Patents
Literature
173 results about "Arterial wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
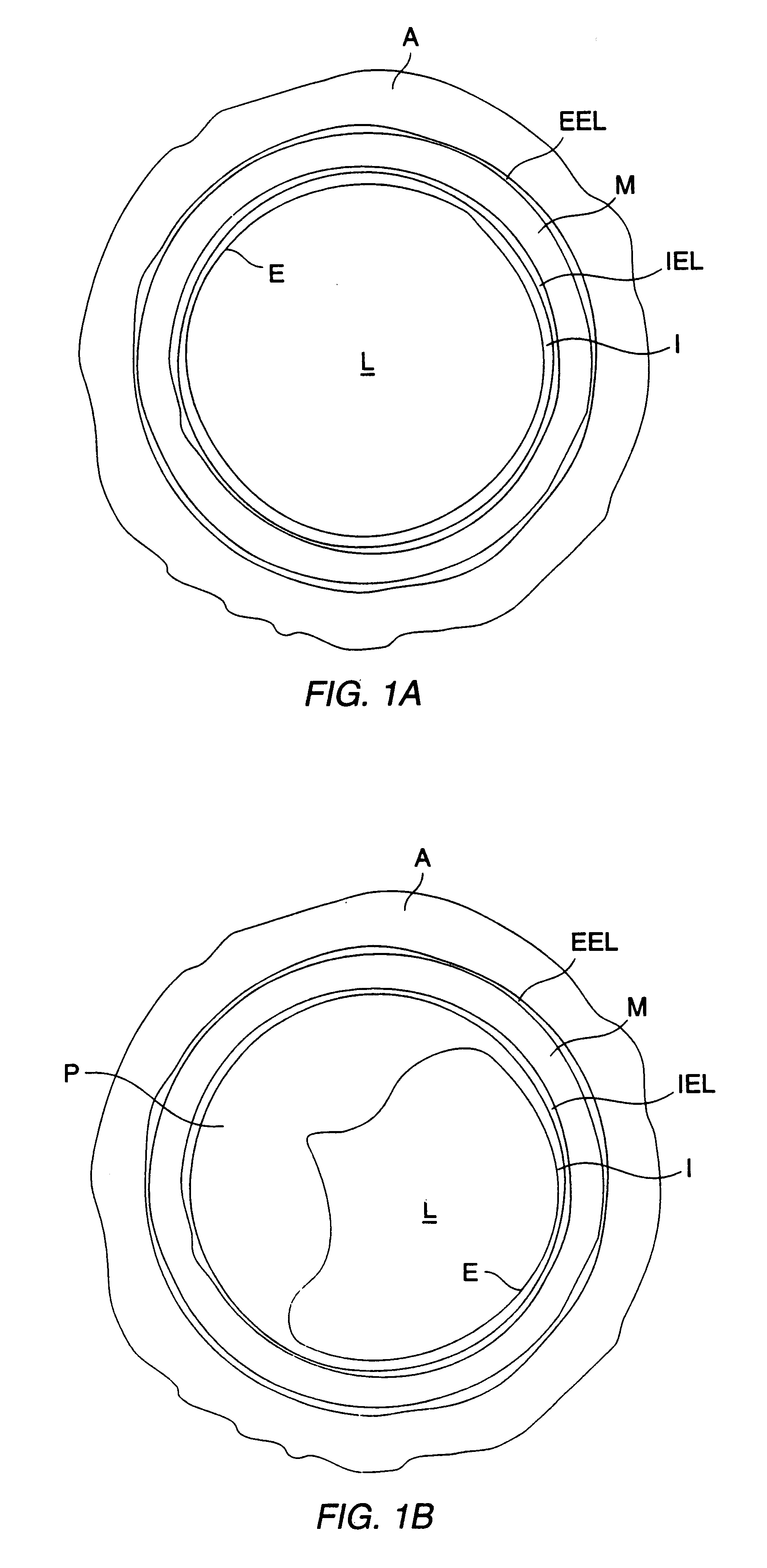
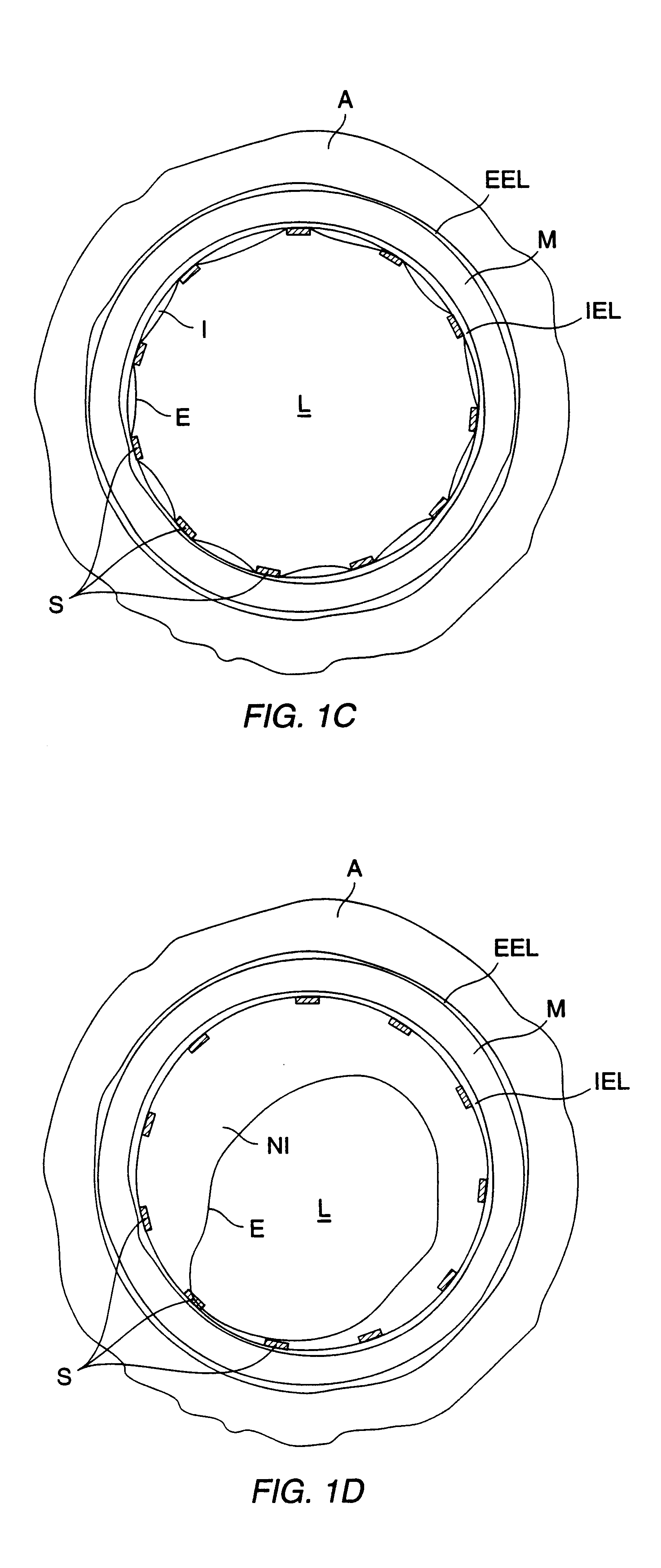
Arterial wall. the fibrous and muscular wall of vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to structures throughout the body, and of the pulmonary arteries that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
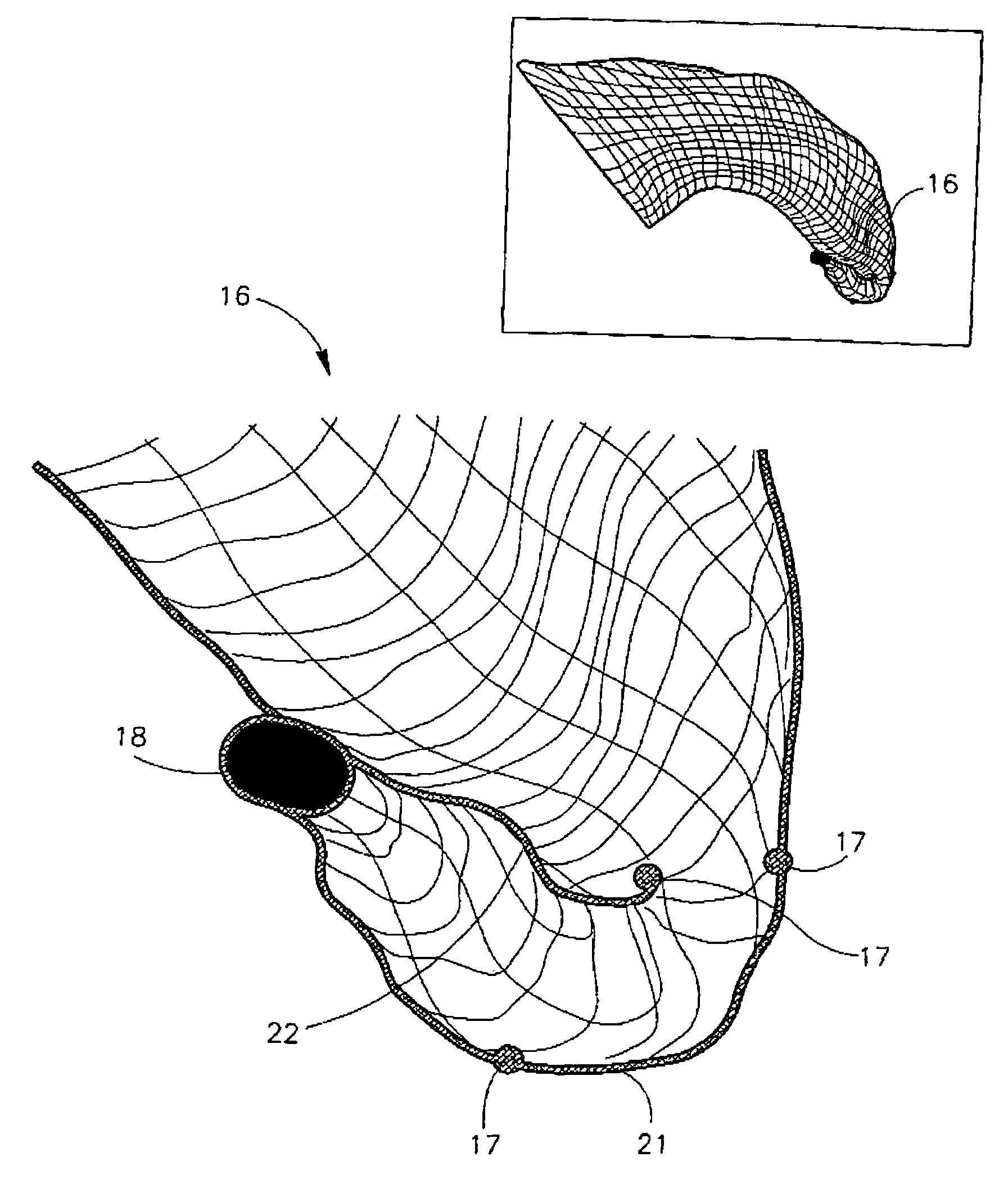
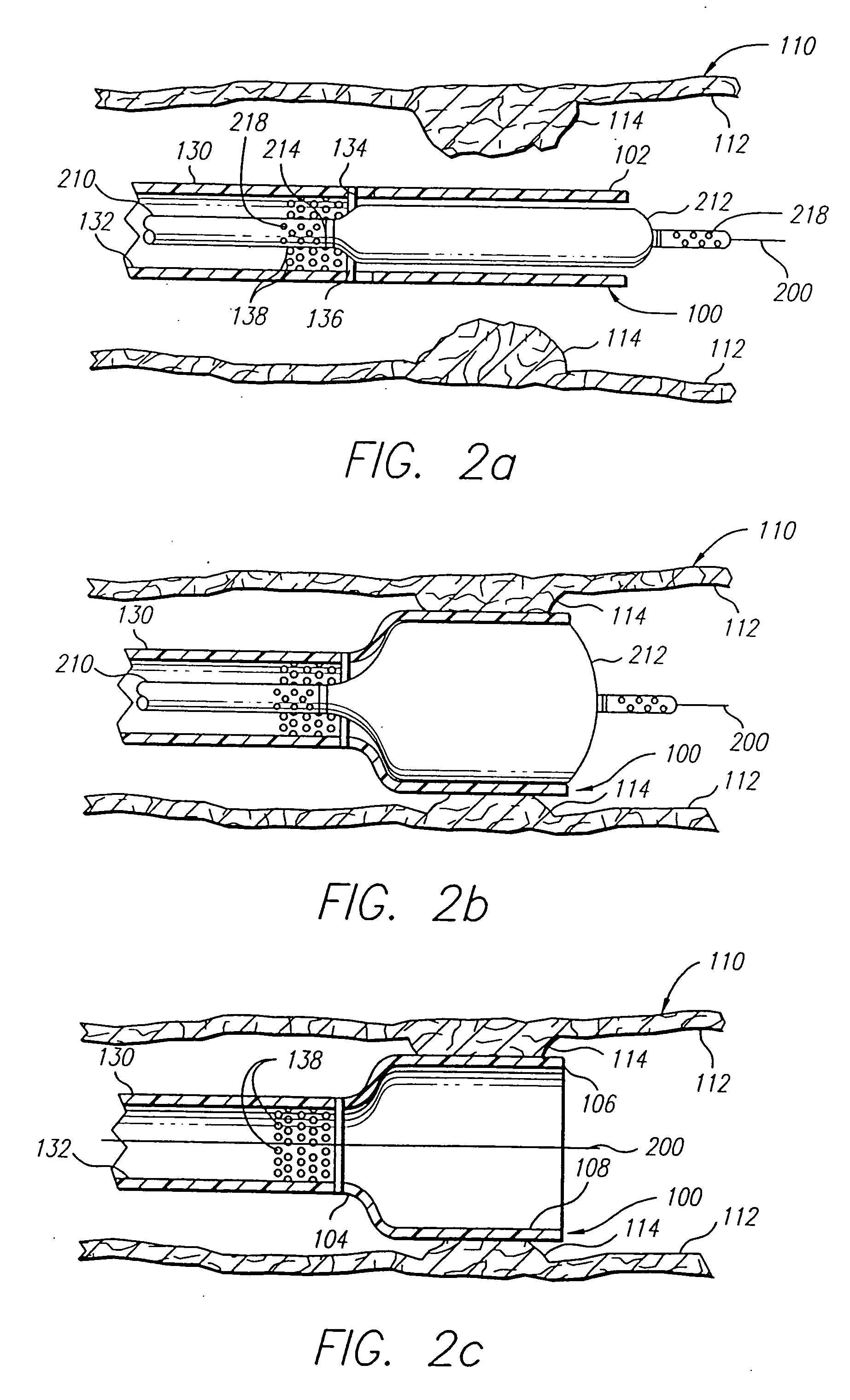
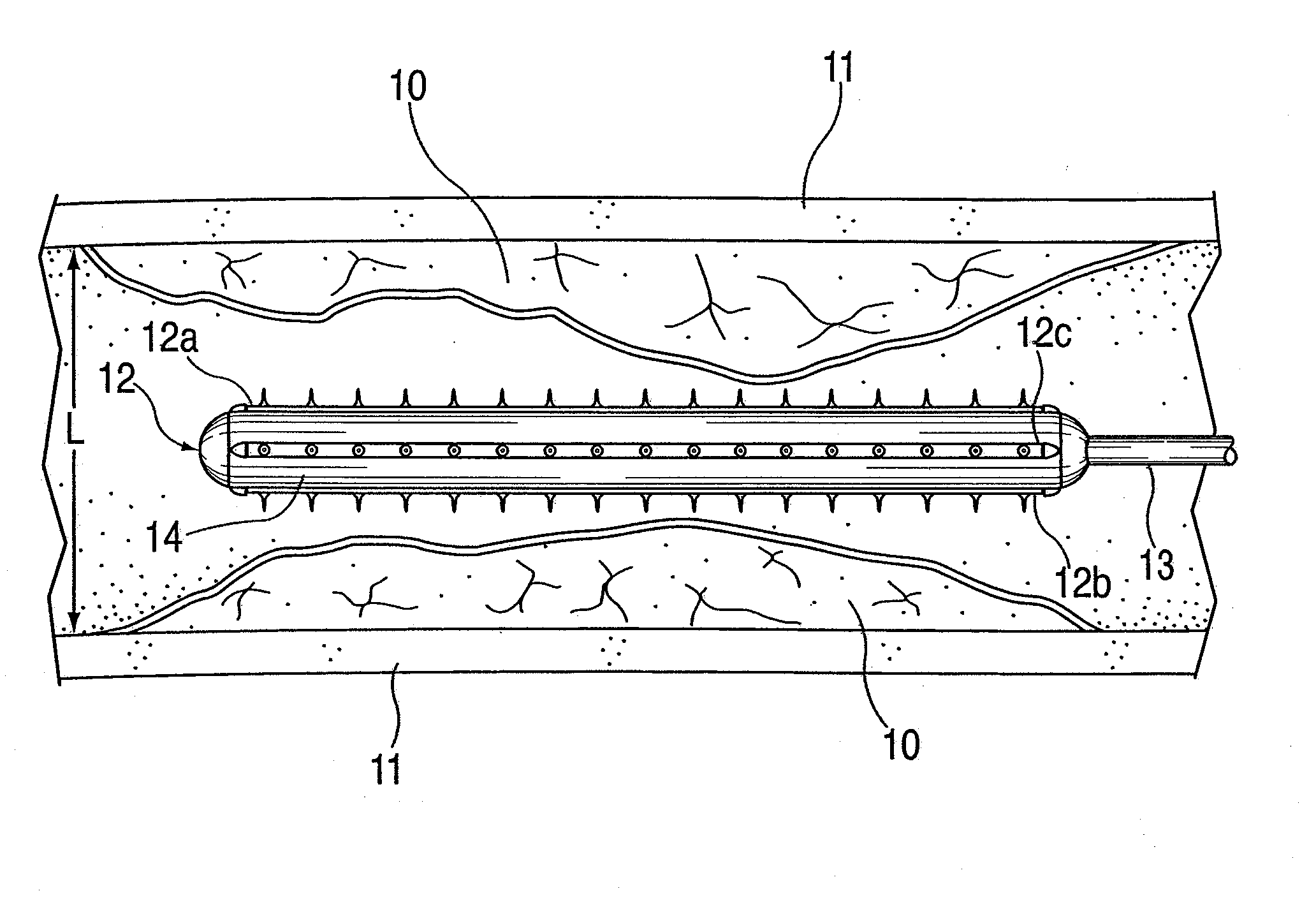
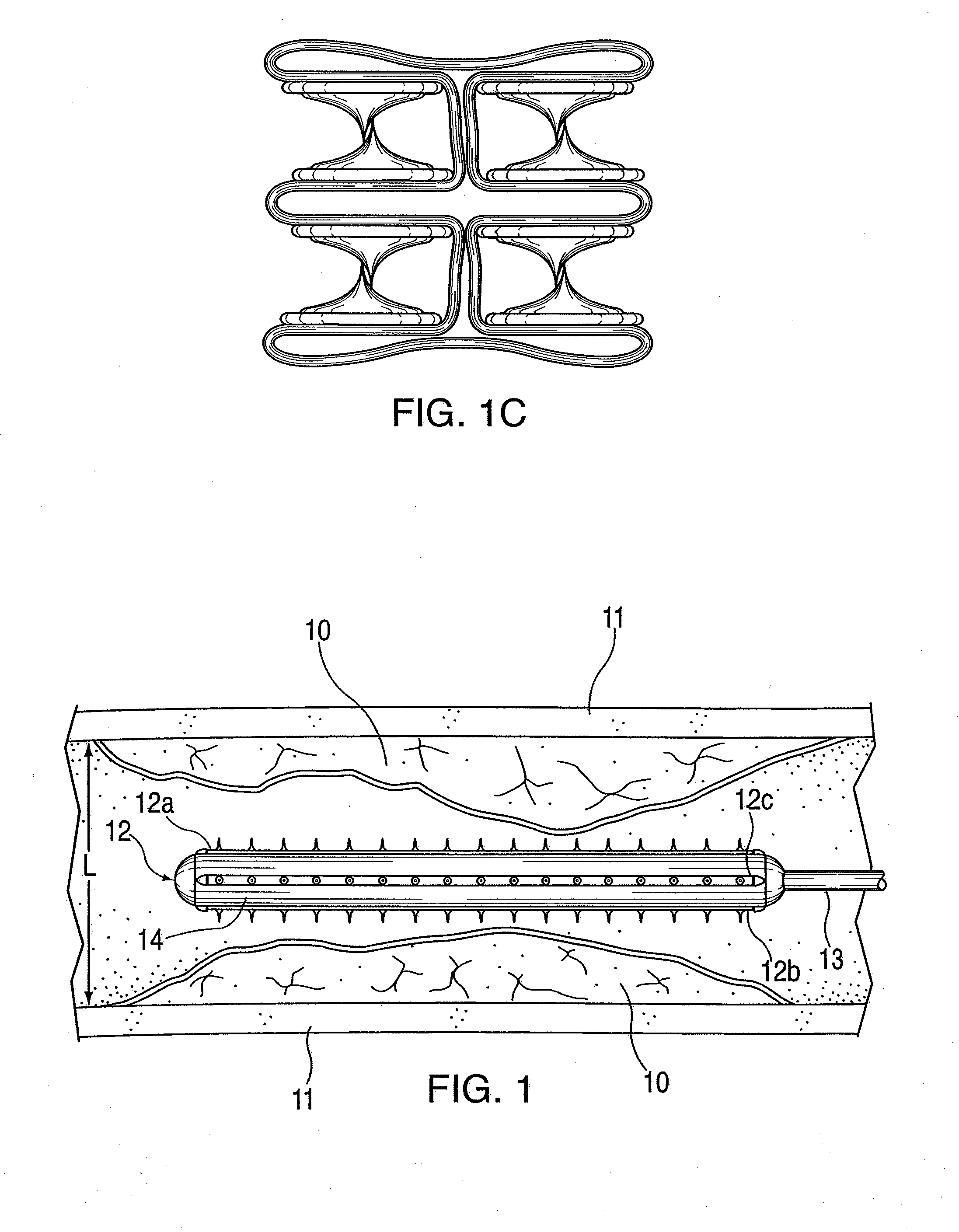
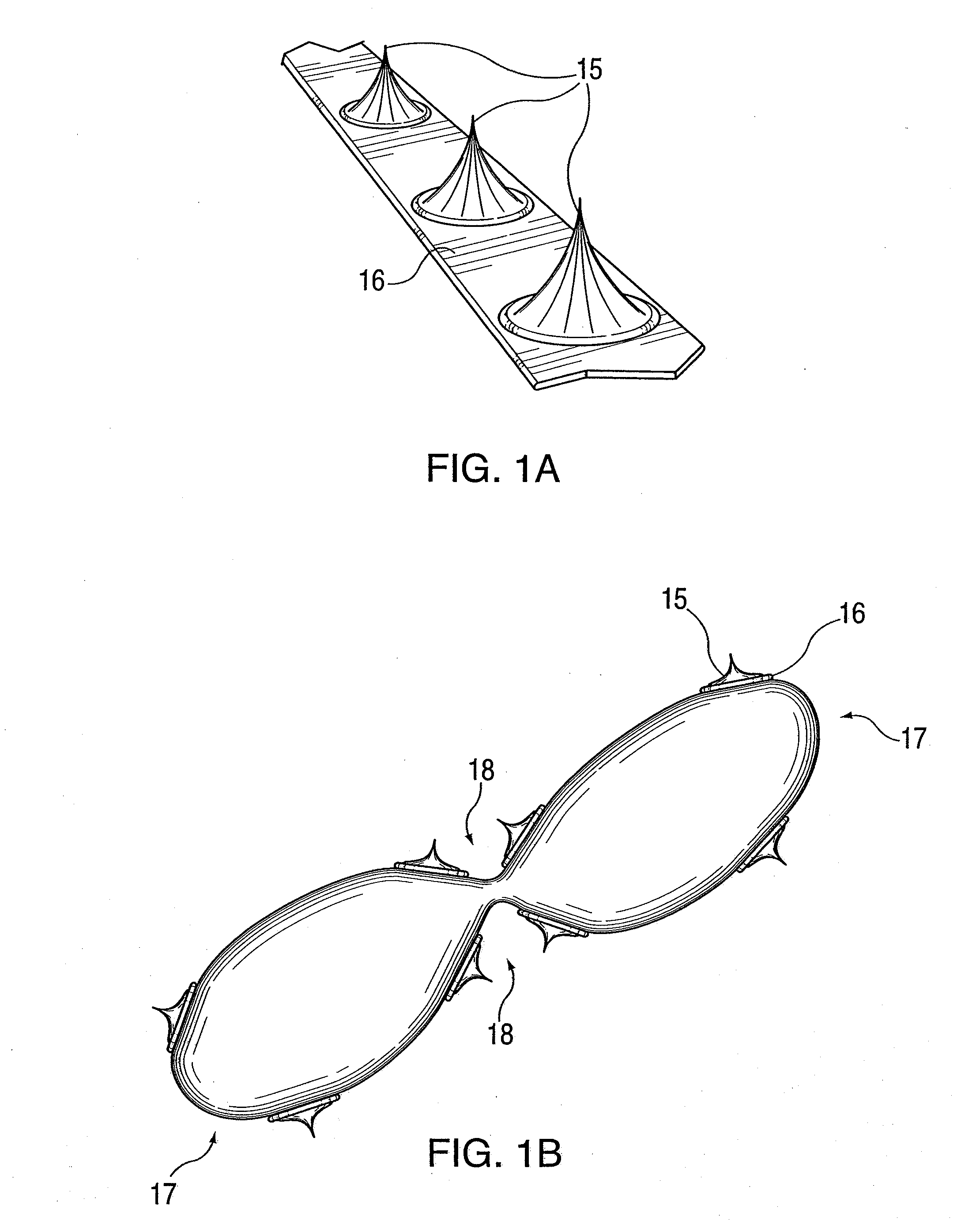
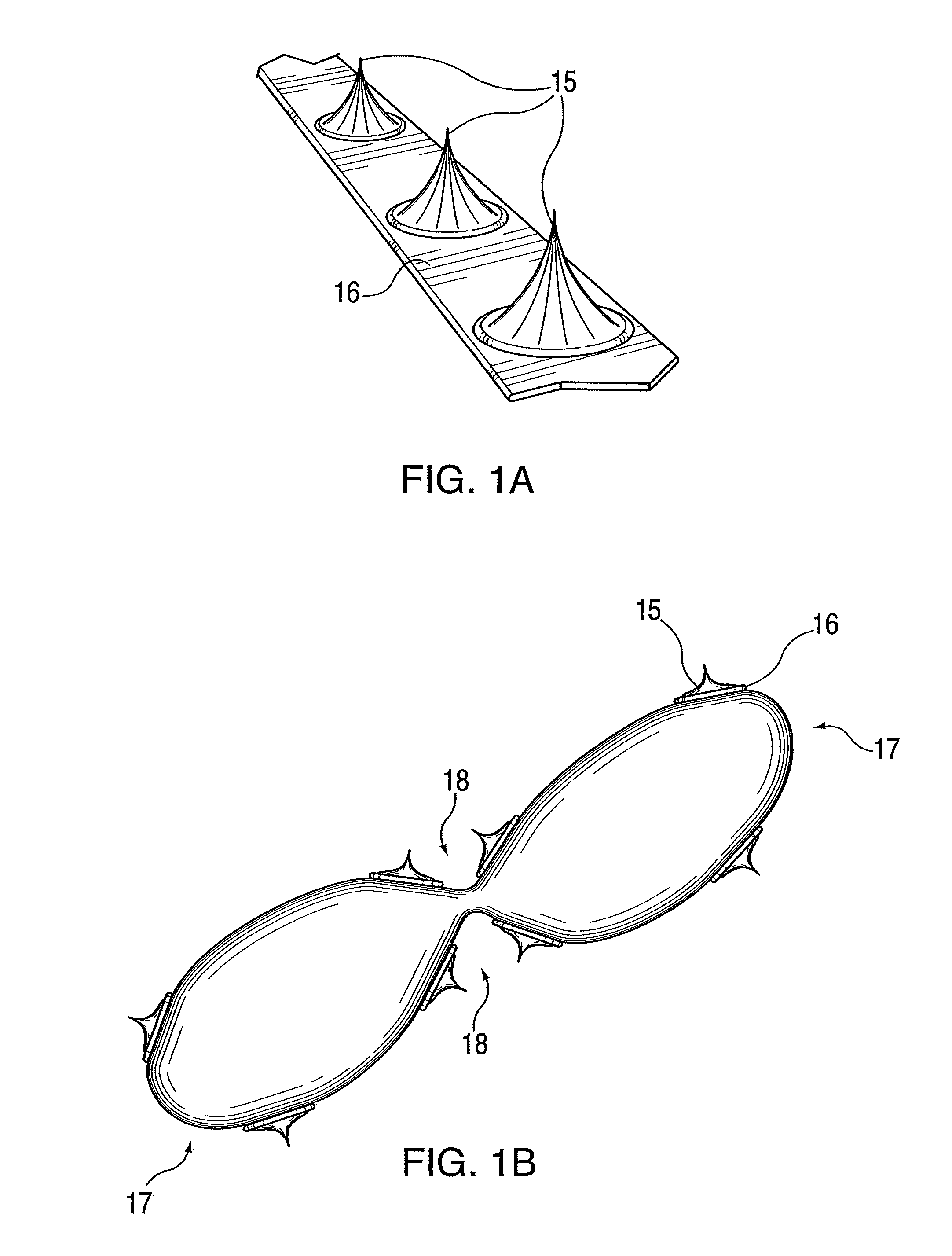
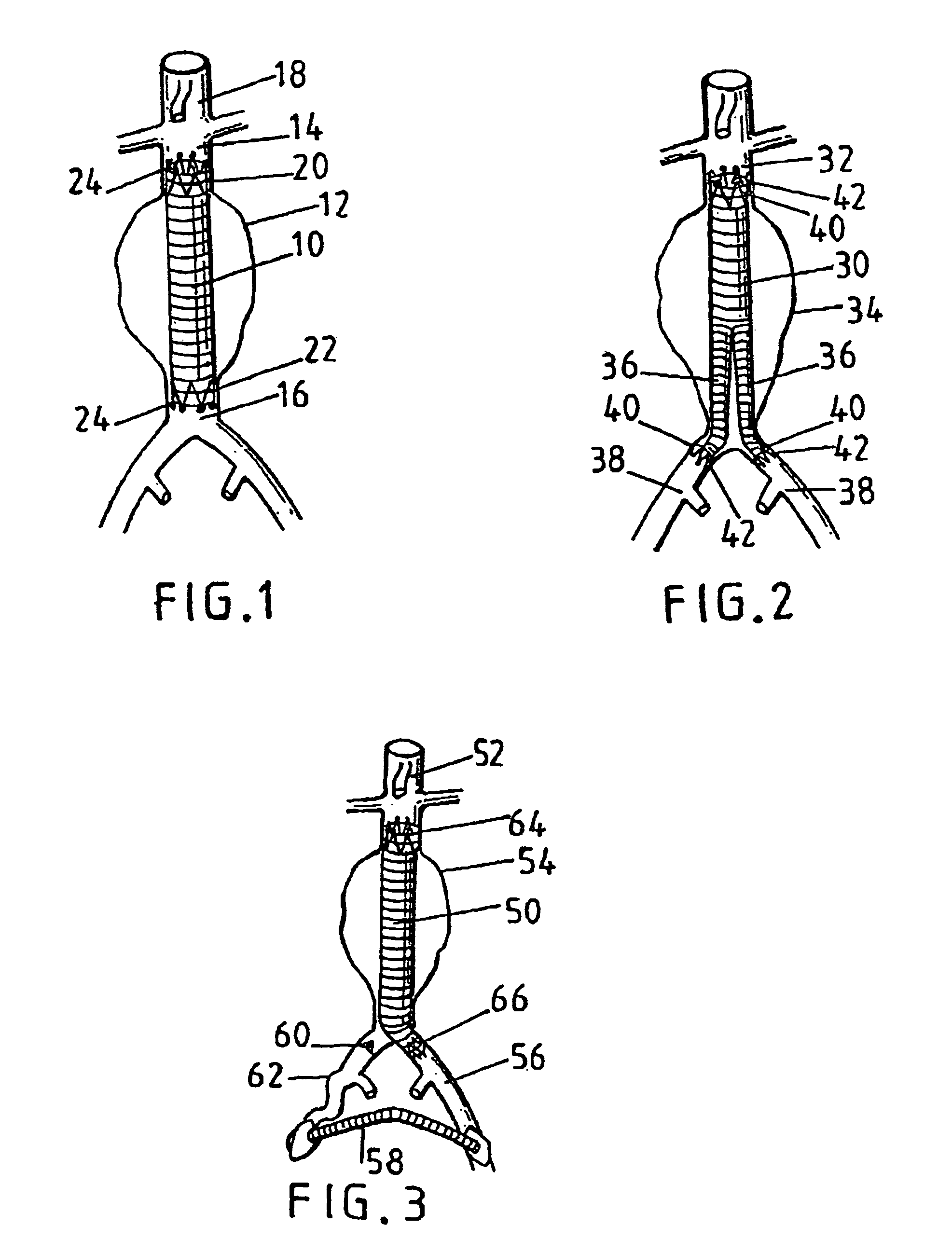
Vascular treatment method and device
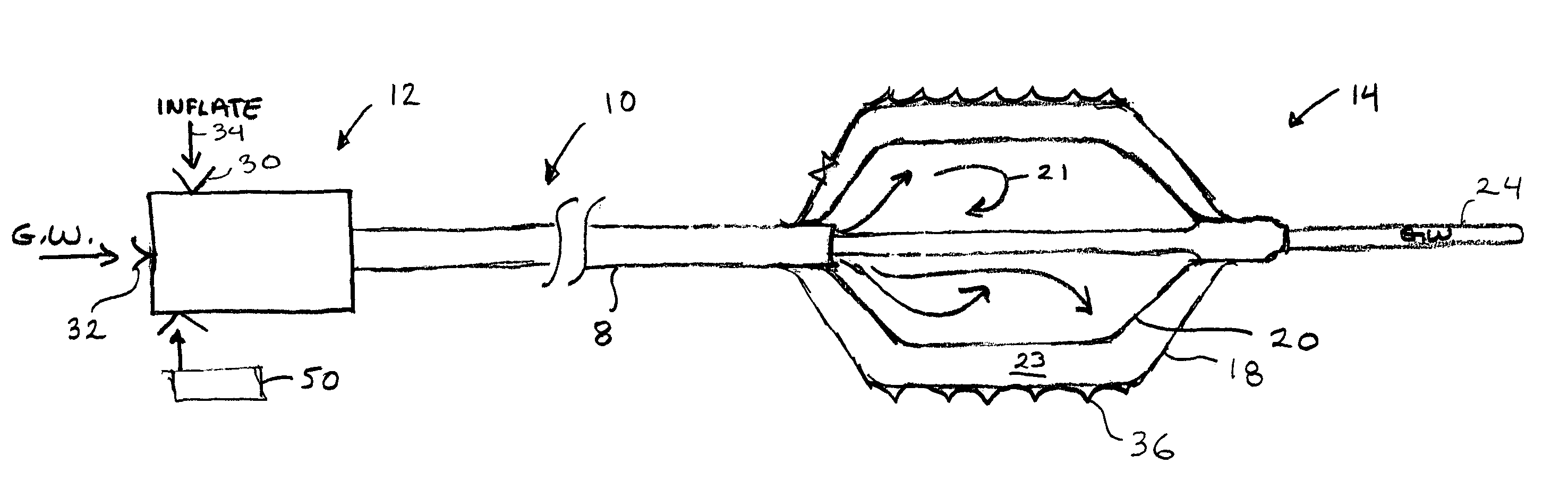
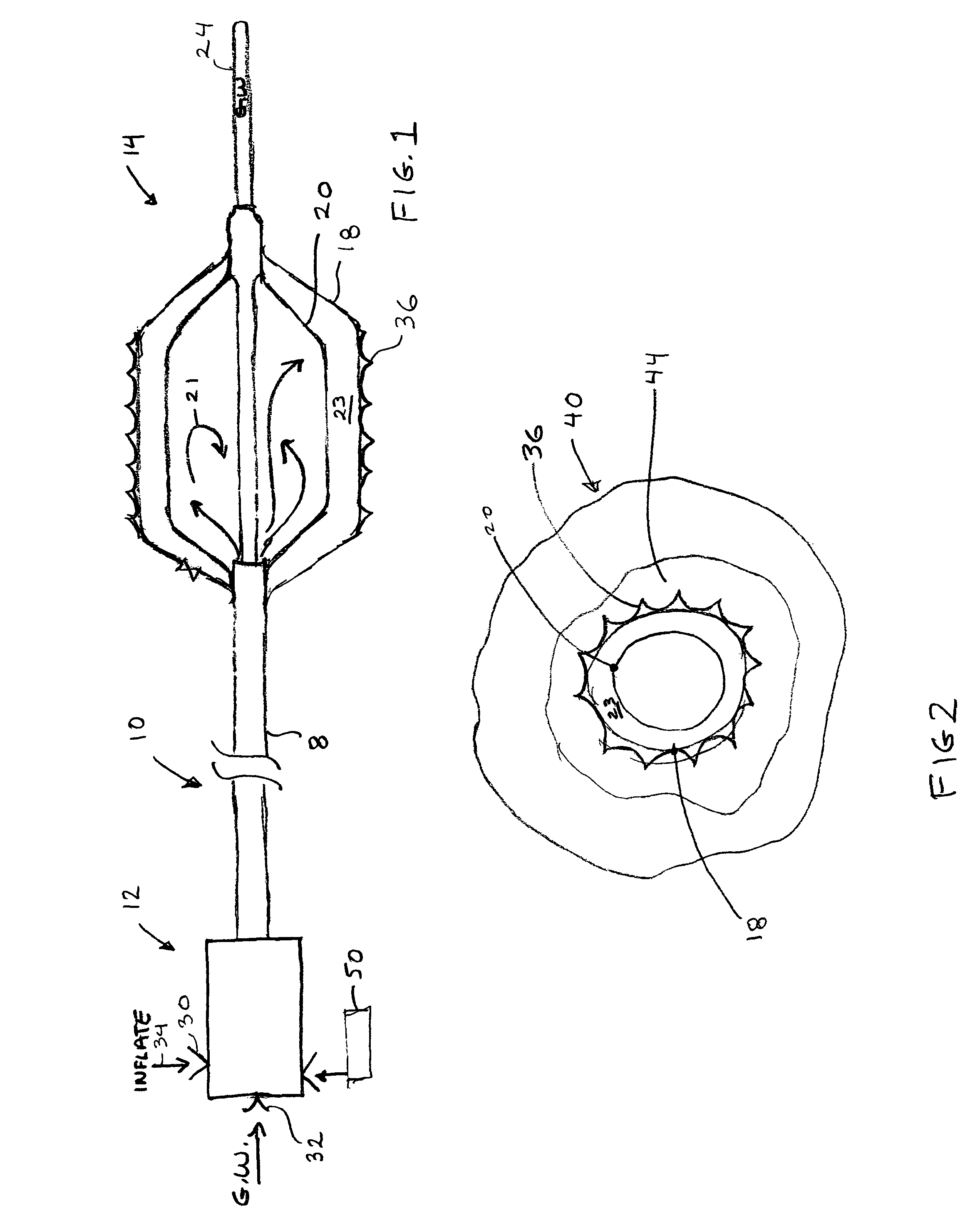
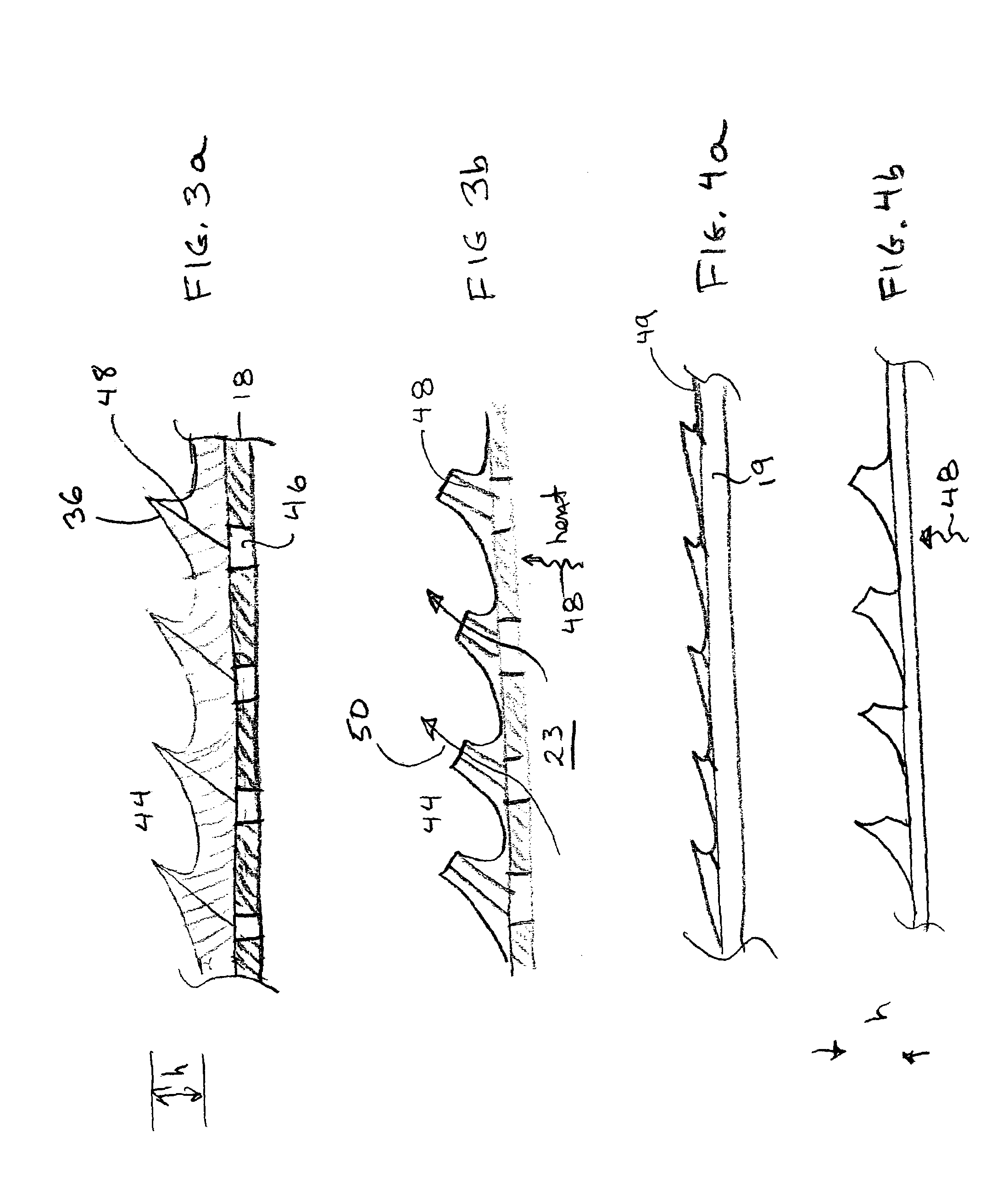
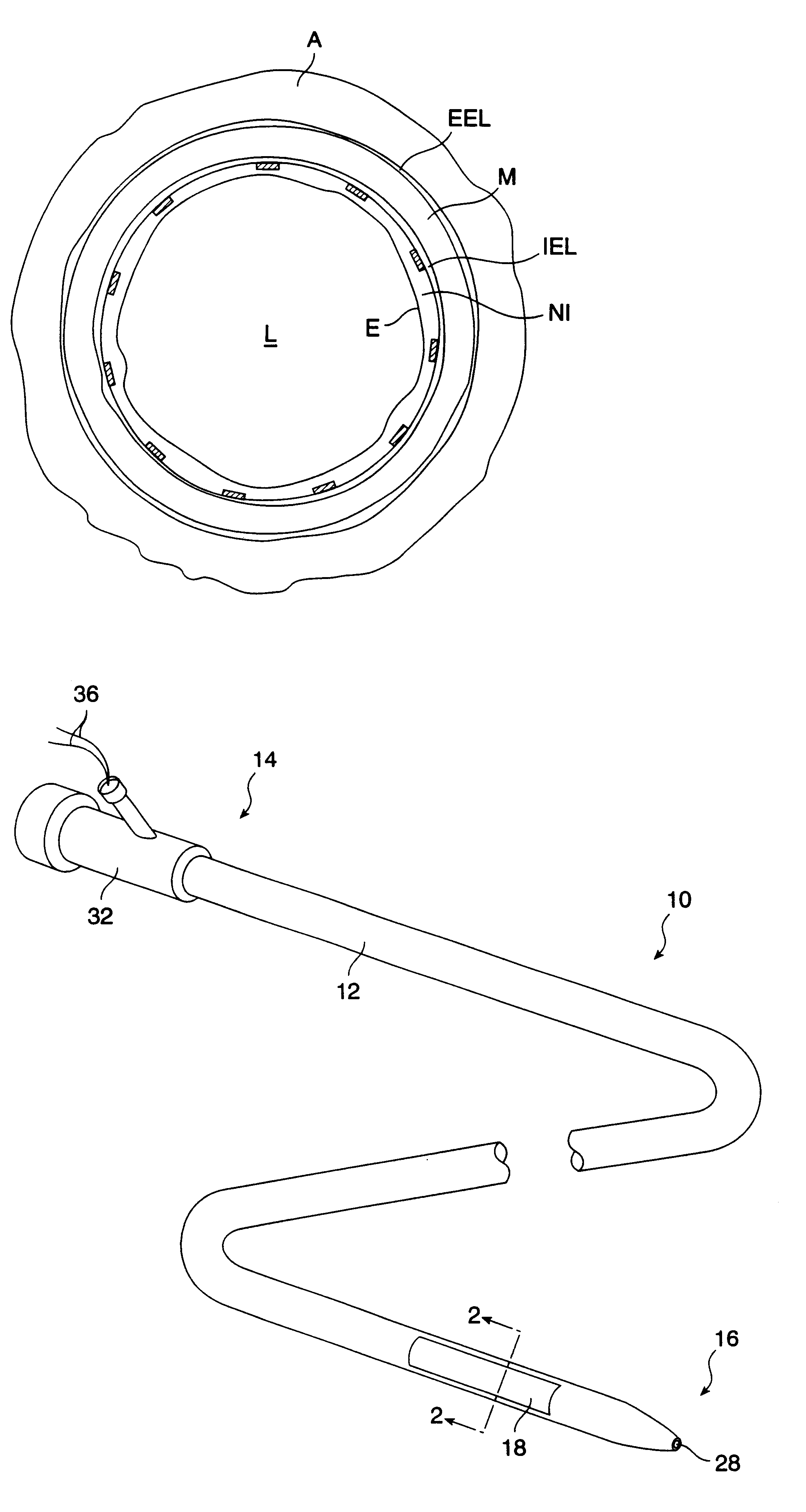
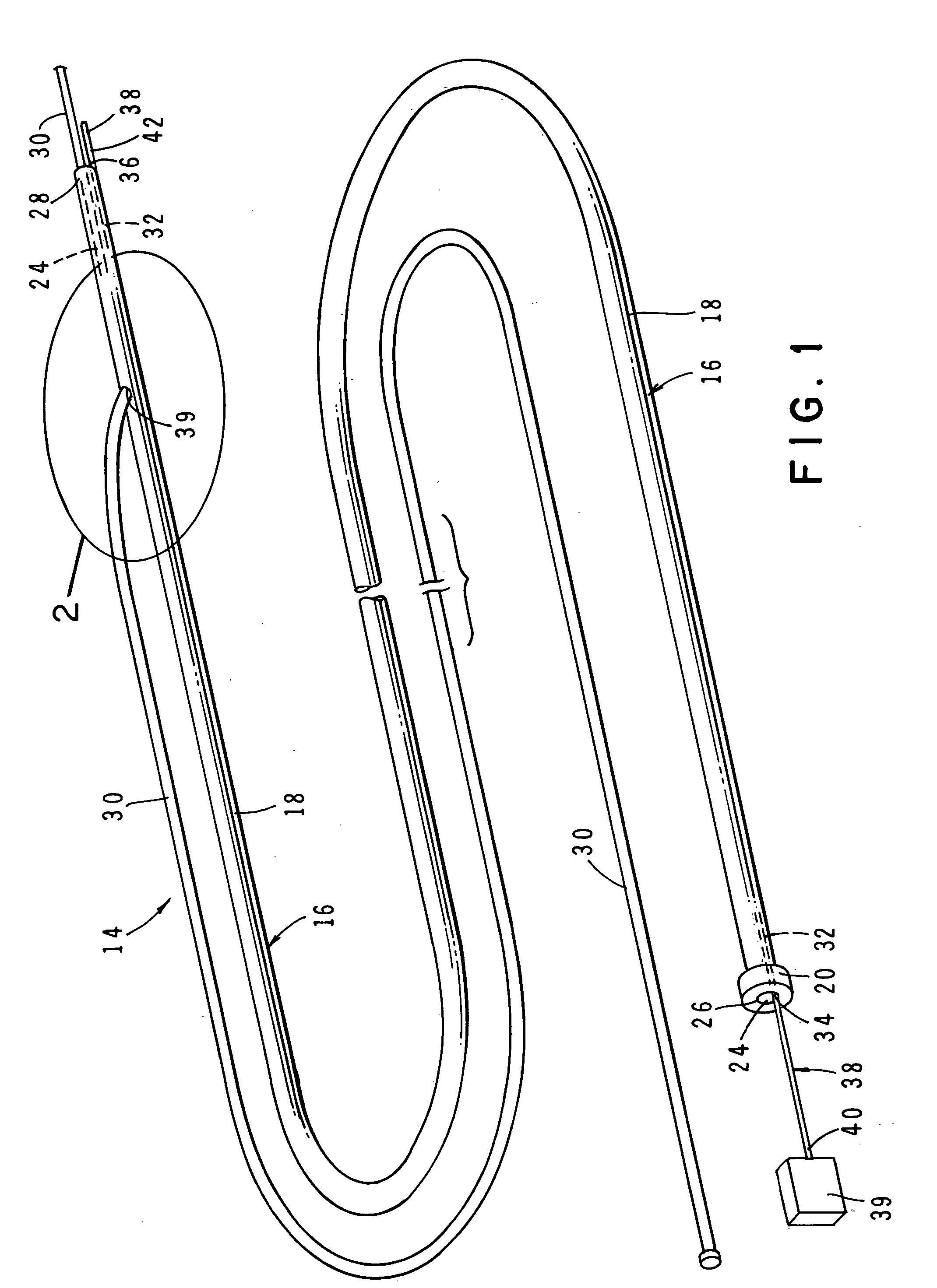
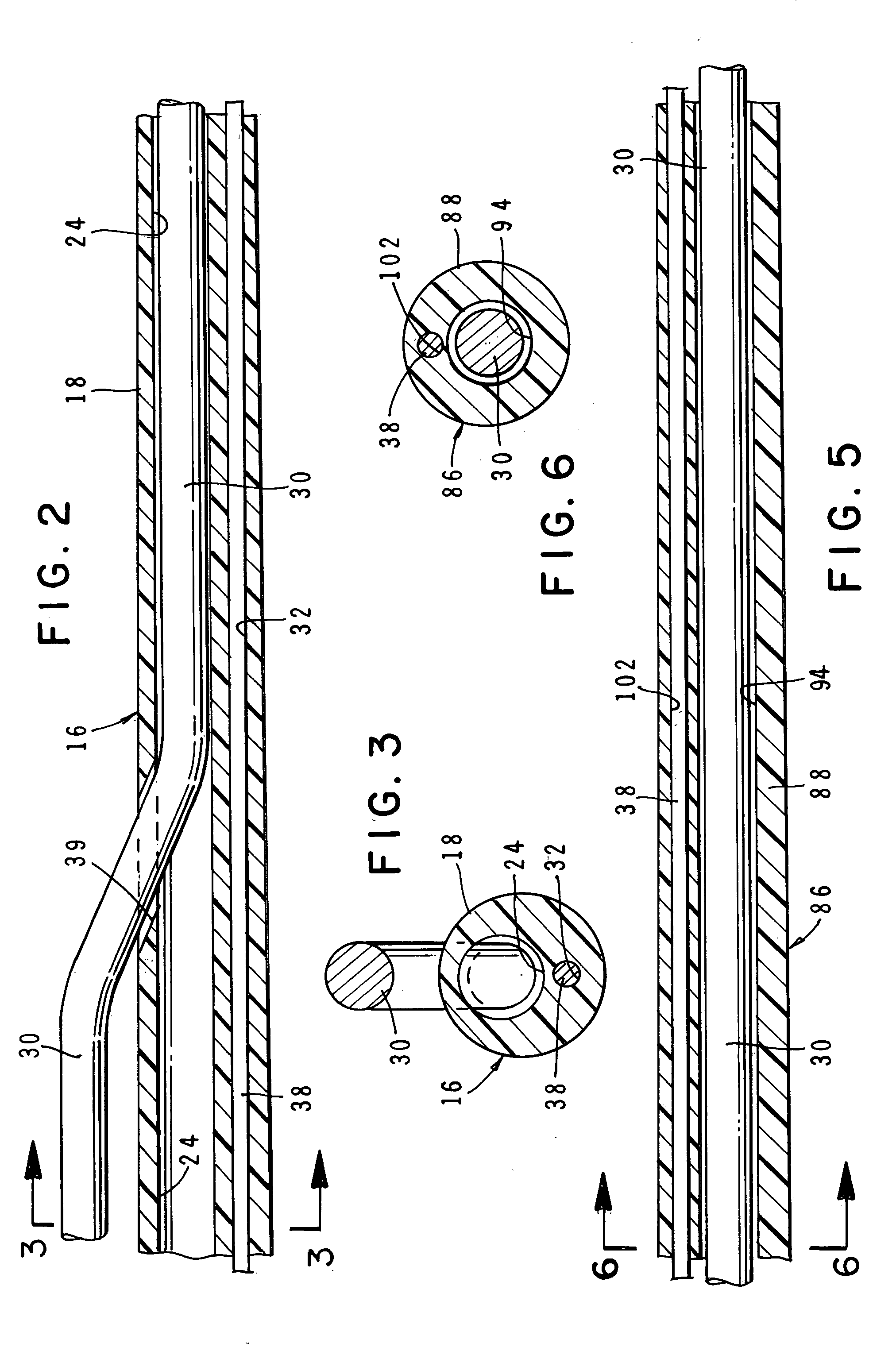
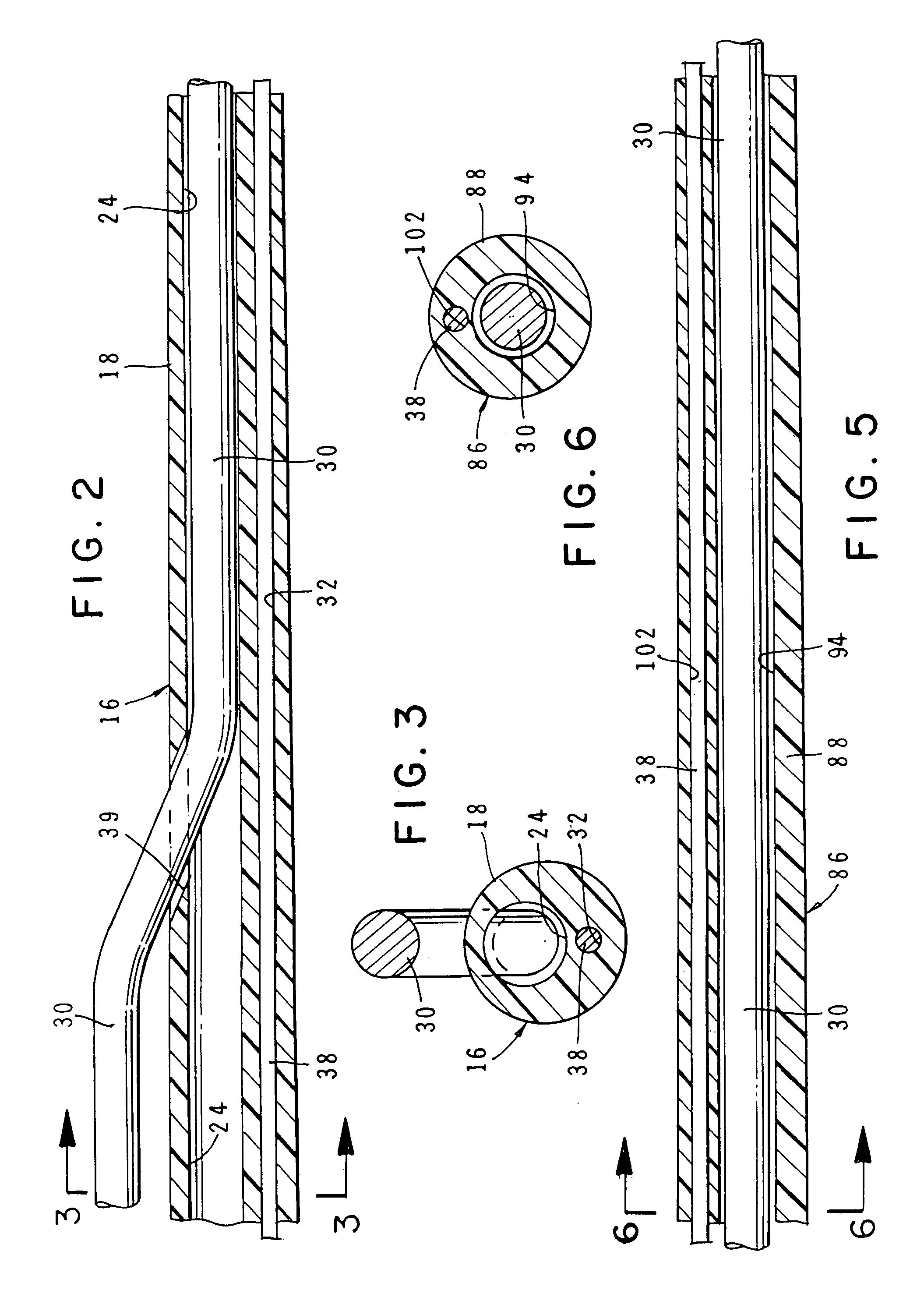
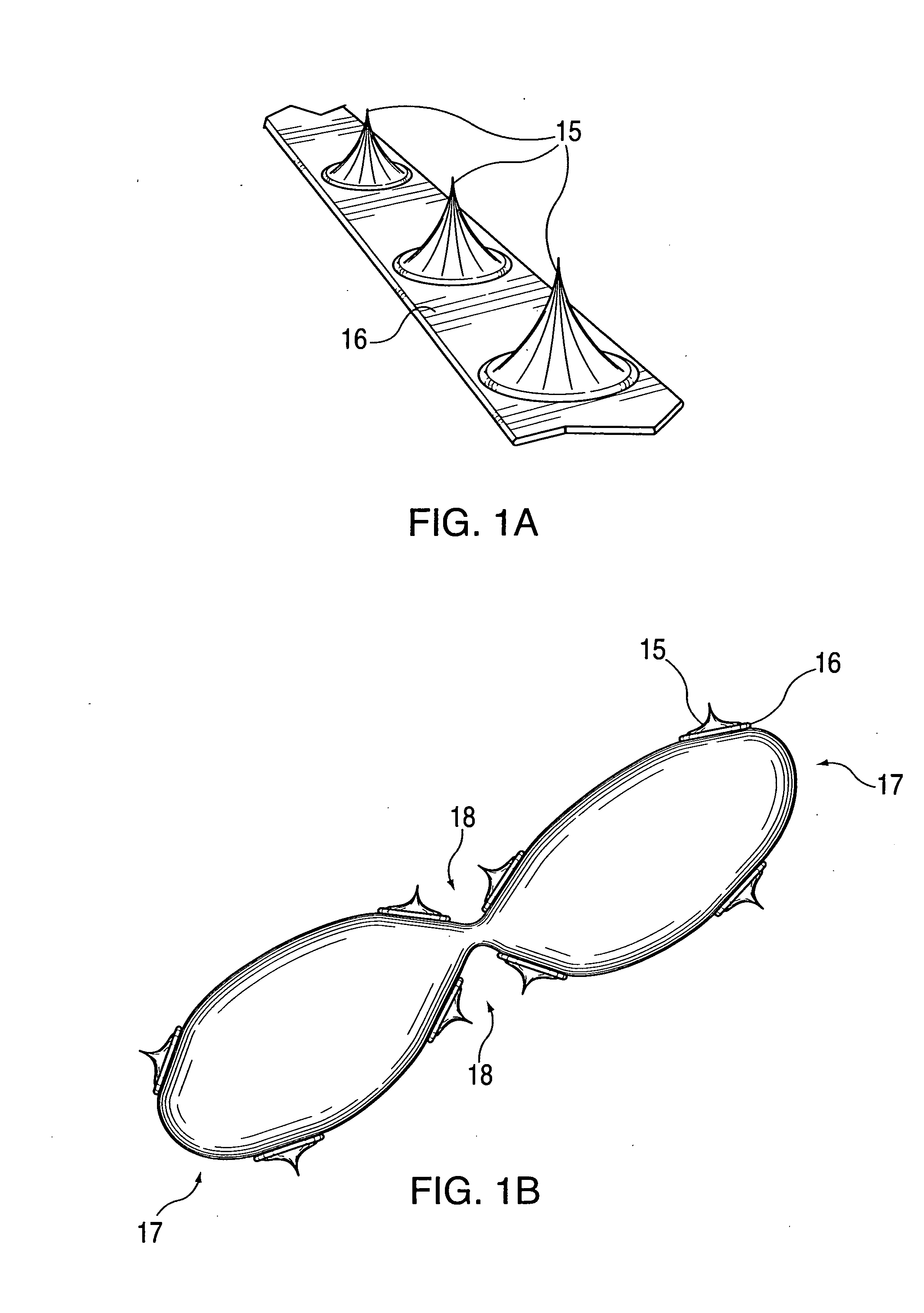
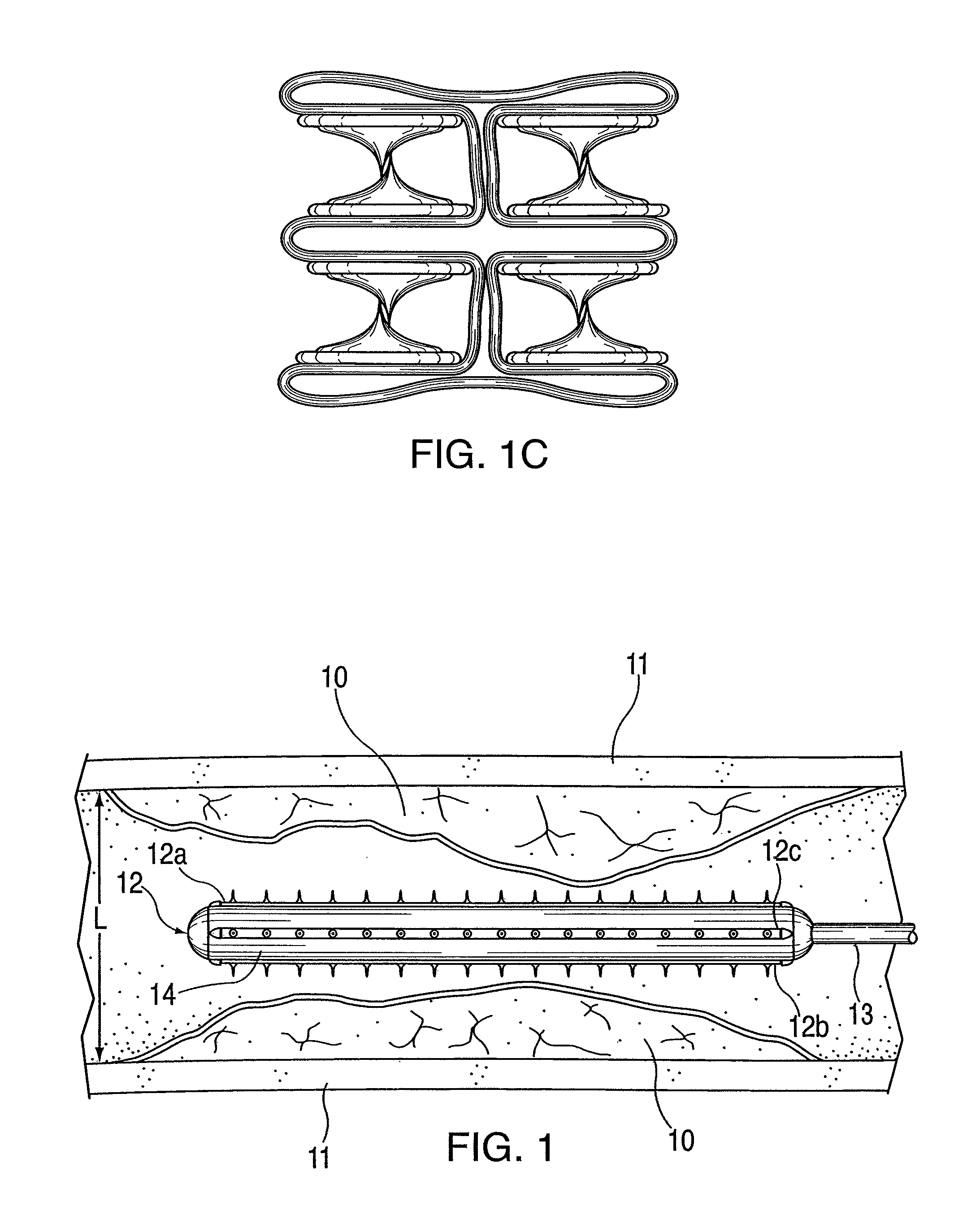
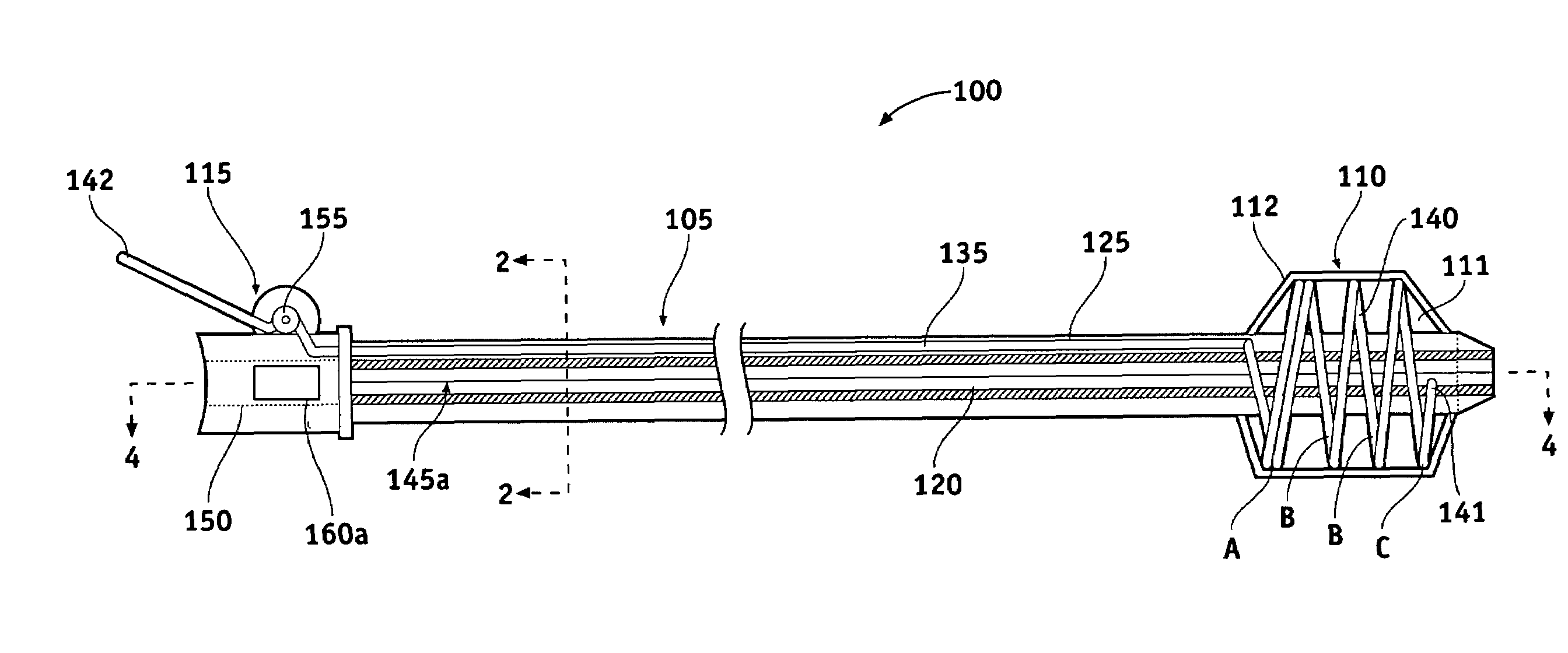
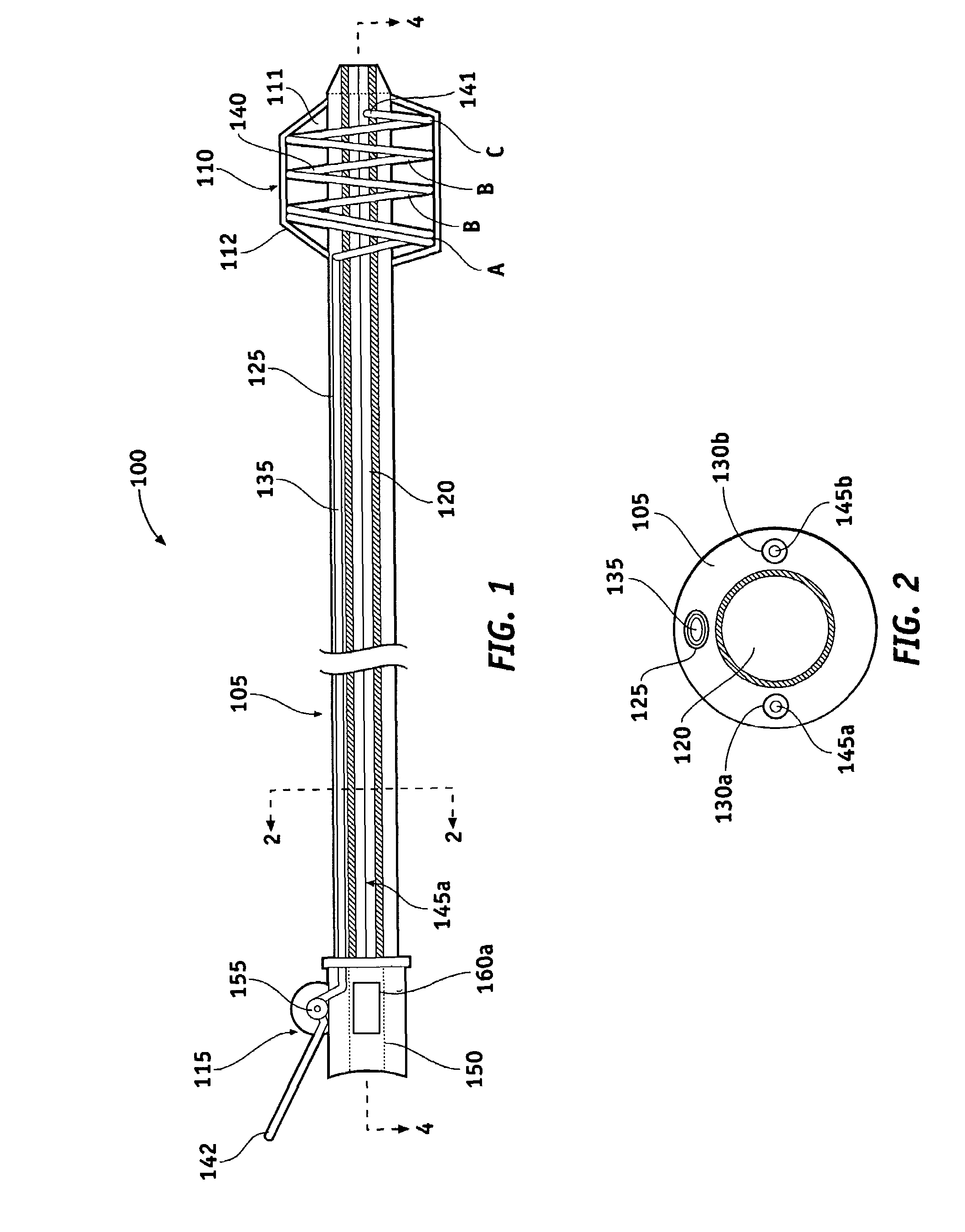
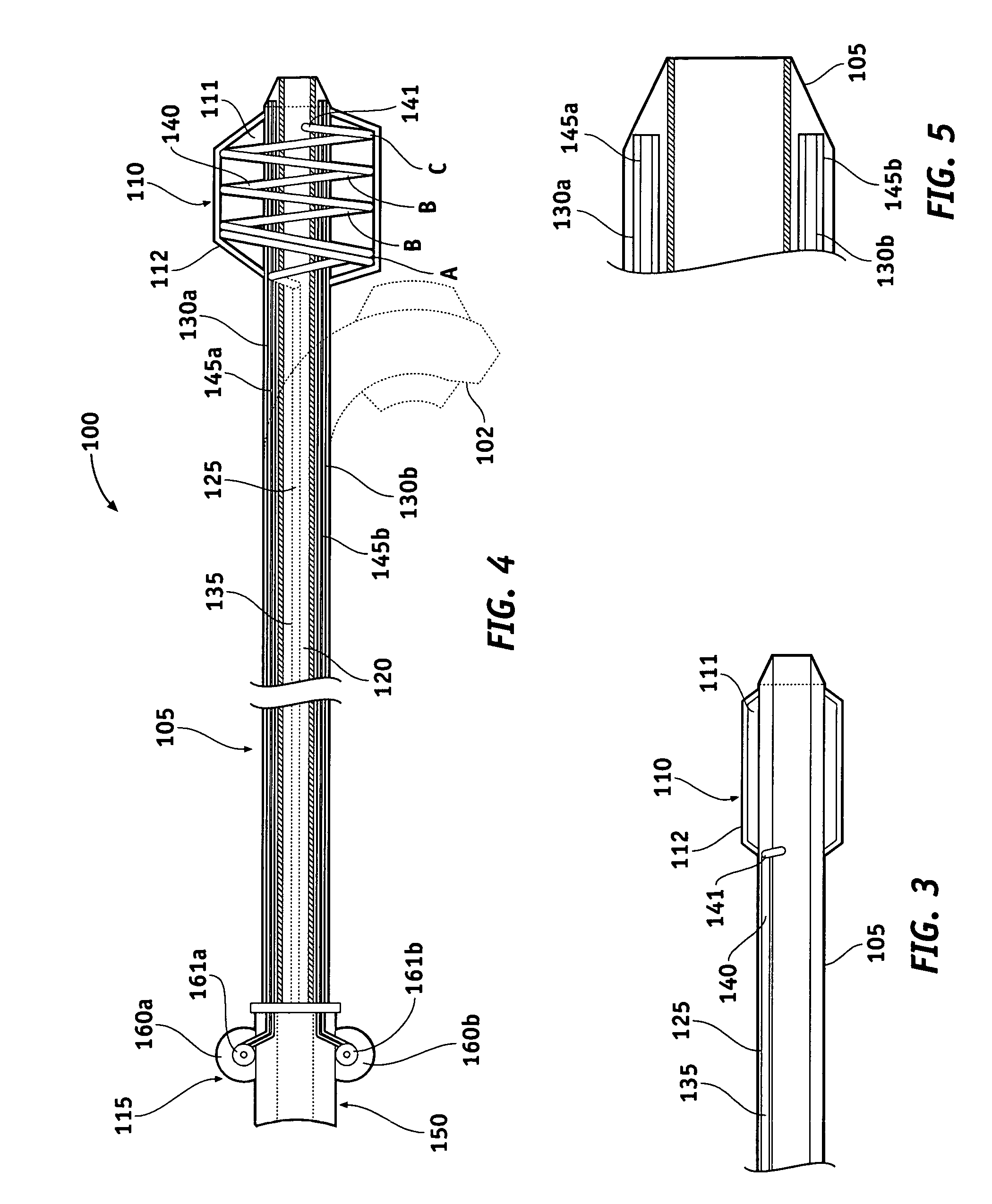
An intravascular catheter with micro spines that penetrate arterial wall to delivery drug or mechanical injury to the vessel wall inducing a “stent” like healing process in the vessel.
Owner:NFOCUS NEUROMEDICAL
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
Methods for bypassing total or near-total obstructions in arteries or other anatomical conduits
Methods for bypassing total or near-total obstructions in arteries or other anatomical conduits. A guidewire is advanced through the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit upstream of the obstruction and past the obstruction. In navigating past the obstruction, this guidewire may advance through tissue that is located within the wall of the artery or anatomical conduit and / or through tissue that is located outside of the wall of the artery or anatomical conduit. After this guidewire has been advanced past the obstruction, a penetrating catheter that is equipped with an orientation element is advanced over that guidewire. The orientation element is then used to aim a penetrator back into the lumen of the obstructed artery or conduit, downstream of the obstruction. The penetrator is then advanced into the lumen of the obstructed artery or conduit, downstream of the obstruction, and a final guidewire is advanced through the penetrator and into the lumen of the artery or conduit downstream of the obstruction. The catheter (and the guidewire that was initially used to pass the obstruction) may then be removed, leaving the final guidewire in place. A balloon or other tract enlarging device may be used to dilate or otherwise enlarge the bypass tract through which the final guidewire extends. Also, a covered or uncovered stent may be placed within the tract to facilitate flow from the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit upstream of the obstruction, through the newly created bypass tract and back into the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit downstream of the obstruction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Endovascular device for entrapment of particulate matter and method for use
A device and method for protecting a blood vessel, and hence bodily tissues, against damage caused by particulate such as an embolus. The device may be a stent, for insertion in a large artery such as the ascending aorta, and may be combined with a filter. In one embodiment, the device includes an outer wire frame rather than a stent. The stent may be made of at least one layer of mesh, which is typically attached or mounted to the arterial wall. Typically only part of the stent is attached (for example at a reinforcing ring structure). Typically the size of the apertures of the mesh at the top portion of the stent is smaller than the bottom portion of the stent. The device and method are particularly useful in preventing blockages of flow to the brain, but have other uses as well. An electric charge may be placed on the device, for example, to prevent blood components from collecting.
Owner:KEYSTONE HEART
Control of arterial smooth muscle tone
InactiveUS8019435B2Efficiently broadcastedInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsSmooth muscleEngineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
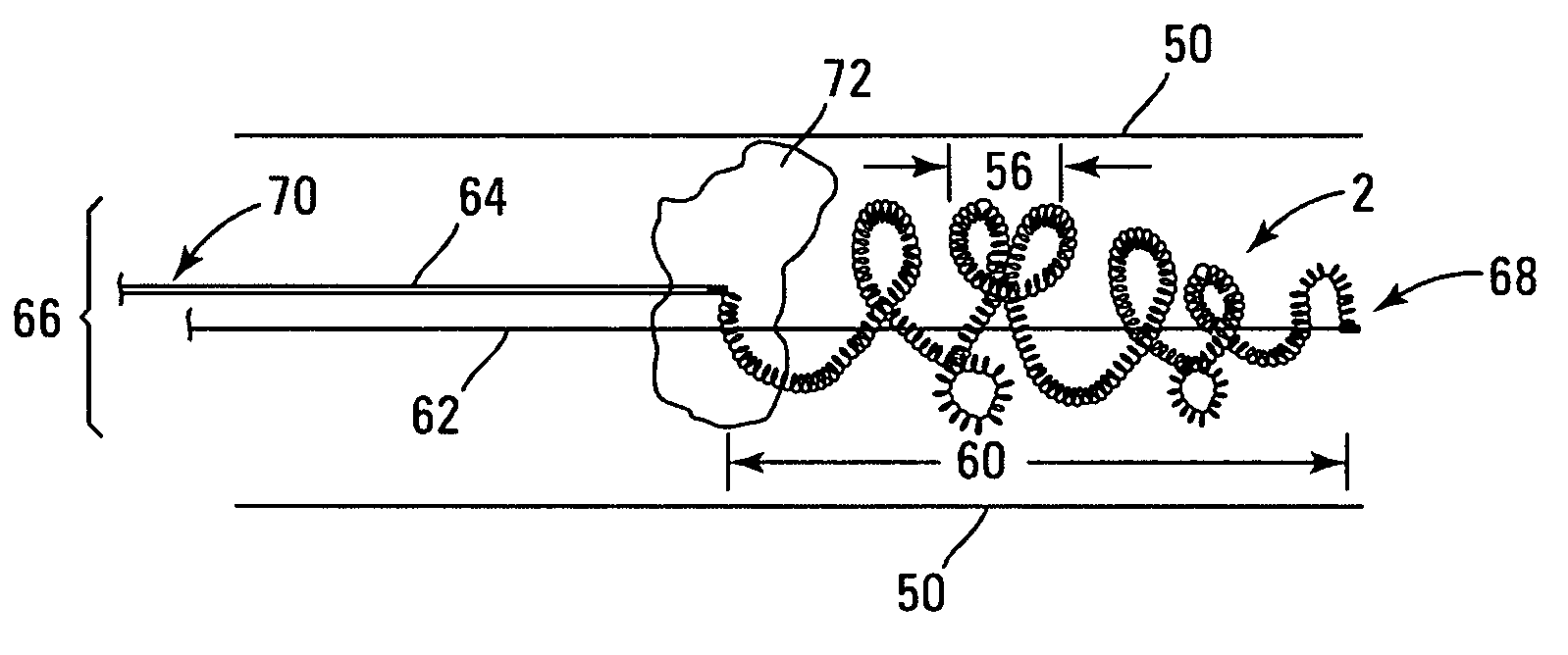
Thrombus removal system and process
InactiveUS20060224177A1Reducing non-rigid contactReduce contactCannulasDilatorsGrip forceSmall artery
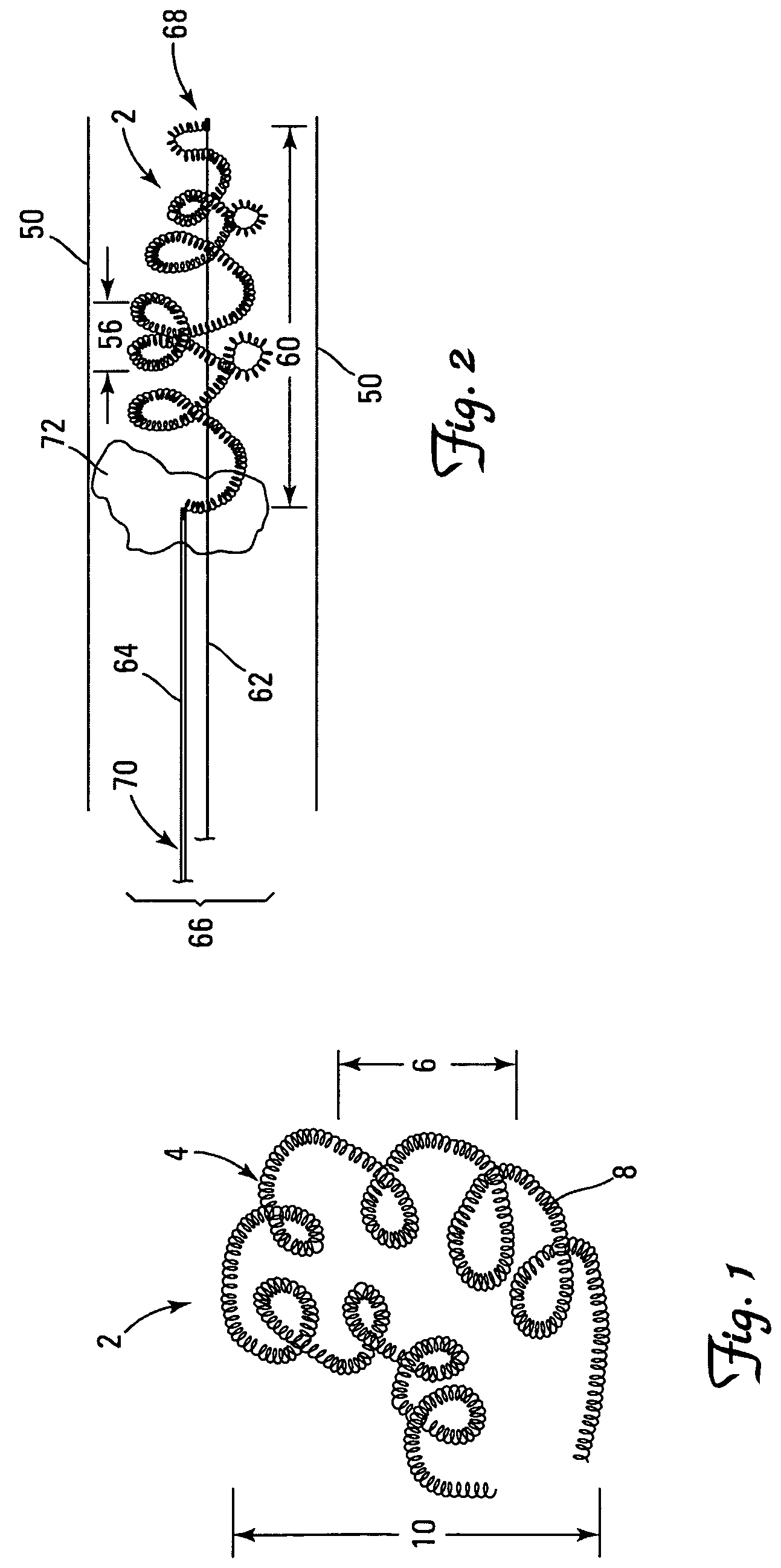
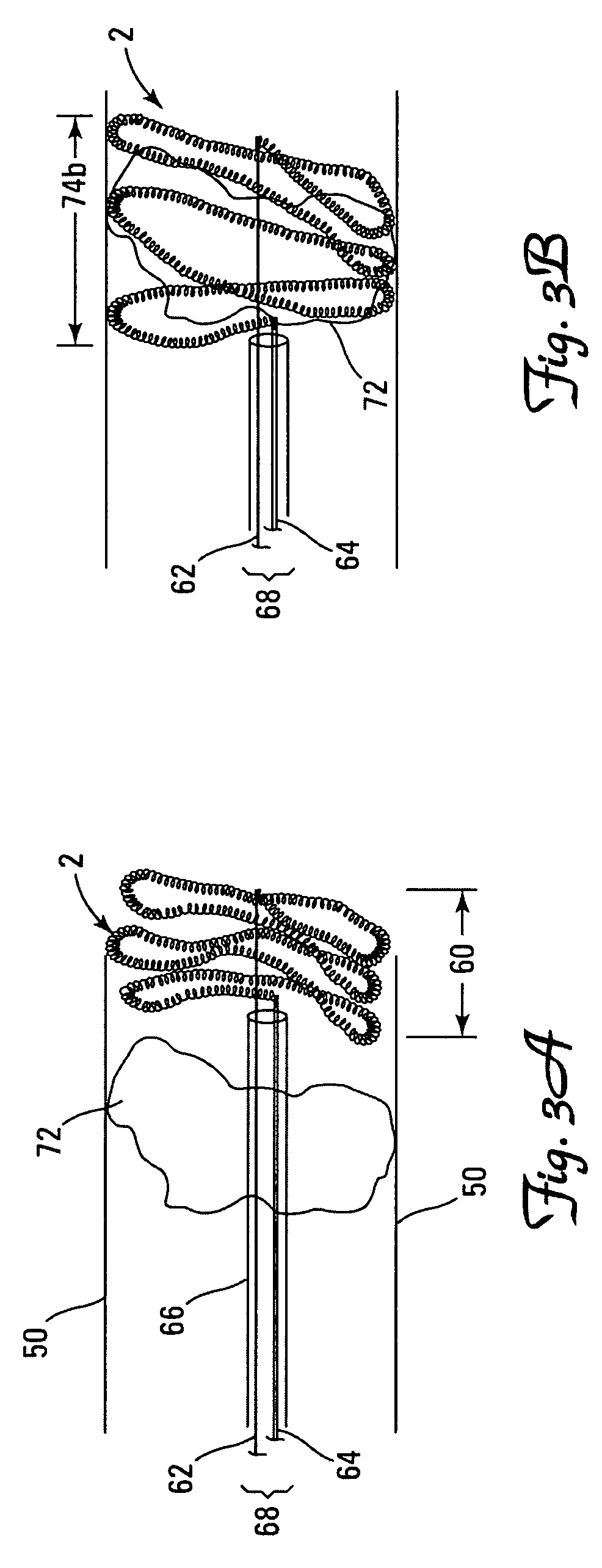
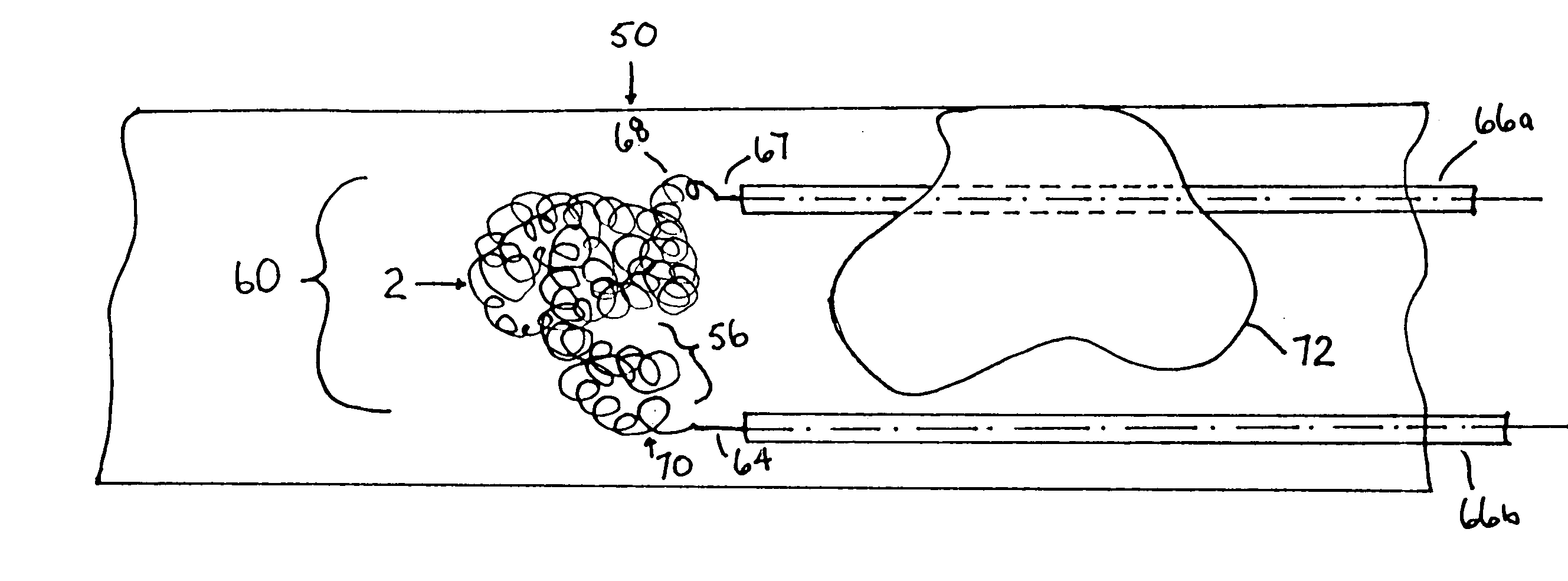
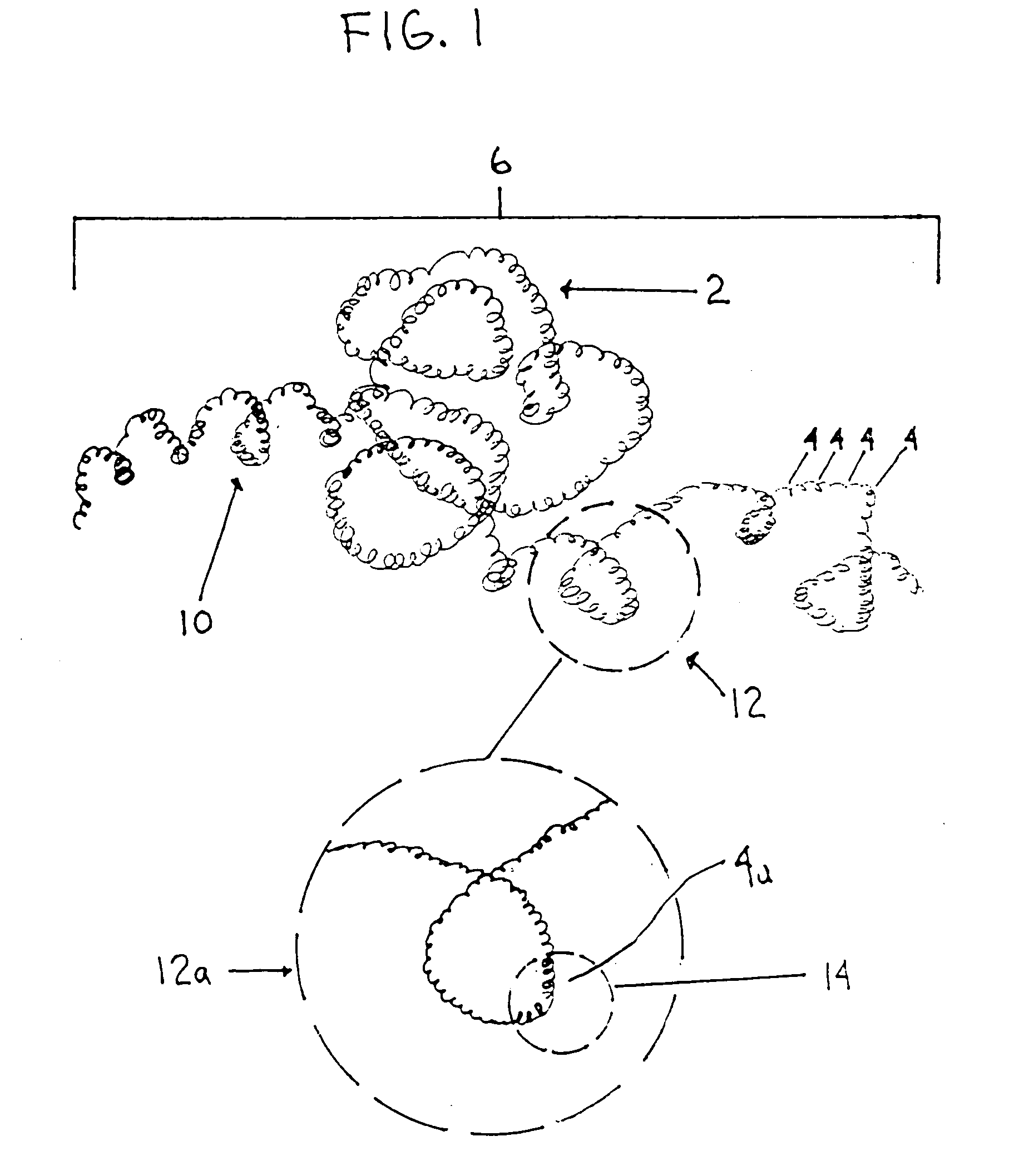
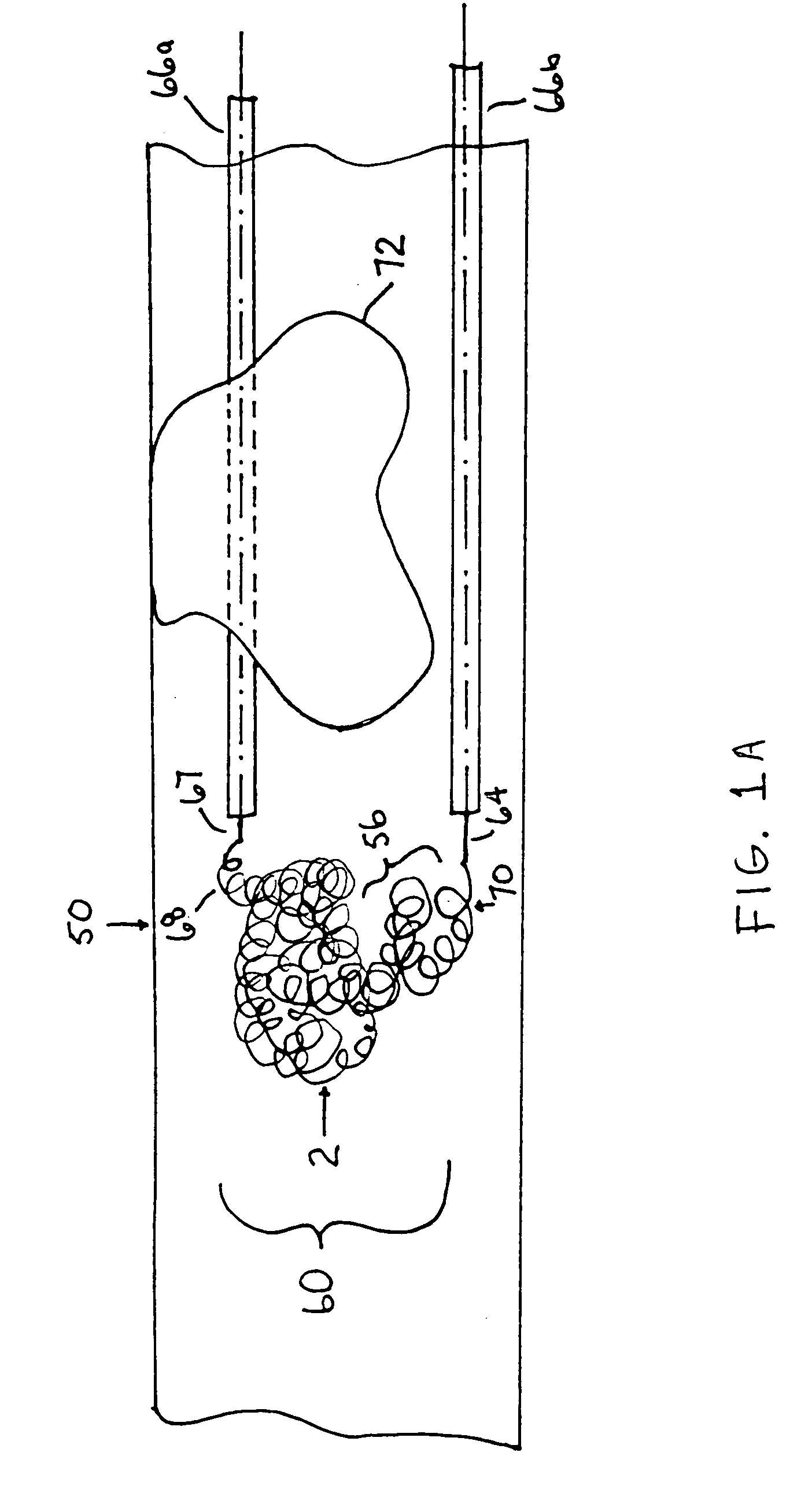
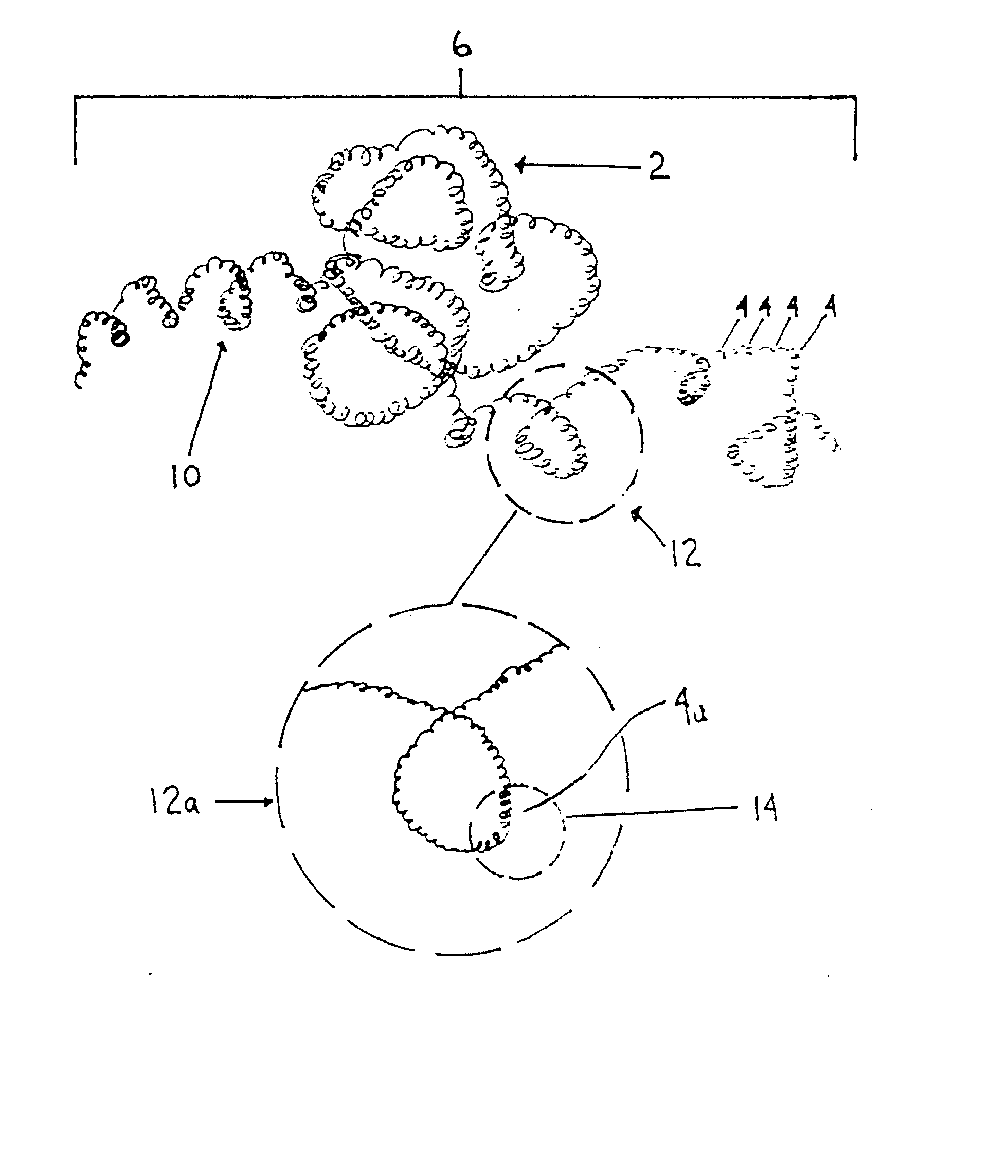
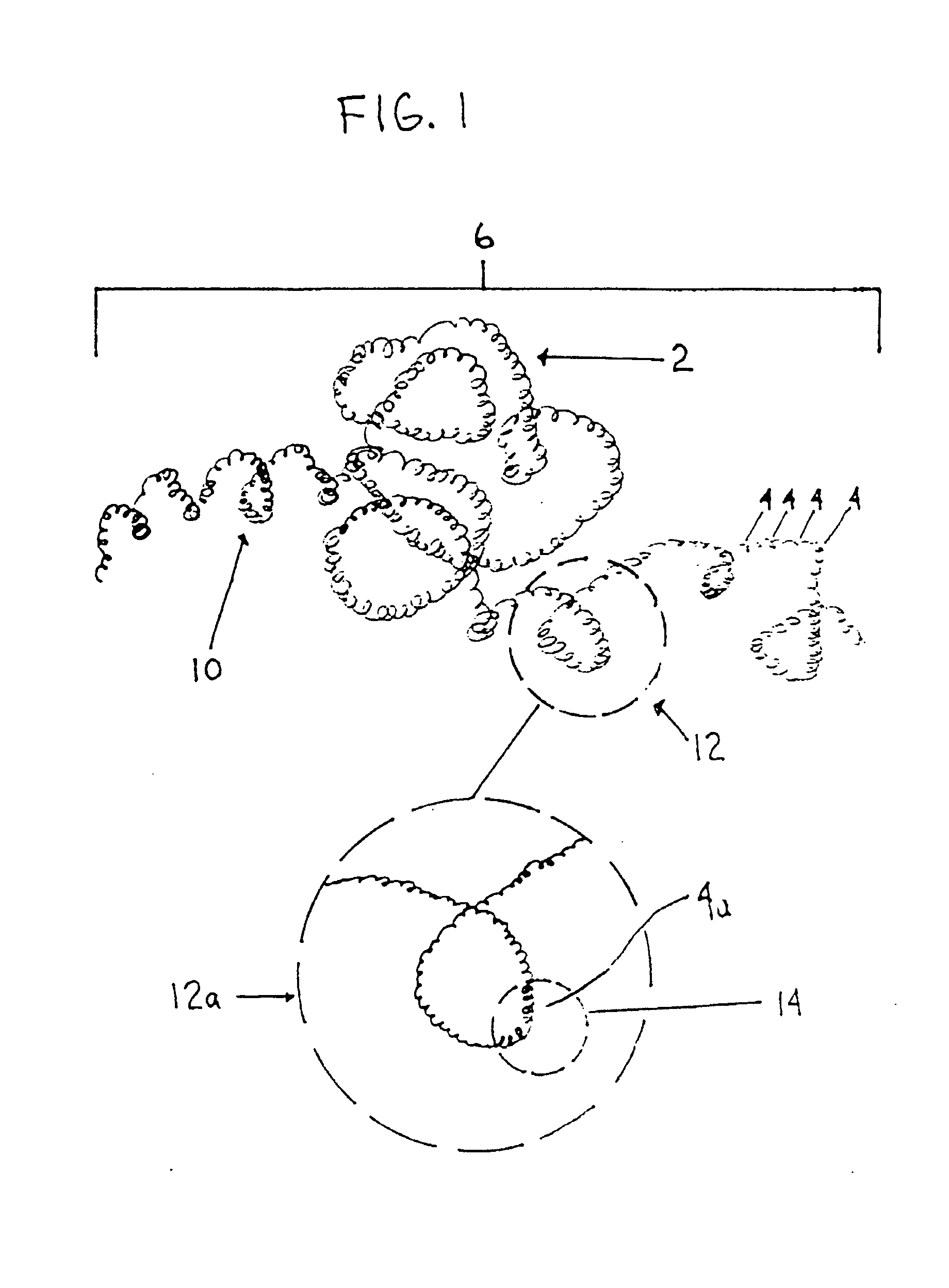
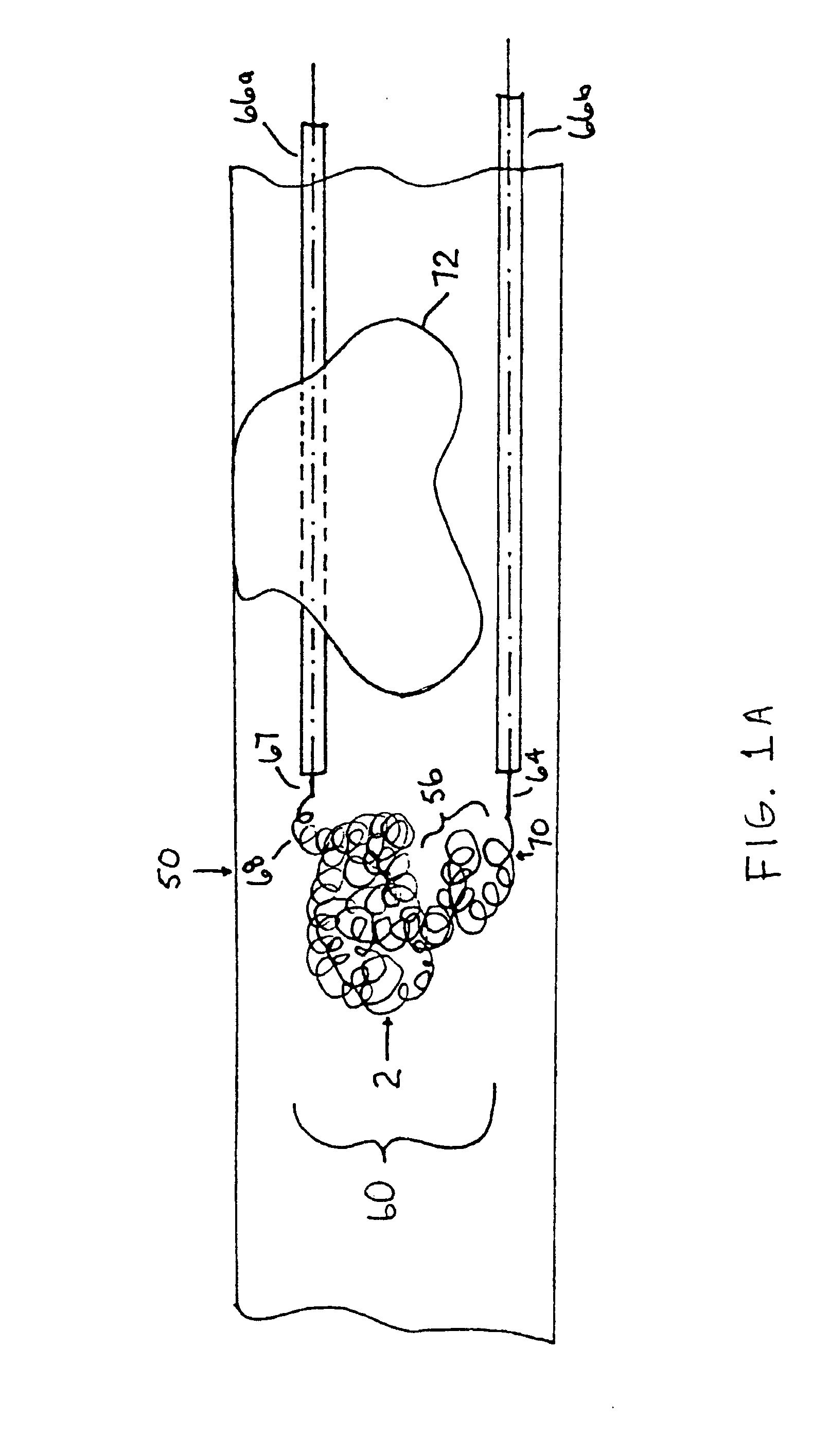
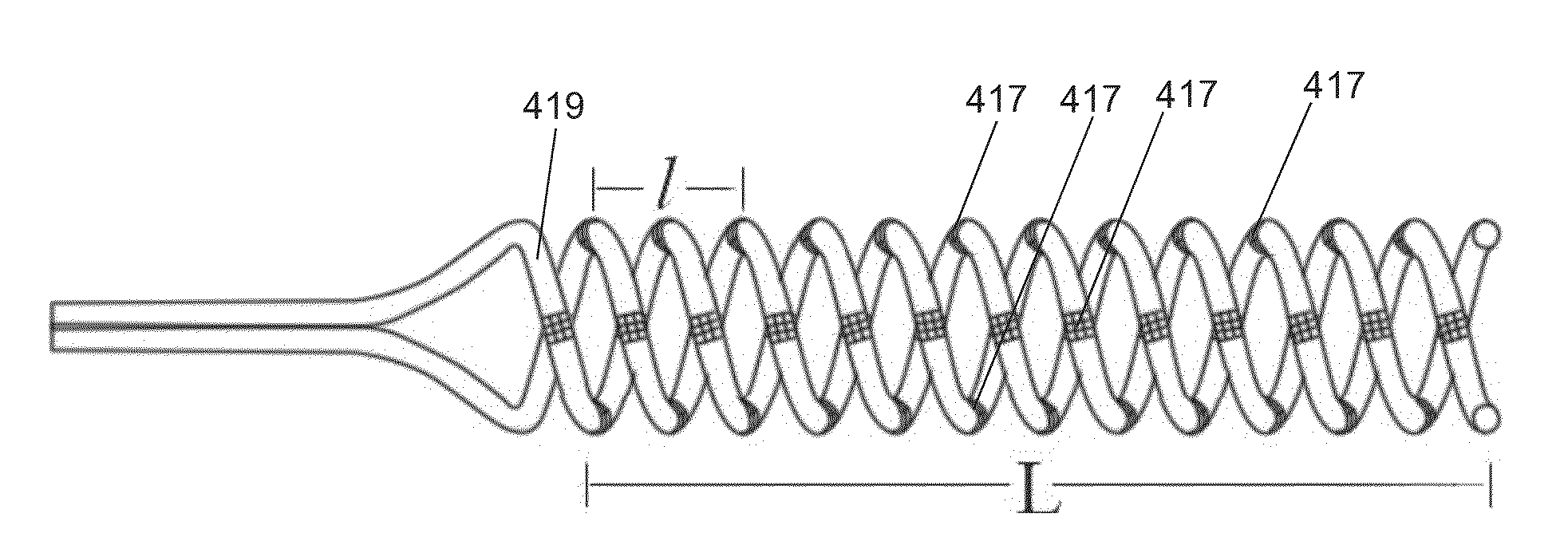
A device captures and assists in the removal of a thrombus in arteries, even in small arteries. The device uses a soft coil mesh to engage the surface of a thrombus, and a guidewire is used to retract the soft coil mesh with the captured thrombus. The soft coil is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical element forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
Methods and devices for denervation
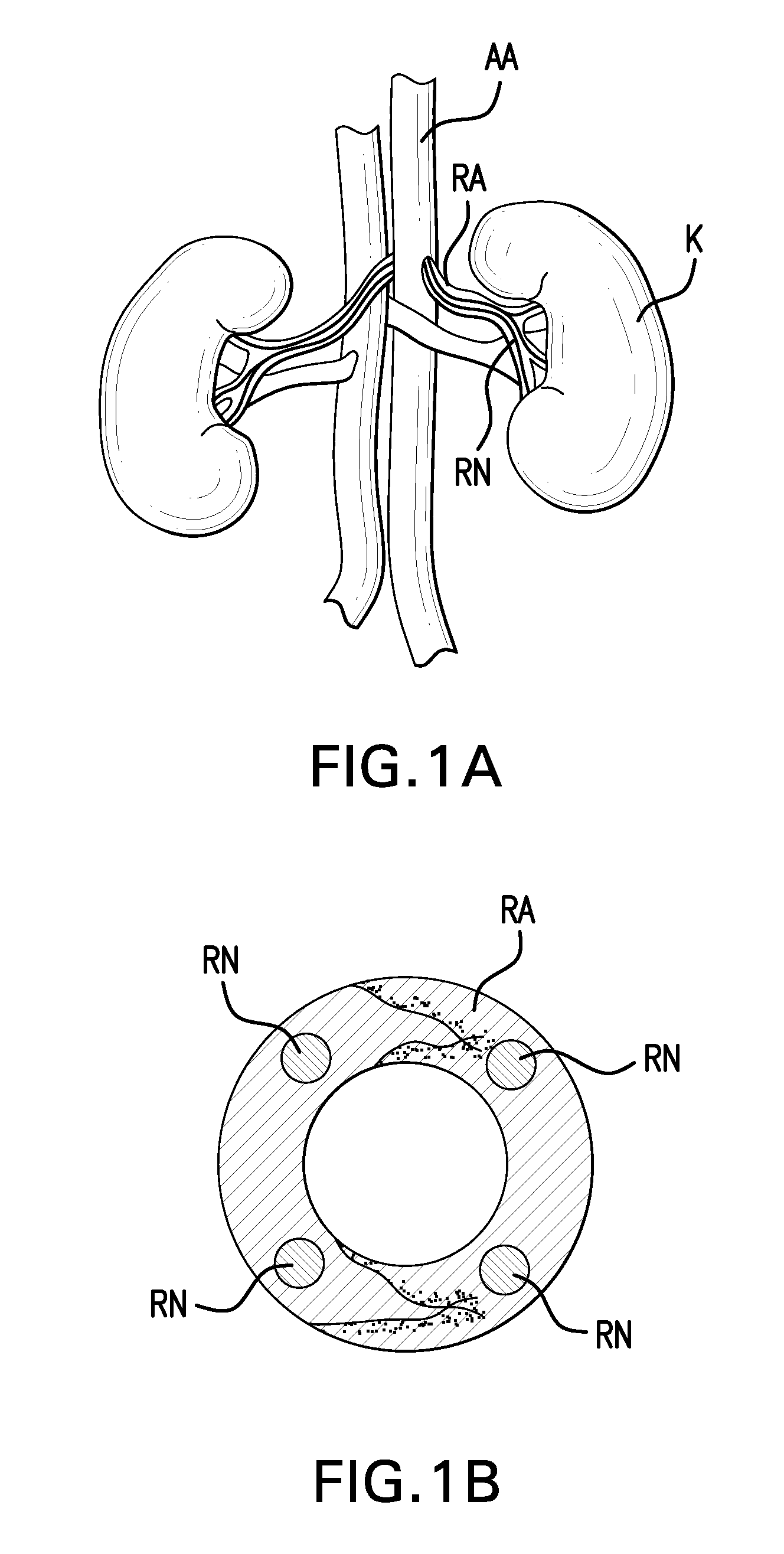
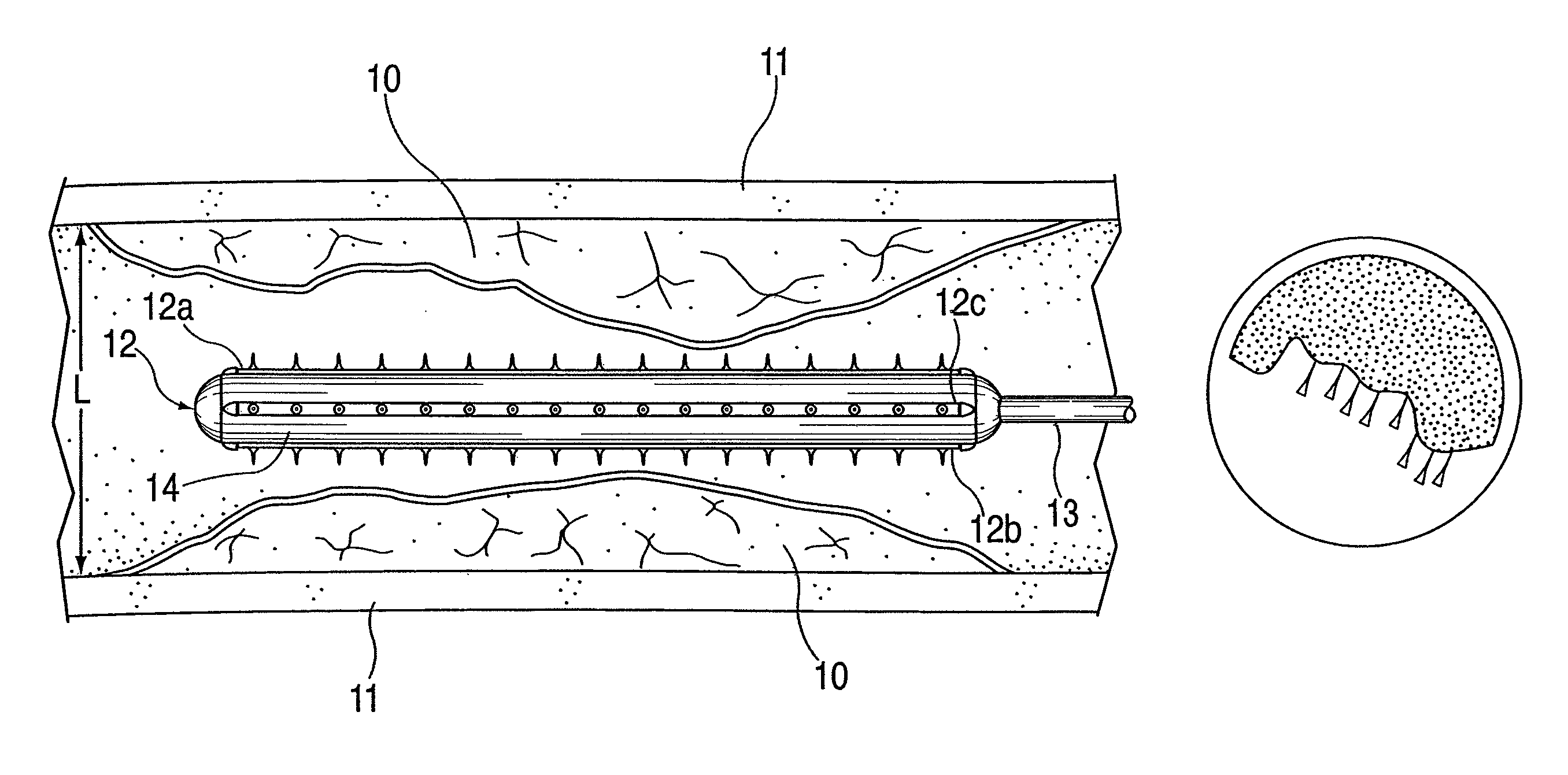
Various delivery devices are described to deliver an agent locally to the renal nerves. The delivery devices are positioned in the renal artery and penetrate into the wall of the renal artery to deliver the agent to the renal nerves. The delivery devices may be used to deliver the agent according to longitudinal position, radial position, and depth of the renal nerves relative to the renal artery. In addition, various methods are described to denervate, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue. Also, various agents are described to denerve, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue.
Owner:NORTHWIND MEDICAL
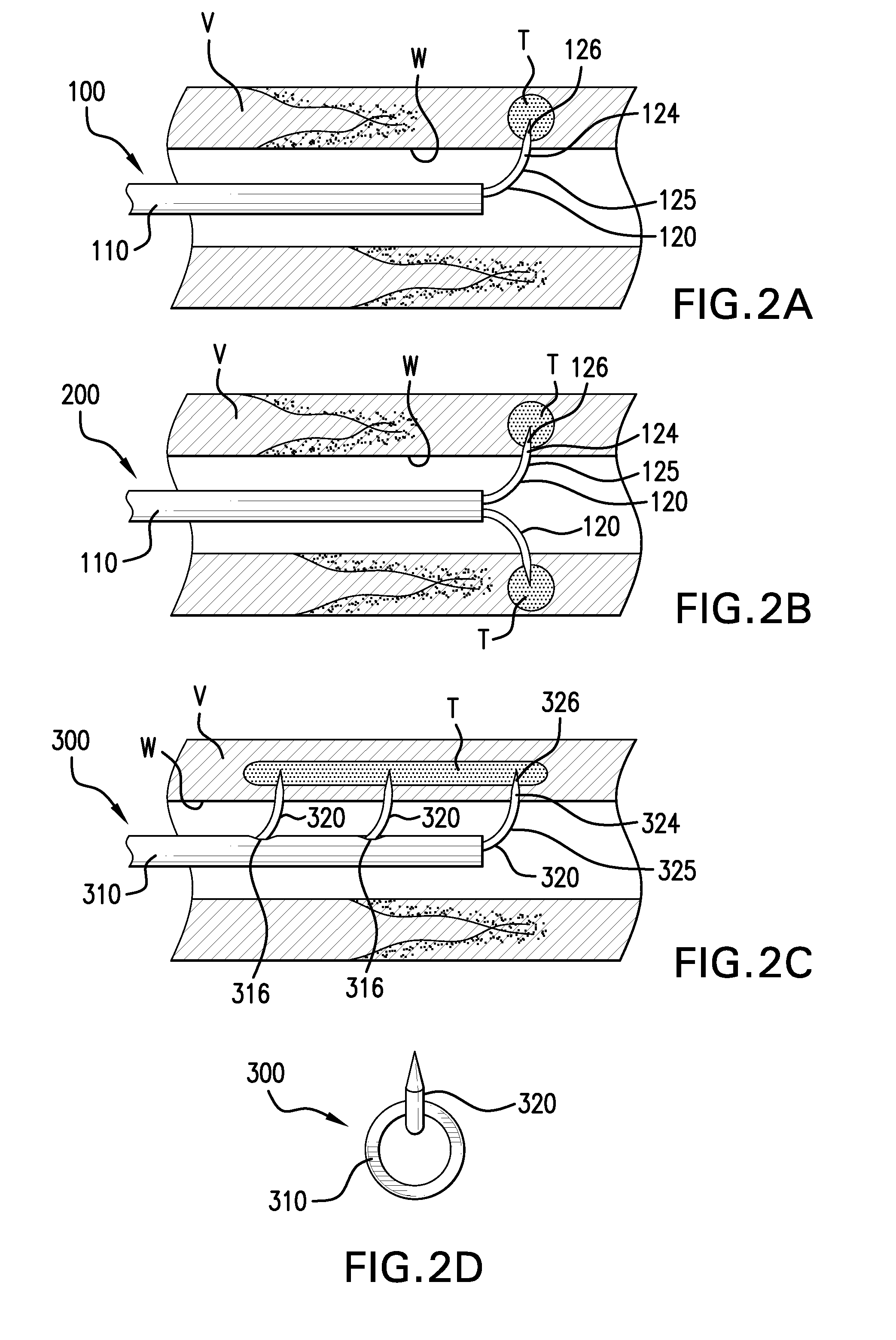
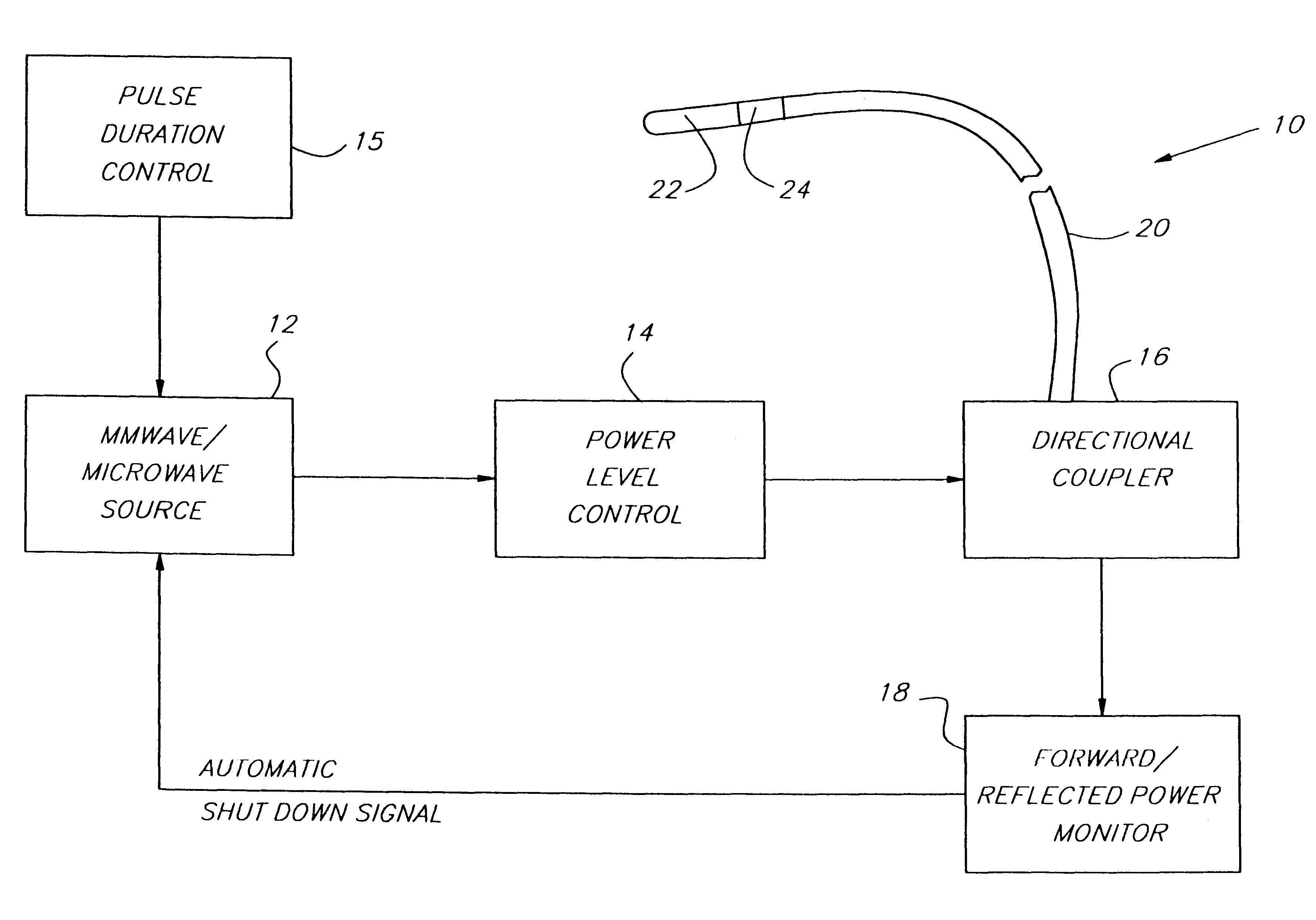
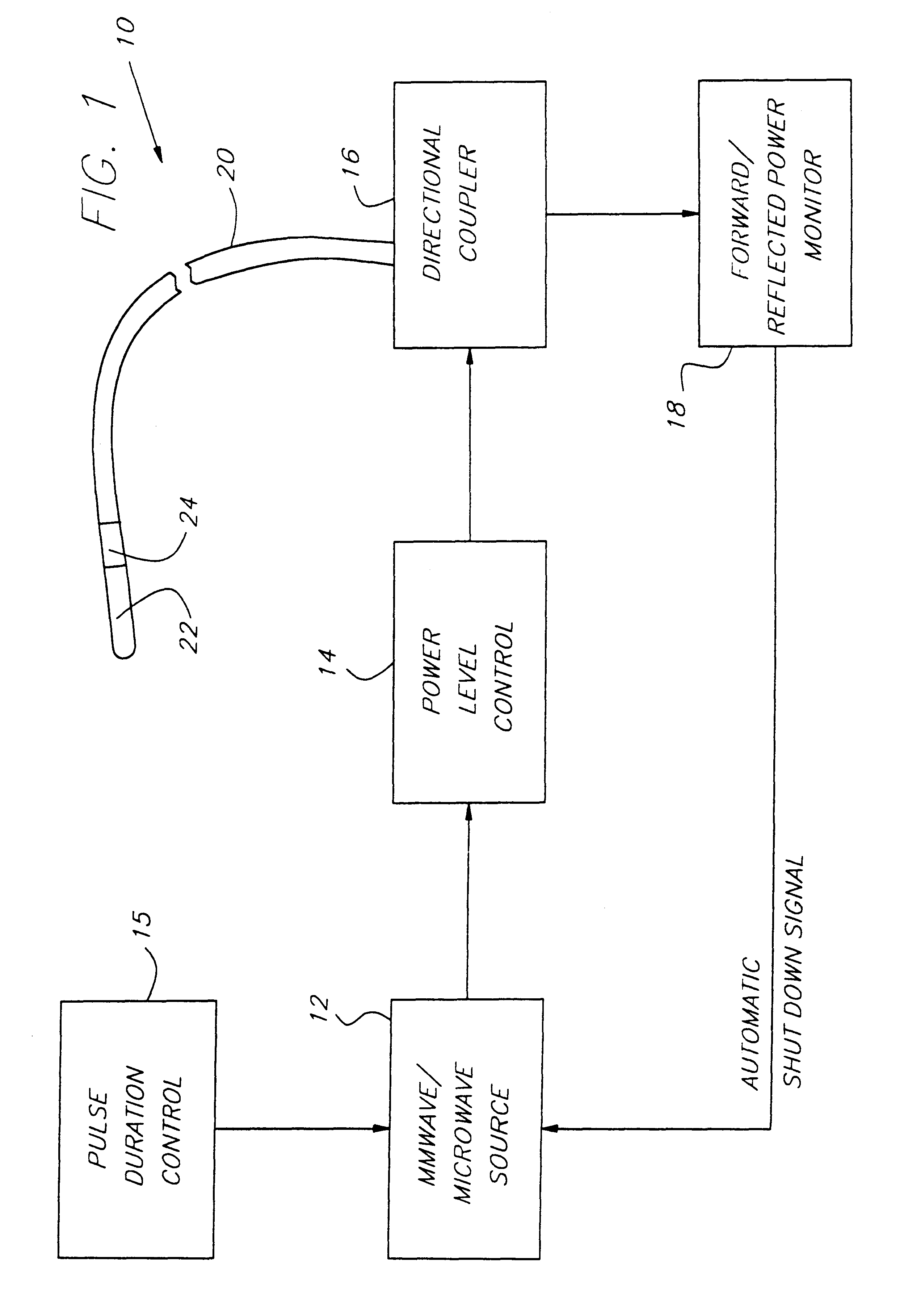
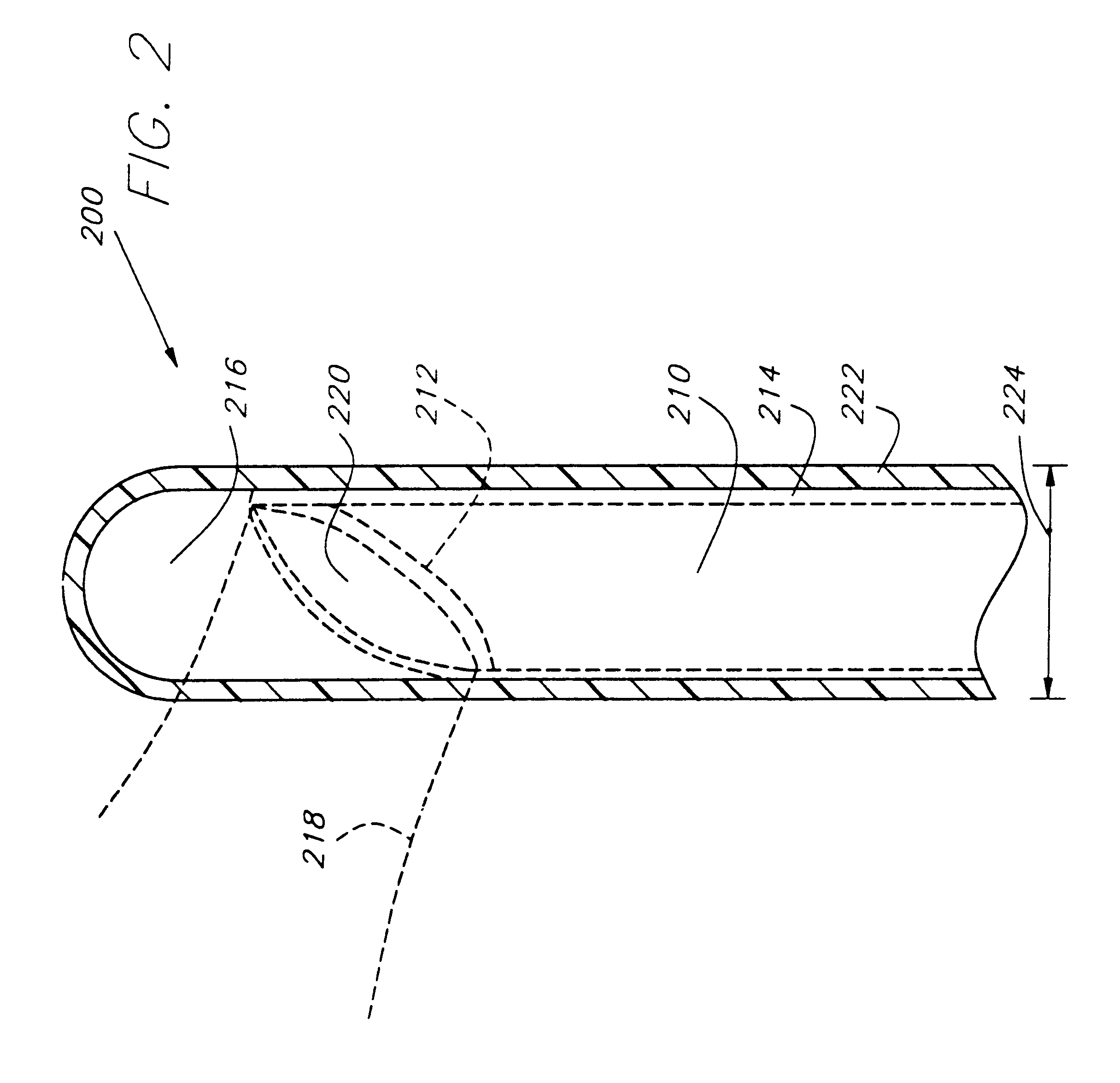
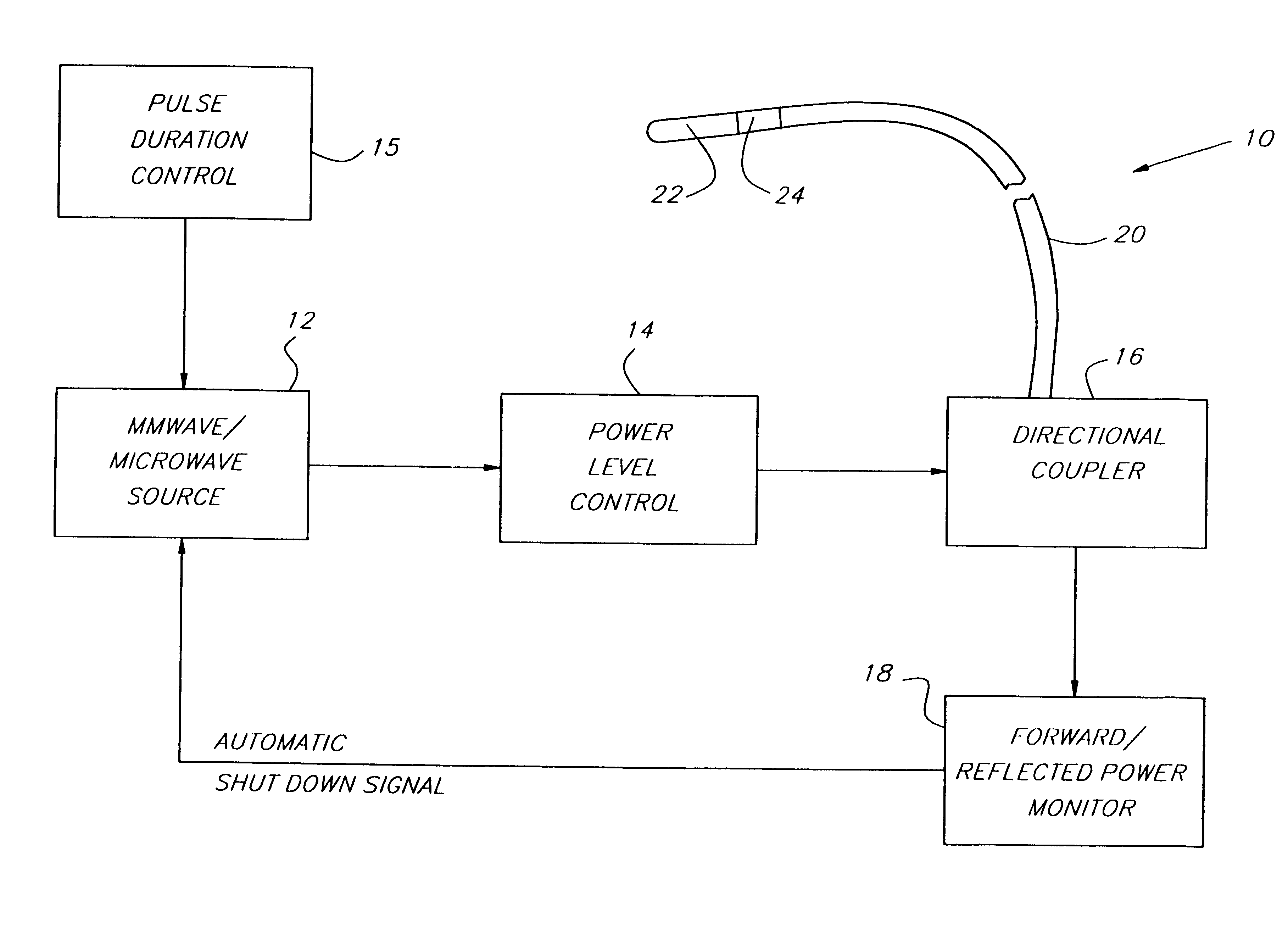
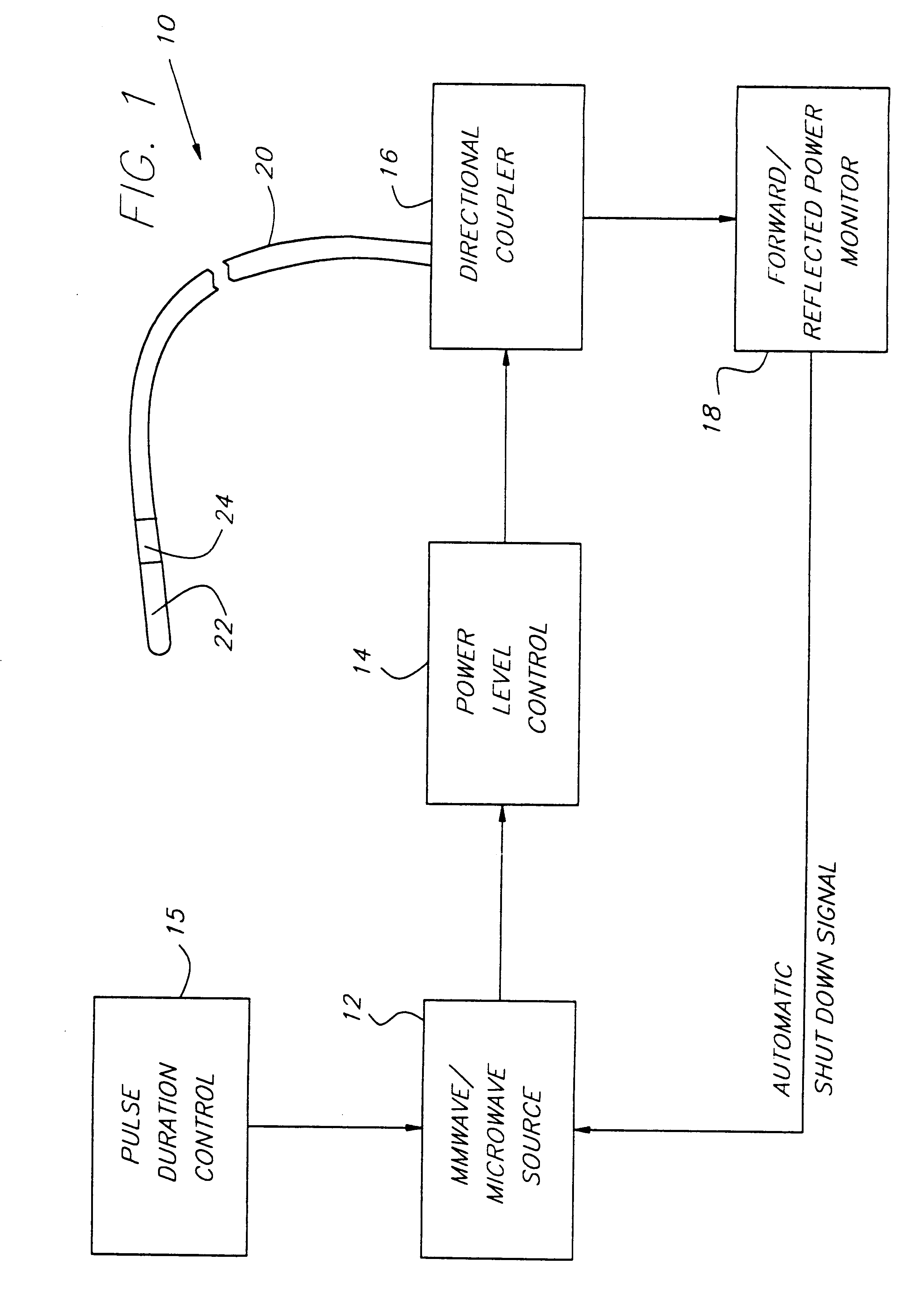
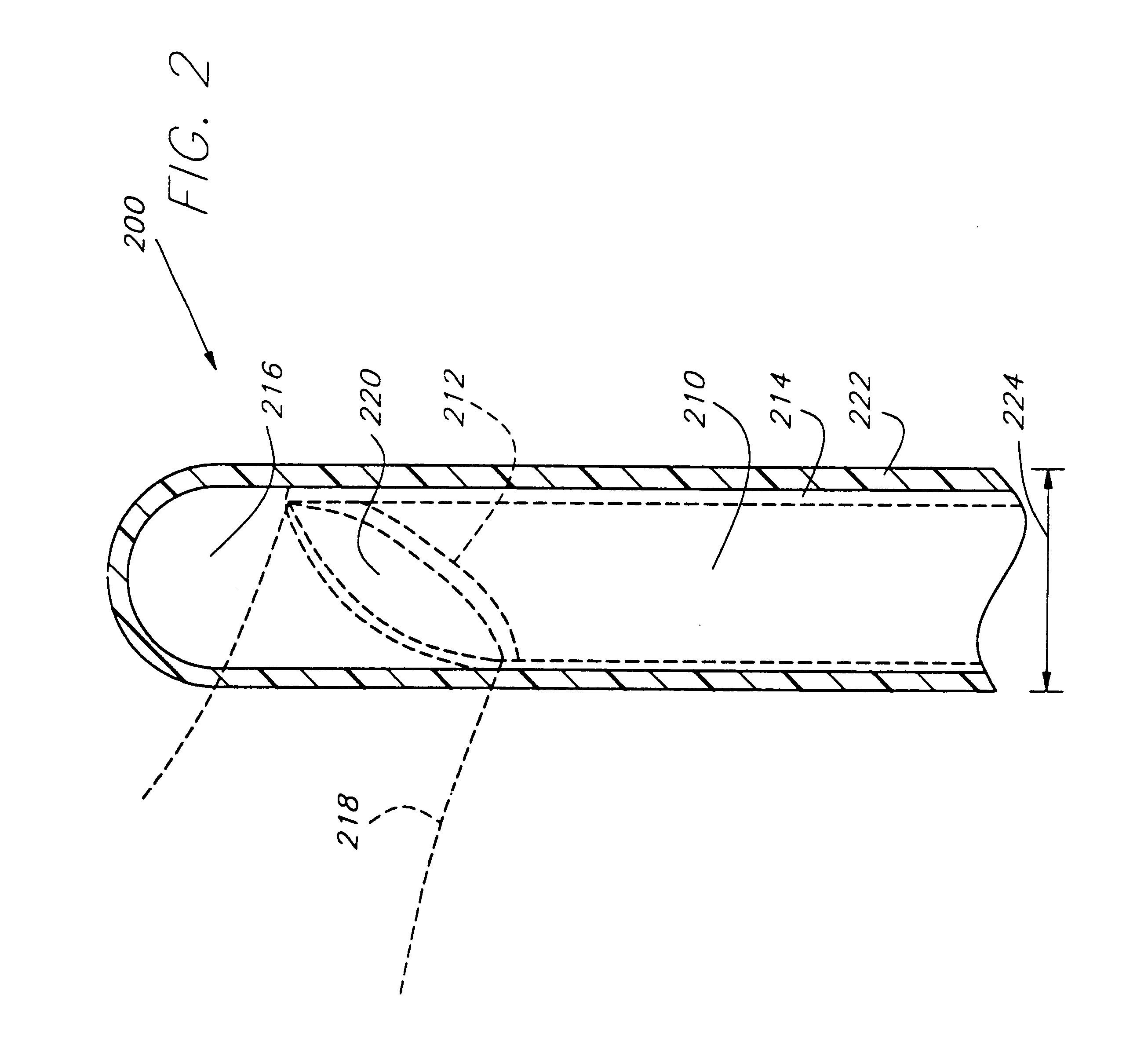
Endothelium preserving microwave treatment for atherosclerosis
Method and apparatus are provided to treat atherosclerosis wherein the artery is partially closed by dilating the artery while preserving the vital and sensitive endothelial layer thereof. Microwave energy having a frequency from 3 GHz to 300 GHz is propagated into the arterial wall to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally necrosing connective tissue and softening fatty and waxy plaque while limiting heating of surrounding tissues including the endothelial layer and / or other healthy tissue, organs, and blood. The heating period for raising the temperature a potentially desired amount, about 20° C. within the atherosclerotic lesion may be less than about one second. In one embodiment of the invention, a radically beveled waveguide antenna is used to deliver microwave energy at frequencies from 25 GHz or 30 GHz to about 300 GHz and is focused towards a particular radial sector of the artery. Because the atherosclerotic lesions are often asymmetrically disposed directable or focussed heating preserves healthy sectors of the artery and applies energy to the asymmetrically positioned lesion faster than a non-directed beam. A computer simulation predicts isothermic temperature profiles for the given conditions and may be used in selecting power, pulse duration, beam width, and frequency of operation to maximize energy deposition and control heat rise within the atherosclerotic lesion without harming healthy tissues or the sensitive endothelium cells.
Owner:NASA
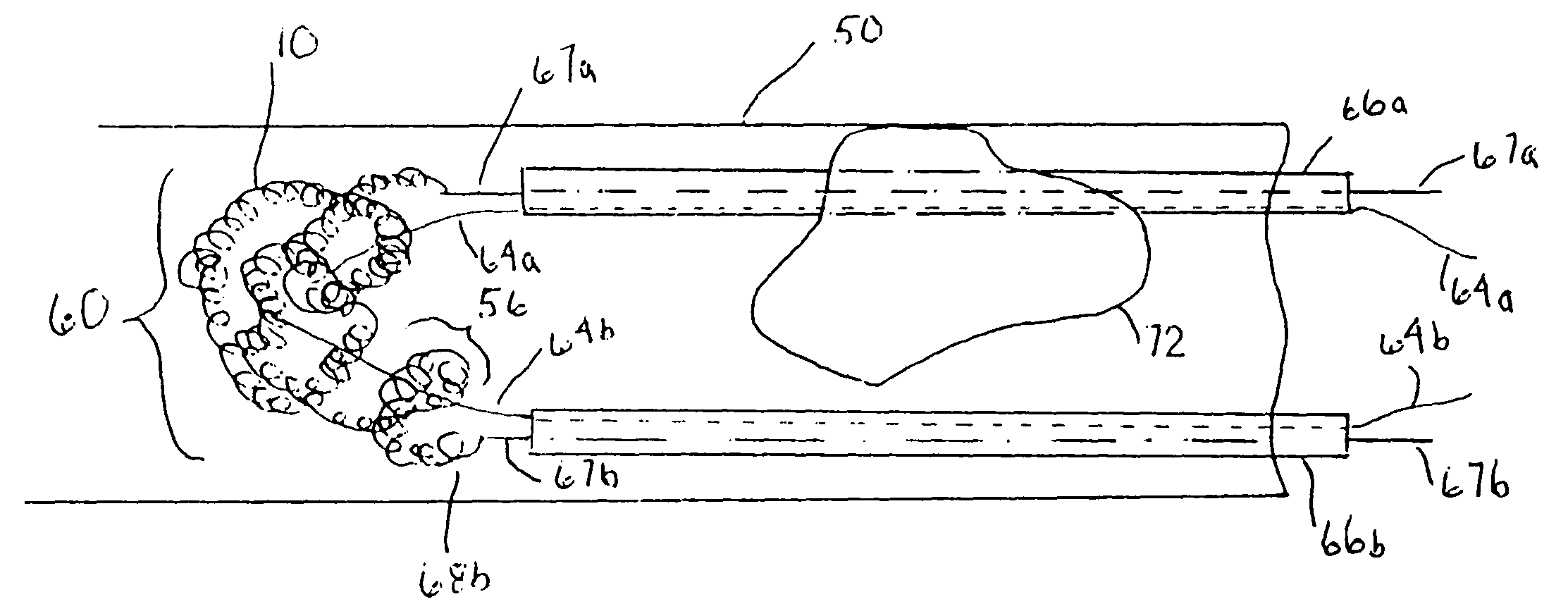
Thrombus removal system and process
A device capable of capturing and facilitating the removal of a thrombus in blood vessels (or stones in biliary or urinary ducts, or foreign bodies) uses a soft coil mesh with the aid of a pull wire or string to engage the surface of a thrombus, and remove the captured thrombus. The soft coil mesh is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical elements forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls. The use of multiple coil mesh elements, delivered through a single lumen or multiple lumens, preferably with separate control of at least one end of each coil, provides a firm grasp on a distal side of a thrombus, assisting in non-disruptive or minimally disrupted removal of the thrombus upon withdrawal of the device.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
Thrombus removal system and process
A device capable of capturing and facilitating the removal of a thrombus in blood vessels (or stones in biliary or urinary ducts, or foreign bodies) uses a soft coil mesh with the aid of a pull wire or string to engage the surface of a thrombus, and remove the captured thrombus. The soft coil mesh is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical elements forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls. The use of multiple coil mesh elements, delivered through a single lumen or multiple lumens, preferably with separate control of at least one end of each coil, provides a firm grasp on a distal side of a thrombus, assisting in non-disruptive or minimally disrupted removal of the thrombus upon withdrawal of the device.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
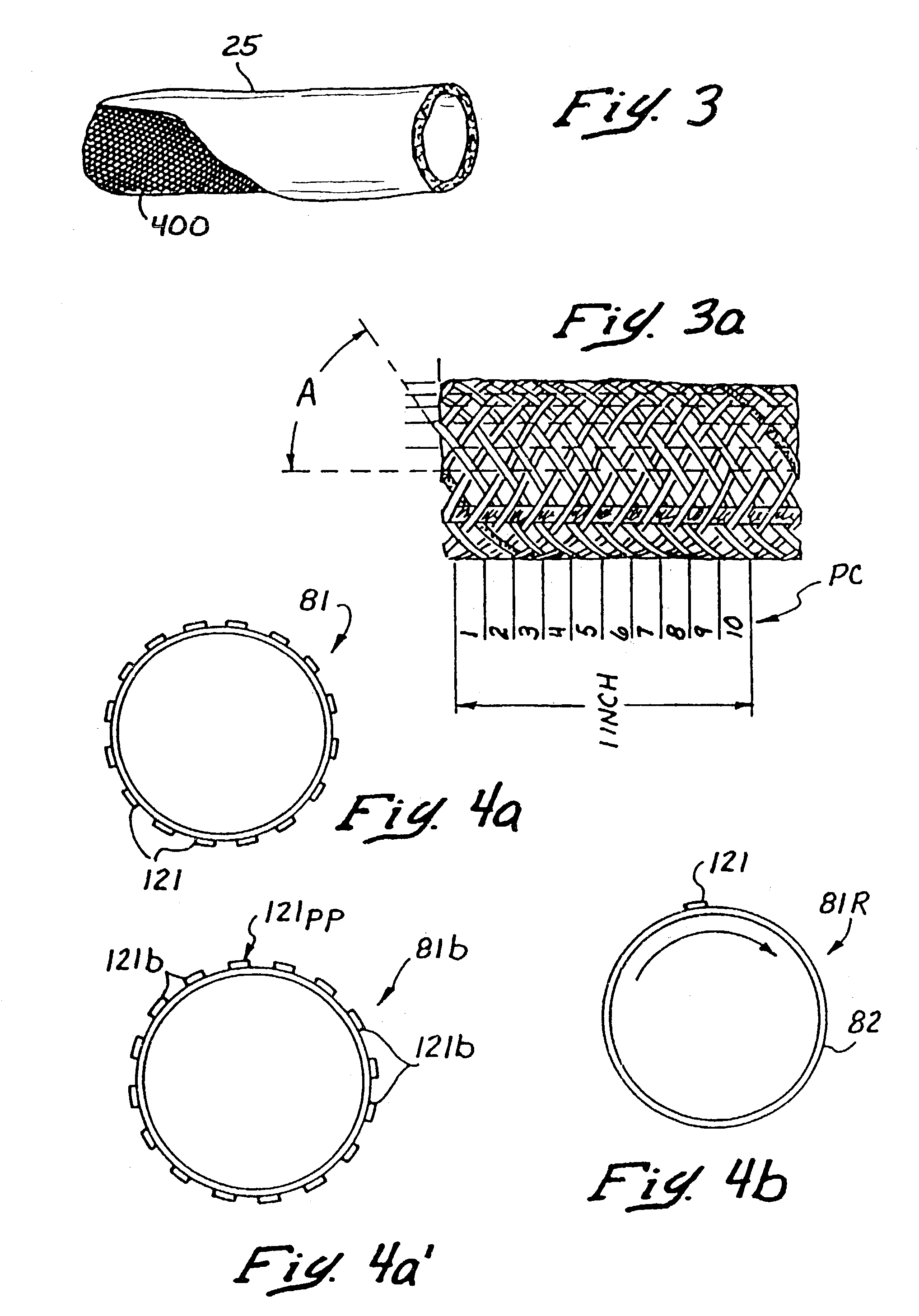
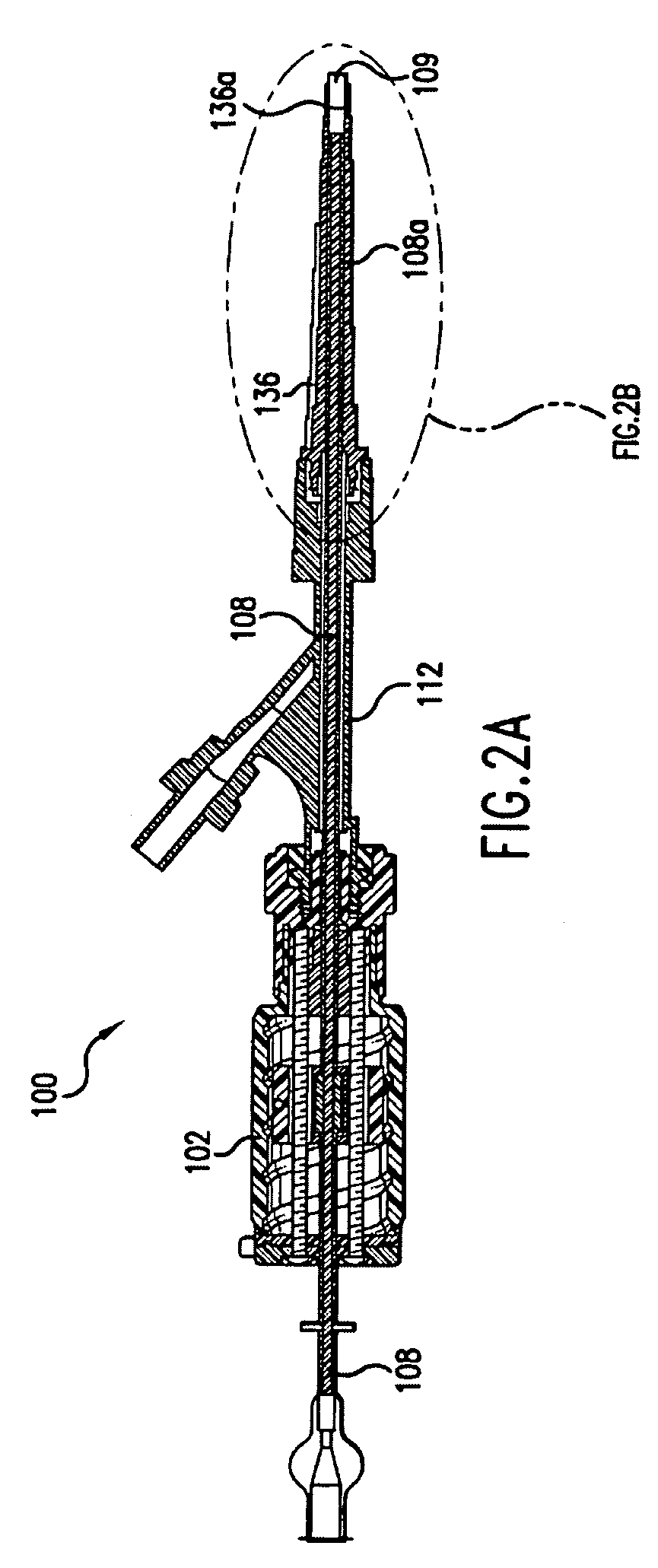
Stent delivery catheter and method of use
A deformable sheath is attached to a catheter and introduced intravascularly to be expanded against an arterial wall and entrap plaque therebetween. A stent is subsequently deployed within the expanded sheath and the sheath is then withdrawn from within the vasculature to leave the stent expanded against the arterial wall with the plaque entrapped therebetween.
Owner:STACK RICHARD S +4
Pre-angioplasty serration of atherosclerotic plaque enabling low-pressure balloon angioplasty and avoidance of stenting
ActiveUS20100042121A1Large caliberSafely and accurately dilated and stretchedBalloon catheterCannulasPercutaneous angioplastyDrug eluting balloon
A device and method for intravascular treatment of atherosclerotic plaque prior to balloon angioplasty which microperforates the plaque with small sharp spikes acting as serrations for forming cleavage lines or planes in the plaque. The spikes may also be used to transport medication into the plaque. The plaque preparation treatment enables subsequent angioplasty to be performed at low balloon pressures of about 4 atmospheres or less, reduces dissections, and avoids injury to the arterial wall. The subsequent angioplasty may be performed with a drug-eluting balloon (DEB) or drug-coated balloon (DCB). The pre-angioplasty perforation procedure enables more drug to be absorbed during DEB or DCB angioplasty, and makes the need for a stent less likely. Alternatively, any local incidence of plaque dissection after balloon angioplasty may be treated by applying a thin, ring-shaped tack at the dissection site only, rather than applying a stent over the overall plaque site.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
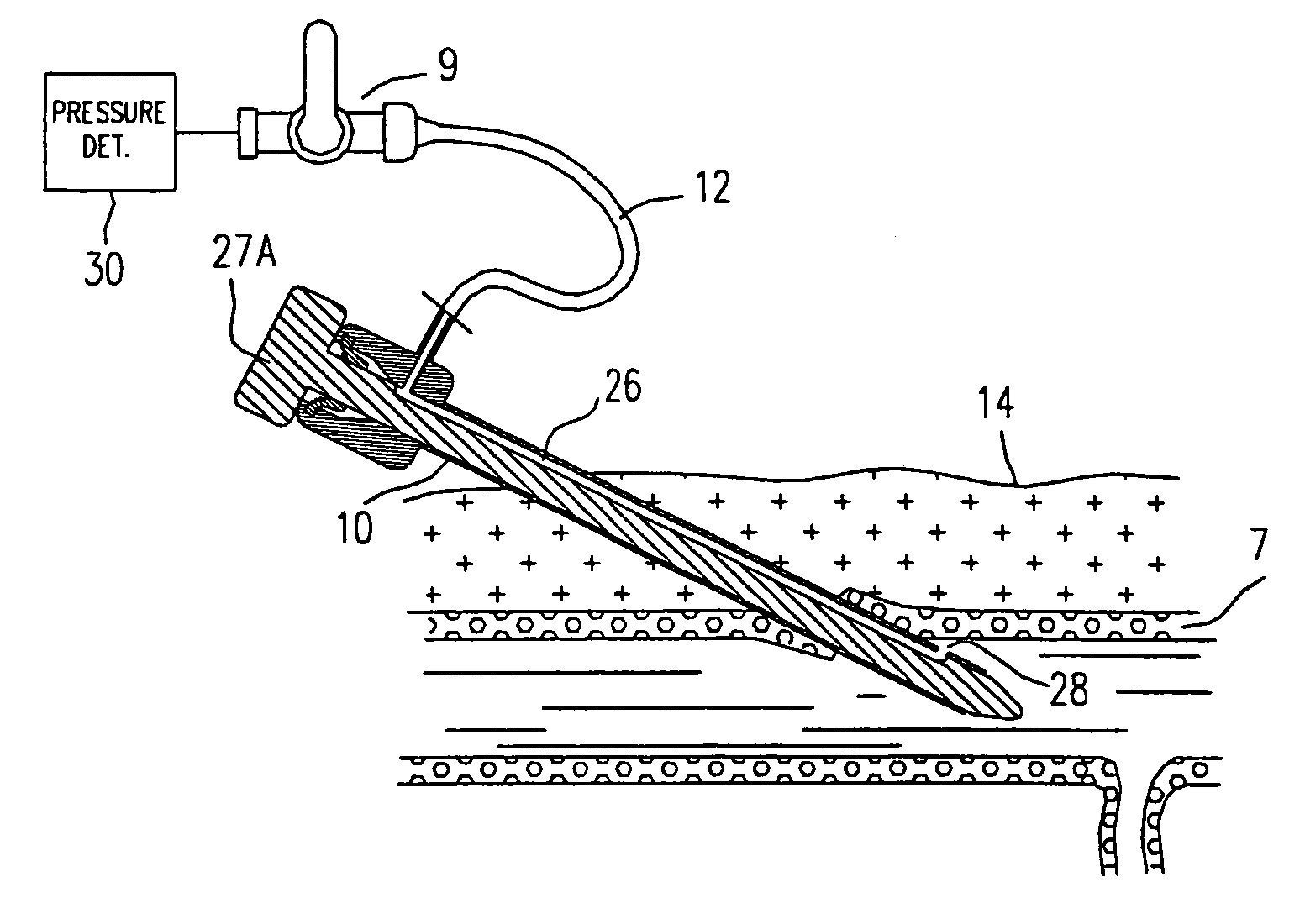
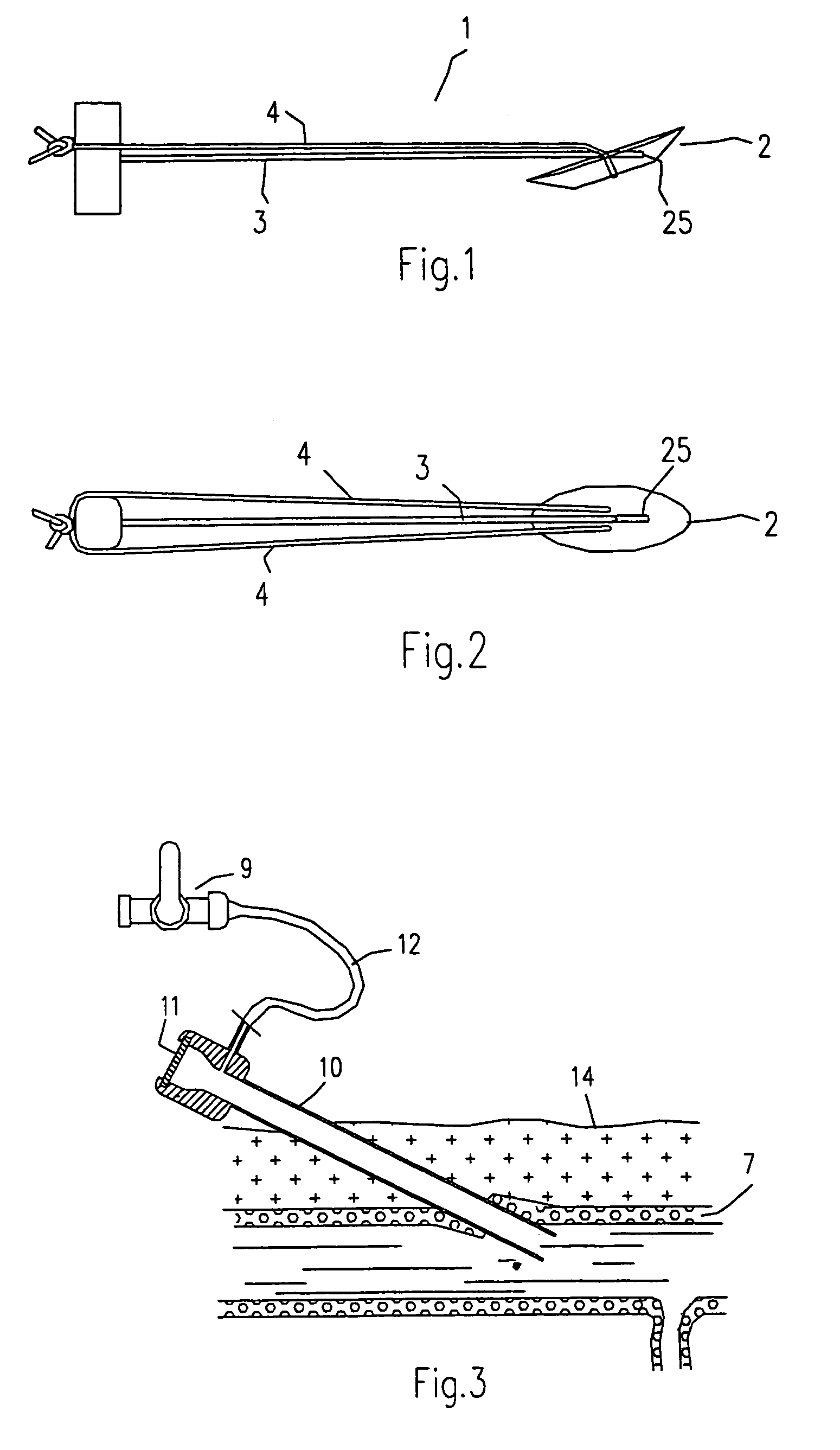
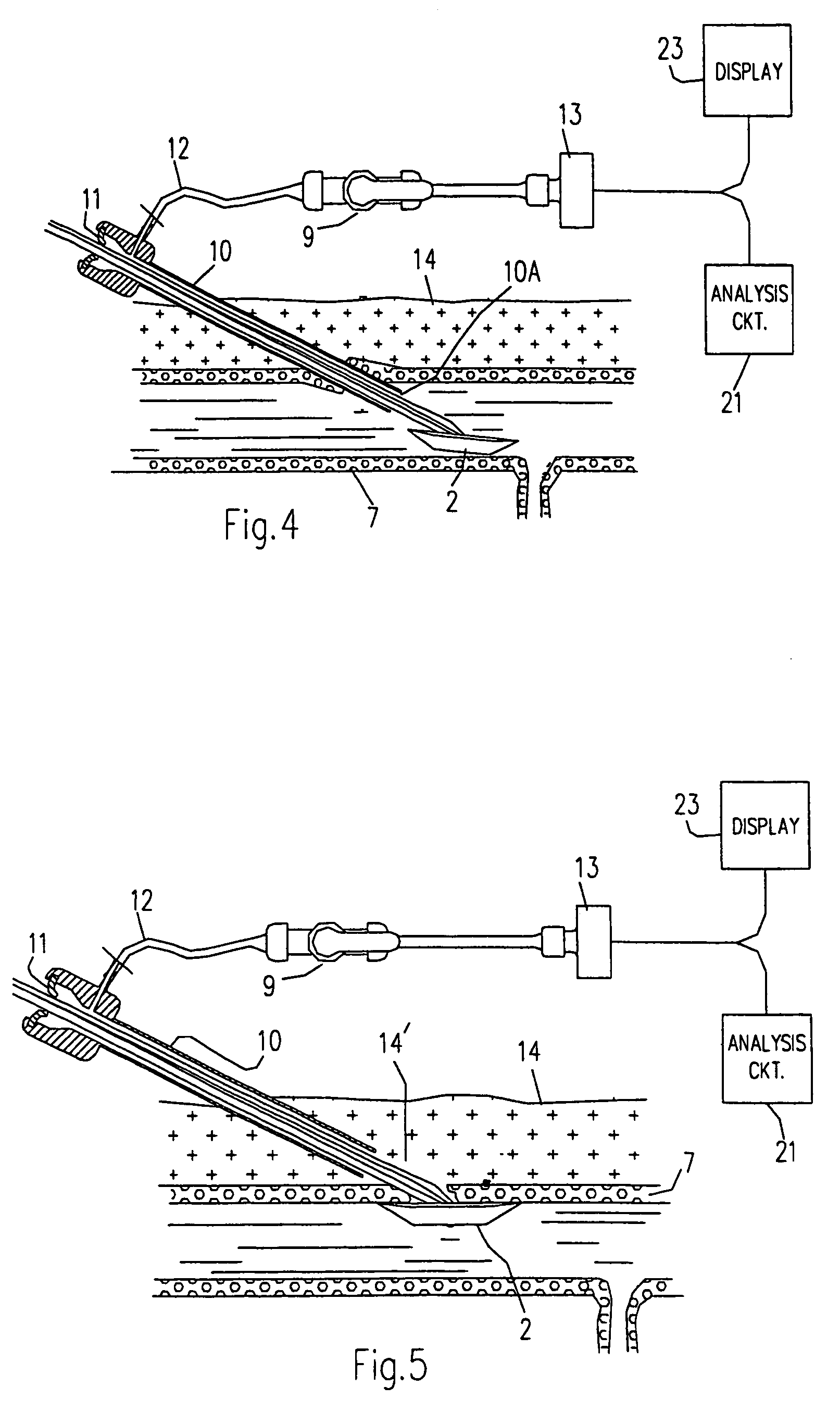
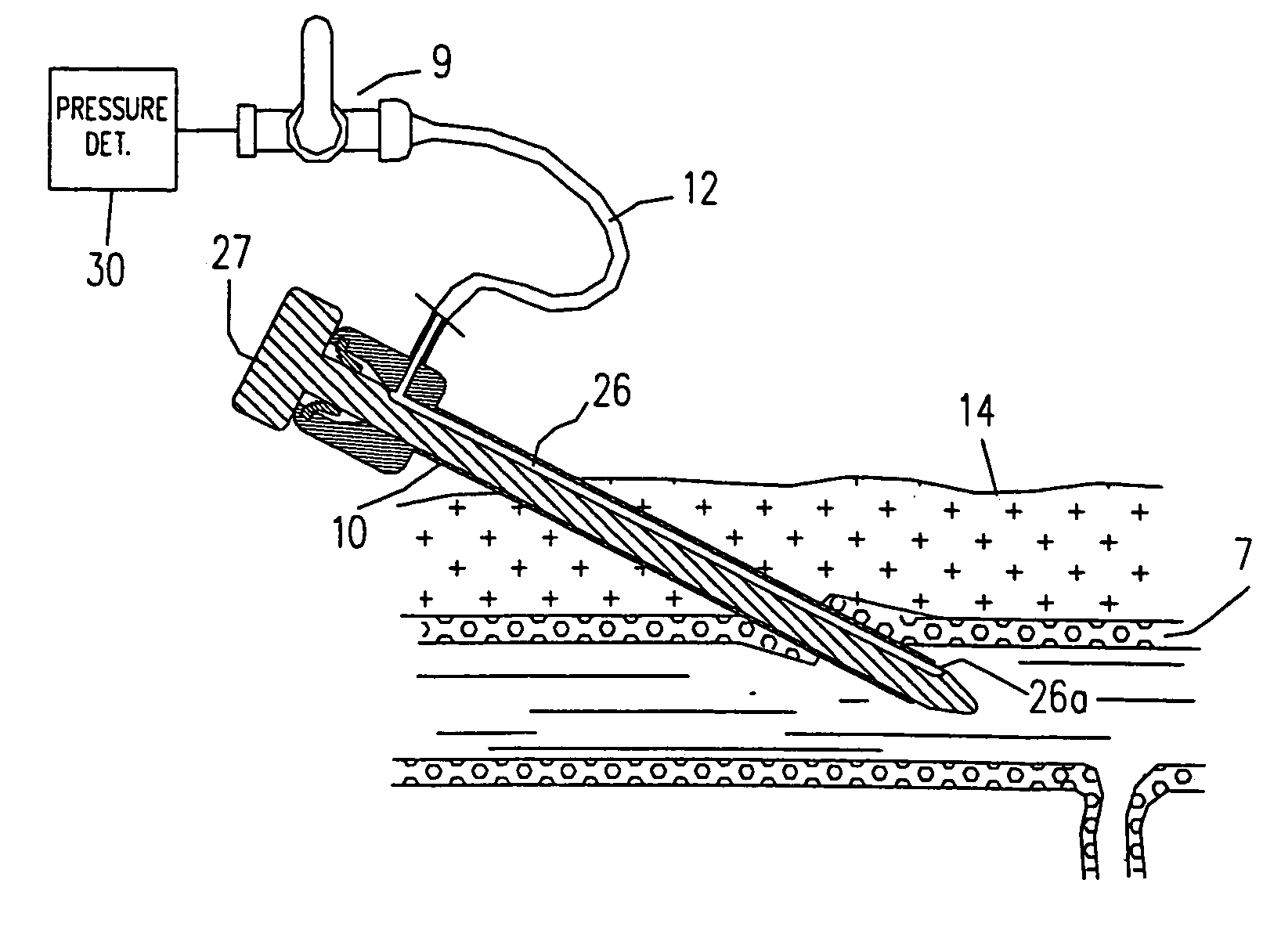
Technique to confirm correct positioning of arterial wall sealing device
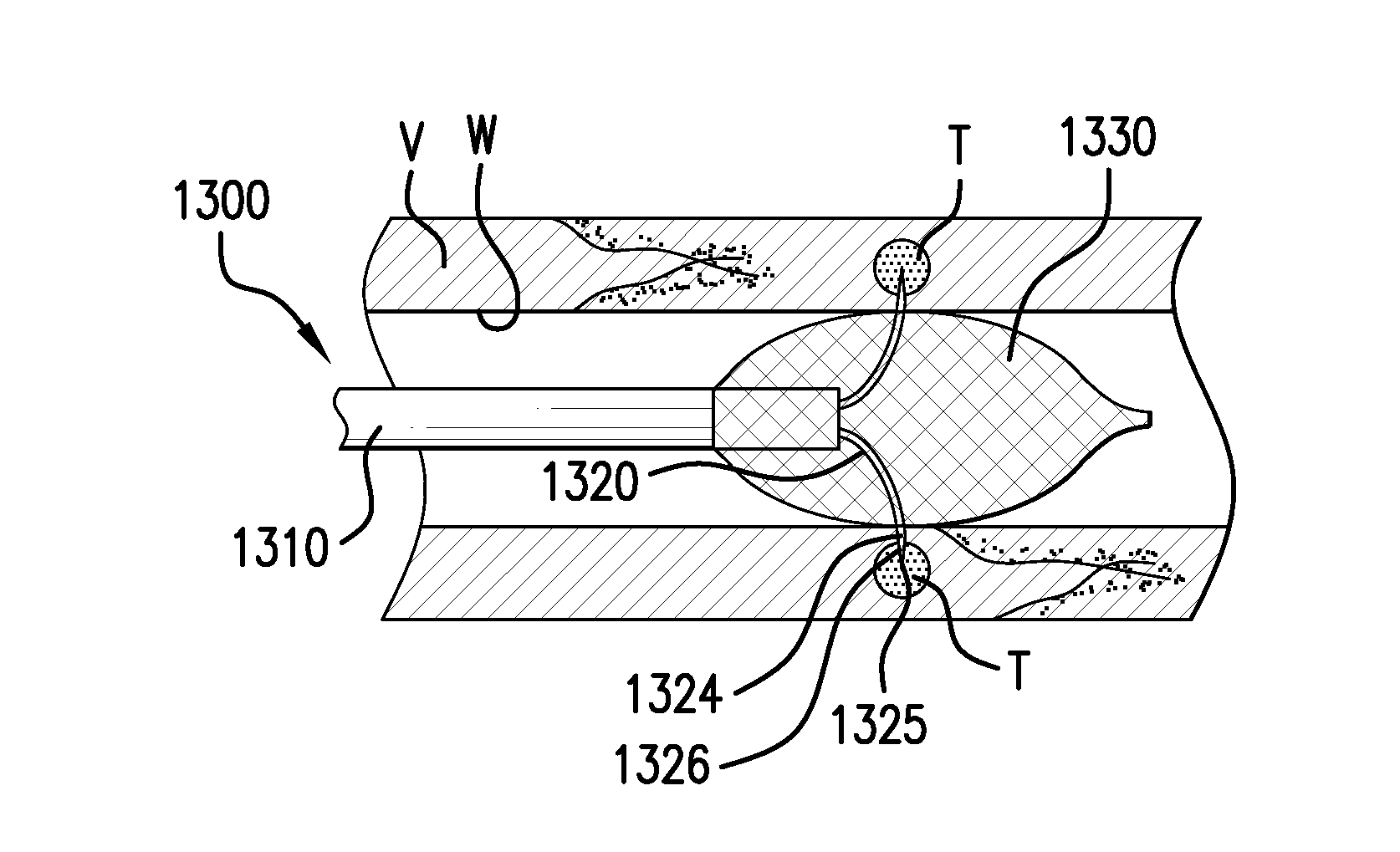
Methods and systems related to sealing punctures in blood vessels (such as following an angio or PTCA procedure) are disclosed. The position of a distal end of an introducer assembly in tissue is determined using a pressure sensor. The pressure sensor is connected to the proximal end of the introducer assembly. The introducer assembly has a fluid path between its distal end and its proximal end. Measured blood pressure is outputted as an indication of the position of the distal end of the introducer assembly in the tissue. Proper positioning of a seal is confirmed by placing the introducer assembly such that its distal end is in tissue outside a puncture in a blood vessel wall and observing a characteristic of blood at the proximal end of the introducer assembly. In both techniques, a waveform of the blood pressure at the distal end of the introducer assembly may be displayed on a display to provide additional information to a surgeon as to the relative position of the components with respect to various tissues.
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
Ultrasonic blood vessel measurement apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050096528A1Effective filteringAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisTissue architectureMedicine
Disclosed are systems and methods for identifying various tissue structure aspects, such as boundaries of arterial walls, within an image, such as an ultrasound image. Various measurements may be made using information with respect to the identified aspects of tissue structure. For example, intima-media thickness measurements may be made. Additionally or alternatively, tissue structure aspects, such as plaque within an artery, may be characterized, such as by determining a density thereof. Various information, such as measurement datums, used in identification of aspects of tissue structure in one image may be stored and applied to subsequent images, such as images of a video sequence.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Catheter deployment device
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Thrombus removal system and process
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
Devices and methods for percutaneous endarterectomy
Devices and methods are provided for percutaneously treating atherosclerotic plaques within blood vessels. Atherosclerotic plaques cause significant morbidity and mortality by narrowing the arteries, which adversely affects blood flow, and by acting as a source for thrombi and emboli thus causing acute organ ischemia. Current treatments include open surgery with its inherent drawbacks, and stenting, which is less invasive but leaves the plaque material in the artery, which promotes restenosis. The present invention combines the advantages of both approaches. In general, the invention provides tools that enable percutaneously dissecting the plaque from the arterial wall and removing it from the body.
Owner:ANGIOWORKS MEDICAL
Intravascular catheter
InactiveUS20050159731A1Effective treatmentEasily and safely navigatedDiagnosticsSurgeryArterial occlusionsSurgical department
An intravascular catheter system includes an intravascular catheter that can be easily and safely navigated through severely occluded arteries. The system uniquely includes both an optical fiber for use in providing data for guiding the catheter and a conventional metal guide wire for use in navigating the catheter through the artery passageway. The system further includes optical imaging of the arterial occlusion during guidance of the catheter through the artery passageway. More particularly the system provides a visual indication to the surgeon to determine if the catheter assembly is approaching the arterial wall.
Owner:LEE DON W
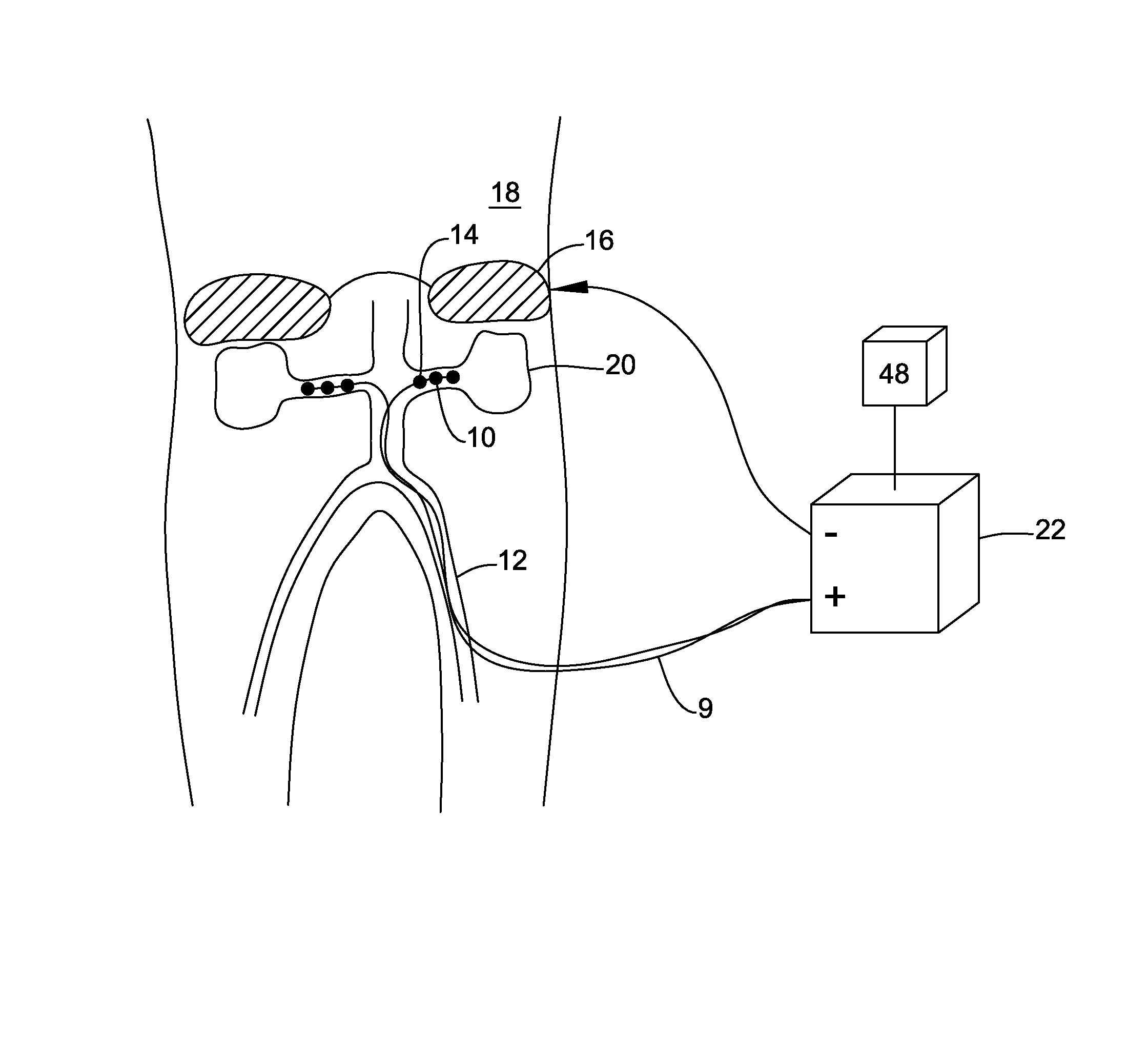
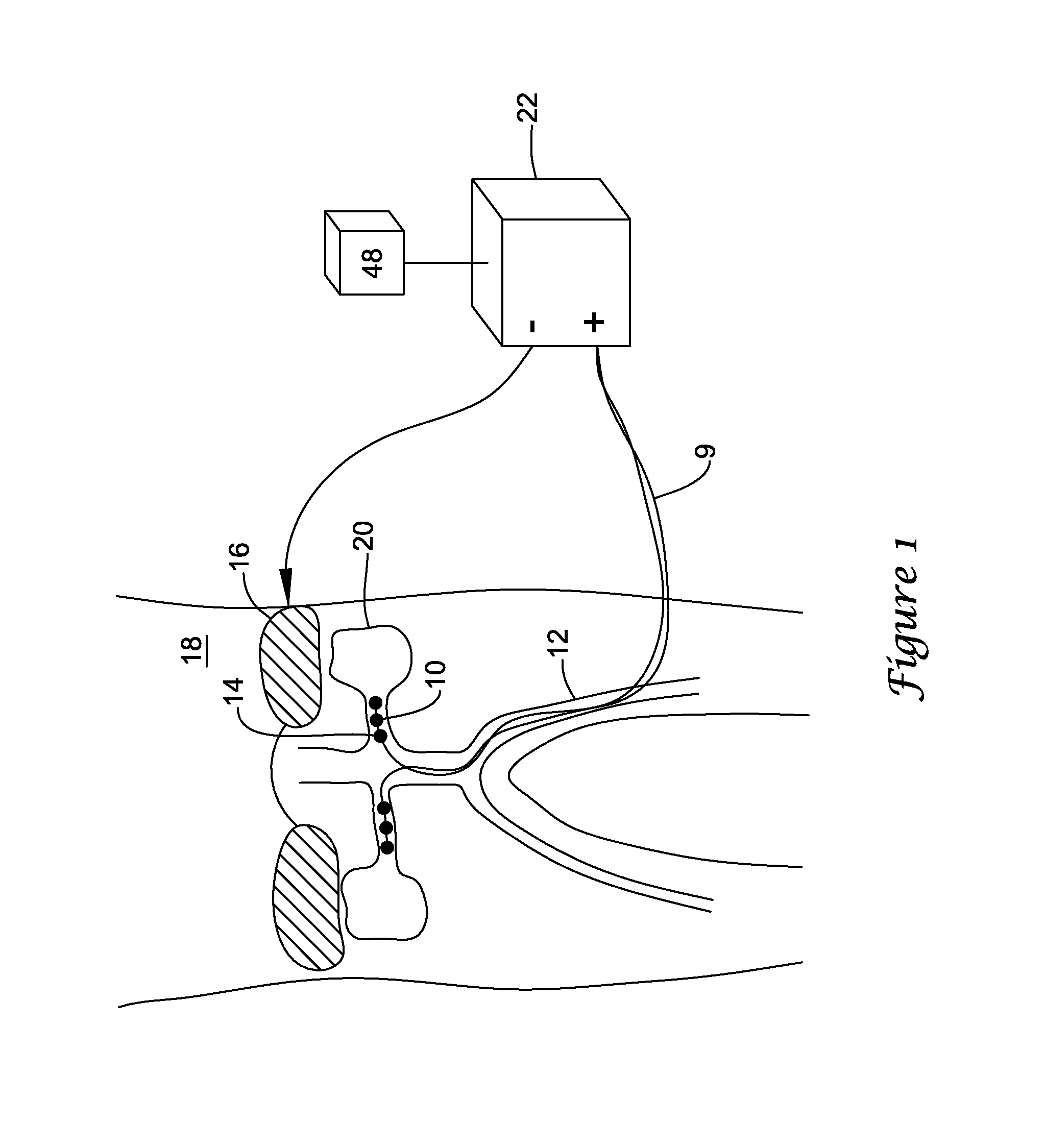
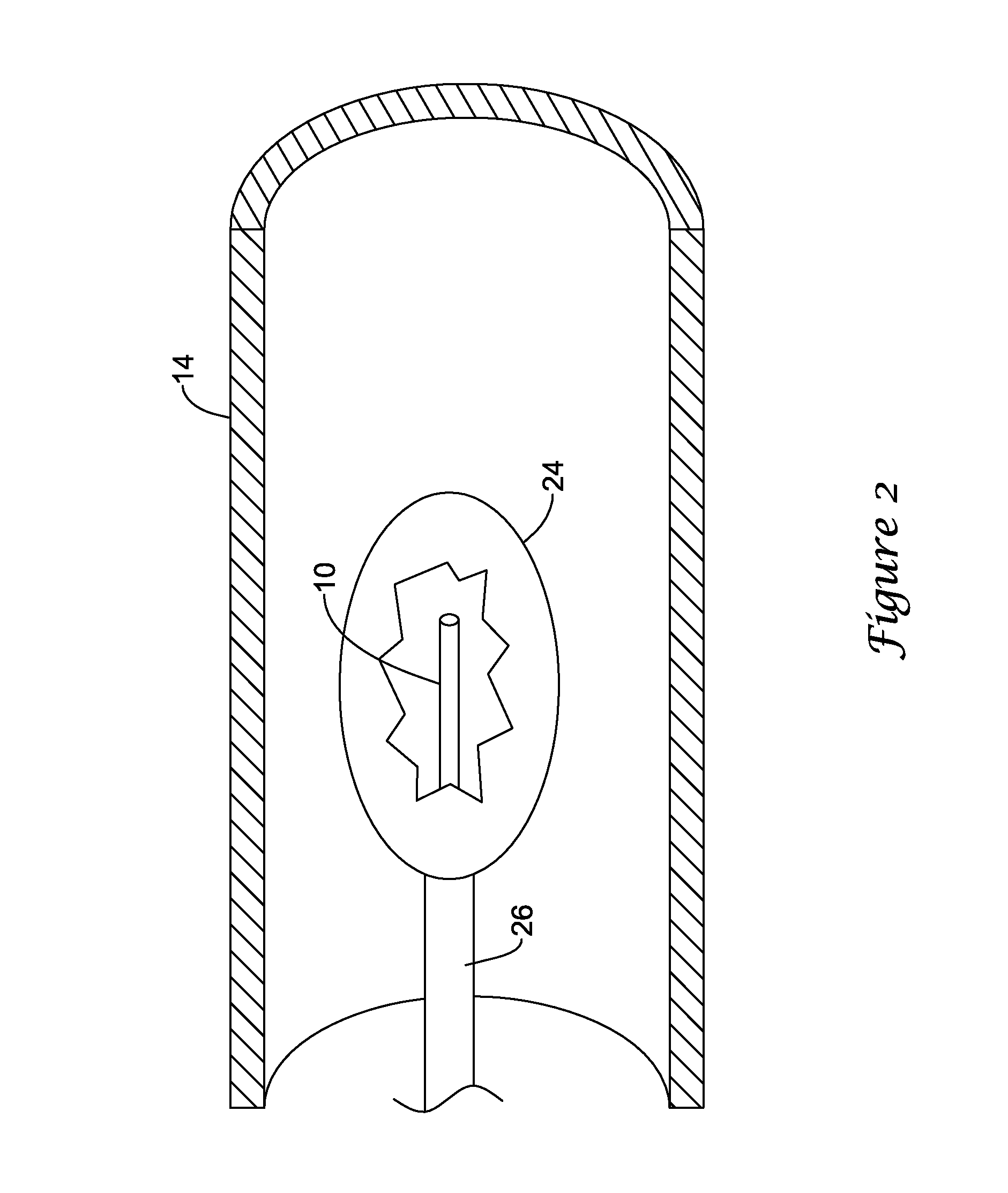
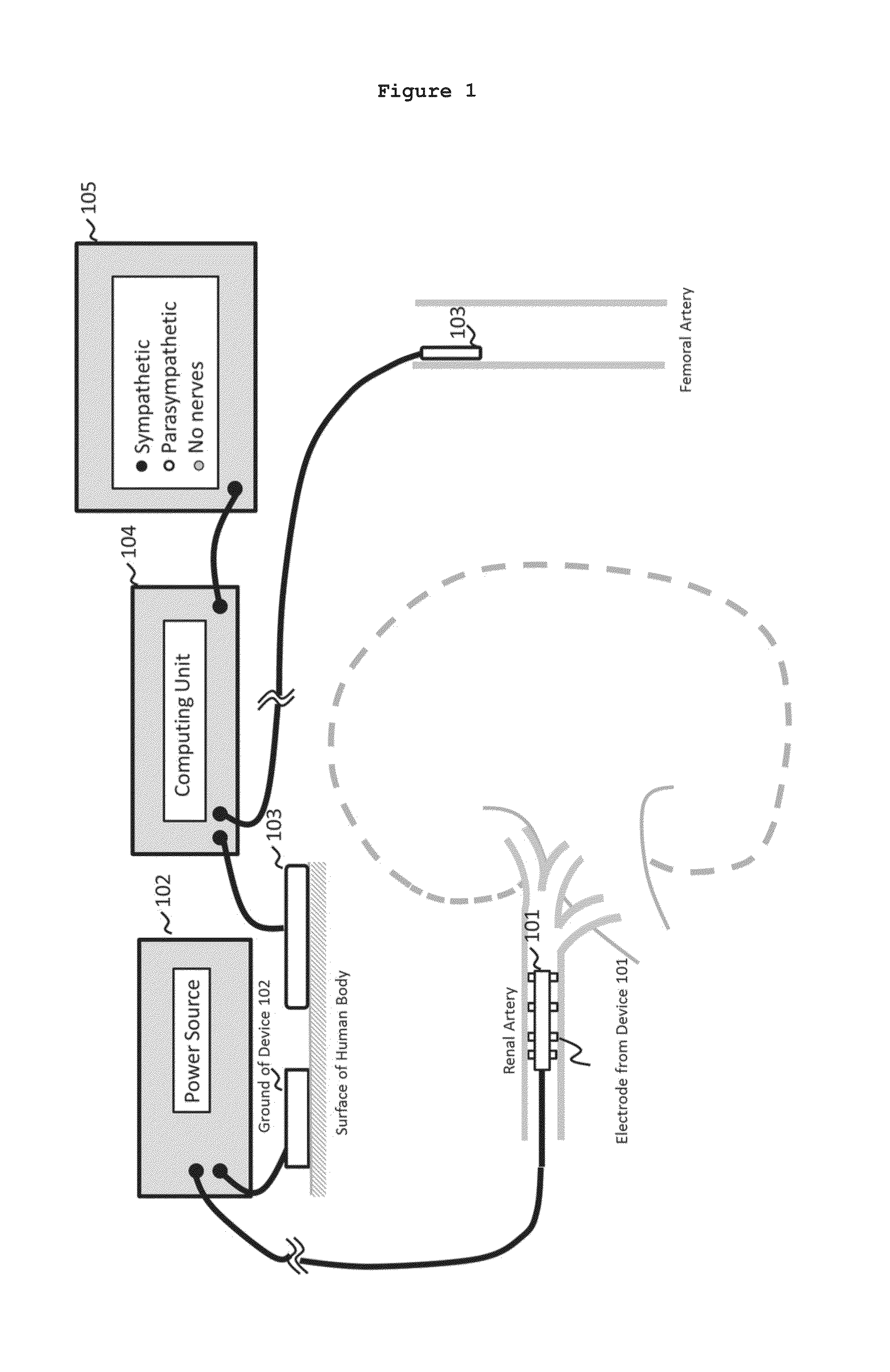
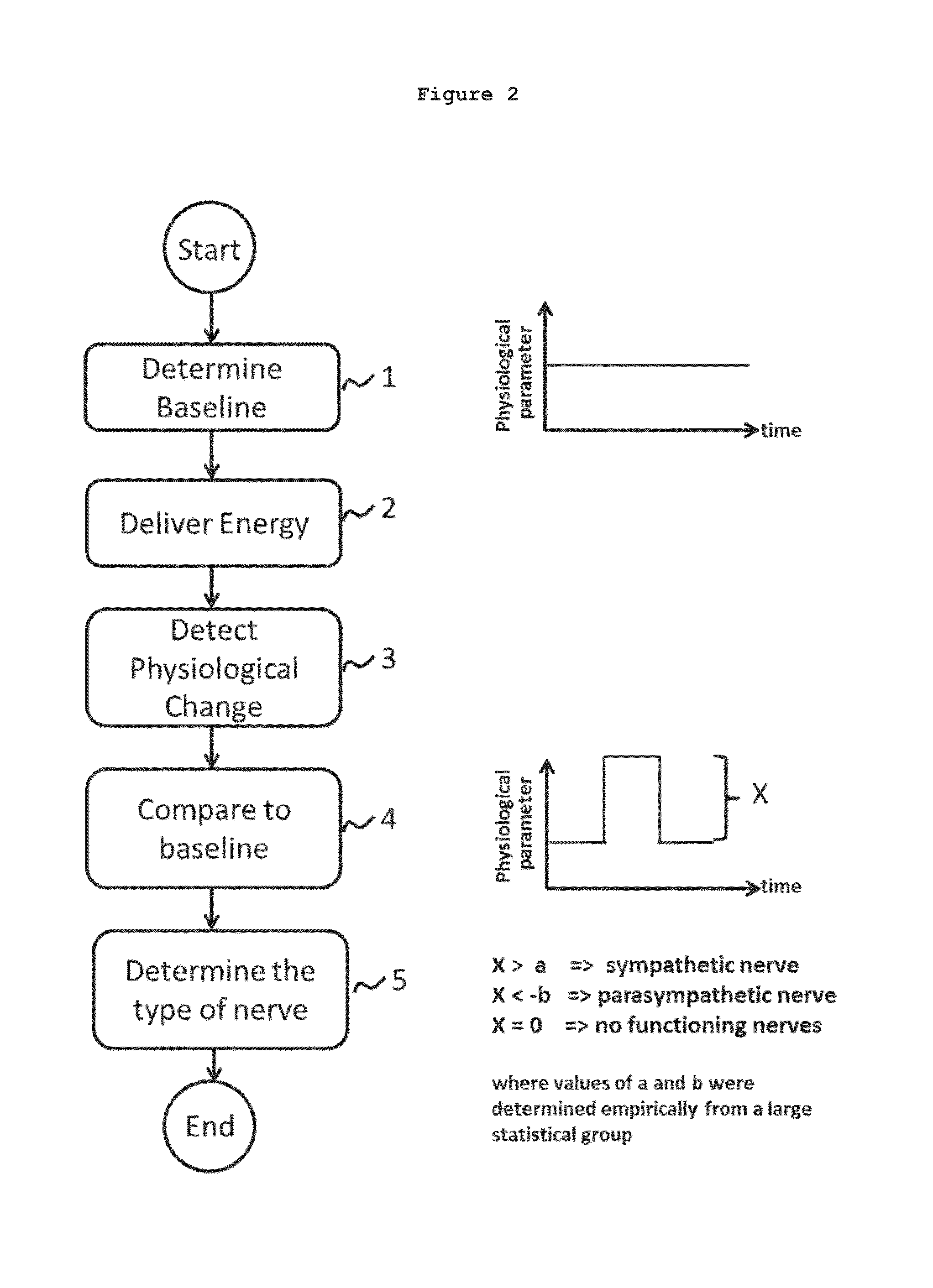
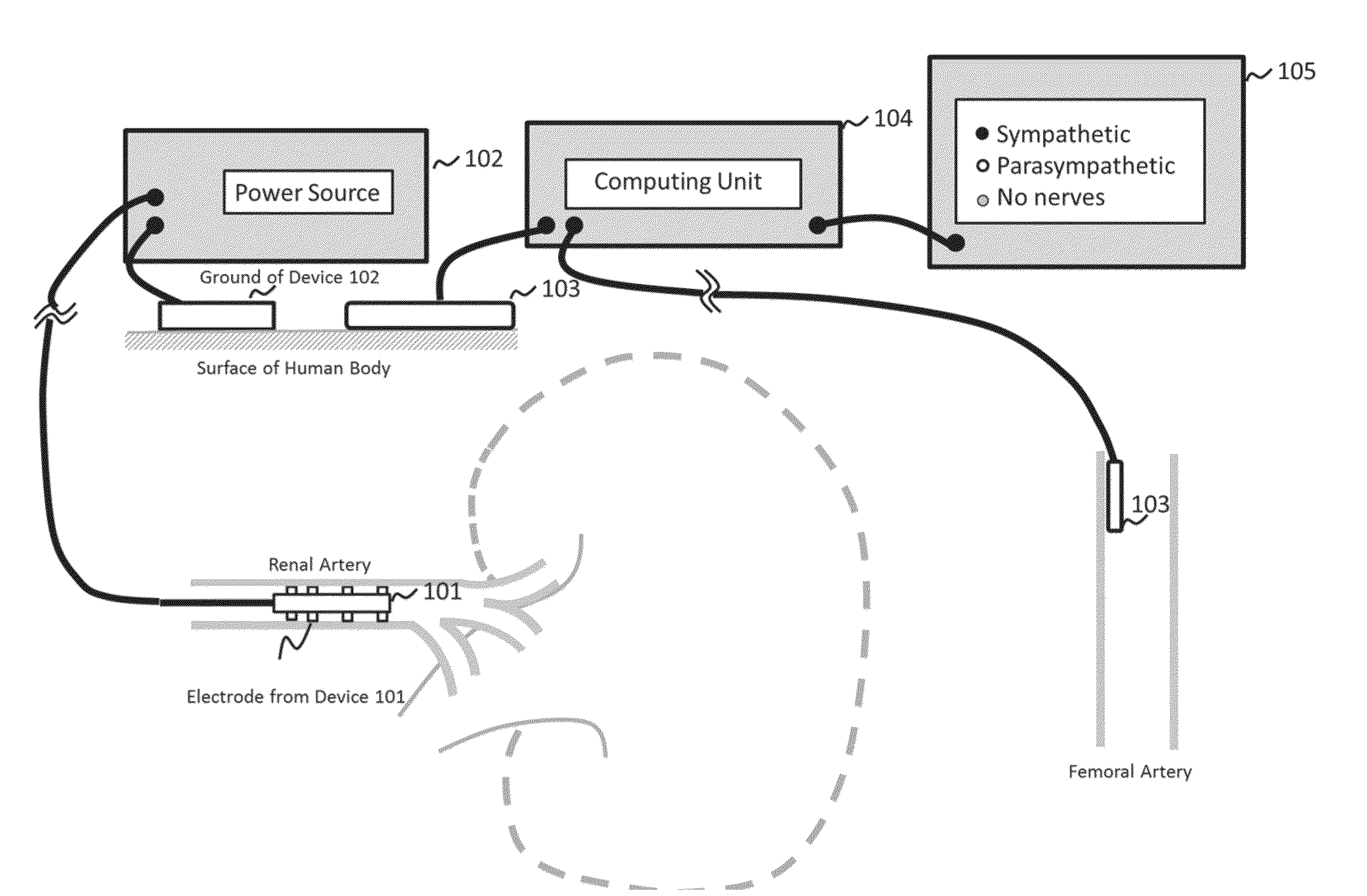
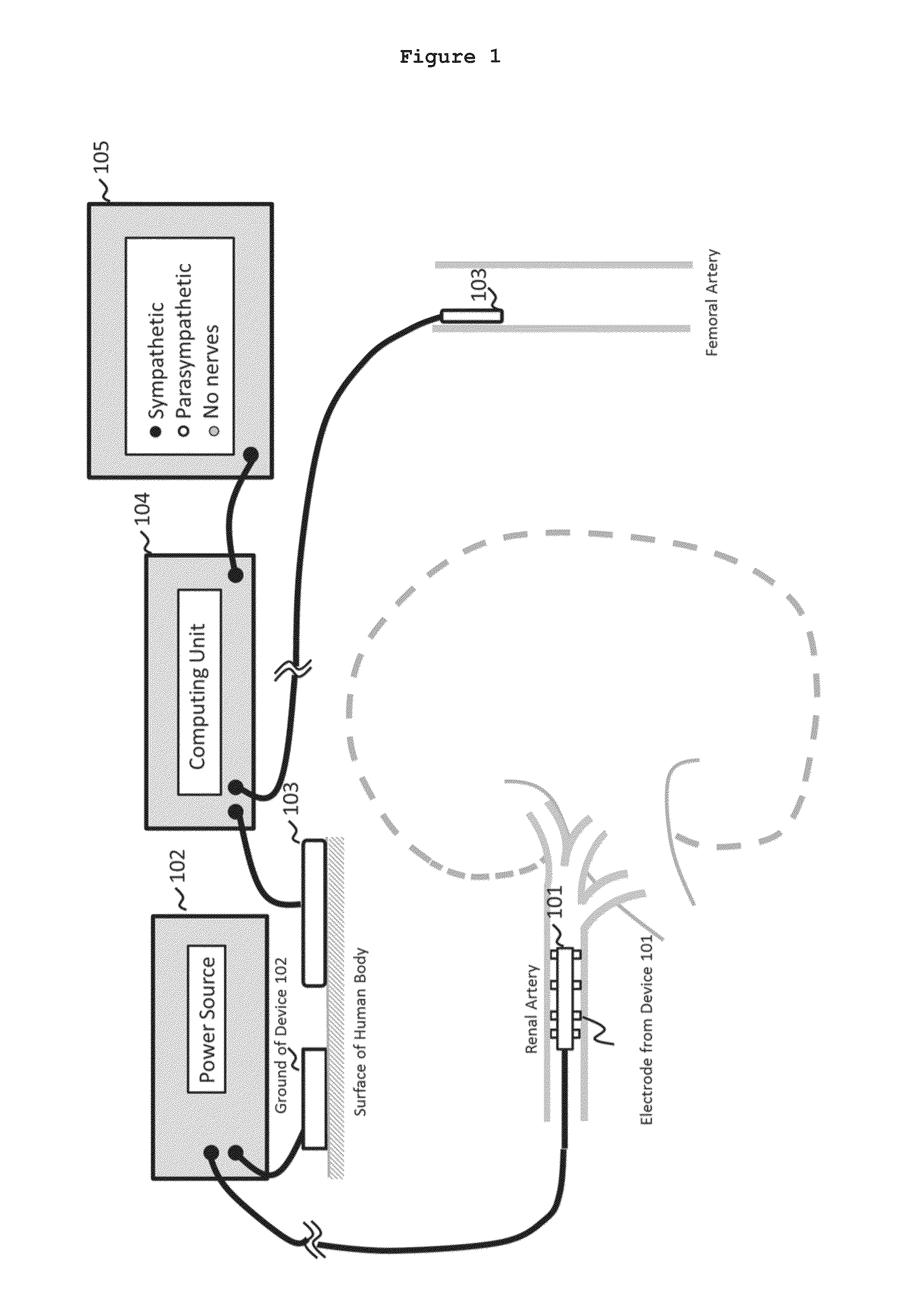
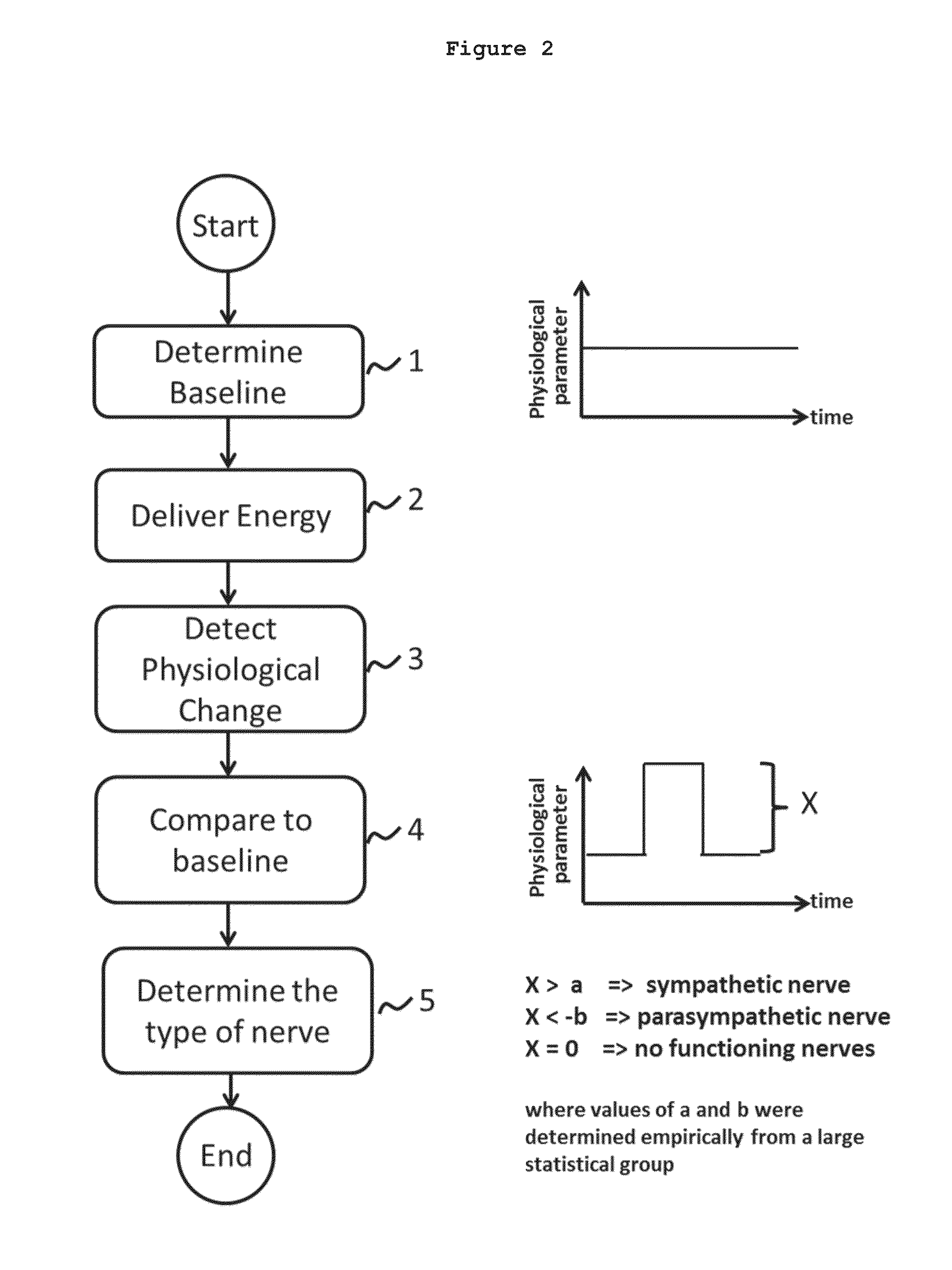
System and method for locating and identifying the functional nerves innervating the wall of arteries and catheters for same
ActiveUS20140213873A1Accurate locationPrecise deliveryUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyArterial wallCatheter
System and method for and identifying nerves innervating the wall of arteries such as the renal artery are disclosed. The present invention identifies areas on vessel walls that are innervated with nerves; provides indication on whether energy is delivered accurately to a targeted nerve; and provides immediate post-procedural assessment of the effect of energy delivered to the nerve. The method includes at least the steps to evaluate a change in physiological parameters after energy is delivered to an arterial wall; and to determine the type of nerve that the energy was directed to (none, sympathetic or parasympathetic) based on the evaluated results. The system includes at least a device for delivering energy to the wall of blood vessel; sensors for detecting physiological signals from a subject; and indicators to display results obtained using said method. Also provided are catheters for performing the mapping and ablating functions.
Owner:SYMAP MEDICAL (SUZHOU) LIMITED
Endothelium preserving microwave treatment for atherosclerois
Method and apparatus are provided to treat atherosclerosis wherein the artery is partially closed by dilating the artery while preserving the vital and sensitive endothelial layer thereof. Microwave energy having a frequency from 3 GHz to 300 GHz is propagated into the arterial wall to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally necrosing connective tissue and softening fatty and waxy plaque while limiting heating of surrounding tissues including the endothelial layer and / or other healthy tissue, organs, and blood. The heating period for raising the temperature a potentially desired amount about 20° C., within the atherosclerotic lesion may be less than about one second. In one embodiment of the invention, a radically beveled waveguide antenna is used to deliver microwave energy at frequencies from 25 GHz or 30 GHz to about 300 GHz and is focused towards a particular radial sector of the artery. Because the atherosclerotic lesions are often asymmetrically disposed, directable or focussed heating preserves healthy sectors of the artery and applies energy to the asymmetrically positioned lesion faster than a non-directed beam. A computer simulation predicts isothermic temperature profiles for the given conditions and may be used in selecting power, pulse duration, beam width, and frequency of operation to maximize energy deposition and control heat rise within the atherosclerotic lesion without harming healthy tissues or the sensitive endothelium cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTRATOR NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTRATION
Technique to confirm correct positioning of arterial wall sealing device
Methods and systems related to sealing punctures in blood vessels (such as following an angio or PTCA procedure) are disclosed. The position of a distal end of an introducer assembly in tissue is determined using a pressure sensor. The pressure sensor is connected to the proximal end of the introducer assembly. The introducer assembly has a fluid path between its distal end and its proximal end. Measured blood pressure is outputted as an indication of the position of the distal end of the introducer assembly in the tissue. Proper positioning of a seal is confirmed by placing the introducer assembly such that its distal end is in tissue outside a puncture in a blood vessel wall and observing a characteristic of blood at the proximal end of the introducer assembly. In both techniques, a waveform of the blood pressure at the distal end of the introducer assembly may be displayed on a display to provide additional information to a surgeon as to the relative position of the components with respect to various tissues.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Technique to confirm correct positioning with respect to arterial wall
Methods and systems related to sealing punctures in blood vessels (such as following an angio or PTCA procedure) are disclosed. The invention provides a system to sense the location of a distal portion of a member within a body. The system includes an introducer portion having a distal end adapted to be placed within a body and a pressure sensor. The pressure sensor is in fluid communication with the distal end and is adapted to provide a pulsation which can be sensed by an operator when the distal end is placed within a pulsating portion of the body.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Diagnostics and the therapeutics for macular degeneration
InactiveUS7108982B1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisArterial wallMacular degeneration
The invention relates to diagnostics and therapeutics and animal models for macular degeneration, specifically as they relate to the association described herein between macular degeneration and arterial wall disruptive disorders. In one embodiment, the invention provides kits and methods for diagnosing macular degeneration comprising identifying a marker for an arterial wall disruptive disorder, including an aneurysm. In one embodiment, the invention provides therapeutics for treating macular degeneration comprising delivering to a subject an agent useful for treating an arterial wall disruptive disorder, including an aneurysm.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Intravascular catheter
InactiveUS20060229591A1Effective treatmentEasily and safely navigatedDiagnosticsSurgeryArterial occlusionsArterial occlusion
Owner:LEE DON W
Device and method for opening blood vessels by pre-angioplasty serration and dilatation of atherosclerotic plaque
ActiveUS20090240270A1Safely and accurately dilated and stretchedDilated more evenly and smoothlyBalloon catheterCannulasBlood vessel spasmPercutaneous angioplasty
A device and method for intravascular treatment of atherosclerotic plaque perforates the plaque with microperforations by small sharp spikes to act as serrations for forming cleavage lines or planes in the plaque. In preferred embodiments, expansion may be obtained by mechanical apparatus, expansion balloon, or balloon-assisted deployment. The plaque treatment enables a subsequent balloon angioplasty to be performed without creating substantial dissections and at low balloon pressure so as to avoid injury to the arterial wall. The plaque treatment may include dilatation of the plaque at low pressure, sufficiently that no subsequent balloon angioplasty is needed. The plaque preparation may be followed by applying one or a few ring tacks to secure the compressed plaque with minimal emplacement of foreign material.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
System and method for locating and identifying the functional nerves innervating the wall of arteries
ActiveUS20140194866A1Accurate locationPrecise deliveryUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyArterial wallBlood vessel
System and method for locating and identifying nerves innervating the wall of arteries such as the renal artery are disclosed. The present invention identifies areas on vessel walls that are innervated with nerves; provides indication on whether a dose of energy is delivered accurately to a targeted nerve; and provides immediate post-procedural assessment of the effect of the energy delivered to the nerve. The method includes at least the steps to evaluate a change in physiological parameters after a dose of energy is delivered to an arterial wall; and to determine the type of nerve that the energy was directed to (none, sympathetic or parasympathetic) based on the results of the evaluation. The system includes at least a device for delivering a dose of energy to the wall of an artery; sensors for detecting physiological signals from a subject; and indicators to display the results obtained using the said method.
Owner:SYMAP MEDICAL (SUZHOU) LIMITED
Intravascular device
ActiveUS9480826B2Large caliberSafely and accurately dilated and stretchedBalloon catheterCannulasEngineeringPercutaneous angioplasty
A device and method for intravascular treatment of atherosclerotic plaque prior to balloon angioplasty. An intravascular device can comprise a carrier configured for expansion within a vessel. The carrier can have a s plurality of ribbon strips extending longitudinally between a first end and a second end. An open slot can be positioned between adjacent ribbon strips. A plurality of spikes can be positioned on each of the ribbon strips. The spikes can act as serrations for forming cleavage lines or planes in plaque in the vessel. The spikes may also be used to transport medication into the plaque. The plaque preparation treatment can enables subsequent angioplasty to be performed at low balloon pressures, can reduces dissections, and avoids injury to the arterial wall.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
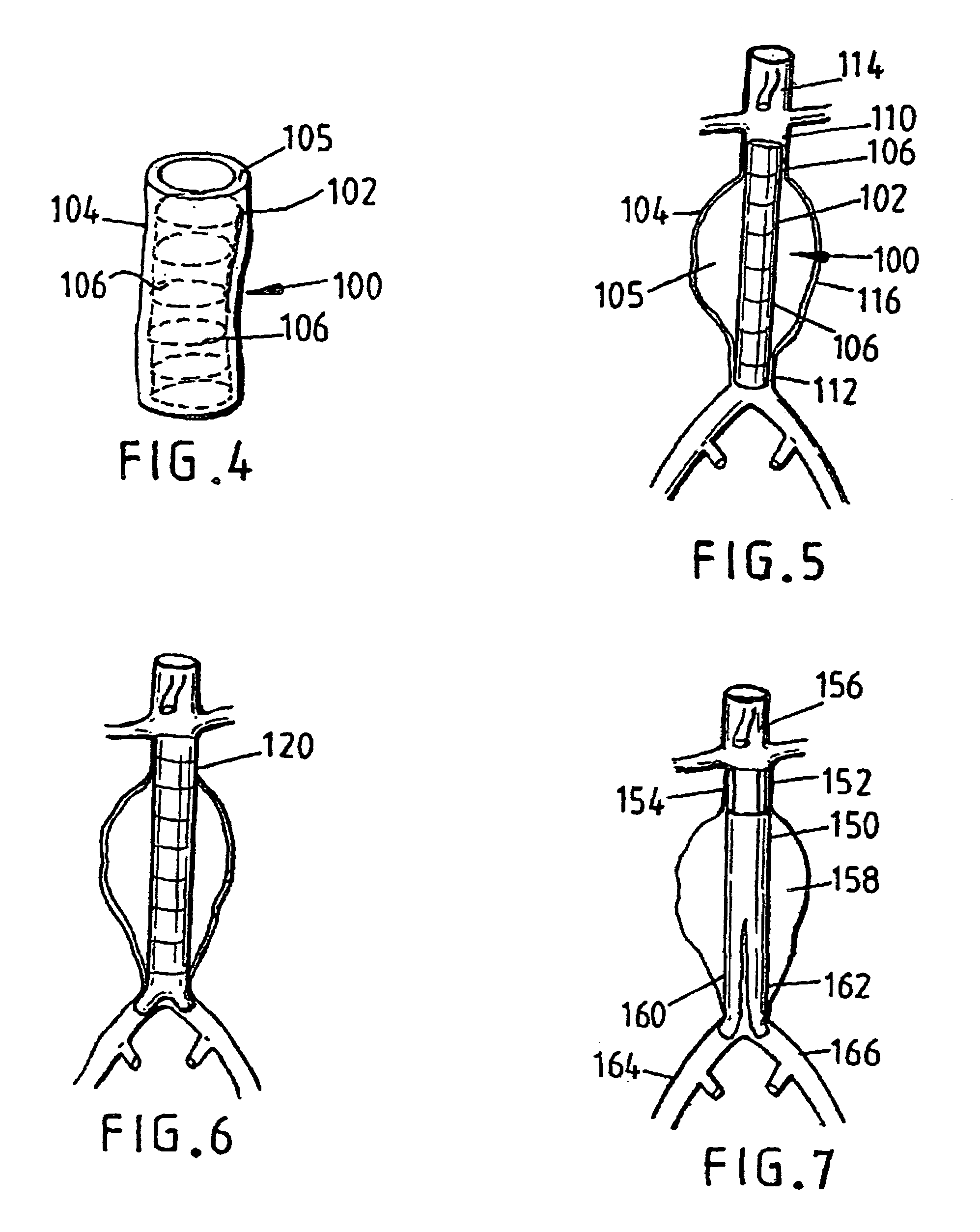
Devices for repairing aneurysms
A device for repairing an aneurysm by deployment within the aneurysm comprises a graft tube, at least part thereof having an inflatable wall whereby the tube can be deployed in an artery and inflated to grip at least part of the arterial wall.
Owner:ENDOLOGIX LLC
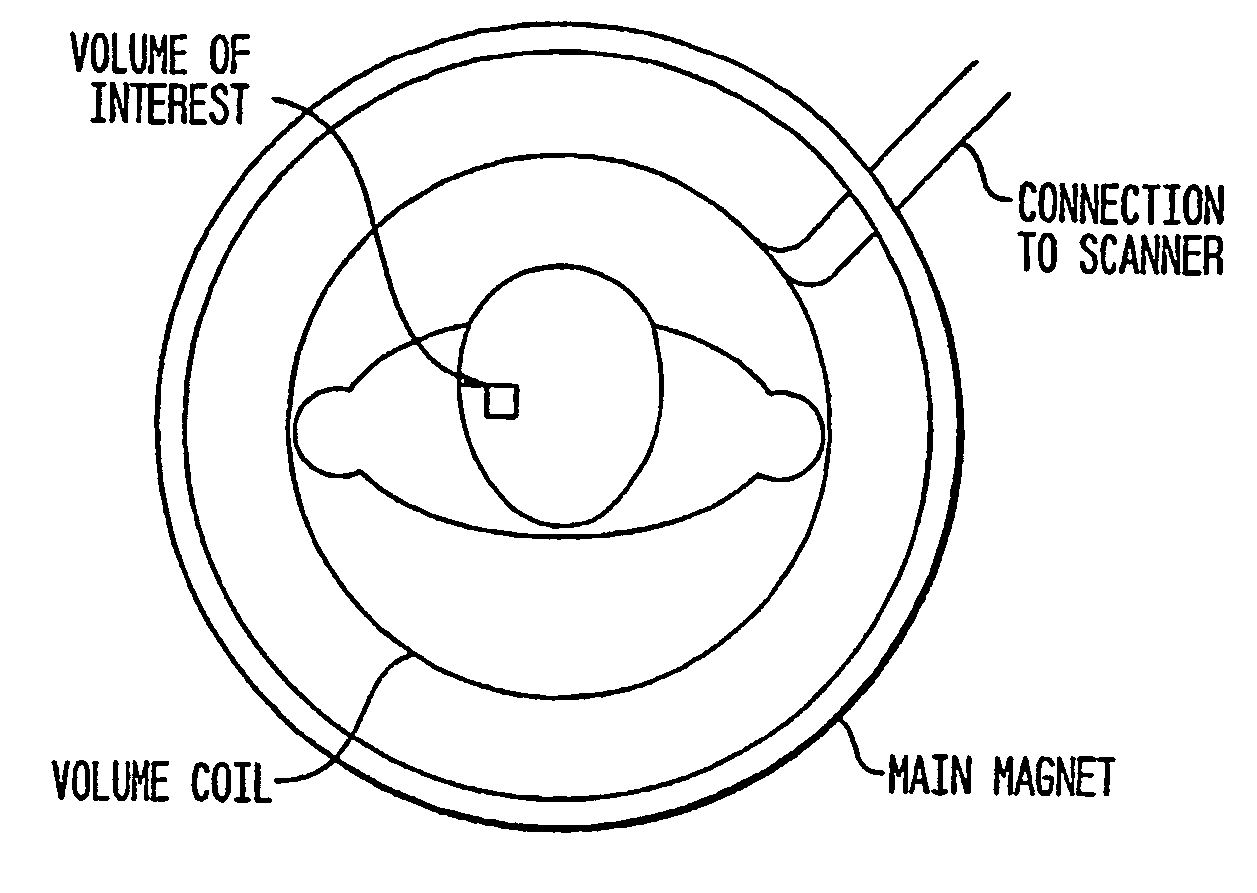
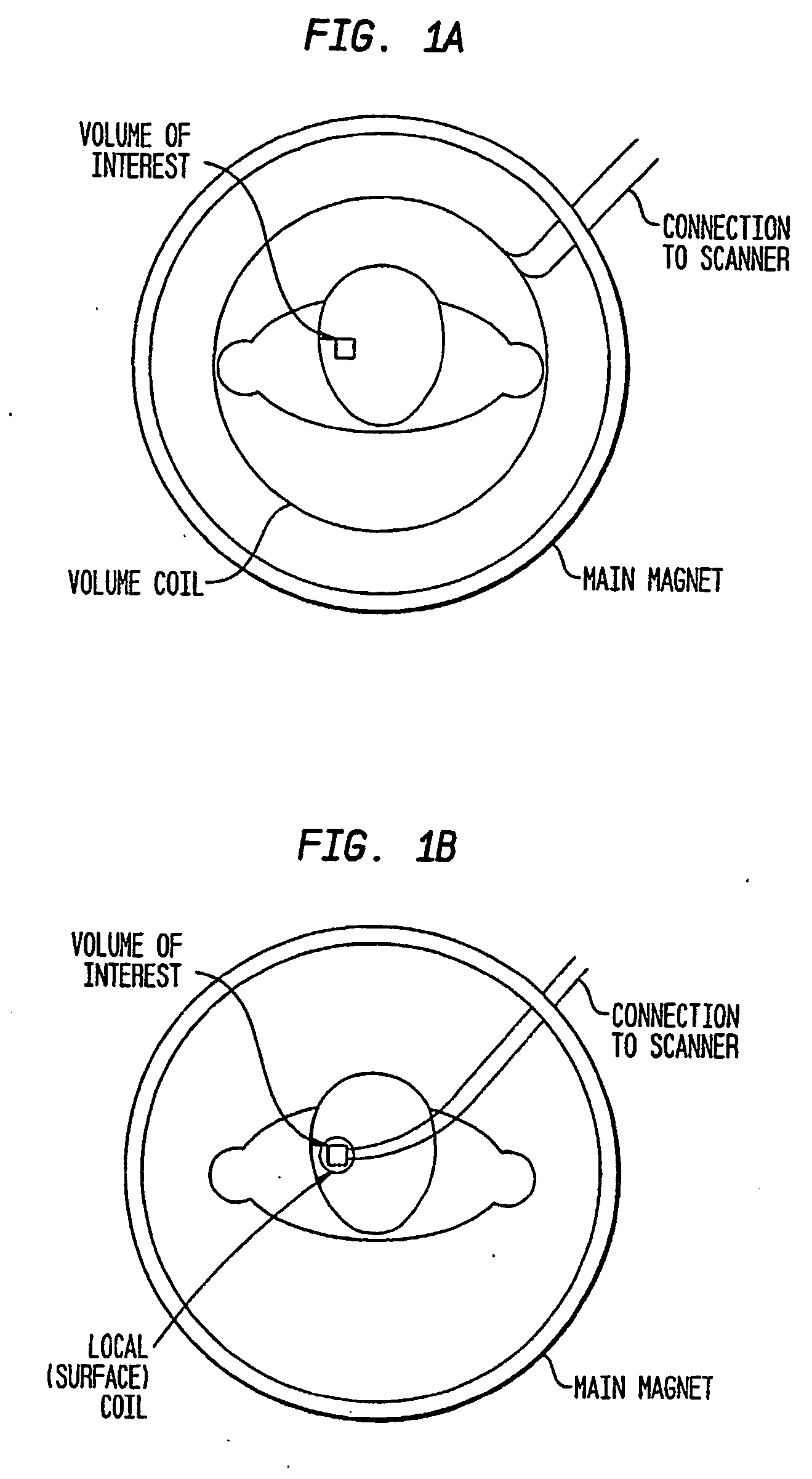
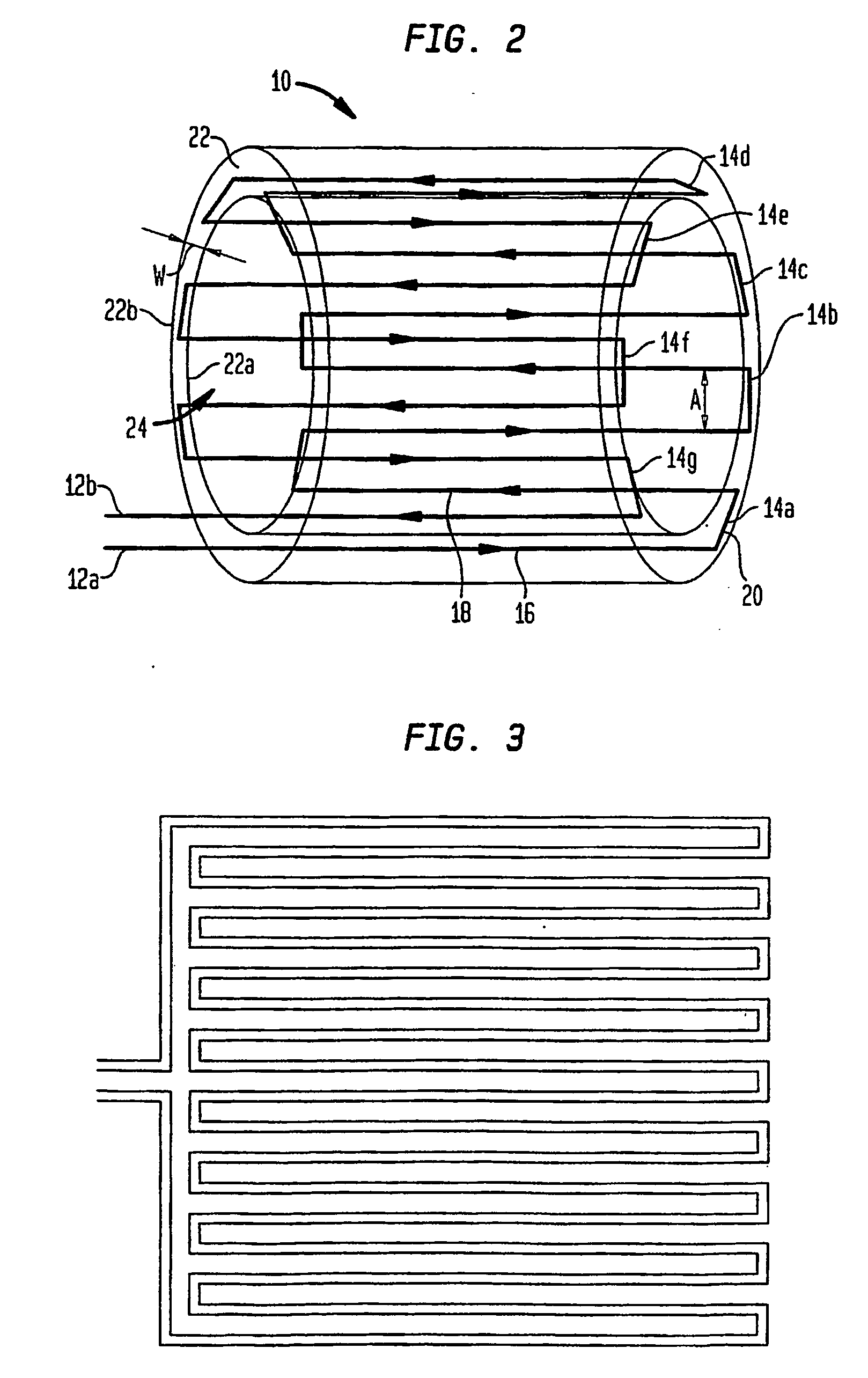
Radiofrequency coil and catheter for surface nmr imaging and spectroscopy
In one aspect, the present invention provides a cylindrical meanderline coil that can significantly improve the performance and usefulness of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) catheter radiofrequency (RF) coils by shaping the spatial dimensions of the volume of excitation and reception of signal. This can provide improved accuracy in defining the volume of excitation and reception of the subject or specimen, and increase the signal to noise ratio of a received signal. In another aspect, the invention provides an intravascular catheter having a coil at its tip for generating and / or detecting magnetic excitations. A preamplifer coupled to the catheter in proximity of the coil allows amplifying signals generated and / or detected by the coil. Although in one application, a coil and / or a catheter of the invention can be employed, for example, for MR spectroscopy or imaging of biological tissue, such as atherosclerotic plaques arterial walls in the human body, the invention provides similar advantages in any situation where a magnetic resonance or other magnetic induction signal is to be received from a thin cylindrical shell or sector of a cylindrical shell.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Guiding catheter with embolic protection by proximal occlusion
A guiding catheter includes an elongate shaft with a central lumen and a mechanically expandable sealing membrane mounted about the distal end of the shaft. An expansion wire is slidably disposed in a dedicated lumen within the catheter, the expansion wire having an expandable distal portion with a pre-formed expanded shape capable of expanding the sealing membrane into sealing engagement with the wall of an artery to provide occlusion of blood flowing through the artery. In one embodiment, a steering wire is slidably disposed in a dedicated lumen within the catheter and is fixed adjacent the shaft distal end. Pushing or pulling the steering wire deflects the distal end of the catheter. In another embodiment, the guiding catheter has a pre-formed curve adjacent the distal end of the shaft.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com