Patents
Literature
58 results about "Vascular ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
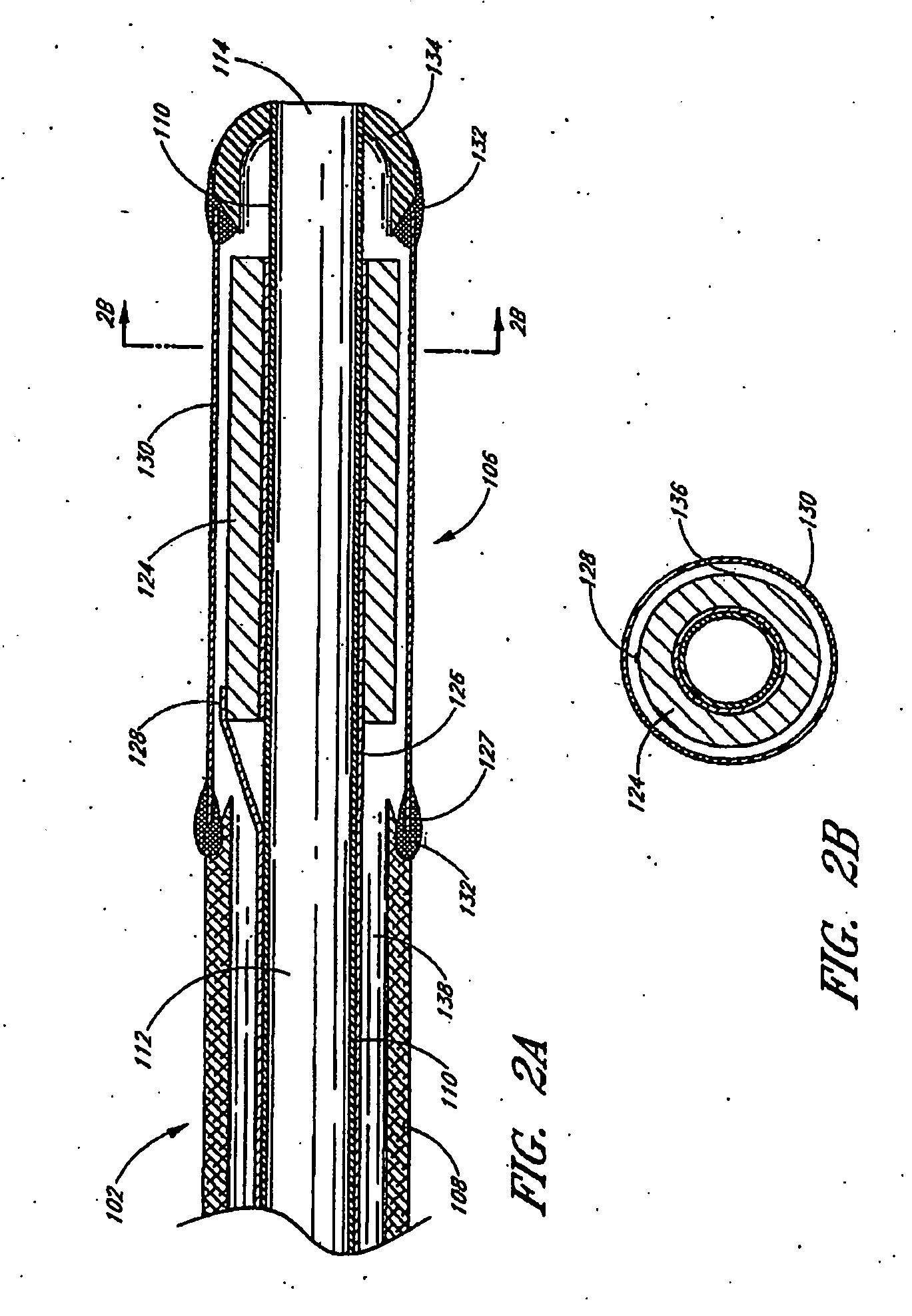
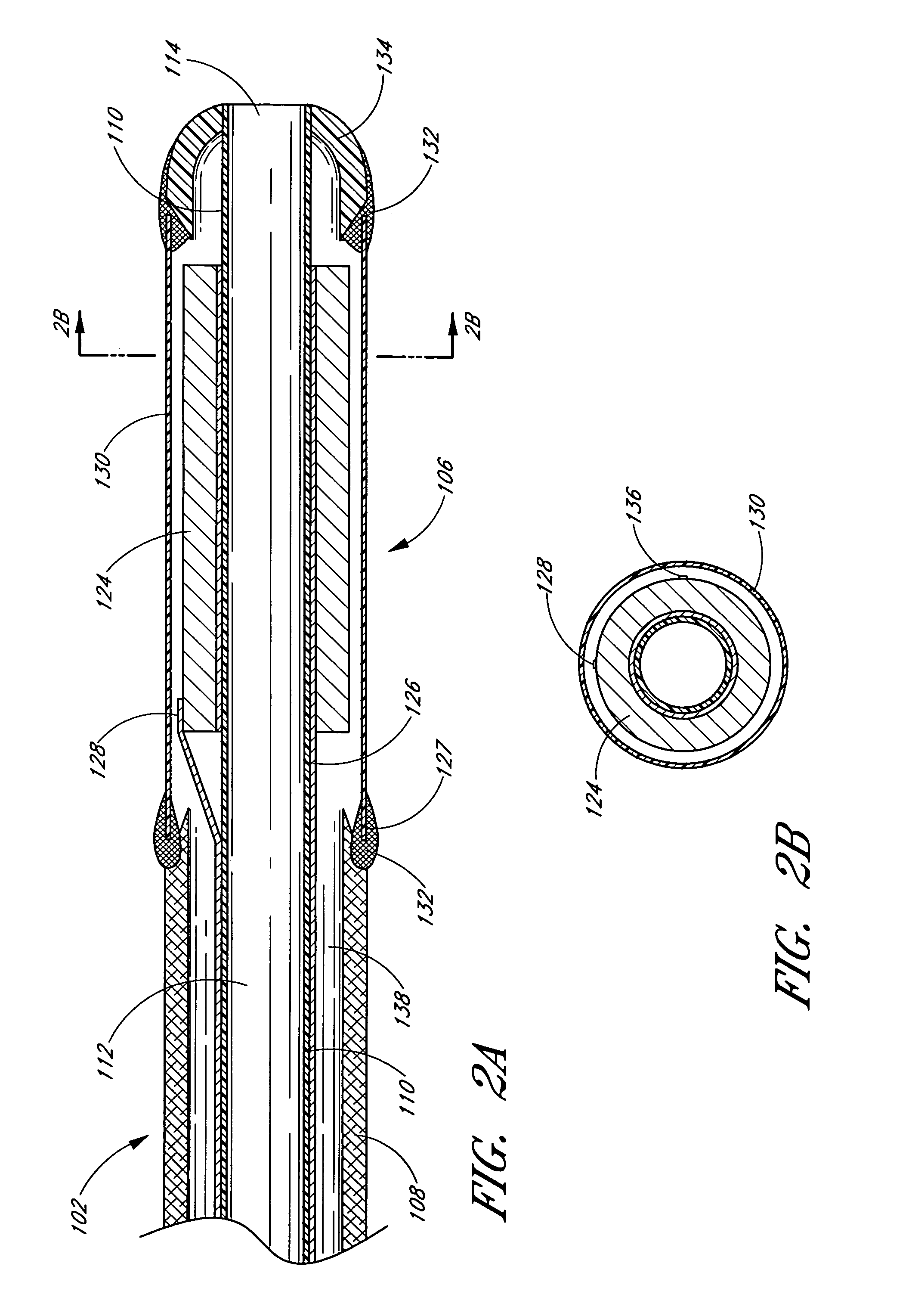
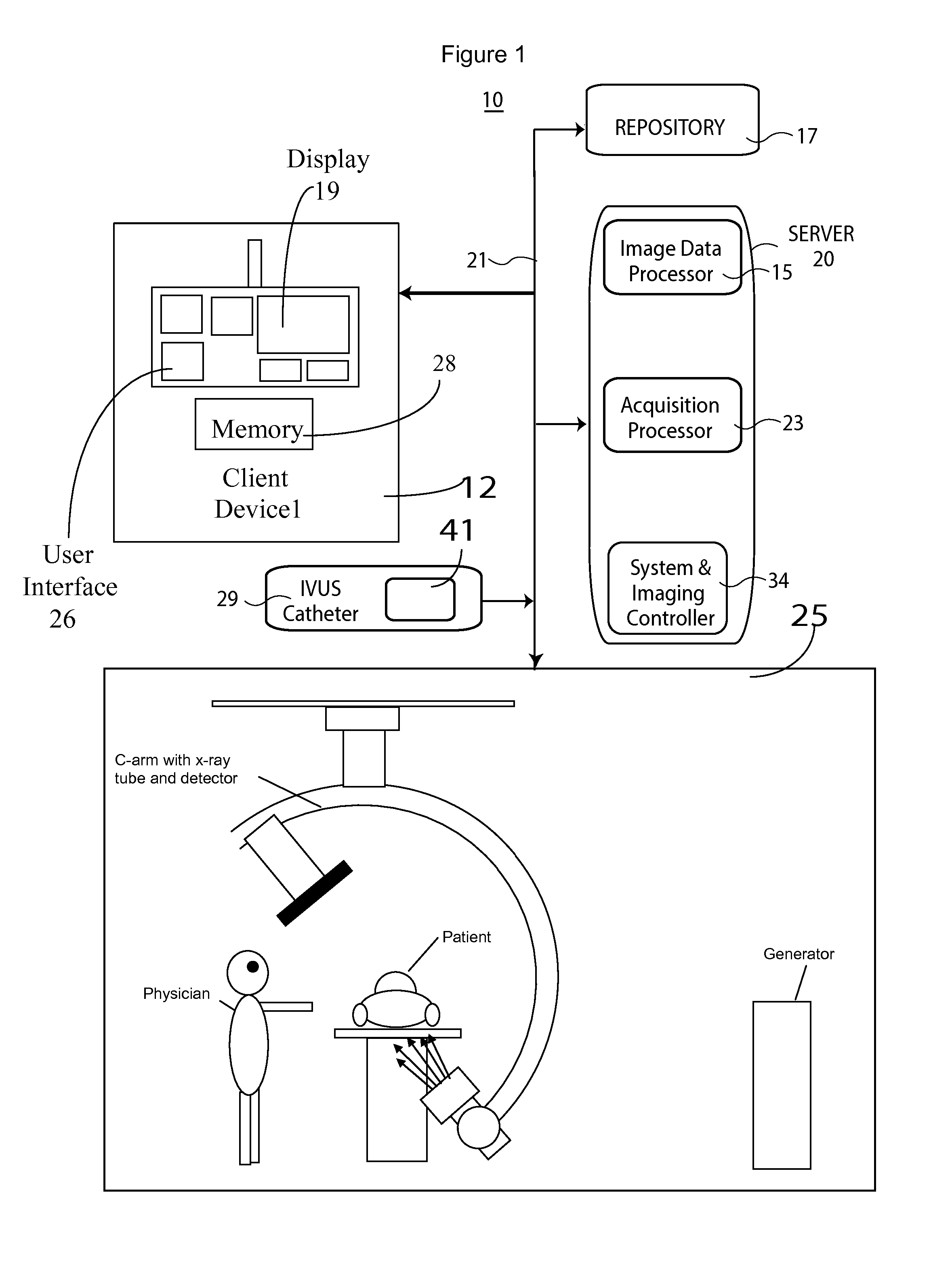
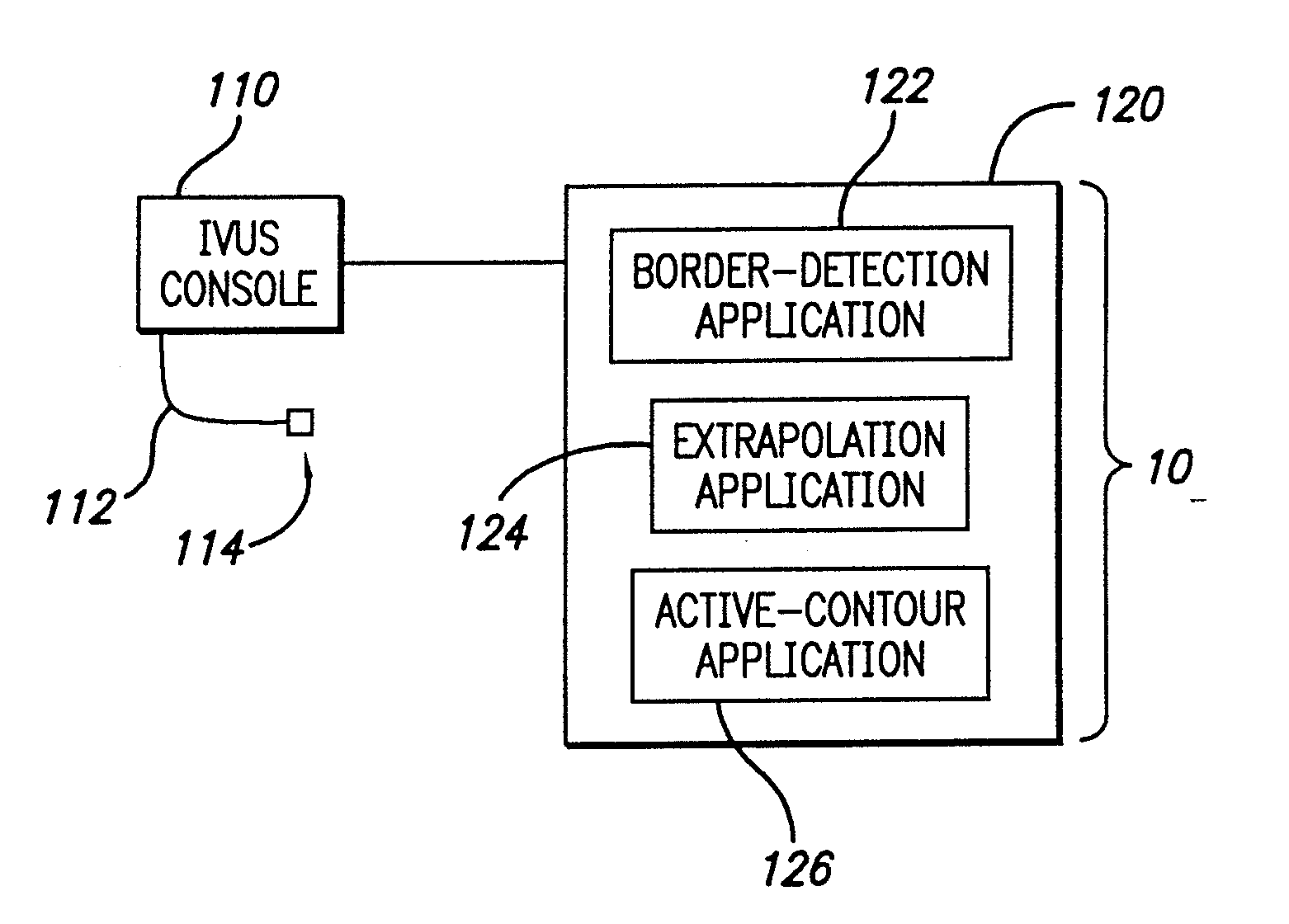
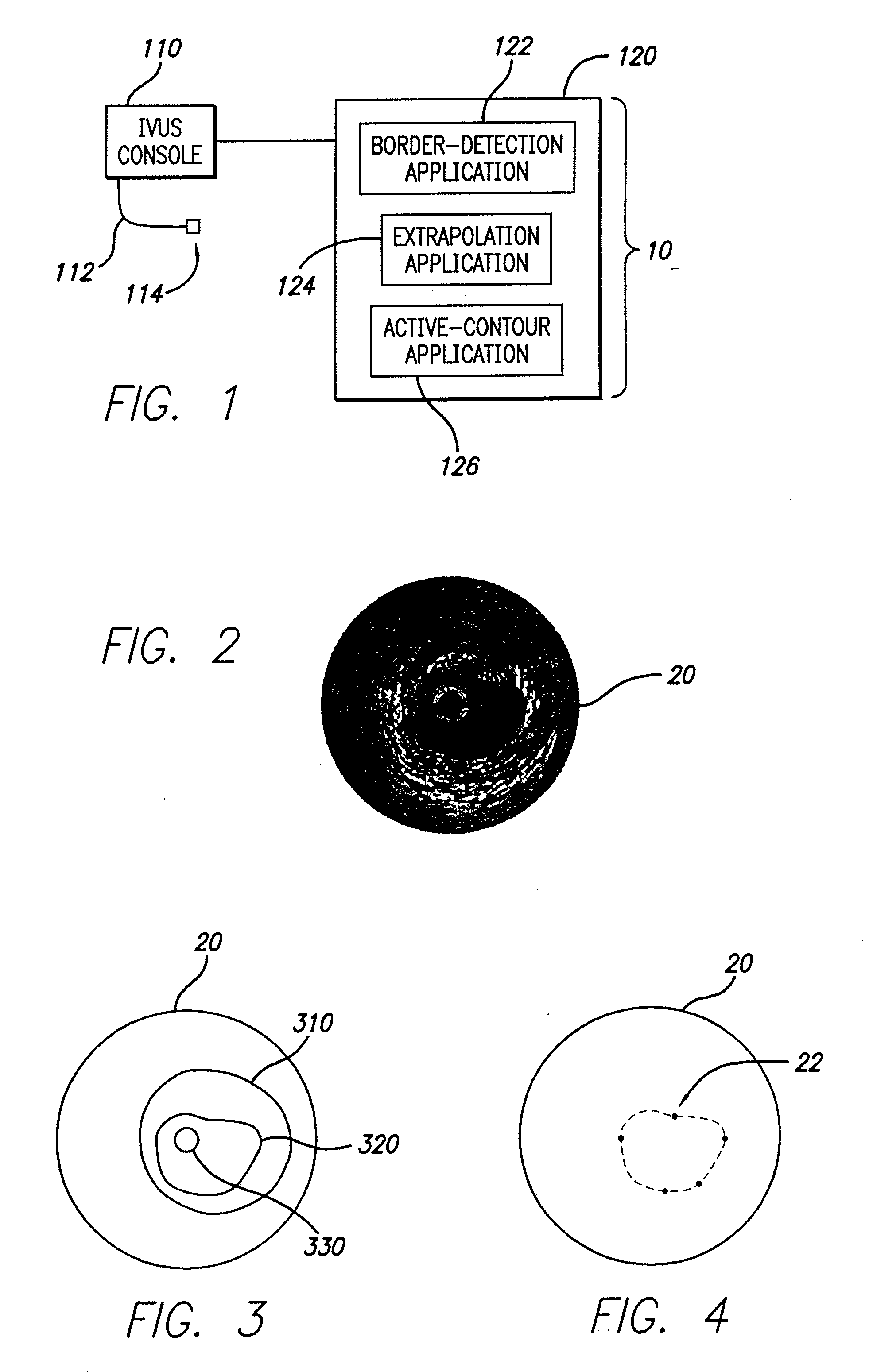
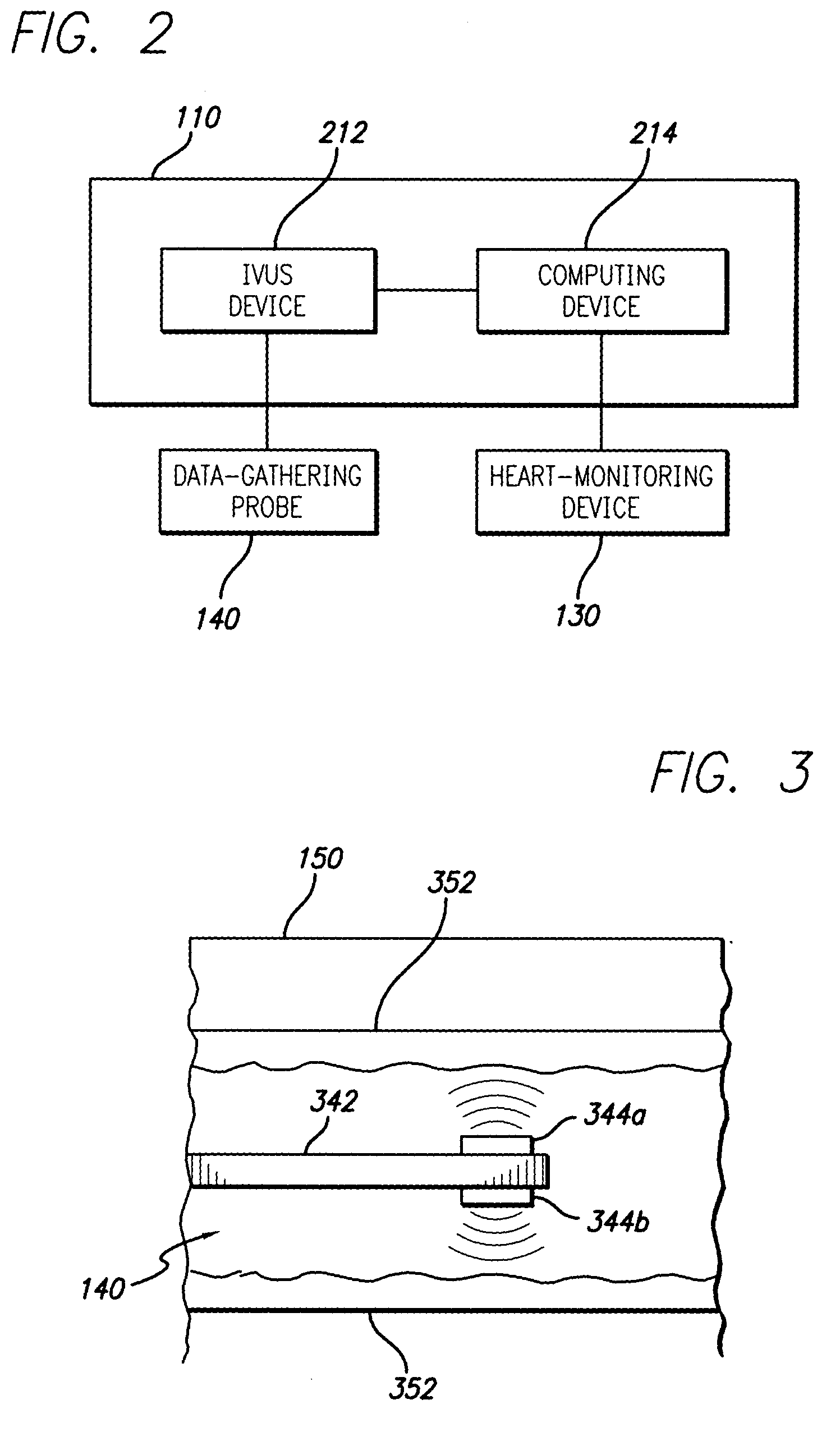
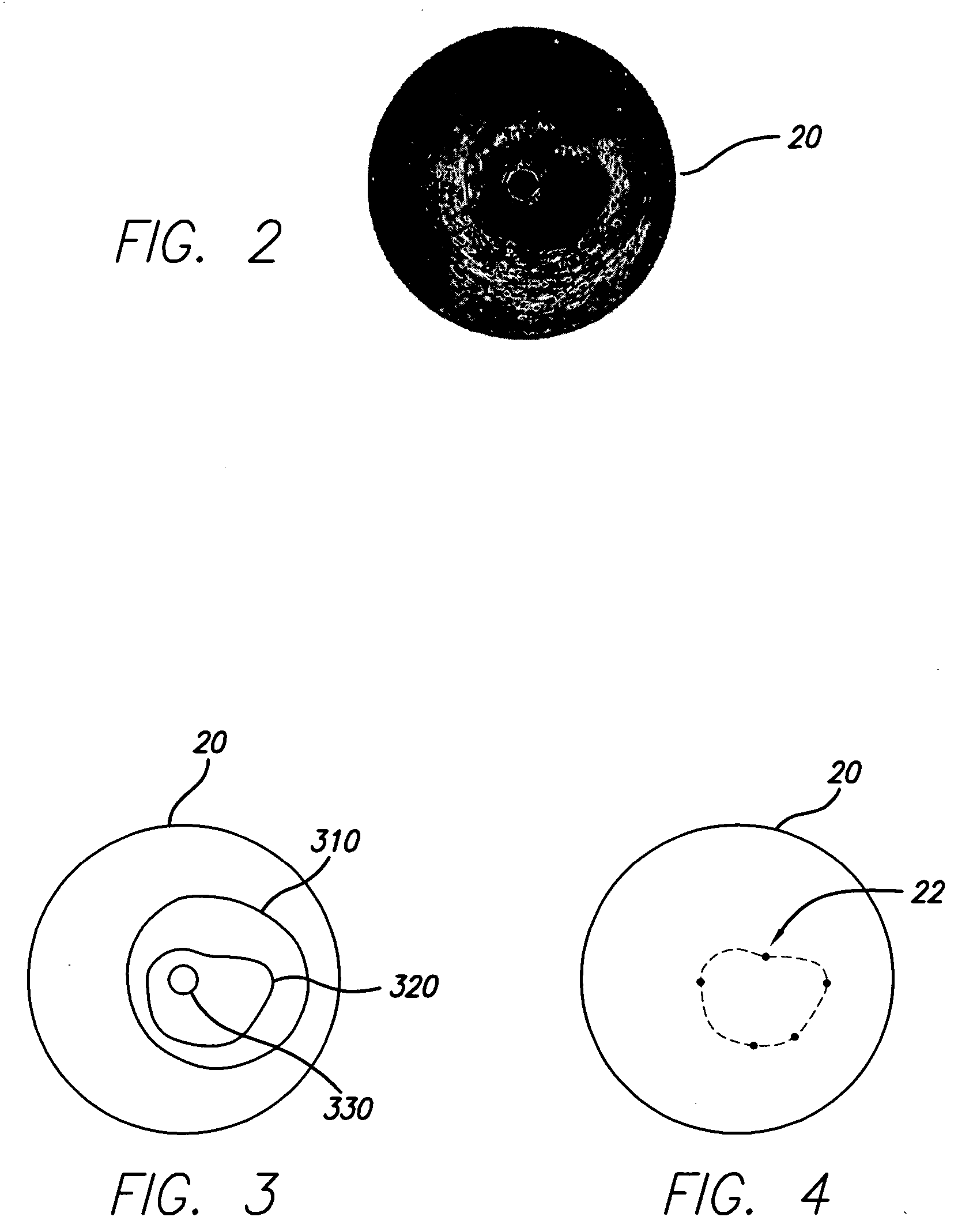
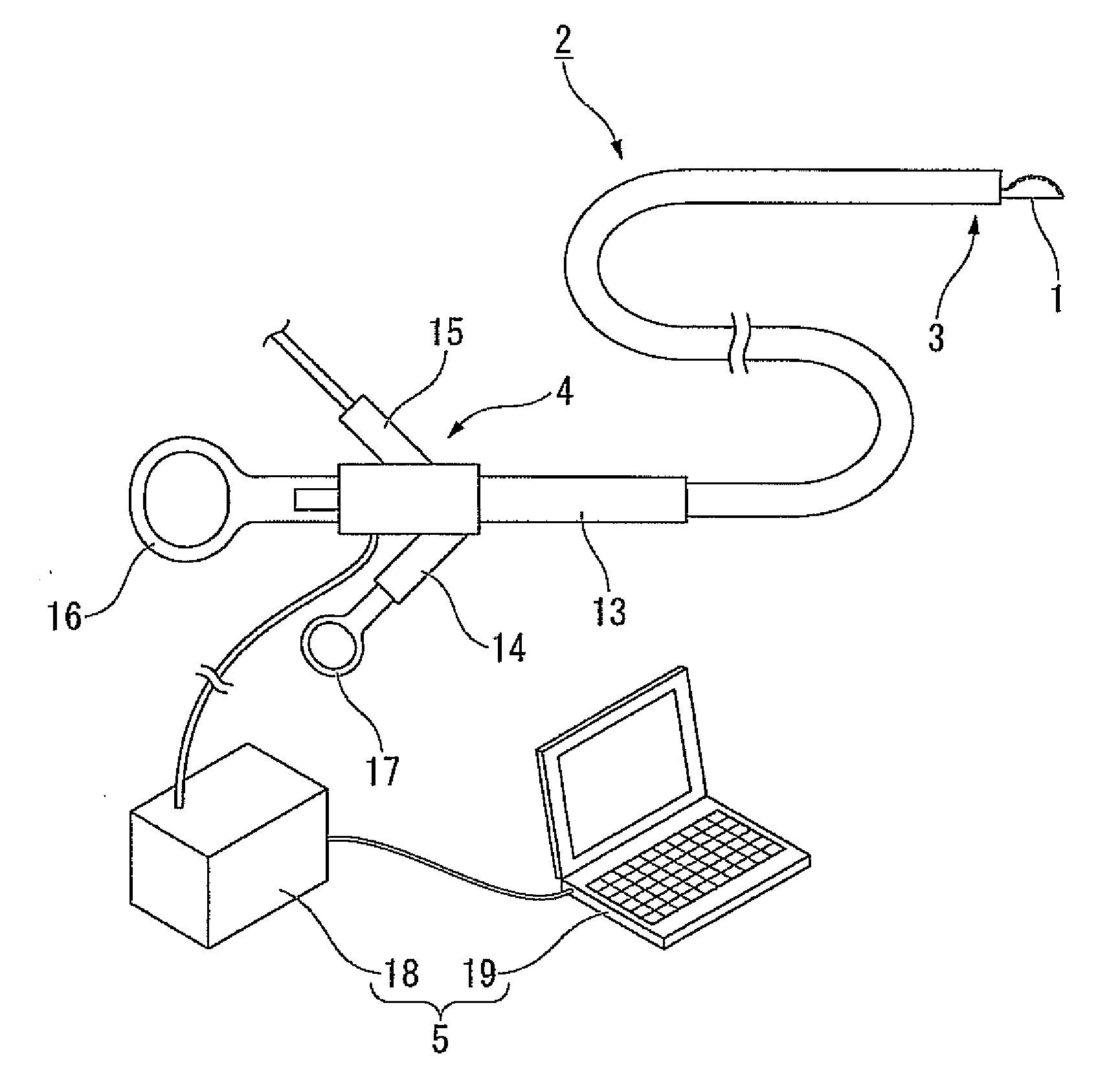
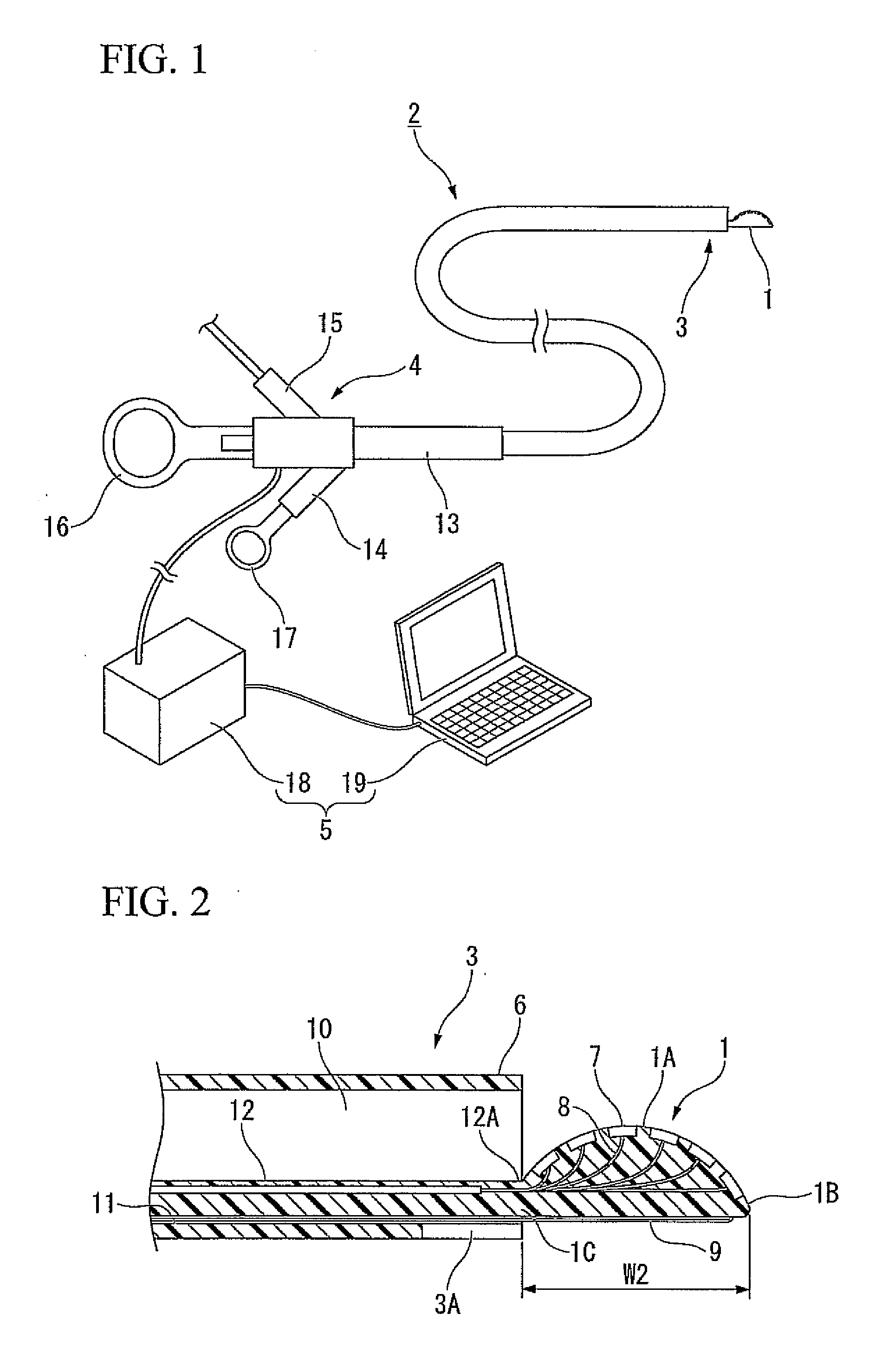
System and method for identifying a vascular border
InactiveUS7359554B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementElectricityVascular ultrasound
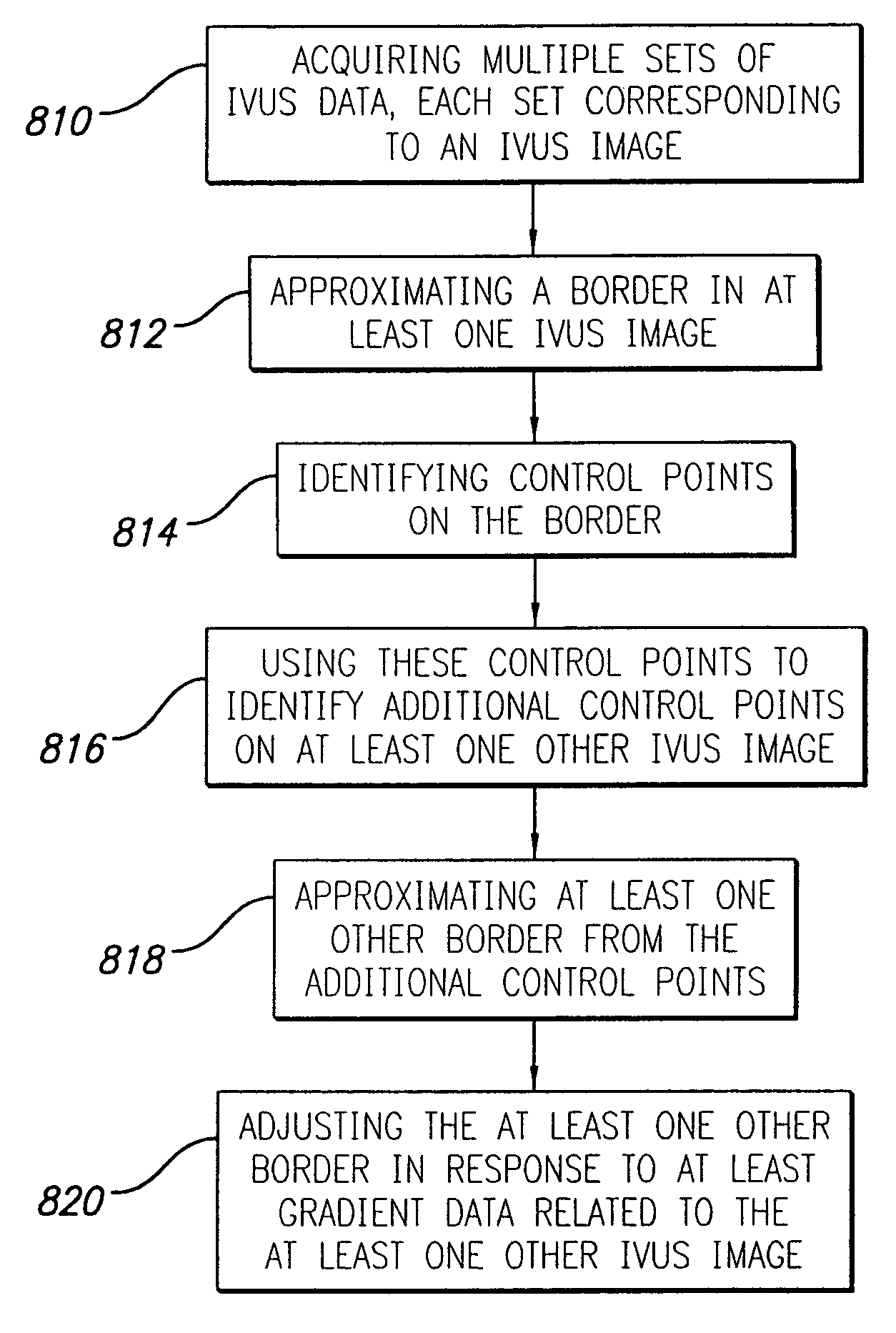
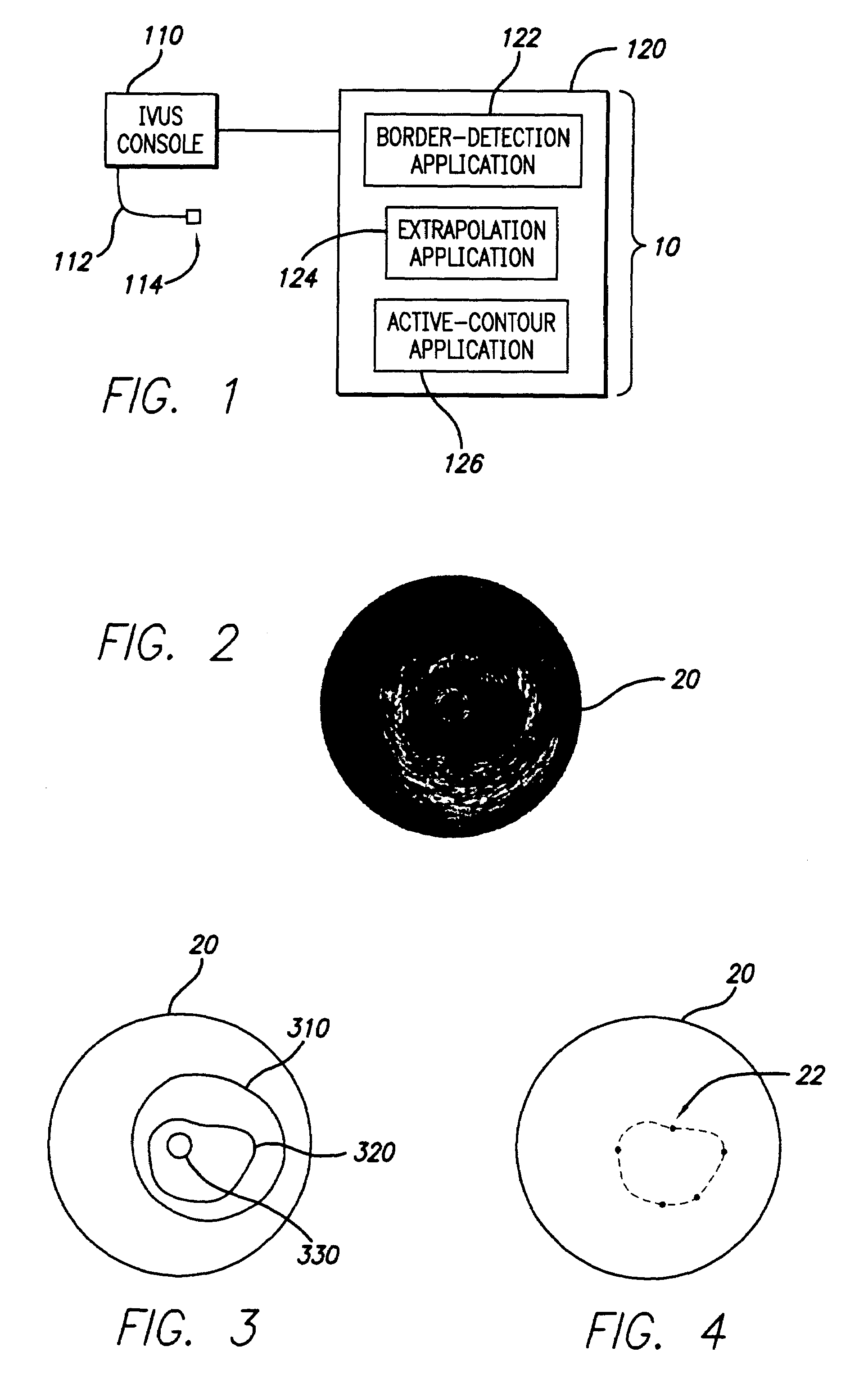
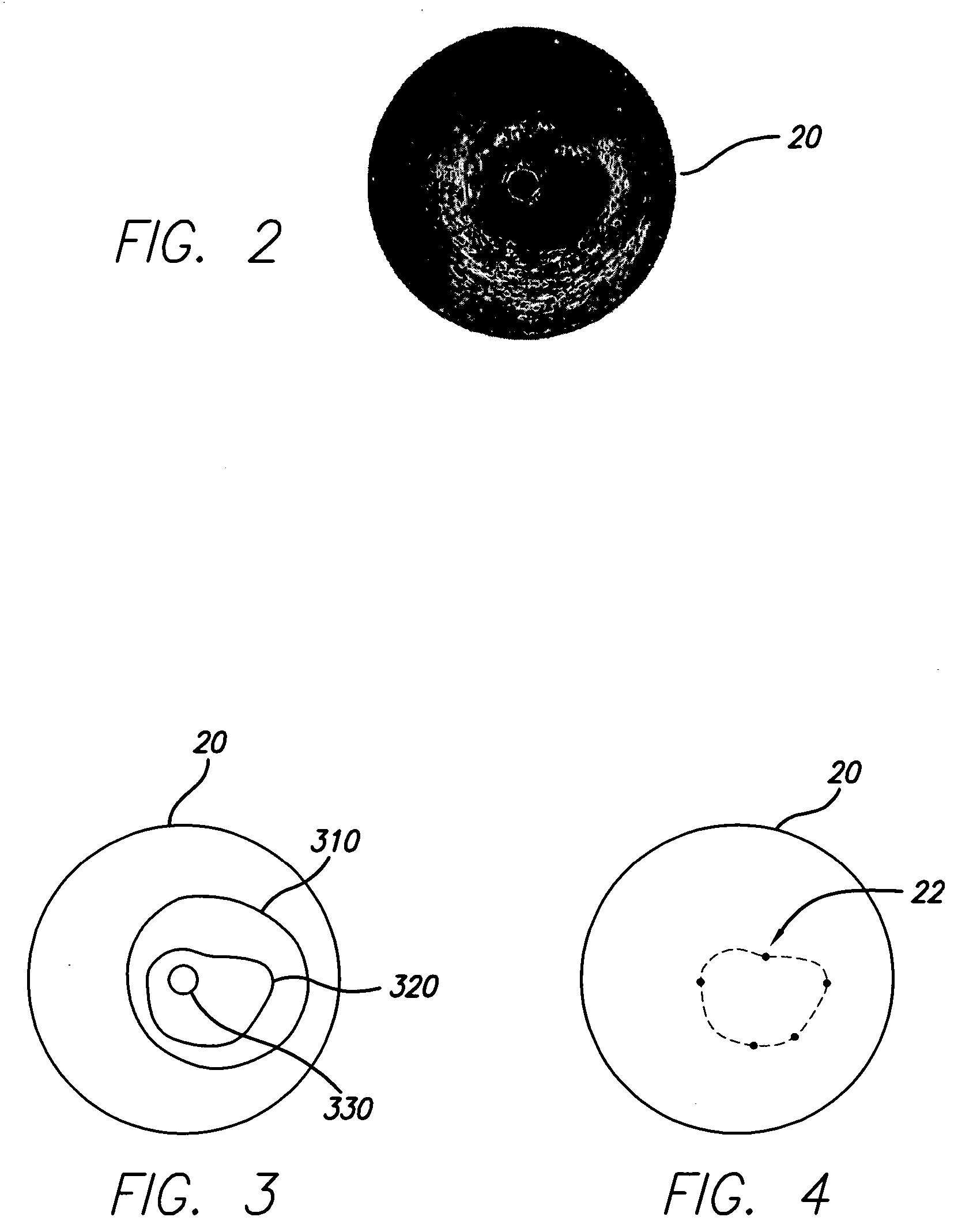
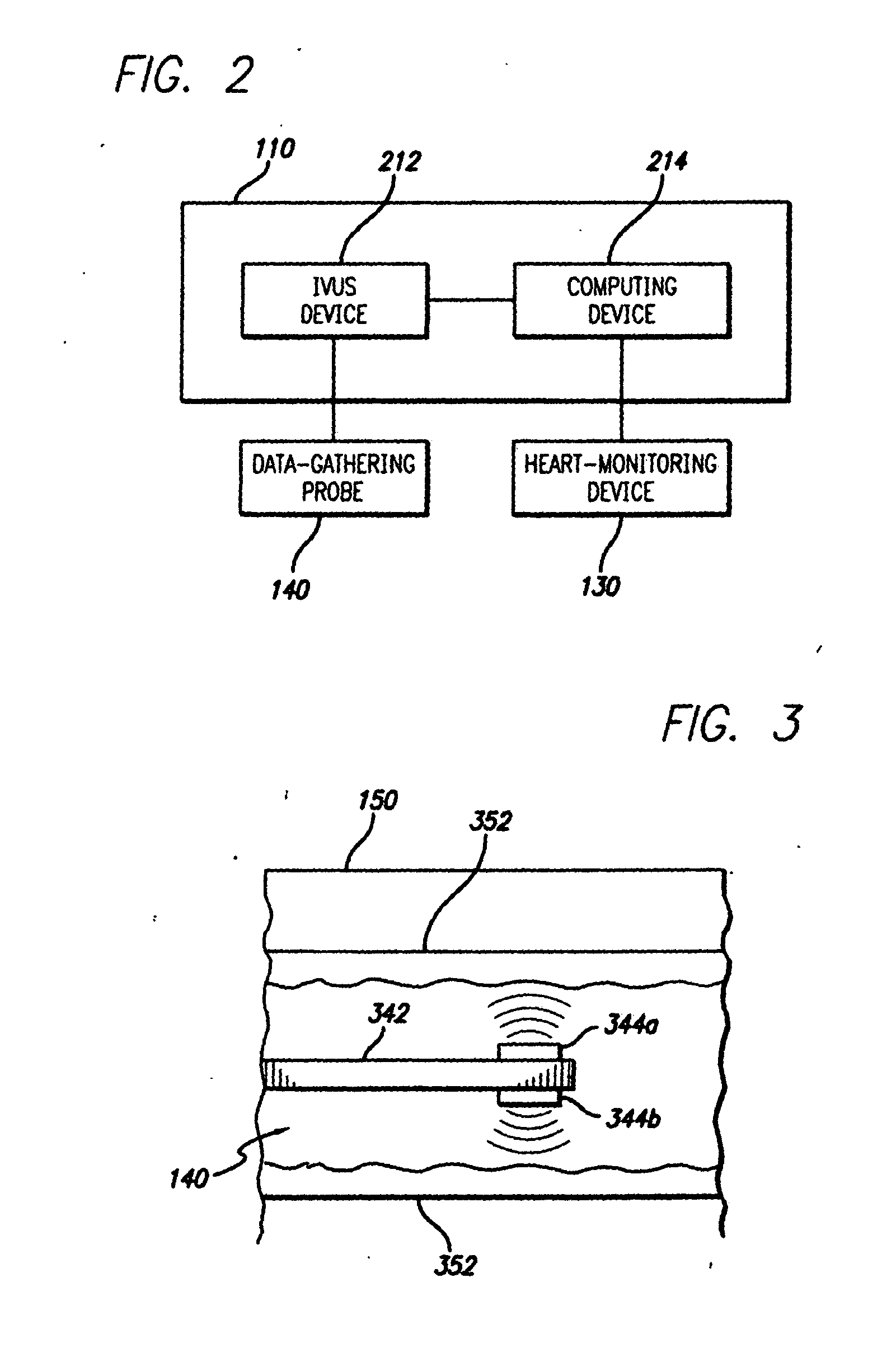
A system and method is provided for using a first vascular image, or more particularly a plurality of control points located thereon, to identify a border on a second vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device electrically connected thereto. Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, an IVUS console is electrically connected to a computing device and adapted to acquire IVUS data. The IVUS data (or multiple sets thereof) is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes a plurality of applications operating thereon—i.e., a border-detection application, an extrapolation application, and an active-contour application. These applications are used to (i) identify a border and control points on a first IVUS image (i.e., any IVUS image), (ii) extrapolate the control points to a second IVUS image (i.e., another IVUS image), (iii) identify a border on the second IVUS image, and (iv) adjust the border on the second IVUS image in accordance with at least one factor. In one embodiment of the present invention, the at least one factor is selected from a group consisting of gradient factor, continuity factor, and curvature factor.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
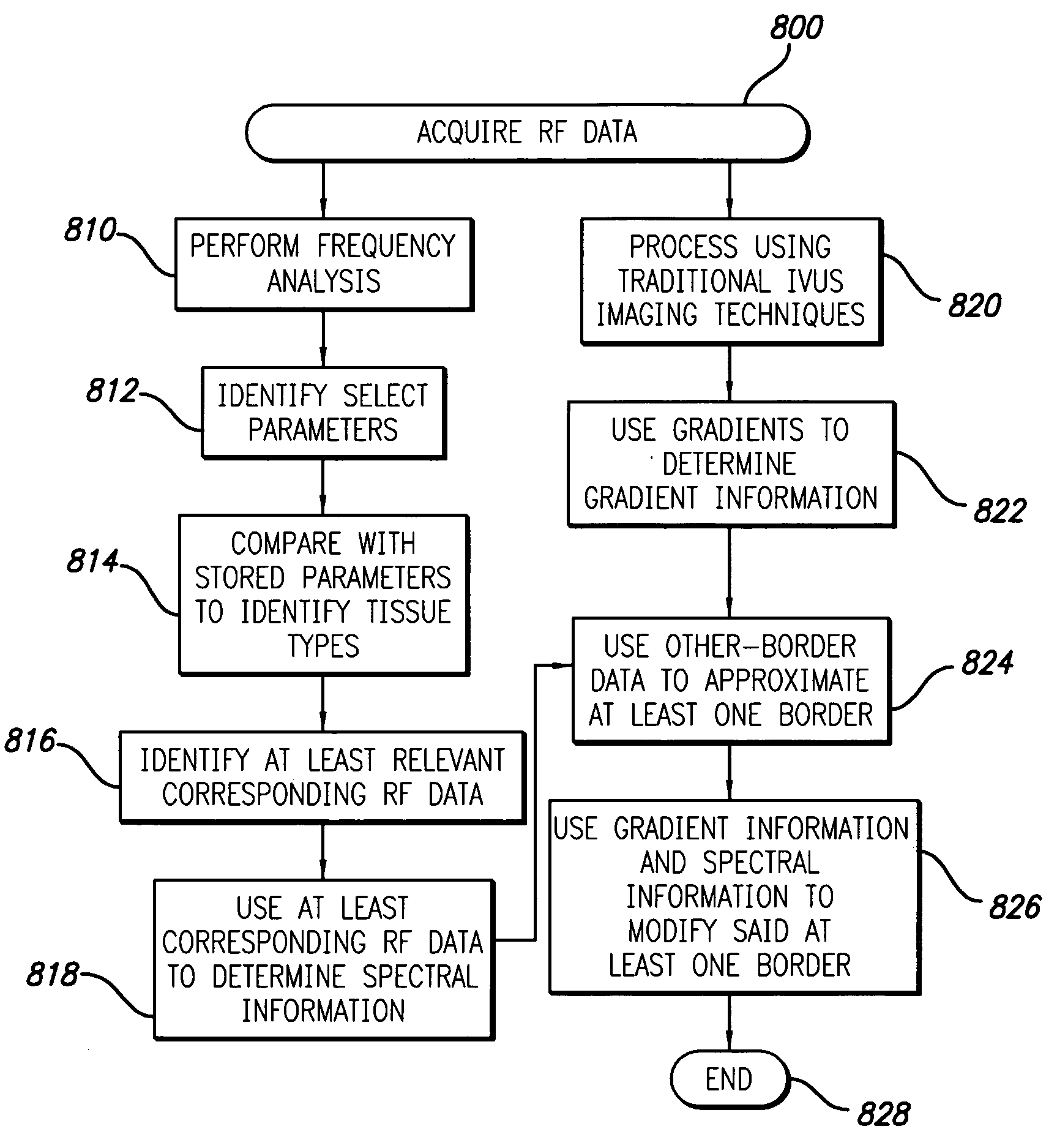
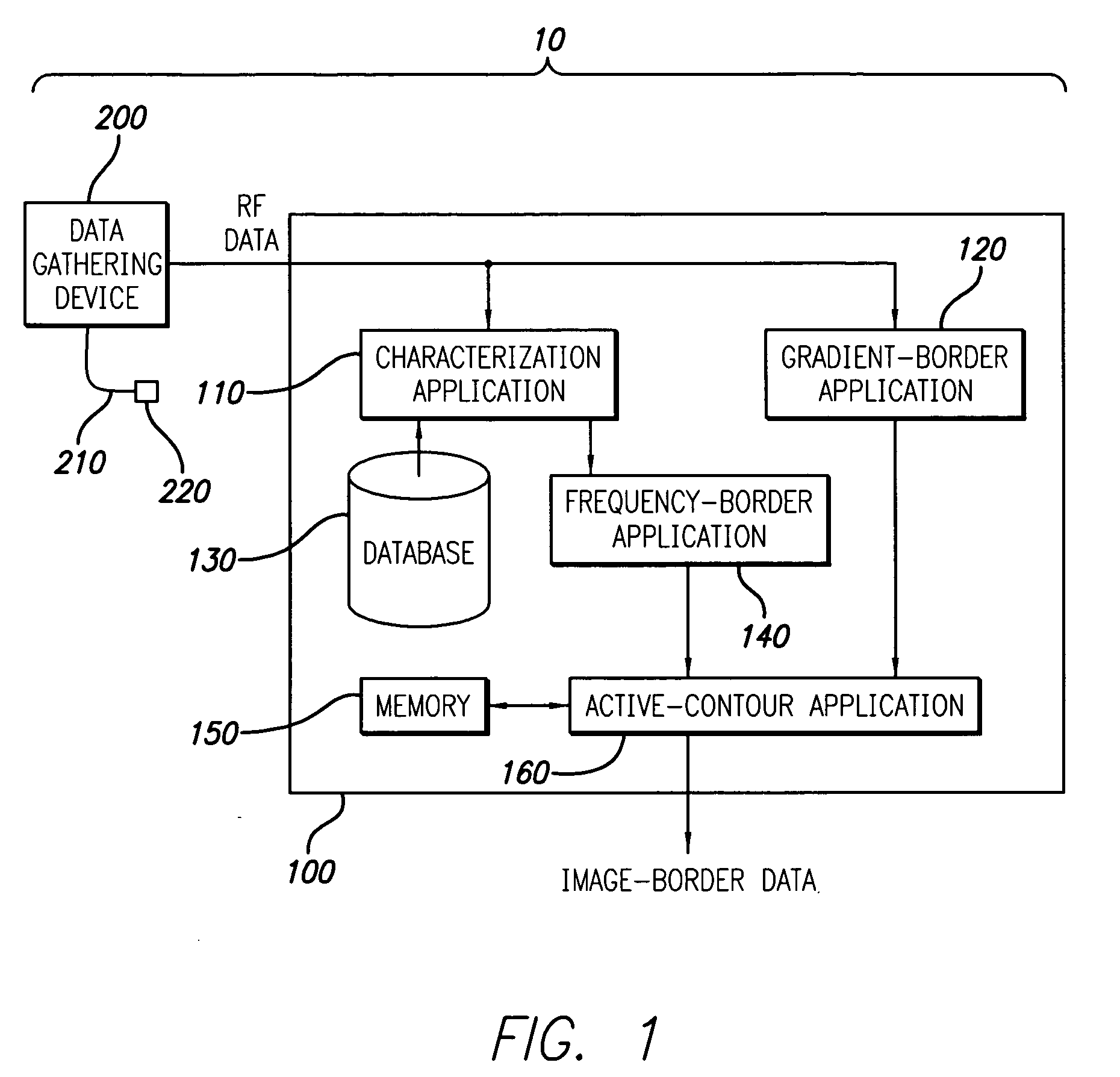
System and method for vascular border detection
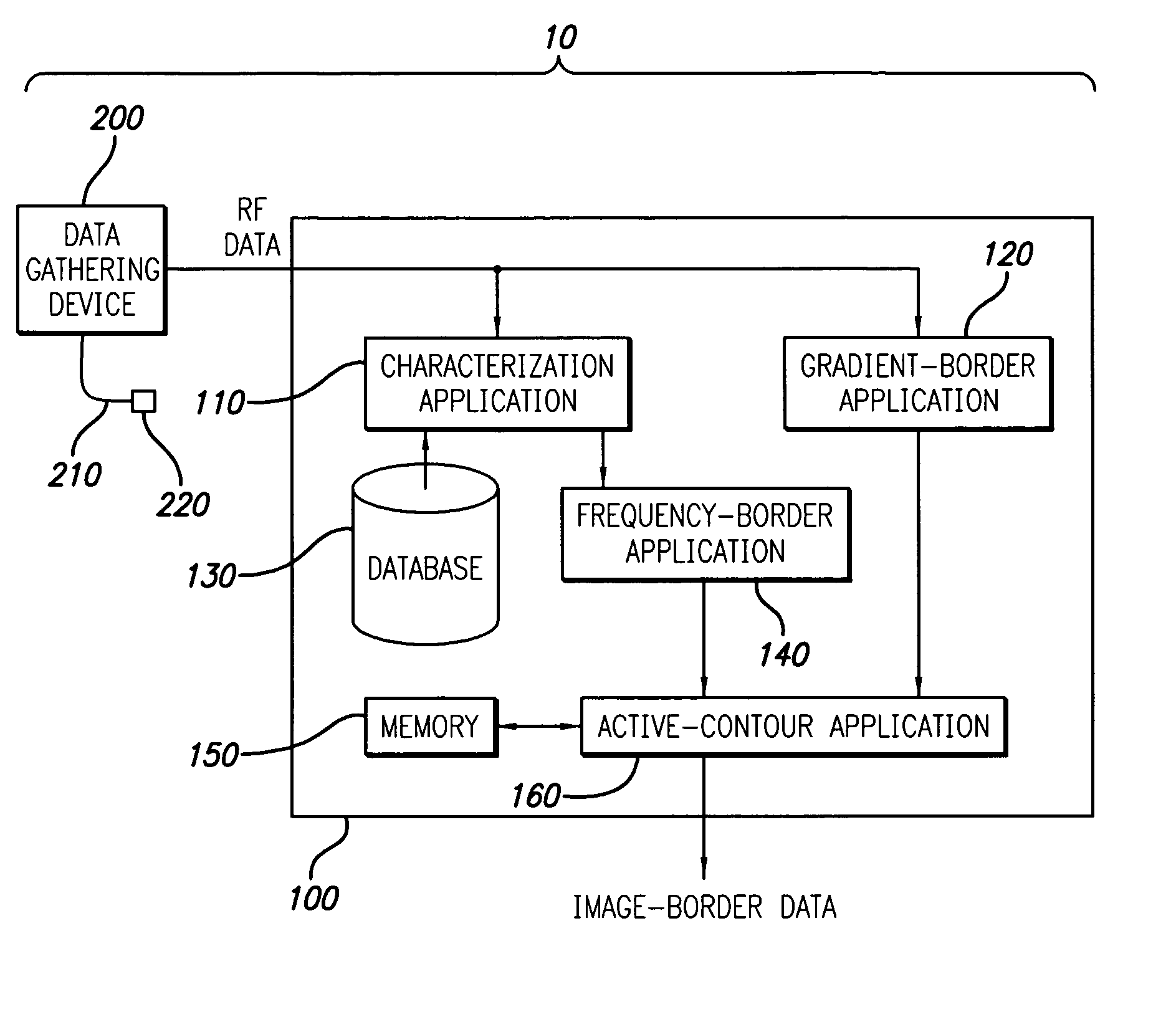
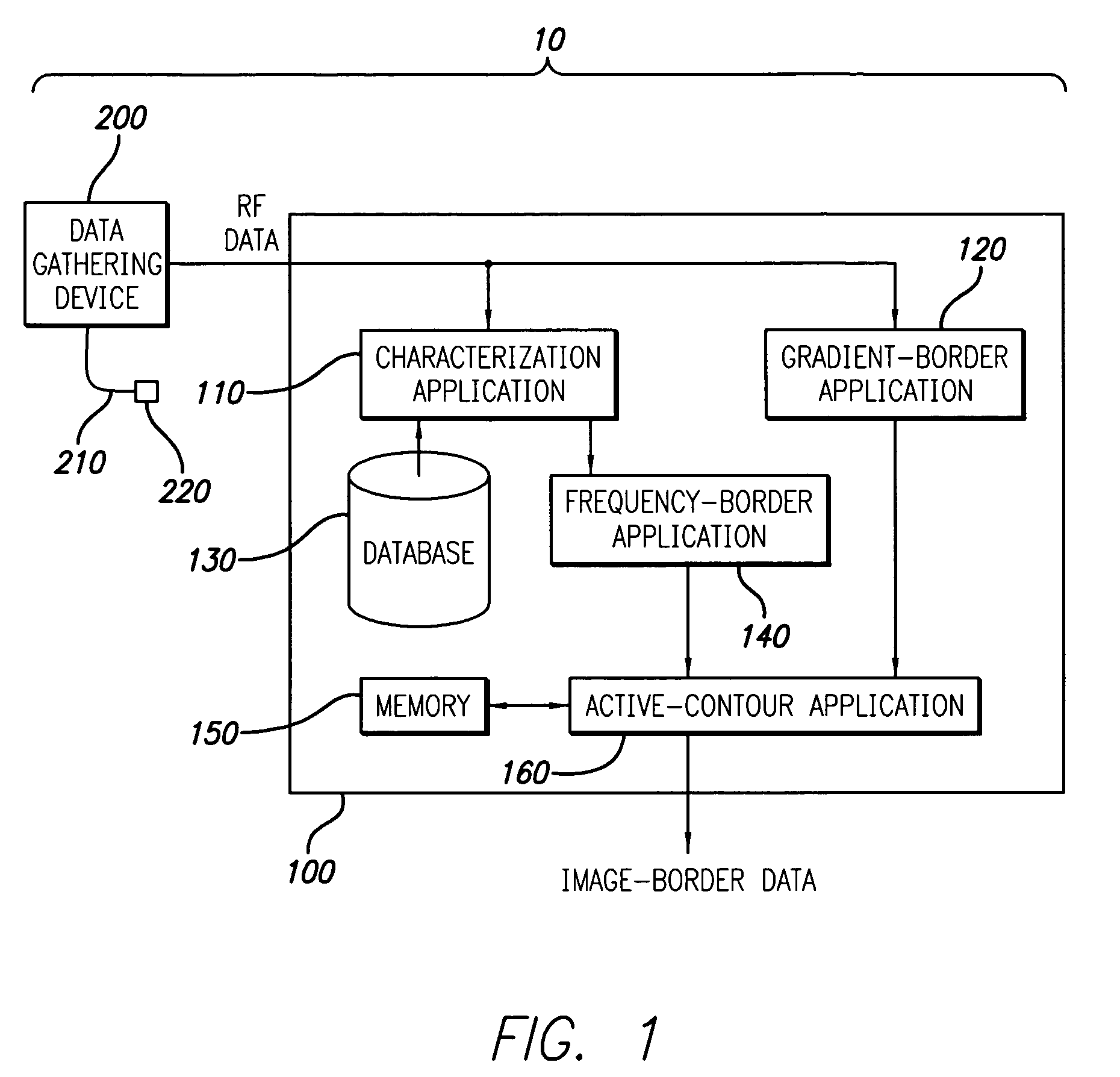
A system and method is provided for using the frequency spectrum of a radio frequency (RF) signal backscattered from vascular tissue to identify at least one border (e.g., tissue interface, etc.) on a vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with a data gathering device (e.g., an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device, etc.) electrically connected to a computing device and a transducer via a catheter. The transducer is used to gather radio frequency (RF) data backscattered from vascular tissue. The RF data is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device via the data-gathering device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes (i) at least one data storage device (e.g., database, memory, etc.) for storing a plurality of tissue types and parameters related thereto and (ii) at least one application (e.g., a characterization application, a gradient-border application, a frequency-border application and / or an active-contour application). The characterization application is used to convert (or transform) the RF data into the frequency domain and to identify a plurality of parameters associated therewith. The identified parameters are then compared to the parameters stored in the data storage device to identify the corresponding tissue type. This information (e.g., tissue type, corresponding RF data, etc.) is then used, either alone or together with other border-related information (e.g., gradient information, other-border information, etc.), to determine at least one border on a vascular image.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
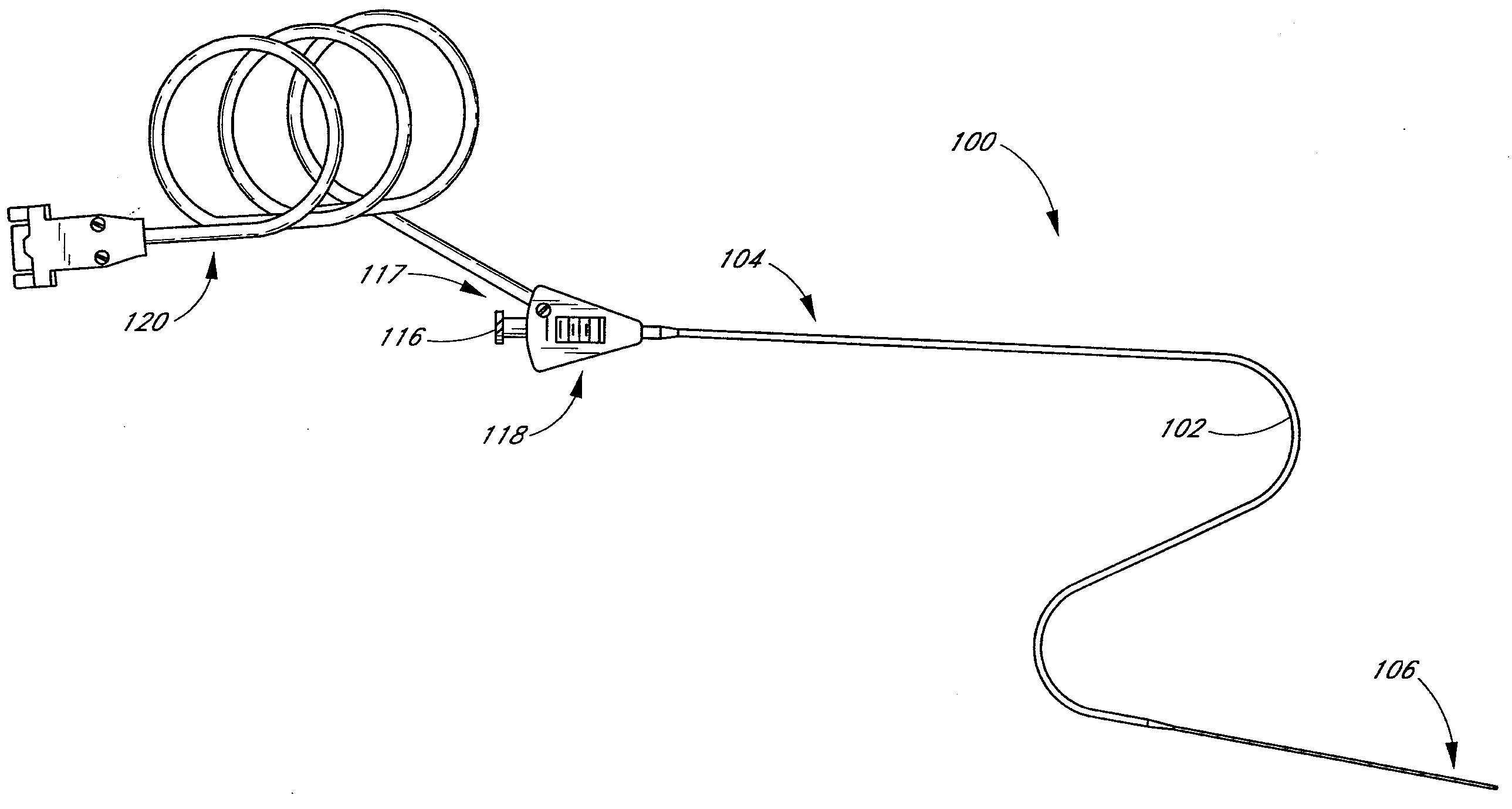
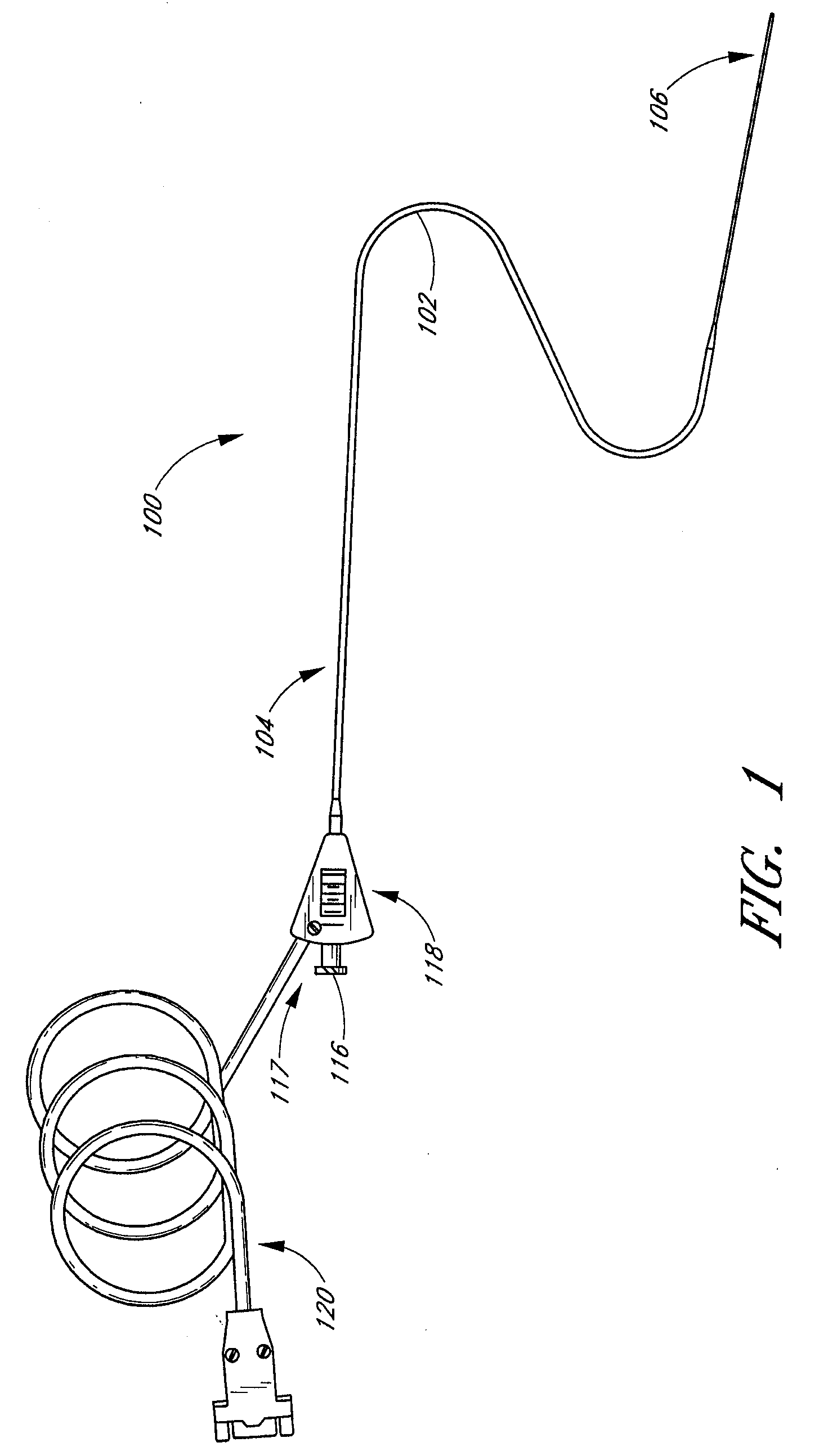
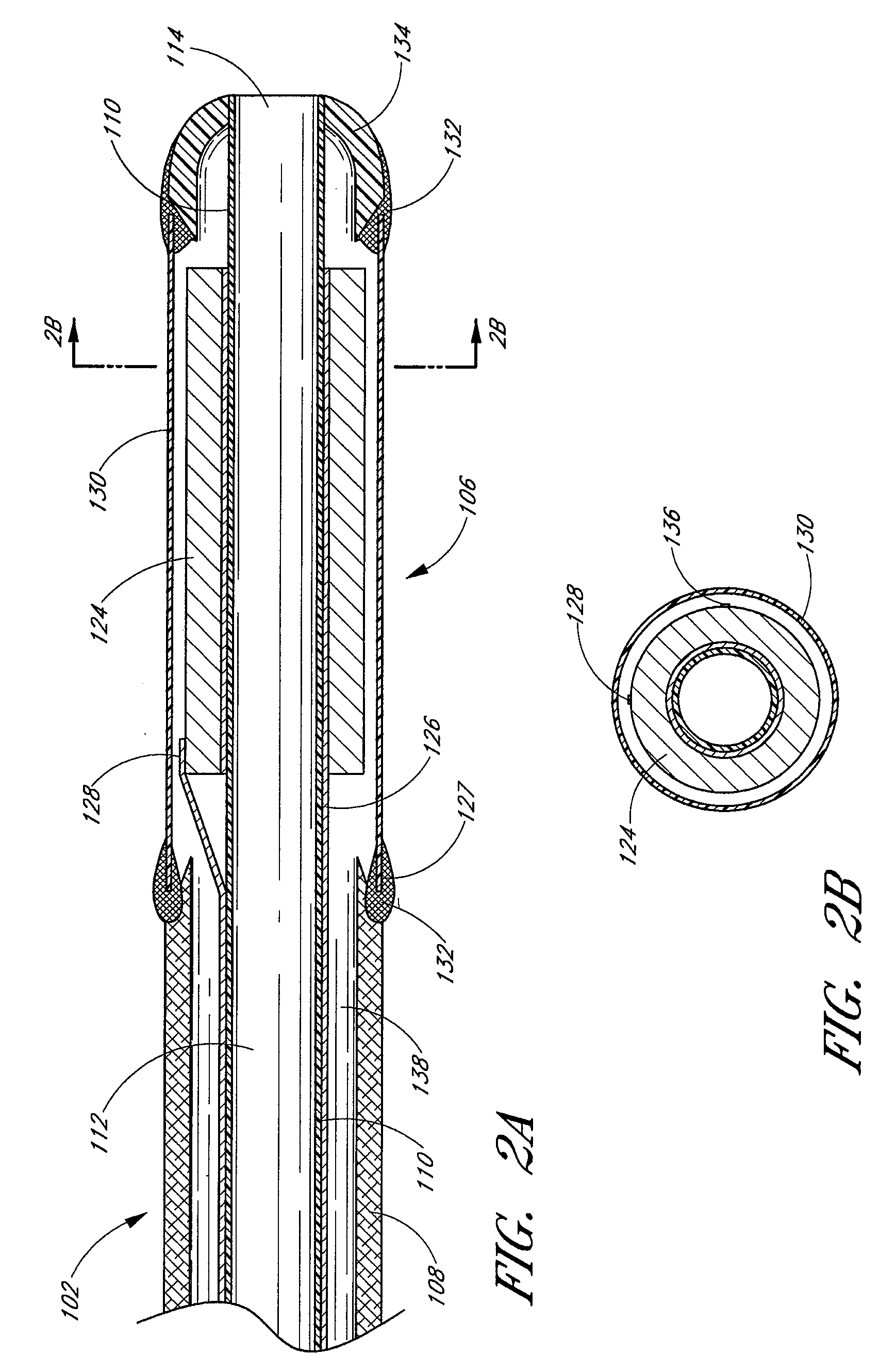
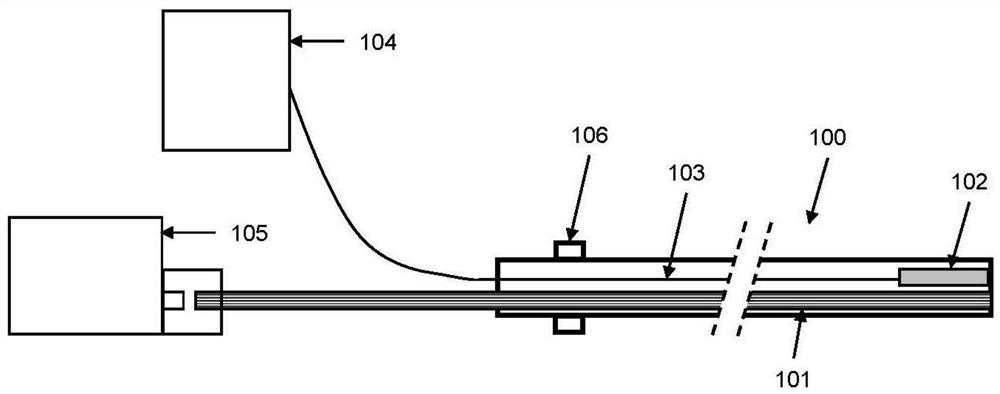
Small vessel ultrasound catheter
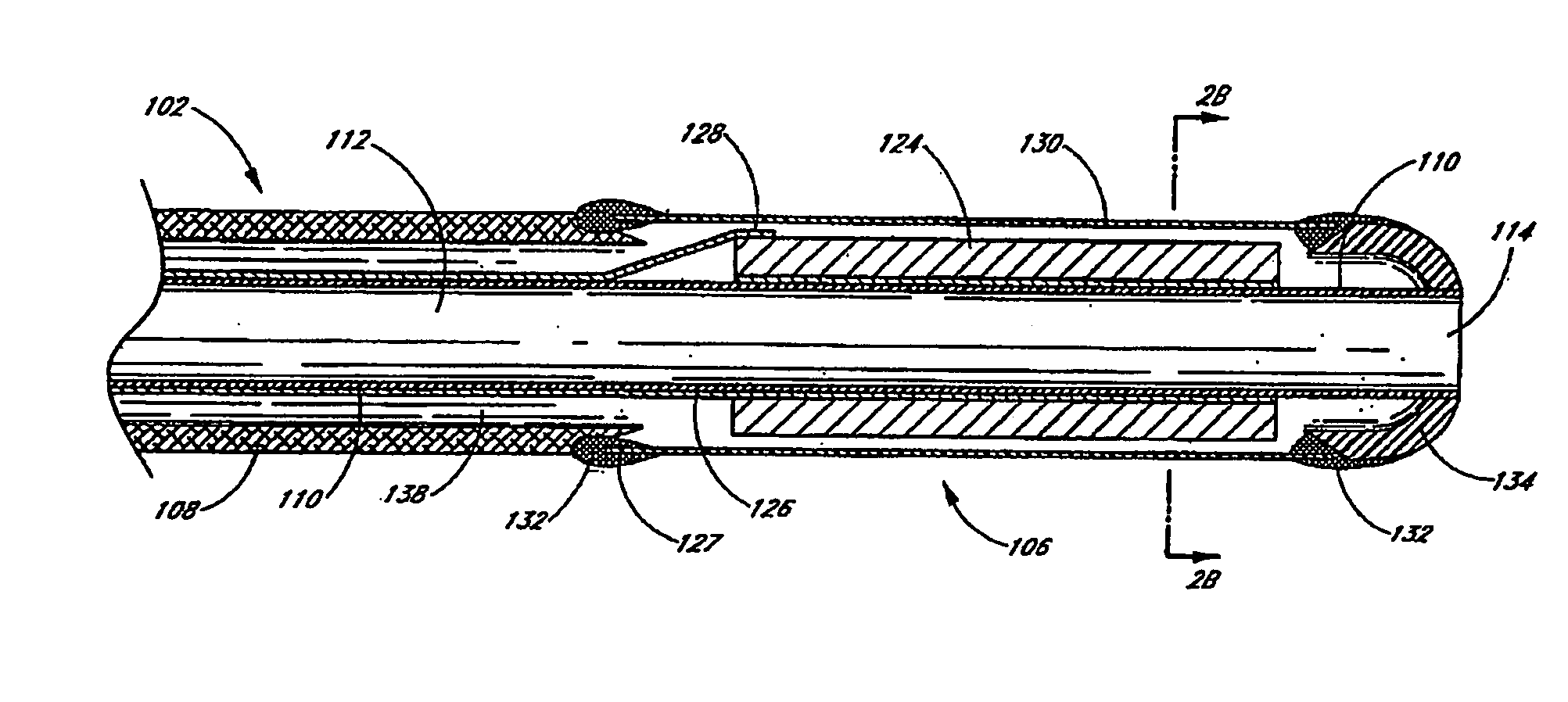
InactiveUS20050215942A1Increase stiffnessSufficient flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Small vessel ultrasound catheter
ActiveUS7384407B2Promote progressReduced bending resistanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:EKOS CORP
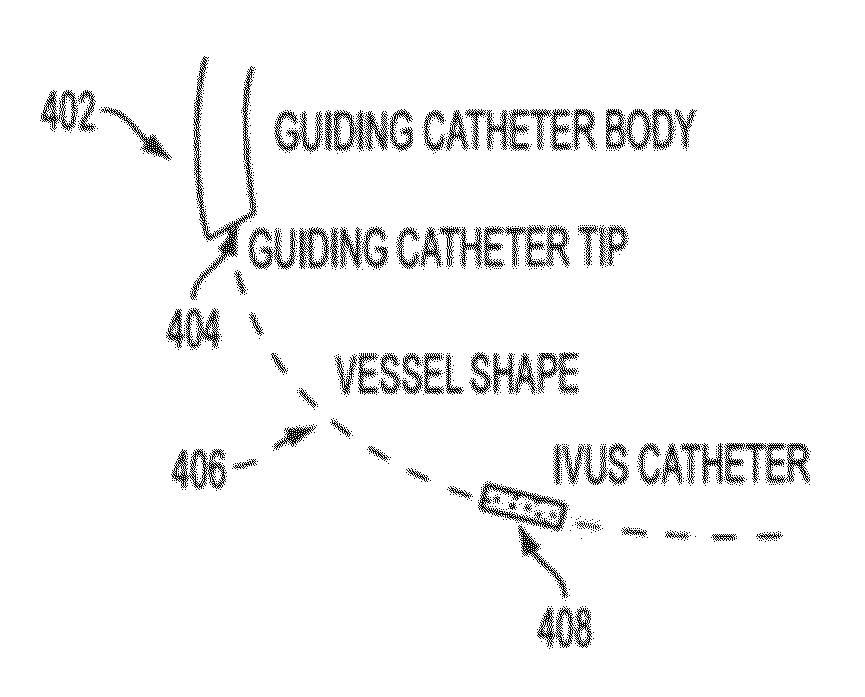
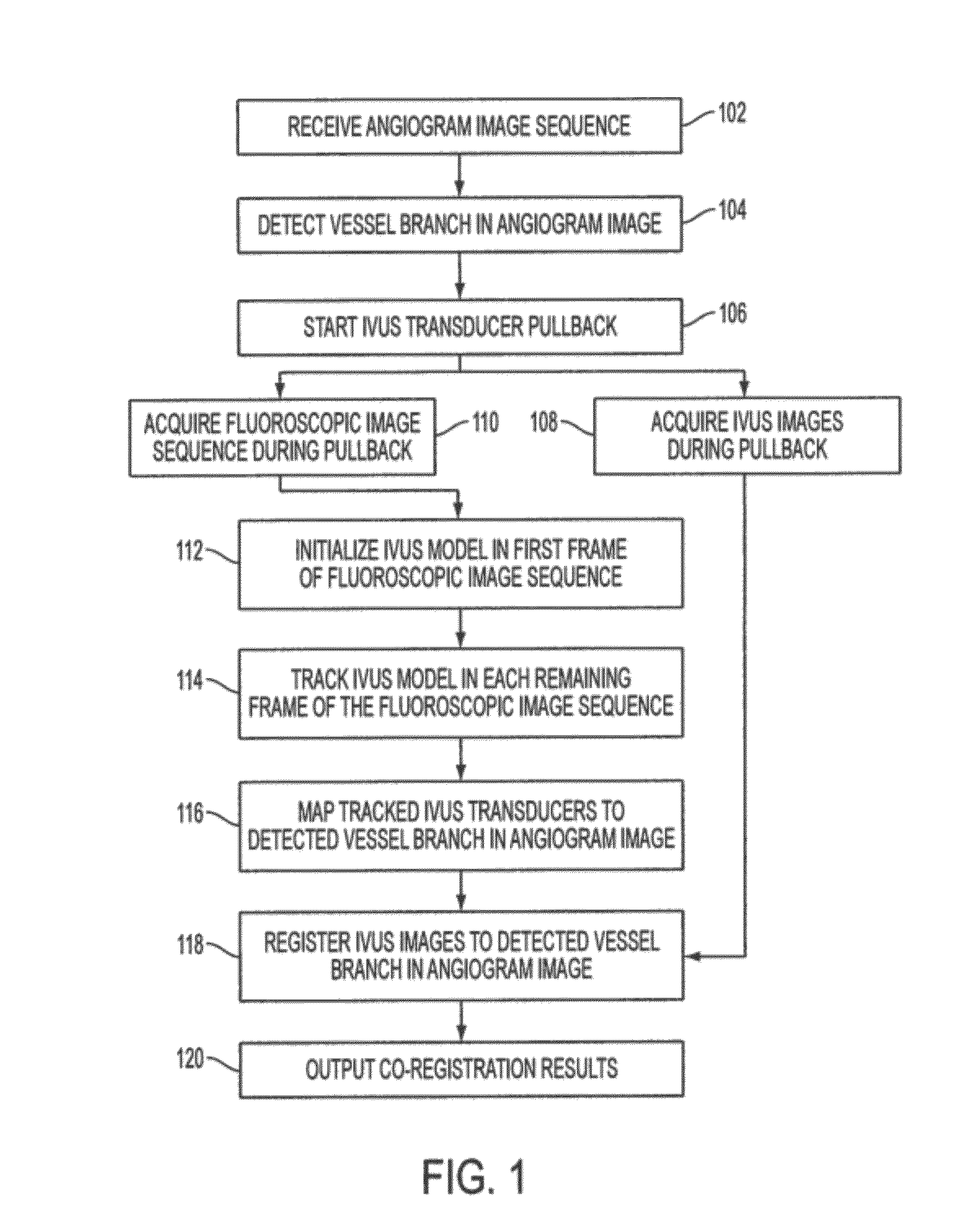
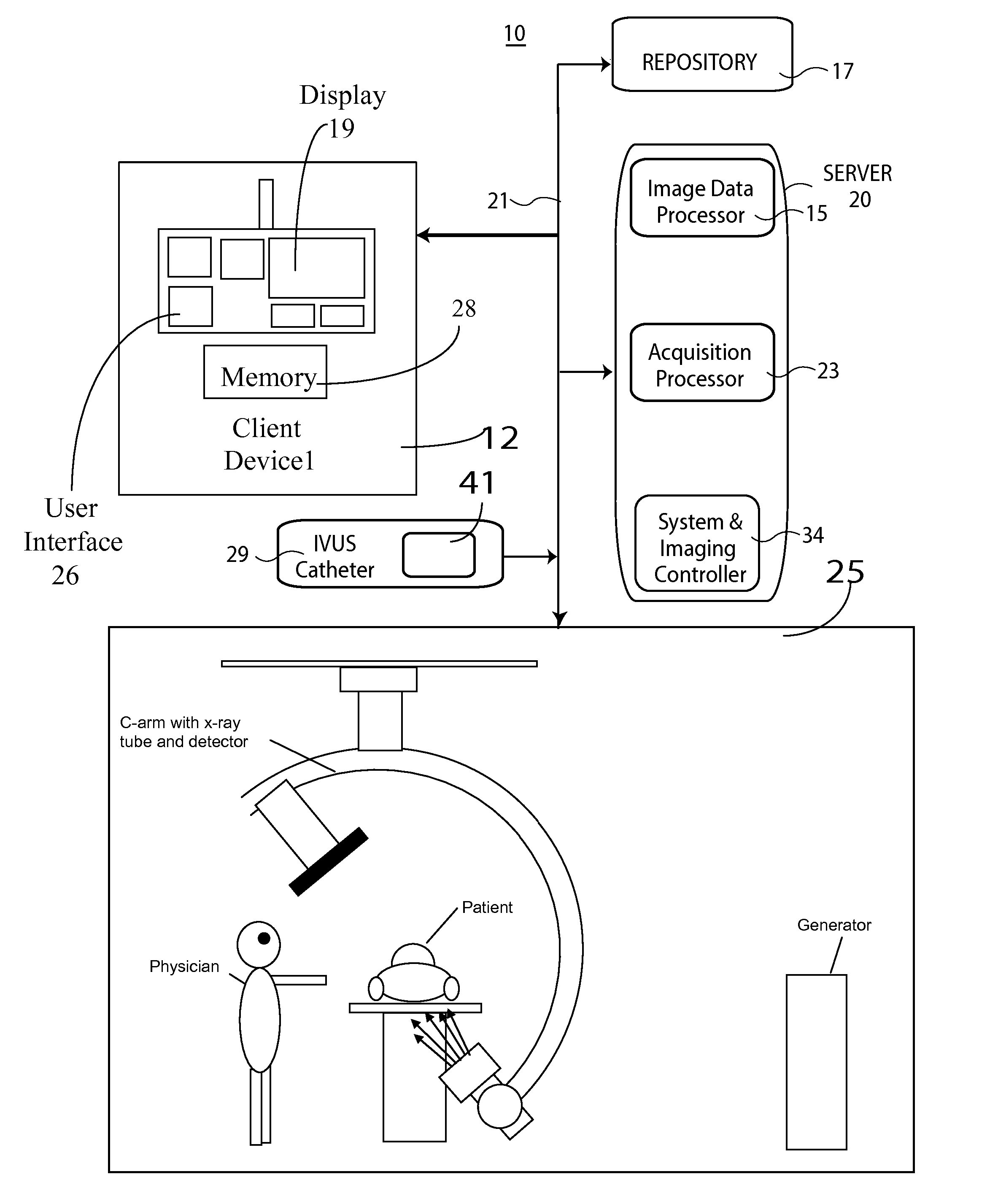
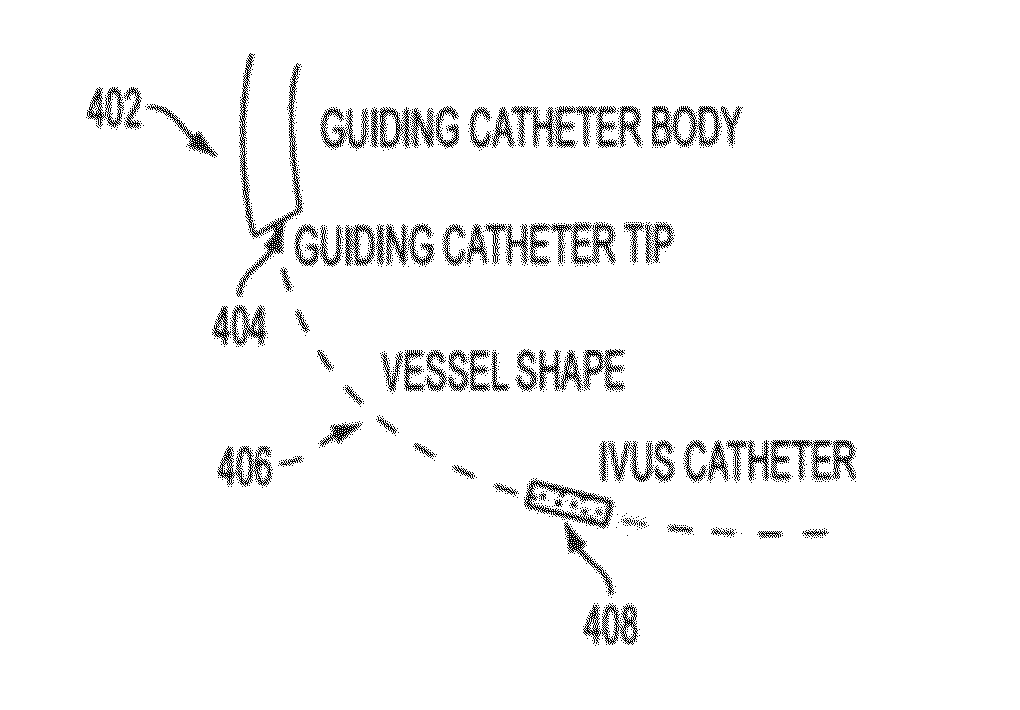
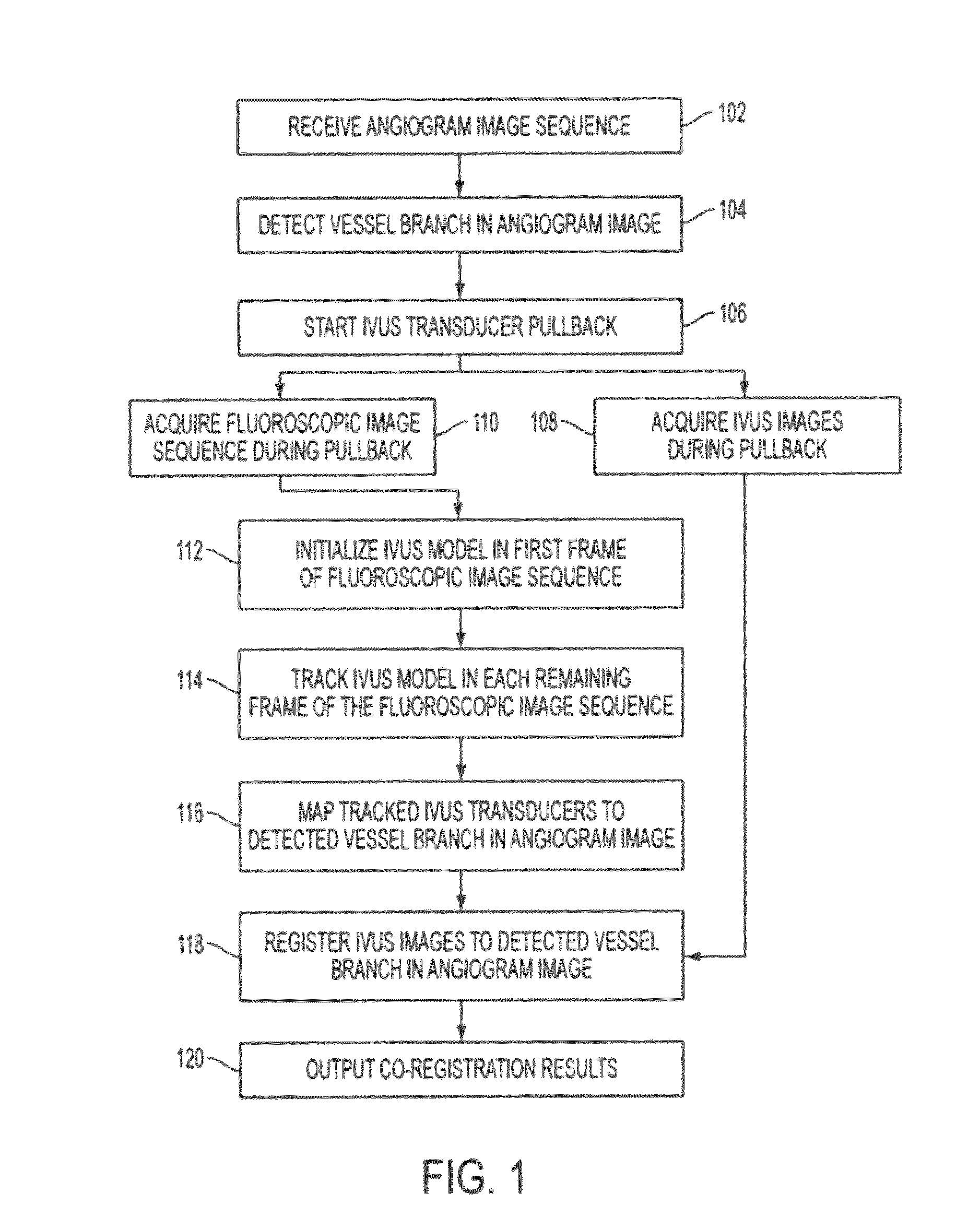
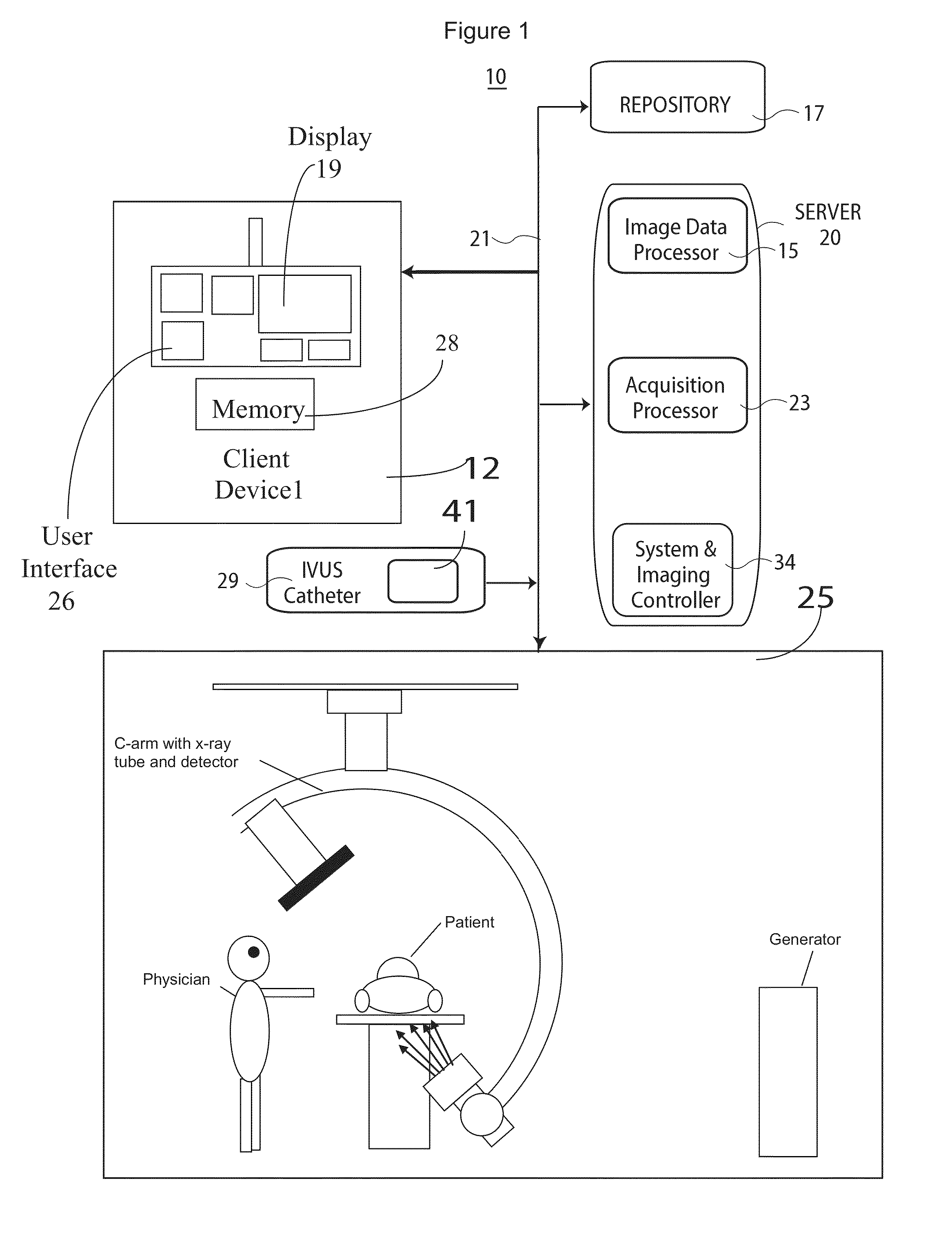
Method and System for Image Based Device Tracking for Co-registration of Angiography and Intravascular Ultrasound Images
ActiveUS20120059253A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundFluorescence
A method and system for co-registration of angiography data and intra vascular ultrasound (IVUS) data is disclosed. A vessel branch is detected in an angiogram image. A sequence of IVUS images is received from an IVUS transducer while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. A fluoroscopic image sequence is received while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. The IVUS transducer and a guiding catheter tip are detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence. The IVUS transducer detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence is mapped to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image. Each of the IVUS images is registered to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image based on the mapped location of the IVUS transducer detected in a corresponding frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System for Detecting Rotation Angle of a Catheter in an X-ray Image
An IVUS catheter is advantageously provided with a particular radio-opaque pattern enabling detection of catheter rotation angle with respect to an X-ray imaging source for co-registering IVUS image data with angiographic X-ray or CT image data, for example. An ultrasound catheter system supports orientation and display of intra-vascular ultrasound imaging data. The system comprises an ultrasound catheter for acquiring ultrasound images comprising a body having a pattern of radio-opaque material on the external surface of the catheter body. The pattern varies with angular rotation of the catheter and indicates an angle of rotation of a predetermined reference orientation of the catheter relative to an X-ray radiation source, so that an X-ray image of the catheter body indicates the pattern and the pattern is analyzable by an image data processor to determine the angle of rotation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
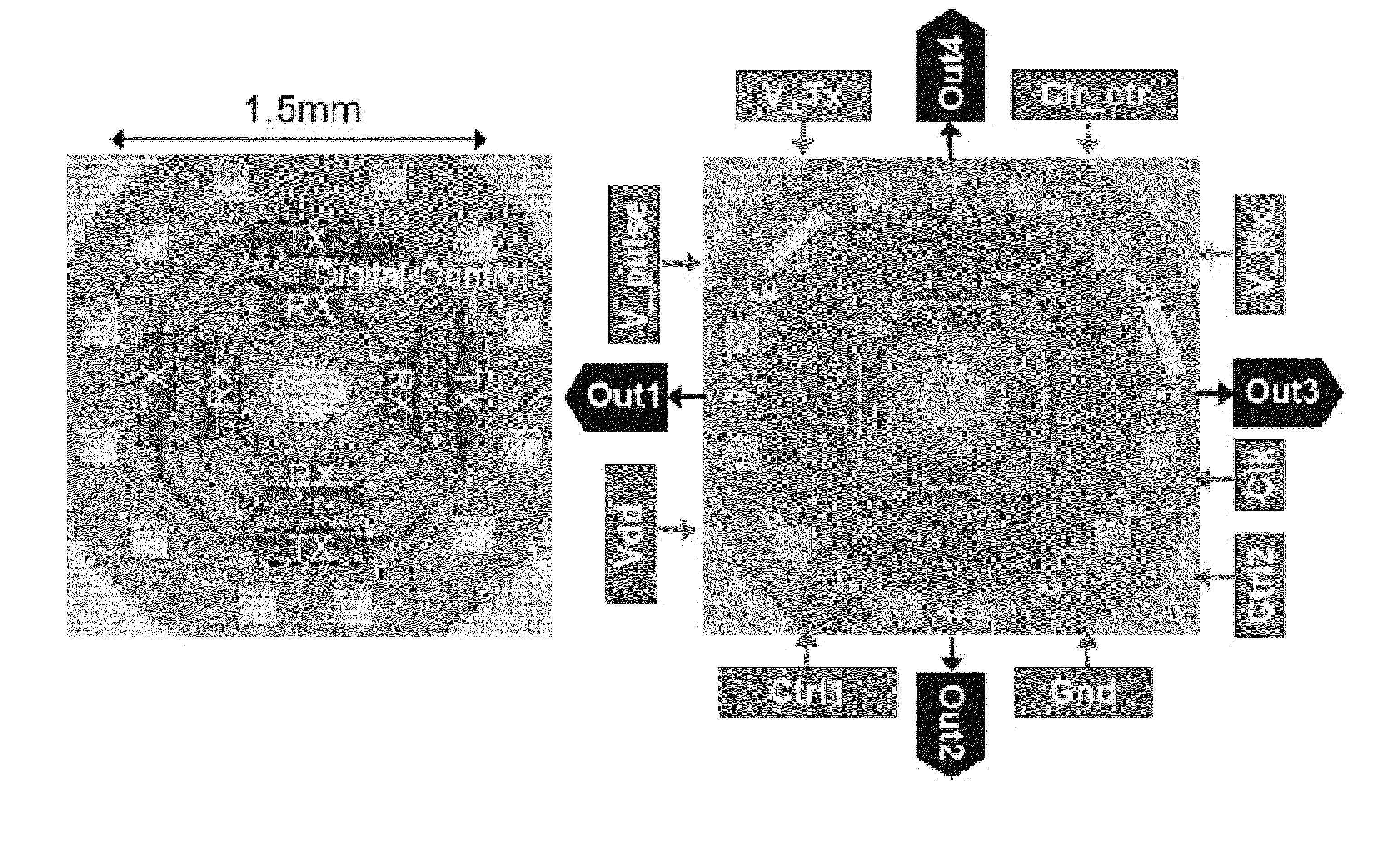
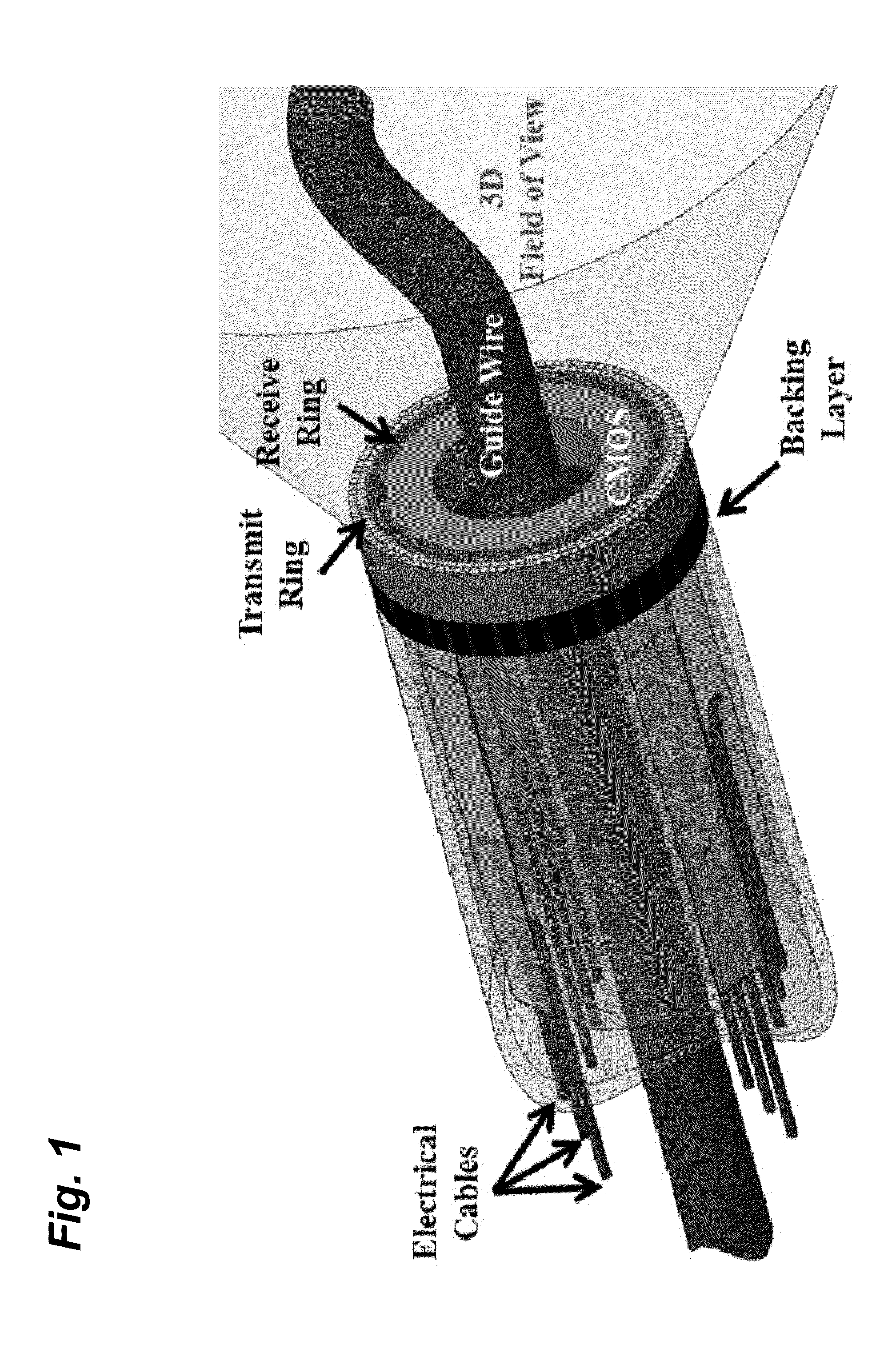
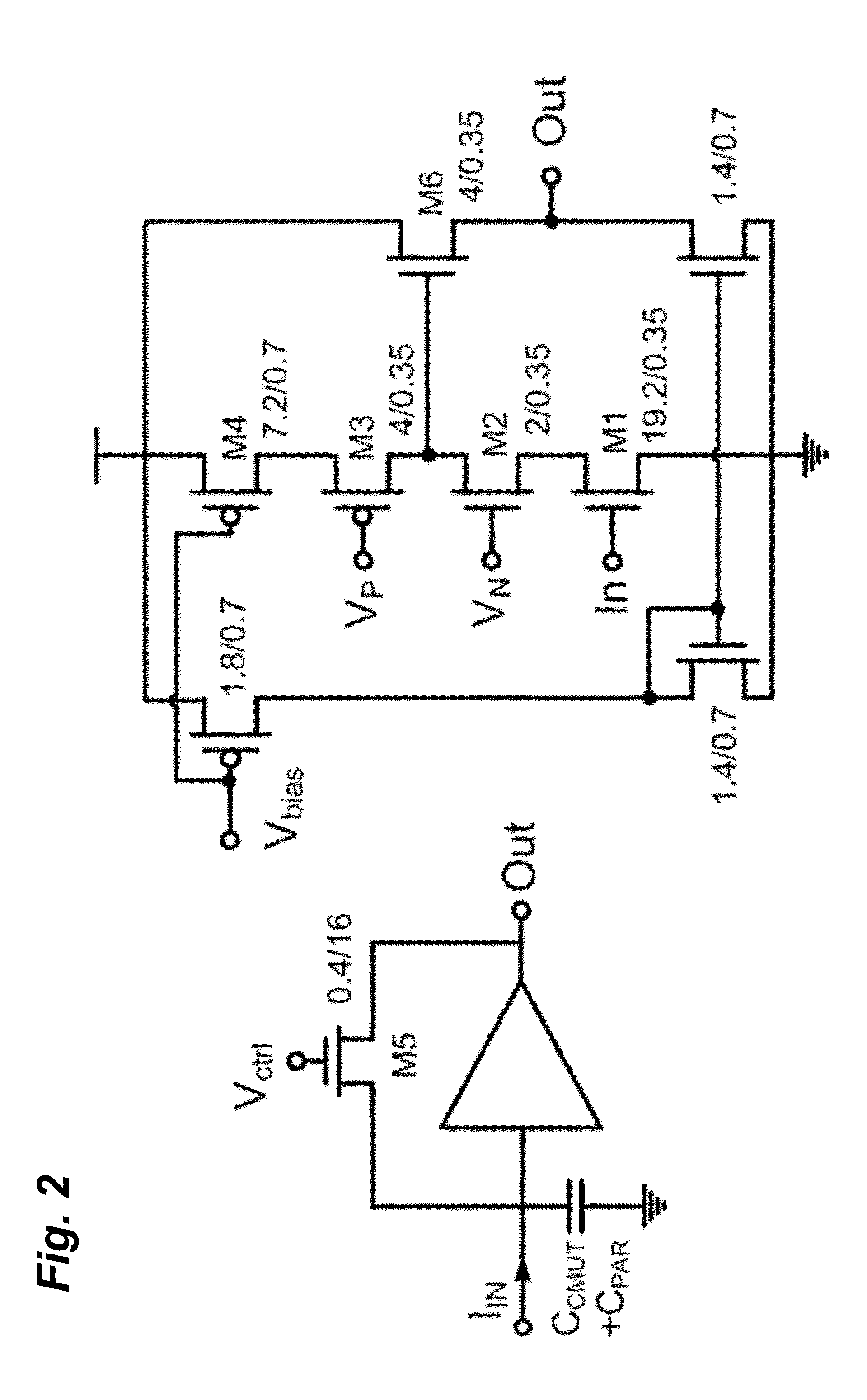
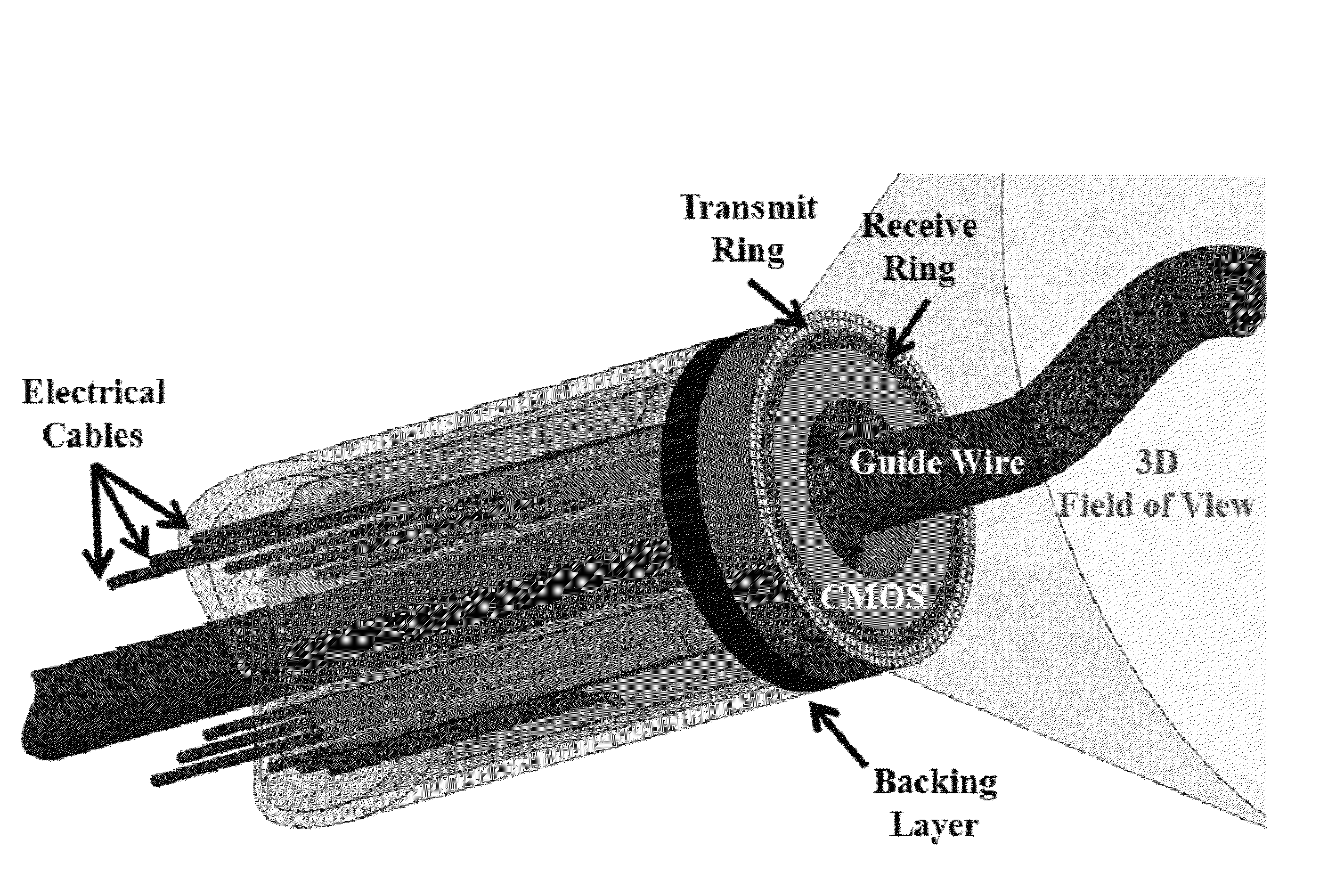
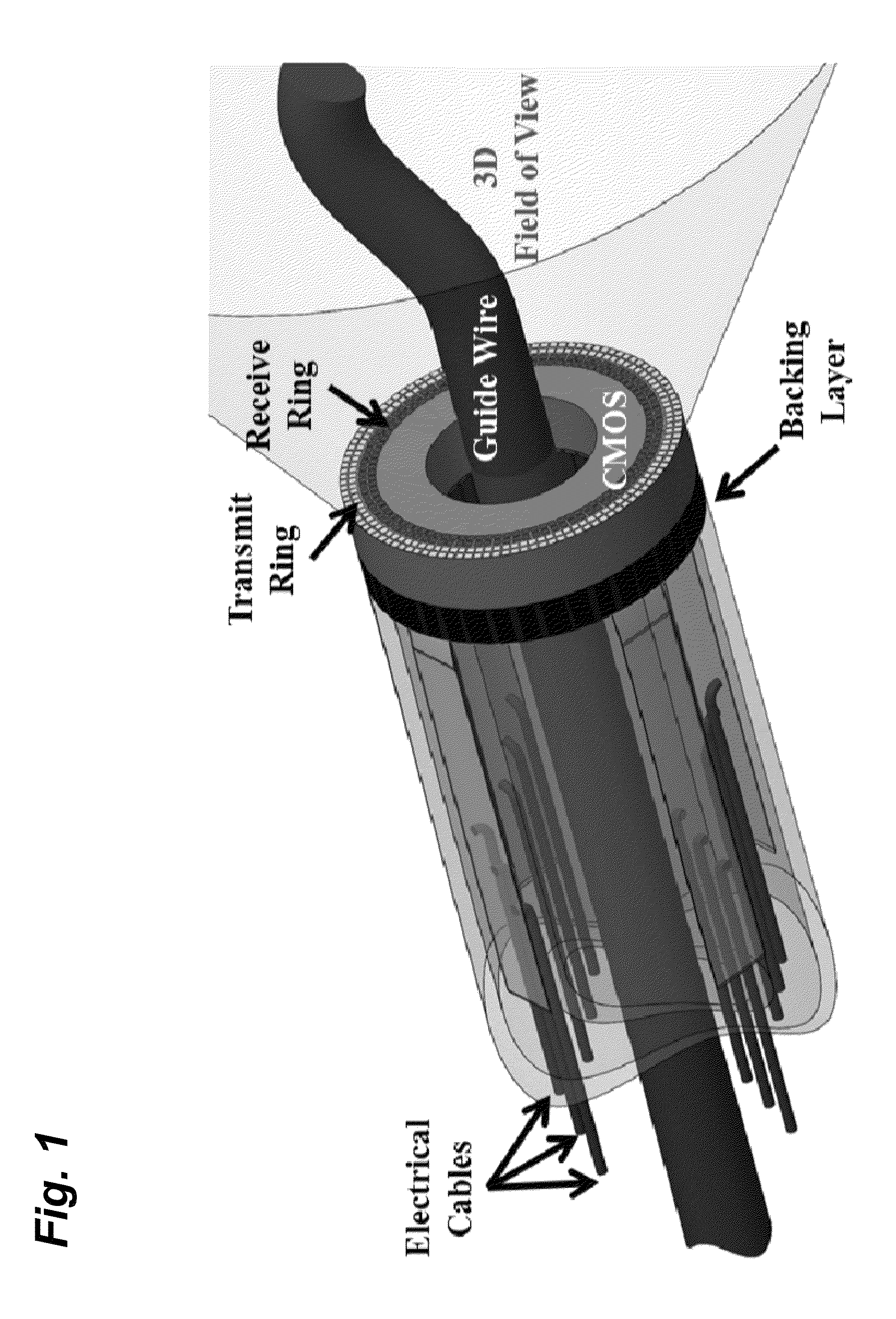
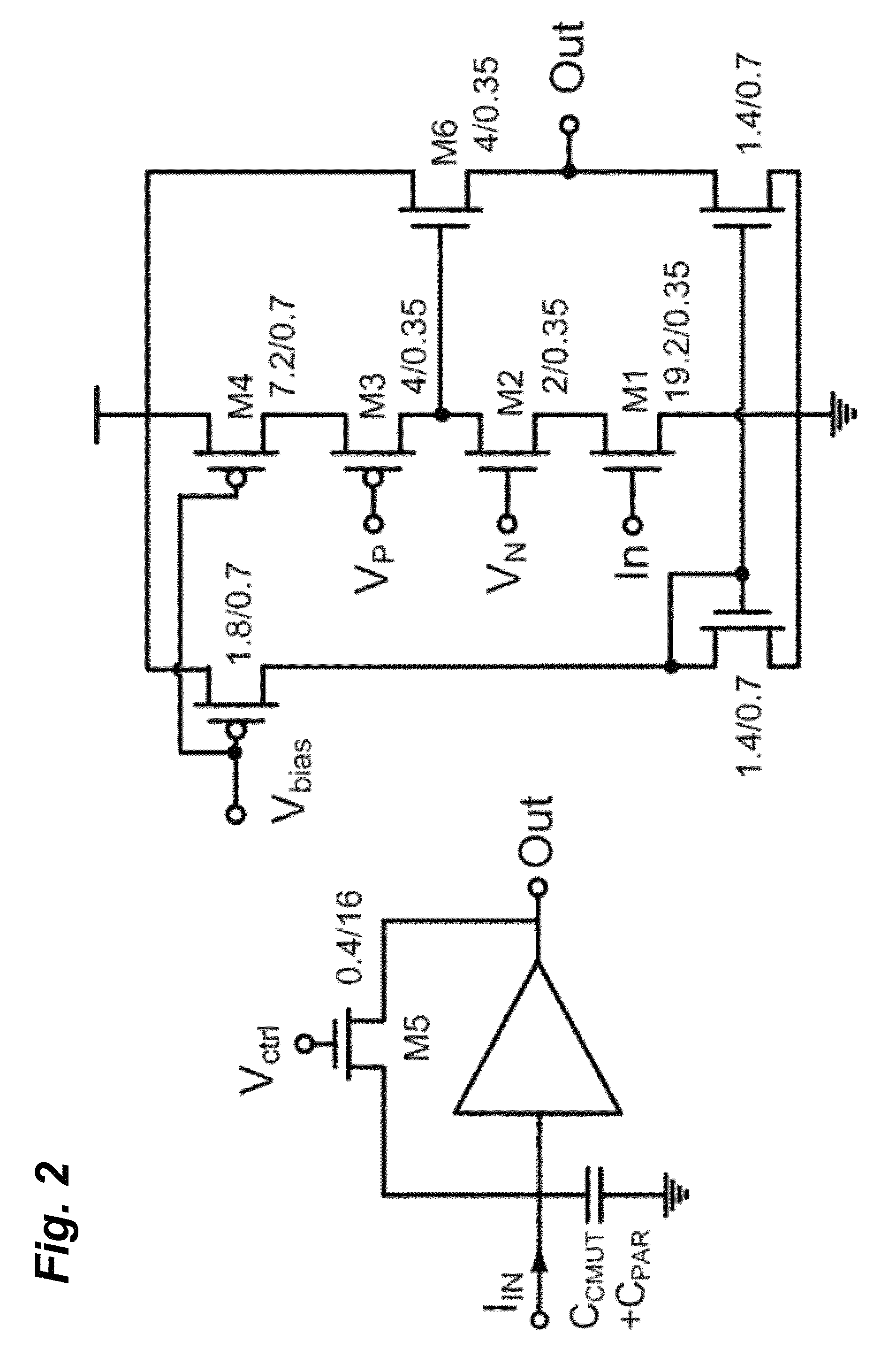
Compact, energy-efficient ultrasound imaging probes using CMUT arrays with integrated electronics
ActiveUS20130064043A1Enhance the imageReduce energy consumptionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound imagingTemperature control
A CMUT on CMOS imaging chip is disclosed. The imaging chip can use direct connection, CMOS architecture to minimize both internal and external connection complexity. Intelligent power management can enable the chip to be used for various imaging applications with strict power constraints, including forward-looking intra-vascular ultrasound imaging. The chip can use digital logic to control transmit and receive events to minimize power consumption and maximize image resolution. The chip can be integrated into a probe, or catheter, and requires minimal external connections. The chip can comprise integrated temperature control to prevent overheating.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Small vessel ultrasound cathter
InactiveUS20080221506A1Promote progressReduce resistanceUltrasound therapyMulti-lumen catheterDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:RODRIGUEZ OSCAR E +7
System And Method For Identifying A Vascular Border
InactiveUS20080287795A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundBoundary detection
A system and method is provided for using a first vascular image, or more particularly a plurality of control points located thereon, to identify a border on a second vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device electrically connected thereto. Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, an-IVUS console is electrically connected to a computing device and adapted to acquire IVUS data. The IVUS data (or multiple sets thereof) is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes a plurality of applications operating thereon—i.e., a border-detection application, an extrapolation application, and an active-contour application. These applications are used to (i) identify a border and control points on a first IVUS image (i.e., any IVUS image), (ii) extrapolate the control points to a second IVUS image (i.e., another IVUS image), (iii) identify a border on the second IVUS image, and (iv) adjust the border on the second IVUS image in accordance with at least one factor. In one embodiment of the present invention, the at least one factor is selected from a group consisting of gradient factor, continuity factor, and curvature factor.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and system for image based device tracking for co-registration of angiography and intravascular ultrasound images
ActiveUS8565859B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationVascular ultrasound
A method and system for co-registration of angiography data and intra vascular ultrasound (IVUS) data is disclosed. A vessel branch is detected in an angiogram image. A sequence of IVUS images is received from an IVUS transducer while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. A fluoroscopic image sequence is received while the IVUS transducer is being pulled back through the vessel branch. The IVUS transducer and a guiding catheter tip are detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence. The IVUS transducer detected in each frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence is mapped to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image. Each of the IVUS images is registered to a respective location in the detected vessel branch of the angiogram image based on the mapped location of the IVUS transducer detected in a corresponding frame of the fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
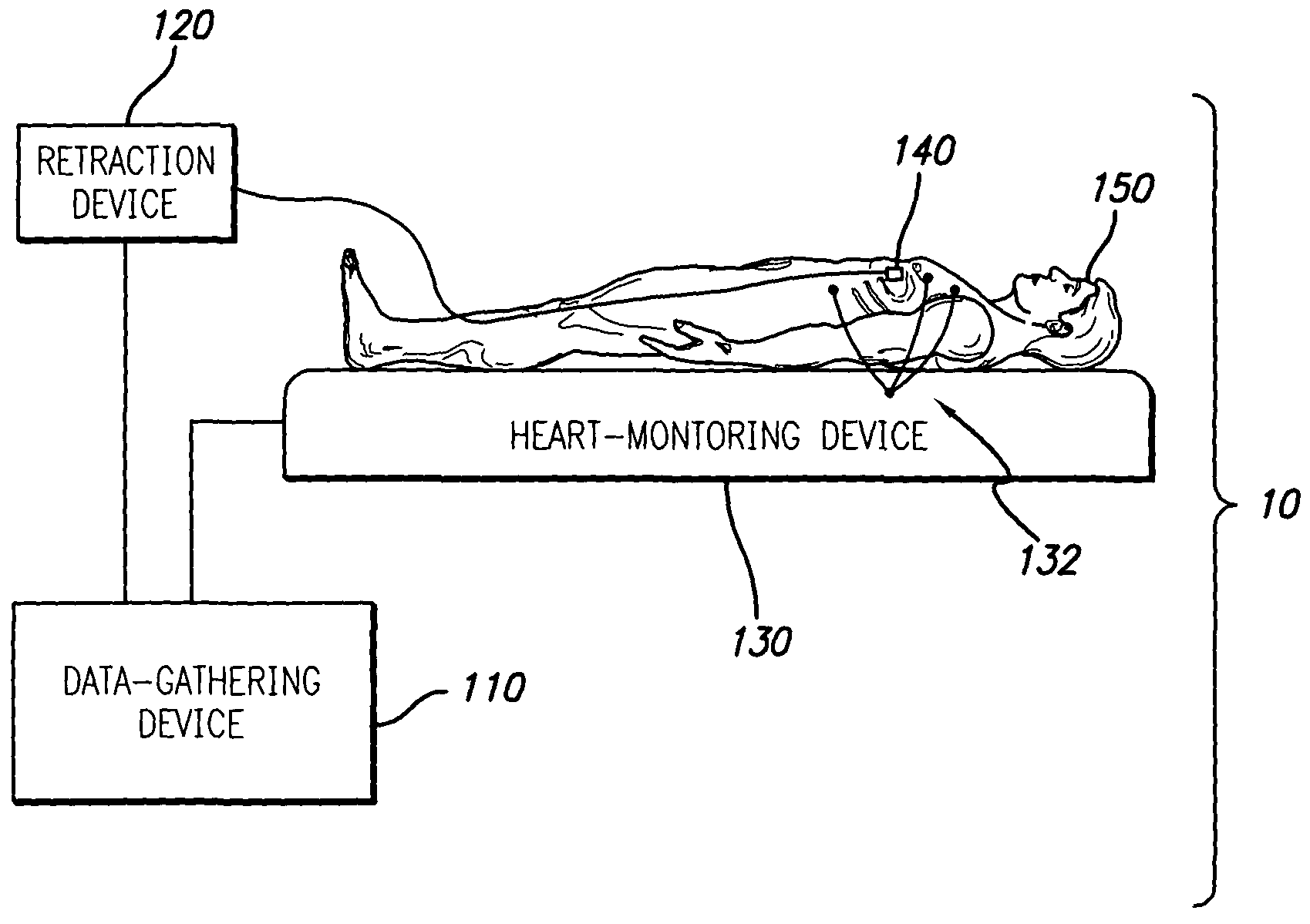
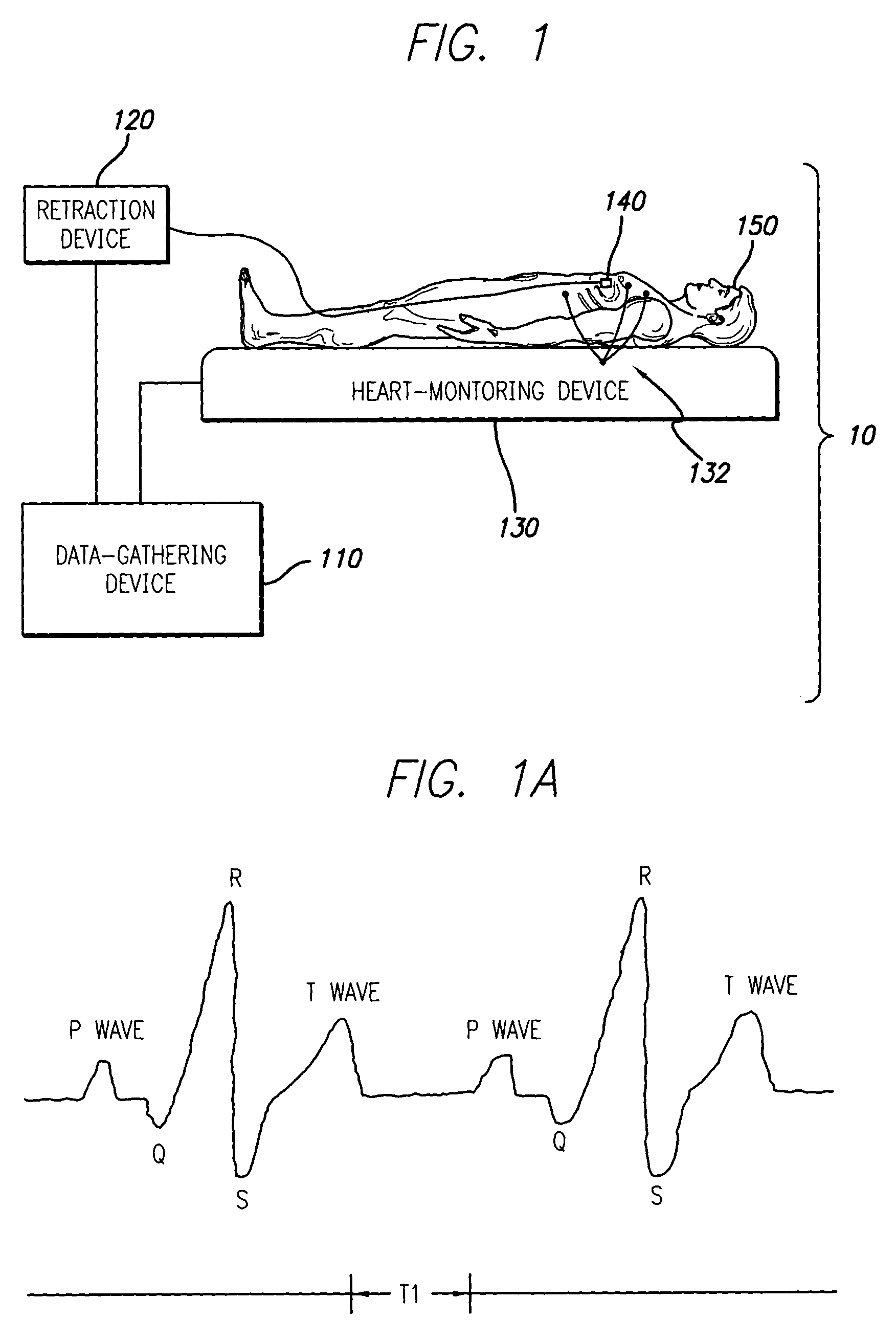
System and method of aquiring blood-vessel data
ActiveUS7927275B2Stable speedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundData acquisition
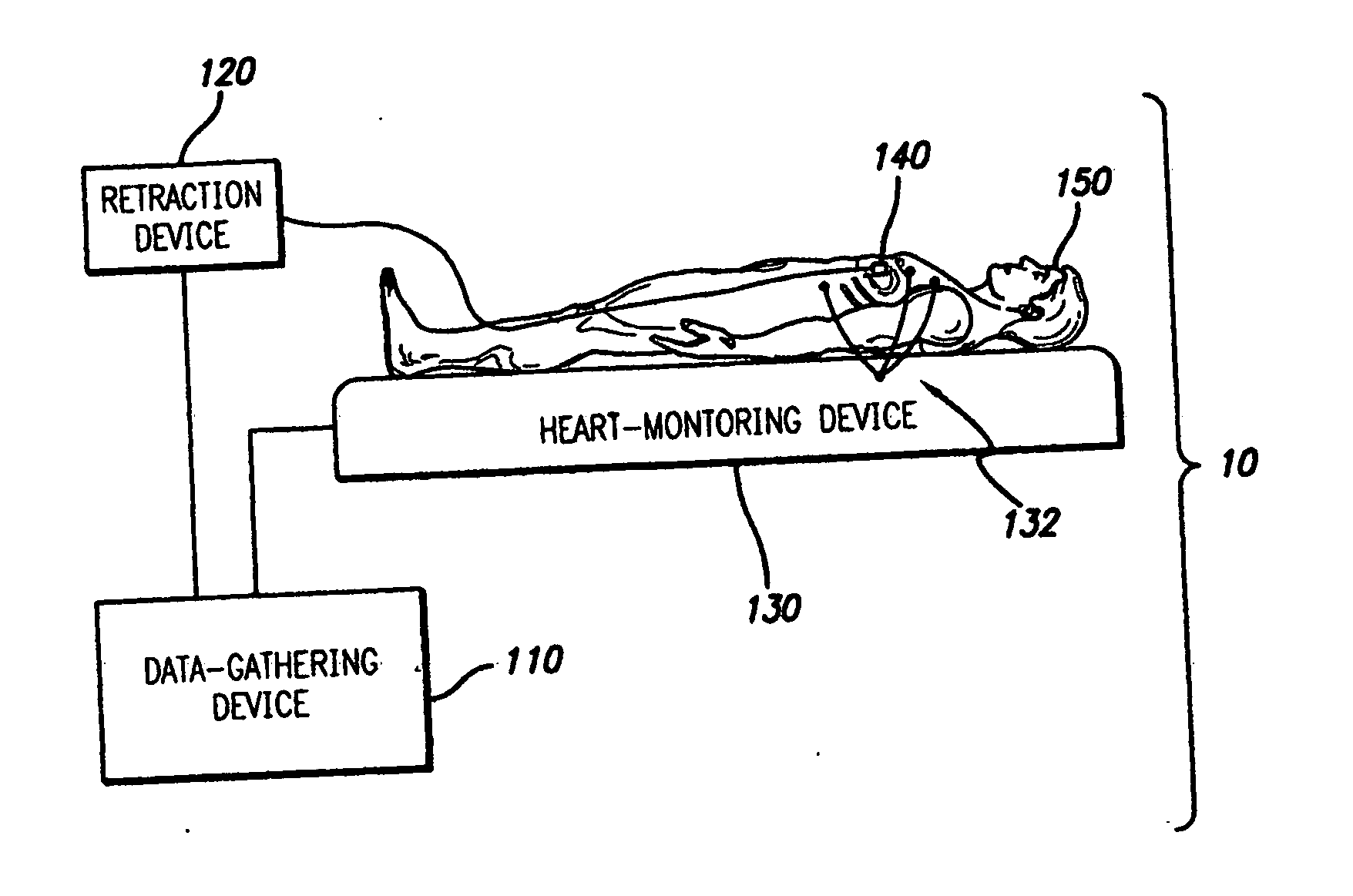
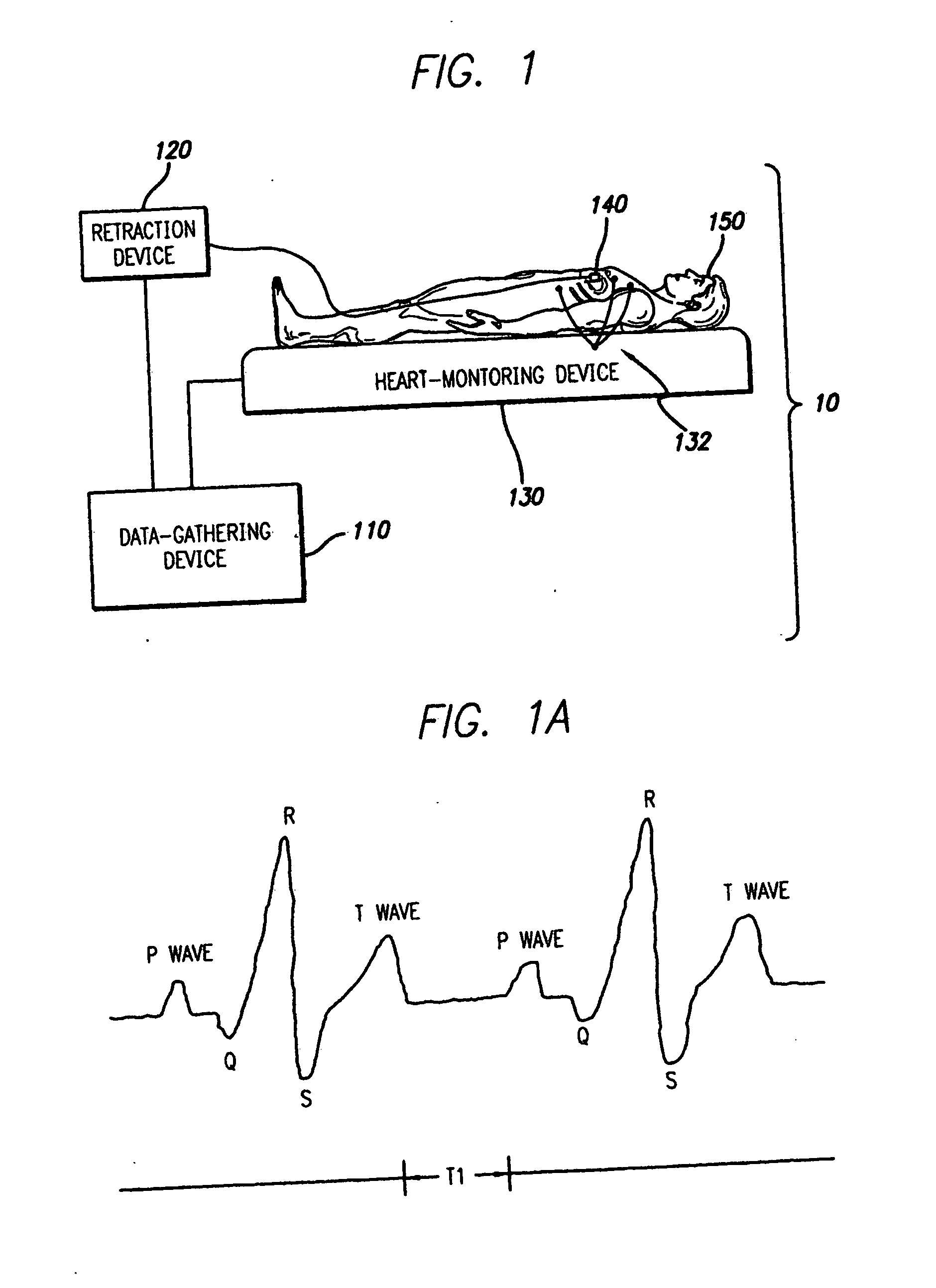
A system and method is provided for substantially synchronizing the acquisition of blood-vessel data to an identifiable portion of heartbeat data. Specifically, a data-gathering device is adapted to acquire heartbeat data and blood-vessel data from a heart-monitoring device and a data-gathering probe, respectively. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the blood-vessel data is acquired during a cyclical portion of the heartbeat data. By identifying a cyclical (or commonly reoccurring) portion of the heartbeat data and acquiring blood-vessel data during this cyclical portion (or during an interval that substantially corresponds thereto), the blood vessel can be analyzed as if it were standing still—i.e., not expanding and relaxing. In one embodiment of the present invention, the heart-monitoring device includes an EKG device, the data-gathering device includes an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device, and the data-gathering probe includes at least one transducer. In another embodiment of the present invention, the data-gathering system further includes a retraction device adapted to move the data-gathering probe though a blood vessel at a substantially steady speed.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System and method for vascular border detection
ActiveUS20050196026A1Closely matchedOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryFrequency spectrumSonification
A system and method is provided for using the frequency spectrum of a radio frequency (RF) signal backscattered from vascular tissue to identify at least one border (e.g., tissue interface, etc.) on a vascular image. Embodiments of the present invention operate in accordance with a data gathering device (e.g., an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device, etc.) electrically connected to a computing device and a transducer via a catheter. The transducer is used to gather radio frequency (RF) data backscattered from vascular tissue. The RF data is then provided to (or acquired by) the computing device via the data-gathering device. In one embodiment of the present invention, the computing device includes (i) at least one data storage device (e.g., database, memory, etc.) for storing a plurality of tissue types and parameters related thereto and (ii) at least one application (e.g., a characterization application, a gradient-border application, a frequency-border application and / or an active-contour application). The characterization application is used to convert (or transform) the RF data into the frequency domain and to identify a plurality of parameters associated therewith. The identified parameters are then compared to the parameters stored in the data storage device to identify the corresponding tissue type. This information (e.g., tissue type, corresponding RF data, etc.) is then used, either alone or together with other border-related information (e.g., gradient information, other-border information, etc.), to determine at least one border on a vascular image.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Cardiovascular ultrasound probe and ultrasound image system
InactiveUS20090093726A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterVascular ultrasoundUltrasound probe
An ultrasound image system includes: an ultrasound probe; a signal-transmitting-and-receiving section for transmitting signals to the ultrasound probe and receiving signals from the ultrasound probe; and an image-displaying section for displaying an ultrasound image obtained by means of the signal-transmitting-and-receiving section, wherein the ultrasound probe includes: a tip section which is provided with: a plurality of ultrasound-wave-transmitting sections for transmitting ultrasound waves to an tissue; and a plurality of ultrasound-wave-receiving sections for receiving signals reflected by the tissue and obtained by means of the ultrasound-wave-transmitting section; and a flexible catheter tube provided with: a first lumen capable of inserting an instrument for treating the tissue from a proximal end section of the ultrasound probe therethrough and exposing the instrument at a position facing the tip section; and a second lumen having an maneuvering wire inserted therethrough and being capable of moving the tip section.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP +1
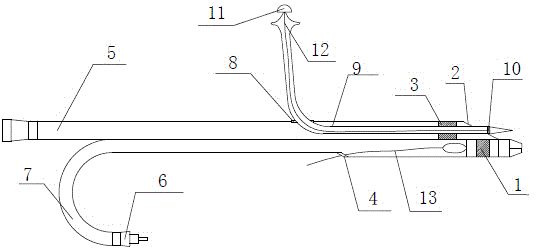
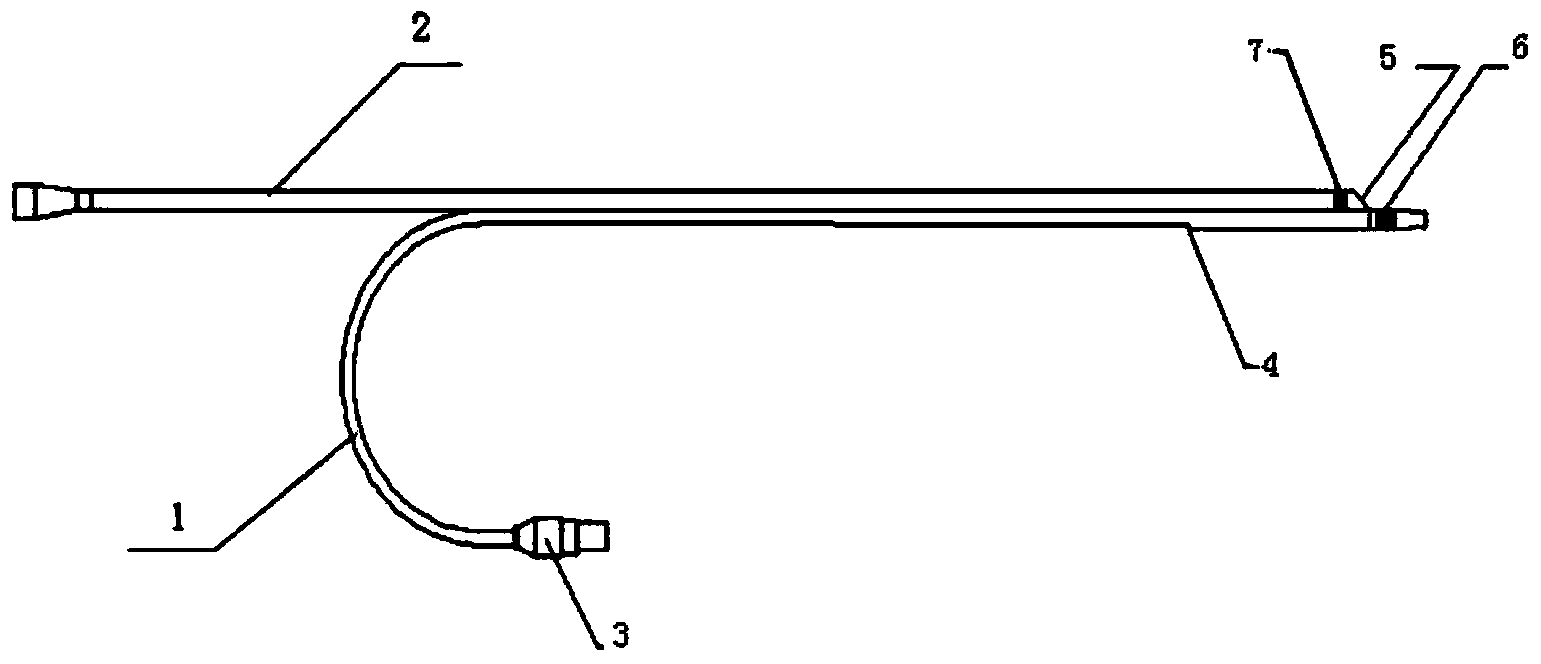
Instrument for arterial occlusion lesion treating and application thereof
ActiveCN104161548AImprove handlingStrong penetrating powerGuide wiresSurgeryCoronary arteriesArterial occlusions
The invention discloses an instrument for arterial occlusion lesion treating and the application thereof. The instrument comprises a vascular ultrasound catheter, a treating micro catheter and a treating guiding line. The vascular ultrasound catheter and the treating micro catheter are integrally connected in parallel. One part of the treating guiding line is placed in the treating micro catheter, and the other part of the treating guiding line penetrates out of the treating micro catheter from a side wall outlet. According to the instrument, the vascular ultrasound catheter and the treating micro catheter are integrally connected in parallel, a double-cavity micro catheter is used for adjusting the treating guiding line to enter a vessel true lumen, thrombus is sucked out through the treating guiding line, and post-operation hidden danger is removed through one-time curing. The problem that in an intervention recanalization treating operation of blocking of coronary arteries, peripheral arteries and other organ pipelines, a treating guiding line cannot enter a true lumen easily is solved.
Owner:马永红
Compact, energy-efficient ultrasound imaging probes using CMUT arrays with integrated electronics
ActiveUS8891334B2Enhance the imageReduce energy consumptionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersMechanical vibrations separationVascular ultrasoundSonification
A CMUT on CMOS imaging chip is disclosed. The imaging chip can use direct connection, CMOS architecture to minimize both internal and external connection complexity. Intelligent power management can enable the chip to be used for various imaging applications with strict power constraints, including forward-looking intra-vascular ultrasound imaging. The chip can use digital logic to control transmit and receive events to minimize power consumption and maximize image resolution. The chip can be integrated into a probe, or catheter, and requires minimal external connections. The chip can comprise integrated temperature control to prevent overheating.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
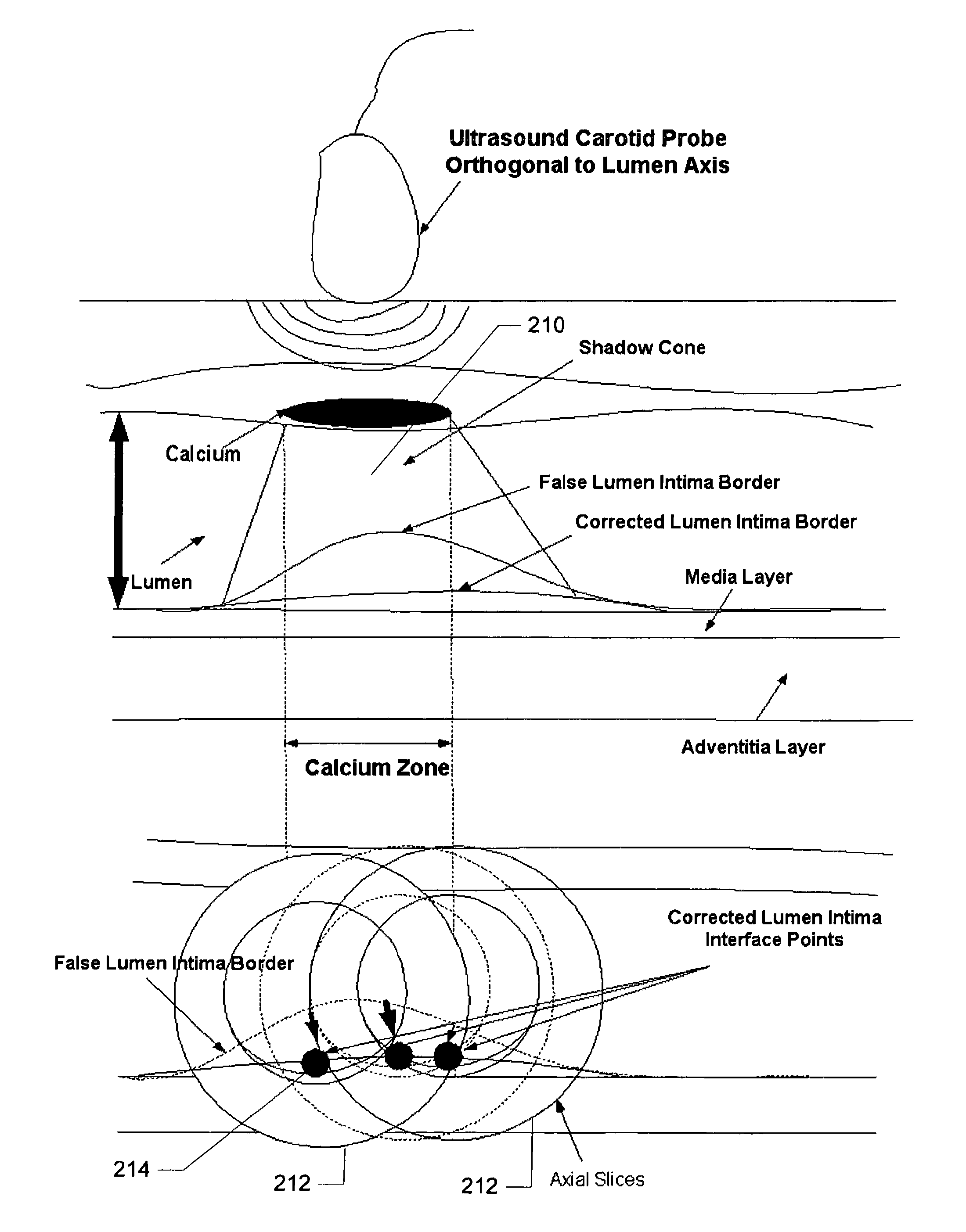
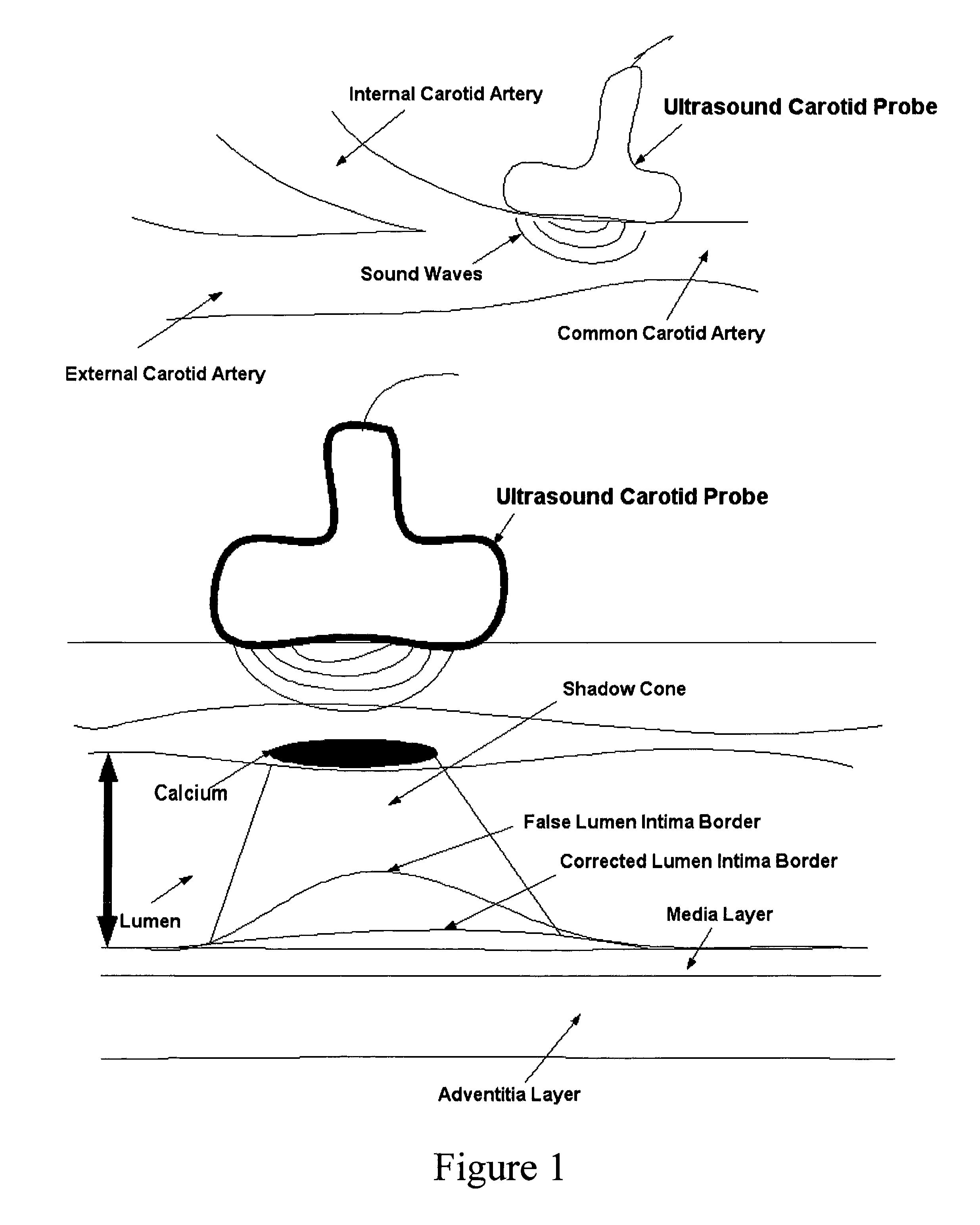
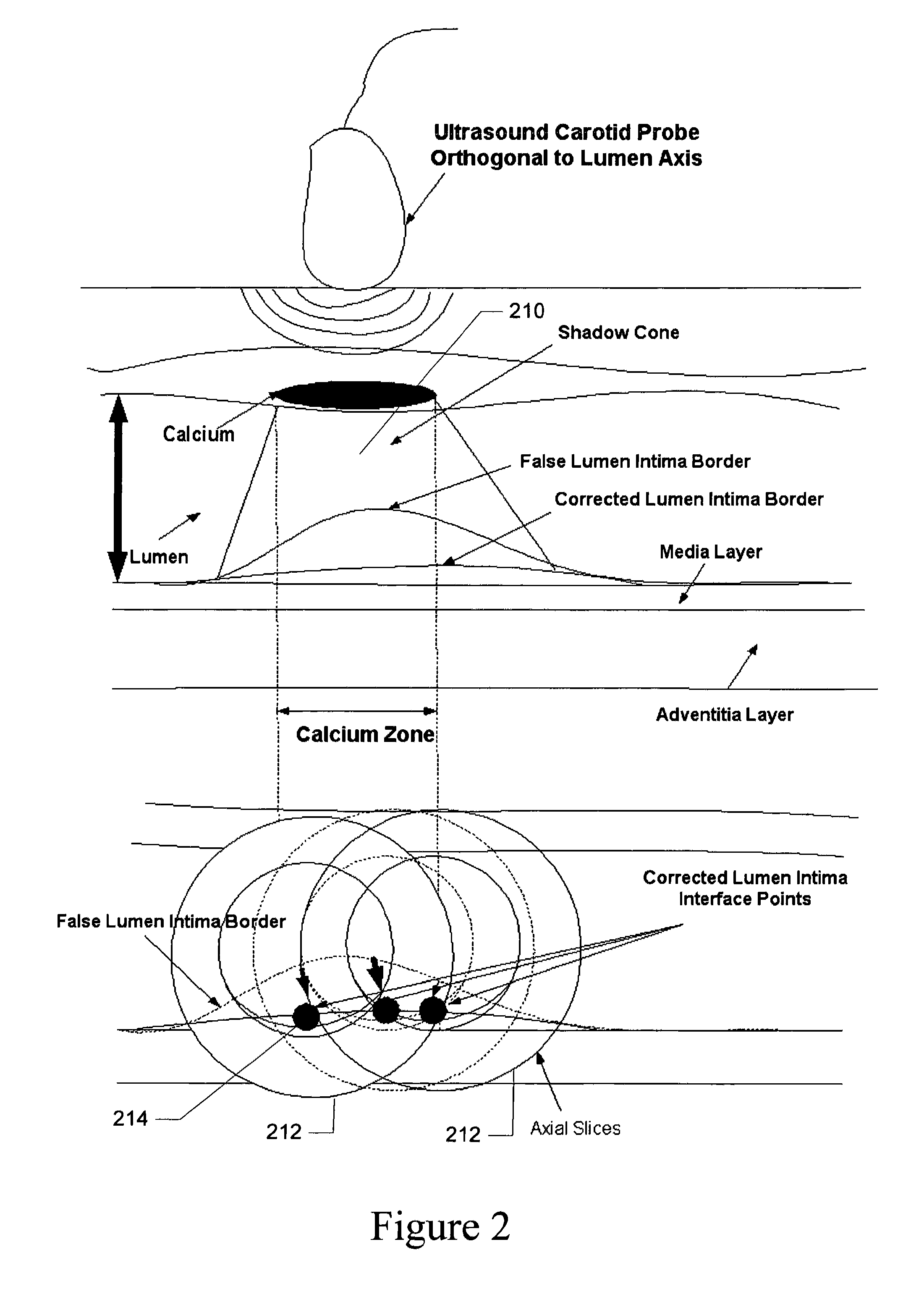
Vascular ultrasound intima-media thickness (IMT) measurement system
InactiveUS8313437B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundSonification
A computer-implemented system and method for fast, reliable and automated processing for intima-media thickness (IMT) measurements. Various embodiments include receiving biomedical imaging data and patient demographic data corresponding to a current scan of a patient; checking the biomedical imaging data in real-time to determine if an artery of the patient has a calcium deposit in a proximal wall of the artery; acquiring arterial data of the patient as a combination of longitudinal B-mode and transverse B-mode data; using a data processor to automatically recognize the artery; using the data processor to calibrate a region of interest around the automatically recognized artery; and determining the intima-media thickness (IMT) of an arterial wall of the automatically recognized artery.
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
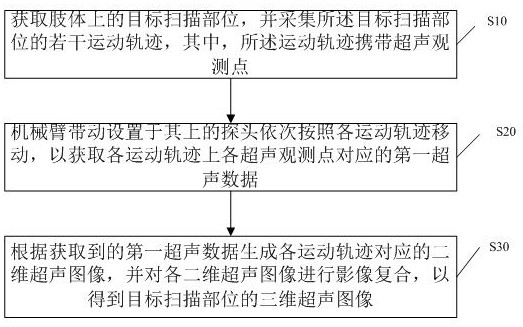
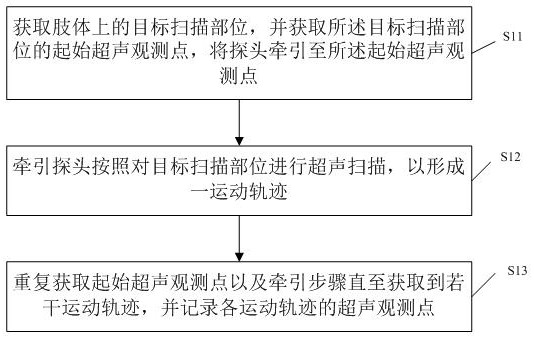
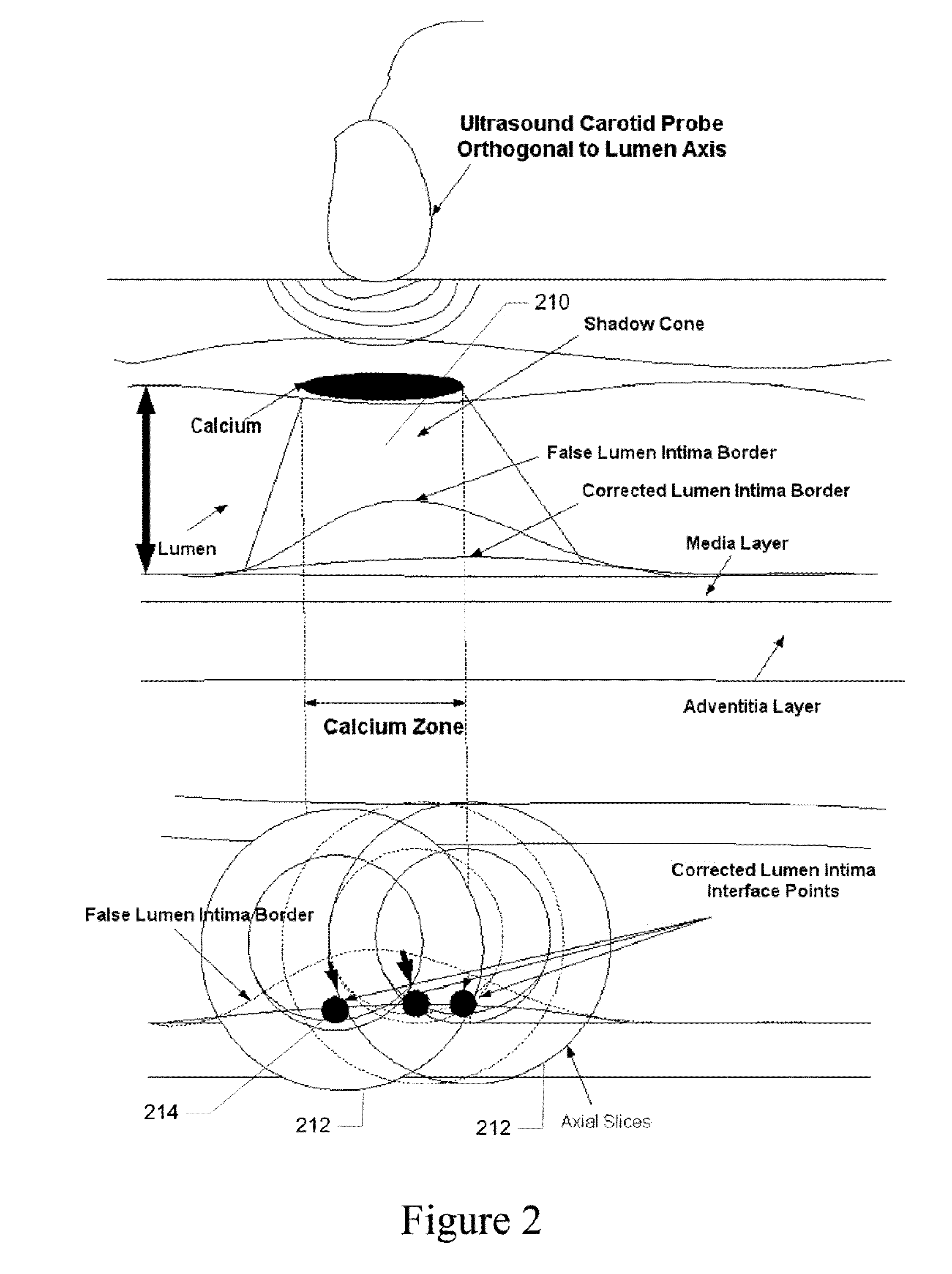
Imaging method of three-dimensional blood vessel ultrasonic image and navigation equipment in ultrasonic operation
ActiveCN112057110AImprove securityOrgan movement/changes detectionComputer-aided planning/modellingHuman bodySurgical operation
The invention discloses an imaging method of a three-dimensional blood vessel ultrasonic image and navigation equipment in an ultrasonic operation. The method comprises the following steps: a plurality of movement tracks at a target scanning part on a limb are determined; a mechanical arm drives a probe to move in sequence according to each movement track to obtain first ultrasonic data; and a plurality of ultrasonic images are generated according to the first ultrasonic data, and the generated ultrasonic images are subjected to image composite reconstruction to obtain a three-dimensional ultrasonic image of the target scanning part. According to the method, the mechanical arm controls the probe to move, three-dimensional image reconstruction is carried out on images collected by the probe, large-range ultrasonic image scanning and three-dimensional image reconstruction on the surface of a human body are achieved, and therefore, a complete three-dimensional ultrasonic image of large-range blood vessels in the human body is obtained, image matching and fusion can be carried out on the three-dimensional ultrasonic image and a three-dimensional DSA (or MRA and the like) image, a three-dimensional fusion image for guiding surgical operation is formed, and the vascular surgery is navigated through the three-dimensional fusion image, and the safety of the vascular surgery is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Validation embedded segmentation method for vascular ultrasound images
InactiveUS20110299754A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundSonification
A computer-implemented system and method for intima-media thickness (IMT) measurements using a validation embedded segmentation method. Various embodiments include receiving biomedical imaging data and patient demographic data corresponding to a current scan of a patient; checking the biomedical imaging data in real-time to determine if an artery of the patient has a calcium deposit in a proximal wall of the artery; acquiring arterial data of the patient as a combination of longitudinal B-mode and transverse B-mode data; using a data processor to automatically recognize the artery by embedding anatomic information; using the data processor to calibrate a region of interest around the automatically recognized artery; automatically computing the weak or missing edges of intima-media and media-adventitia walls using edge flow, labeling and connectivity; and determining the intima-media thickness (IMT) of an arterial wall of the automatically recognized artery.
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
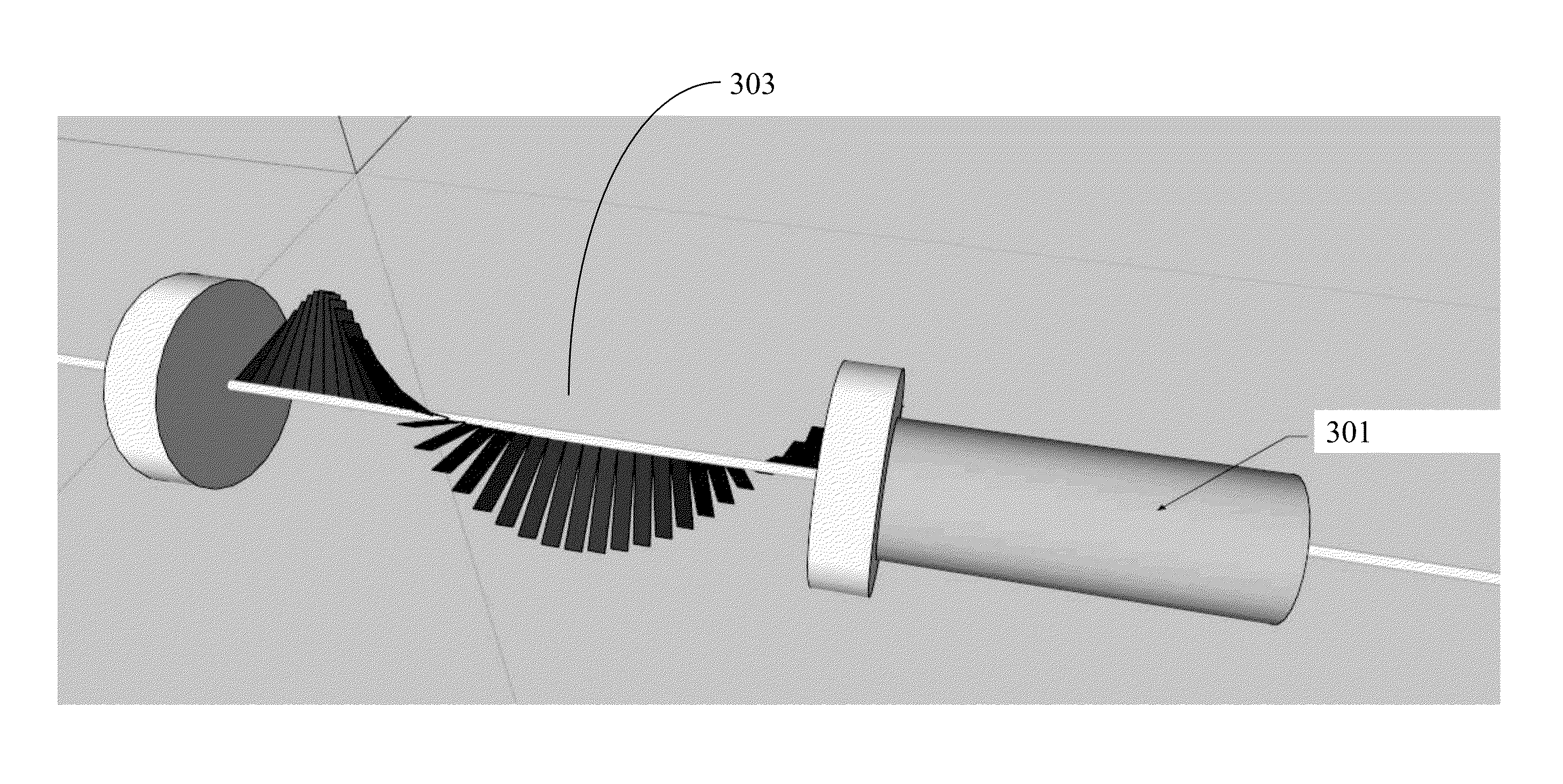
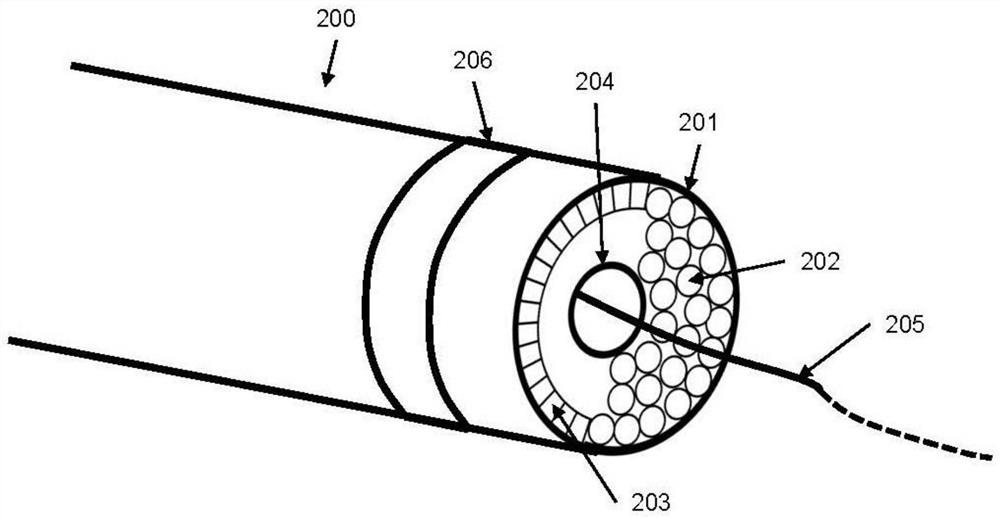
Intravascular ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter
InactiveCN104068897AImprove handlingSmall instrument diameterSurgical needlesCatheterVascular ultrasoundUltrasound angiography
The invention discloses an intravascular ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter. The intravascular ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter is characterized by being composed of a vascular ultrasound catheter and a treatment micro-catheter integrally in parallel connection with the vascular ultrasound catheter. The intravascular ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter is small in outer diameter, a puncture lead wire is easily and synchronously brought into the lesion with the ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter, and the ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter effectively improves the controllability of the lead wire. In addition, the intravascular ultrasound double-cavity micro-catheter can show the tube wall and lesion characteristics. Due to the fact that two catheters are conjoined, when the lead wire puncture is performed under the vascular ultrasound guidance, the puncture lead wire and an ultrasound probe are relatively fixed in position, and relation of the guide lead wire and a target objective is easily confirmed, correct grasp of the puncture direction is facilitated, the success rate that the lead wire is fed into the true lumen can be greatly improved, and the operation achievement ratio can be improved.
Owner:汝磊生
System for detecting rotation angle of a catheter in an X-ray image
An IVUS catheter is advantageously provided with a particular radio-opaque pattern enabling detection of catheter rotation angle with respect to an X-ray imaging source for co-registering IVUS image data with angiographic X-ray or CT image data, for example. An ultrasound catheter system supports orientation and display of intra-vascular ultrasound imaging data. The system comprises an ultrasound catheter for acquiring ultrasound images comprising a body having a pattern of radio-opaque material on the external surface of the catheter body. The pattern varies with angular rotation of the catheter and indicates an angle of rotation of a predetermined reference orientation of the catheter relative to an X-ray radiation source, so that an X-ray image of the catheter body indicates the pattern and the pattern is analyzable by an image data processor to determine the angle of rotation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
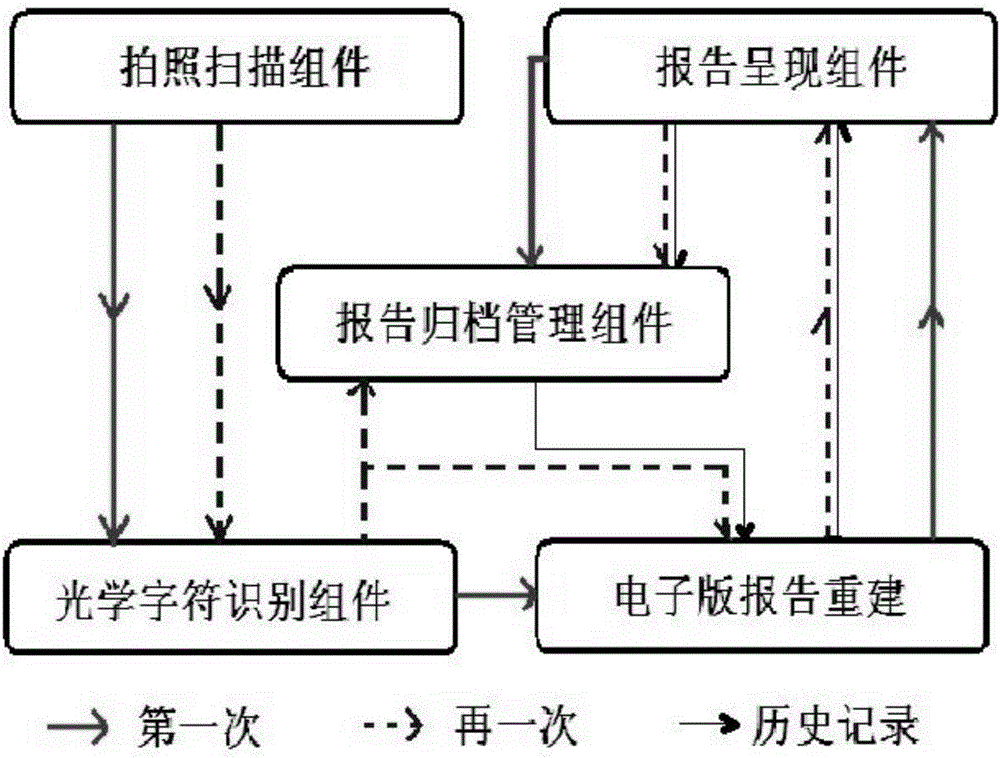
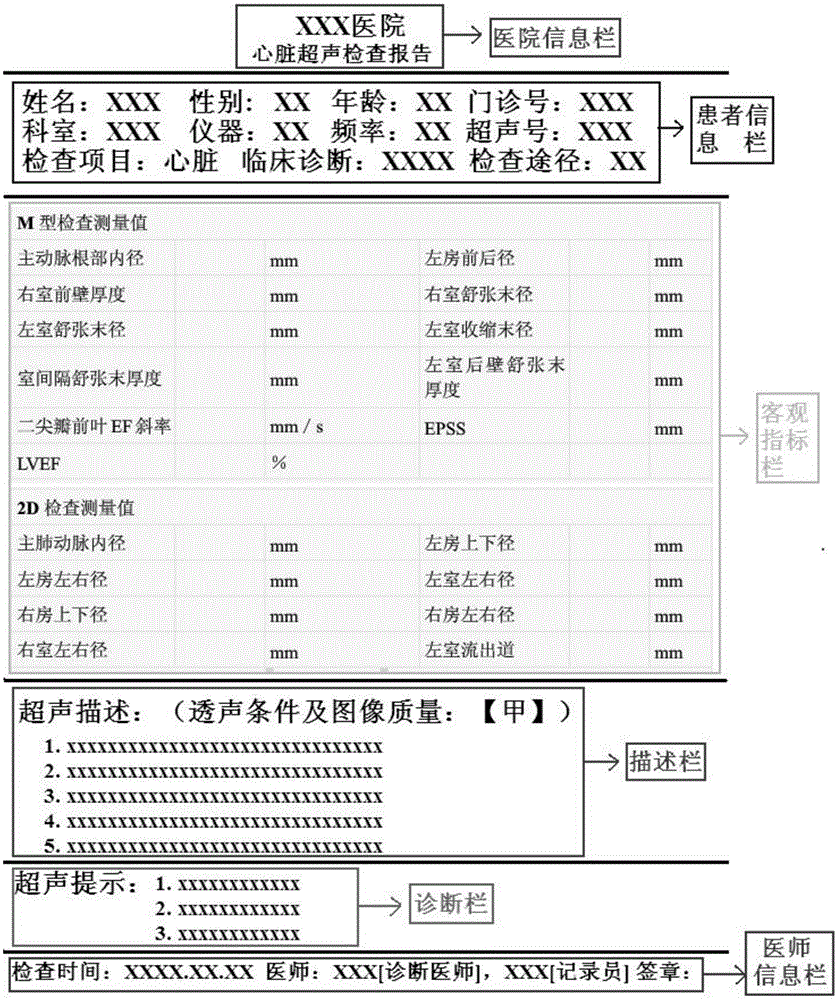
Digitalization ultrasonic kinetocardiogram report automatic management method and system
ActiveCN106202948AEasy transferEasy to manageCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseSonification
The invention relates to a digitalization ultrasonic kinetocardiogram report automatic management method and a system. The system comprises five modules which are a photographing scanning assembly, an optical character recognition assembly, an electronic edition report reconstruction and presentation assembly, and a report filing management assembly; the method comprises a first processing of the ultrasonic kinetocardiogram and a second processing of the ultrasonic kinetocardiogram. The system and the method are advantageous in that the system and the method can be widely applied to the archiving, transmission, classification and comparison of various inspection reports (such as vascular ultrasound report, various inspection reports and the like) mainly based on objective indicators and long-term warning and disease management of large groups of large-scale data cloud, both to achieve the commonality of the results of various hospital tests, reduce medical costs, save medical resources, and to fulfill a network medical mode which integrates big data cloud calculation disease pre-warning and disease individual management.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
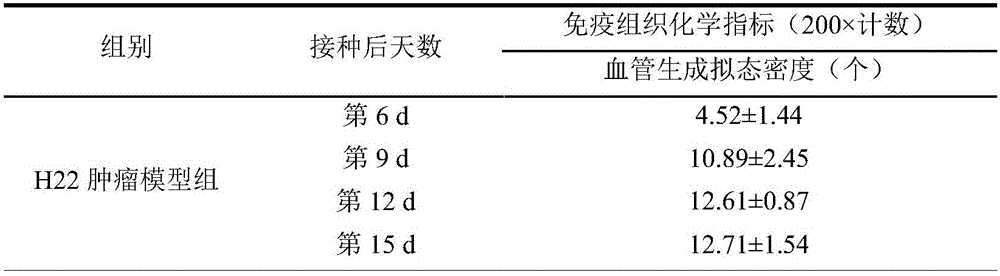
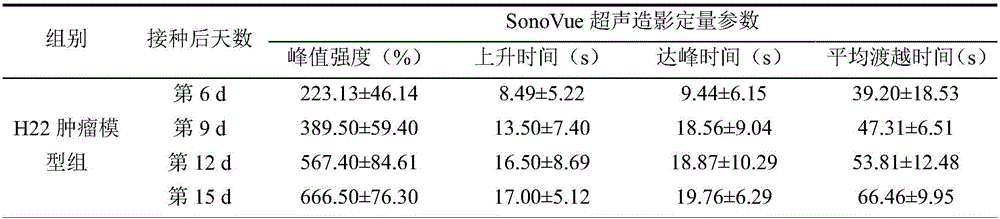
Examination indexes of SonoVue ultrasonic contrast technology in diagnosis and treatment of tumor angiogenesis mimicry
InactiveCN105879064AEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsAbnormal tissue growthVascular ultrasound
The invention discloses examination indexes of a SonoVue ultrasonic contrast technology in diagnosis and treatment of tumor angiogenesis mimicry and belongs to the technical field of clinical tumor vessel ultrasonic examination. The situation that ultrasonic examination indexes including the rising time, the time to peak and the average transition time can be used for clinical diagnosis and treatment of tumor angiogenesis mimicry is found for the first time, a basis is provided for clinical early noninvasive diagnosis of tumor angiogenesis mimicry, the grade malignancy, the blood supply mode and other characters of a tumor of a patient can be clinically diagnosed easily, and a diagnosis basis is provided for drug selection or operation treatment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
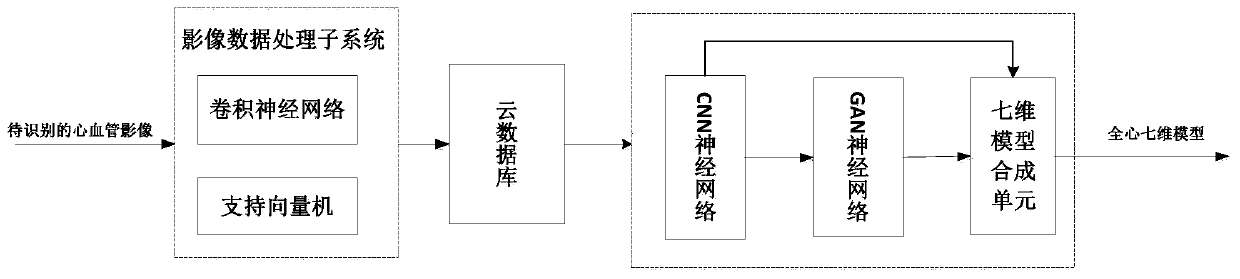
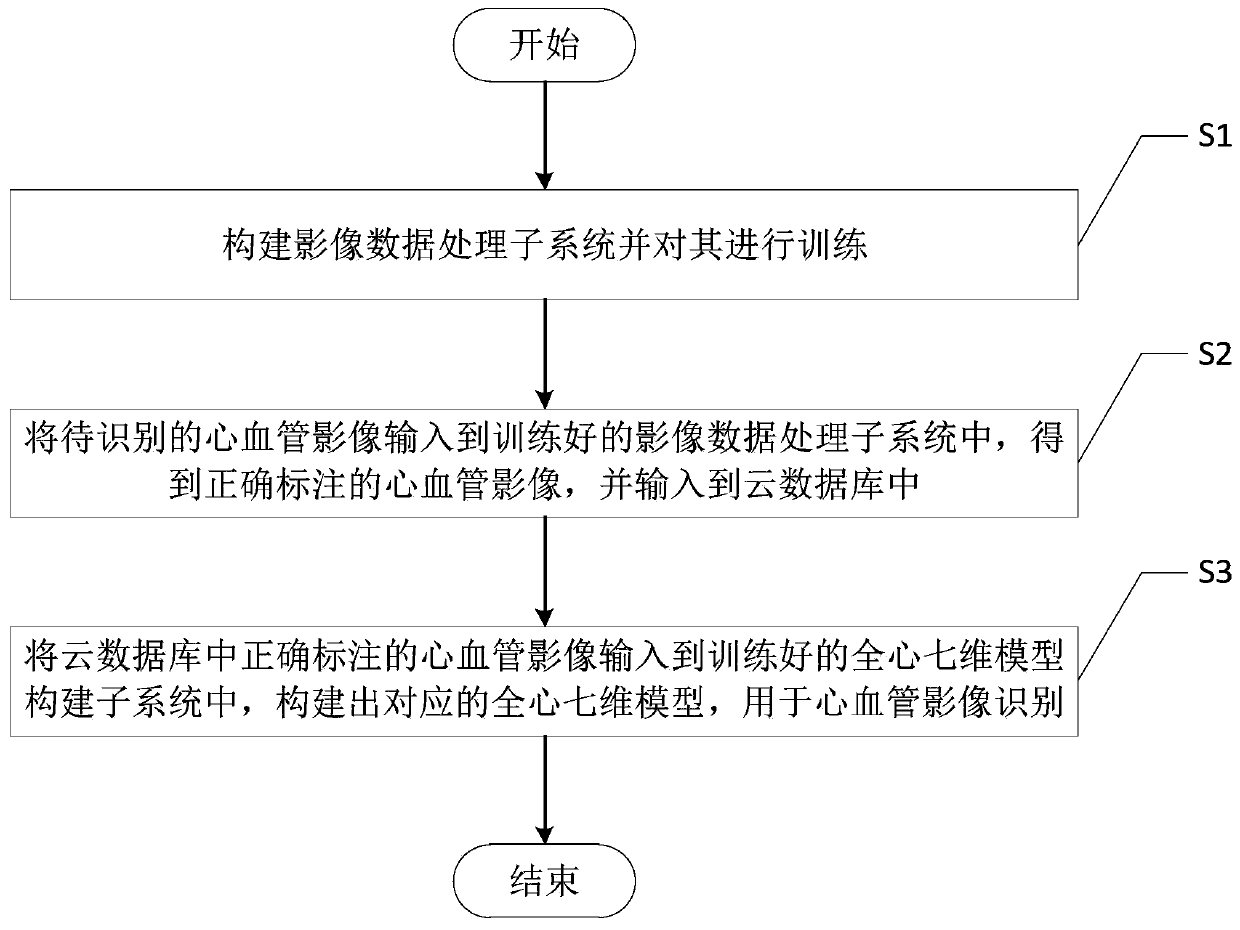
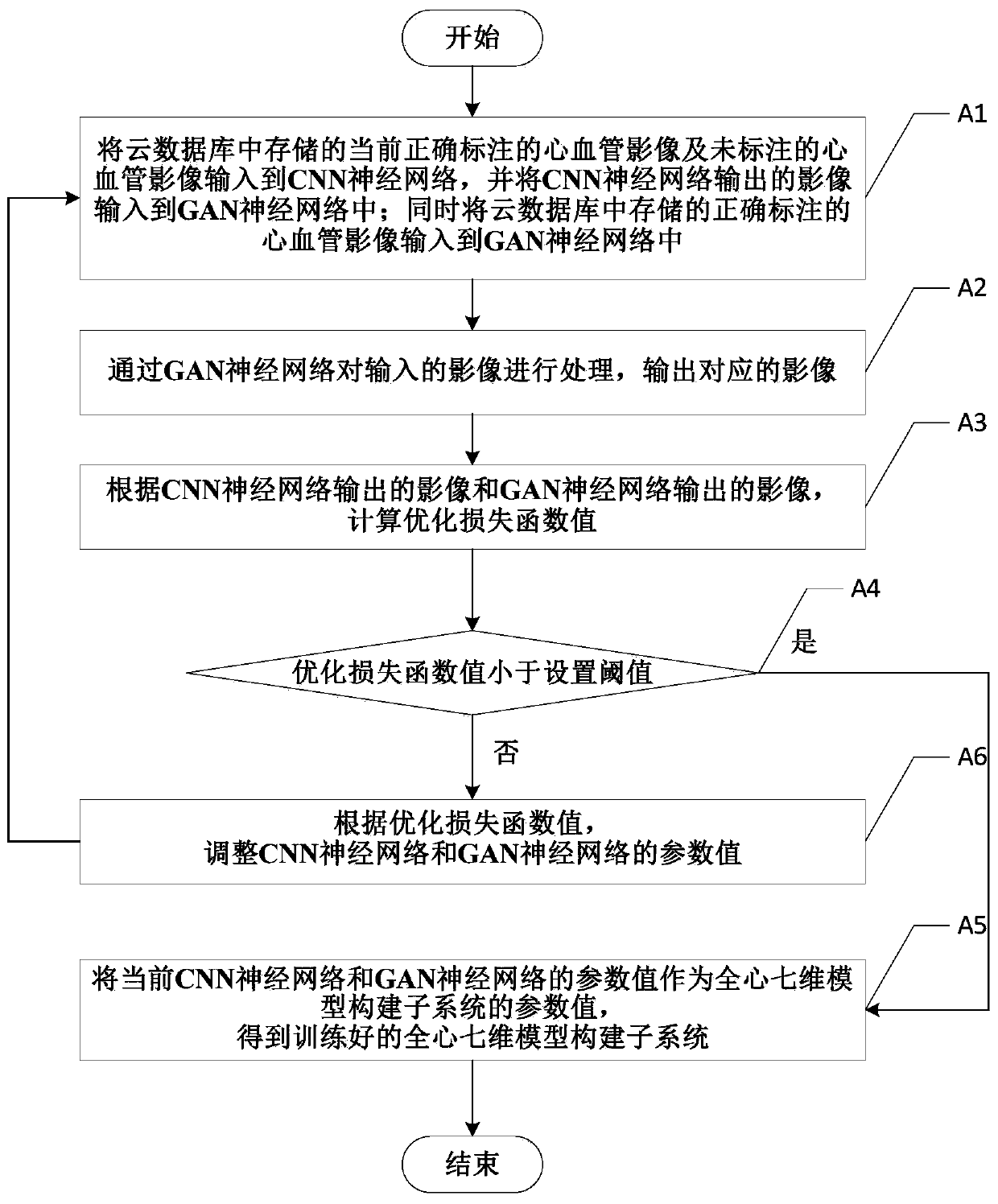
Cardiovascular image recognition system and method based on whole-heart seven-dimensional model
ActiveCN111341420AAccurate identificationComparableMedical imagesNeural architecturesVascular ultrasoundImaging study
The invention discloses a cardiovascular image recognition system and method based on a whole-heart seven-dimensional model. The system comprises an image data processing subsystem, a cloud database and a whole-heart seven-dimensional model construction subsystem which are connected in sequence. The image data processing subsystem is used for processing an input cardiovascular image to be identified, accurately labeling the cardiovascular image and uploading the cardiovascular image to be identified to the cloud database; the cloud database is used for storing all accurately marked cardiovascular images; and the whole-heart seven-dimensional model construction subsystem is used for constructing a corresponding whole-heart seven-dimensional model according to the required cardiovascular image in the cloud database, and recognizing the cardiovascular image according to the constructed whole-heart seven-dimensional model. The cardiovascular ultrasound image can be accurately recognized, and the recognition quality is guaranteed; a high-compatibility modeling system is provided, and the method is suitable for various imaging inspection modes; the time consumed by an imaging doctor in image reading and modeling is reduced, and the burden of the imaging doctor is greatly reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
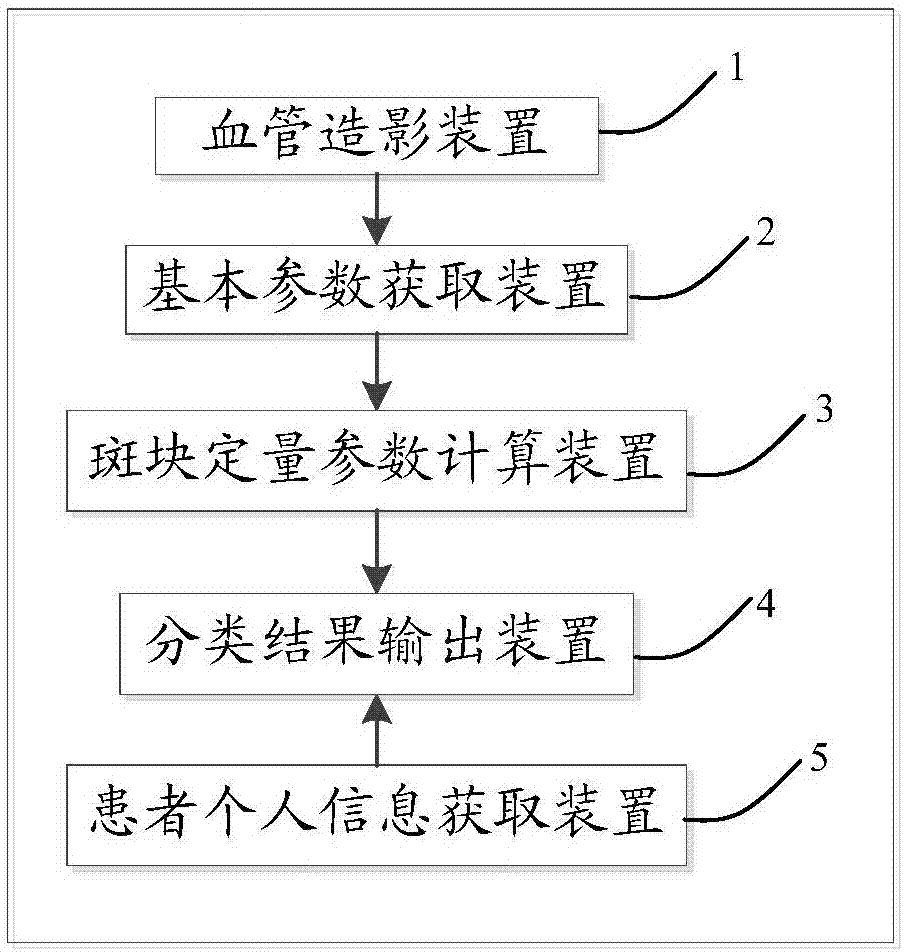
Atherosclerotic plaque classifying system
ActiveCN107506791AEarly classificationQuick classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSonificationVascular ultrasound
The invention provides an atherosclerotic plaque classifying system. The system comprises an angiography device which is used for acquiring a vascular ultrasound contrastographic image, a basic parameter acquisition device which is used for analyzing the vascular ultrasound contrastographic image to acquire the maximum plaque area A, an intraluminal time-intensity curve and an intra-plaque time-intensity curve, extracting the intraluminal contrast agent peak time TTP1, the peak intensity IMAX1 and the area under the curve AUC1 from the intraluminal time-intensity curve, and extracting the intra-plaque contrast agent peak time TTP2, the peak intensity IMAX2 and the area under the curve AUC2 from the intra-plaque time-intensity curve, a plaque quantitative parameter calculation device which is used for acquiring the enhancement intensity IMAX, the maximum enhancement density DMAX, the relative peak time delta TTP, the area under the curve delta AUC and the relative average transit time delta mTT, and a classification result output device which is used for classifying atherosclerotic plaques according to the plaque quantitative parameter.
Owner:哈尔滨声诺医疗科技有限公司
Catheter system integrating ultrasonic imaging and laser ablation
ActiveCN113017827APreserve the effect of treatmentDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionVascular ultrasoundLaser light
The invention provides a catheter system integrating ultrasonic imaging and laser ablation. The catheter system comprises a catheter, the left end and the right end of the catheter are the catheter near end and the catheter far end respectively, an optical waveguide and an ultrasonic signal channel are arranged in an inner cavity of the catheter, the near end of the optical waveguide is connected with a pulse laser light source, and the far end of the optical waveguide ends at the end face of the catheter far end. Laser pulses emitted by the pulse laser light source are emitted from the front of the far end of the catheter through the optical waveguide and erode tissues in front of the catheter; The near end of the ultrasonic signal channel is connected with an ultrasonic imaging engine, the far end of the ultrasonic signal channel is connected with an ultrasonic imaging probe for foresight imaging, and the ultrasonic imaging probe is used for focusing and scanning imaging to assist laser ablation. Vascular ultrasonic imaging and laser ablation are combined into a catheter system, the treatment effect of the laser ablation is reserved, image guidance of the vascular ultrasonic imaging is provided, and application of the laser ablation in eccentric vascular stenosis can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
System and method of aquiring blood-vessel data
ActiveUS20110208017A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundData acquisition
A system and method is provided for substantially synchronizing the acquisition of blood-vessel data to an identifiable portion of heartbeat data. Specifically, a data-gathering device is adapted to acquire heartbeat data and blood-vessel data from a heart-monitoring device and a data-gathering probe, respectively. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the blood-vessel data is acquired during a cyclical portion of the heartbeat data. By identifying a cyclical (or commonly reoccurring) portion of the heartbeat data and acquiring blood-vessel data during this cyclical portion (or during an interval that substantially corresponds thereto), the blood vessel can be analyzed as if it were standing still—i.e., not expanding and relaxing. In one embodiment of the present invention, the heart-monitoring device includes an EKG device, the data-gathering device includes an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device, and the data-gathering probe includes at least one transducer. In another embodiment of the present invention, the data-gathering system further includes a retraction device adapted to move the data-gathering probe though a blood vessel at a substantially steady speed.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Vein puncture robot operation trajectory planning method based on ultrasonic image guidance
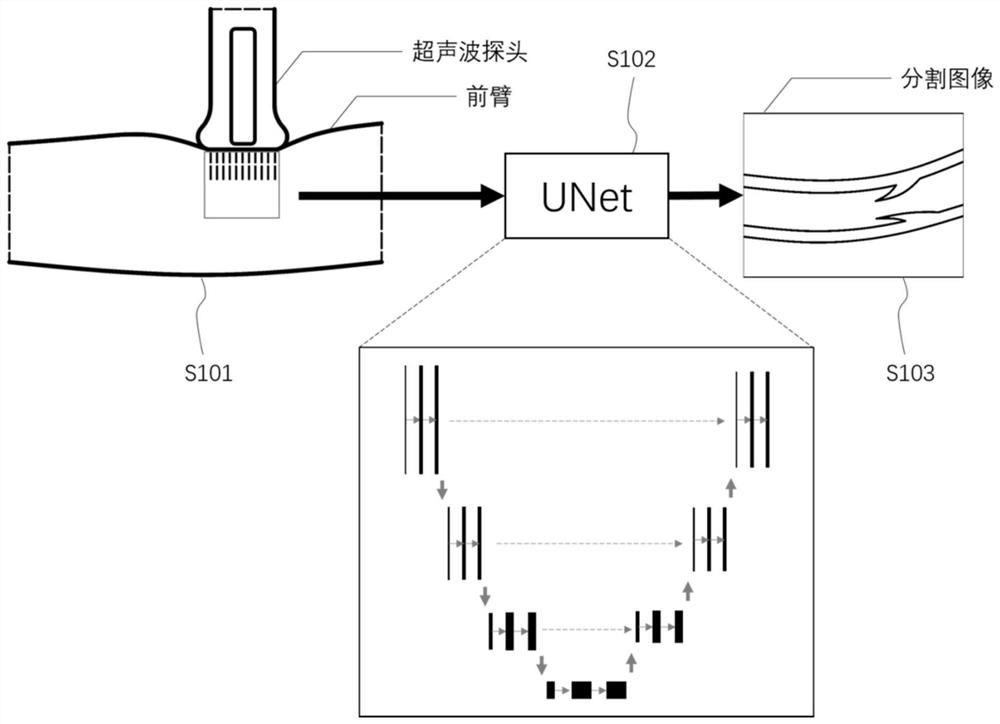
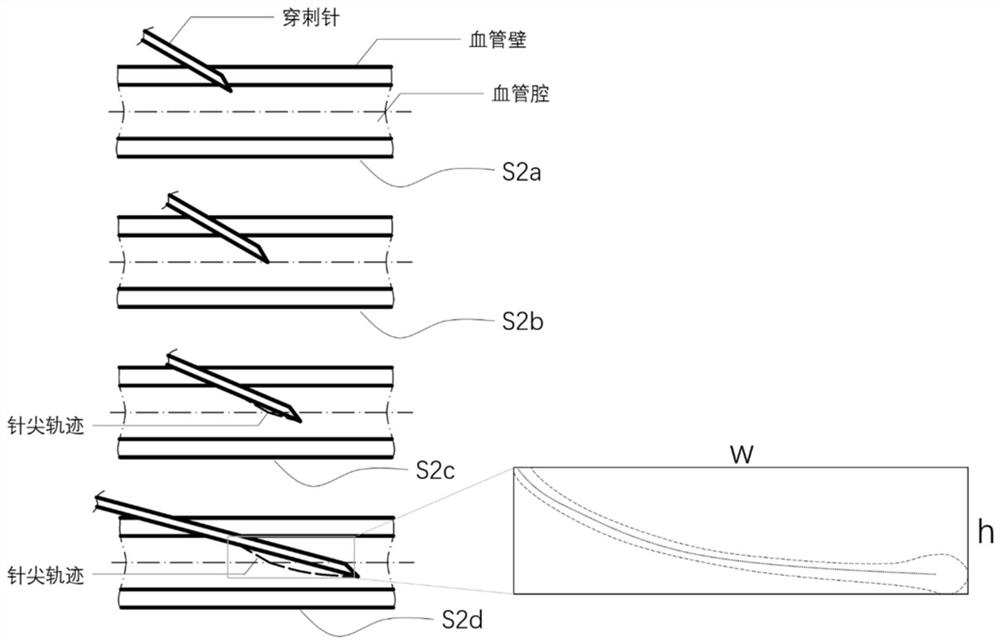
ActiveCN112022294AEnsure safetyRealize automatic punctureImage enhancementImage analysisVascular ultrasoundImage guidance
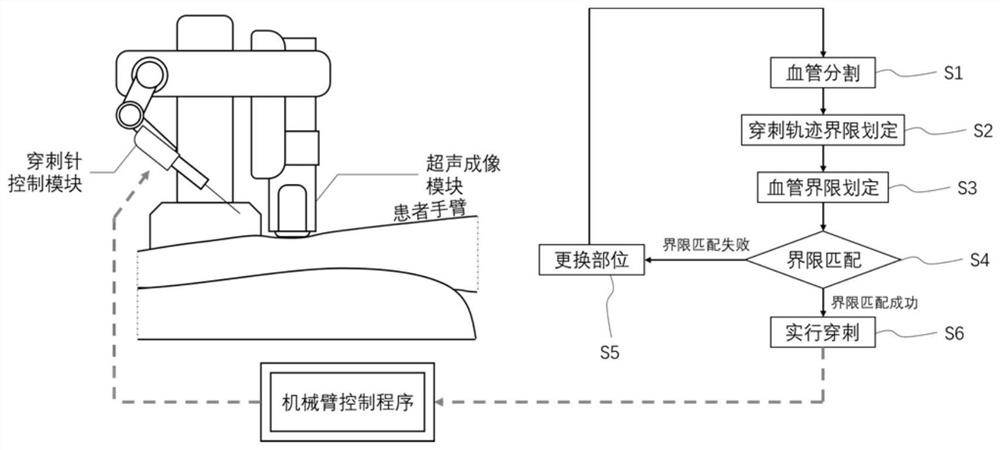
The invention relates to a vein puncture robot operation trajectory planning method based on ultrasonic image guidance. The vein puncture robot operation trajectory planning method based on the ultrasonic image guidance is characterized by performing vein puncture through a puncture piece controlled by the vein puncture robot, and comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring a blood vessel ultrasonic image of a certain part of a subject to be punctured, and acquiring a blood vessel segmentation map from the blood vessel ultrasonic image; 2) defining bounds of a puncture trajectory according toa preset first puncture trajectory of the puncture piece in the blood vessel; 3) dividing a safe area from the blood vessel segmentation map to obtain boundaries of the blood vessel; 4) matching the bounds of the puncture trajectory with the boundaries of the blood vessel, and generating a second puncture trajectory on basis of matched positions and the first puncture trajectory if the bounds of the puncture trajectory are completely covered by the boundaries of the blood vessel, or changing the part of the subject to be punctured and performing the above steps again. Compared with the prior art, the vein puncture robot operation trajectory planning method based on the ultrasonic image guidance includes trajectory planning so that automatic puncture can be achieved, thereby realizing highdegree of automation and guaranteeing safety of the puncture trajectory.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
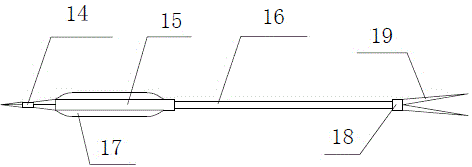
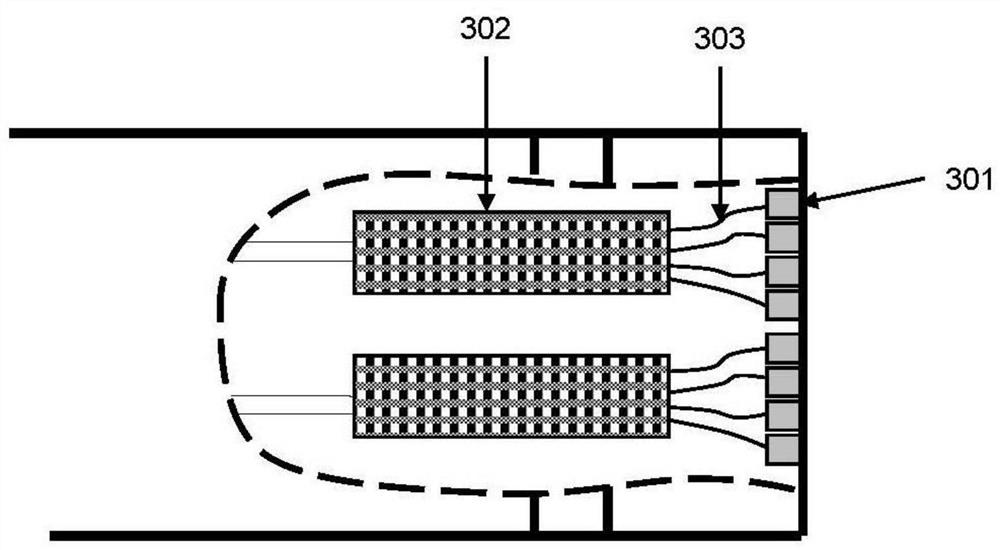
Ultrasound transducer assembly and method for manufacturing an ultrasound transducer assembly
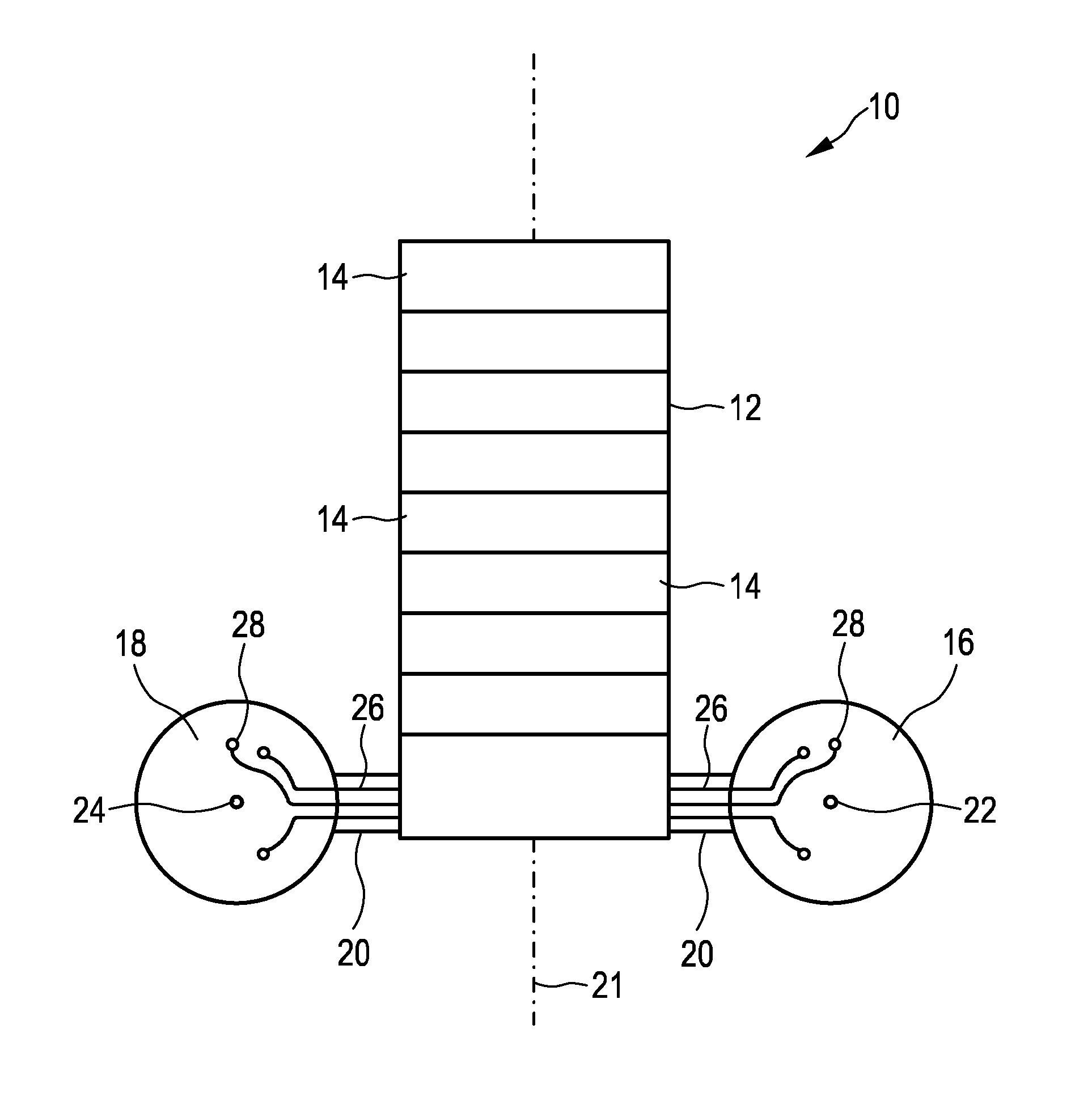
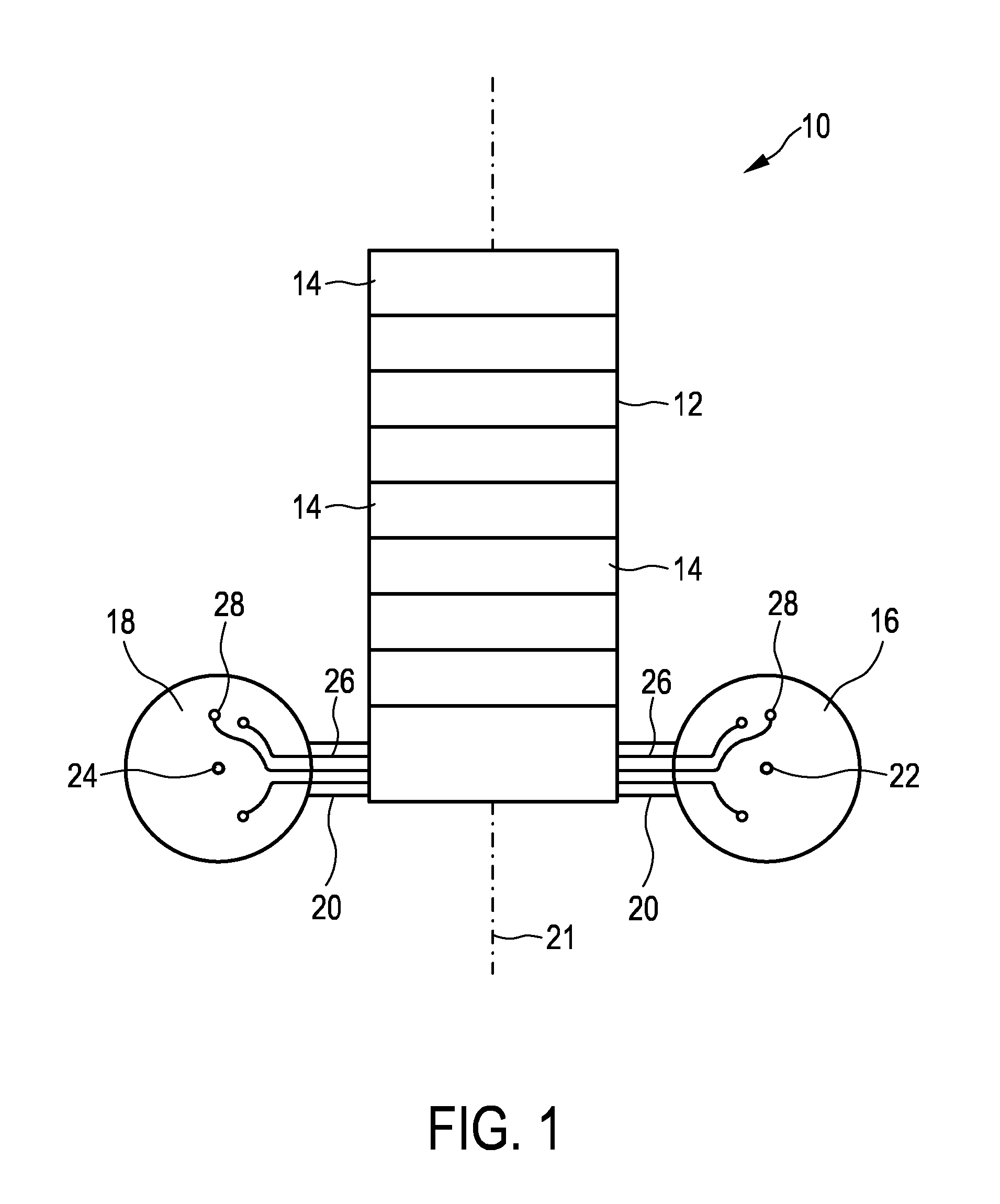
ActiveUS20160207068A1Small sizeLow effortUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyUltrasonic sensorSonification
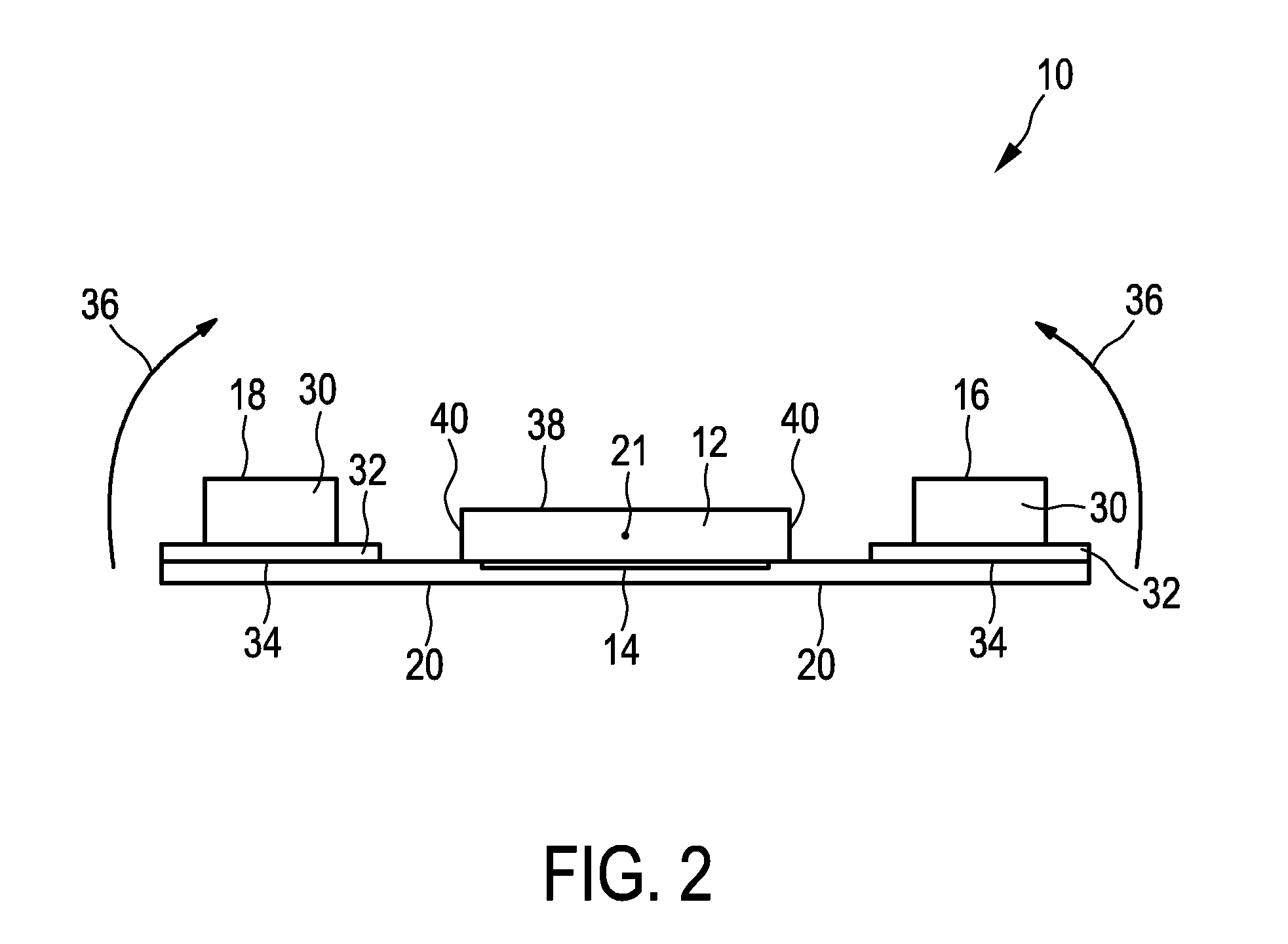
The present invention relates to an ultrasound transducer assembly (10), in particular for intra vascular ultrasound systems. The assembly (10) comprises a transducer array (12) including a plurality of transducer elements (14) for transmitting and receiving ultrasound waves. Two support elements (16, 18) are provided for supporting the transducer array (12) in a curved or polygonal shape. The support elements (16, 18) are connected via a flexible connection layer (20) to the transducer array (12) for flexibly connecting the support elements (16, 18) to the transducer array (12).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Blood flow automatic measurement method and device based on ultrasonic image
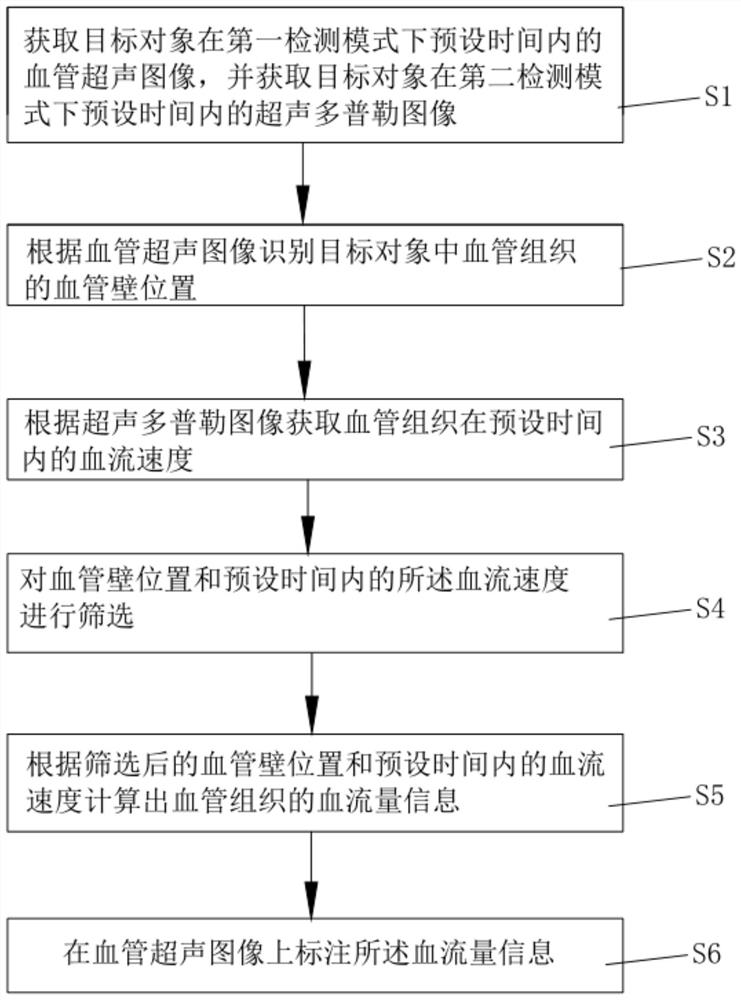
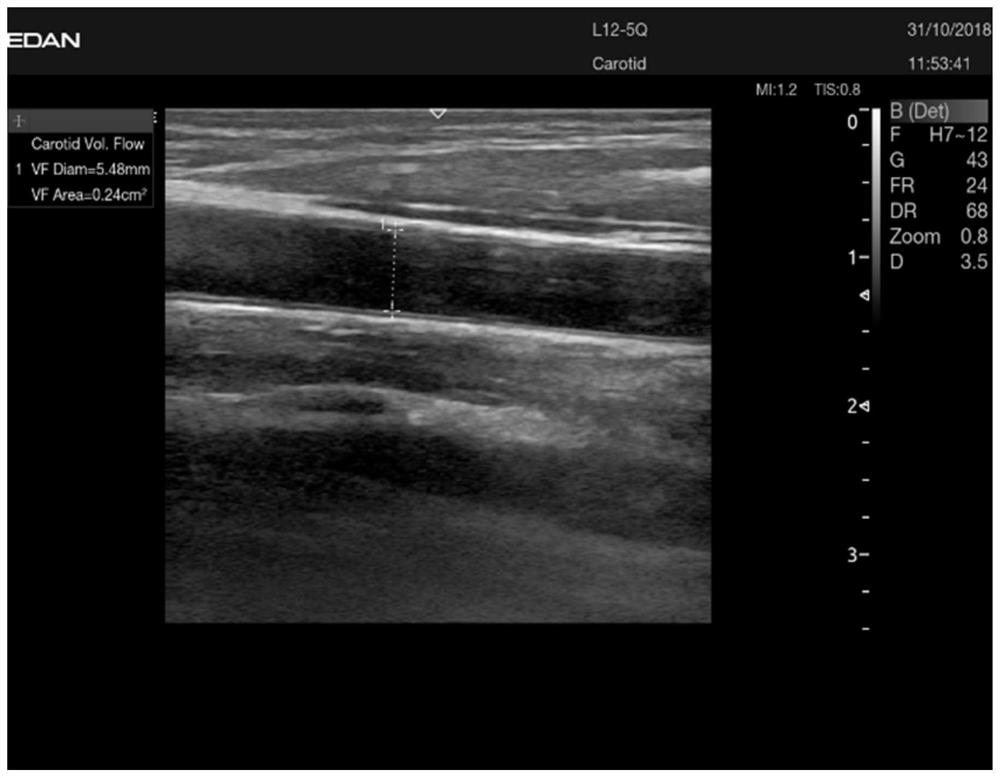
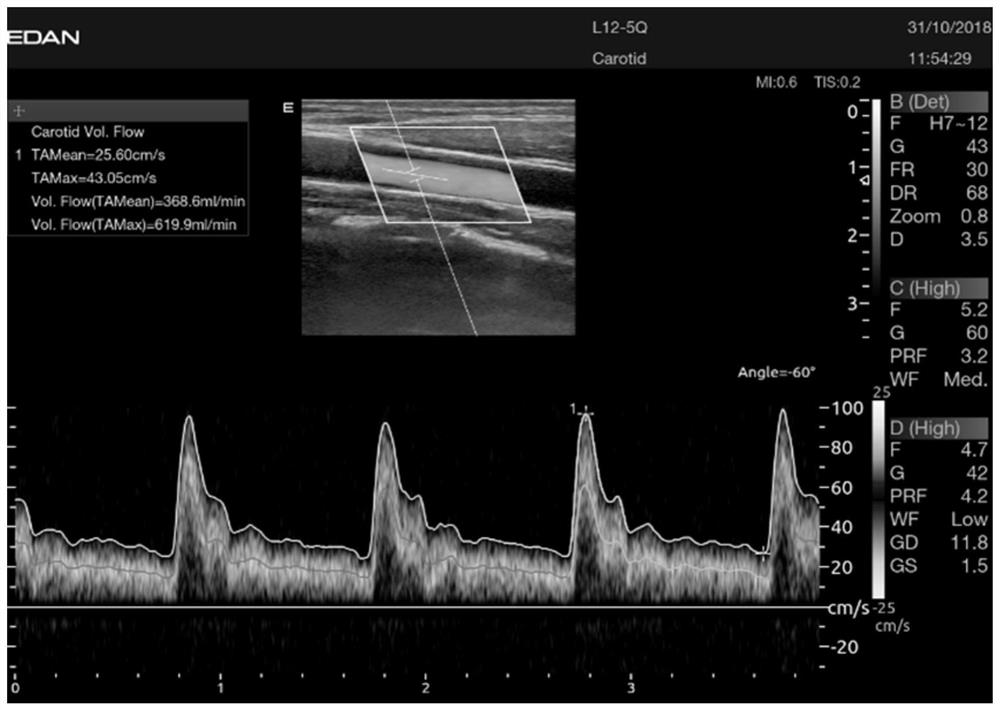
PendingCN112037163ARobustEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisVascular ultrasoundBlood Vessel Tissue
The invention discloses a blood flow automatic measurement method and device based on an ultrasonic image, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a blood vessel ultrasonic image of a target object in a preset time under a first detection mode, and obtaining an ultrasonic Doppler image of the target object in a preset time under a second detection mode; identifying the blood vessel wall position of the blood vessel tissue in the target object according to the blood vessel ultrasonic image; acquiring the blood flow velocity of the vascular tissue within a preset time according to the ultrasonic Doppler image; and calculating blood flow information of the vascular tissue according to the position of the vascular wall and the blood flow velocity within the preset time. According to theblood flow measurement mode, the operation process is simpler, medical staff do not need to manually label and switch image modes back and forth, and the examination efficiency is improved; and meanwhile, the blood flow is calculated by utilizing the blood vessel diameter data and the blood flow speed data within the preset time, so that the blood flow calculation result is more robust, random interference caused by instantaneous measurement is reduced, and the measurement result is more accurate.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
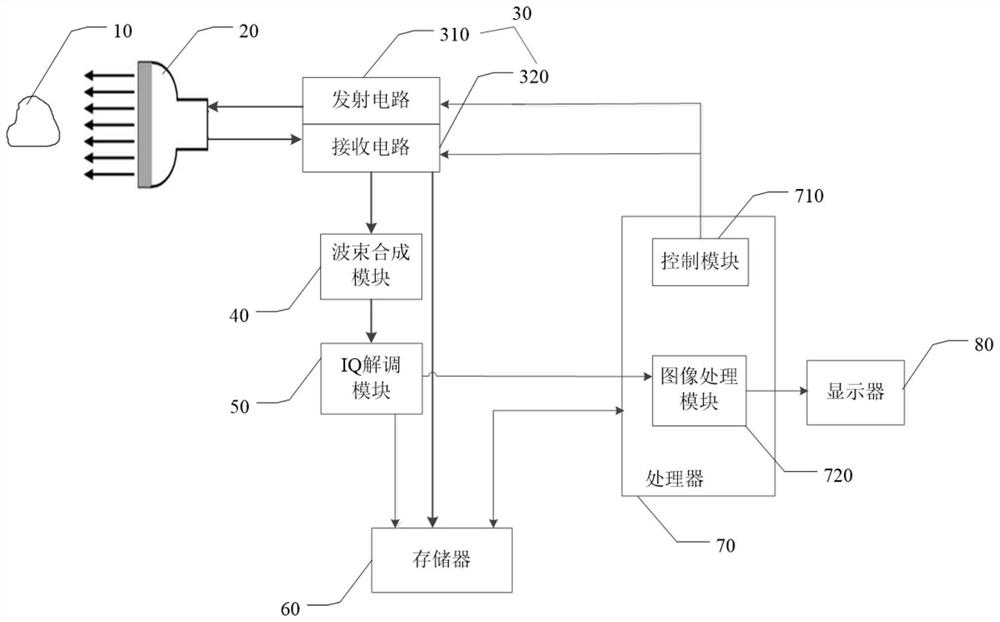
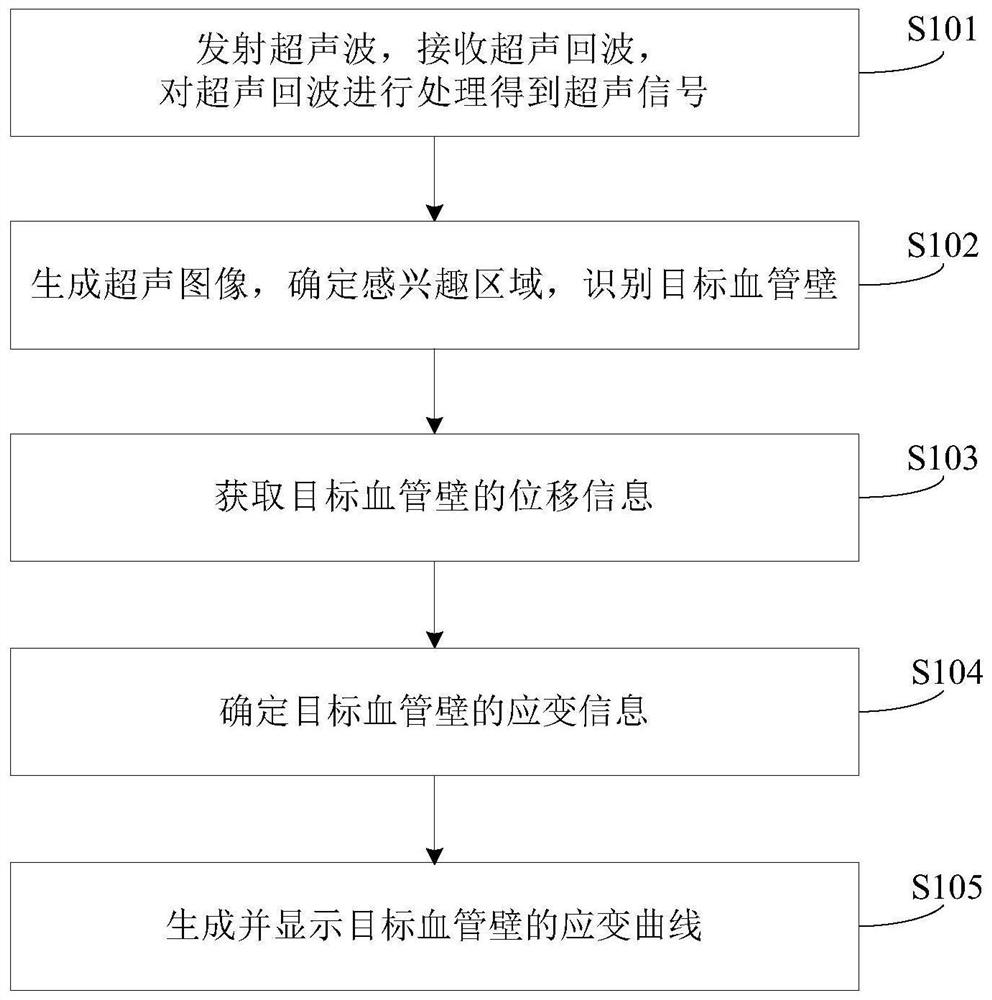
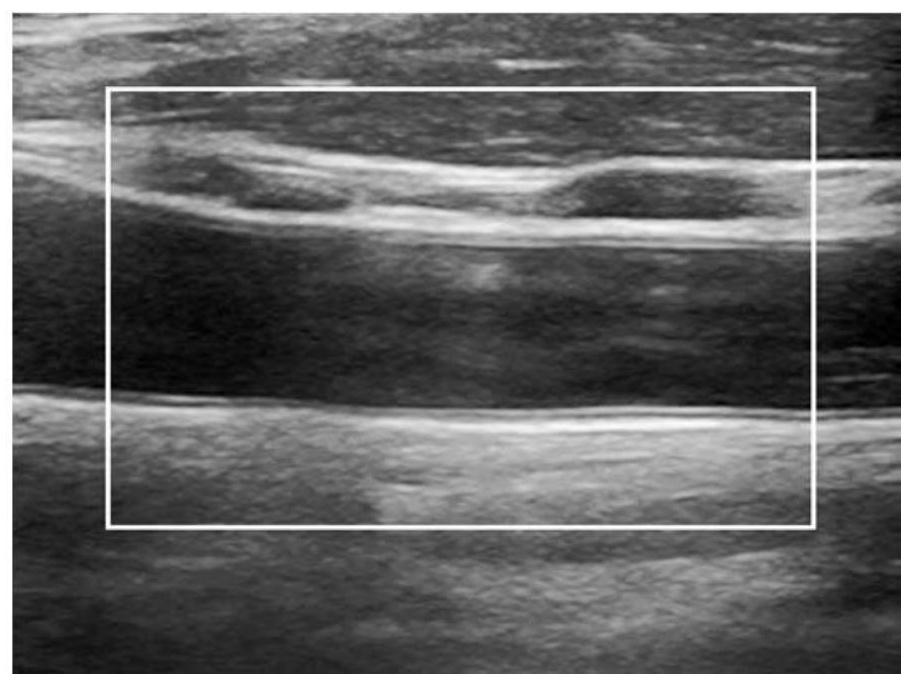
Vascular ultrasound data processing method and device and storage medium
PendingCN114680936AEasy to capture the law of elastic changesOrgan movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionVascular ultrasoundRadiology
The embodiment of the invention provides a blood vessel ultrasonic data processing method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: transmitting ultrasonic waves to a target tissue containing blood vessels, receiving ultrasonic echoes based on the ultrasonic waves returned from the target tissue, and processing the ultrasonic echoes to obtain ultrasonic signals; generating an ultrasonic image of the blood vessel according to the ultrasonic signal, determining a region of interest in the ultrasonic image, and identifying a target blood vessel wall in the region of interest; acquiring displacement information of the target blood vessel wall according to the ultrasonic signal; determining strain information of the target blood vessel wall according to the displacement information of the target blood vessel wall; and generating and displaying a strain curve of the target blood vessel wall according to the strain information of the target blood vessel wall, wherein the strain curve is used for representing a change track of the strain information of the target blood vessel wall along with time. According to the method, the change track of the strain information of the target blood vessel wall along with time is reflected through the strain curve, and the elastic change rule of the blood vessel is conveniently captured.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com