Patents
Literature
218 results about "Small vessel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
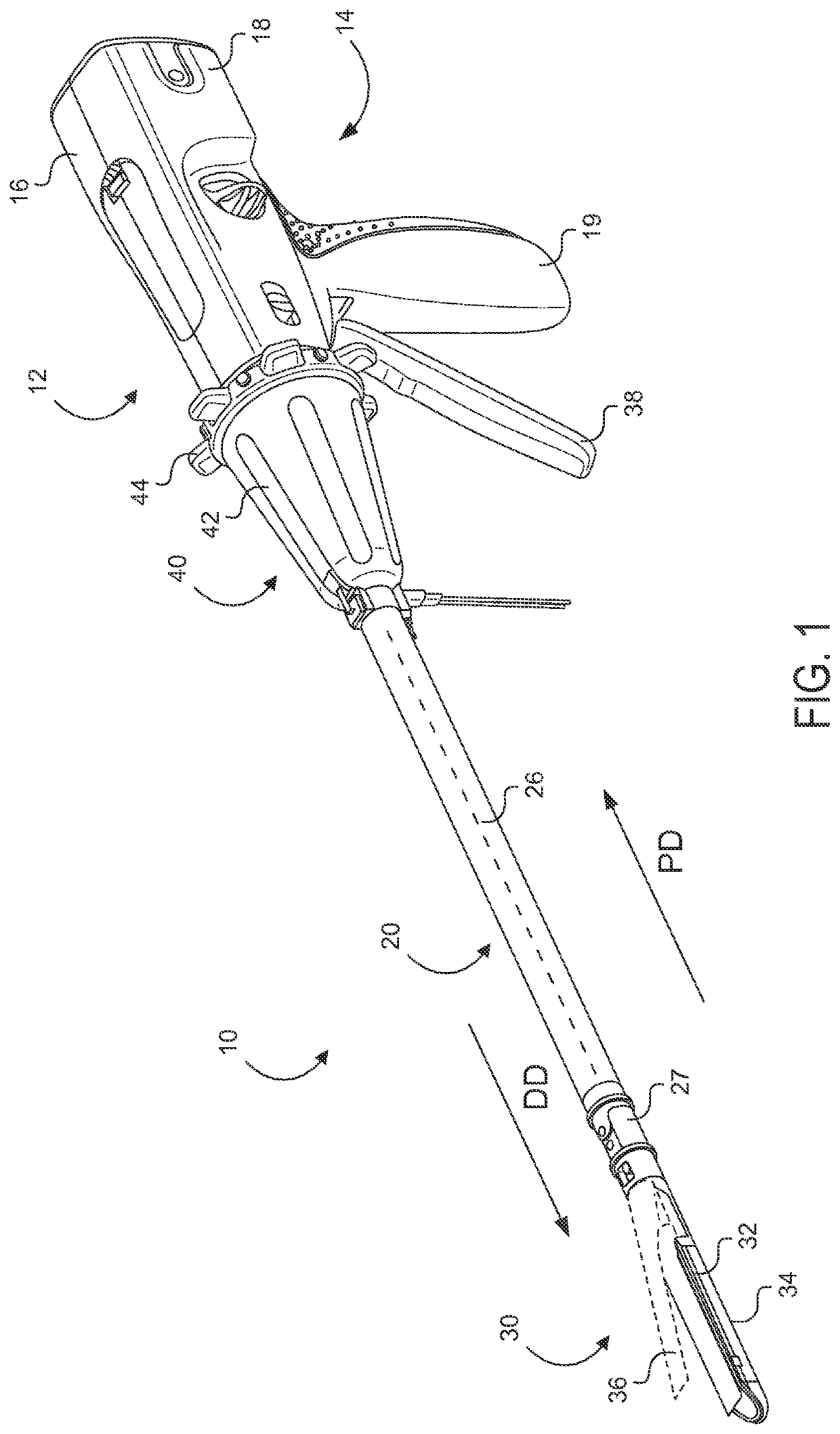
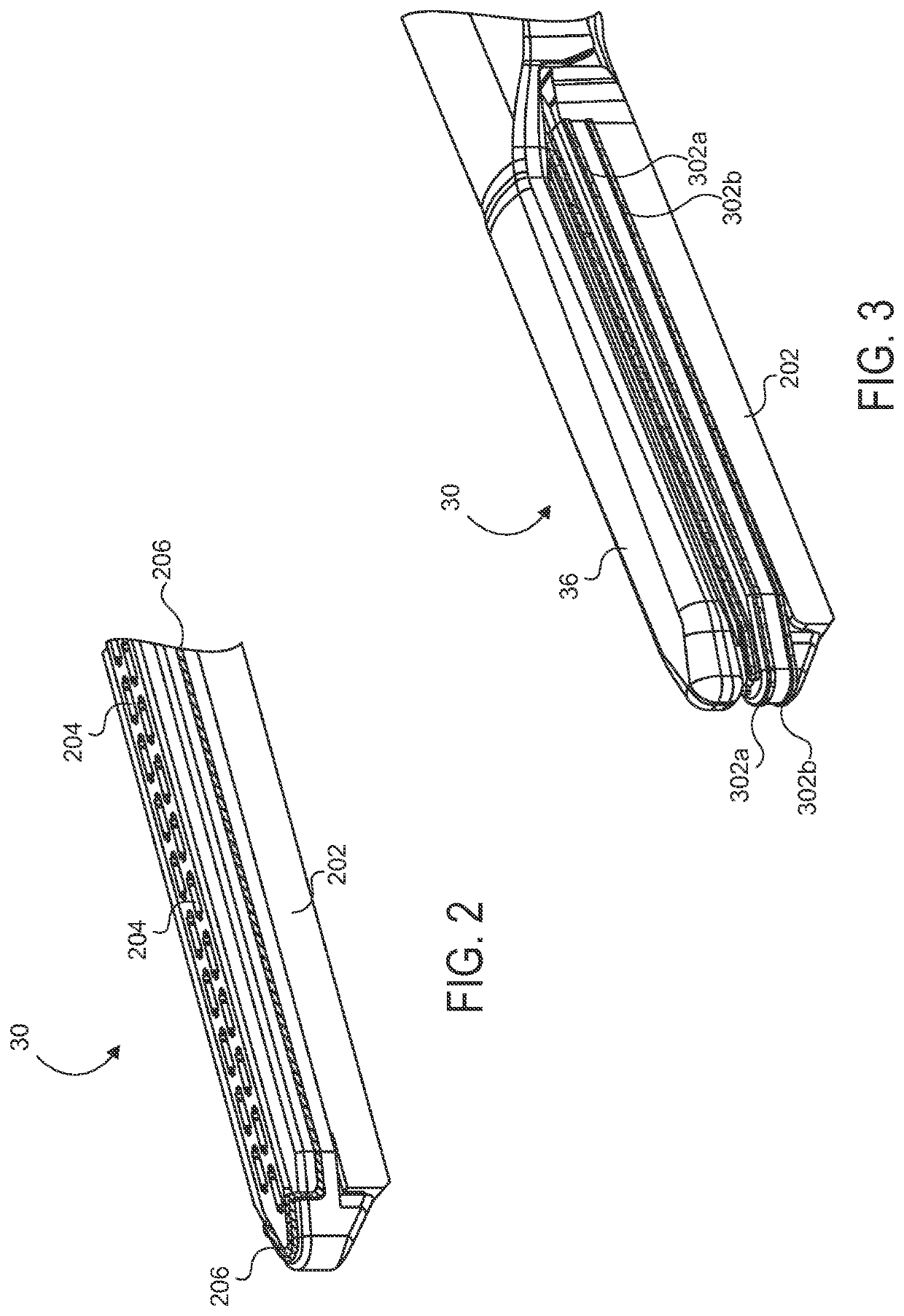
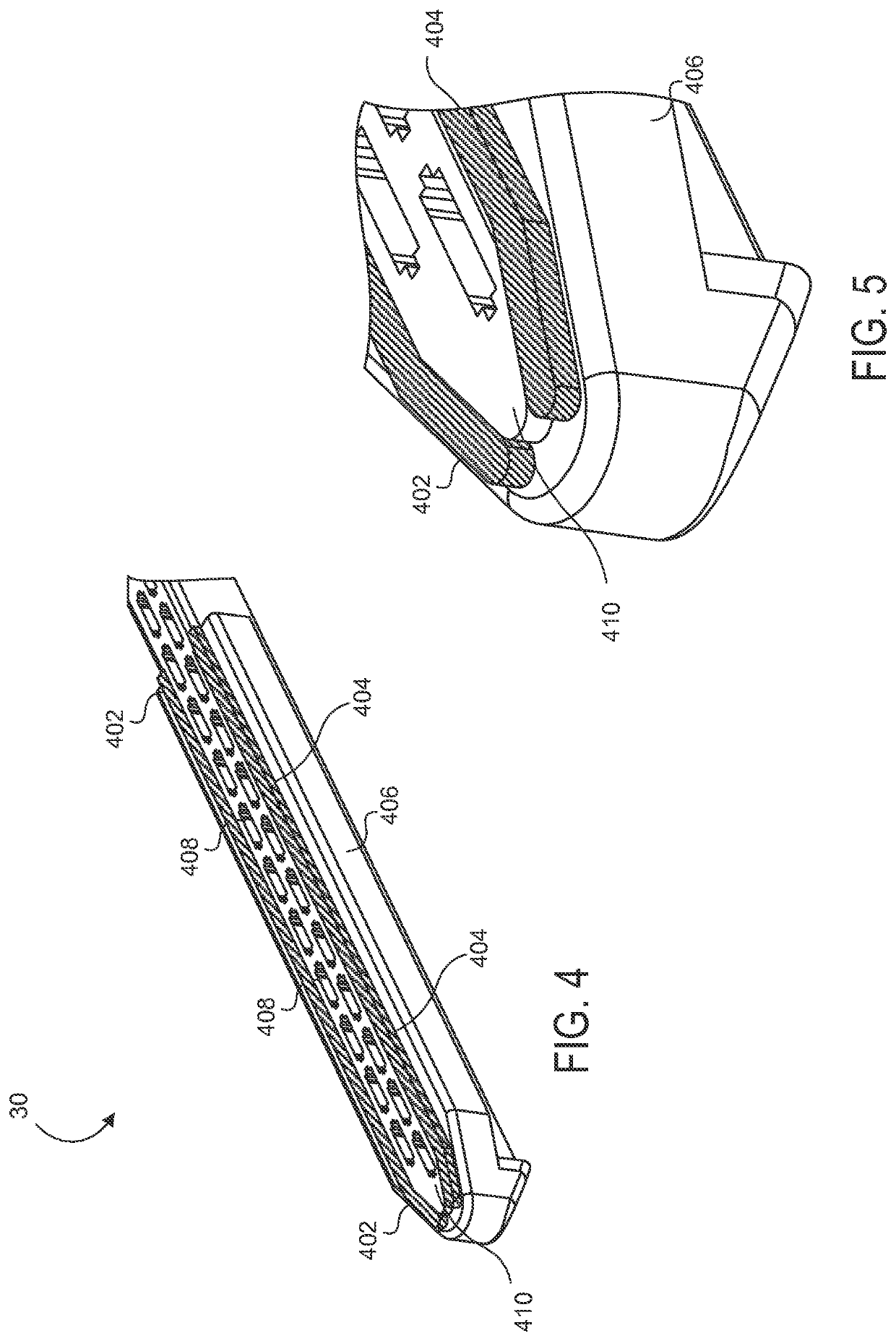
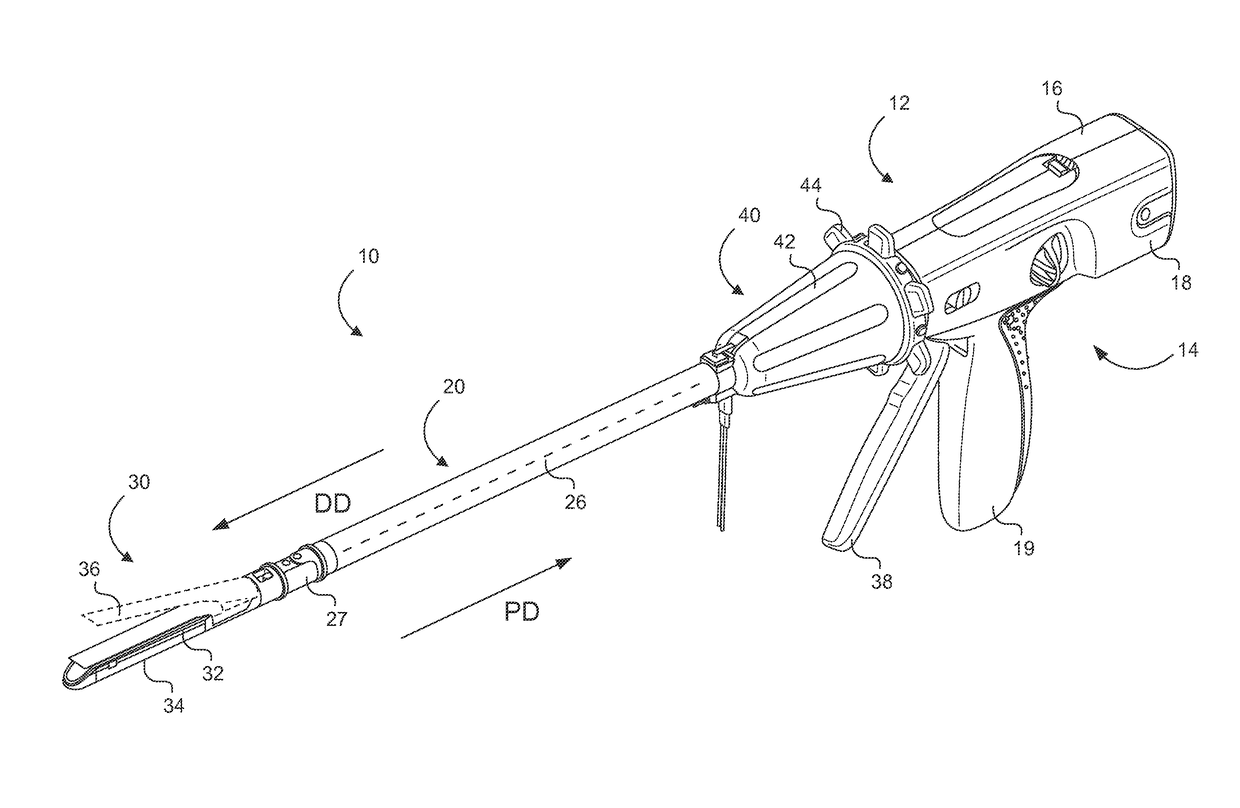
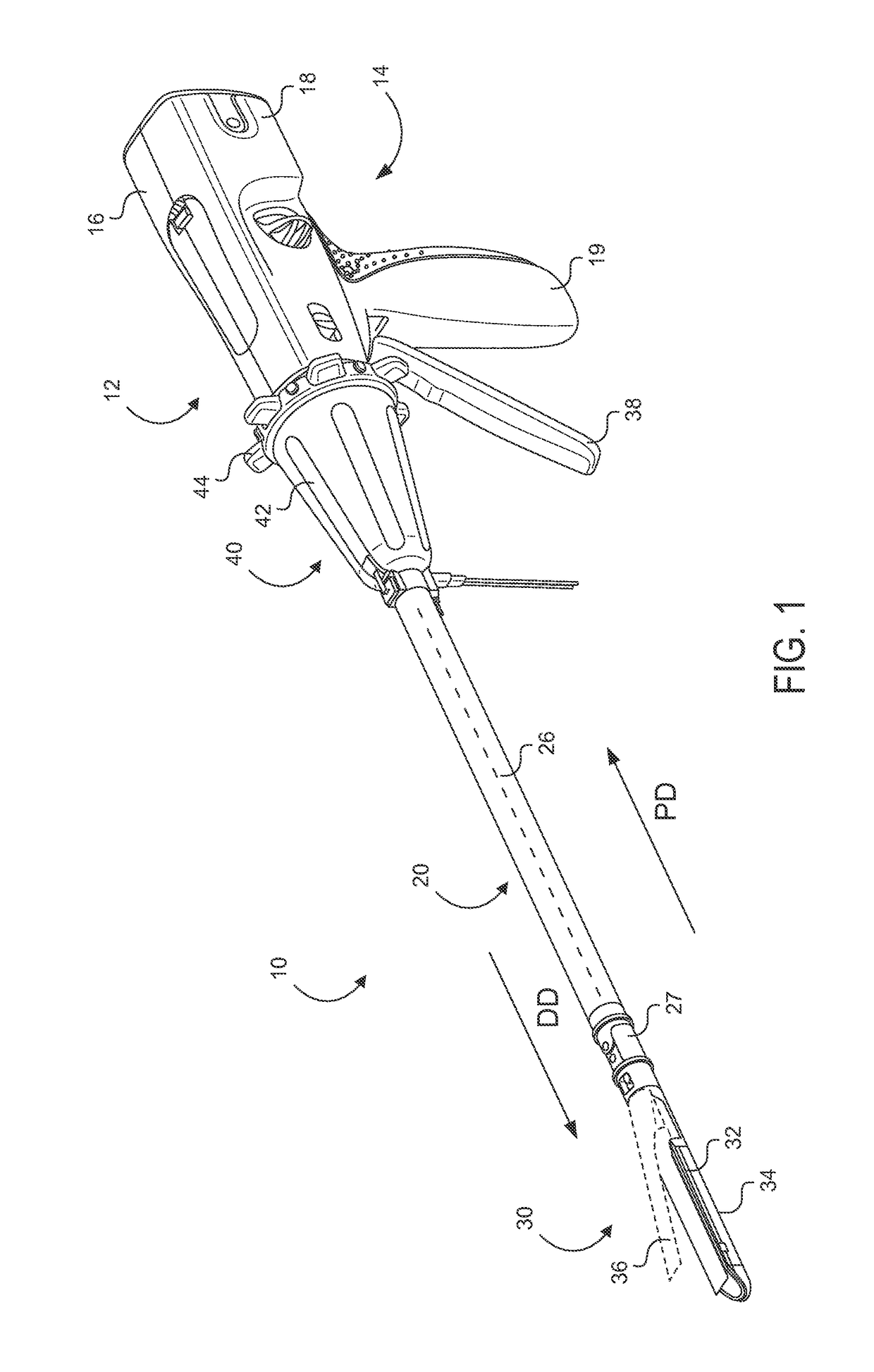
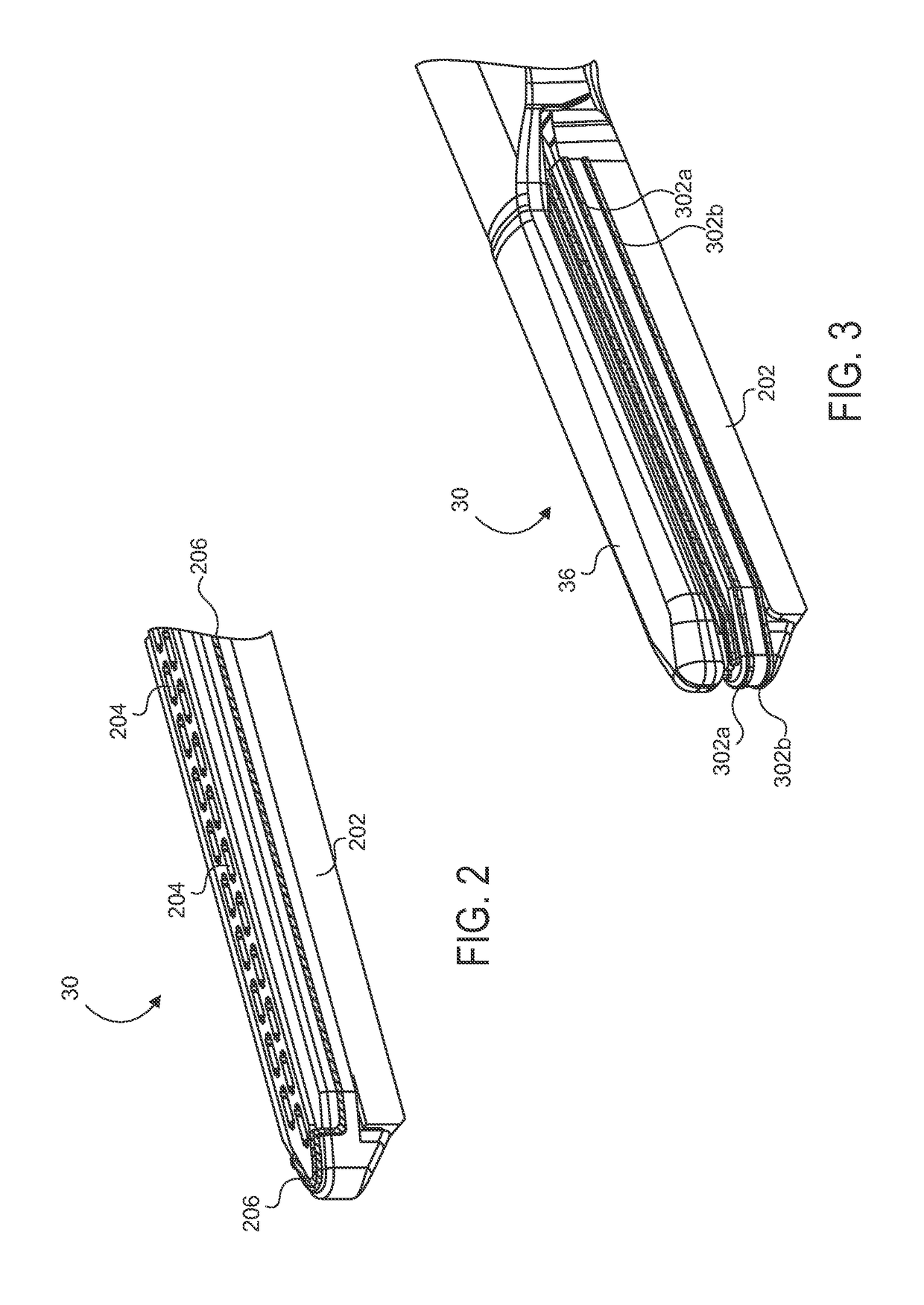
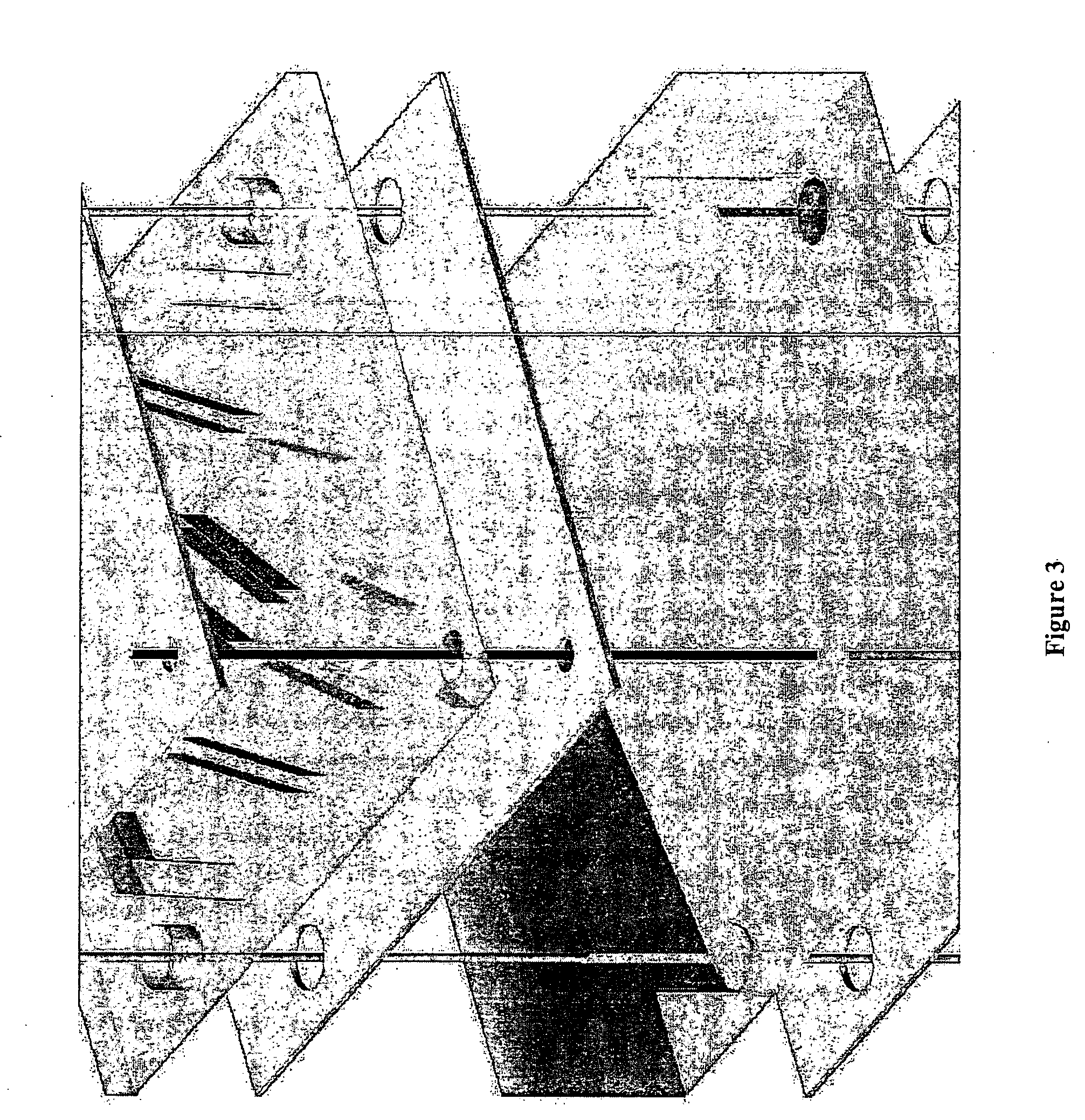
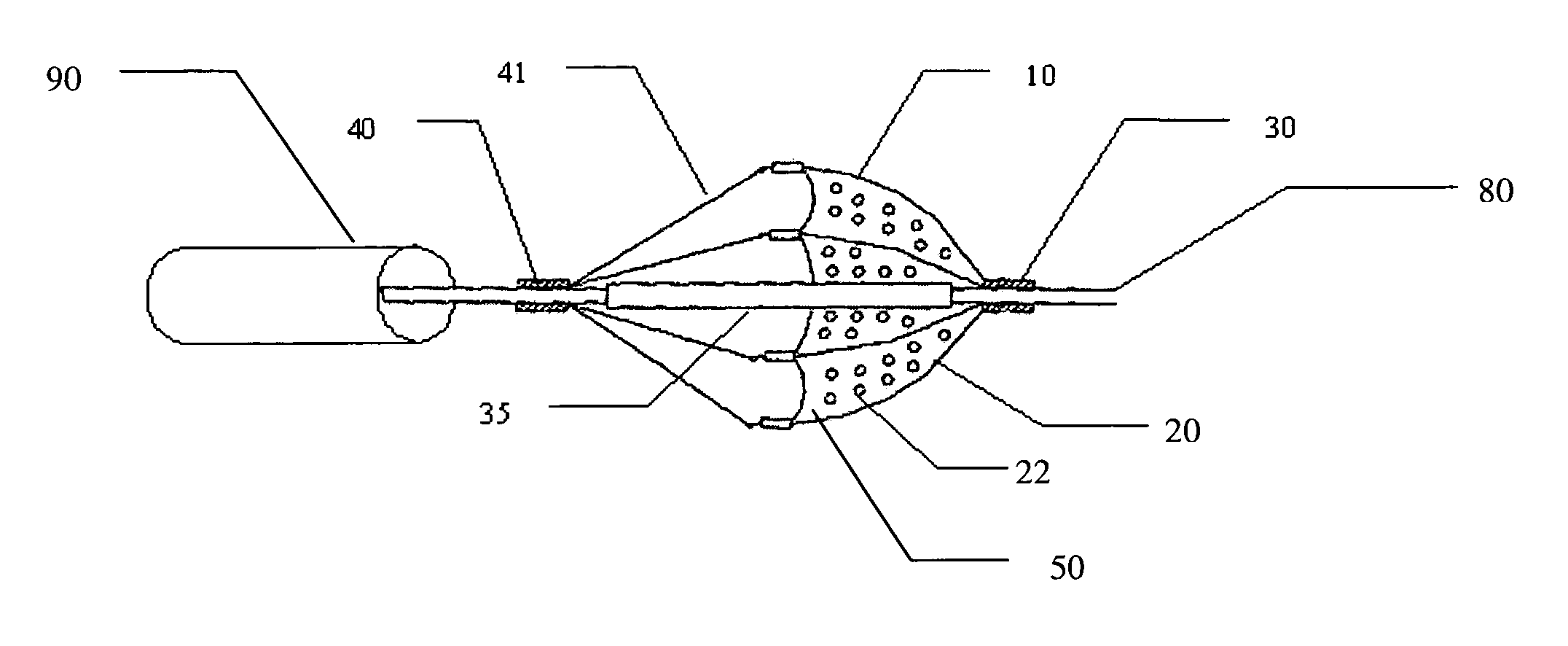
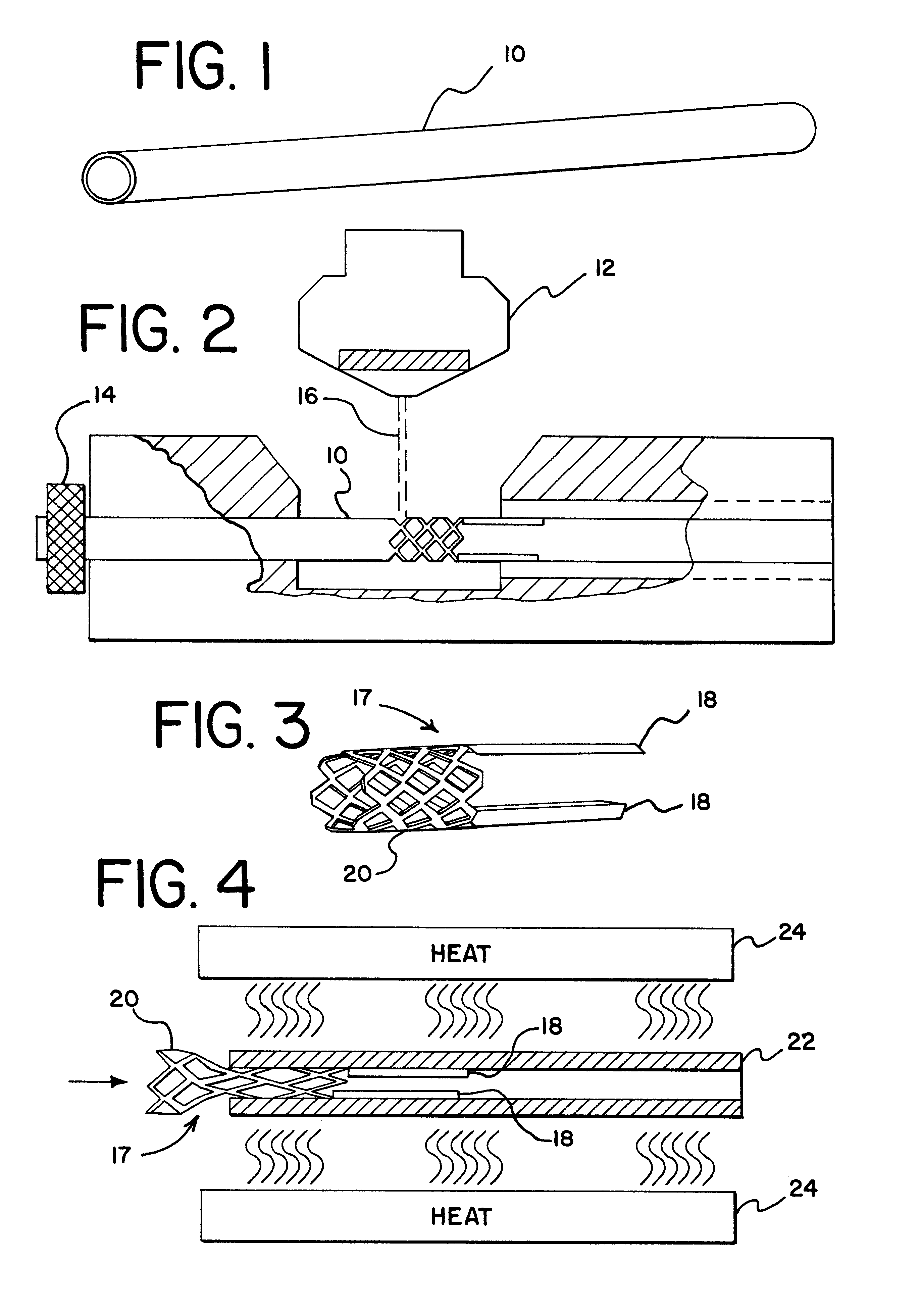
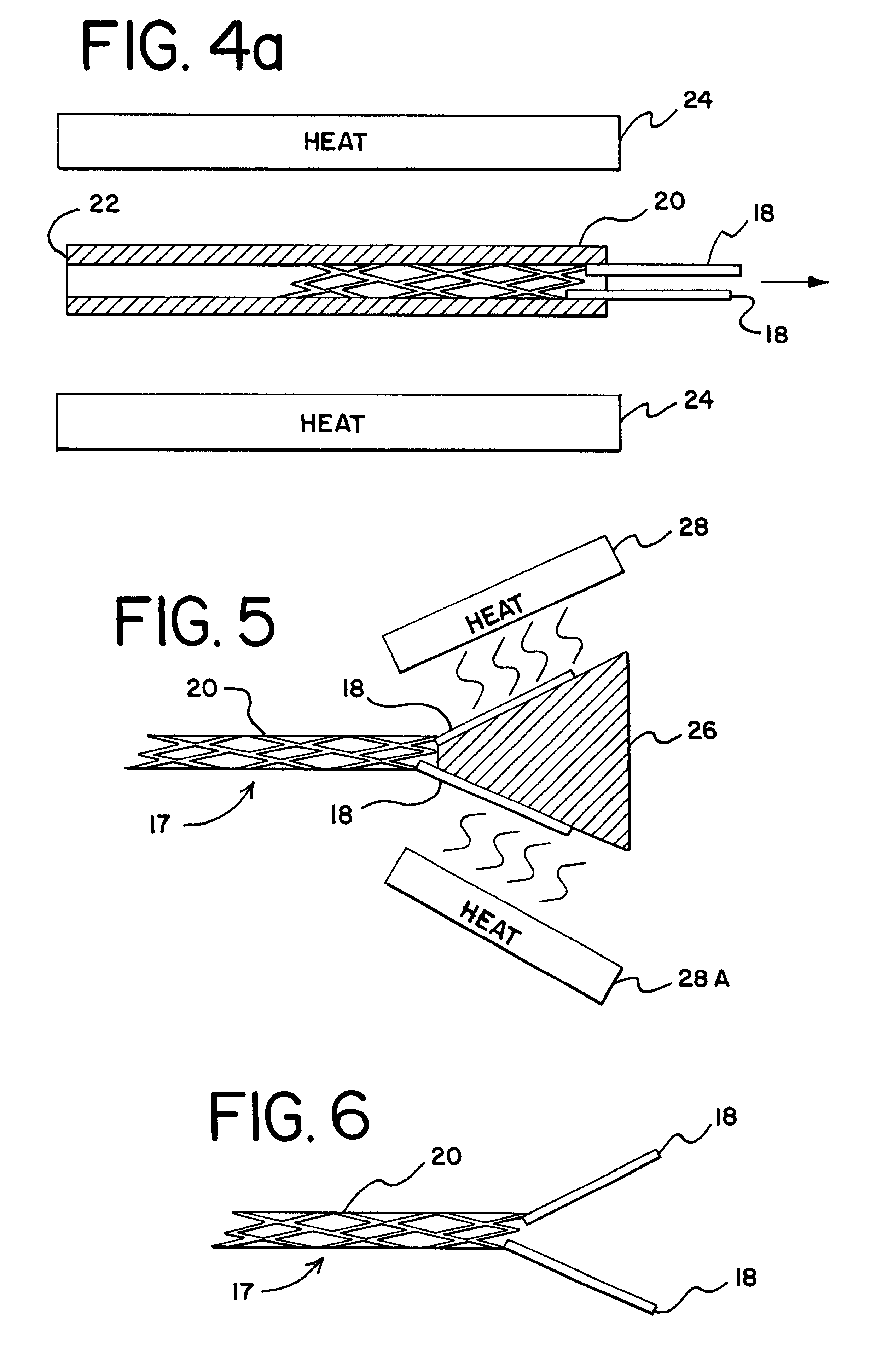
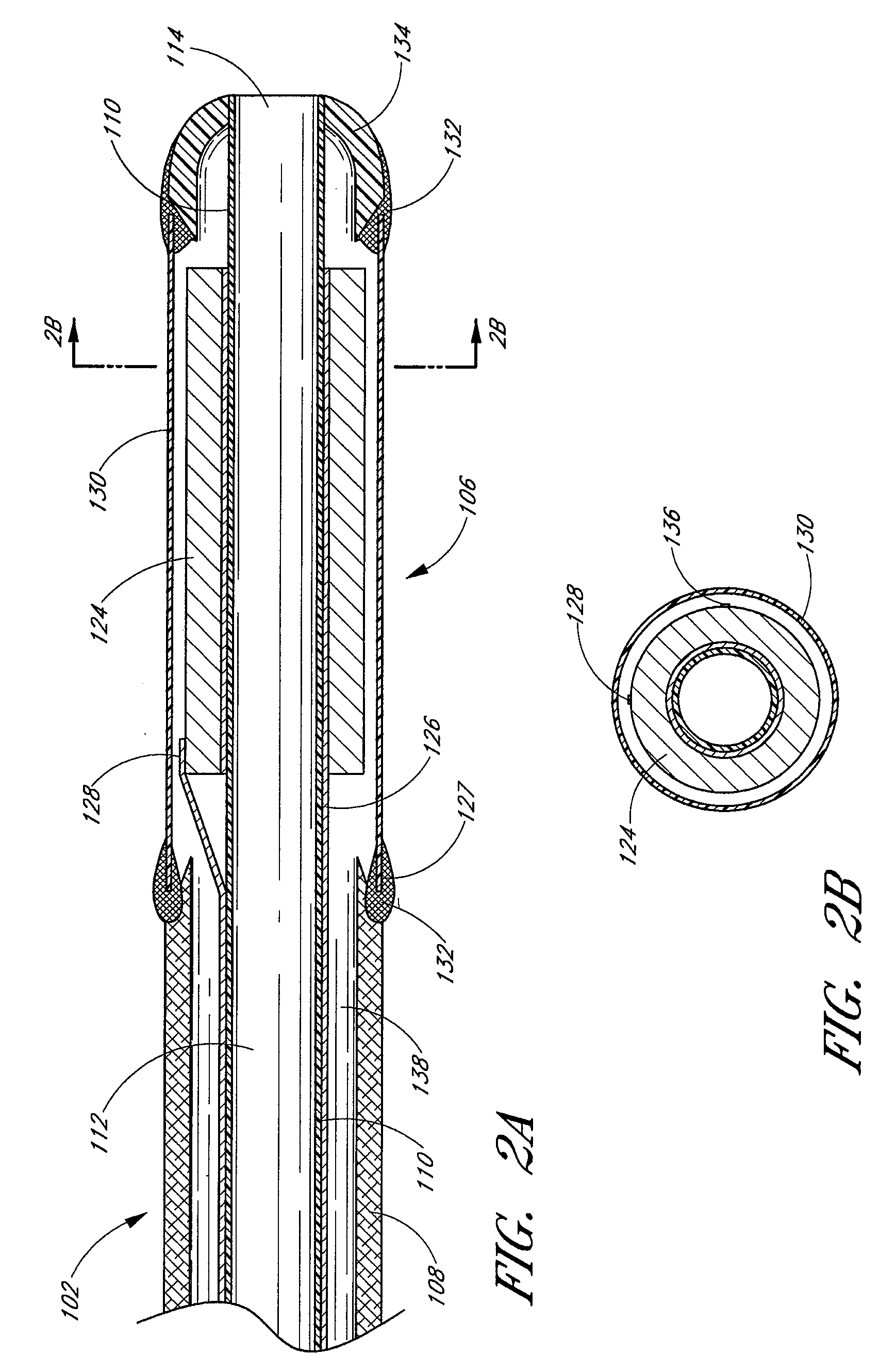
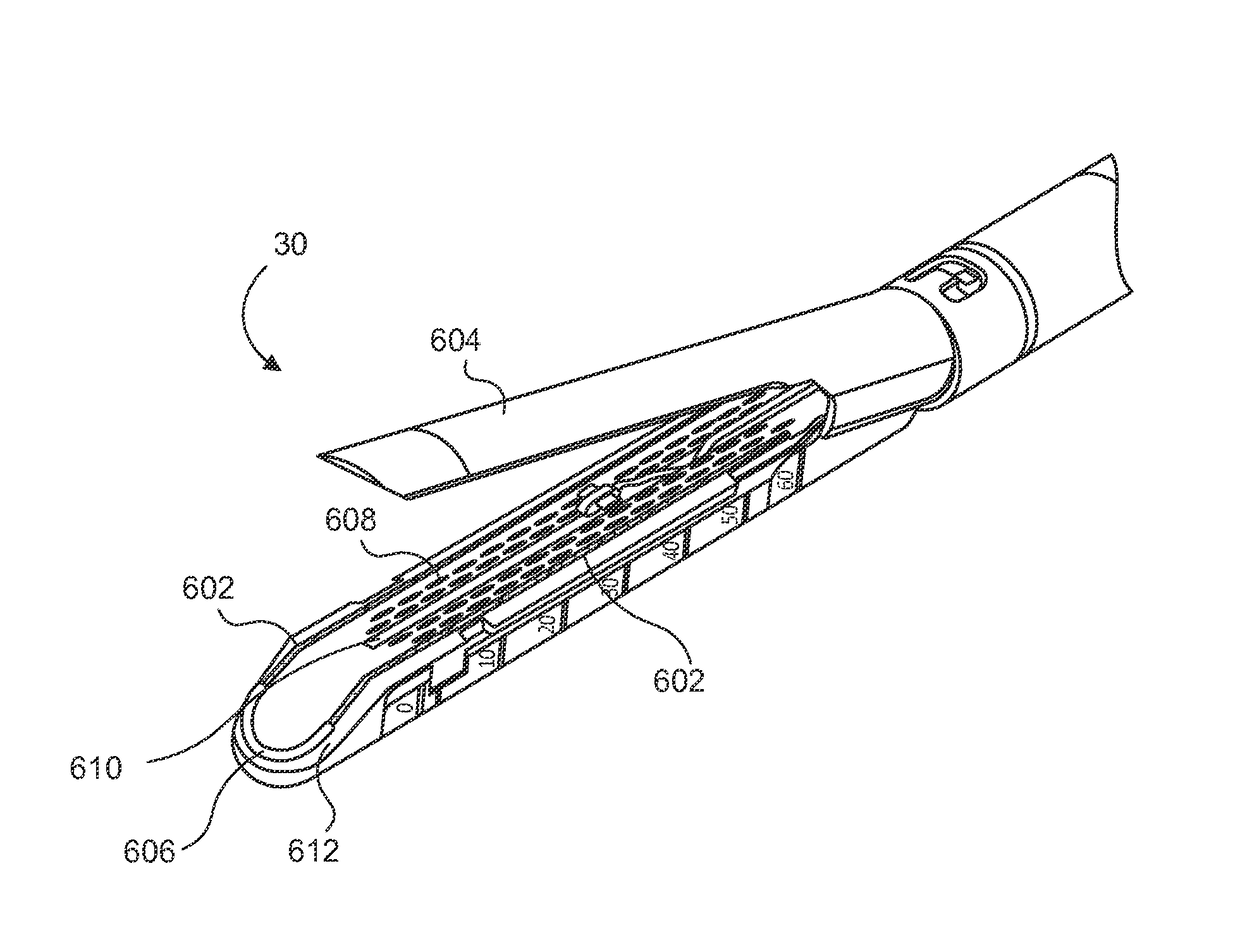
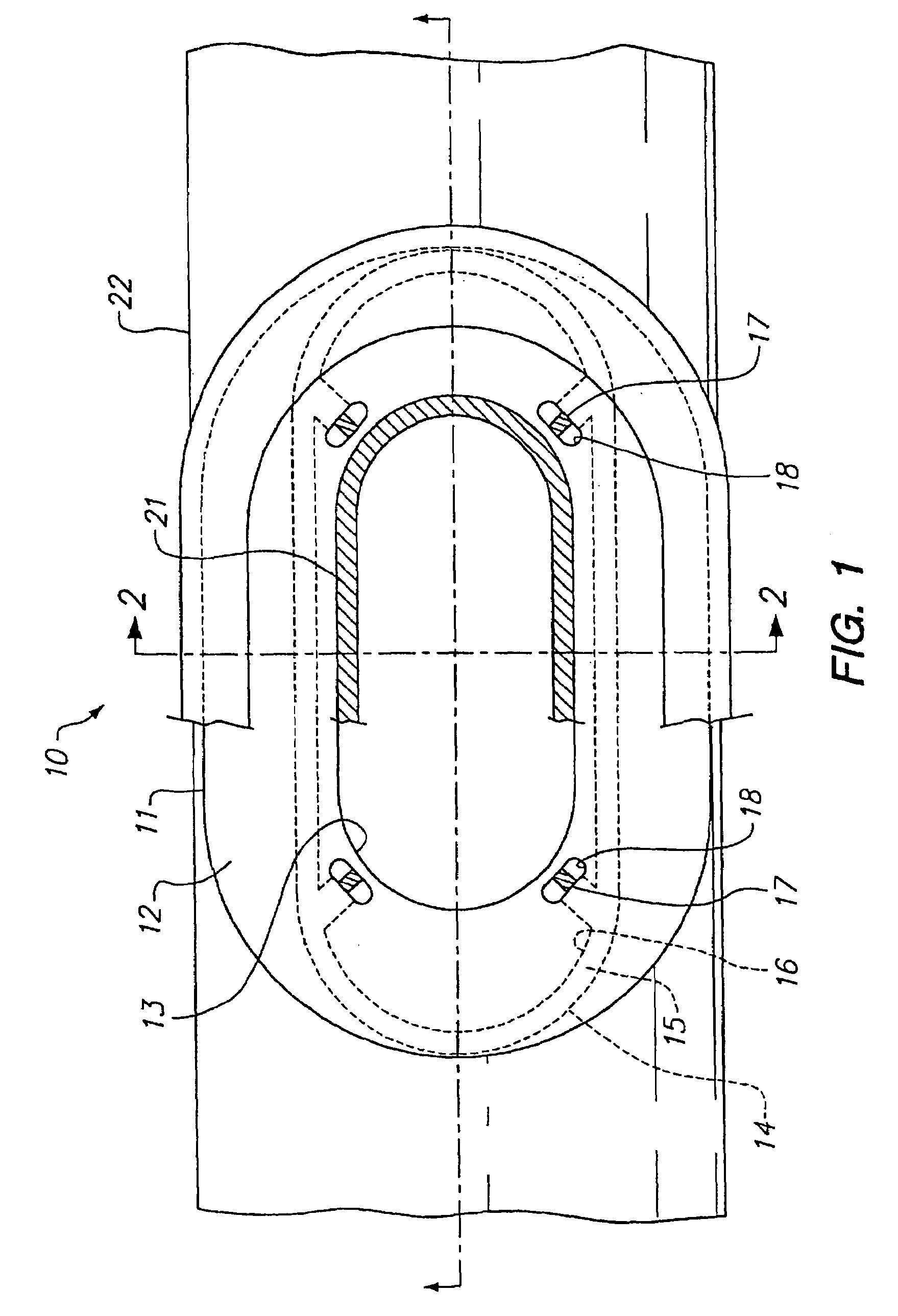
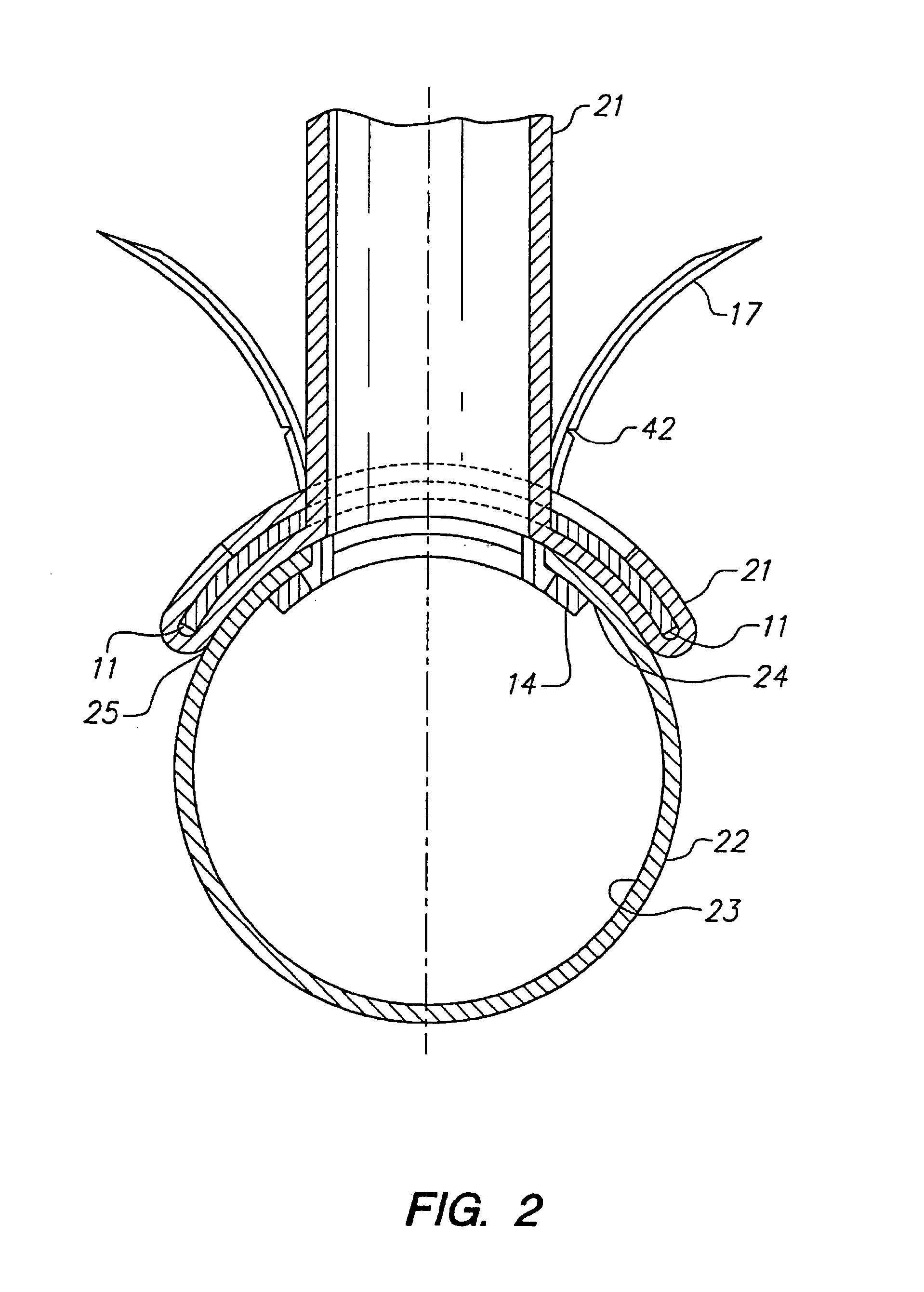
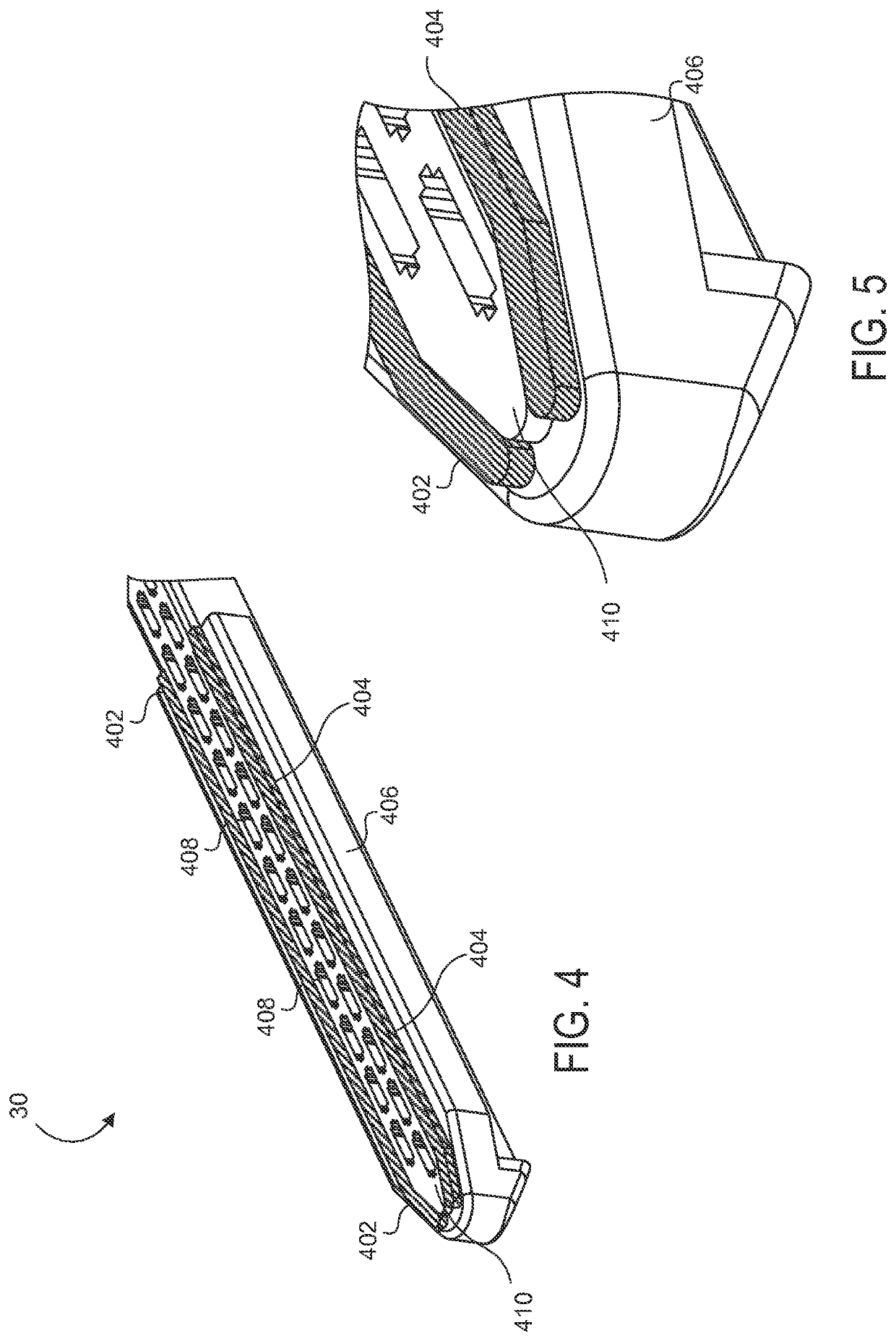
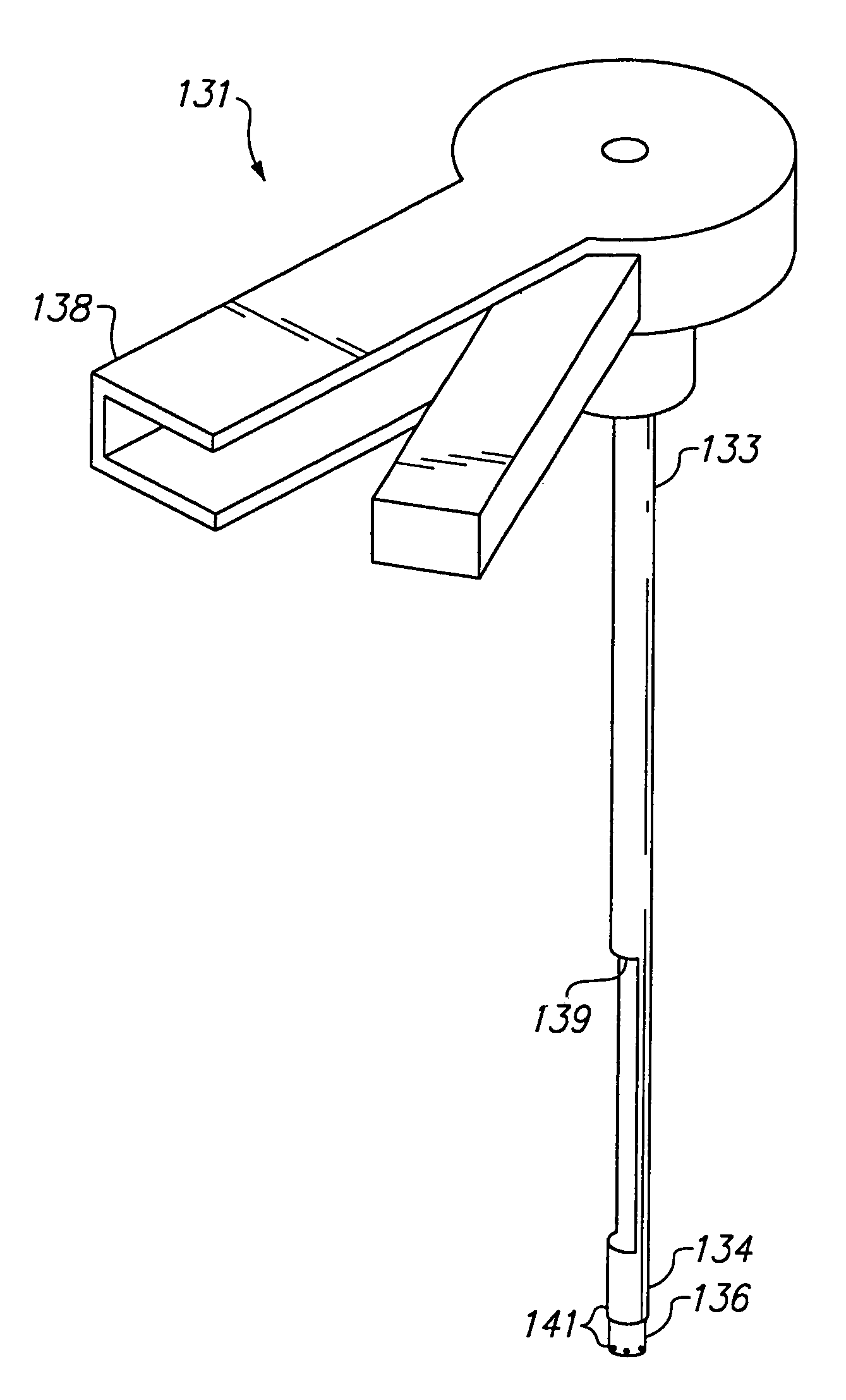
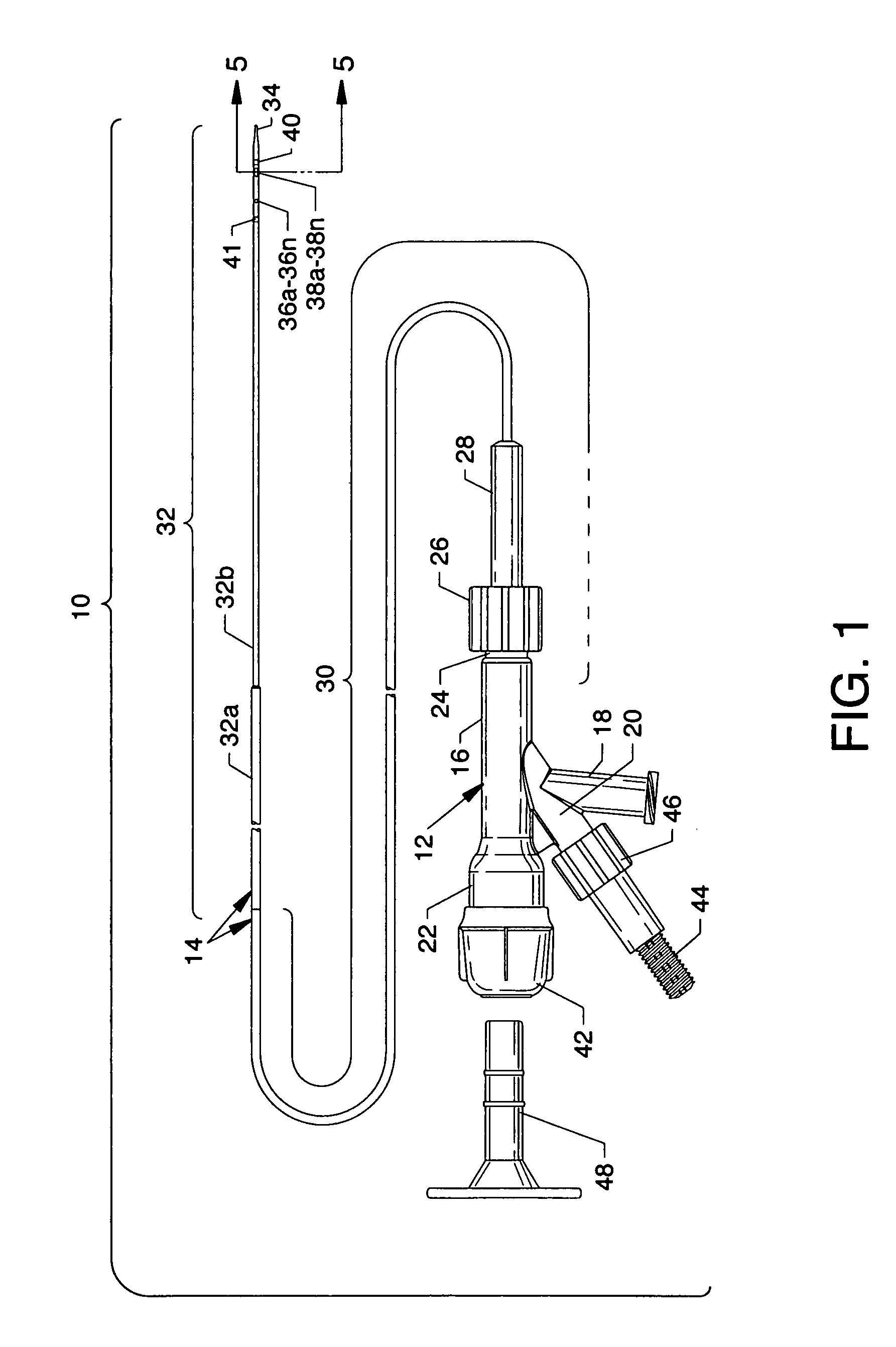
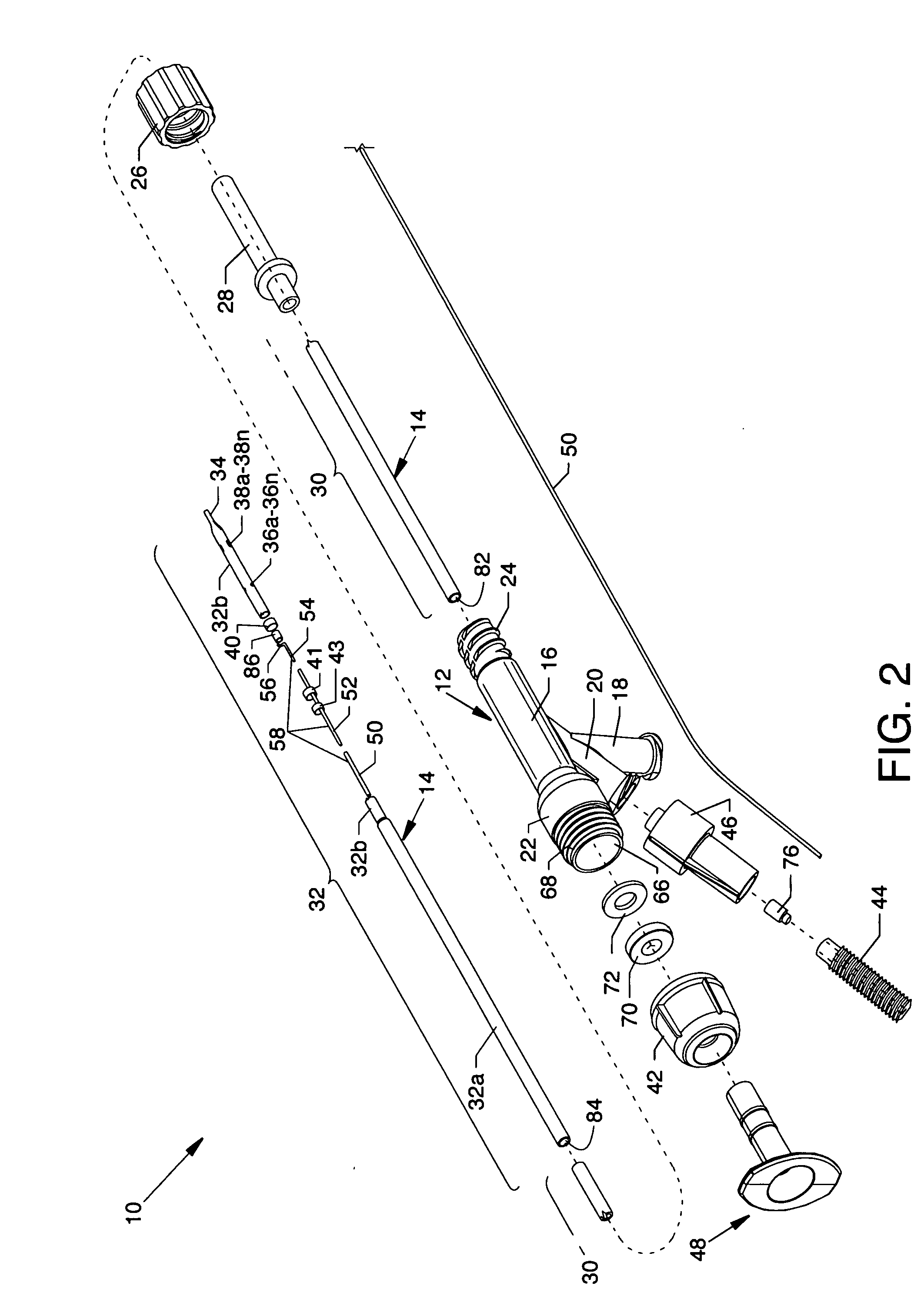
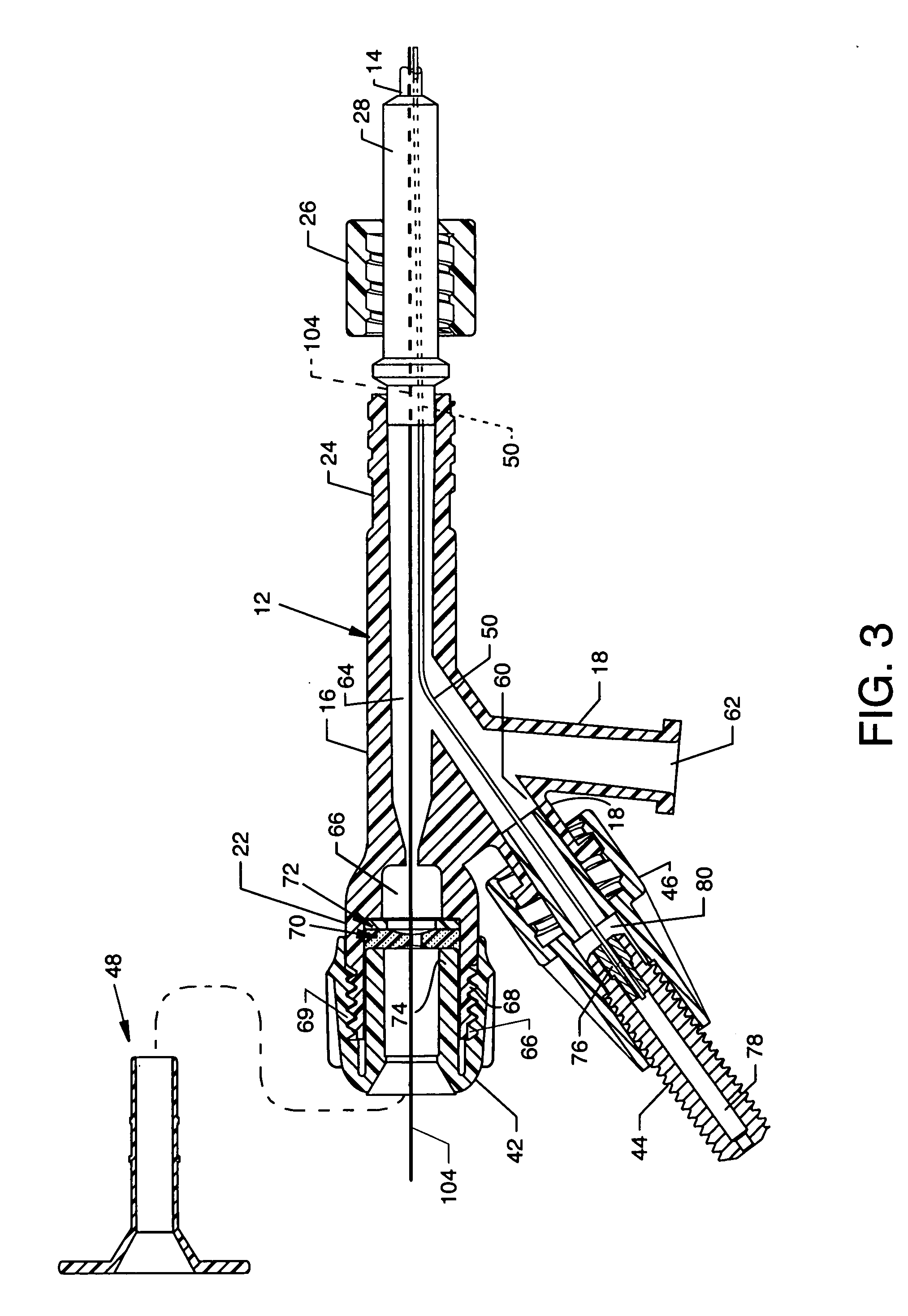
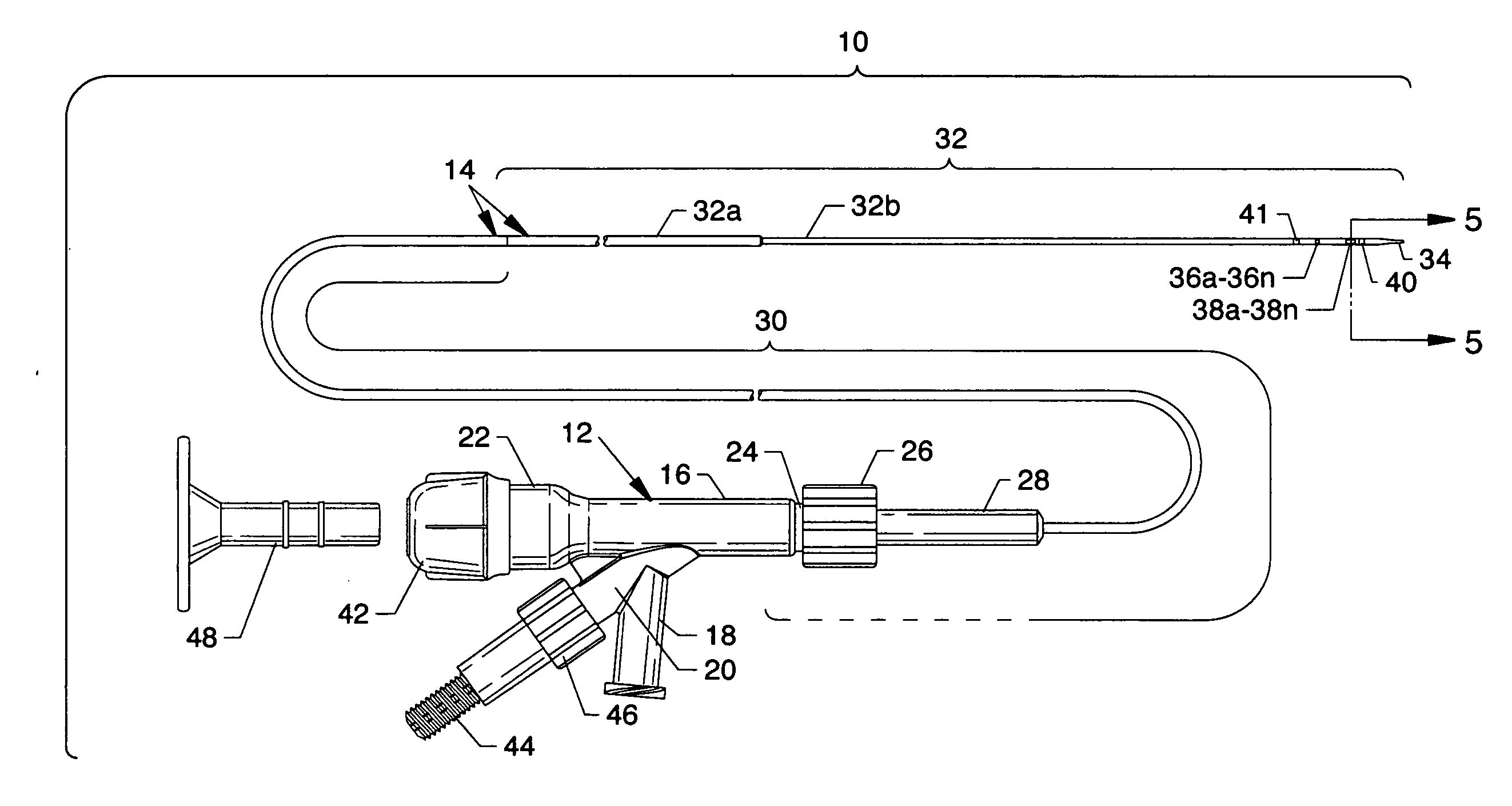
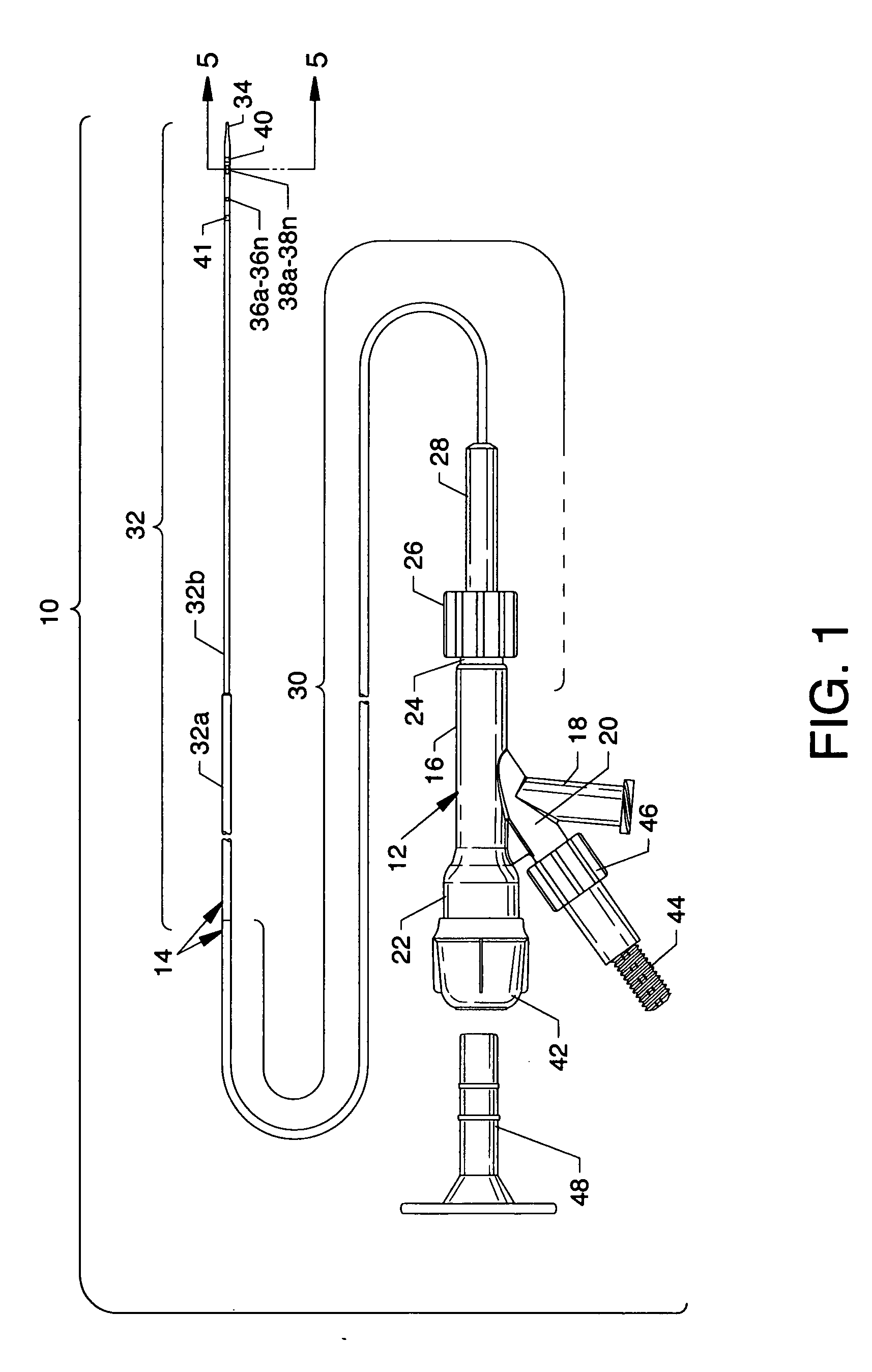
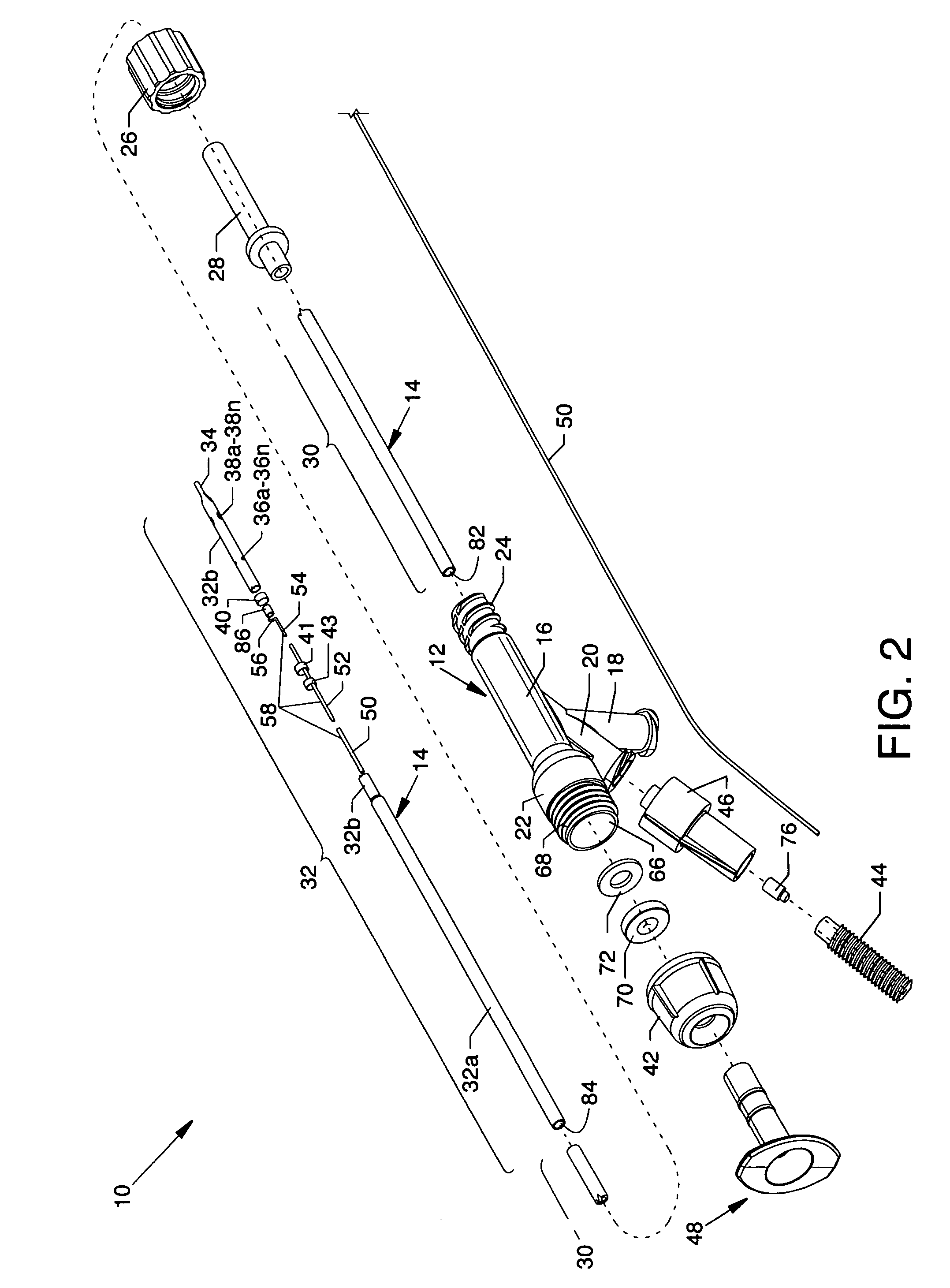
Electrode wiping surgical device
Aspects of the present disclosure include a surgical device comprising electrodes on the sides of an end of an effector to aide in sealing during various surgical procedures, such as a liver resection. During a sealing procedure, the surgeon may wipe the surgical site with the end effector, causing the electrodes to touch the fractured area. Electrosurgical energy may be applied to the electrodes during the wiping, causing coagulation of smaller vessels, such as tiny blood vessels and bile ducts in the parenchyma of the liver. In some cases, due to the nature of some smaller vessels, electrosurgical energy should be delicately applied to cause sealing but to avoid overly damaging the remaining tissue. In some embodiments, the thin design of the electrodes allows for an appropriate amount of electrosurgical energy to be applied to the fractured area.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Electrode wiping surgical device
Aspects of the present disclosure include a surgical device comprising electrodes on the sides of an end of an effector to aide in sealing during various surgical procedures, such as a liver resection. During a sealing procedure, the surgeon may wipe the surgical site with the end effector, causing the electrodes to touch the fractured area. Electrosurgical energy may be applied to the electrodes during the wiping, causing coagulation of smaller vessels, such as tiny blood vessels and bile ducts in the parenchyma of the liver. In some cases, due to the nature of some smaller vessels, electrosurgical energy should be delicately applied to cause sealing but to avoid overly damaging the remaining tissue. In some embodiments, the thin design of the electrodes allows for an appropriate amount of electrosurgical energy to be applied to the fractured area.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
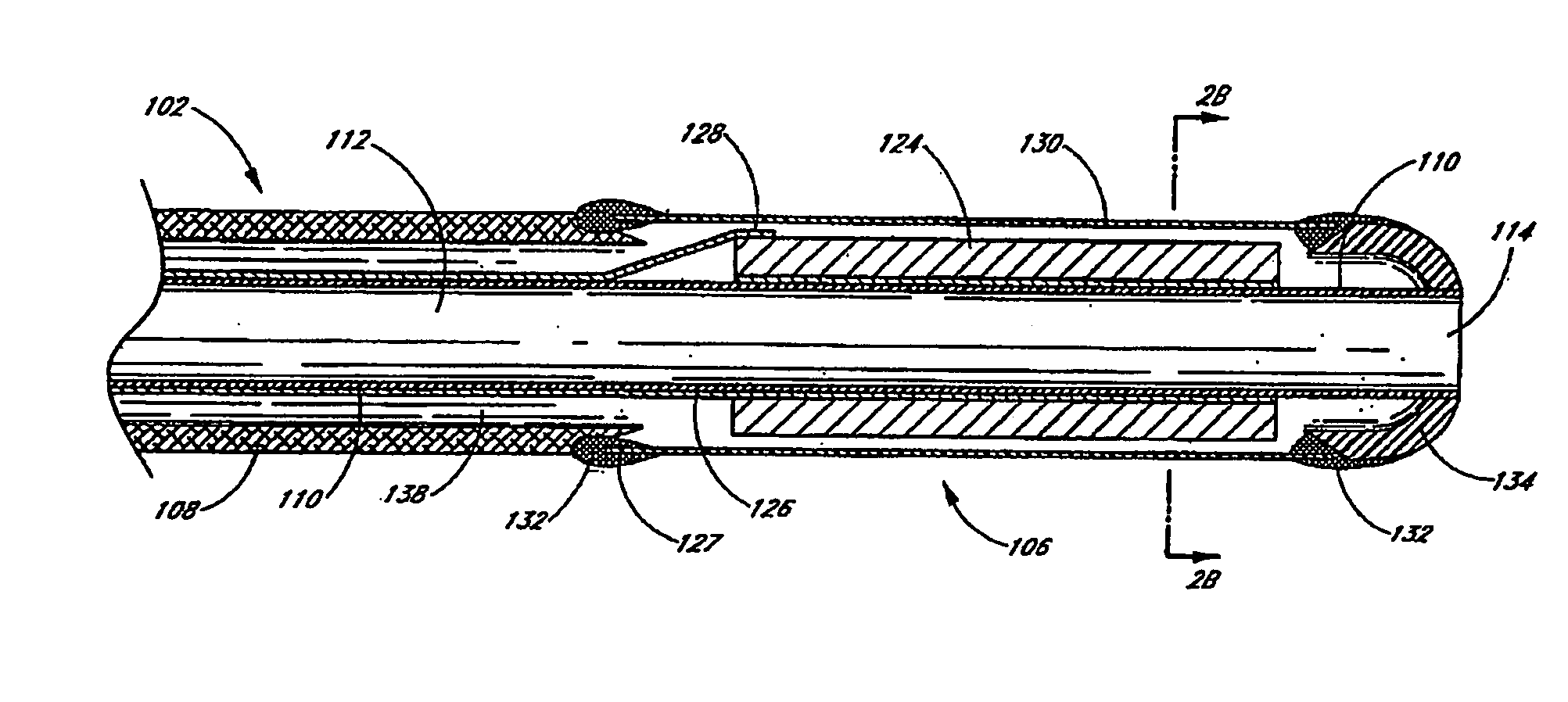
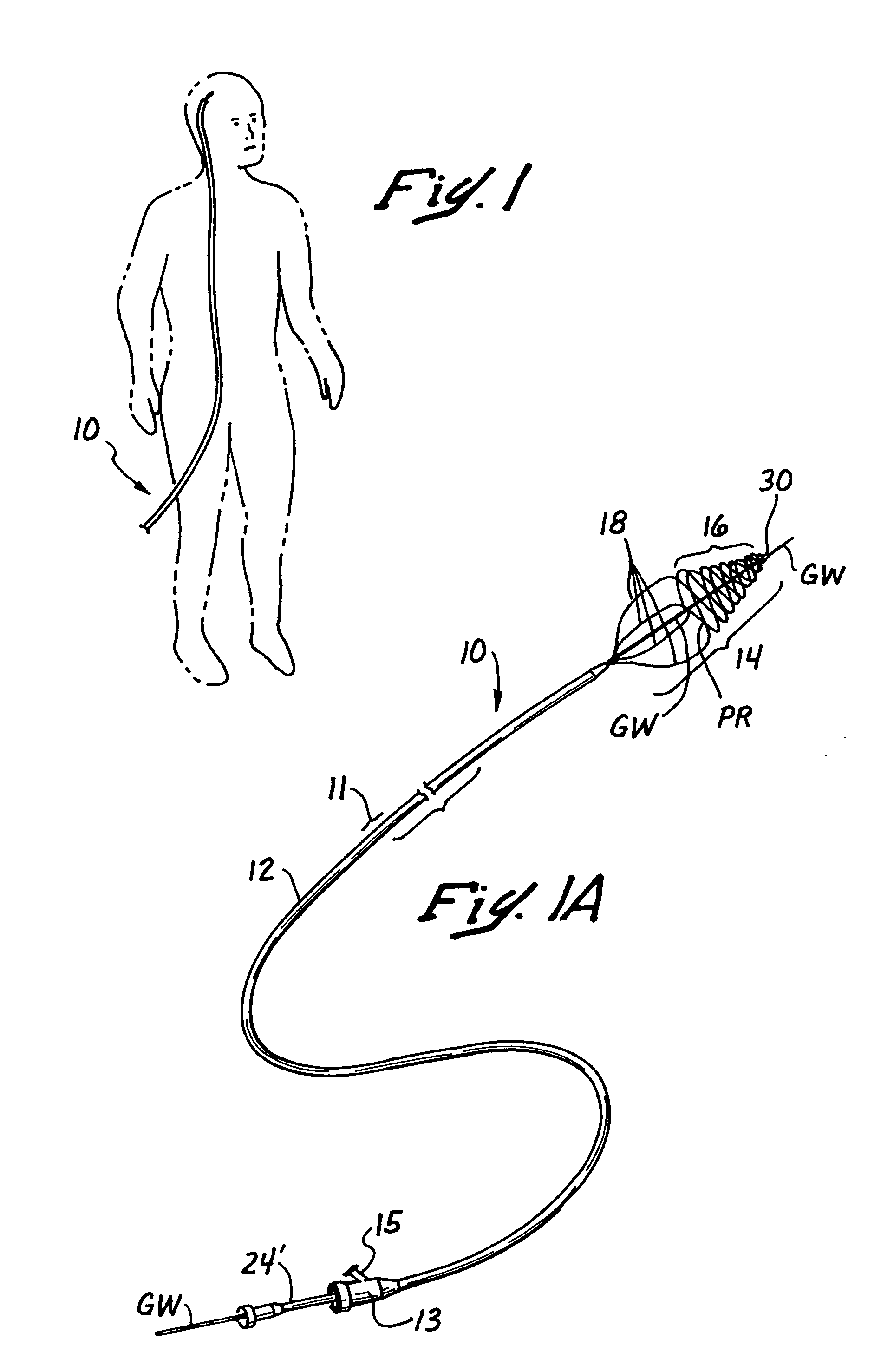
Small vessel ultrasound catheter
InactiveUS20050215942A1Increase stiffnessSufficient flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:EKOS CORP
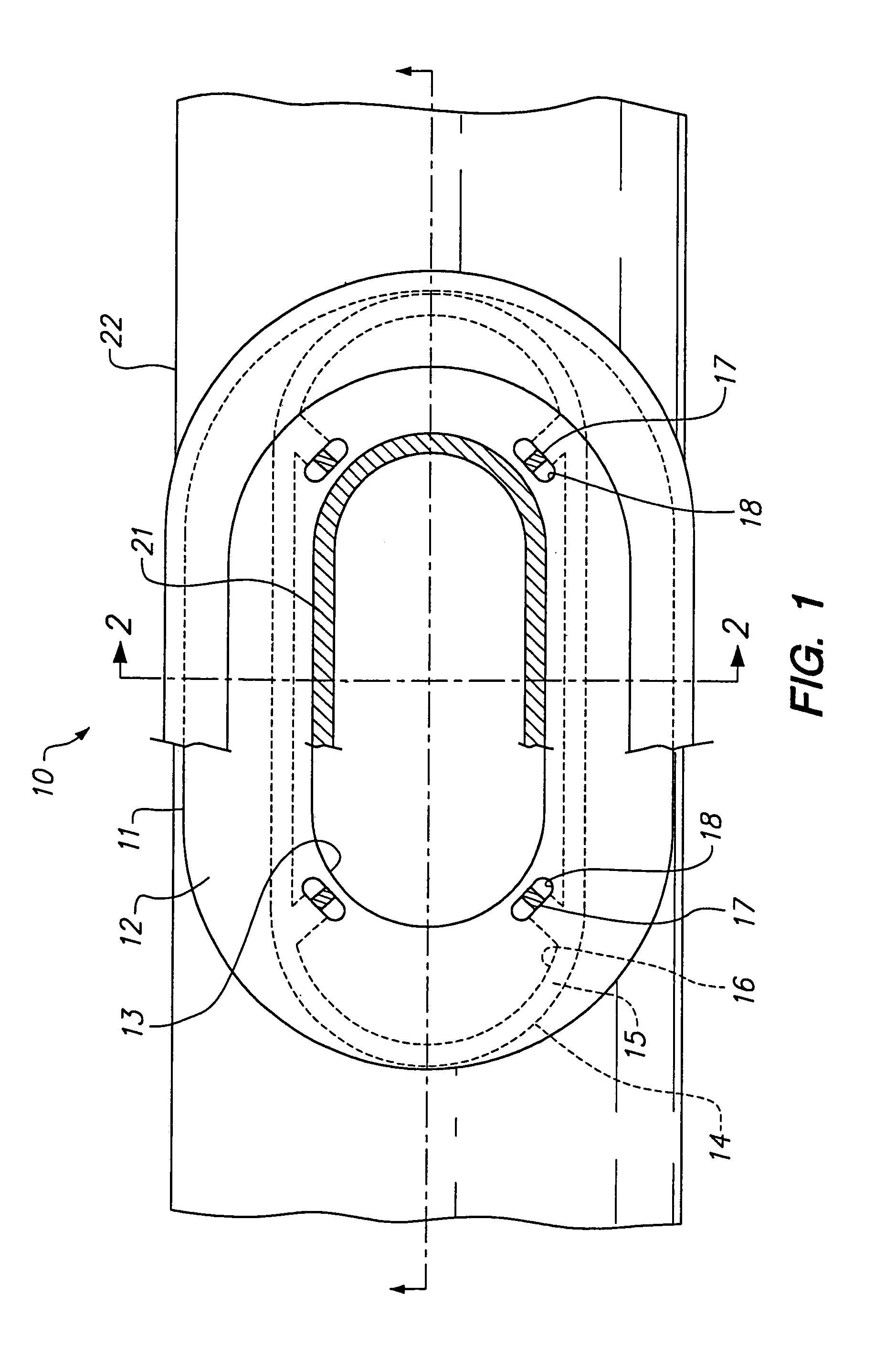
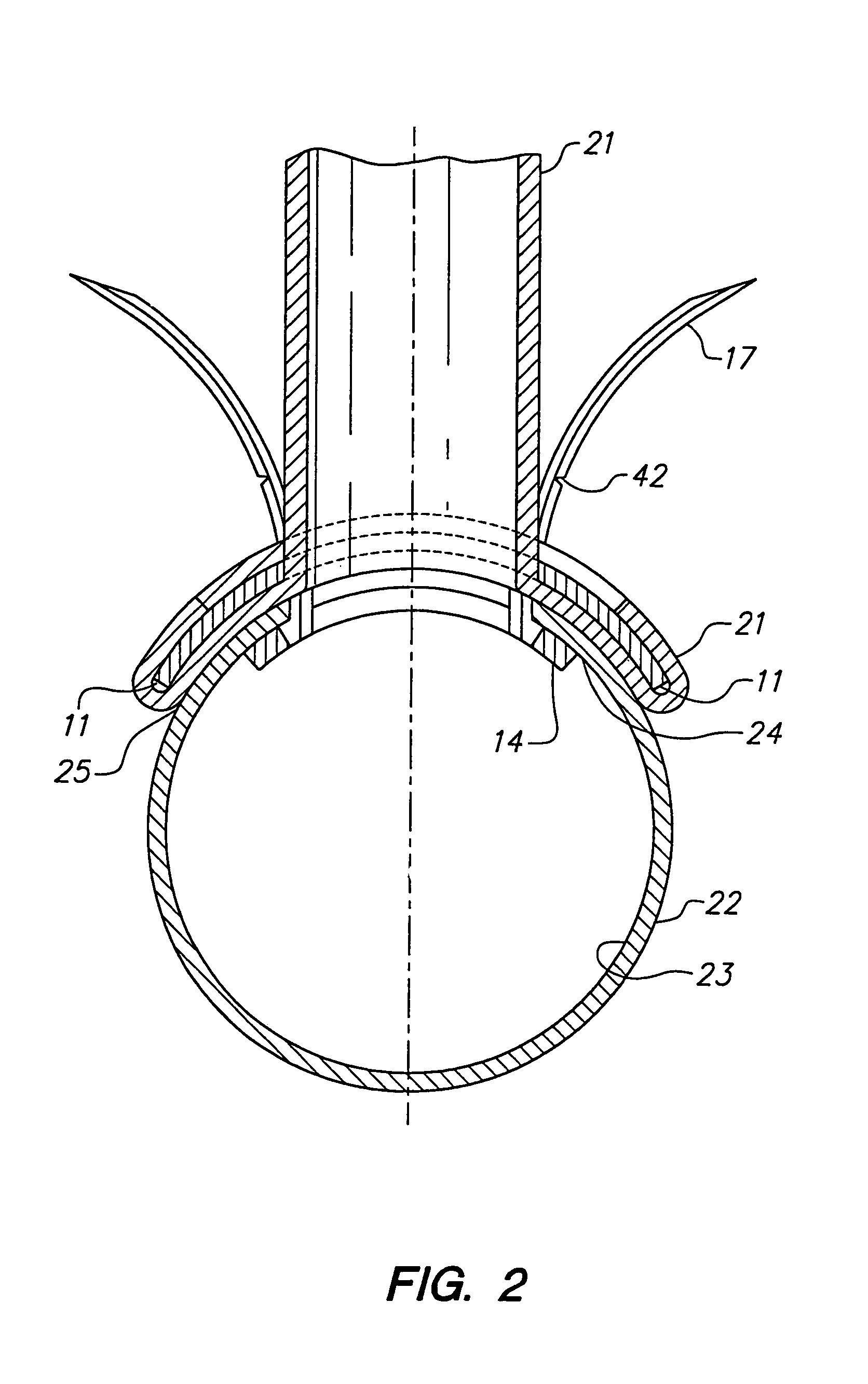
Embolic filter
InactiveUS7004955B2Maintaining and restoring patencyImprove the immunitySurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryBiomedical engineering
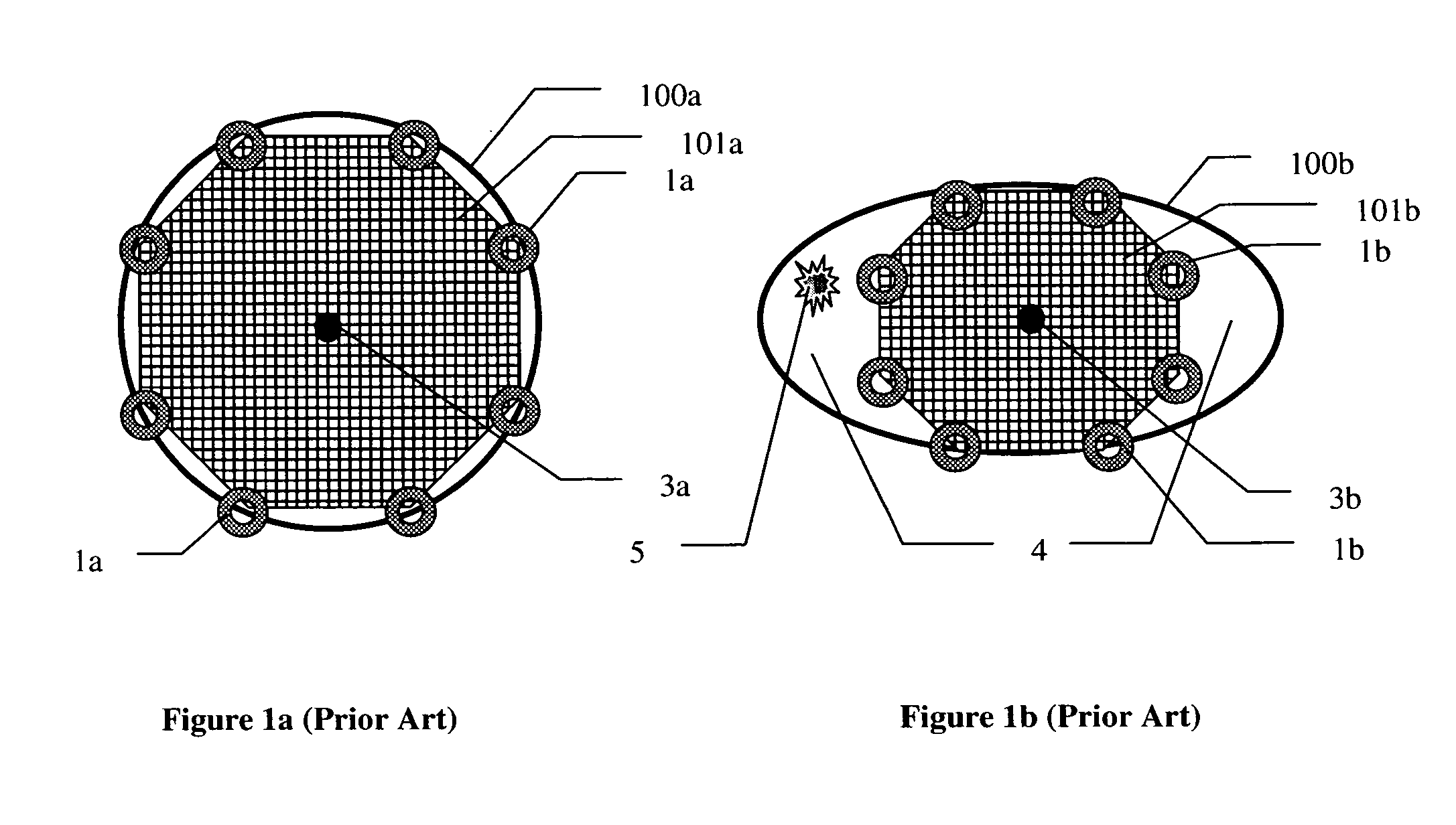
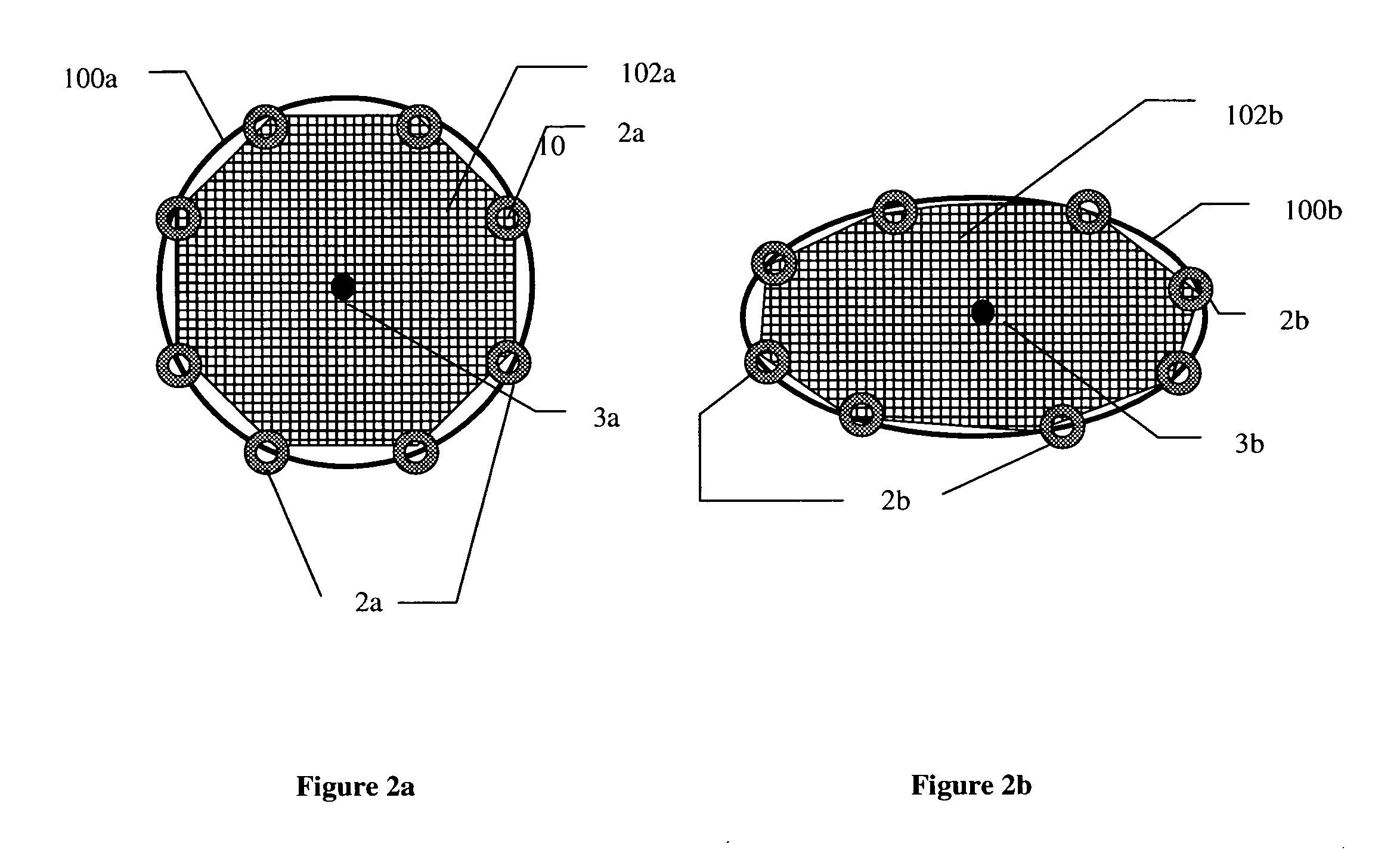
An intravascular filter device for use in capturing debris which may occur as a result of an intravascular procedure. The filter device includes a proximal section, a distal section and a mid-section. The mid-section includes three rings configured in a sixteen apices alternating V-pattern. The filter device specifically embodies structure that provides enhanced radial opening and angular resistance to collapse in its expanded state. While, in its compressed state the filter device provides an extremely small compressed profile giving it the desired ability to be delivered into very small vessels of the human vasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
Small vessel ultrasound catheter
ActiveUS7384407B2Promote progressReduced bending resistanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Embolectomy catheters and methods for treating stroke and other small vessel thromboembolic disorders
InactiveUS7691121B2Prevent and minimize severityEasy extractionStentsDilatorsThrombosis embolismThromboembolic disorder
Embolectomy catheters, rapid exchange microcatheters, systems and methods for removing clots or other obstructive matter (e.g., thrombus, thromboemboli, embolic fragments of atherosclerotic plaque, foreign objects, etc.) from blood vessels. This invention is particularly useable for percutaneous removal of thromboemboli or other obstructive matter from small blood vessels of the brain, during an evolving stroke or period of cerebral ischemia. In some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters of this invention are advanceable with or over a guidewire which has been pre-inserted through or around the clot. Also, in some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters include clot removal devices which are deployable from the catheter after the catheter has been advanced at least partially through the clot. The clot removal device may included a deployable wire nest that is designed to prevent a blood clot from passing therethrough. The delivery catheter may include telescoping inner and outer tubes, with the clot removal device being radially constrained by the outer tube. Retraction of the outer tube removes the constraint on the clot removal device and permits it to expand to its deployed configuration. An infusion guidewire is particularly useful in conjunction with the embolectomy catheter, and permits infusion of medicaments or visualization fluids distal to the clot.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
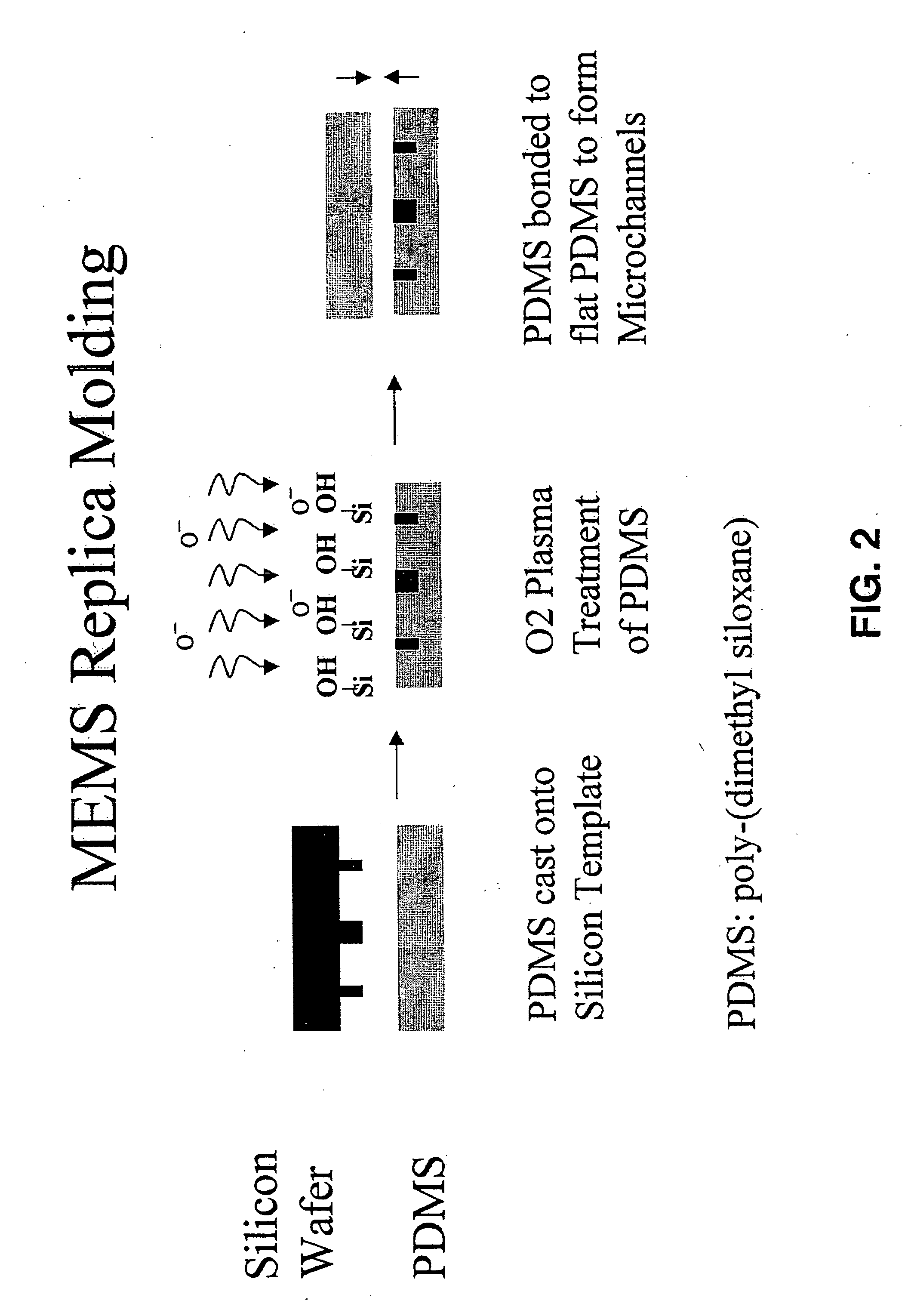
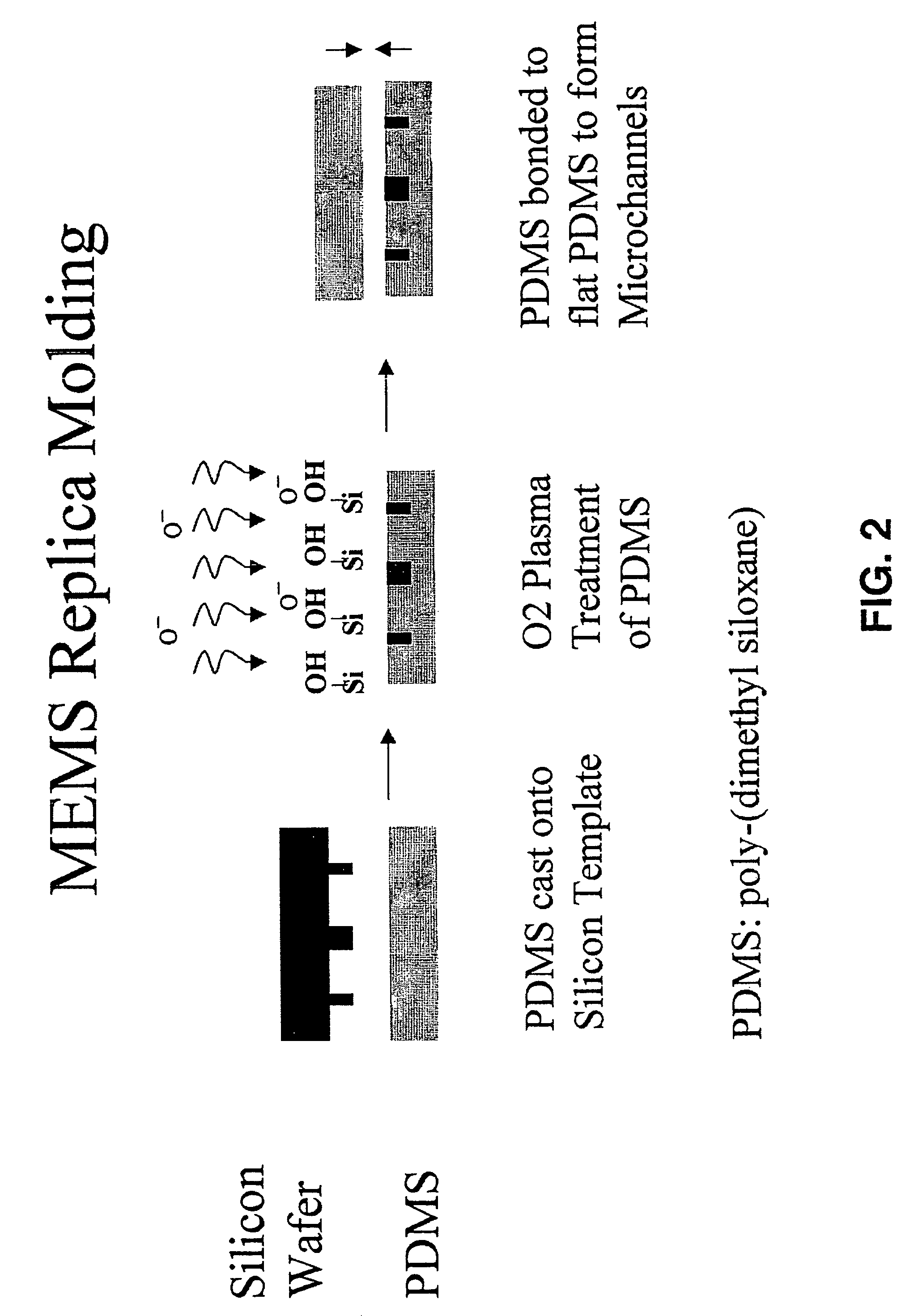
Three dimensional construct for the design and fabrication of physiological fluidic networks
ActiveUS20060136182A1Increase cell densityIncrease the number ofMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringSmall vessel
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Distal protection apparatus with improved wall apposition
InactiveUS20060149313A1Easy loadingPrevent thrombosisSurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryEmbolization material
In accordance with the present invention, a distal protection and embolic material retrieval device with improved apposition to both large and small vessel walls of varying geometries for enhancing the filtering of embolic material during intravascular procedures while allowing for the passage of blood is provided. The device includes a filter basket designed to maximize apposition of the filtering portion to that of the vessel wall and may include struts which provide circumferential support to the filtering membrane and thereby minimizing or eliminating in-folding of the filter basket. Thin film materials may also be utilized for the filtering membrane of the filter basket. In addition one can incorporate biological and / or pharmaceutical agents in combination with the present invention.
Owner:ARGUELLO EDWARD +3
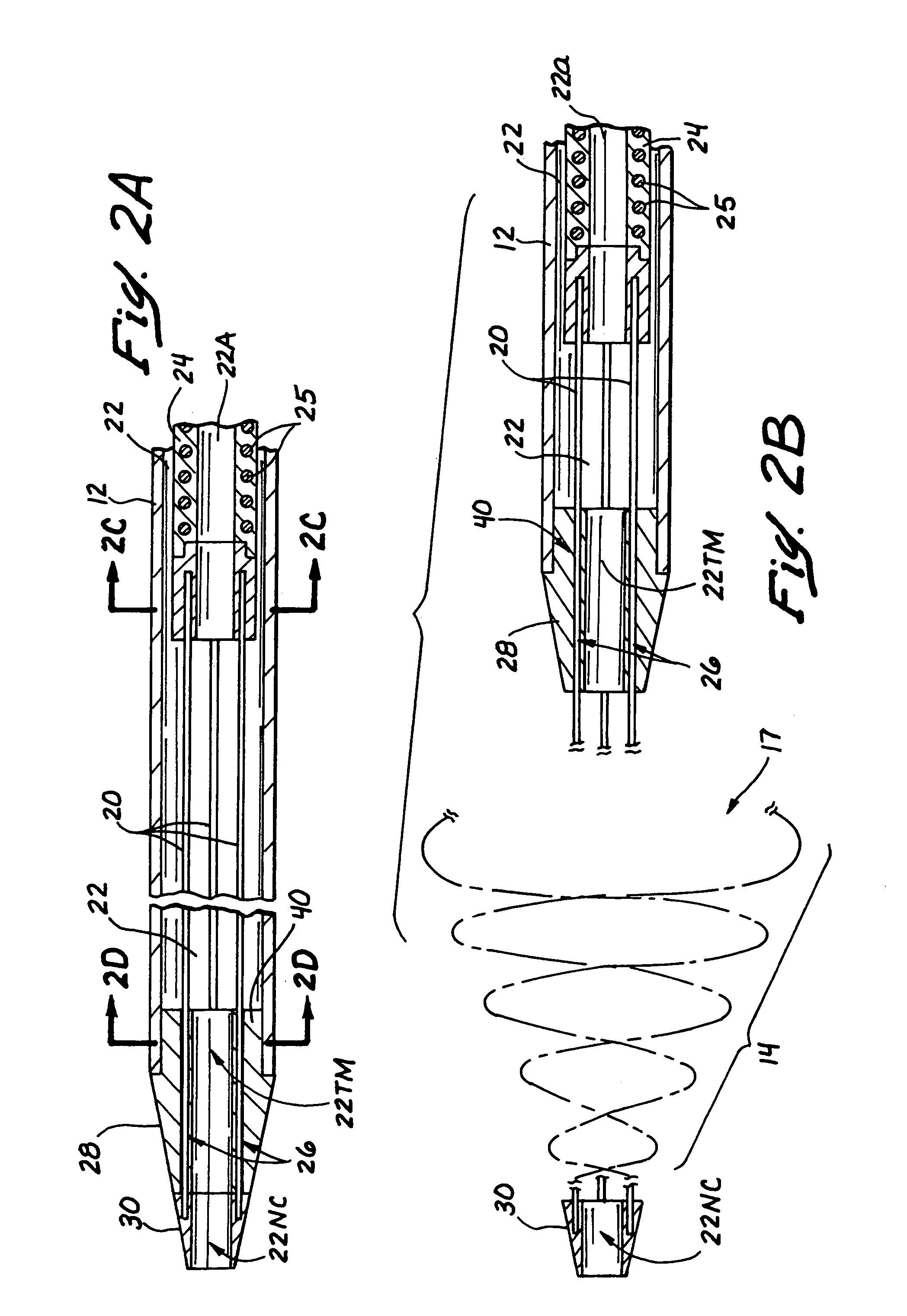
Endovascular medical device with plurality of wires
InactiveUS7025758B2Increase resistanceEasy to installStentsInfusion syringesProsthesisMedical device
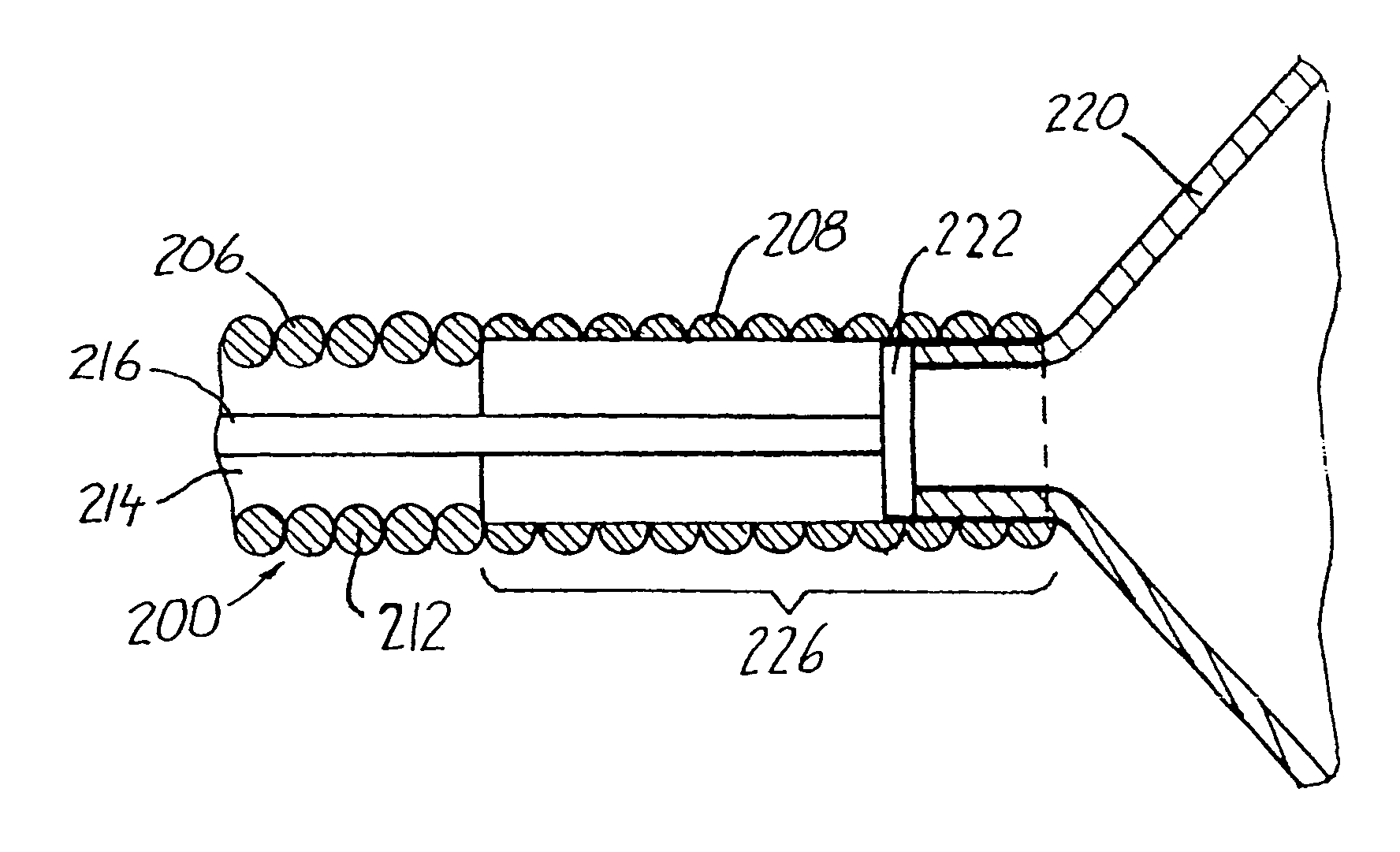
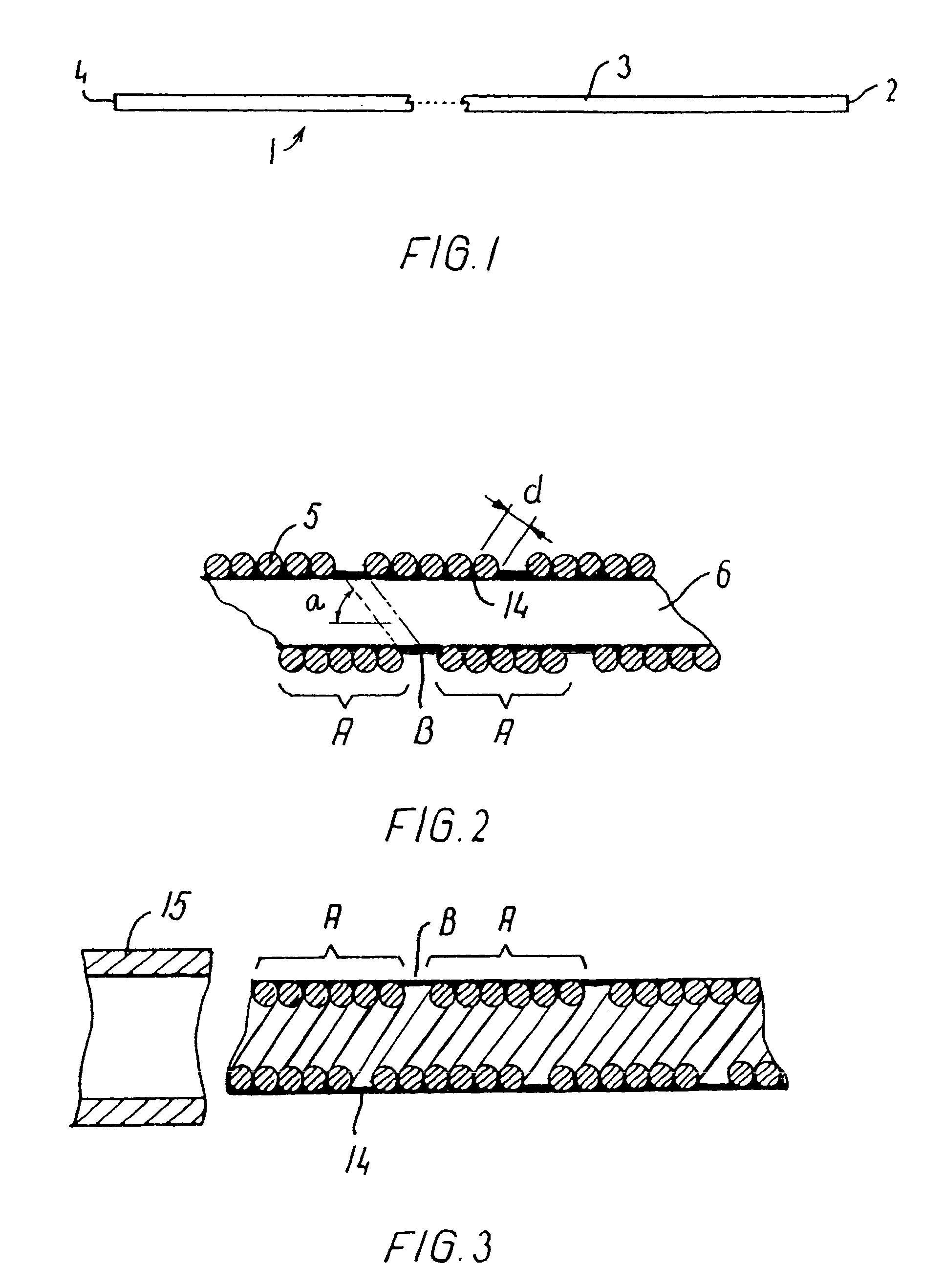
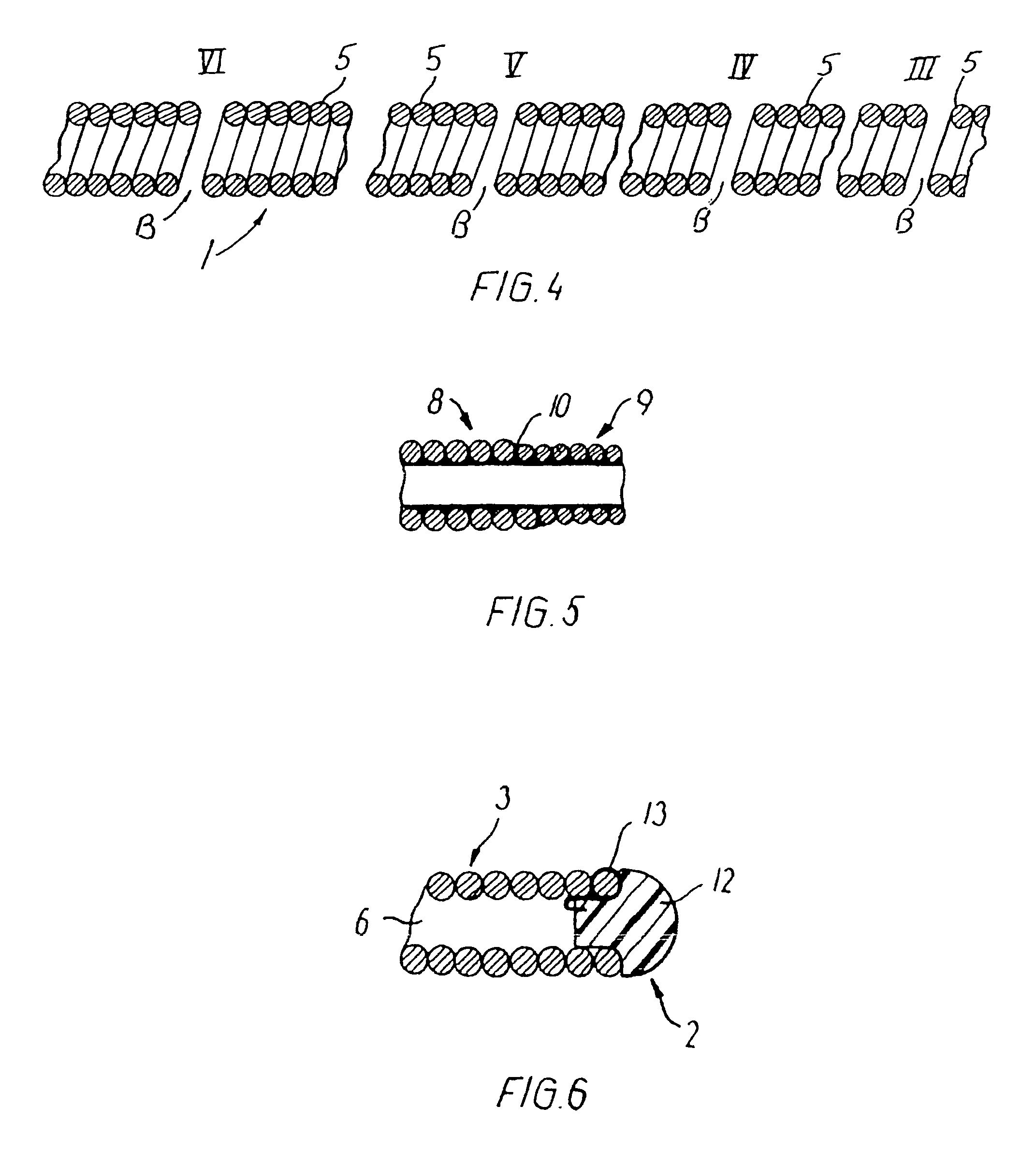
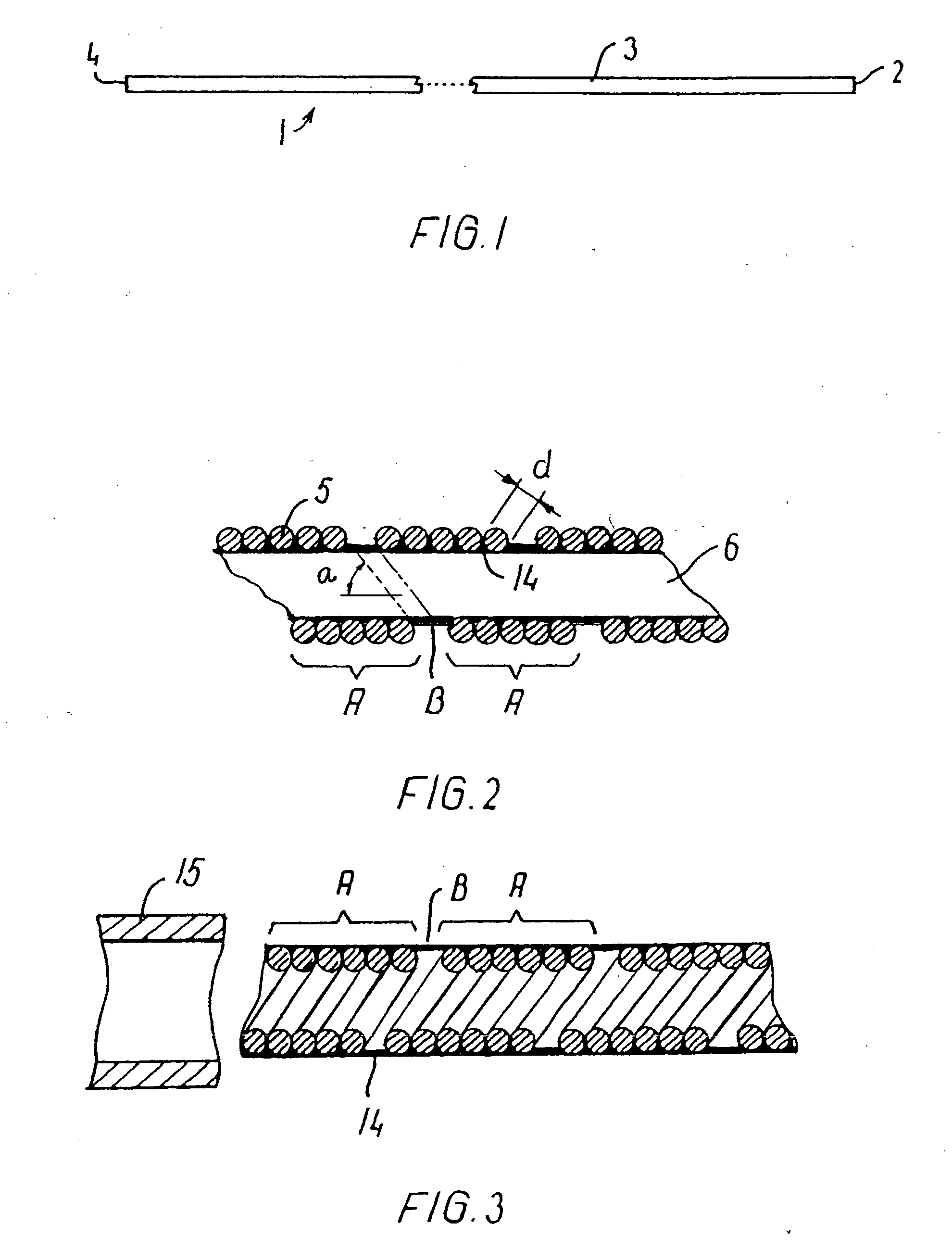
An endovascular device (1, 100, 200, 300) having a distal end (2), a proximal end (4) and a body portion (3) therebetween. The body portion is made of a multiple filament helically wound row (A) of wires (5), provided with a sealing coating (14) on the inside surface or the outside surface or both. The device may be a catheter (1), a sheath, an introducer, a delivery device, a pusher (100), an embolization coil delivery device (300), or a receptacle (208) for an expandable prosthesis (220) used with a delivery device (200). From 2 to 12, and preferably from 4 to 8, wires (5) are used in the row, and fewer wires may be used proceeding toward the distal end (2) for greater flexibility. The helically wound row of wires transmits torque and provides pushability to the device while resisting kinking, and enables a small outside diameter for reaching very small vessels and extending through very tortuous vessels.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method of manufacturing small profile medical devices
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC +1
Small vessel ultrasound cathter
InactiveUS20080221506A1Promote progressReduce resistanceUltrasound therapyMulti-lumen catheterDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:RODRIGUEZ OSCAR E +7
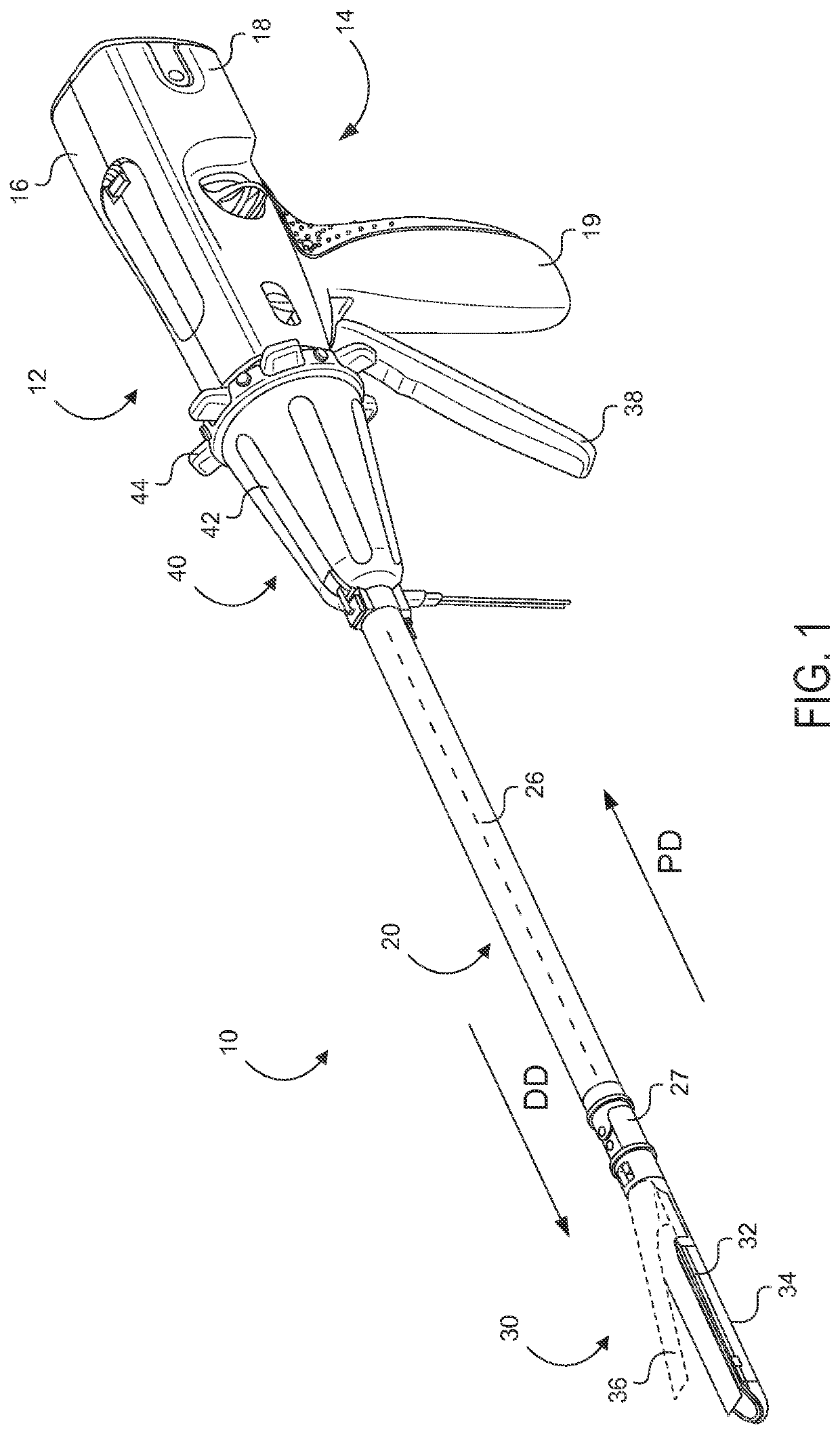
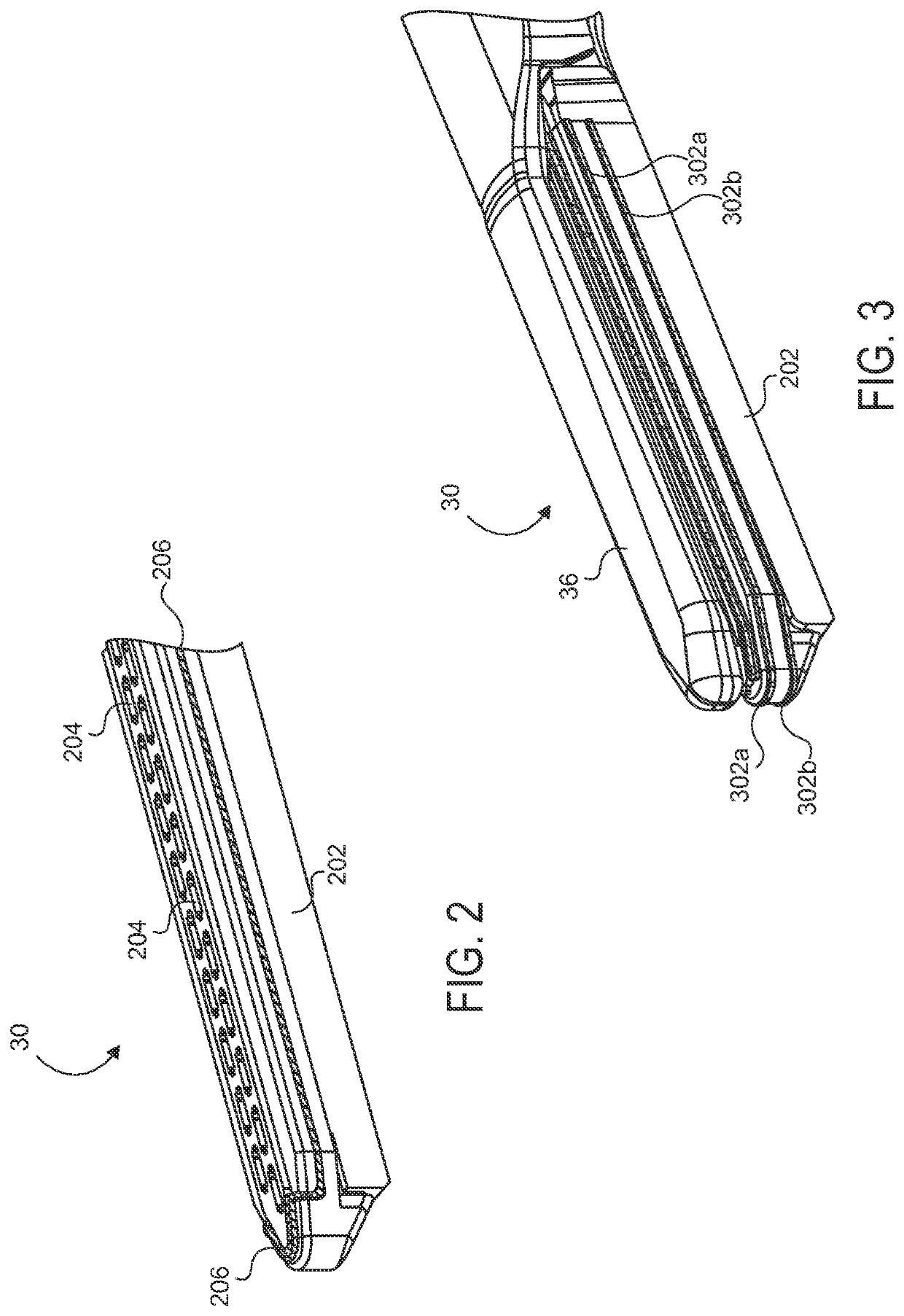
Control and electrical connections for electrode endocutter device
Aspects of the present disclosure include an attachable power and control system to supply energy to electrodes of a wiping electrode coagulation system of a surgical device. A surgical device includes electrodes at an end of effector to aide in sealing during various surgical procedures. During the procedure, the surgeon may wipe the surgical site with the end effector, causing the electrodes to touch the fractured area. Electrosurgical energy may be applied to the electrodes during the wiping, causing coagulation of smaller vessels. The attachable power and control system may be configured to slide over the shaft of the surgical device. The power and control system also may be configured to supply power to the electrodes and to control when energy is applied to the electrodes, based in part, for example, on measuring a distance or angle of the opening of the jaws at the end effector.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
An attention mechanism U-shaped densely connected retinal blood vessel segmentation method
ActiveCN109448006AImprove performanceExtract accurate and moreImage enhancementImage analysisData setNetwork model
The invention relates to an attention mechanism U-shaped densely connected retinal (a novel retinal blood vessel segmentation method fusing DenseNet and Attention U-net network) blood vessel segmentation method, comprising the steps of retinal blood vessel image preprocessing and constructing a retinal blood vessel segmentation model. The method of the invention can effectively solve the problemsthat adjacent blood vessels are easy to connect, the micro blood vessels are too wide, the small blood vessels are easy to break, the blood vessel intersection is insufficient in segmentation, the image noise is too sensitive, the gray value of the object and the background is crossed, the optic disc and the lesion focus are missegmented, and the like. The method of the invention integrates a plurality of network models under the condition of low complexity, the excellent segmentation results are obtained on DRIVE dataset, the accuracy and sensitivity are 96.95% and 85.94%, respectively, whichare about 0.59% and 7.92% higher than those published in the latest literature.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
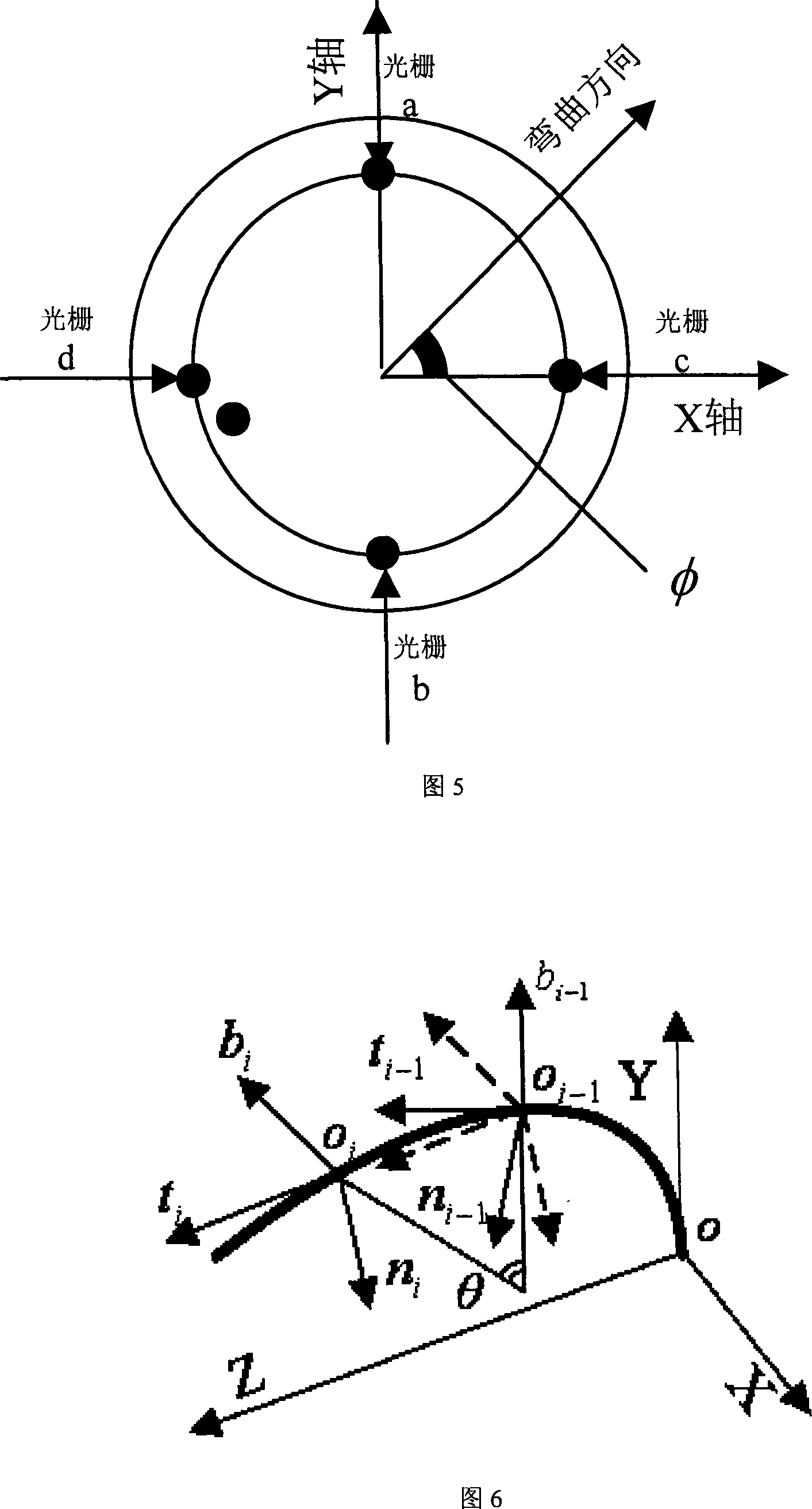
Thin long flexible rod spatial shape detecting device and method
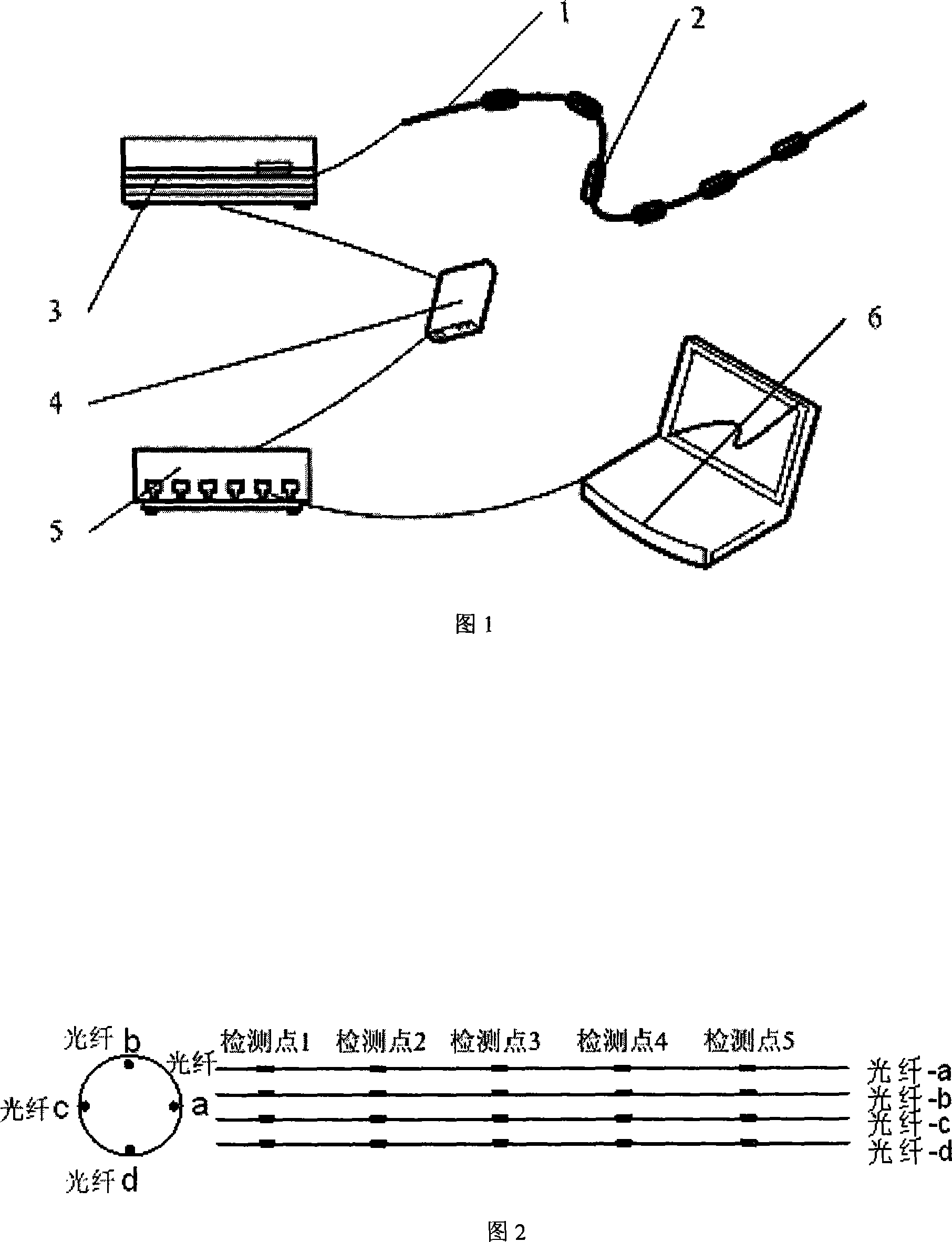
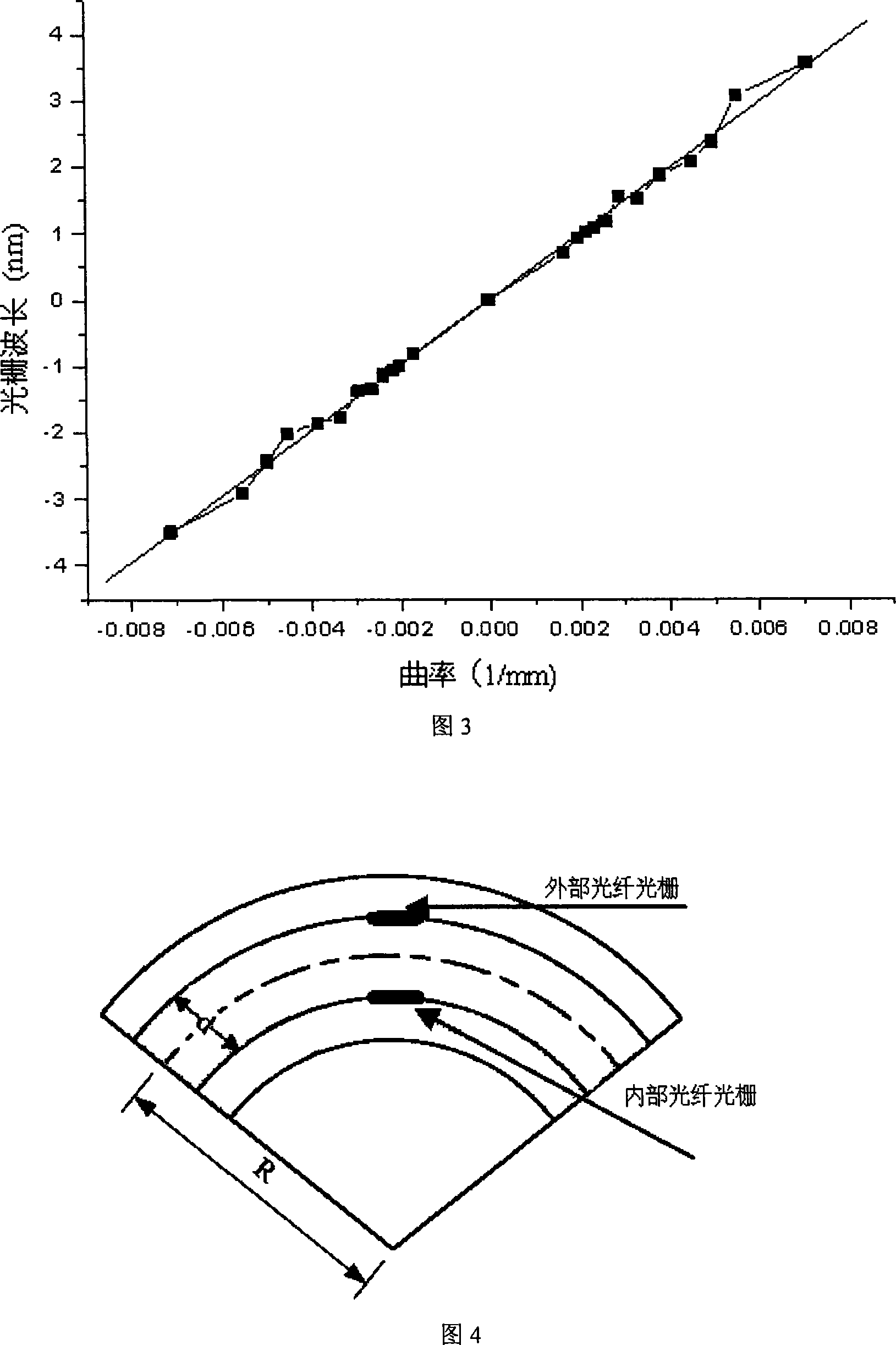
InactiveCN101099657AImprove real-time response performanceSmall sizeSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayFiber
The present invention relates to a space form detection device of fine-long flexible bar and its detection method. Said device is composed of fine-long flexible bar, fiber-optic grating sensor array, fiber-optic grating modulator-demodulator, local area network router, data acquisition and data processing module and display equipment. The space form detection method of fine-long flexible bar includes the following steps: utilizing a group of grating array formed from four optical fibers arranged on the fine-long flexible bar, utilizing scale factor between the off-line labeled curvature and wavelength and utilizing fiber-optic grating modulator and demodulator to measure wavelengths of 20 raster points in five discrete points of fine-long flexible bar in the space so as to obtain the space curvature size and direction of discrete point position, then utilizing data processing module to reconstruct the form of said fine-long flexible bar in space. Said device can be used for making real-time tracking detection of human body cavity channel and fine-small vessel forms in the therapeutic process.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
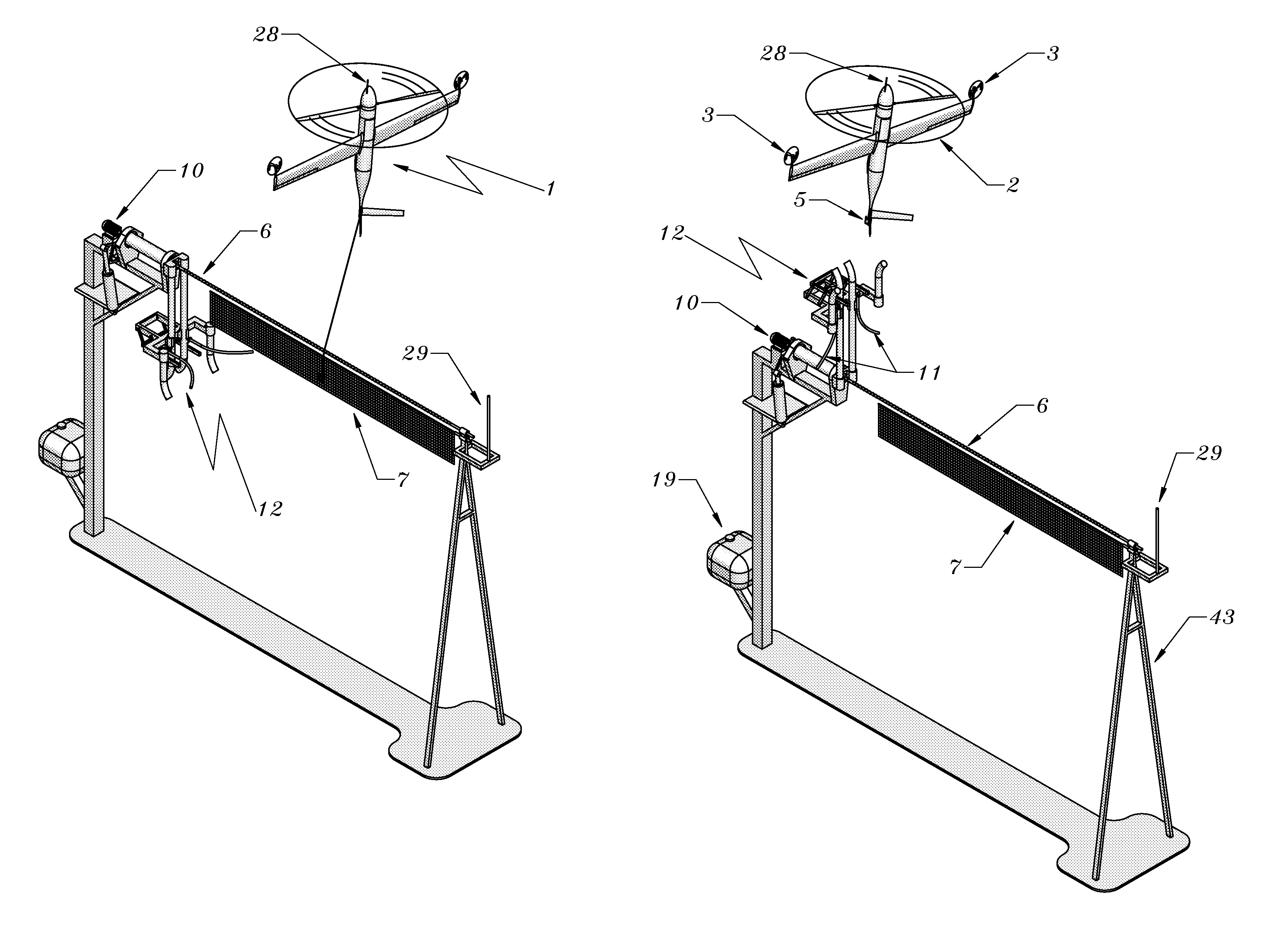
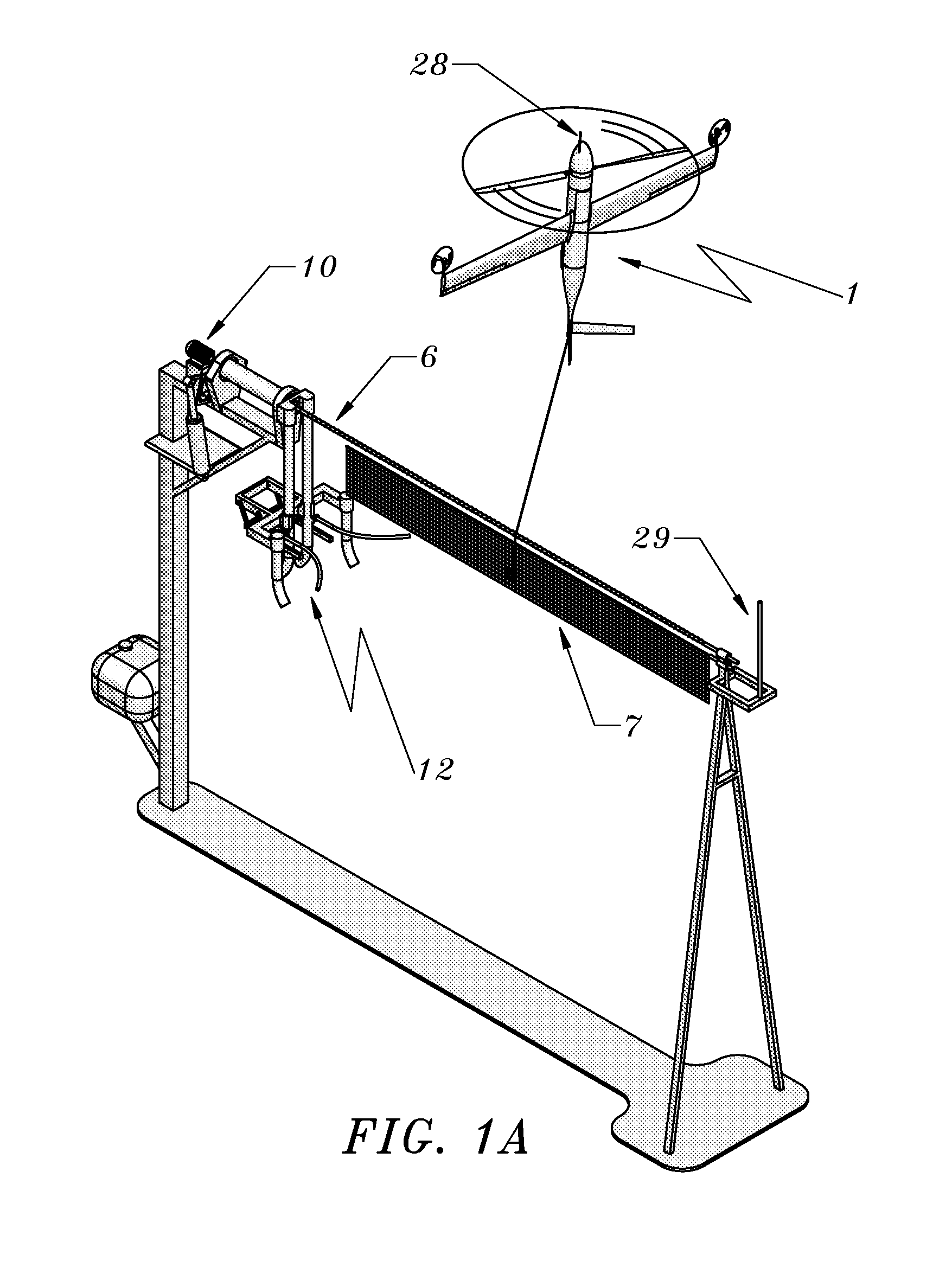
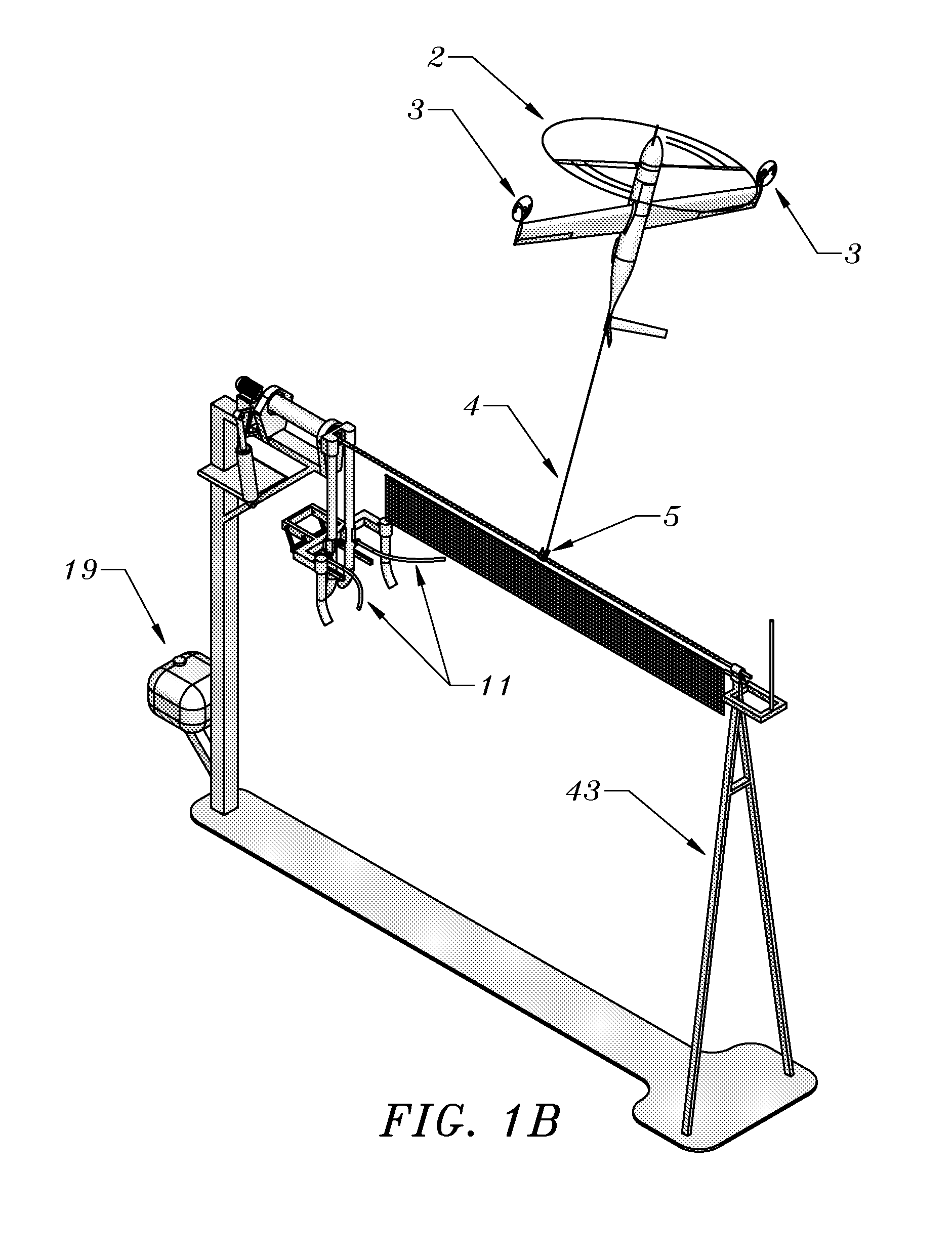
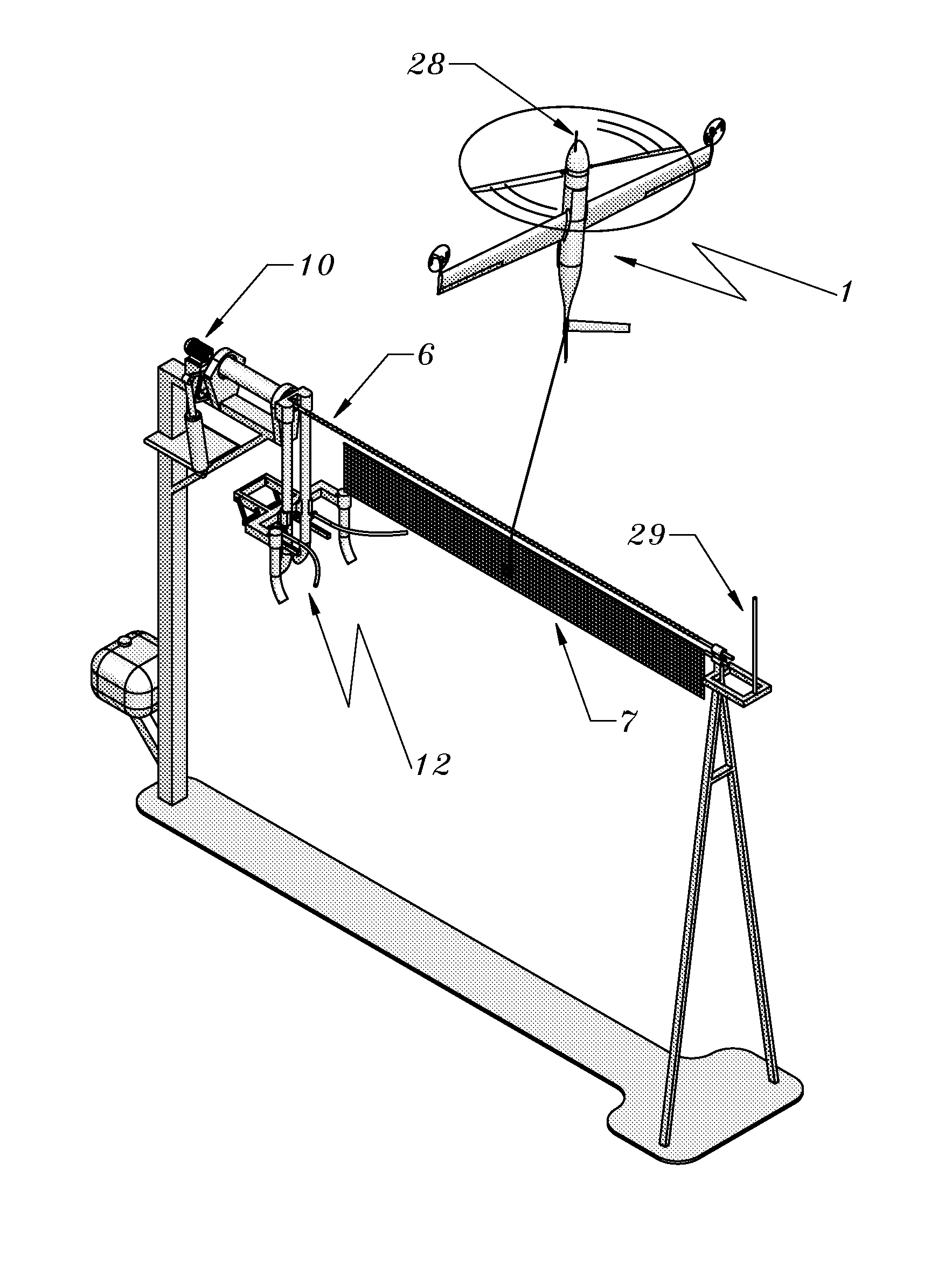
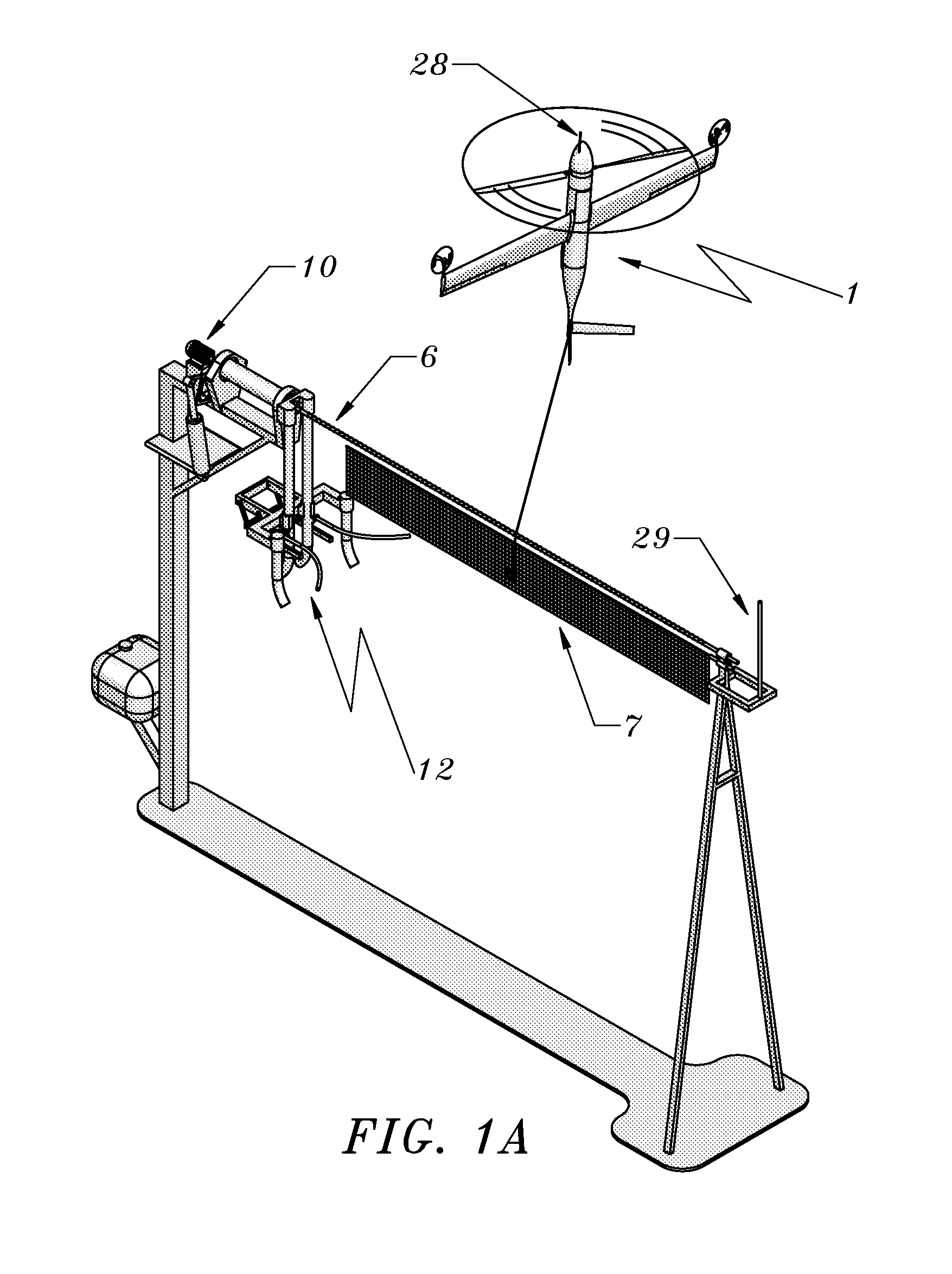
Rail recovery system for aircraft
The present invention's side-arm recovery system enables large Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UASs) to operate from small vessels or from ground sites with a minimal footprint. The side-arm recovery system allows arresting an UAS independent of a runway. On the ground or on a ship, the system makes use of a specialized crane system that includes capture and energy absorption devices. A fuselage-mounted top hook snags a horizontal cable and the arresting forces act in the plane of symmetry through the central structure of the UAS. After the capture energy is absorbed, the recovery system safely lowers the aerial vehicle to a ground handling cart. The same system can be combined into a launcher and retriever system which further reduces the footprint by eliminating the need for a separate launcher.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
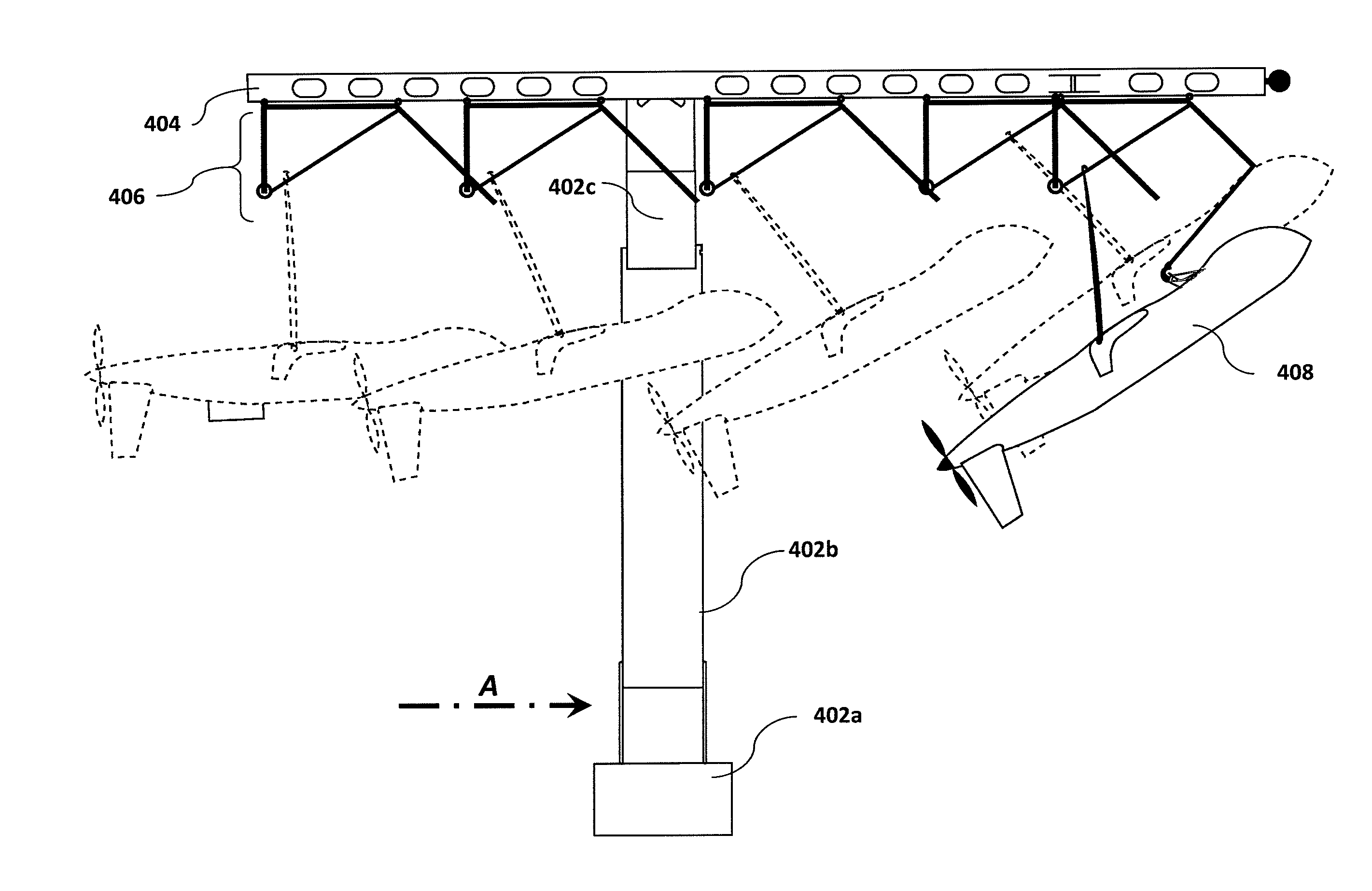
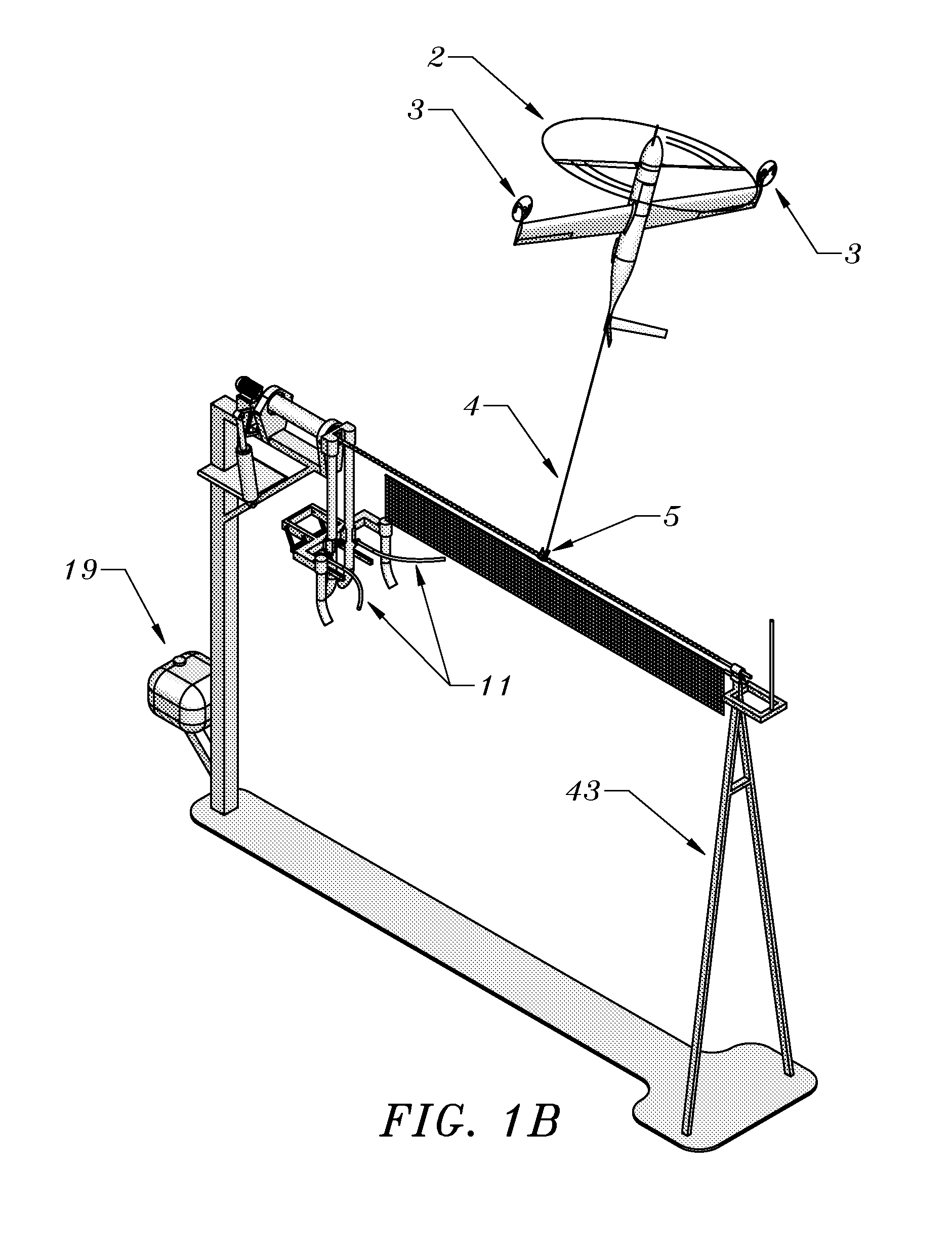
Method and apparatus for automated launch, retrieval, and servicing of a hovering aircraft
An aircraft capable of thrust-borne flight can be automatically retrieved, serviced, and launched using equipment suitable for use on a small vessel, or at a base with similarly limited space or irregular motion. For retrieval, the aircraft drops a tether, and pulls the tether at low relative speed into contact with a horizontal guide. The tether is pulled across the guide until the guide is captured by a hook or other end effector. The tether length is then adjusted as necessary, and the aircraft swings on the guide to hang in an inverted position. Translation of the tether along the guide then brings the aircraft to a docking carriage, in which the aircraft parks for servicing. For launch the carriage is swung upright, the end effector is released from the guide, and the aircraft thrusts into free flight. A full ground-handling cycle can thus be accomplished automatically with simple and economical apparatus. It can be used with low risk of damage, and requires only moderate accuracy in manual or automatic flight control.
Owner:AEROVEL CORP
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
InactiveUS7018388B2Minimizing restenosisMinimizing thrombosisDiagnosticsStaplesCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Anastomotic stents for connecting a graft vessel to a target vessel, and methods of use thereof. The anastomotic stents of the invention are suitable for use in a variety of anastomosis procedures, including coronary artery bypass grafting. One embodiment of the invention comprises a large vessel anastomotic stent for use with large diameter target vessels such as the aorta or its major side branches. Another embodiment of the invention comprises a small vessel anastomotic stent for use on a target vessel which has a small diameter such as a coronary artery. Another aspect of the invention involves applicators for use with the stents of the invention.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Control and electrical connections for electrode endocutter device
Aspects of the present disclosure include an attachable power and control system to supply energy to electrodes of a wiping electrode coagulation system of a surgical device. A surgical device includes electrodes at an end of effector to aide in sealing during various surgical procedures. During the procedure, the surgeon may wipe the surgical site with the end effector, causing the electrodes to touch the fractured area. Electrosurgical energy may be applied to the electrodes during the wiping, causing coagulation of smaller vessels. The attachable power and control system may be configured to slide over the shaft of the surgical device. The power and control system also may be configured to supply power to the electrodes and to control when energy is applied to the electrodes, based in part, for example, on measuring a distance or angle of the opening of the jaws at the end effector.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Method and apparatus for automated launch, retrieval, and servicing of a hovering aircraft
ActiveUS8955800B2Avoid problemsEconomical and simpleArresting gearLaunching/towing gearJet aeroplaneAirplane
Owner:AEROVEL CORP
Method and system for attaching a graft to a blood vessel
InactiveUS7041110B2Prevent movementMinimizing restenosisStaplesNailsCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Owner:AESCULAP AG
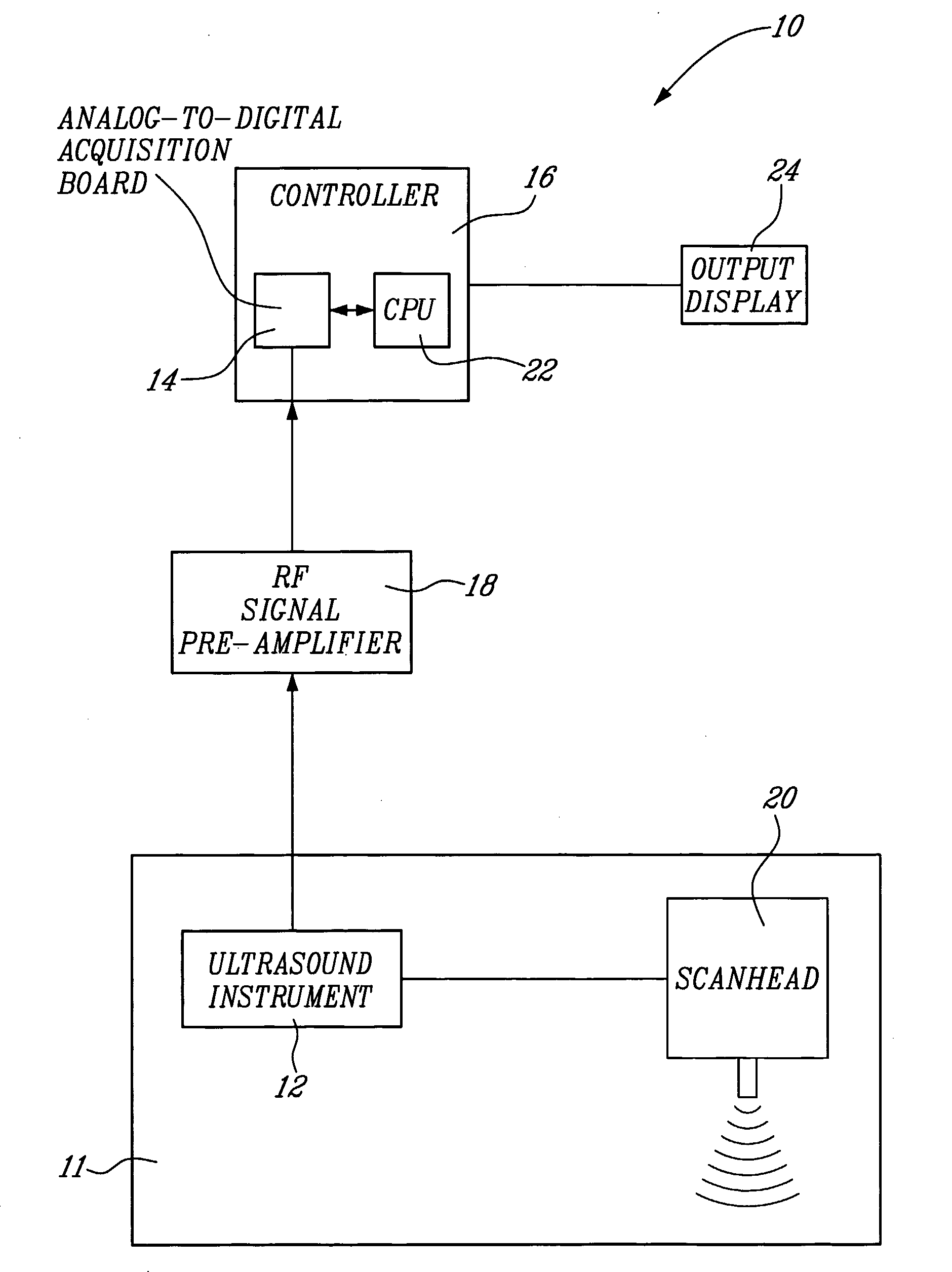
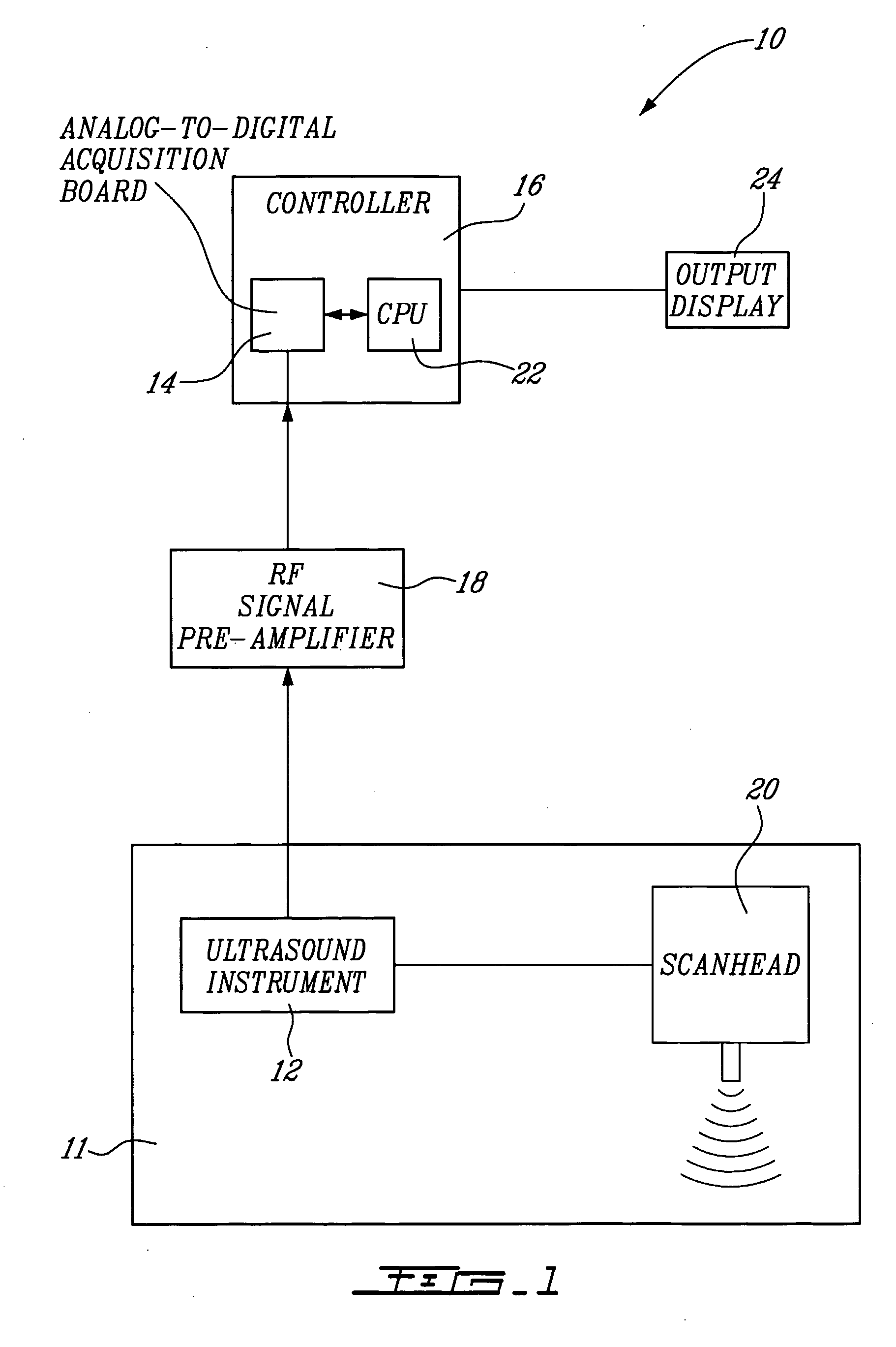
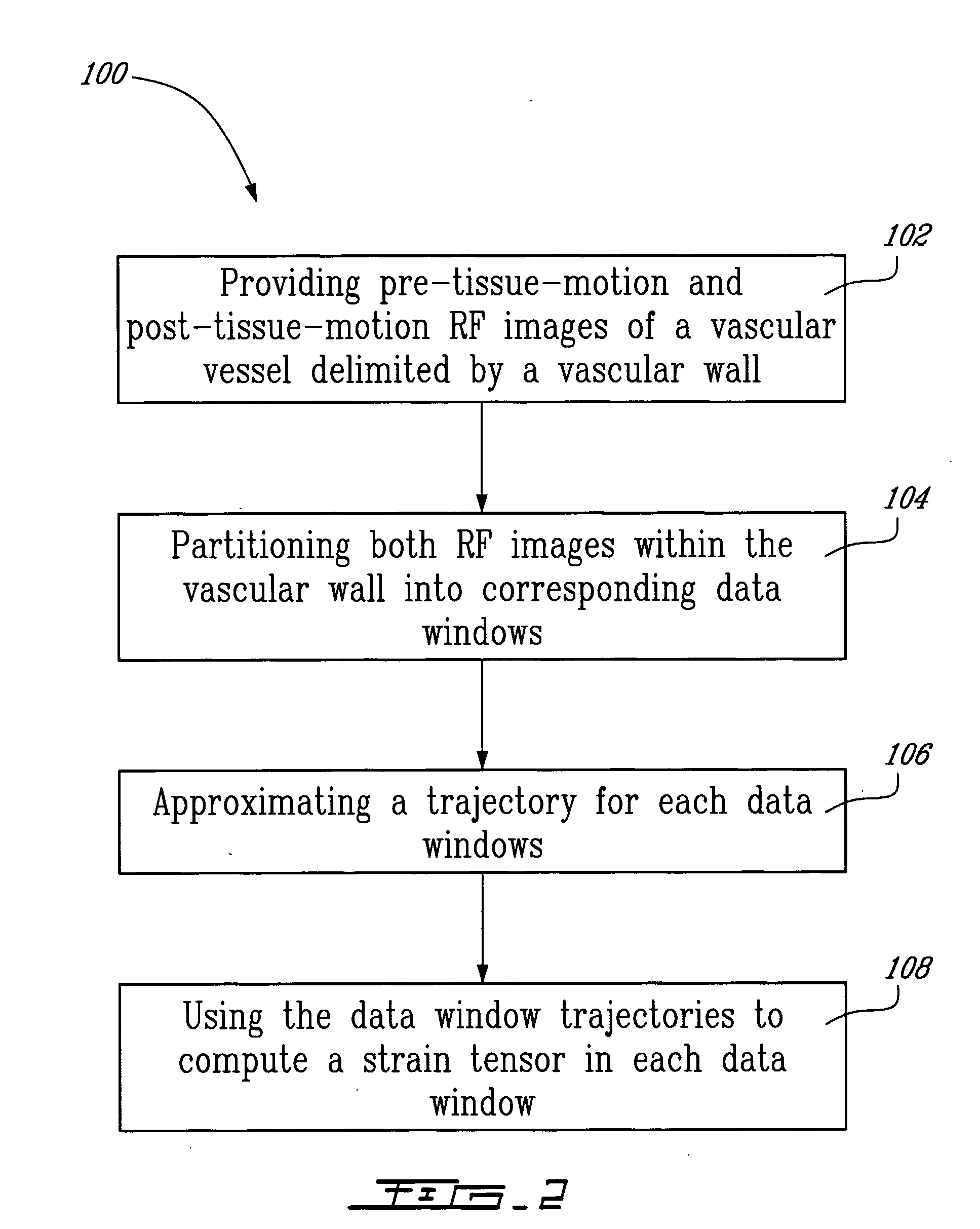
Method And System For Vascular Elastography
The method for vascular elastography comprises: i) obtaining a sequence of radio-frequency (RF) images including pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images in digital form of a vessel delimited by a vascular wall; the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images being representative of first and second time-delayed configuration, of the whole vessel; ii) partitioning both the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images within the vascular wall into corresponding data windows; approximating a trajectory between the pre- and post-tissue-motion for corresponding data windows; and using the trajectory for each data window to compute the full strain tensor in each data window, which allow determining the Von Mises coefficient. The method can be adapted for non-invasive vascular elastography (NIVE), for non-invasive vascular micro-elastography (MicroNIVE) on small vessels, and for endovascular elastography (EVE).
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
Endovascular medical device with plurality of wires
InactiveUS20060100602A1Influence is negligiblePrecise maintenanceGuide wiresOcculdersProsthesisIntravascular device
An endovascular device (1, 100, 200, 300) having a distal end (2), a proximal end (4) and a body portion (3) therebetween. The body portion is made of a multiple filament helically wound row (A) of wires (5), provided with a sealing coating (14) on the inside surface or the outside surface or both. The device may be a catheter (1), a sheath, an introducer, a delivery device, a pusher (100), an embolization coil delivery device (300), or a receptacle (208) for an expandable prosthesis (220) used with a delivery device (200). From 2 to 12, and preferably from 4 to 8, wires (5) are used in the row, and fewer wires may be used proceeding toward the distal end (2) for greater flexibility. The helically wound row of wires transmits torque and provides pushability to the device while resisting kinking, and enables a small outside diameter for reaching very small vessels and extending through very tortuous vessels.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Rear seat and support for watercraft
An improved seat design for a small watercraft increases the ability of a rider on the watercraft to monitor activities taking place behind the watercraft. The watercraft includes a contoured rear seat that is wider than the front seat. The wider surface area provides riders with the ability to quickly turn and look behind the watercraft. The rear seat also includes several handles or grips to provide added stability to a watercraft rider.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Miniature flexible thrombectomy catheter
ActiveUS20080188831A1Maximize thrombectomy actionGood effectGuide wiresFluid jet surgical cuttersDistal portionGuide tube
The present invention pertains to a miniature flexible thrombectomy catheter having one or more flexible miniature noncollapsing tubular portions including pushable and torqueable structure for introduction into the smaller vessels in neurovascular regions. A jet body having an arcuate fluid jet emanator is incorporated in order to minimize size at the distal portion of a minimally sized catheter tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
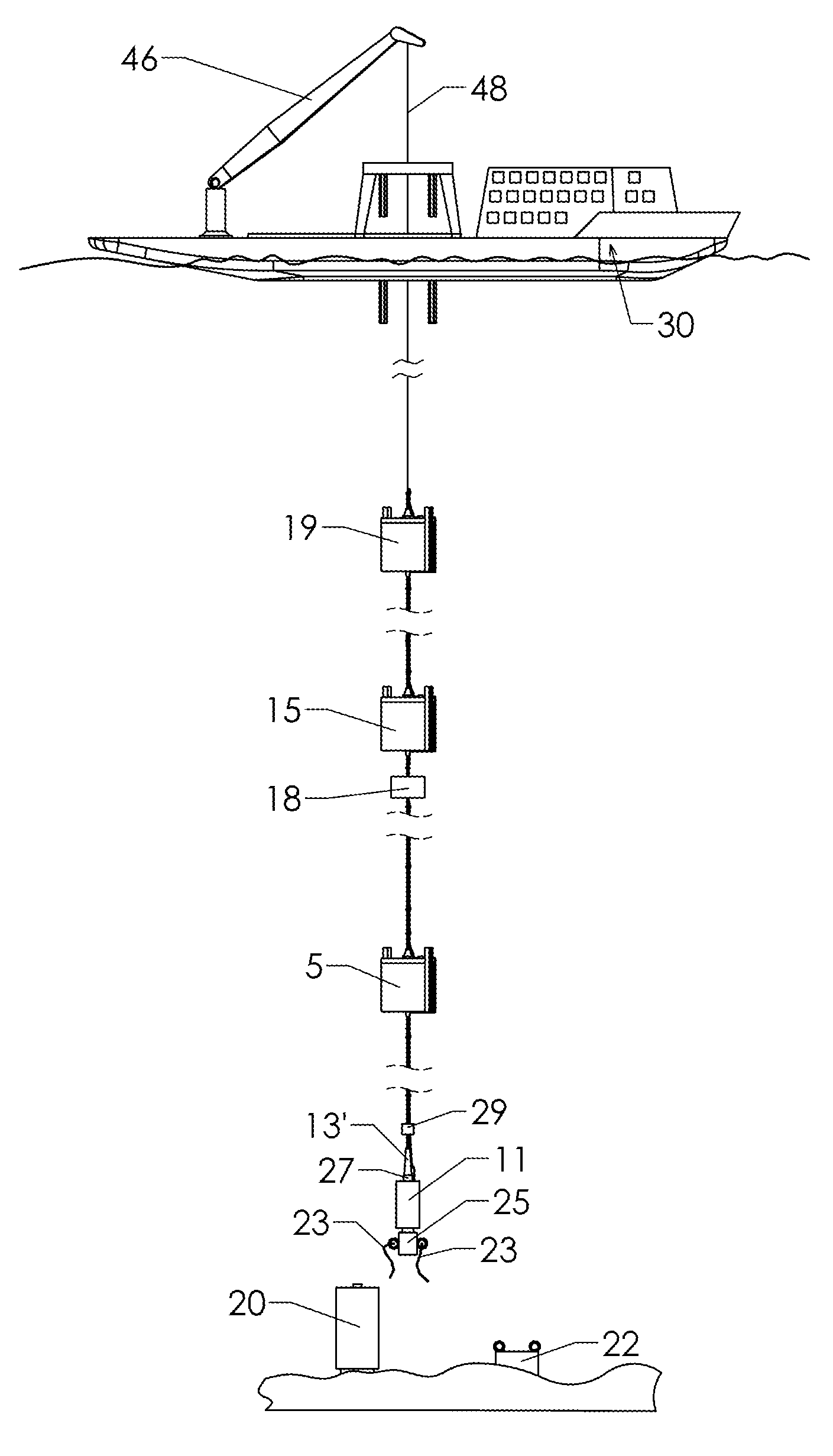
Riser technology
InactiveUS20110011320A1Low costDrilling rodsWell/borehole valve arrangementsSystems designWater flow
The present invention is directed to novel methods and apparatus for the design, installation, use, recovery, and reuse of a Self Supporting Riser (SSR) for wells that are not under a platform. The SSR of the present invention uses standardized joints that can be recovered, potentially warehoused, and recombined in different configurations for different purposes or locations. Emphasis is on methods and apparatus that use relatively small vessels subject to high motions in the installation, use and recovery of the SSR. The SSR is adapted for high current and / or deep water applications for purposes of downhole well intervention and subsea equipment installation. In contrast to the apparatus and processes of the prior art, this invention addresses a comprehensive system design.
Owner:MY TECH L LC
Container for a vial or ampoule
InactiveUS6467299B1Lighting and heating apparatusPharmaceutical containersPlastic materialsEngineering
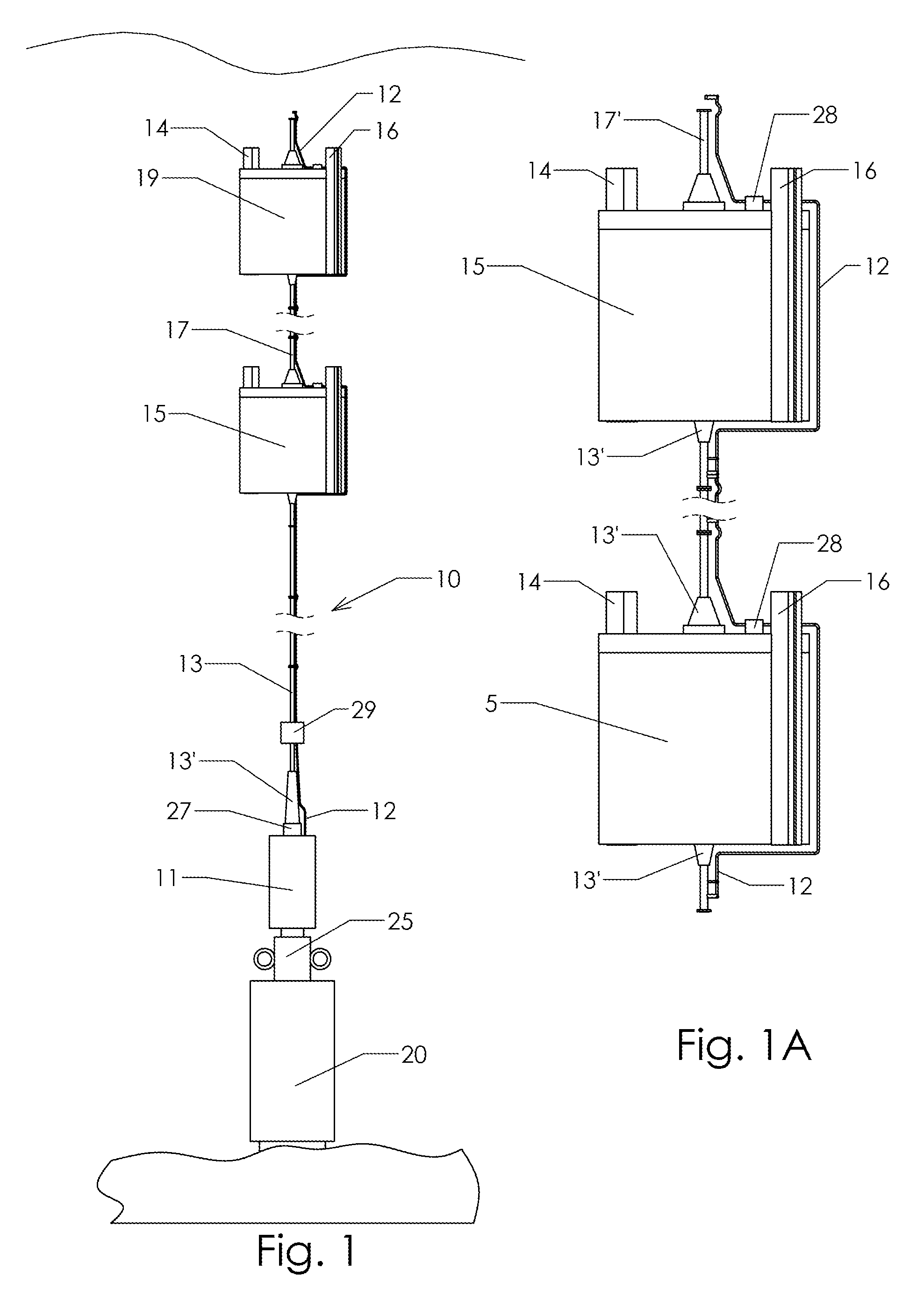
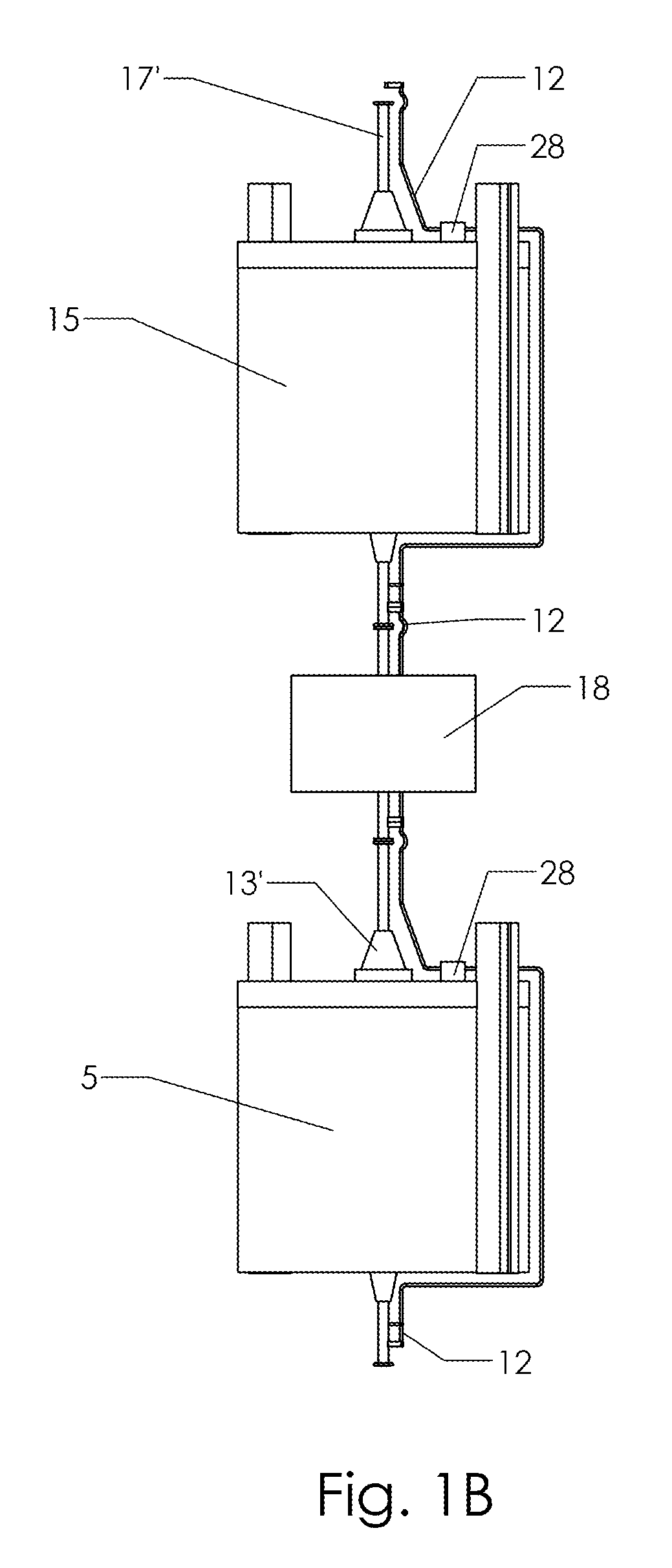
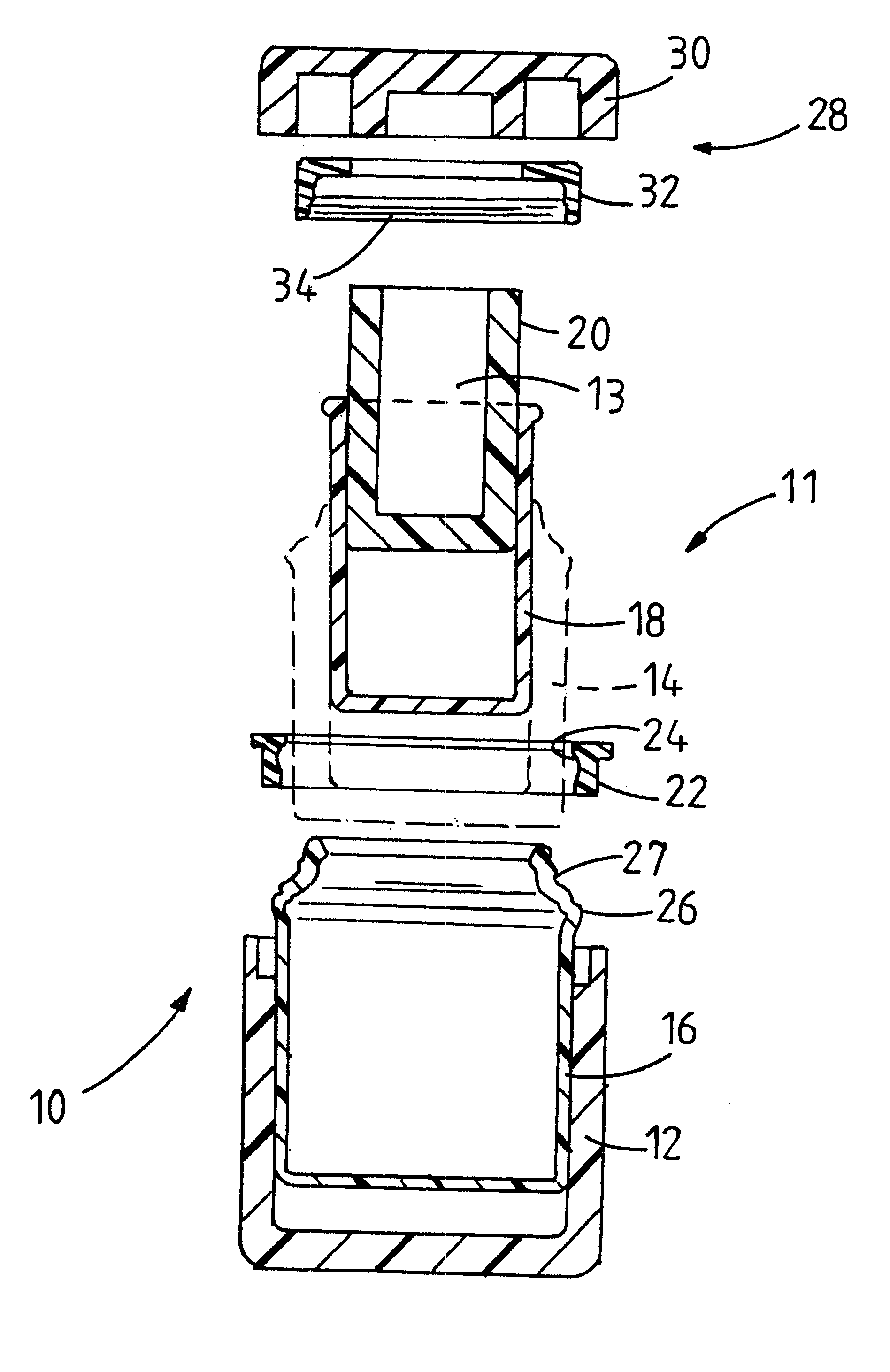
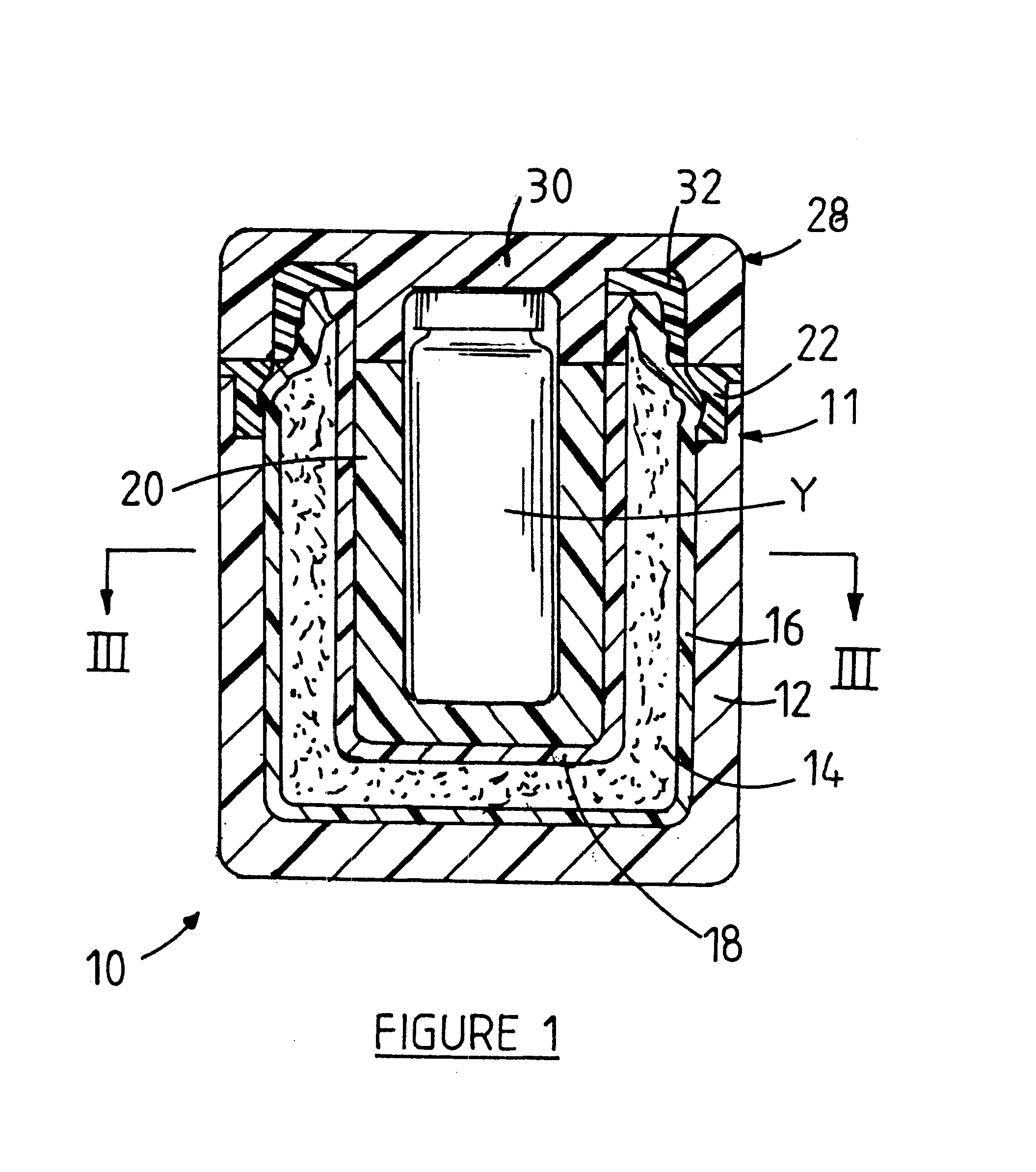
A portable container (10) suitable for housing and protecting vials (Y) ampoules and other small vessels containing pharmaceutical or veterinary preparations such as vaccines, which are sensitive to changes in temperature or to relatively high temperature, is provided. The container (10) comprises a layered wall (11) defining a centrally located cavity (13) for receiving the vial (Y). The wall (11) includes an outer thermally insulating layer (12) surrounding a substance (14) for providing a passive cold source to the cavity (13) and two spaced inner layers (16 and 18) of a relatively hard plastics material providing an annular chamber wherein the substance (14) is received.
Owner:TRIPLE CCC CC
Method and apparatus for automated launch, retrieval, and servicing of a hovering aircraft
ActiveUS20110233329A1Light and portableReduce loadPower plant fuel tanksArresting gearActuatorAirplane
An aircraft capable of thrust-borne flight can be automatically retrieved, serviced, and launched using equipment suitable for use on a small vessel, or at a base with similarly limited space or irregular motion. For retrieval, the aircraft drops a tether, and pulls the tether at low relative speed into contact with a horizontal guide. The tether is pulled across the guide until the guide is captured by a hook or other end effector. The tether length is then adjusted as necessary, and the aircraft swings on the guide to hang in an inverted position. Translation of the tether along the guide then brings the aircraft to a docking carriage, in which the aircraft parks for servicing. For launch the carriage is swung upright, the end effector is released from the guide, and the aircraft thrusts into free flight. A full ground-handling cycle can thus be accomplished automatically with simple and economical apparatus. It can be used with low risk of damage, and requires only moderate accuracy in manual or automatic flight control.
Owner:AEROVEL CORP
Miniature flexible thrombectomy catheter
InactiveUS20080188793A1Efficient and reliable and less-costlyImprove pushabilityCannulasCatheterDistal portionBlood vessel
The present invention pertains to a miniature flexible thrombectomy catheter having one or more flexible miniature noncollapsing tubular portions including pushable and torqueable structure for introduction into the smaller vessels in neurovascular regions. A jet body having an arcuate fluid jet emanator is incorporated in order to minimize size at the distal portion of a minimally sized catheter tube.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Three dimensional construct for the design and fabrication of physiological fluidic networks
ActiveUS8147562B2Increase cell densityIncrease the number ofMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringSmall vessel
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Small watercraft with improved suspension system
InactiveUS6152062AEasy and convenient accessImprove comfortCabin furnitureVessel partsEngineeringWatercraft
An improved cushioning apparatus on a watercraft enhances the comfort of the ride, reduce rider fatigue, and cushion impact forces experienced by the watercraft hull, while allowing for convenient and easy access to various engine components for maintenance and repair of the engine. The cushioning apparatus absorbs at least a portion of any impact force which the rider experienced from the hull, as well as provides at least one degree of movement between the seated rider and the hull in order to cushion such impact forces. The cushioning apparatus may also isolate the rider, at least to some degree, from vibrations experienced by the hull. In one mode, the cushioning apparatus is connected to the watercraft by quick-disconnect fittings, which allow the seat and support frame to be easily moved away from an engine access opening for maintenance of the engine. Furthermore, a quick-access opening is disclosed which allows a rider to access various engine components without requiring that the cushioning apparatus be disconnected from the watercraft. Moreover, the cushioning apparatus increases the convenience and stability of the watercraft for heavier load conditions such as when multiple riders are riding on the watercraft.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com