Patents
Literature
84 results about "Tissue heating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
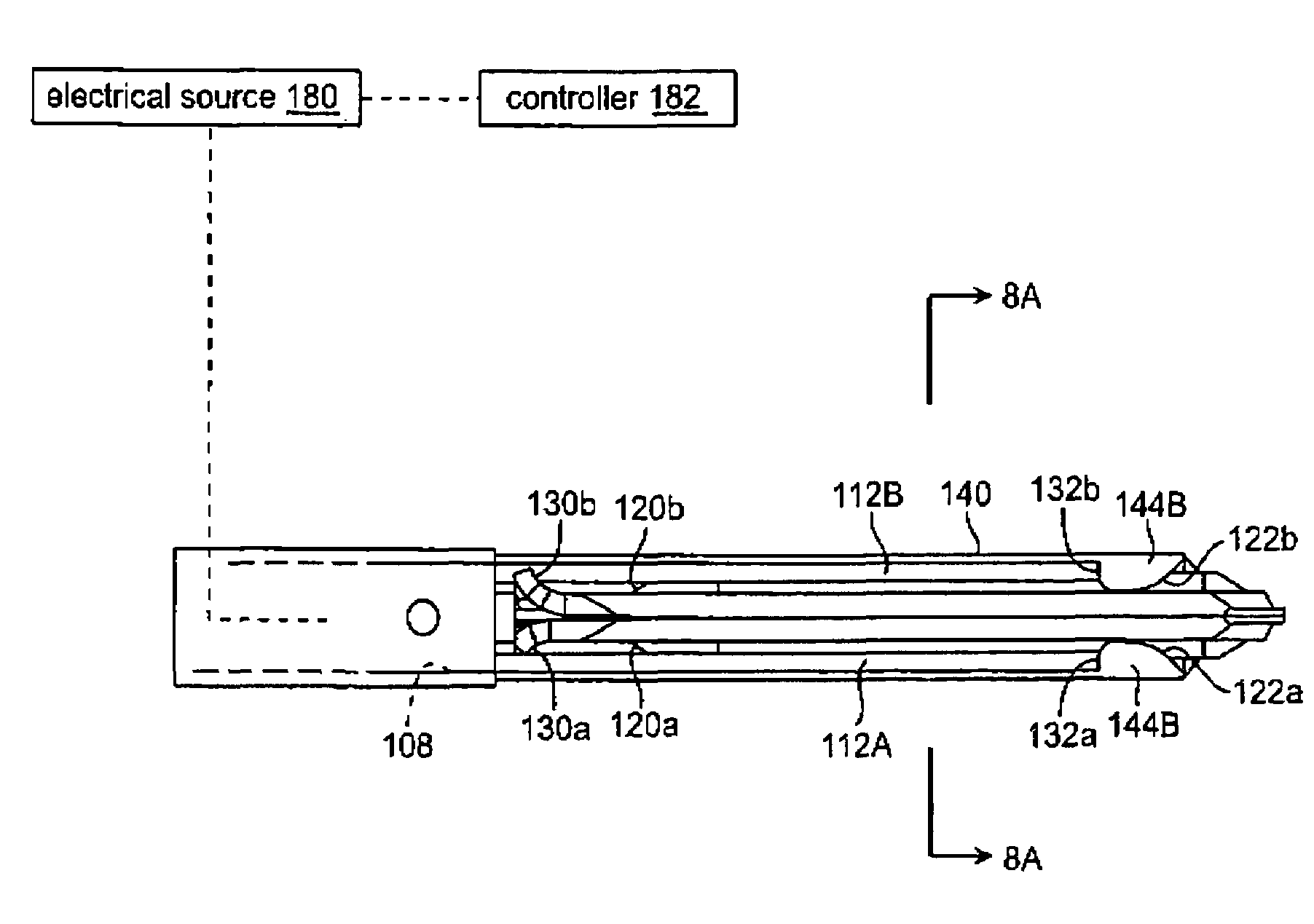
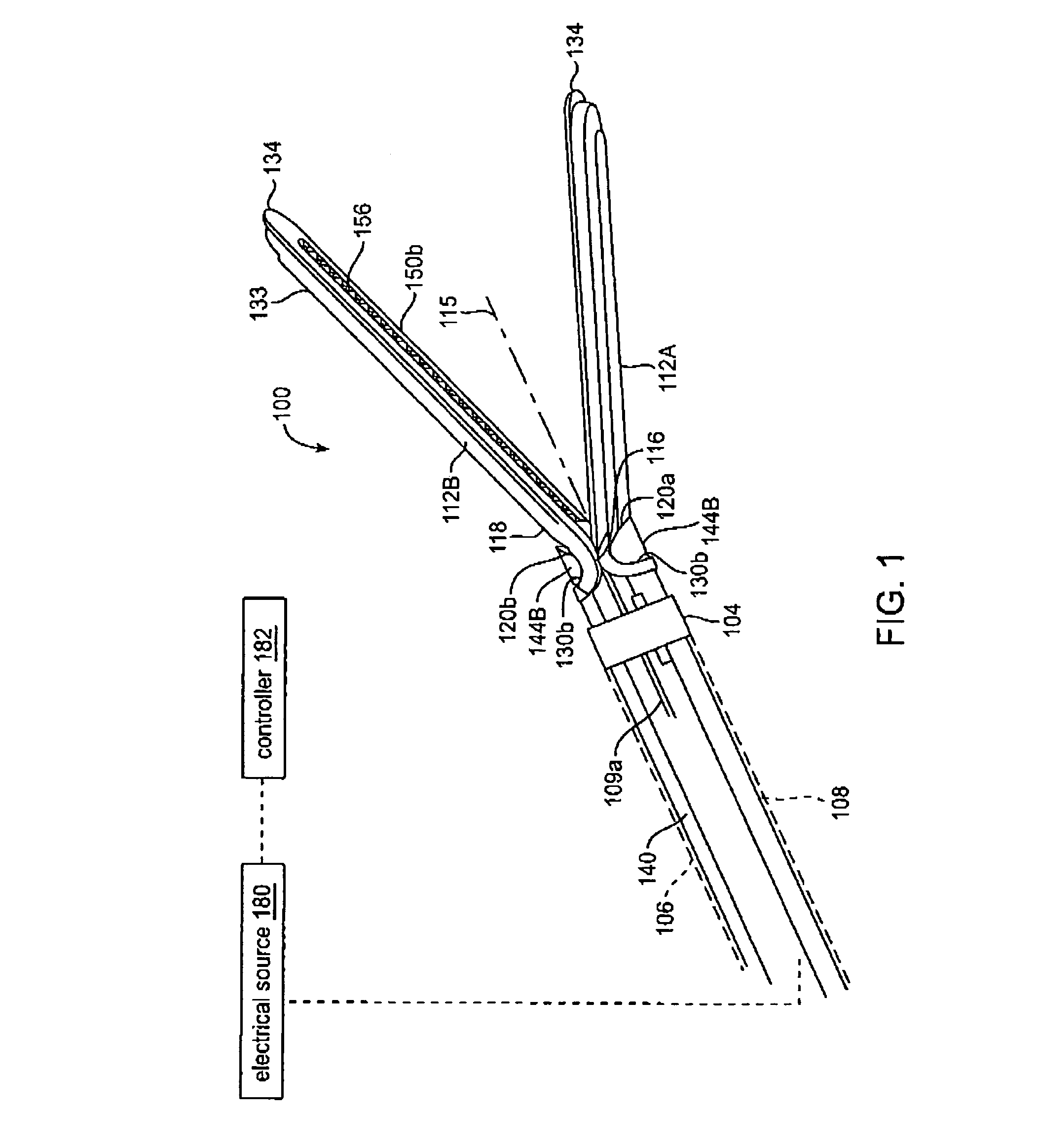
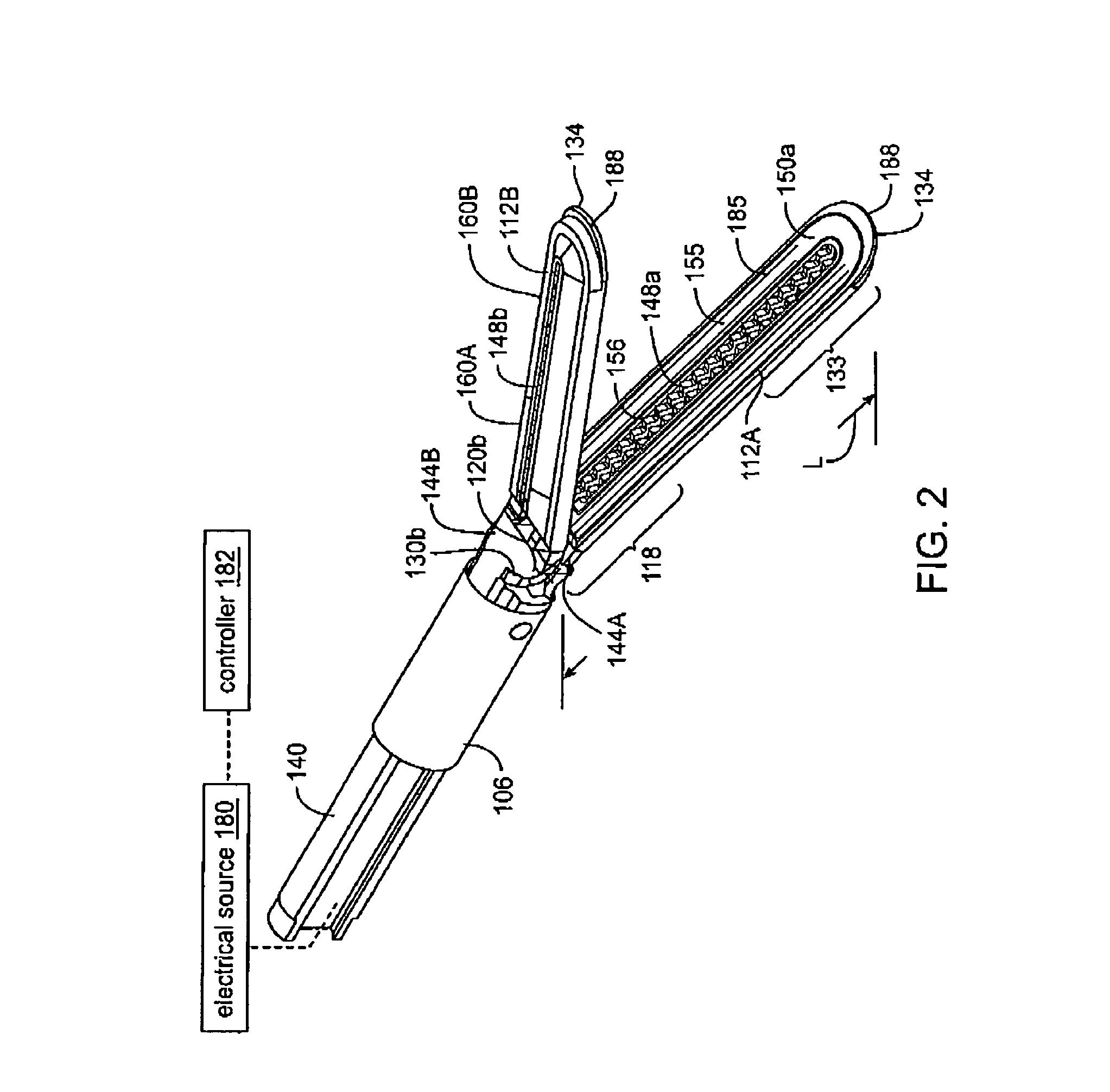
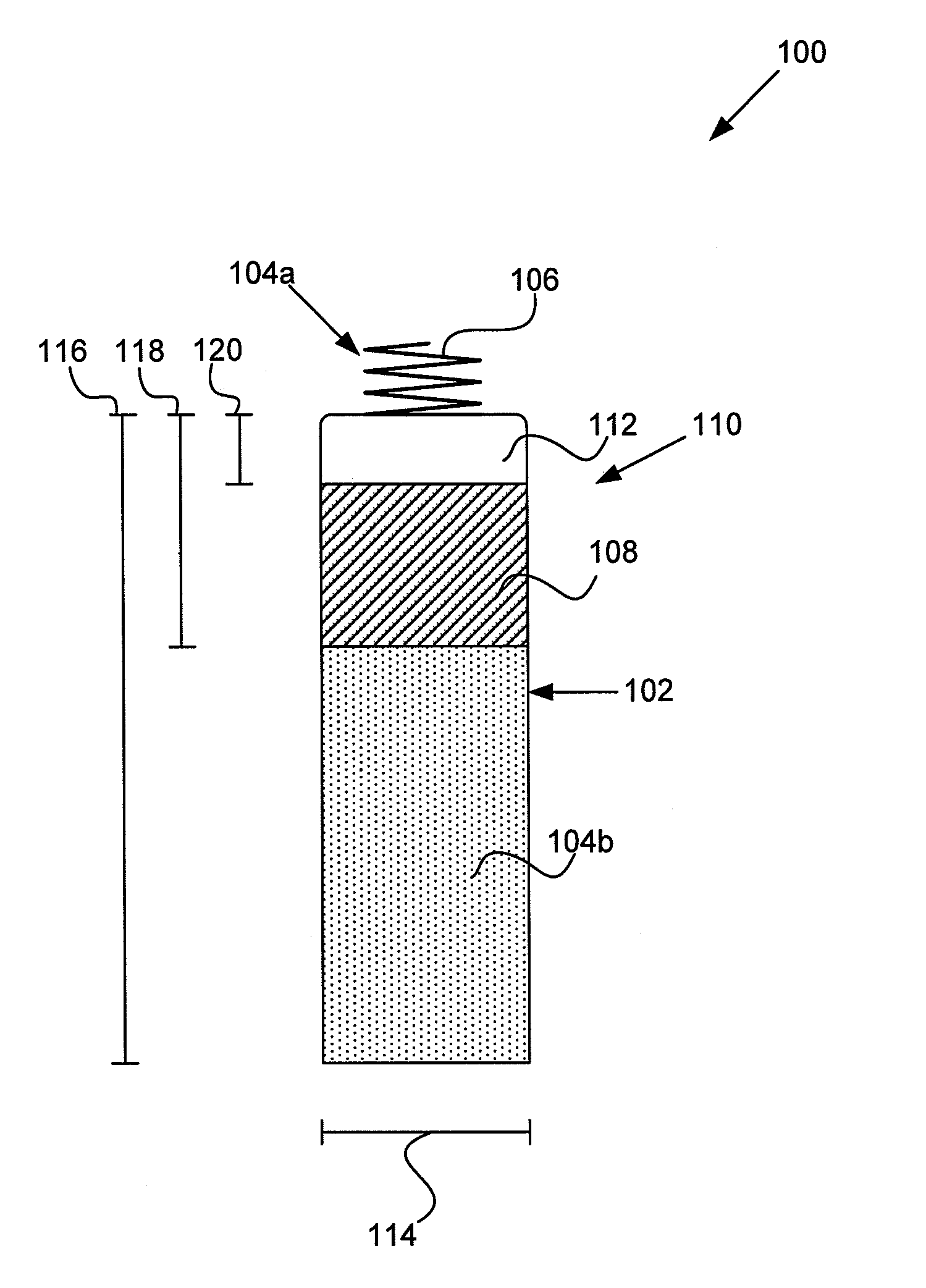
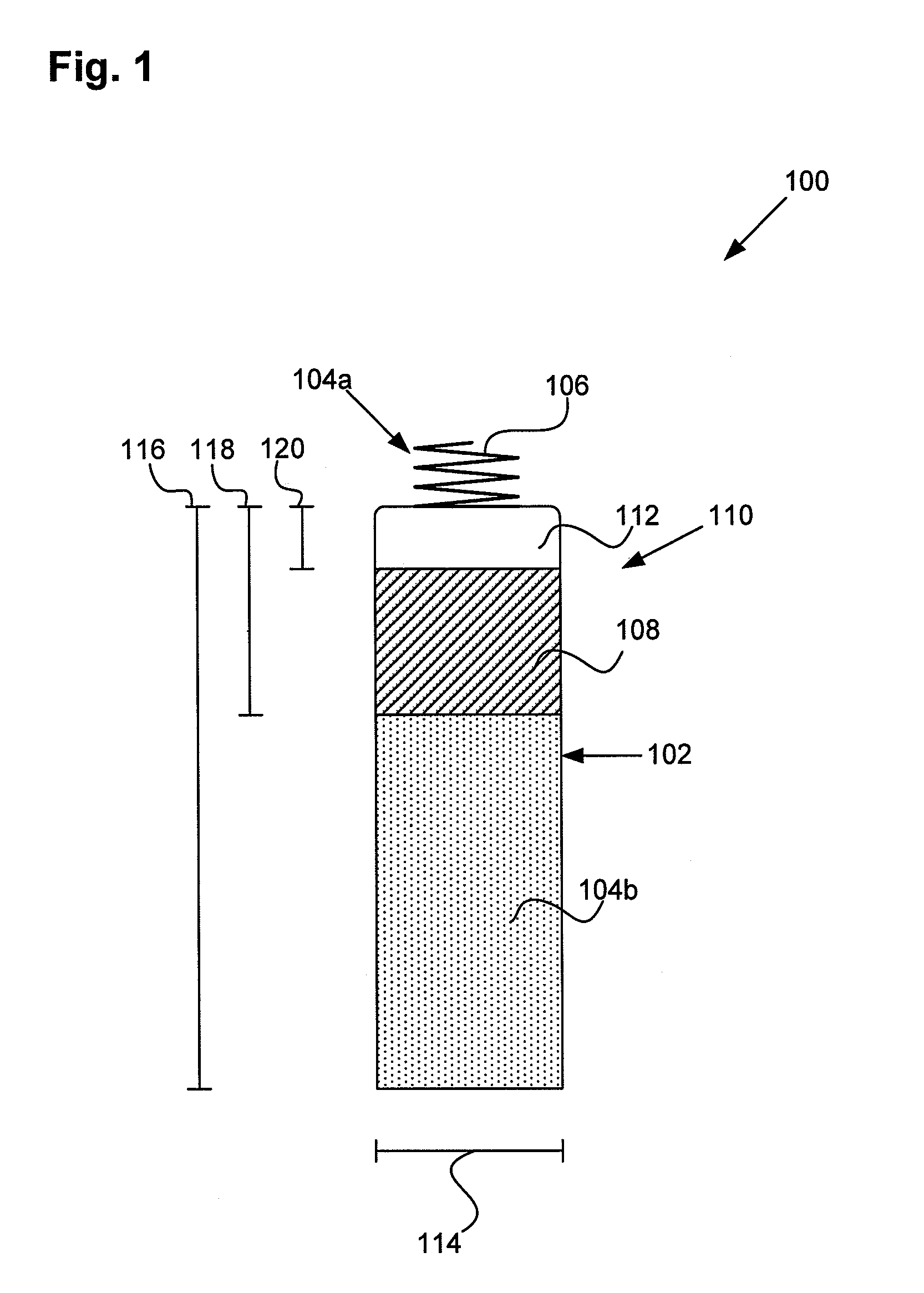
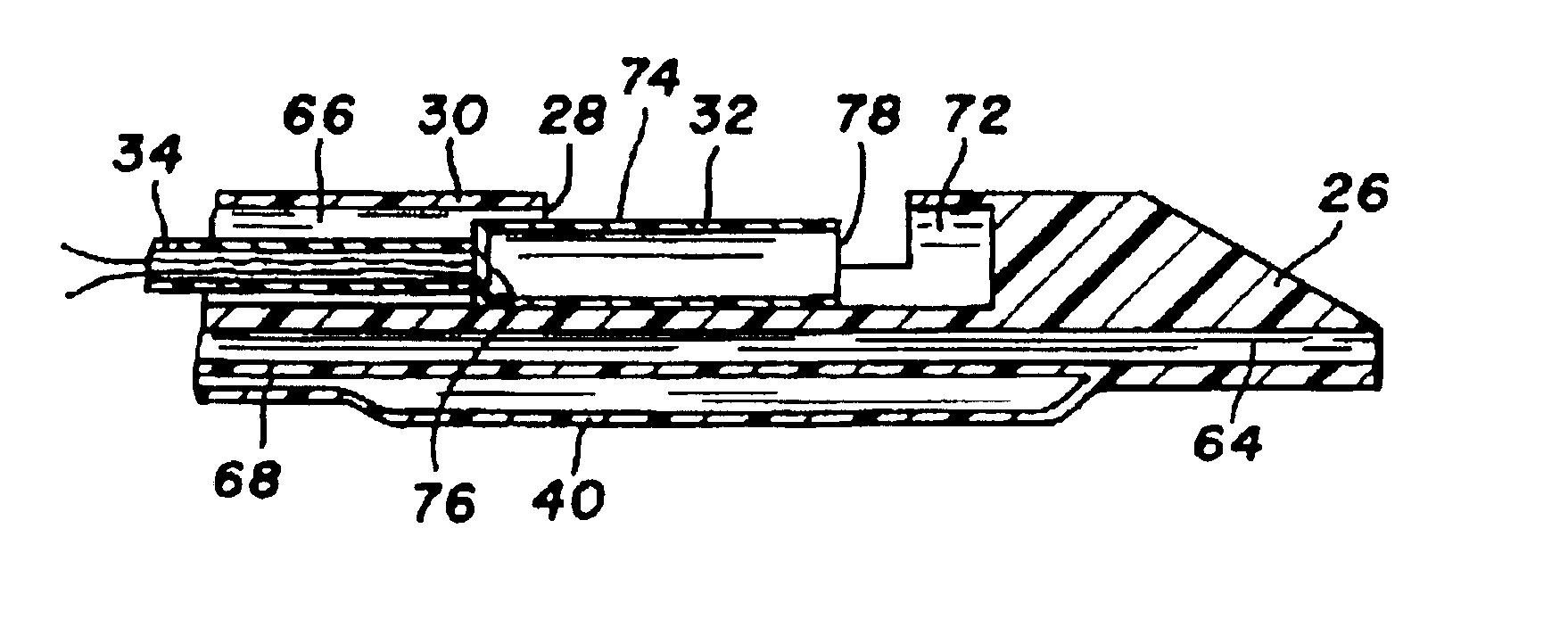
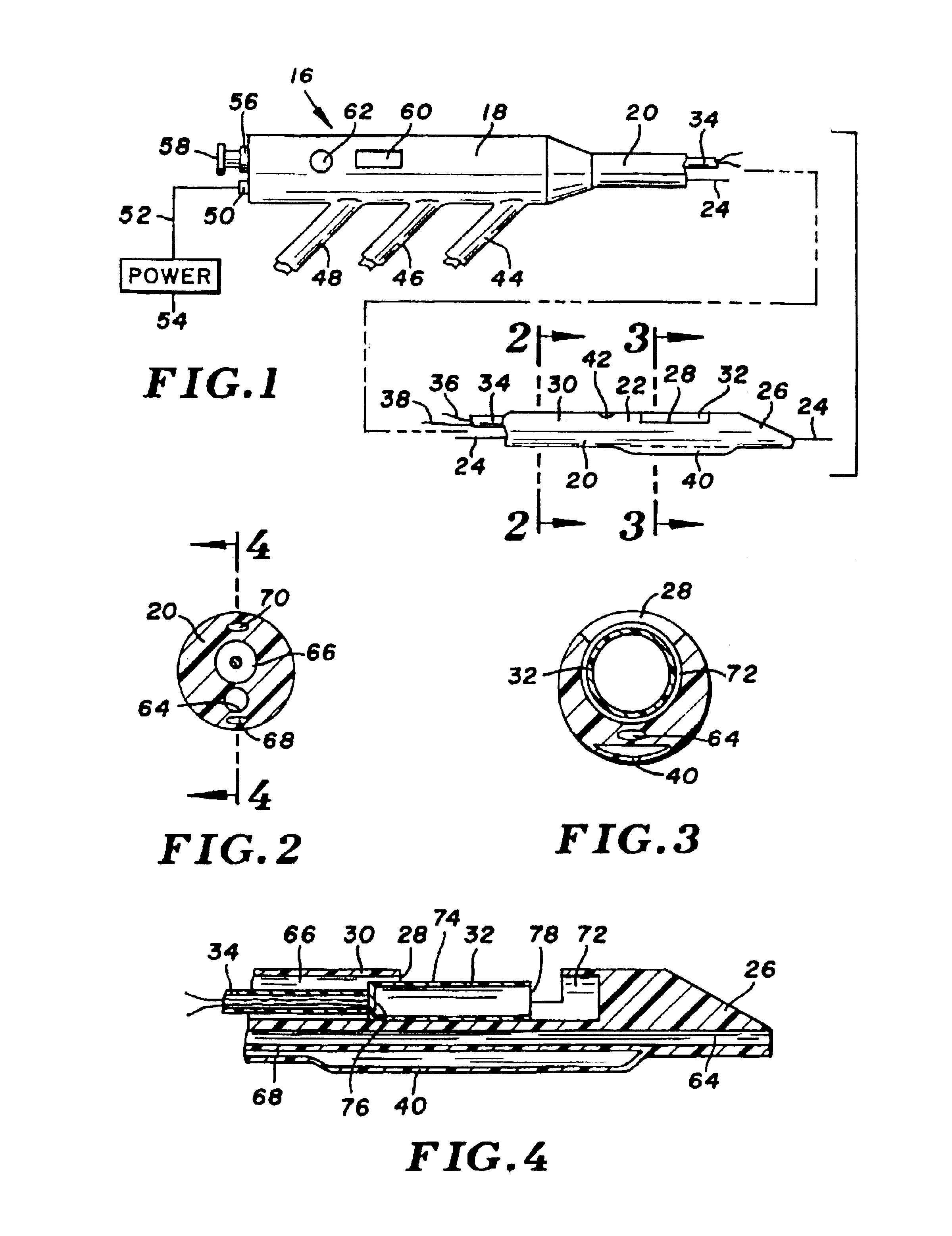
Jaw structure for electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7011657B2Improve the immunityEfficient weldingElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical medical device and technique for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue that provides very high compressive forces. In one exemplary embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying first and second surface portions that comprise (i) an electrically conductive material and (ii) a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material having a selected increased resistance that differs at each selected increased temperature over a targeted treatment range. One type of PTC material is a doped ceramic that can be engineered to exhibit a selected positively sloped temperature-resistance curve over about 37° C. to 100° C. The 70° C. to 100° C. range can bracket a targeted “thermal treatment range” at which tissue welded can be accomplished. The engineered resistance of the PTC matrix at the upper end of the temperature range will terminate current flow through the matrix. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane cause ohmic heating within tissue from Rf energy delivery tissue PTC matrix is heated to exceed the treatment range. Thereafter, energy density in the engaged tissue will be modulated as the conductivity of the second portion hovers within the targeted treatment range to thereby provide optical tissue heating for purposes of tissue welding.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
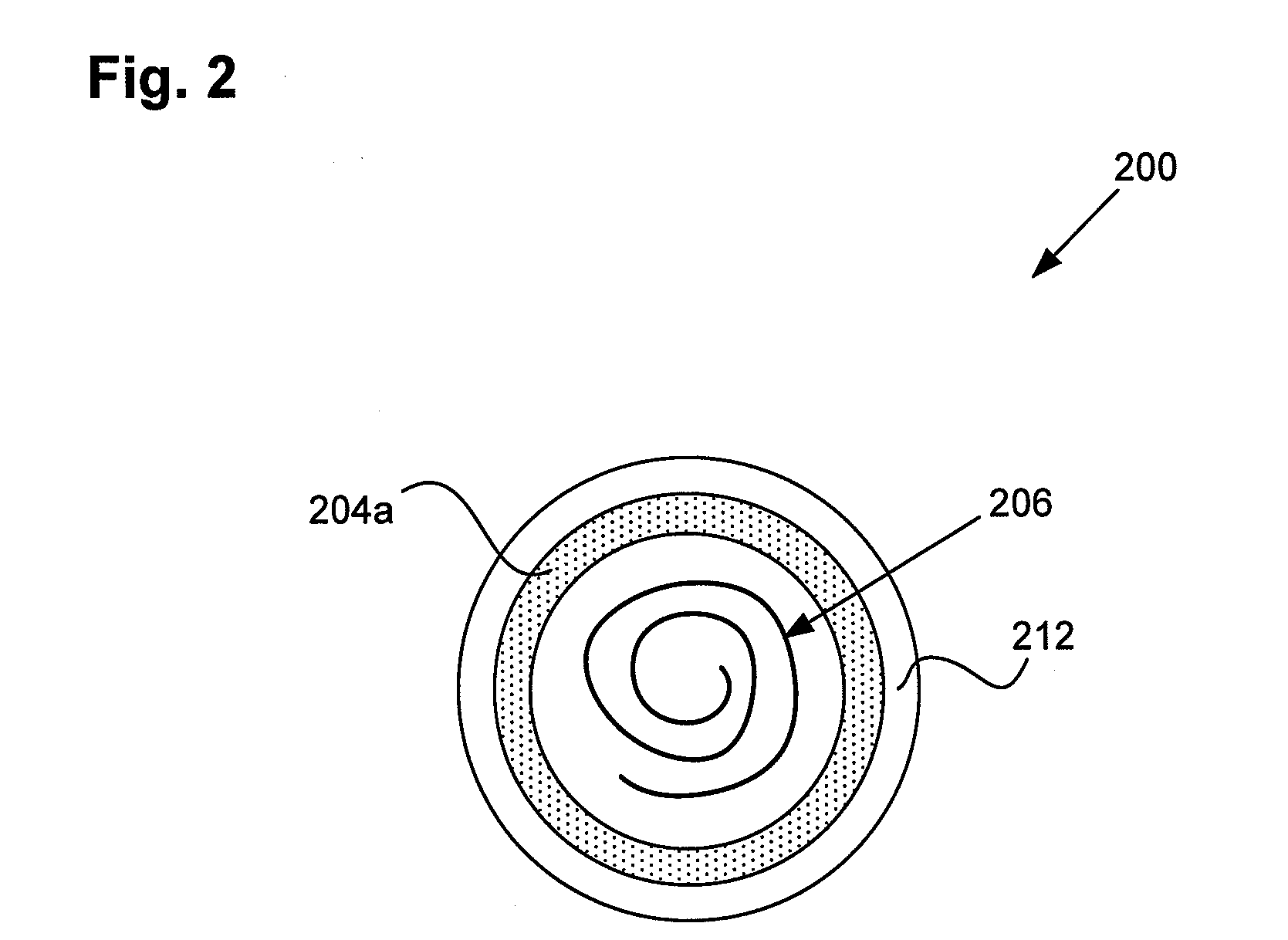
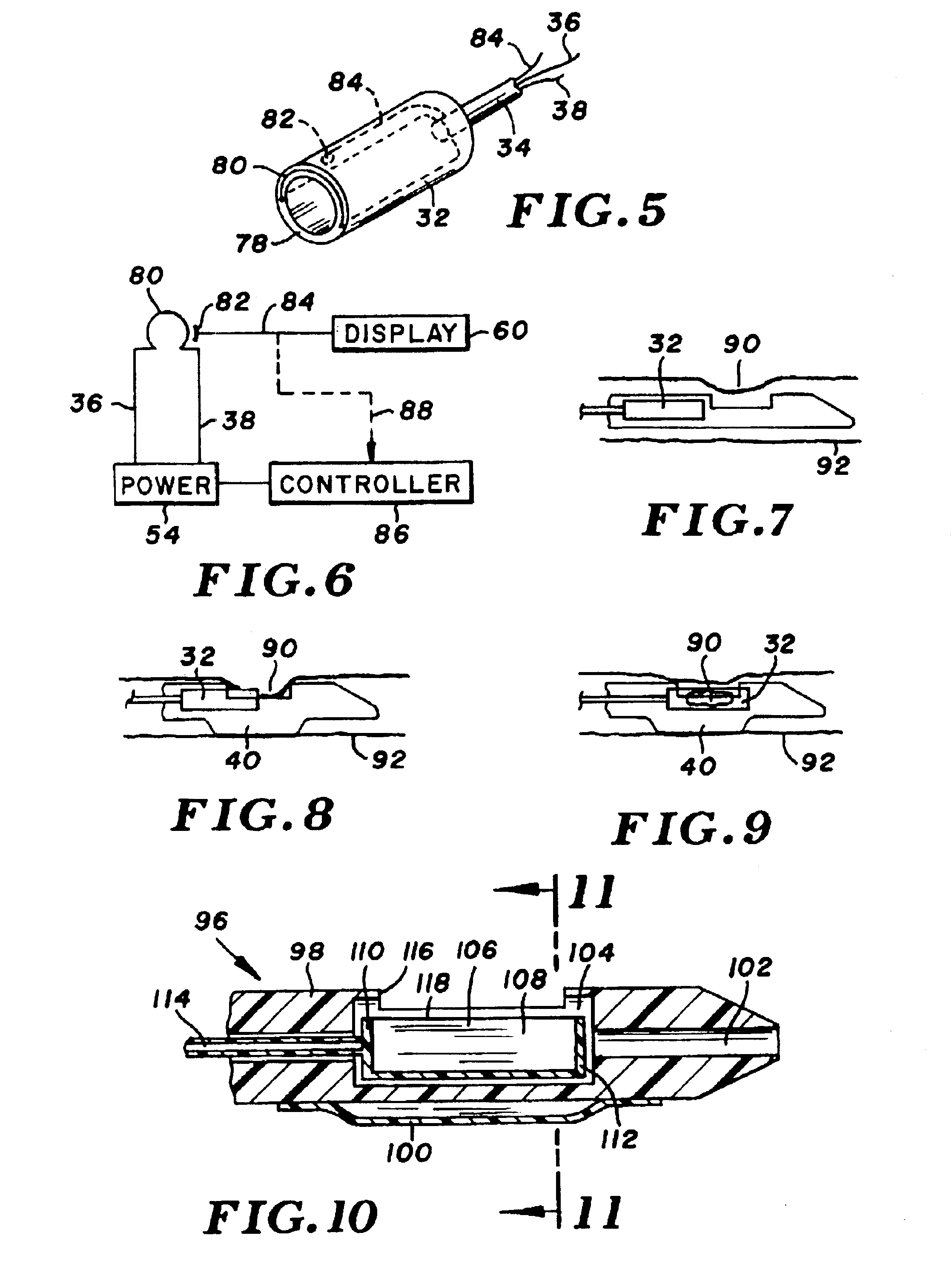
Electrothermal instrument for sealing and joining or cutting tissue
InactiveUS6860880B2Promote sticking togetherReduce lossesSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsField conditionsTissue heating
An instrument and method are provided for sealing and joining or hemostatically dividing tissue, which is particularly suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery. The instrument makes use of the controlled application of a combination of heat and pressure to seal adjacent tissues, to join adjacent tissues, or to anastomose tissues, whereby tissue is heated for an optimal time and at an optimal temperature under optimal pressure to maximize tissue seal strength while minimizing collateral tissue damage. The instrument of the present invention is lightweight and therefore portable, and is particularly useful in field conditions where a source of external power may not be readily available.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Electrothermal device for coagulating, sealing and cutting tissue during surgery
InactiveUS6908463B2Promote sticking togetherMinimal lossSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsTissue heatingField conditions
An instrument and method are provided for sealing and joining or hemostatically dividing tissue, which is particularly suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery. The instrument makes use of the controlled application of a combination of heat and pressure to seal adjacent tissues, to join adjacent tissues, or to anastomose tissues, whereby tissue is heated for an optimal time and at an optimal temperature under optimal pressure to maximize tissue seal strength while minimizing collateral tissue damage. The instrument of the present invention is lightweight and therefore portable, and is particularly useful in field conditions where a source of external power may not be readily available.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
MRI Compatible Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker
InactiveUS20110077708A1Maintain safe operationEpicardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowPath length
An implantable battery powered leadless pacemaker or biostimulator is provided that may include any of a number of features. One feature of the biostimulator is that it safely operates under a wide range of MRI conditions. One feature of the biostimulator is that it has a total volume small enough to avoid excessive image artifacts during a MRI procedure. Another feature of the biostimulator is that it has reduced path lengths between electrodes to minimize tissue heating at the site of the biostimulator. Yet another feature of the biostimulator is that a current loop area within the biostimulator is small enough to reduce an induced current and voltage in the biostimulator during MRI procedures. Methods associated with use of the biostimulator are also covered.
Owner:NANOSTIM
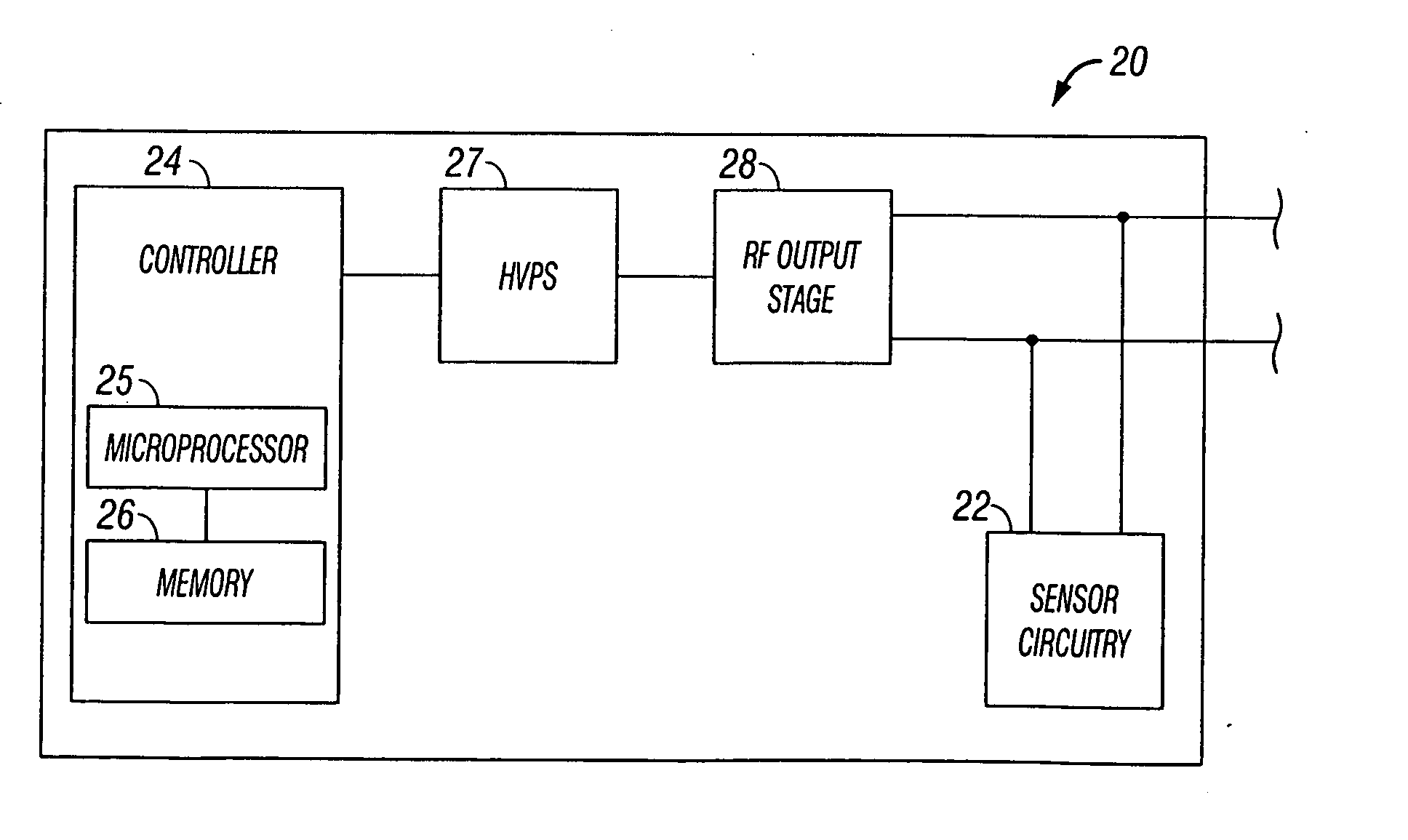
System and method for controlling tissue heating rate prior to cellular vaporization
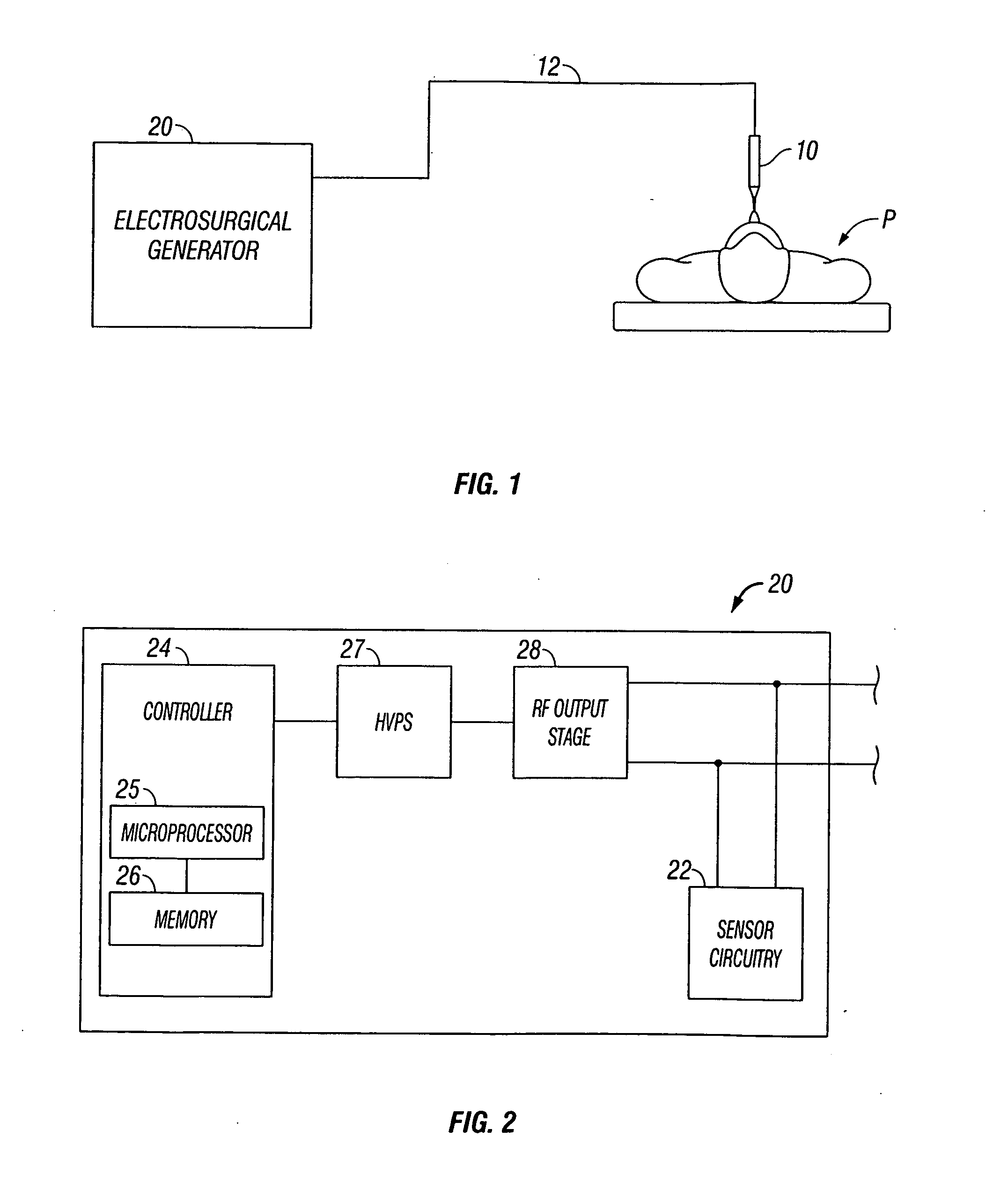
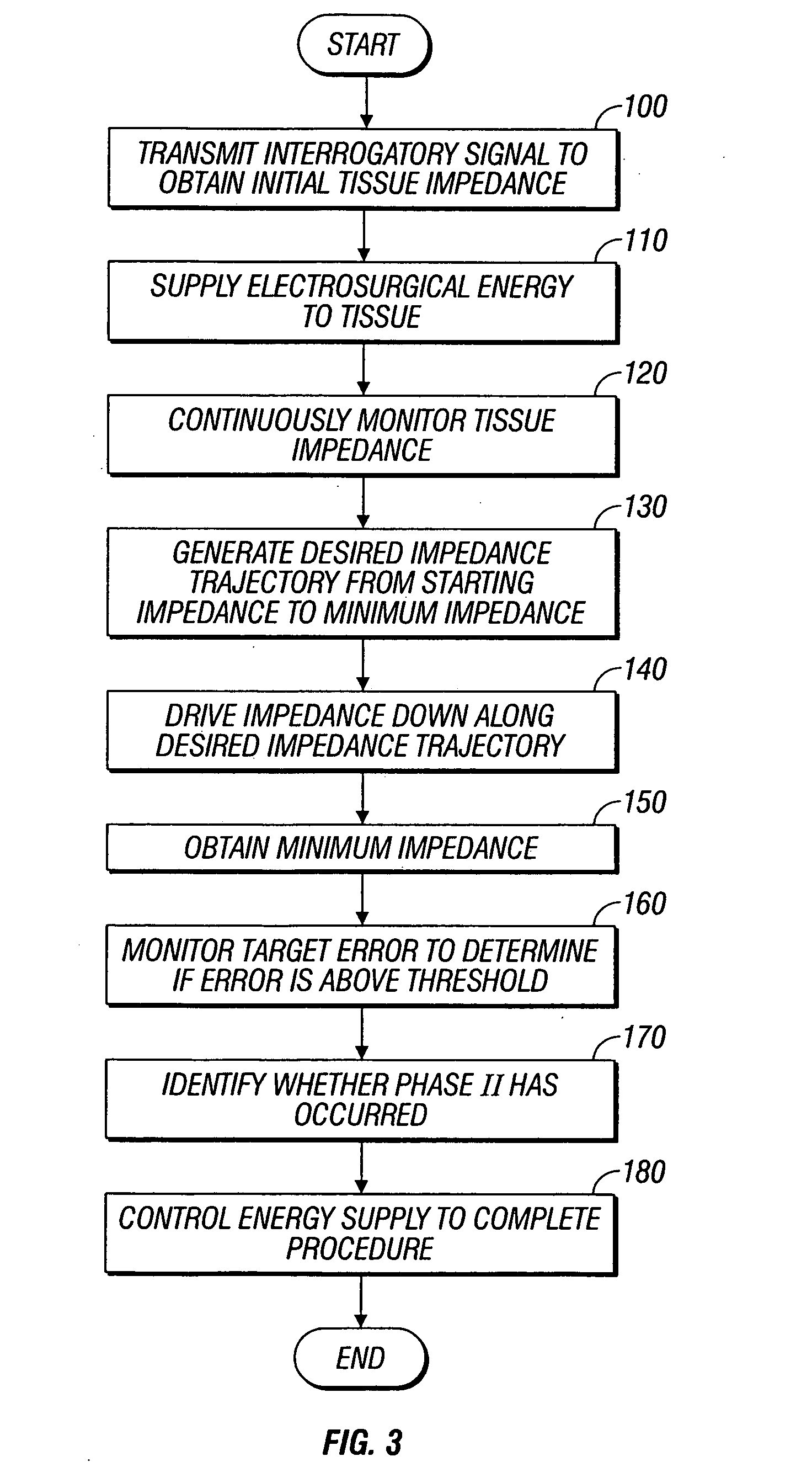
InactiveUS20070282320A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for coolingElectricityTissue heating
A system and method for performing electrosurgical procedures are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator adapted to supply energy at an output level to tissue and to transmit an interrogatory signal to obtain initial tissue impedance to derive a starting impedance value. The electrosurgical generator includes a microprocessor adapted to generate a desired impedance trajectory as a function of either of the initial tissue impedance or the starting impedance value. The desired impedance trajectory includes a plurality of target impedance values. The electrosurgical generator is further adapted to drive tissue impedance along the desired impedance trajectory by adjusting the output level to match tissue impedance to a corresponding target impedance value. The system also includes an electrosurgical instrument including at least one active electrode adapted to apply electrosurgical energy to tissue.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Method and device for fat treatment
InactiveUS20110112520A1Good electrode couplingEvenly distributedElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingVoltage pulseTissue heating
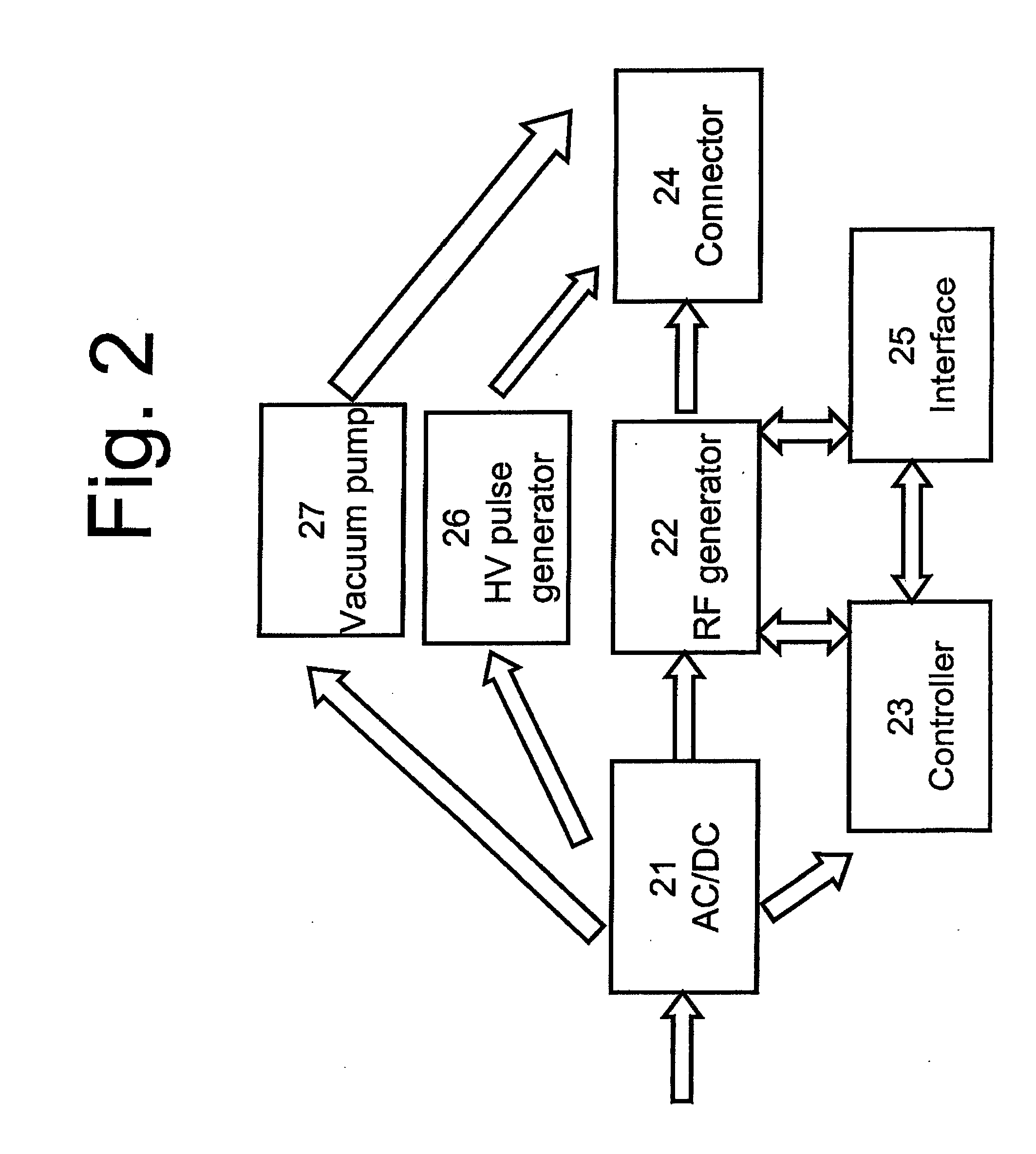
A method and apparatus for fat destruction and body contouring. The method comprises pre-heating treated tissue and applying a high voltage pulse to destroy adipose tissue. The device includes an energy source for tissue heating and an HV pulse generator for applying voltage pulsed in the range of 200V to 5 kV.
Owner:INVASIX
MRI Compatible Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker
InactiveUS20130274847A1Maintain safe operationEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesTissue heatingPath length
An implantable battery powered leadless pacemaker or biostimulator is provided that may include any of a number of features. One feature of the biostimulator is that it safely operates under a wide range of MRI conditions. One feature of the biostimulator is that it has a total volume small enough to avoid excessive image artifacts during a MRI procedure. Another feature of the biostimulator is that it has reduced path lengths between electrodes to minimize tissue heating at the site of the biostimulator. Yet another feature of the biostimulator is that a current loop area within the biostimulator is small enough to reduce an induced current and voltage in the biostimulator during MRI procedures. Methods associated with use of the biostimulator are also covered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Reduction of RF induced tissue heating using conductive surface pattern
InactiveUS20090099555A1Providing mechanical stabilityInteraction is limitedElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsSurface patternTissue heating
The present invention provides, among other things, means to suppress AC current propagation along elongated medical devices incorporating long conductive structures. AC currents in the frequency range from approximately 10 MHz to 3 GHz can be substantially suppressed without altering the low and DC frequency response of the medical device.
Owner:RENTENDO CORP
Tissue cutting catheter and RF cutting method
InactiveUS6872204B2Highly accurate and fine cutReduce pullingDiagnosticsCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceTissue heating
A tissue cutting device includes a catheter with a window at its distal tip for admitting tissue into a catheter compartment. A cylindrical cartridge in the compartment has a cutting edge that supports an electrically conductive cutting element, e.g. a band or wire. The cutting element and adjacent tissue can be heated to a selected temperature by generating an electrical current through the cutting element. The catheter is maneuverable to position its distal end near the tissue to be cut. The catheter incorporates a dilatation balloon or other feature to urge the catheter against the tissue, so that at least part of the tissue may enter the compartment through the window. Then, the cartridge is manipulated from the catheter's proximal end to move the cutting edge across the window, cutting the tissue. According to alternative embodiments, the cartridge is either rotated or moved axially relative to the catheter and, in either event may be capable of closing the catheter window when the cut is complete. Further alternatives involve either placing an indifferent electrode on the patient and providing an RF signal via a single conductor to the cutting element for ohmic heating, or providing an RF (or a DC) current through the cutting element and two separate conductors for direct resistive heating of the cutting element.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR TECH INC
Microwave applicator with margin temperature sensing element
InactiveUS20080033422A1ElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingAmplitude control
A microwave applicator for applying microwave radiation to body tissue includes a temperature sensor positioned along the applicator to measure the temperature of body tissue at a margin of the tissue to be treated. By monitoring the temperature of the tissue at the margin of the tissue to be treated, the heating of the tissue can be better controlled to ensure that the tissue to be treated is heated to the required temperature while damage to surrounding normal tissue is minimized. Treatment can include positioning one or more applicators into body tissue and applying microwave radiation to the applicators. Phase and amplitude control of the microwave radiation can be used to produce a desired heating pattern. Optimization of the number and location of microwave applicators and the phase and amplitude of microwave energy applied thereto can be determined through pretreatment simulation.
Owner:BSD MEDICAL
System method and apparatus for localized heating of tissue
InactiveUS6850804B2Important utilityPrecision therapyUltrasound therapyStentsTissue heatingPercent Diameter Stenosis
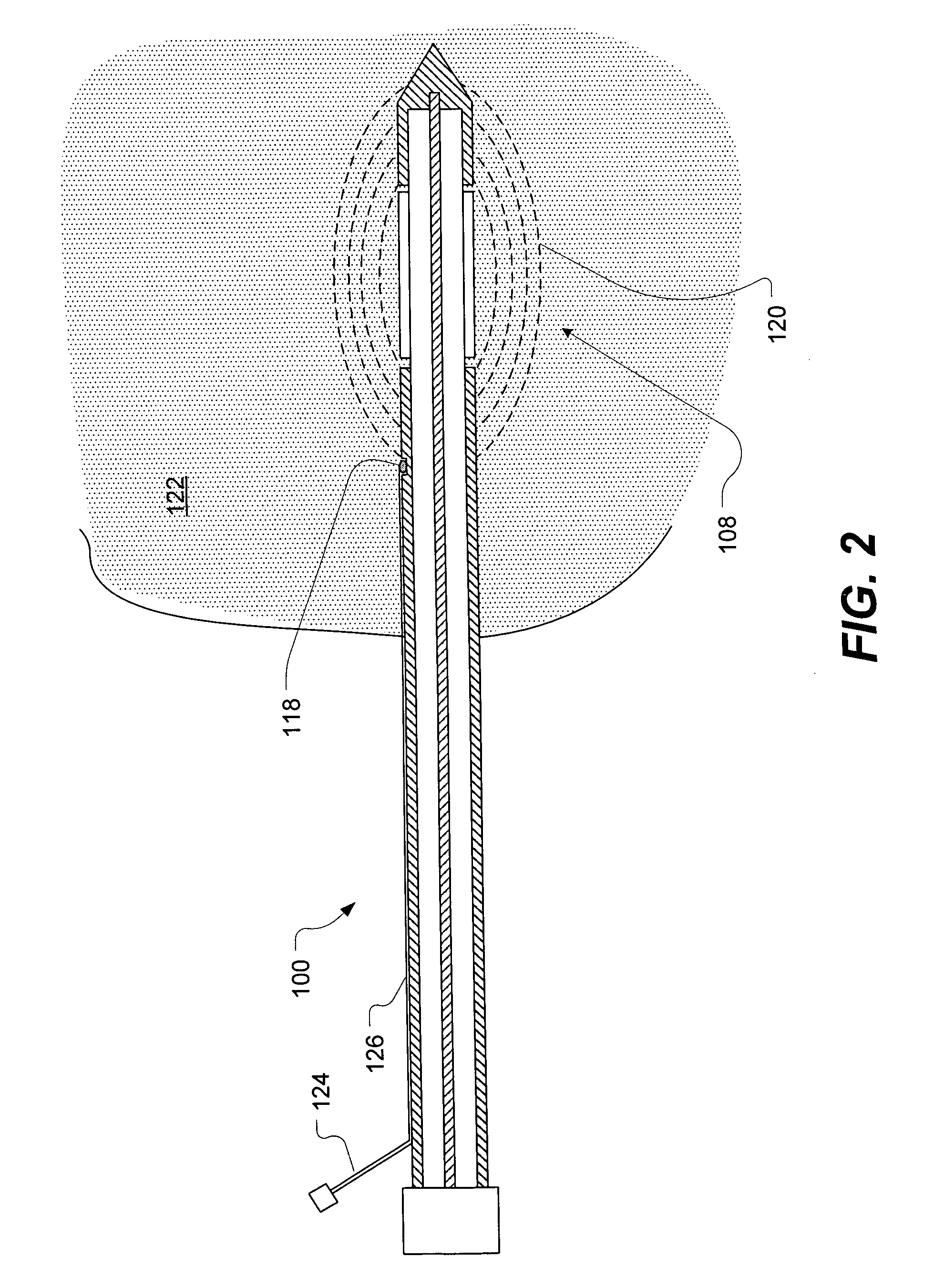
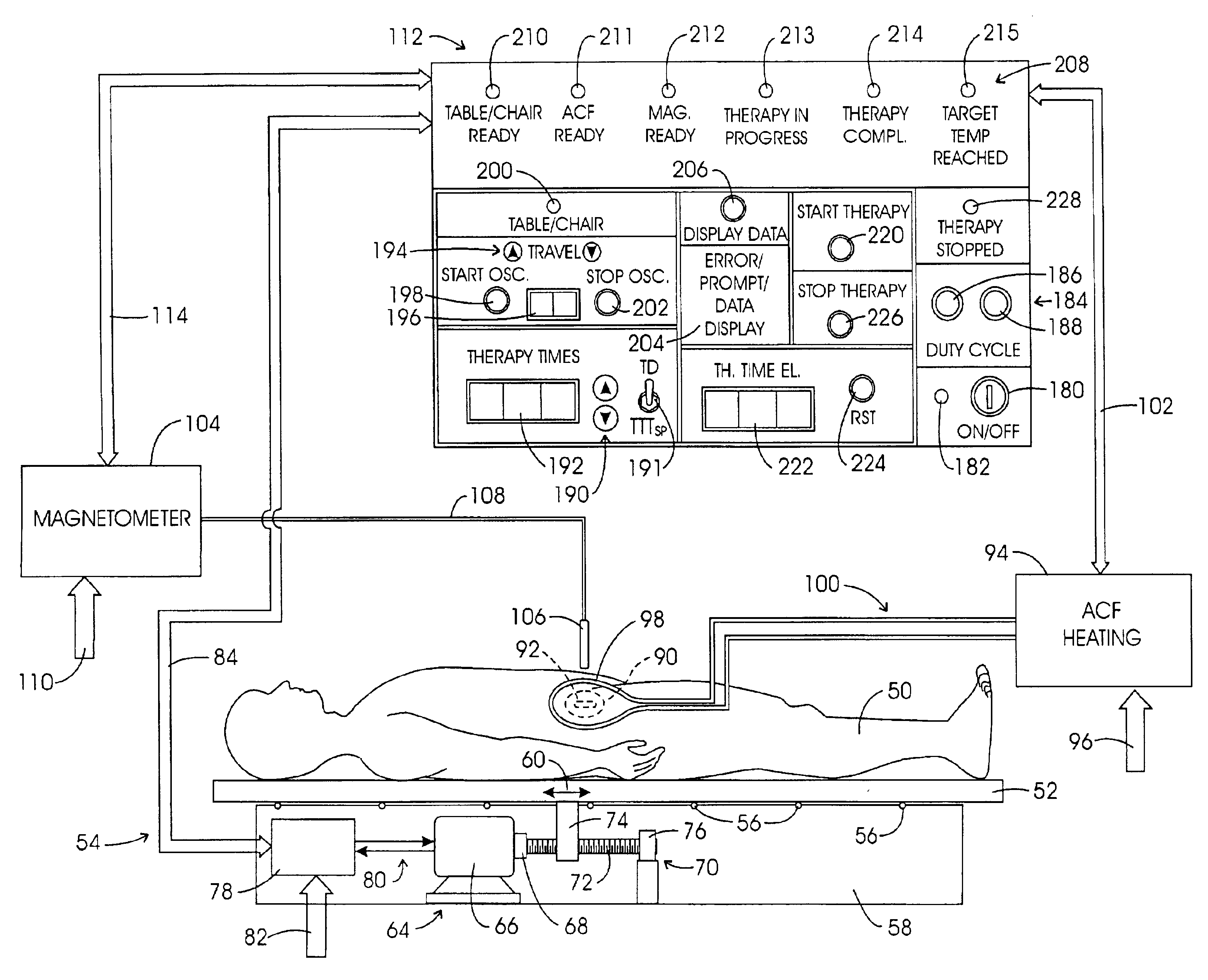
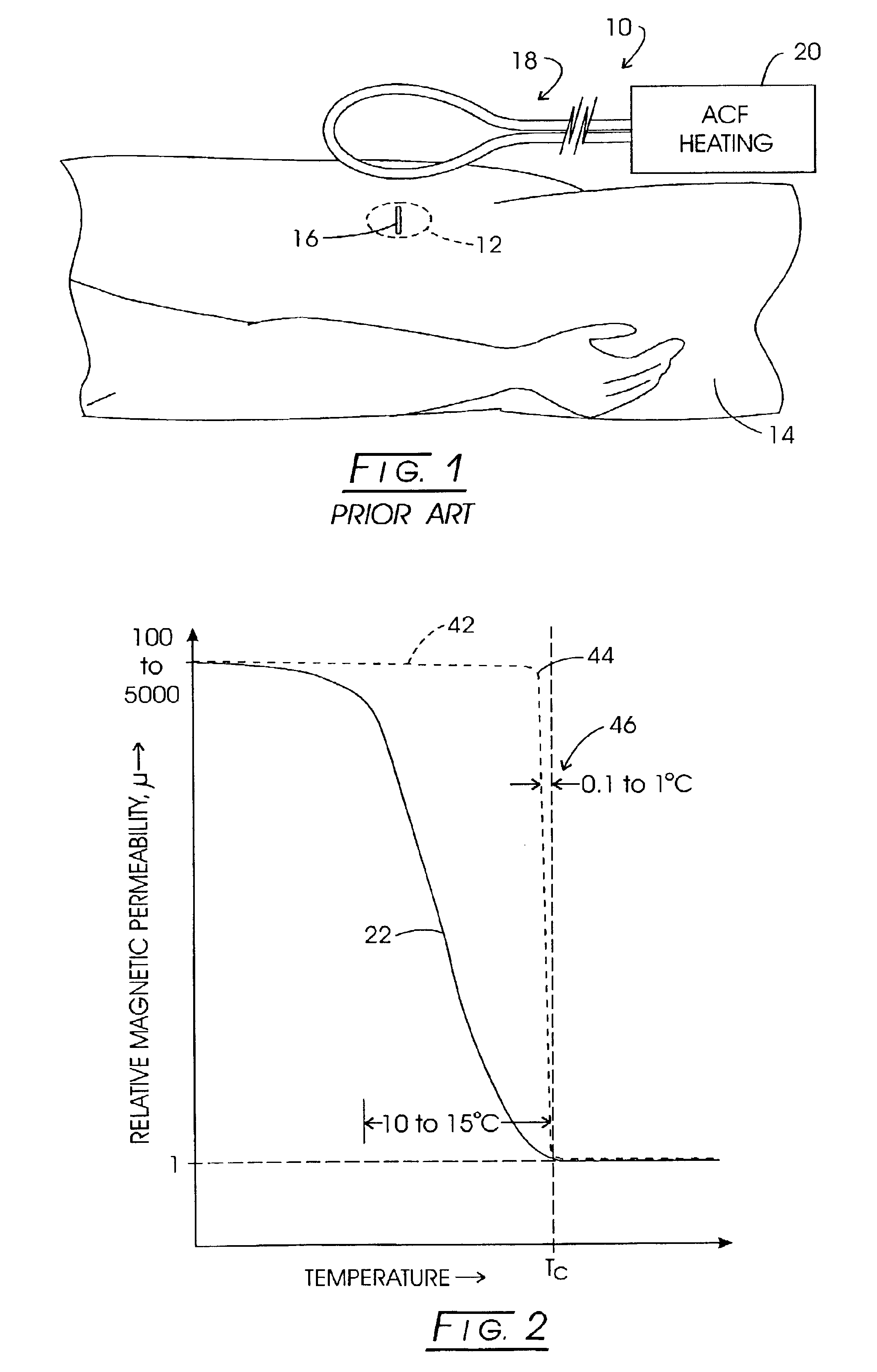
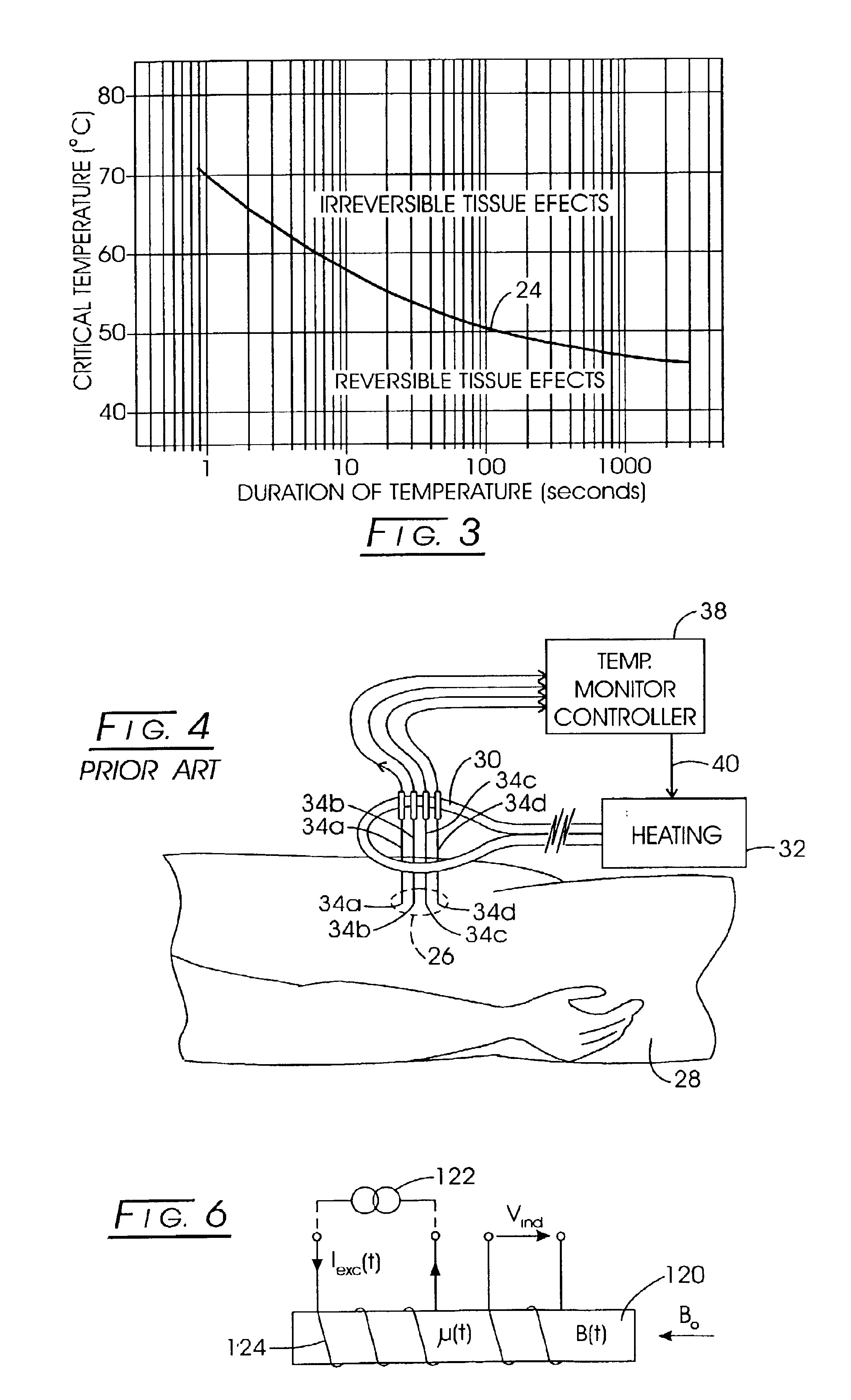
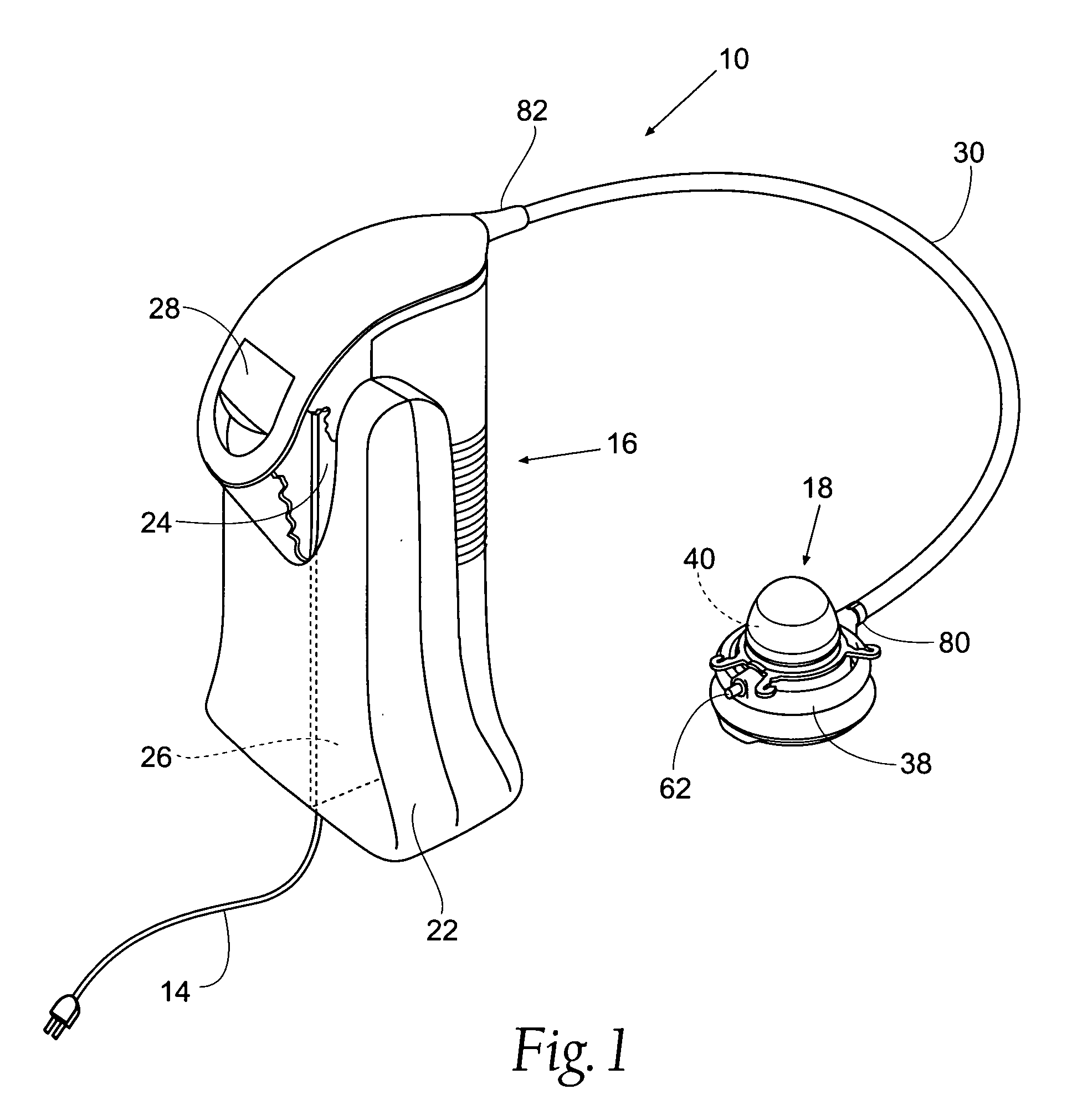
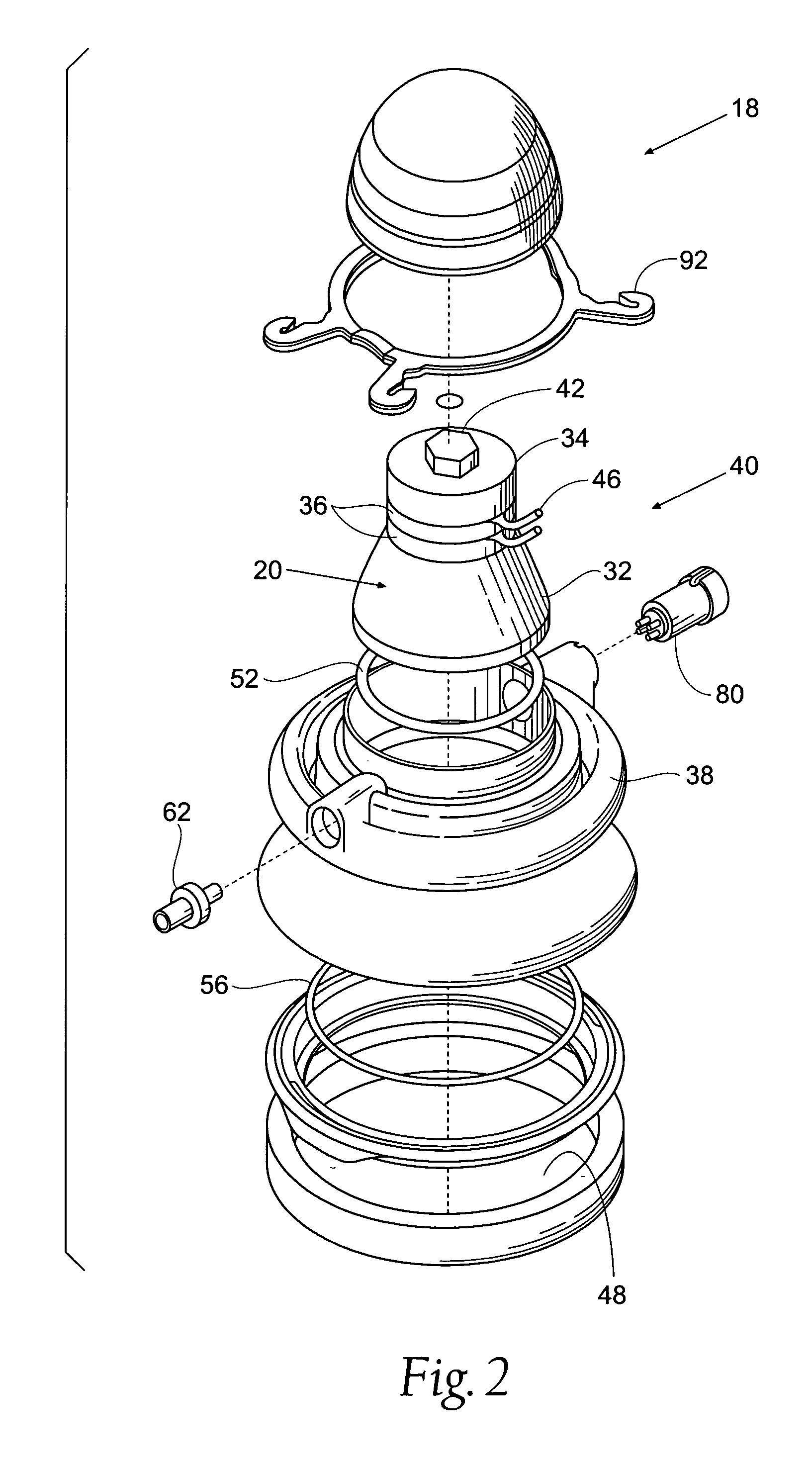
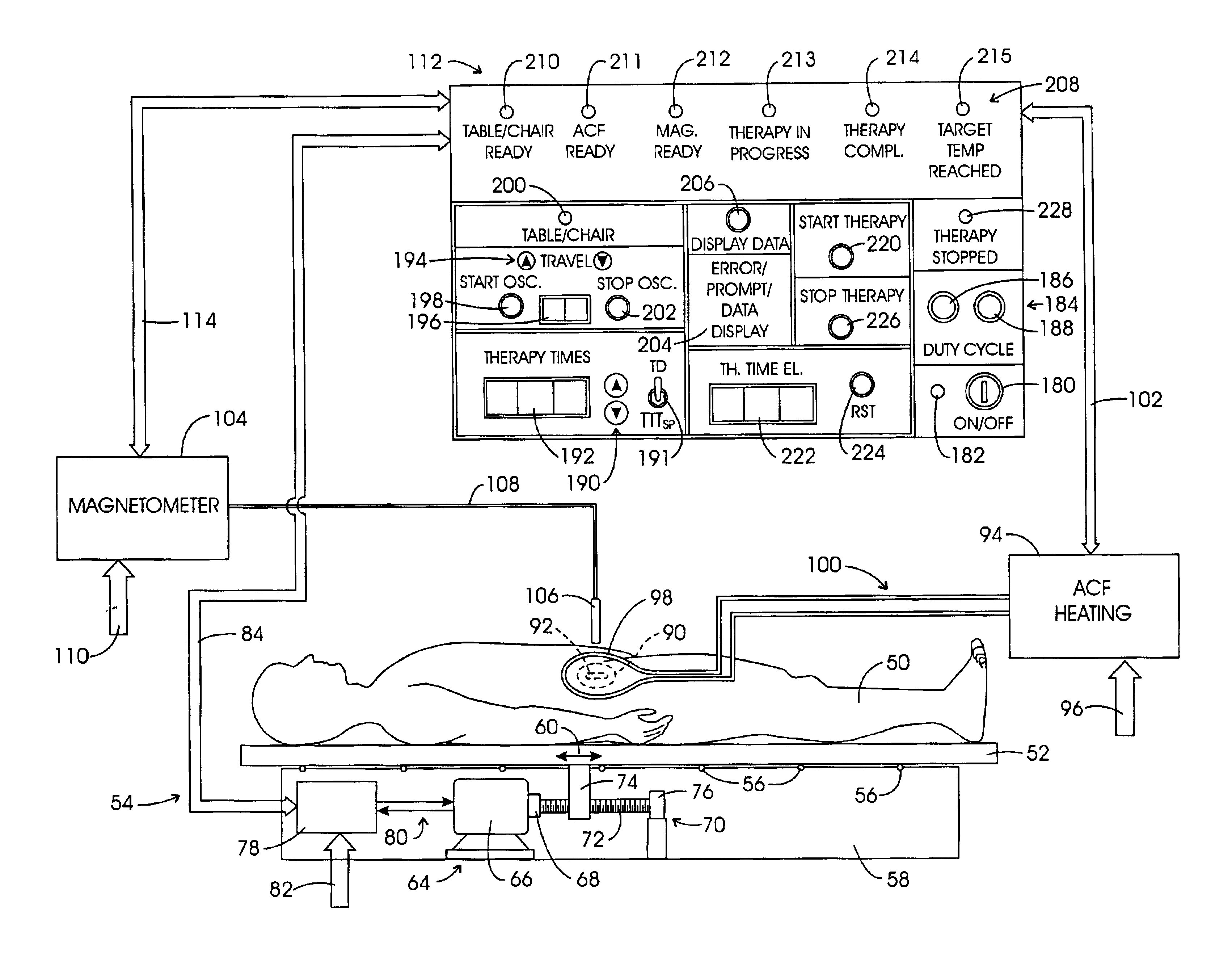
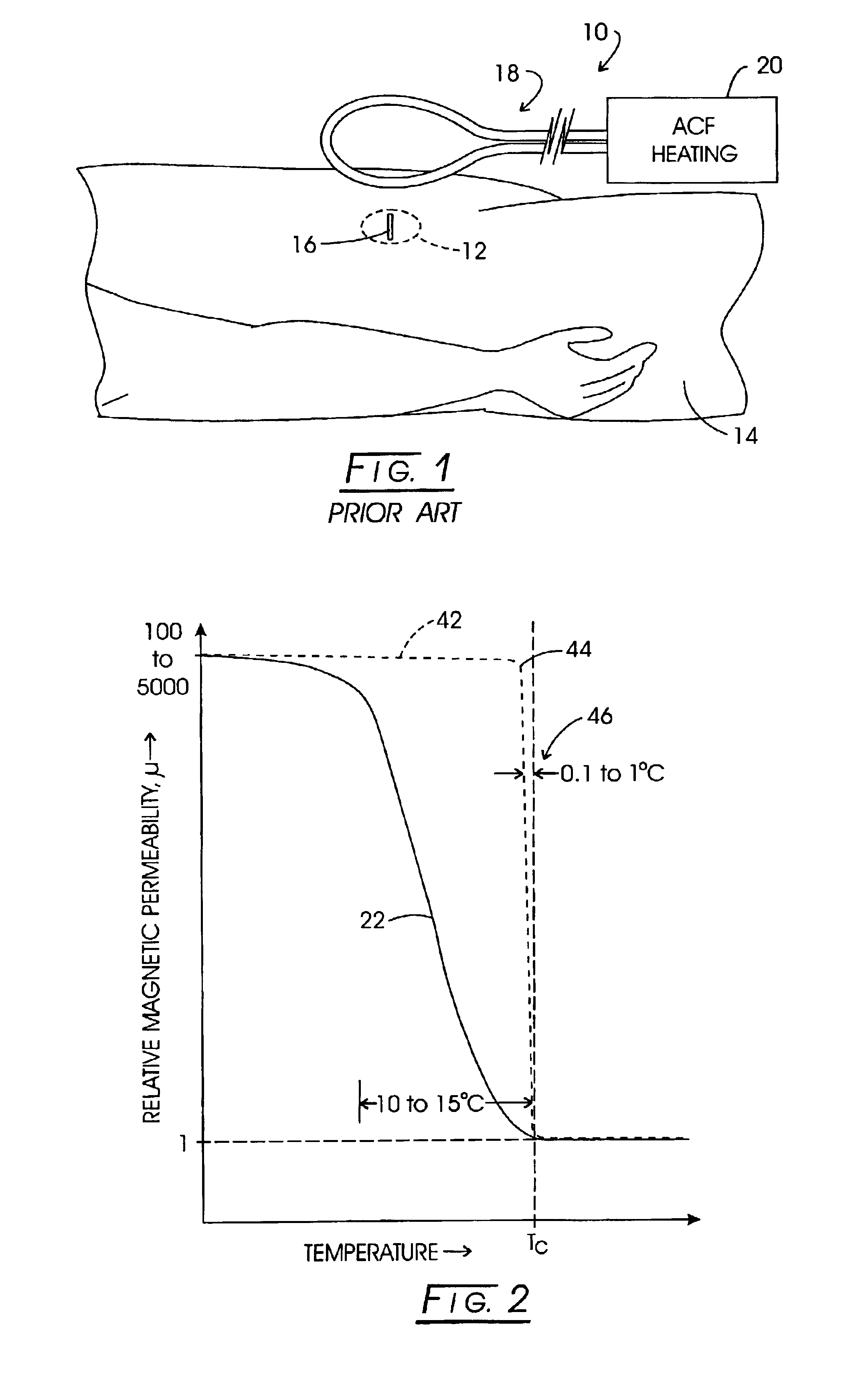
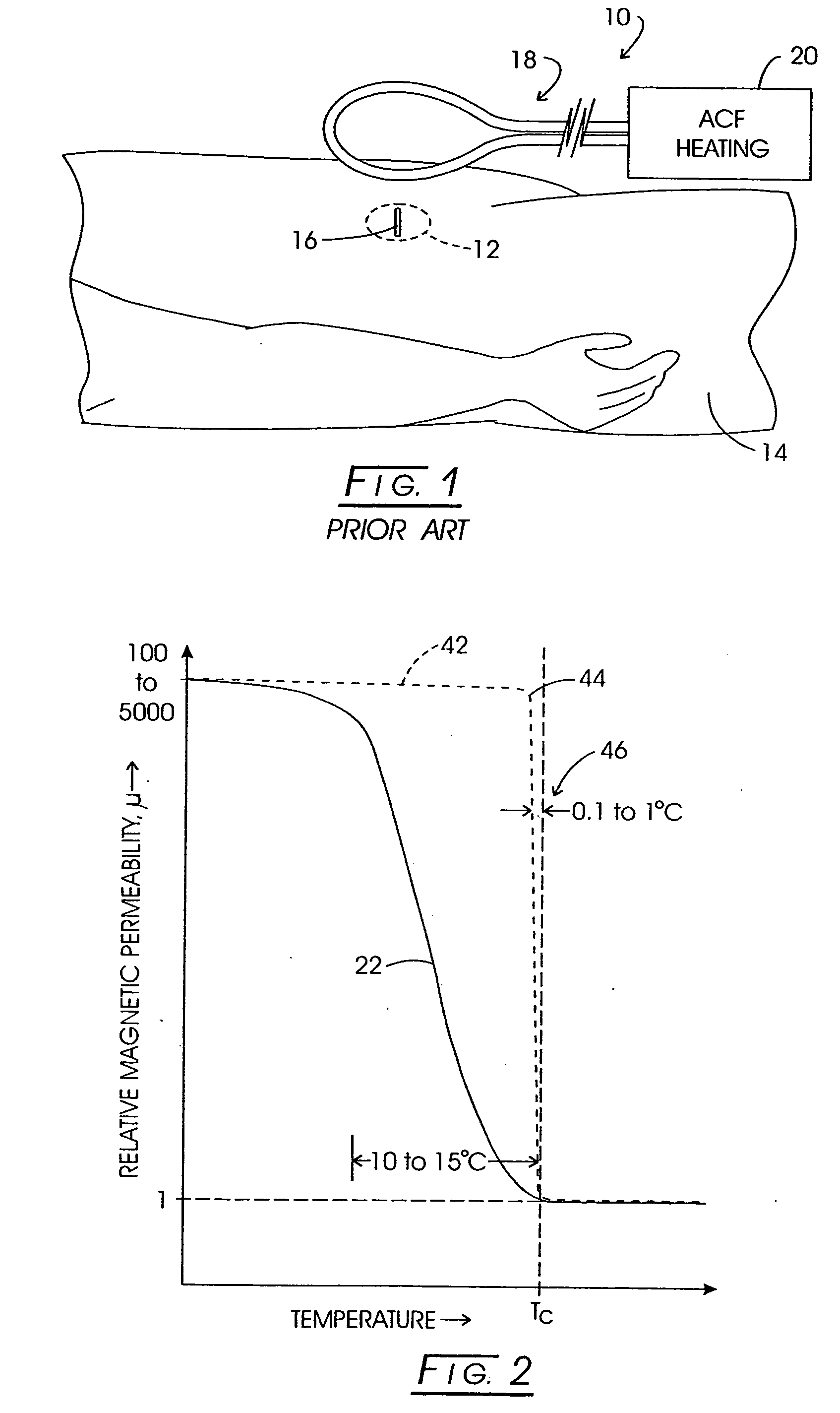
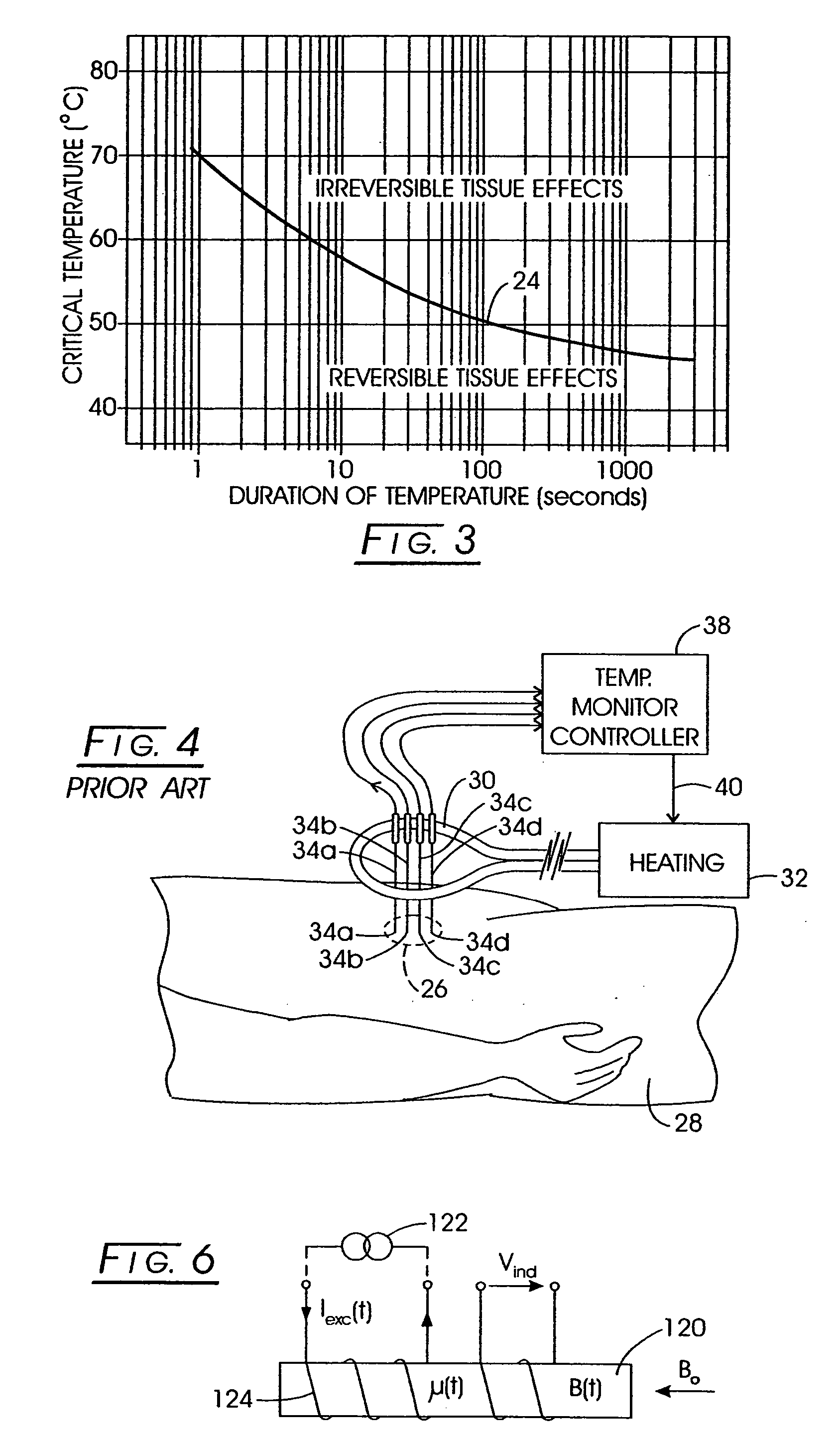
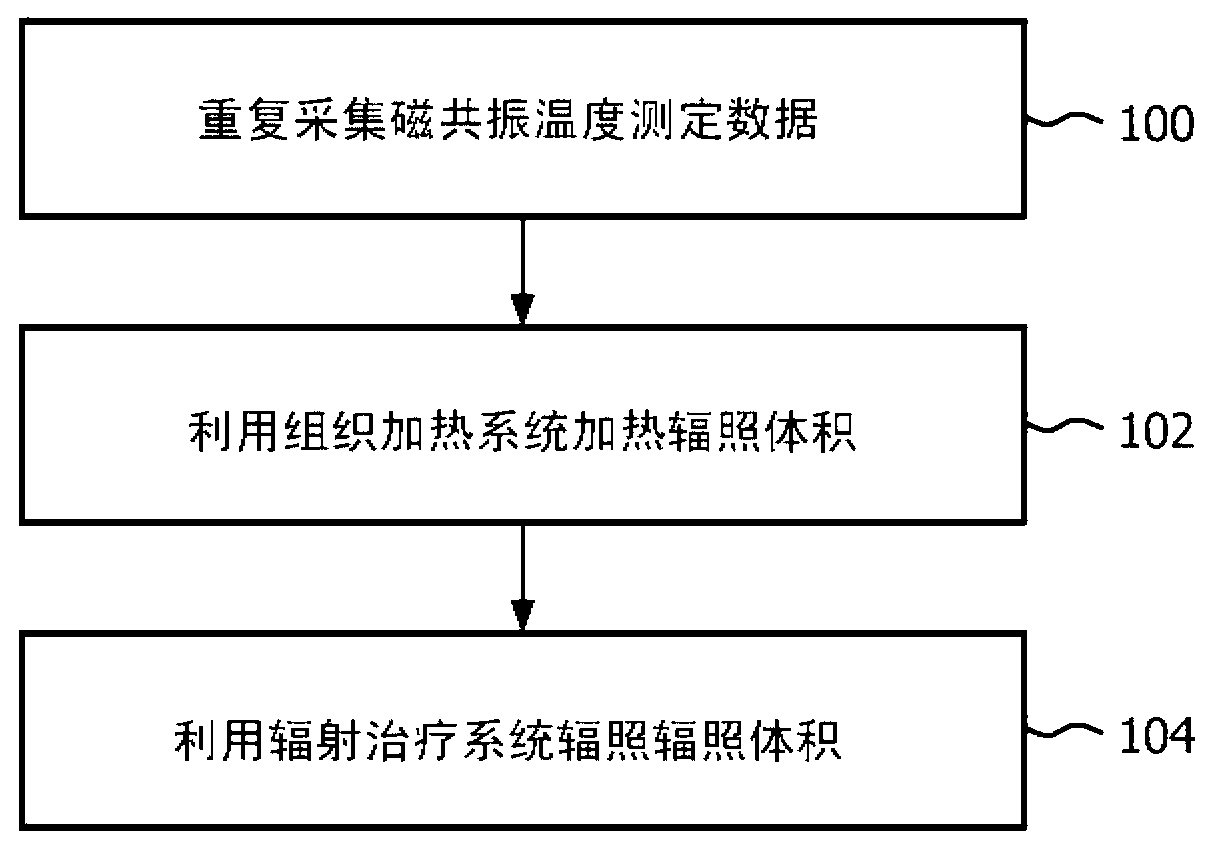
System method and apparatus for accurately carrying out the in situ heating of a targeted tissue. Small implants are employed with the targeted tissue which exhibit an abrupt change of magnetic permeability at an elected Curie temperature. The permeability state of the implant is monitored utilizing a magnetometer. The implants may be formed as a setpoint temperature determining component combined with a non-magnetic heater component to enhance the tissue heating control of the system. With the system, a very accurate quantum of heat energy can be supplied to a neoplastic lesion or tissue carrying infectious disease so as to maximize the induction of heat shock proteins. The system also may be utilized in conjunction with non-magnetic arterially implanted stents for the hyperthermia therapy treatment of restenosis and in conjunction with the mending of boney tissue.
Owner:APSARA MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for measuring catheter contact force during a medical procedure
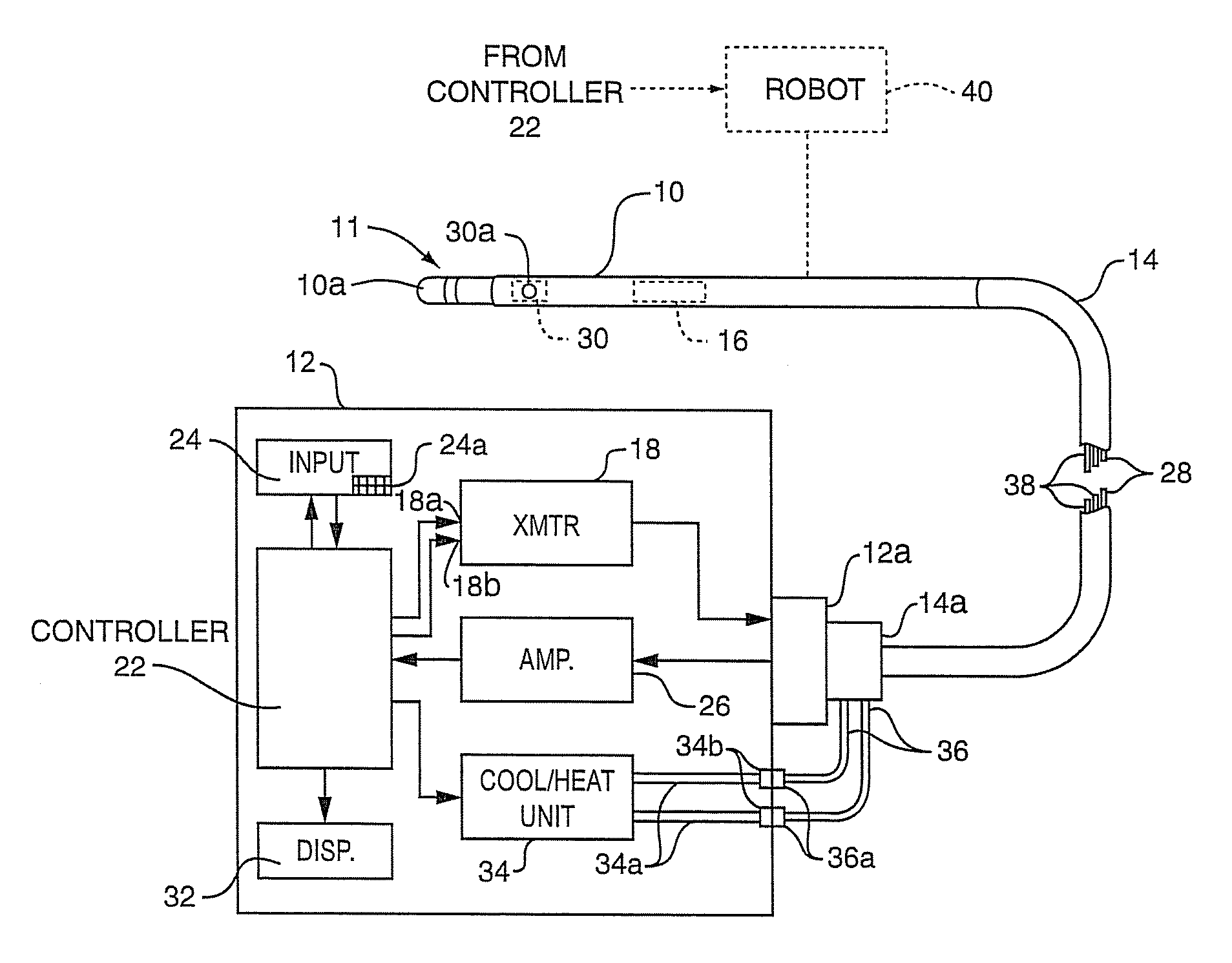
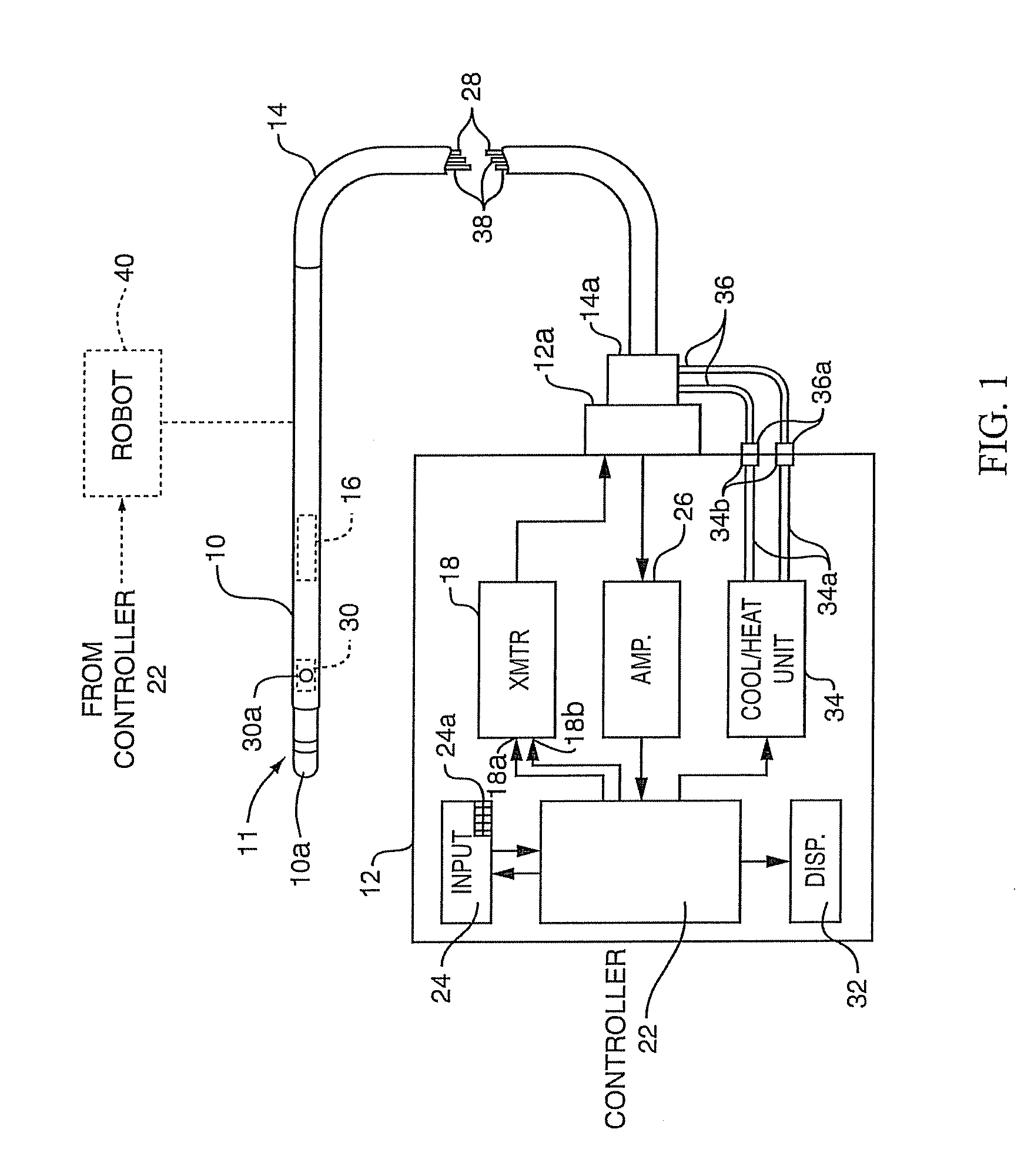
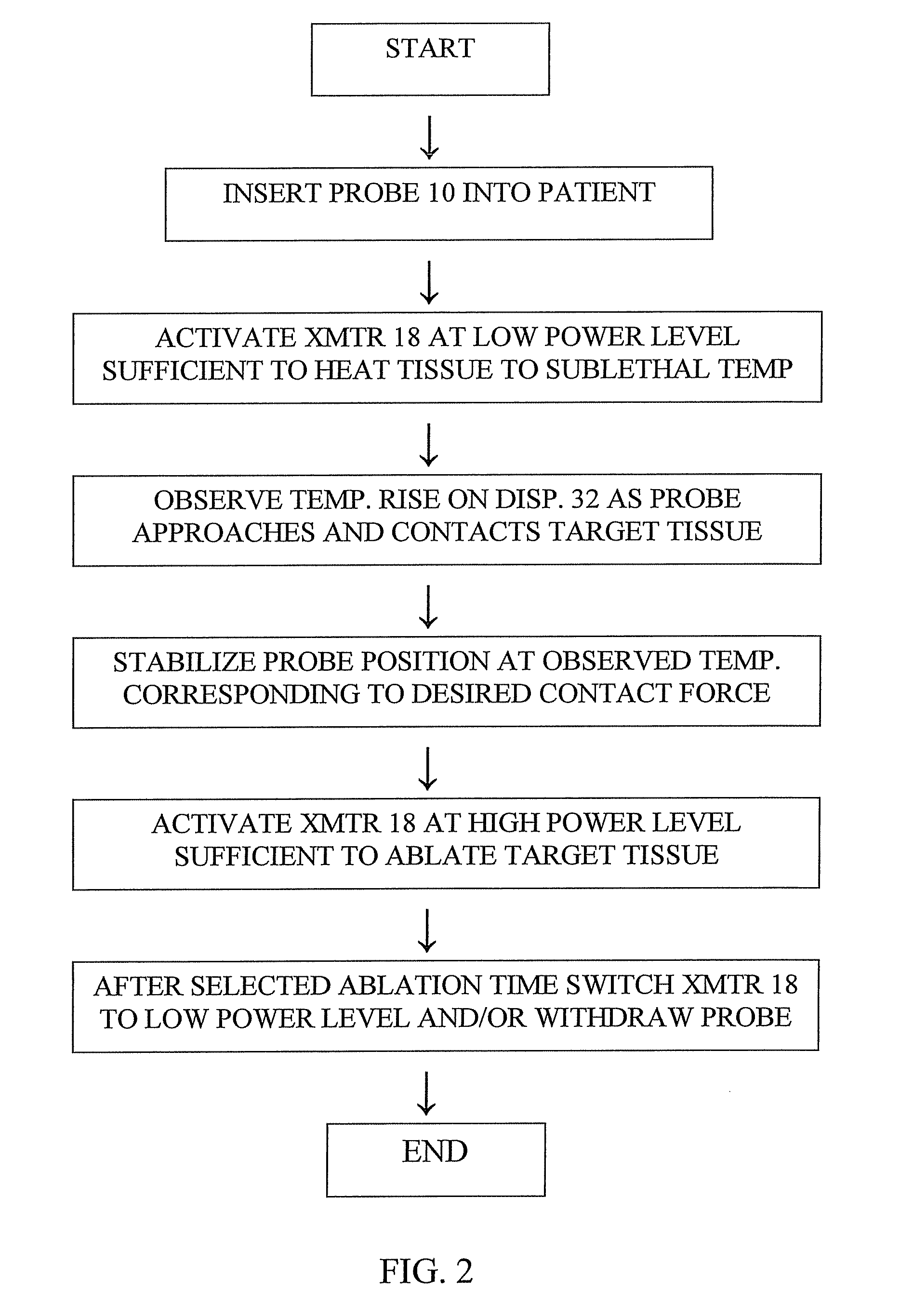
ActiveUS8206380B2Accurate measurementMinimizing chanceDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingSufficient time
A method for measuring the contact force exerted on tissue by a probe for heating the tissue and containing an antenna which is connected to a radiometer whose output reading indicates the temperature at depth of the tissue contacted by the probe comprises displaying the output reading of the radiometer, applying sufficient power to the probe to heat the tissue to a selected first temperature that is not lethal to the tissue, moving the probe into contact with the tissue, observing the increase in the displayed temperature reading that occurs when the probe contacts the tissue, and advancing the probe toward the tissue until the displayed temperature reading reaches a value corresponding to a selected tissue contact force. After the probe position in the tissue has stabilized, the applied power to the probe may be increased to heat the tissue to a selected second temperature that is lethal to tissue for a sufficient time to ablate the tissue followed by lowering the tissue heating to a sub-lethal temperature. Apparatus for practicing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED CARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
System and method for estimating tissue heating of a target ablation zone for electrical-energy based therapies
Systems and methods are provided for modeling and for providing a graphical representation of tissue heating and electric field distributions for medical treatment devices that apply electrical treatment energy through one or a plurality of electrodes. In embodiments, methods comprise: providing one or more parameters of a treatment protocol for delivering one or more electrical pulses to tissue through a plurality of electrodes; modeling electric and heat distribution in the tissue based on the parameters; and displaying a graphical representation of the modeled electric and heat distribution. In another embodiment, a treatment planning module is adapted to generate an estimated target ablation zone based on a combination of one or more parameters for an irreversible electroporation protocol and one or more tissue-specific conductivity parameters.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method for increasing saliva and tear production with ultrasound
InactiveUS20080269648A1Avoid side effectsIncrease tear productionUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesSonificationTissue heating
A non-invasive apparatus and method for increasing saliva and tear production from the salivary and lacrimal glands with the application of high frequency low intensity ultrasound. An ultrasound transducer coated with connecting gel placed in contact with the facial tissues transmitting 1.5 MHz frequency ultrasound pressure waves into the tissues and into the glands. The time-averaged intensity of the ultrasound pressure waves is typically limited to approximately 30 milliwatts per square centimeter to avoid tissue heating.
Owner:ROBERT T BOCK CONSULTANCY
System and method for tissue treatment using non-symmetric radio-frequency energy waveform
ActiveUS9168096B2Minimize shocking effectReducing the IEP thresholdSurgical instruments for heatingNon symmetricTissue heating
A method for soft tissue destruction comprises applying high voltage pulses causing irreversible electroporation alternating with low amplitude pulses of opposite polarity balanced to provide negligible average current and minimize risk of electrical shock. The method may be accompanied by tissue heating to reduce the electroporation threshold and negative pressure for skin shaping and optimal voltage distribution.
Owner:INVASIX
System and method for estimating tissue heating of a target ablation zone for electrical-energy based therapies
Systems and methods are provided for modeling and for providing a graphical representation of tissue heating and electric field distributions for medical treatment devices that apply electrical treatment energy through one or a plurality of electrodes. In embodiments, methods comprise: providing one or more parameters of a treatment protocol for delivering one or more electrical pulses to tissue through a plurality of electrodes; modeling electric and heat distribution in the tissue based on the parameters; and displaying a graphical representation of the modeled electric and heat distribution. In another embodiment, a treatment planning module is adapted to generate an estimated target ablation zone based on a combination of one or more parameters for an irreversible electroporation protocol and one or more tissue-specific conductivity parameters.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Systems and methods for applying ultrasound energy to increase tissue perfusion and/or vasodilation without substantial deep heating of tissue
InactiveUS20080208084A1Less-deep heatingMinimizes attenuationUltrasound therapyImage enhancementTissue heatingSonification
Owner:TIMI 3 SYST
System method and apparatus for localized heating of tissue
InactiveUS6993394B2Wide applicationImportant utilityUltrasound therapyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsTissue heatingPercent Diameter Stenosis
System method and apparatus for accurately carrying out the in situ heating of a targeted tissue. Small implants are employed with the targeted tissue which exhibit an abrupt change of magnetic permeability at an elected Curie temperature. The permeability state of the implant is monitored utilizing a magnetometer. The implants may be formed as a setpoint temperature determining component combined with a non-magnetic heater component to enhance the tissue heating control of the system. With the system, a very accurate quantum of heat energy can be supplied to a neoplastic lesion or tissue carrying infectious disease so as to maximize the induction of heat shock proteins. The system also may be utilized in conjunction with non-magnetic arterially implanted stents for the hyperthermia therapy treatment of restenosis and in conjunction with the mending of boney tissue.
Owner:APSARA MEDICAL
Integrated cryosurgical system with refrigerant and electrical power source
ActiveUS20120265278A1Improve appearanceSufficient powerSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for coolingRefrigerantEngineering
A system for treating tissue in a patient includes a body having a cooling fluid supply path and a tissue piercing probe in fluid communication with the cooling fluid supply path. The probe extends distally from the body and is insertable into the tissue through the patient's skin. A cooling fluid source is fluidly coupled with the probe such that when cooling is initiated, cooling fluid flows in the probe thereby cooling the probe and any adjacent tissue. A heater element is in thermal engagement with the cooling fluid source and a power source provides power to the heater element thereby heating the cooling fluid. The power source has sufficient power to heat the cooling fluid to at least a desired temperature but has insufficient power to heat the cooling fluid above a critical temperature which results in rupture of the cooling fluid source.
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
System and method for estimating tissue heating of a target ablation zone for electrical-energy based therapies
Systems and methods are provided for modeling and for providing a graphical representation of tissue heating and electric field distributions for medical treatment devices that apply electrical treatment energy through one or a plurality of electrodes. In embodiments, methods comprise: providing one or more parameters of a treatment protocol for delivering one or more electrical pulses to tissue through a plurality of electrodes; modeling electric and heat distribution in the tissue based on the parameters; and displaying a graphical representation of the modeled electric and heat distribution. In another embodiment, a treatment planning module is adapted to generate an estimated target ablation zone based on a combination of one or more parameters for an irreversible electroporation protocol and one or more tissue-specific conductivity parameters.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
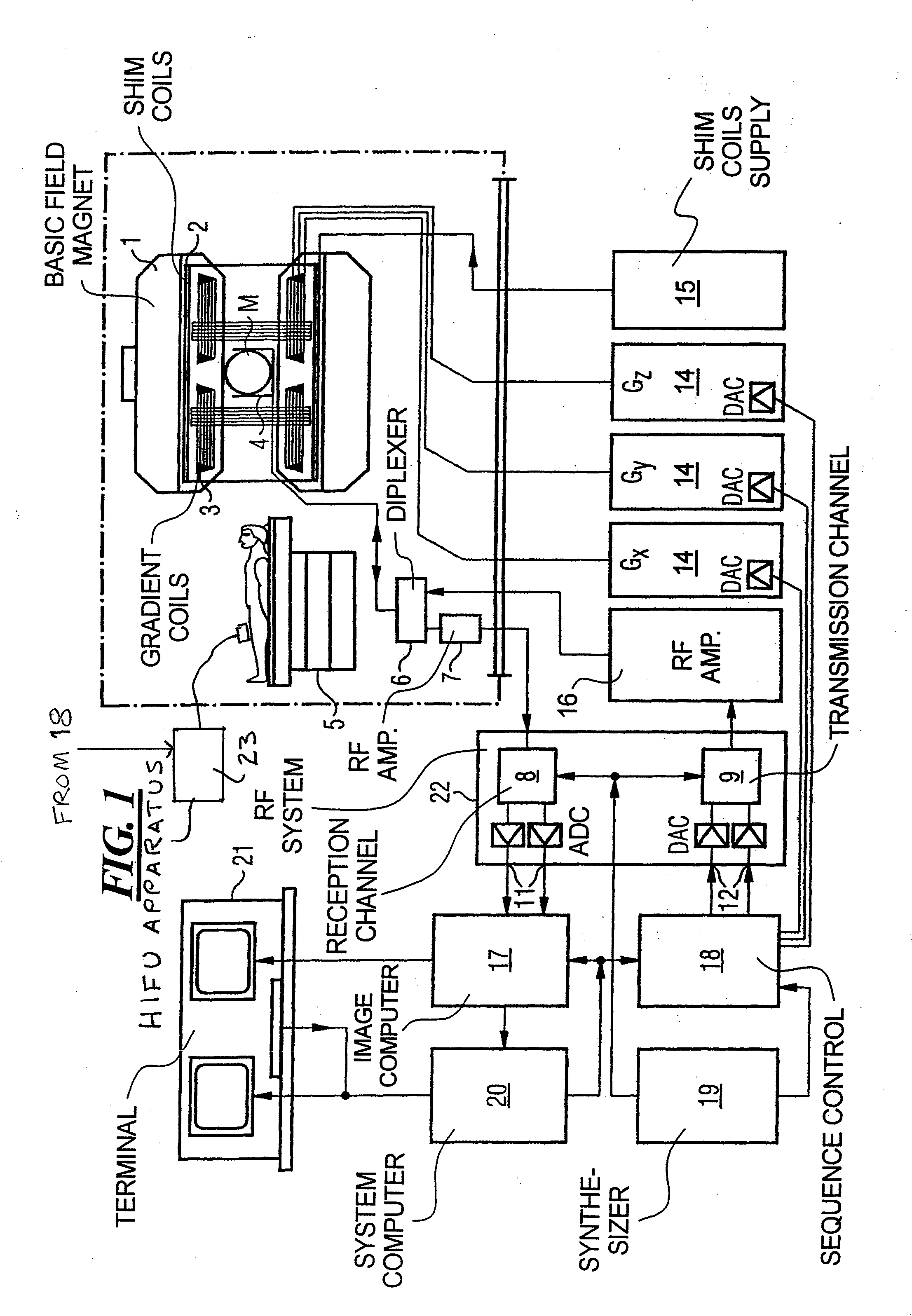
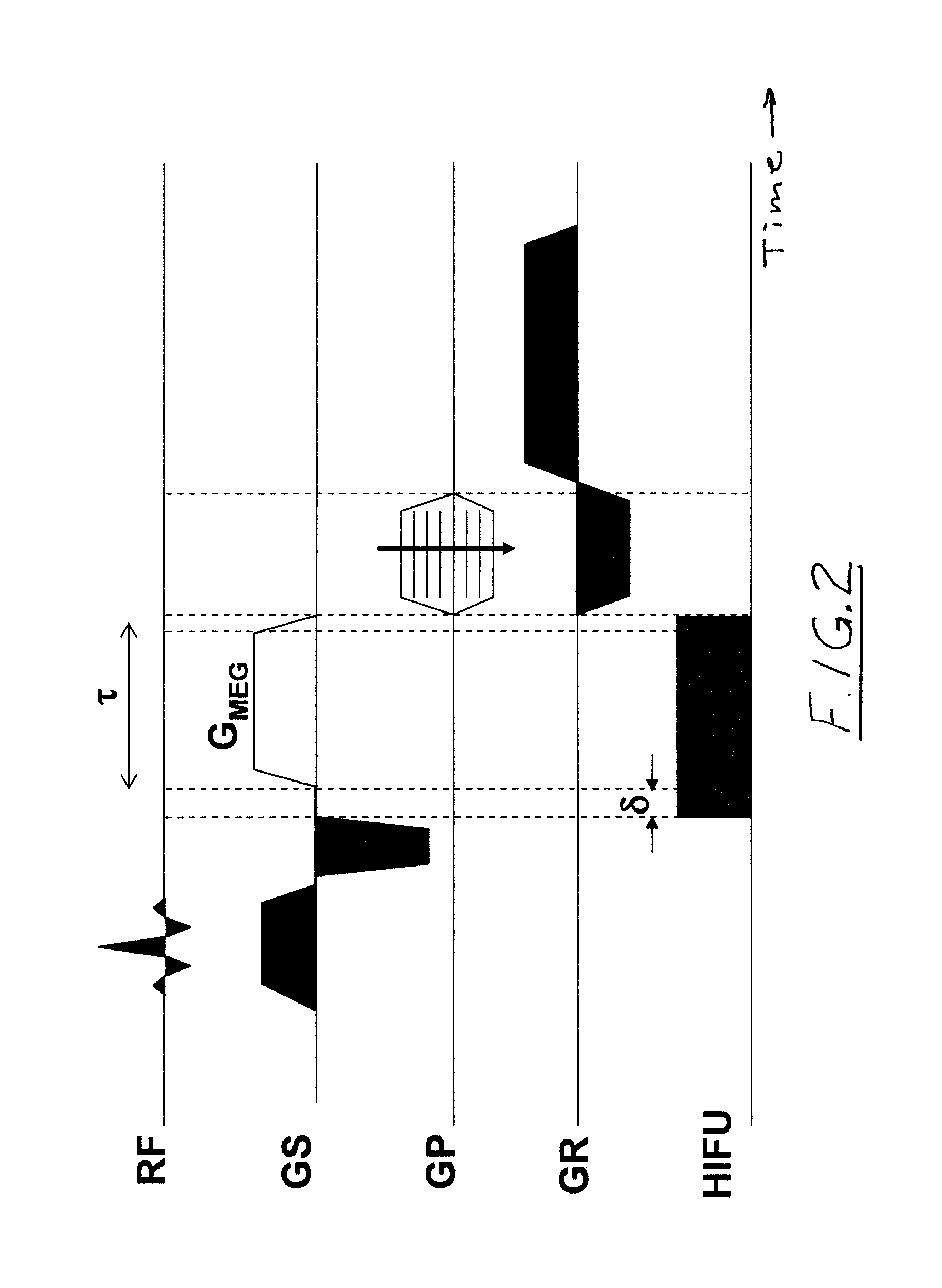
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound focusing under simultaneous temperature monitoring
ActiveUS20110248714A1Precise positioningHigh resolutionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSonificationTissue heating
In a method and an apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), precise localization of the focal point of the HIFU is determined by imaging an examination subject in parallel with GRE sequences that respectively include a positive monopolar gradient pulse and a negative monopolar gradient pulse, that respectively encode the acoustic radiation force (ARF)-induced phase shift that is induced by the simultaneous activation of HIFU during the sequences. A GRE phase image is reconstructed from each acquisition sequence, and a difference image is formed between the two GRE phase images, from which the HIFU focal point is determined. An average image is formed of the two GRE phase images from which PRFS temperature map is determined simultaneously to ARFI map. The use of parallel imaging and the use of partial Fourier reconstruction for reconstructing the GRE phase images allows the data to be acquired sufficiently rapidly so as to minimize the adverse effect of tissue heating that occurs with conventional longer-duration, and repetitious, techniques.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
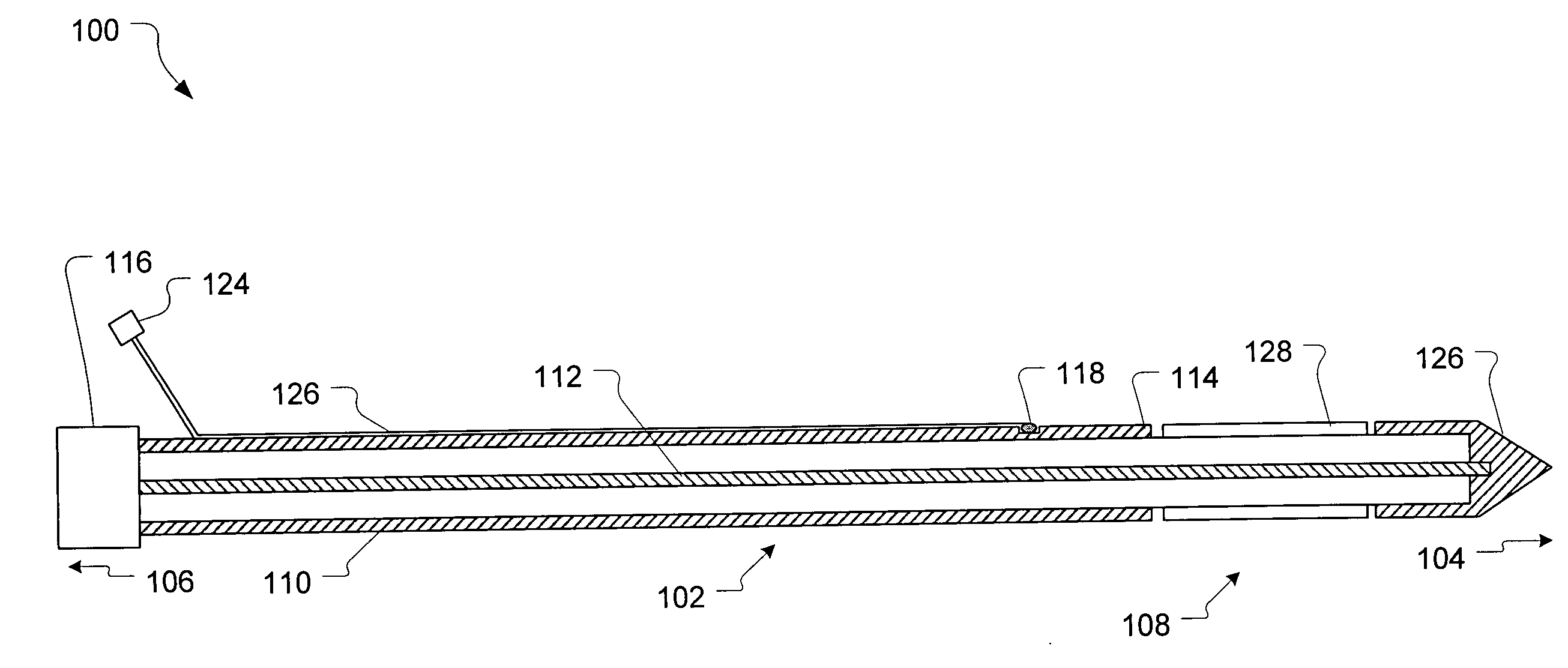
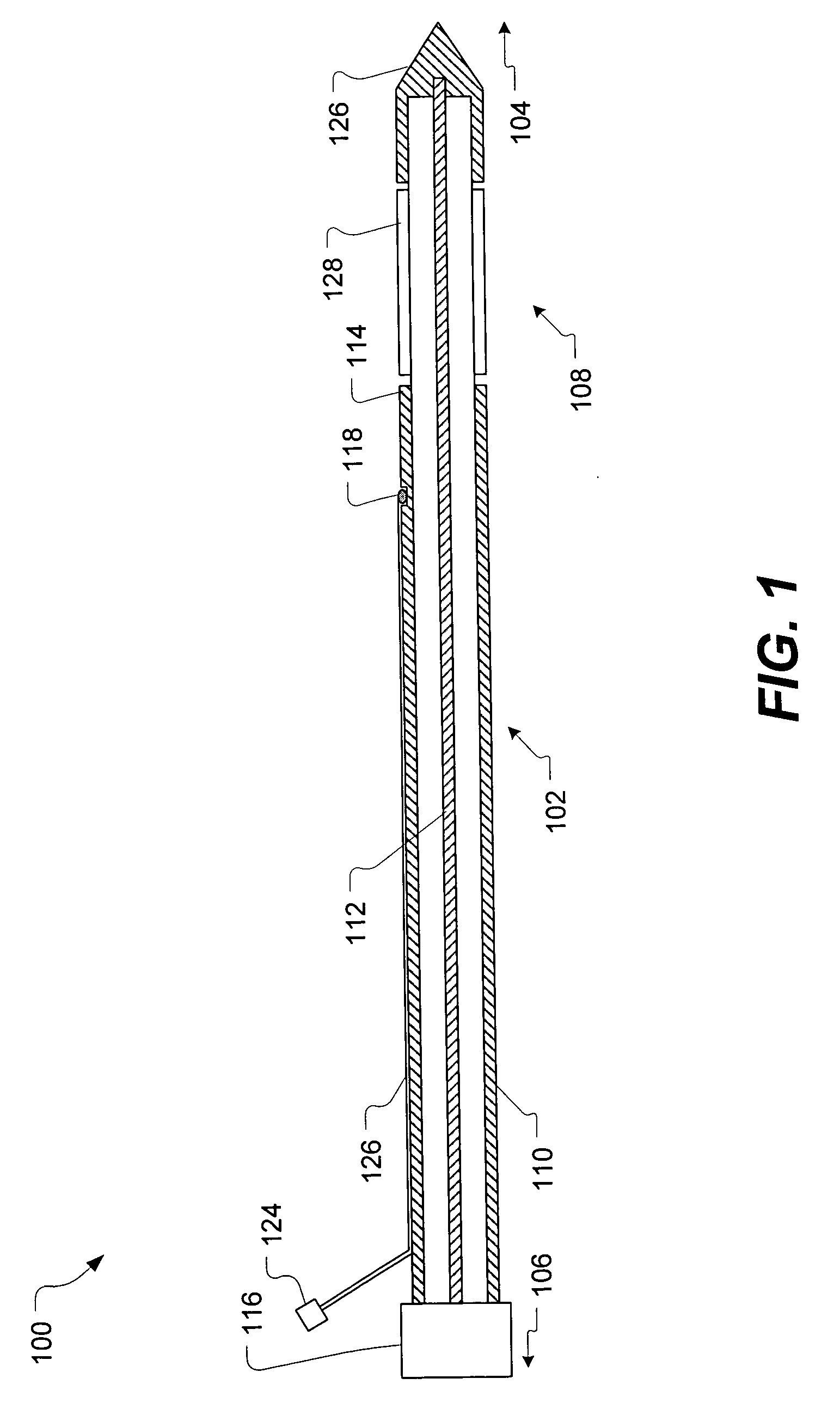
Thermotherapy catheter and method of prostate thermotherapy with improved guide and heat confinement
InactiveUS6868290B2Facilitates orientingEasy maintenanceSurgical instruments using microwavesTherapeutic coolingTissue heatingAcute angle
A thermotherapy catheter for heat treating the prostate gland includes an O-ring positioned within a chamber between an outer tube and an interior heat generation device guide tube. The O-ring supports a distal end portion of a probe guide tube at a desired acute angle so that a temperature probe can be advanced from the end of the probe guide tube into the prostate gland at a predetermined desired acute angle for calculating tissue heating and tissue necrosis information from temperature sensors located on a distal end of the temperature probe. The O-ring also separates a still liquid chamber from a circulatory flow path so that heated liquid surrounding the generation device is applied effectively to heat the prostate gland, while the circulating cooling fluid effectively removes heat from a feed cable which supplies energy to the heat generation device.
Owner:PROSTALUND OPERATIONS
Adjustable open loop control devices and methods
InactiveUS20070050001A1More reliableLess-costly to manufactureControlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingPower applicationLoop control
Noninvasive methods for therapeutically heating a collagenous structural support tissue of a pelvic support system to a desired temperature range are provided. One method comprises delivering energy to the structural support tissue to heat the tissue to the desired temperature range by ramping up a power level for a first period of time. A first constant high power level is then maintained for a second period of time. The power level is then ramped down for a third period of time. A second constant lower power level is then maintained for a fourth period of time. This power application treatment yields a favorable heat treatment maximizing predictability and efficacy while maintaining sufficient levels of safety. Further, such open loop power algorithms advantageously provide control without the need for subsidiary tissue temperature feedback measurements from sensors or tissue penetrating needles.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
Ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm
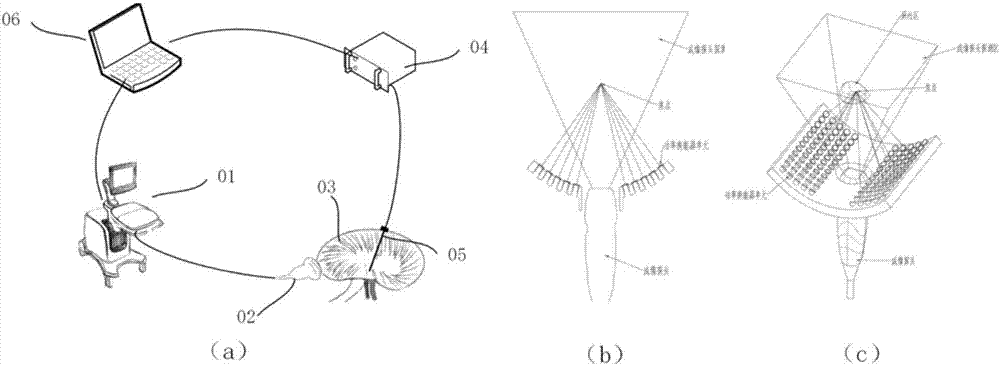
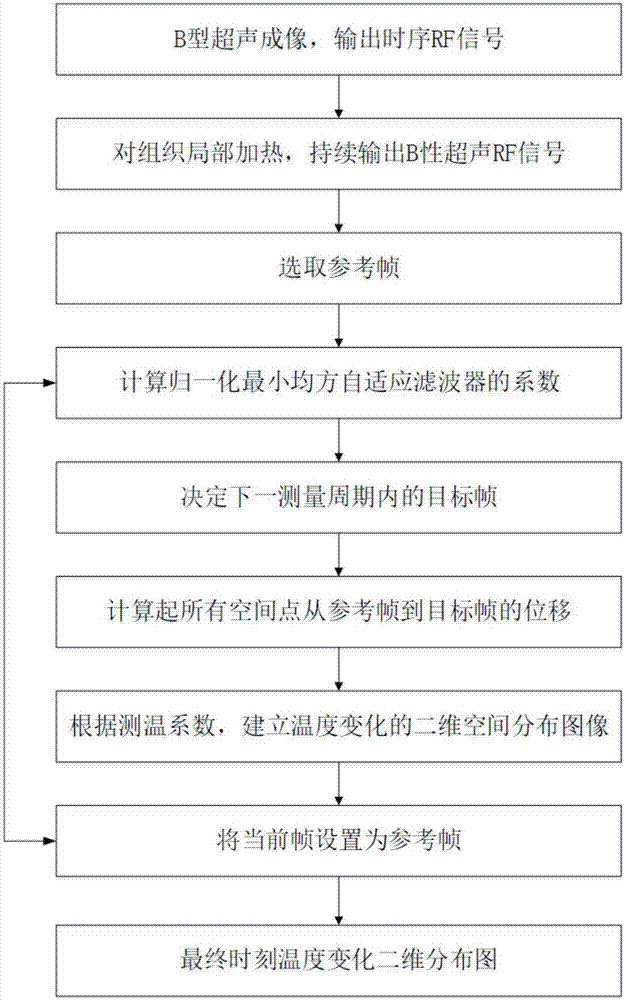
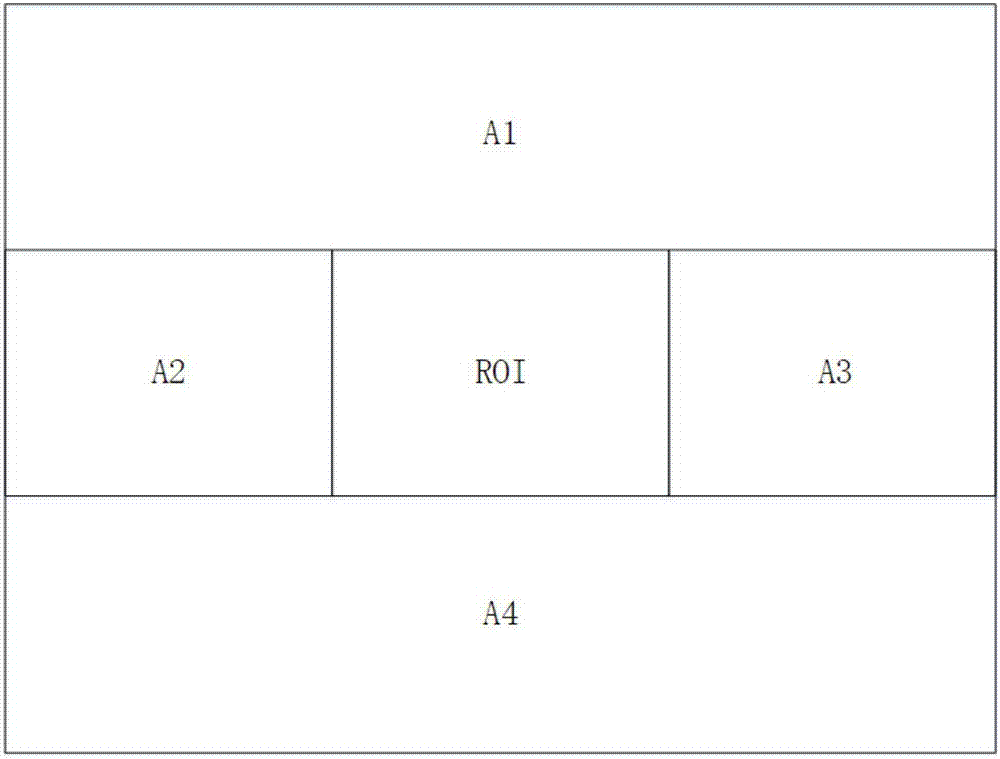
ActiveCN107569256ALow costEasy to deploy at scaleOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseTissue heating
The invention discloses an ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm. Aiming at the problem that temperature increment ofa target area cannot be effectively monitored in methods for treating diseases based on various current body tissue heating modes, a method for evaluating the temperature change of the biological tissue by using B-mode ultrasound RF signals is established. According to the method, methods such as focused ultrasound, radio frequency and microwave are used for locally heating the biological tissue,B-mode ultrasound is used for imaging the target area and collecting the RF signals of the target area, a target frame is selected based on B-mode ultrasound timing sequence images, time delay imagesthat ultrasound passes through the tissue are calculated, and accordingly temperature change images are obtained; according to images outside a heating area, the coefficient of a self-adaption filteris calculated, and the obtained temperature change images are subjected to noise suppression. According to the ultrasonic method, the error in the temperature increment range of 18 DEG C is smaller than or equal to 2 DEG C, the temperature increment monitoring technology of B-mode ultrasound is promoted to be applied to thermal therapy, and the safety and effectiveness of the thermal therapy can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
System method and apparatus for localized heating of tissue
InactiveUS20050234532A1Wide applicationImportant utilityUltrasound therapyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsTissue heatingPercent Diameter Stenosis
System method and apparatus for accurately carrying out the in situ heating of a targeted tissue. Small implants are employed with the targeted tissue which exhibit an abrupt change of magnetic permeability at an elected Curie temperature. The permeability state of the implant is monitored utilizing a magnetometer. The implants may be formed as a setpoint temperature determining component combined with a non-magnetic heater component to enhance the tissue heating control of the system. With the system, a very accurate quantum of heat energy can be supplied to a neoplastic lesion or tissue carrying infectious disease so as to maximize the induction of heat shock proteins. The system also may be utilized in conjunction with non-magnetic arterially implanted stents for the hyperthermia therapy treatment of restenosis and in conjunction with the mending of boney tissue.
Owner:APSARA MEDICAL
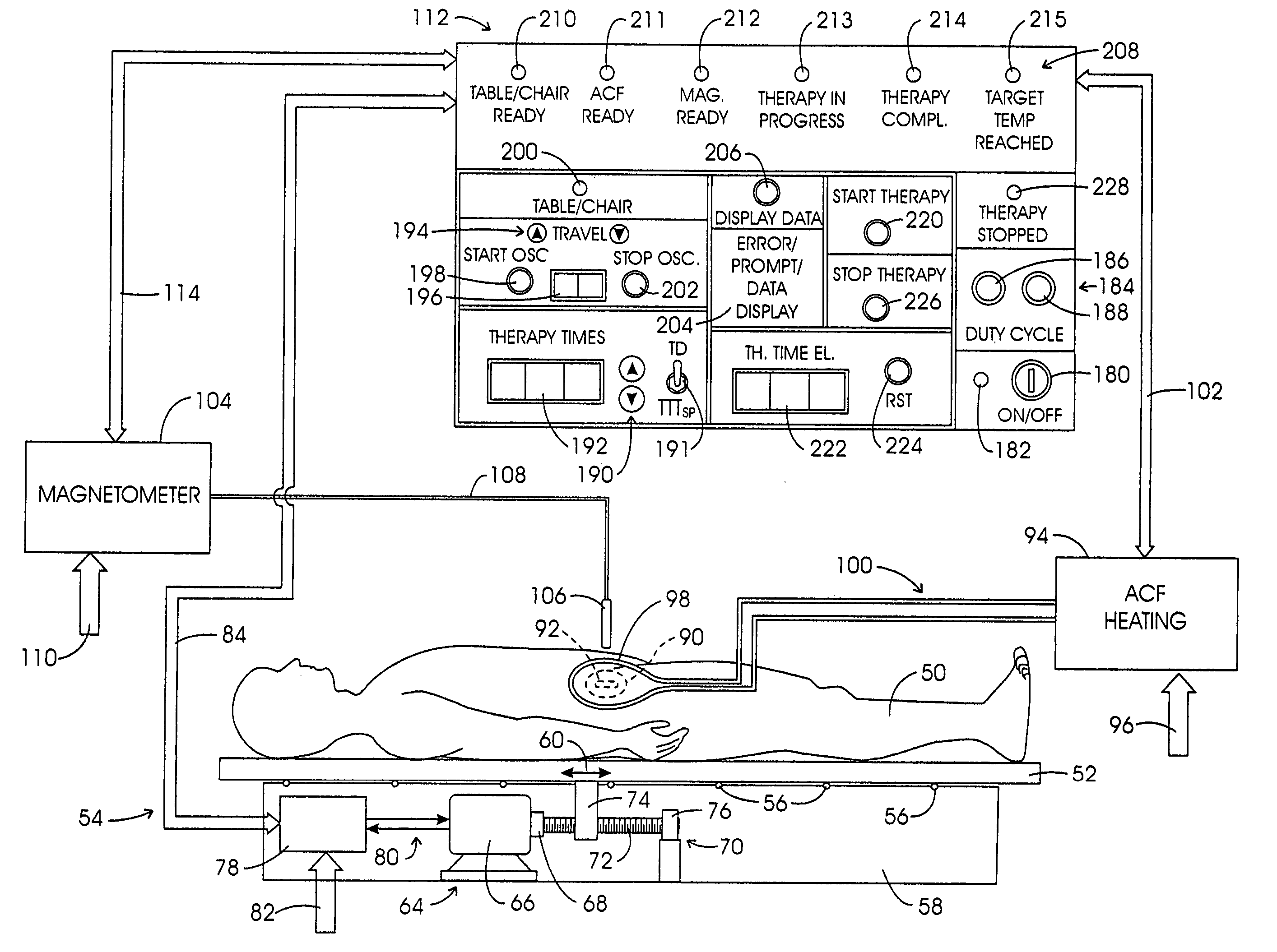
Therapeutic apparatus
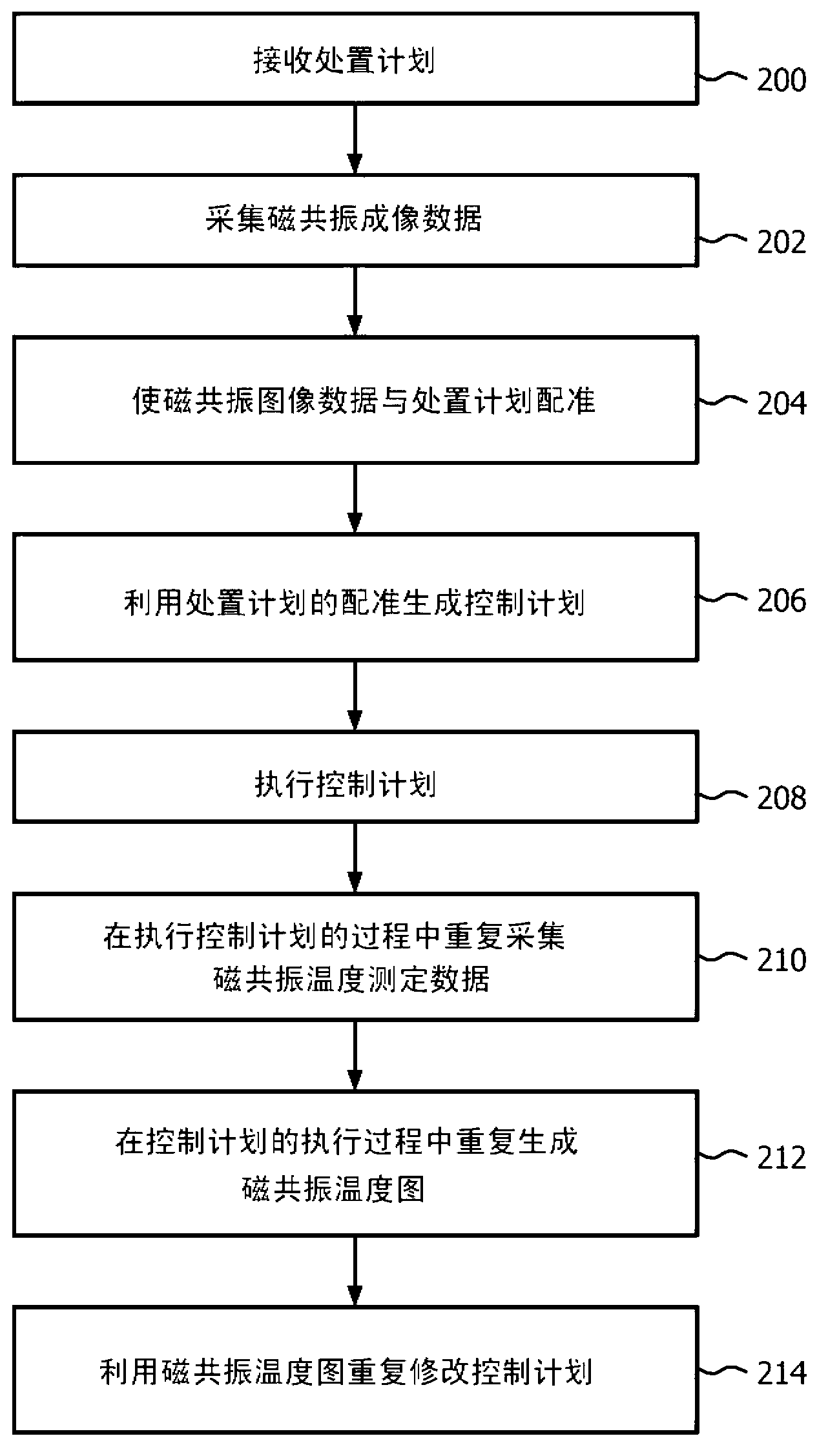
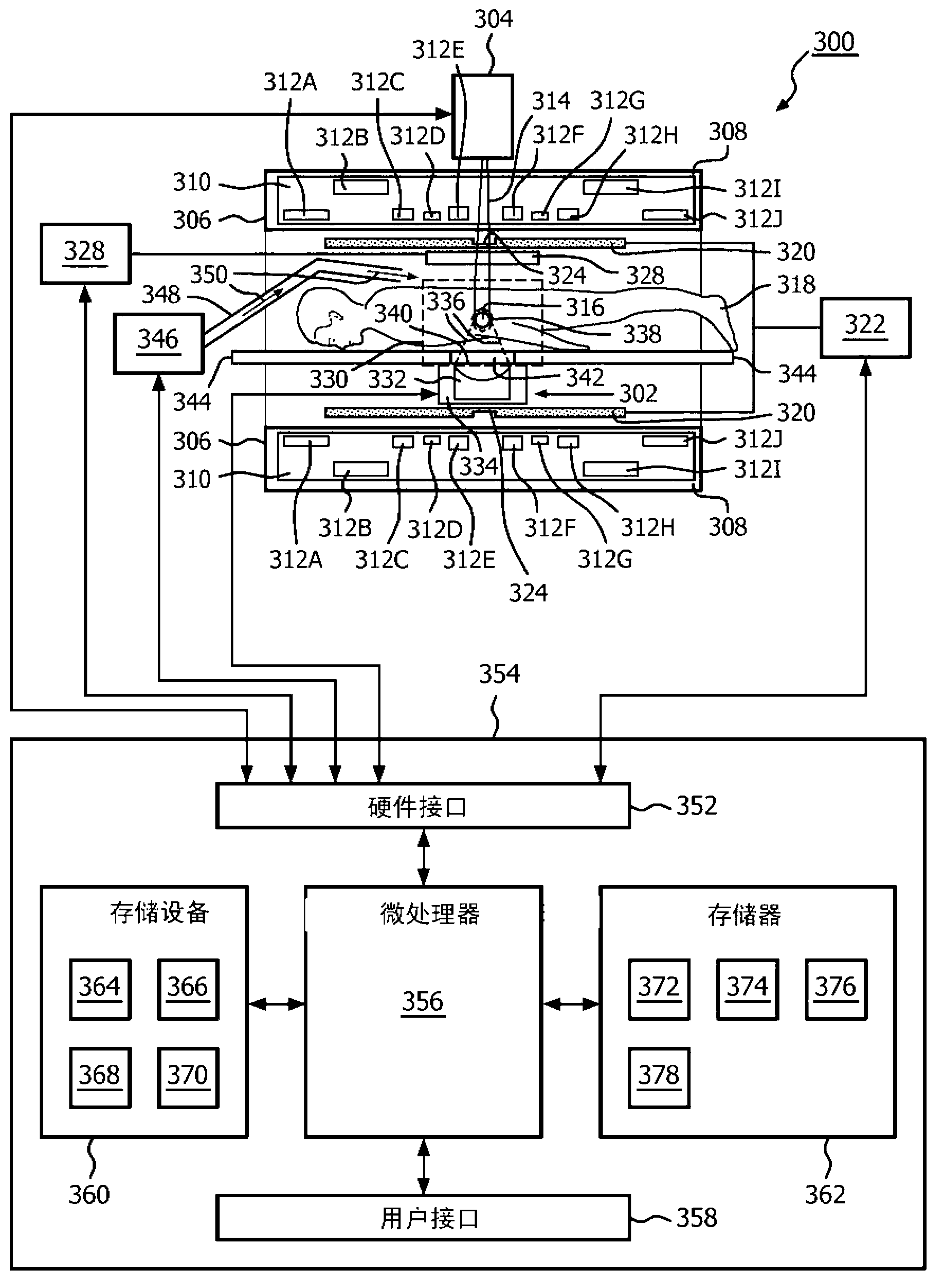
The invention provides for a therapeutic apparatus comprising a tissue heating system (302, 480, 482). The therapeutic apparatus further comprises a magnetic resonance imaging system (300) for acquiring magnetic resonance thermometry data (366) from nuclei of a subject (318) located within an imaging volume (330). The therapeutic apparatus further comprises a radiation therapy system (304, 592) for irradiating an irradiation volume (316, 516) of the subject, wherein the irradiation volume is within the imaging volume. The therapeutic apparatus further comprises a controller (354) for controlling the therapeutic apparatus. The controller is adapted for acquiring (100, 210) magnetic resonance thermometry data repeatedly using the magnetic resonance imaging system. The controller is adapted for heating (102, 208) at least the irradiation volume using the tissue heating system. The heating is controlled using the magnetic resonance thermometry data. The controller is adapted for irradiating (104, 208) the irradiation volume.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic nanometer temperature measuring method based on effective relaxation time
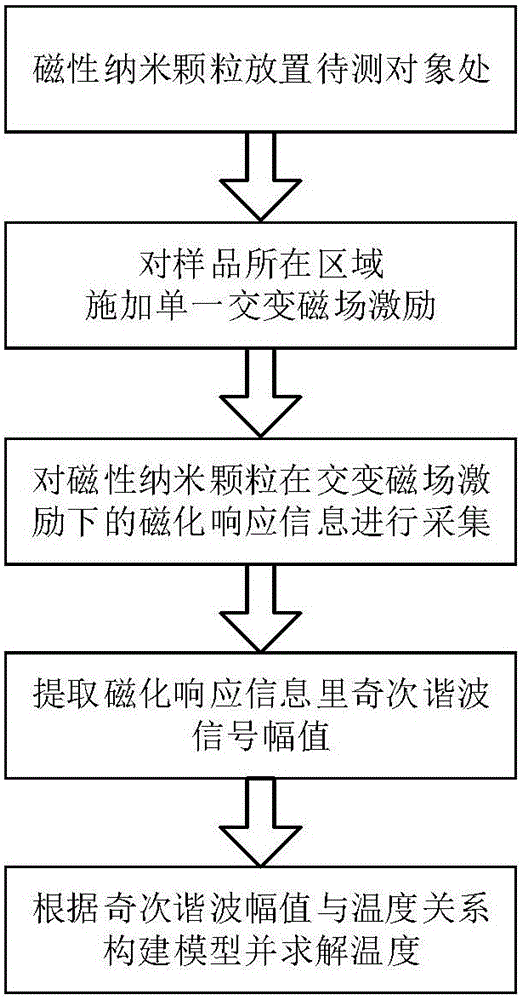
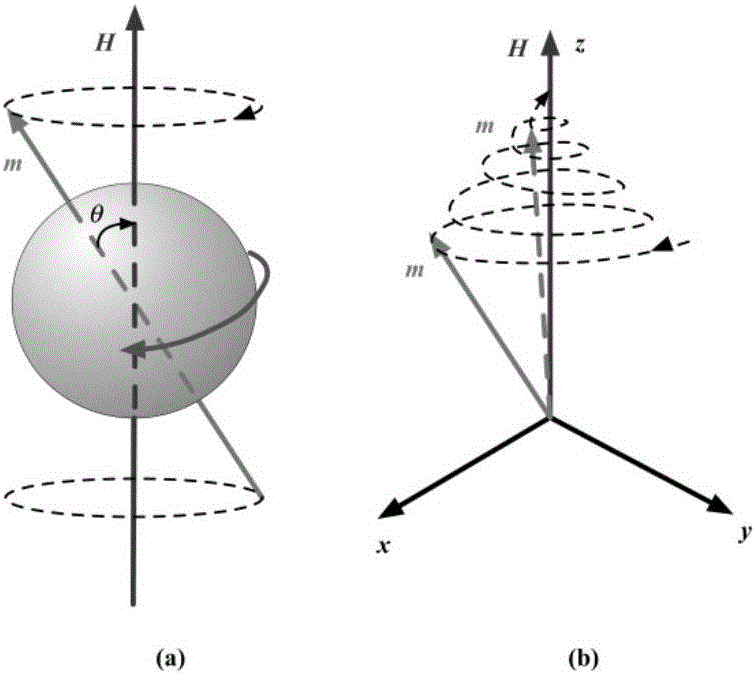
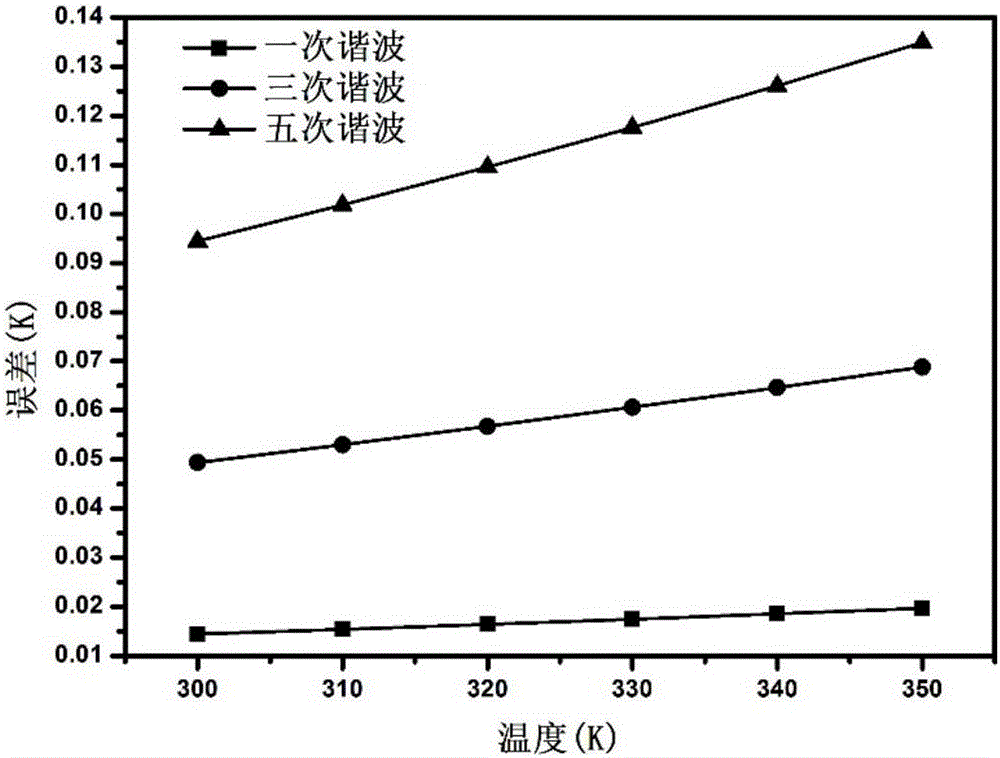
ActiveCN106137519AHigh temperature sensitivityRealize temperature measurementMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue heatingMathematical model
The invention discloses a magnetic nanometer temperature measuring method based on effective relaxation time. The method comprises the following steps that magnetic nanometer particles are placed in an object area to be detected inside a nontransparent article; the magnetic nanometer particles in the object area to be detected are subjected to tissue heating with a radio frequency magnetic field, and meanwhile magnetizing response information of the magnetic nanometer particles under the excitation of the radio frequency magnetic field is obtained with a coil of a hollow structure; the amplitude value of any harmonic signal in magnetizing response signals of the magnetic nanometer particles is extracted; effective relaxation time serves as an intermediate variable, and the relation between the amplitude values of harmonic signals and the absolute temperature is established with the harmonic information to solve the absolute temperature. According to the method, a mathematical model between the magnetizing response harmonic amplitude value information of the magnetic nanometer particles and temperatures is established with the effective relaxation time, the temperature information of the article can be rapidly and accurately obtained, and especially the temperatures are measured while a radio frequency field is heated under the premise that no excitation magnetic field is added in magnetic nanometer thermal therapy.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY +1
Tissue ablation device using a lens to three dimensionally focus electromagnetic energy
InactiveUS20050267457A1Minimize impactMinimal effectDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingSide effectTissue heating
This invention provides a device that uses a lens to focus electromagnetic energy to a singular three dimensionally focused point. The invention has three-dimensional target positioning capability. This invention can be used in tissue ablation, tissue thermography, tissue heating, and tissue hyperthermia. Possible specific treatment applications include, but are not limited to: cancer ablation, scar tissue ablation, epithelial tissue ablation, infected tissue ablation, herniated disk removal, tissue growth stimulation. The main advantage of this device is that it maximizes the effect on the target tissue and greatly reduces the effect of the surrounding tissue to the point of there being close to no side effects from radiation therapy.
Owner:HRUSCHKA CYNTHIA RUYBA
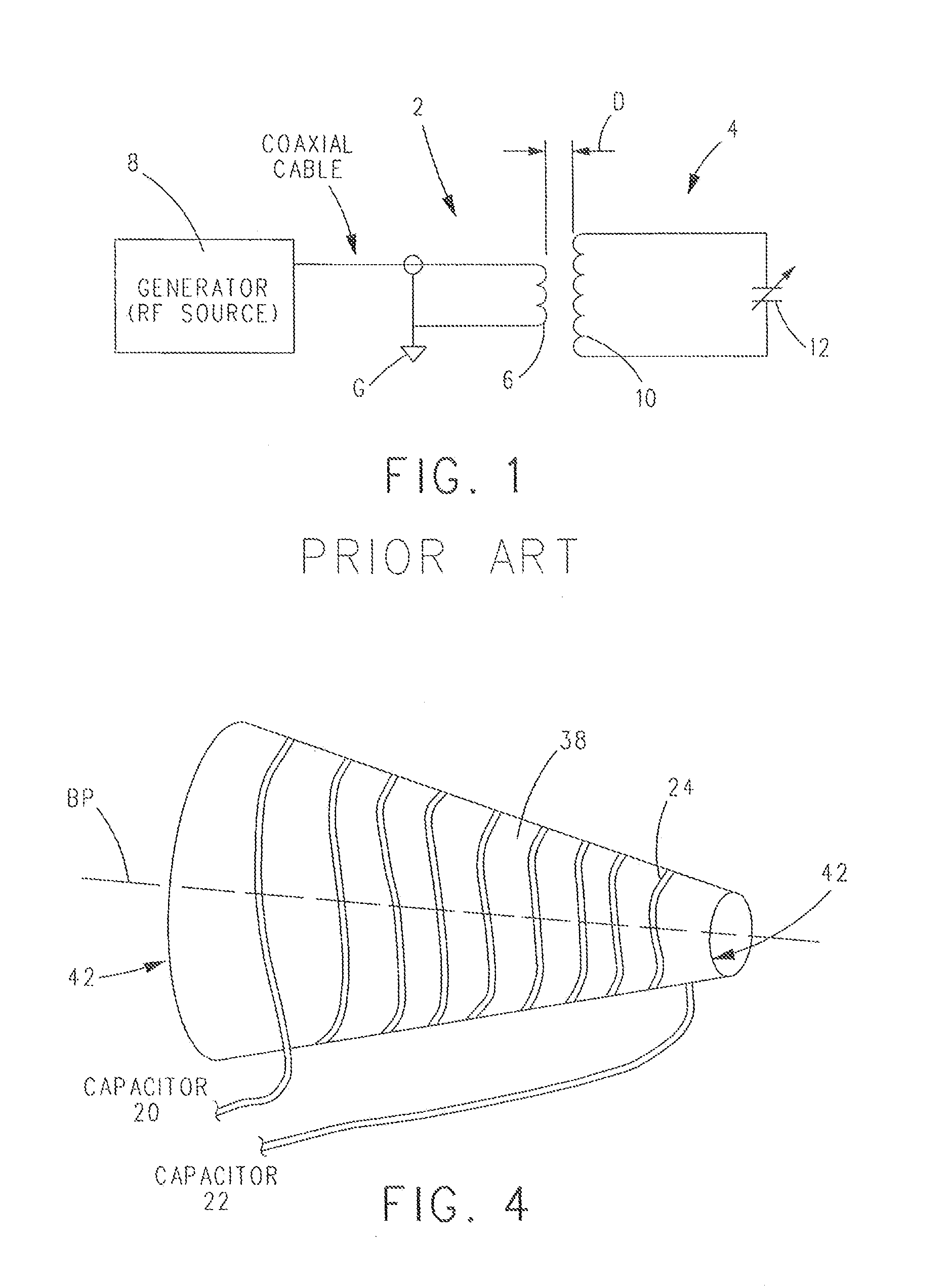
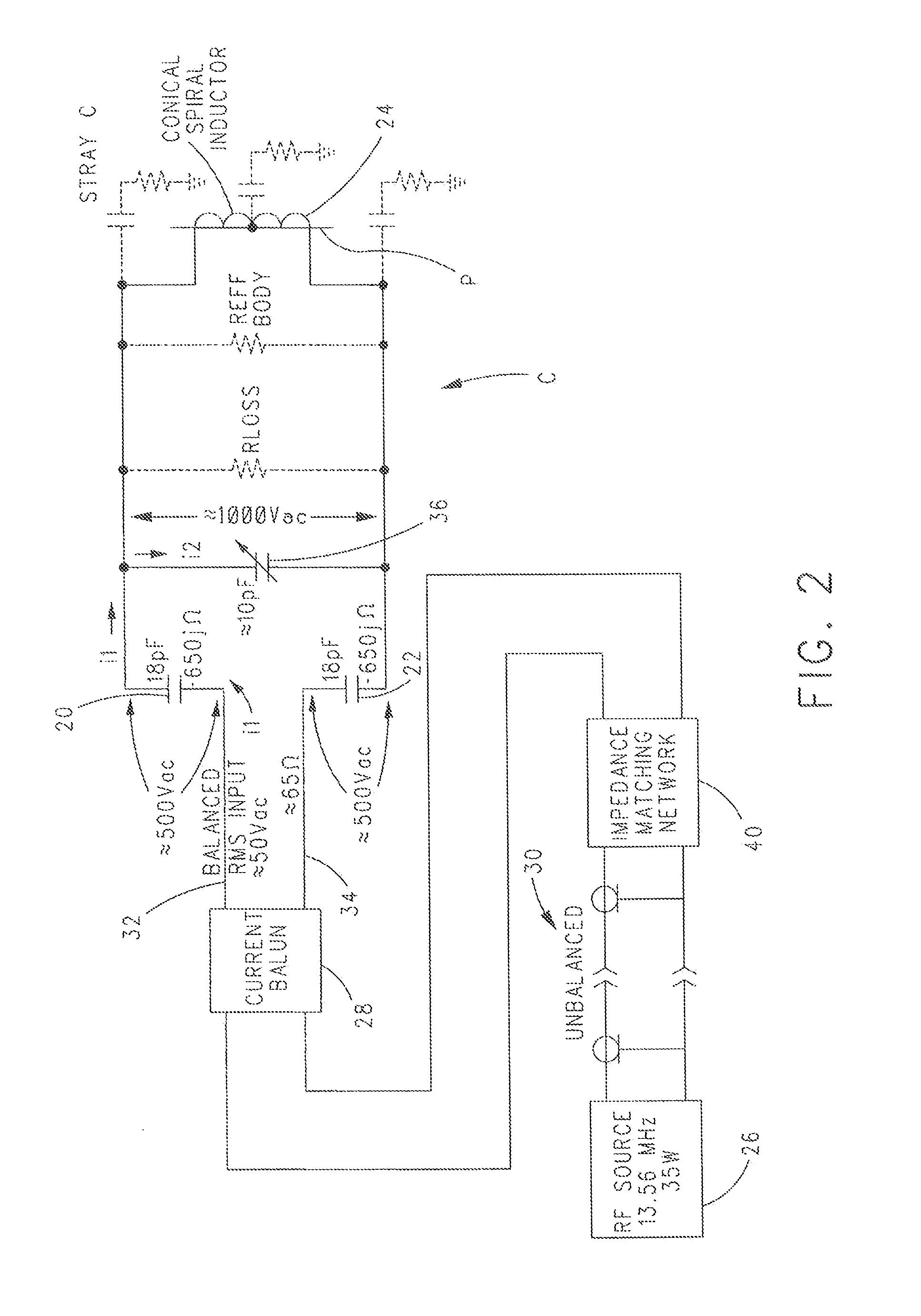
Coupling Method for Resonant Diathermy and Other Bio-Tissue Heating Applicators
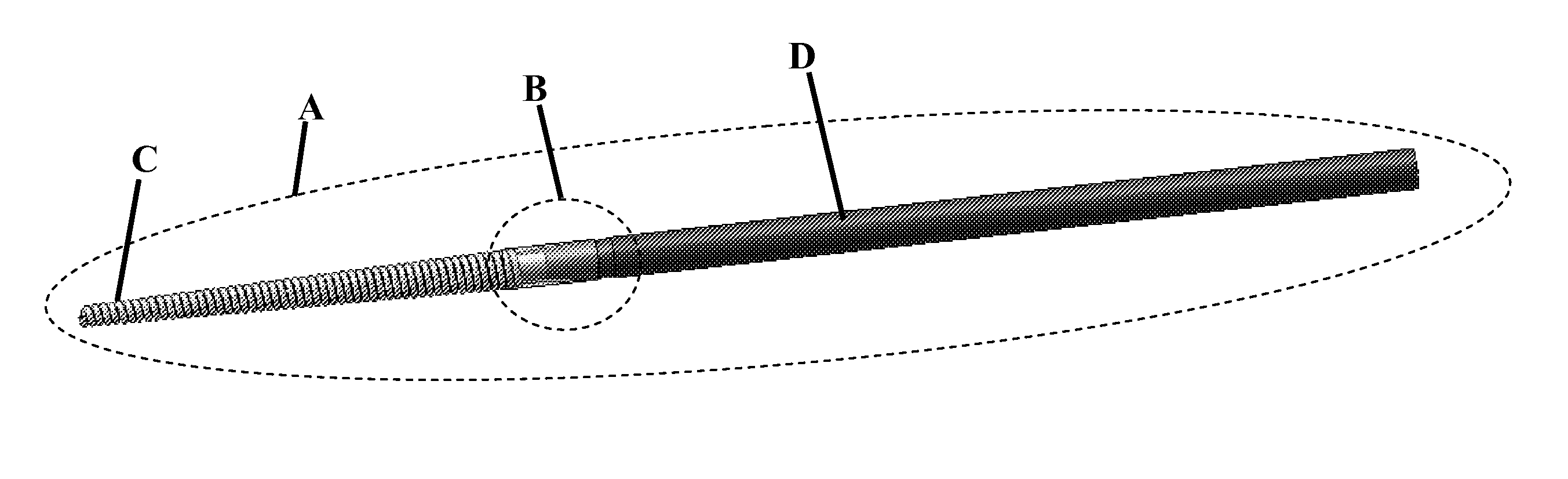
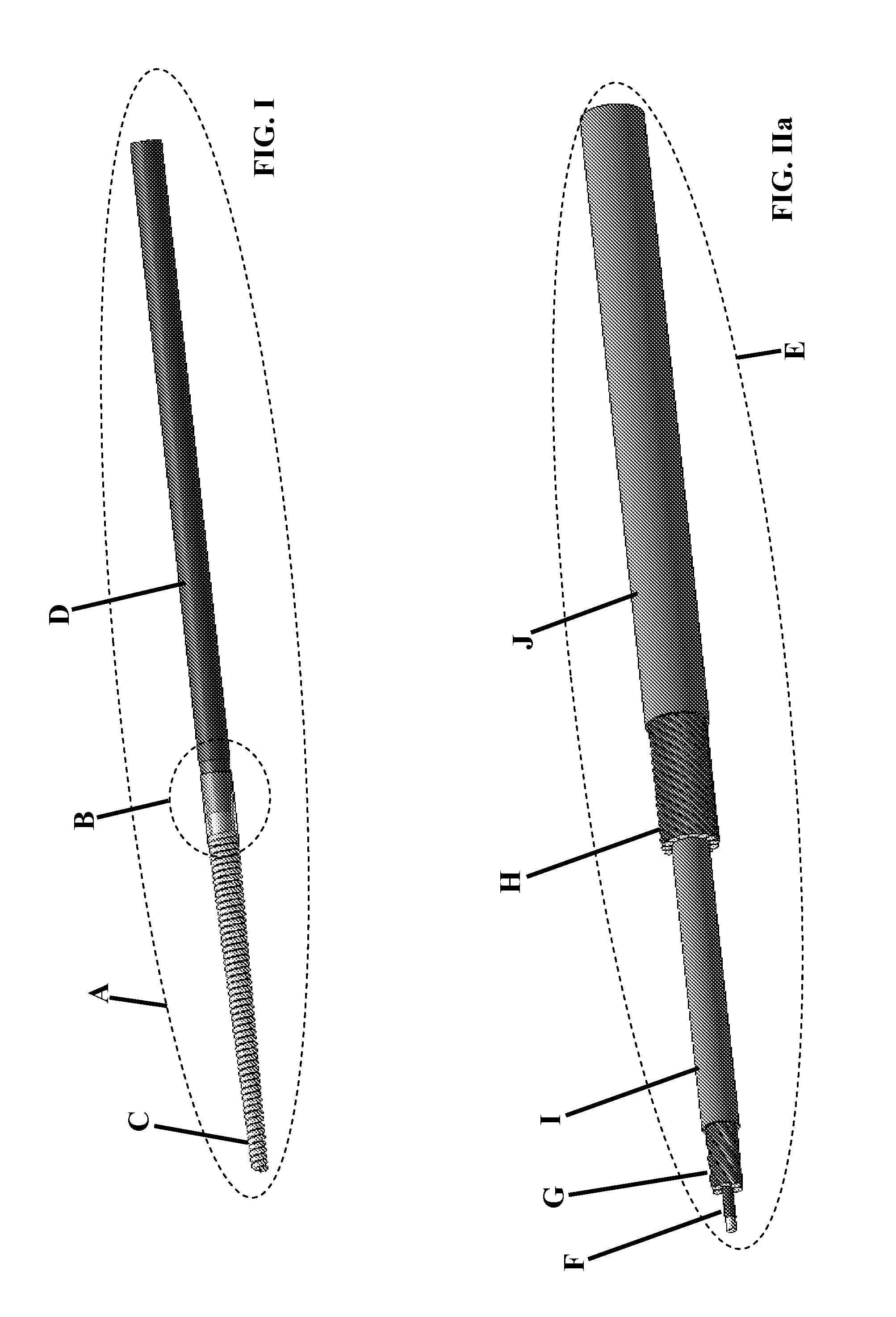
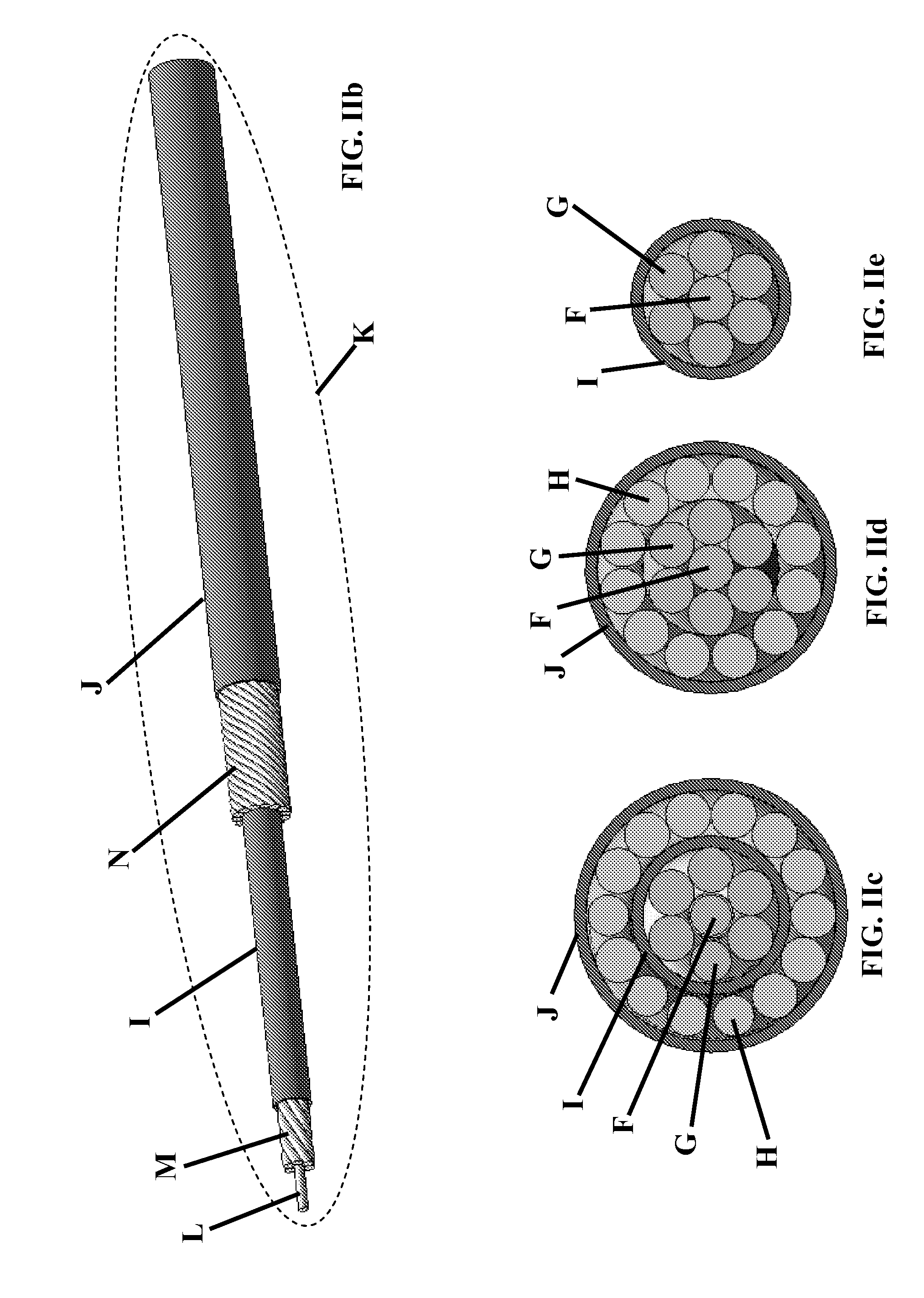
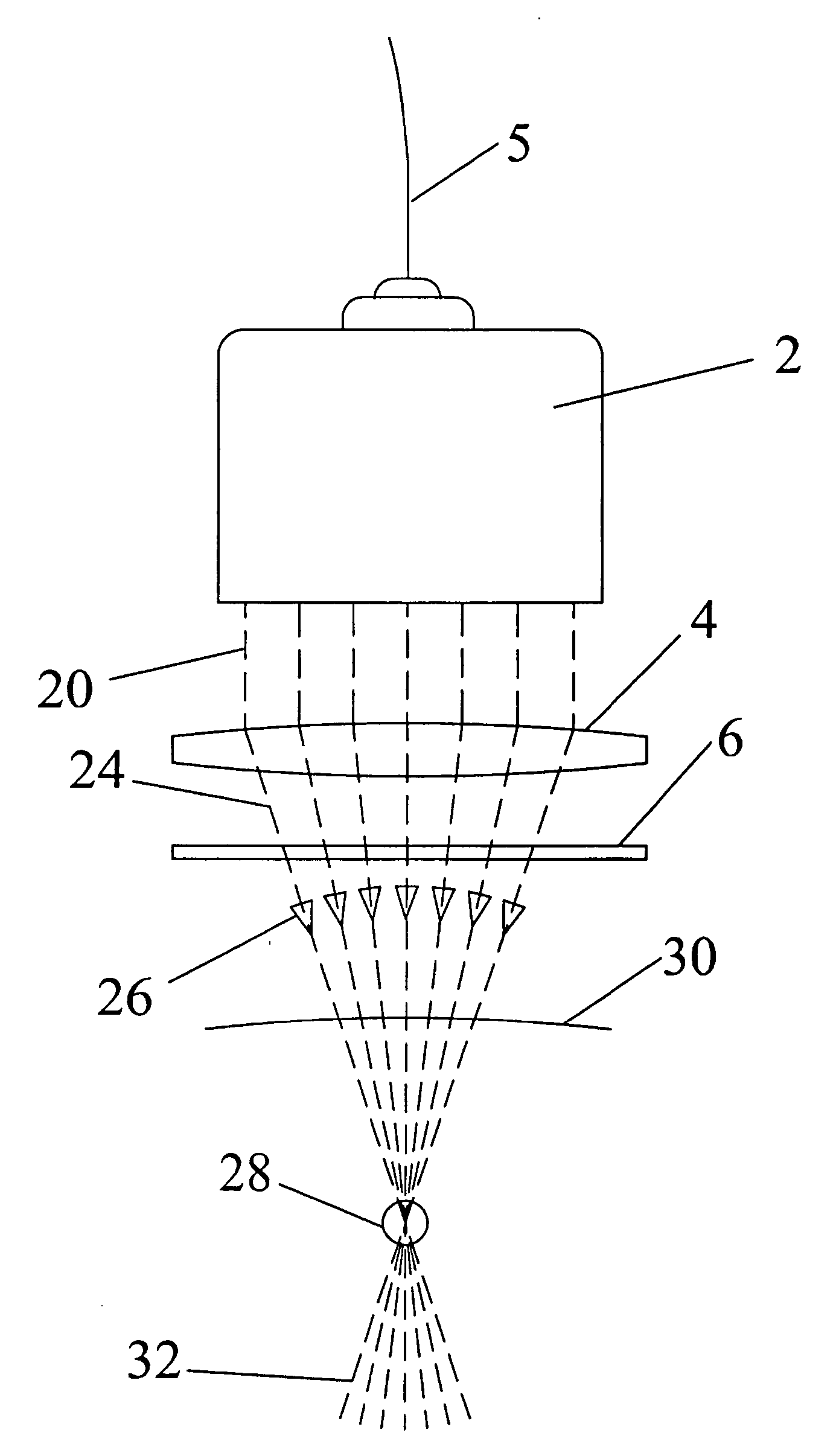
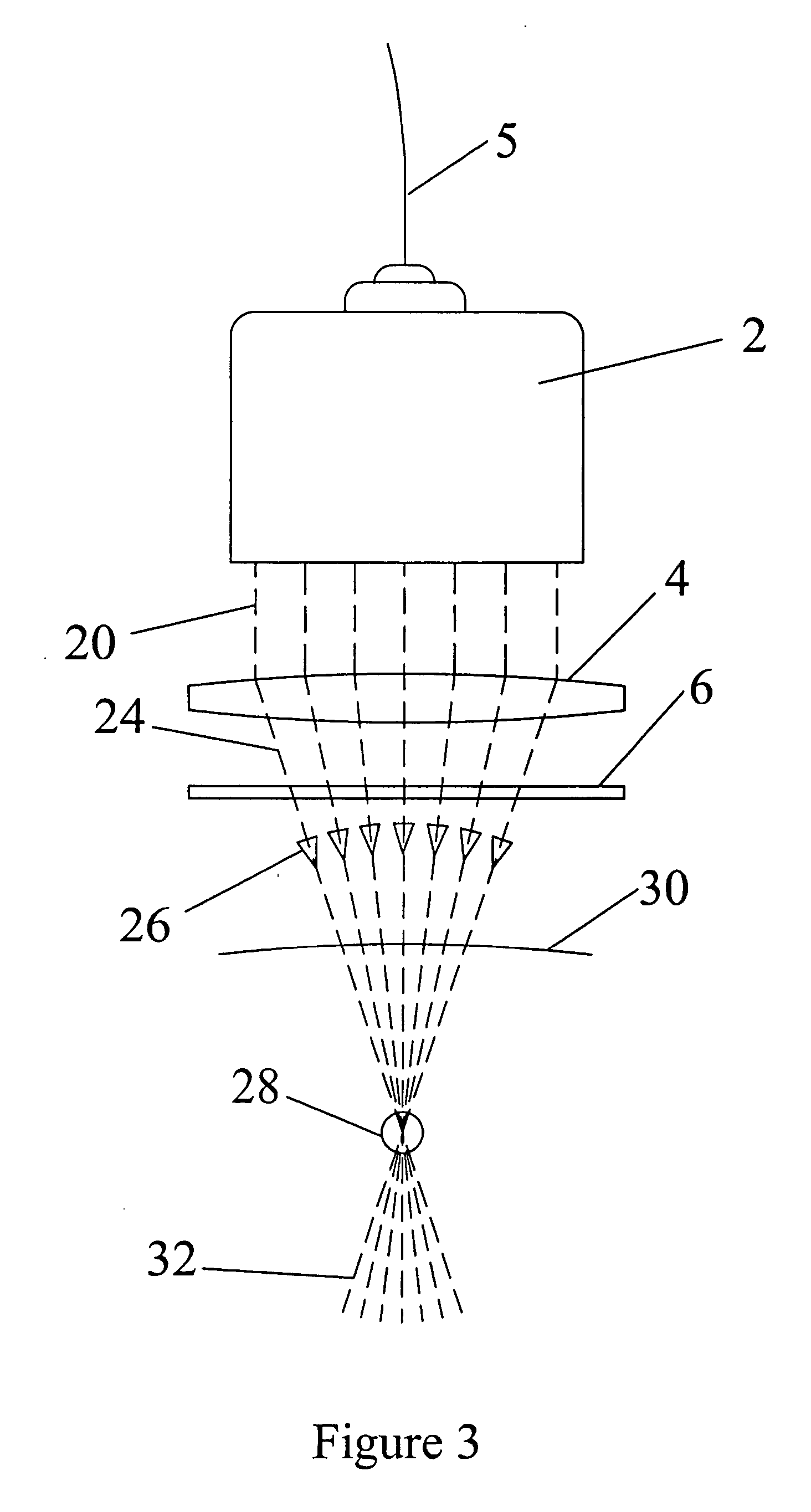
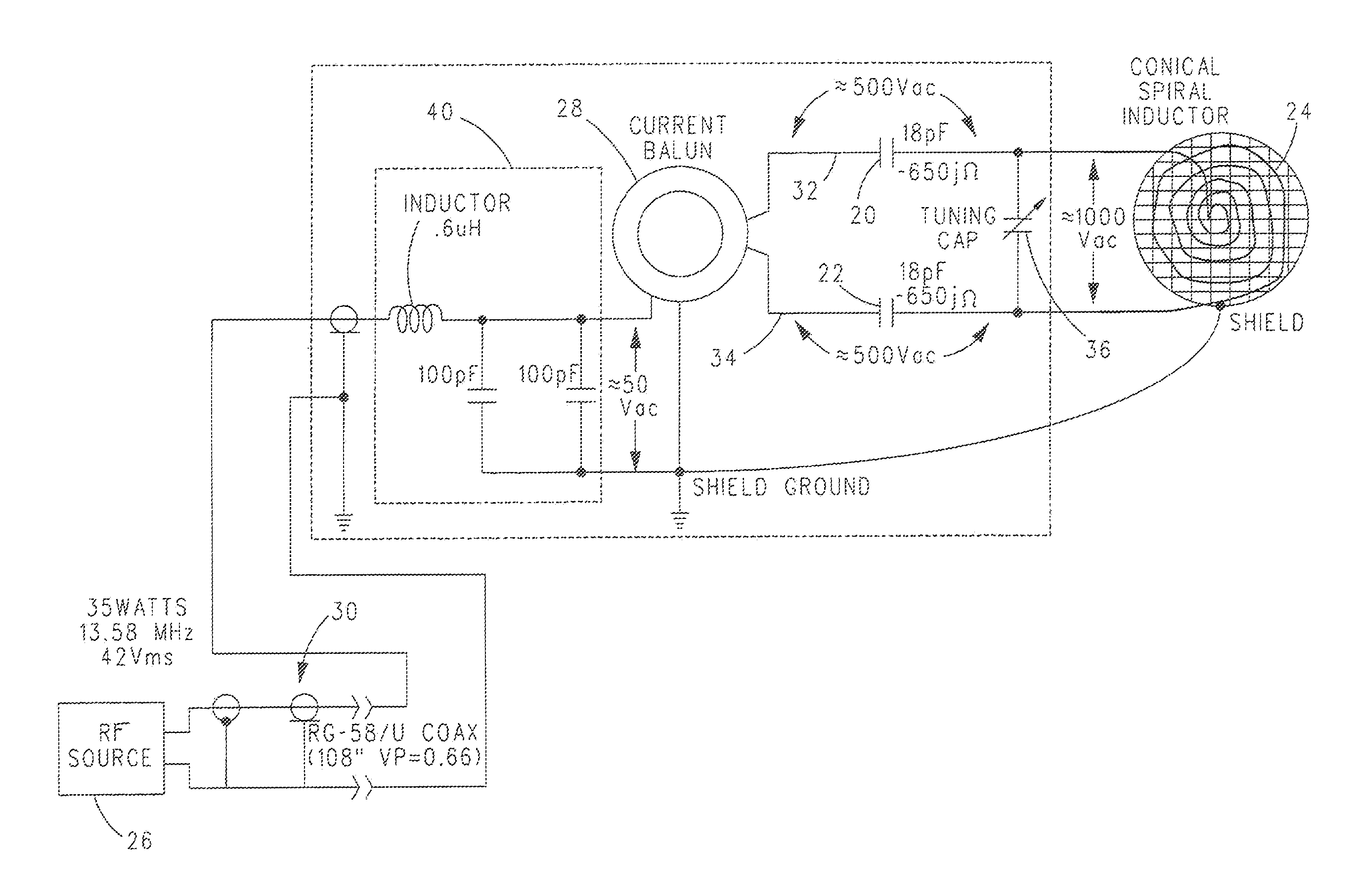
ActiveUS20120265277A1Eliminating inductive couplingEfficiently boosting the common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR)Magnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSurgical instrument detailsCapacitanceTissue heating
A diathermy apparatus includes a cylindrical coil (24) defining an opening (42), a pair of capacitors of substantially similar capacitance (20 and 22), each capacitor connected to one end of the coil, an RF signal source (26), and a balun (28) connected between the RF signal source (26) and the pair of capacitors (20 and 22). The balun (28) is operative for converting an unbalanced signal received from the RF signal source (26) into a balanced signal supplied to coil (24) via the pair of capacitors (20 and 22). Desirably, the cylindrical coil is a conical cylindrical (or cone-shaped) spiral coil.
Owner:VIATHERM THERAPEUTICS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com