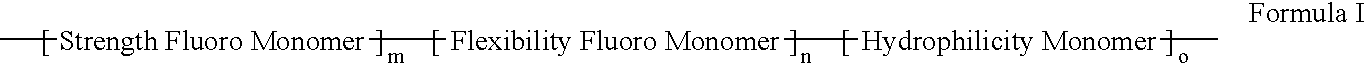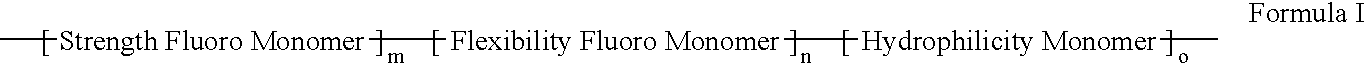Patents
Literature
152 results about "Patent foramen ovale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
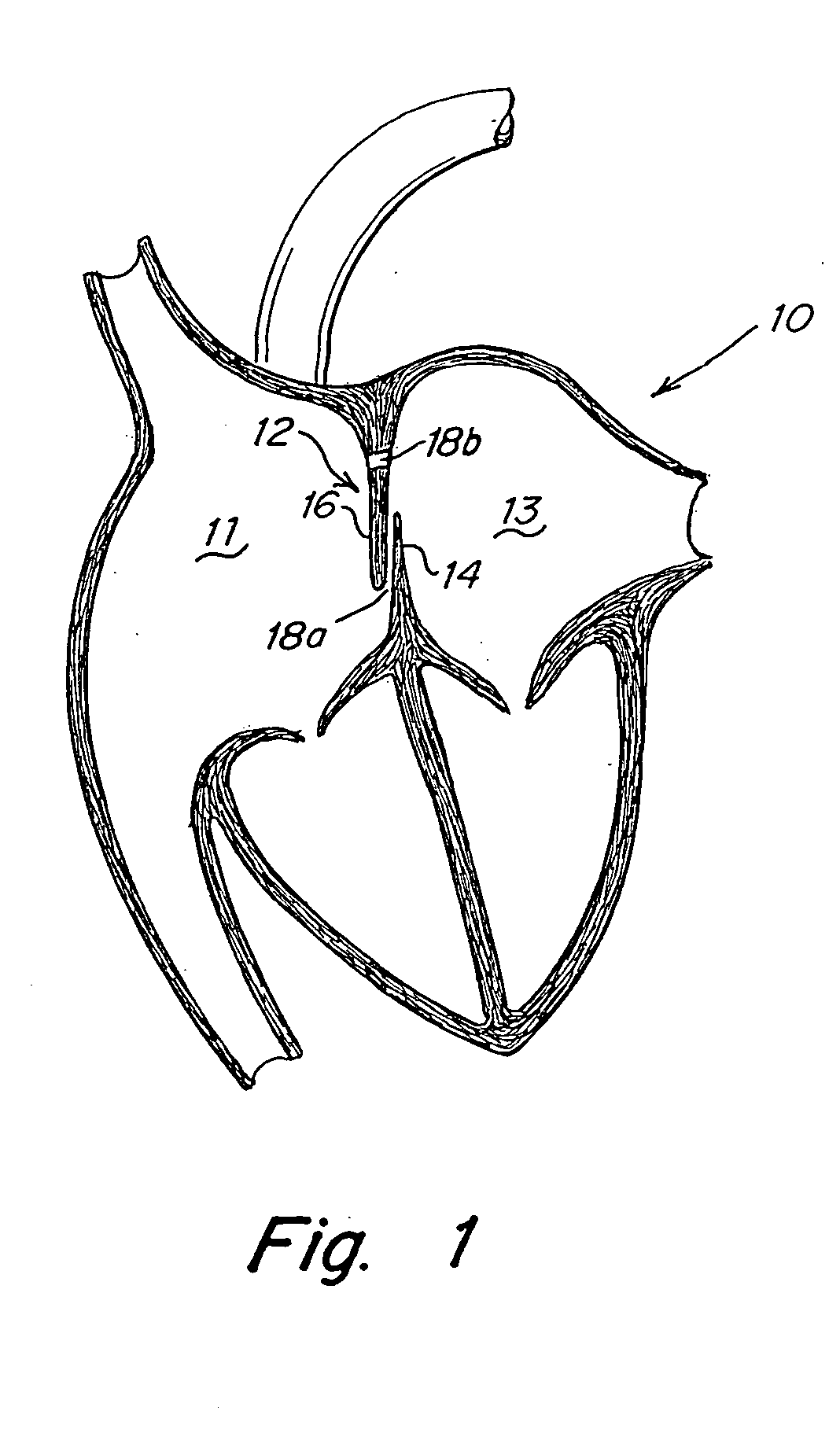
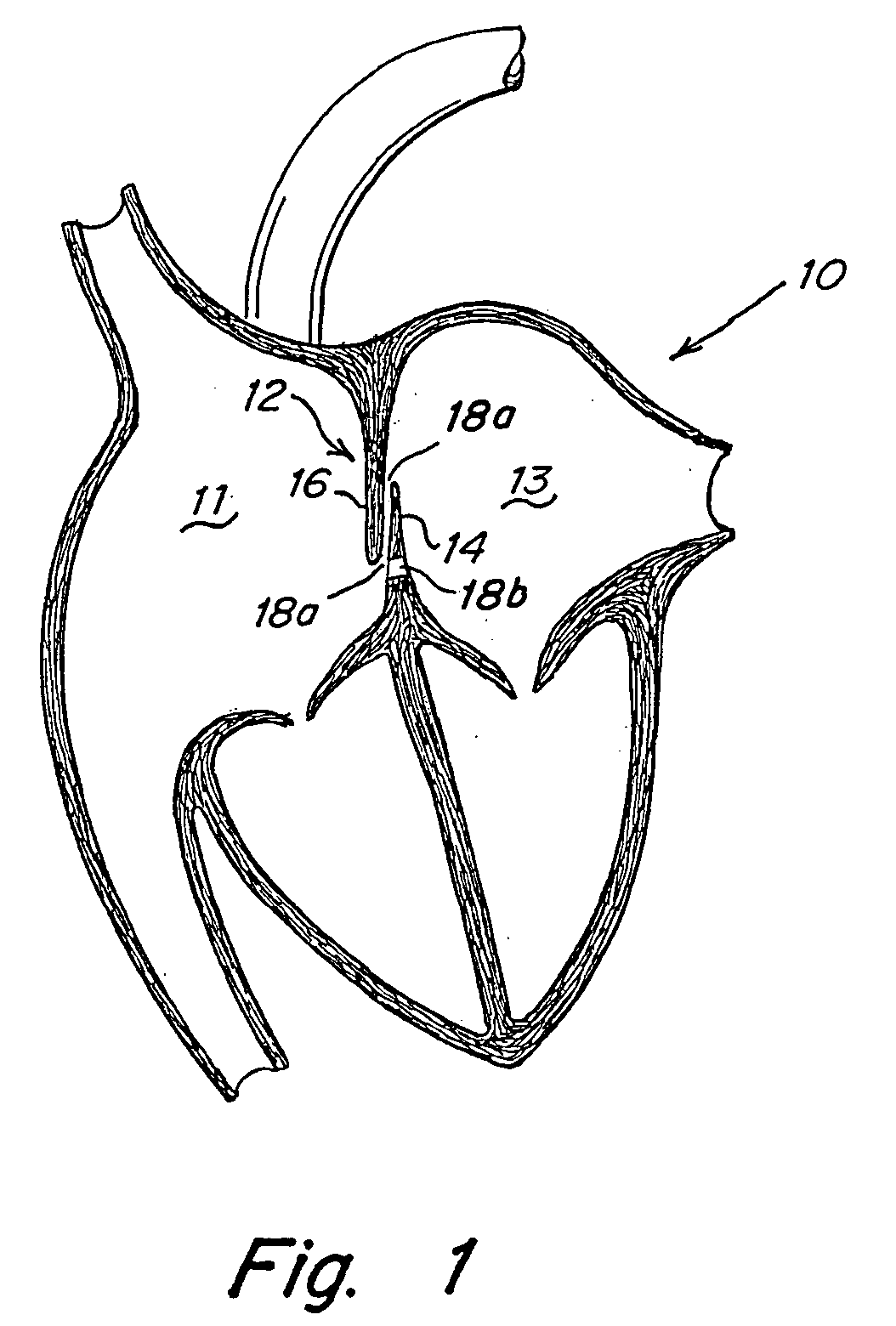
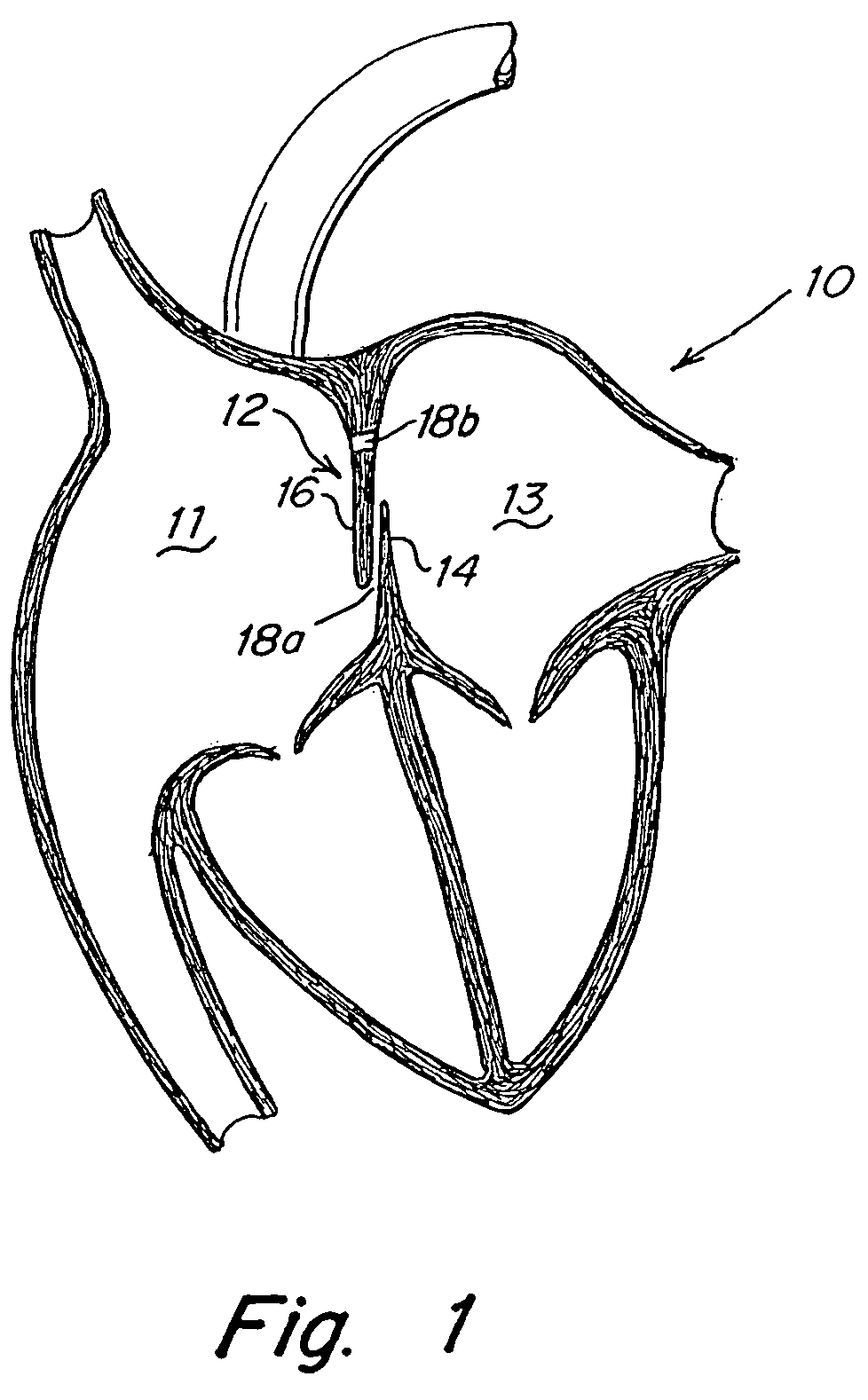
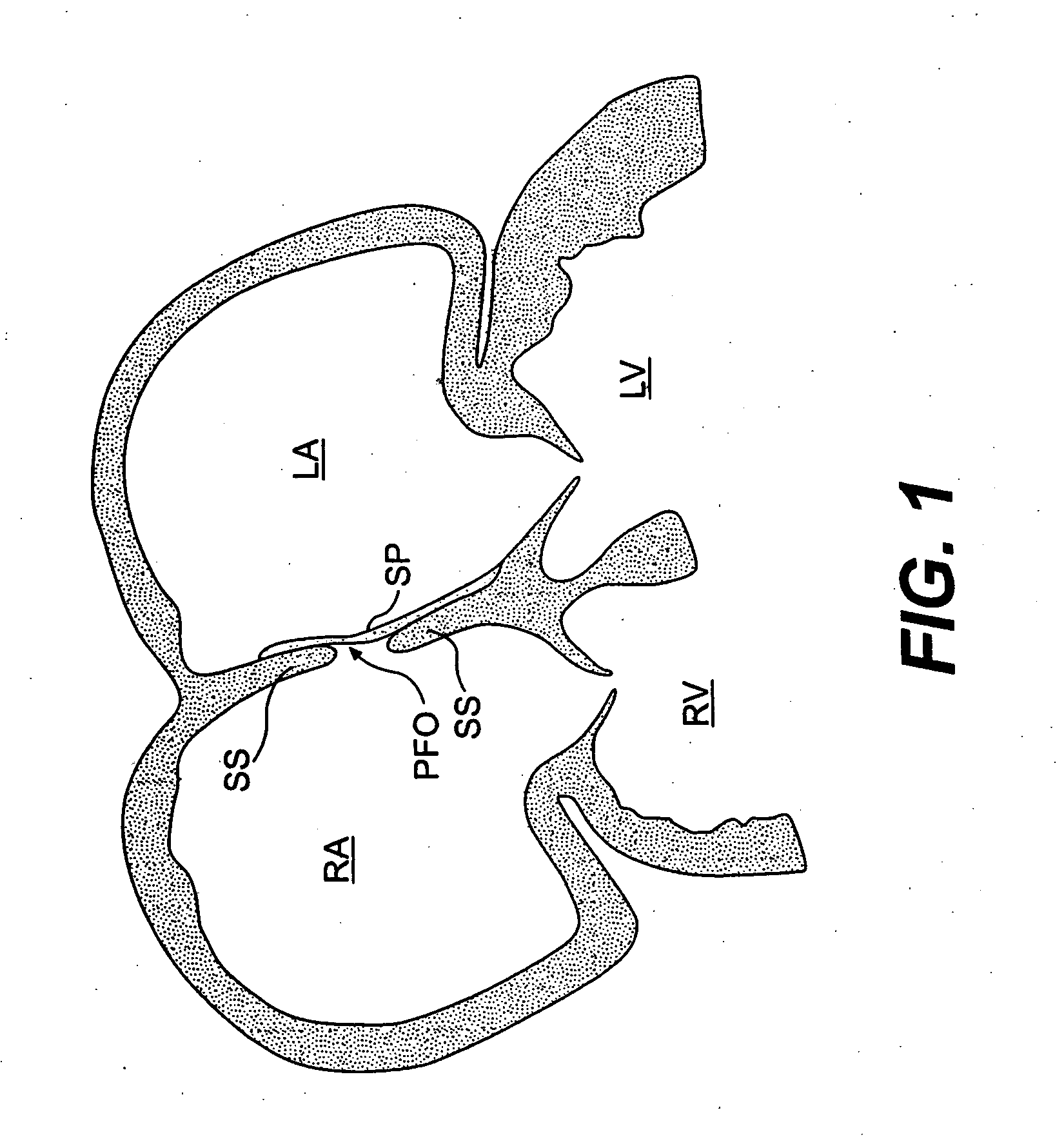
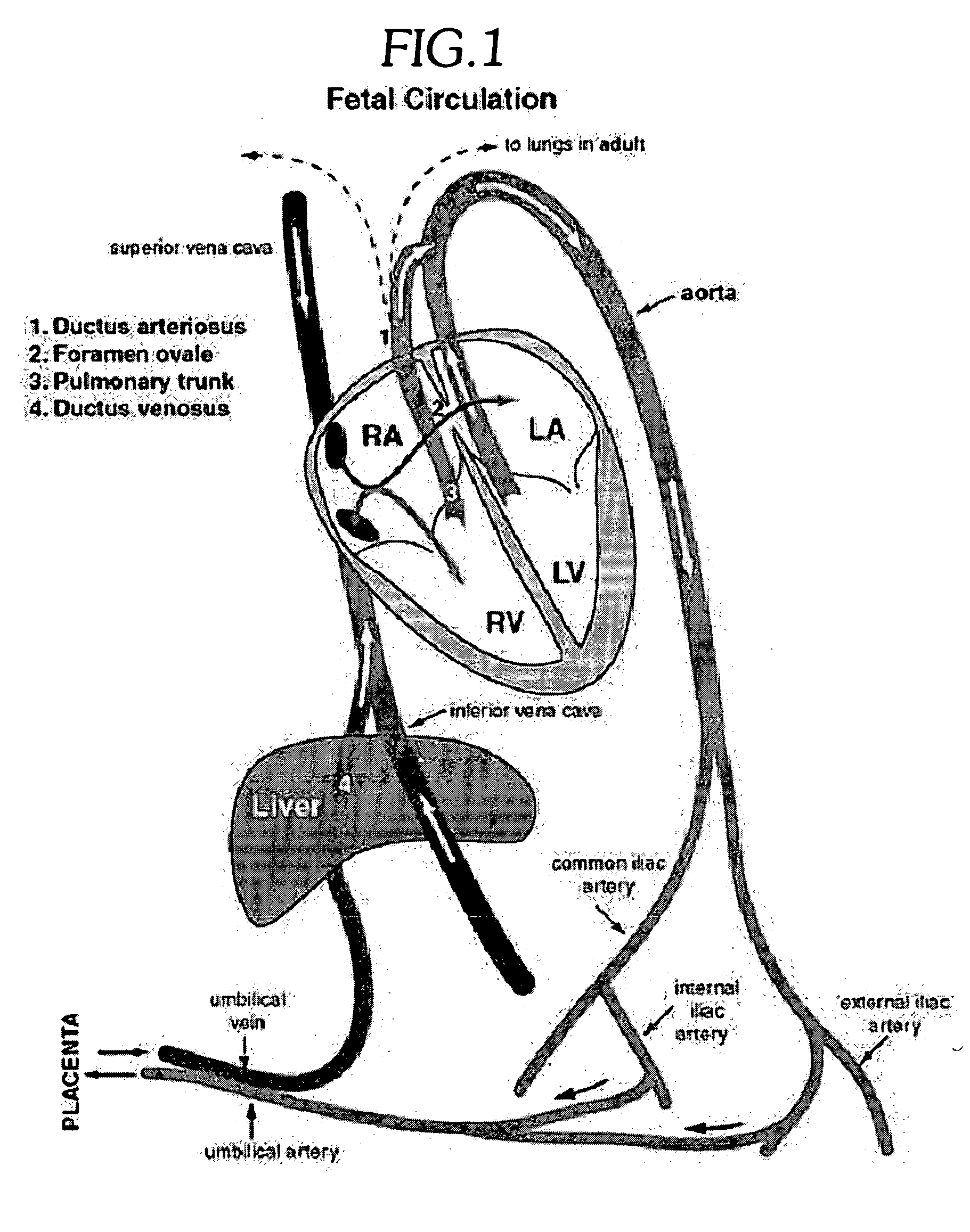
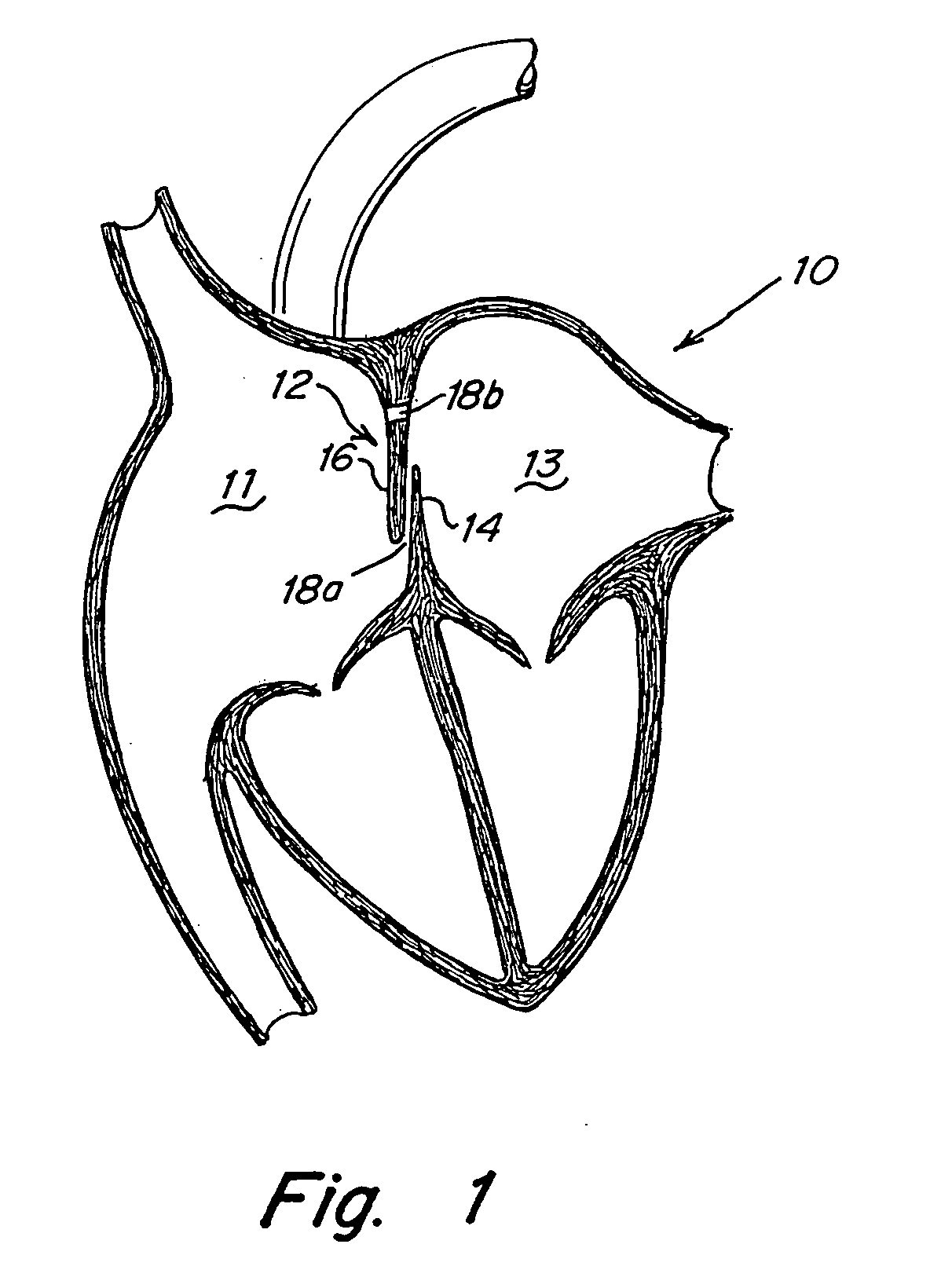
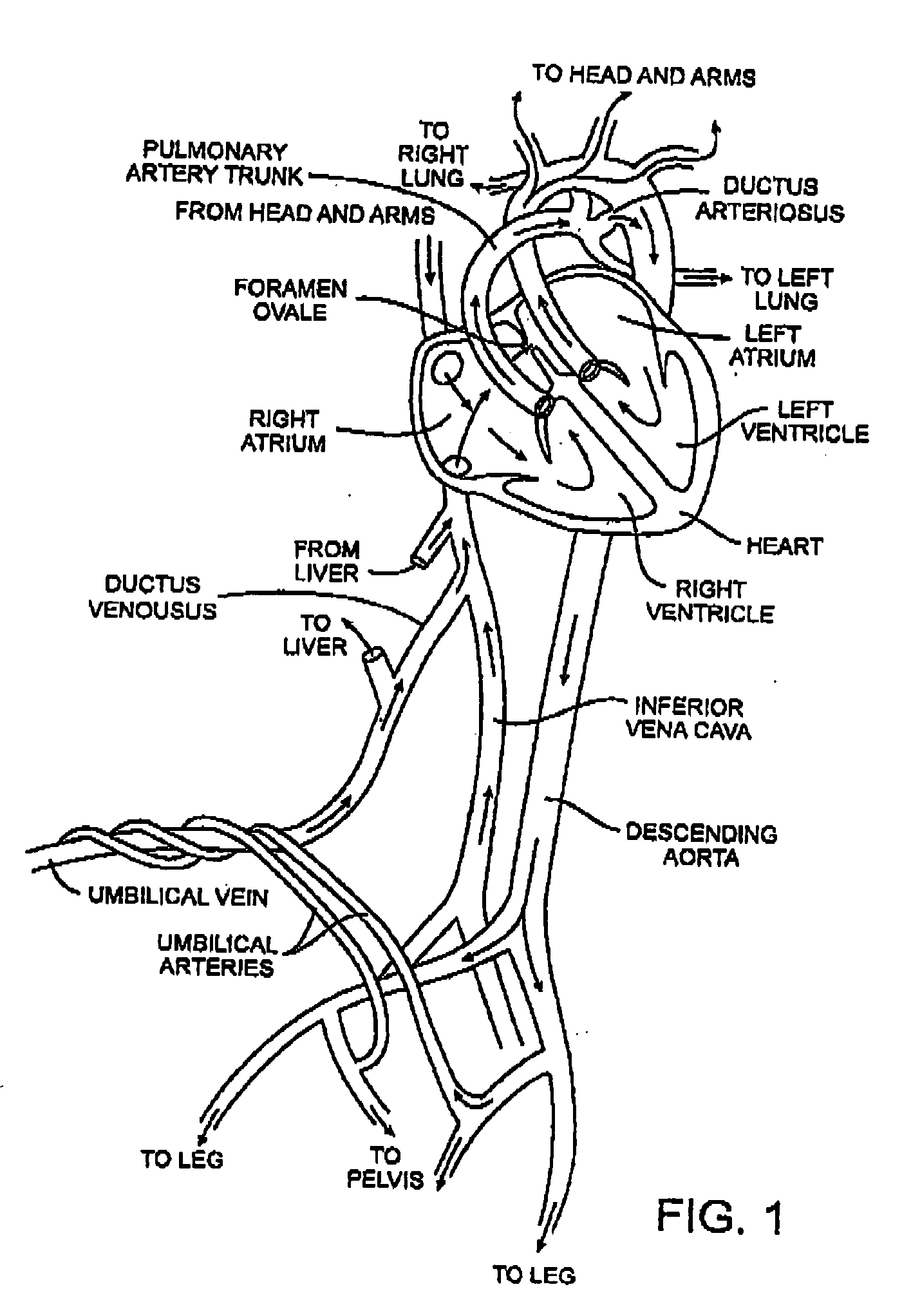
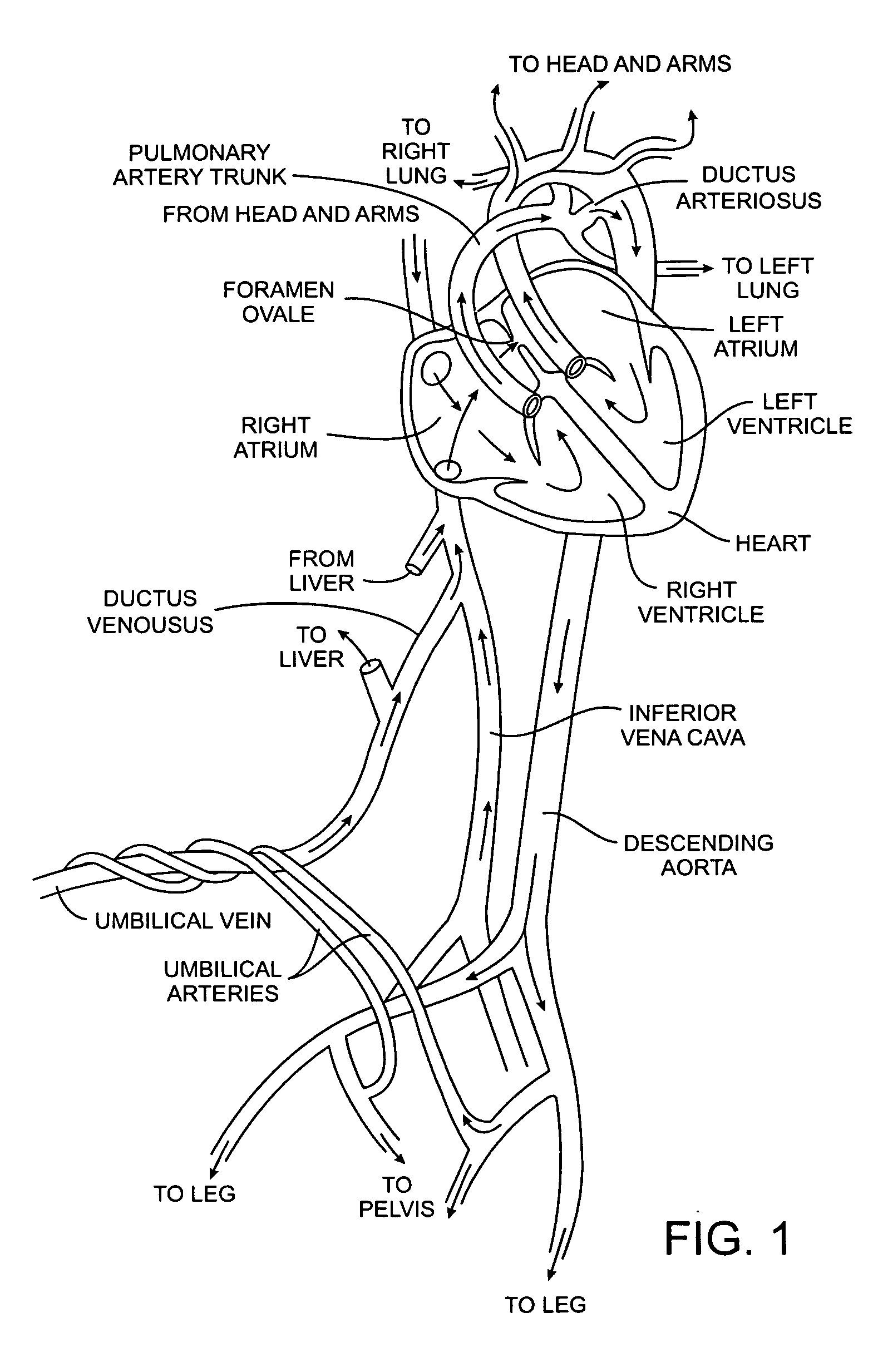
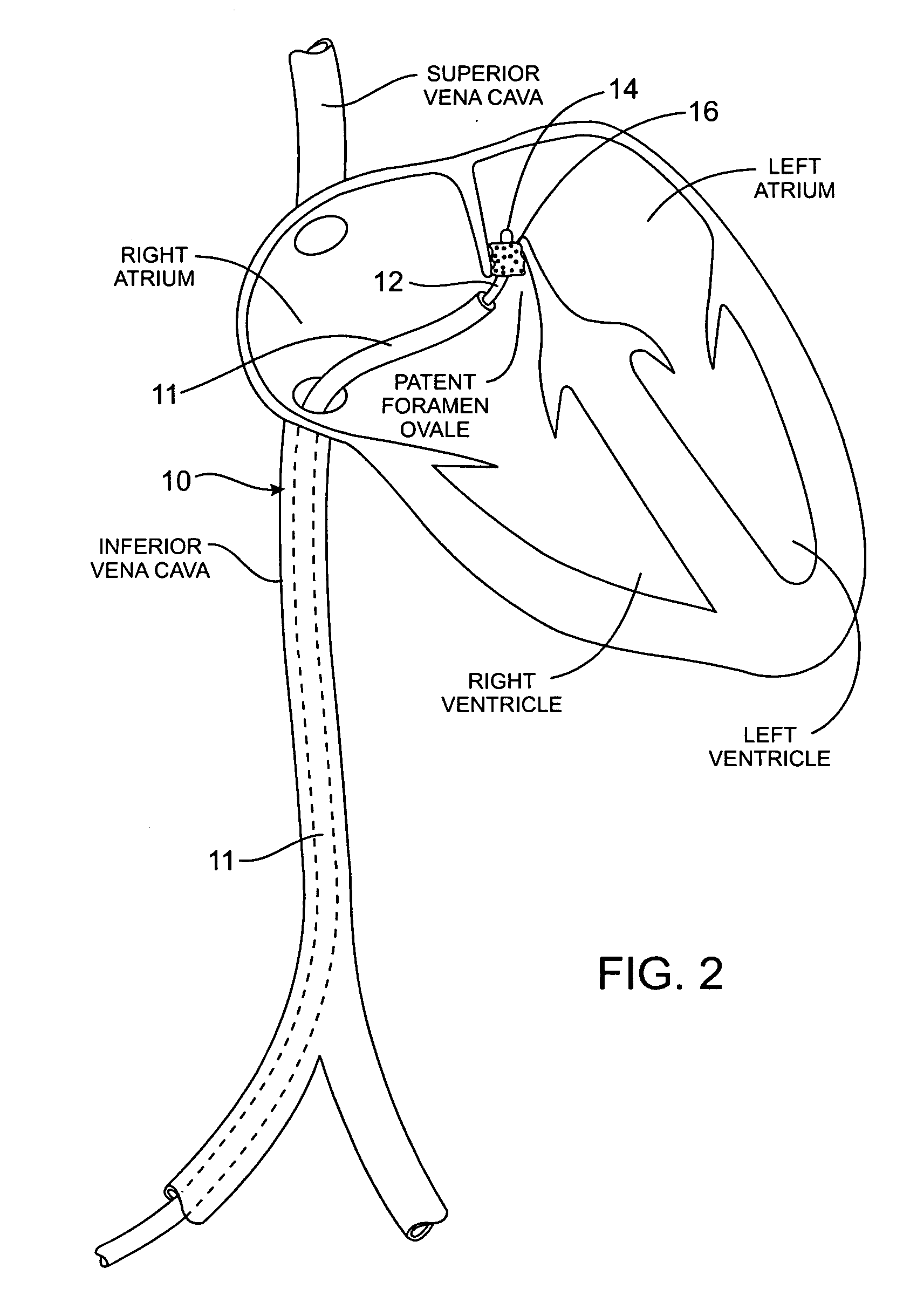
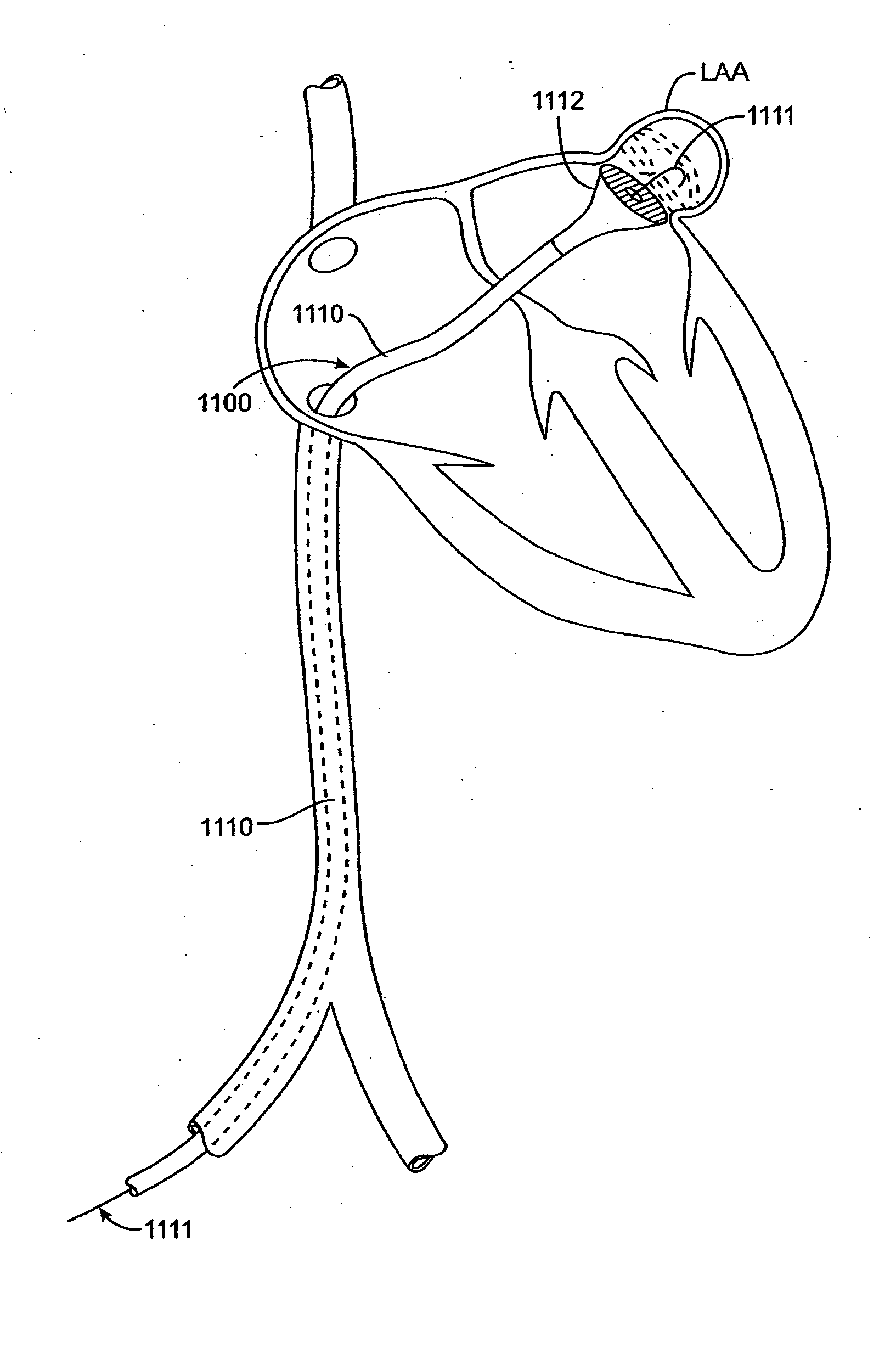
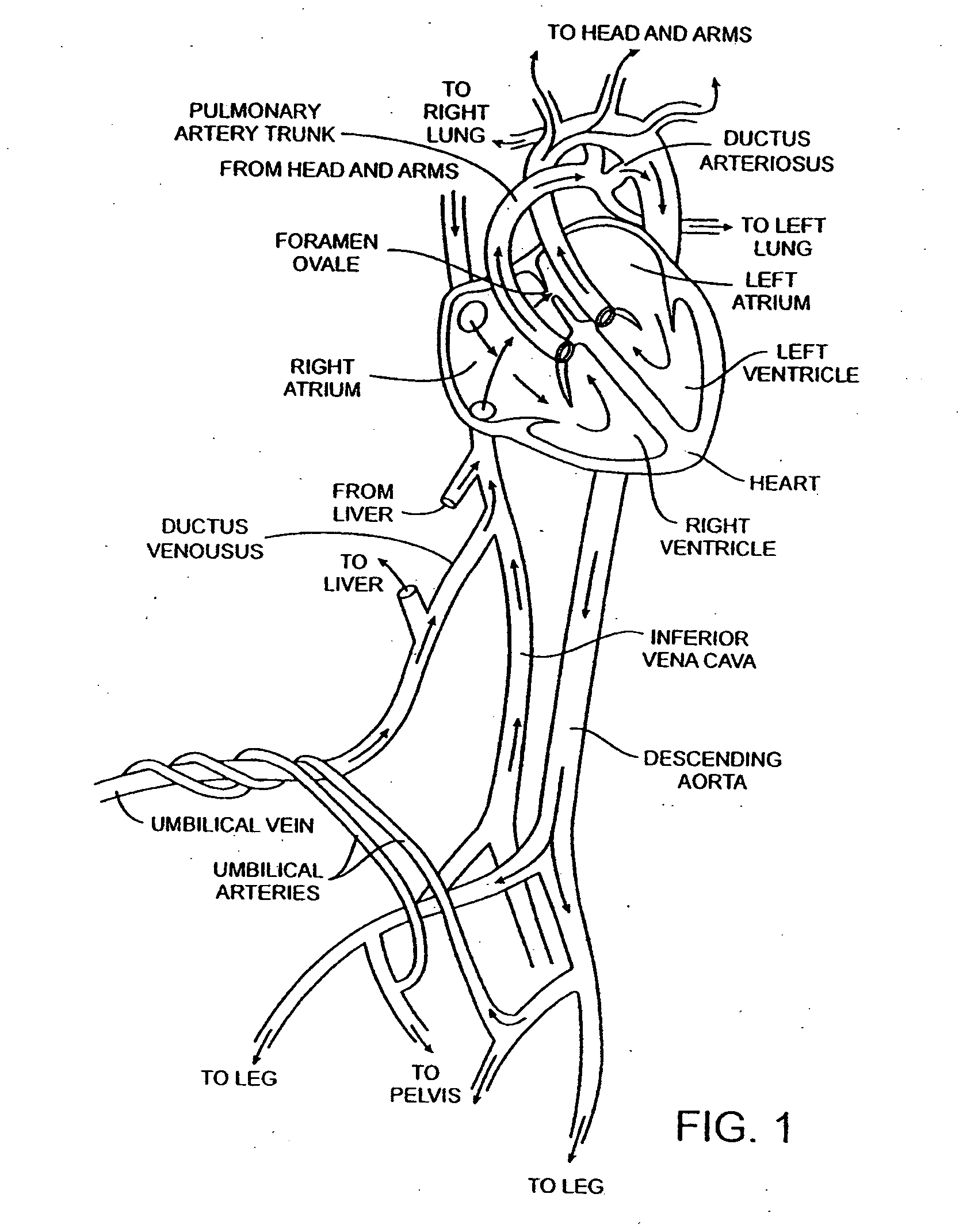
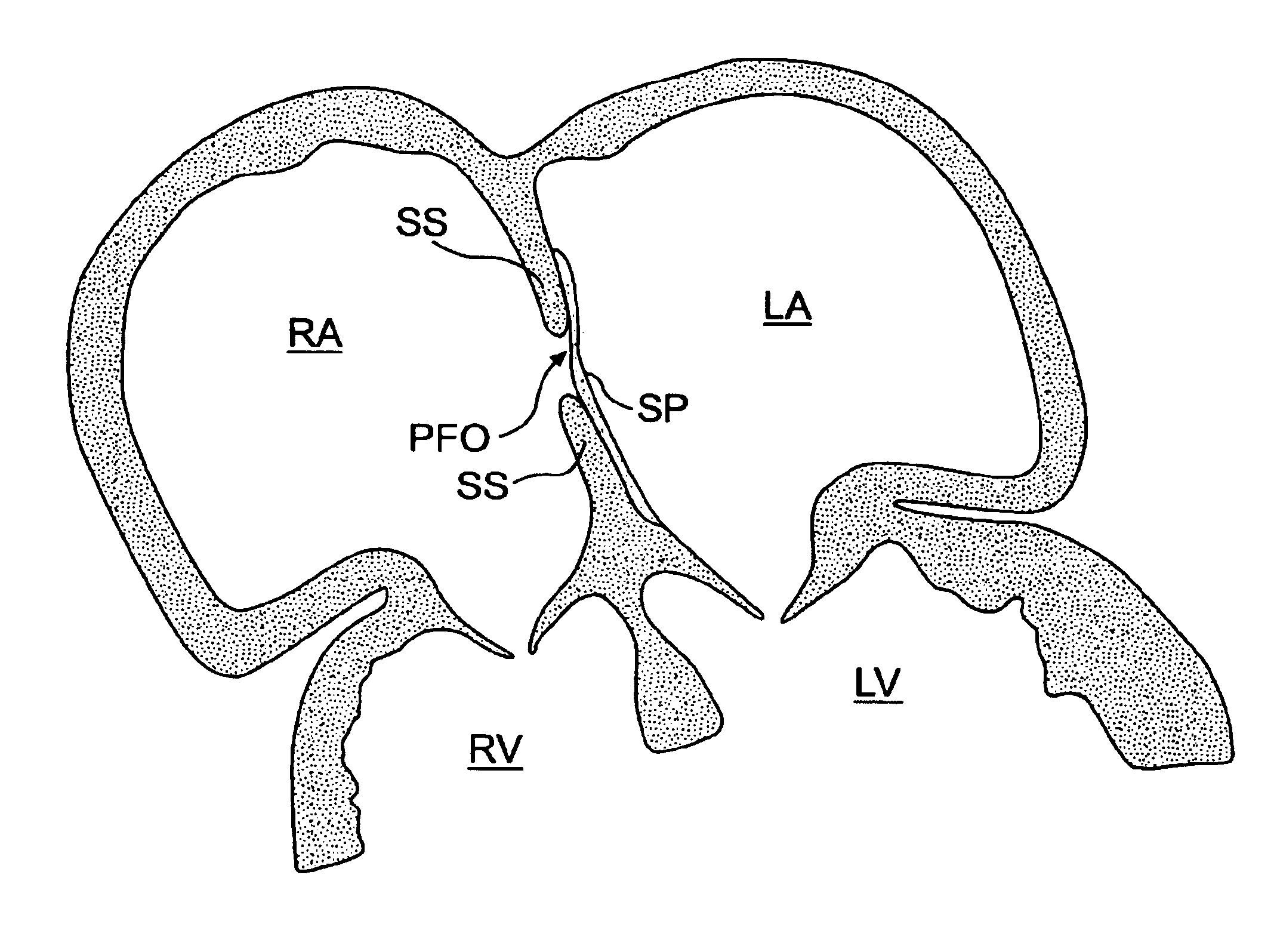
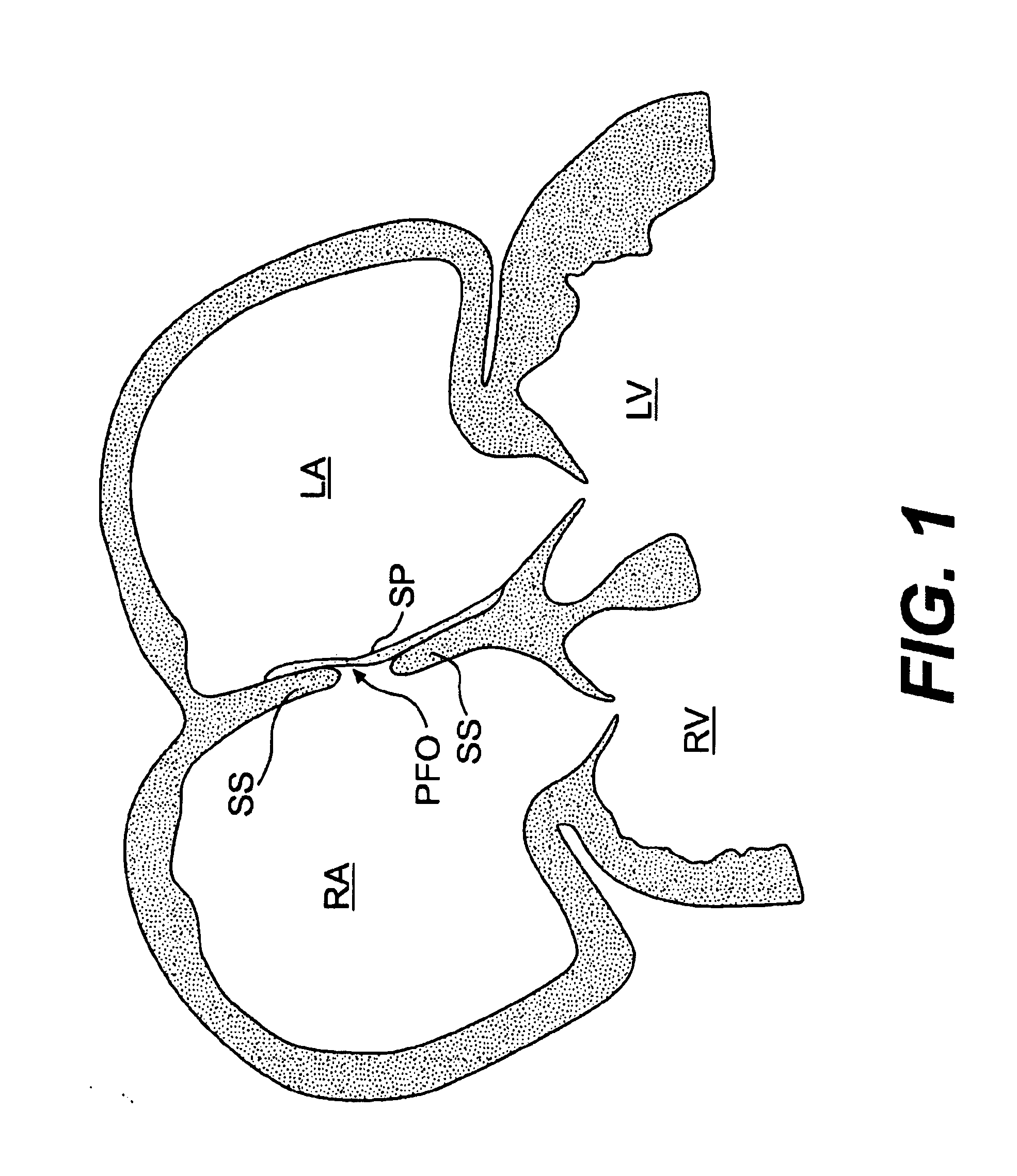
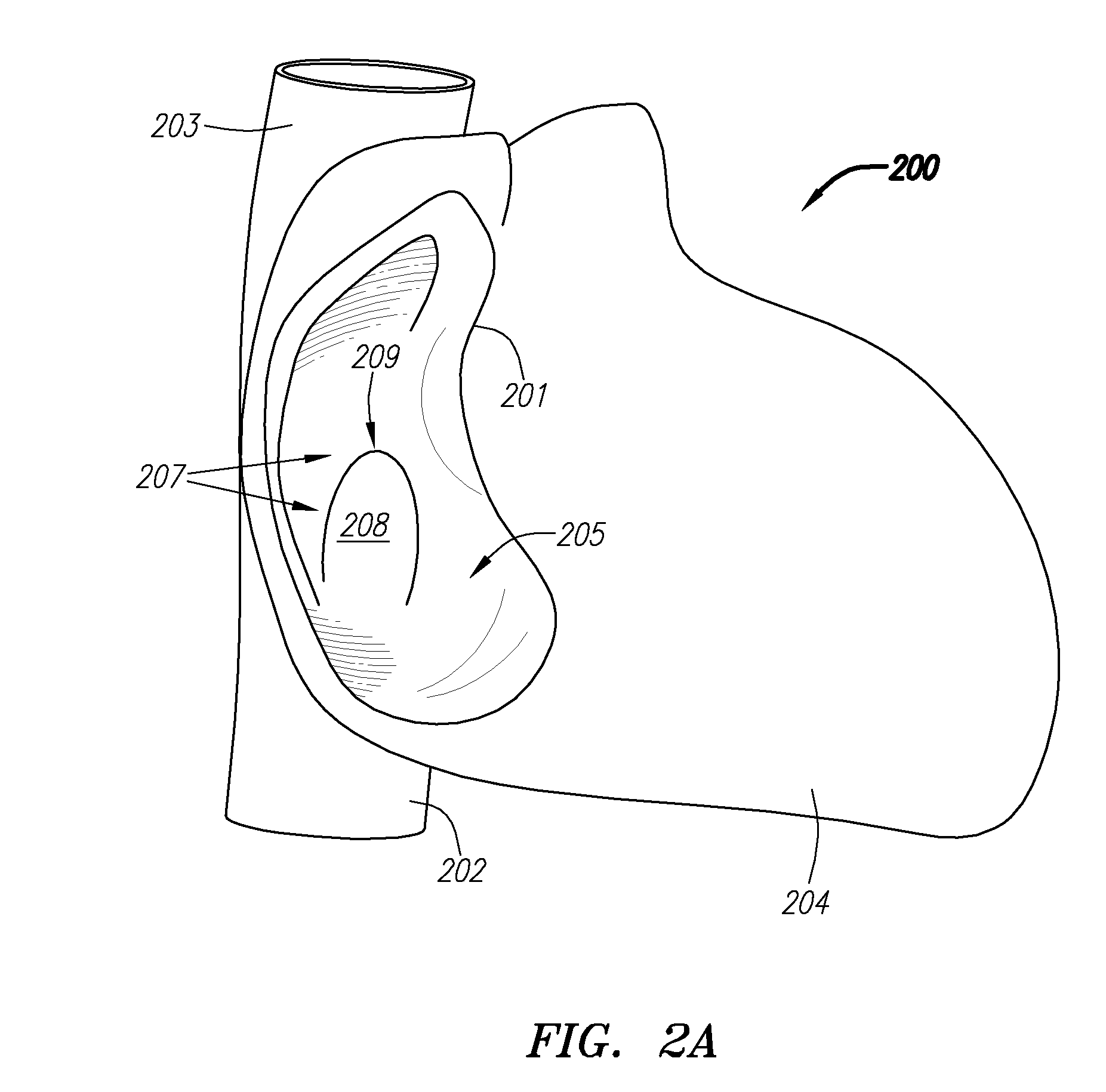
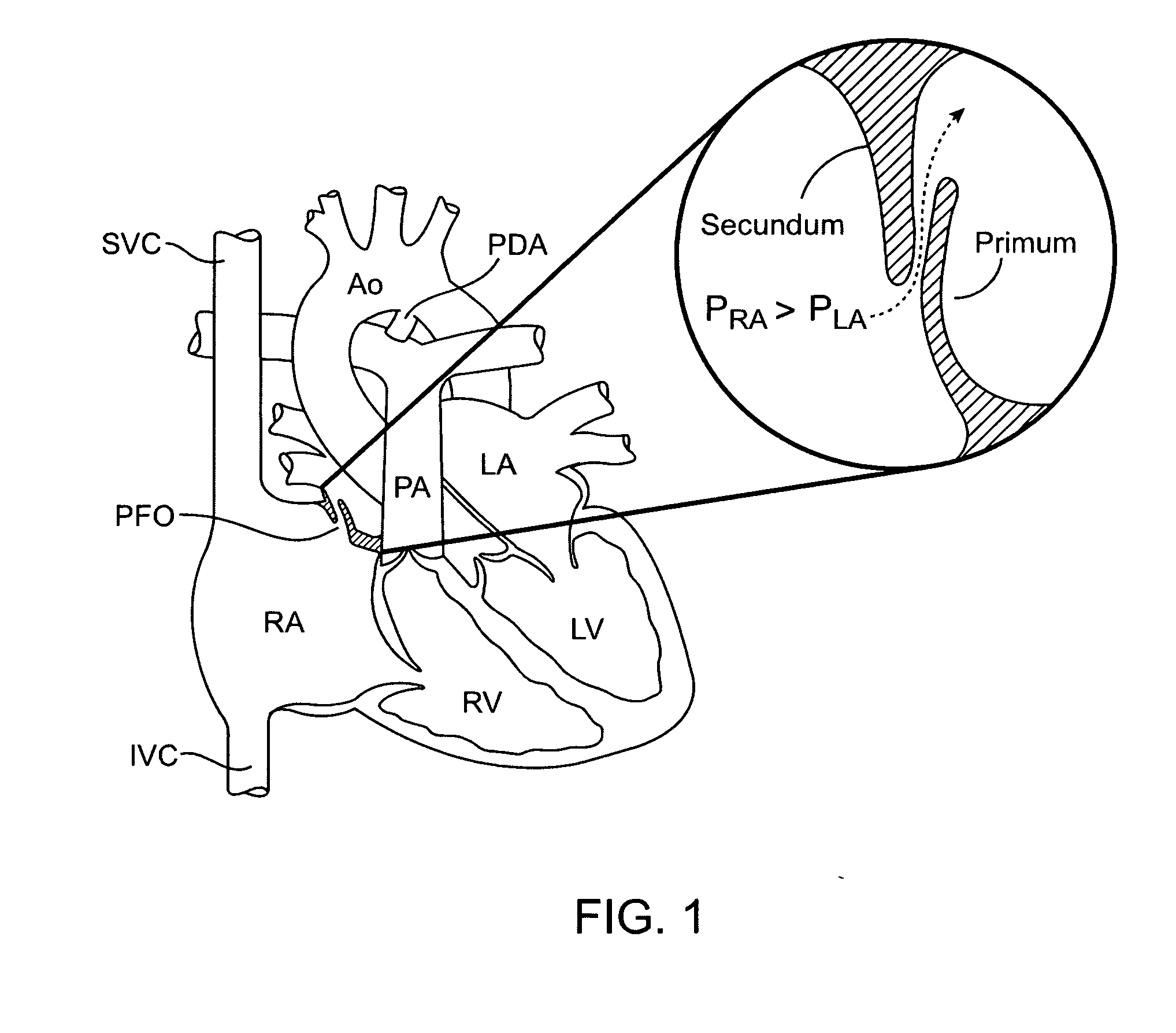
A congenital defect characterized by a hole in the wall between the atria.
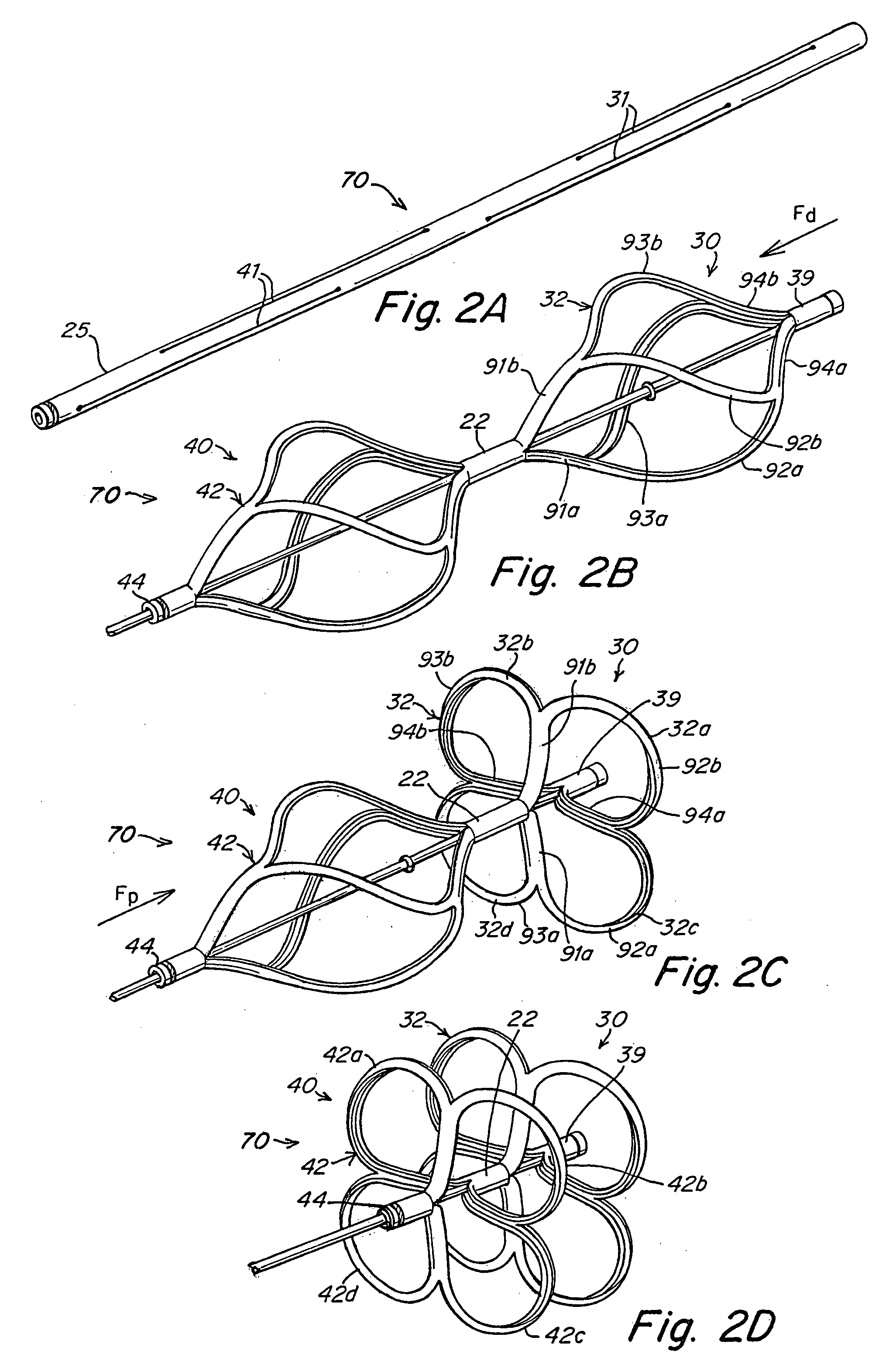
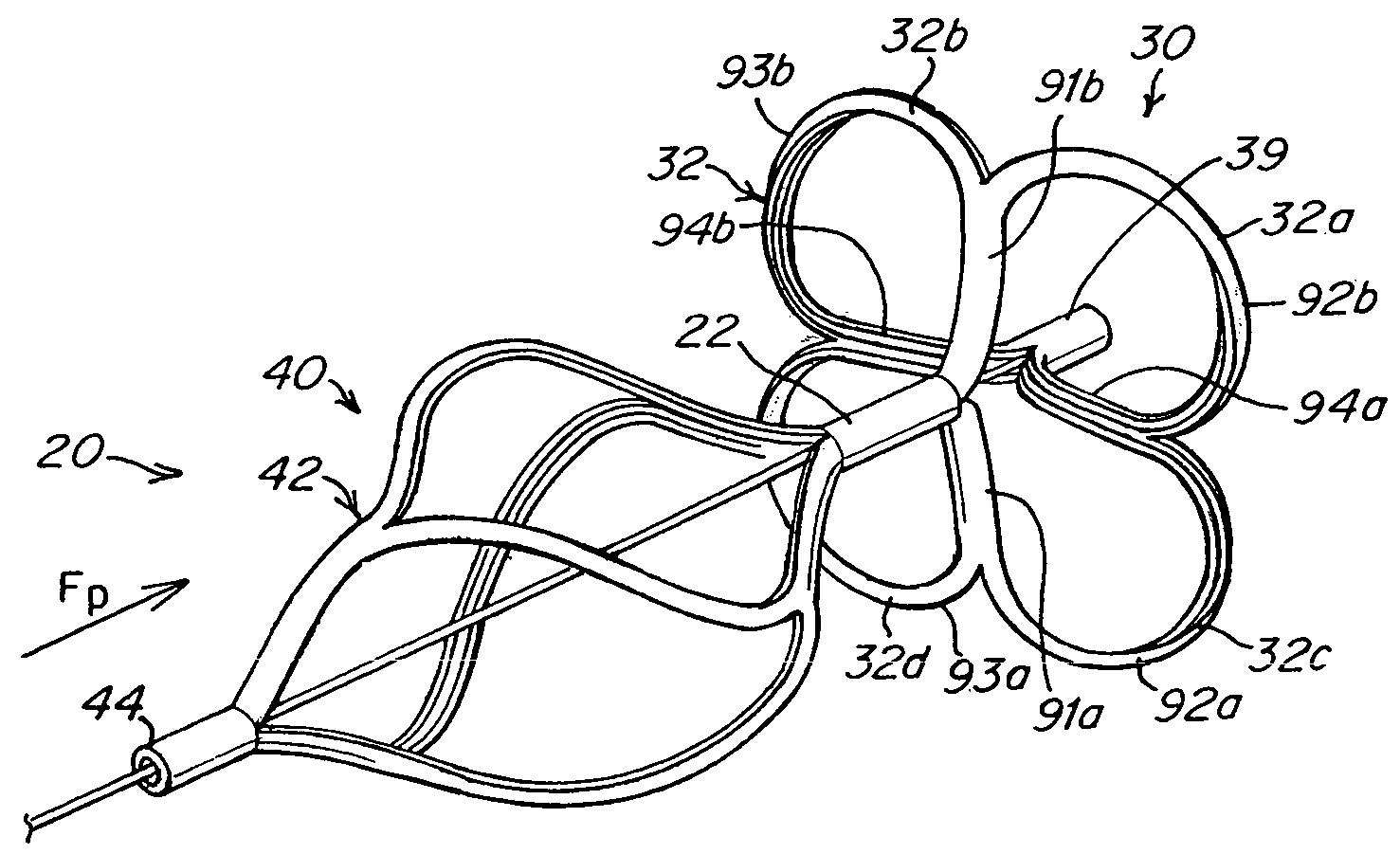
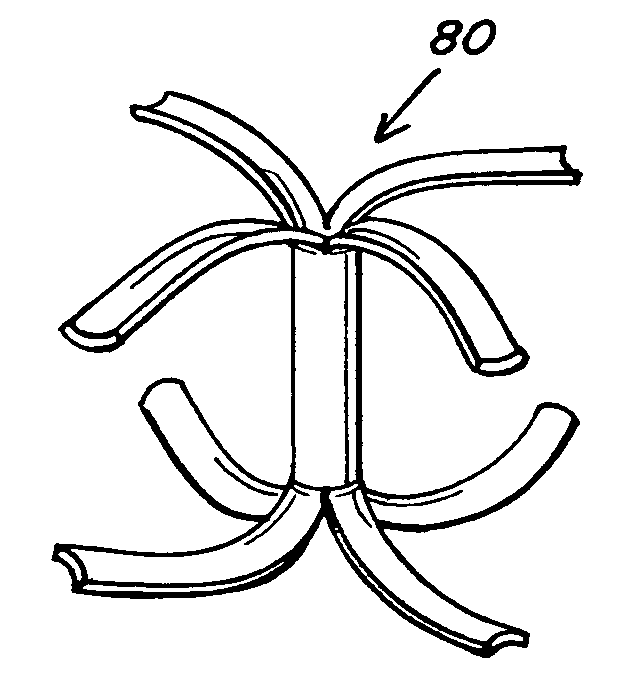
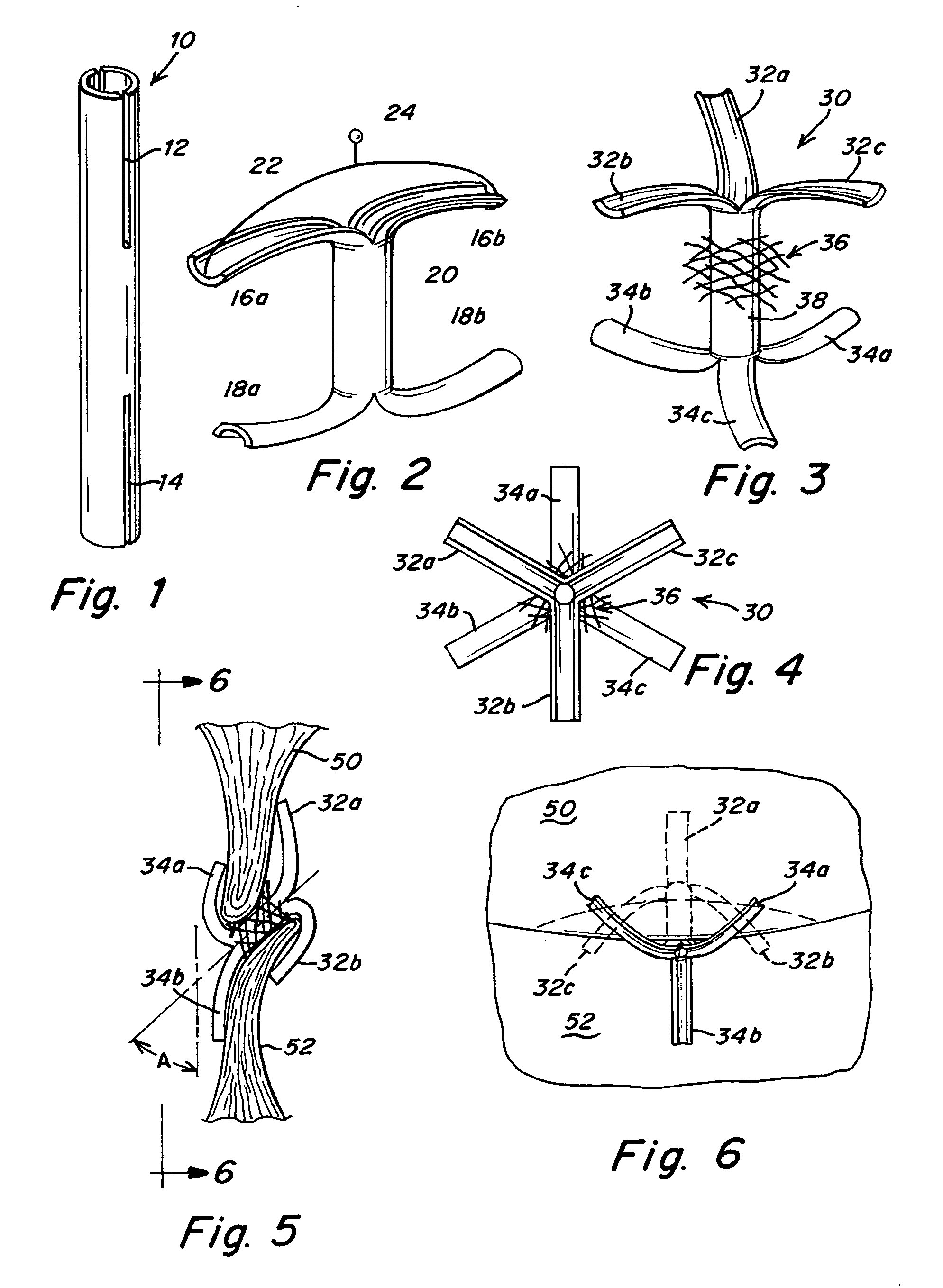
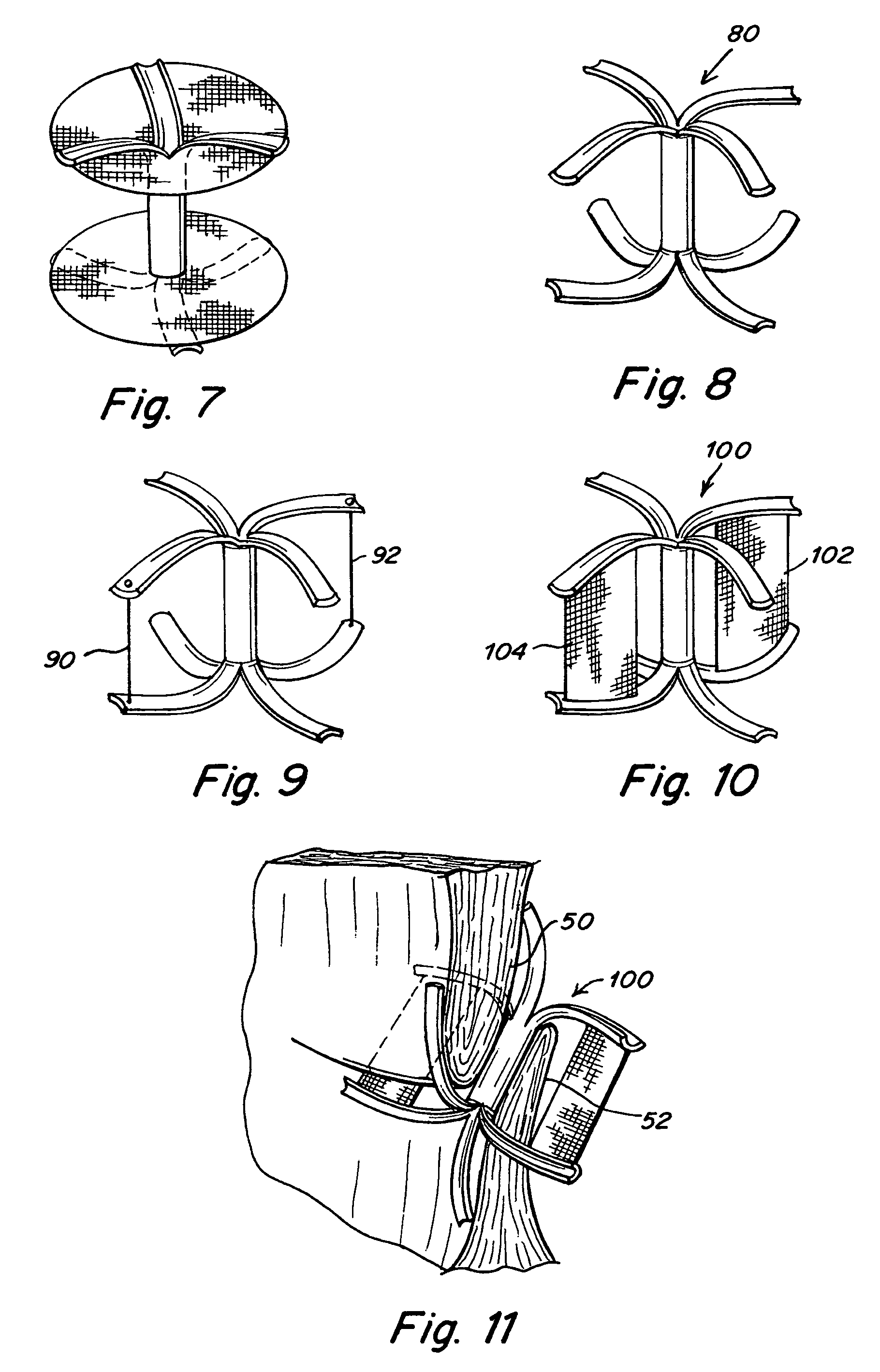
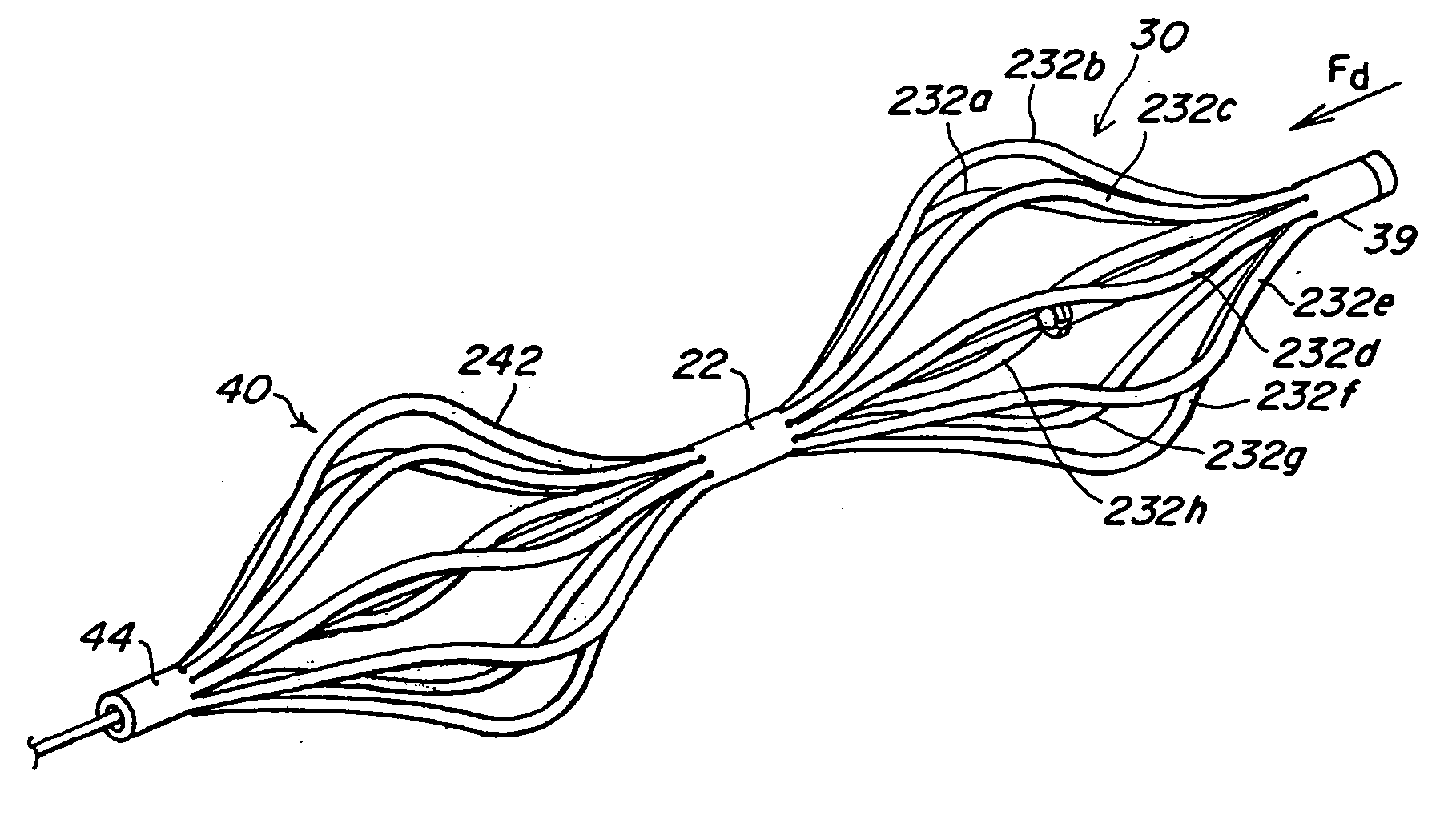
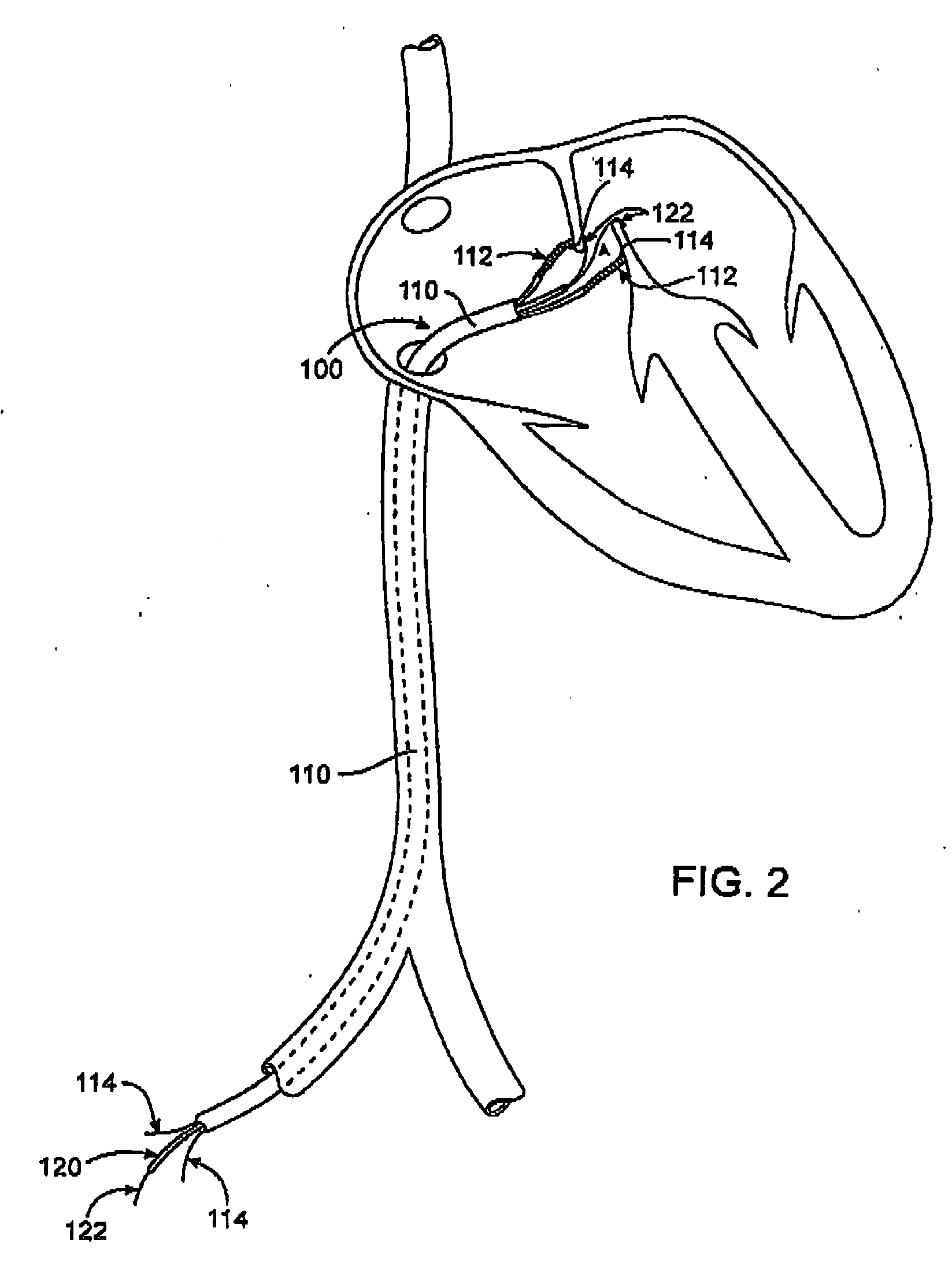
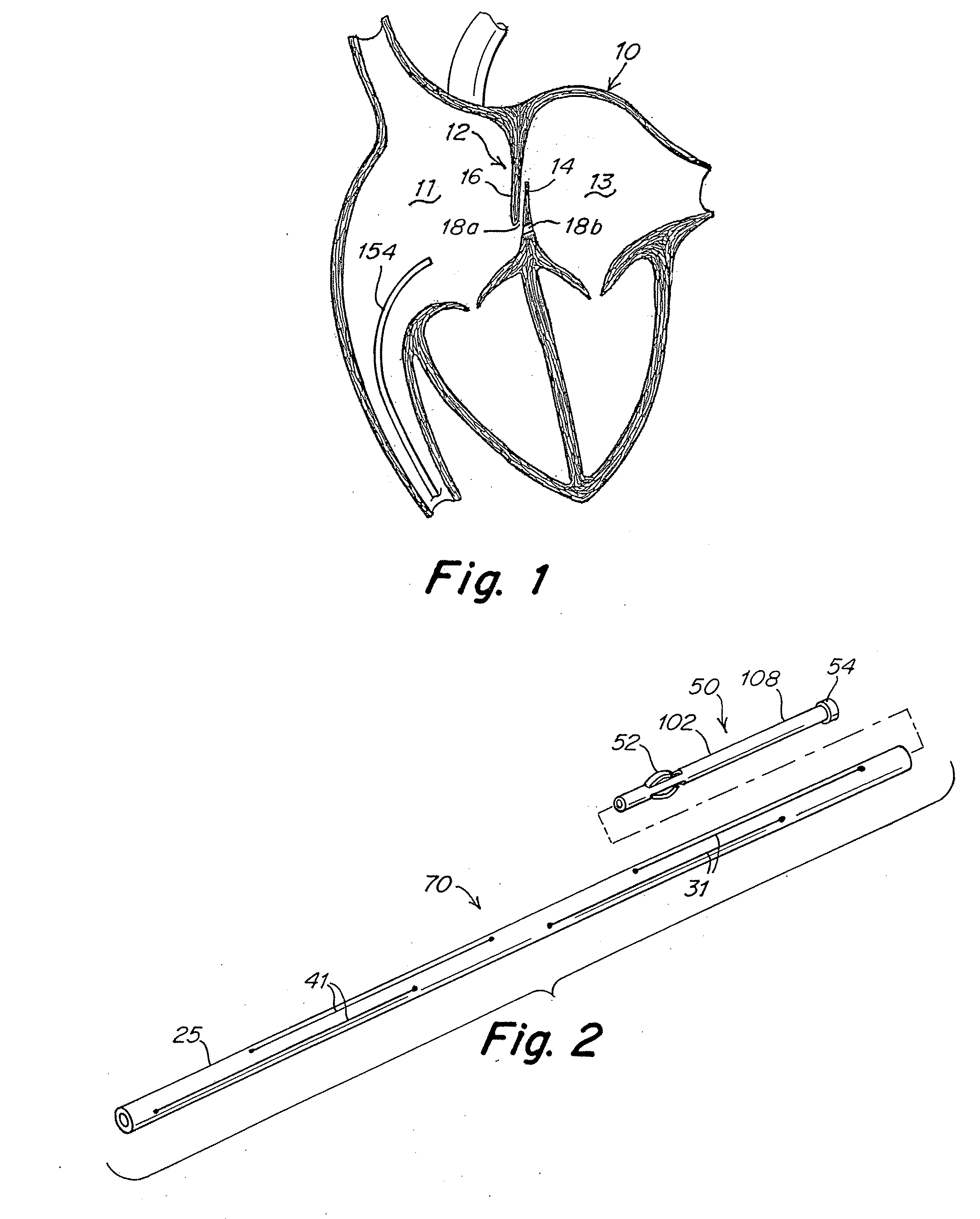
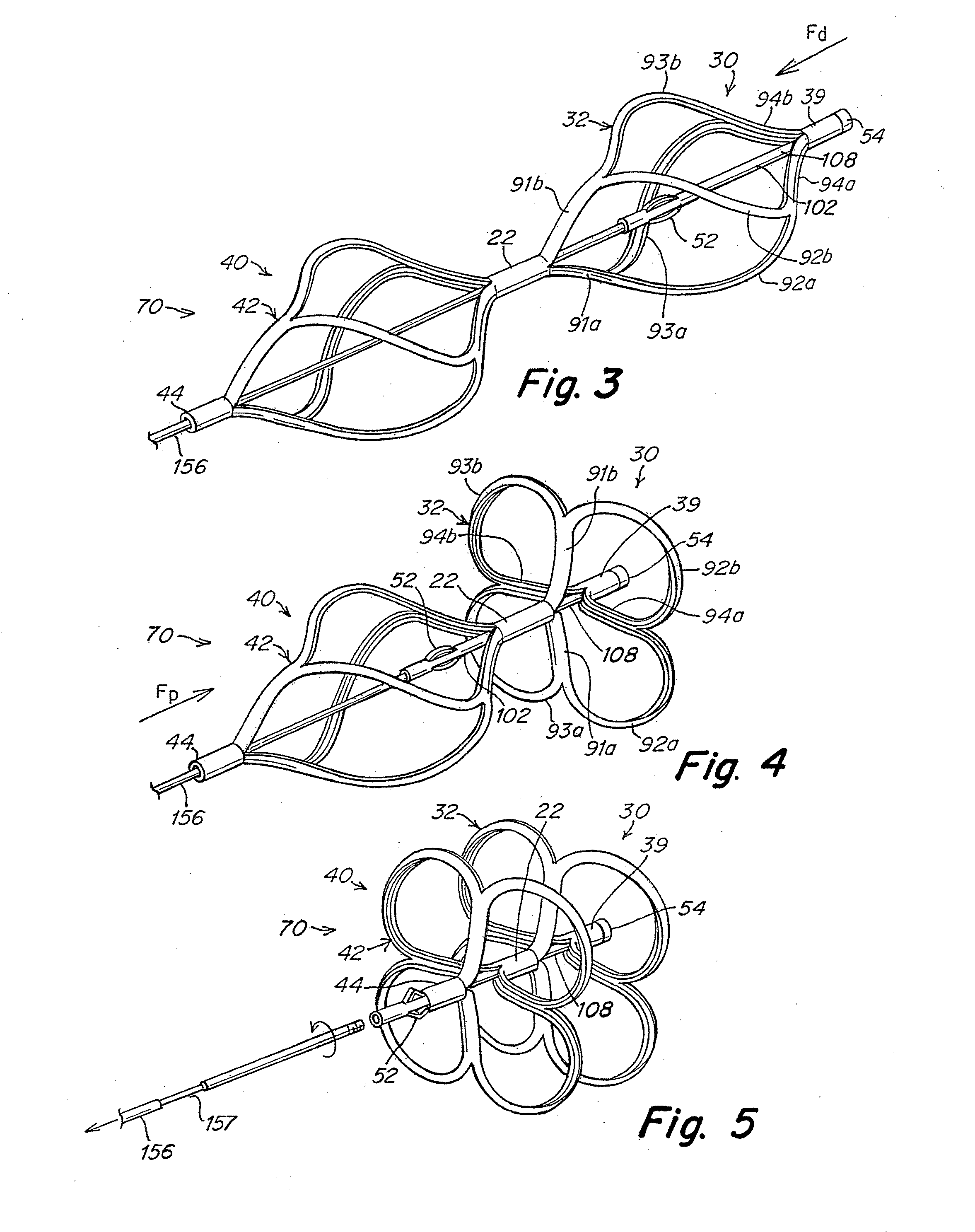
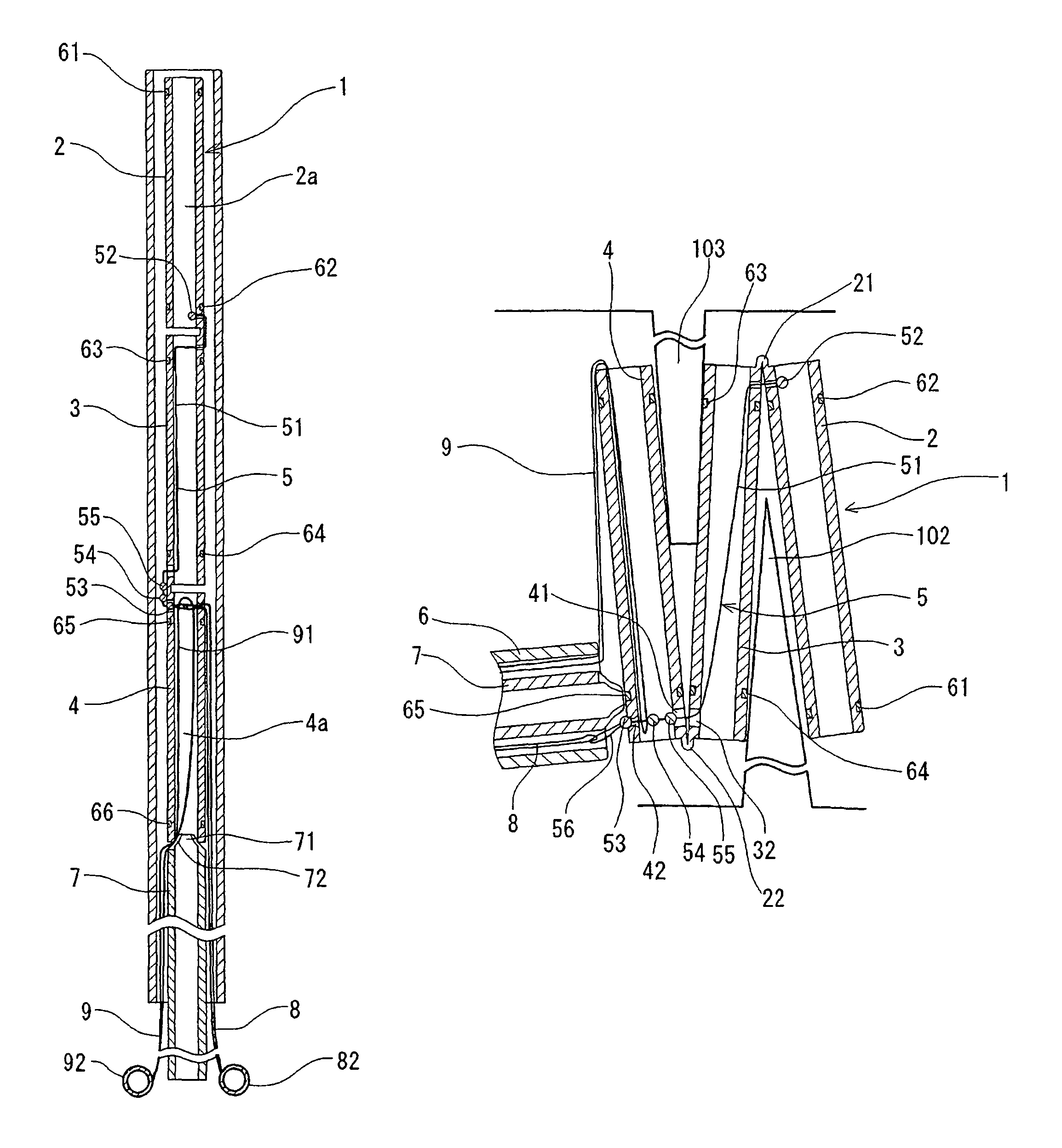
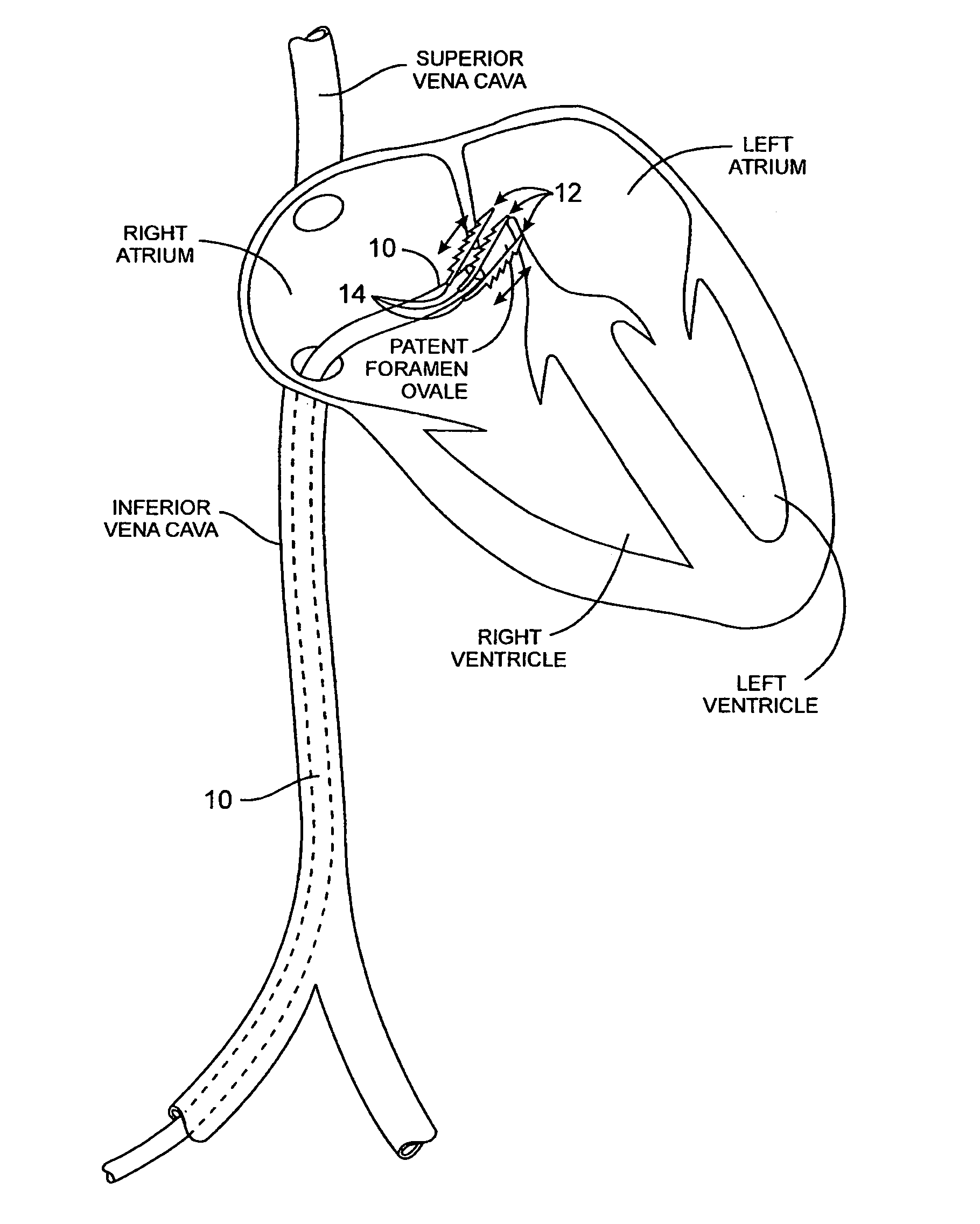
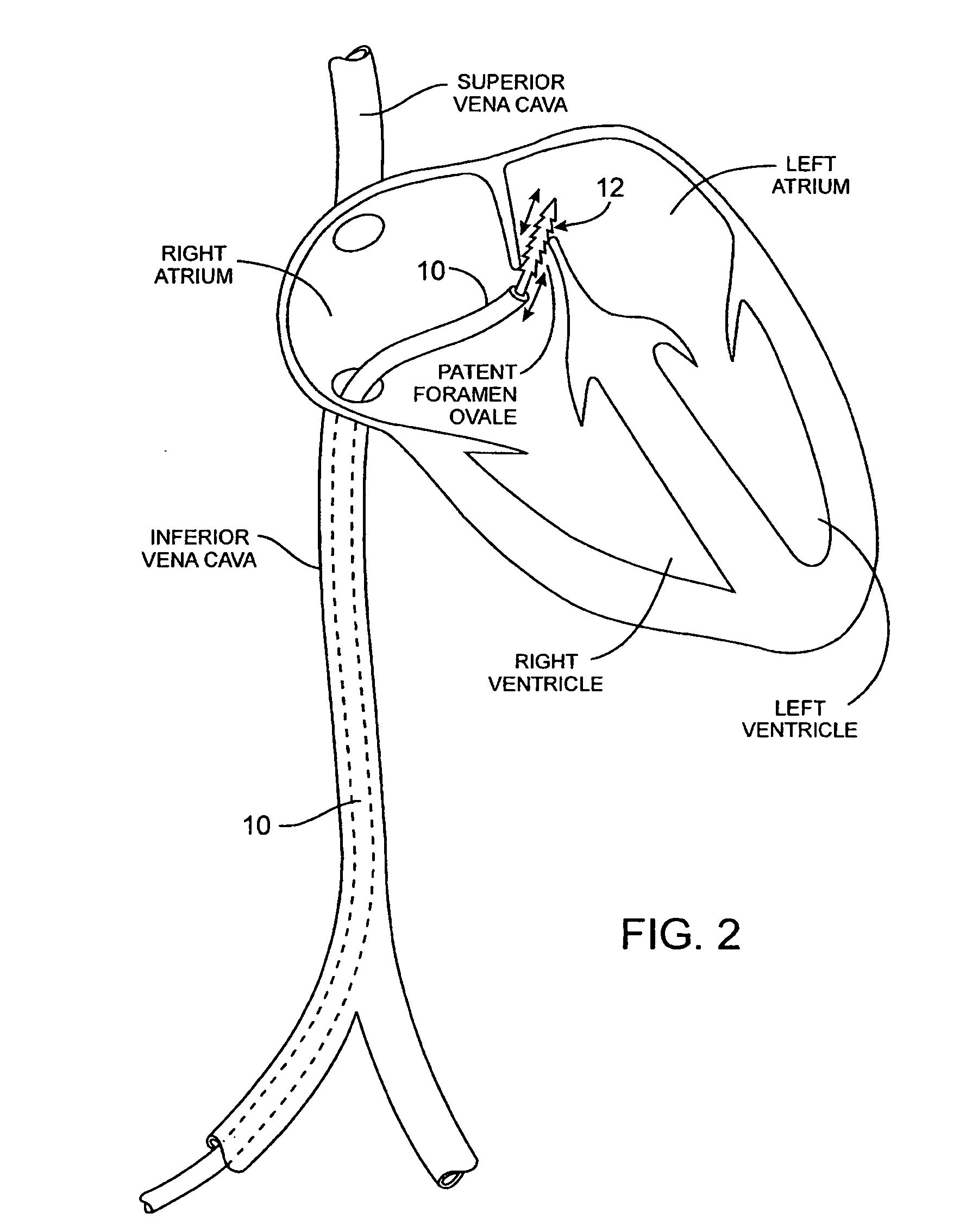
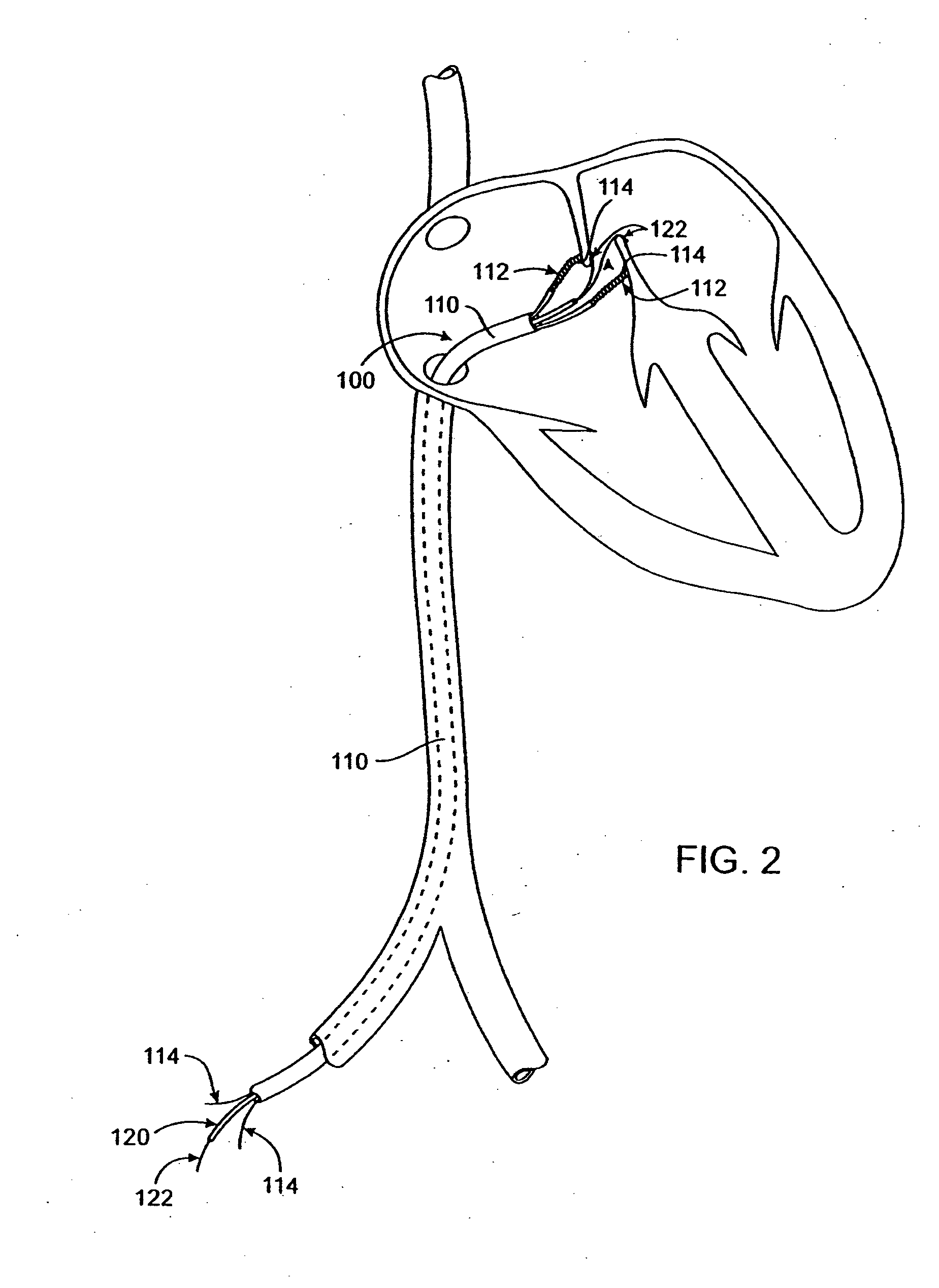
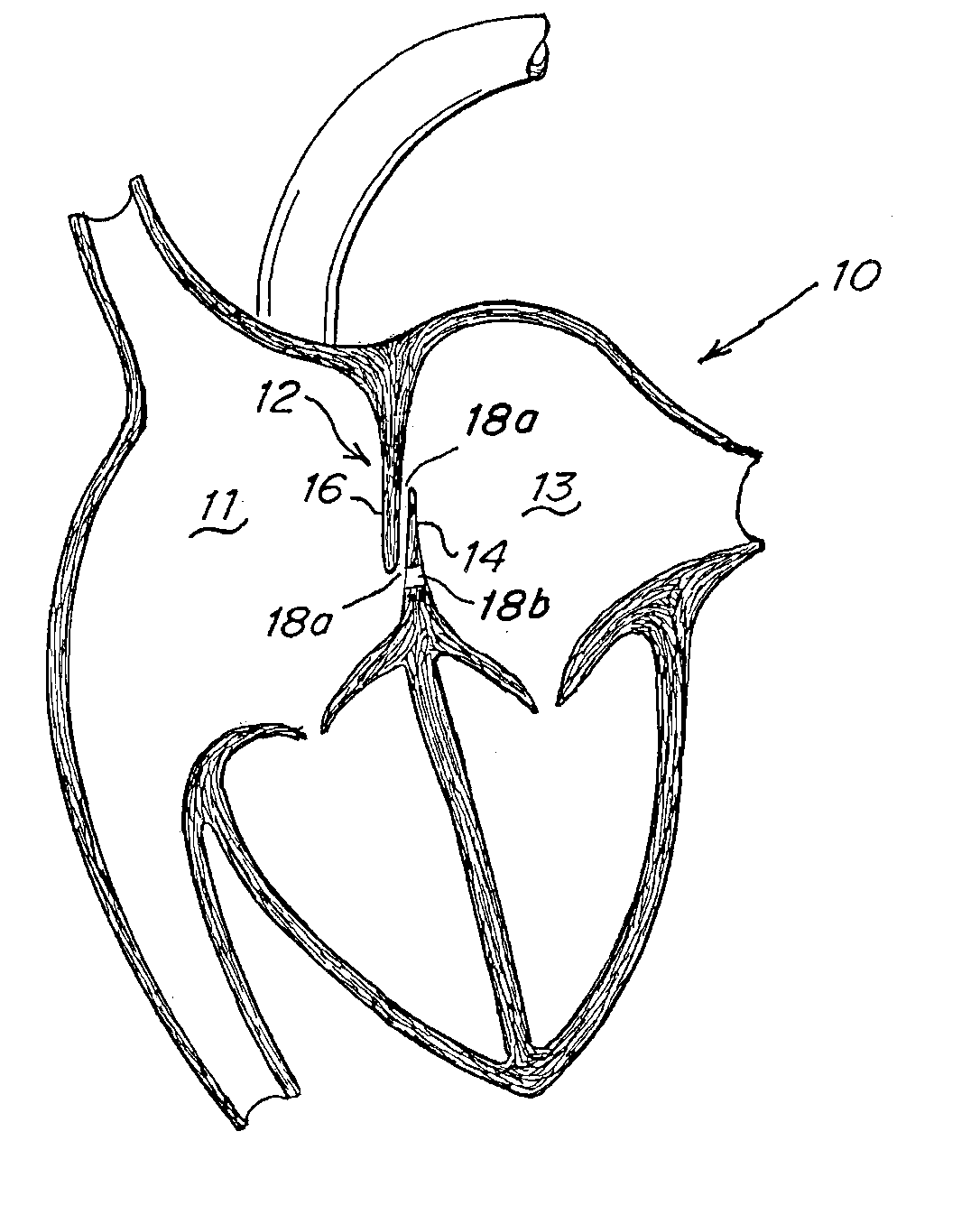
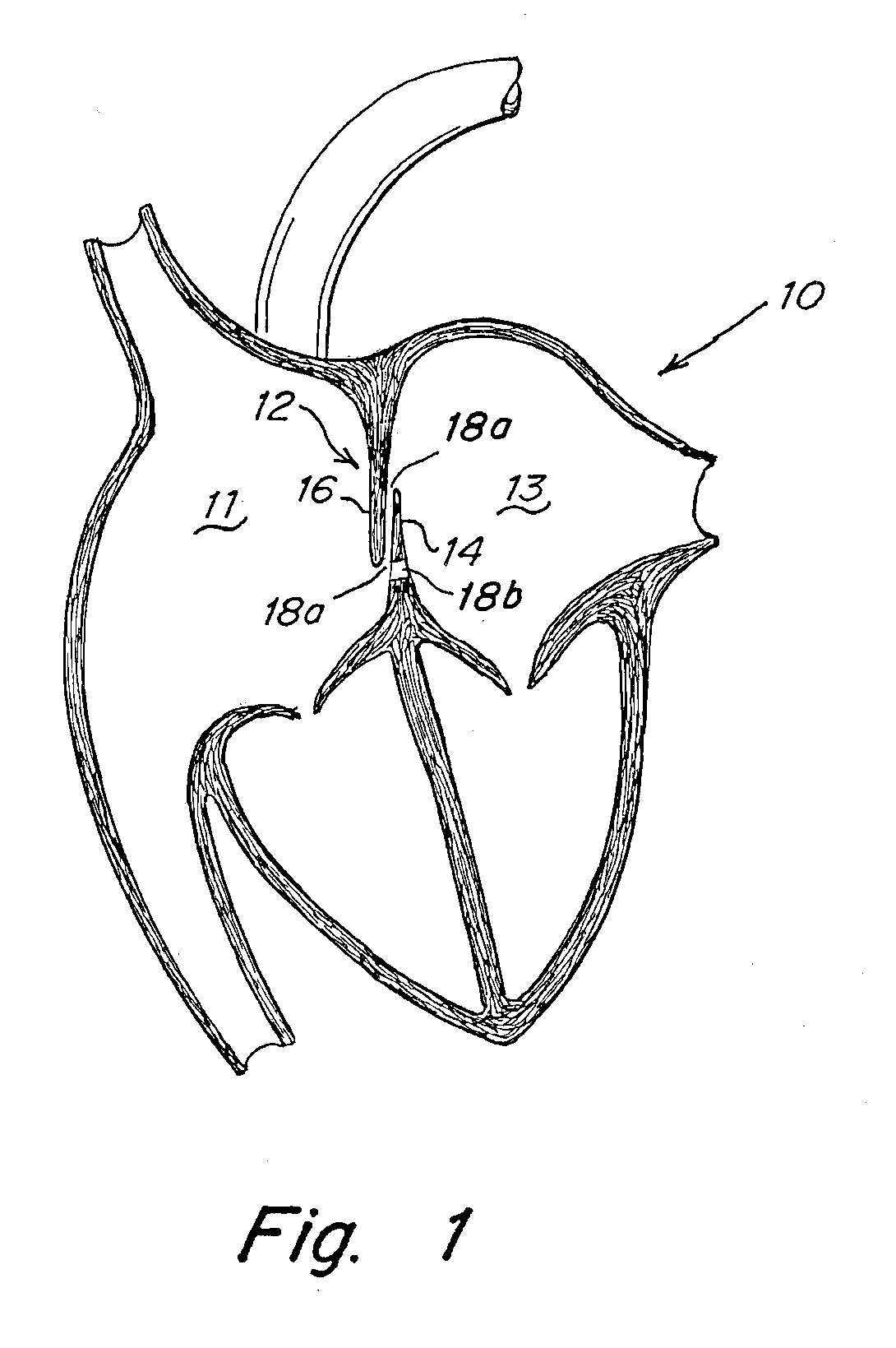
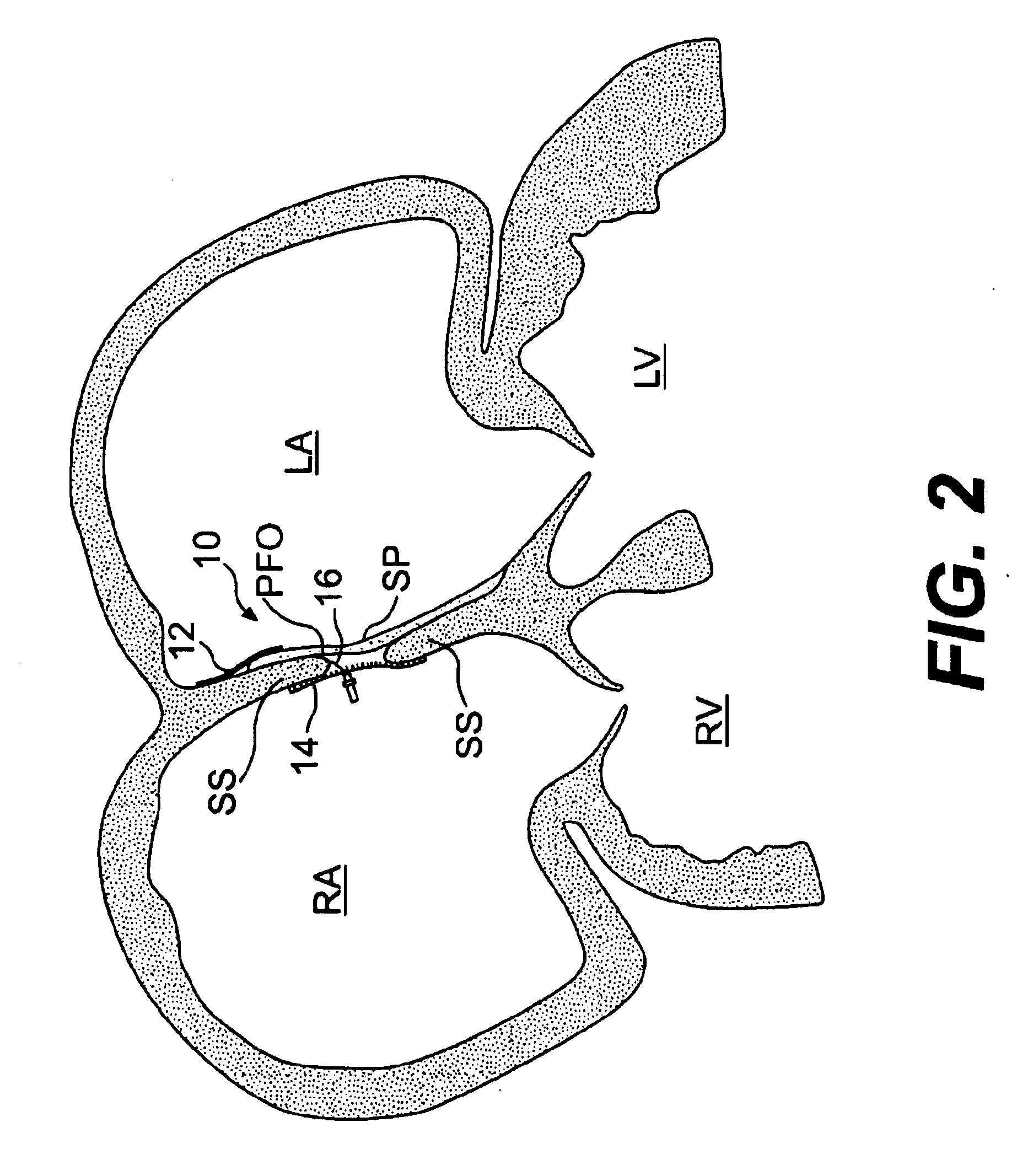
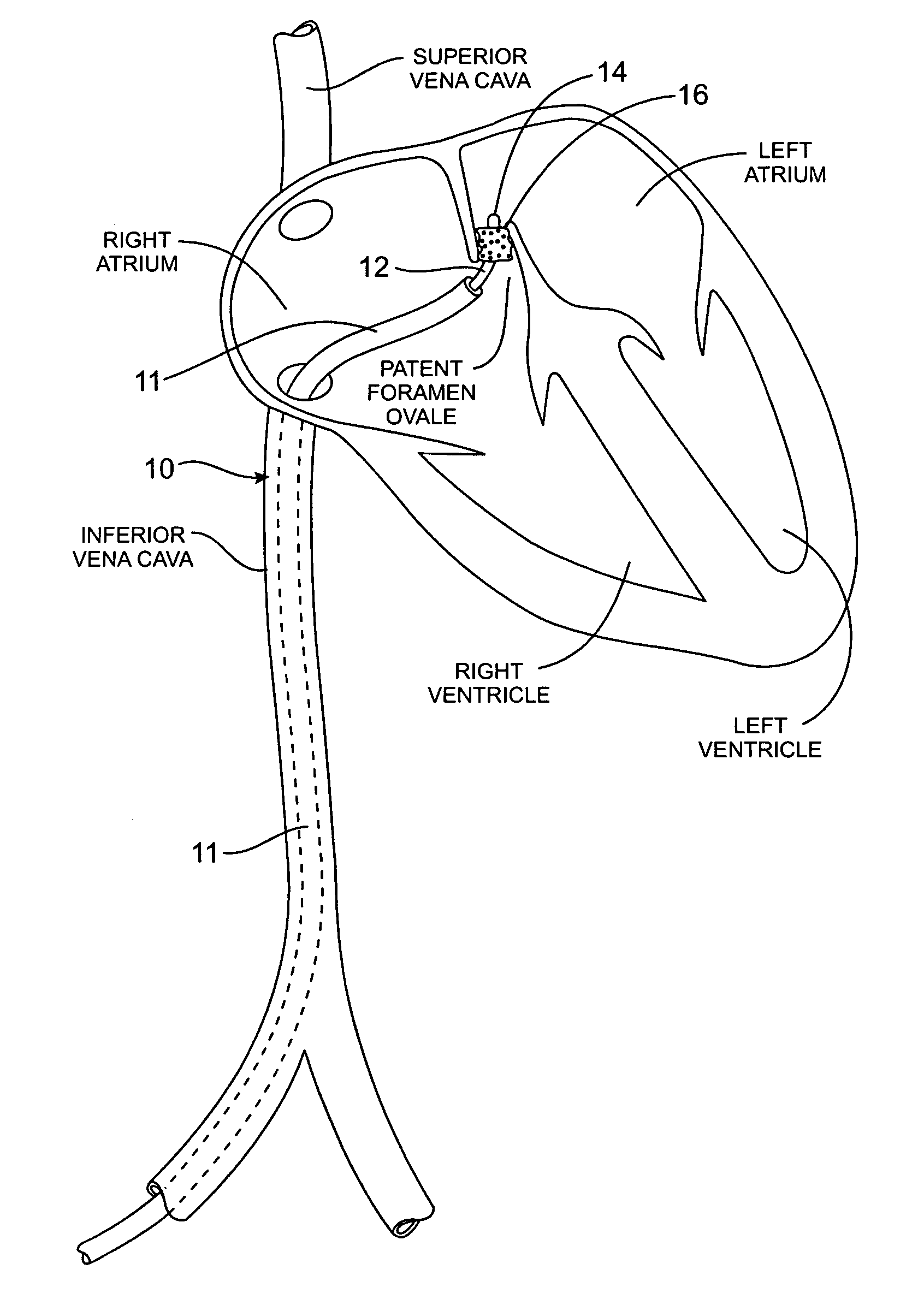
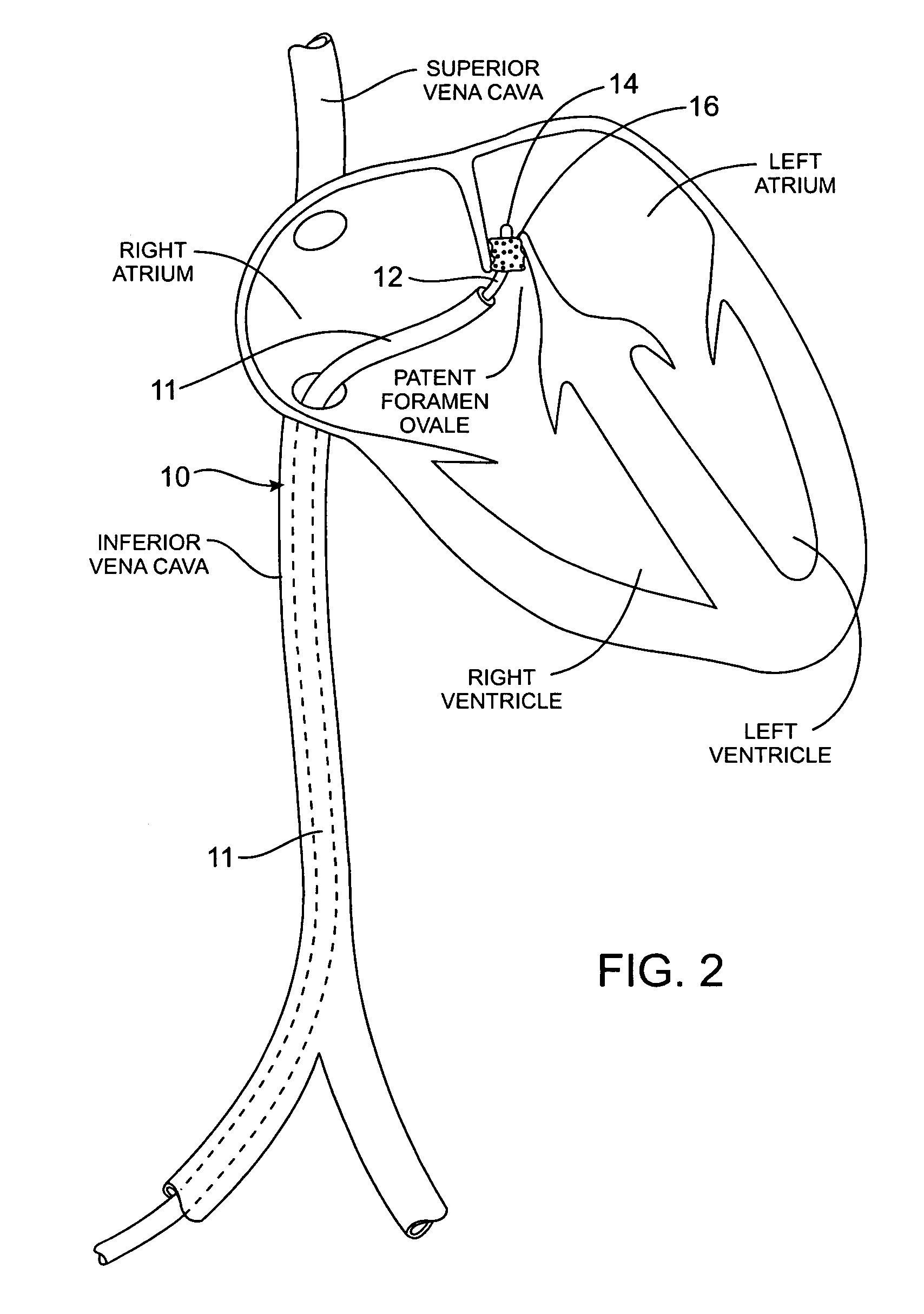
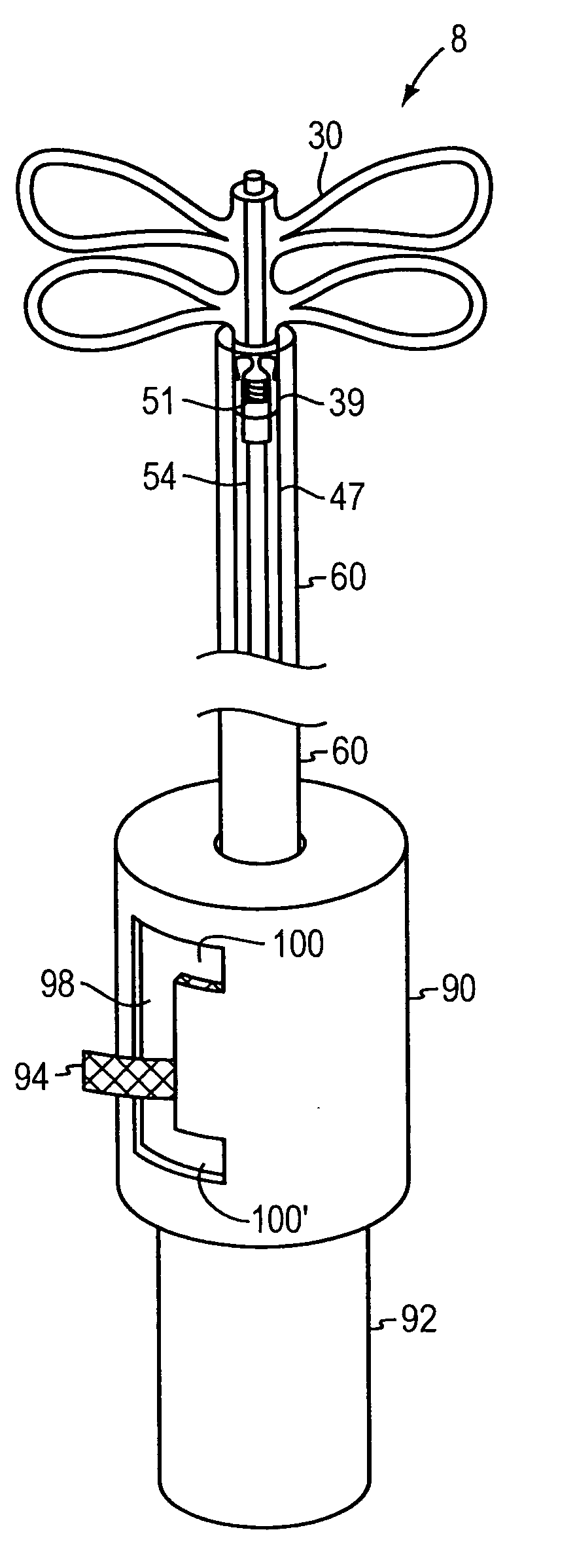
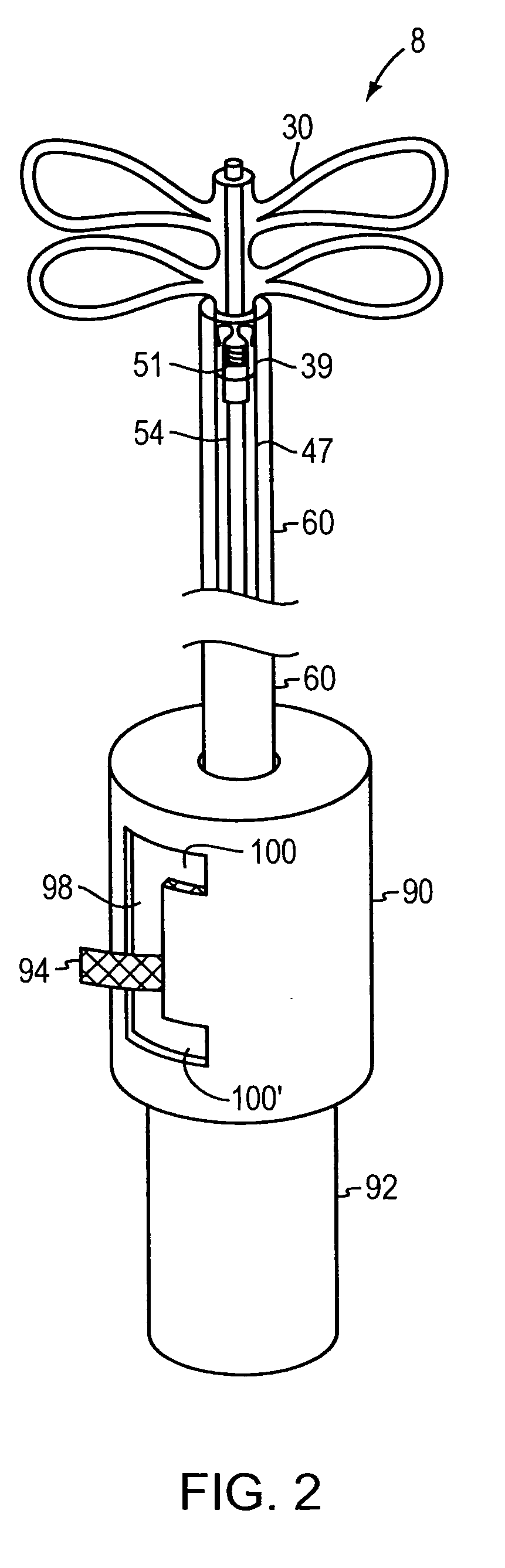
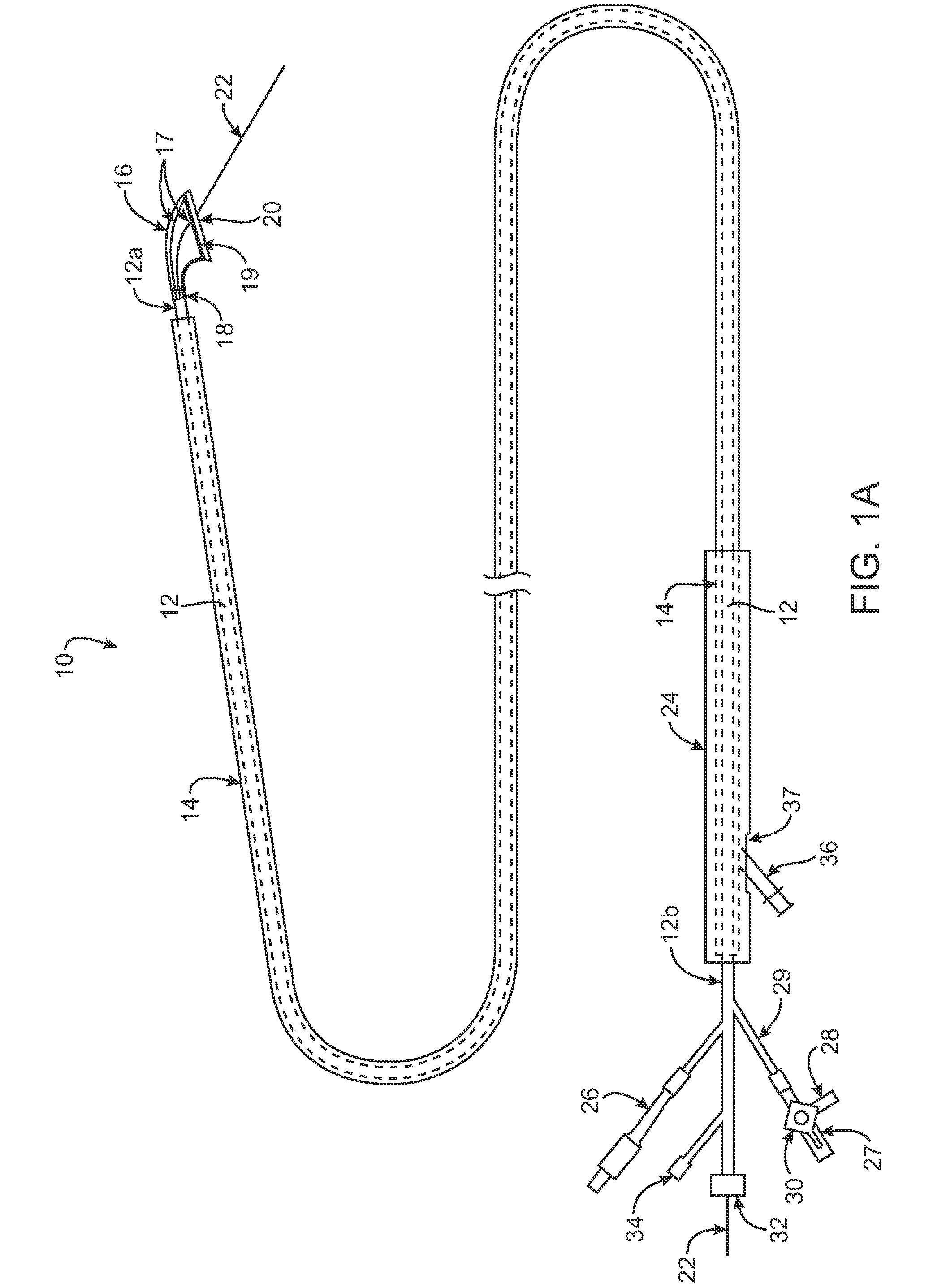
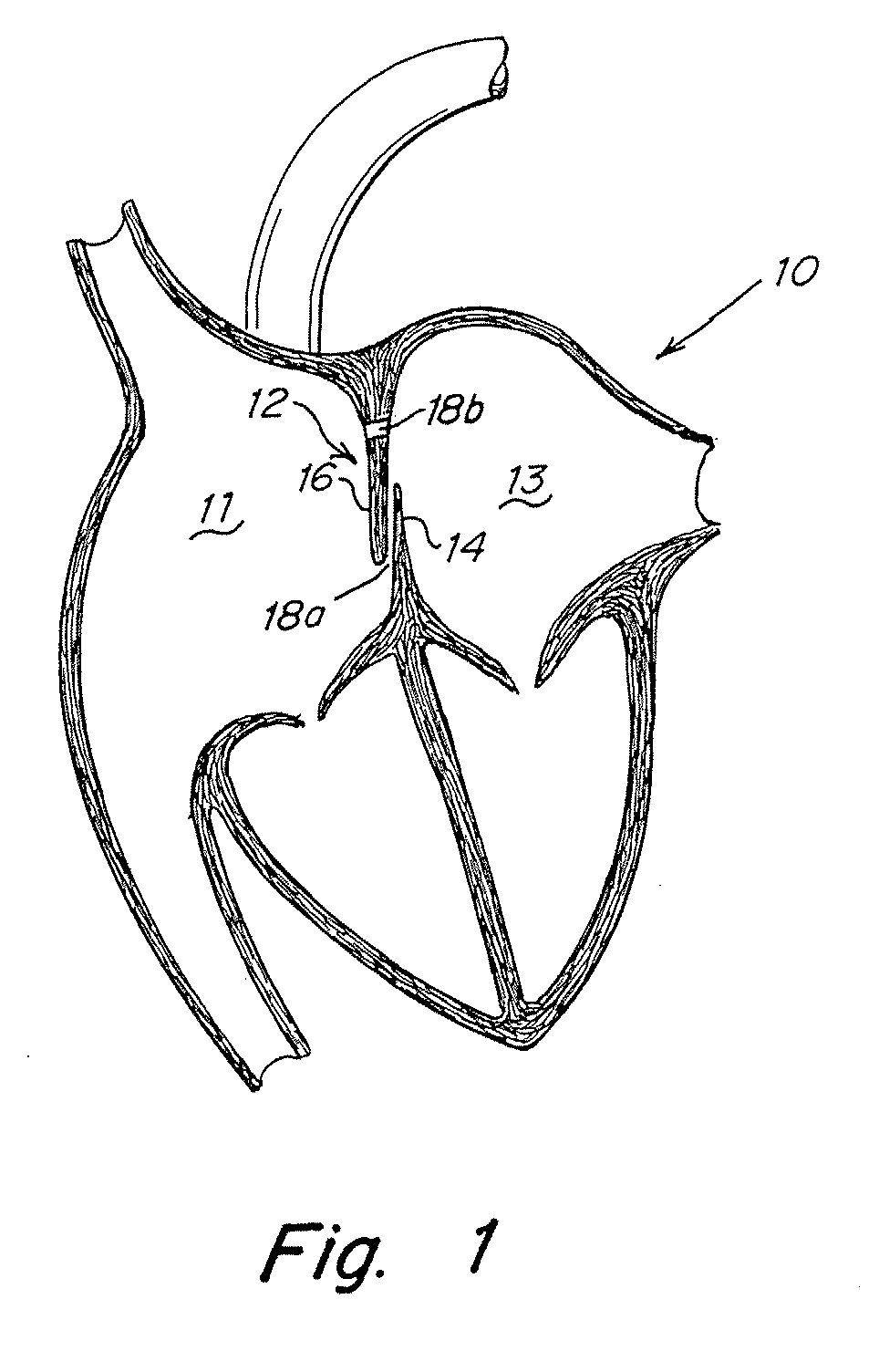
Tubular patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure device with catch system
ActiveUS20050043759A1Minimize traumaMinimize distortion to the septal tissue surroundingSurgical veterinaryWound clampsEngineeringAtrial septal defects
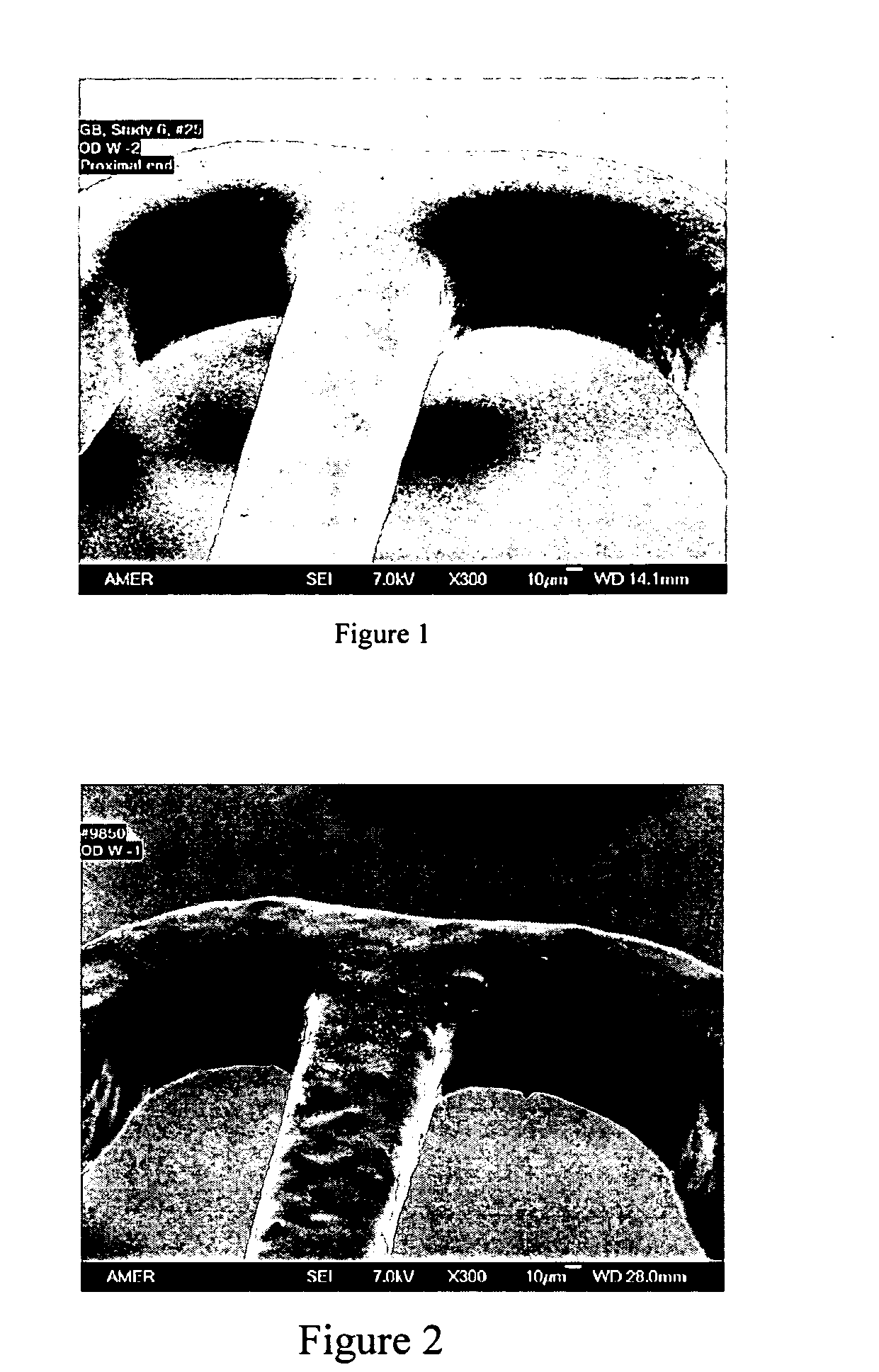
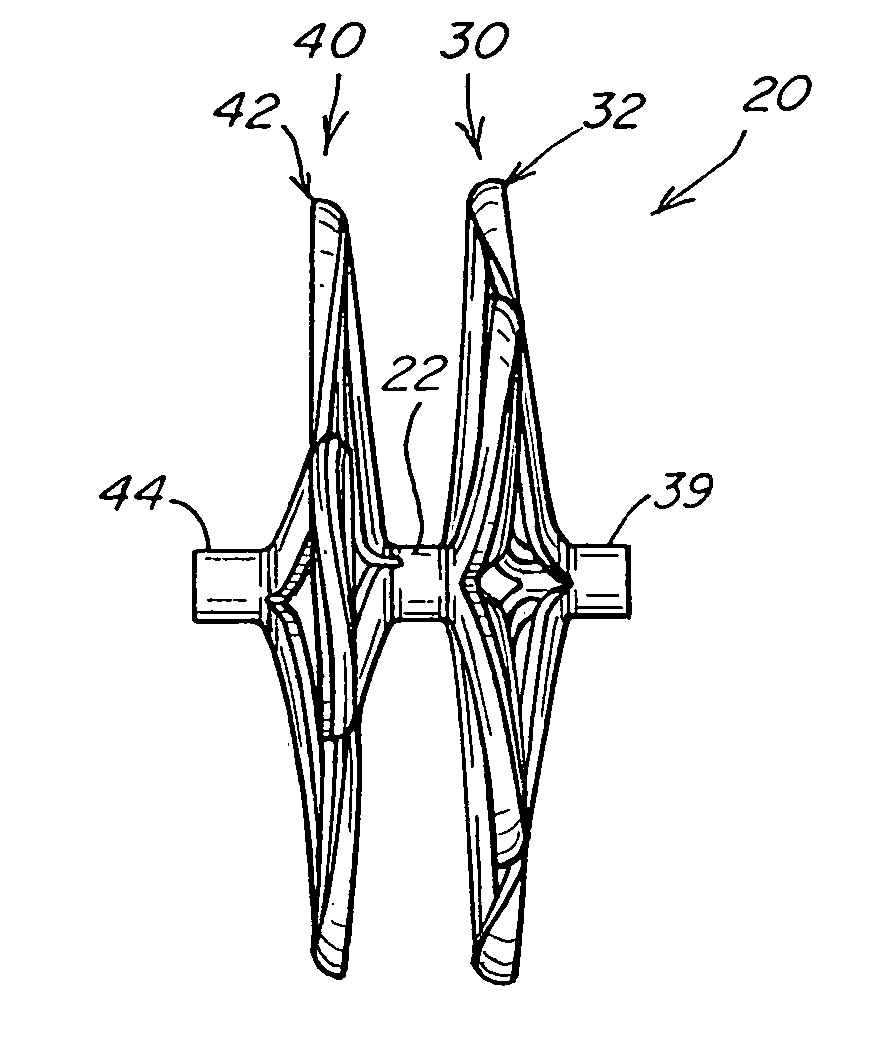
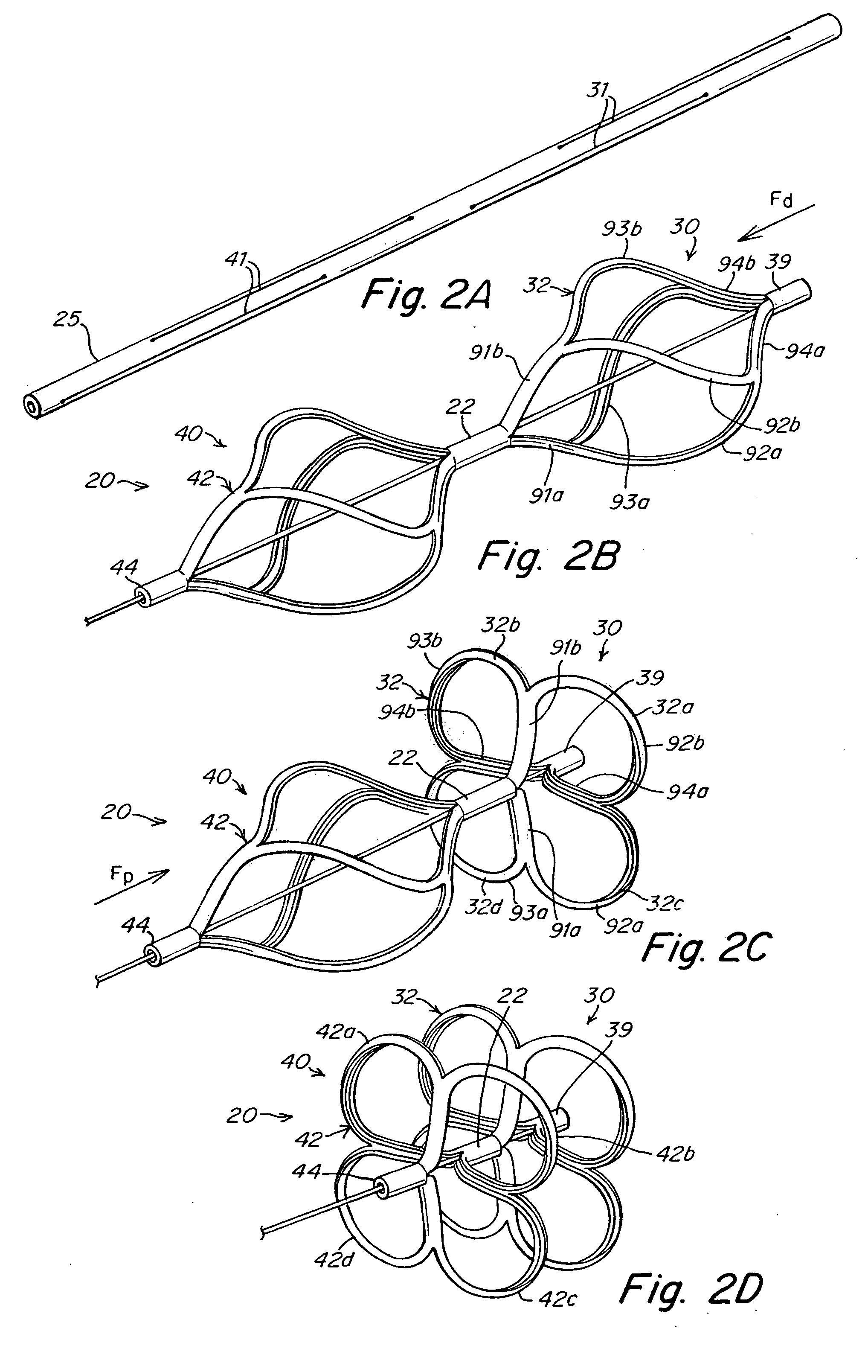
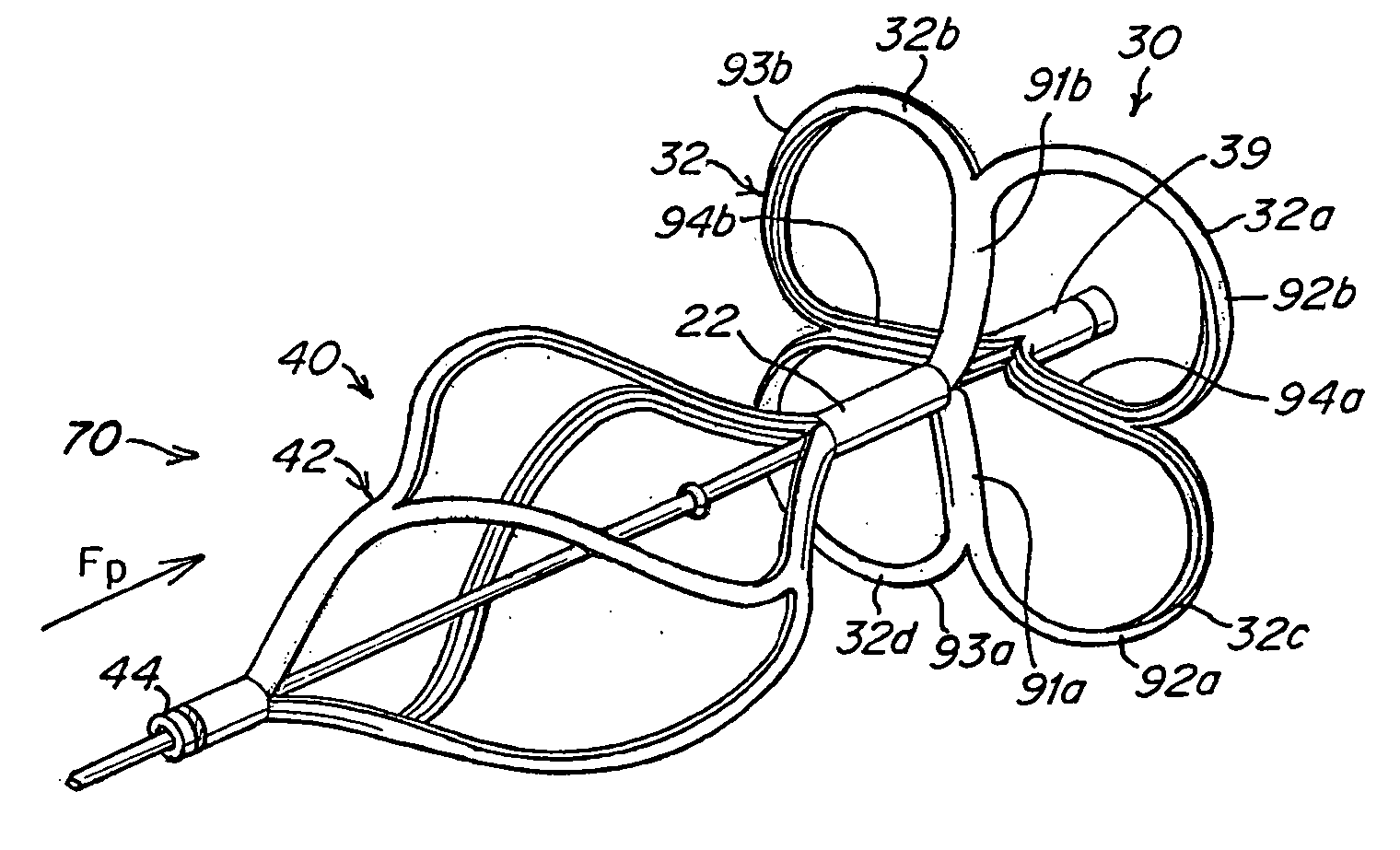
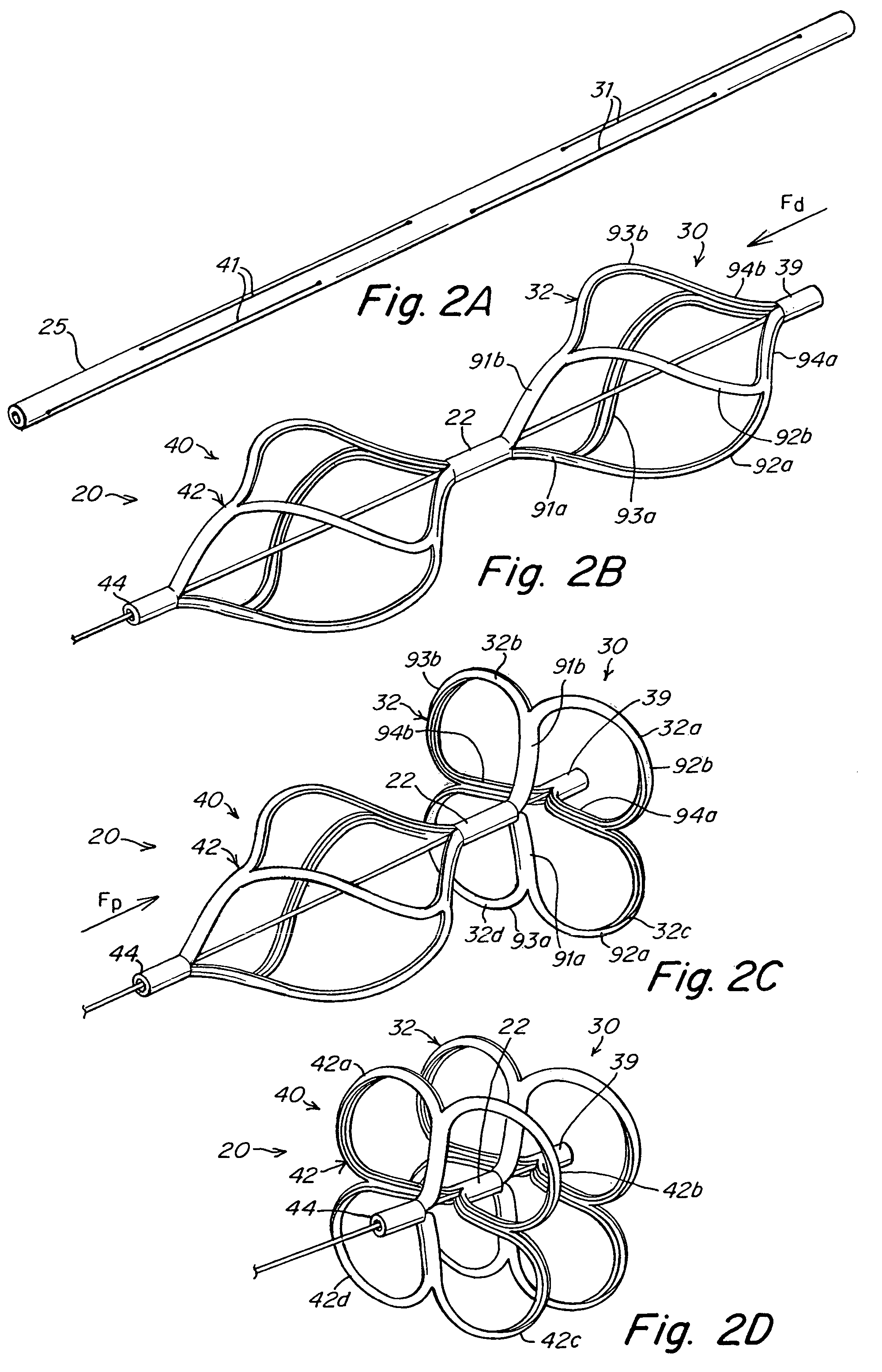
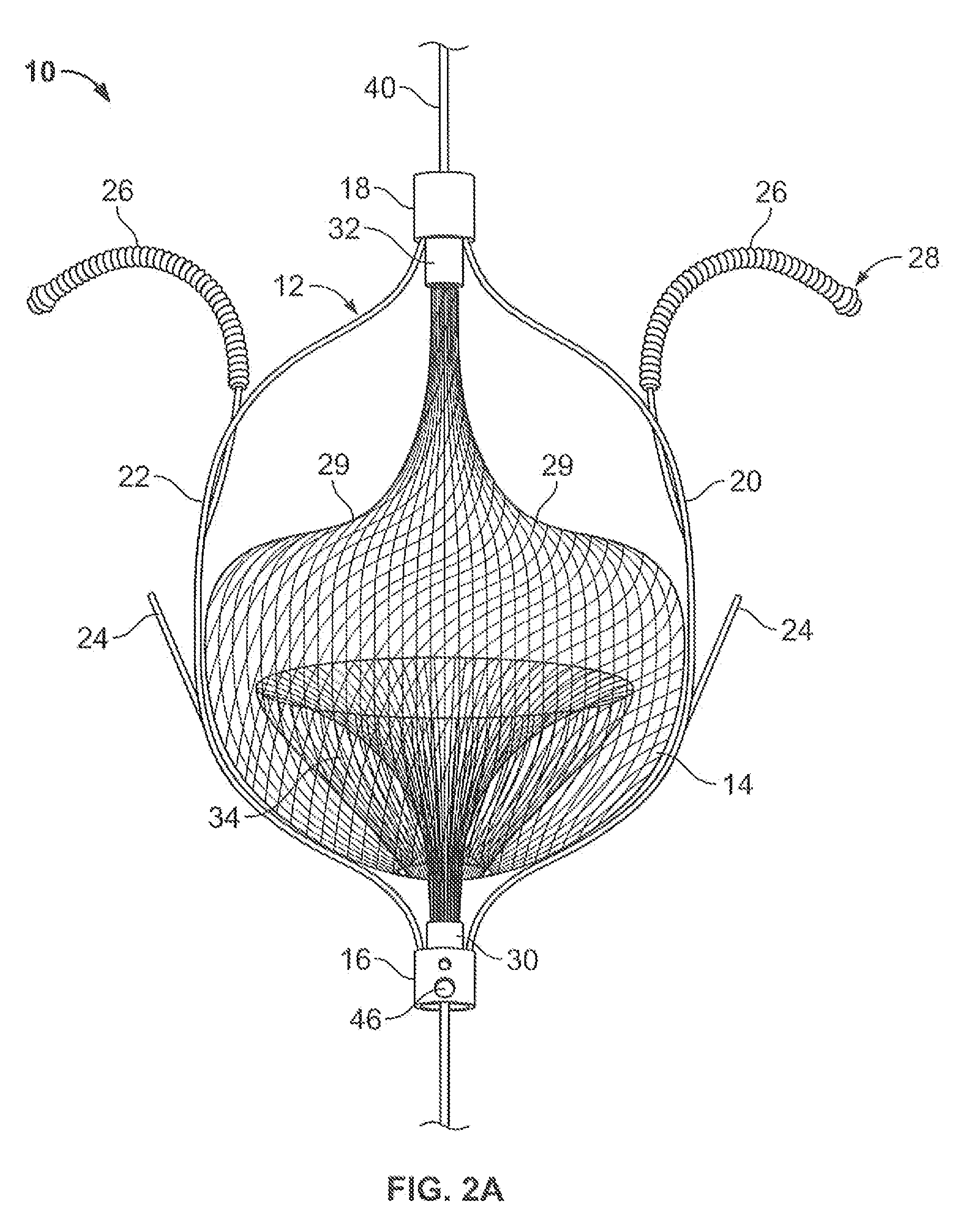
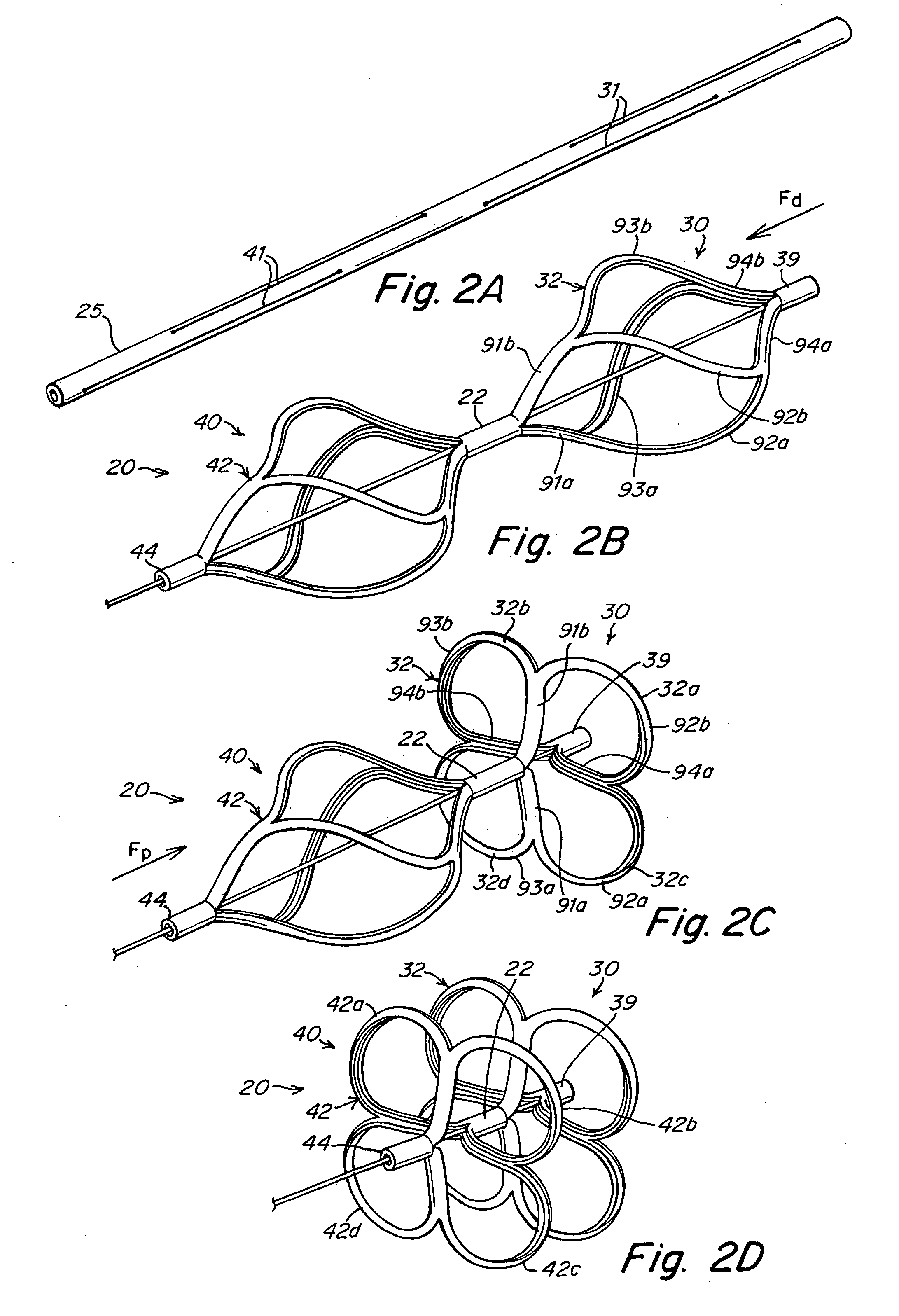
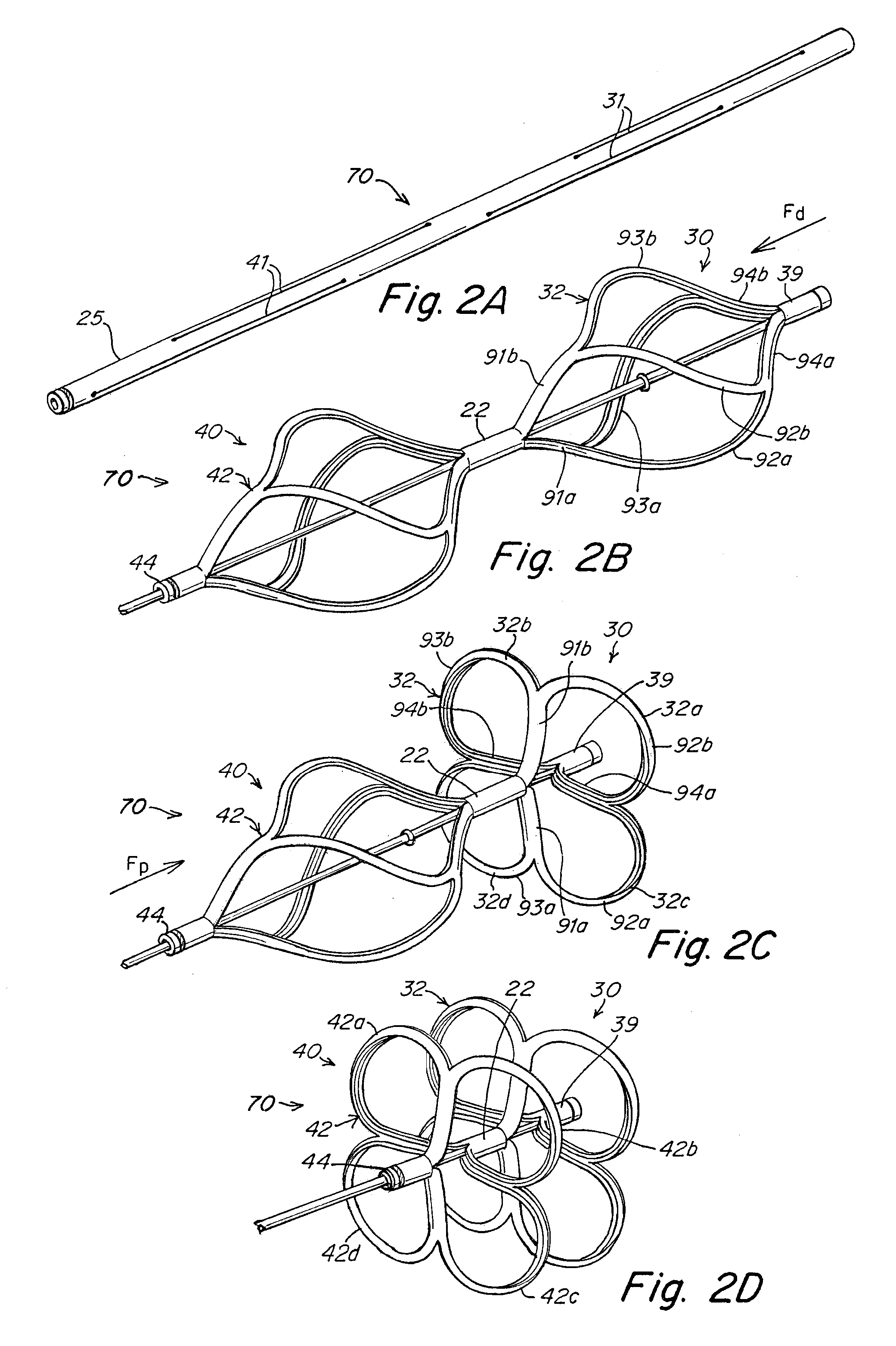
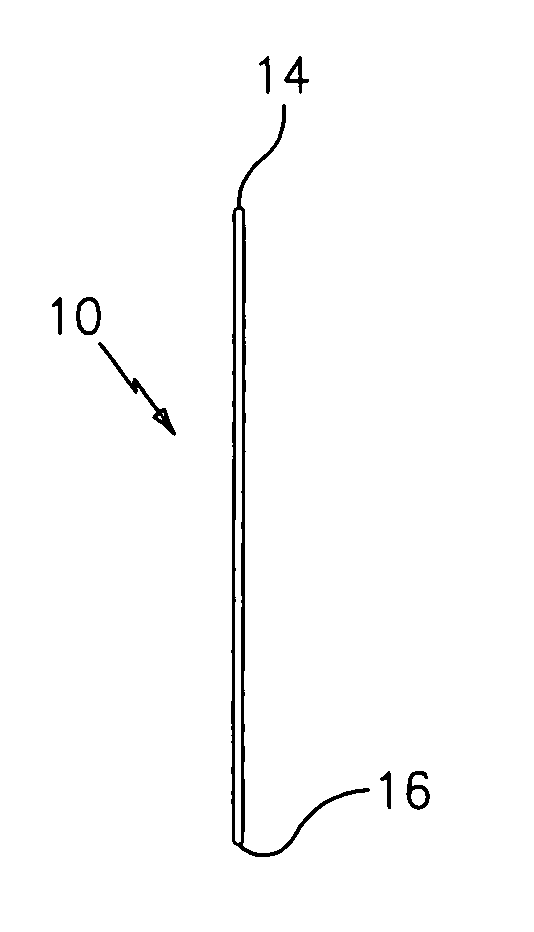
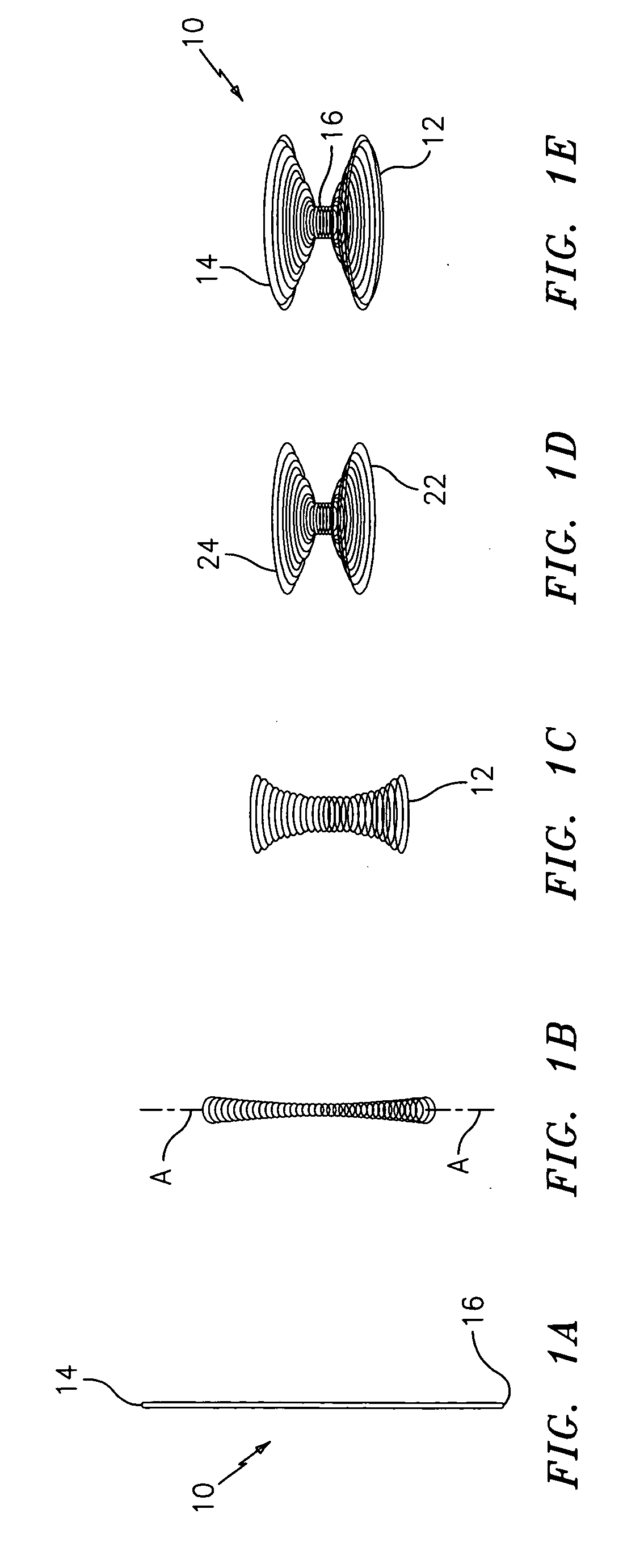
The present invention provides a device for occluding an anatomical aperture, such as an atrial septal defect (ASD) or a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder includes two sides connected by a central tube. The occluder is formed from a tube, which is cut to produce struts in each side. Upon the application of force, the struts deform into loops. The loops may be of various shapes, sizes, and configurations, and, in at least some embodiments, the loops have rounded peripheries. In some embodiments, at least one of the sides includes a tissue scaffold. The occluder further includes a catch system that maintains its deployed state in vivo. When the occluder is deployed in vivo, the two sides are disposed on opposite sides of the septal tissue surrounding the aperture and the catch system is deployed so that the occluder exerts a compressive force on the septal tissue and closes the aperture.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
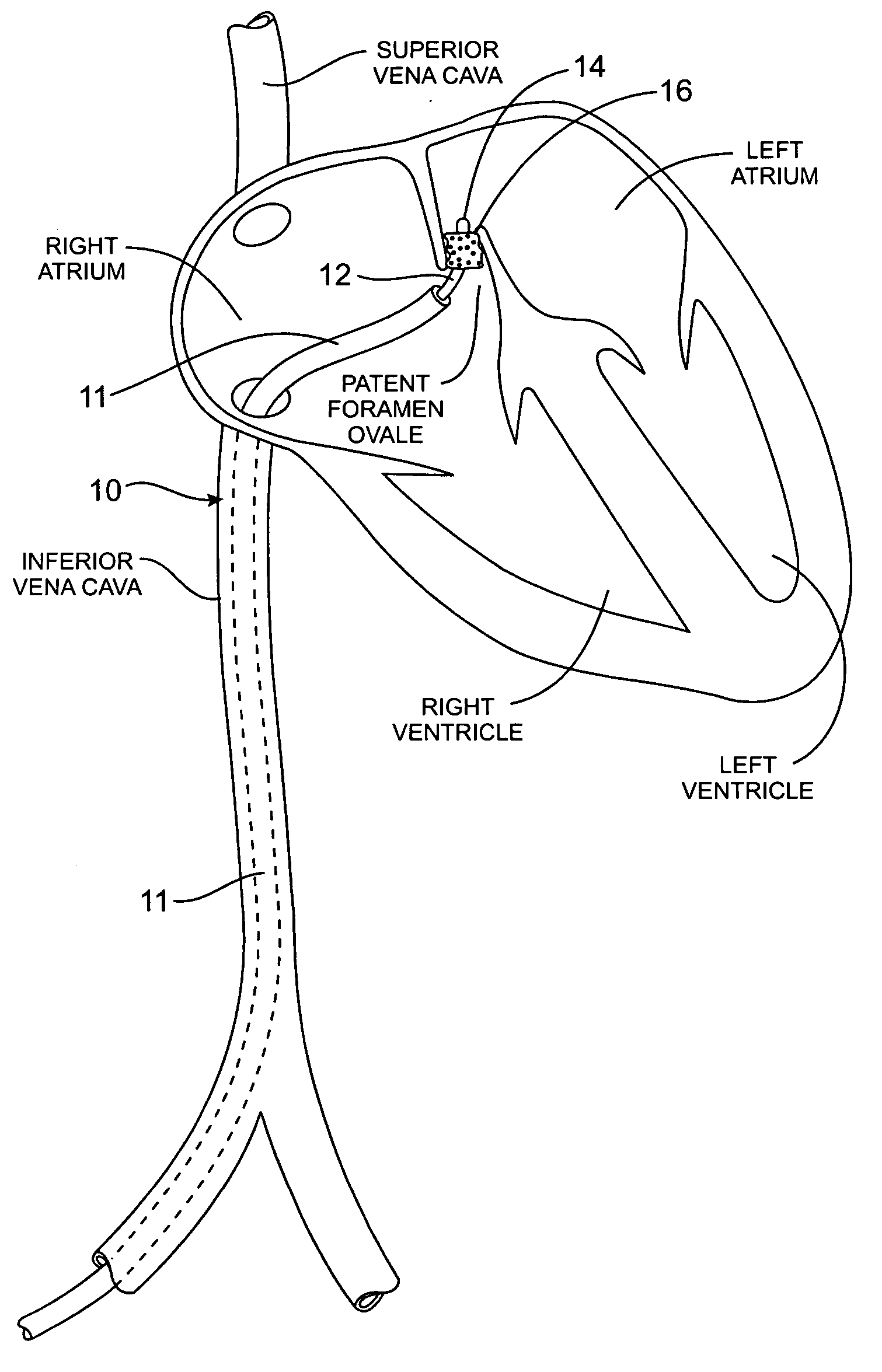
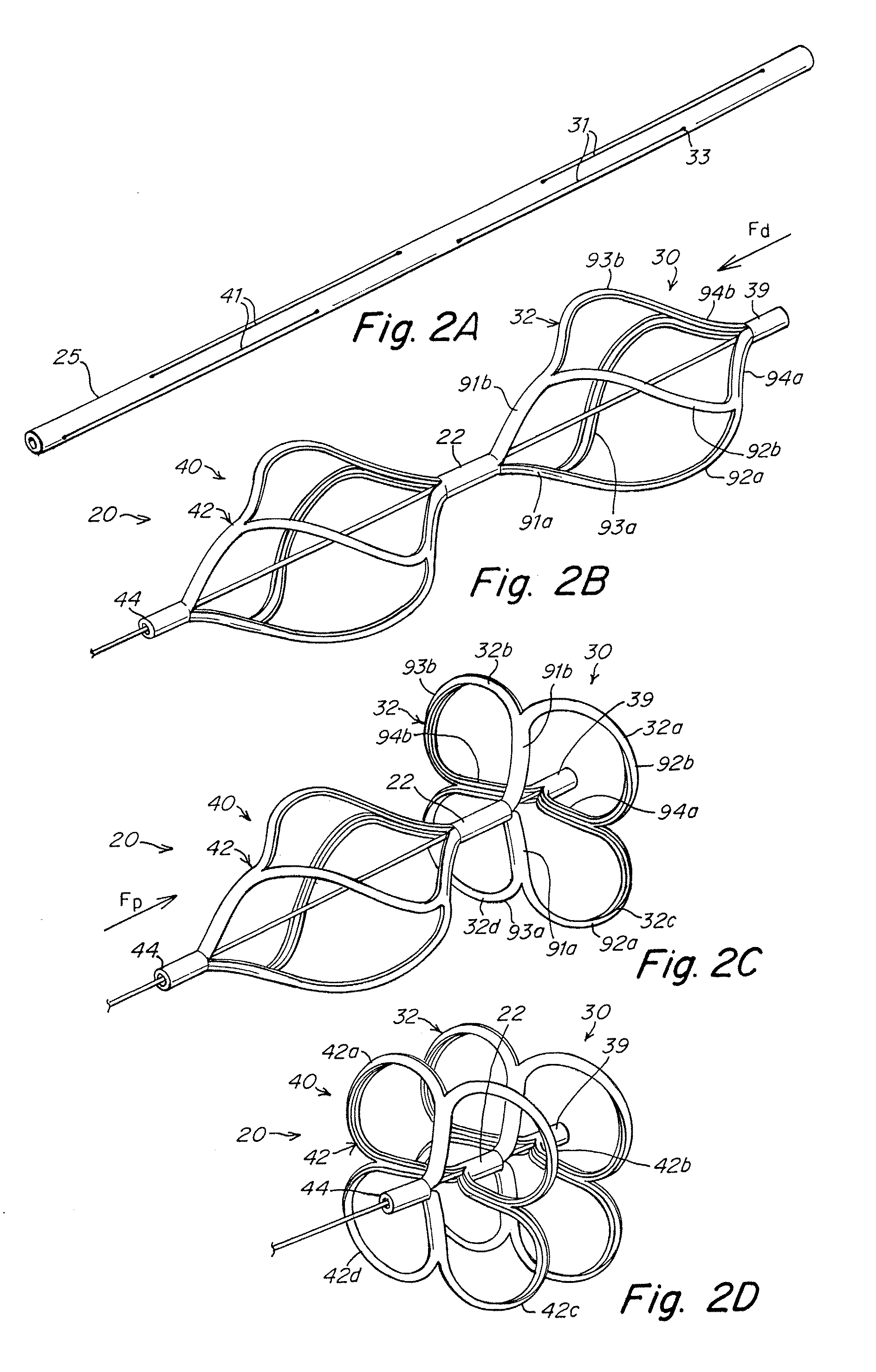
Occluder device double securement system for delivery/recovery of such occluder device
Devices, delivery systems and delivery techniques for an occlusion device for the closure of physical anomalies, such as an atrial septal defect, a patent foramen ovale (PFO), and other septal and vascular defects are described. The devices, delivery systems and delivery techniques relate particularly to, but are not limited to, a patent foramen ovale (PFO) occluder made from a polymer tube. Specifically, a petal-shaped occluder with a catch system is provided within a delivery sheath. In certain embodiments, the delivery system includes a first securement system for securing a first end of the occluder and a second securement system for securing a second end of the occluder to a delivery catheter and a delivery wire contained in the delivery system. The securement enable the deployment (and retrieval) of the device. The securement systems enable pushing and pulling of respective ends of the occluder to expand and contract the device by varying its axial length. In one aspect, the first securement system employs a threaded connection and the second securement system employs a suture connection. In another aspect, the first securement system employs a threaded connection and the second securement system employs a collet finger connection. The securement systems are detached when the device has been properly positioned. The securement systems can be manipulated by control systems provided in the control portion of the delivery system.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Tubular patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure device with catch system
ActiveUS7678123B2Minimize distortion to the septal tissue surroundingMinimize distortionSurgical veterinaryWound clampsAtrial septal defectsEngineering
The present invention provides a device for occluding an anatomical aperture, such as an atrial septal defect (ASD) or a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder includes two sides connected by a central tube. The occluder is formed from a tube, which is cut to produce struts in each side. Upon the application of force, the struts deform into loops. The loops may be of various shapes, sizes, and configurations, and, in at least some embodiments, the loops have rounded peripheries. In some embodiments, at least one of the sides includes a tissue scaffold. The occluder further includes a catch system that maintains its deployed state in vivo. When the occluder is deployed in vivo, the two sides are disposed on opposite sides of the septal tissue surrounding the aperture and the catch system is deployed so that the occluder exerts a compressive force on the septal tissue and closes the aperture.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Closure devices, related delivery methods, and related methods of use
ActiveUS20060009800A1Prevent proximal movementPrevent movementDiagnostic markersSurgical veterinaryRight atriumLeft atrial
A device for sealing a patent foramen ovale (PFO) in the heart is provided. The device includes a left atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a left atrium of the heart, a right atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a right atrium of the heart, and an elongate member adapted to extend through the passageway and connect the left and right atrial anchors. A system for delivering the closure device includes side-by-side tubes. A device for retrieving a mis-deployed closure device includes a shaft portion and an expandable retrieval portion.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Split ends closure device
InactiveUS20050267524A1Improve conformitySmall diameter delivery sheathSurgical veterinaryWound clampsBlood flowEngineering
A device closes a patent foramen ovale (PFO), thus reducing or eliminating blood flow through the defect. The device is formed from a tubular structure having split ends, such that, after insertion, struts defined by the split ends pivot in a radial direction away from the tube, thereby securing the device within the septal defect.
Owner:NMT MEDICAL
Mechanical tissue device and method
InactiveUS20080119886A1Rigid enoughLength of device being increasedDilatorsOcculdersVeinVenous blood
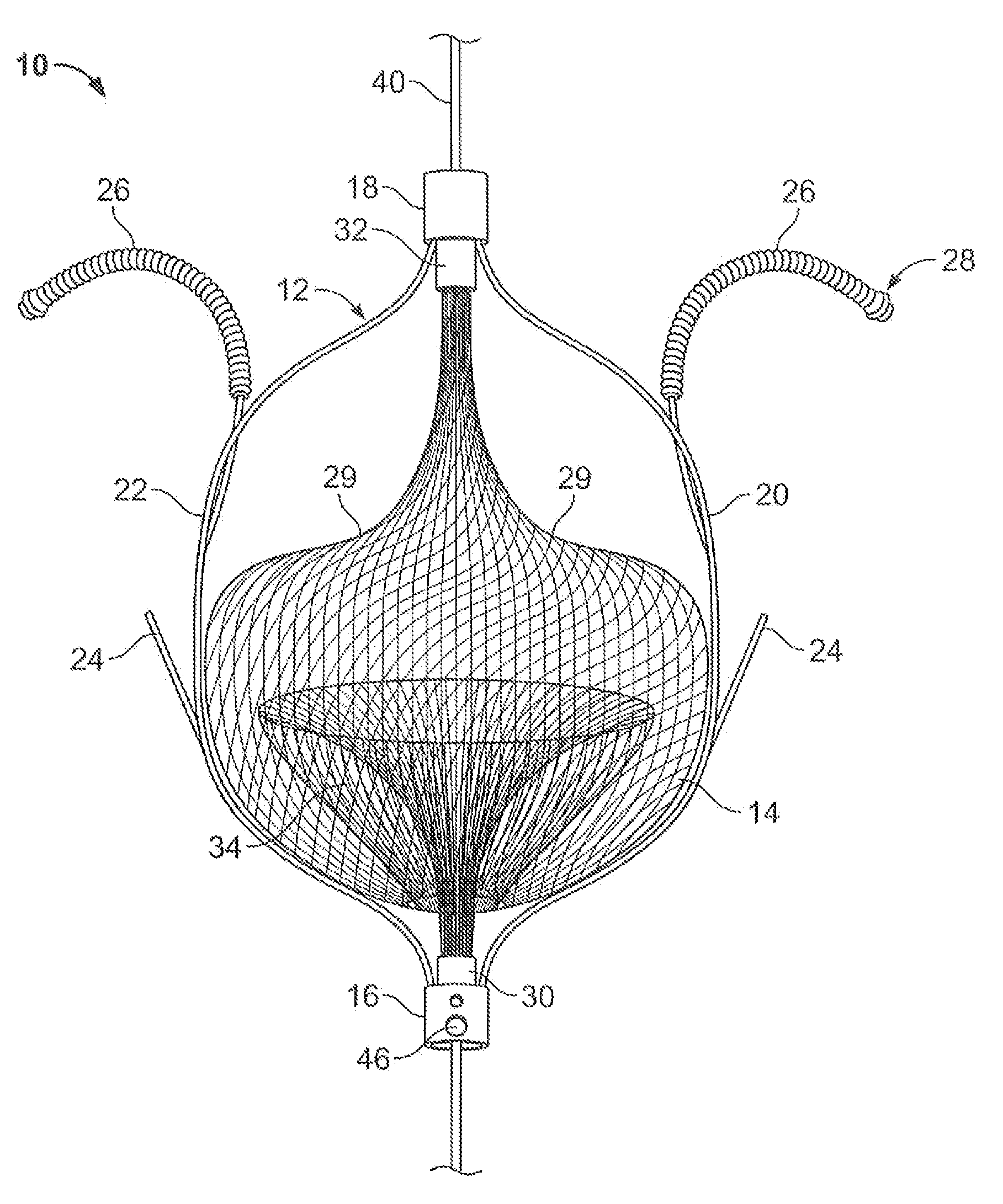
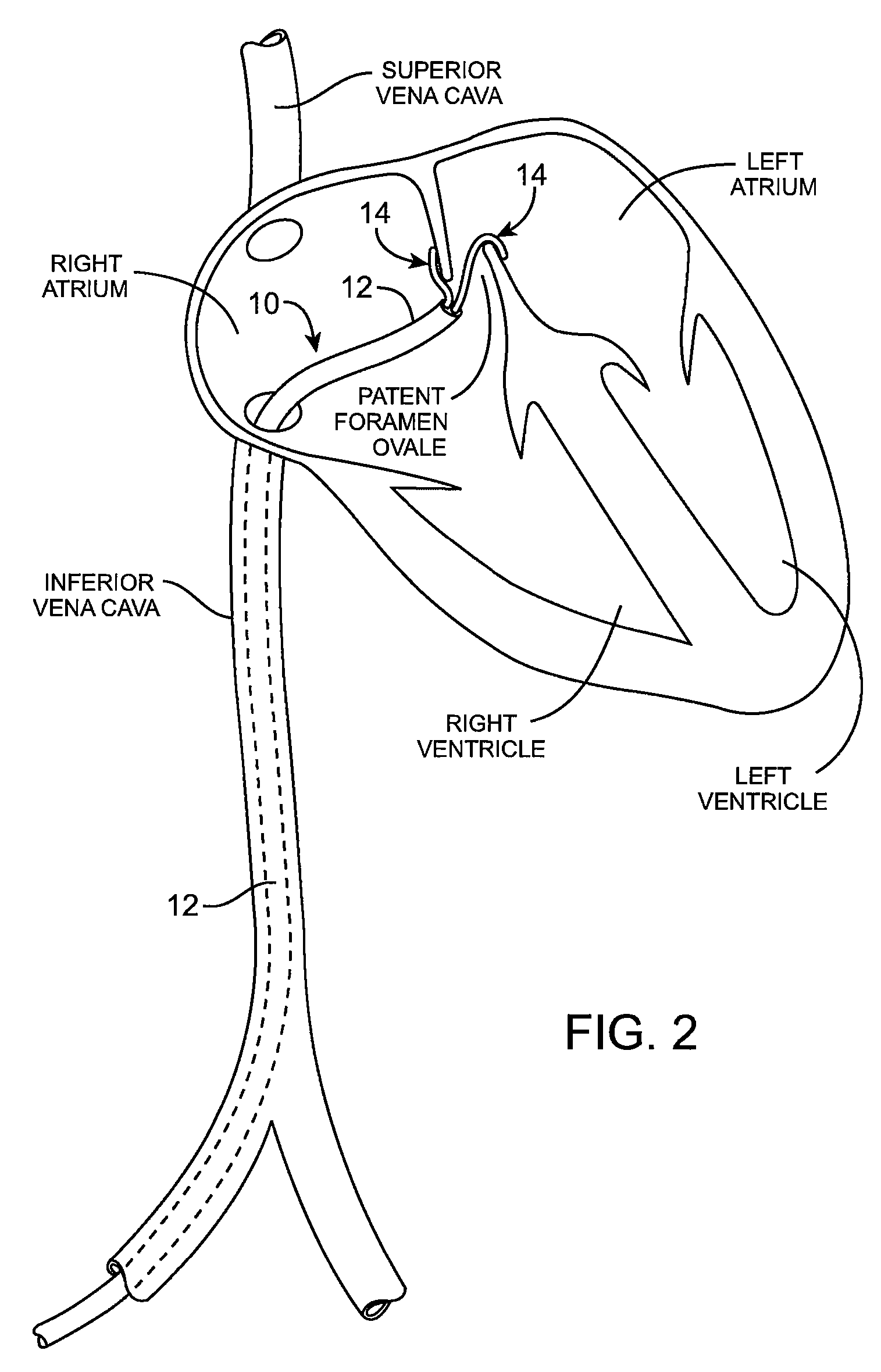
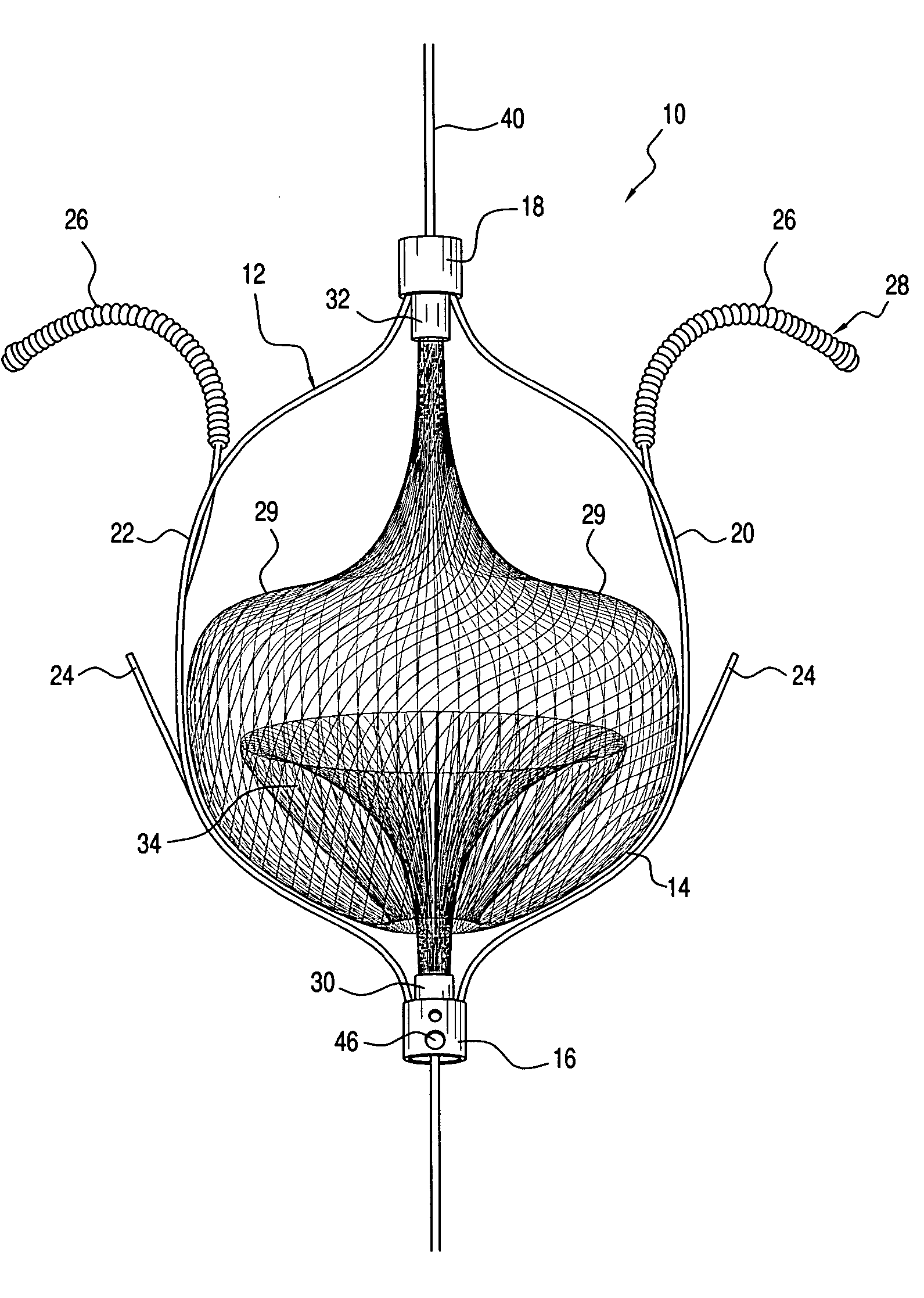
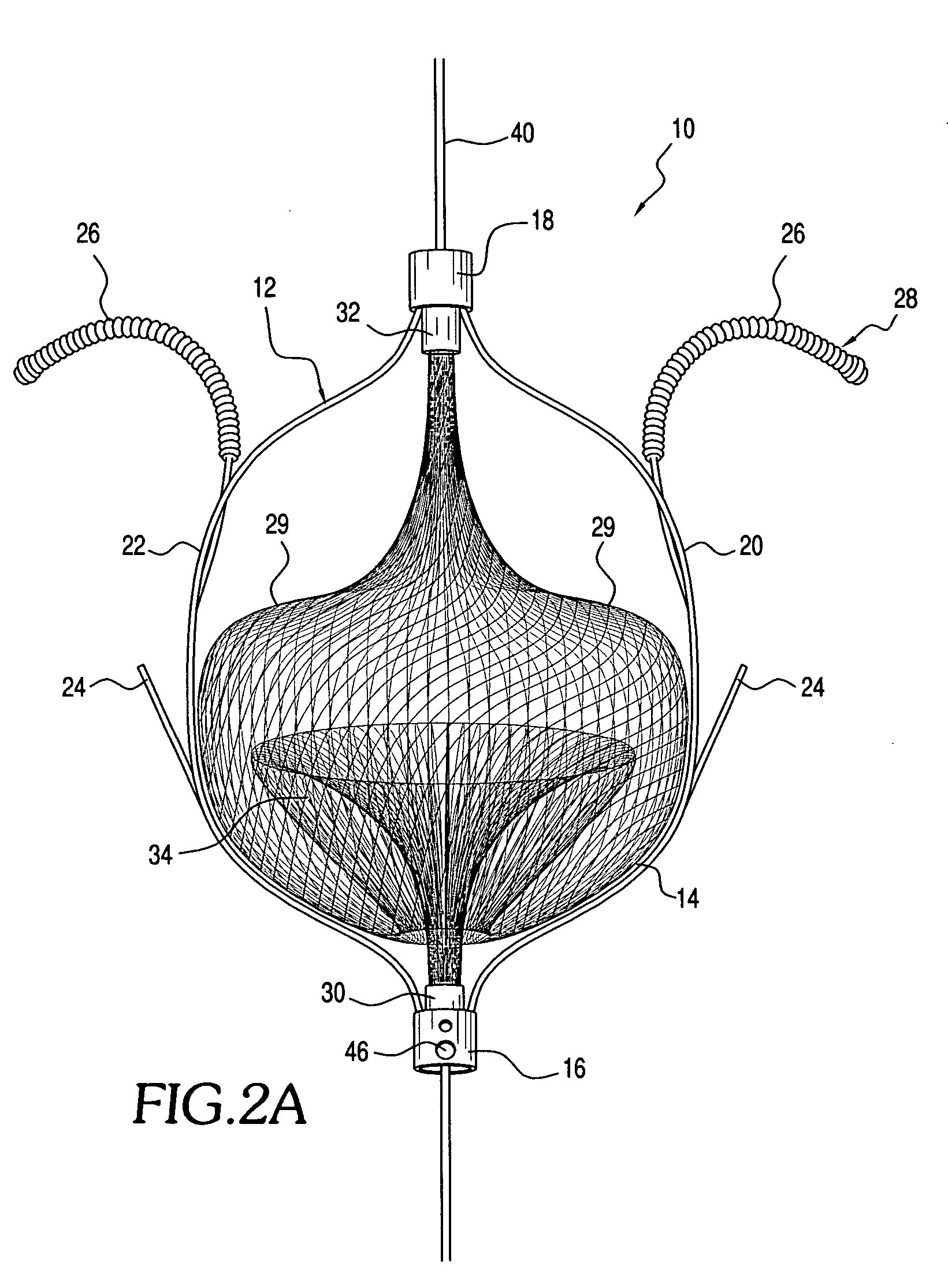
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as Nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Energy based devices and methods for treatment of patent foramen ovale
Methods, devices and systems for treating patent foramen ovale (PFO) involve advancing a catheter device to a position in a heart for treating a PFO, bringing tissues adjacent the PFO at least partially together, and applying energy to the tissues to substantially close the PFO acutely. Catheter devices generally include an elongate catheter body, at least one tissue apposition member at or near the distal end for bringing the tissues together, and at least one energy transmission member at or near the distal end for applying energy to the tissues. In some embodiments, the tissue apposition member(s) also act as the energy transmission member(s). Applied energy may be monoploar or bipolar radiofrequency energy or any other suitable energy, such as laser, microwave, ultrasound, resistive heating or the like.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Embolic filtering method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009799A1Obstruct passageEncourage and facilitate growth of tissueAnnuloplasty ringsDilatorsVenous bloodCardiac defects
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Tubular patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure device with catch system
ActiveUS20070010851A1Minimize traumaMinimize distortion to the septal tissue surroundingSurgical veterinaryWound clampsAtrial septal defectsEngineering
The present invention provides a device for occluding an anatomical aperture, such as an atrial septal defect (ASD) or a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder includes two sides connected by a central tube. The occluder is formed from a tube, which is cut to produce struts in each side. Upon the application of force, the struts deform into loops. The loops may be of various shapes, sizes, and configurations, and, in at least some embodiments, the loops have rounded peripheries. In some embodiments, at least one of the sides includes a tissue scaffold. The occluder further includes a catch system that maintains its deployed state in vivo. When the occluder is deployed in vivo, the two sides are disposed on opposite sides of the septal tissue surrounding the aperture and the catch system is deployed so that the occluder exerts a compressive force on the septal tissue and closes the aperture.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Energy based devices and methods for treatment of anatomic tissue defects
Methods and apparatus for treatment of anatomic defects in human tissues, such as patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial or ventricular septal defects, left atrial appendage, patent ductus arteriosis, blood vessel wall defects and certain electrophysiological defects, involve positioning a distal end of an elongate catheter device at the site of the anatomic defect, engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to bring the tissues together, and applying energy to the tissues with the catheter device to substantially close the anatomic defect acutely. Apparatus generally includes an elongate catheter having a proximal end and a distal end, a vacuum application member coupled with the distal end for engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect and applying vacuum to the tissues to bring them together, and at least one energy transmission member coupled with the vacuum application member for applying energy to tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to substantially close the defect acutely.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
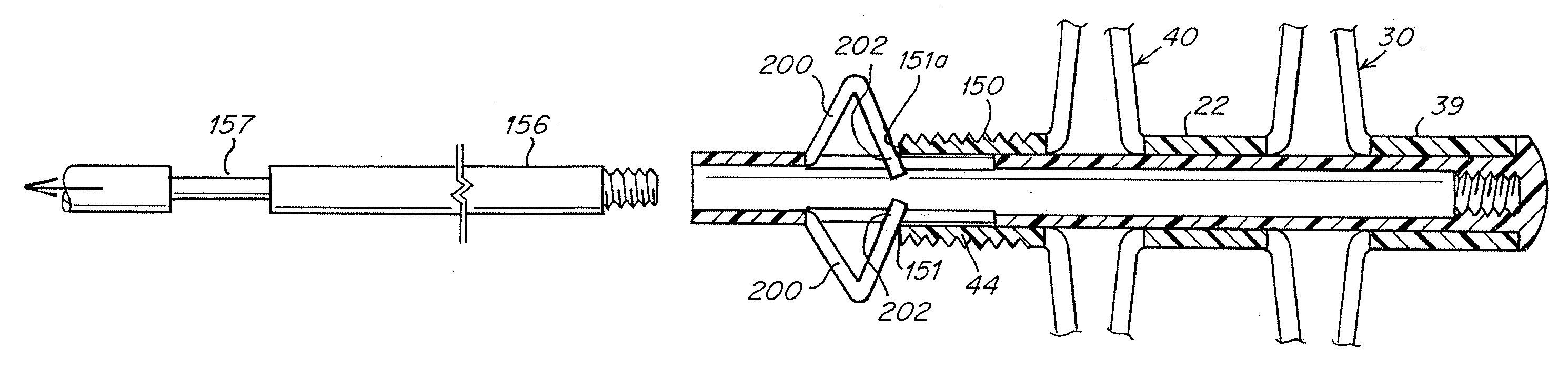
Catch members for occluder devices
InactiveUS20070167981A1Shorten the axial lengthPrevent slidingOcculdersSurgical veterinaryMedicineAtrial septal defects
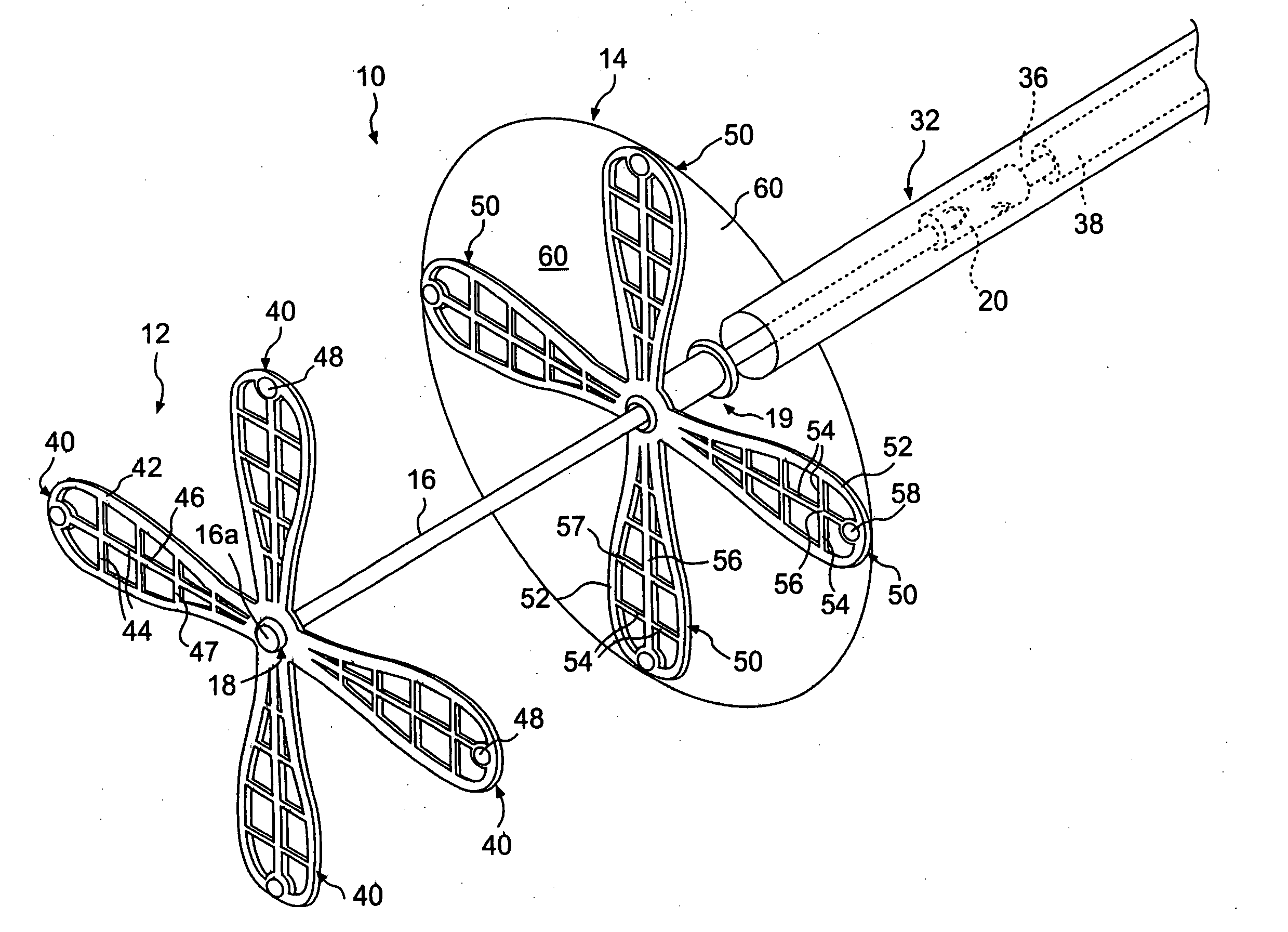
Devices and techniques for modifying and maintaining a configuration of an occlusion device for the closure of physical anomalies, such as an atrial septal defect, a patent foramen ovale (PFO), and other septal and vascular defects are described. The devices and techniques relate particularly to, but are not limited to, modifying and maintaining a configuration of a PFO occluder made from a polymer tube. The proximal portion of a catch member may be provided with one or more protrusions, or arms, or bump or other raised element for securing the occluder in a partial or fully deployed configuration, either temporarily or permanently.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
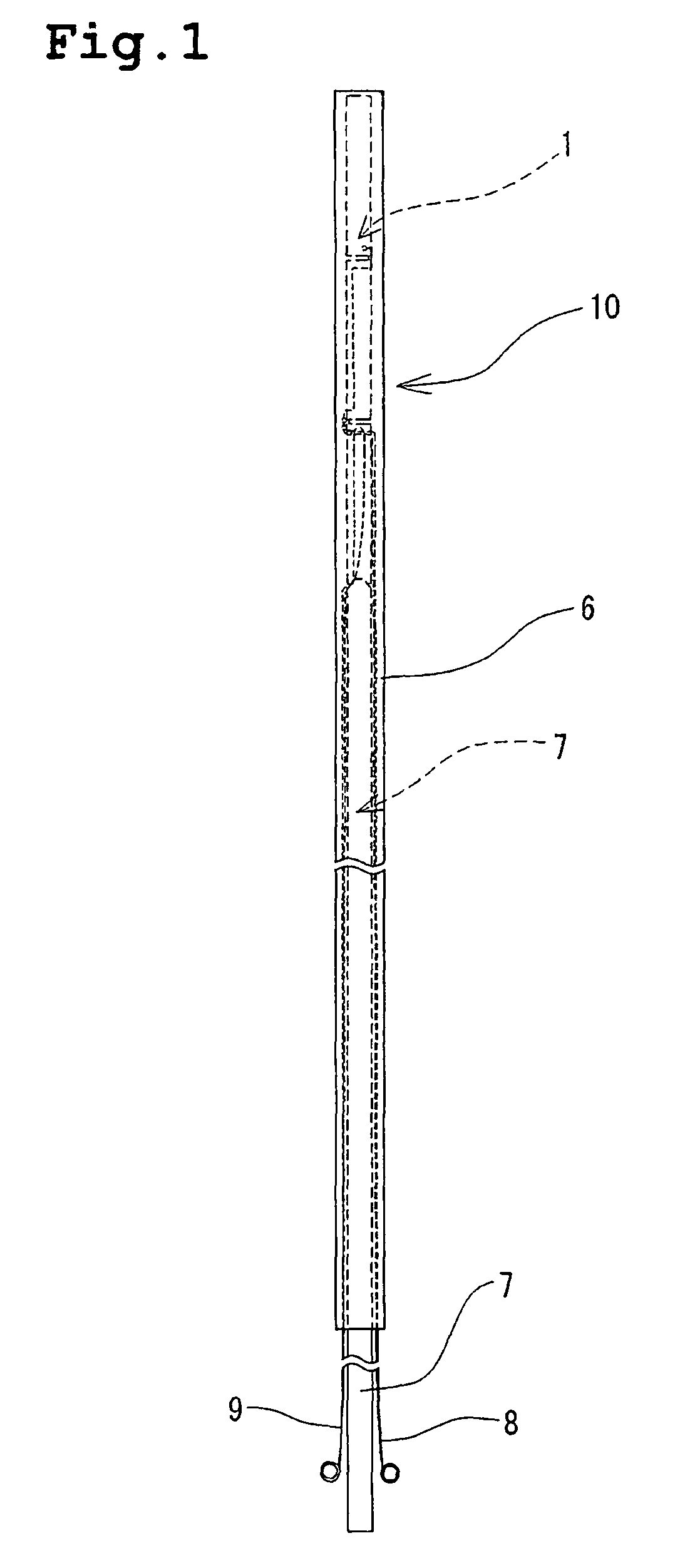
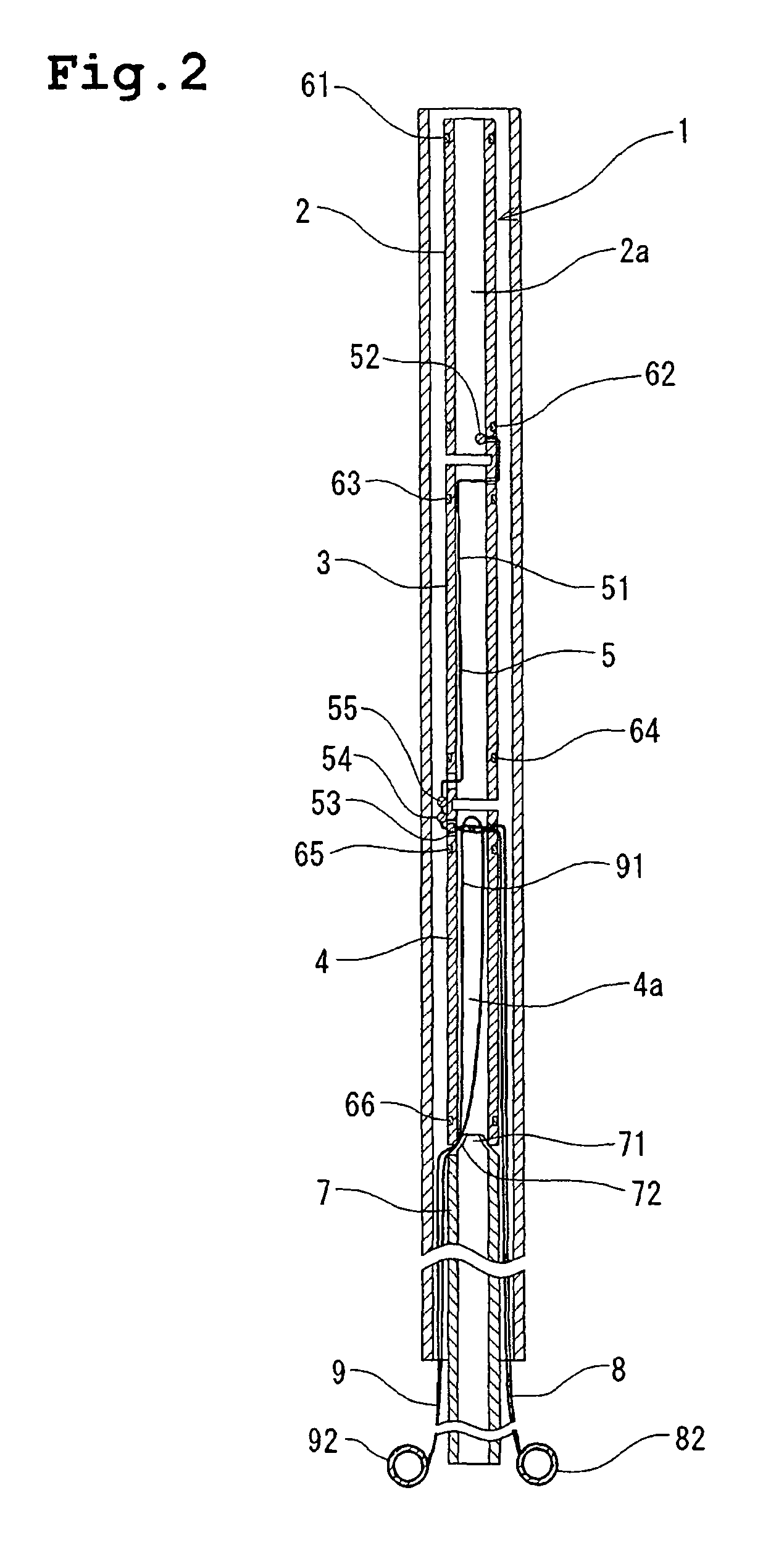
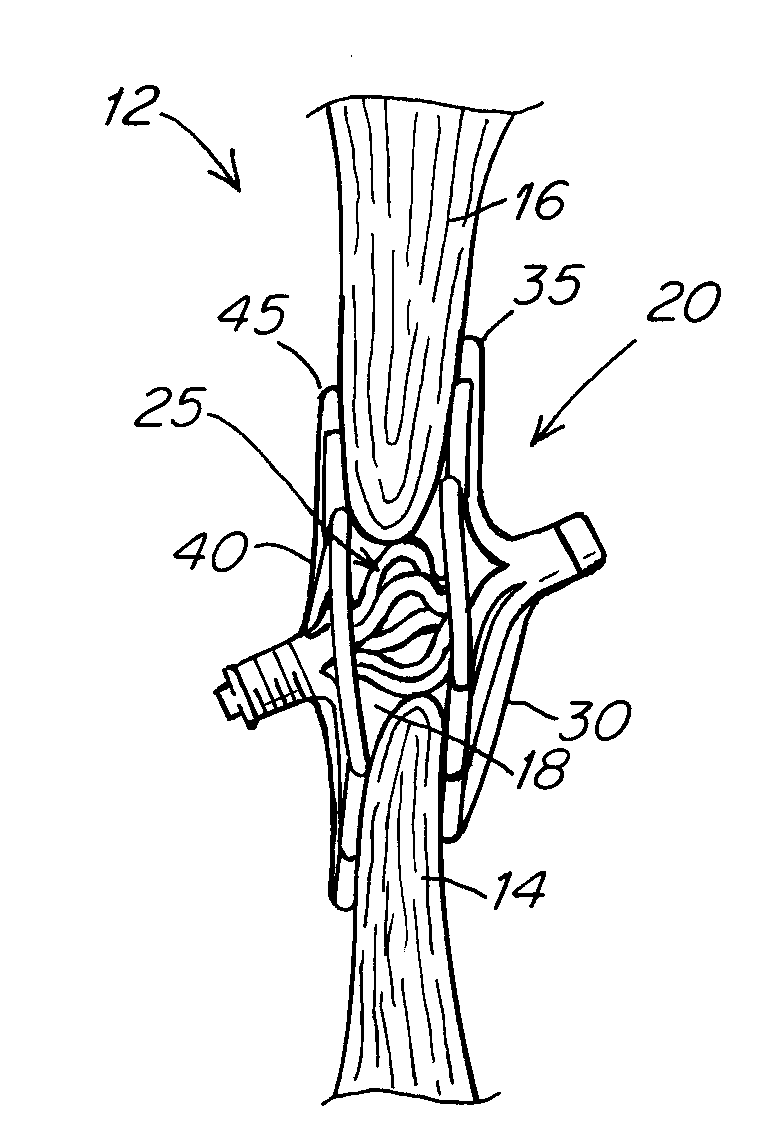
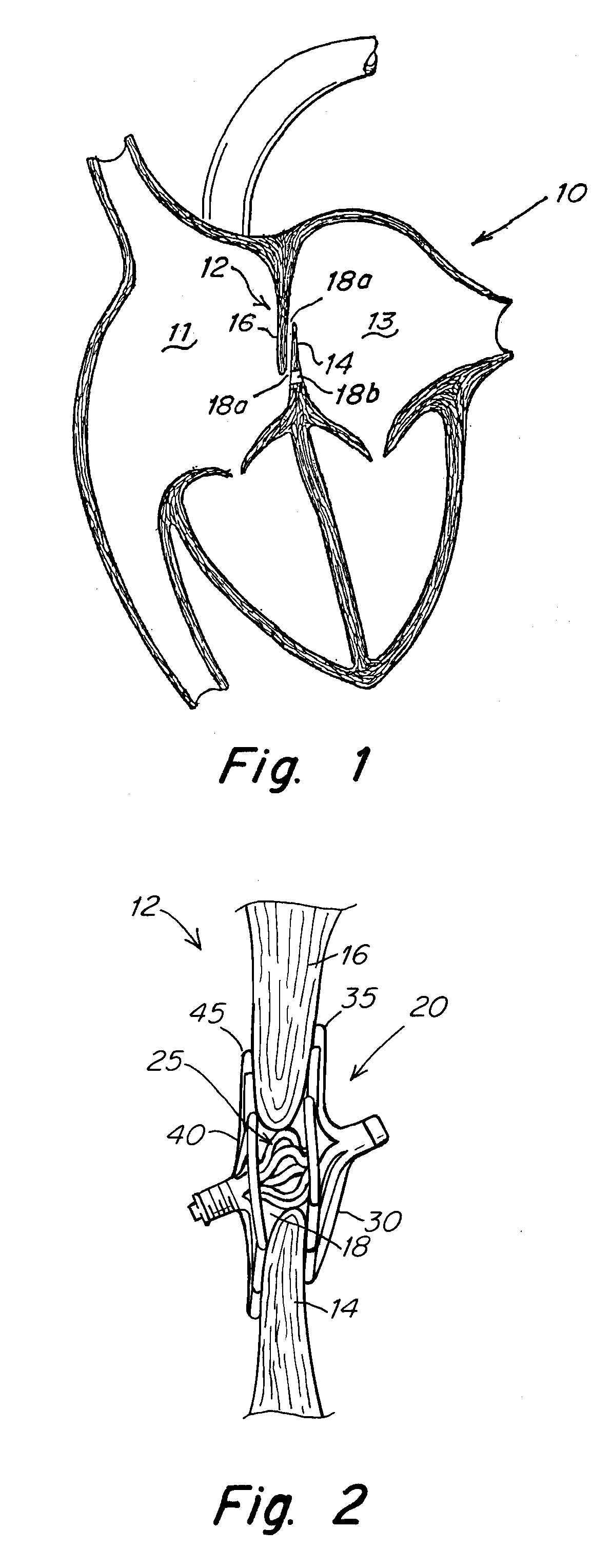
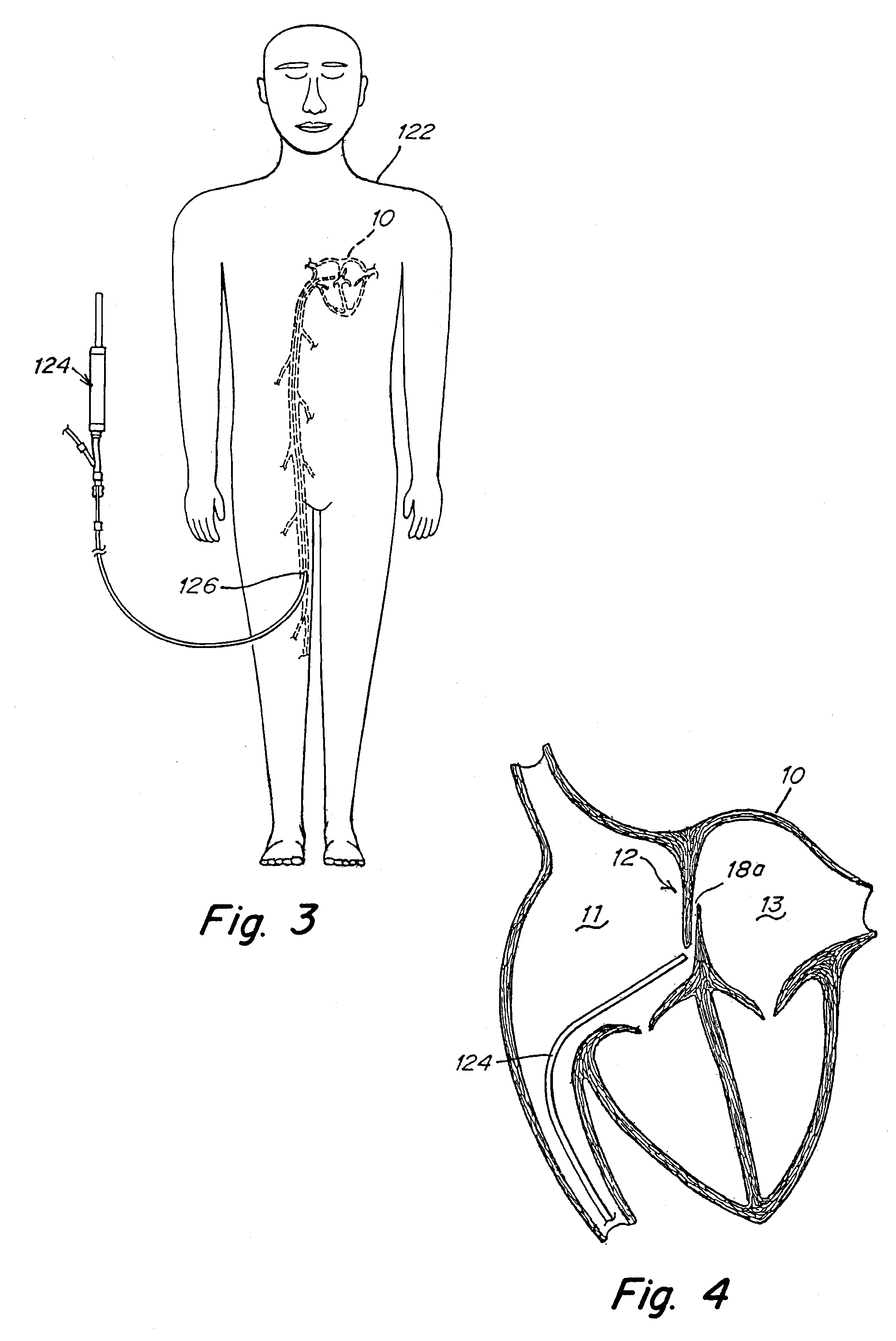
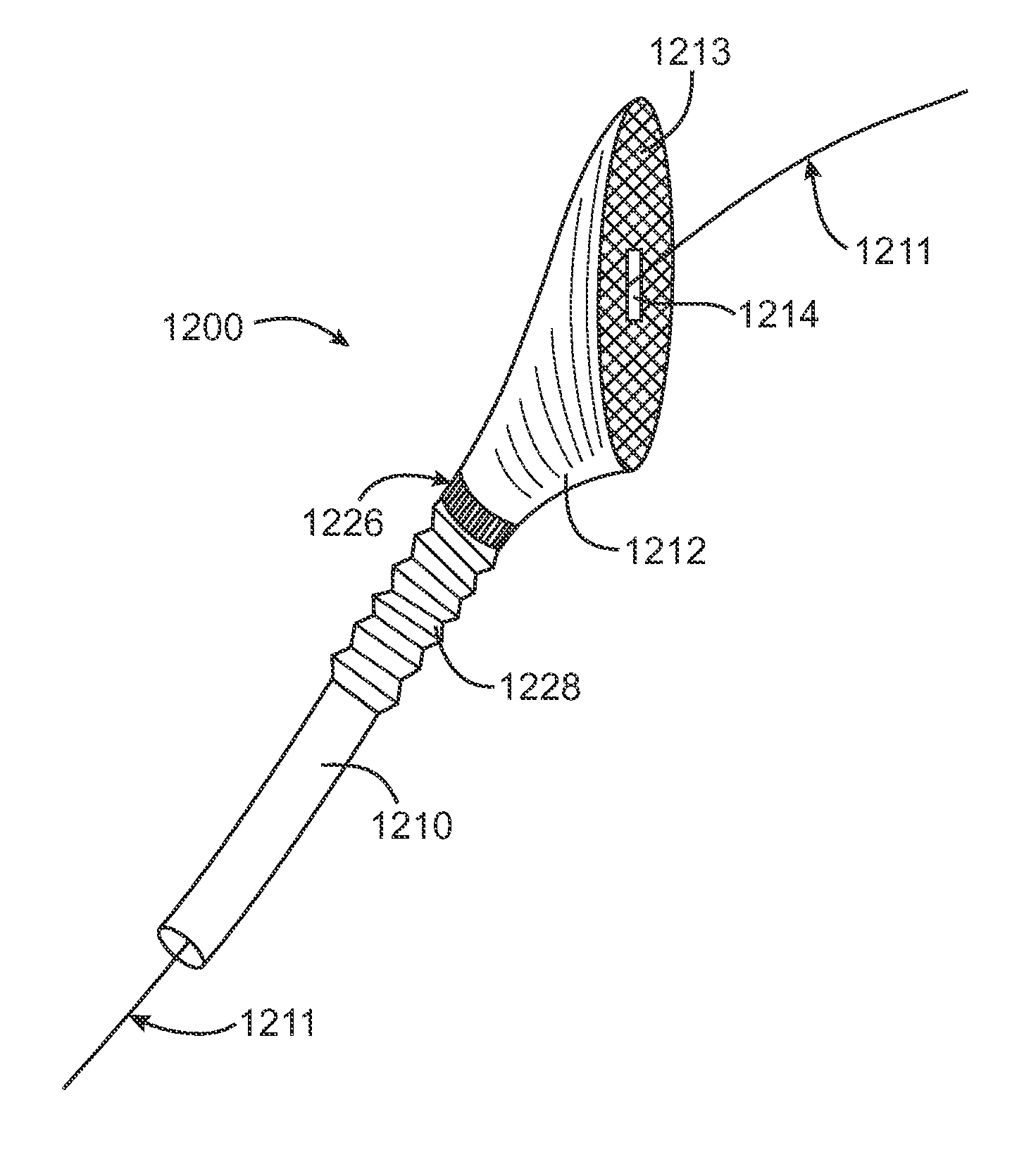
Device for treating a patent foramen ovale
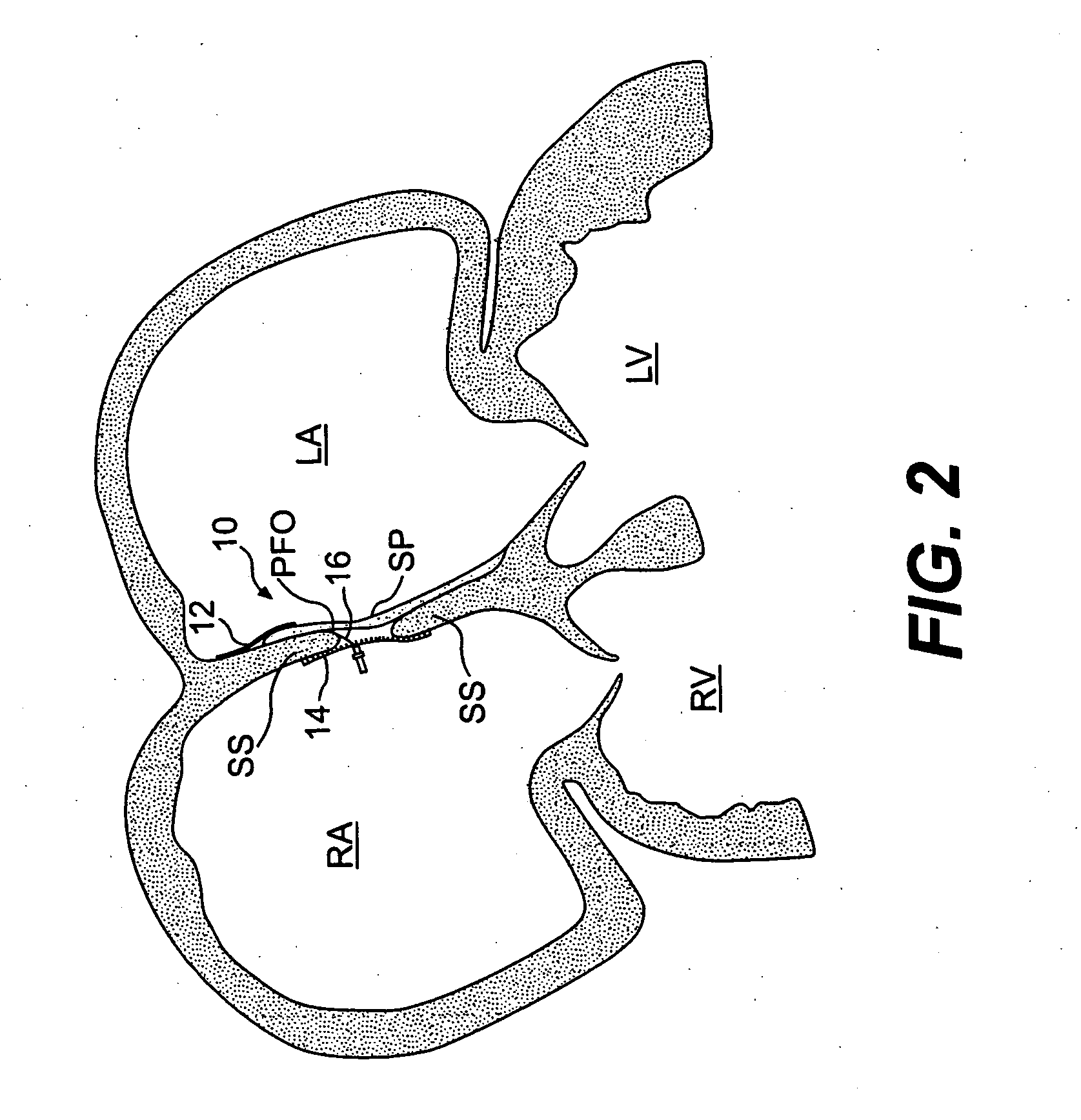
A device for treating a patent foramen ovale has a first part having a predetermined length; a second part having a predetermined length; a third part having a predetermined length; and a pulling member which penetrates into the second part from a side face of a distal portion of the second part, crosses the second cylindrical part obliquely and extends from a side face of a proximal portion of the second part and penetrates into the third part from a side face of a distal portion of the third part, with one end of the pulling member held by a proximal portion of the first part. A part of a locking mechanism provided at other end of the pulling member and a part of the locking mechanism provided at the third part are locked to each other, when the pulling member is pulled to allow the first part and the second part proximate to each other and the second part and the third part to be proximate to each other.
Owner:TERUMO KK
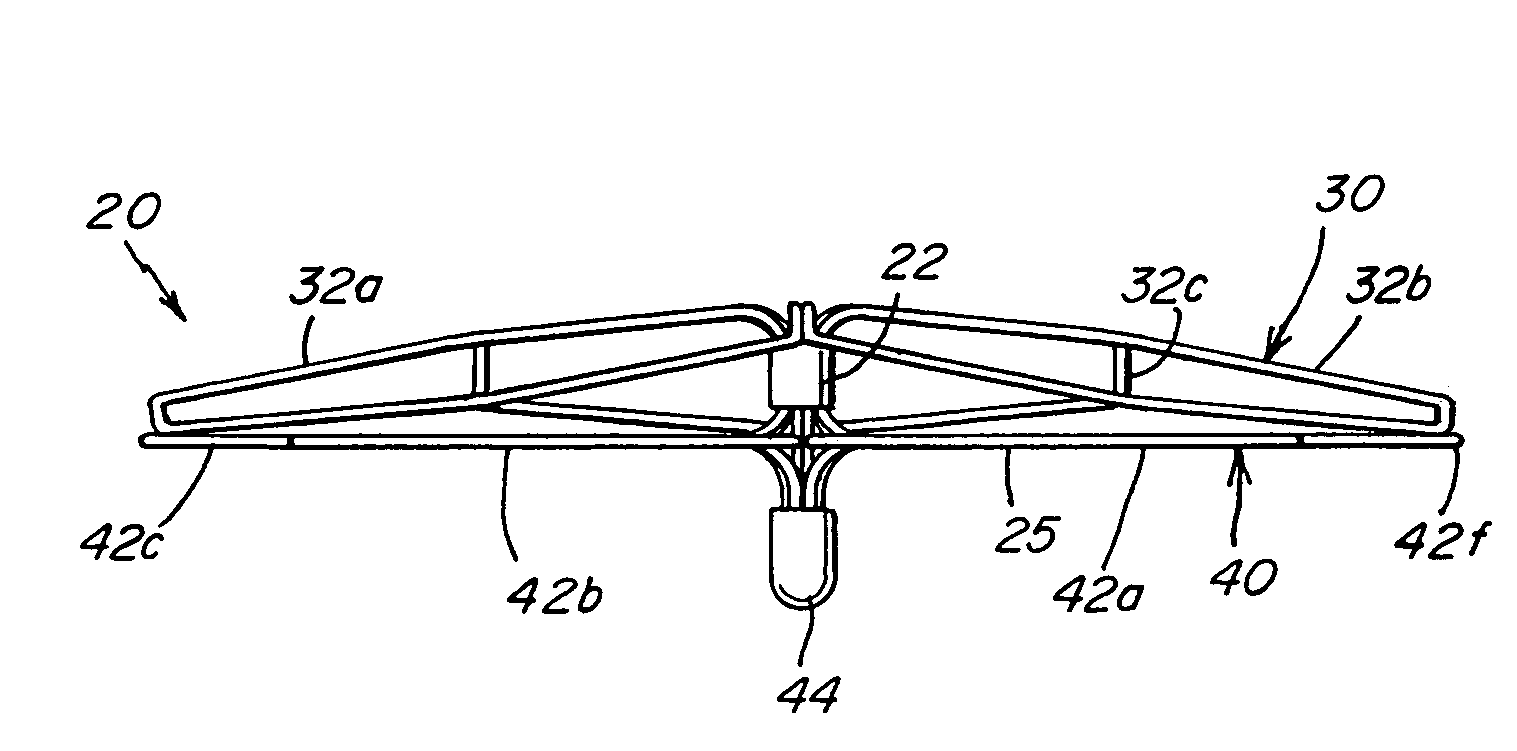
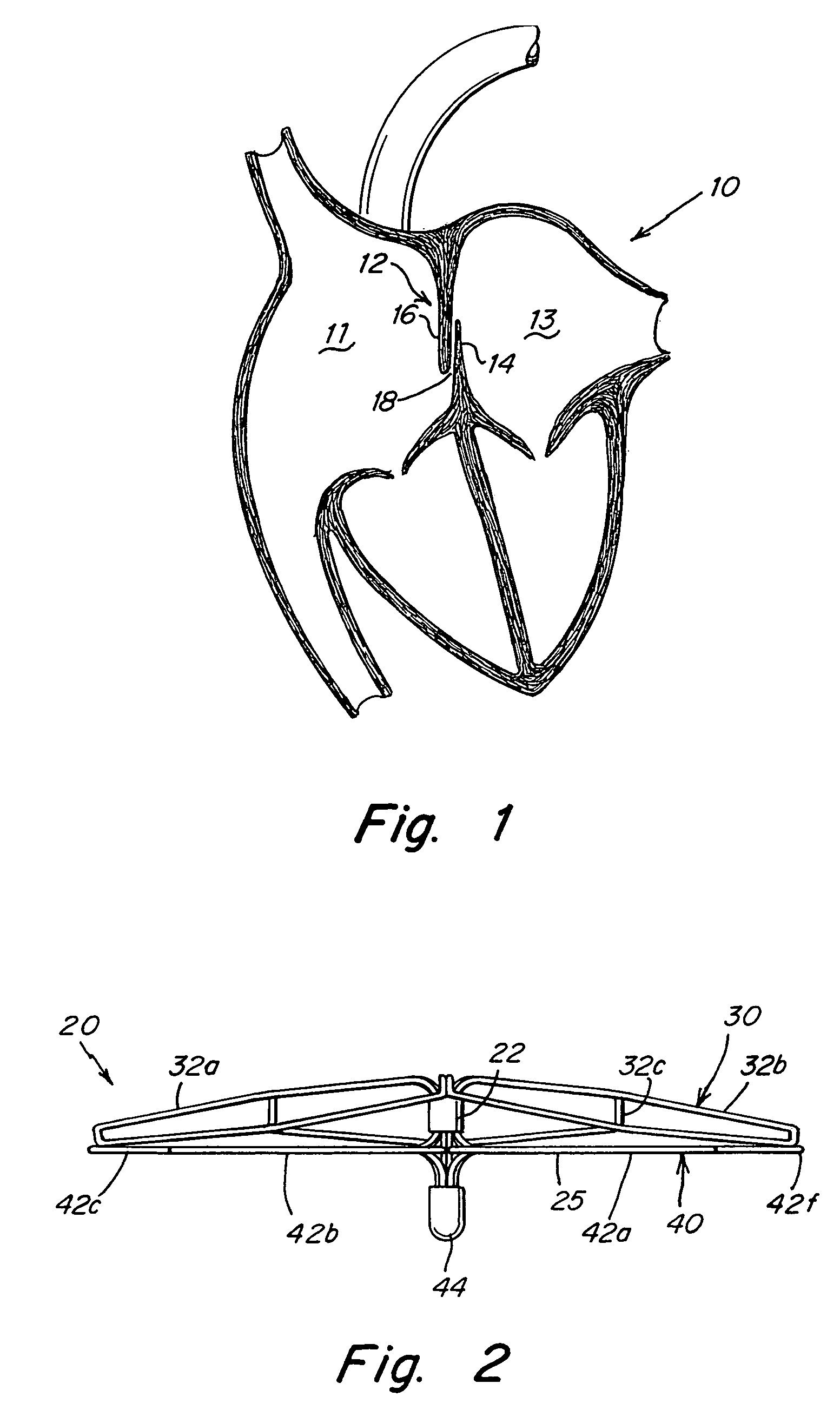
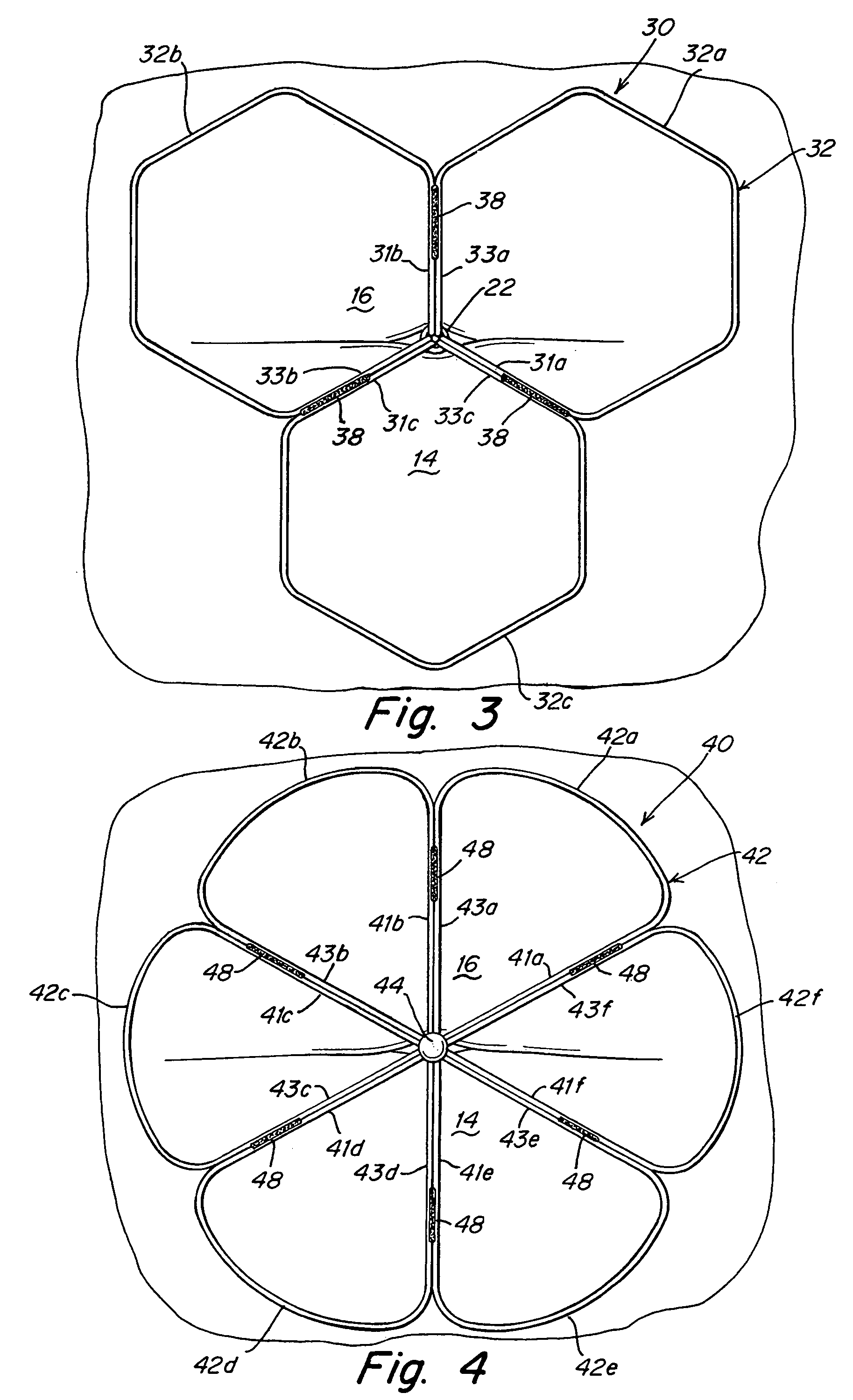
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure device with radial and circumferential support
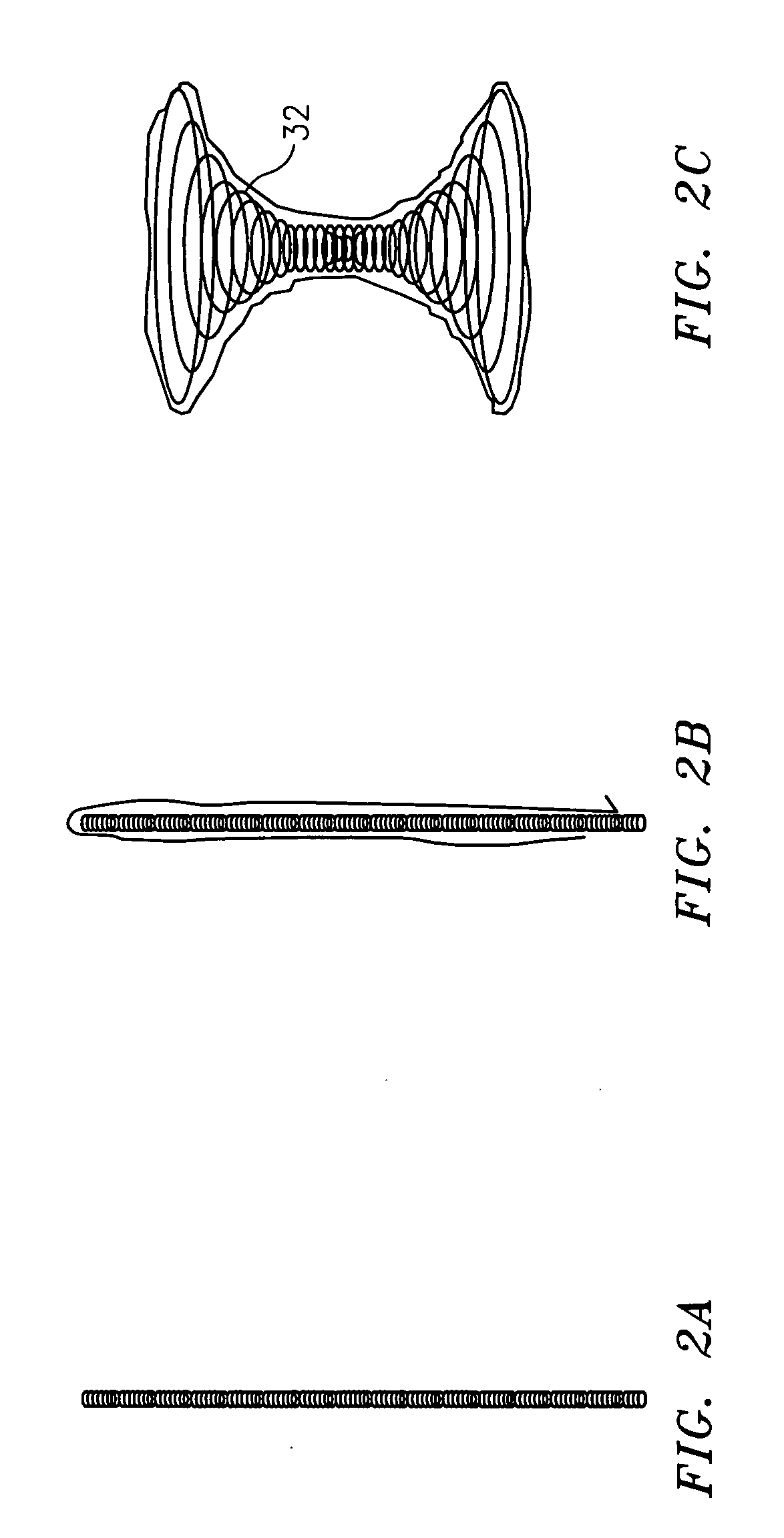
The present invention provides a device for occluding an anatomical aperture, such as a septal defect or patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder includes two sides connected by an intermediate joint. Each of the sides includes at least one elongate element, which is arranged to form non-overlapping loops. Each loop has at least one radially-extending segment that is adjacent to a radially-extending segment of another loop. In at least some embodiments, at least one pair of adjacent radially-extending segments is connected. The loops of the device may be of various shapes, sizes, and configurations, and, in at least some embodiments, the loops have rounded peripheries. In some embodiments, at least one of the sides includes a tissue scaffold. When the occluder is deployed in vivo, the two sides are disposed on opposite sides of the septal tissue surrounding the aperture, thereby exerting a compressive force on the septal tissue that is distributed along both the outer periphery of the occluder and the radially-extending segments.
Owner:NMT MEDICAL +1
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale
ActiveUS20050131460A1Extended stayExtension of timeUltrasound therapyBalloon catheterPatent foramen ovaleCatheter device
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale (PFO) generally involve use of a catheter having treatment means at its distal end. In some embodiments, the treatment means includes one or more abrasive needles used to abrade tissue adjacent the PFO to induce closure of the PFO. In other embodiments, treatment means includes an energy transmission member or more apertures for dispensing a fluid to contact and close the PFO. An exemplary method involves advancing a catheter device to position the distal end adjacent the PFO, exposing a plurality of abrasive needles from the catheter, advancing the needles through the PFO and / or tissue adjacent the PFO, and retracting the needles relative to the PFO to abrade at least a portion of the tissue.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale
ActiveUS20050034735A1Easy positioningEasy retentionElectrotherapyDiagnosticsElectrical resistance and conductanceForamen
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale (PFO) generally involve use of a catheter having at least one closure device at its distal end. In some embodiments, the catheter also includes one or more energy transmission members for delivering energy to the closure device(s) and to the tissue adjacent the PFO to induce closure of the PFO. Closure devices may comprise, for example, a bioresorbable matrix or a non-resorbable matrix. In some embodiments, the closure device contains particles dispersed within the closure device to increase conductance and / or to reduce resistance and / or impedance. An exemplary method involves advancing a catheter to position its distal end into the tunnel of the PFO and fixing the closure device within the tunnel of the patent foramen PFO.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Septal closure device with centering mechanism
ActiveUS20080249562A1Prevent leakageEqually distributedSurgical veterinaryWound clampsDevices fixationEngineering
In one aspect, the present invention provides a device for occluding an aperture in a body, for example, a patent foramen ovale (PFO), including a first side adapted to be disposed on one side of the septum and a second side adapted to be disposed on the opposite side of the septum. The device has an elongated, low-profile delivery configuration and a shortened, radially expanded deployment configuration. The first and second sides are adapted to occlude the aperture upon deployment of the device at its intended delivery location. The device also includes a radially expandable center portion. In some embodiments, the center portion includes a plurality of ribs provided by slits in device. The ribs expand radially when the device is deployed. The expandable center portion facilitates the positioning of the device in the aperture. The device can be secured in the deployed configuration using a catch system.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Implant-catheter attachment mechanism using snare and method of use
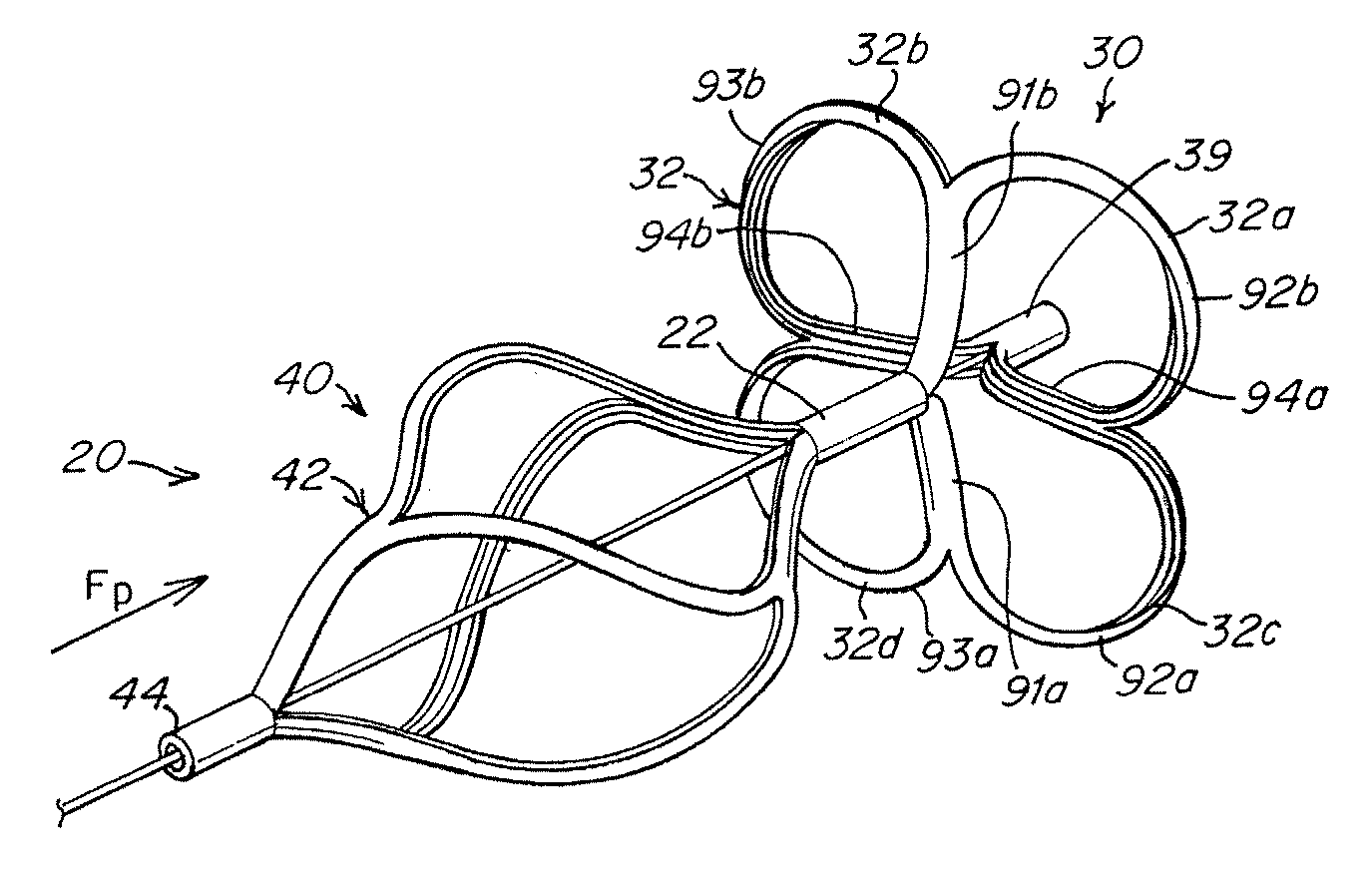
Devices, delivery systems and delivery techniques for an occlusion device for the closure of physical anomalies, such as an atrial septal defect, a patent foramen ovale (PFO), and other septal and vascular defects are described. The devices, delivery systems and delivery techniques relate particularly to, but are not limited to, a patent foramen ovale (PFO) occluder made from a polymer tube. The securement systems enable the deployment (and retrieval) of the device. In one aspect, the second securement system employs a snare connection. The snare connection may have various configurations, including a single snare, double snare, and double criss-cross snare. The securement systems are detached when the device has been properly positioned. The securement systems can be manipulated by control systems provided in the control portion of the delivery system.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
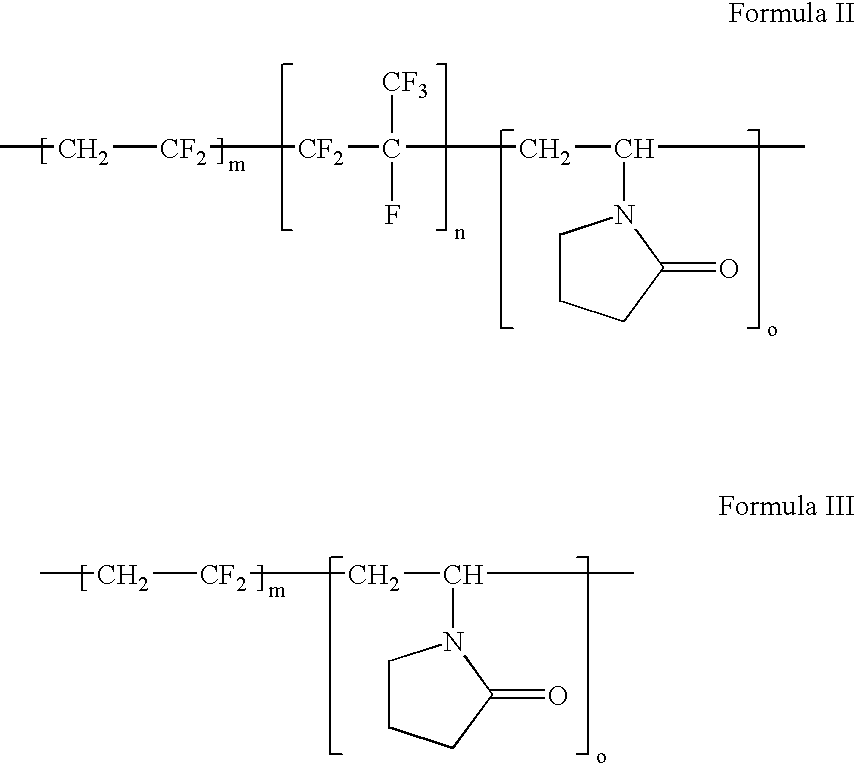
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers
ActiveUS20060047095A1Improve propertiesProvide flexibilityFibre treatmentSurgeryDiseasePolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer of fluorinated monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer of fluorinated monomers or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Closure devices, related delivery methods, and related methods of use
A device for sealing a patent foramen ovale (PFO) in the heart is provided. The device includes a left atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a left atrium of the heart, a right atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a right atrium of the heart, and an elongate member adapted to extend through the passageway and connect the left and right atrial anchors. The right atrial anchor preferably includes a plurality of arms and a cover attached to the arms. The left atrial anchor preferably also includes a plurality of arms and preferably does not include a cover. Preferably, the elongate member has a first end fixedly connected to the left atrial anchor and a portion, proximal to the first end, passing through the right atrial anchor. Preferably, the elongate member is flexible.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale
ActiveUS7165552B2Facilitate positioning and retentionElectrotherapyDiagnosticsForamenPatent foramen ovale
Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale (PFO) generally involve use of a catheter having at least one closure device at its distal end. In some embodiments, the catheter also includes one or more energy transmission members for delivering energy to the closure device(s) and to the tissue adjacent the PFO to induce closure of the PFO. Closure devices may comprise, for example, a bioresorbable matrix or a non-resorbable matrix. In some embodiments, the closure device contains particles dispersed within the closure device to increase conductance and / or to reduce resistance and / or impedance. An exemplary method involves advancing a catheter to position its distal end into the tunnel of the PFO and fixing the closure device within the tunnel of the patent foramen PFO.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Delivery device for implant with dual attachment sites
InactiveUS20070088388A1Improve accuracyEasy to controlSurgical veterinaryWound clampsSurgeryAttachment site
The invention generally relates to systems and methods for percutaneous closure of intra-cardiac openings, such as a patent foramen ovale (PFO). In one embodiment, a delivery system includes a first attachment mechanism and a second attachment mechanism attached to a closure device for implantation in an intra-cardiac opening. The delivery system can be used to deliver a closure device to the intra-cardiac opening, or to retrieve or re-position a closure device within the intra-cardiac opening.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Methods and apparatus for closing a layered tissue defect
Methods and apparatus for treatment of layered tissue defects having a majority of the surfaces of the defect layers in contact generally involve use of a catheter having at least one energy transmission member at its distal end. The distal end of the apparatus also typically has a force applying member which can apply a force to the tissue defect. Often this force is a lateral force or vacuum which helps the tissue to appose itself. An exemplary method of closing a patent foramen ovale (PFO) involves positioning a closure device between layers of the PFO. Energy is then applied to the layered tissue defect with the closure device so as to substantially close the tissue defect. The energy is often monopolar or bipolar radiofrequency energy. A force may also be applied by the closure device to the layered tissue defect so as to bring the layered tissue defect together.
Owner:TERUMO KK
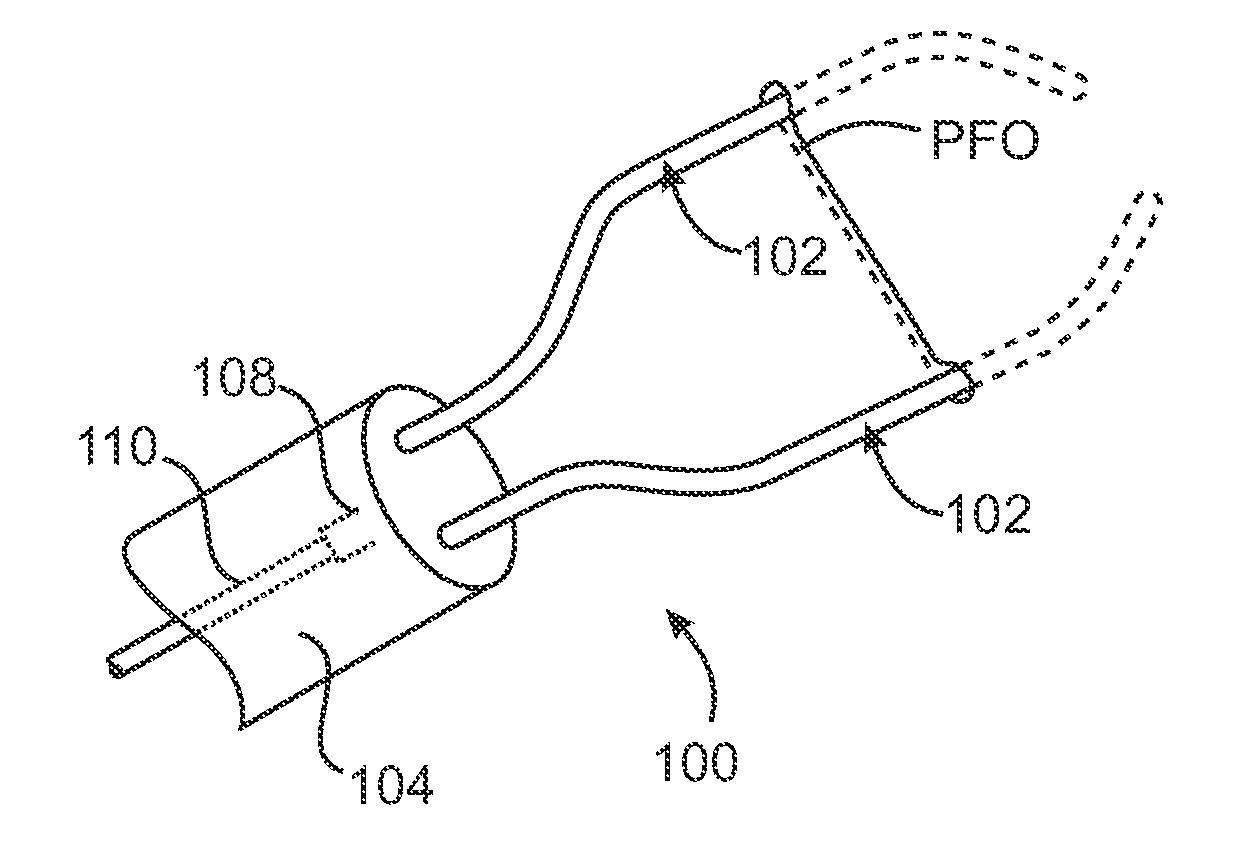
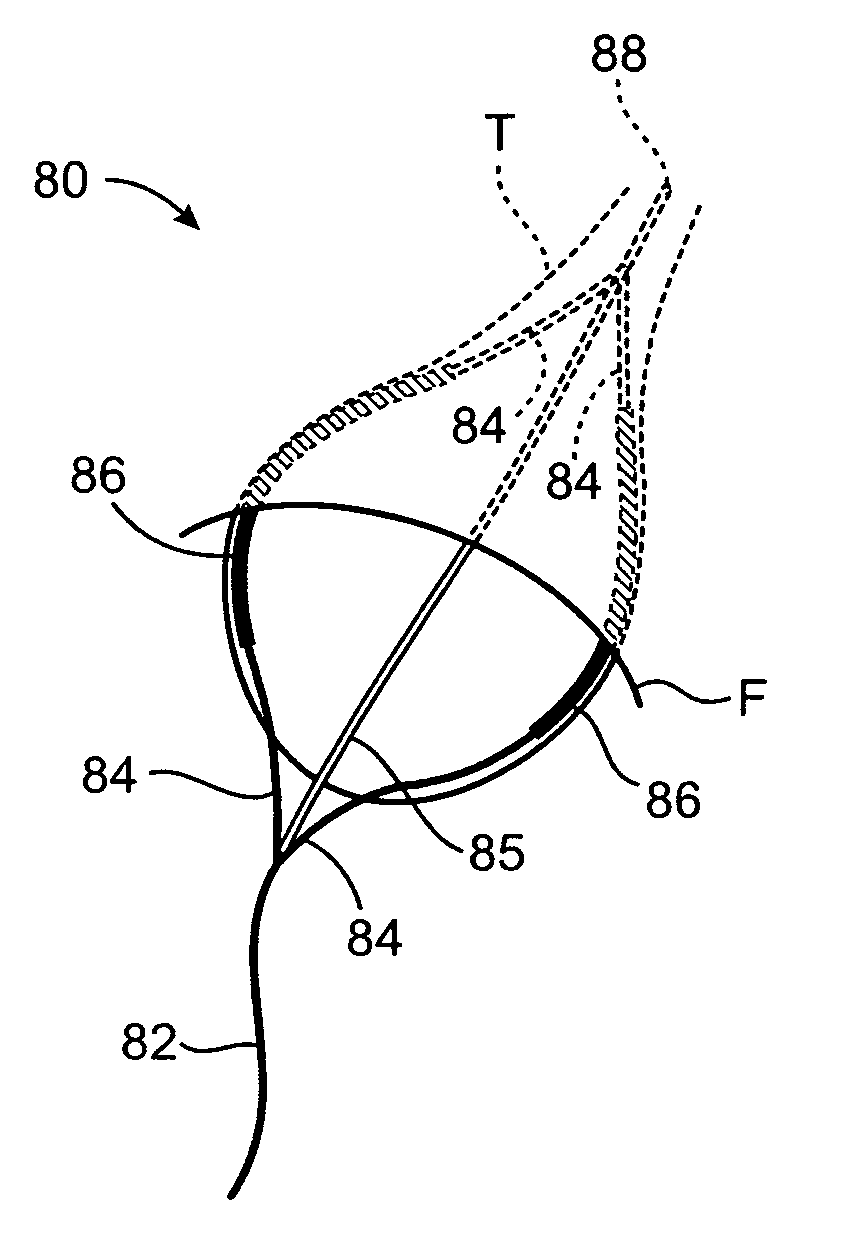
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects with Capture Devices and Other Devices
InactiveUS20080154286A1Convenient treatmentSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTissue defectSeptal wall
Systems, devices and methods for treating internal tissue defects, such as septal defects, are provided. An exemplary method of treating an internal tissue defect, specifically a method of closing a patent foramen ovale (PFO), can include passing a closure element from a right atrium through a septal wall in a first location and into the left atrium. A capture device, which can be configured as a snare-like device, can be used to capture the closure element in the left atrium and pull the closure element back through the septal wall in a different, second location, such that the closure element is routed over the PFO. The closure element can then be anchored and / or locked against the septal wall such that the PFO is at least partially closed.
Owner:OVALIS
Energy based devices and methods for treatment of anatomic tissue defects
ActiveUS20070287999A1Promote sportsImprove foldabilityCatheterSurgical instrument detailsTissue defectEnergy based
Methods for treating anatomic tissue defects such as patent foramen ovale (PFO) generally involve positioning a distal end of an elongate catheter device at the site of the anatomic defect, exposing an expandable housing and energy transmission member out of the distal end of the catheter device, engaging the housing with tissues at the site of the anatomic defect, applying suction to the tissues via the housing to bring the tissues together; and applying energy to the tissues with the energy transmission member to substantially close the anatomic defect acutely. Apparatus generally include an elongate catheter body, a housing extending from a distal end of the catheter body for engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect, and an energy transmission member adjacent a distal end of the housing, the energy transmission member having at least one substantially planar surface.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Intravascular occlusion device
InactiveUS20050055050A1Inherent abilityPromote localizationSurgical veterinaryWound clampsBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
A device for repairing an anatomical defect such as a patent foramen ovale possesses spring-like characteristics enabling it to be stored within, and discharged from, the distal end of a catheter when the device is in the compressed state and to assume a defect-occluding configuration when the device is in the expanded, or noncompressed, state.
Owner:ALFARO ARTHUR A
Scaffold for tubular septal occluder device and techniques for attachment
InactiveUS20080077180A1Minimize traumaMinimize distortion to the septal tissue surroundingSurgical veterinaryWound clampsEngineeringSeptal Occluder Device
The present invention provides a device for occluding an anatomical aperture, such as an atrial septal defect (ASD) or a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder includes two sides connected by a central tube. A tissue scaffold material is disposed on the occluder. The occluder is formed from a tube, which is cut to produce struts in each side. Upon the application of force, the struts deform into loops. The loops may be of various shapes, sizes, and configurations, and, in at least some embodiments, the loops have rounded peripheries. In some embodiments, at least one side of the occluder includes a tissue scaffold. The occluder further includes a catch system that maintains its deployed state in vivo. When the occluder is deployed in vivo, the two sides are disposed on opposite sides of the septal tissue surrounding the aperture and the catch system is deployed so that the occluder exerts a compressive force on the septal tissue and closes the aperture.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Methods and apparatus to achieve a closure of a layered tissue defect
InactiveUS20060271089A1Improve sealingEffective seal of defectBalloon catheterDiagnosticsTissue defectGuide tube
Methods for treating anatomic tissue defects such as a patent foramen ovale generally involve positioning a distal end of a catheter device at the site of the defect, exposing a housing and energy transmission member from the distal end of the catheter, engaging the housing with tissues at the site of the defect, applying suction or other approximating tool to the tissue via the housing to bring the tissue together, and applying energy to the tissue with the energy transmission member or to deliver a clip or fixation device to substantially close the defect. Apparatus generally include a catheter body, a housing extending from a distal end of the catheter body for engaging tissue at the site of the defect, and further adapted to house a fusing or fixation device such as an energy transmission member adjacent a distal end of the housing, or a clip or fixation delivery element.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Closure devices, related delivery methods and tools, and related methods of use
A device for sealing a patent foramen ovale (PFO) in the heart is provided. The device includes a left atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a left atrium of the heart, a right atrial anchor adapted to be placed in a right atrium of the heart, and an elongate member adapted to extend through the passageway and connect the left and right atrial anchors. The right atrial anchor preferably includes a plurality of arms and a cover attached to the arms. The left atrial anchor also includes a plurality of arms and preferably does not include a cover. Preferably, the elongate member has a first end of fixedly connected to the left atrial anchor and a portion, proximal to the first end, releasably connected to the right atrial anchor. Preferably, the elongate member is flexible.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com