Patents
Literature
10382 results about "Film material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Raw Materials. A roll of film consists of the emulsion and base that compose the film itself, the cassette or cartridge, and outer protective packaging. The materials used to make the emulsion are silver, nitric acid, and gelatin.
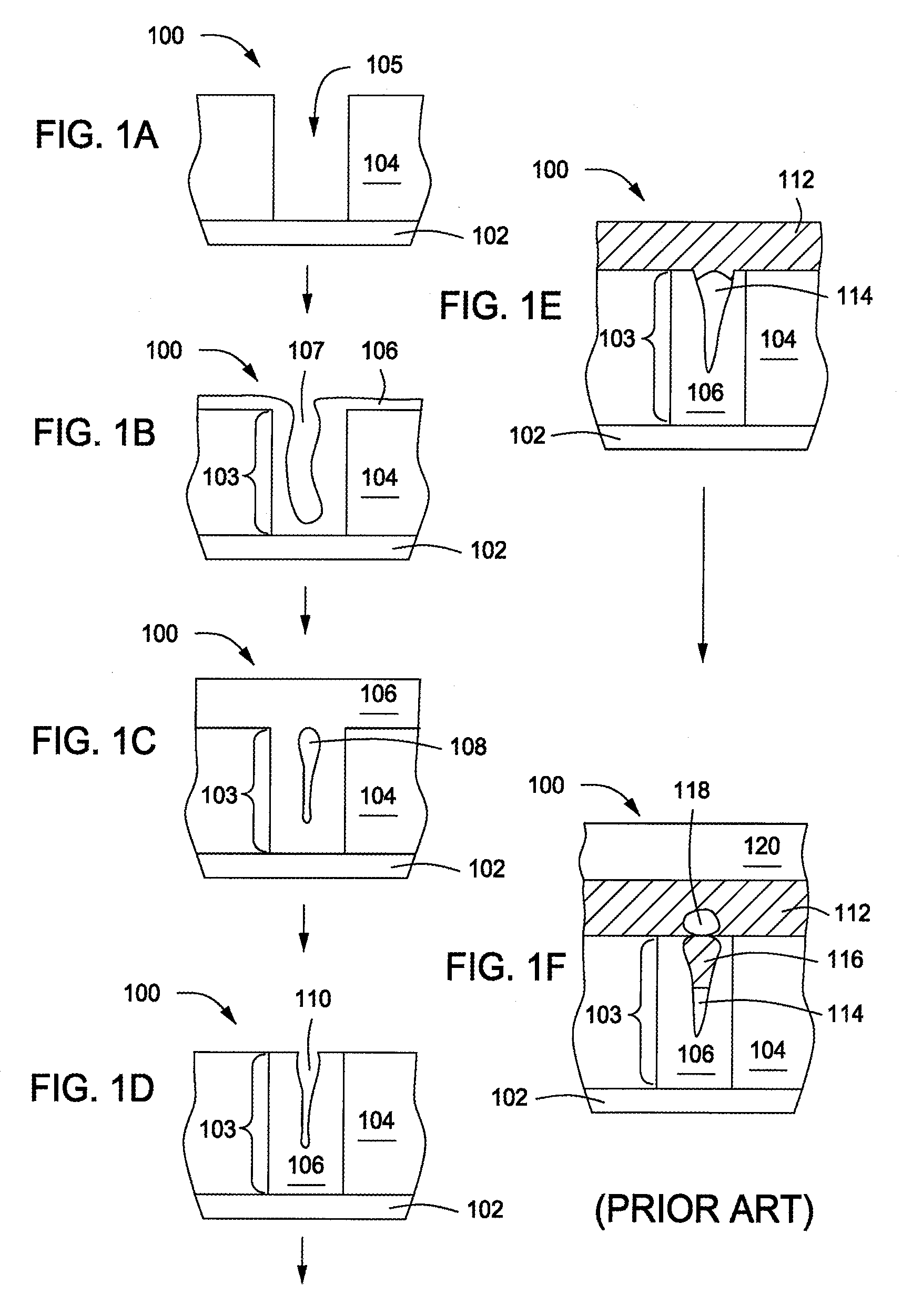
Heat-shrinkable anti-fomitic device
Owner:M TECH INC
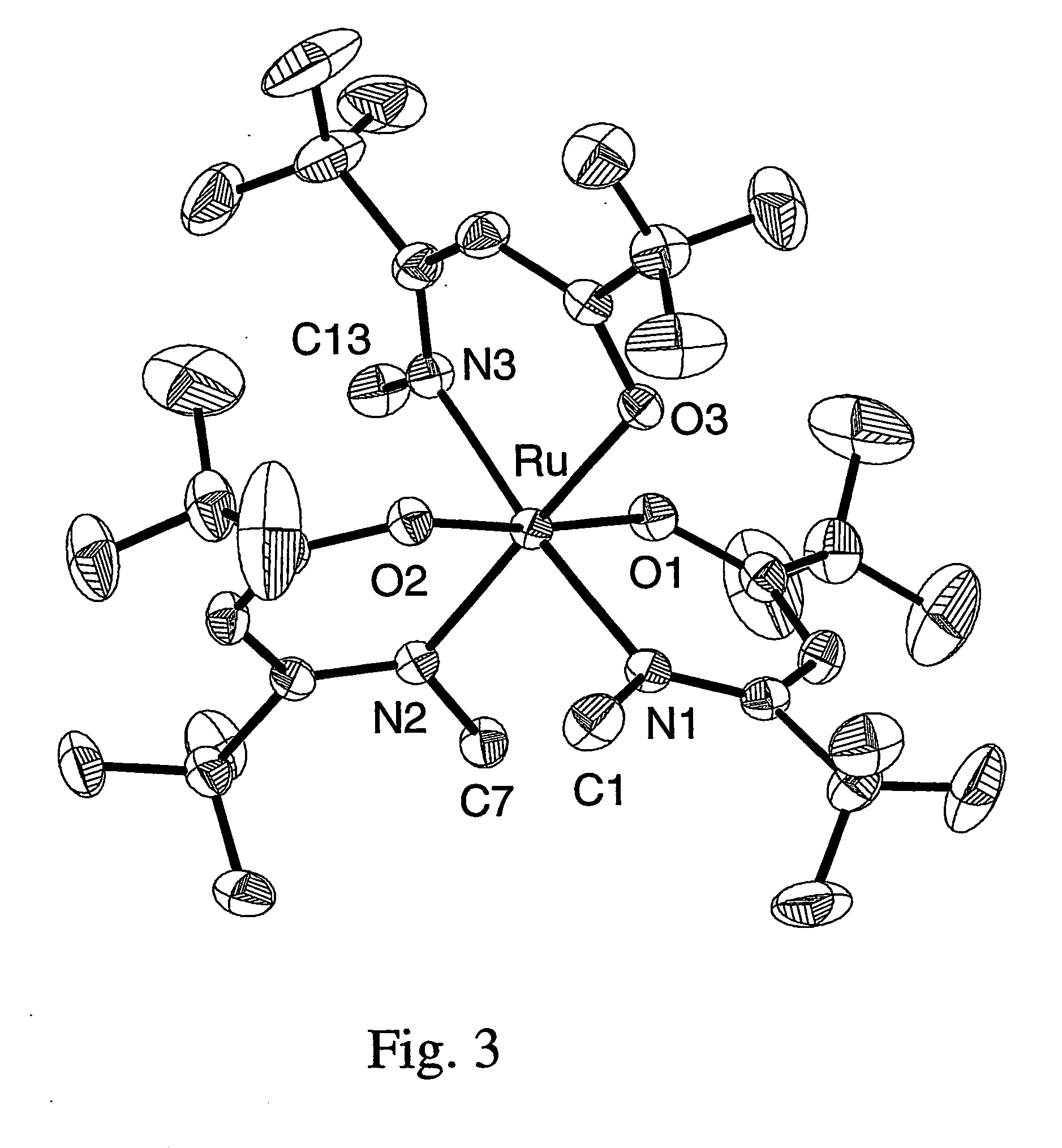
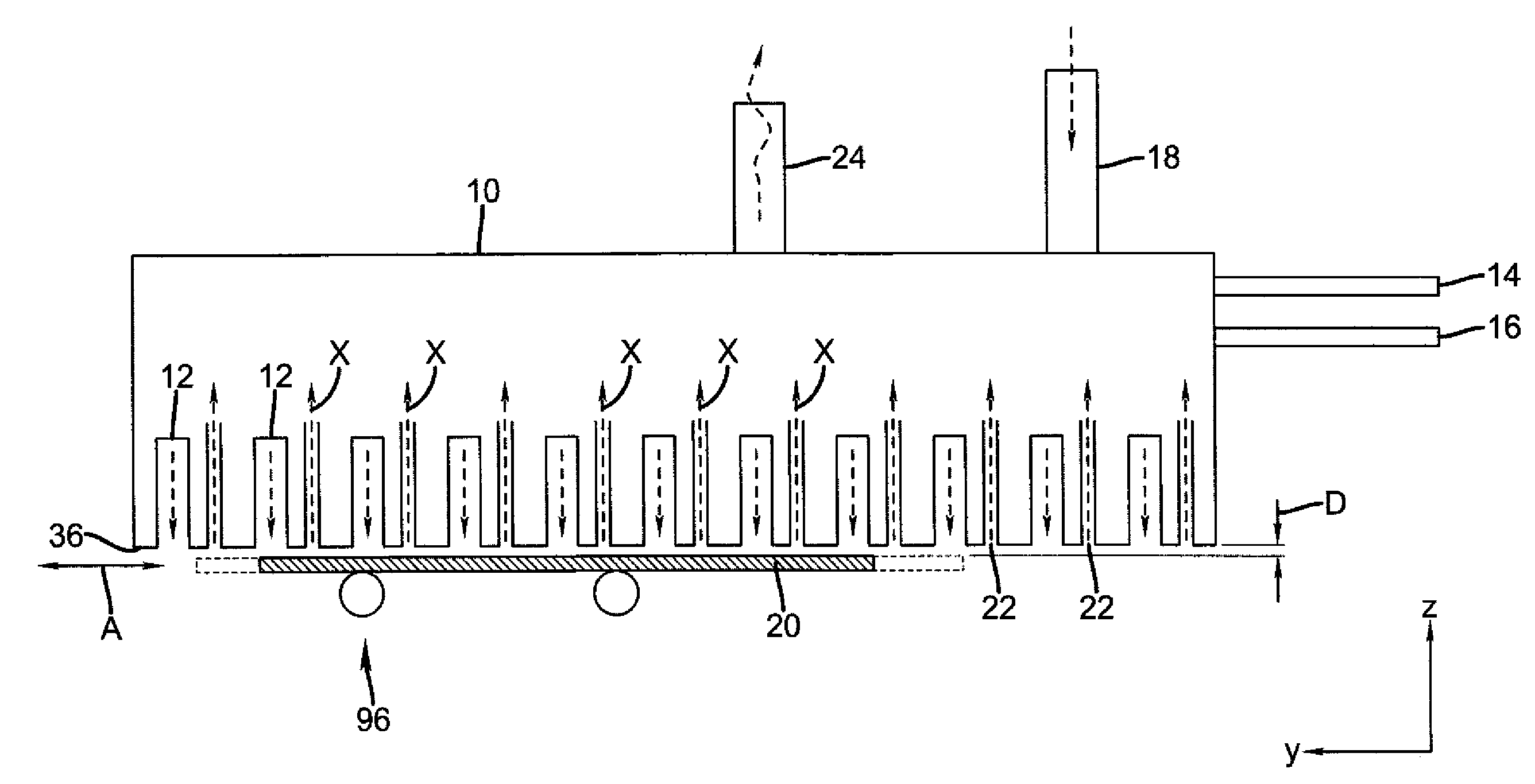
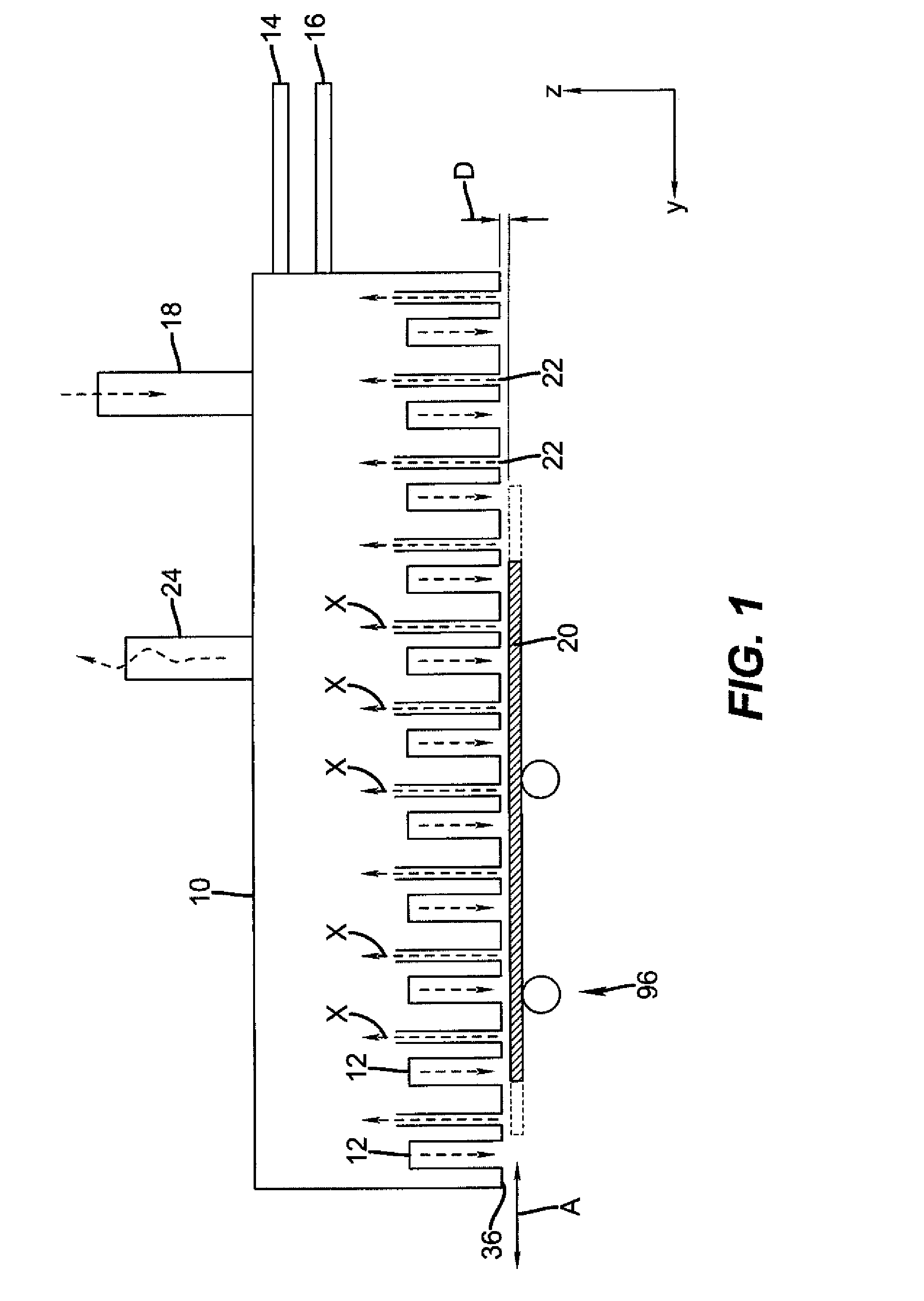
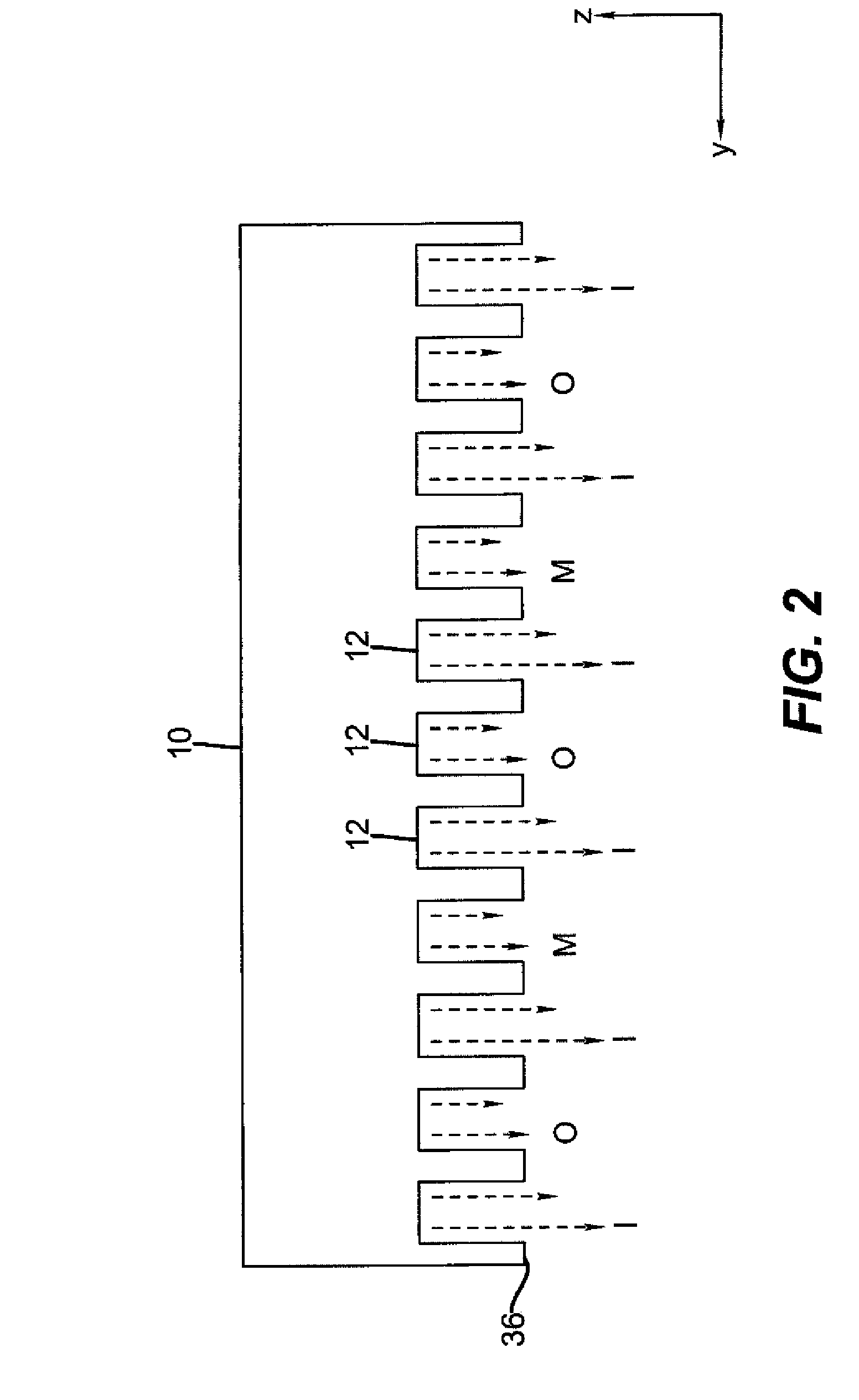
Apparatus for atomic layer deposition
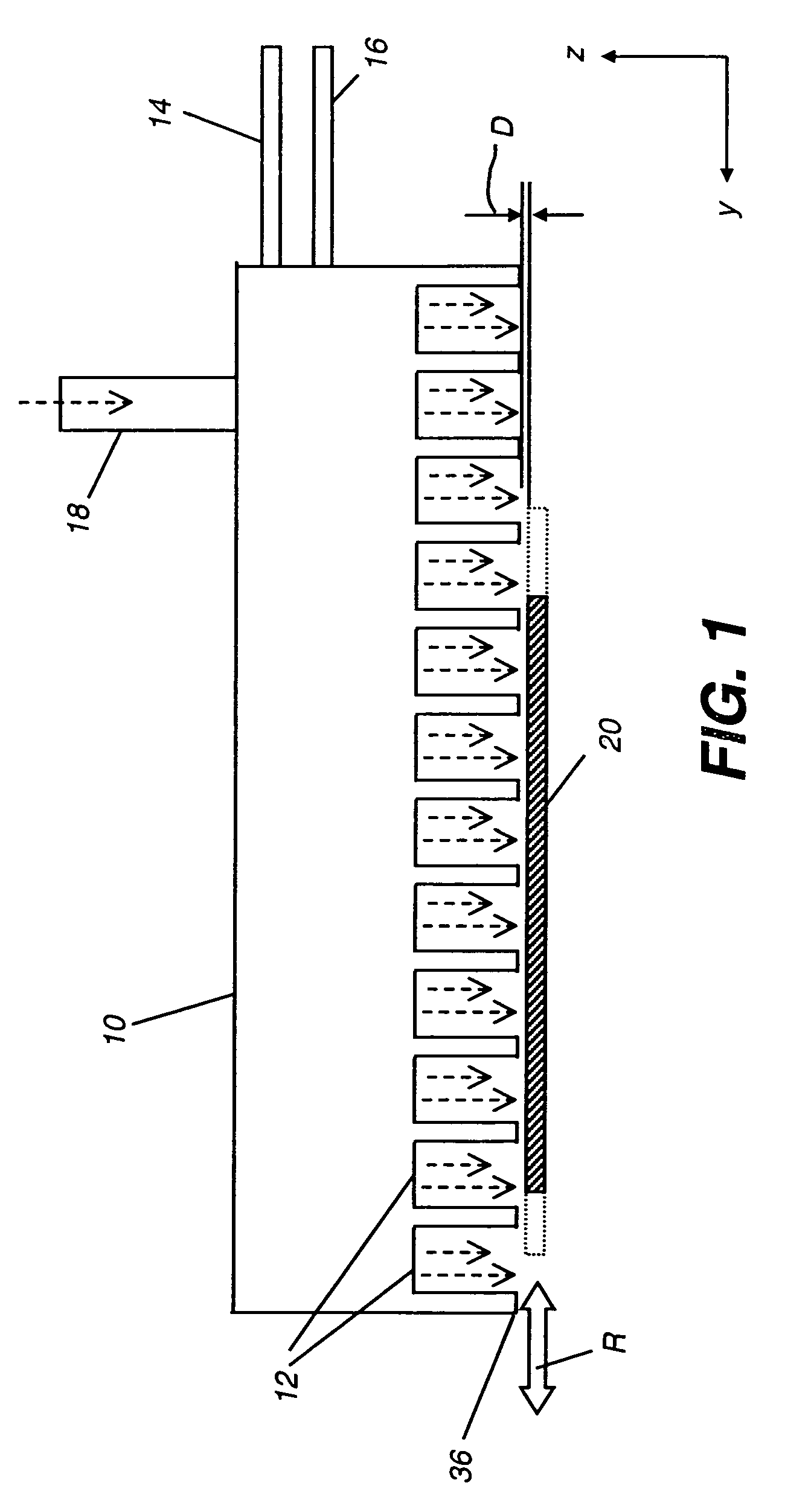
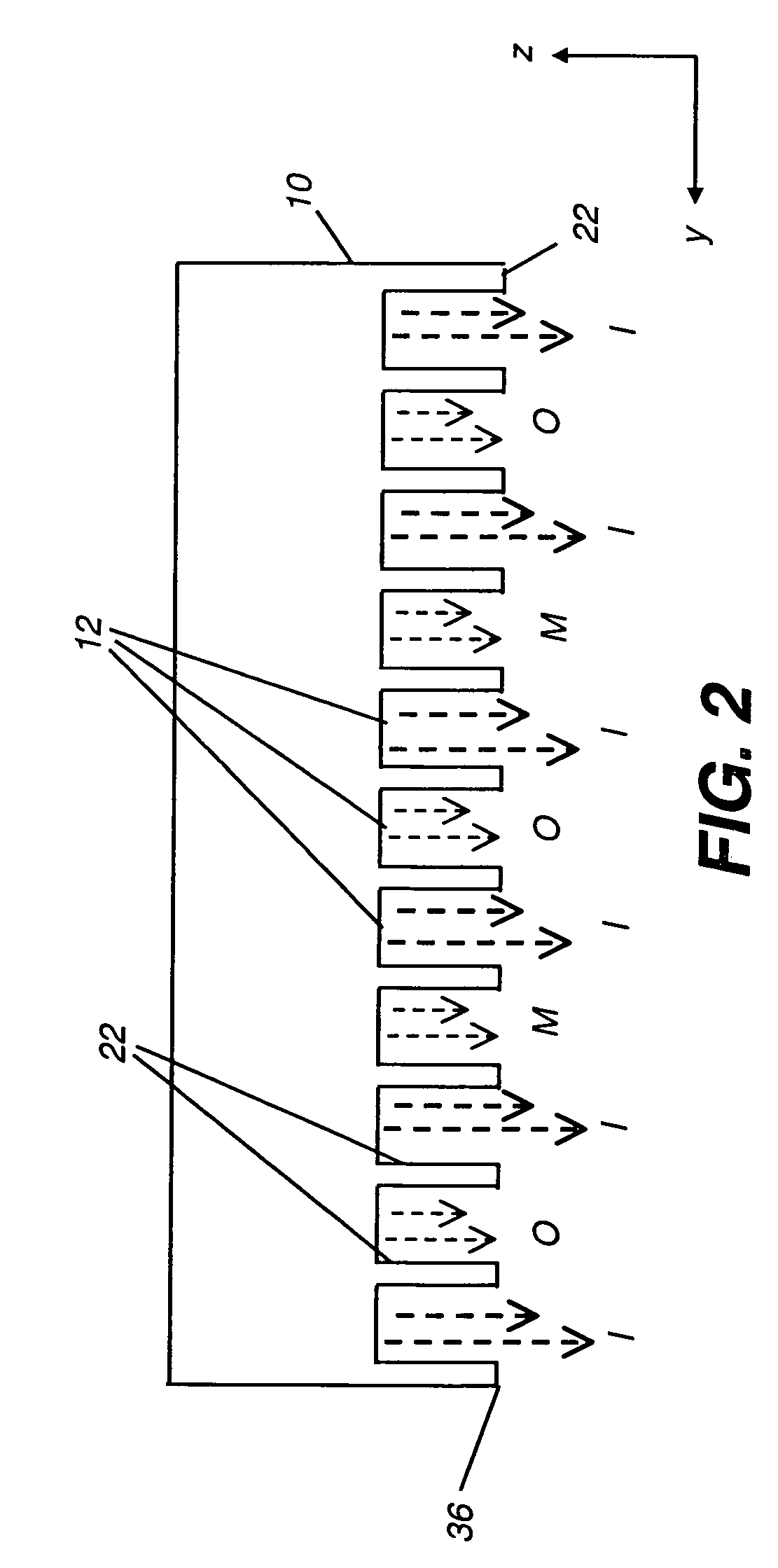
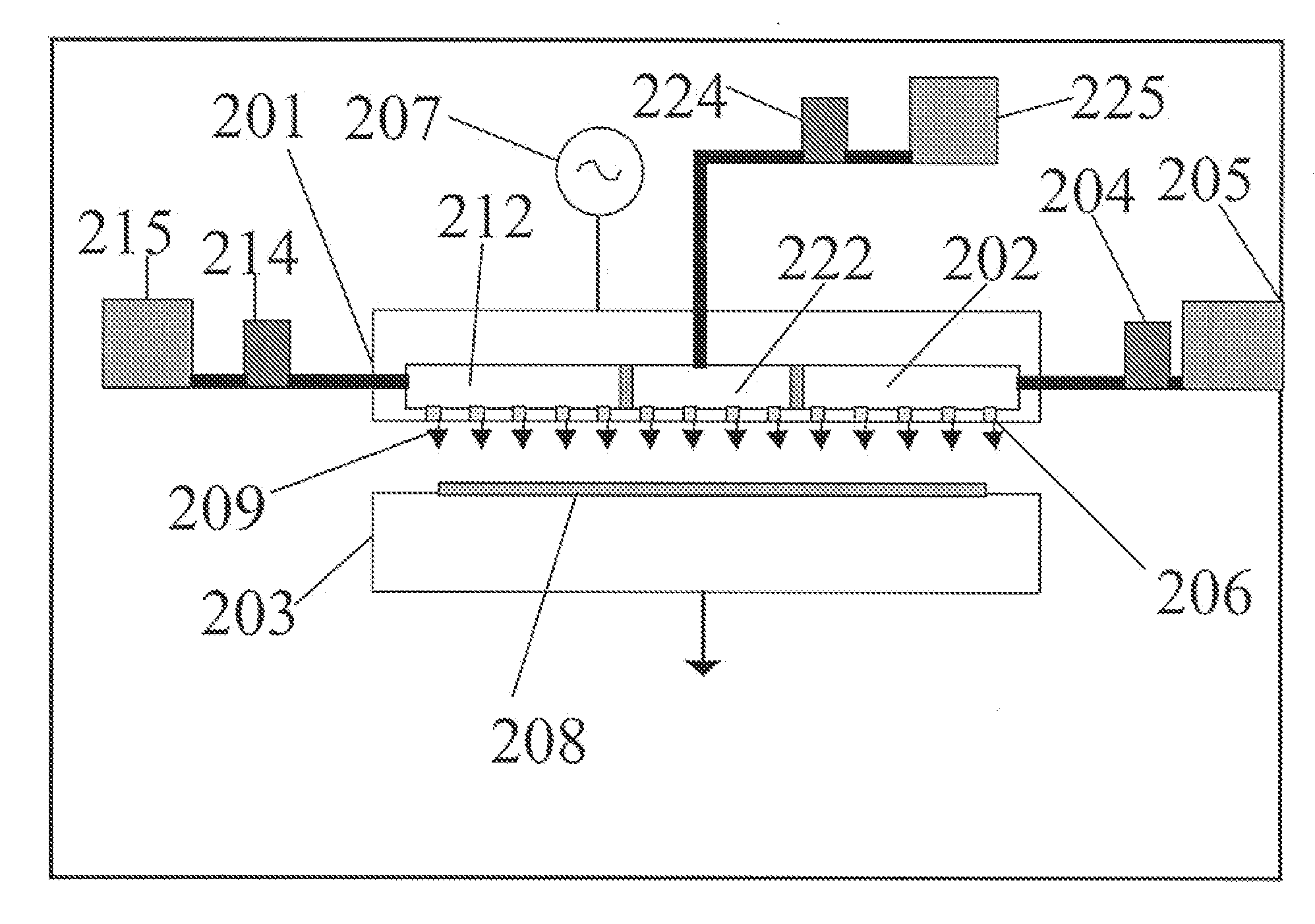
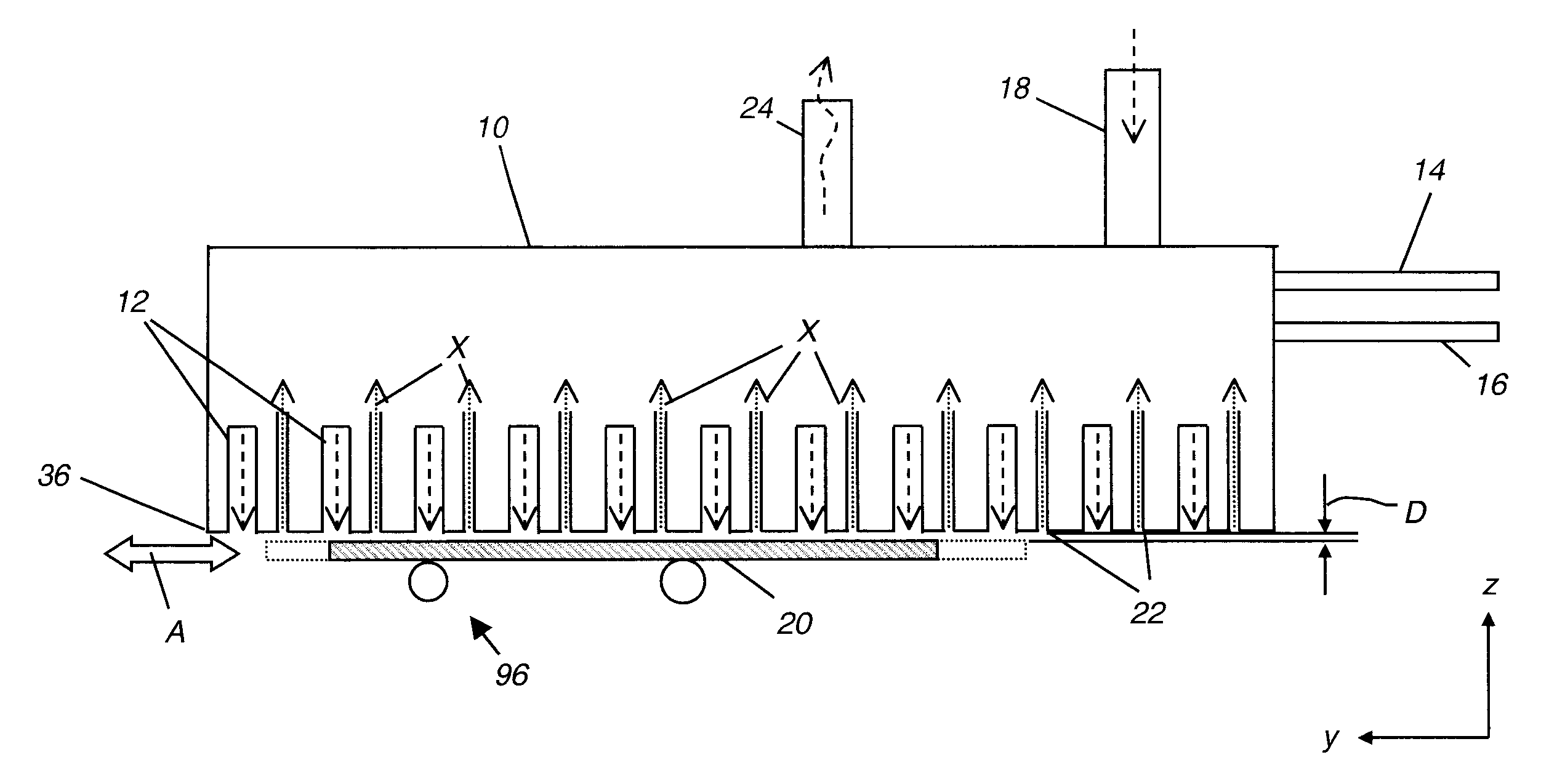
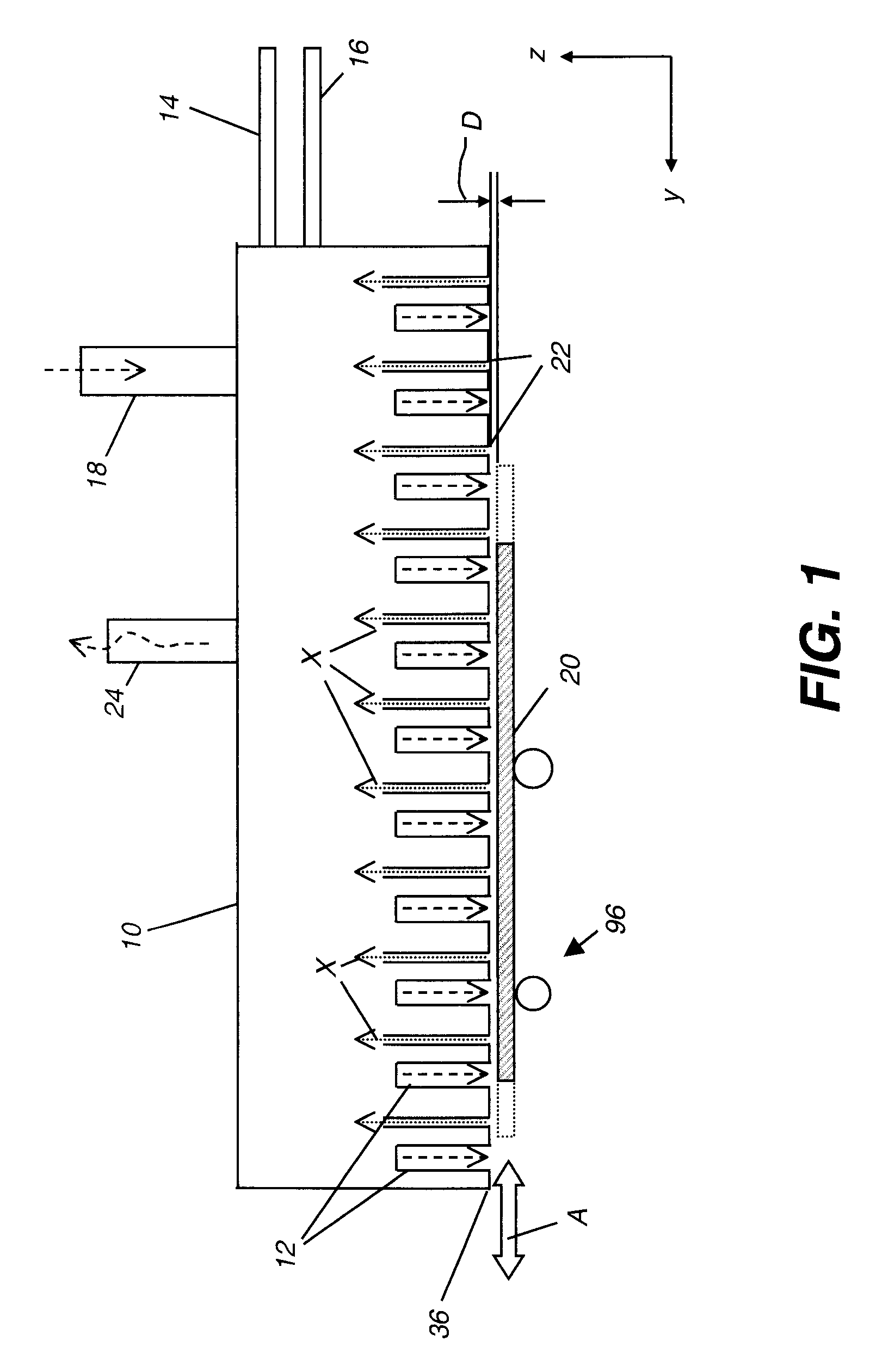
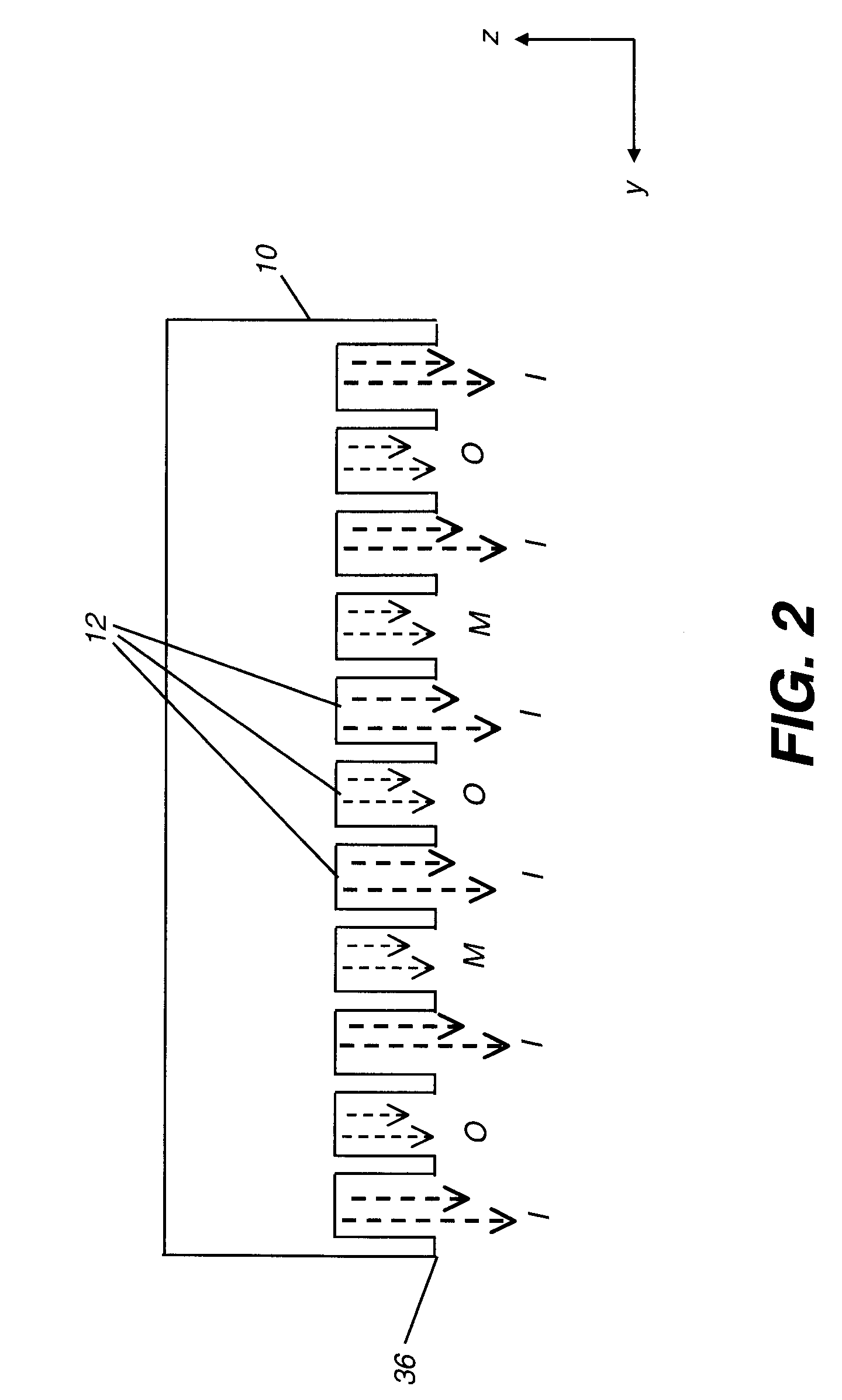
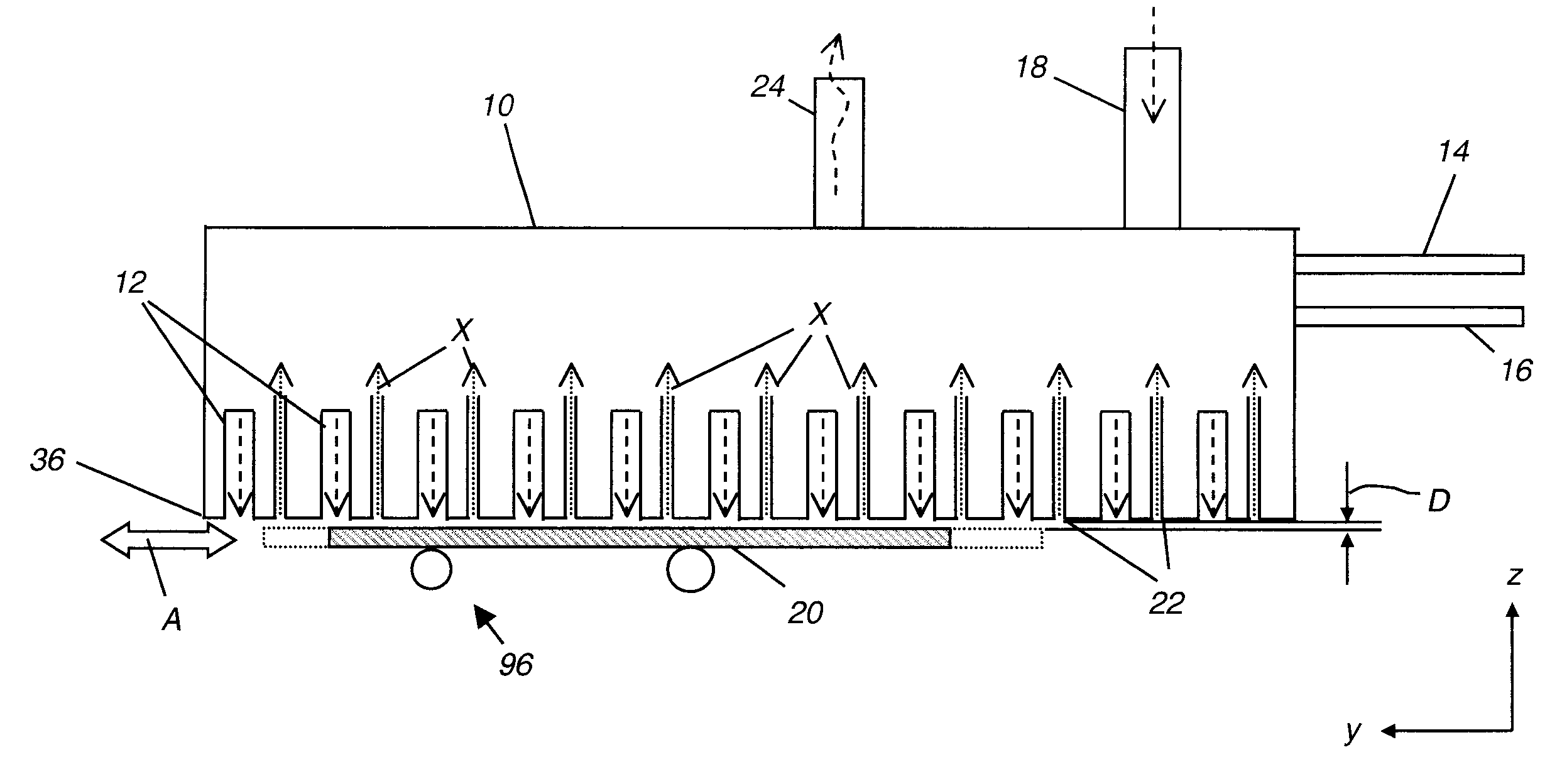
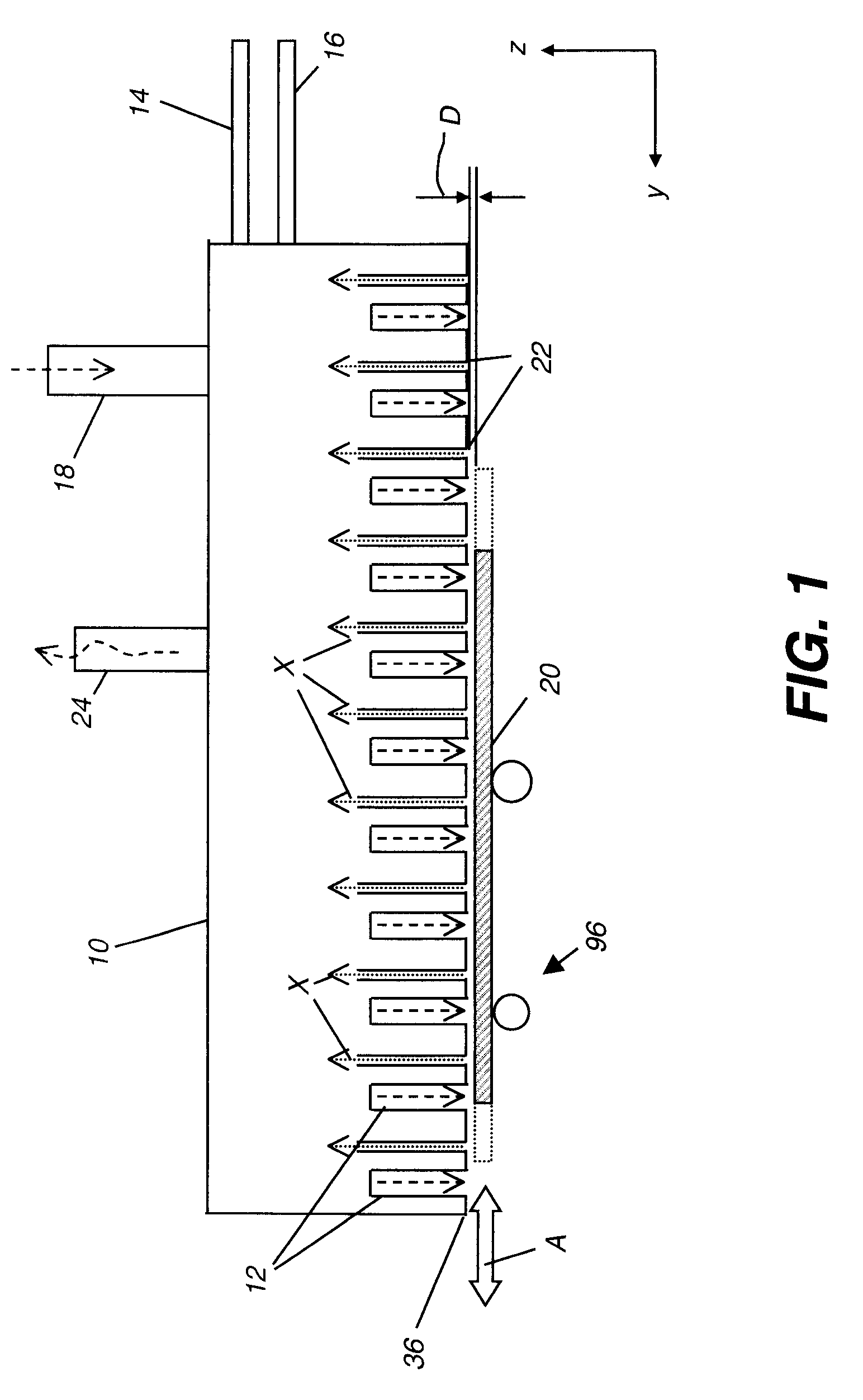
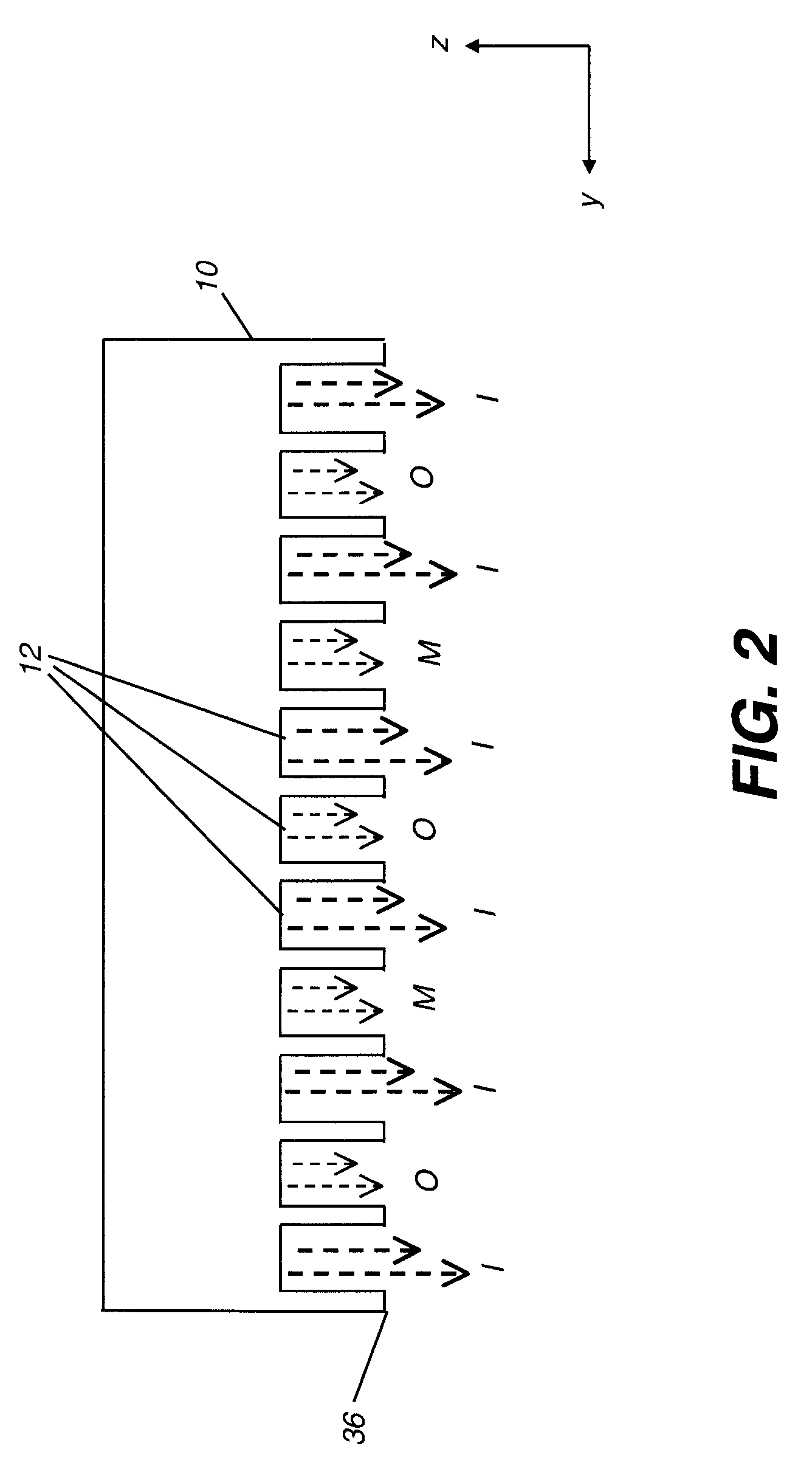
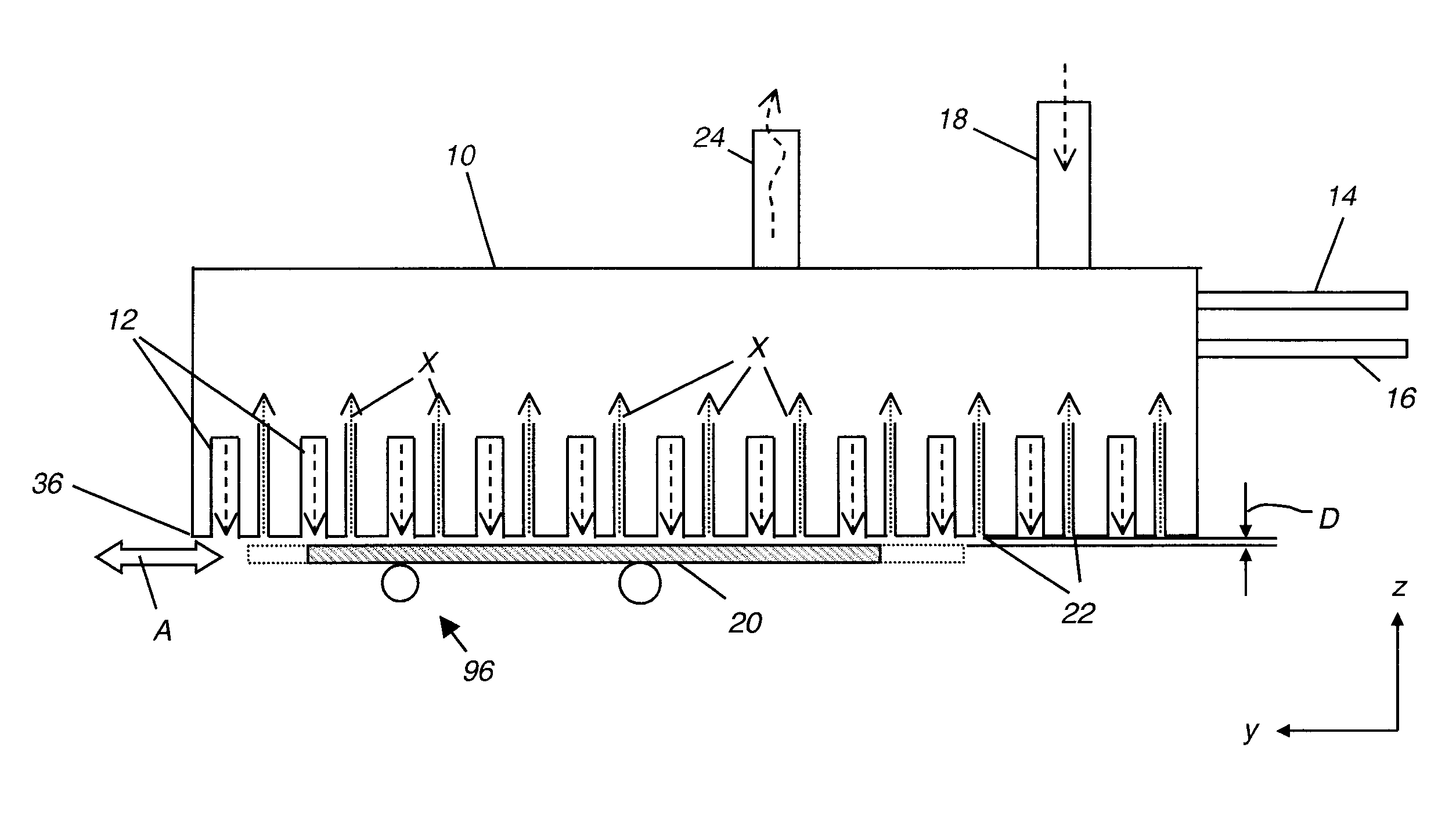
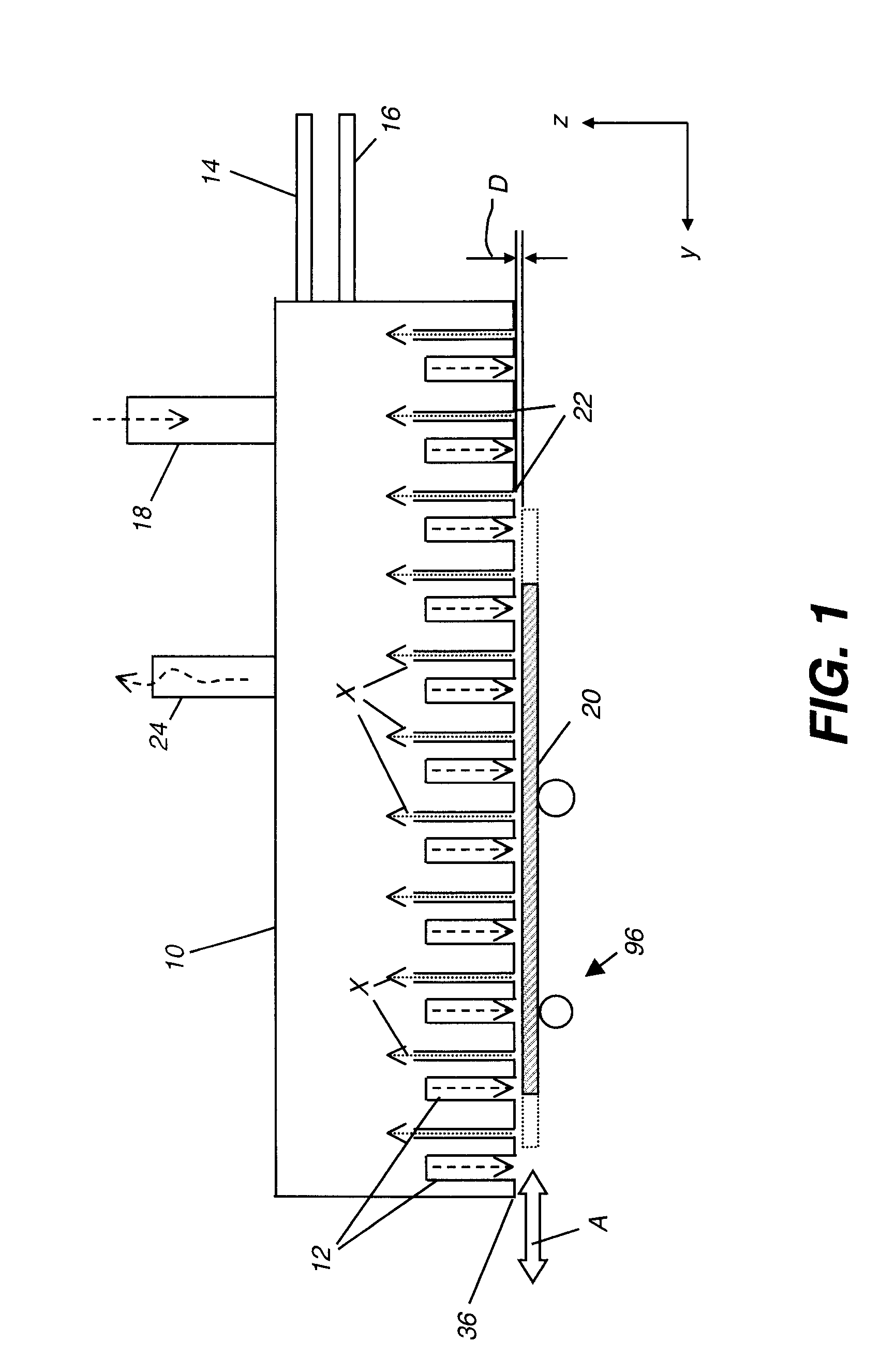
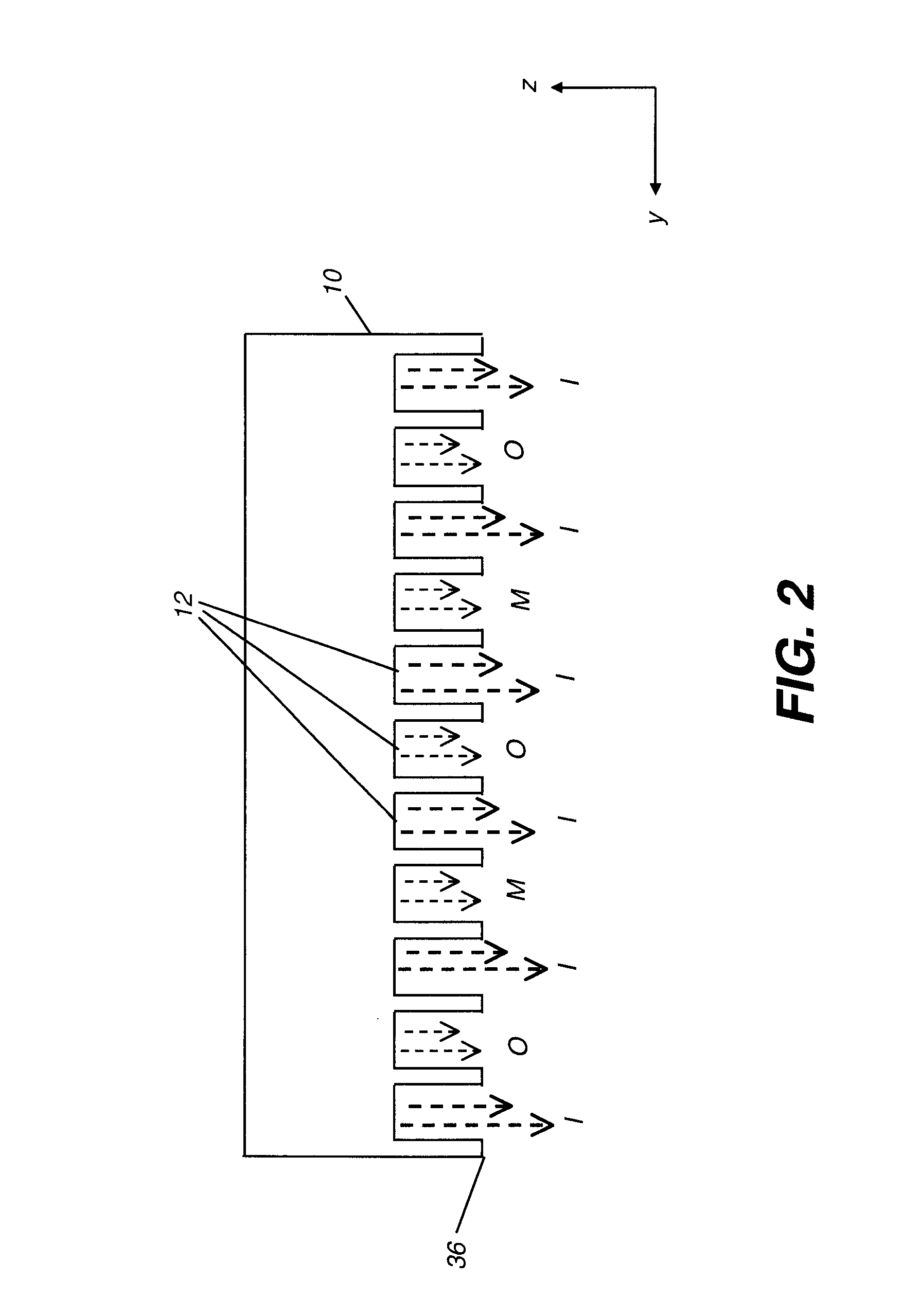
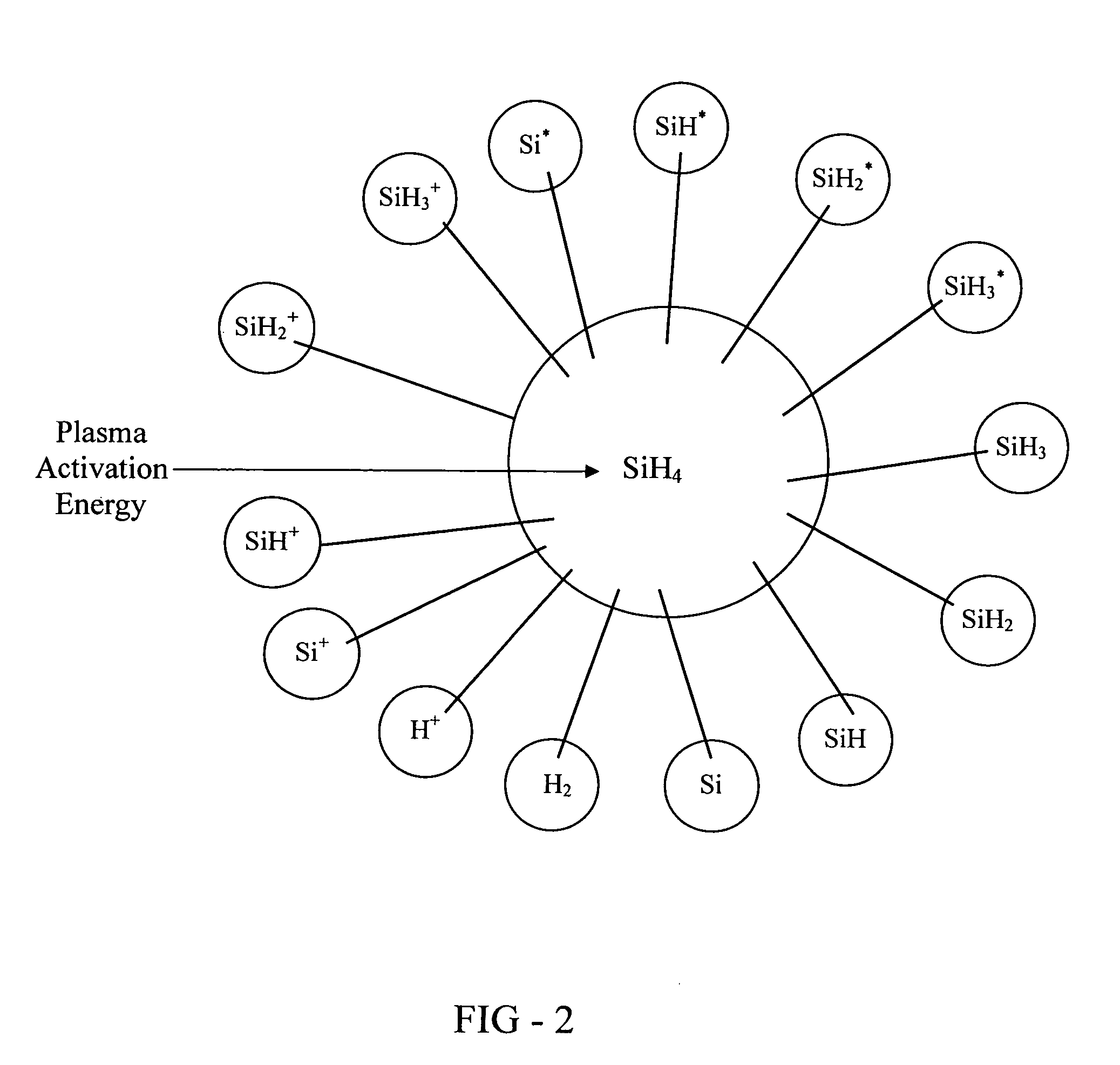
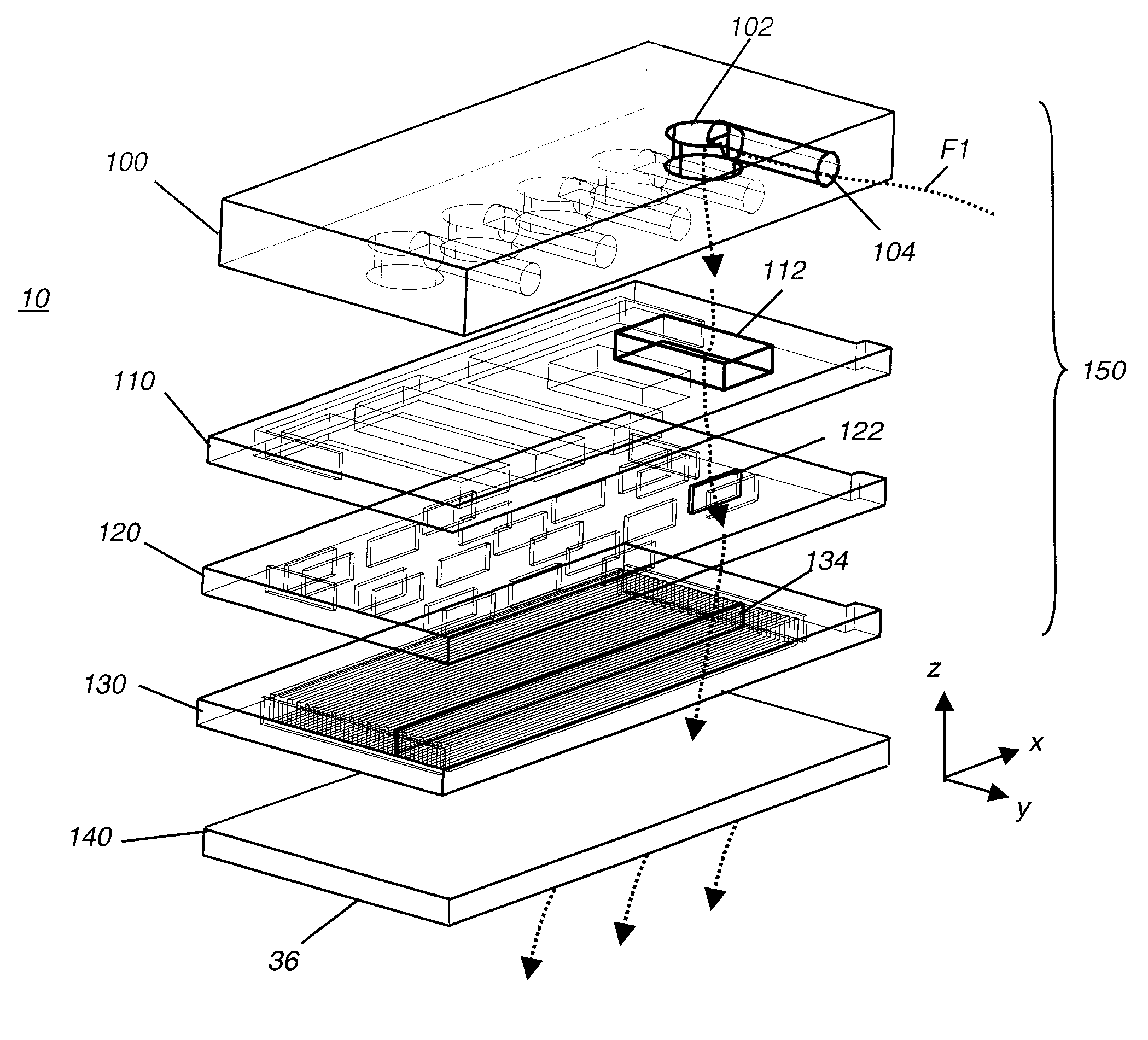
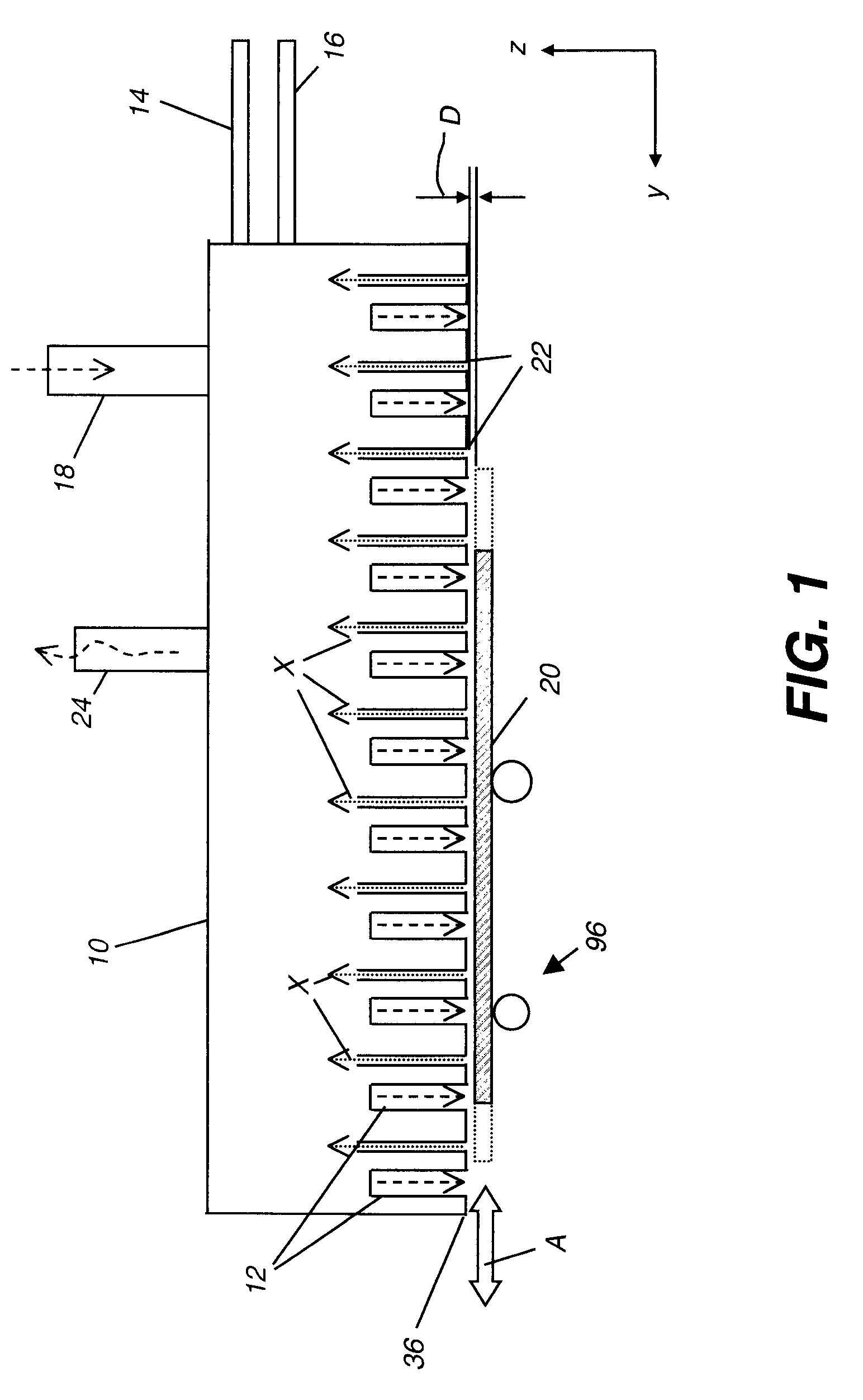
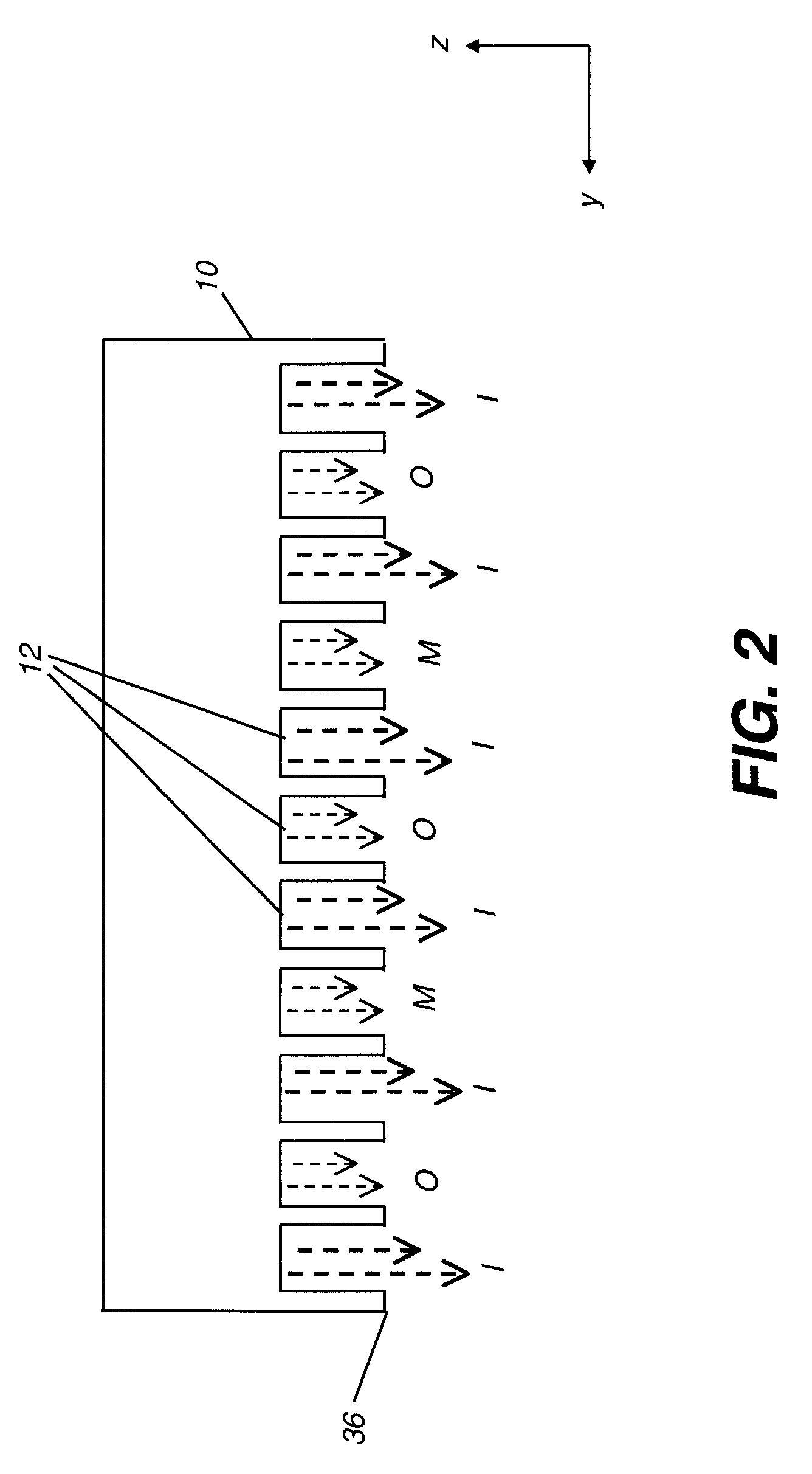
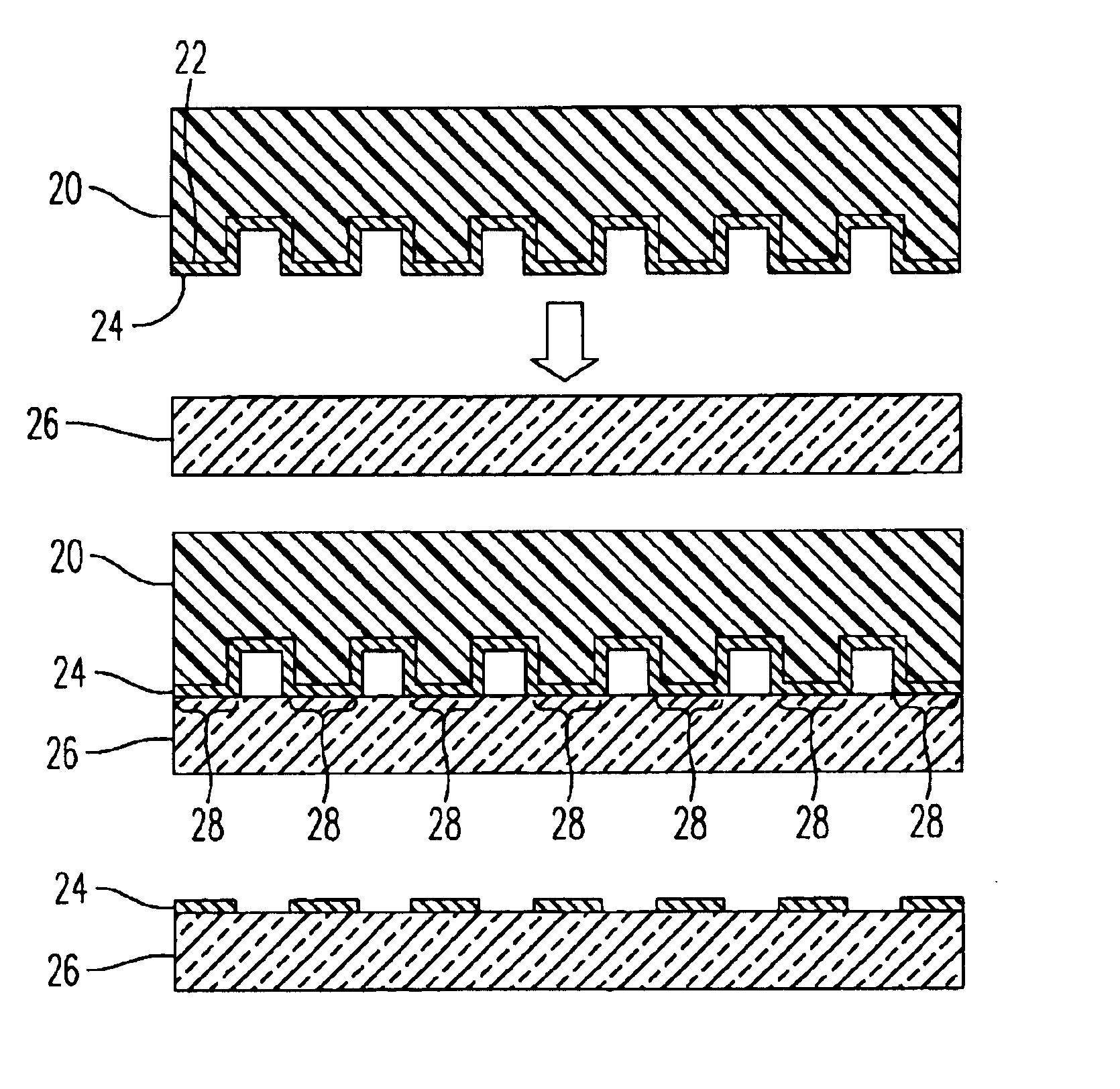
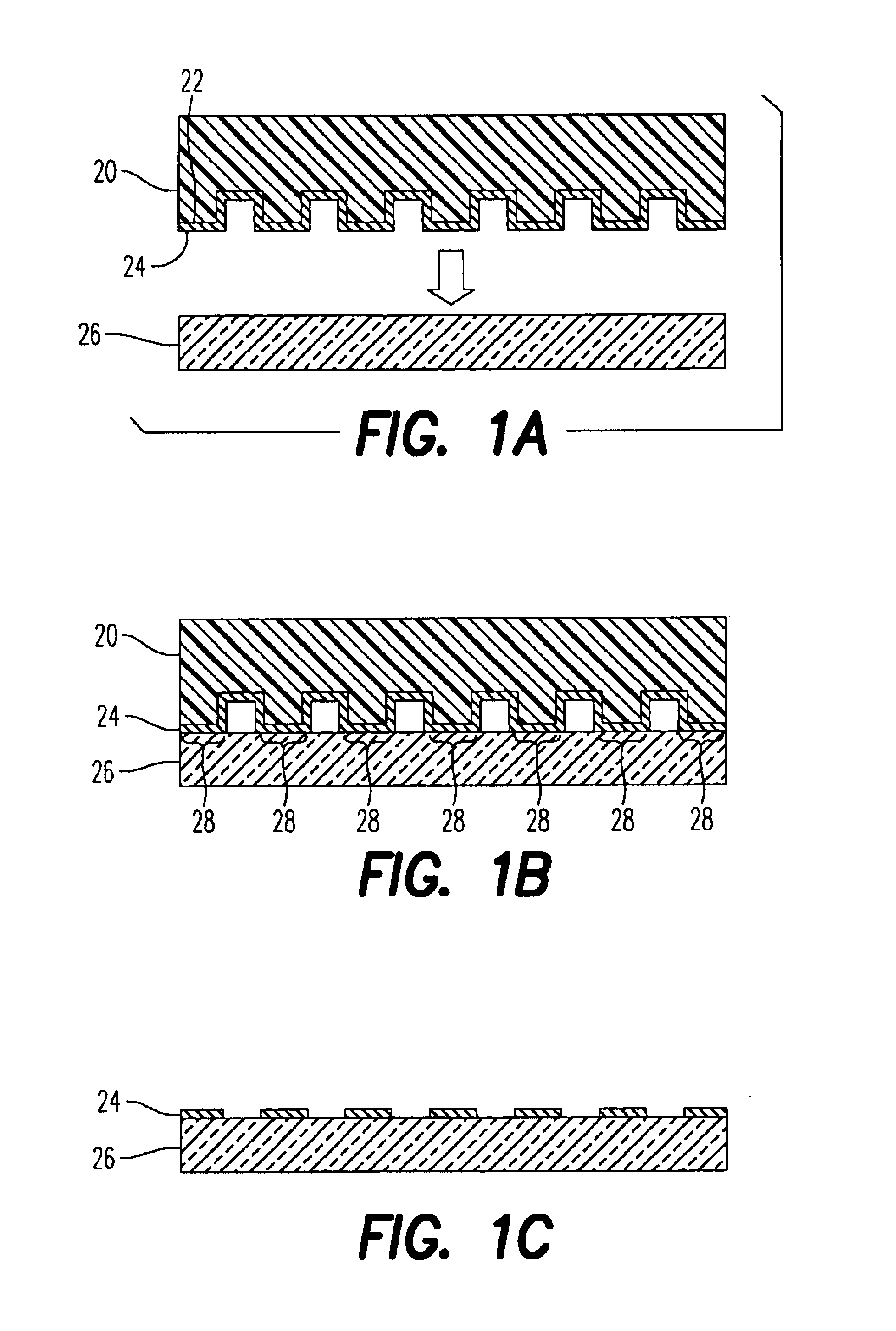
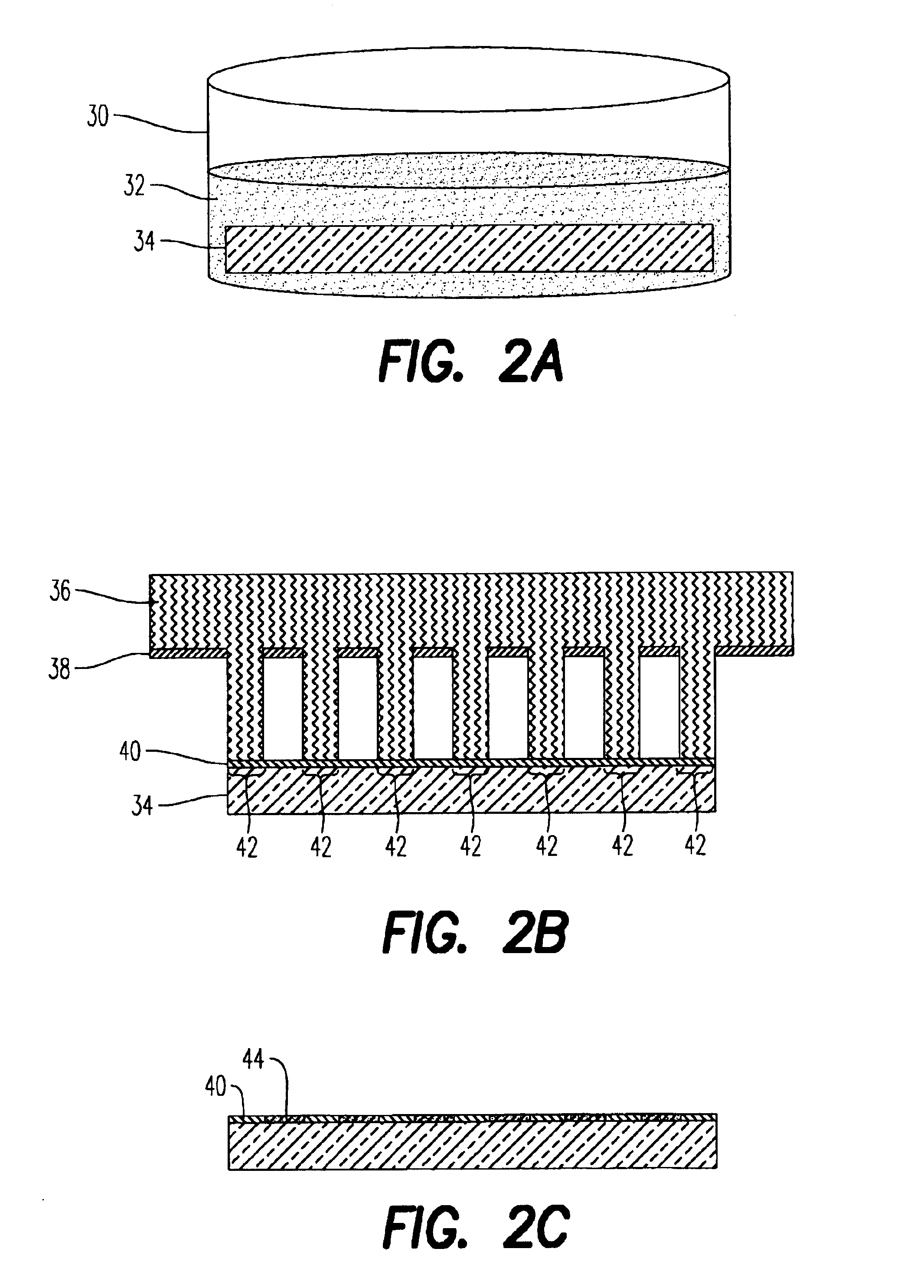
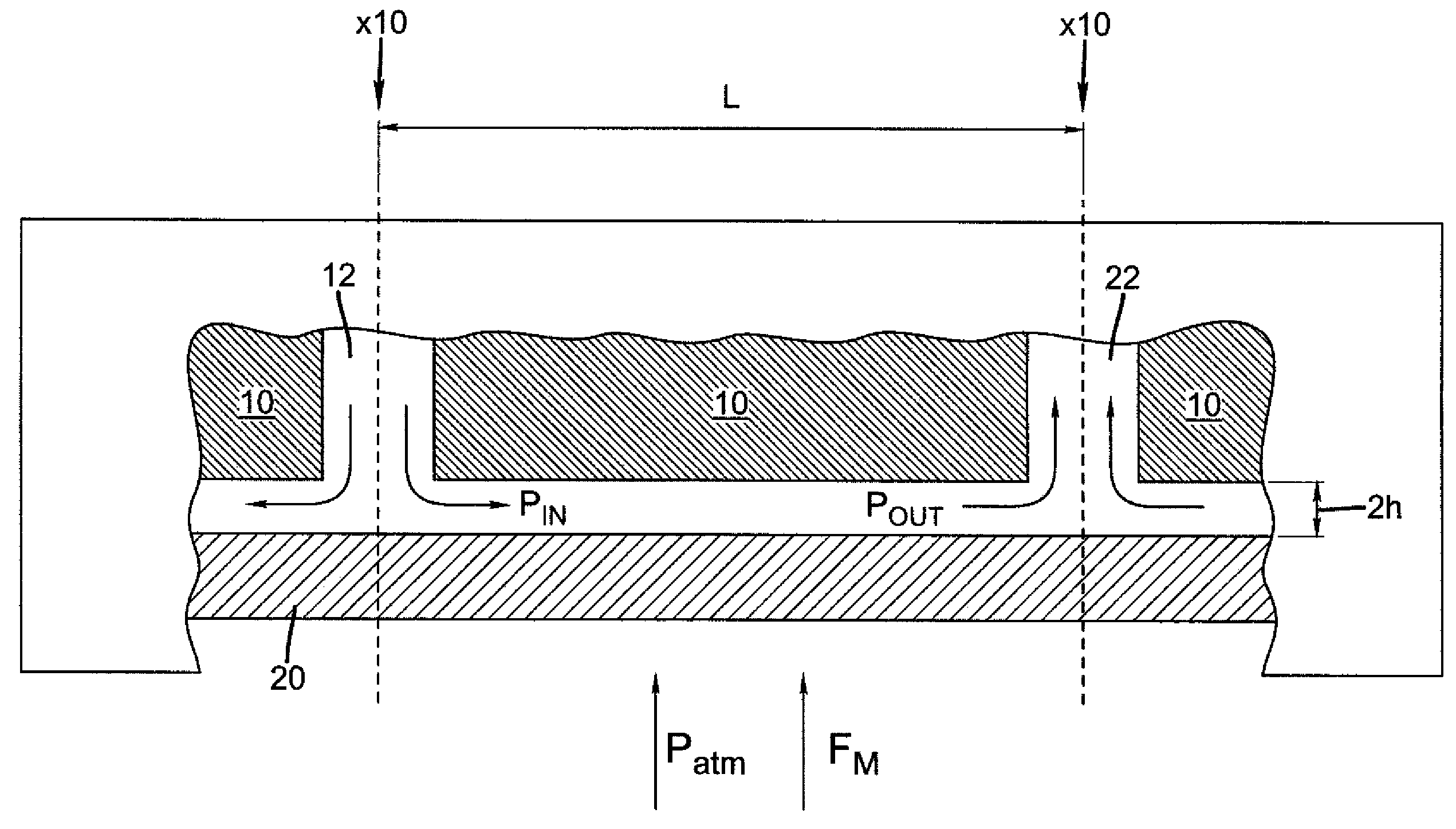
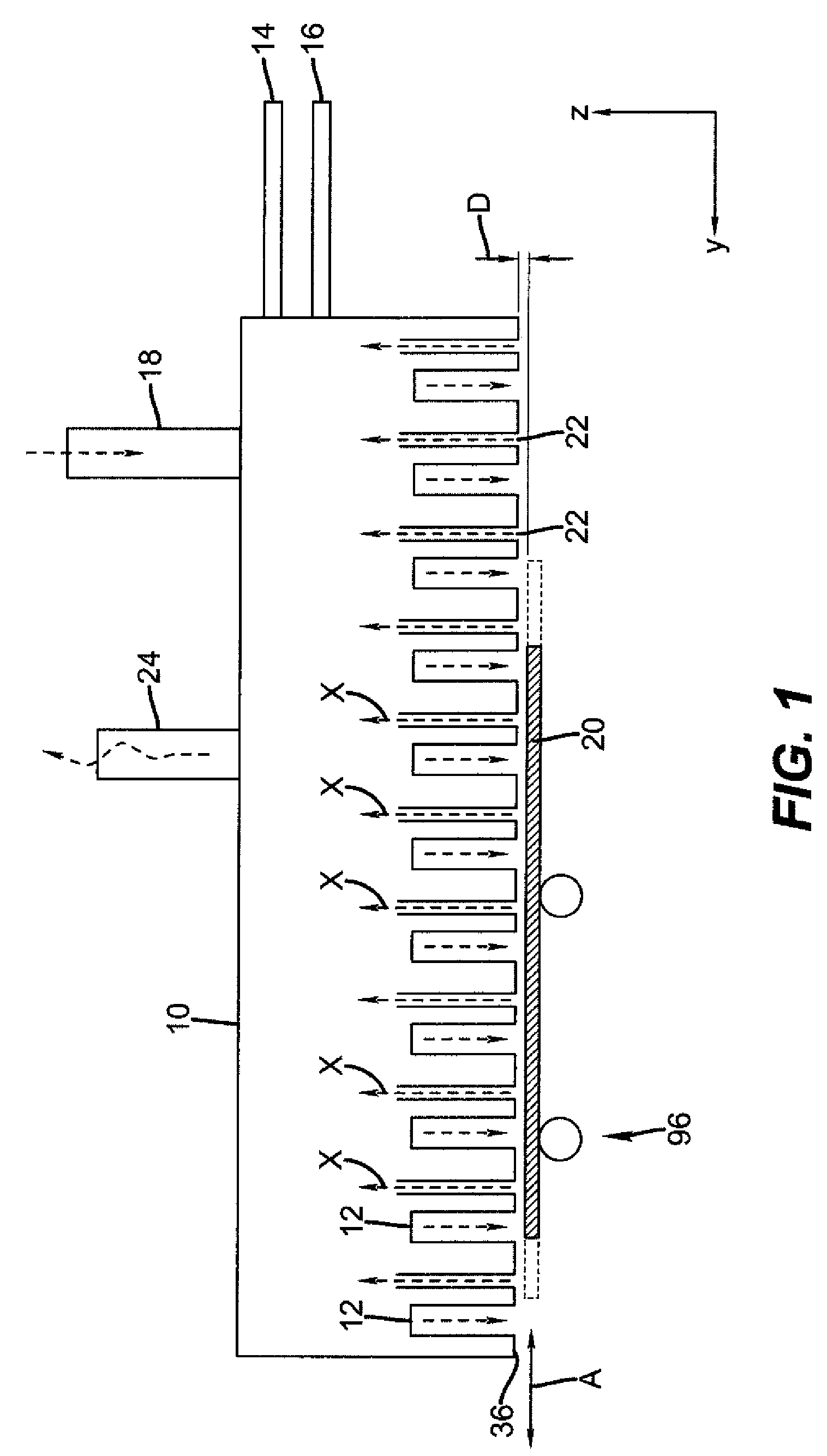
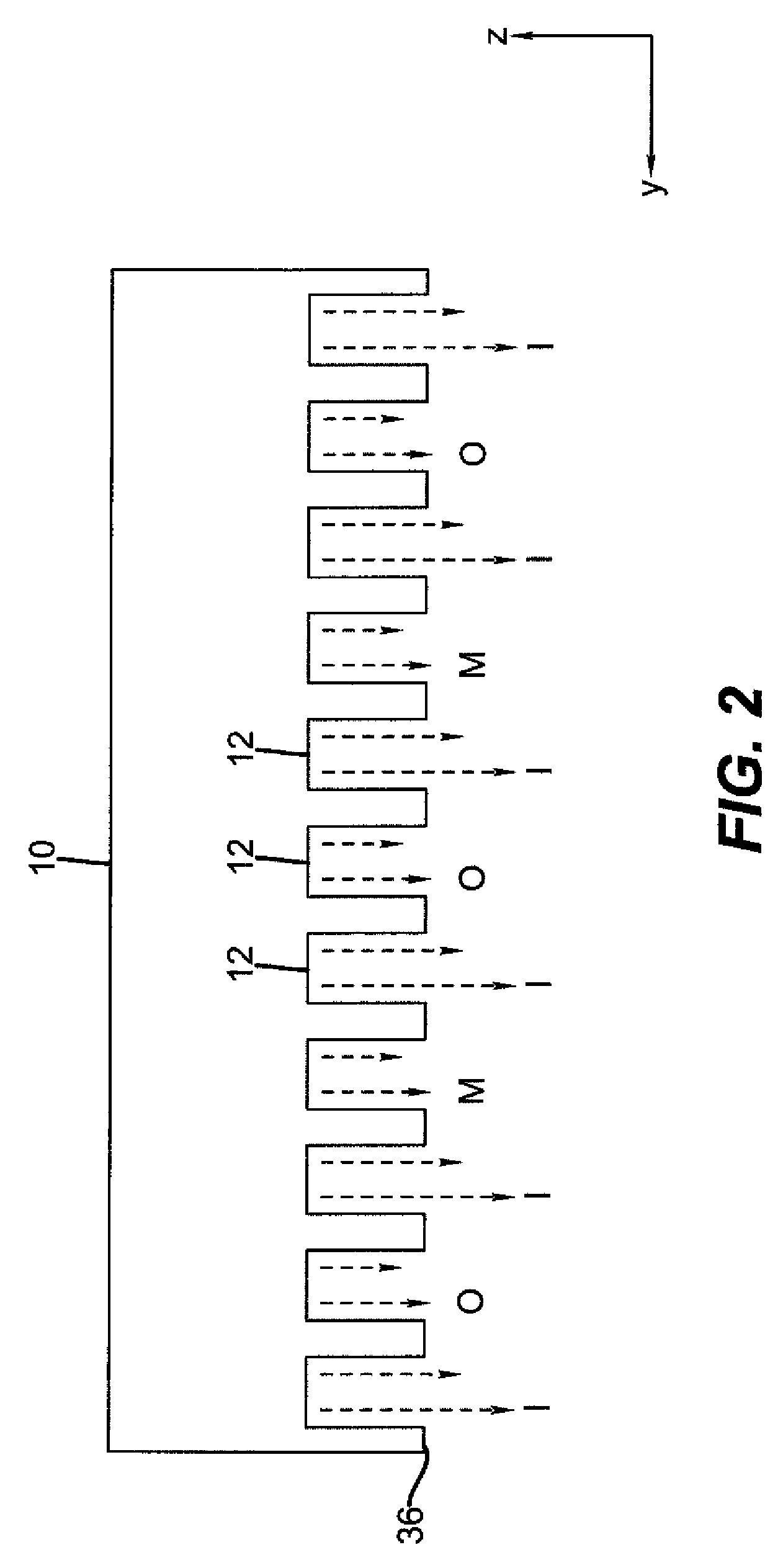
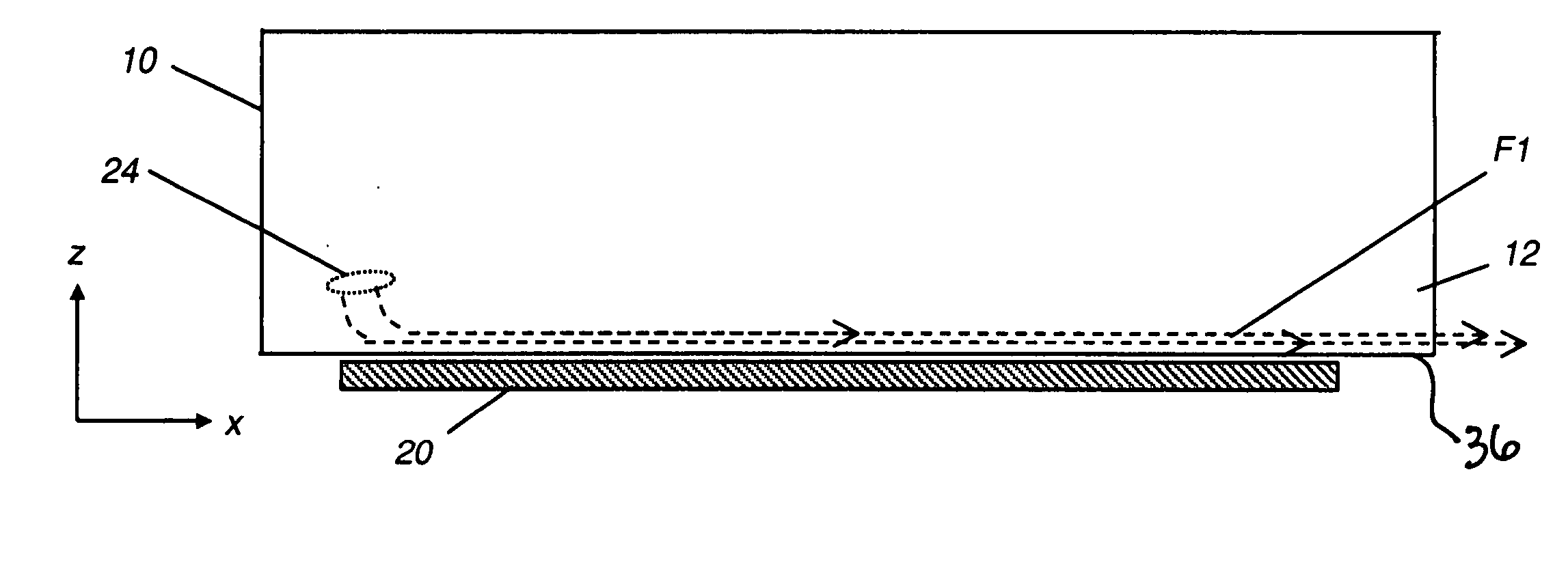
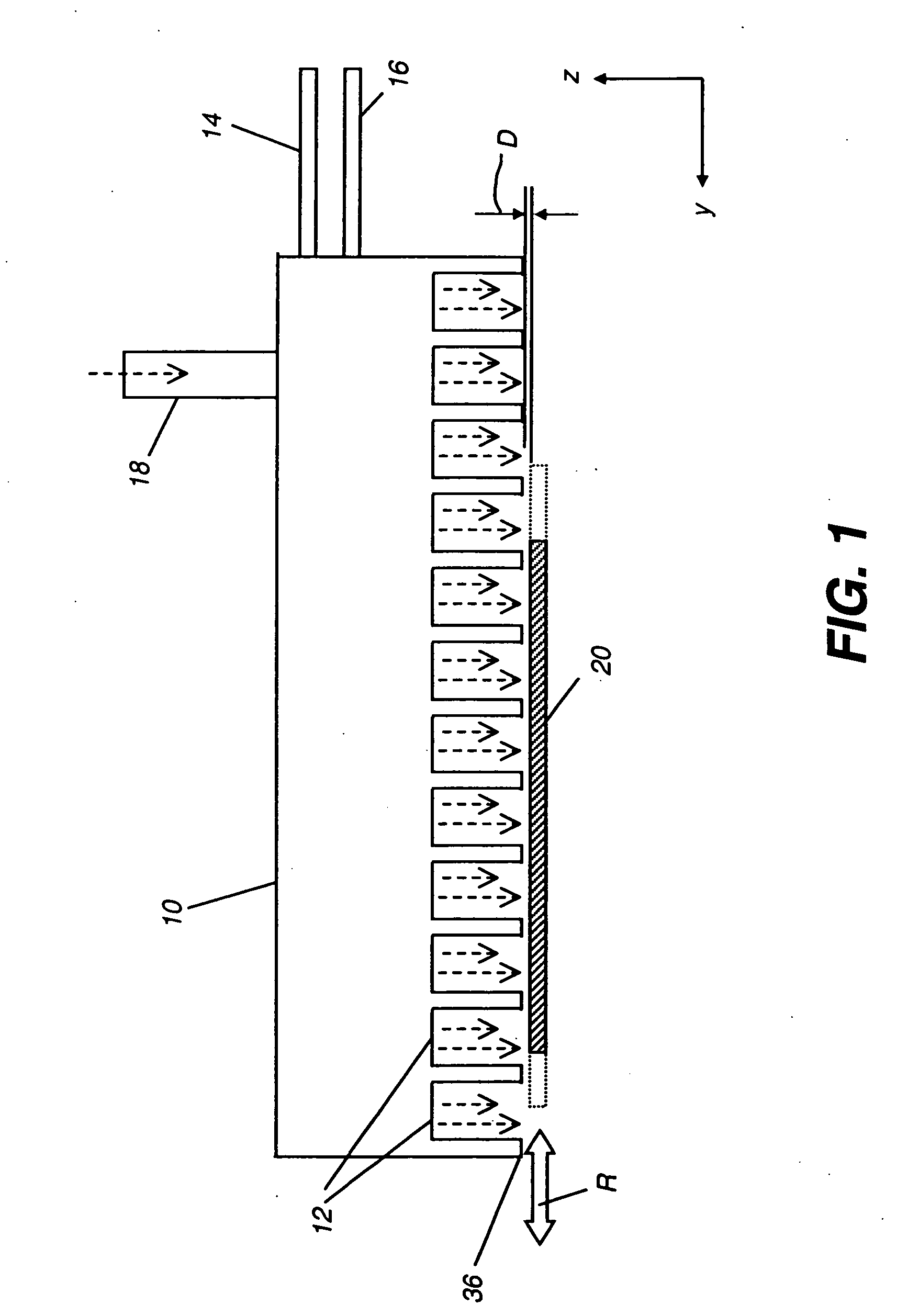
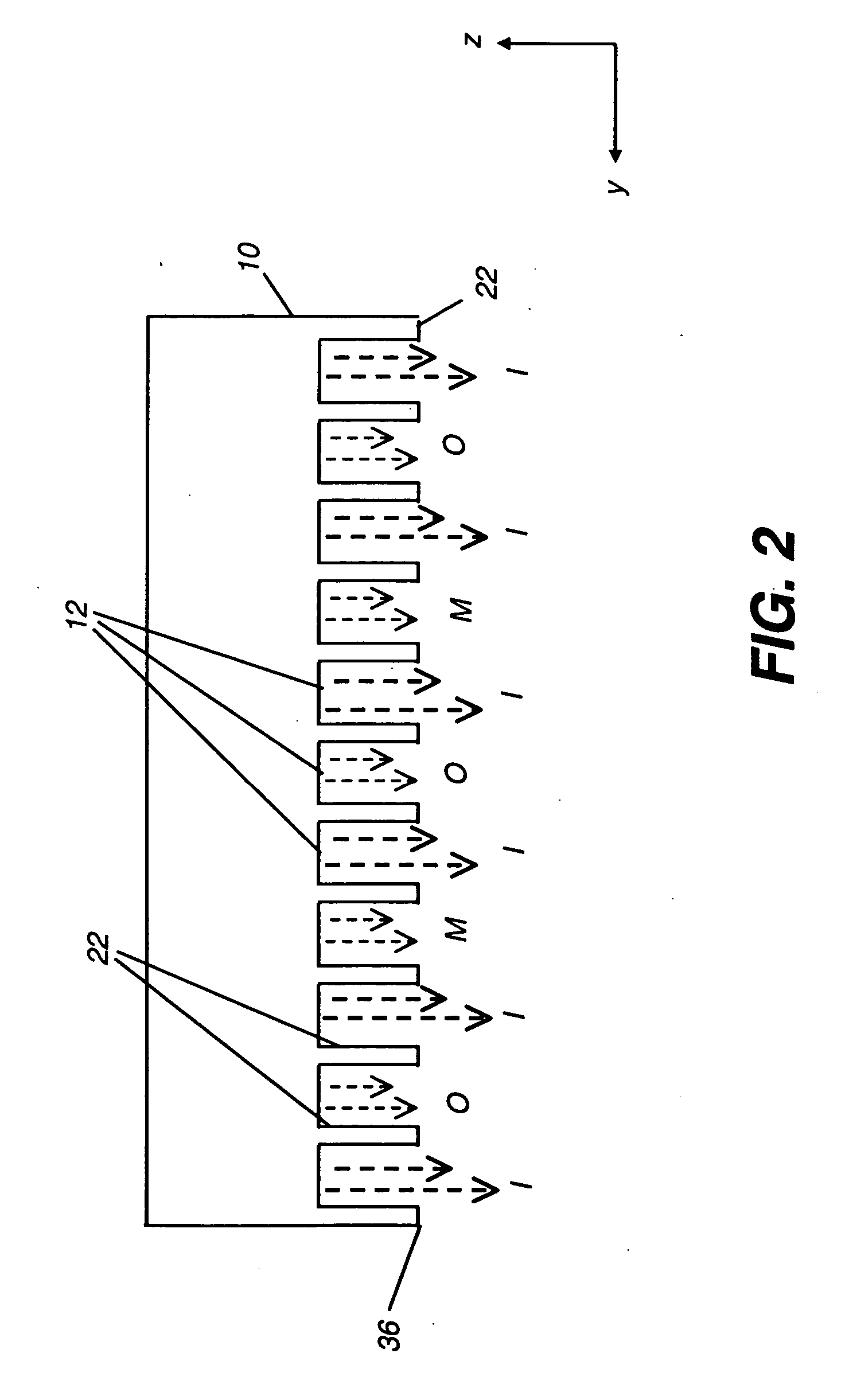
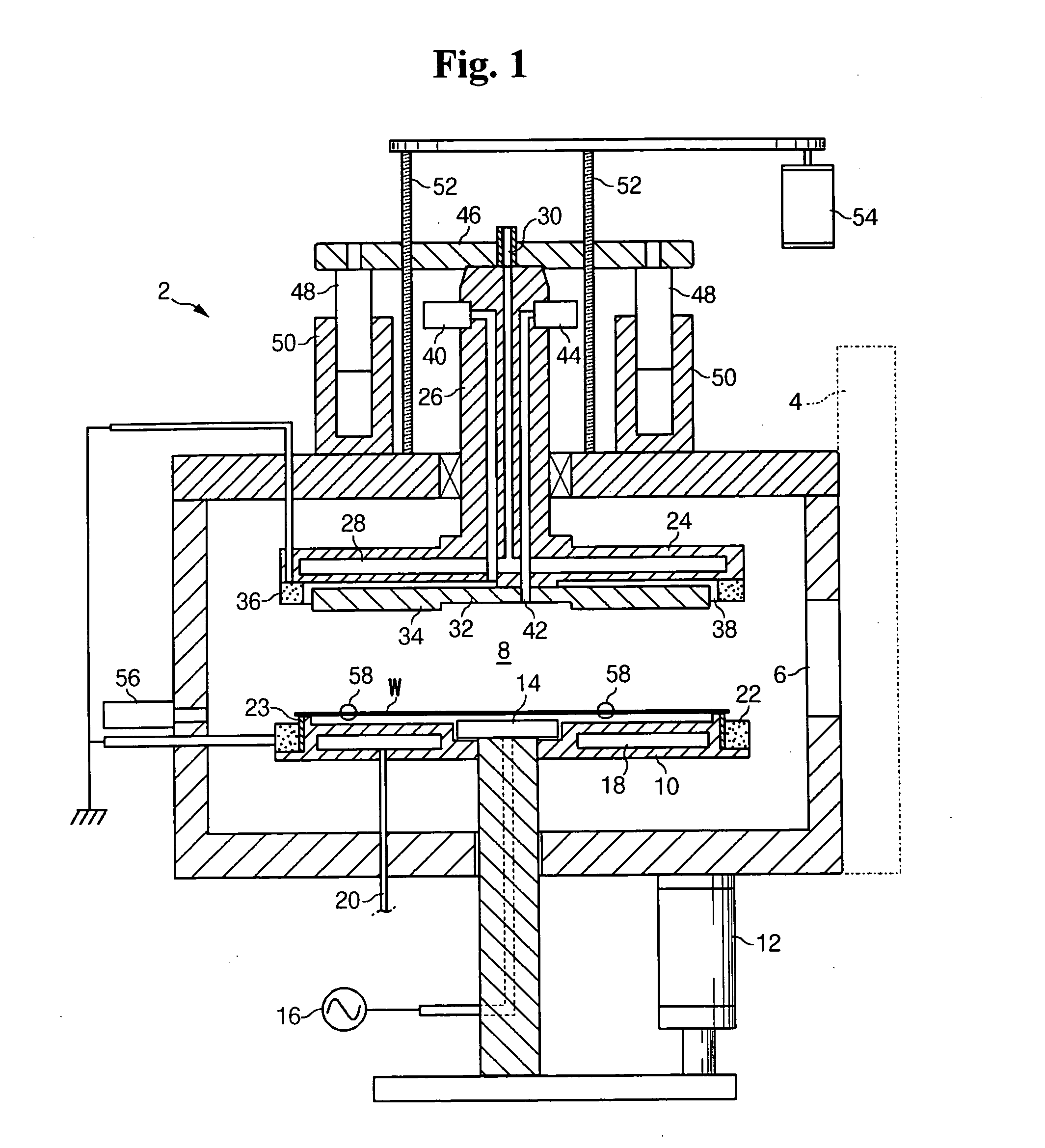
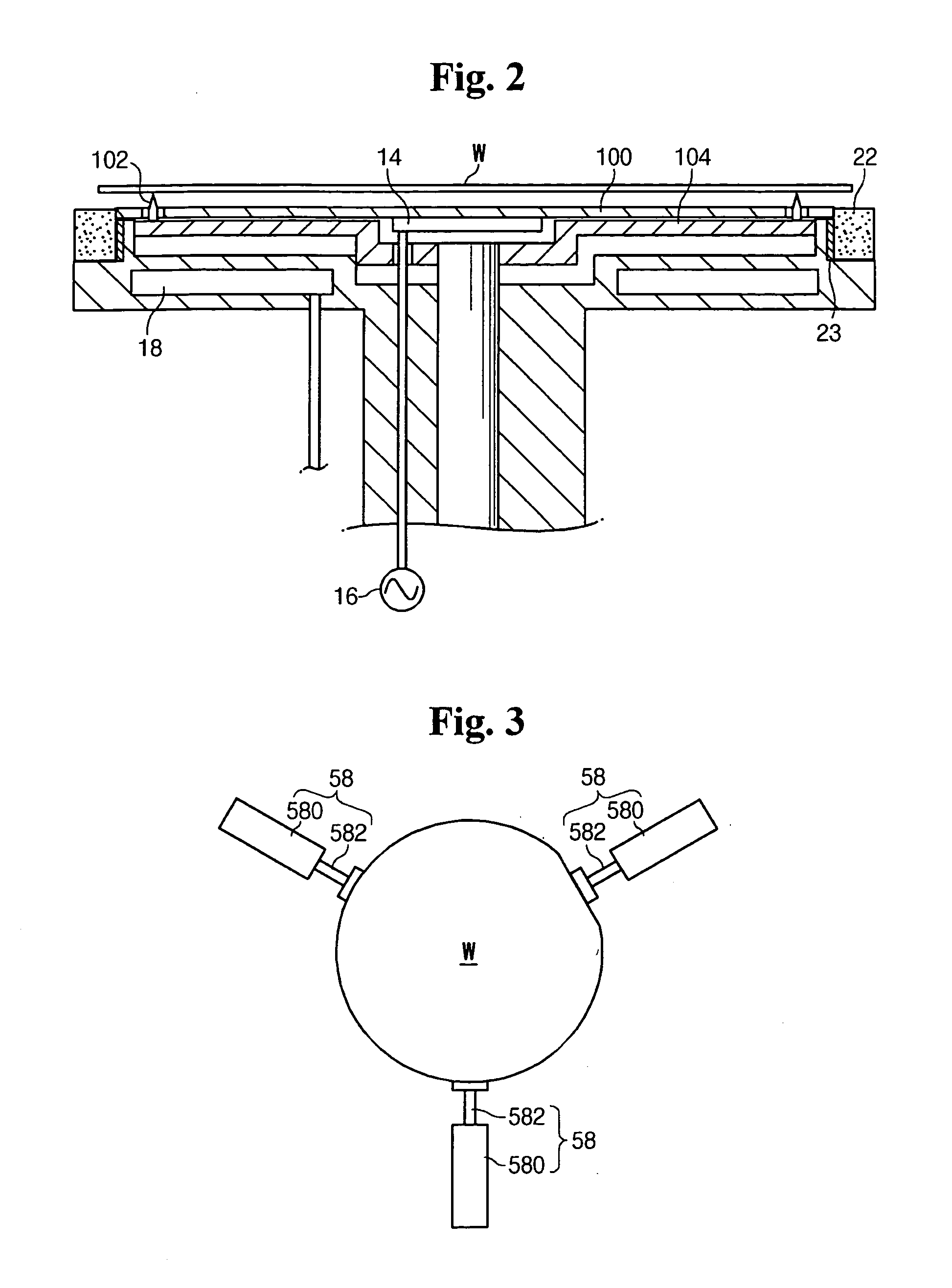
The present invention provides a distribution manifold for thin-film material deposition onto a substrate comprising a plurality of inlet ports for a sequence of gaseous materials, an output face comprising a plurality of open elongated output channels, each channel extending in a length direction substantially in parallel. The distribution manifold can be employed in a deposition system for thin film deposition, further comprising a plurality of sources for a plurality of gaseous materials and a support for positioning a substrate in pre-designed close proximity to the output face of the distribution manifold. During operation of the system, relative movement between the output face and the substrate support is accomplished.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
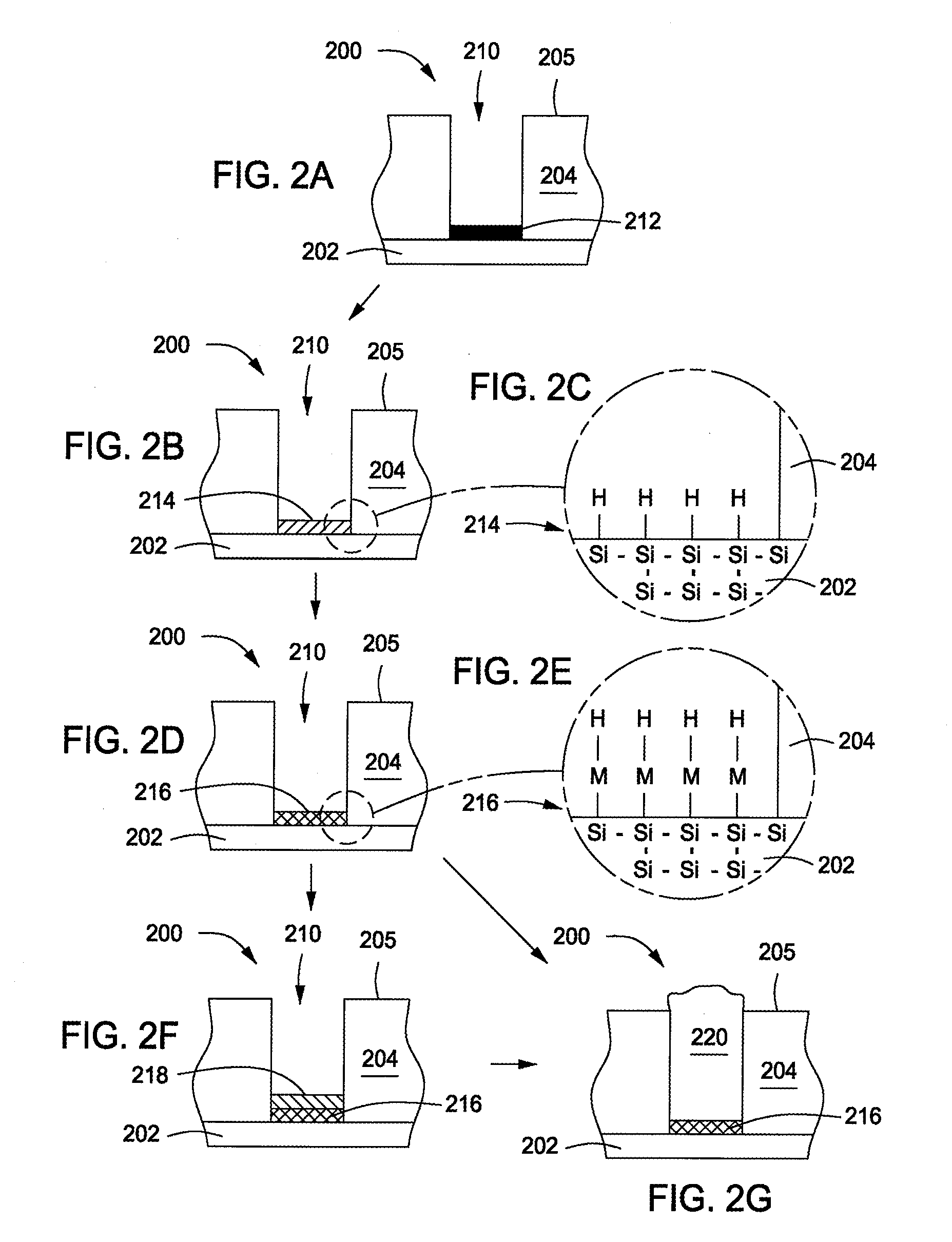
Self-supporting laminated films, structural materials and medical devices manufactured therefrom and methods of making same
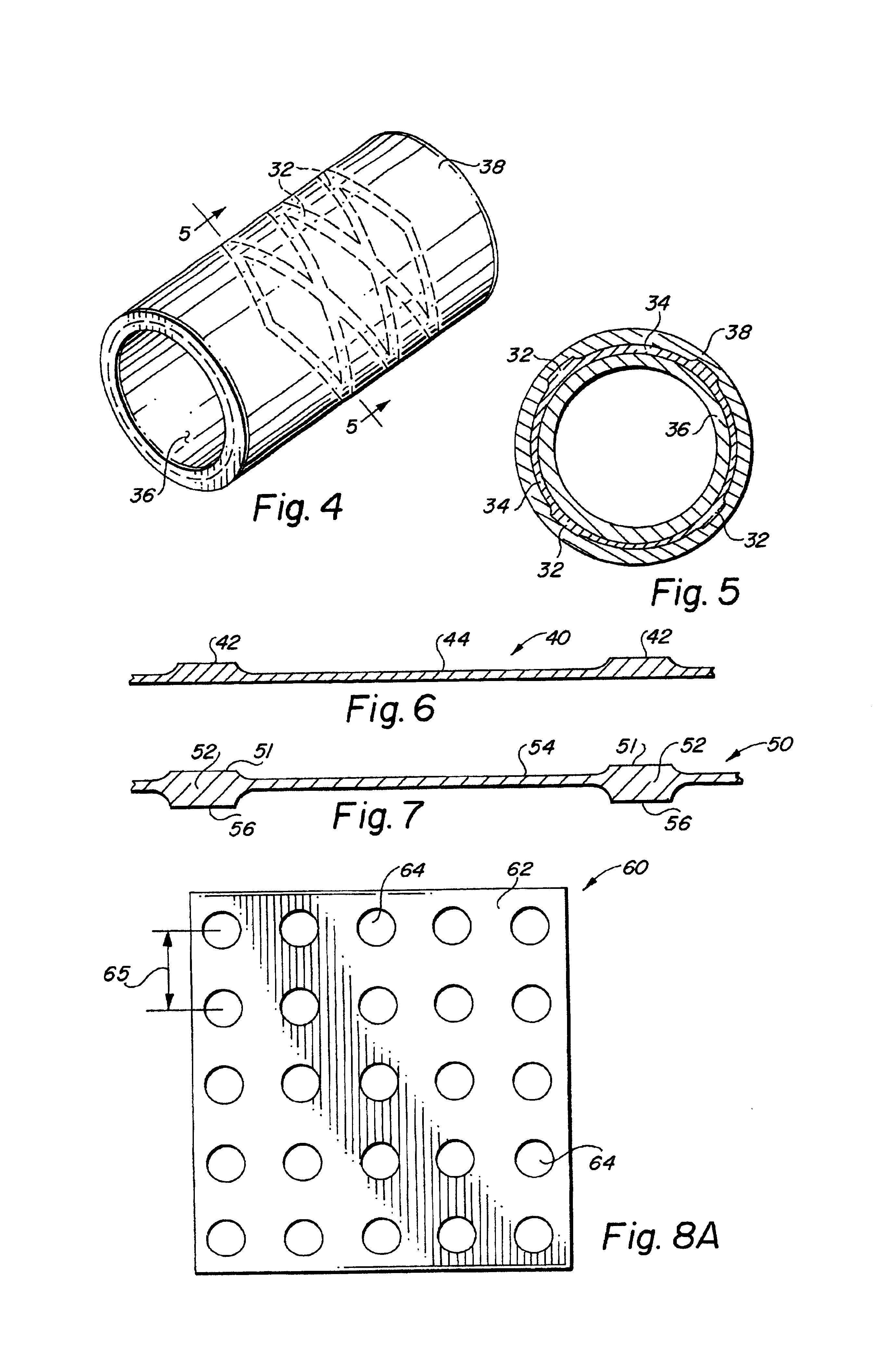
Metal foils, wires, and seamless tubes with increased mechanical strength are provided. As opposed to wrought materials that are made of a single metal or alloy, these materials are made of two or more layers forming a laminate structure. Laminate structures are known to increase mechanical strength of sheet materials such as wood and paper products and are used in the area of thin films to increase film hardness, as well as toughness. Laminate metal foils have not been used or developed because the standard metal forming technologies, such as rolling and extrusion, for example, do not lend themselves to the production of laminate structures. Vacuum deposition technologies can be developed to yield laminate metal structures with improved mechanical properties. In addition, laminate structures can be designed to provide special qualities by including layers that have special properties such as superelasticity, shape memory, radio-opacity, corrosion resistance etc. Examples of articles which may be made by the inventive laminate structures include implantable medical devices that are fabricated from the laminated deposited films and which present a blood or body fluid and tissue contact surface that has controlled heterogeneities in material constitution. An endoluminal stent-graft and web-stent that is made of a laminated film material deposited and etched into regions of structural members and web regions subtending interstitial regions between the structural members. An endoluminal graft is also provided which is made of a biocompatible metal or metal-like material. The endoluminal stent-graft is characterized by having controlled heterogeneities in the stent material along the blood flow surface of the stent and the method of fabricating the stent using vacuum deposition methods.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Etching Apparatus and Process with Thickness and Uniformity Control
InactiveUS20060191637A1Improve uniformityReduce unevennessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringFilm material
Apparatus and process for etching semiconductor wafers and the like in which a substrate is supported by a pedestal within a chamber, and at least one gas capable of etching the substrate or a film material on the substrate is introduced into the chamber through a segmented gas injection element which is separated from the substrate by a distance approximately less than its size from which the distribution of the flow or mixture of gas can be altered spatially proximate to the substrate in a controlled and variable way, for each wafer or substrate if desired, by having a varying amount or mixture of gas flow to some or all of the segments such as to cause the etching rate distribution to vary across the substrate.
Owner:ZAJAC JOHN +1
Deposition system and method using a delivery head separated from a substrate by gas pressure
ActiveUS20090130858A1Different from numberAllowed to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringProduct gas
A process for depositing a thin film material on a substrate is disclosed, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows from the output face of a delivery head of a thin film deposition system toward the surface of a substrate, and wherein the series of gas flows comprises at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material, wherein one or more of the gas flows provides a pressure that at least contributes to the separation of the surface of the substrate from the face of the delivery head. A system capable of carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method of selectively depositing a thin film material at a semiconductor interface
InactiveUS20070108404A1Detergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formMetal silicide
Embodiments of the invention provide processes to form a high quality contact level connection to devices formed on a substrate. In one embodiment, a method for depositing a material on a substrate is provided which includes exposing the substrate to a buffered oxide etch solution to form a silicon hydride layer during a pretreatment process, depositing a metal silicide layer on the substrate, and depositing a first metal layer (e.g., tungsten) on the metal silicide layer. The buffered oxide etch solution may contain hydrogen fluoride and an alkanolamine compound, such as ethanolamine diethanolamine, or triethanolamine. The metal silicide layer may contain cobalt, nickel, or tungsten and may be deposited by an electroless deposition process. In one example, the substrate is exposed to an electroless deposition solution containing a solvent and a complexed metal compound.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
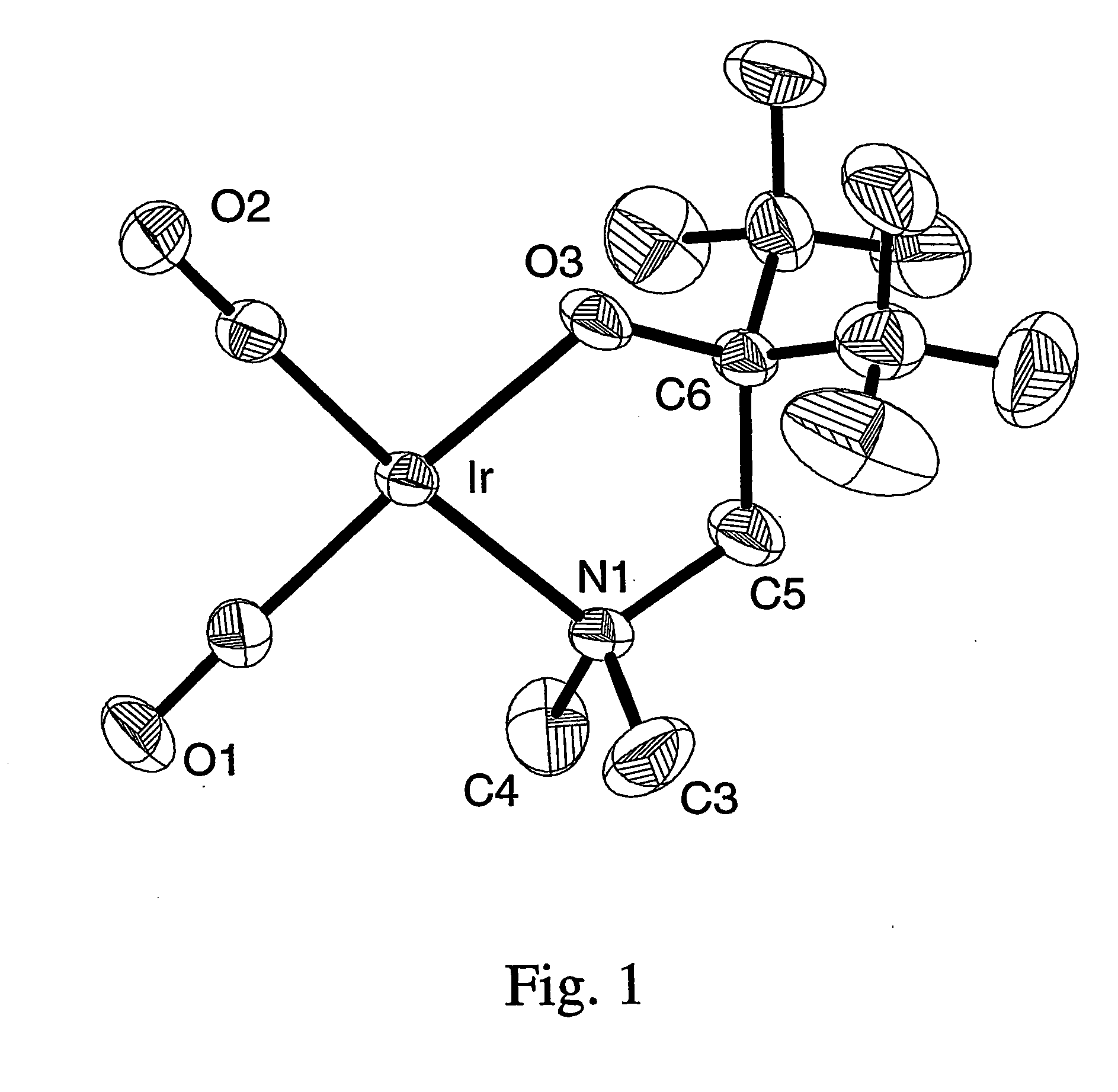
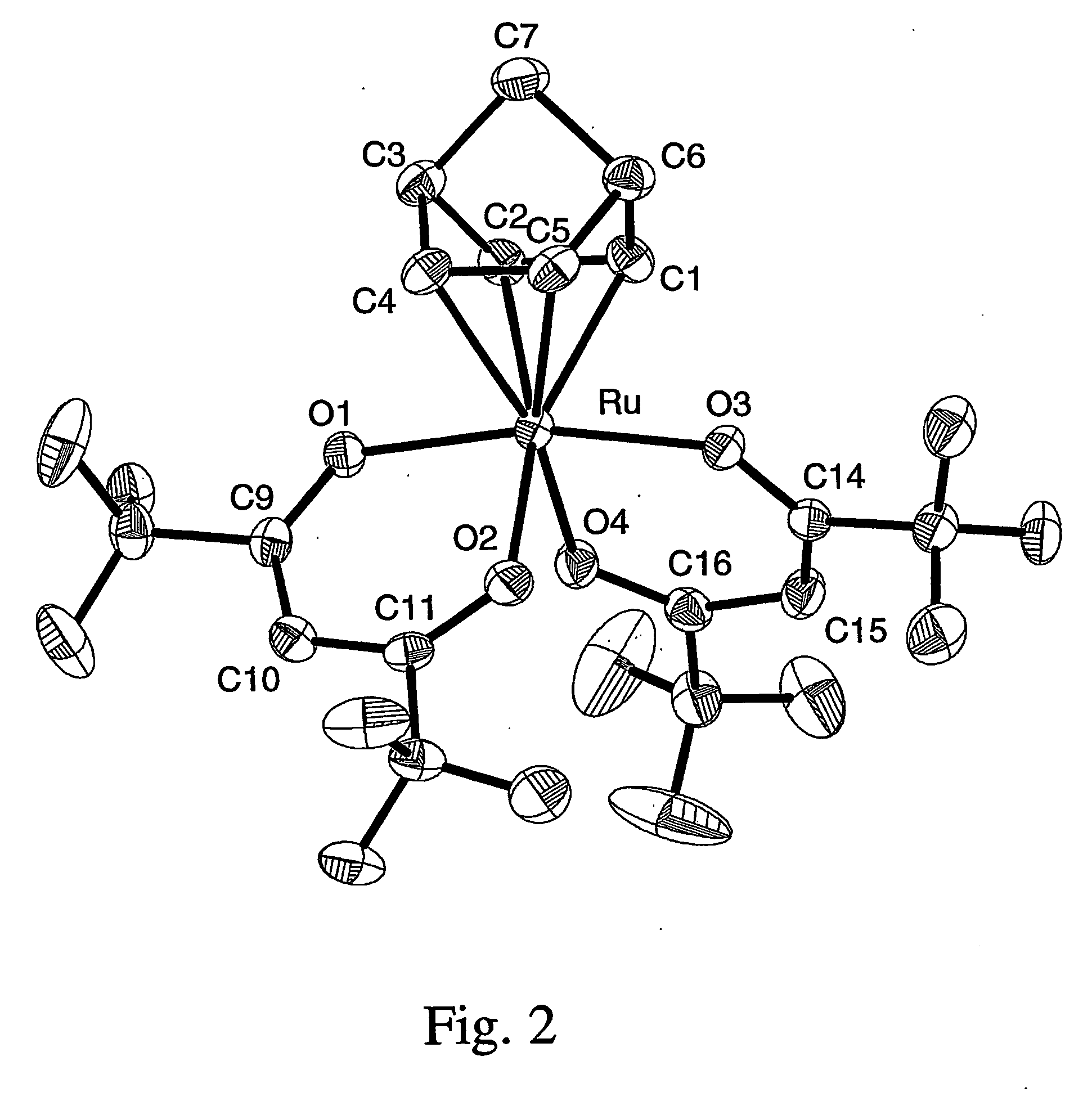
Volatile noble metal organometallic complexes
InactiveUS20050033075A1Reduce Van der Waals interactionBoiling and sublimation temperatureFurnaces without endless coreRuthenium organic compoundsIridiumIodide
A series of noble metal organometallic complexes of the general formula (I): MLaXb(FBC)c, wherein M is a noble metal such as iridium, ruthenium or osmium, and L is a neutral ligand such as carbonyl, alkene or diene; X is an anionic ligand such as chloride, bromide, iodide and trifluoroacetate group; and FBC is a fluorinated bidentate chelate ligand such as beta diketonate, beta-ketoiminate, amino-alcoholate and amino-alcoholate ligand, wherein a is an integer of from zero (0) to three (3), b is an integer of from zero (0) to one (1) and c is an 10 integer of from one (1) to three (3). The resulting noble metal complexes possess enhanced volatility and thermal stability characteristics, and are suitable for chemical vapor deposition(CVD) applications. The corresponding noble metal complex is formed by treatment of the FBC ligand with a less volatile metal halide. Also disclosed are CVD methods for using the noble metal complexes as source reagents for deposition of noble metal-containing films such as Ir, Ru and Os, or even metal oxide film materials IrO2, OsO2 and RuO2.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Deposition system for thin film formation
ActiveUS20090081885A1Different from numberAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduct gasFilm material
A process for depositing a thin film material on a substrate is disclosed, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows from the output face of a delivery head of a thin film deposition system toward the surface of a substrate, and wherein the series of gas flows comprises at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material, wherein one or more of the gas flows provides a pressure that at least contributes to the separation of the surface of the substrate from the face of the delivery head. A system capable of carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Delivery device comprising gas diffuser for thin film deposition
ActiveUS20080166884A1Good suitAllowed to operateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFilm material
A process for depositing a thin film material on a substrate is disclosed, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows from the output face of a delivery head of a thin film deposition system toward the surface of a substrate, and wherein the series of gas flows comprises at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material. A system capable of carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
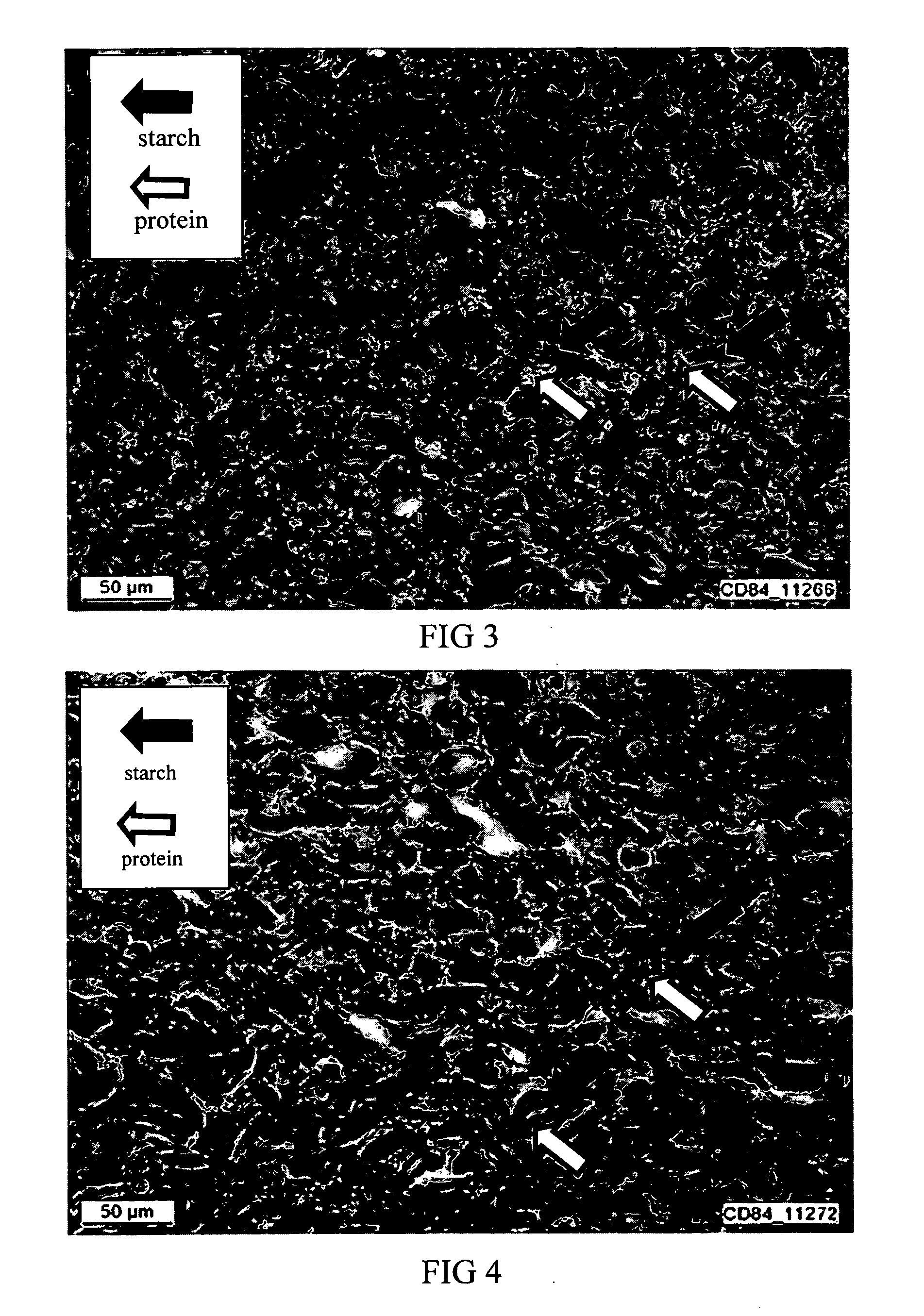
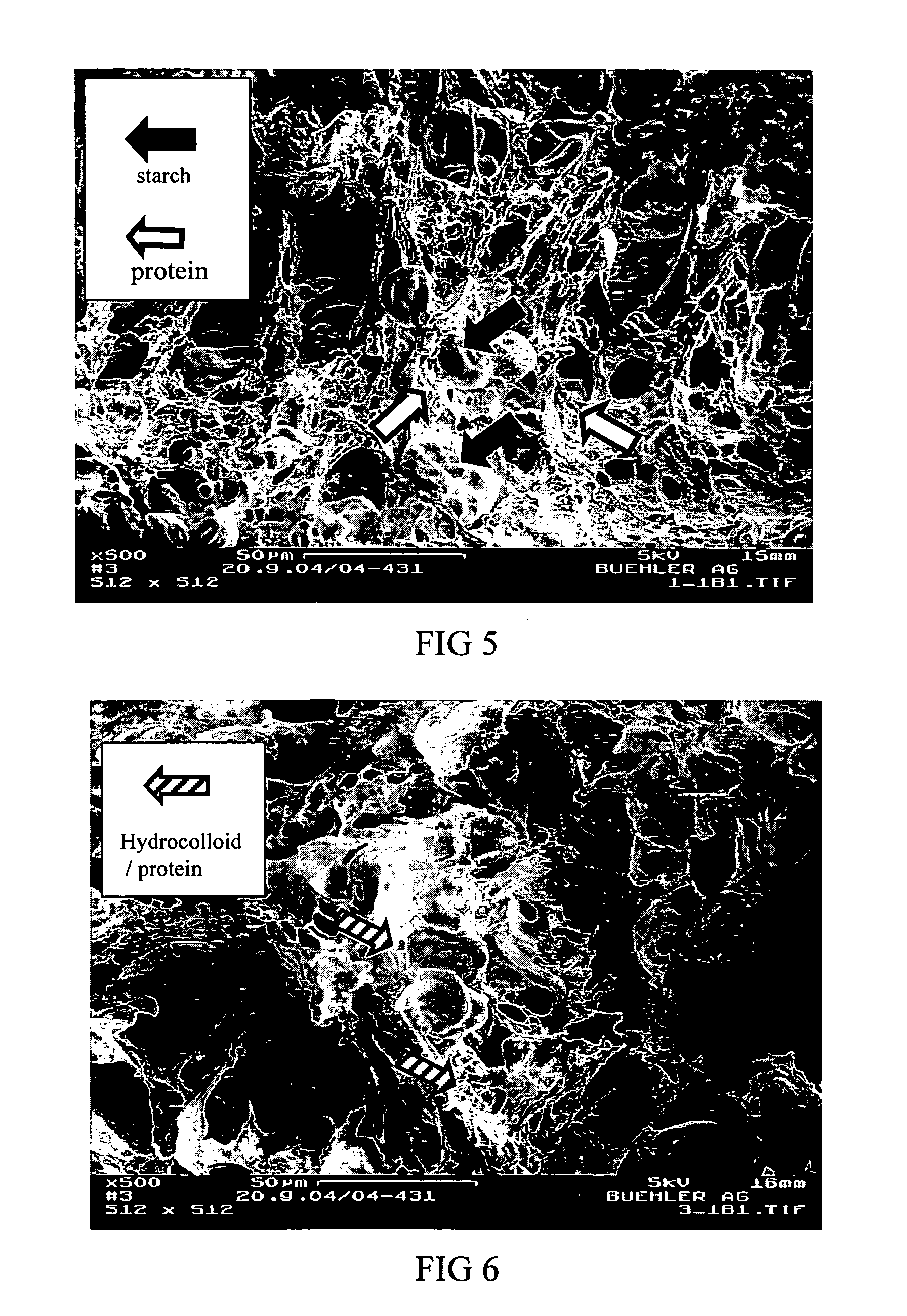
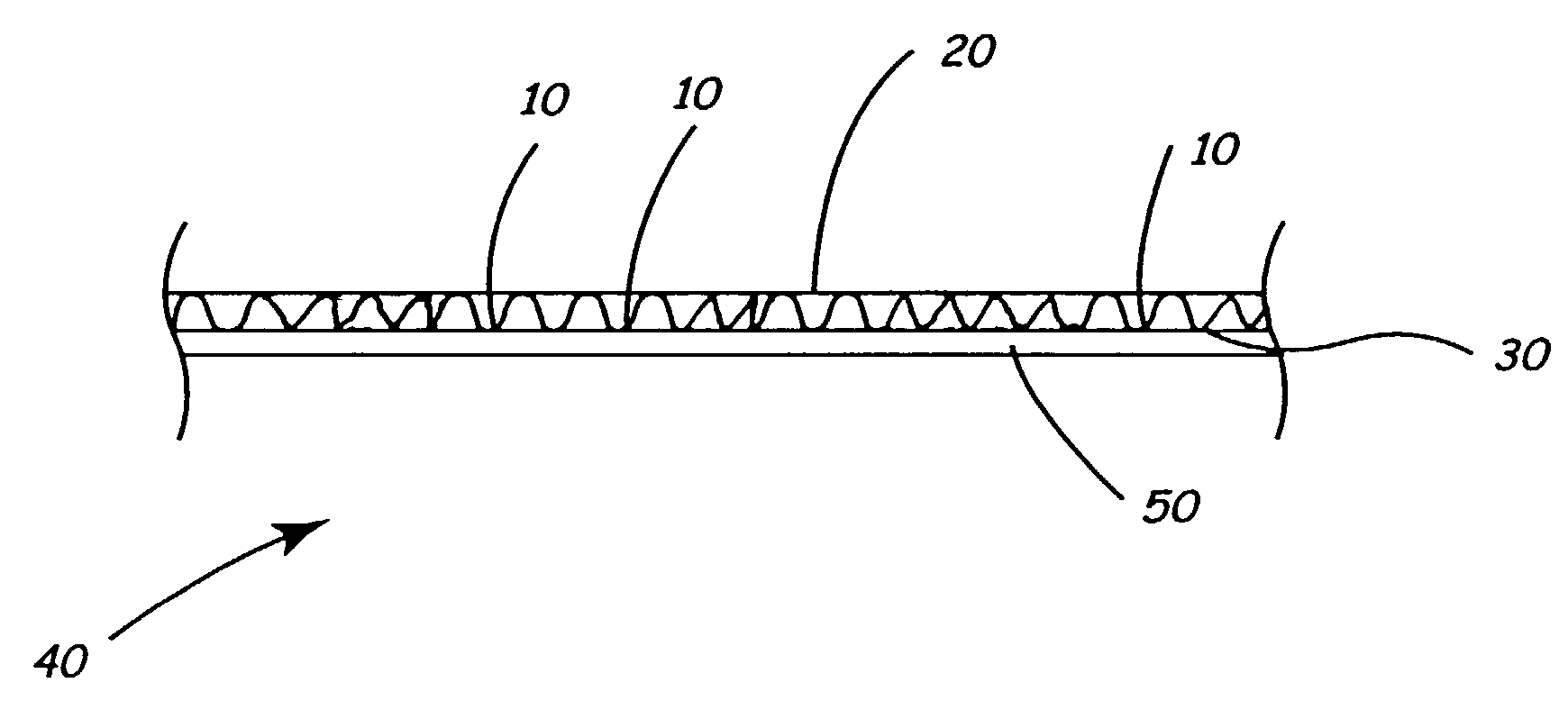
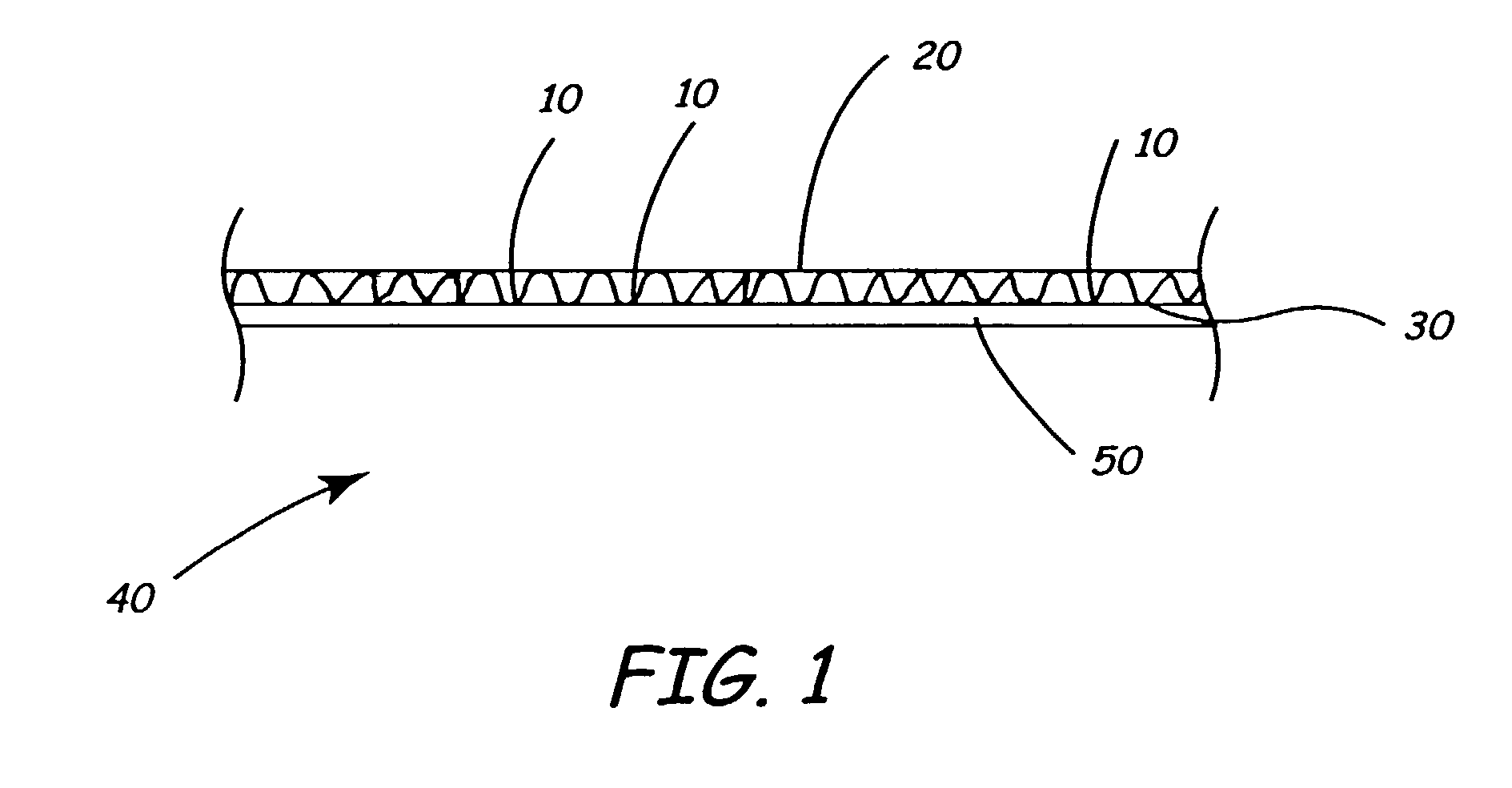
Reduced digestible carbohydrate food having reduced blood glucose response
ActiveUS20050118326A1Hypoglycemic responseReduced digestibleDough treatmentLeguminous plant bakery productsAdditive ingredientFood material
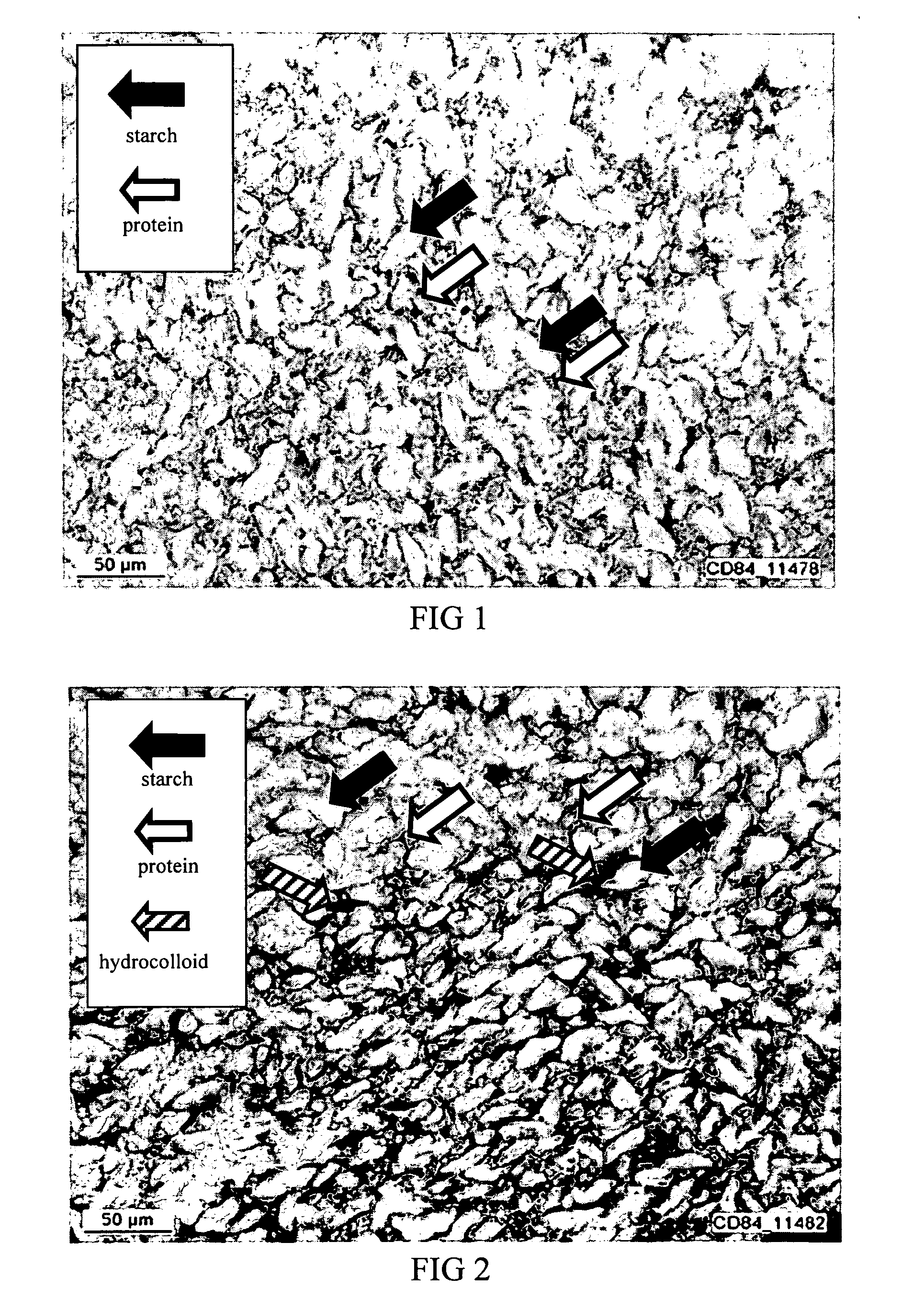
Reducing the digestion of digestible carbohydrates in a digestible carbohydrate-based material, and reducing the absorption of the digestion product(s) of digestible carbohydrates (that is, simple sugars) within the small intestine. The undigested digestible carbohydrate and the unabsorbed digestion products pass through the small intestines and into the colon, where they are fermented. In effect, the food materials made by practicing the present invention cause a controlled amount of digestible carbohydrate to by-pass the small intestine, resulting in the fermentation of digestible carbohydrates in the colon. The invention also provides for processing of a digestible carbohydrate-based ingredient with a non-digestible food film material, to form a reduced digestible carbohydrate food having a protective food film network, which can inhibit or prevent digestion of the digestible carbohydrate. The present invention also provides for processing of a digestible carbohydrate-based ingredient with a non-digestible food film material, to provide a resulting reduced digestible carbohydrate food containing a viscosity-building component that contributes to the formation of a viscous intestinal chyme that can inhibit or prevent digestion of the digestible carbohydrate and can inhibit adsorption of digestion products of digestible carbohydrates in the small intestine.
Owner:TECHCOM GRP LLC
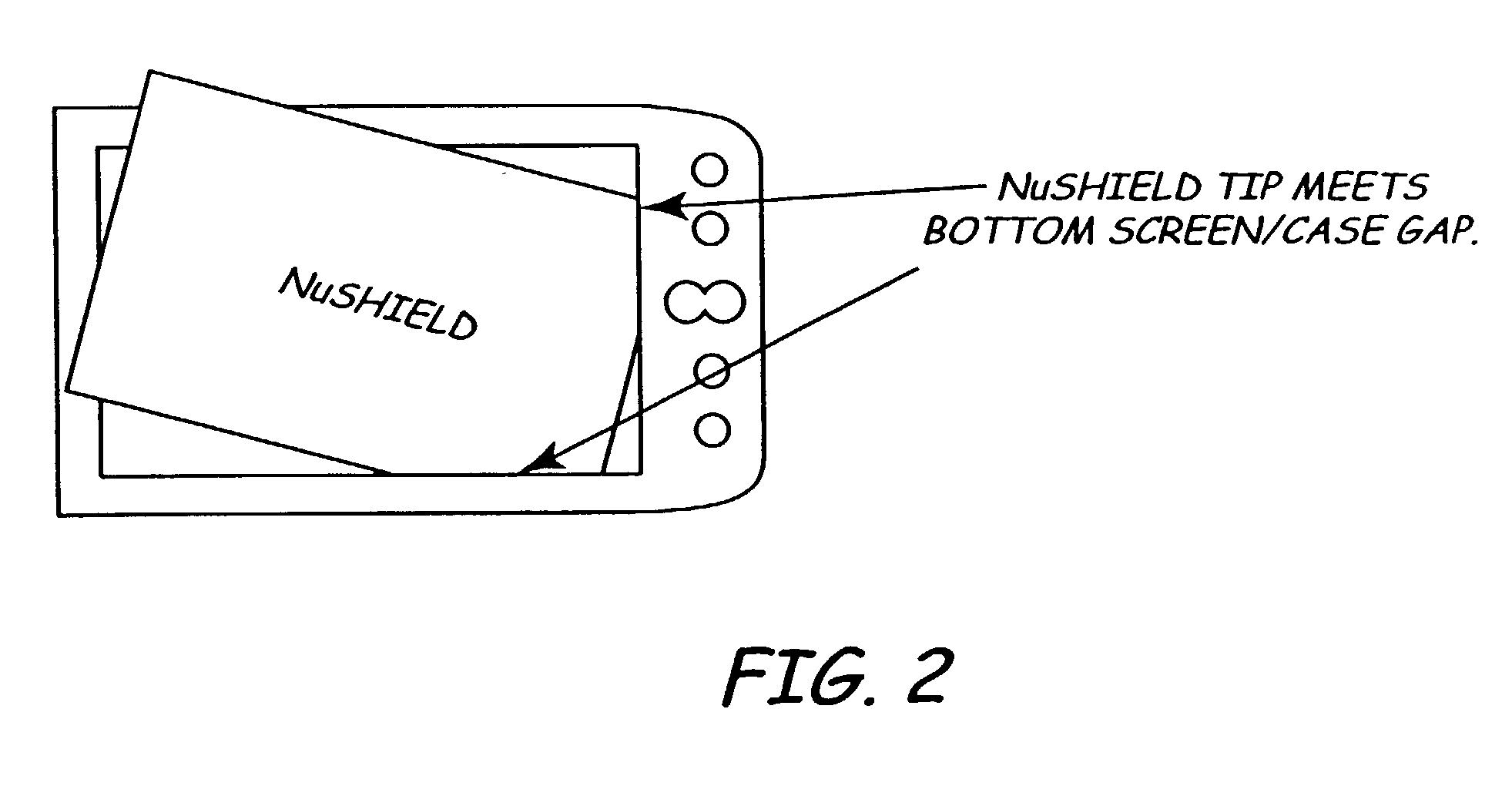
Screen protector
InactiveUS7070837B2Prevents orMinimize formationLiquid crystal compositionsAdhesive processesRefractive indexEngineering
A plastic film screen protector that prevents interference patterns from arising when the film touches the screen is described. The advantages are accomplished by the film having a slightly roughened surface so that the majority of the film facing an electronic device screen does not substantially touch the screen. These physical aberrations prevent Newton ring interference patterns and spots caused by refractive index differences between air and the film material.
Owner:ROSS MARK
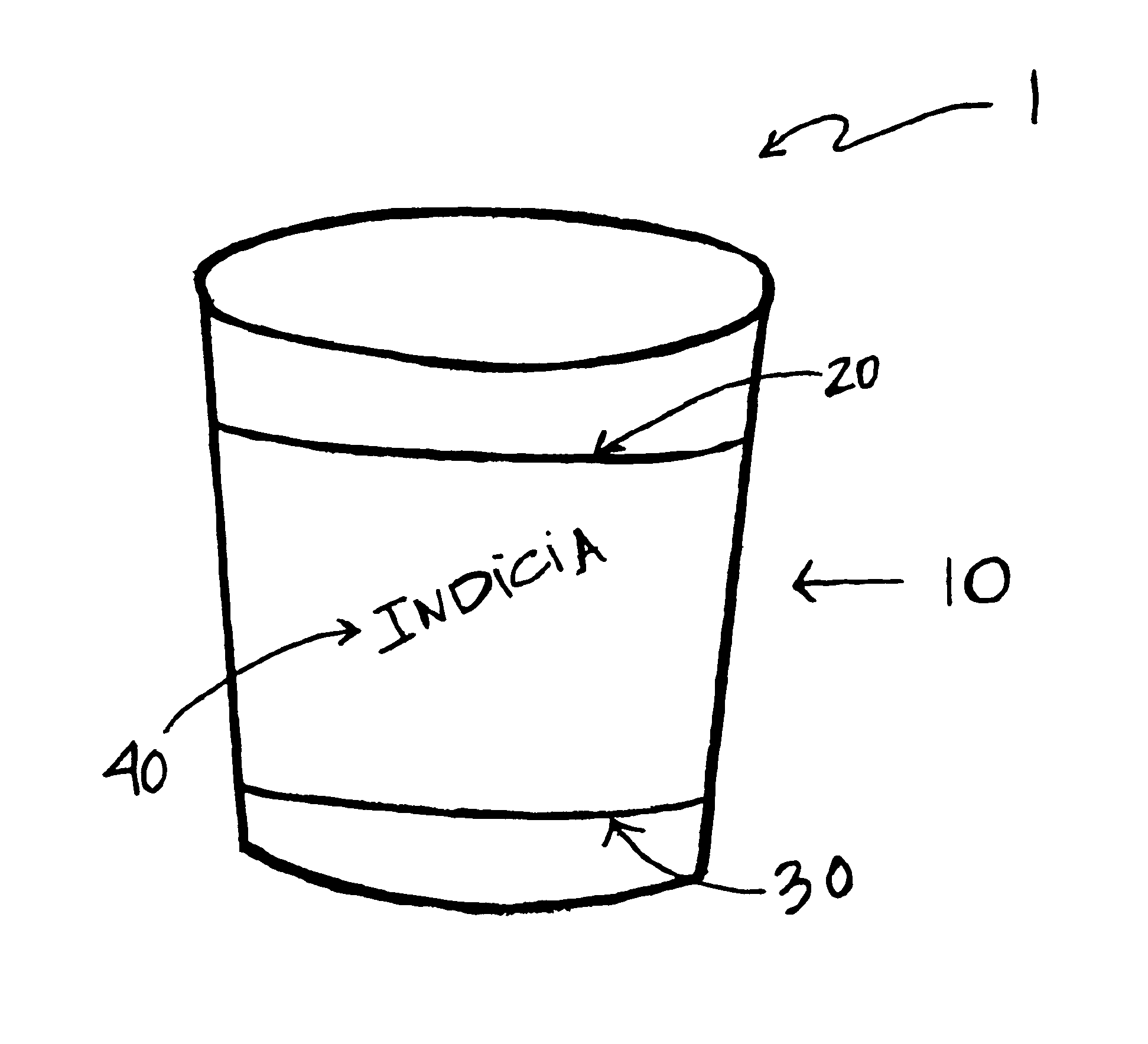
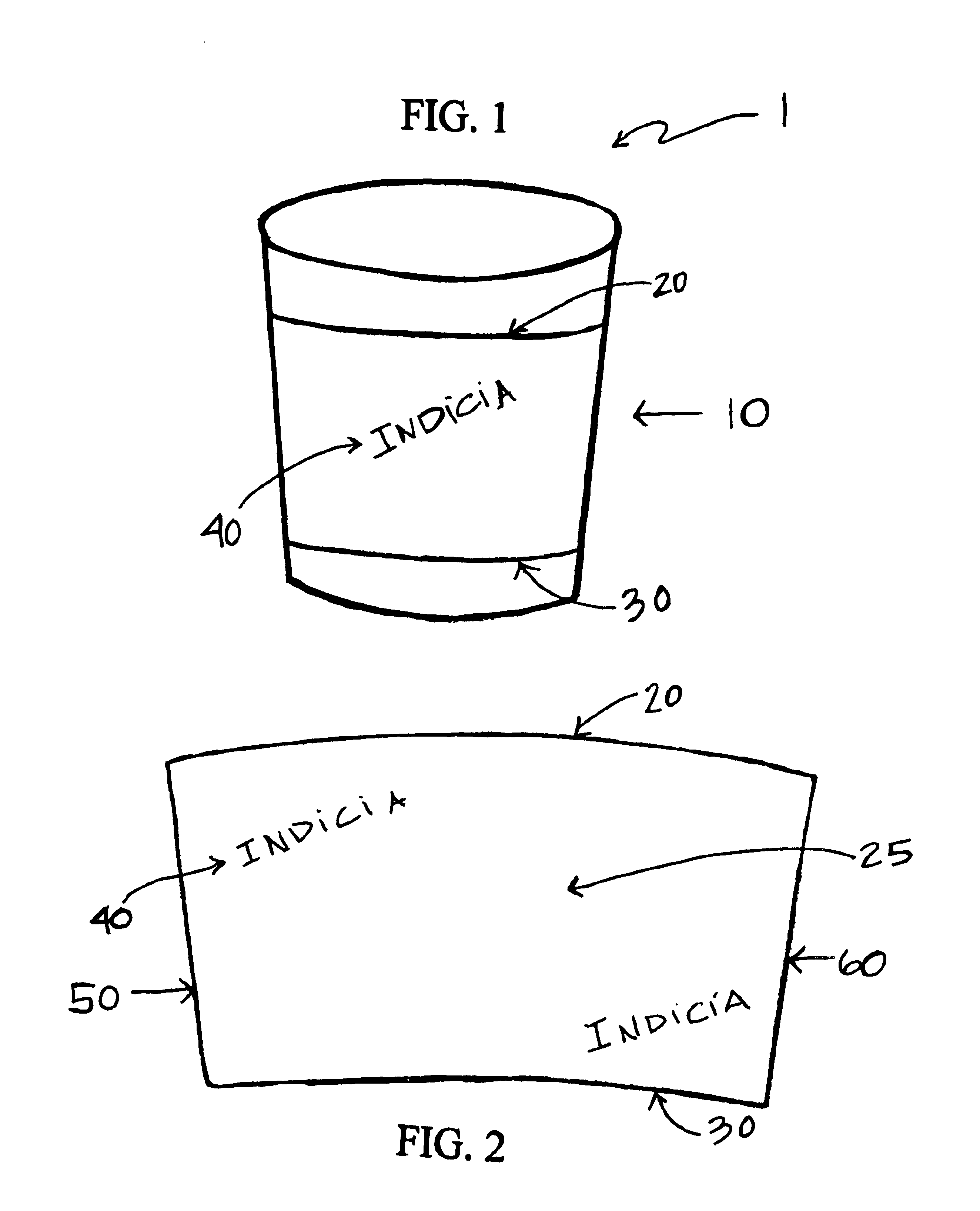
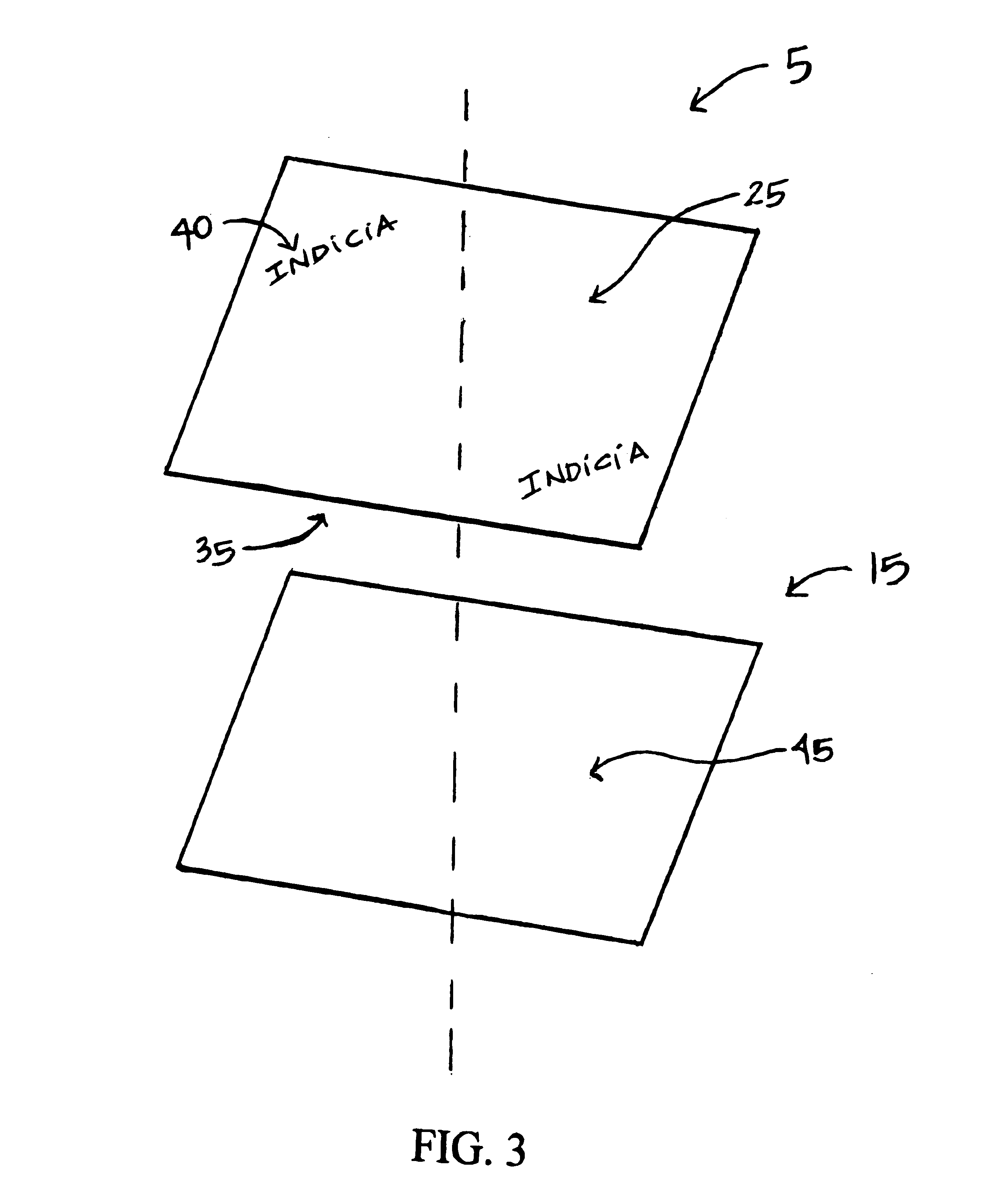
Insulating sleeve for grasping container and manufacturing method
InactiveUS6814253B2Easy to masterEasy to useSynthetic resin layered productsRefuse receptaclesPlastic materialsVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:DOUBLE TEAM
Delivery device for deposition
InactiveUS20080166880A1Different from numberAllowed to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringFilm material
A delivery device for thin-film material deposition has at least first, second, and third inlet ports for receiving a common supply for a first, a second and a third gaseous material, respectively. Each of the first, second, and third elongated emissive channels allow gaseous fluid communication with one of corresponding first, second, and third inlet ports. The delivery device is formed from apertured plates, superposed to define a network of interconnecting supply chambers and directing channels for routing each of the gaseous materials from its corresponding inlet port to its corresponding plurality of elongated emissive channels.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
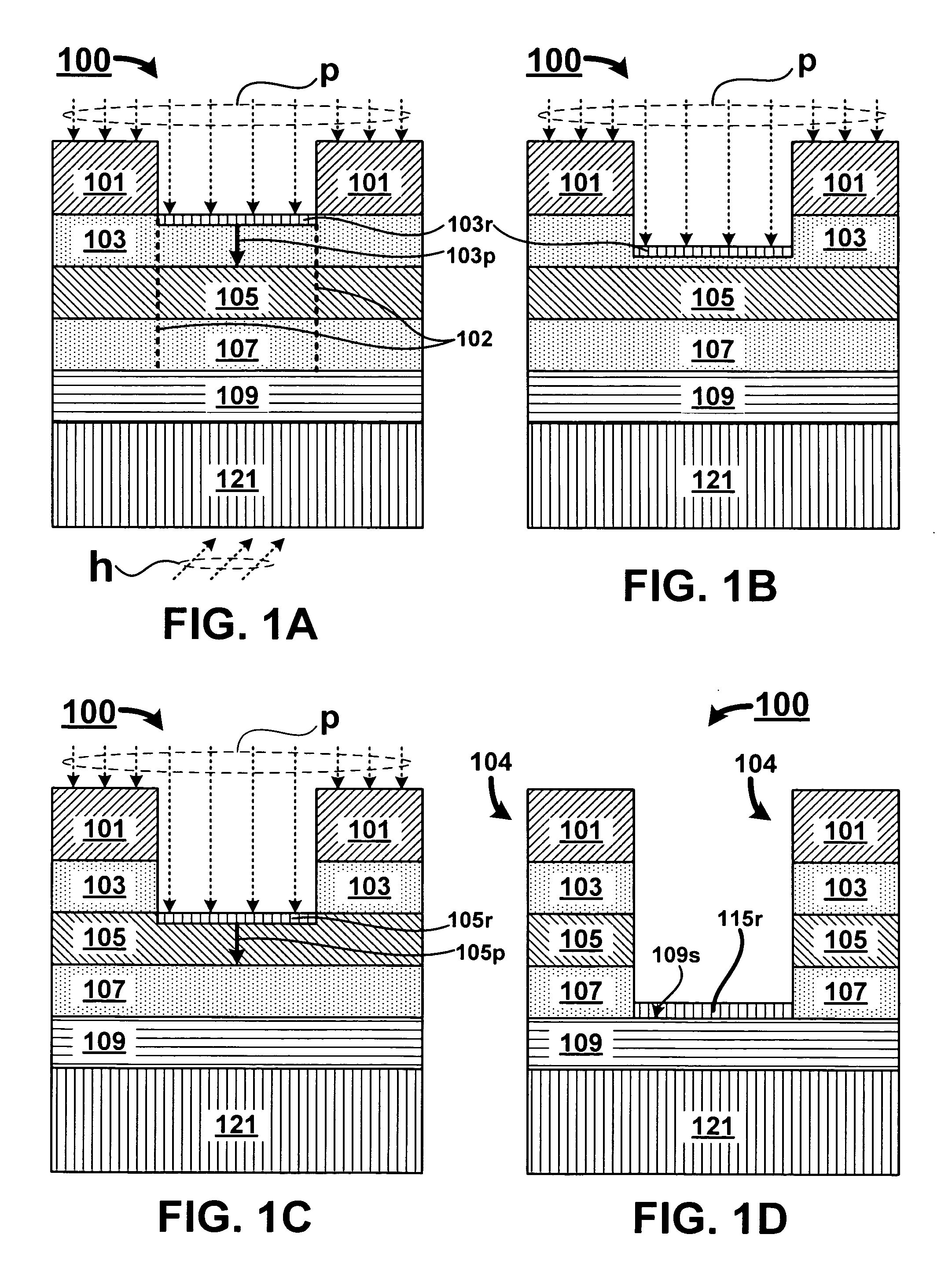
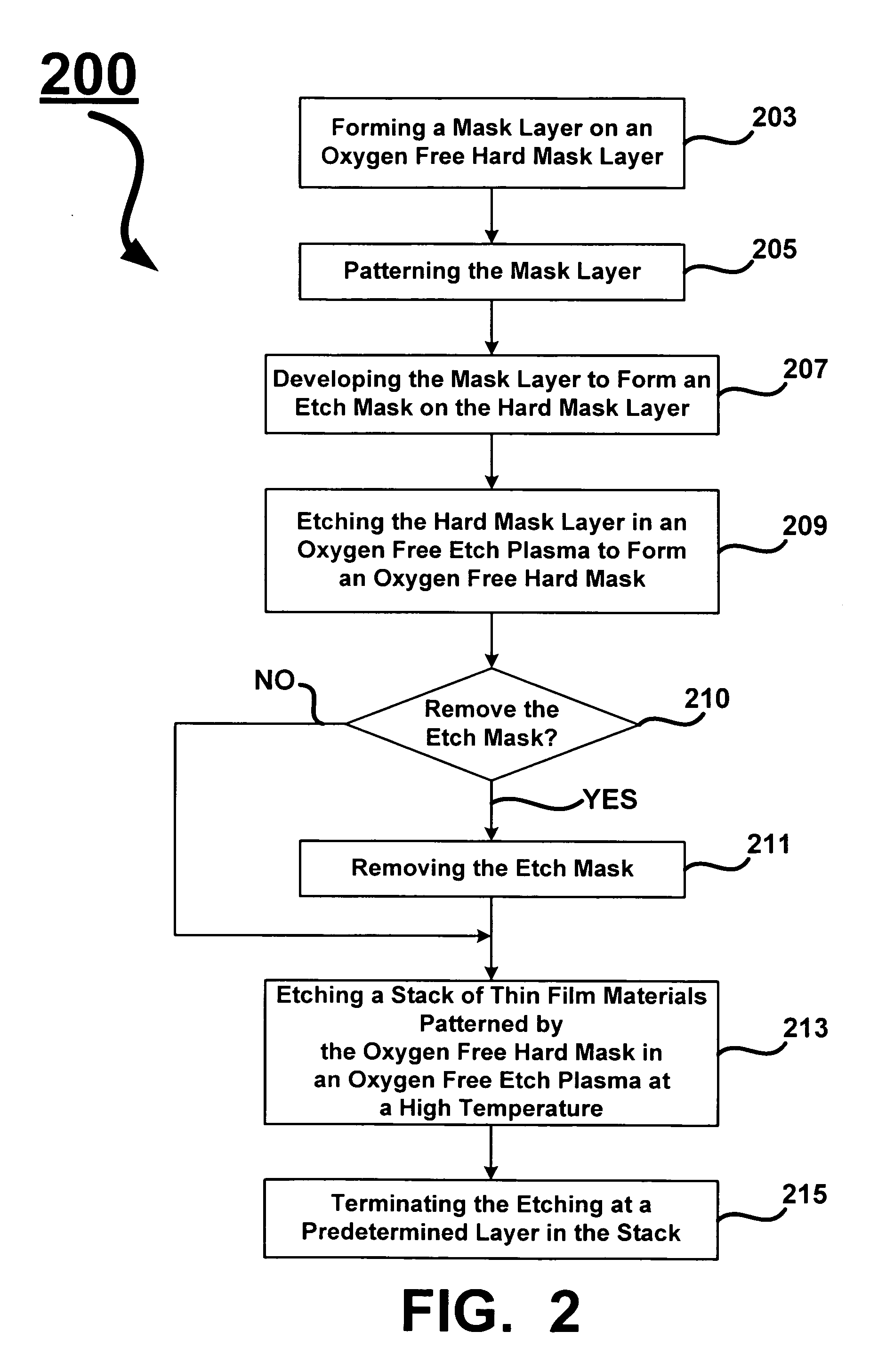
Oxygen depleted etching process
A method for oxygen depleted plasma etching and mixed mode plasma etching are disclosed. The method includes using an oxygen free etch plasma or a substantially oxygen free etch plasma at a high temperature to etch a stack including a plurality of layers of thin film materials. The oxygen depleted etching prevents or substantially reduces by-product re-deposition of titanium oxides generated by etching of titanium thin films in the stack. The titanium oxides can serve as a secondary mask layer that can cause defects in devices formed from the stack. Mixed mode plasma etching can include etching the stack with an oxygen free plasma, a substantially oxygen free plasma, and an oxygen containing plasma at different stages of a process.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Thin film deposition via a spatially-coordinated and time-synchronized process
InactiveUS20100151149A1Increase deposition rateImprove photovoltaic efficiencyFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesRemote plasmaSource material
A deposition system and process for the formation of thin film materials. In one embodiment, the process includes forming an initial plasma from a first material stream and allowing the plasma to evolve in space and / or time to extinguish species that are detrimental to the quality of the thin film material. After the initial plasma evolves to an optimum state, a second material stream is injected into the deposition chamber to form a composite plasma that contains a distribution of species more conducive to formation of a high quality thin film material. The deposition system includes a deposition chamber having a plurality of delivery points for injecting two or more streams (source materials or carrier gases) into a plasma region. The delivery points are staggered in space to permit an upstream plasma formed from a first material stream deposition source material to evolve before combining a downstream material stream with the plasma. Injection of different material streams is also synchronized in time. The net effect of spatial coordination and time synchronization of material streams is a plasma whose distribution of species is optimized for the deposition of a thin film photovoltaic material at high deposition rates. Delivery devices include nozzles and remote plasma sources.
Owner:OVSHINSKY TECH
Delivery device comprising gas diffuser for thin film deposition
ActiveUS7789961B2Different from numberShorten the timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin membraneFilm material
A process for depositing a thin film material on a substrate is disclosed, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows from the output face of a delivery head of a thin film deposition system toward the surface of a substrate, and wherein the series of gas flows comprises at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material. A system capable of carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor device having the organic thin film transistor
InactiveUS20040023447A1Simple manufacturing processThin thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMan-hourEngineering
There have been problems in that a dedicated apparatus is needed for a conventional method of manufacturing an organic thin film transistor and in that: a little amount of an organic semiconductor film is formed with respect to a usage amount of a material; and most of the used material is discarded. Further, apparatus maintenance such as cleaning of the inside of an apparatus cup or chamber has needed to be frequently carried out in order to remove the contamination resulting from the material that is wastefully discarded. Therefore, a great cost for materials and man-hours for maintenance of apparatus have been required. In the present invention, a uniform organic semiconductor film is formed by forming an aperture between a first substrate for forming the organic semiconductor film and a second substrate used for injection with an insulating film formed at a specific spot and by injecting an organic semiconductor film material into the aperture due to capillarity to the aperture. The insulating film formed at the specific spot enables formation of the organic semiconductor film with high controllability. Further, the insulating film can also serve as a spacer that holds the aperture, that is, an interval (gap) between the substrates.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
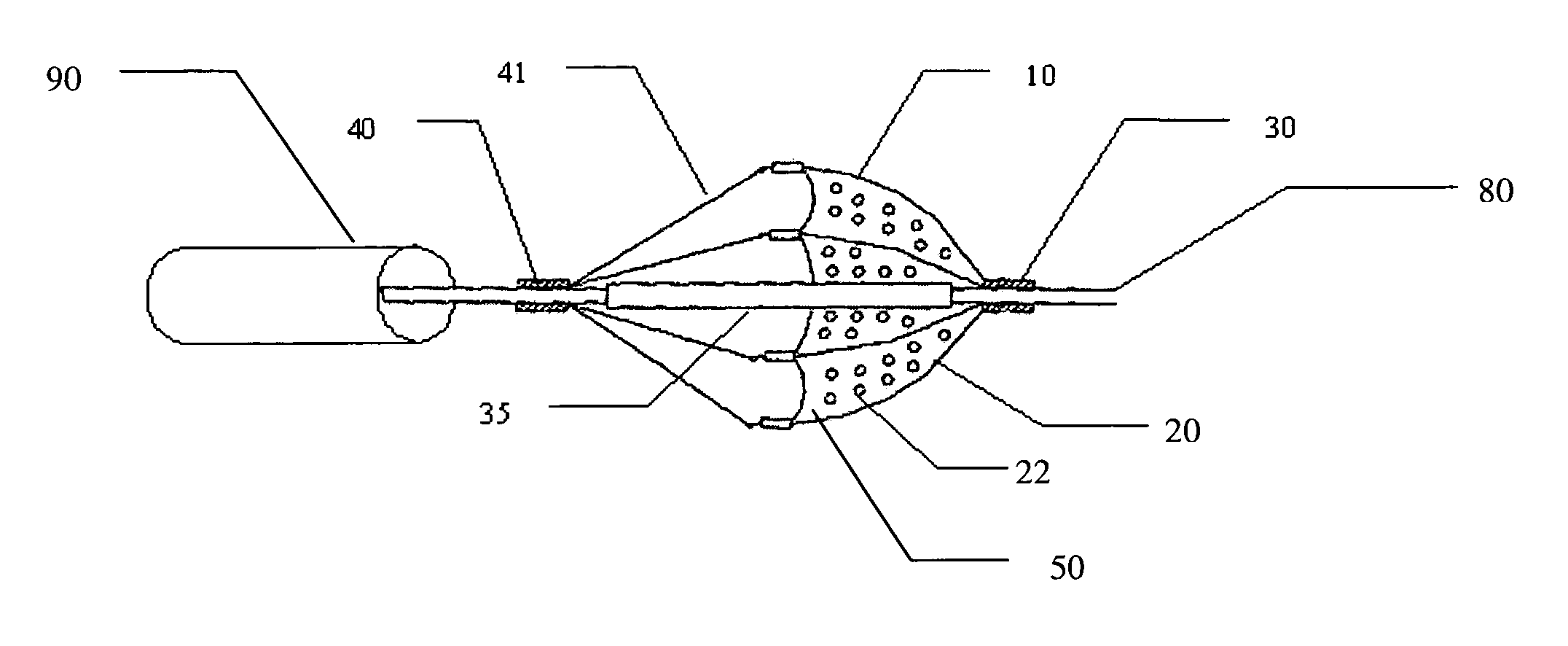
Distal protection apparatus with improved wall apposition
InactiveUS20060149313A1Easy loadingPrevent thrombosisSurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryEmbolization material
In accordance with the present invention, a distal protection and embolic material retrieval device with improved apposition to both large and small vessel walls of varying geometries for enhancing the filtering of embolic material during intravascular procedures while allowing for the passage of blood is provided. The device includes a filter basket designed to maximize apposition of the filtering portion to that of the vessel wall and may include struts which provide circumferential support to the filtering membrane and thereby minimizing or eliminating in-folding of the filter basket. Thin film materials may also be utilized for the filtering membrane of the filter basket. In addition one can incorporate biological and / or pharmaceutical agents in combination with the present invention.
Owner:ARGUELLO EDWARD +3
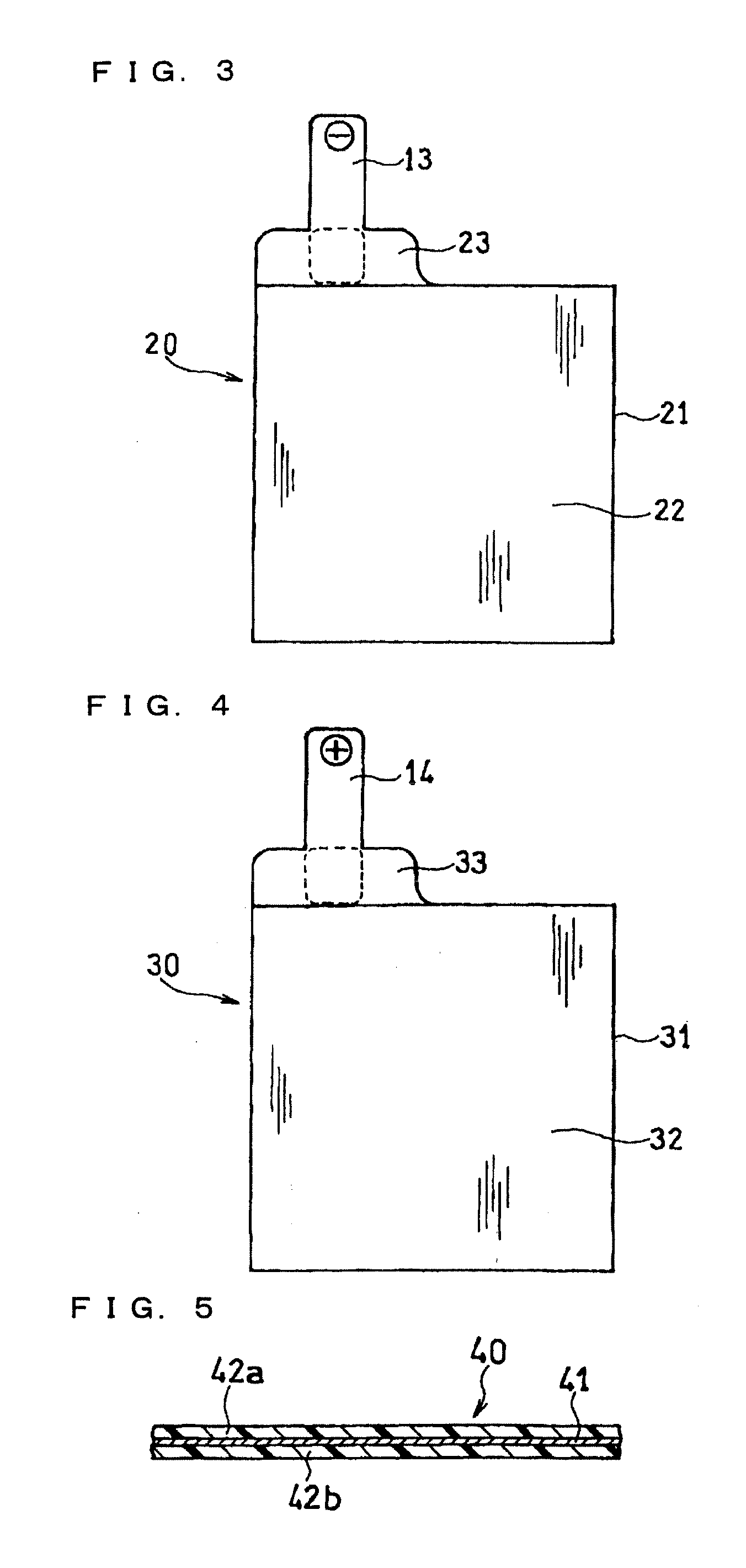
Flexible battery and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20130101884A1Impart high flexibilityImproves sealing reliabilityFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsEngineeringFlexible battery
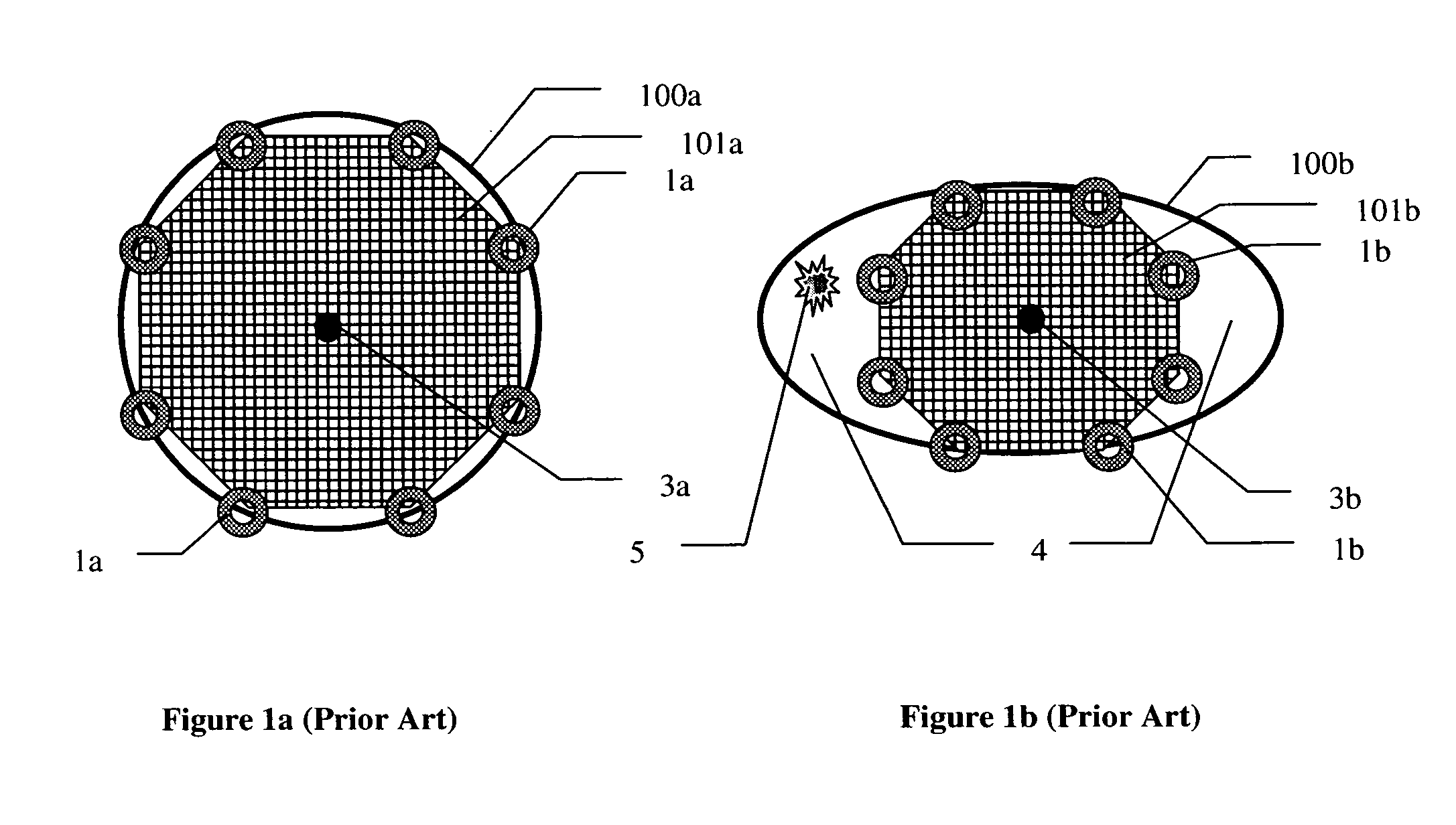
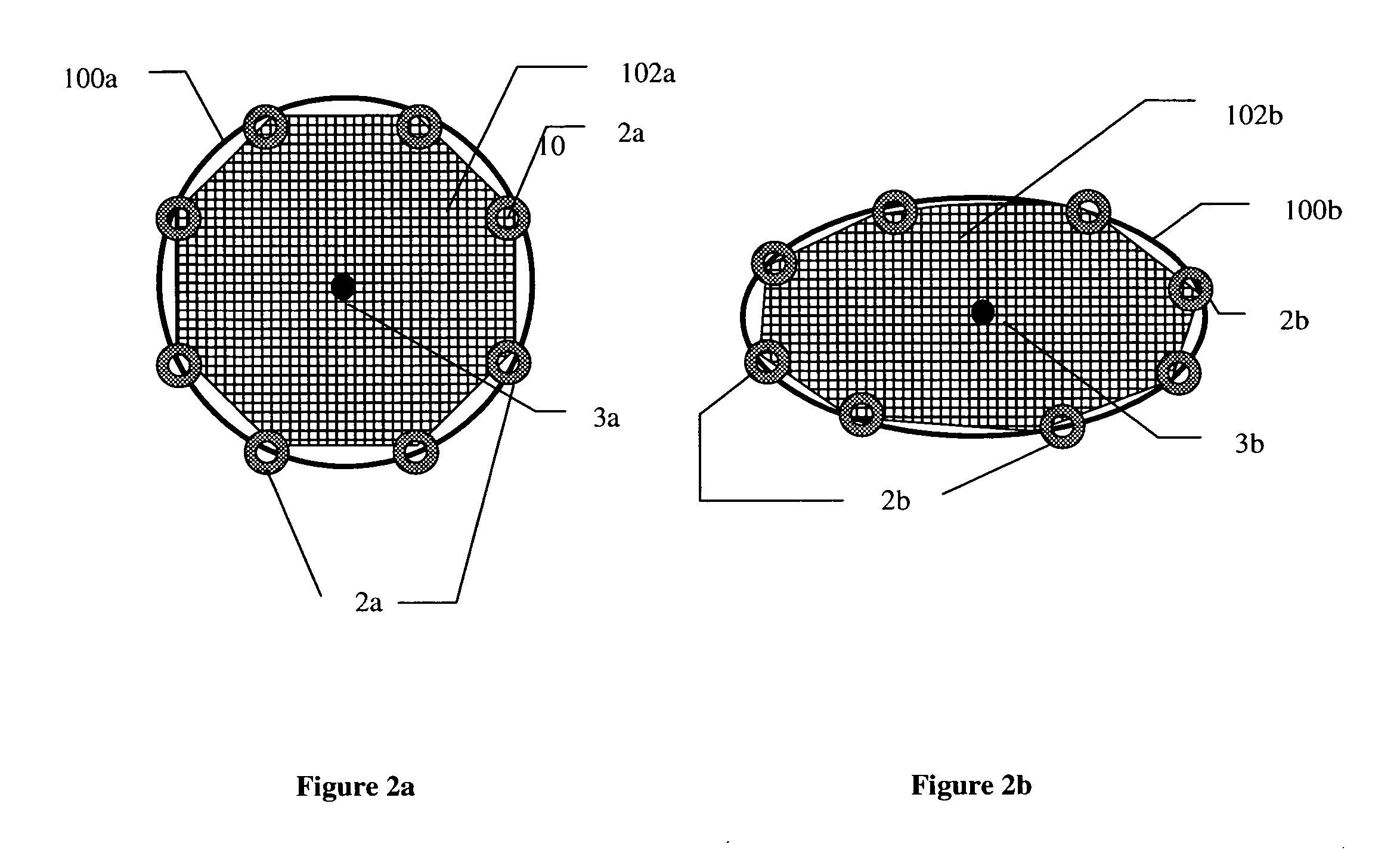
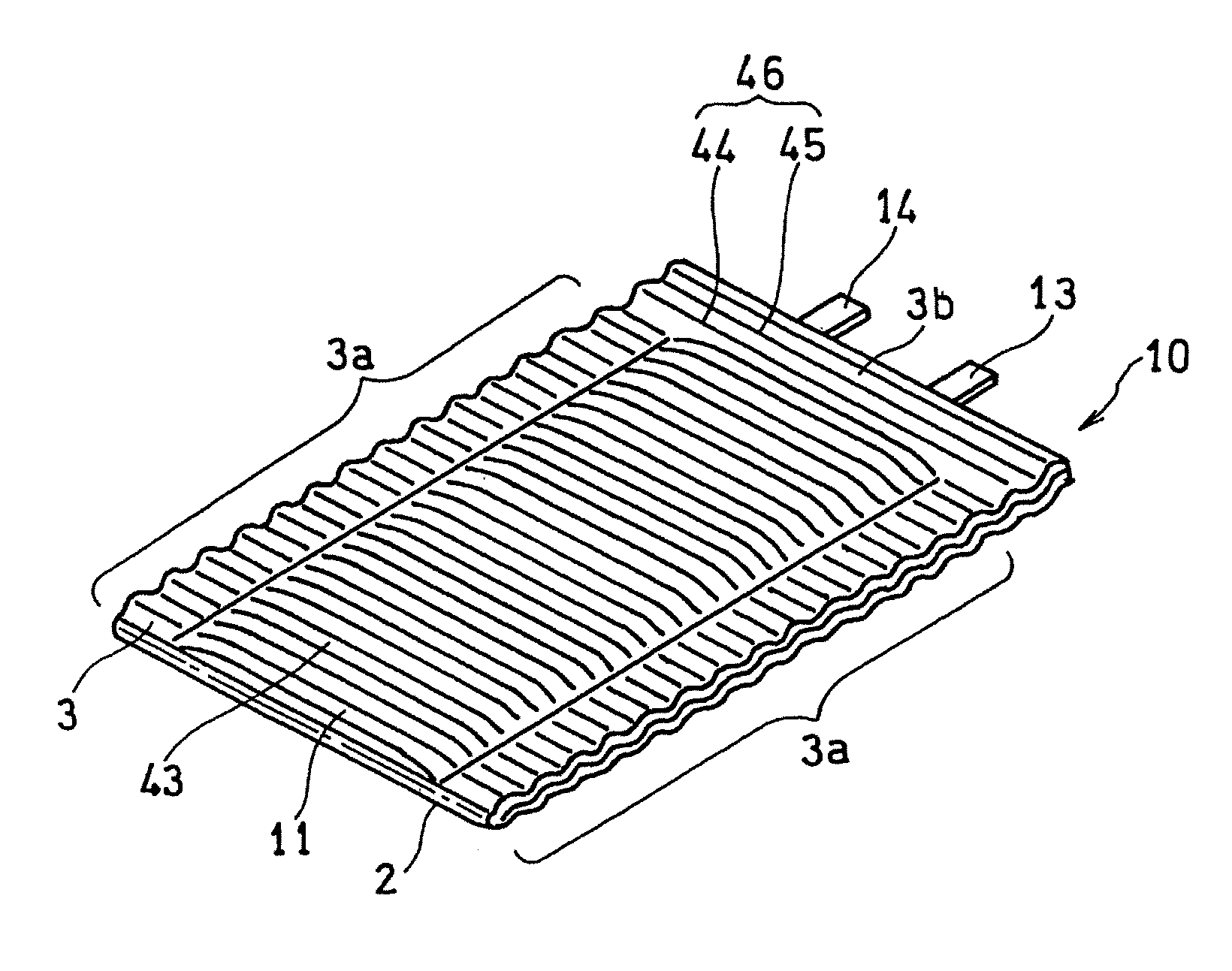
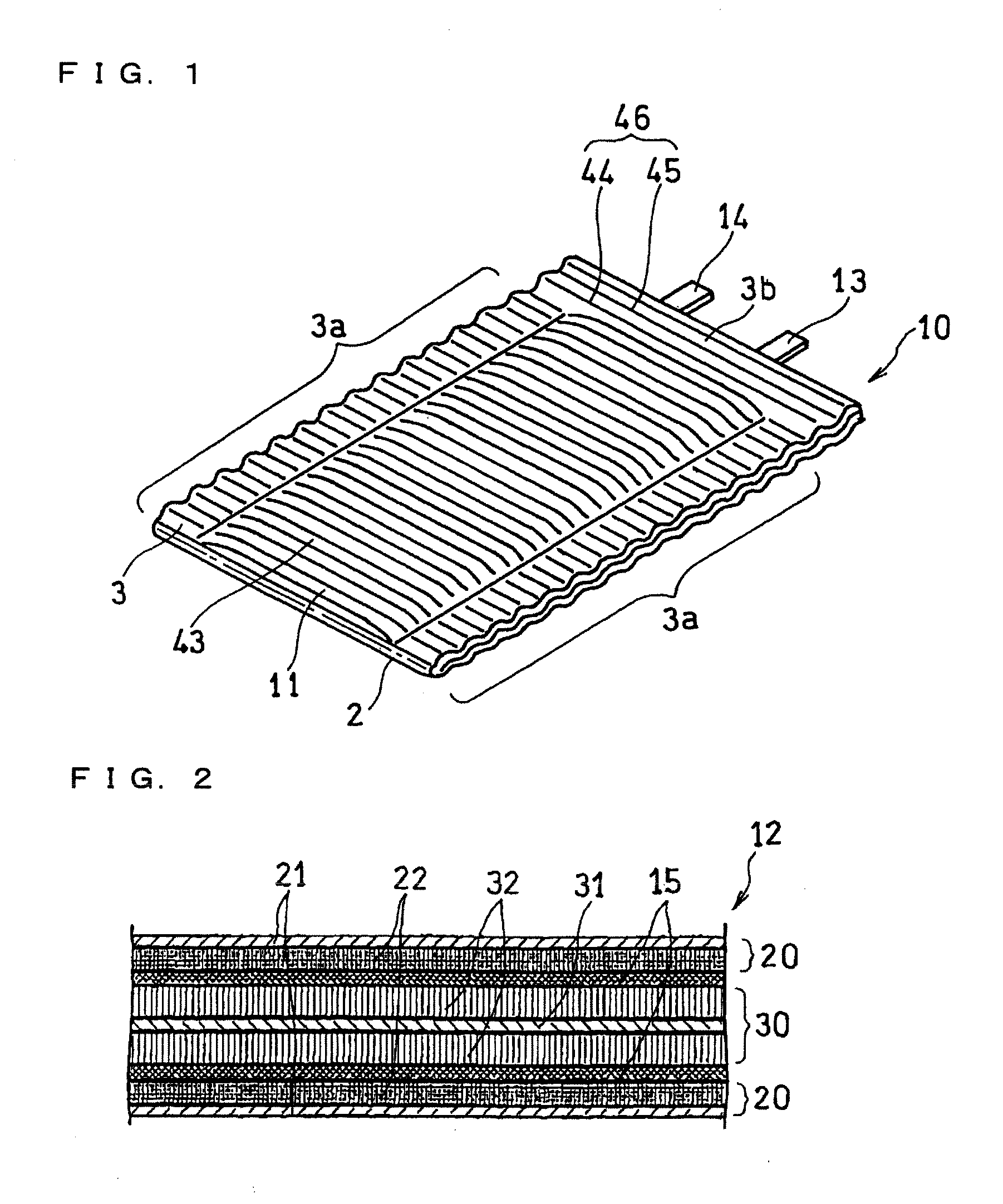
Disclosed is a flexible battery including a sheet-like electrode group, an electrolyte, and a housing with flexibility enclosing the electrode group and electrolyte. The housing includes a film material folded into two in which the electrode group is inserted. The film material has two facing portions respectively facing two principal surfaces of the electrode group, a fold line which is between the two facing portions and along which the film material is folded, and two bonding margins respectively set around the two facing portions. The two bonding margins are bonded to each other into a bonded portion. At least the two facing portions of the film material are formed in a corrugated shape having a plurality of ridge and valley lines arranged in parallel to each other. The ridge lines in one of the two facing portions are overlapped with the valley lines in the other. The fold line is parallel to the ridge and valley lines.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
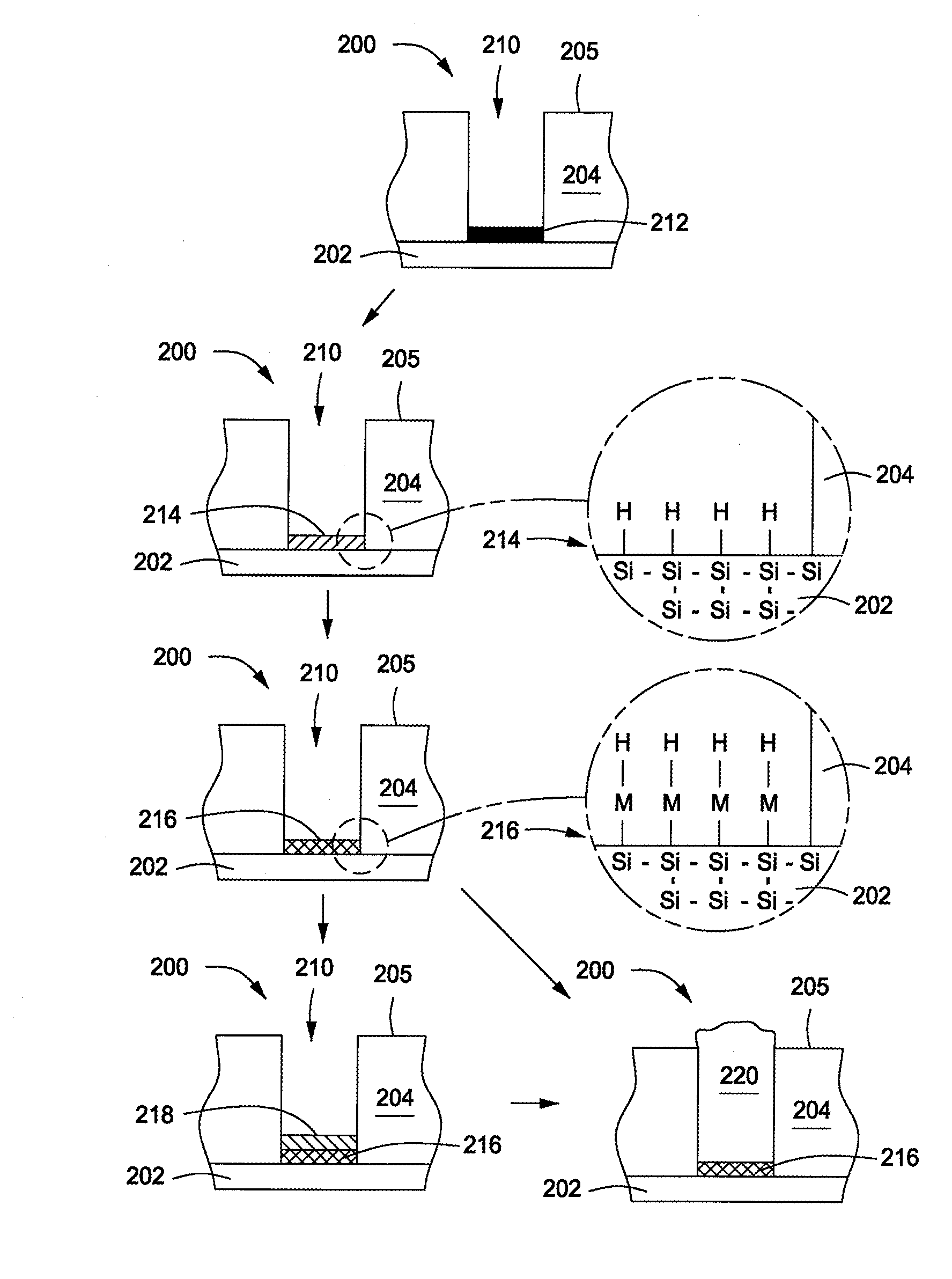
Patterning solution deposited thin films with self-assembled monolayers
InactiveUS6887332B1Low costMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsSelf-assembled monolayerDeposition process
The present invention provides a method of forming a patterned thin film on a surface of a substrate having thereon a patterned underlayer of a self-assembled monolayer. The method comprises depositing a thin film material on the self-assembled monolayer to produce a patterned thin film on the surface of the substrate. The present invention further provides processes for preparing the self-assembled monolayer. The present invention still further provides solution-based deposition processes, such as spin-coating and immersion-coating, to deposit a thin film material on the self-assembled monolayer to produce a patterned thin film on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Grapheme-organic material layered assembling film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101474897ALow priceLight in massLayered productsPretreated surfacesChemical industryElectromagnetic shielding
The invention relates to a graphene-organic material layered assembly film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: using a graphene material and an organic material as raw materials, utilizing interaction of static electricity, hydrogen bonds, coordinate bonds or charge transfer and the like between the graphene and the organic material, and superposing films layer by layer through the film preparation methods such as spin coating, spraying, dipping, lifting and pulling and the like to prepare the film, wherein the thickness of each layer of the film can be controlled between 10 nanometers and 2 millimeters according to requirement. The layered assembly film and the preparation method have the characteristics that multilayer film materials with different functions are prepared by utilizing unique electric, magnetic, mechanical and chemical properties of the grapheme, and can be used as biomaterials, conductive materials, electromagnetic shielding and wave absorbing materials, photovoltaic materials, electrode materials, film filtering and separating materials, and the like to be applied to chemistry and chemical industry, biology and precision instruments, and manufacture of micro electrons, machinery and aviation and aerospace devices according to the selected different organic materials.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Semiconductor device
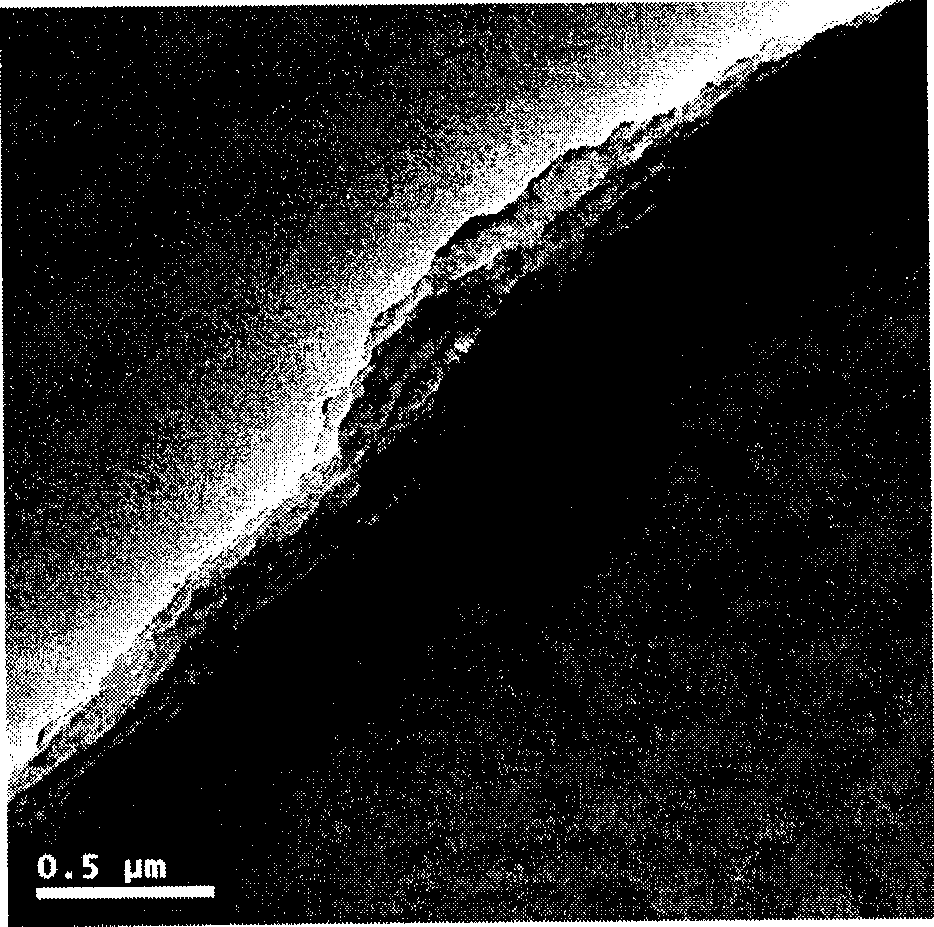
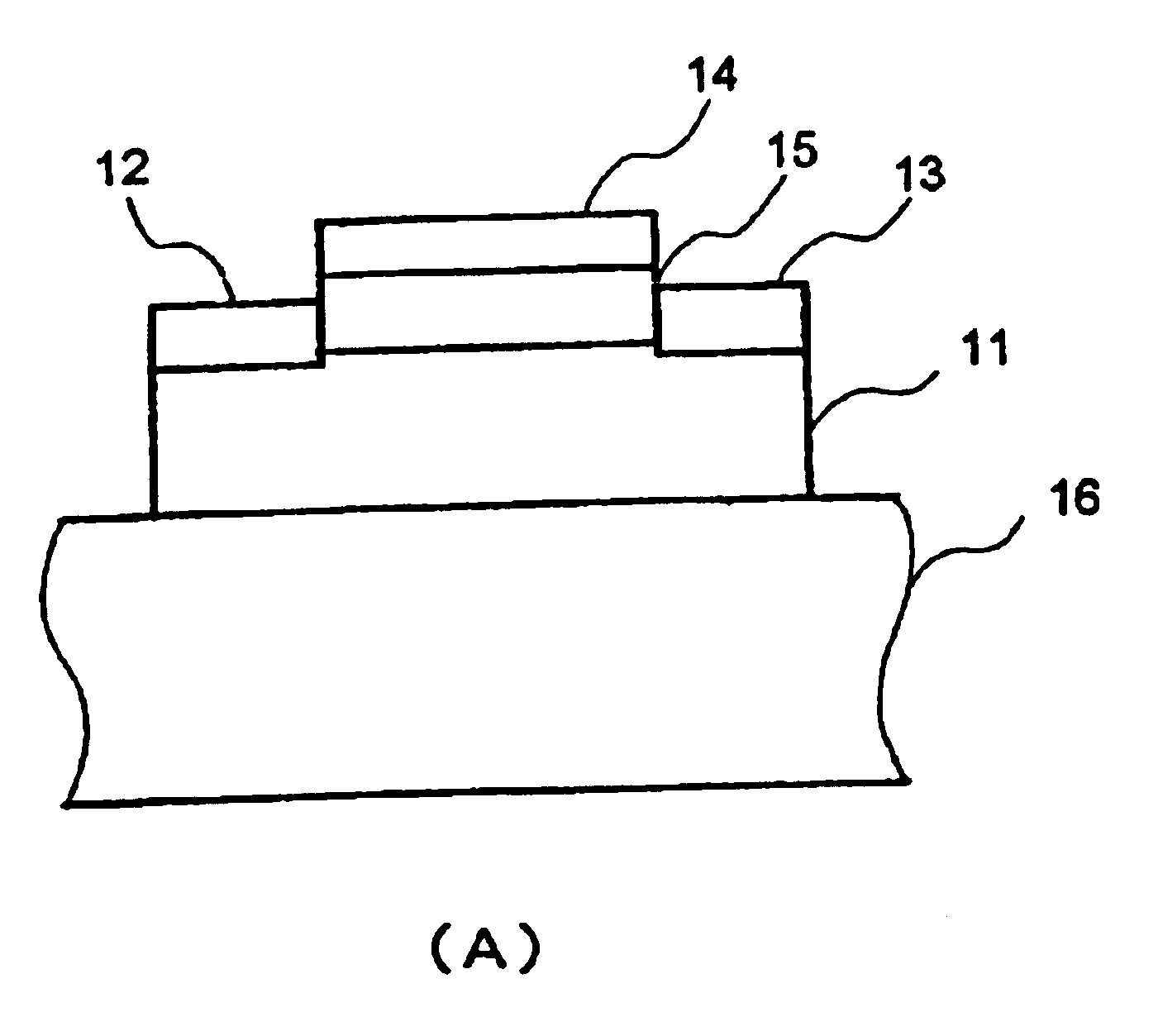
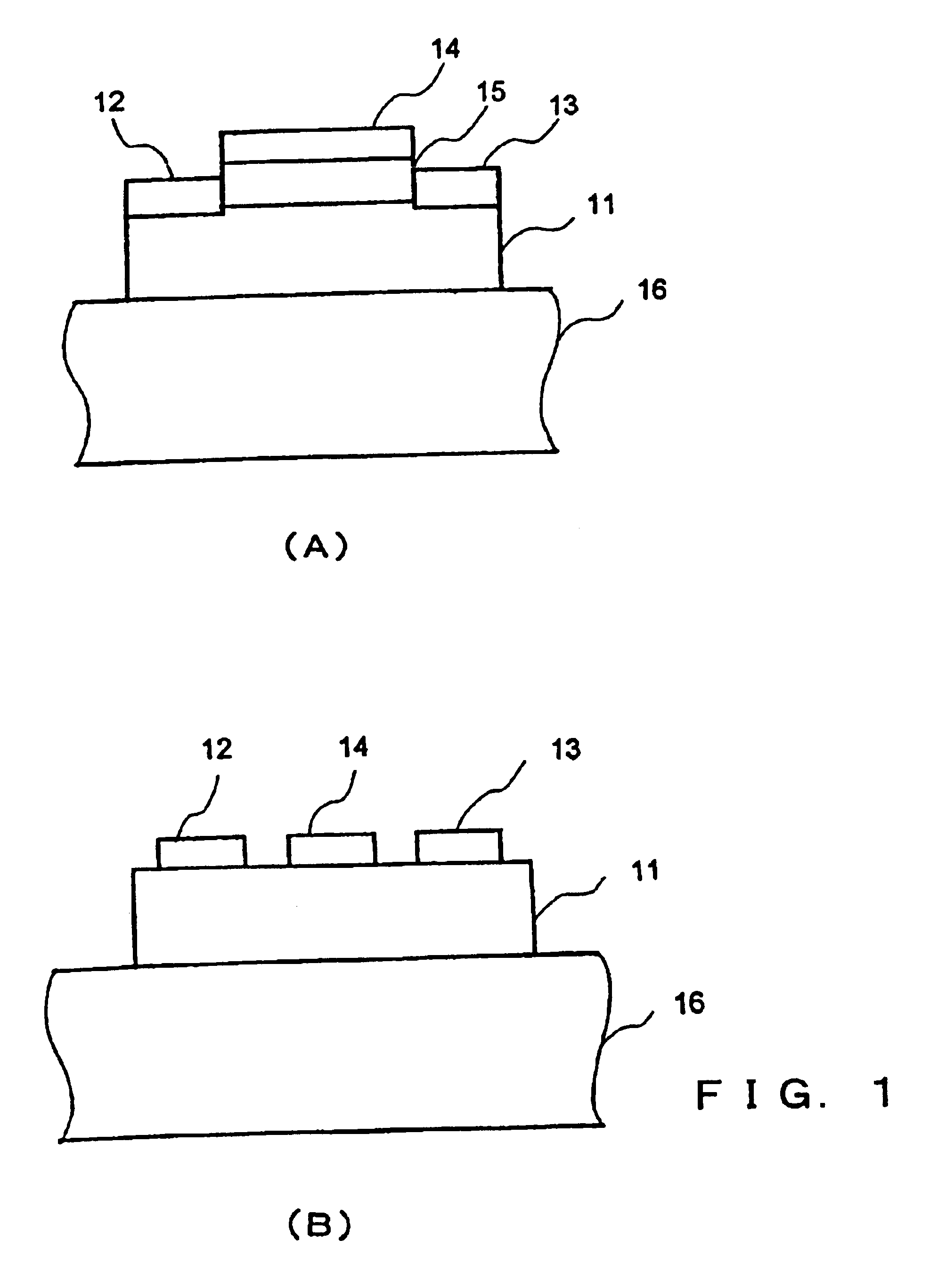
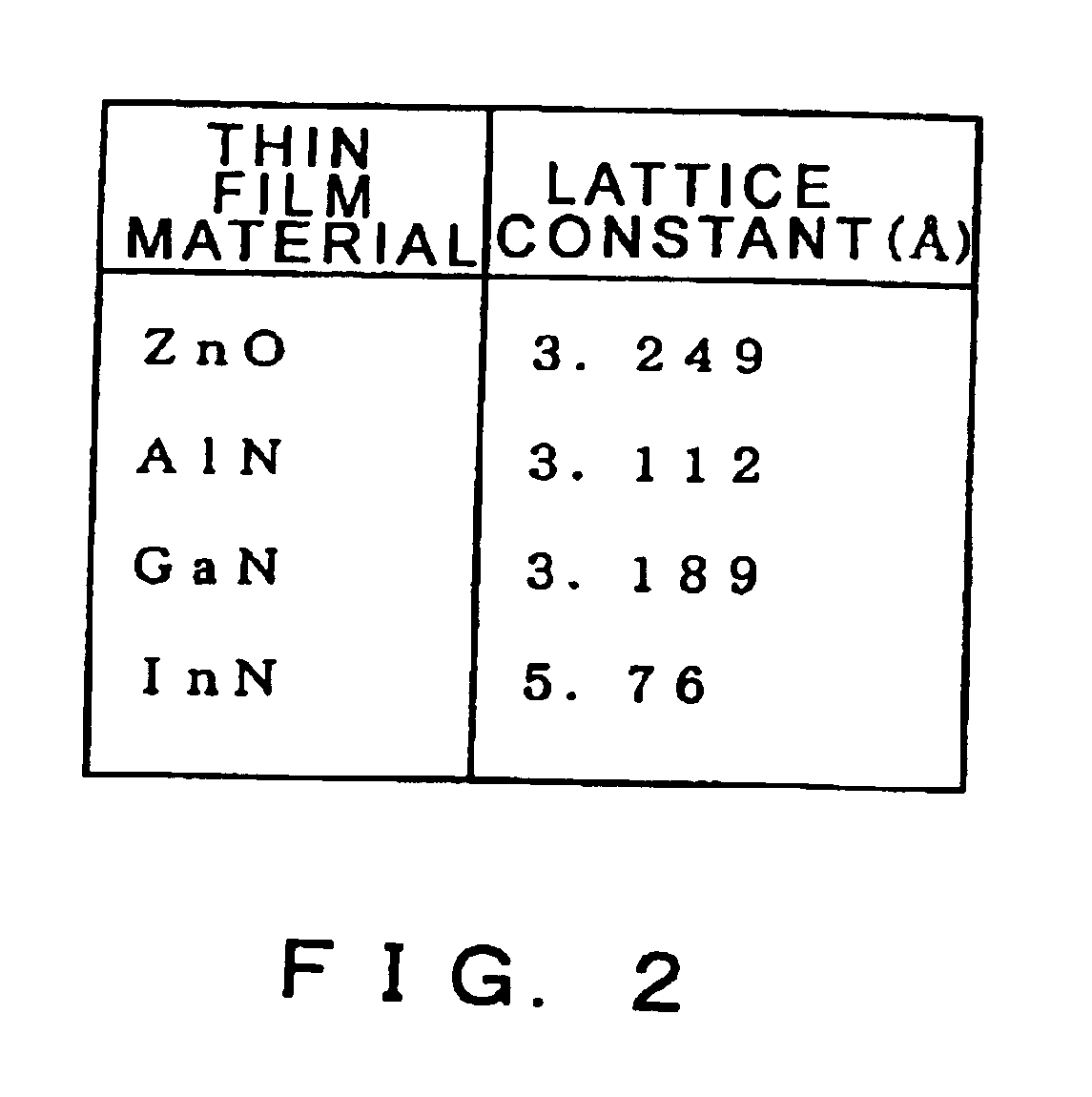
The present invention provides a high quality thin film comparable to a bulk single crystal and providres a semiconductor device with superior characteristics. A channel layer 11, for example, is formed of a semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO or the like. A source 12, a drain 13, a gate 14 and a gate insulating layer 15 are formed on the channel layer 111 to form an FET. For a substrate 16, a proper material is selected depending on a thin film material of the channel layer 11 in consideration of compatibility of both lattice constants. For example, if ZnO is used for the semiconductor of the channel layer as a base material, ScAlMgO4 or the like can be used for the substrate 16.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
System for thin film deposition utilizing compensating forces
ActiveUS7572686B2Different from numberShorten the timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFilm material
A process for depositing a thin film material on a substrate is disclosed, comprising simultaneously directing a series of gas flows from the output face of a delivery head of a thin film deposition system toward the surface of a substrate, and wherein the series of gas flows comprises at least a first reactive gaseous material, an inert purge gas, and a second reactive gaseous material, wherein the first reactive gaseous material is capable of reacting with a substrate surface treated with the second reactive gaseous material. A system capable of carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
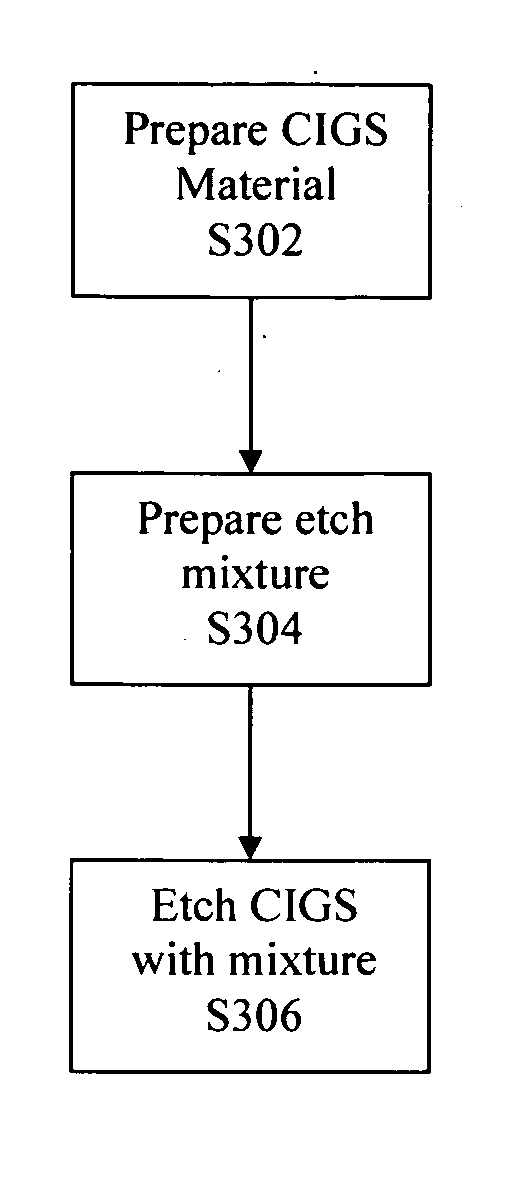
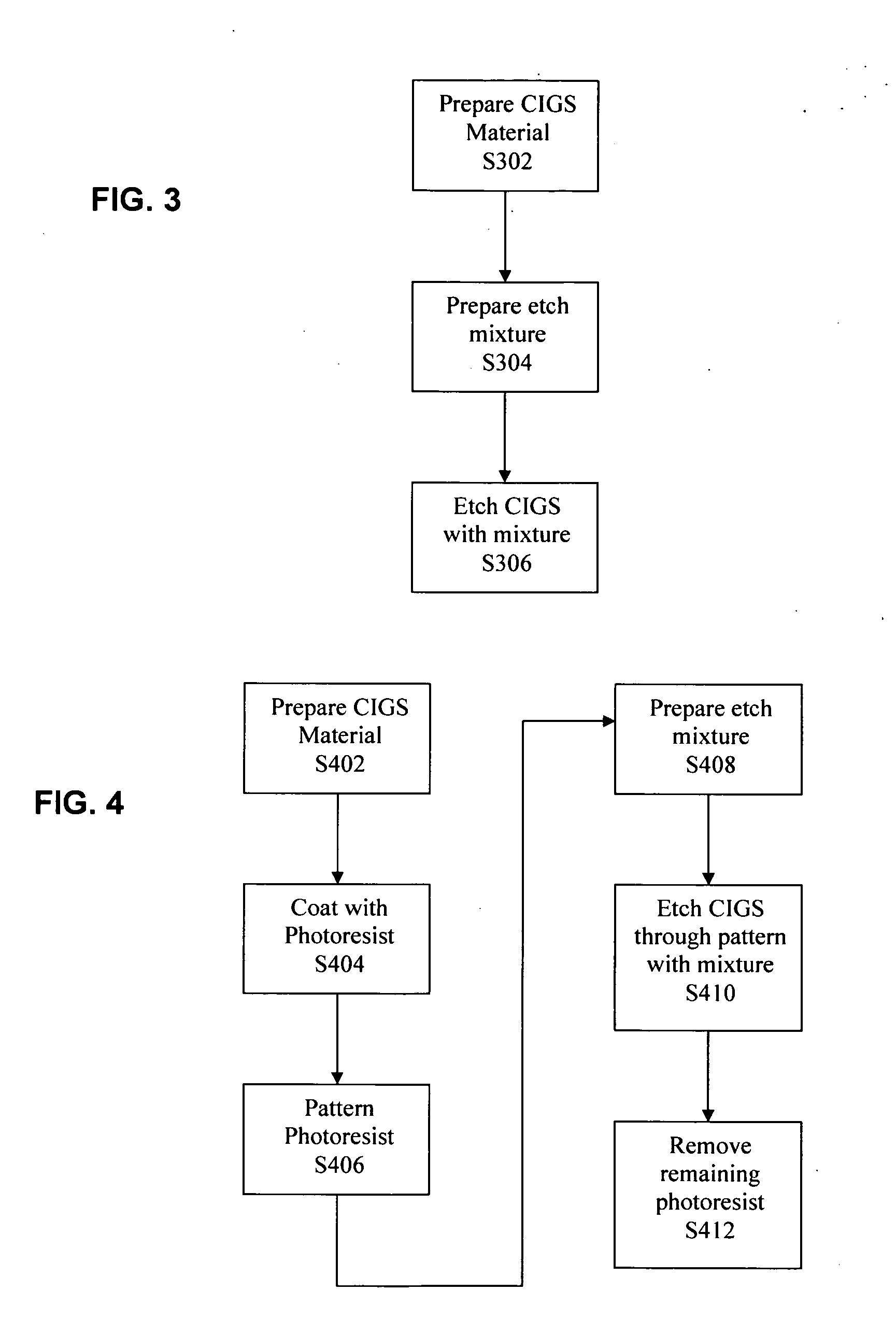
Method for patterning a photovoltaic device comprising CIGS material using an etch process
InactiveUS20070227578A1High selectivityBetter and more efficient photovoltaic modulesPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationEtchingFilm material
A processing method herein enables patterning a thin-film photovoltaic module into cells and / or sub-cells using an etch process. According to one aspect, an etch mixture is identified that is capable etching through a thin-film material such as CIGS with high selectivity to both photoresist and underlying layers such as metal. According to another aspect, the etch process enables patterning a photovoltaic device using lithographic techniques. Among other things, the invention enables forming interconnect structures with feature sizes that are substantially smaller than is possible with prior art techniques, and avoids many of the problems associated with laser and mechanical scribes, thus resulting in better and more efficient photovoltaic modules.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for selective area deposition of inorganic materials
ActiveUS20090081827A1Allowed to operateSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingMetallurgyOrganic compound
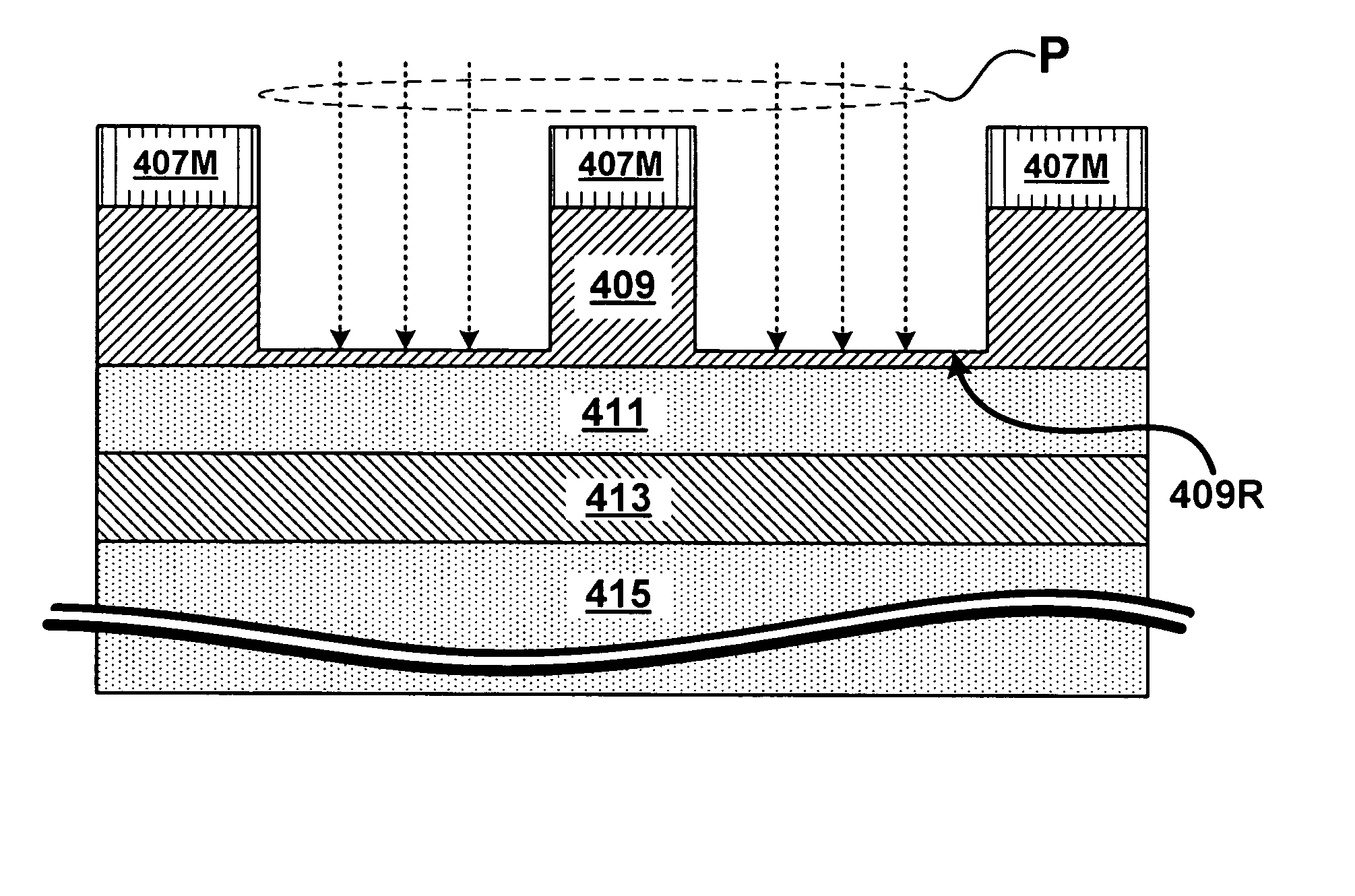
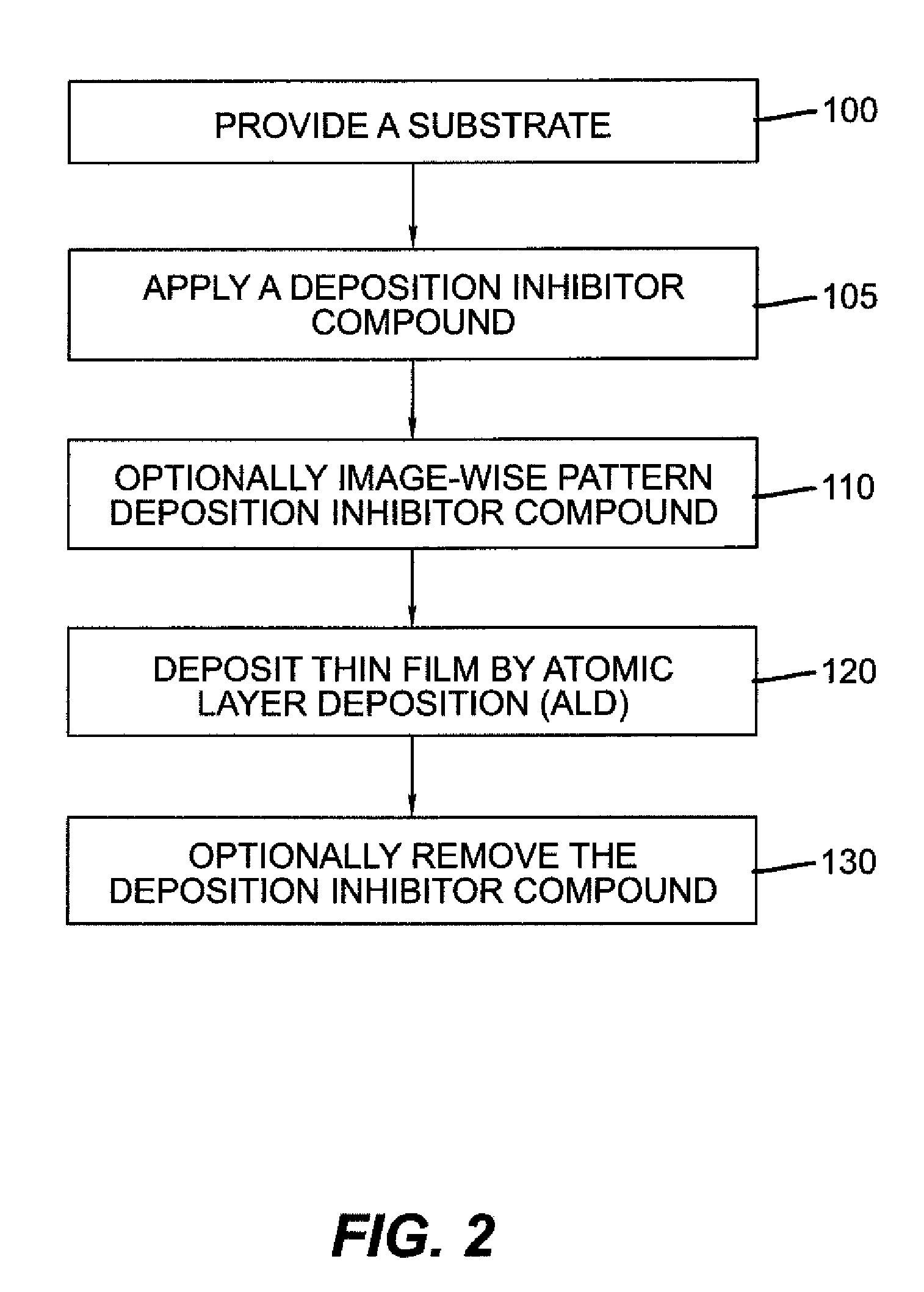
An atomic-layer-deposition process for forming a patterned thin film comprising providing a substrate, applying a deposition inhibitor material to the substrate, wherein the deposition inhibitor material is an organic compound or polymer; and patterning the deposition inhibitor material either after step (b) or simultaneously with applying the deposition inhibitor material to provide selected areas of the substrate effectively not having the deposition inhibitor material. An inorganic thin film material is substantially deposited only in the selected areas of the substrate not having the deposition inhibitor material.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Apparatus for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20070228470A1Allowed to operateTransistorSolid-state devicesFilm materialAtomic layer deposition
The present invention provides a distribution manifold for thin-film material deposition onto a substrate comprising a plurality of inlet ports for a sequence of gaseous materials, an output face comprising a plurality of open elongated output channels, each channel extending in a length direction substantially in parallel. The distribution manifold can be employed in a deposition system for thin film deposition, further comprising a plurality of sources for a plurality of gaseous materials and a support for positioning a substrate in pre-designed close proximity to the output face of the distribution manifold. During operation of the system, relative movement between the output face and the substrate support is accomplished.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Photochromic film material
InactiveUS20050136260A1Improve the immunityMinimizing penetrationPhotosensitive materialsSynthetic resin layered productsHeat stabilityNear infrared radiation
The invention is directed to a photochromic material that filters, from solar radiation, near infrared radiation and sufficient portions of ultraviolet radiation while transmitting actinic radiation in the wavelength range of about 341±5 nm. The light-transmitting photochromic material provides light and heat stability to achieve a longer useful life. This photochromic material is preferably incorporated in a multilayered structure with constituents provided on or contained within one or more layers to enhance the resistance to light fatigue.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Plasma etching chamber and plasma etching system using same
ActiveUS20050173067A1Limited spaceImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadio frequencyFilm material
Disclosed is a plasma etching chamber for completely dry-cleaning a film material and particles deposited at the periphery of a wafer through plasma etching while generating plasma at the top to the bottom sides of the periphery of the wafer. A pair of top and bottom anodes facing each other is placed around the periphery of the wafer under the application of radio frequency through a cathode. Alternatively, a top cathode and a bottom anode are placed around the periphery of the wafer while facing each other and a view-ring shields the area of the cathode, the anode and the wafer from the outside. A plasma etching system includes a plurality of the above-structured etching chambers. A handler takes wafers from a plurality of cassette stands or load ports, and posture-corrects the orientation frat locations of the wafers by a wafer alignment unit. The wafers are charged into the plasma etching chambers directly or via load lock chambers. The handler takes the etched wafers from the chambers, and returns the wafers to the cassettes or the load ports directly or via the load lock chambers.
Owner:SOSUL
Method of forming thin film patterning substrate including formation of banks
InactiveUS20050186403A1Improve accuracyHigh yieldLayered productsDecorative surface effectsDisplay deviceThin membrane
Display devices such as EL elements or LED elements, are formed from thin film elements having banks of prescribed height and a thin film layer formed by an ink jet method in areas to be coated that are partitioned by those banks. The banks may be formed of an organic material on a bank formation surface configured of an inorganic material, plasma treatment is performed under conditions that the induction gas is fluorine-based and that fluorine is present excessively, and the areas enclosed by the banks subjected to surface treatment are filled with the liquid thin film material to form the thin film layer or layers.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Disposable bioreactor
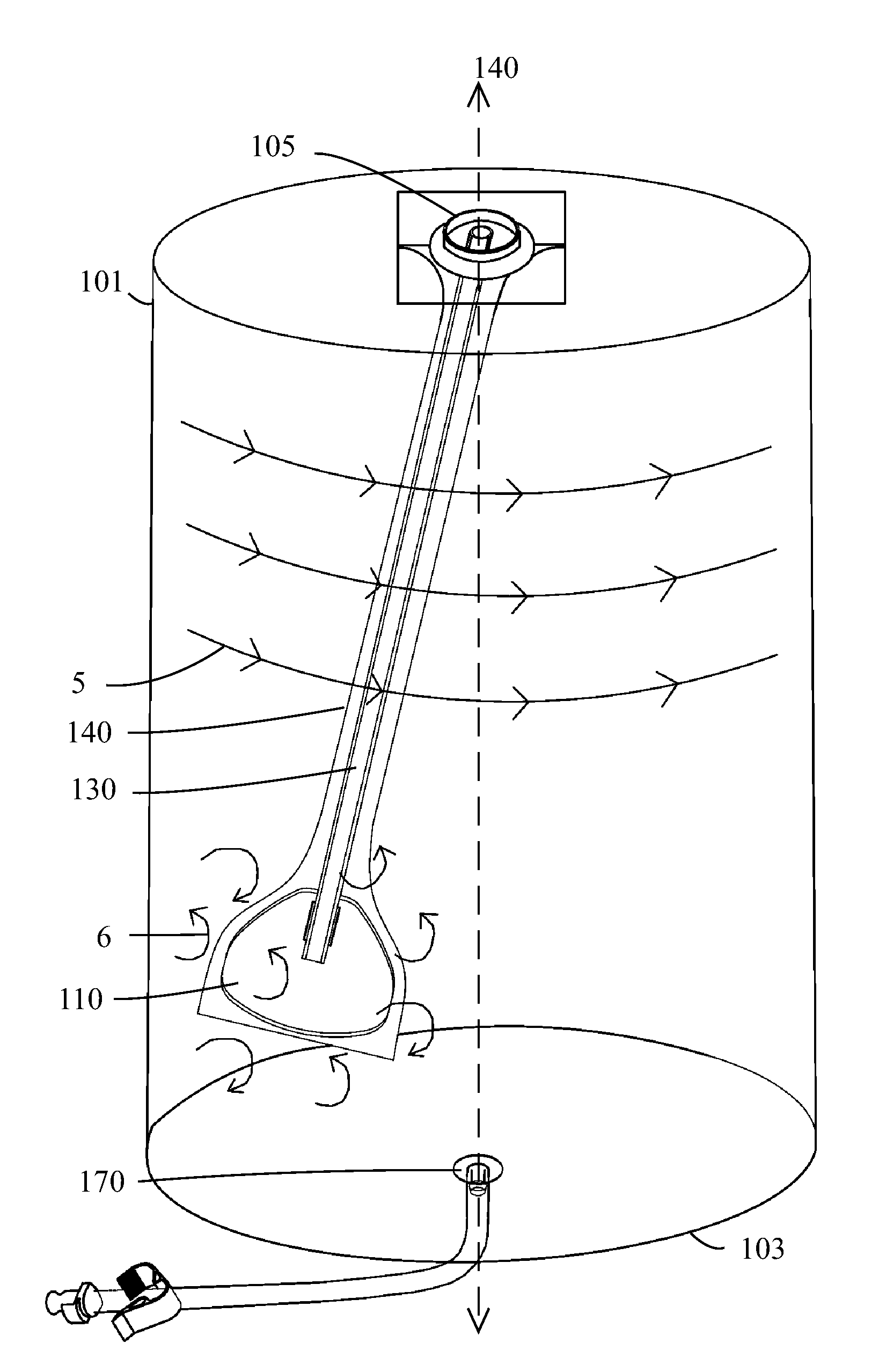
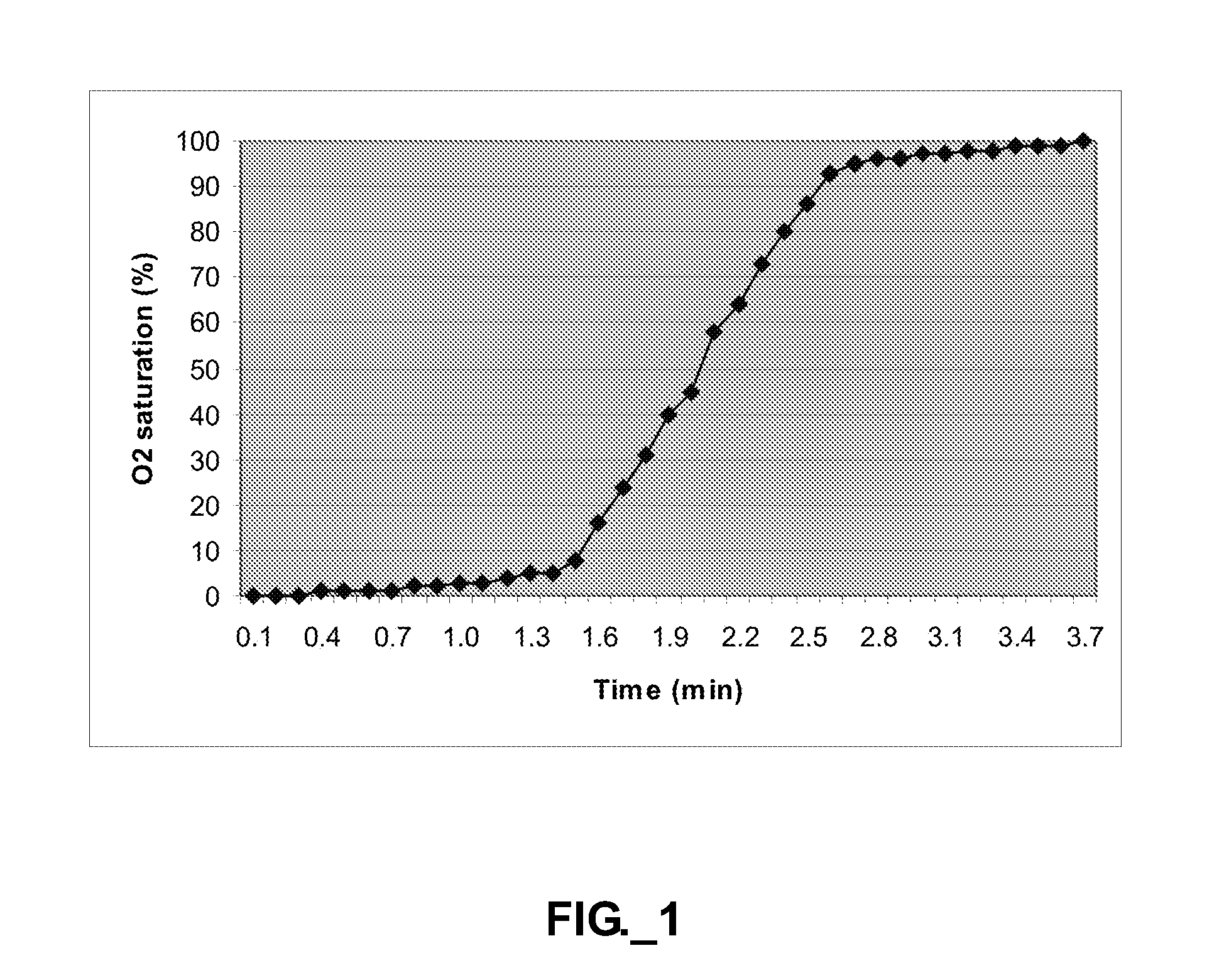
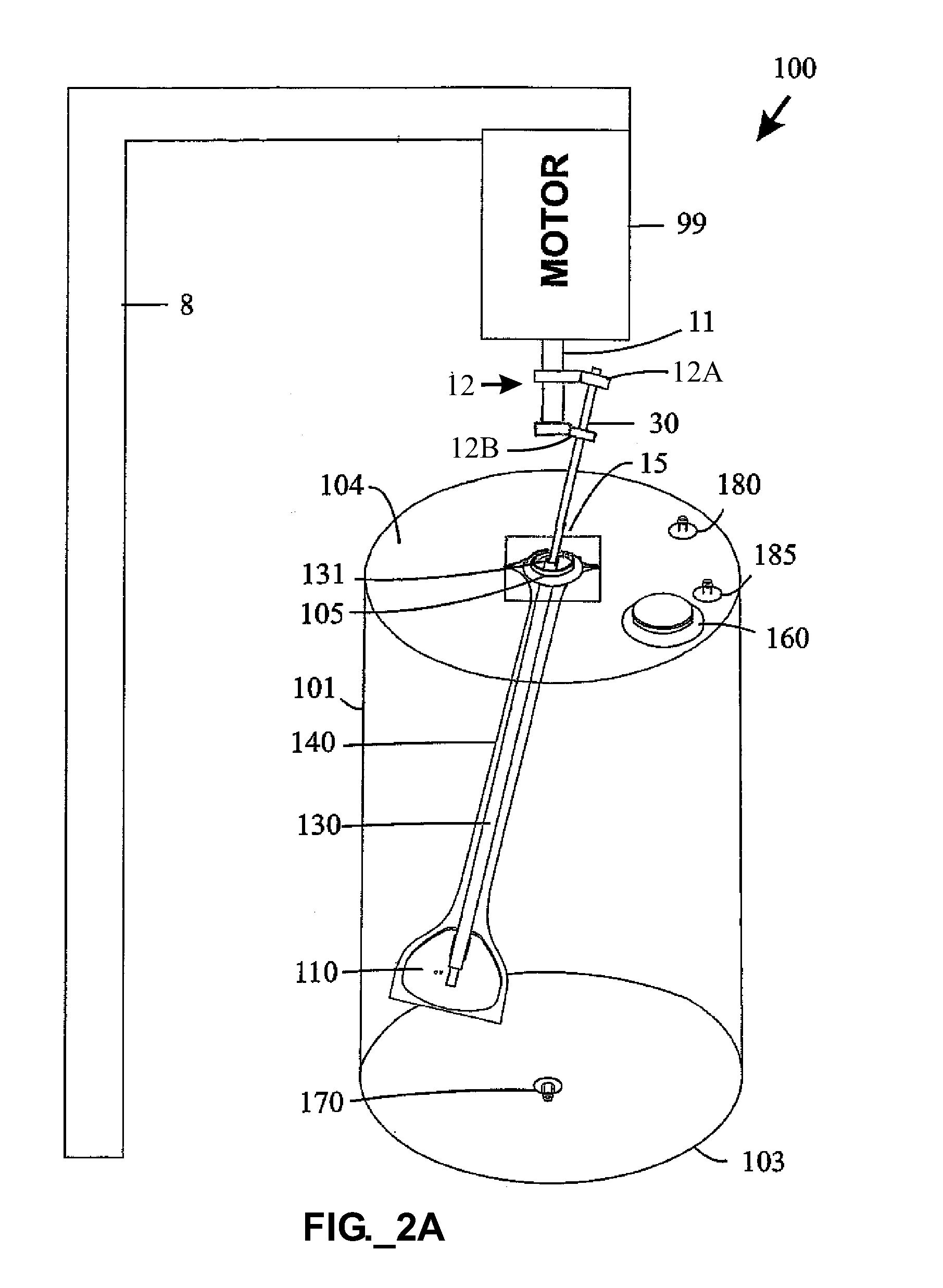
ActiveUS20100015696A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCatheterEngineering
A disposable material processing apparatus, useable as a bioreactor or fermenter, includes a hollow tank (101) and a mixing paddle (110) disposed within the interior of the tank and adapted to mix contents therein. The paddle may be isolated within a flexible sleeve (140). Various functional elements, such as a sparger, sensor, material extraction conduit, material addition conduit, and / or heat exchange element may be provided, and optionally arranged to travel with the paddle within the tank interior. Baffles may protrude into a mixing tank to enhance mixing. A tank and / or sleeve may comprise polymeric film materials.
Owner:PALL LIFE SCI BELGIUM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com