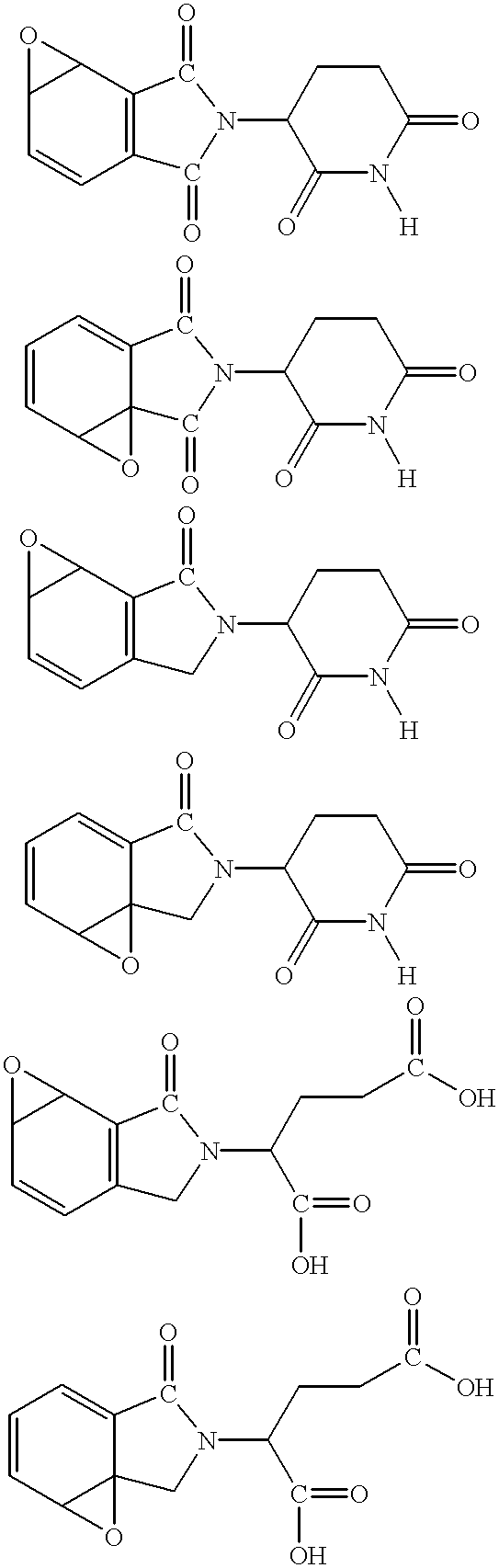
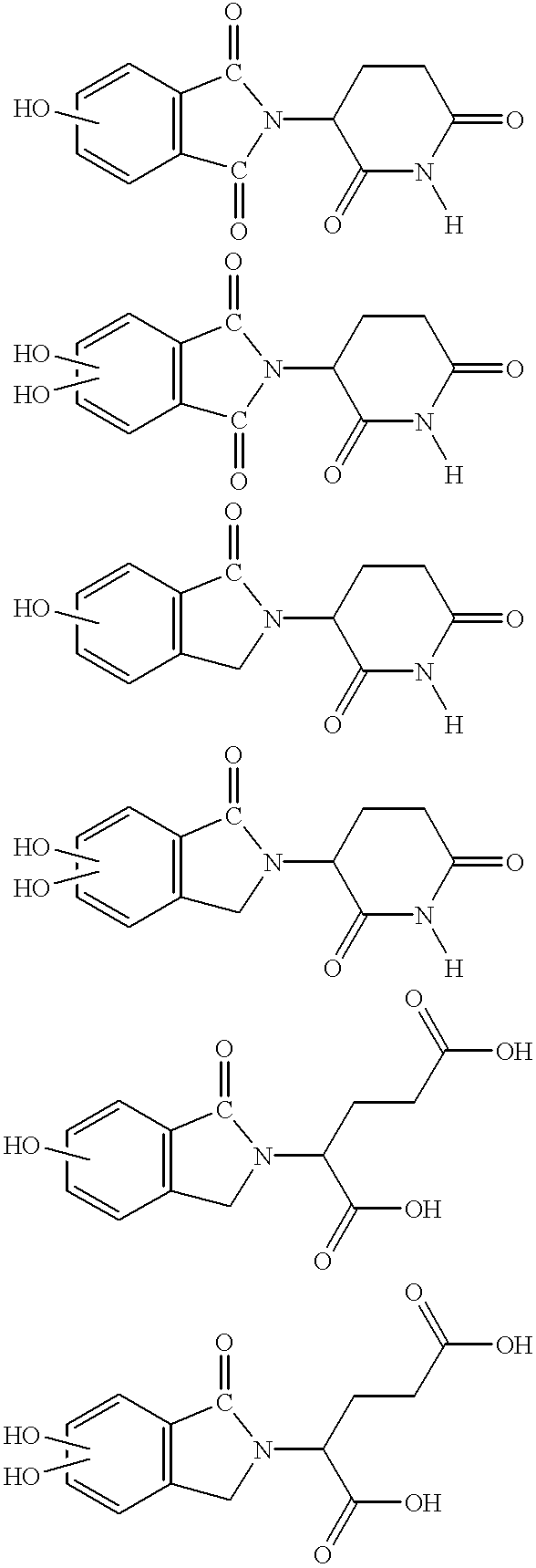
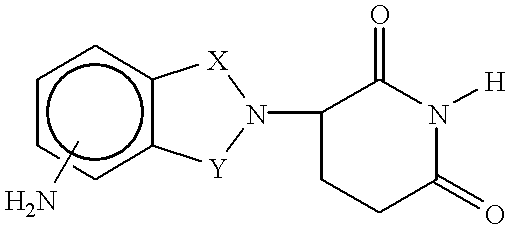
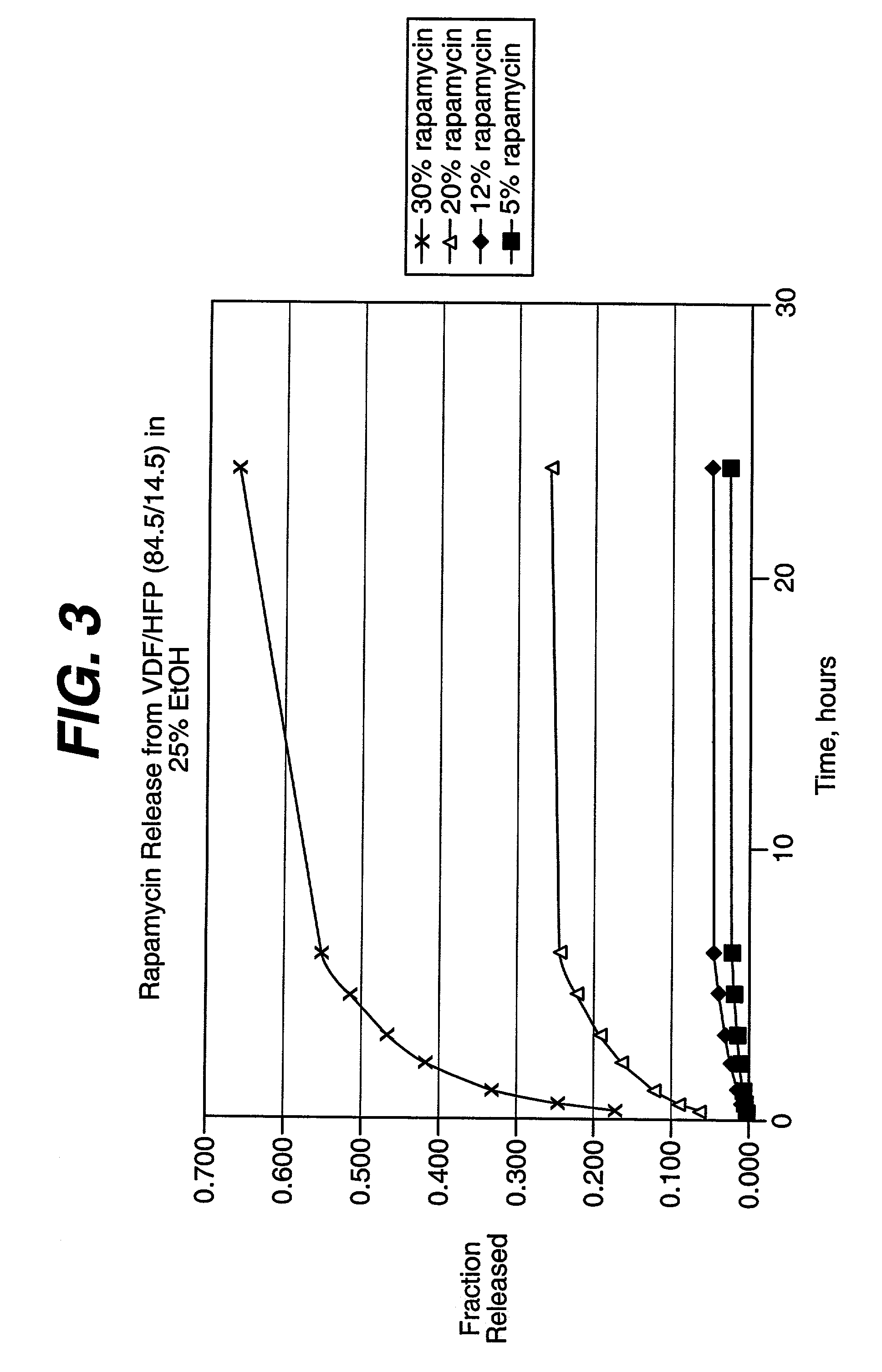
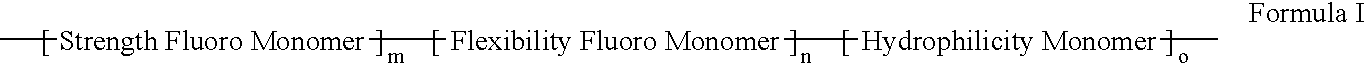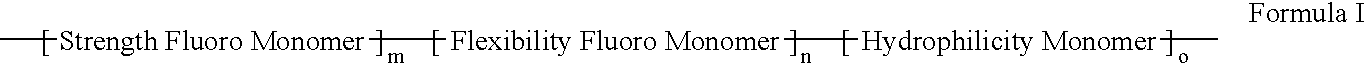Patents
Literature
1128 results about "Percent Diameter Stenosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Binary restenosis is traditionally defined as a reduction in the percent diameter stenosis of 50% or more (≥50%). It is also known as just "binary stenosis". The term "binary" means that patients are placed in 2 groups, those who have ≥50% stenosis and those who have <50% stenosis.
Targeted and high density drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002852A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
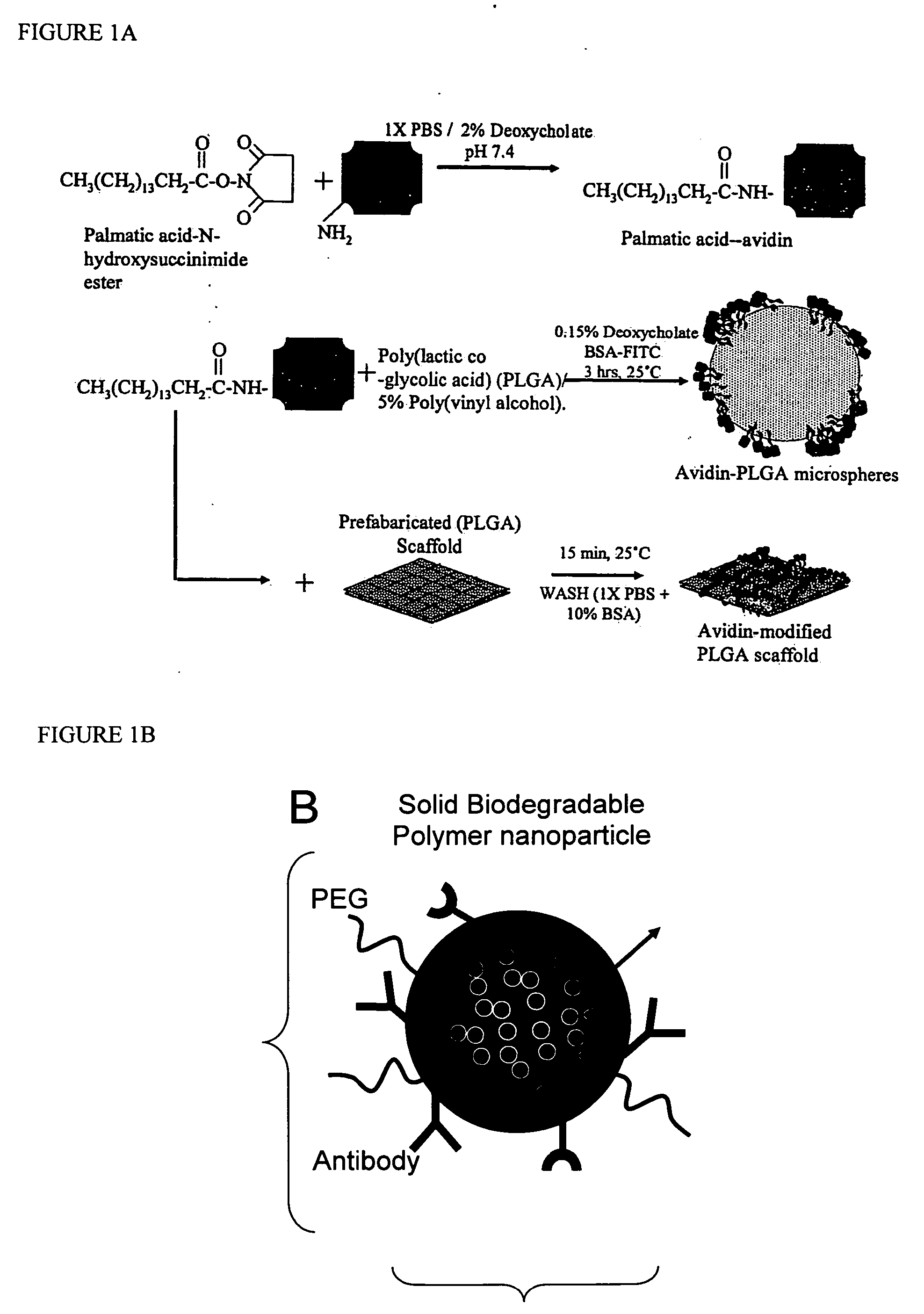
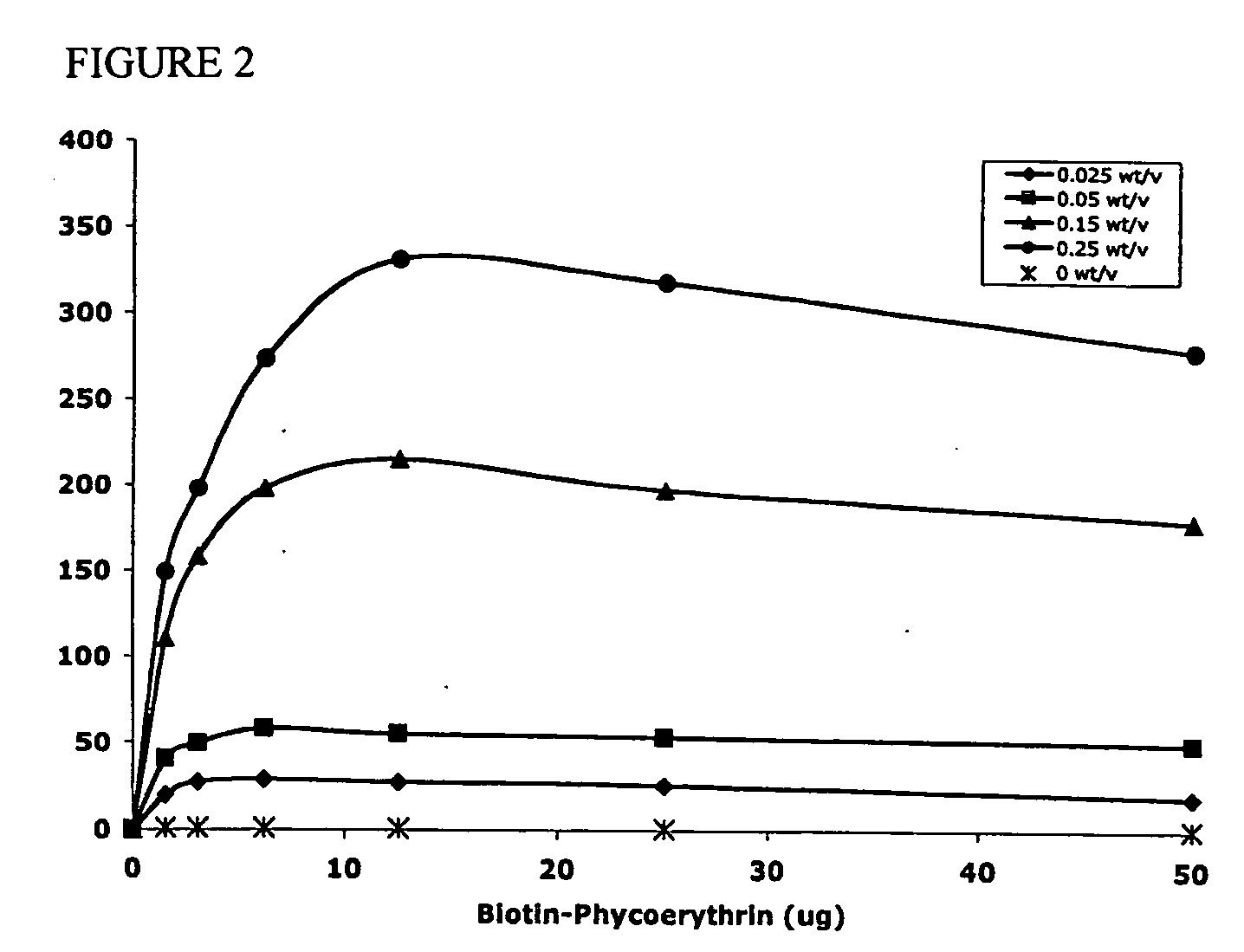
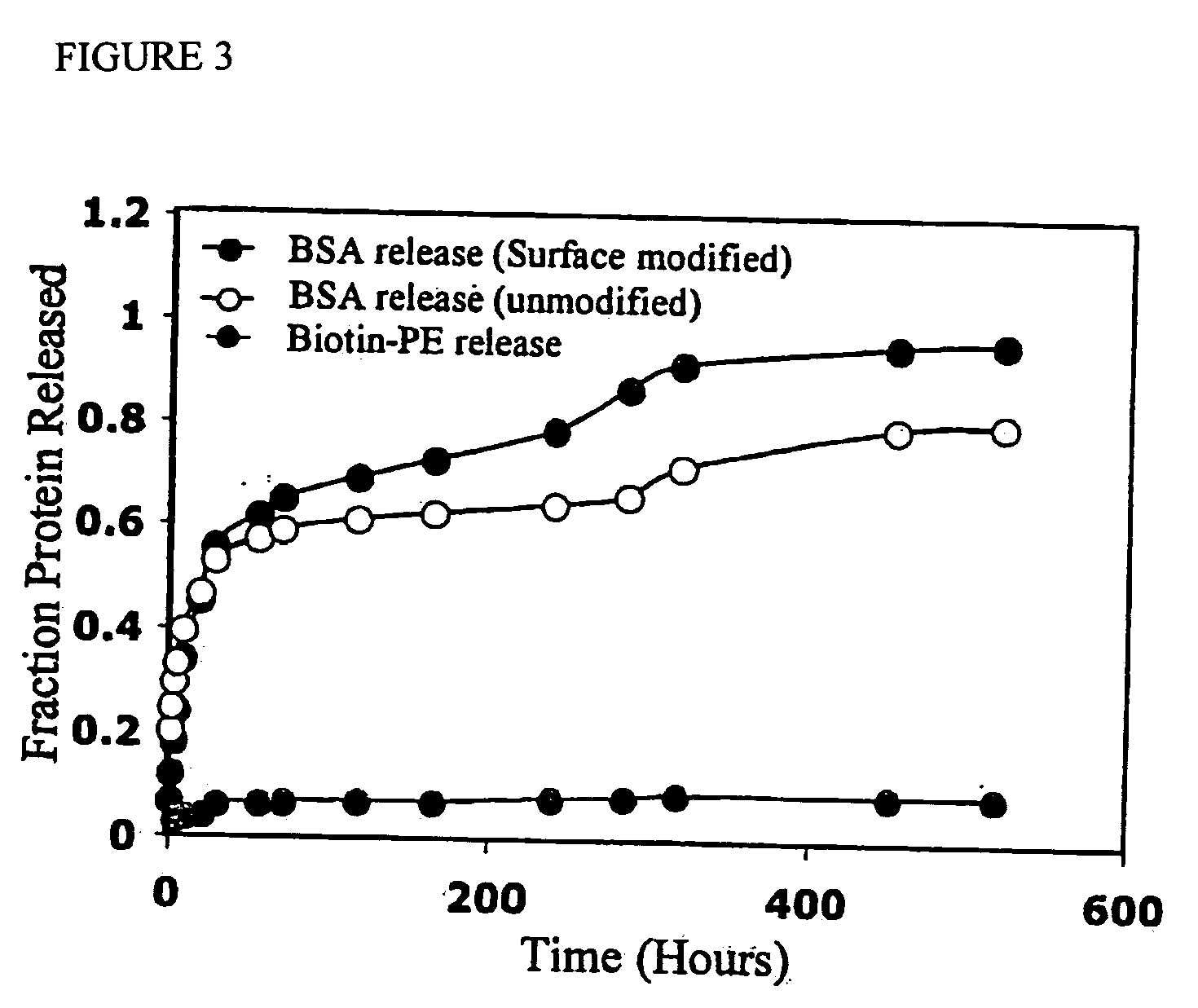
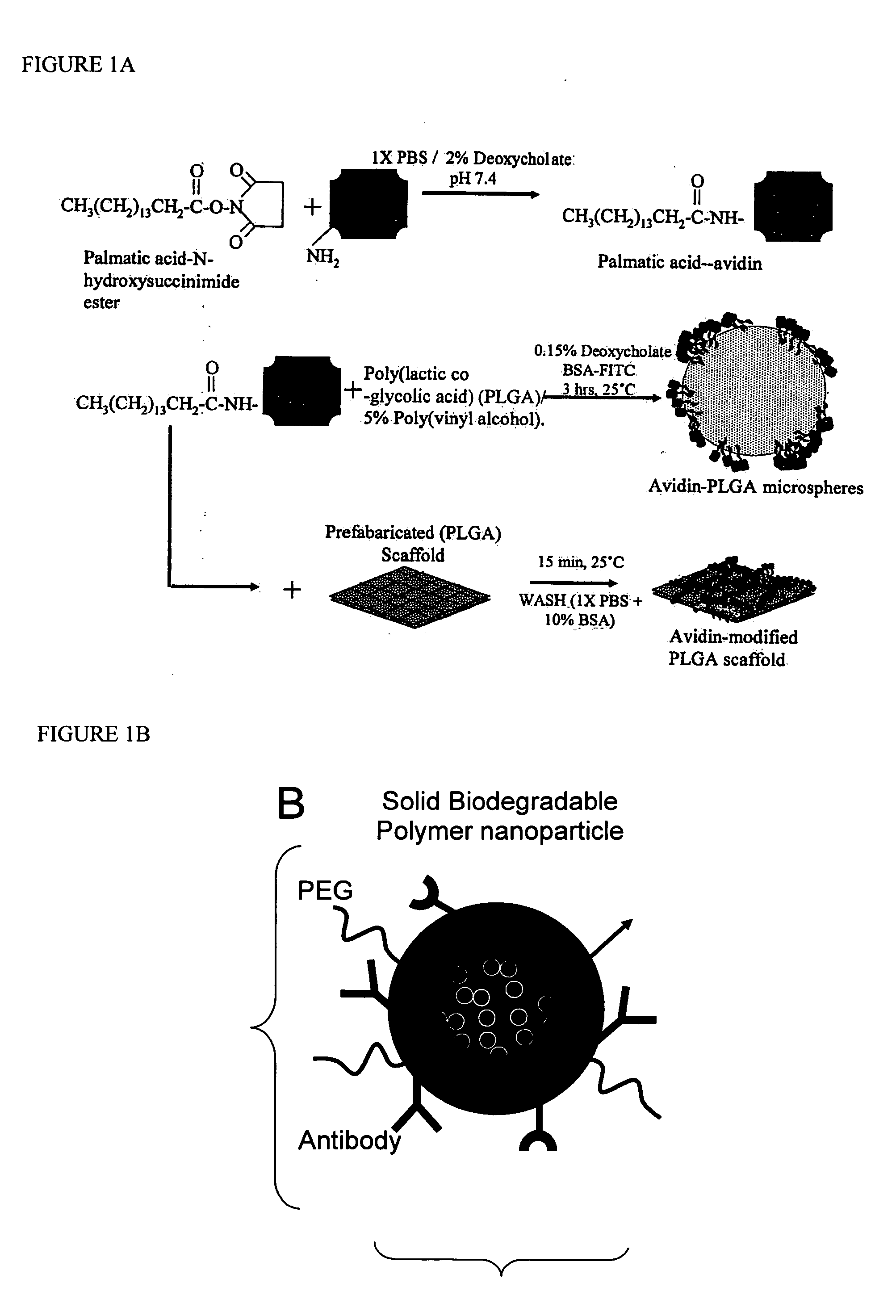
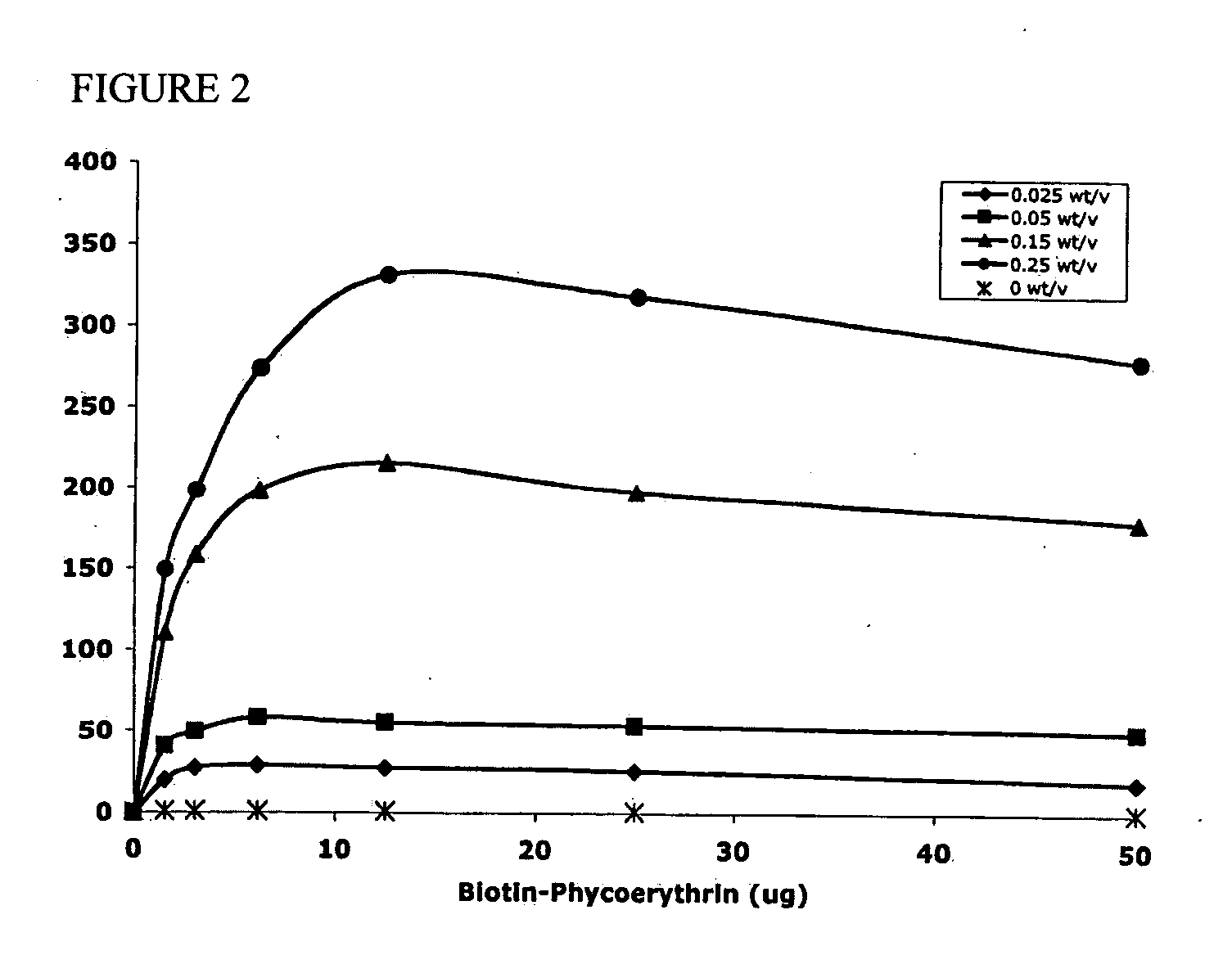
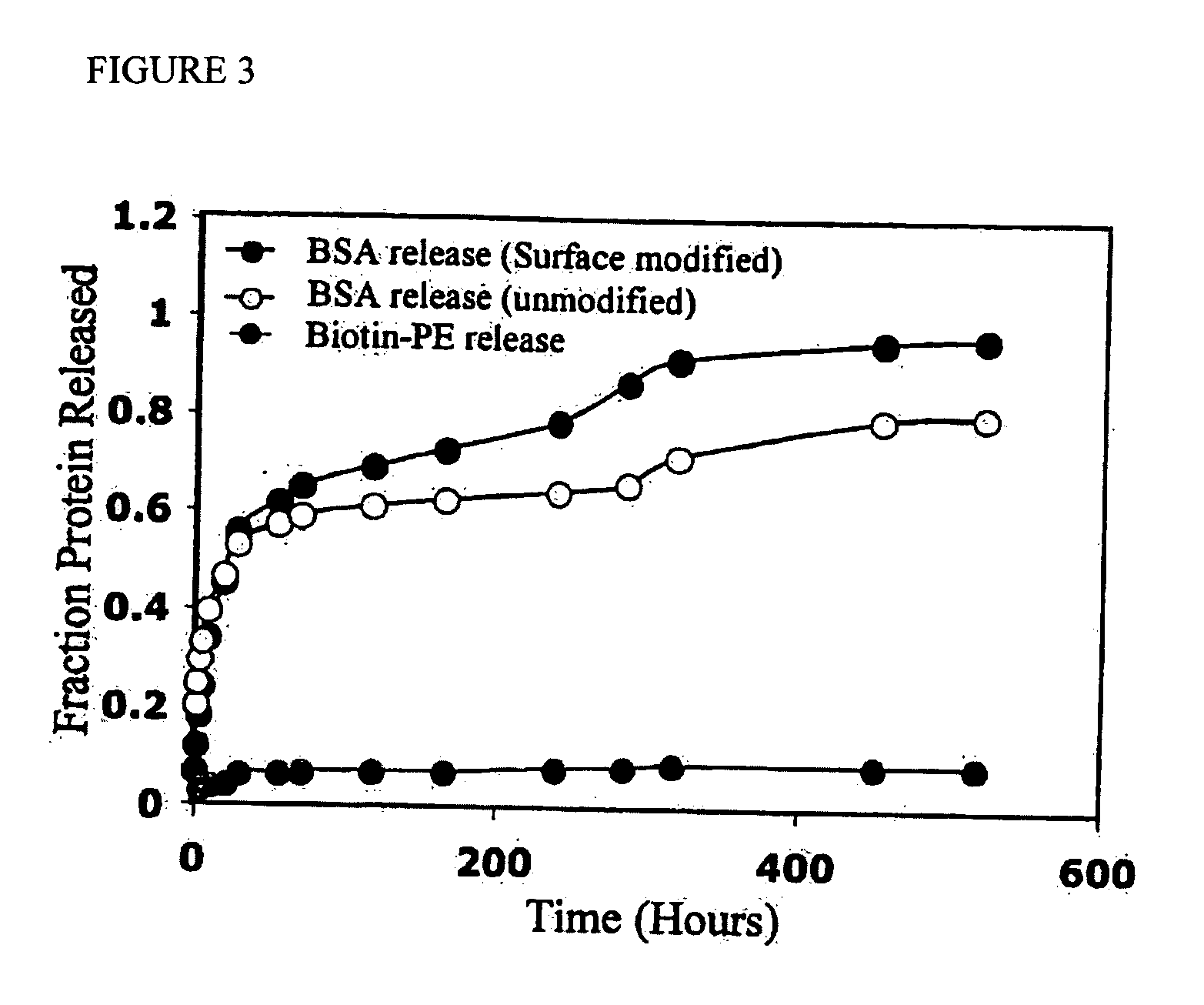
Polymeric delivery devices have been developed which combine high loading / high density of molecules to be delivered with the option of targeting. As used herein, “high density” refers to microparticles having a high density of ligands or coupling agents, which is in the range of 1000-10,000,000, more preferably between 10,000 and 1,000,000 ligands per square micron of microparticle surface area. A general method for incorporating molecules into the surface of biocompatible polymers using materials with an HLB of less than 10, more preferably less than 5, such as fatty acids, has been developed. Because of its ease, generality and flexibility, this method has widespread utility in modifying the surface of polymeric materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering, as well other other fields. Targeted polymeric microparticles have also been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Electrosurgical systems and methods for recanalization of occluded body lumens
InactiveUS6855143B2Speed up the flowEliminate potentialSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingCoronary arteriesDistal portion
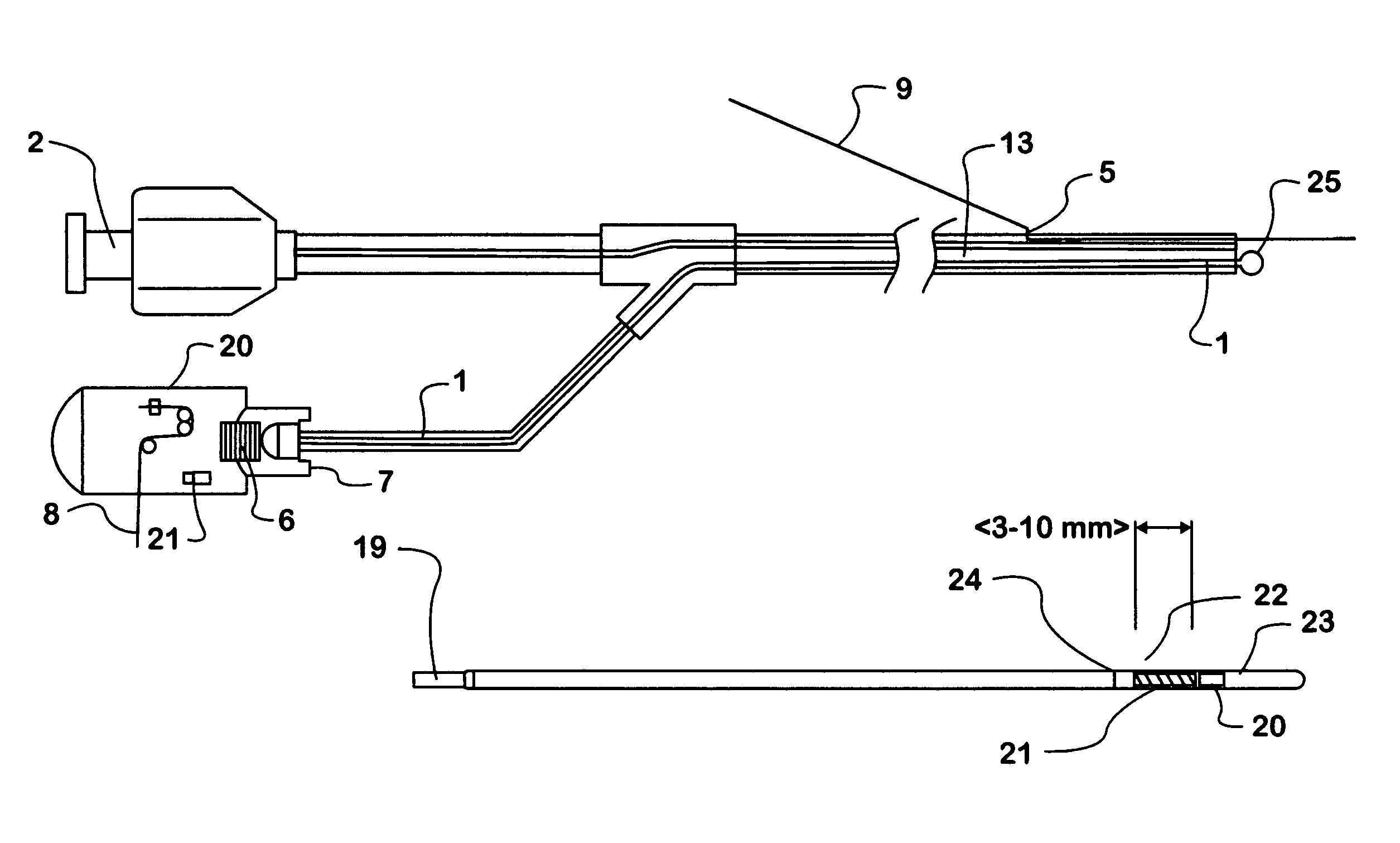
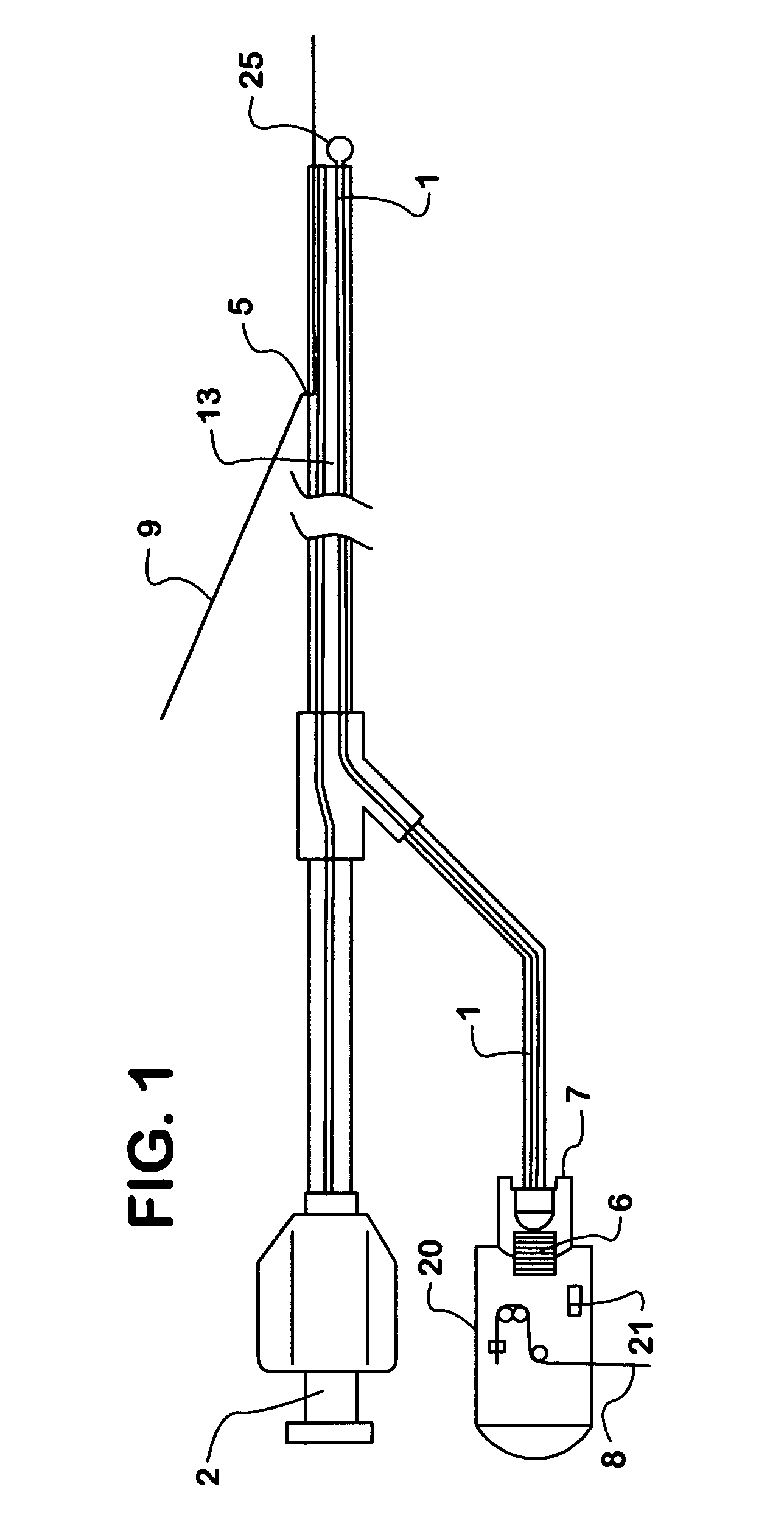
The present invention comprises electrosurgical apparatus and methods for maintaining patency in body passages subject to occlusion by invasive tissue growth. The apparatus includes an electrode support disposed at a shaft distal end having at least one active electrode arranged thereon, and at least one return electrode proximal to the at least one active electrode. In one embodiment, a plurality of active electrodes each comprising a curved wire loop portion are sealed within a distal portion of the electrode support. The apparatus and methods of the present invention may be used to open and maintain patency in virtually any hollow body passage which may be subject to occlusion by invasive cellular growth or invasive solid tumor growth. Suitable hollow body passages include ducts, orifices, lumens, and the like, with exemplary body passages including the coronary arteries. The present invention is particularly useful for reducing or eliminating the effects of restenosis in coronary arteries by selectively removing tissue in-growth in or around stents anchored therein.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
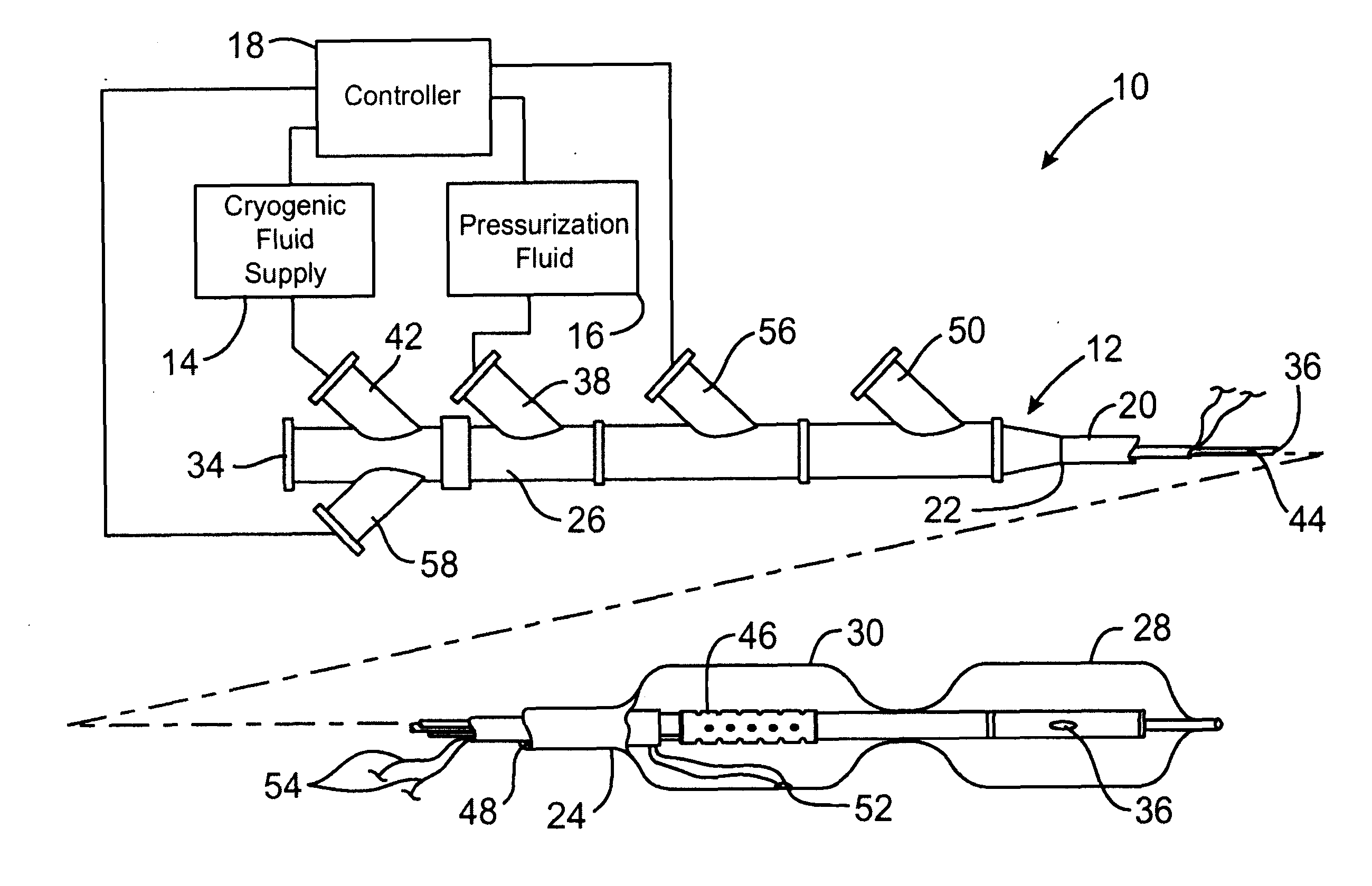
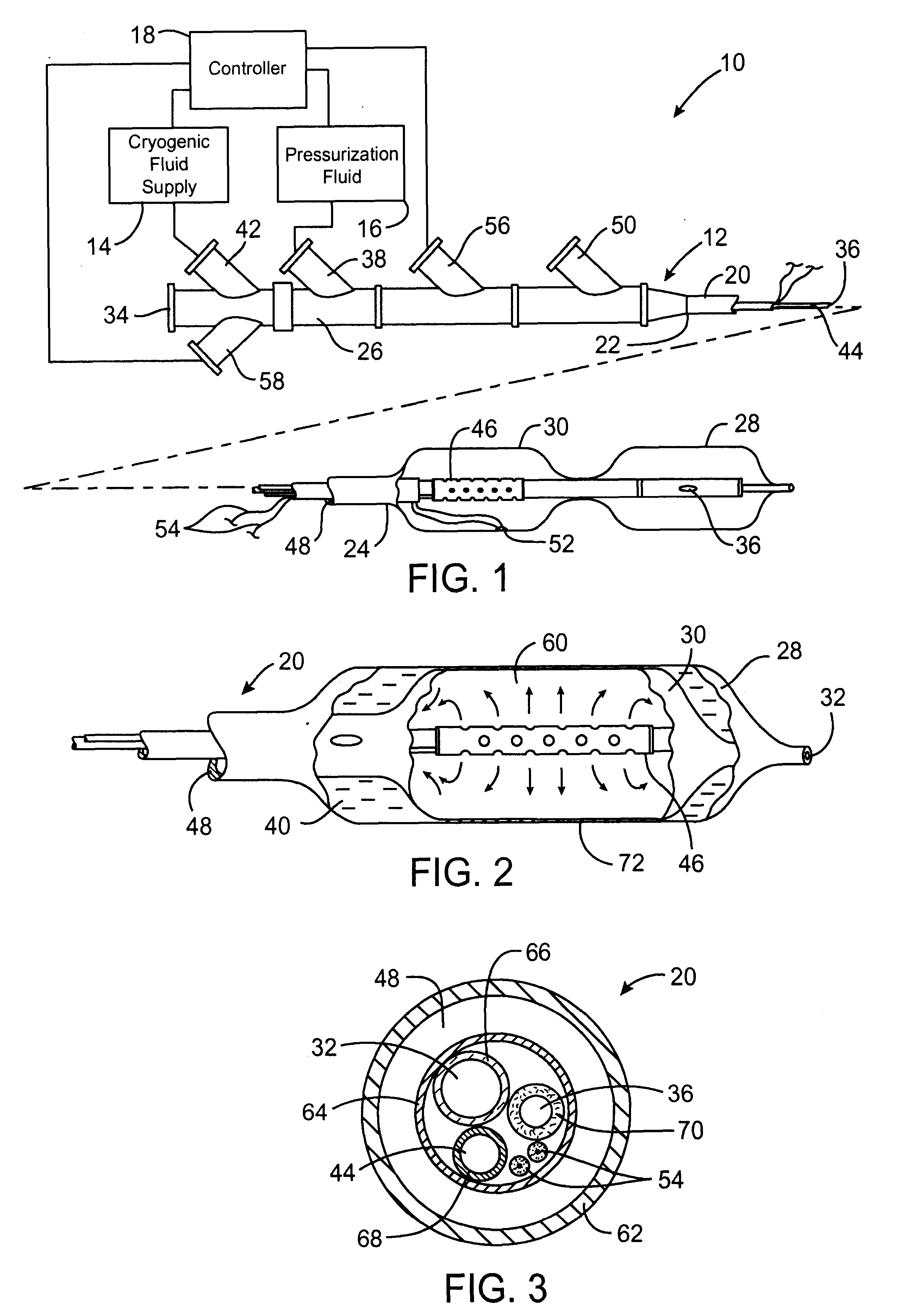
Cryogenically enhanced intravascular interventions
InactiveUS6468297B1Less stenosisLowering indexCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
Techniques and devices for treating atherosclerotic disease use controlled cryogenic cooling, often in combination with angioplasty and / or stenting. A combination cryogenic / angioplasty catheter may cool the diseased blood vessel before, during, and / or after dilation. Controlled cooling of the vessel wall reduces actual / observed hyperplasia as compared to conventional uncooled angioplasty. Similar reductions in restenosis may be provided for other primary treatments of the blood vessel, including directional arthrectomy, rotational arthrectomy, laser angioplasty, stenting, and the like. Cooling of vessel wall tissues will often be performed through plaque, and the cooling process will preferably take the thermodynamic effects of the plaque into account.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Therapy via targeted delivery of nanoscale particles
InactiveUS20050090732A1Destroying inhibiting vascularityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiseaseProstate cancer
Disclosed are compositions, systems and methods for treating a subject's body, body part, tissue, body fluid cells, pathogens, or other undesirable matter involving the administration of a targeted thermotherapy that comprises a bioprobe (energy susceptive materials that are attached to a target-specific ligand). Such targeted therapy methods can be combined with at least one other therapy technique. Other therapies include hyperthermia, direct antibody therapy, radiation, chemo- or pharmaceutical therapy, photodynamic therapy, surgical or interventional therapy, bone marrow or stem cell transplantation, and medical imaging, such as MRI, PET, SPECT, and bioimpedance. The disclosed therapies may be useful in the treatment of a variety of indications, including but not limited to, cancer of any type, such as bone marrow, lung, vascular, neuro, colon, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer, epitheleoid sarcomas, AIDS, adverse angiogenesis, restenosis, amyloidosis, tuberculosis, cardiovascular plaque, vascular plaque, obesity, malaria, and illnesses due to viruses, such as HIV.
Owner:NANOTX INC
Methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, restenosis and related disorders
Methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of all forms of atherosclerosis are described. Administration of compounds such as thalidomide, its analogs, hydrolysis products, metabolites, derivatives and precursors as well as additional compounds capable of inhibiting tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) are used in the invention. Also disclosed is the coating of prosthetic devices, such as stents, with the compounds of the invention for the prevention and / or treatment of restenosis.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
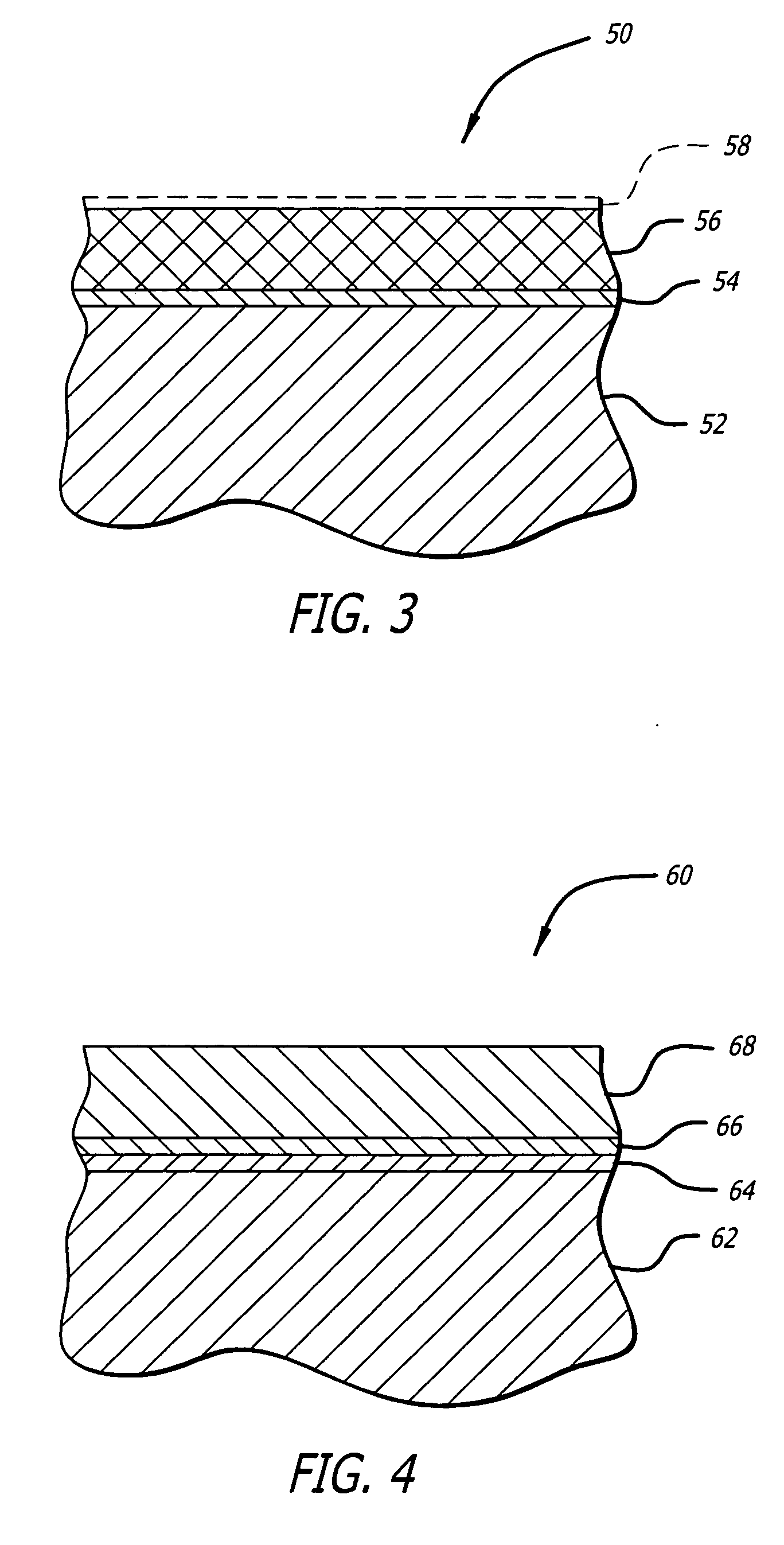
Stent with outer slough coating
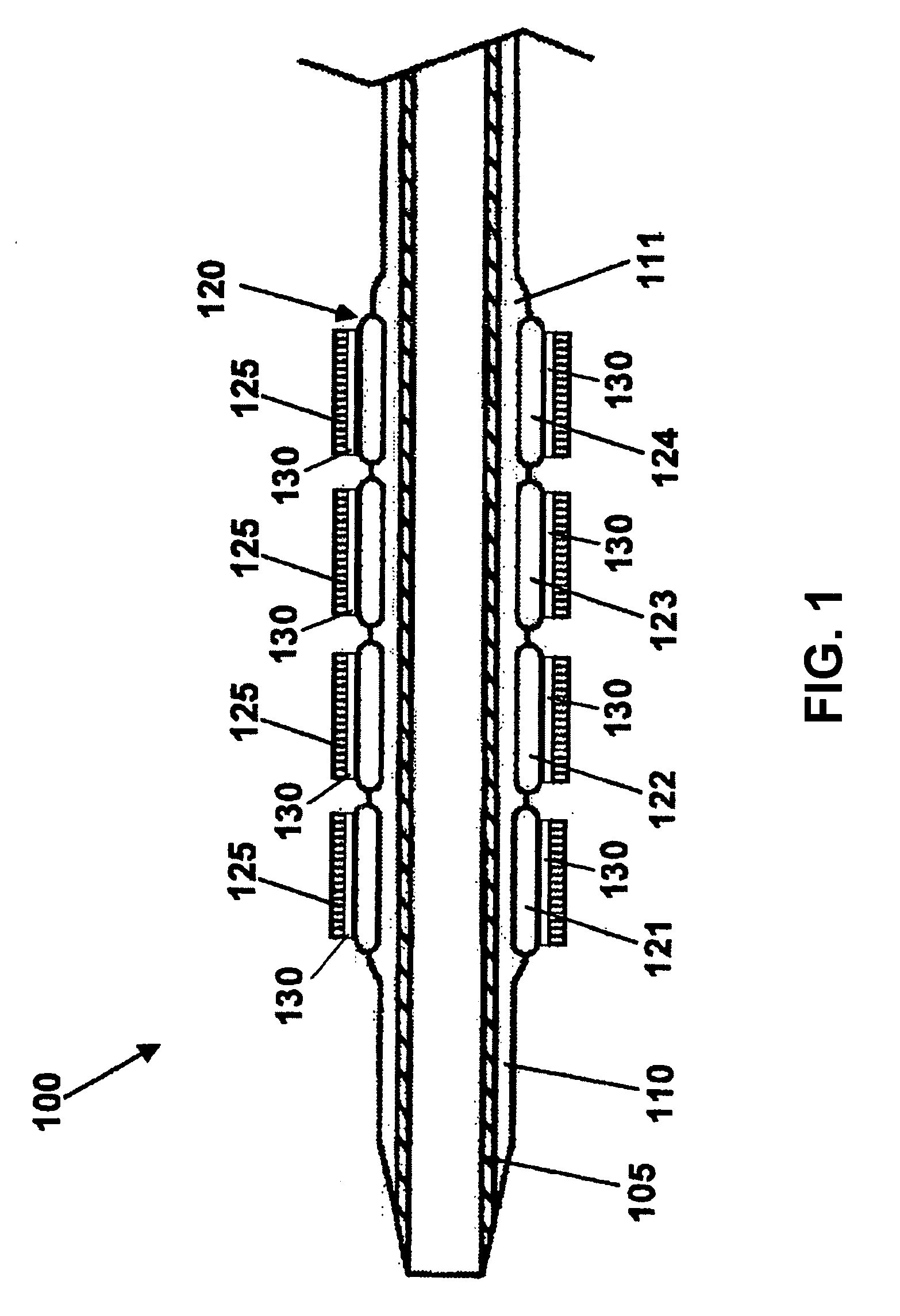
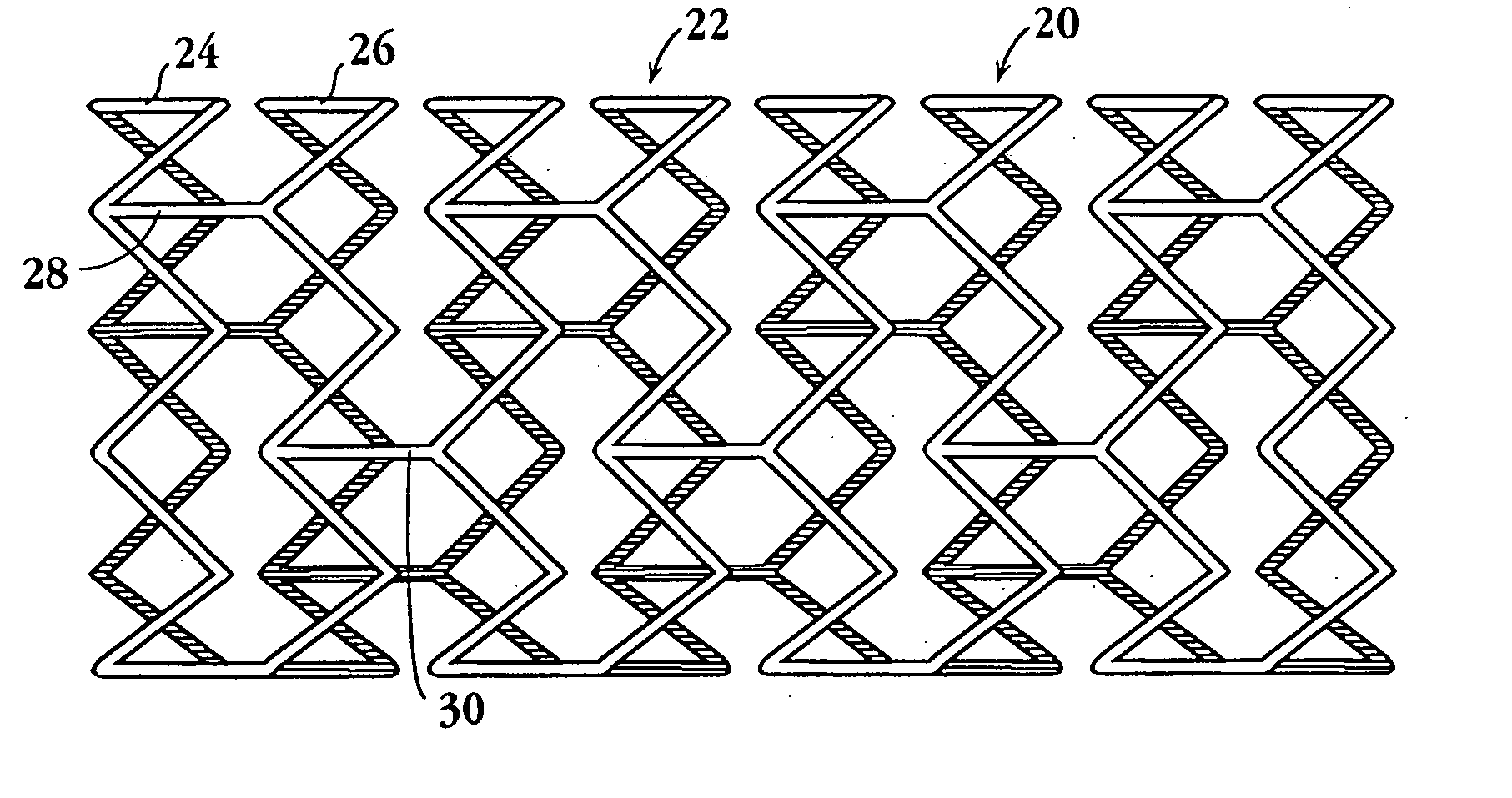
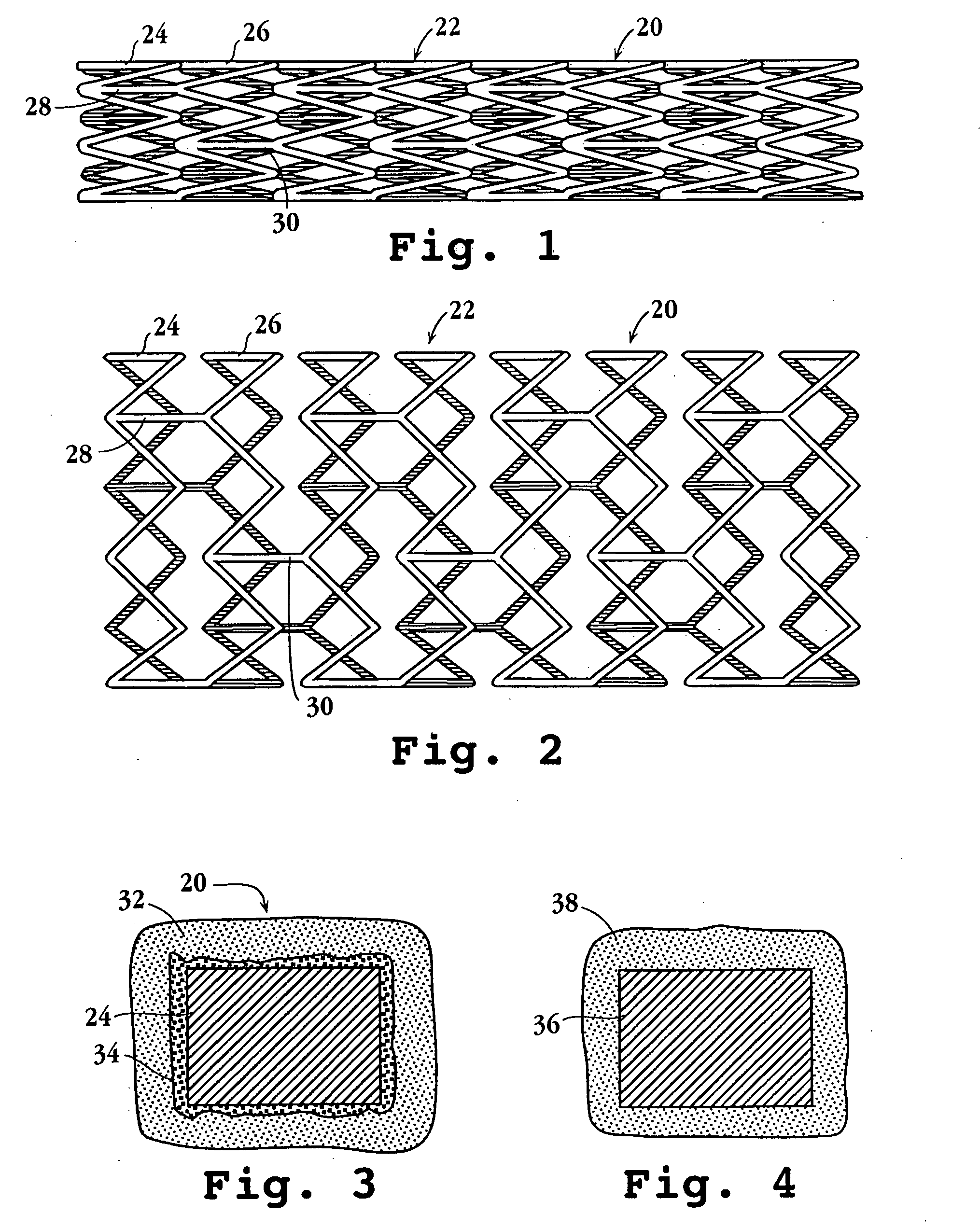
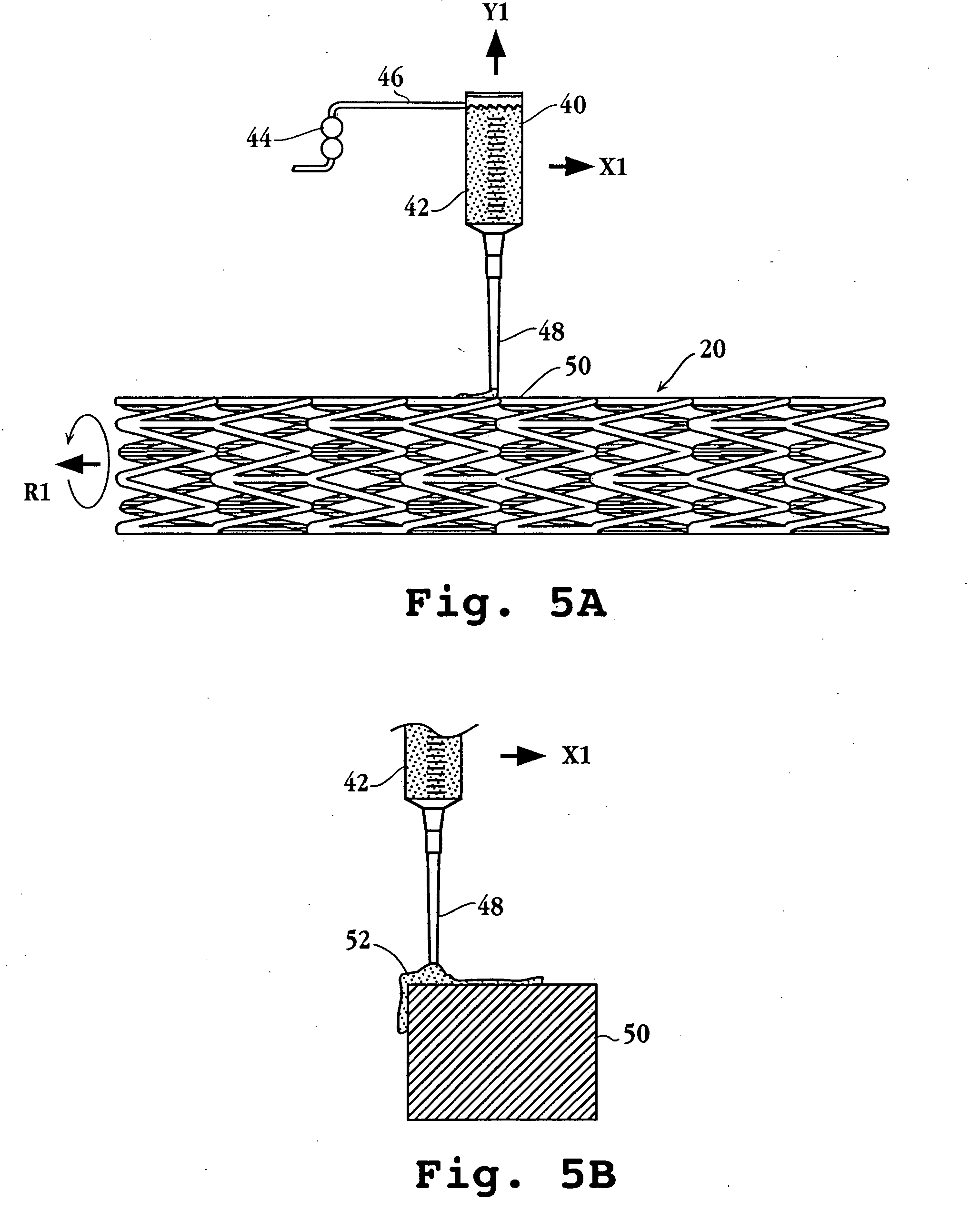
The stent with an outer slough coating 125 of the present invention provides a coated stent having a permanent coating 130 disposed on the stent and a slough coating 125 disposed on the permanent coating 130. The permanent coating 130 includes an anti-proliferative agent and the slough coating 125 includes an anti-inflammatory agent. The slough coating 125 erodes shortly after stent implantation to deliver the anti-inflammatory agent, which treats tissue trauma from the angioplasty and the presence of the stent. Once the slough coating 125 has substantially eroded, the permanent coating 130 delivers the anti-proliferative agent long-term to prevent tissue growth on the stent or within the body lumen, and prevent restenosis. The permanent coating 130 can also include an anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Angioplasty stent
A prosthesis for use in preventing restenosis after angioplasty is formed of plastic or sheet metal, and is expandable and contractable for placement. The prosthesis can be inserted while in a collapsed position, then expanded and locked at the larger diameter. Spring force can be provided by the material itself, or metal springs can be embedded within the walls of the prosthesis. Preferably, the walls have holes therethrough to promote tissue growth; and, in one embodiment, the holes are in the form of slots so that the prosthesis is segmented and can bend longitudinally.
Owner:W H WALL FAMILY HLDG LLLP
Stent system for preventing restenosis
A system for treating a body lumen is disclosed. The system comprises an outer stent and an inner stent disposed within the lumen of the outer stent. At least one end of the inner stent extends outside of the lumen of the outer stent, so that the end of the inner stent contacts and conforms to the body lumen wall that is adjacent the end of the outer stent. A coating can be disposed on a surface, preferably the outer surface, of the inner stent. The coating contains a therapeutic substance that may be released into the body lumen wall to help in preventing restenosis. Also disclosed is a stent having a balloon-expandable portion connected to a self-expanding portion. Methods for deploying the system and the stent are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
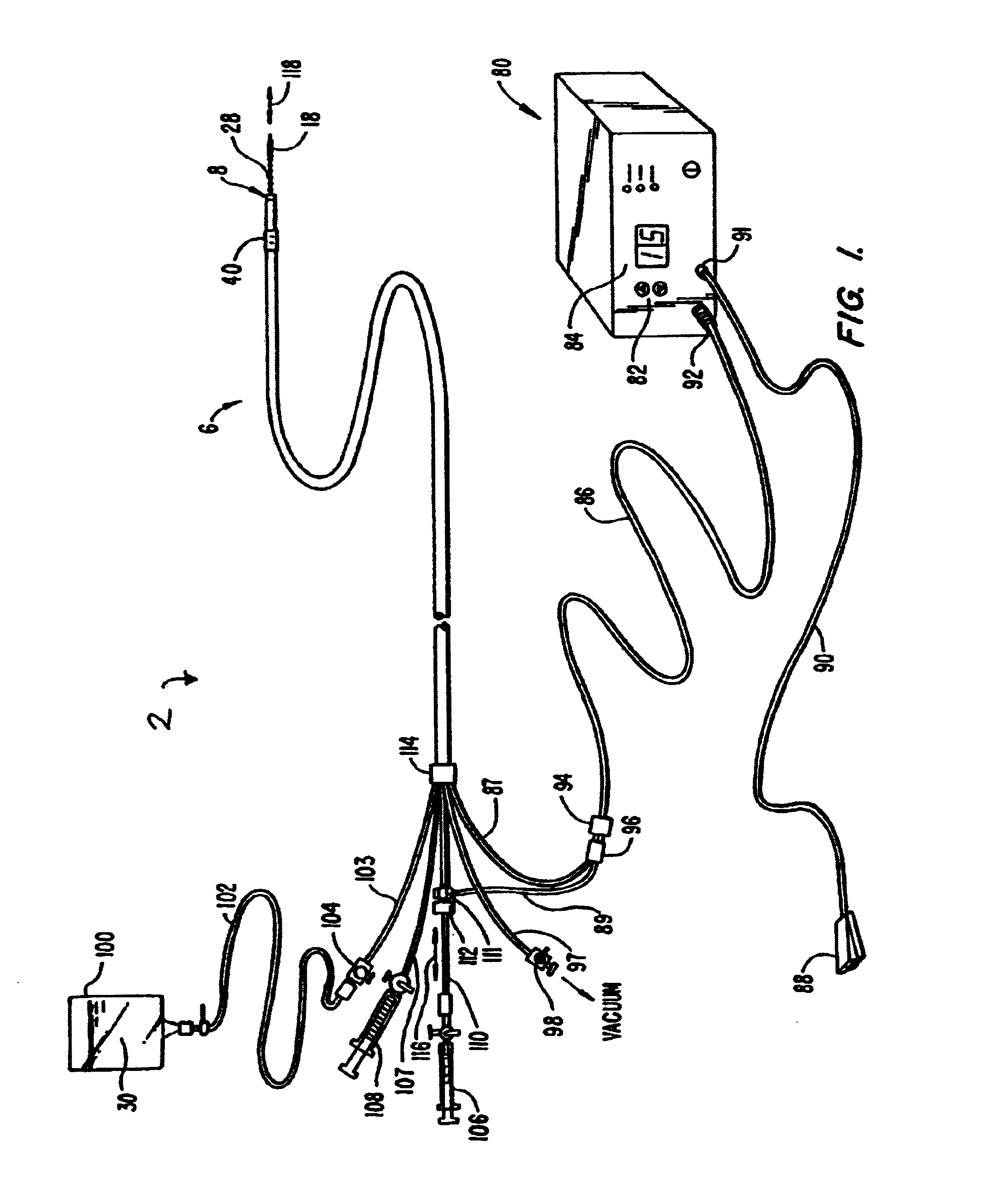
Method and device for performing cooling or cryo-therapies, for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS7001378B2Minimize and inhibit bio-chemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS6156500AImprove throughputBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsClinical trialPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease, including, but not limited to, atherosclerosis, ischemia / reperfusion, hypertension, restenosis, and arterial inflammation. Specifically, the present invention identifies and describes genes which are differentially expressed in cardiovascular disease states, relative to their expression in normal, or non-cardiovascular disease states, and / or in response to manipulations relevant to cardiovascular disease. Further, the present invention identifies and describes genes via the ability of their gene products to interact with gene products involved in cardiovascular disease. Still further, the present invention provides methods for the identification and therapeutic use of compounds as treatments of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, the present invention provides methods for the diagnostic monitoring of patients undergoing clinical evaluation for the treatment of cardiovascular disease, and for monitoring the efficacy of compounds in clinical trials. Additionally, the present invention describes methods for the diagnostic evaluation and prognosis of various cardiovascular diseases, and for the identification of subjects exhibiting a predisposition to such conditions.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Medical device with porous surface containing bioerodable bioactive composites and related methods
InactiveUS20050119723A1Reduced responseImproving device-tissue interfaceStentsLiquid surface applicatorsActive agentNanoparticle
An implantable medical device includes a porous surface with a composite material located within the pores that includes a bioerodable material in combination with a bioactive agent. The composite material is adapted to erode upon exposure to the body of a patient, thus releasing the bioactive agent into the patient, whereas the porous surface remains on the device. In one embodiment, the composite material includes micro- or nano-particles that are deposited within the pores. In a further embodiment, the porous surface is an electrolessly electrochemically deposited material. Certain tie layer and other surface modification aspects are described to enhance various aspects of the bioactive composite surface. The bioactive composite surface is of particular benefit when provided on an endolumenal stent assembly in a manner adapted to elute anti-restenosis or anti-thrombosis agents or combinations thereof.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
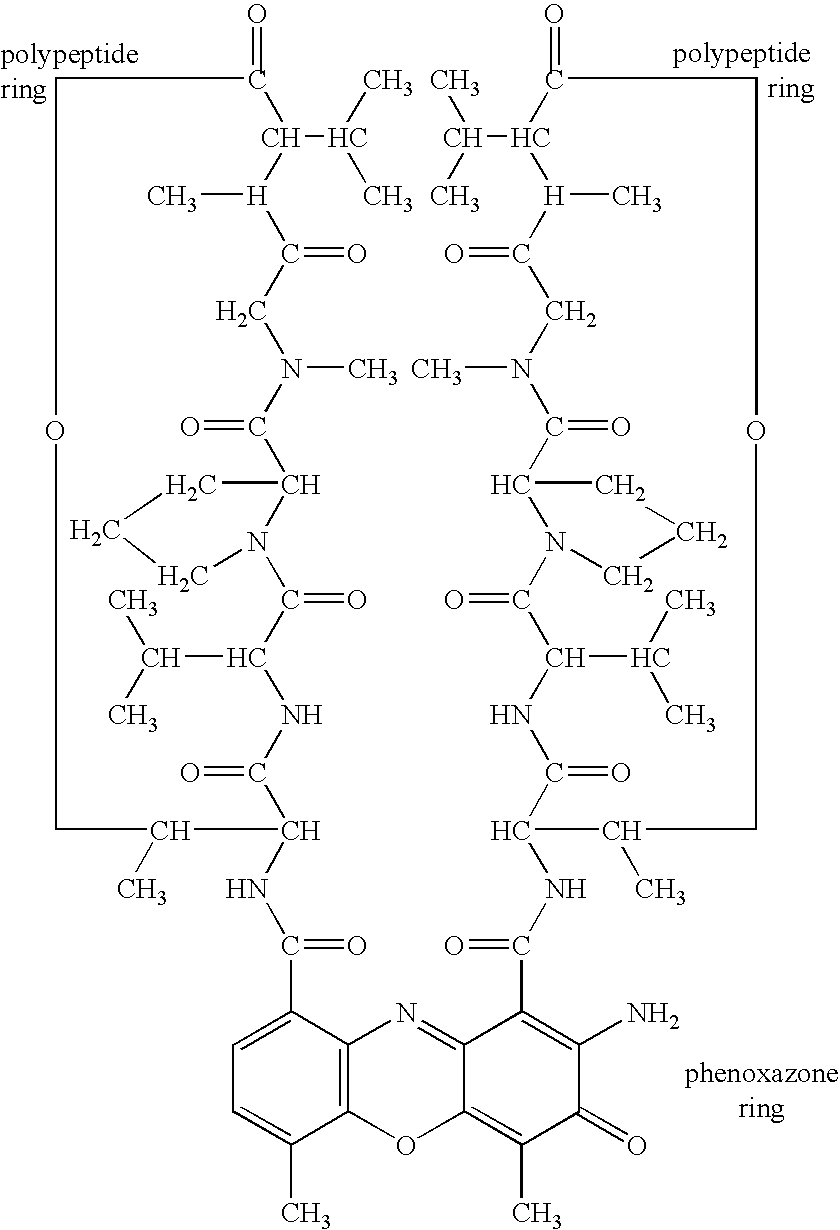
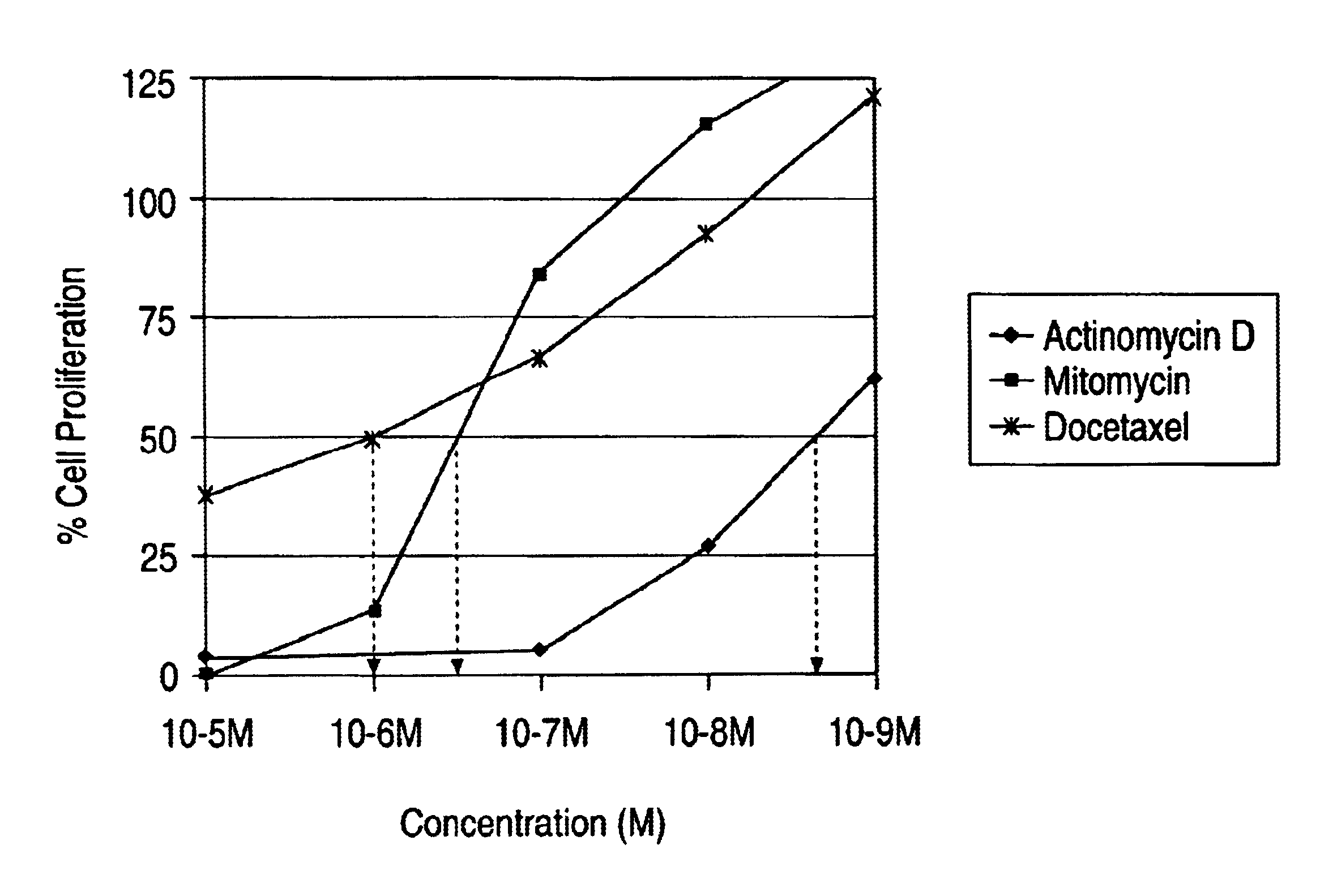
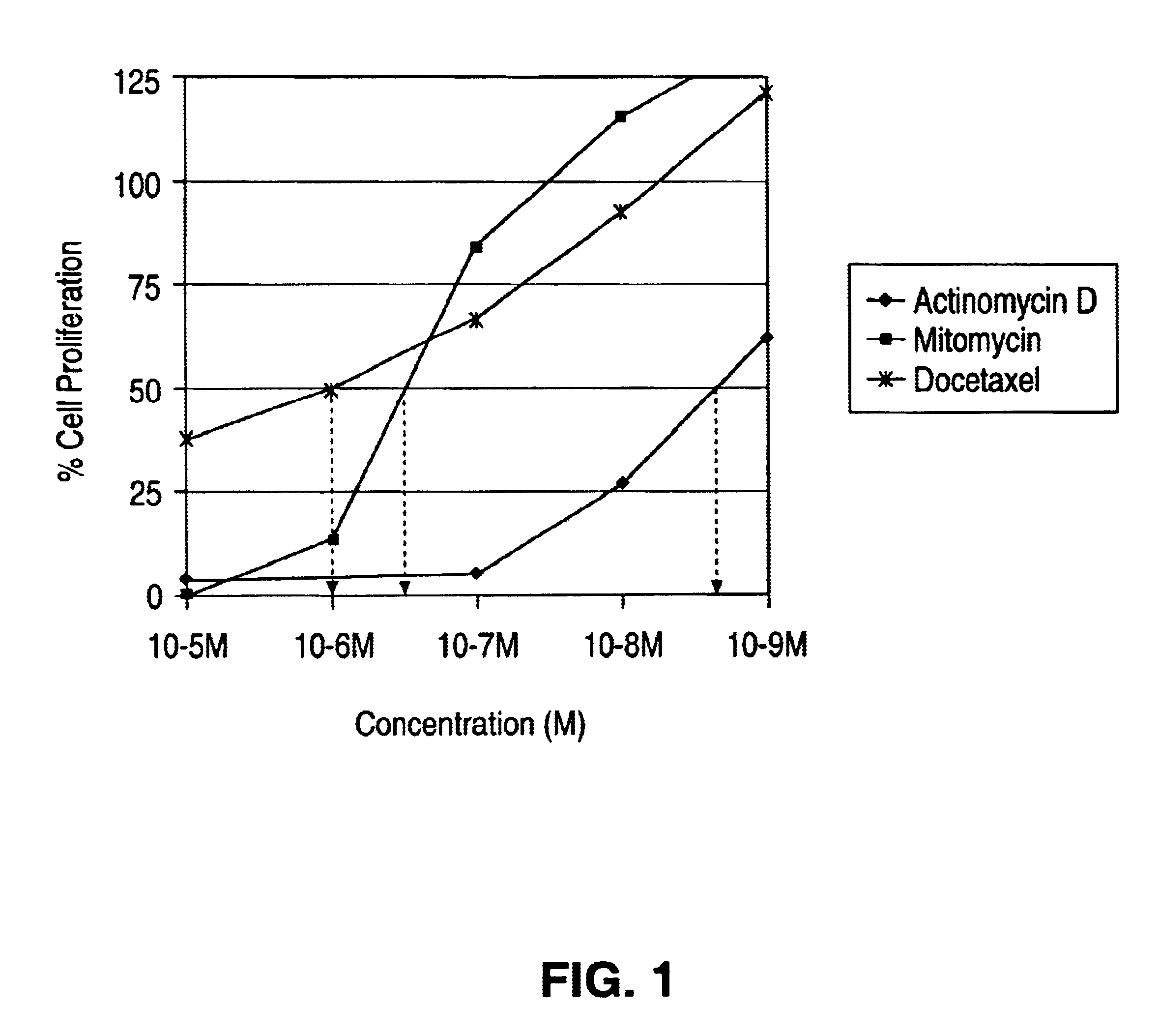
Actinomycin D for the treatment of vascular disease
A composition, comprising actinomycin D, is locally or systemically administered for the treatment of a blood vessel, such as caused by recurring stenosis or restenosis following vascular trauma or disease.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Drug-delivery endovascular stent and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20050038505A1Prevent restenosisEfficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPolymer substrateInsertion stent
An intravascular stent and method for inhibiting restenosis, following vascular injury, is disclosed. The stent has an expandable, linked-filament body and a drug-release coating formed on the stent-body filaments, for contacting the vessel injury site when the stent is placed in-situ in an expanded condition. The coating releases, for a period of at least 4 weeks, a restenosis-inhibiting amount of a monocyclic triene immunosuppressive compound having an alkyl group substituent at carbon position 40 in the compound. The stent, when used to treat a vascular injury, gives good protection against clinical restenosis, even when the extent of vascular injury involves vessel overstretching by more than 30% diameter. Also disclosed is a stent having a drug-release coating composed of (i) 10 and 60 weight percent poly-d / -lactide polymer substrate and (ii) 40-90 weight percent of an anti-restenosis compound, and a polymer undercoat having a thickness of between 1-5 microns.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
Devices, systems, and methods for debulking restenosis of a blood vessel
Devices, systems, and methods are employed to restore patency to arterial lesions, e.g., by debulking restenosis in a blood vessel or within a stent or coil.
Owner:ATHEROMED
Cryotreatment device and method
InactiveUS7220257B1Reduce adverse reactionsReduced responseStentsOther blood circulation devicesCoronary artery angioplastyPercent Diameter Stenosis
Devices and methods for cooling vessel walls to inhibit restenosis in conjunction with medical procedures such as coronary artery angioplasty. Stenosed vessel walls can be cooled prior to angioplasty, after angioplasty, or both. The invention is believed to inhibit restenosis through cooling to a temperature near freezing, preferably without causing substantial vessel wall cell death. One catheter device includes a distal tube region having coolant delivery holes radially and longitudinally distributed along the distal region. In some devices, holes spray coolant directly onto the vessel walls, with the coolant absorbed into the blood stream. In other embodiments, a balloon or envelope is interposed between the coolant and the vessel walls and the coolant returned out of the catheter through a coolant return lumen. Some direct spray devices include an occlusion device to restrict blood flow past the region being cooled. Pressure, temperature, and ultrasonic probes are included in some cooling catheters. Pressure control valves are included in some devices to regulate balloon interior pressure within acceptable limits. In applications using liquid carbon dioxide as coolant, the balloon interior pressure can be maintained above the triple point of carbon dioxide to inhibit dry ice formation. Some cooling catheters are coiled perfusion catheters supporting longer cooling periods by allowing perfusing blood flow simultaneously with vessel wall cooling. One coiled catheter is biased to assume a coiled shape when unconstrained and can be introduced into the body in a relatively straight shape, having a stiffening wire inserted through the coil strands.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods for modulating thermal and mechanical properties of coatings on implantable devices
InactiveUS20050245637A1Narrow molecular weight distributionHigh molecular weightStentsSurgical adhesivesVulnerable plaquePercent Diameter Stenosis
Methods for modulating and enhancing thermal and mechanical properties and biocompatibilities of coatings on implantable devices are disclosed. Implantable devices containing the enhanced thermal and mechanical properties and biocompatibilities are also described. The implantable devices can be used to treat a medical condition such as vulnerable plaque or restenosis.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for reducing restenosis in the presence of an intravascular stent
InactiveUS6939345B2Reduce generationLot of damageDilatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCoronary arteriesProximate
A first electrode is positioned within an artery proximate an implanted intravascular stent. A second electrode is positioned at a separate location relative the position of the first electrode. Electrical energy is then delivered between the first and the second electrodes to produce an electrical field adjacent the implanted intravascular stent. When a intravascular stent is implanted in a coronary artery, the delivery of the electrical energy is coordinated to cardiac cycles detected in sensed cardiac signals, where the delivery of the electrical energy between the first electrode and the second electrode occurs during a predetermined portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS6905494B2Minimize and inhibit biochemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Balloon catheter method for reducing restenosis via irreversible electroporation
InactiveUS20090247933A1Promote resultsPrevent excessive cell lysingElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisIrreversible electroporation
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a balloon catheter with a particular electrode configuration. Also provided is a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Cryoplasty device and method
InactiveUS7022120B2Preventing or slowing the post-procedure reclosure of a dilated lesionPrevent and slow recoilDilatorsCatheterPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
A cryoplasty catheter and method for preventing or slowing reclosure of a lesion following angioplasty. The cryoplasty catheter includes a shaft having proximal and distal ends and a dilatation balloon disposed at the distal end. An intake lumen and exhaust lumen are defined by the shaft to deliver coolant to the balloon and to exhaust or drain coolant from the balloon. The method in accordance with the present invention includes cooling a lesion to aid in remodeling the lesion through dilatation and / or freezing a portion of the lesion adjacent the dilatation balloon to kill cells within the lesion to prevent or retard restenosis.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Irreversible electroporation device and method for attenuating neointimal
InactiveUS20090248012A1Promote resultsPrevent excessive cell lysingElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisTunica intima
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a device and a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of treatment with drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002971A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
Polymeric microparticles have been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and can have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Electromagnetic photonic catheter for reducing restenosis
InactiveUS6962584B1Reduce spreadImprove scalabilitySurgical instrument detailsCatheterPhotonicsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The method of vascular treatment for restenosis or vulnerable plaque after an invasive procedure, such as for example angioplasty, stenting with or without drug coating, or drug delivery, comprises: inserting a catheter or hollow guide wire to the treatment location; delivering light through the catheter in the wavelength range of about 700–2500 nm; and moving the light to treat the affected region.
Owner:STONE GREGG W +5
Stent coatings containing HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
InactiveUS20030077310A1Hydrolysis can be preventedAvoid accessStentsSurgeryHMG-CoA reductaseDepressant
Stents with coatings comprising a combination of a restenosis inhibitor comprising an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor and a carrier. Also provided are methods of coating stents with a combination of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor and a carrier. A preferred example of a restenosis inhibitor is cerivastatin. The stent coatings have been shown to release restenosis inhibitors in their active forms.
Owner:ZIMMER ORTHOBIOLIGICS
Stent with polymeric coating
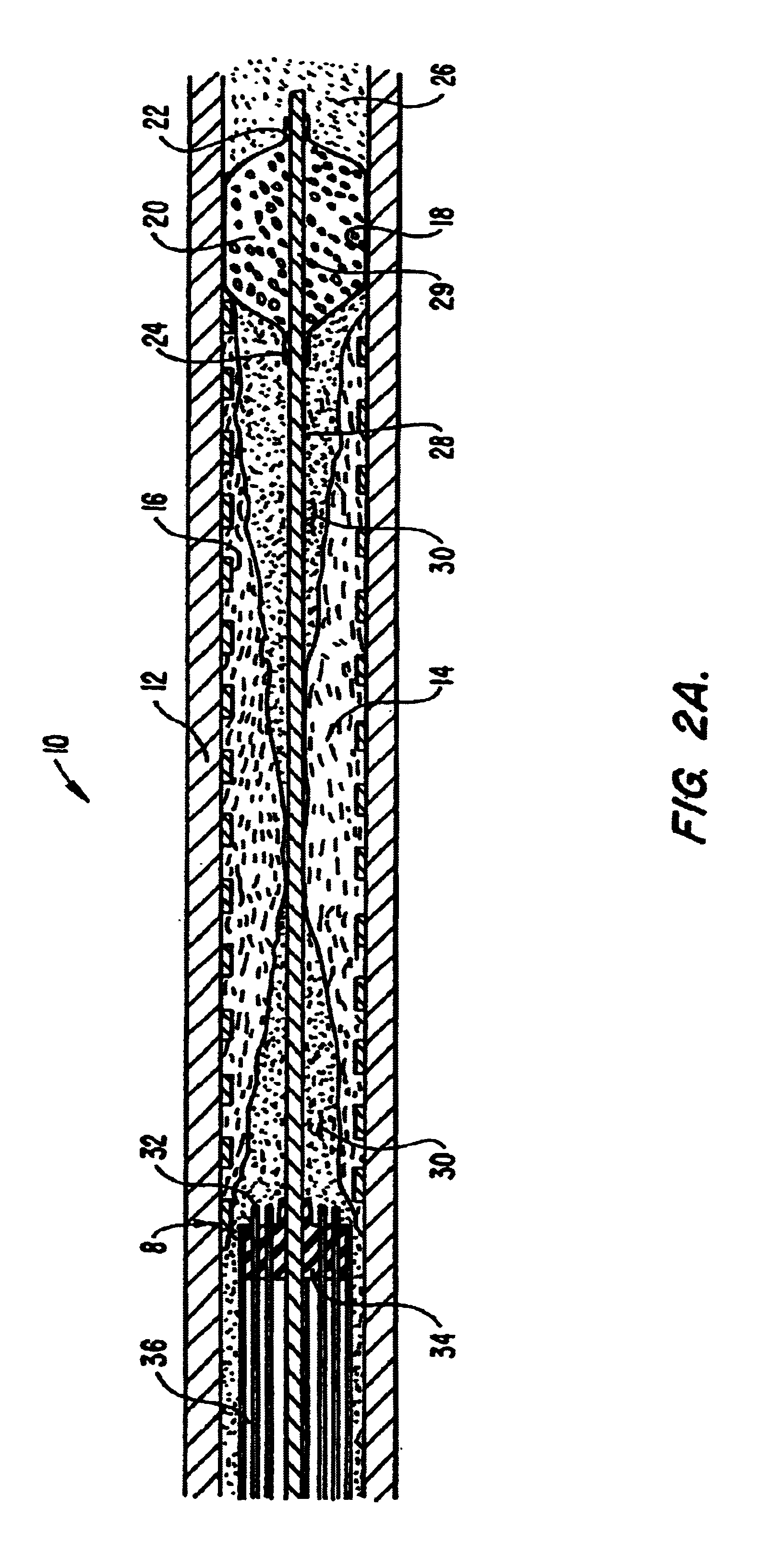
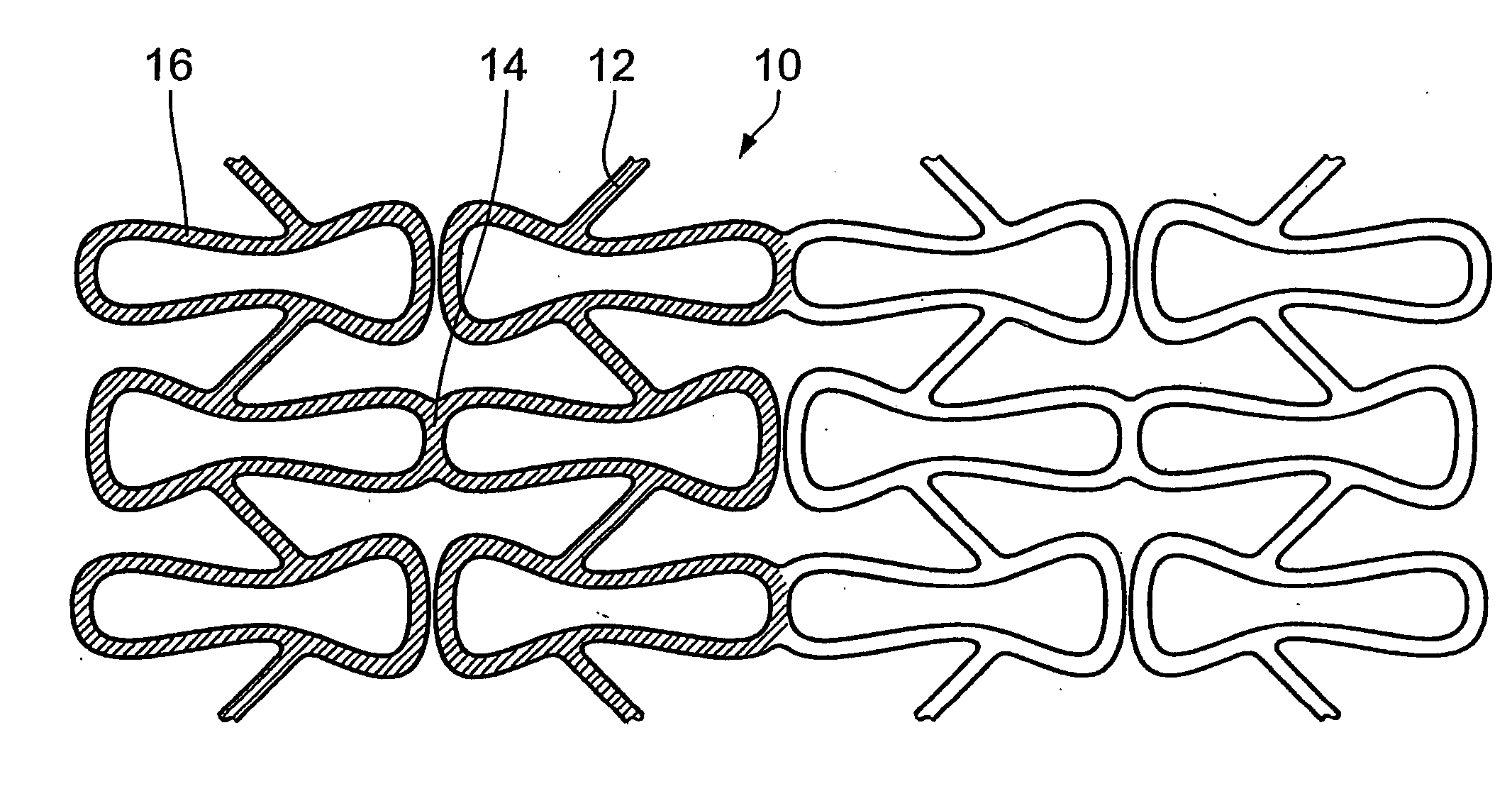
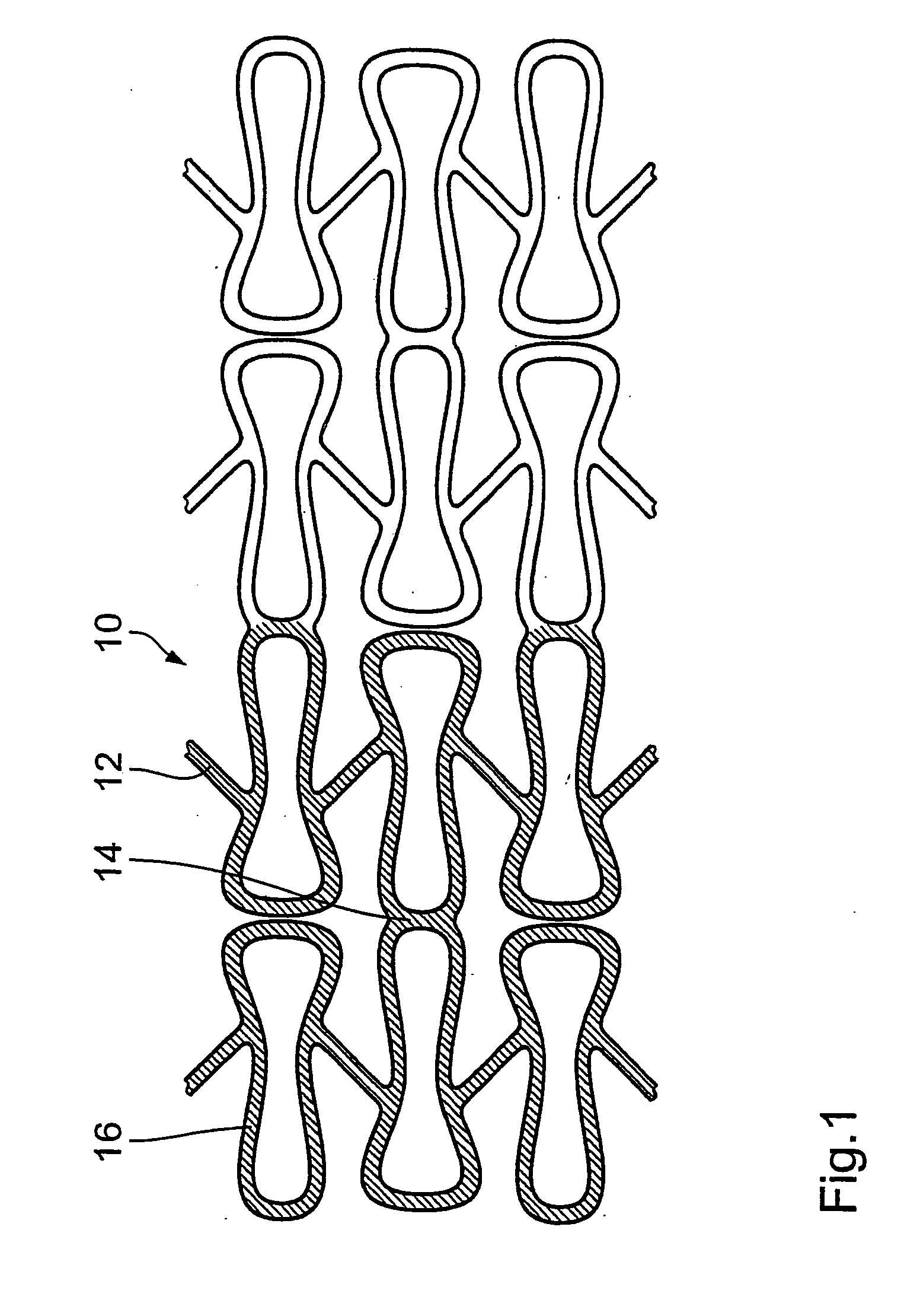
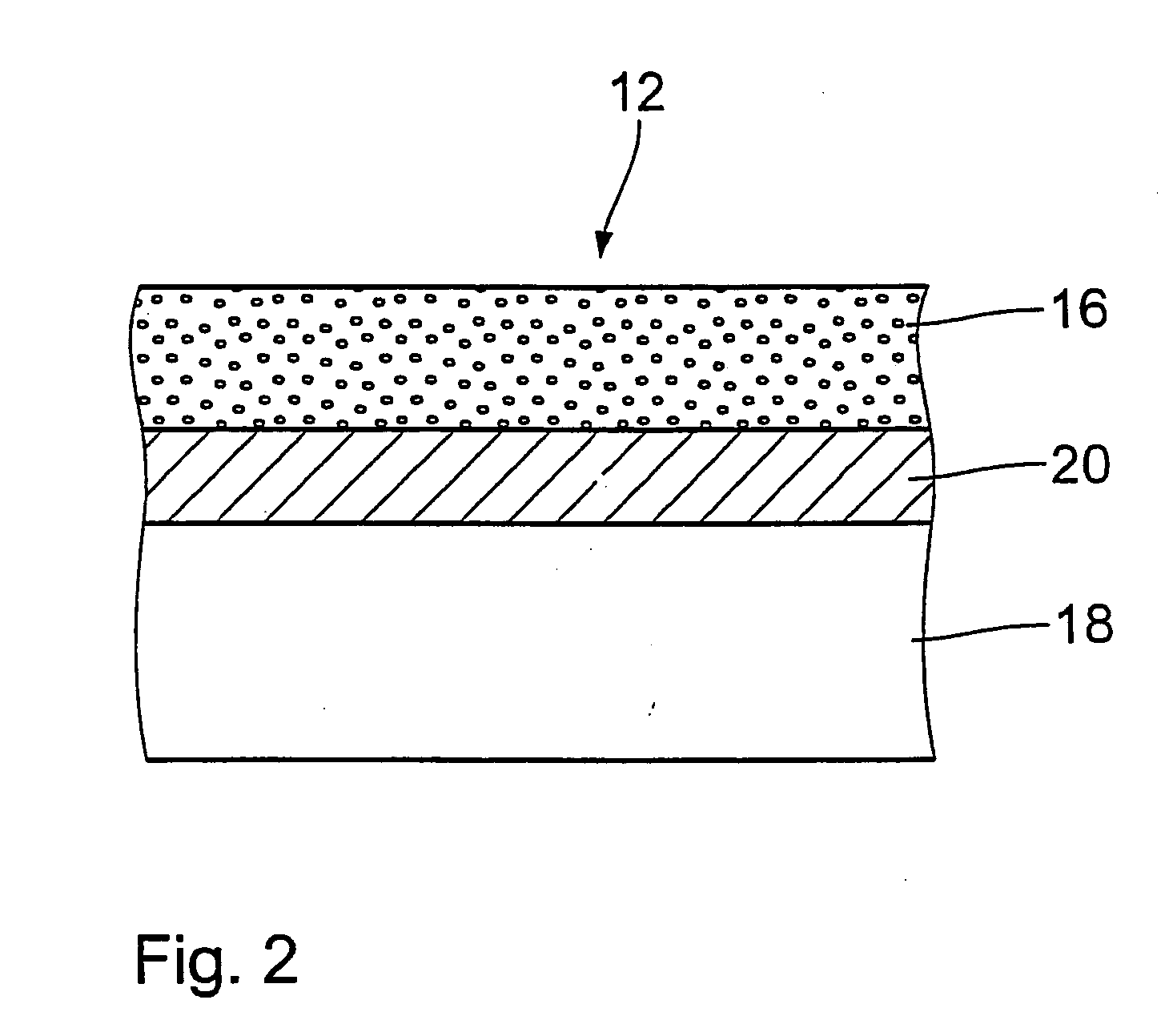
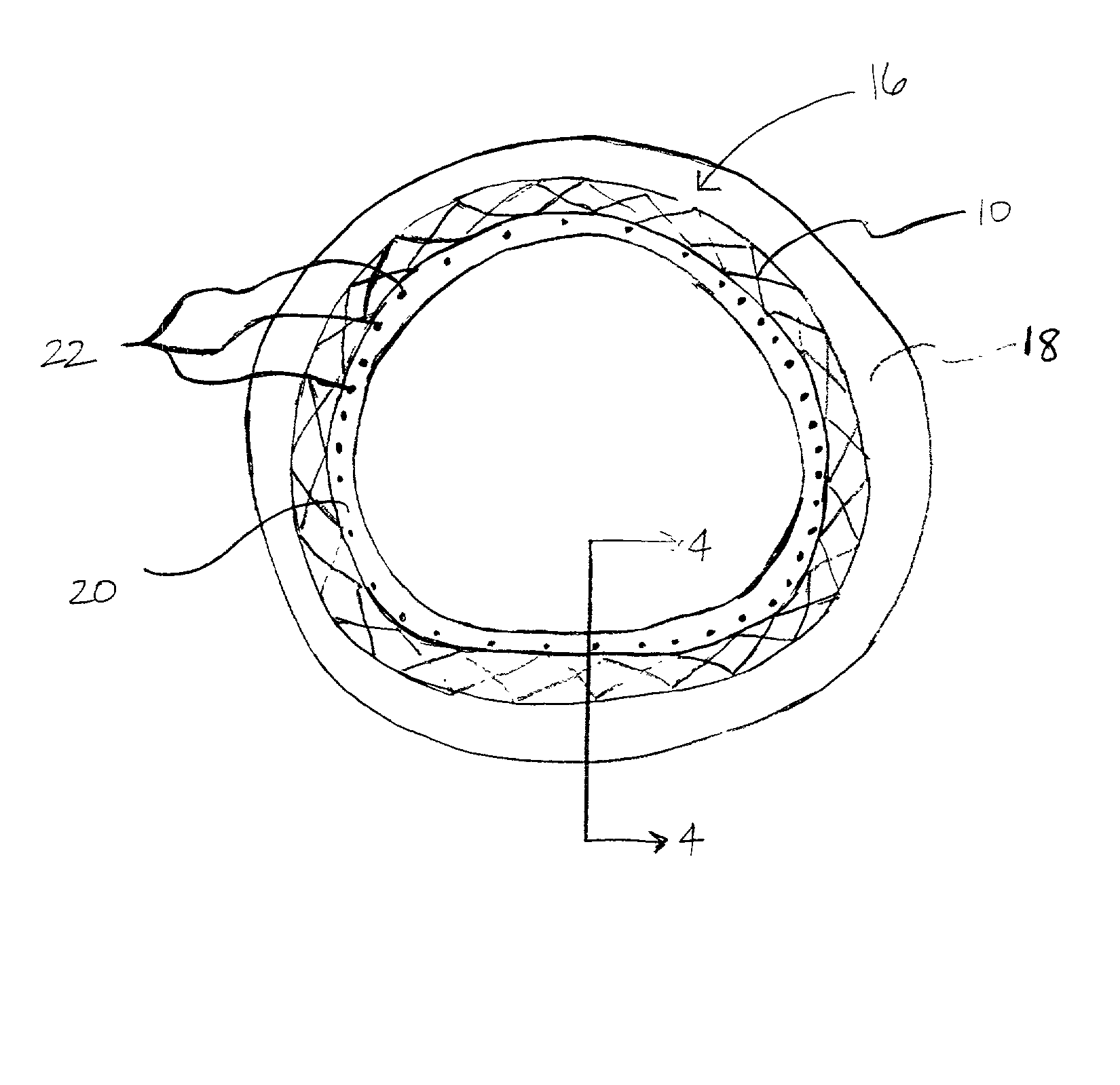
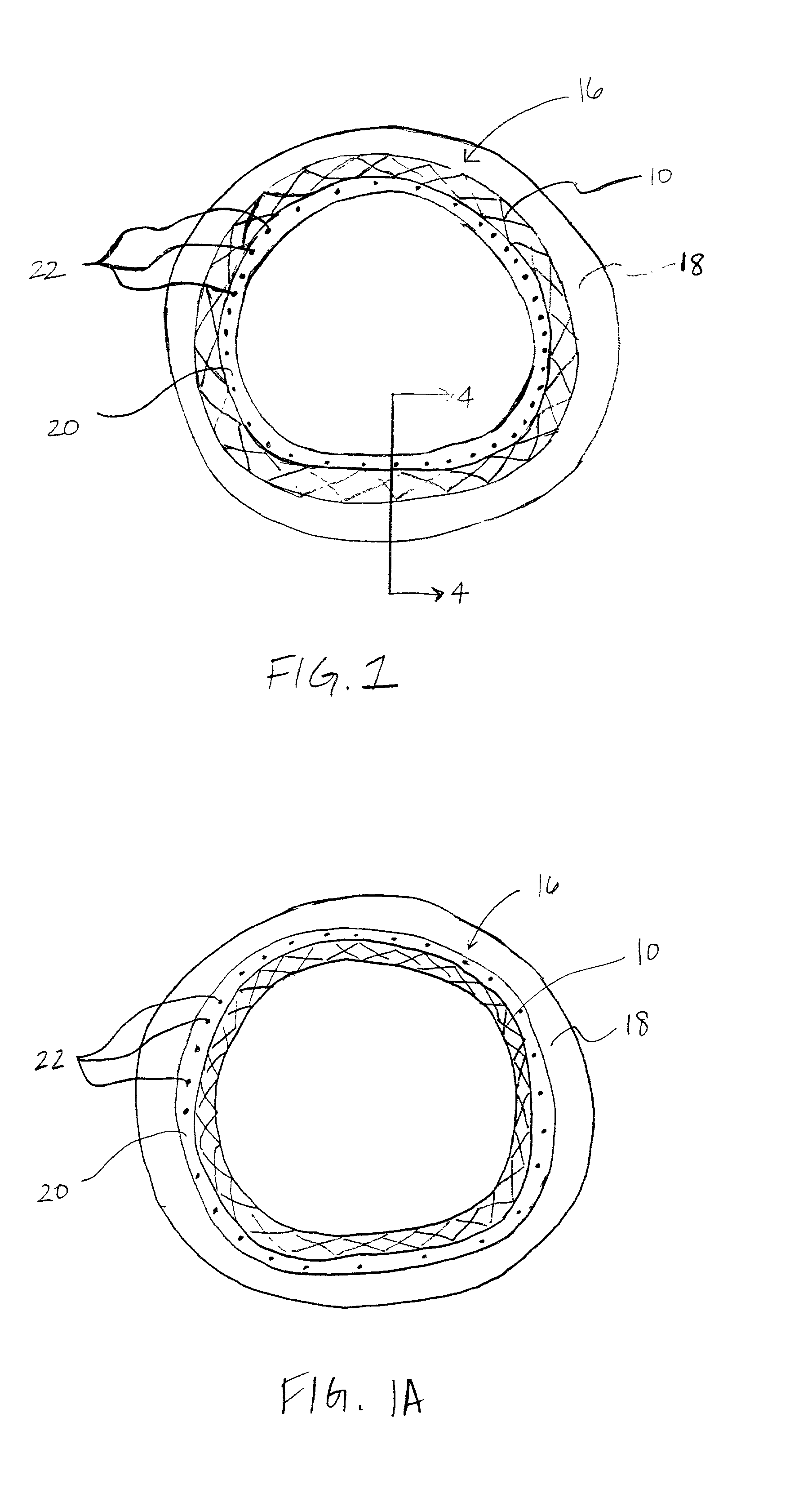
InactiveUS20040034409A1Effectively suppress the restenosis-triggering factorsReduce spreadPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesPercent Diameter StenosisPolymer
The invention concerns an implantable stent (10) with an at least portion-wise polymeric coating (16). The coating material is admittedly intended to bond to known materials but by virtue of its properties it is intended to enjoy improved compatibility and reduce inflammatory and proliferative processes which can lead to restenosis. That is achieved in that the polymeric coating (16) in the implantable condition after production and sterilization contains poly-L-lactide of a mean molecular weight of more than 200 kDa.
Owner:BIOTRONIK
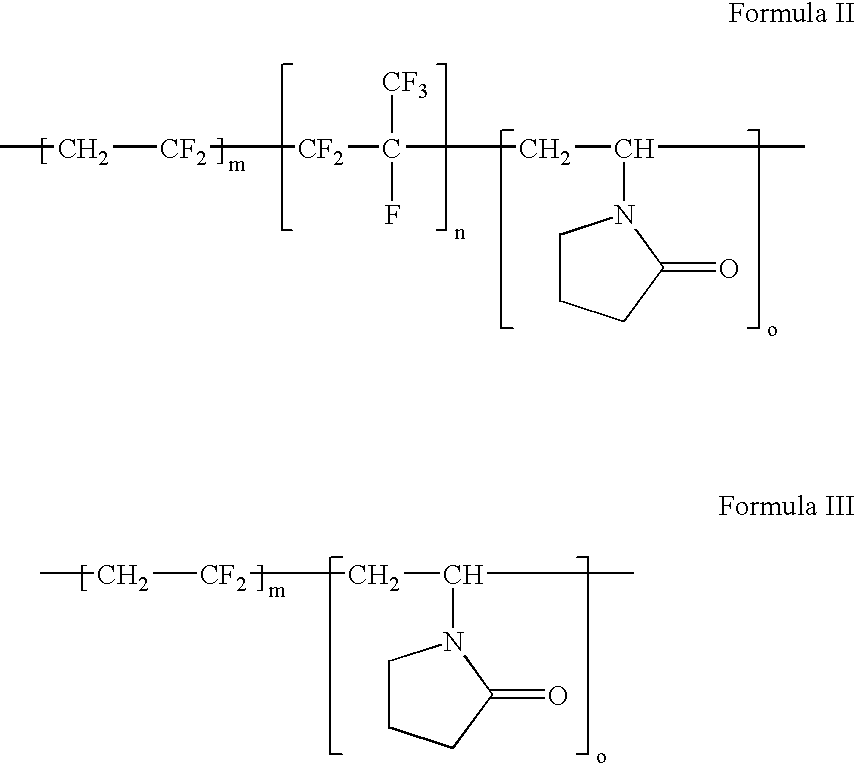
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers
ActiveUS20060047095A1Improve propertiesProvide flexibilityFibre treatmentSurgeryDiseasePolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer of fluorinated monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer of fluorinated monomers or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Apparatus and methods for controlled substance delivery from implanted prostheses
InactiveUS20020082685A1Improve drug delivery efficiencyReduce lossesStentsSurgeryPercent Diameter StenosisControl substances
The present invention provides improved devices and methods for inhibiting restenosis and hyperplasia after intravascular intervention. In particular, the present invention provides luminal prostheses which allow for programmed and controlled substance delivery with increased efficacy to selected locations within a patient's vasculature to inhibit restenosis. The luminal delivery prosthesis comprises a scaffold which is implantable within a body lumen and means on the scaffold for releasing a substance from the scaffold. The substance is released over a predetermined time pattern comprising an initial phase wherein the substance delivery rate is below a threshold level and a subsequent phase wherein the substance delivery rate is above a threshold level.
Owner:ALTAI MEDICAL TECH
Coated medical devices for the treatment of vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS7195640B2Reduce drug toxicityGood curative effectSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesPercent Diameter StenosisCoating
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. In addition to reducing or substantially eliminating a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism, the medical device in combination with one or more therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to treat various vascular diseases, for example, restenosis and vulnerable plaque. In the case of vulnerable plaque, one or more drugs, agents or compounds may be utilized to treat the various aspects of vulnerable plaque and these drugs, agents and / or compounds may be released with a given release profile for the most effective treatment. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH +1
Methods for treating restenosis with p21
InactiveUS6218372B1Treating and preventing restenosis in vivoFacilitate immune recognitionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisGene product
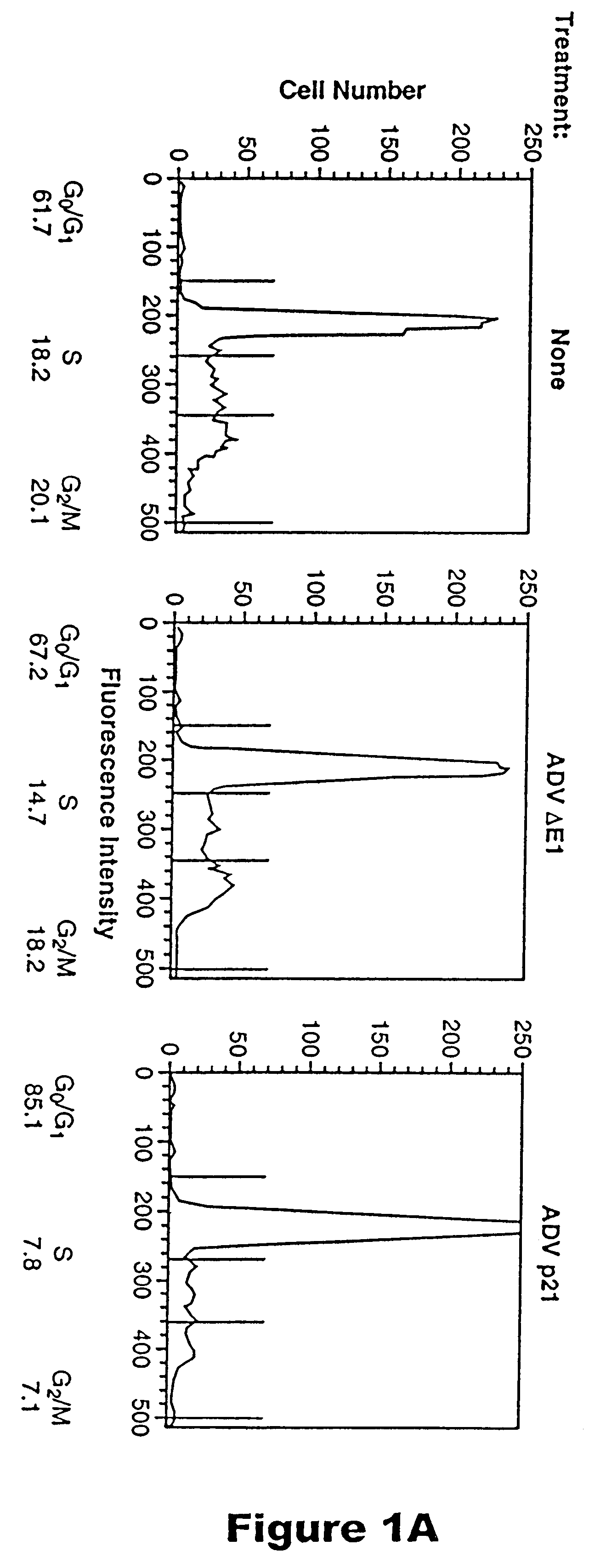
The p21 gene encodes a cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor which affects cell cycle progression, but the role of this gene product in altering tumor growth has not been established. The present inventors have now discovered that the growth of malignant cells in vivo is inhibited by expression of p21. Expression of p21 resulted in an accumulation of cells in G0 / G1, alteration in morphology, and cell differentiation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com