Patents
Literature
678 results about "Blood arterial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arterial blood. Arterial blood is the oxygenated blood in the circulatory system found in the pulmonary vein, the left chambers of the heart, and in the arteries. It is bright red in color, while venous blood is dark red in color (but looks purple through the translucent skin).
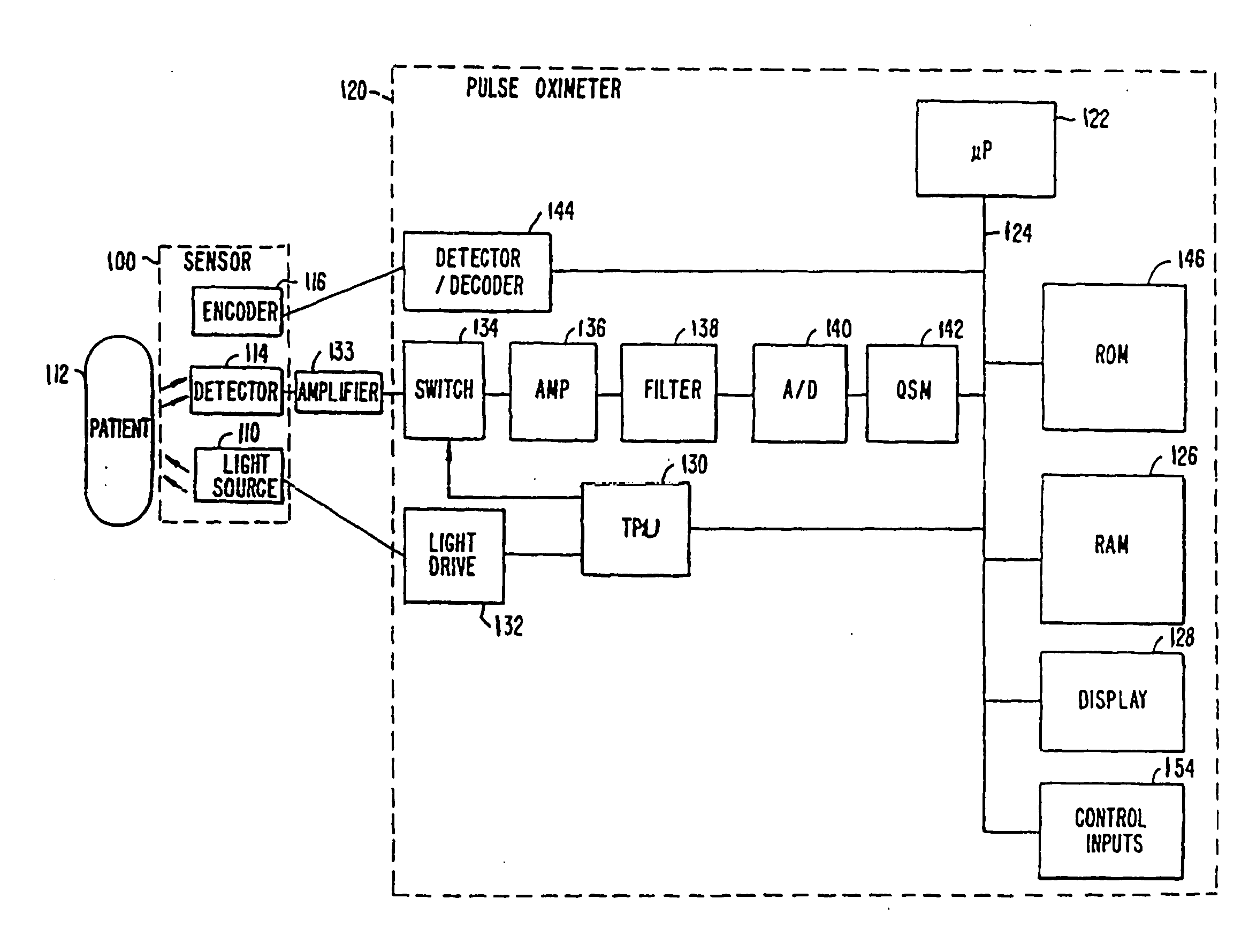
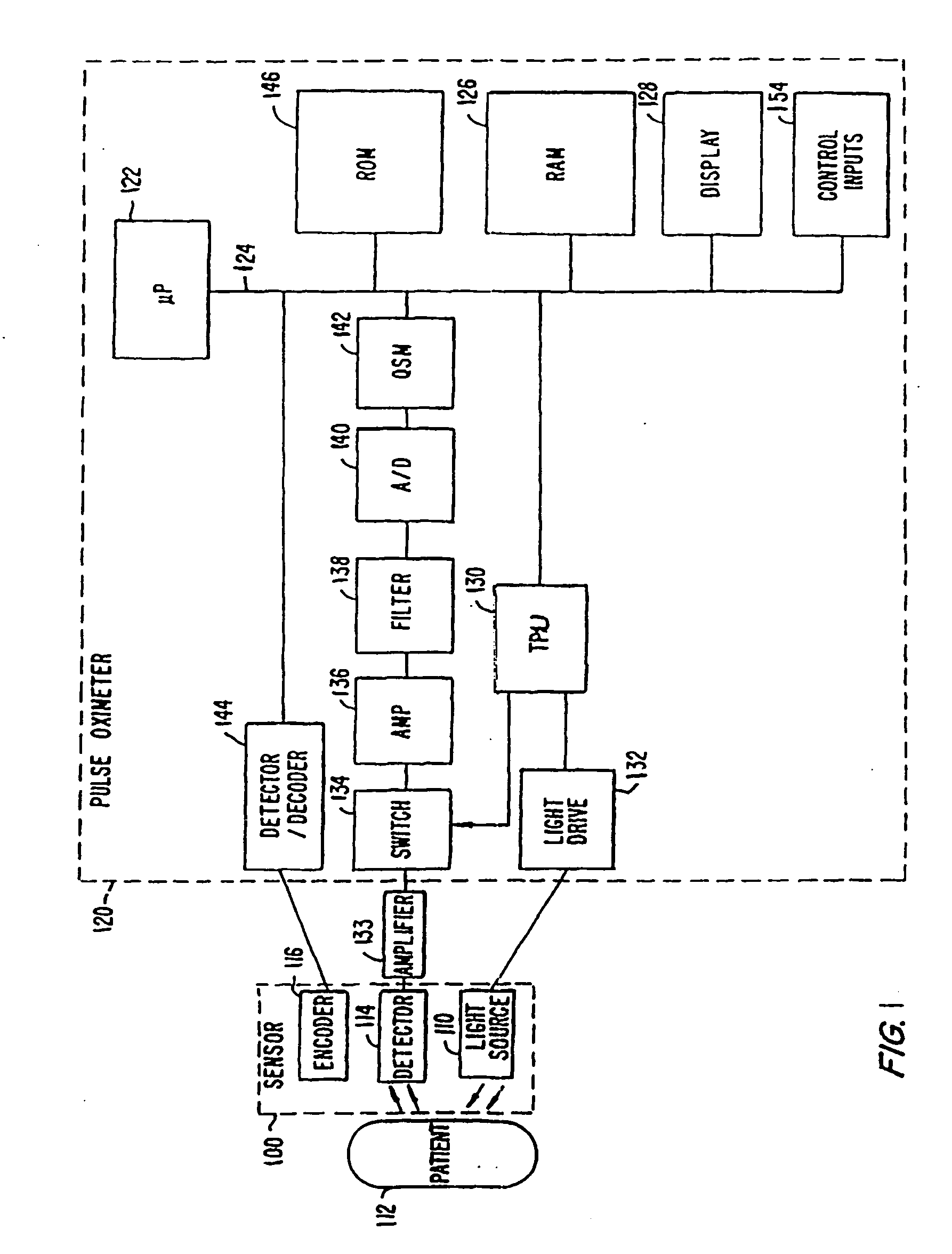
Systems and methods for making noninvasive physiological assessments
InactiveUS6875176B2Improve accuracySensitive highOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryDiseaseNon invasive
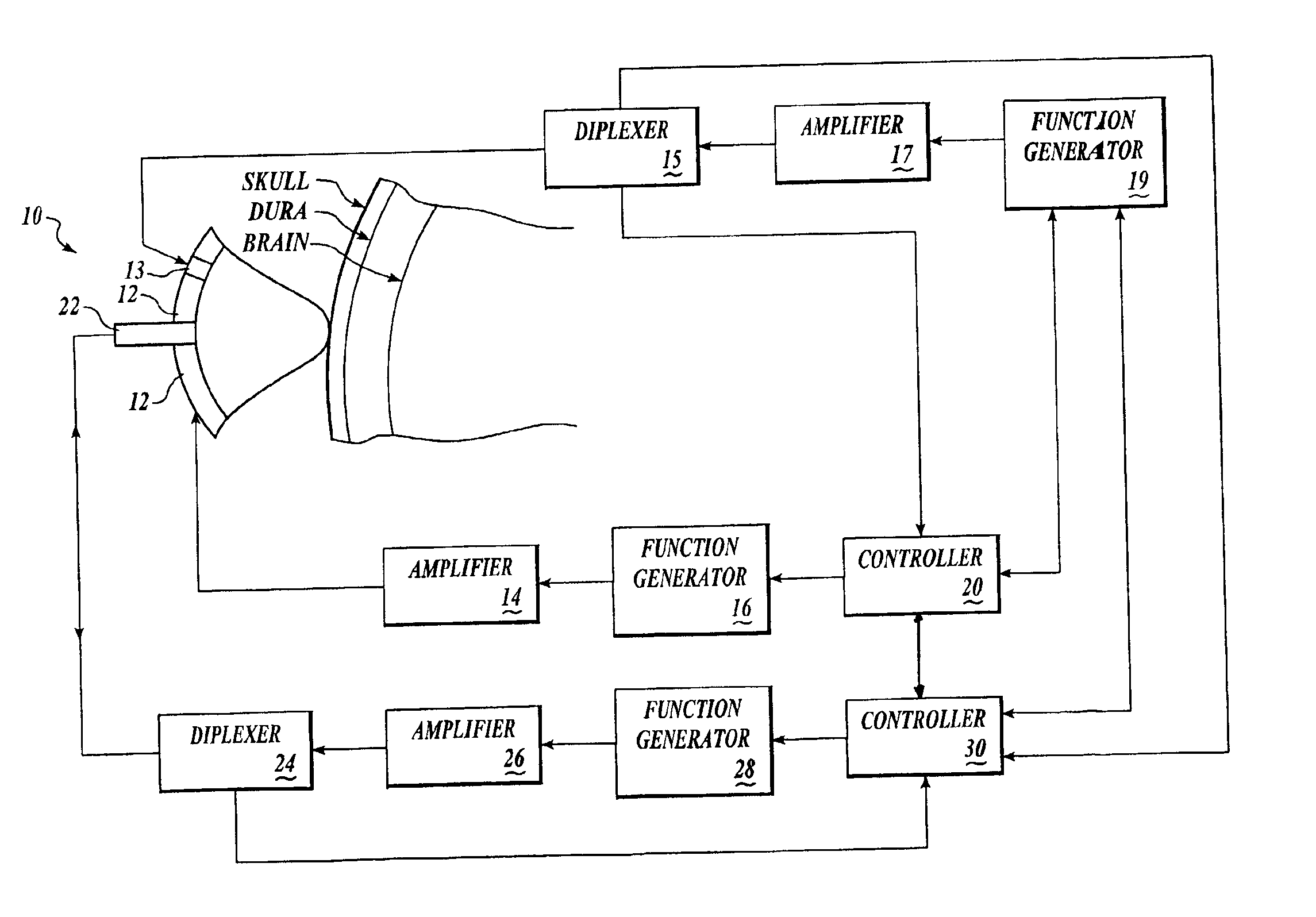
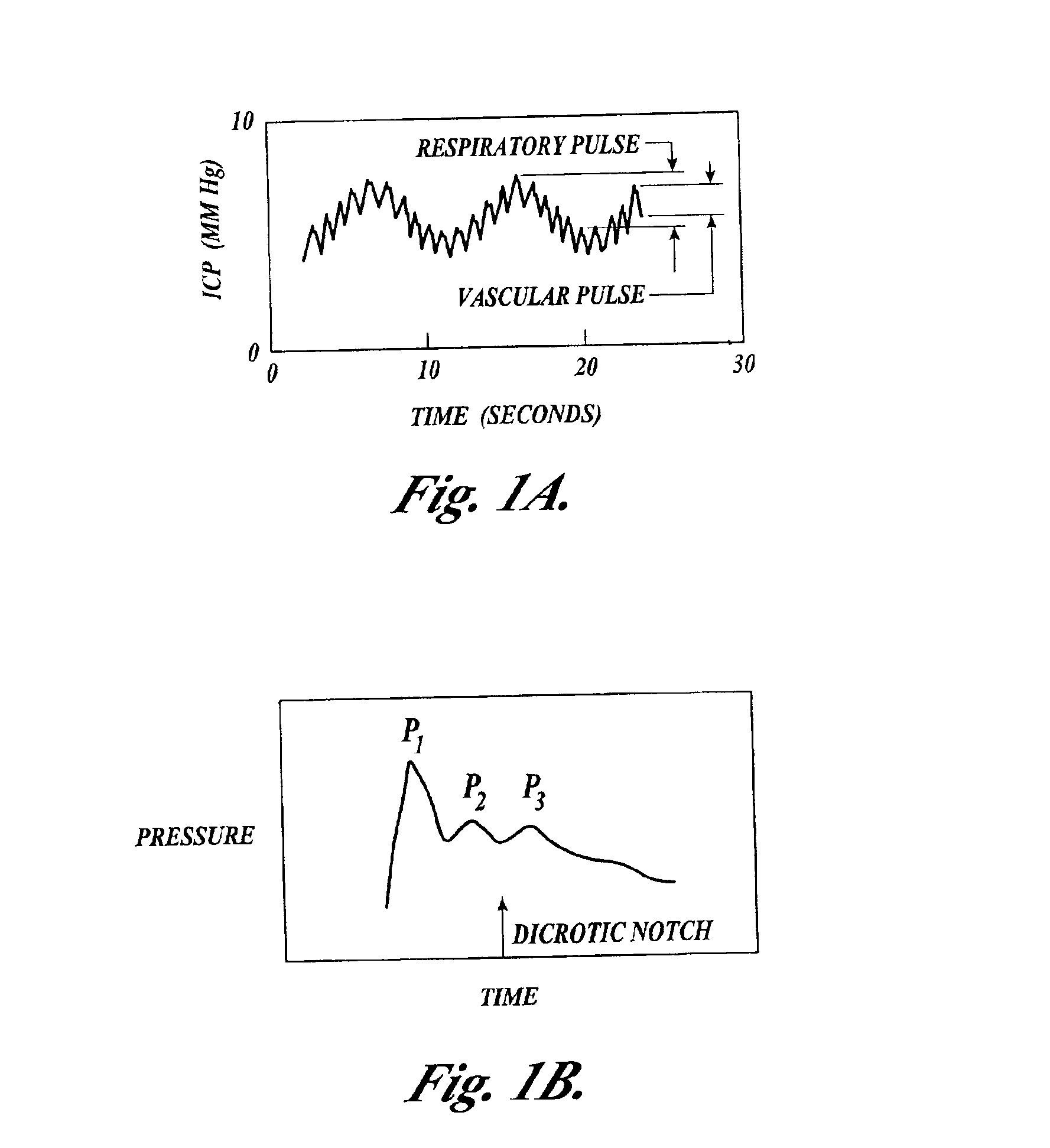
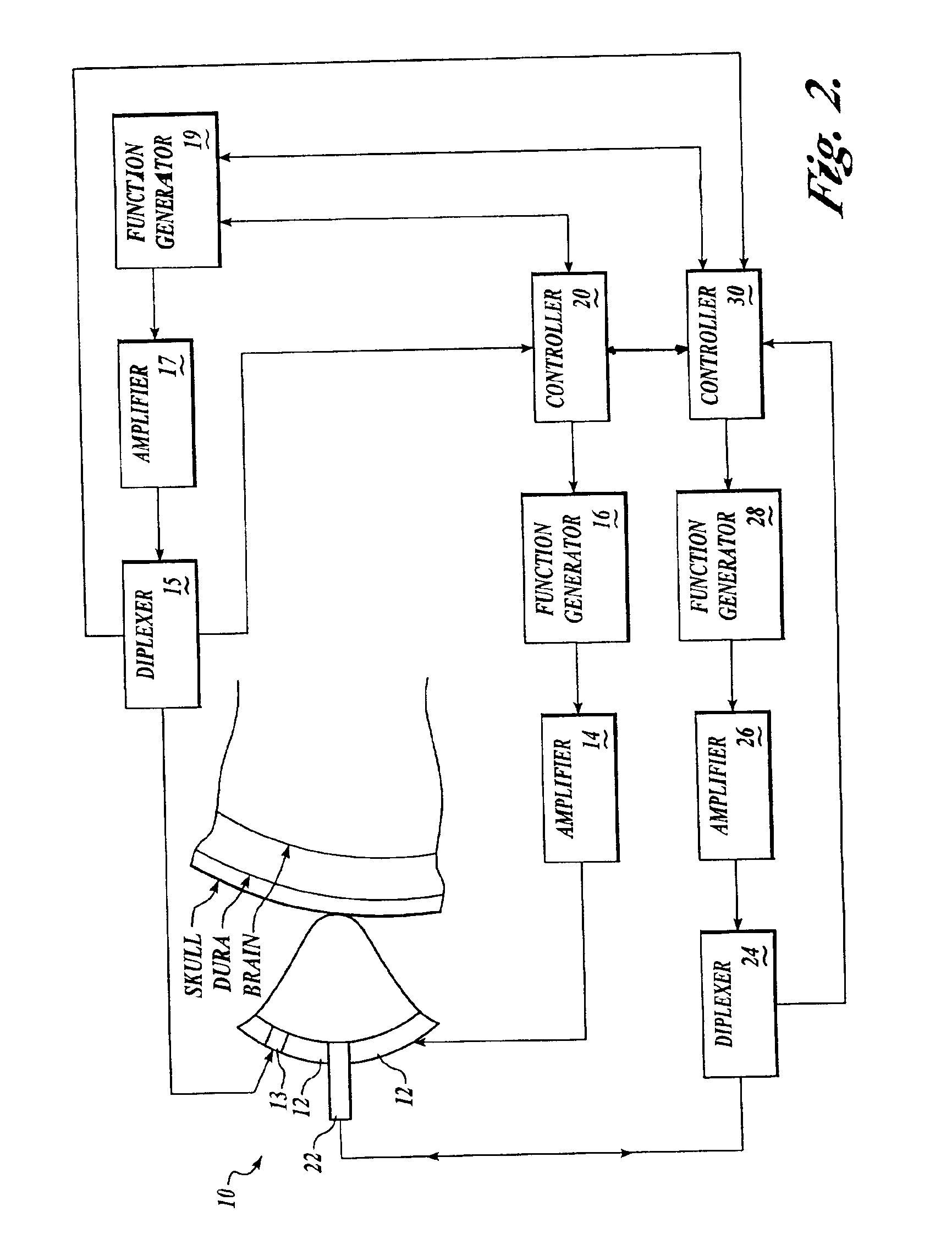
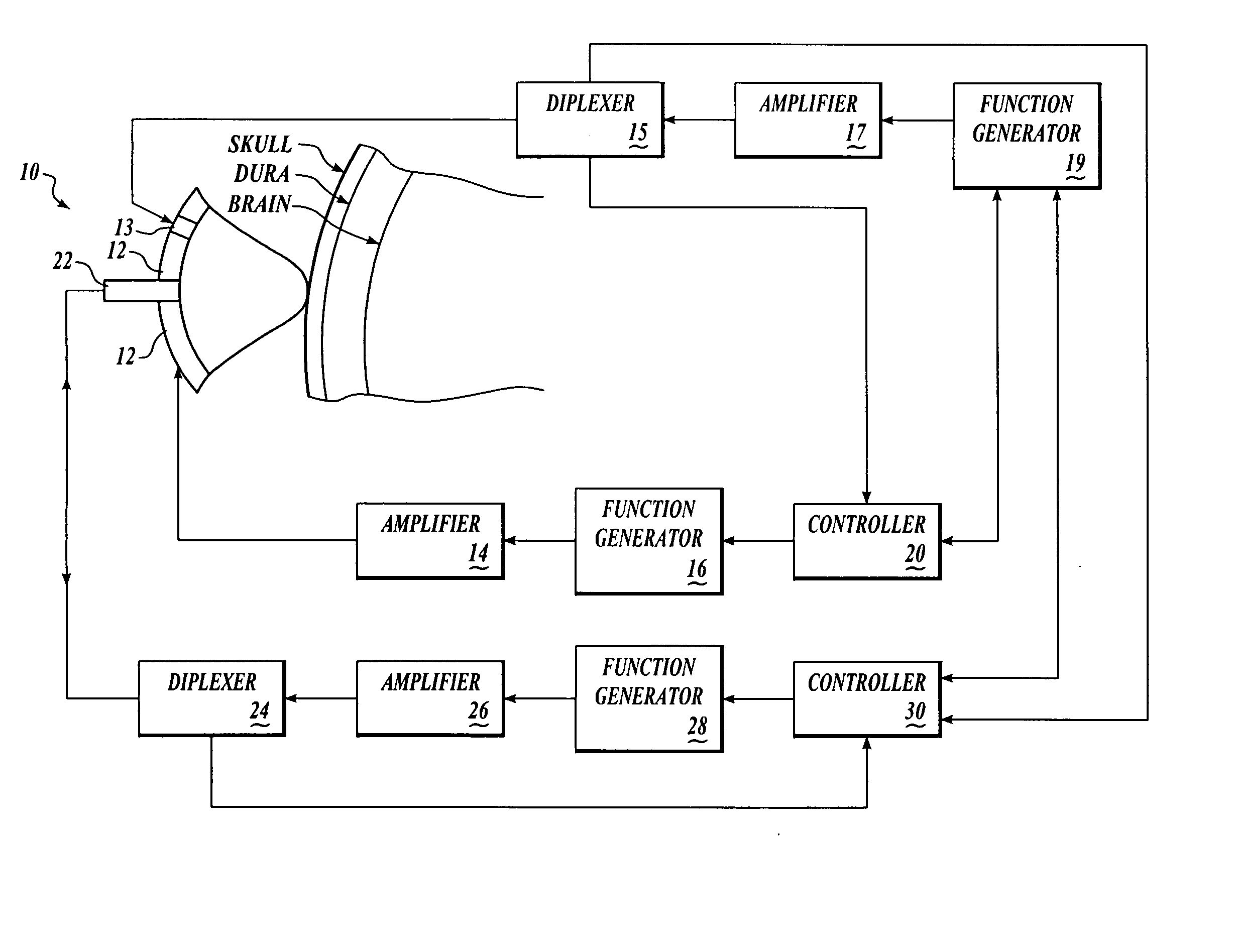
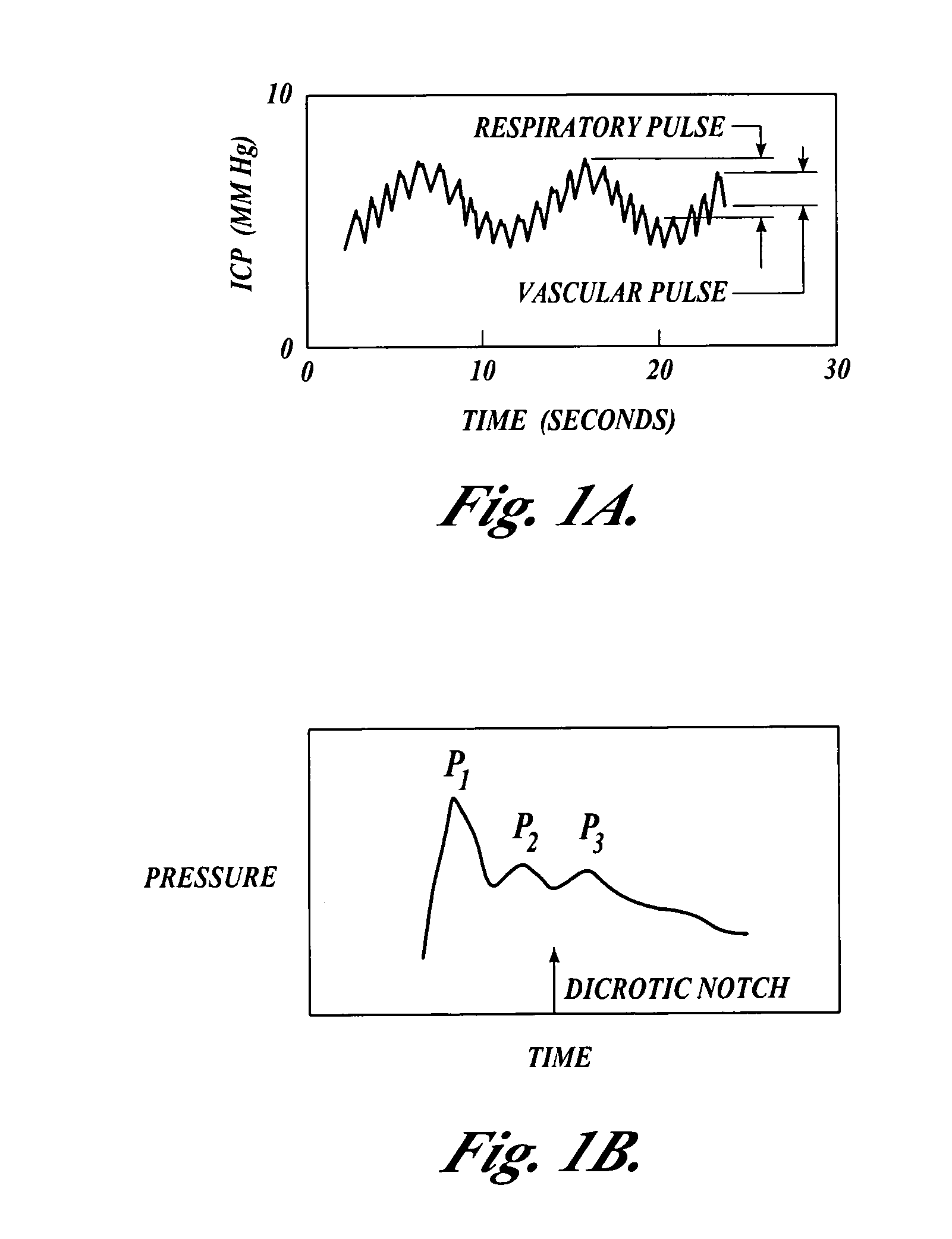
Systems and methods for assessment of tissue properties, noninvasively, by acquiring data relating to at least one aspect of intrinsic and / or induced tissue displacement, or associated biological responses, are provided. Data relating to tissue displacement and associated biological changes may be acquired by detecting acoustic properties of tissue using ultrasound interrogation pulses, preferably in a scatter or Doppler detection mode. Based on this data, tissue properties are assessed, characterized and monitored. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include non-invasive assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties. Methods and systems for localizing physiological condition(s) and / or biological response(s), such as pain, by targeting and selectively probing tissues using the application of focused ultrasound are also provided.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
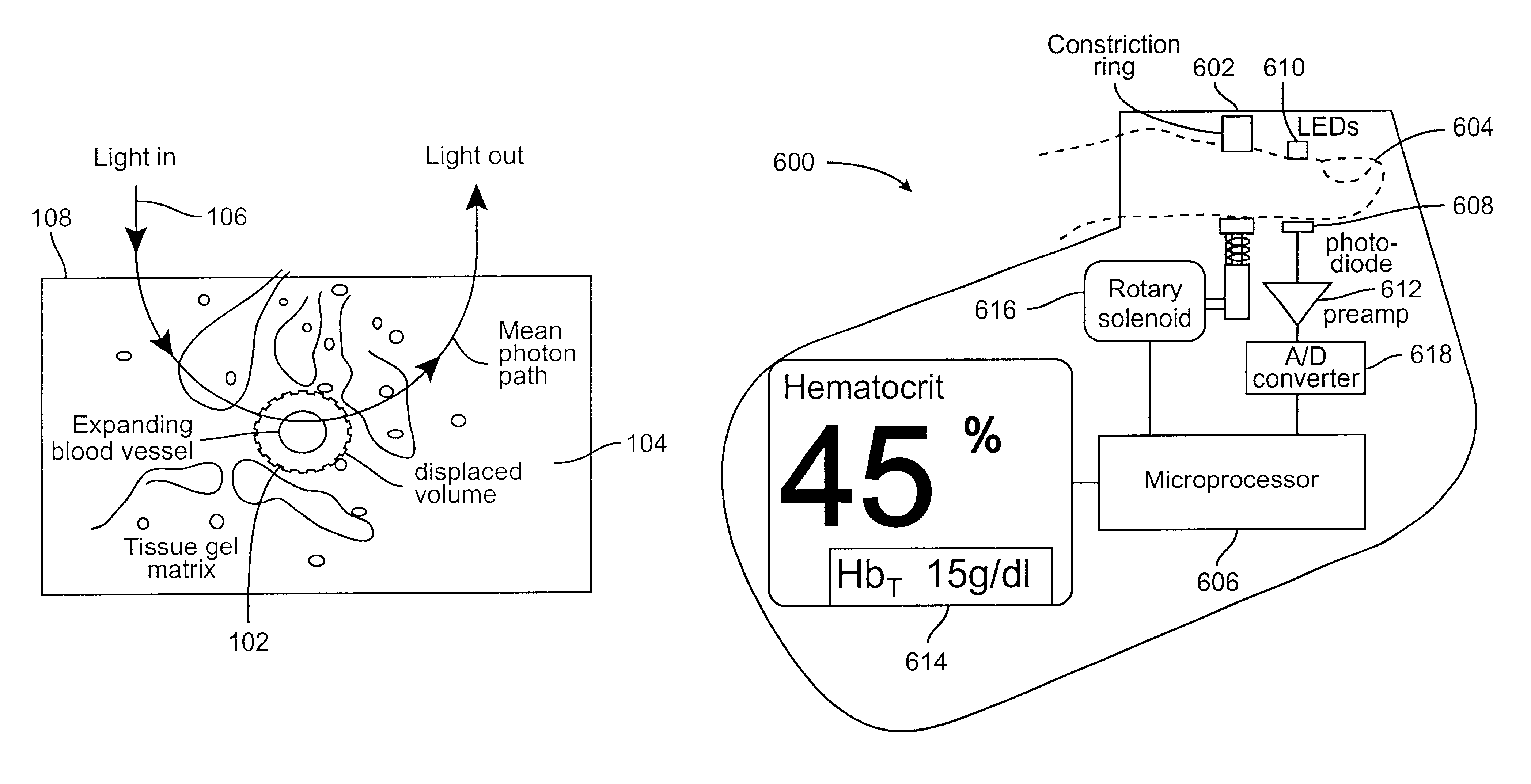
Method and apparatus for improving the accuracy of noninvasive hematocrit measurements
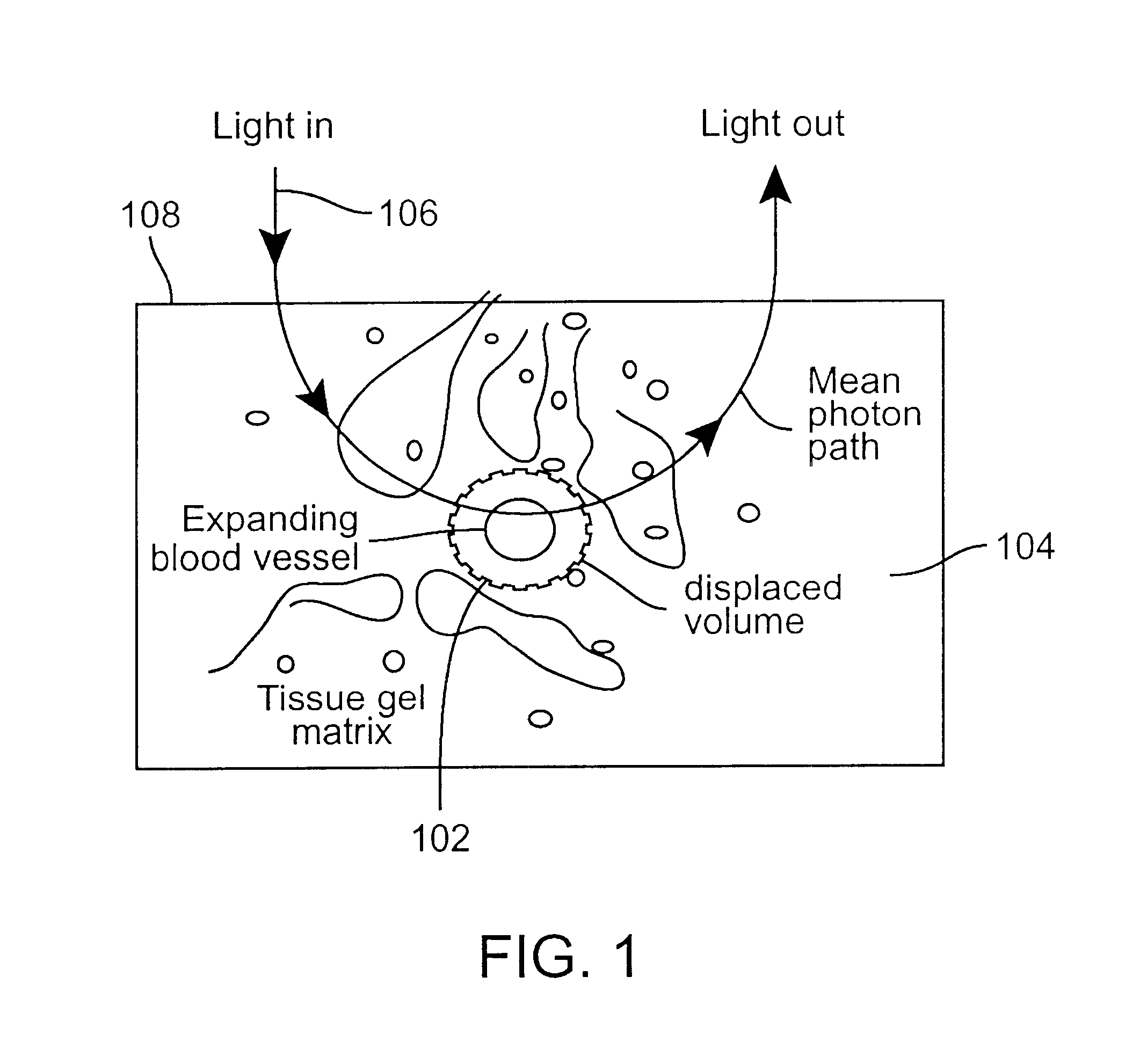
A device and a method to provide a more reliable and accurate measurement of hematocrit (Hct) by noninvasive means. The changes in the intensities of light of multiple wavelengths transmitted through or reflected light from the tissue location are recorded immediately before and after occluding the flow of venous blood from the tissue location with an occlusion device positioned near the tissue location. As the venous return stops and the incoming arterial blood expands the blood vessels, the light intensities measured within a particular band of near-infrared wavelengths decrease in proportion to the volume of hemoglobin in the tissue location; those intensities measured within a separate band of wavelengths in which water absorbs respond to the difference between the water fractions within the blood and the displaced tissue volume. A mathematical algorithm applied to the time-varying intensities yields a quantitative estimate of the absolute concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. To compensate for the effect of the unknown fraction of water in the extravascular tissue on the Hct measurement, the tissue water fraction is determined before the occlusion cycle begins by measuring the diffuse transmittance or reflectance spectra of the tissue at selected wavelengths.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Vital signs probe
InactiveUS20050209516A1Improve performanceAccurate calculationEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPulse oximetryCore temperature
A combination of a patient core temperature sensor and the dual-wavelength optical sensors in an ear probe or a body surface probe improves performance and allows for accurate computation of various vital signs from the photo-plethysmographic signal, such as arterial blood oxygenation (pulse oximetry), blood pressure, and others. A core body temperature is measured by two sensors, where the first contact sensor positioned on a resilient ear plug and the second sensor is on the external portion of the probe. The ear plug changes it's geometry after being inserted into an ear canal and compress both the first temperature sensor and the optical assembly against ear canal walls. The second temperature sensor provides a reference signal to a heater that is warmed up close to the body core temperature. The heater is connected to a common heat equalizer for the temperature sensor and the pulse oximeter. Temperature of the heat equalizer enhances the tissue perfusion to improve the optical sensors response. A pilot light is conducted to the ear canal via a contact illuminator, while a light transparent ear plug conducts the reflected lights back to the light detector.
Owner:FRADEN JACOB
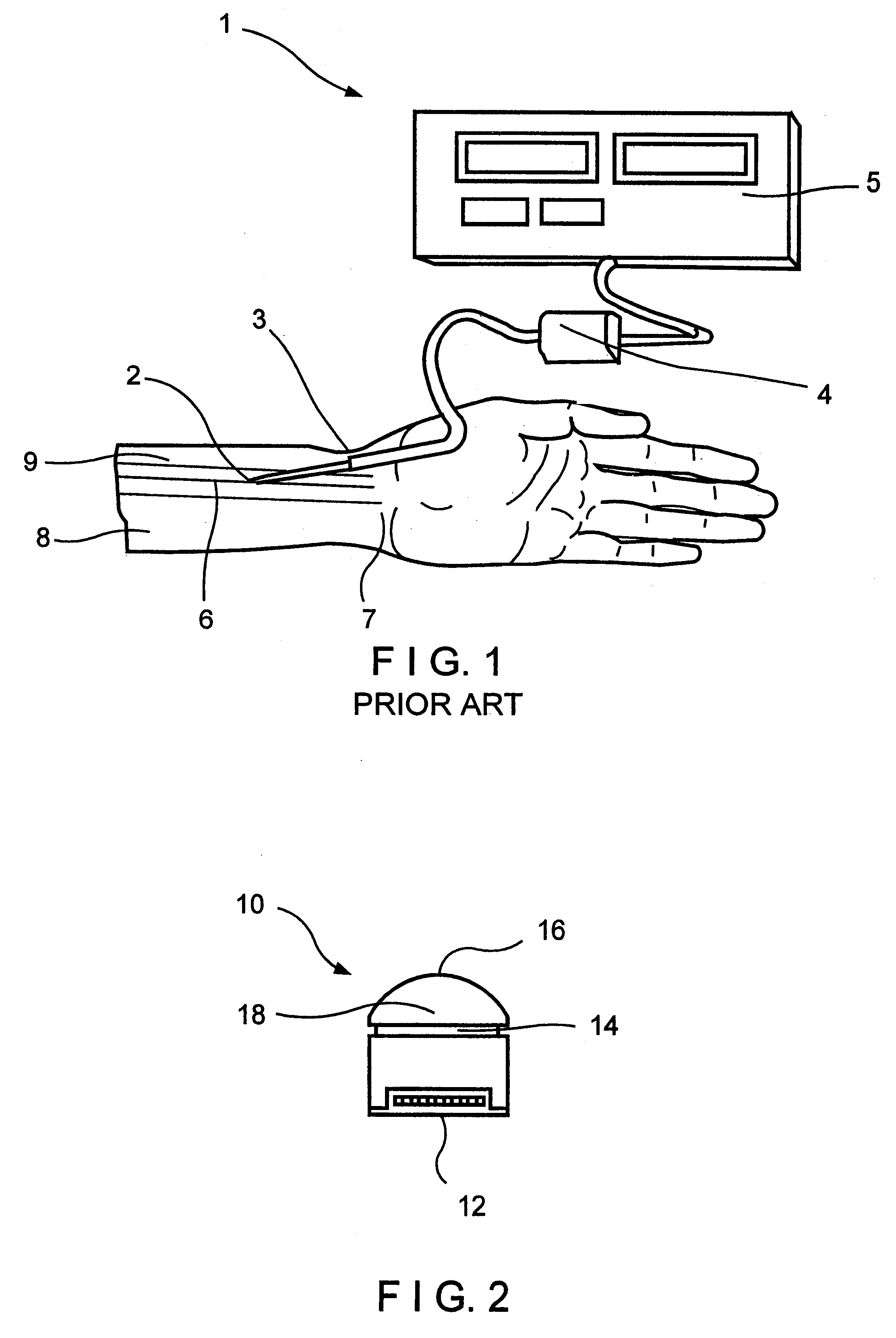
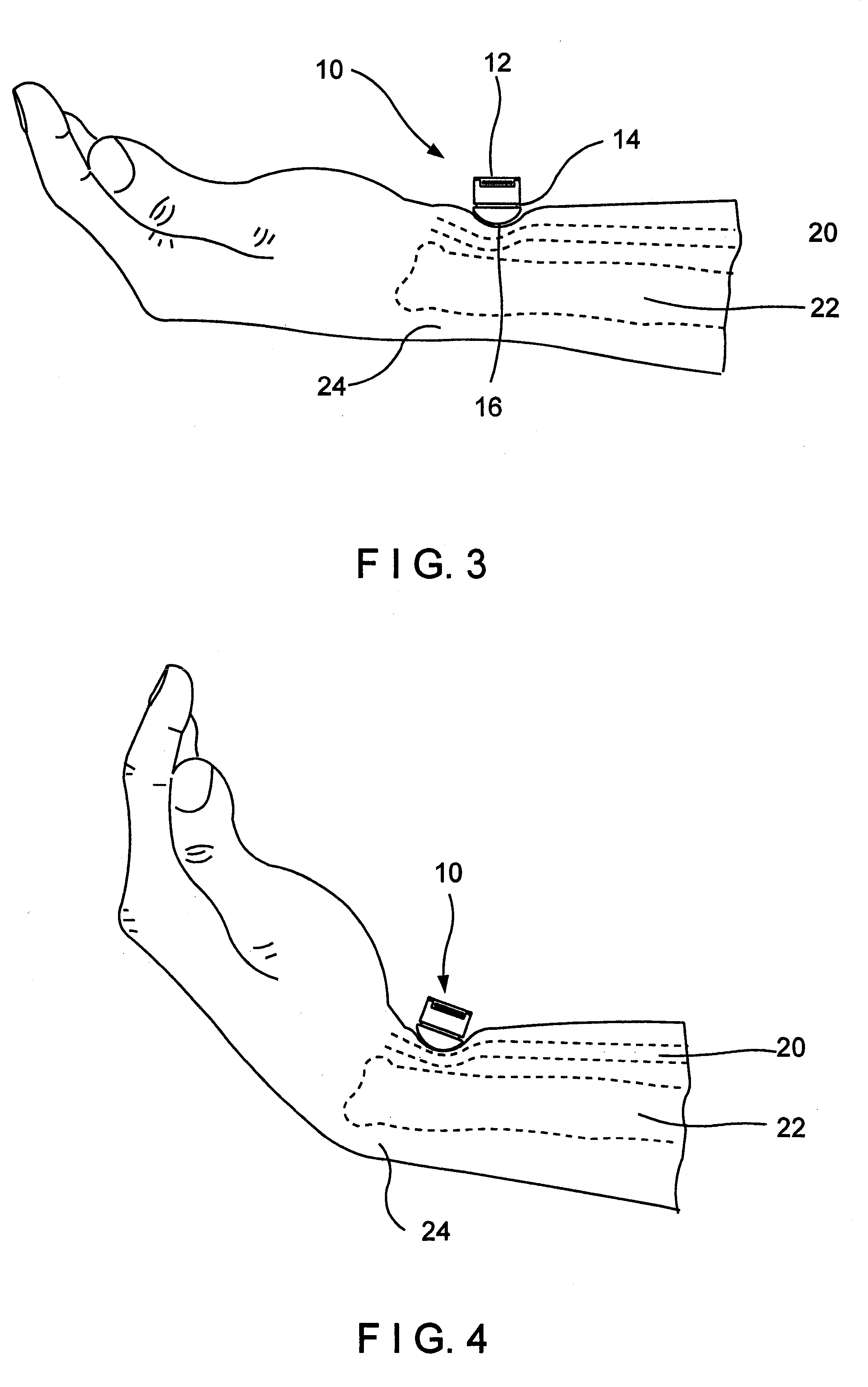
Pressure applicator devices particularly useful for non-invasive detection of medical conditions
InactiveUS6461305B1Low mobilityEasy constructionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterVeinBlood arterial
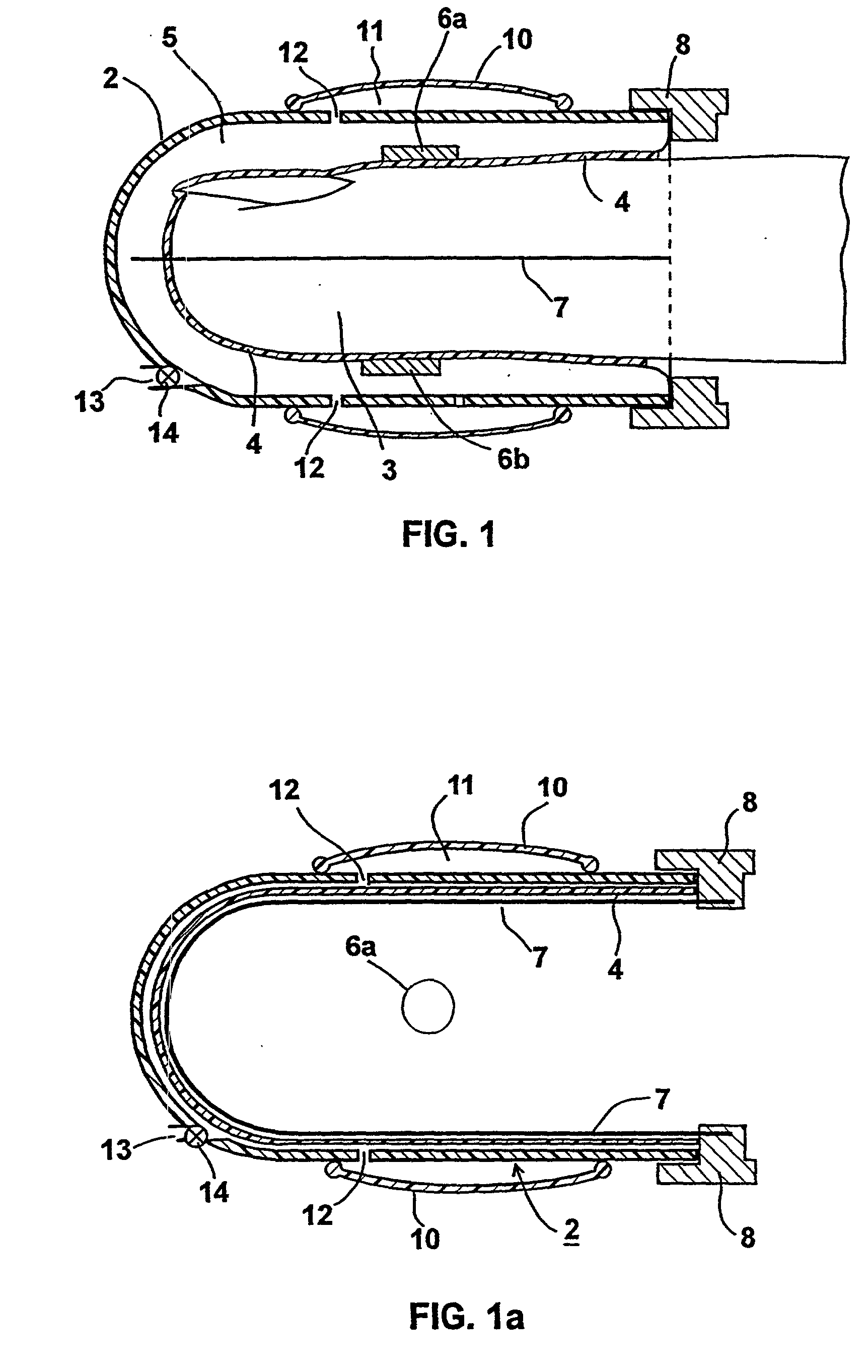
A probe for application to a body part particularly a finger of a patient to detect a change in the physical condition of the patient includes a housing defining a compartment closed at one end and open at the opposite end for receiving the distal end of the patient's finger and a medium wholly self-contained within the probe for applying a static pressure field substantially uniformly around the distal end of the patient's finger, of a predetermined magnitude sufficient to substantially prevent distention of the venous vasculature, uncontrolled venous backflow, and retrognade shockwave propagation into the distal end, and to partially unload the wall tension of, but not to occlude, the arteries in the distal end when at heart level or below. A sensor senses changes in the distal end of the patient's finger related to changes in arterial blood volume therein.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
Mechanical tissue device and method
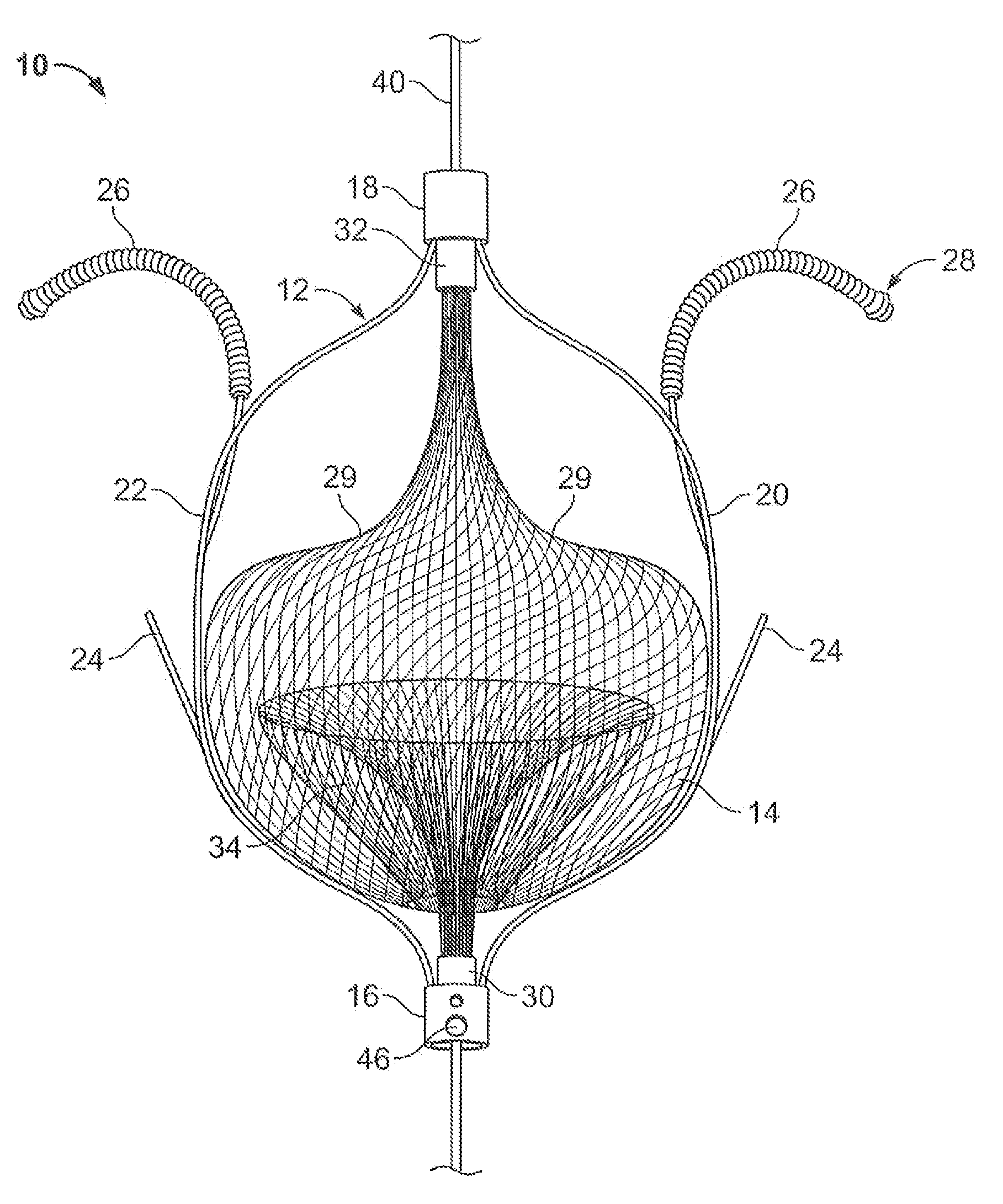
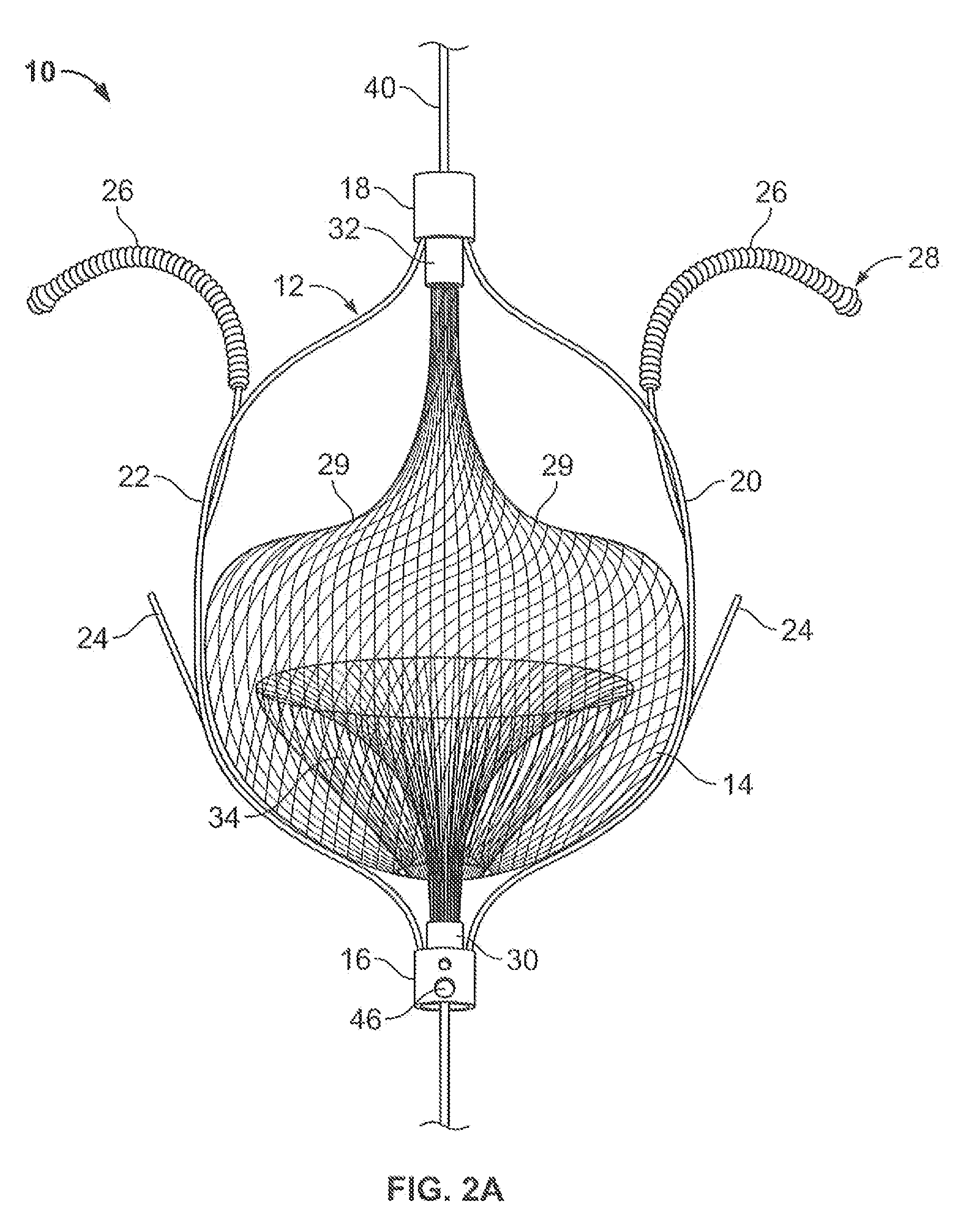
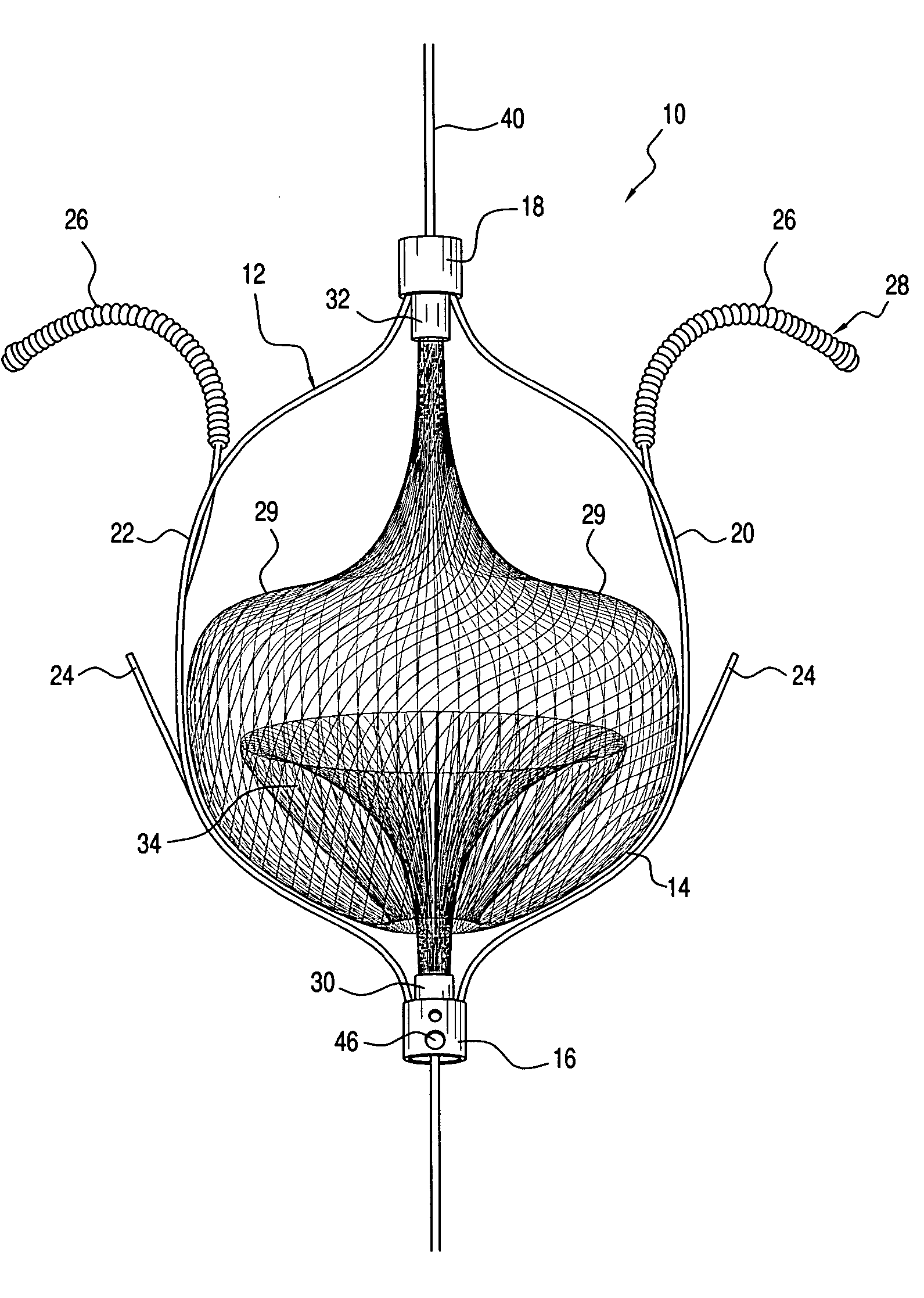
InactiveUS20080119886A1Rigid enoughLength of device being increasedDilatorsOcculdersVeinVenous blood
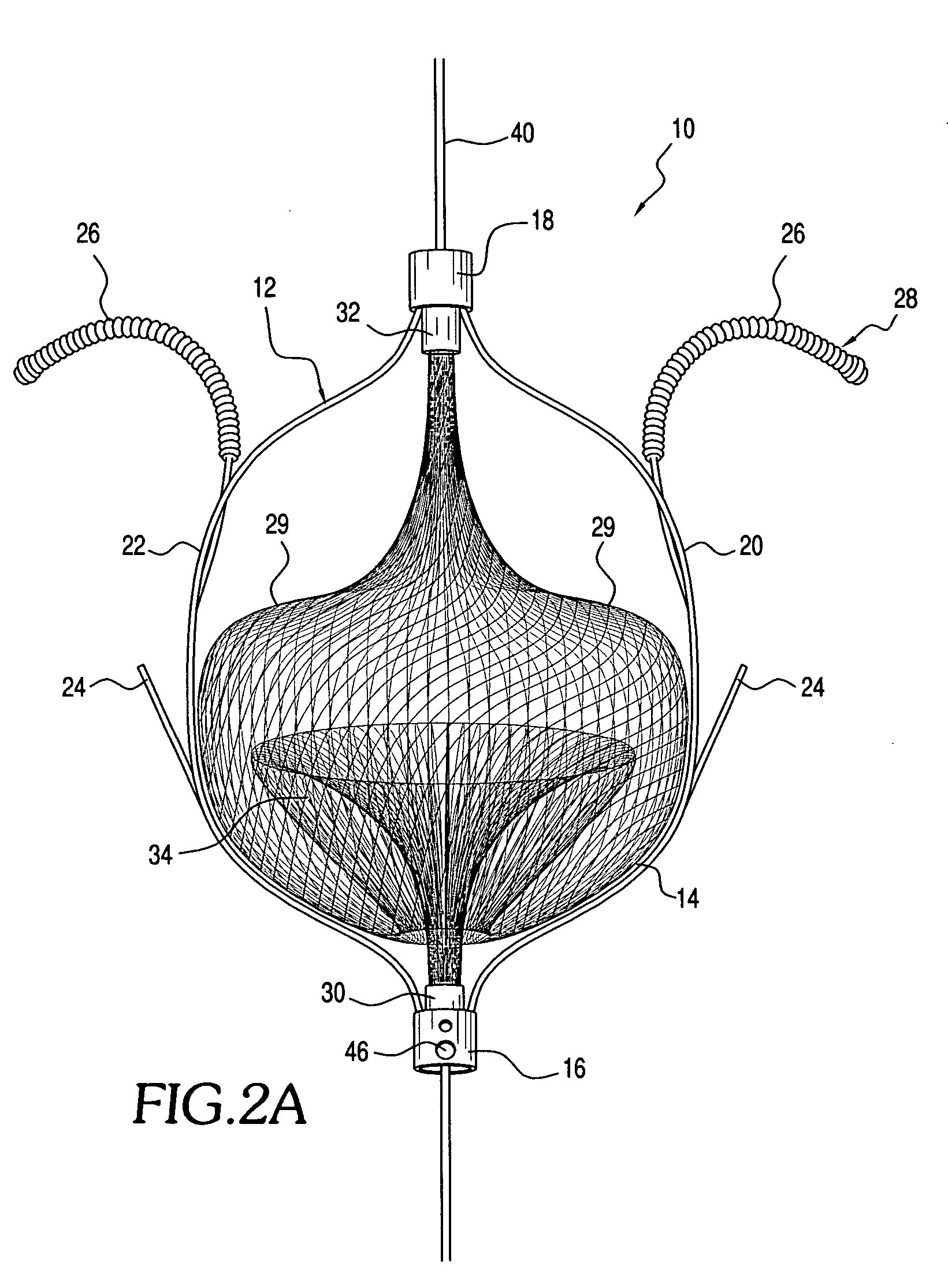
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as Nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Embolic filtering method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009799A1Obstruct passageEncourage and facilitate growth of tissueAnnuloplasty ringsDilatorsVenous bloodCardiac defects
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
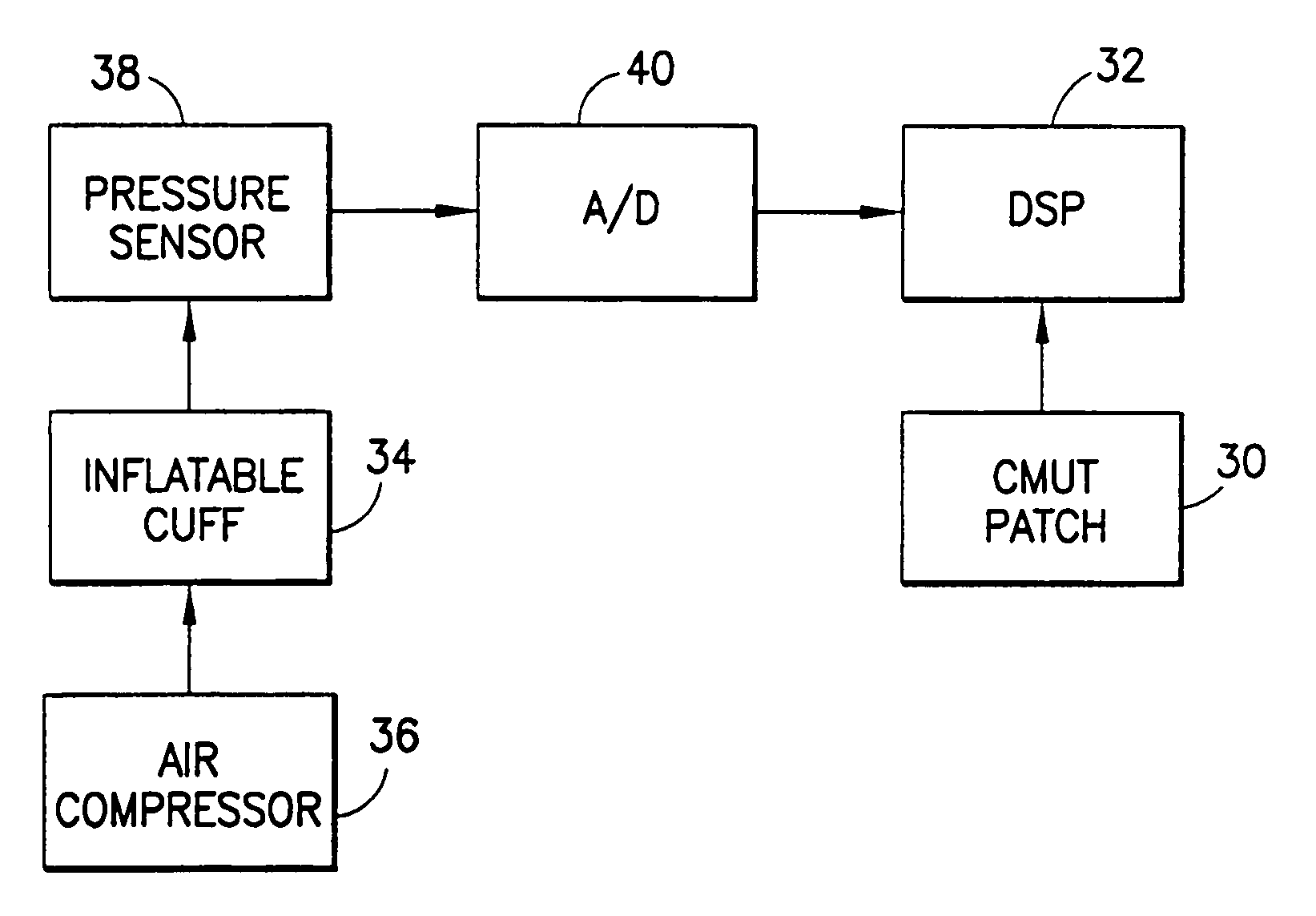
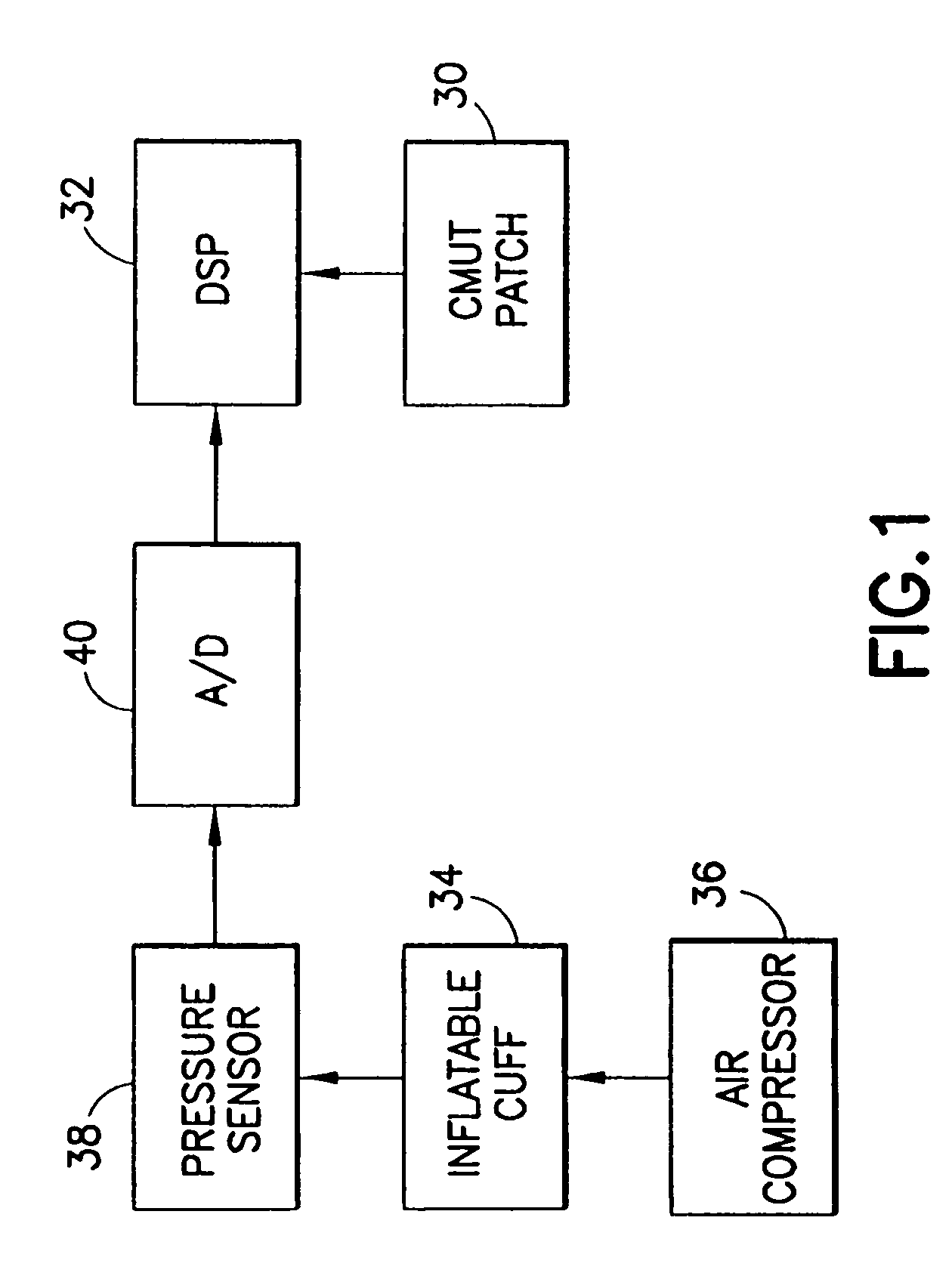
Wearable blood pressure sensor and method of calibration
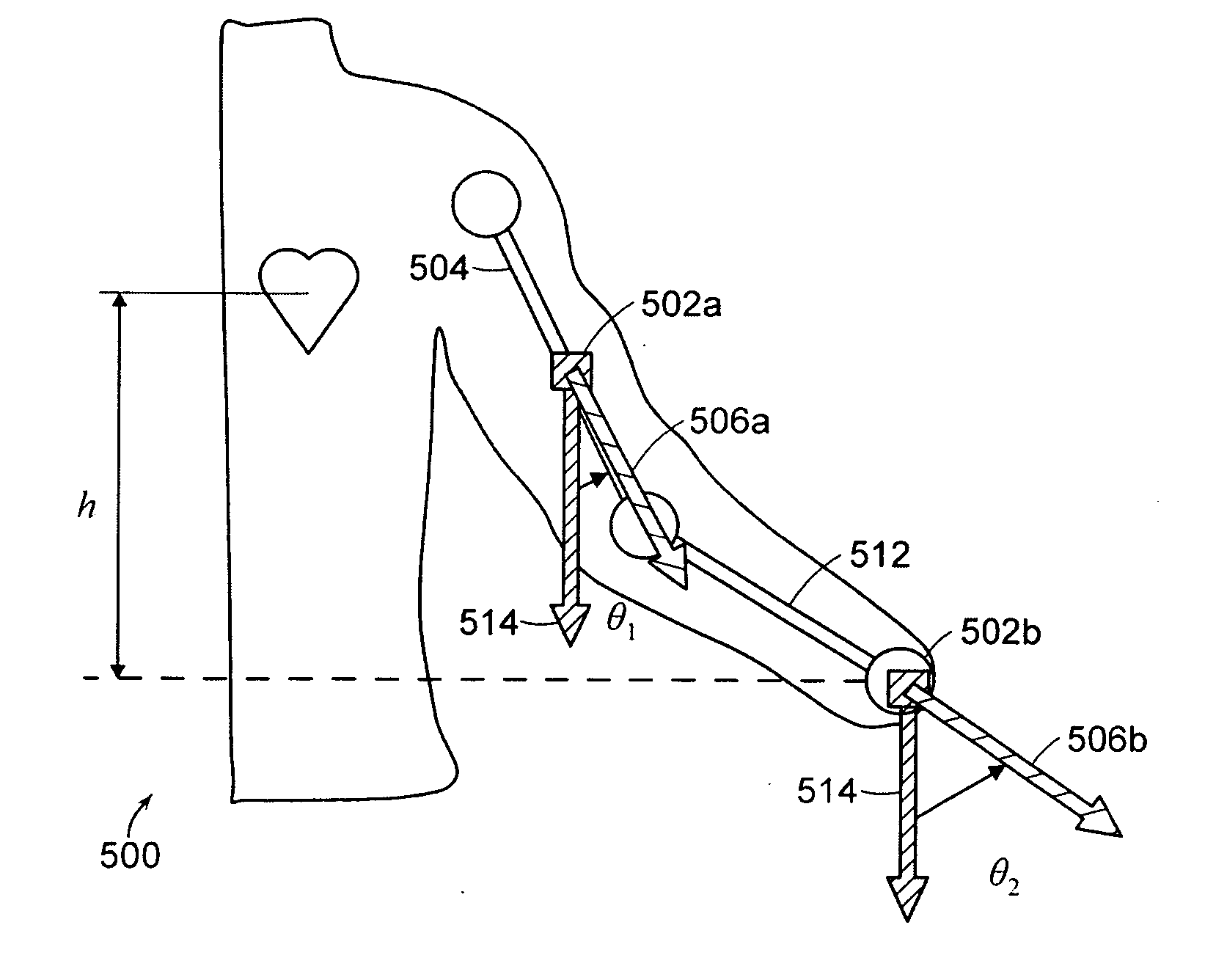
Methods and apparatus for measuring arterial blood pressure at an extremity of a subject. Arterial blood pressure is derived from a circulatory measurement performed on an extremity of a subject and the circulatory measurement is normalized to account for the instantaneous vertical displacement of the extremity. The vertical displacement of the extremity relative to the heart of the subject is obtained using the angular orientation of the subject's extremity. An improved photoplethysmograph can discriminate light traversing the extremity from ambient light on the basis of differential response. The apparatus may have a conducting polymer actuator for applying pressure to the extremity of the subject. A pulsatile waveform from the photoplethysmographic signal may be obtained at a plurality of externally applied pressures to calibrate the photoplethysmograph.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
InactiveUS20050015009A1Accurate assessmentAccurate monitoringMedical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
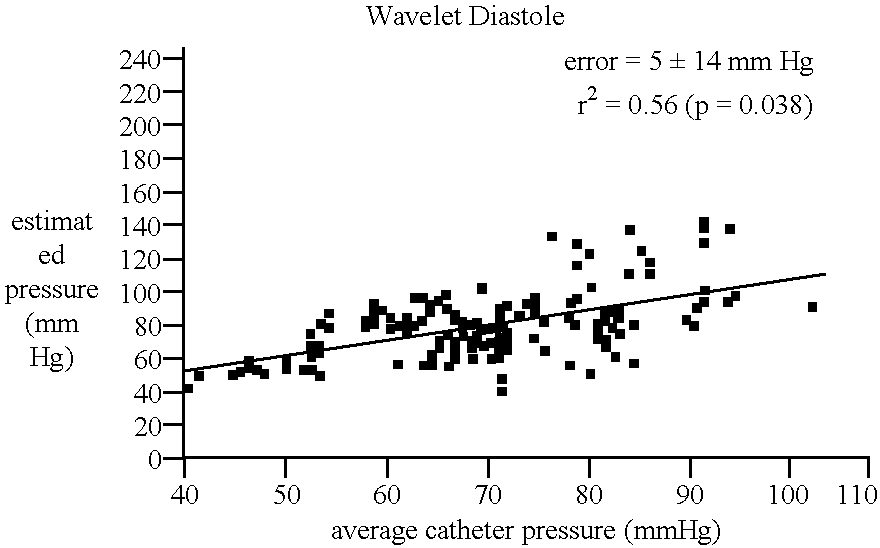
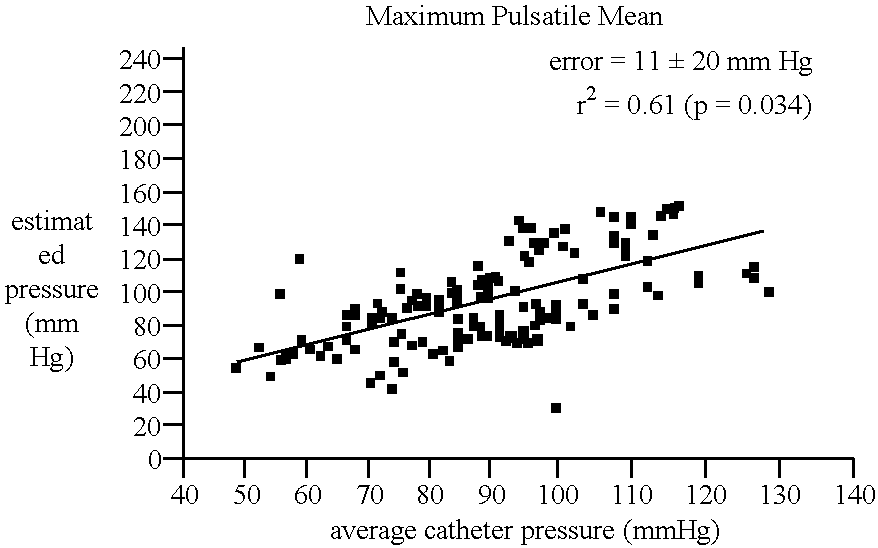
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and device for monitoring blood pressure
A device for continuously monitoring a user's arterial blood pressure has a sensor adapted to continuously detect the blood pressure and to generate signals representative thereof by contact with an external surface of the user's body at a location adjacent an artery. The sensor is securely held in operable contact with the user's body at the location. A microprocessor interprets the signals generated by the sensor to determine actual arterial blood pressure. The sensor includes a projecting portion for detecting and transmitting changes in blood pressure, wherein the projecting portion is adapted to effect at least partial occlusion of the artery at the location.
Owner:HEALTHSTATS INT PTE
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Optical apparatus and method of use for non-invasive tomographic scan of biological tissues
The present invention relates to a non-invasive optical system equipped with optical tomographic scanning method and algorithm for quantifying scattering and absorption properties and chromophore concentrations of highly scattering medium such as biological tissues, for 3D mapping and imaging reconstruction of the spatial and temporal variations in such properties. The invention further relates to a method and an apparatus for simultaneous measurement of concentrations of biochemical substances and blood oxygen saturation inside a biological tissue and arterial blood.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH +1
Method and apparatus for the noninvasive determination of arterial blood pressure
InactiveUS6514211B1Blood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsUltrasonic sensorTransmural pressure
Owner:TENSYS MEDICAL INC
Non-invasive blood component measurement system
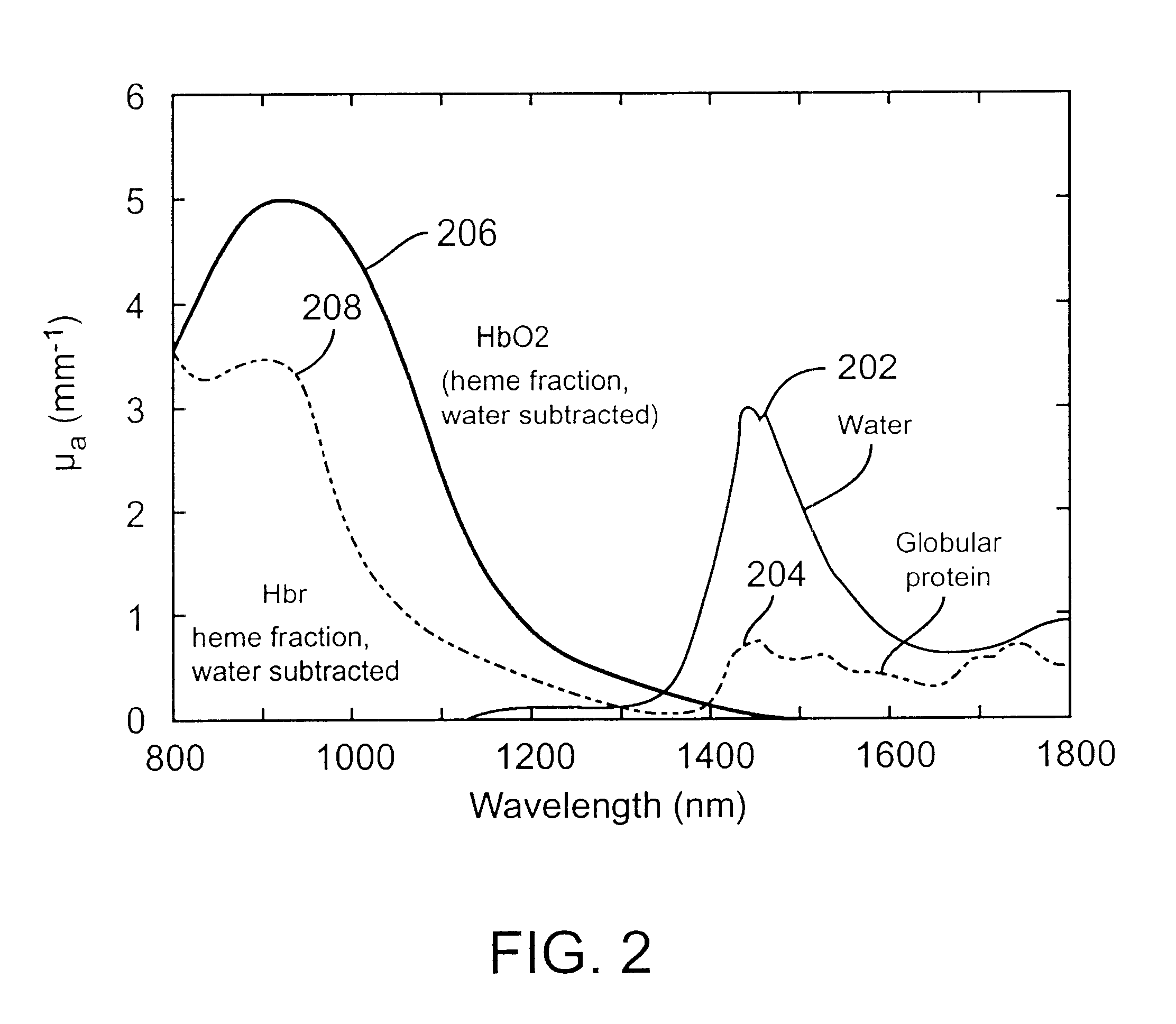
Non-invasive, optical apparatus and methods for the direct measurement of hemoglobin derivatives and other analyte concentration levels in blood using diffuse reflection and transmission spectroscopy in the wavelength region 400-1350 nm which includes the transparent tissue window from approximately 610 to 1311 nanometers and, using diffuse reflection spectroscopy, the mid-infrared region from 4.3-12 microns in wavelength. Large area light collection techniques are utilized to provide a much larger pulsate signal than can be obtain with current sensor technology. Sensors used in separate or simultaneous precision measurements of both diffuse reflection and transmission, either separately or simultaneously, from pulsate, blood-perfused tissue for the subsequent determination of the blood analytes concentrations such as arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2), carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), oxyhemoglobin (OHb), deoxyhemoglobin (dOHb), methemoglobin (metHb), water (H2O), hematocrit (HCT), glucose, cholesterol and proteins such as albumin and other analytes components.
Owner:3WAVE OPTICS
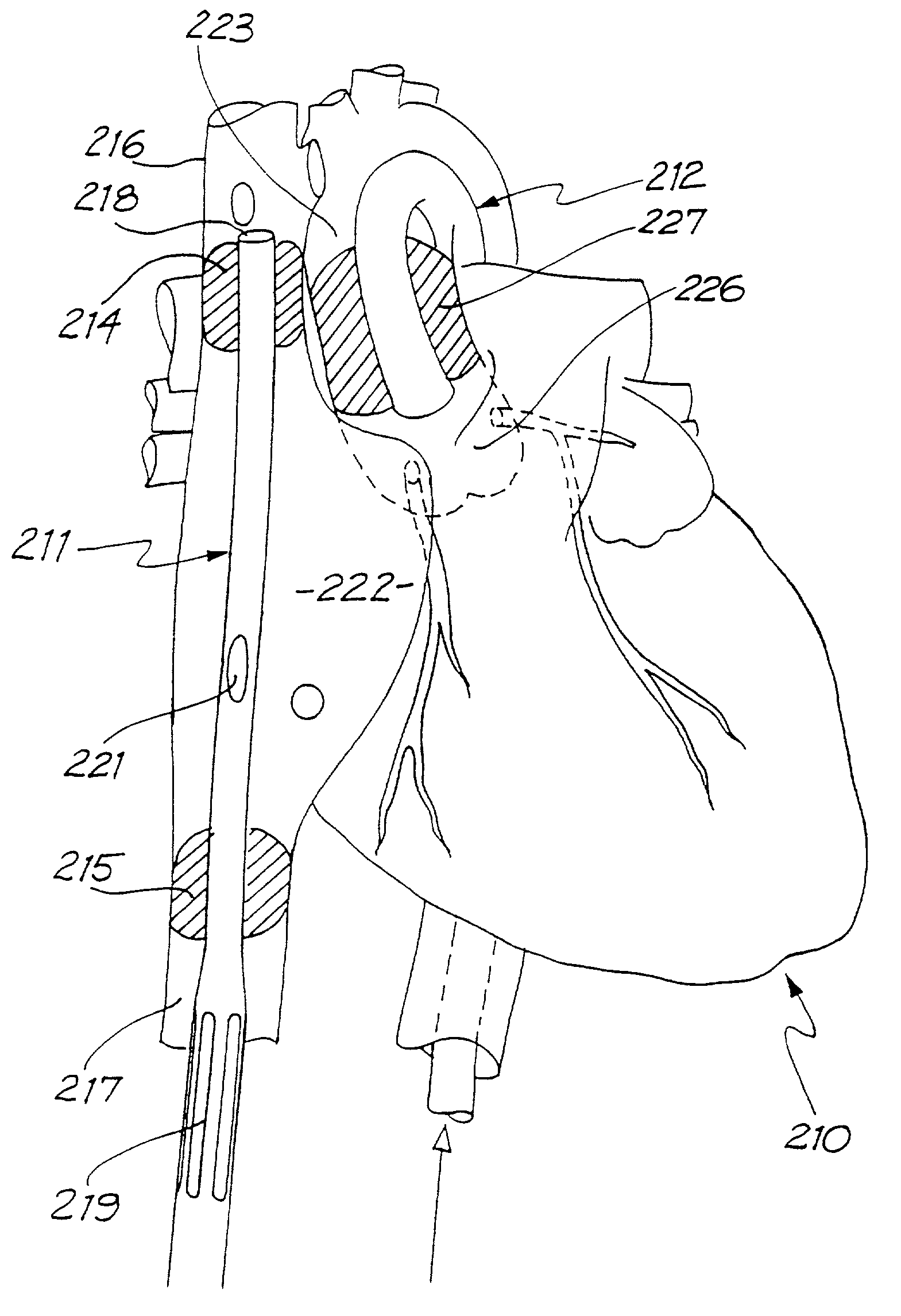
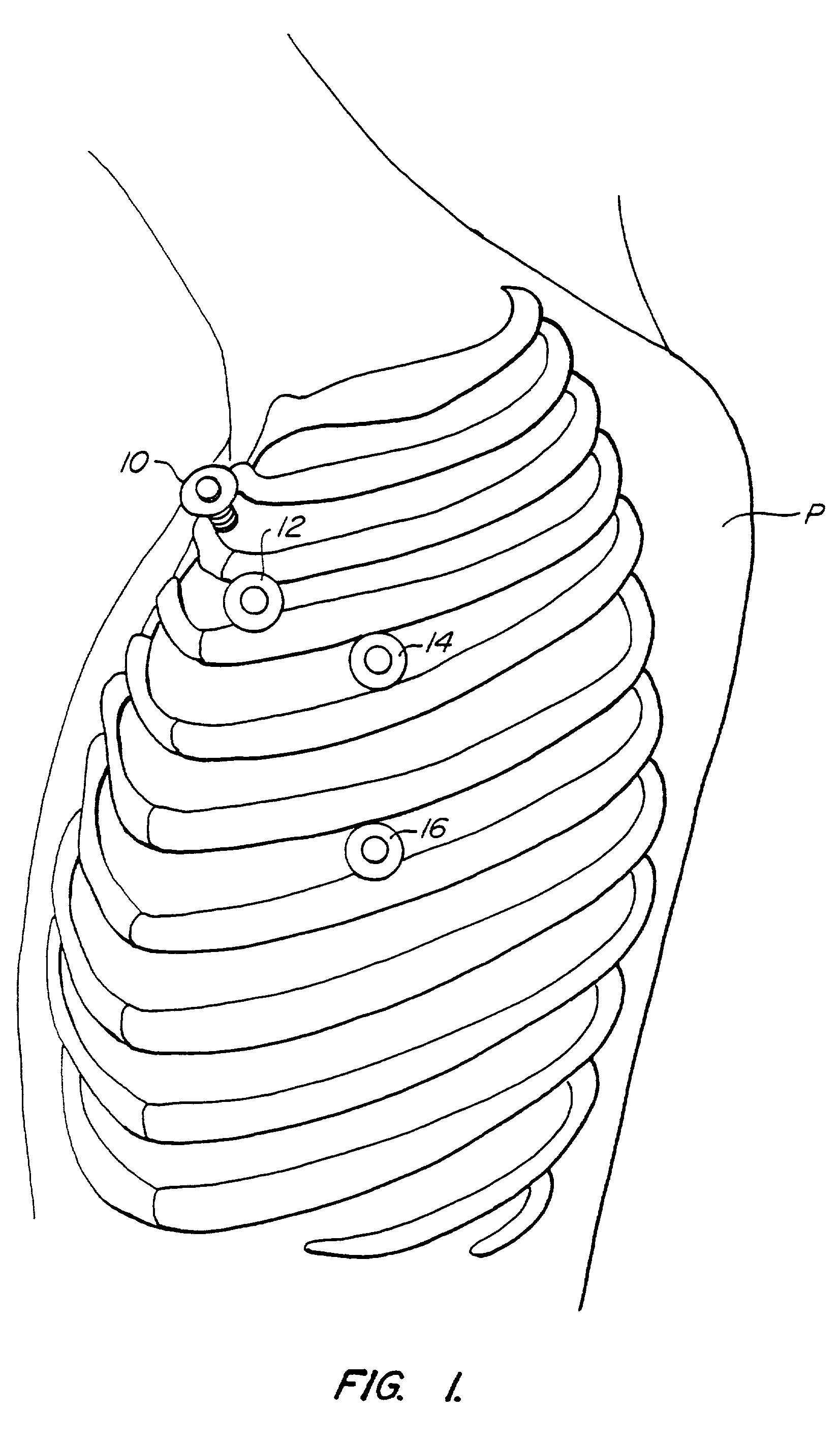
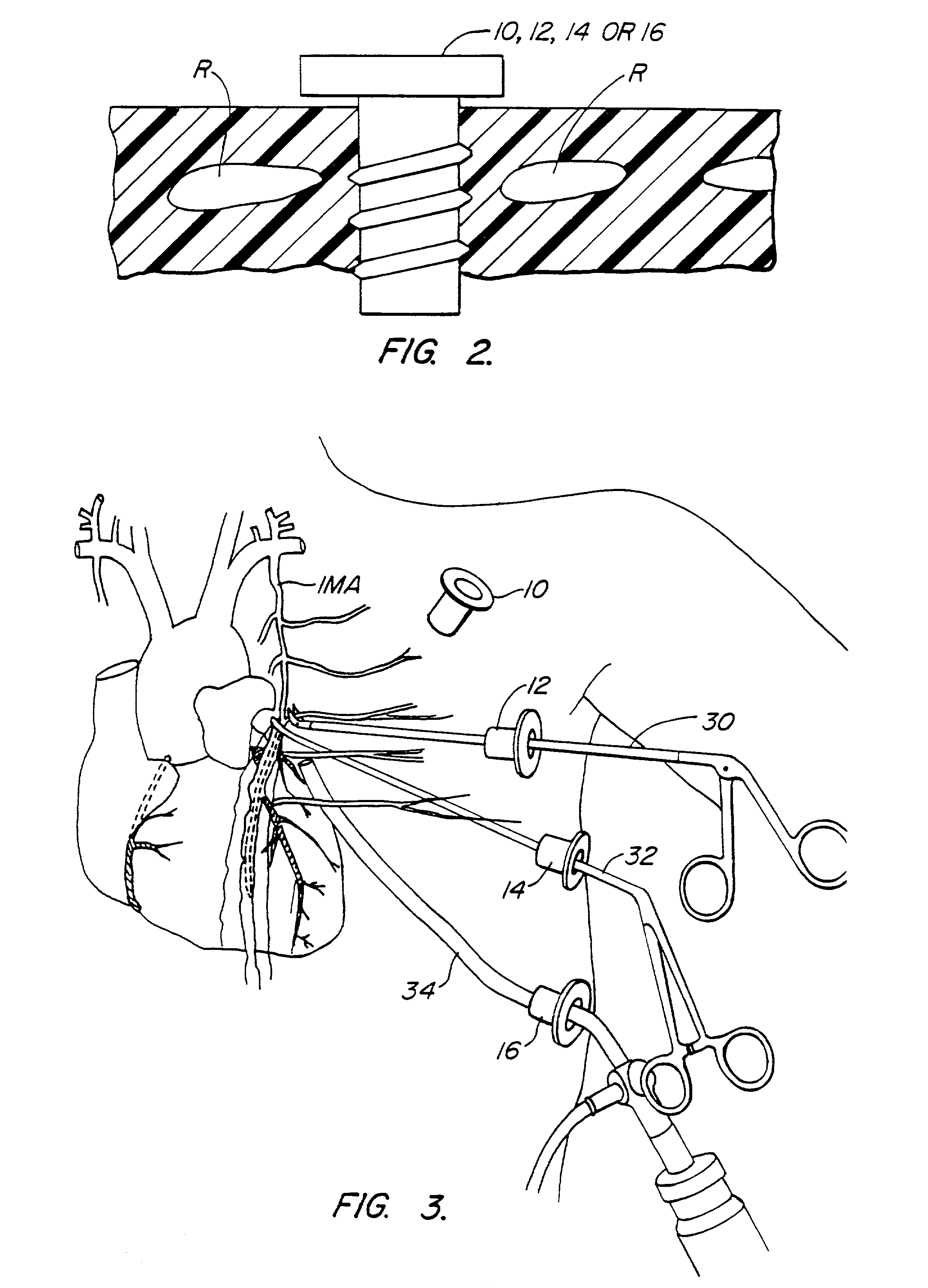
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6027476AImprove isolationReduce complicationsSuture equipmentsCannulasThoracoscopeHeart operations
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Fetal pulse oximetry
InactiveUS7047055B2Minimize measurement errorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsObstetricsPulse oximetry
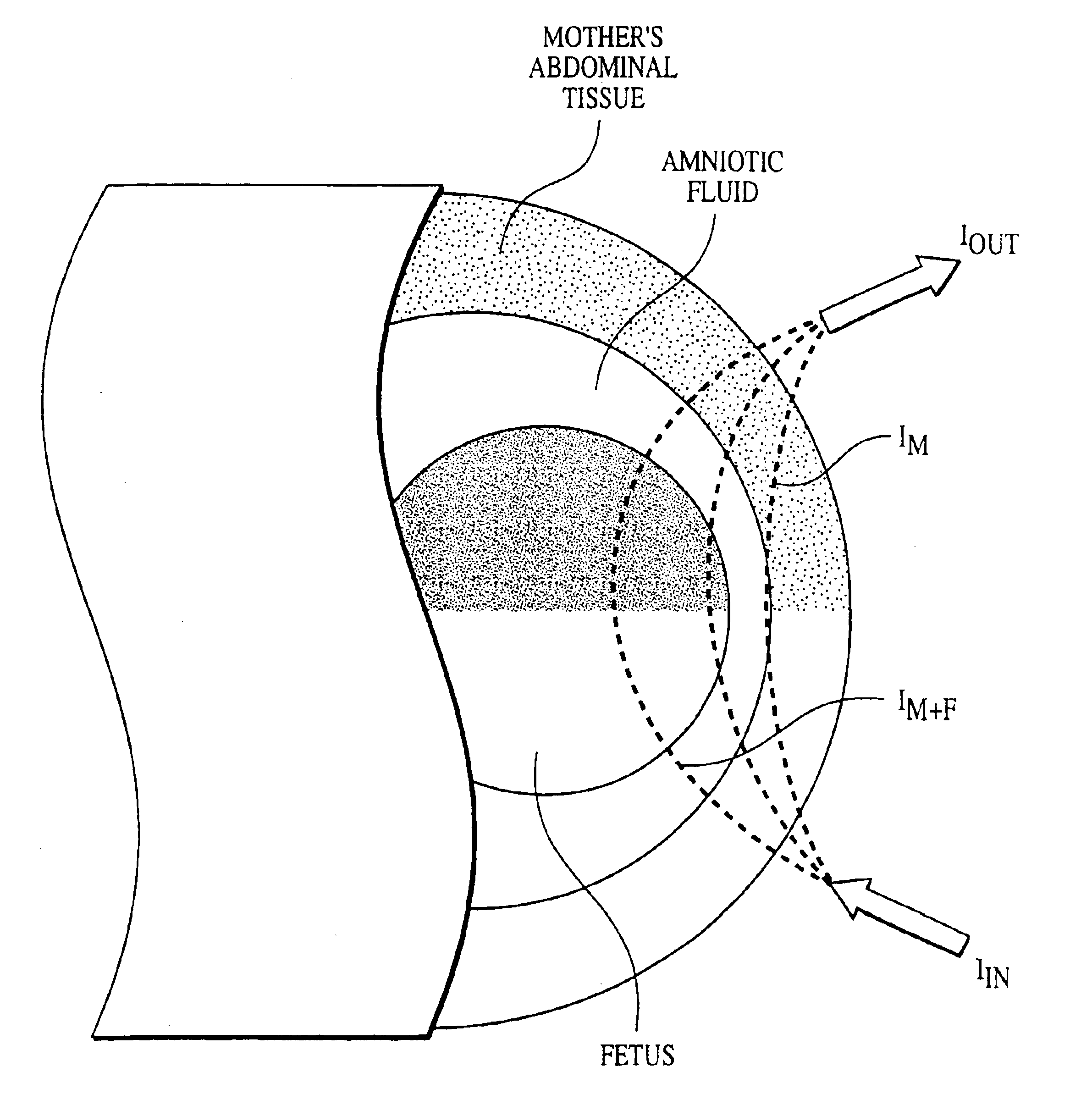
A fetal blood pulse oximetry method and apparatus using a first wavelength of light at about 655 to 705 nm and a second wavelength of light at about 820 to 900 nm. Measurements are taken through a mother's abdomen. Processing is performed to extract absorption information related to fetal arterial blood with calculation of fetal oxygen saturation from the extracted data.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for the noninvasive assessment of hemodynamic parameters including blood vessel location
InactiveUS20020055680A1Blood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsUltrasonic sensorTherapeutic Devices
A method and apparatus for determining the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of a subject during tonometric conditions. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises one or more pressure and ultrasound transducers placed over the radial artery of a human subject's wrist, the latter transmitting and receiving acoustic energy so as to permit the measurement of blood velocity during periods of variable compression of the artery. In another aspect of the invention, a wrist brace useful for measuring blood pressure using the aforementioned apparatus is disclosed. In yet another aspect of the invention, backscattered acoustic energy is used to identify the location of the blood vessel of interest, and optionally control the position of measurement or treatment equipment with respect thereto.
Owner:TENSYS MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Pulse oximetry sensor and technique for using the same on a distal region of a patient's digit
ActiveUS20060224058A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOxygen Saturation MeasurementDistal portion
A sensor may be placed on a distal portion of a patient's finger or toe to obtain pulse oximetry measurements. The distal portion of a digit contains few if any large vascular structures that could adversely affect pulse oximetry measurements, but the distal portion does contain microvasculature that carries arterial blood that facilitates pulse oximetry measurements. The sensor may include an emitter and a detector that are spaced apart by an appropriate distance so that they may be located on the distal portion of a patient's digit during pulse oximetry measurements.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods for measuring blood pressure with automatic compensations
Disclosed is a method for measuring an arterial blood pressure of a subject comprising detecting a pulse-wave-related signal of the subject; extracting a feature from the signals; determining a factor that can affect the arterial blood pressure of the subject; and determining the arterial blood pressure based on the feature with an automatic compensation for the factors. The disclosed method reduces the error in measuring the blood pressure based on characteristics of the pulse-wave-related signals.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS20060029578A1Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
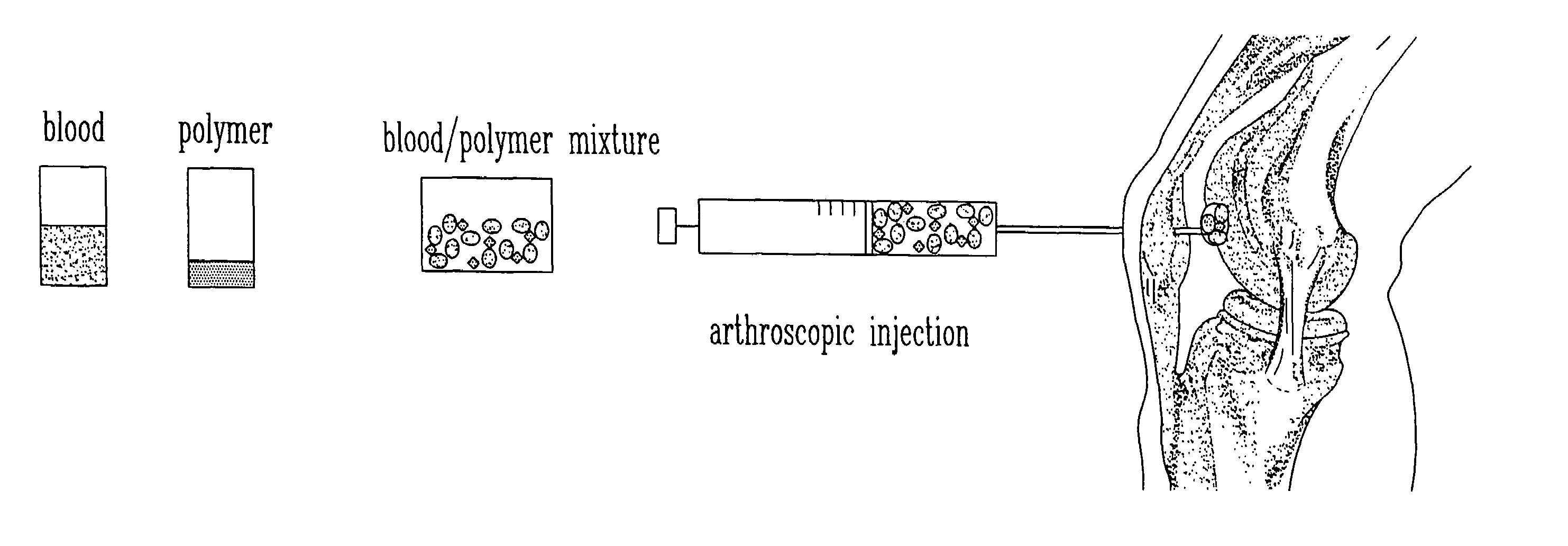
The present invention relates to a new method for repairing human or animal tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, ligament, tendon, bone, skin, cornea, periodontal tissues, abscesses, resected tumors, and ulcers. The method comprises the step of introducing into the tissue a temperature-dependent polymer gel composition such that the composition adhere to the tissue and promote support for cell proliferation for repairing the tissue. Other than a polymer, the composition preferably comprises a blood component such as whole blood, processed blood, venous blood, arterial blood, blood from bone, blood from bone-marrow, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta blood, erythrocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin and platelet rich plasma. The present invention also relates to a new composition to be used with the method of the present invention.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
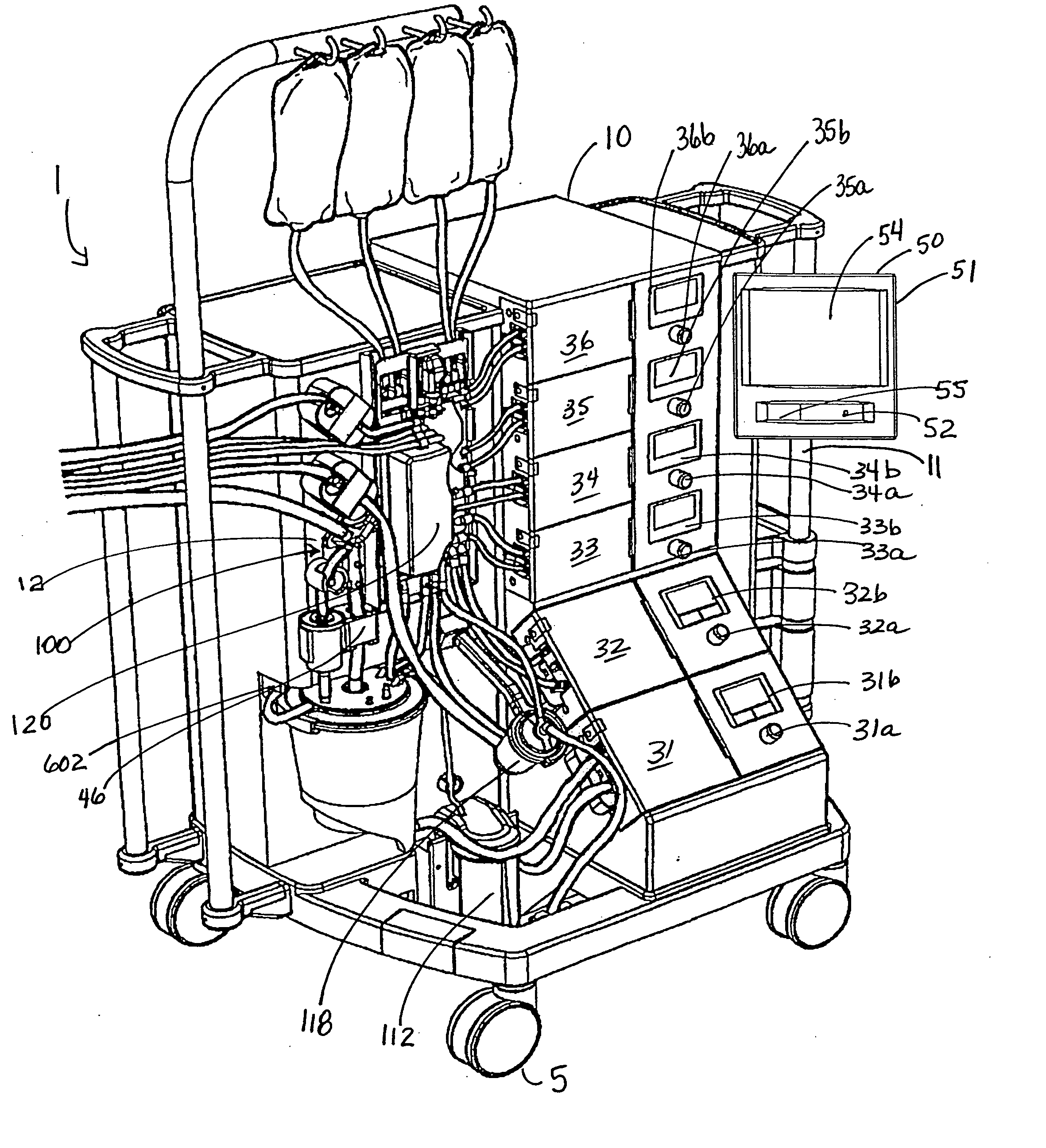
Blood perfusion system
ActiveUS20060167400A1Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesVenous bloodDisplay device
An extracorporeal blood perfusion system includes a disposable assembly and a control unit having a control interface region. The interface region includes pump assemblies for selective pumping of venous blood, arterial blood, cardioplegia solution, suctioned blood and blood removed from the left ventricle. Valve assemblies control the flow of fluids through the assembly and to / from the patient and sensors monitor various fluid parameters including temperature and pressure within the various fluid circuits. The user interface is a functional screen interface for effecting the operation of the control unit and valve assemblies. The screen interface may be a touch screen having objects that corresponds to the component interface region. The display may be selectively controlled to provide graphic depictions of disposable assembly components with corresponding narrative instructions.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
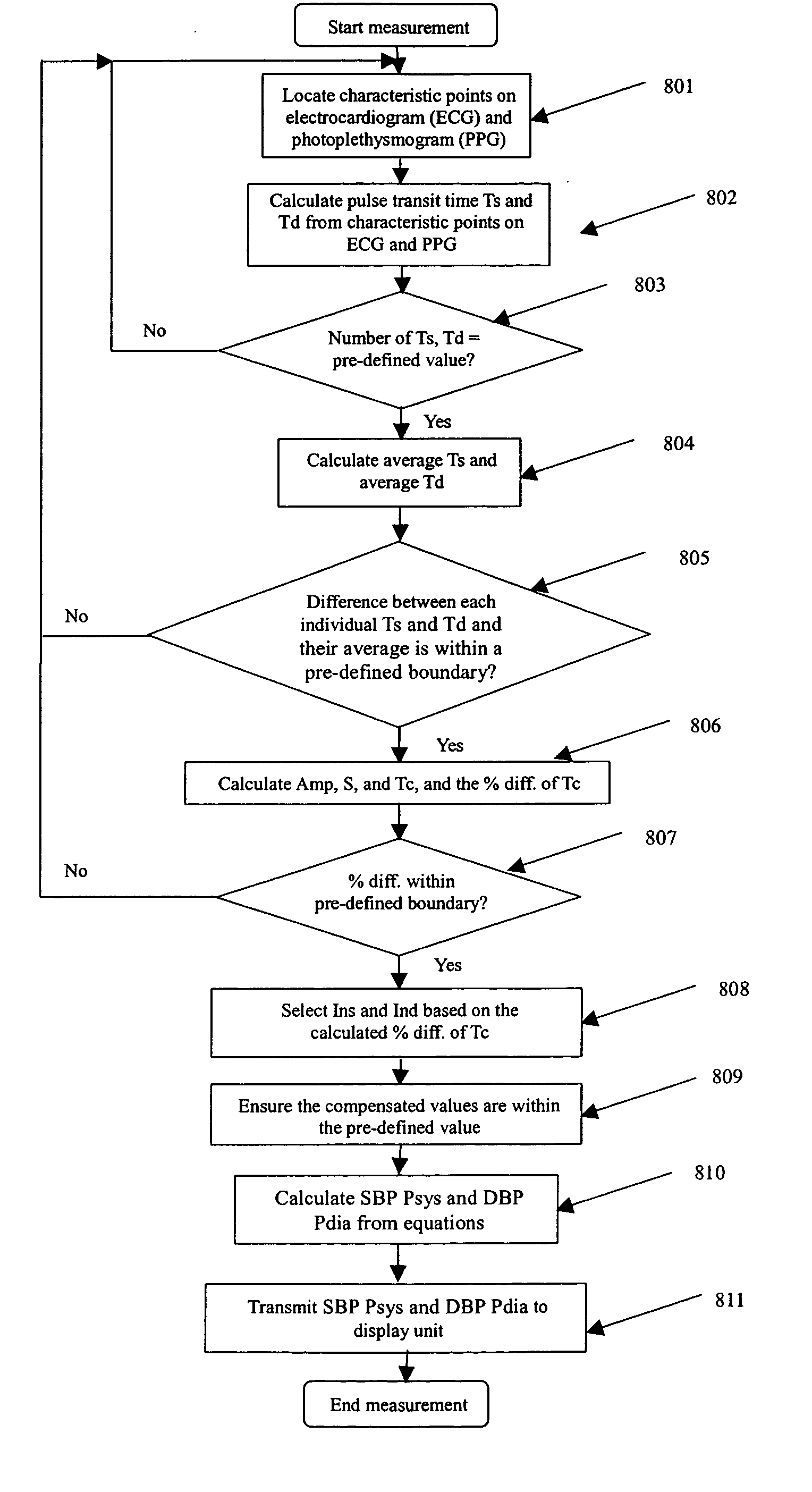
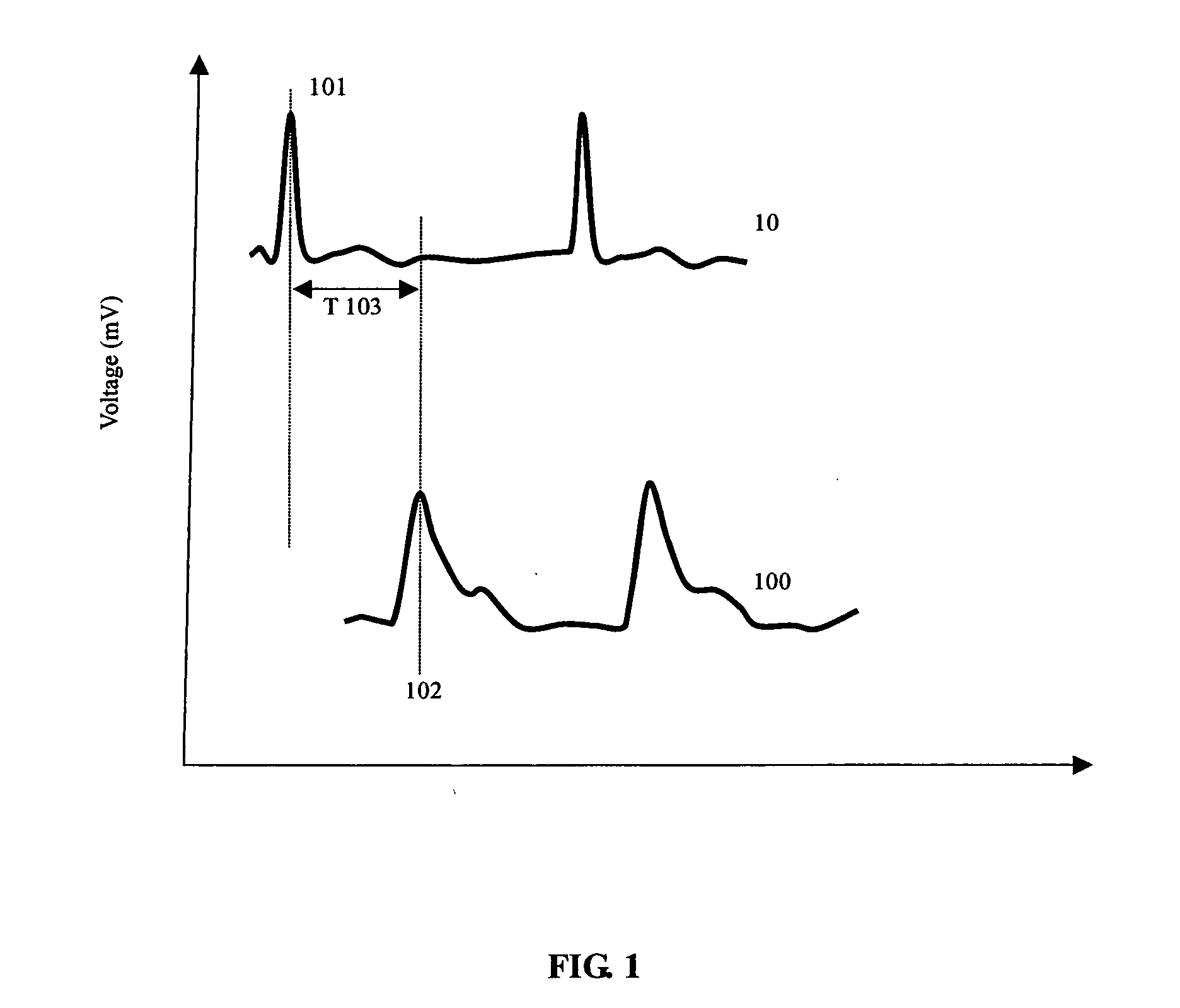
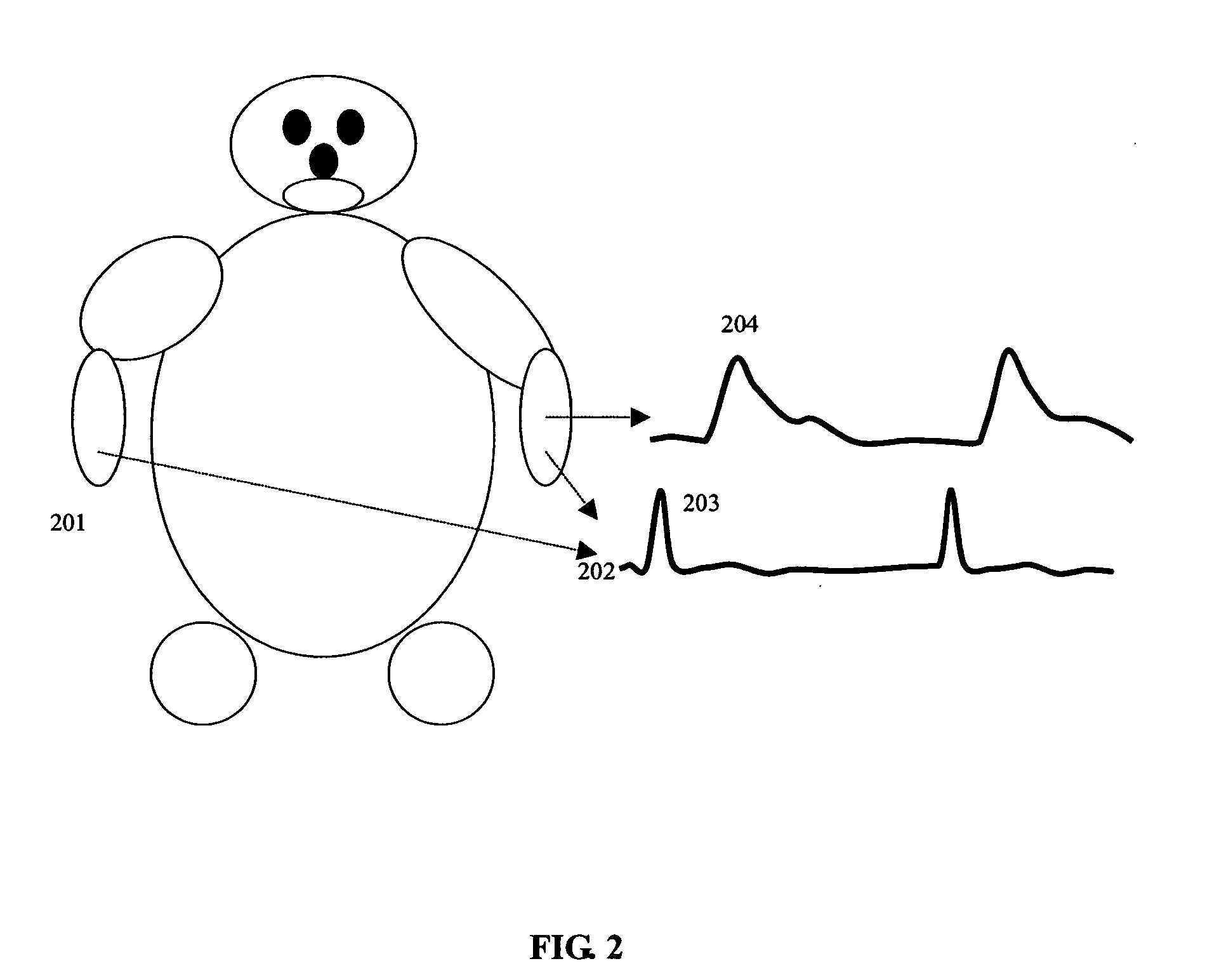
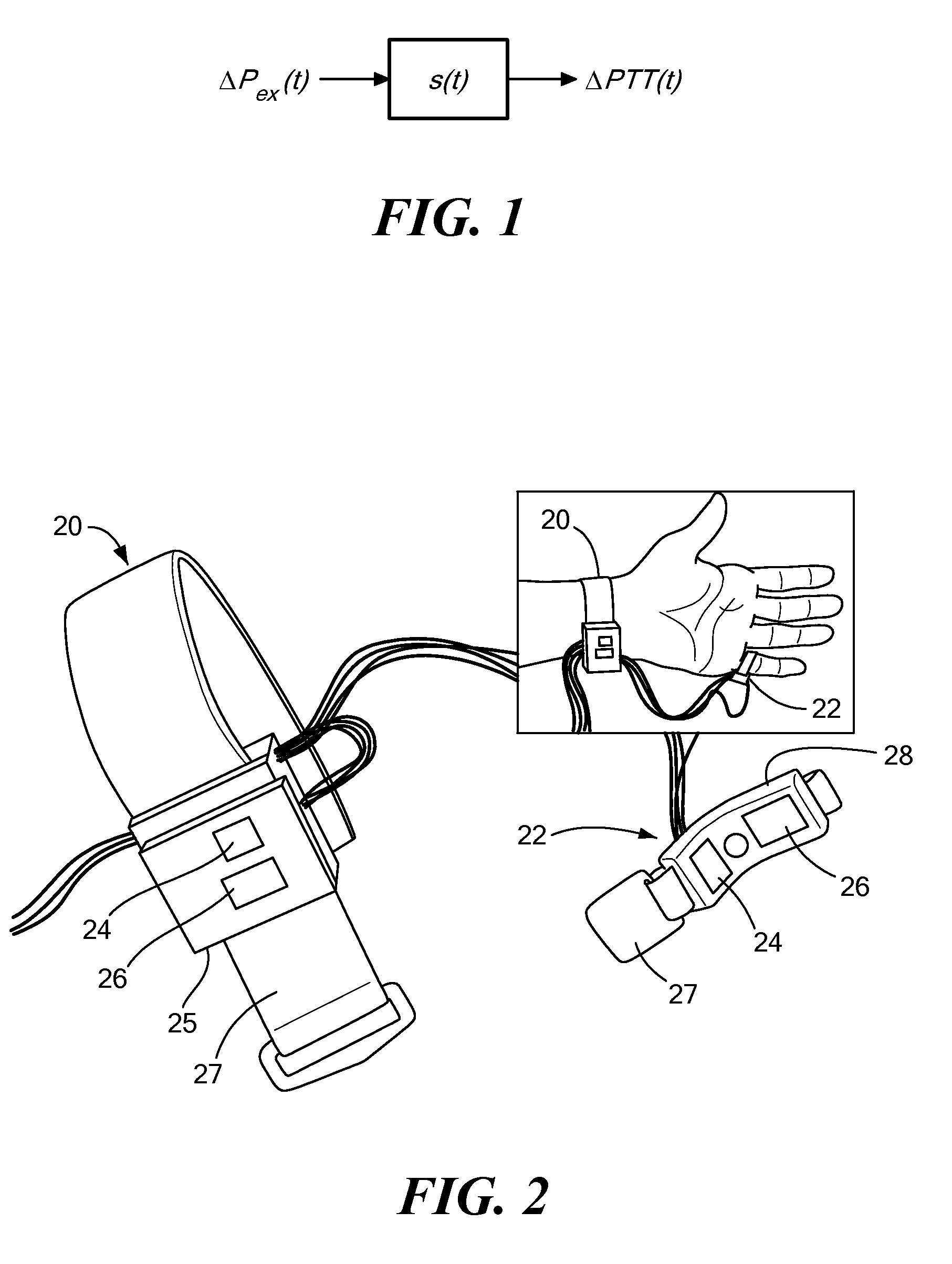
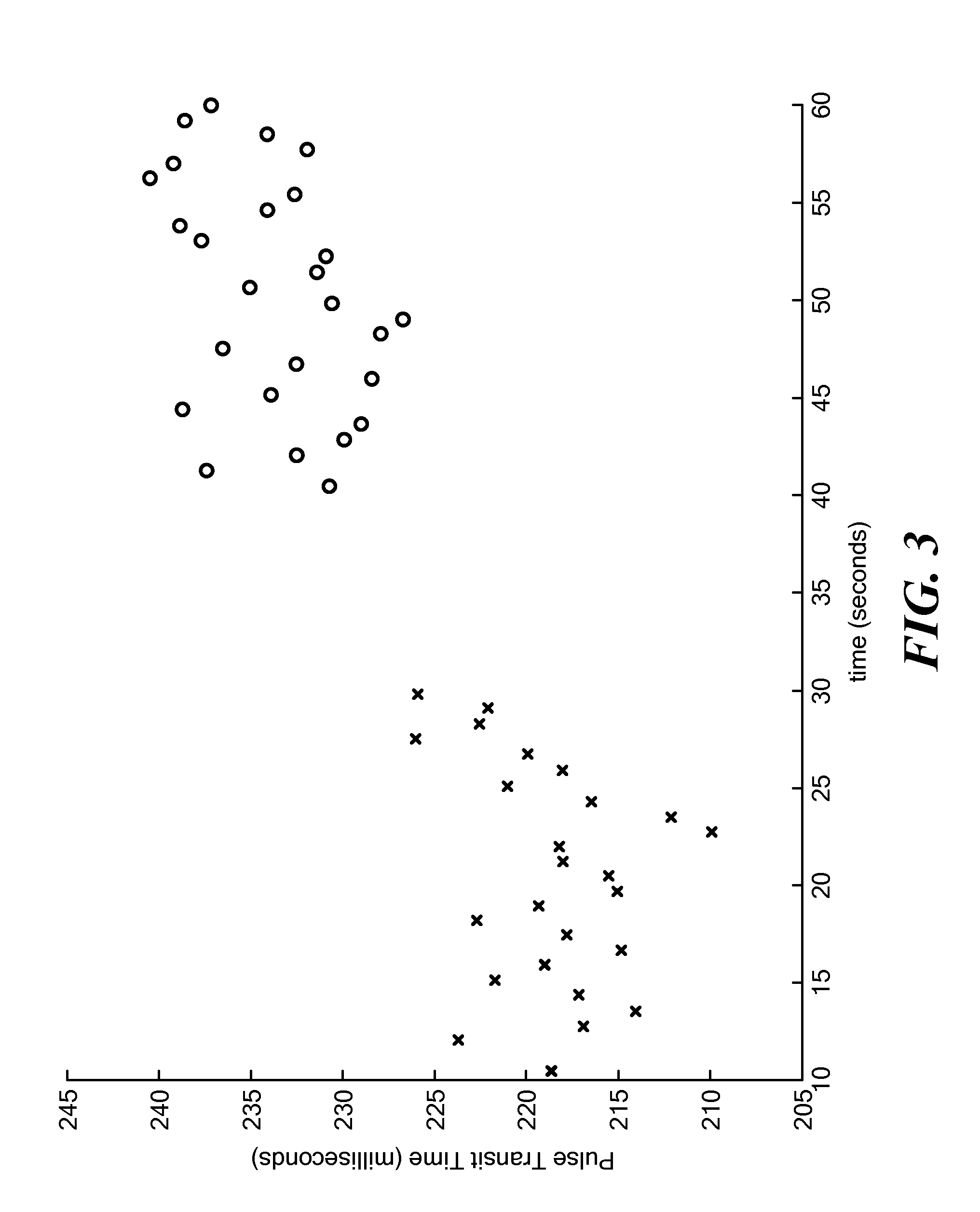
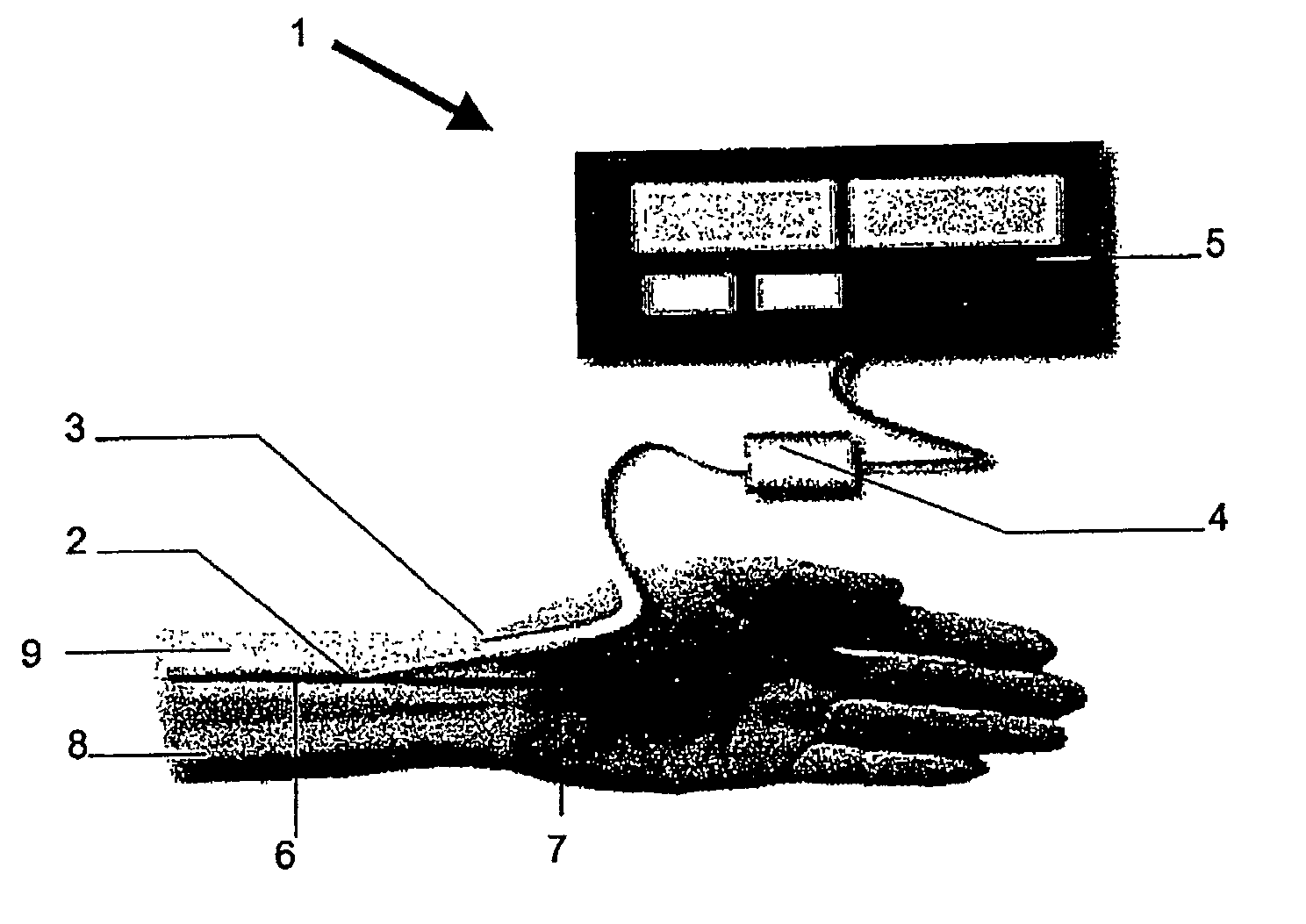
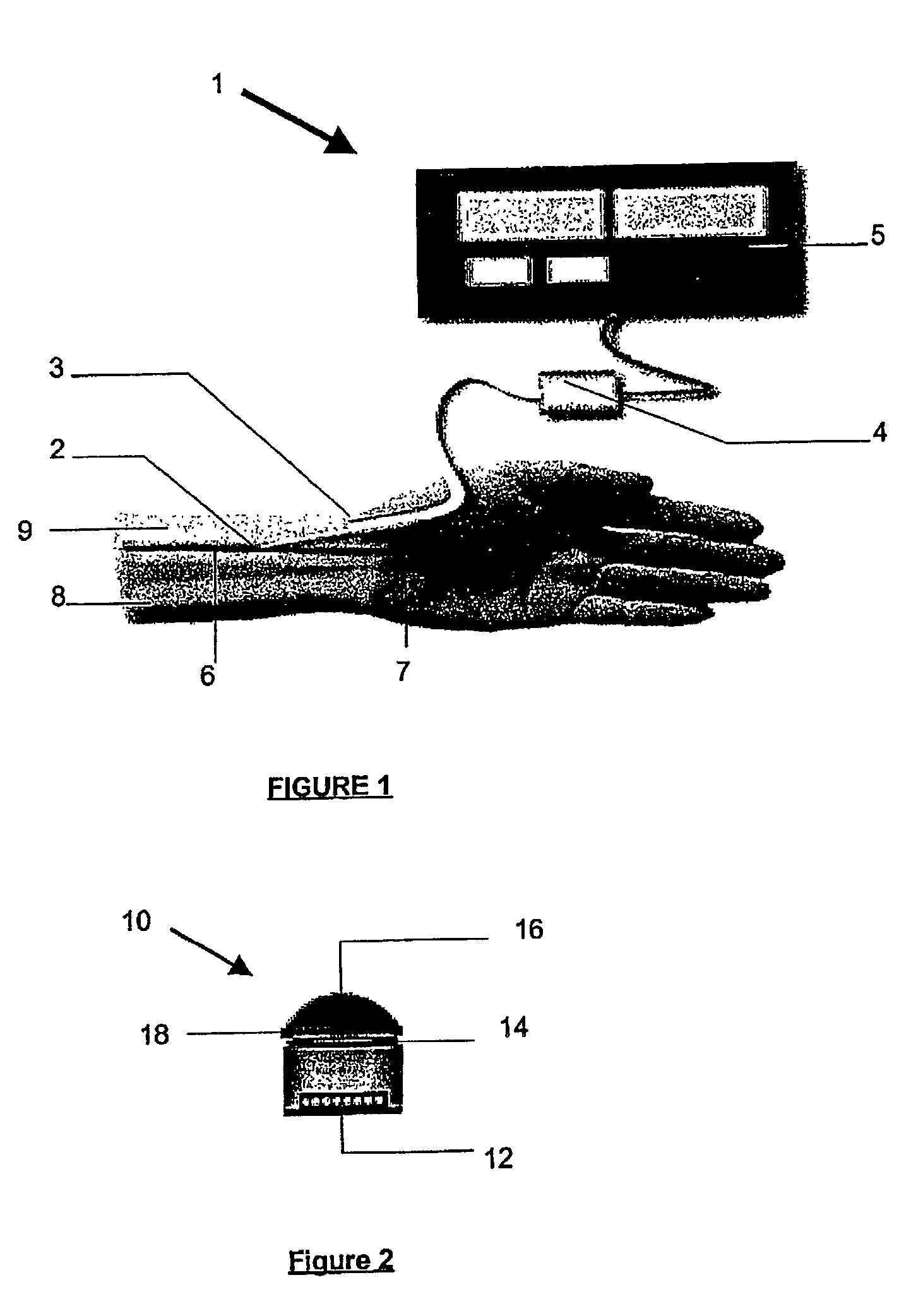
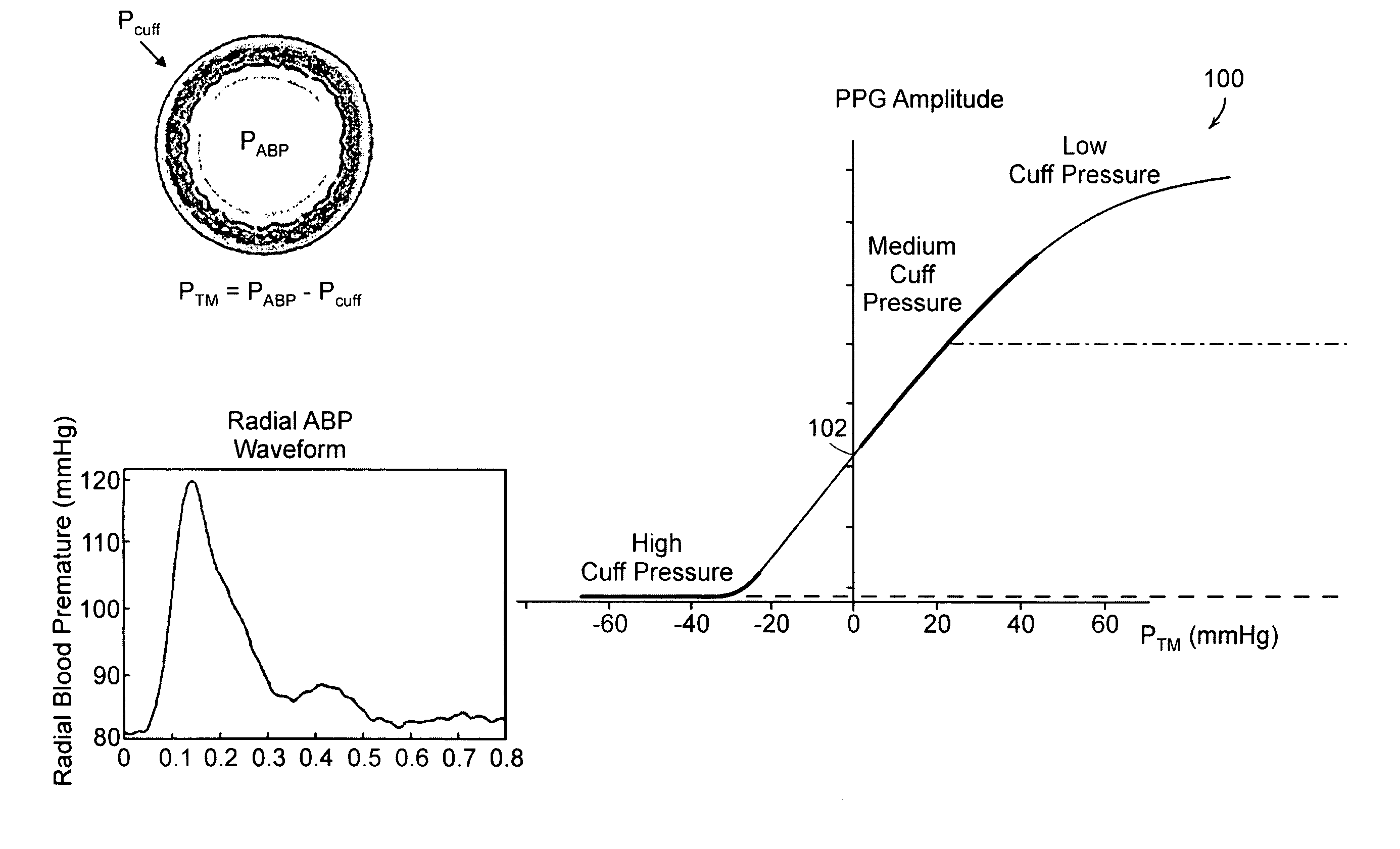
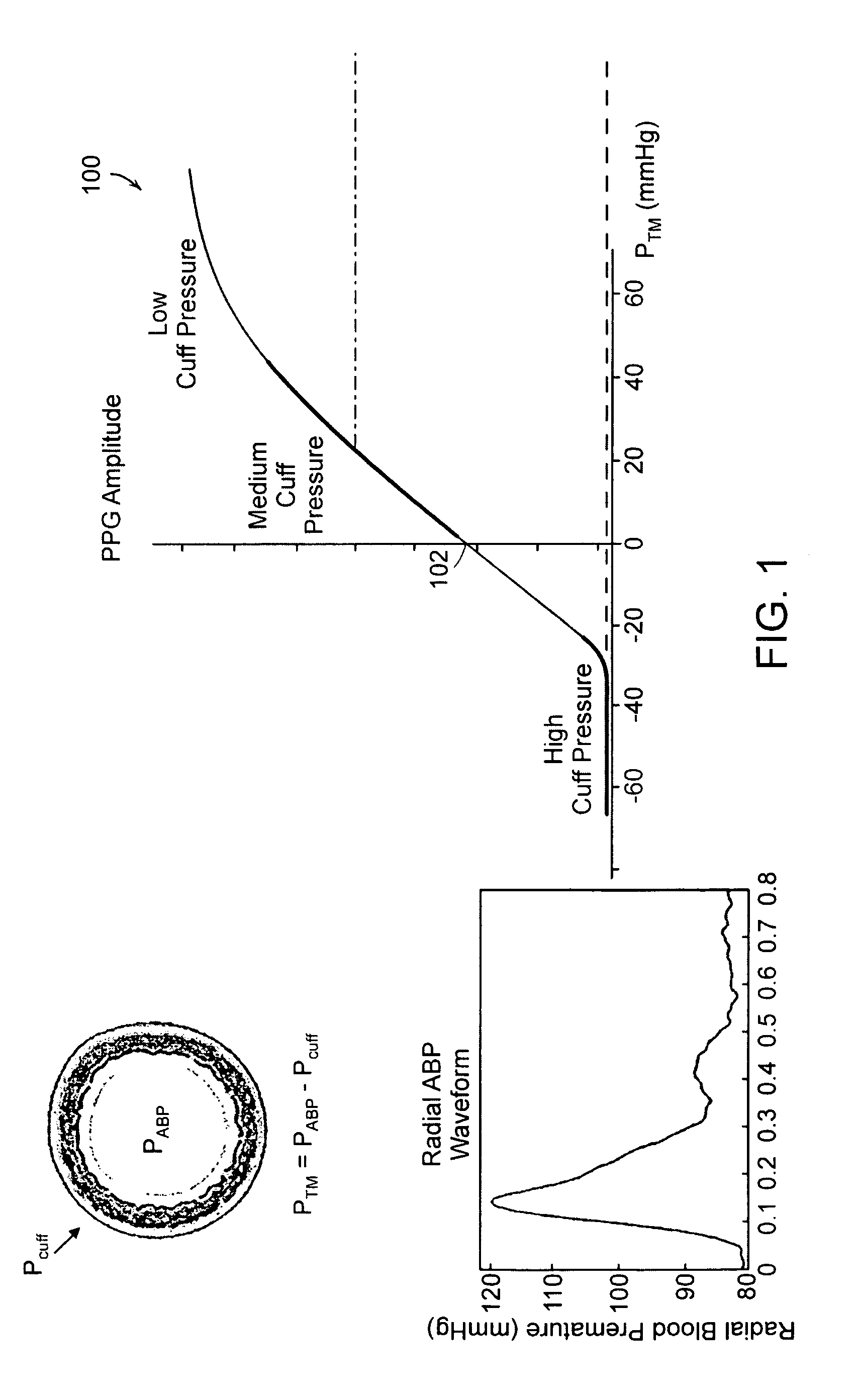
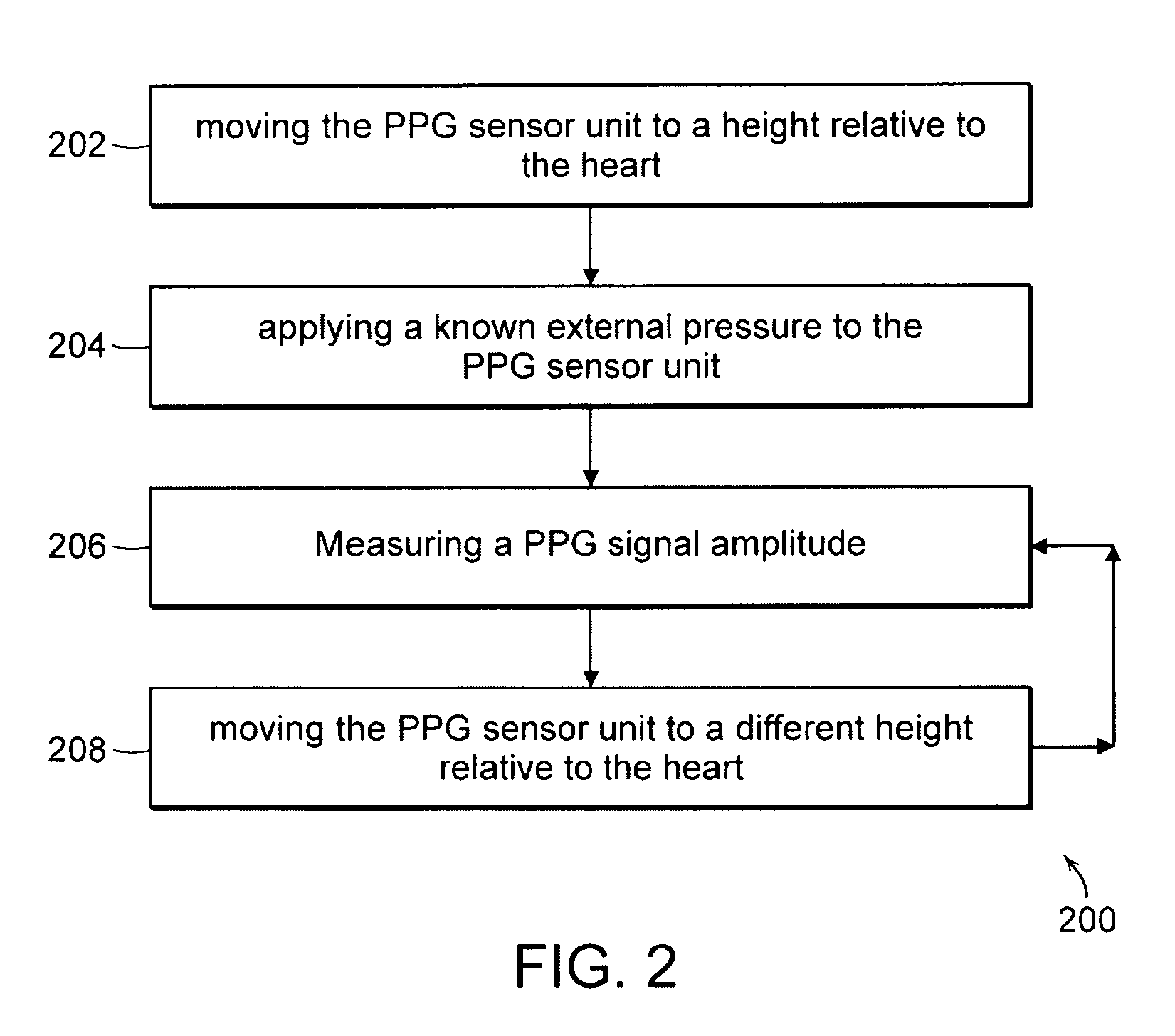
Calibration of Pulse Transit Time Measurements to Arterial Blood Pressure using External Arterial Pressure Applied along the Pulse Transit Path
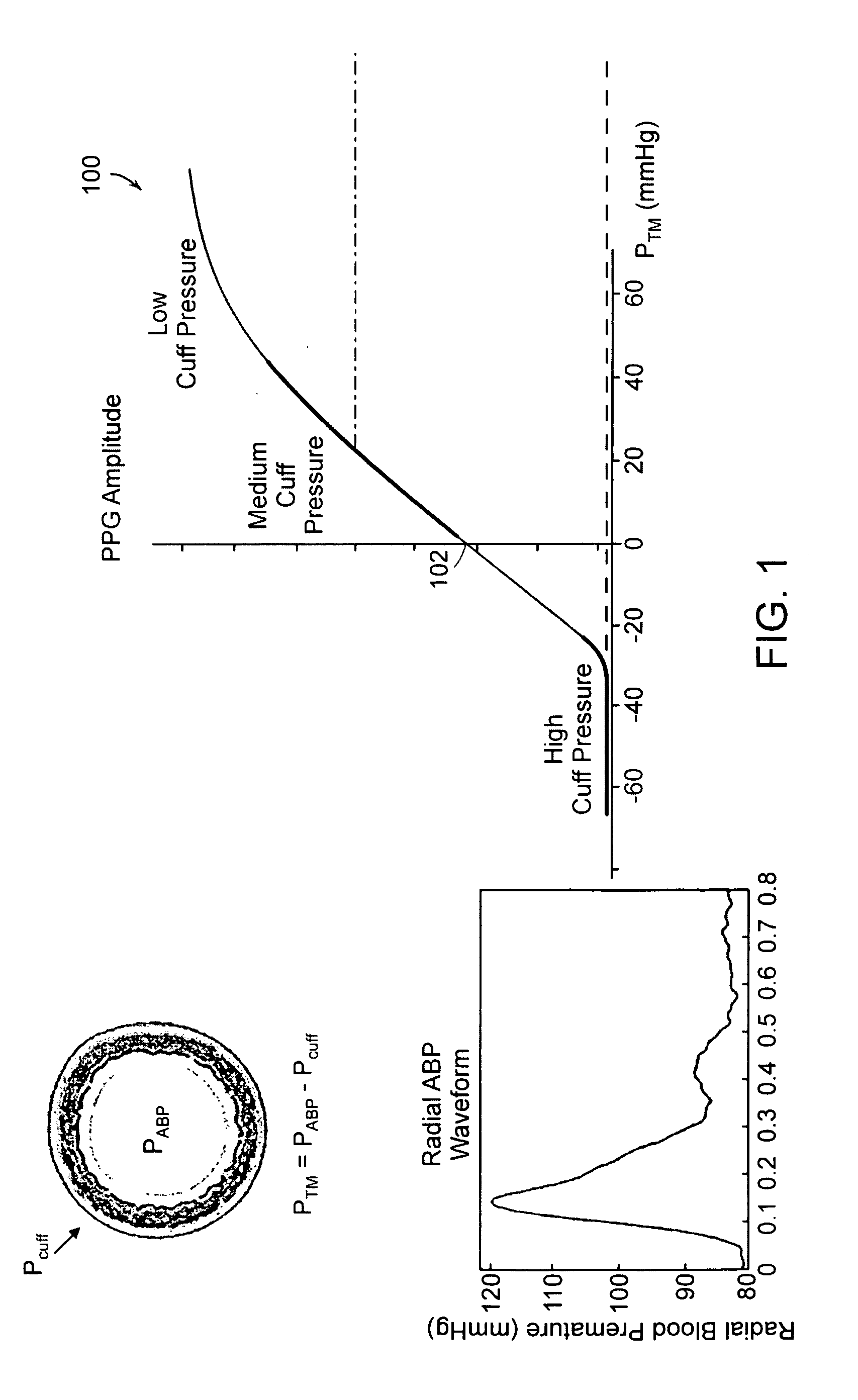
An apparatus and methods for adaptive and autonomous calibration of pulse transit time measurements to obtain arterial blood pressure using arterial pressure variation. The apparatus and methods give pulse transit time (PTT) devices an ability to self-calibrate. The methods apply a distributed model with lumped parameters, and may be implemented, for example, using pulse transit time measurements derived from a wearable photoplethysmograph (PPG) sensor architecture with an intervening pressurizing mechanism.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and device for monitoring blood pressure
A device for continuously monitoring a user's arterial blood pressure has a sensor adapted to continuously detect the blood pressure and to generate signals representative thereof by contact with an external surface of the user's body at a location adjacent an artery. The sensor is securely held in operable contact with the user's body at the location. A microprocessor interprets the signals generated by the sensor to determine the actual arterial blood pressure. The sensor includes a projecting portion for detecting and transmitting changes in blood pressure, wherein the projecting portion is adapted to effect at least partial occlusion of the artery at the location.
Owner:HEALTHSTATS INT PTE
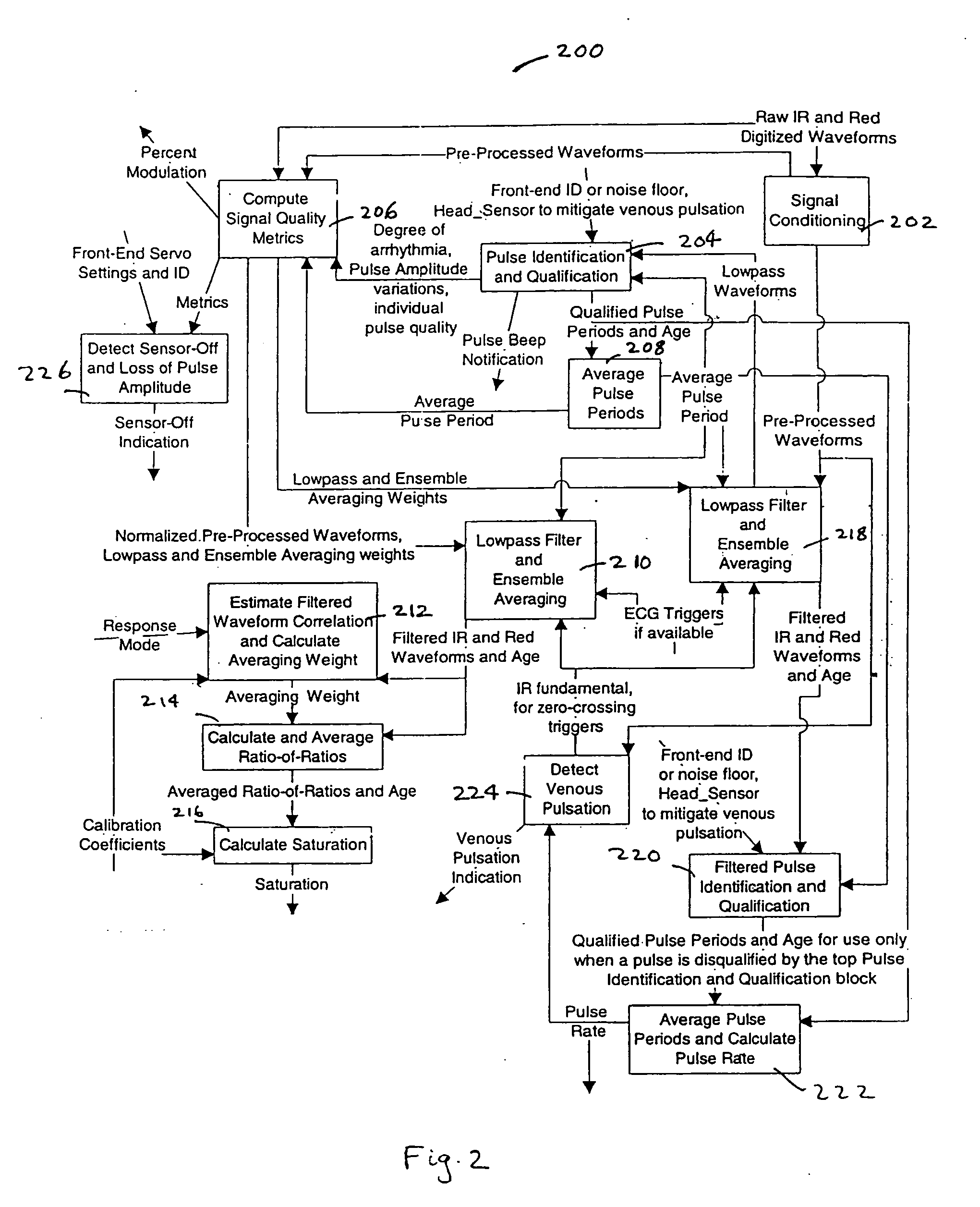
Method and apparatus for optical detection of mixed venous and arterial blood pulsation in tissue
A method and device for detecting the presence of mixed venous and arterial blood pulsation in tissue, including receiving first and second electromagnetic radiation signals from a blood perfused tissue portion corresponding to infrared and red wavelengths of light, obtaining a measure of a phase difference between the first and second electromagnetic radiation signals, comparing the measure with a threshold value to form a comparison, and detecting the presence or absence of venous pulsation using the comparison.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Wearable blood pressure sensor and method of calibration
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
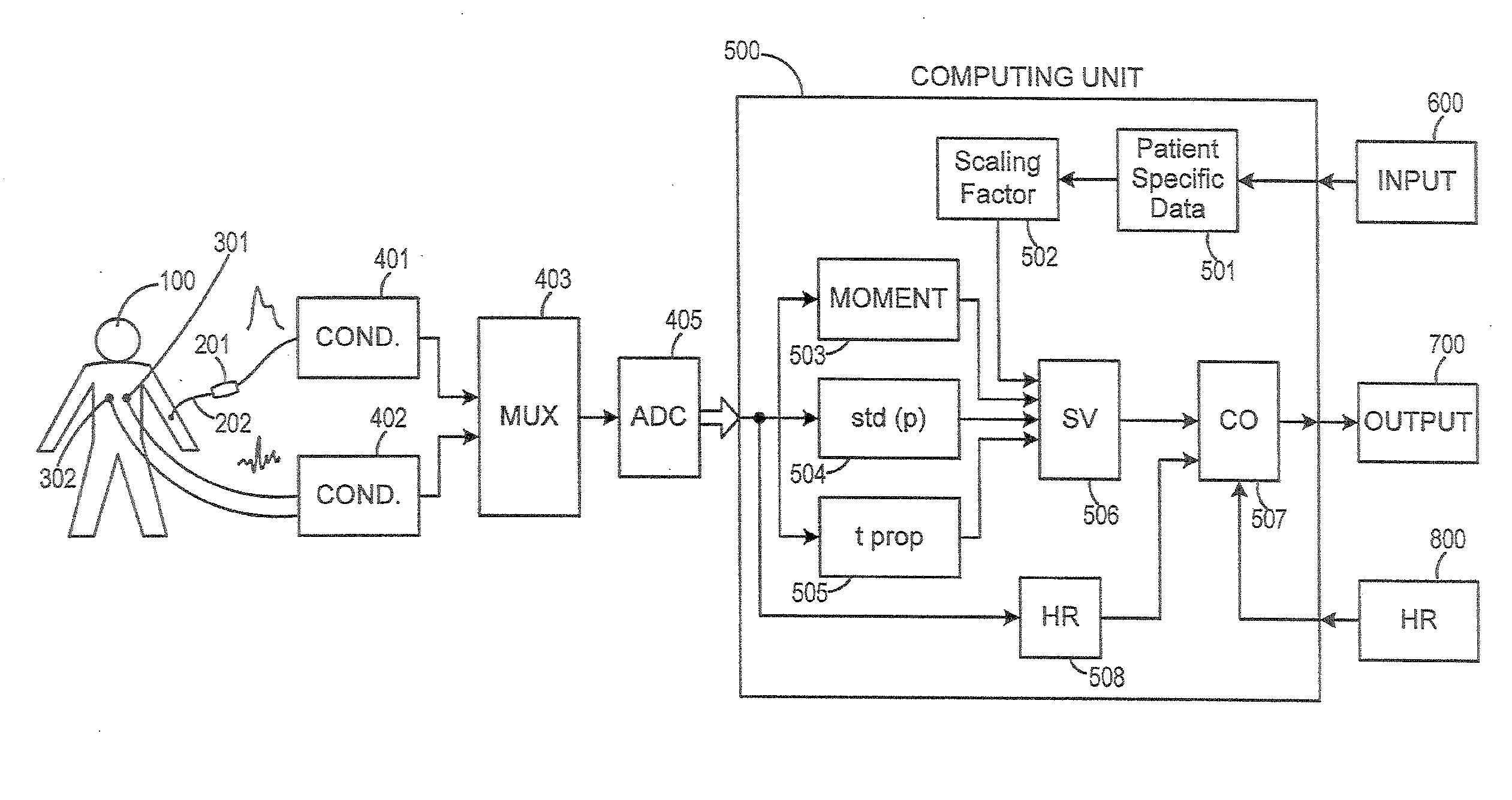
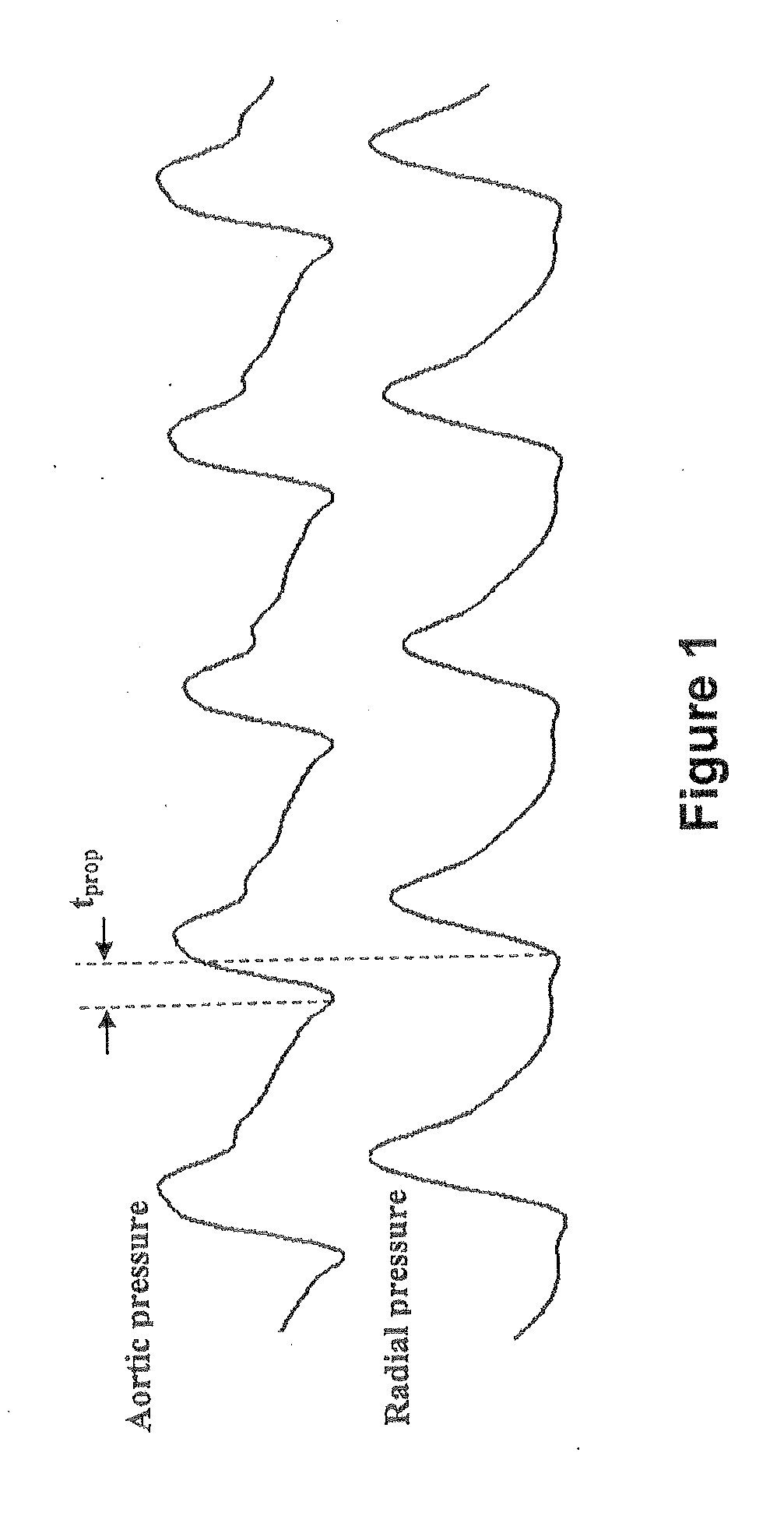
Method and Apparatus for Continuous Assessment of a Cardiovascular Parameter Using the Arterial Pulse Pressure Propagation Time and Waveform
InactiveUS20080015451A1ElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesCardiac cycleArterial pulse pressure
A method and apparatus for determining a cardiovascular parameter including receiving an input signal corresponding to an arterial blood pressure measurement over an interval that covers at least one cardiac cycle, determining a propagation time of the input signal, determining at least one statistical moment of the input signal, and determining an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter using the propagation time and the at least one statistical moment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods and apparatuses related to blood analyte measurement system
InactiveUS20100168535A1Accurate measurementEfficient implementationMedical devicesCatheterOperational systemPotassium
The present invention relates to a blood analyte measurement system for the procurement of blood samples for measurement of blood properties such as analyte concentration or analyte presence. A blood access system can be coupled with a measurement system such as an electrochemical sensor, and can also be used with other measurement modalities. Embodiments of the present invention can facilitate accurate measurement of blood glucose by the clinician in a sterile manner. Embodiments of the present invention can also enable the calibration of the sensor at one or more calibration points. One desired analyte of measurement is glucose for the effective implementation of glycemic control protocols. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used for the measurement of other analytes such as arterial blood gases, lactate, hemoglobin, potassium and urea. Additionally, embodiments of the present invention can function effectively on a variety of blood access points and specifically enables glucose monitoring in an existing arterial line that is already in place for hemodynamic monitoring. The present invention does not consume a significant amount of blood. Some embodiments of the present invention can re-infuse the blood into the patient, which can facilitate operation of the system in a sterile manner.
Owner:ROBINSON MARK RIES +4
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS20020013569A1Reduce complicationsEvenly distributedSuture equipmentsCannulasSurgical operationCoronary artery graft bypass
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia
Owner:HEARTPORT
Pressure applicator devices particularly useful for non-invasive detection of medical conditions
InactiveUS20020072681A1Low mobilityEasy constructionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterVeinBlood arterial
A probe for application to a body part particularly a finger of a patient to detect a change in the physical condition of the patient includes a housing defining a compartment closed at one end and open at the opposite end for receiving the distal end of the patient's finger and means consituted of a medium wholly self-contained within the probe for applying a static pressure field substantially uniformly around the distal end of the patient's finger, of a predetermined magnitude sufficient to substantially prevent distention of the venous vasculature, uncontrolled venous backflow, and retrognade shockwave propagation into the distal end, and to partially unload the wall tension of, but not to occlude, the arteries in the distal end when at heart level or below. A sensor senses changes in the distal end of the patient's finger related to changes in arterial blood volume therein.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com