Patents
Literature
2514 results about "Glycemic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The glycemic response to a food or meal is the effect that food or meal has on blood sugar (glucose) levels after consumption. It is normal for blood glucose and insulin levels to rise after eating and then return again to fasting levels over a short period of time. This is particularly so after consumption of meals rich in certain carbohydrates. Glycemic management refers to the selection of foods to manage your blood sugar levels.
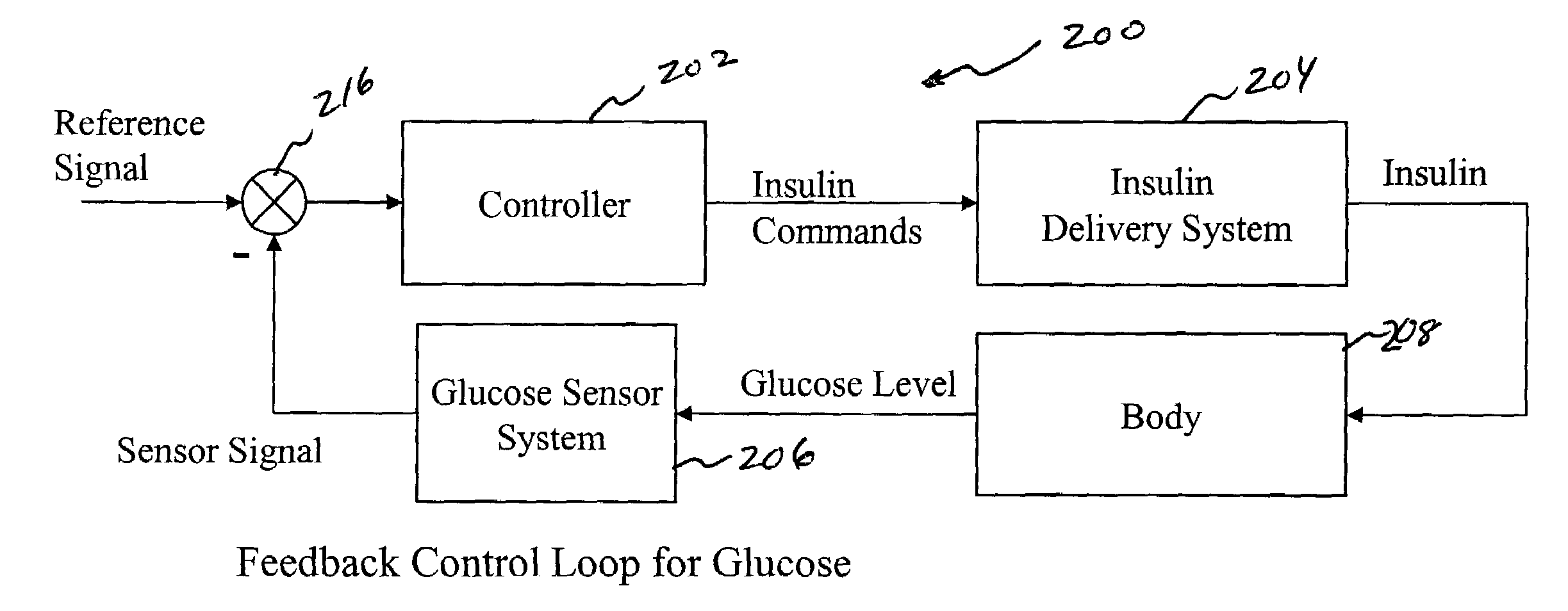
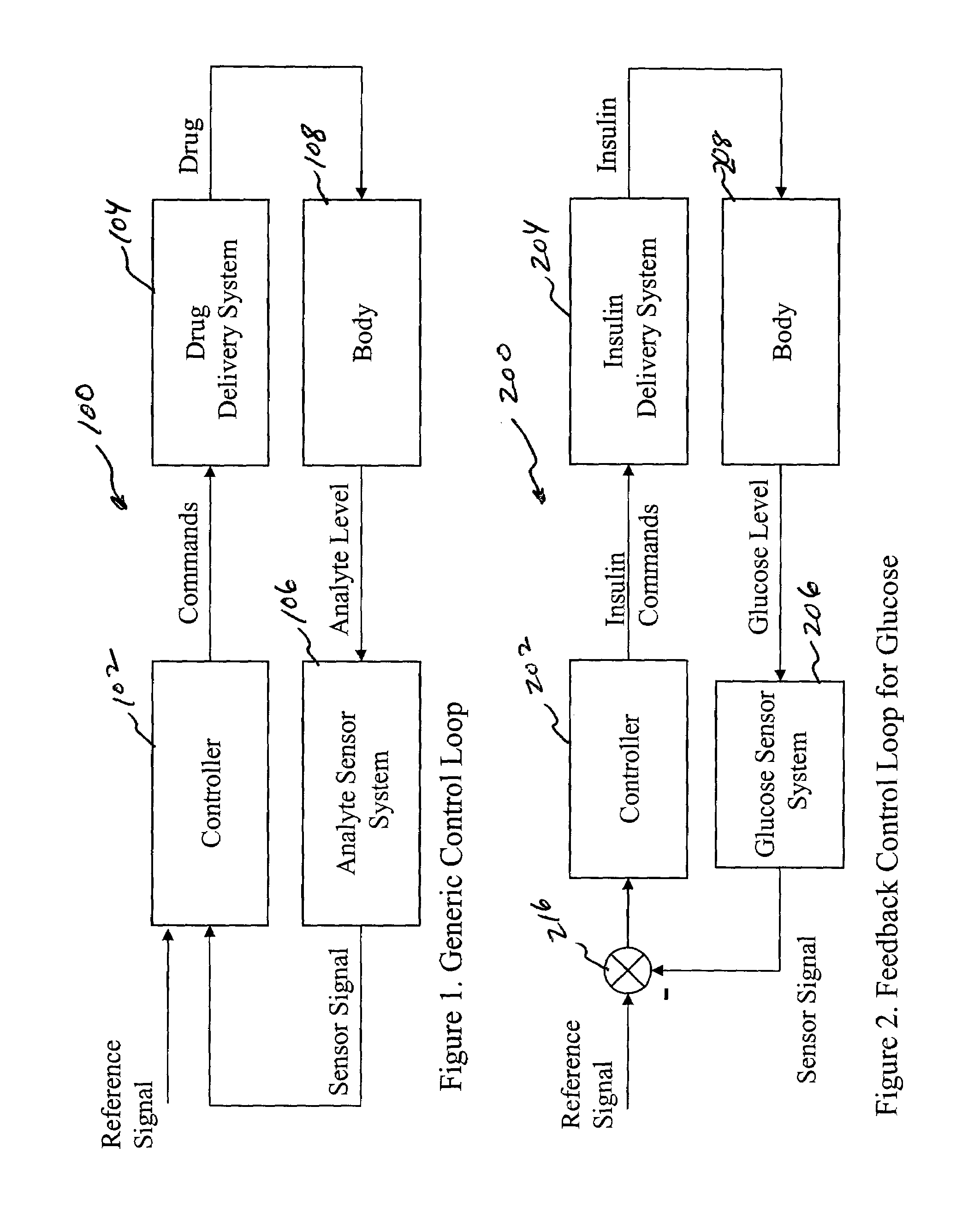
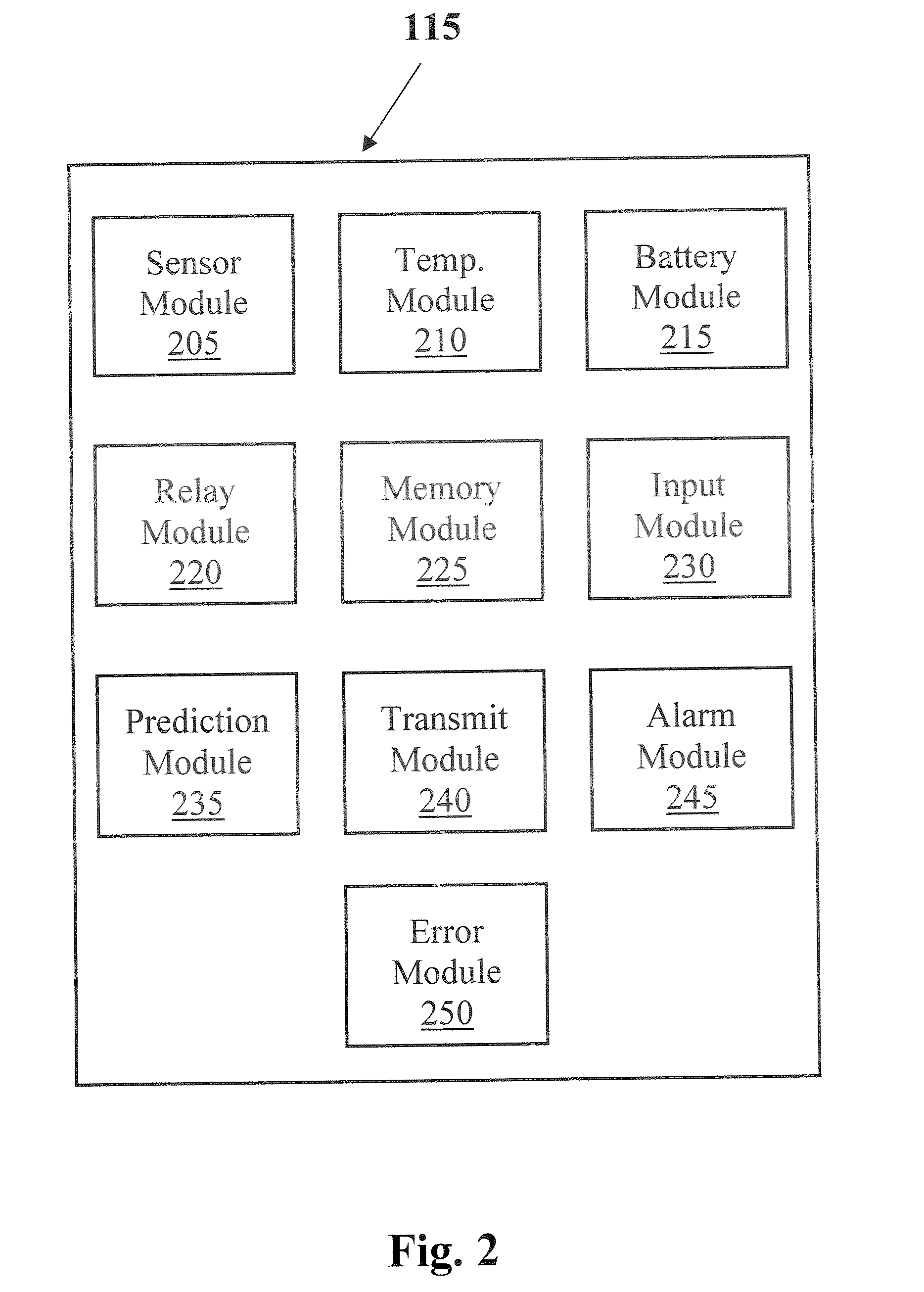
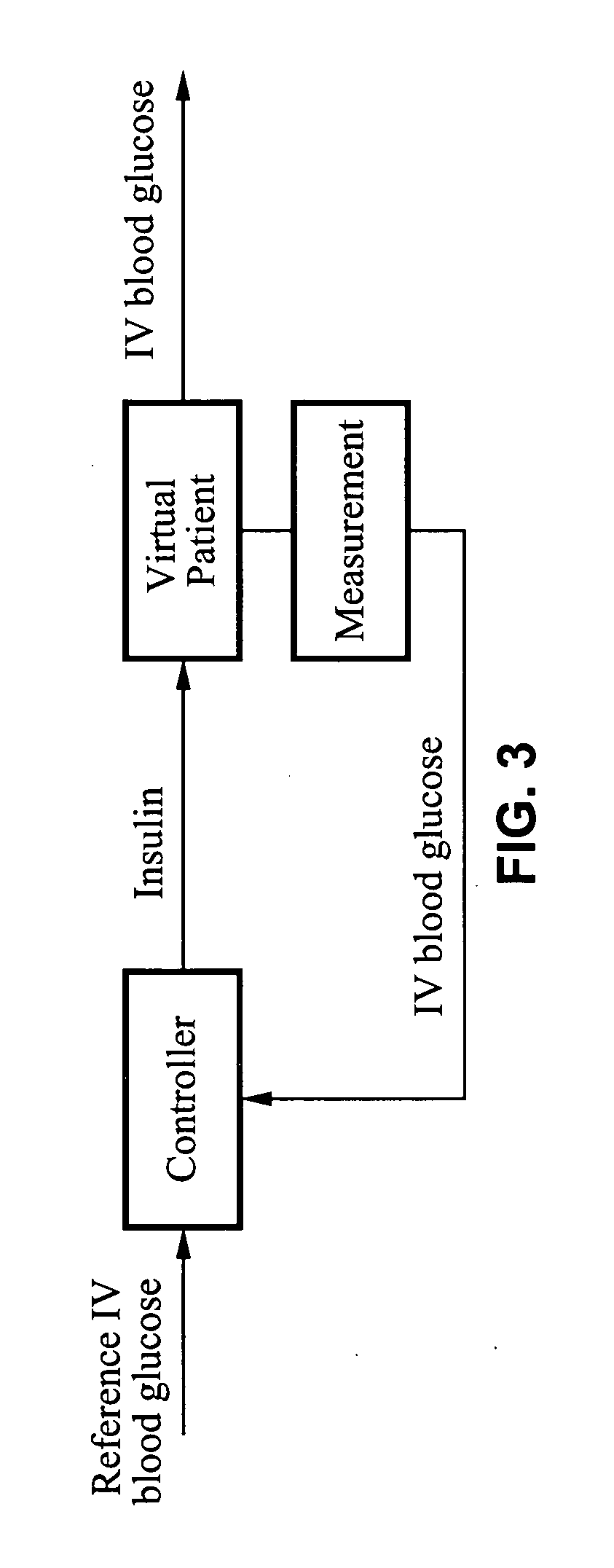
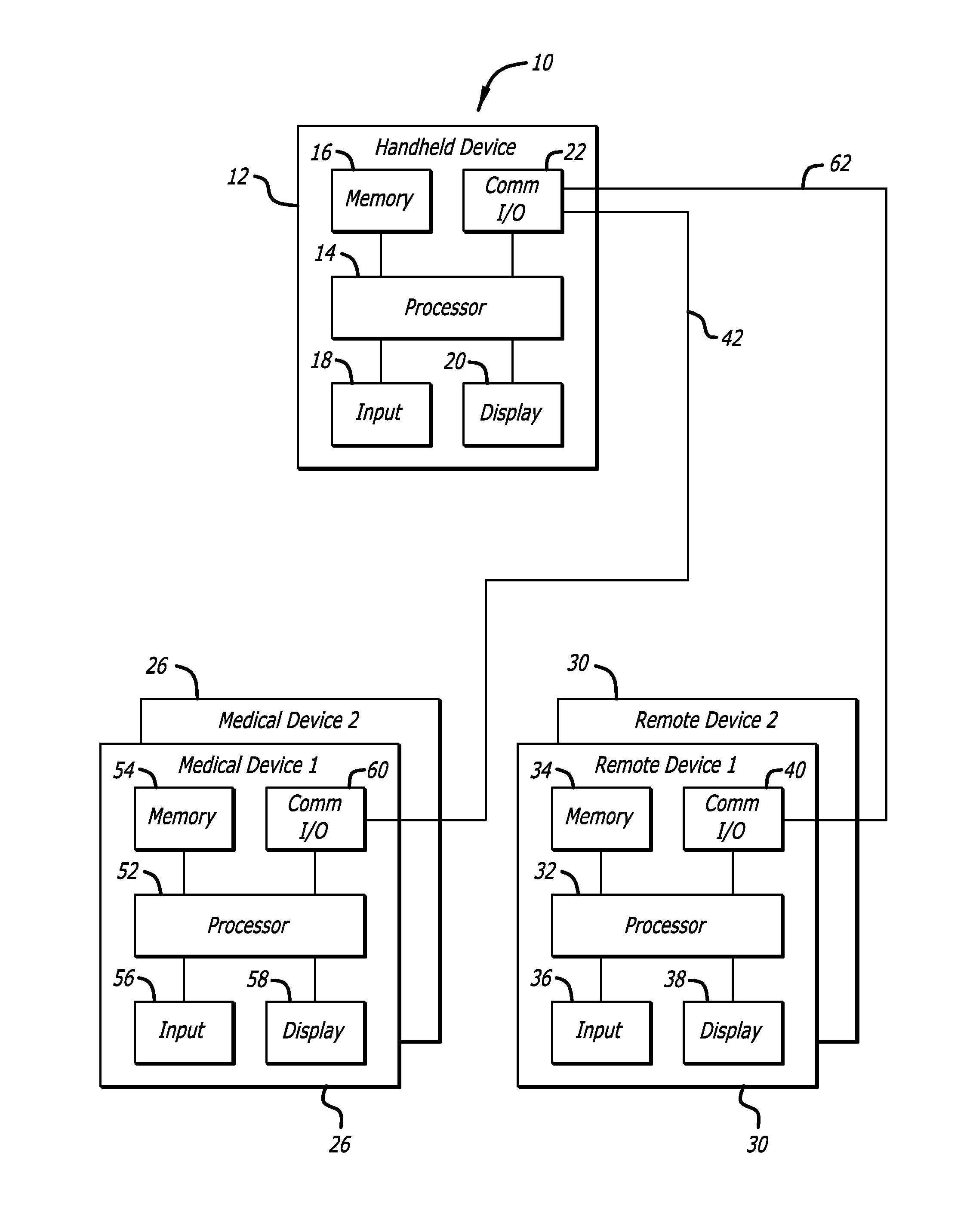
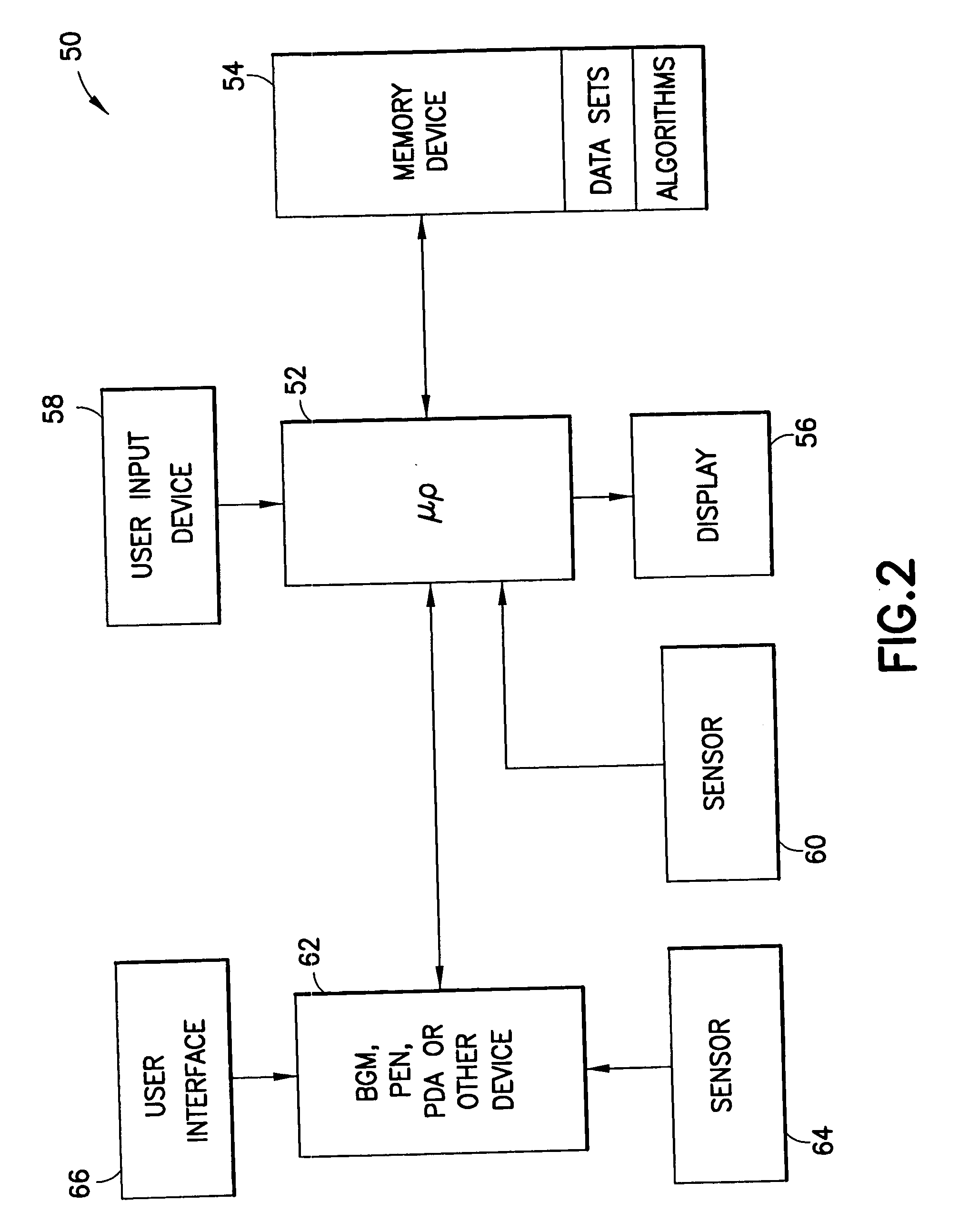
System and method for initiating and maintaining continuous, long-term control of a concentration of a substance in a patient using a feedback or model-based controller coupled to a single-needle or multi-needle intradermal (ID) delivery device
ActiveUS7060059B2Maintaining continuous, long-term control of the blood glucose concentrationsImprove performancePeptide/protein ingredientsDrug and medicationsInsulin infusionClosed loop
A closed loop therapy system for controlling a concentration of a substance, such as blood glucose concentration, in the body of a user. The system and method employ a sensor system that measures a glucose level in the body, a controller that uses the measured glucose levels to generate an output that can be used to automatically or manually control an intradermal insulin infusion system to set a constant or time-varying profile of target blood glucose concentrations in a user, and then infuse an appropriate amount of insulin into the body of the user so as to reach and maintain the target values of the blood glucose concentration.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
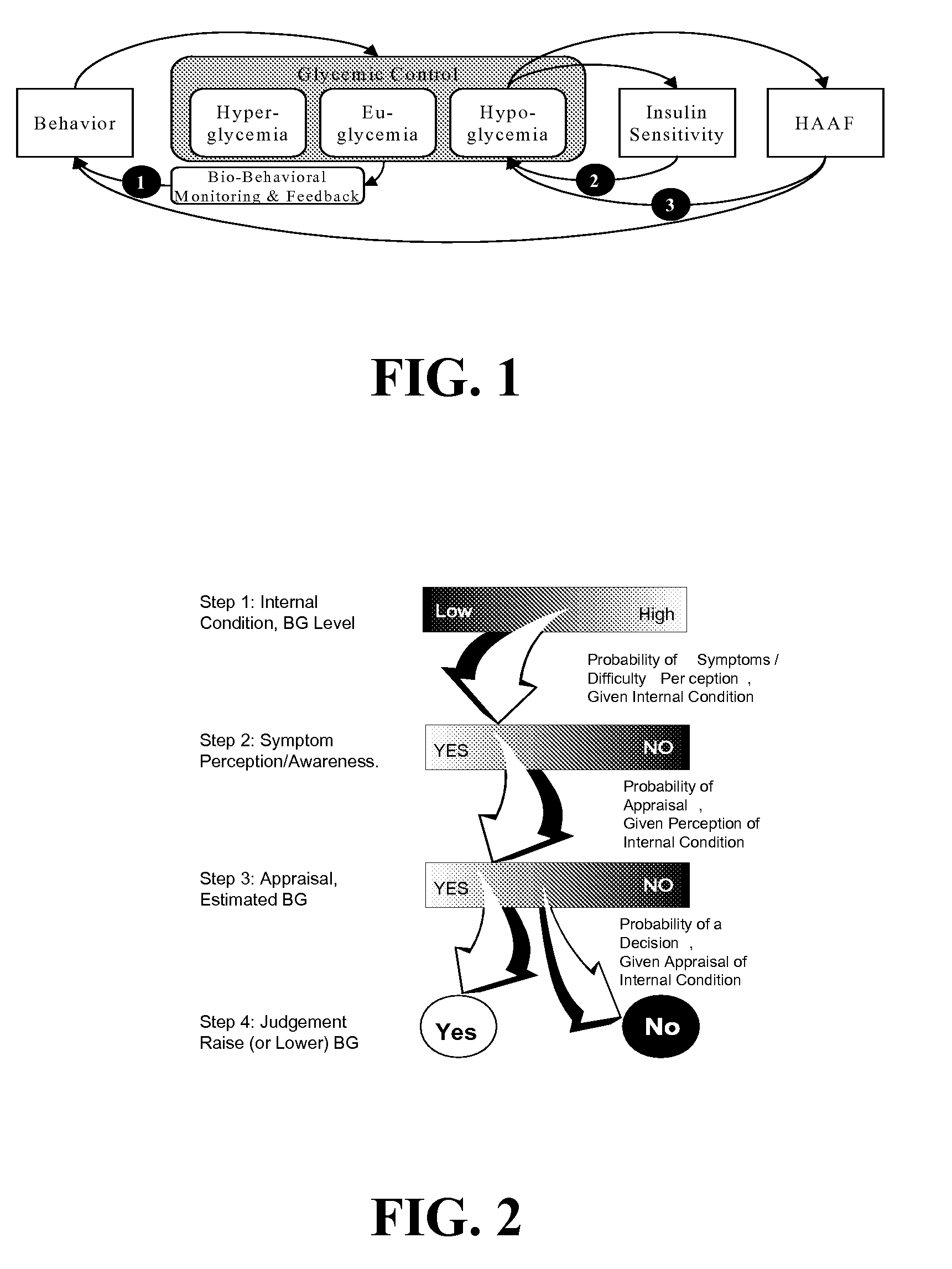
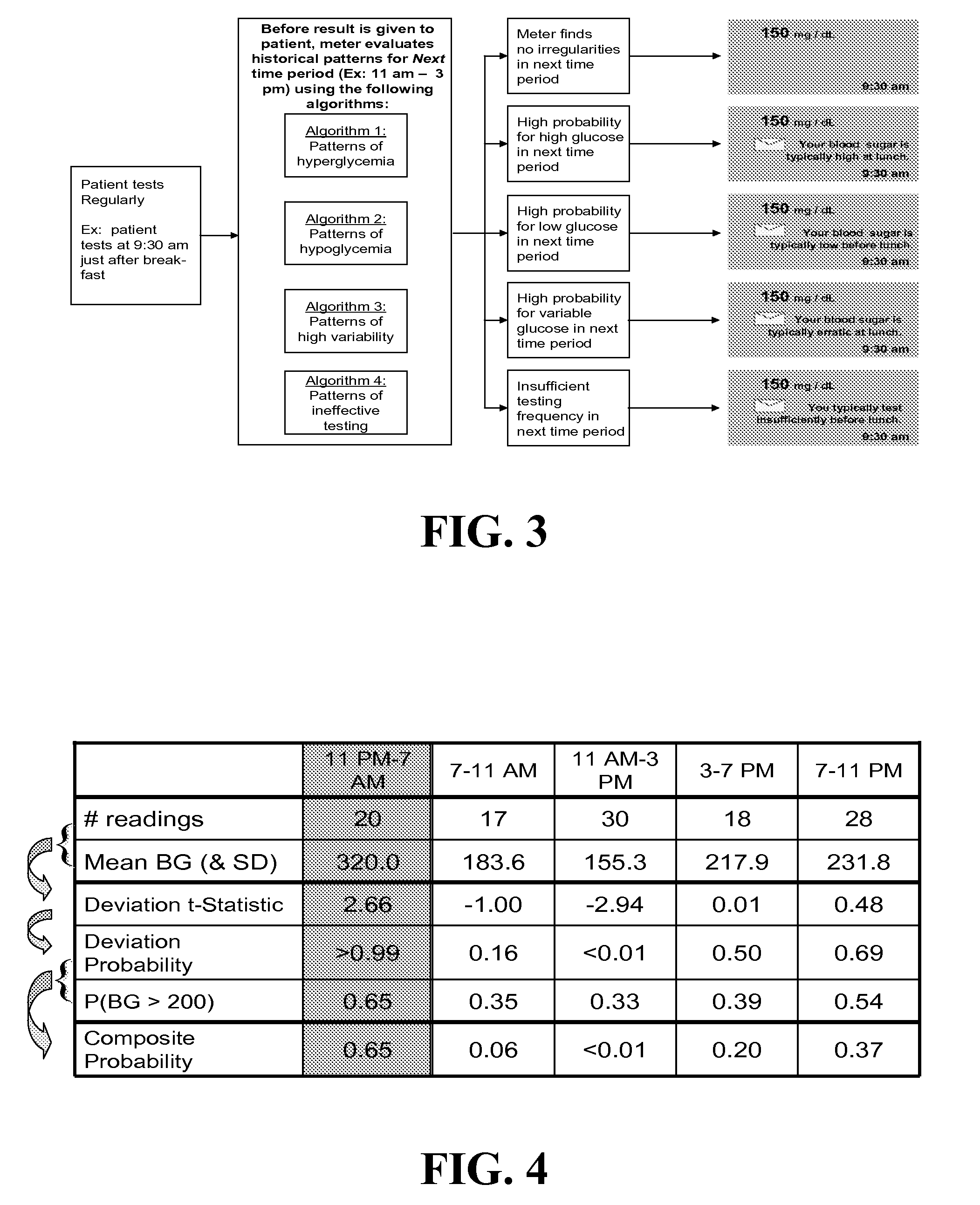
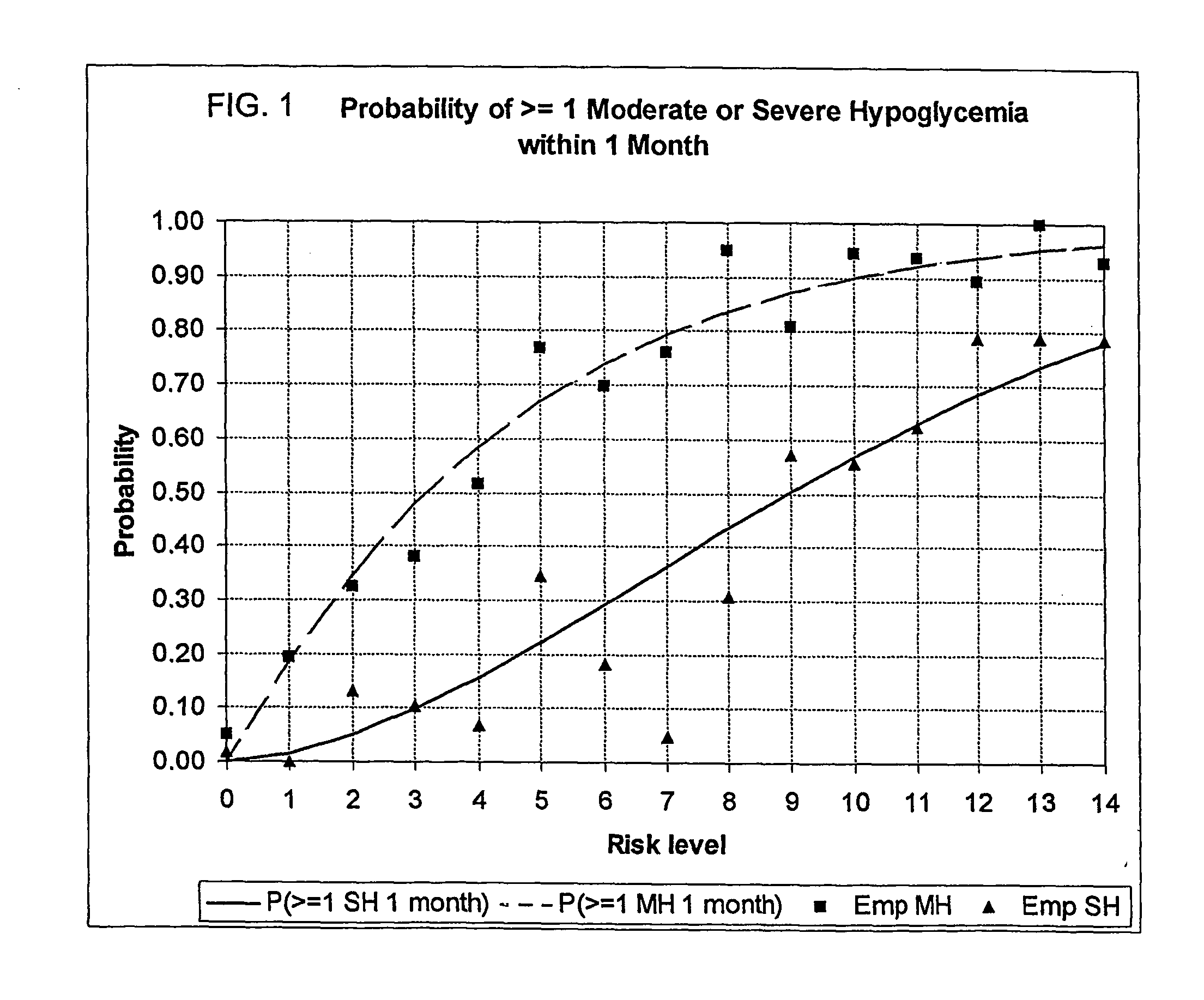
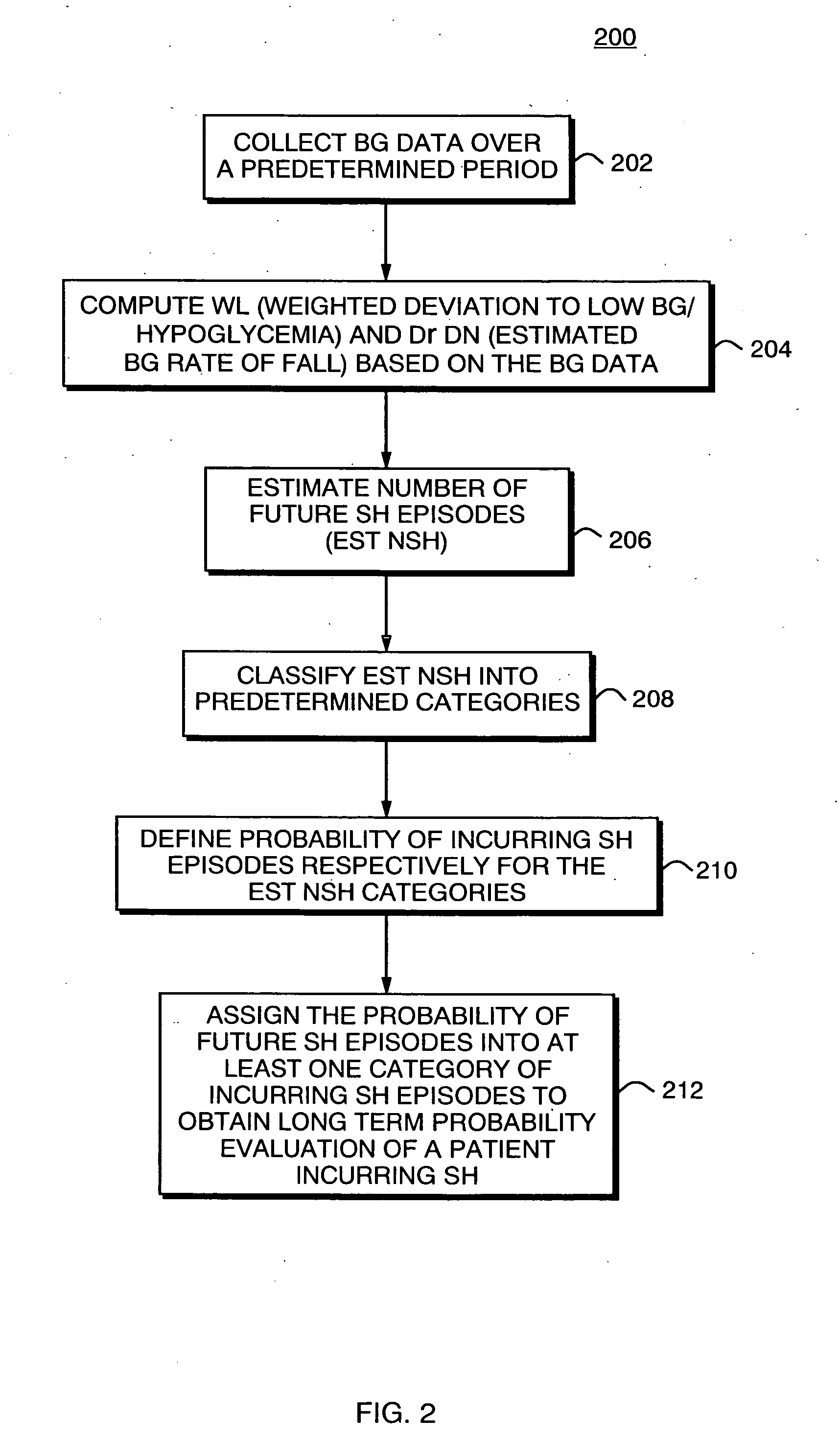
Systems, Methods and Computer Program Codes for Recognition of Patterns of Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia, Increased Glucose Variability, and Ineffective Self-Monitoring in Diabetes
InactiveUS20080154513A1Evaluate effectivenessEnhance existing SMBG devicesDrug and medicationsDigital computer detailsAcute hyperglycaemiaOptimal control
A method, system, and computer program product related to the maintenance of optimal control of diabetes, and is directed to predicting patterns of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, increased glucose variability, and insufficient or excessive testing for the upcoming period of time, based on blood glucose readings collected by a self-monitoring blood glucose device. The method, system, and computer program product pertain directly to the enhancement of existing home blood glucose monitoring devices, by introducing an intelligent data interpretation component capable of predicting and alerting the user to periods of increased risk for hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, increased glucose variability, and ineffective testing, and to the enhancement of emerging self-monitoring blood glucose devices by the same features. With these predictions the diabetic can take steps to prevent the adverse consequences associated with hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and increased glucose variability.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
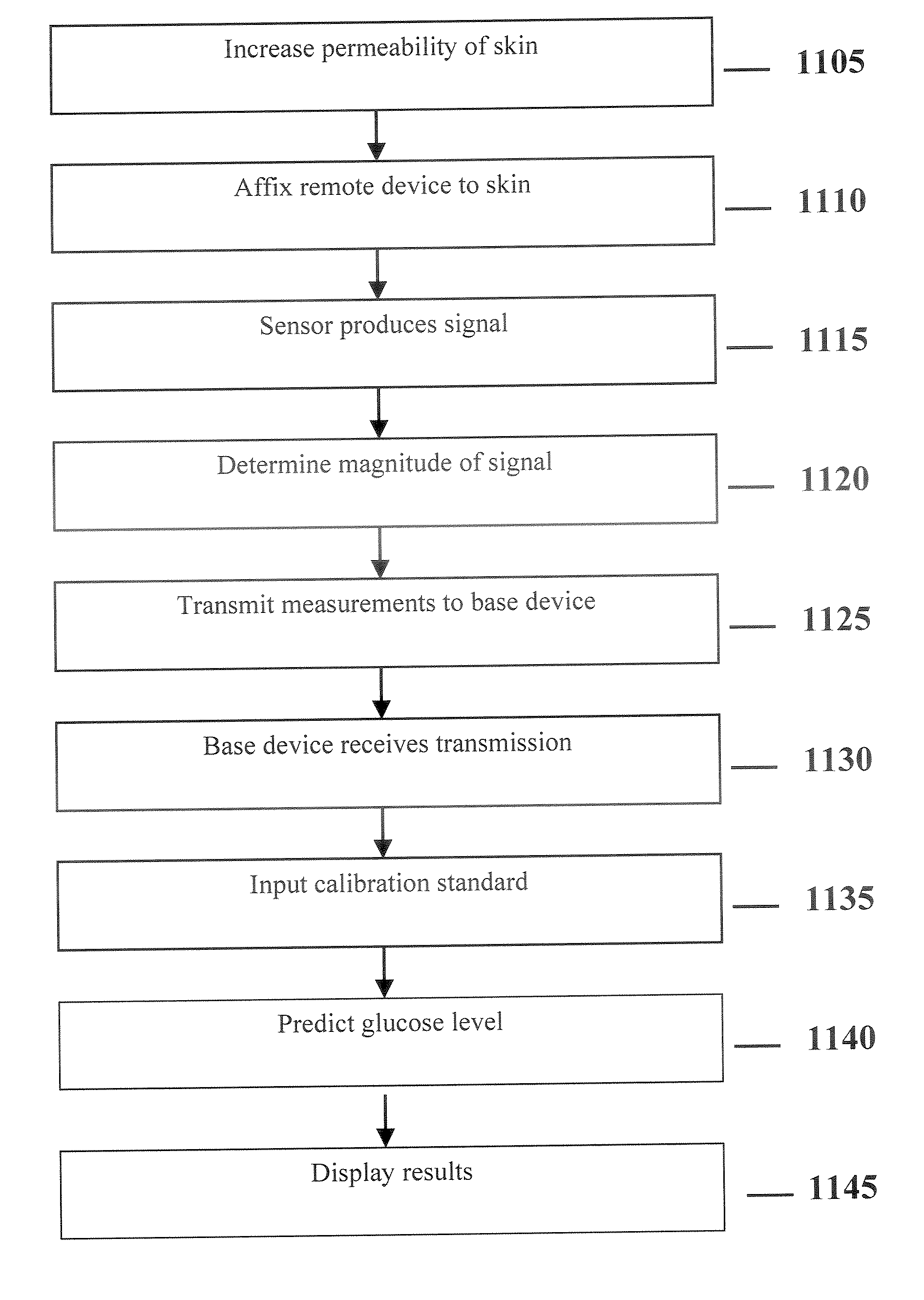
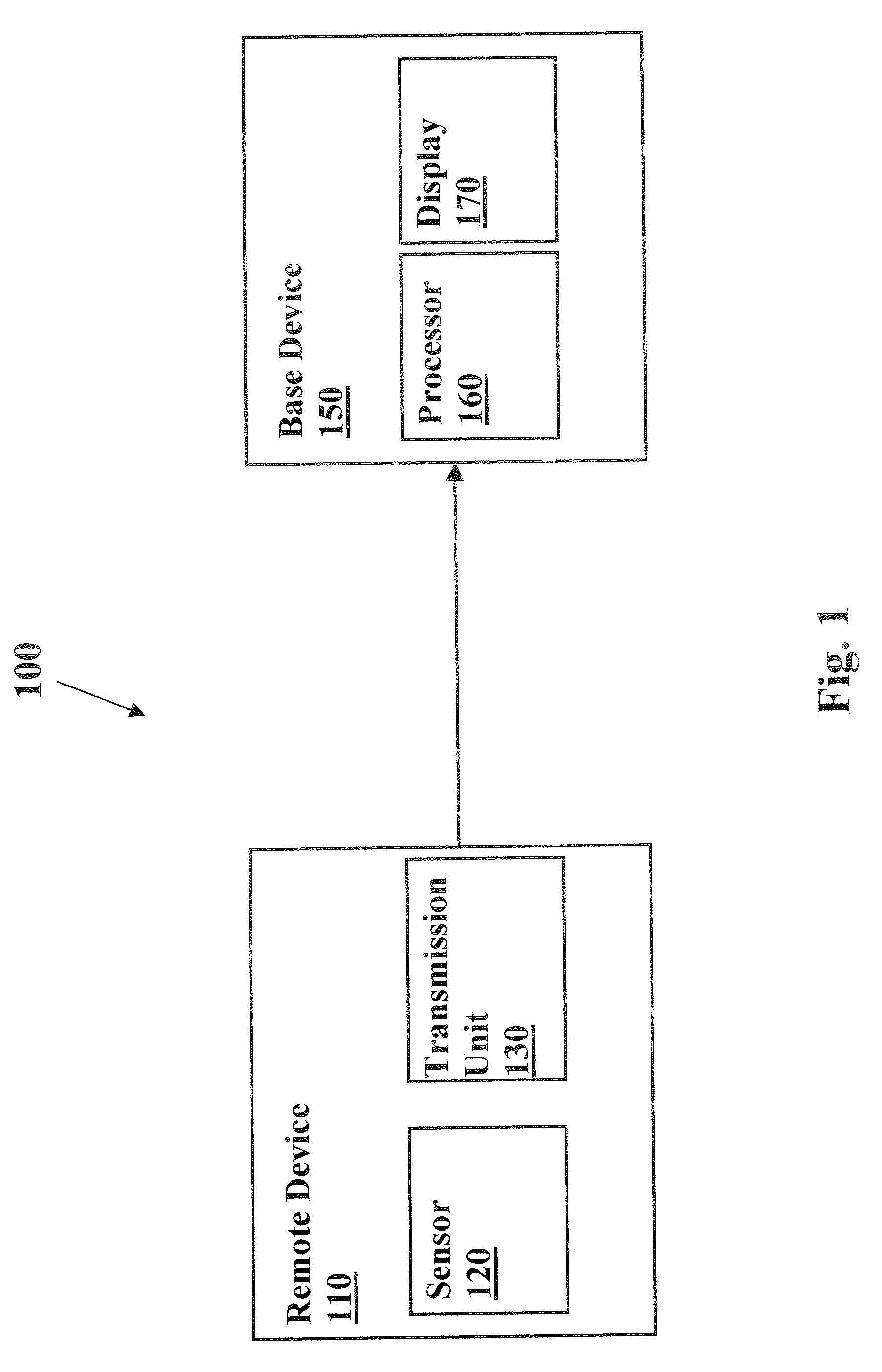
System and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring
A system and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the method includes the steps of (1) contacting a remote device to an area of biological membrane having a permeability level, the remote device comprising a sensor and a transmitter; (2) extracting the at least one analyte through and out of the area of biological membrane and into the sensor; (3) generating an electrical signal representative of a level of the at least one analyte; (4) transmitting the electrical signal to a base device; (5) processing the electrical signal to determine the level of the at least one analyte; and (6) displaying the level of the at least one analyte in real time. The system includes a remote device that includes a sensor that generates an electrical signal representative of the concentration of the at least one analyte; and a transmitter that transmits the electrical signal. The system further includes a base device that includes a receiver that receives the electrical signal; a processor that processes the electrical signal; and a display that displays the processed signal in real time.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for advising patients concerning doses of insulin
A method for guiding a user to select a dose of insulin, including the steps of calculating a firsts pecific dose of insulin by applying information provided by the user to an insulin dose calculation algorithm, wherein such information includes at least the user's current blood glucose level and the user's desired blood glucose level, calculating at least a second specific dose of insulin that is different from the first specific dose, and presenting to the user a range of doses comprising at least two of the specific doses.
Owner:INSULET CORP
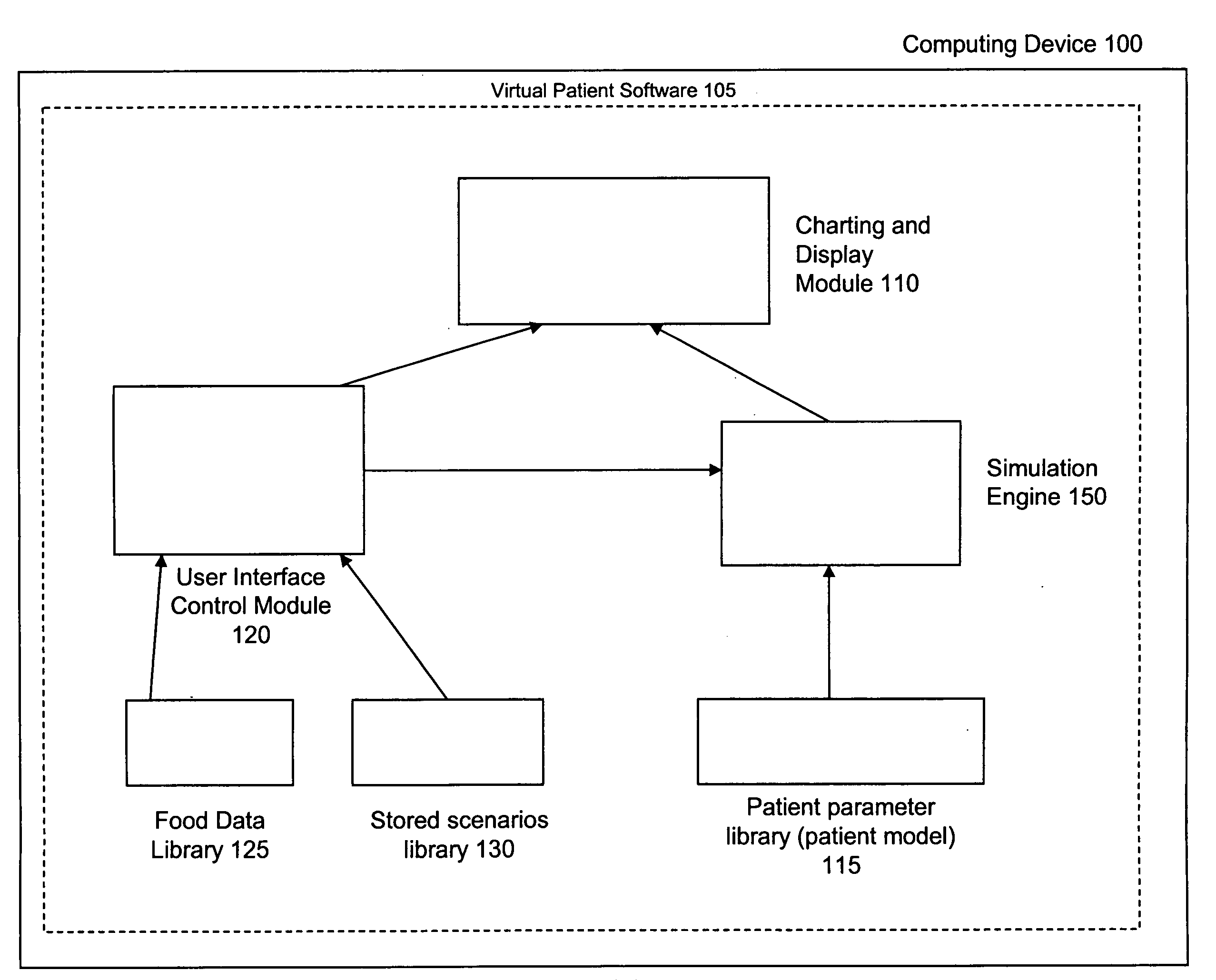
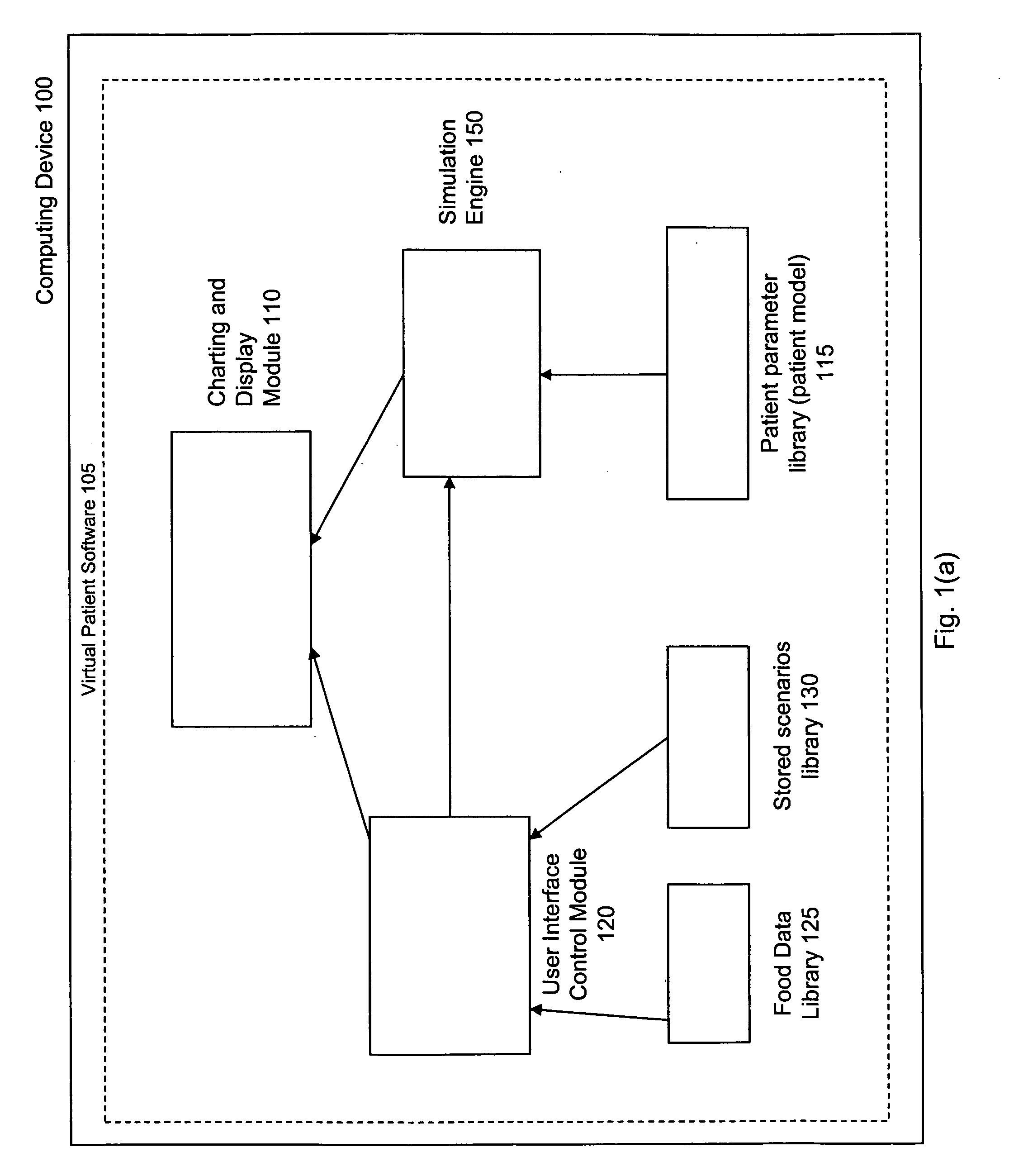
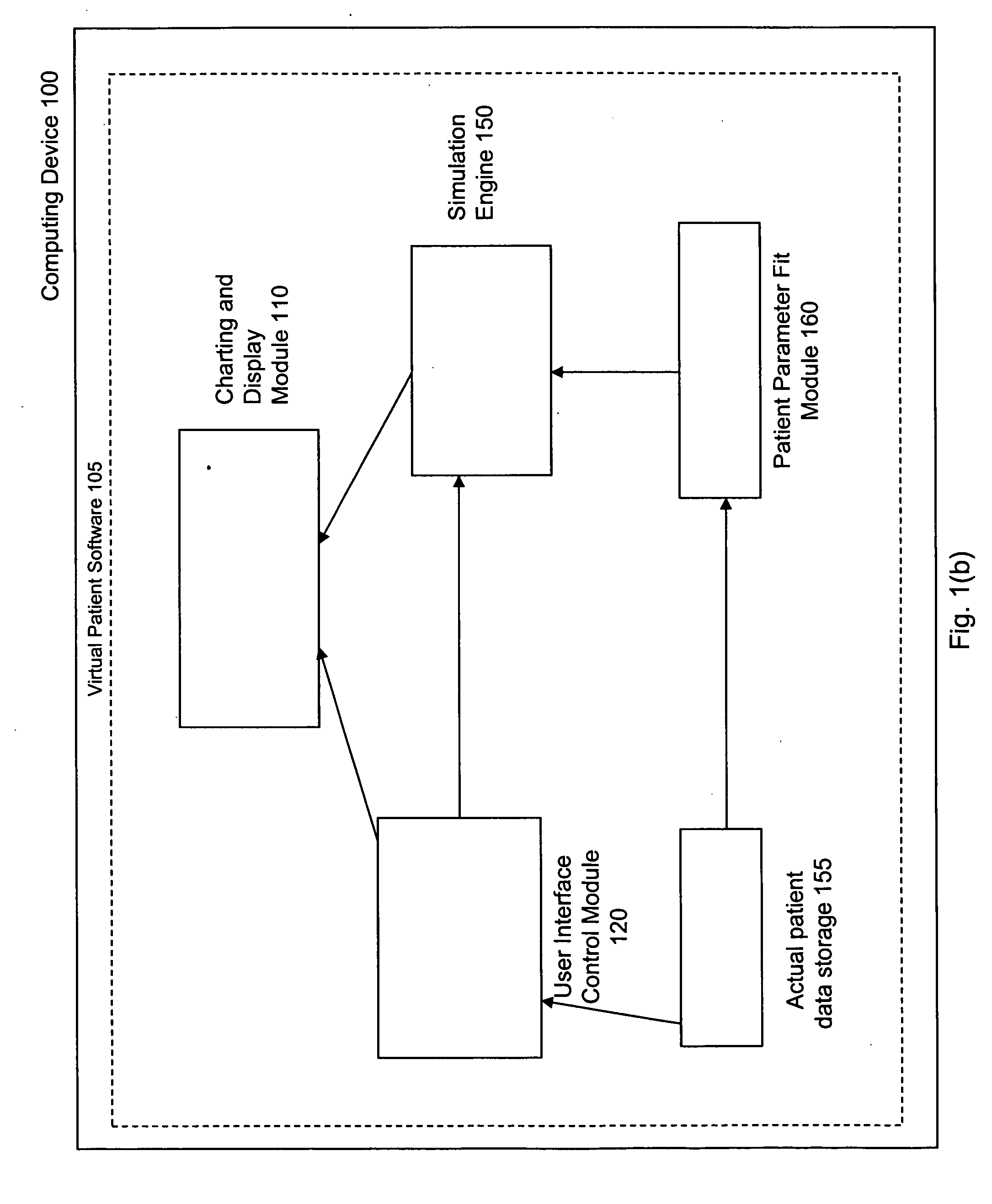
Virtual patient software system for educating and treating individuals with diabetes
A system to assist an individual in developing a therapy in diabetes treatment of a patient includes a user interface control module, a simulation engine, a charting and display module. The user interface control module receives an input related to the patient and captures a current time of the simulation. The simulation engine receives the input, generates a plurality of blood glucose readings for the patient up to the current time of the simulation based on the input, and to transfers the plurality of blood glucose readings. The charting and display module receives the plurality of blood glucose readings and display the plurality of blood glucose readings. The simulation engine receives patient parameters from a patient parameter library based on a selected patient model.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
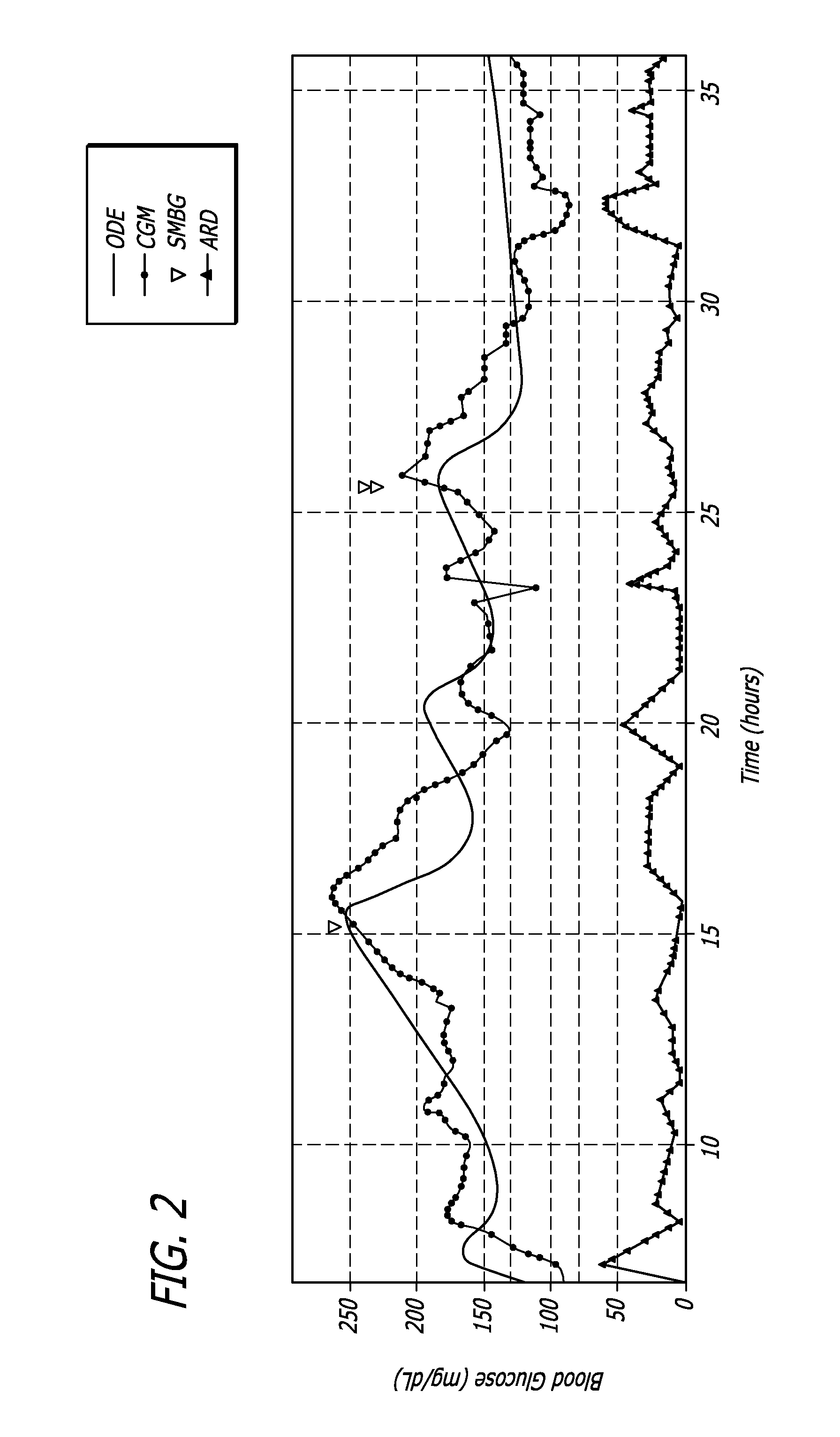
Method, system, and computer program product for the processing of self-monitoring blood glucose(smbg)data to enhance diabetic self-management
ActiveUS20050214892A1Easy to monitorContinuous informationMedical simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute hyperglycaemiaOptimal control
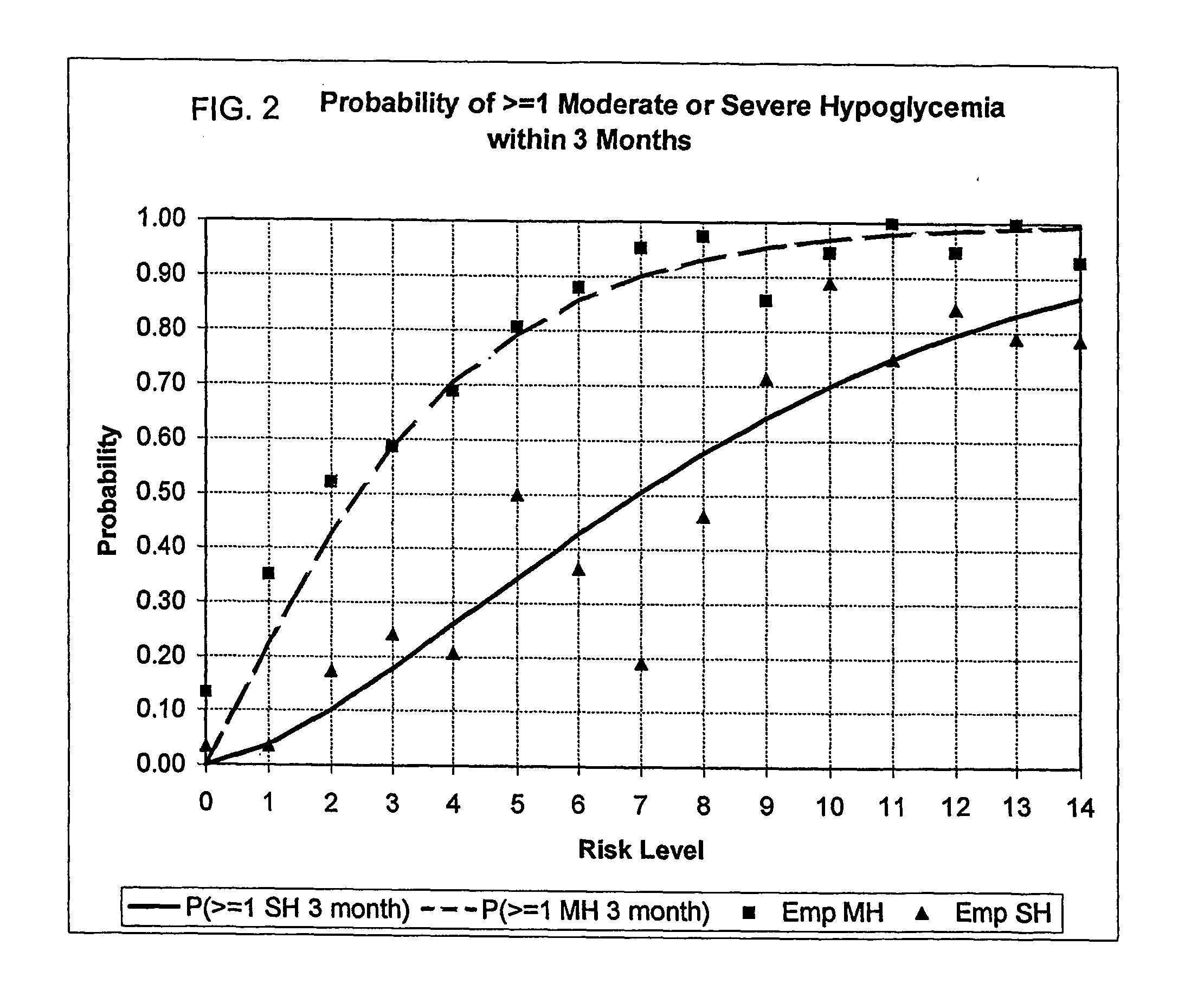
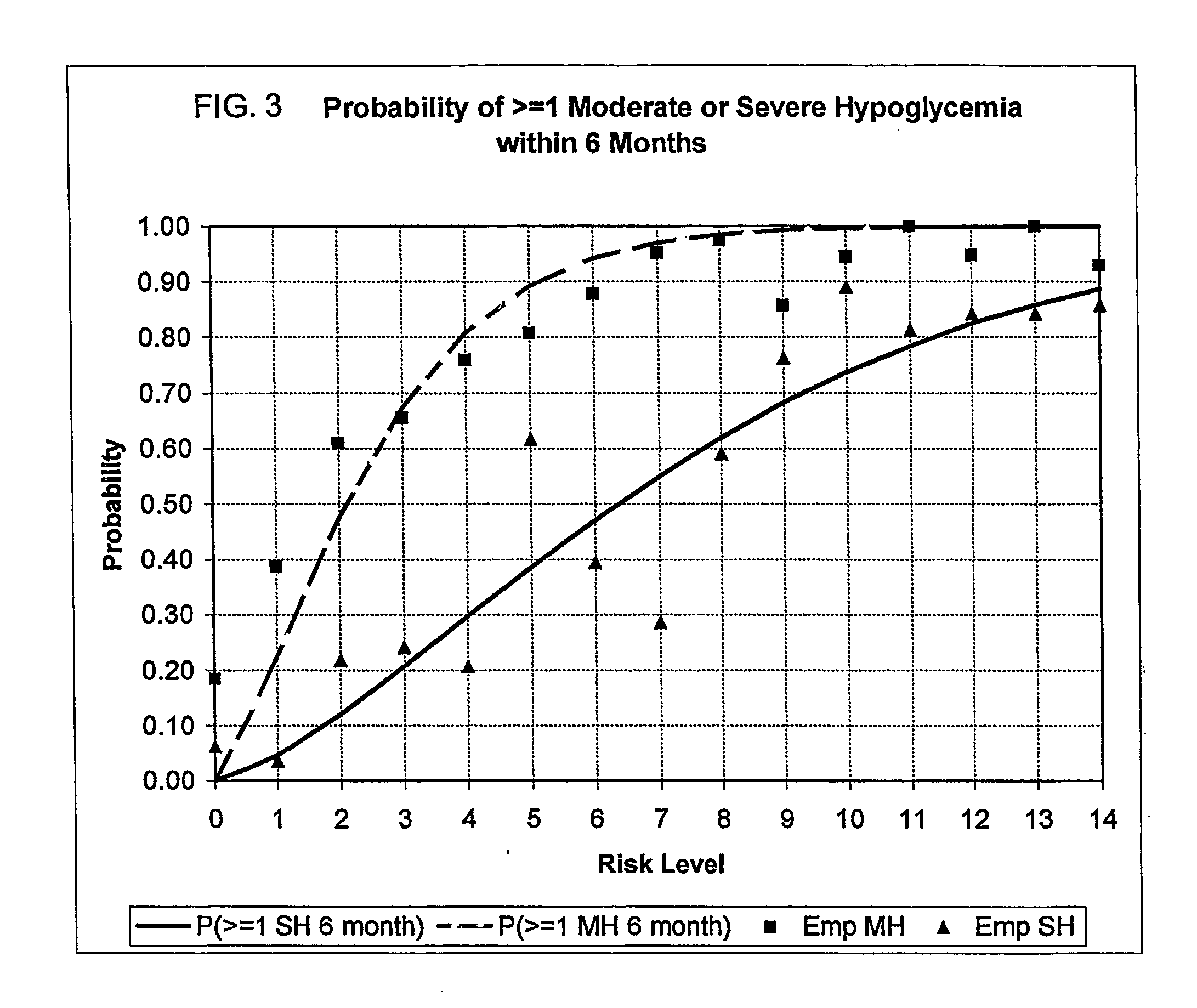
A method, system, and computer program product related to the maintenance of optimal control of diabetes, and is directed to predicting the long-term exposure to hyperglycemia, and the long-term and short-term risks of severe or moderate hypoglycemia in diabetics, based on blood blucose readings collected by a self-monitoring blood glucose device. The method, system, and computer program product pertain directly to the enhancement of existing home blood glucose monitoring devices, by introducing an intelligent data interpretation component capable of predicting both HbA1c and periods of increased risk of hypoglycemia, and to the enhancement of emerging continuous monitoring devices by the same features. With these predictions the diabetic can take steps to prevent the adverse consequences associated with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
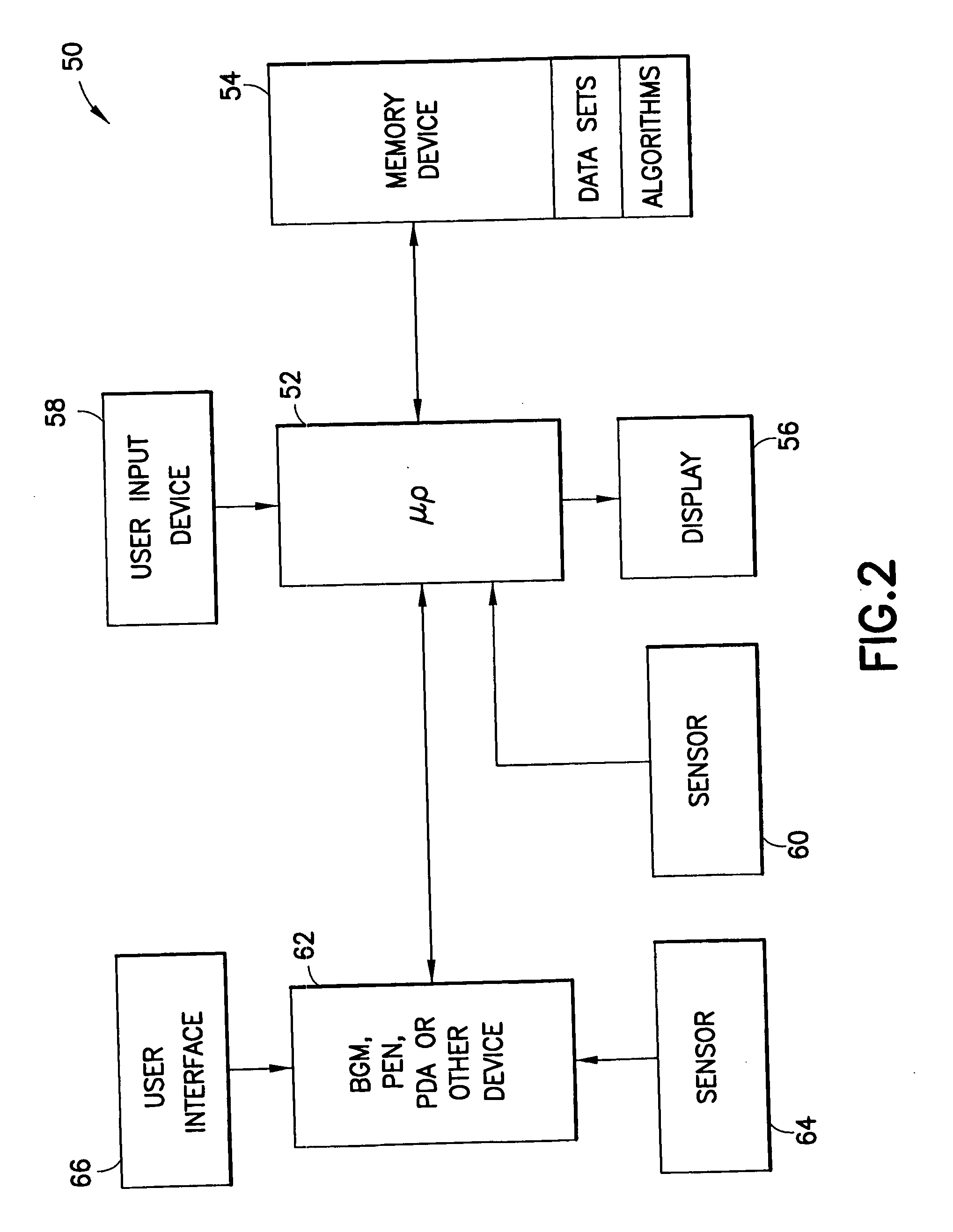
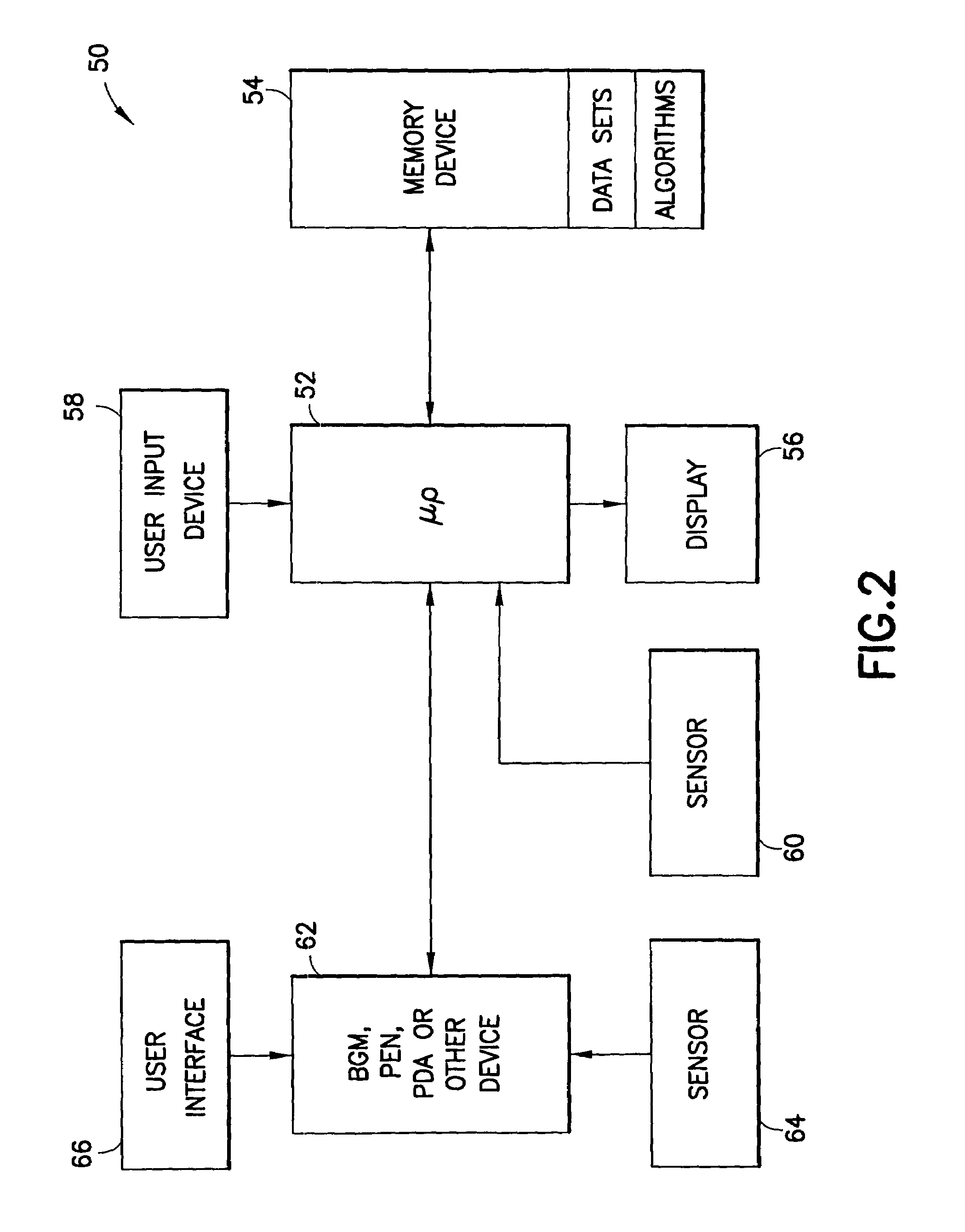
System for determining insulin dose using carbohydrate to insulin ratio and insulin sensitivity factor
An apparatus and method are provided for determining a patient's carbohydrate to insulin ratio (CIR) and insulin sensitivity factor (ISF), and using these values, along with values for current blood glucose level and deviation from target blood glucose level, for determining insulin dose in view of carbohydrate intake during a particular time period. The apparatus and method employ algorithms that can be implemented in any of a personal computer, personal data assistant, hand held computing device, blood glucose monitor, infusion pump, medication delivery pen, meter, calculator, among other therapeutic, diagnostic or informational devices used for managing a patient's blood glucose levels.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
System for determining insulin dose using carbohydrate to insulin ratio and insulin sensitivity factor
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Use of an equilibrium intravascular sensor to achieve tight glycemic control
A method for achieving tight glycemic control in a patient in need thereof is disclosed. The method comprises deploying an equilibrium glucose sensor within a blood vessel in the patient, coupling the sensor to a monitor that displays the blood glucose concentration, and administering a blood glucose regulator when the blood glucose concentration varies outside of the predetermined concentration range. The blood glucose regulator is administered in an amount sufficient to return the blood glucose concentration to within the predetermined concentration range, thereby achieving tight glycemic control.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Method and apparatus for glucose control and insulin dosing for diabetics
ActiveUS20050272640A1Ensure robustnessAccurately predicting insulin bolus dosagesPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug and medicationsPhysiologyMonitors blood glucose
A computer implemented method and associated apparatus for the combined control of insulin bolus dosing and basal delivery for the goal of achieving normal glycemic response to meals, exercise, stressors, and other perturbations to blood glucose levels. A run-to-run algorithm is used to monitor blood glucose levels and adjust insulin delivery as conditions are varied.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptide agonists of GLP-1 activity
InactiveUS6528486B1Lower blood sugar levelsEffective and stablePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderD-GlucoseGlycemic
The present invention relates to novel peptide conjugates which have increased stability and are useful in the treatment of excess levels of blood glucose.
Owner:ZP HLDG SPV
Method and apparatus for glucose control and insulin dosing for diabetics
ActiveUS7651845B2Accurately predicting insulin bolus dosagesProcess controlPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug and medicationsMonitors blood glucoseGlycemic
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
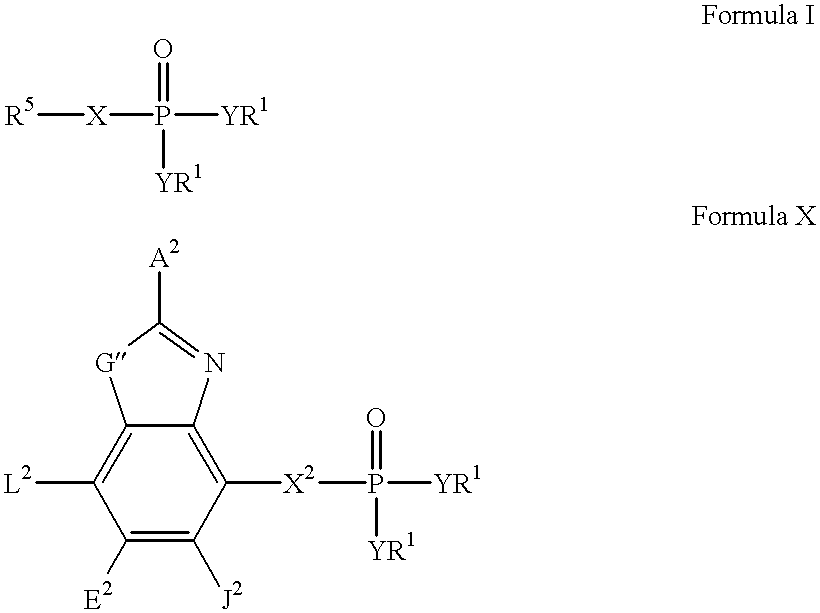
Heteroaromatic compounds containing a phosphonate group that are inhibitors of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
FBPase inhibitors of the formula I and Xare useful in the treatment of diabetes and other conditions associated with elevated blood glucose or excess glycogen storage.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
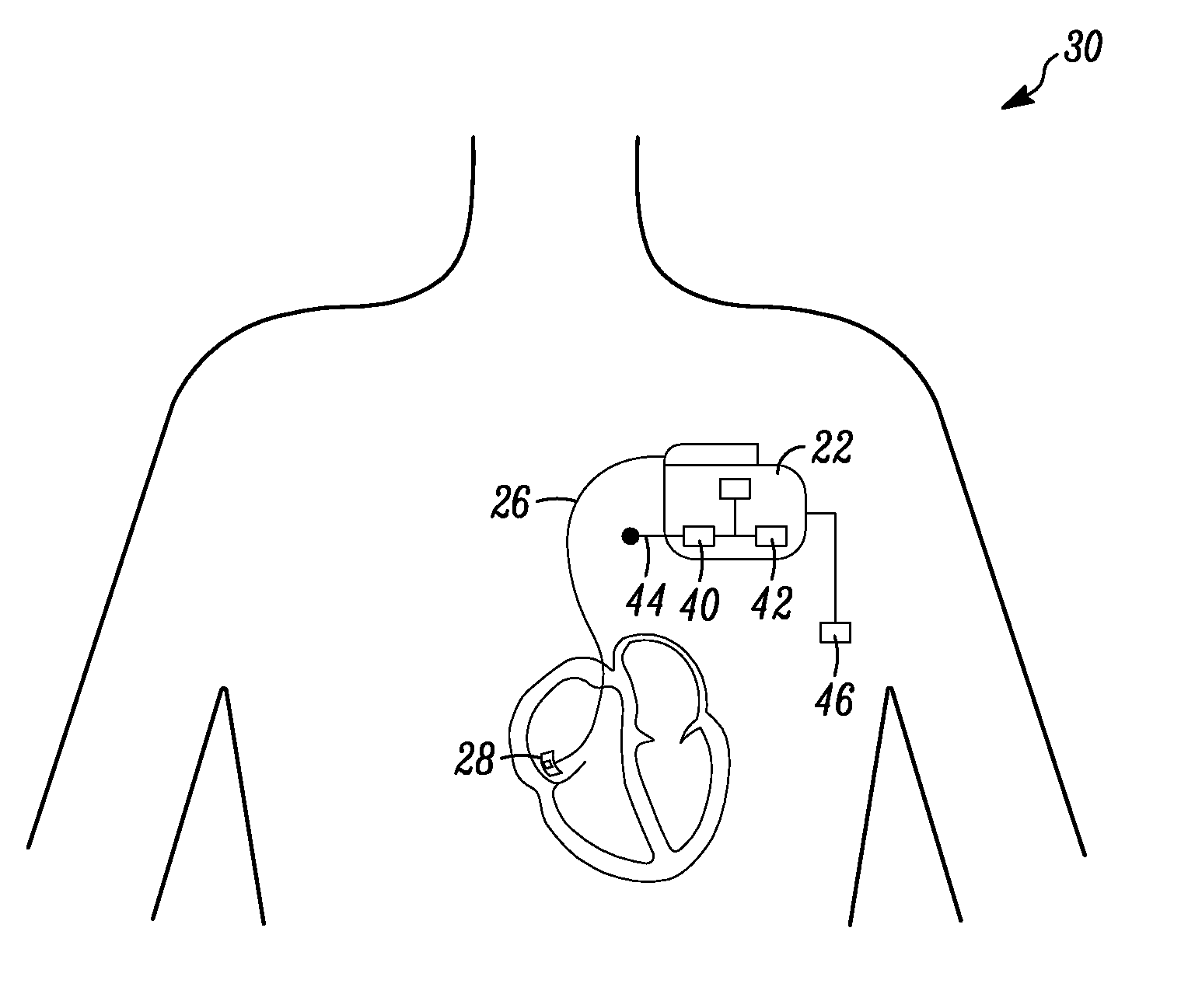
Glycemic control monitoring using implantable medical device
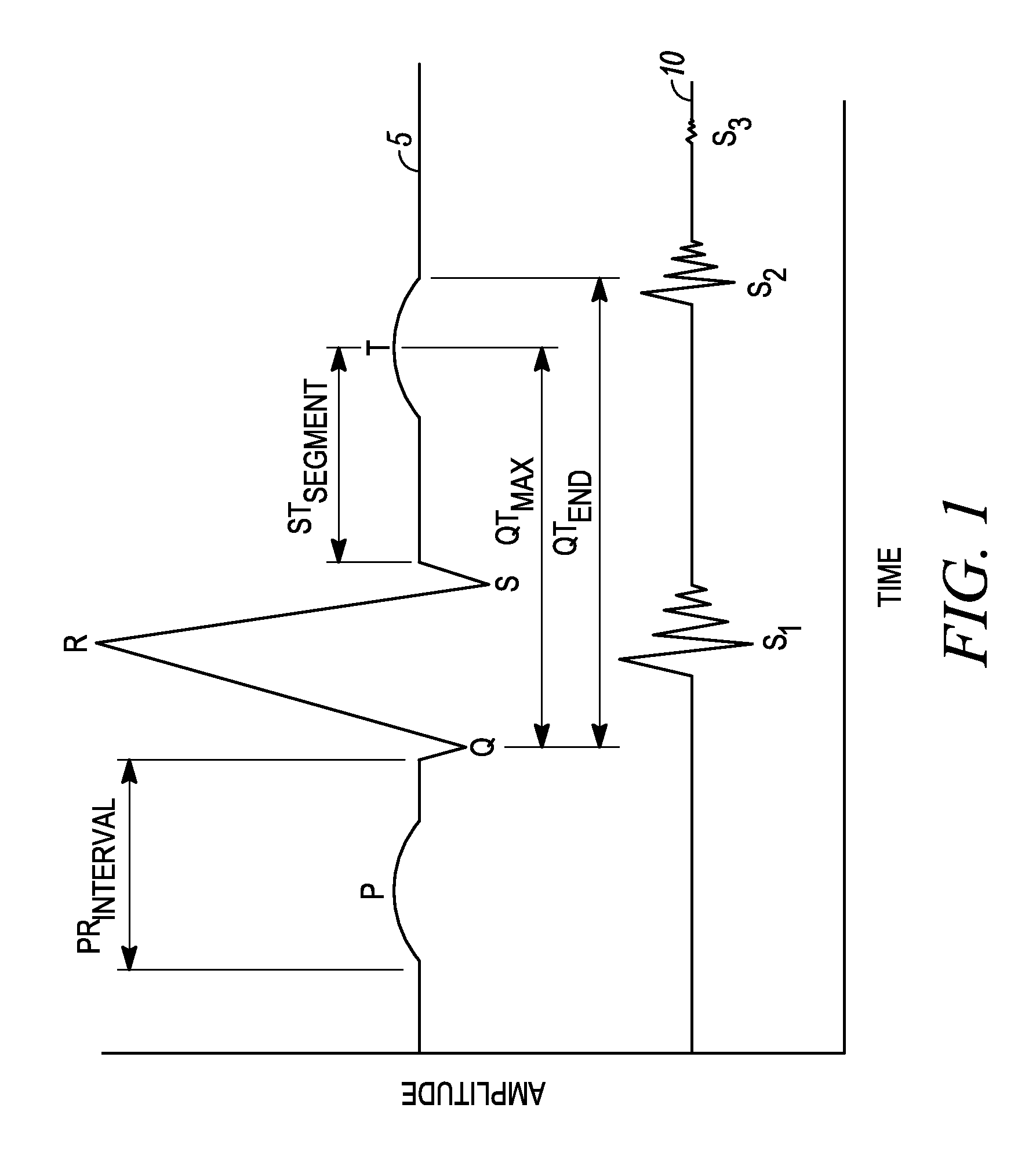
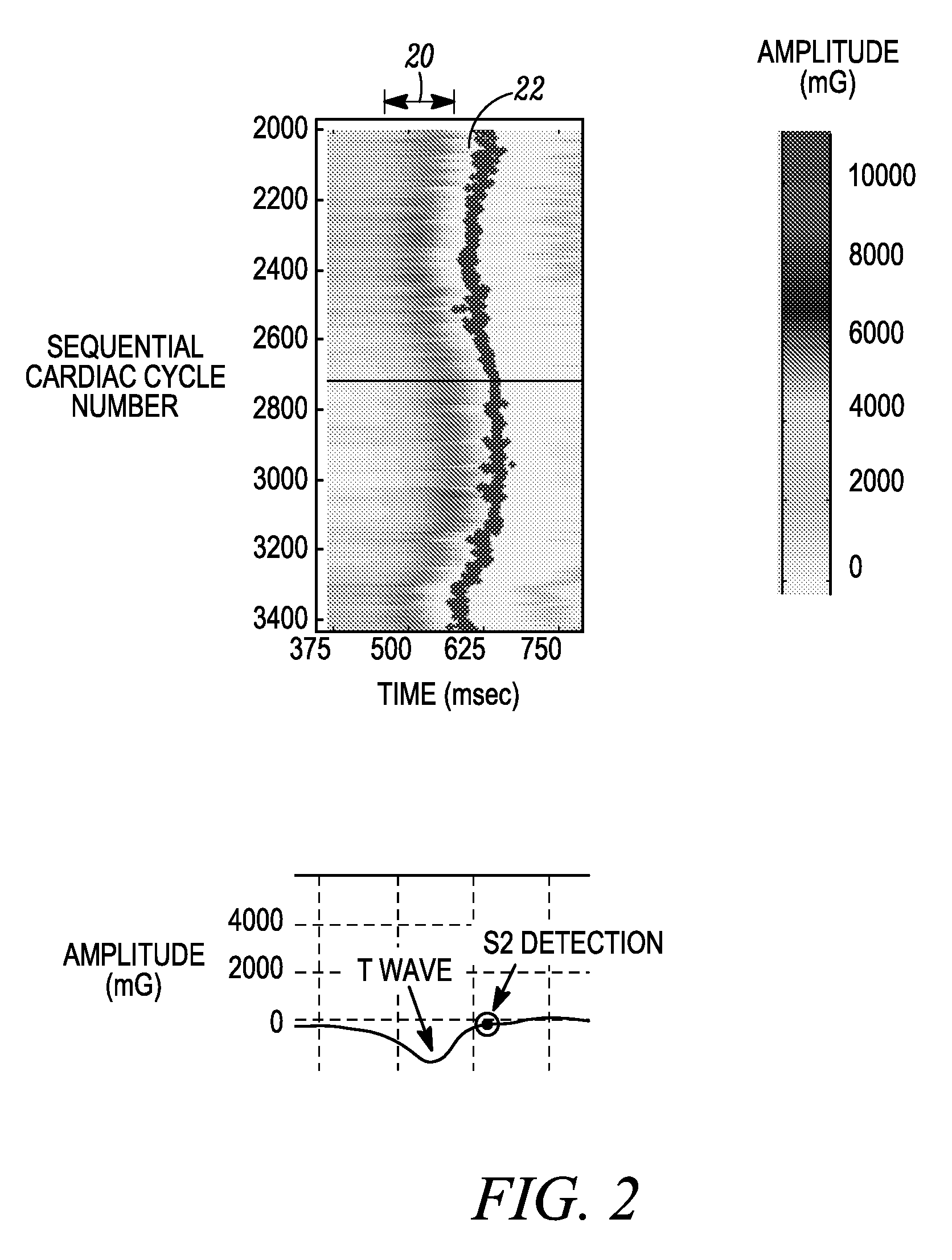
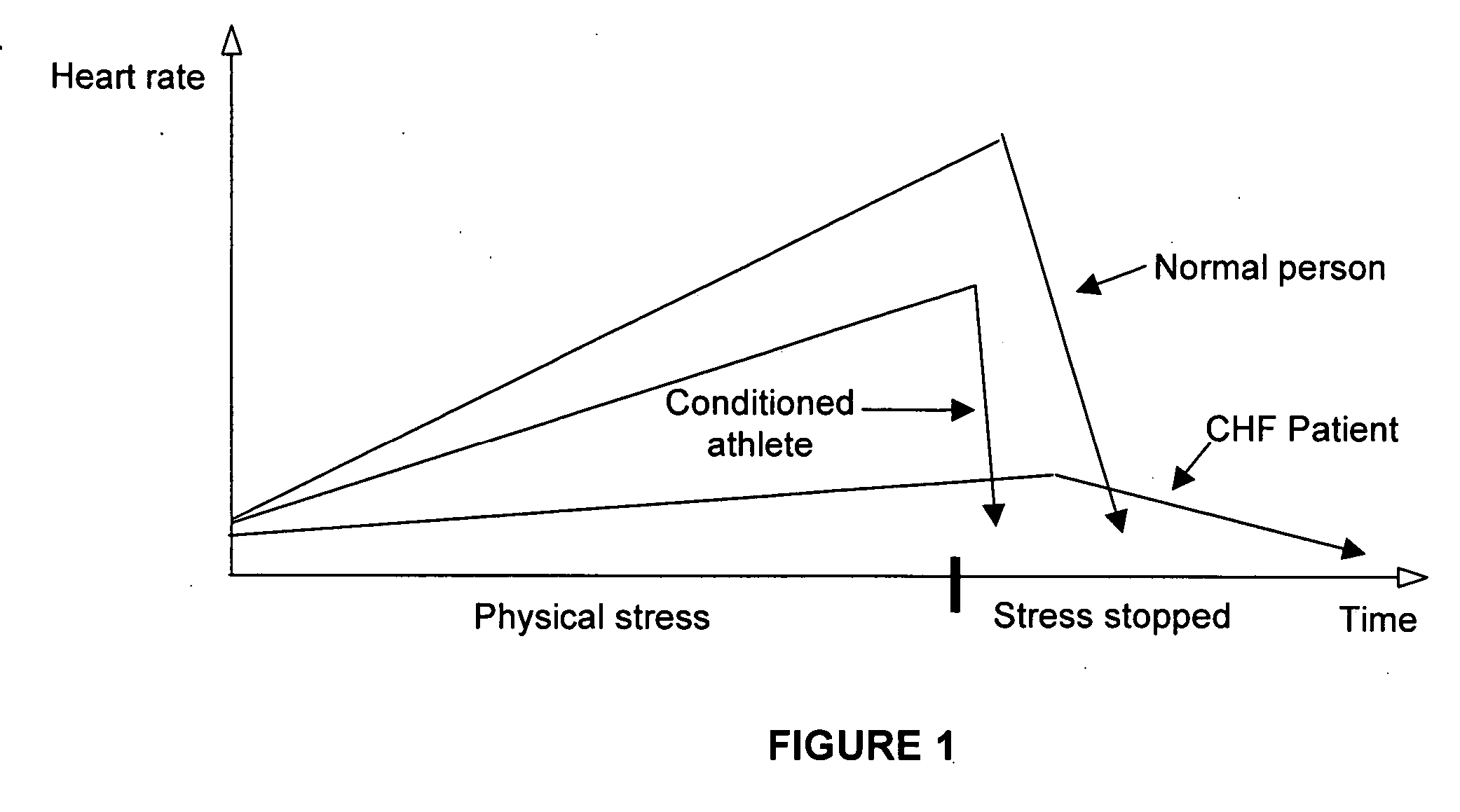
An apparatus for monitoring a patient's blood glucose level. The apparatus includes an implantable medical device having a controller and an implantable heart sounds sensor configured to transmit signals to the controller of the implantable medical device. The controller is configured to determine if a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic based on the signals from the heart sounds sensor. A method is also disclosed that includes sensing the patient's heart sounds, determining the amplitude of the S2 heart sound, determining the length of the interval from the S1 heart sound to the S2max heart sound, determining the length of the interval from the S1 heart sound to the S2end heart sound, and determining the patient's blood glucose status based on the patient's heart sounds.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
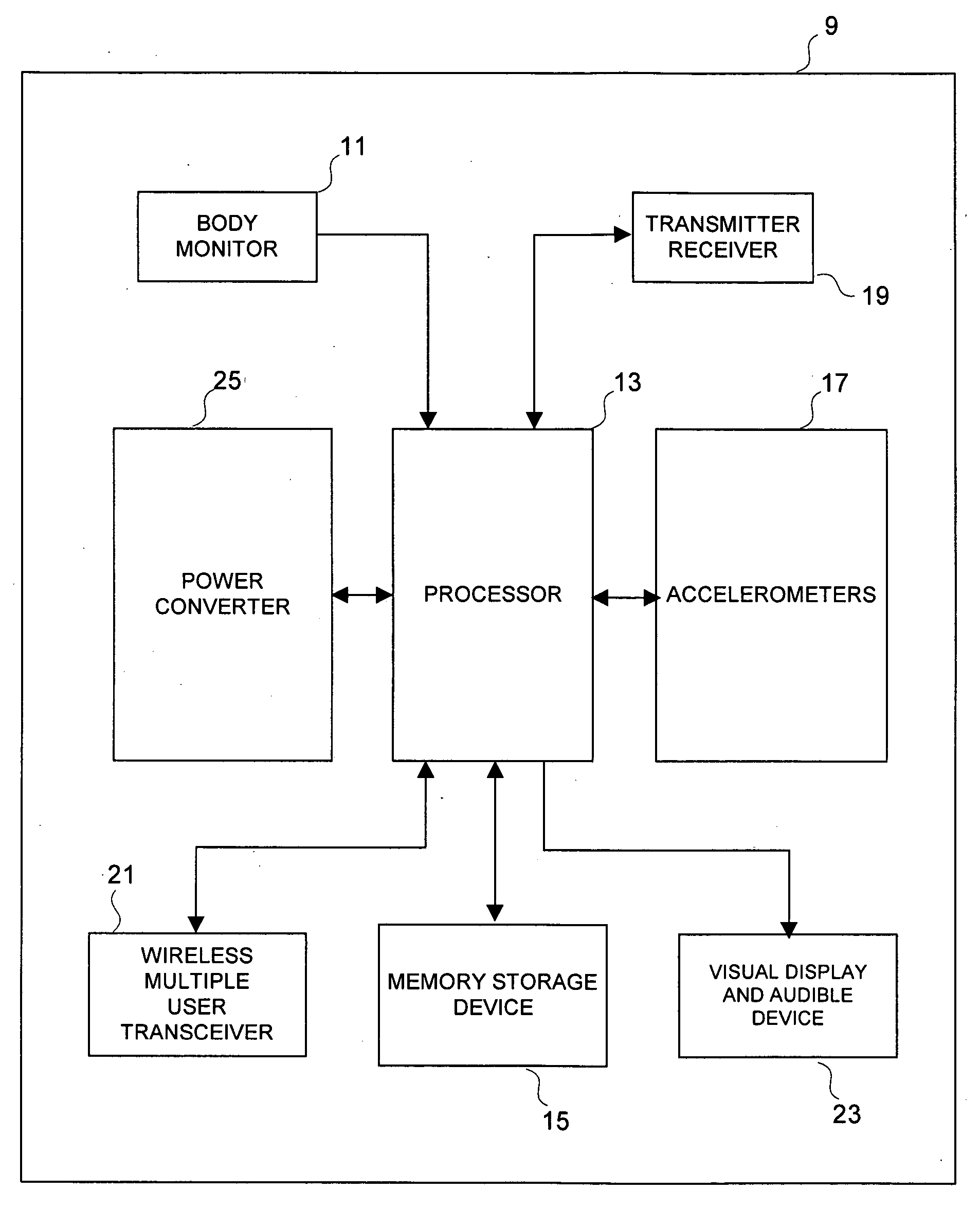
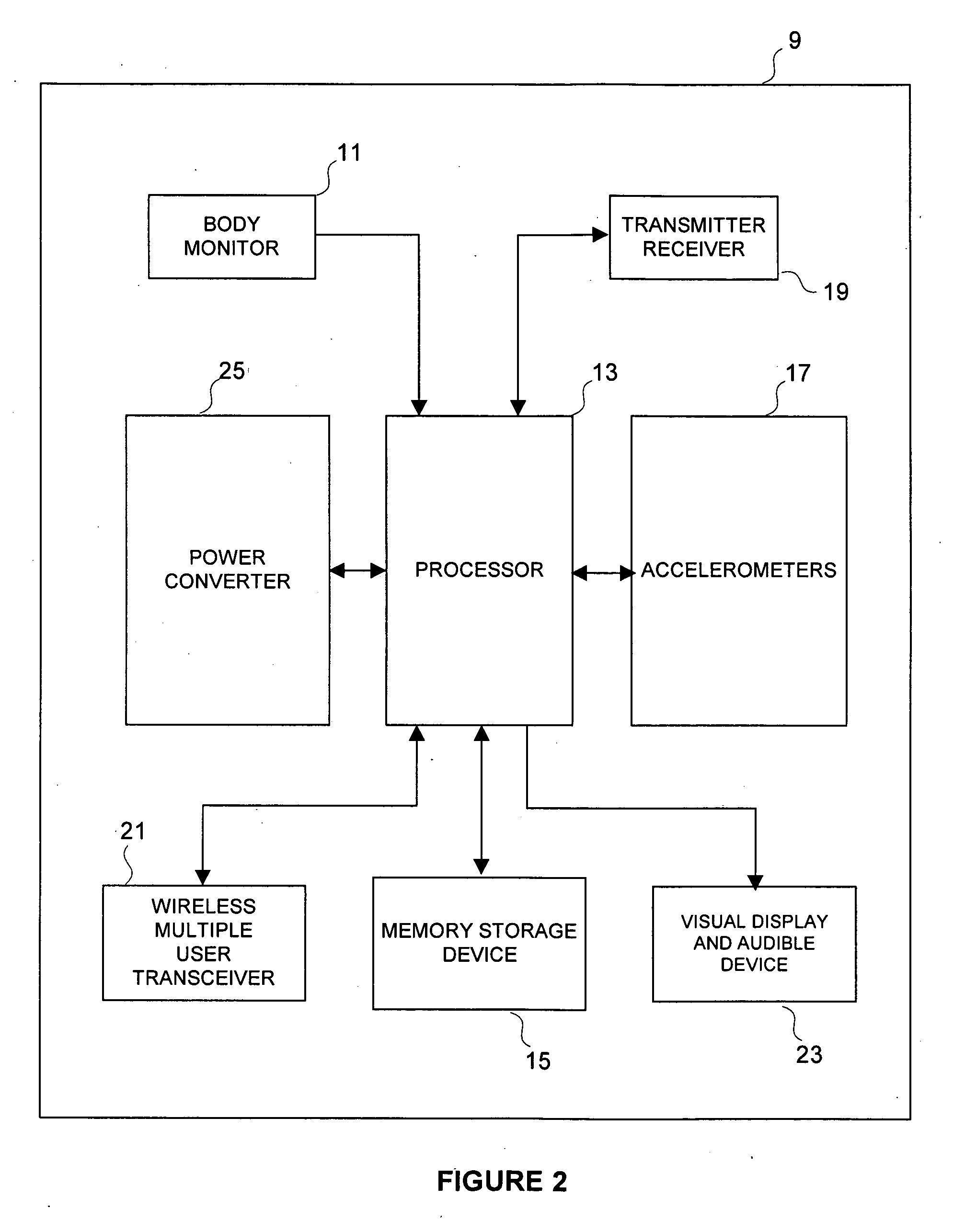
Method and apparatus including altimeter and accelerometers for determining work performed by an individual
Method and calculations determine an individual's, or several individuals' simultaneous rates of oxygen consumption, maximum rates of oxygen consumption, heart rates, calorie expenditures, and METS (multiples of metabolic resting rate) in order to determine the amounts of work that is performed by the individual's body. A heart monitor measures the heart rate, and an accelerometer measures the acceleration of the body along one or more axes. An altimeter measures change in altitude, a glucose monitor measures glucose in tissue and blood, and thermometers, thermistors, or thermocouples measure body temperature. Data including body fat and blood pressure measurements are stored locally and transferred to a processor for calculation of the rate of physiological energy expenditure. Certain cardiovascular parameters are mathematically determined. Comparison of each axis response to the individual's moment can be used to identify the type of activity performed and the information may be used to accurately calculate total energy expenditure for each physical activity. Energy expenditure may be calculated by assigning a separate proportionality coefficient to each axis and tabulating the resulting filtered dynamic acceleration over time, or by comparison with previously predetermined expenditures for each activity type. A comparison of total energy expenditure from the current activity is compared with expenditure from a previous activity, or with a baseline expenditure rate to assess the level of current expenditure. A measure of the individual's cardio-vascular health may be obtained by monitoring the heart's responses to various types of activity and to total energy expended.
Owner:TELECOM MEDICAL
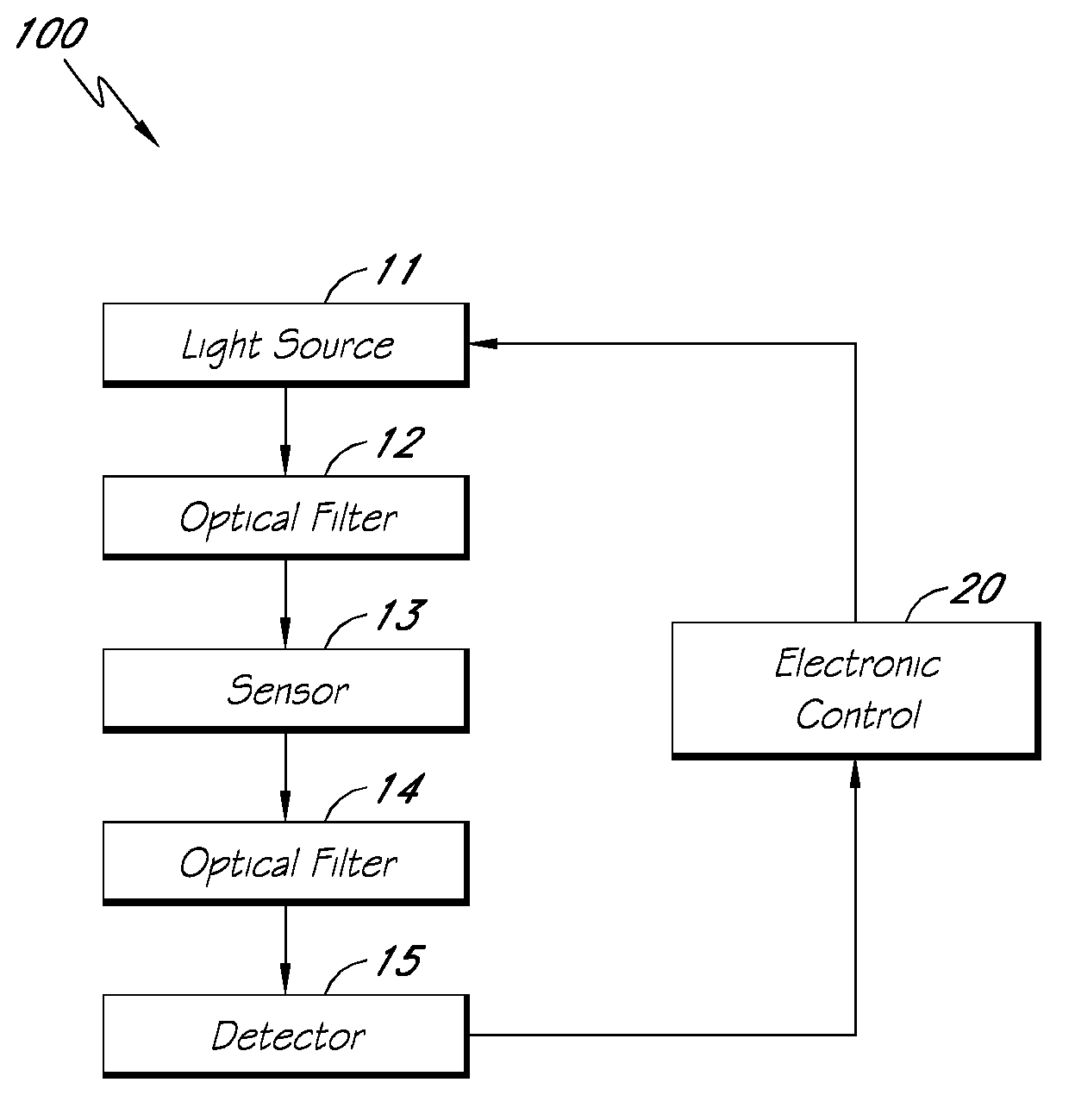
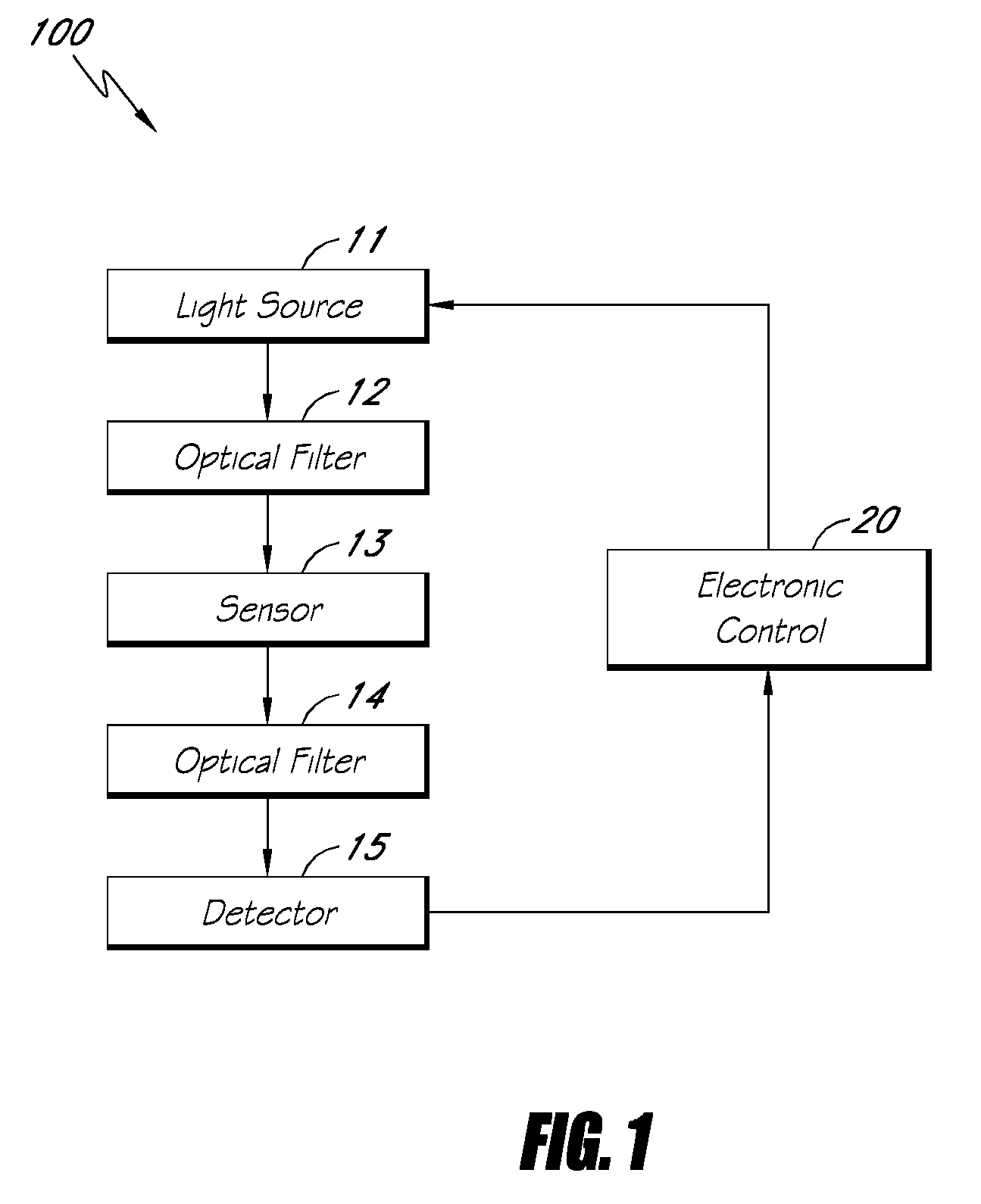
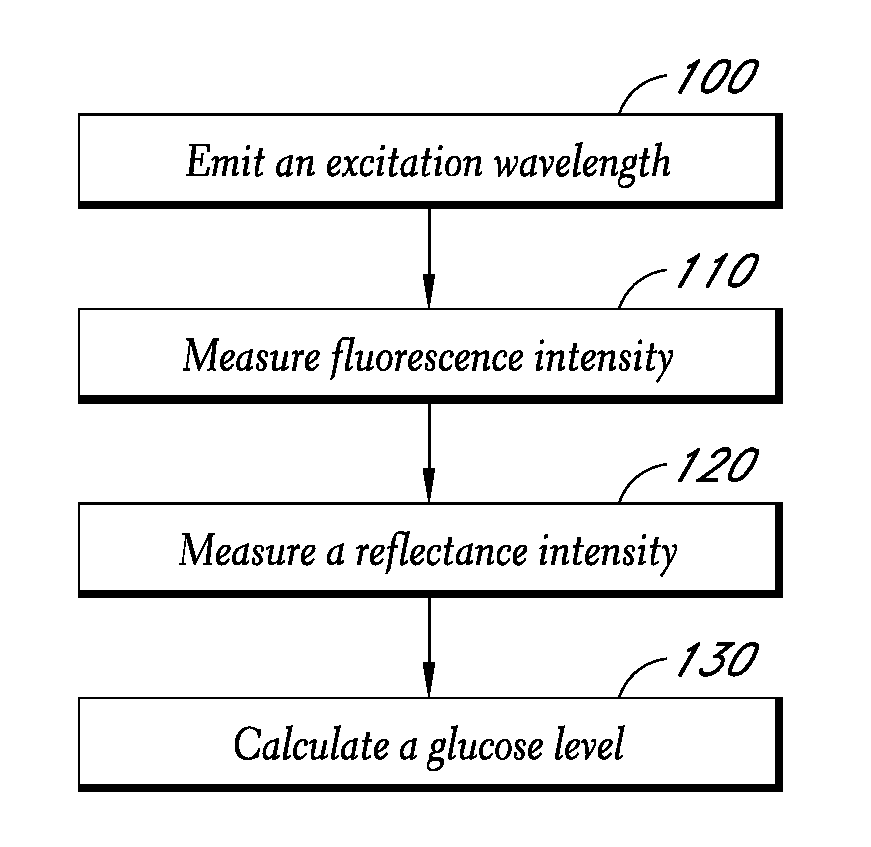
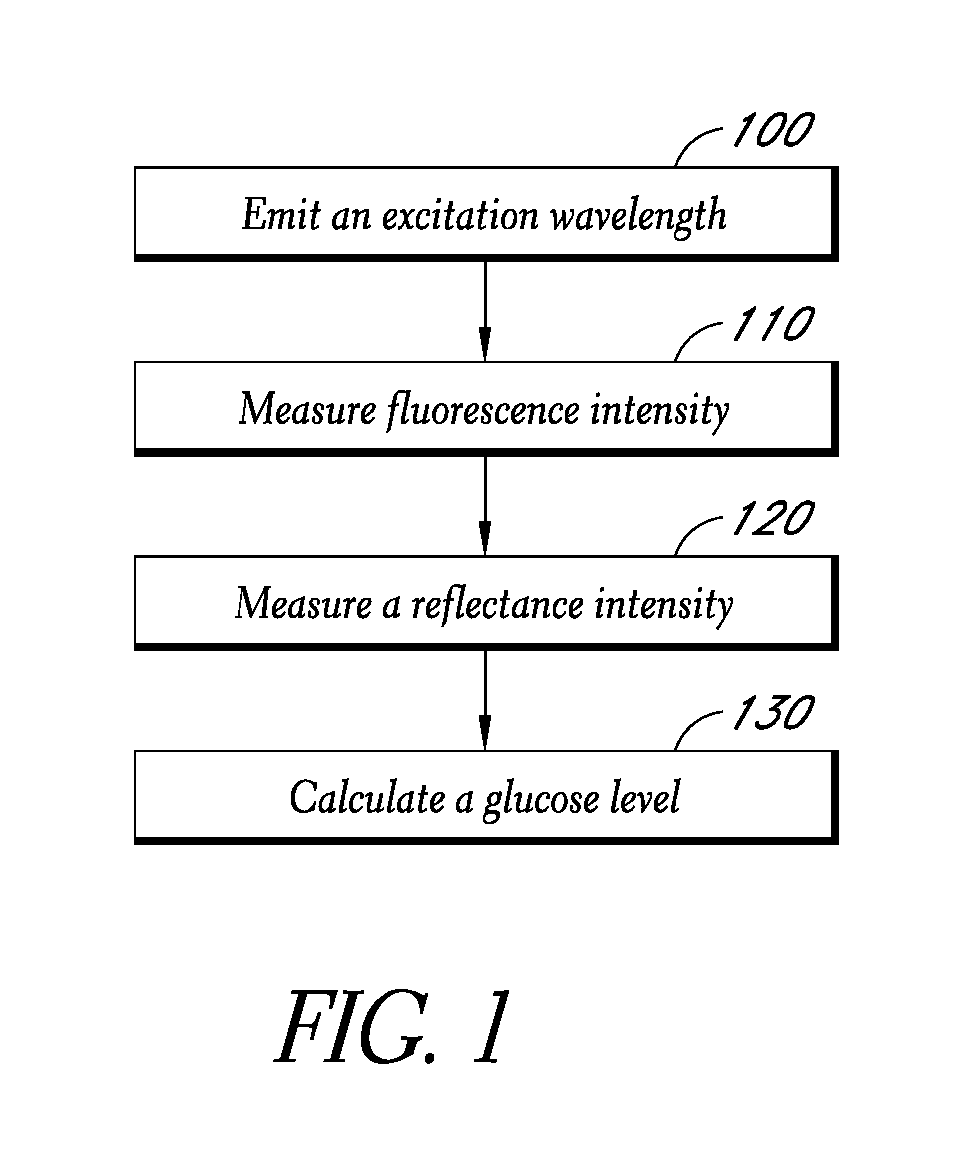
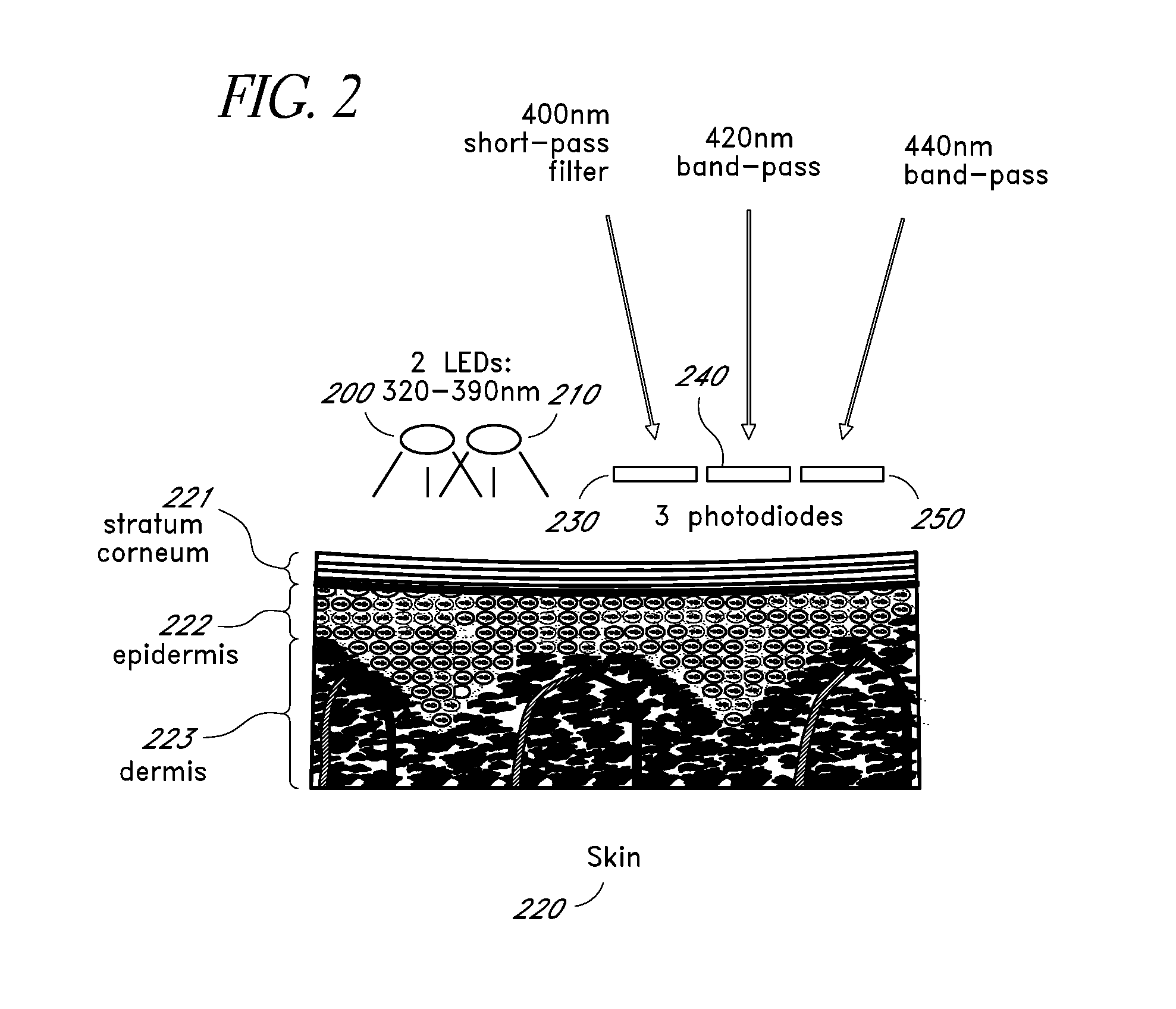
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20110028806A1Easily detected fluorescenceEasy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteLight energy
A noninvasive or minimally invasive procedure and system for measuring blood glucose levels is disclosed. A set of photodiodes detects the fluorescence and reflectance of light energy emitted from one or more emitters, such as LEDs, into a patient's skin. In an embodiment, small molecule metabolite reporters (SMMRs) that bind to glucose are introduced to the measurement area to provide more easily detected fluorescence.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
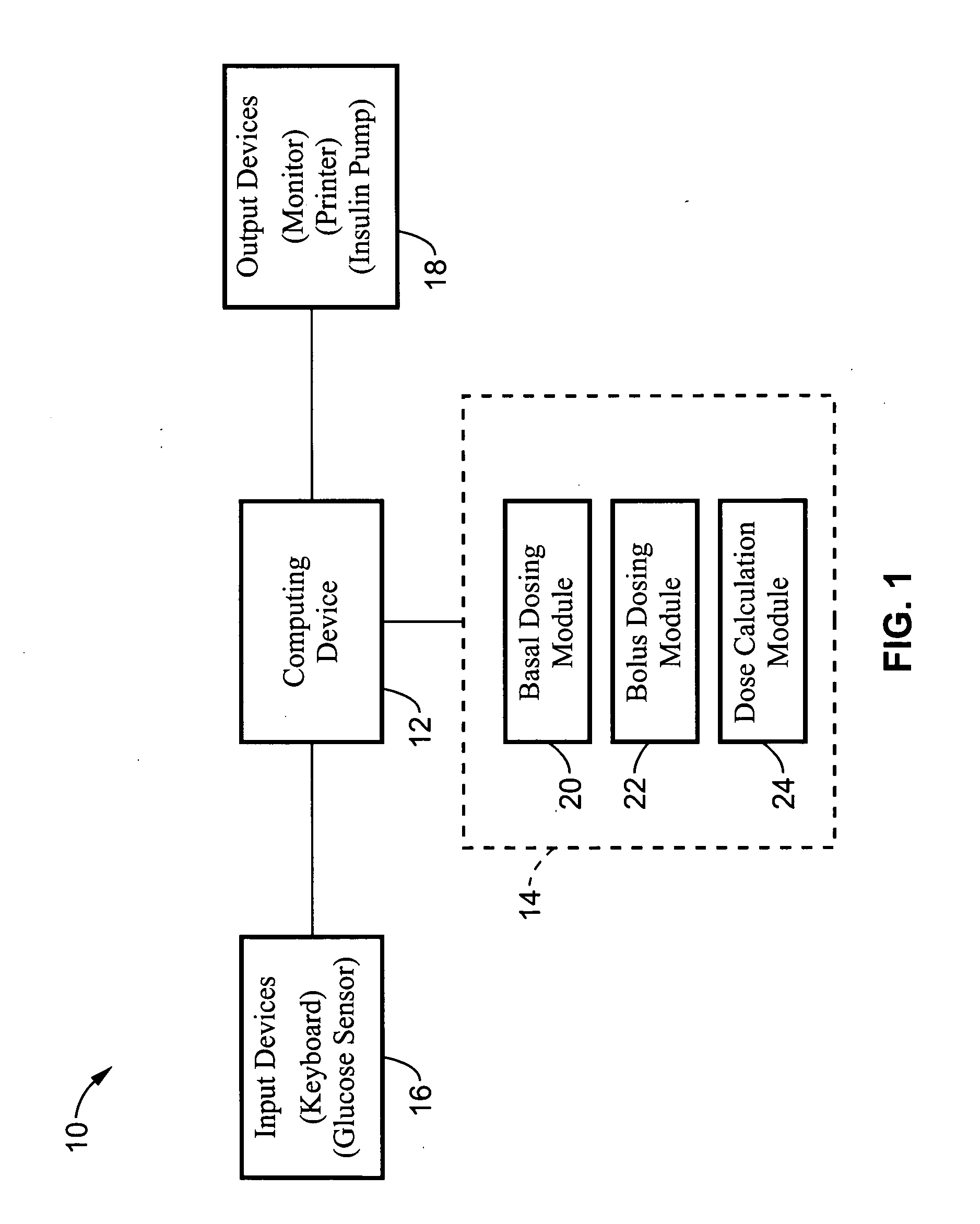
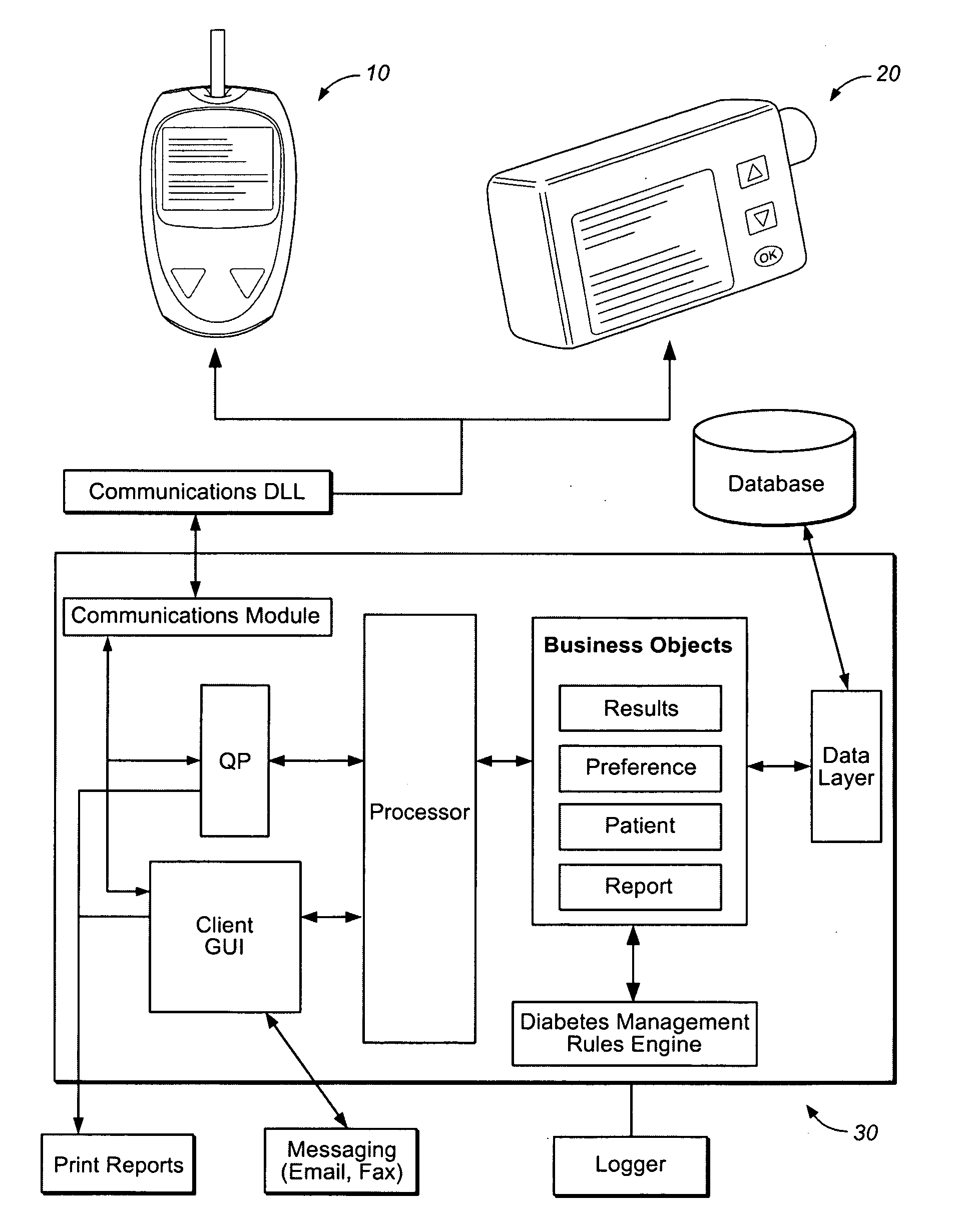
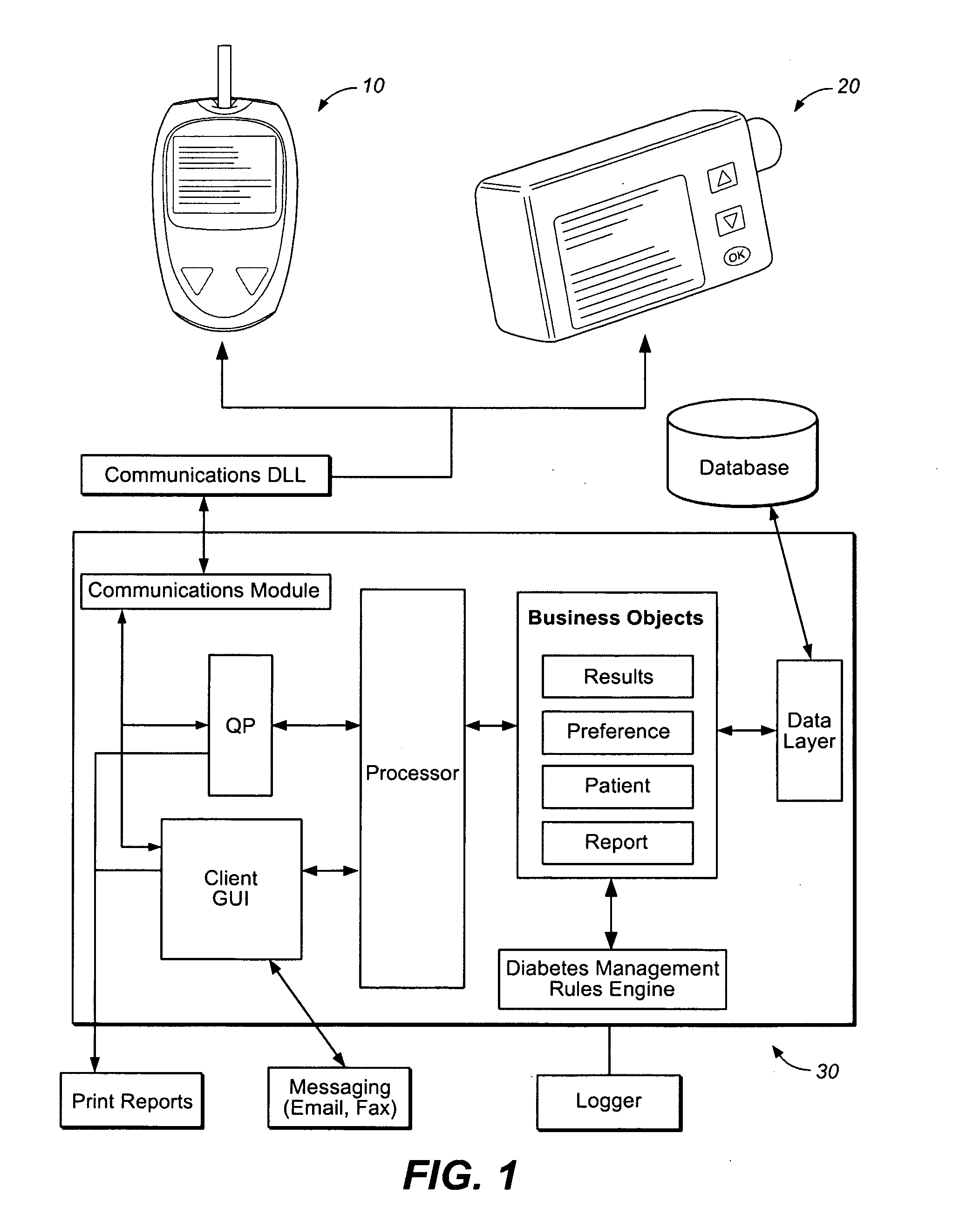
Diabetes Management System
In one embodiment, a diabetes management system comprises a glucose monitoring system, a pump system, and a remote device. The glucose monitoring system and pump system are attached to a patient and covered by a soft shell. The glucose monitoring system and the pump system are controlled by the small, touch-screen remote device such a patient can discreetly monitor blood glucose levels and administer insulin dosages. The remote device has a small and durable form factor that can be worn or carried in various ways.
Owner:ADAPTIVE PATH
Correction factor testing using frequent blood glucose input
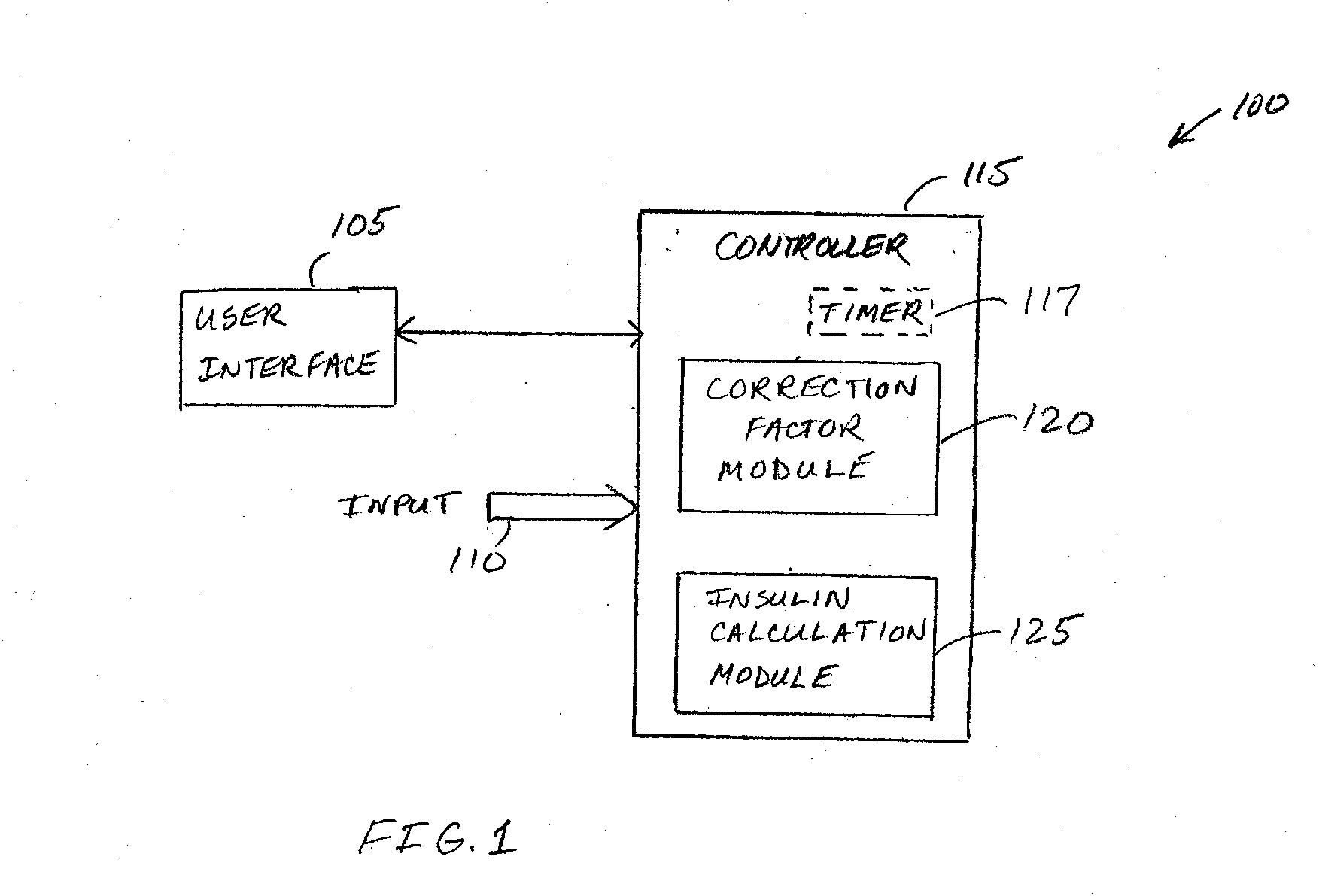
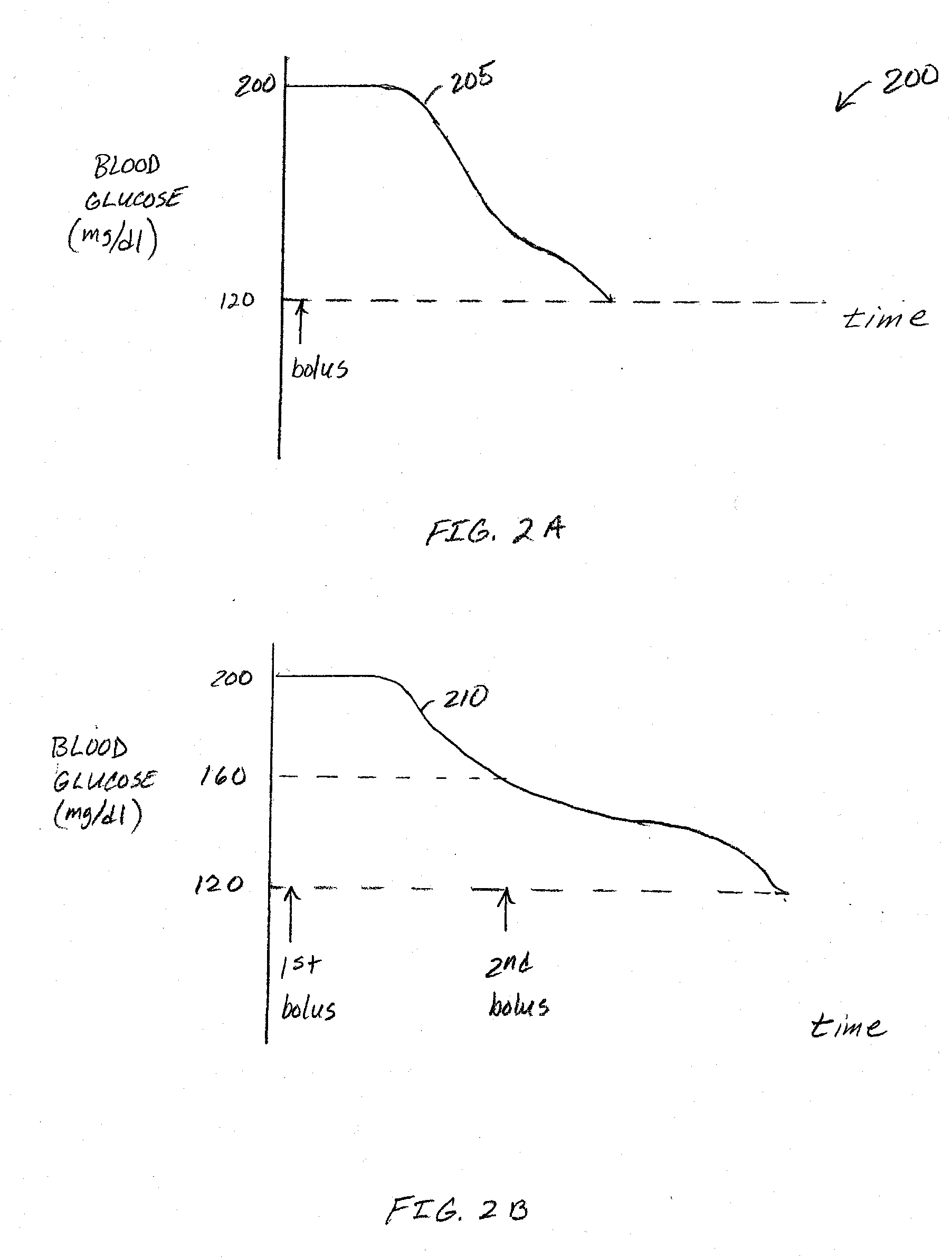
An apparatus comprising a user interface configured to generate an electrical signal to begin determination of an effective correction factor when prompted by a user, an input configured to receive sampled blood glucose data of a patient that is obtained during a specified time duration, including a time duration after delivery of an initial insulin correction bolus, and a controller in electrical communication with the input and the user interface. The controller includes a correction factor module configured for determining an effective correction factor according to an amount of insulin in the initial insulin correction bolus and a decrease in the blood glucose level determined using the sampled blood glucose data. Other devices and methods are disclosed.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
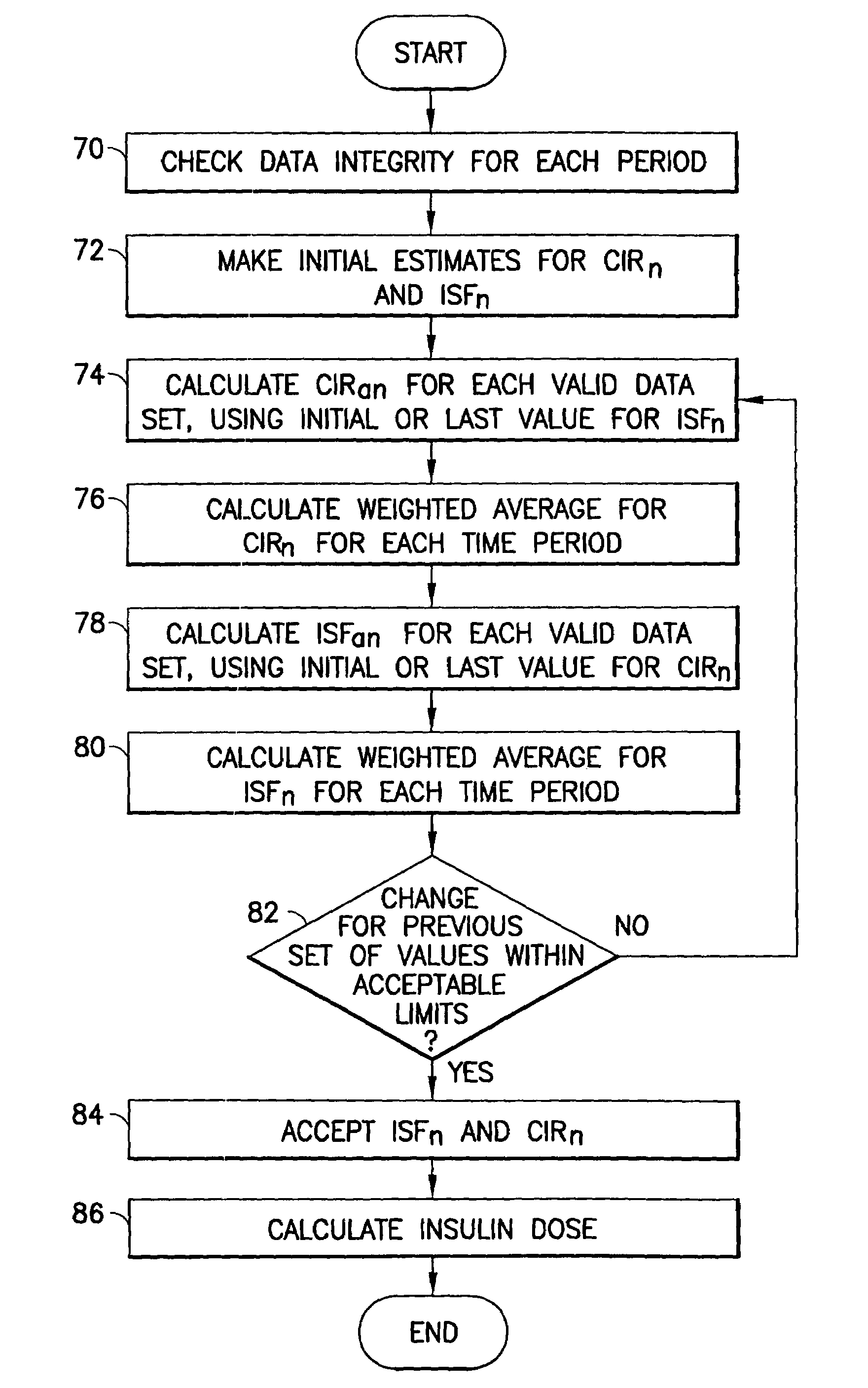
Method and apparatus to calculate diabetic sensitivity factors affecting blood glucose
InactiveUS20100262434A1Reasonable expectationPhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsGlucose polymersD-Glucose
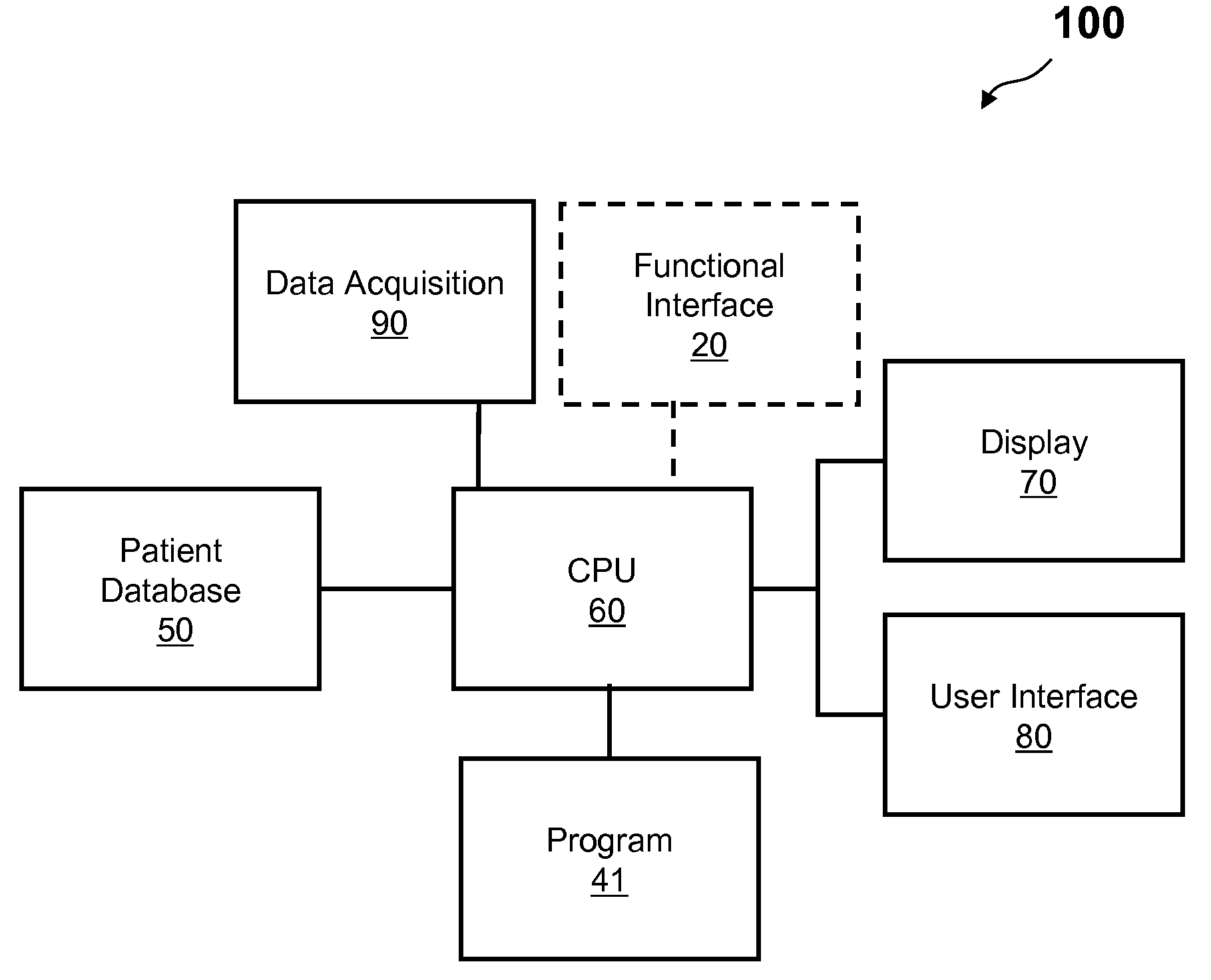
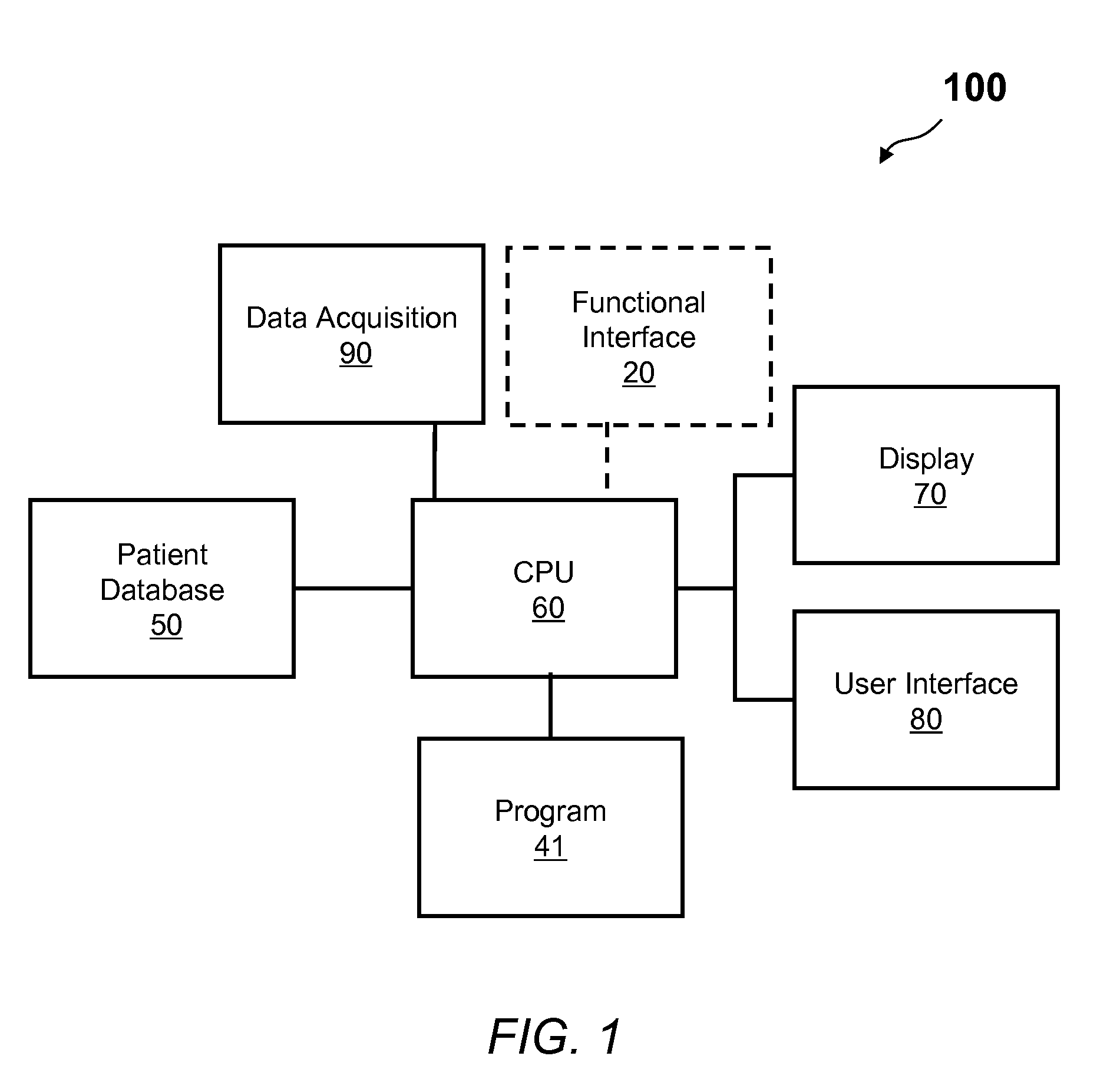
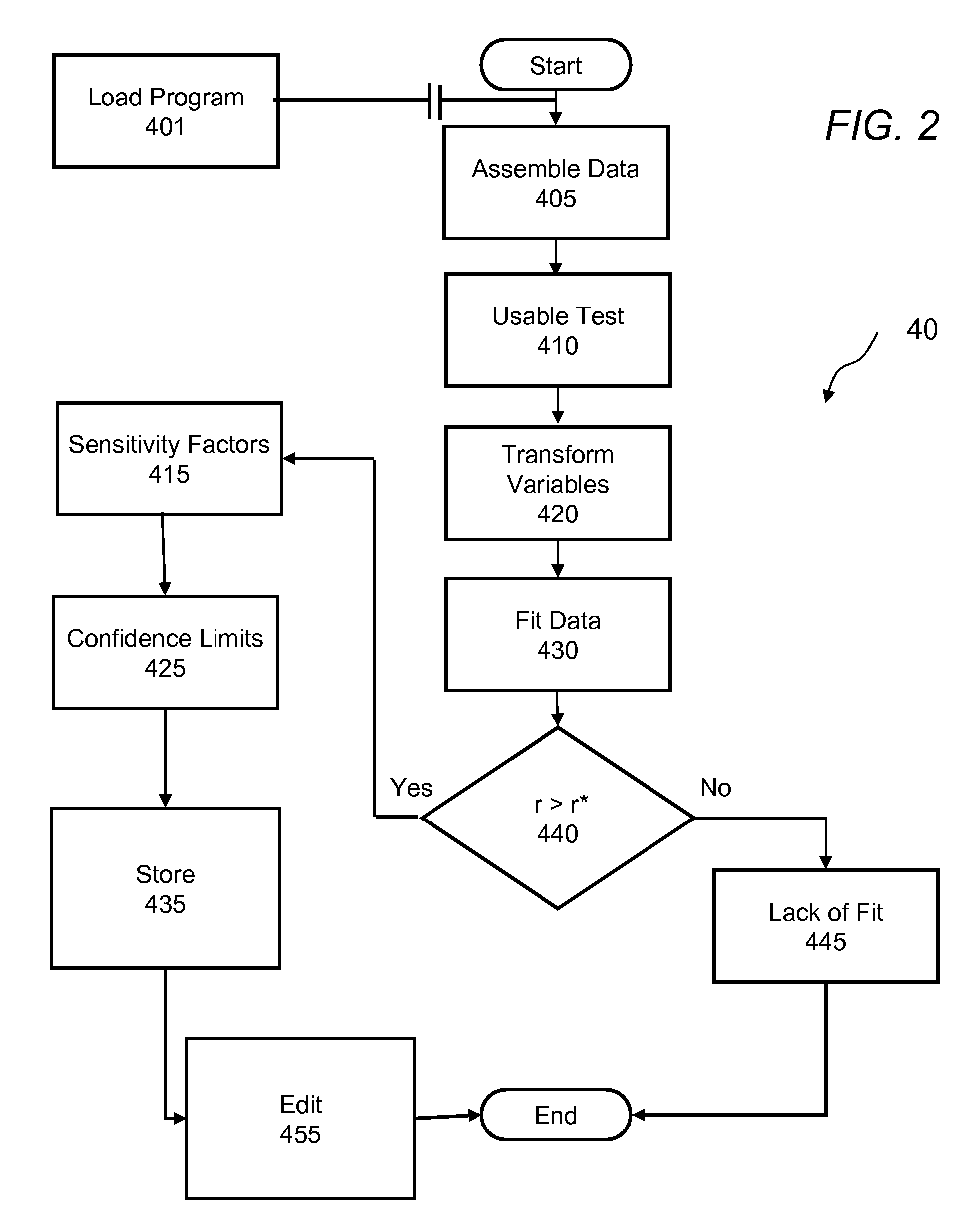
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining a diabetic patient's carbohydrate to insulin ratio (CIR), carbohydrate to blood glucose ratio (CGR), and insulin sensitivity factor (ISF) using the patient's record of blood glucose readings, carbohydrate consumption and insulin doses. The method provides the sensitivity factors that best account for the patient's observed blood glucose changes by linear regression of appropriately transformed variables. An apparatus that can collect and store the blood glucose readings, insulin dosages, and carbohydrate intake data and process these data according to this invention can generate statistically characterized sensitivity factors to advise the diabetic patient on optimal bolus insulin dosages.
Owner:SHAYA STEVEN A
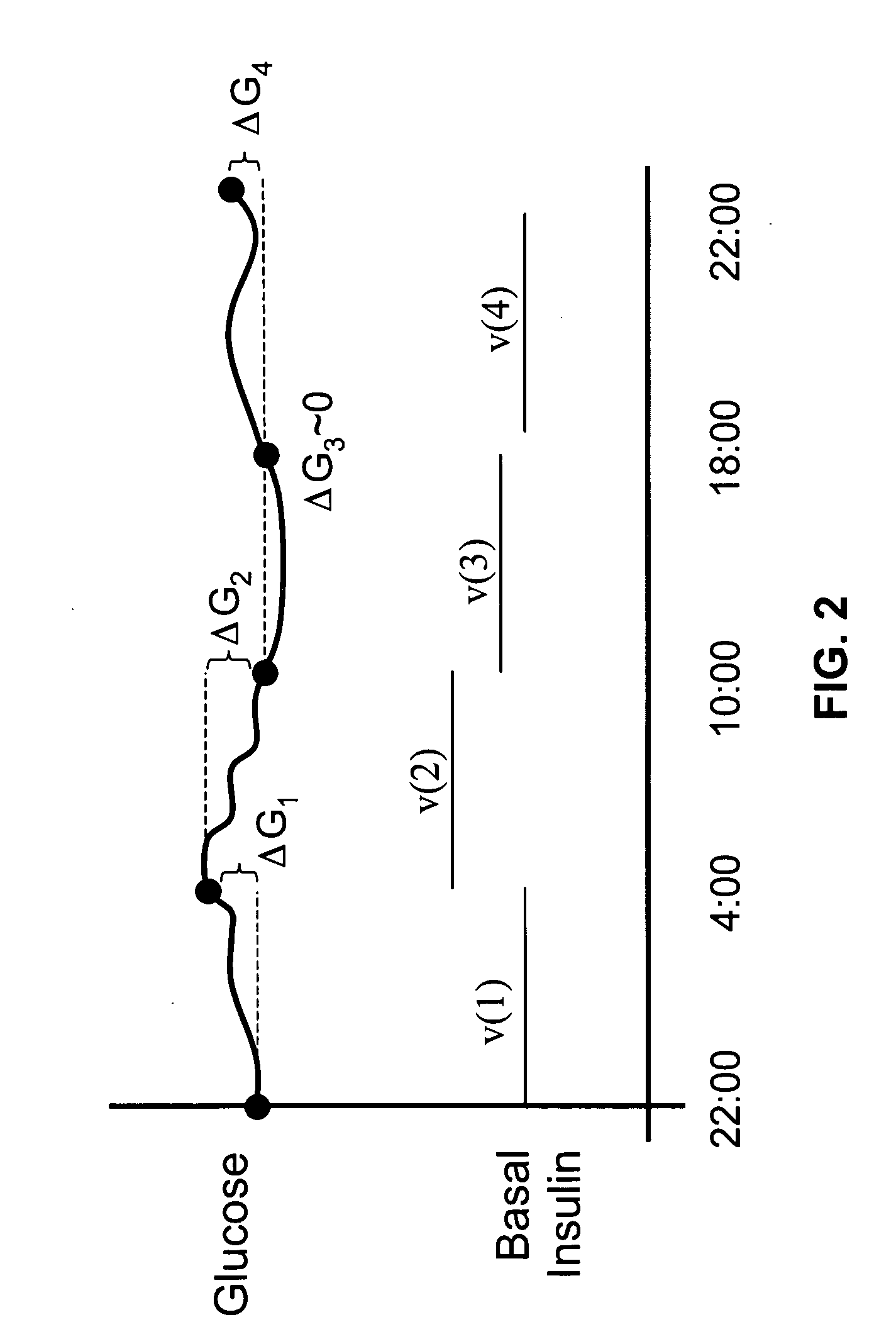
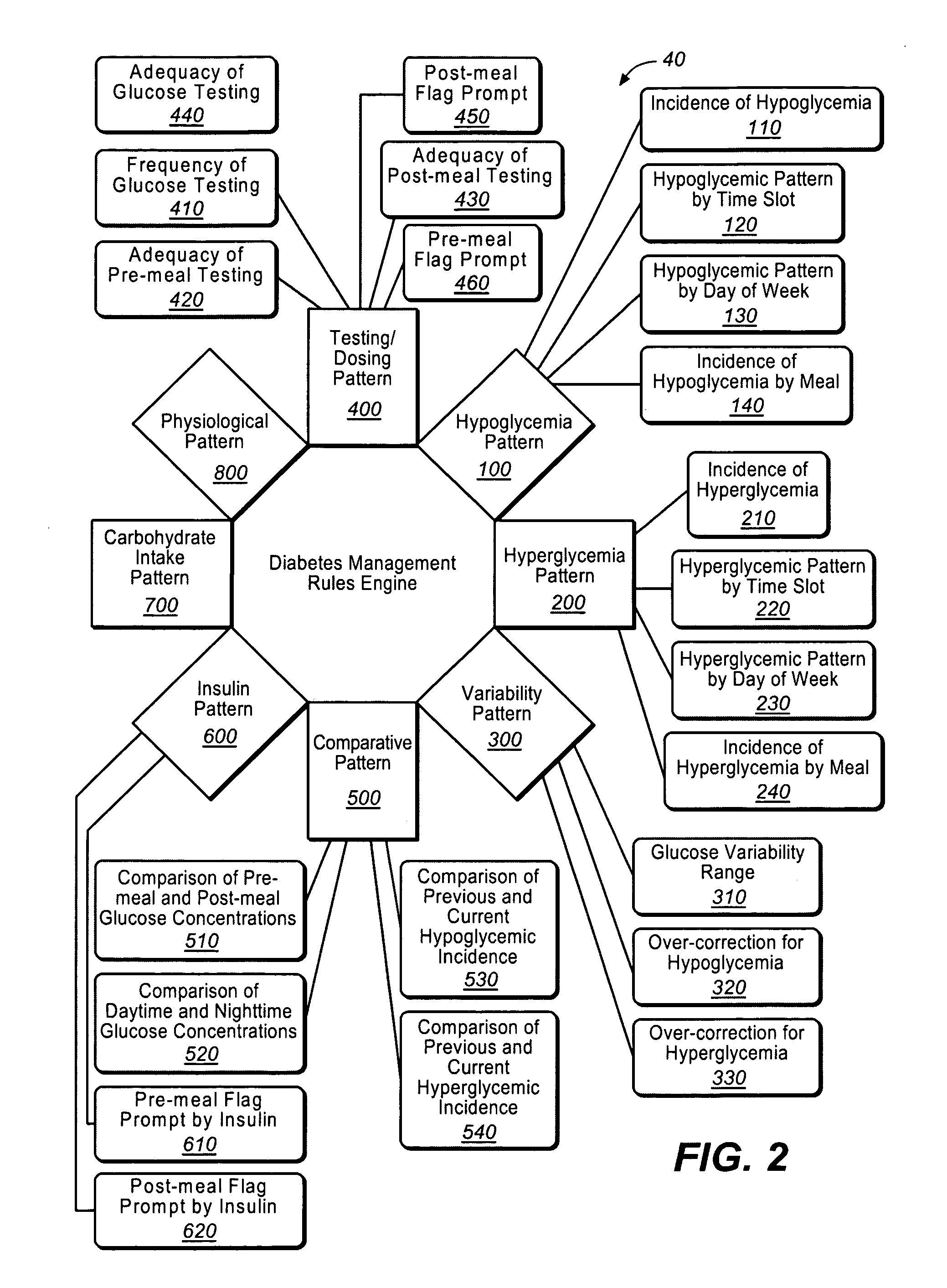
Methods of determining pre or post meal time slots or intervals in diabetes management
A diabetes management system or process is provided herein that may be used to analyze and recognize patterns for a large number of blood glucose concentration measurements and other physiological parameters related to the glycemia of a patient. In particular, a method of monitoring glycemia in a patient may include storing a patient's data on a suitable device, such as, for example, a blood glucose meter. The patient's data may include blood glucose concentration measurements. The diabetes management system or process may be installed on, but is not limited to, a personal computer, an insulin pen, an insulin pump, or a glucose meter. The diabetes management system or process may identify a plurality of pattern types from the data including a testing / dosing pattern, a hypoglycemic pattern, a hyperglycemic pattern, a blood glucose variability pattern, and a comparative pattern. After identifying a particular pattern with the data management system or process, a warning message may be displayed on a screen of a personal computer or a glucose meter. Other messages can also be provided to ensure compliance of any prescribed diabetes regiments or to guide the patient in managing the patient's diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
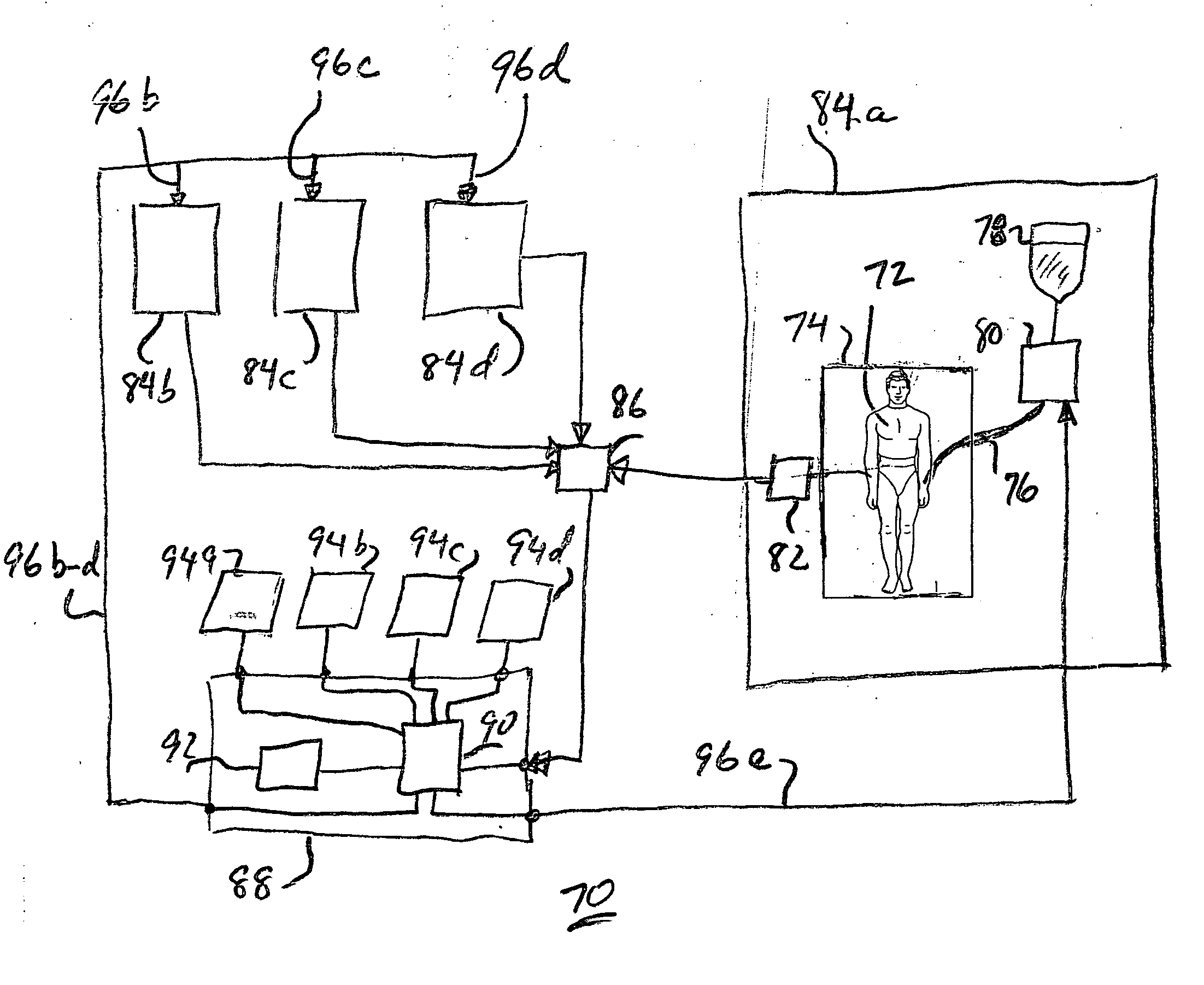
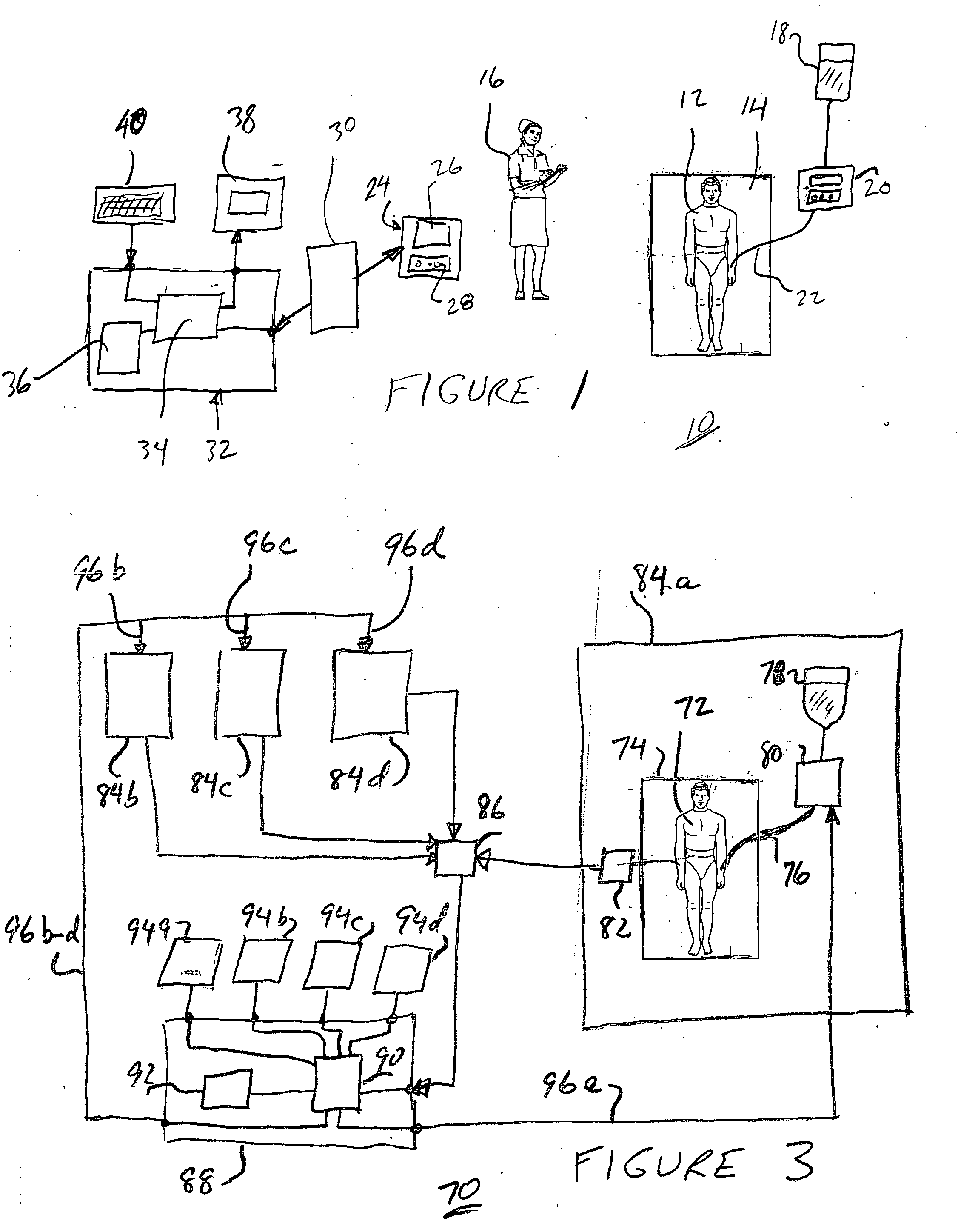
System for managing glucose levels in patients with diabetes or hyperglycemia
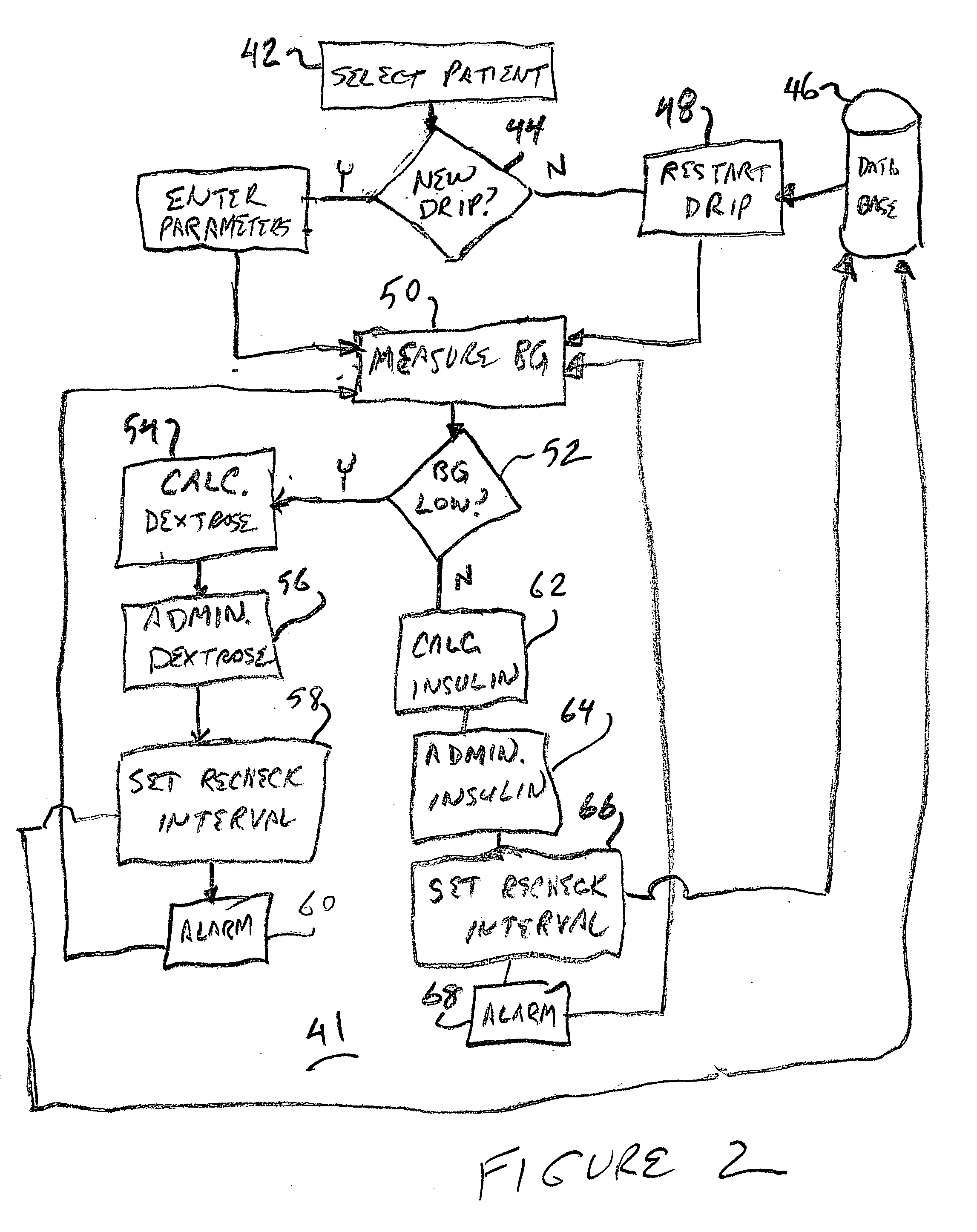
A blood glucose maintenance system for use by hyperglycemic individuals measures their blood glucose level and calculates an appropriate glucose or insulin dosage based on the measurement. Recheck intervals responsive to dosage history are determined. Warning or alert messages or signals are produced if certain measurements or calculations fall outside established normal ranges. It is particularly useful for patients in a hospital or in-patient environment.
Owner:INDIANA UNIVERSITY HEALTH
Test plug and cable for a glucose monitor
Owner:MINIMED
Methods for modeling insulin therapy requirements
InactiveUS20110098548A1Improve fitShorten the timeMedical simulationDrug and medicationsGlycemicGlucose control
Various methods for improving the use of model based prediction of future blood glucose control in a patient having diabetes are described. A system for processing diabetes related information, including glucose information, for accurately predicting future glucose levels as a function of glucose data, carbohydrate intake, insulin delivery history and exercise history and then providing recommendations related to the predicted future glucose levels, is also described.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
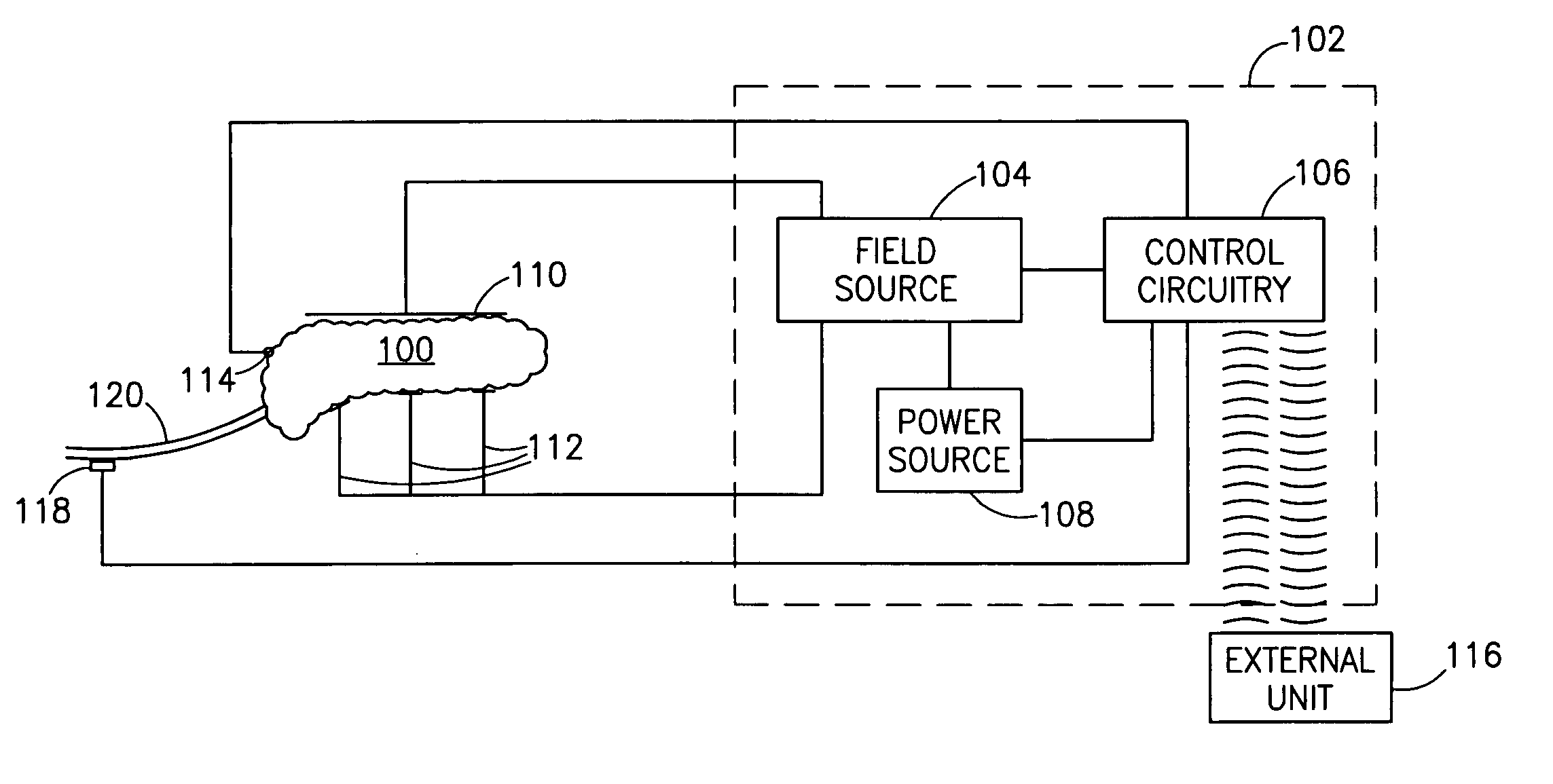
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS7006871B1Increased insulin secretionAvoiding unacceptable calcium level profileElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsLevel insulin
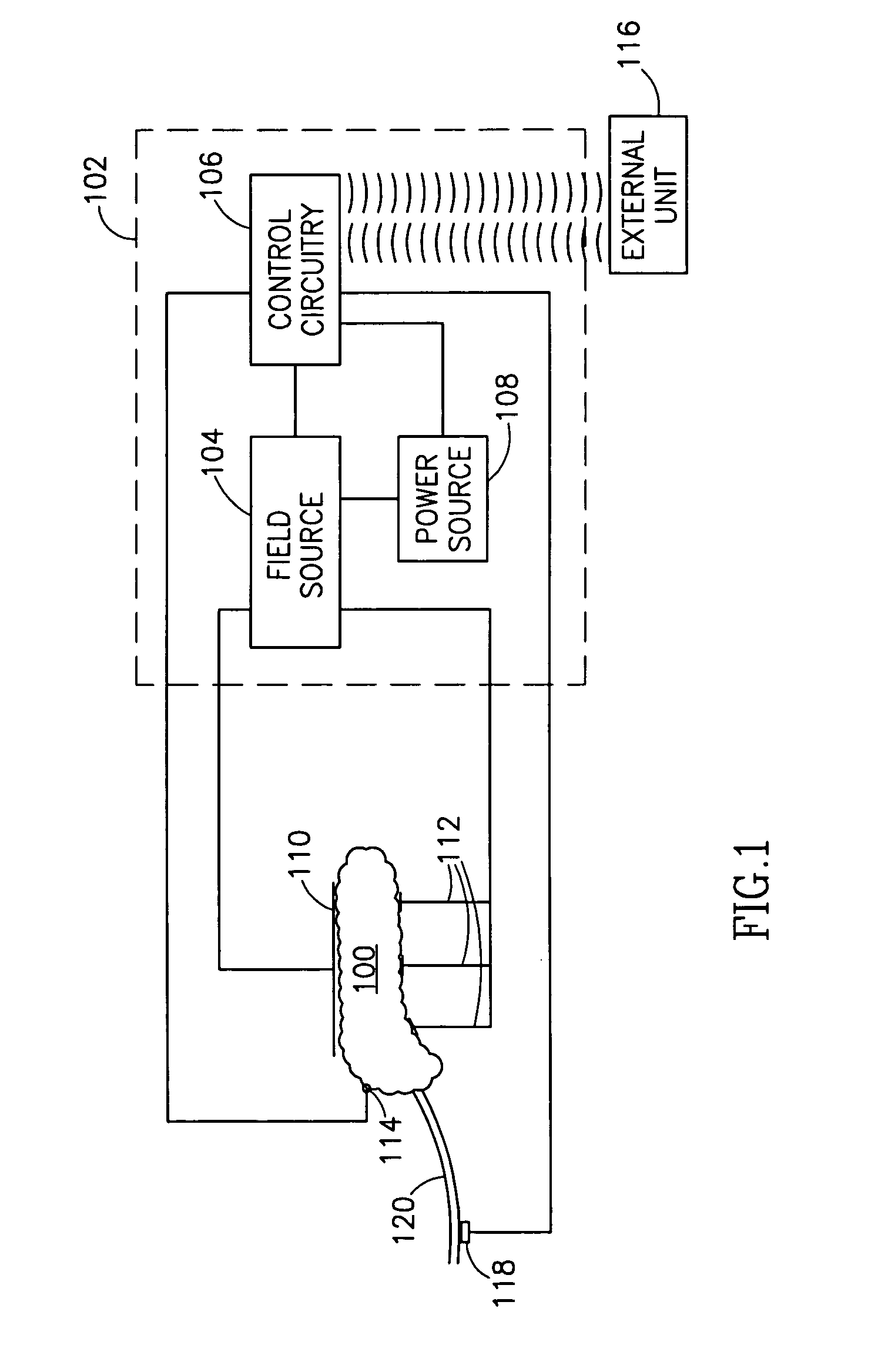
A pancreatic controller (102), comprising: a glucose sensor (118), for sensing a level of glucose or insulin in a body serum; at least one electrode (110, 112), for electrifying an insulin producing cell or group of cells; a power source (104) for electrifying said electrode with a pulse that does not initiate an action potential in said cell and has an effect of increasing insulin secretion; and a controller (106) which receives the sensed level and controls said power source to electrify said electrode to have a desired effect on said level.
Owner:METACURE
System for determining insulin dose using carbohydrate to insulin ratio and insulin sensitivity factor
An apparatus and method are provided for determining a patient's carbohydrate to insulin ratio (CIR) and insulin sensitivity factor (ISF), and using these values, along with values for current blood glucose level and deviation from target blood glucose level, for determining insulin dose in view of carbohydrate intake during a particular time period. The apparatus and method employ algorithms that can be implemented in any of a personal computer, personal data assistant, hand held computing device, blood glucose monitor, infusion pump, medication delivery pen, meter, calculator, among other therapeutic, diagnostic or informational devices used for managing a patient's blood glucose levels.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
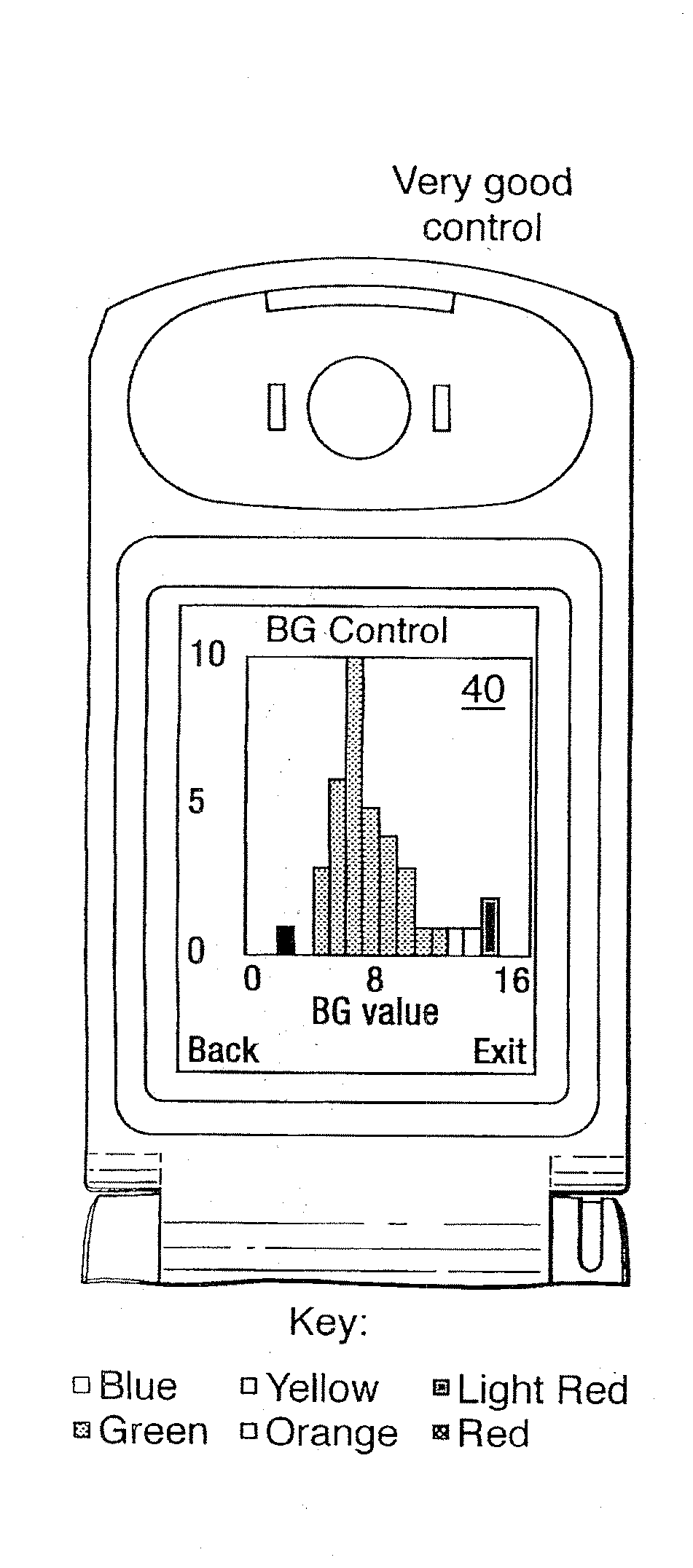
Medical Data Display
InactiveUS20100259543A1Quality is easy to controlMedical simulationDrawing from basic elementsData displayBlood Glucose Measurement
A method of displaying medical data, particularly data representative of the condition of patients suffering from chronic medical conditions such as asthma, diabetes and hypertension. The display consists of two graphical elements, one of which indicates the current value of a parameter indicative of the patient's condition, this being displayed against another graphical element which represents a model of normality for that patient. The graphical element indicating the current condition may be, for example, a needle, against a scale which is constructed according to the patient-specific model of normality. This is particularly advantageous in the case of displays which have a small display area, such as mobile telephones and PDAs. Other forms of display are disclosed, such as histograms with the display being dynamically colour-coded and auto-scaled, or displays including limits which may vary. Another form of display is also disclosed which illustrates administrations of a pharmacological agent and corresponding measurements of the patient's condition, with a visual link such as colour-coding linking the administration to the corresponding condition measurement. For example several days of insulin administration dosages may be displayed alongside several days of blood glucose measurements, with the administrations colour-coded to the corresponding blood glucose measurement, to assist the patient in determining whether the insulin administration is stably controlling their condition.
Owner:E SAN LTD
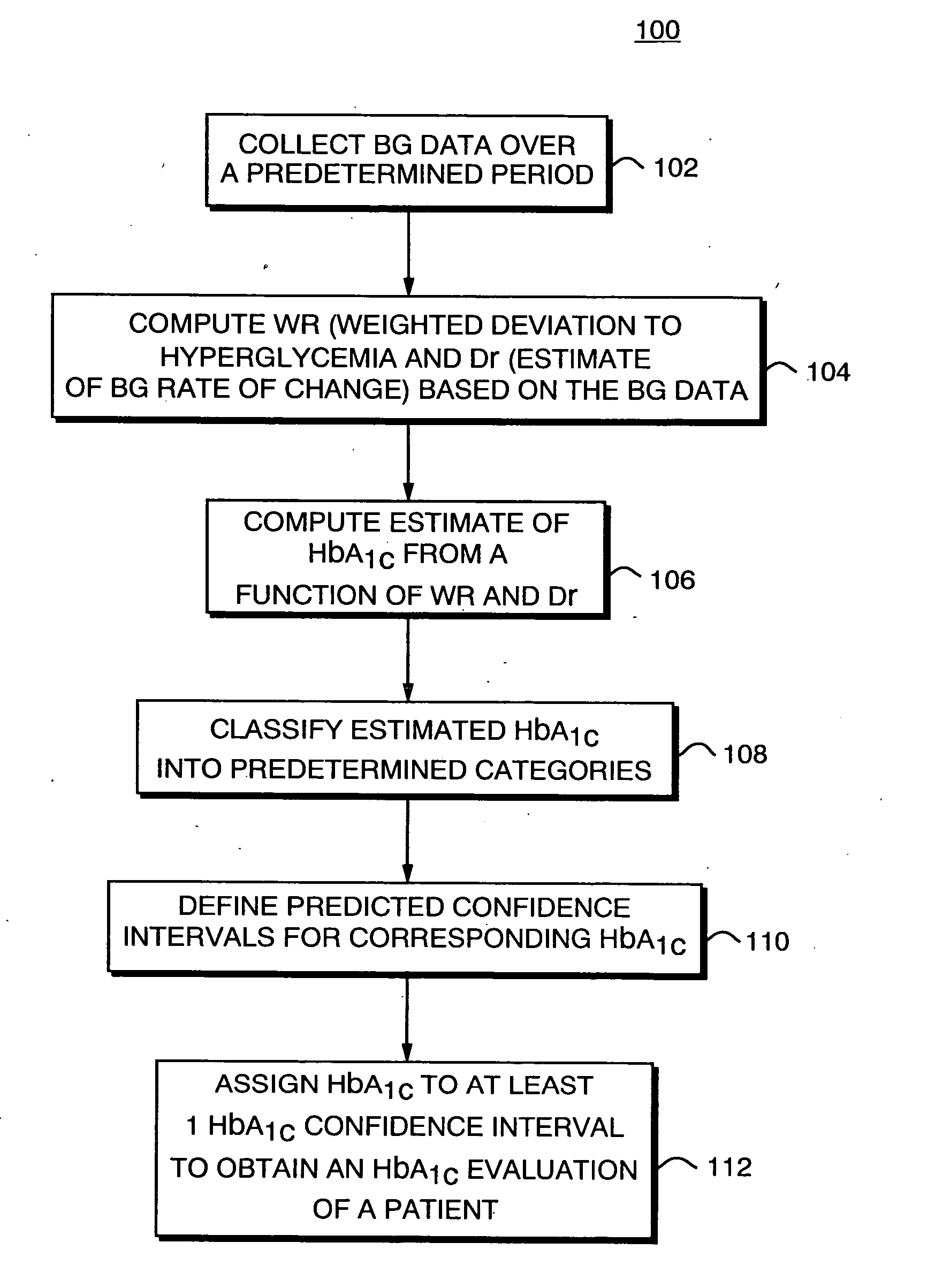
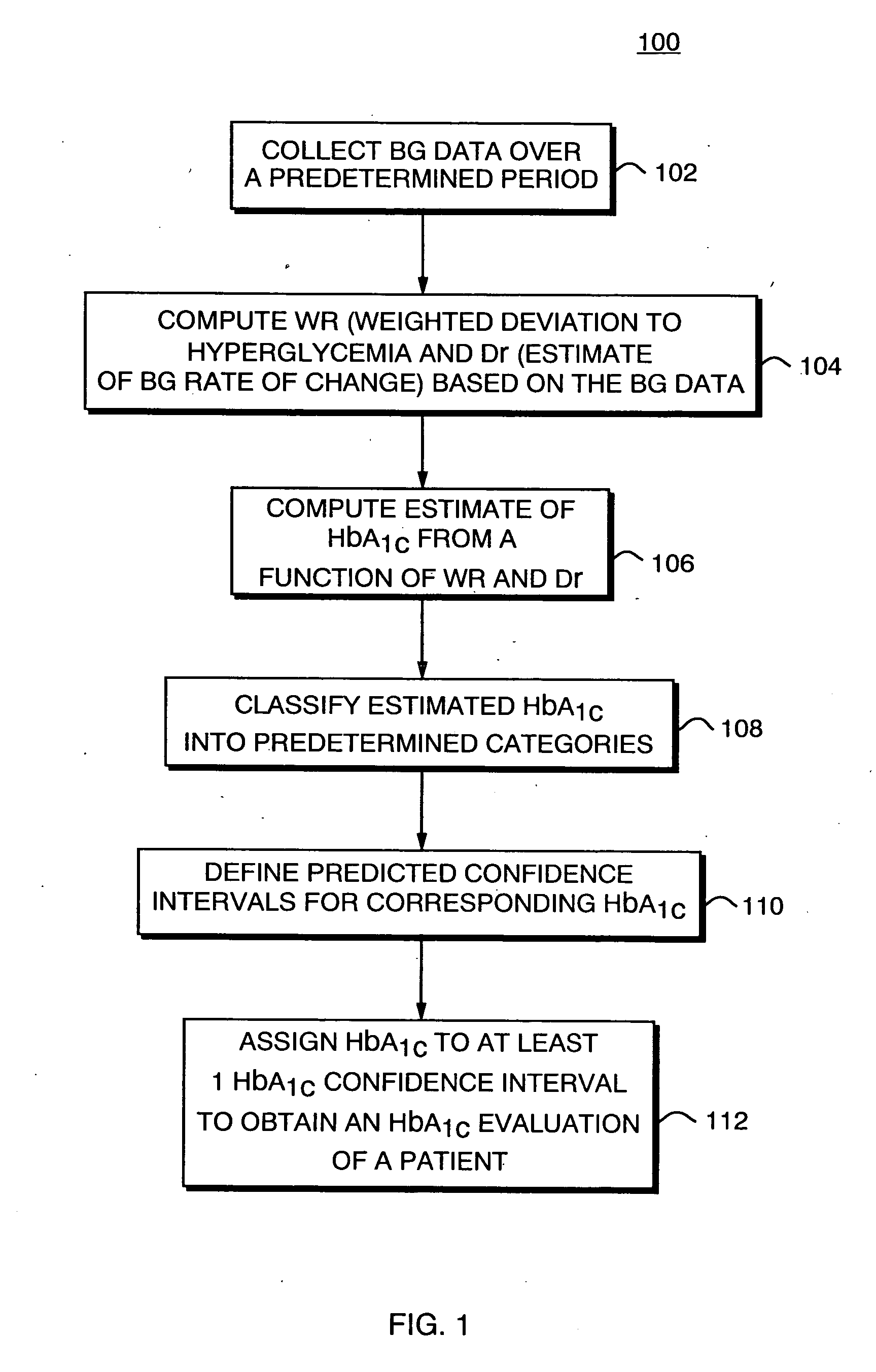
Method, system, and computer program product for the evaluation of glycemic control in diabetes from self-monitoring data
ActiveUS20060094947A1Easy to monitorContinuous informationMedical simulationTelemedicineLow glucoseAcute hyperglycaemia
A method, system, and computer program product related to the diagnosis of diabetes, and is directed to predicting the long-term risk of hyperglycemia, and the long-term and short-term risks of severe hypoglycemia in diabetics, based on blood glucose readings collected by a self-monitoring blood glucose device. The method, system, and computer program product pertain directly to the enhancement of existing home blood glucose monitoring devices, by introducing an intelligent data interpretation component capable of predicting both HbA1c and periods of increased risk of hypoglycemia, and to the enhancement of emerging continuous monitoring devices by the same features. With these predictions the diabetic can take steps to prevent the adverse consequences associated with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
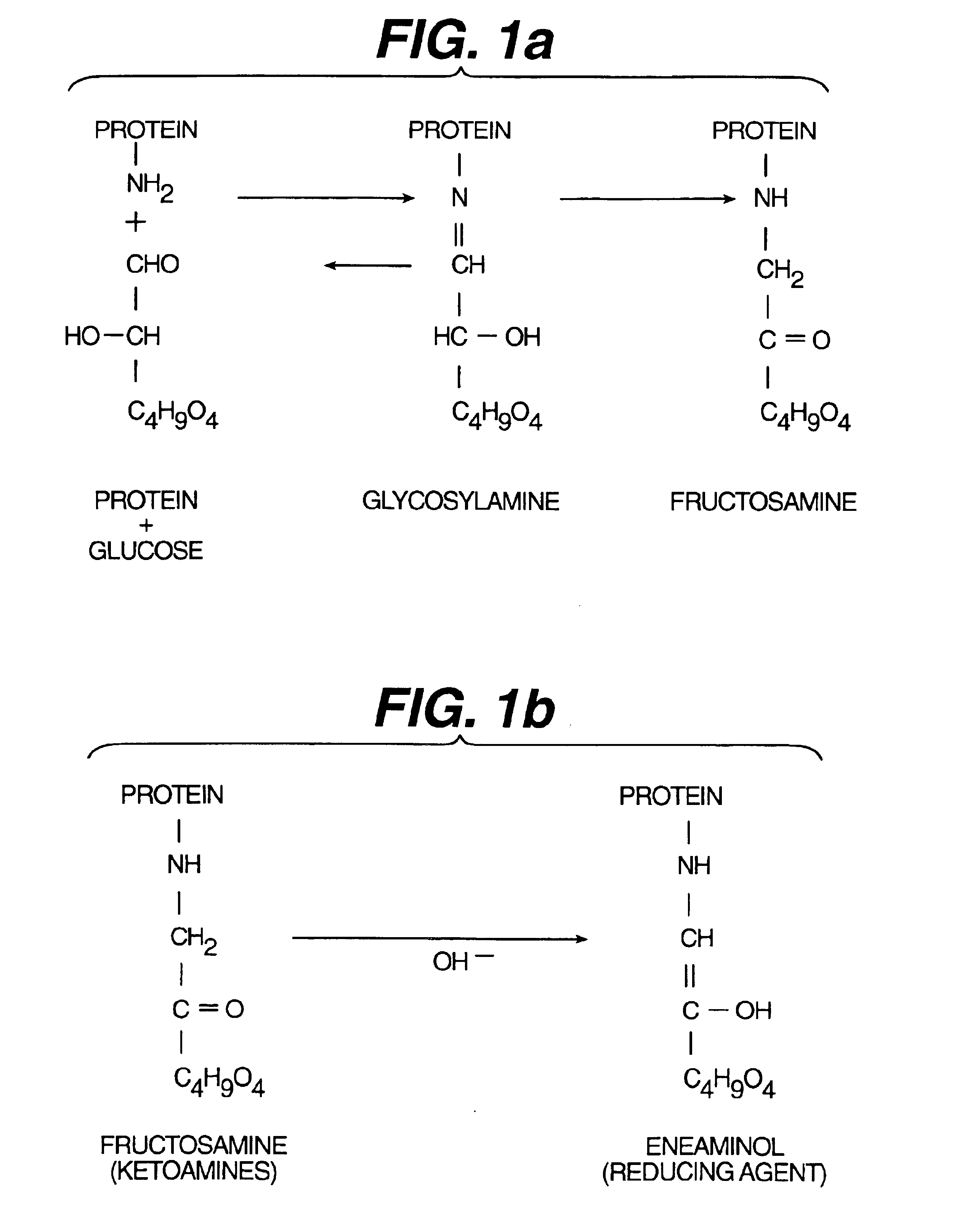
Combined assay for current glucose level and intermediate or long-term glycemic control
InactiveUS6958129B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteConcentrations glucose
The present invention is directed to a single test system and method for determining the integrated glycemic condition of a subject by measuring the concentration of glucose and the level of protein-bound glucose in a subject's body fluid, such as whole blood. The glucose concentration is indicative of the subject's immediate glycemic condition, whereas the protein-bound glucose concentration is indicative of either intermediate or long-term glycemic condition. Optionally, other analytes indicative of glycemic condition, such as ketone bodies or fatty acid derivatives, can also be measured. The present invention also provides a method of diagnosing diabetes. The invention additionally provides a method for analyzing the concentration of fructosamine in less than or equal to five minutes without the use of a reaction accelerator.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
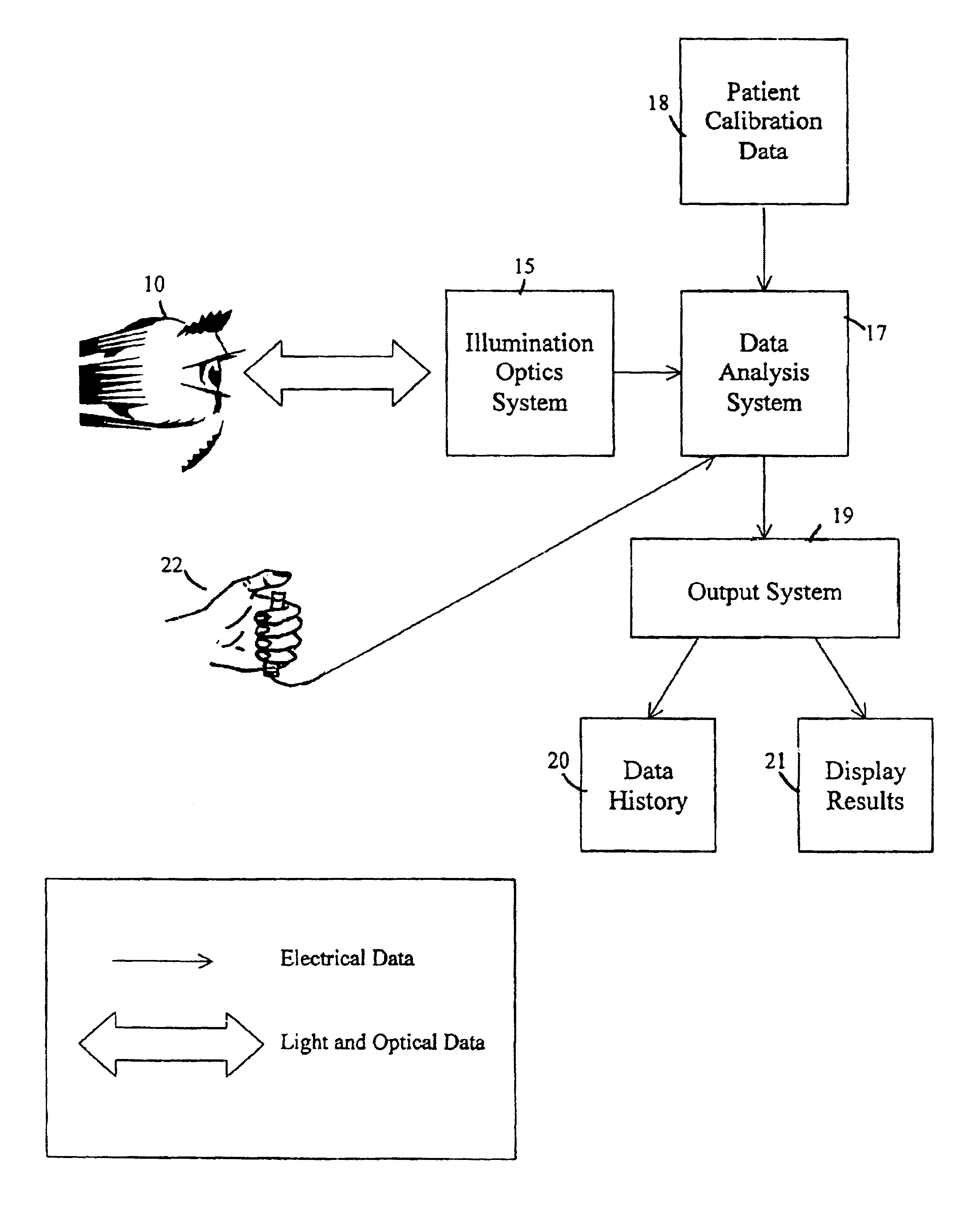
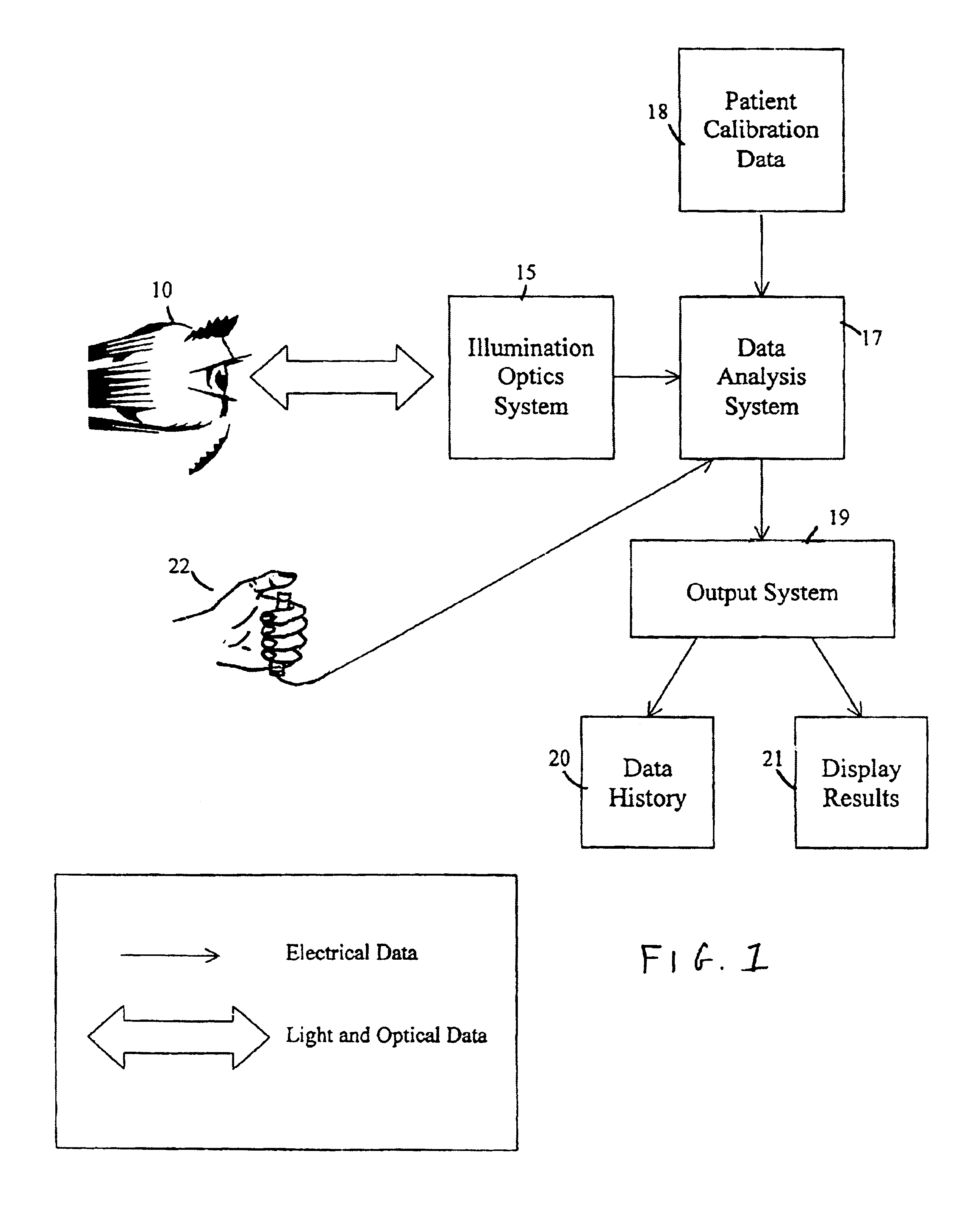
Non-invasive psychophysical measurement of glucose using photodynamics
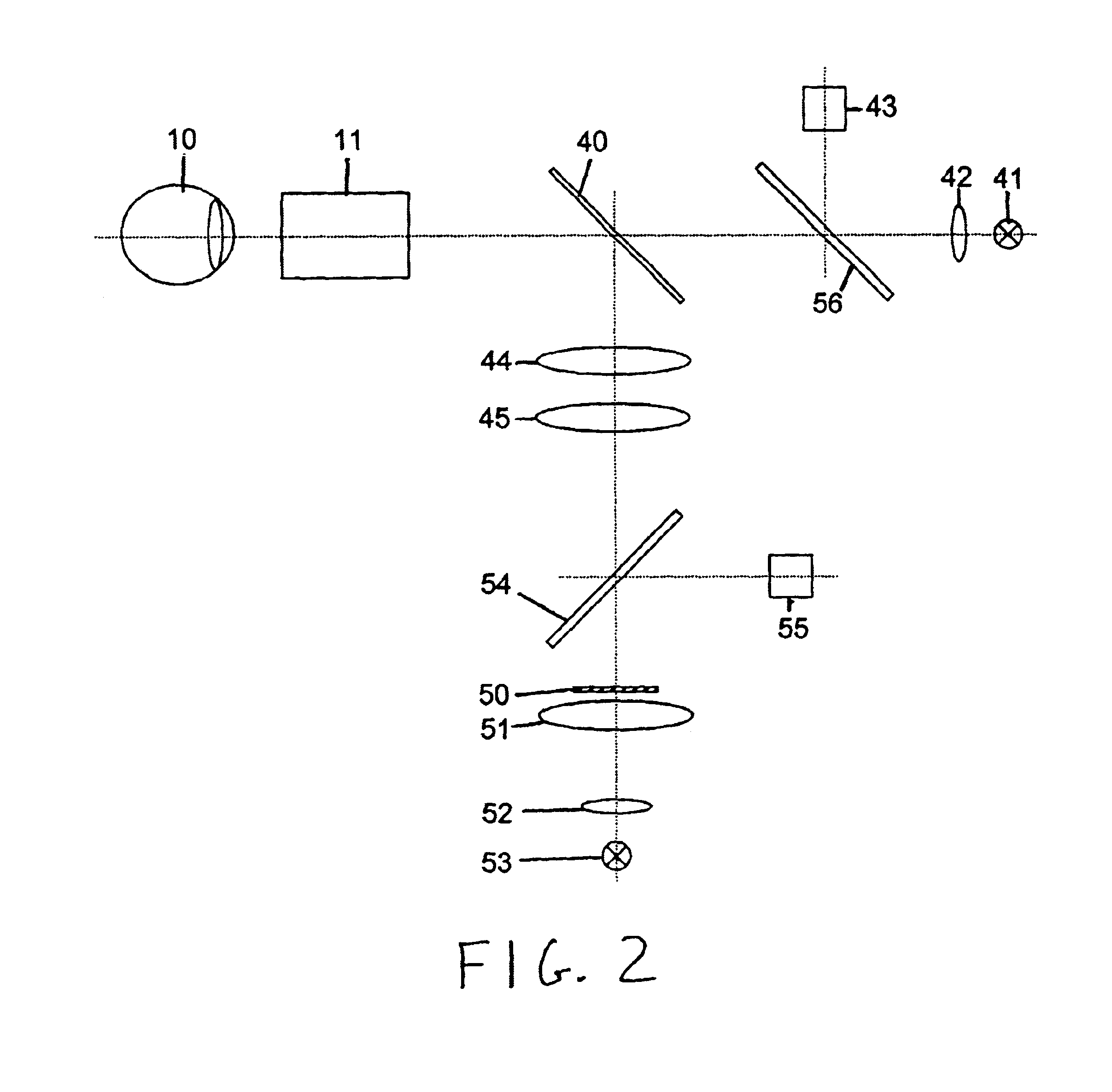
Blood glucose concentrations are measured by non-invasive methods and apparatus using visual pigment bleaching in conjunction with psychophysical methodologies. Bleaching light of selected wavelengths is projected through the pupil of the eye of an observer onto the fundus to bleach visual pigments in the eye. The observer's psychophysical response to a visual stimulus is then measured to obtain information regarding the rate of regeneration of the visual pigments. From the rate of pigment regeneration, blood glucose concentrations are measured accurately. The psychophysical methodologies that may be used with the invention include visual acuity tests and color-matching tests.
Owner:FOVIOPTICS INC
Reduced digestible carbohydrate food having reduced blood glucose response
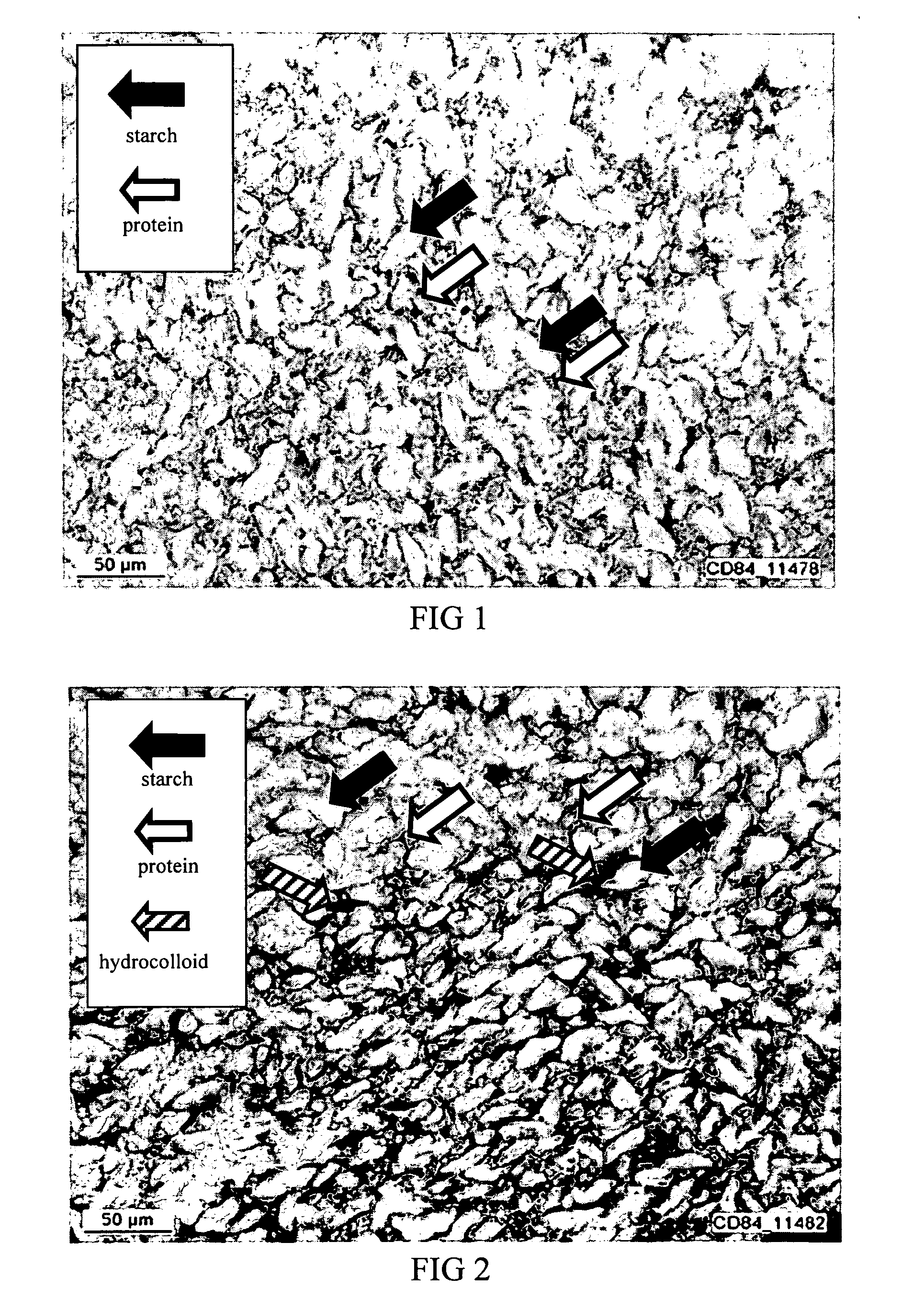
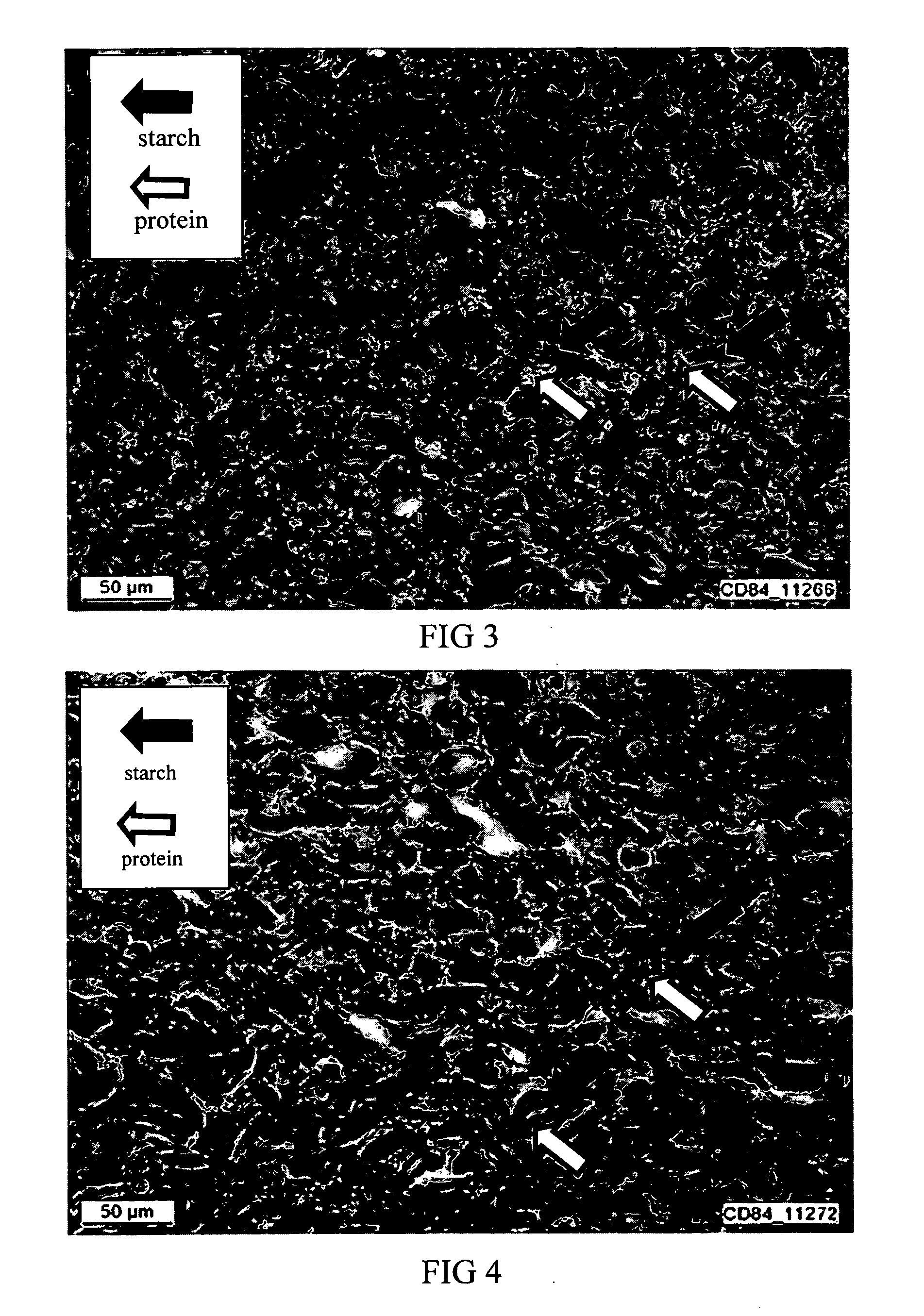
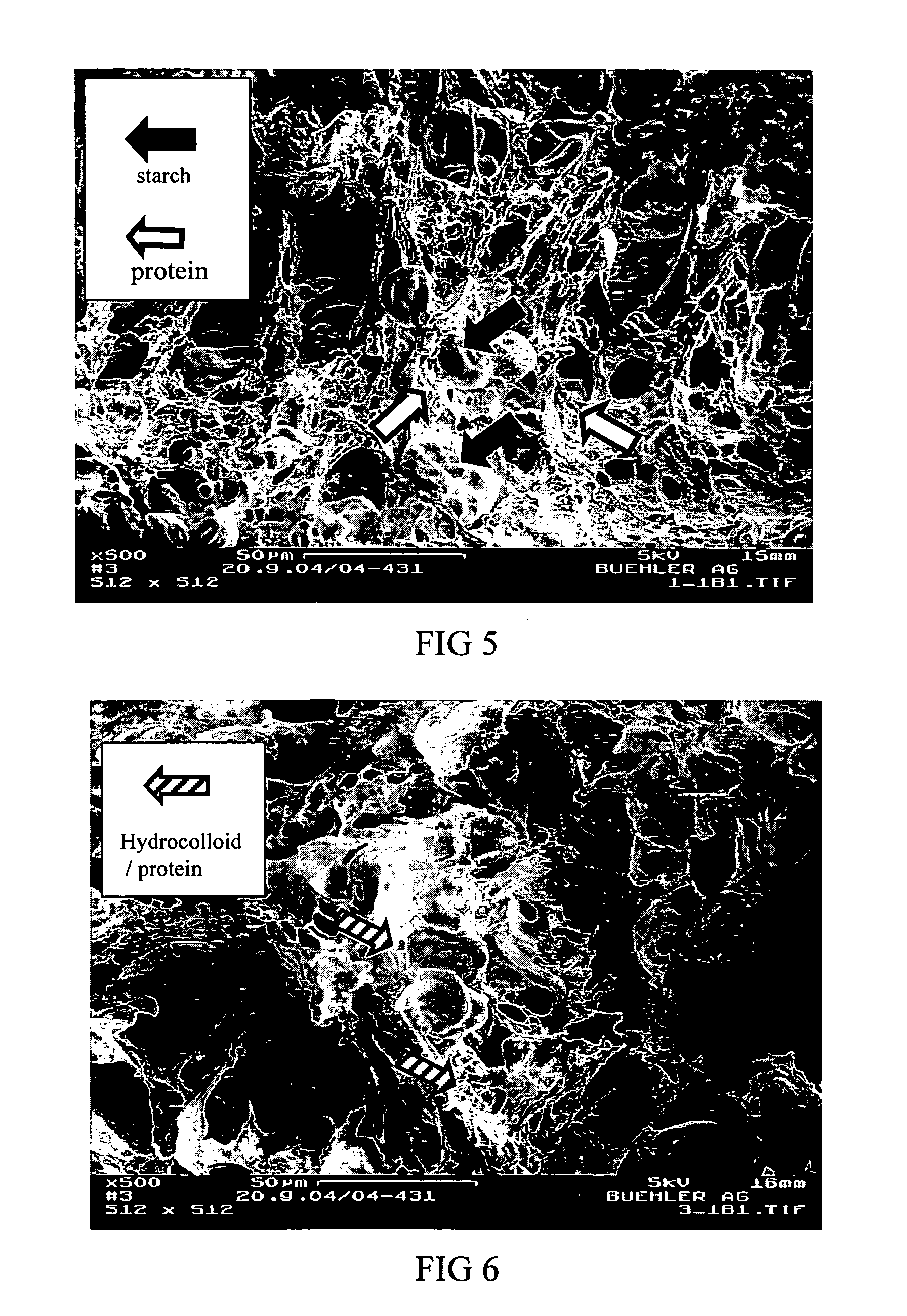
ActiveUS20050118326A1Hypoglycemic responseReduced digestibleDough treatmentLeguminous plant bakery productsAdditive ingredientFood material
Reducing the digestion of digestible carbohydrates in a digestible carbohydrate-based material, and reducing the absorption of the digestion product(s) of digestible carbohydrates (that is, simple sugars) within the small intestine. The undigested digestible carbohydrate and the unabsorbed digestion products pass through the small intestines and into the colon, where they are fermented. In effect, the food materials made by practicing the present invention cause a controlled amount of digestible carbohydrate to by-pass the small intestine, resulting in the fermentation of digestible carbohydrates in the colon. The invention also provides for processing of a digestible carbohydrate-based ingredient with a non-digestible food film material, to form a reduced digestible carbohydrate food having a protective food film network, which can inhibit or prevent digestion of the digestible carbohydrate. The present invention also provides for processing of a digestible carbohydrate-based ingredient with a non-digestible food film material, to provide a resulting reduced digestible carbohydrate food containing a viscosity-building component that contributes to the formation of a viscous intestinal chyme that can inhibit or prevent digestion of the digestible carbohydrate and can inhibit adsorption of digestion products of digestible carbohydrates in the small intestine.
Owner:TECHCOM GRP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com