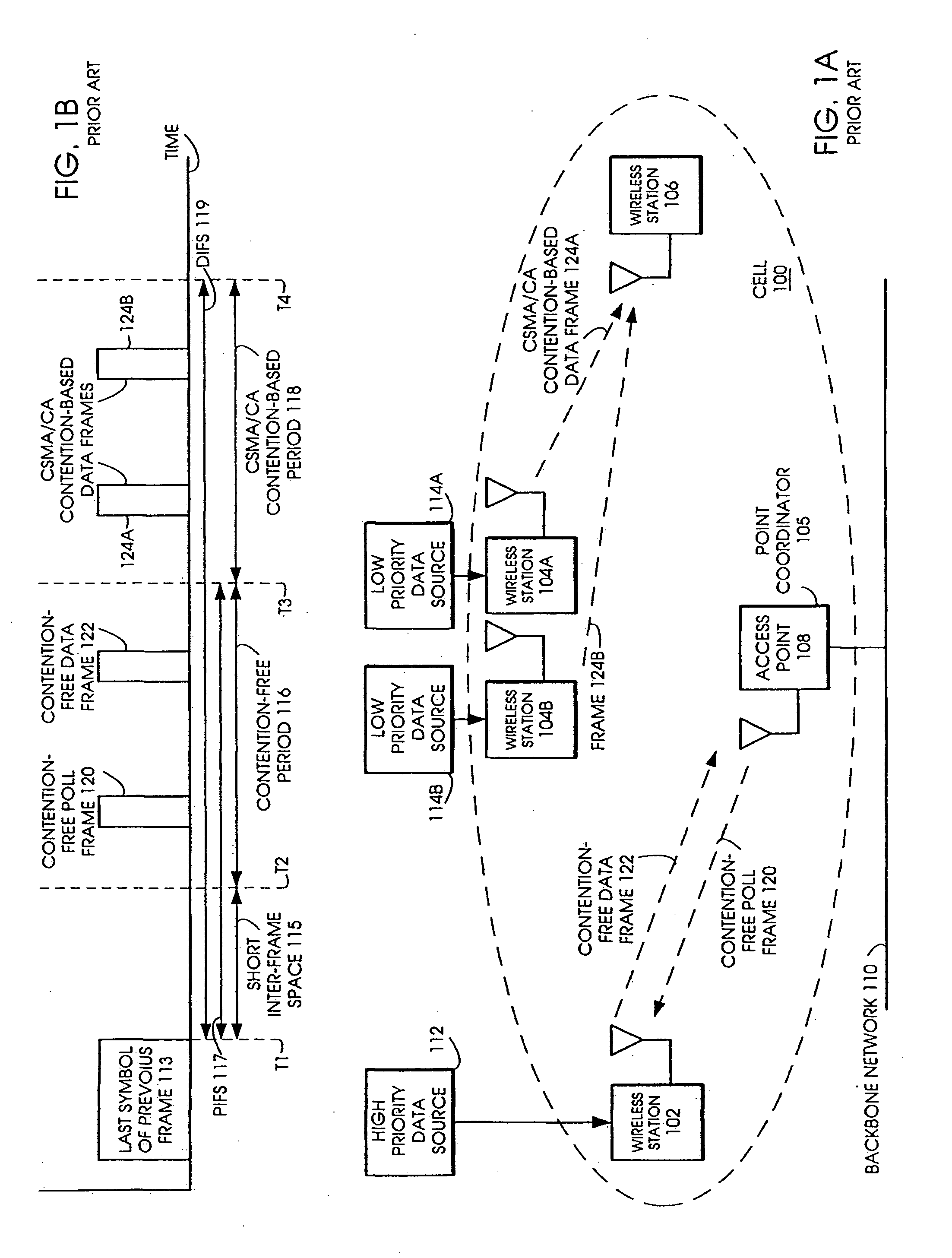
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
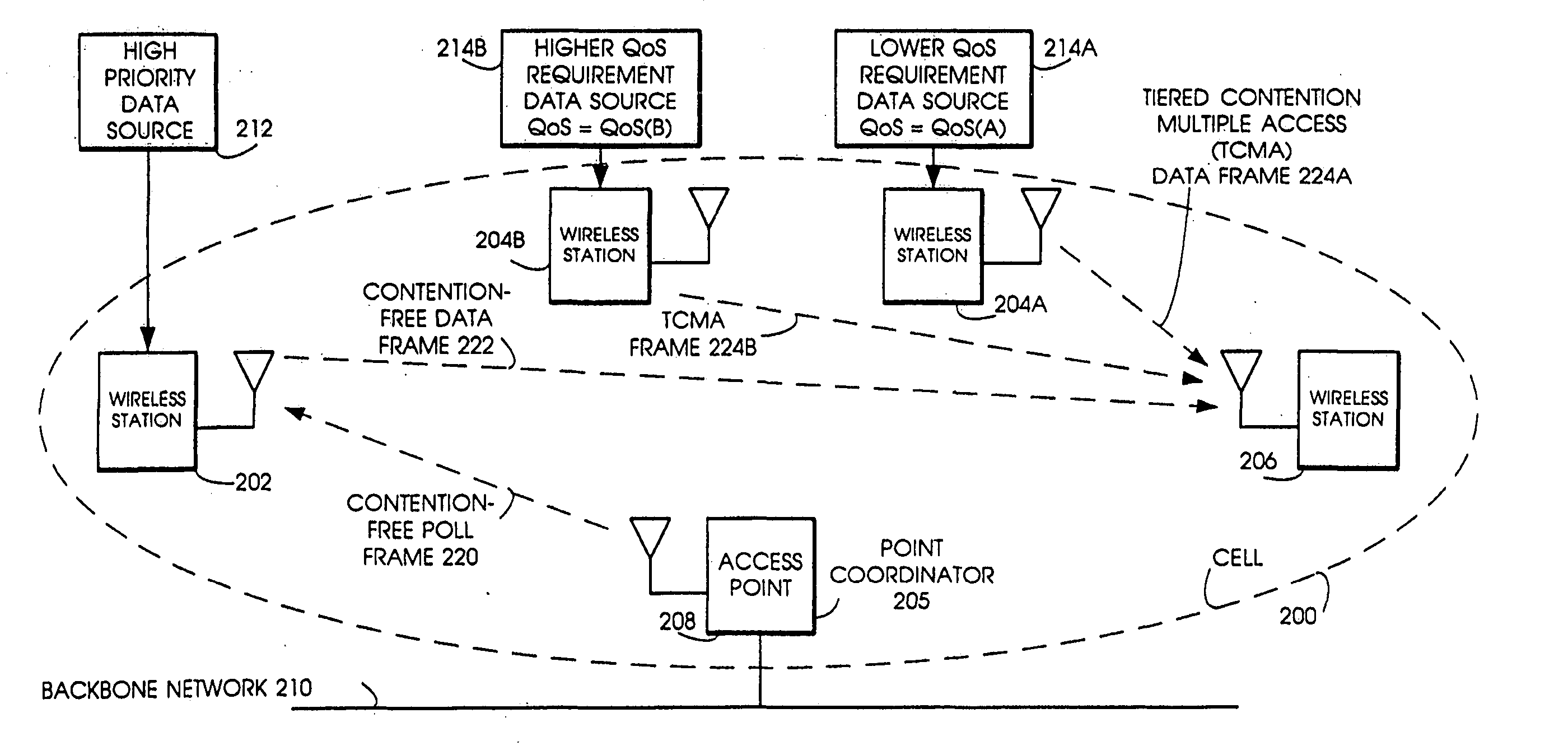
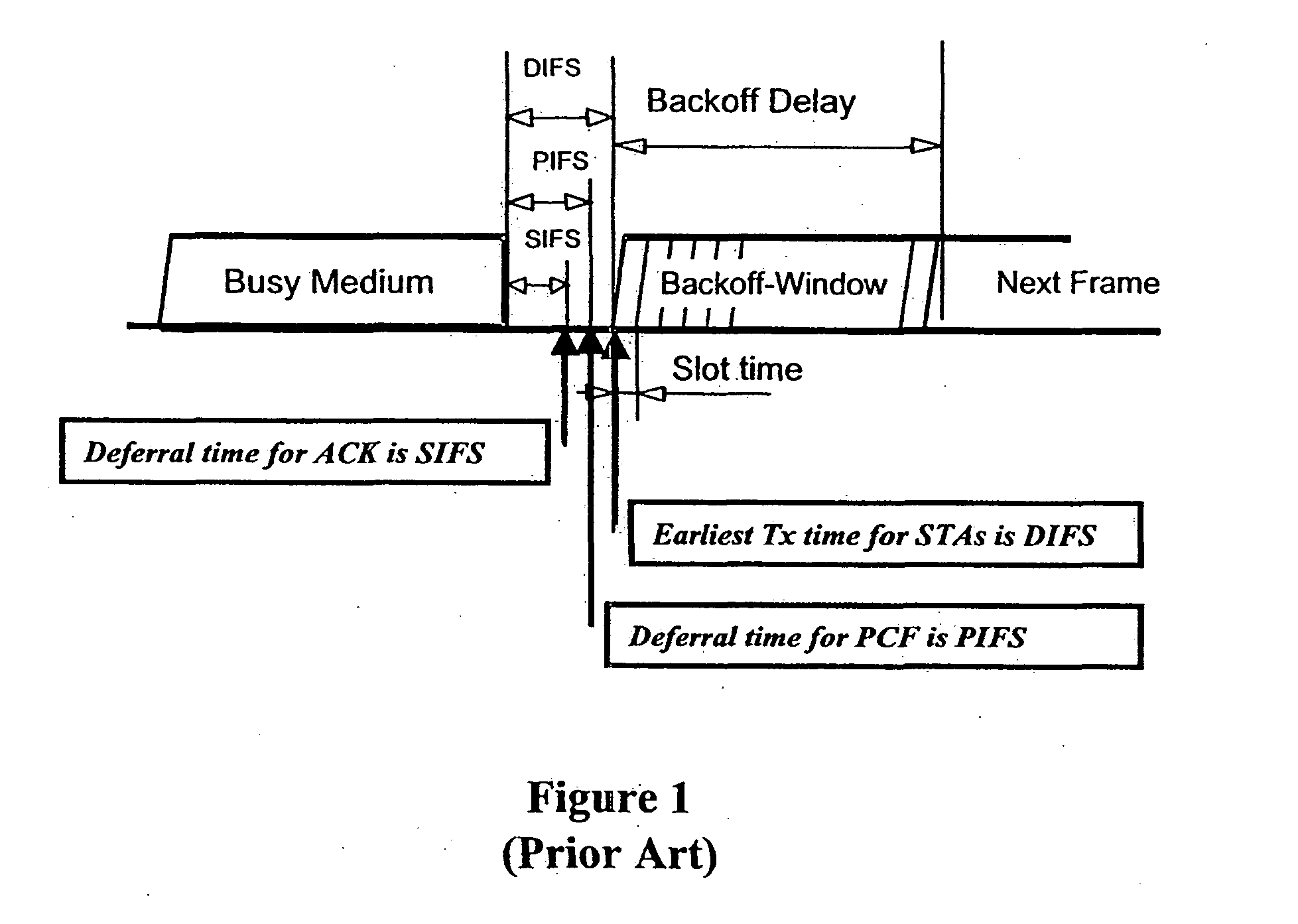
InactiveUS20070019664A1Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementError preventionService-level agreementClass of service
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
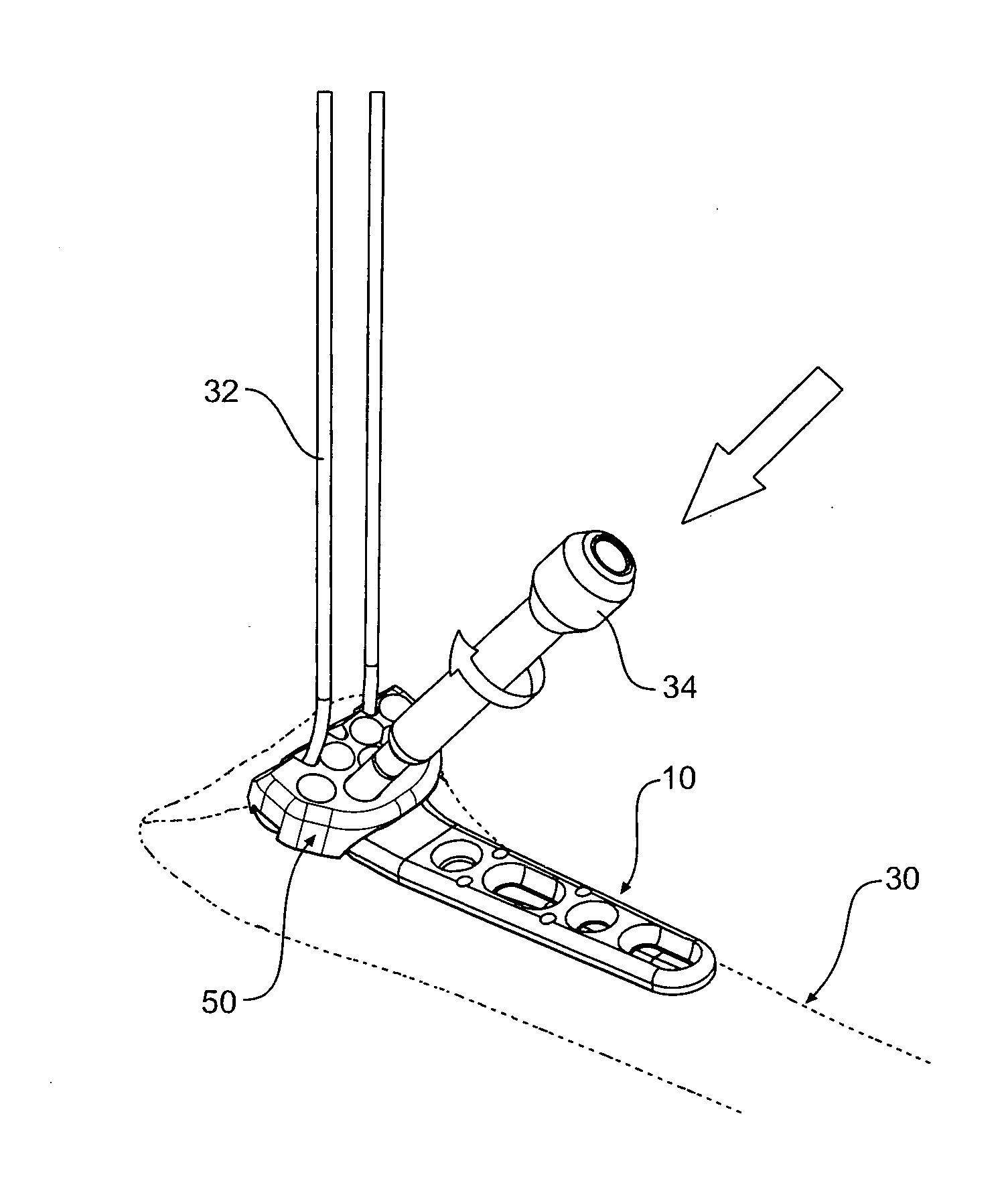
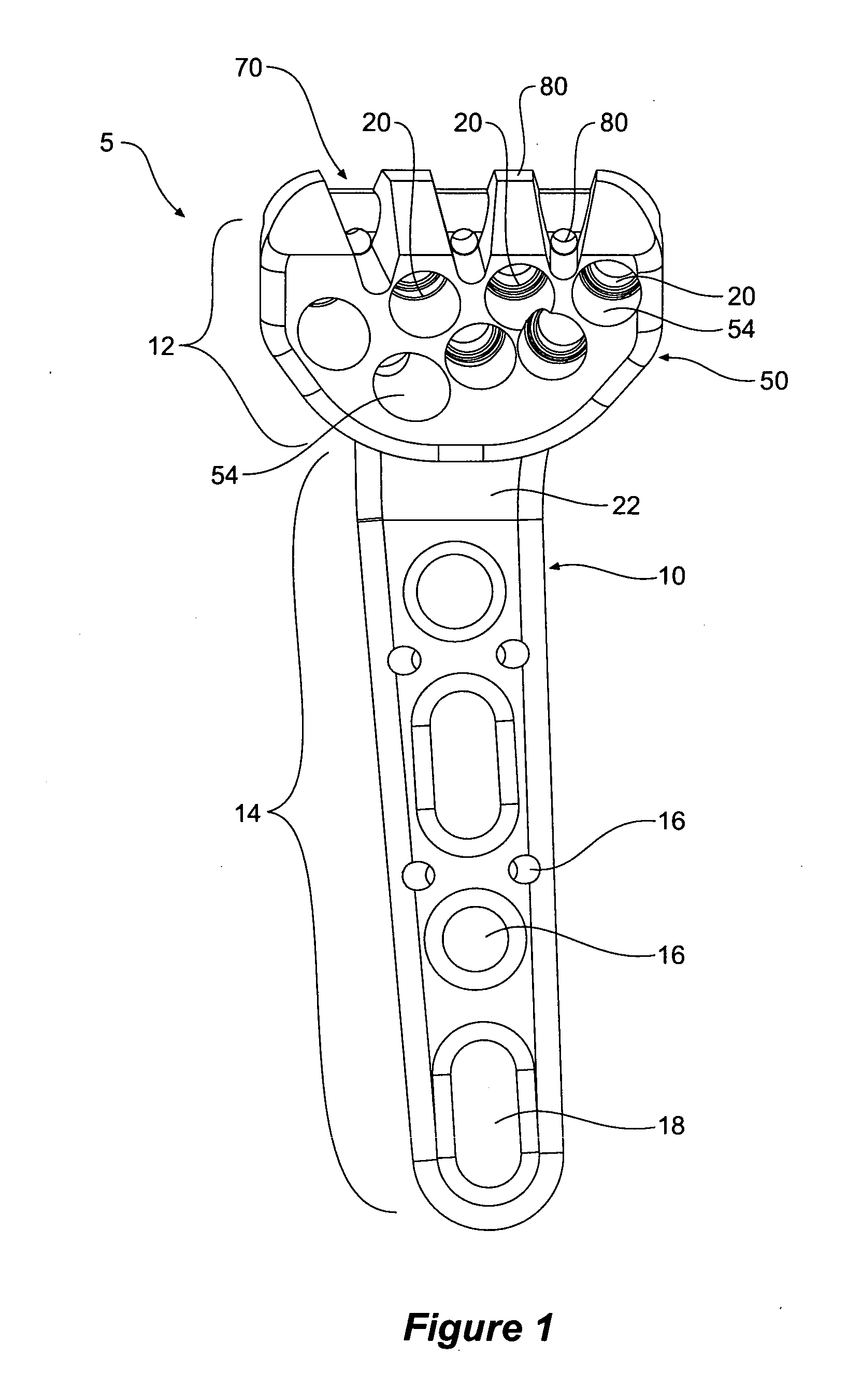
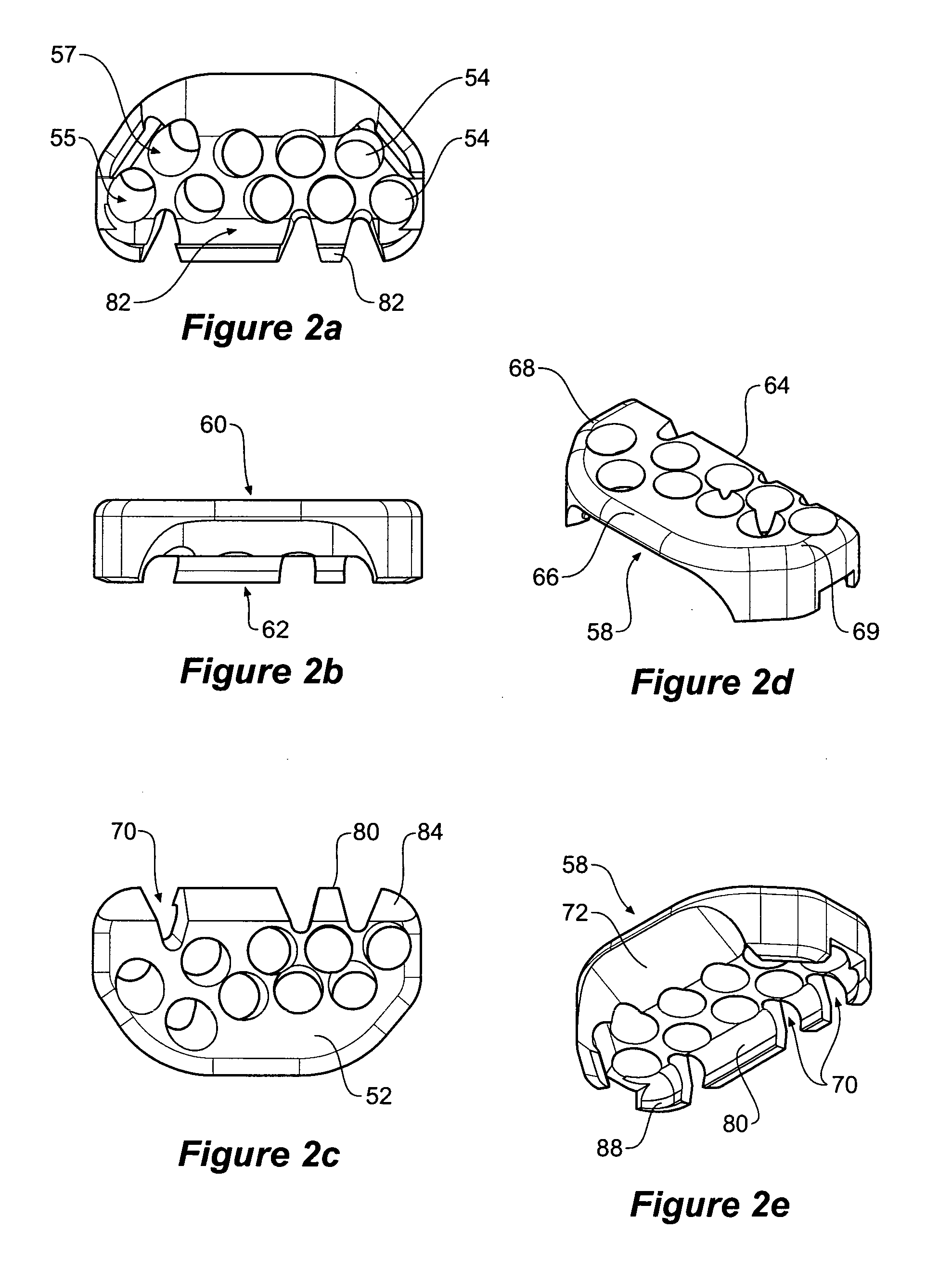
Tool jig for bone implant assembly
InactiveUS20110106086A1Strengthen the relative fixedAids fixation of the boneJoint implantsBone drill guidesBone implantBONES BONE
The invention provides a tool jig (50) for use with a bone plate (10) having one or more fixing element apertures (20), wherein the tool jig (50) guides placement of a drill sleeve (34) to enable the drill sleeve (34) to be attached to a fixing element aperture (20), the tool jig (50) comprising a body (52), a securing means (80) on the body adapted to releasably secure the tool jig (50) to the bone plate (10) such that the tool jig (50) can be firstly secured in position to the bone plate (10) and secondly removed, and one or more tool jig apertures (54) defined in the body (52) wherein an at least one or all tool jig apertures (54) are adapted to be substantially aligned with an at least one or all fixing element apertures (20); wherein, in use, the tool jig aperture (54) guides the drill sleeve (34) so that the longitudinal axis of the drill sleeve (34) substantially aligns with the axis of the fixing element aperture (20) prior to attaching the drill sleeve (34) to the fixing element aperture (20). The invention also provides a medical implant assembly (5) comprising the tool jig (50) and the bone plant (10), a kit comprising the medical implant assembly and at least one drill sleeve (34), and methods of using same.
Owner:AUSTOFIX GRP
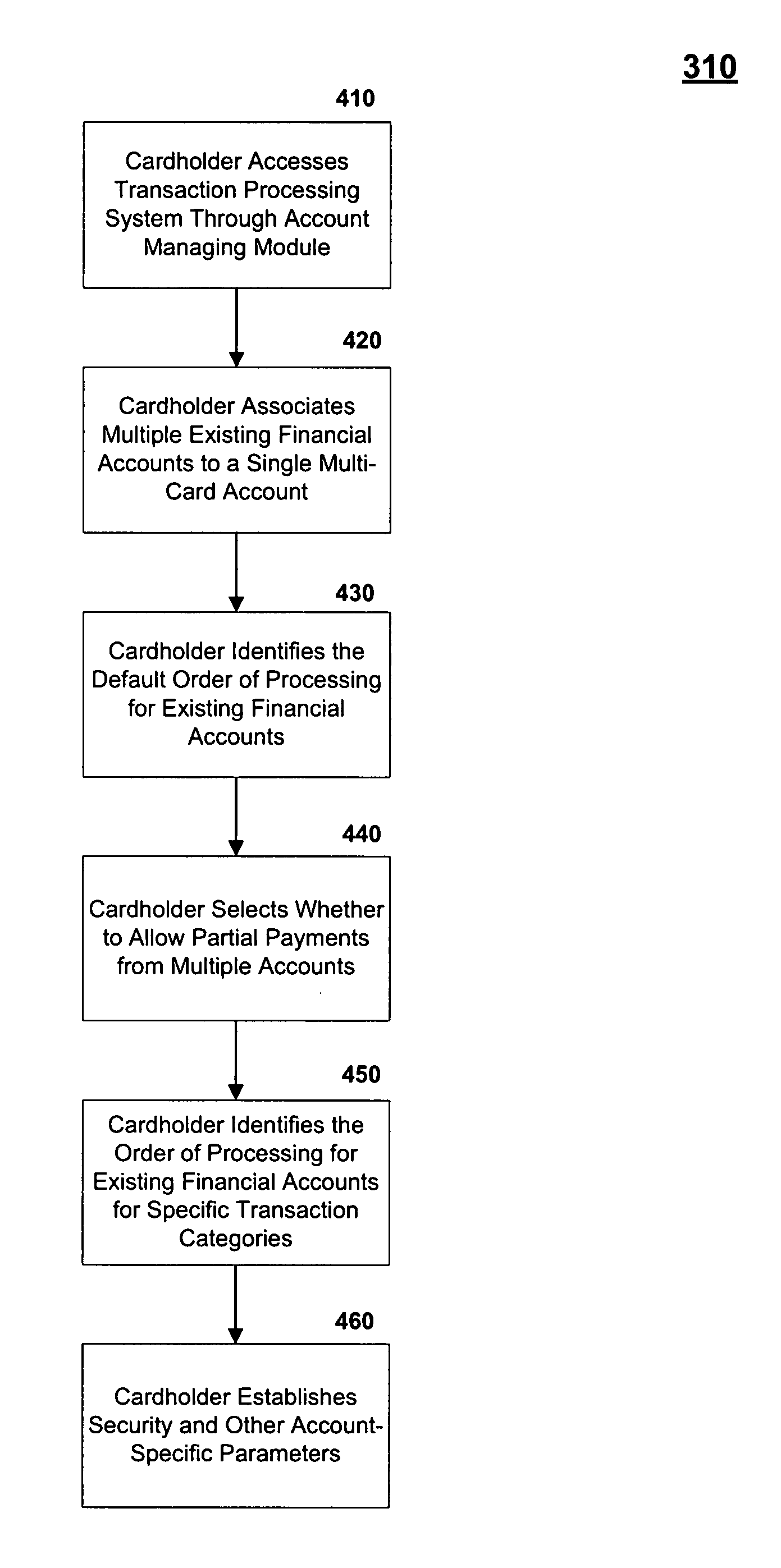
Method and system for processing financial transactions using multiple financial accounts
InactiveUS20080301041A1Minimizing chanceMinimize the numberFinanceCredit schemesFinancial transactionFinancial trading
Associating multiple existing financial accounts with a multi-card account. The single multi-card account may allow a cardholder to determine an order for processing a financial transaction among the multiple financial accounts. This ordering may be dependent on the type of financial transaction. Also, the cardholder may allows partial payments from multiple financial accounts, such that a single purchase could be allocated to multiple accounts associated with the multi-card account. These systems and methods minimize the number of cards a cardholder must carry, thus minimizing the chance of losing cards or otherwise having an unauthorized use of an account and also minimizing the chance of an embarrassing rejection of a transaction.
Owner:BRUK MARK EDWARD
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
InactiveUS20070041398A1Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementService-level agreementTraffic capacity
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Controllable sealed chamber for surveillance camera
InactiveUS20020140848A1Easy to deployMinimizing chanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensDisplay device
A chamber for a surveillance camera that is designed to be mounted inside a larger camera housing. The chamber is sealed and provides a controlled internal environment for sensitive camera optics and internal electronics. A flush mount window is provided for the front lens of the camera, and a sealed feed-through electronic connector is provided for attachment to external controls. Valves for both adding and removing gasses to / from the chamber are provided. In one embodiment, temperature, pressure and / or humidity sensors may be deployed inside the chamber and connected electronically to a display or computer for monitoring and adjustment. In another embodiment of, a heating element is provided to evaporate moisture from the camera lens and / or from the window, and to help control the temperature inside the chamber.
Owner:PELCO INC
Interlaminar Stabilizing System
ActiveUS20110106163A1Intervertebral space is reducedReduce spacingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsVertebraEngineering
A spinal stabilization system includes a first engagement member and a support structure. The first engagement member is adapted to be disposed between a first vertebra and a second vertebra. The engagement member generally includes a seating surface for accommodating at least a portion of a laminar region of the first vertebra. The support structure engages a portion of the second vertebra. The structural cooperation of the first engagement member and the support structure is such that the engagement member restricts reduction of the intervertebral spacing between the first and second vertebrae.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com